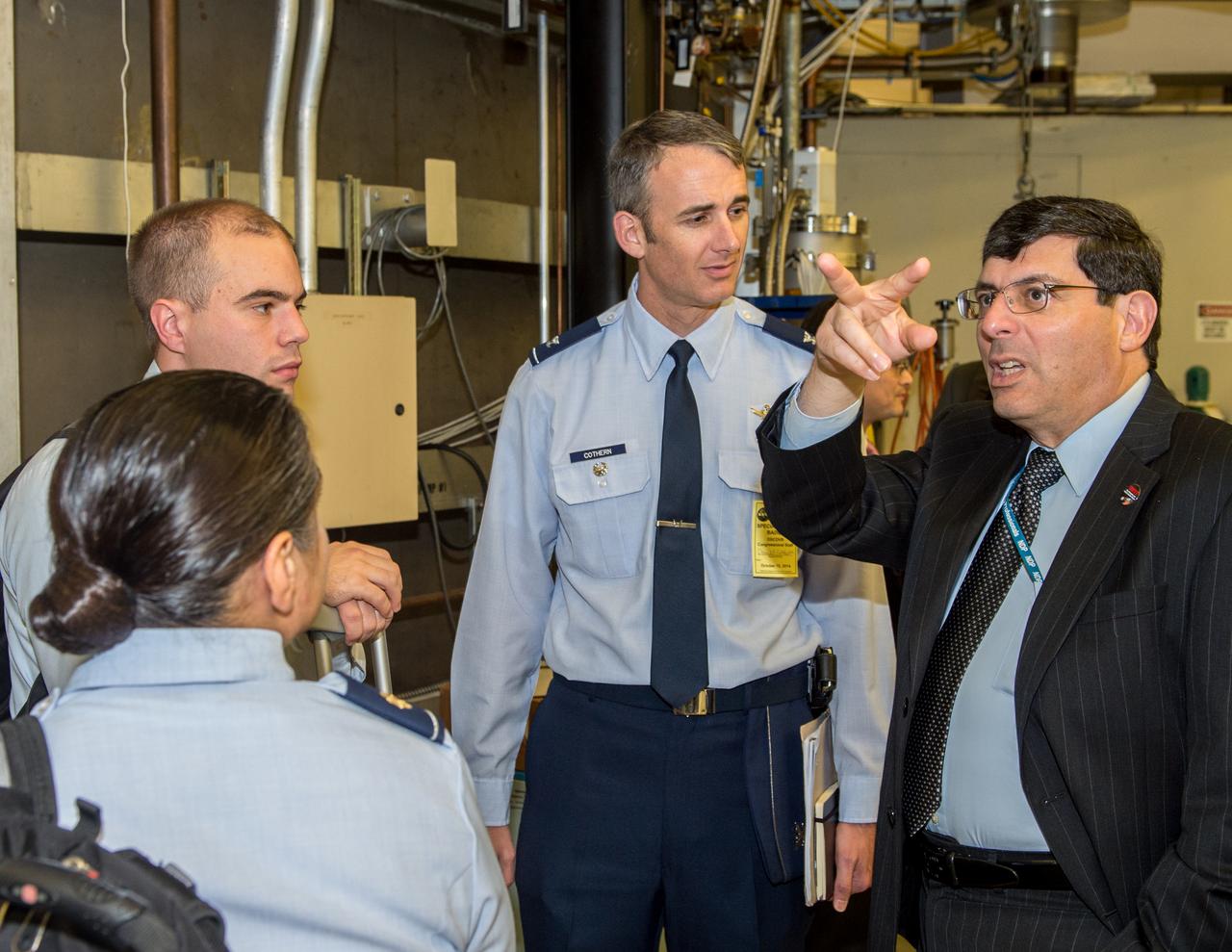

Joint NASA-NOAA-Air Force Congressional Staff Day Goddard Space Flight Center
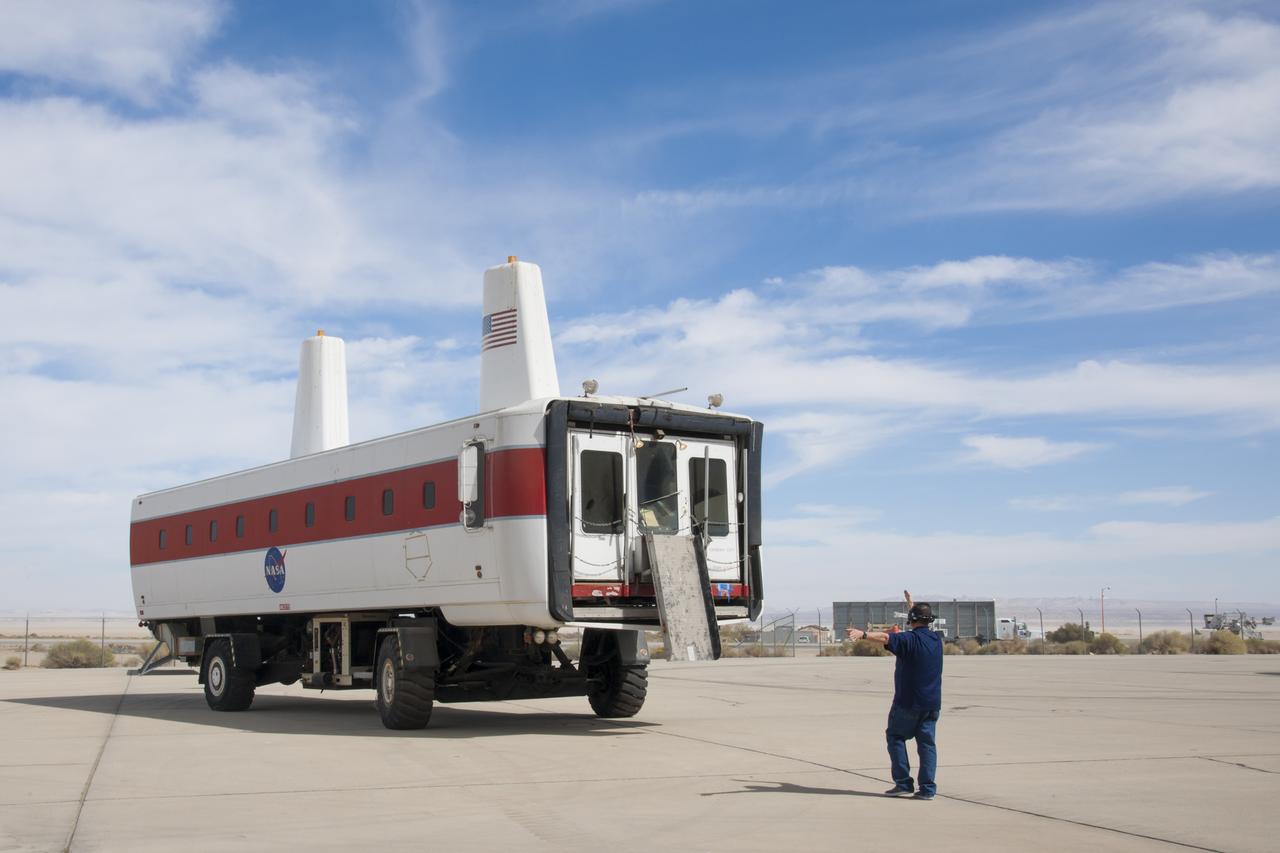

Workers drive the space shuttle Crew Transport Vehicle, or CTV, to the Edwards Air Force Base Flight Test Museum in California for display.
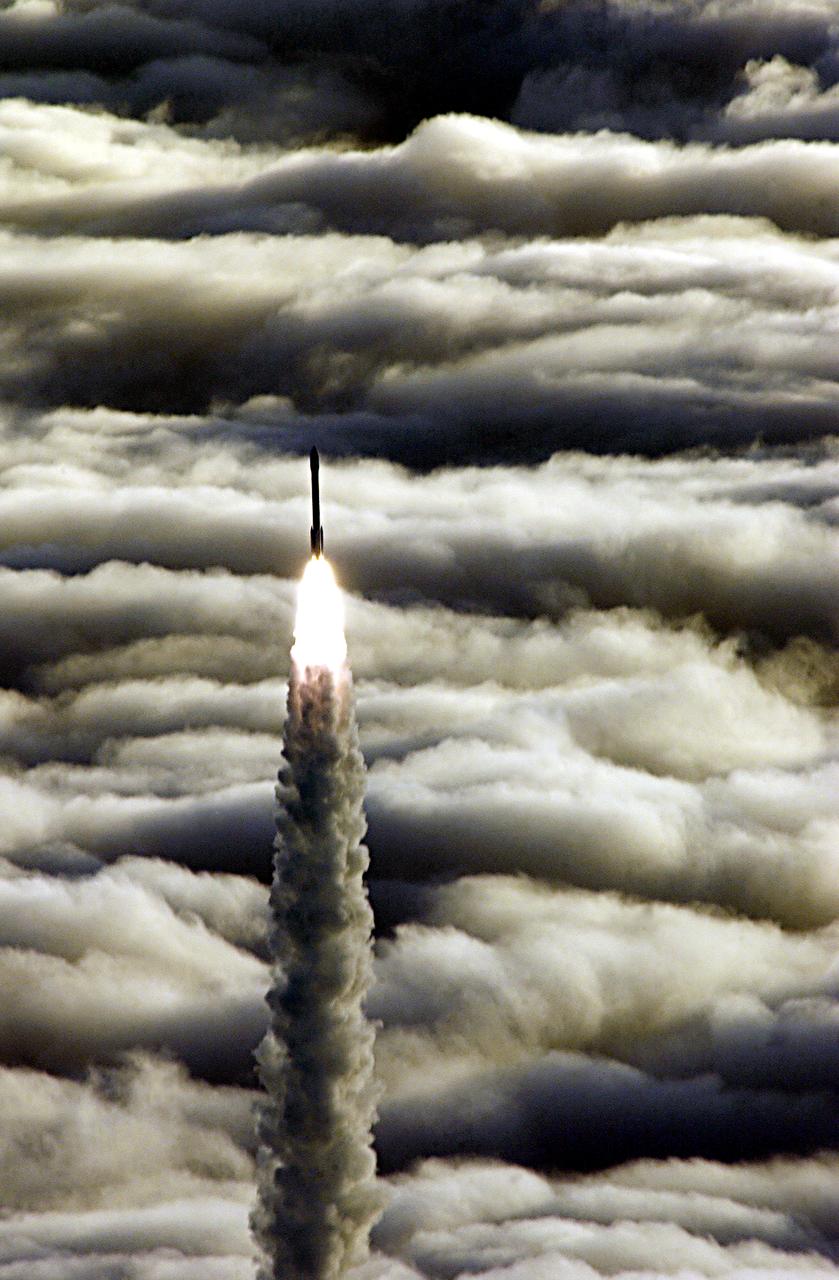

Vandenberg AFB CA-- A Boeing Delta II rocket soars above the clouds here today at Vandenberg AFB CA. The NASA payload aboard the rocket is the ICESat, an Ice Cloud and land Elevation Satellite, and CHIPSat, a Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer. ICESat, a 661-pound satellite, is a benchmark satellite for the Earth Observing System that will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will observe the ice sheets that blanket the Earth’s poles to determine if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate affect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Geoscience Laser Altimeter System is the sole instrument on the satellite. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide information about the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This launch, marks the first Delta from Vandenberg this year. (USAF photo by: SSgt Lee A Osberry Jr.)
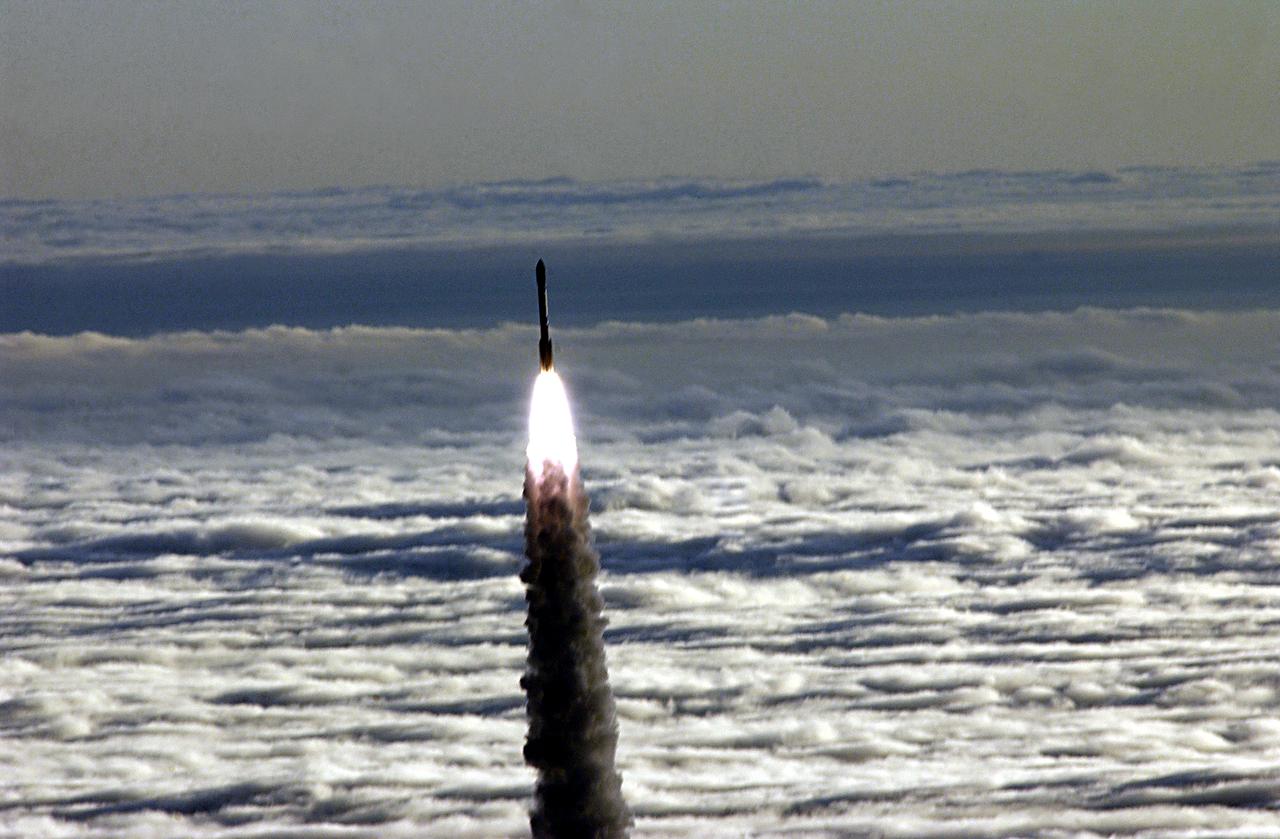

Vandenberg AFB CA-- A Boeing Delta II rocket soars above the clouds here today at Vandenberg AFB CA. The NASA payload aboard the rocket is the ICESat, an Ice Cloud and land Elevation Satellite, and CHIPSat, a Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer. ICESat, a 661-pound satellite, is a benchmark satellite for the Earth Observing System that will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will observe the ice sheets that blanket the Earth’s poles to determine if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate affect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Geoscience Laser Altimeter System is the sole instrument on the satellite. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide information about the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This launch, marks the first Delta from Vandenberg this year. (USAF photo by: SSgt Lee A Osberry Jr.)
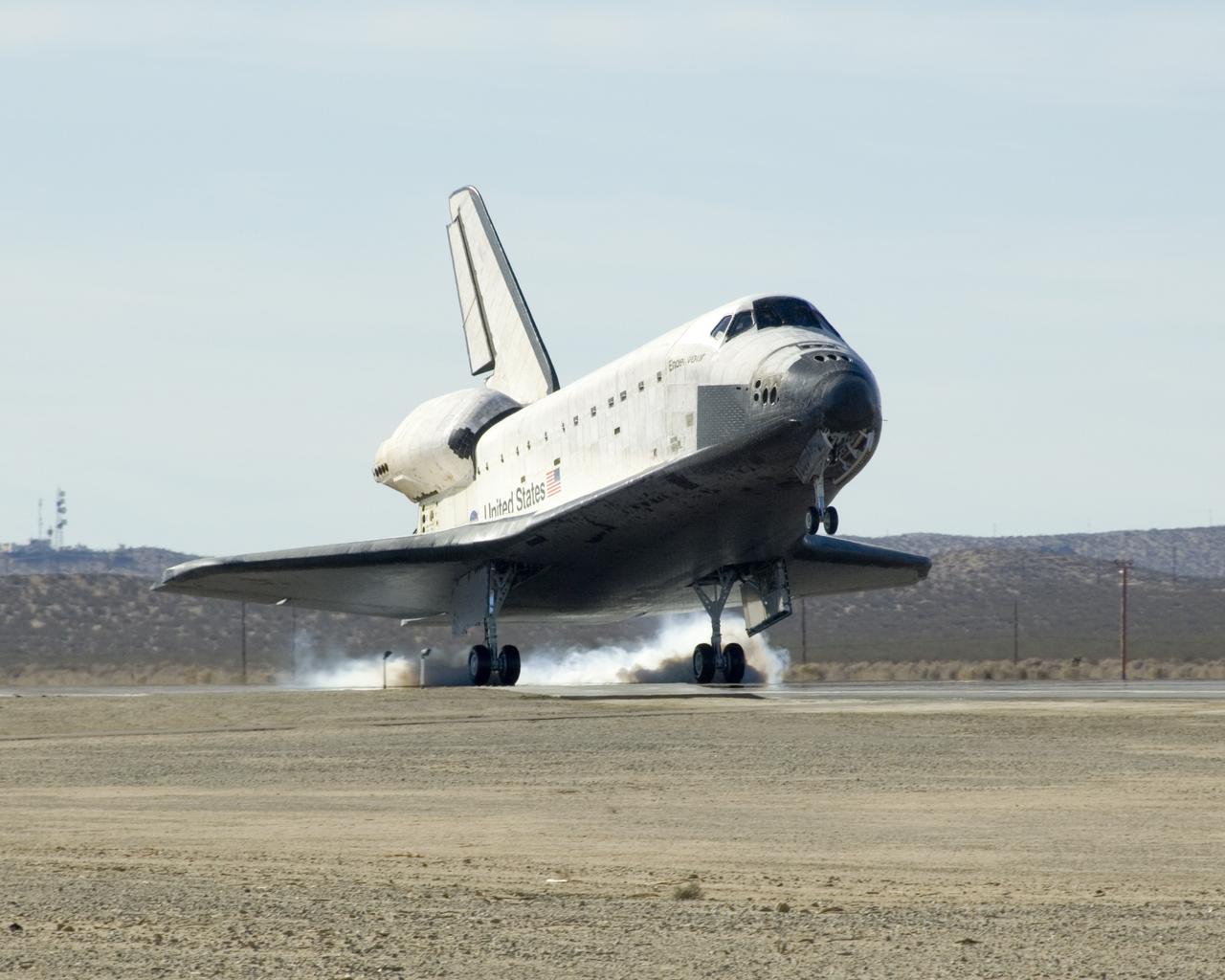

Space Shuttle Endeavour touches down at Edwards Air Force Base Nov. 30, 2008 to conclude mission STS-126 to the International Space Station.
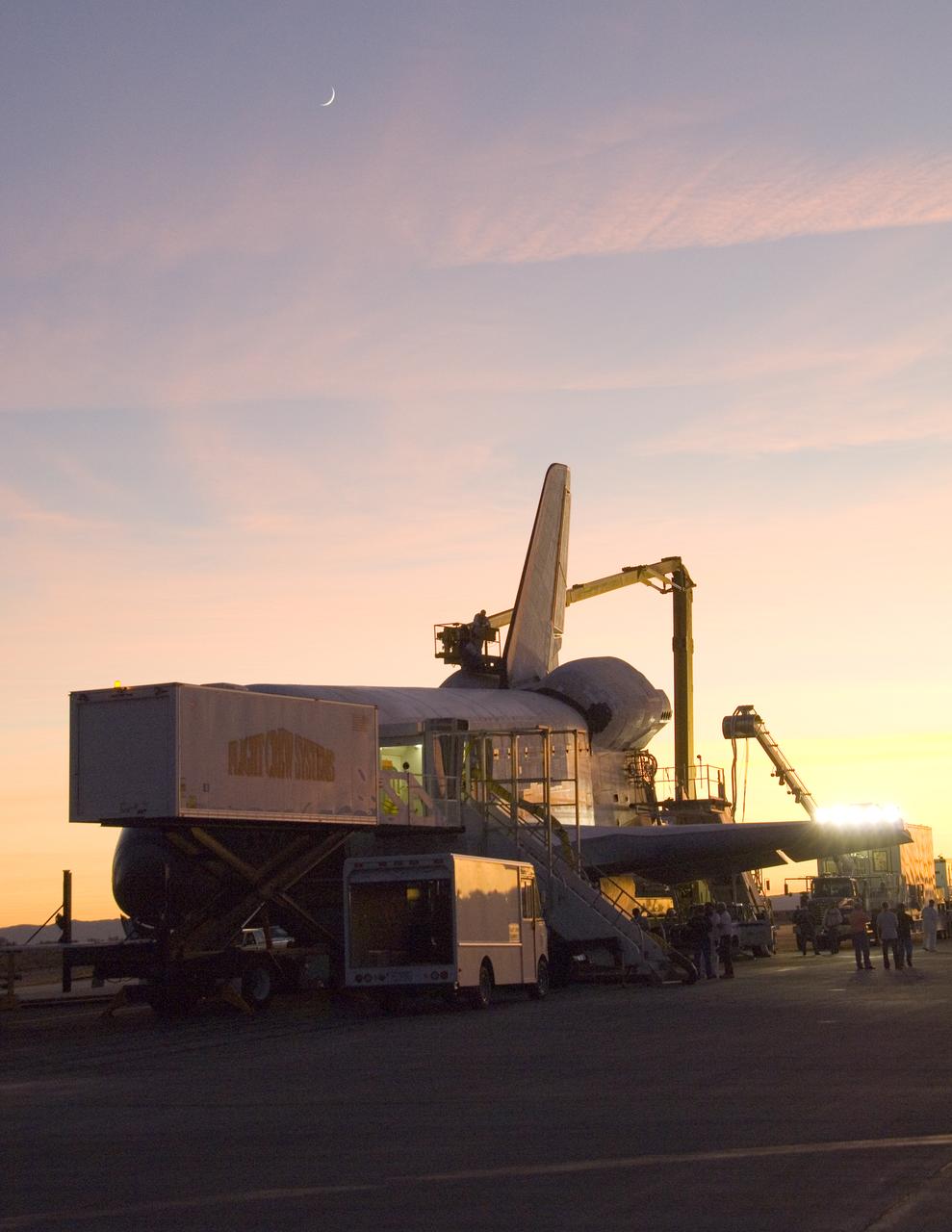

Its STS-126 mission over, Space Shuttle Endeavour is surrounded by recovery equipment before being towed off the Edwards Air Force Base runway.
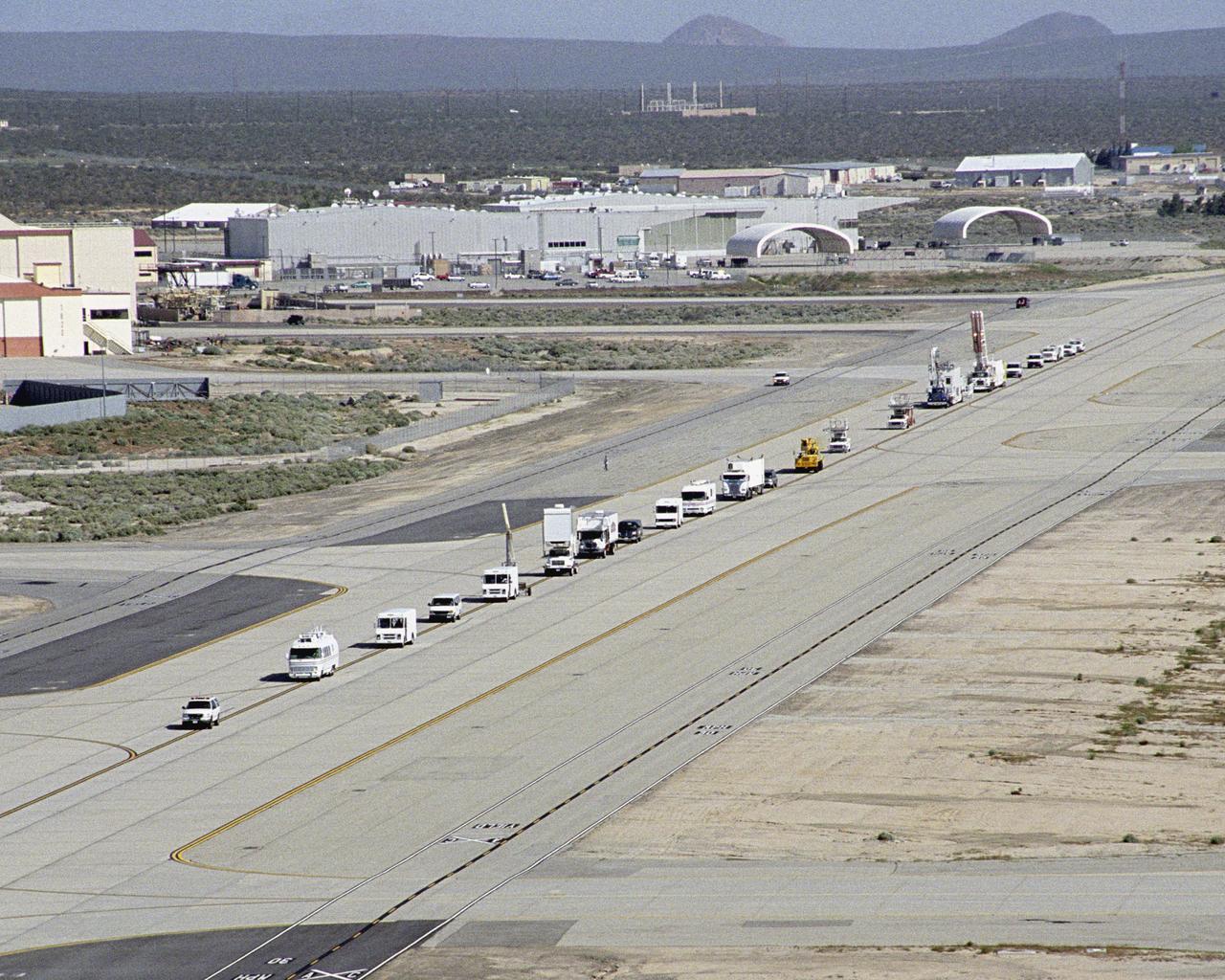

A long string of specialized NASA vehicles convoys down a taxiway at Edwards Air Force Base to begin a Space Shuttle rescue and recovery training exercise.
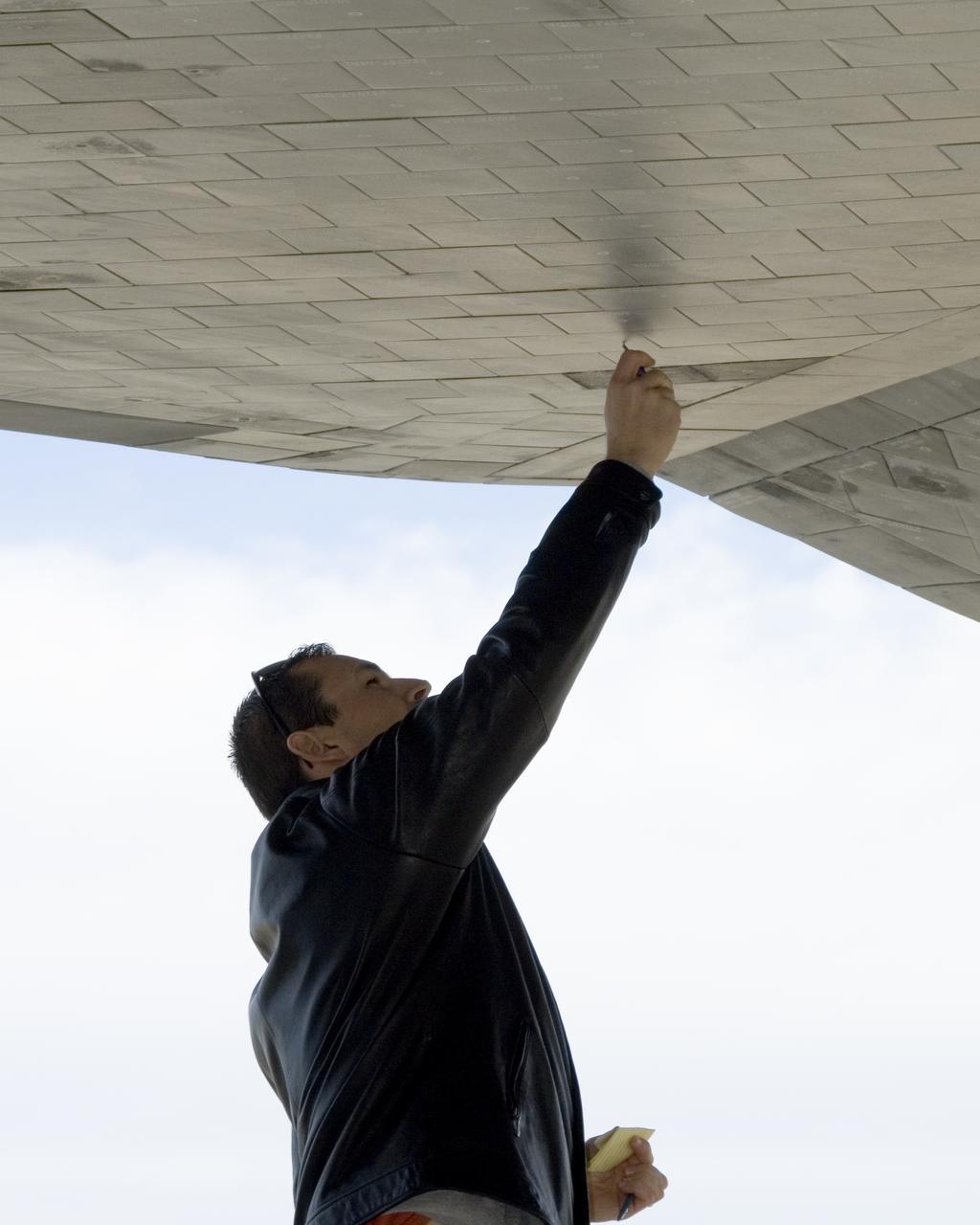

A United Space Alliance technician carefully checks the thermal tiles on the underside of Space Shuttle Endeavour for nicks and dings following its landing at Edwards Air Force Base to conclude mission STS-126.
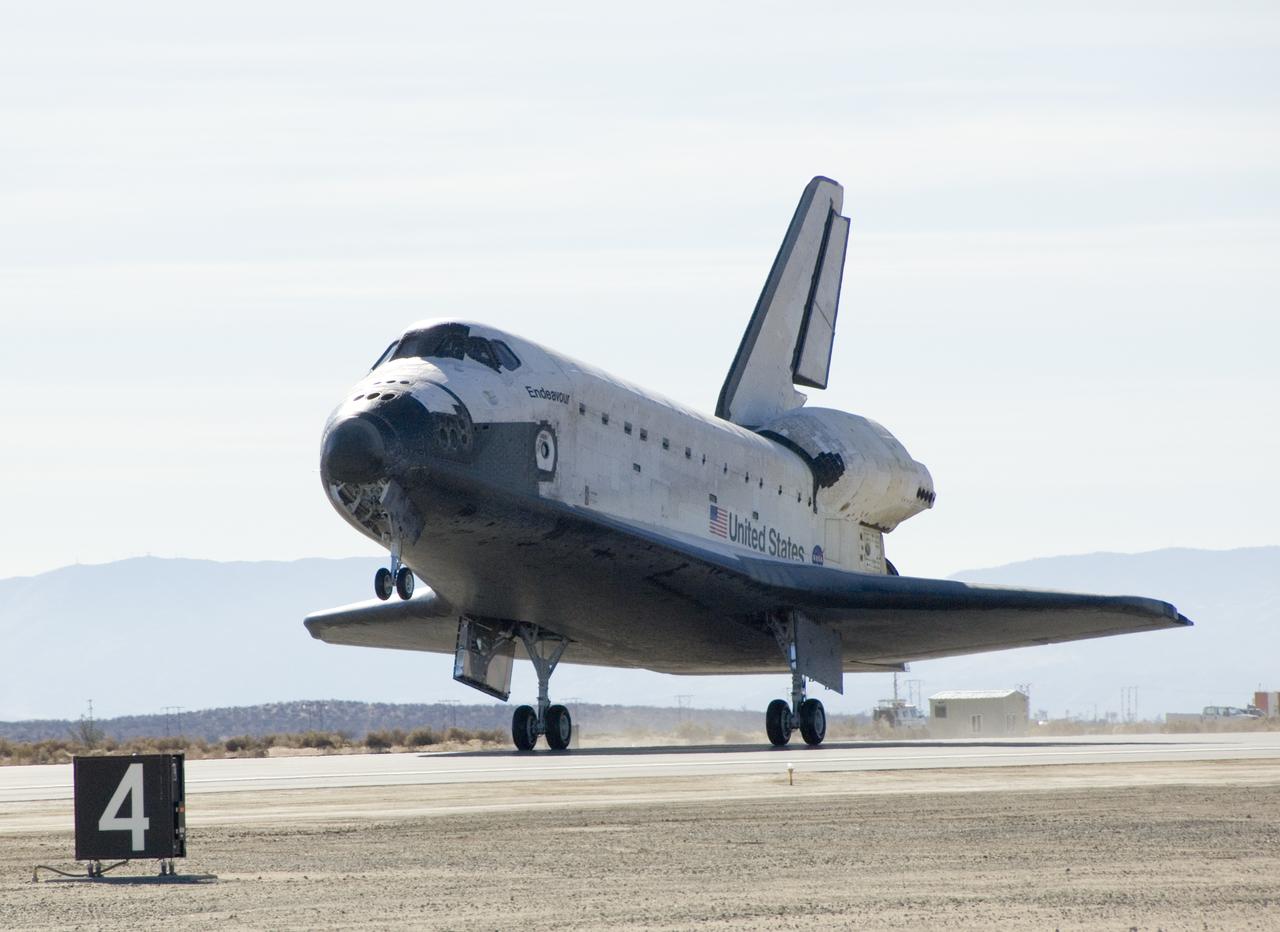

Space Shuttle Endeavour rolls out on runway 04-L at Edwards Air Force Base moments after touchdown, ending mission STS-126 to the International Space Station.
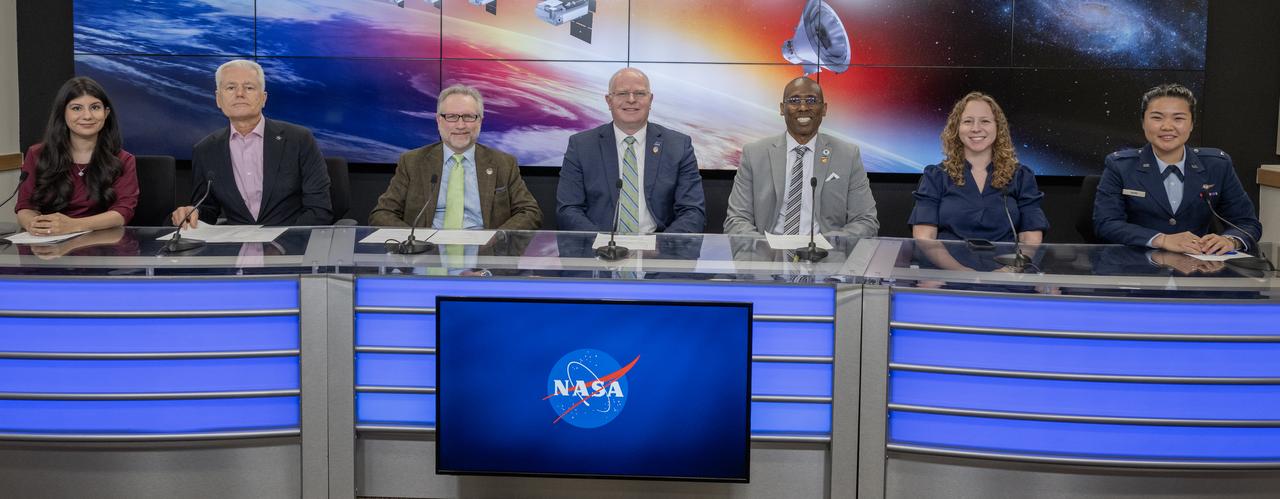

NASA, SpaceX and U.S. Air Force participate in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
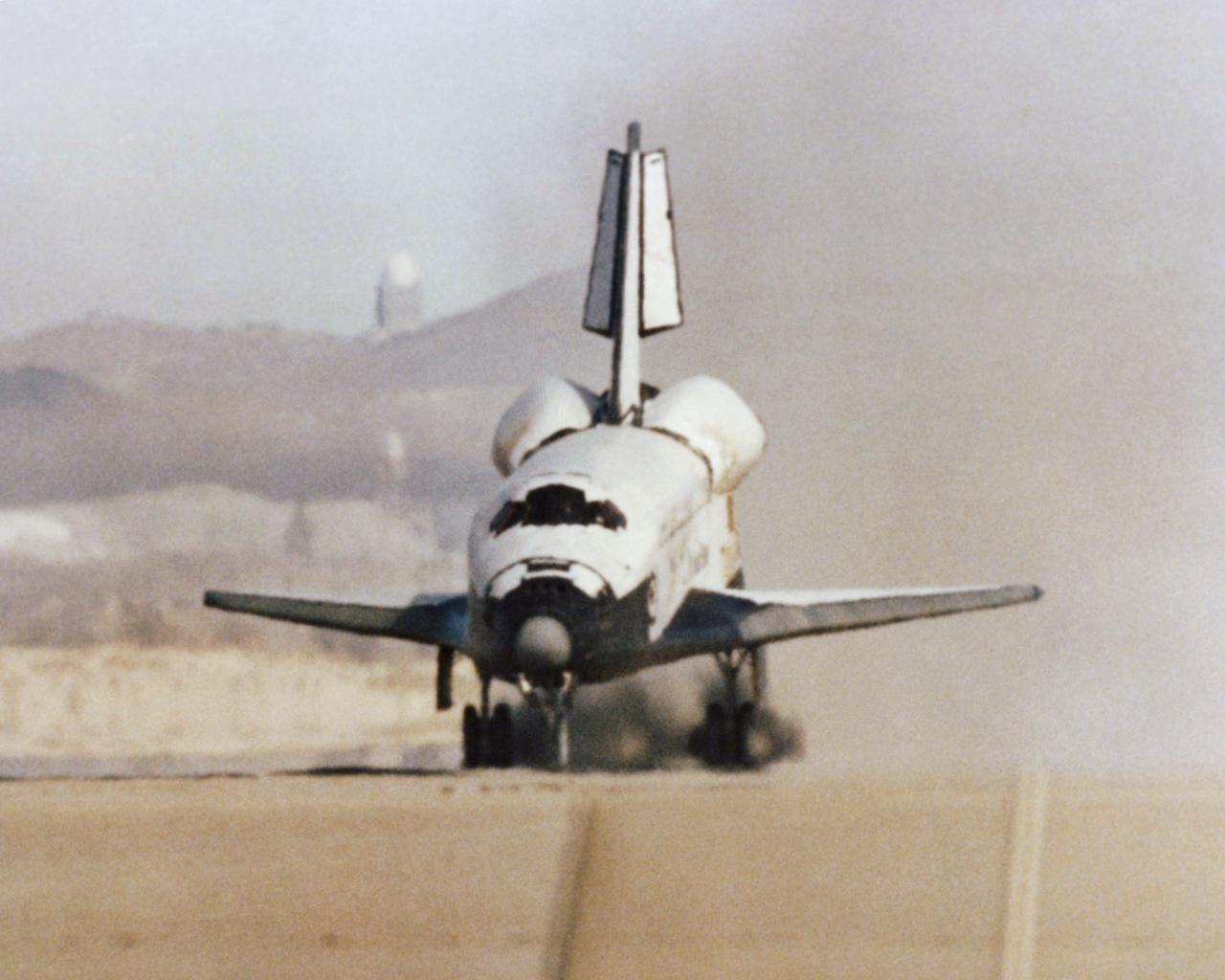

The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on lakebed runway 23 at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to conclude the first orbital shuttle mission.
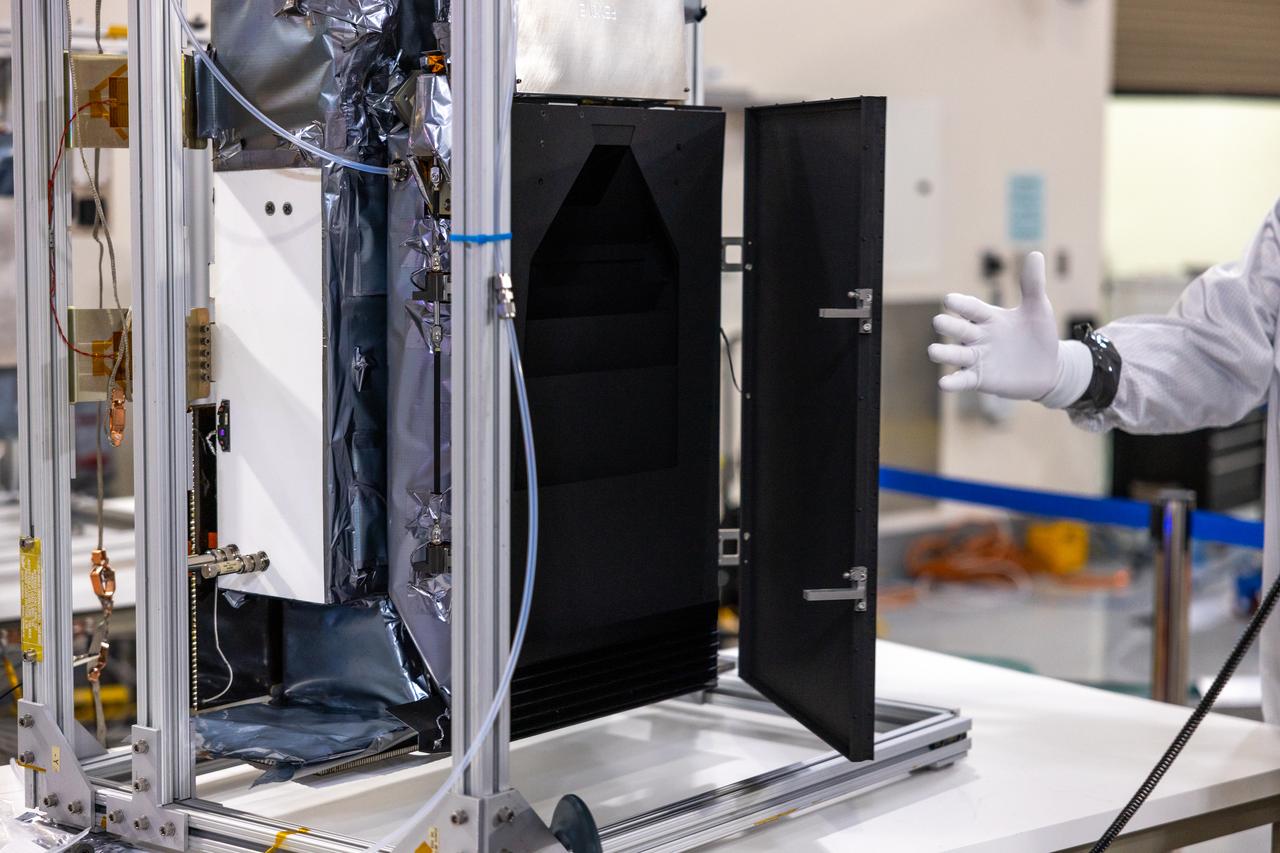

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
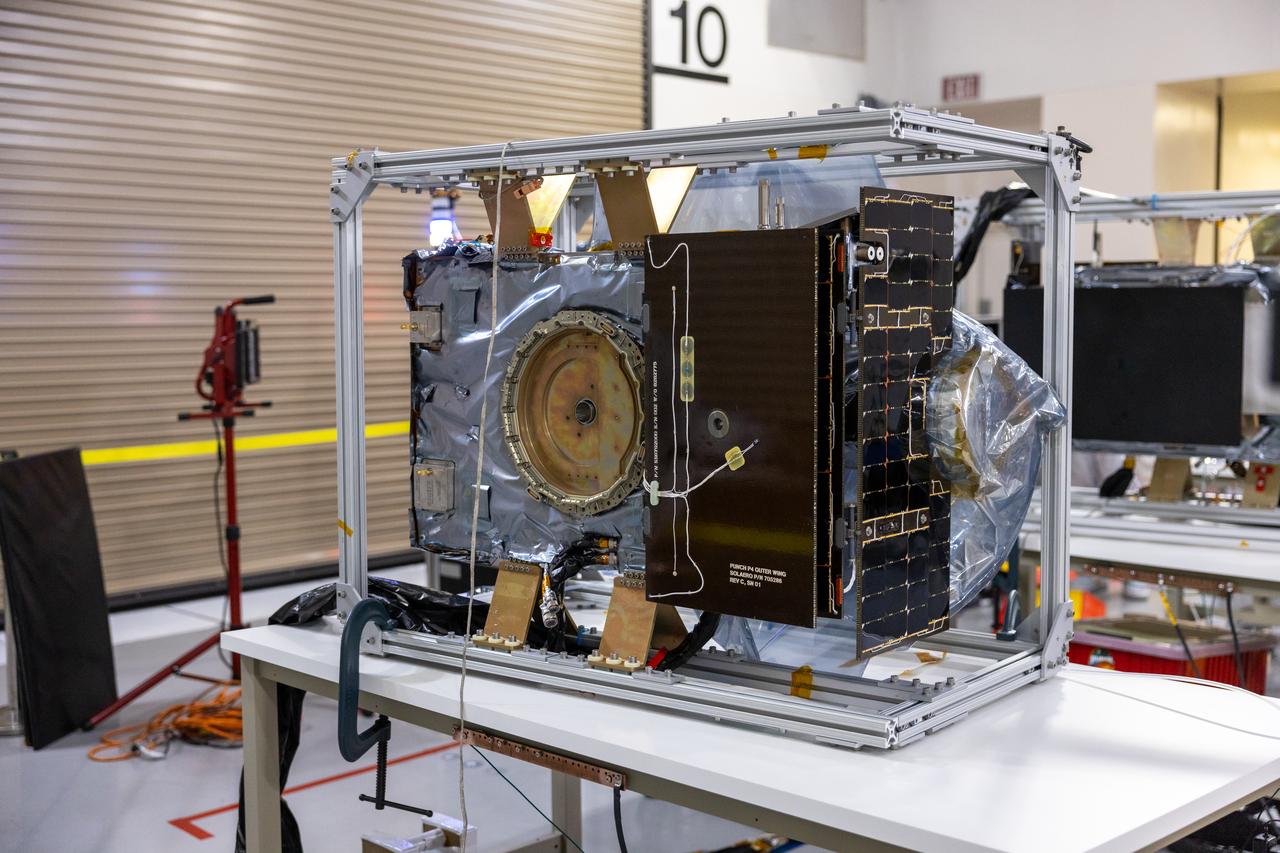
Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
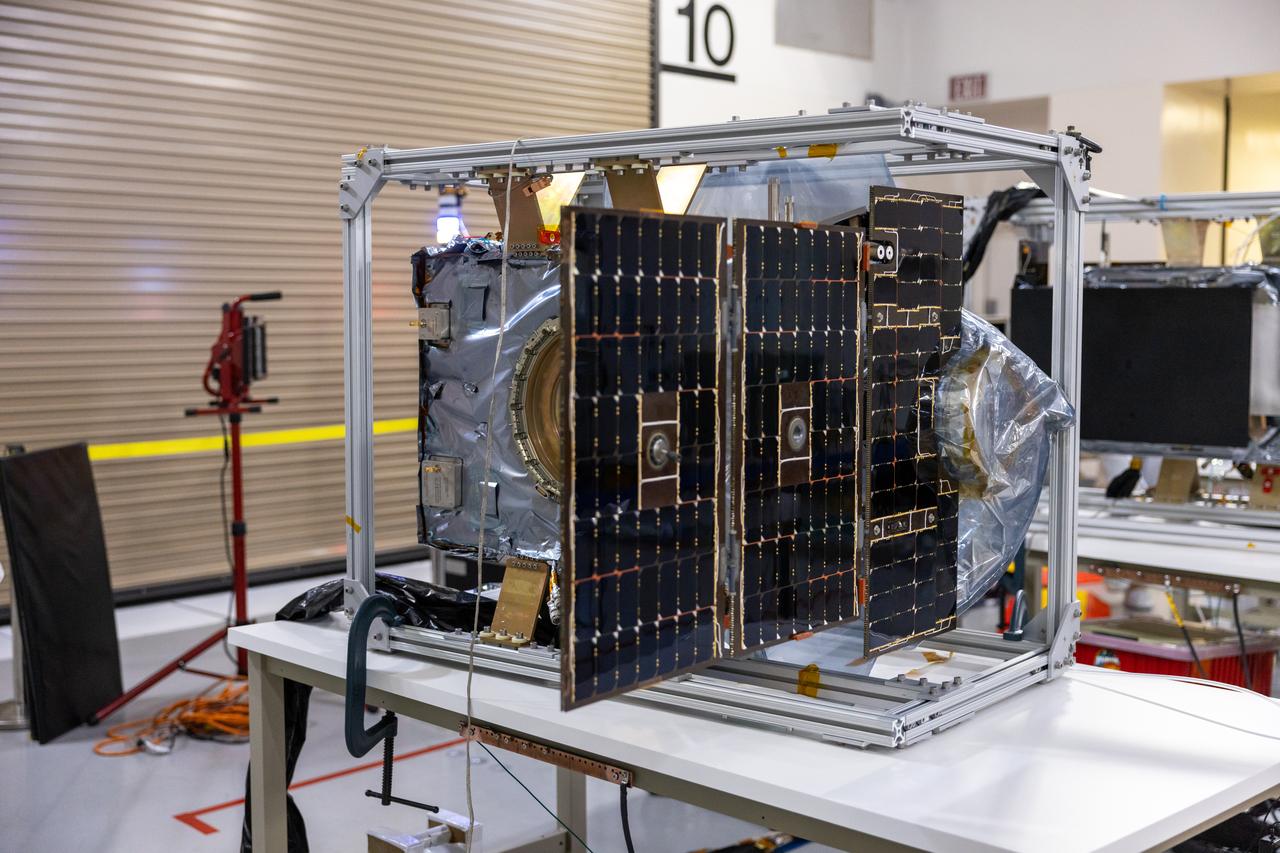

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
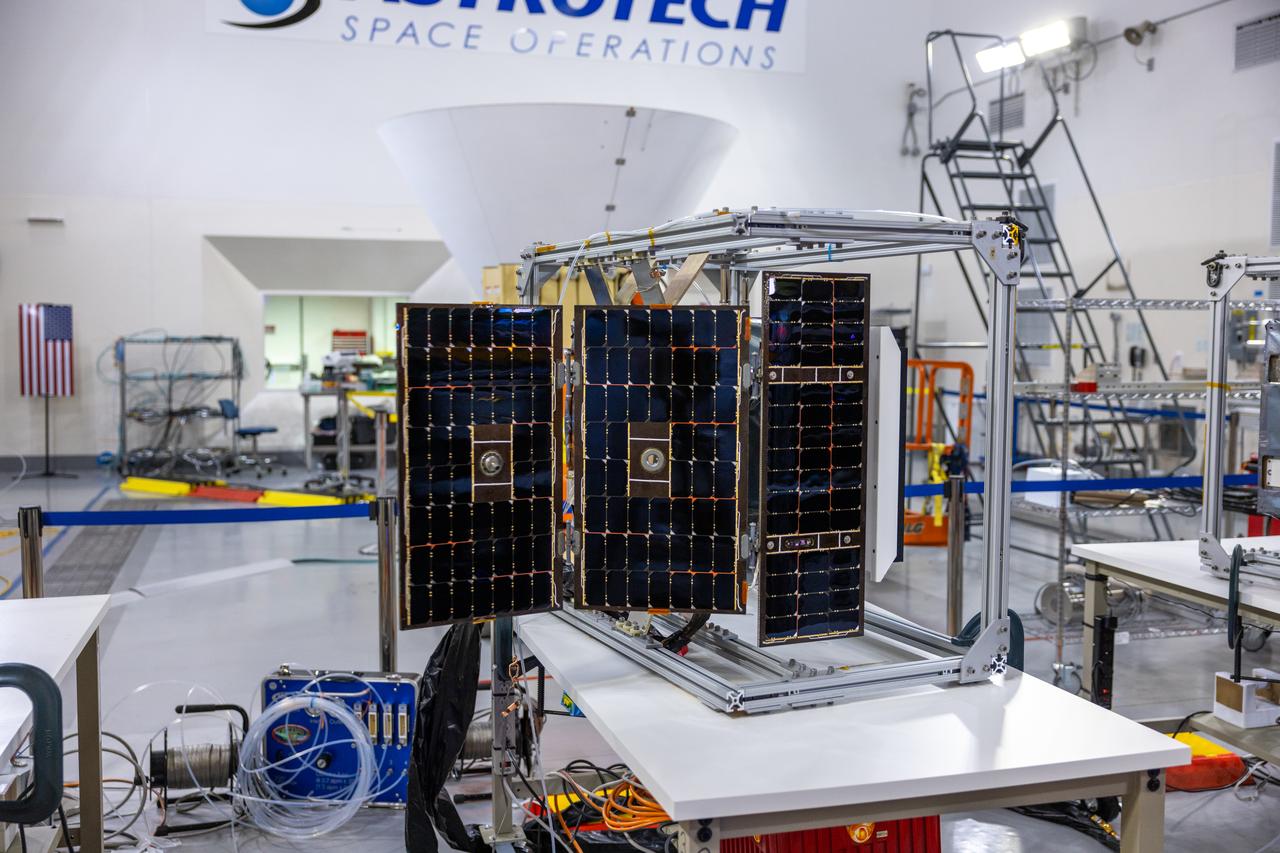

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
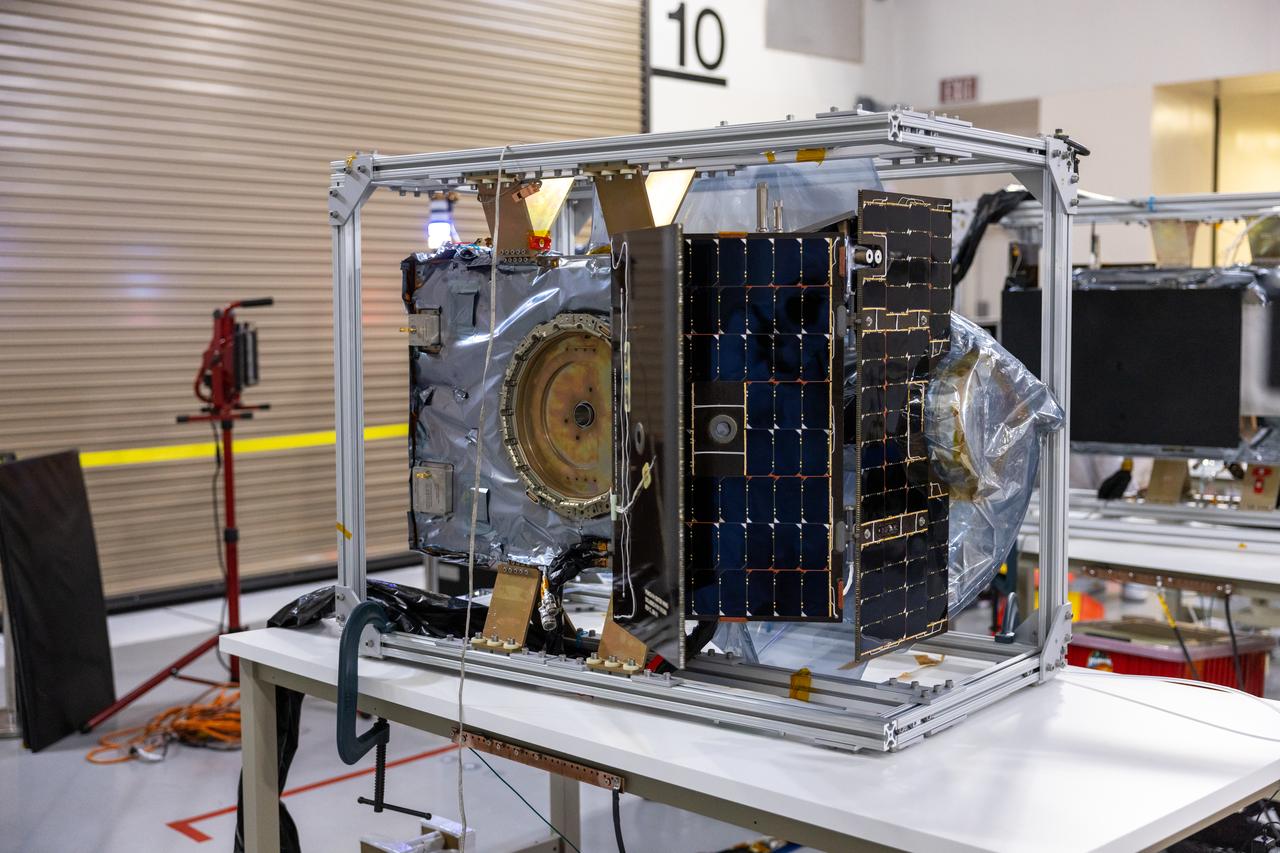

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
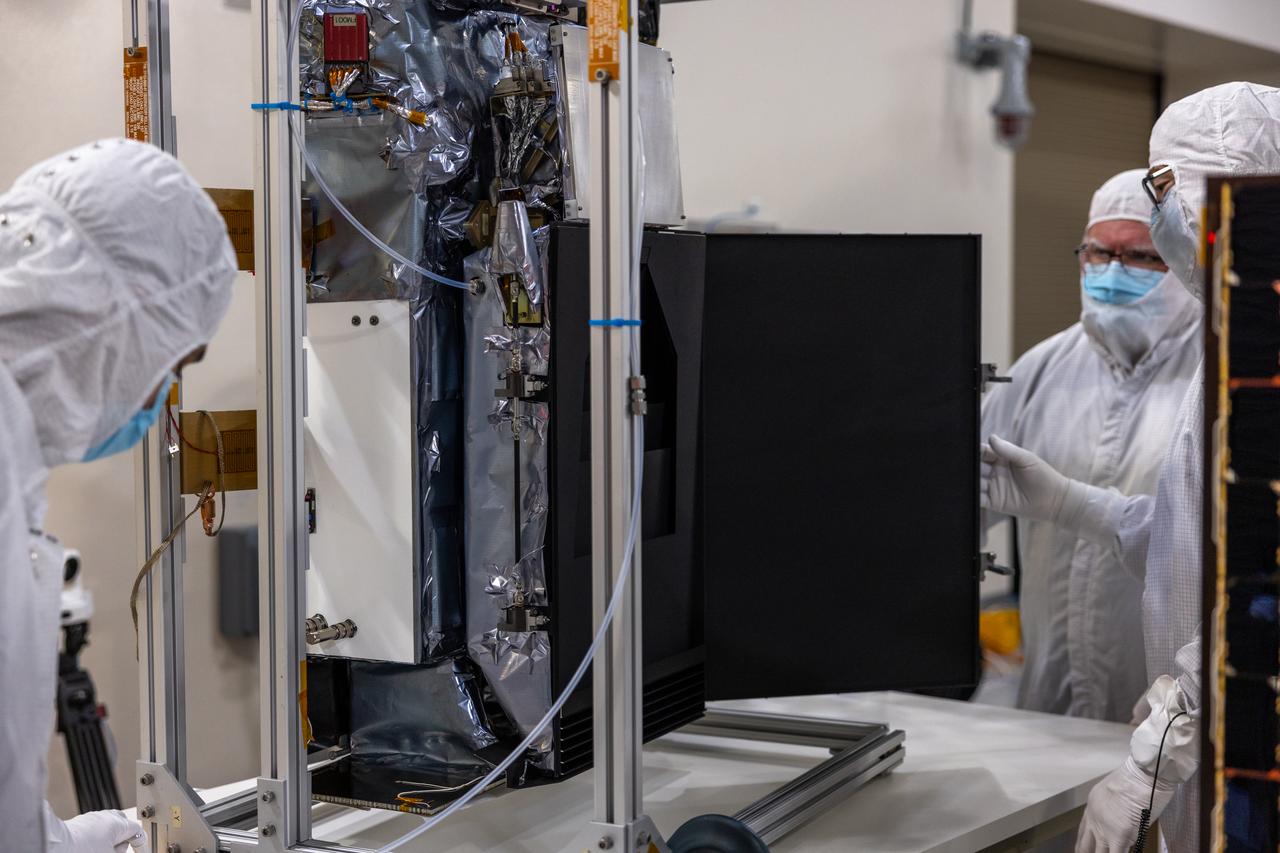

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
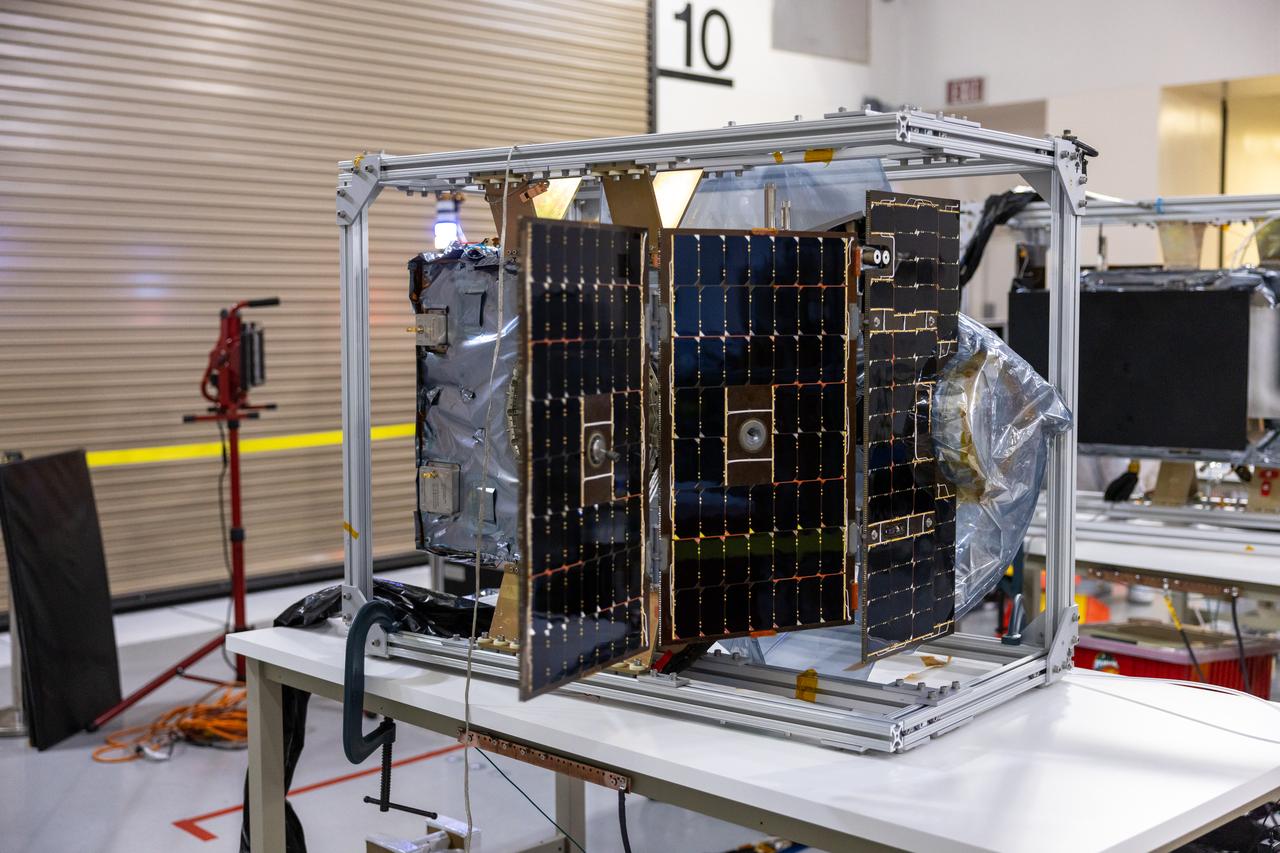

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
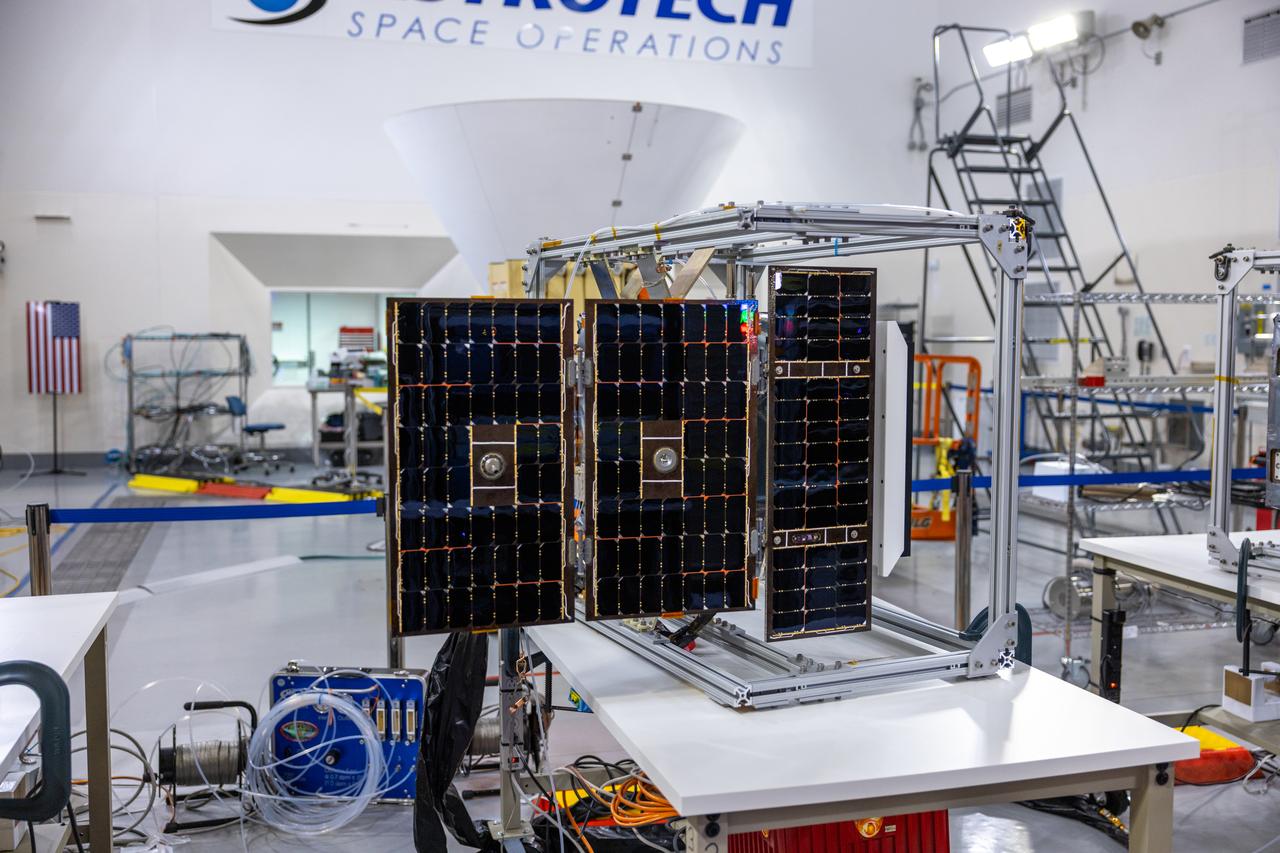

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
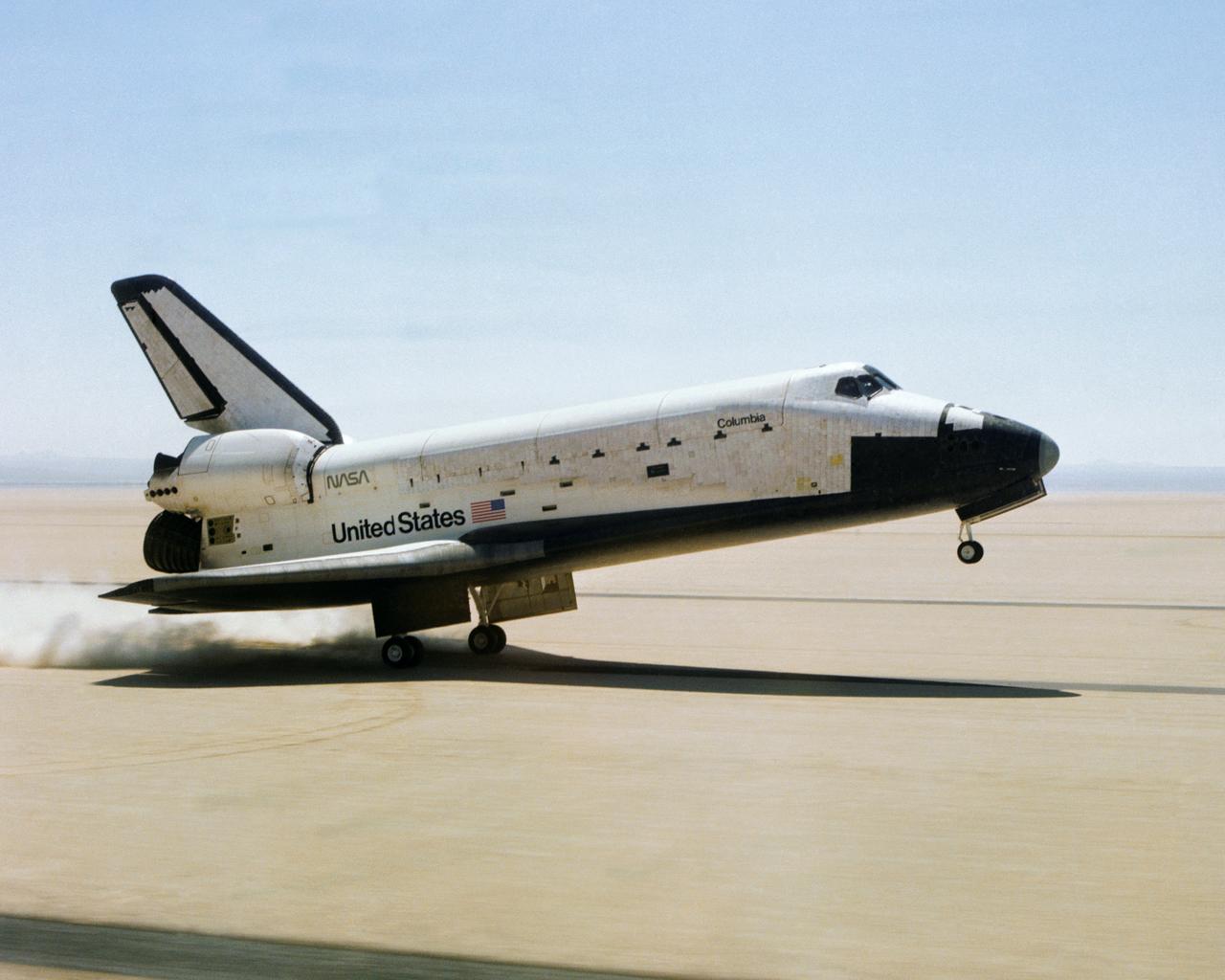

The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on lakebed runway 23 at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to conclude the first orbital shuttle mission. (JSC photo # S81-30734)
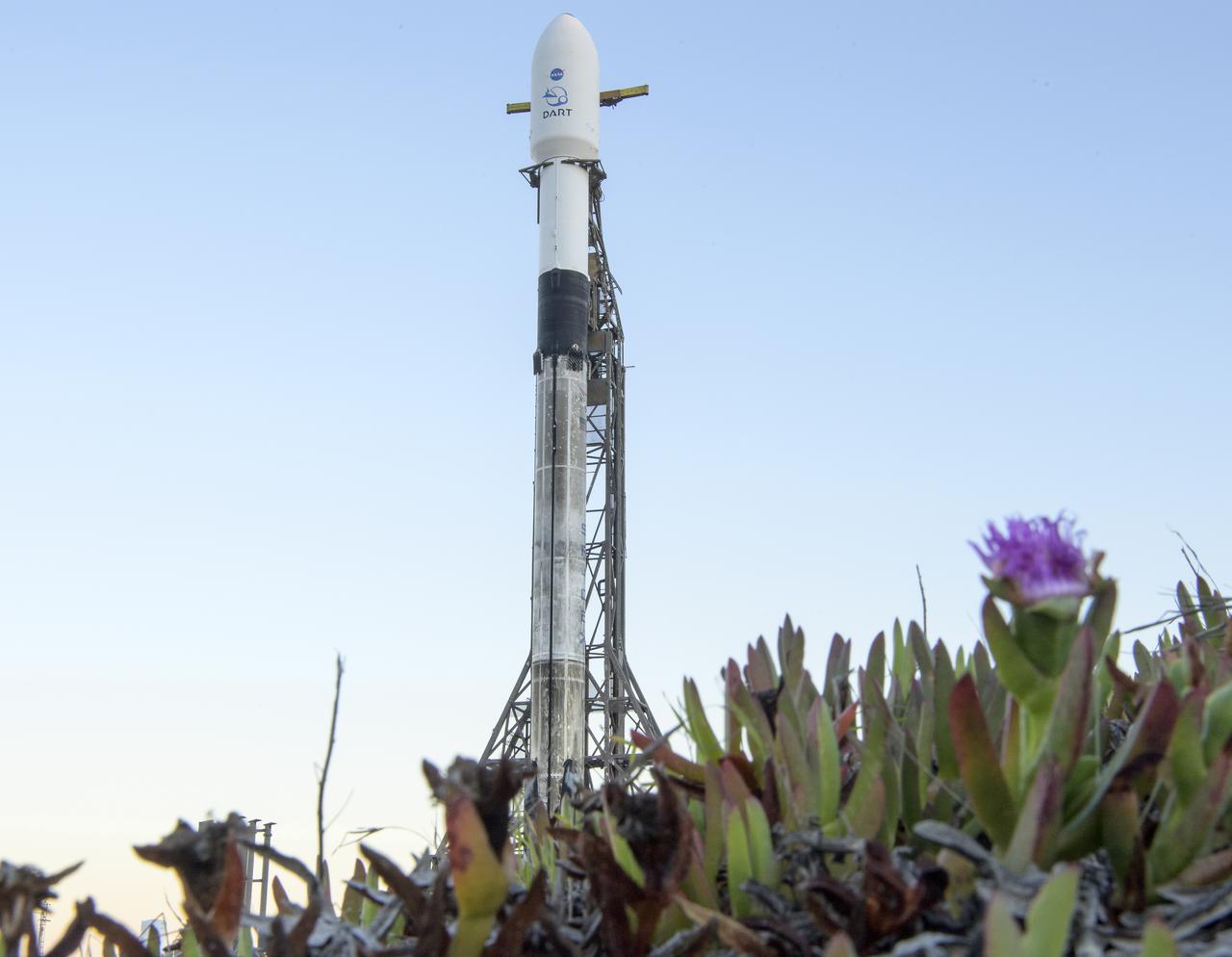

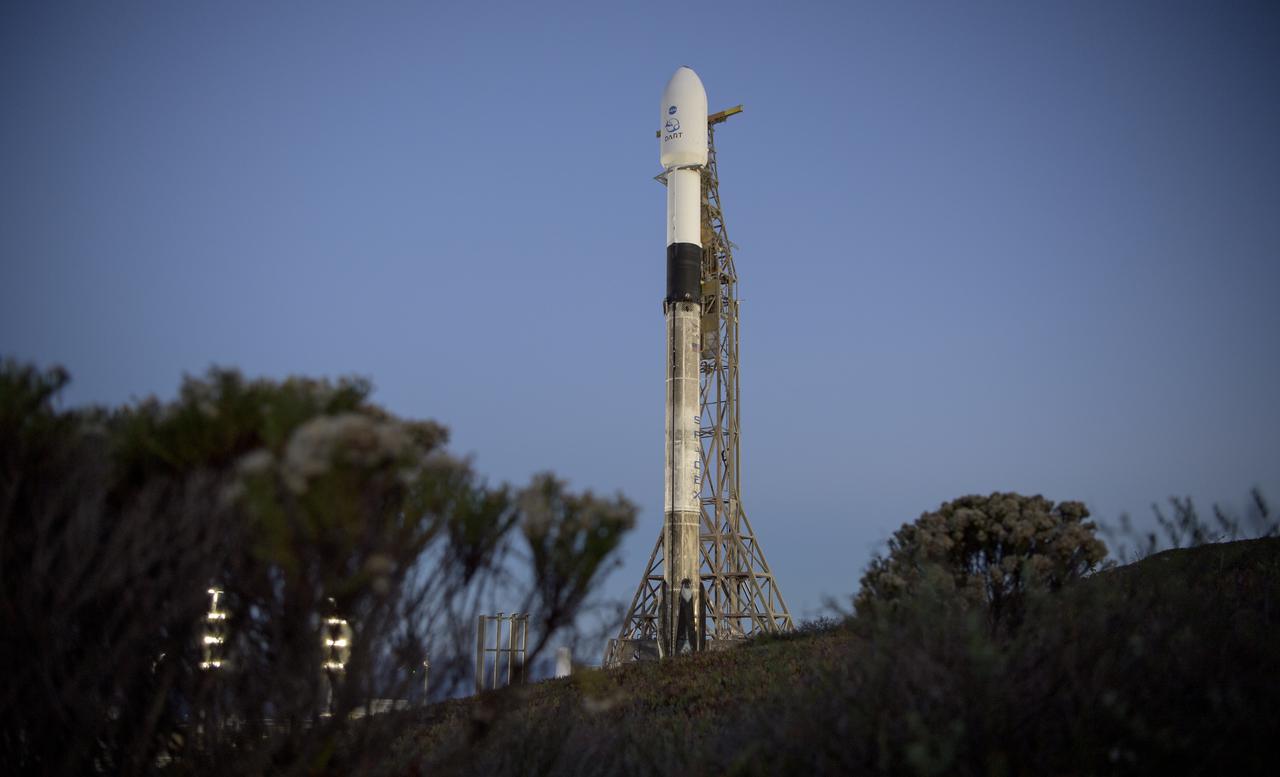
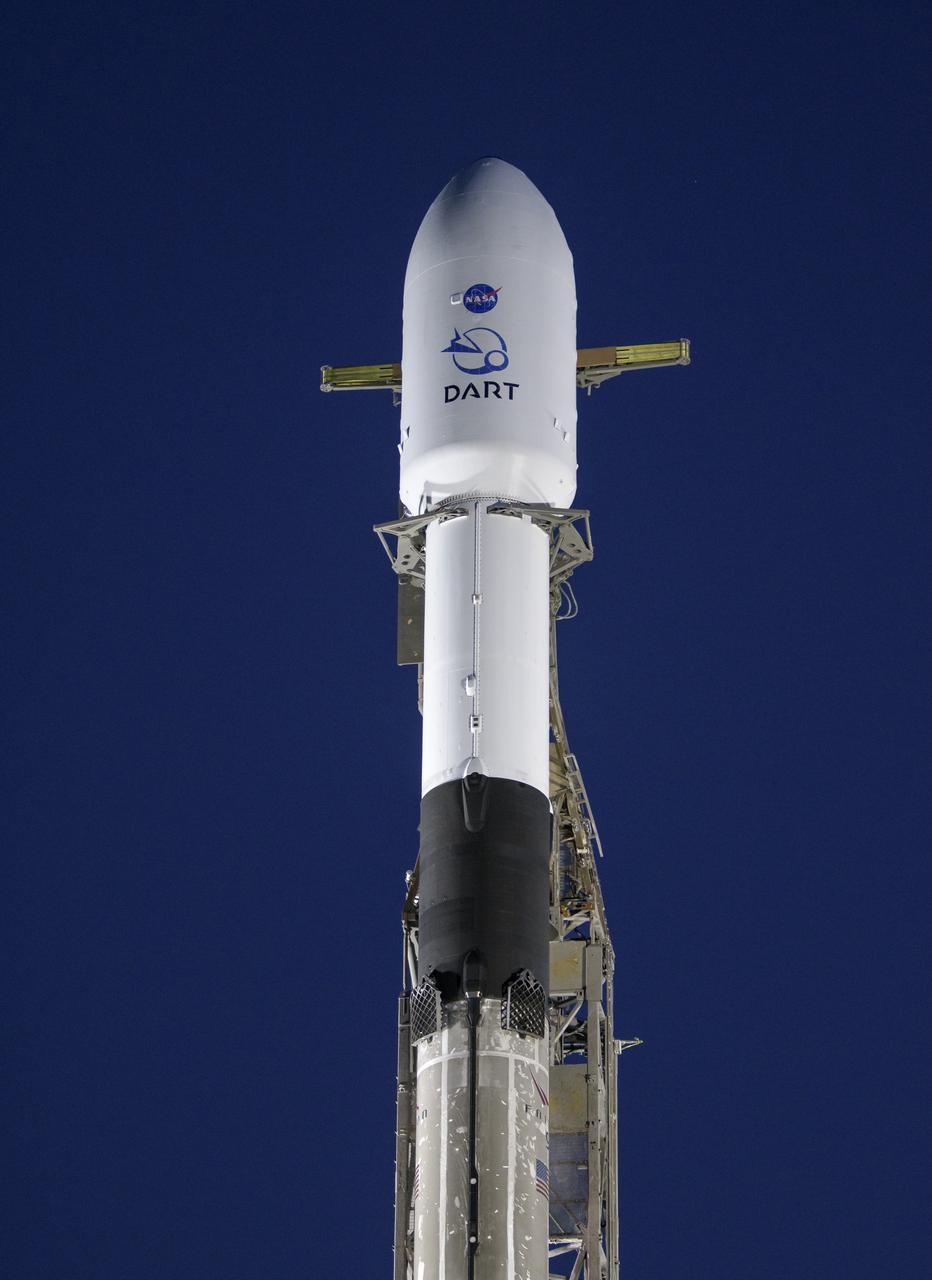
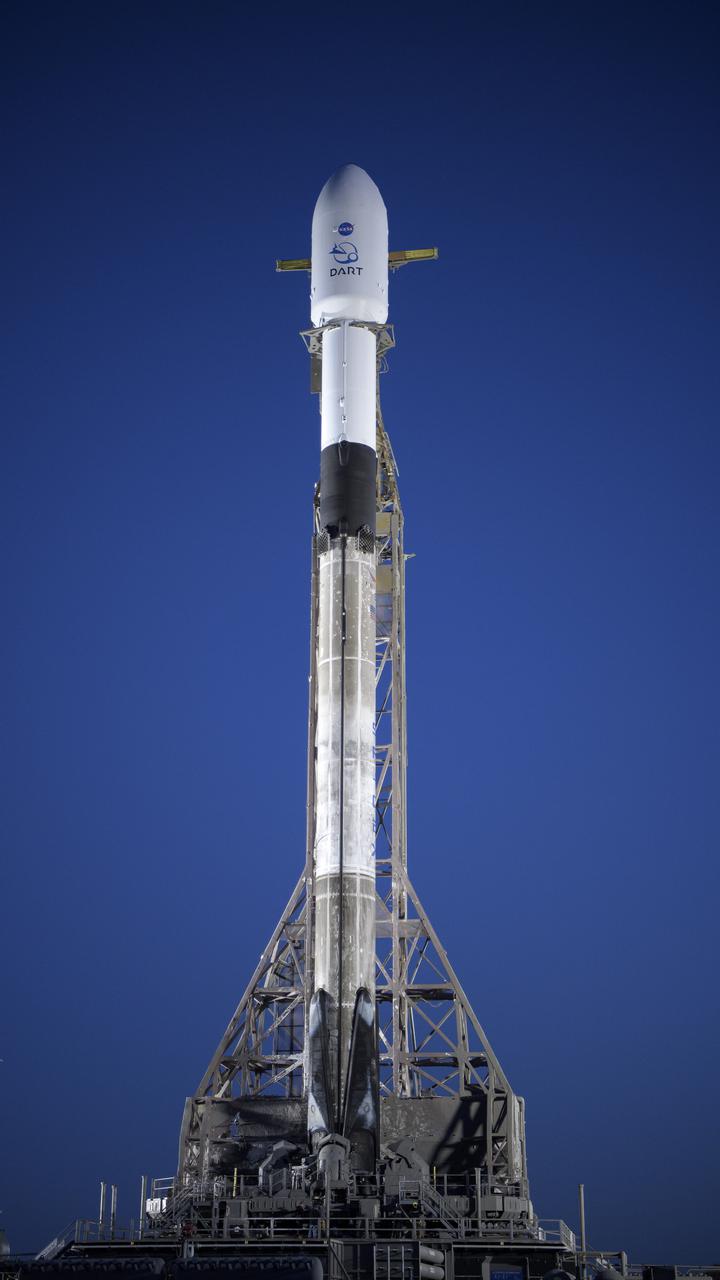
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
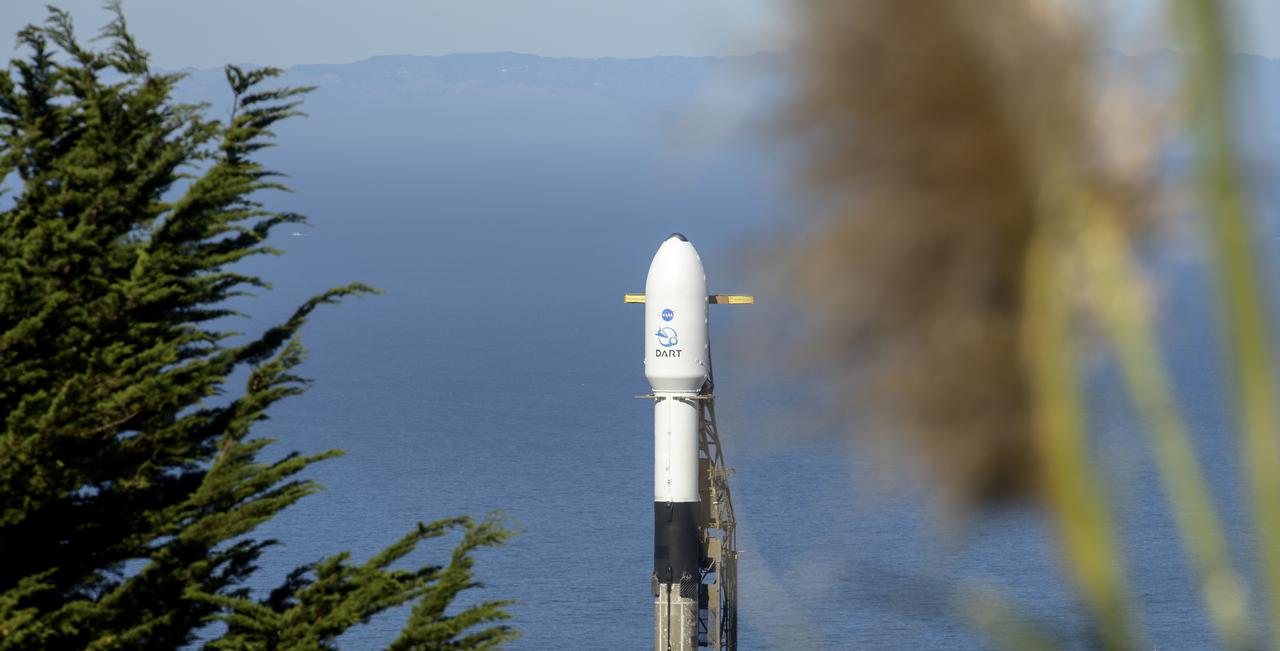

