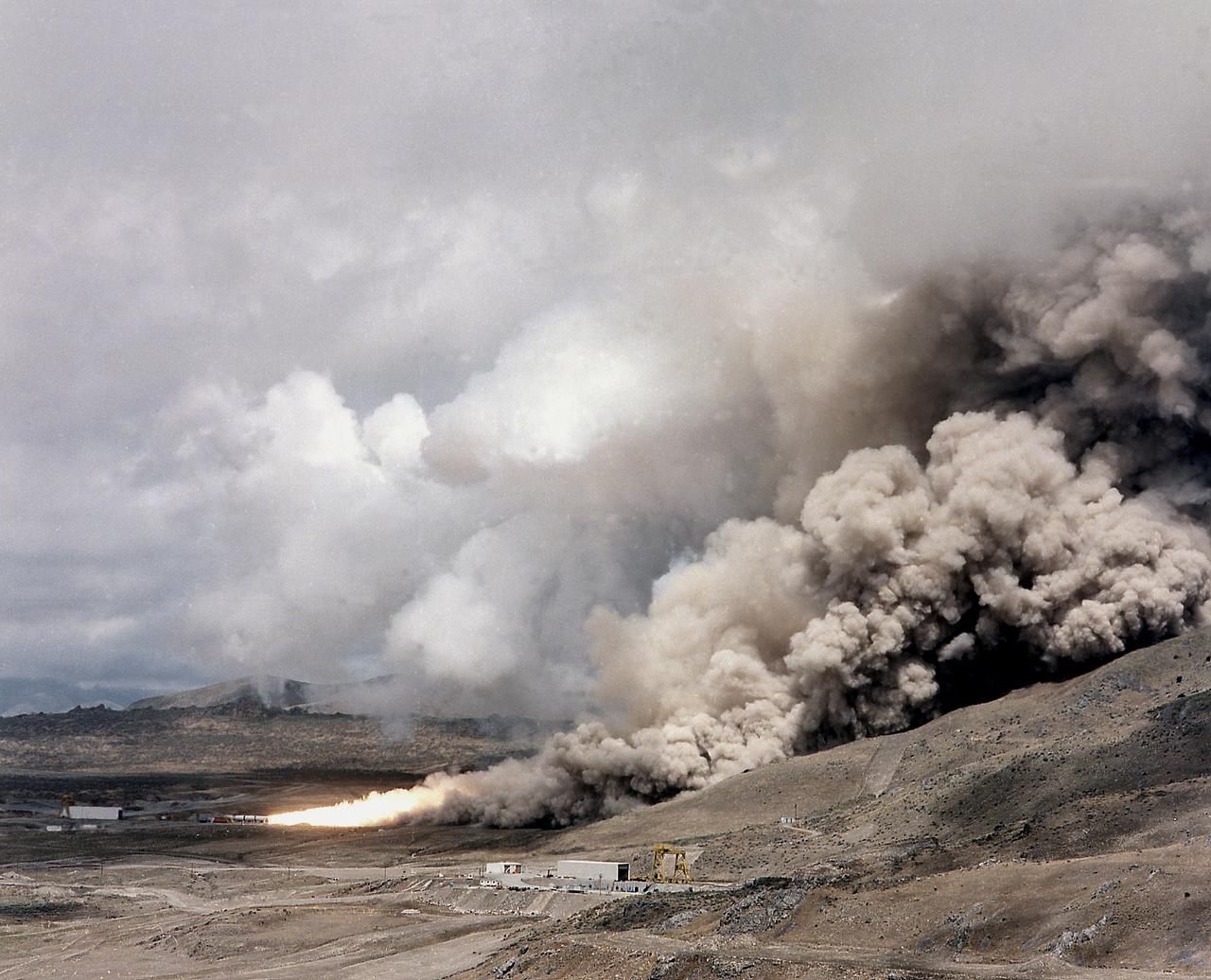

This photograph is a long shot view of a full scale solid rocket motor (SRM) for the solid rocket booster (SRB) being test fired at Morton Thiokol's Wasatch Operations in Utah. The twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the SRM's were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
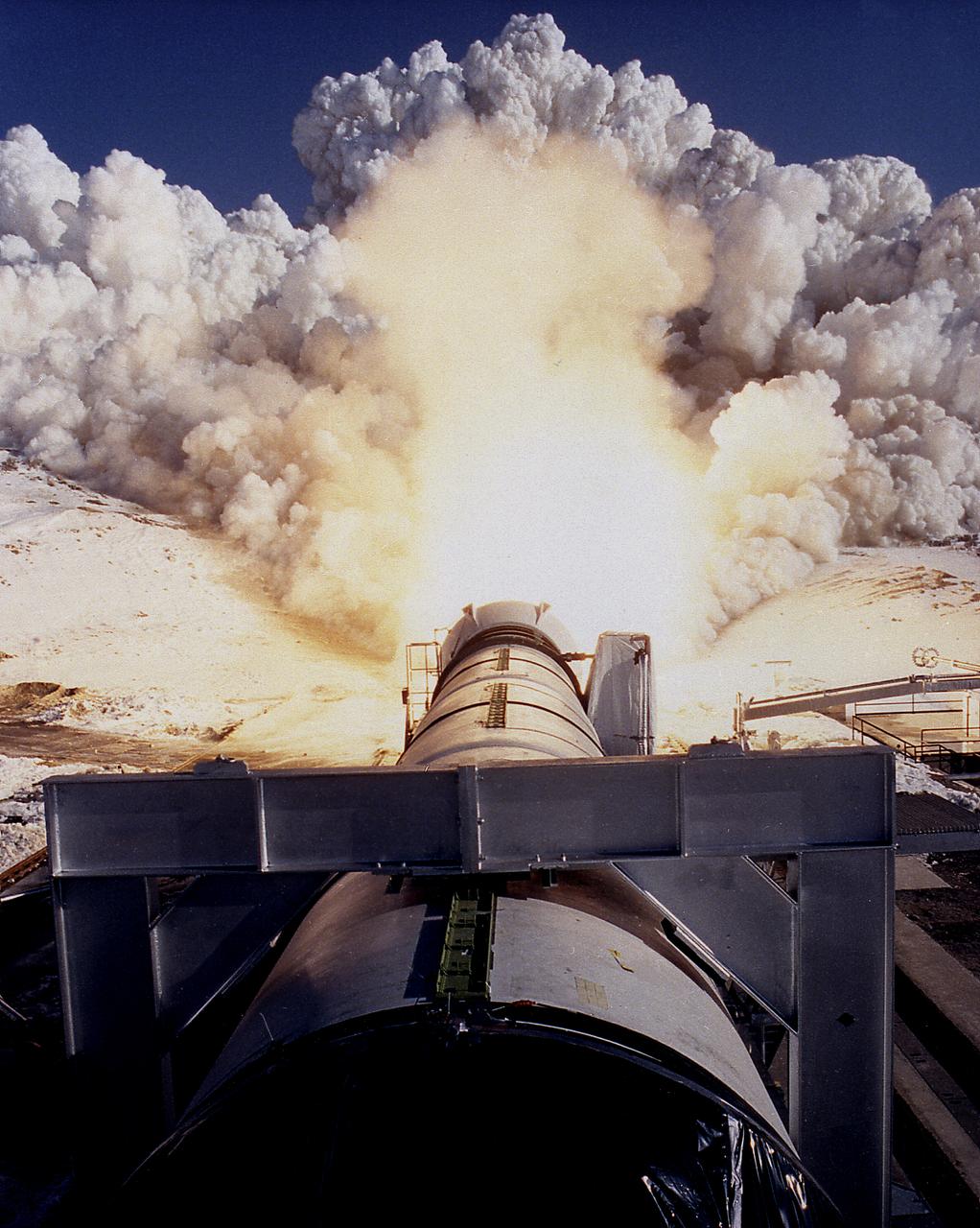

This photograph shows a static firing test of the Solid Rocket Qualification Motor-8 (QM-8) at the Morton Thiokol Test Site in Wasatch, Utah. The twin solid rocket boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
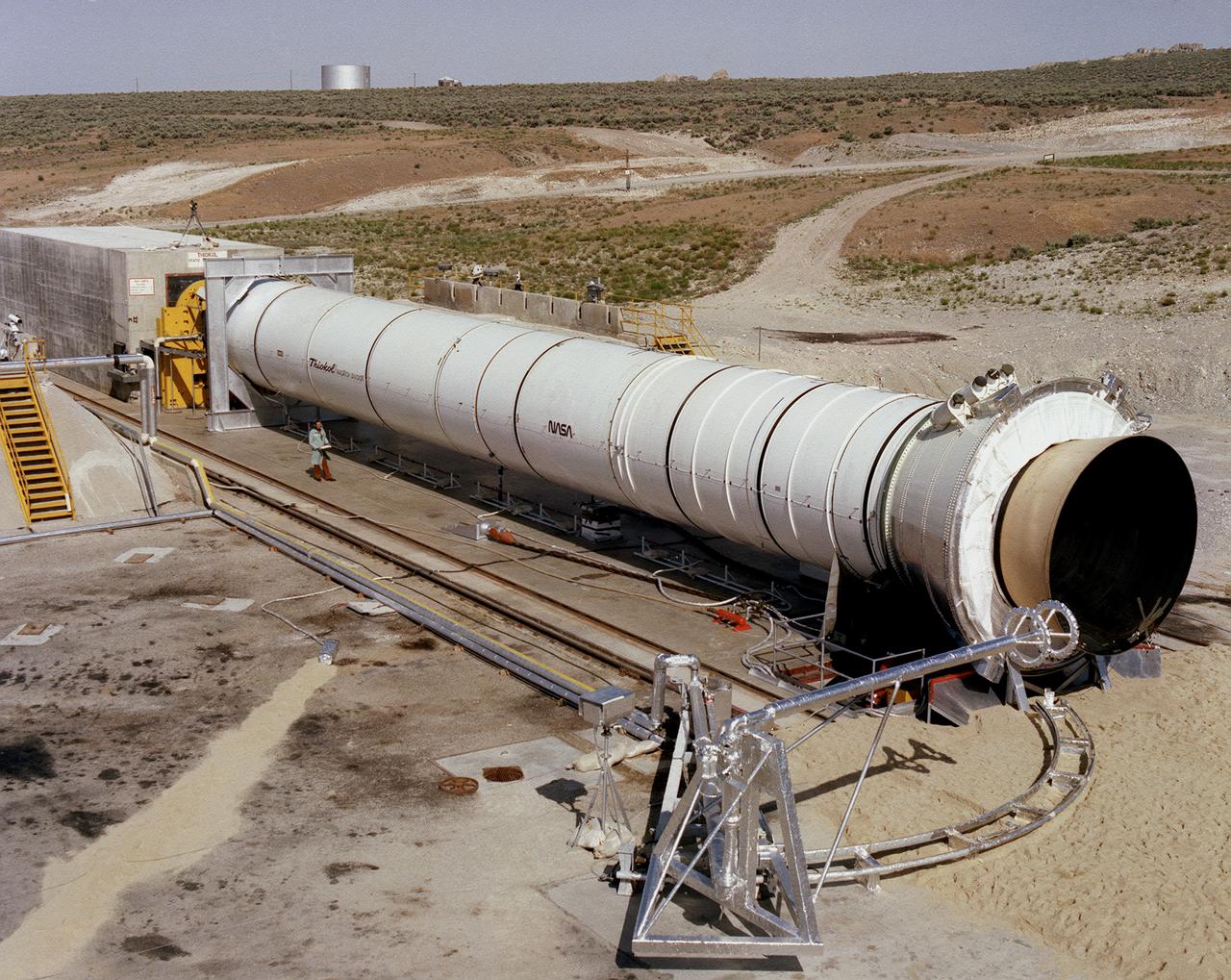

This is a photograph of the solid rocket booster's (SRB's) Qualification Motor-1 (QM-1) being prepared for a static firing in a test stand at the Morton Thiokol Test Site in Wasatch, Utah, showing the aft end of the booster. The twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. Under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
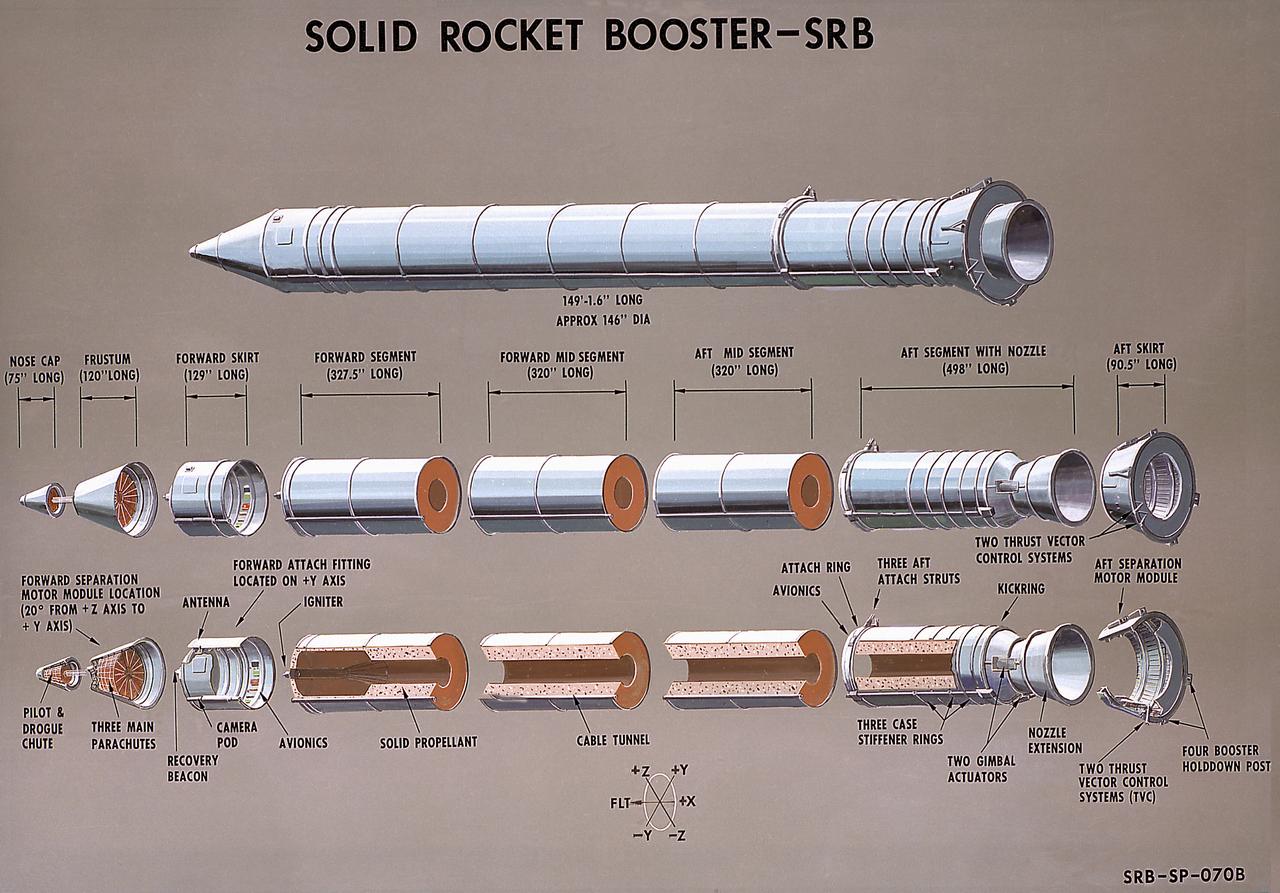
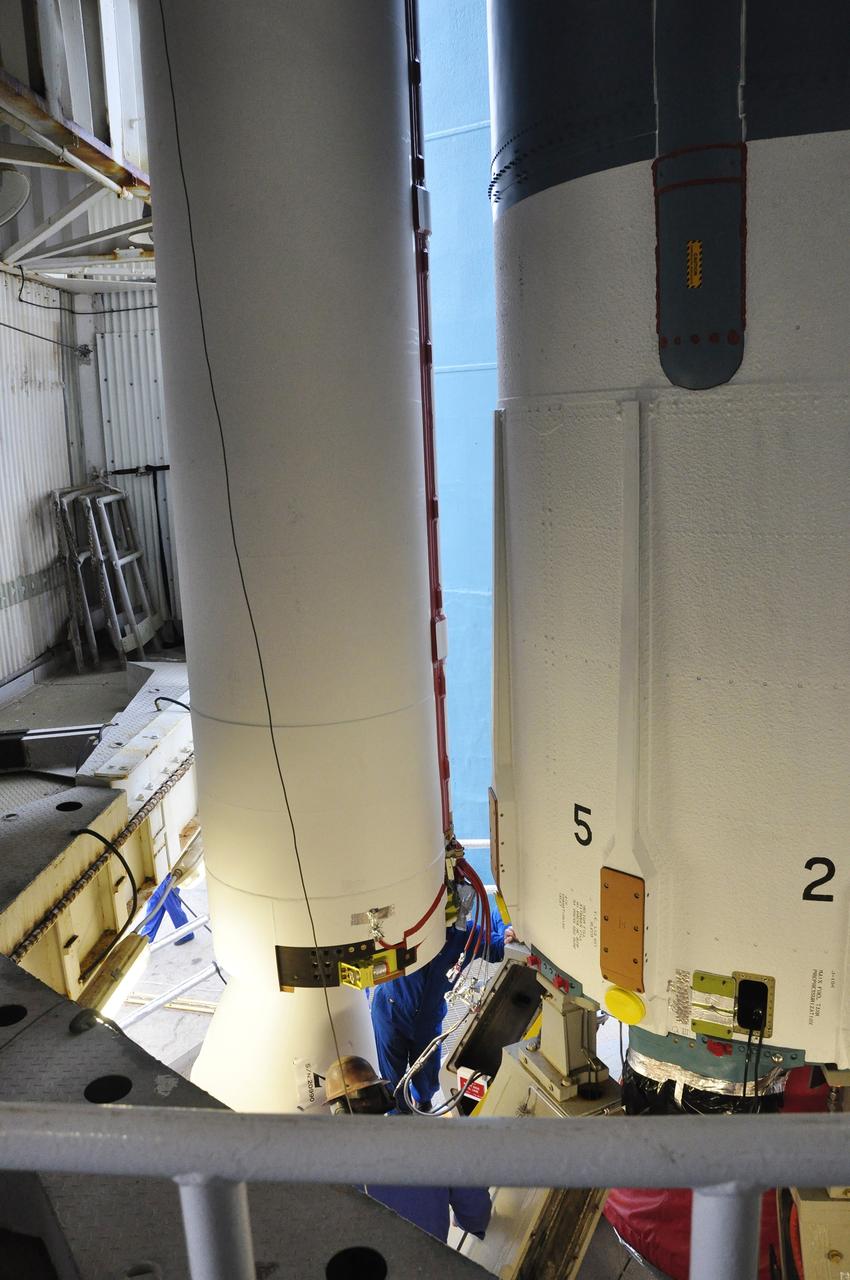
This illustration is a cutaway of the solid rocket booster (SRB) sections with callouts. The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment. The boosters are designed to survive water impact at almost 60 miles per hour, maintain flotation with minimal damage, and preclude corrosion of the hardware exposed to the harsh seawater environment. Under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRB's are assembled and refurbished by the United Space Boosters. The SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
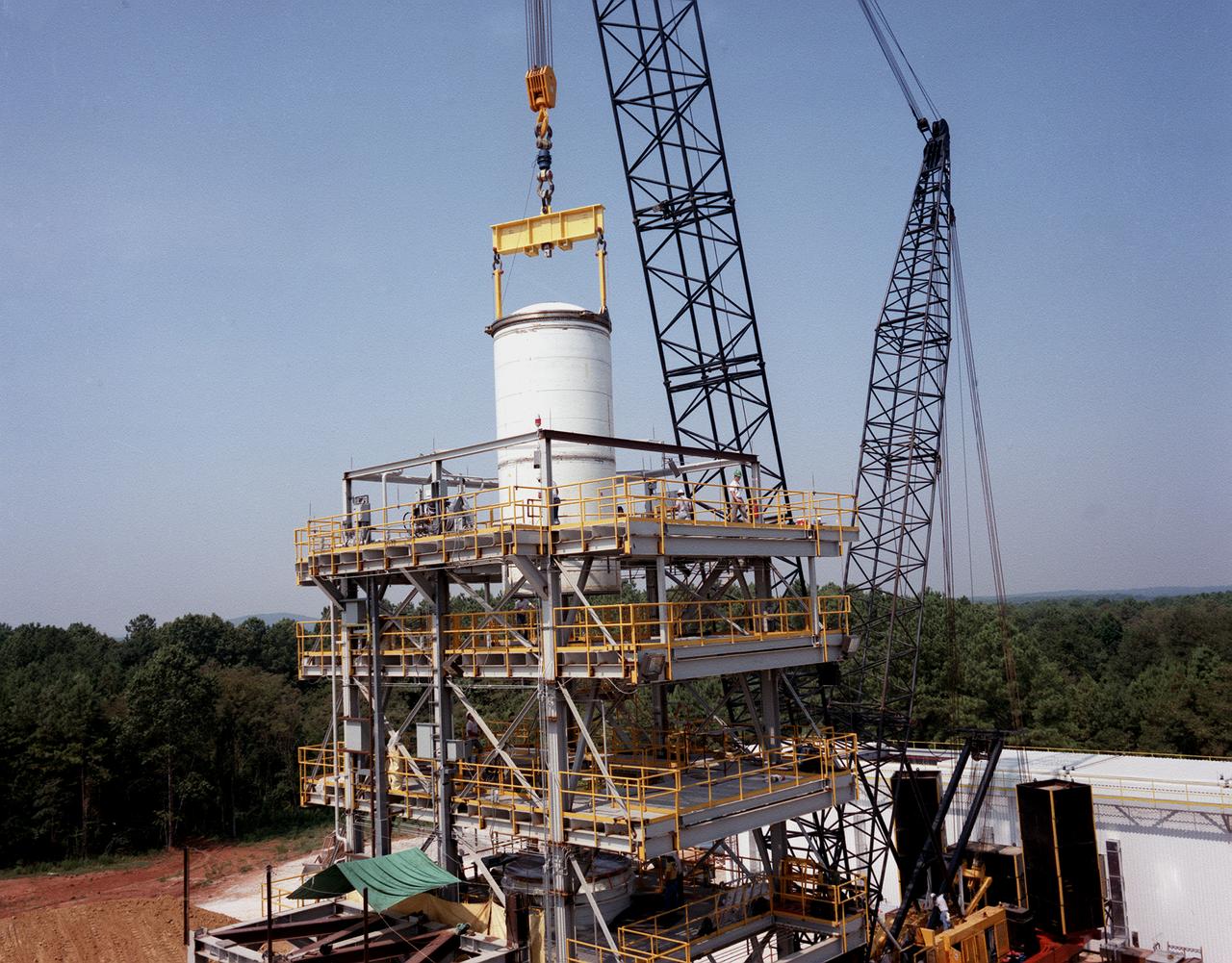

A forward segment is being lowered into the Transient Pressure Test Article (TPTA) test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) east test area. The TPTA test stand, 14-feet wide, 27-feet long, and 33-feet high, was built in 1987 to provide data to verify the sealing capability of the redesign solid rocket motor (SRM) field and nozzle joints. The test facility applies pressure, temperature, and external loads to a short stack of solid rocket motor hardware. The simulated SRM ignition pressure and temperature transients are achieved by firing a small amount of specially configured solid propellant. The pressure transient is synchronized with external programmable dynamic loads that simulate lift off loads at the external tank attach points. Approximately one million pounds of dead weight on top of the test article simulates the weight of the other Shuttle elements.
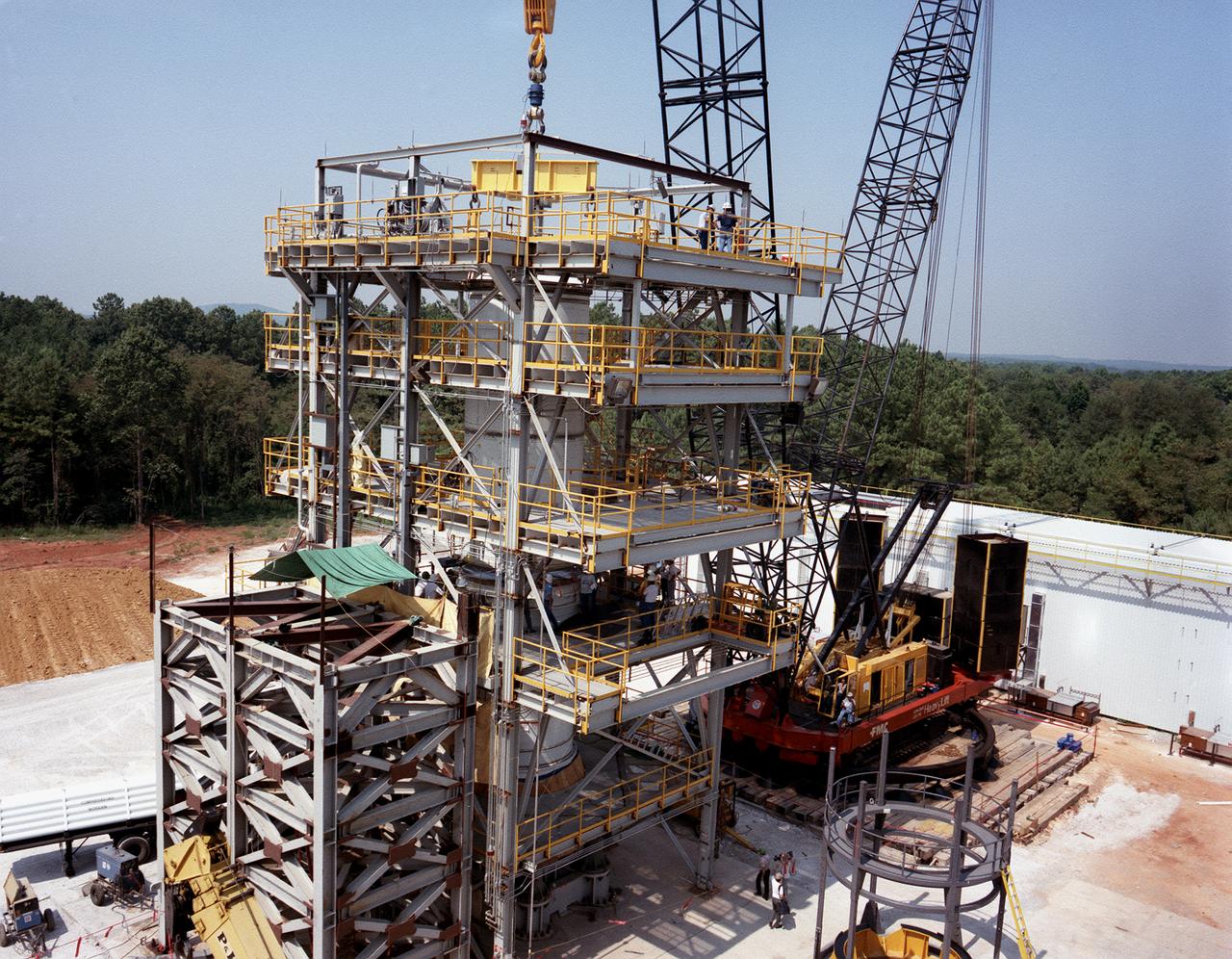

A forward segment is being lowered into the Transient Pressure Test Article (TPTA) test stand at thw Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) east test area. The TPTA test stand, 14-feet wide, 27-feet long, and 33-feet high, was built in 1987 to provide data to verify the sealing capability of the redesign solid rocket motor (SRM) field and nozzle joints. The test facility applies pressure, temperature, and external loads to a short stack of solid rocket motor hardware. The simulated SRM ignition pressure and temperature transients are achieved by firing a small amount of specially configured solid propellant. The pressure transient is synchronized with external programmable dynamic loads that simulate lift off loads at the external tank attach points. Approximately one million pounds of dead weight on top of the test article simulates the weight of the other Shuttle elements.
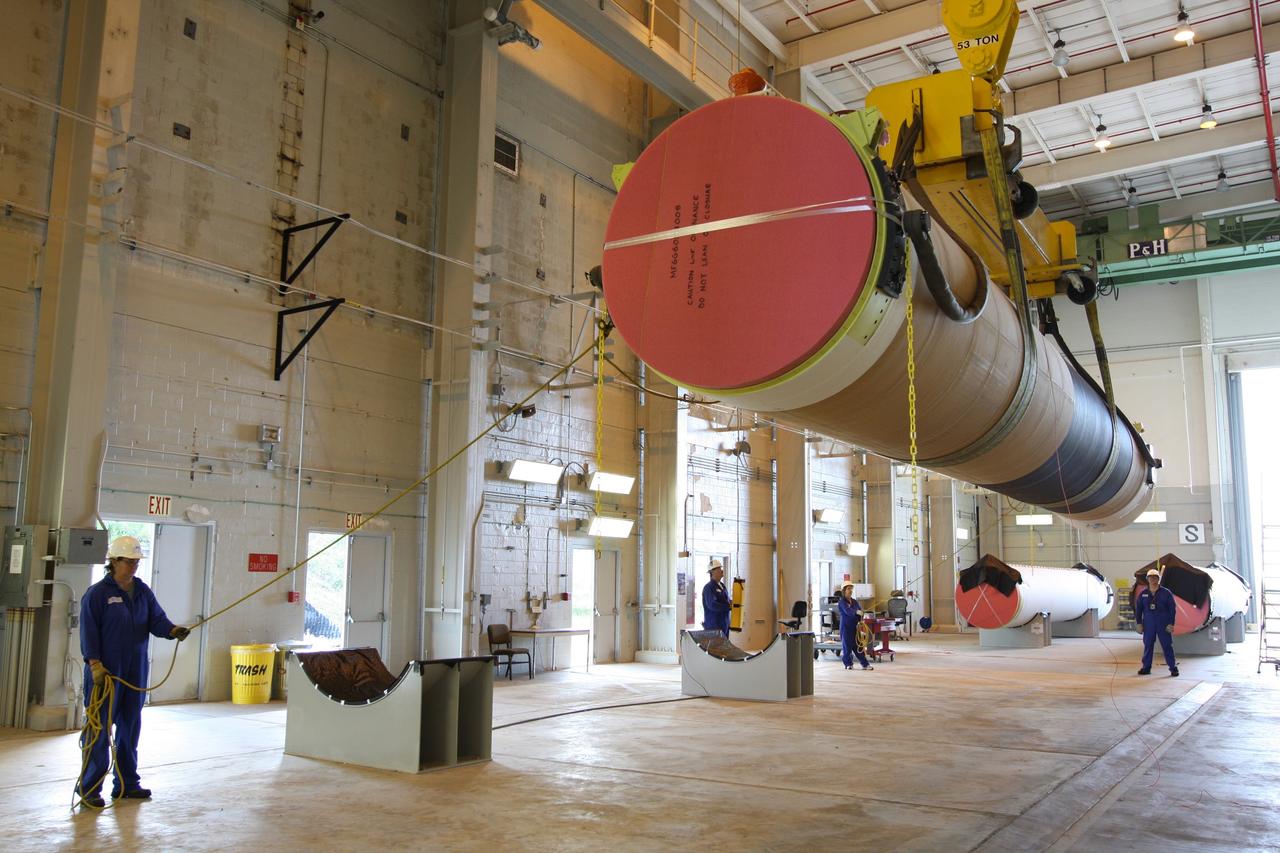

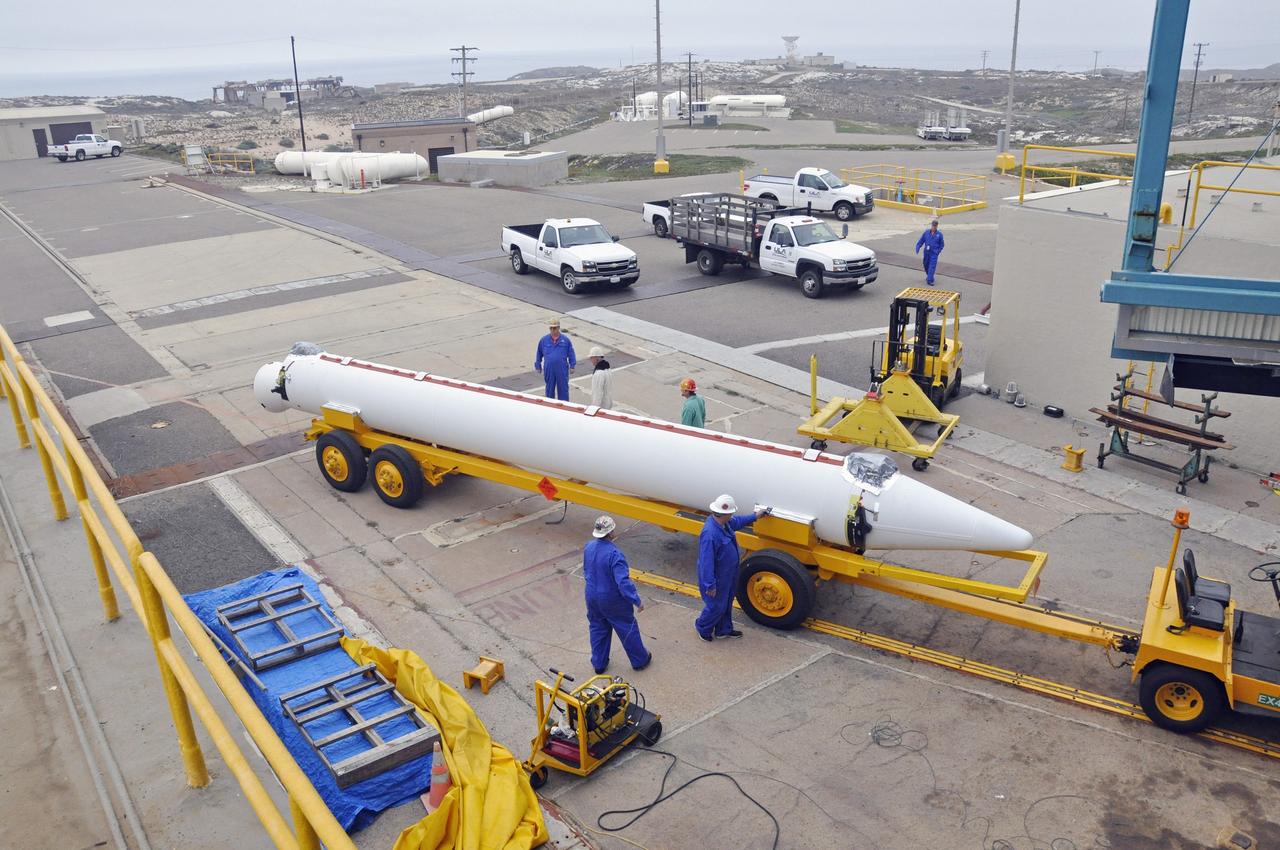
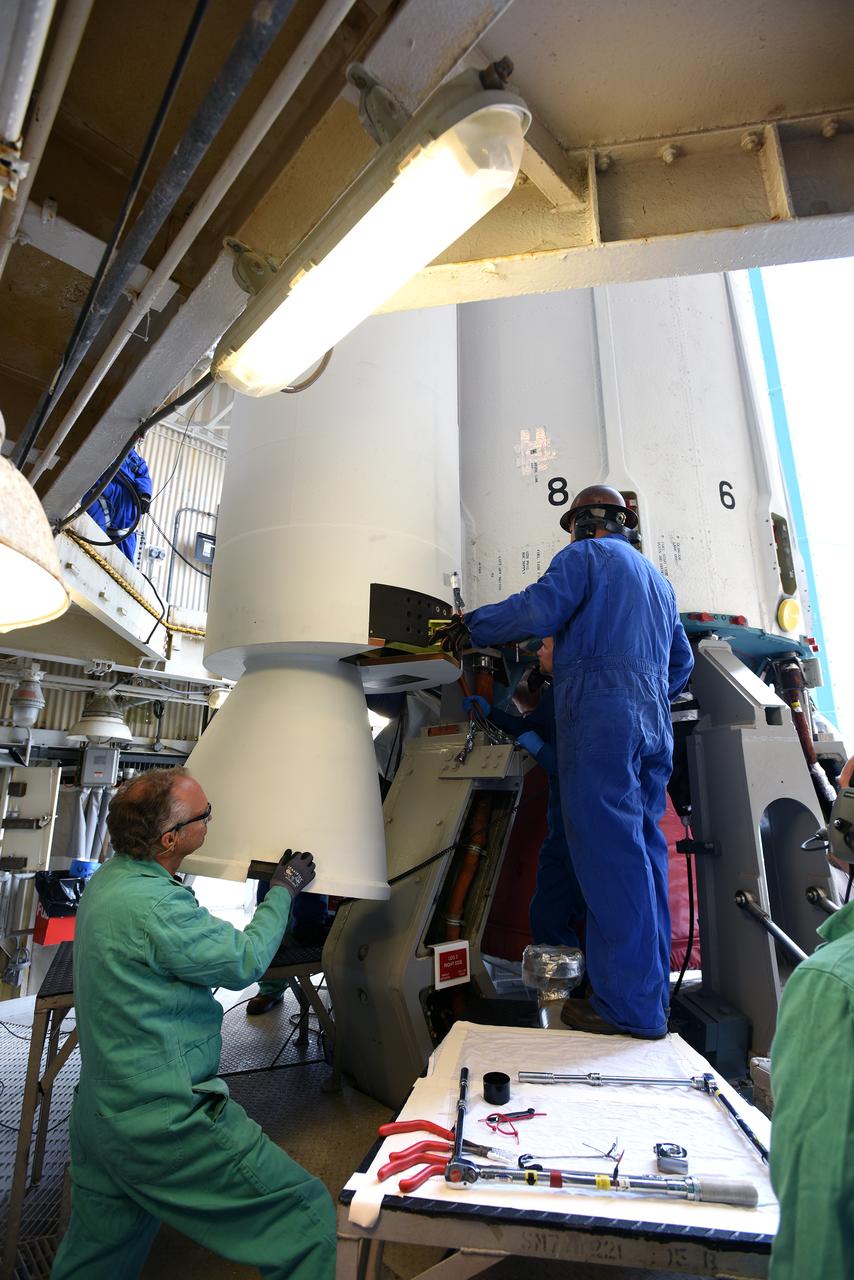
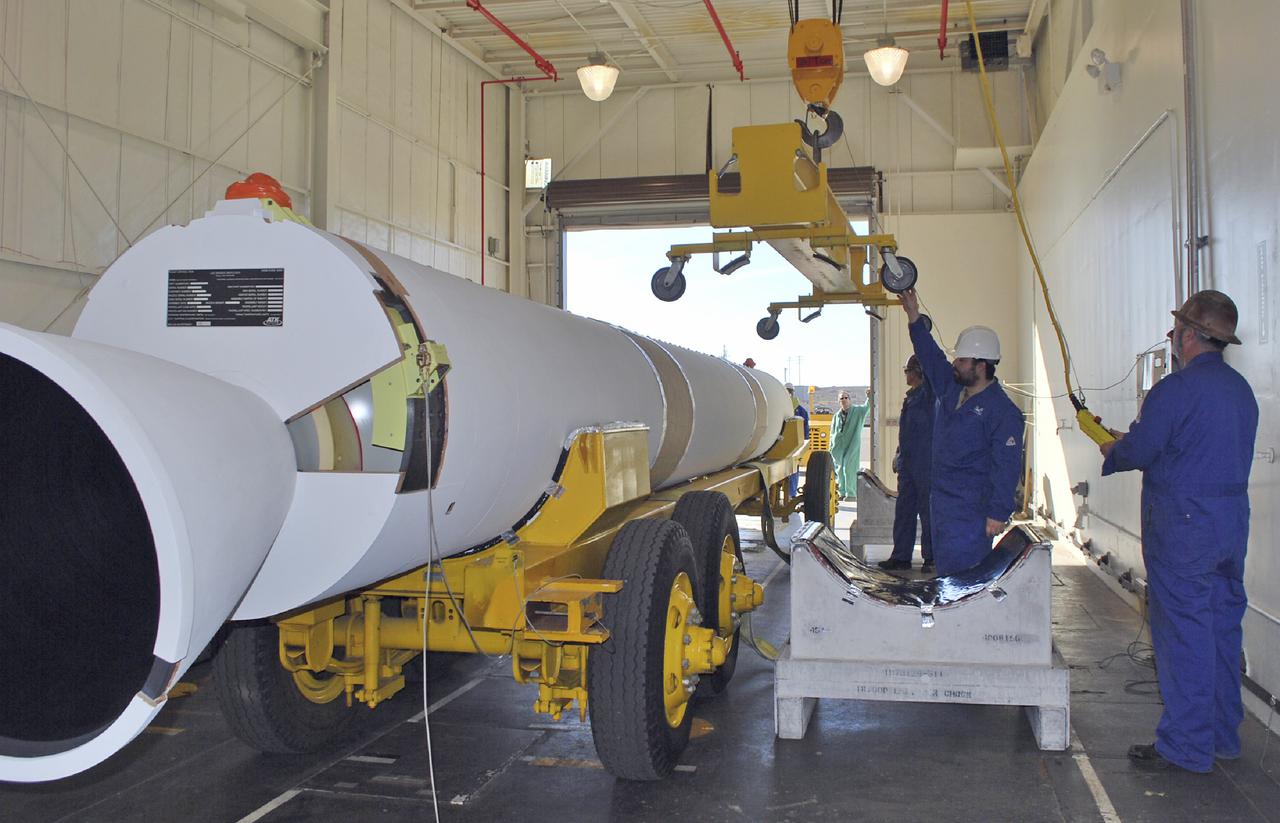
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, ATK Space Systems workers guide a 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft as it is lowered toward a work stand. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
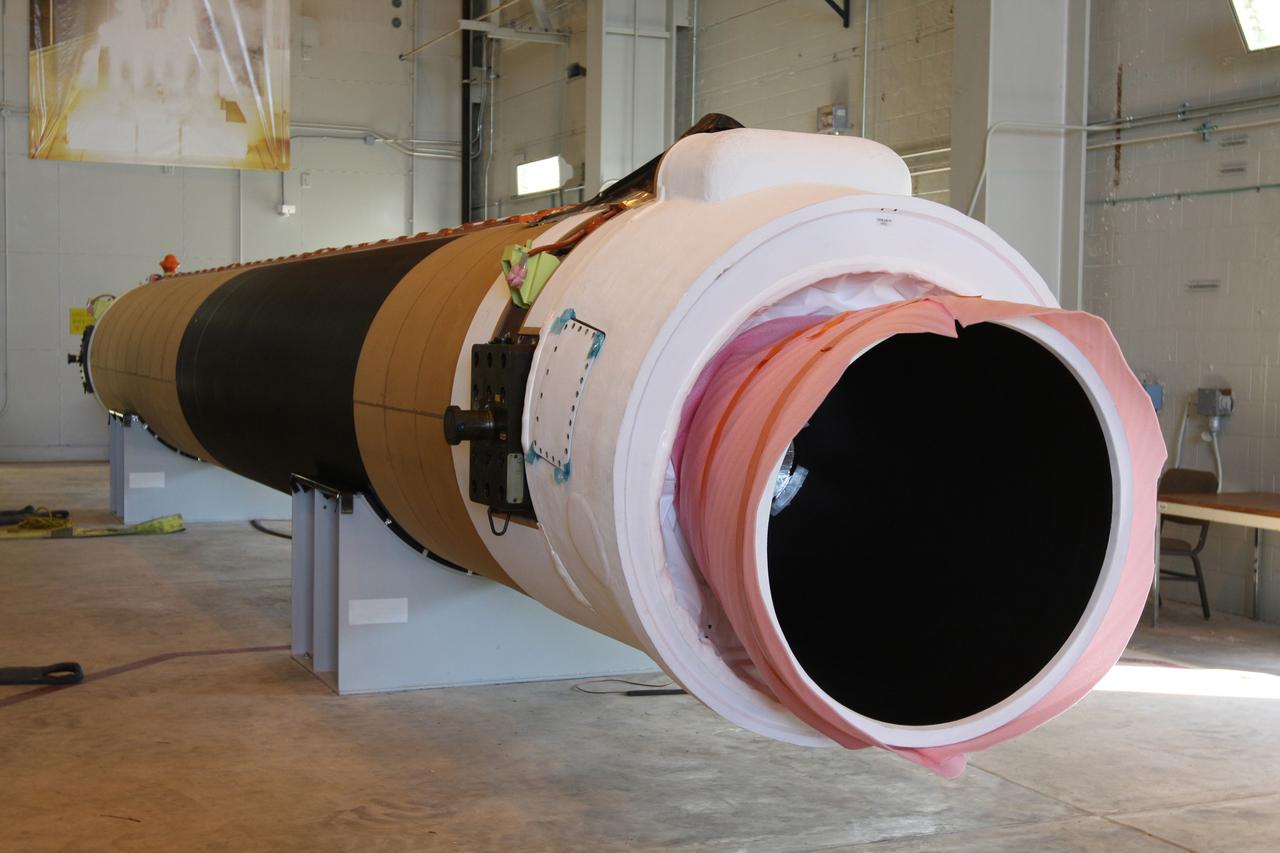

