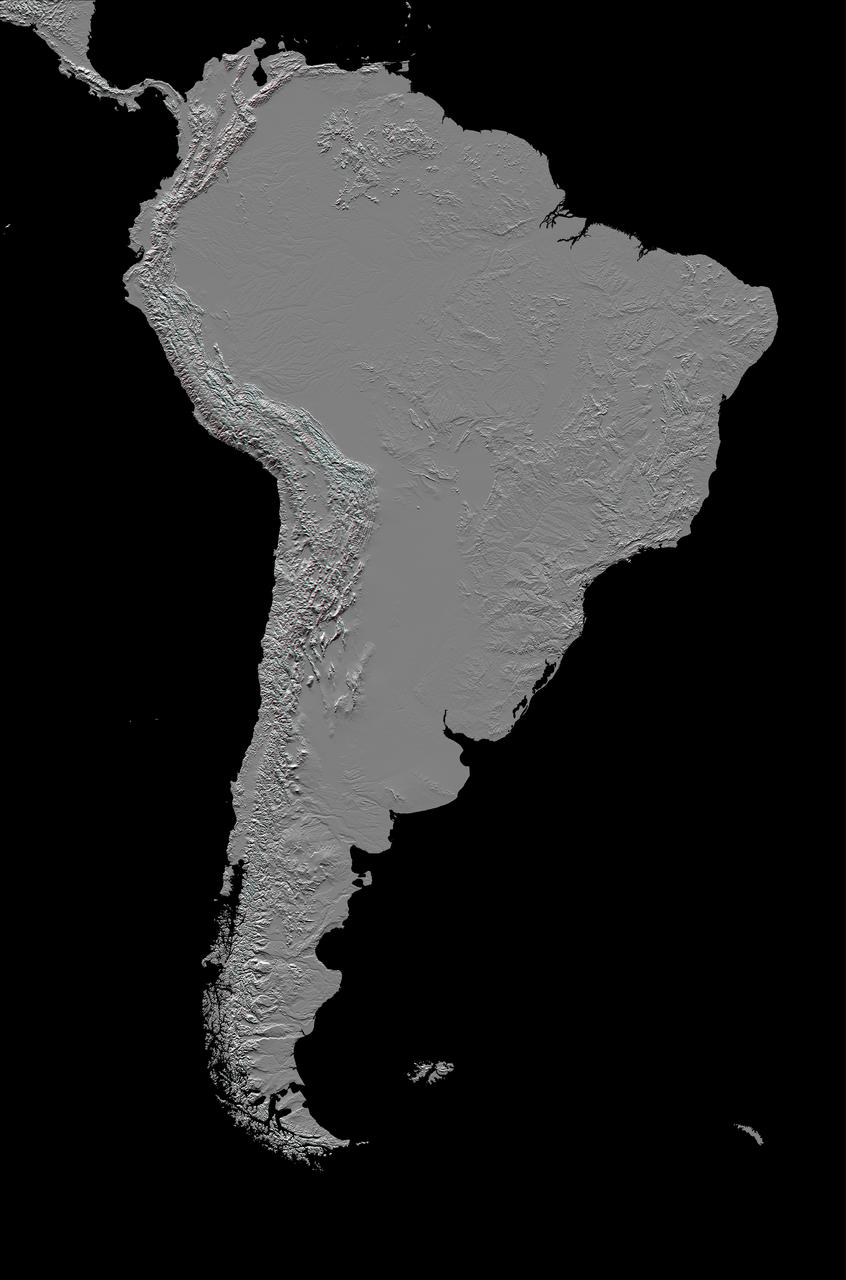
This anaglyph, from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, in South America is dominated by the Andes Mountains, which extend all along the Pacific Coast. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
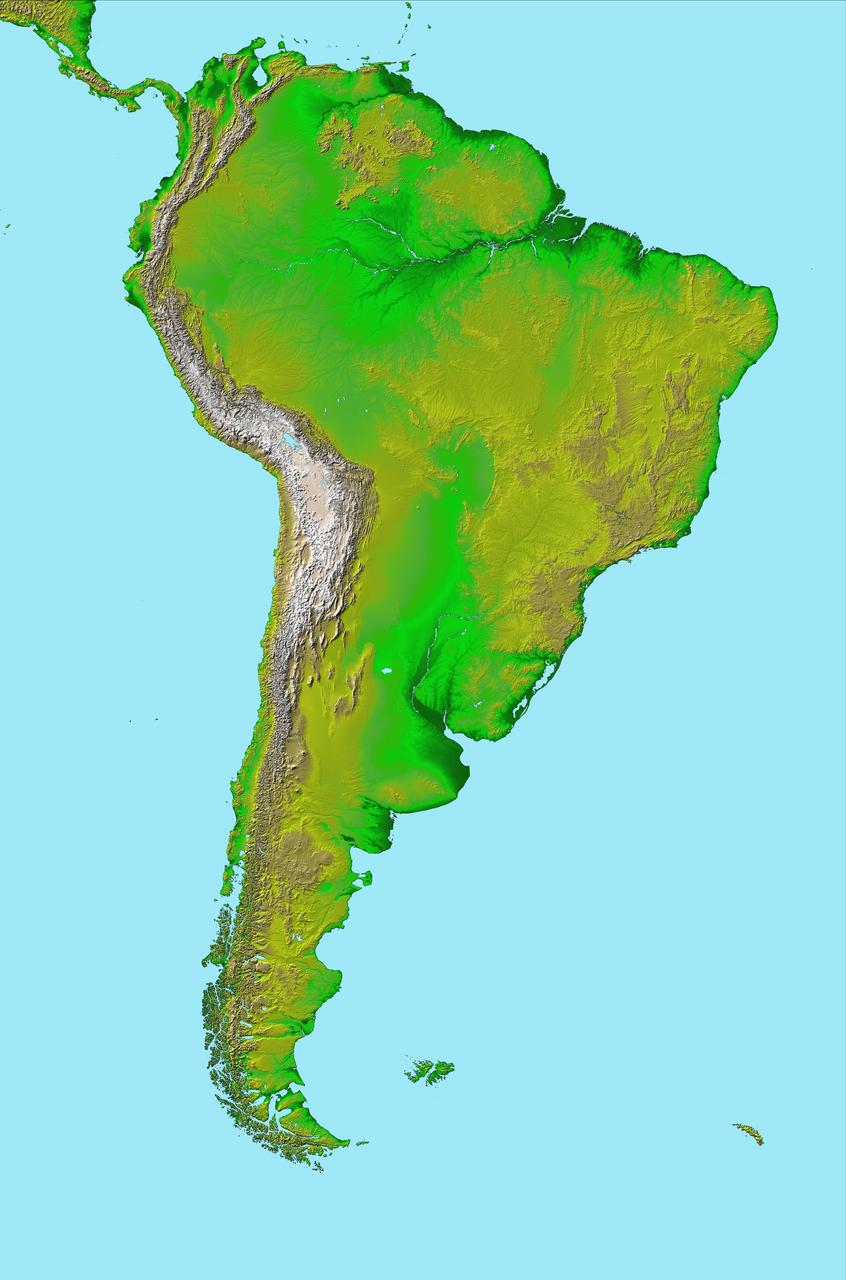
This image of South America was generated with data from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM.
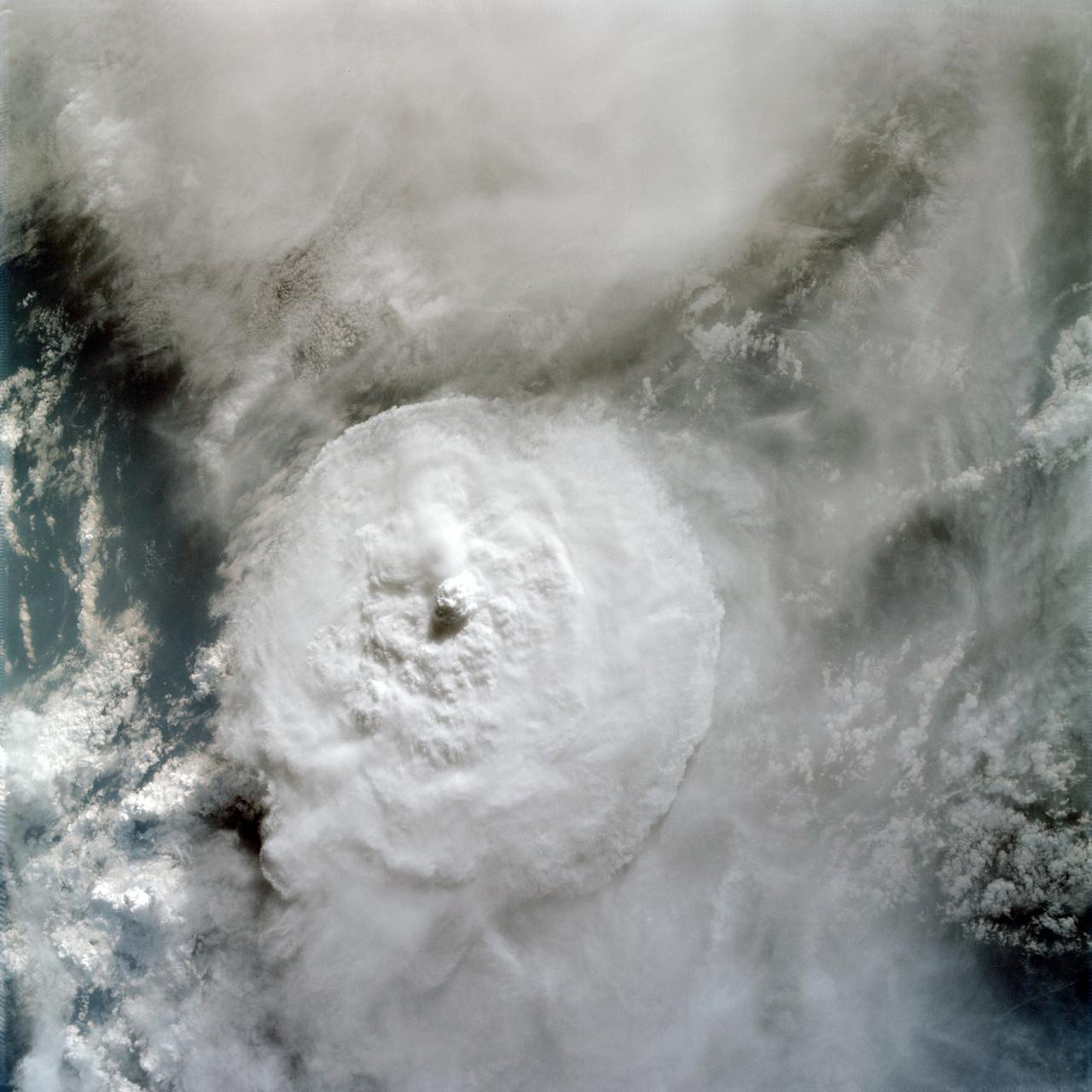

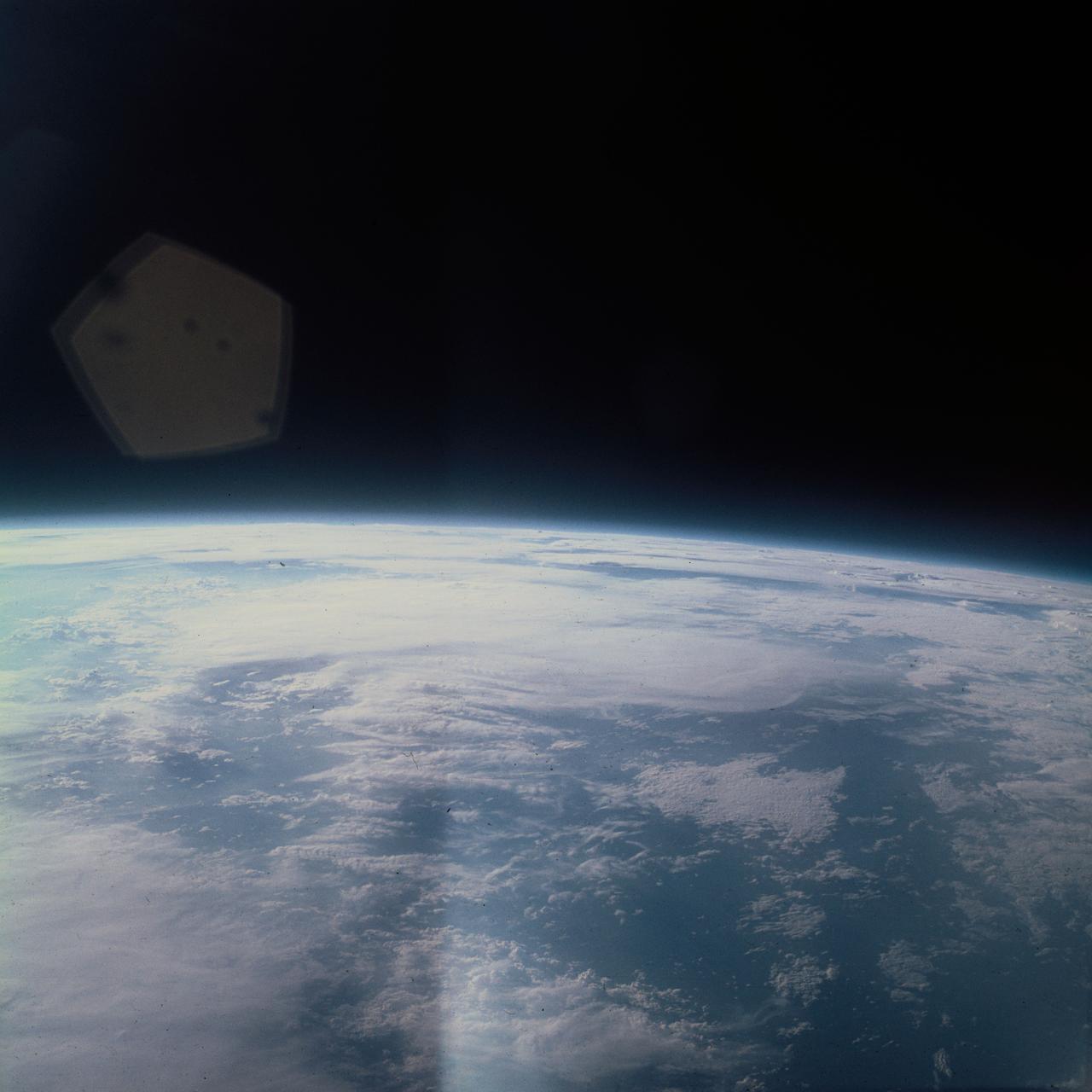
AS09-22-3374 (March 1969) --- Near vertical view of thunderhead over South America as photographed from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its Earth-orbital mission.
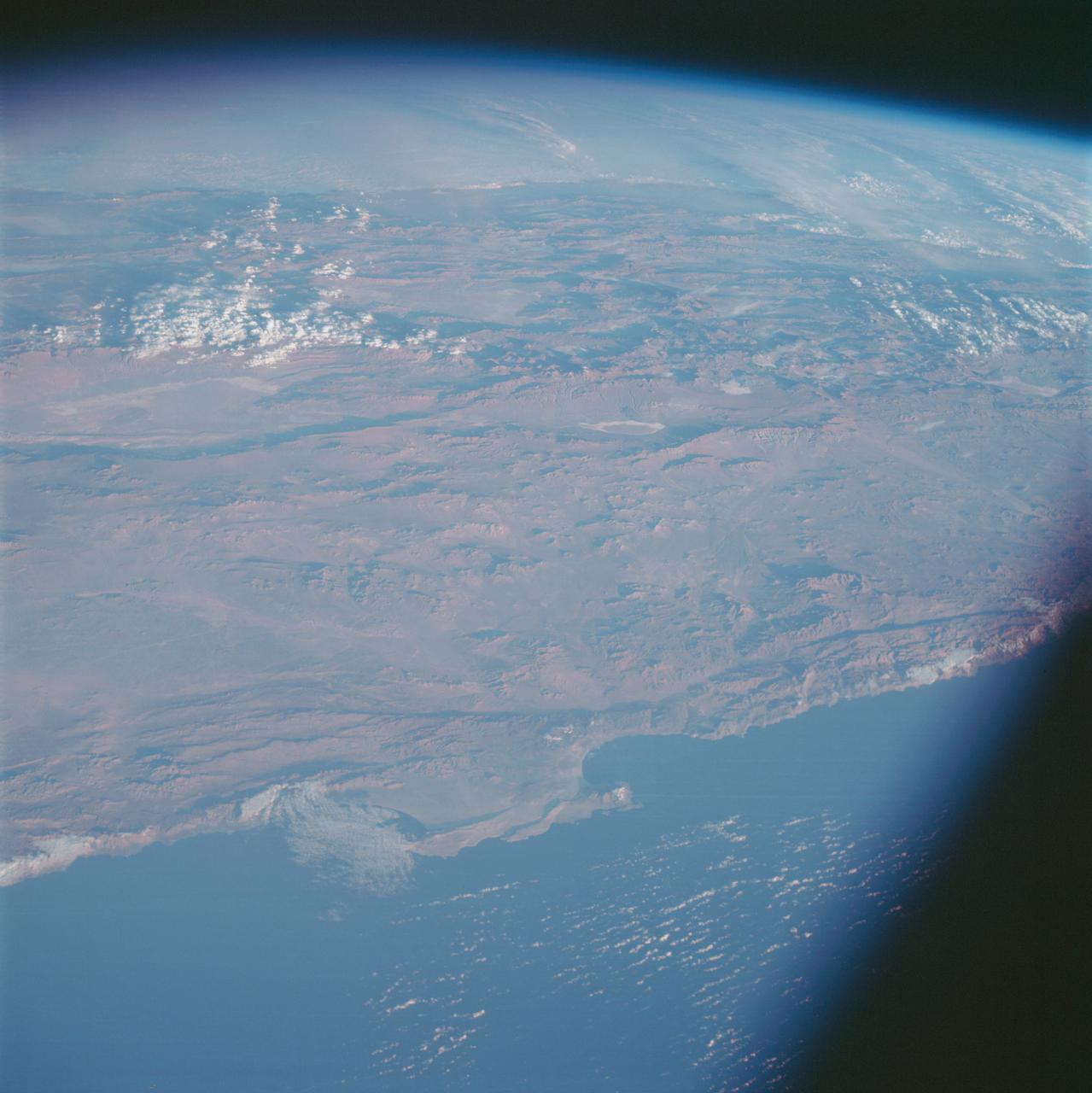

AS07-07-1826 (17 Oct. 1968) --- This view of South America was photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 81st revolution of Earth from an altitude of 120 nautical miles. The port city of Antofagasta, Chile, is located in the half-moon shaped bay in the lower left portion of the picture. Beyond the coast is the Andean peak of Llullaillaco Volcano which rises 22,000 feet above sea level. At left center is the Chuquicamata copper mines located near Coloma. At the center of the photo, behind the large salt lake and atop a 19,000 foot high volcano, the countries of Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile meet at a common point. Below the clouds in the upper portion of the photo are the Great Plains known as the Gran Chaco.
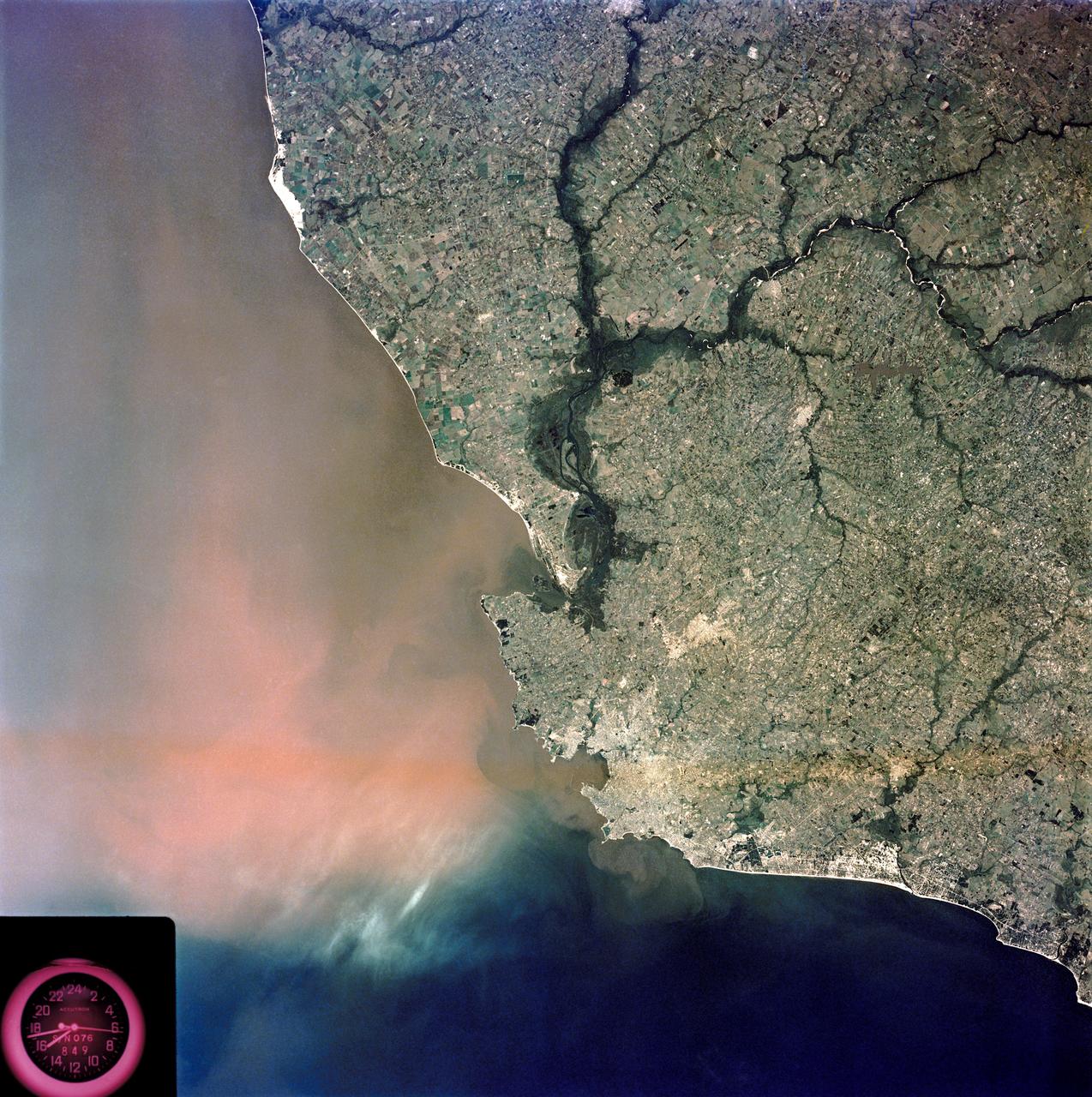

SL3-84-202 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Montevideo, Uruguay area of South America is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The large body of water is Rio de la Plata which flows into the South Atlantic Ocean at the bottom of the picture. The red plum in the Rio de la Plata is probably sediment moving seaward. The Santa Lucia River enters the Rio de la Plata west of Montevideo and is the major drainage for the region. Note the small Isla del Tigre at the mouth of the Santa Lucia. The white beach and sand dune areas are plainly visible along the coast. A major airport can be seen immediately east of downtown Montevideo. Major thoroughfares and residential areas, such as the bright one in the suburbs, are clearly visible, also. Farm tracts in green and grey rectangular patterns indicate agricultural regions. Photo credit: NASA
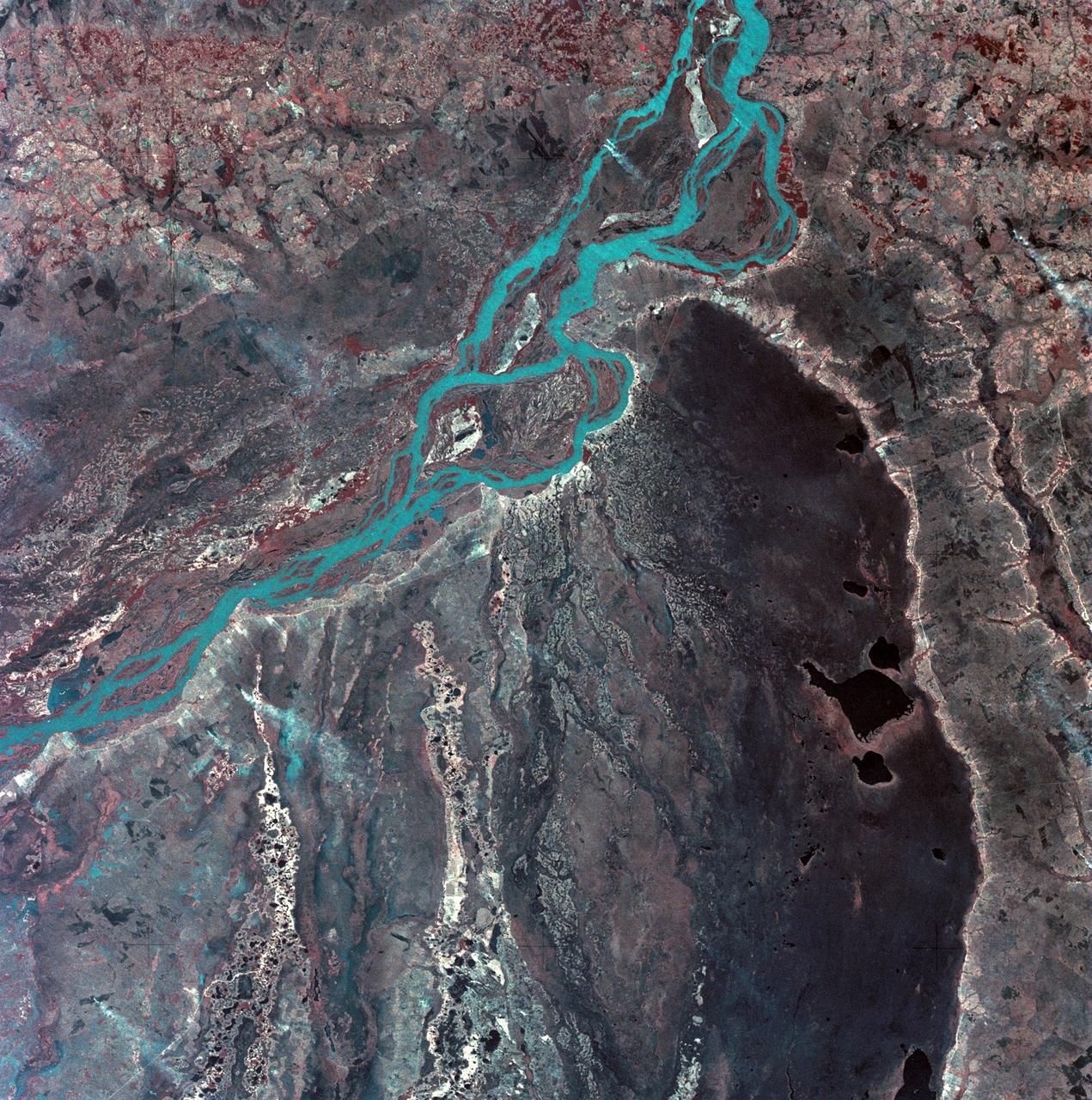

SL3-33-167 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Argentina-Paraguay border area of South America as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. This picture was taken with type 2443 infrared color film. The Parana River flows from east to west across the picture. This part of the Rio Parana is located between the towns of Posadas, Argentina, and Resistencia, Argentina. The major body of water in the large swamp area is Laguna Ibera. Note the several fires burning in this area. The largest land mass (Argentina) is south of the river. Paraguay is north of the river. Isla Apipe Grande is near the center of the photograph. The S190-A experiment is part of the Skylab Earth Resources Experiments Package. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
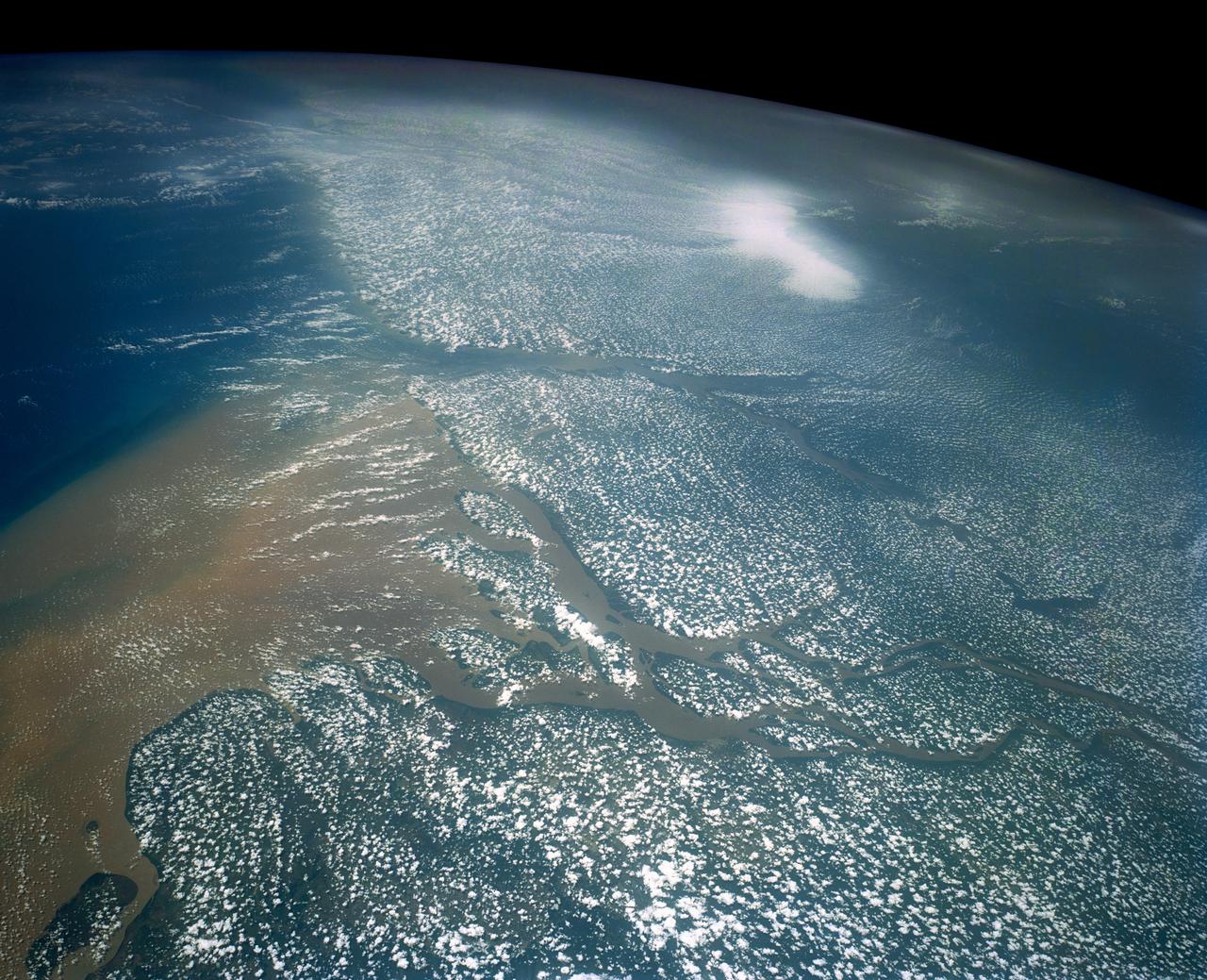

Huge sediment loads from the interior of the country flow through the Mouths of the Amazon River, Brazil (0.5S, 50.0W). The river current carries hundreds of tons of sediment through the multiple outlets of the great river over 100 miles from shore before it is carried northward by oceanic currents. The characteristic "fair weather cumulus" pattern of low clouds over the land but not over water may be observed in this scene.
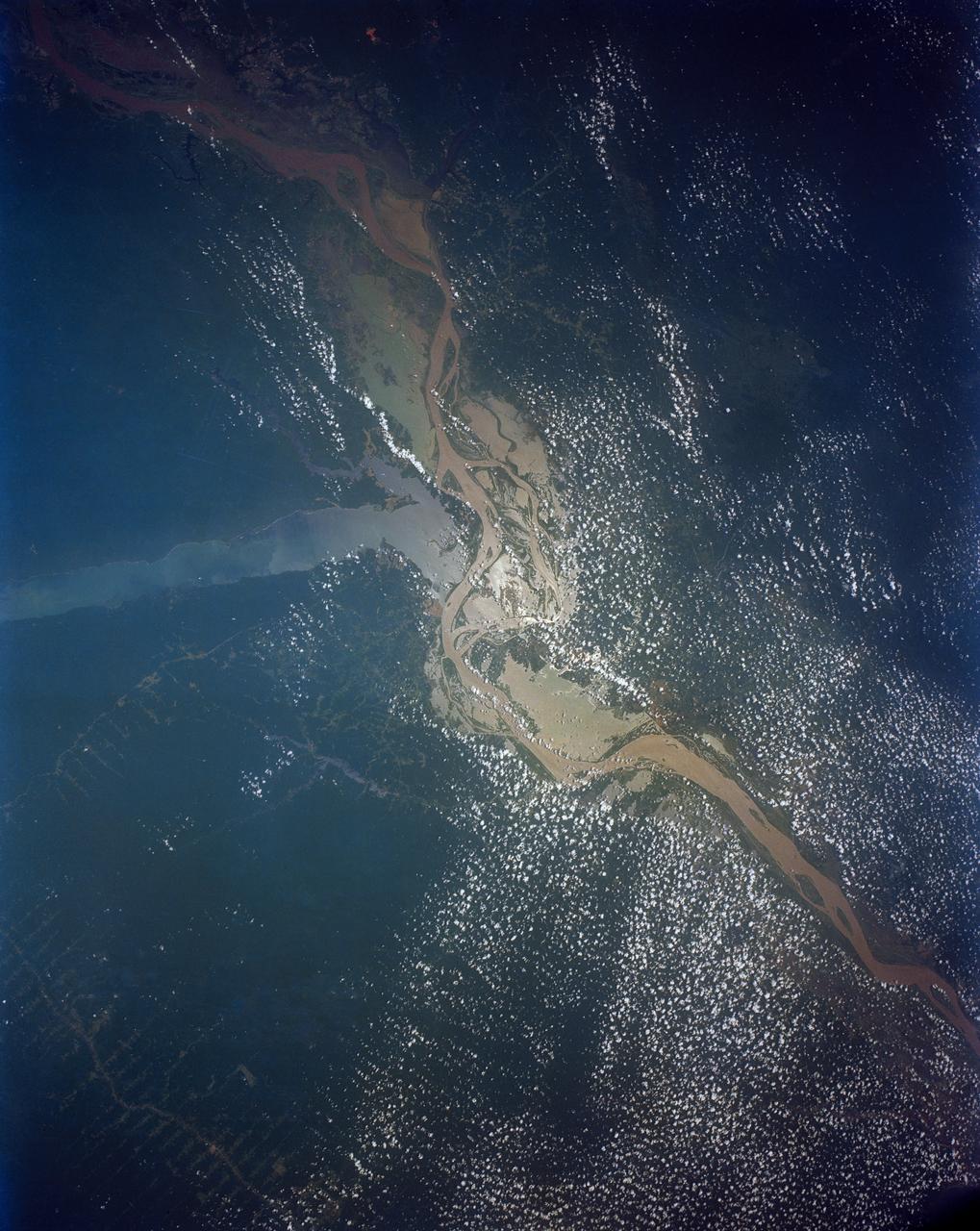

This view shows the confluence of the Amazon and the Topajos Rivers at Santarem, Brazil (2.0S, 55.0W). The Am,azon flows from lower left to upper right of the photo. Below the river juncture of the Amazon and Tapajos, there is considerable deforestation activity along the Trans-Amazon Highway.
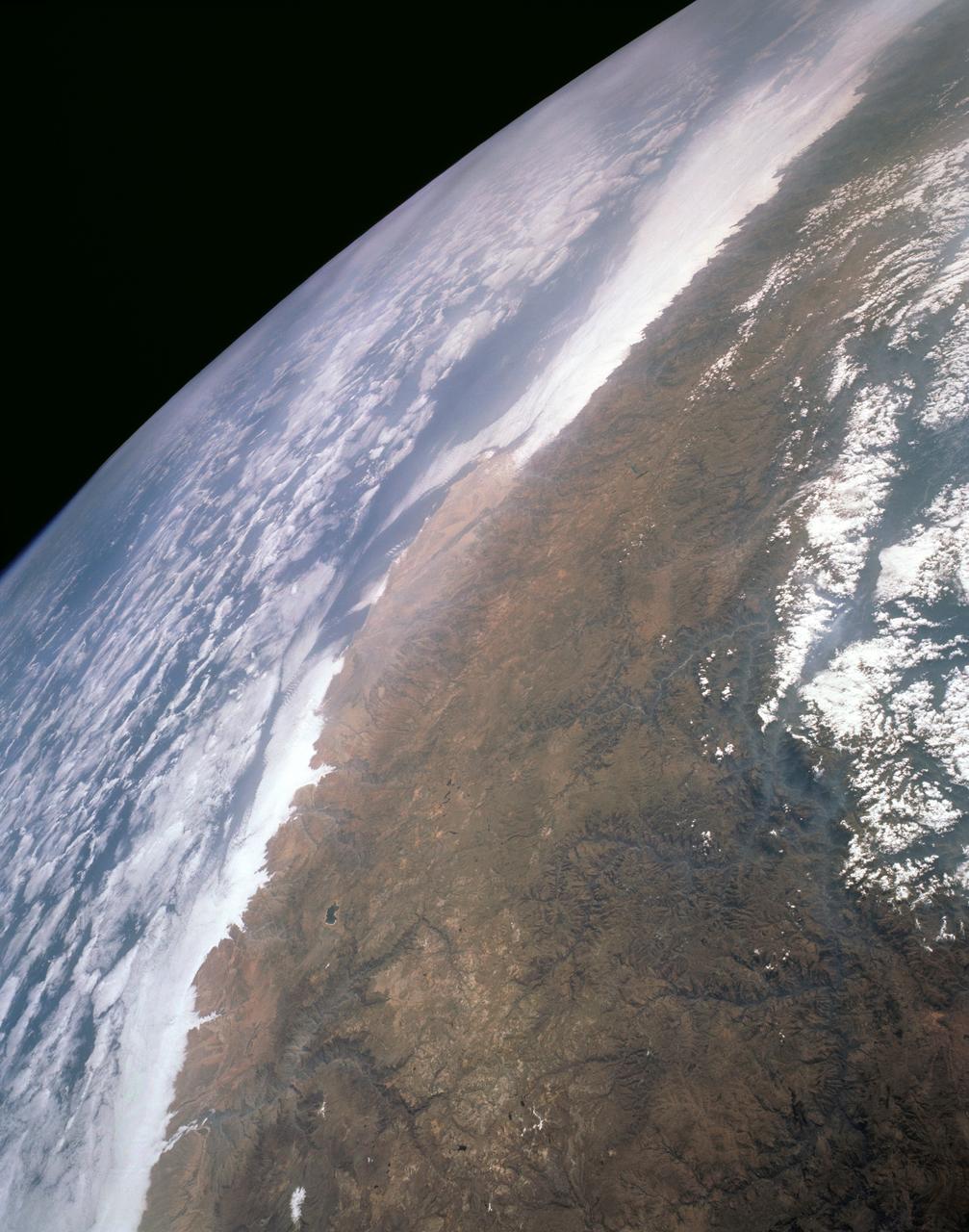

STS043-151-159 (2-11 August 1991) --- This photograph looks westward over the high plateau of the southern Peruvian Andes west and north of Lake Titicaca (not in field of view). Lima, Peru lies under the clouds just north of the clear coastal area. Because the high Andes have been uplifted 10,000 to 13,000 feet during the past 20 million years, the rivers which cut down to the Pacific Ocean have gorges almost that deep, such as the Rio Ocona at the bottom of the photograph. The eastern slopes of the Andes are heavily forested, forming the headwaters of the Amazon system. Smoke from burning in the Amazon basin fills river valleys on the right side of the photograph. A Linhof camera was used to take this view.

