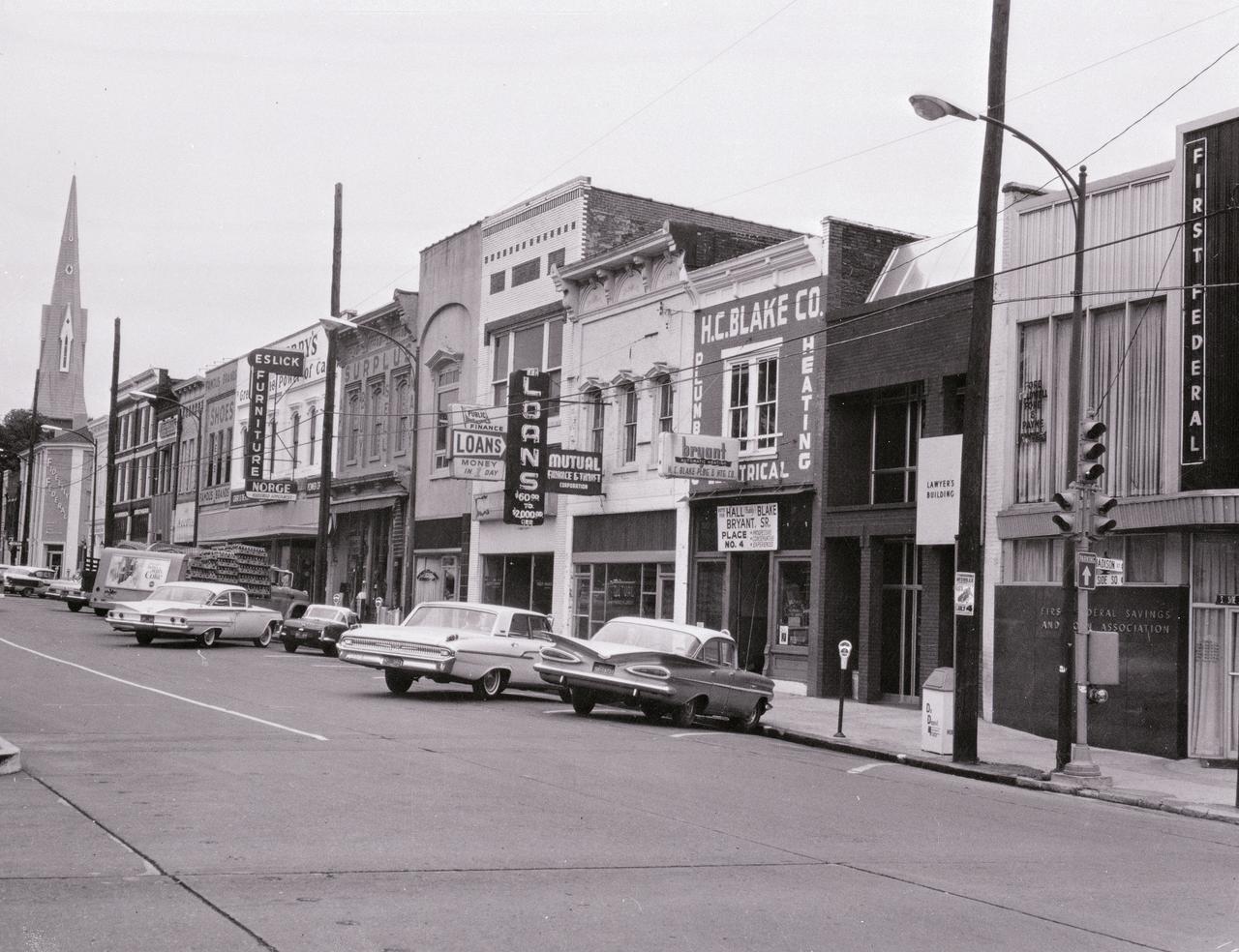

This historical photo of the South side of Square in downtown Huntsville, Alabama was taken in 1965. (Courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)
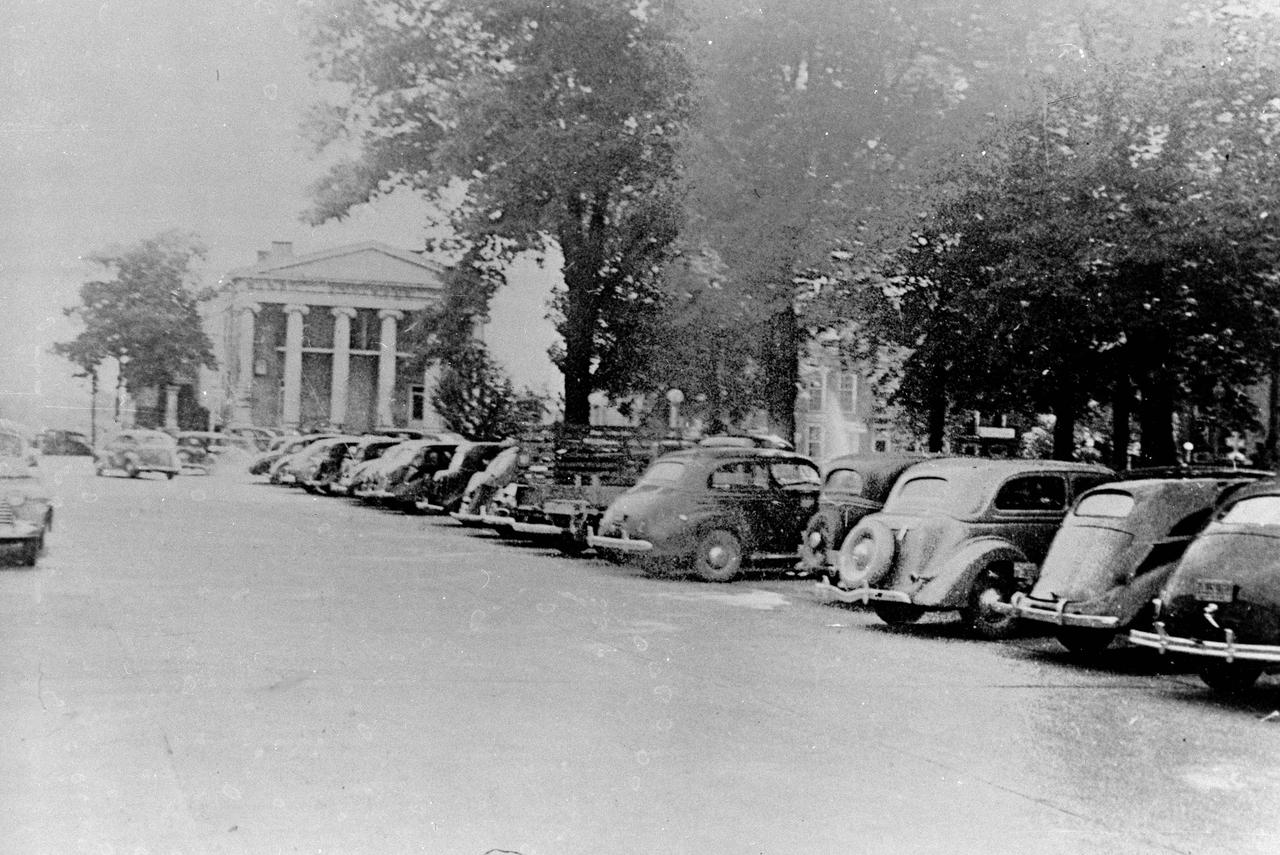

This 1940s photo of the South side of Square in downtown Huntsville, Alabama, looking west, shows a historical bank in the background with cars parked just South of the Courthouse (not shown in photo). (Courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)
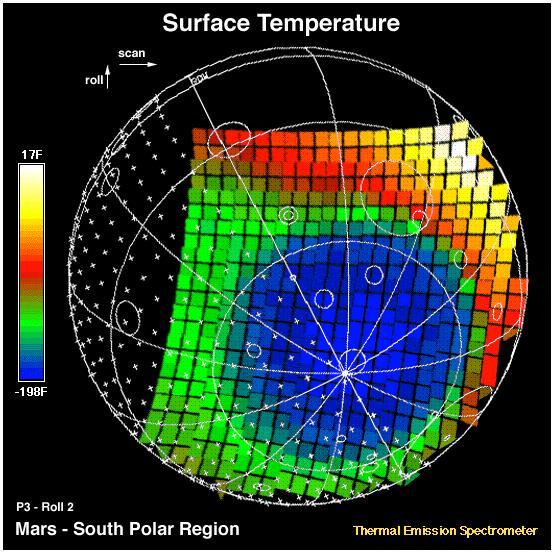
This image shows the temperature of the martian surface measured by the Mars Global Surveyor Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) instrument. On September 15, 3 hours and 48 minutes after the spacecrafts third close approach to the planet, the TES instrument was commanded to point at Mars and measure the temperature of the surface during a four minute scan. At this time MGS was approximately 15,000 miles (~24,000 km) from the planet, with a view looking up from beneath the planet at the south polar region. The circular blue region (- 198 F) is the south polar cap of Mars that is composed of CO2 ice. The night side of the planet, shown with crosses, is generally cool (green). The sunlit side of the planet reaches temperatures near 15 F (yellow). Each square represents an individual observation