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft rests on a work stand awaiting further processing. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
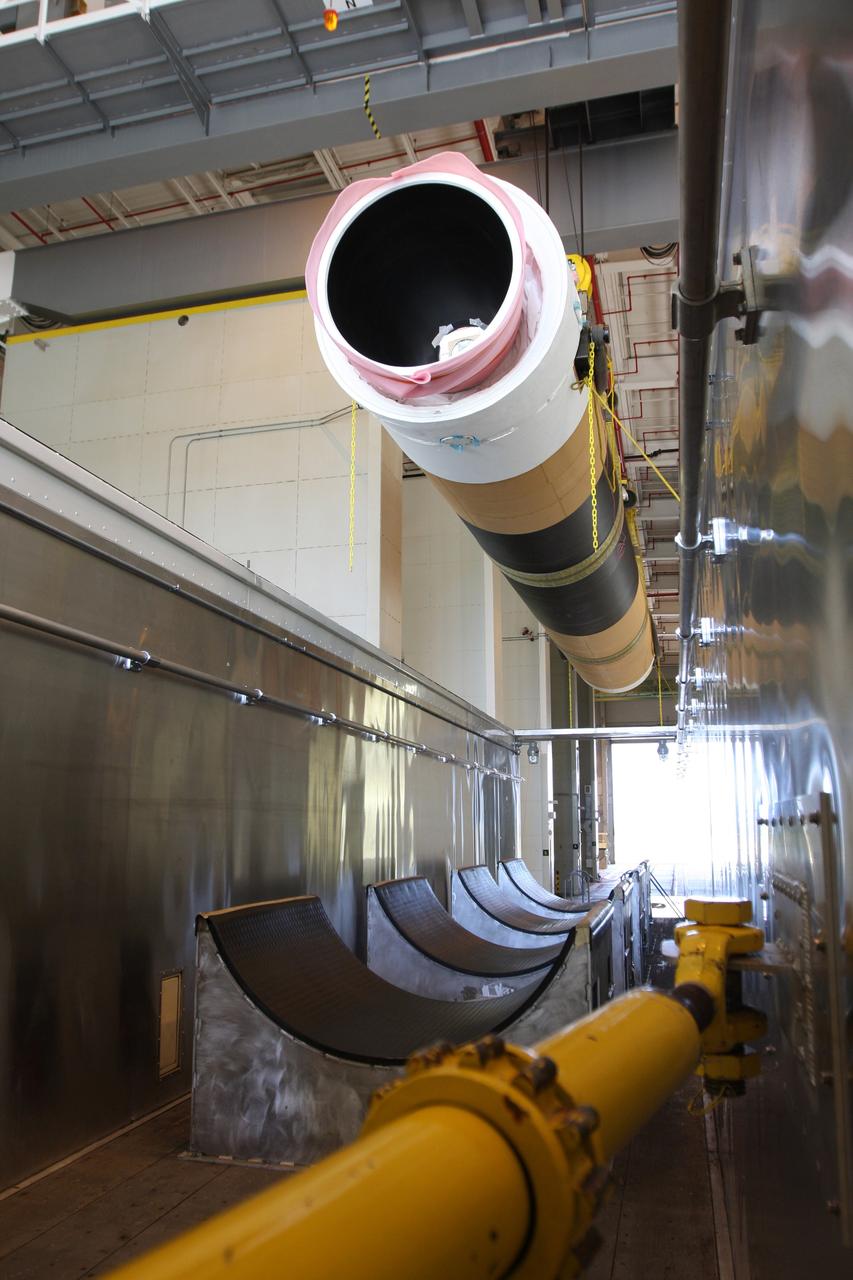

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft is lifted from the tractor-trailer in which it was delivered. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
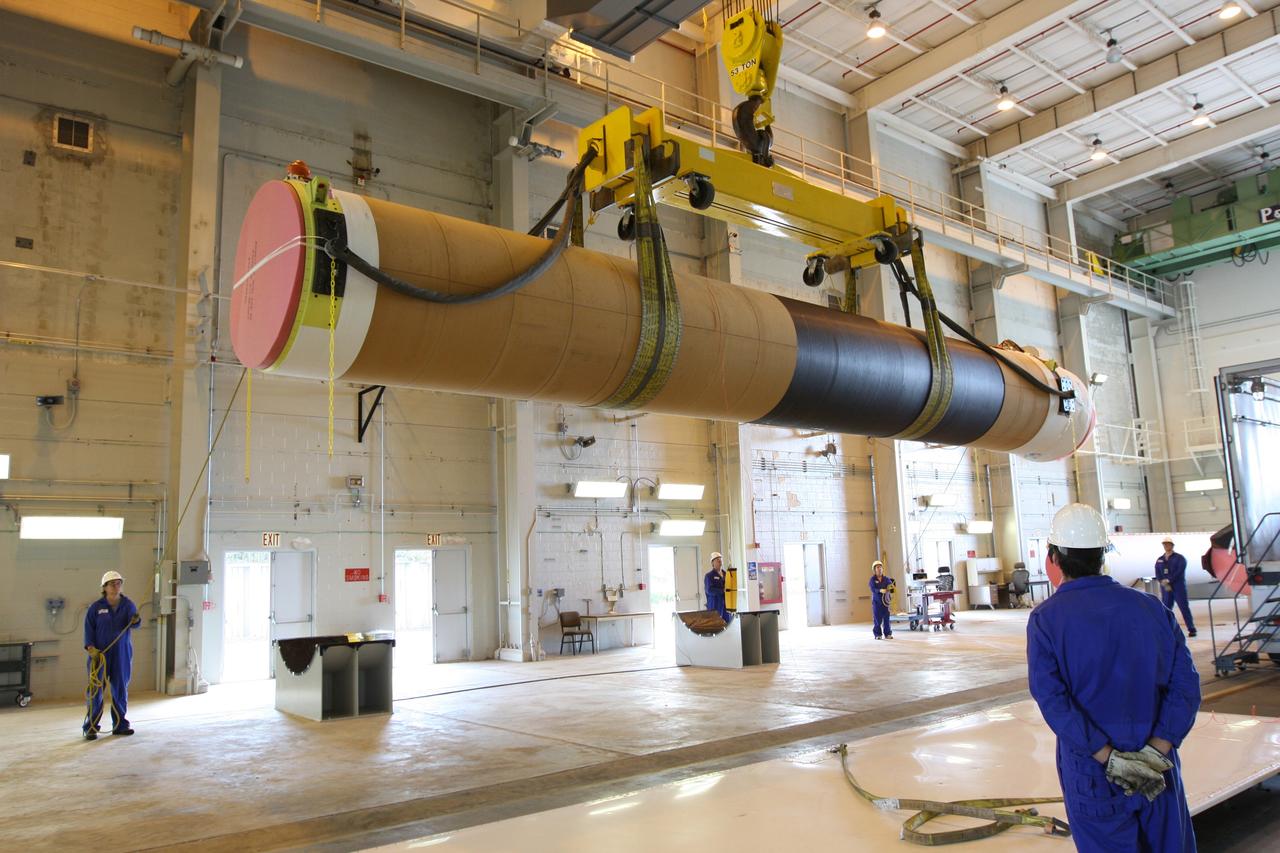

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, ATK Space Systems workers guide a 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft as it is moved toward a work stand. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
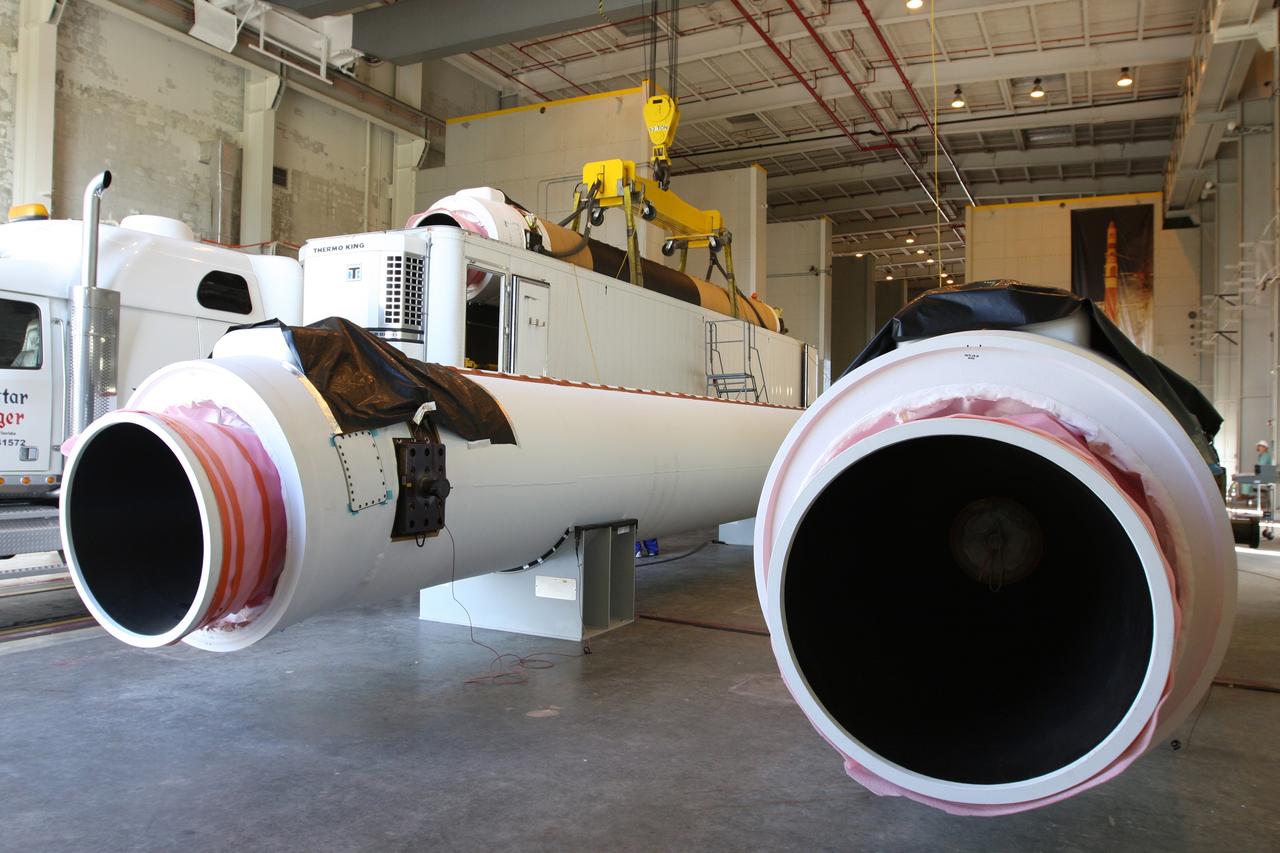

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Receipt Inspection Shop on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an ATK Space Systems' 60-inch graphite epoxy motor, or GEM, slated for launch of the GOES-P spacecraft is lifted from the tractor-trailer in which it was delivered. The two GEMs in the foreground were delivered previously to support another mission. The United Launch Alliance Delta IV is the launch vehicle for GOES-P, the latest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. Launch is targeted for March 4, 2010, from Launch Complex 37. For information on GOES-P, visit http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/goes-n-o-p. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
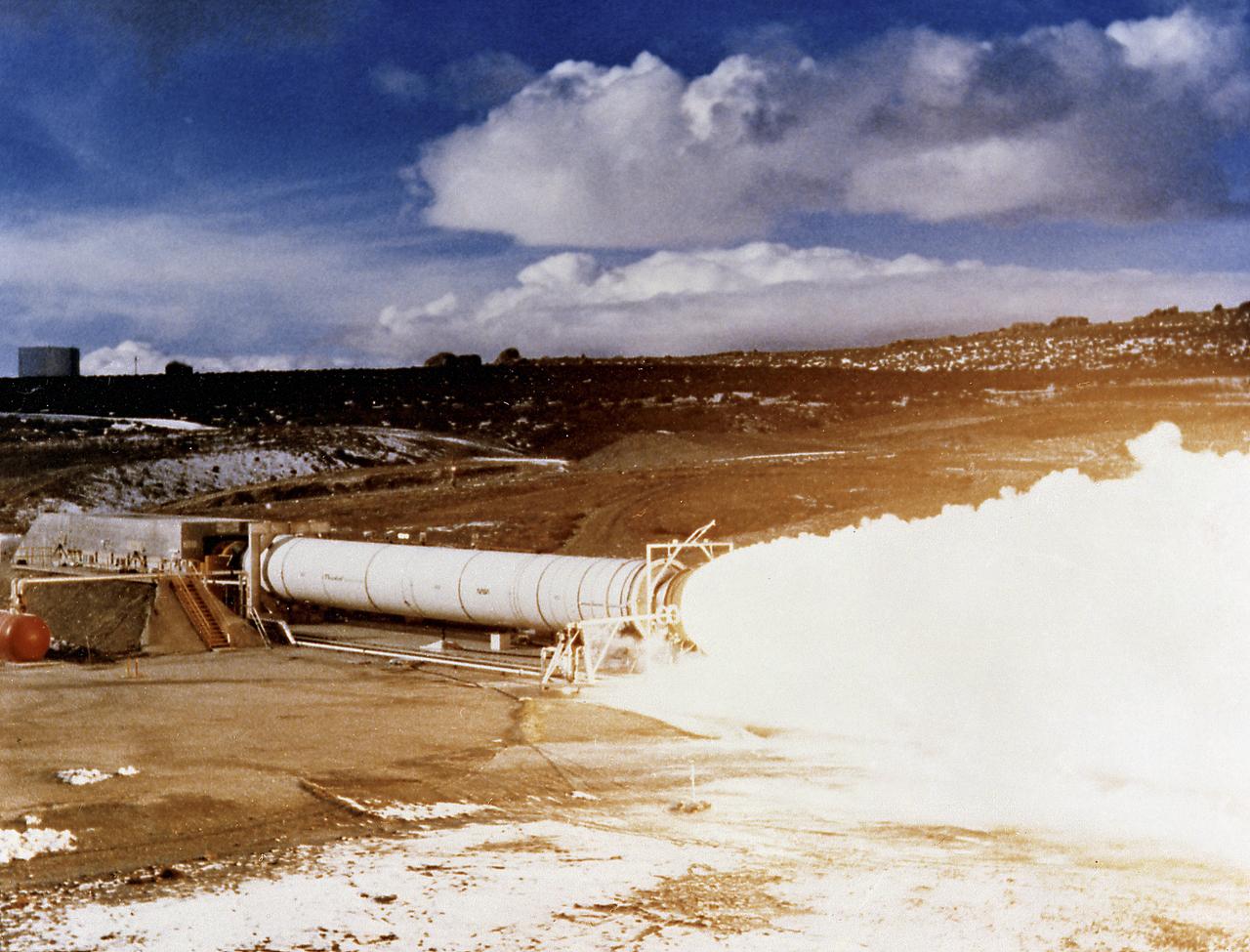

Pictured is an early testing of the Solid Rocket Motor (SRM) at the Thiokol facility in Utah. The SRMs later became known as Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) as they were more frequently used on the Space Shuttles.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 Solid Rocket Motor in support of the Ares/CLV first stage at ATK, Utah . Constellation/Ares project. This image is extracted from a high definition video file and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 Solid Rocket Motor in support of the Ares/CLV first stage at ATK, Utah . Constellaton/Ares project. This image is extracted from a high definition video file and is the highest resolution available.

Shown is a test of the TEM-13 solid rocket motor at the ATK test facility in Utah in support of the Ares/CLV first stage. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.
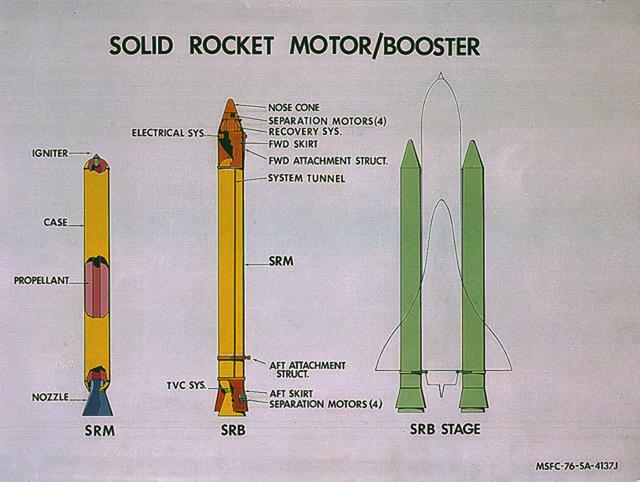
This image illustrates the solid rocket motor (SRM)/solid rocket booster (SRB) configuration. The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the SRM's were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment. The boosters are designed to survive water impact at almost 60 miles per hour, maintain flotation with minimal damage, and preclude corrosion of the hardware exposed to the harsh seawater environment. Under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the SRB's are assembled and refurbished by the United Space Boosters. The SRM's are provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.
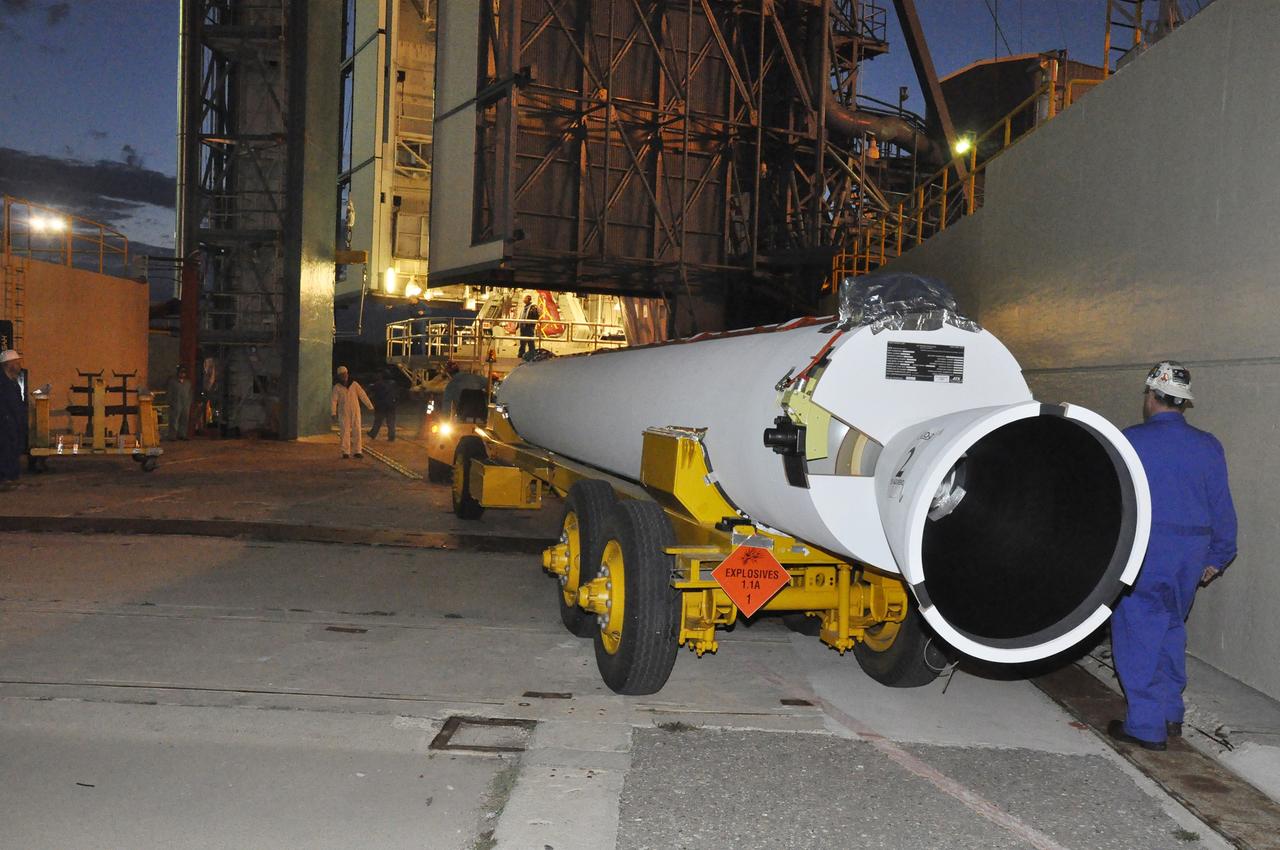

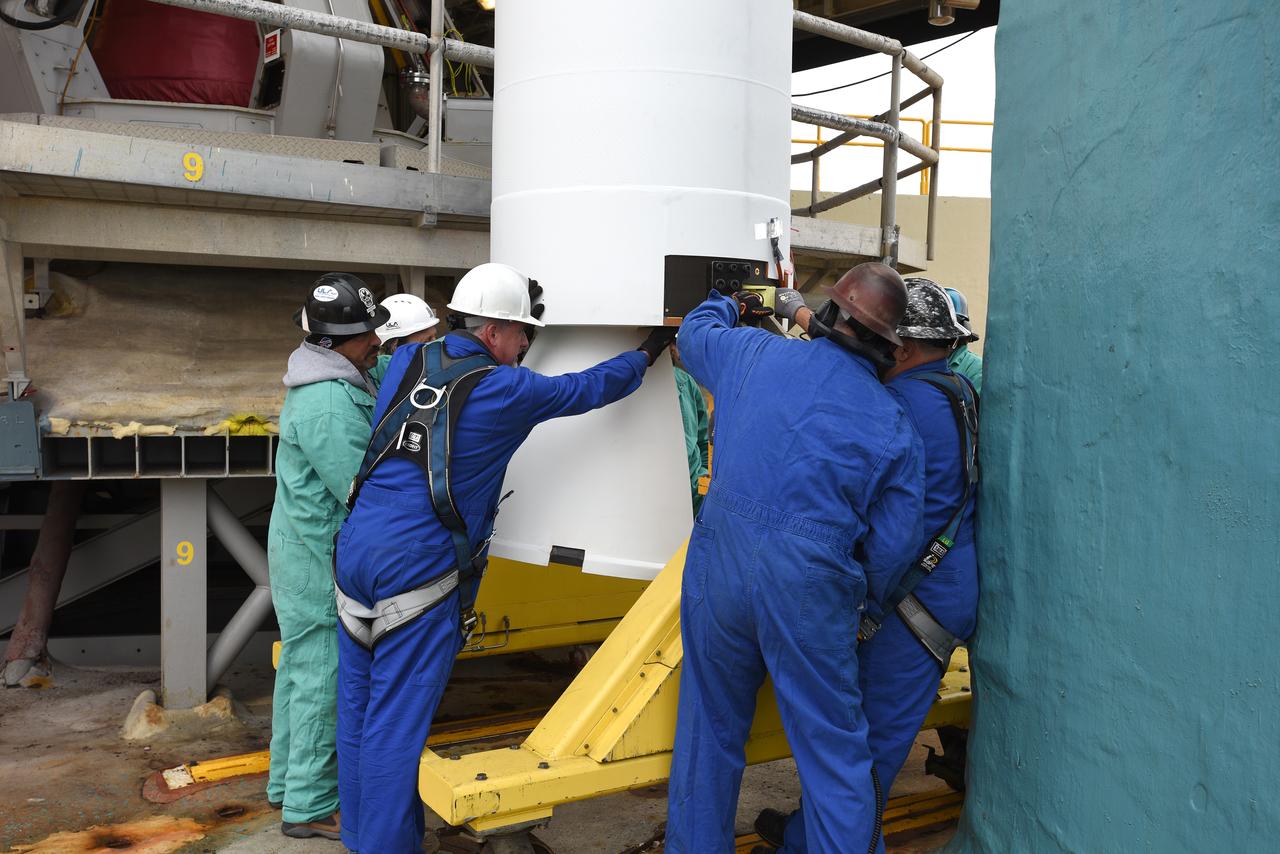
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A second solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is towed to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
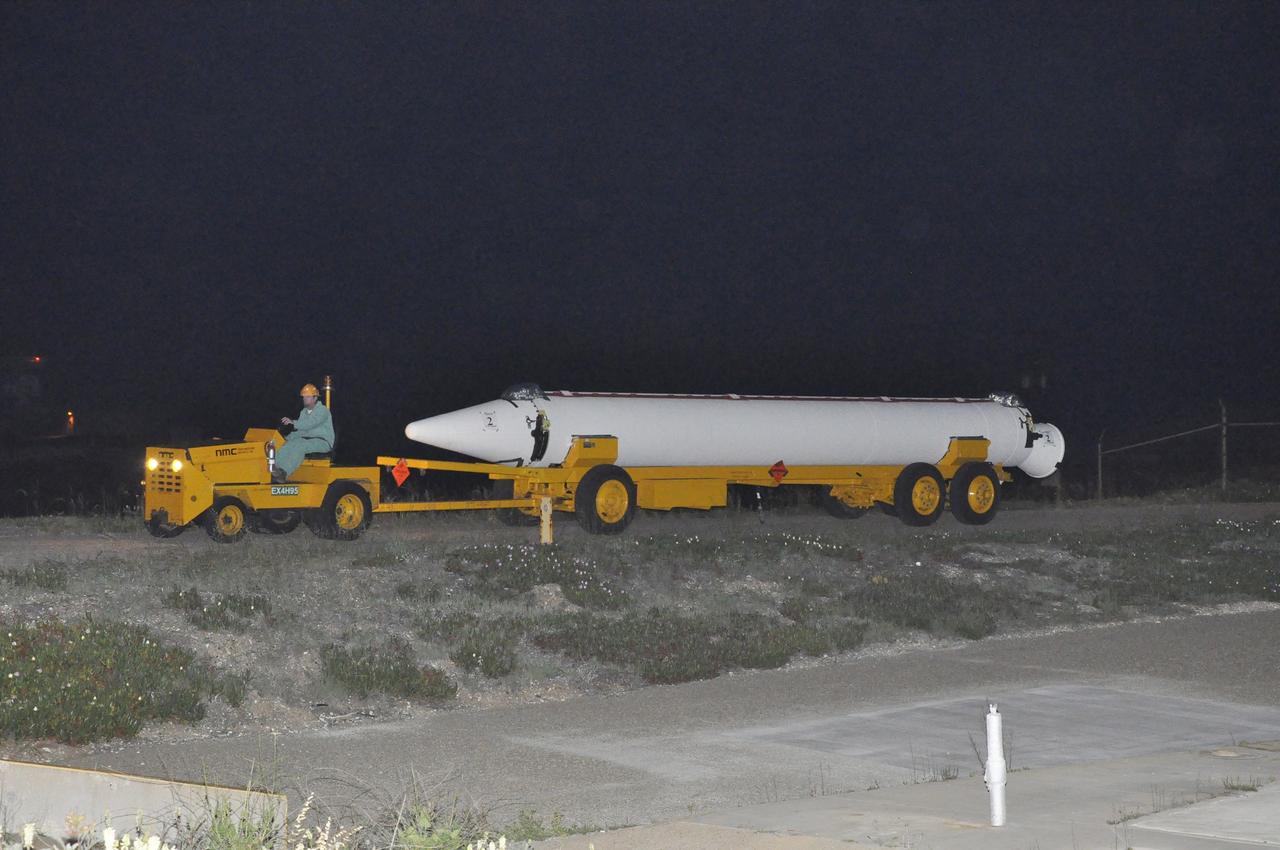

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is towed to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

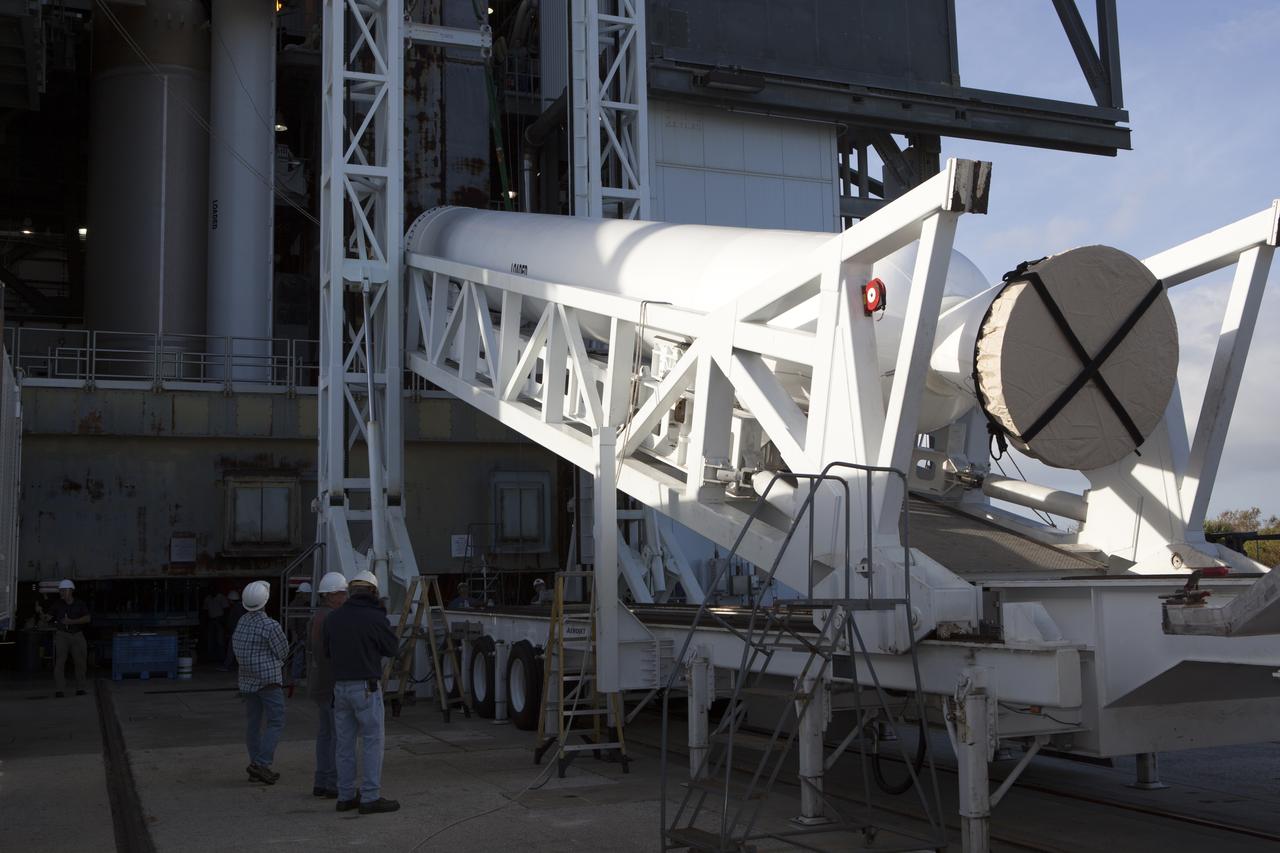
Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket stands at Space Launch Complex 2 as preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

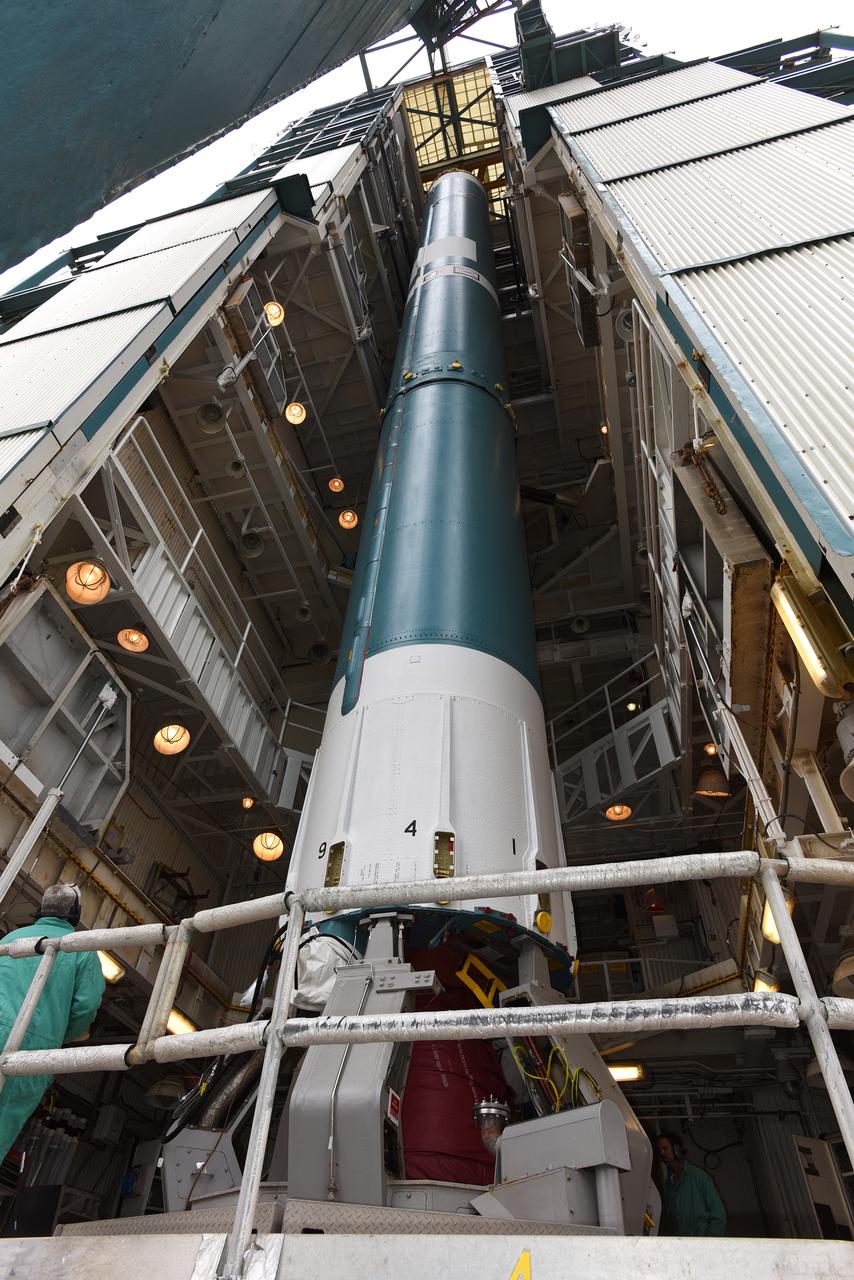
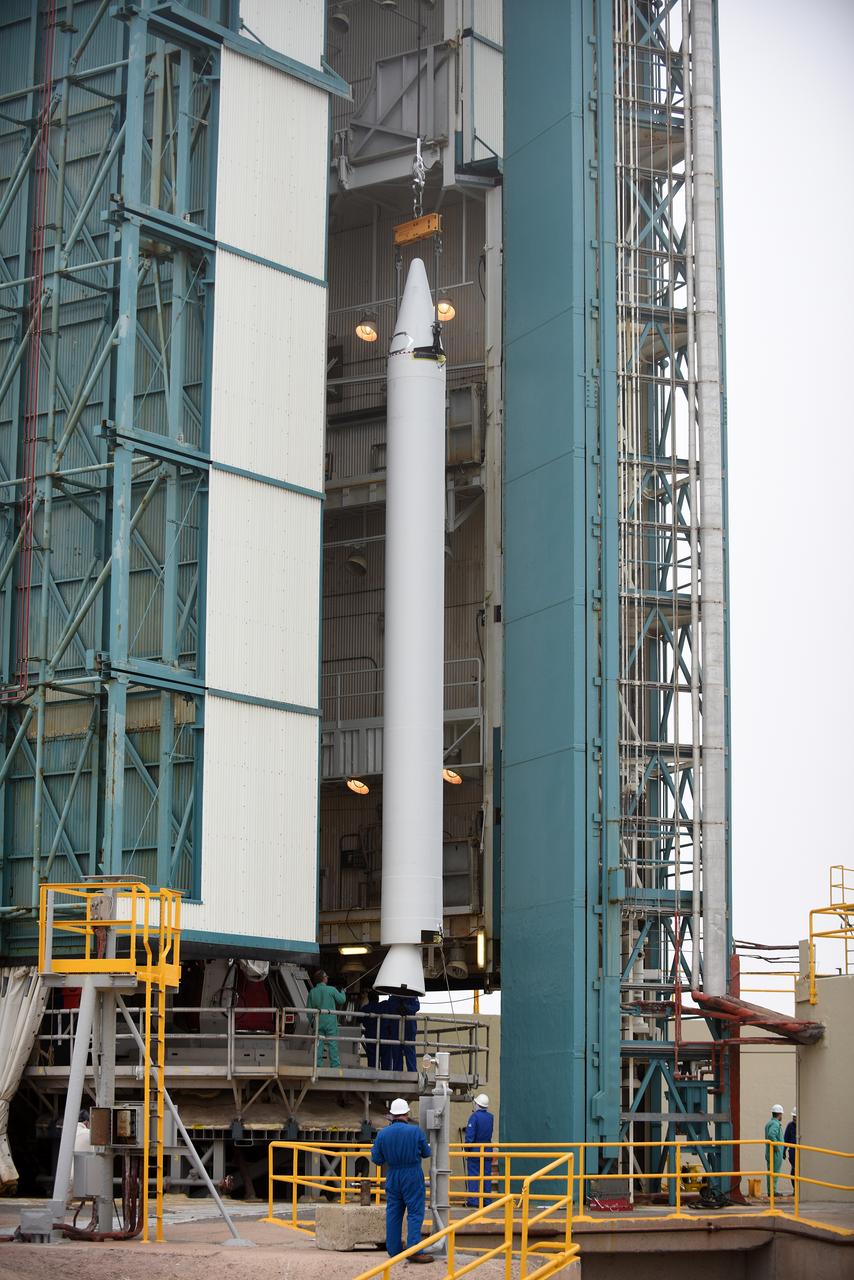
The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
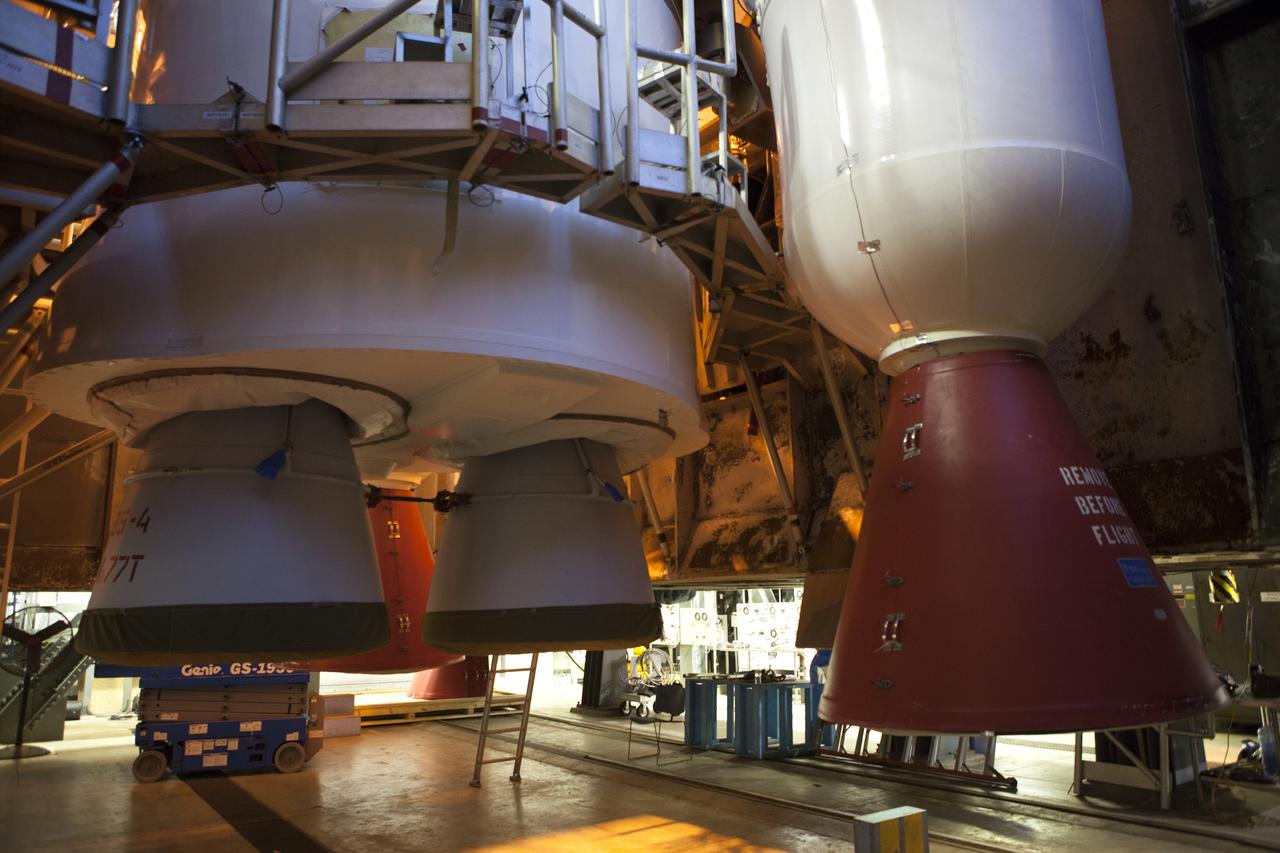

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is being mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

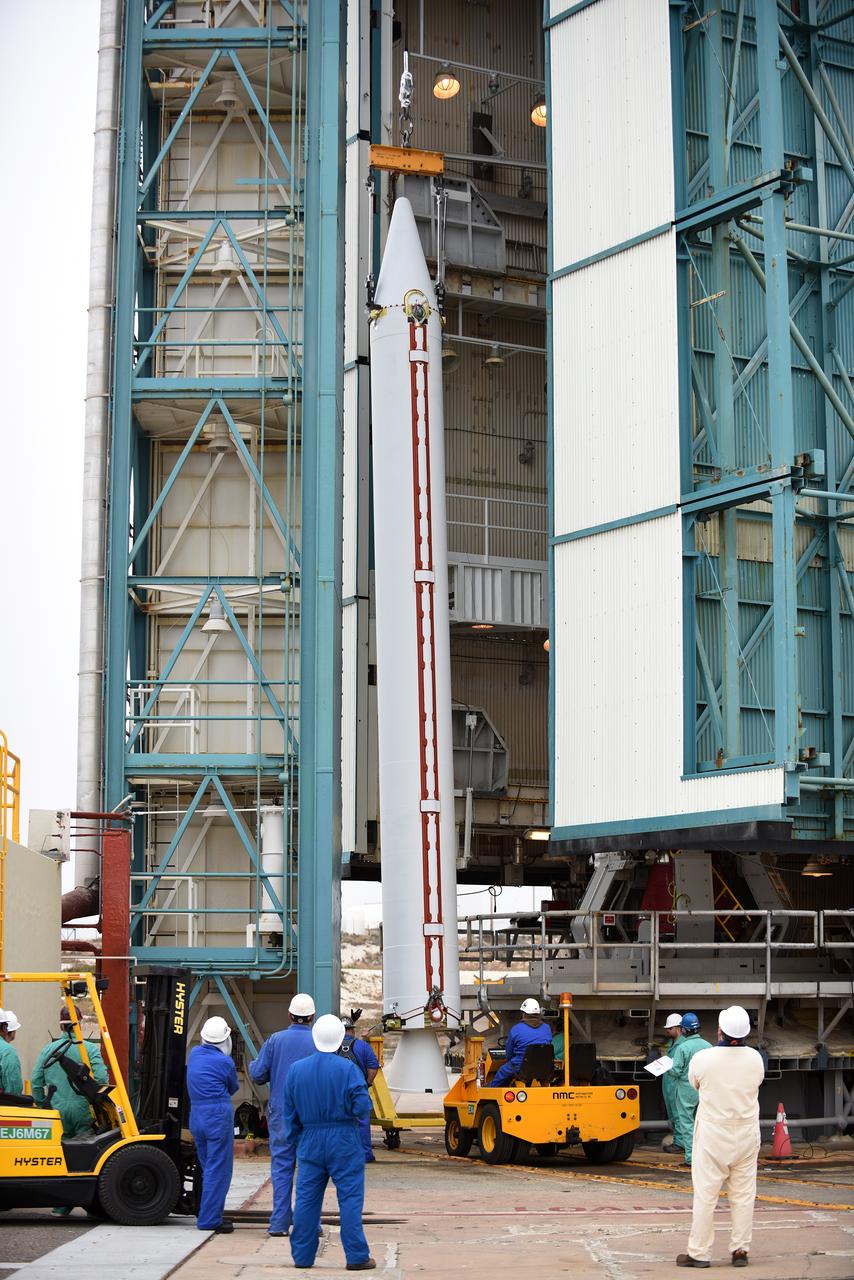
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

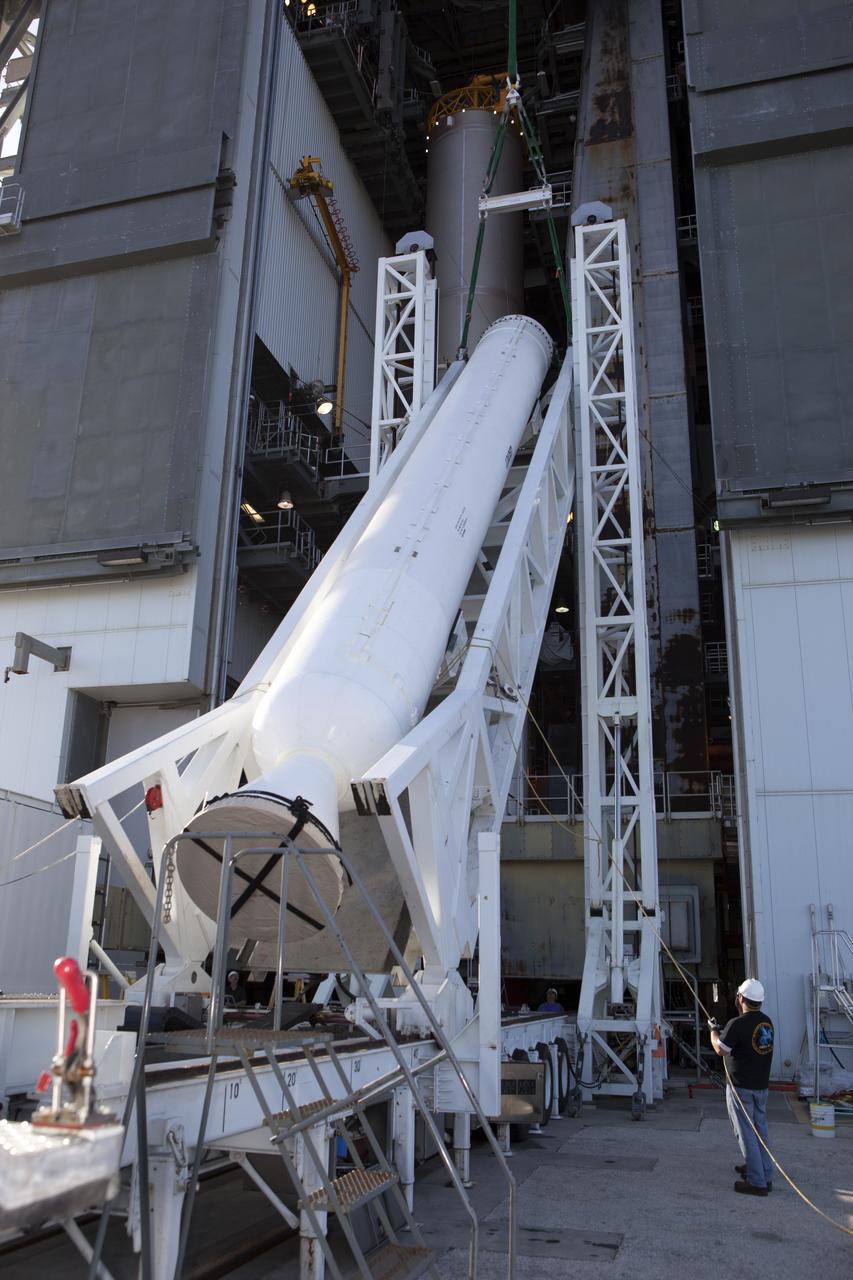
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) monitor the progress as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
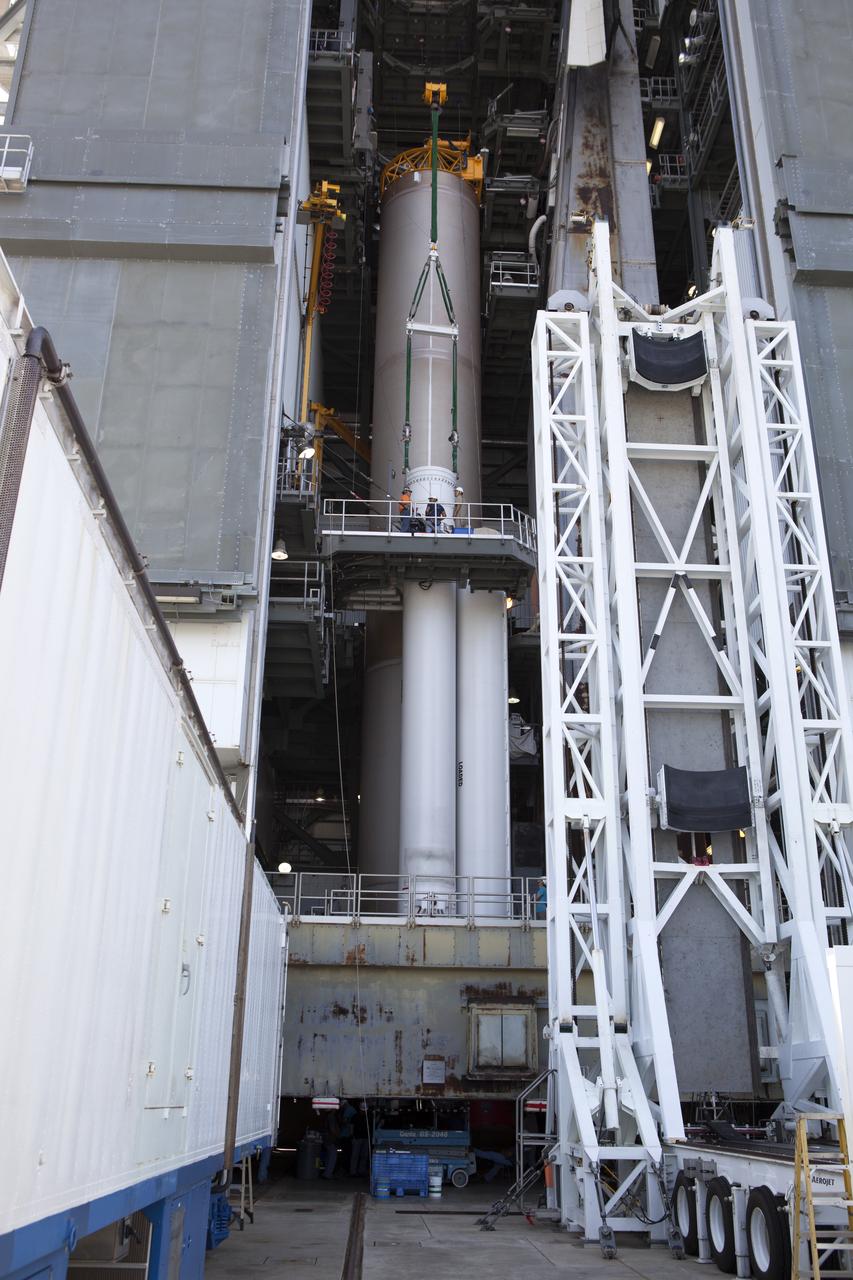

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the solid rocket motor is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for its upcoming launch. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect a solid rocket motor at Space Launch Complex 2 as it is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect a solid rocket motor at Space Launch Complex 2 as it is attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor is lifted at Space Launch Complex 2 to be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Preparations are continuing for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft on March 27, 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position and moved into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
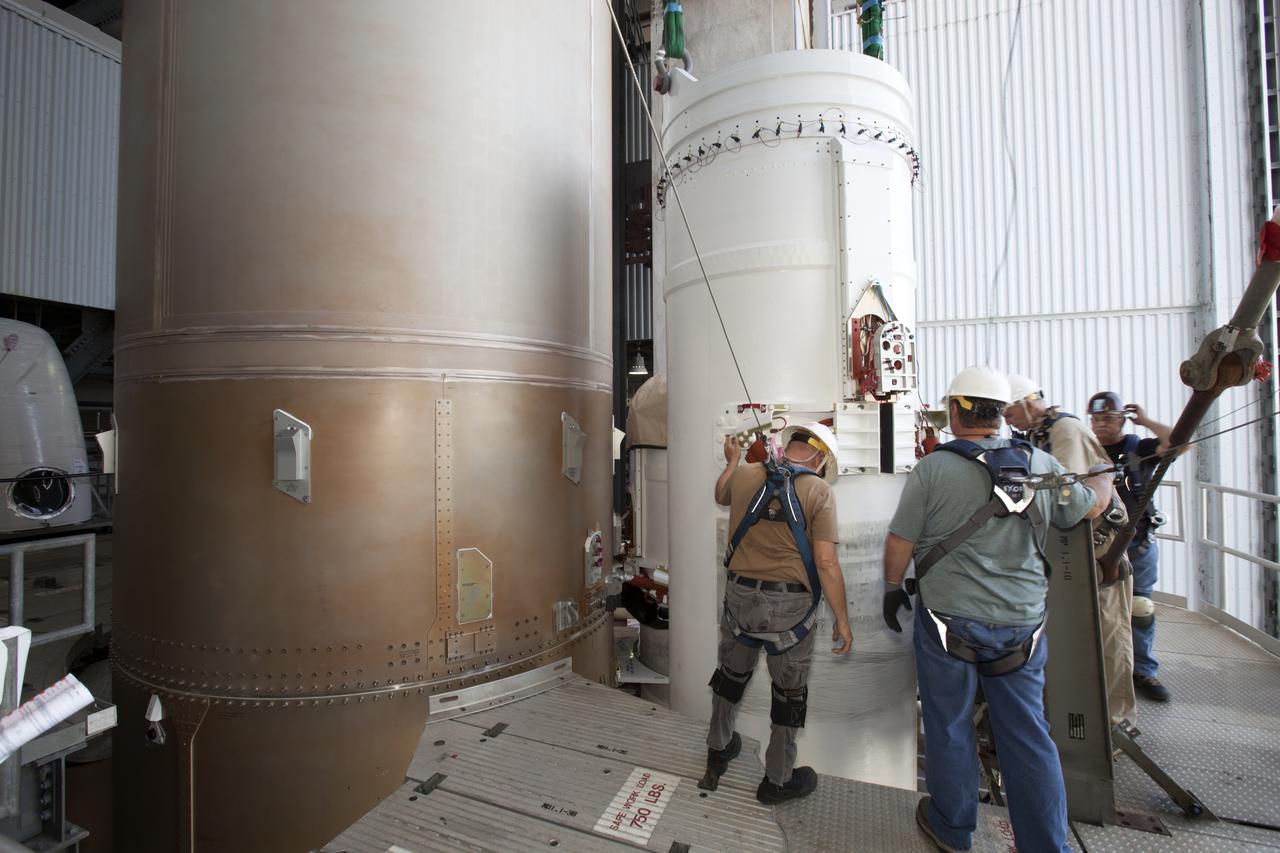

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) assist as the solid rocket motor is mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

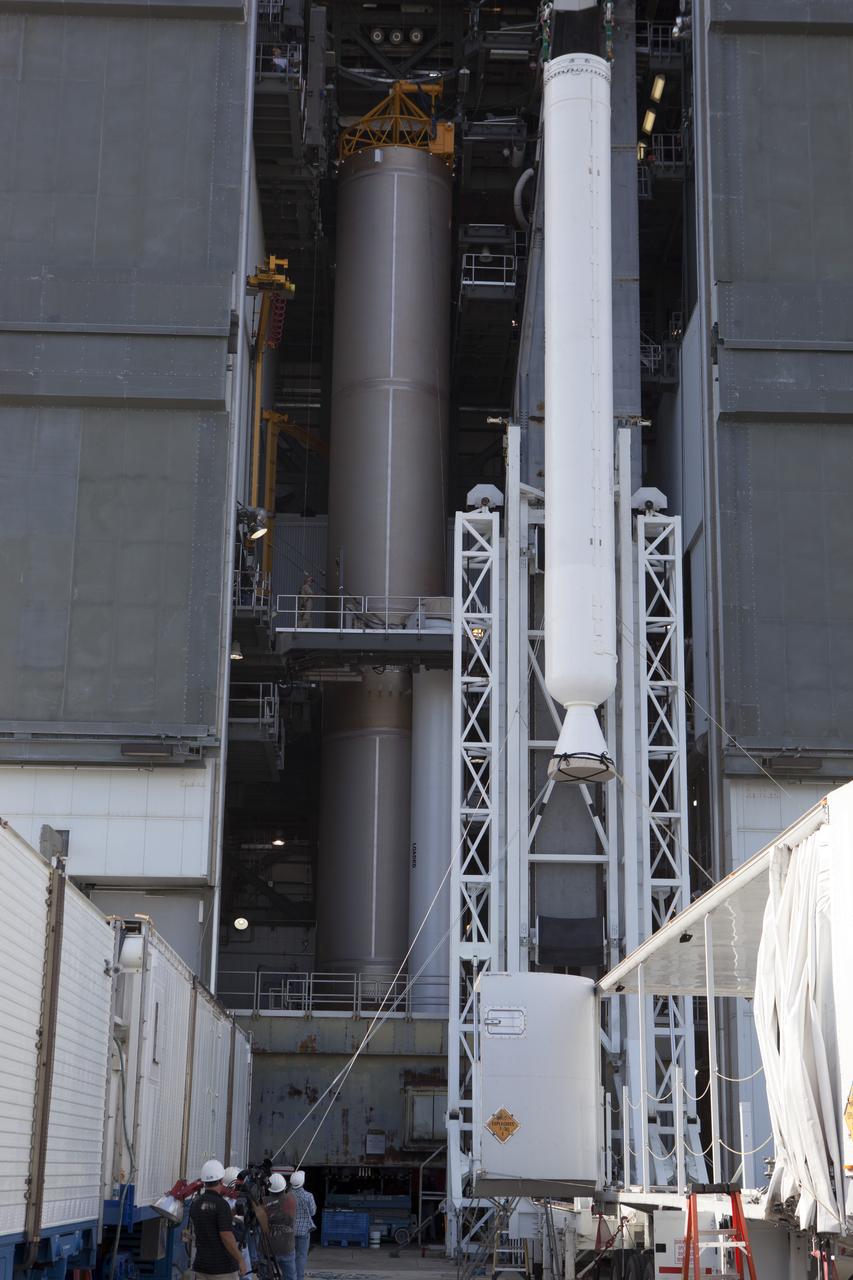
Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
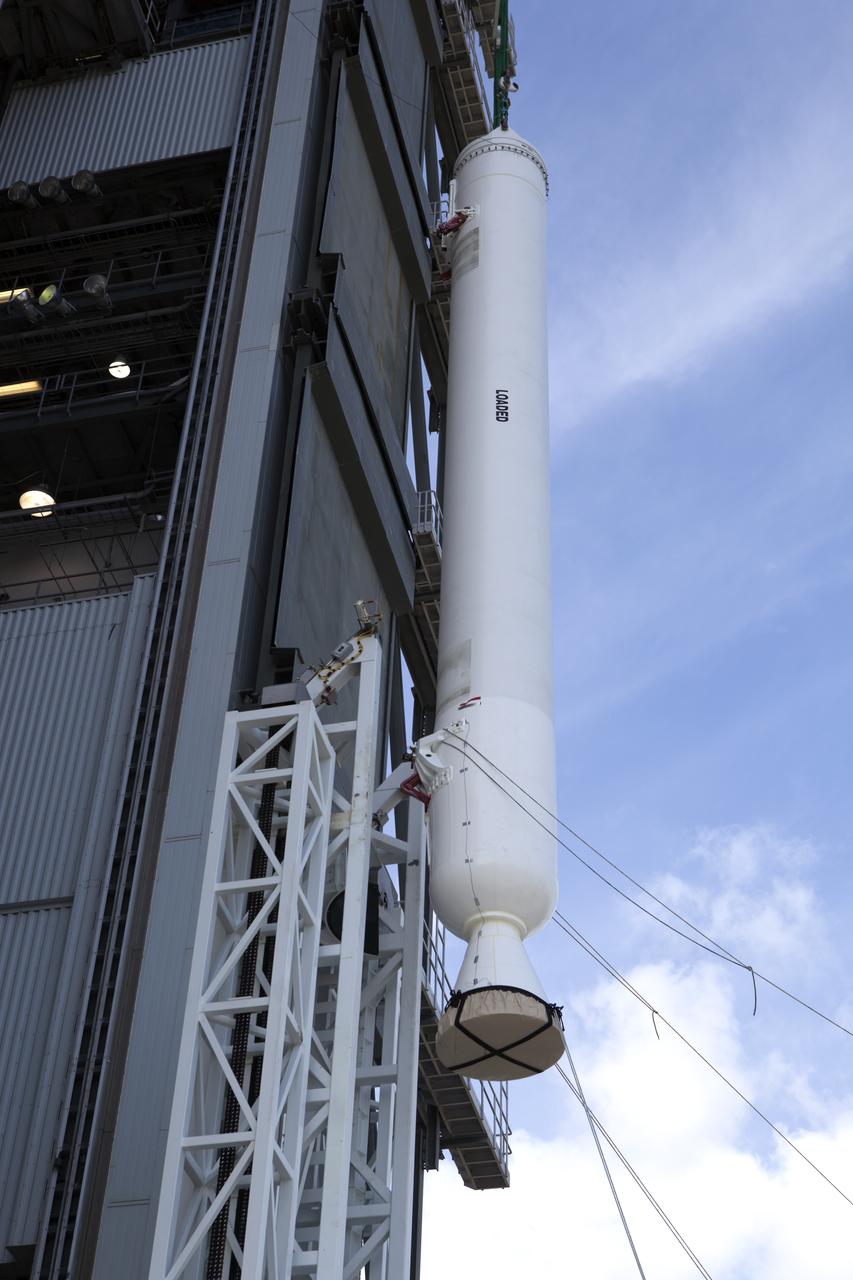

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) technician inspects the solid rocket motor for the ULA Atlas V rocket on its transporter near the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solid rocket motor will be lifted and mated to the rocket in preparation for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
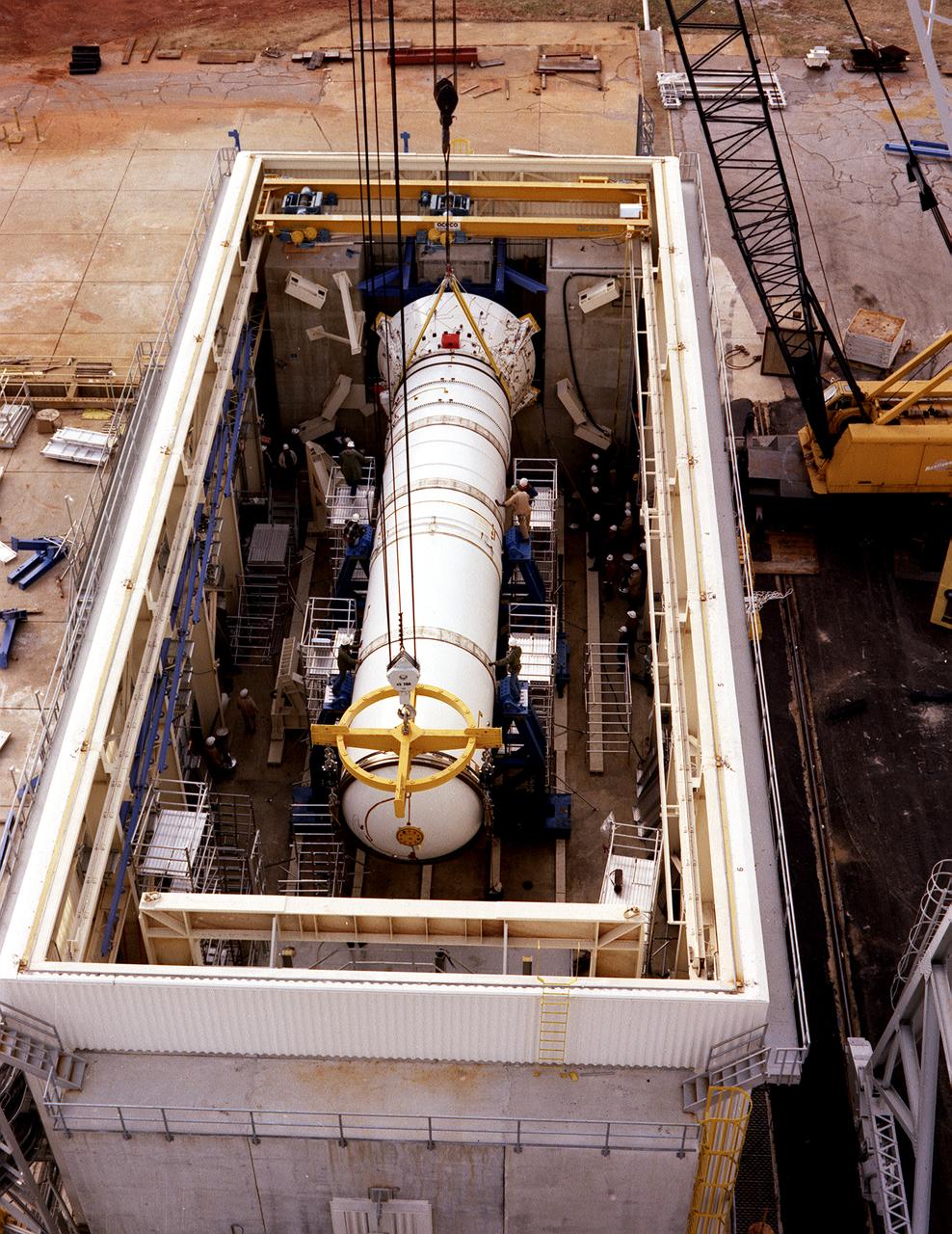
The solid rocket booster (SRB) structural test article is being installed in the Solid Rocket Booster Test Facility for the structural and load verification test at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment.
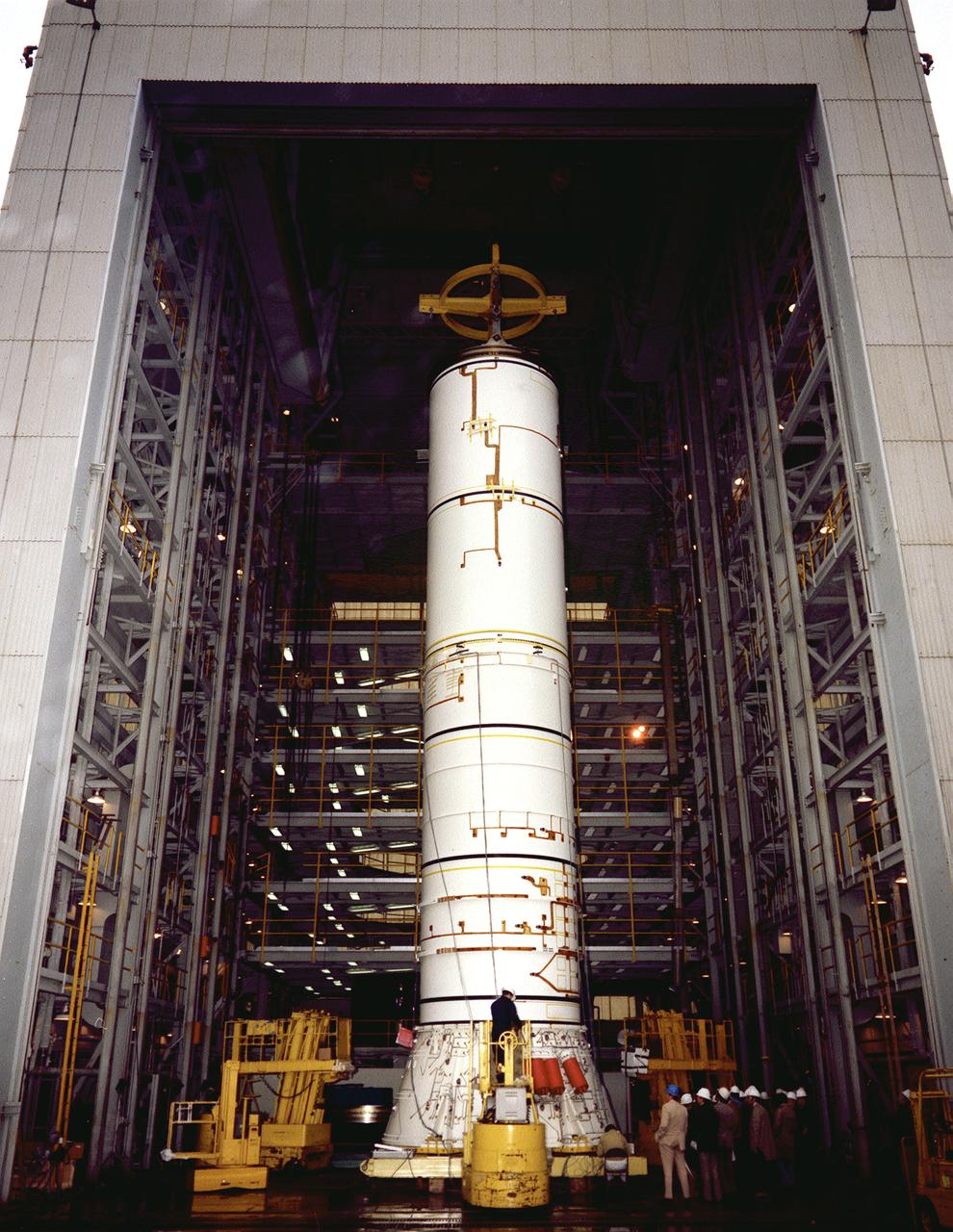

The structural test article to be used in the solid rocket booster (SRB) structural and load verification tests is being assembled in a high bay building of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment.
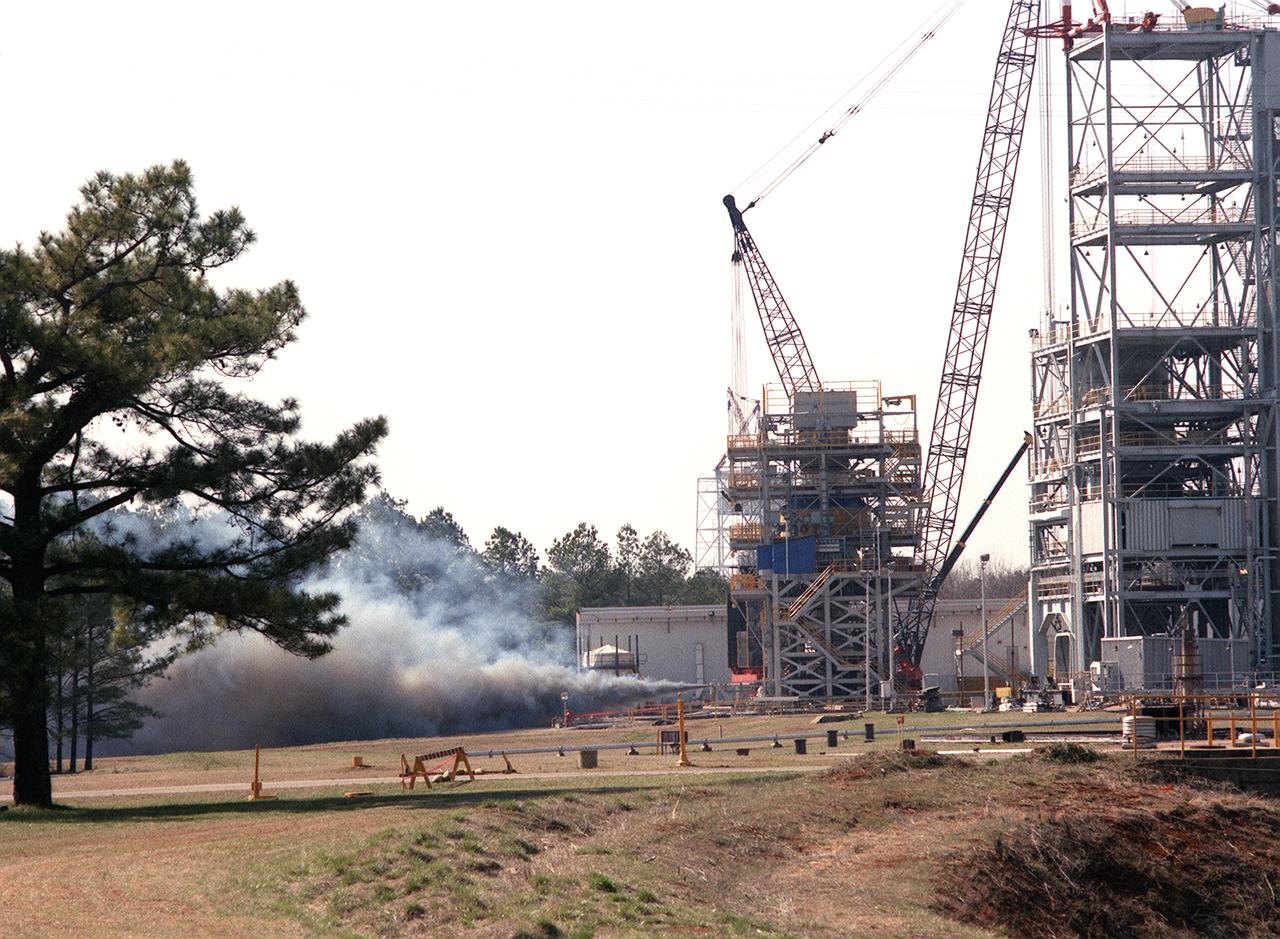

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) successfully test fired the third in a series of Transient Pressure Test Articles (TPTA) in its east test area. The test article was a short-stack solid rocket motor 52-feet long and 12-feet in diameter. The TPTA tests were designed to evaluate the effects of temperature, pressure and external loads encountered by the SRM, primarily during ignition transients. Instrumentation on the motor recorded approximately 1,000 charnels of data to verify the structural performance, thermal response, sealing capability of the redesign field, and case-to-nozzle joints. The TPTA test stand, 14-feet wide by 26-feet long by 33-feet high, was built in 1987. The TPTA series was a joint effort among Morton Thiokol, Inc., United Space Boosters, Inc., Wyle Laboratories, and MSFC. Wyle Laboratories conducted the tests for the MSFC, which manages the redesigned SRM program for NASA.
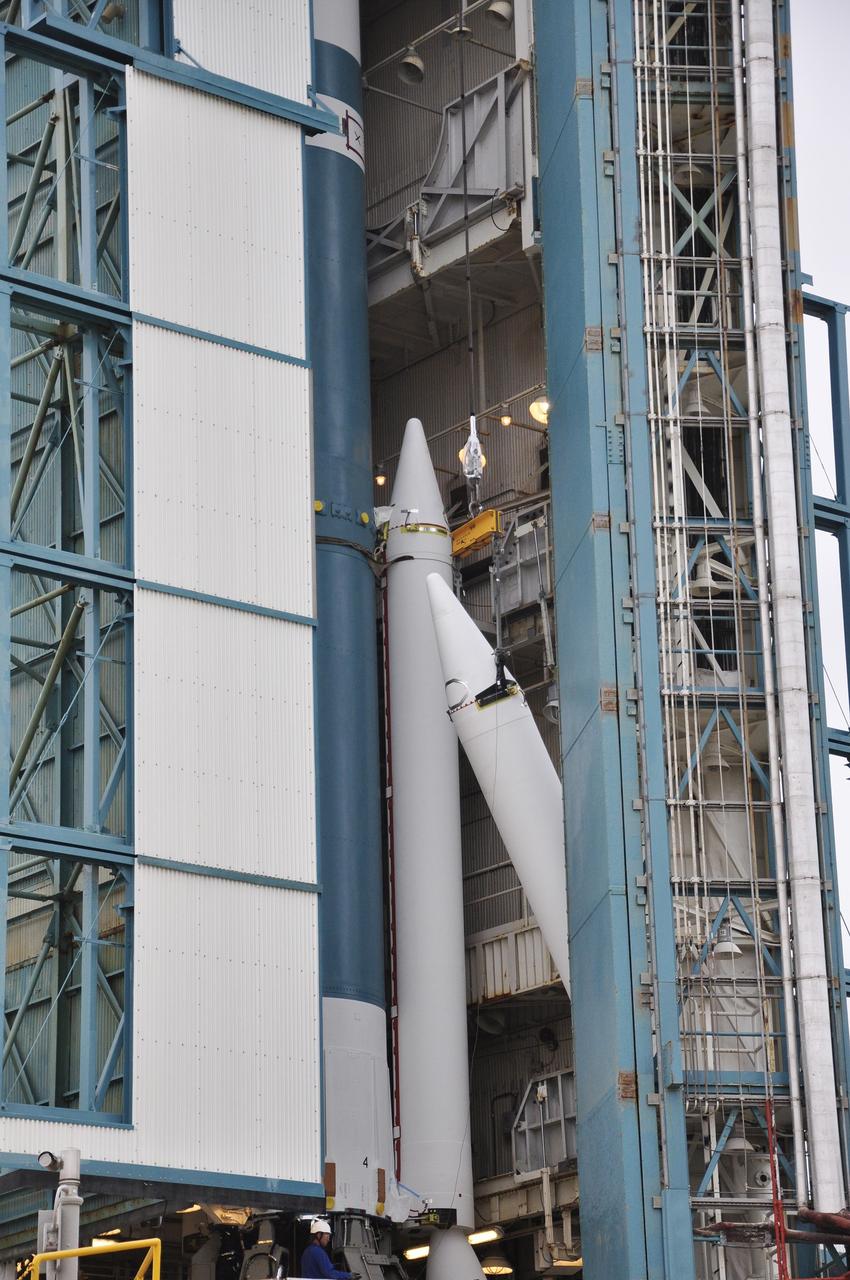

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into place beside the Delta II first stage, with two SRMs already attached, in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
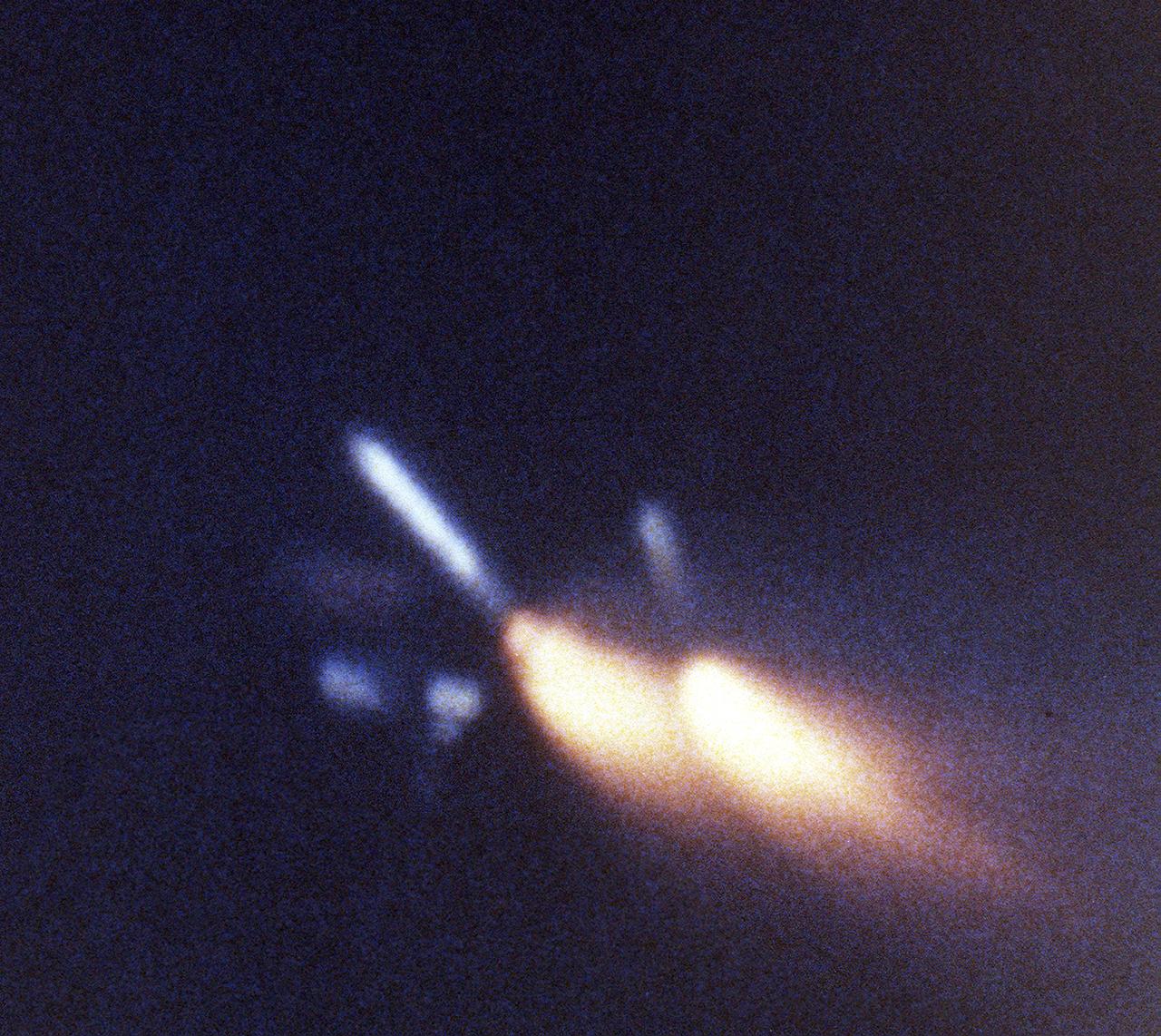

This view, taken by a motion picture tracking camera for the STS-3 mission, shows both left and right solid rocket boosters (SRB's) at the moment of separation from the external tank (ET). After impact to the ocean, they were retrieved and refurbished for reuse. The Shuttle's SRB's and solid rocket motors (SRM's) are the largest ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds. That is equivalent to 44 million horsepower, or the combined power of 400,000 subcompact cars.
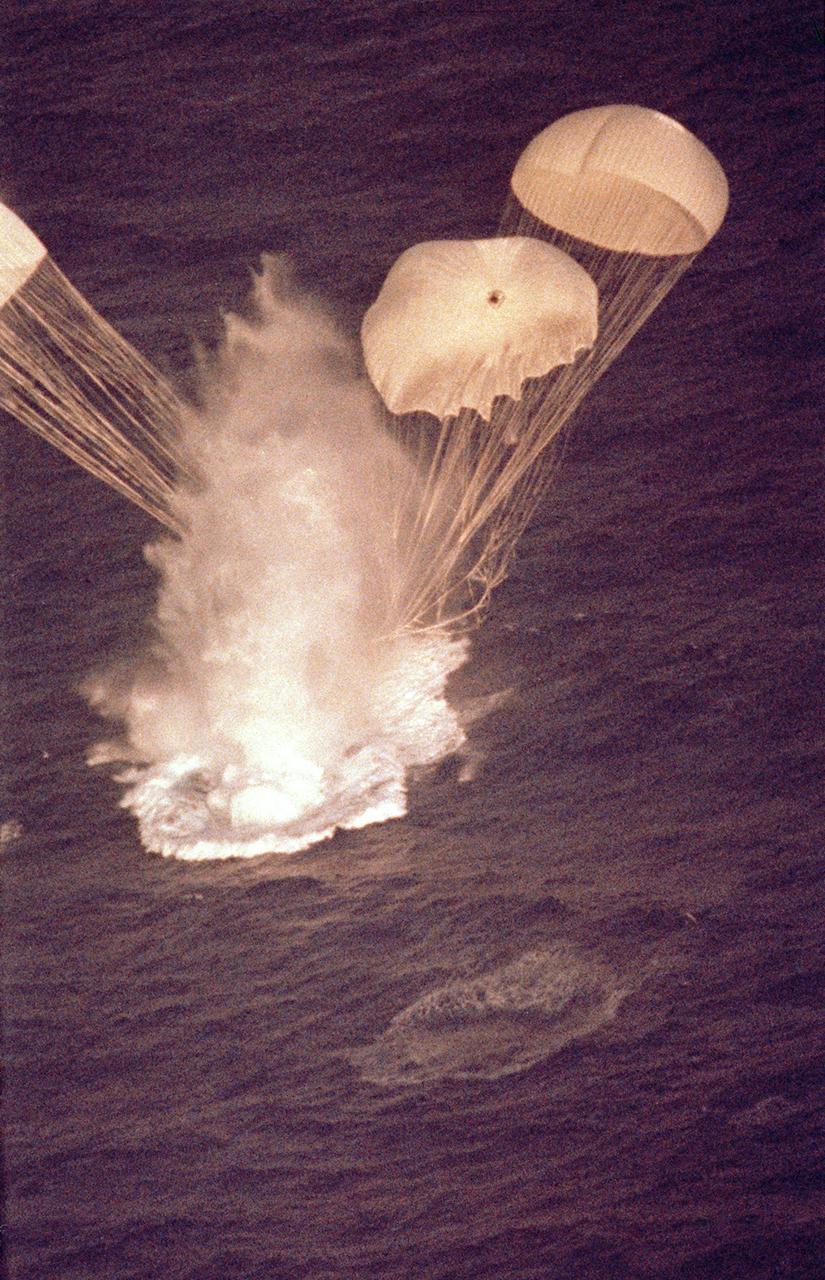
he left solid rocket booster (SRB) for the STS-5 mission is shown in this photograph at the moment of splashdown after its separation from the external tank. This view was photographed from a Cast Glance aircraft. After impact to the ocean, it was retrieved and refurbished for reuse. The Shuttle's SRB's and solid rocket motors (SRM's) are the largest ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds. That is equivalent to 44 million horsepower, or the combined power of 400,000 subcompact cars.
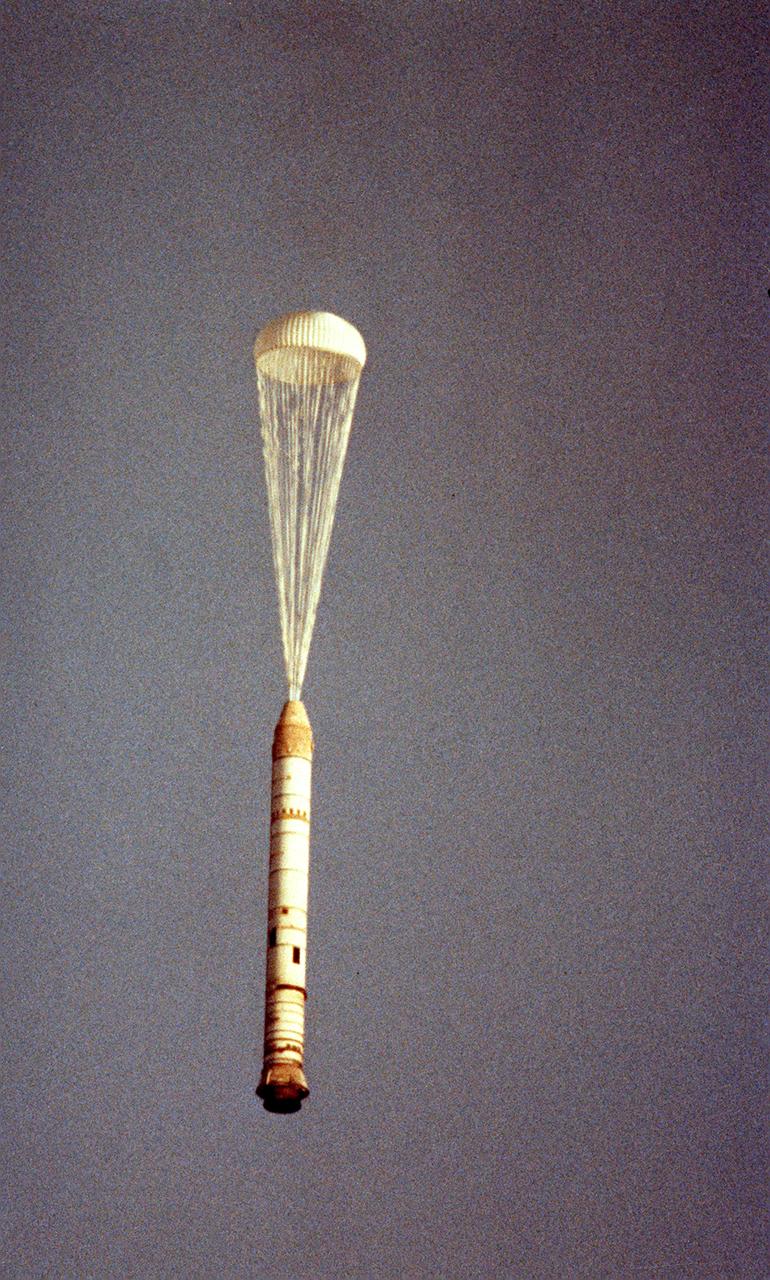

The right solid rocket booster (SRB) for the STS-5 mission, with one chute opened, falls after its separation from the external tank (ET). This view was photographed from a Cast Glance aircraft. After impact to the ocean, it was retrieved and refurbished for reuse. The Shuttle's SRB's and solid rocket motors (SRM's) are the largest ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds. That is equivalent to 44 million horsepower, or the combined power of 400,000 subcompact cars.
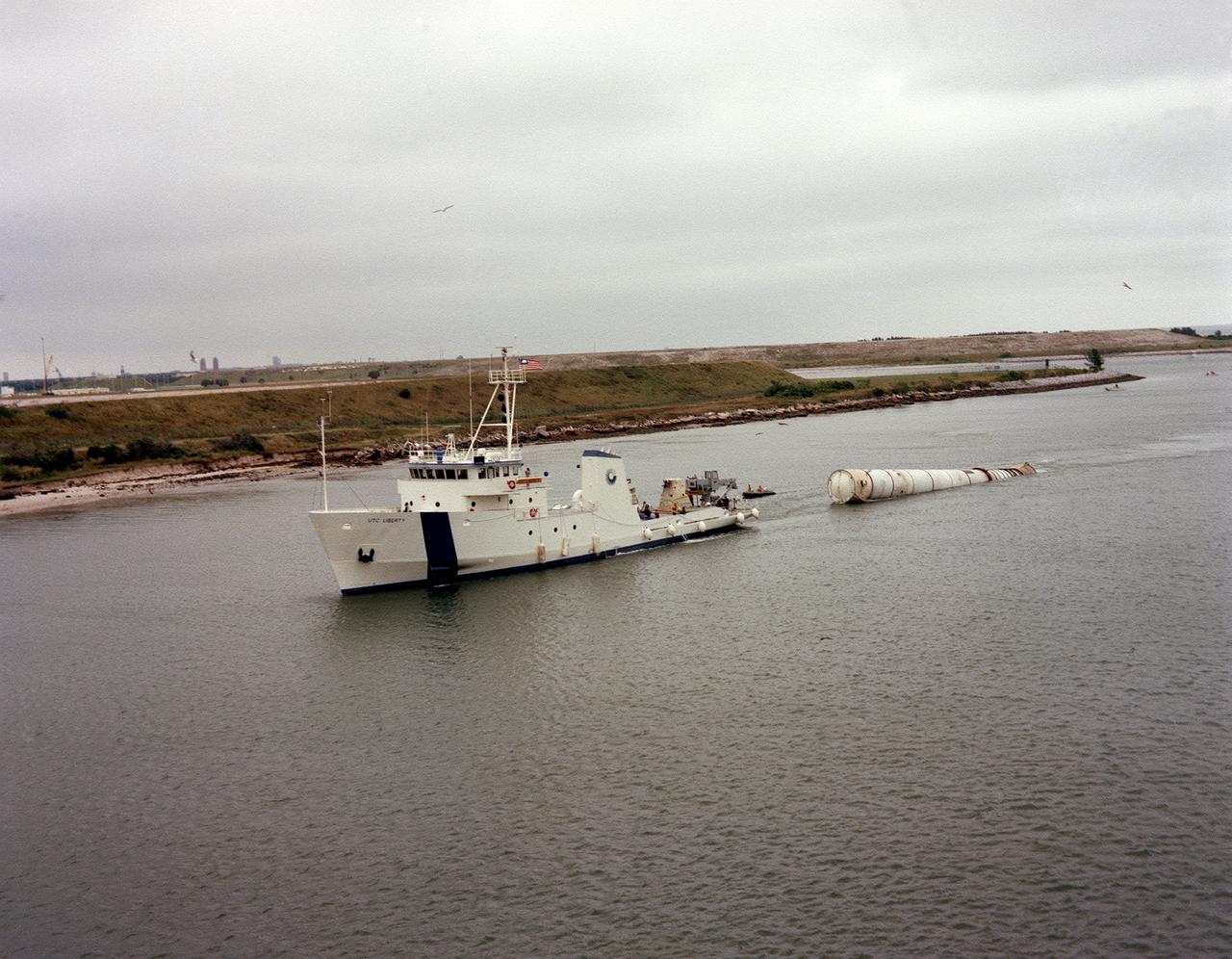

The towing ship, Liberty, towed a recovered solid rocket booster (SRB) for the STS-5 mission to Port Canaveral, Florida. The recovered SRB would be inspected and refurbished for reuse. The Shuttle's SRB's and solid rocket motors (SRM's) are the largest ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds. The requirement for reusability dictated durable materials and construction to preclude corrosion of the hardware exposed to the harsh seawater environment. The SRB contains a complete recovery subsystem that includes parachutes, beacons, lights, and tow fixture.
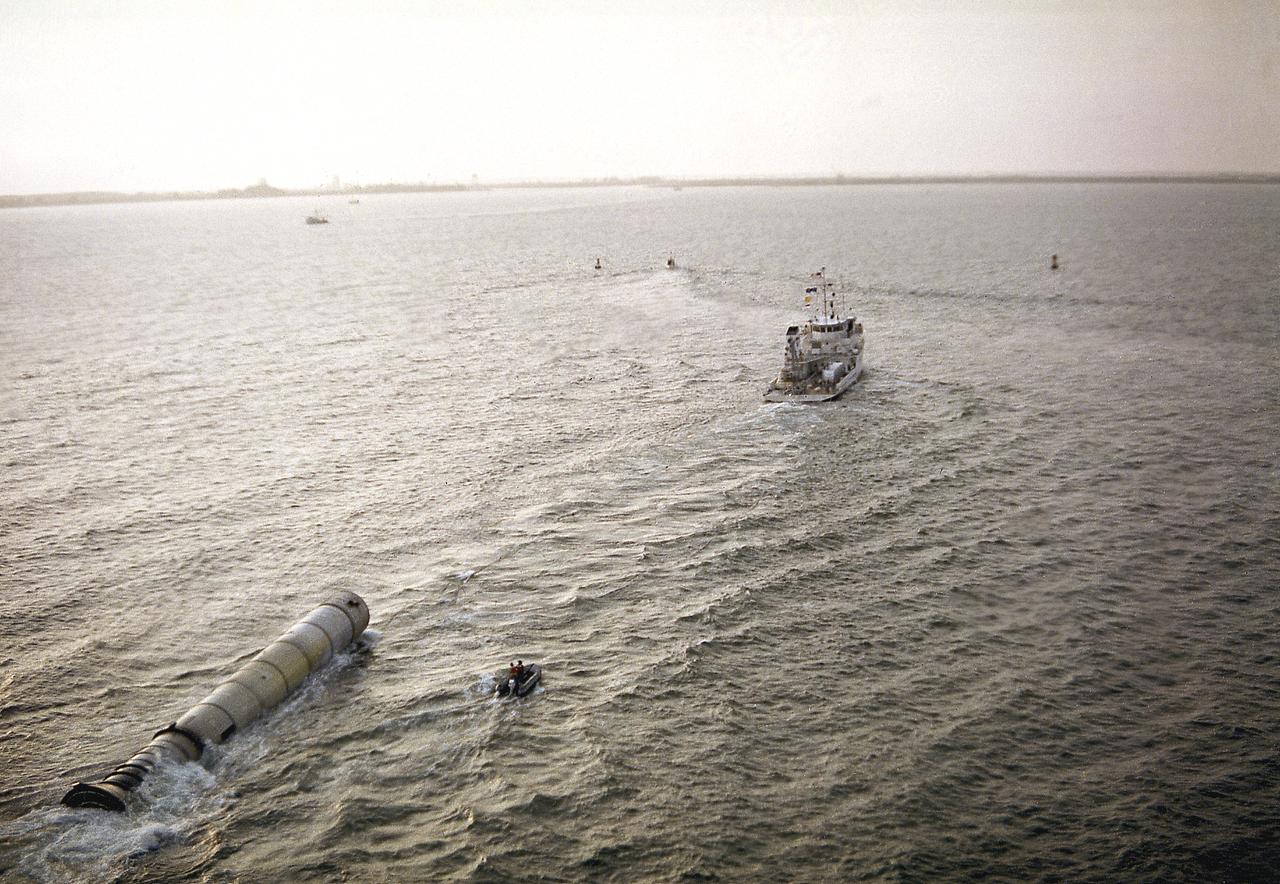

The towing ship, Liberty, towed a recovered solid rocket booster (SRB) for the STS-3 mission to Port Canaveral, Florida. The recovered SRB would be inspected and refurbished for reuse. The Shuttle's SRB's and solid rocket motors (SRM's) are the largest ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds. The requirement for reusability dictated durable materials and construction to preclude corrosion of the hardware exposed to the harsh seawater environment. The SRB contains a complete recovery subsystem that includes parachutes, beacons, lights, and tow fixture.
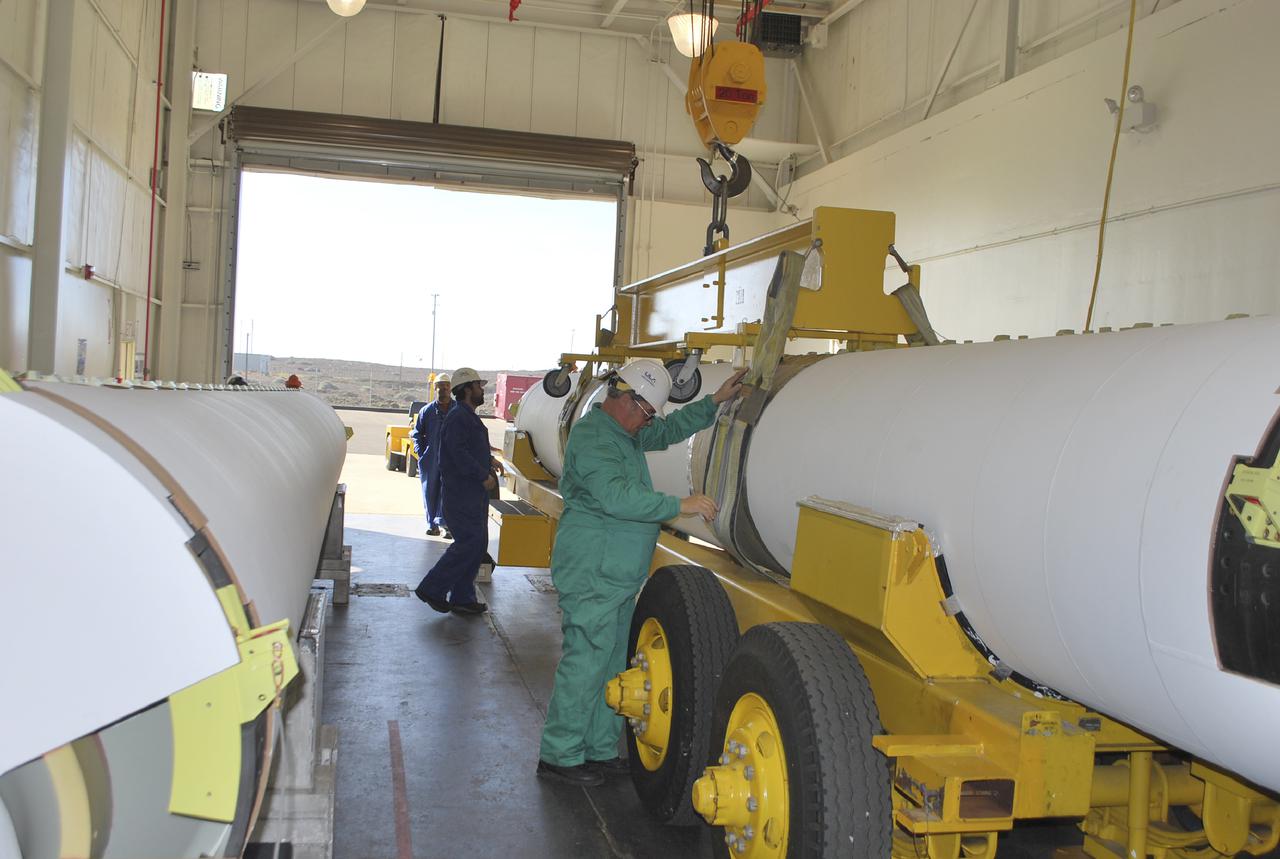

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to hoist a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, from a transporter onto a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
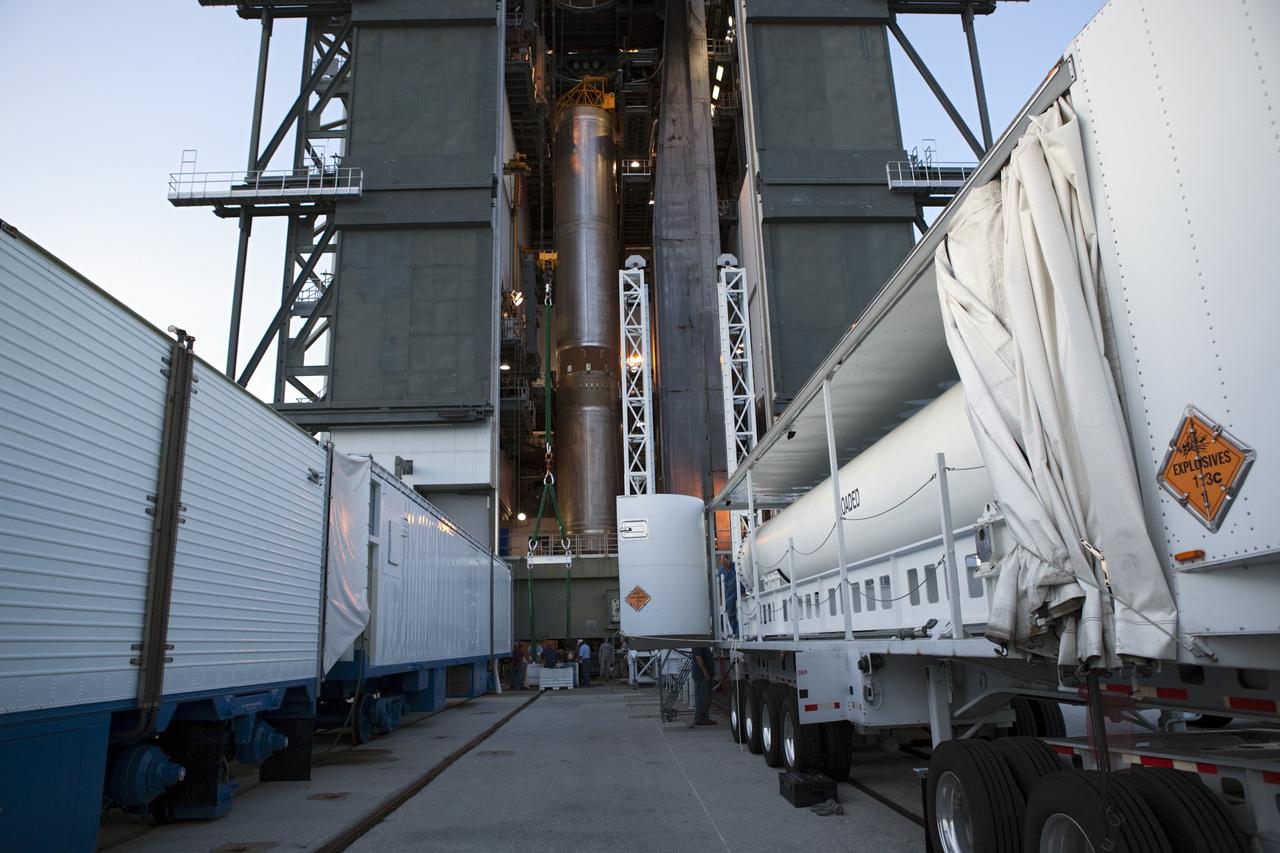

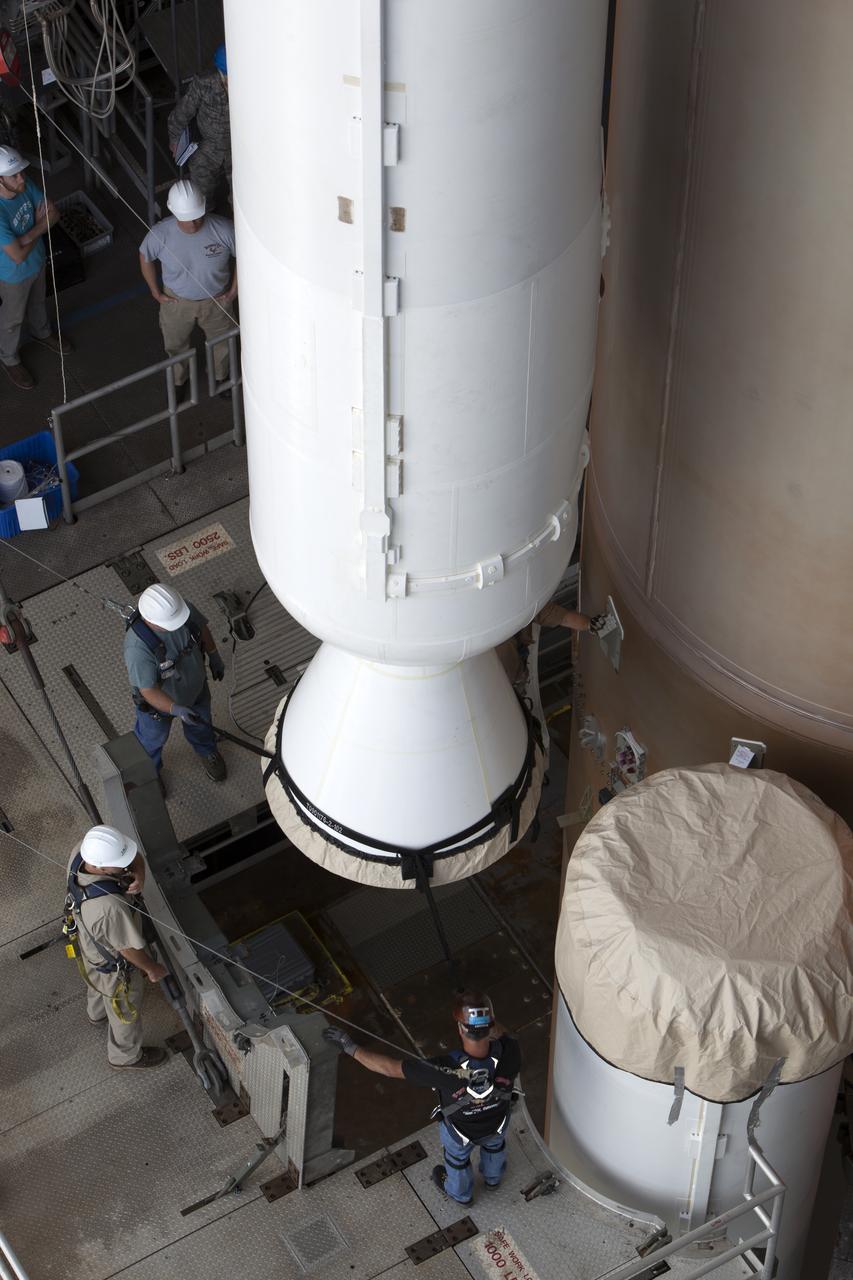
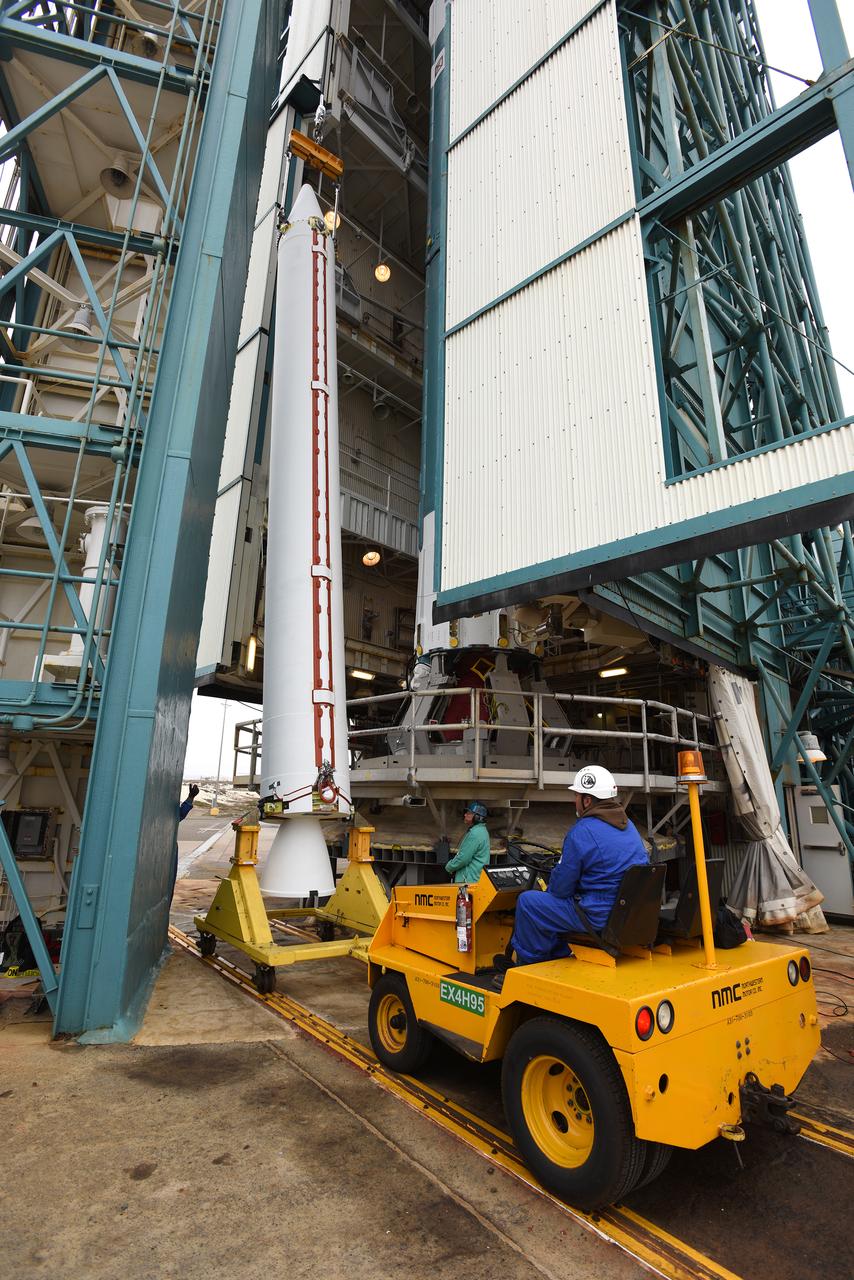
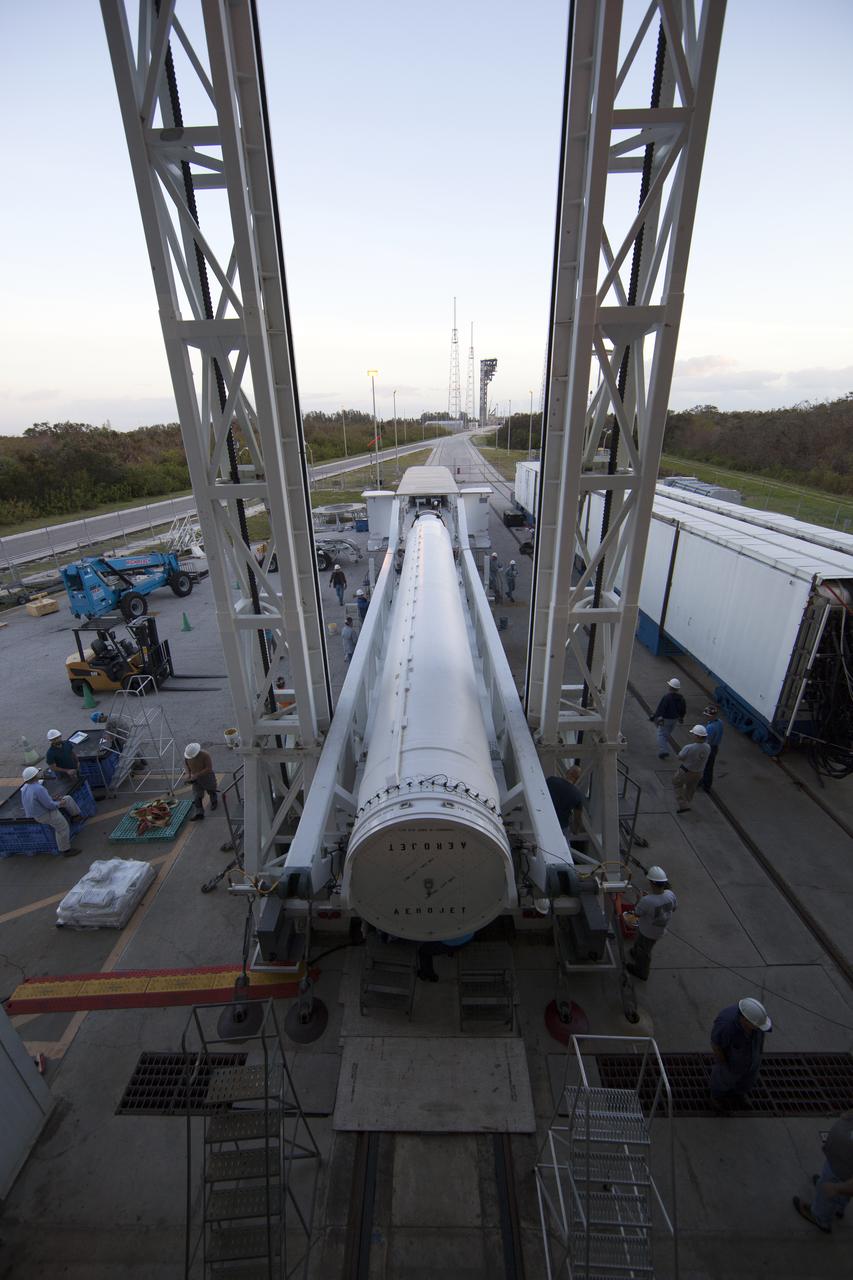
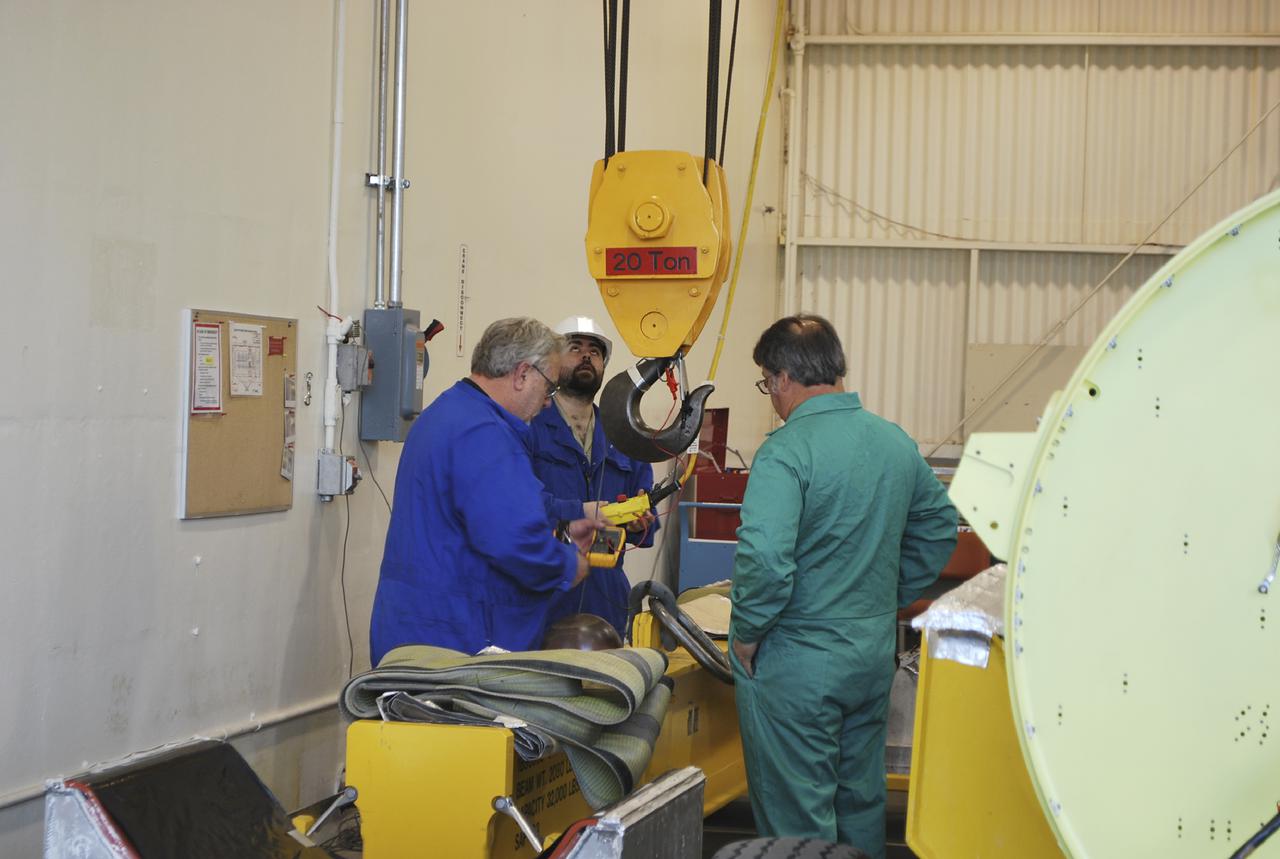
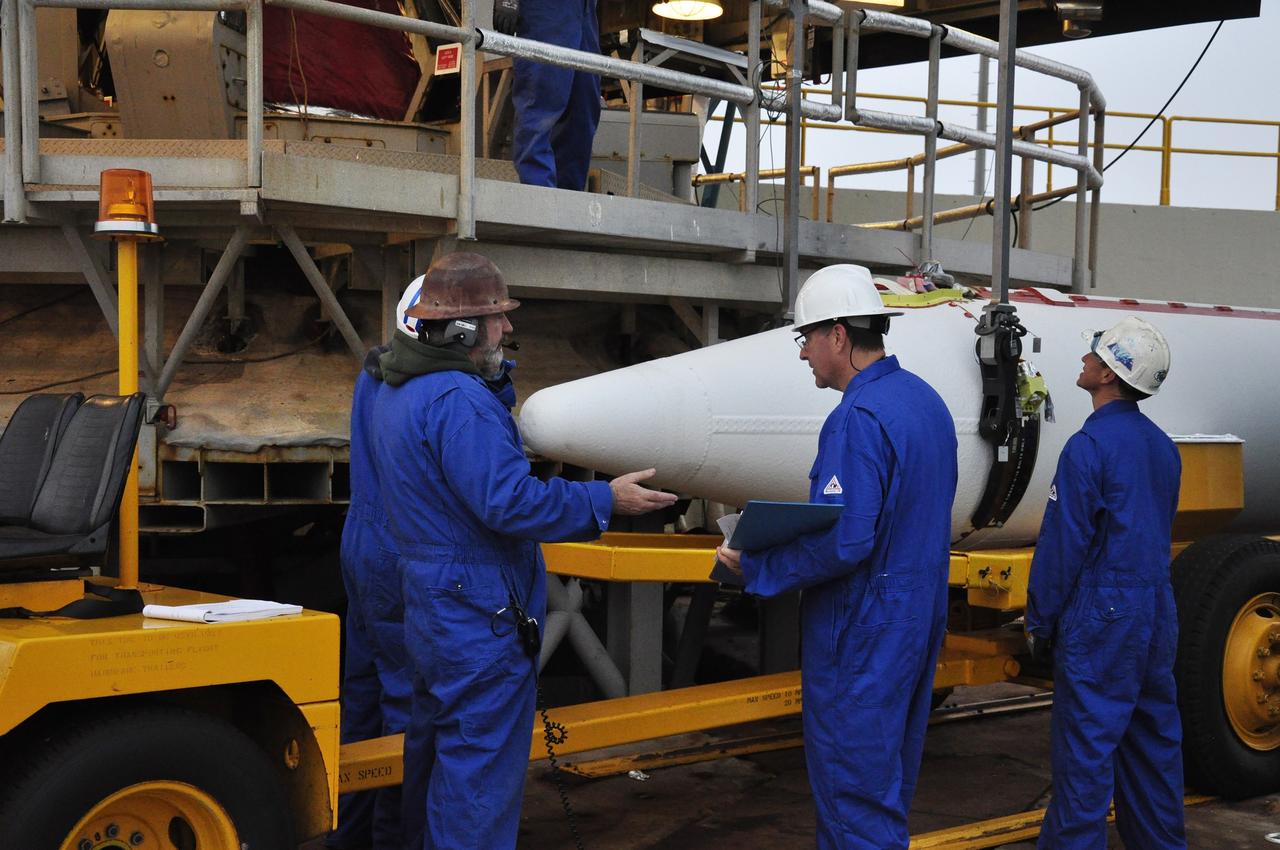
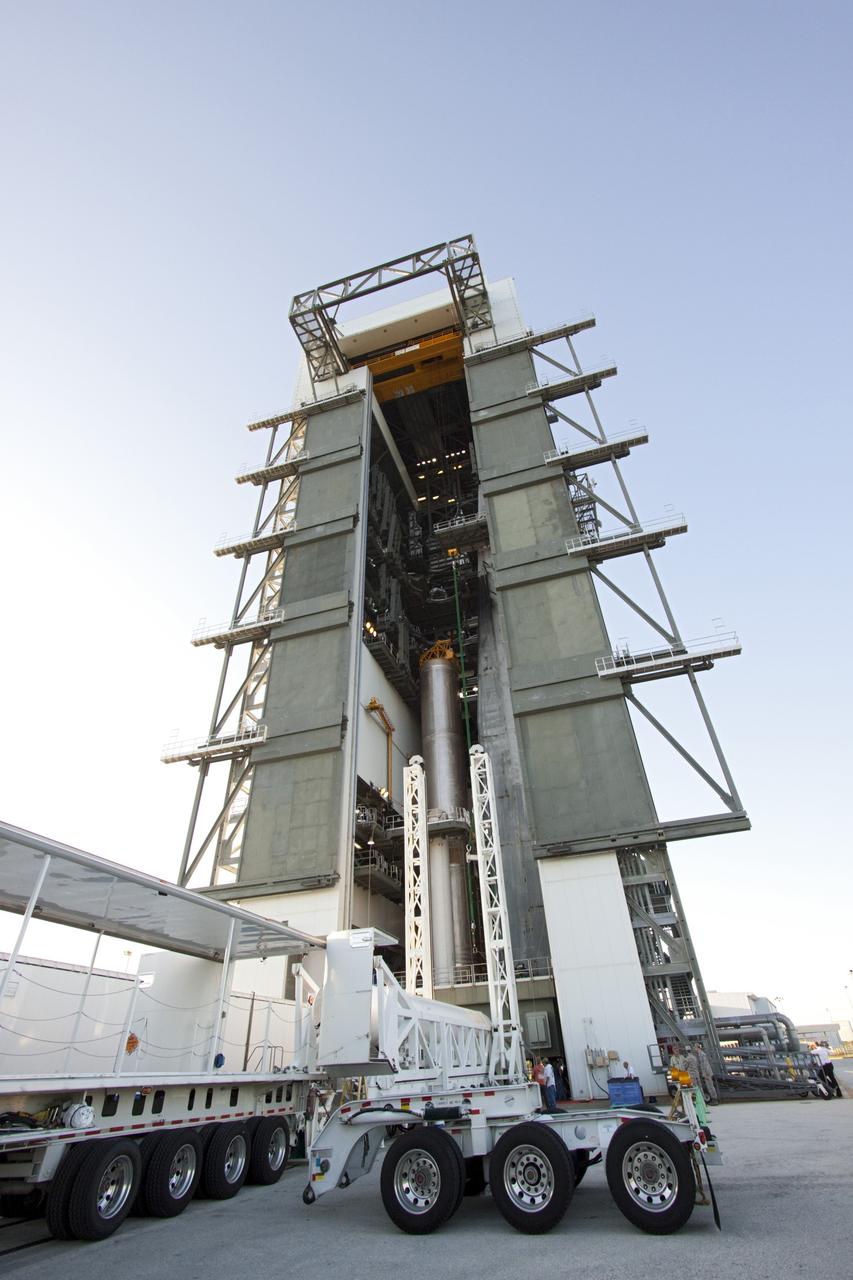
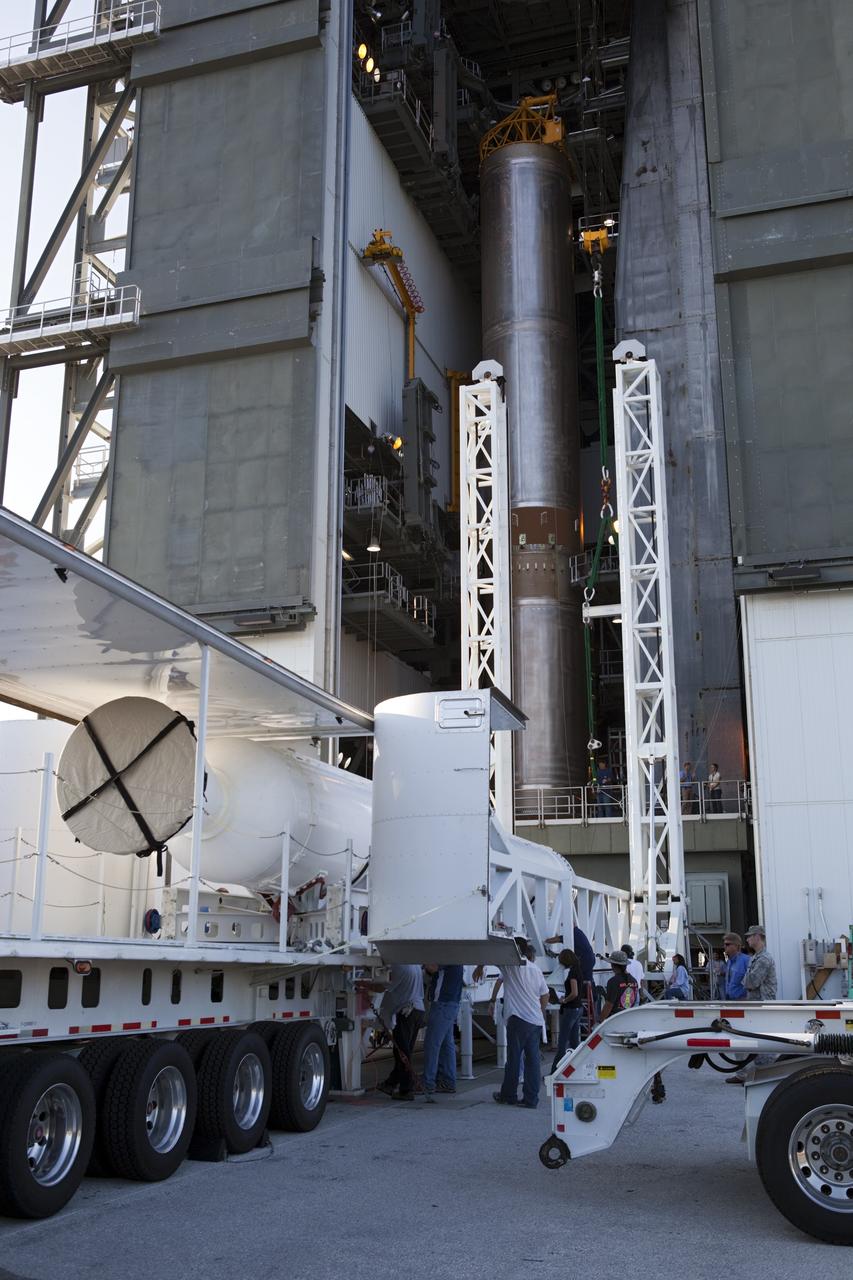
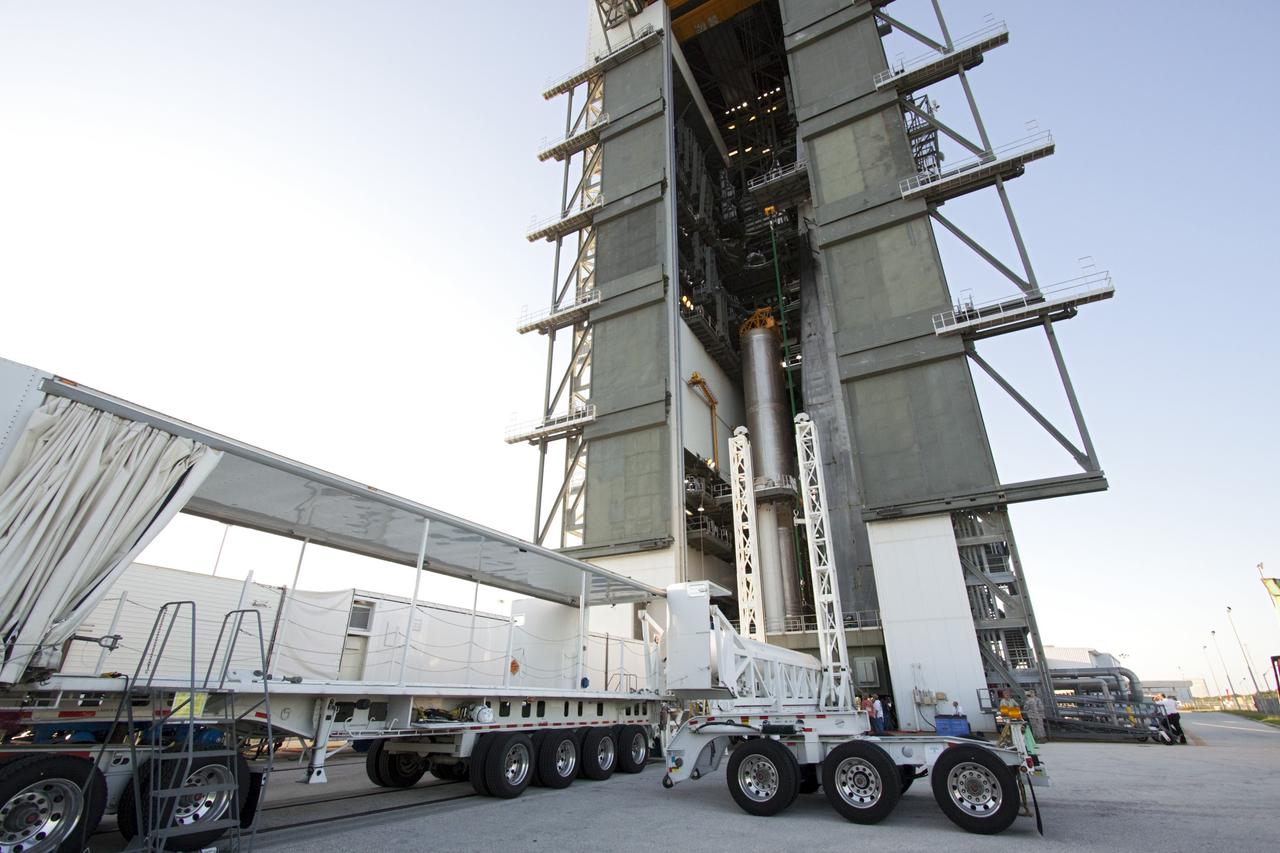
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a trailer carrying a solid rocket motor (SRM) awaits unloading. The SRM will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket being prepared to launch NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
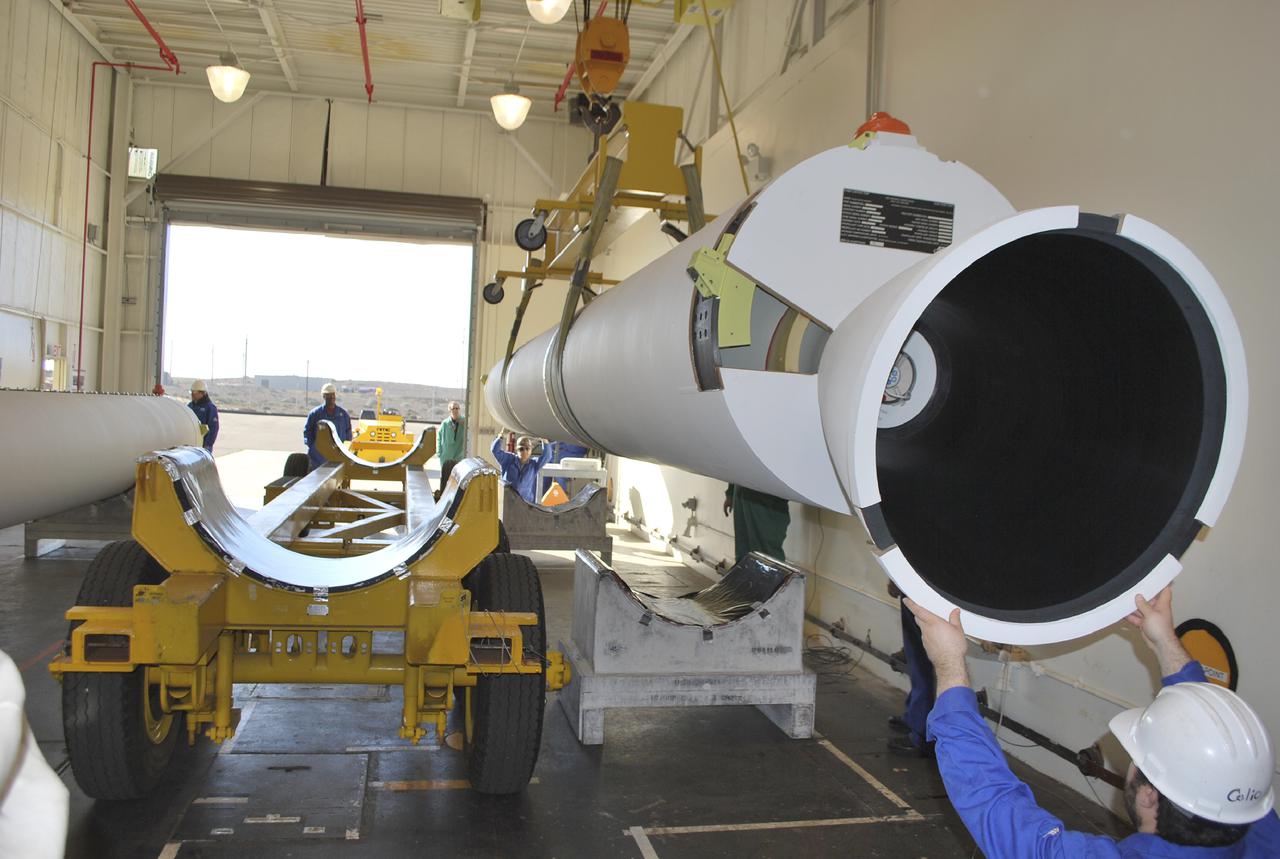

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California lower a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, onto a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to lift a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, from a transporter onto a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
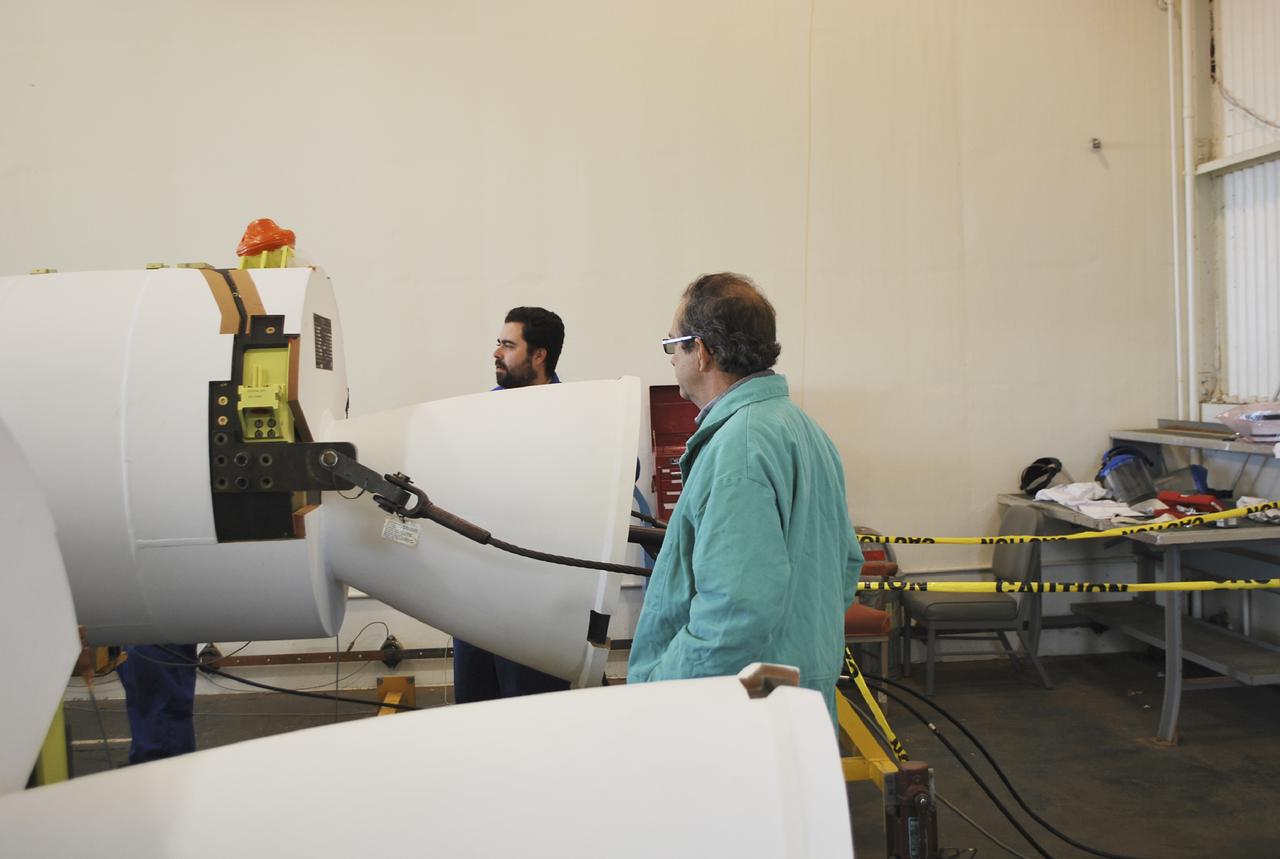

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California conduct a leak check on the solid rocket motors, or SRMs, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
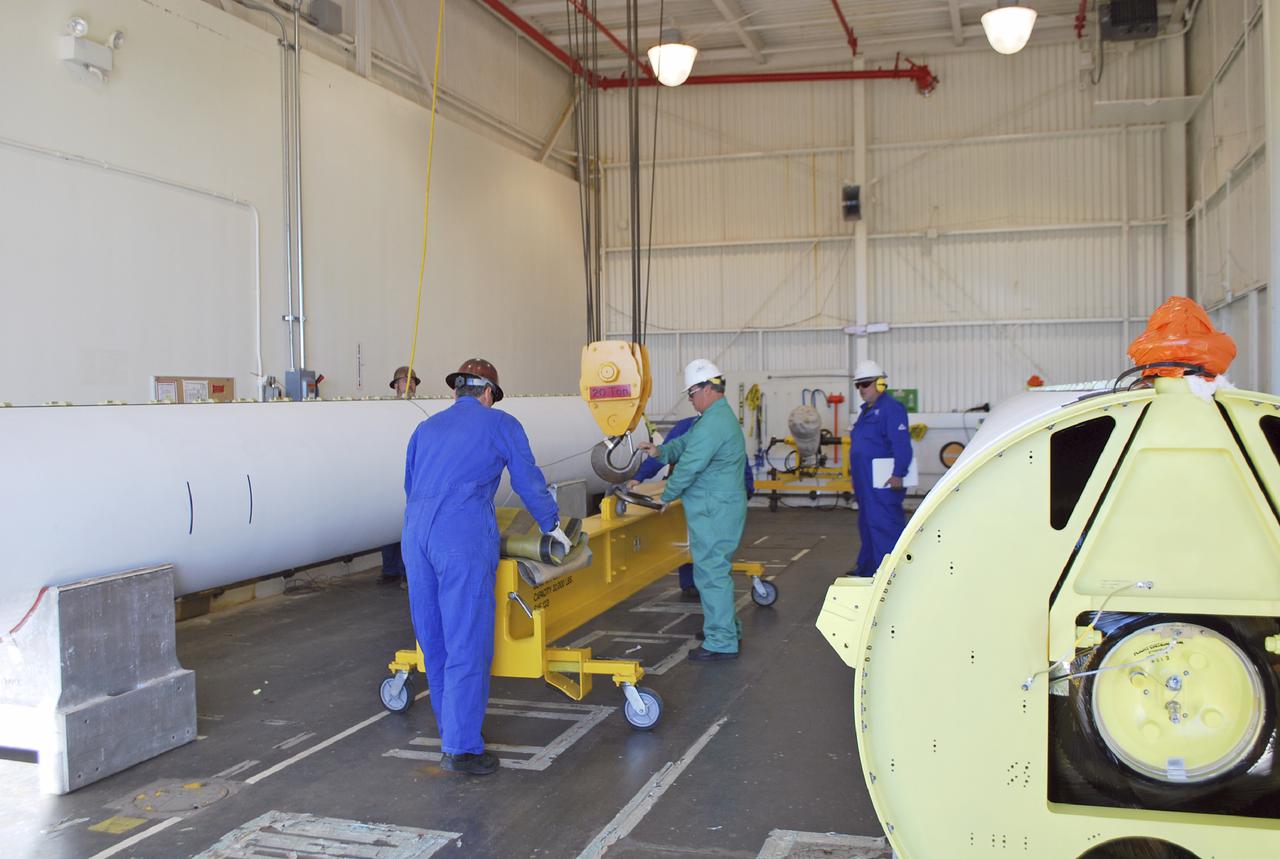

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, rests on a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to lift a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, from a transporter onto a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California lift a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission, from a transporter onto a storage chock where it will be kept until needed. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to conduct a leak check on the solid rocket motors, or SRMs, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, the OCO-2 mission. The SRMs will be attached to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket slated to launch the OCO-2 spacecraft from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it moves into position beside the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane lifts the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, following its delivery to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted from its transportation cradle upon its delivery to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker inspects the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, after it is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage in place in the tower. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane supports the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, following its delivery to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers inspect the nosecone of a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, upon its delivery to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane lifts the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker monitors the solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is moved into position in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to the rocket's first stage in place in the tower. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solid rocket motor, or SRM, is lifted alongside the mobile service tower. The SRM will be moved inside the tower and attached to the Delta II first stage, which is the launch vehicle for the OSTM/Jason-2 spacecraft. The OSTM, or Ocean Topography Mission, on the Jason-2 satellite is a follow-on to Jason-1. It will take oceanographic studies of sea surface height into an operational mode for continued climate forecasting research and science and industrial applications. This satellite altimetry data will help determine ocean circulation, climate change and sea-level rise. OSTM is a joint effort by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NASA, France’s Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales and the European Meteorological Satellite Organisation. OSTM/Jason-2 will be launched aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320 from Vandenberg on June 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The first solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, has been attached to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker prepares to attach a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it moves into position beside the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into the mobile service tower next to the Delta II first stage at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane lifts the third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position at the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane lifts the second solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the second solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach a third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage are nearing completion. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the second solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted into a vertical position beside the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the Delta II rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach a third solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage are nearing completion. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker attaches a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers complete the task of attaching a solid rocket motor, or SRM, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to attach the rocket's three SRMs, known as graphite epoxy motors, to its first stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

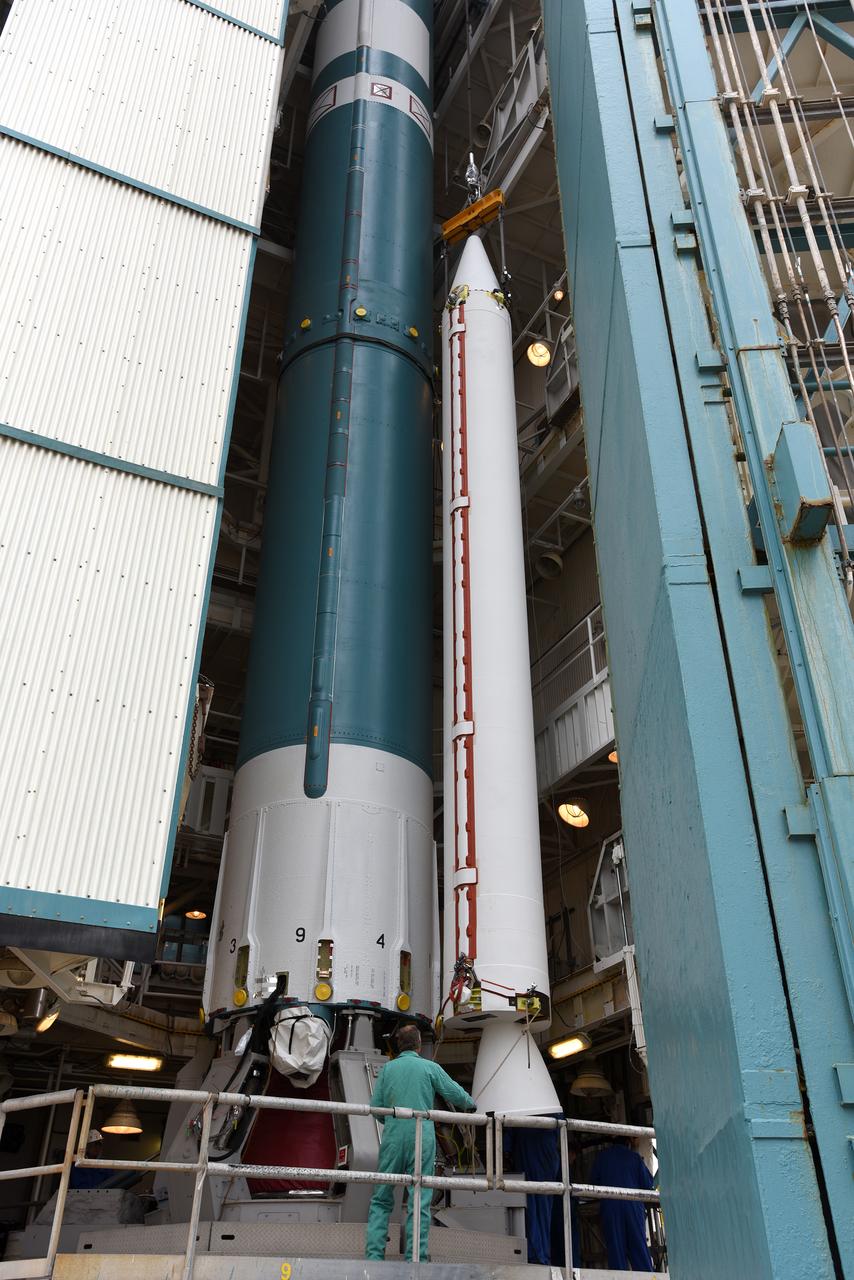
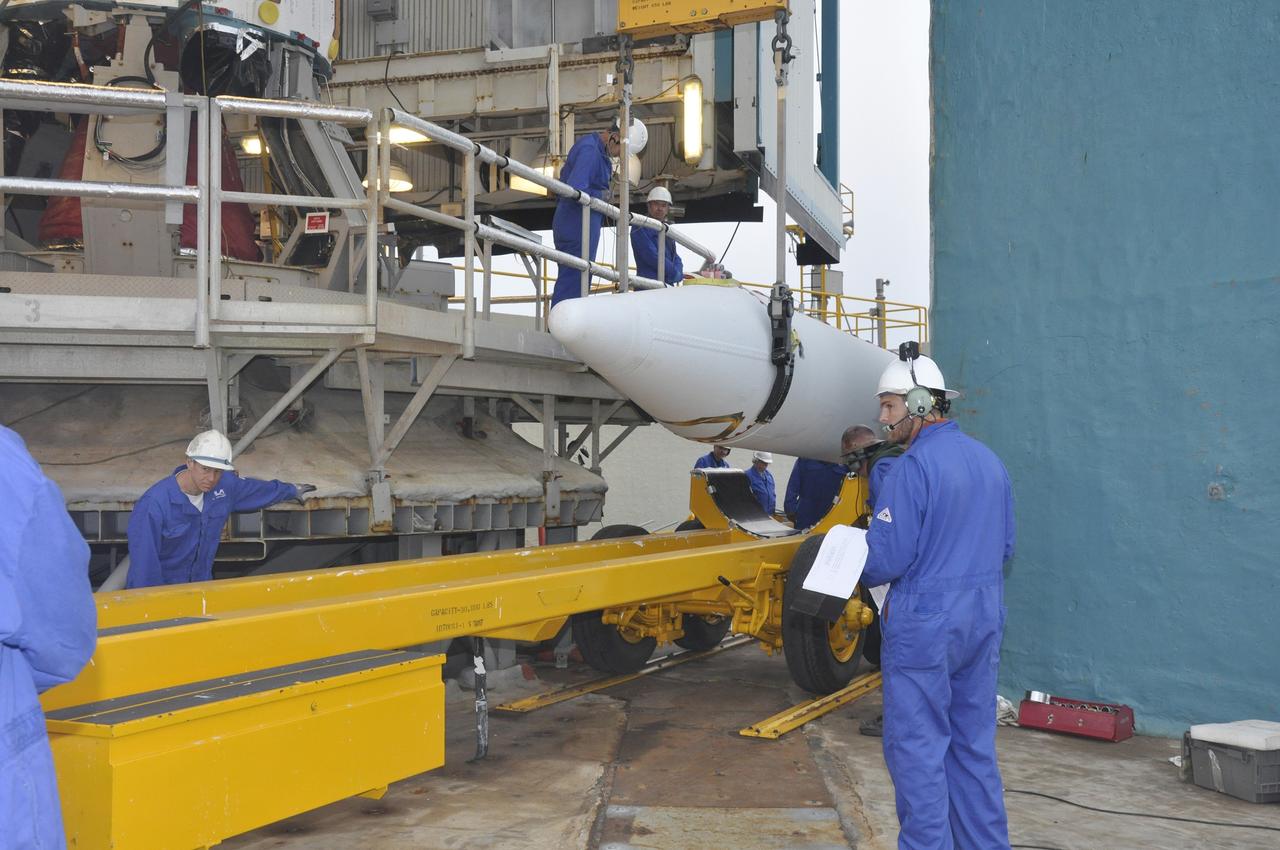
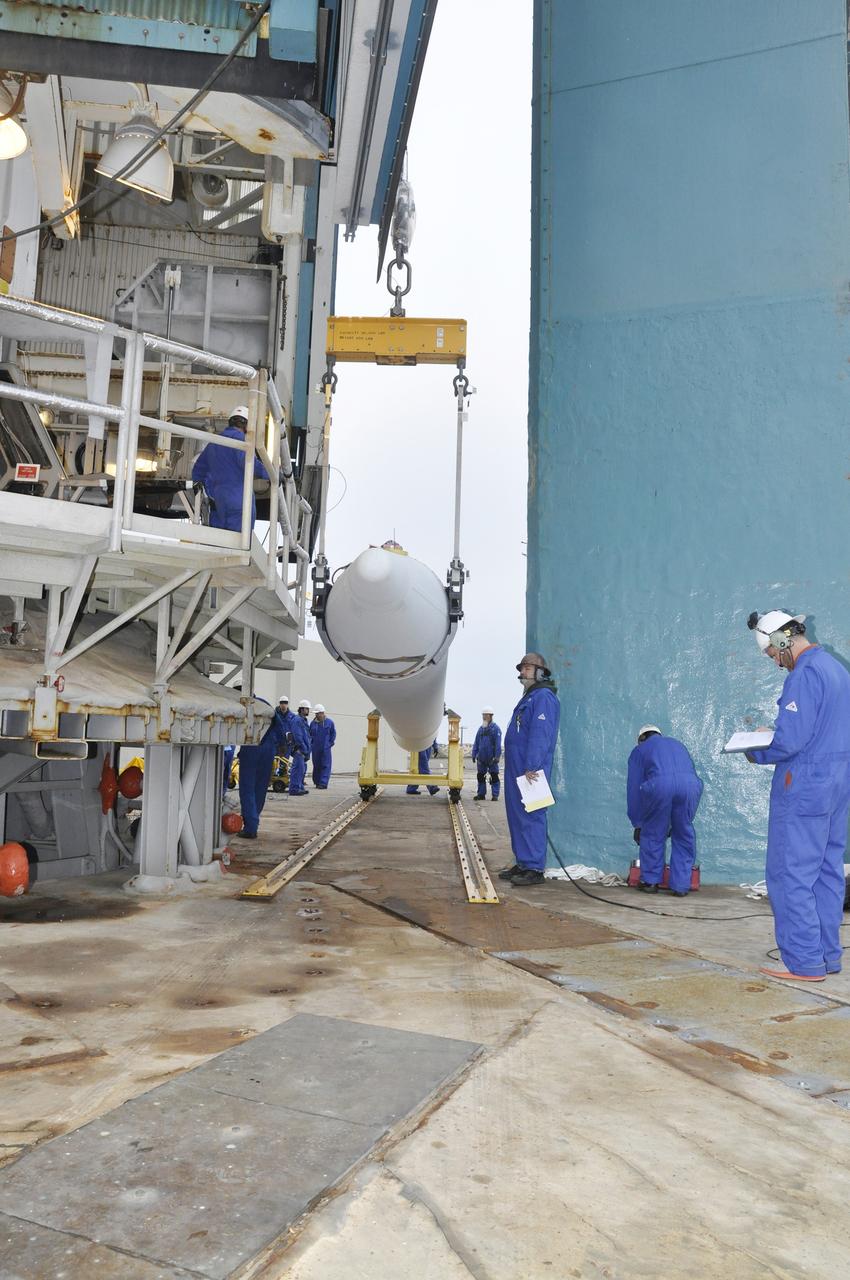
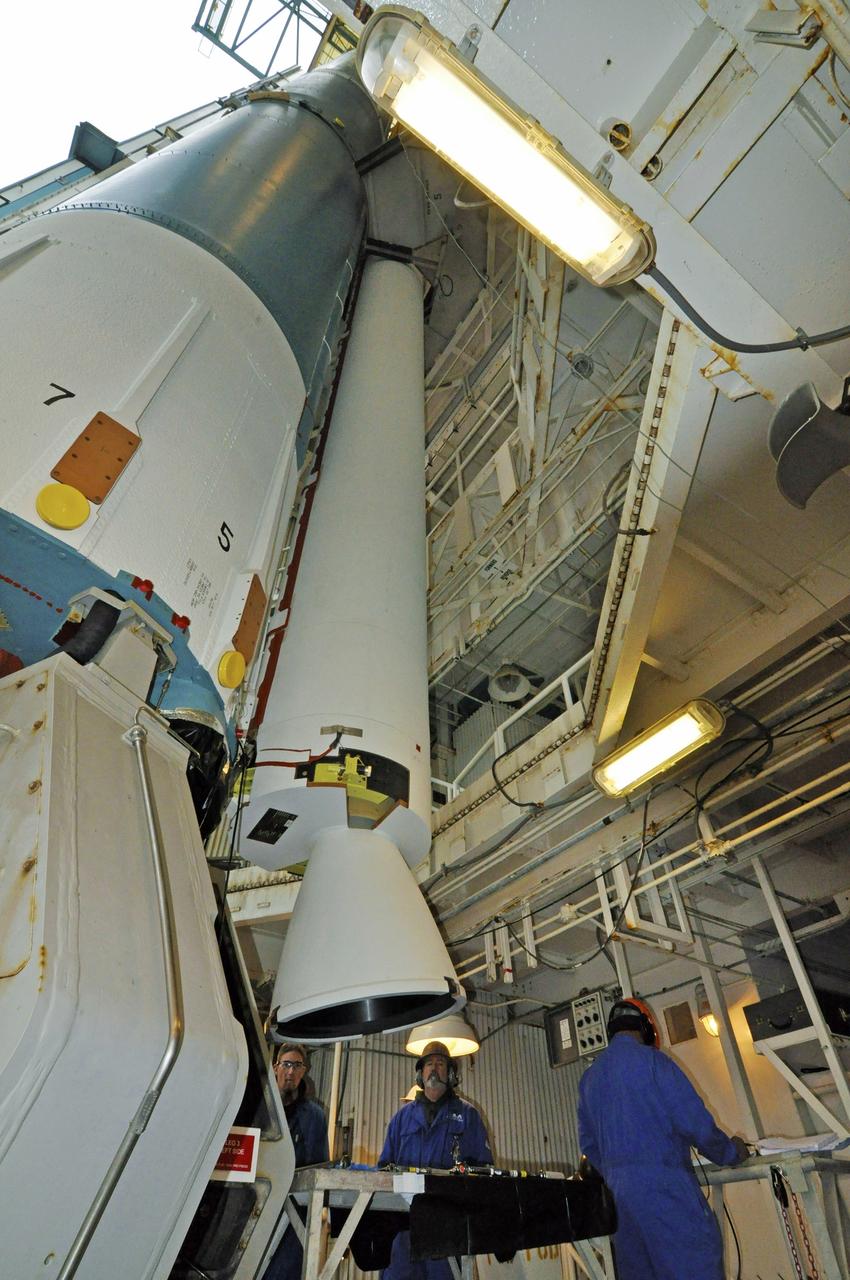
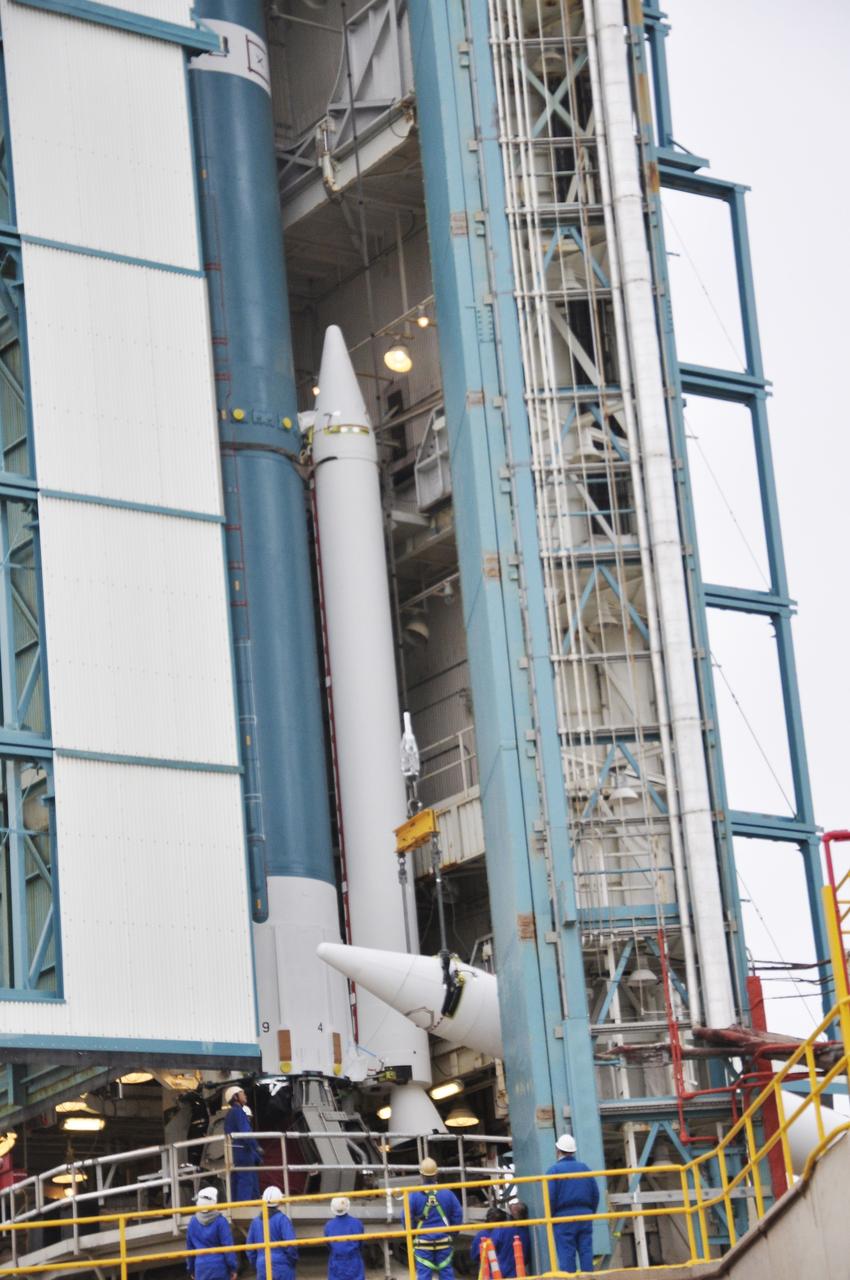
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians guide the final solid rocket motor (SRM) off a trailer. The motor will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians guide a solid rocket motor (SRM) off a trailer. The motor will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians guide the final solid rocket motor (SRM) off a trailer. The motor will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Operations to attach three solid rocket motors, or SRMs, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California are complete. The SRMs used to give the first stage additional thrust are known as graphite epoxy motors. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
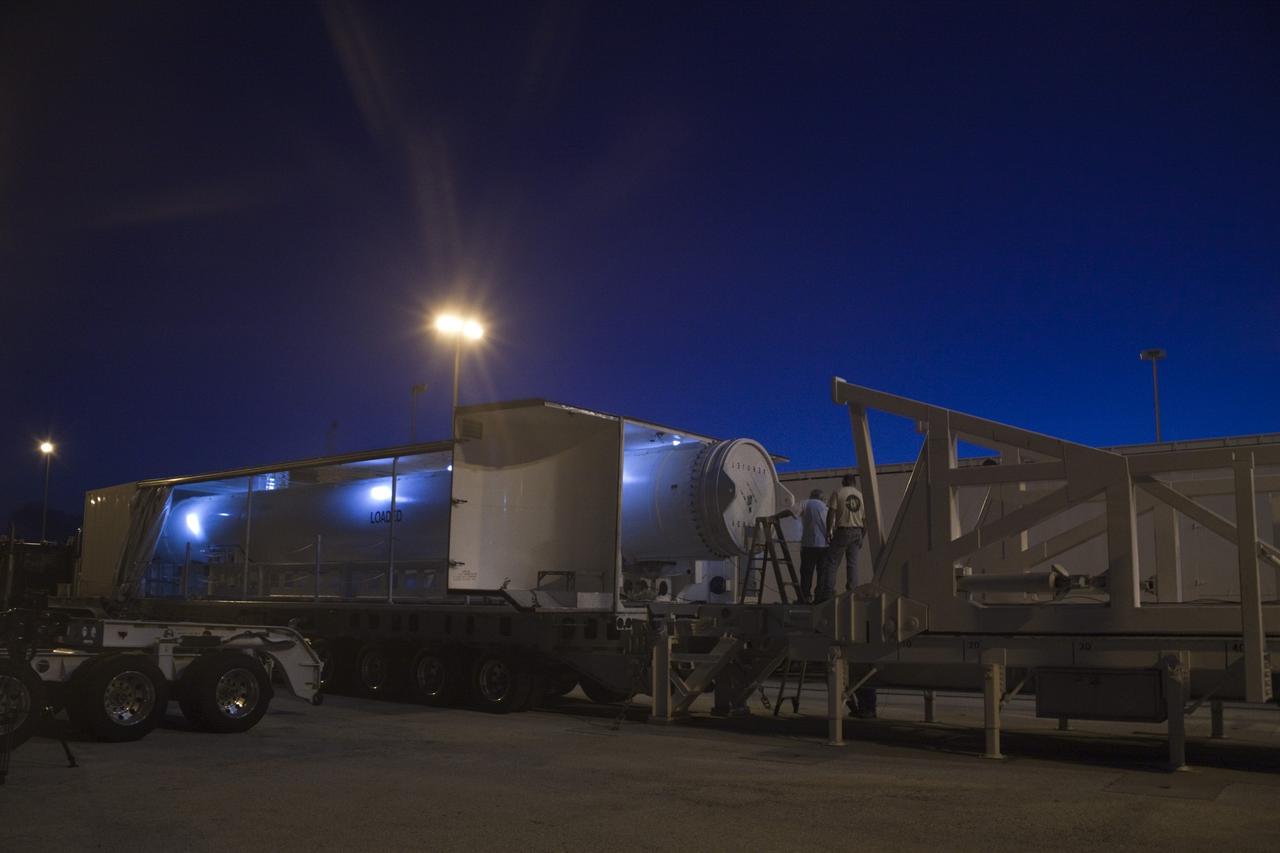

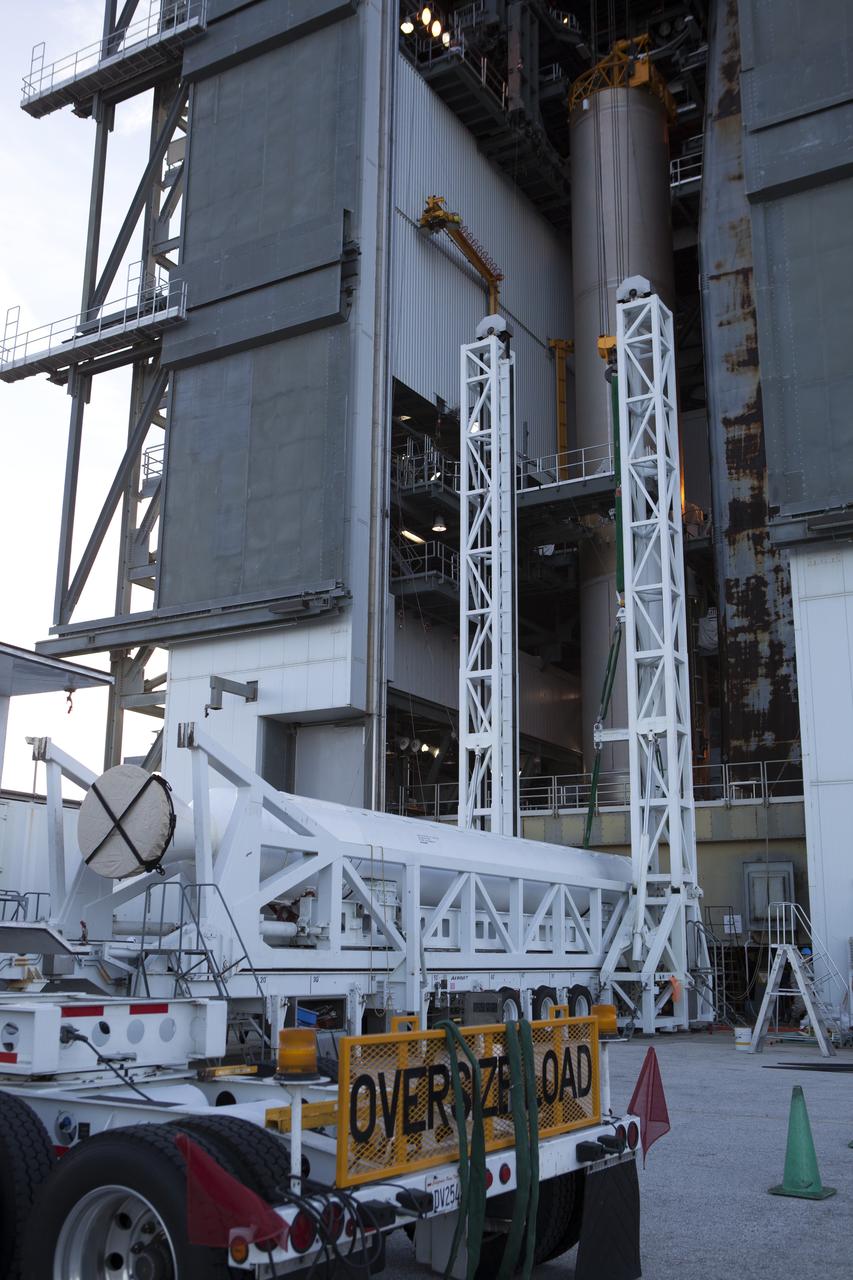
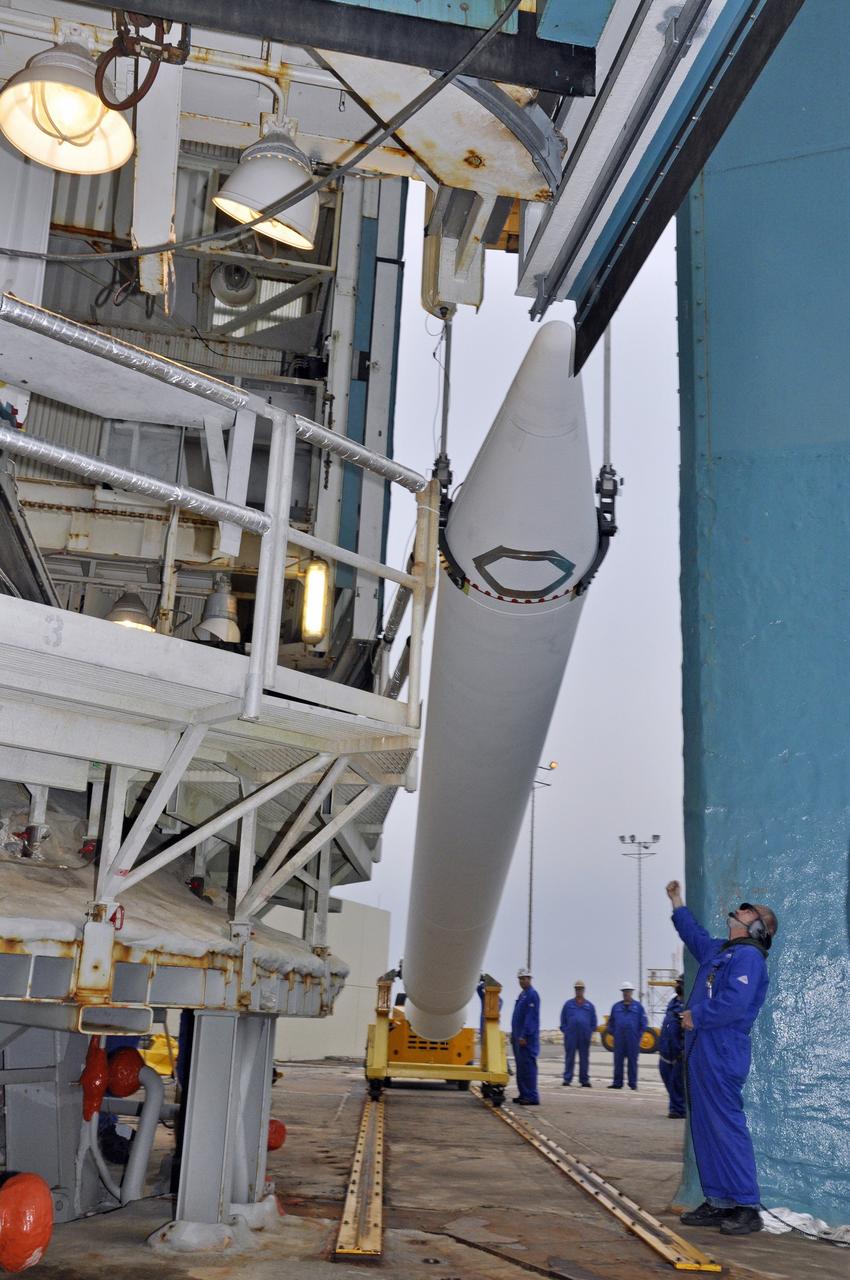
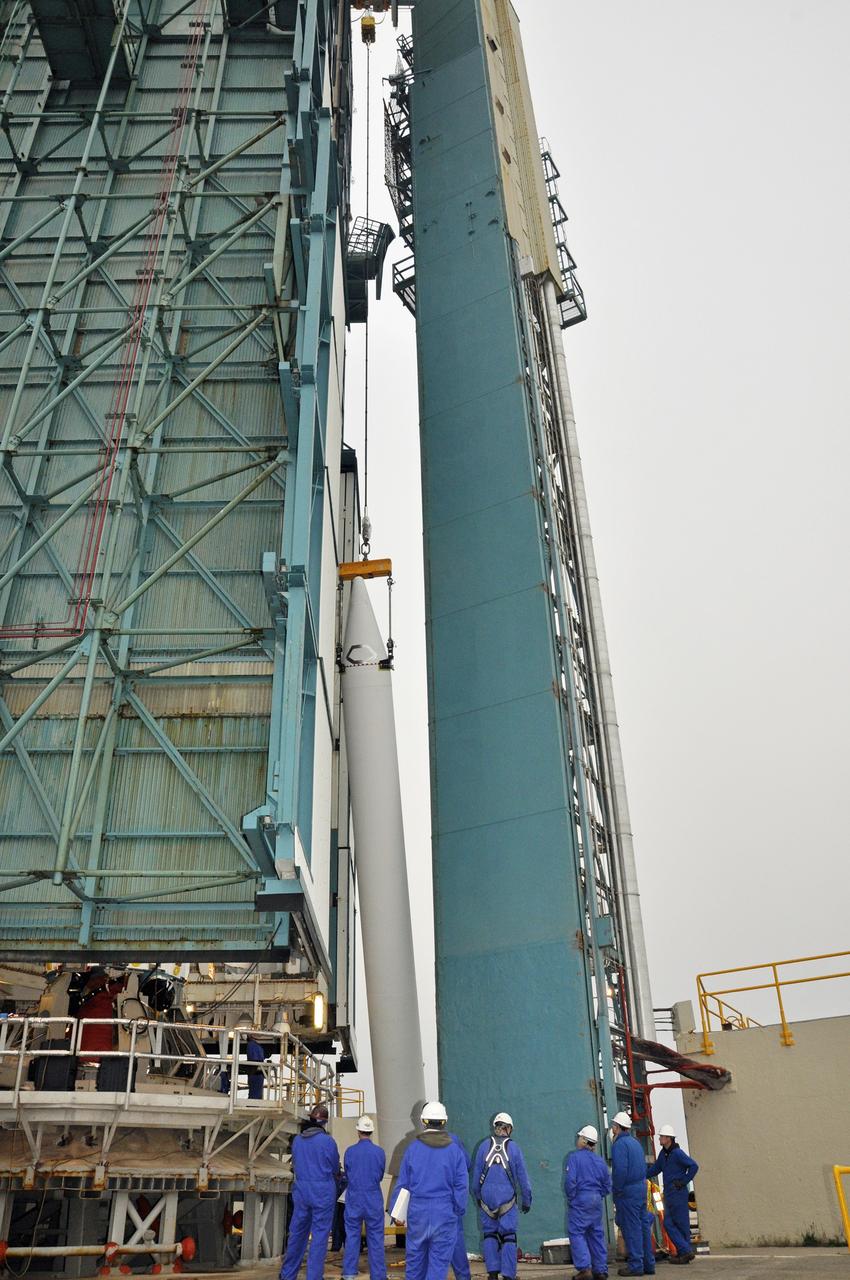
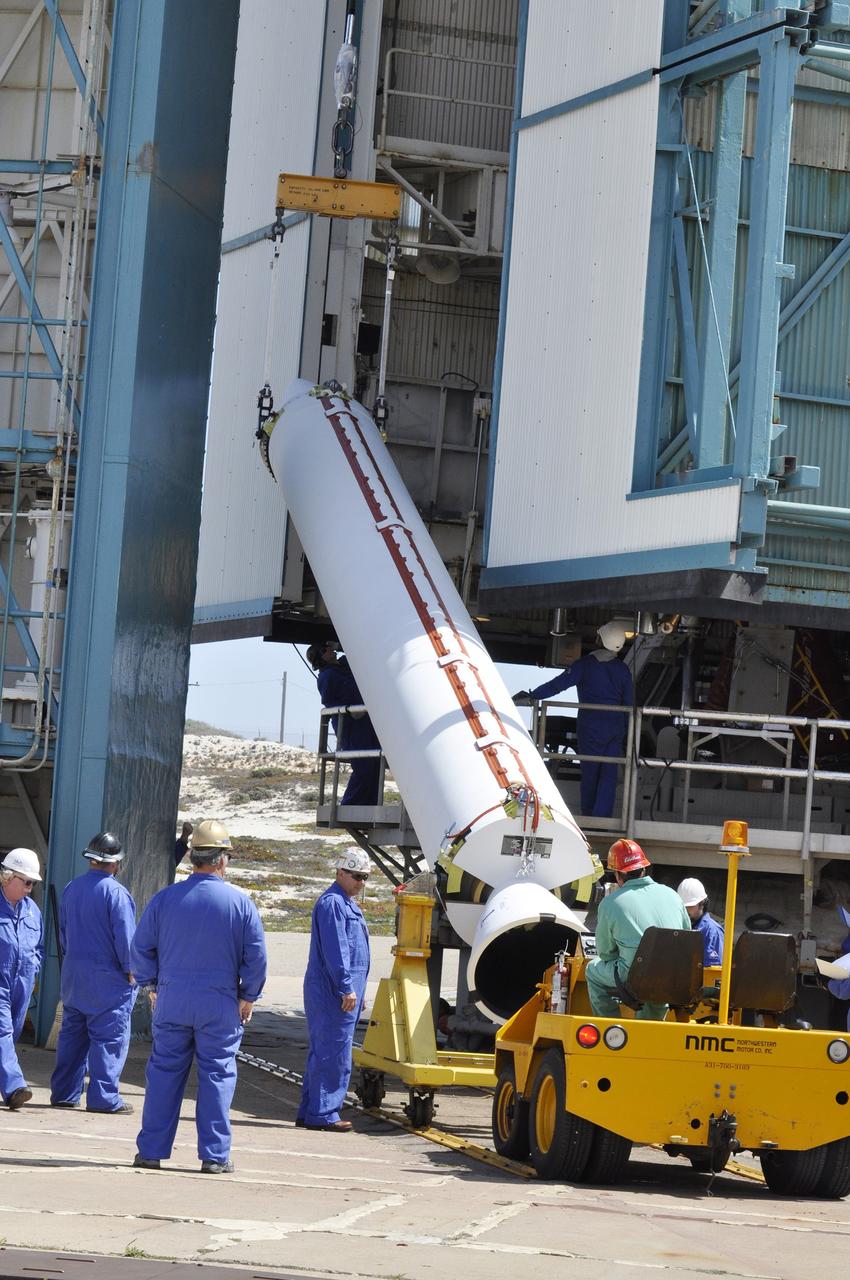
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Under the night sky at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers prepare the final solid rocket motor (SRM) for lifting into the Vertical Integration Facility. The SRM will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket being prepared to launch NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
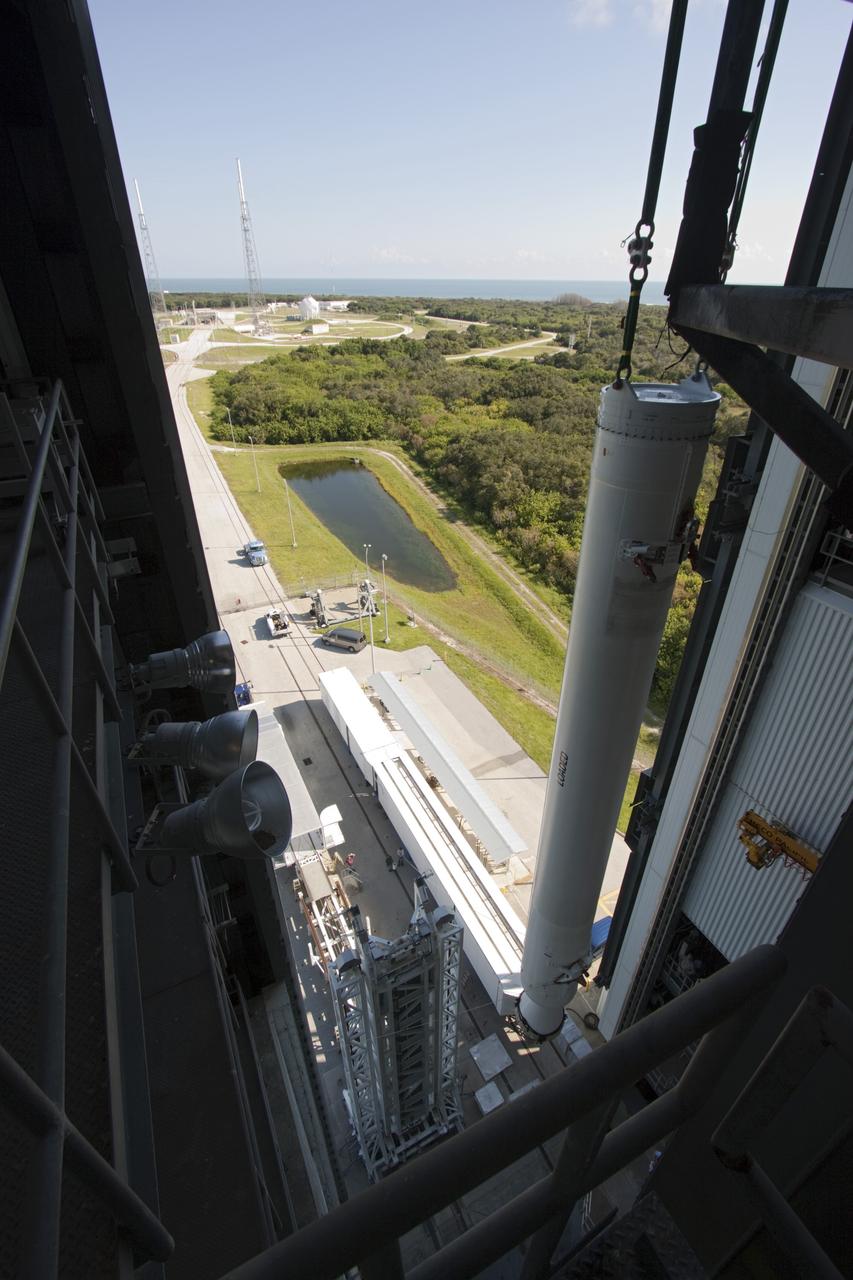

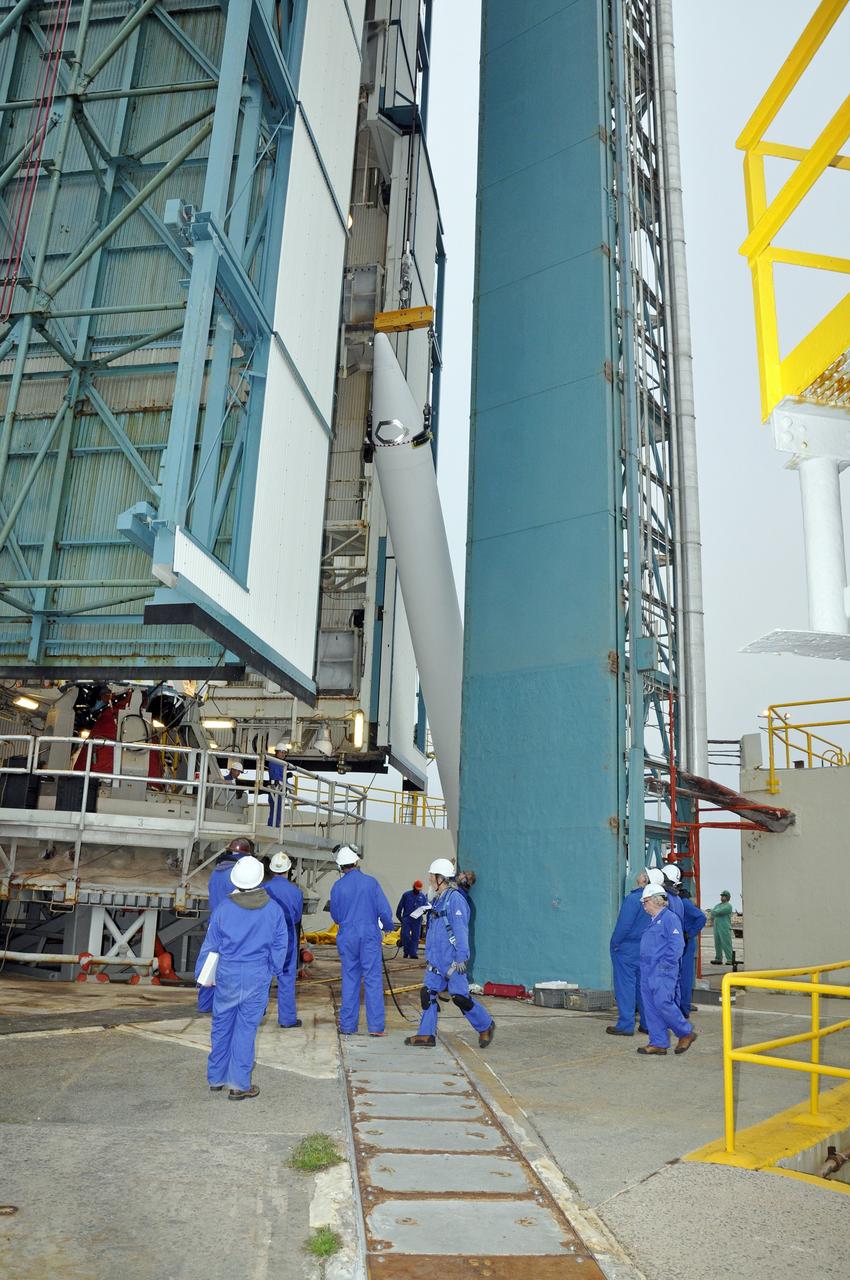
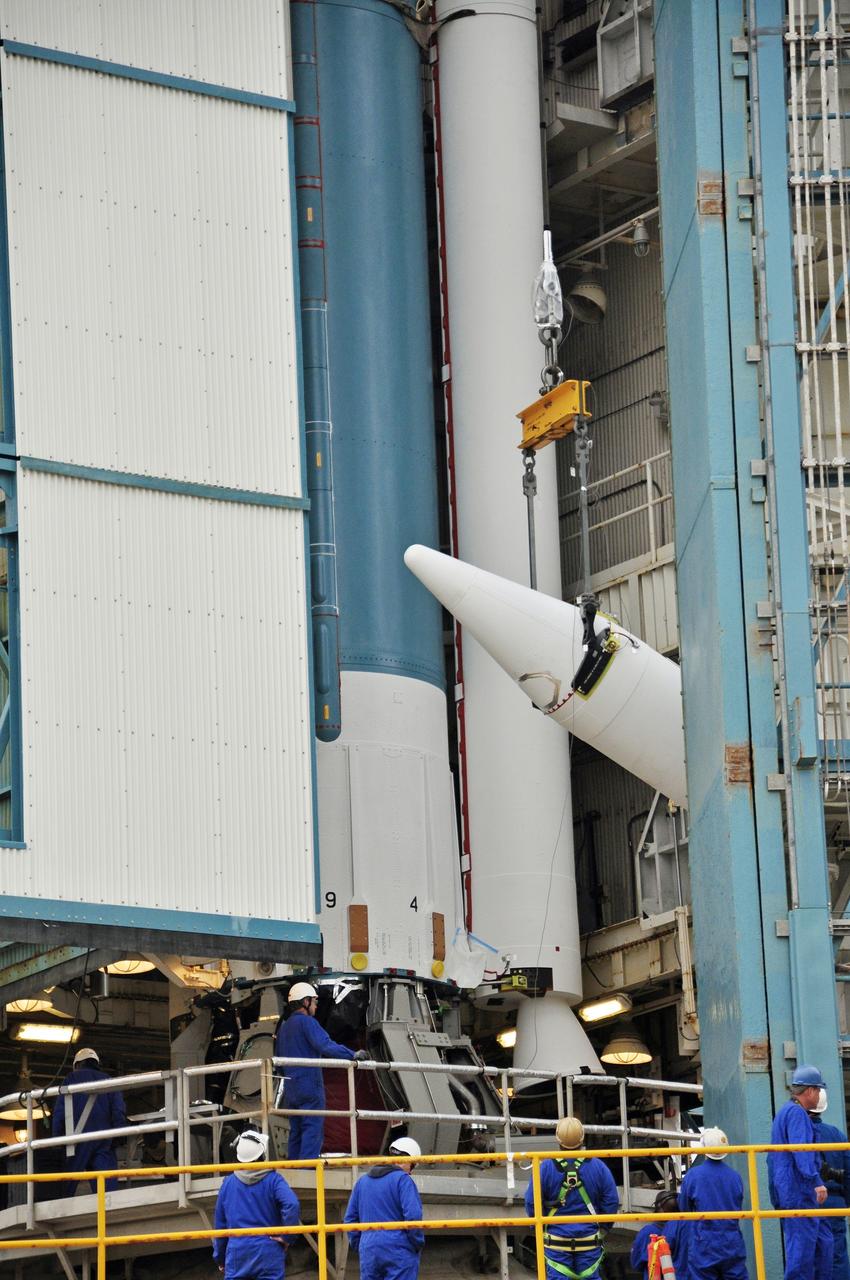
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A unique view is offered at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, as the final solid rocket motor (SRM) hangs in an upright position for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
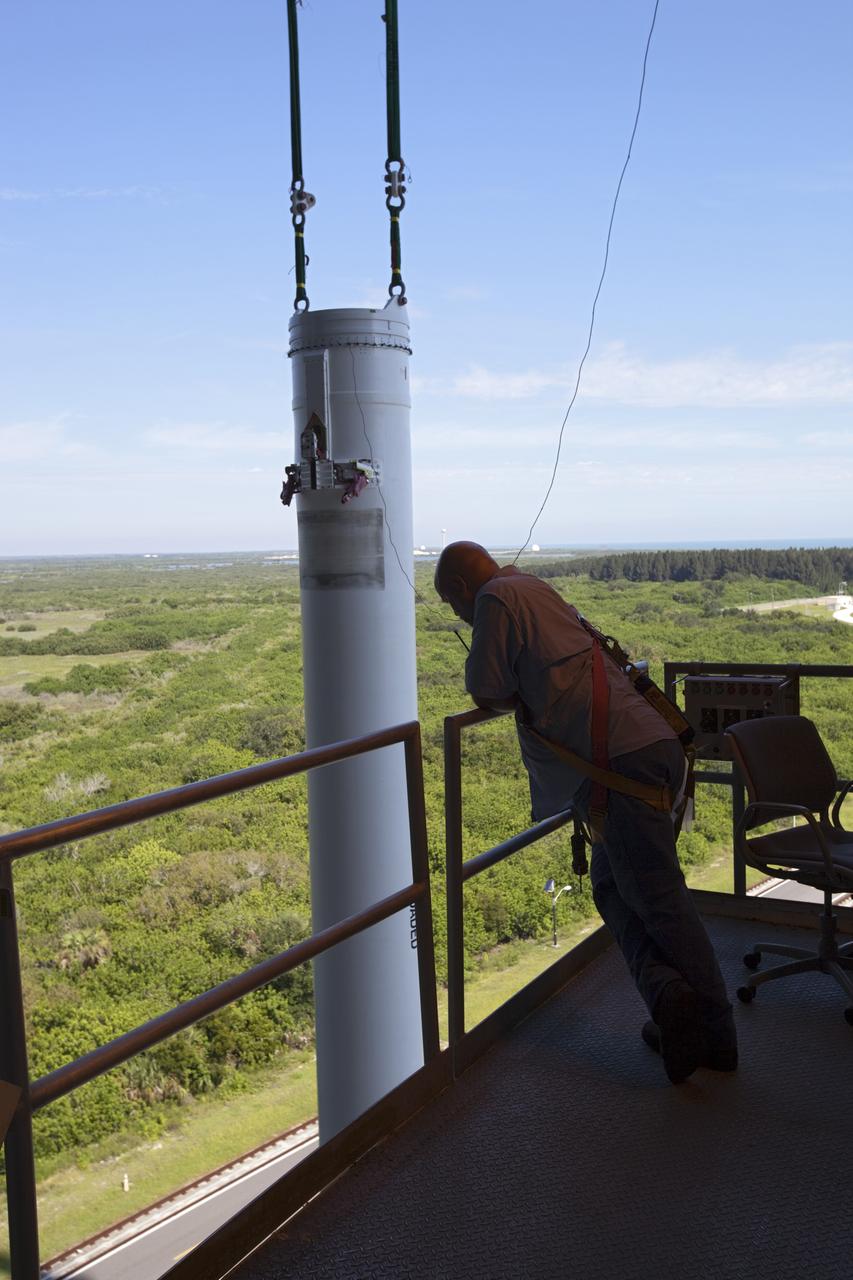

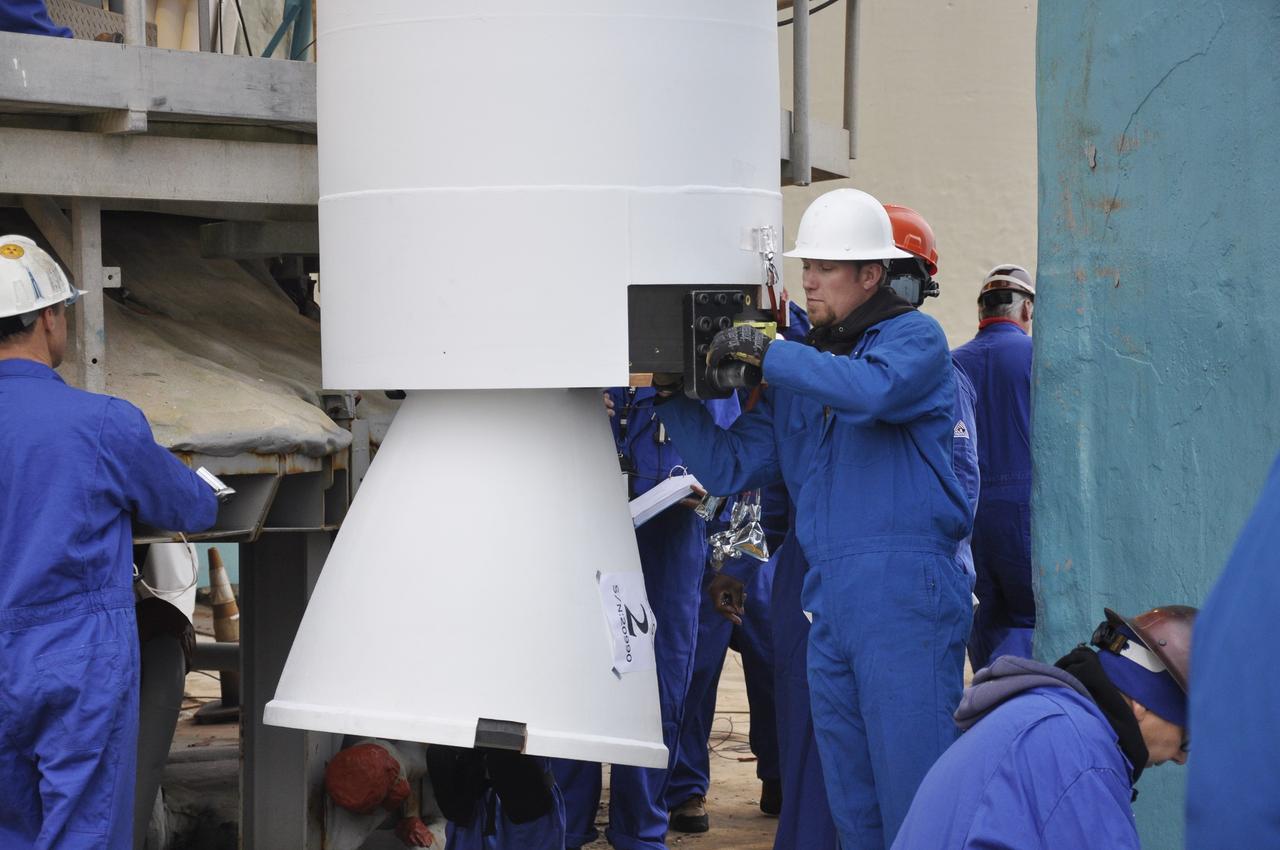
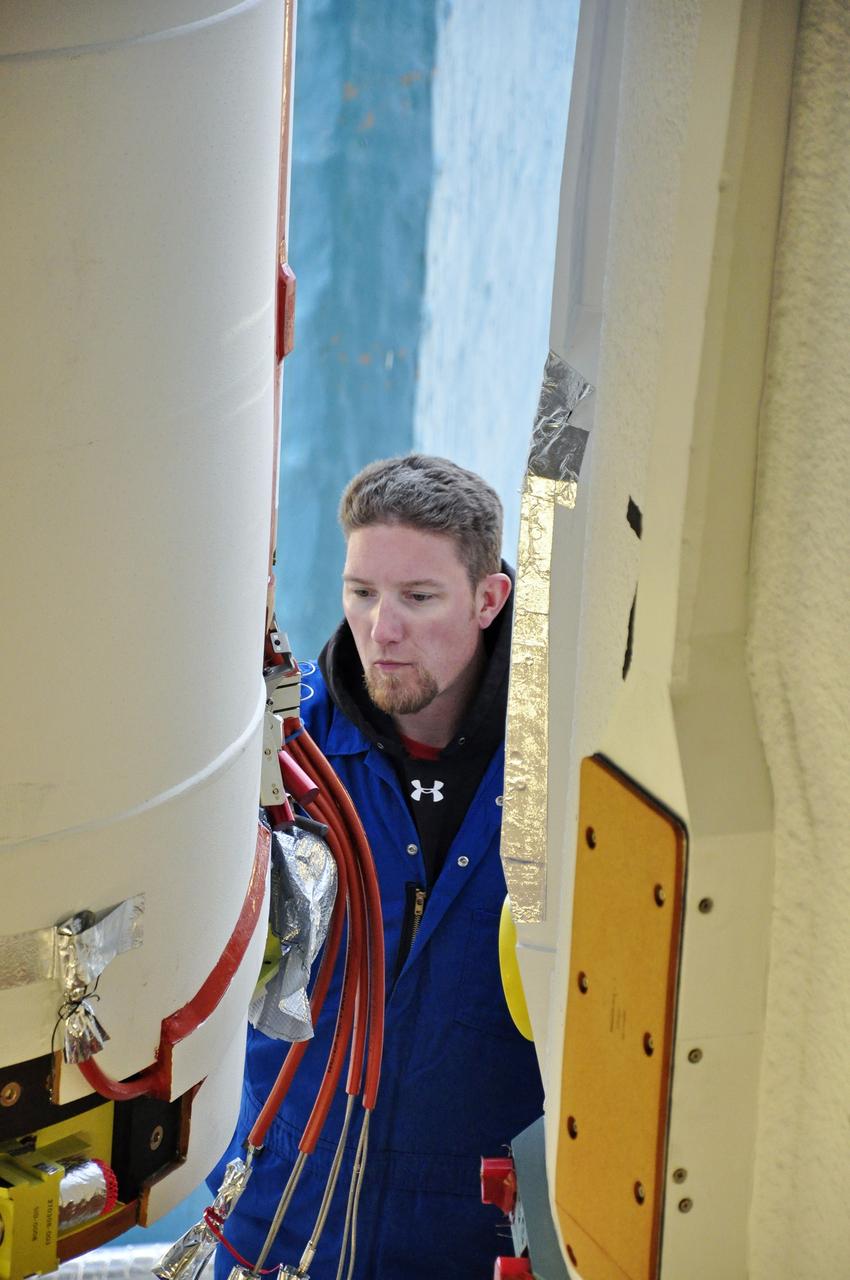
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A technician at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida monitors the lifting of a solid rocket motor (SRM) for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
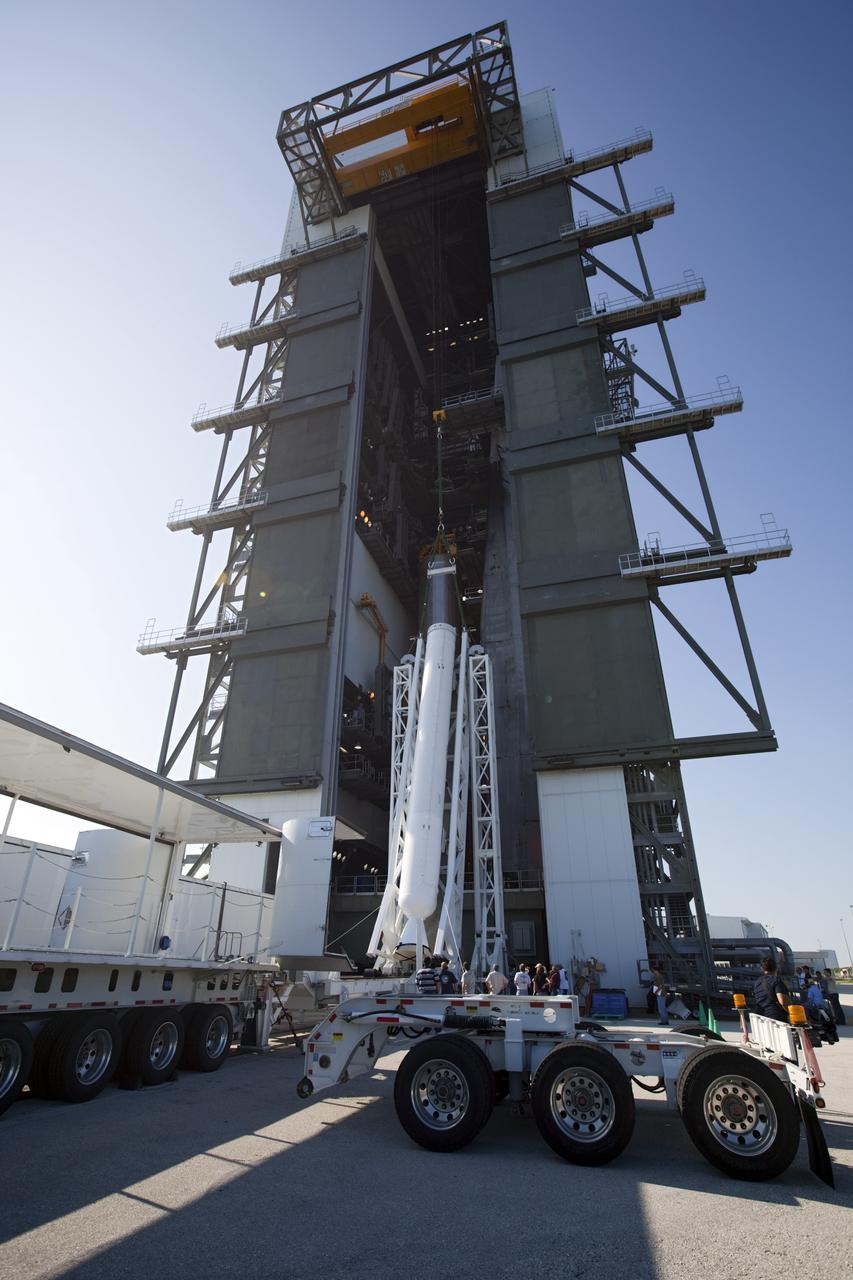

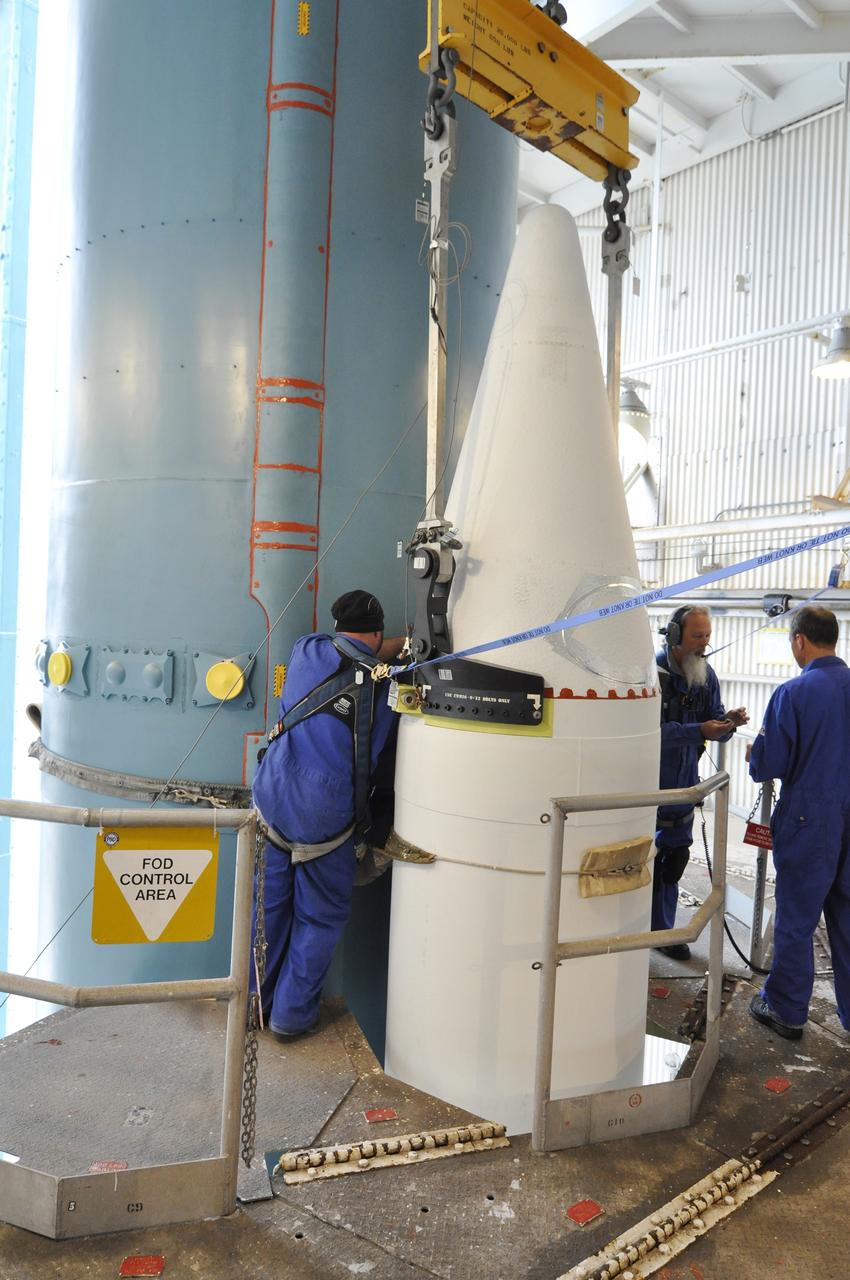
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians use a lifting device to elevate a solid rocket motor (SRM) into an upright position for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
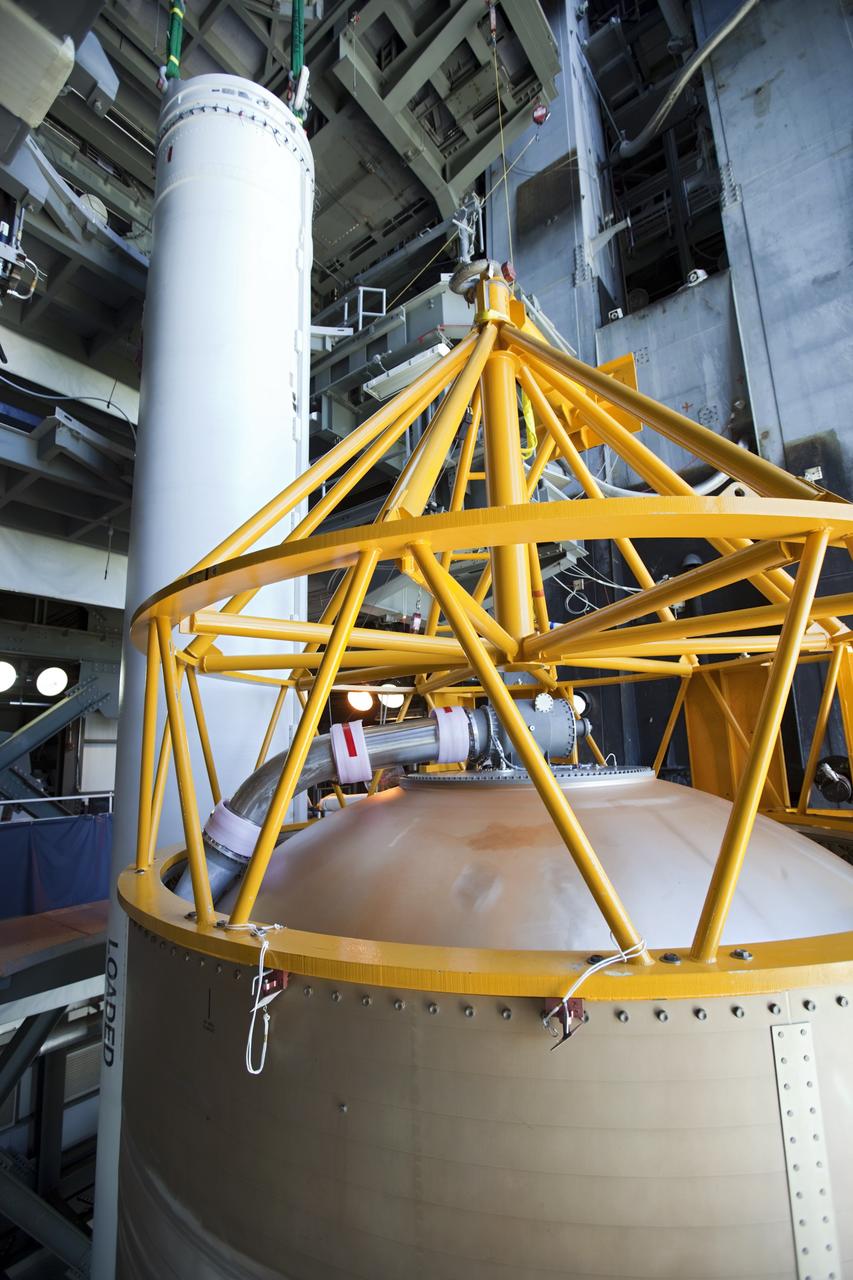
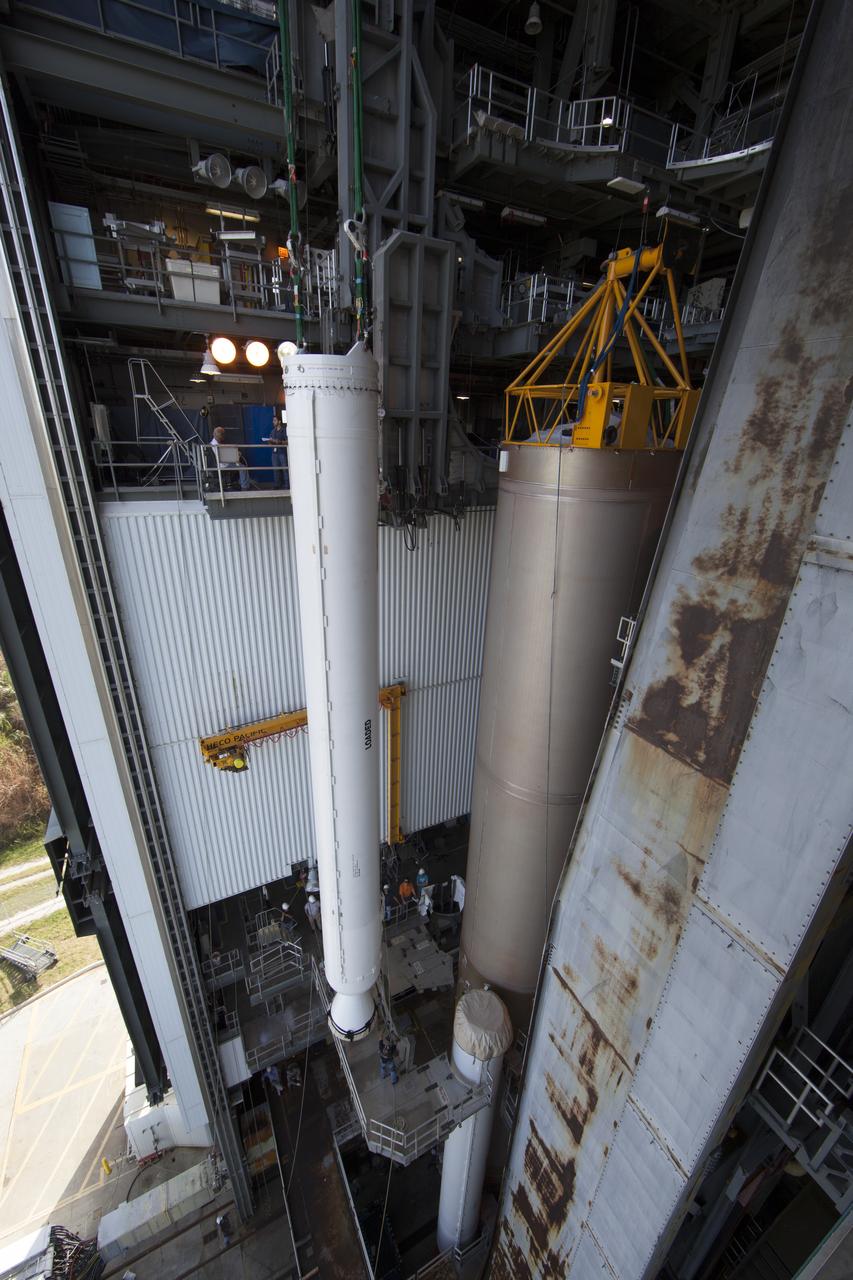
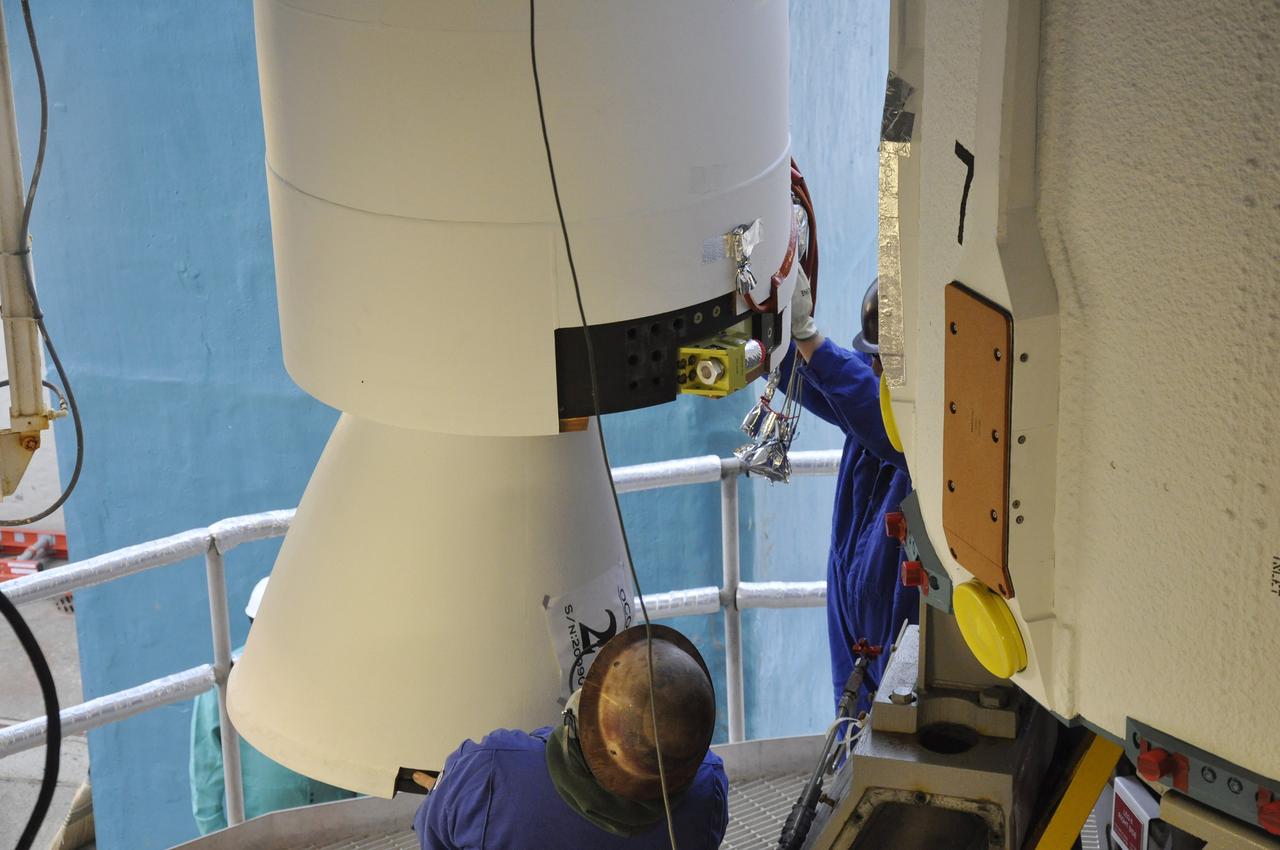
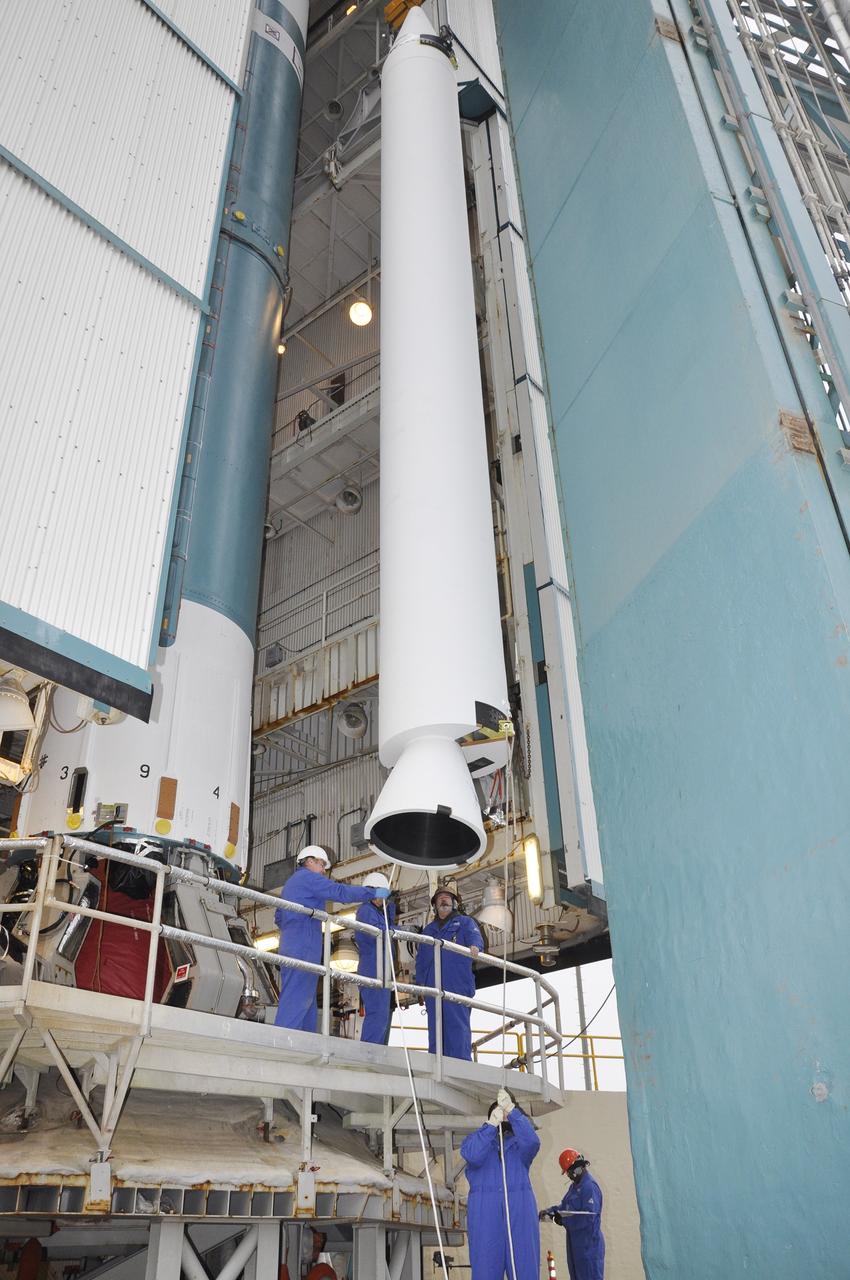
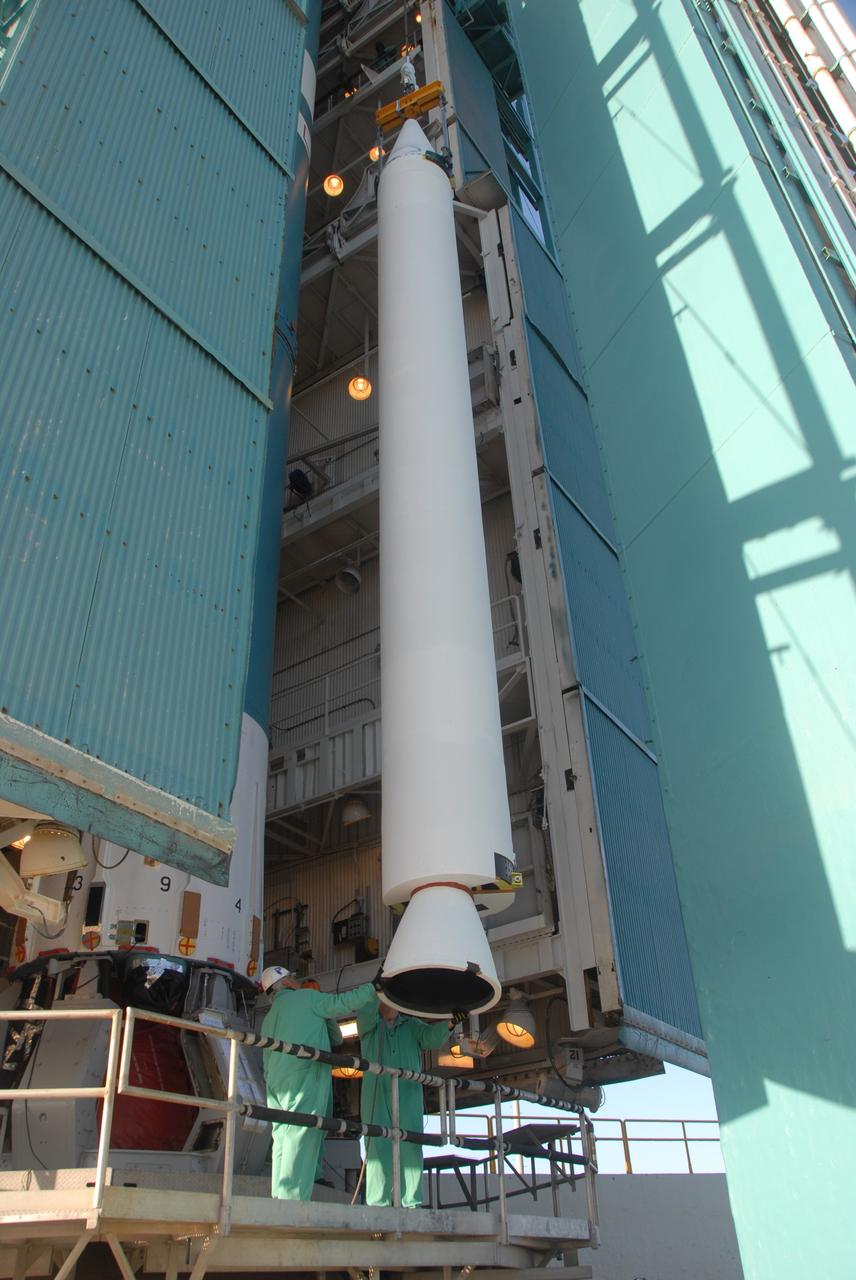
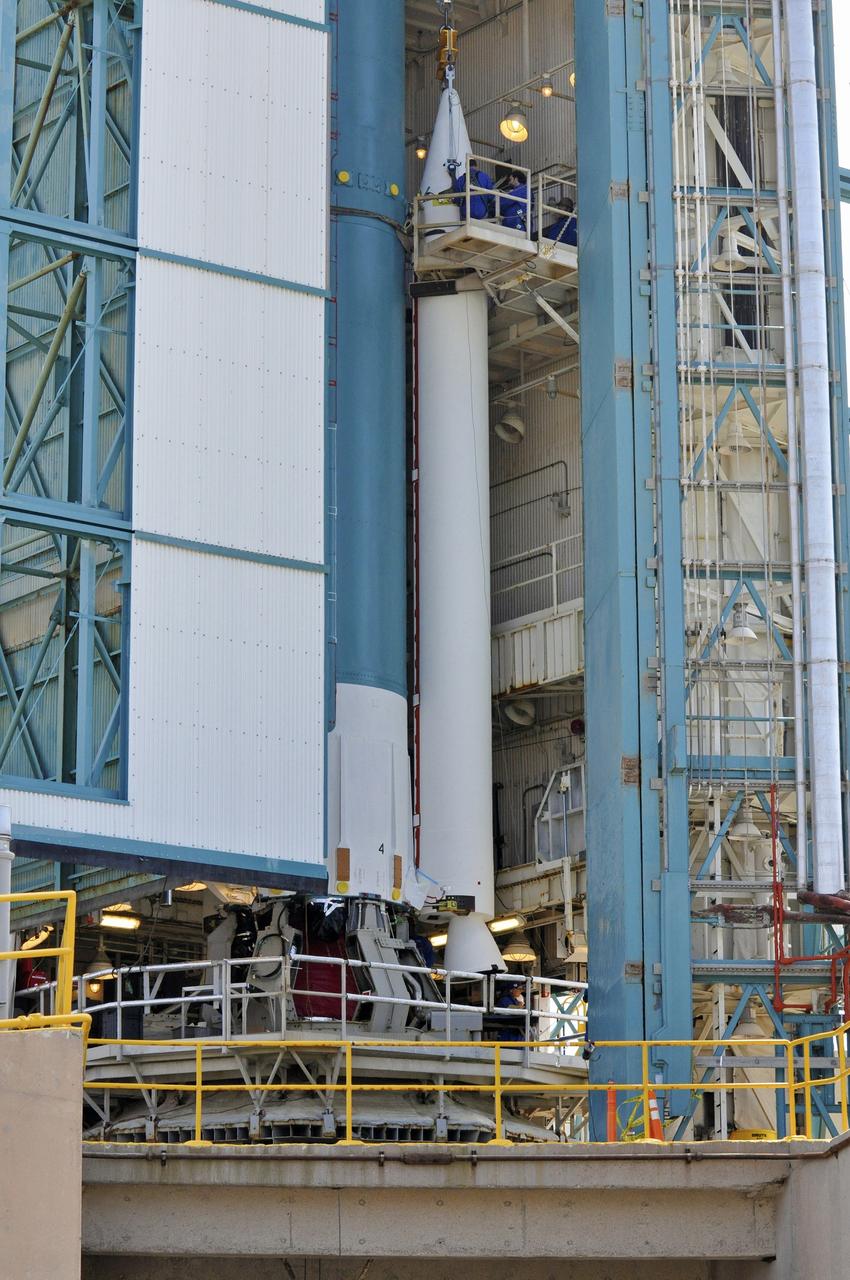
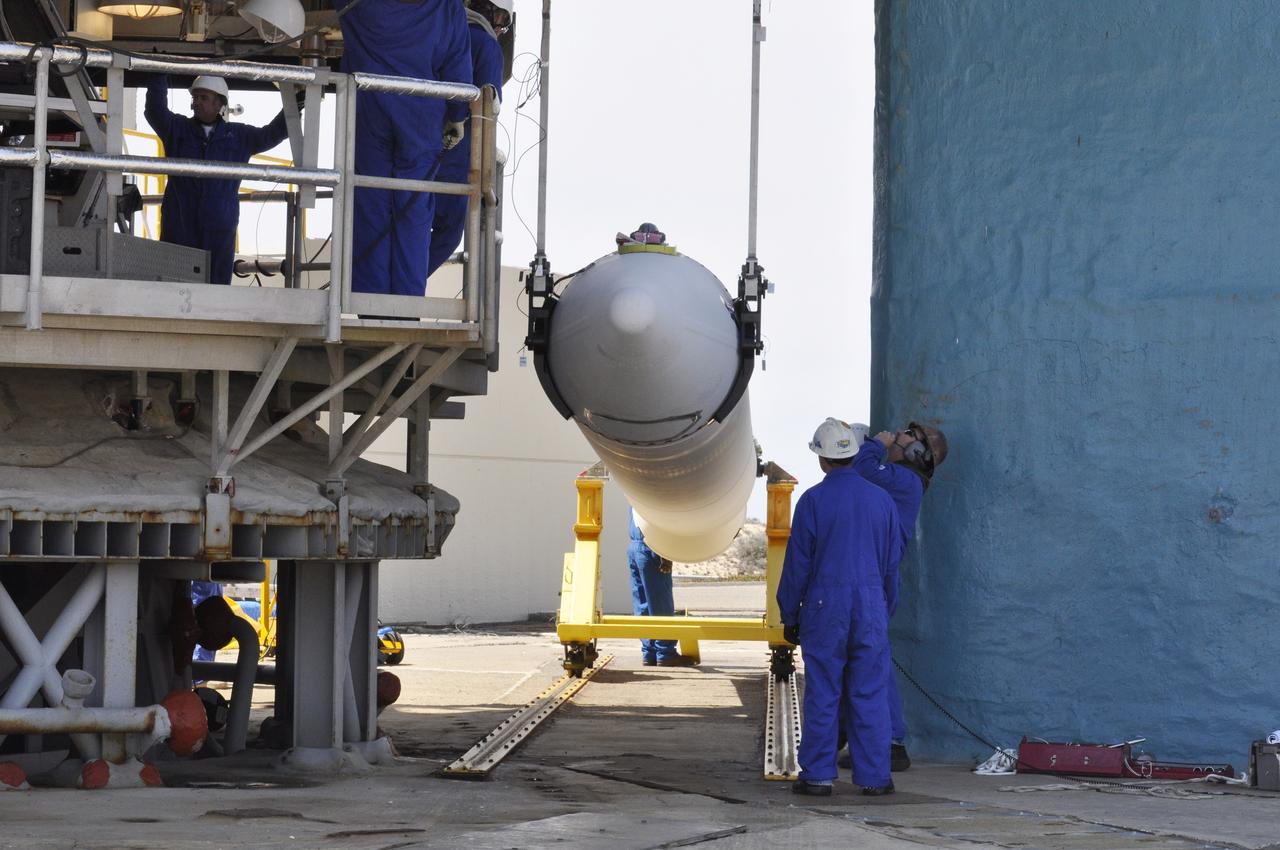
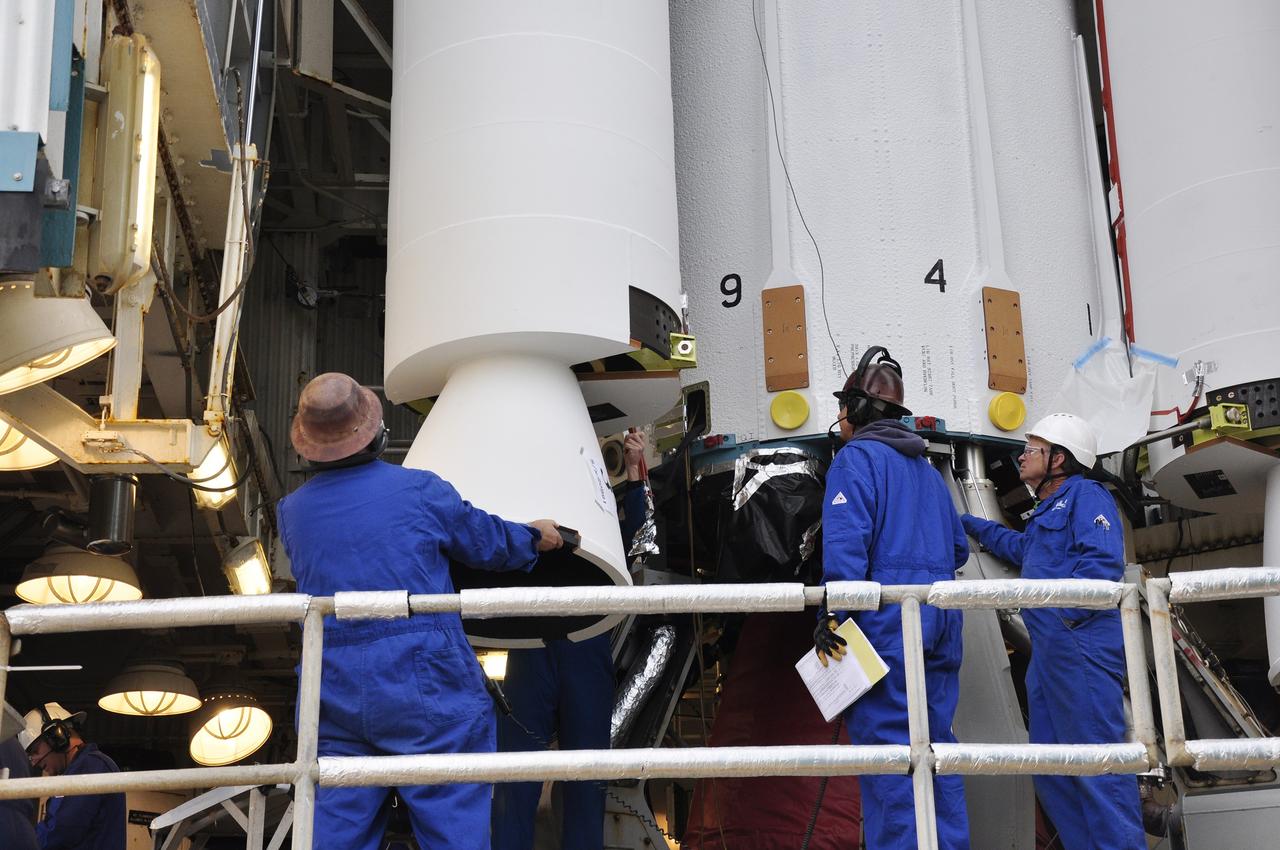
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane lowers a solid rocket motor (SRM) for mating to the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Atlas V will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into space. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
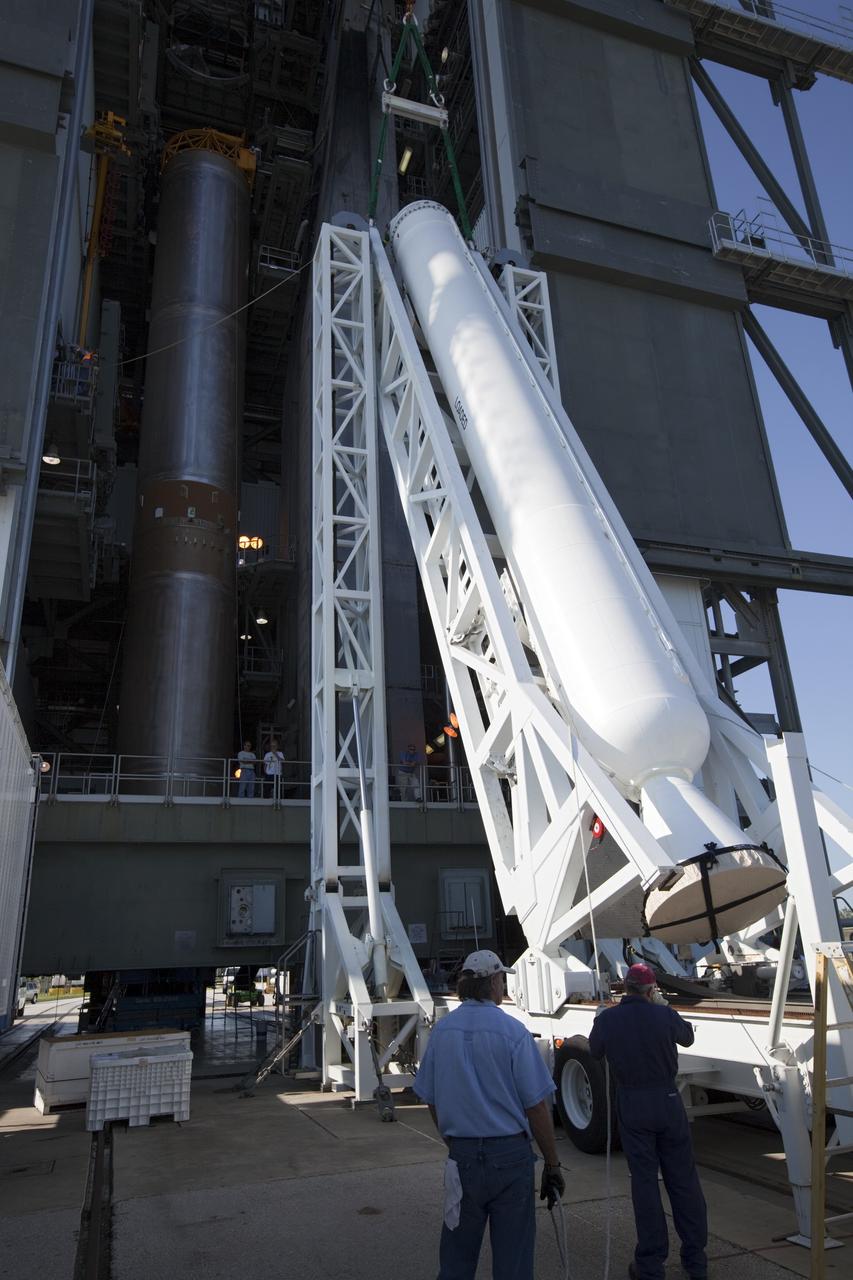

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians use a lifting device to elevate a solid rocket motor (SRM) into an upright position for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
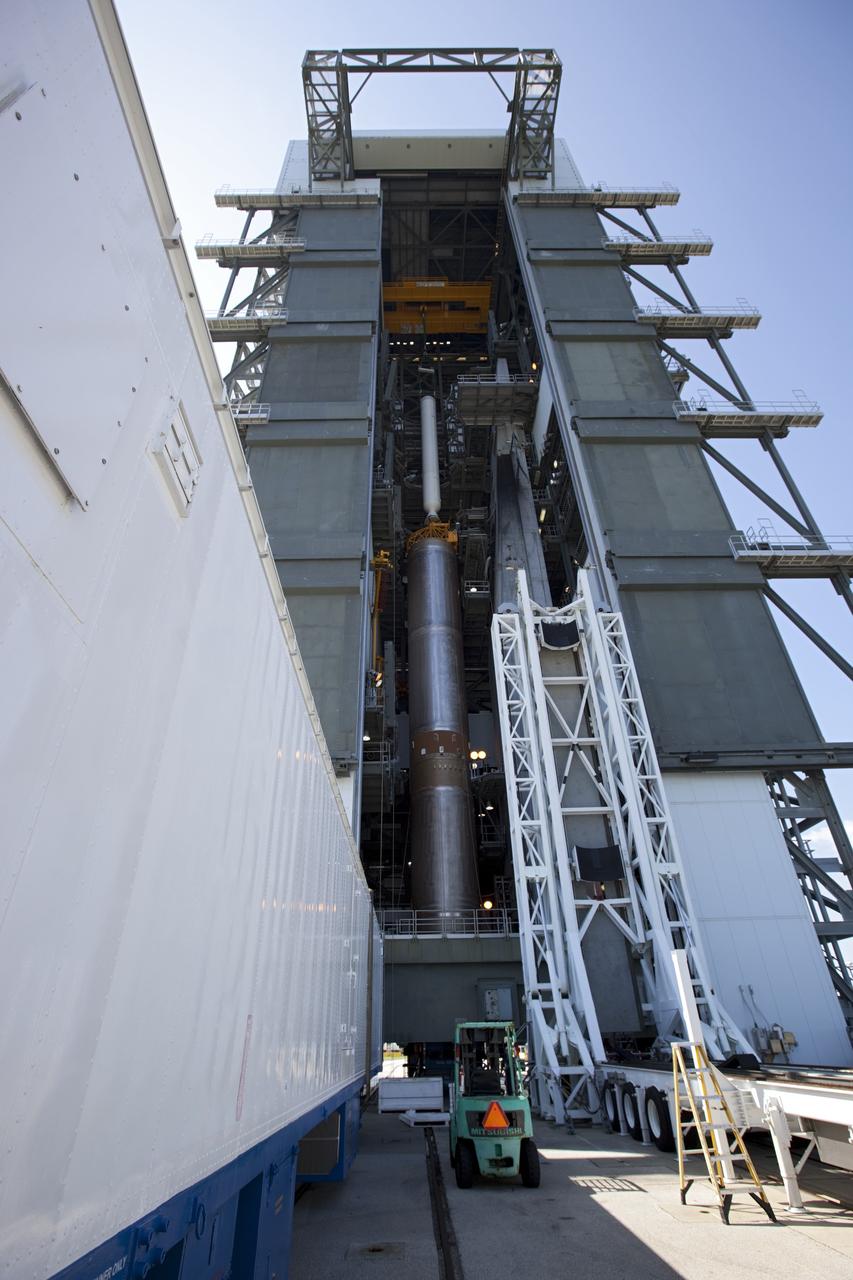

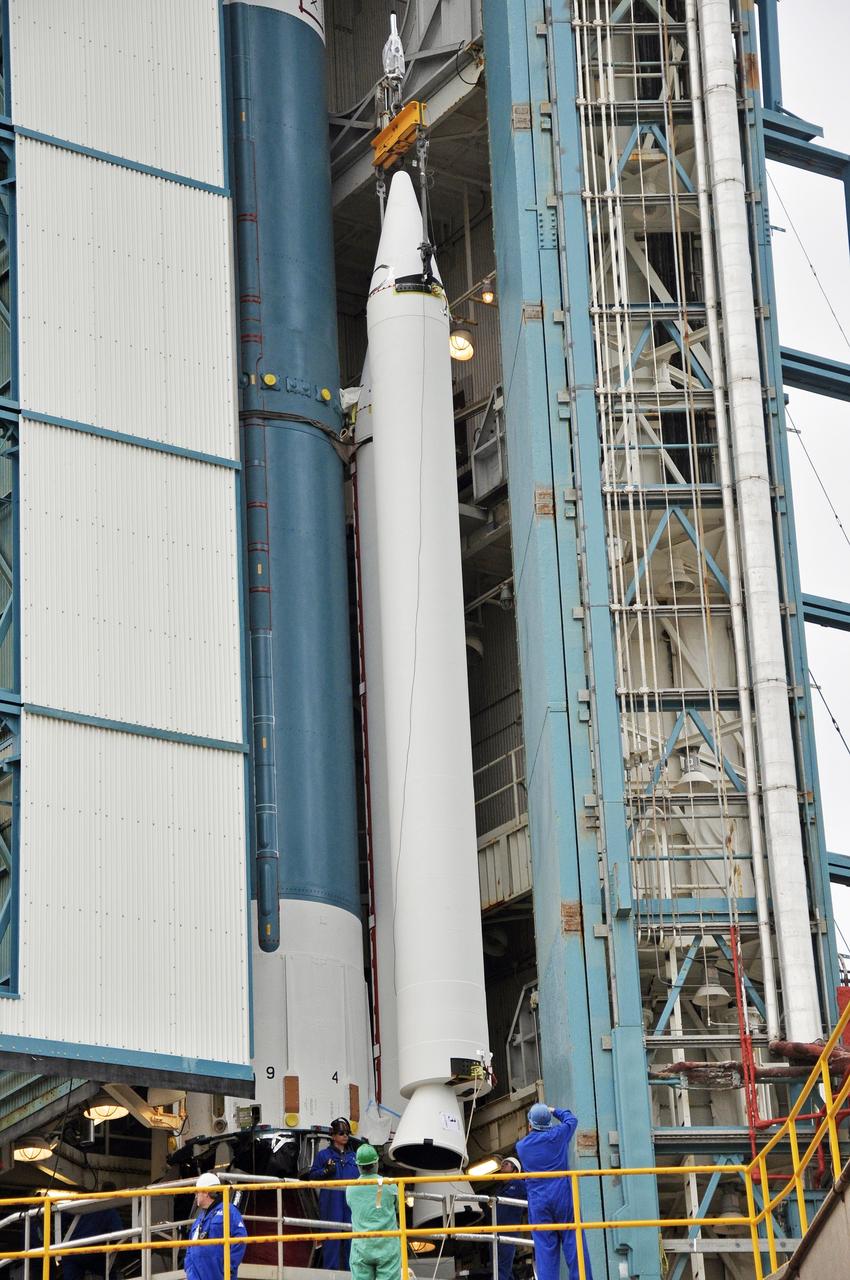
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane positions a solid rocket motor (SRM) for mating to the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Atlas V will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into space. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane positions a solid rocket motor (SRM) for mating to the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Atlas V will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into space. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

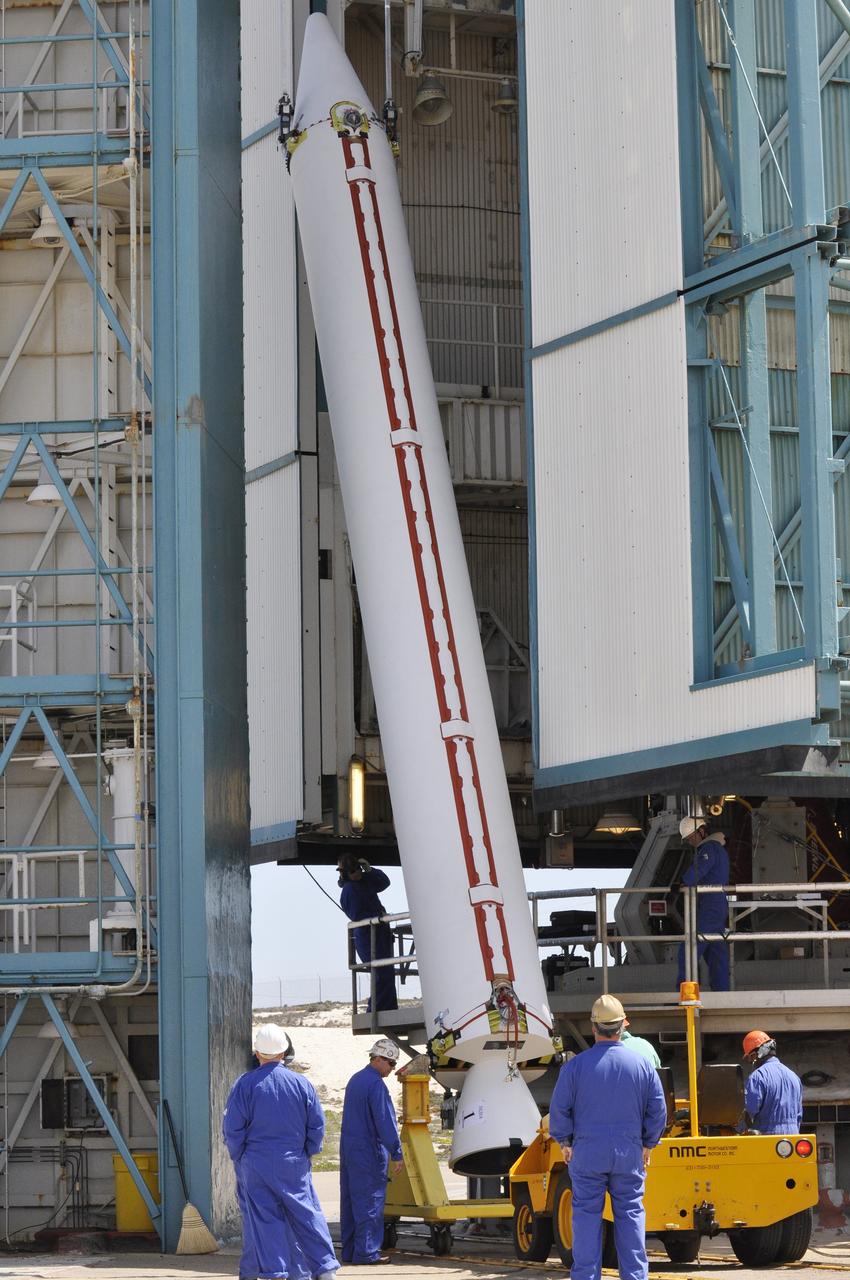
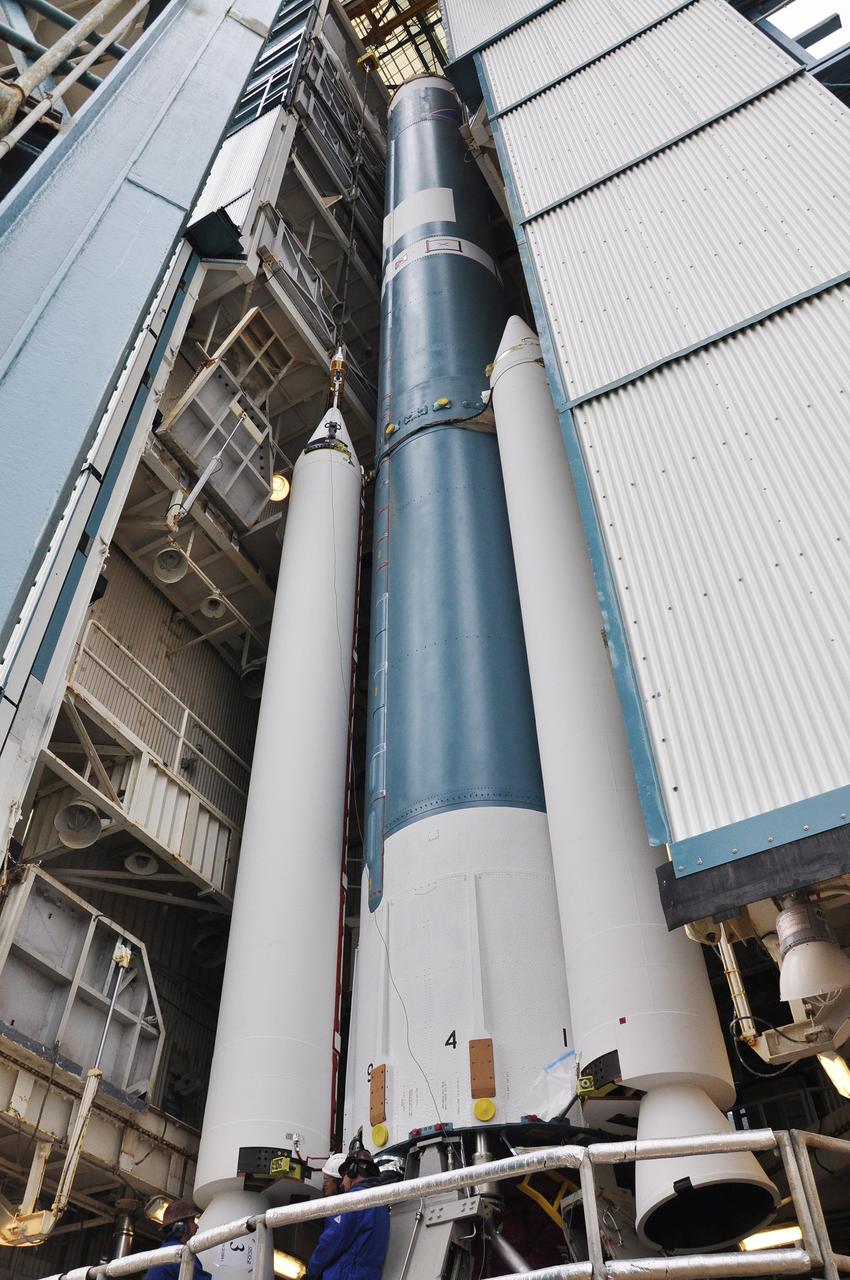
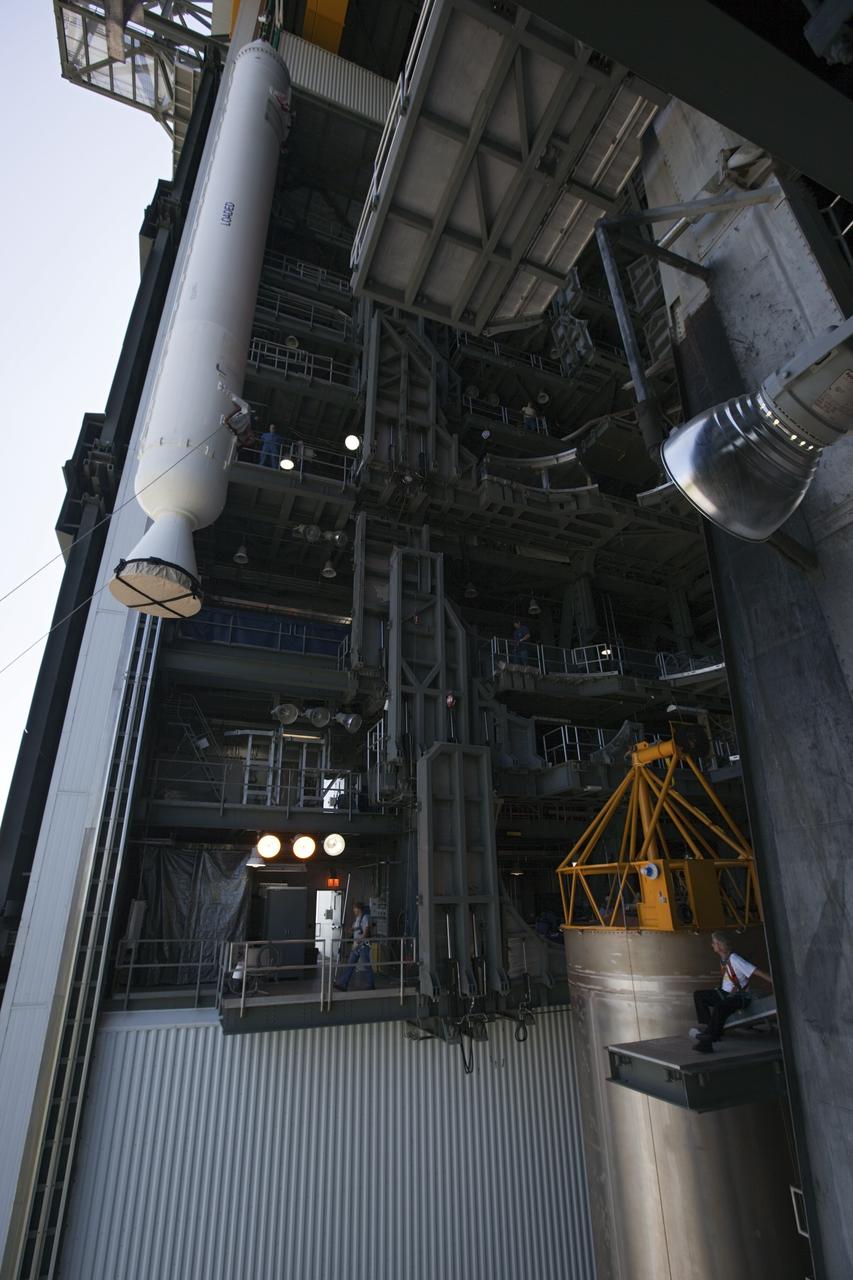
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the final solid rocket motor (SRM) is ready for mating to the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Atlas V will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into space. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
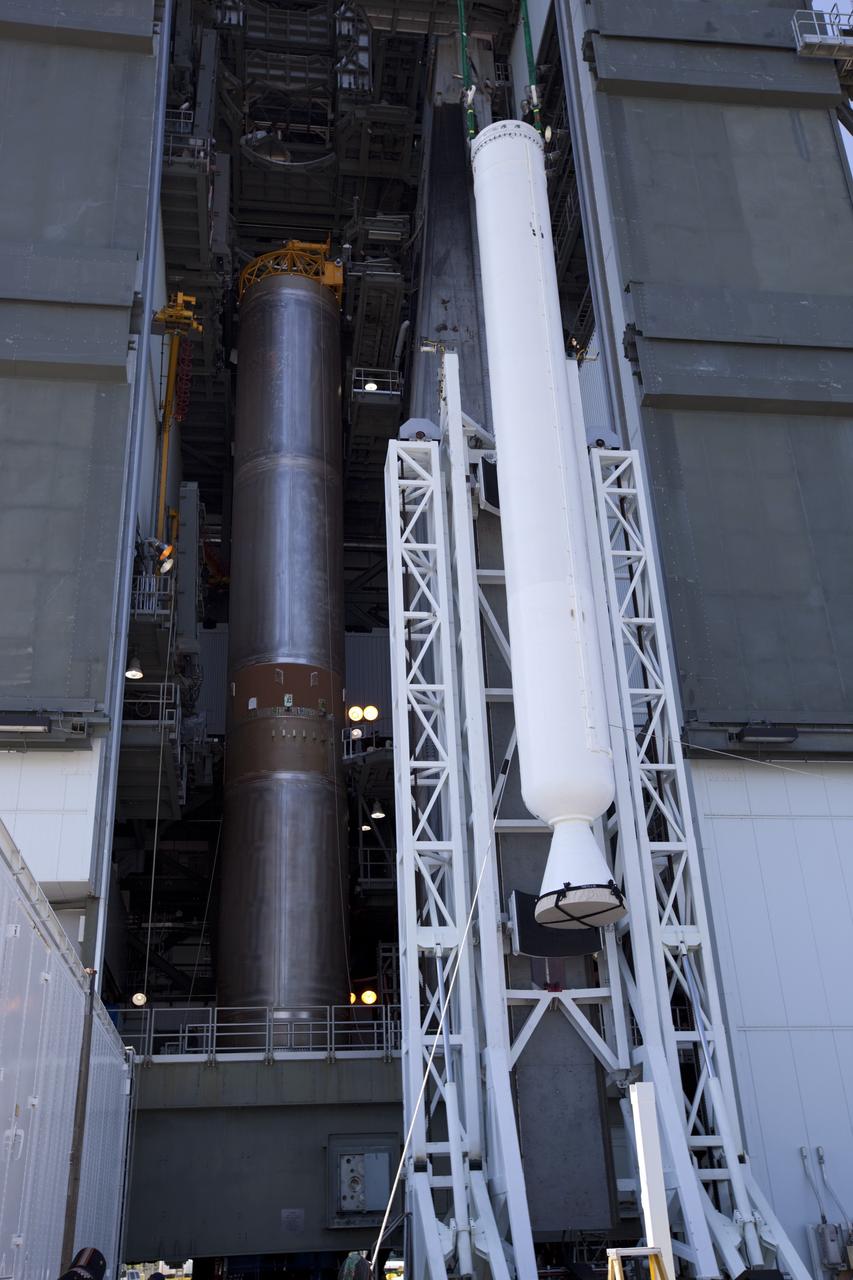

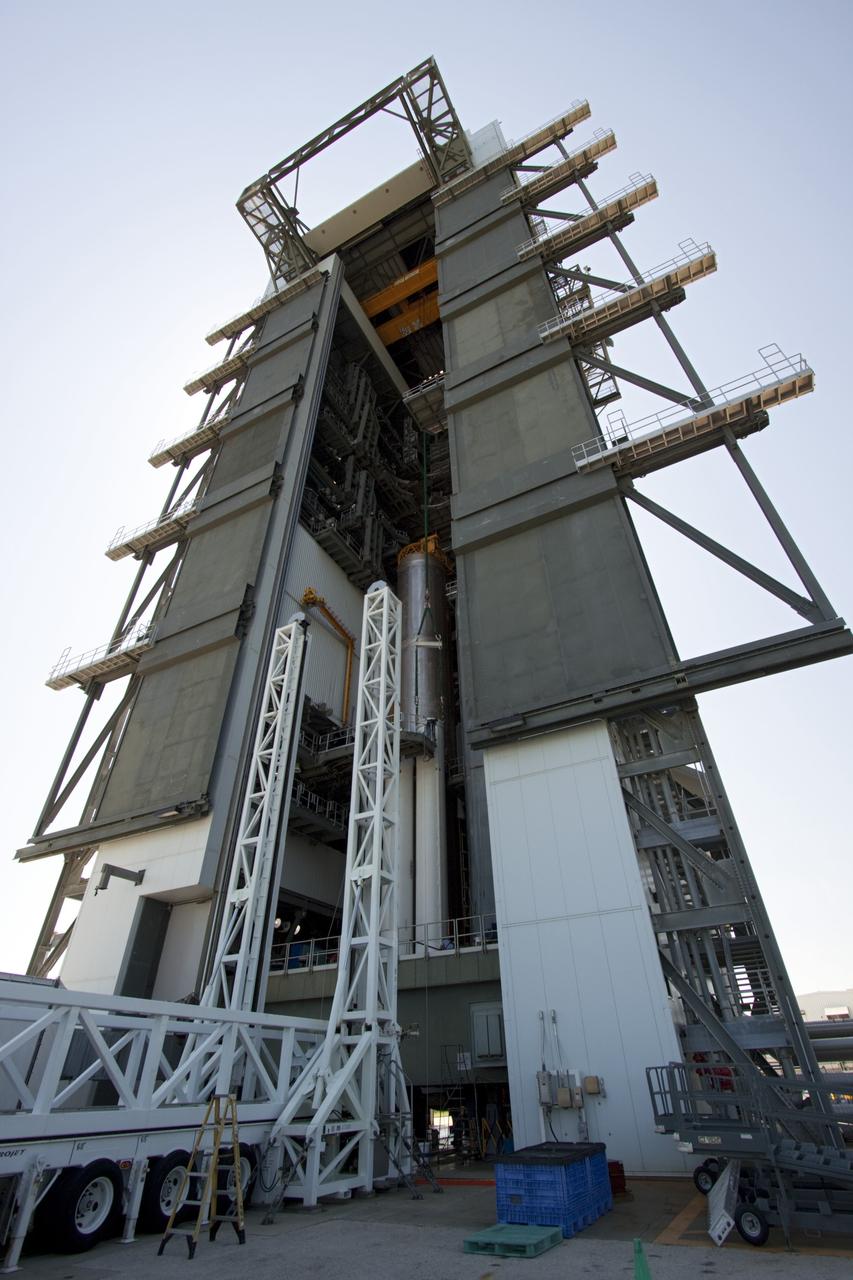
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a solid rocket motor (SRM) hangs in an upright position for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
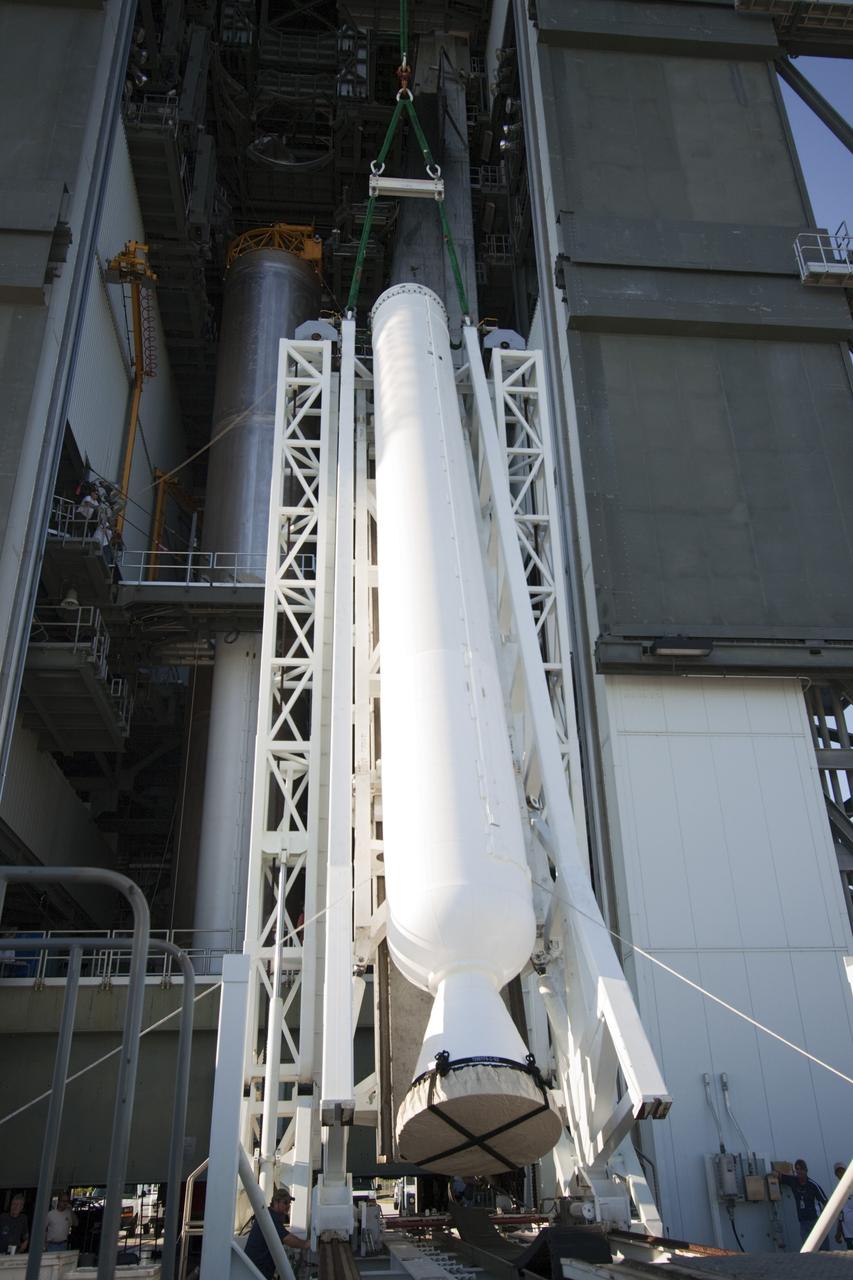

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the final solid rocket motor (SRM) hangs in an upright position for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which will carry NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
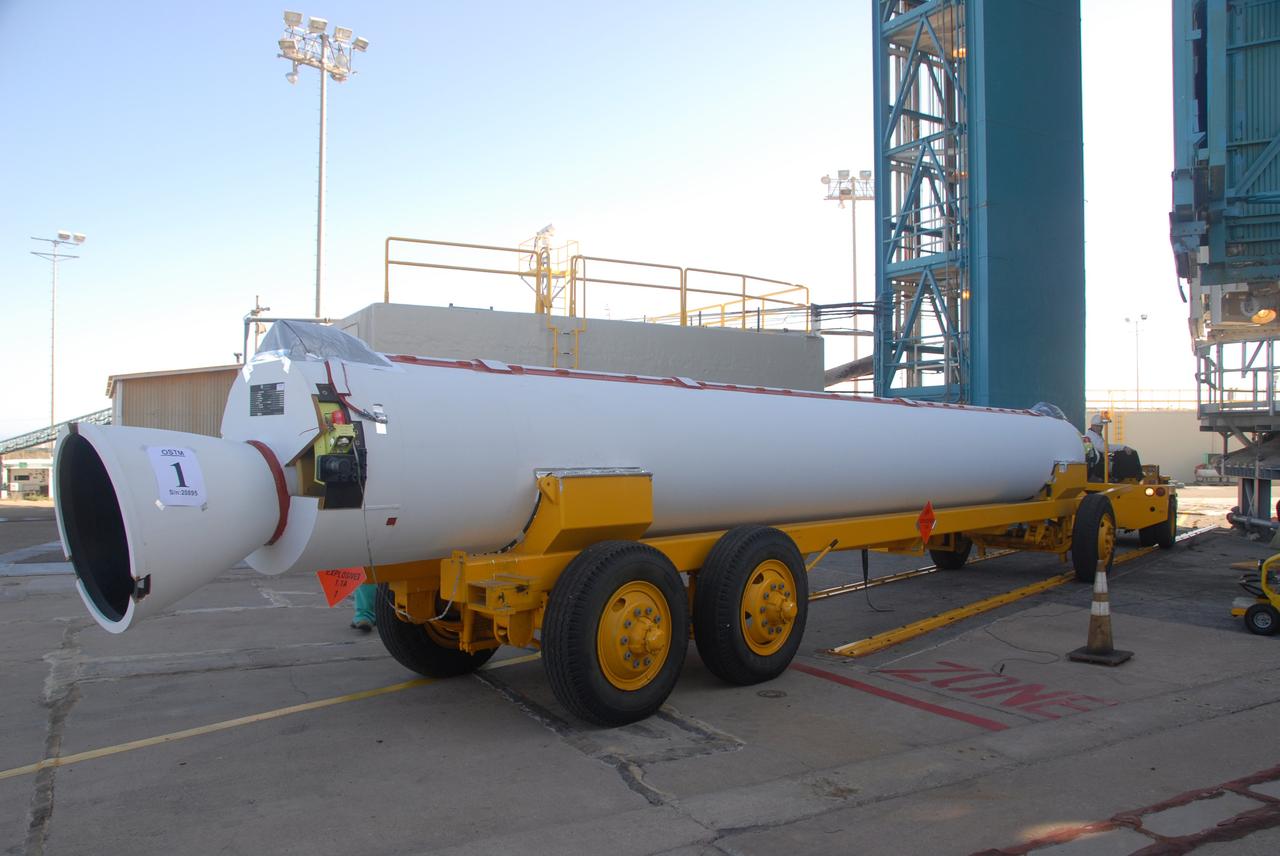

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A second solid rocket motor, or SRM, to arrive on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California is moved into place for lifting into the mobile service tower. The SRM will be attached to the Delta II first stage inside the tower. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the OSTM/Jason-2 spacecraft. The OSTM, or Ocean Topography Mission, on the Jason-2 satellite is a follow-on to Jason-1. It will take oceanographic studies of sea surface height into an operational mode for continued climate forecasting research and science and industrial applications. This satellite altimetry data will help determine ocean circulation, climate change and sea-level rise. OSTM is a joint effort by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NASA, France’s Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales and the European Meteorological Satellite Organisation. OSTM/Jason-2 will be launched aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320 from Vandenberg on June 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti
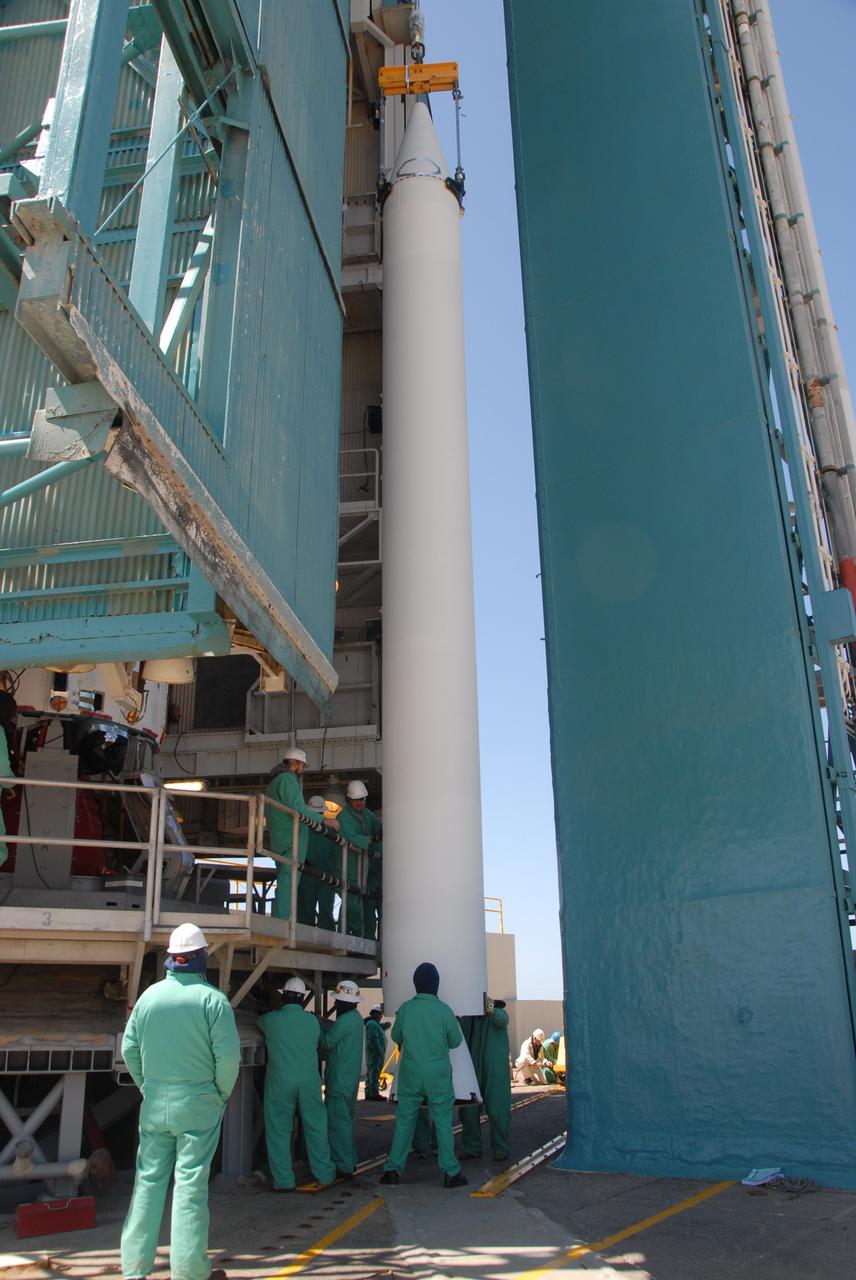

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second solid rocket motor, or SRM, is suspended in front of the mobile service tower. The SRM will be lifted into the tower and attached to the Delta II first stage inside. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the OSTM/Jason-2 spacecraft. The OSTM, or Ocean Topography Mission, on the Jason-2 satellite is a follow-on to Jason-1. It will take oceanographic studies of sea surface height into an operational mode for continued climate forecasting research and science and industrial applications. This satellite altimetry data will help determine ocean circulation, climate change and sea-level rise. OSTM is a joint effort by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, NASA, France’s Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales and the European Meteorological Satellite Organisation. OSTM/Jason-2 will be launched aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320 from Vandenberg on June 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti