
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) technician inspects the solid rocket motor for the ULA Atlas V rocket on its transporter near the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solid rocket motor will be lifted and mated to the rocket in preparation for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
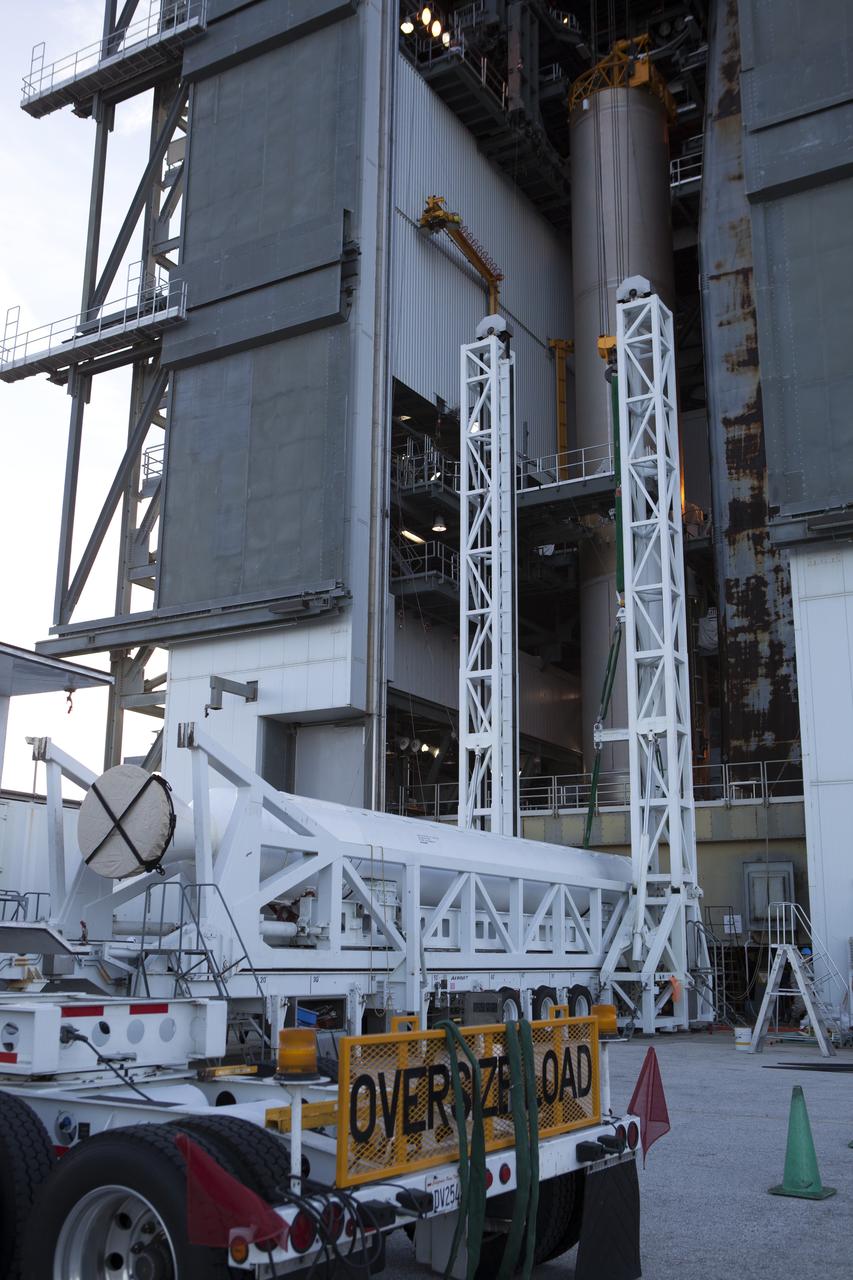

Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
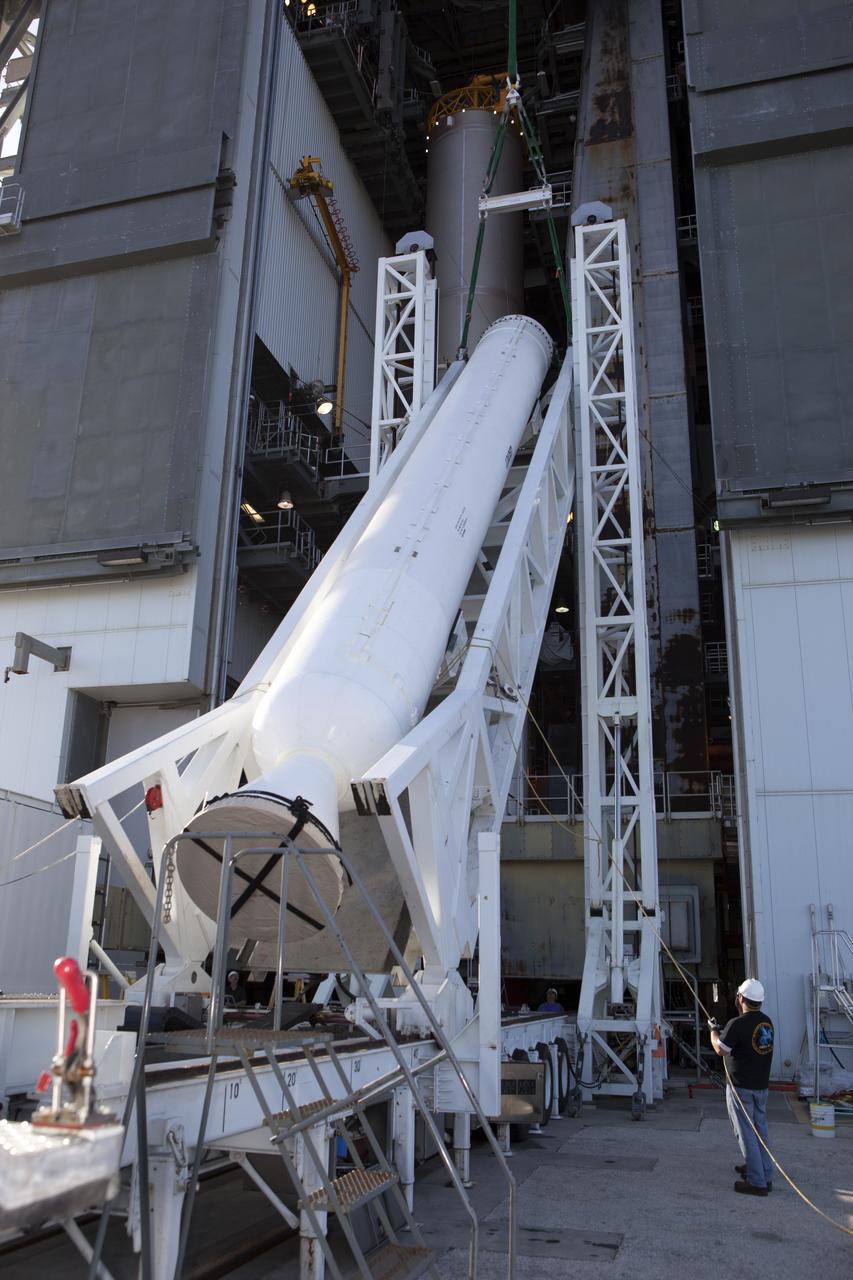

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
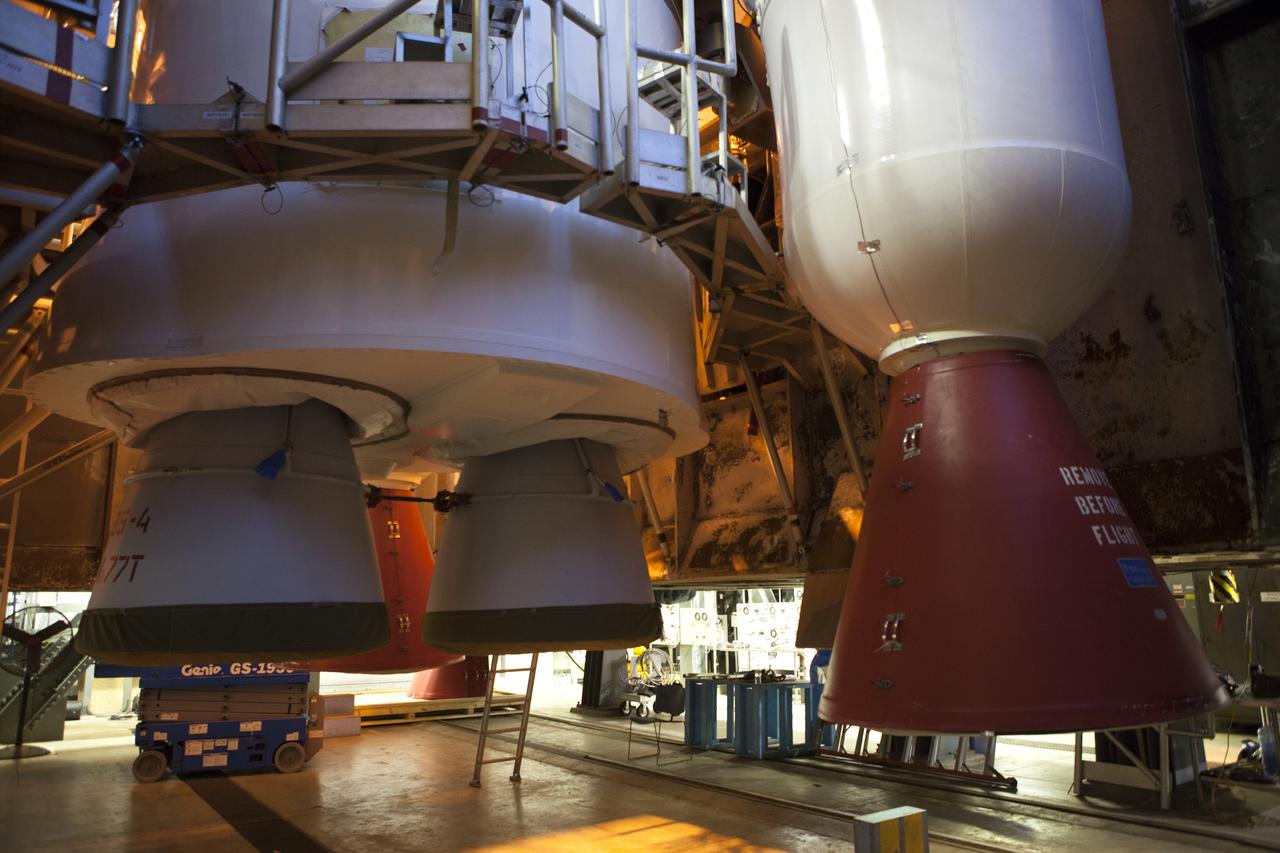

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is being mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
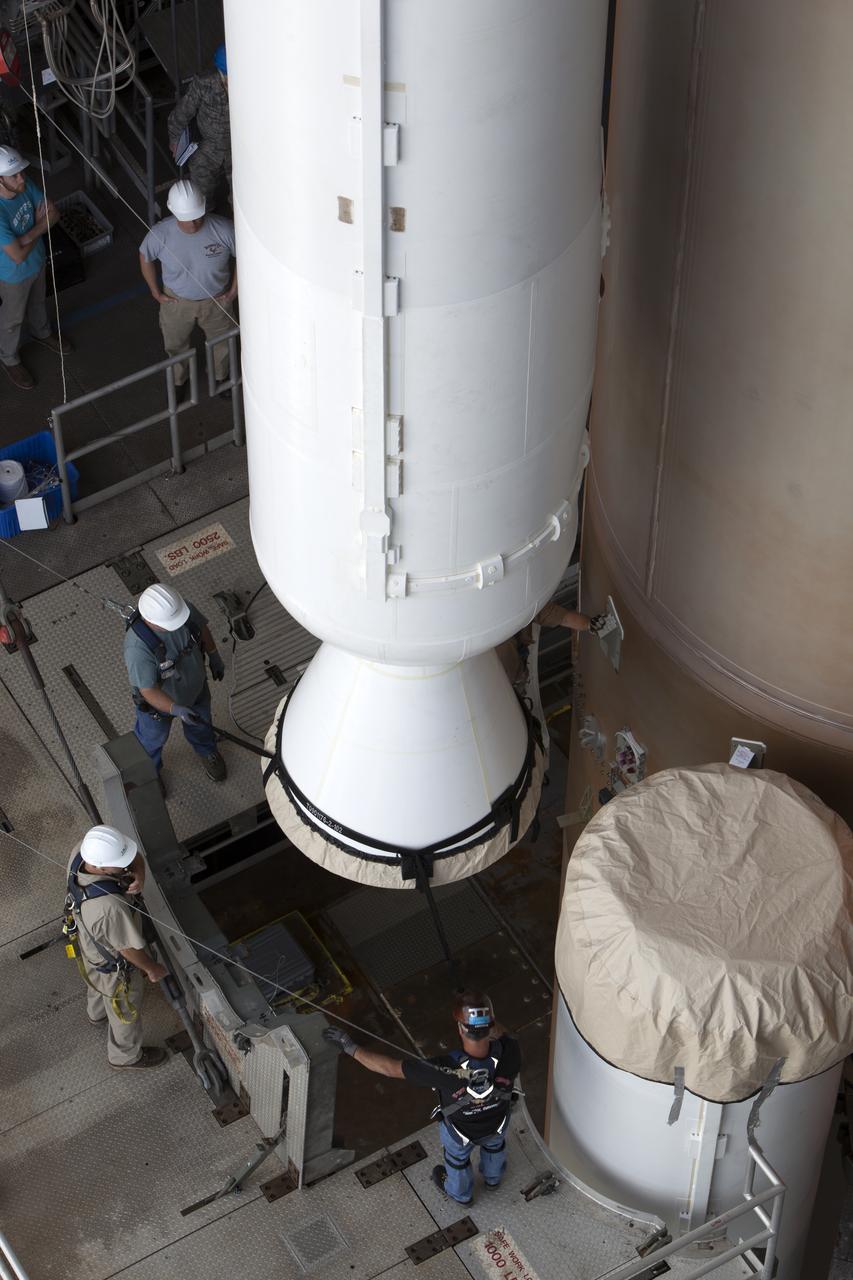

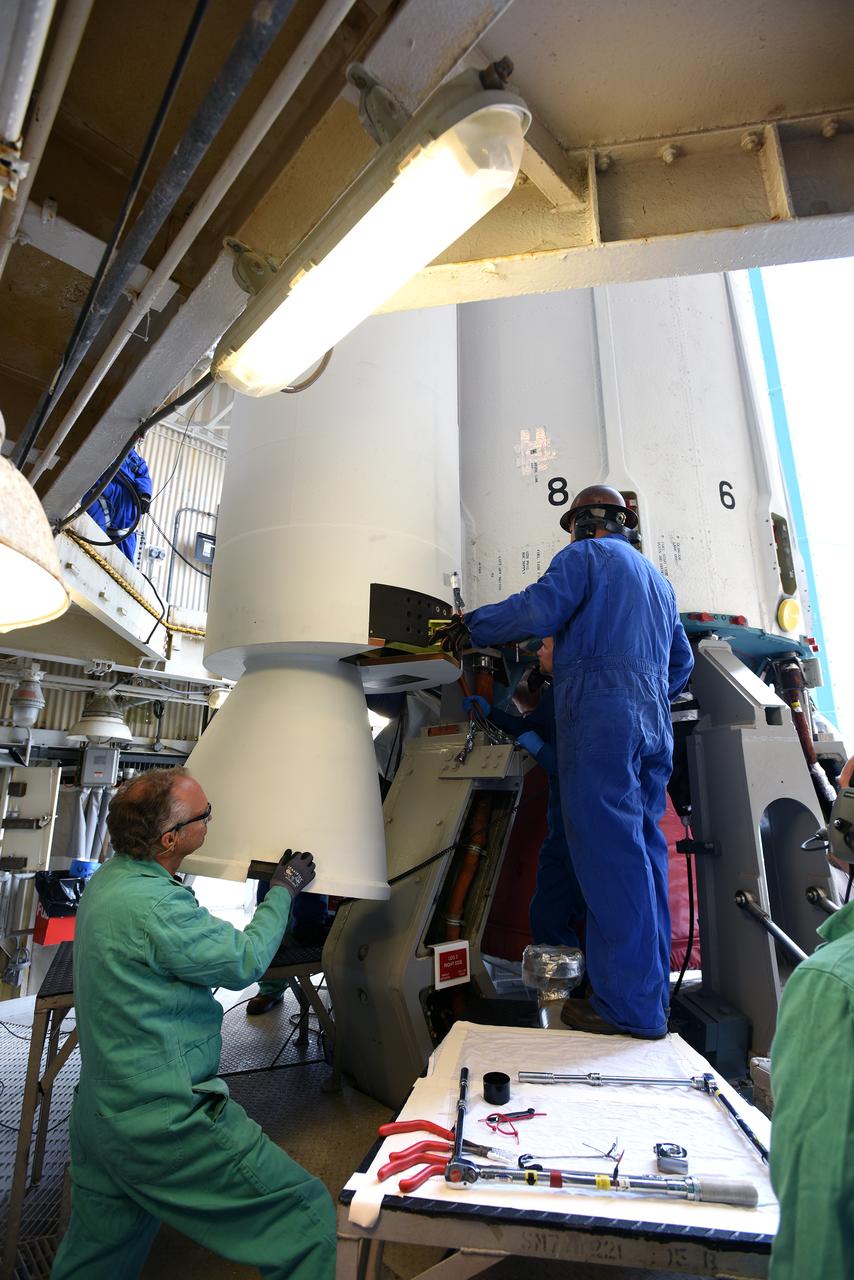
Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) monitor the progress as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
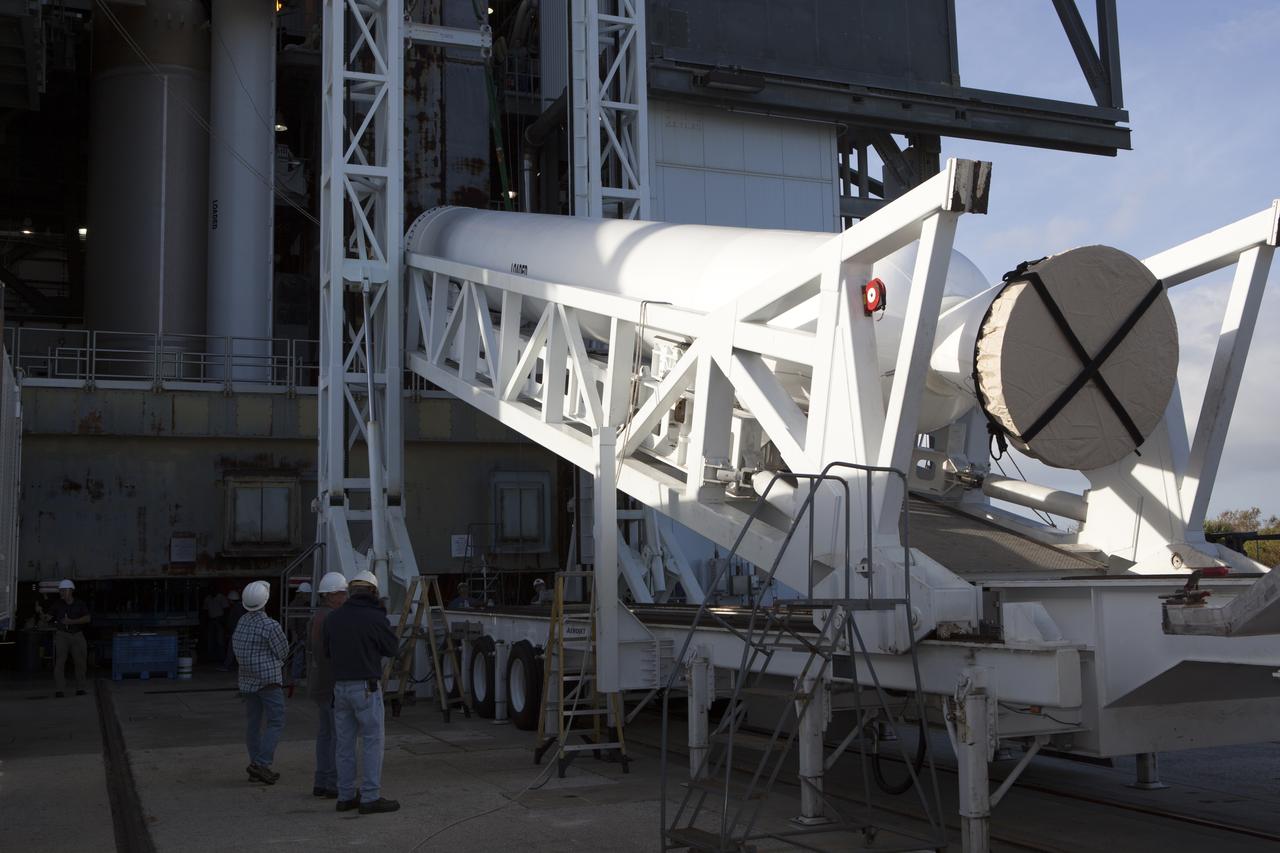

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
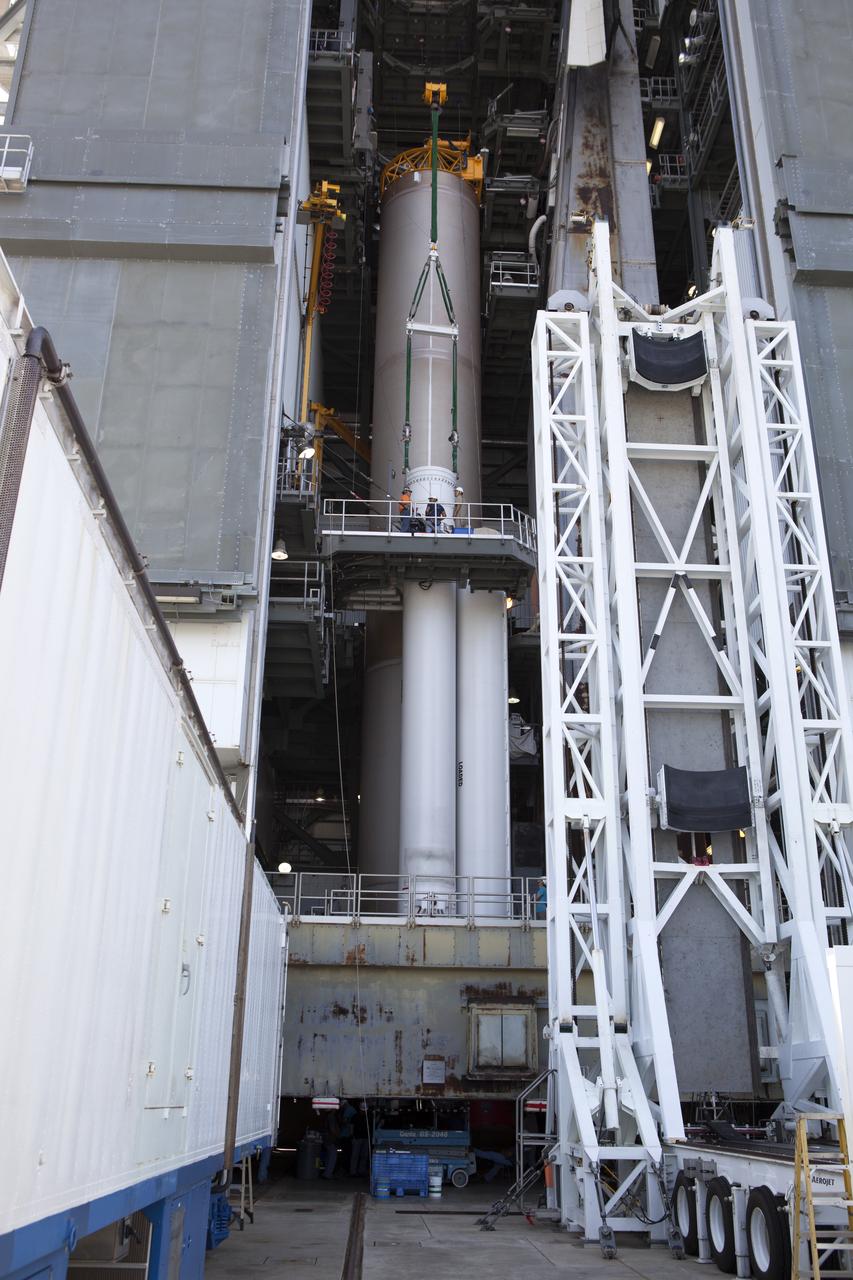

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
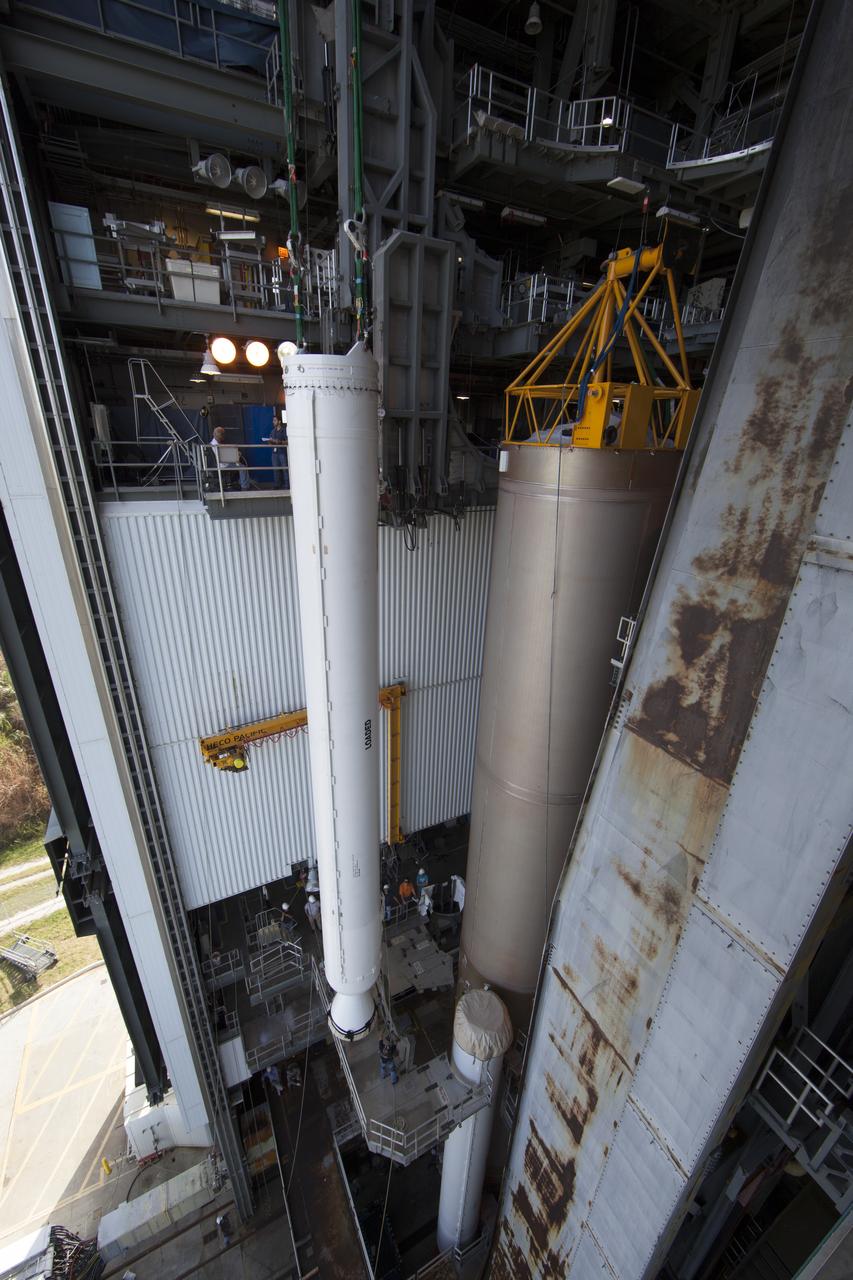

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position and moved into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
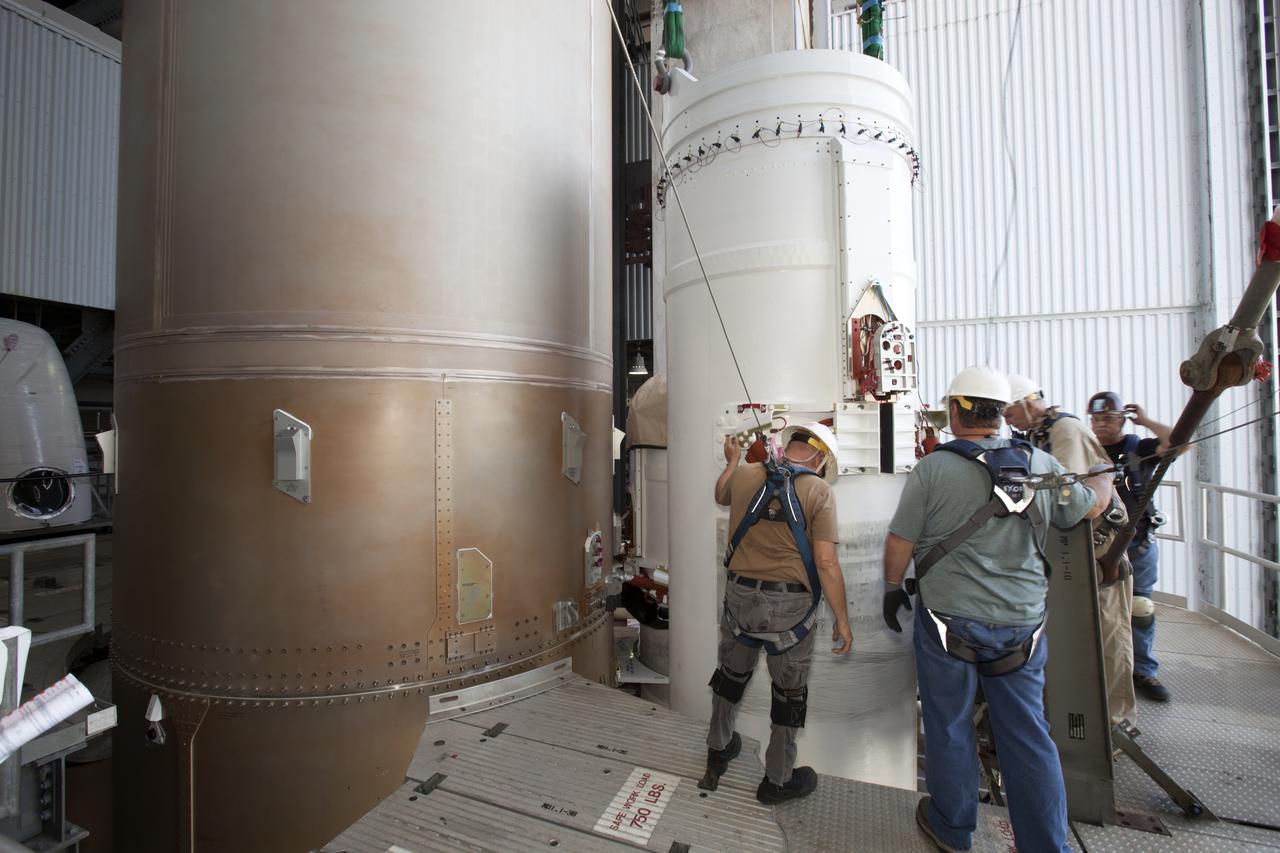

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) assist as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
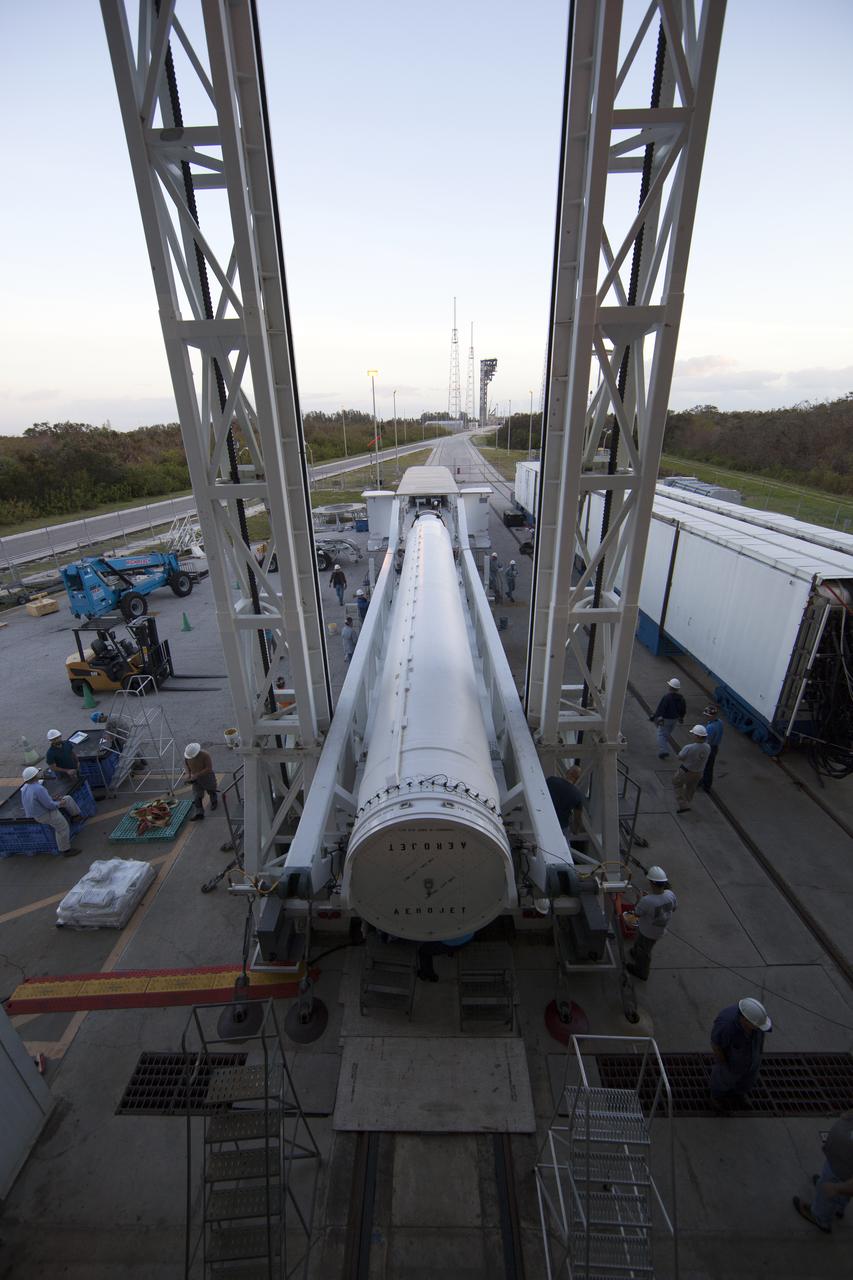

Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
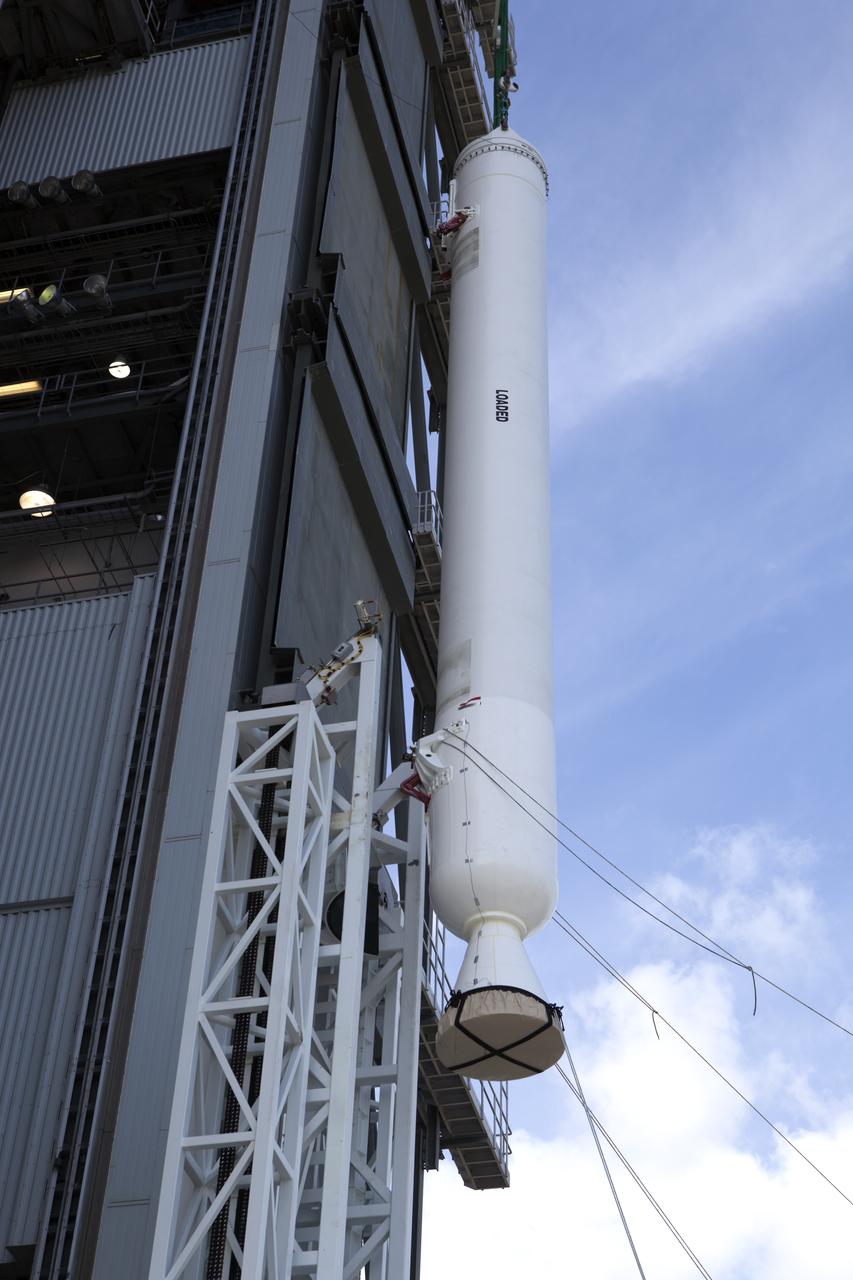

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
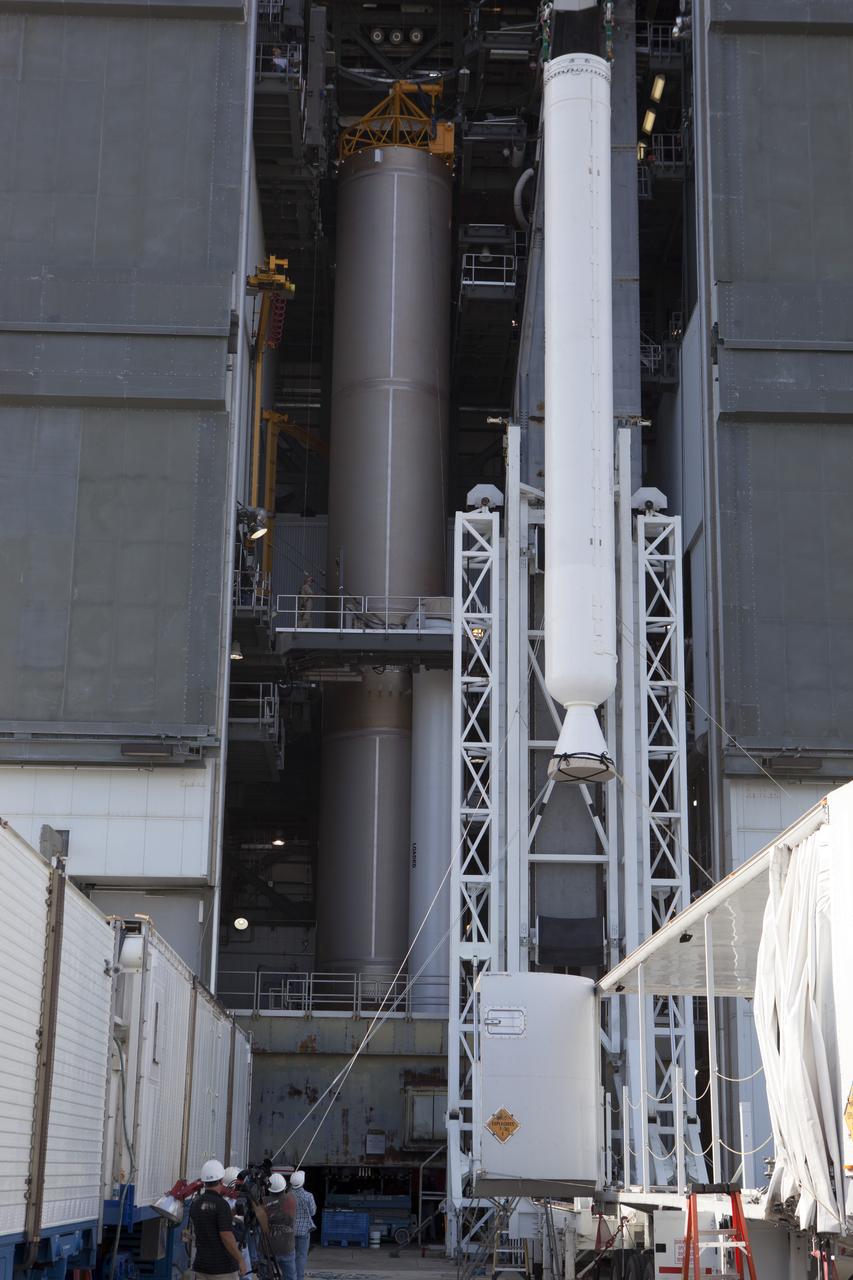

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

A scaled-down 24-inch version of the Space Shuttle's Reusable Solid Rocket Motor was successfully fired for 21 seconds at a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Test Stand. The motor was tested to ensure a replacement material called Lycocel would meet the criteria set by the Shuttle's Solid Motor Project Office. The current material is a heat-resistant, rayon-based, carbon-cloth phenolic used as an insulating material for the motor's nozzle. Lycocel, a brand name for Tencel, is a cousin to rayon and is an exceptionally strong fiber made of wood pulp produced by a special "solvent-spirning" process using a nontoxic solvent. It will also be impregnated with a phenolic resin. This new material is expected to perform better under the high temperatures experienced during launch. The next step will be to test the material on a 48-inch solid rocket motor. The test, which replicates launch conditions, is part of Shuttle's ongoing verification of components, materials, and manufacturing processes required by MSFC, which oversees the Reusable Solid Rocket Motor project. Manufactured by the ATK Thiokol Propulsion Division in Promontory, California, the Reusable Solid Rocket Motor measures 126 feet (38.4 meters) long and 12 feet (3.6 meters) in diameter. It is the largest solid rocket motor ever flown and the first designed for reuse. During its two-minute burn at liftoff, each motor generates an average thrust of 2.6 million pounds (1.2 million kilograms).
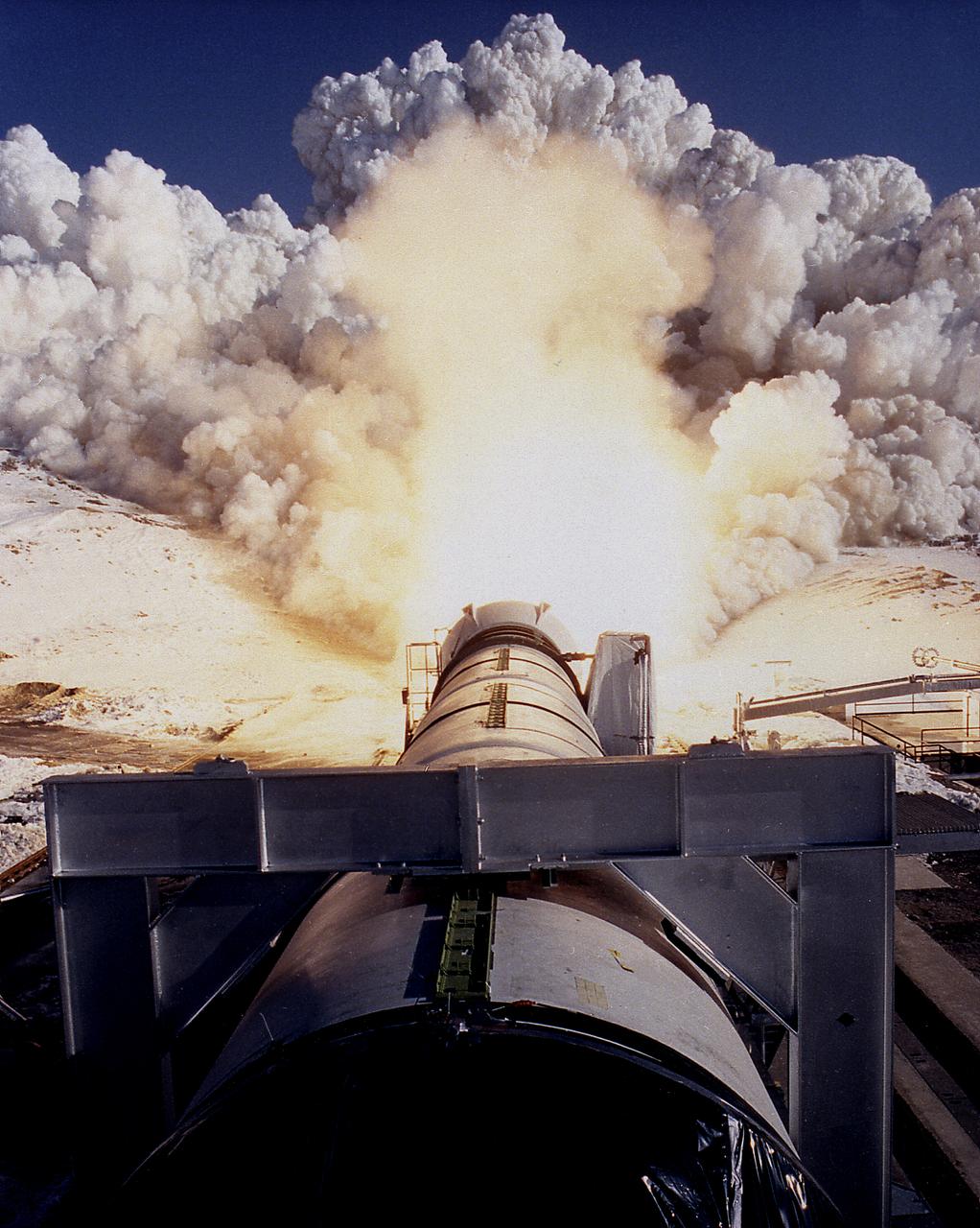

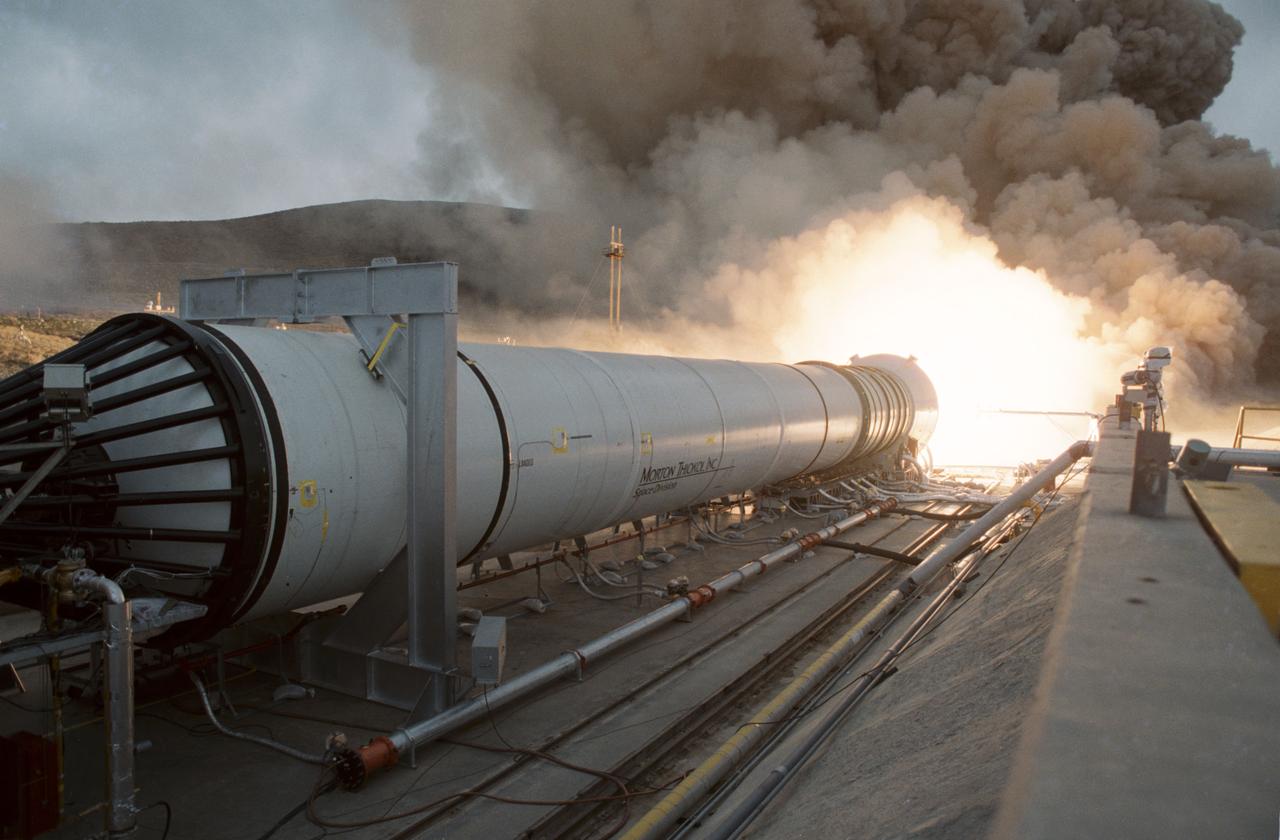
This photograph shows a static firing test of the Solid Rocket Qualification Motor-8 (QM-8) at the Morton Thiokol Test Site in Wasatch, Utah. The twin solid rocket boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
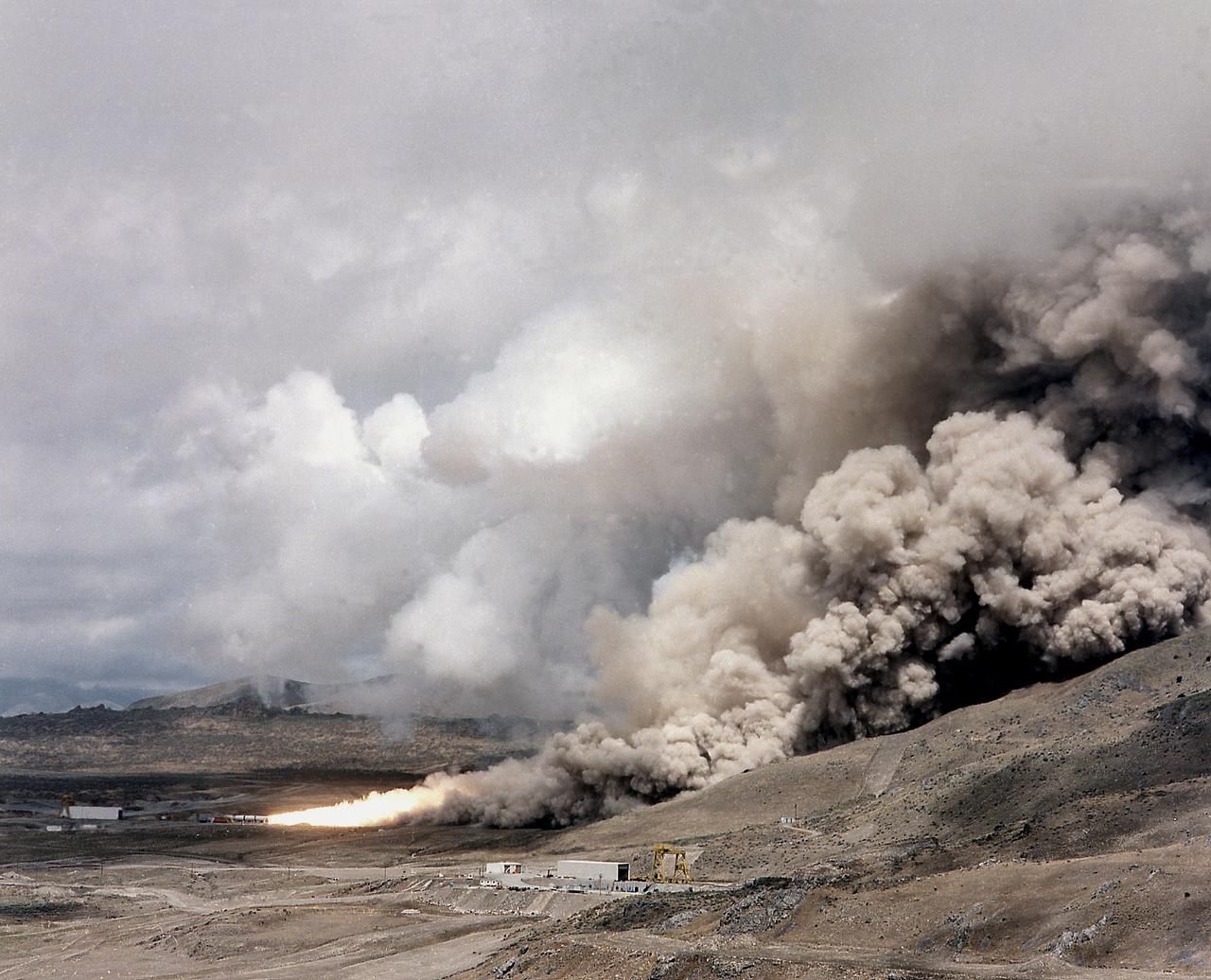

This photograph is a long shot view of a full scale solid rocket motor (SRM) for the solid rocket booster (SRB) being test fired at Morton Thiokol's Wasatch Operations in Utah. The twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the SRM's were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
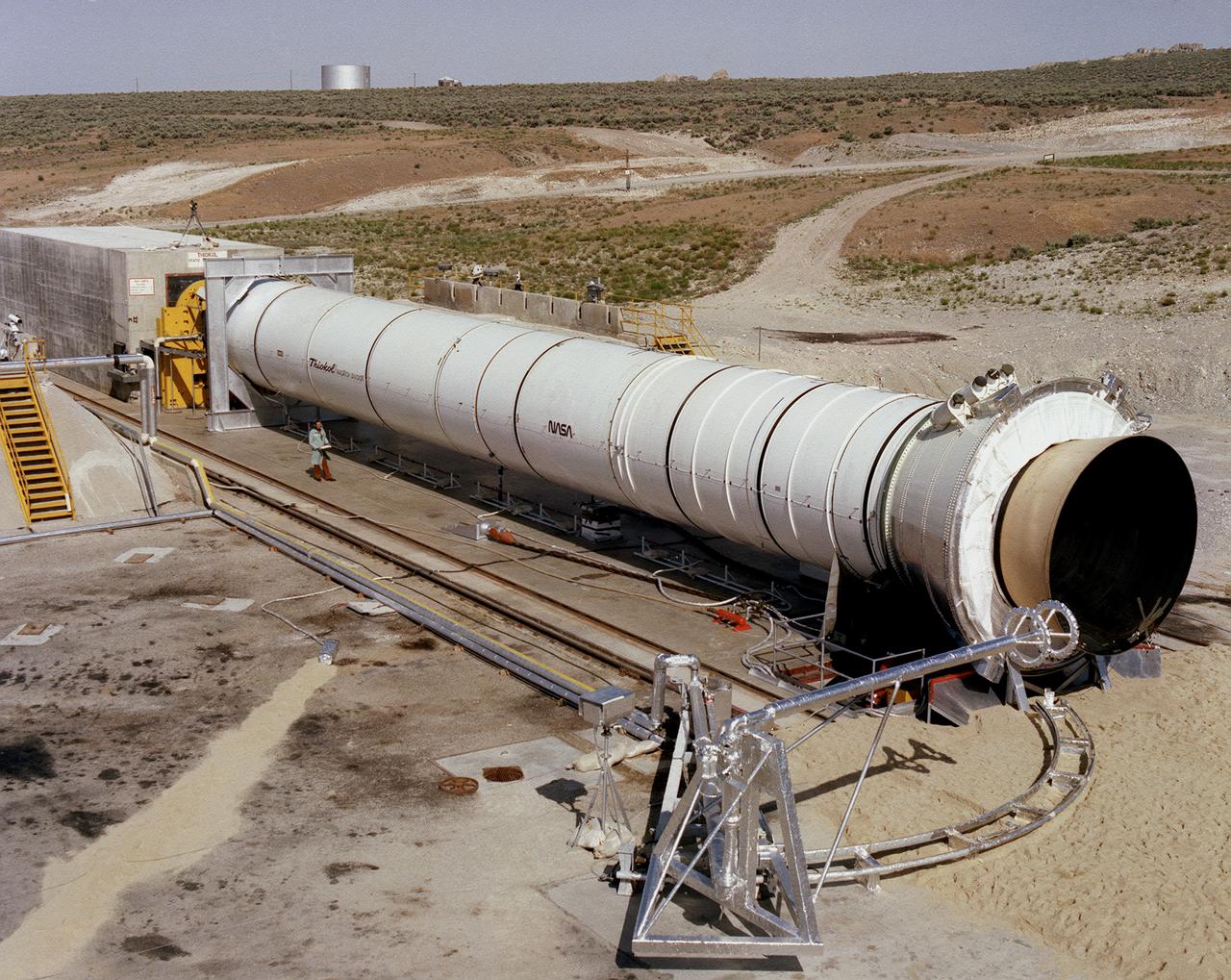

This is a photograph of the solid rocket booster's (SRB's) Qualification Motor-1 (QM-1) being prepared for a static firing in a test stand at the Morton Thiokol Test Site in Wasatch, Utah, showing the aft end of the booster. The twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
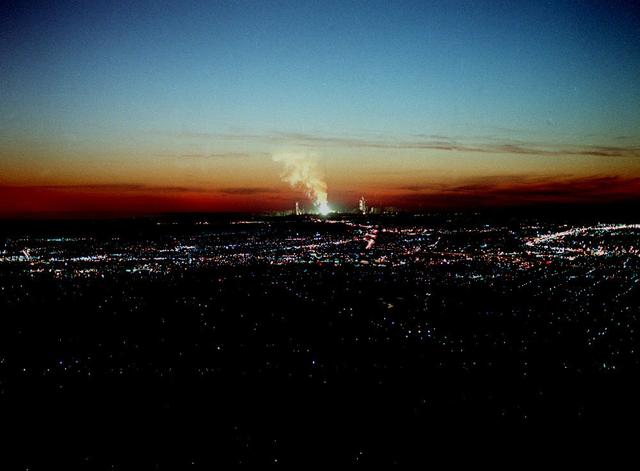

A 48 inch Advanced Solid Rocket Motor is test fired at Marshall's Solid Propulsion Research Test Article facility for M-NASA Project.
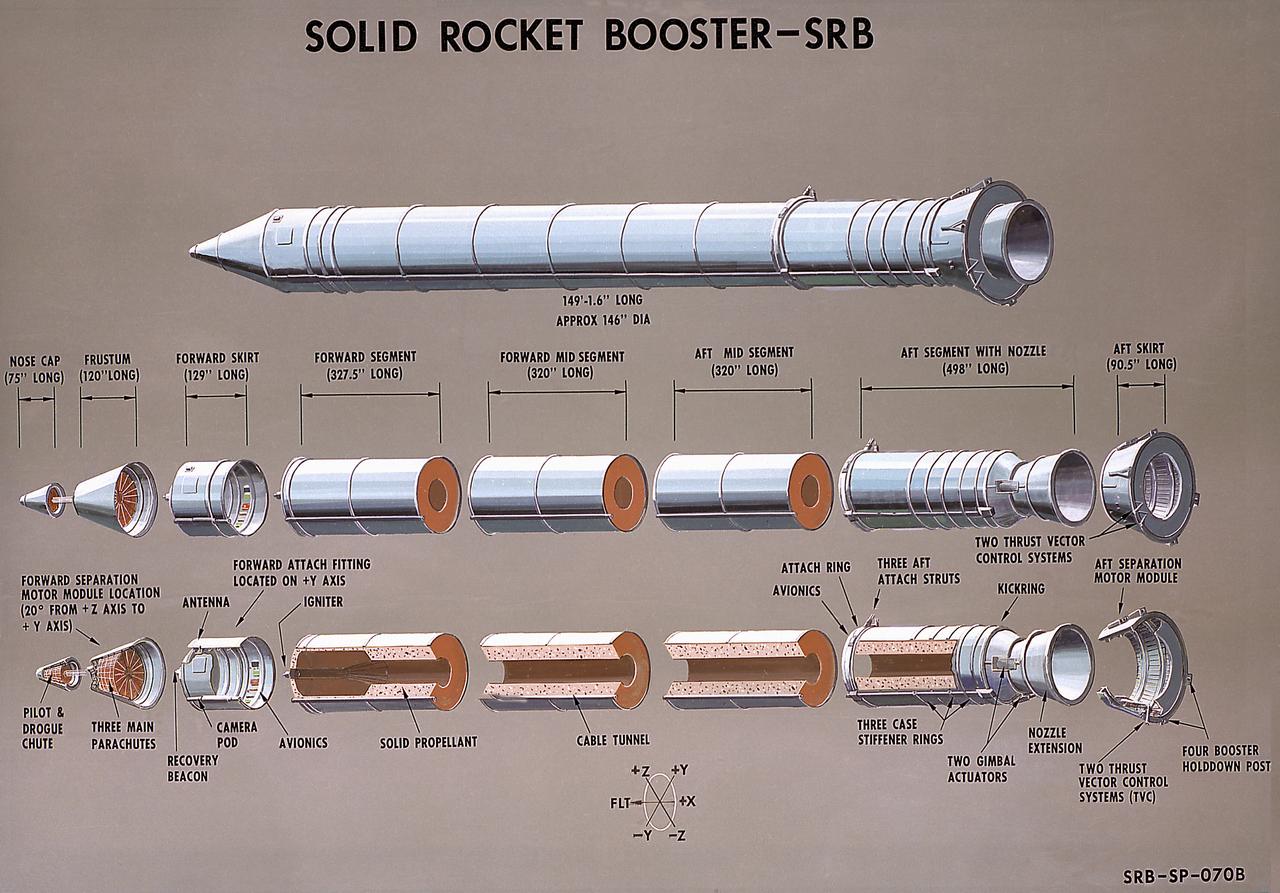
This illustration is a cutaway of the solid rocket booster (SRB) sections with callouts. The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment. The boosters are designed to survive water impact at almost 60 miles per hour, maintain flotation with minimal damage, and preclude corrosion of the hardware exposed to the harsh seawater environment. Under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRB's are assembled and refurbished by the United Space Boosters. The SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.

Solid Rocket Qualification Motor Firing at the Morton Thiokol facility at Brigham City, Utah on 20 April 1988.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 Solid Rocket Motor in support of the Ares/CLV first stage at ATK, Utah . Constellation/Ares project. This image is extracted from a high definition video file and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 Solid Rocket Motor in support of the Ares/CLV first stage at ATK, Utah . Constellaton/Ares project. This image is extracted from a high definition video file and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.
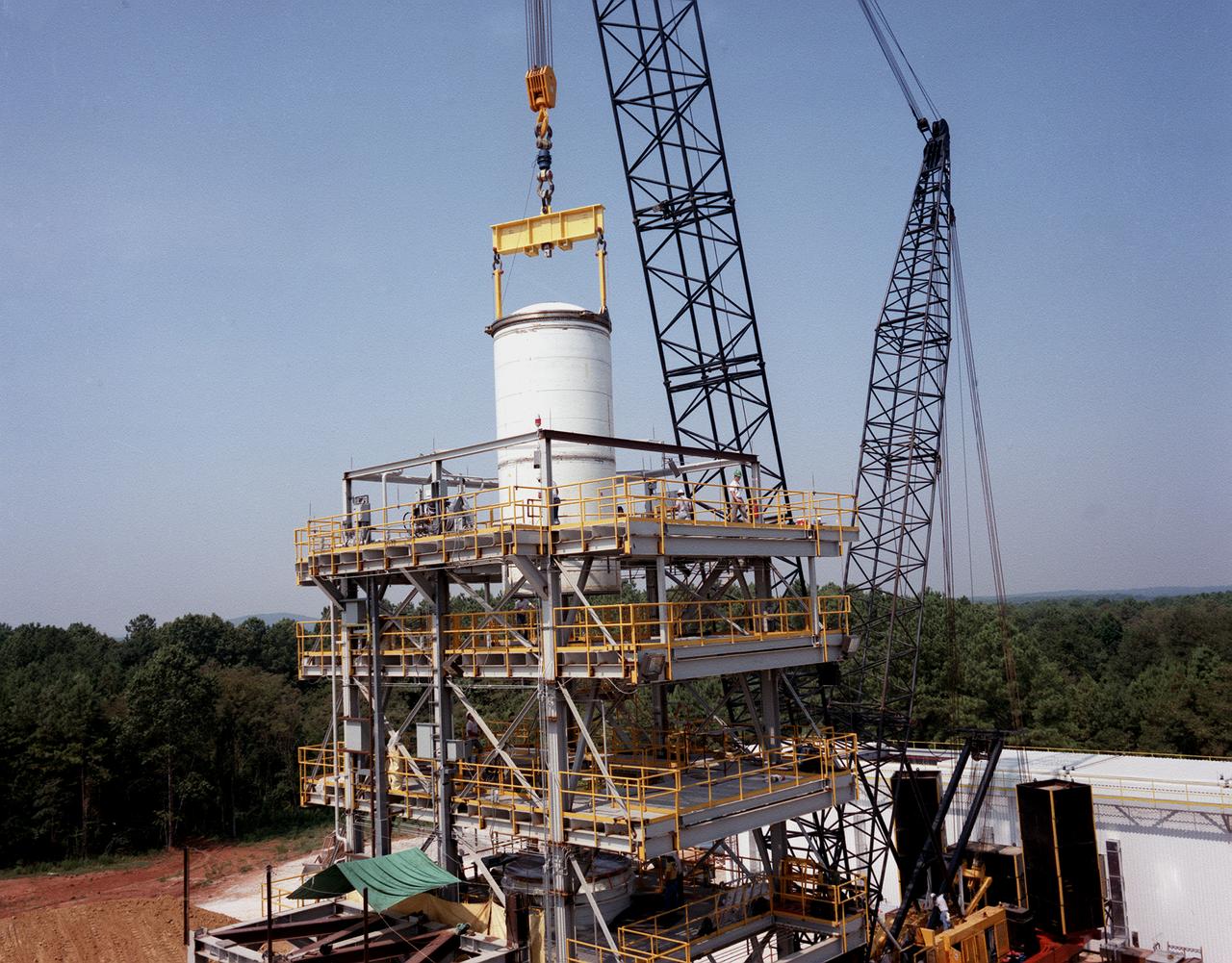

A forward segment is being lowered into the Transient Pressure Test Article (TPTA) test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) east test area. The TPTA test stand, 14-feet wide, 27-feet long, and 33-feet high, was built in 1987 to provide data to verify the sealing capability of the redesign solid rocket motor (SRM) field and nozzle joints. The test facility applies pressure, temperature, and external loads to a short stack of solid rocket motor hardware. The simulated SRM ignition pressure and temperature transients are achieved by firing a small amount of specially configured solid propellant. The pressure transient is synchronized with external programmable dynamic loads that simulate lift off loads at the external tank attach points. Approximately one million pounds of dead weight on top of the test article simulates the weight of the other Shuttle elements.
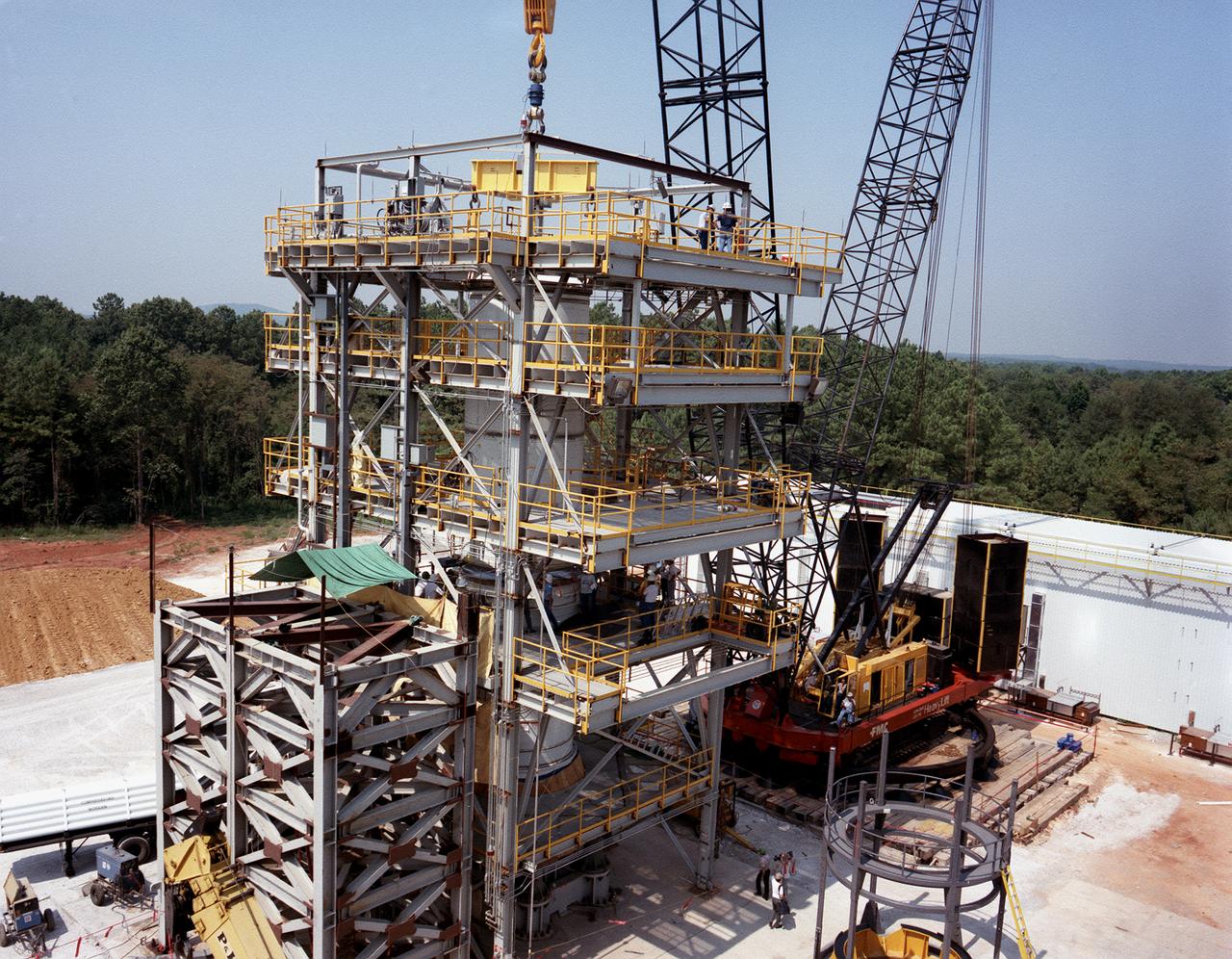

A forward segment is being lowered into the Transient Pressure Test Article (TPTA) test stand at thw Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) east test area. The TPTA test stand, 14-feet wide, 27-feet long, and 33-feet high, was built in 1987 to provide data to verify the sealing capability of the redesign solid rocket motor (SRM) field and nozzle joints. The test facility applies pressure, temperature, and external loads to a short stack of solid rocket motor hardware. The simulated SRM ignition pressure and temperature transients are achieved by firing a small amount of specially configured solid propellant. The pressure transient is synchronized with external programmable dynamic loads that simulate lift off loads at the external tank attach points. Approximately one million pounds of dead weight on top of the test article simulates the weight of the other Shuttle elements.
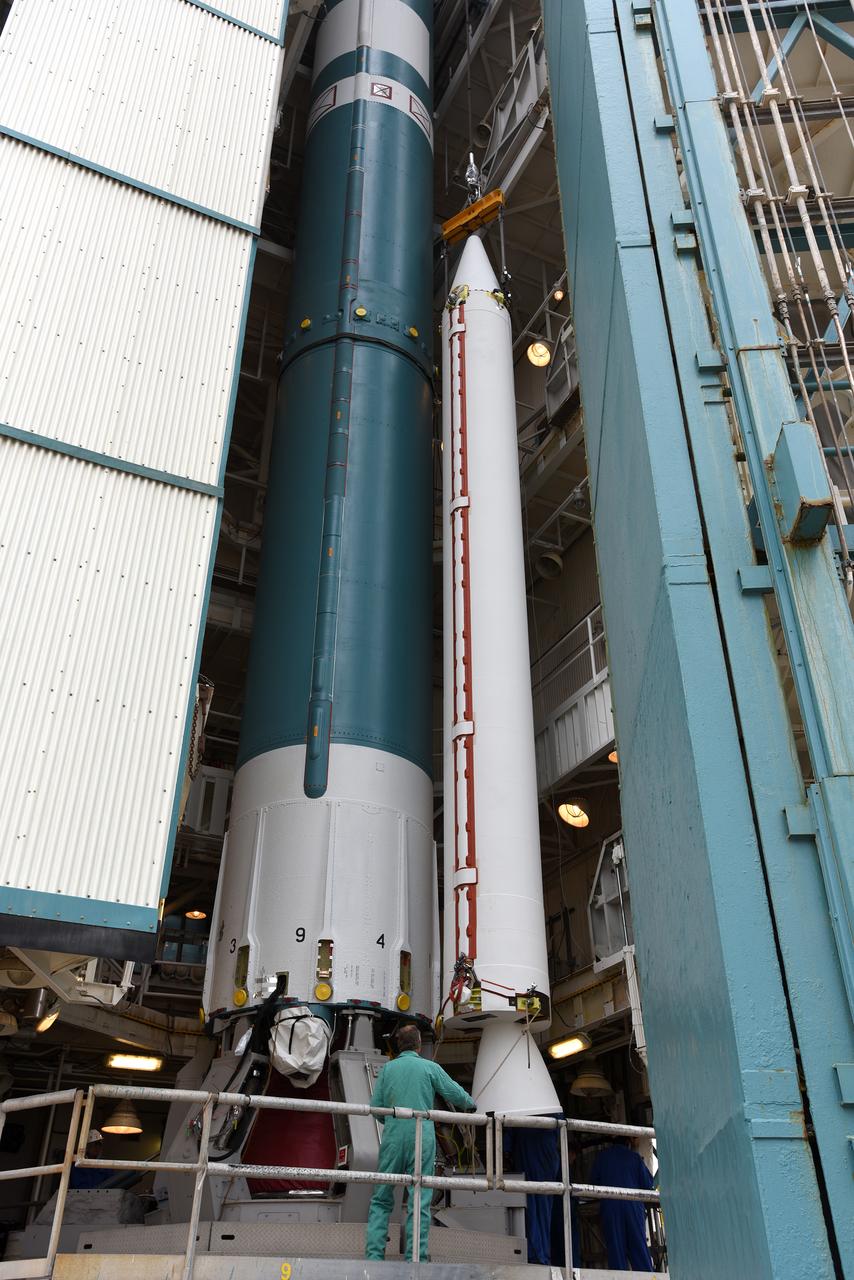