This image of part of the Atlantic coast of South America was acquired by the Suomi NPP satellite on the night of July 20, 2012. The image was made possible by the “day-night band” of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe dim signals such as city lights, gas flares, auroras, wildfires, and reflected moonlight. “Nothing tells us more about the spread of humans across the Earth than city lights,” says Chris Elvidge, who leads the Earth Observation Group at NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center. Named for satellite meteorology pioneer Verner Suomi, NPP flies over any given point on Earth's surface twice each day at roughly 1:30 a.m. and p.m. The polar-orbiting satellite flies 824 kilometers (512 miles) above the surface, sending its data once per orbit to a ground station in Svalbard, Norway, and continuously to local direct broadcast users distributed around the world. Suomi NPP is managed by NASA with operational support from NOAA and its Joint Polar Satellite System, which manages the satellite's ground system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79822" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
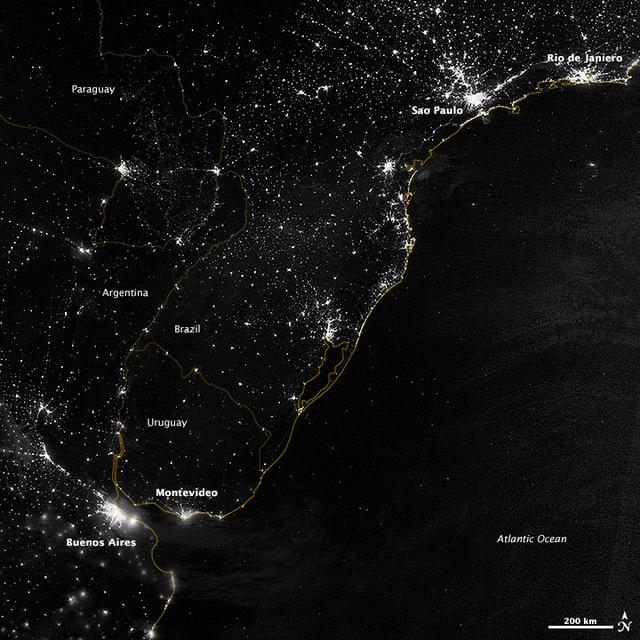
This image of part of the Atlantic coast of South America was acquired by the Suomi NPP satellite on the night of July 20, 2012. The image was made possible by the “day-night band” of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe dim signals such as city lights, gas flares, auroras, wildfires, and reflected moonlight. “Nothing tells us more about the spread of humans across the Earth than city lights,” says Chris Elvidge, who leads the Earth Observation Group at NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center. Named for satellite meteorology pioneer Verner Suomi, NPP flies over any given point on Earth's surface twice each day at roughly 1:30 a.m. and p.m. The polar-orbiting satellite flies 824 kilometers (512 miles) above the surface, sending its data once per orbit to a ground station in Svalbard, Norway, and continuously to local direct broadcast users distributed around the world. Suomi NPP is managed by NASA with operational support from NOAA and its Joint Polar Satellite System, which manages the satellite's ground system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79822" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

AS08-16-2593 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- A striking view from the Apollo 8 spacecraft showing nearly the entire Western Hemisphere, from the mouth of the St. Lawrence River, including nearby Newfoundland, extending to Tierra del Fuego at the southern tip of South America. Central America is clearly outlined. Nearly all of South America is covered by clouds, except the high Andes Mountain chain along the west coast. A small portion of the bulge of West Africa shows along the sunset terminator.

Filled with briny lakes, the Quisquiro salt flat in South America's Altiplano represents the kind of landscape that scientists think may have existed in Gale Crater, which NASA's Curiosity rover is exploring. This salt flat is located in Chile, though the Altiplano sprawls across countries. Streams and rivers flowing from mountain ranges into this arid, high-altitude plateau lead to closed basins similar to Mars' ancient Gale Crater. Lakes on the Altiplano are heavily influenced by climate in the same way as Gale. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23374
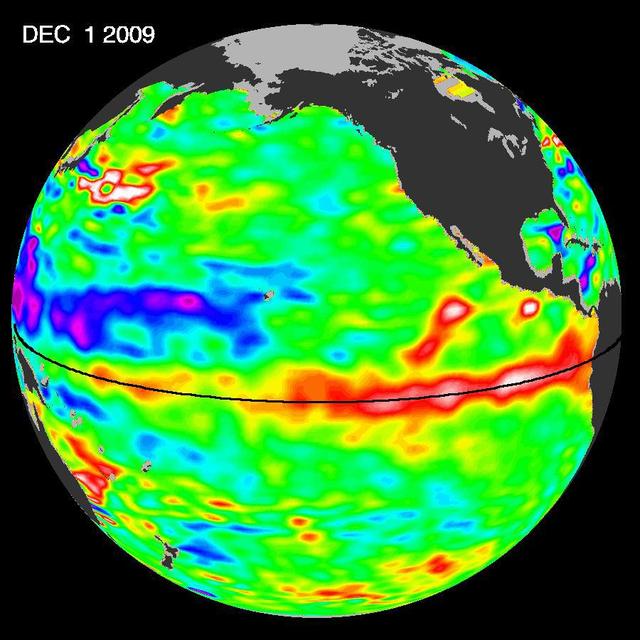
The most recent sea-level height data from the NASA/European Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2 oceanography satellite show the continued eastward progression of a strong wave of warm water, known as a Kelvin wave, now approaching South America.
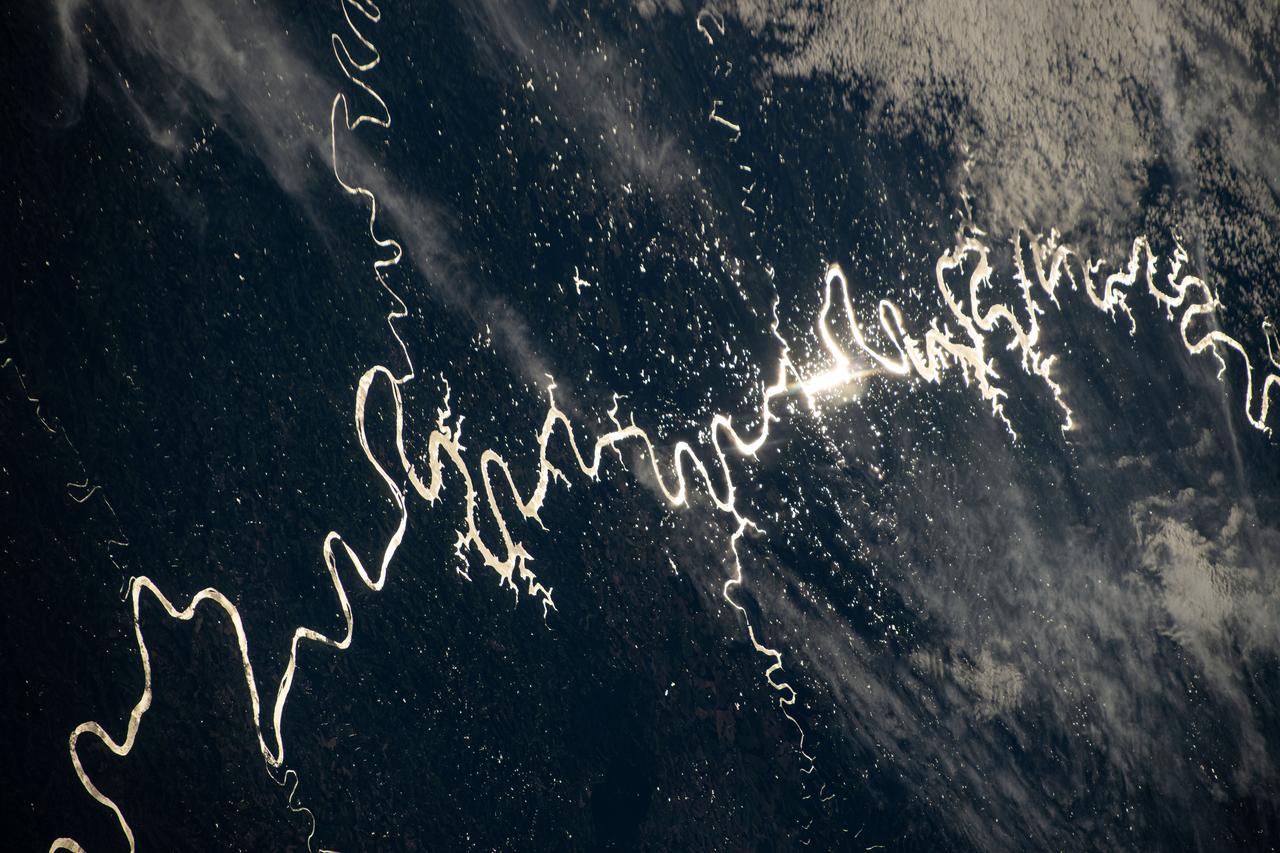

iss072e311451 (Dec. 3, 2024) --- The Sun's glint beams off one of the many rivers that snake throughout South America's fertile, low grasslands region, also known as the Pampas. The International Space Station was orbiting 261 miles above the border of Paraguay and Argentina at the time of this photograph. Credit: NASA/Don Pettit
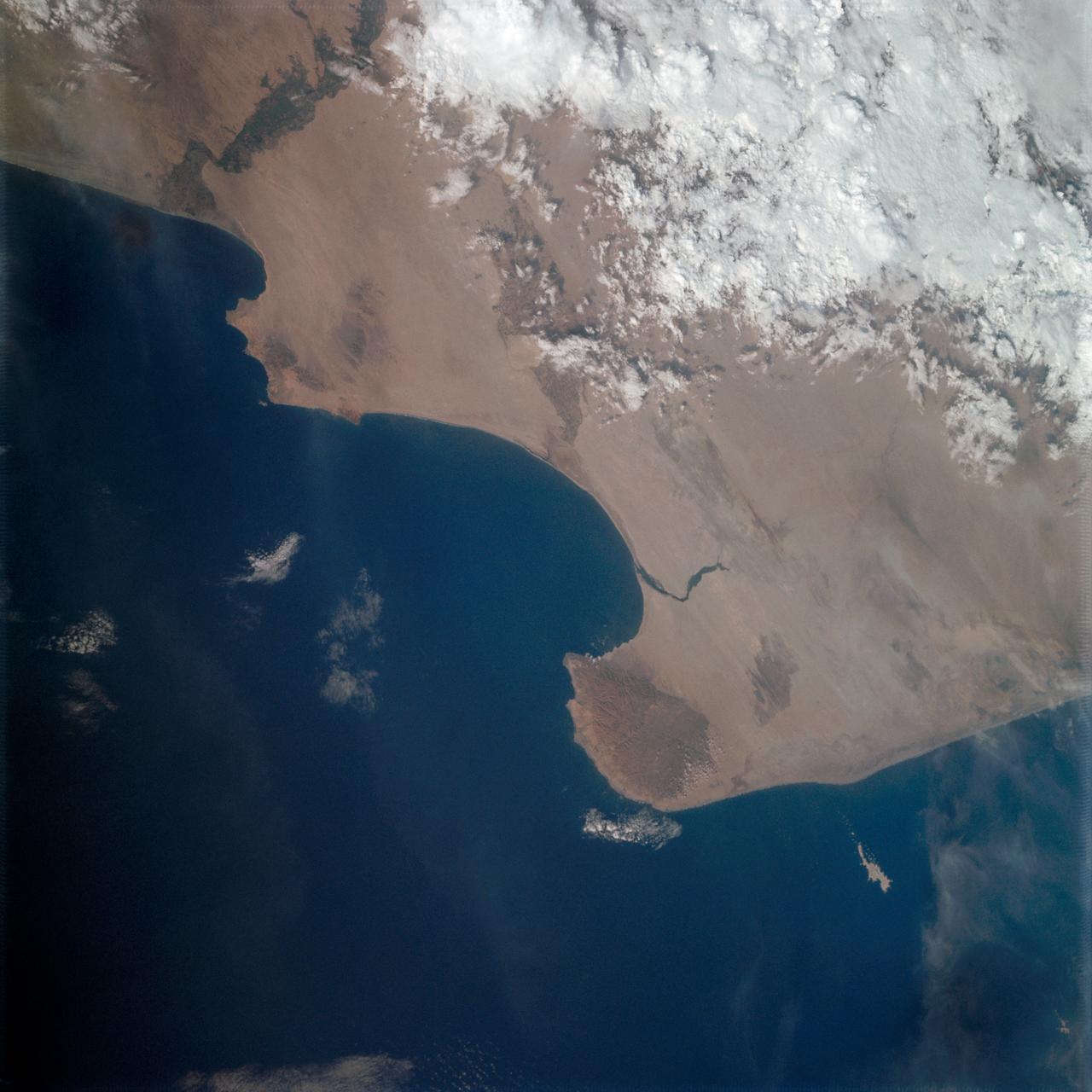

Vertical Earth Observation taken by the Apollo 9 crew. View is of Peru and South America including Aguja Point and Piura. Film magazine was E,film type was SO-368 Ektachrome with 0.460 - 0.710 micrometers film / filter transmittance response and haze filter,80mm lens. Latitude was 5.35 S by Longitude 81.05 W, Overlap was 0%, Altitude miles were 125 and cloud cover was 20%.
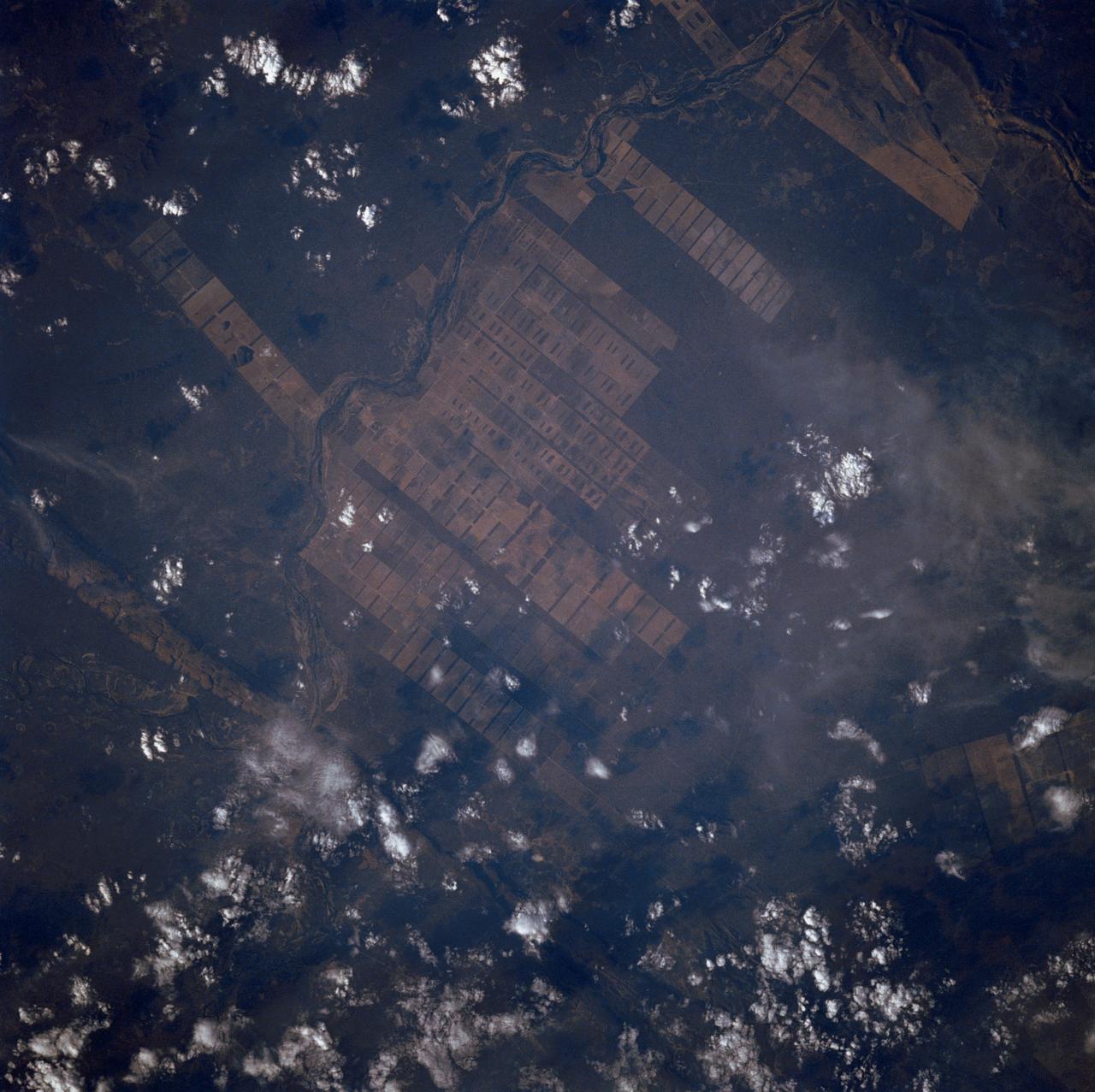

The large field patterns in this view of the Rio Sao Francisco basin, Brazil, South America, (11.5S, 43.5W) indicate a commercial agriculture venture; family subsistence farms are much smaller and laid out in different patterns. Land clearing in Brazil has increased at an alarming rate in recent years and preliminary estimates suggest a 25 to 30% increase in deforestation since 1984. The long term impact on the ecological processes are still unknown.

S62-06606 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Cloud formation over Western Atlantic Ocean north of South America taken during the fourth orbit pass of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission by astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. with a hand-held camera. Photo credit: NASA

S62-06604 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Western horizon over South America taken during the sixth orbit pass of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission by astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. with a hand-held camera. Photo credit: NASA

S62-06612 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Cloud formation over South America taken during the fifth orbit pass of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission by astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. with a hand-held camera. Photo credit: NASA

S62-06607 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Western horizon over South America taken during the sixth orbit pass of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission by astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. with a hand-held camera. Photo credit: NASA
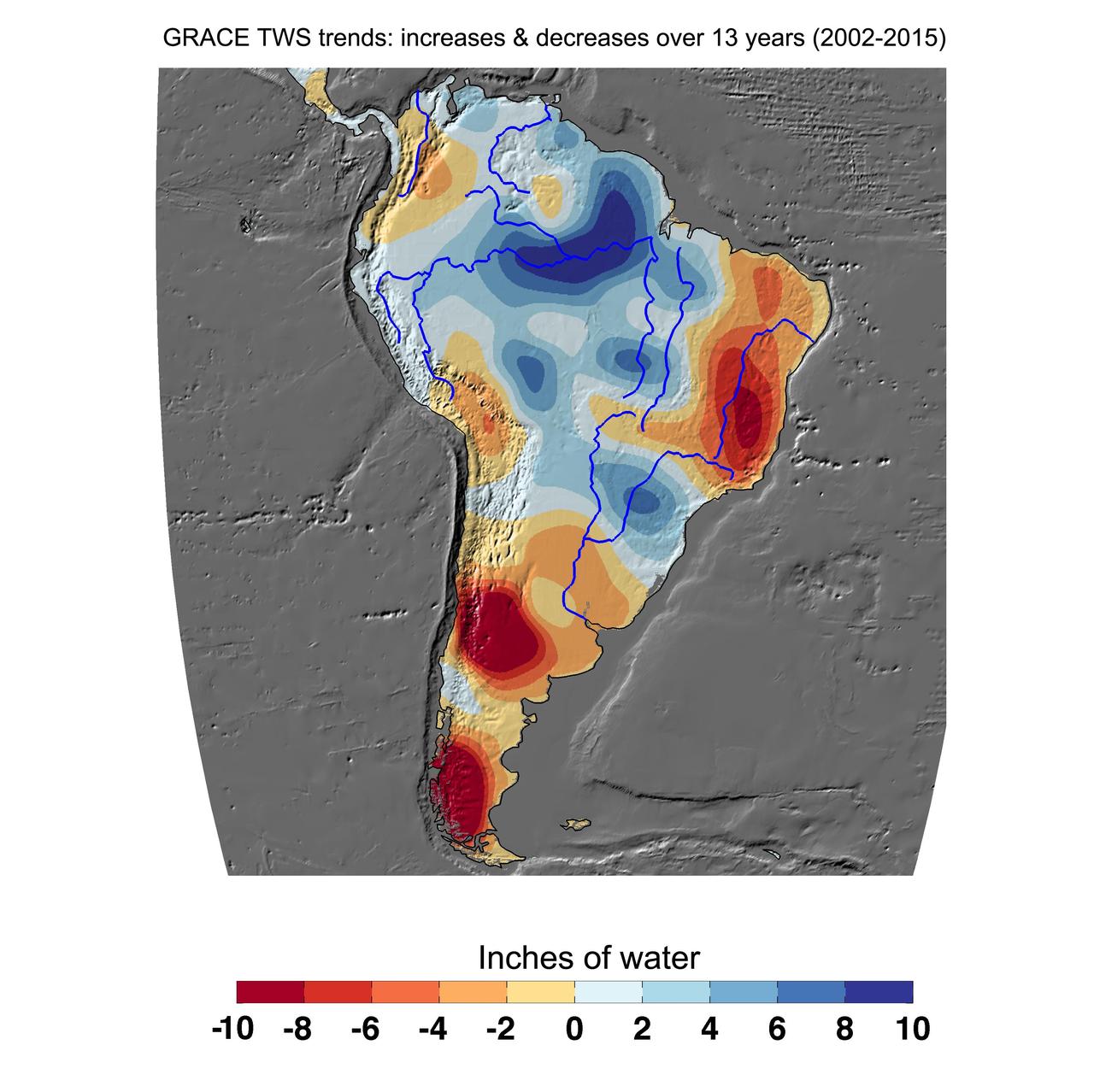
Cumulative total freshwater losses in South America from 2002 to 2015 (in inches) observed by NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission. Total water refers to all of the snow, surface water, soil water and groundwater combined. Much of the Amazon River basin experienced increasing total water storage during this time period, though the persistent Brazilian drought is apparent to the east. Groundwater depletion strongly impacted total water losses in the Guarani aquifer of Argentina and neighboring countries. Significant water losses due to the melting ice fields of Patagonia are also observed. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20205

STS-65 Earth observation taken aboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, shows Northern Chile and the Andes Mountains. This color photograph is a panoramic (southern view) that features Chile and the Andes Mountains of South America. The Atacama Desert, one of the driest regions on Earth, is clearly visible along the Chilean coast. In the near left foreground is the Salar de Arizaro. Salar Punta Negra in the center foreground appears to be partially filled with water. On the right side of the view, a coastal plateau rises from the Pacific Ocean and meets the Andes Mountains that appear as a backbone running north to south along the border of Chile and Argentina. In the distant left portion of the view can be seen the hazy Chaco Plains and Pampas.

This color image of the Earth was obtained by NASA's Galileo at about 6:10 a.m. Pacific Standard Time on Dec. 11, 1990, when the spacecraft was about 1.3 million miles from the planet during the first of two Earth flybys on its way to Jupiter. The color composite used images taken through the red, green and violet filters. South America is near the center of the picture, and the white, sunlit continent of Antarctica is below. Picturesque weather fronts are visible in the South Atlantic, lower right. This is the first frame of the Galileo Earth spin movie, a 500- frame time-lapse motion picture showing a 25-hour period of Earth's rotation and atmospheric dynamics. A movie is availalble at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00114
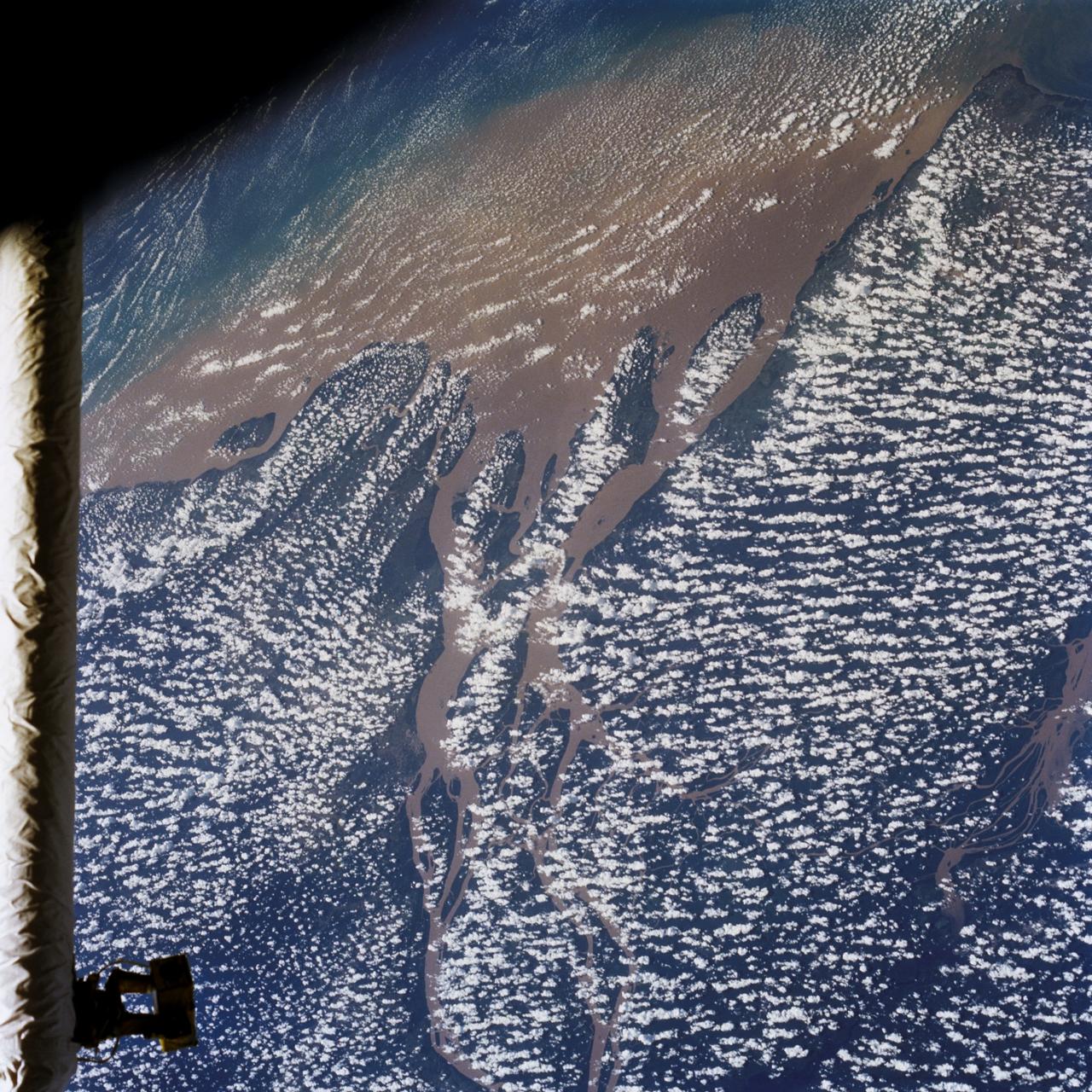

STS046-80-009 (31 July-8 Aug. 1992) --- A view of the mouth of the Amazon River and the Amazon Delta shows a large sediment plume expanding outward into the Atlantic Ocean. The sediment plume can be seen hugging the coast north of the Delta. This is caused by the west-northwest flowing Guyana Current. The large island of Marajo is partially visible through the clouds.
This is a three-dimensional view of Isabela, one of the Galapagos Islands located off the western coast of Ecuador, South America.

These two images show exactly the same area in South America, the Guiana Highlands straddling the borders of Venezuela, Guyana and Brazil.
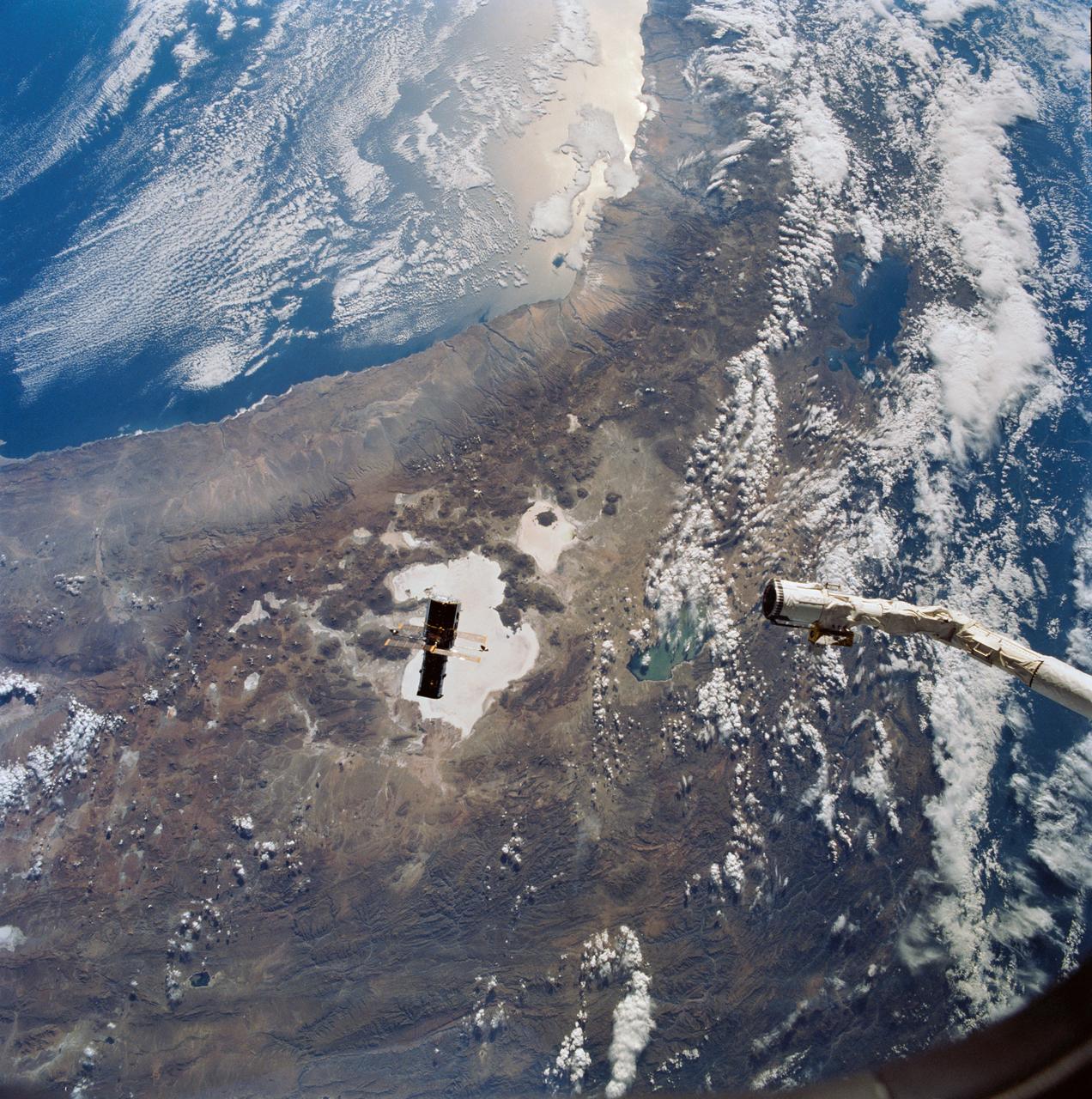

Hubble Space Telescope (HST), with its solar array (SA) wings and high gain antennae (HGA) fully extended,is released from Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector and is set free into Earth orbit by the STS-31 crew. HST drifts away from the end effector over the Andes Mountains.Parts of Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina are visible. The view covers a huge area of the western half of South America stretching from 14 degrees south latitude to 23 degrees, about 1,000 kilometers.

L to R; NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein (in tan flight suit), JPL AirSAR Scientist Tim Miller, and Mission Manager David Bushman briefing press in Santiago, Chile, for NASA's AirSAR 2004 mission. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with school children that visited the DC-8 during AirSAR 2004 in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

Dr. Tom Mace, NASA DFRC Director of Airborne Sciences, talks with a student from Punta Arenas, Chile, during a tour of the DC-8 aircraft while it was in the country supporting the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
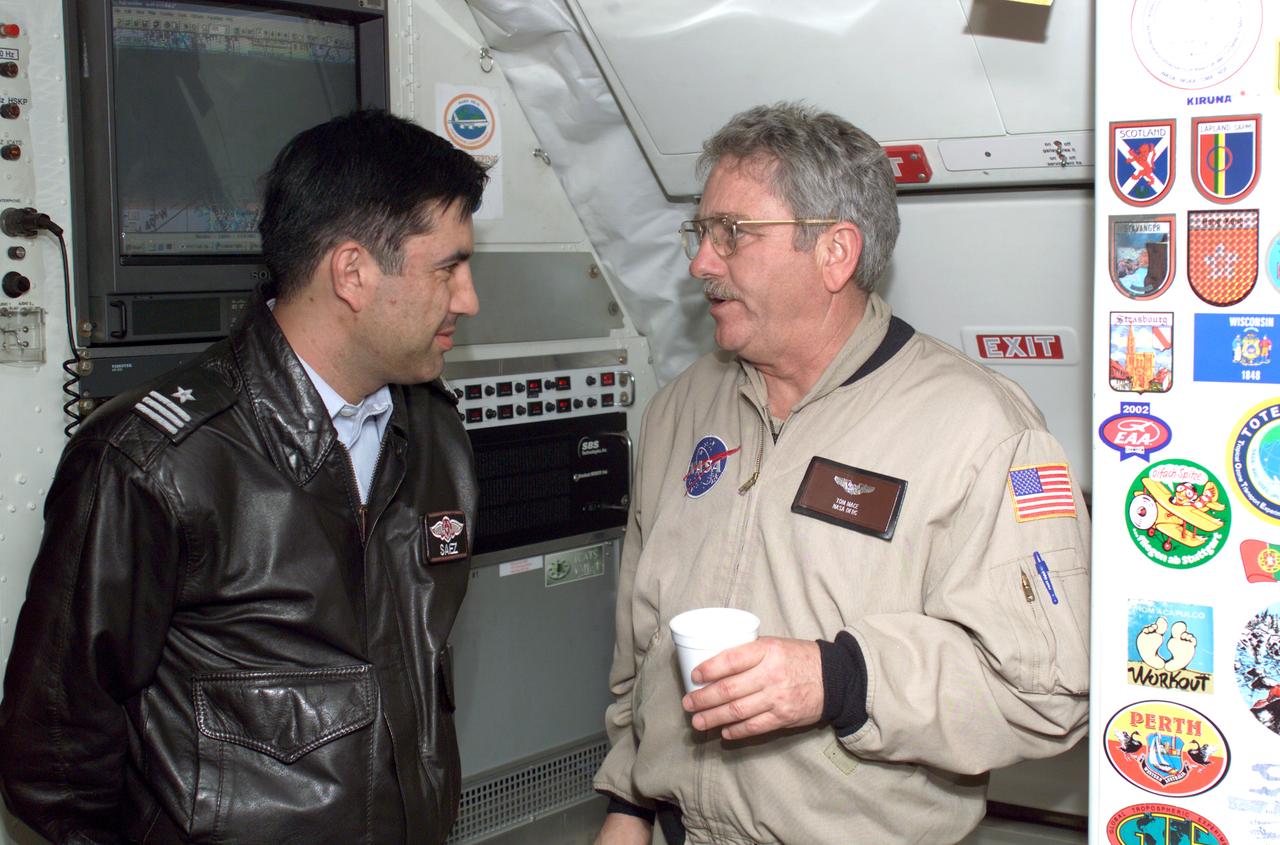

Chilean Air Force Captain Saez and Dr. Tom Mace, DFRC Director of Airborne Sciences, discuss airborne science during a DC-8 ferry flight from Santiago to Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
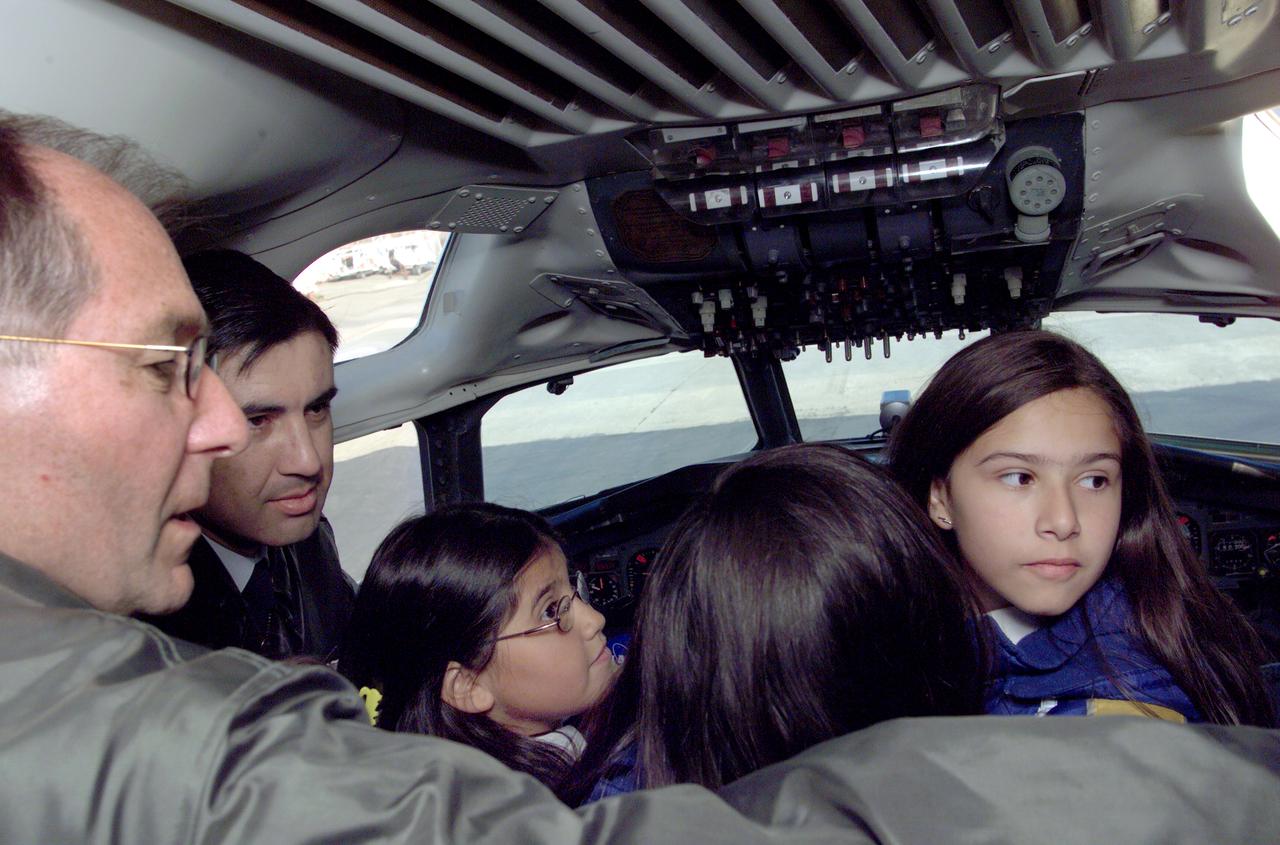

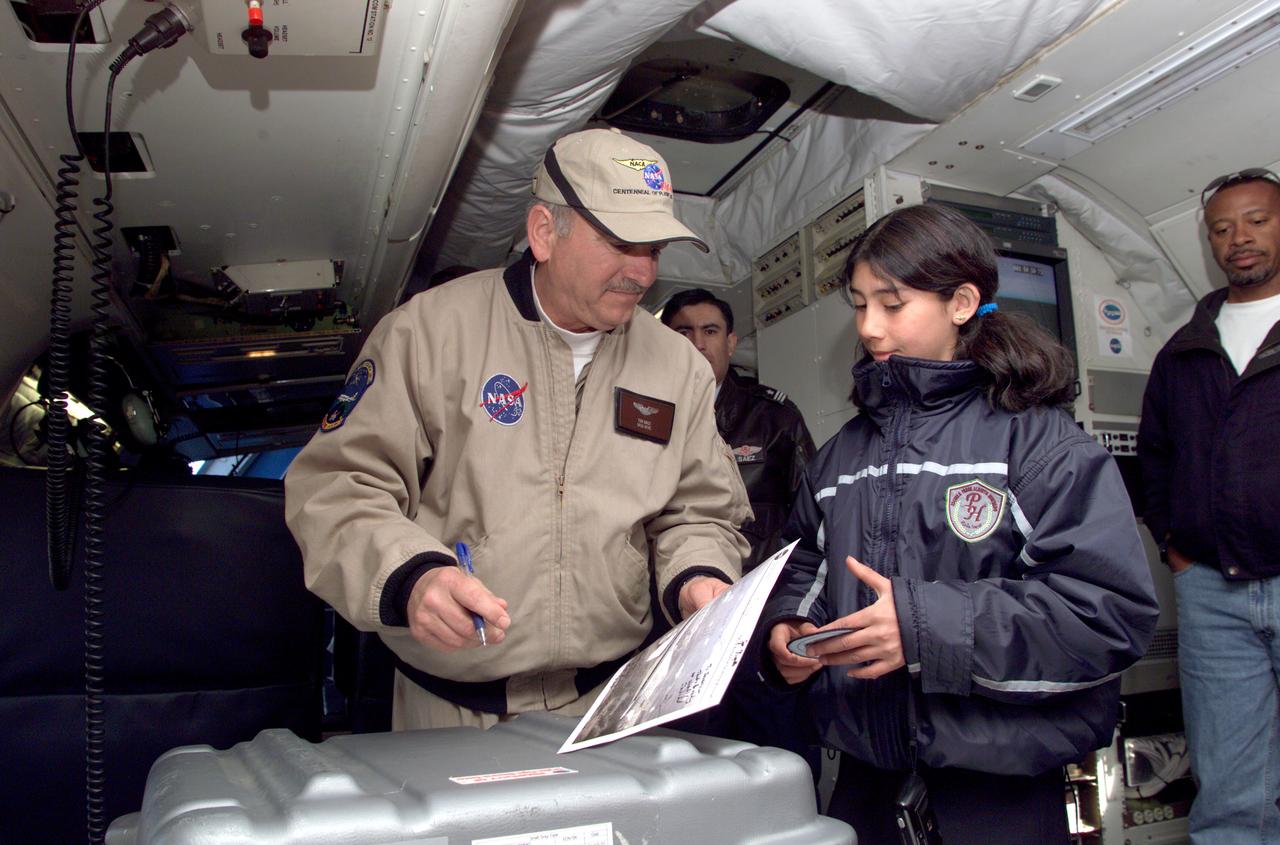
Pilot Bill Brockett (left) and Chilean Air Force Captain Saez with school children in the cockpit of NASA Dryden's DC-8 flying laboratory. Brockett explained NASA's AirSAR 2004 mission in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
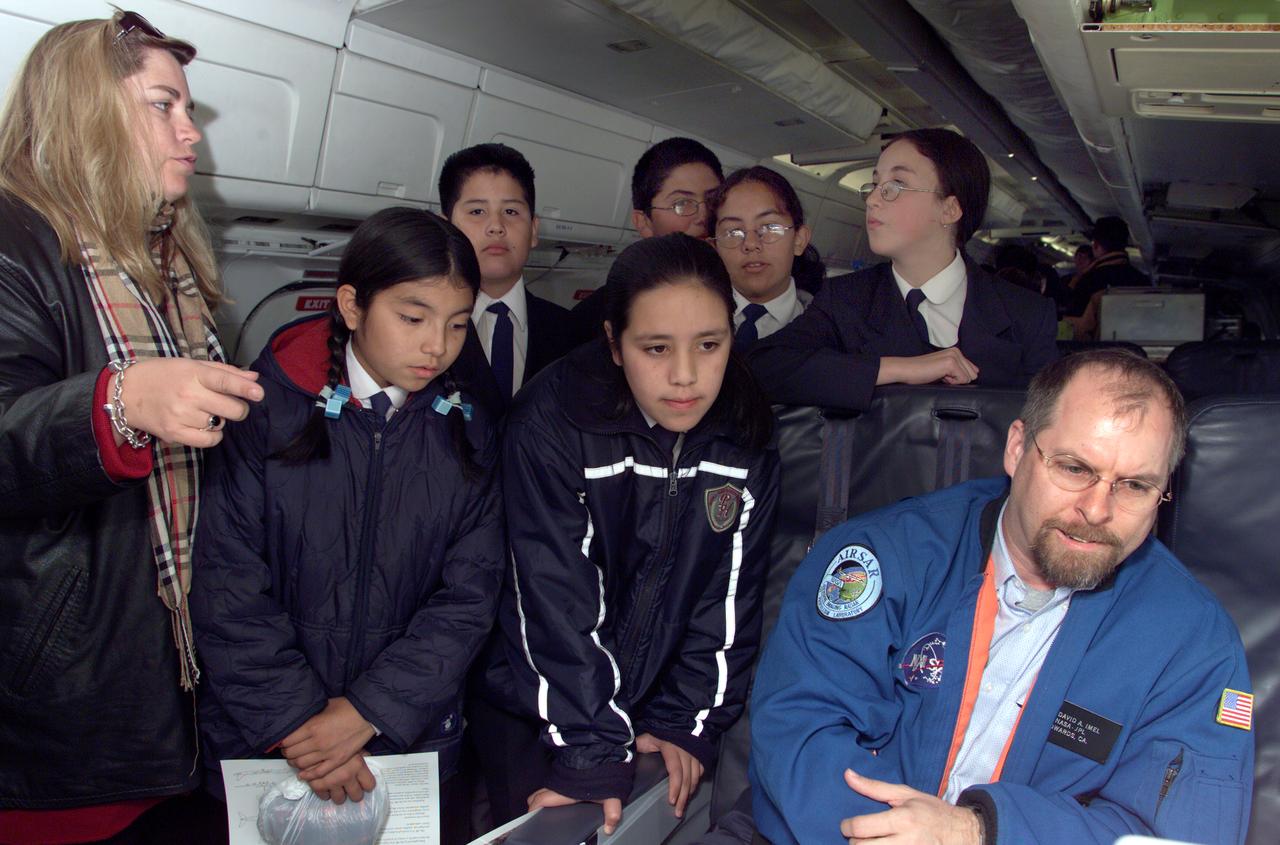

School children from Punta Arenas, Chile, talk with Dr. David Imel, an AirSAR scientist from NASA JPL, during AirSAR 2004. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
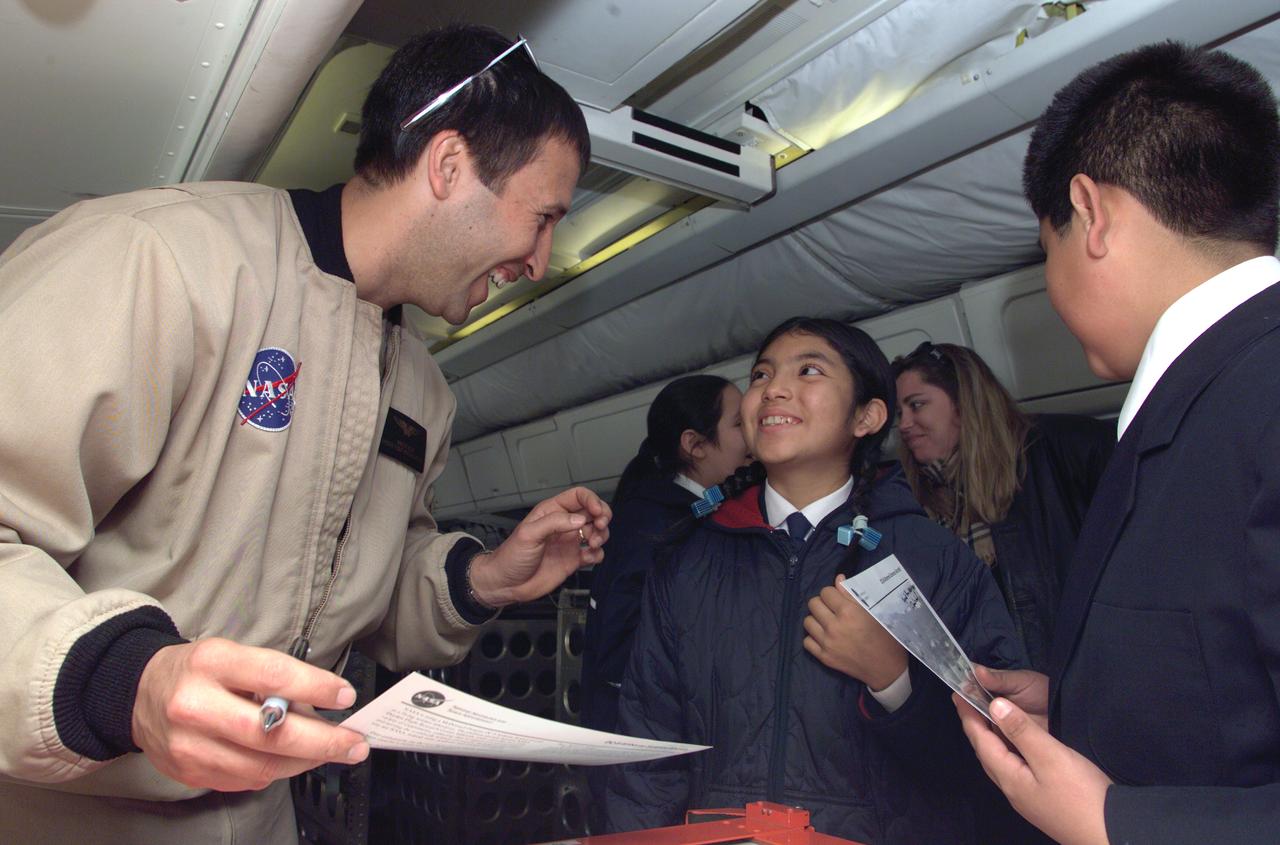

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein talks with school children from Punta Arenas, Chile, during a tour of the DC-8 aircraft while it was in the country supporting the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
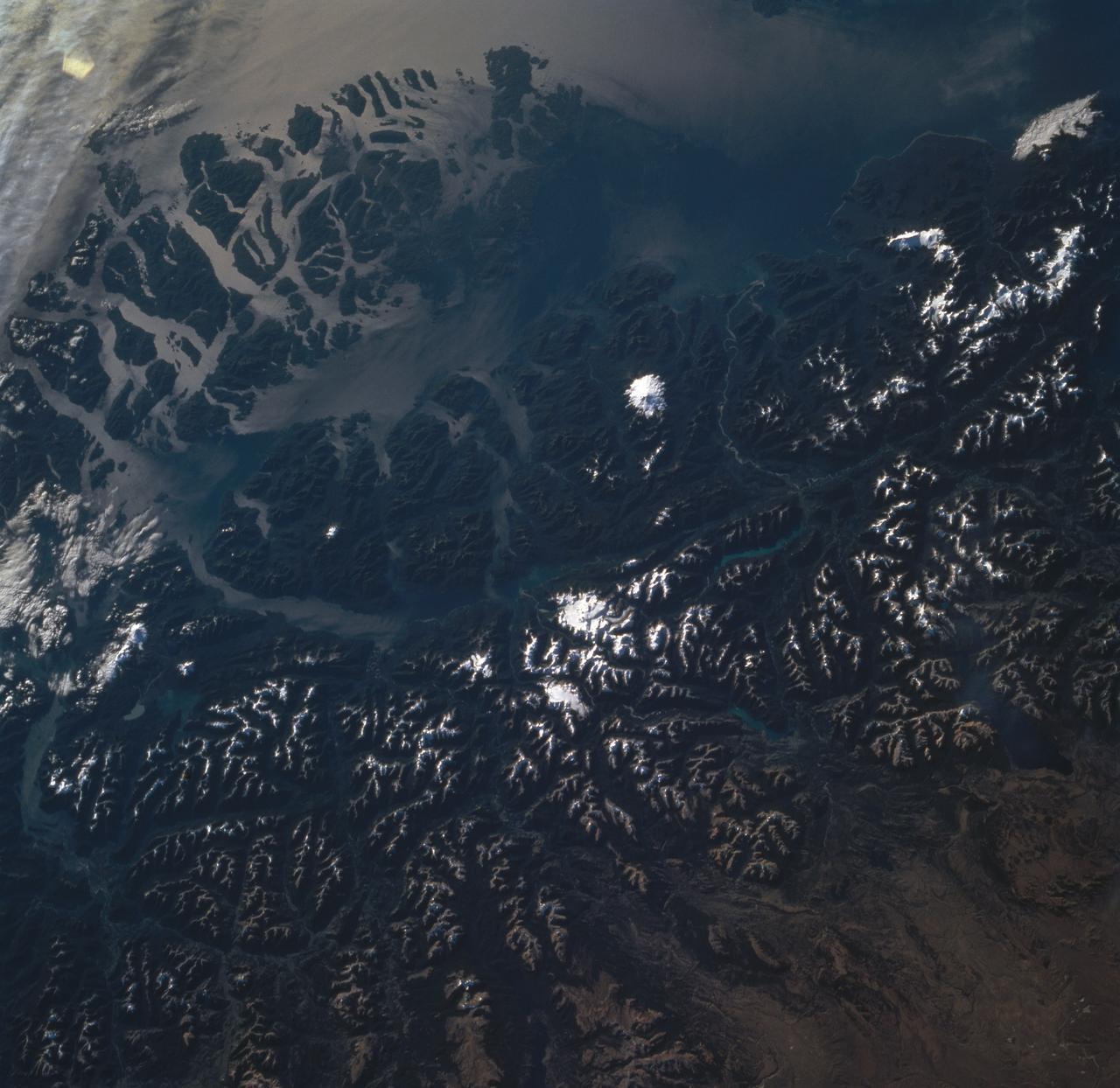

STS060-85-000AH (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This view is centered at about 44 degrees south along the Chilean continental margin of South America. The dark-colored coastal region is heavily forested by dense old-growth forests that are now being cut, but east of the mountains in Argentina the dry climate supports very little vegetation. This desert region known as Patagonia appears as light brown colors. The coastline is especially dramatic because it is shaped by the tortuous channels carved by glaciers which have left fjords. These fjords have effectively cut across the continental divide, and are bordered by active volcanoes which reach elevations between 2, 000 - 3,000 meters. The prominent volcanic peak in the center of the frame is Mt. Melimoya. To the north is a long, snow-covered volcanic ridge called Cerro Yantales. Cerro Yantales recently reported greatly increased fumarolic activity, including the emission of yellow gases near the summit. Russian and American scientists will use this photography to look for further evidence of increased activity like snow melt around the peak. Other Russian and American scientists are particularly interested in mapping the summertime snowline and firm (permanent snow field) elevations as early indications of any potential climatic variation in the making.
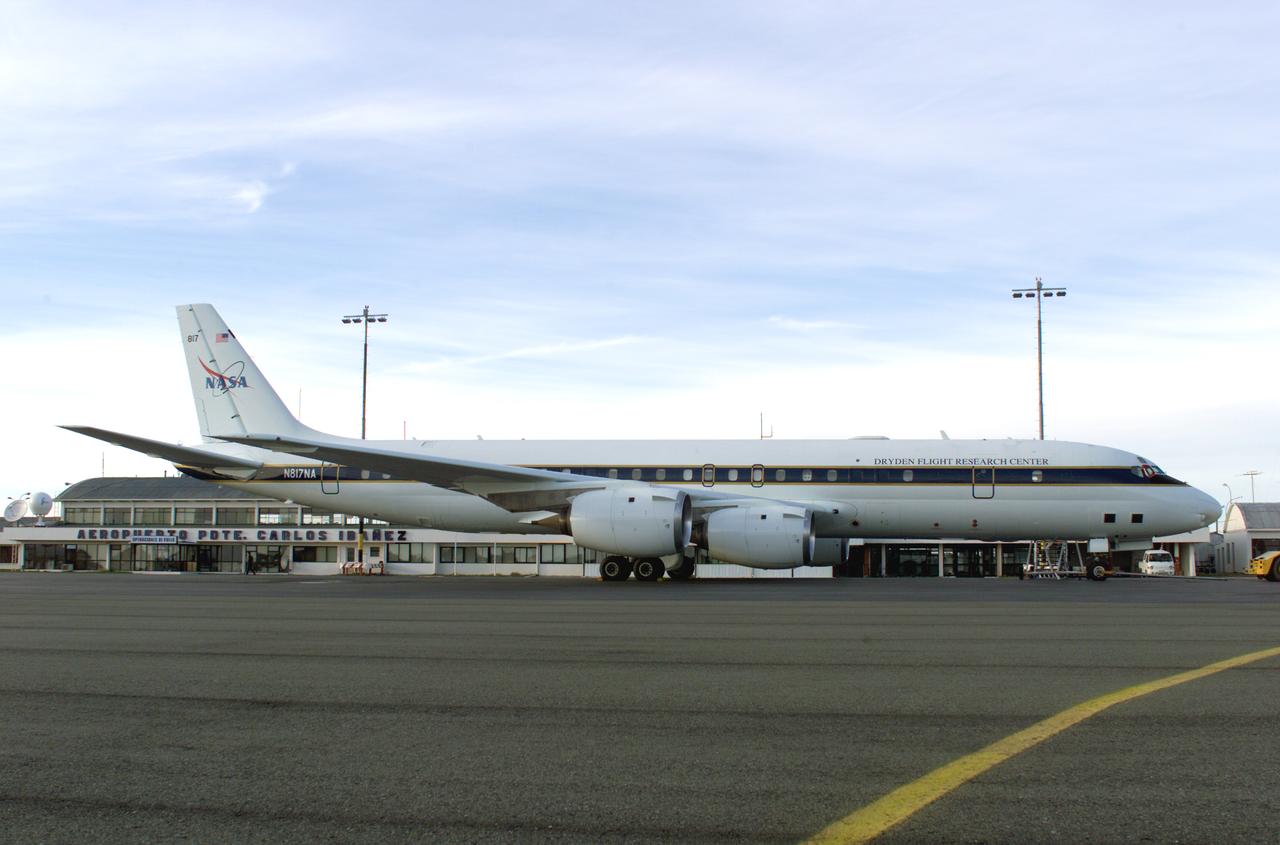

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft prior to launch from Carlos Ibanez International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile, during AirSAR 2004. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct.
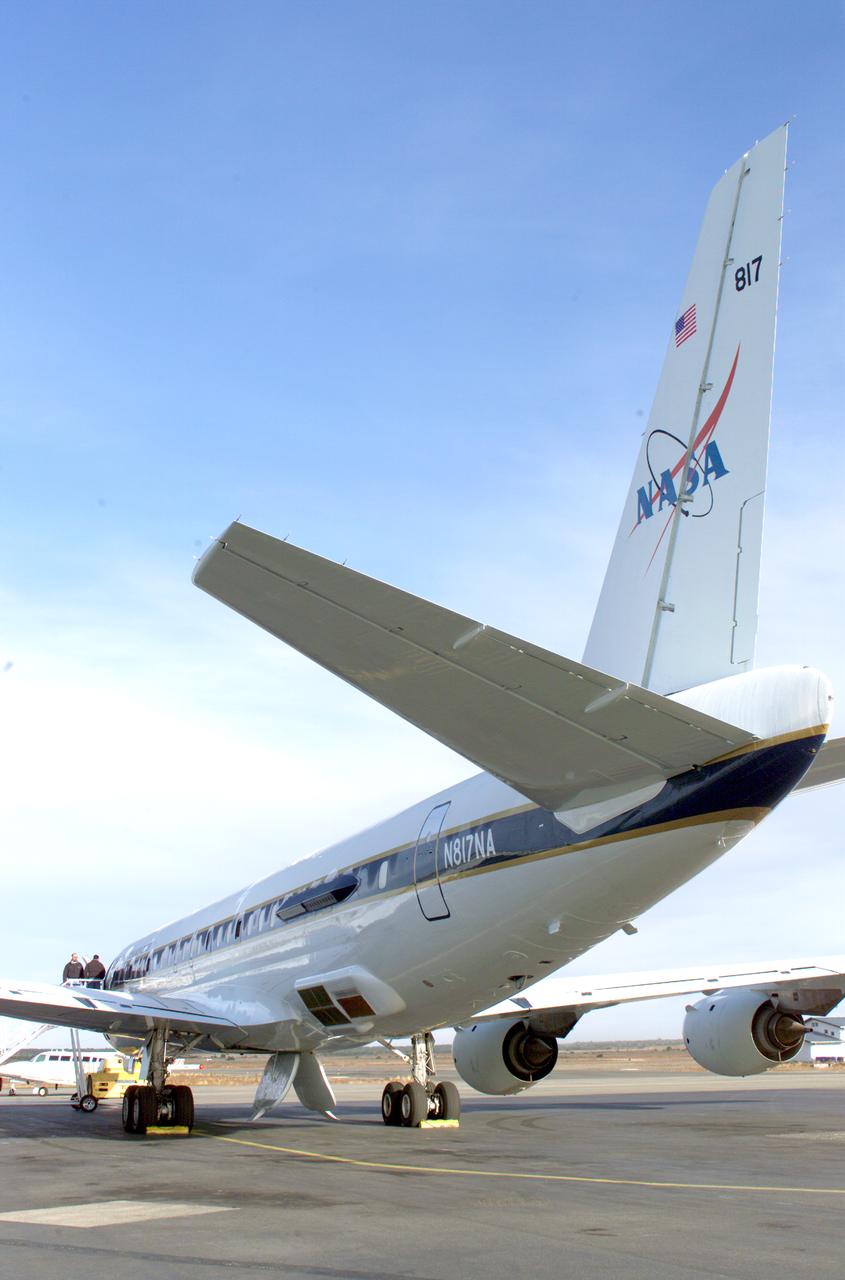

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft at Carlos Ibanez International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. A portion of AirSAR hardware is visible on the left rear fuselage. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct.
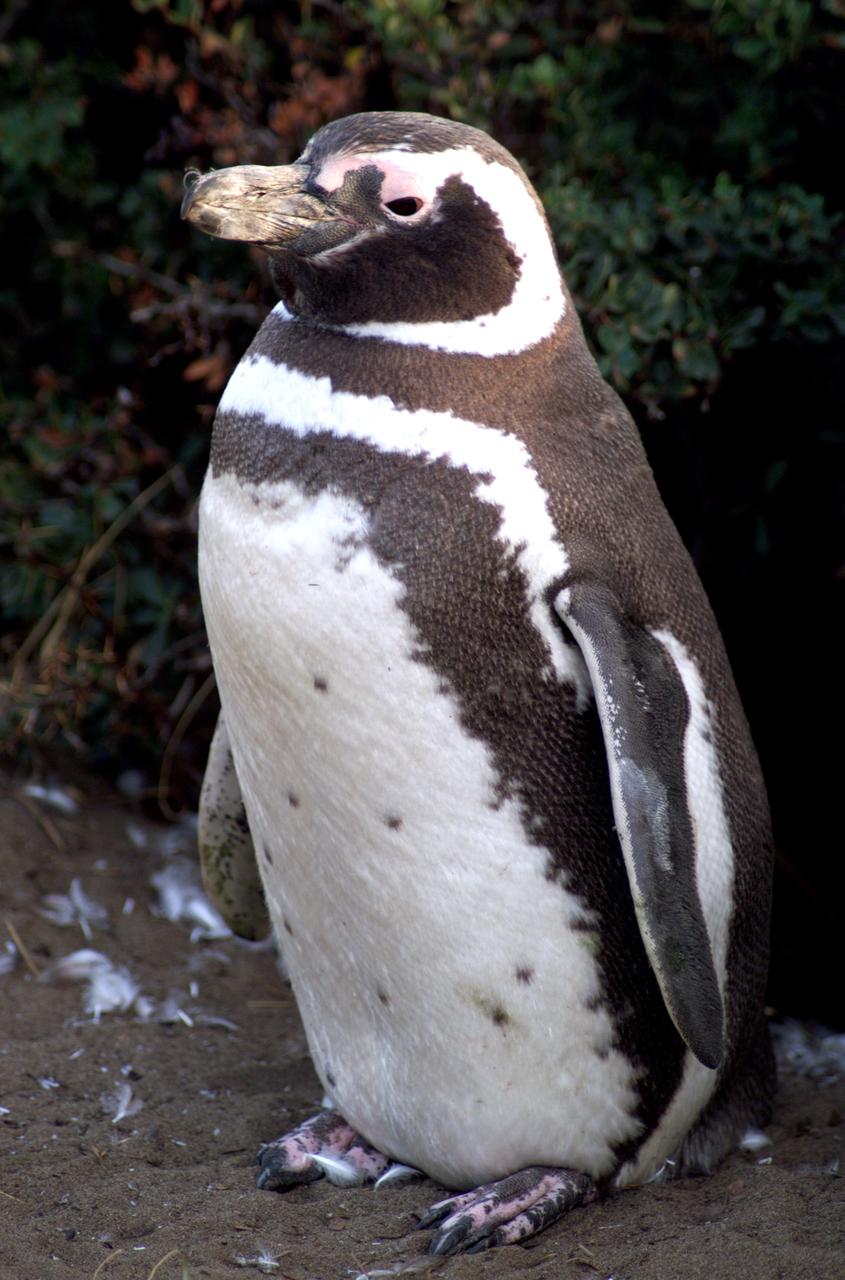

A penguin near Punta Arena, Chile, photographed in its natural summer habitat during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct.
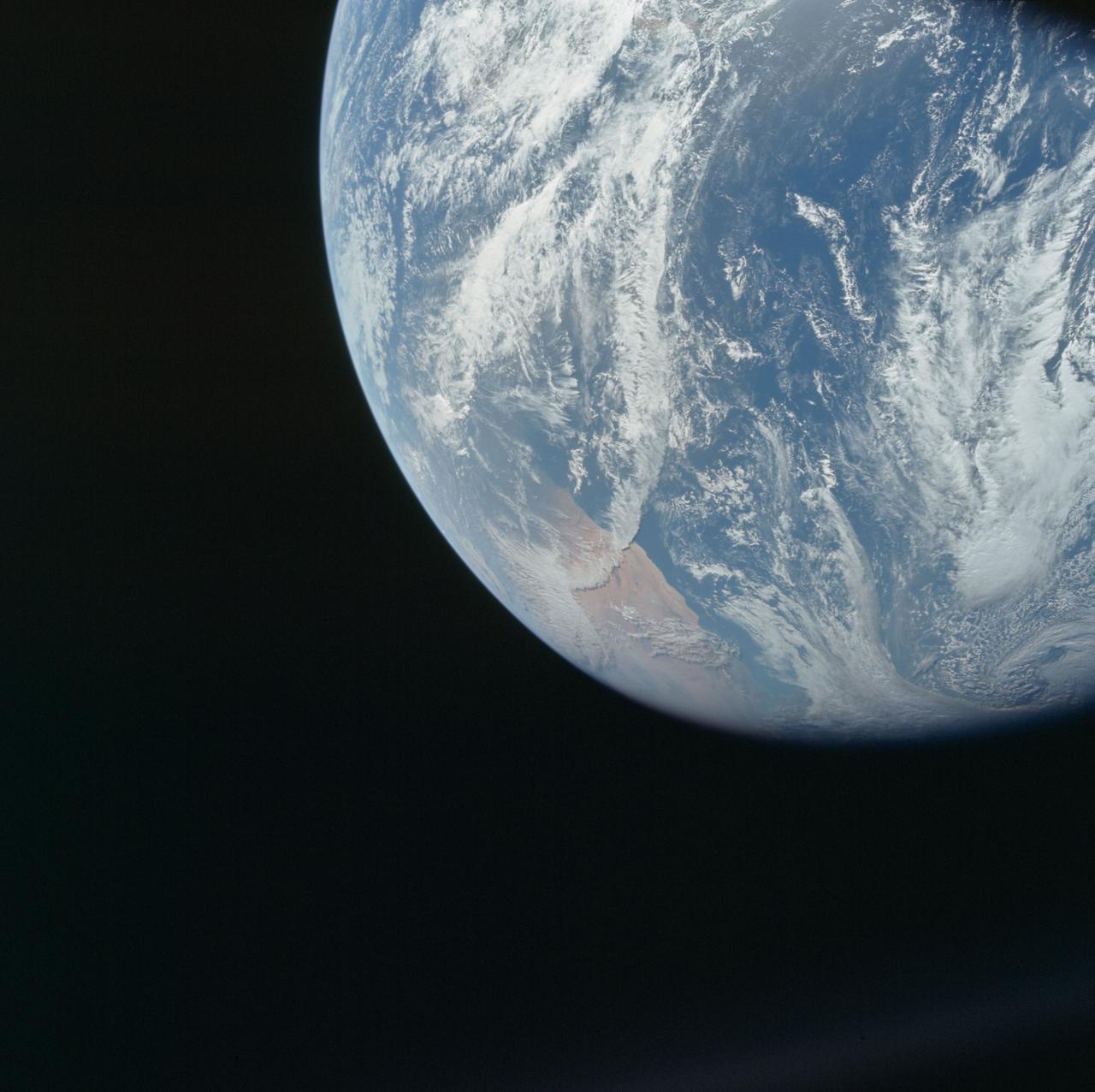

AS08-16-2588 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Both sides of the Atlantic Ocean are visible in this view from Apollo 8 spacecraft. (Hold picture with Earth at bottom left). The large, most prominent land mass is the bulge of West Africa. The portion of Africa near the equator is dark and cloudy, but the more northerly portions are clear, showing the prominent cape at Dakar and the Senegal River in Senegal; Cap Blanc; the Adrar Plateau in Mauretania; the wide expanse of desert in Algeria and Spanish Sahara; and the far edge, the Atlas and Anti-Atlas Mountains in Morocco. Clouds cover the eastern coast of South America, southward from Surinam and Guyana to near the city of Salvador, Brazil. The view was photographed following trans-lunar insertion.
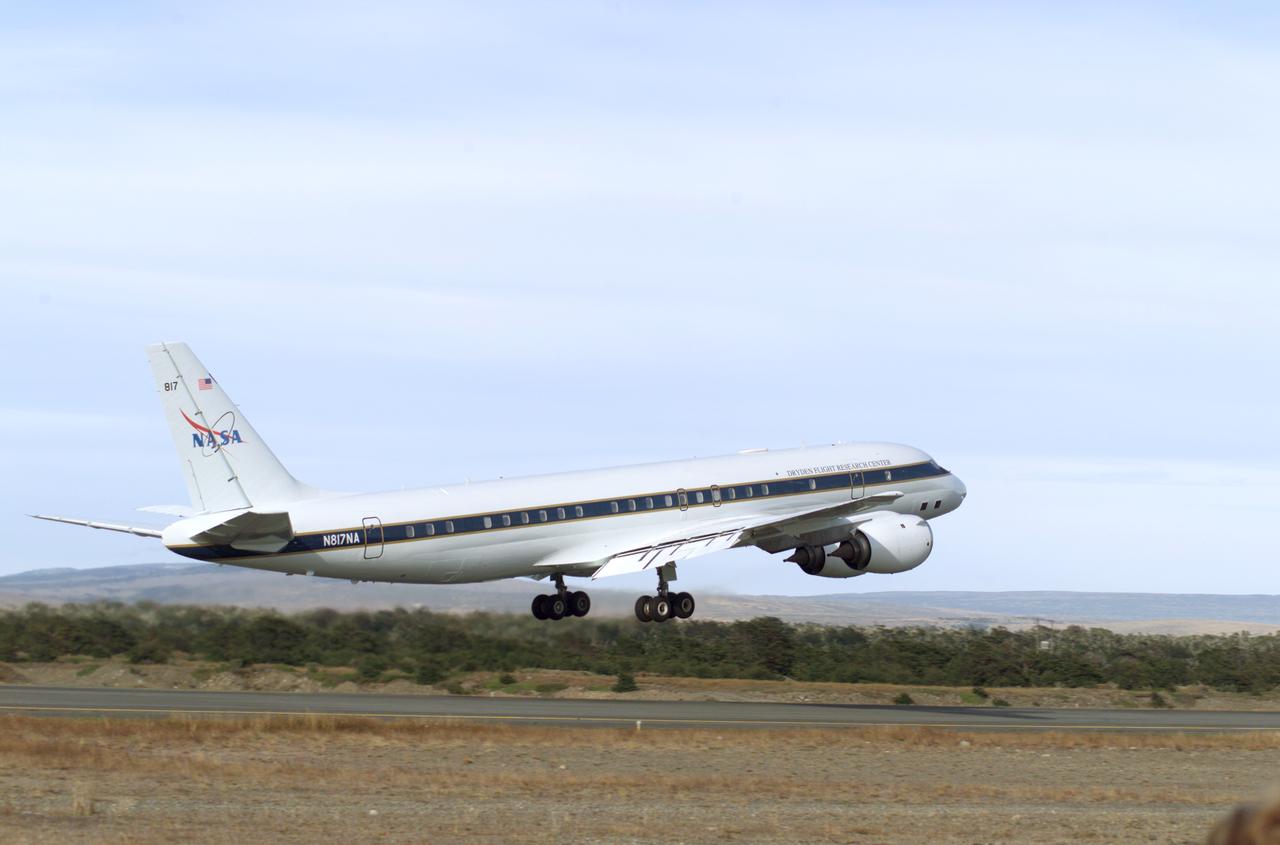

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Carlos Ibanez International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile, during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct.
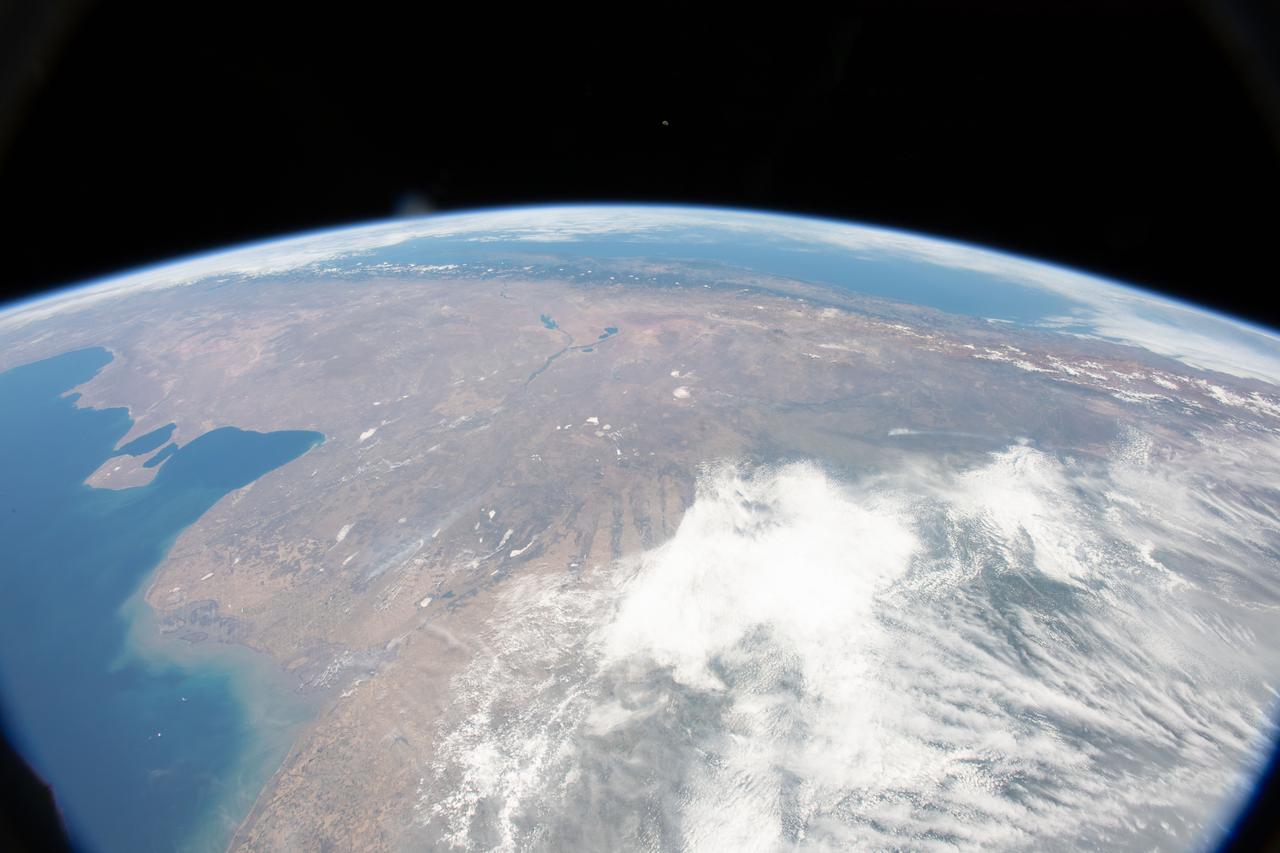

iss058e006004 (Jan. 26, 2019) --- This photograph of South America from bottom to top looks from the northeast coast of Argentina to southwest across Chile, the Andes mountains and the Pacific Ocean. The International Space Station was orbiting 259 miles above the Atlantic coast of the South American continent.
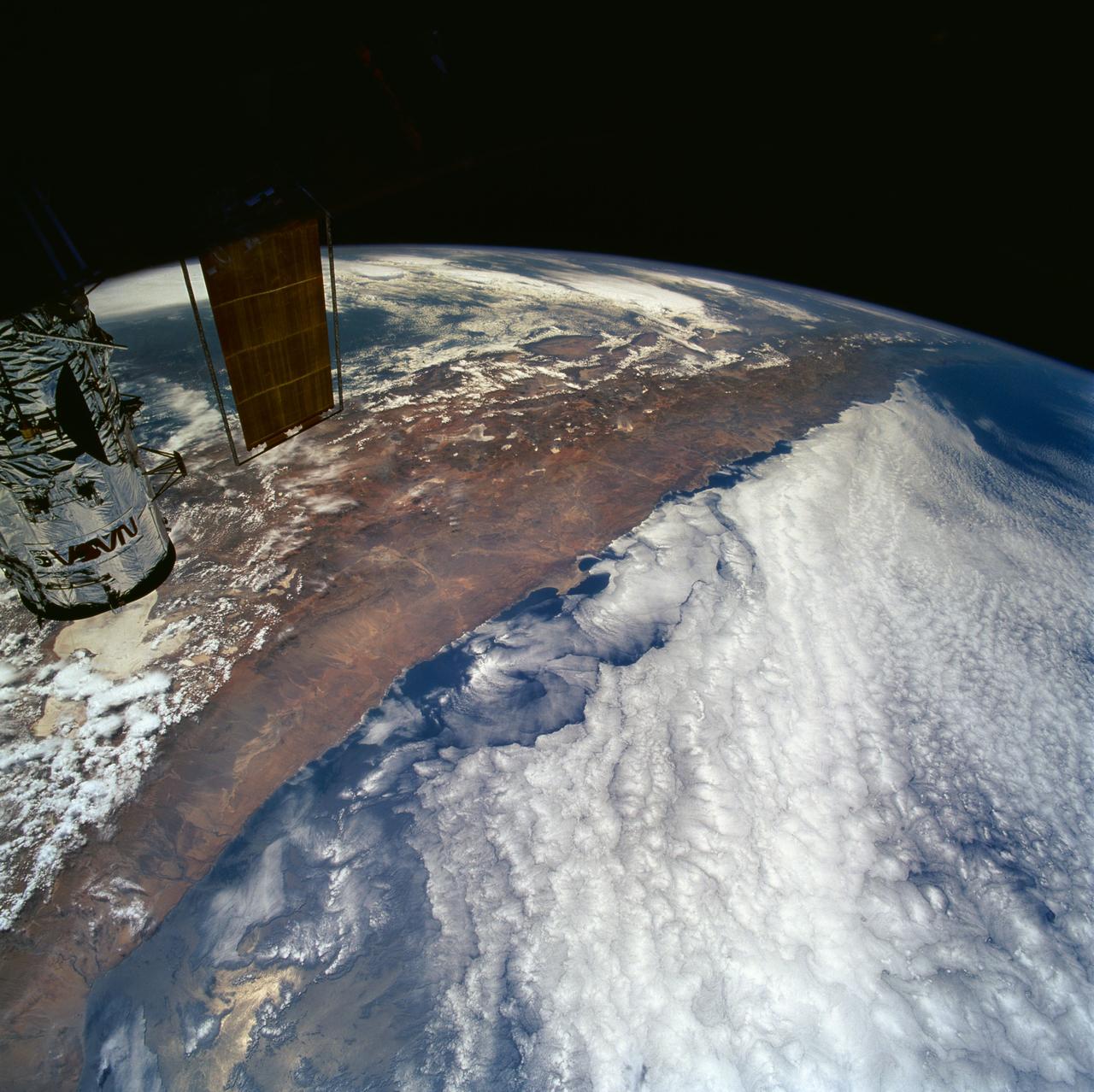

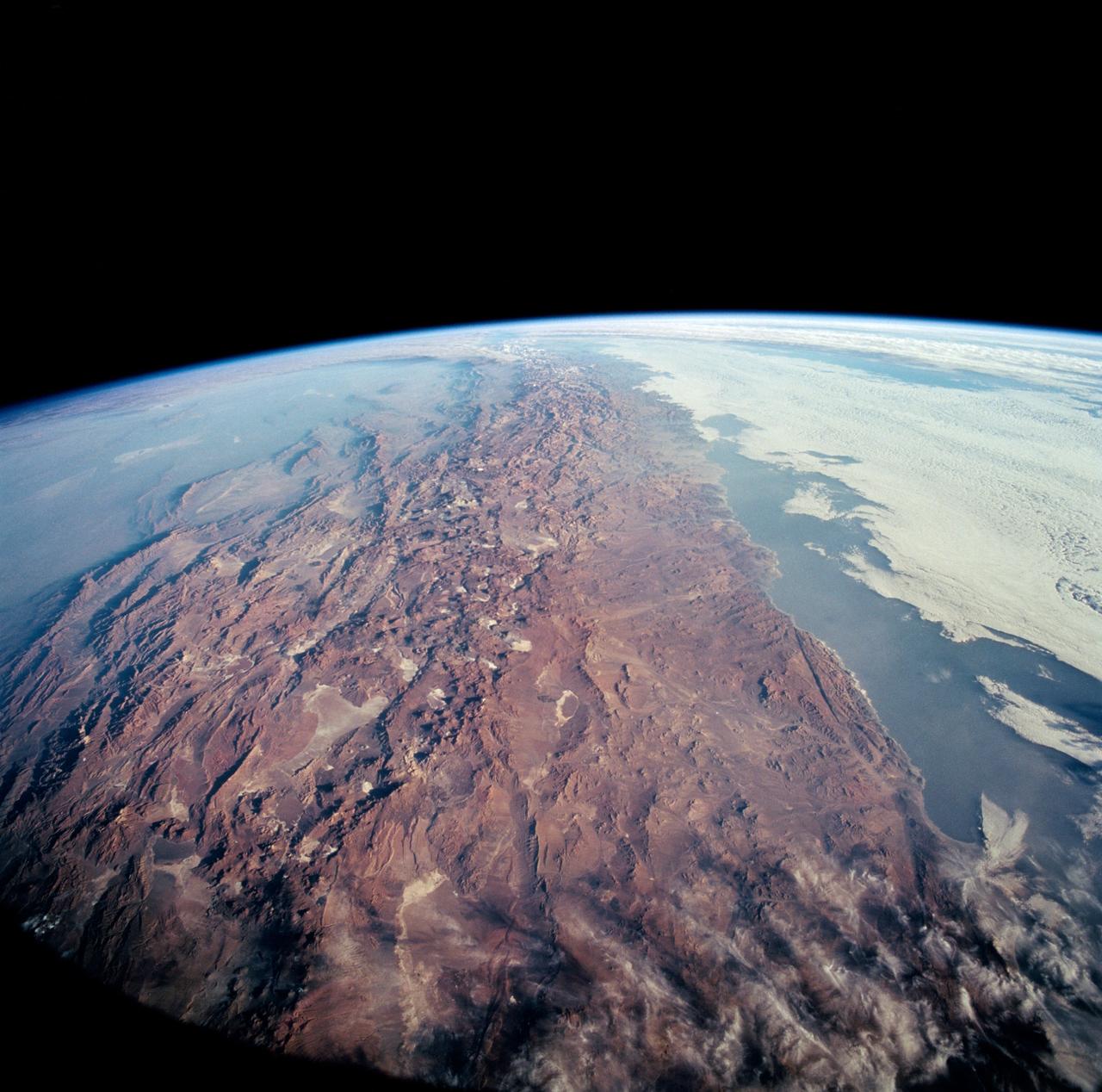
STS061-101-023 (8 Dec 1993) --- This color photograph is a spectacular, panoramic (southeastern view) shot that features the northern half of the country of Chile and the Andes Mountains of South America. The Atacama Desert, one of the driest regions on earth, is clearly visible along the northern Chilean coast. This desert extends from roughly Arica in the north to the city of Caldera in the south, a distance of six hundred miles. Some parts of this very arid region go for more than twenty years without measurable precipitation. It is an area of dramatic and abrupt elevation changes. For example, from the waters edge there is an escarpment of the coastal plateau that rises like an unbroken wall two or three thousand feet above the Pacific Ocean. From the coastal plateau, there is an even more dramatic increase in elevation -- from two thousand feet above sea level to an average elevation of thirteen thousand feet above sea level in the Bolivian Altiplano. This elevation change occurs within a one hundred to two hundred mile distance from the Pacific Ocean. The north-south trending spine of the Andes Mountains can be seen on this photograph. Several of the volcanic peaks in this mountain chain exceed 20,000 feet above sea level. Interspersed with these volcanic peaks, numerous dry lake beds (salars) can be seen as highly reflective surfaces. The largest of these salars (Salar de Uyuni) is visible at the edge of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Offshore, the cold Peruvian current produces low stratus clouds that can be found along this coastline at certain times of the year. This is the same type of meteorological phenomena that is found along the southern California coast and the Skeleton coast of southwestern Africa.
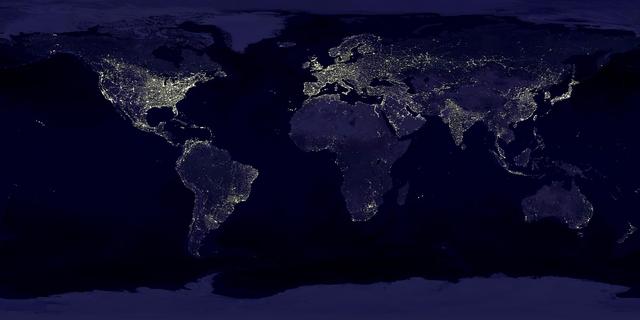
The Eastern U.S., Europe, and Japan are brightly lit by their cities, while interiors of Africa, Asia, Australia, and South America are dark and lightly populated in this image created in 2000 by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.

This near-infrared photograph of the Earth was taken by the Galileo spacecraft at 6:07 a.m. PST on Dec. 11, 1990, at a range of about 1.32 million miles. South America is prominent near the center. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00226
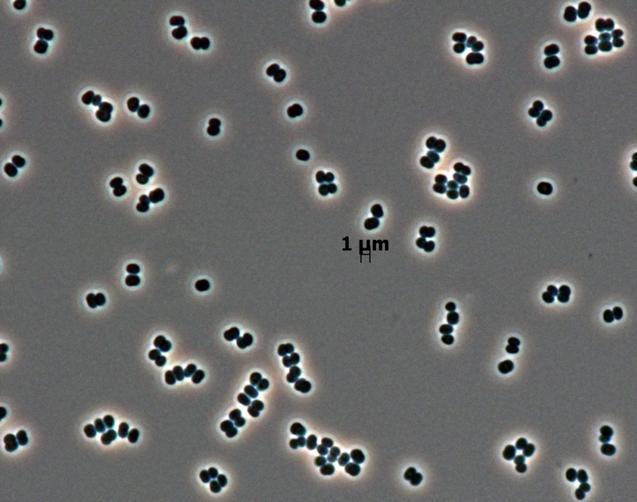
This microscopic image shows dozens of individual bacterial cells of the recently discovered species, Tersicoccus phoenicis, found in only two places: clean rooms in Florida and South America where spacecraft are assembled for launch.
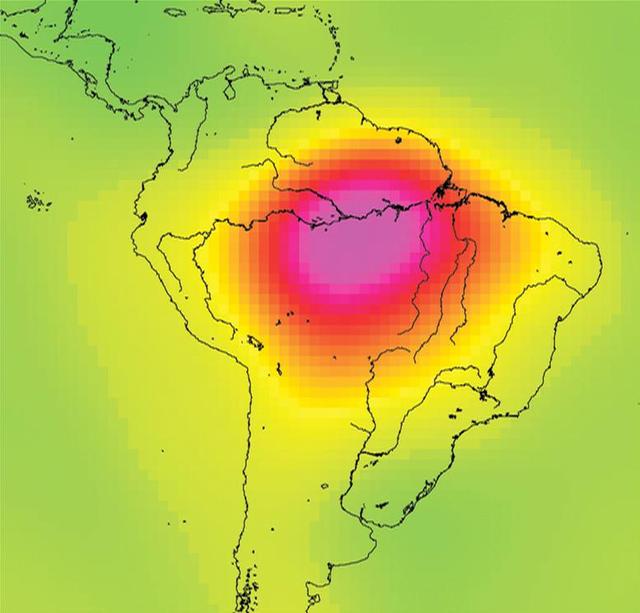
This image is from data taken by NASA Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment showing the Amazon basin in South America. The amount of water stored in the Amazon basin varies from month to month. Animations are available at the Photojournal.
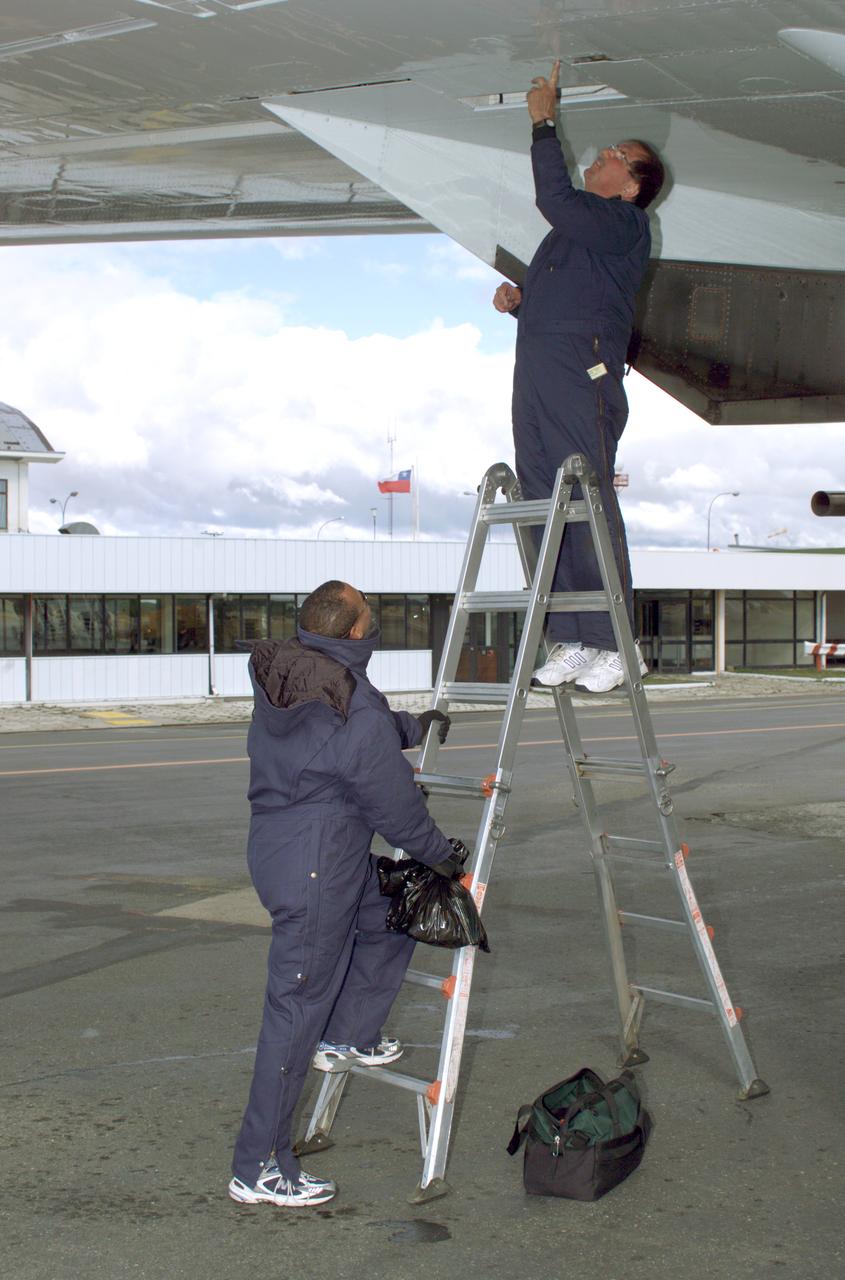

NASA DC-8 Ground Support Technicians Mark Corlew and Mike Lakowski perform routine maintenance on the aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

JPL scientist Dr. David Imel and U.S. Air Force Colonel Gwen Linde, the Defense Department Attache Officer assigned to the Chilean Embassy, lead Chilean students on a tour of the DC-8 aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
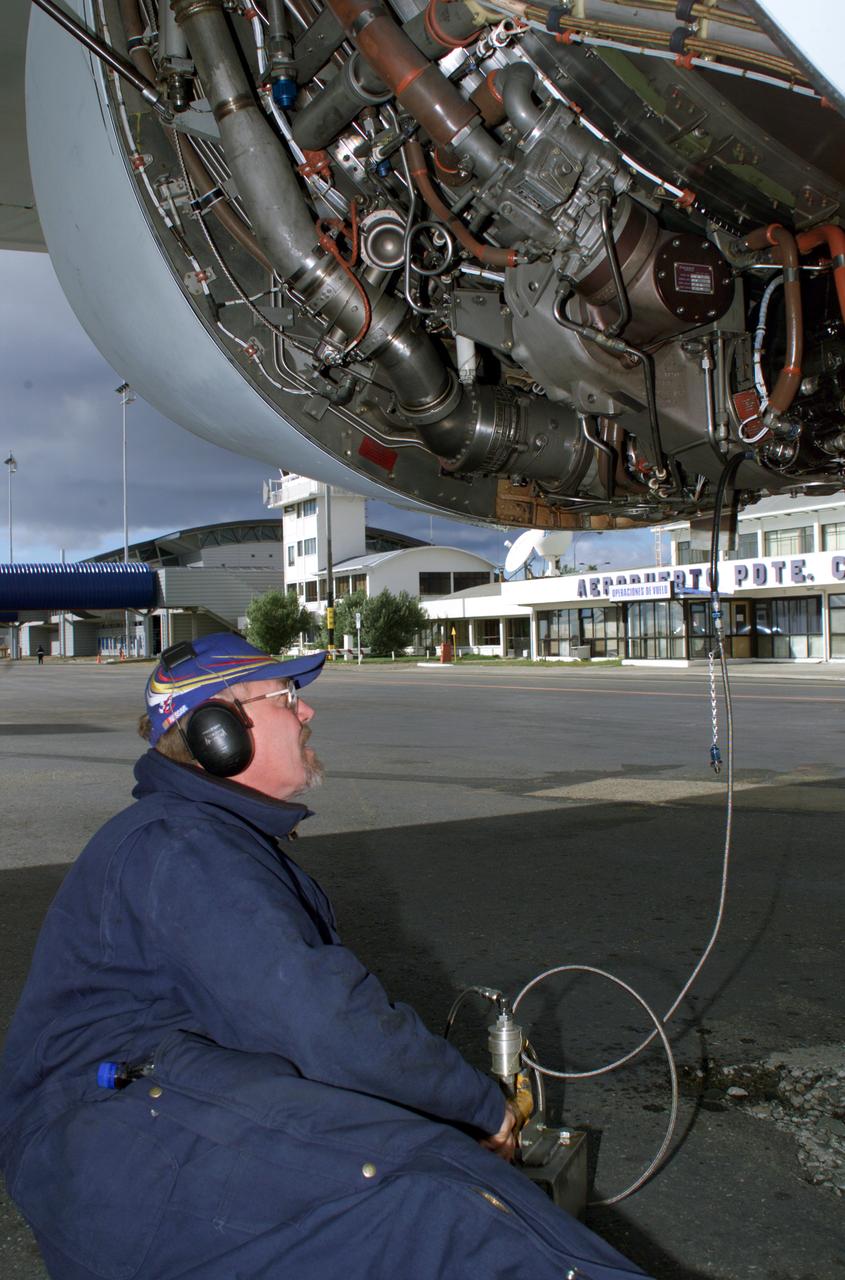

NASA DC-8 Ground Support Technician Joe Niquette performs routine maintenance on the DC-8 aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
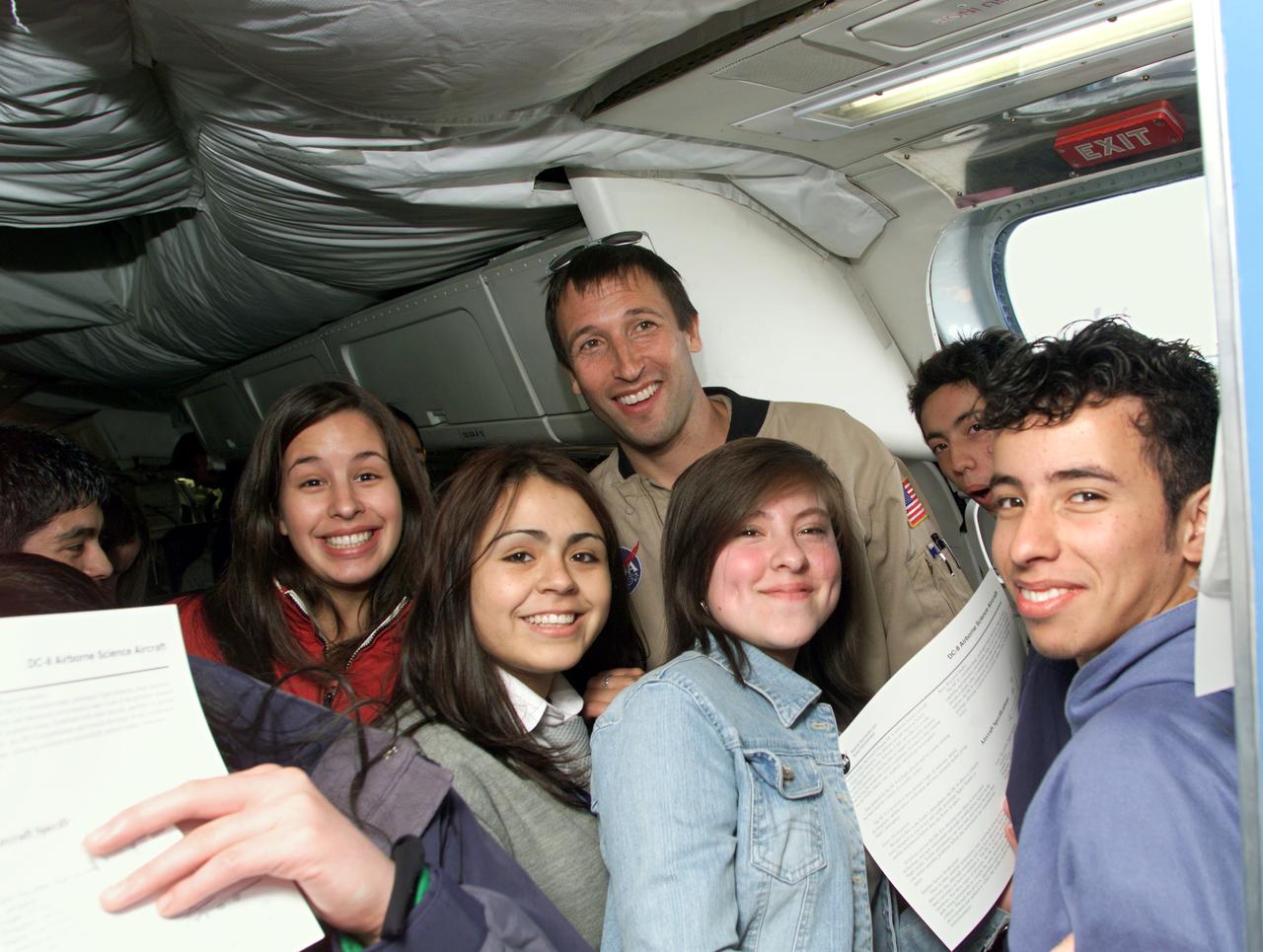

NASA DC-8 Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with a group of Chilean Students onboard the aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
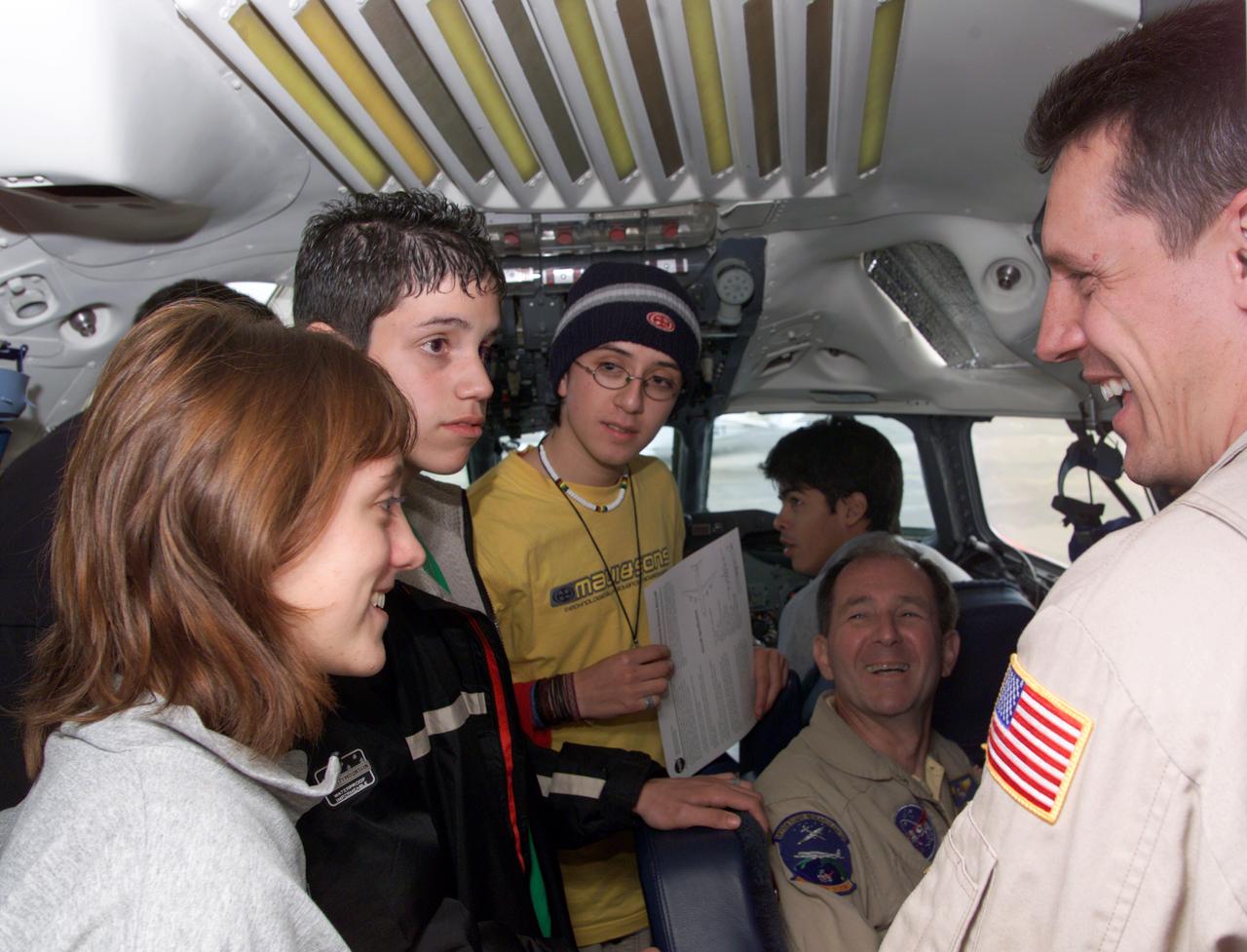

NASA DC-8 Pilots Craig Bomben and Bill Brockett explain the DC-8 cockpit to Chilean students onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
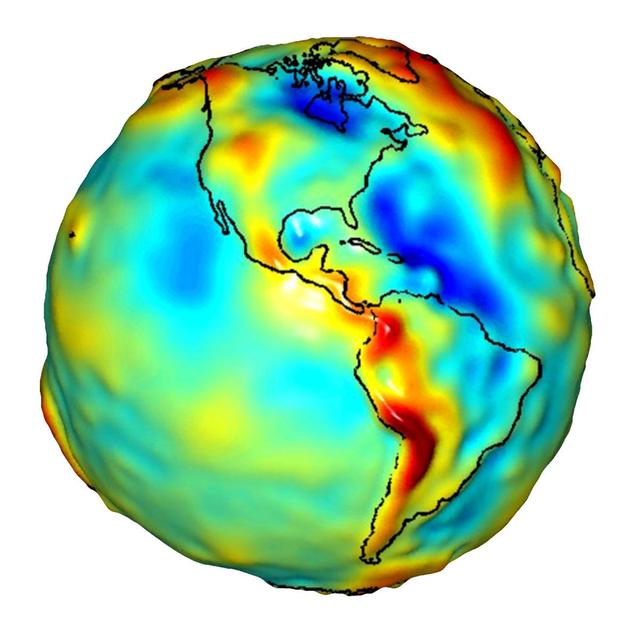
This visualization of a gravity model was created with data from NASA Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment and shows variations in the gravity field across the Americas.
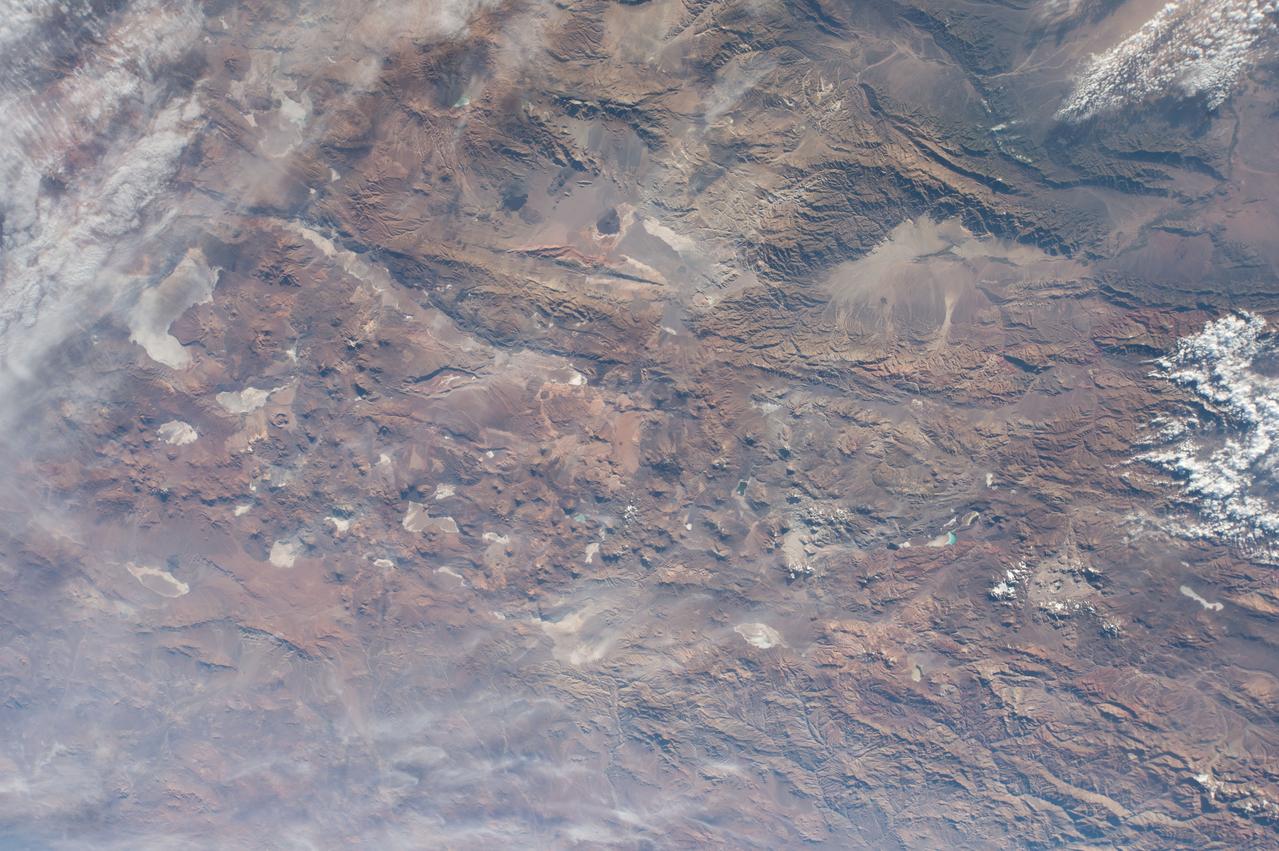

GMT362_00_58_Terry Virts_chile andes central south america amazon start in mountains_123
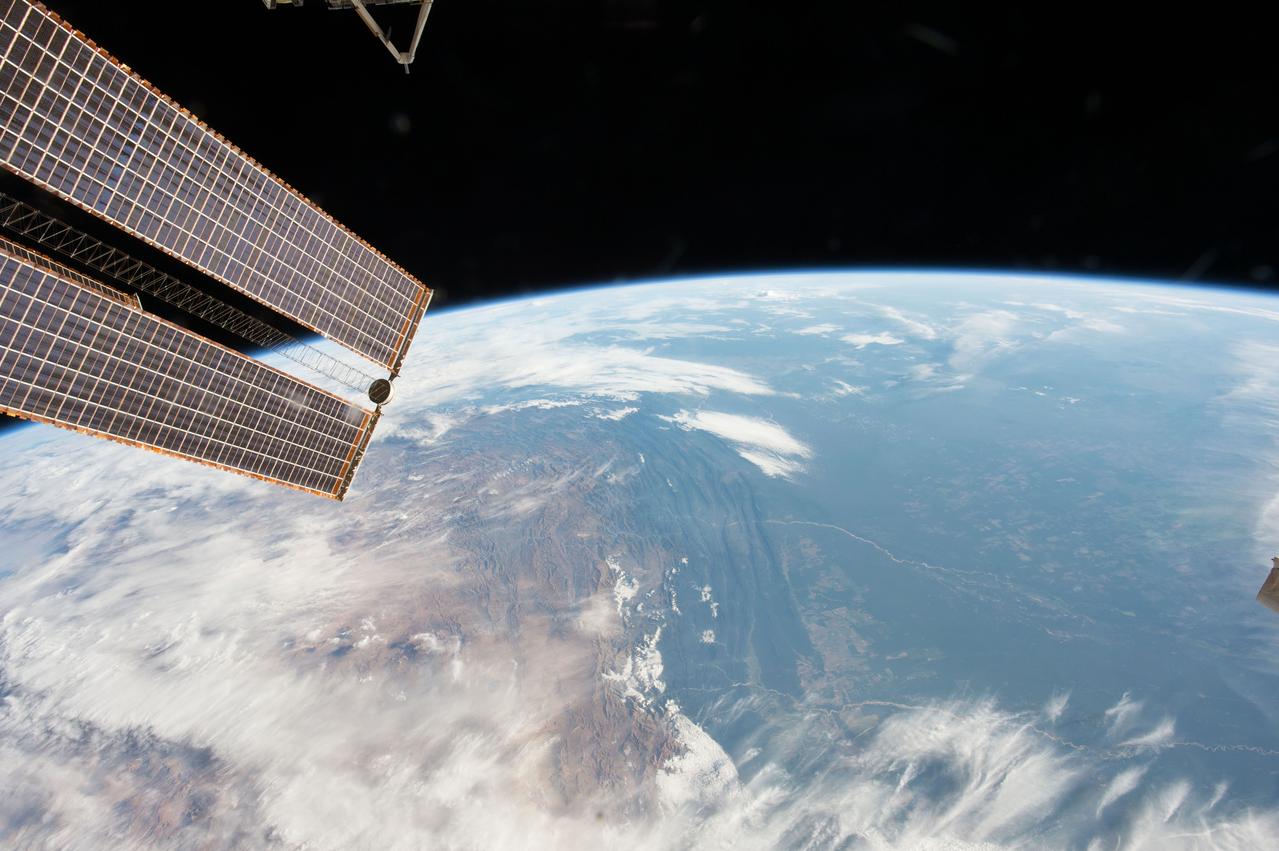

GMT362_00_58_Terry Virts_chile andes central south america amazon start in mountains_123
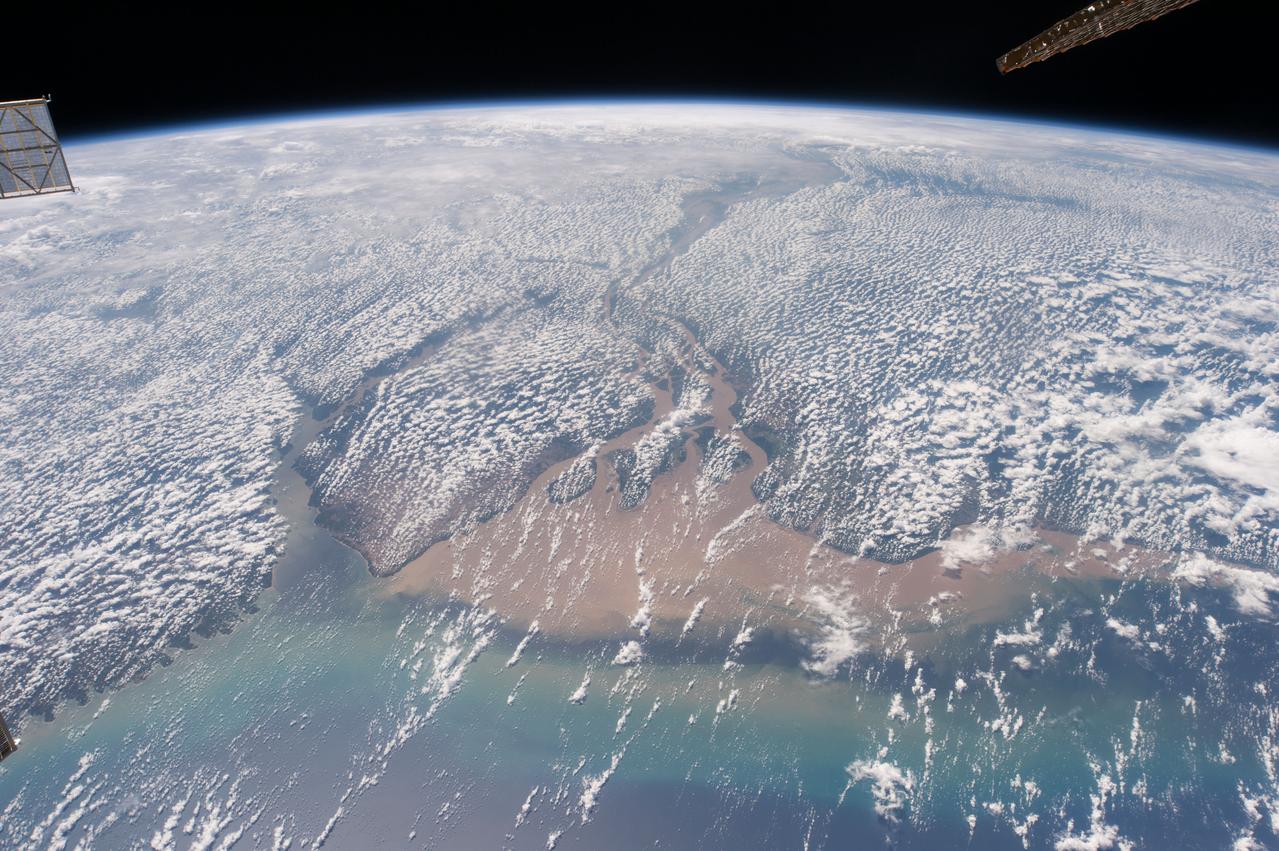

GMT350_20_59_For Huntsville_Terry Virts_SSRMS MSG amazon south america arm movie_128
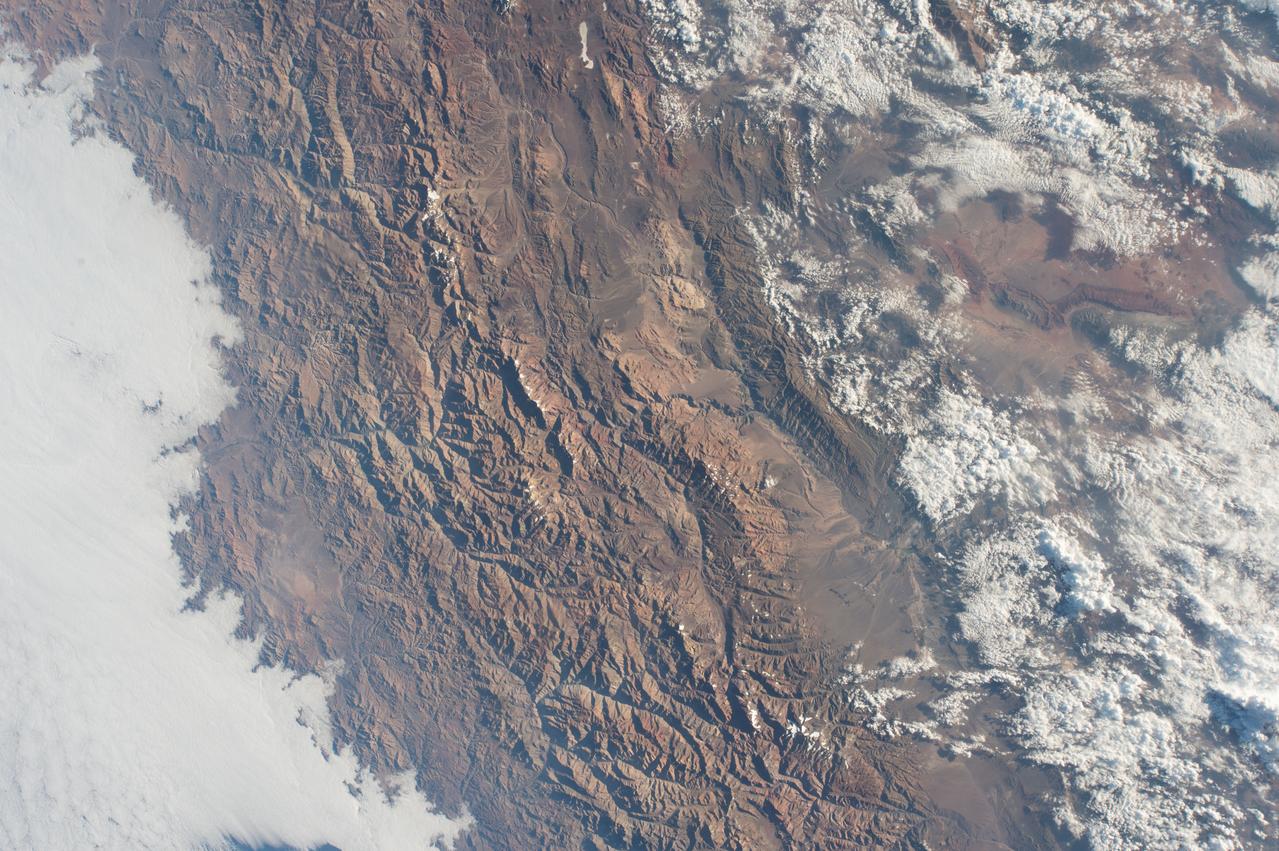

GMT362_00_58_Terry Virts_chile andes central south america amazon start in mountains_123
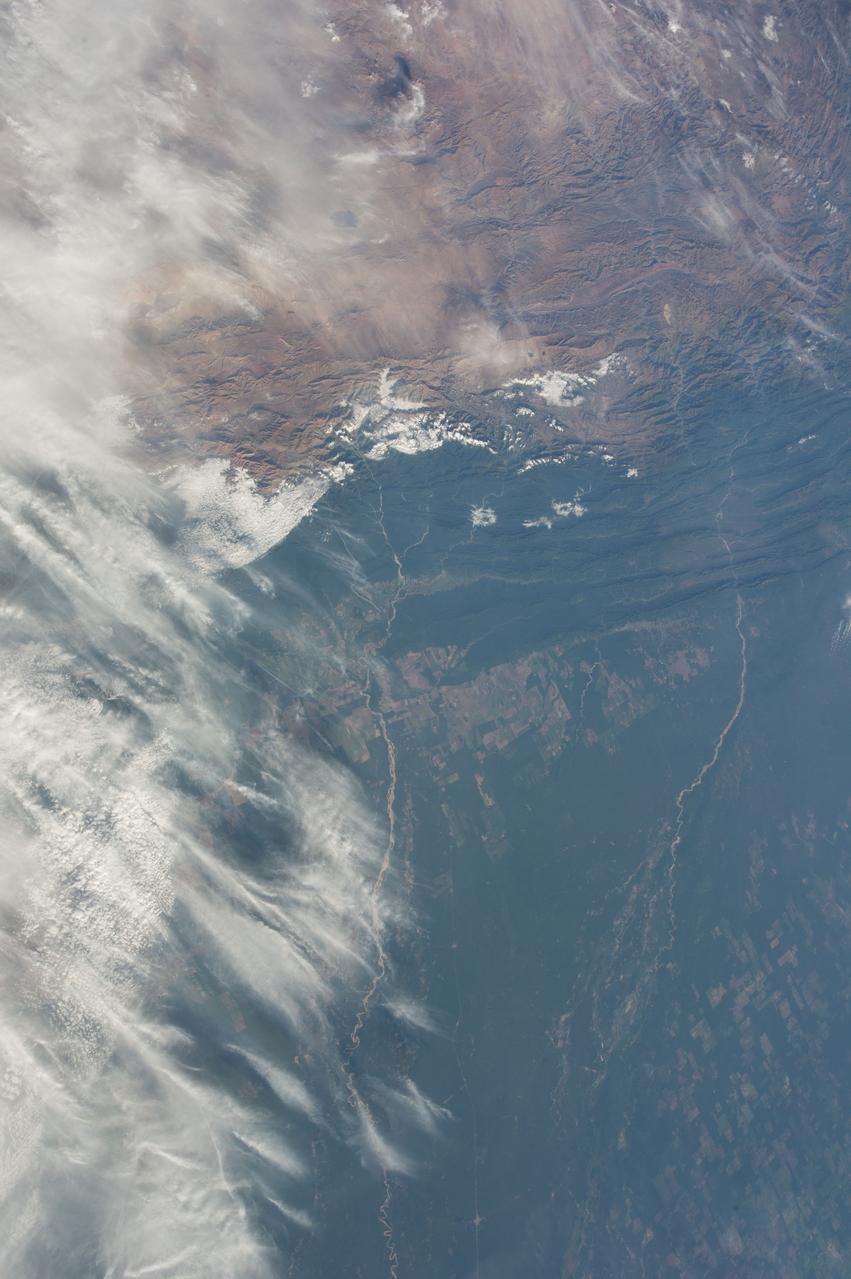

GMT362_00_58_Terry Virts_chile andes central south america amazon start in mountains_123
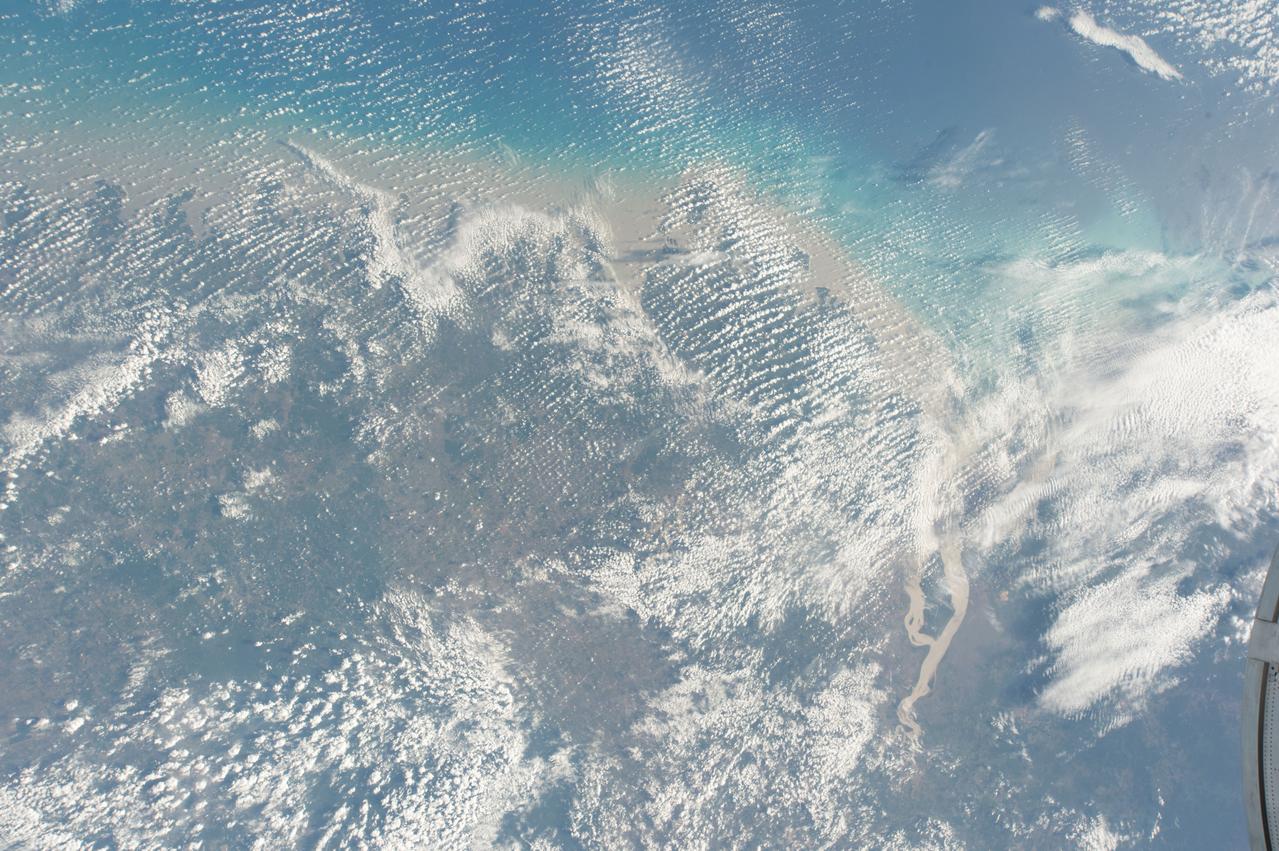

GMT362_00_58_Terry Virts_chile andes central south america amazon start in mountains_123

iss060e013481 (July 18, 2019) --- A full Moon is pictured from the International Space Station as the orbiting complex flew 270 miles above the South Pacific Ocean off the coast of South America.
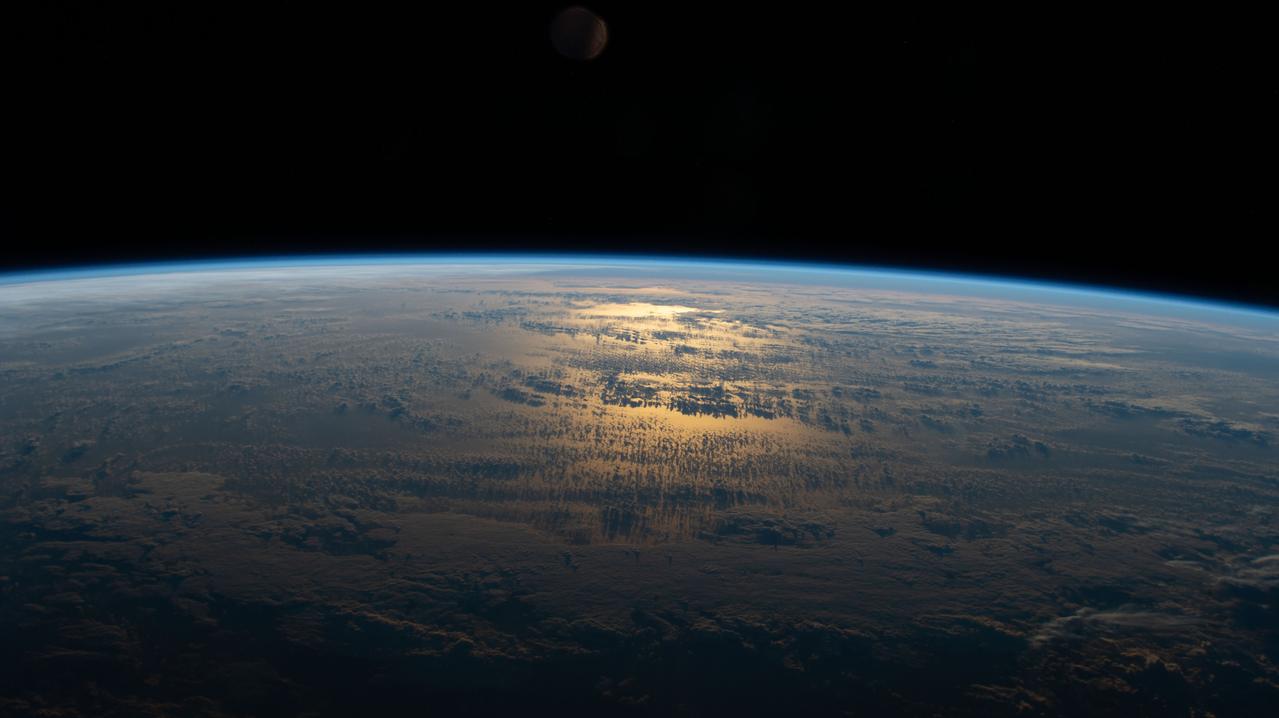

iss063e050668 (July 18, 2020) --- The sun's glint beams off a partly cloudy South Pacific as the International Space Station's orbital track took it halfway between Australia and South America.
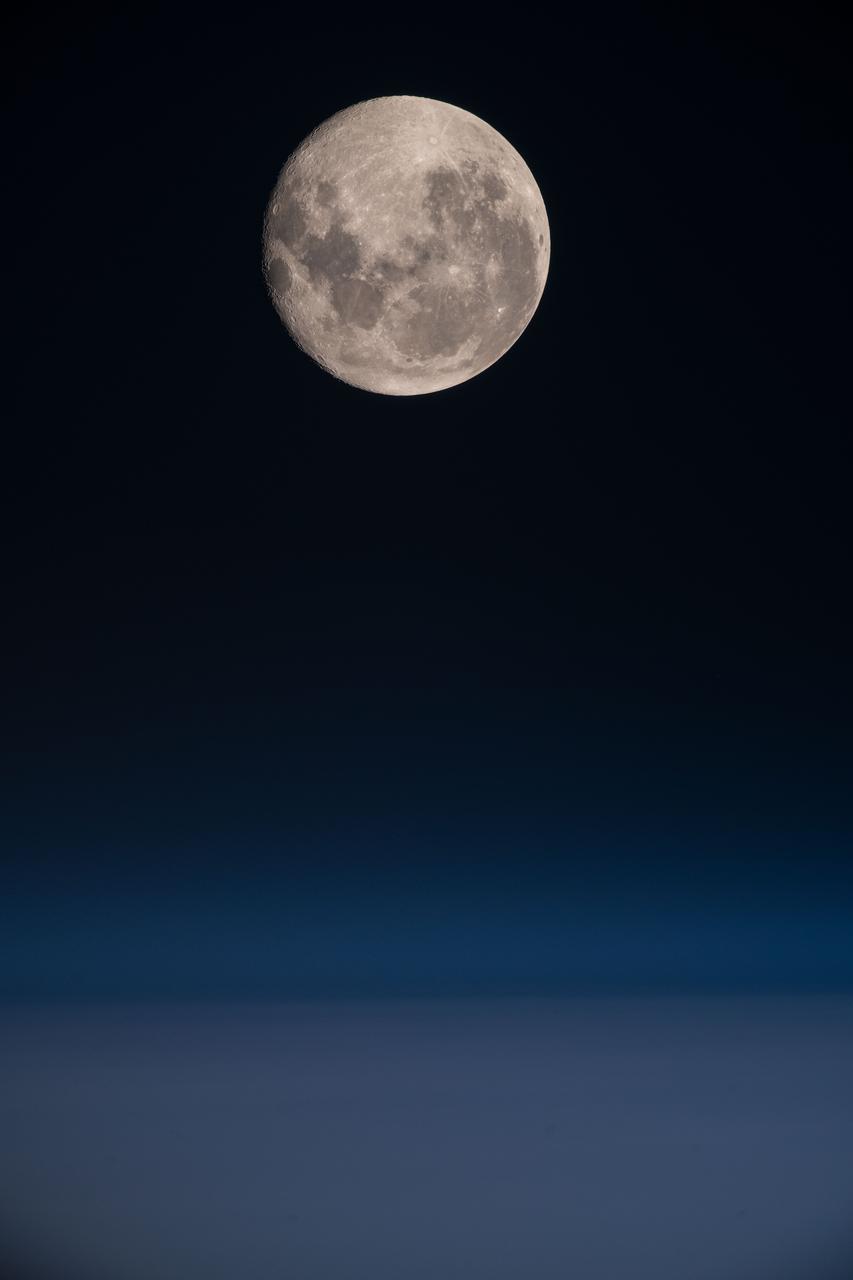

iss060e013471 (July 18, 2019) --- A full Moon is pictured from the International Space Station as the orbiting complex flew 270 miles above the South Pacific Ocean off the coast of South America.
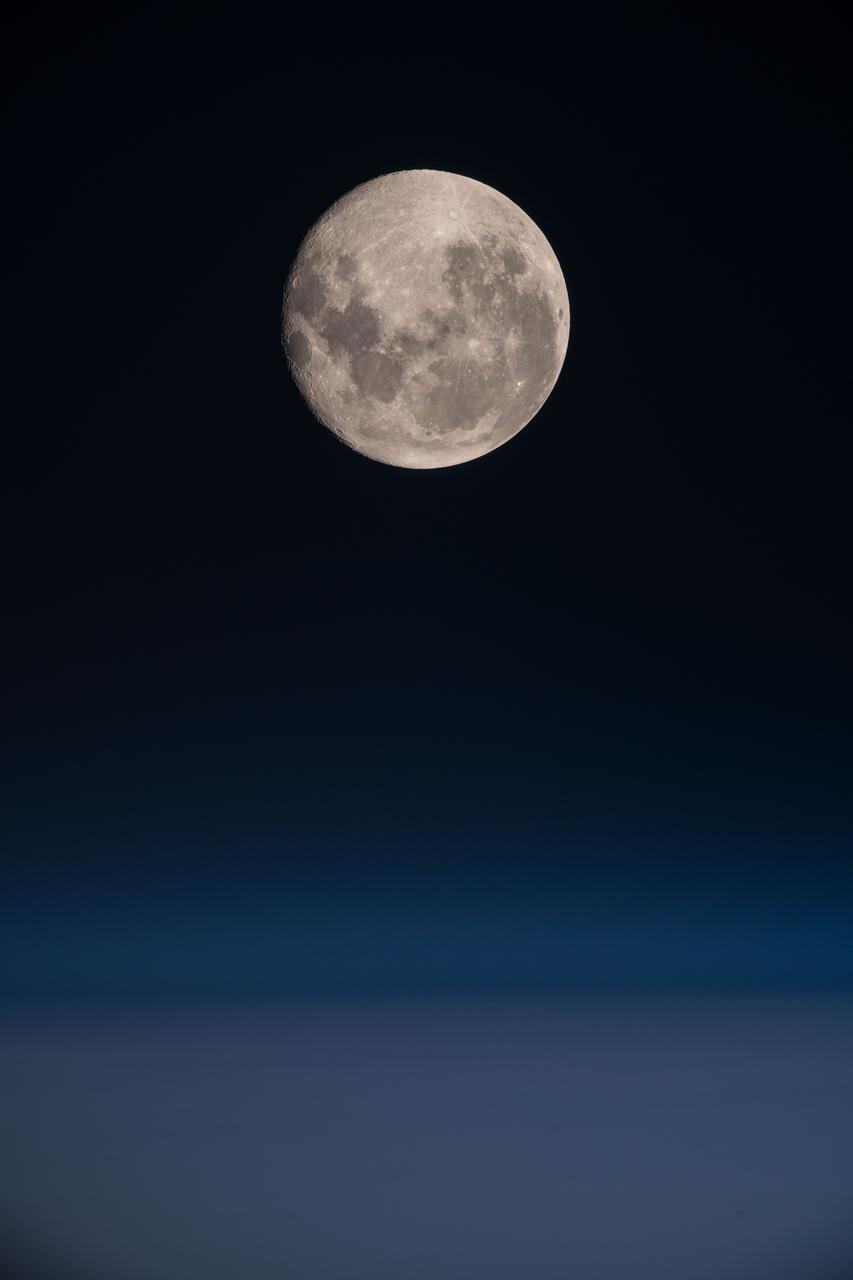

iss060e013472 (July 18, 2019) --- A full Moon is pictured from the International Space Station as the orbiting complex flew 270 miles above the South Pacific Ocean off the coast of South America.
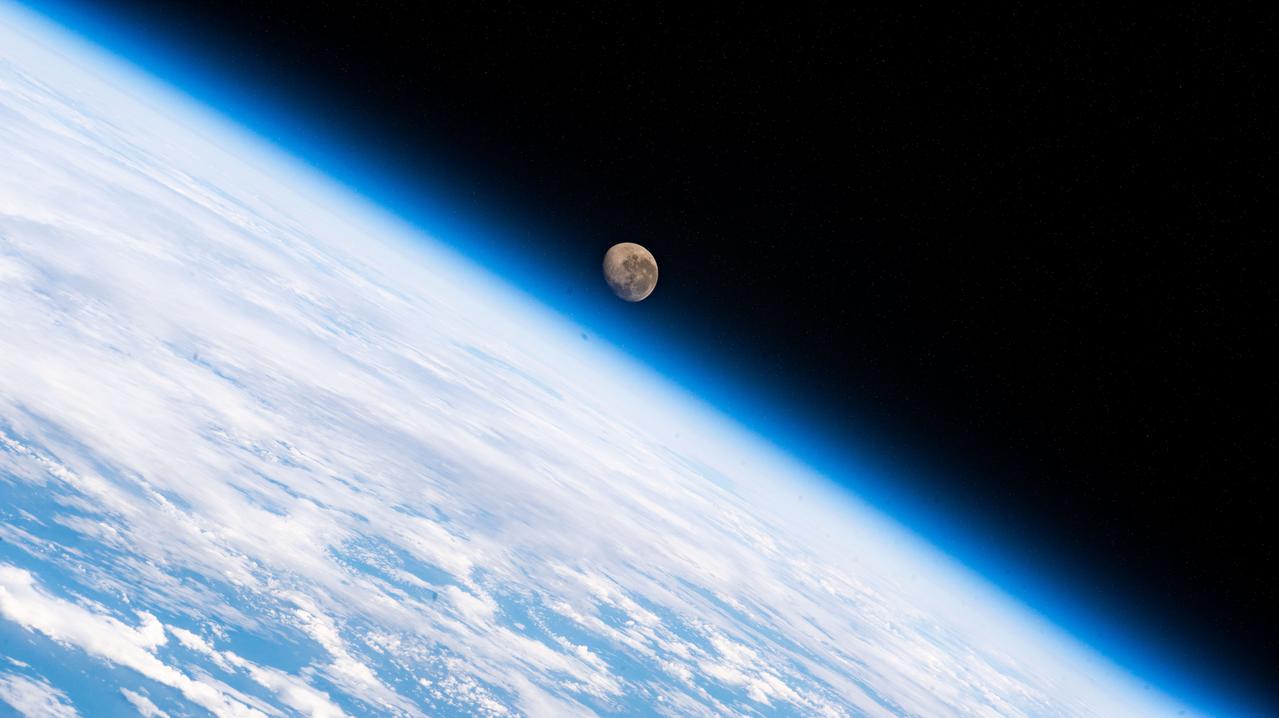

iss066e123388 (Jan. 21, 2022) --- The waning gibbous Moon is pictured above the Earth's horizon as the International Space Station orbited 272 miles above the Atlantic Ocean in betweenthe tips of South America and South Africa.
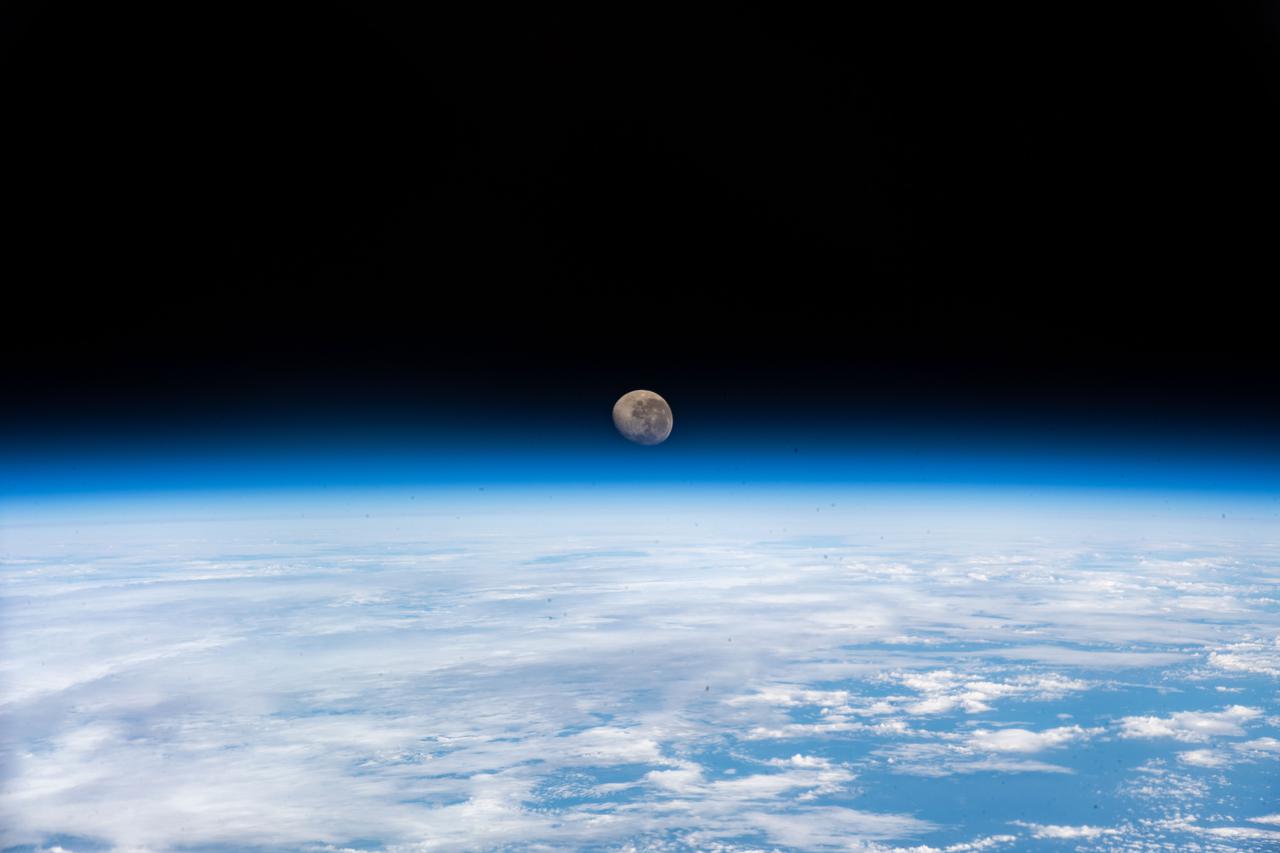

iss066e124140 (Jan. 21, 2022) --- The waning gibbous Moon is pictured above the Earth's horizon as the International Space Station orbited 272 miles above the Atlantic Ocean in bnetween the tips of South America and South Africa.
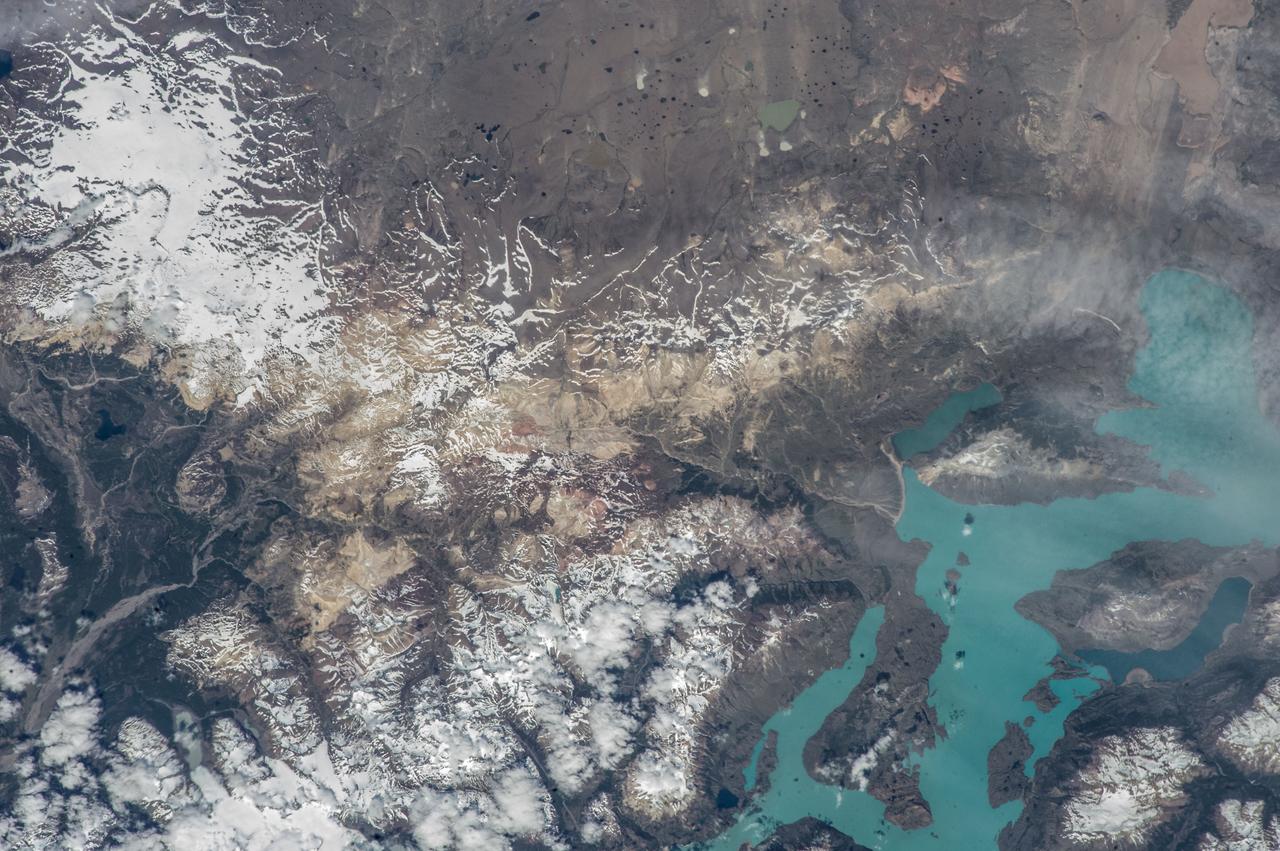

Earth Observations taken by Expedition 38 crewmember. Crewmember indicates South America. Image was released by astronaut on Twitter.
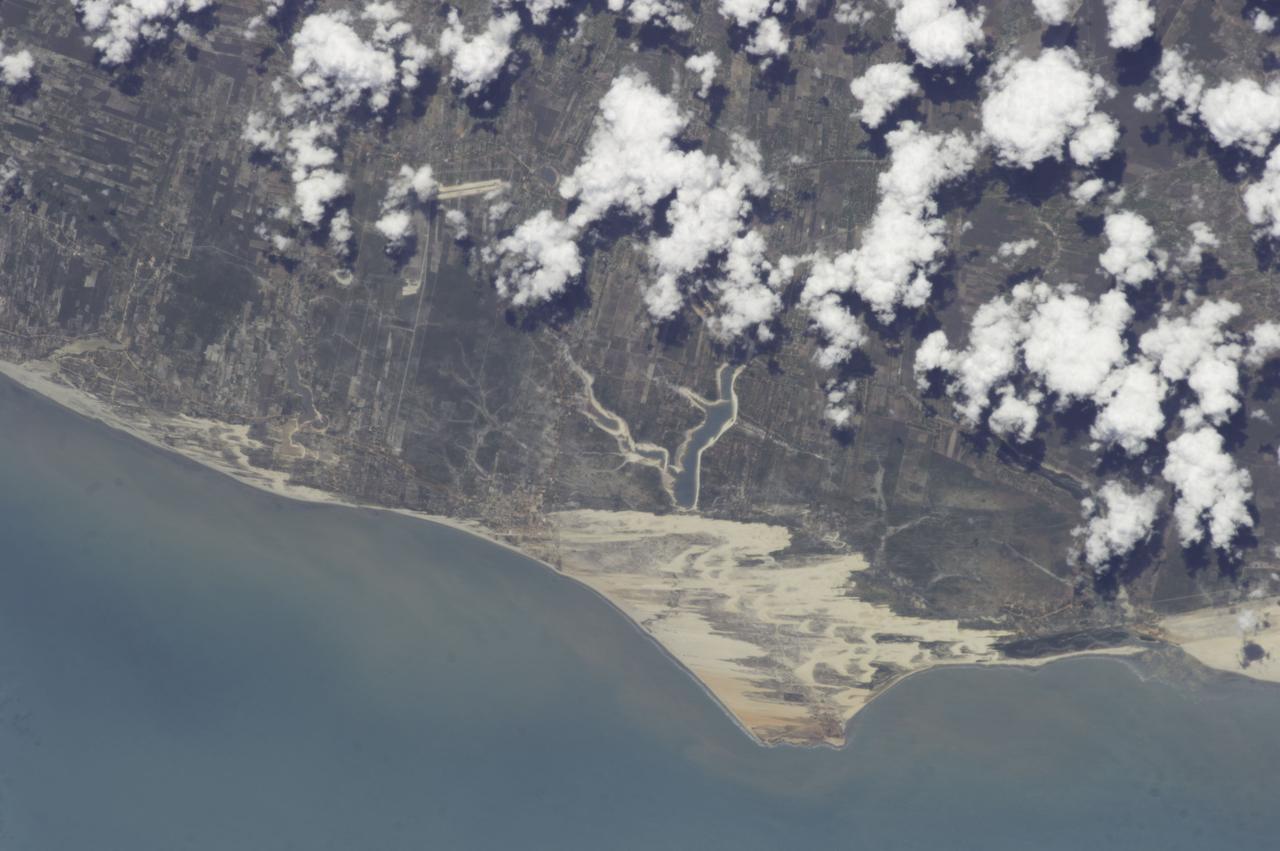

Earth observations taken by Expedition 38 crewmember. Crewmember indicates South America. Image was released by astronaut on Twitter.
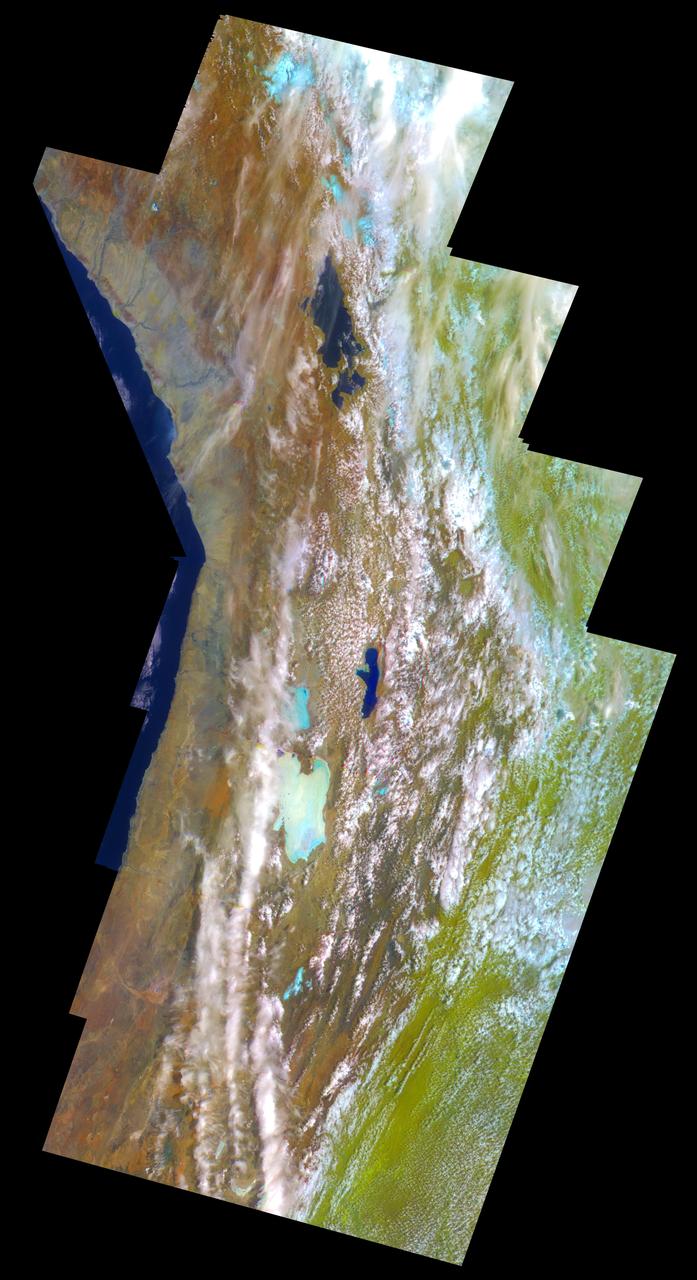
This false-color mosaic of the central part of the Andes mountains of South America 70 degrees w. longitude, 19 degrees s. latitude is made up of 42 images acquired by NASA’s Galileo spacecraft from an altitude of about 25,000 kilometers 15,000 miles. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00133
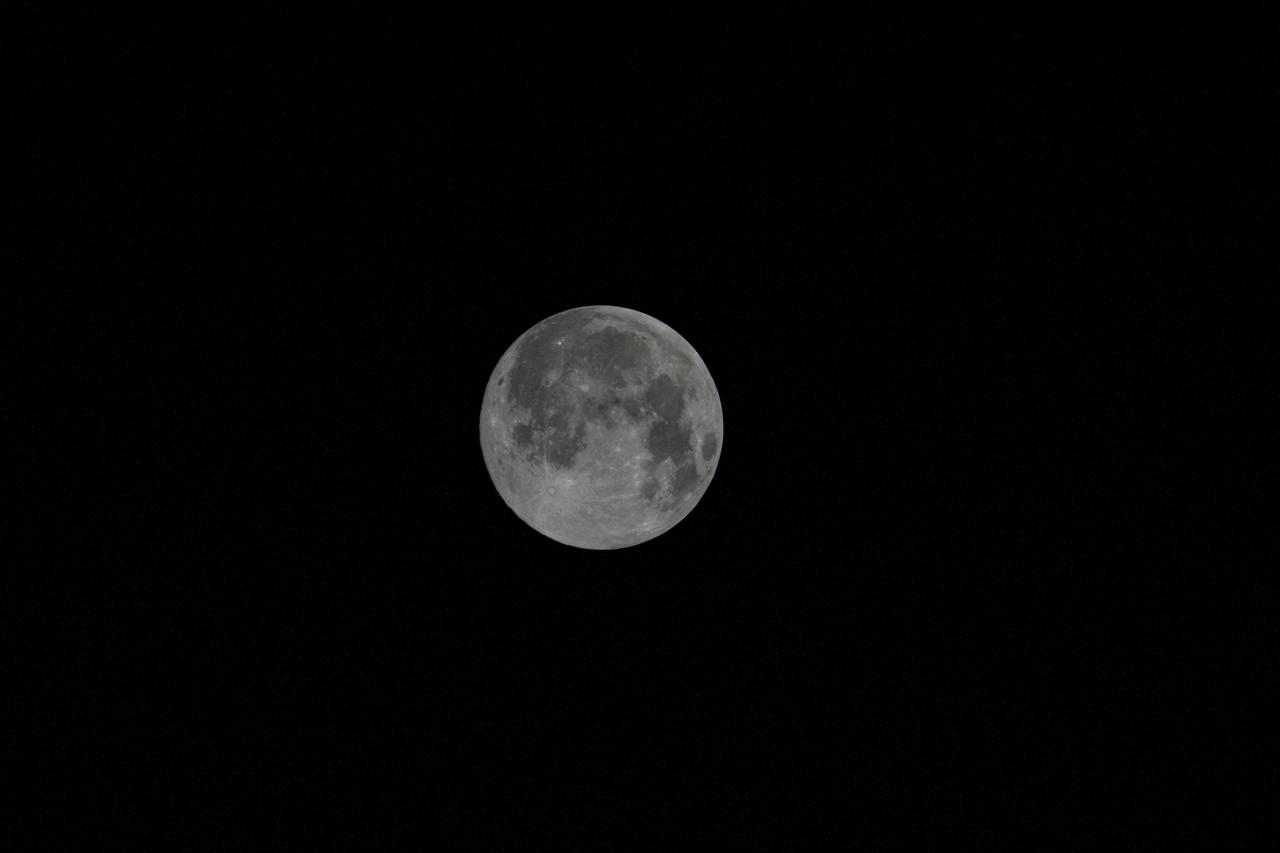

iss064e016494 (Dec. 29, 2020) --- The waxing gibbous Moon, the phase before it becomes a Full Moon, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 272 miles above the South Atlantic in between the tip of South America and the tip of South Africa.
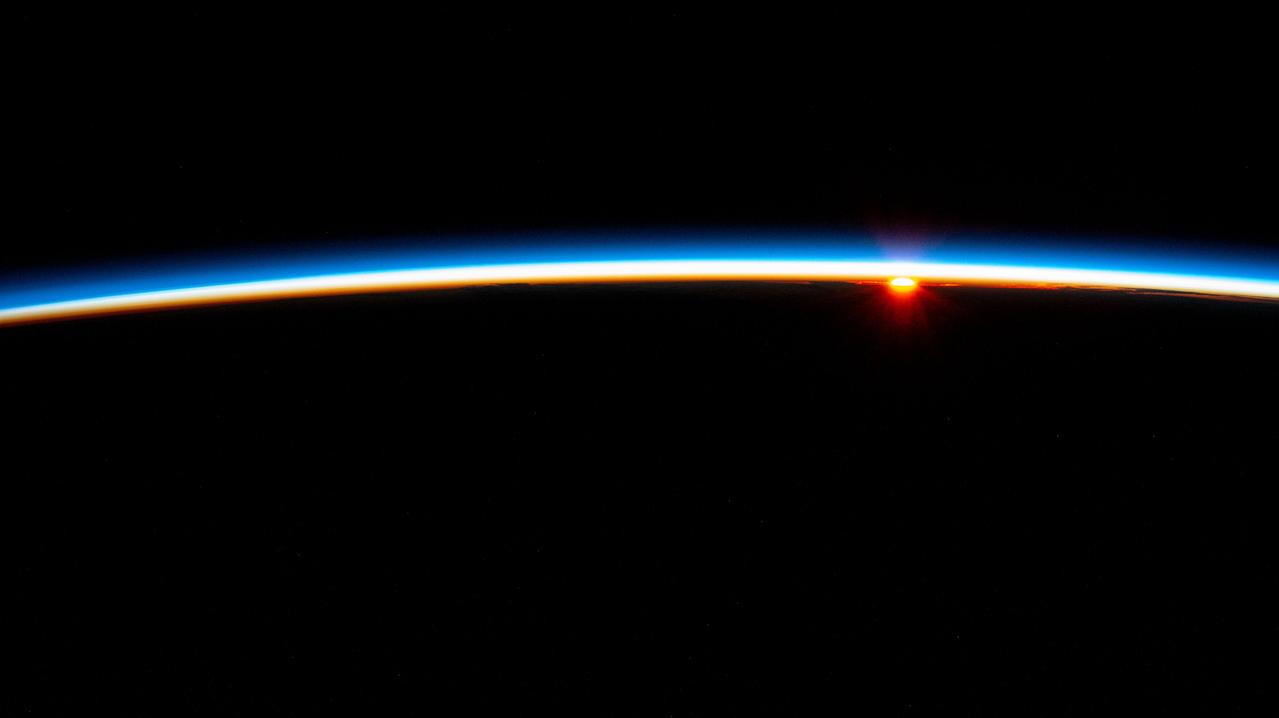

iss071e547275 (Aug. 22, 2024) --- The last rays of an orbital sunset fade below Earth's horizon illuminating the atmosphere in this photograph from the International Space Station as it soared 267 miles above the South Atlantic Ocean in between the tips of South America and South Africa.
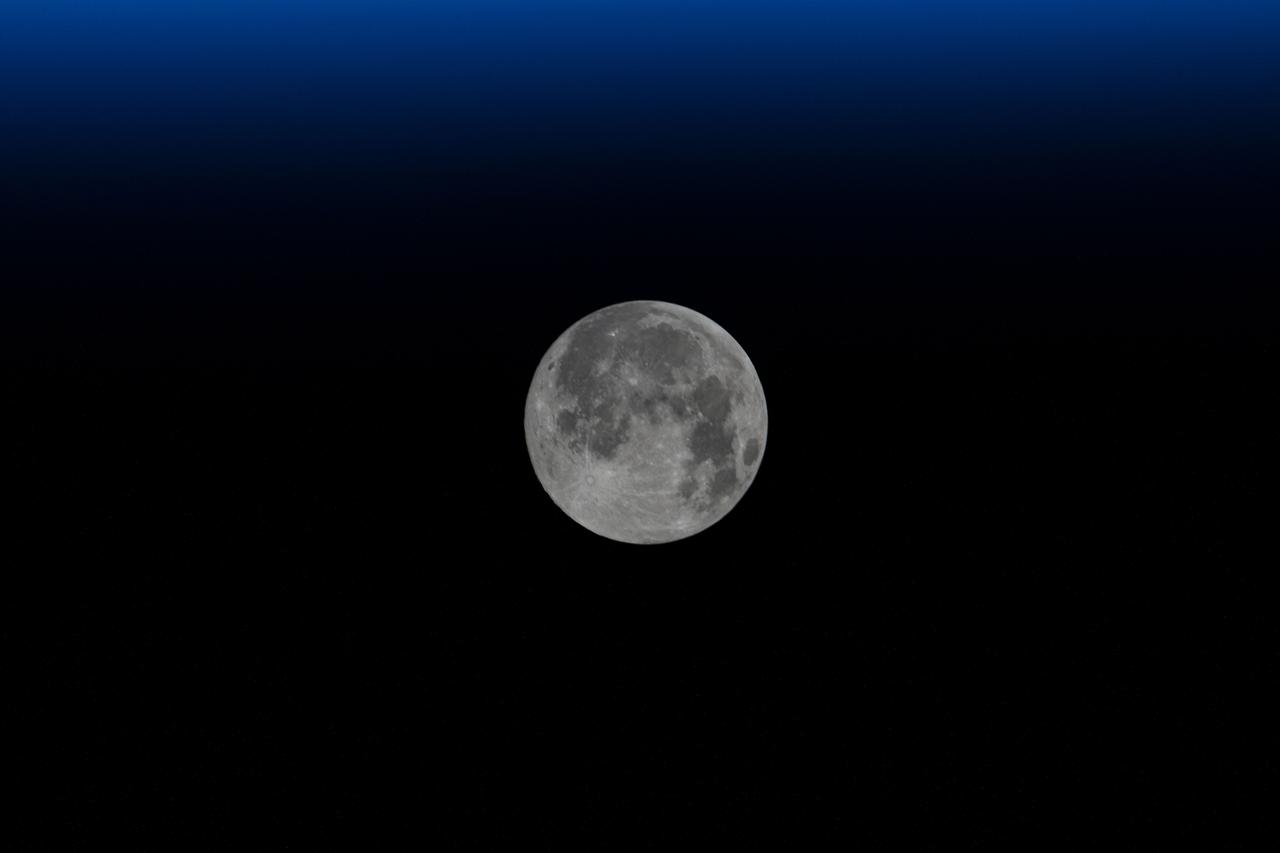

iss064e016473 (Dec. 29, 2020) --- The waxing gibbous Moon, the phase before it becomes a Full Moon, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 272 miles above the South Atlantic in between the tip of South America and the tip of South Africa.
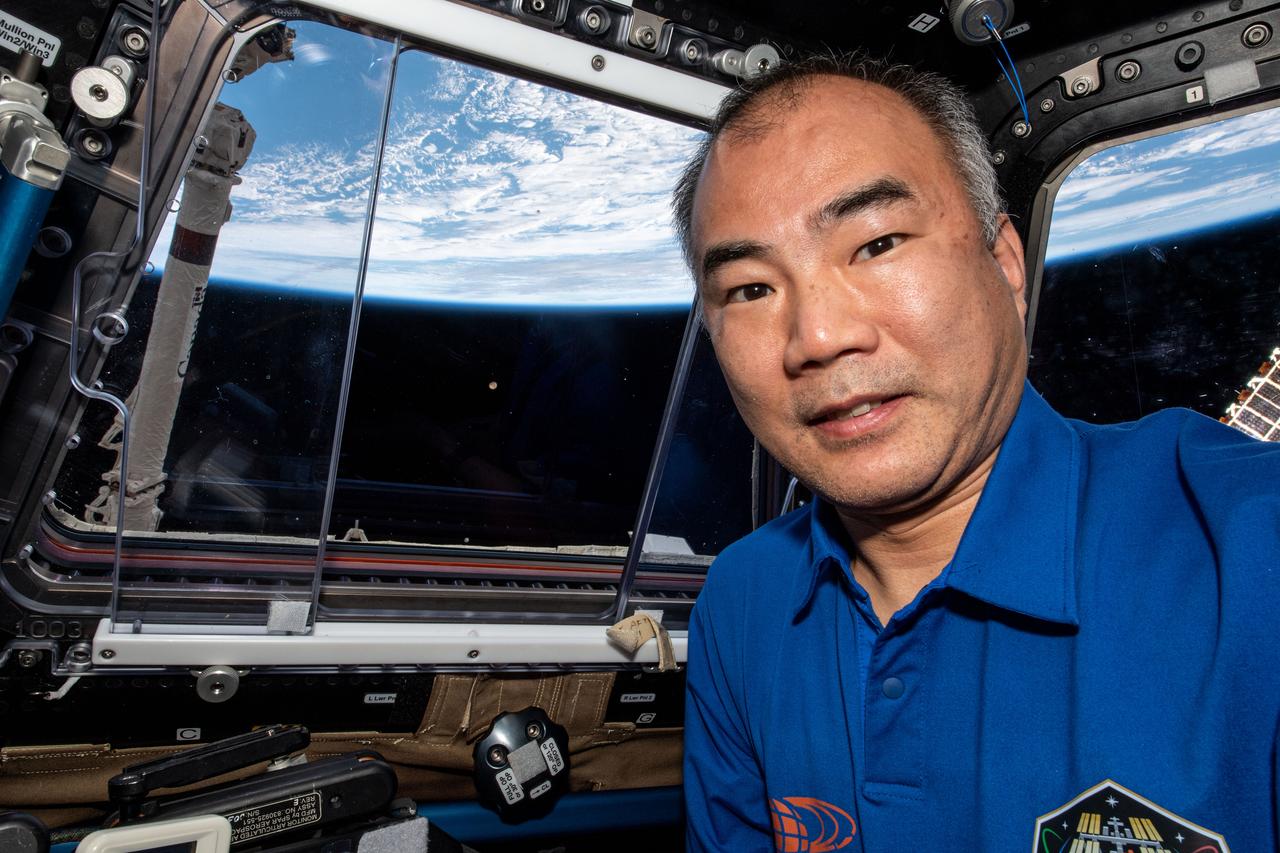
iss064e016183 (Dec. 27, 2020) --- JAXA astronaut Soichi Noguchi is pictured inside the International Space Station's "window to the world," the cupola, as it was orbiting 269 miles above the South Atlantic in between the tip of South America and the tip of South Africa.
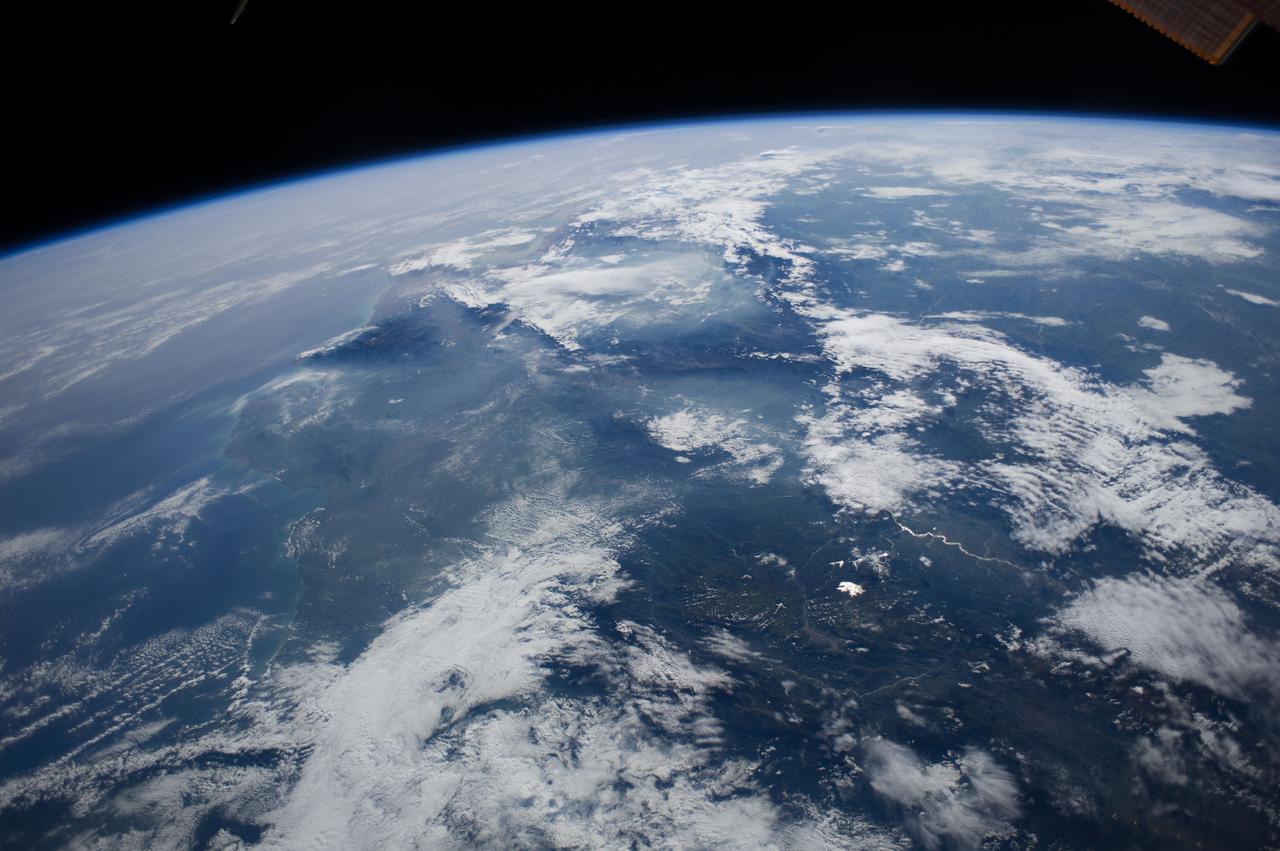

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: Panama and South America.
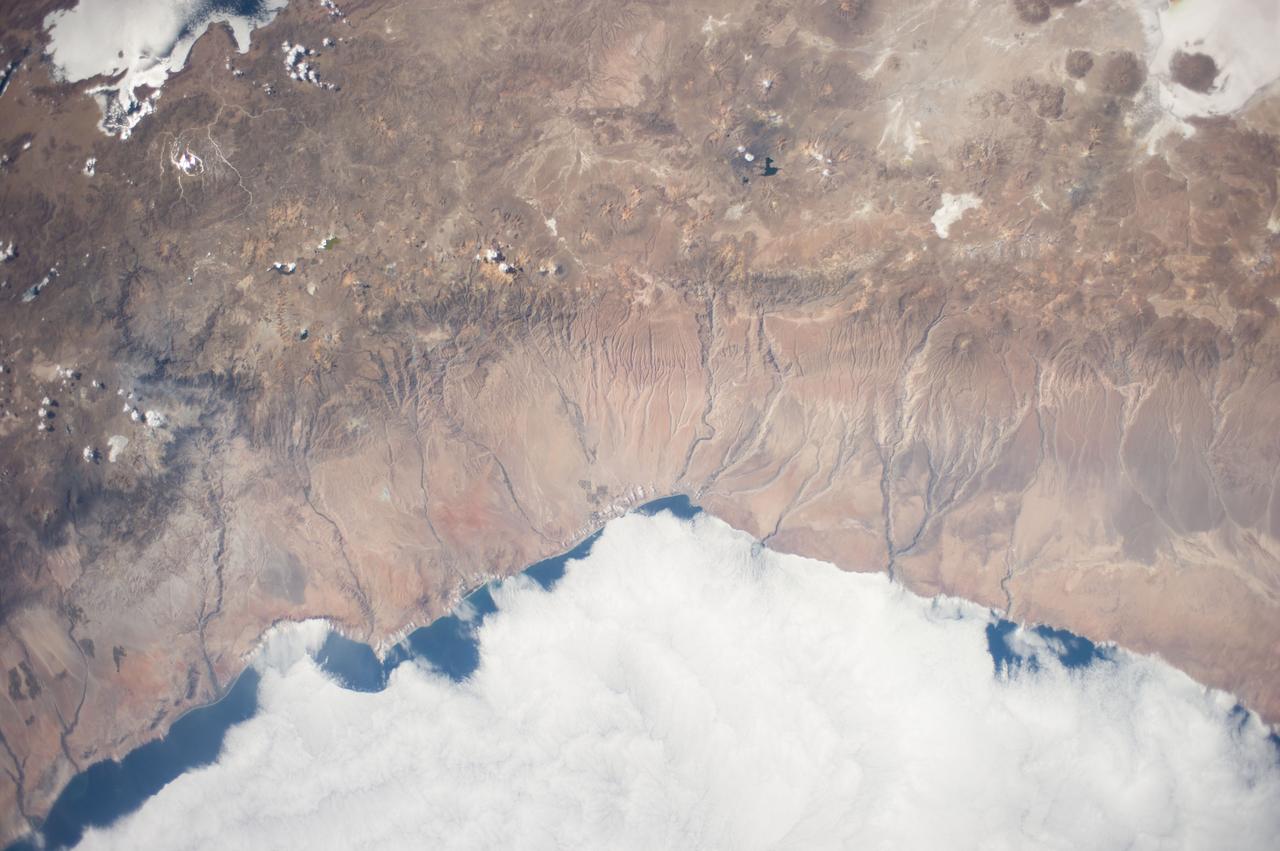

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: South America.
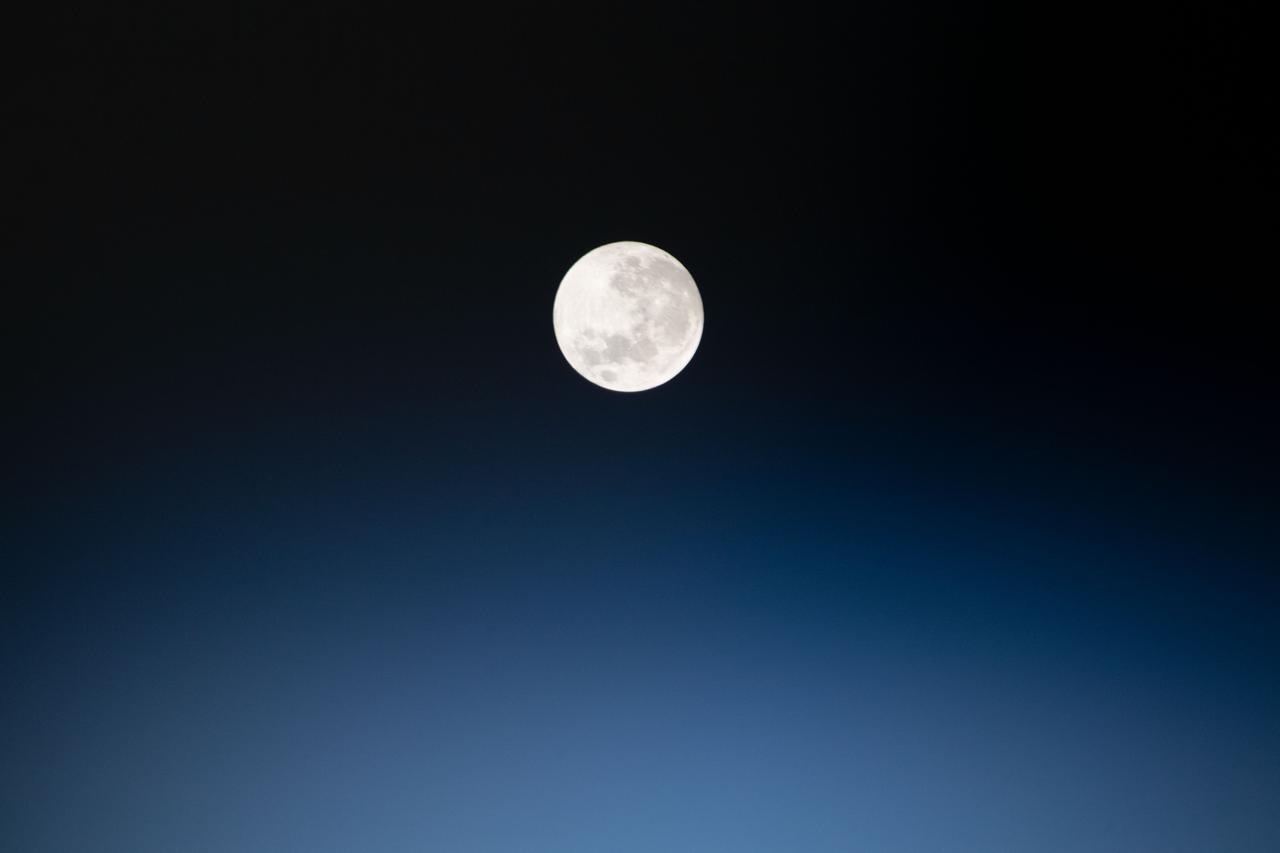

iss060e008815 (July 16, 2019) --- The full moon is pictured as the International Space Station orbited 257 miles above Peru in South America.
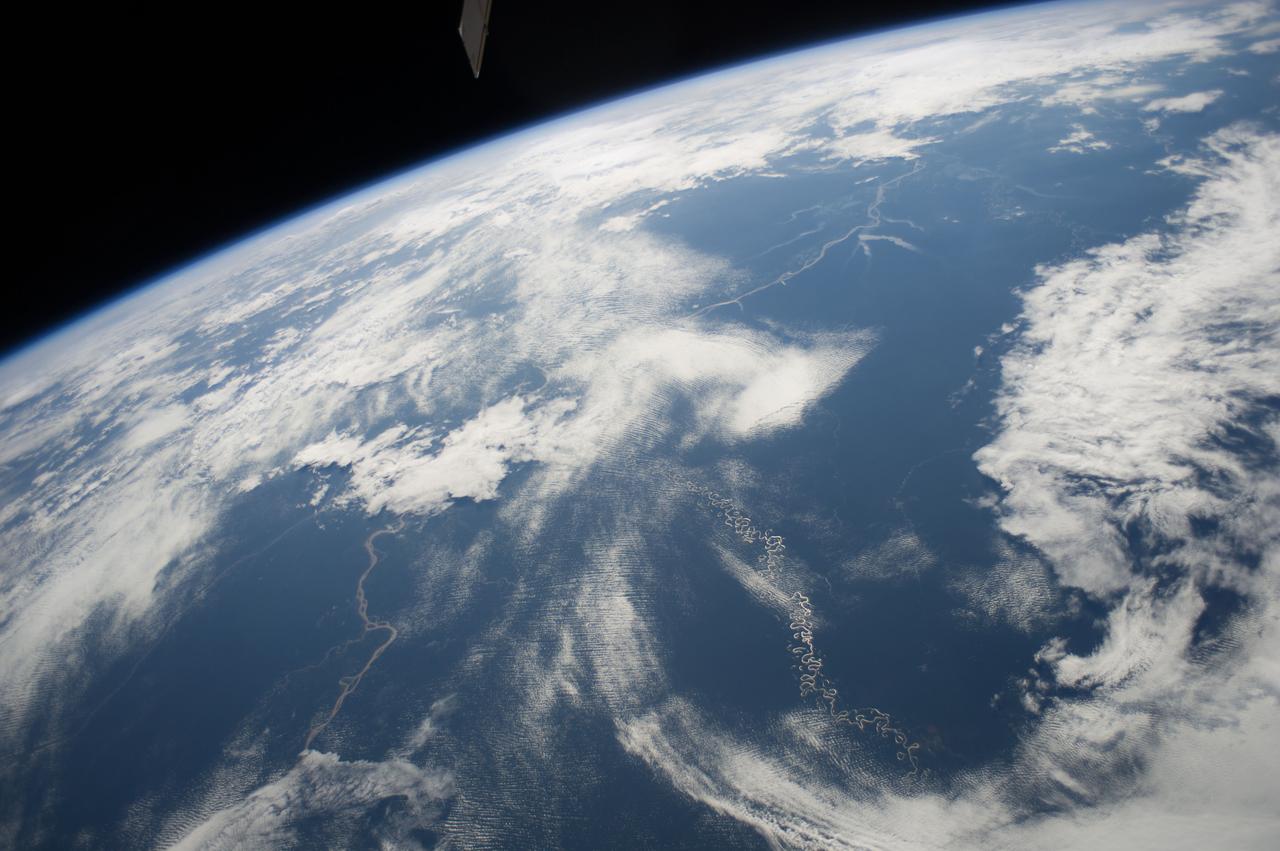

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: Panama and South America.
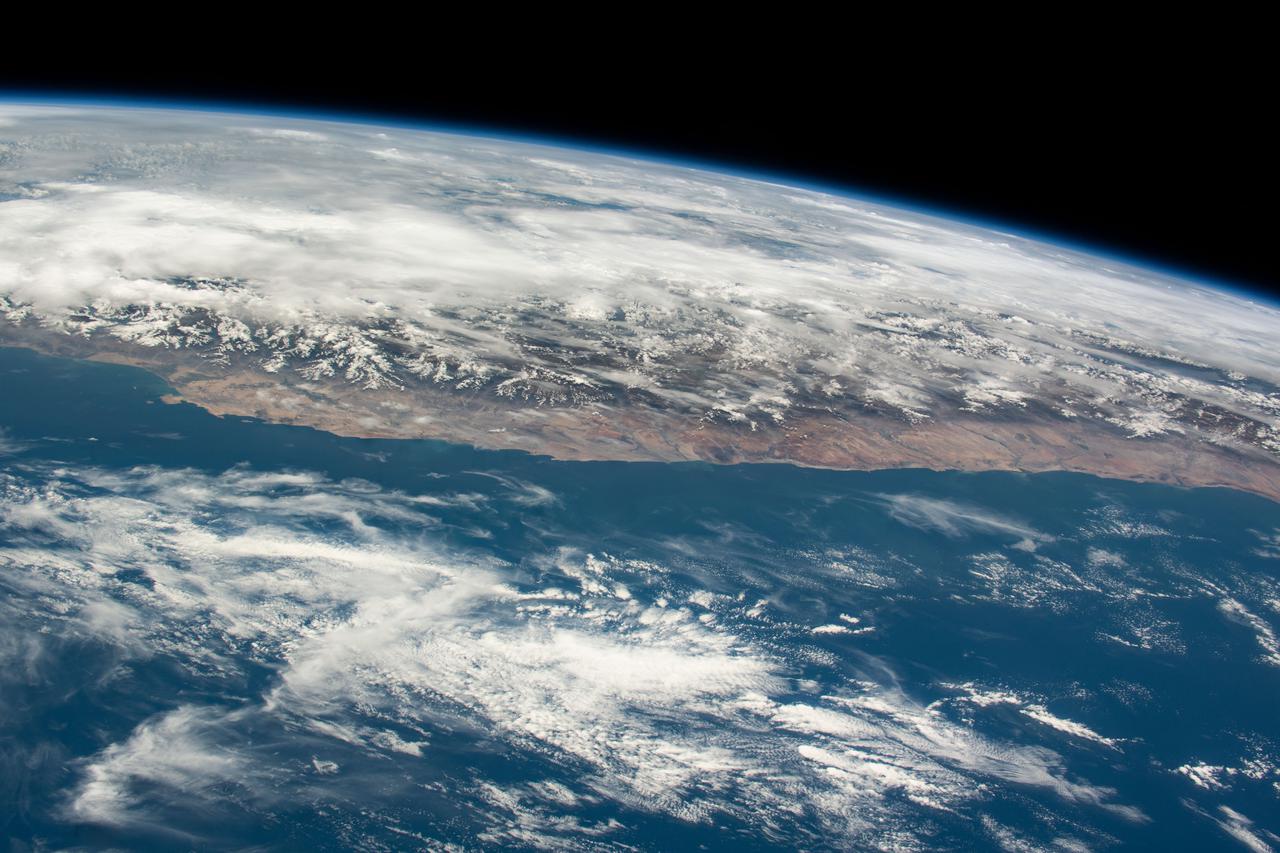

iss064e026455 (Jan. 26, 2021) --- The coast of Peru in South America is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean.

iss064e026467 (Jan. 26, 2021) --- The coast of Peru in South America is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean.
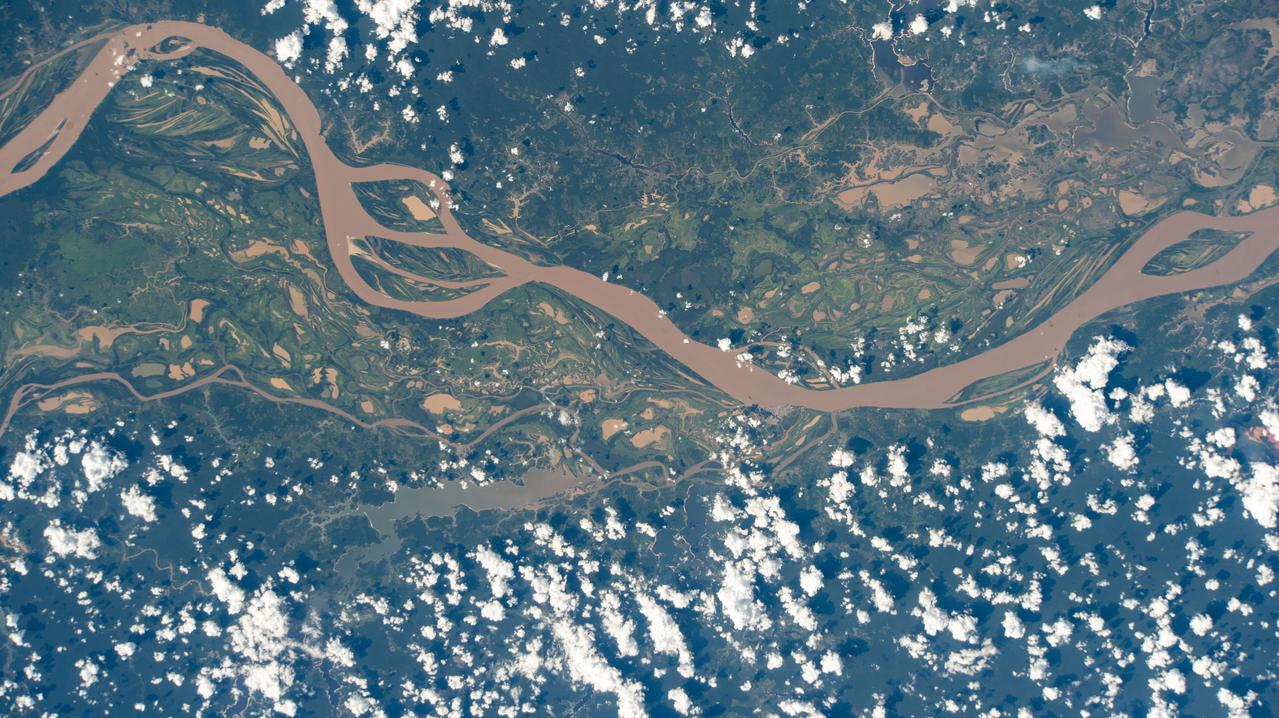

iss064e014990 (Dec. 23, 2020) --- The Amazon River is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above Brazil in South America.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which shares a boundary with the Kennedy Space Center, is winter home to hundreds of waterfowl such as these coots and pintail ducks. The smaller coot inhabits open ponds and marshes, wintering in saltwater bays and inlets. They range from southern Canada to northern South America. The pintail can be found in marshes, prairie ponds and tundra, and salt marshes in winter. They range from Alaska and Greenland south to Central America and the West Indies
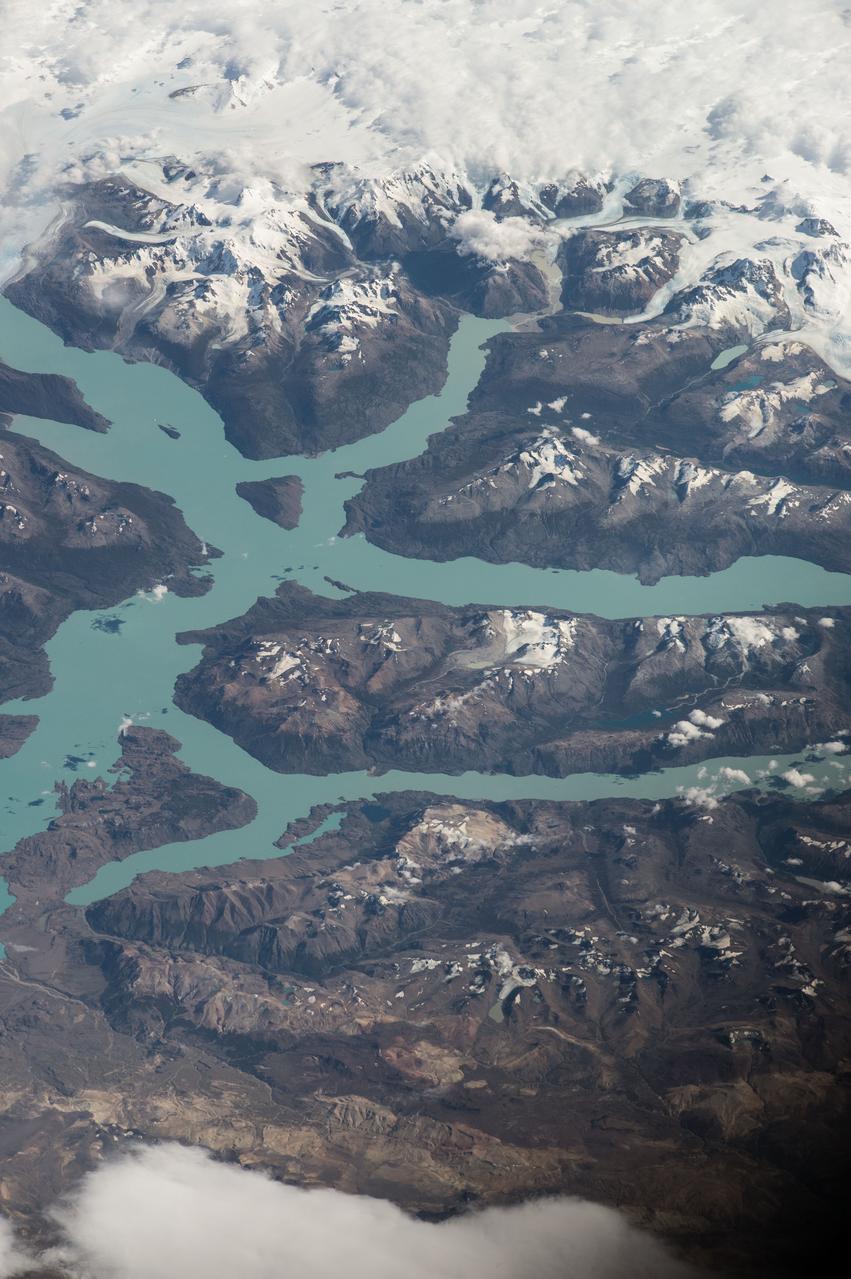

ISS047e014747 (03/22/2016) --- Crewmembers of the International Space Stations Expedition 47 captured this image of southern South America. Patagonia is a sparsely populated region located at the southern end of South America, shared by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes mountains as well as the deserts, steppes and grasslands east of this southern portion of the Andes. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia
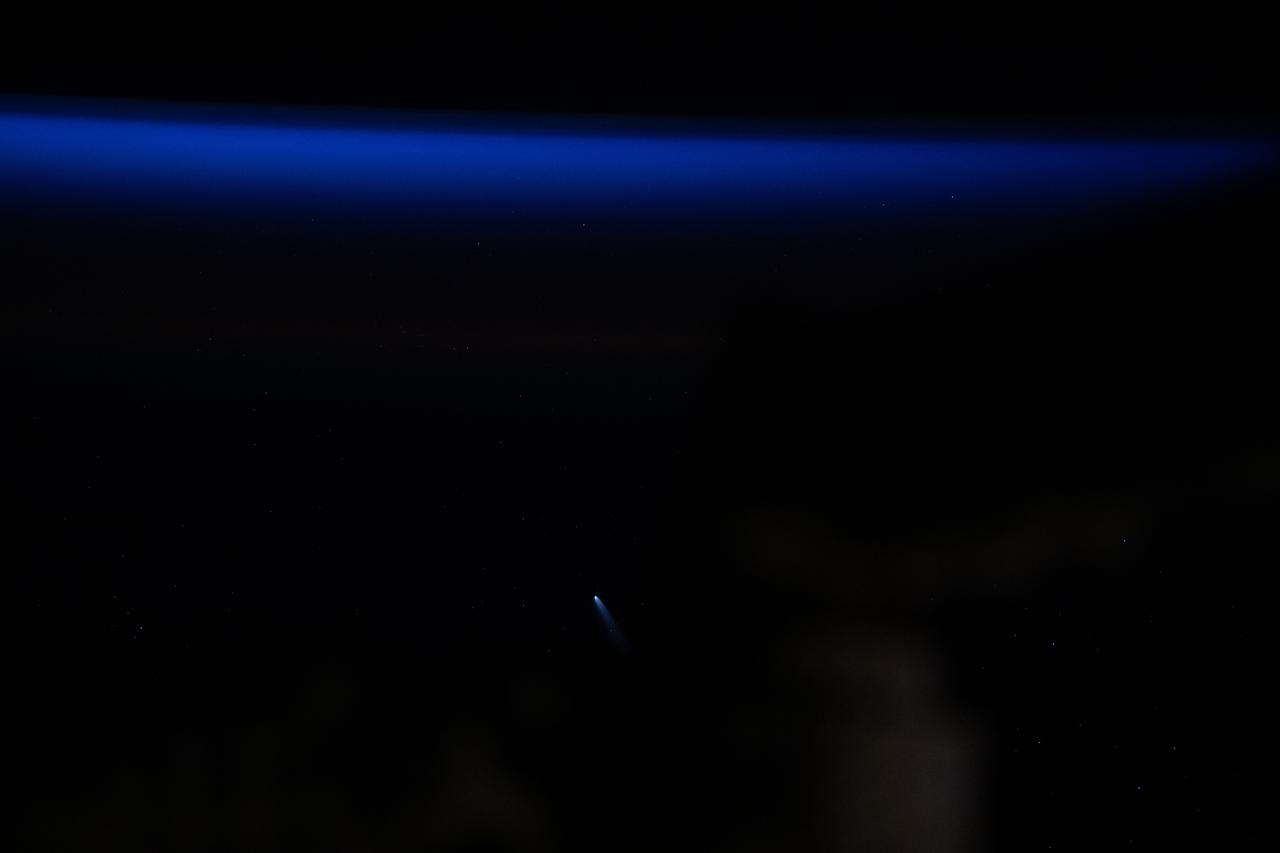

iss072e024551 (Sept. 25, 2024) --- Comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan-ATLAS) was about 44 million miles away from Earth in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 272 miles above the South Pacific Ocean west of the Patagonia region of South America just before sunrise.
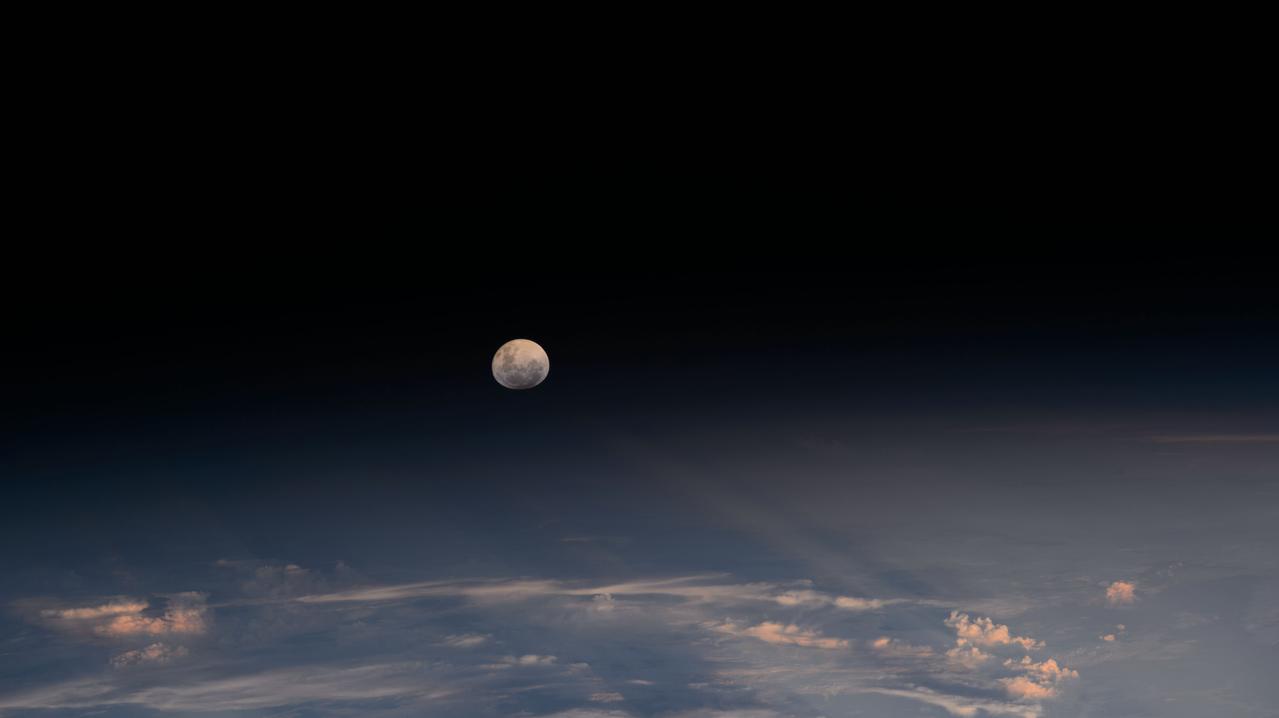

iss072e978997 (April 13, 2025) --- The Moon's light is refracted by the Earth's atmosphere giving it a spheroid shape in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited into a sunset 264 miles above the border between Bolivia and Brazil in South America.

iss063e033229 (June 28, 2020) --- The International Space Station, with the Progress 74 cargo craft in the foreground, is about to orbit over the Pacific coast of South America near the northern tip of Chile.
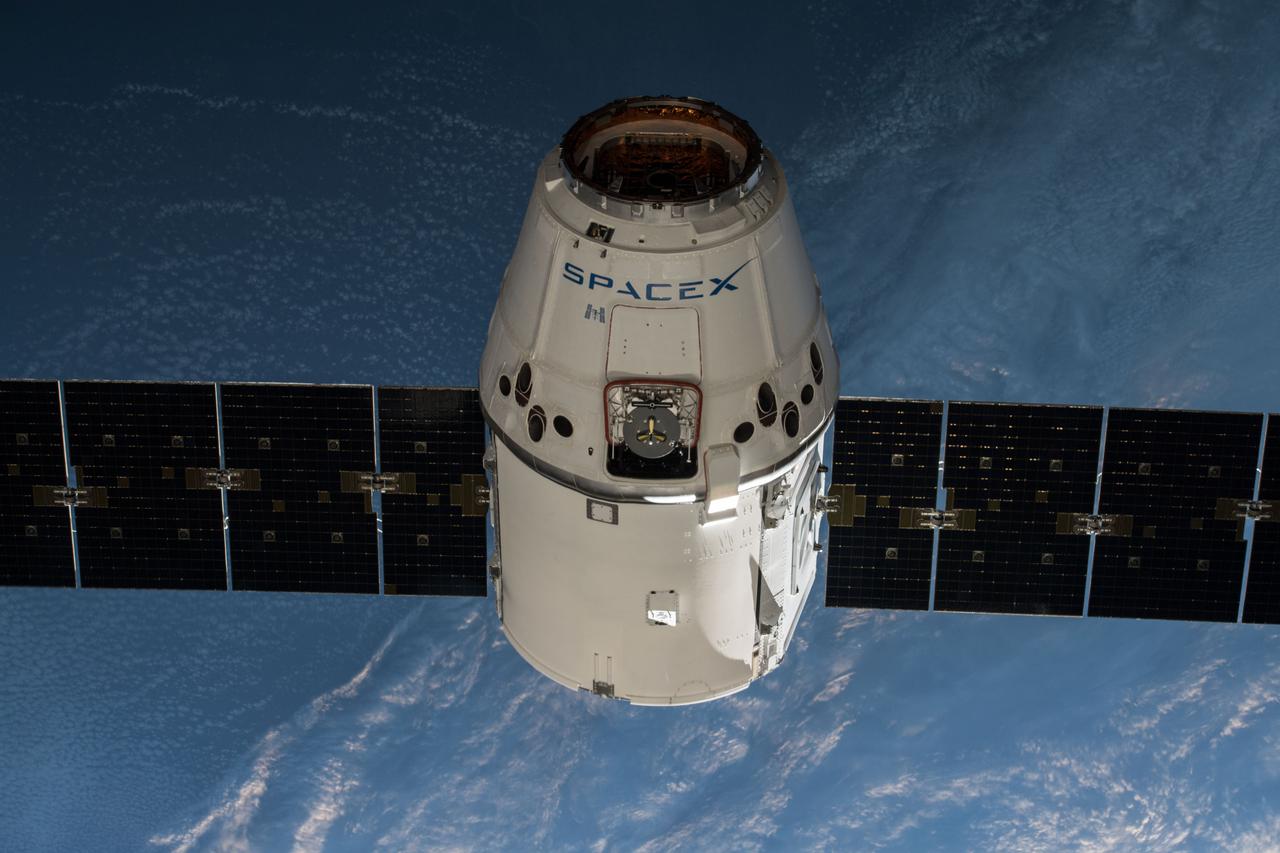

iss055e009903 (April 4, 2018) --- The SpaceX Dragon resupply ship slowly approaches the International Space Station as the two spacecraft orbits off the southern tip of South America.
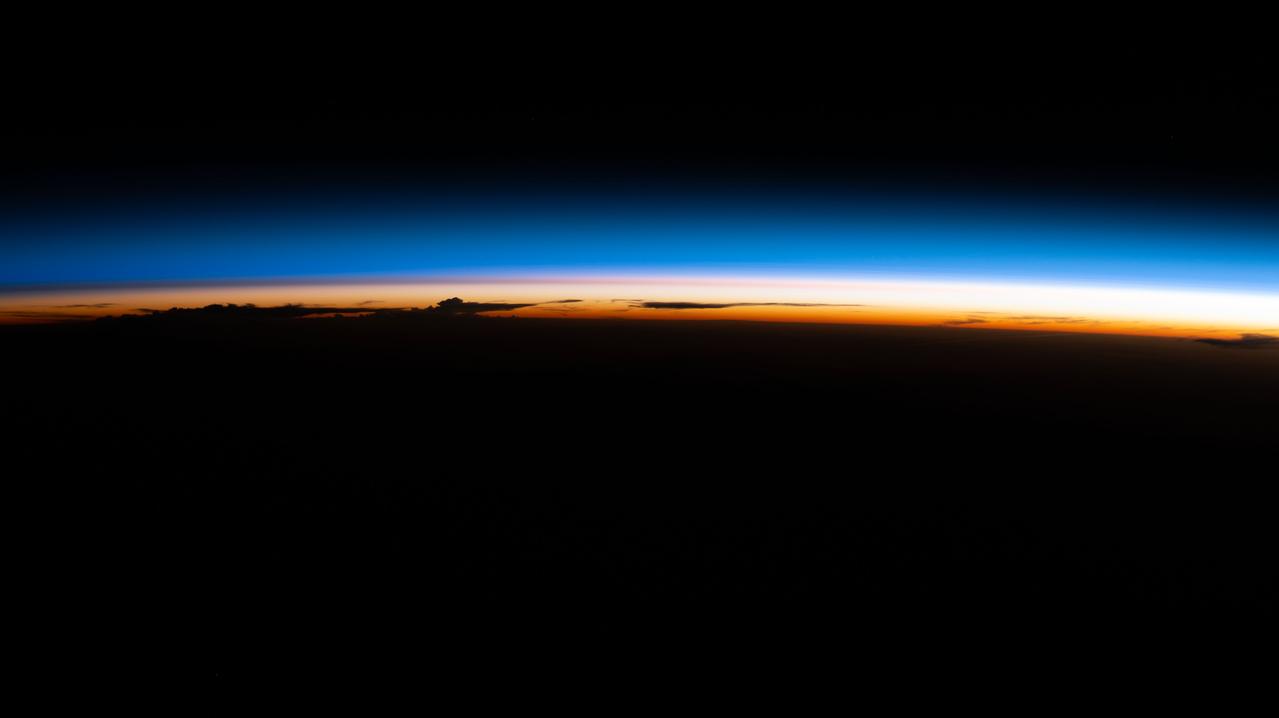

iss067e265876 (Aug. 13, 2022) --- An orbital sunrise illuminate's Earth's atmosphere silhouetting clouds as the International Space Station soared 264 miles above the Paraguay-Brazil border in South America.
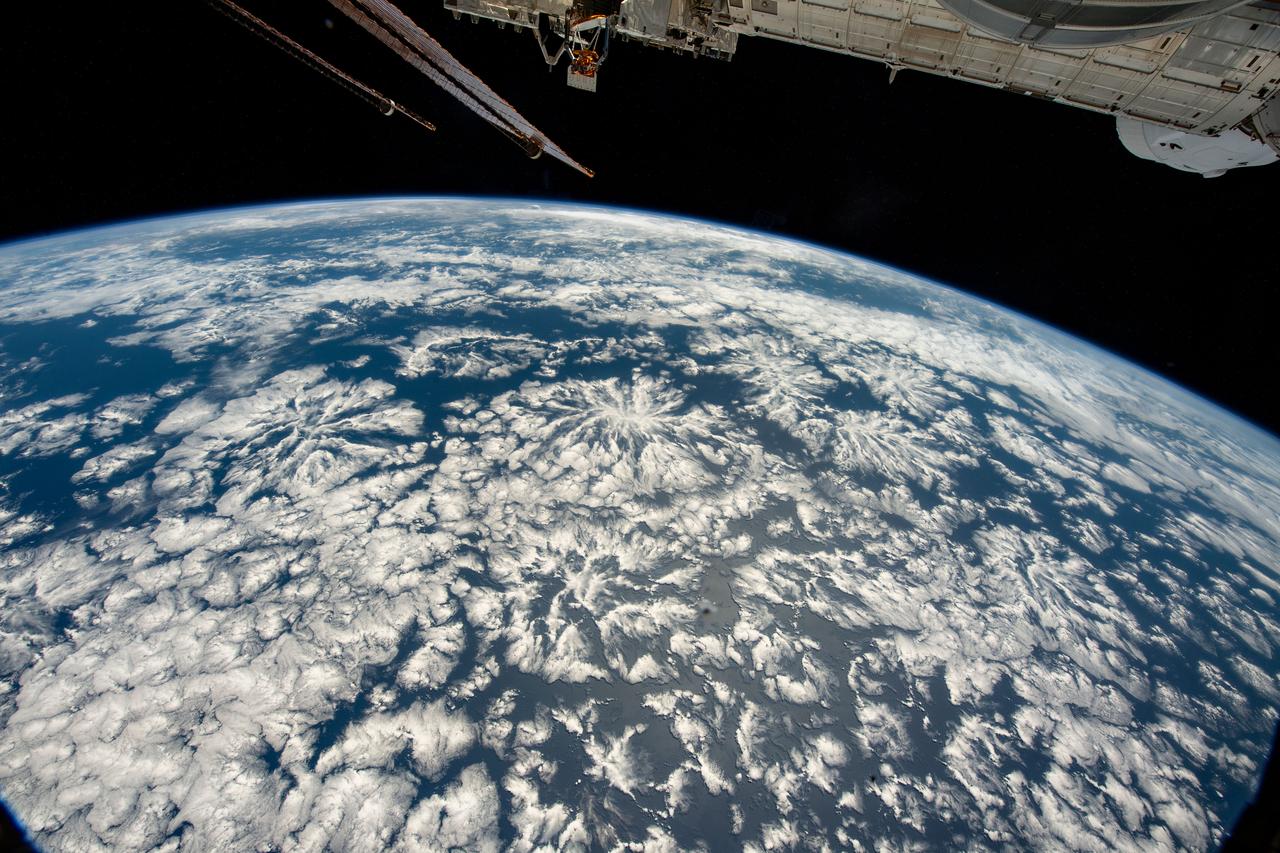

iss067e220400 (July 31, 2022) --- A partly cloudy Pacific Ocean is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above off the coast of Peru in South America.

iss070e000820 (Sept. 30, 2023) --- The waning gibbous Moon is pictured above Earth from the International Space Station as it soared into an orbital nighttime 260 miles above the Atlantic Ocean near the northeast coast of South America.

NASA CTO Douglas Terrier is interviewed by NBC's Tom Costello during an Eclipse Across America broadcast aboard the USS Yorktown in Charleston, South Carolina on Aug. 21, 2017.
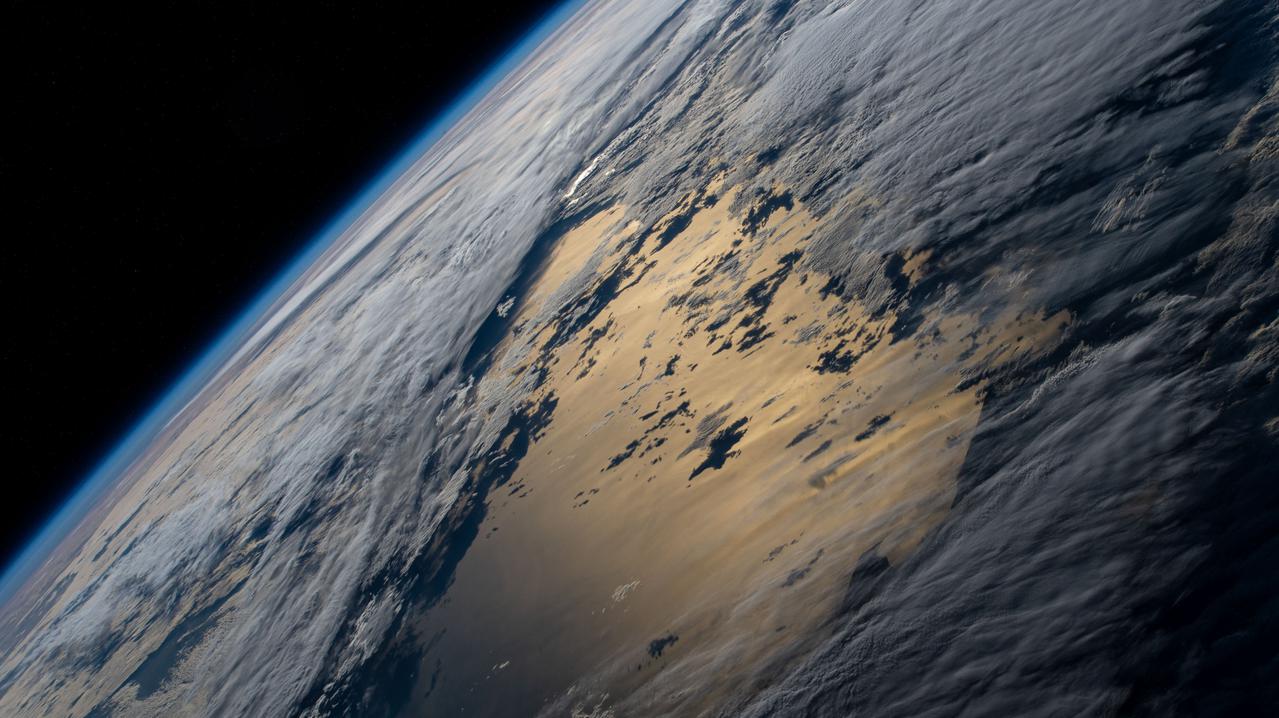

iss064e029010 (Feb. 4, 2021) --- This view of the Earth's horizon looks across a cloudy Pacific Ocean as the International Space Station orbited 271 miles above off the coast of southern Chile in South America.
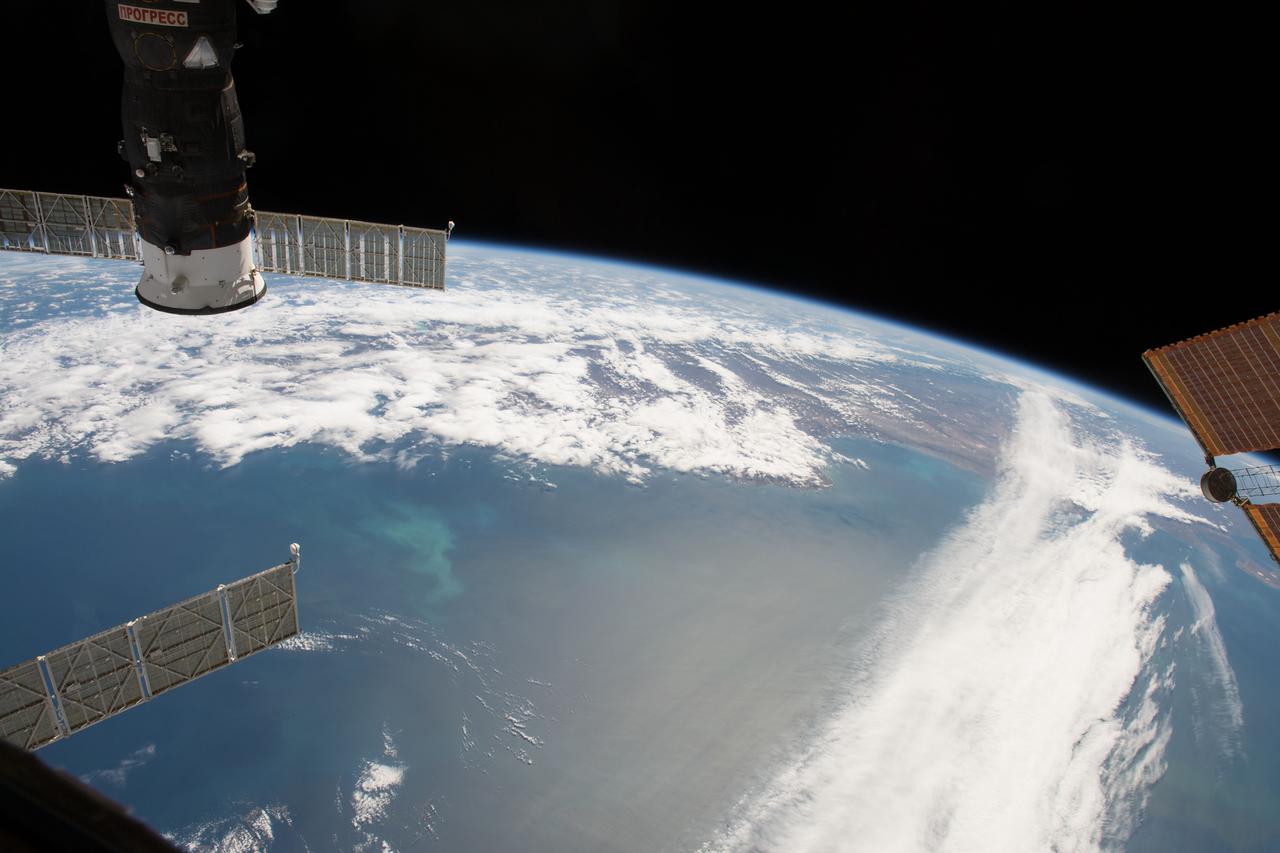

iss054e022072 (Jan. 12, 2018) --- The International Space Station orbits above the Falkland Islands off the coast of the southern-most portion of Argentina on the continent of South America. In the upper-right of the photograph is the docked Progress 68 cargo craft.
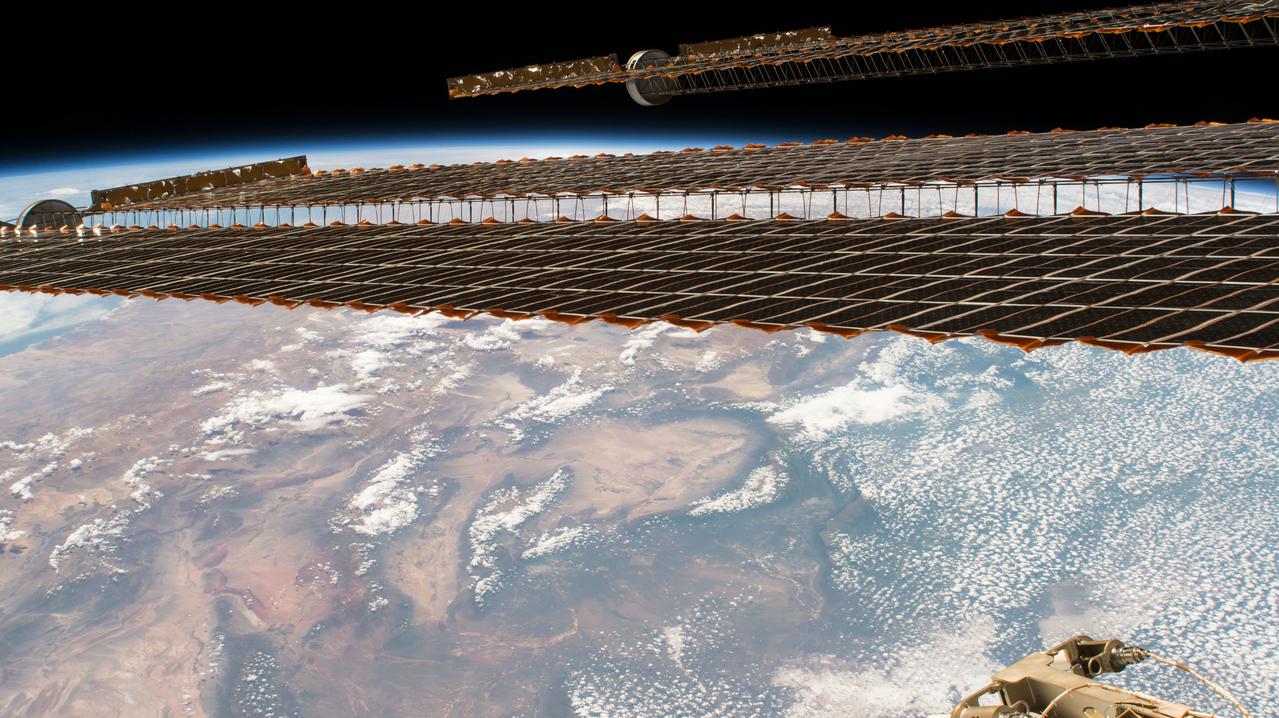

iss050e030665 (01/12/2017) --- The international Space Station (ISS) passes over South America showing Argentina, and the Southern Andes. This angled image of the ISS Solar Arrays frames the Earth scene taken by astronauts of Expedition 50.
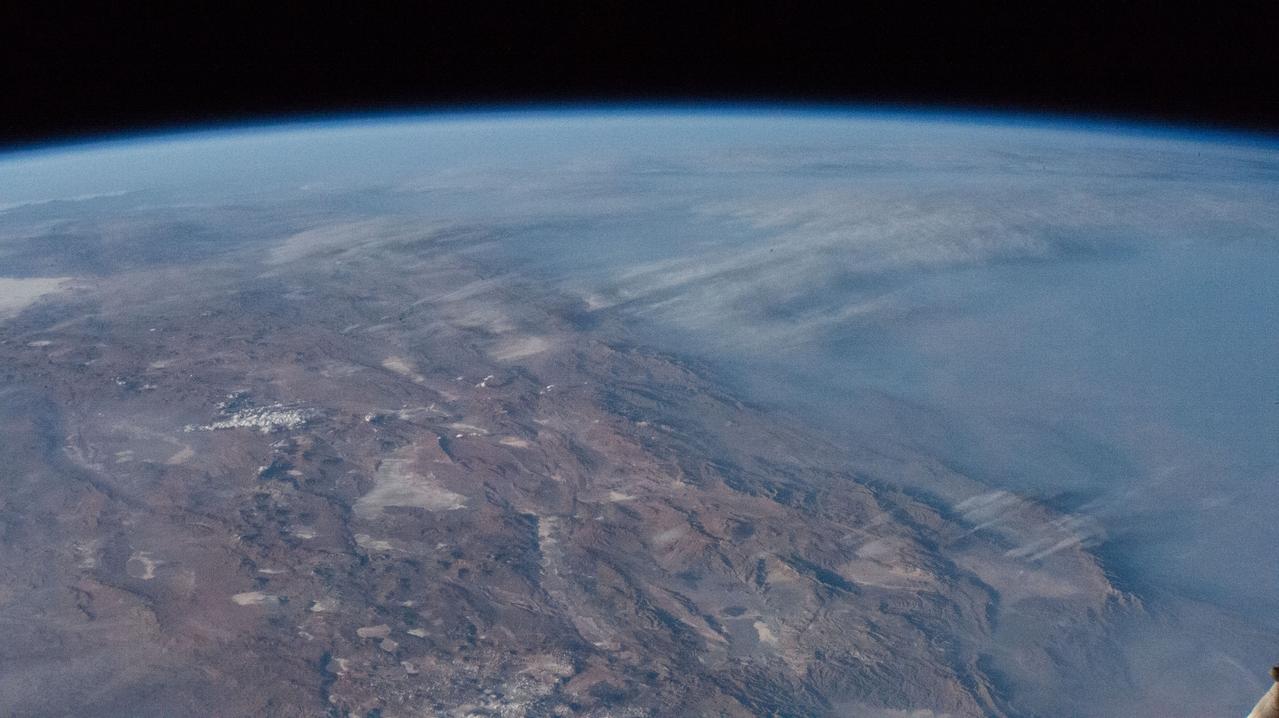

iss067e355983 (Sept. 11, 2022) --- The Andes Mountain range is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above the coast of central Chile in South America.
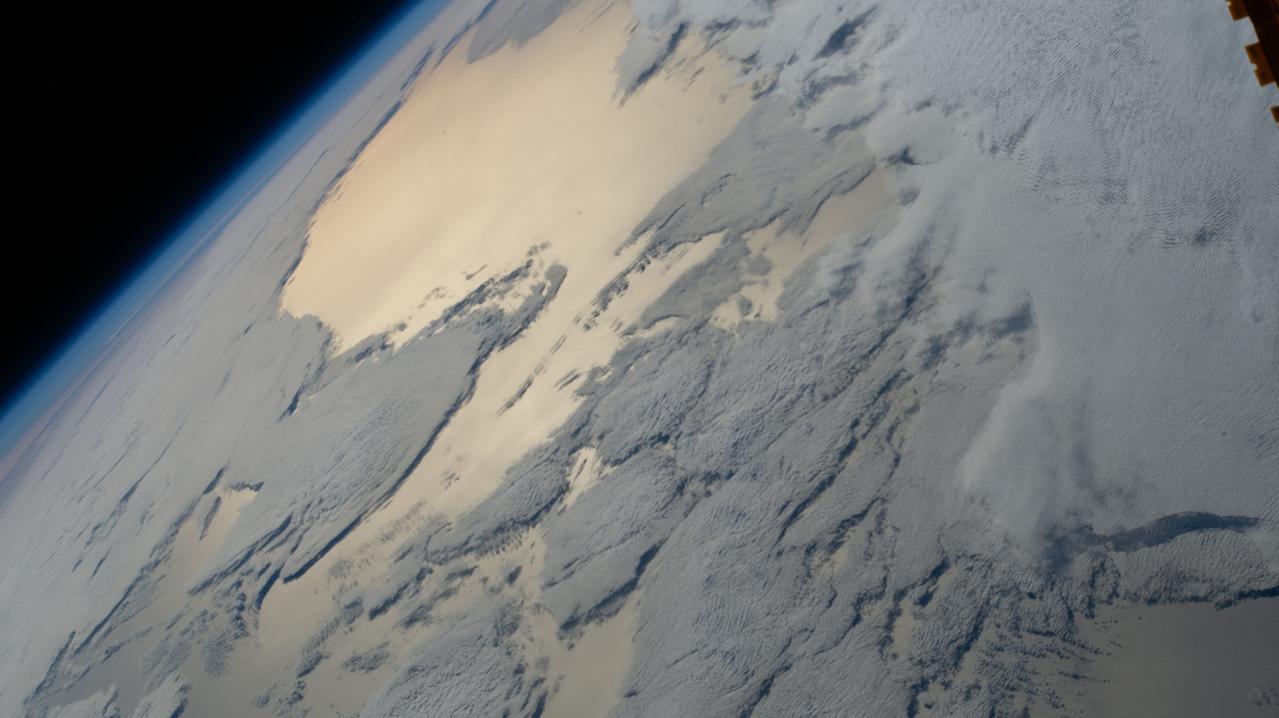

iss064e029006 (Feb. 4, 2021) --- This view of the Earth's horizon looks across a cloudy Atlantic Ocean as the International Space Station orbited 271 miles above off the coast of southern Argentina in South America.
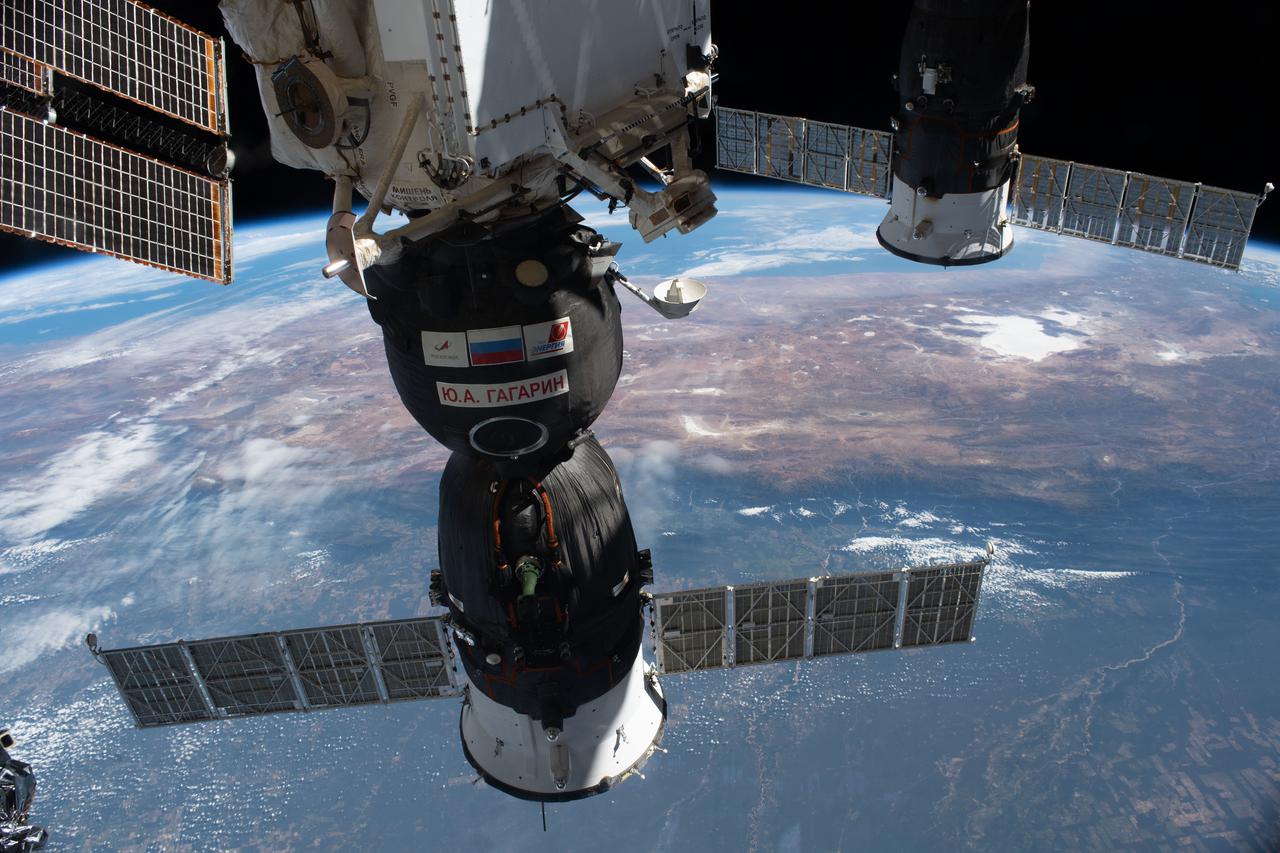

iss065e056881 (May 3, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship (foreground) and the ISS Progress 77 cargo craft are pictured docked to the International Space Station as it orbited 265 miles above South America.

NASA CTO Douglas Terrier talks with the "Today Show's" Al Roker about NASA's science research during an Eclipse Across America broadcast aboard the USS Yorktown in Charleston, South Carolina on Aug. 21, 2017.
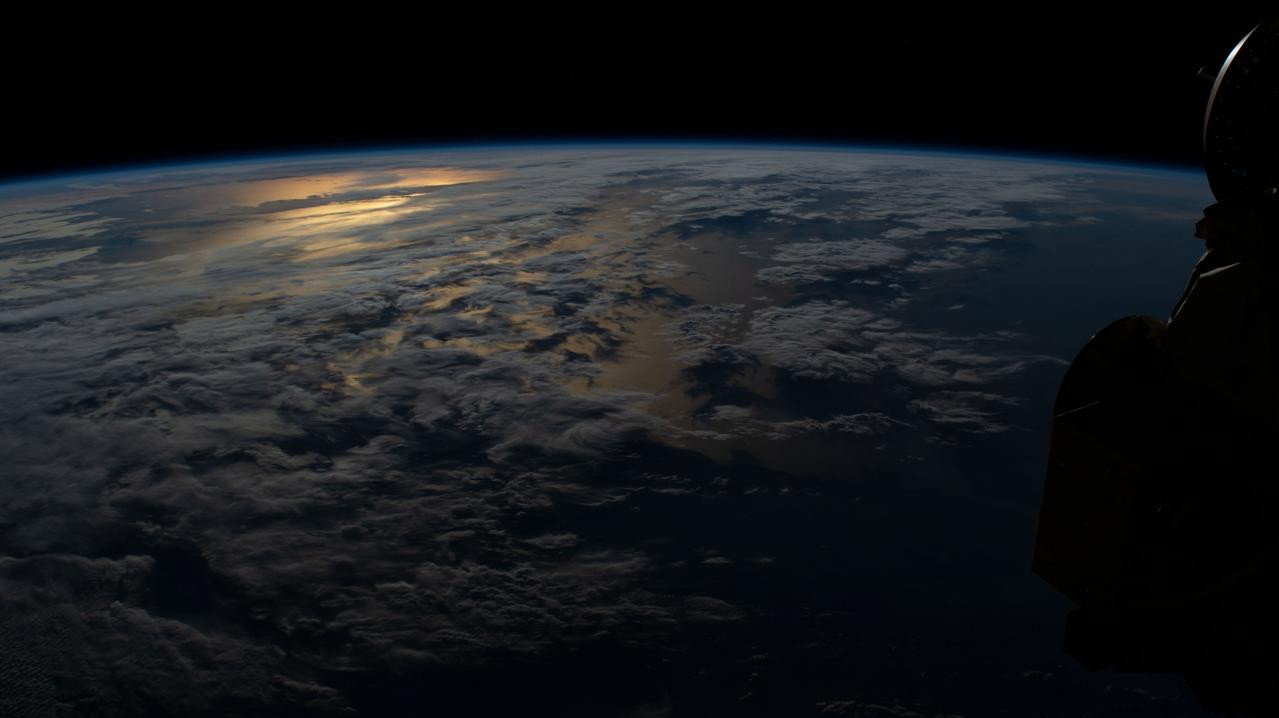

iss061e036737 (Nov. 9, 2019) --- The International Space Station orbits 264 miles above Argentina on its northeast track across South America as this photograph looks across the Atlantic Ocean during an orbital sunset.
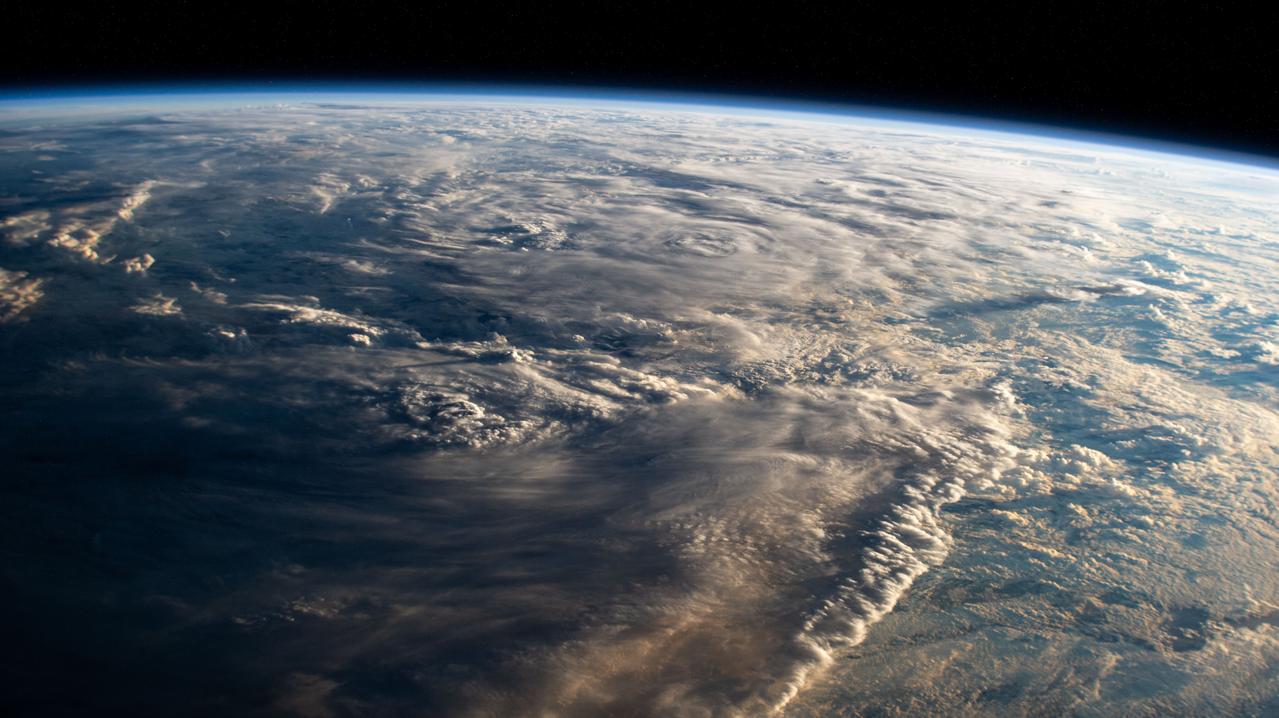

iss071e6649782 (Sept. 12, 2024) --- A tropical depression in the Atlantic Ocean in between Africa and South America is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above.
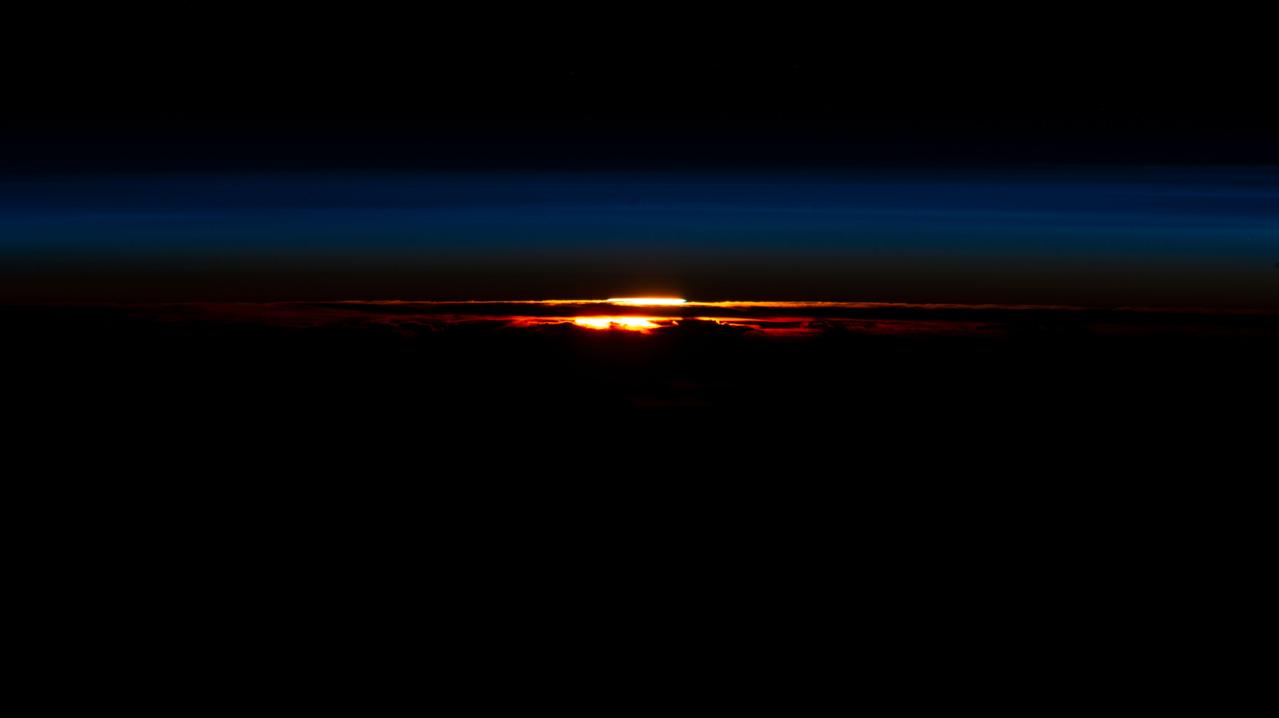

iss069e025337 (June 24, 2023) --- The last rays of an orbital sunset begin fading in Earth's atmosphere silhouetting the cloud tops in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 271 miles above the southernmost tip of South America.
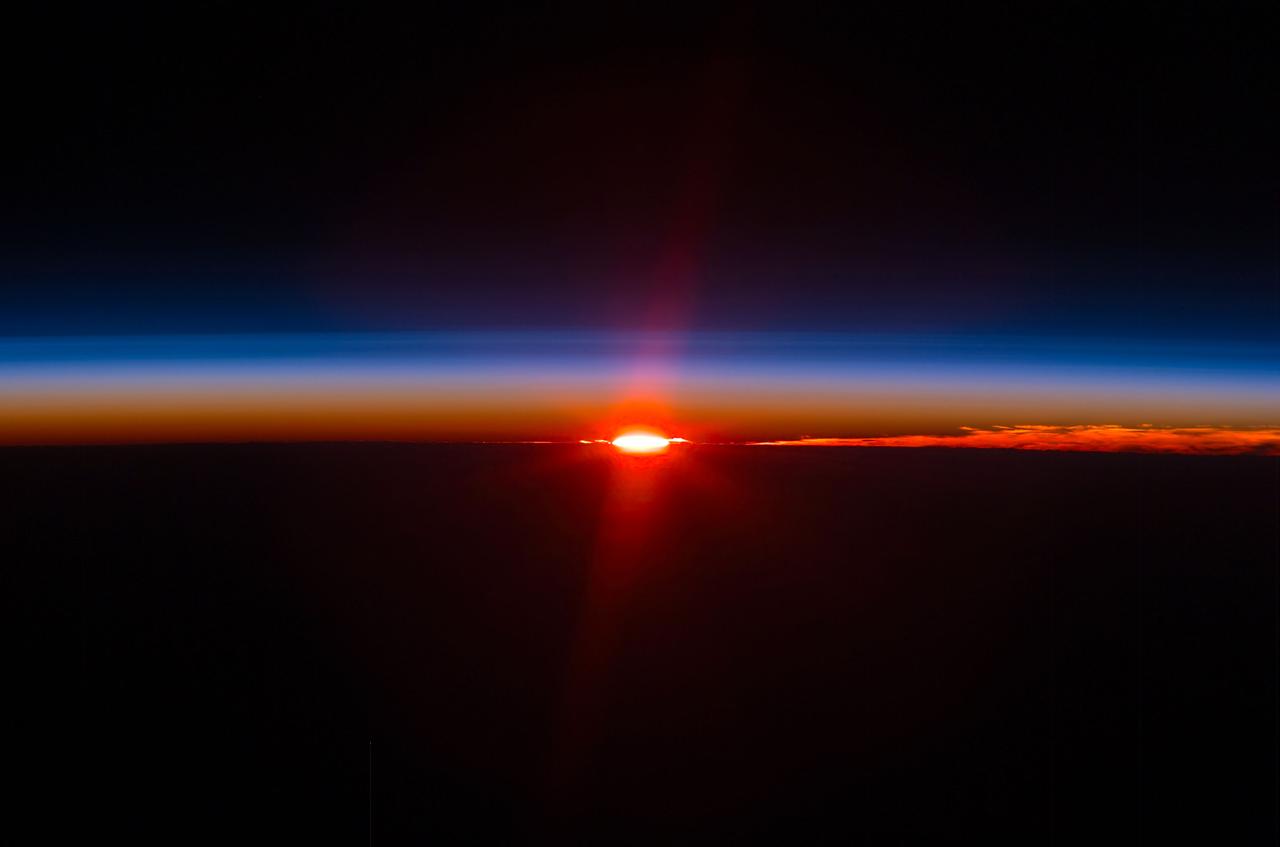

ISS017-E-005452 (26 April 2008) --- Layers of Earth's atmosphere, brightly colored as the sun sets over South America, are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station.