acquired in 2 seconds with a ground resolution of ~125 miles (~200 km). The TES instrument will remain on and collect similar images every 100 minutes to monitor the temperature of the surface and atmosphere throughout the aerobraking phase of the MGS mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00937
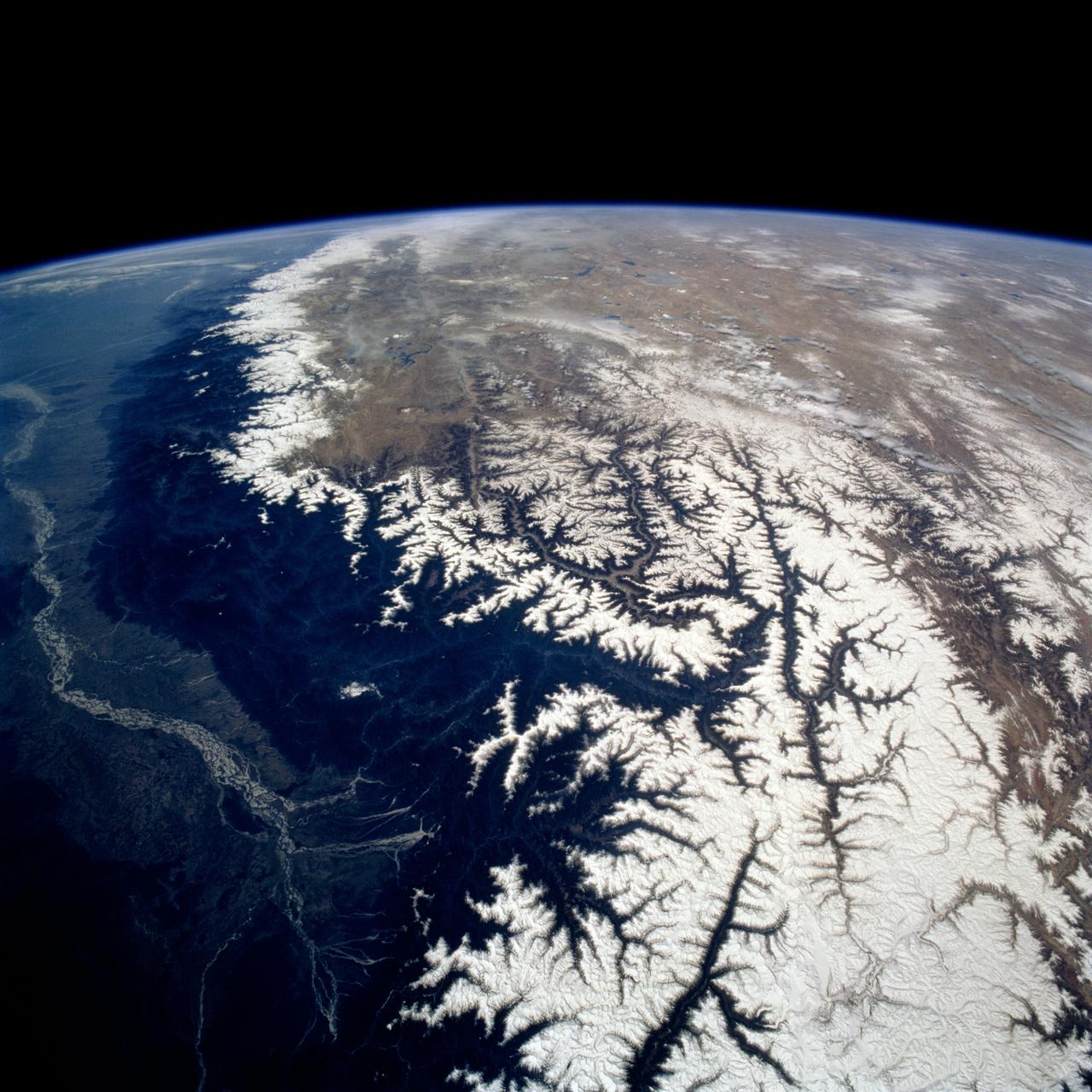

STS075-721-013 (22 Feb.-9 March 1996) --- Snow caps the line of the Himalayas in this 70mm frame photographed by a crew member using a handheld 70mm camera. The green plain of the Ganges-lower Brahamaputra is to the south (left) and the brown Tibetan Plateau desert to the right. The Brahamaputra River, 1,800 miles long, rises on the Tibetan Plateau (top) at the foot of a glacier at the elevation of 22,000 feet. It flows east (towards the camera) for more than half its length, and then descends onto the low plains through some of the deepest gorges in the world. In the low country of northeastern India (left side of photo), it flows west to meet the Ganges. Rainfall totals in this part of the Himalayas are some of the highest in the world, measuring 400 inches at Cherapunji on the Himalayan slopes center left. It has a drainage area of 250,000 square miles.
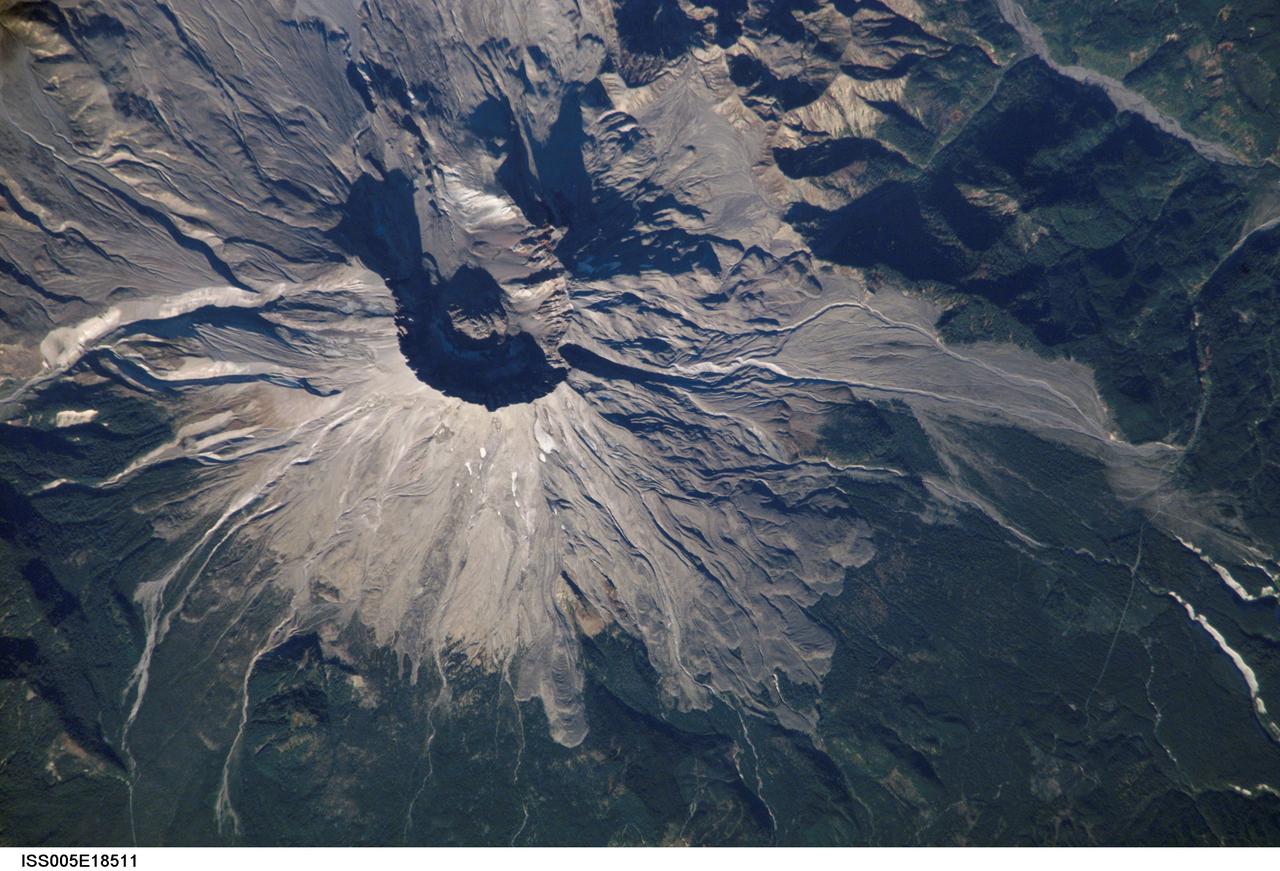
ISS005-E-18511 (25 October 2002) --- Mount Saint Helens, Washington, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 5 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). On May 18, 1980, Mount Saint Helens volcano erupted. A series of earthquakes preceded the eruption, triggering a collapse of the north side of the mountain into a massive landslide. This avalanche coincided with a huge explosion that destroyed over 270 square miles of forest in a few seconds, and sent a billowing cloud of ash and smoke 80,000 feet into the atmosphere. The crewmembers on the Station captured this detailed image of the volcano’s summit caldera. In the center of the crater sits a lava dome that is 876 feet above the crater floor and is about 3,500 feet in diameter. The upper slopes of the 1980 blast zone begin at the gray colored region that extends north (upper left) from the summit of the volcano. The deeply incised valley to the left (west) is the uppermost reach of the South Fork of the Toutle River. Devastating mudslides buried the original Toutle River Valley to an average depth of 150 feet, but in places up to 600 feet. The dark green area south of the blast zone is the thickly forested region of the Gifford Pinchot National Forest.
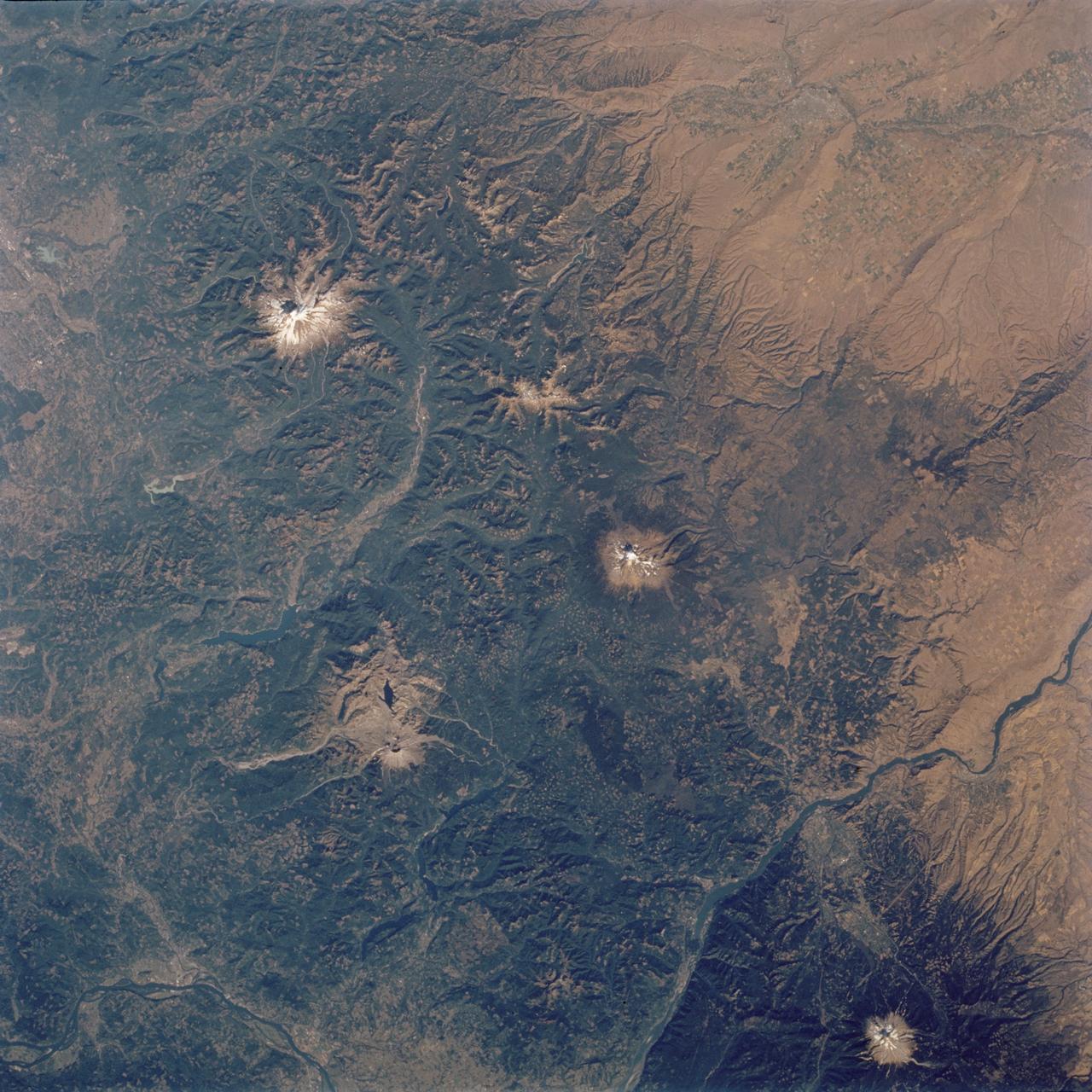

STS112-704-142 (7-18 October 2002) --- (For orientation purposes, north is toward the top left corner). Green colors of the forests of the Cascade Mountains dominate this view, photographed from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis. Browner colors (top right) are the semiarid plains of the Columbia Basin, in the rain shadow of the Cascades. The highest peaks in this part of the Cascades are four volcanoes. The amount of snow is a good indication of their altitude. The highest is Mt. Rainier (14,410 feet) with the greatest amount of white snow (top left). Seattle lies immediately downslope (top left margin). Mt. Adams (12,276) lies due south in the middle of the view. Mt. Hood (11,235 feet) in the lower right corner, lies south of the great gorge of the Columbia River (which crosses the lower right and then the lower left corners of the view). The river flows broadly west (left) to the Pacific Ocean (out of the picture left). Mt. St Helens (8,364 feet), the snow-free brown patch lower left, was too low to retain snow after the recent fall. According to geologists studying the STS-112 photography, even from the altitude of the Space Shuttle, the intact south half of the cone can be discerned. The geologists point out that the famous blast of 1980 not only destroyed the north side of the cone but blew down the green forest for many square miles on the north side (brown signature).
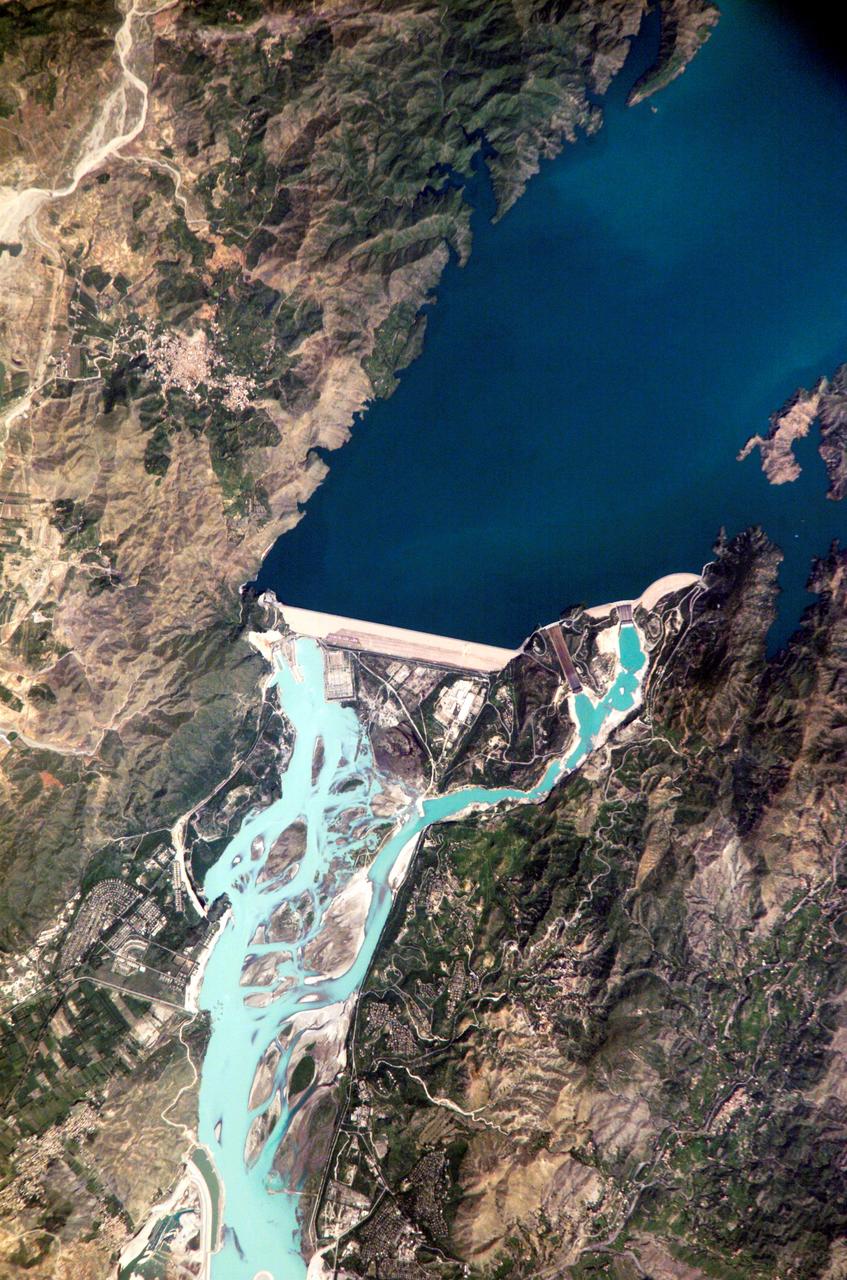

ISS005-E-12804 (6 September 2002) --- Tarbela Dam, Pakistan is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 5 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). The Indus River basin extends from the Himalaya mountain ranges forming the northeastern boundary of Pakistan, to the alluvial plains of Sindh near the Arabian Sea coastline. Tarbela Dam is part of the Indus Basin Project that resulted from a water treaty signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan. This treaty guaranteed Pakistan water supplies independent of upstream control by India. Designed primarily for water storage rather than power generation, the dam was completed in 1977. Turquoise waters of the Indus River (to the south of the dam) reflect the high proportion of silt and clay suspended in waters released by the spillways (chutes on either of side of the main dam). With a volume of 142,000,000 cubic meters, the Tarbela Dam is the largest earth and rockfill dam in the world and stands 147 meters above the Indus riverbed. Its reservoir occupies an area of 37 square kilometers. While the dam has fulfilled its purpose in storing water for agricultural use in Pakistan, there have been environmental consequences to the Indus river delta, according to NASA scientists who are studying the Space Station photography. Reduction of seasonal flooding and reduced water flows to the delta have resulted in decrease of mangrove stands and abundance of some fish species.
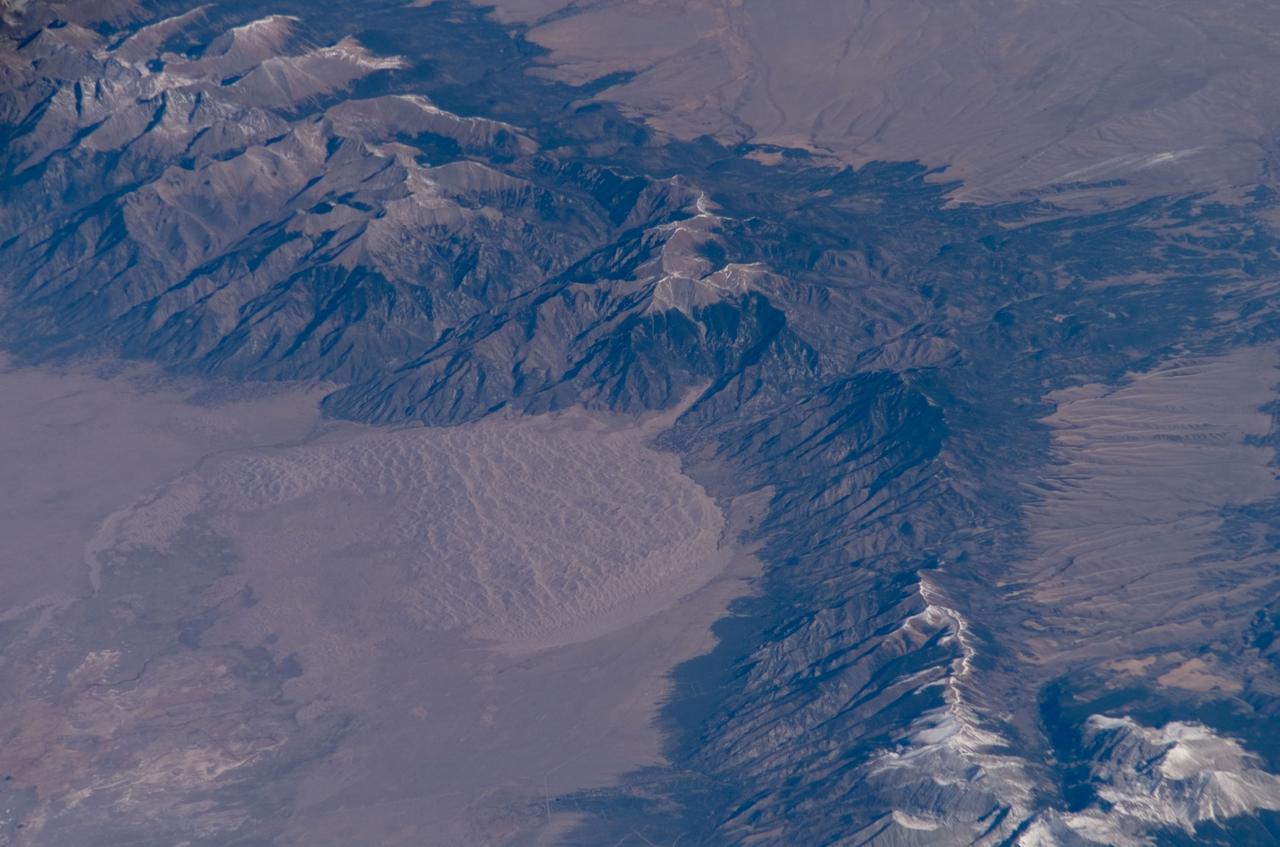

ISS016-E-006986 (26 Oct. 2007) --- Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve, Colorado is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 16 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Sangre de Cristo Mountains of south-central Colorado stretch dramatically from top left to lower right of this image, generally outlined by the dark green of forests with white snow-capped peaks on the highest elevations. Dun-colored dunes, covering an area of 80 square kilometers, are banked up on the west side of the mountains and comprise the Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve. Originally established in 1932 as a National Monument, it was reauthorized as a National Park in 2004. The park contains dunes over 750 feet (227 meters) high -- among the highest in North America. Sand grains that make up the dunes are small enough to be moved along by the wind (a process known as saltation), although much of the dunefield is now anchored by vegetation. Predominant winds blow broadly to the east, so that sand in the San Luis valley (part of which appears at lower left) is driven towards and piled against the Sangre de Cristo Mts. The sand of the dunes is mostly derived from ancient exposed lakebed sediments - now the floor of the San Luis valley - formed by erosion of rocks in the Sangre de Cristo and San Juan Mountains (located to the west). The action of streams and occasional storms today returns some of the impounded sand back to the valley, where the prevailing winds begin the sand's migration to the dunefield anew. Interestingly, the specific location of the sand field appears to be related to a locally lower altitude sector of the Sangre de Cristo Mts. Altitudes can be inferred from the distribution of snow cover on the day this image was taken. Areas to the north (Cleveland Peak and northward) of the dunefield, and to the south around Blanca Peak, are higher than the ridgeline next to the dune field where almost no snow is visible. Since winds are preferentially channeled over the lower parts of any range (hundreds of meters lower here than ridgelines to north and south), sand grains are carried up to (but not over) the low point of the range.
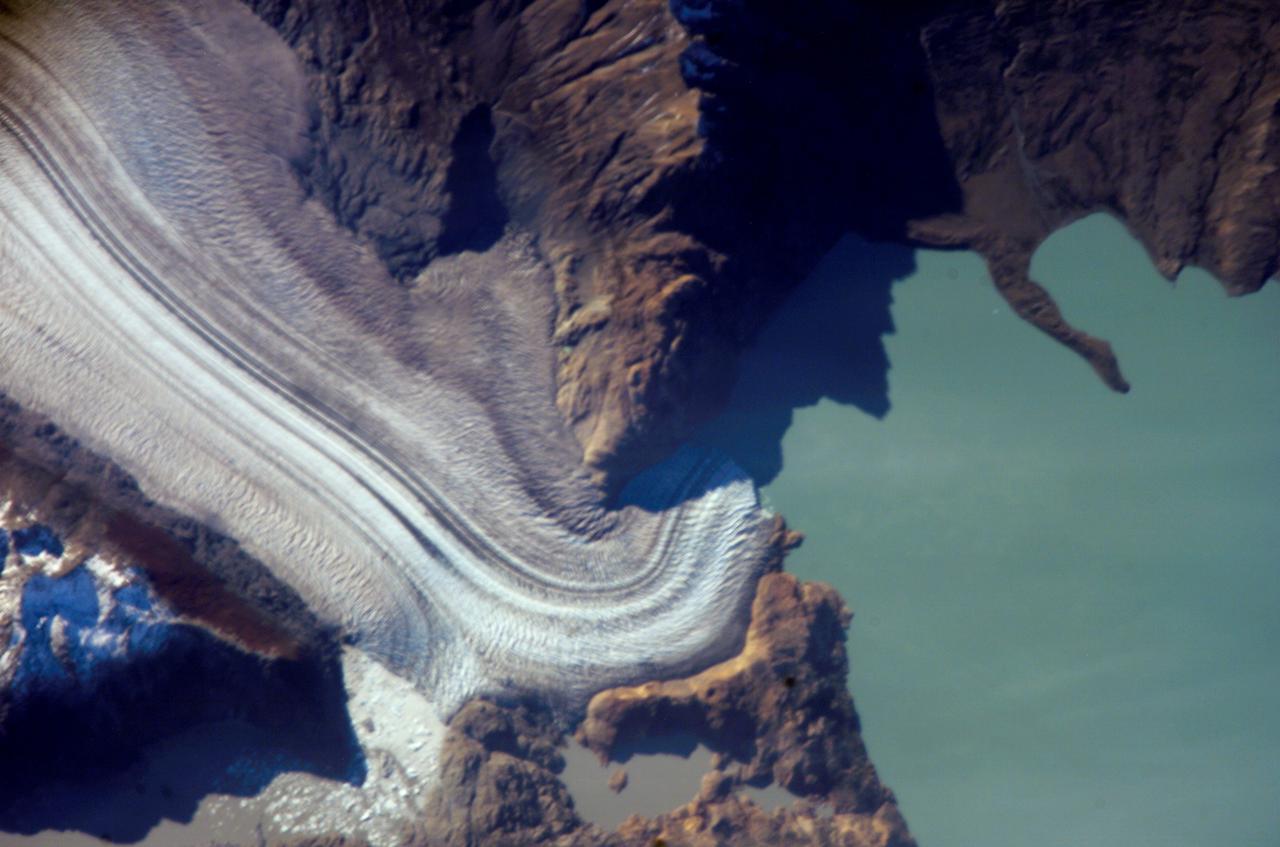

ISS013-E-06947 (12 April 2006) --- Viedma Glacier, Argentina is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. The ice fields of Patagonia, located at the southern end of South America, are the largest masses of ice in the temperate Southern Hemisphere (approximately 55,000 square kilometers in area). The ice fields contain numerous valley glaciers that terminate in melt-water-fed lakes. These are known as "calving" glaciers, as they lose mass by collapse of large ice chunks from the terminus--or end--of the glacier. These newly separated chunks of ice are then free to float away, much like ice cubes in a punch bowl. The Patagonian glaciers are closely monitored using remotely sensed data as they respond to regional climate change. Visual comparison of time series of images is typically performed to quantify change in ice extent and position. The terminus of the Viedma Glacier, approximately two kilometers across where it enters Lake Viedma, is shown in this image. Moraines are accumulations of soil and rock debris that form along the sides and front of a glacier as it flows across the landscape (much like a bulldozer). Independent valley glaciers can merge together as they flow down-slope, and the moraines become entrained in the center of the new ice mass. These medial moraines are visible as dark parallel lines within the white central mass of the glacier (image center and left). Crevasses - oriented roughly perpendicular to the medial moraines - are also visible in the grey-brown ice along the sides of the glacier. According to scientists, the canyon-like crevasses form as a result of stress between the slower moving ice along the valley sides and the more rapidly moving ice in the center of the glacier. Calving of ice from the southwestern fork of the glacier terminus is visible at image lower left.
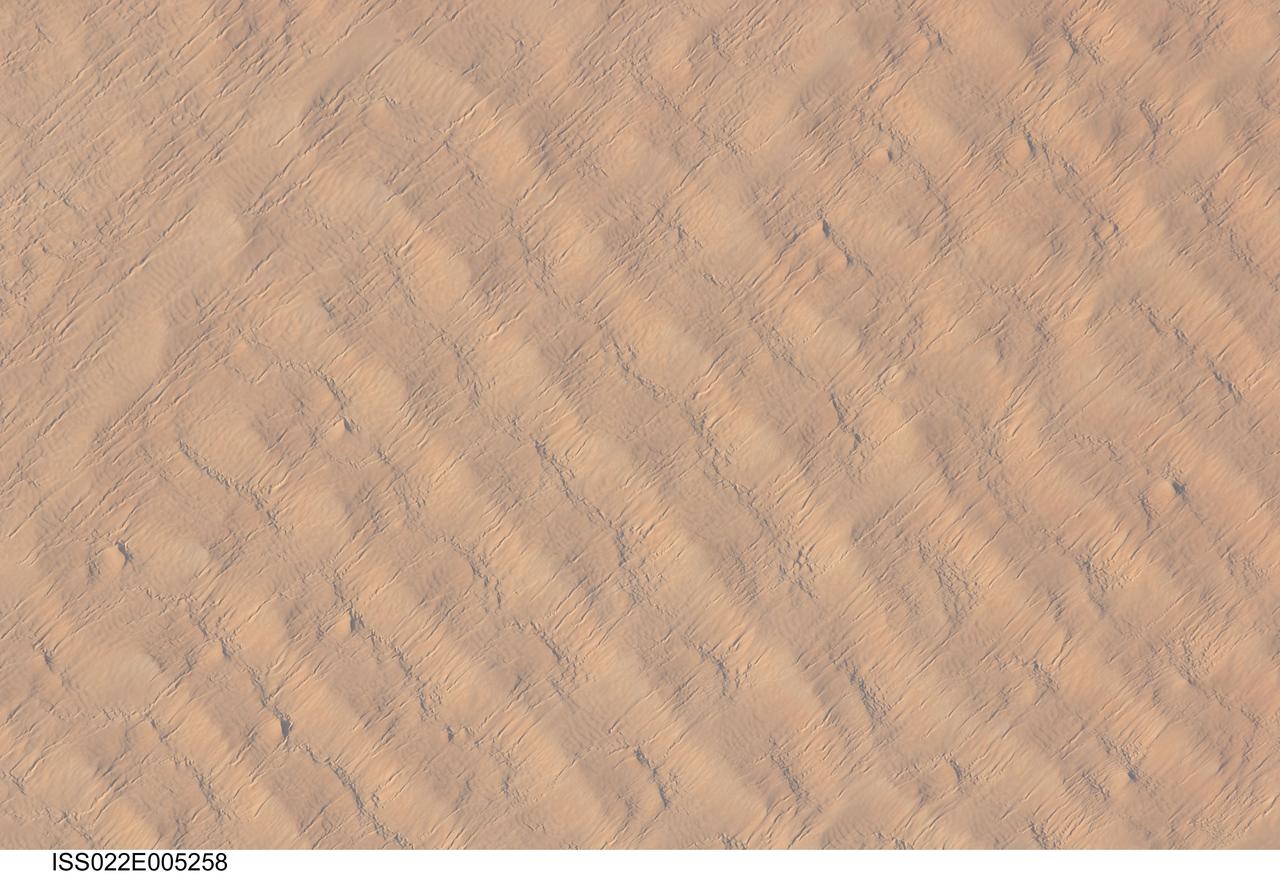

ISS022-E-005258 (1 Dec. 2009) --- This detailed hand-held digital camera?s image recorded from the International Space Station highlights sand dunes in the Fachi-Bilma erg, or sand sea, which is part of the central eastern Tenere Desert. The Tenere occupies much of southeastern Niger and is considered to be part of the larger Sahara Desert that stretches across northern Africa. Much of the Sahara is comprised of ergs ? with an area of approximately 150,000 square kilometers, the Fachi-Bilma is one of the larger sand seas. Two major types of dunes are visible in the image. Large, roughly north-south oriented transverse dunes fill the image frame. This type of dune tends to form at roughly right angles to the dominant northeasterly winds. The dune crests are marked in this image by darker, steeper sand accumulations that cast shadows. The lighter-toned zones between are lower interdune ?flats?. The large dunes appear to be highly symmetrical with regard to their crests. This suggests that the crest sediments are coarser, preventing the formation of a steeper slip face on the downwind side of the dune by wind-driven motion of similarly-sized sand grains. According to NASA scientists, this particular form of transverse dune is known as a zibar, and is thought to form by winnowing of smaller sand grains by the wind, leaving the coarser grains to form dune crests. A second set of thin linear dunes oriented at roughly right angles to the zibar dunes appears to be formed on the larger landforms and is therefore a younger landscape feature. These dunes appear to be forming from finer grains in the same wind field as the larger zibars. The image was taken with digital still camera fitted with a 400 mm lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center.