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.
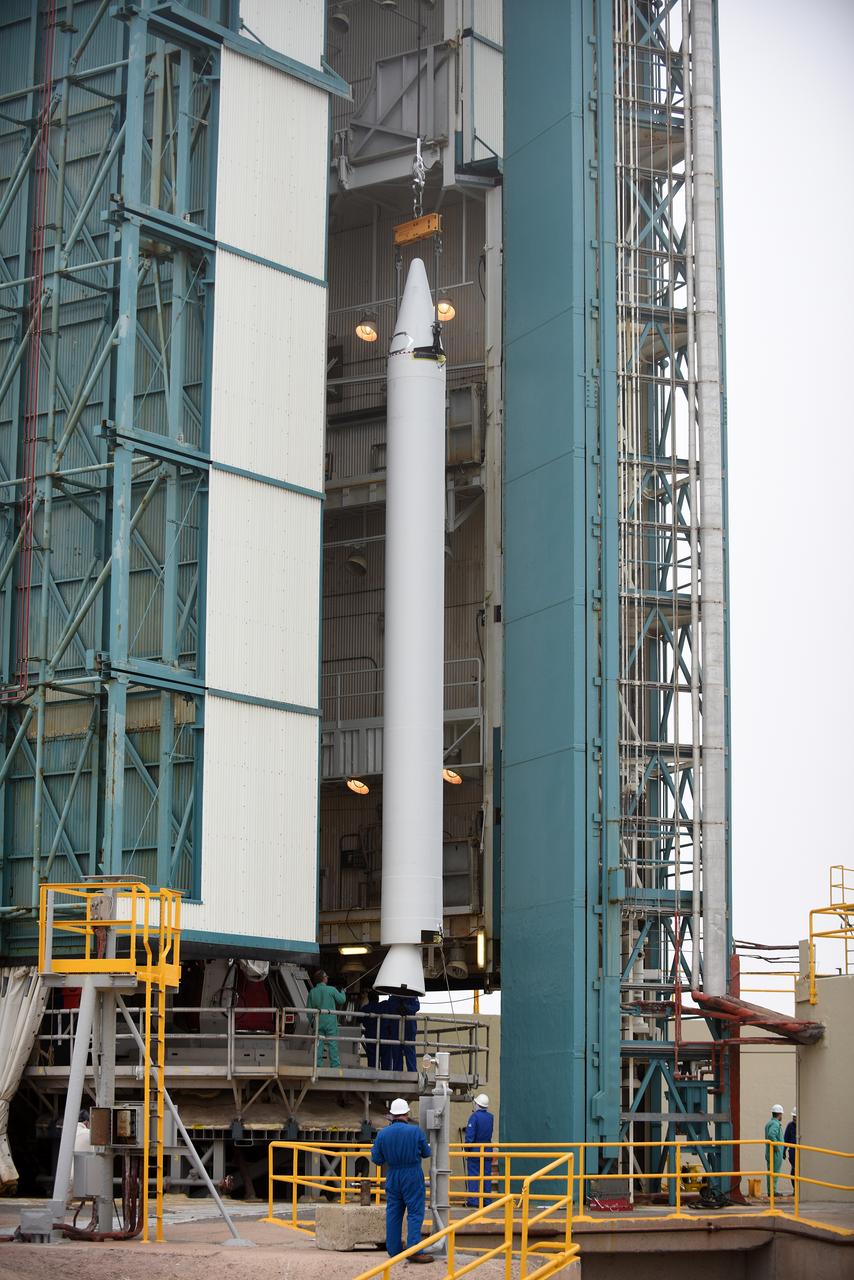

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

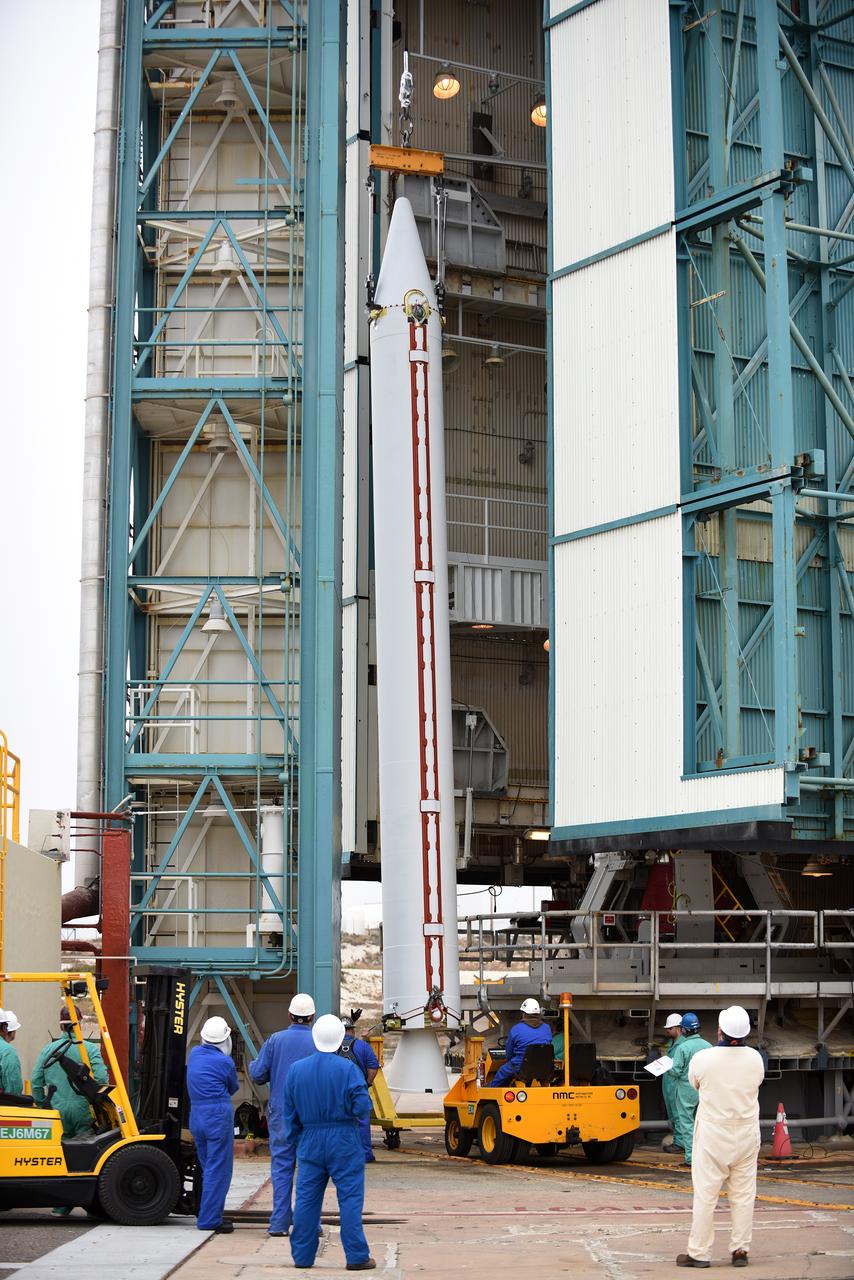
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect a solid rocket motor at Space Launch Complex 2 as it is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect a solid rocket motor at Space Launch Complex 2 as it is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.
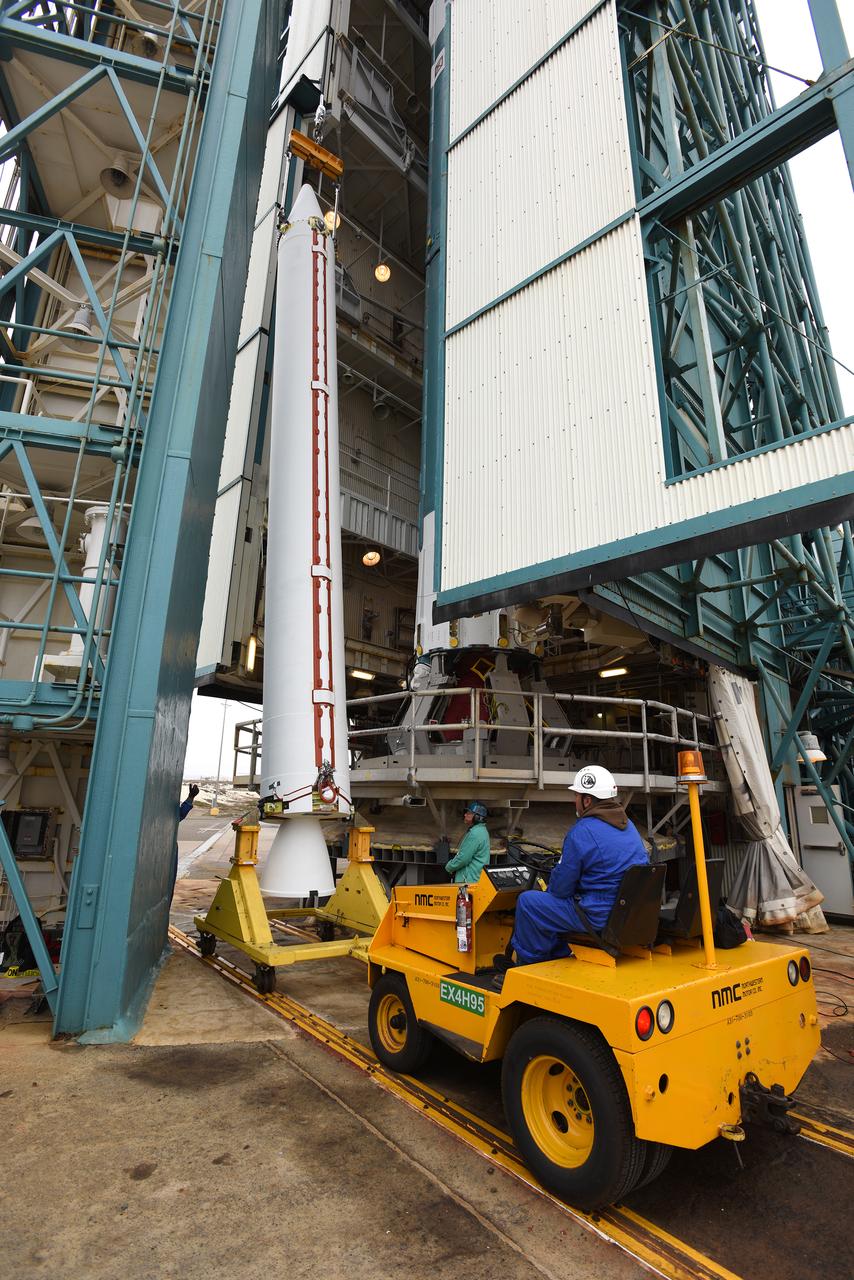

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.
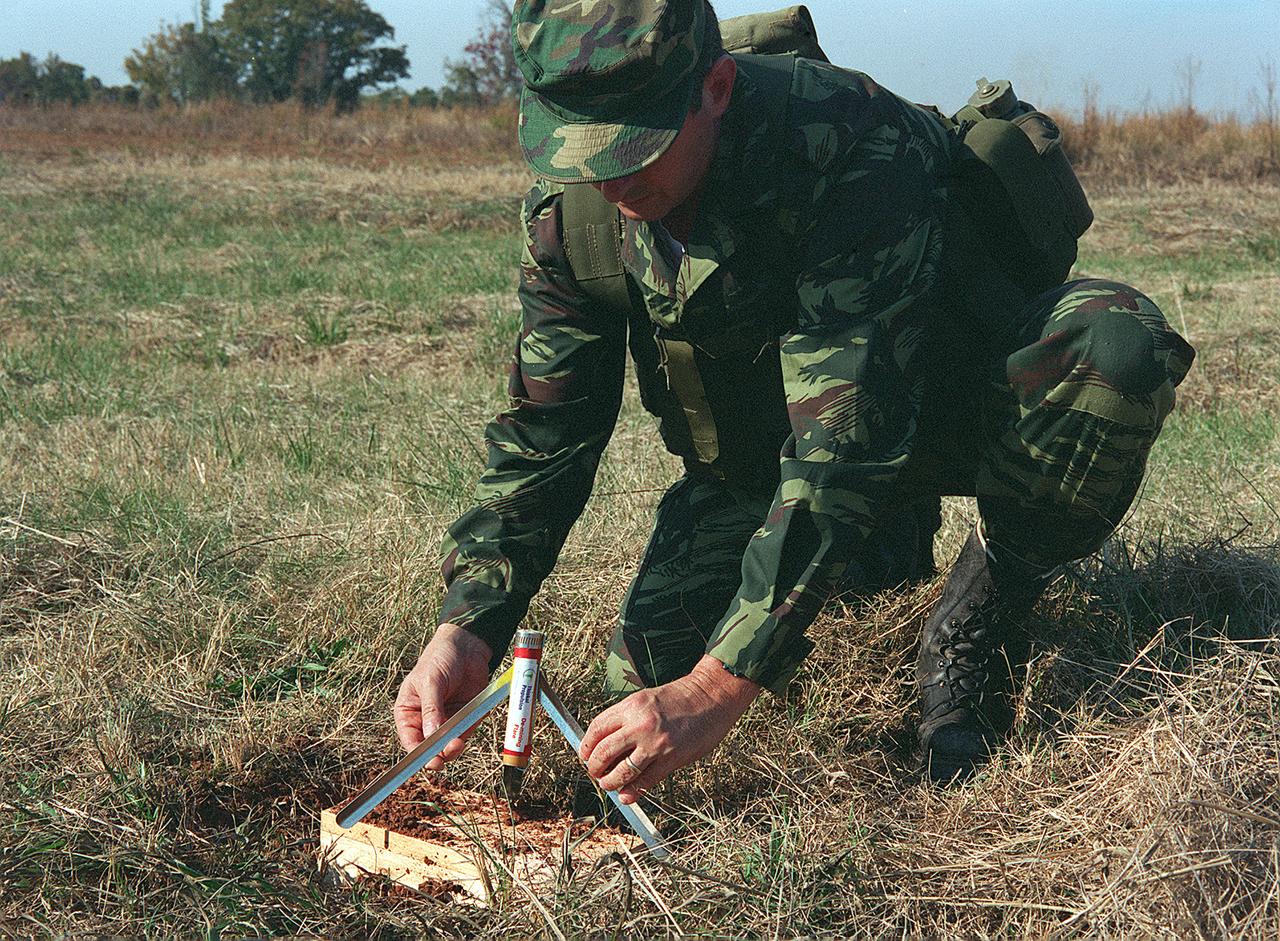

The same rocket fuel that helps power the Space Shuttle as it thunders into orbit will now be taking on a new role, with the potential to benefit millions of people worldwide. Leftover rocket fuel from NASA is being used to make a flare that destroys land mines where they were buried, without using explosives. The flare is safe to handle and easy to use. People working to deactivate the mines simply place the flare next to the uncovered land mine and ignite it from a safe distance using a battery-triggered electric match. The flare burns a hole in the land mine's case and ignites its explosive contents. The explosive burns away, disabling the mine and rendering it harmless. Using leftover rocket fuel to help destroy land mines incurs no additional costs to taxpayers. To ensure enough propellant is available for each Shuttle mission, NASA allows for a small percentage of extra propellant in each batch. Once mixed, surplus fuel solidifies and carnot be saved for use in another launch. In its solid form, it is an ideal ingredient for the new flare. The flare was developed by Thiokol Propulsion in Brigham City, Utah, the NASA contractor that designs and builds rocket motors for the Solid Rocket Booster Space Shuttle. An estimated 80 million or more active land mines are scattered around the world in at least 70 countries, and kill or maim 26,000 people a year. Worldwide, there is one casualty every 22 minutes
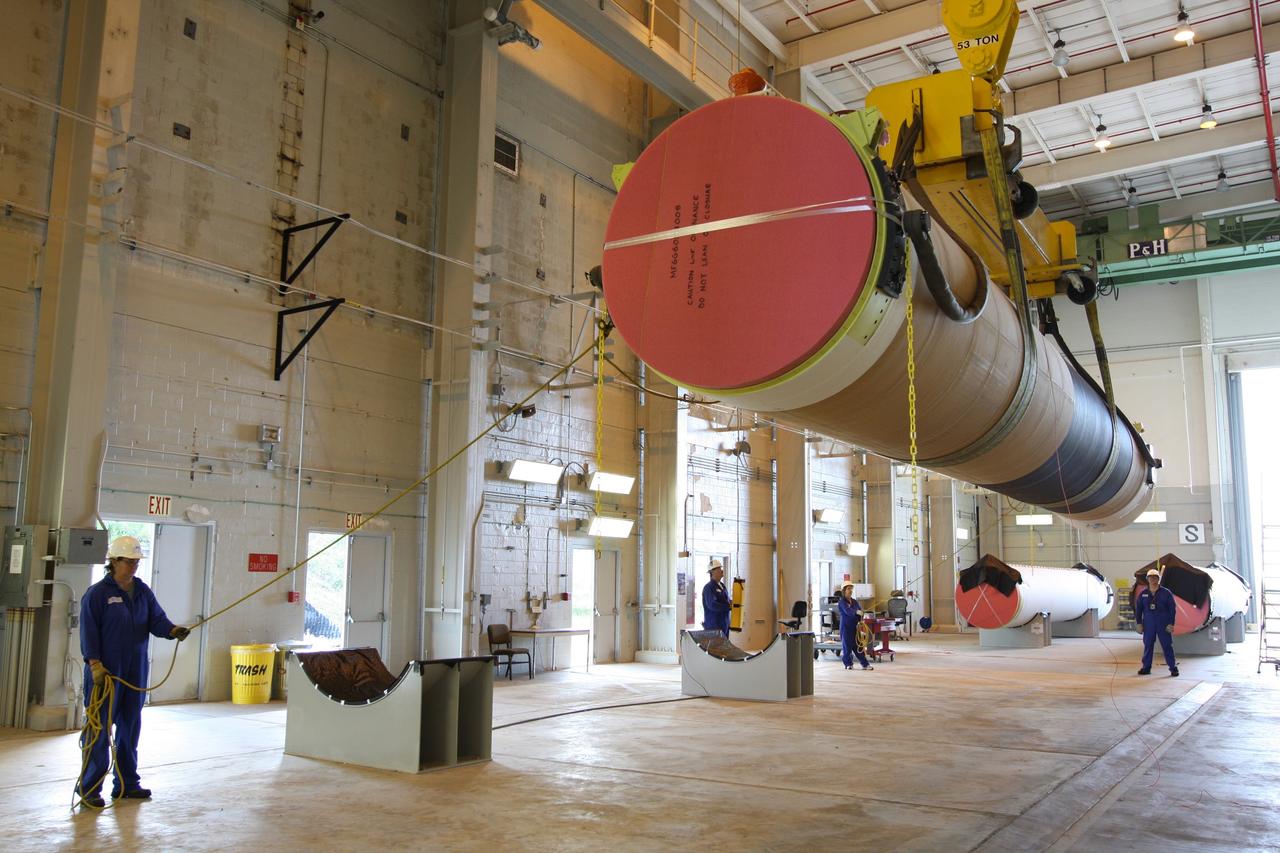

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, ATK Space Systems workers guide a 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft as it is lowered toward a work stand. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
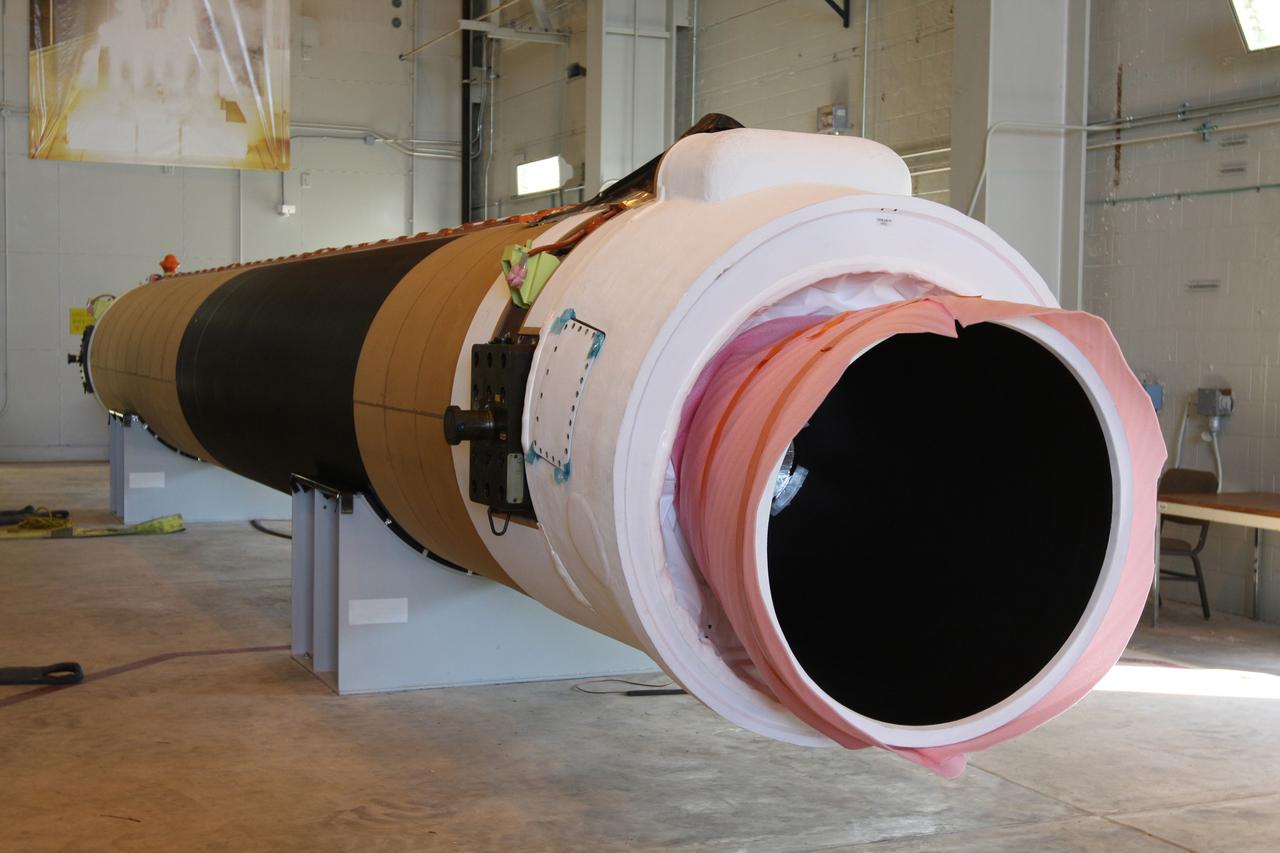

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft rests on a work stand awaiting further processing. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

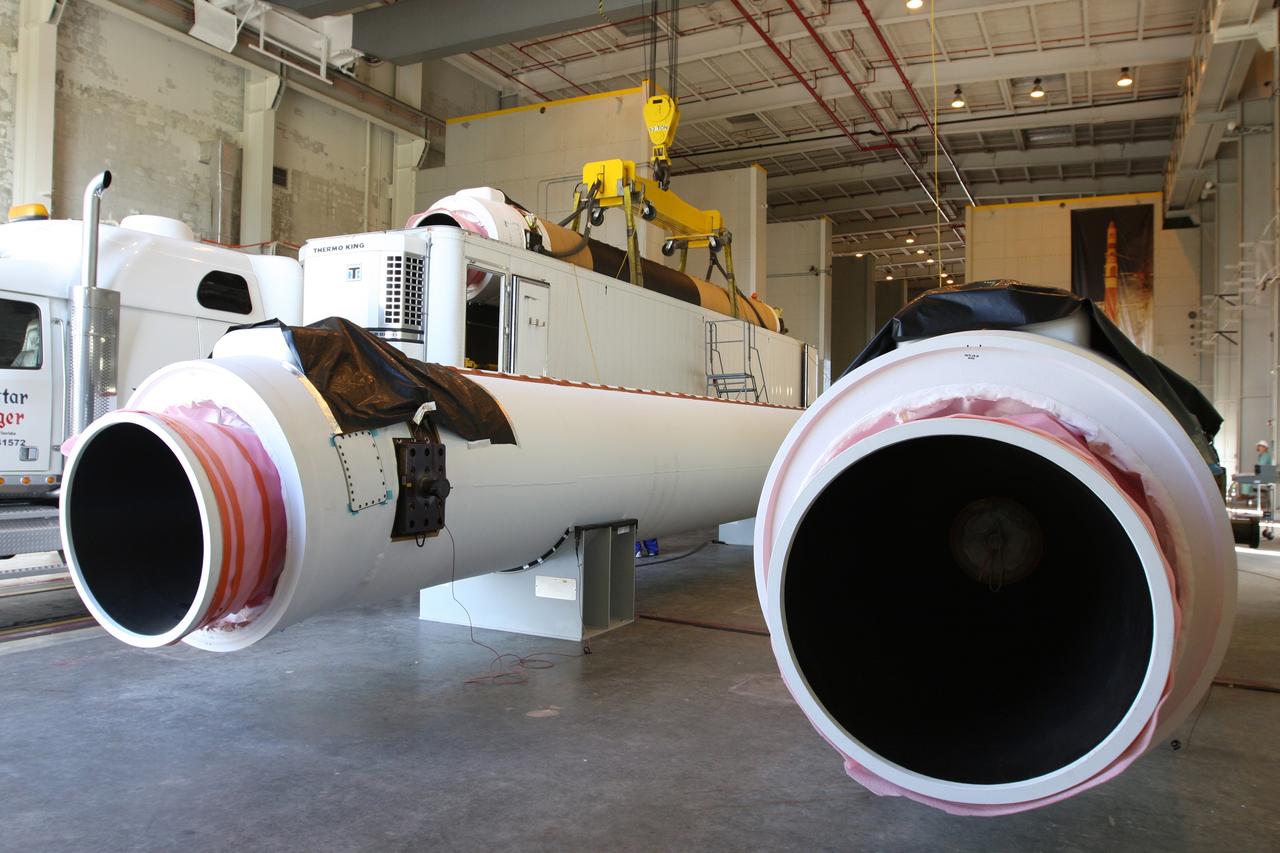
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft is lifted from the tractor-trailer in which it was delivered. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

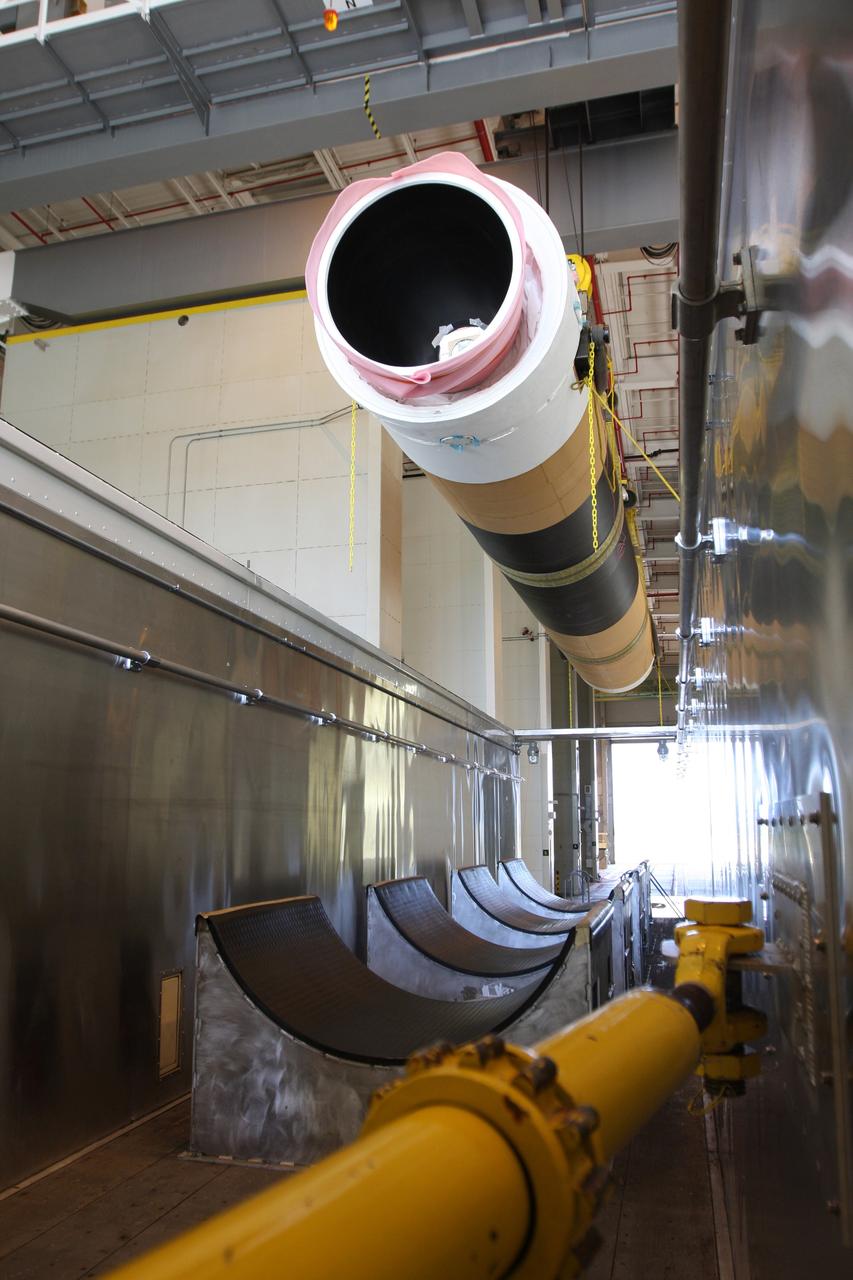
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, ATK Space Systems workers guide a 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft as it is moved toward a work stand. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

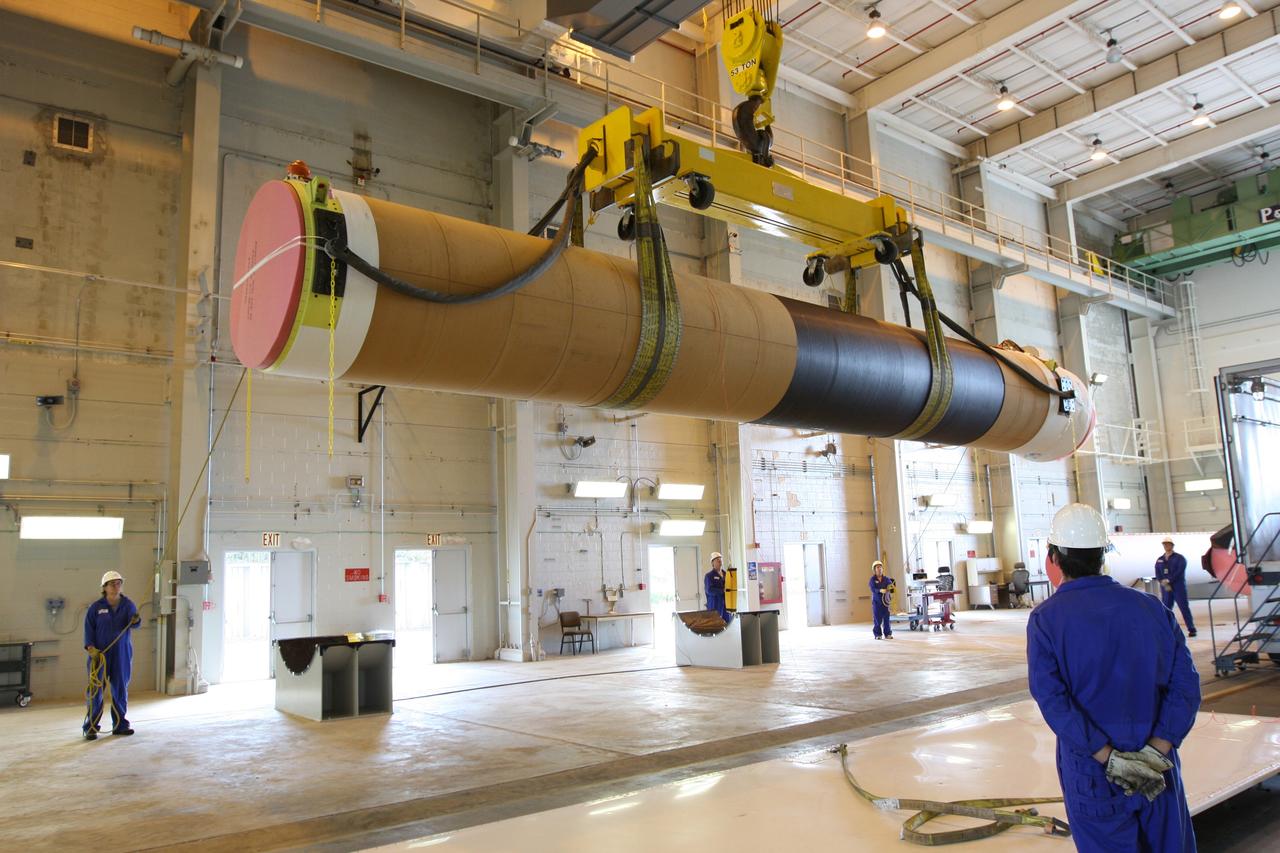
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft is lifted from the tractor-trailer in which it was delivered. The two GEMs in the foreground were delivered previously to support another mission. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
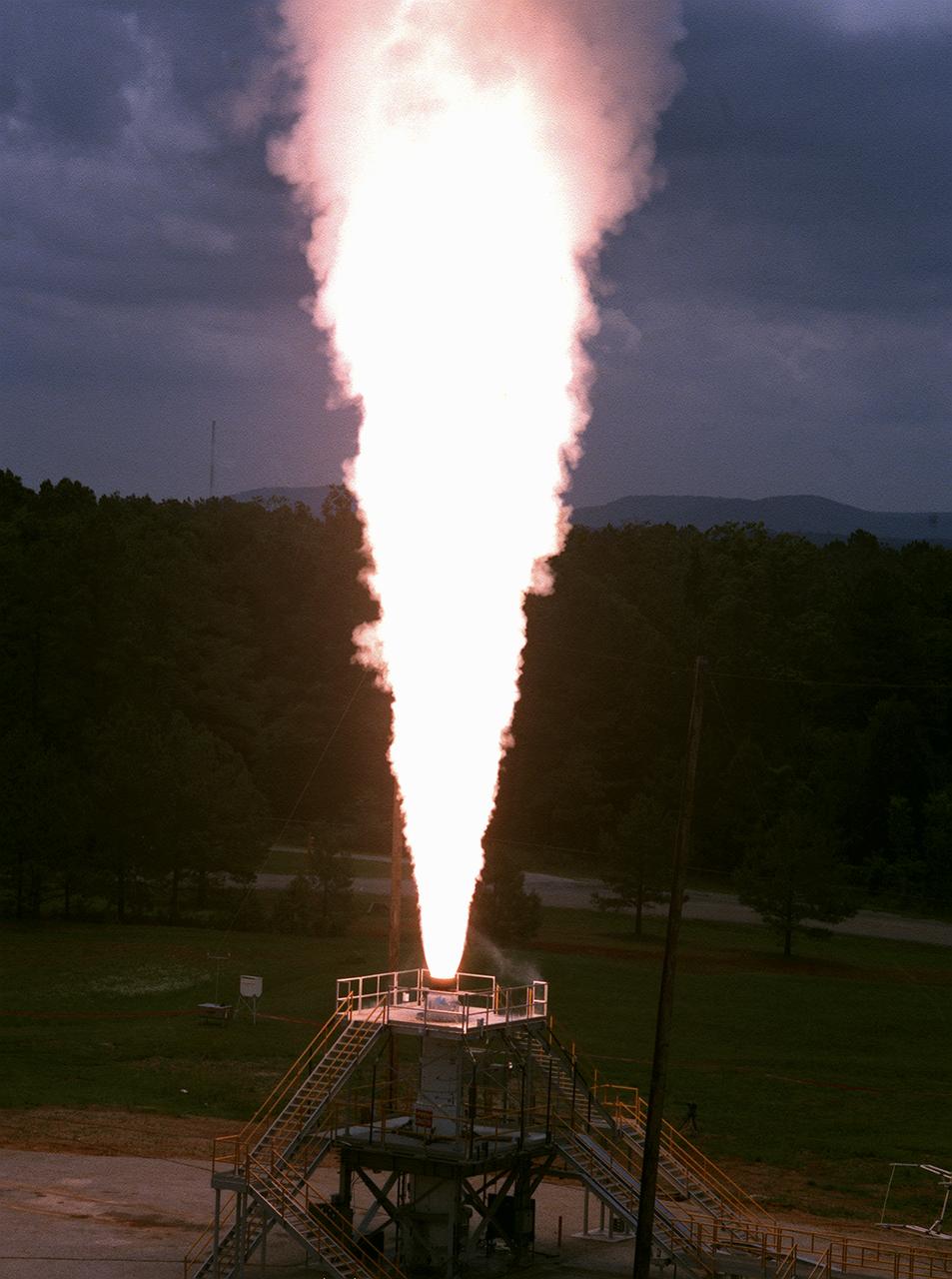

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) engineers test fired a 26-foot long, 100,000-pound-thrust solid rocket motor for 30 seconds at the MSFC east test area, the first test firing of the Modified NASA Motor (M-NASA Motor). The M-NASA Motor was fired in a newly constructed stand. The motor is 48-inches in diameter and was loaded with two propellant cartridges weighing a total of approximately 12,000 pounds. The purpose of the test was to learn more about solid rocket motor insulation and nozzle materials and to provide young engineers additional hands-on expertise in solid rocket motor technology. The test is a part of NASA's Solid Propulsion Integrity Program, that is to provide NASA engineers with the techniques, engineering tools, and computer programs to be able to better design, build, and verify solid rocket motors.
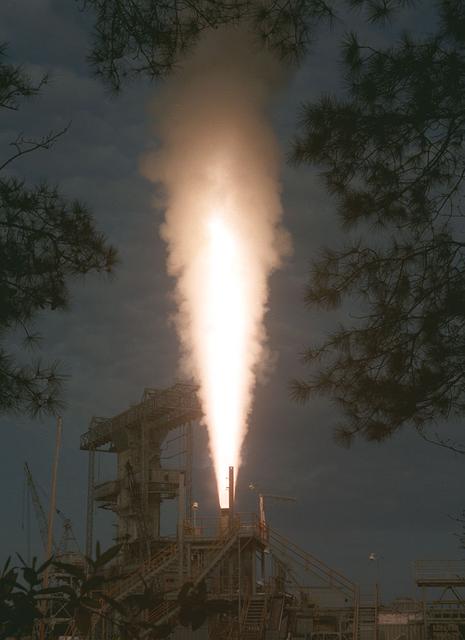