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
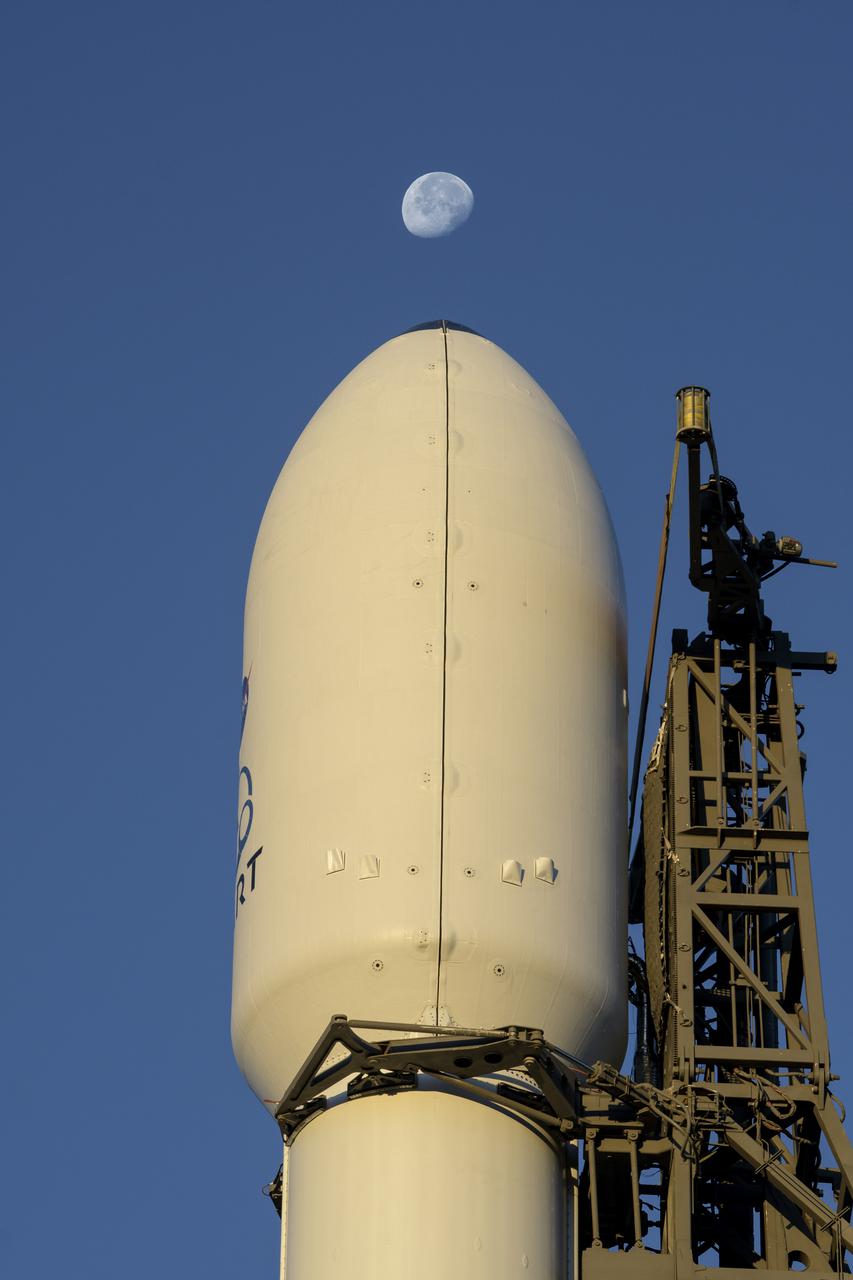

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
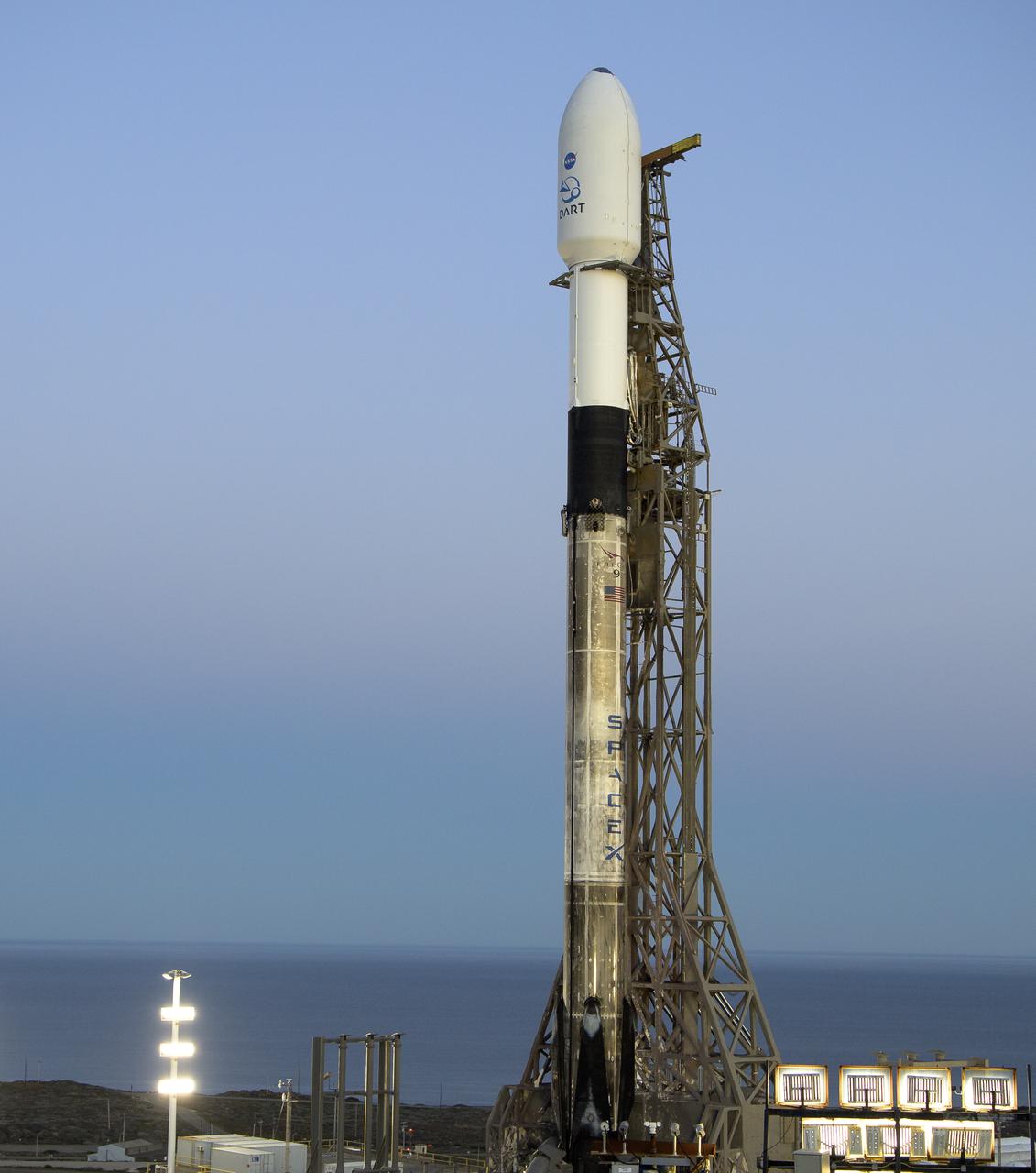

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
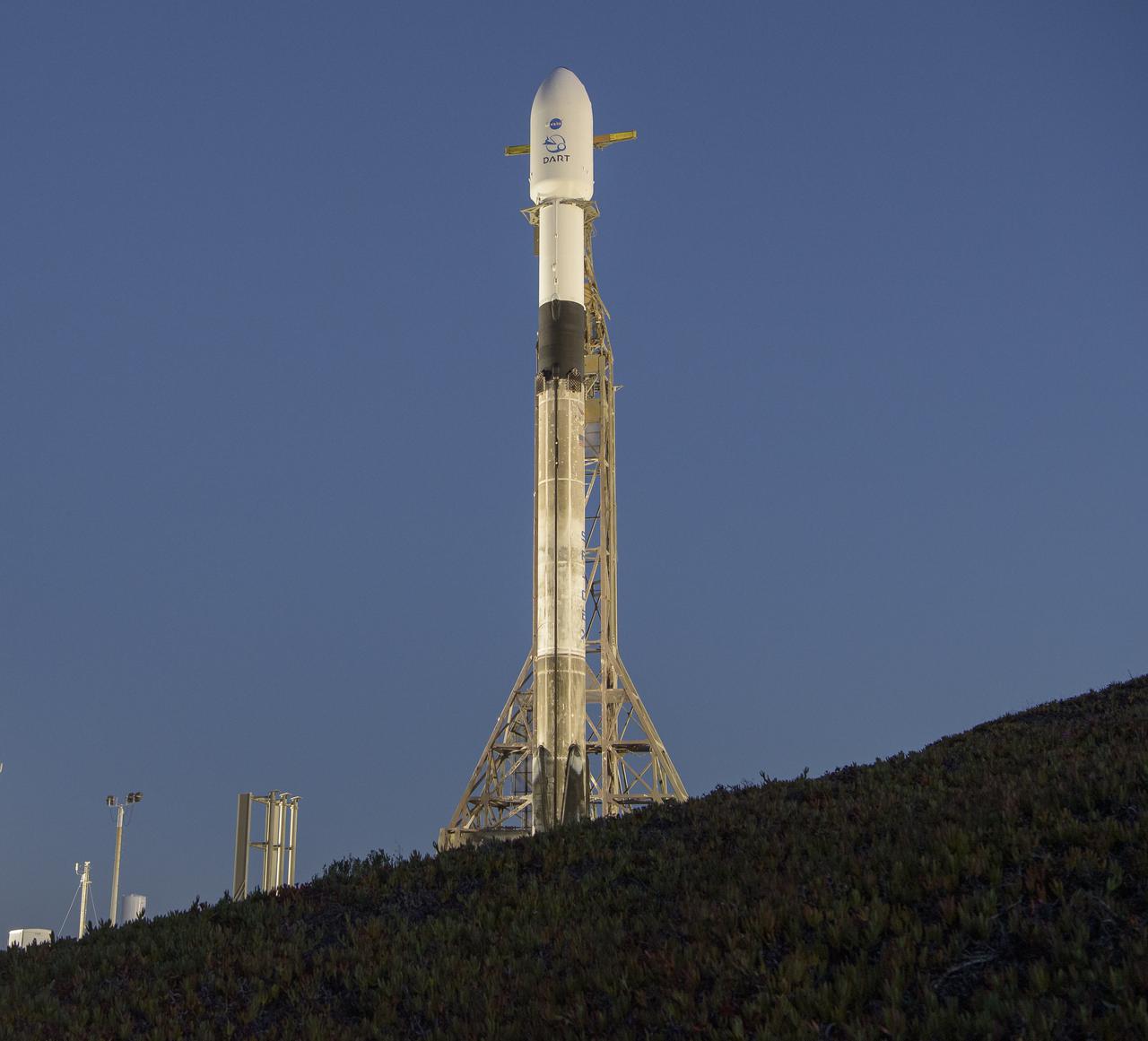

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
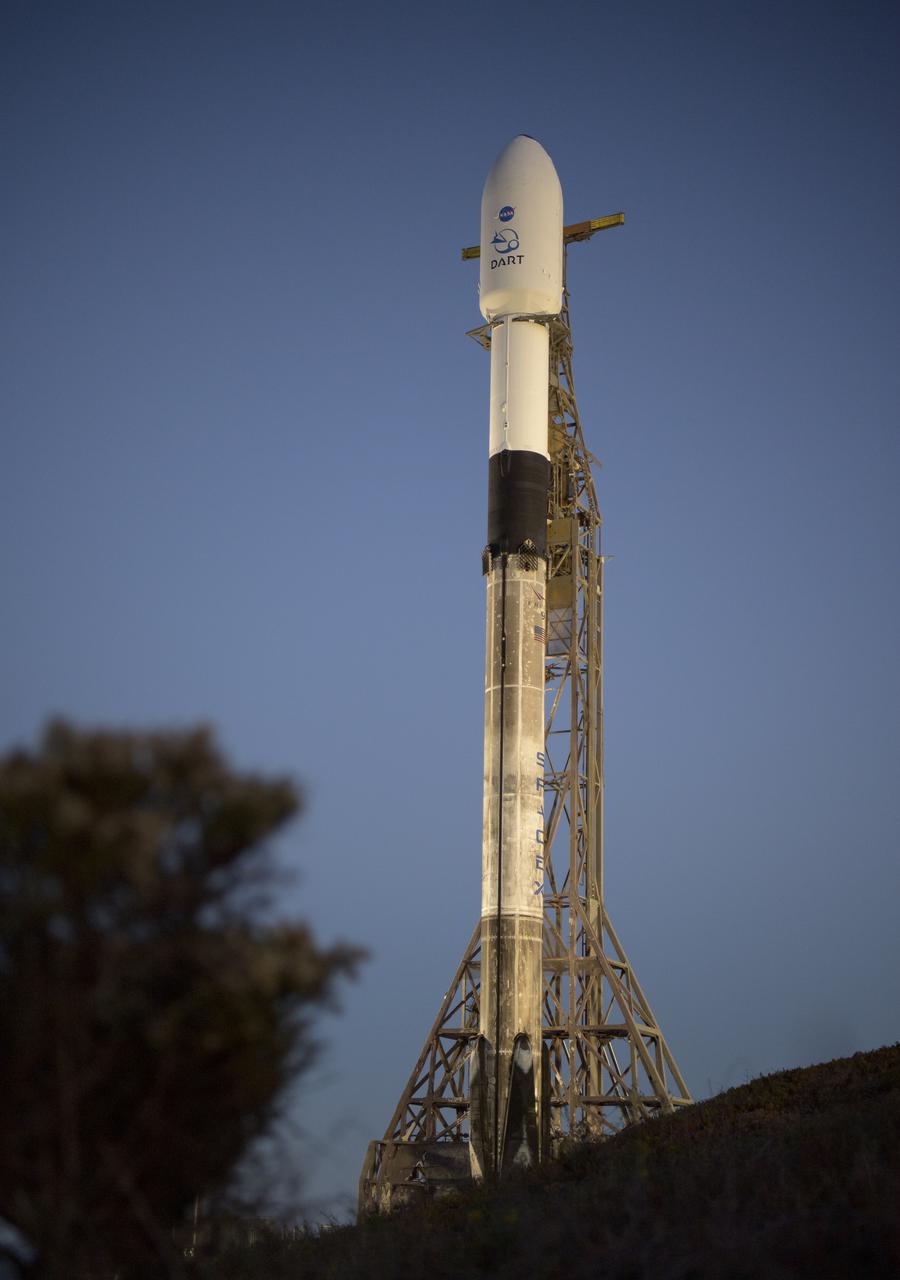

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
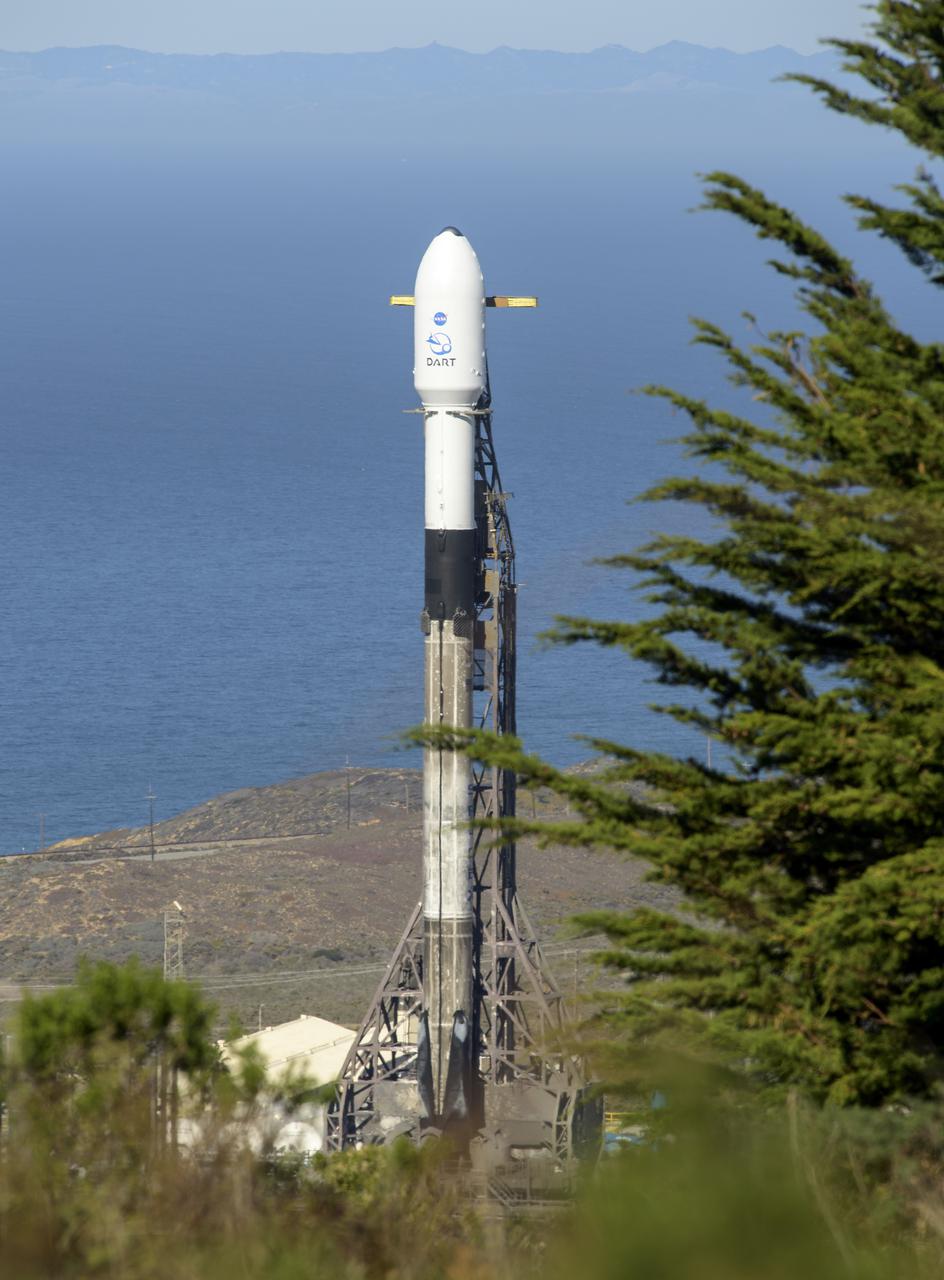

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
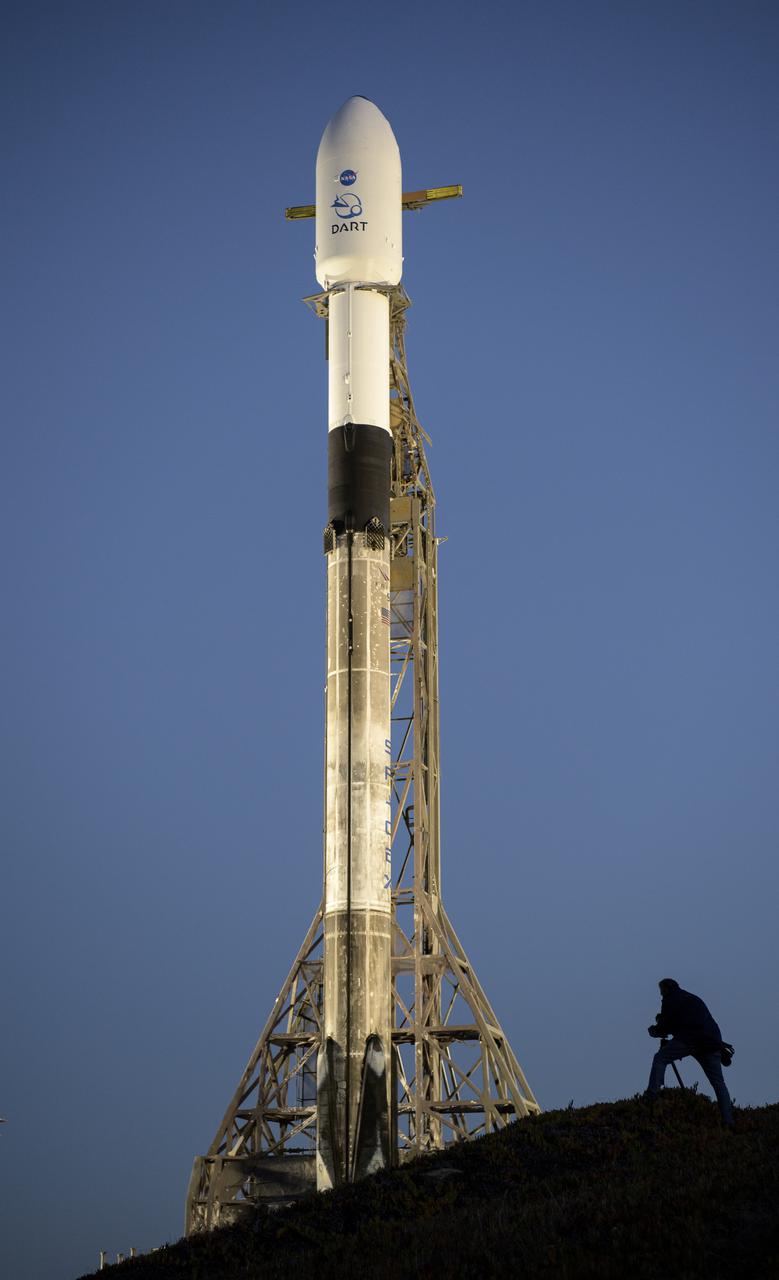

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
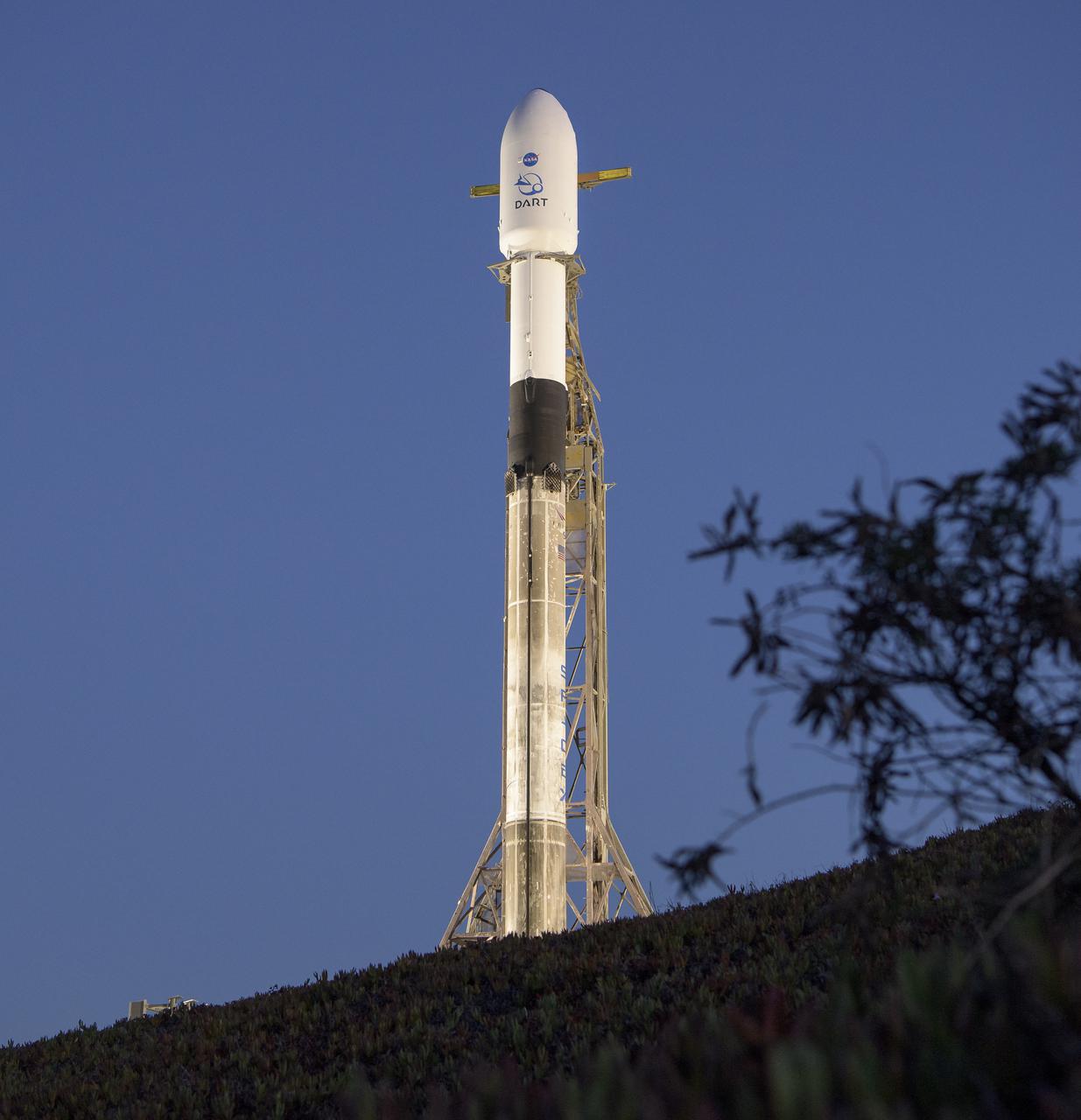

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
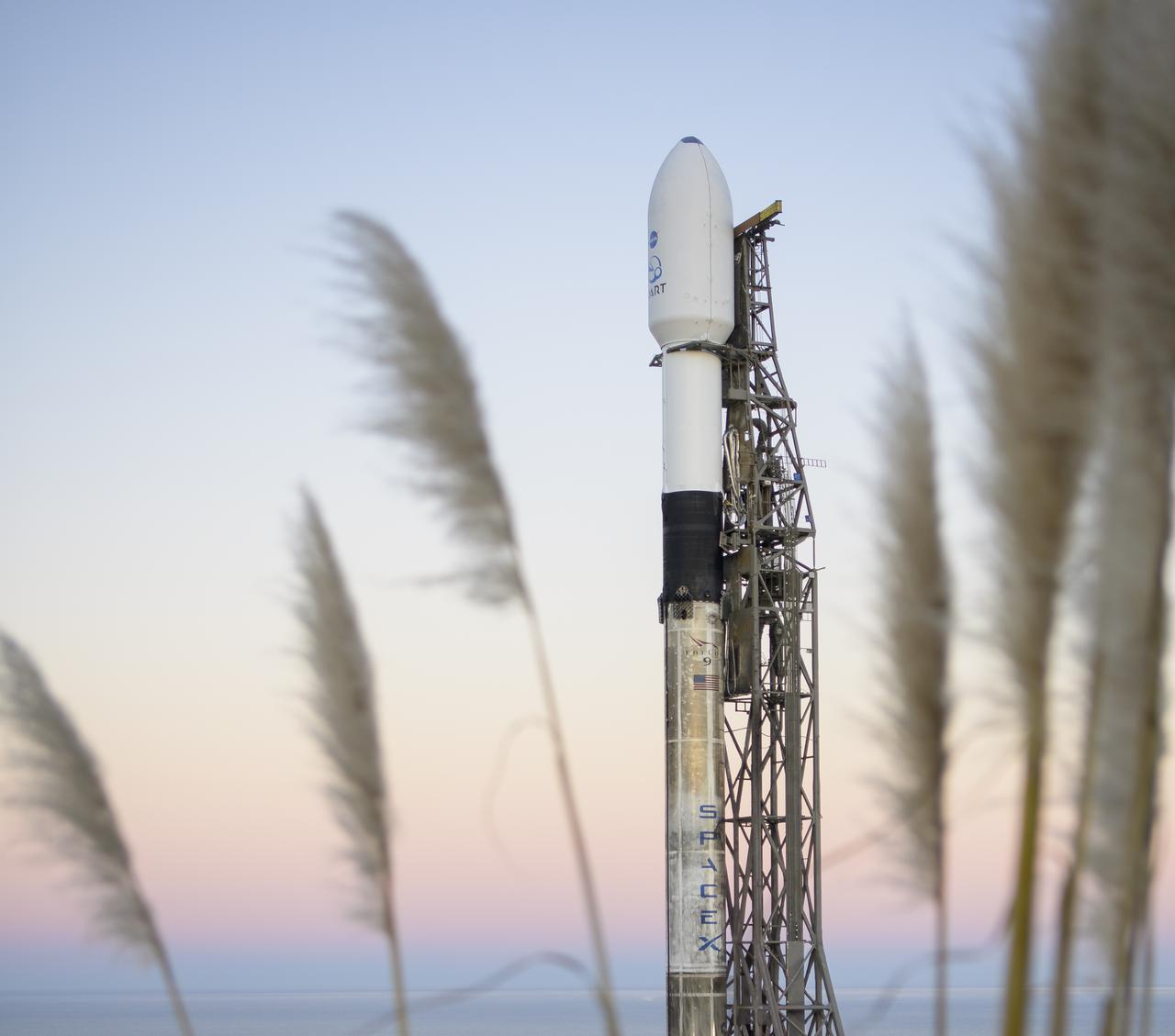

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
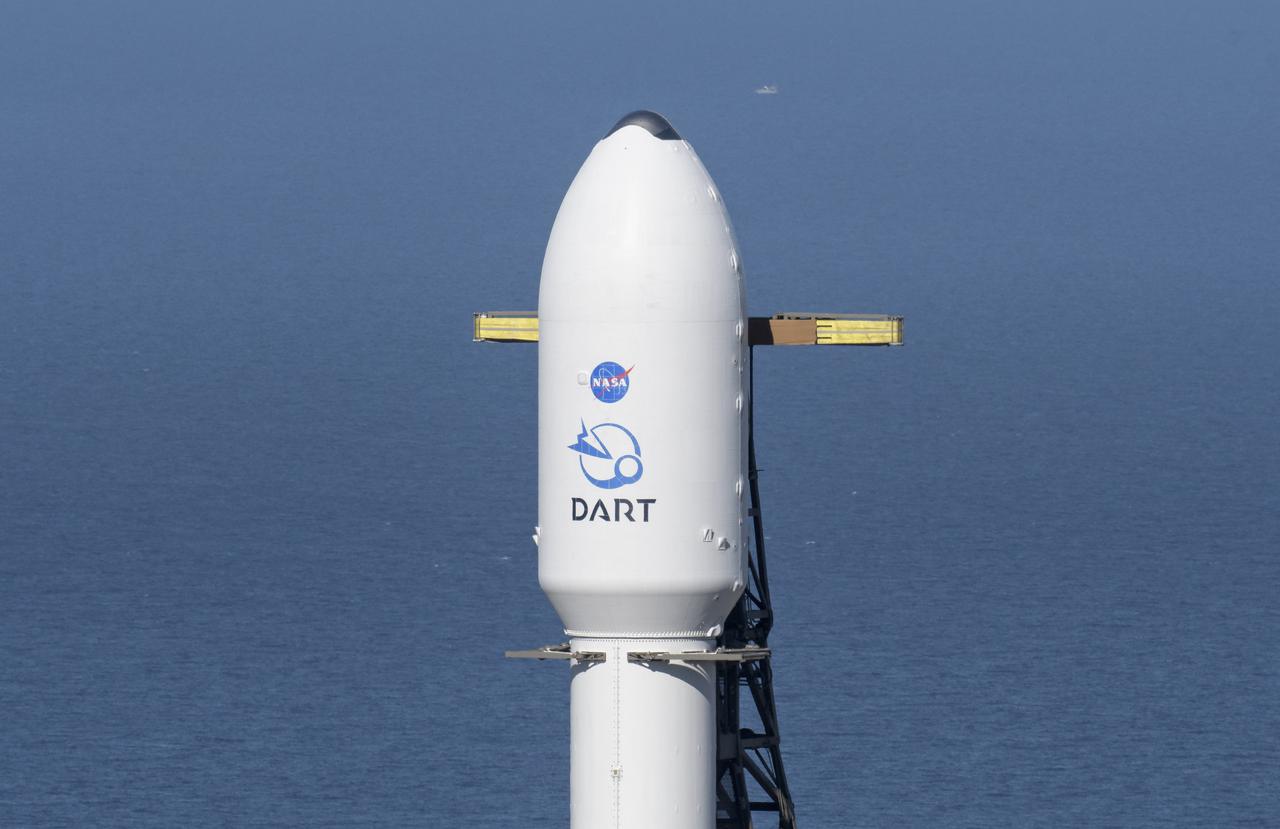

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
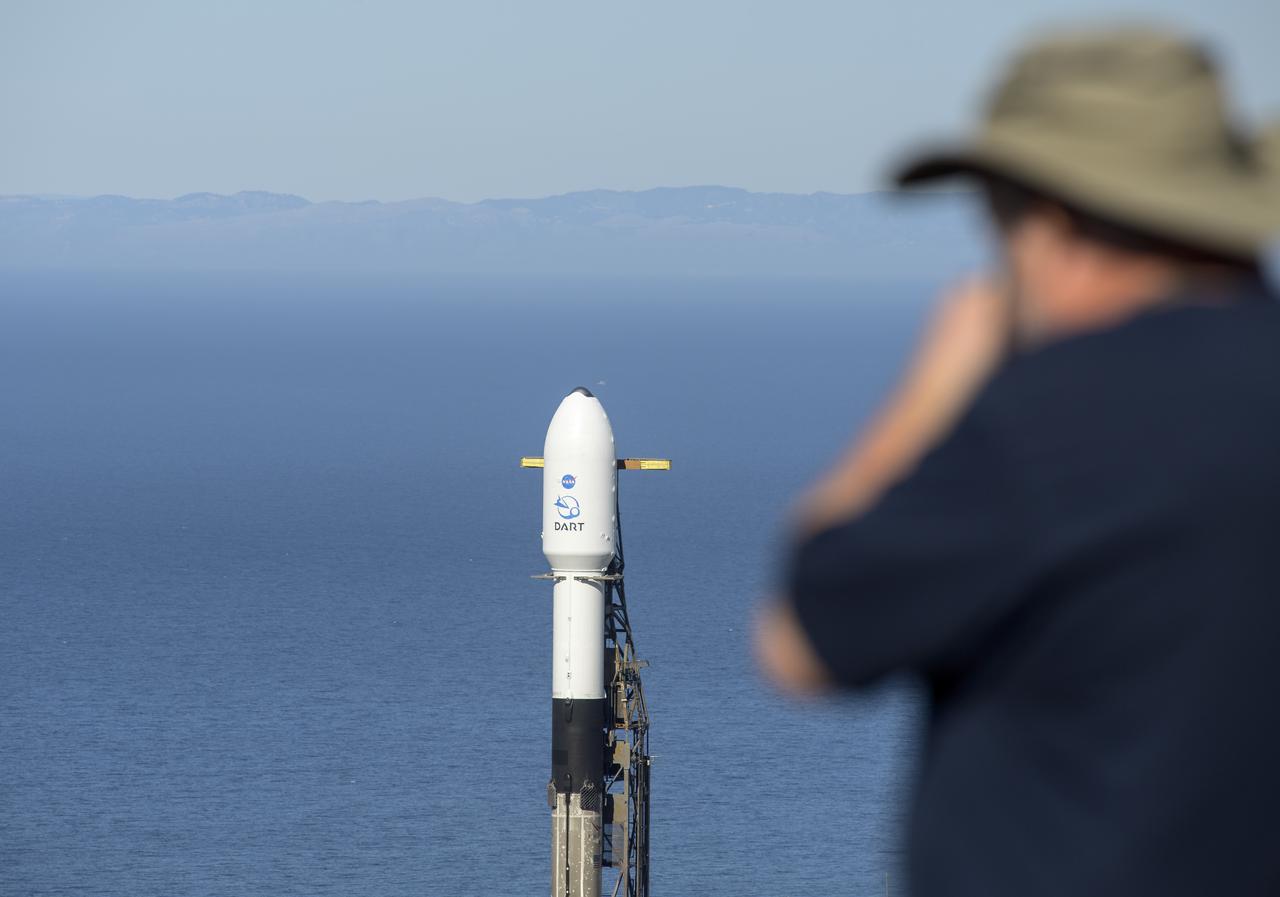

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
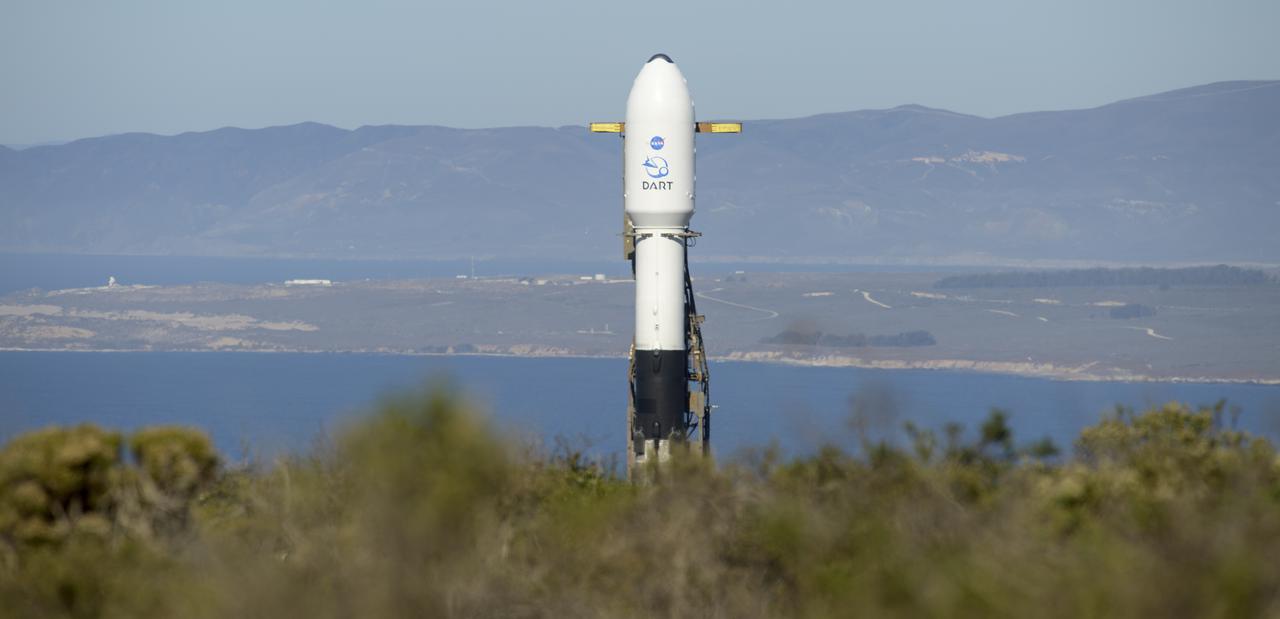

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
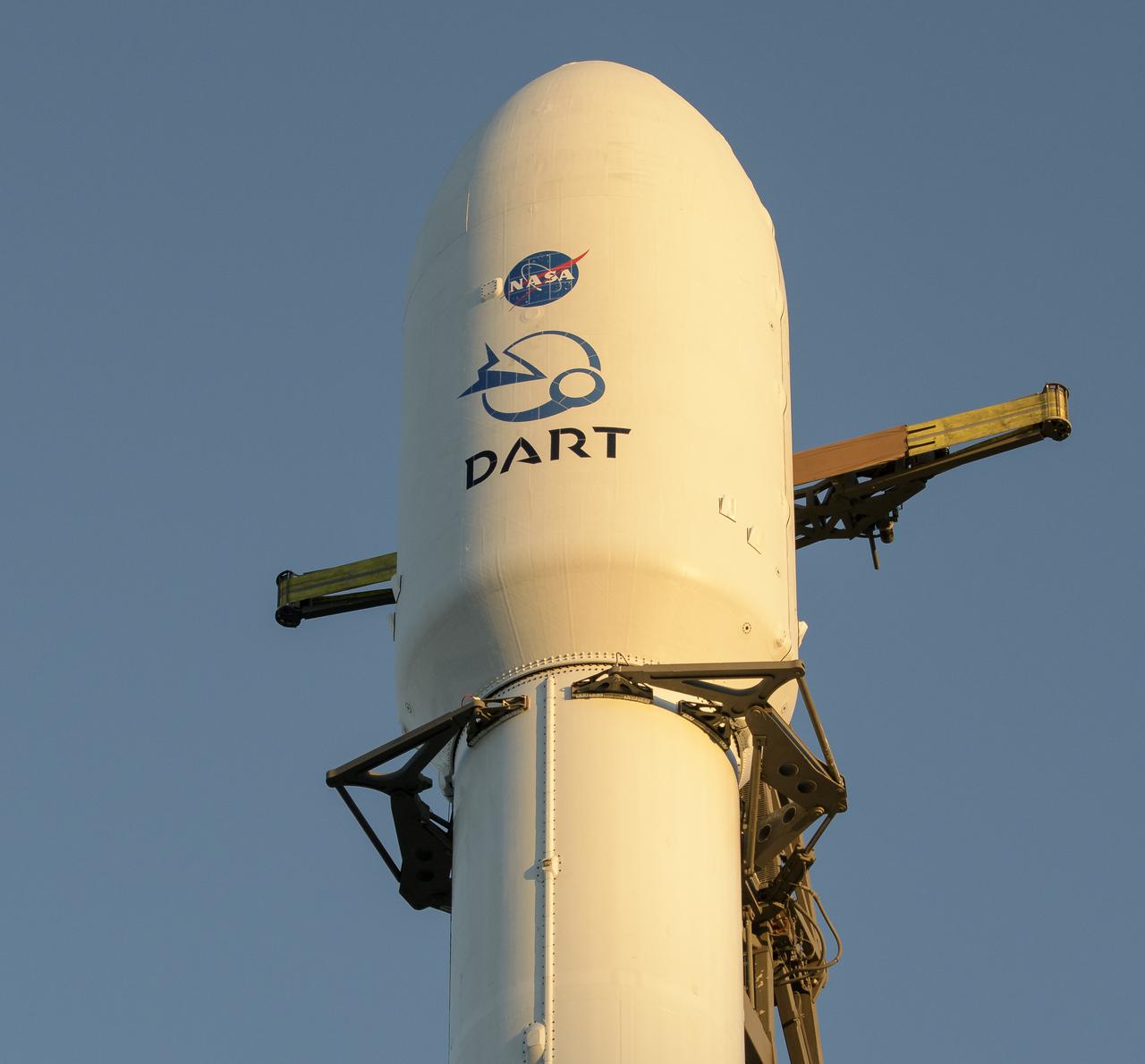

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
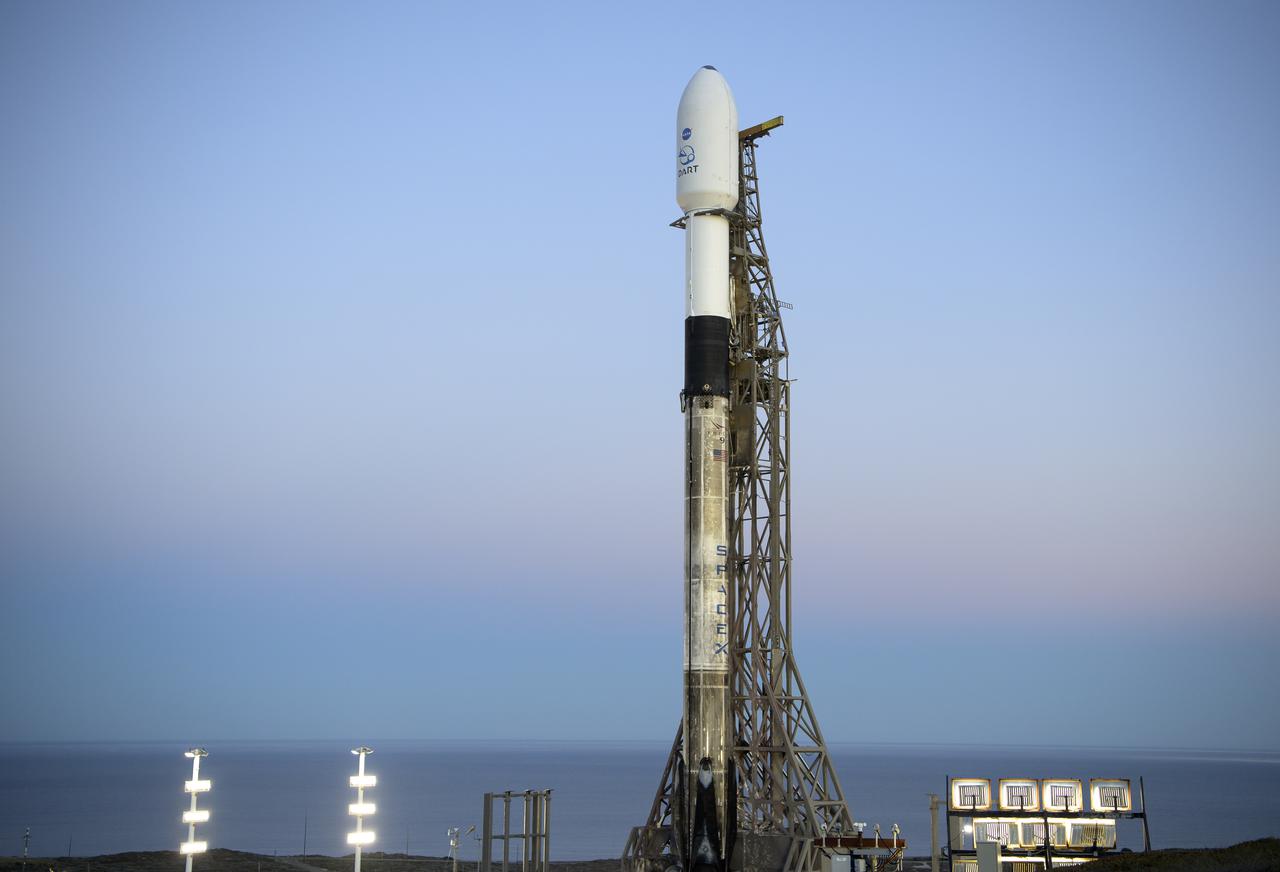

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
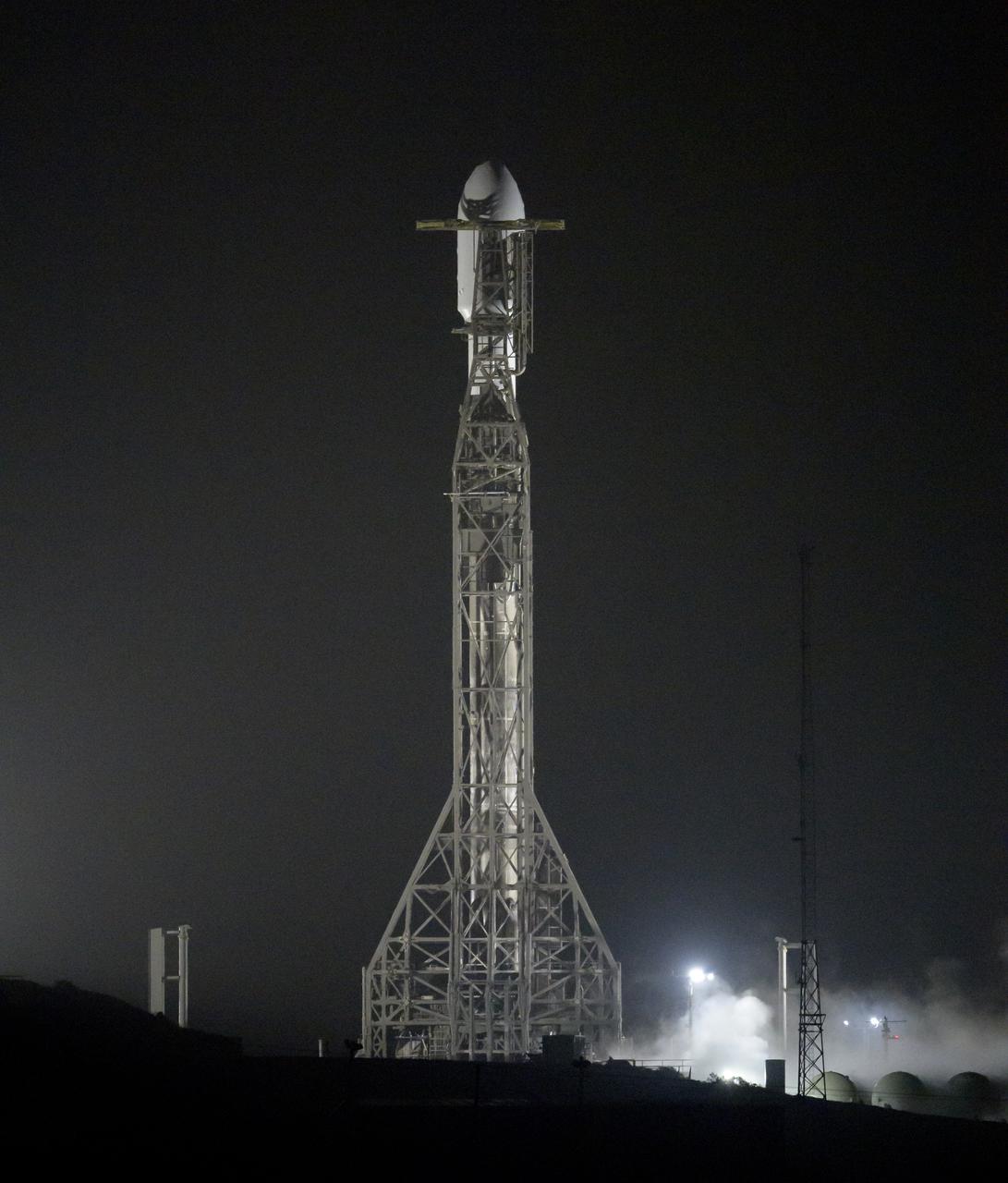

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen ready for launch, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
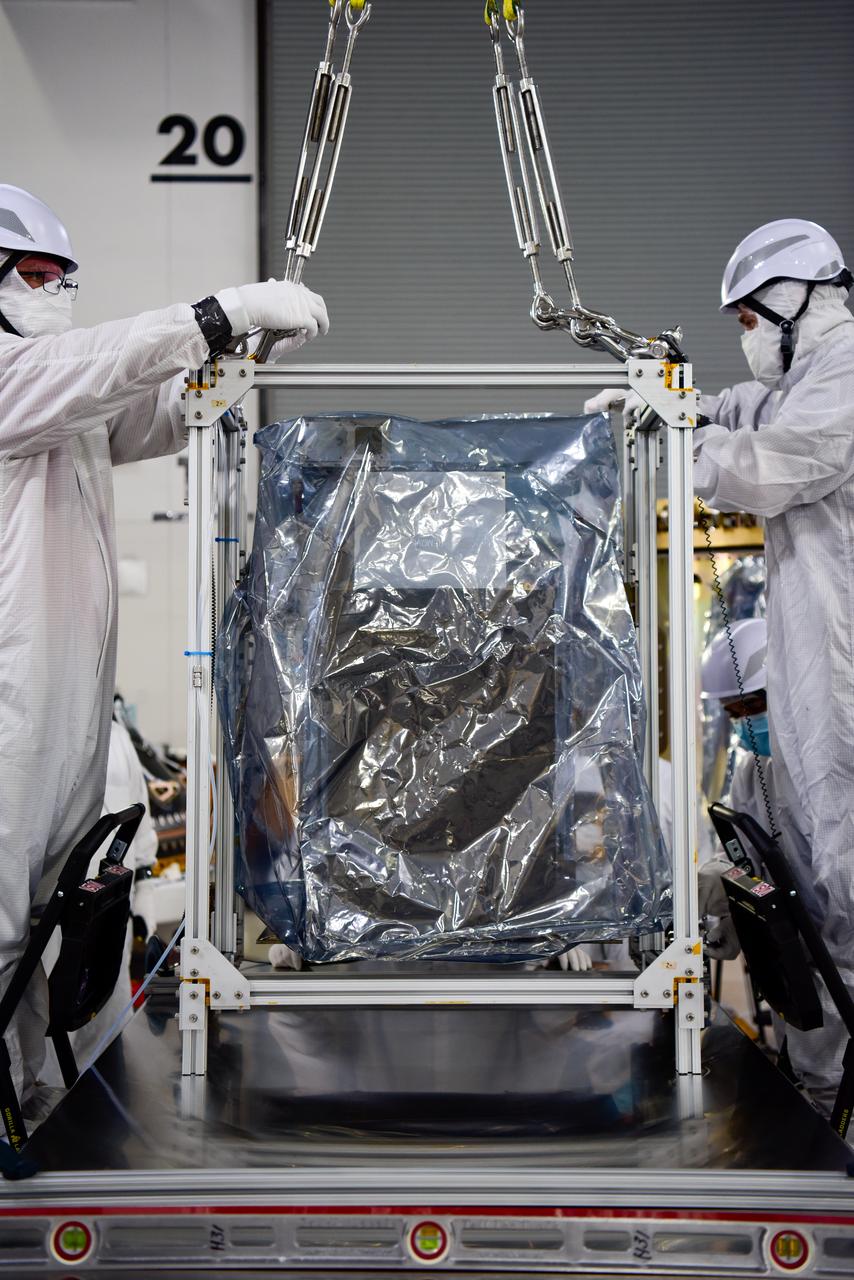

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
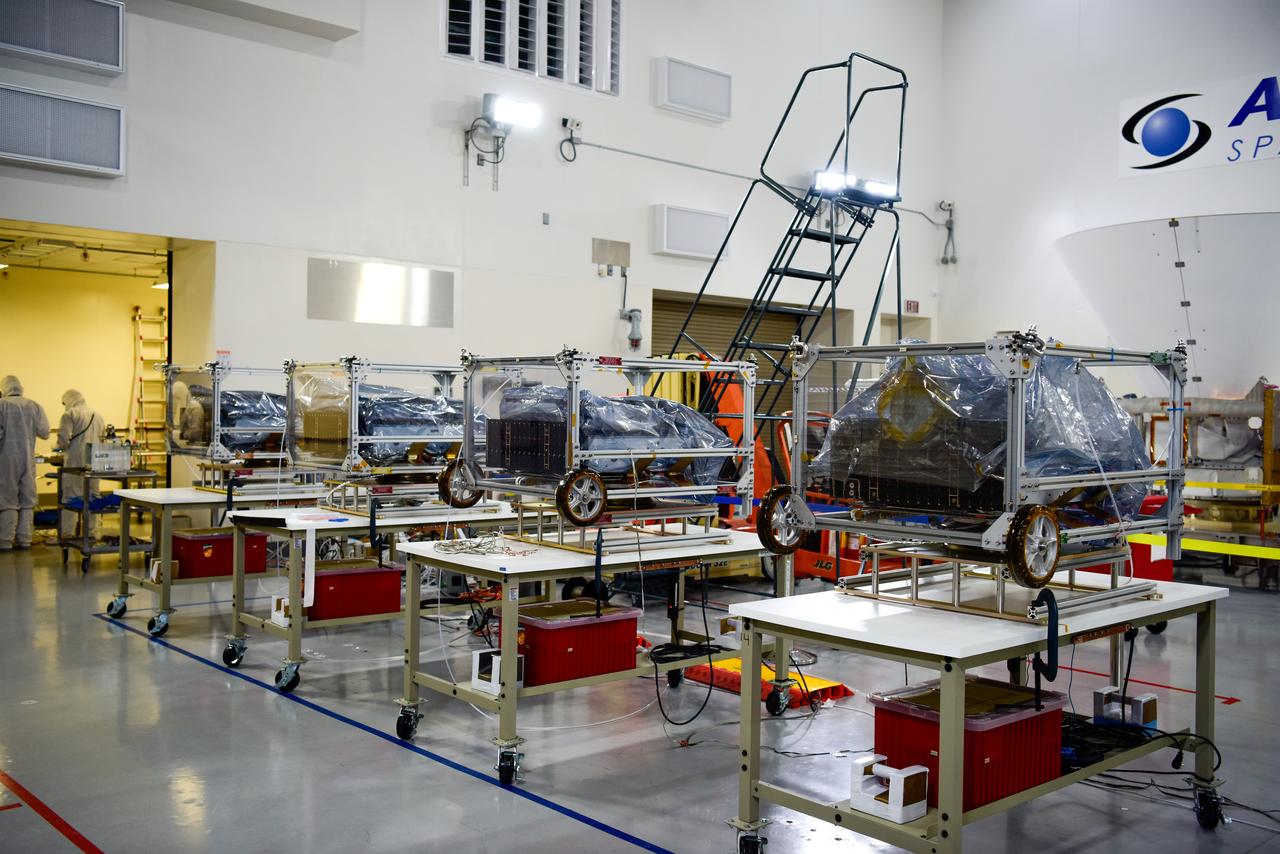

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites await integration to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
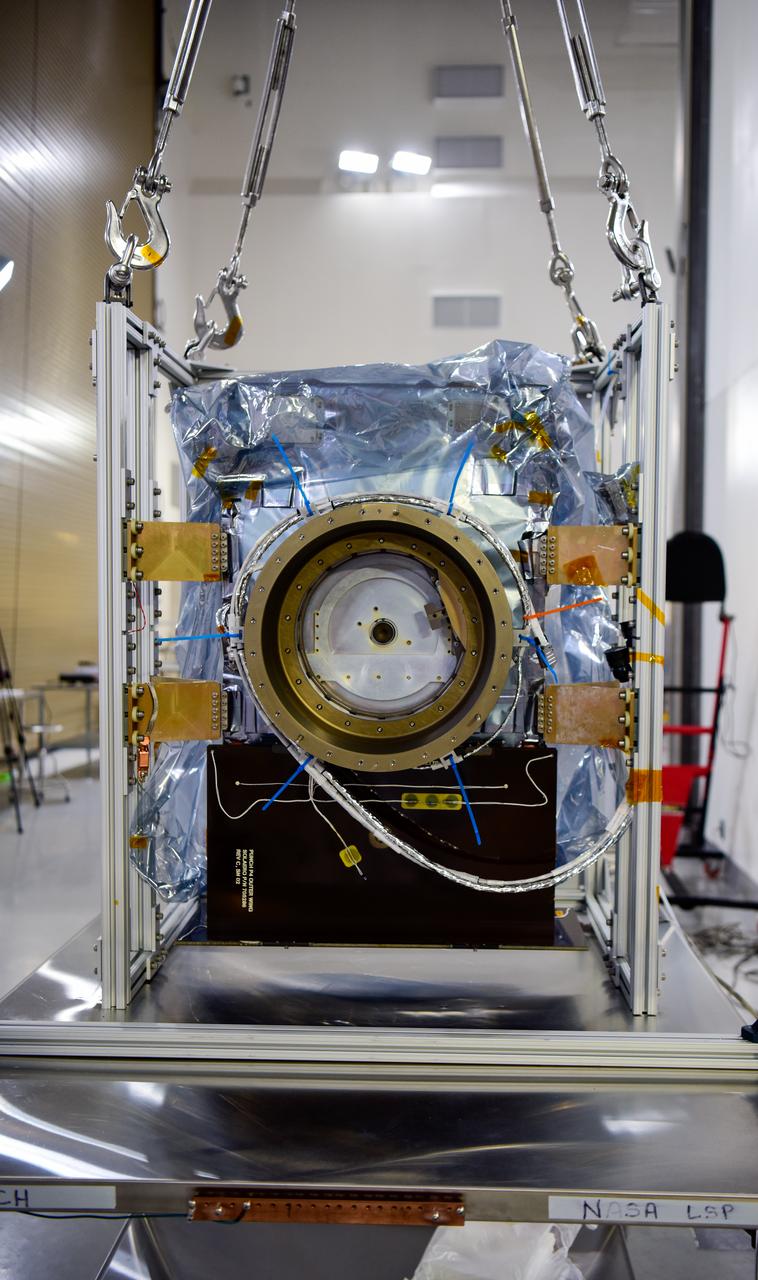

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
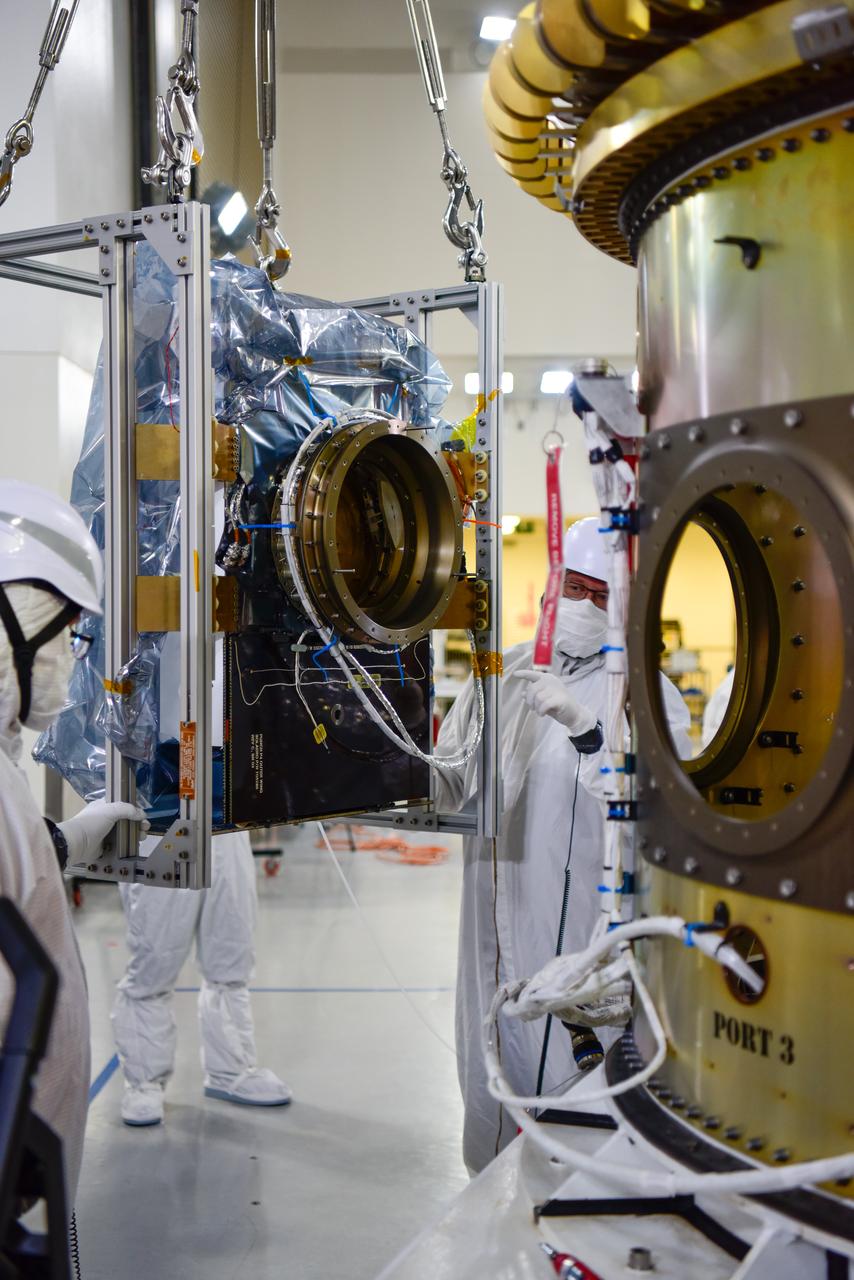

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites await integration to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
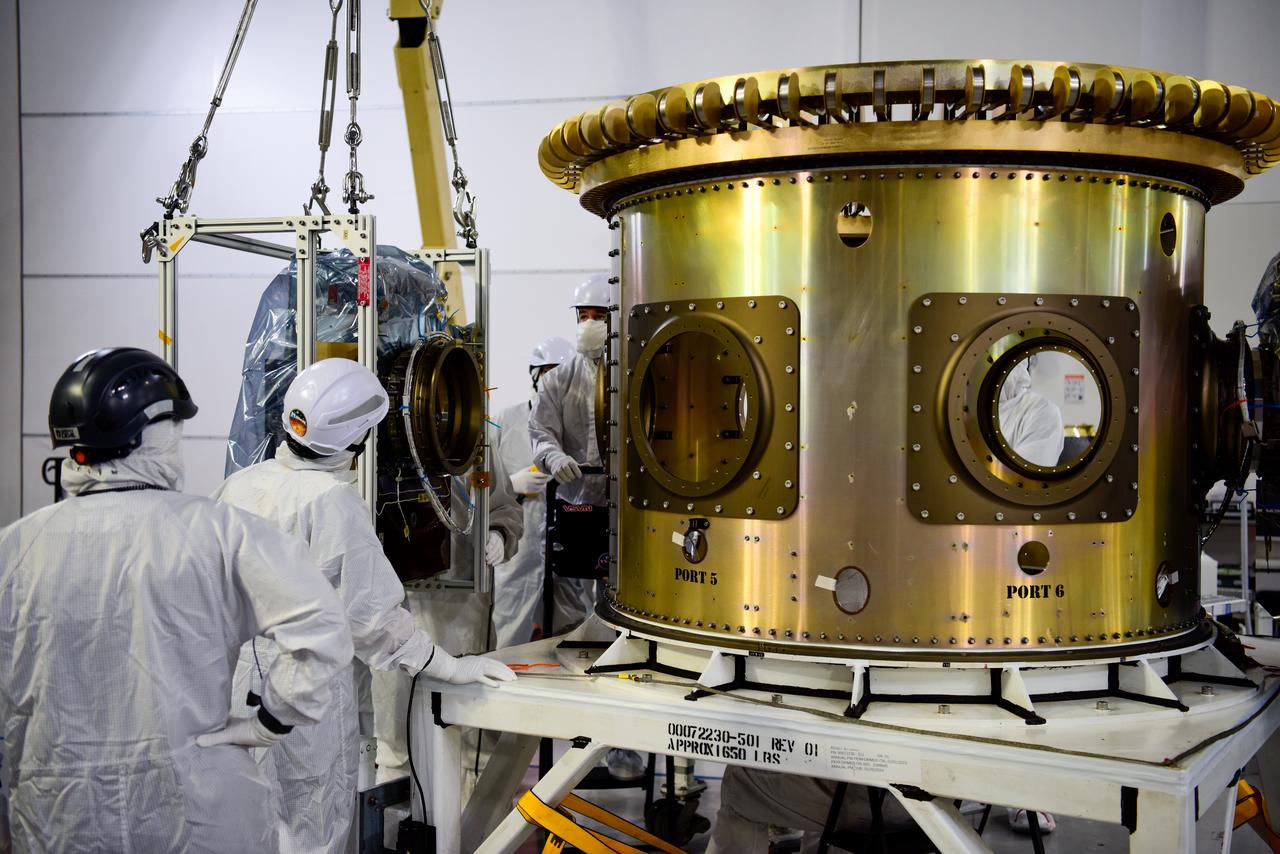

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
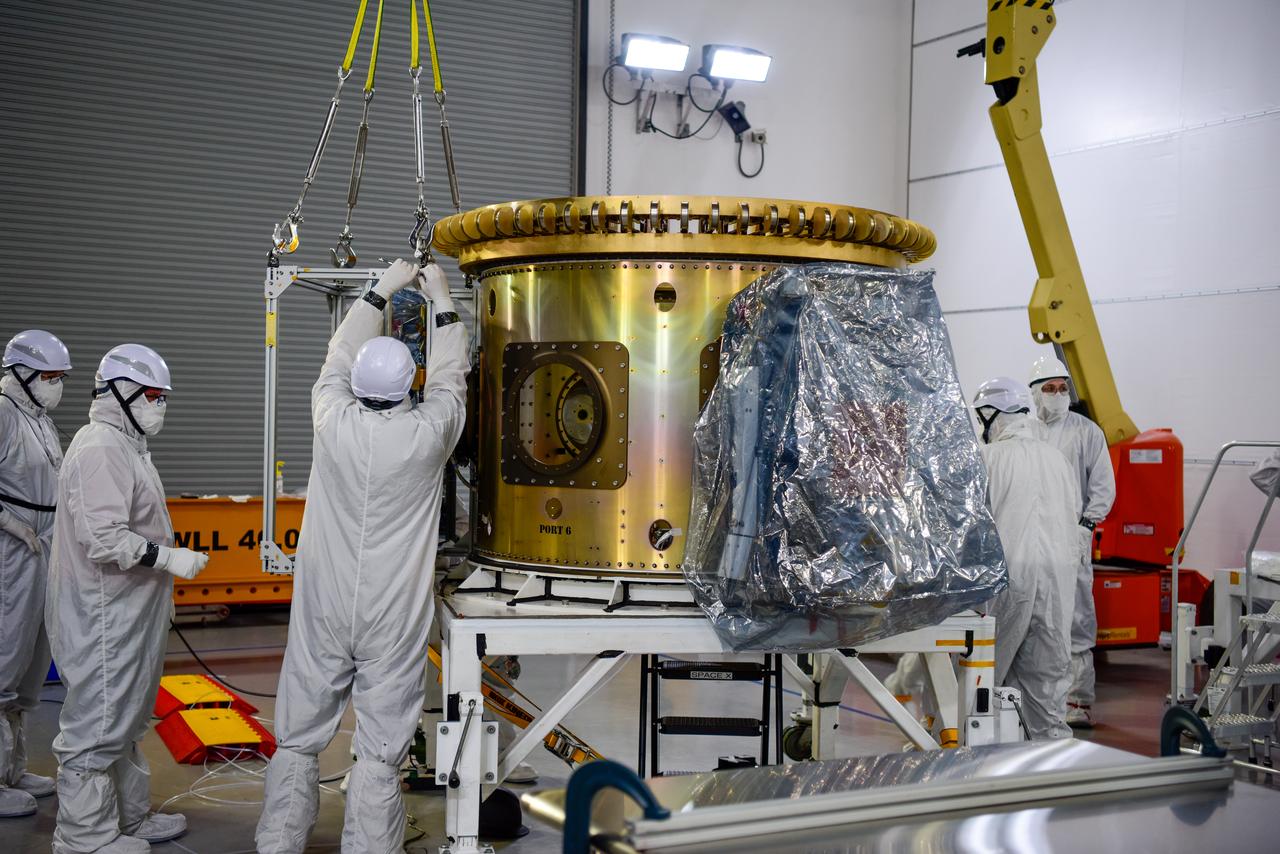

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
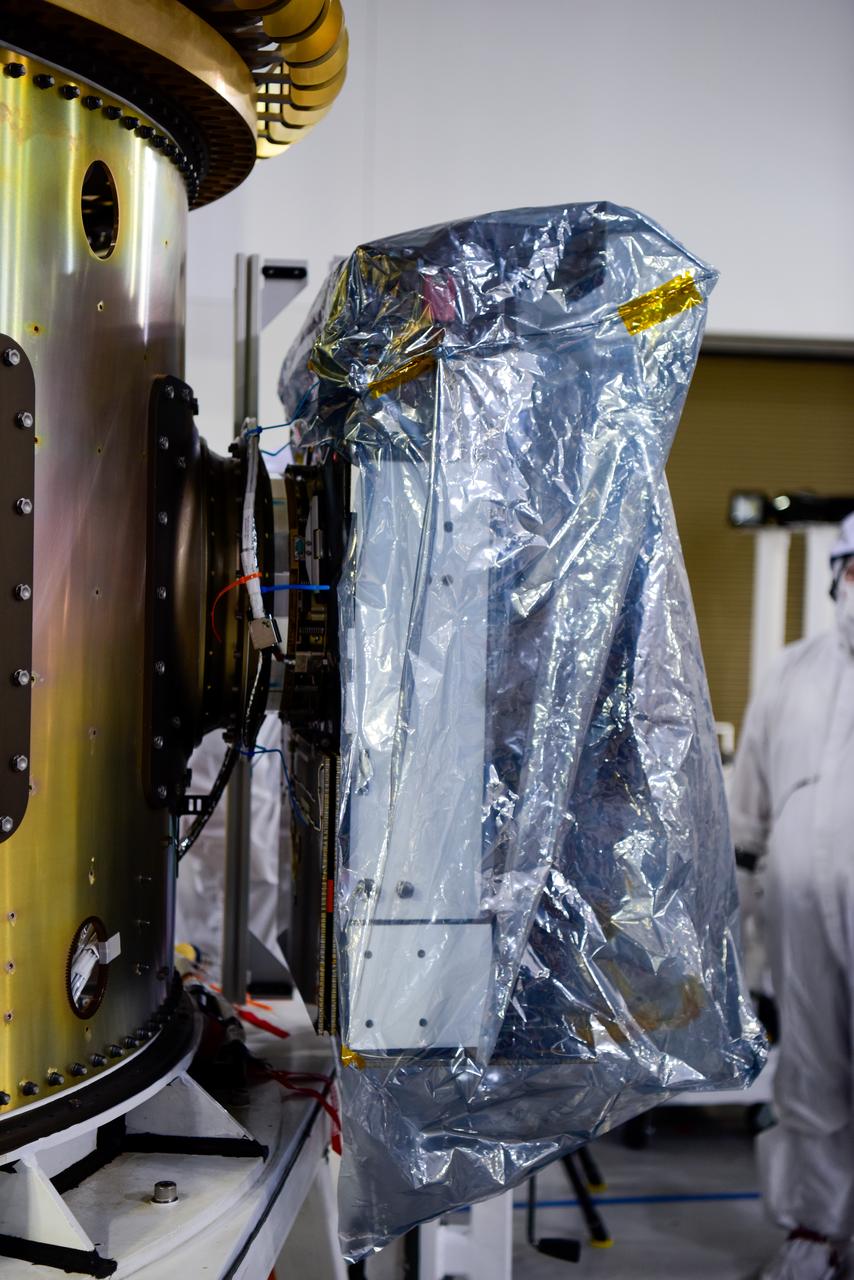

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
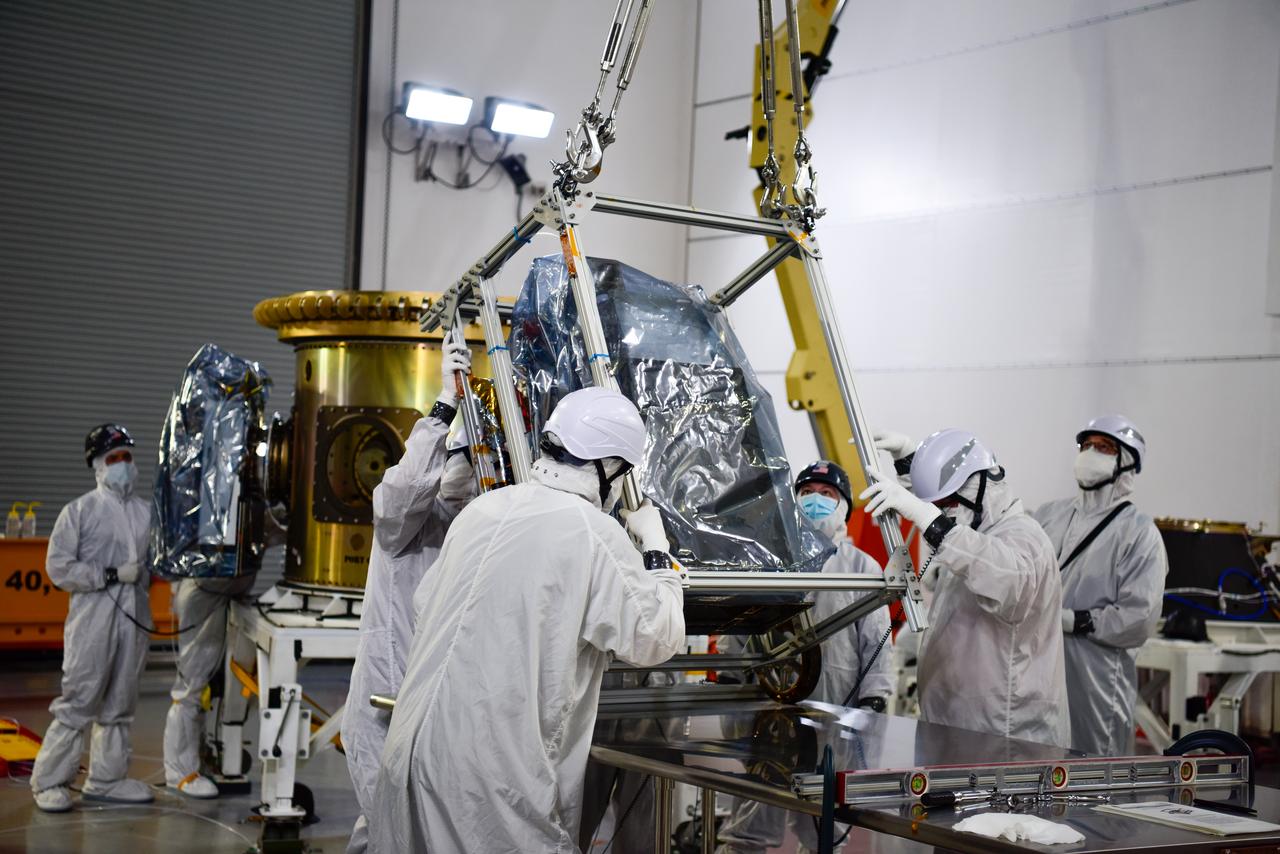

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
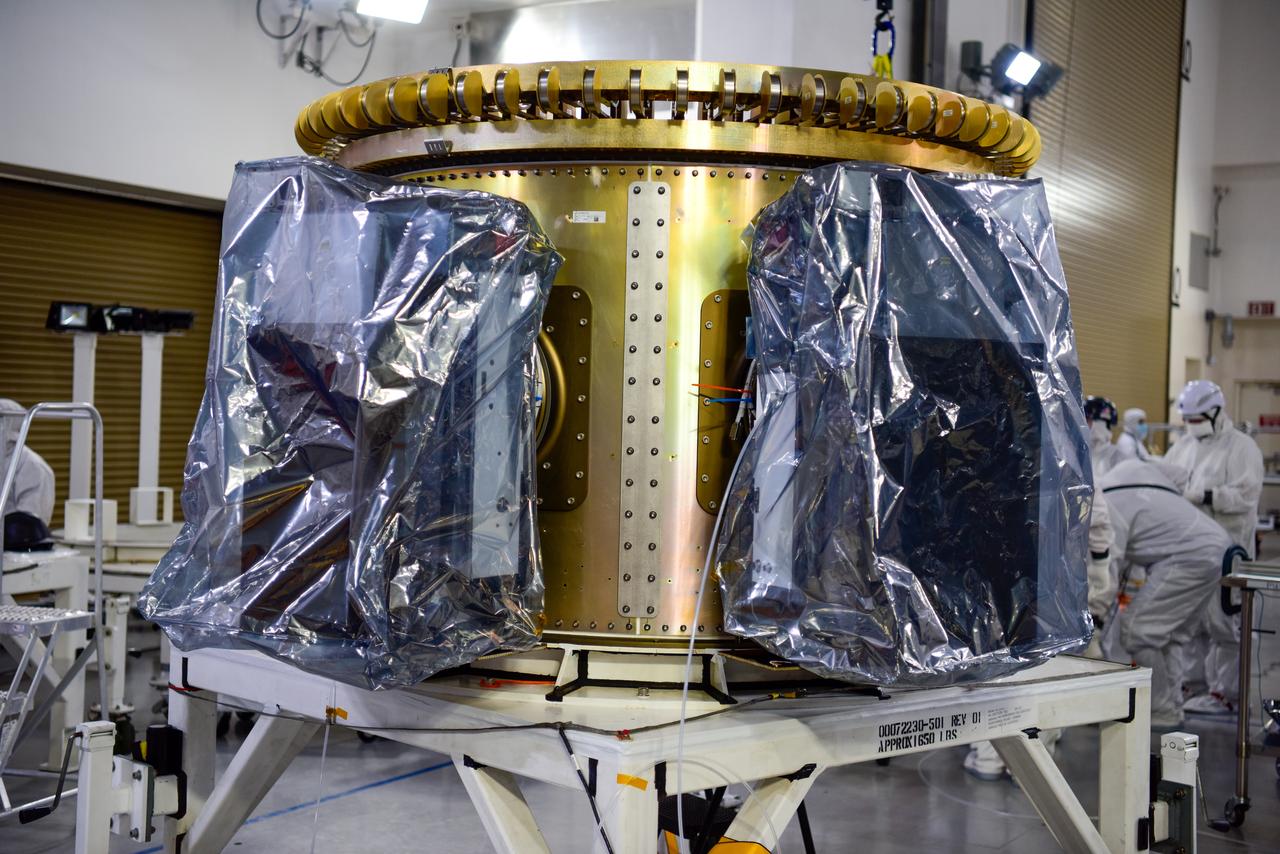

Technicians integrate NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites to the evolved expendable launch vehicle secondary payload adapter array ring inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Feb. 14, 2025. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. The PUNCH mission is launching as a rideshare with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 10:09 p.m. EST (7:09 p.m. PST), Friday, Feb. 28, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
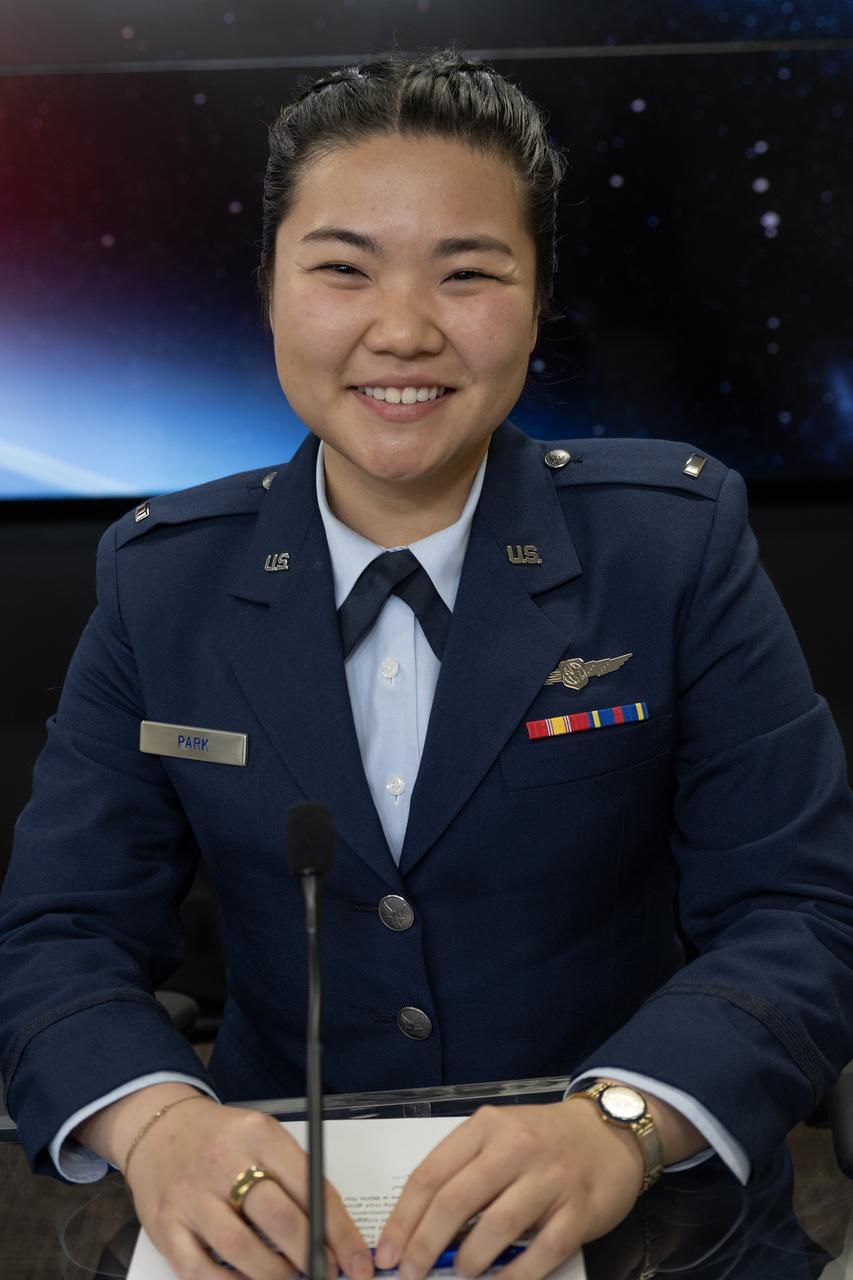

1st Lt. Ina Park, launch weather officer, 30th Operations Support Squadron, U.S. Air Force participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is NET targeted for 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
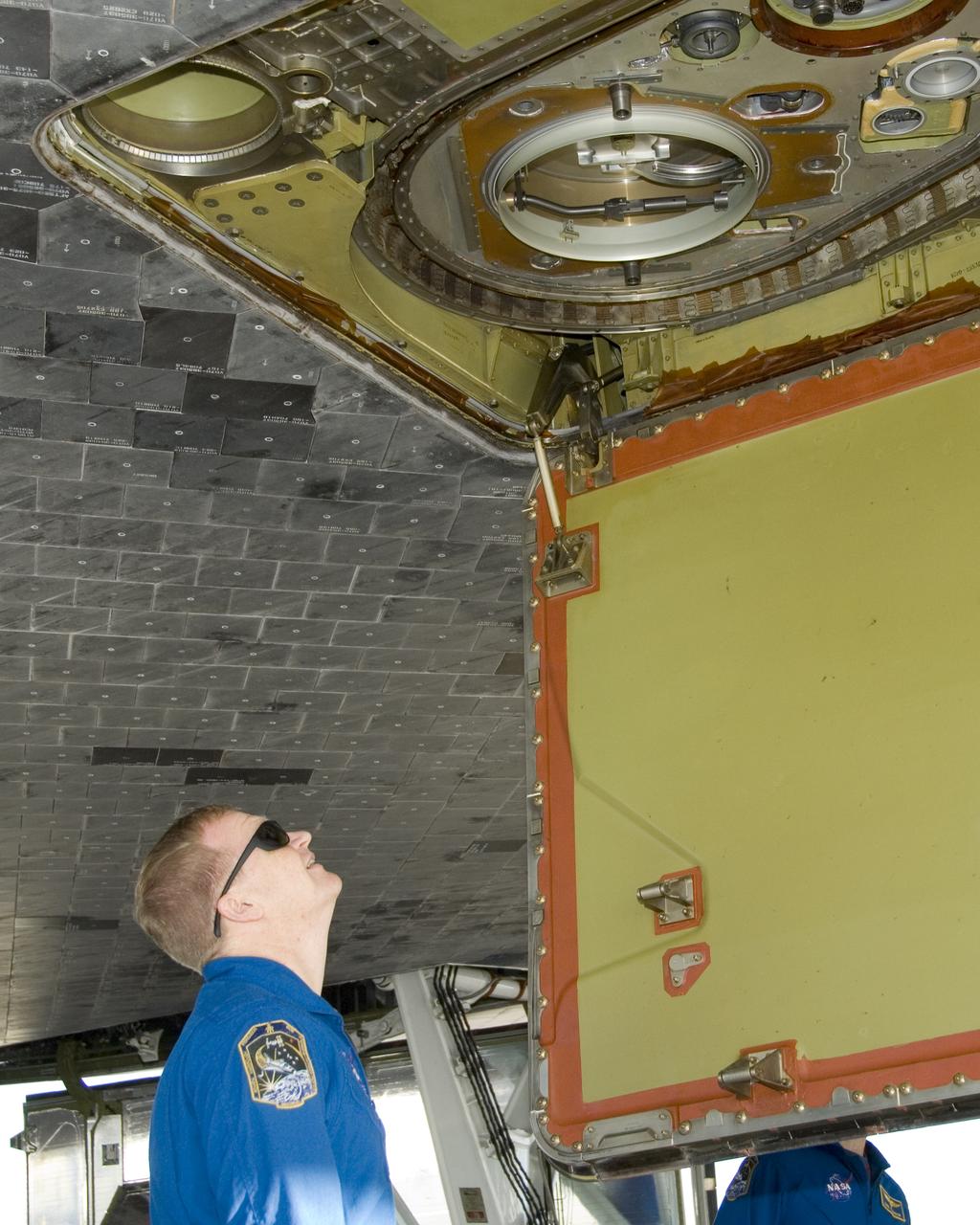

STS-126 pilot Eric Boe inspects the liquid oxygen line connection on the belly of Space Shuttle Endeavour following landing at Edwards Air Force Base Sunday.
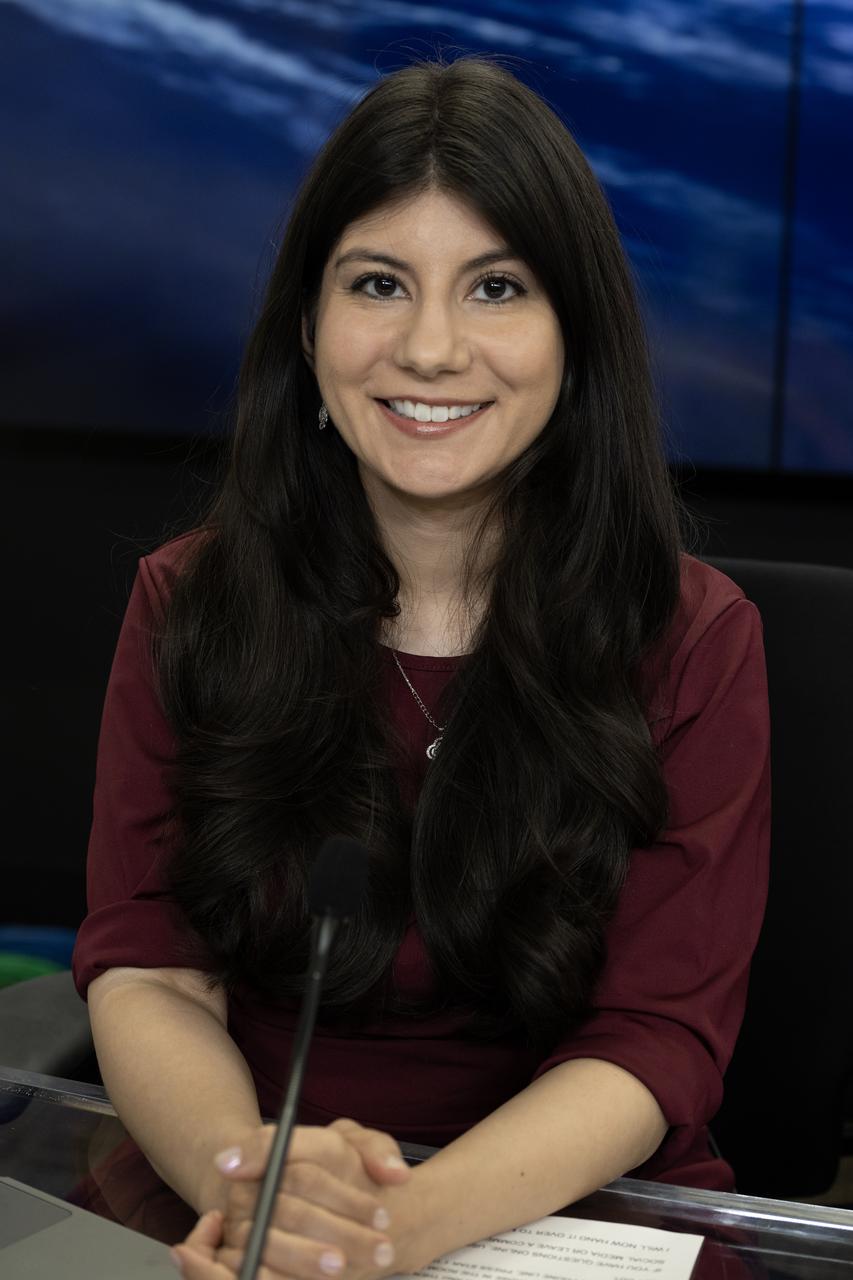

Raquel Villanueva, communications, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
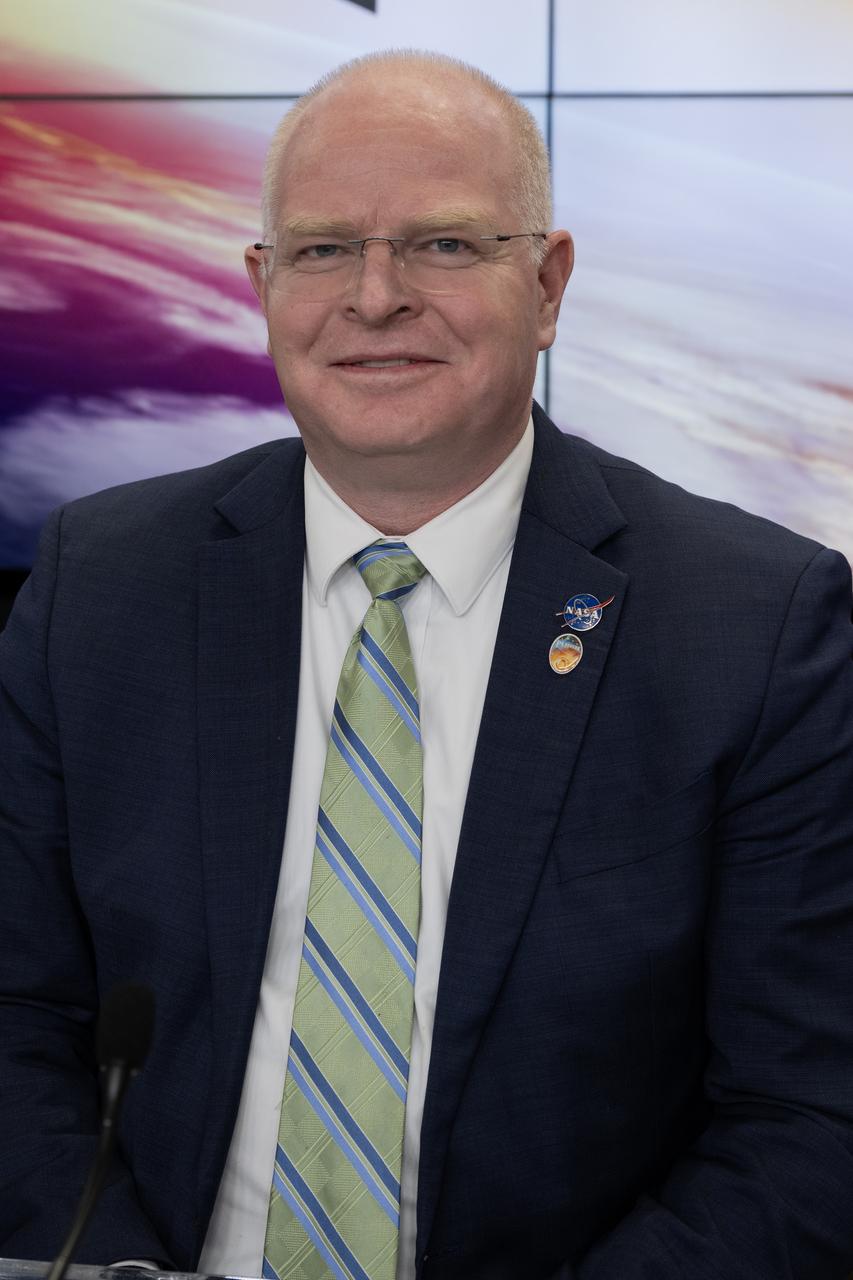

David Cheney, PUNCH program executive, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
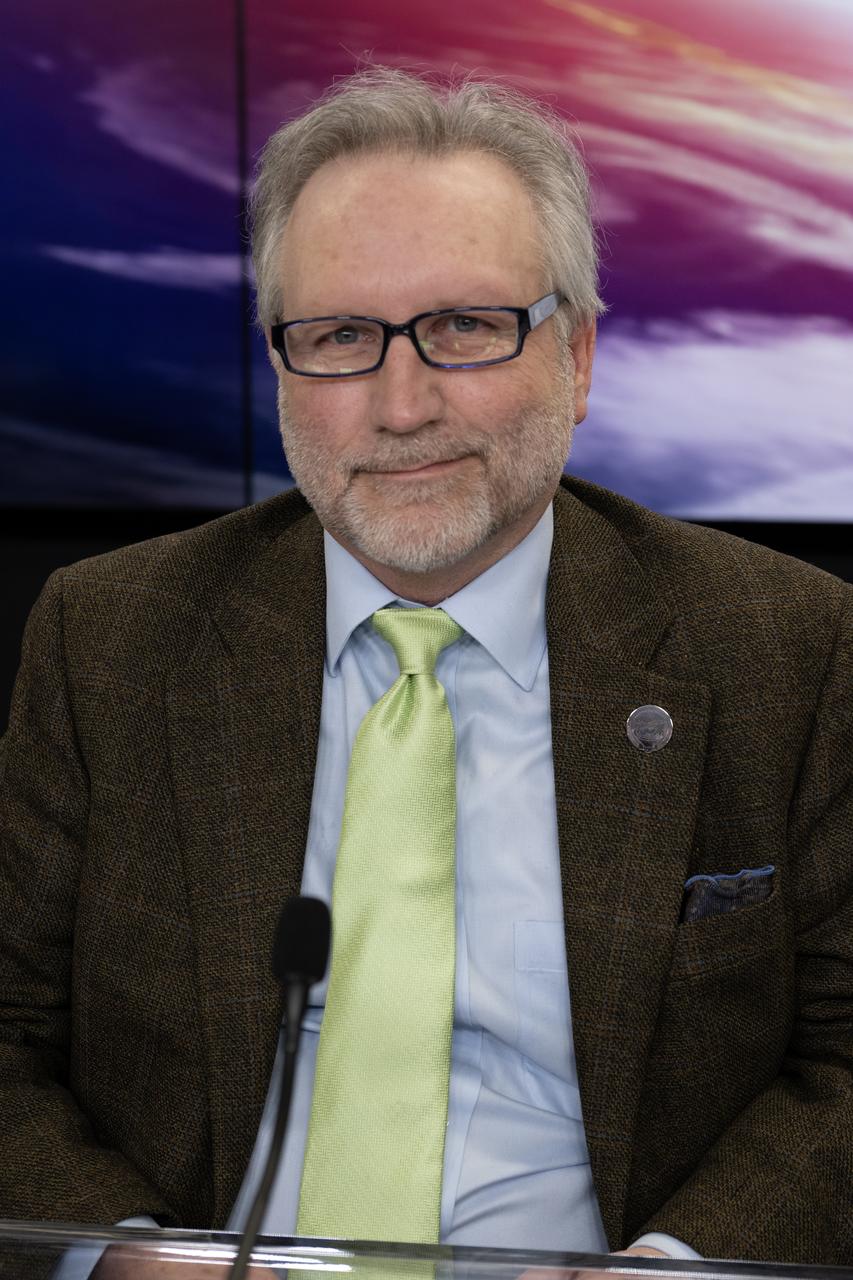

James Fanson, SPHEREx project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
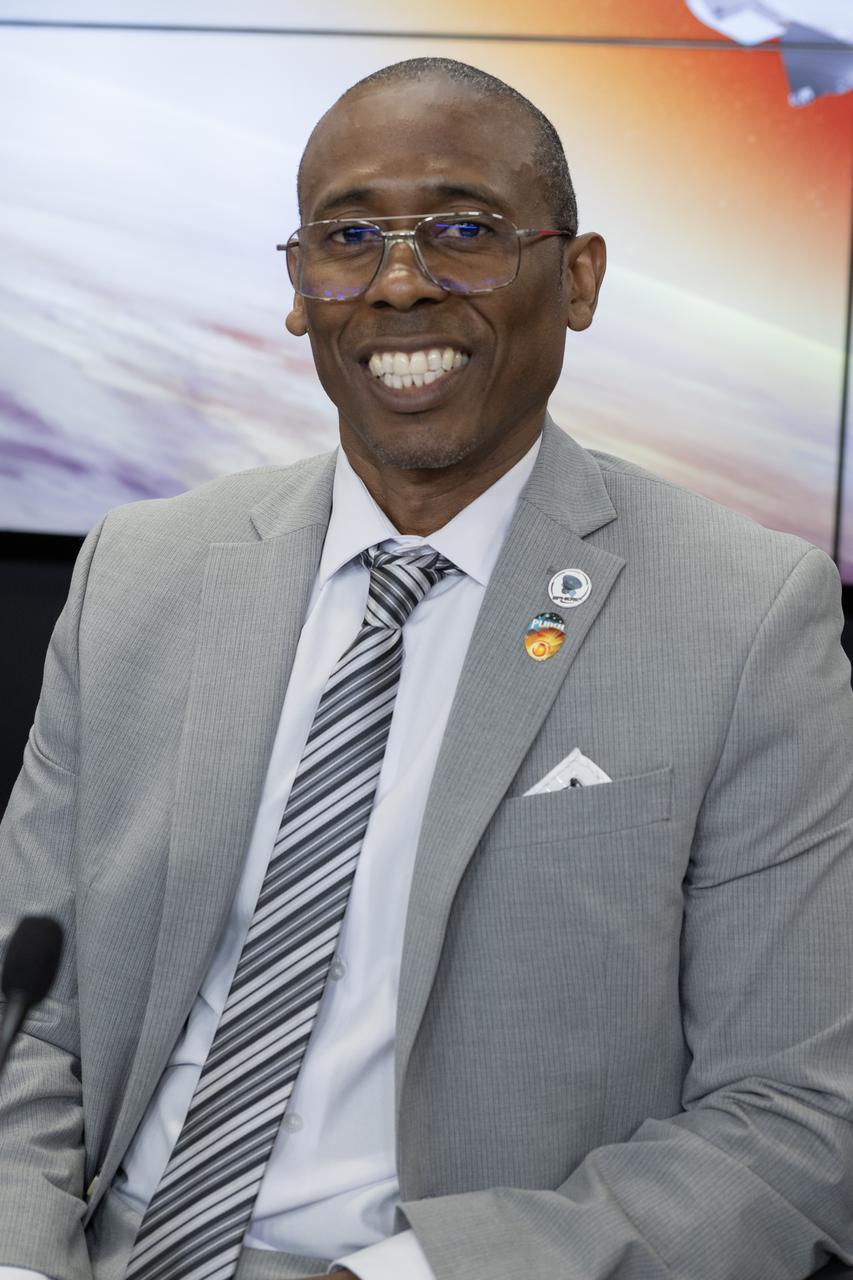

Dr. Denton Gibson, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
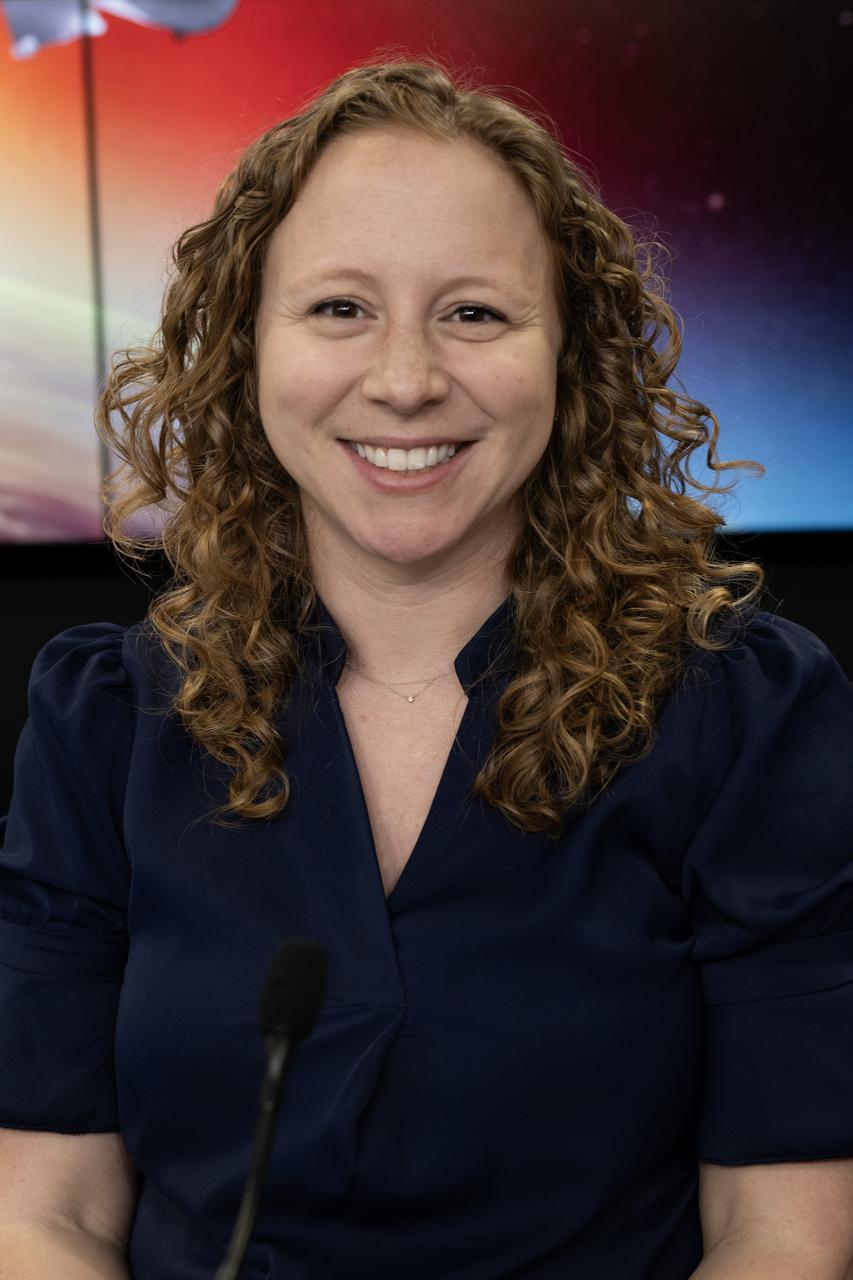

Julianna Scheiman, director, NASA Science Missions, SpaceX, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites arrive at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
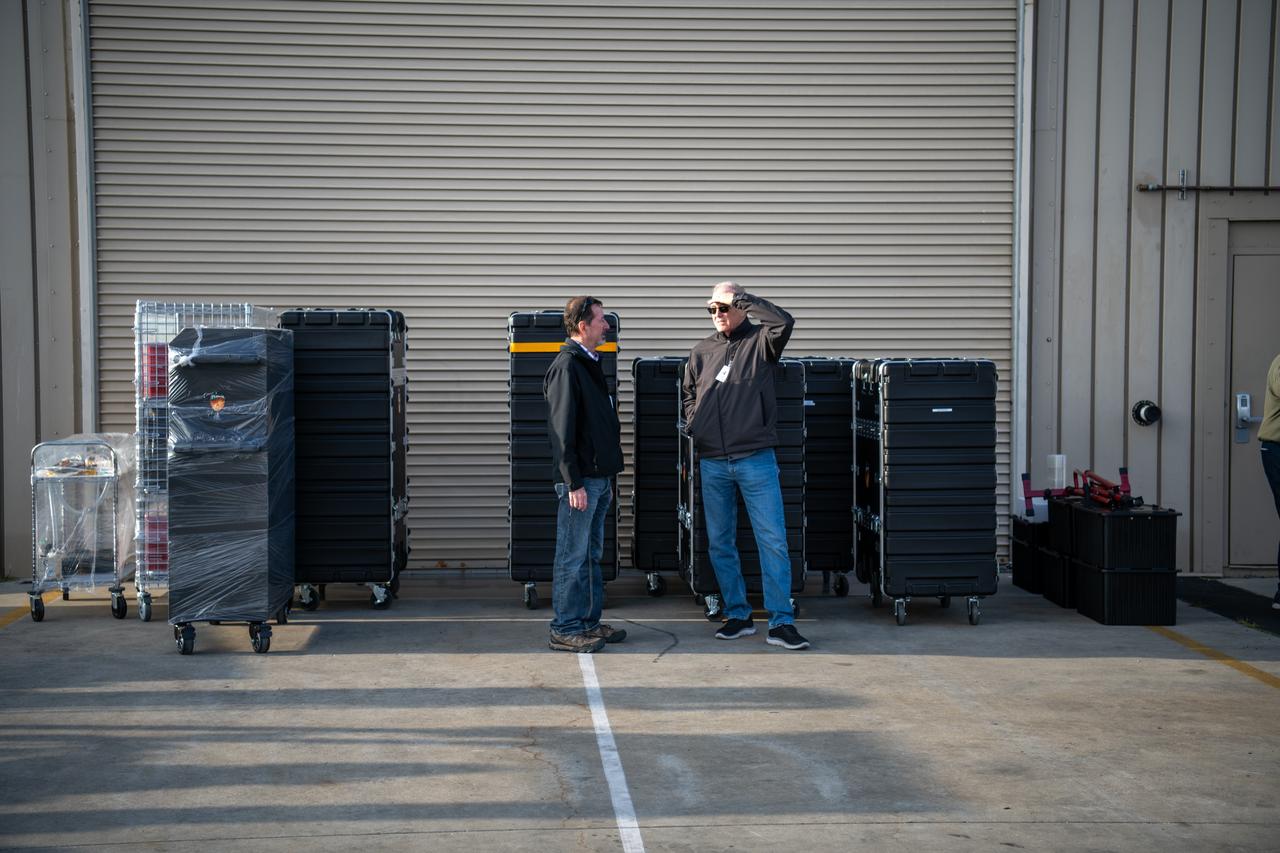

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites arrive at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
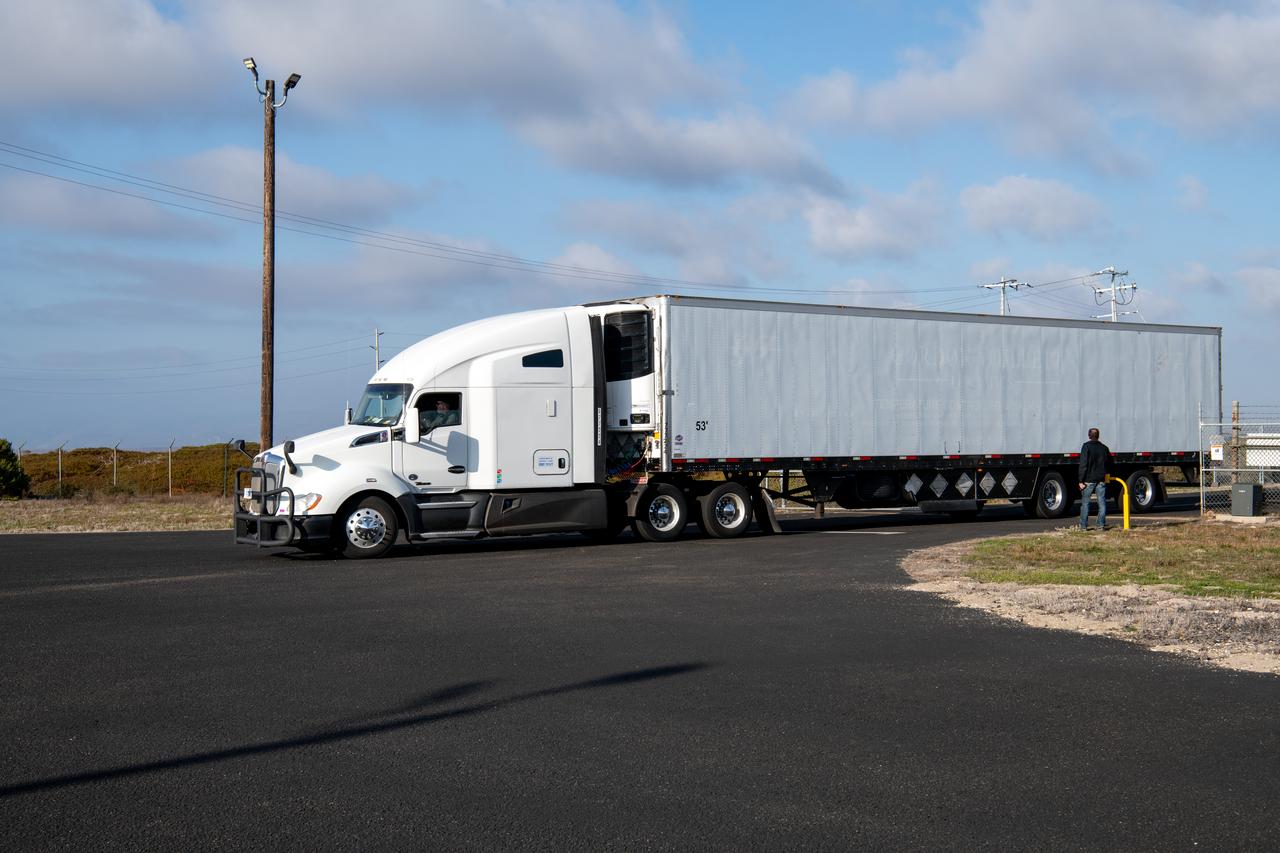

A transport truck carrying four small satellites of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
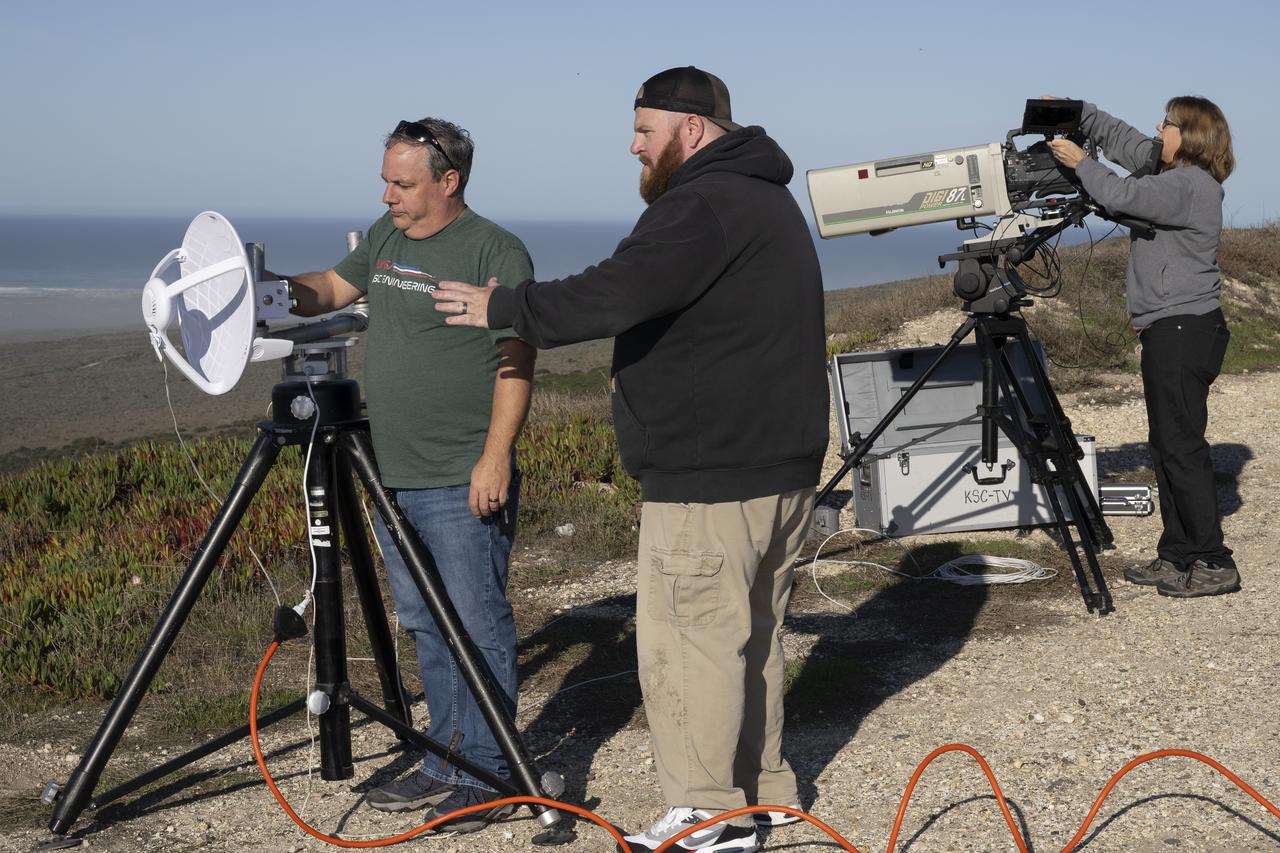

NASA videographer Jacob Shaw and the video team from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, prepare to film the launch of NASA’s SPHEREx mission at Vandenberg Space Force Base. The mission, short for Specto-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer, launched on March 11, 2025, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, continuing NASA’s exploration of the cosmos – and its commitment to visual storytelling.
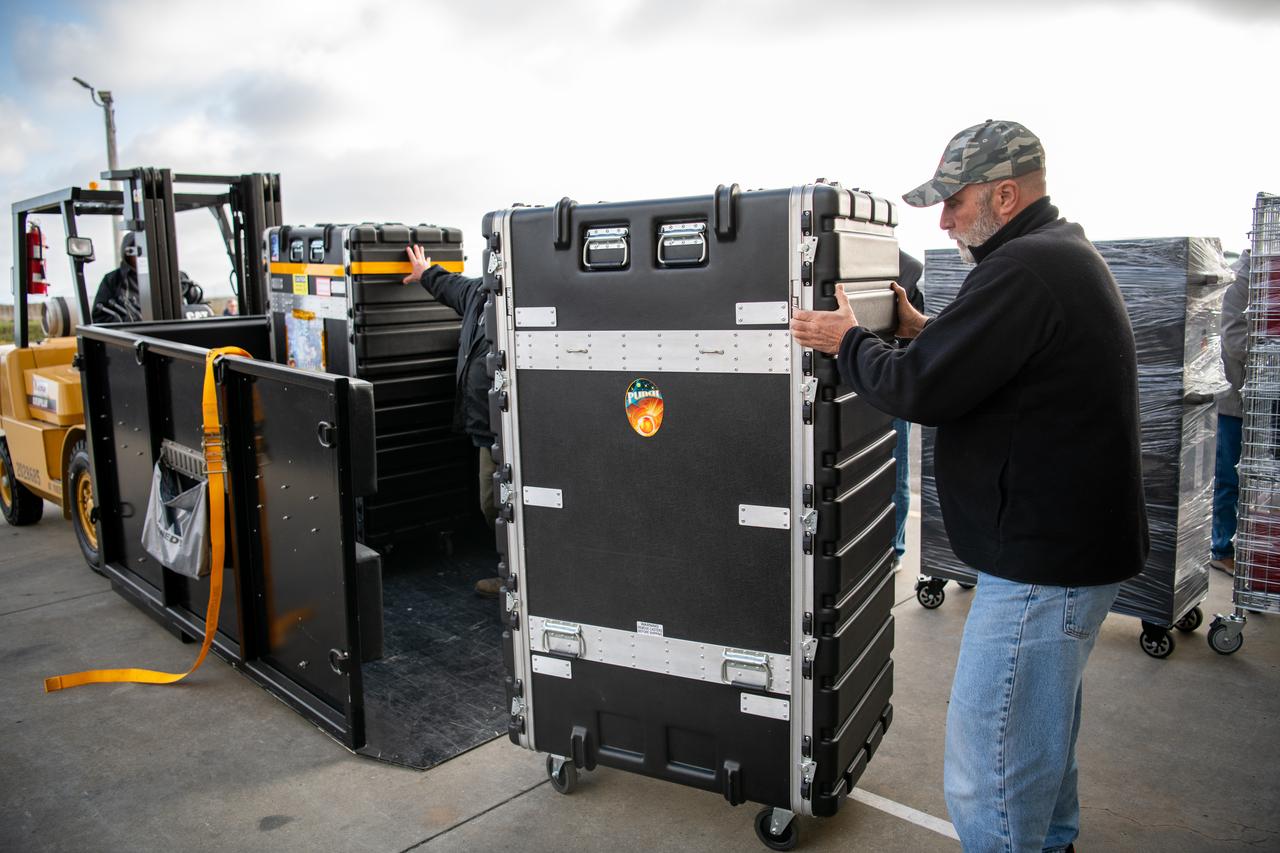

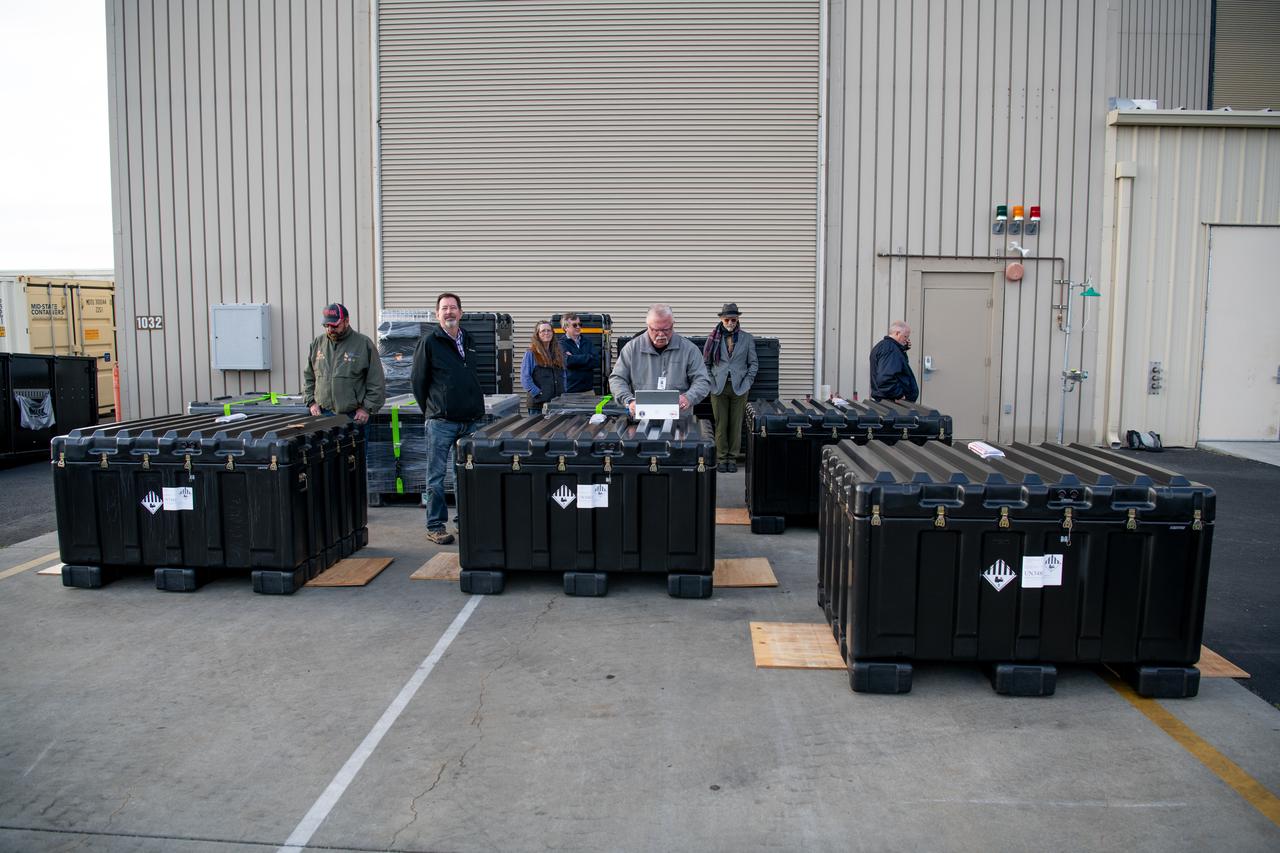
Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
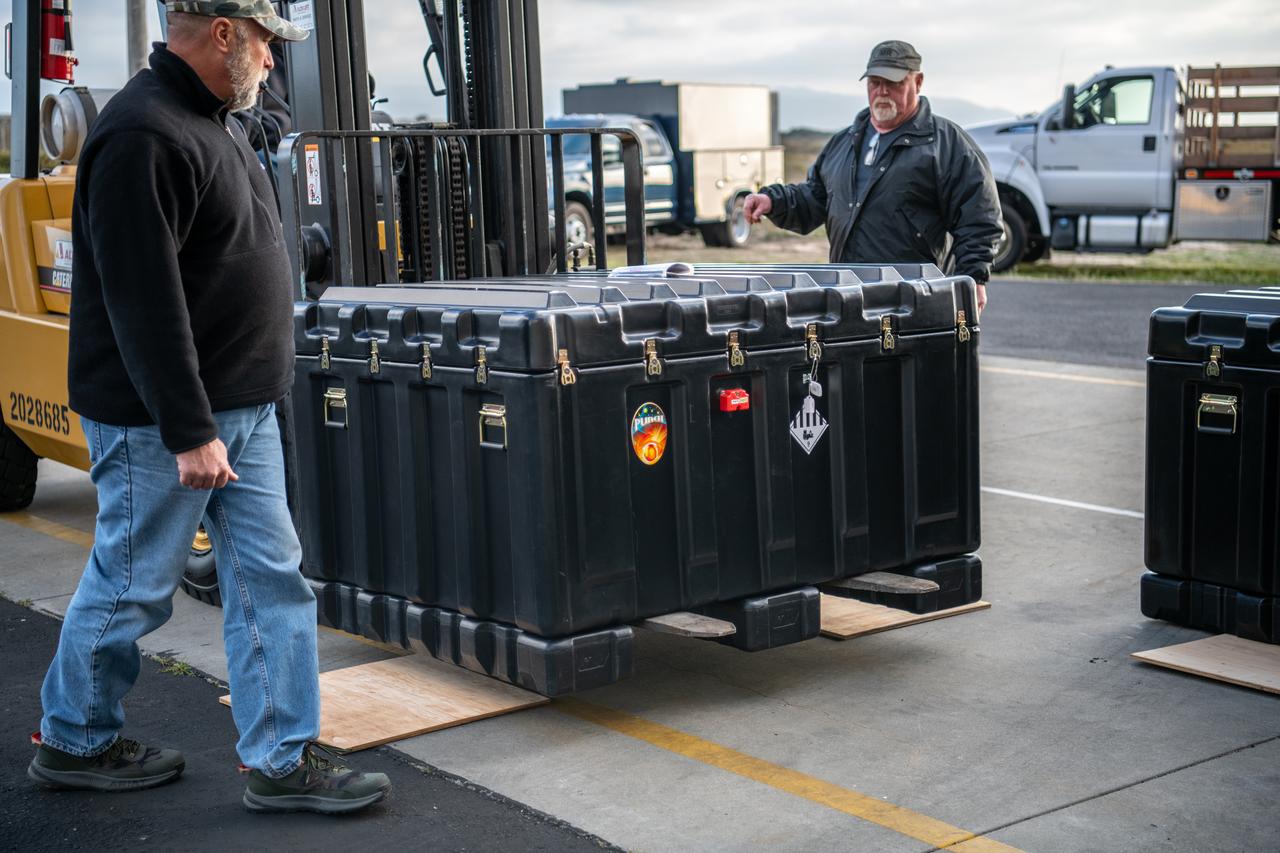

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
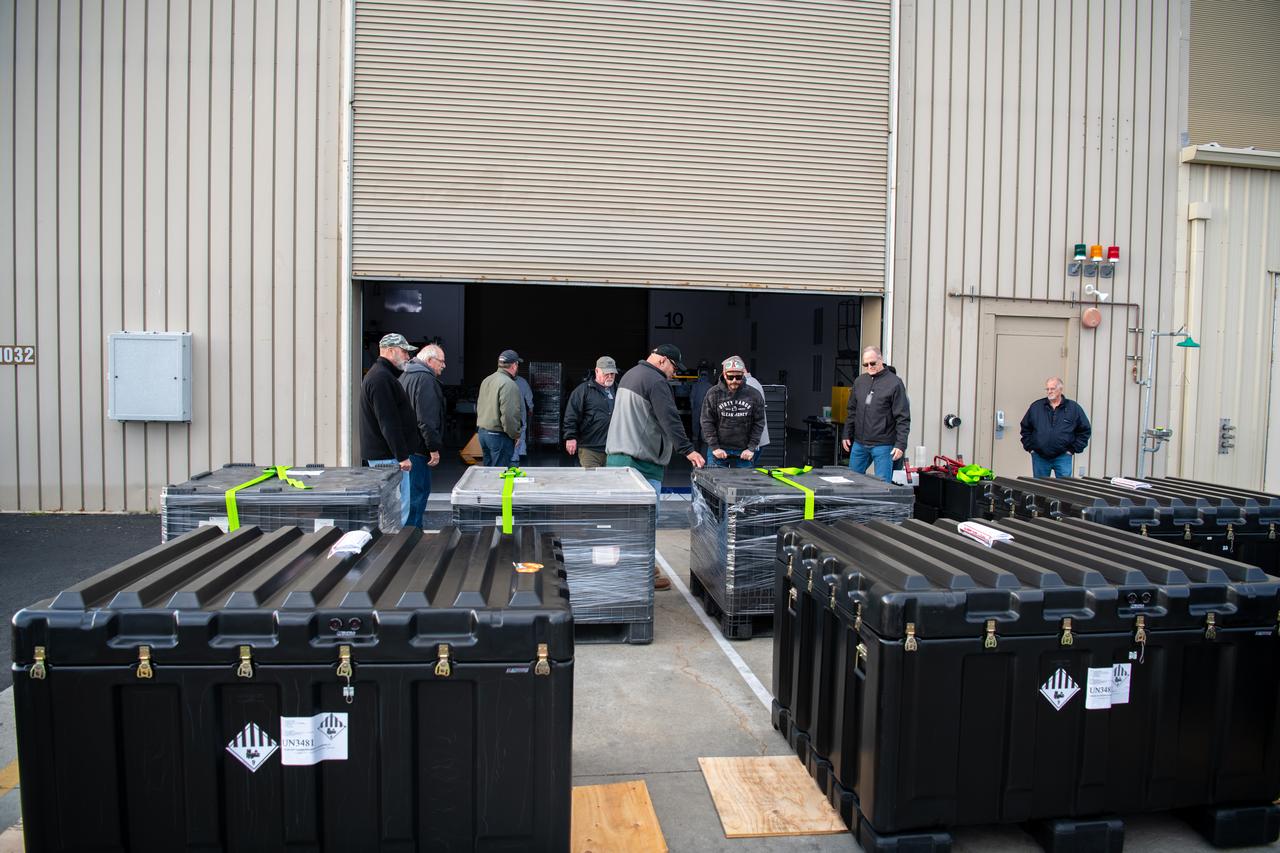

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
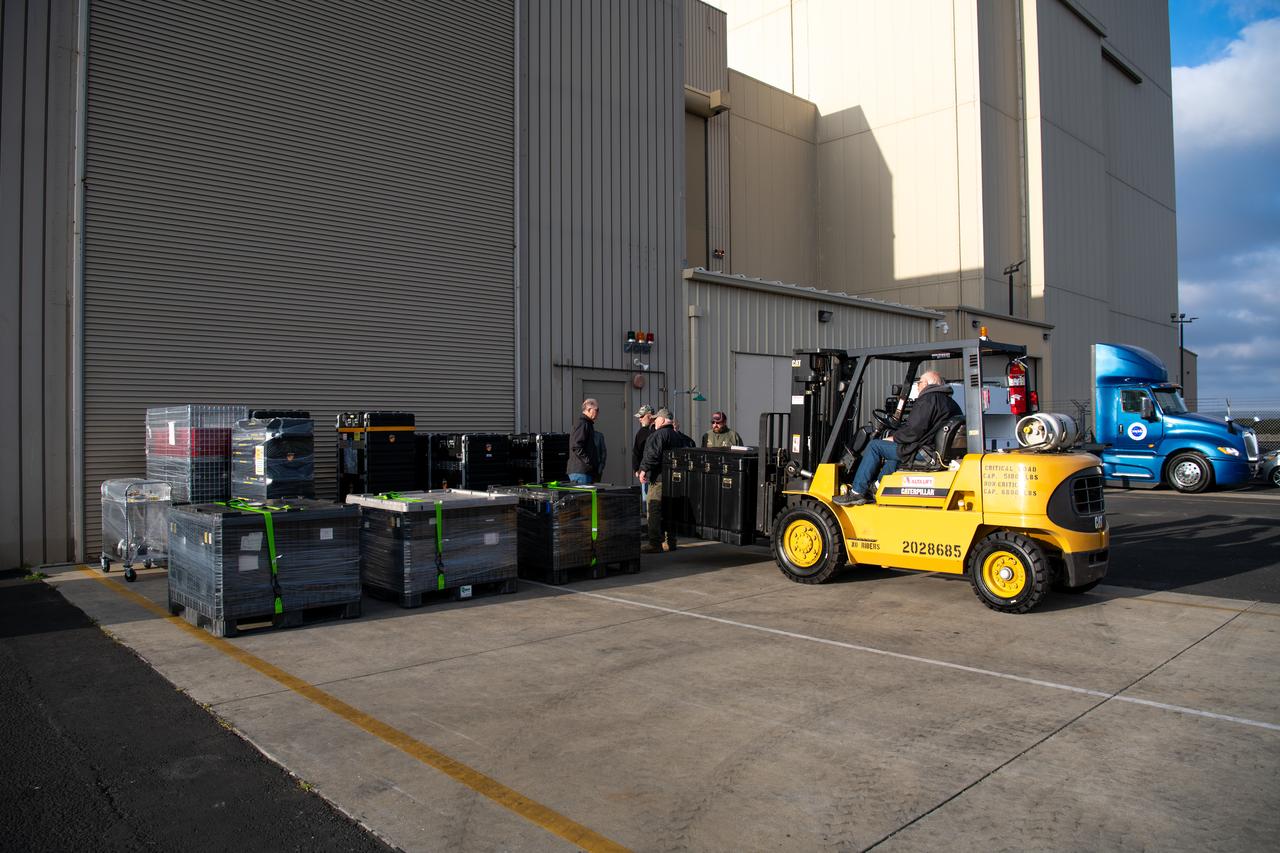

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
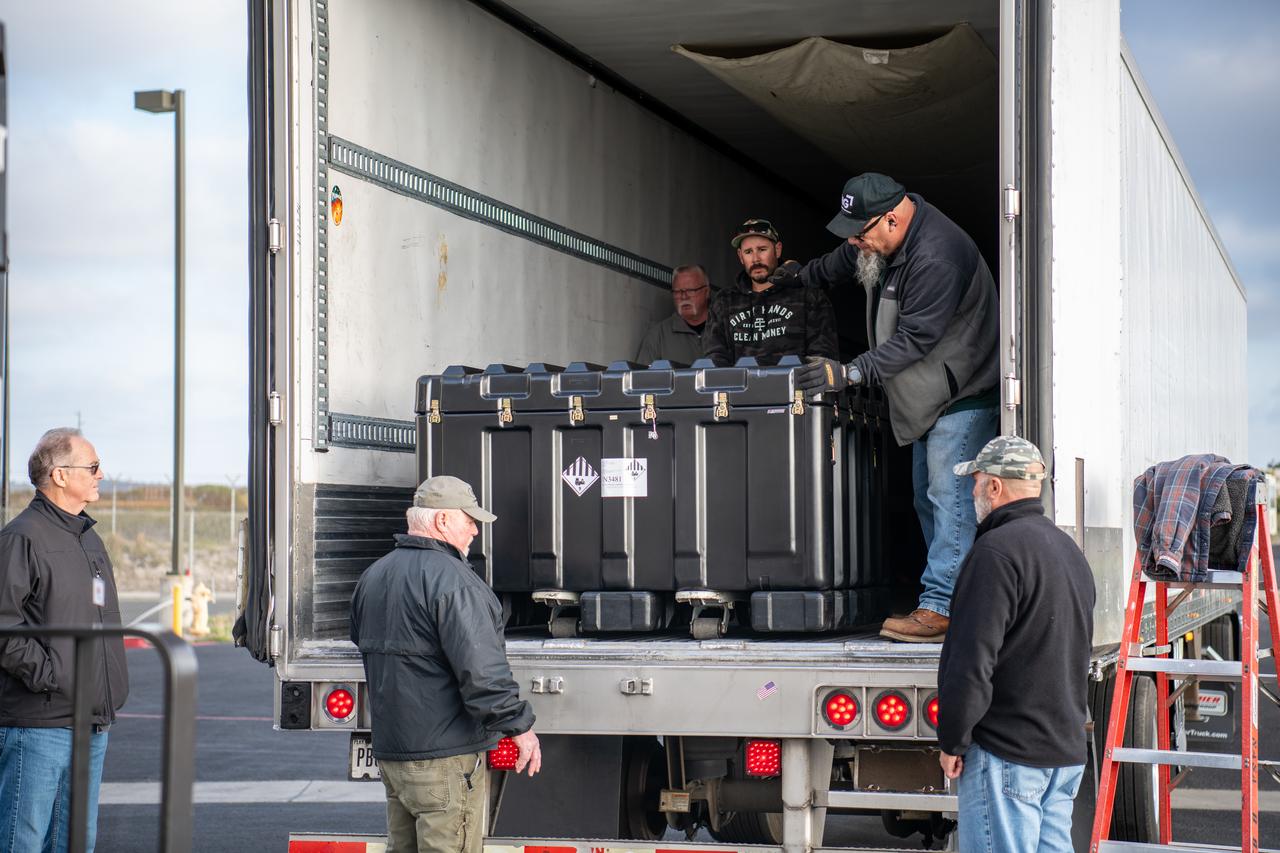

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
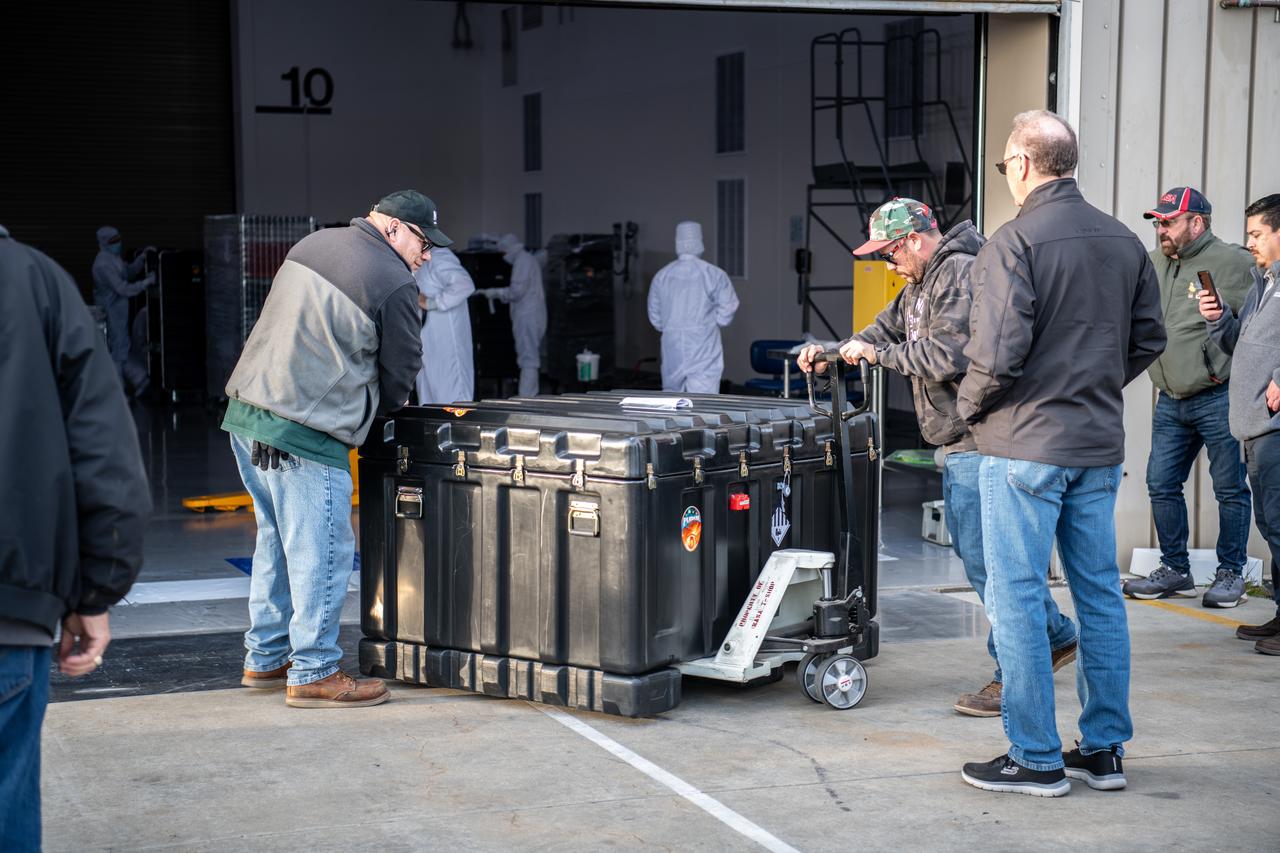

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
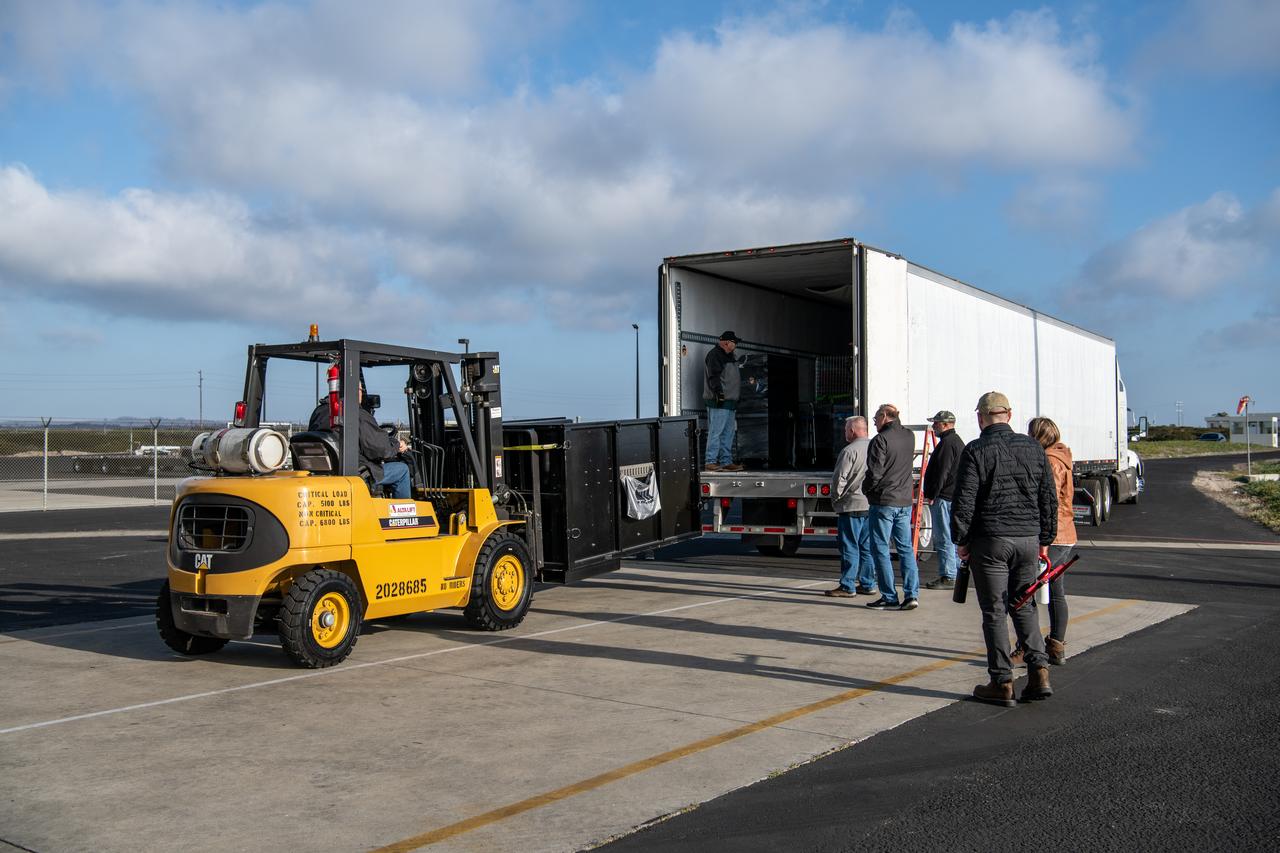

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
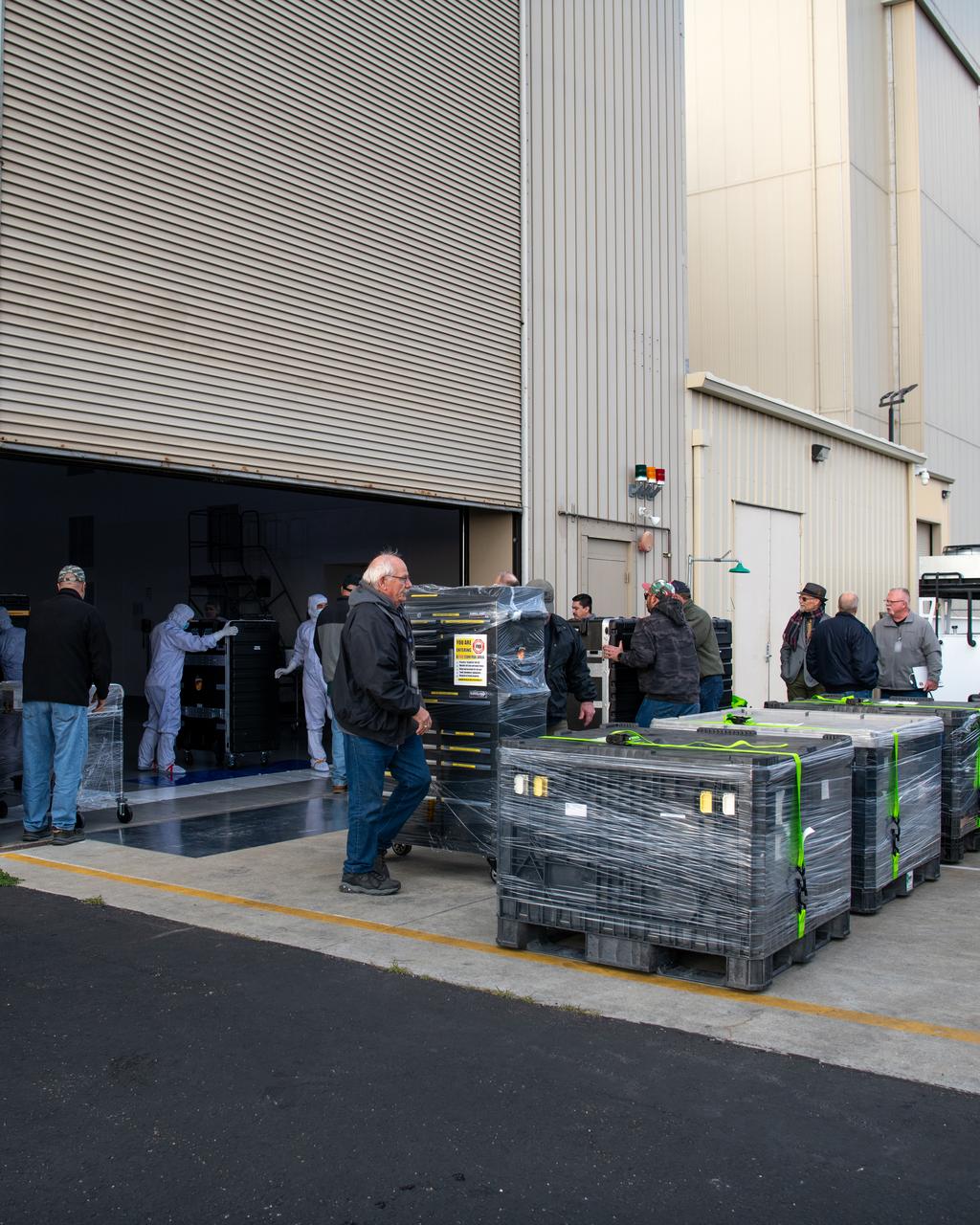

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
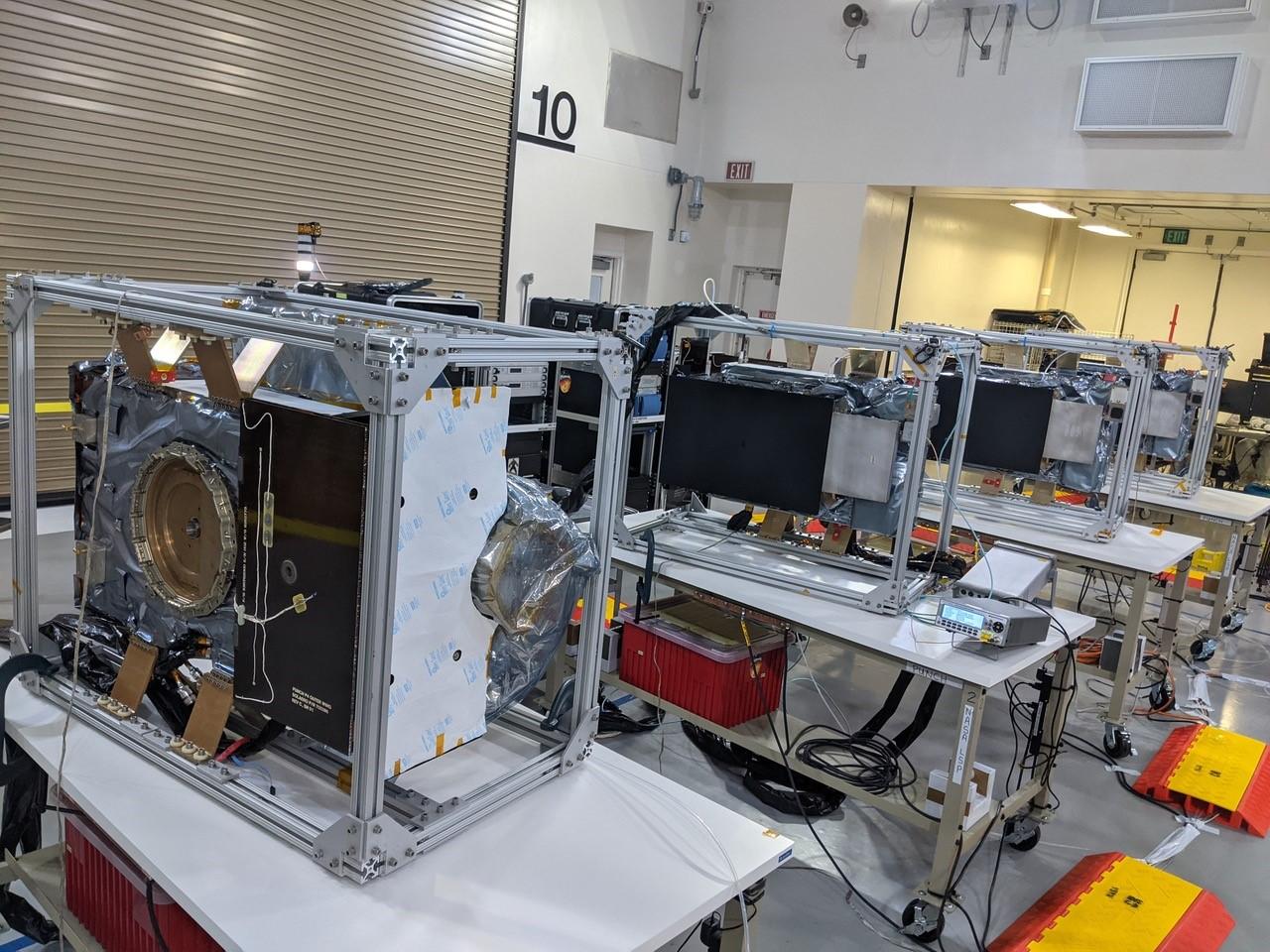

Technicians conduct integration and testing of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites during prelaunch operations inside Astrotech Space Operations on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
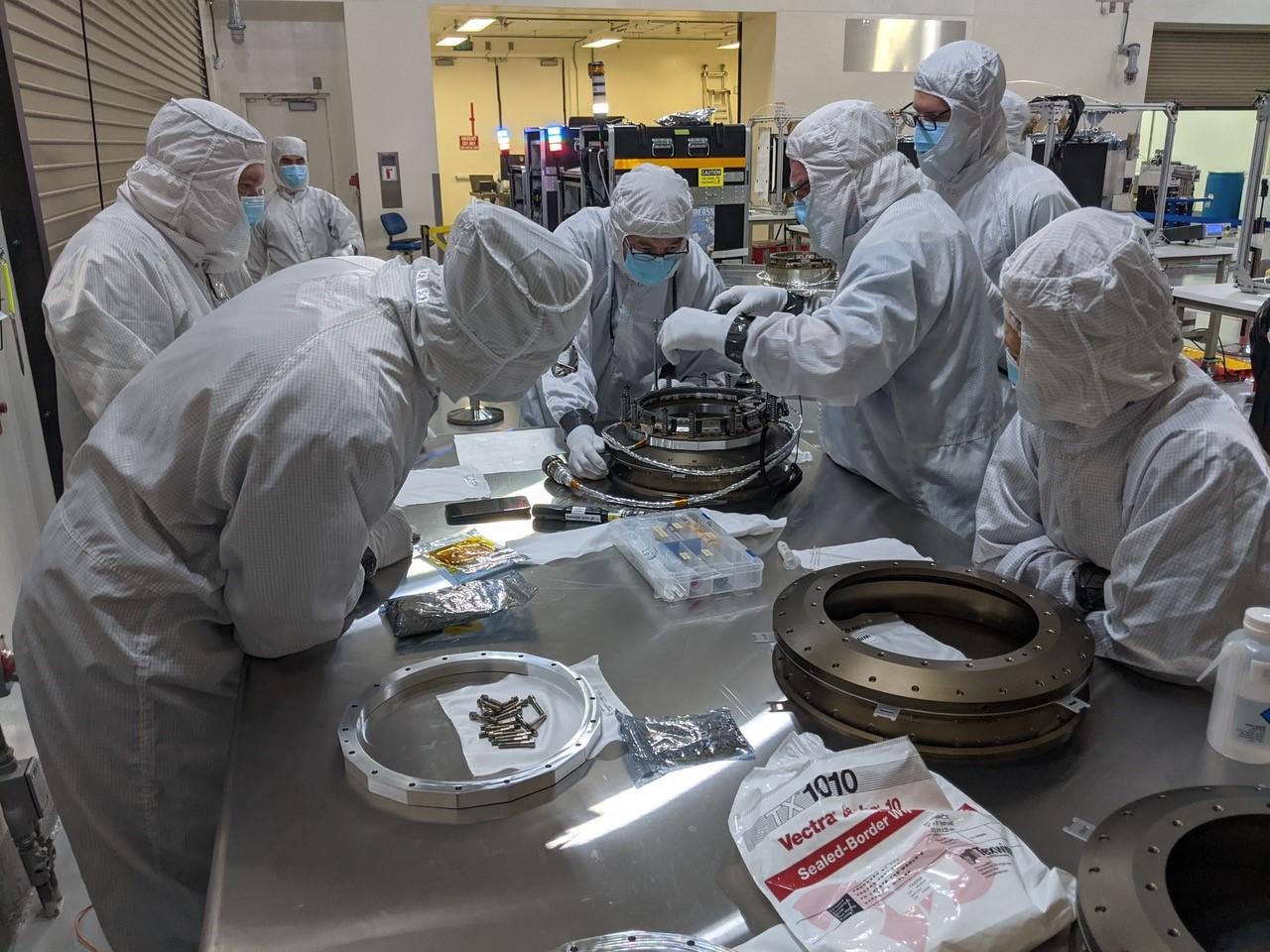

Technicians conduct integration and testing of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites during prelaunch operations inside Astrotech Space Operations on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
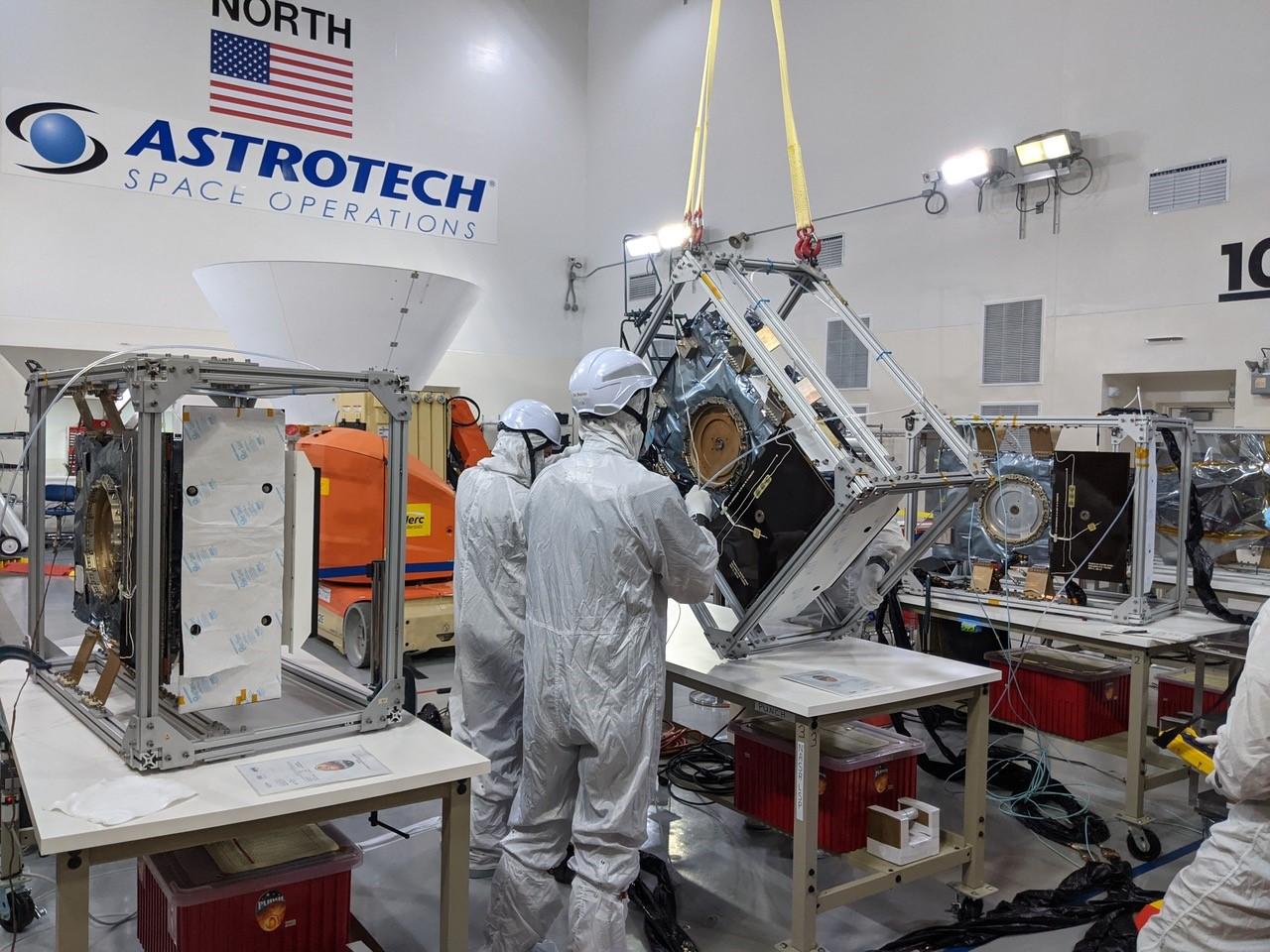

Technicians conduct integration and testing of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites during prelaunch operations inside Astrotech Space Operations on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
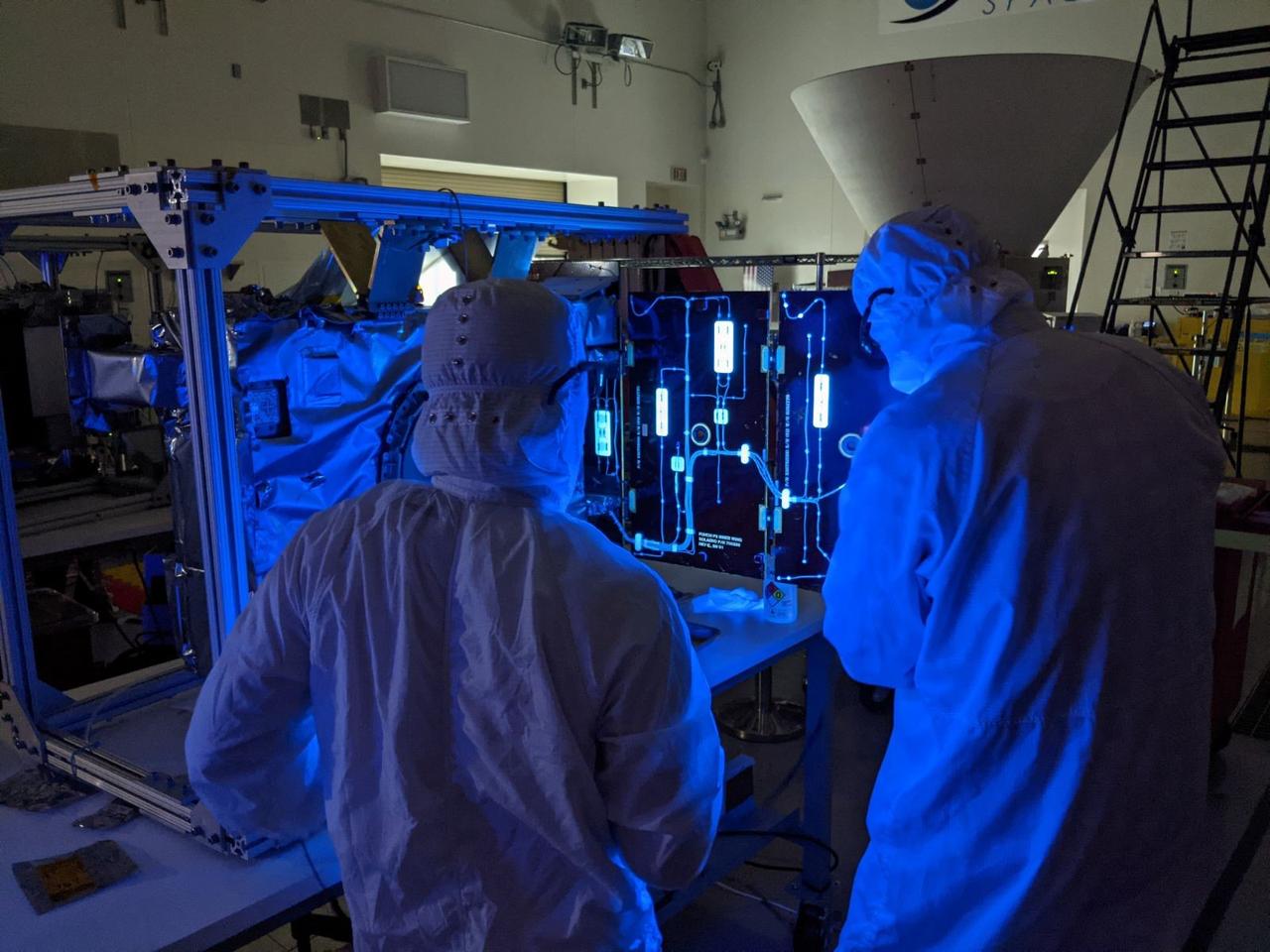

Technicians conduct integration and testing of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites during prelaunch operations inside Astrotech Space Operations on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
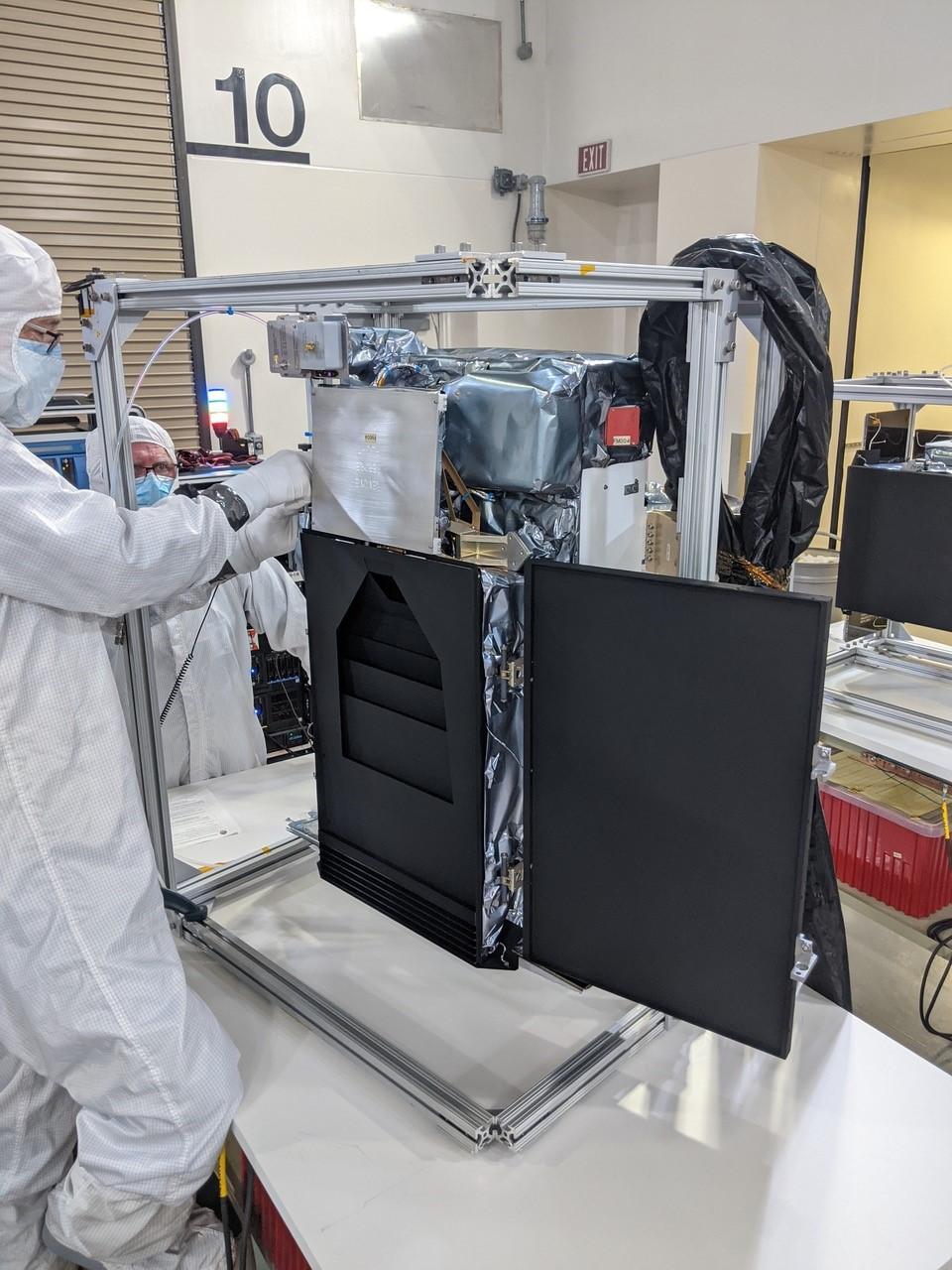

Technicians conduct integration and testing of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites during prelaunch operations inside Astrotech Space Operations on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
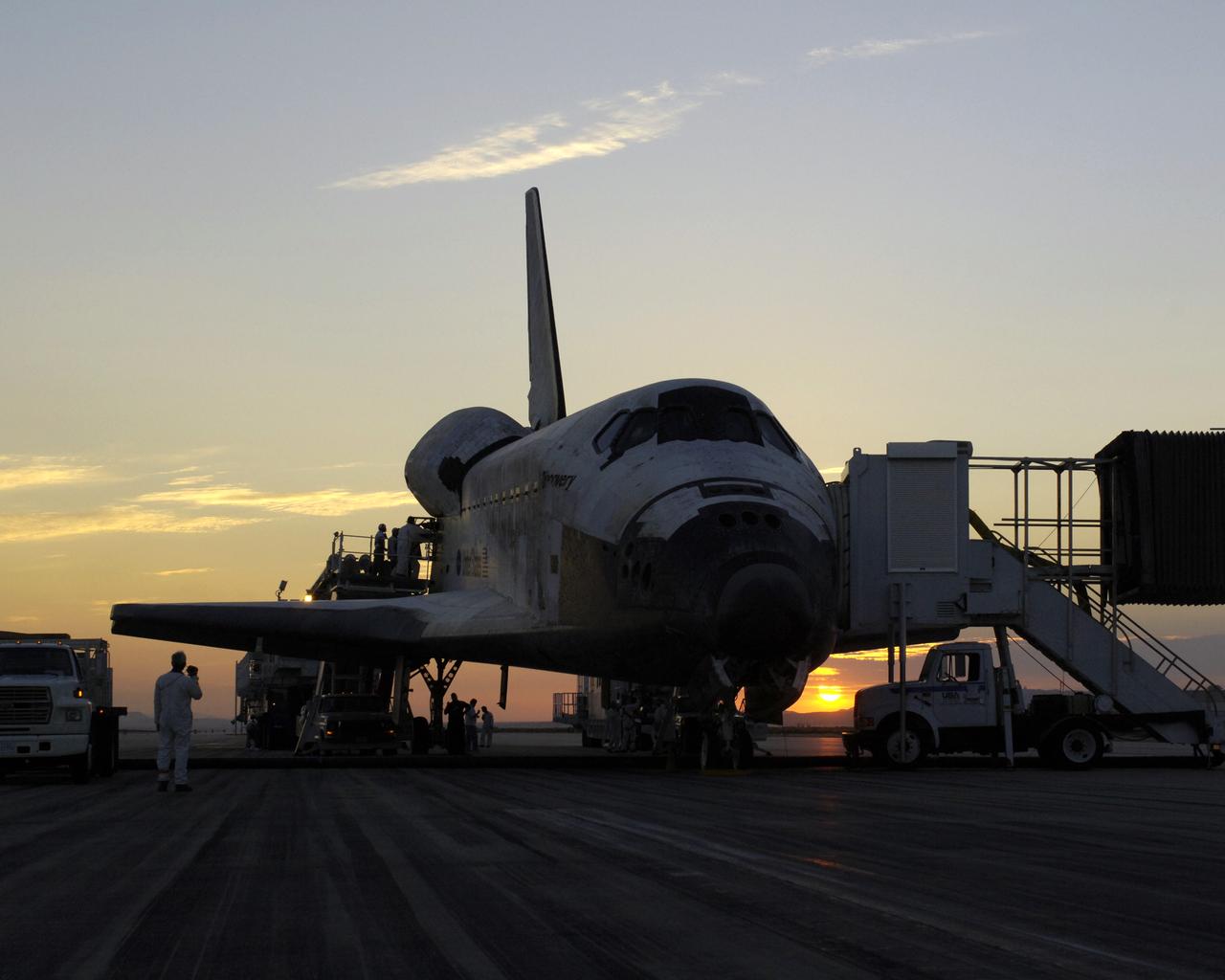

The sun rises on the Space Shuttle Discovery as it rests on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, after a safe landing August 9, 2005 to complete the STS-114 mission. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
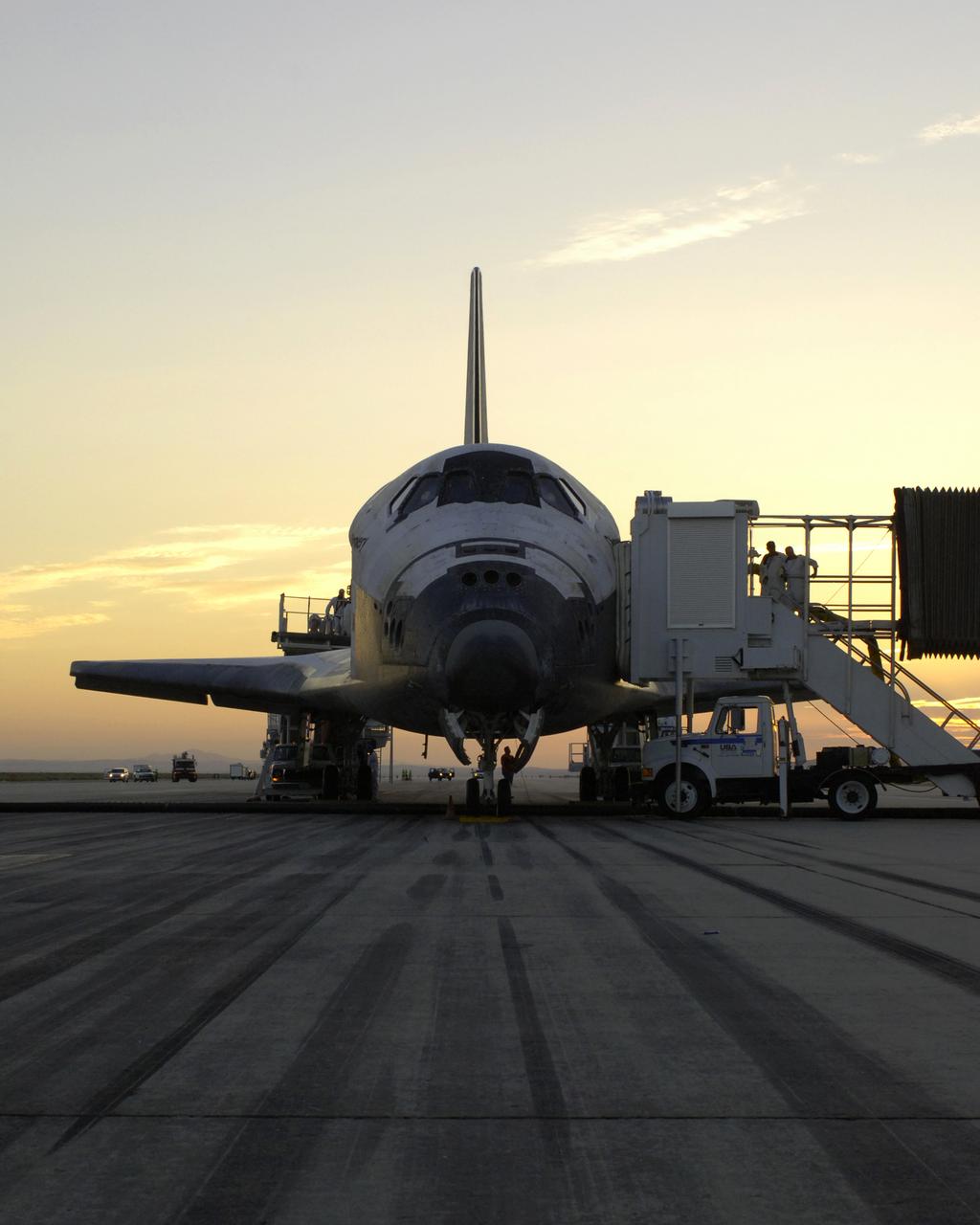

The sun rises on the Space Shuttle Discovery as it rests on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, after a safe landing August 9, 2005 to complete the STS-114 mission. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT this morning, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
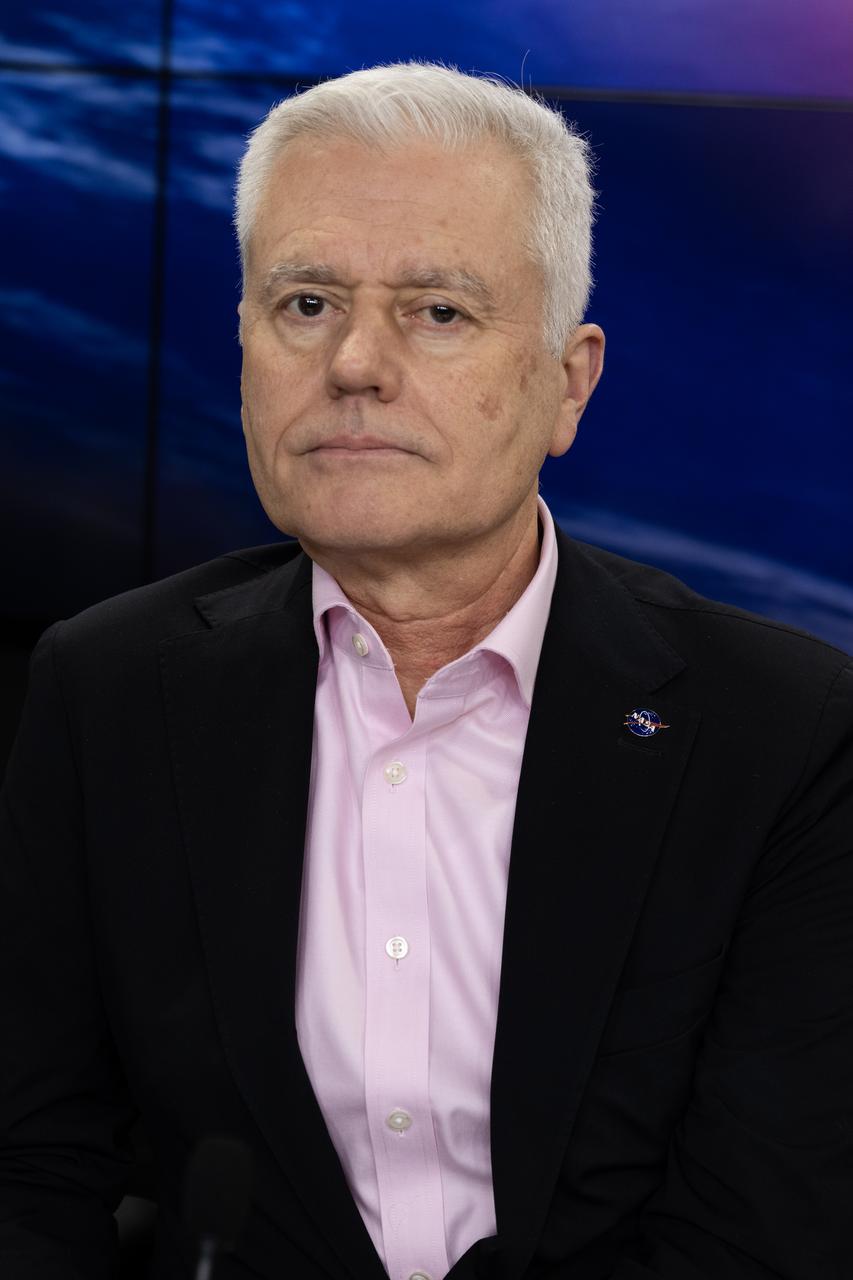

Mark Clampin, acting deputy associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Friday, March 7, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system. Liftoff aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for NET 10:10 p.m. EST (7:10 p.m. PST), Saturday, March 8, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
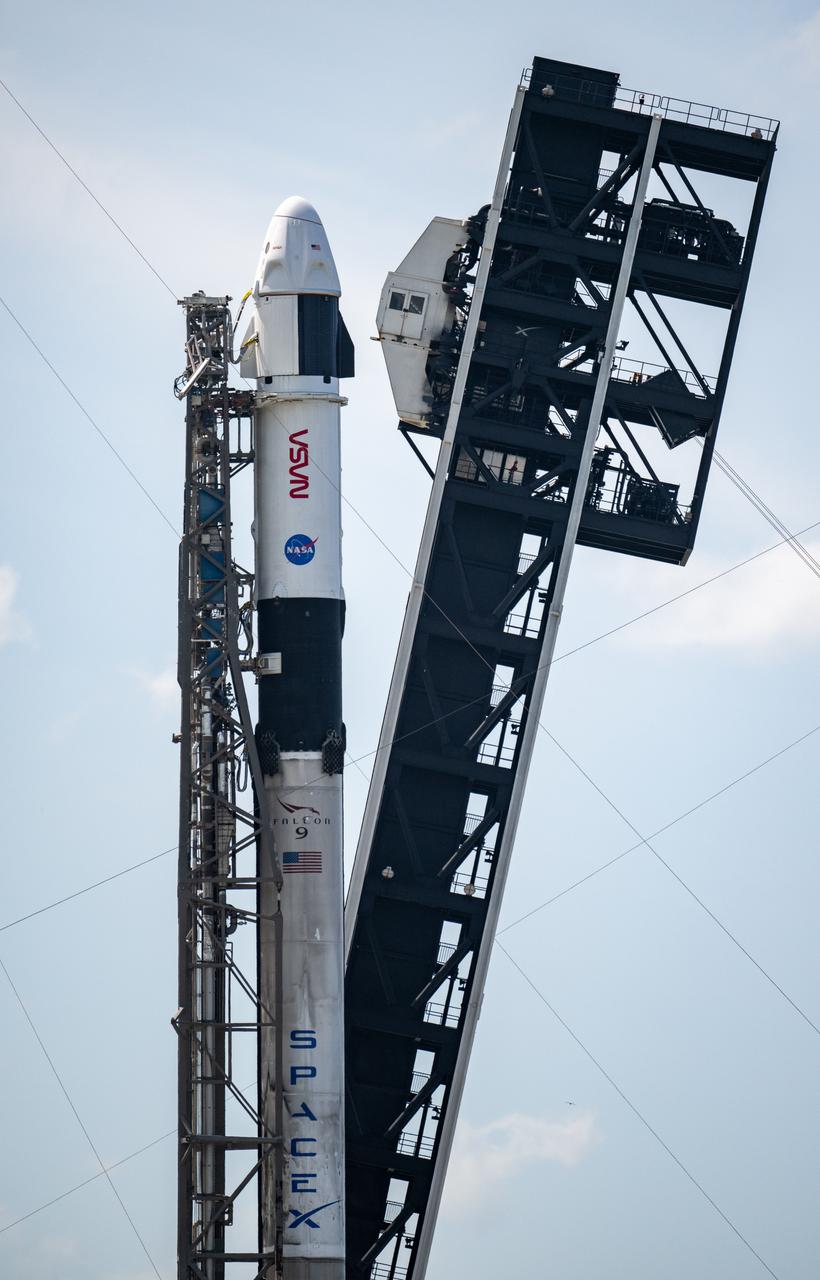

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Dragon spacecraft on top is seen, photographed at an angle, as it is raised into a vertical position on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 40 as preparations continue for the Crew-9 mission, Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission is the ninth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov are scheduled to launch on 1:17 p.m. EDT on Saturday, Sept. 28, from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
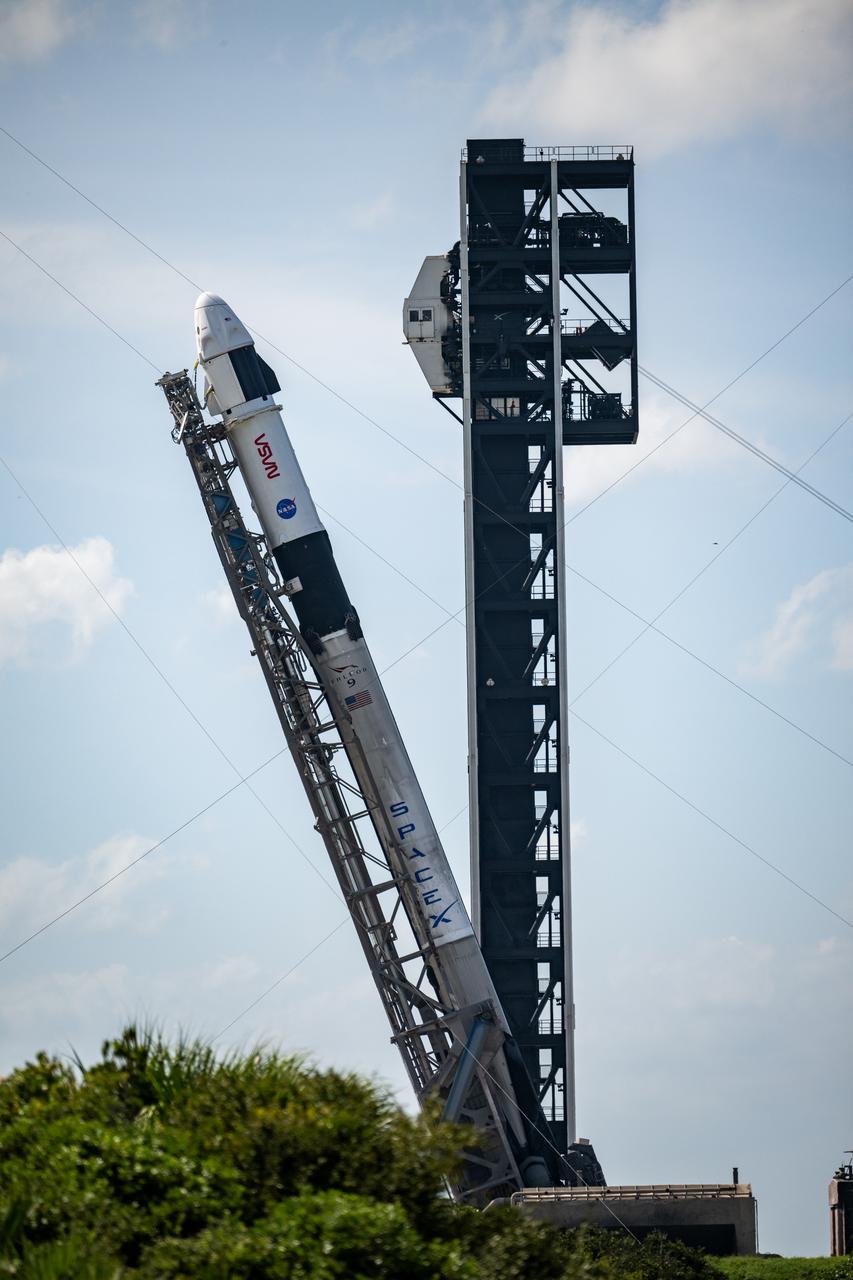

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Dragon spacecraft on top is seen as it is raised into a vertical position on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 40 as preparations continue for the Crew-9 mission, Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission is the ninth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov are scheduled to launch on 1:17 p.m. EDT on Saturday, Sept. 28, from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
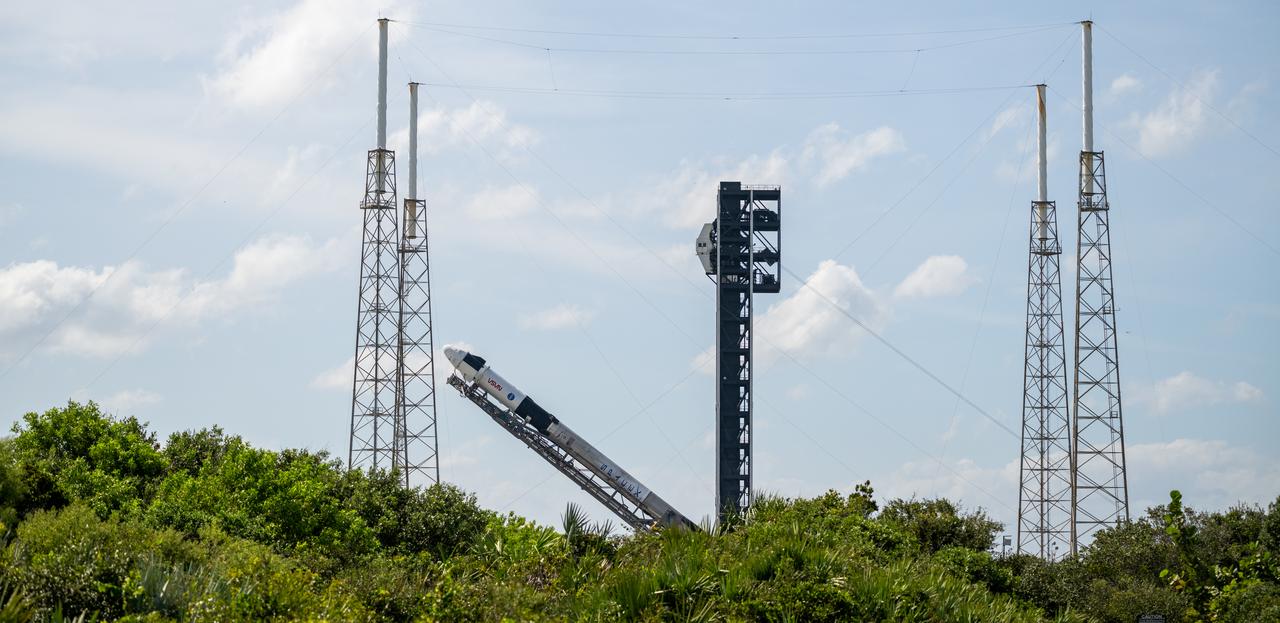

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company's Dragon spacecraft on top is seen as it is raised into a vertical position on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 40 as preparations continue for the Crew-9 mission, Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission is the ninth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov are scheduled to launch on 1:17 p.m. EDT on Saturday, Sept. 28, from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
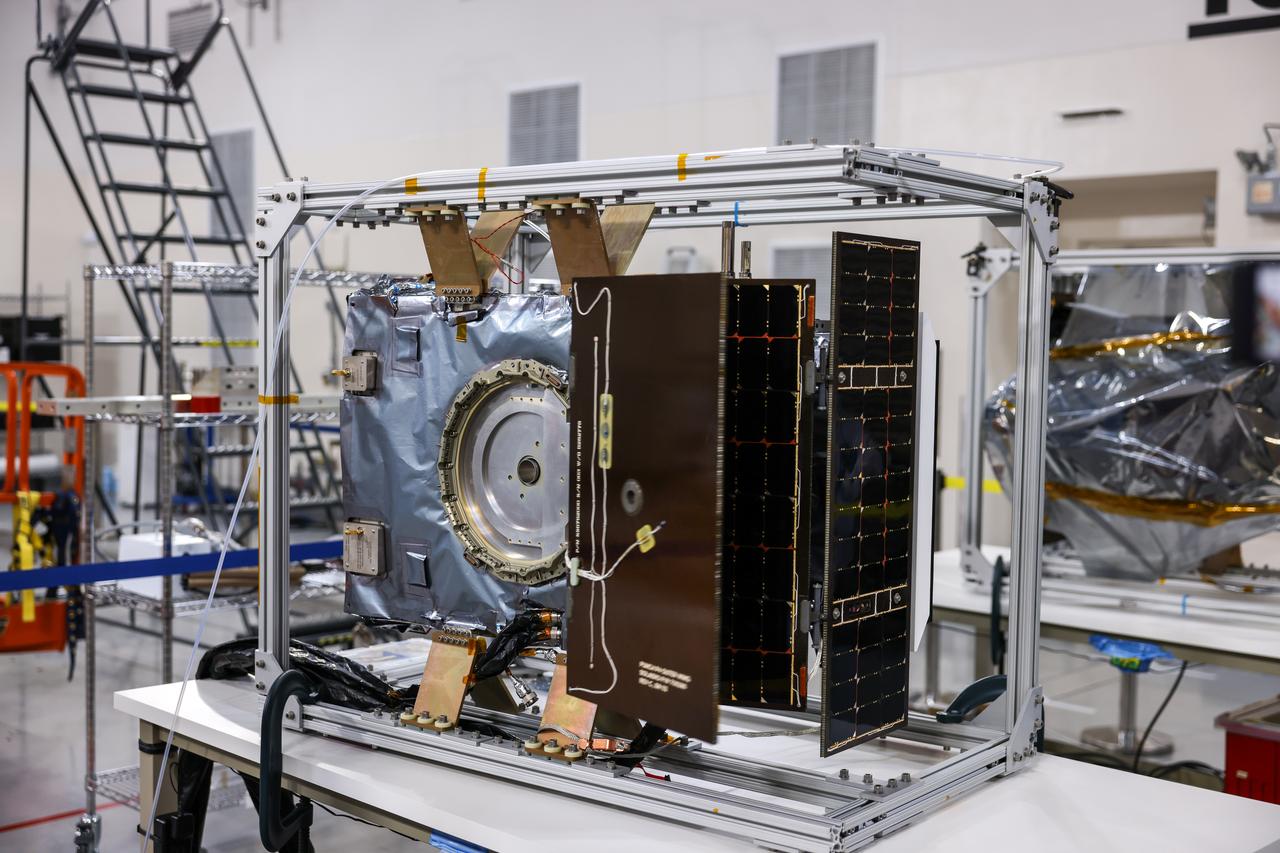

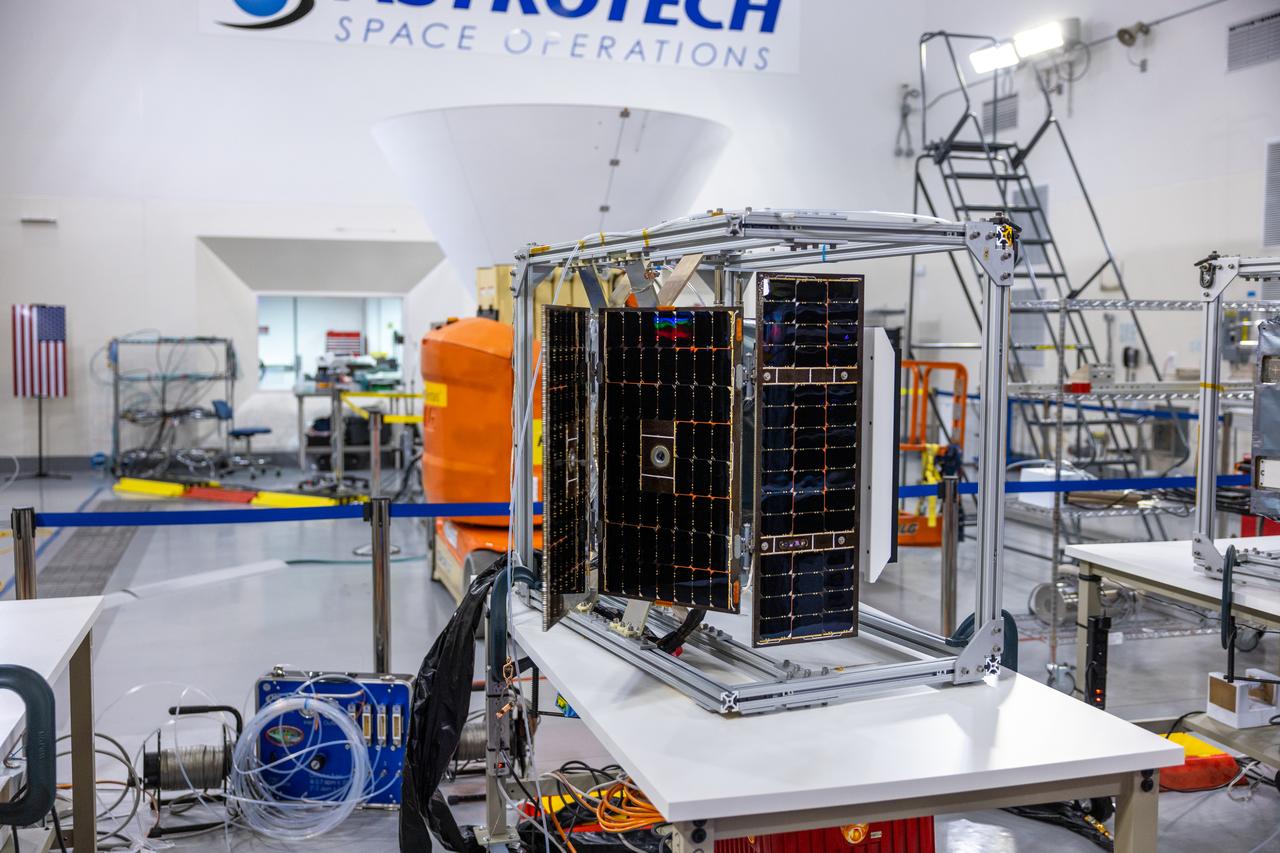
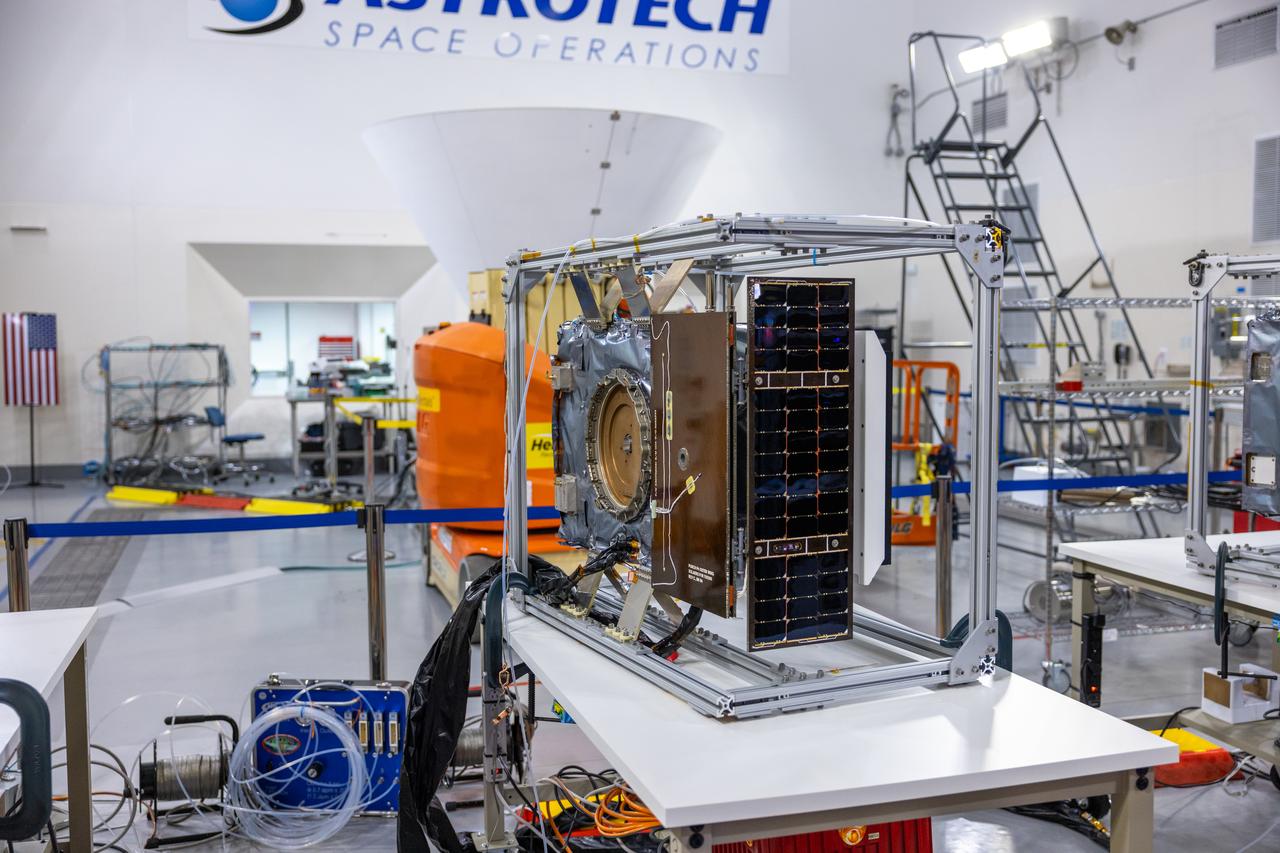
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
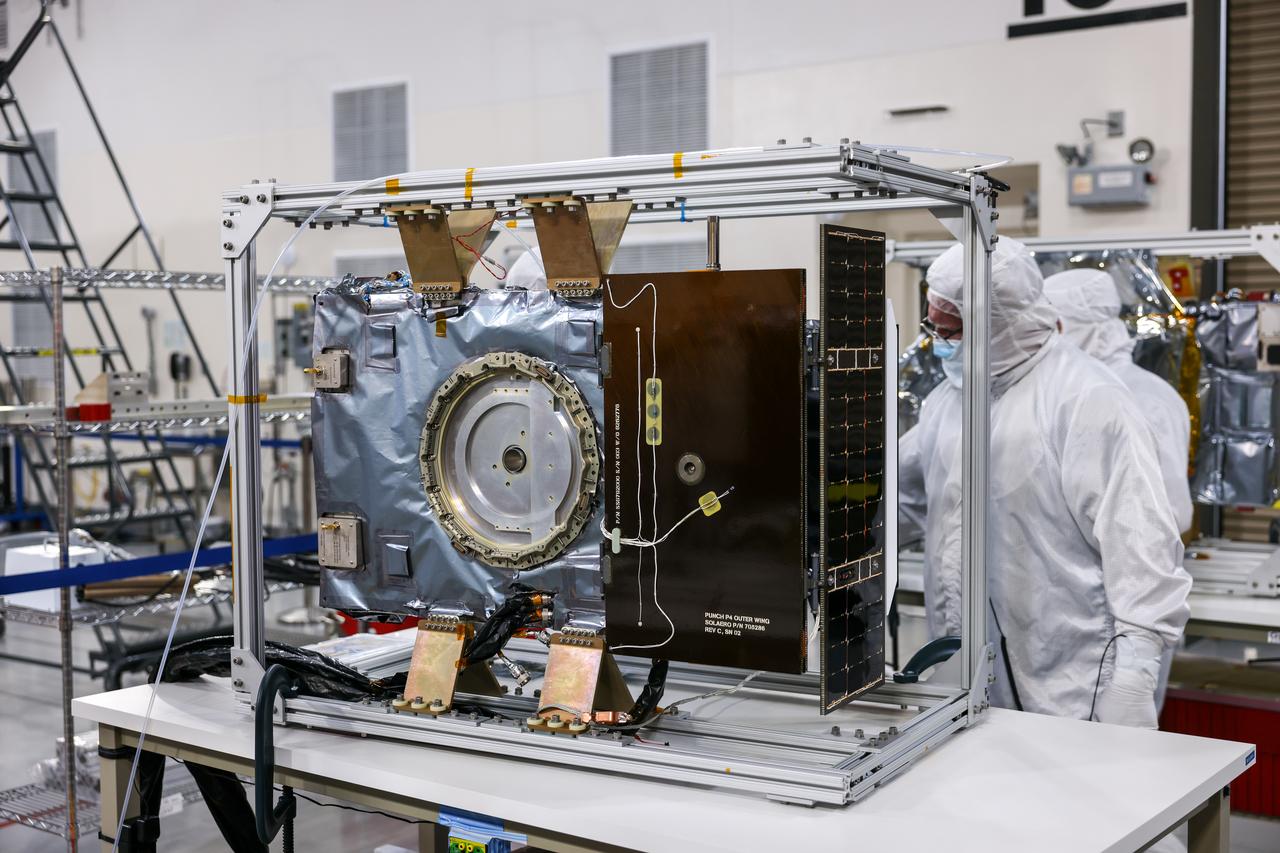
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
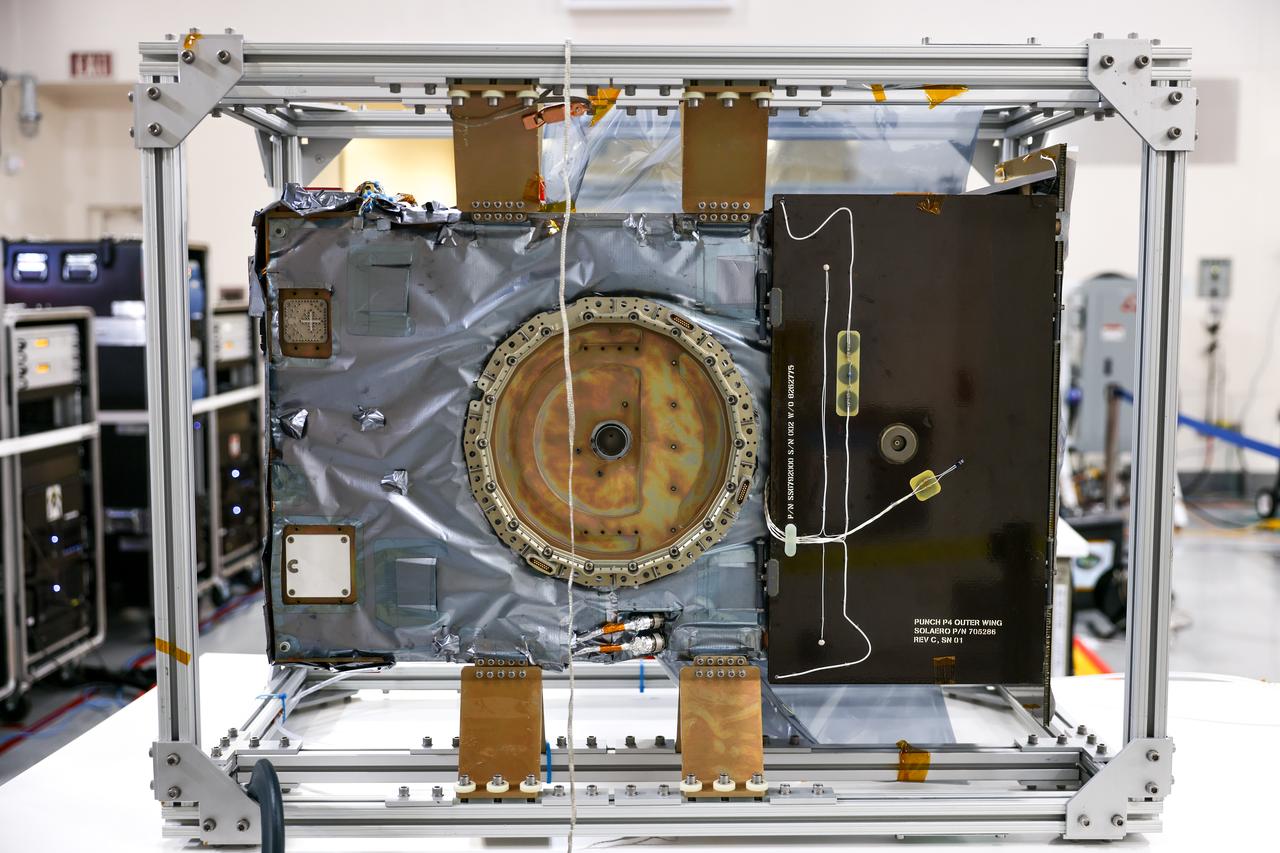
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
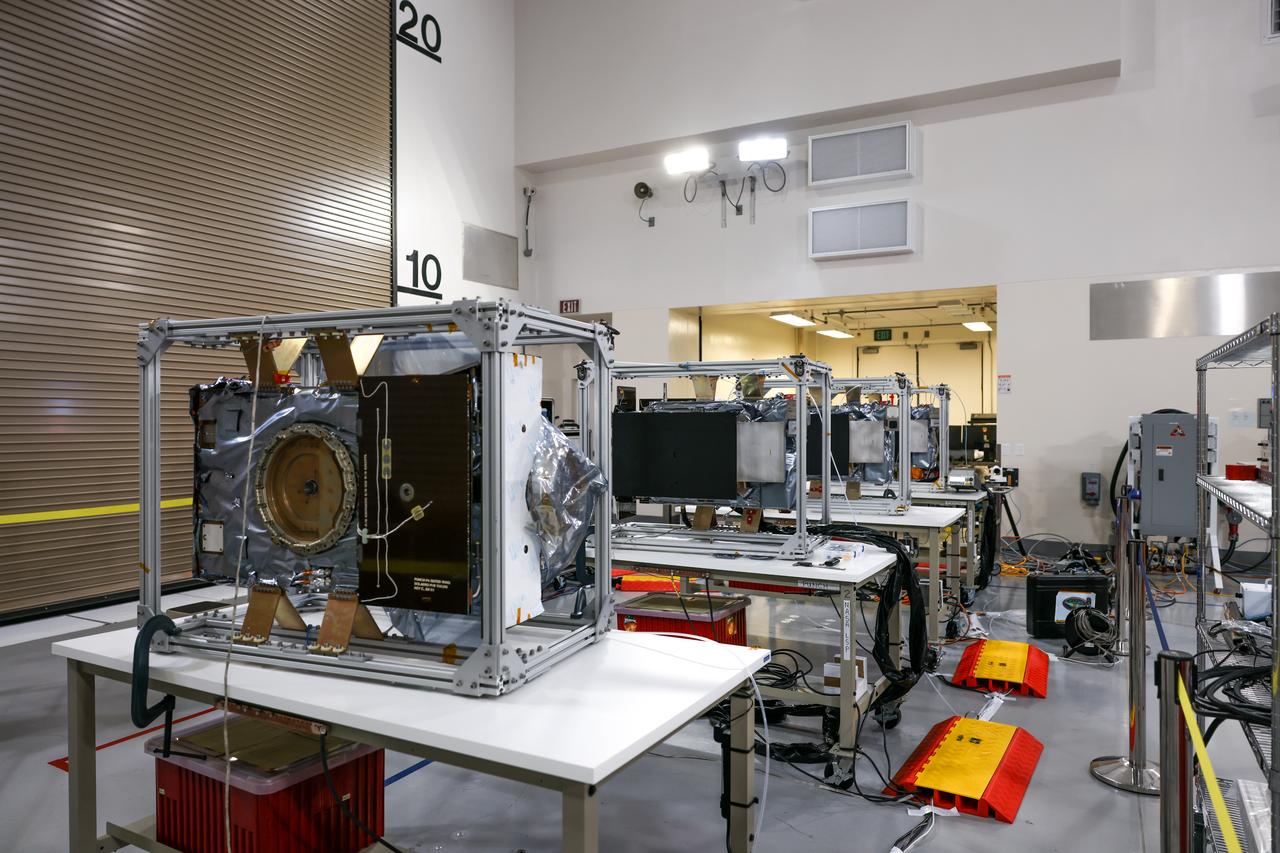

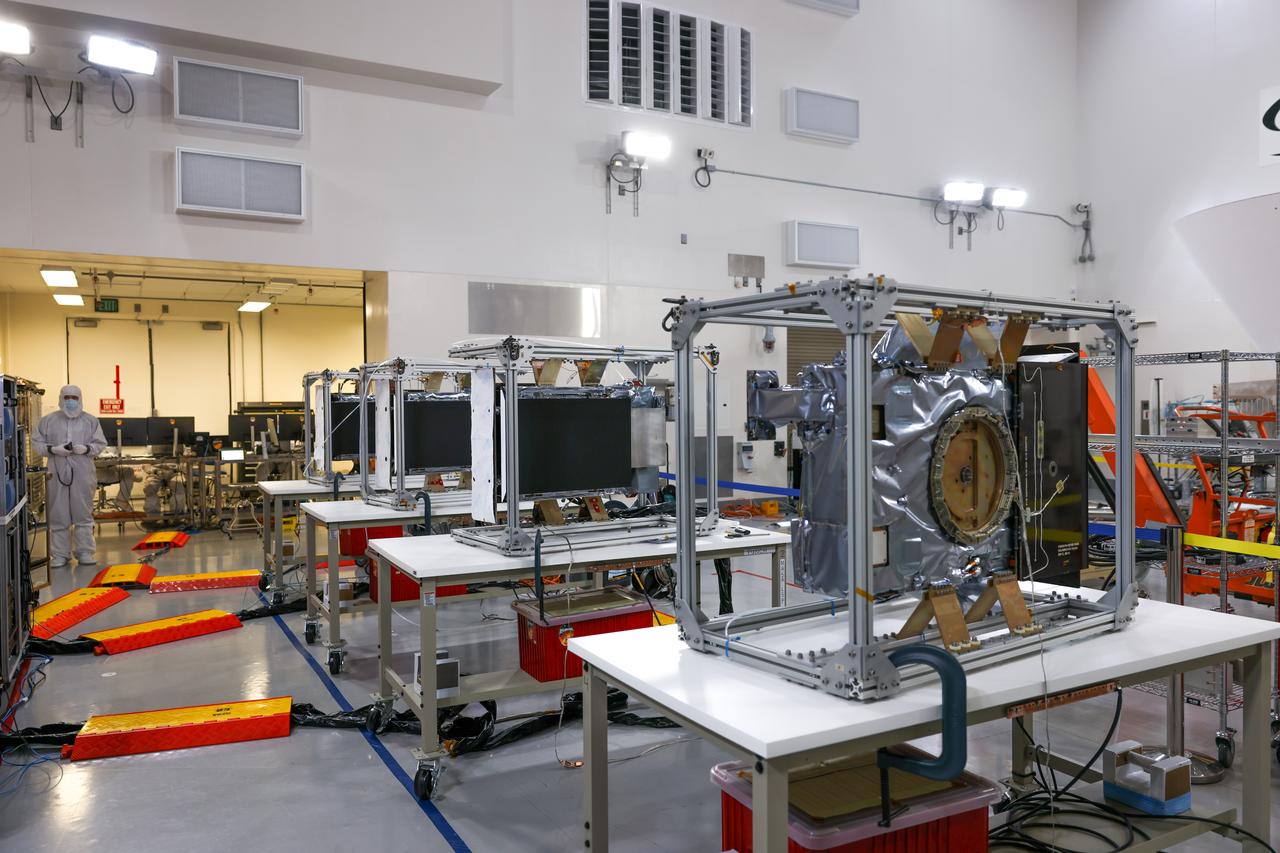
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
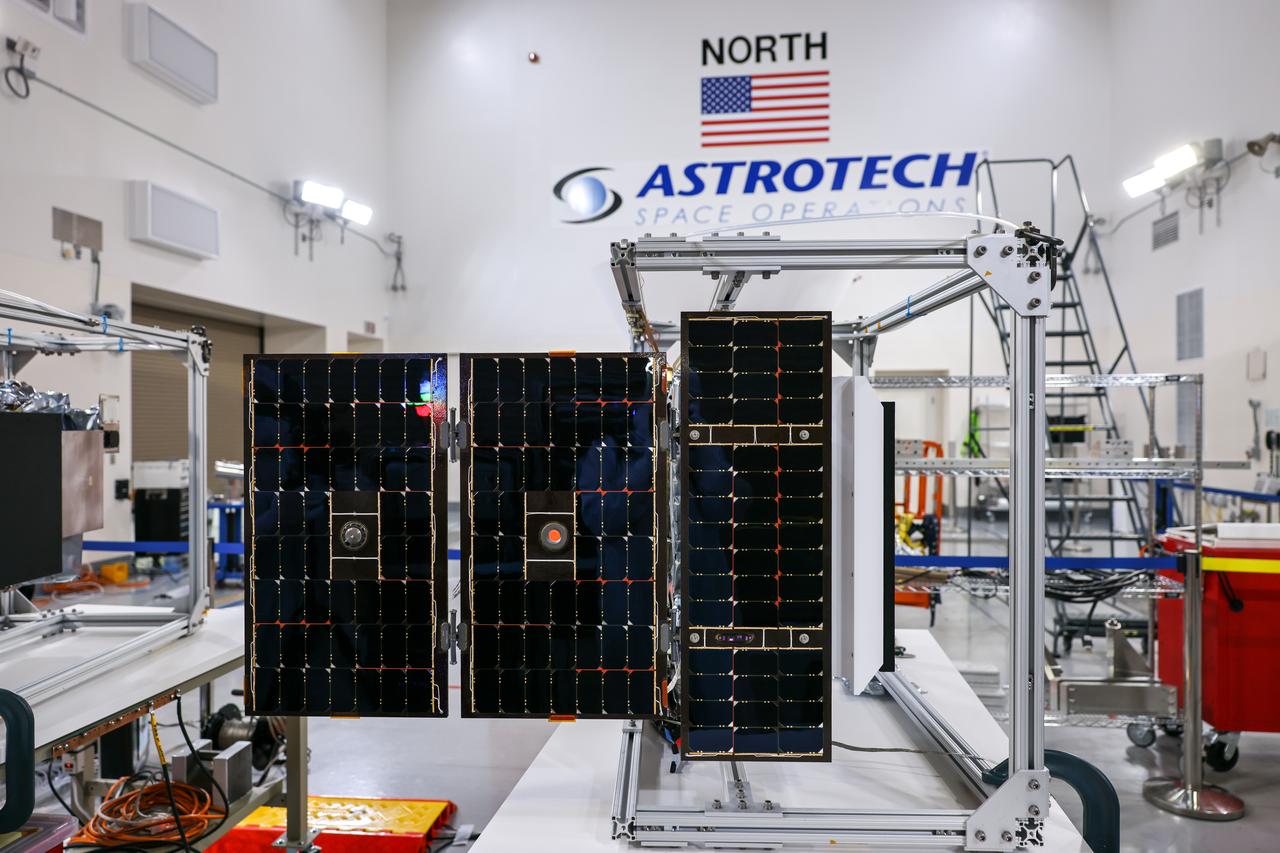

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
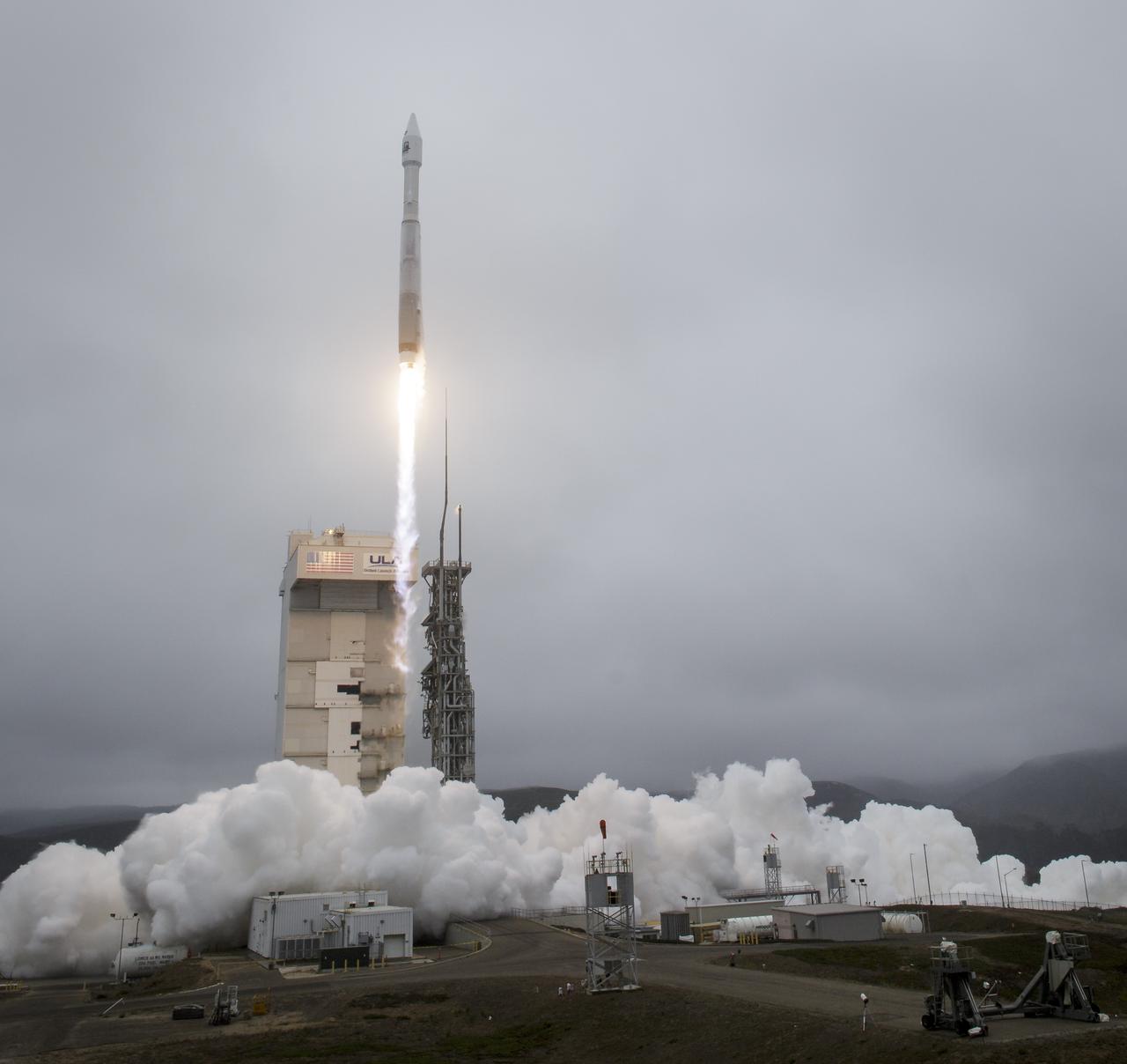

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
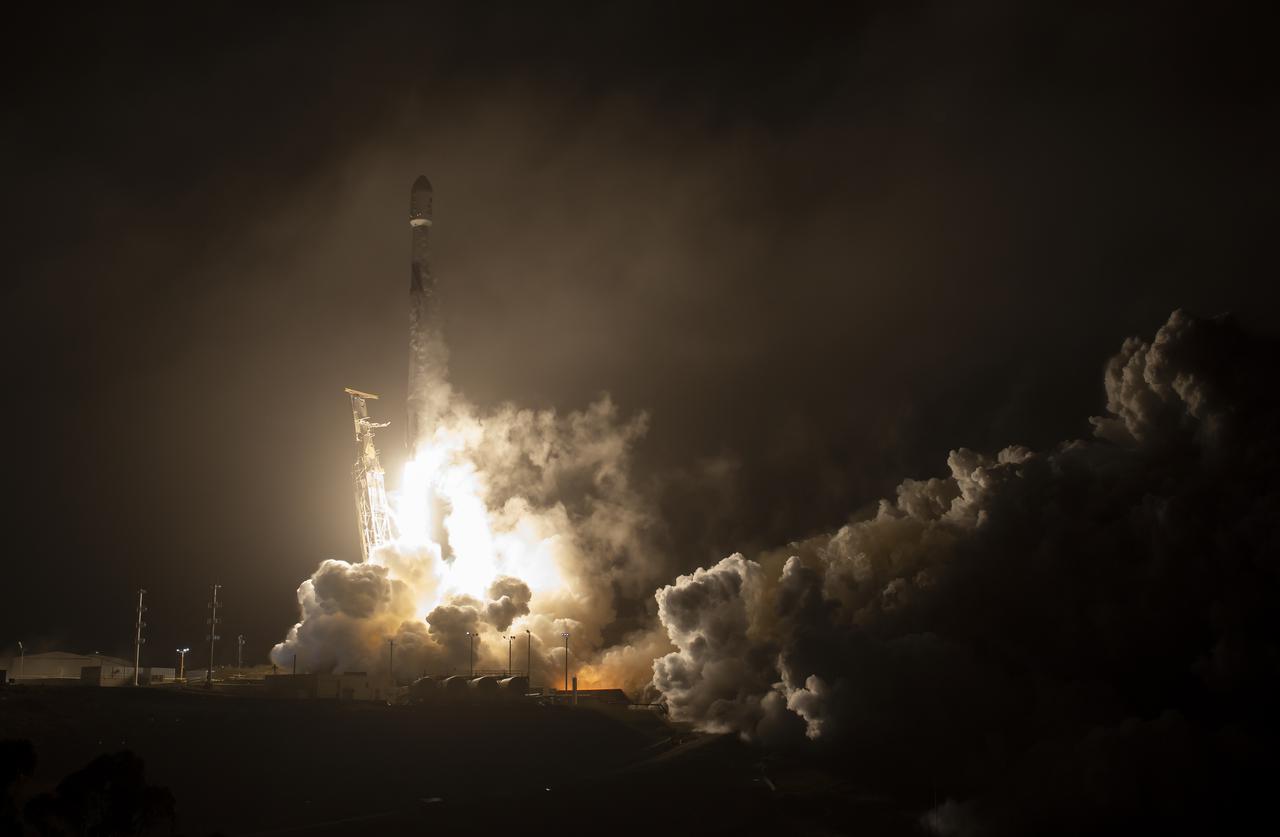

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
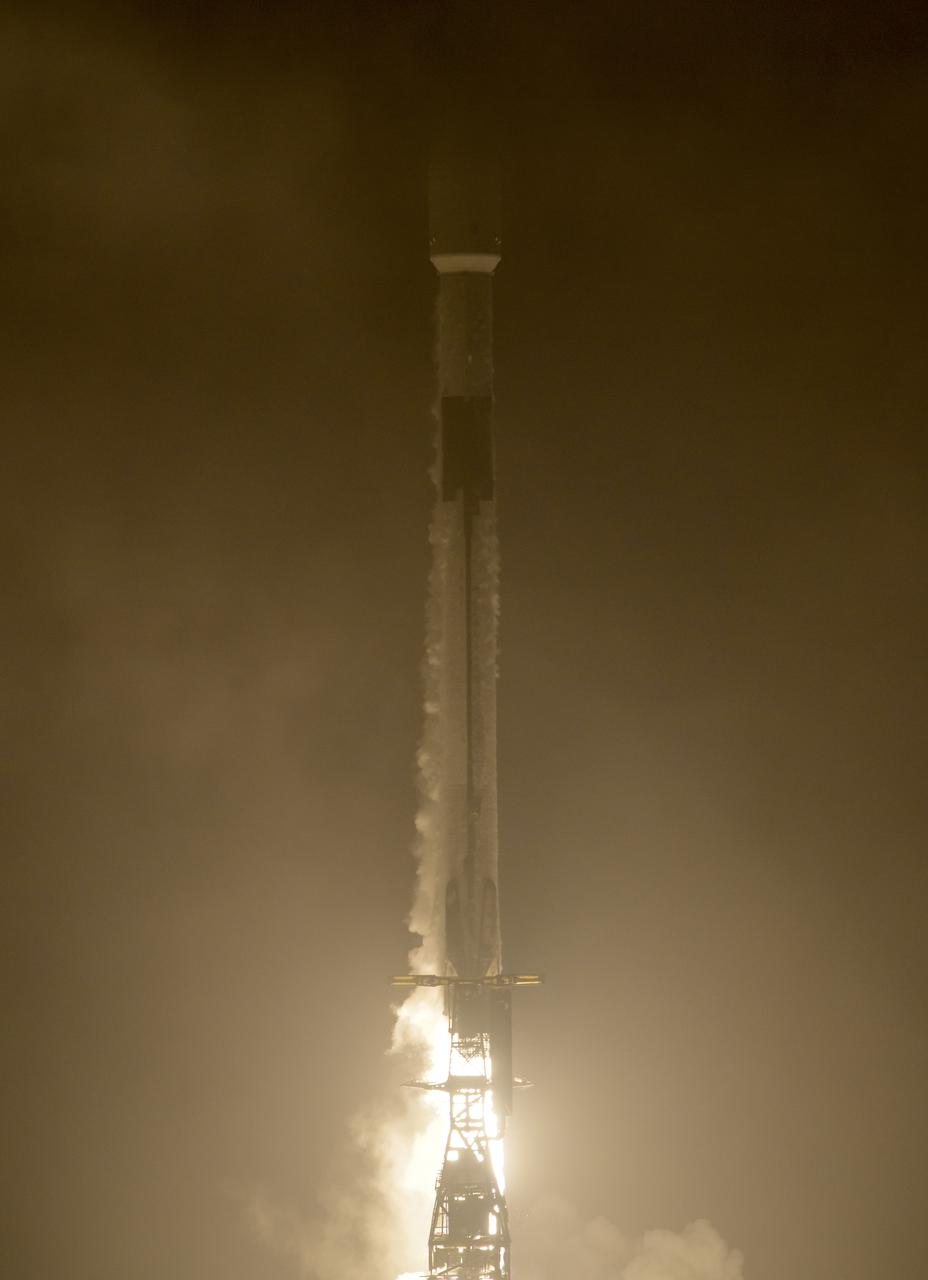

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
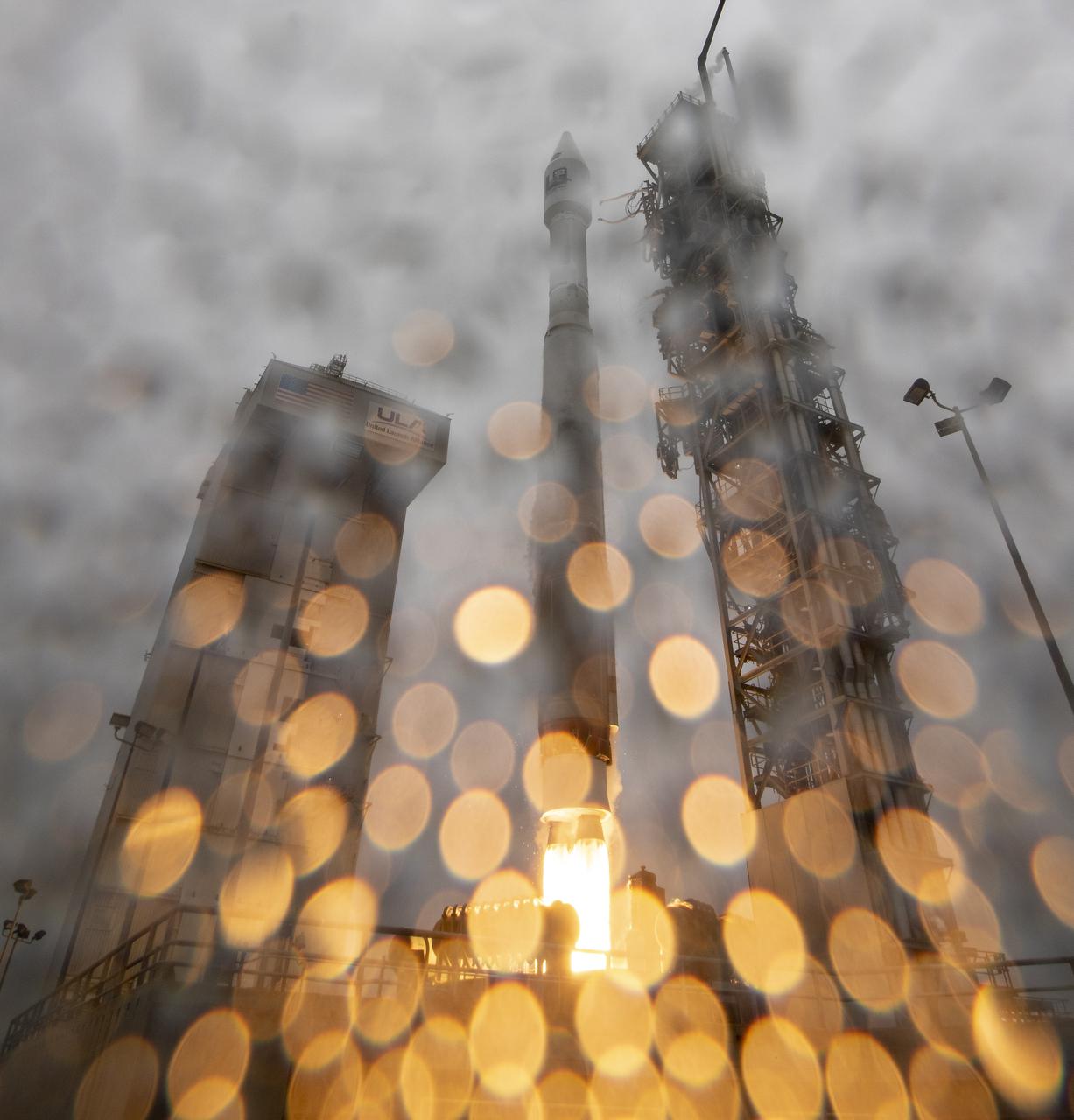

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
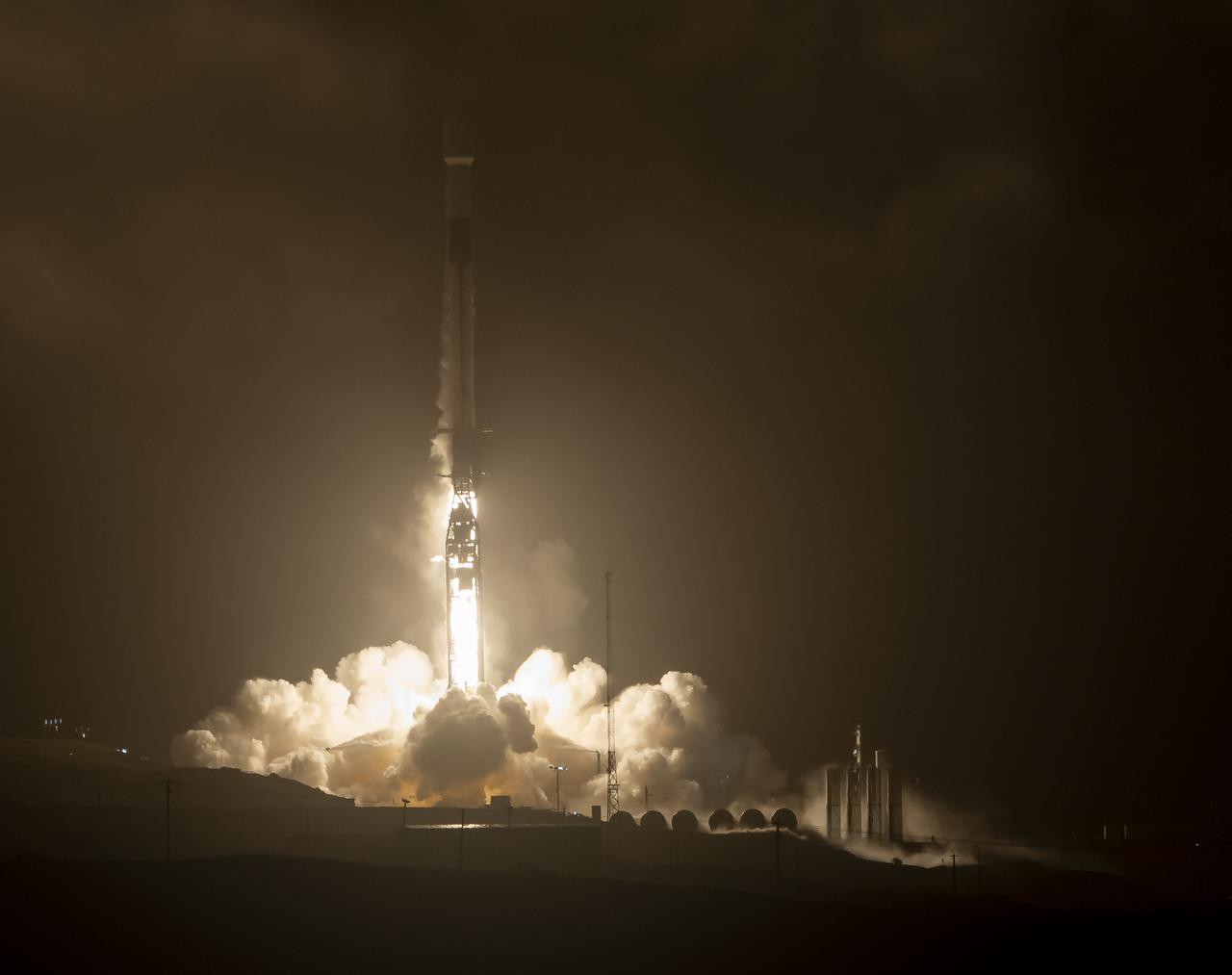

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
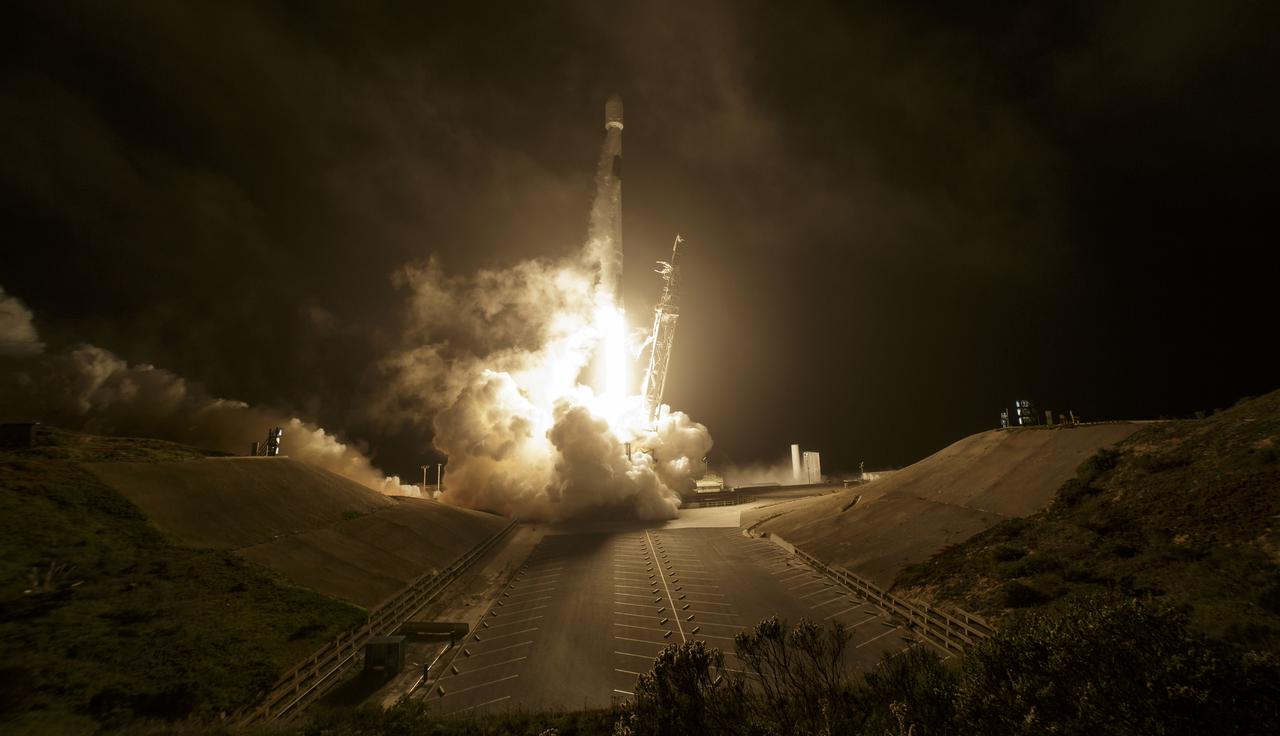

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
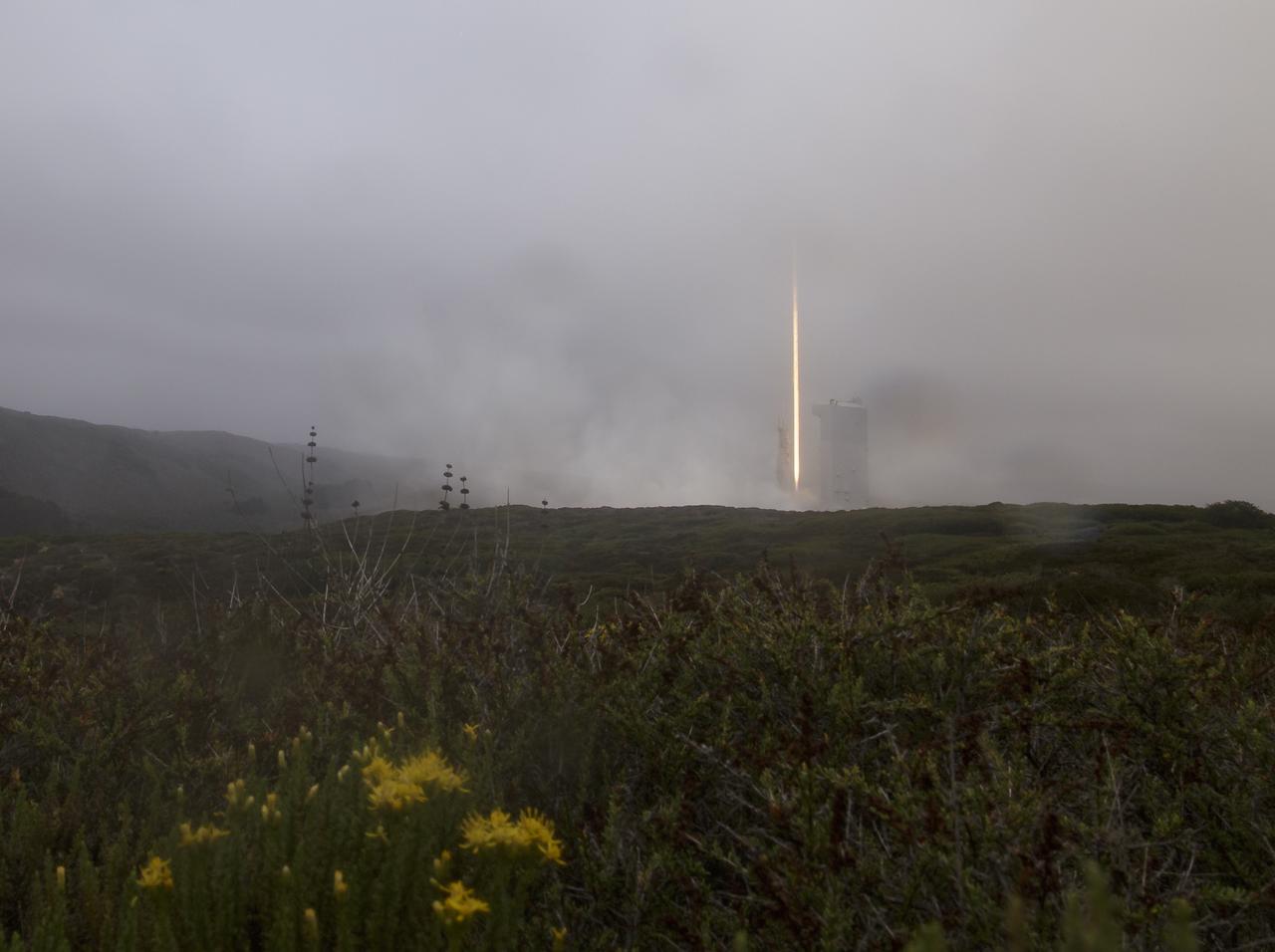

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen in this 30 second exposure as is launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
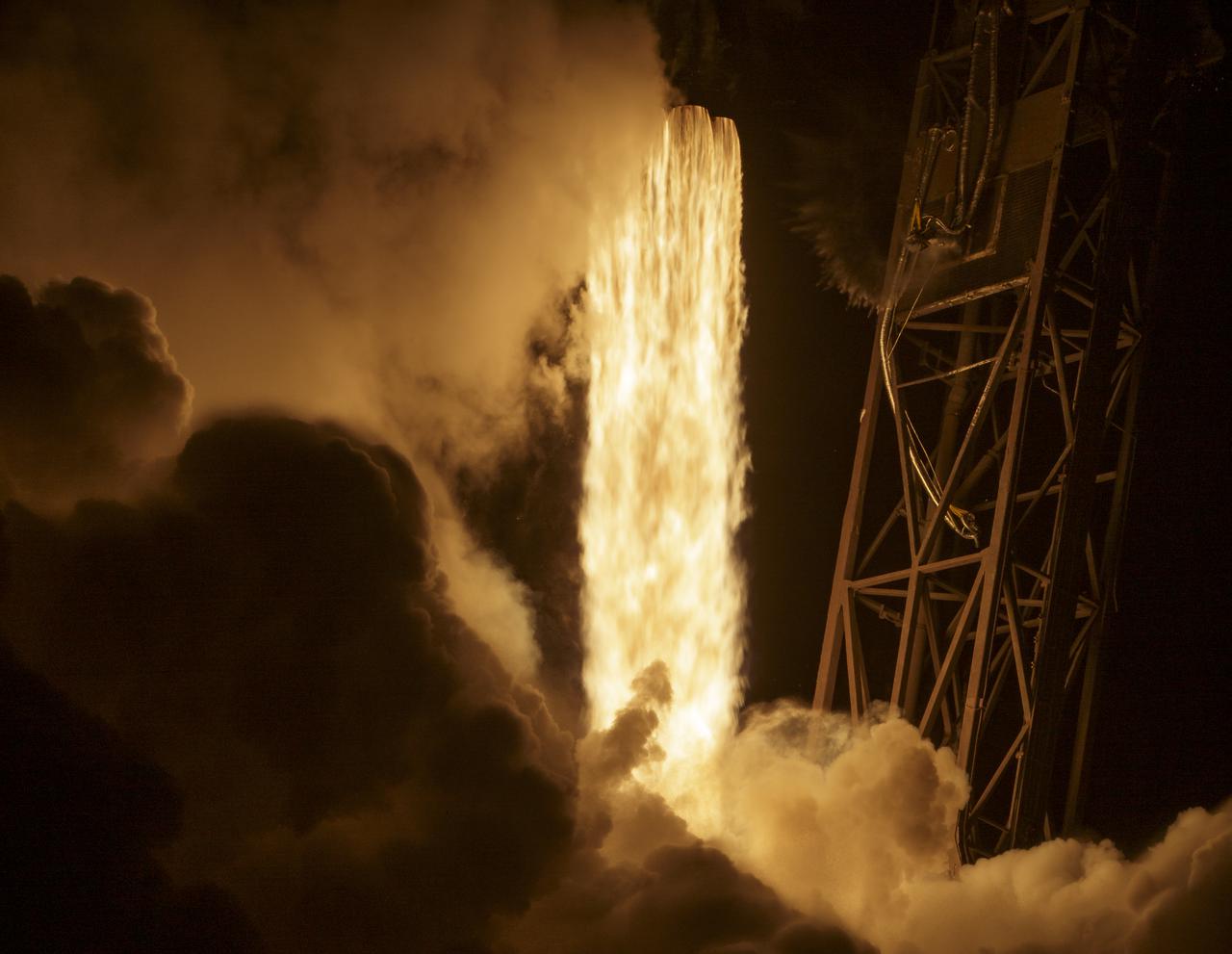

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
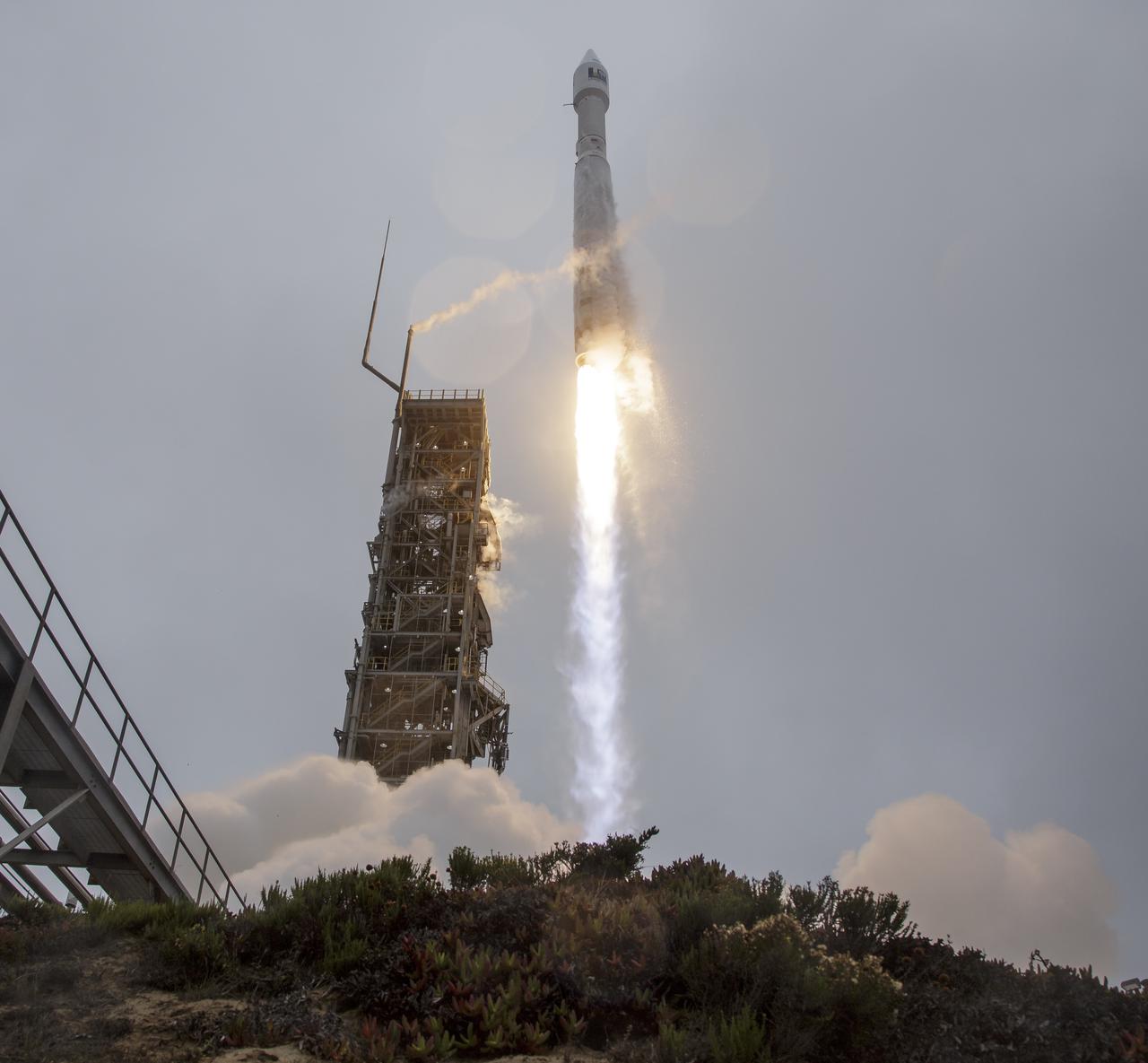

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
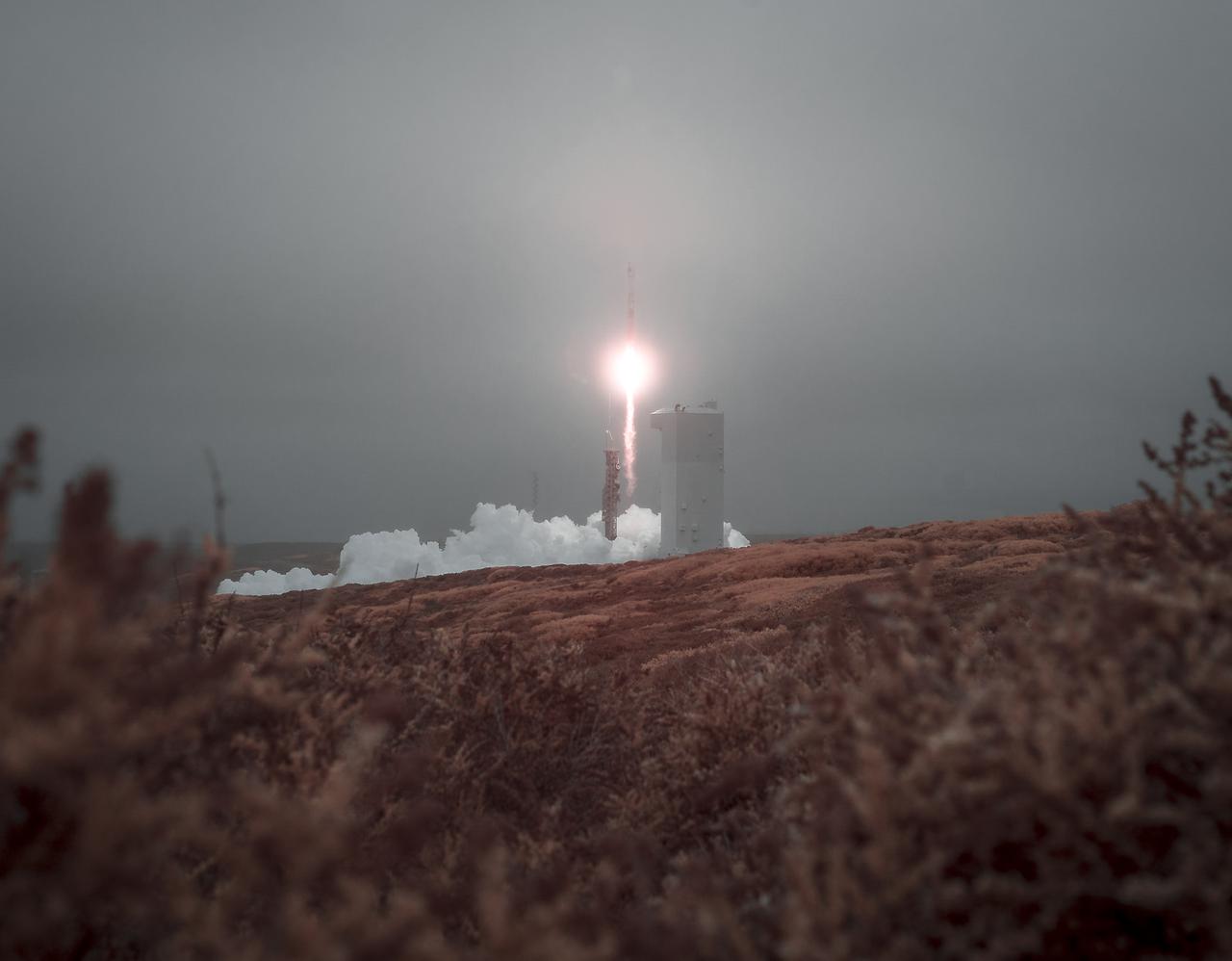

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket with the Landsat 9 satellite onboard is seen in this false color infrared image as it launches, Monday, Sept. 27, 2021, from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The Landsat 9 satellite is a joint NASA/U.S. Geological Survey mission that will continue the legacy of monitoring Earth’s land and coastal regions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)