The roman candle effect as seen in this picture represents the testing of a solid rocket booster (SRB) for unexplained corrosion conditions (EUCC) which have occurred on the nozzles of redesigned solid rocket motors (RSRM). The motor being tested in this photo is a 48 M-NASA motor.
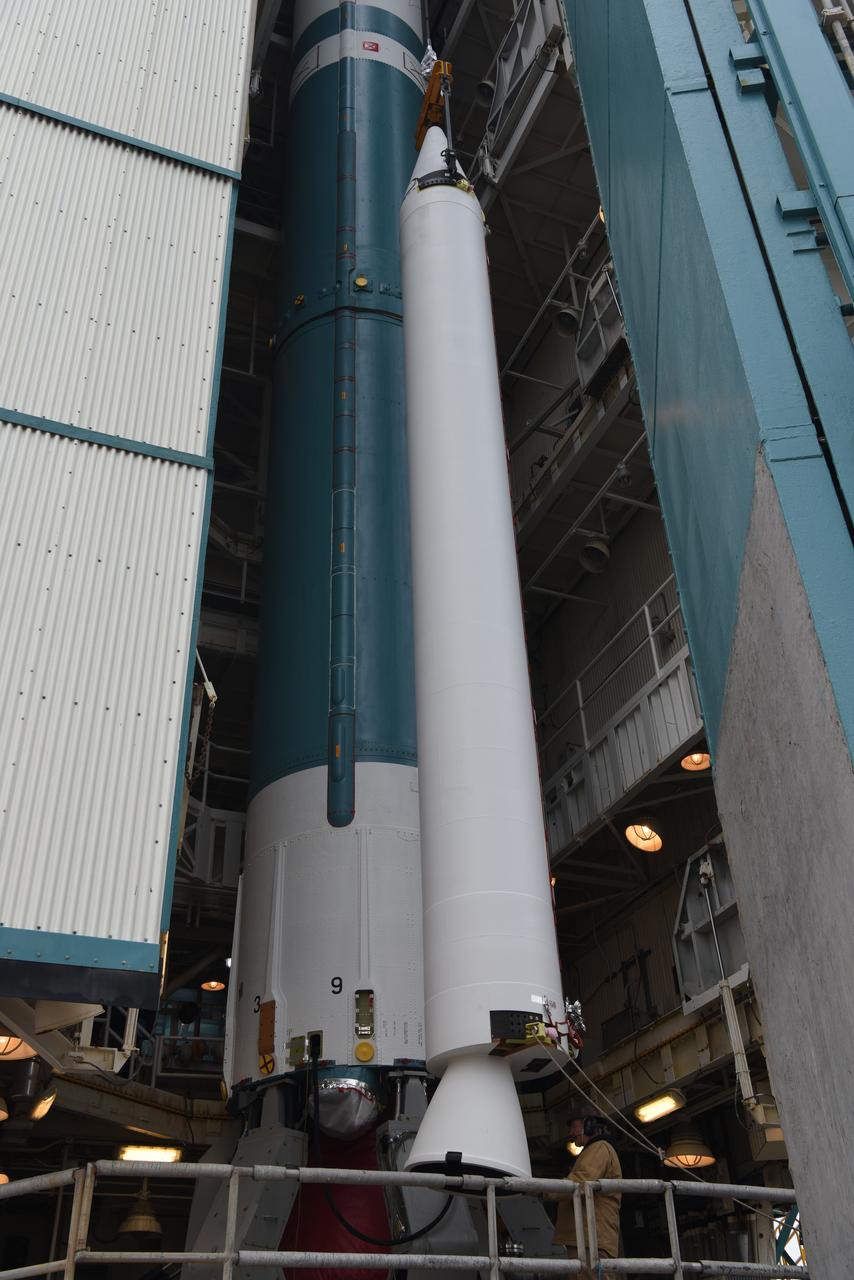

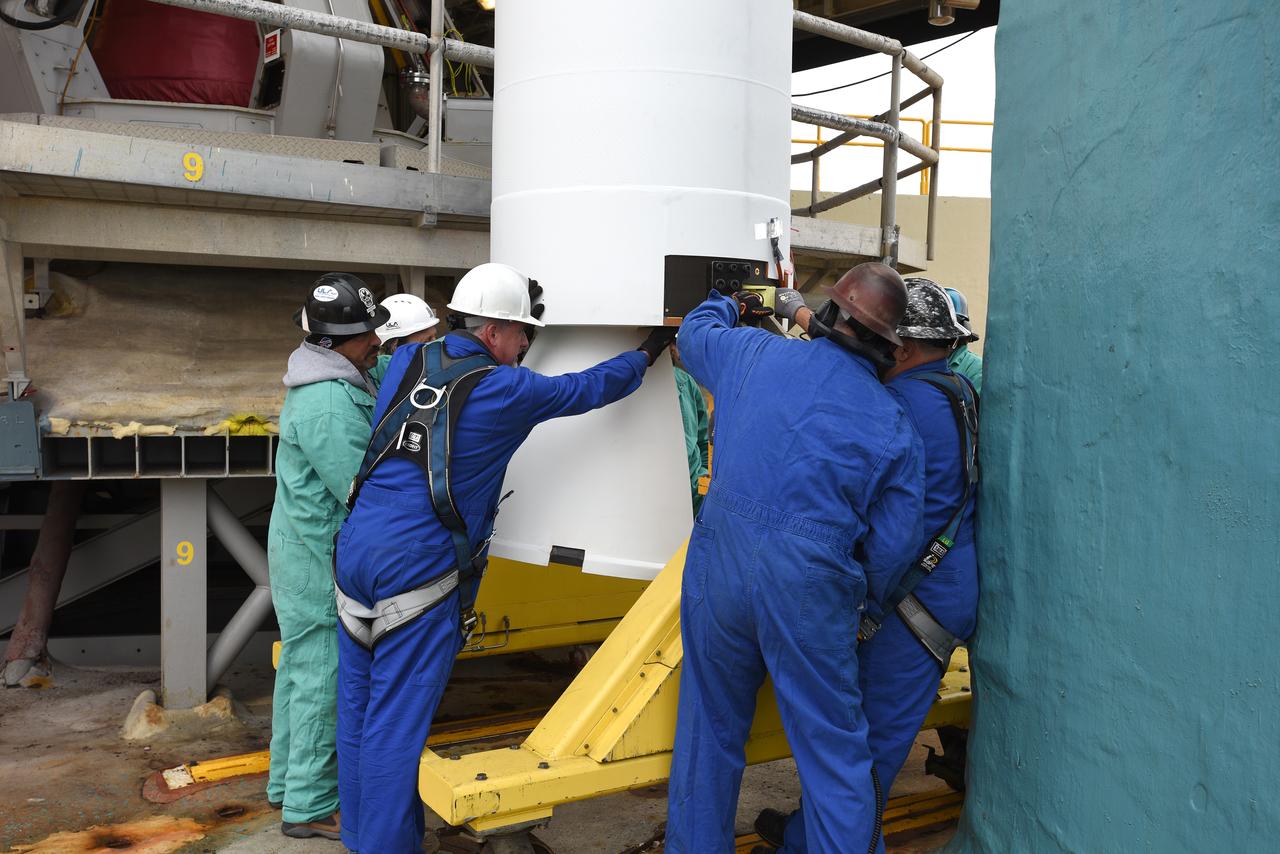
The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
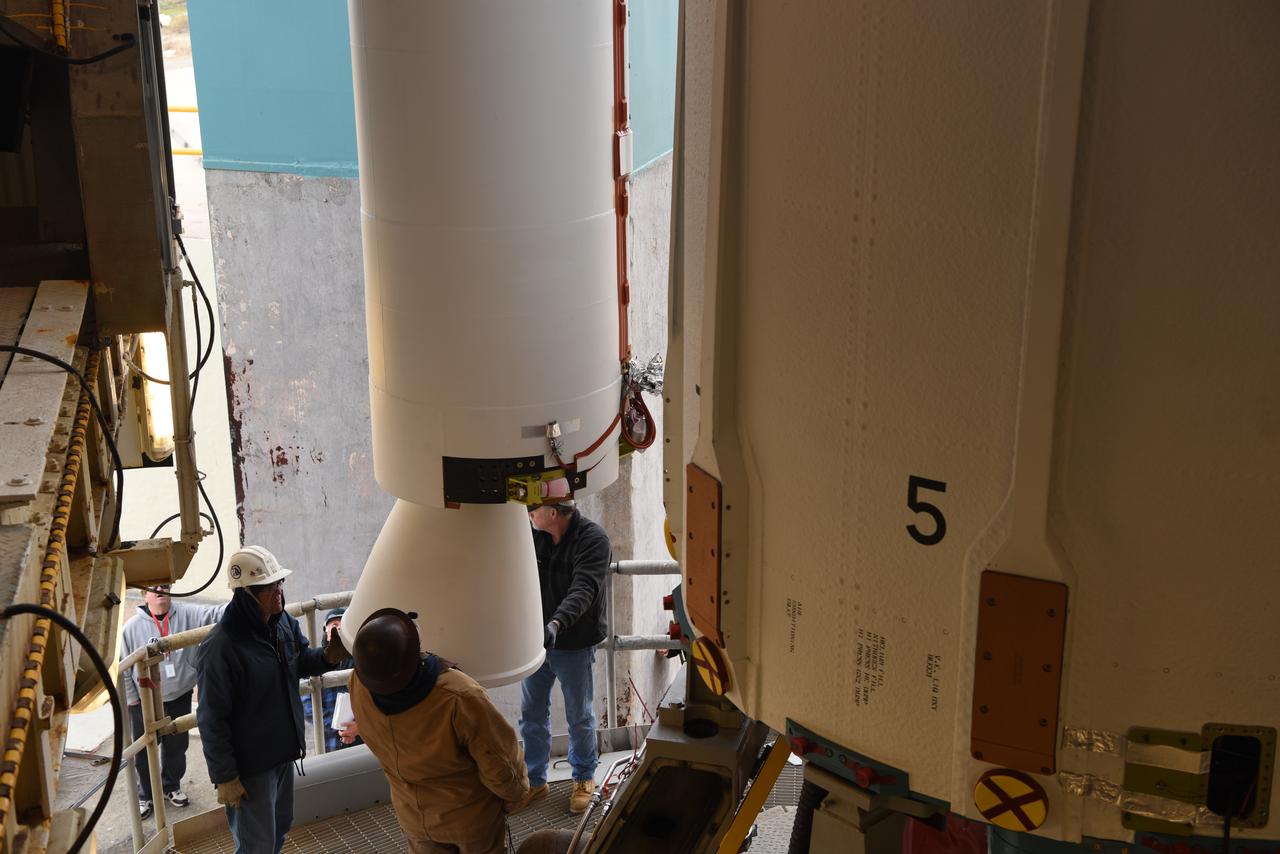

United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians assist as the solid rocket motor is lifted up and moved toward the Delta II launch vehicle in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final ULA Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
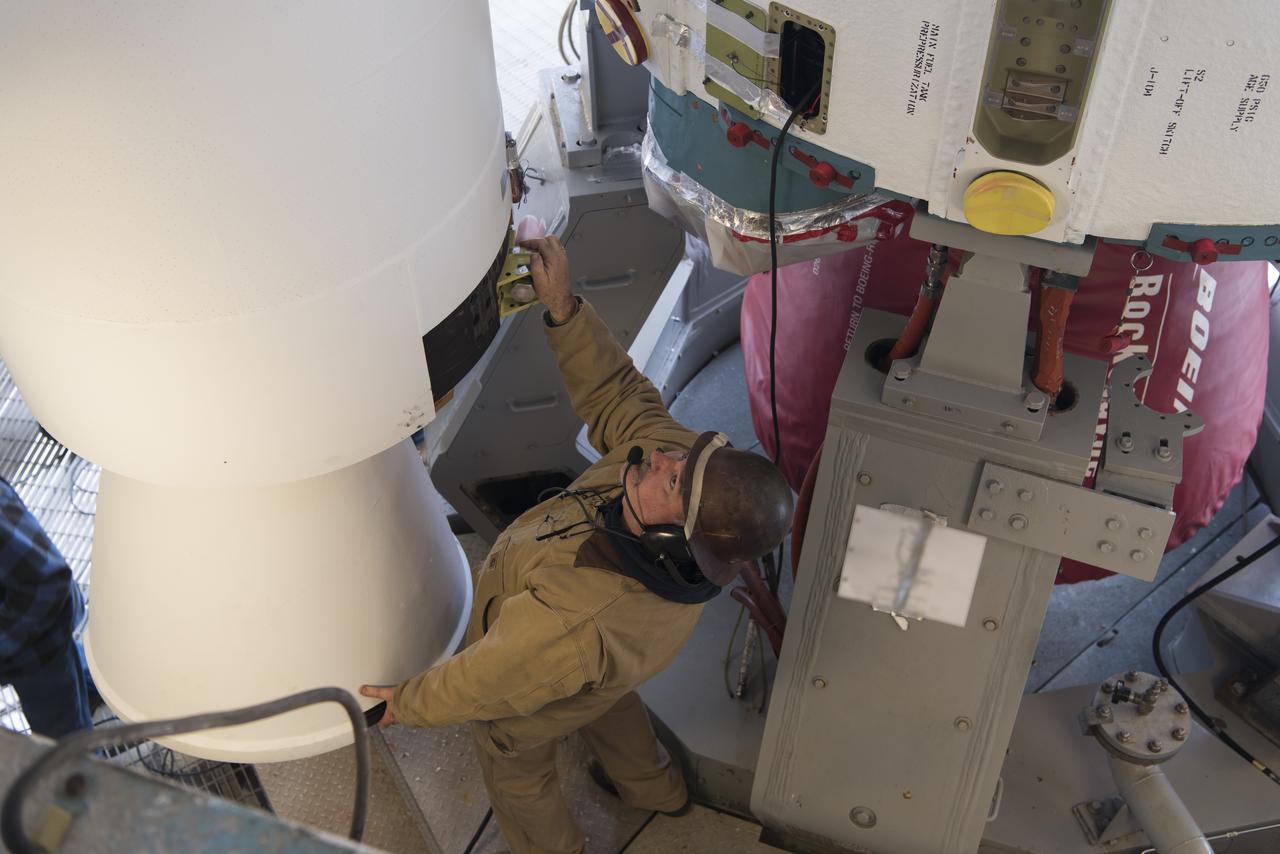

United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians assist as the solid rocket motor is moved toward the Delta II launch vehicle in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final ULA Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
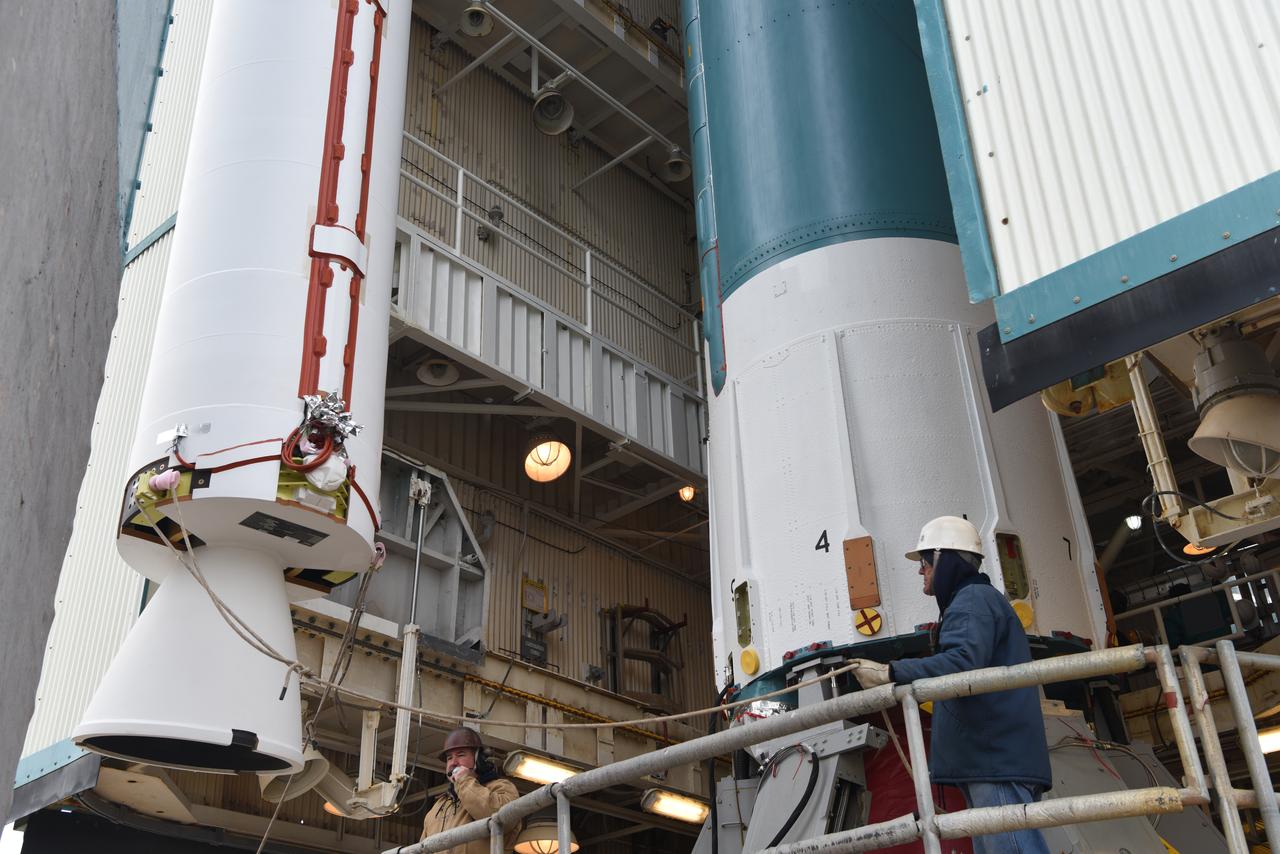

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
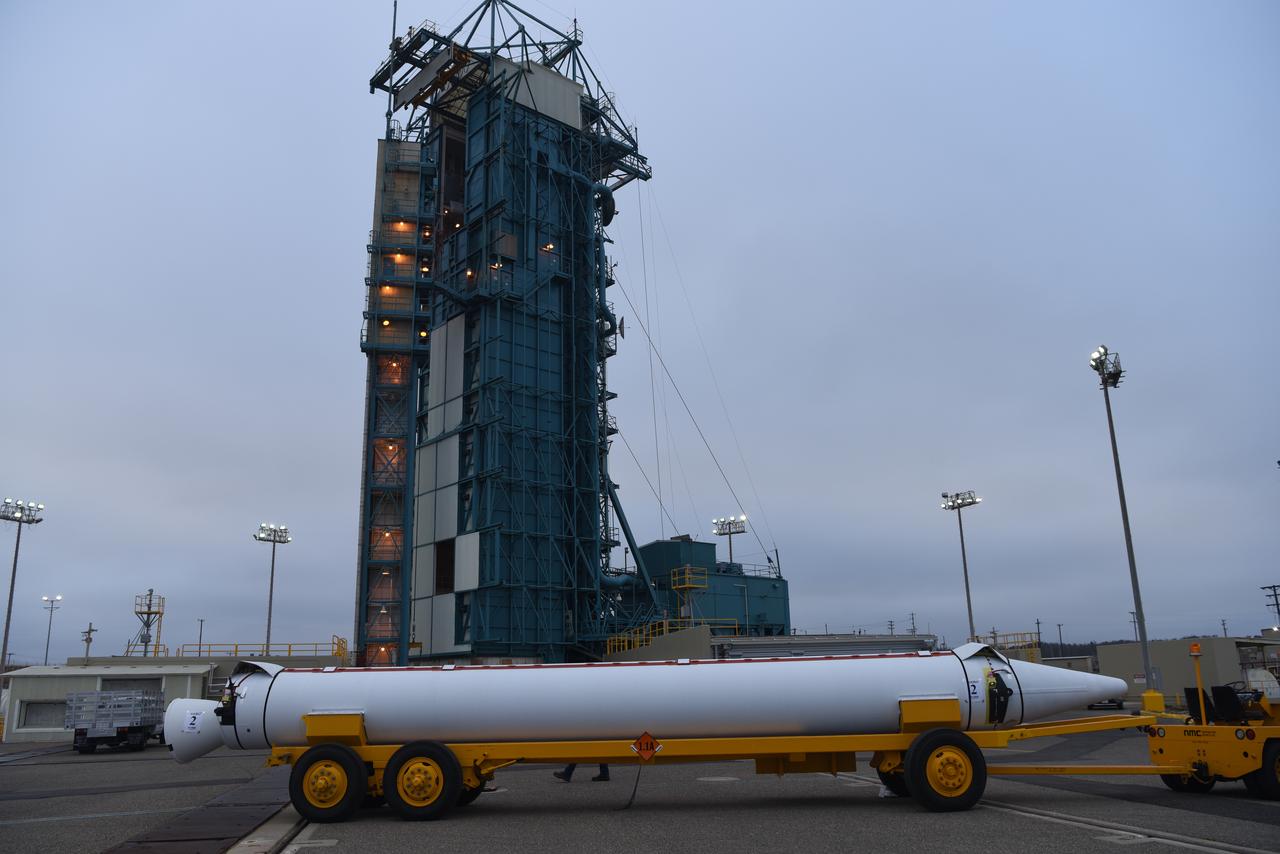

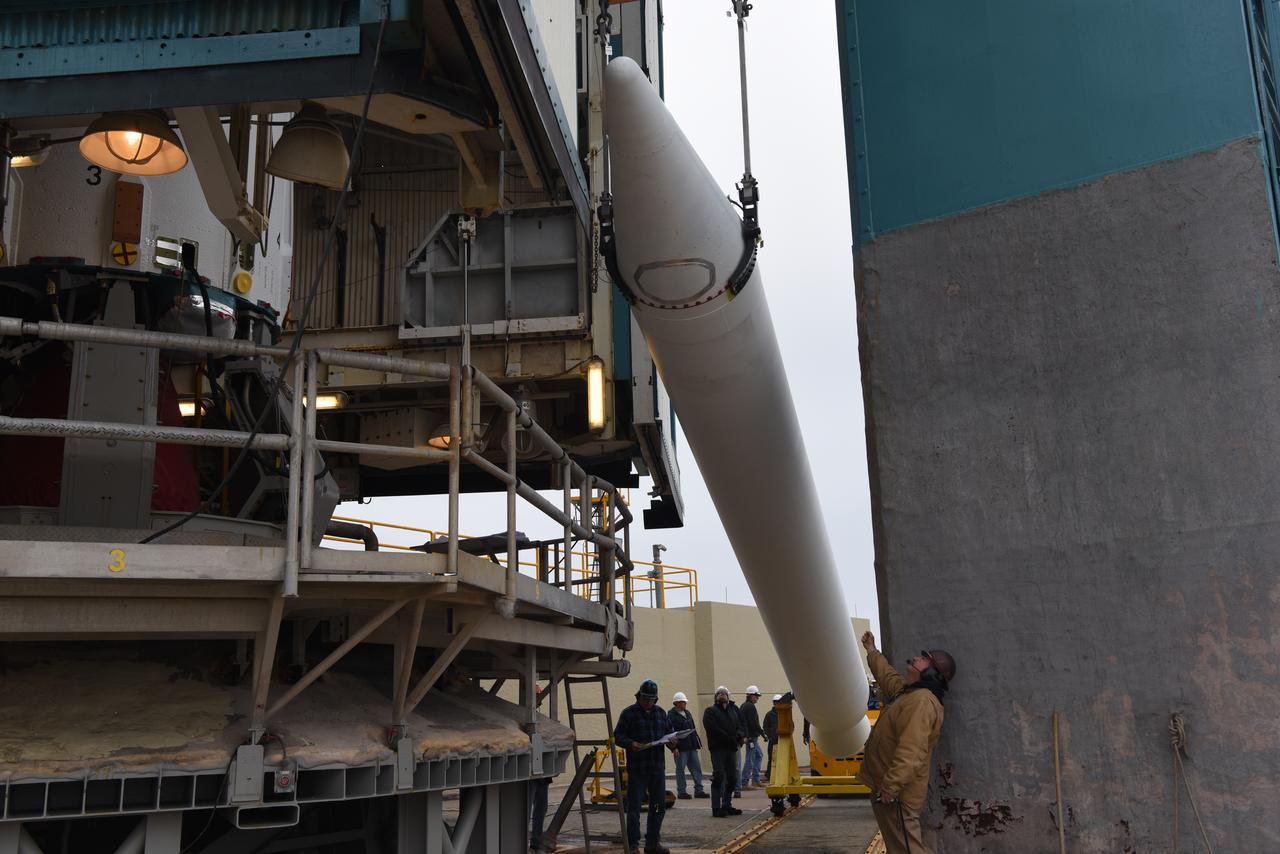
The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be lifted up and attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
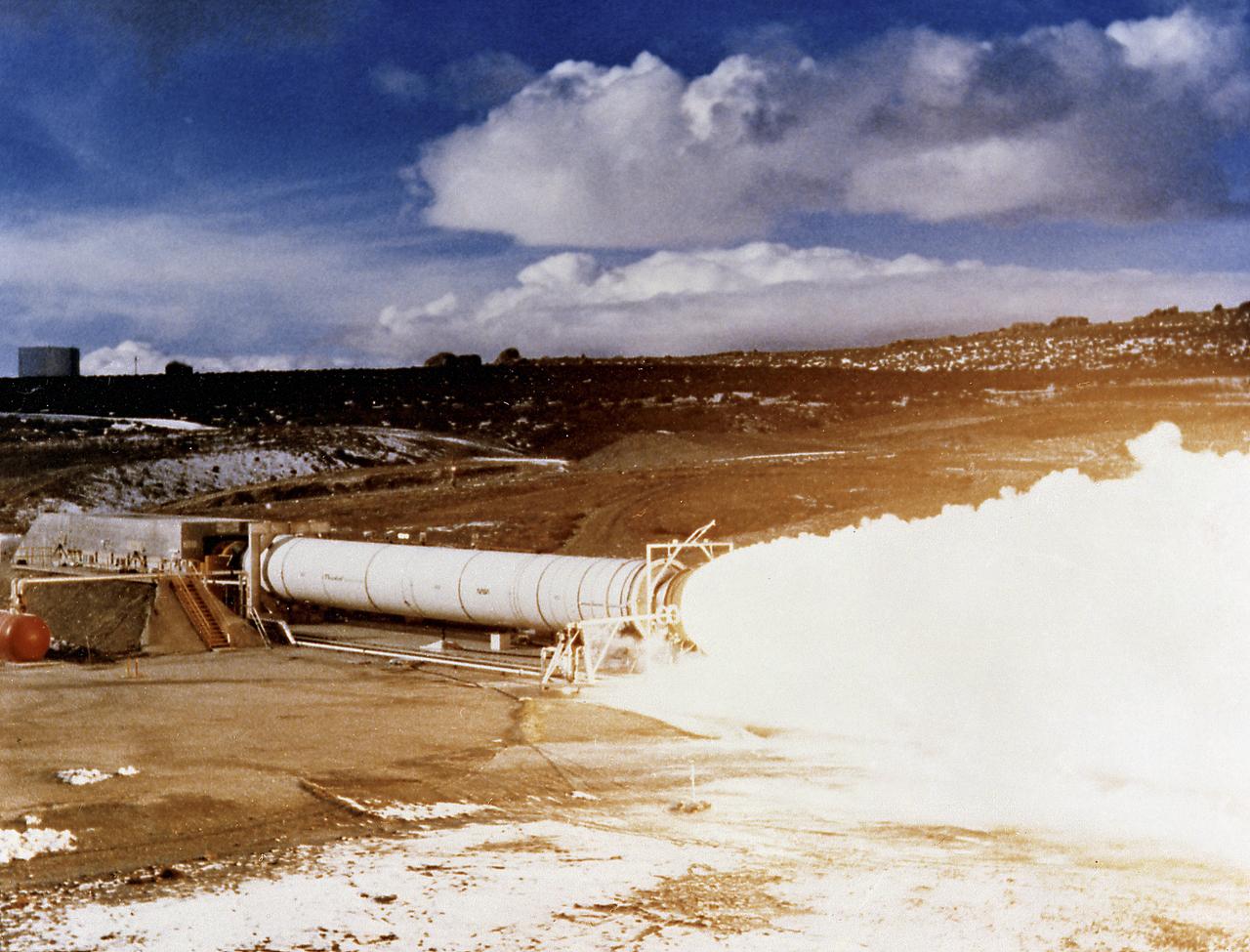

Pictured is an early testing of the Solid Rocket Motor (SRM) at the Thiokol facility in Utah. The SRMs later became known as Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) as they were more frequently used on the Space Shuttles.
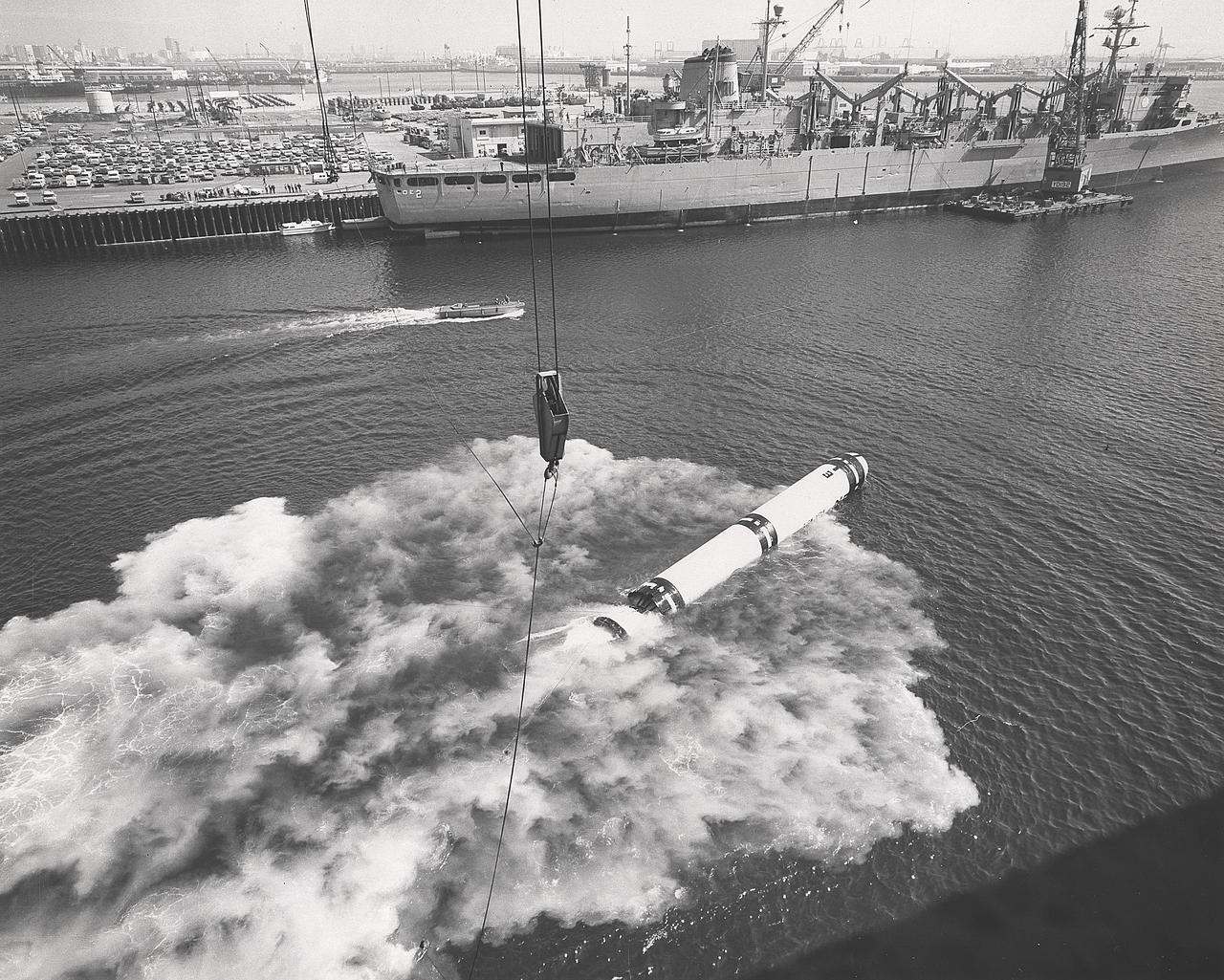

As early as September 1972, the Marshall Space Flight Center arnounced plans for a series of 20 water-entry simulation tests with a solid-fueled rocket casing assembly. The tests would provide valuable data for assessment of solid rocket booster parachute water recovery and aid in preliminary solid rocket motor design.
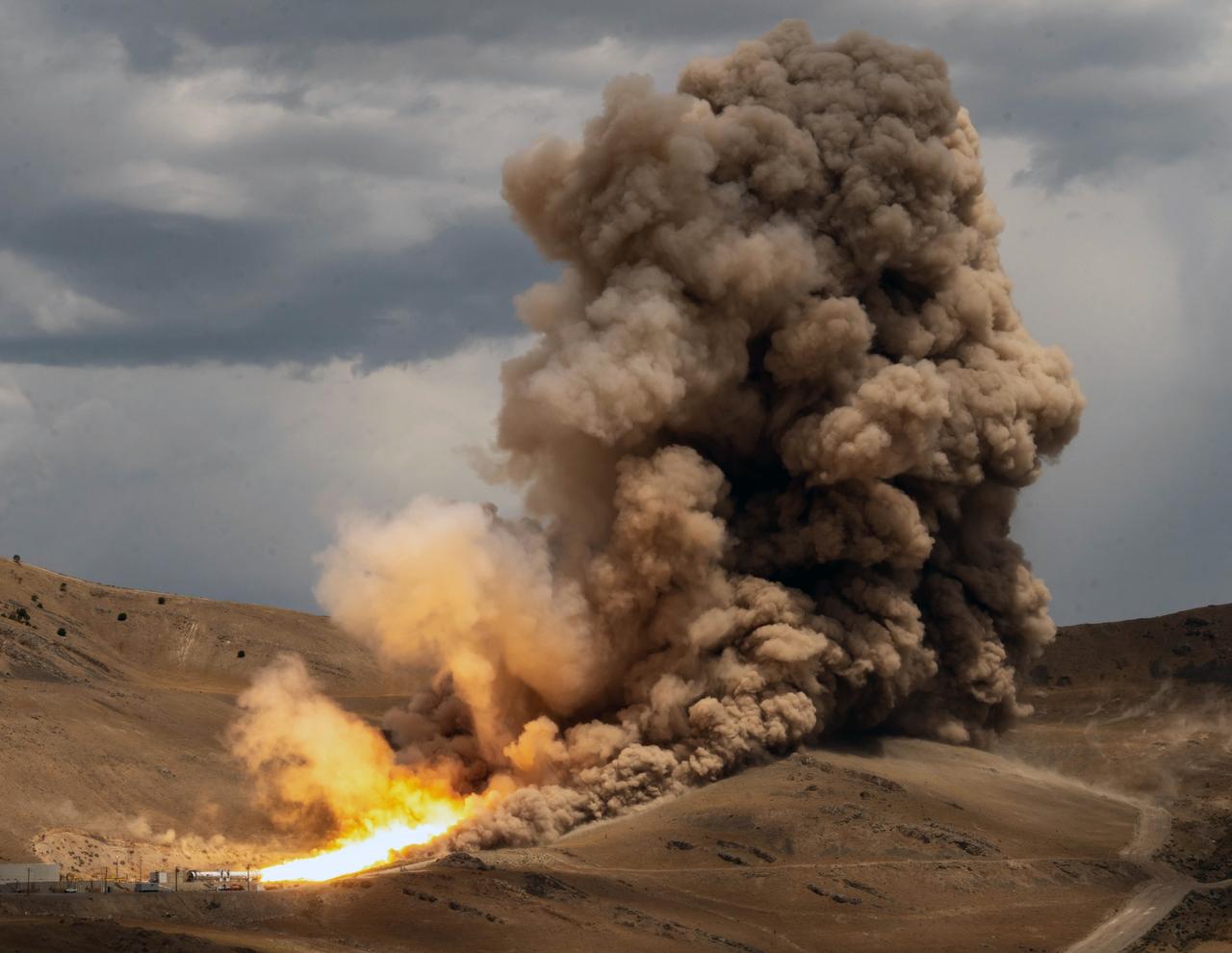

NASA and Northrop Grumman completed a solid rocket booster motor ground test for future flights of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, July 21. The booster motor, called Flight Support Booster-2 (FSB-2), fired for a little over two minutes and produced more than 3.6 million pounds of thrust. Test data will be used to evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters for missions after Artemis III. When SLS launches the Artemis missions to the Moon, its two five-segment solid rocket boosters produce more than 75% of the initial thrust. The SLS boosters are the largest, most powerful boosters ever built for flight. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls
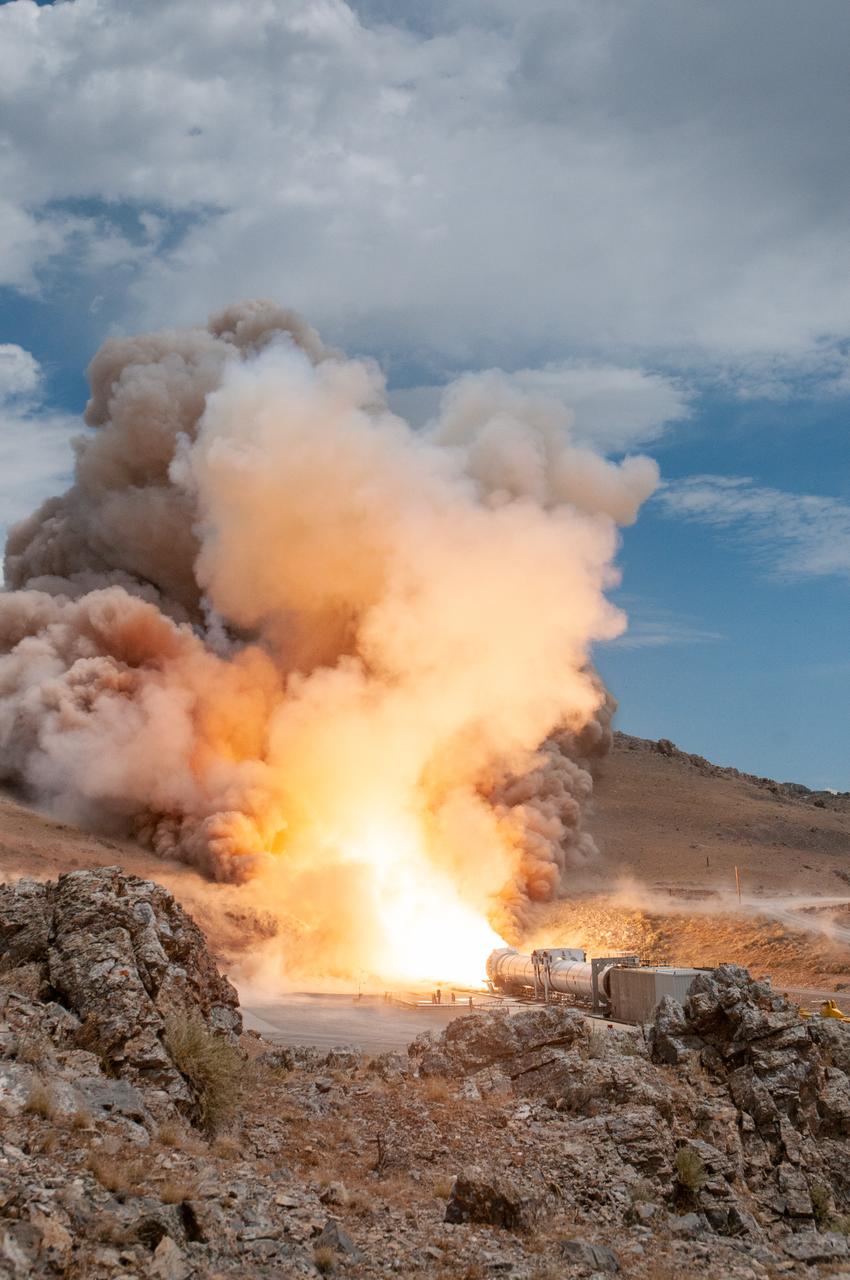

NASA and Northrop Grumman completed a solid rocket booster motor ground test for future flights of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, July 21. The booster motor, called Flight Support Booster-2 (FSB-2), fired for a little over two minutes and produced more than 3.6 million pounds of thrust. Test data will be used to evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters for missions after Artemis III. When SLS launches the Artemis missions to the Moon, its two five-segment solid rocket boosters produce more than 75% of the initial thrust. The SLS boosters are the largest, most powerful boosters ever built for flight. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls
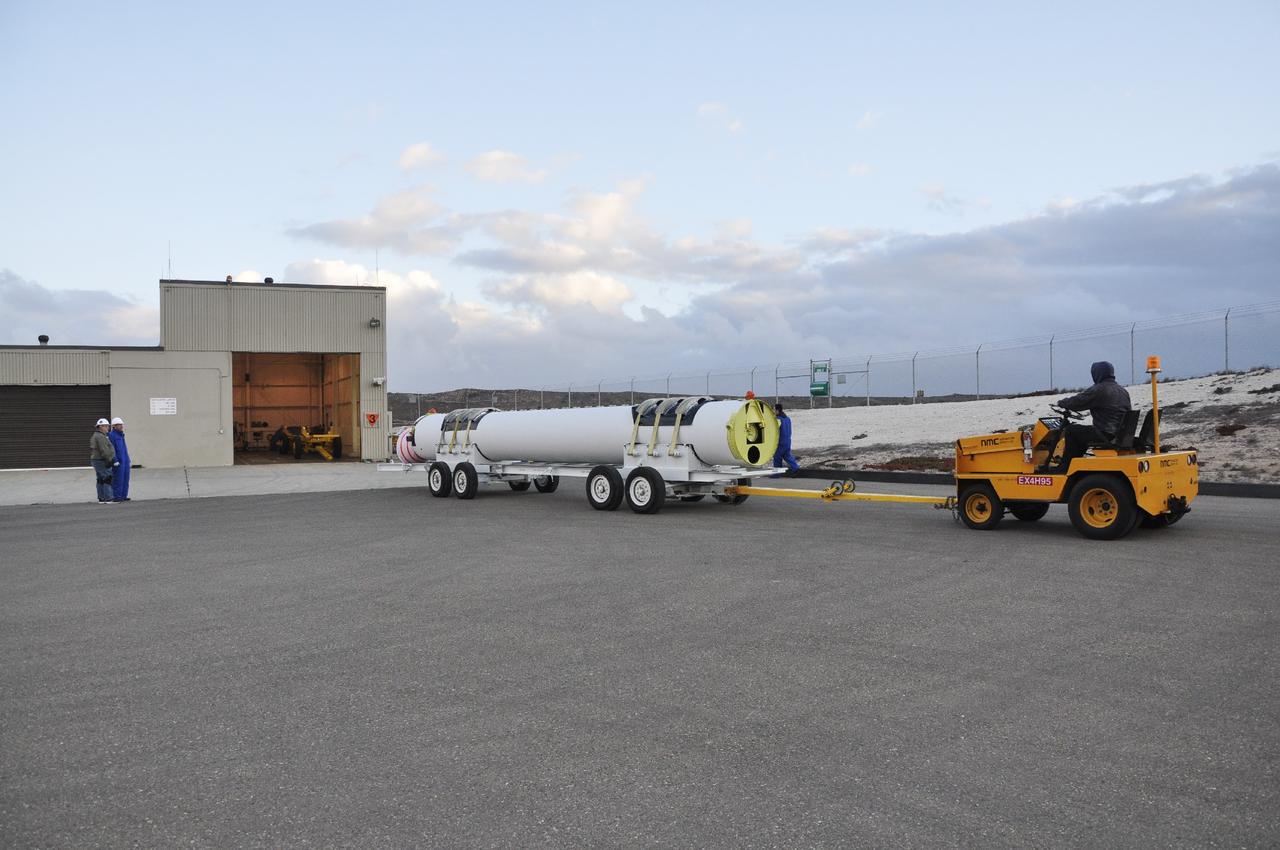

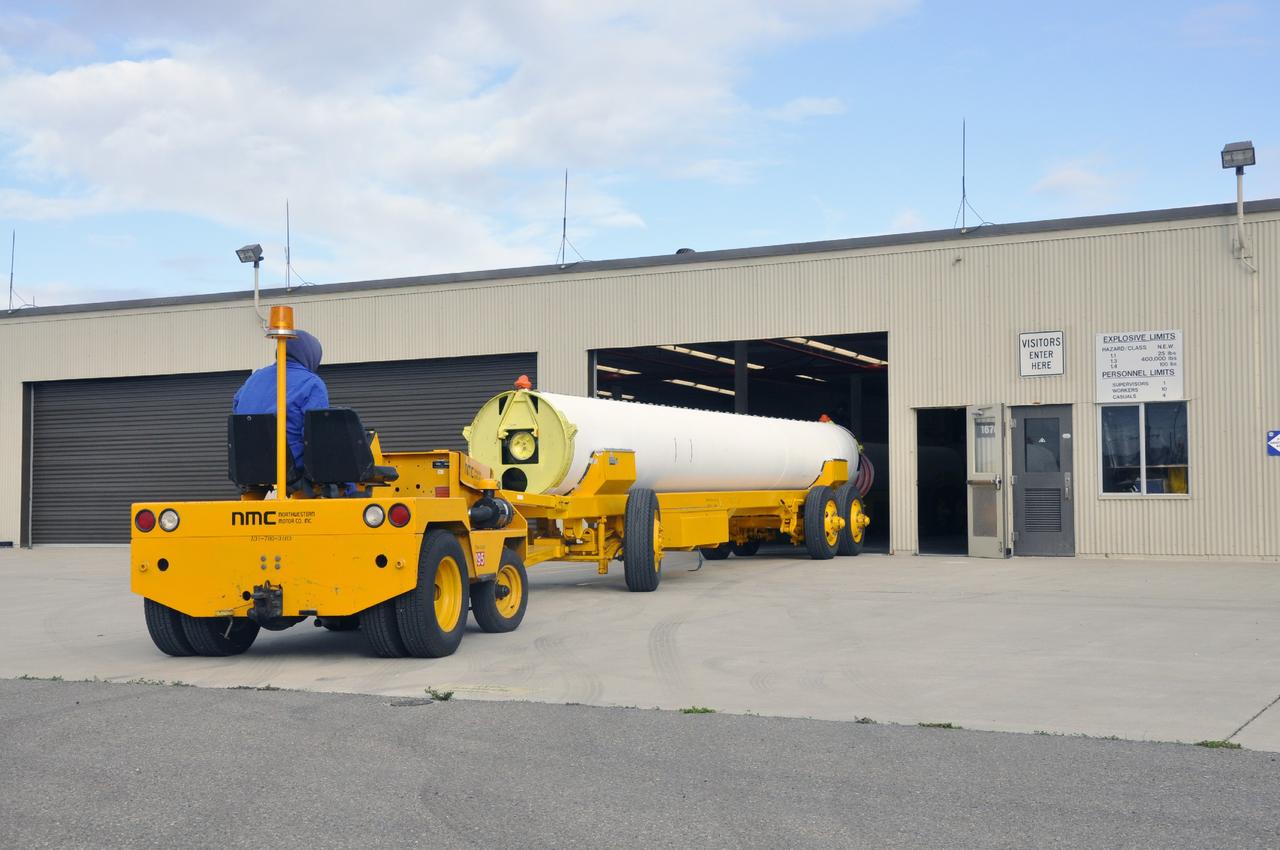
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket rocket motor is maneuvered toward the open high bay door of the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
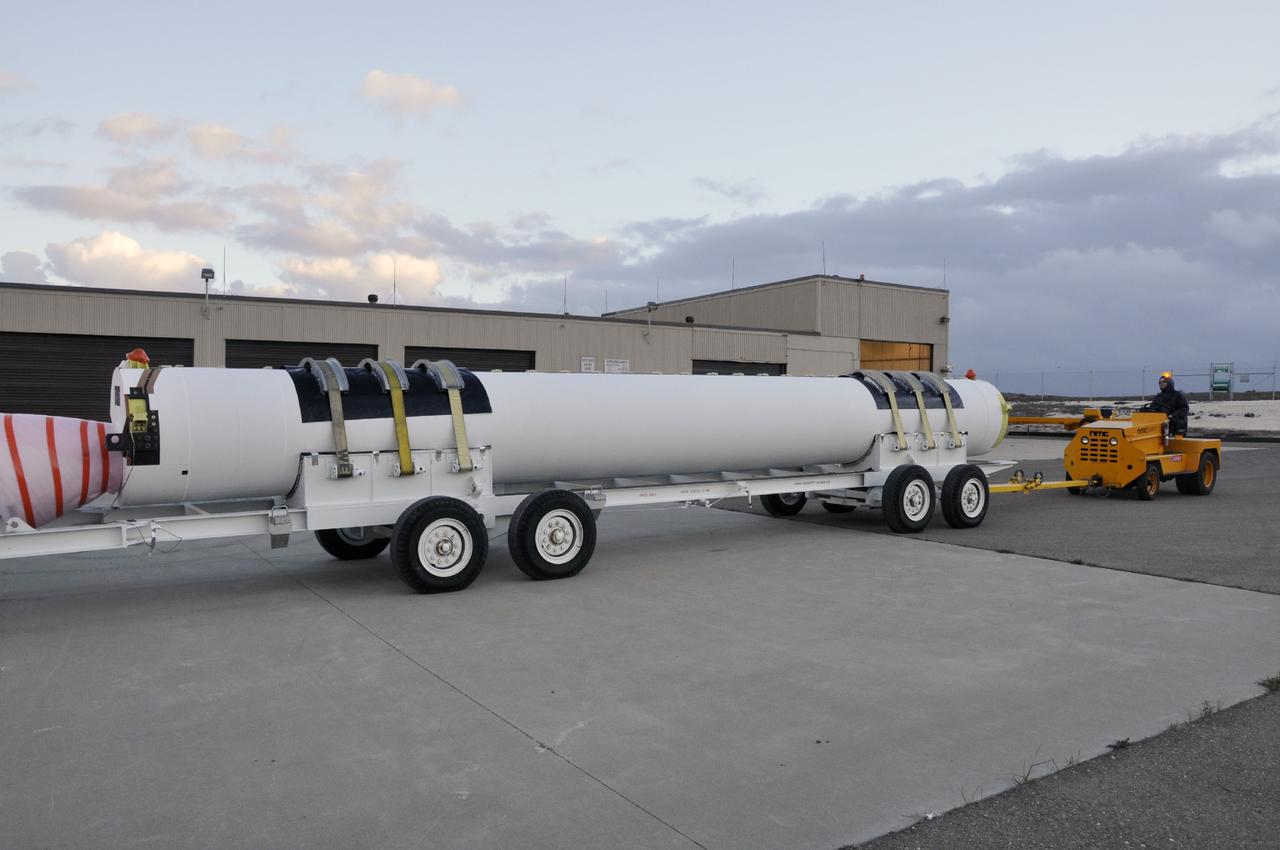

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket rocket motor is hauled away from its delivery truck and toward the open high bay door of the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
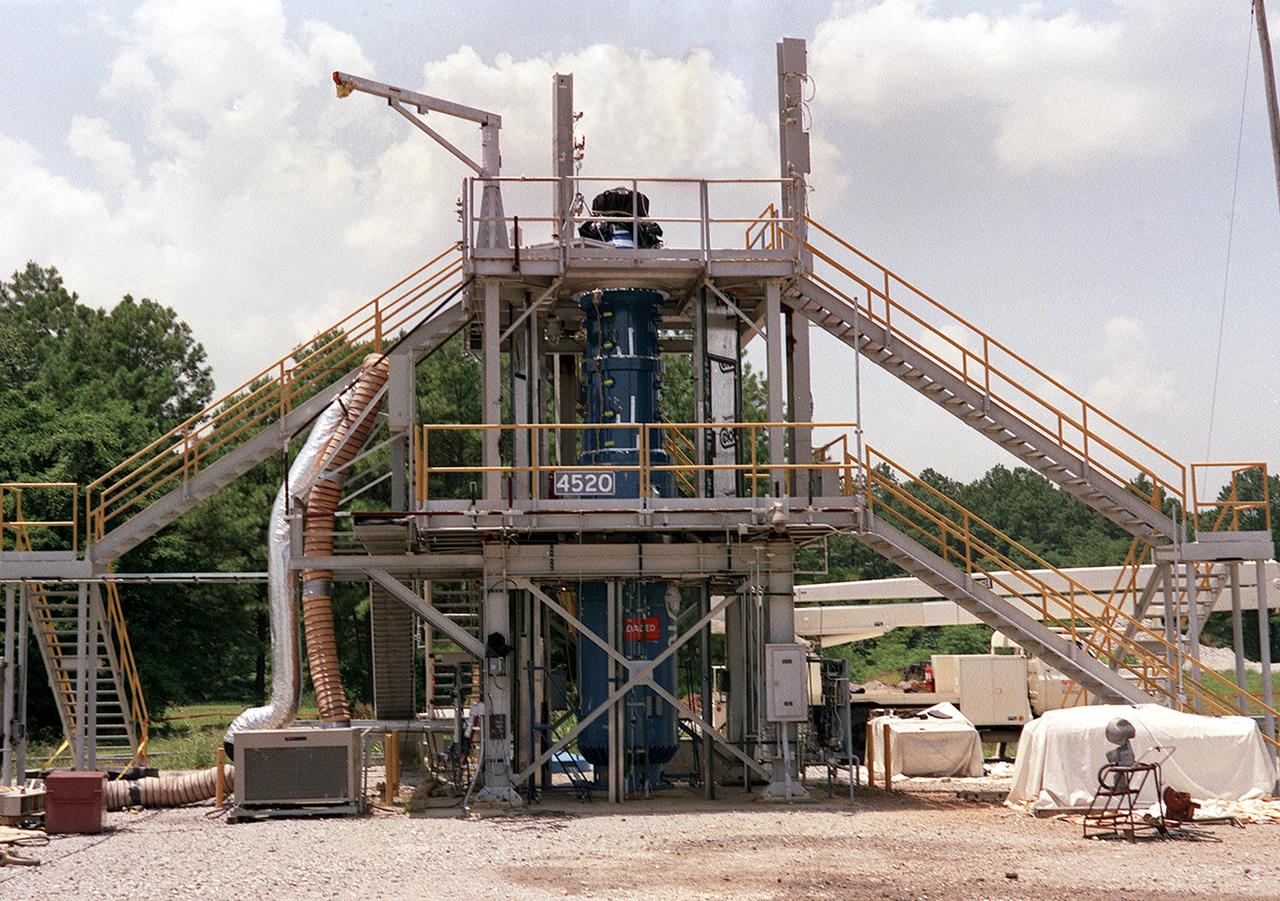

This photograph shows the Solid Propellant Test Article (SPTA) test stand with the Modified Nasa Motor (M-NASA) test article at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The SPTA test stand, 12-feet wide by 12-feet long by 24-feet high, was built in 1989 to provide comparative performance data on nozzle and case insulation material and to verify thermostructural analysis models. A modified NASA 48-inch solid motor (M-NASA motor) with a 12-foot blast tube and 10-inch throat makes up the SPTA. The M-NASA motor is being used to evaluate solid rocket motor internal non-asbestos insulation materials, nozzle designs, materials, and new inspection techniques. New internal motor case instrumentation techniques are also being evaluated.
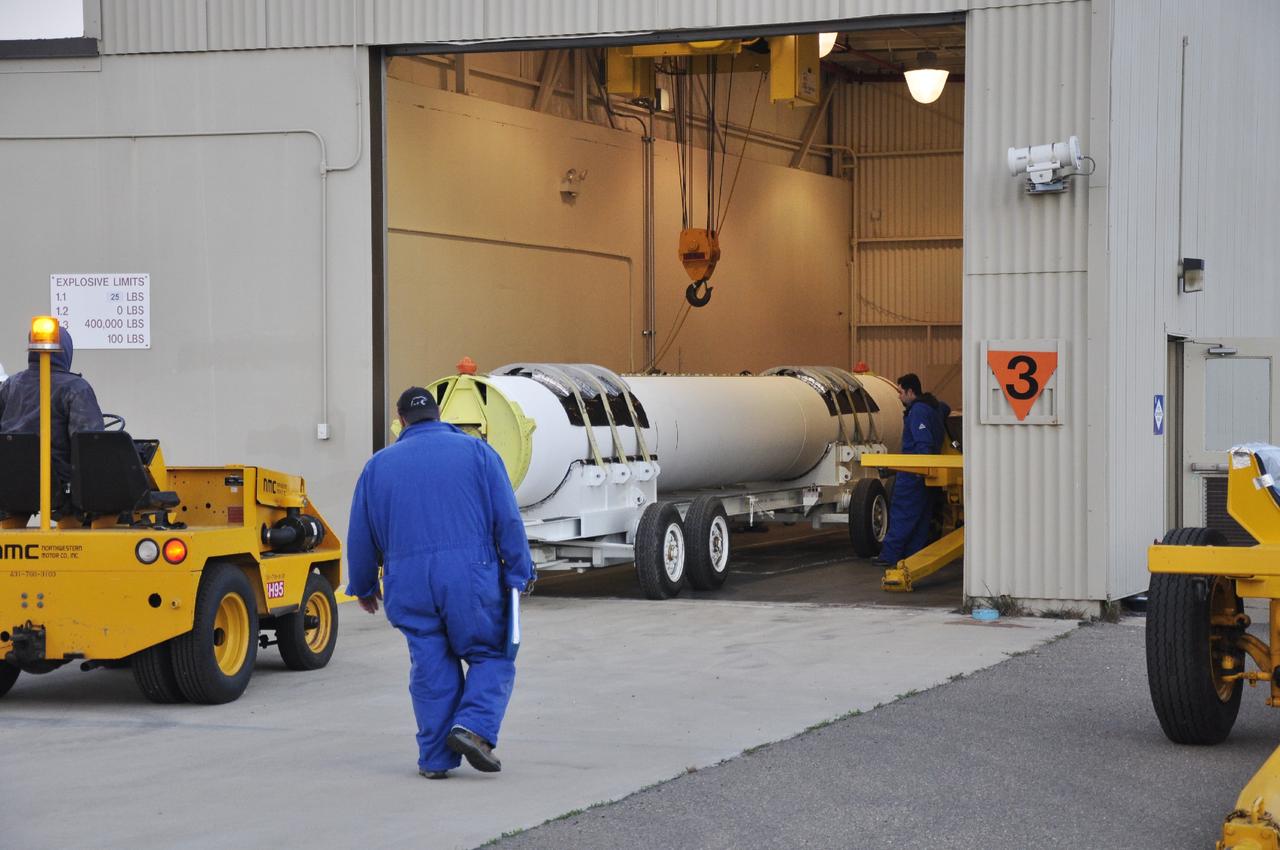

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is rolled into the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
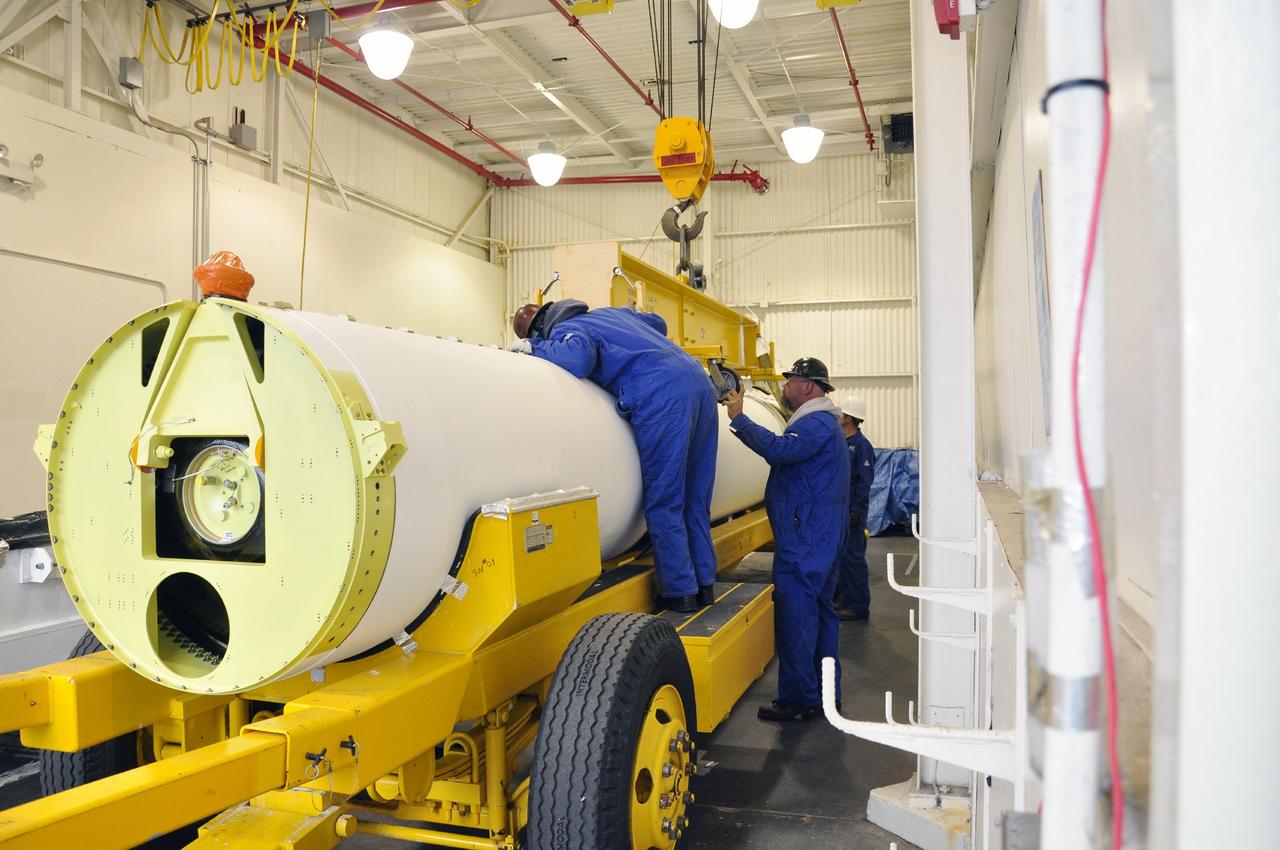

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is secured to a transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
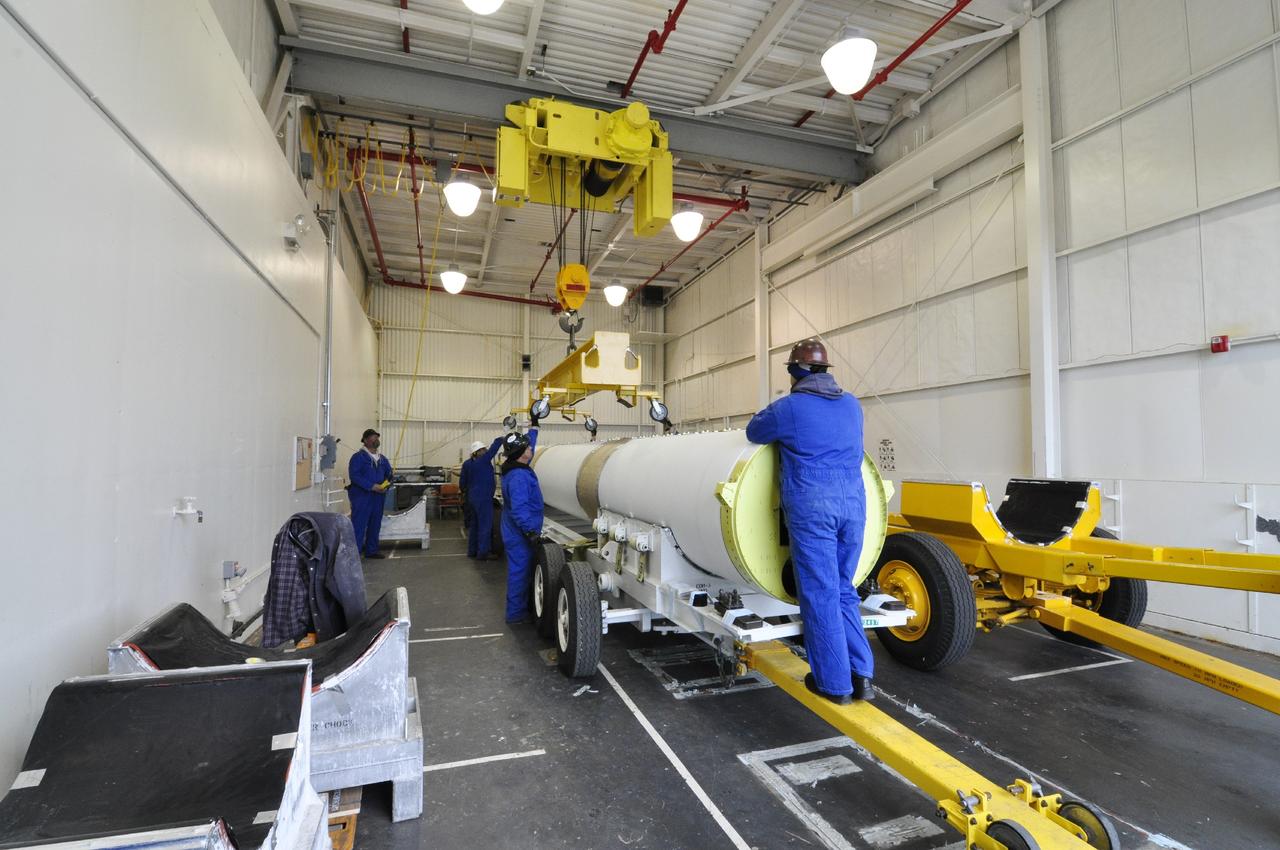

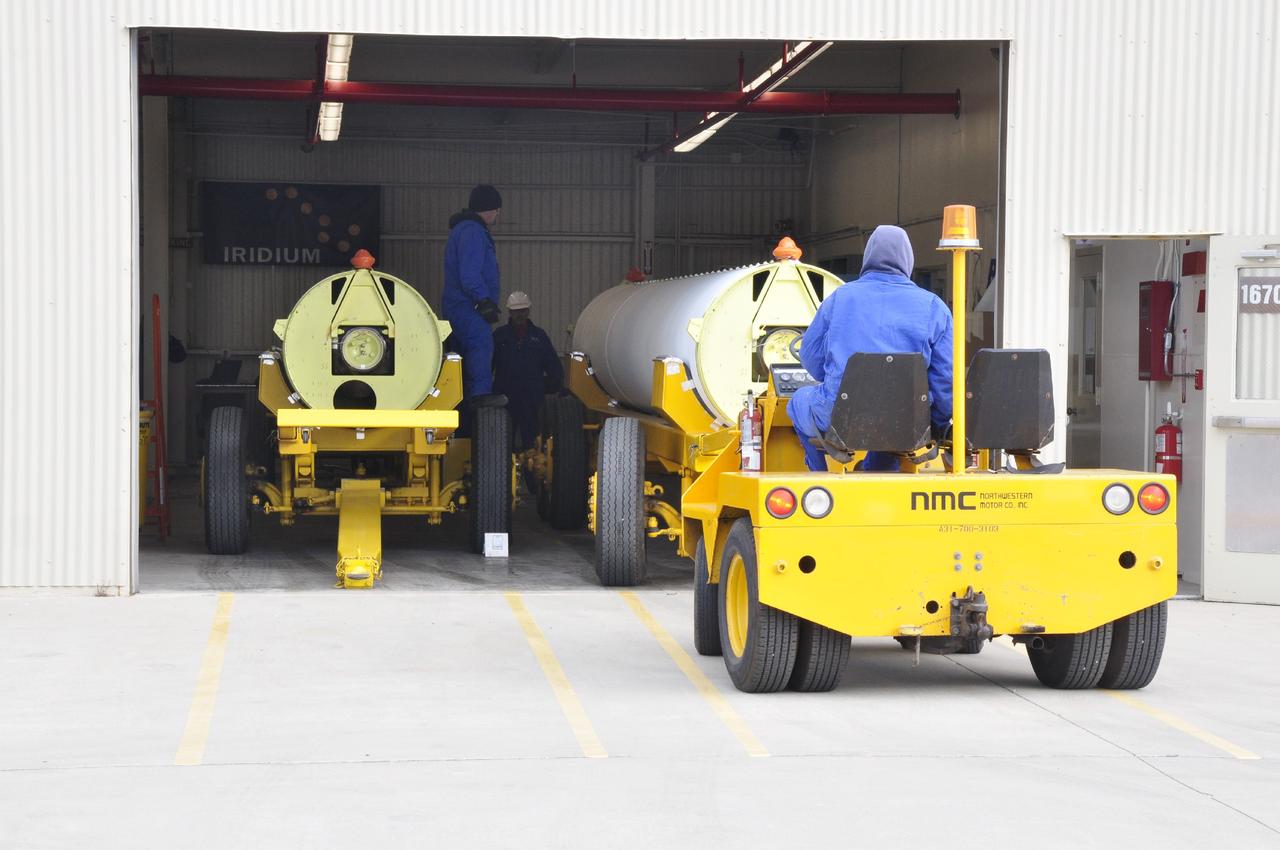
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians prepare to move a solid rocket motor to a different transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
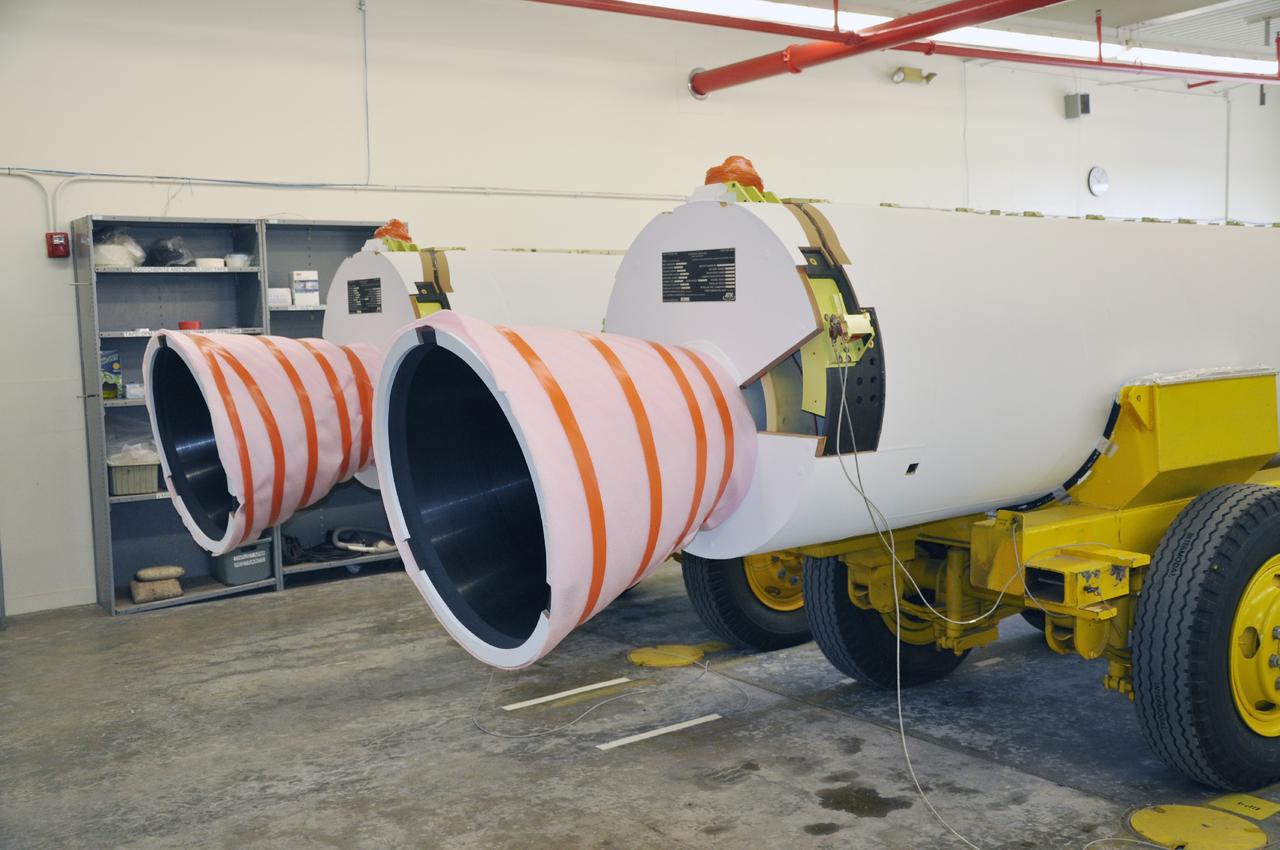

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A pair of solid rocket motors on transporters inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motors will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
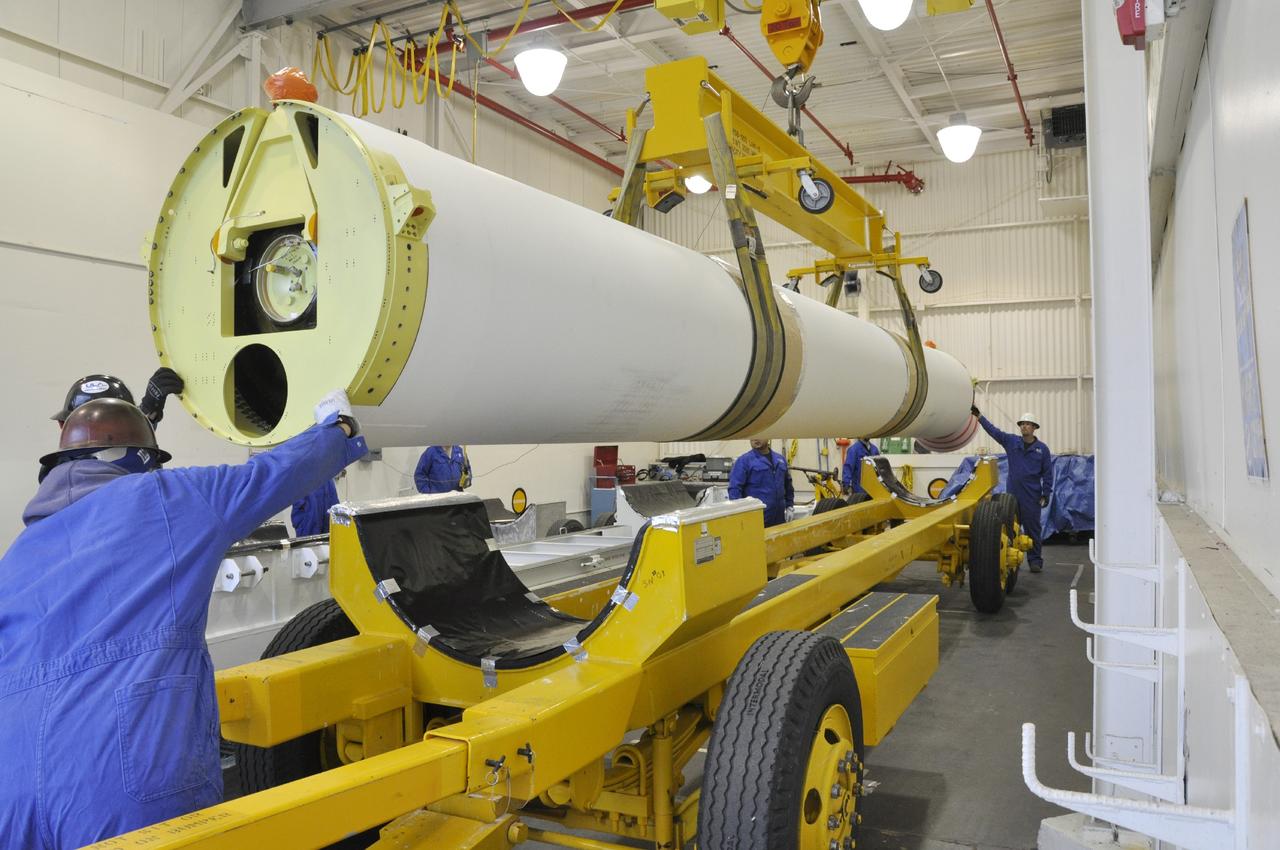

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- An overhead crane moves a solid rocket motor onto a transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
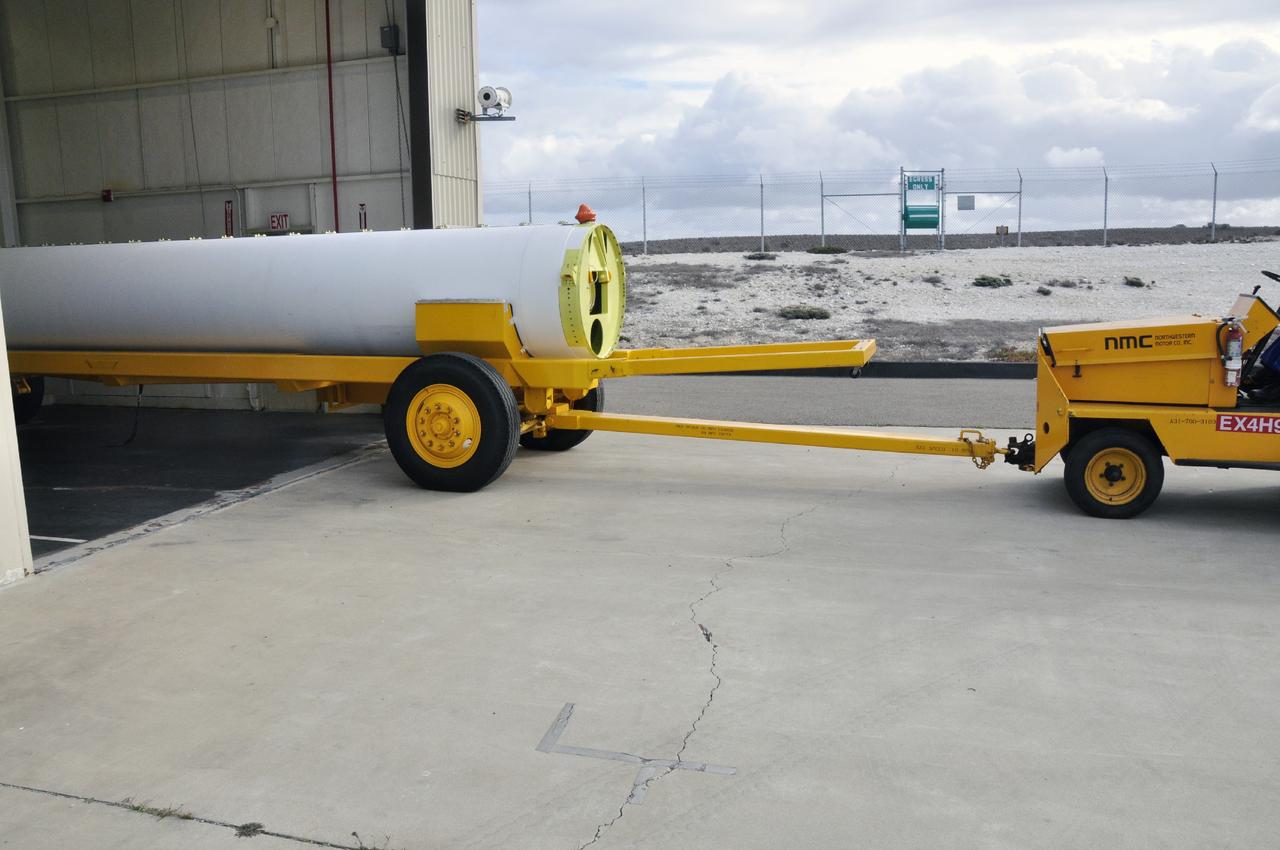

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is moved on a transporter to the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
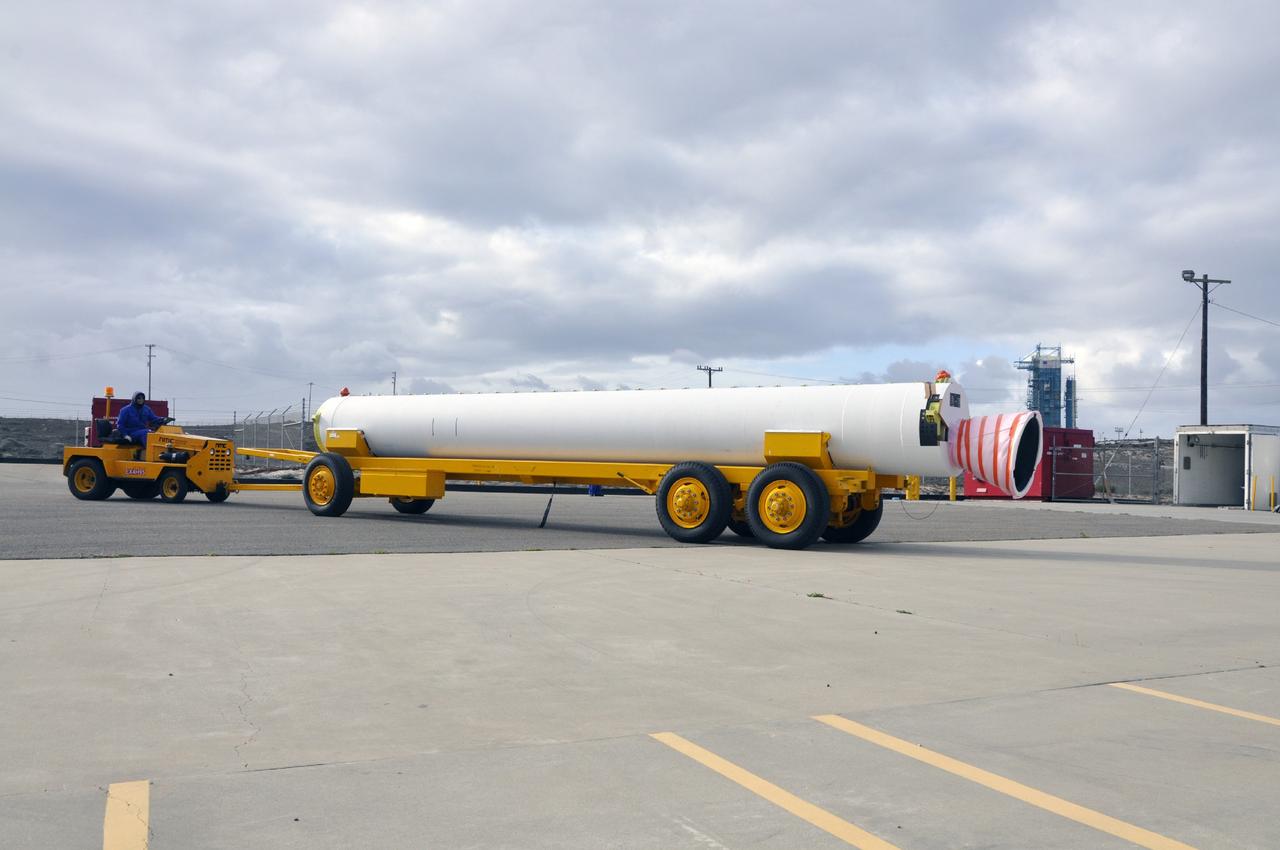

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is moved on a transporter to the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. Space Launch Complex-2, where the mission will launch from, can be seen in the background. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
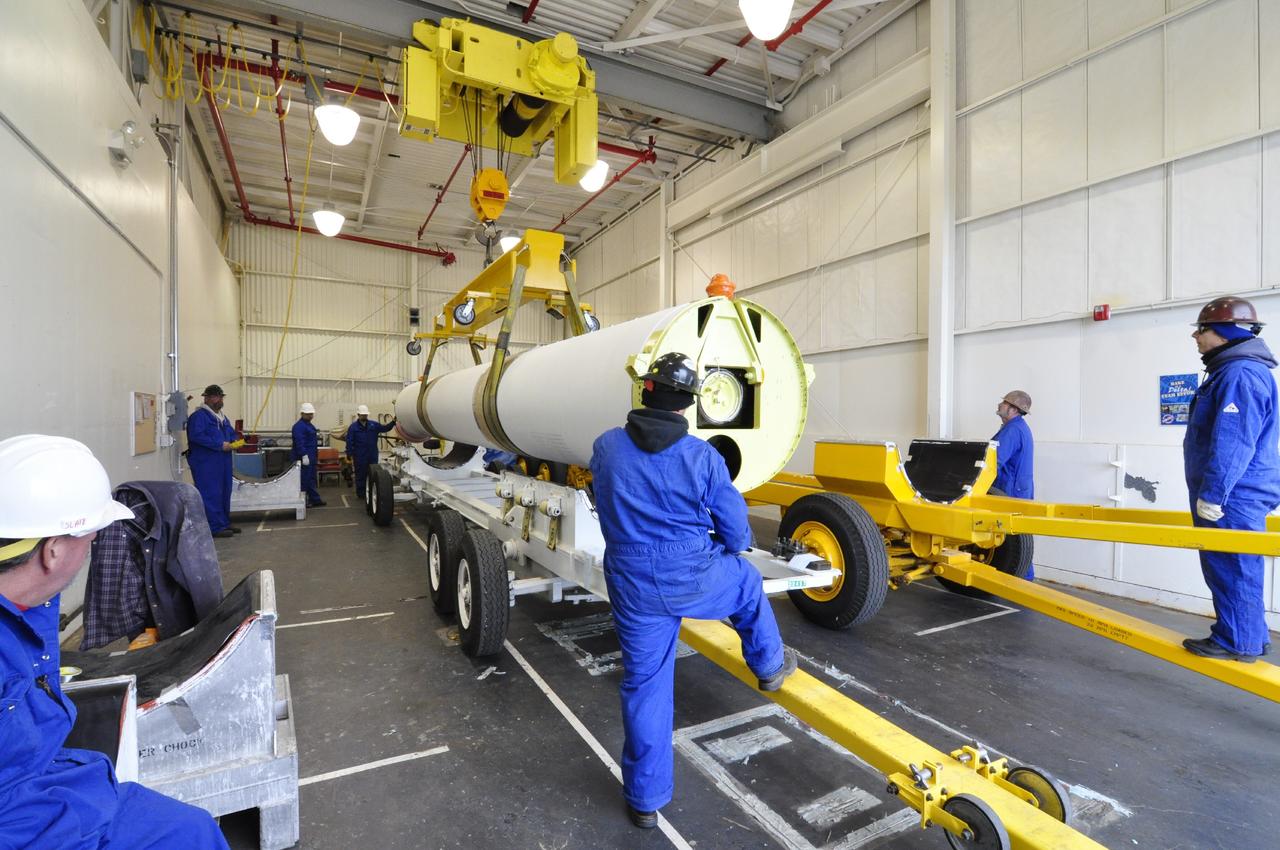

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians move a solid rocket motor to a different transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
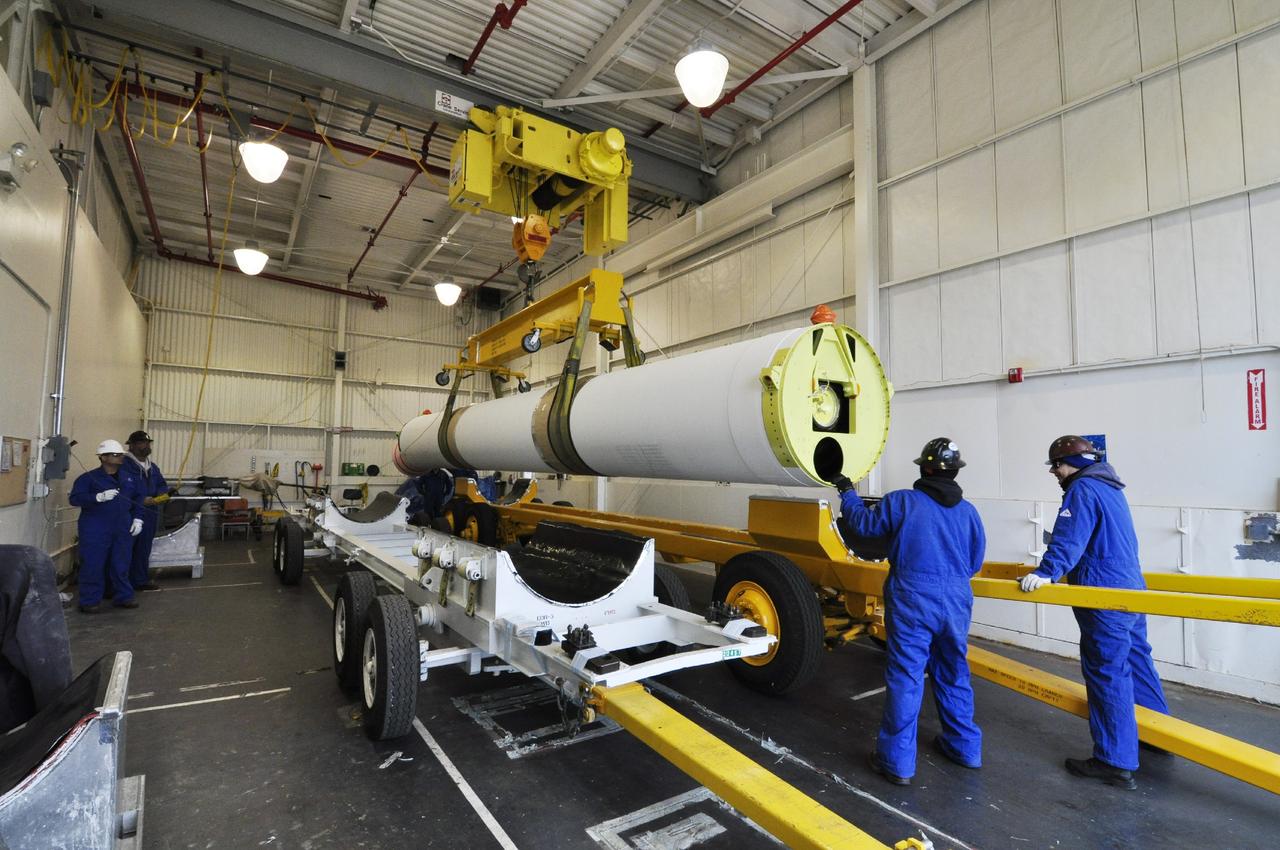

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians move a solid rocket motor to a different transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
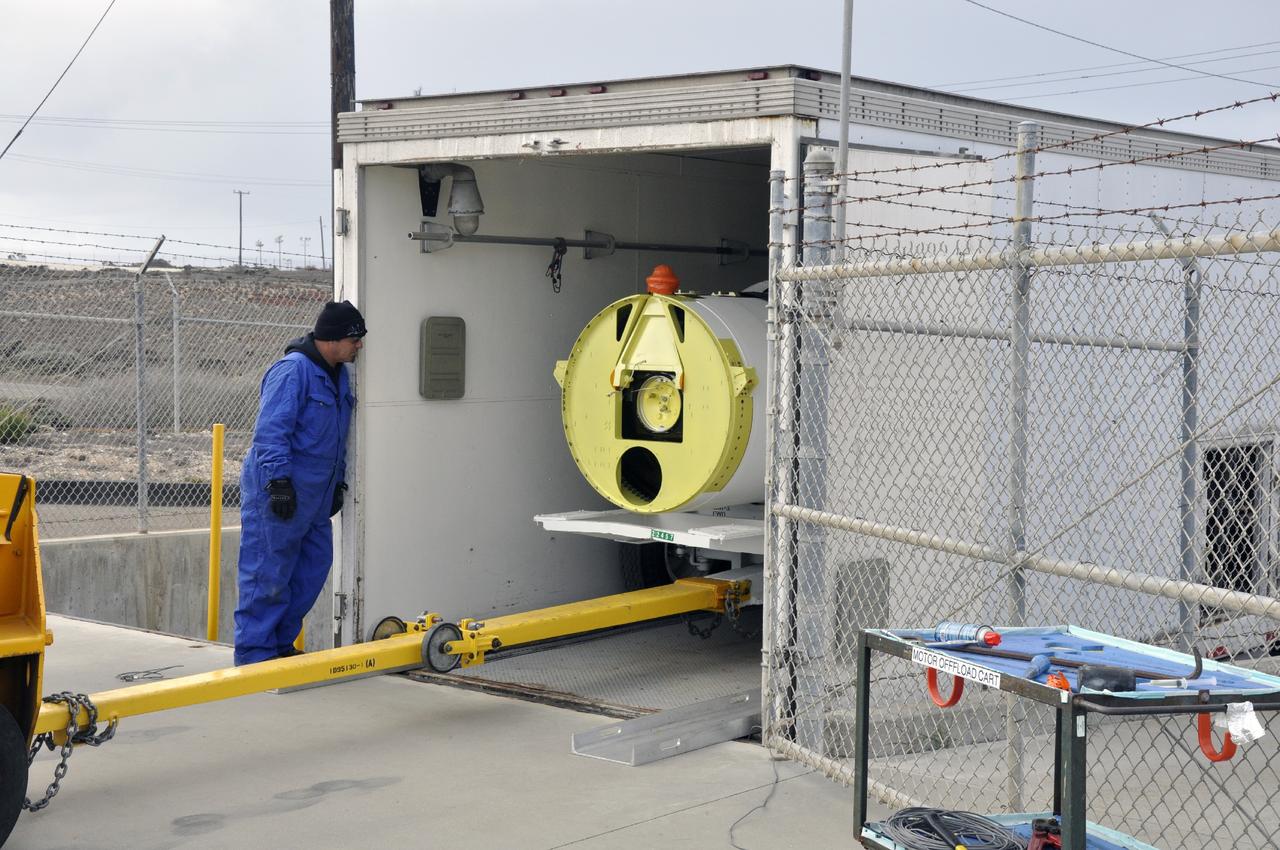

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is moved on a transporter to the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is moved on a transporter to the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor is moved on a transporter to the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
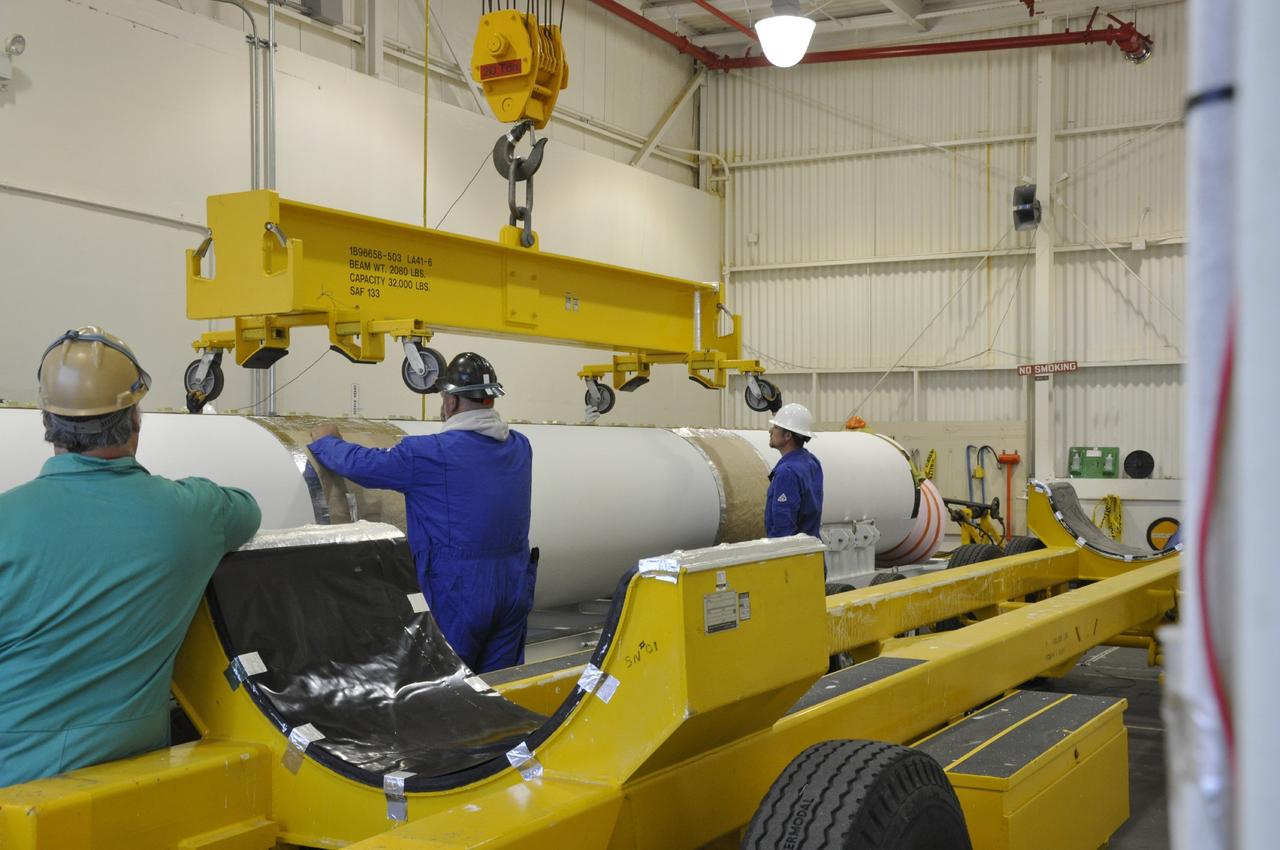

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- An overhead crane is moved into position above a solid rocket motor inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
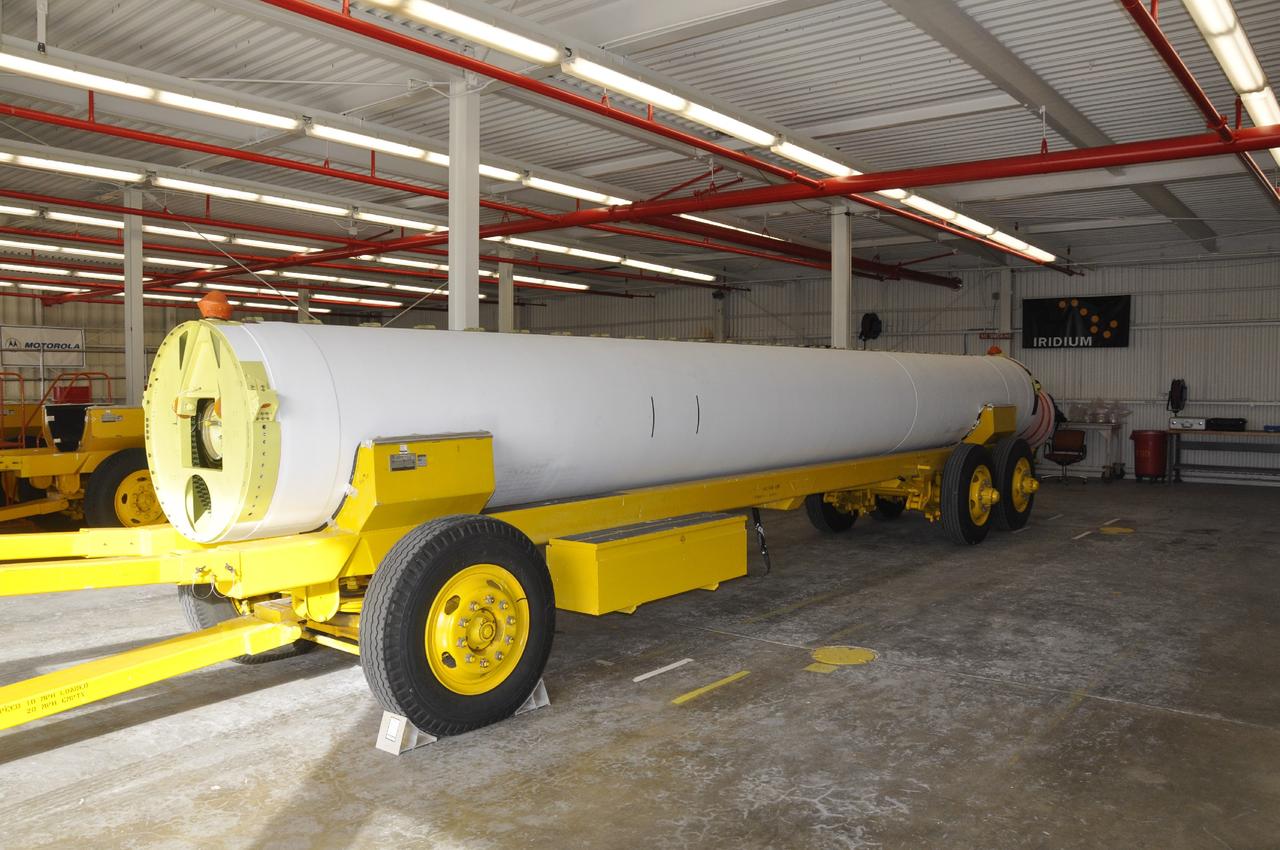

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A solid rocket motor sits on a transporter inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
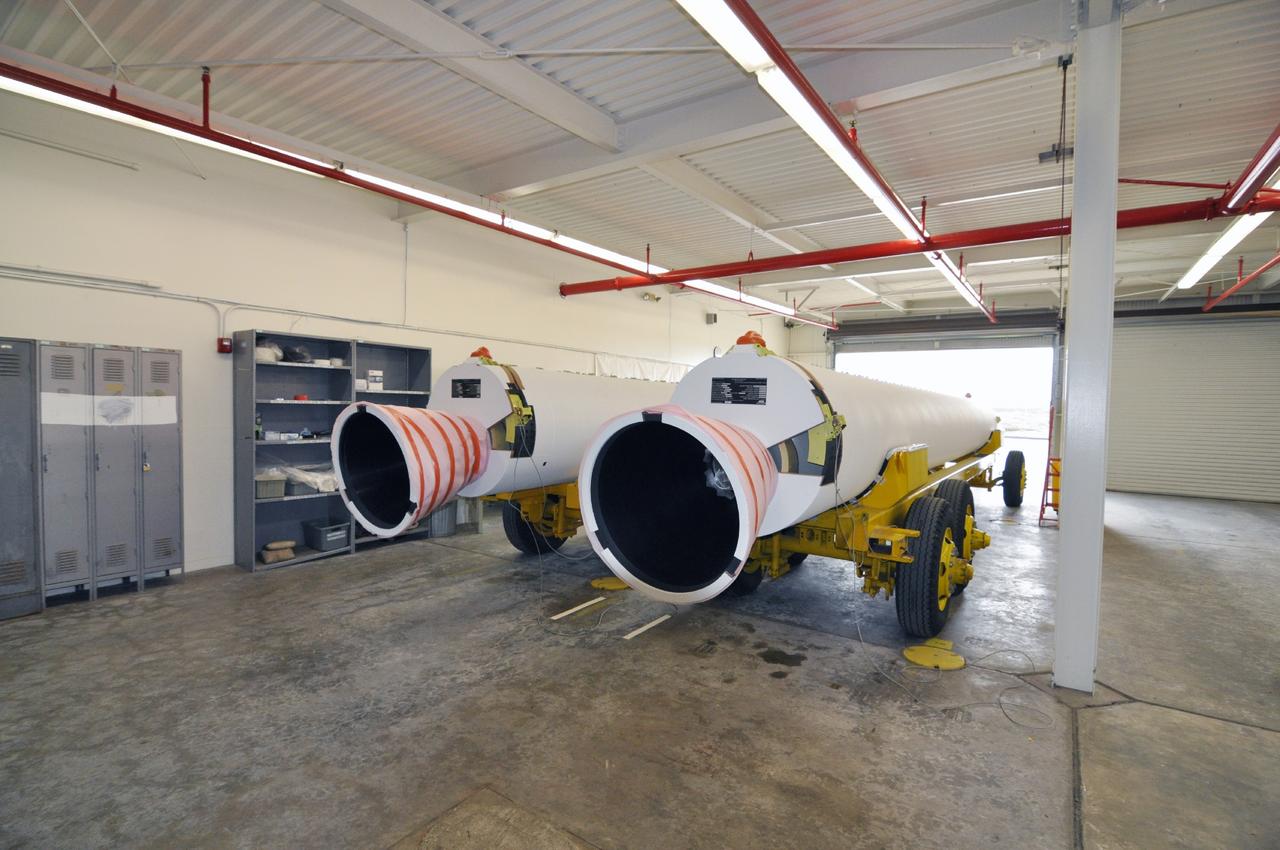

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A pair of solid rocket motors on transporters inside the Solid Rocket Motor Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motors will be attached to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, spacecraft in July 2014. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
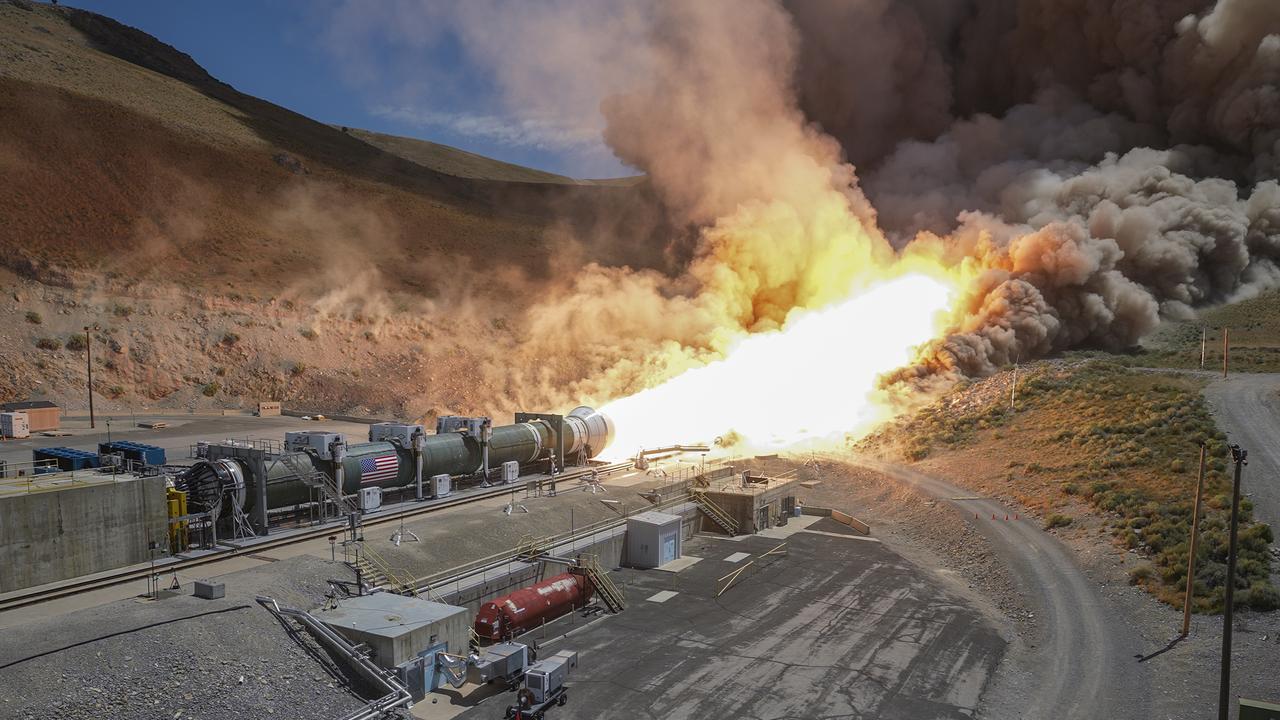

Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. During the test, there was an abnormal event approximately 15 seconds before the end of the motor firing. Despite this event, NASA achieved several of the test’s primary objectives and received valuable data on technical risks identified ahead of the test. Testing this evolved booster for the SLS will help evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters. The BOLE effort was launched to transition to a more efficient, lower cost commercial solution for the boosters for the SLS rocket. Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will send astronauts to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and to build the foundation for the first crewed missions to Mars – for the benefit of all. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

A Titan IVB core vehicle and its twin Solid Rocket Motor Upgrades (SRMUs) depart from the Solid Rocket Motor Assembly and Readiness Facility (SMARF), Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), en route to Launch Complex 40. At the pad, the Centaur upper stage will be added and, eventually, the prime payload, the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings and moon, Titan. Launch of the Cassini mission to Saturn is scheduled for Oct. 6 from Pad 40, CCAS
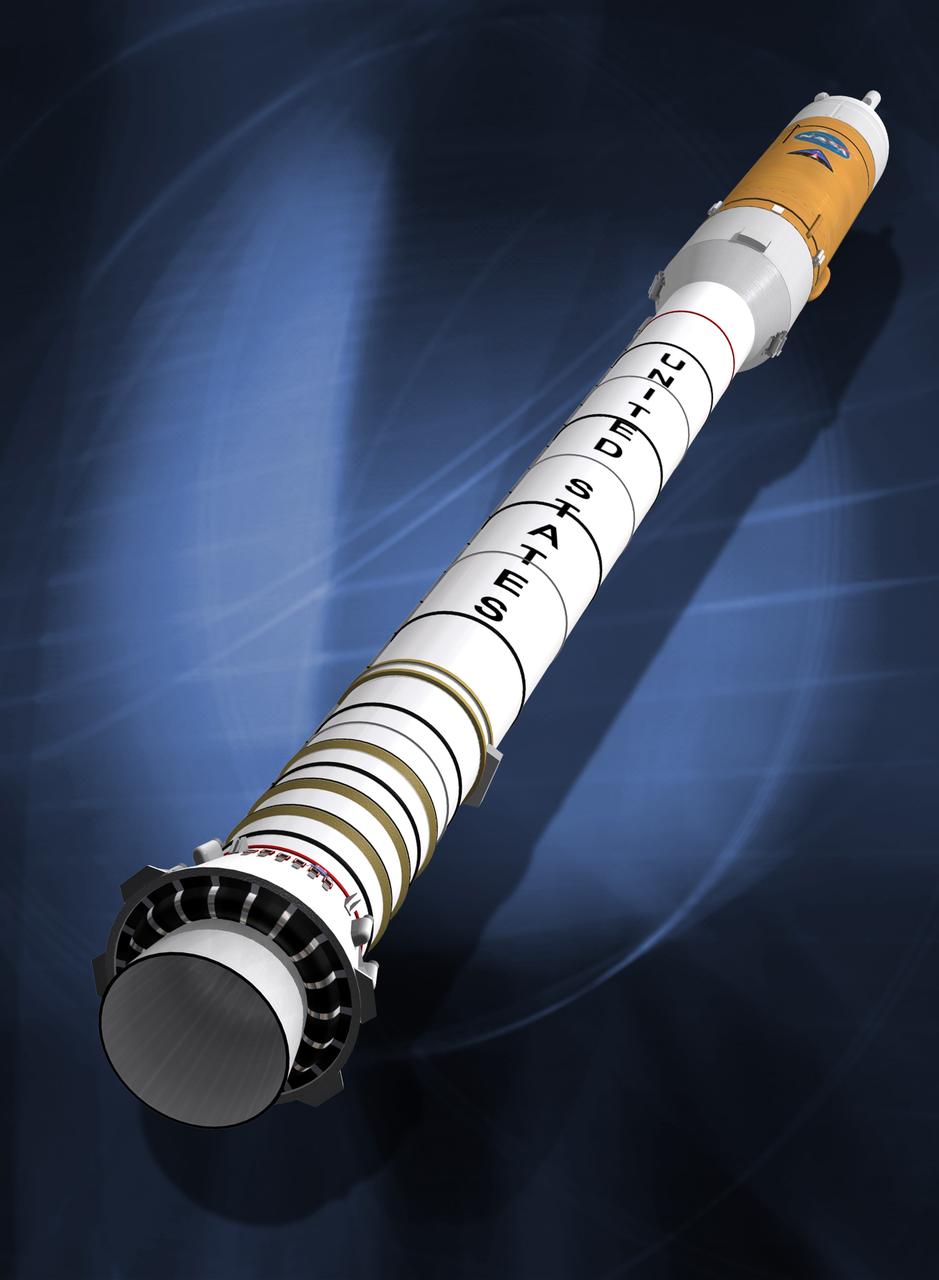

Shown is an illustration of the Ares I concept. The first stage will be a single, five-segment solid rocket booster derived from the space shuttle programs reusable solid rocket motor. The first stage is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama for NASA's Constellation program.
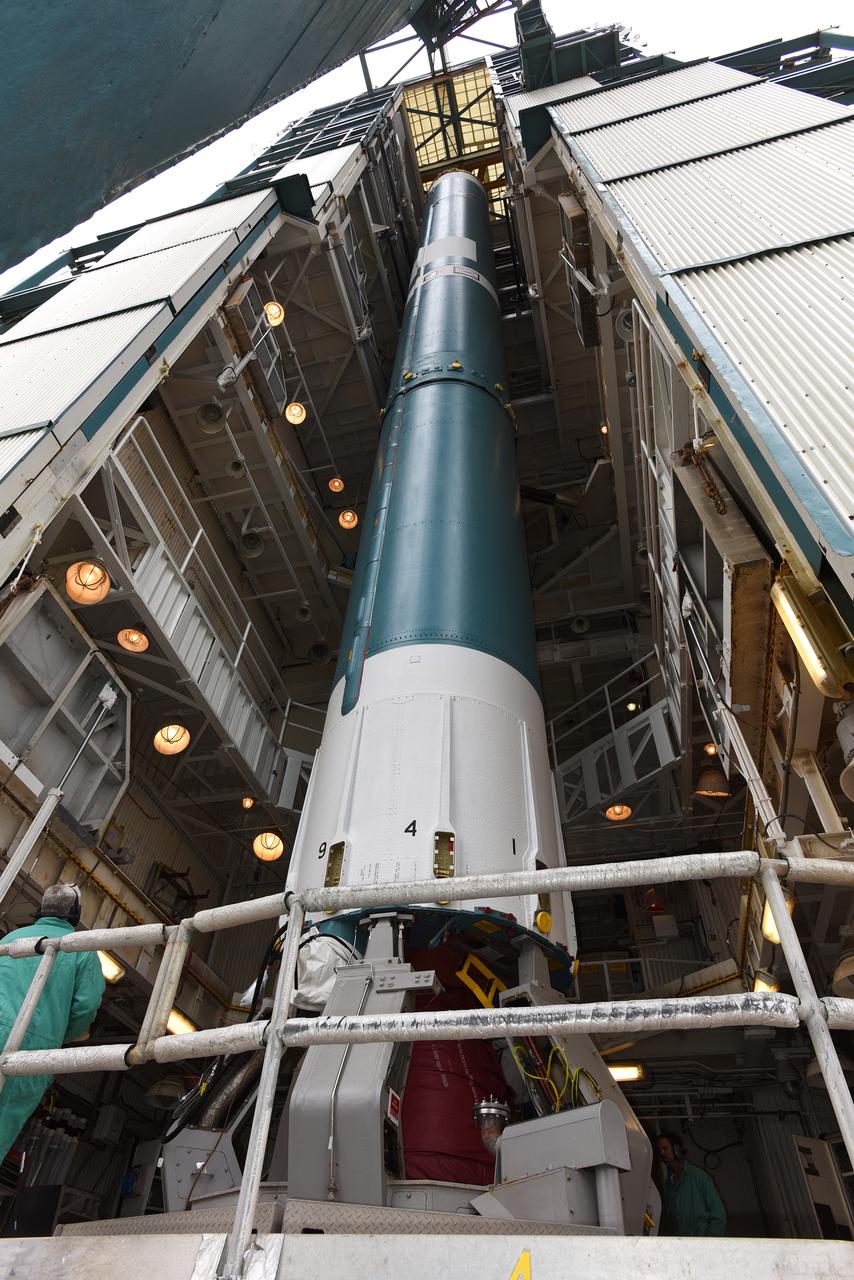

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket stands at Space Launch Complex 2 as preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

A test firing of the Qualification Motor-1 Solid Rocket Motor which will power the Space Launch System and Orion on Artemis I takes place in Promontory, Utah on March 11, 2015. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
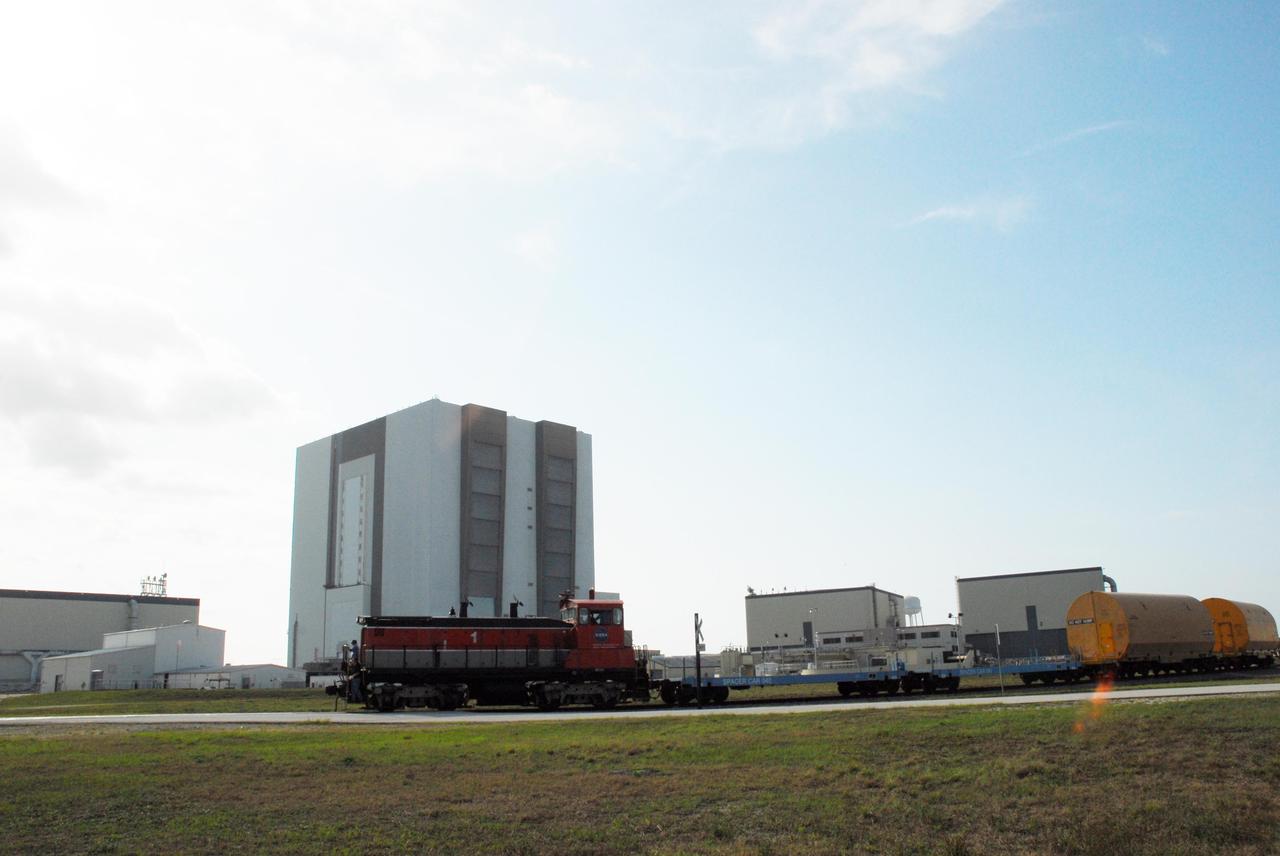

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments roll past the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. The RPSF is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
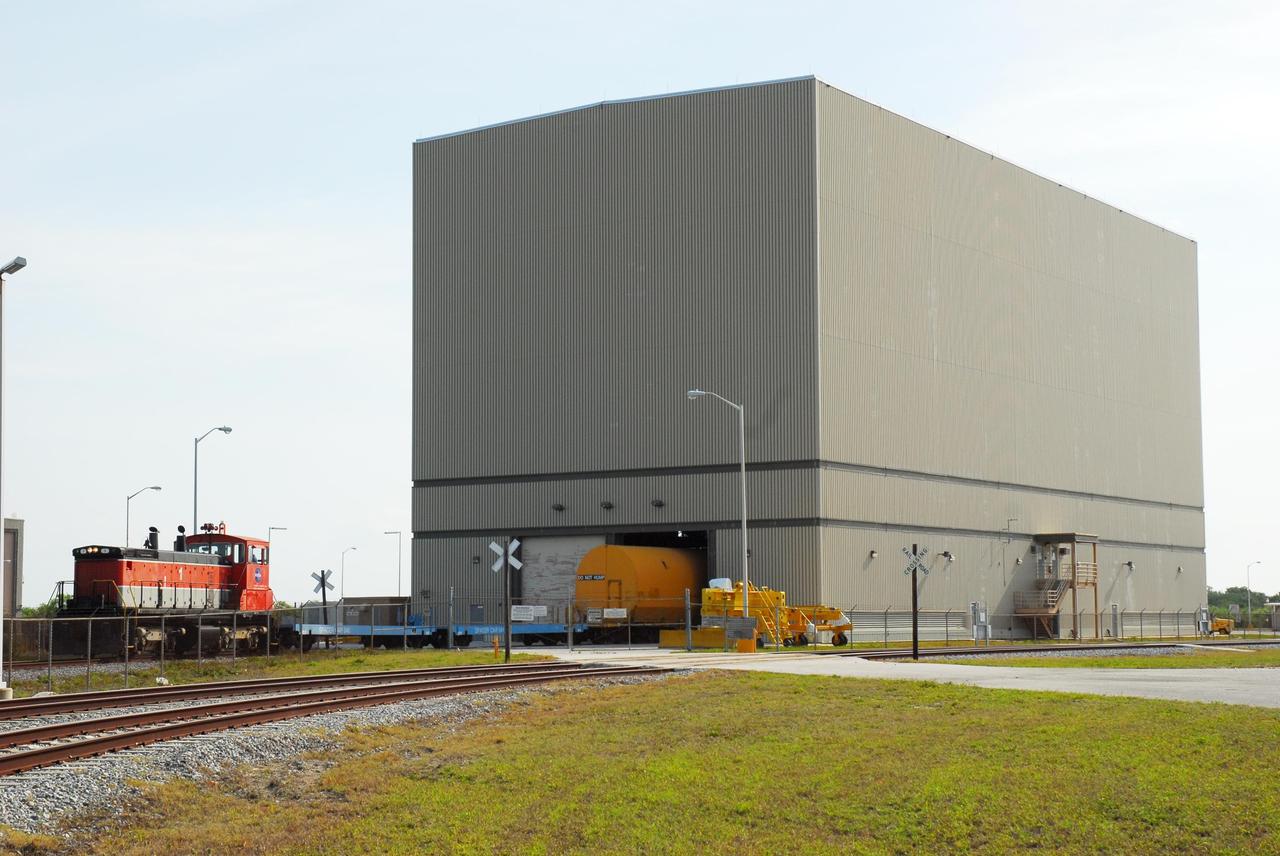

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The final rail car carrying solid rocket booster motor segments moves its cargo into the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. The RPSF is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
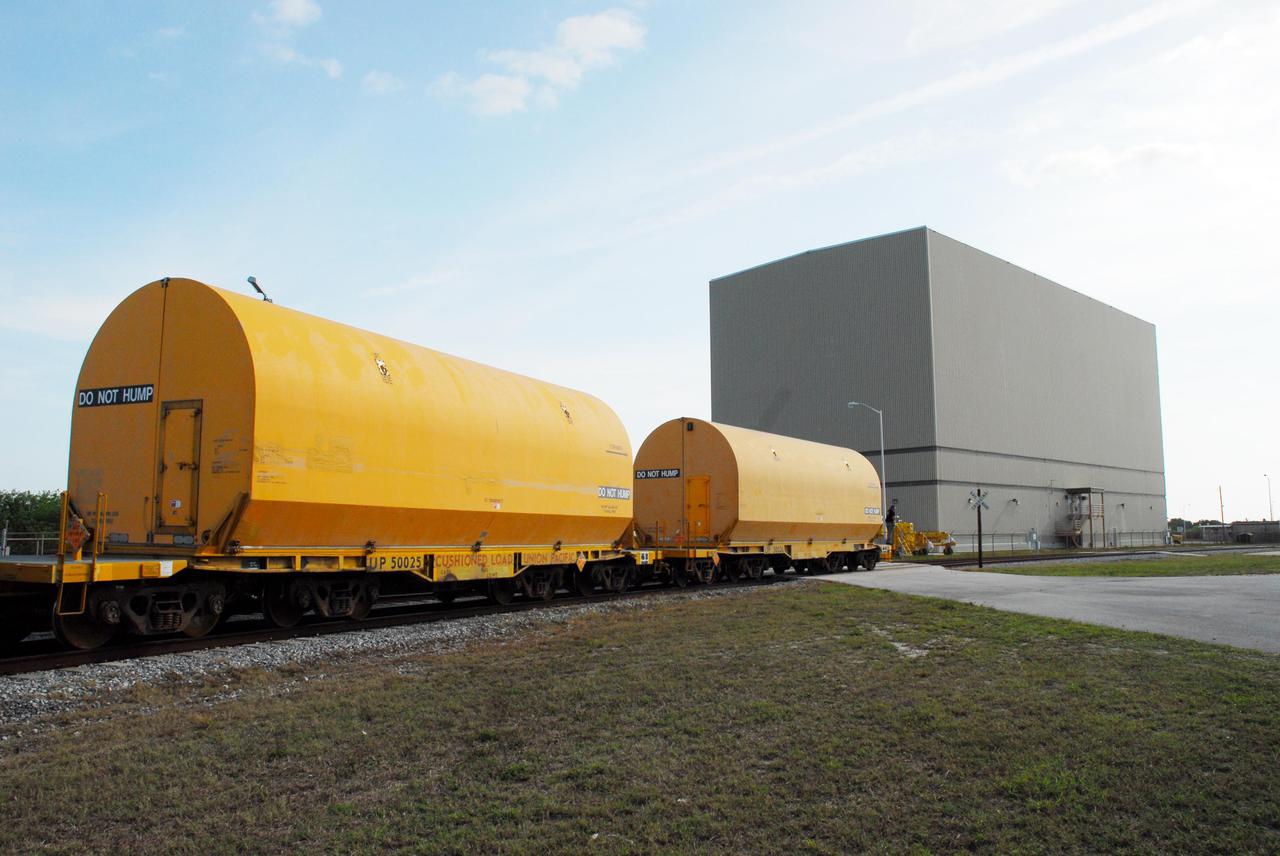

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments roll toward the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. The RPSF is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA_George Shelton
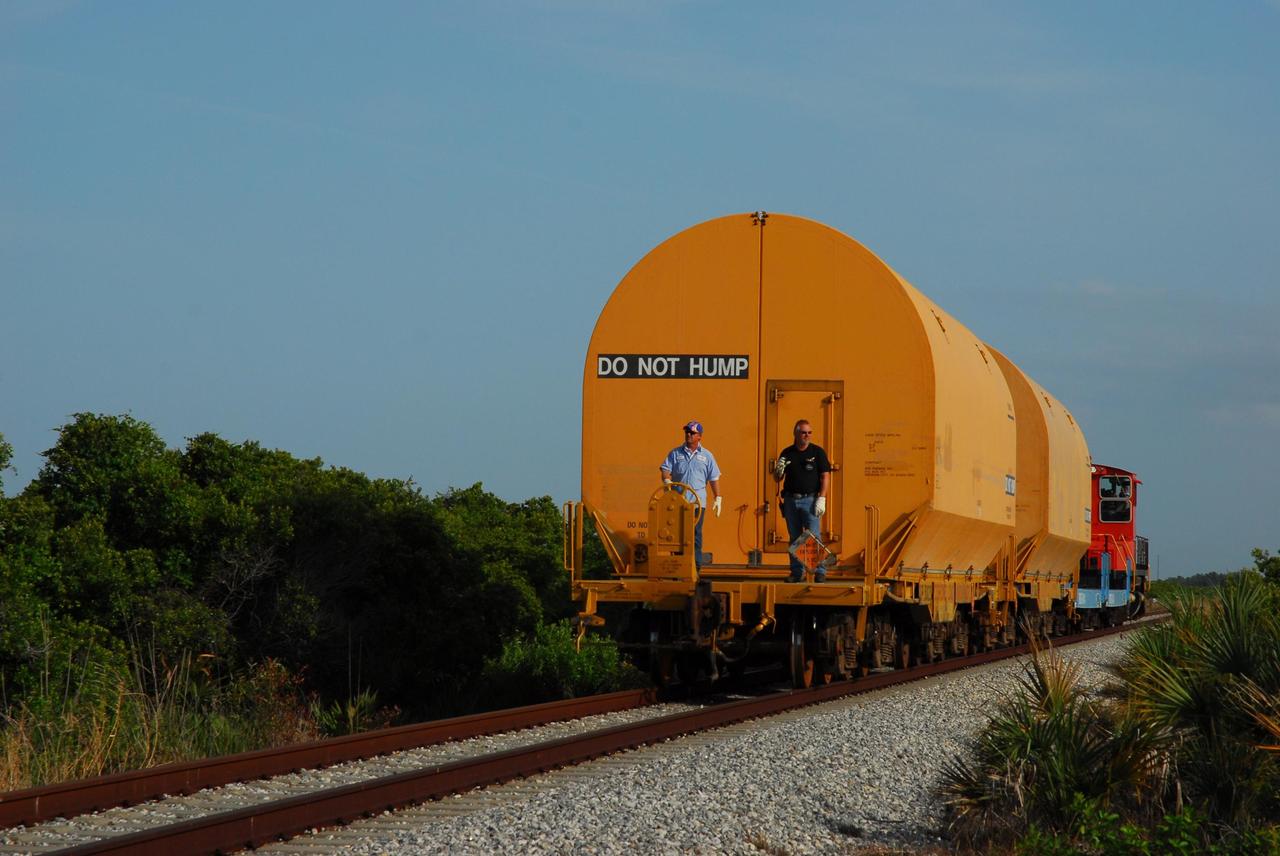

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments roll to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. The main facility is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
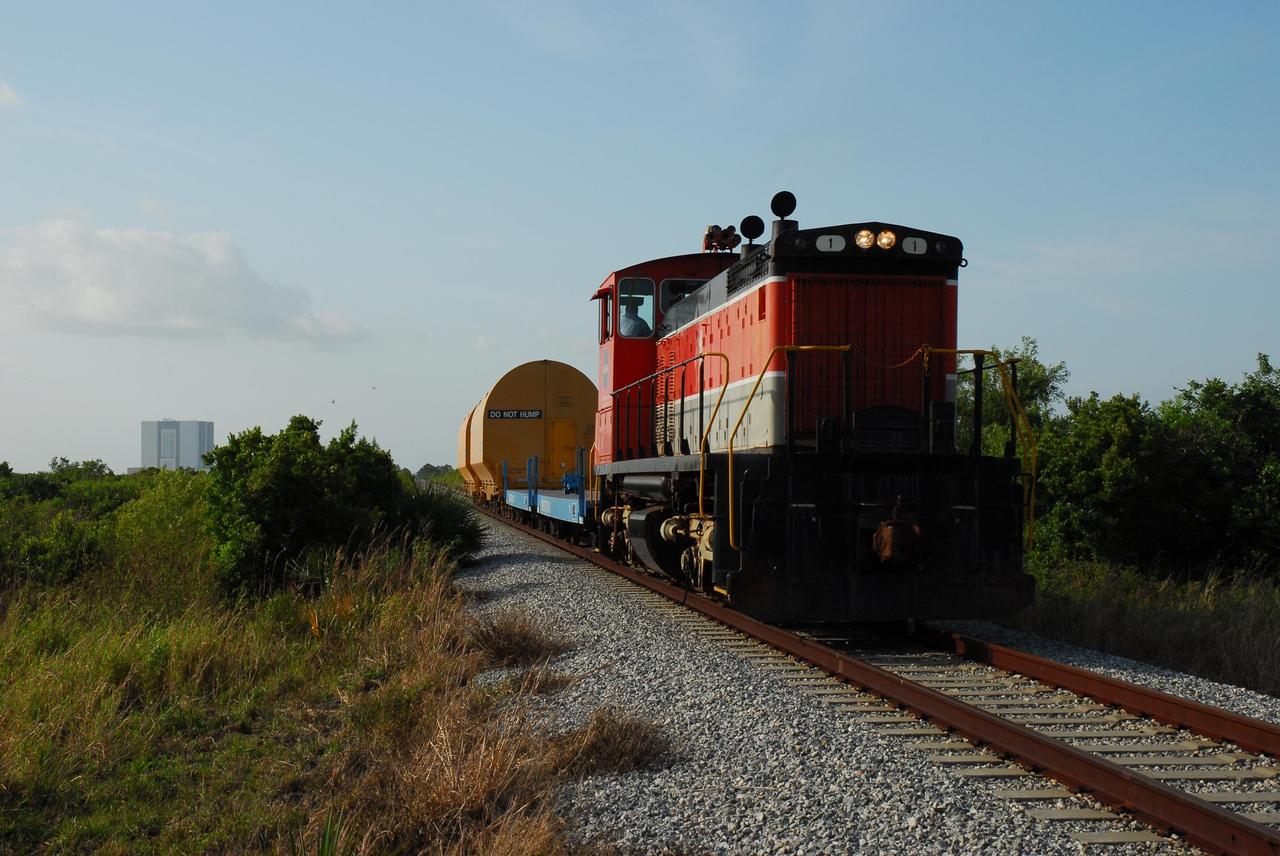

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments roll to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. In the background, at left, is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RPSF is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
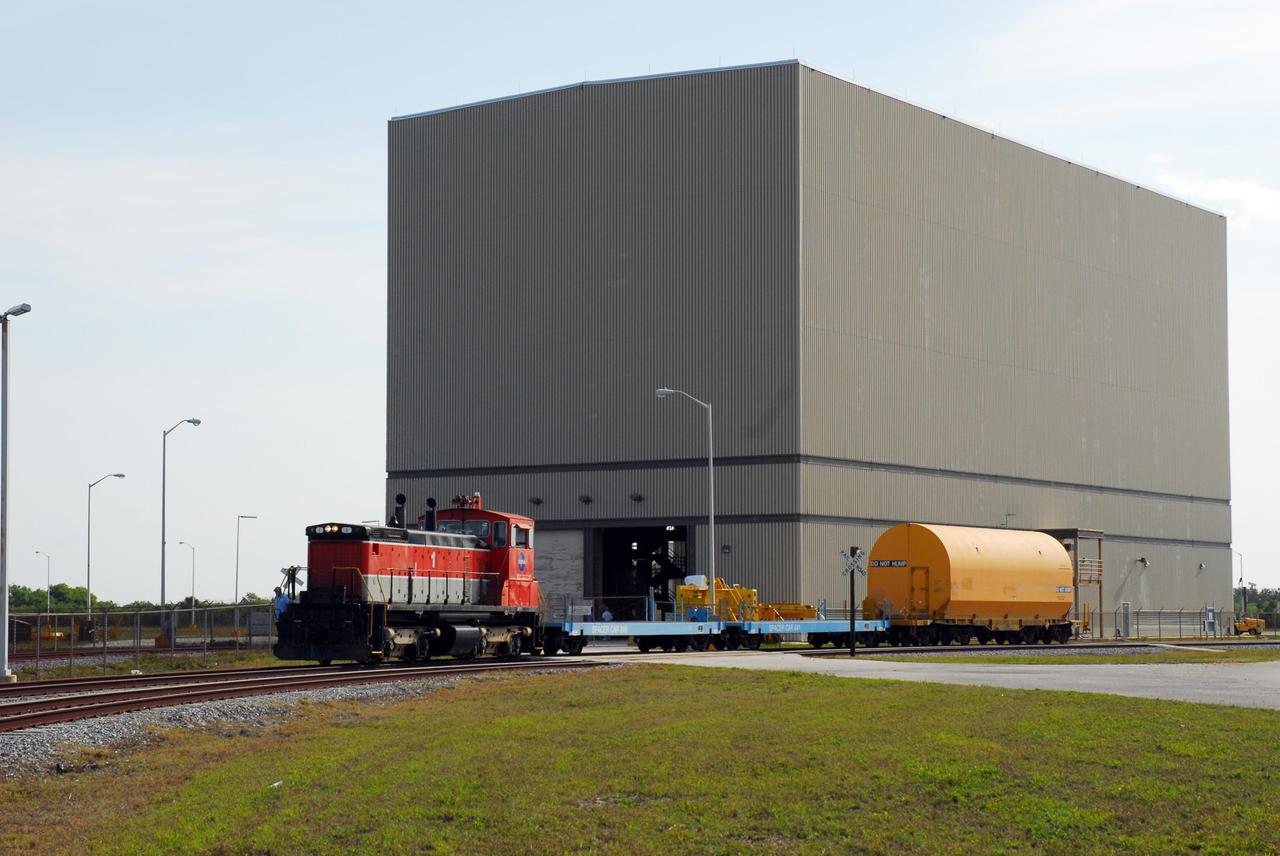

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments deliver their cargo to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 Area. The RPSF is used for solid rocket motor receiving, rotation and inspection, and supports aft booster buildup. When live solid rocket motor segments arrive at the processing facility, they are positioned under one of the cranes. Handling slings are then attached to and remove the railcar cover. The segment is inspected while it remains horizontal. The two overhead cranes hoist the segment, rotate it to a vertical position and place it on a fixed stand. The aft handling ring is then removed. The segment is hoisted again and lowered onto a transportation and storage pallet, and the forward handling ring is removed to allow inspections. It is then transported to one of the surge buildings and temporarily stored until it is needed for booster stacking in the VAB. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
The solid rocket booster (SRB) structural test article is being installed in the Solid Rocket Booster Test Facility for the structural and load verification test at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This young alligator crosses a road near the railroad tracks where the train carrying solid rocket booster motor segments approaches Kennedy Space Center. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
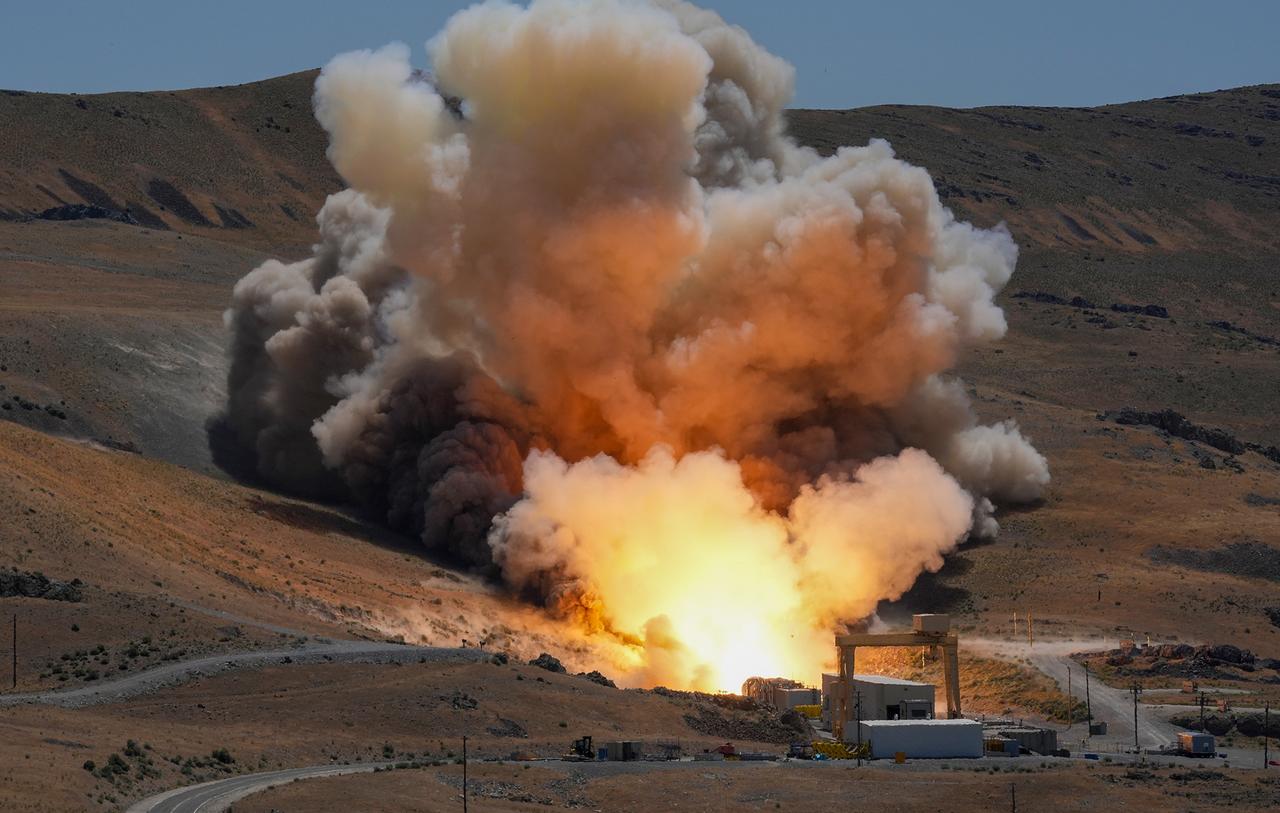

Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. During the test, there was an abnormal event approximately 15 seconds before the end of the motor firing. Despite this event, NASA achieved several of the test’s primary objectives and received valuable data on technical risks identified ahead of the test. Testing this evolved booster for the SLS will help evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters. The BOLE effort was launched to transition to a more efficient, lower cost commercial solution for the boosters for the SLS rocket. Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will send astronauts to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and to build the foundation for the first crewed missions to Mars – for the benefit of all. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
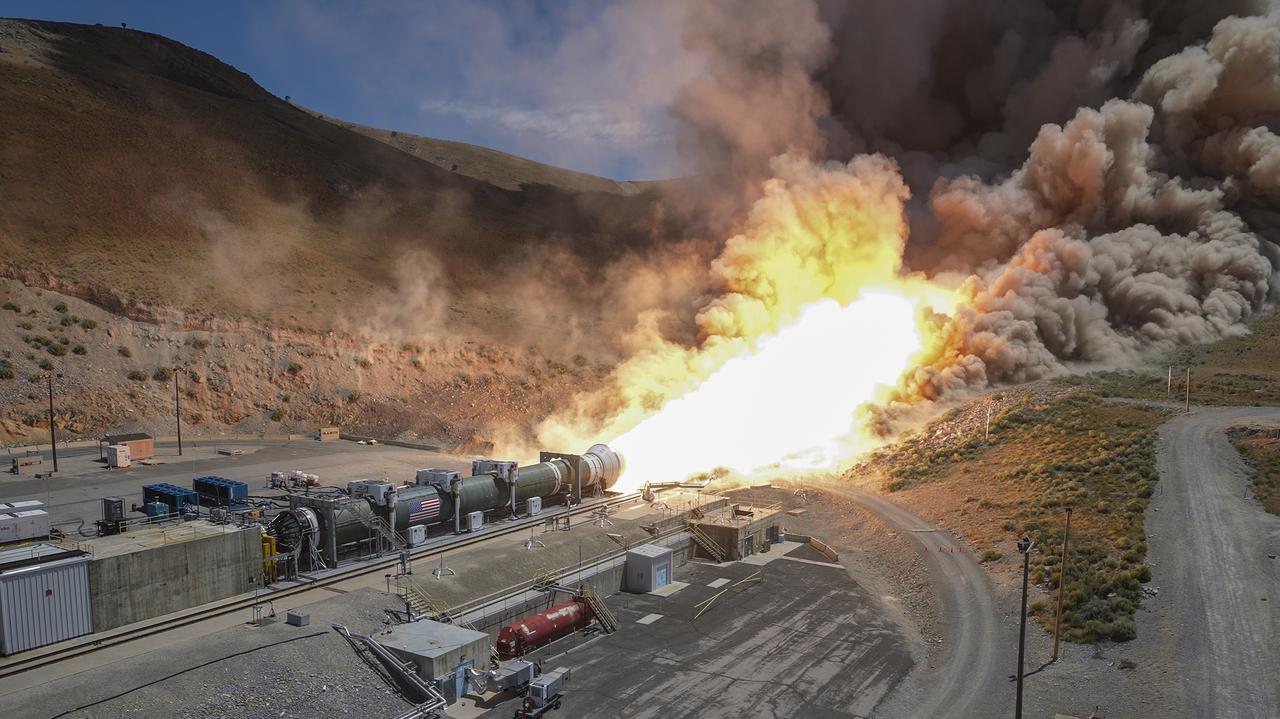

Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. During the test, there was an abnormal event approximately 15 seconds before the end of the motor firing. Despite this event, NASA achieved several of the test’s primary objectives and received valuable data on technical risks identified ahead of the test. Testing this evolved booster for the SLS will help evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters. The BOLE effort was launched to transition to a more efficient, lower cost commercial solution for the boosters for the SLS rocket. Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will send astronauts to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and to build the foundation for the first crewed missions to Mars – for the benefit of all. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
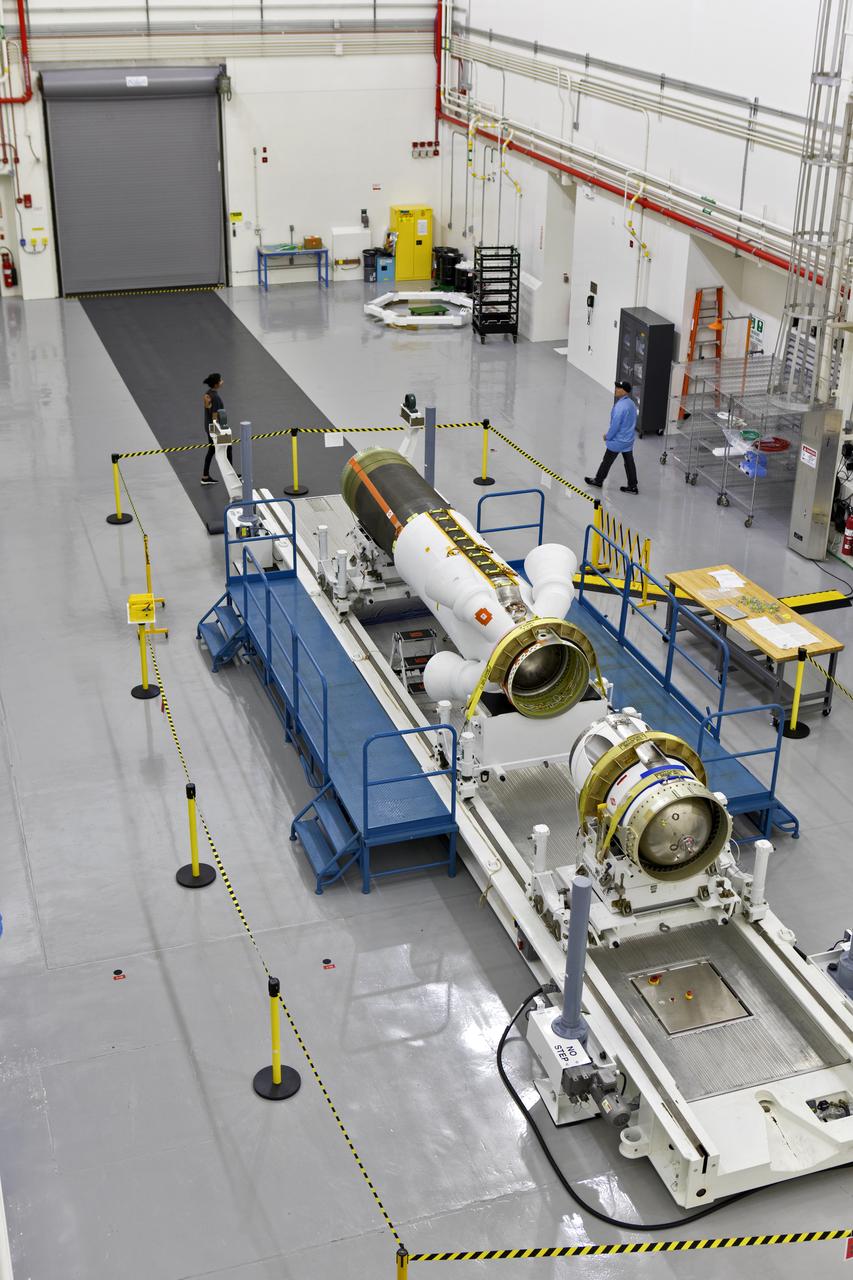

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
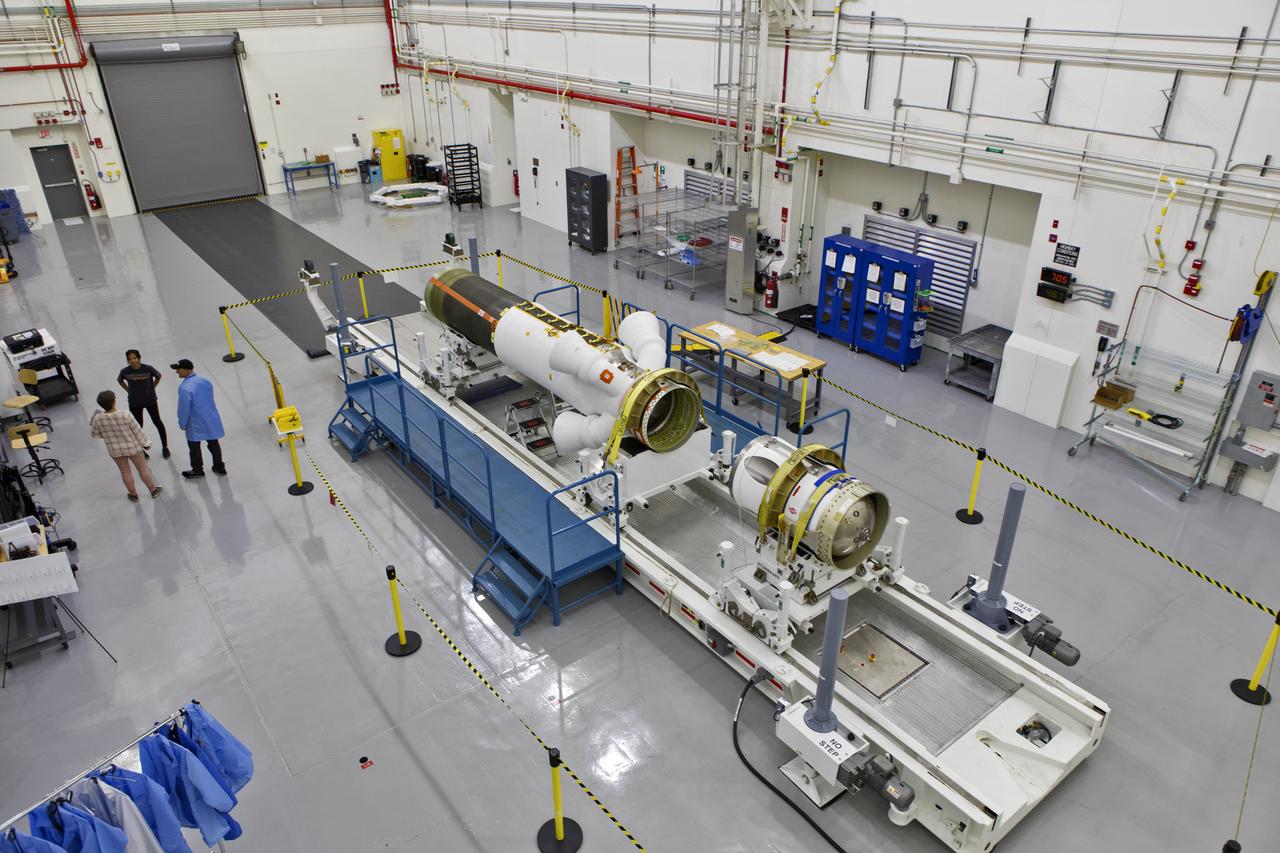

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
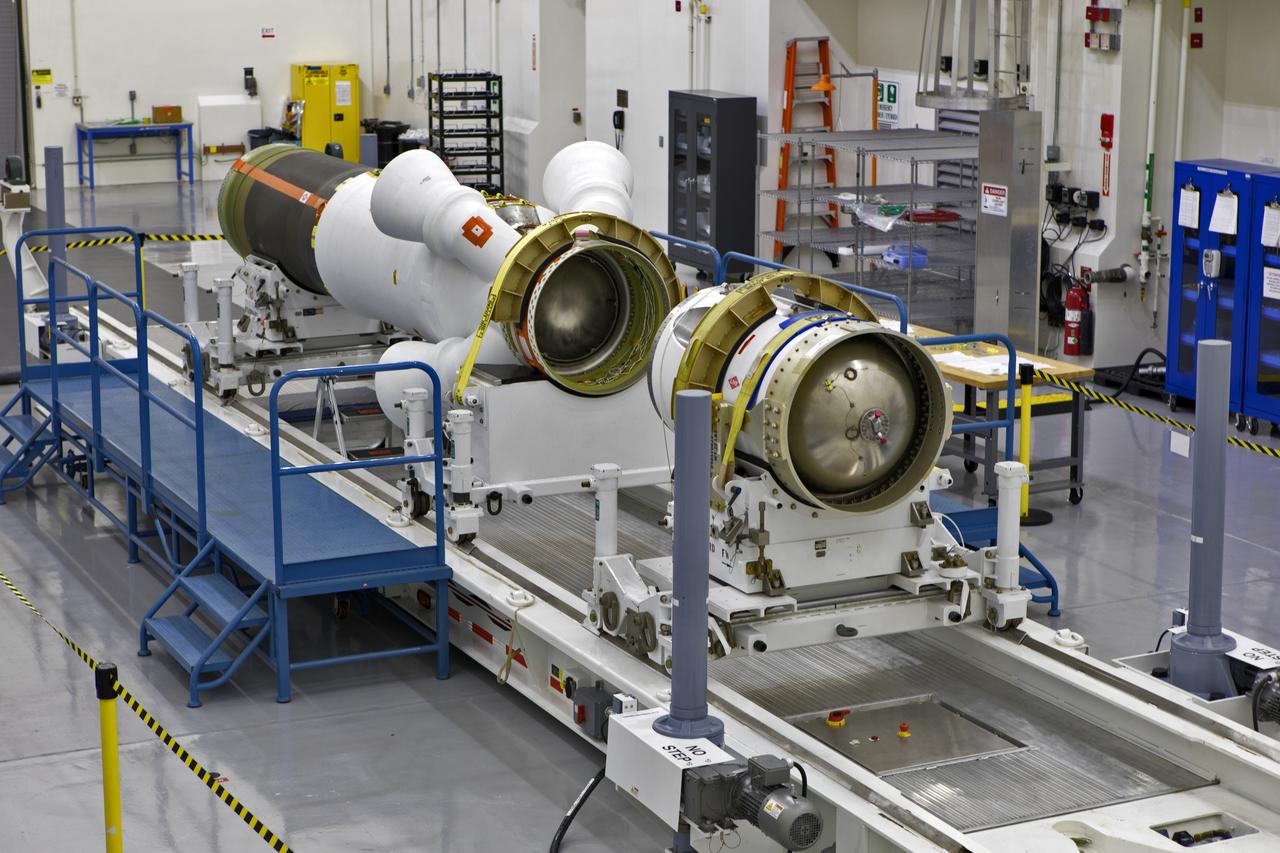

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
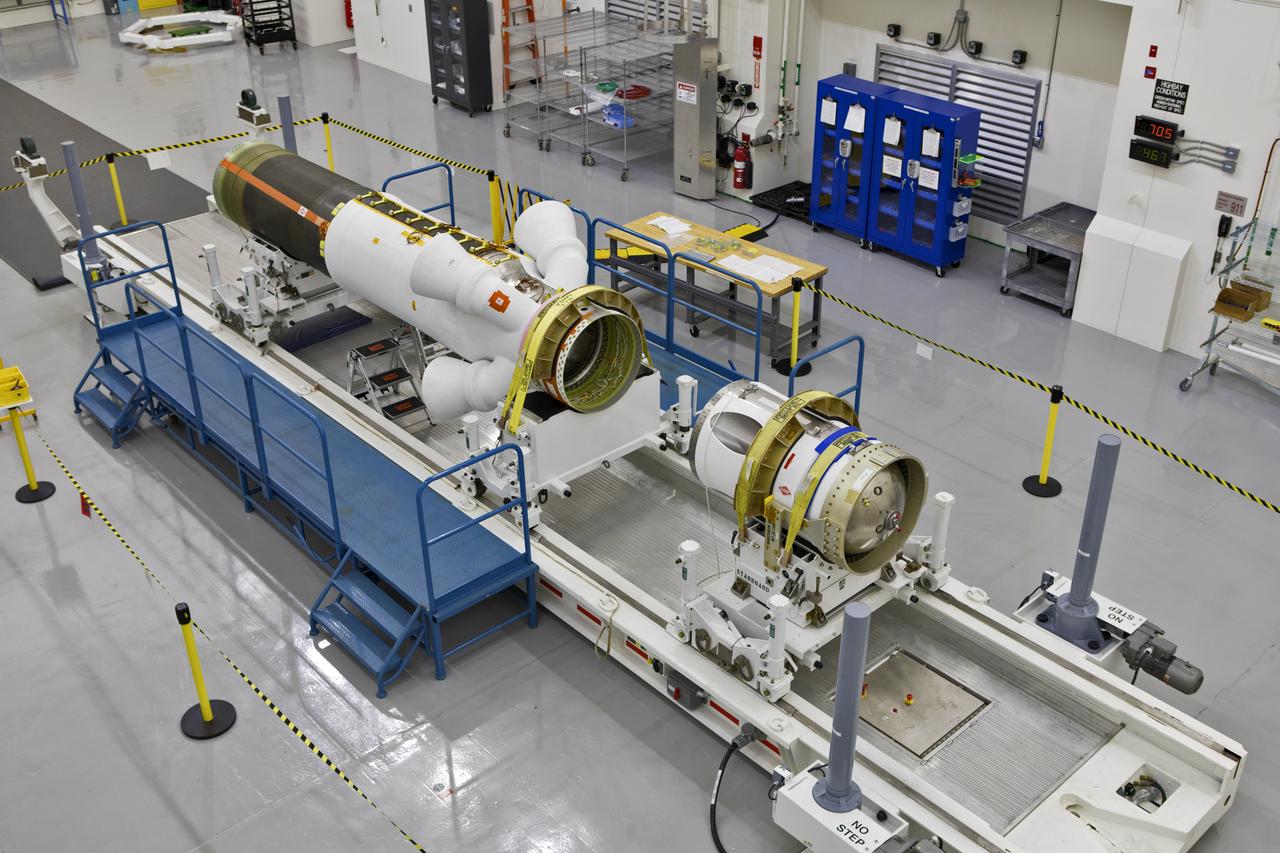

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.

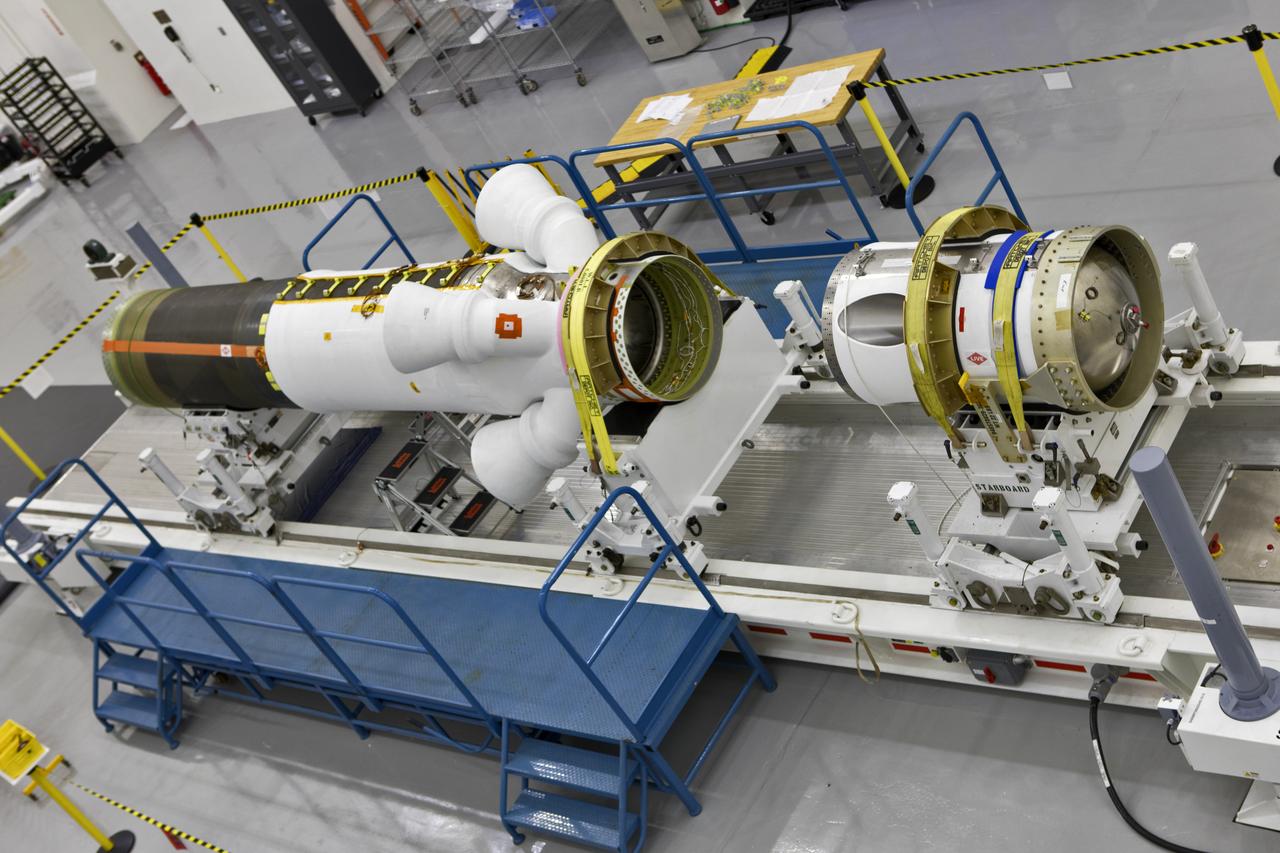
The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
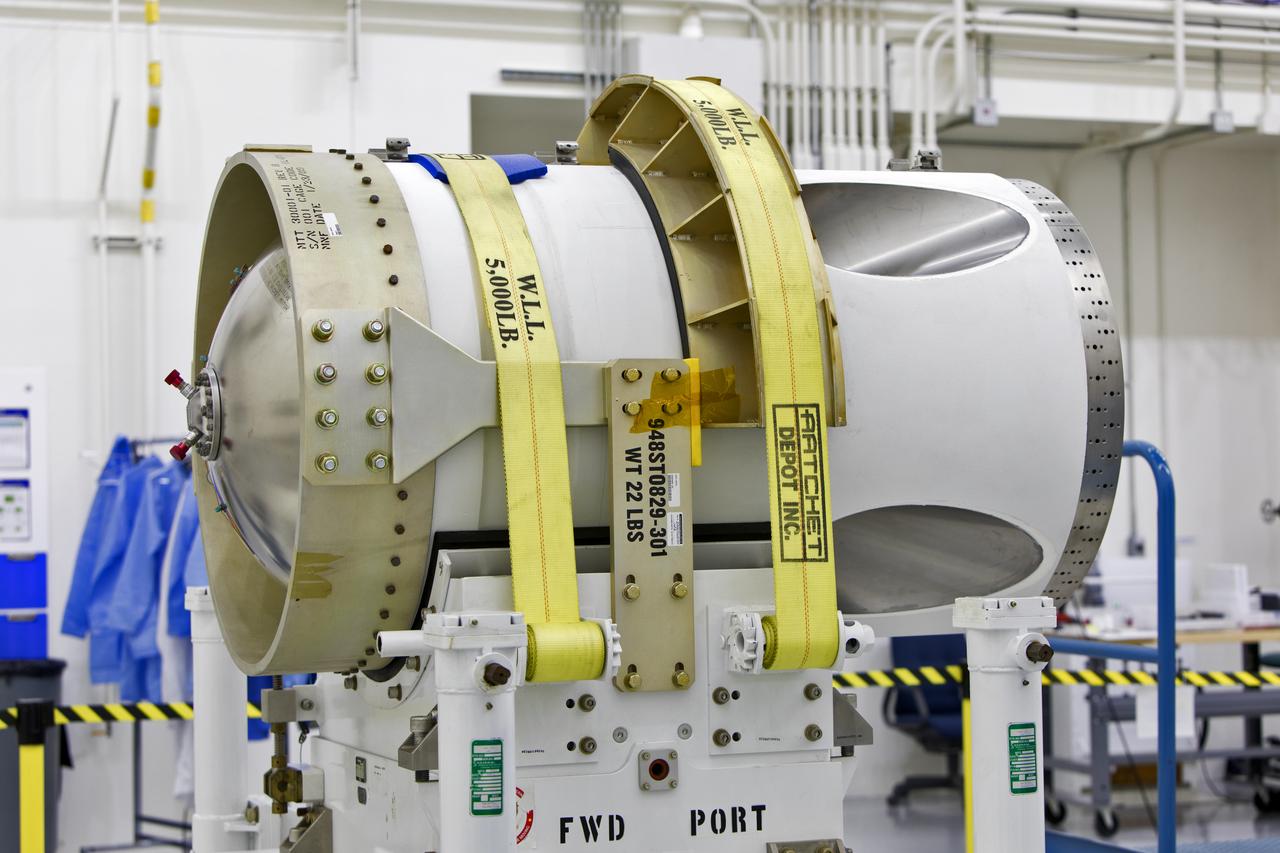
The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
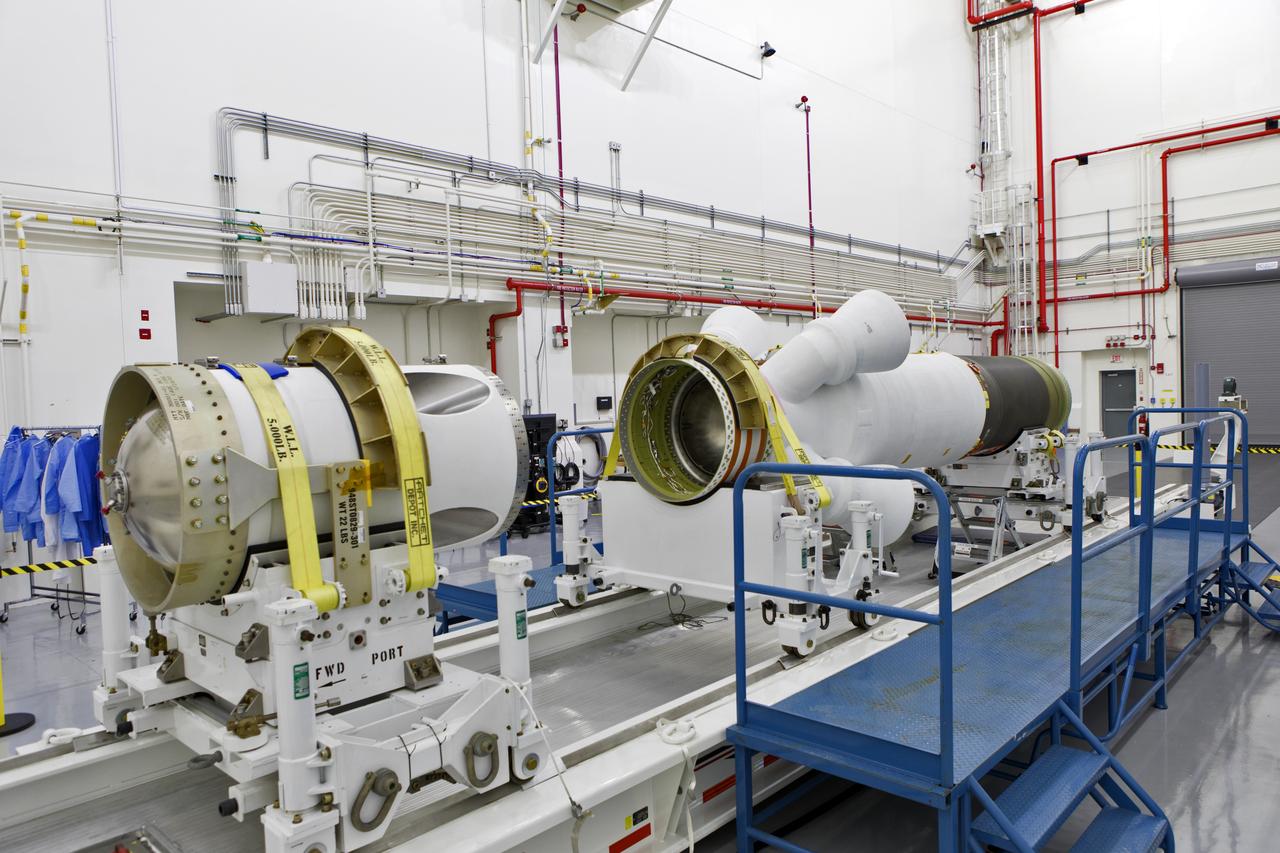

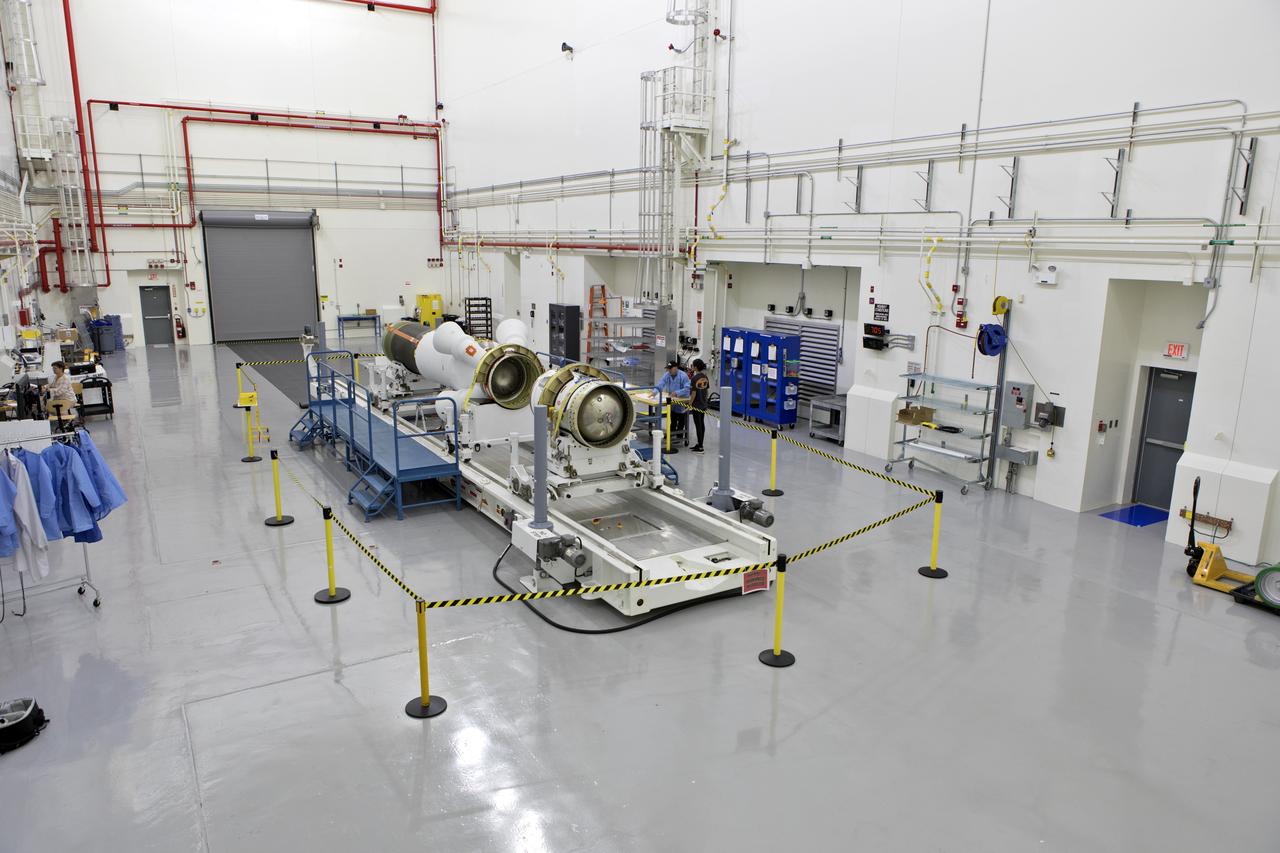
The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
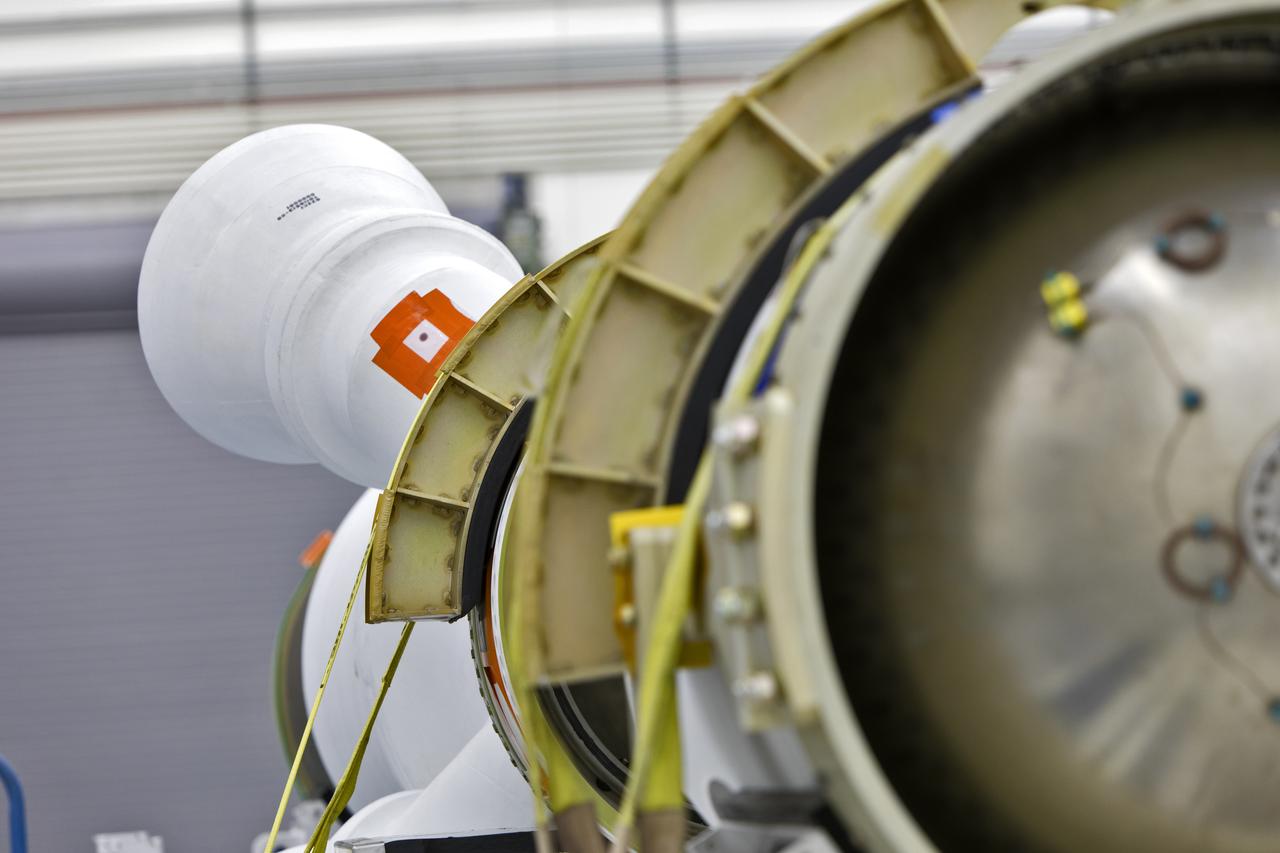

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
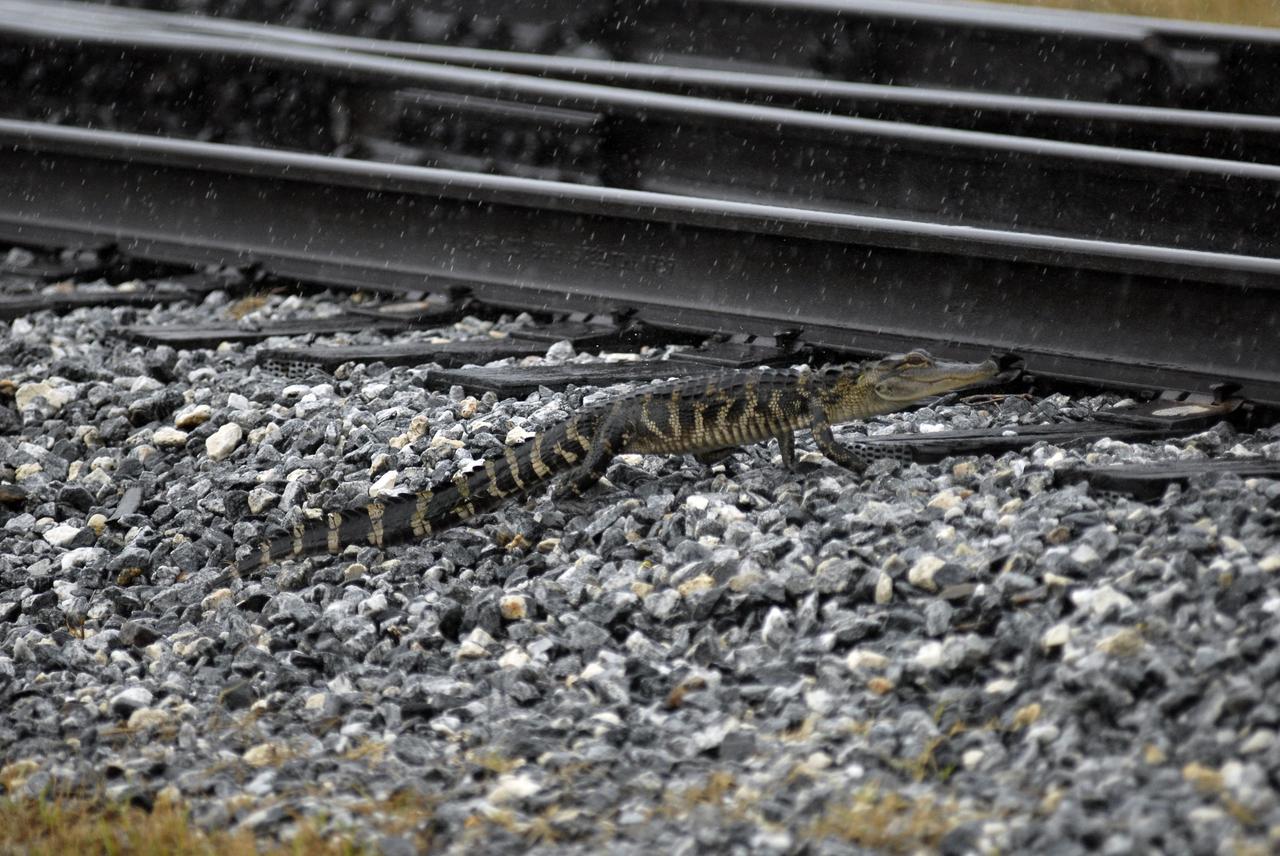

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This young alligator approaches the railroad tracks where the train carrying solid rocket booster motor segments is approaching Kennedy Space Center. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
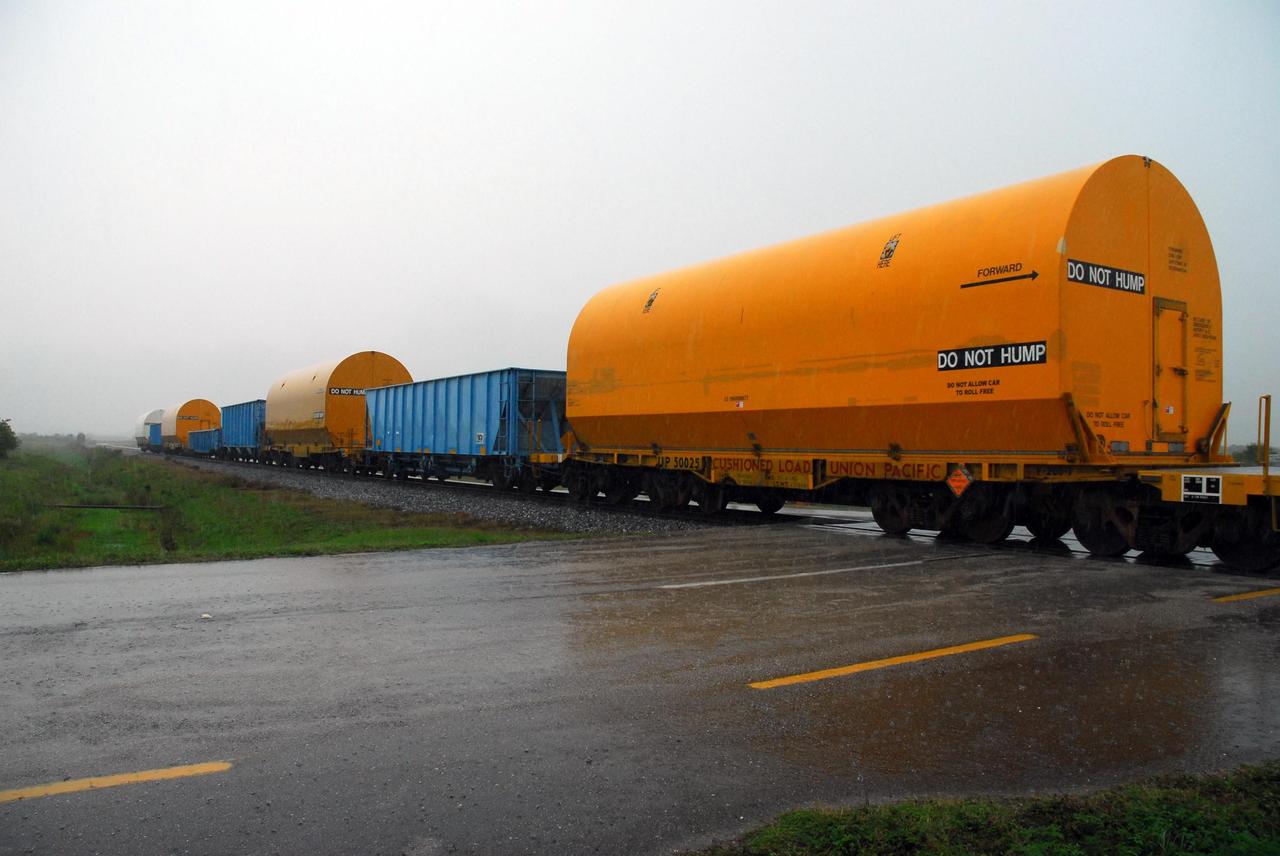

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Solid rocket motor segments and two aft exit cone segments arrive by rail at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
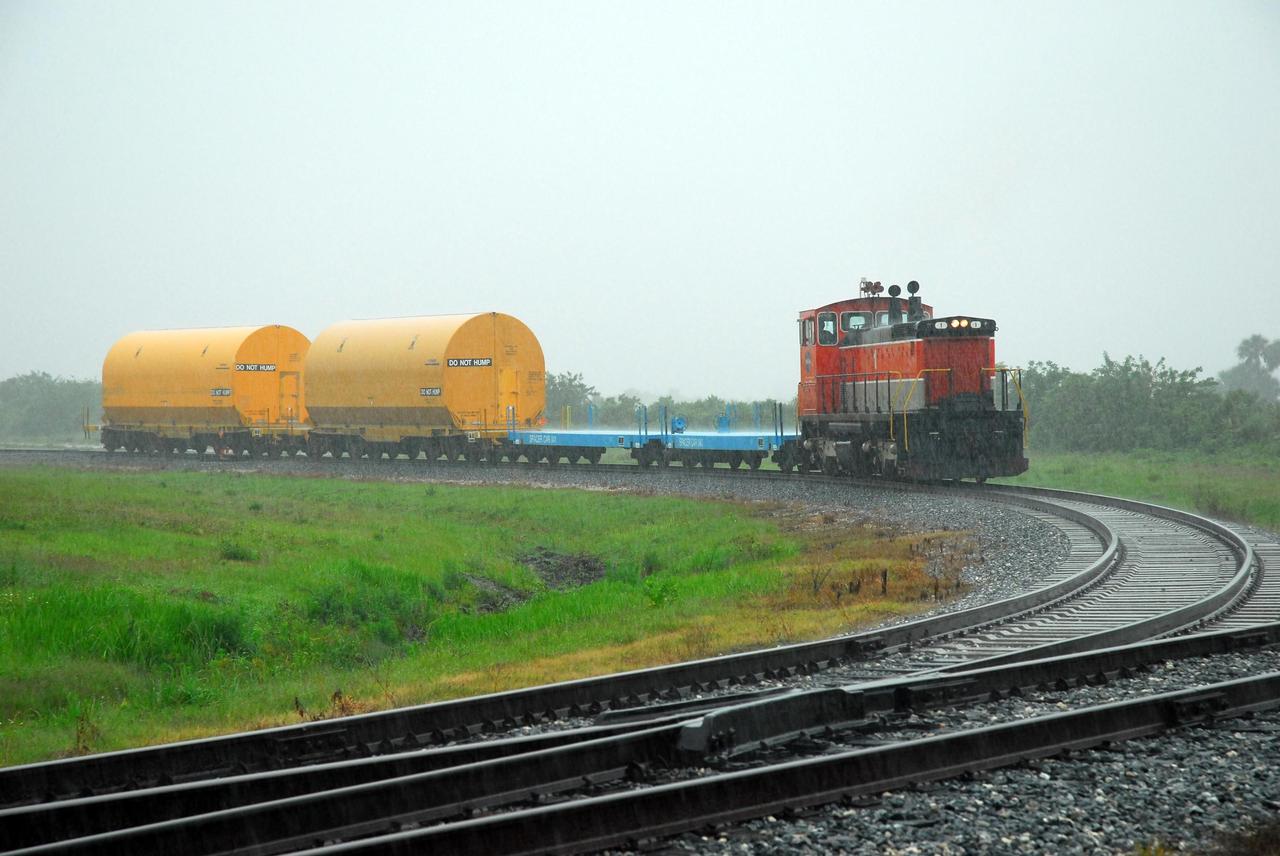

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The locomotive and rail cars carrying solid rocket booster motor segments and two aft exit cone segments cross a road on Kennedy Space Center. These cars are headed for the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
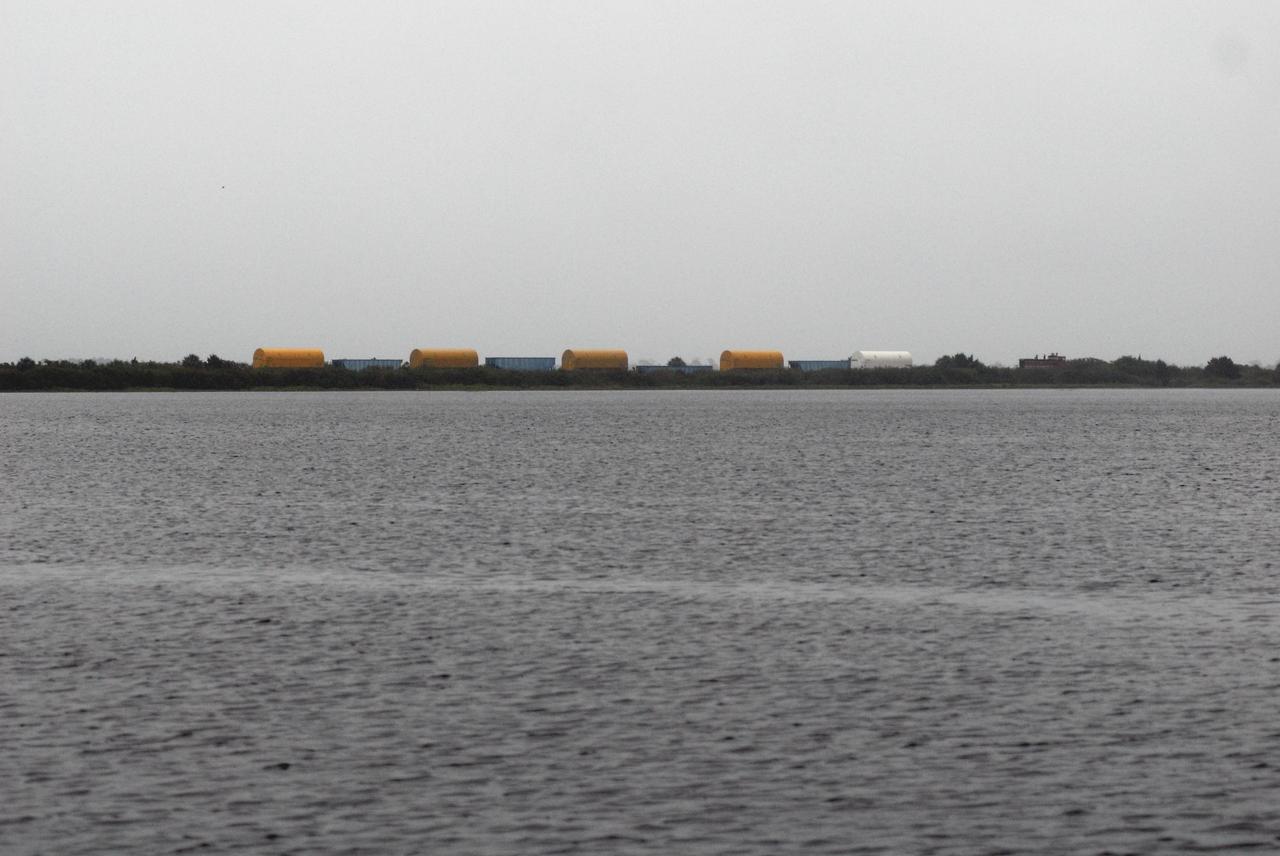

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Solid rocket motor segments and two aft exit cone segments arrive by rail at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
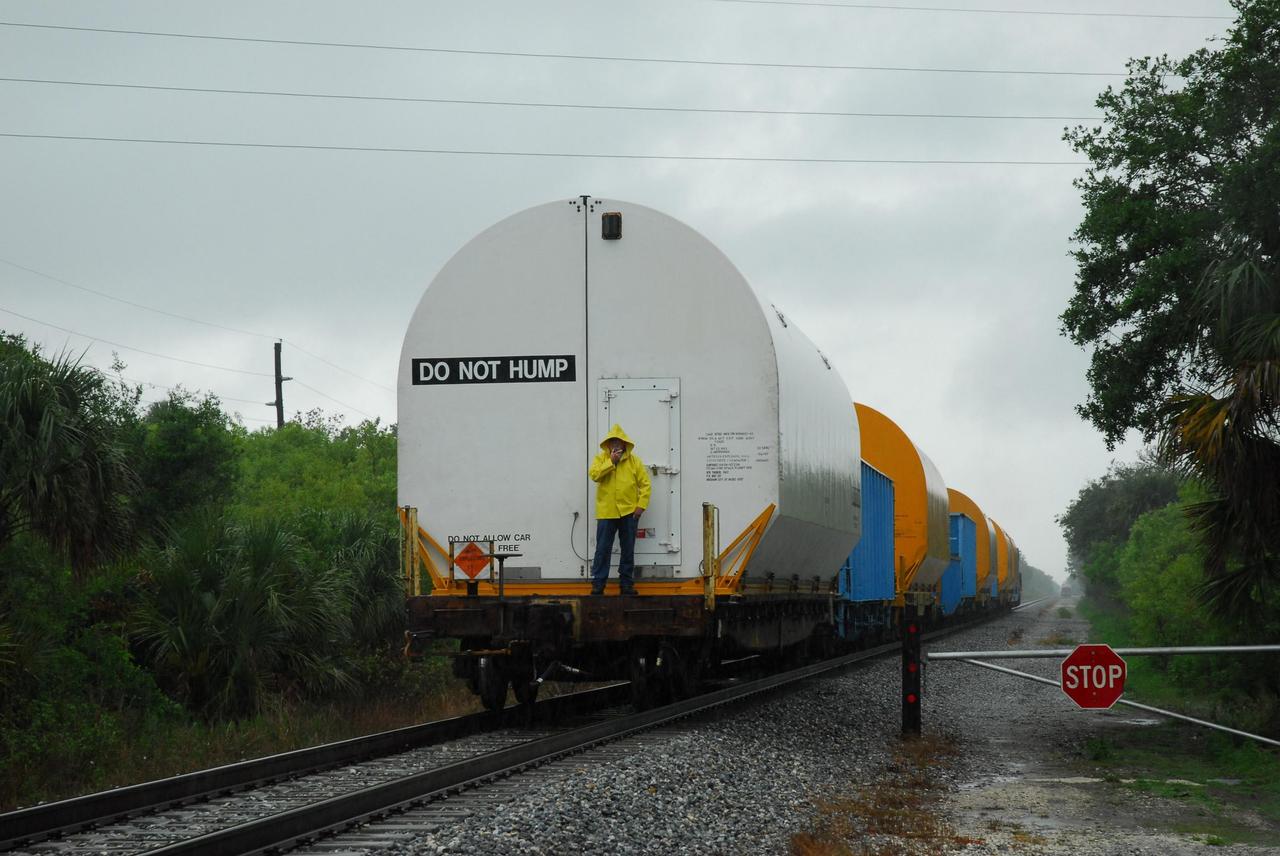

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Solid rocket motor segments and two aft exit cone segments arrive by rail at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This young alligator climbs on the railroad tracks where the train carrying solid rocket booster motor segments is approaching Kennedy Space Center. While enroute, solid rocket motor segments were involved in a derailment in Alabama. The rail cars carrying these segments remained upright and were undamaged. An inspection determined these segment cars could continue on to Florida. The segments themselves will undergo further evaluation at Kennedy before they are cleared for flight. Other segments involved in the derailment will be returned to a plant in Utah for further evaluation. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett