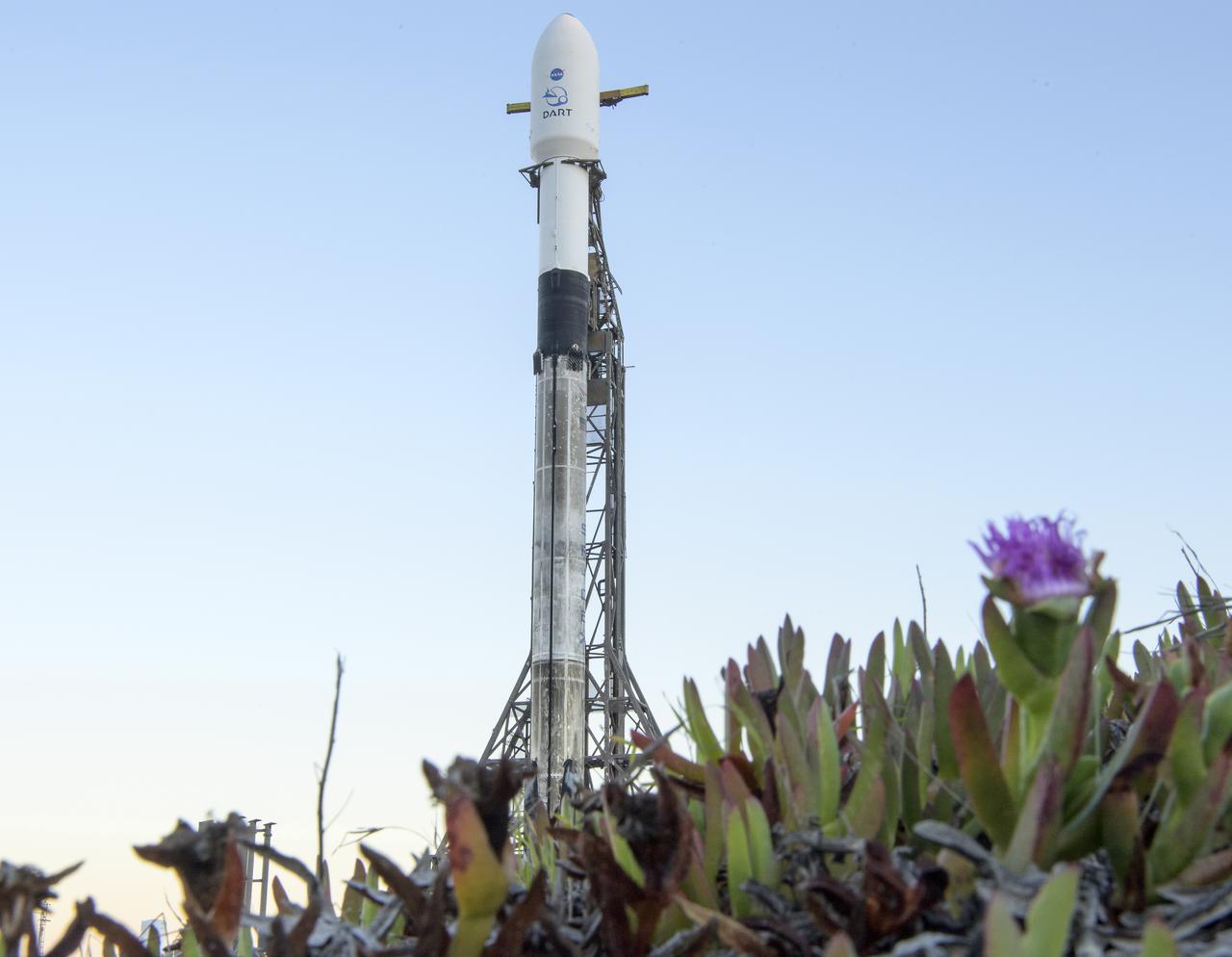

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
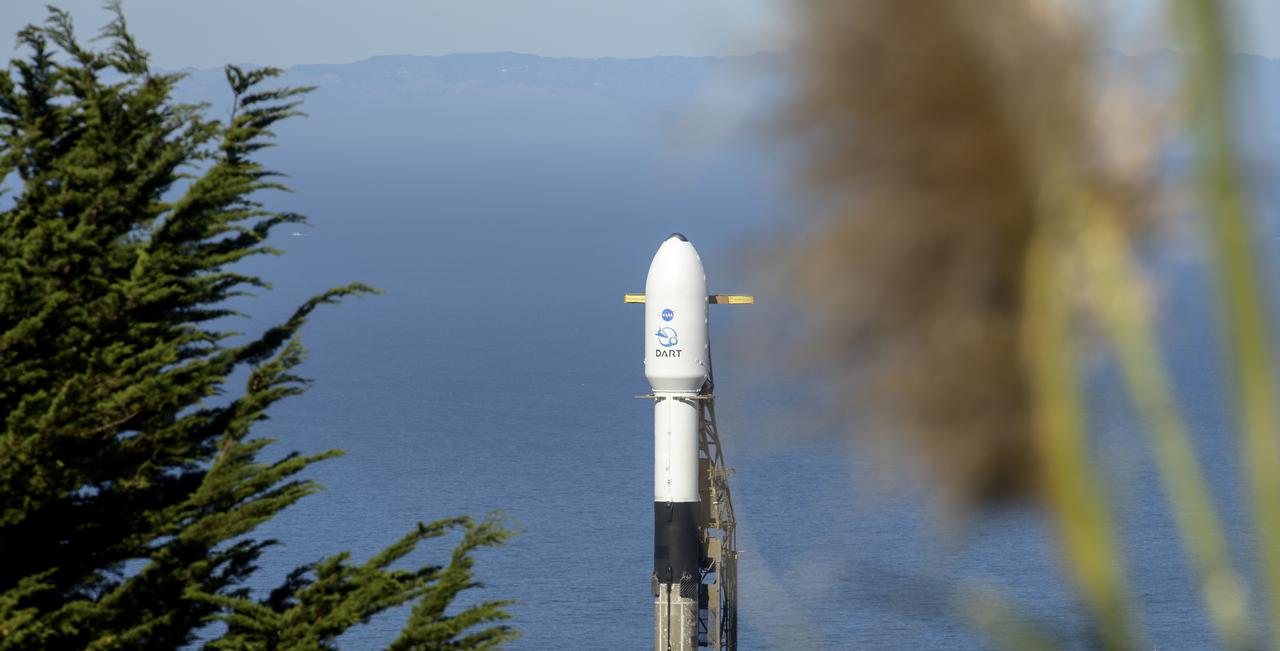

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
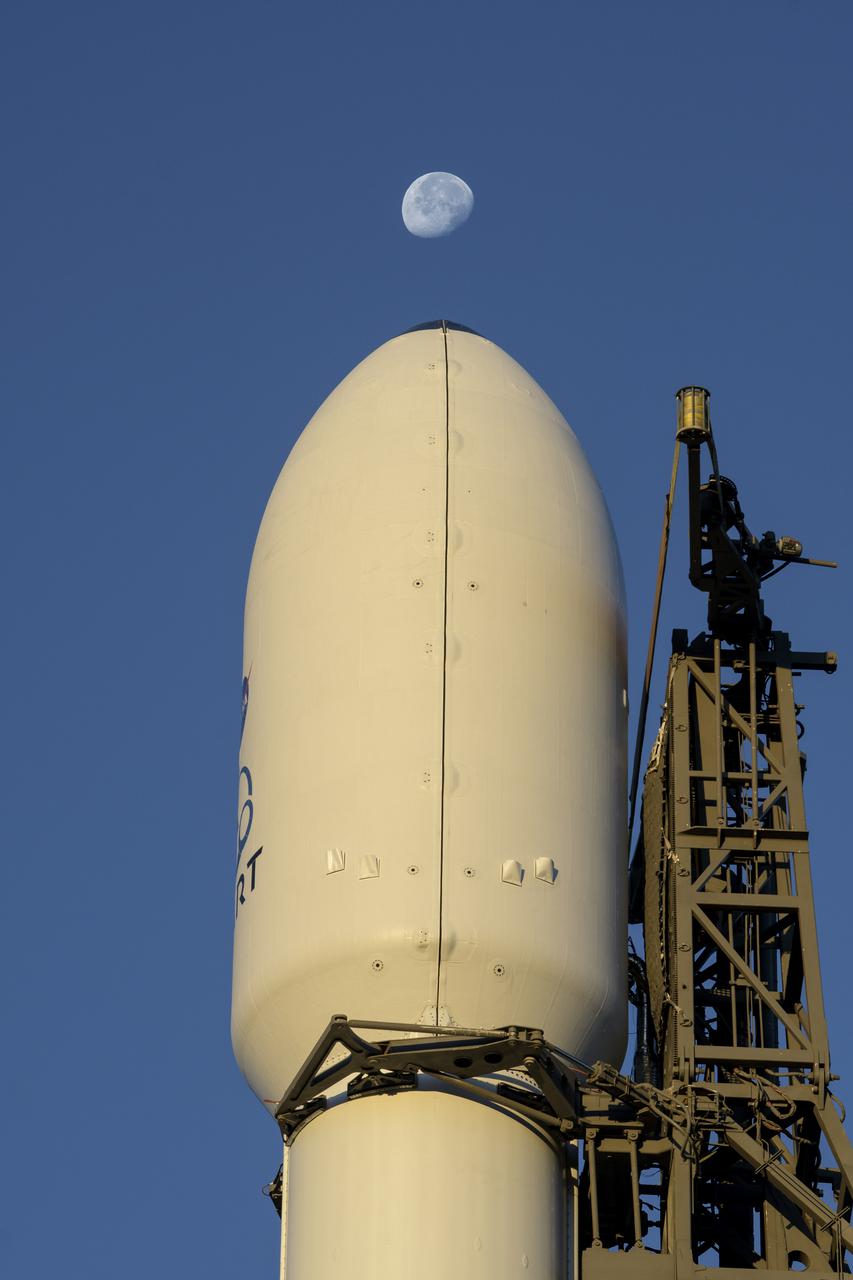

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
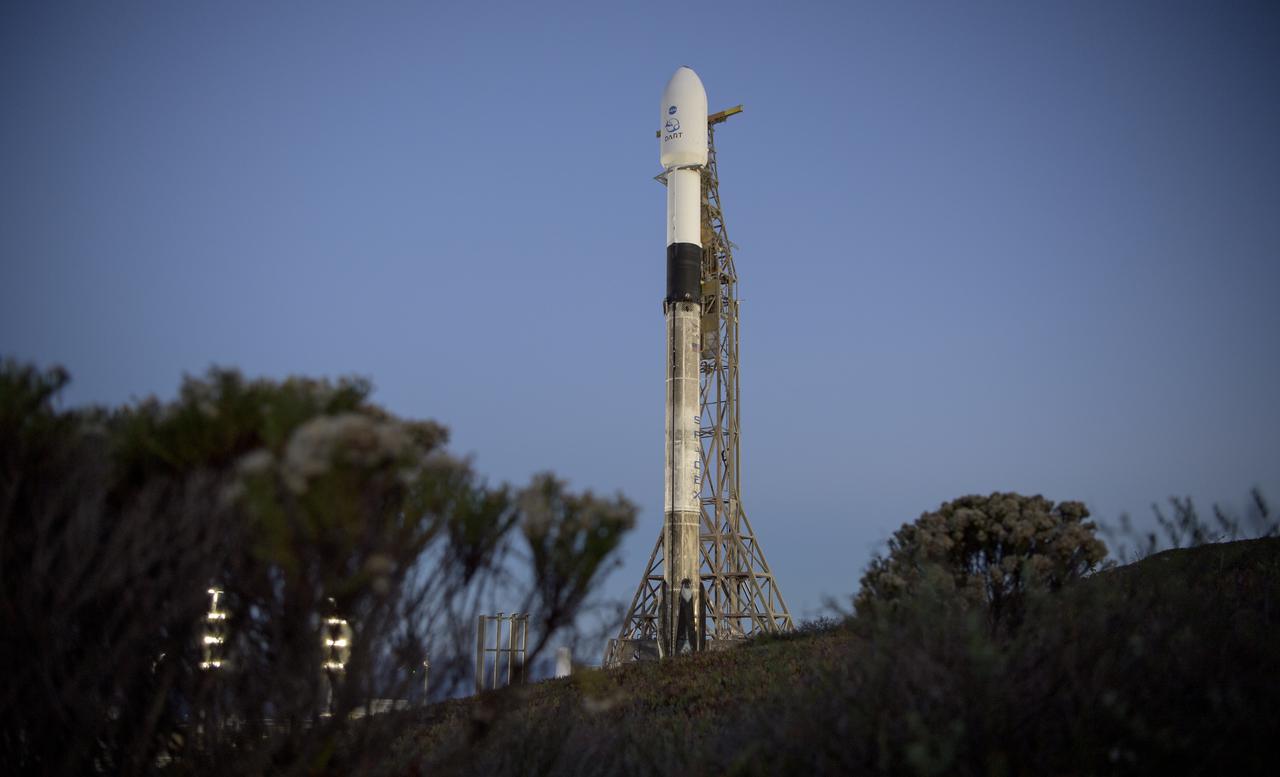

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
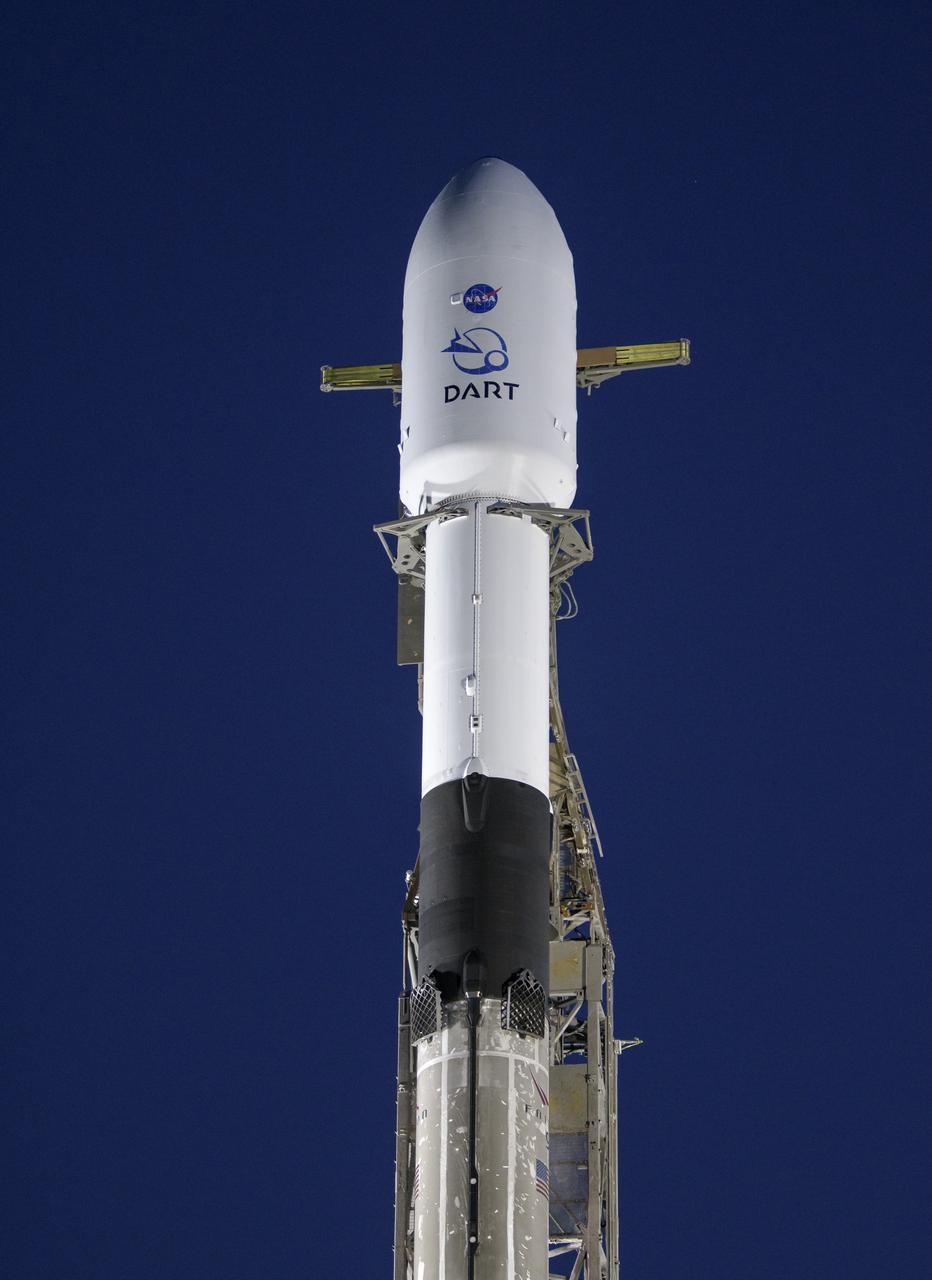

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
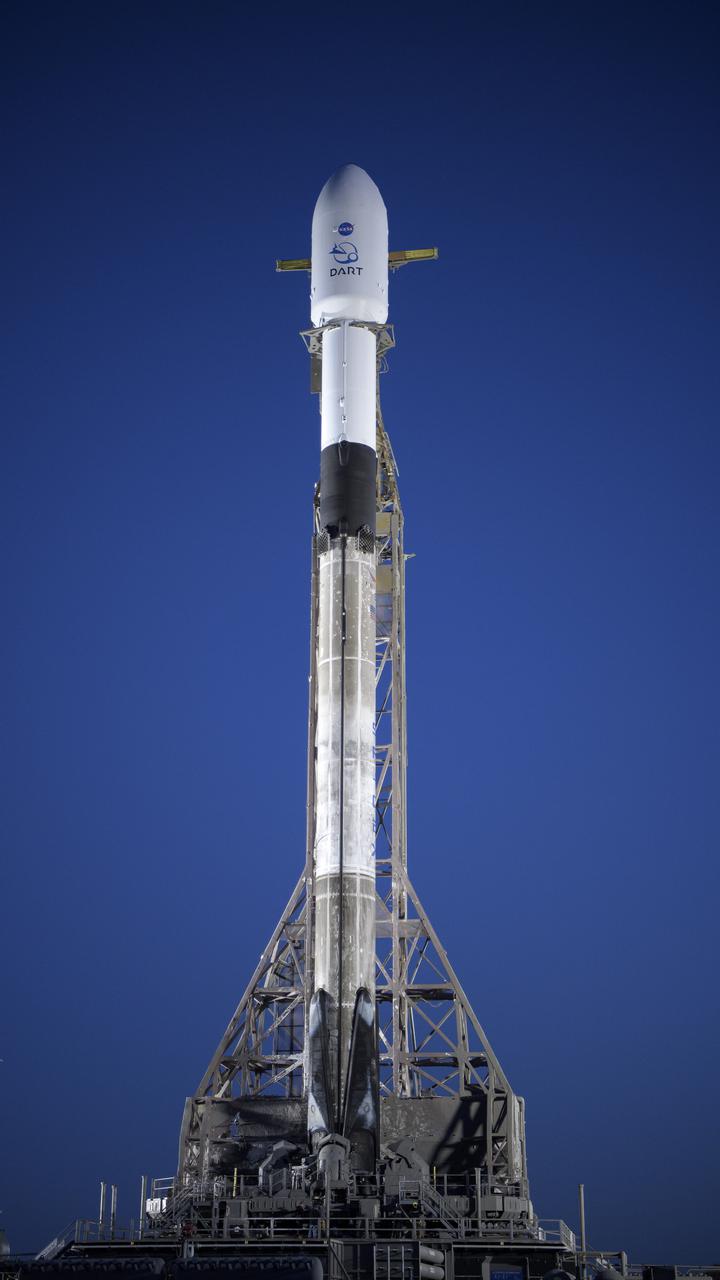

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
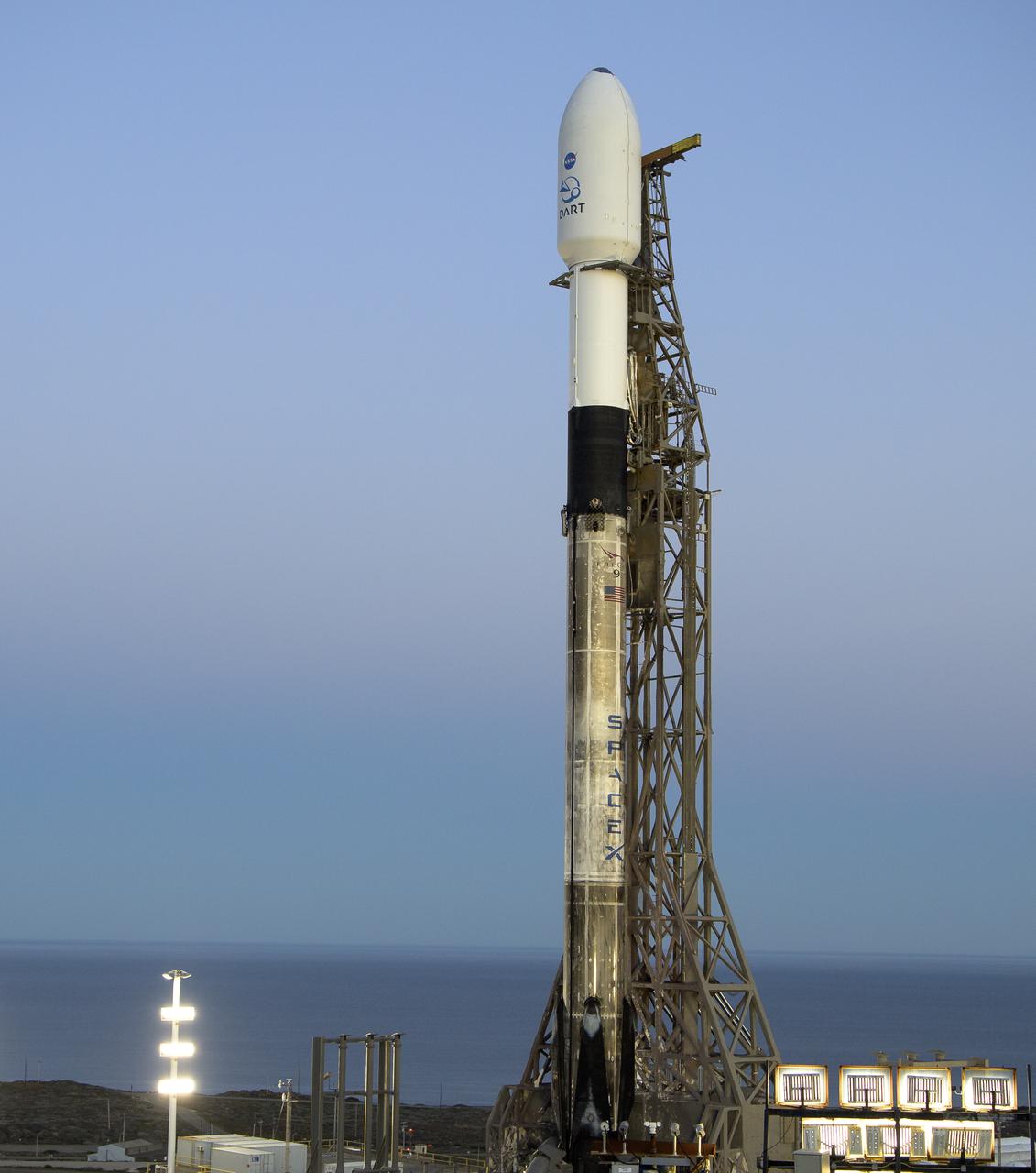

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
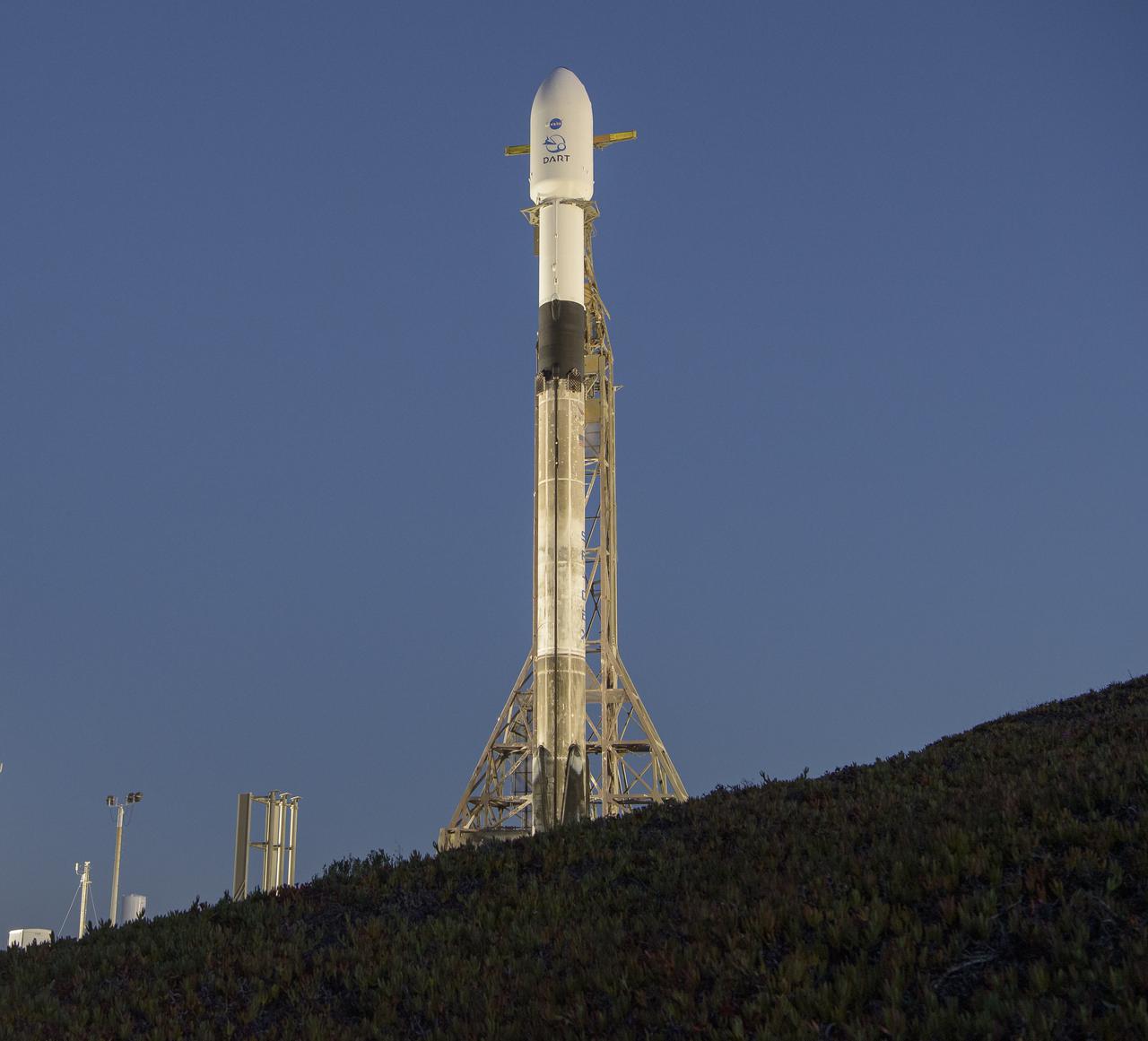

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
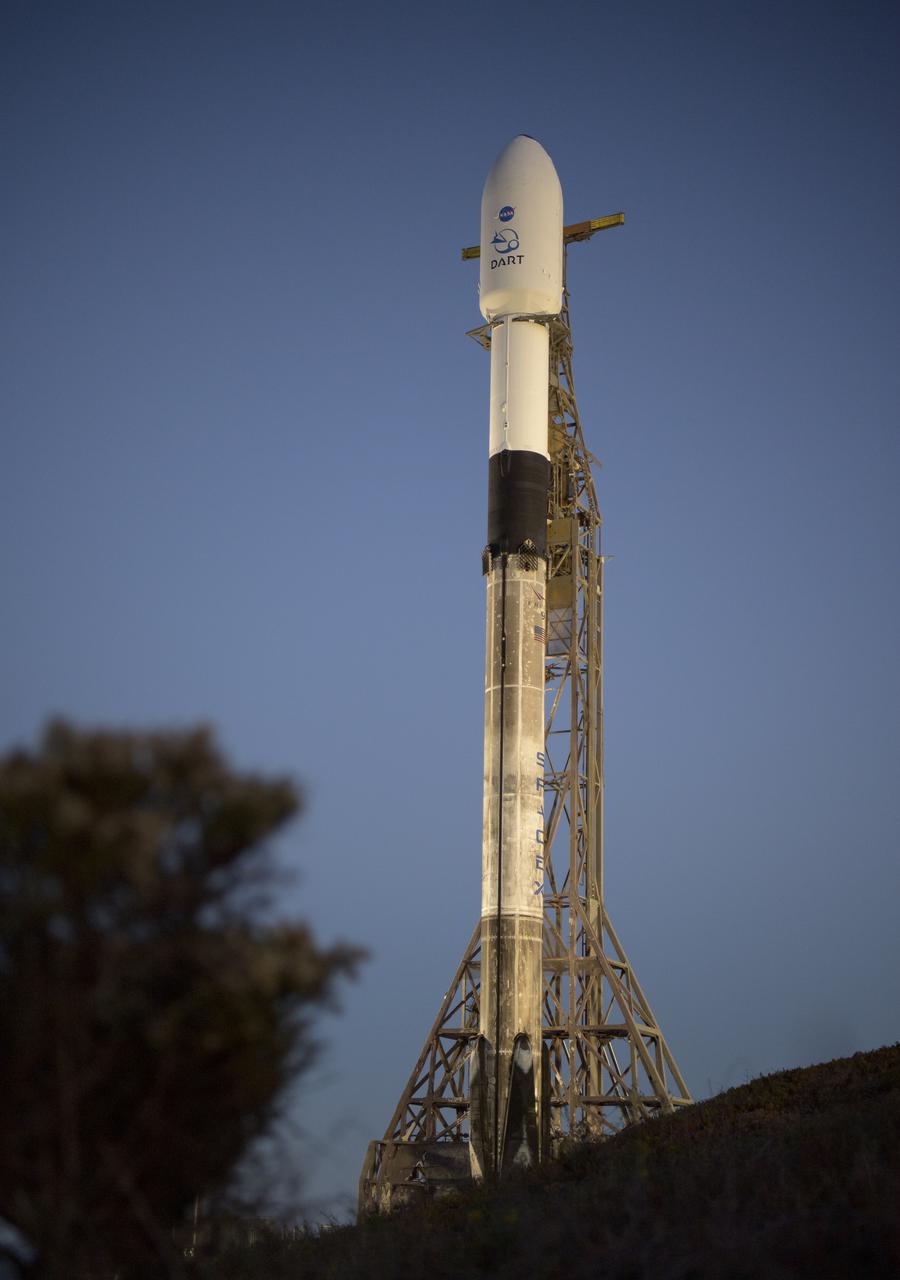

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
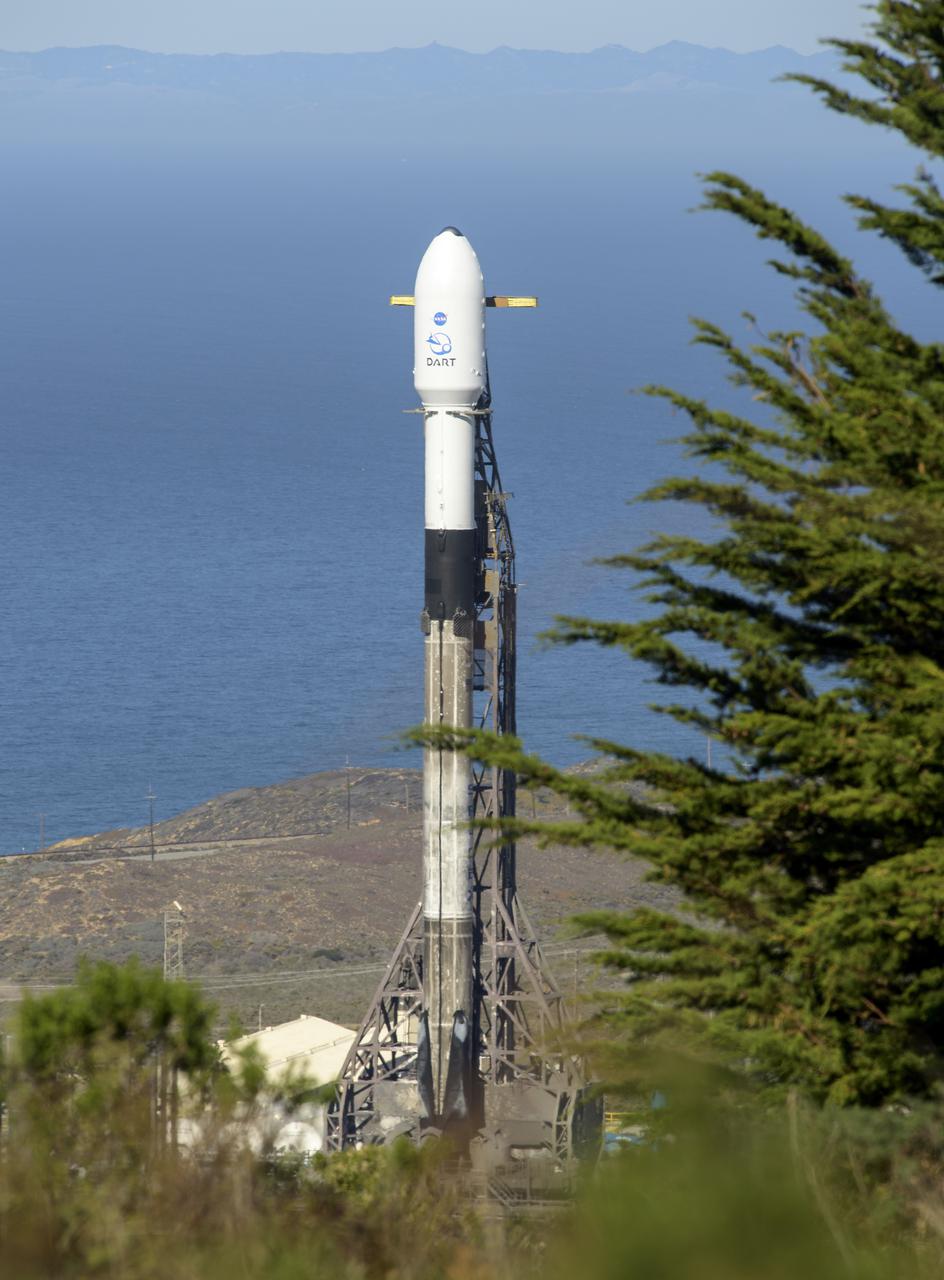

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
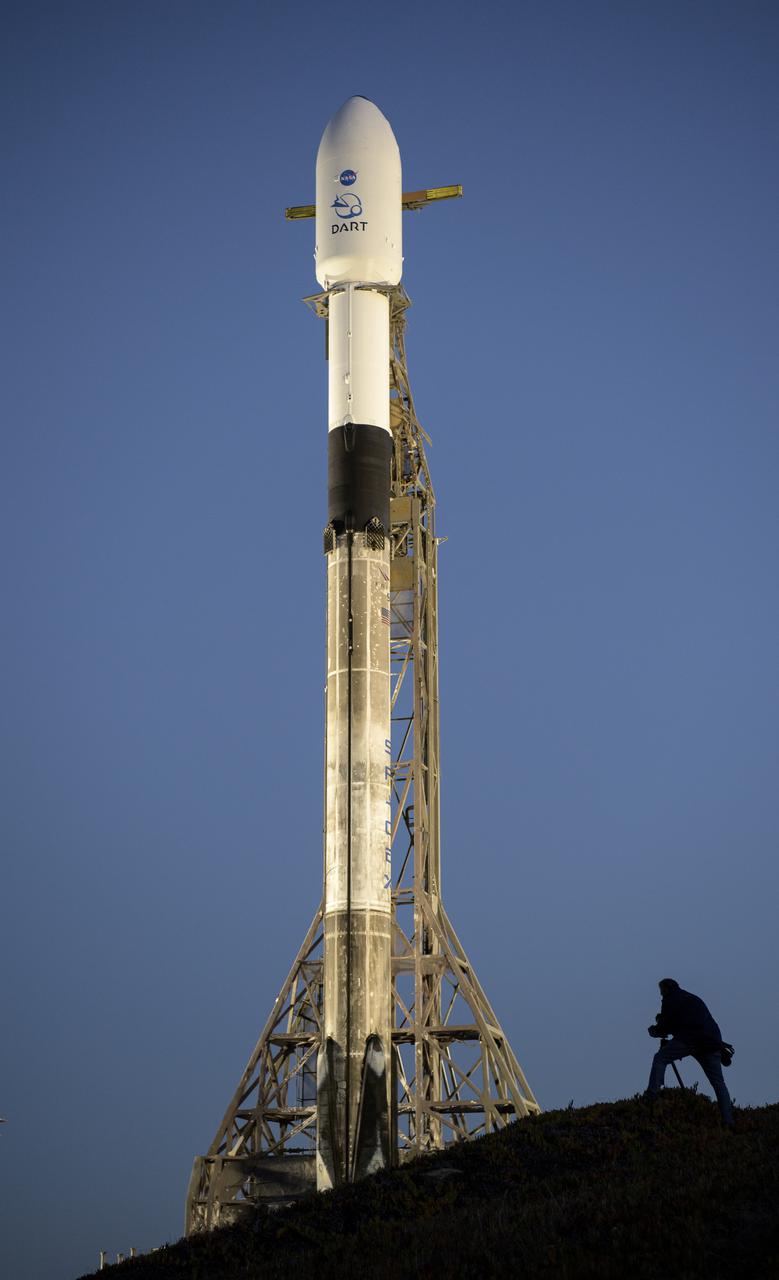

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
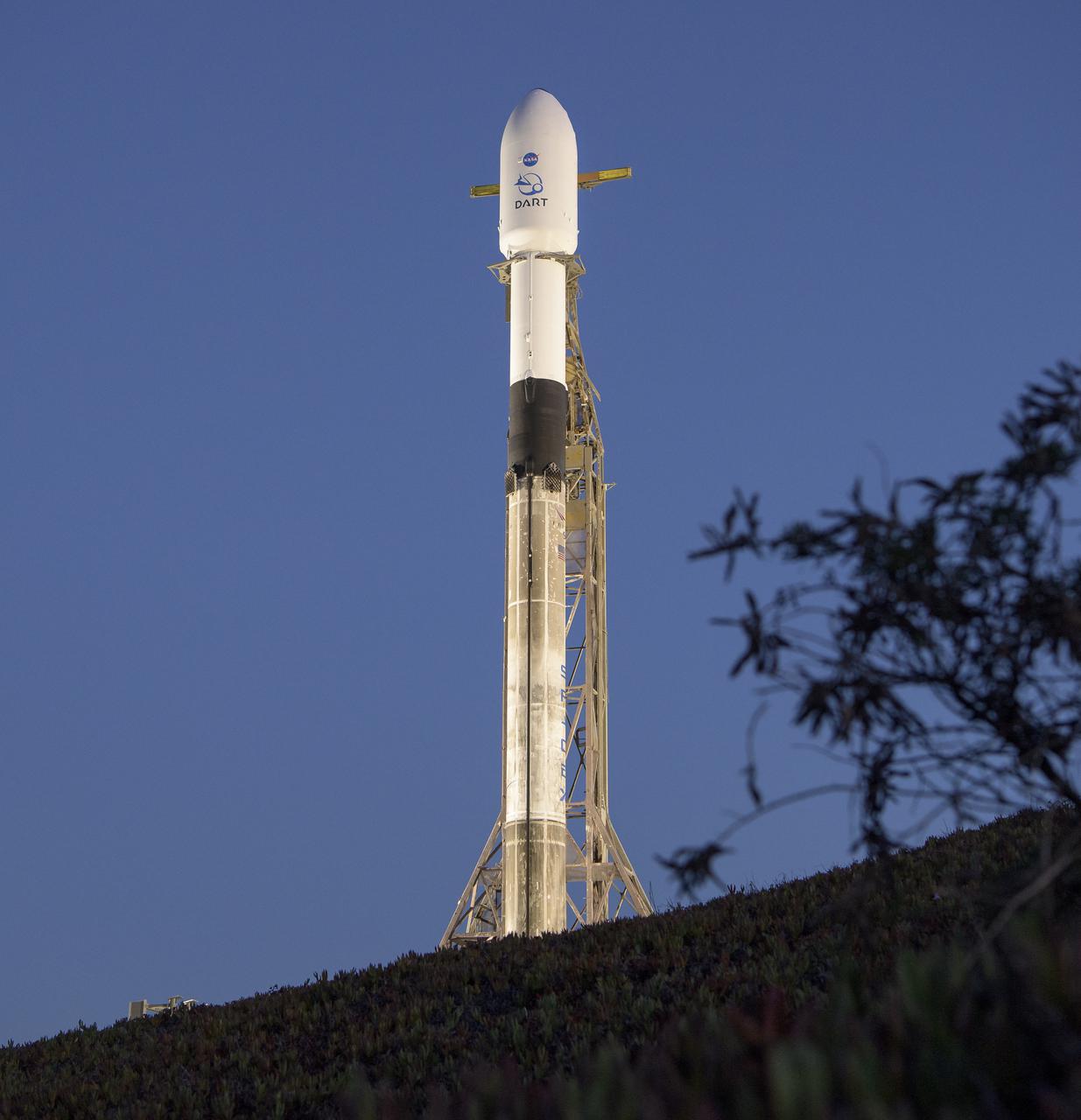

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
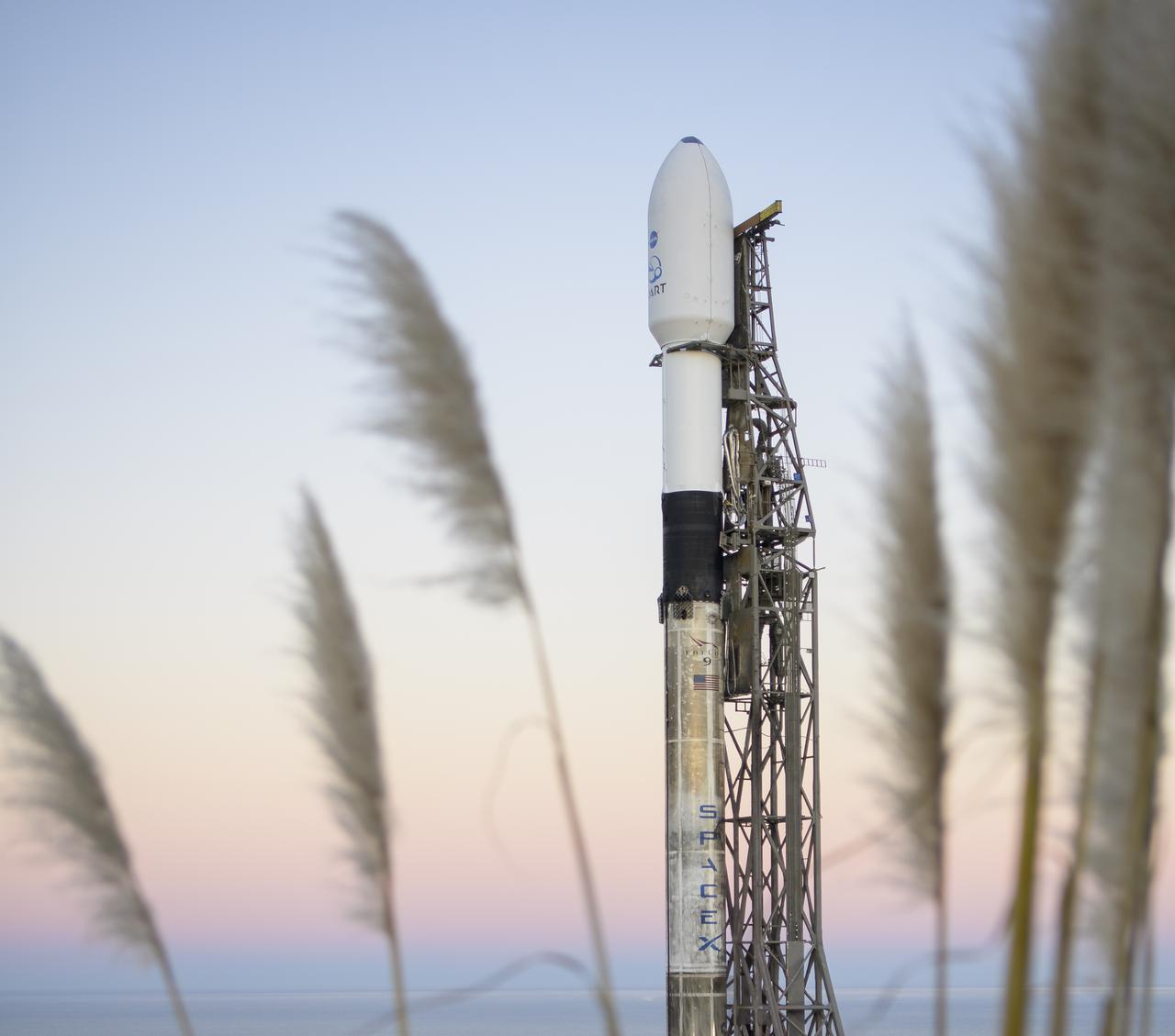

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
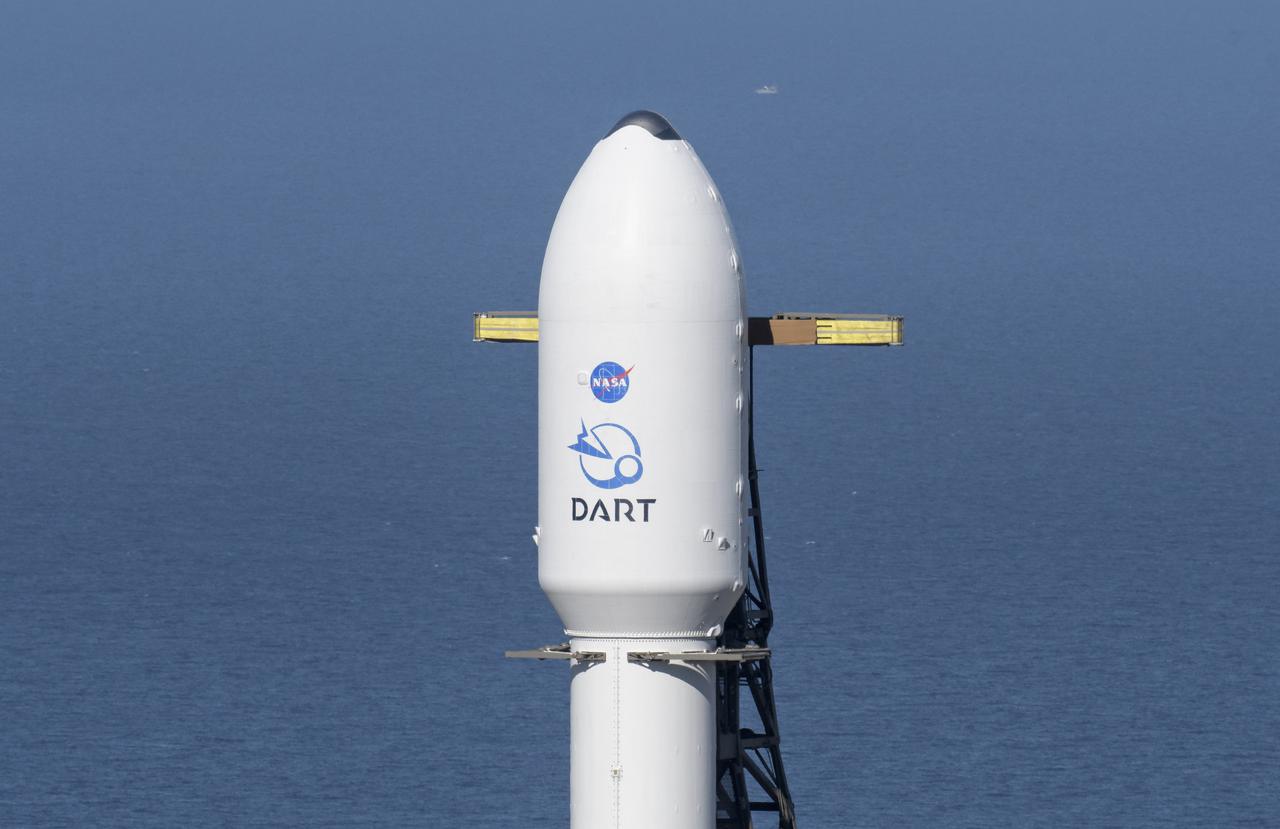

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
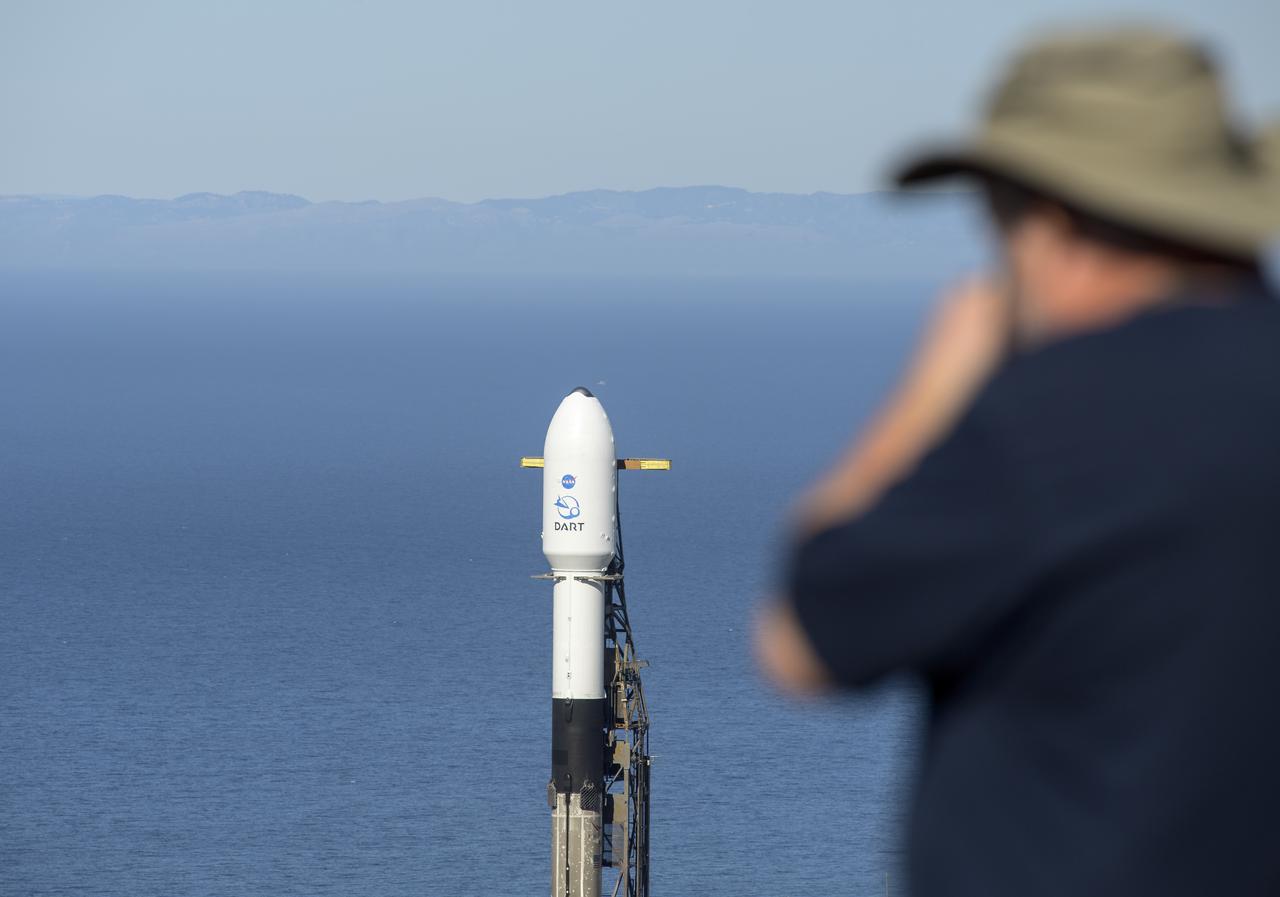

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
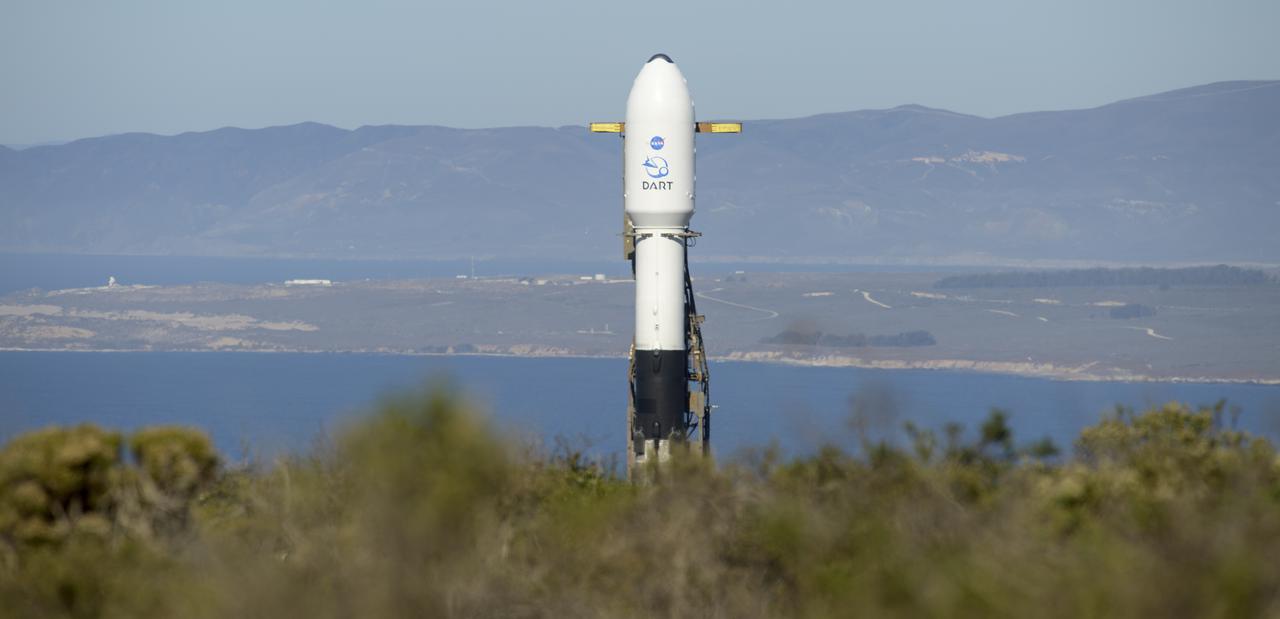

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
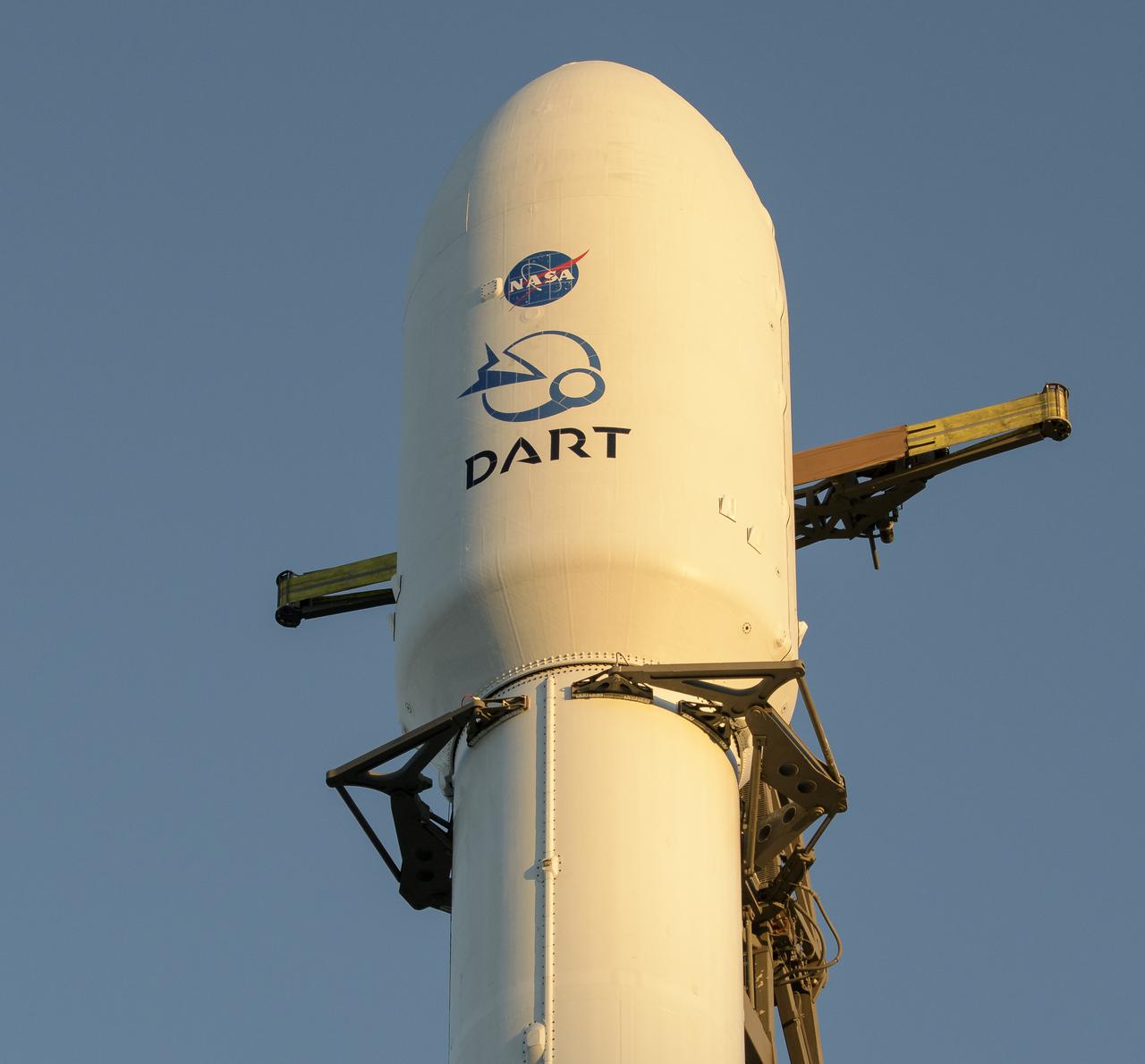

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
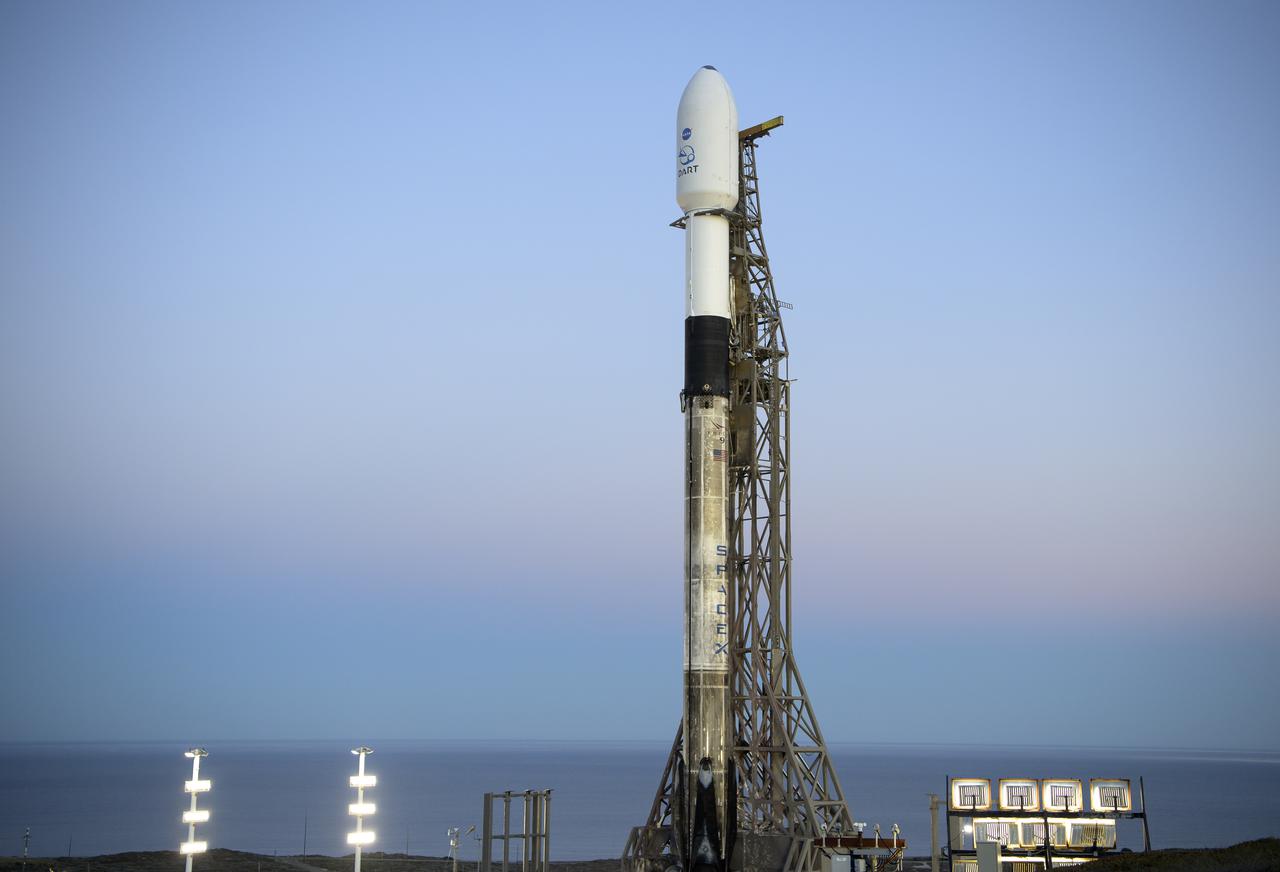

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
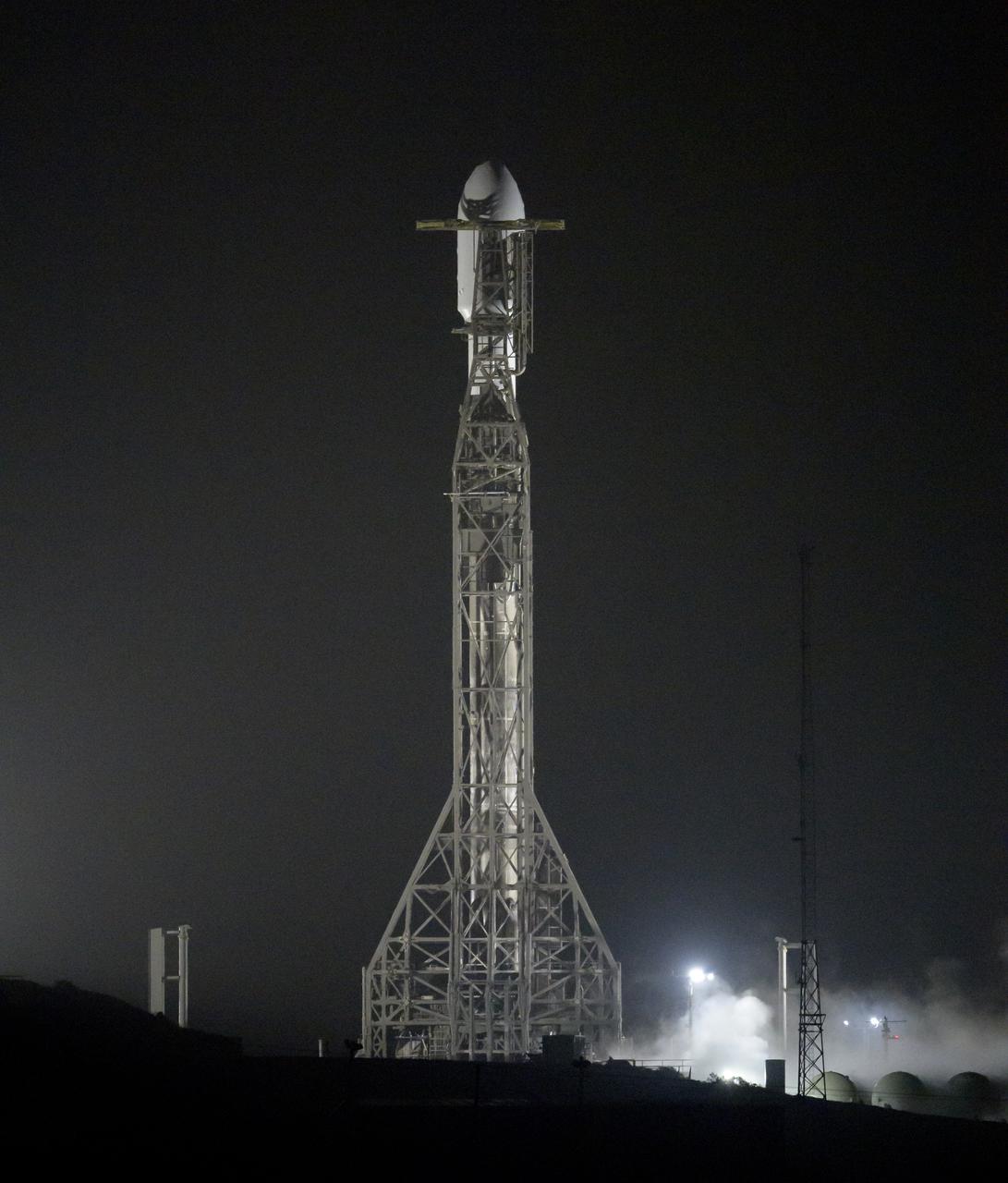

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen ready for launch, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission stands vertical Tuesday, July 22, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
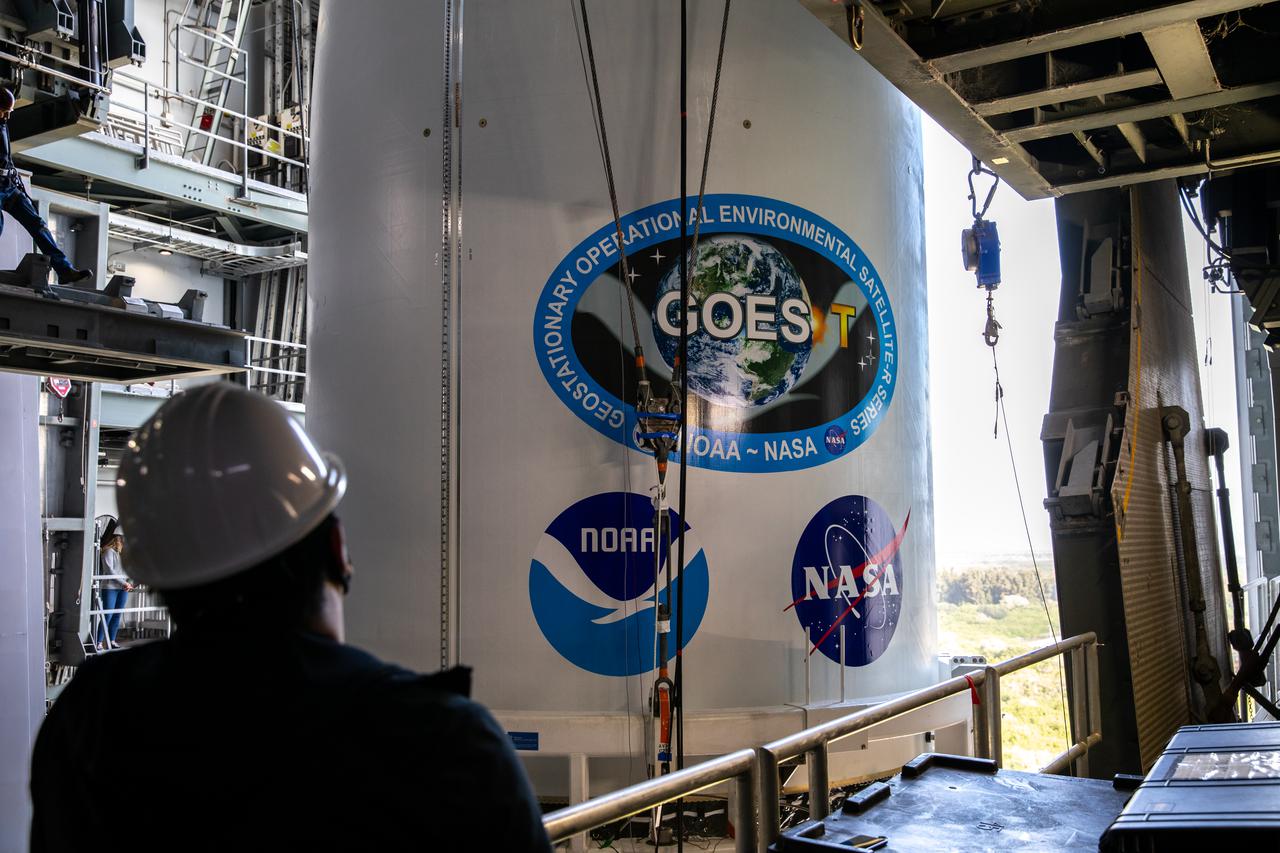

A United Launch Alliance technician monitors the progress as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, is moved into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
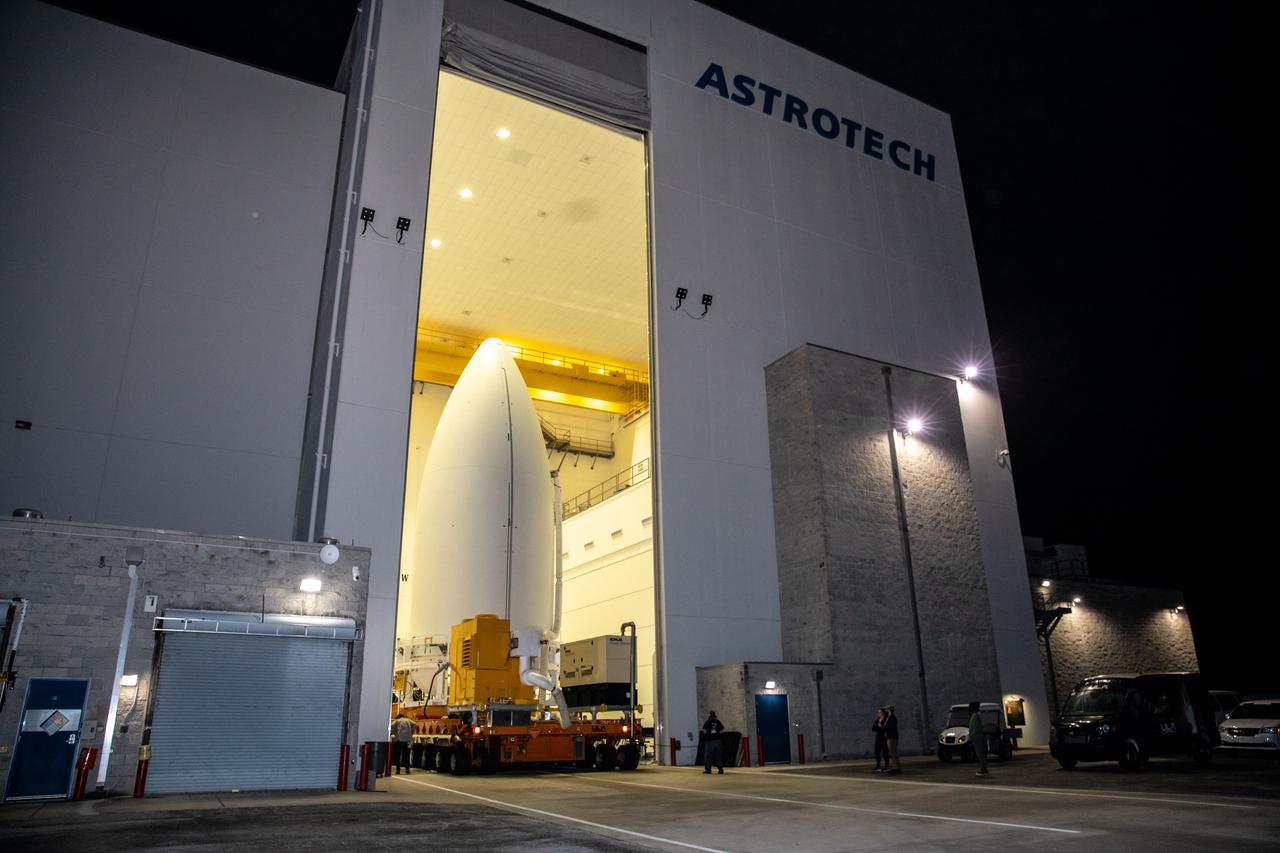

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, begins its move out of the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, for the trip to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be lifted up inside the integration facility and secured to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
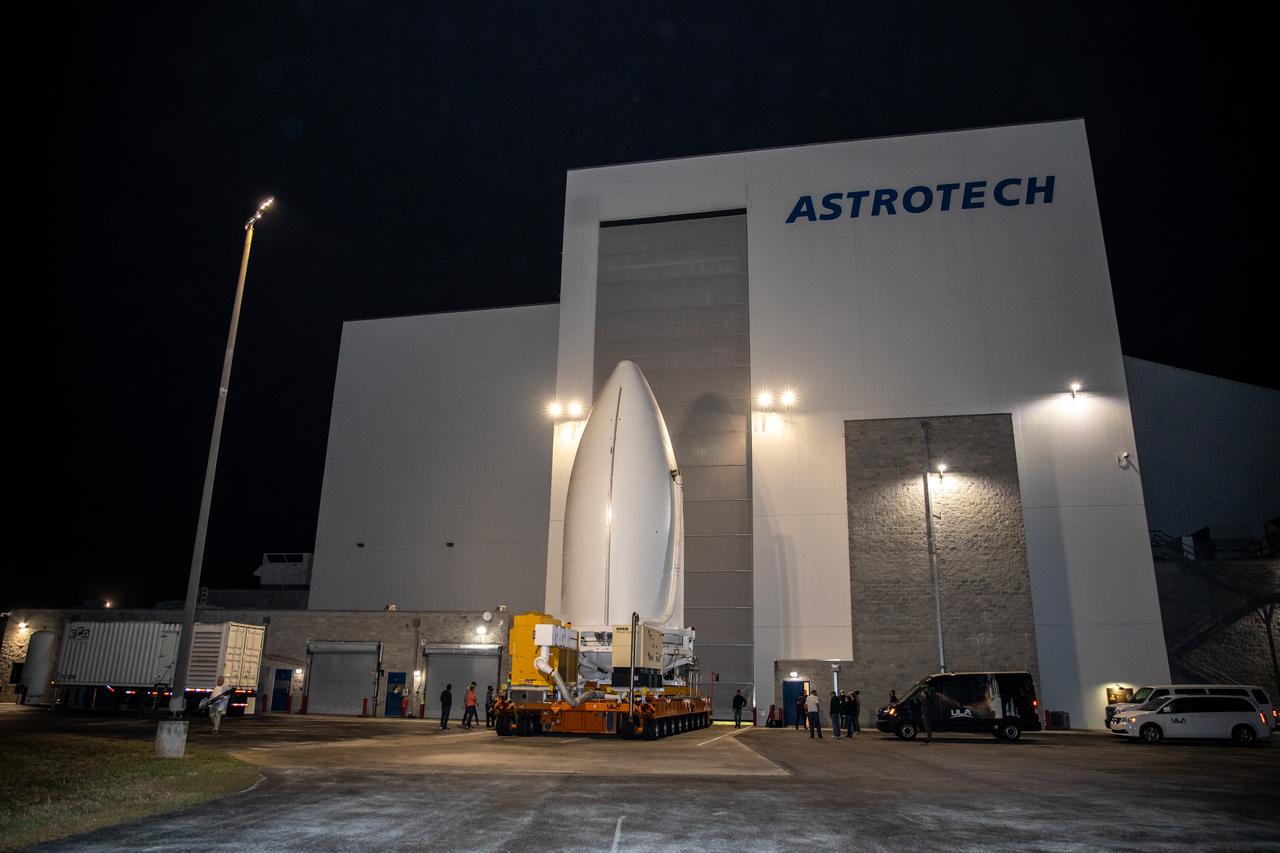

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, exits the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, for its trip to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be lifted up inside the integration facility and secured to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
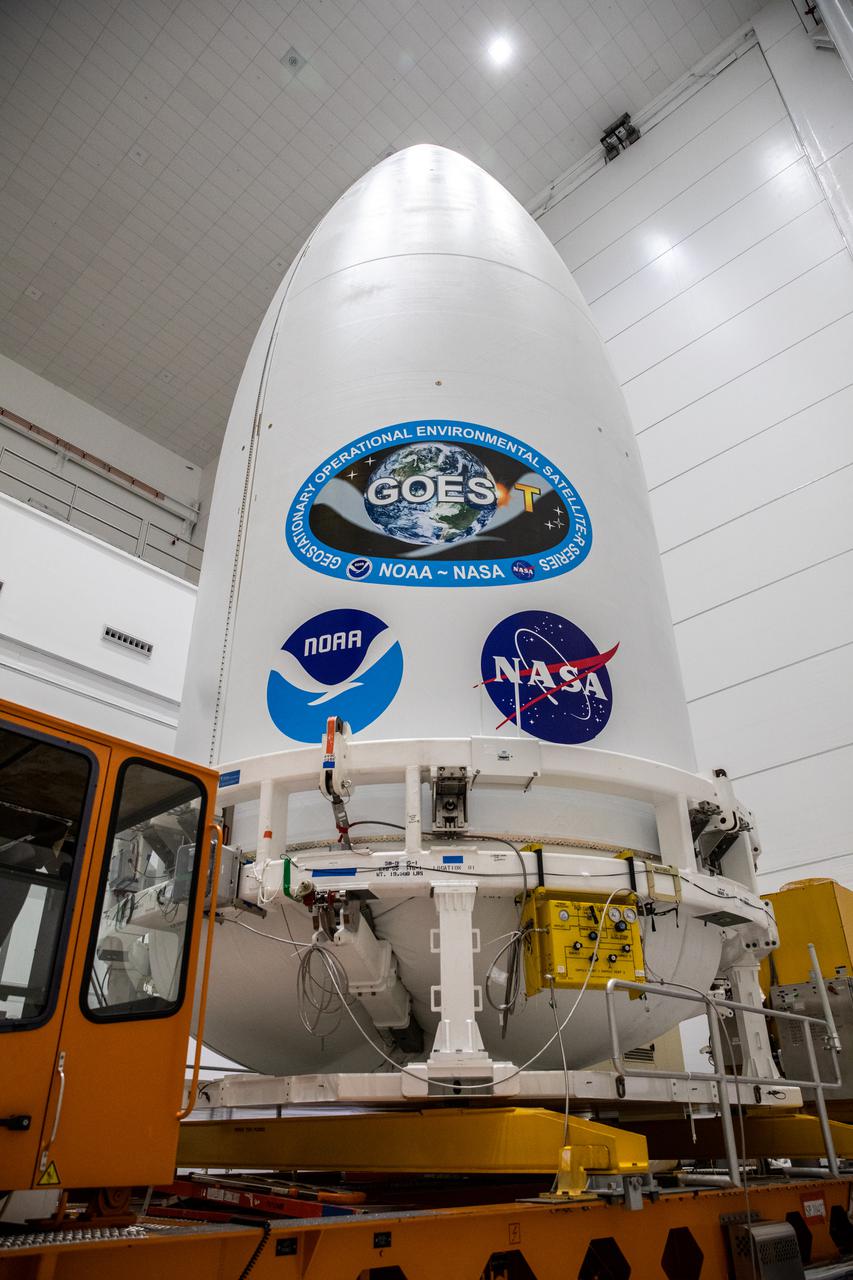

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, is prepared for its move from the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be lifted up inside the integration facility and secured to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
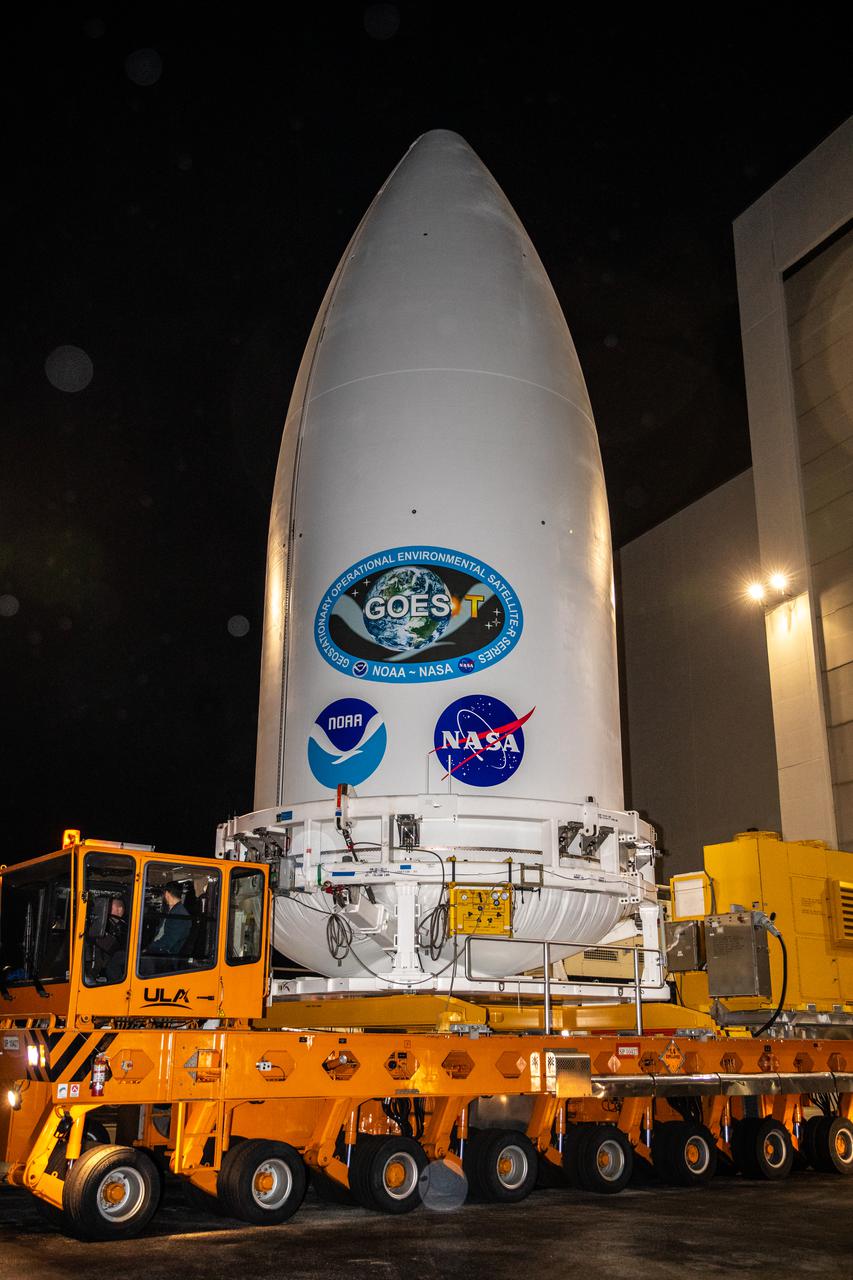

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, exits the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, for its trip to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be lifted up inside the integration facility and secured to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
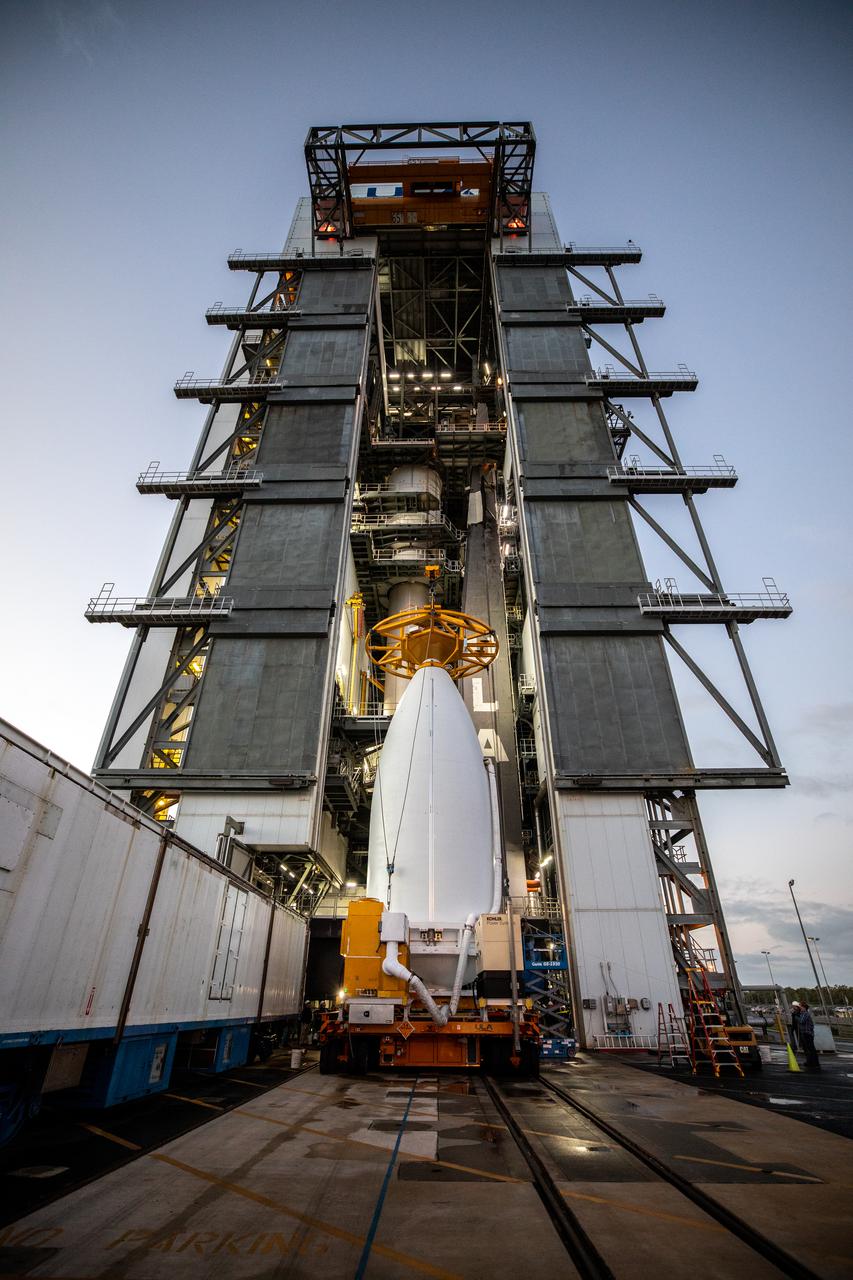

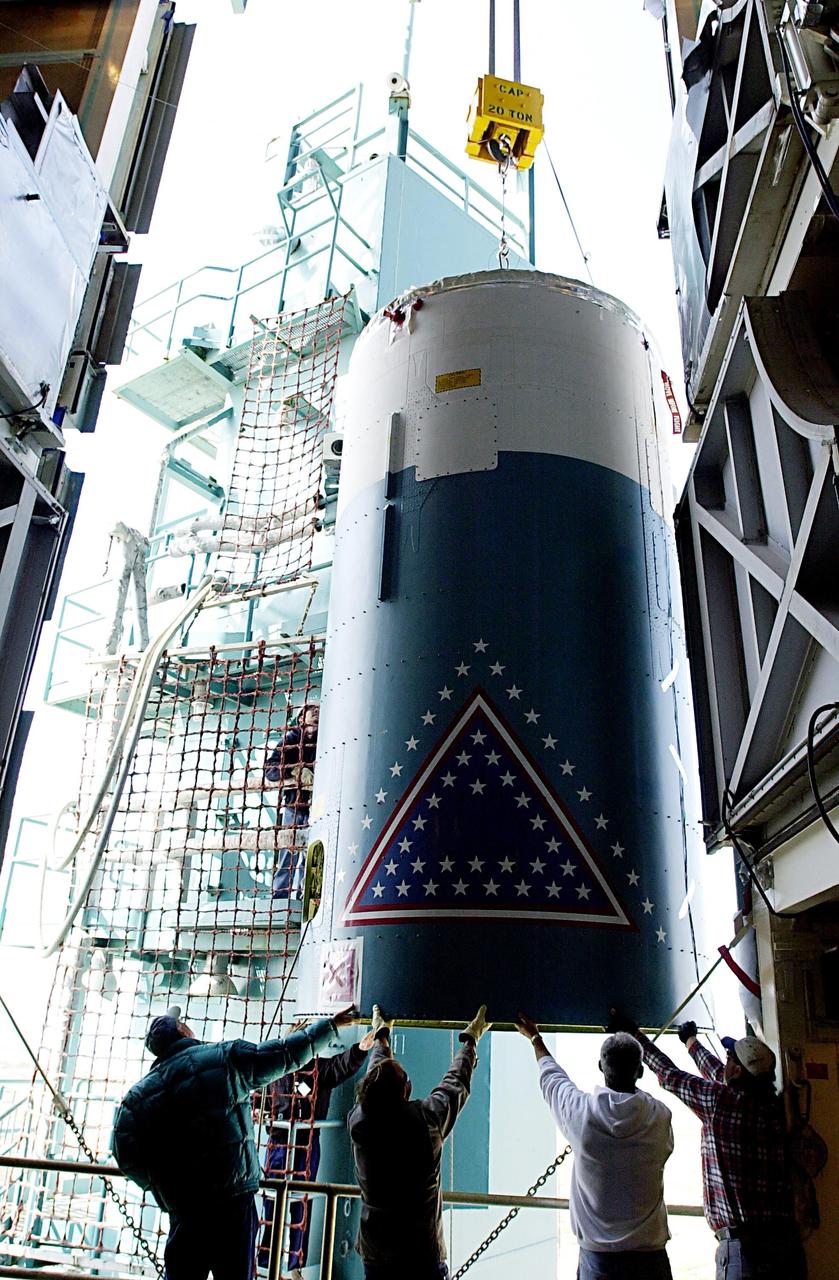
Preparations are underway to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
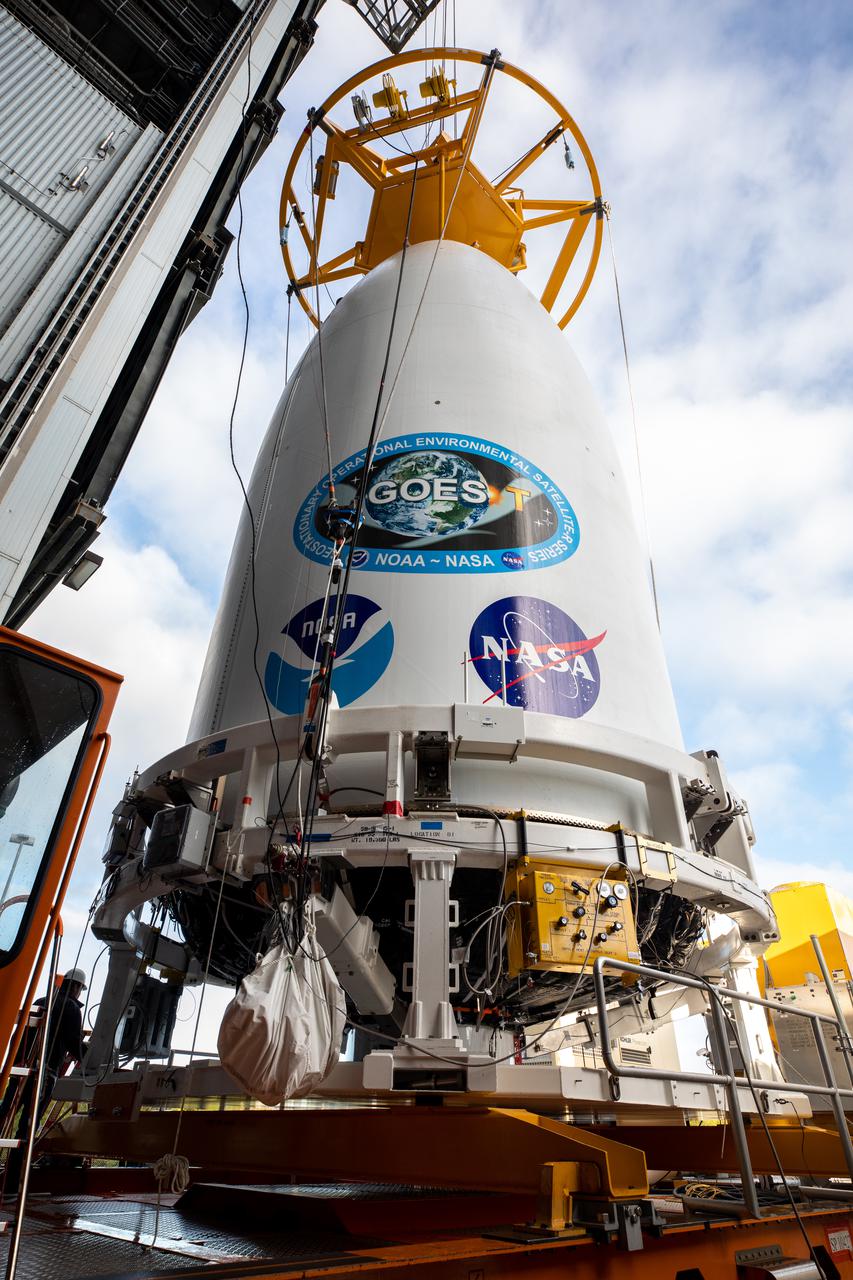

A crane is attached to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, for its lift up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
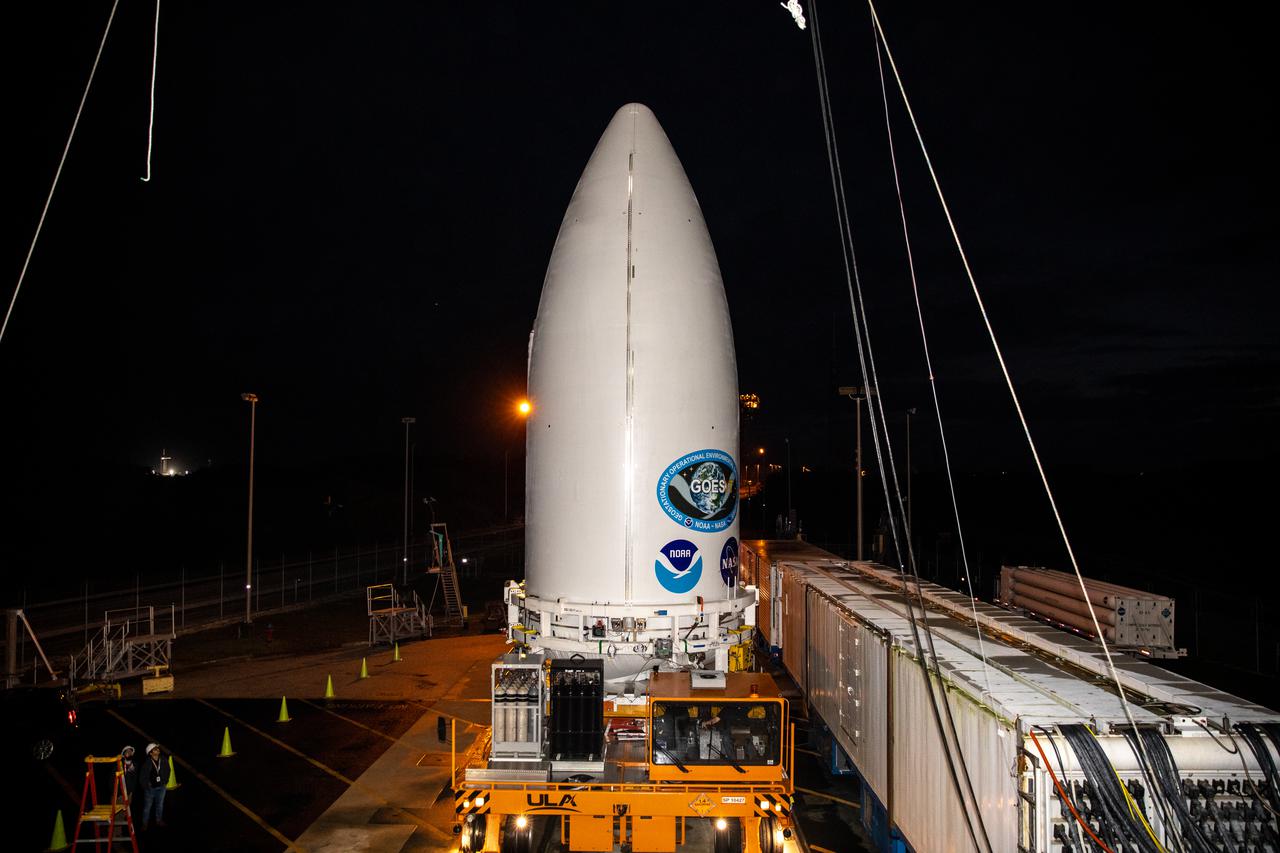

Preparations are underway to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
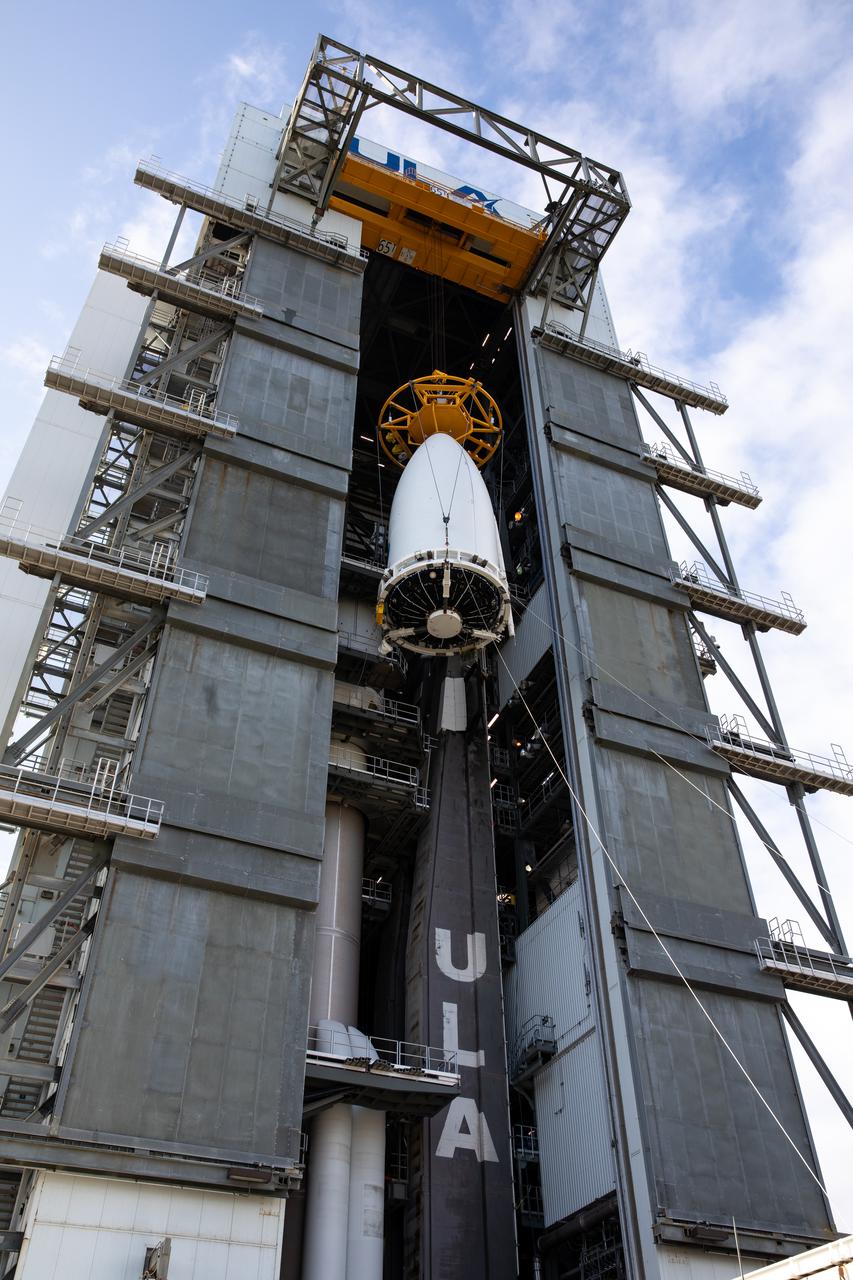

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, is lifted up by crane for its move into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
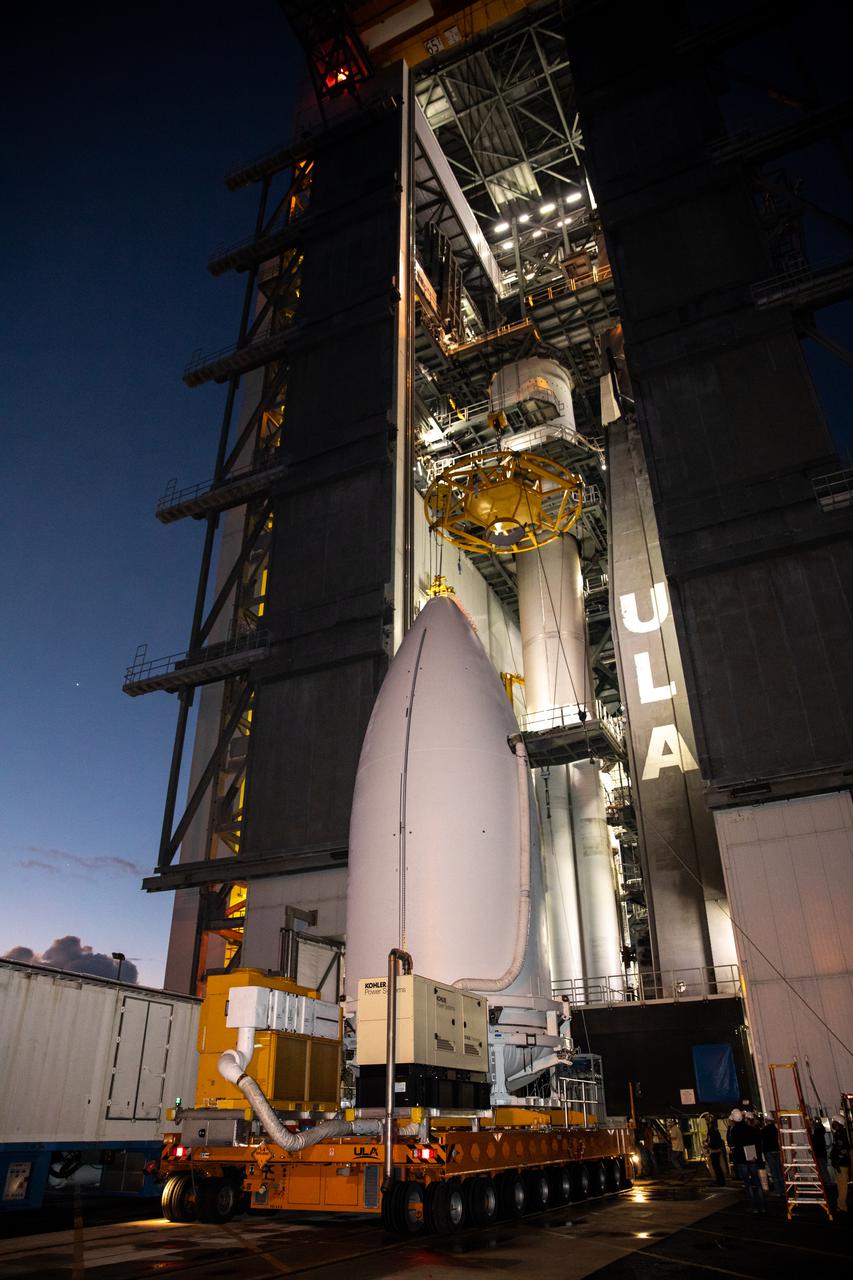

Preparations are underway to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
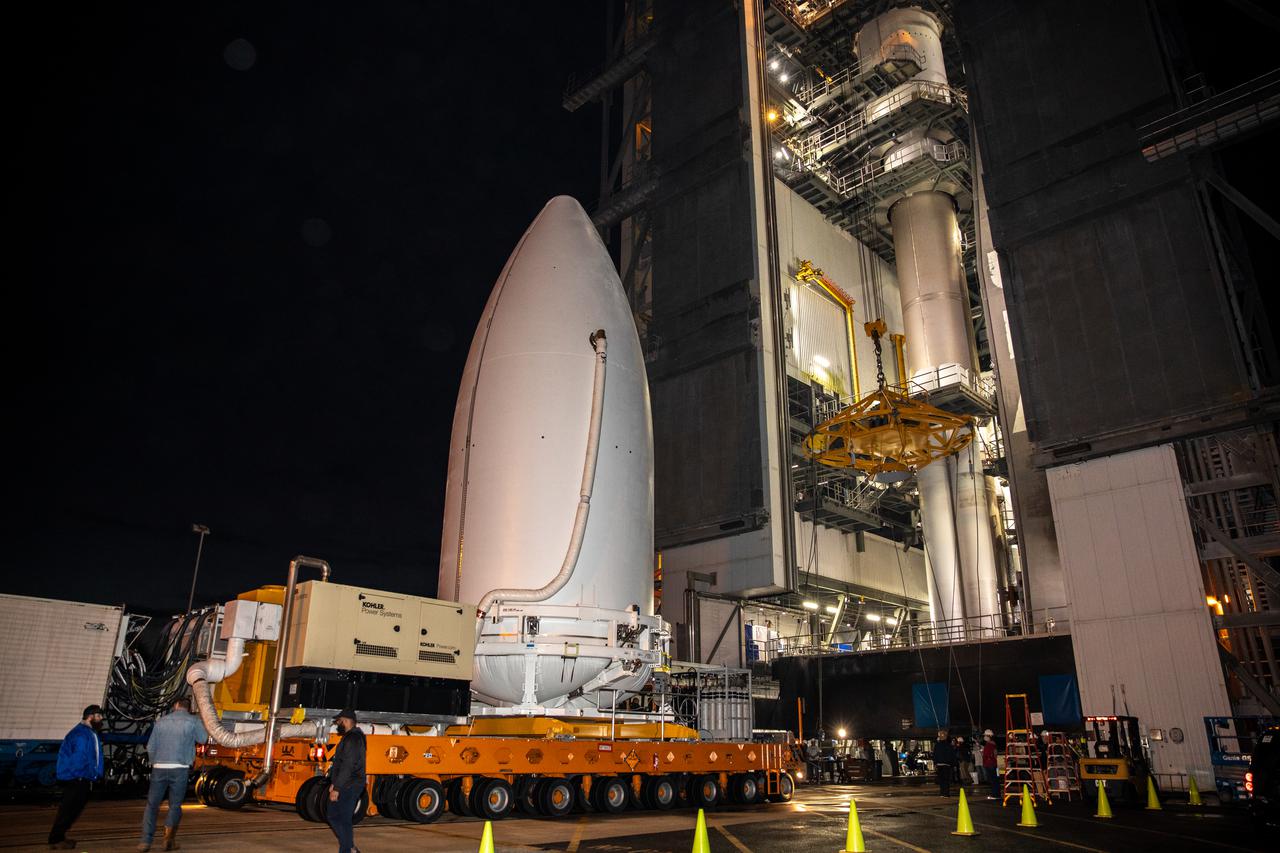

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be lifted up inside the integration facility and secured to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
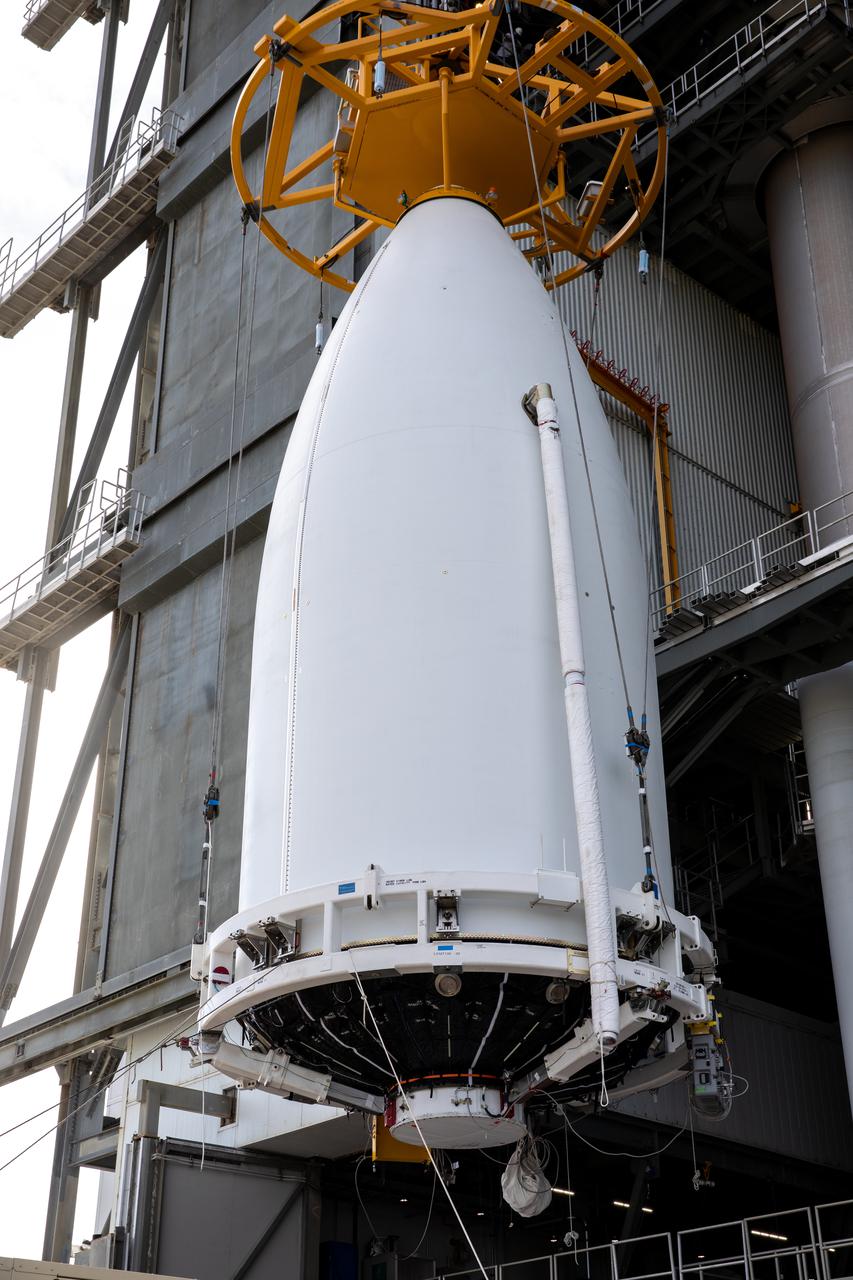

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, is lifted up by crane for its move into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
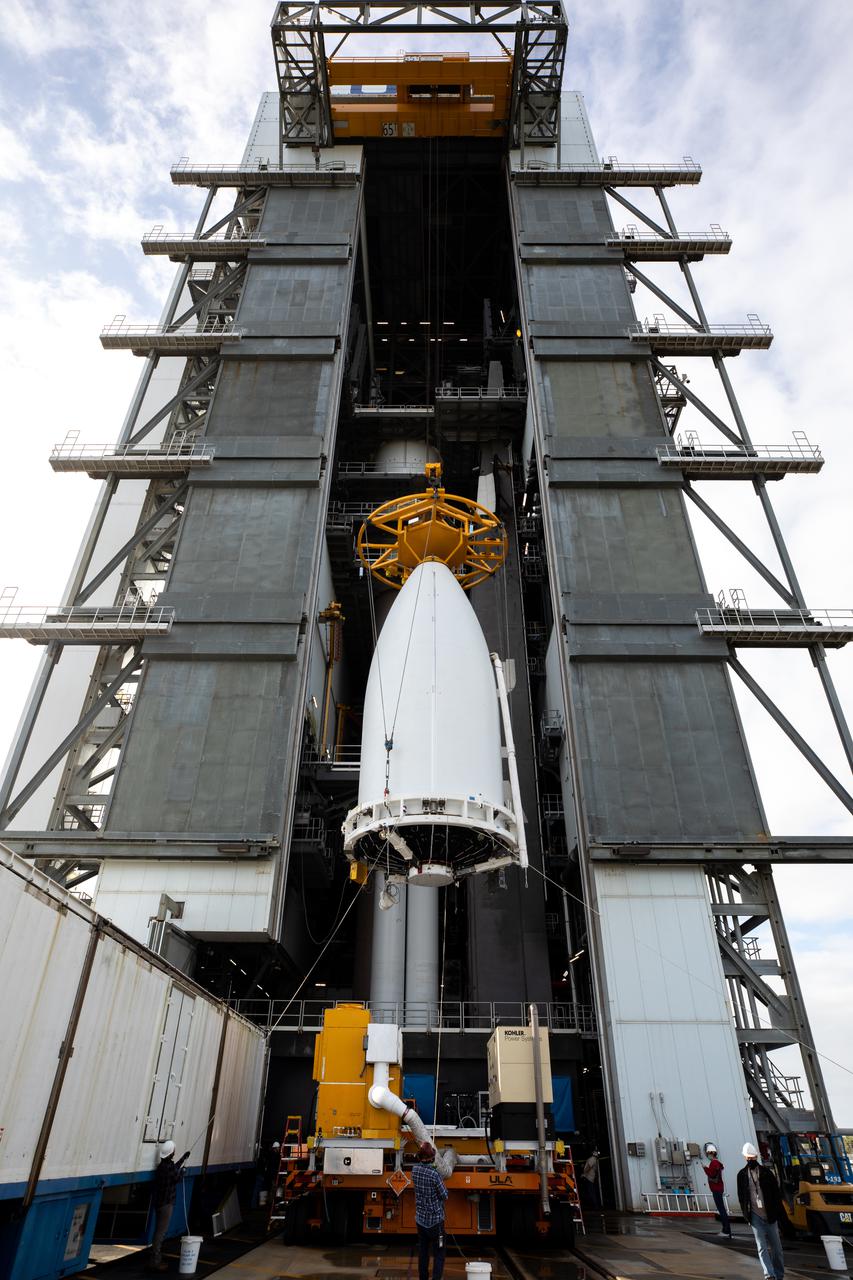

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), enclosed in its payload fairing, is lifted up by crane for its move into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 17, 2022. The satellite will be secured atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket. GOES-T is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V rocket from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.

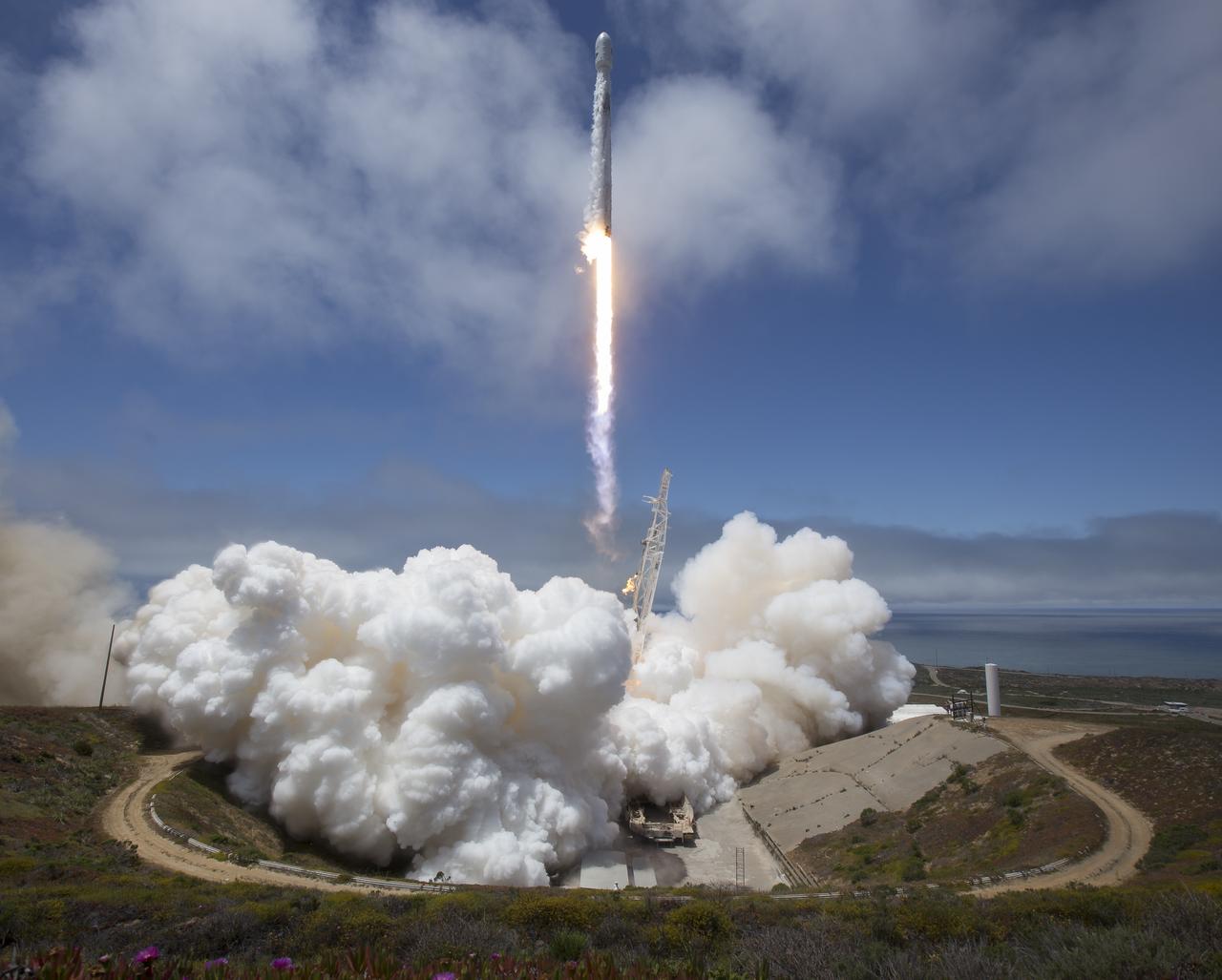
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), is secured on the pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
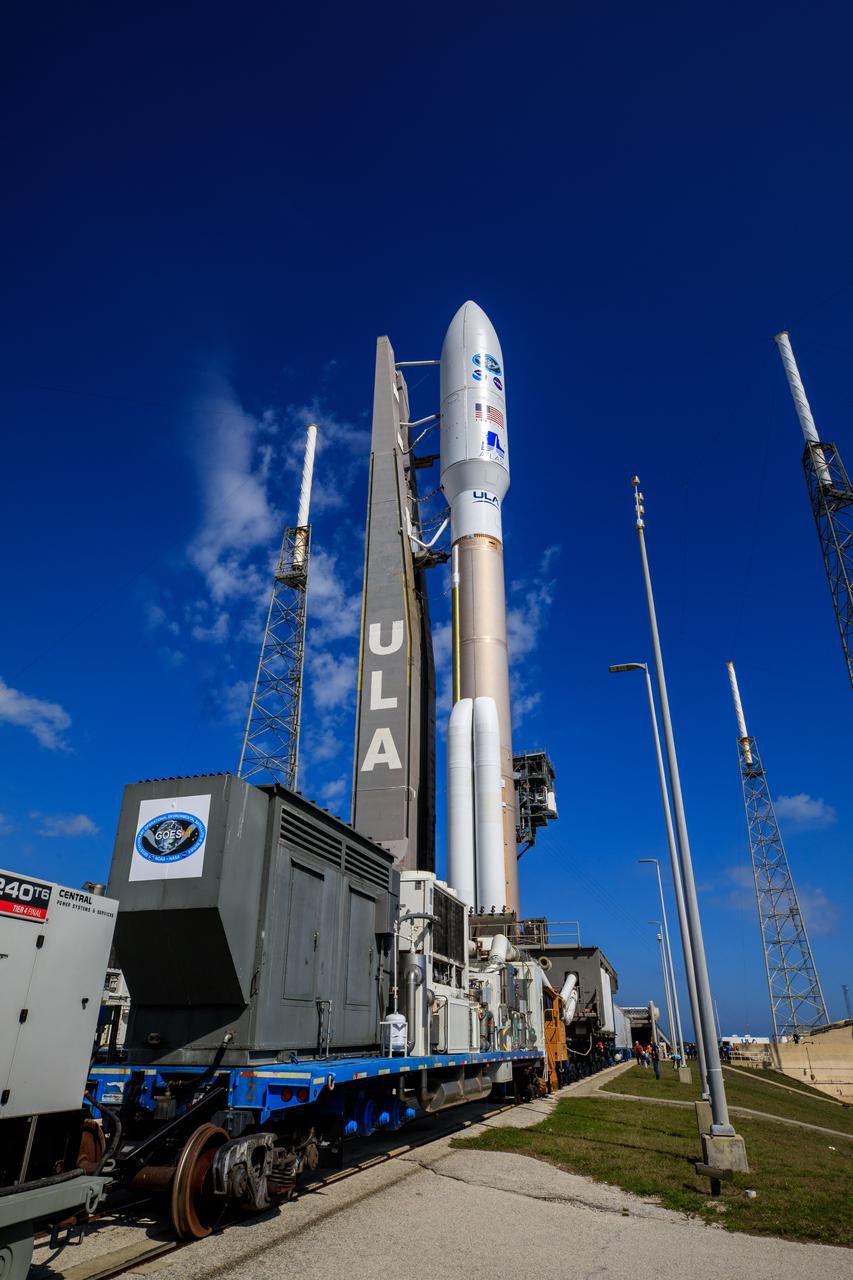

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
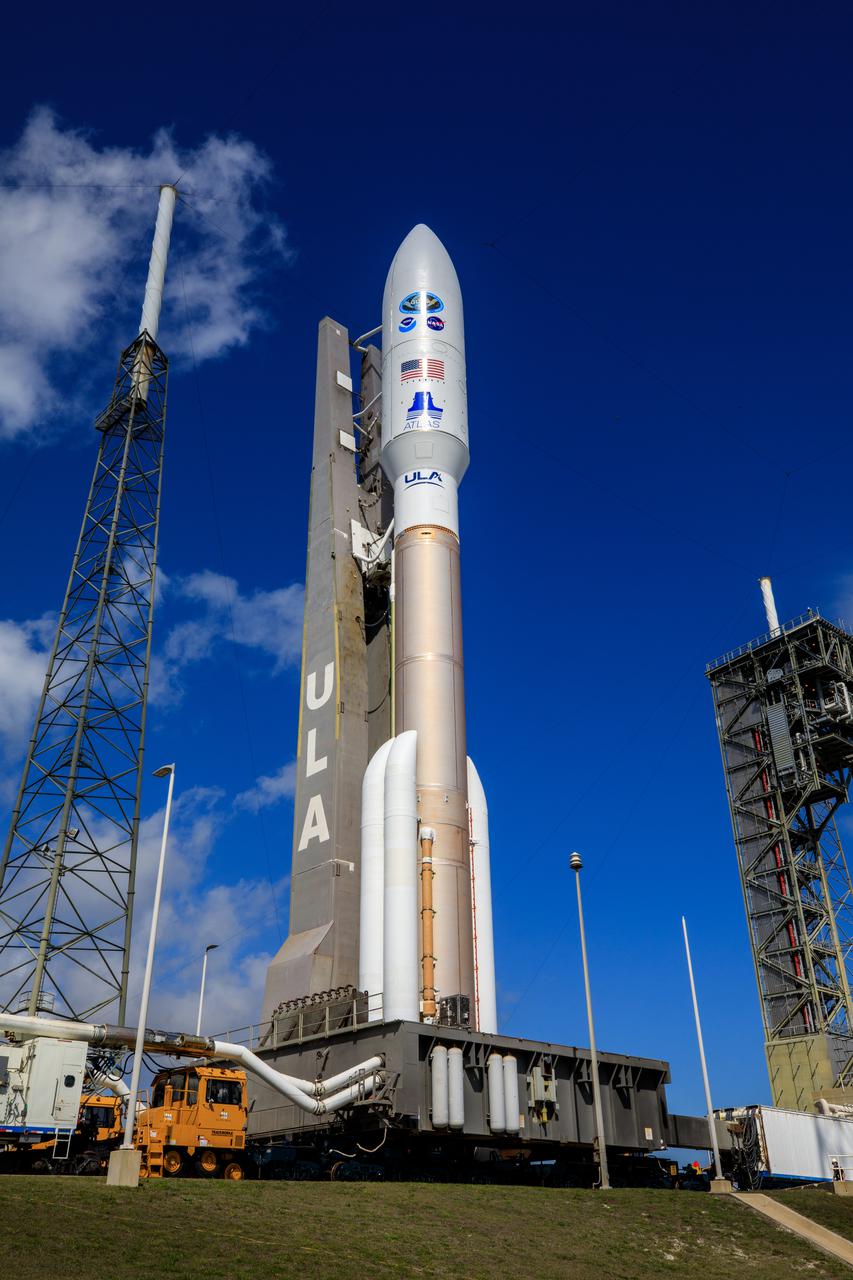

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
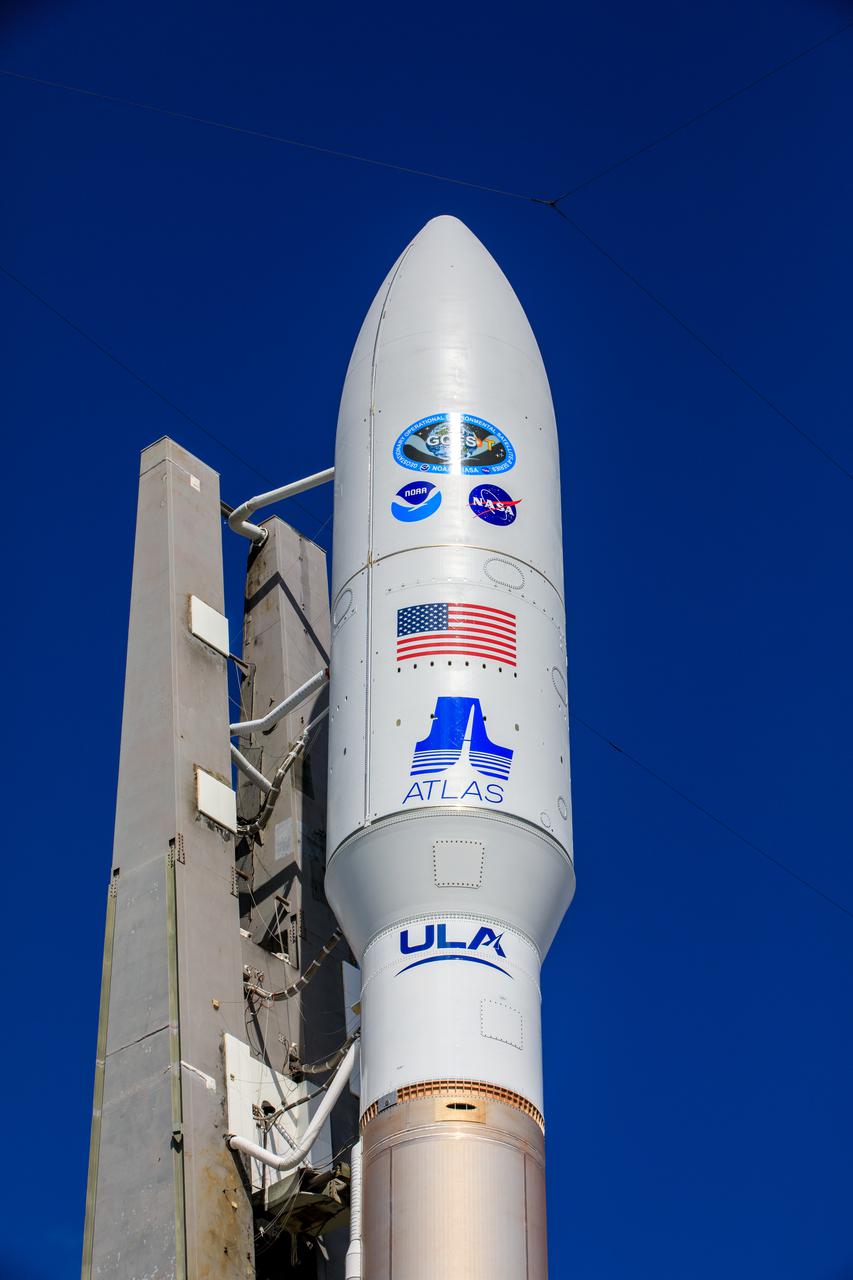

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
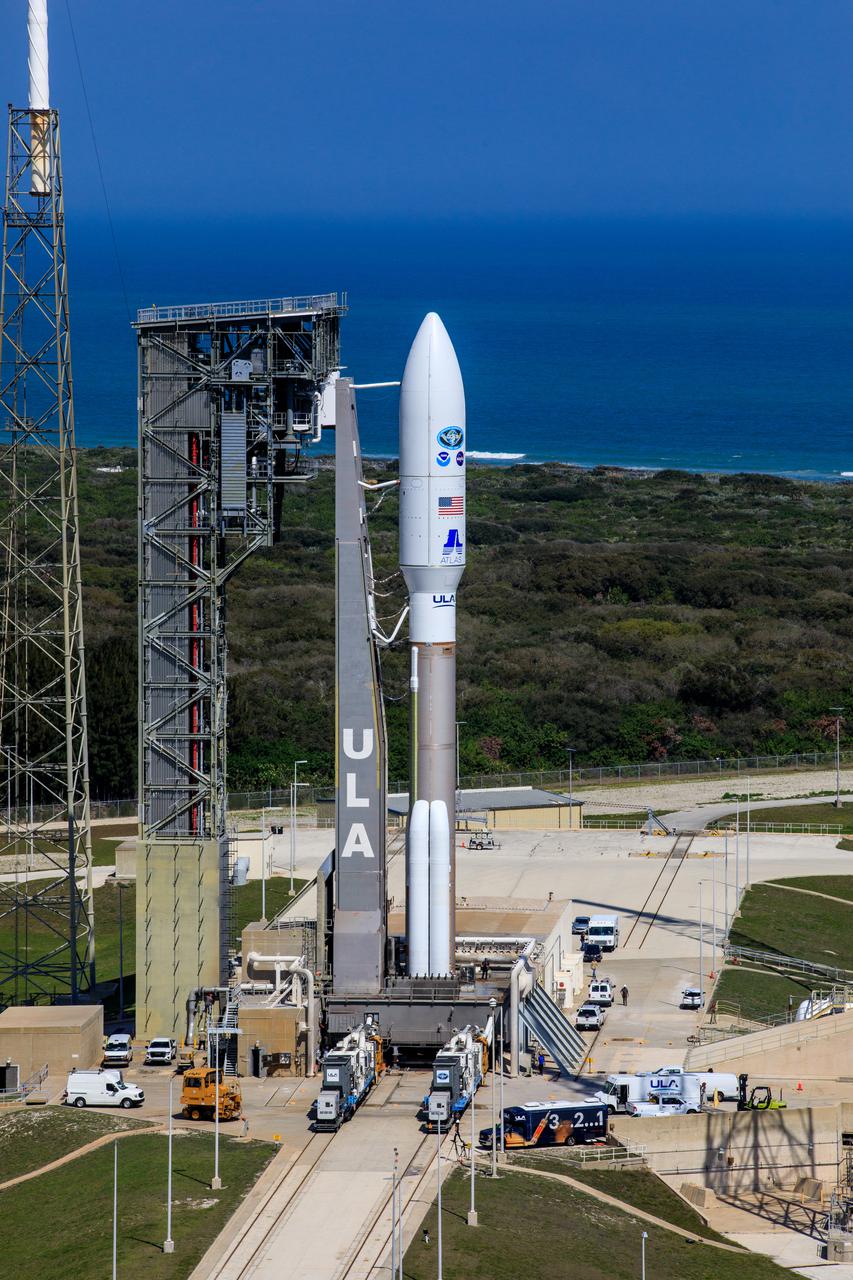

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), is secured on the pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
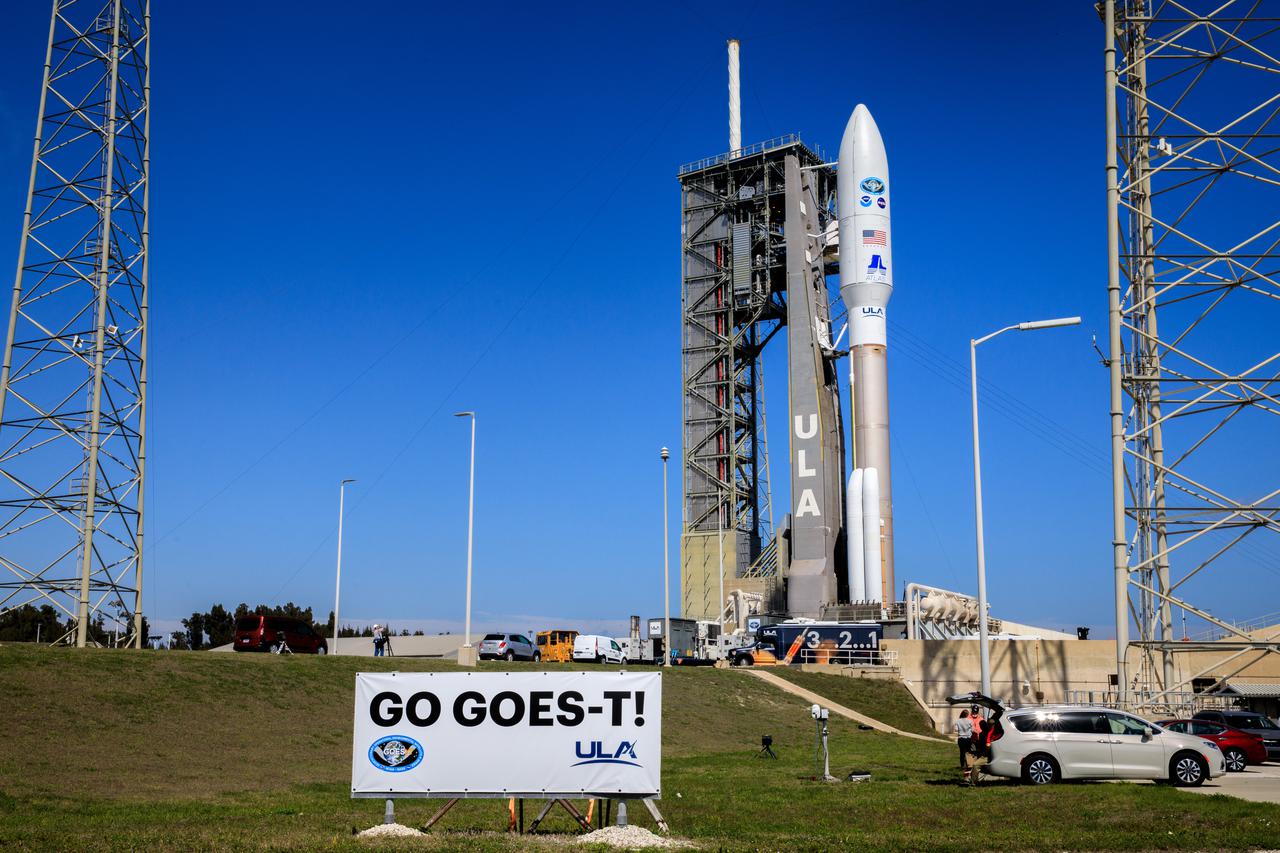

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), is secured on the pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
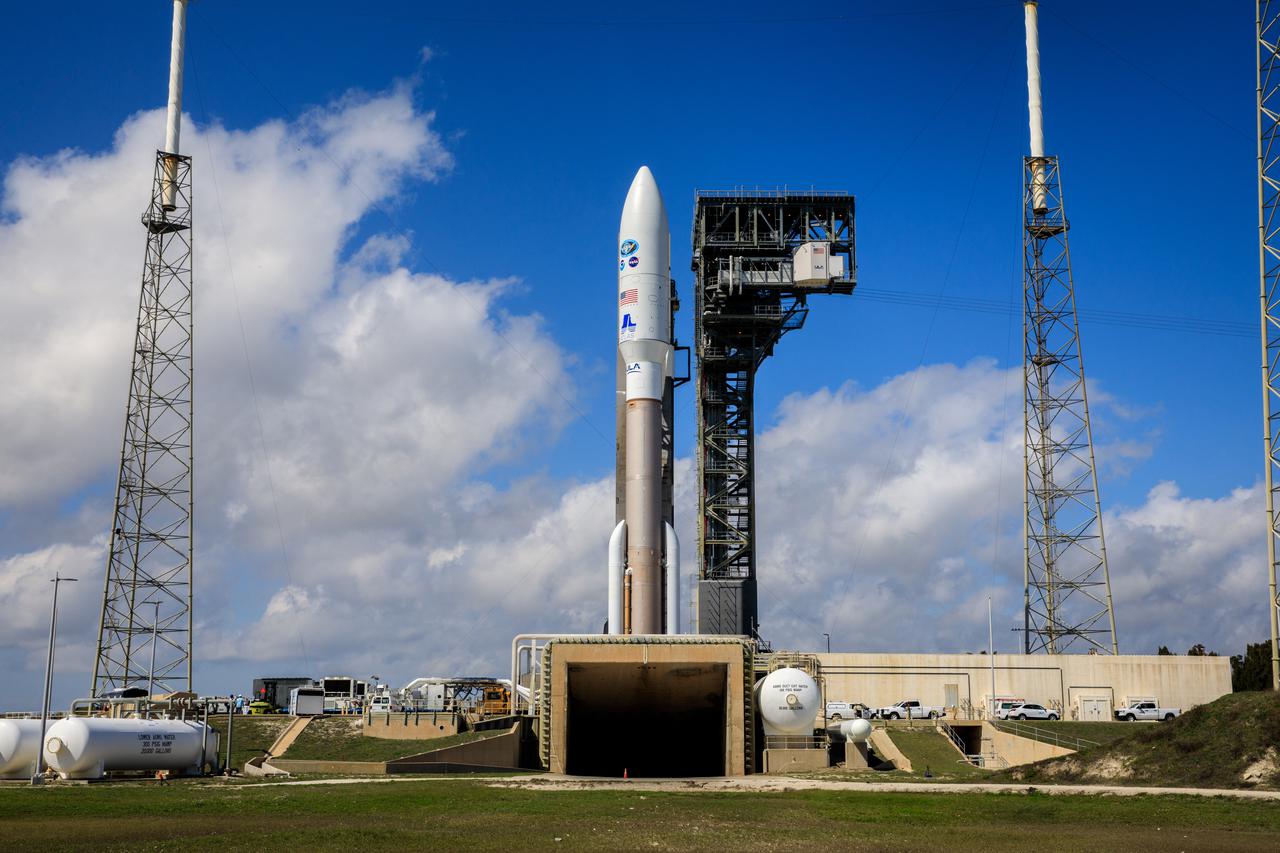

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), is secured on the pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.

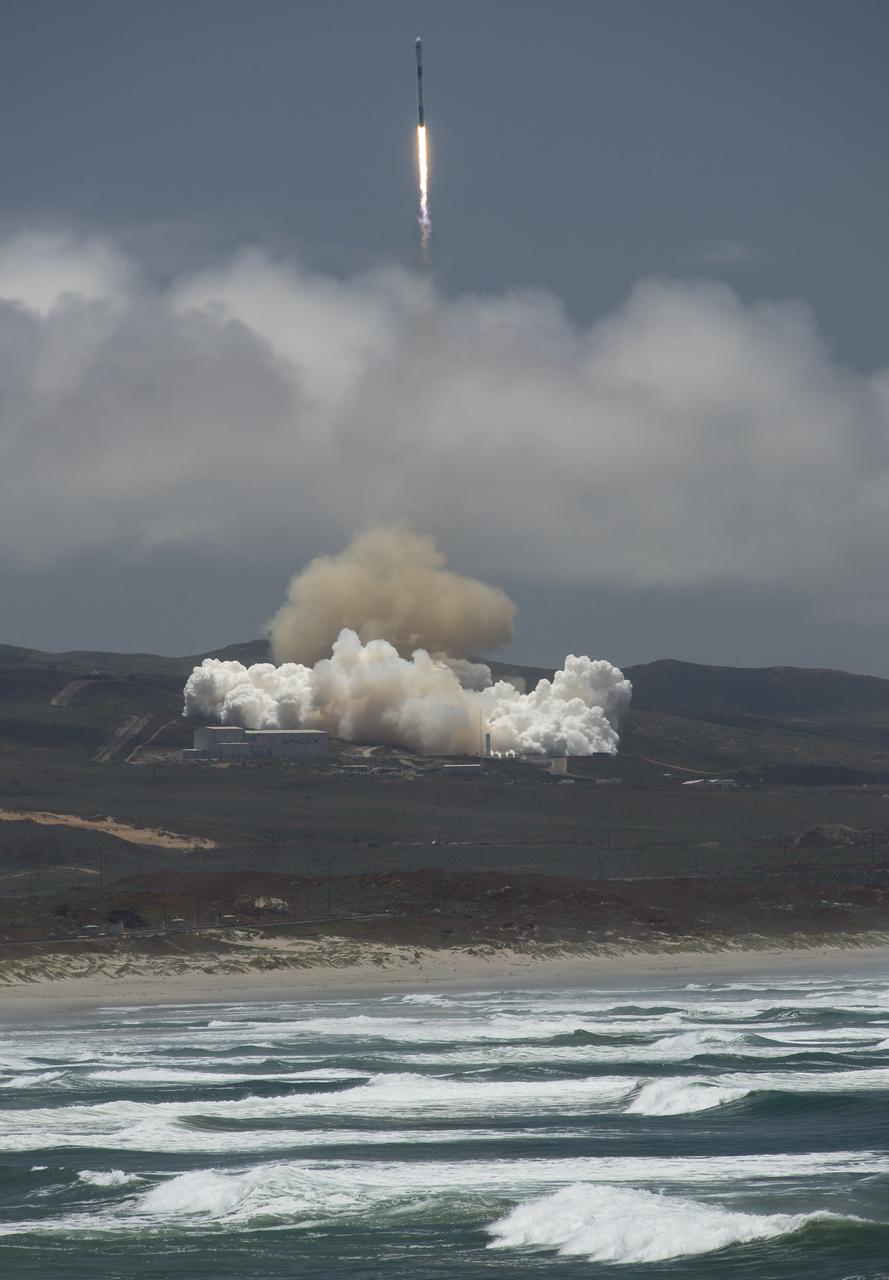
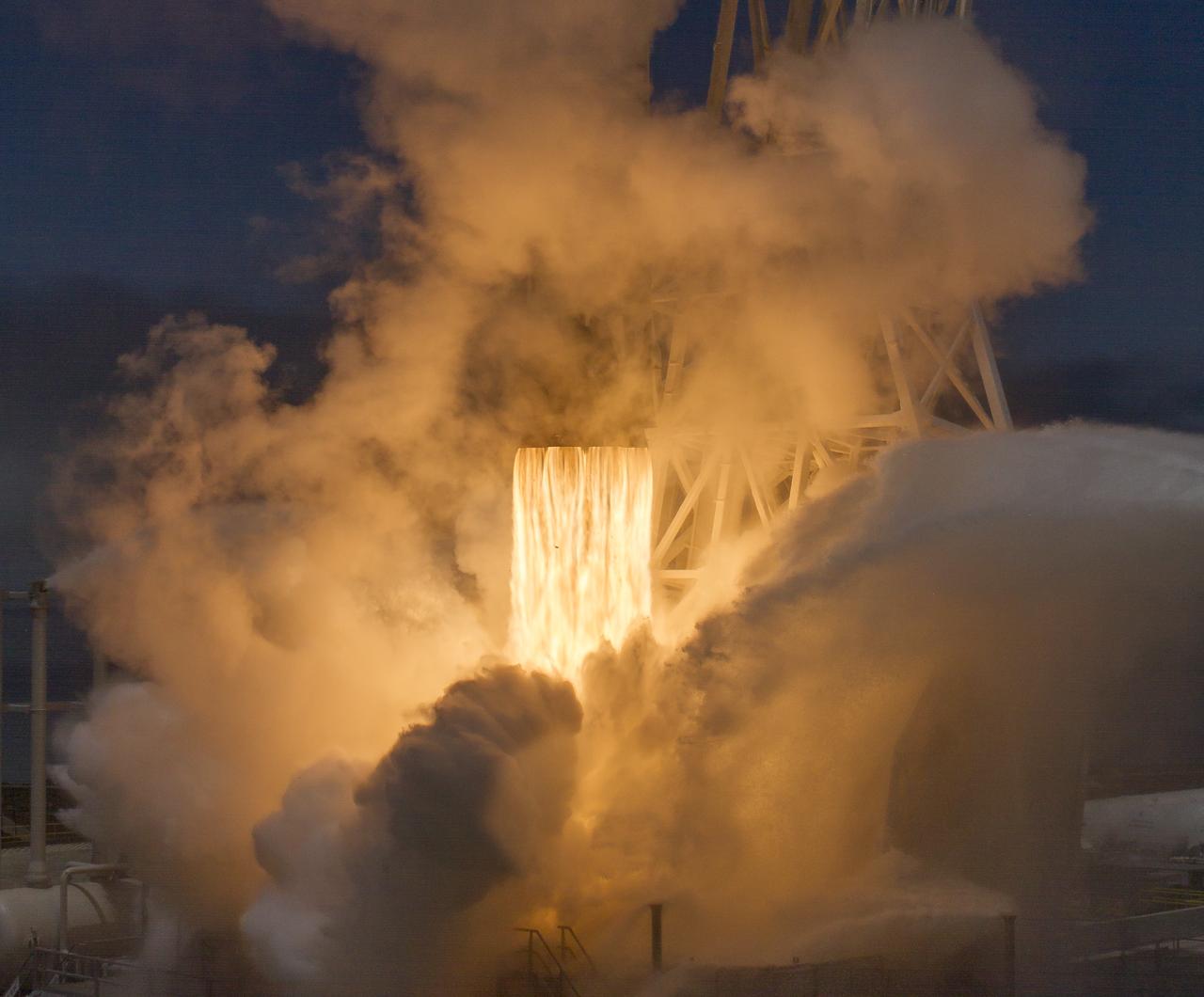
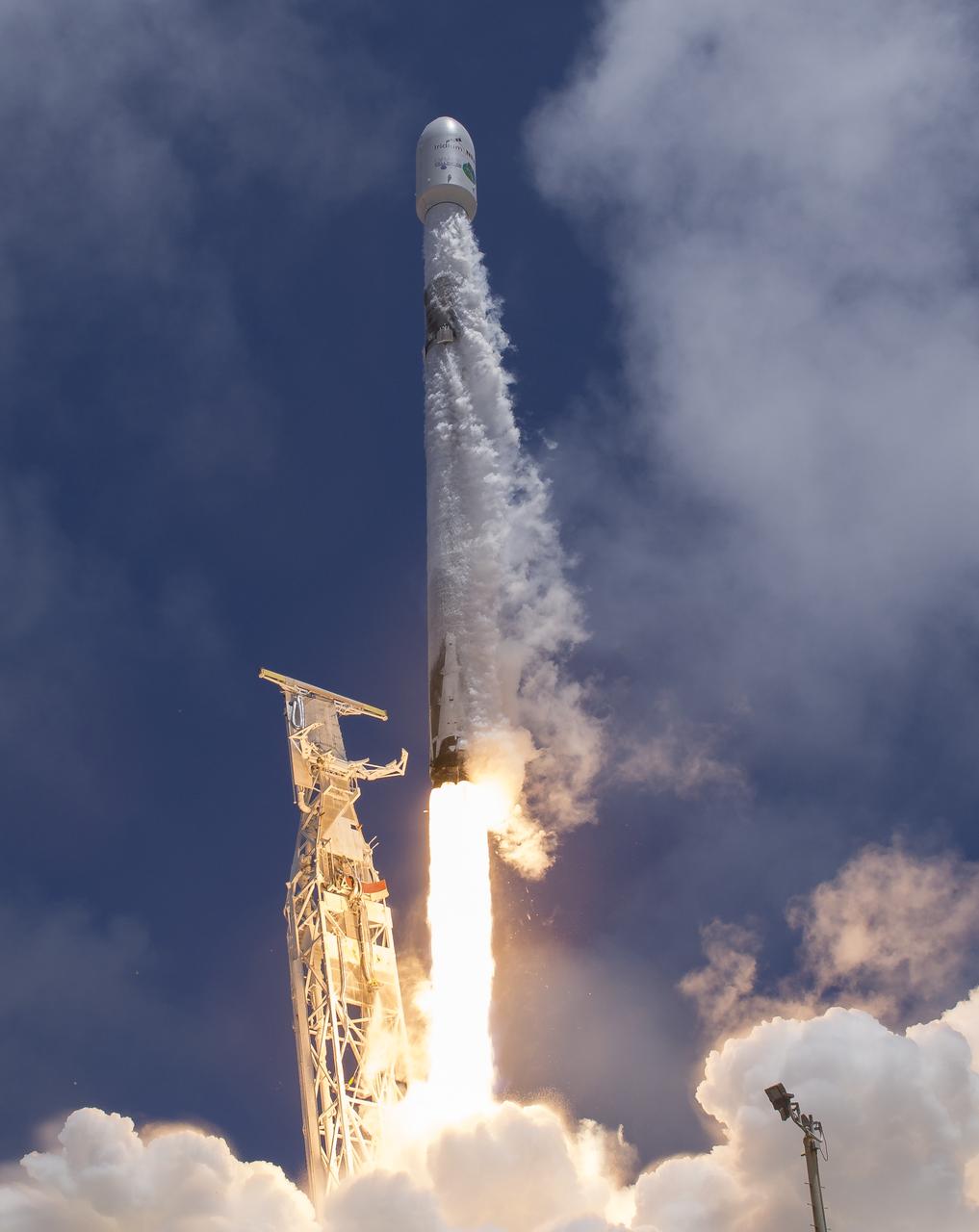
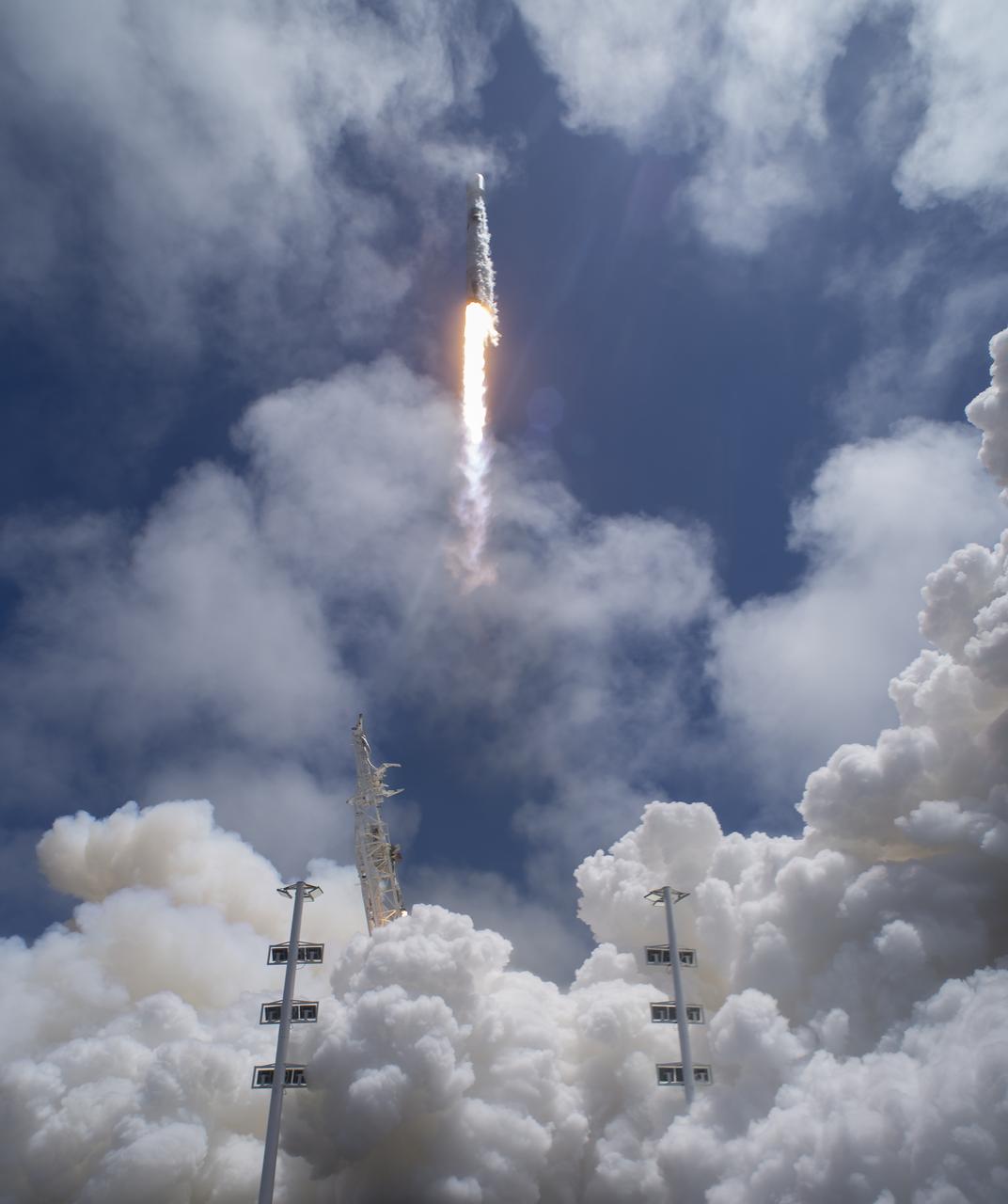
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
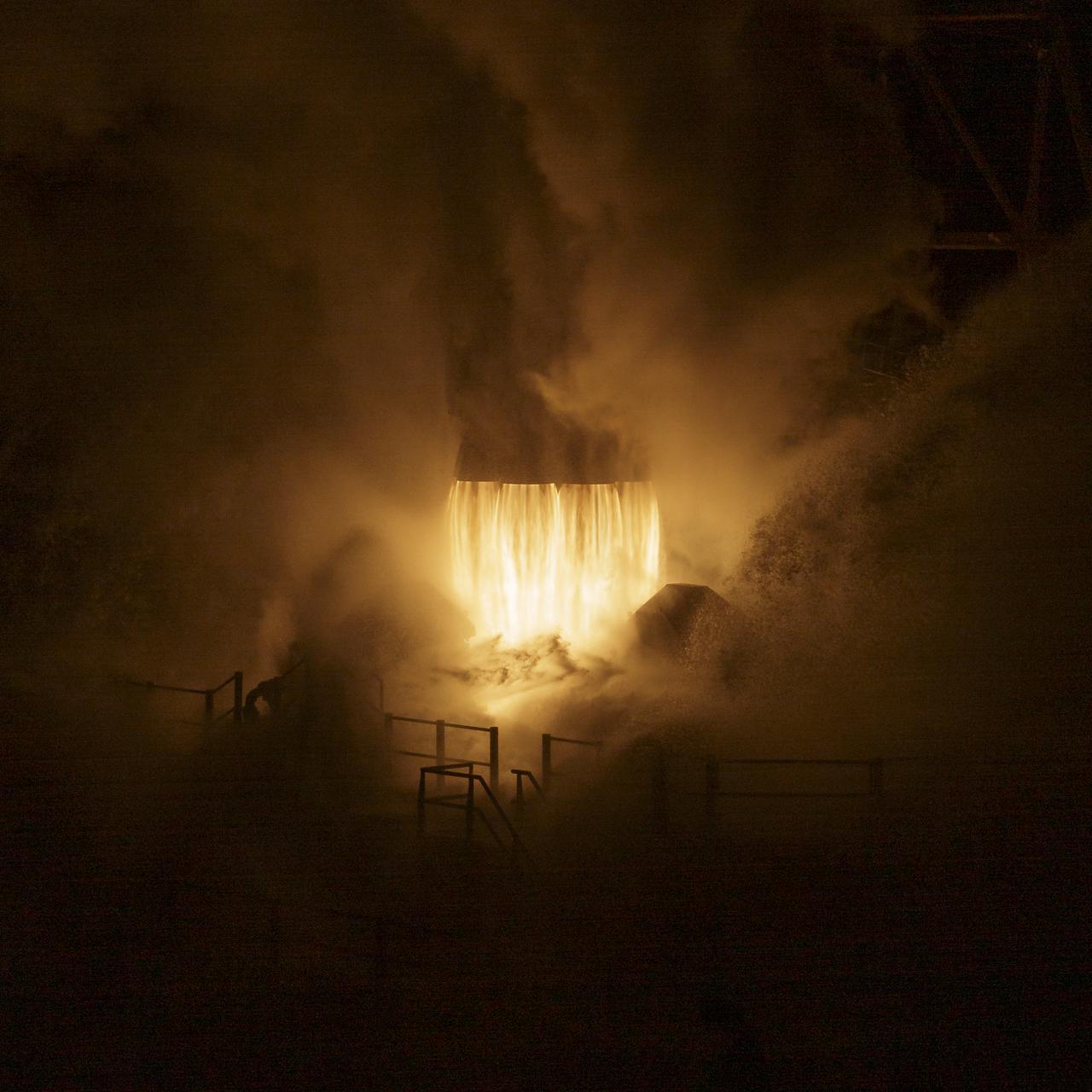

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
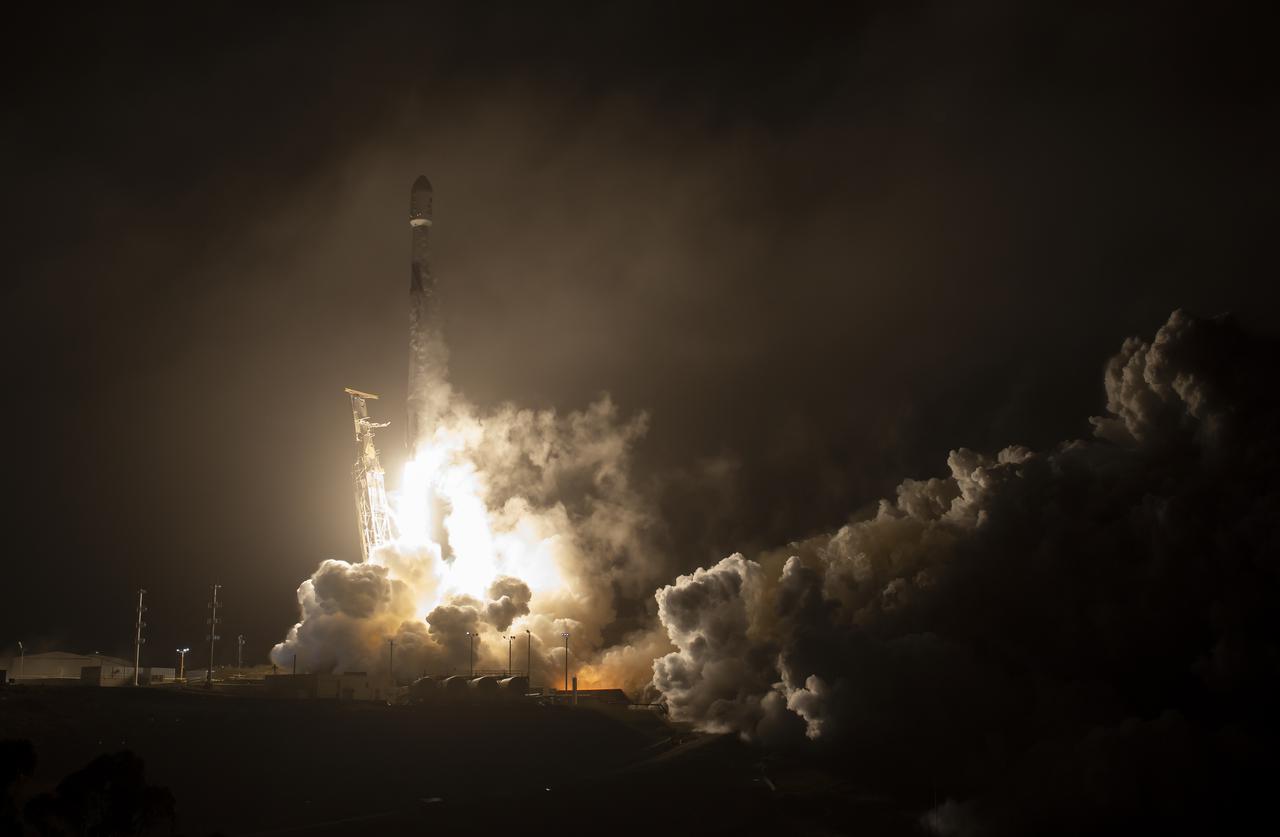

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
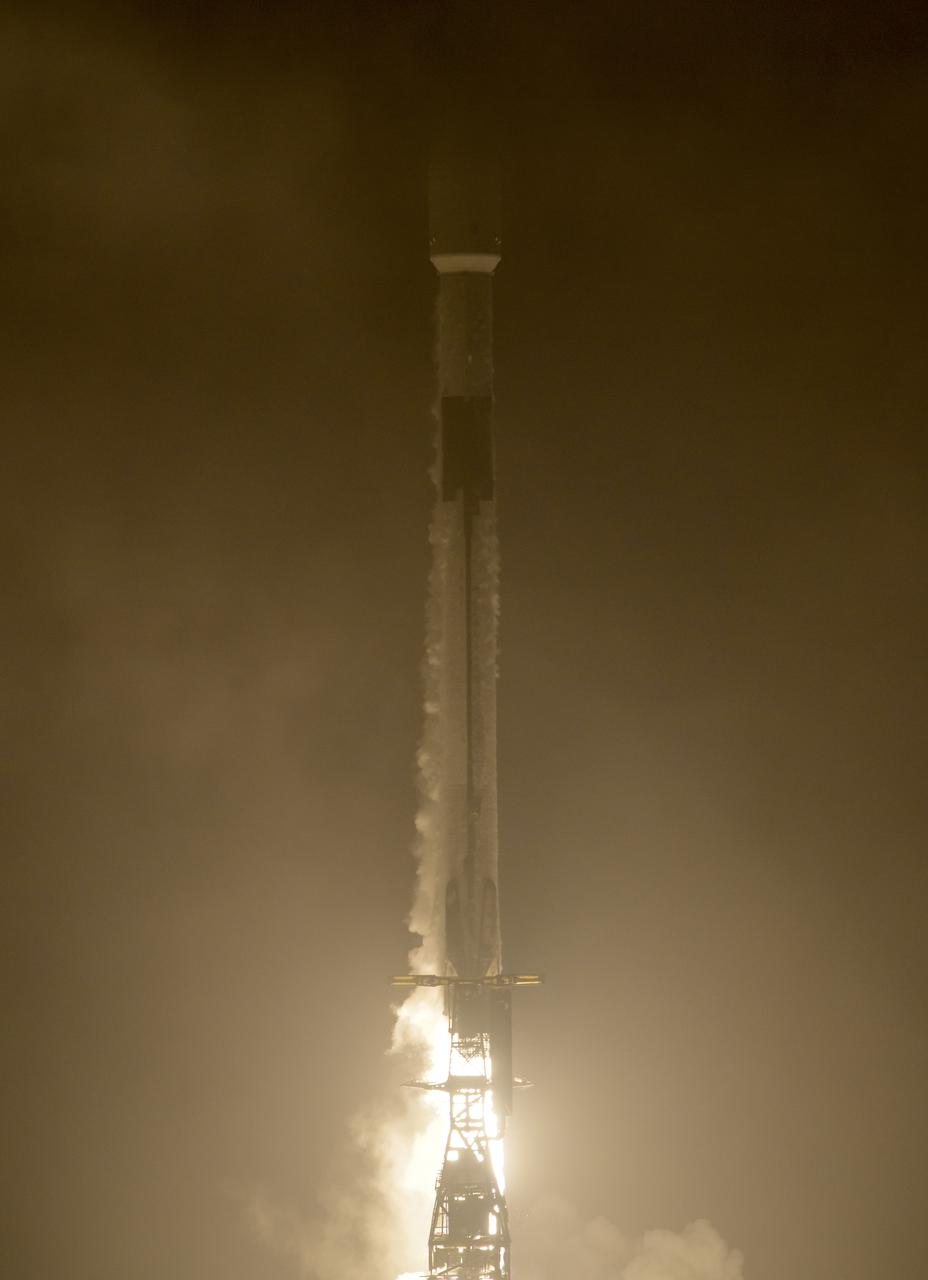

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
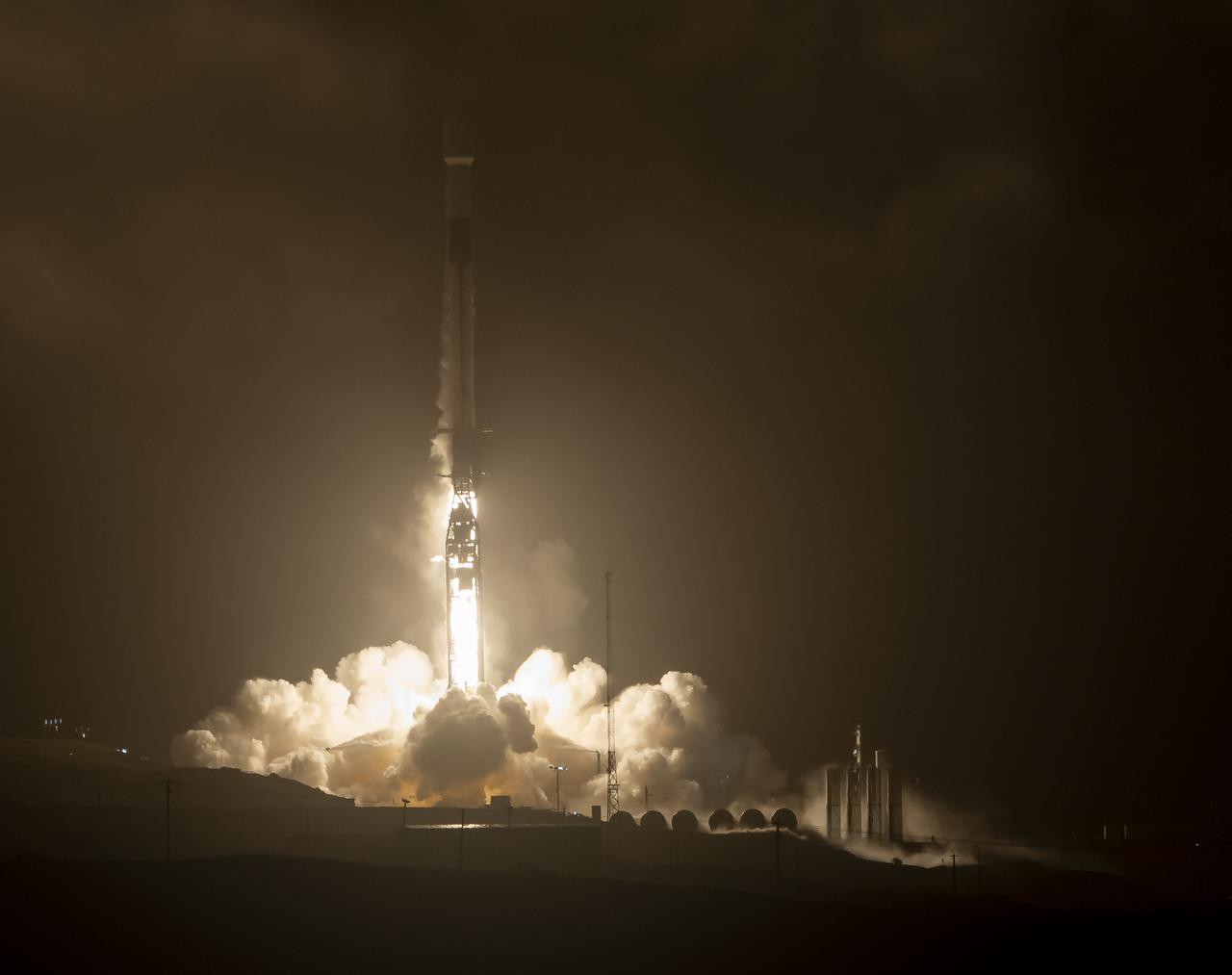

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
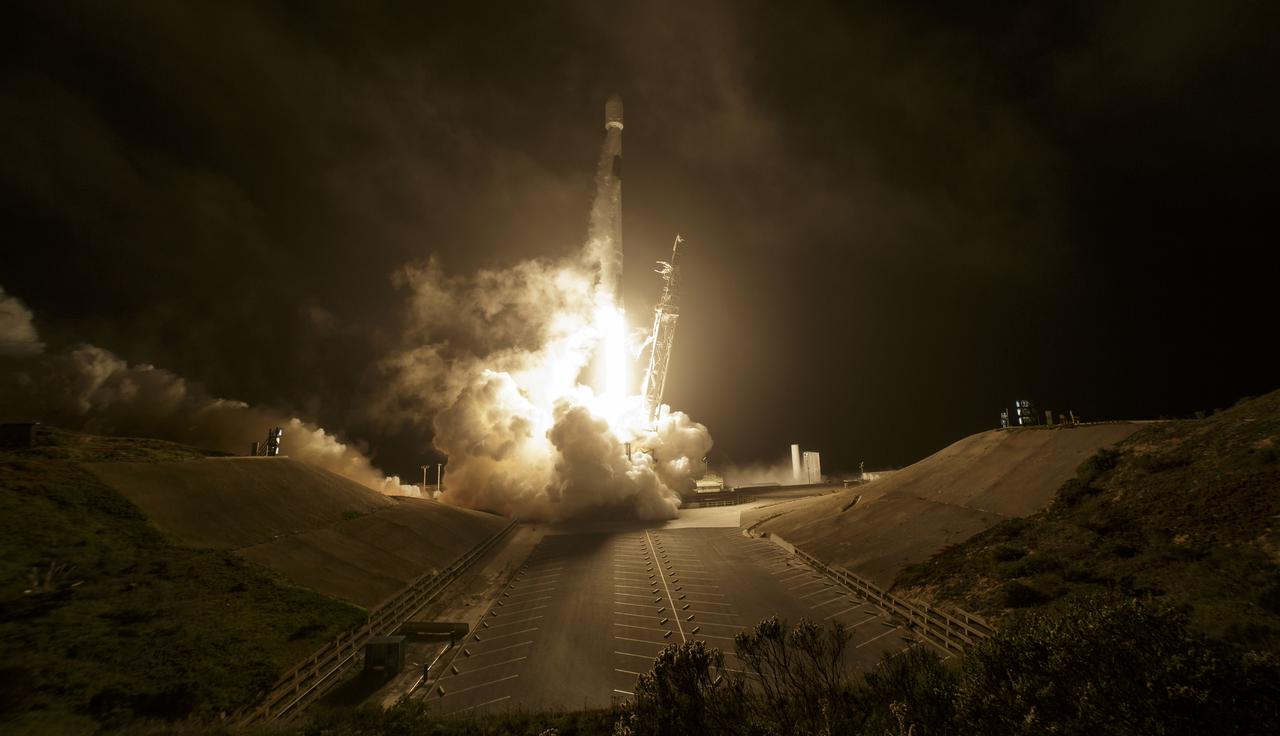

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
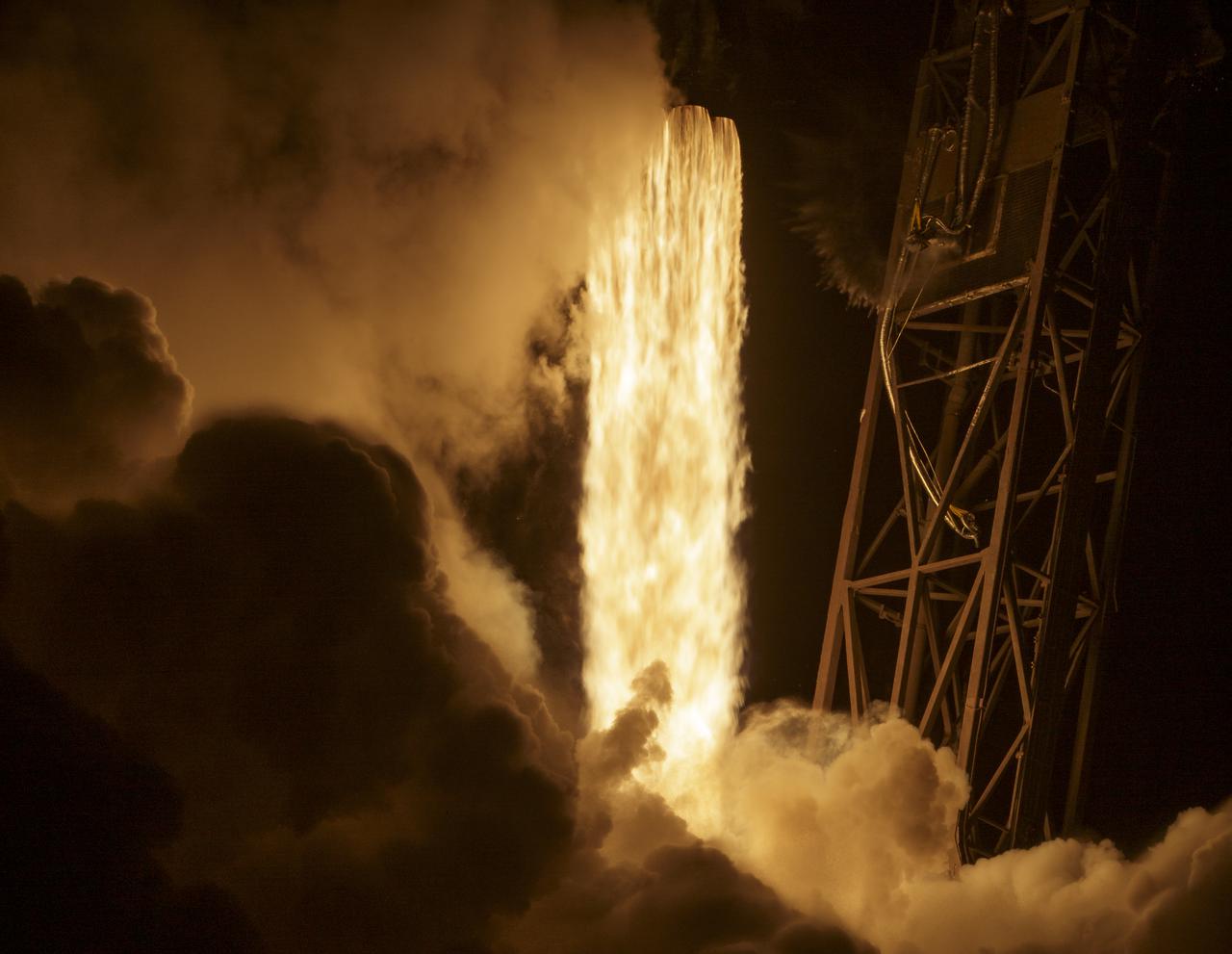

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
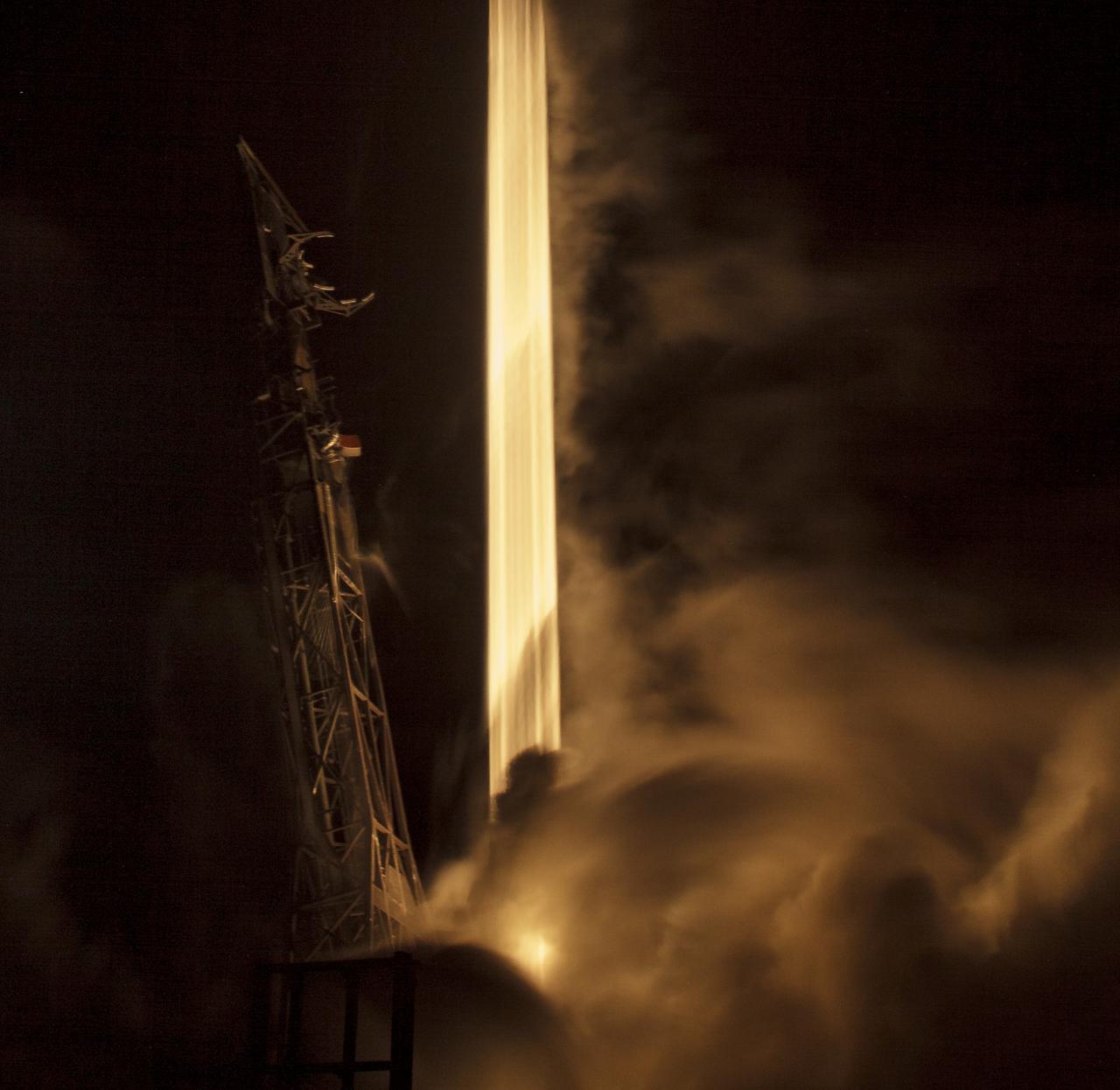

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen in this 30-second exposure photograph as it launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
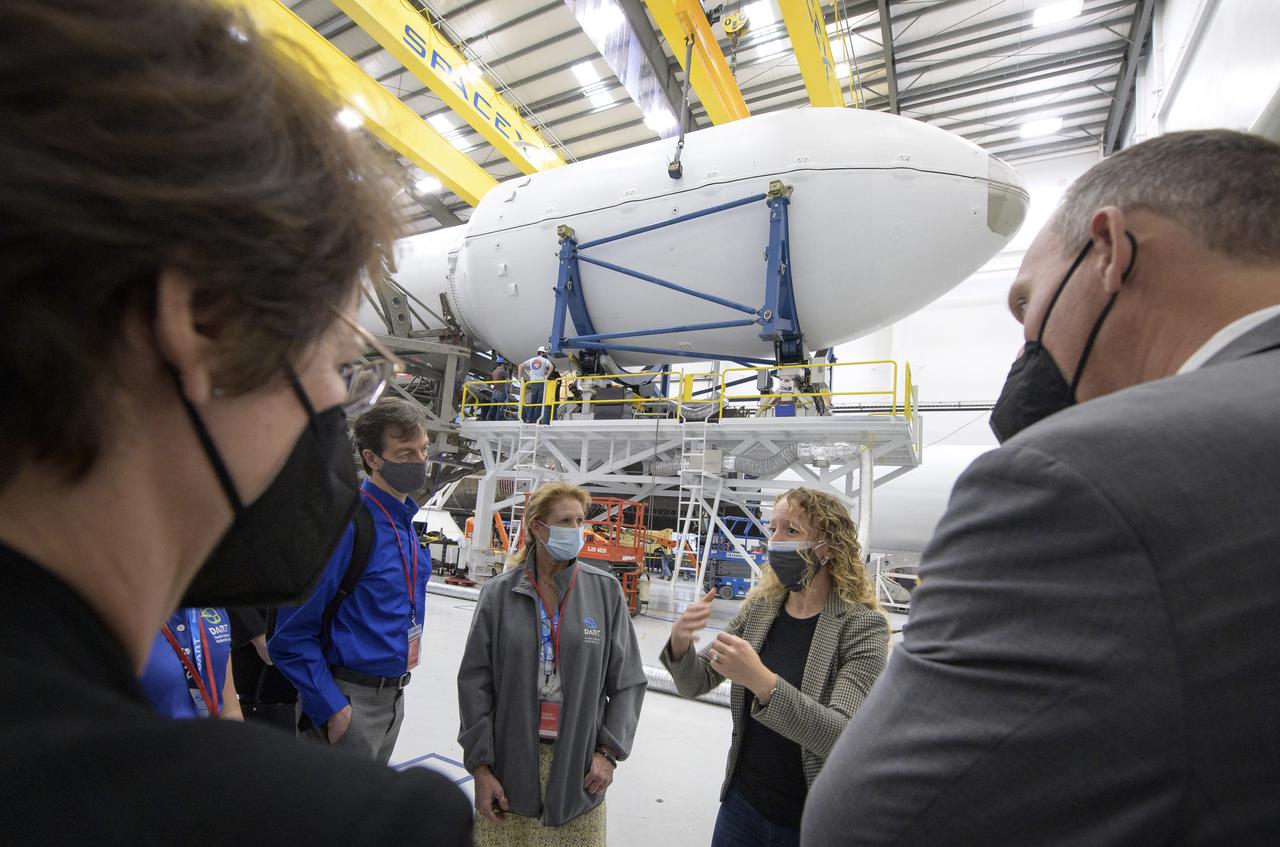

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, right, and other NASA leadership listen as Julianna Scheiman, director for civil satellite missions, SpaceX, center, gives a tour of the hanger where the Falcon 9 rocket and DART spacecraft are being readied for launch, Monday, Nov. 22, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
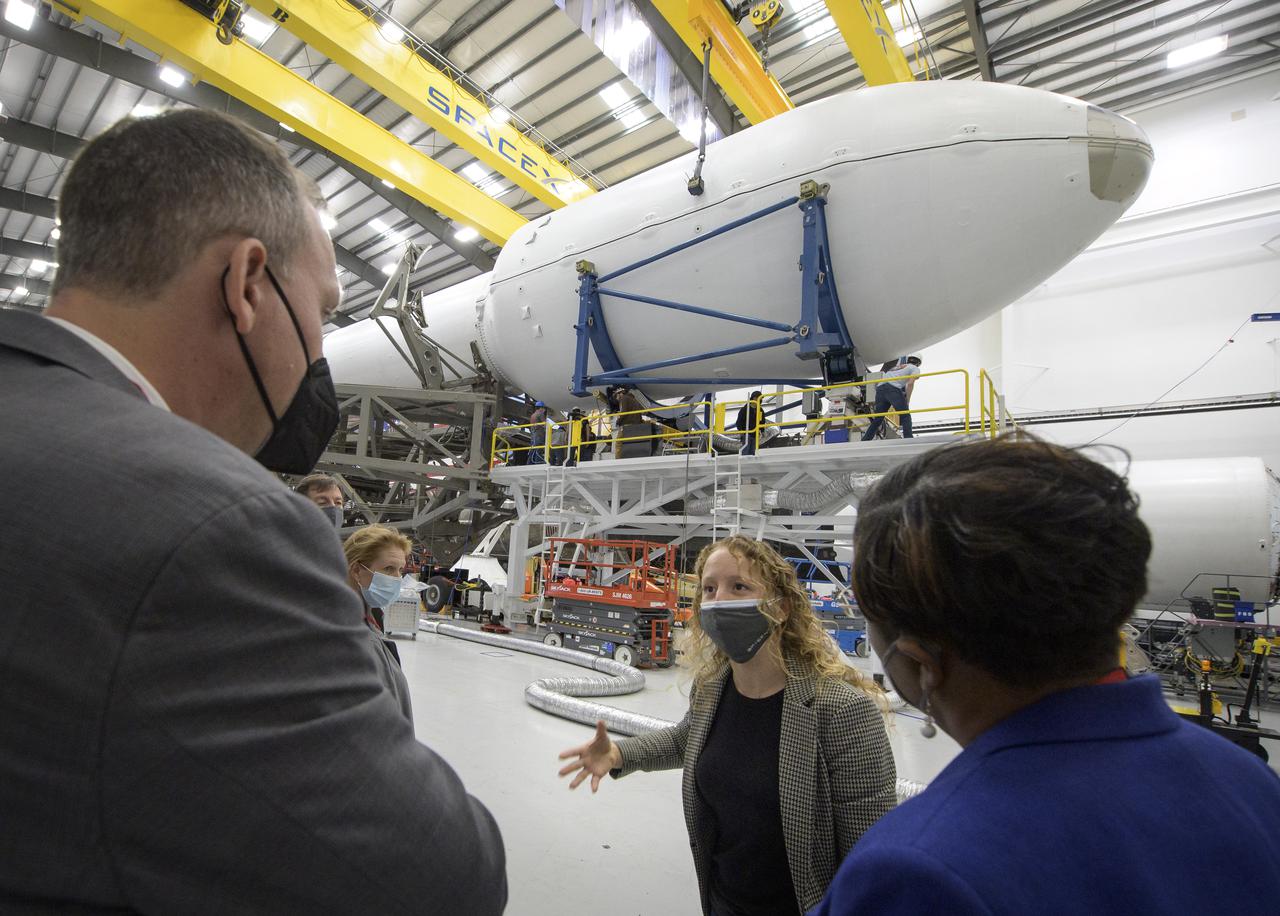

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, left, and other NASA leadership listen as Julianna Scheiman, director for civil satellite missions at SpaceX, center, gives a tour of the hanger where the Falcon 9 rocket and DART spacecraft are being readied for launch, Monday, Nov. 22, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
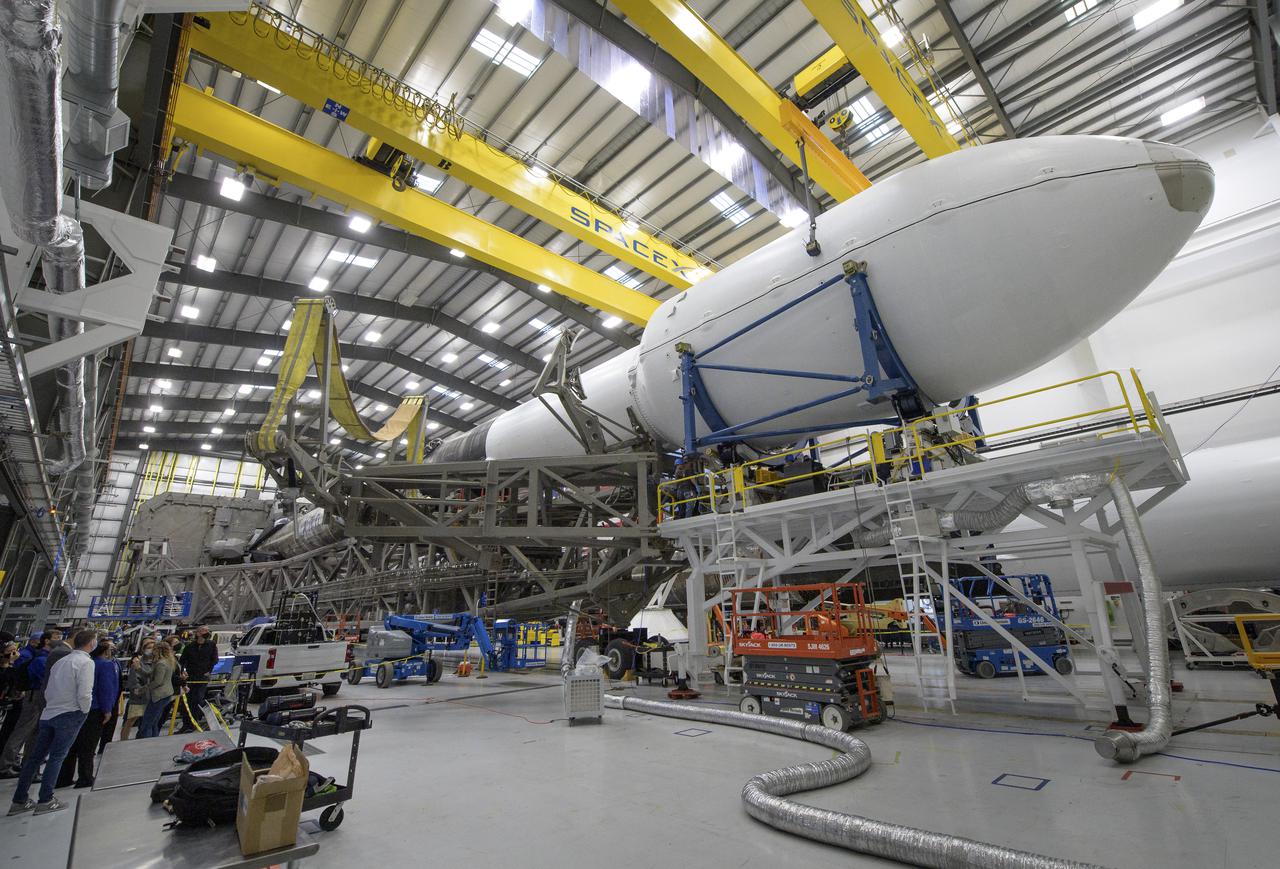

The Falcon 9 rocket and DART spacecraft readied for launch are seen as NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, and other NASA leadership get a tour from Julianna Scheiman, director for civil satellite missions, SpaceX, Monday, Nov. 22, 2021, at the SpaceX hanger, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

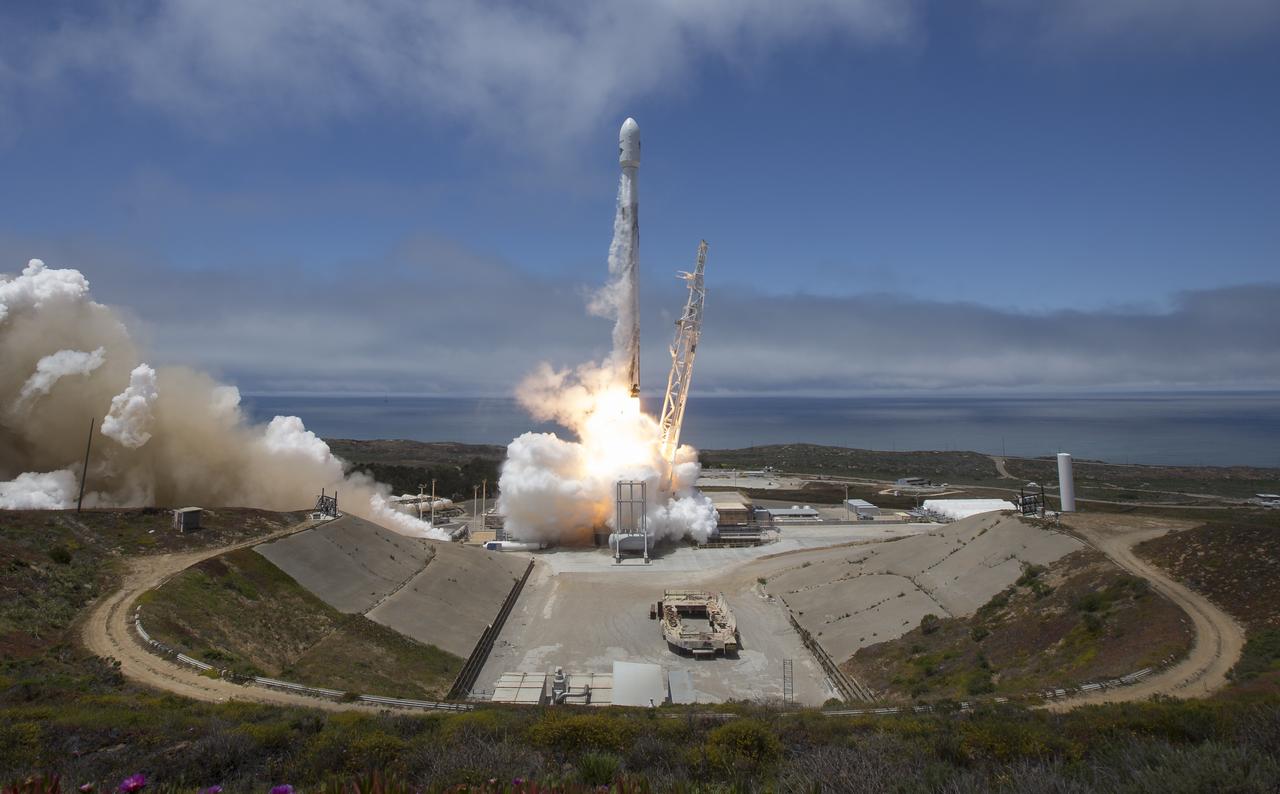
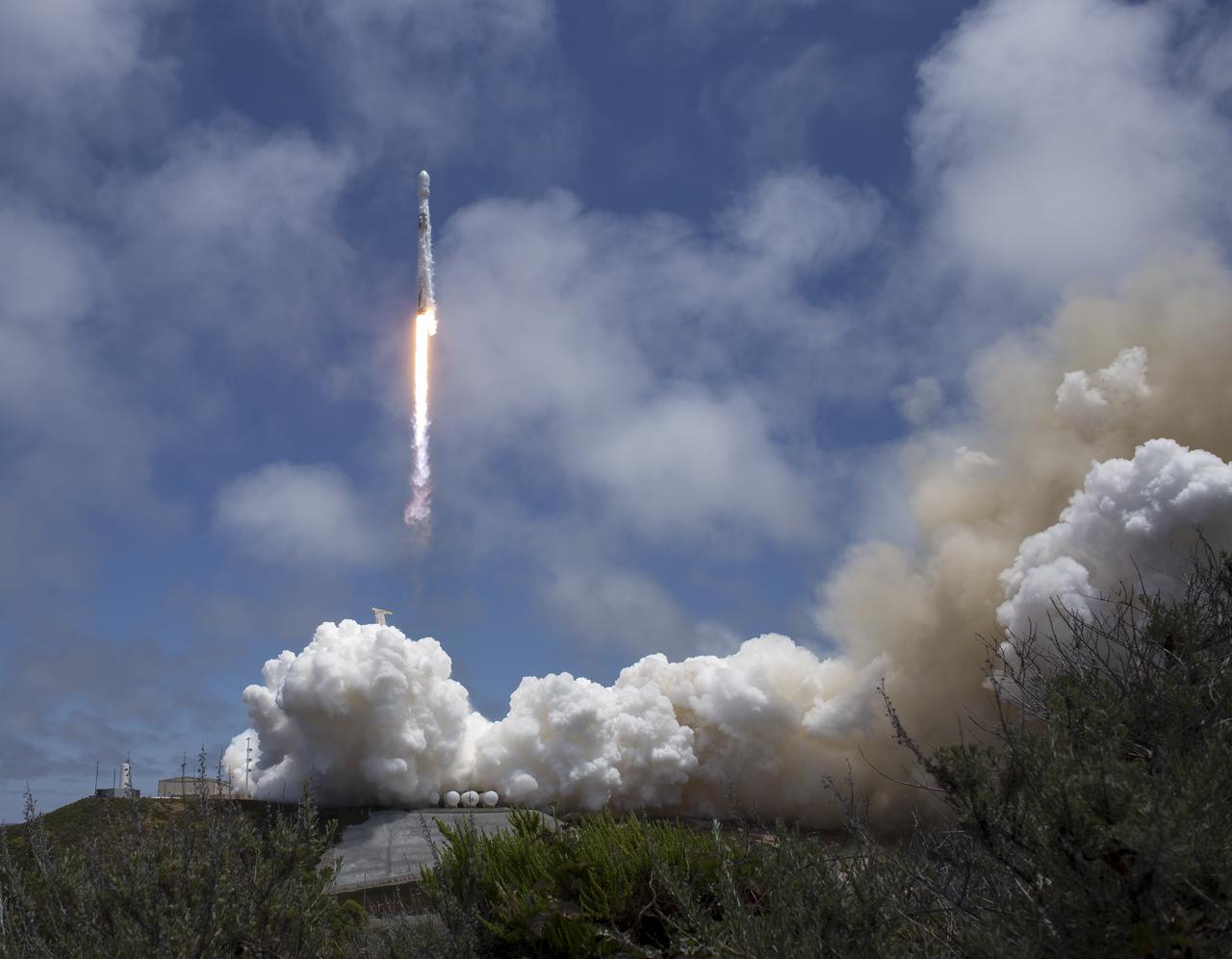
The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

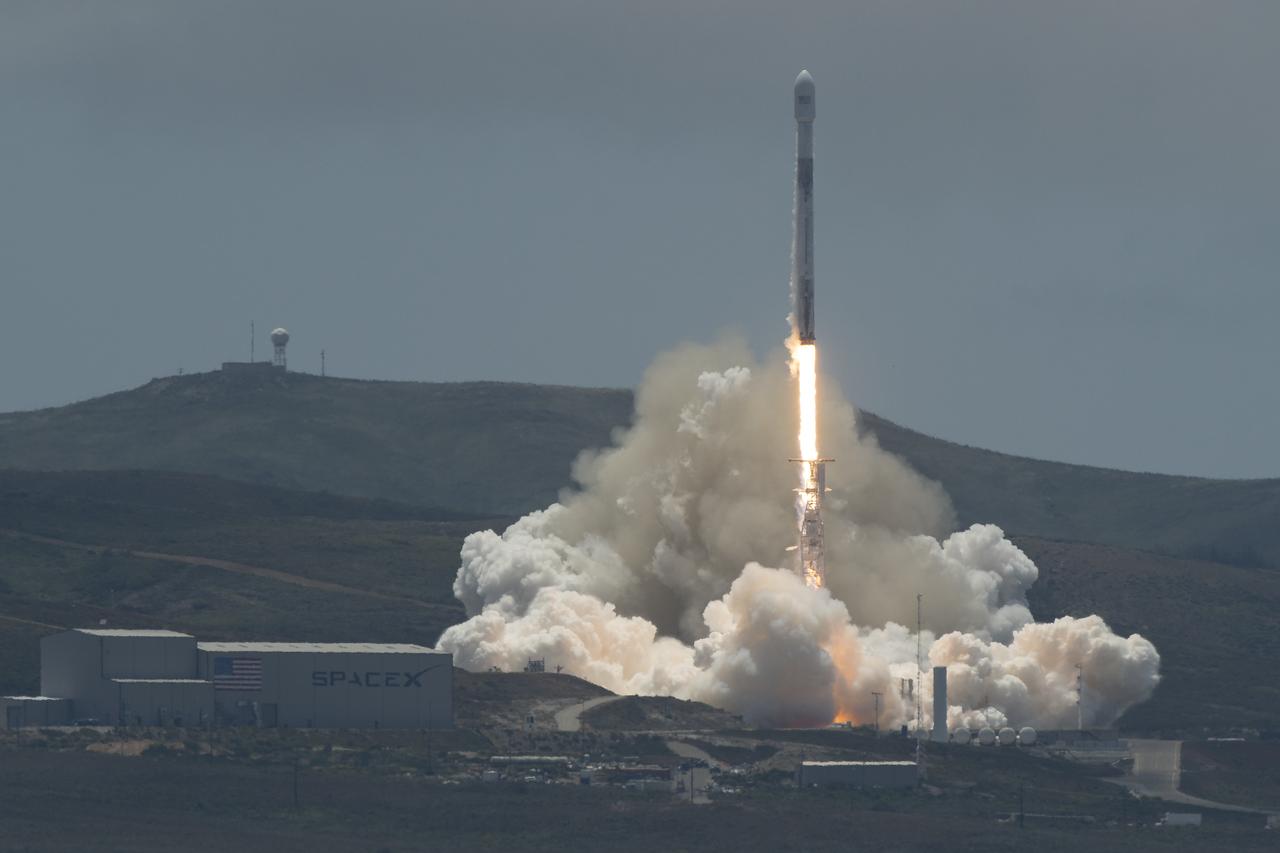
The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
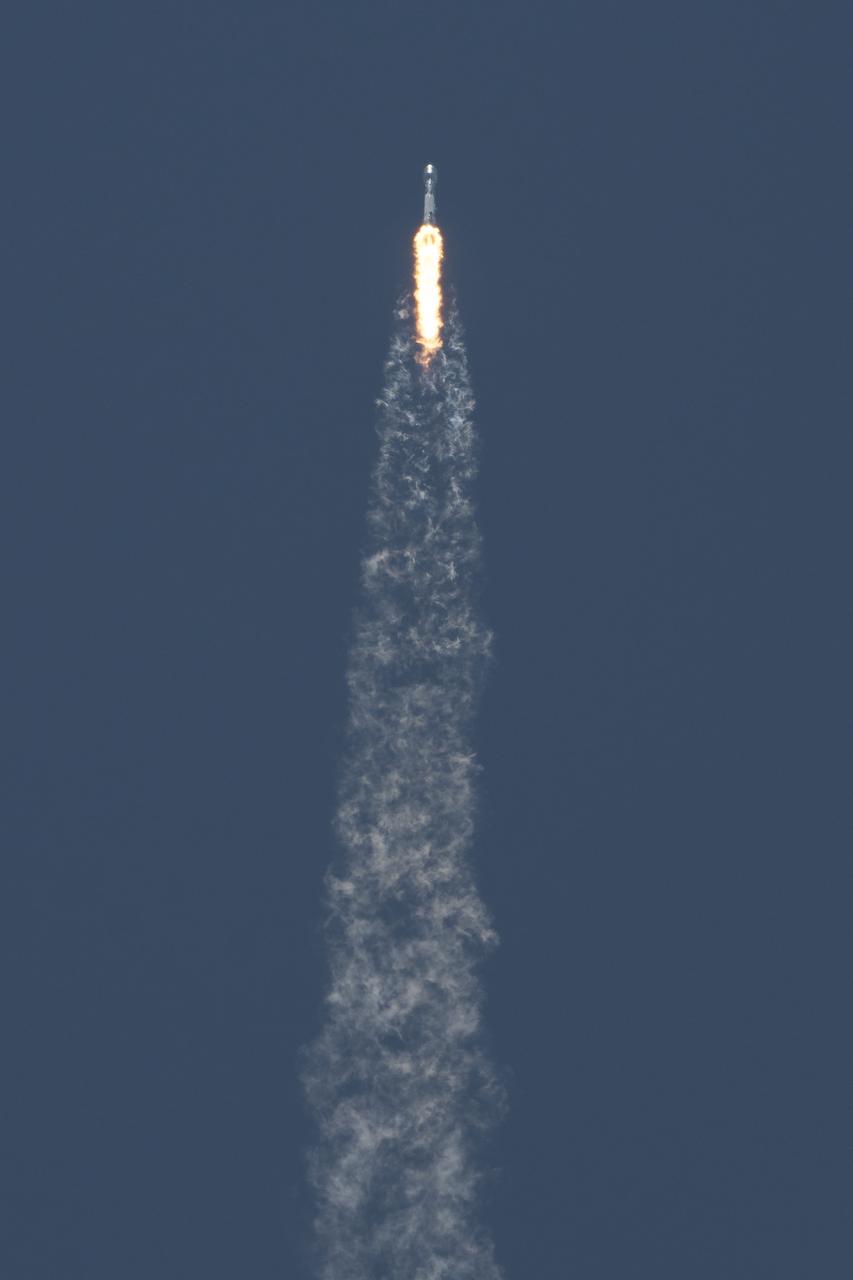

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
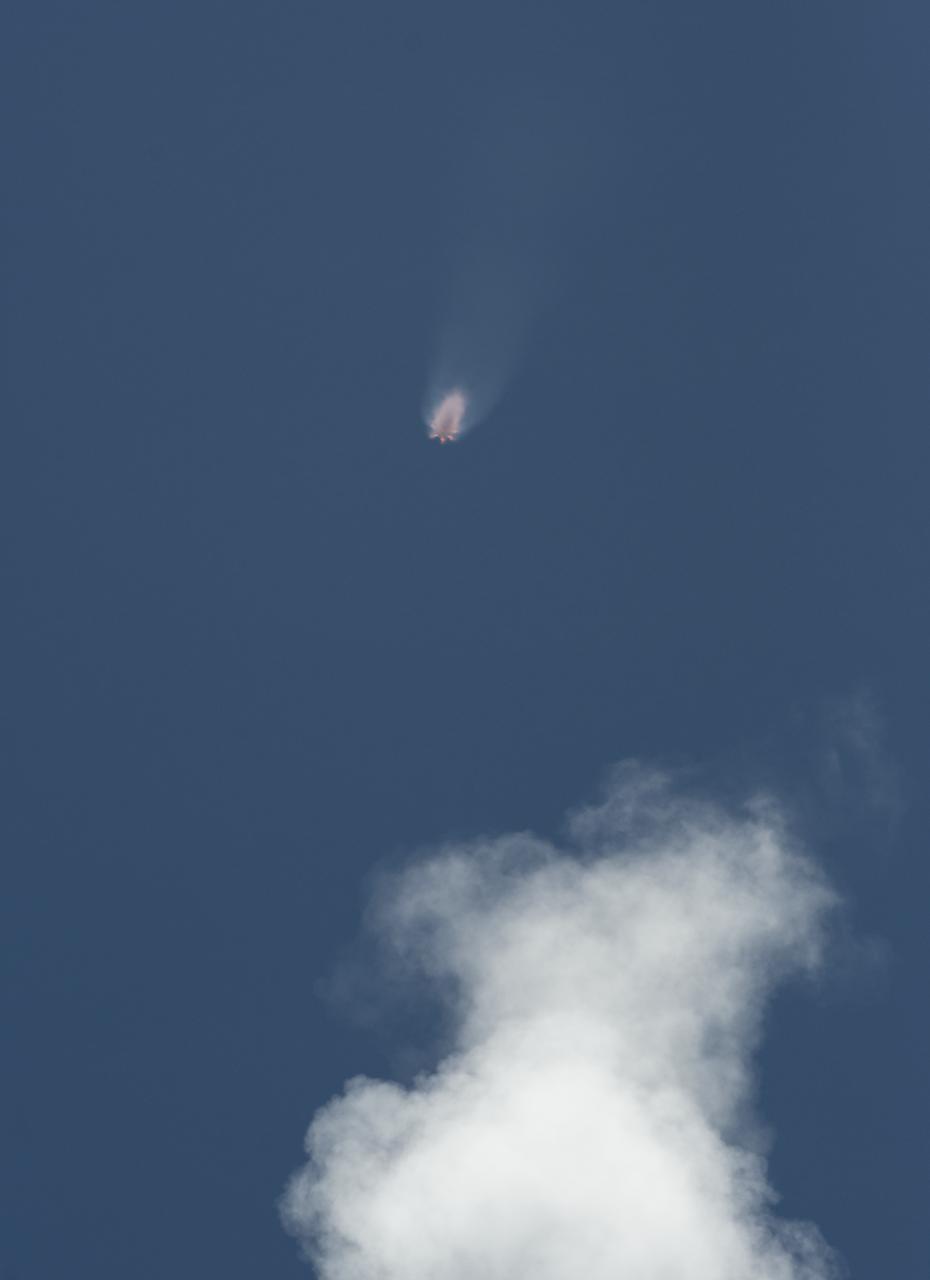

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
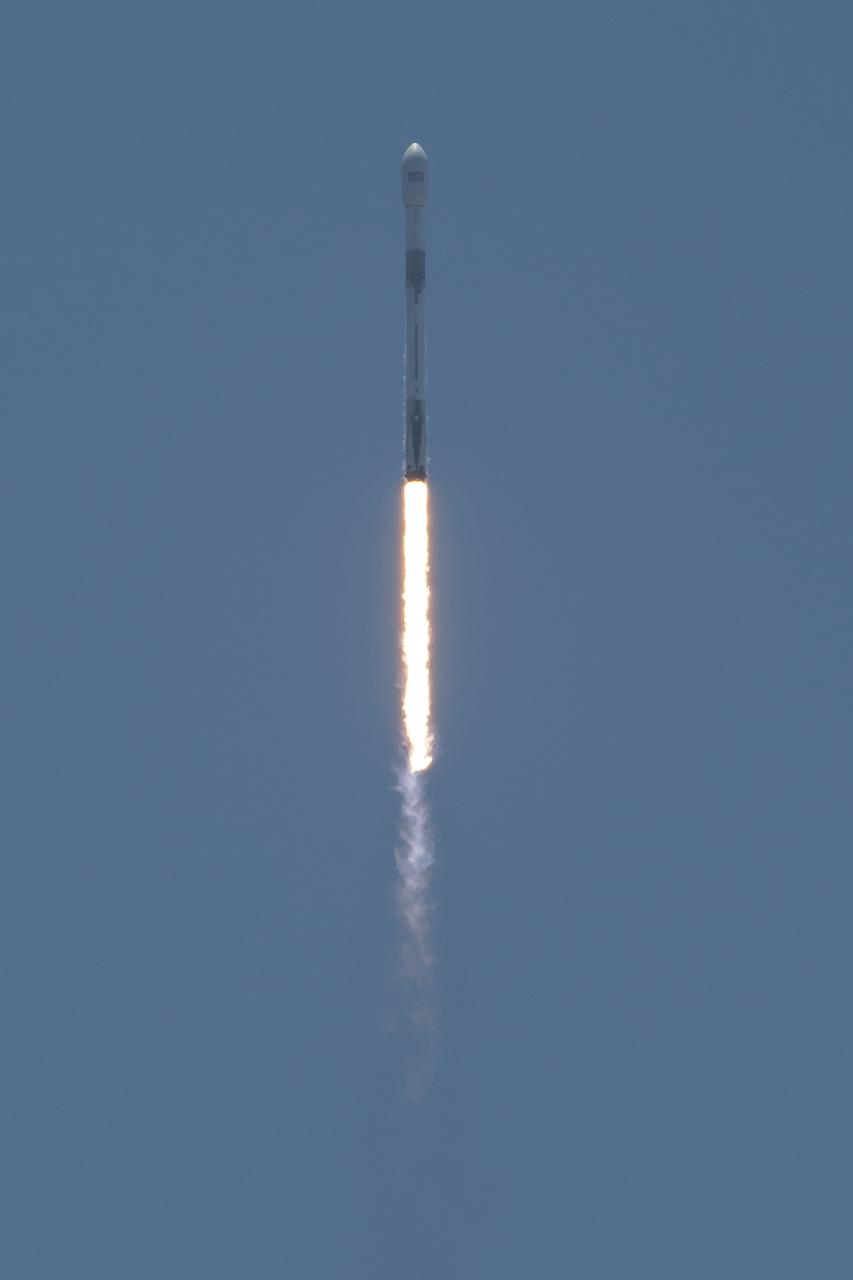

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Long exposure photograph showing the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launching onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
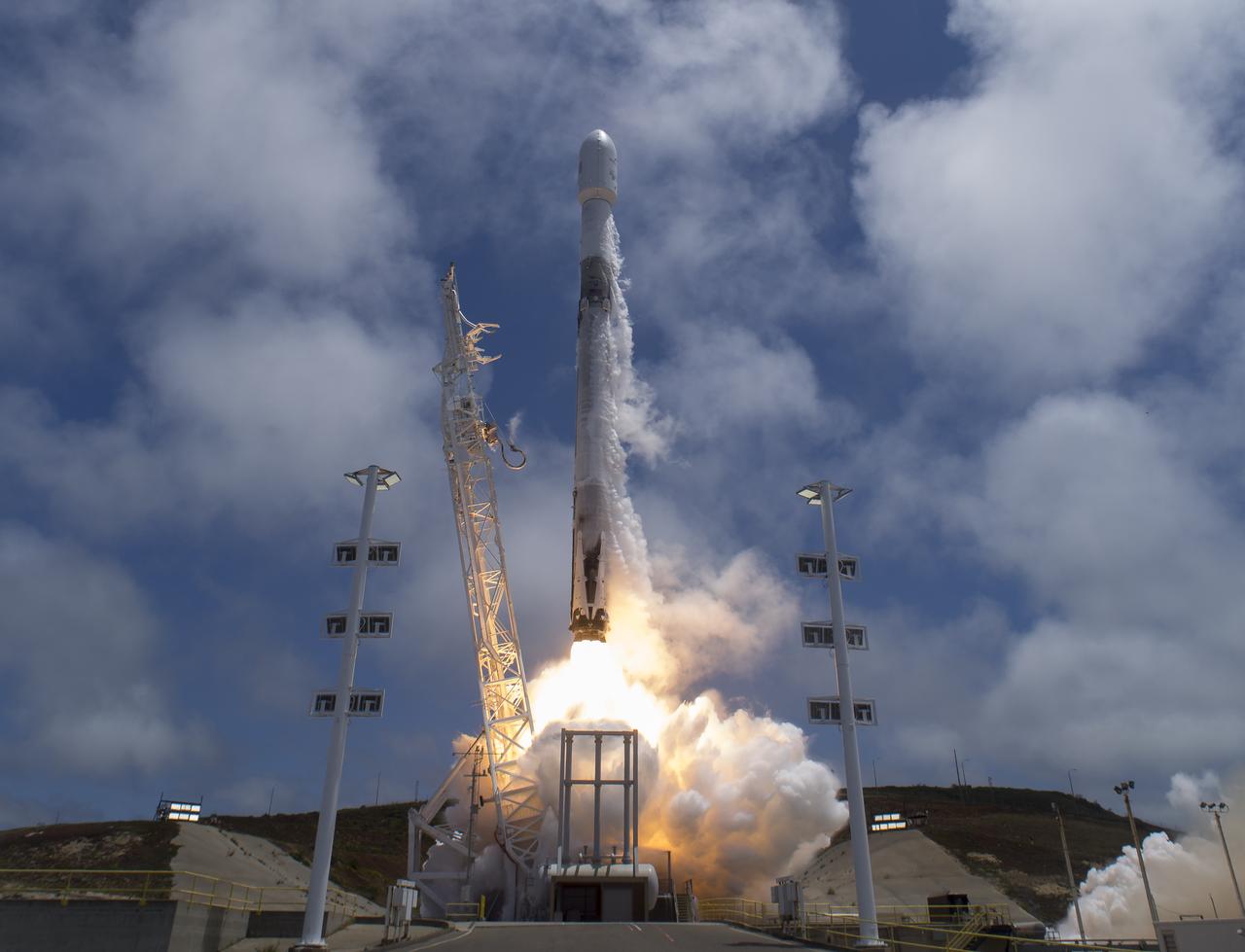

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
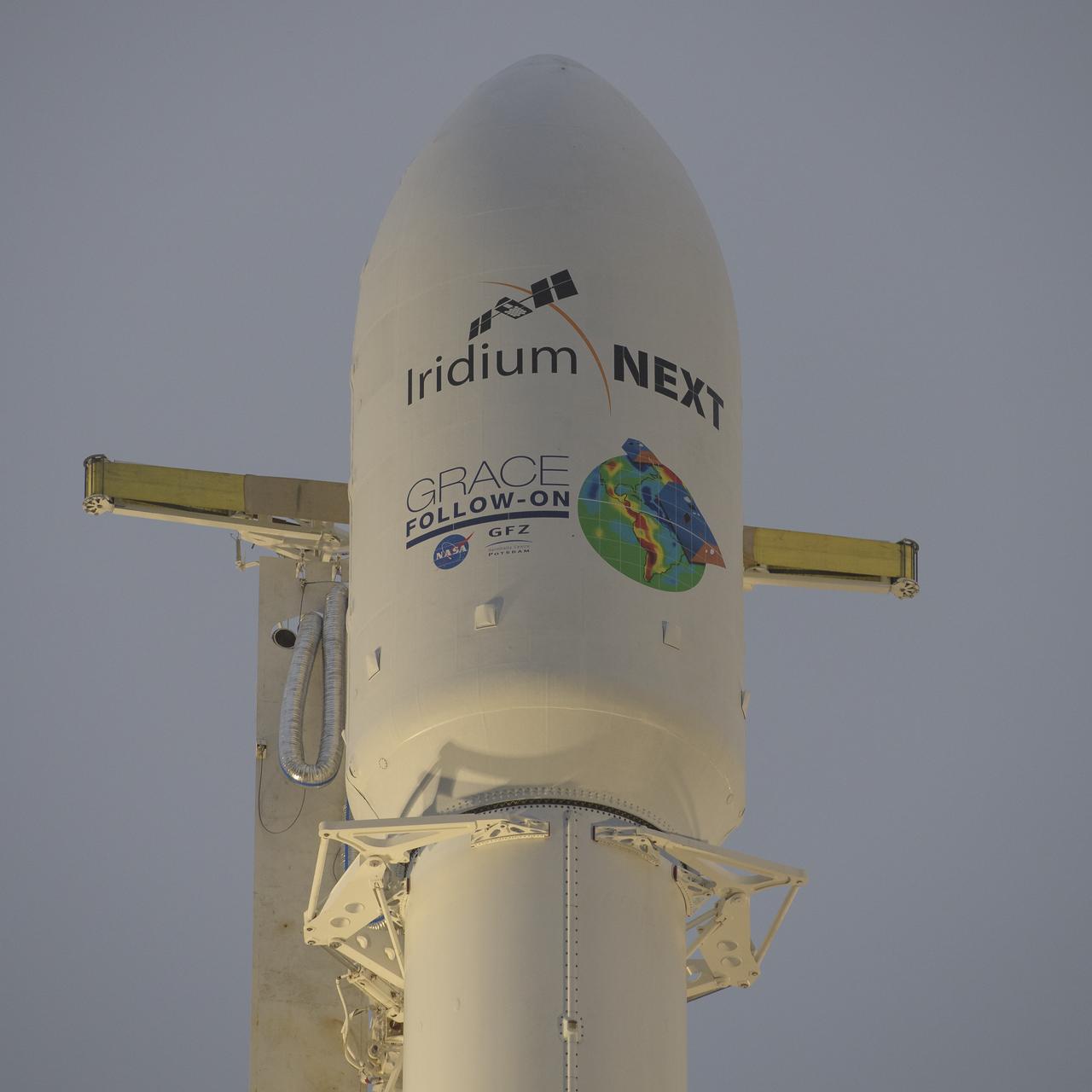

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Monday, May 21, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
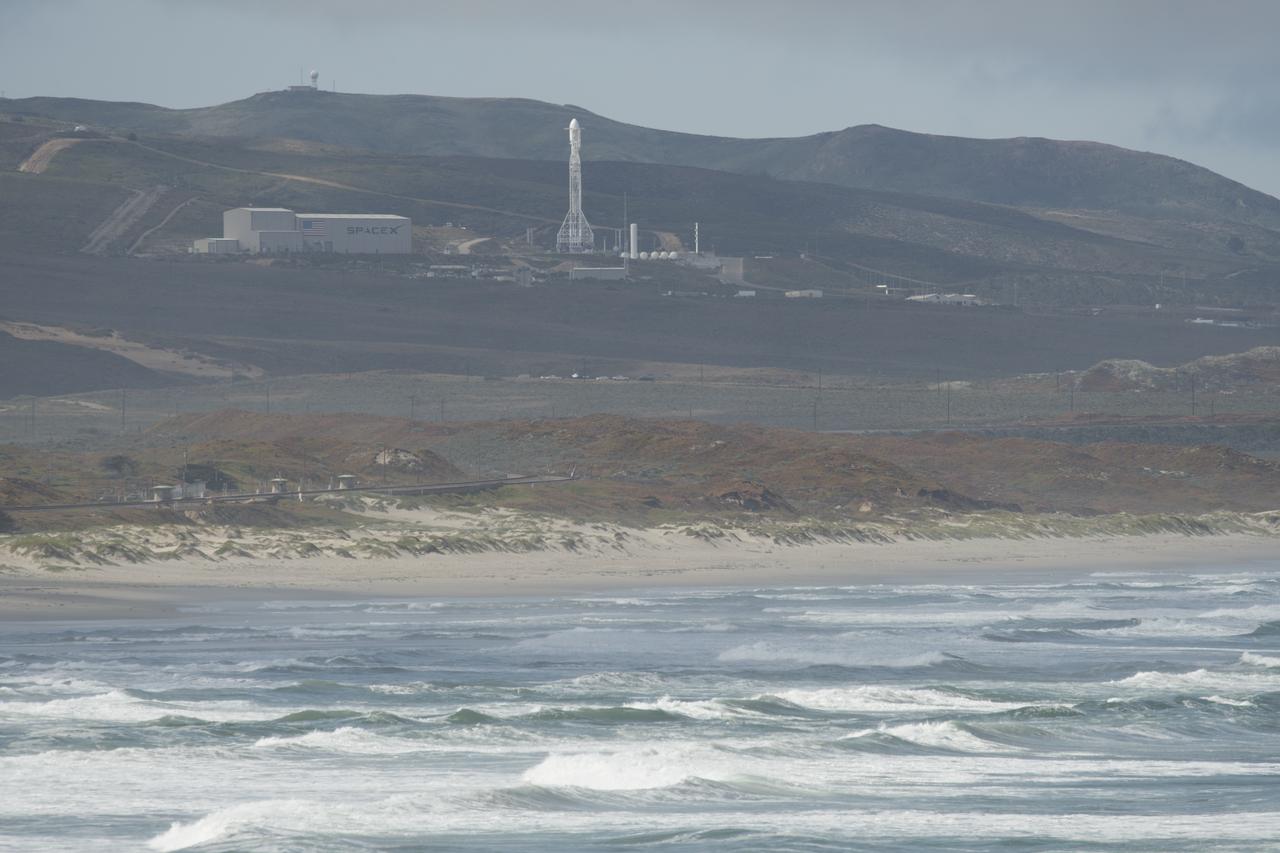

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
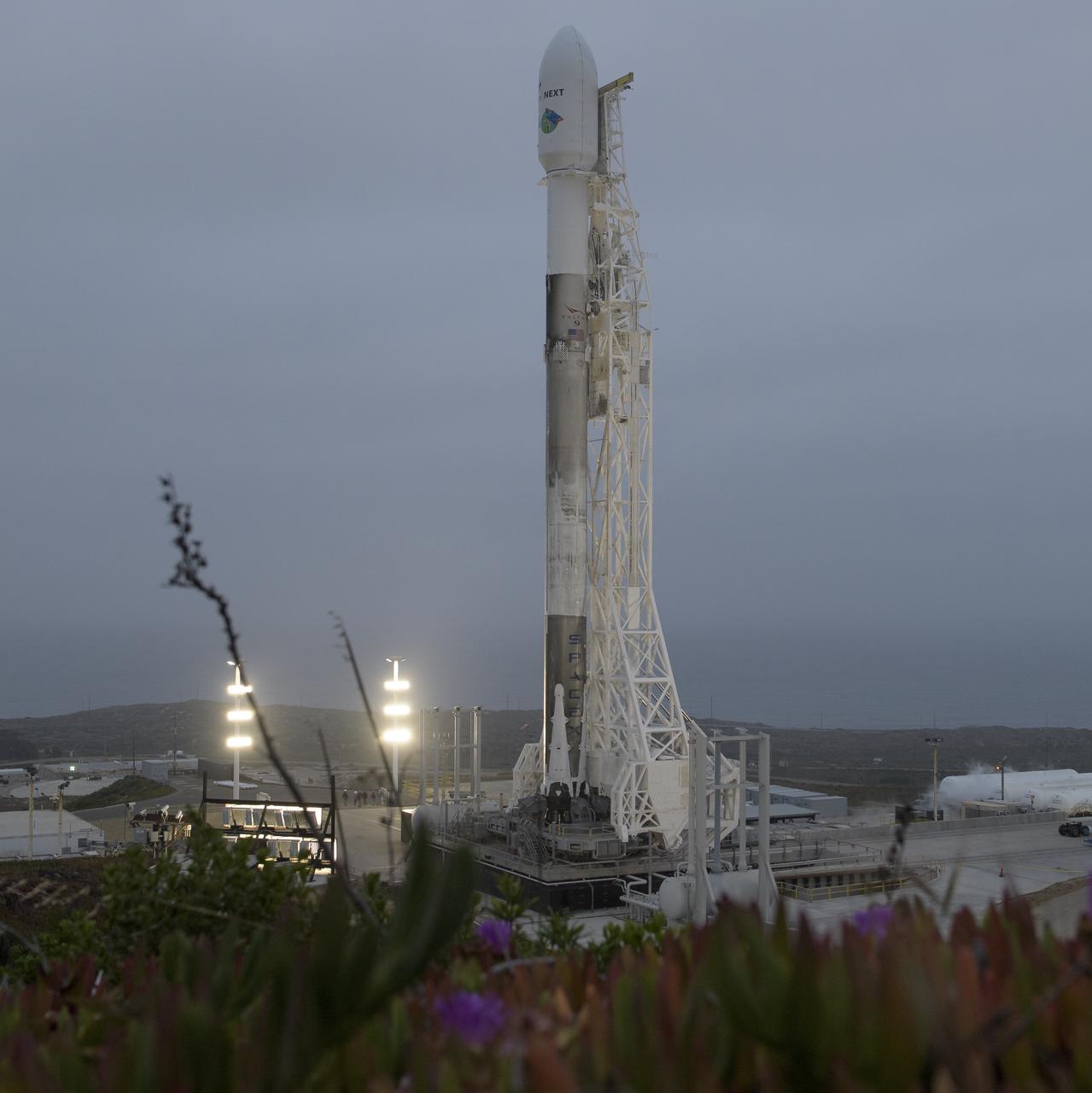

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Monday, May 21, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
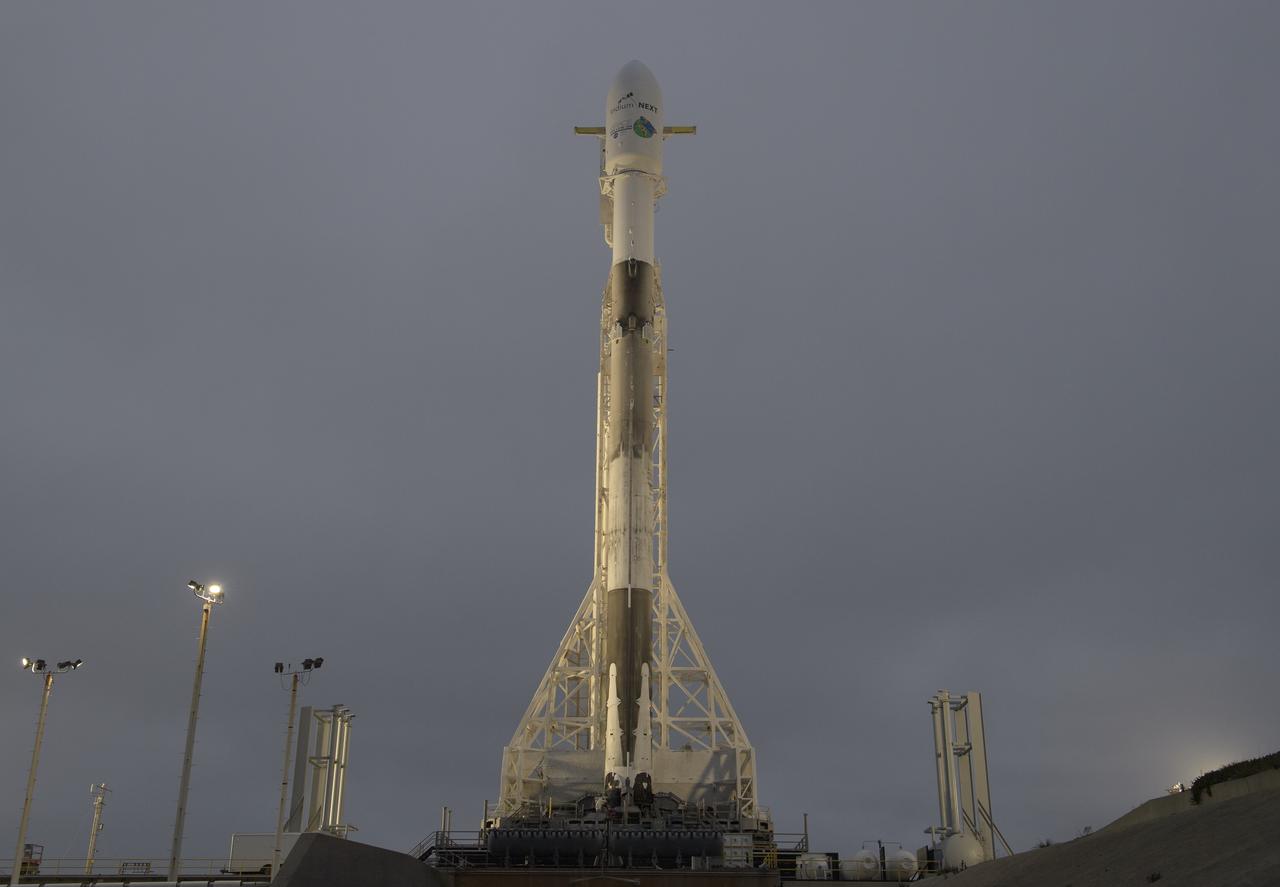

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Monday, May 21, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
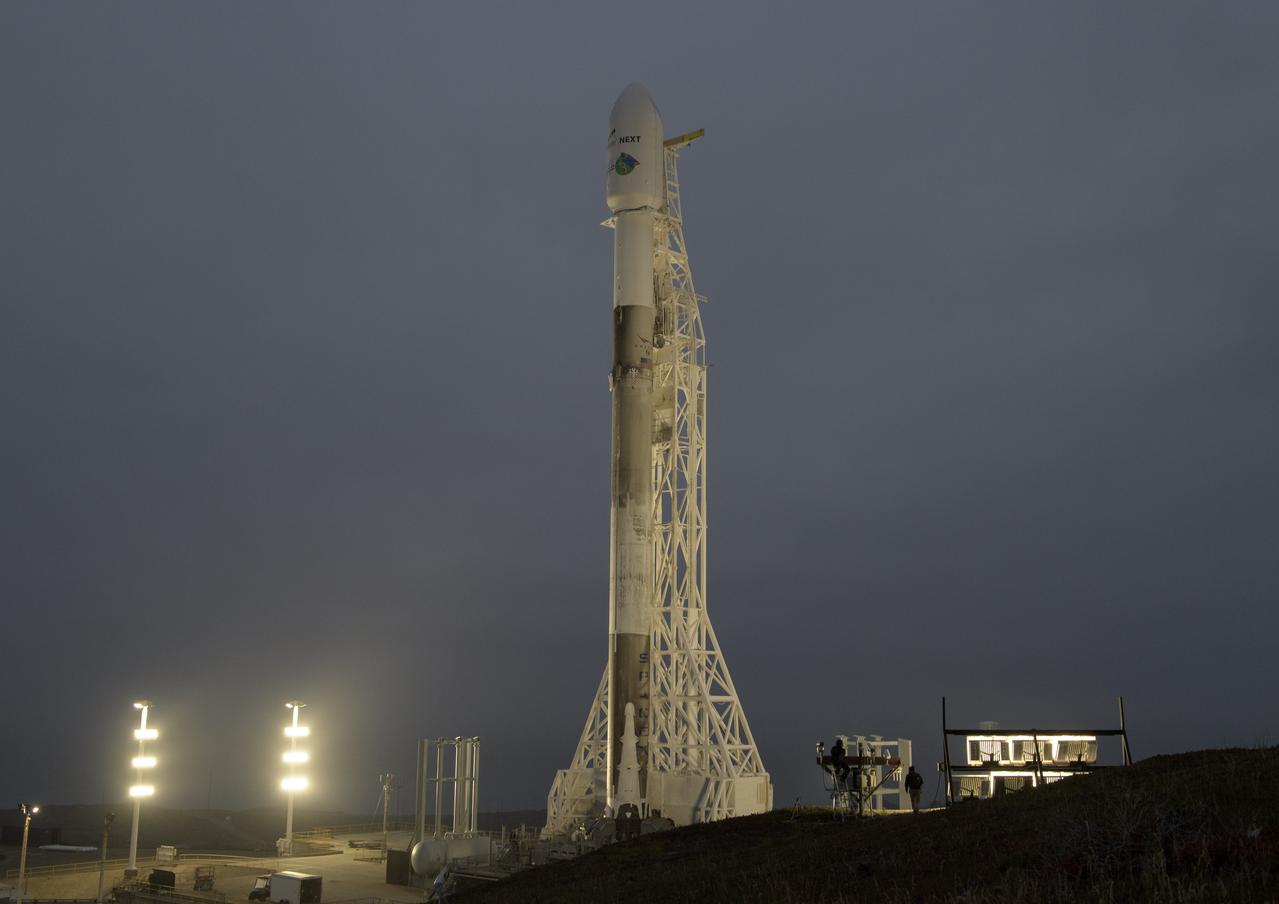

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Monday, May 21, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
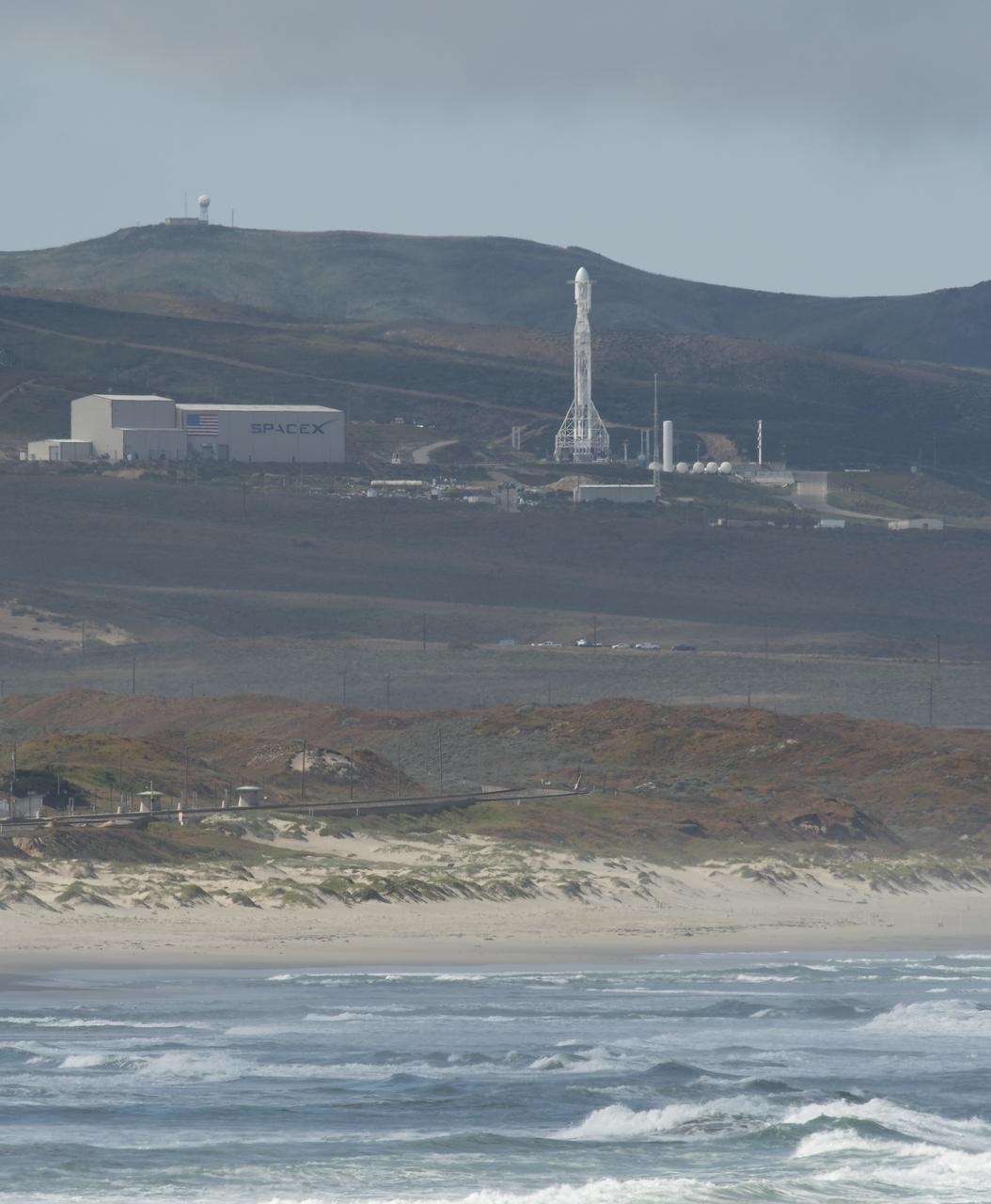

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is seen with the NASA/German Research Centre for Geosciences GRACE Follow-On spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, May 22, 2018, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The mission will measure changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. GRACE-FO is sharing its ride to orbit with five Iridium NEXT communications satellites as part of a commercial rideshare agreement. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
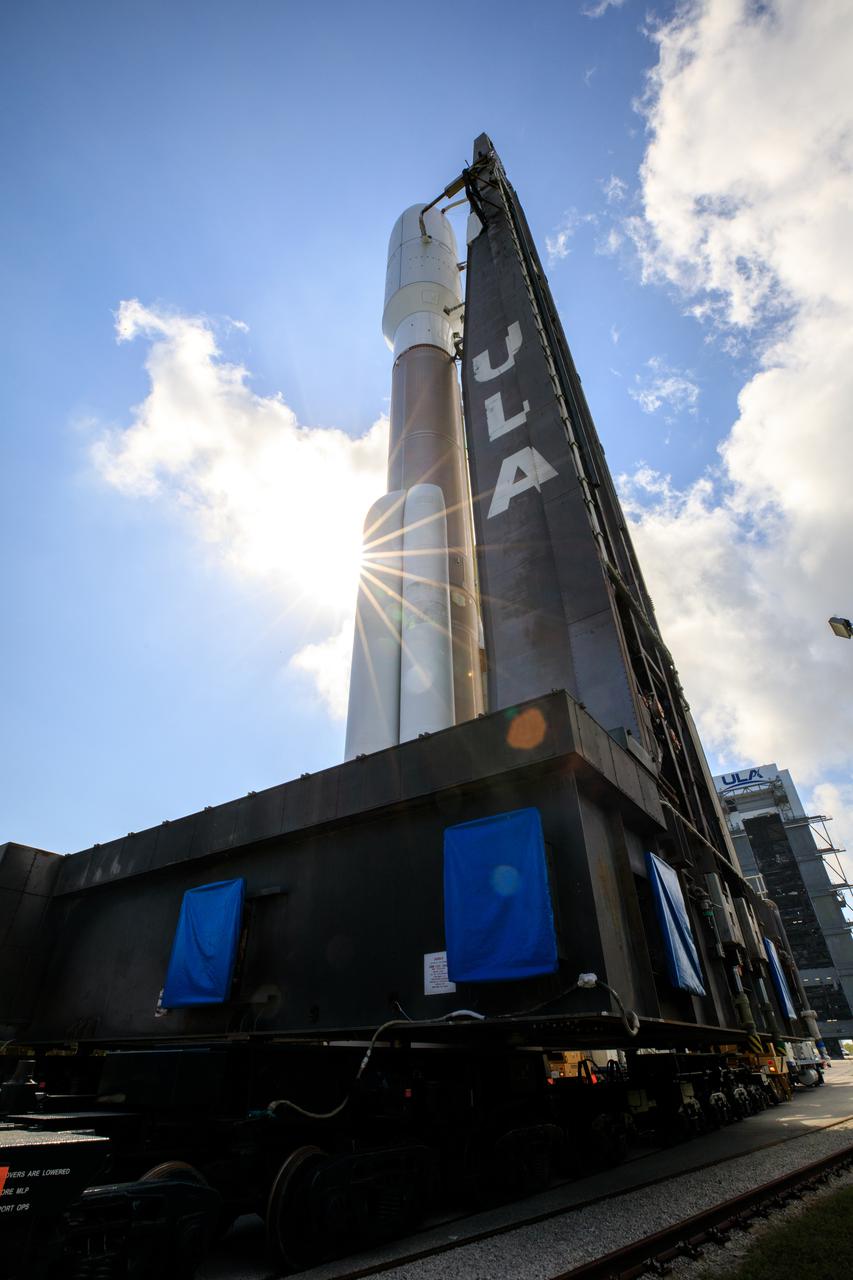

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), rolls out of the Vertical Integration Facility on its way to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
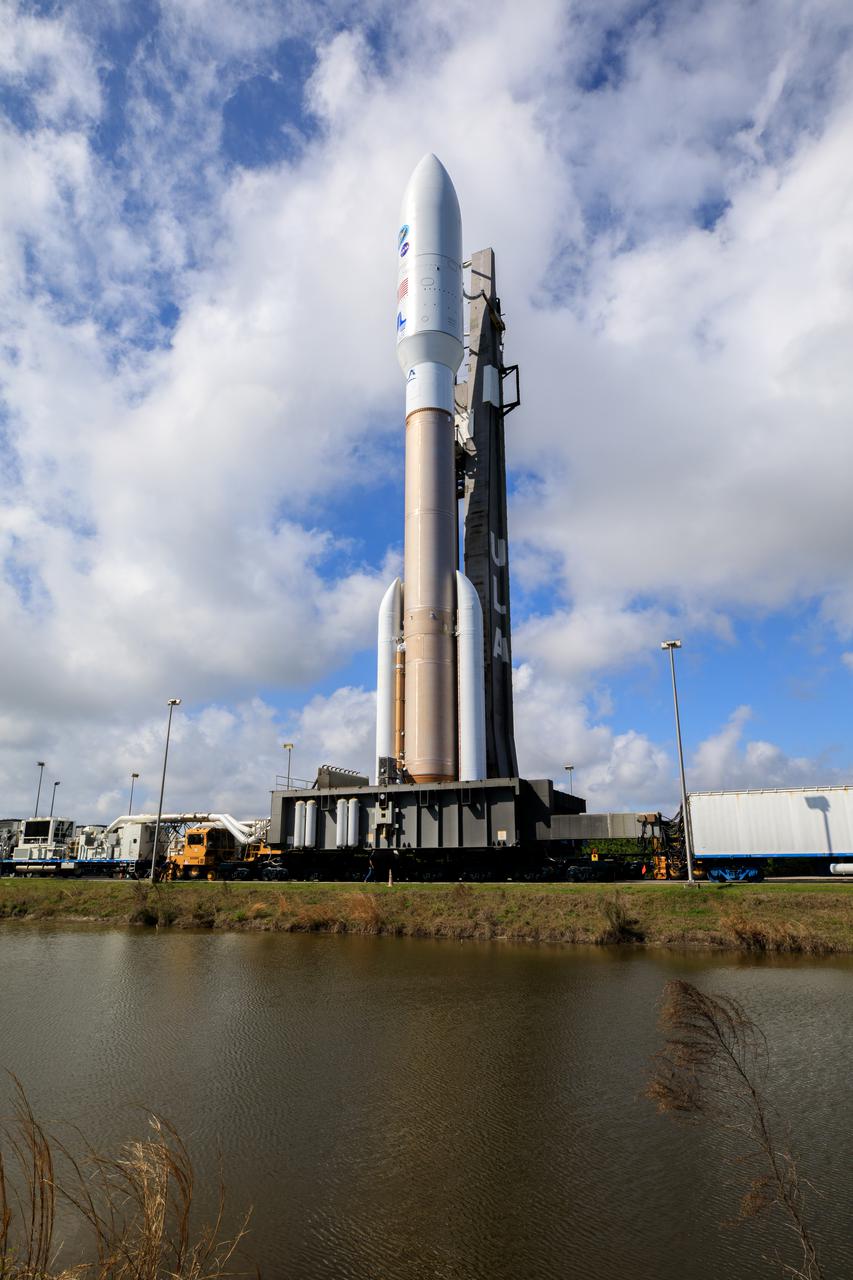

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), rolls out of the Vertical Integration Facility on its way to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
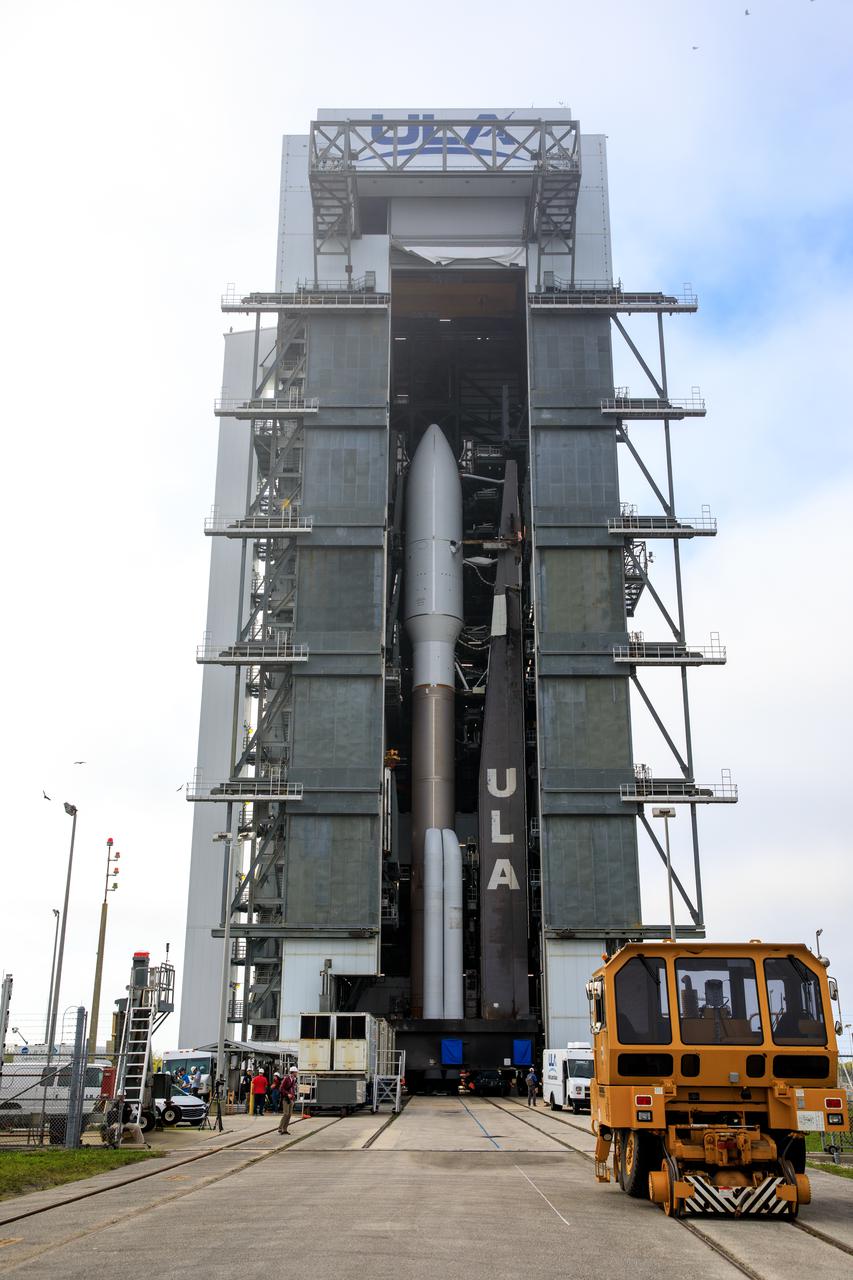

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), begins its rollout from the Vertical Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
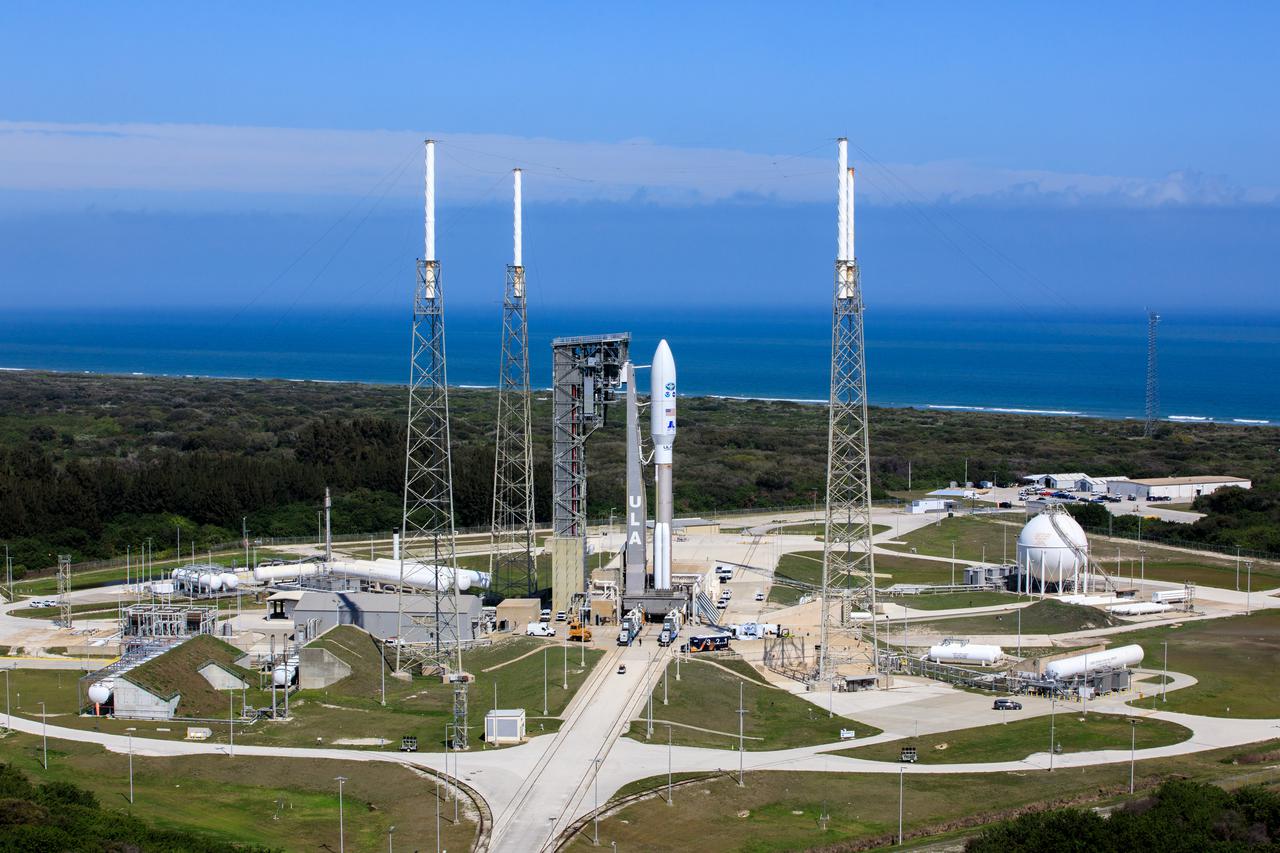

An aerial view shows the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), secured on the pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Feb. 28, 2022. GOES-T will lift off atop the Atlas V from SLC-41 on March 1, 2022, at 4:38 p.m. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T will be renamed GOES-18 once it reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-18 will go into operational service as GOES West to provide critical data for the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, Central America, and the Pacific Ocean. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
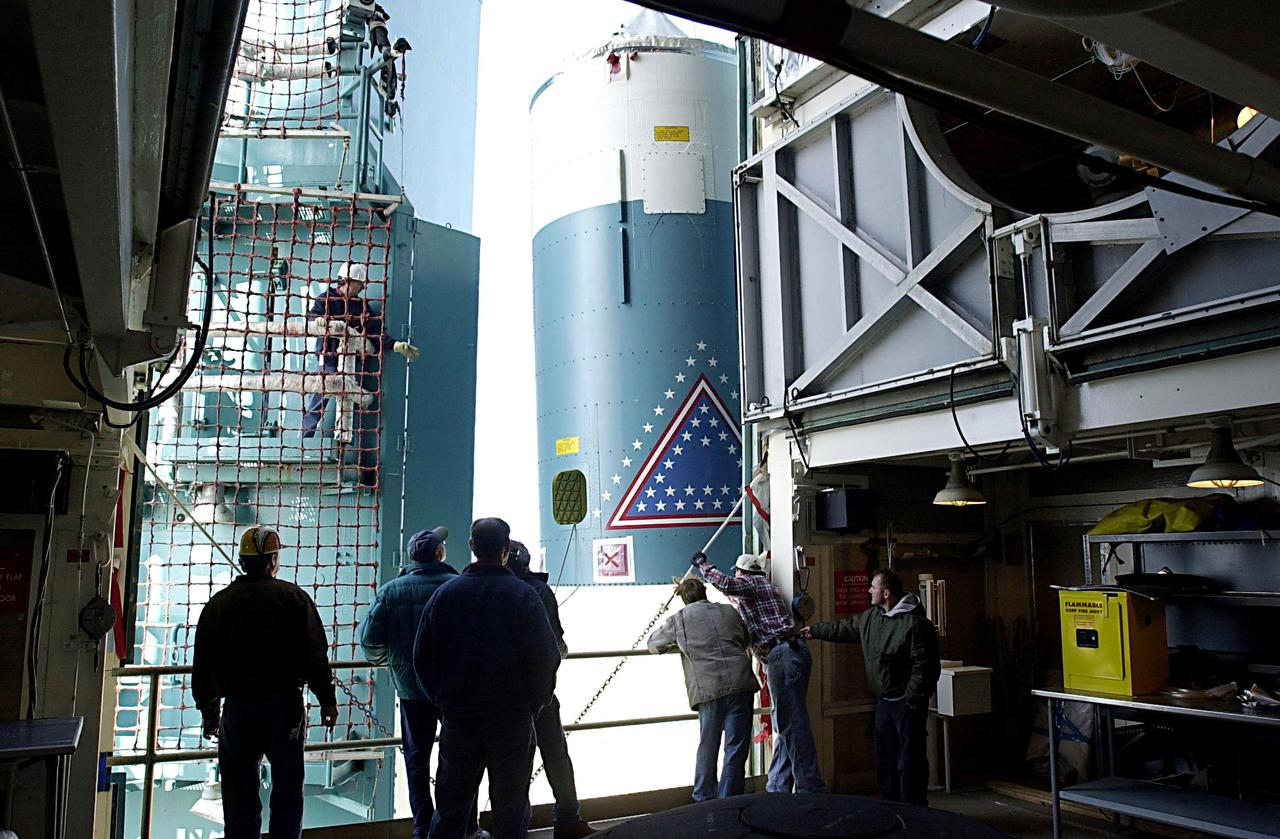

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., watch as the interstage of the Delta II rocket is lifted to a level where it can be mated with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

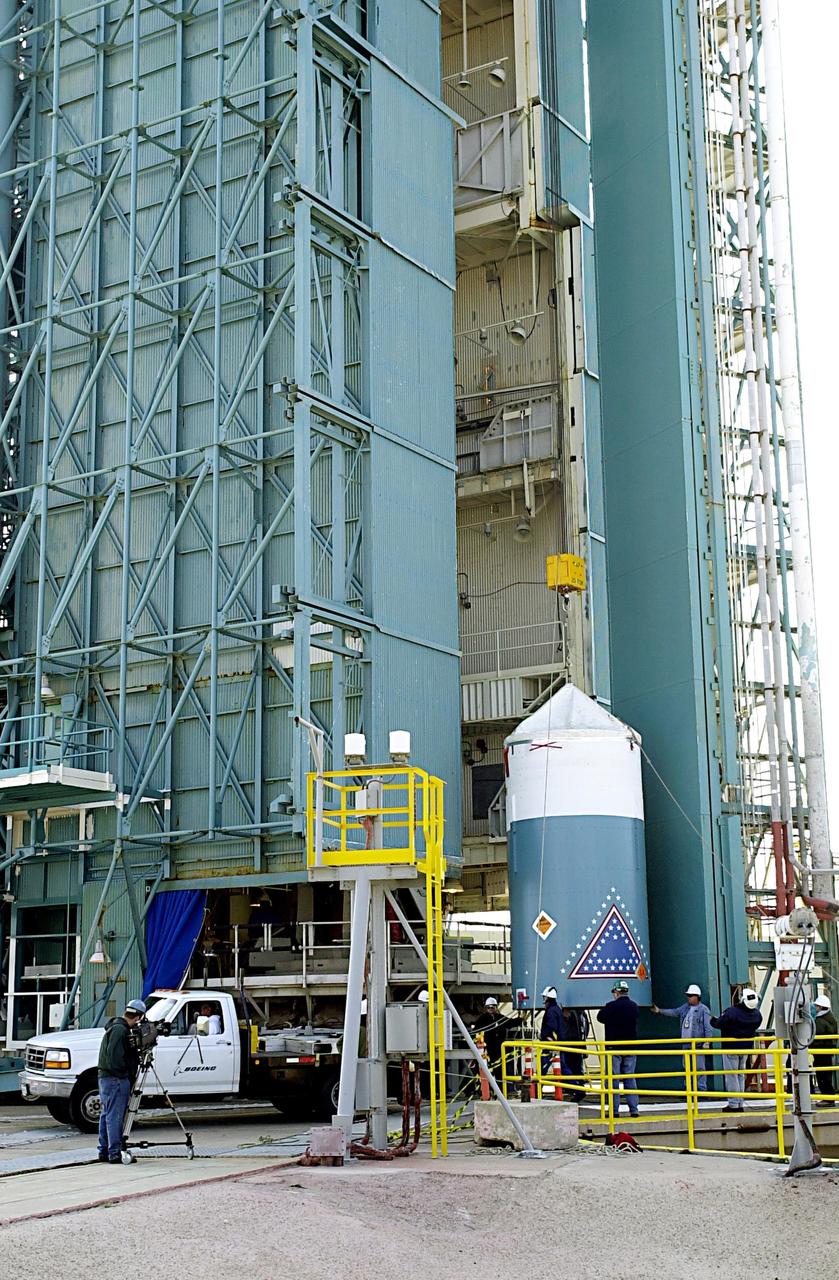
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position as preparations continue to mate it to a Delta II rocket. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position for mating to a Delta II rocket. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

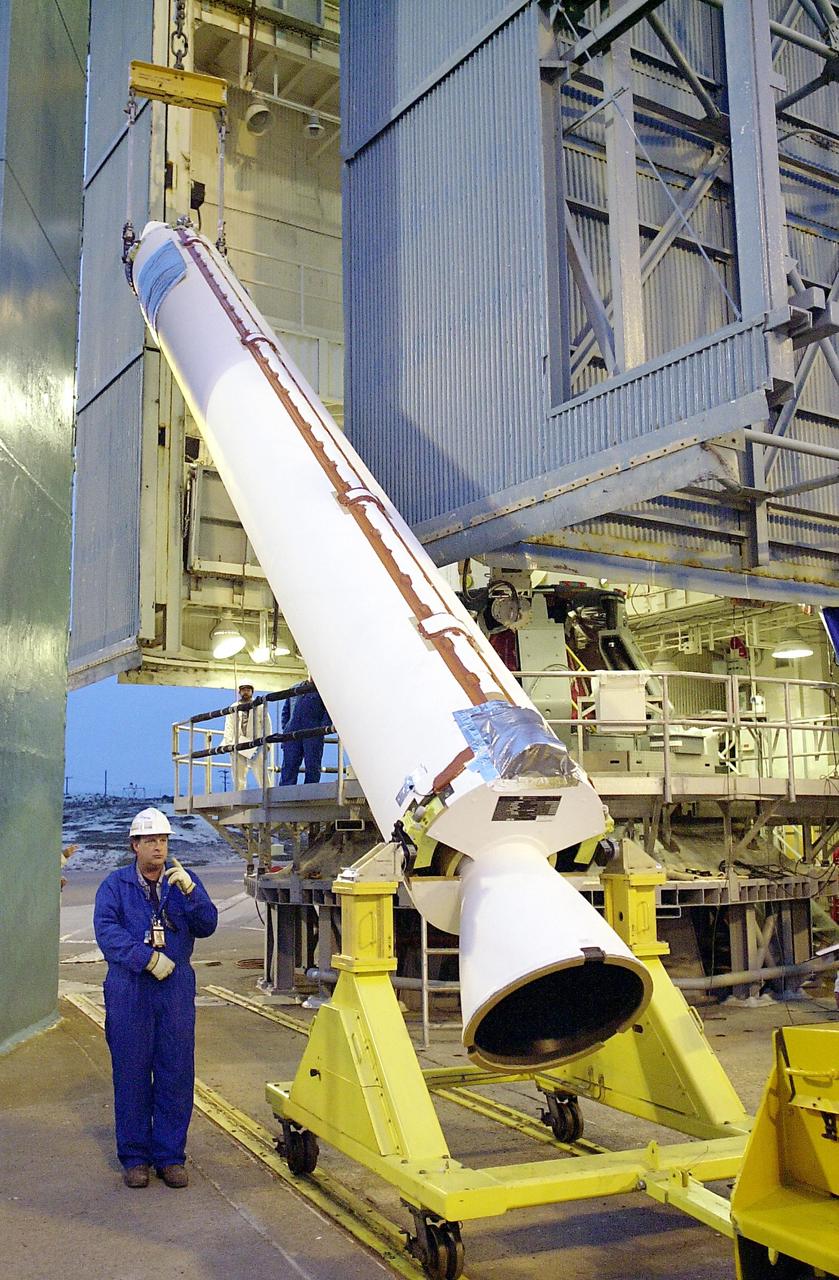
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., help guide the interstage of the Delta II rocket toward the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

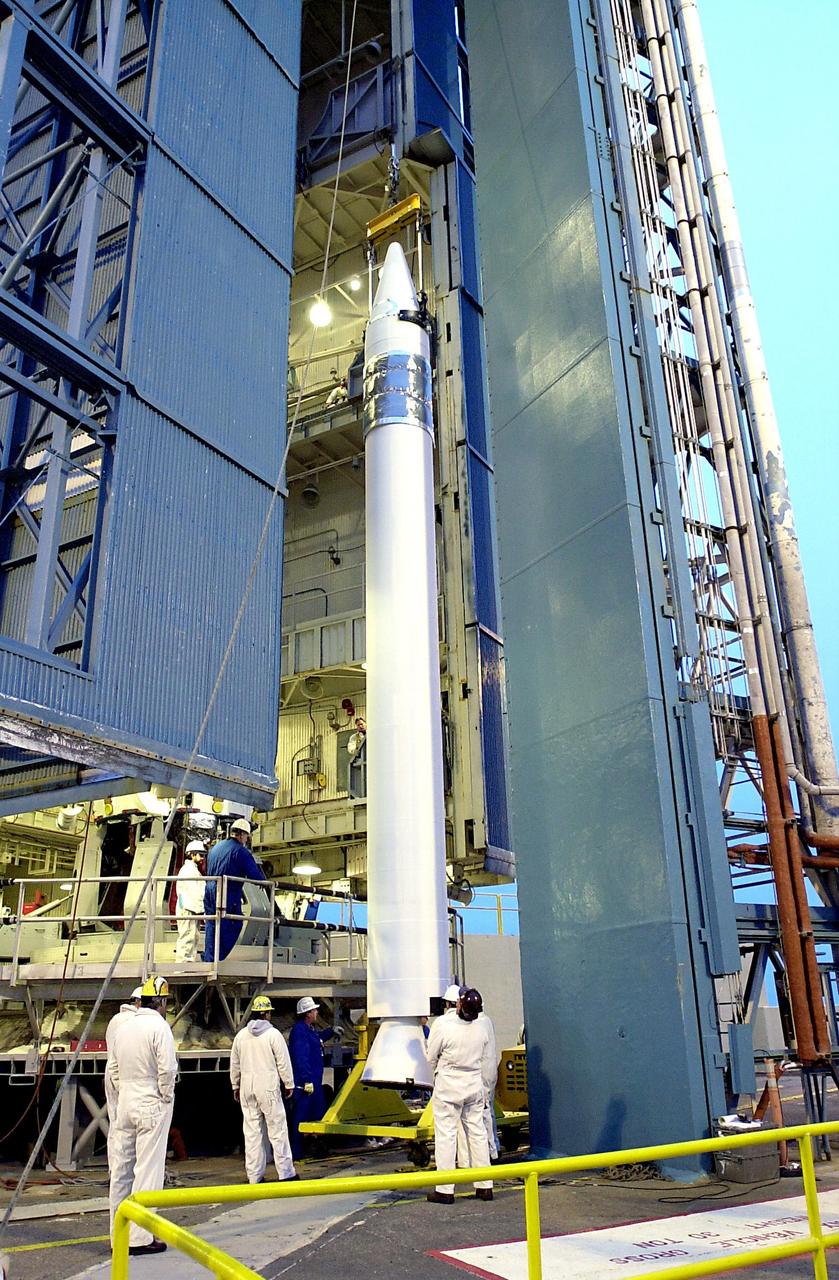
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at the base of the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., watch as the interstage of the Delta II rocket is lifted up the tower. The interstage will eventually house the second stage and will be mated with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
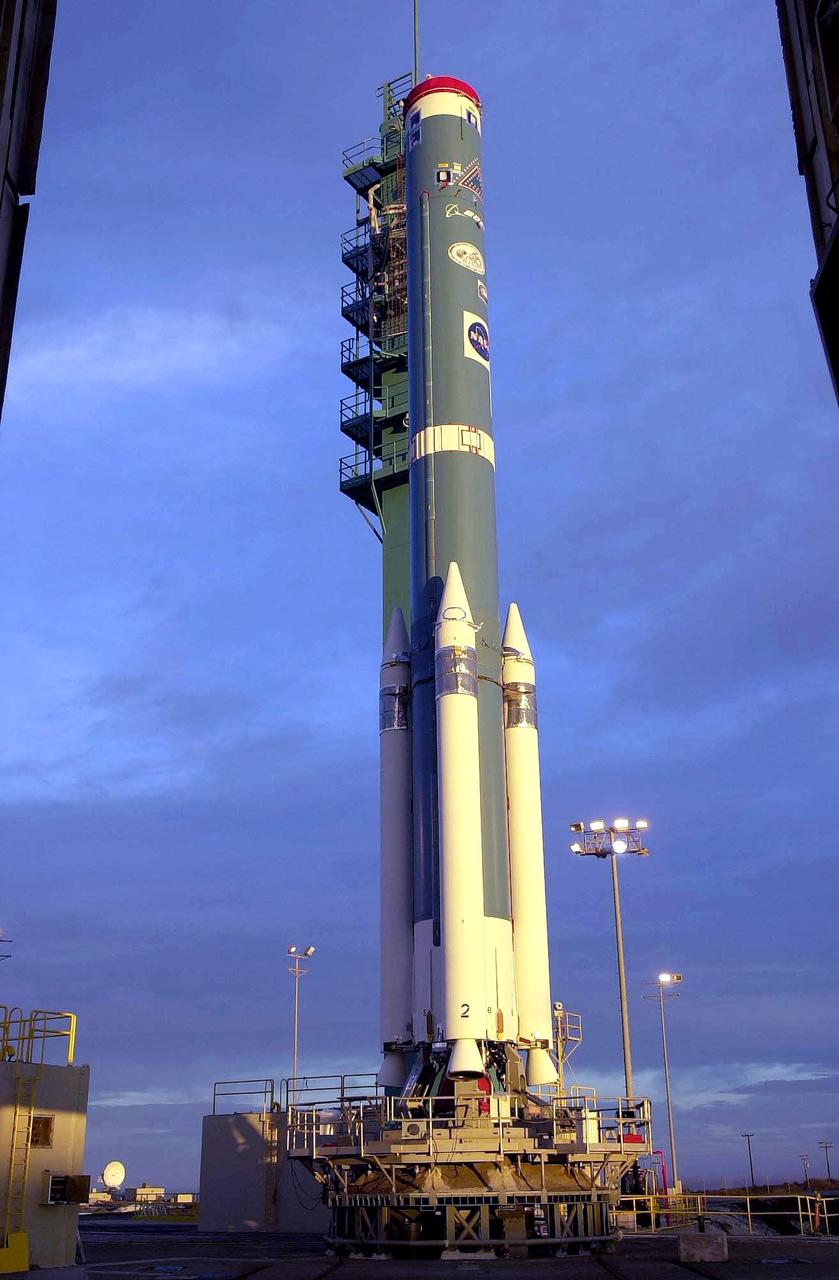

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., the launch tower has been rolled back to reveal a Delta II rocket with its solid rocket boosters attached. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat, is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer, or CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11, 2003, between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., help guide the interstage of the Delta II rocket into position for mating with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., help guide the interstage of the Delta II rocket into position for mating with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

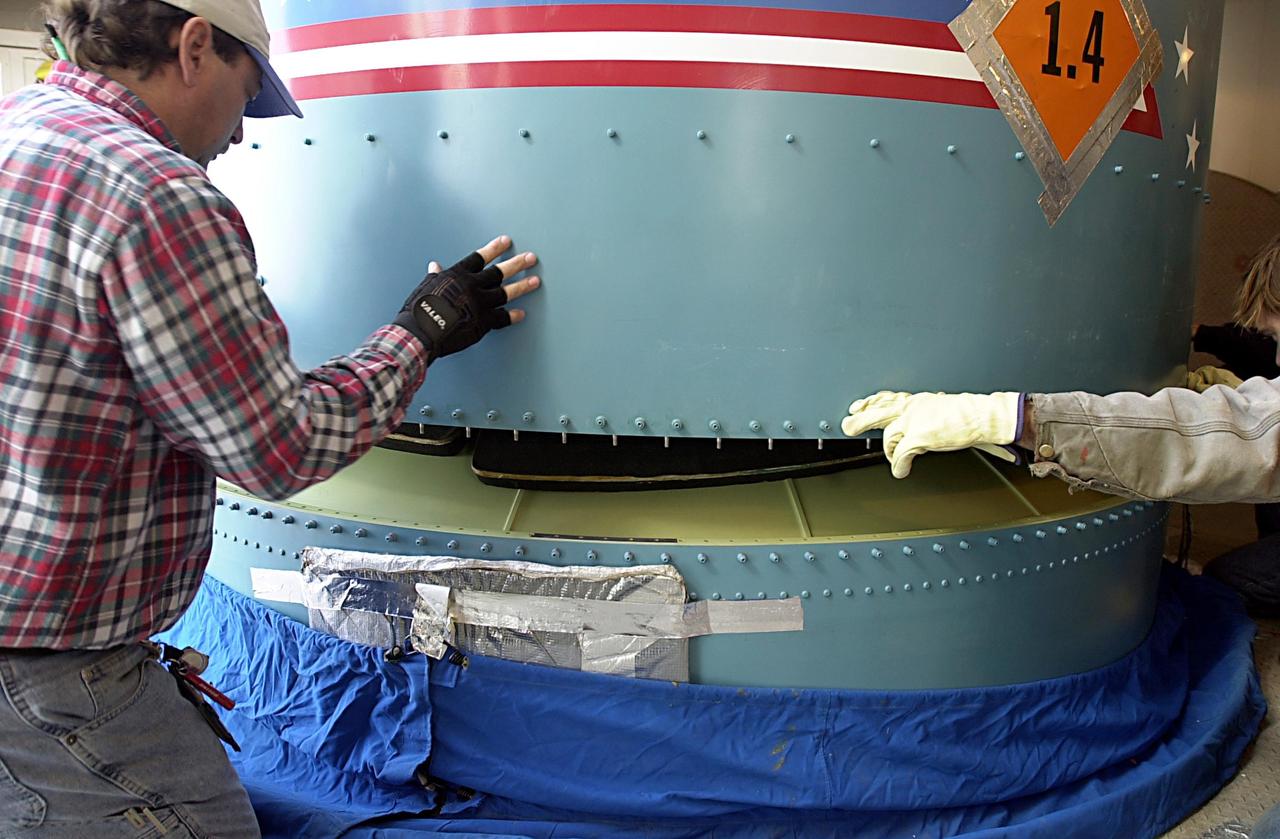
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position beside the Delta II rocket to which it will be attached. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
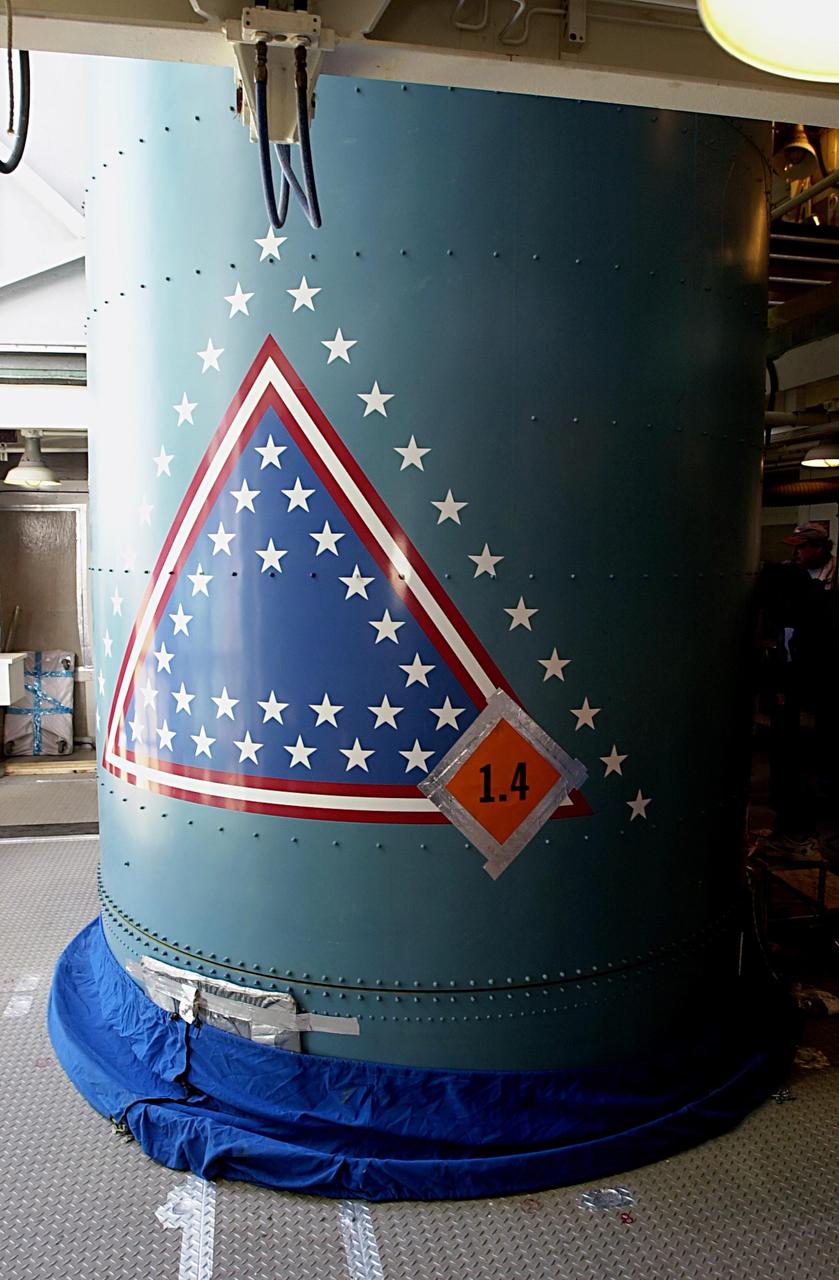

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., the second stage of a Delta II rocket sits mated with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
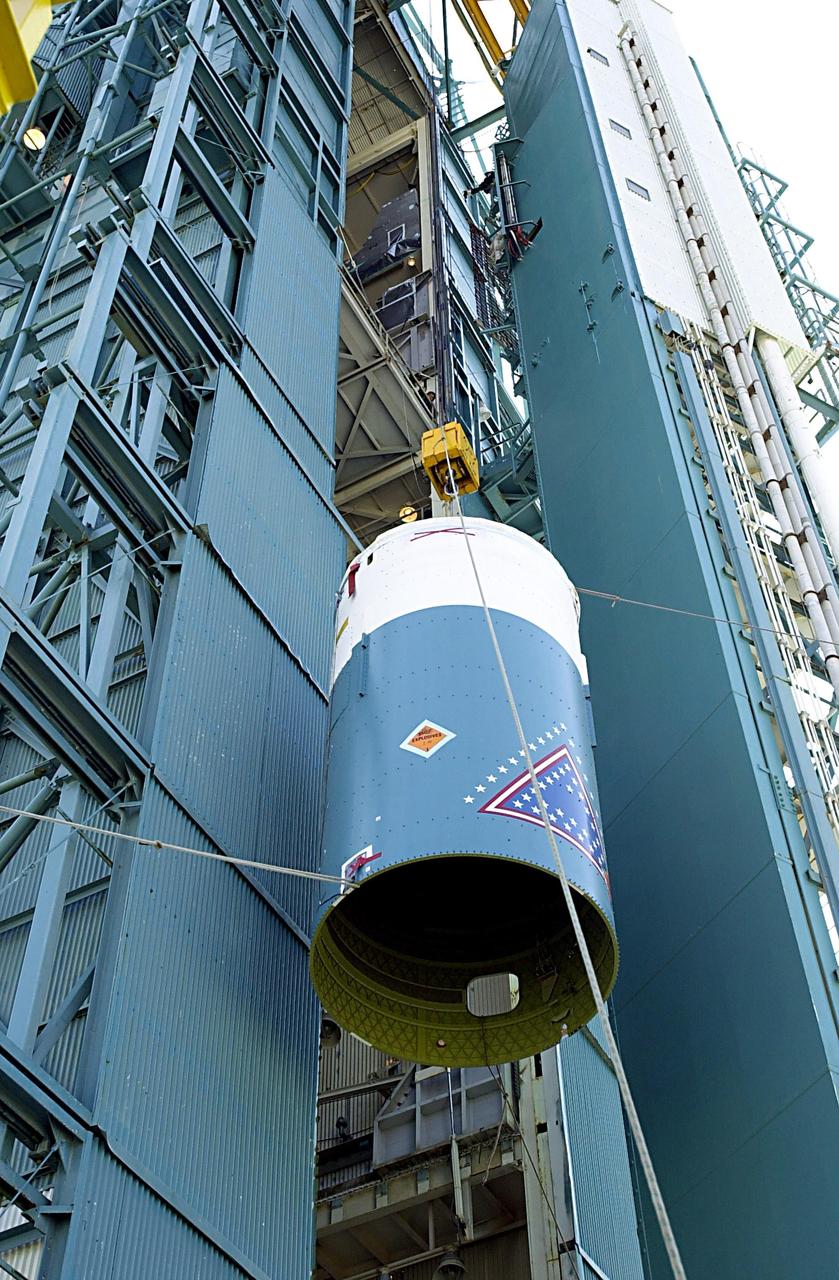

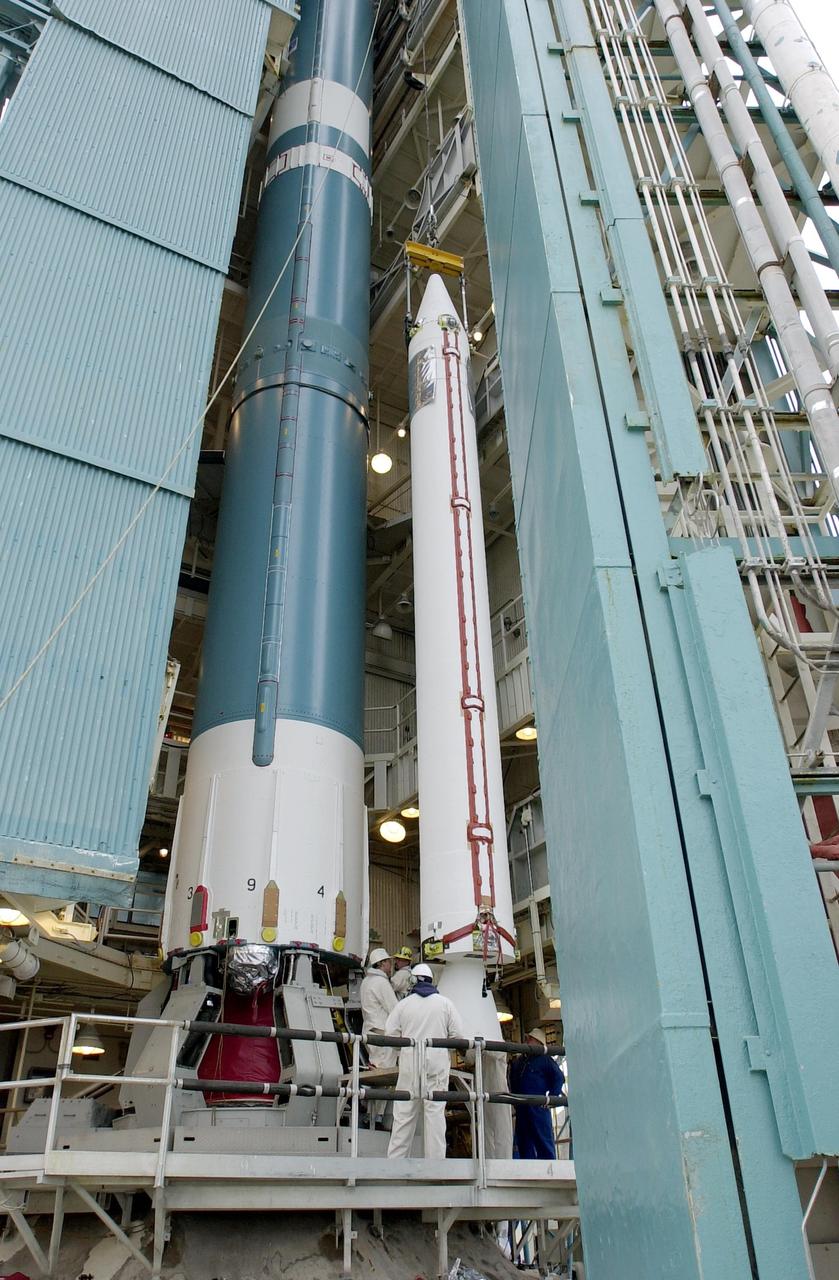
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The interstage of the Delta II rocket is lifted up the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The interstage will eventually house the second stage and will be mated with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
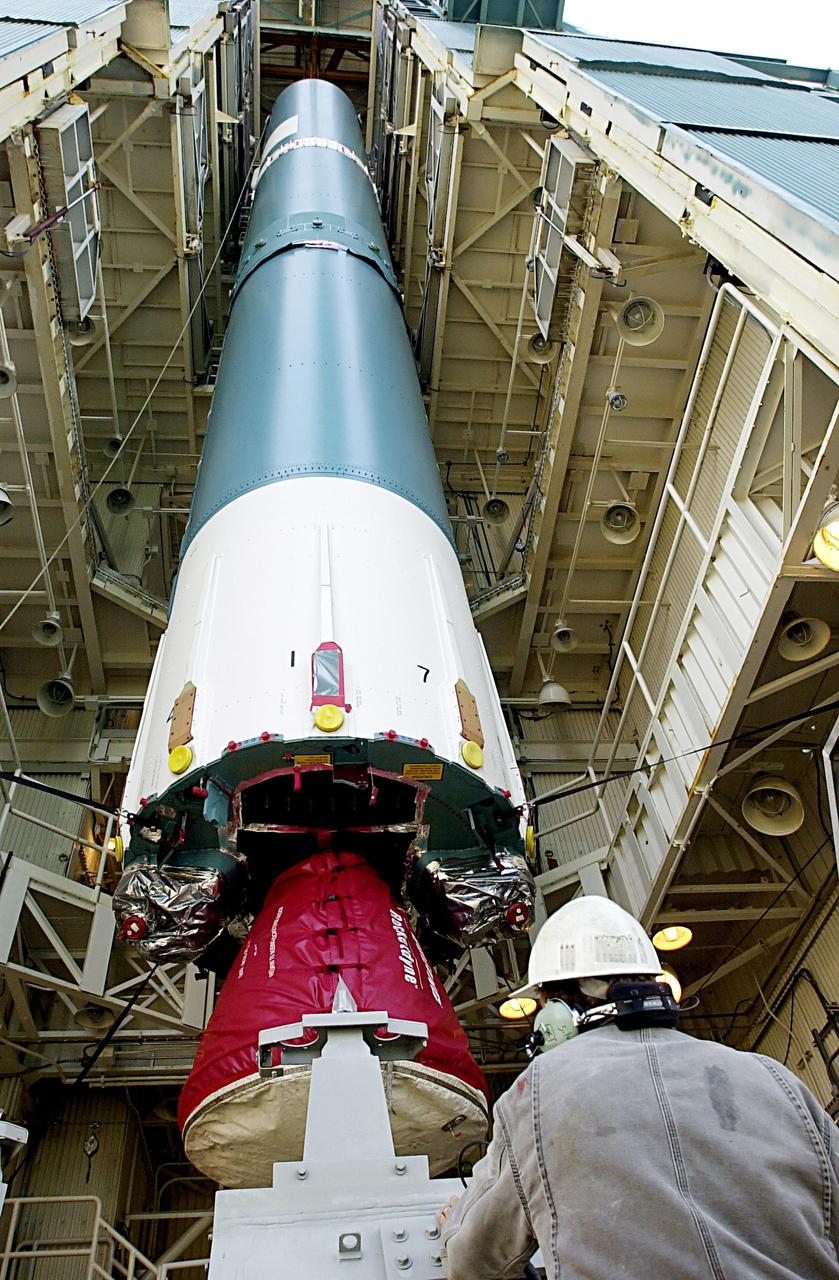

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first stage of the Delta II rocket is moved into place in the tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
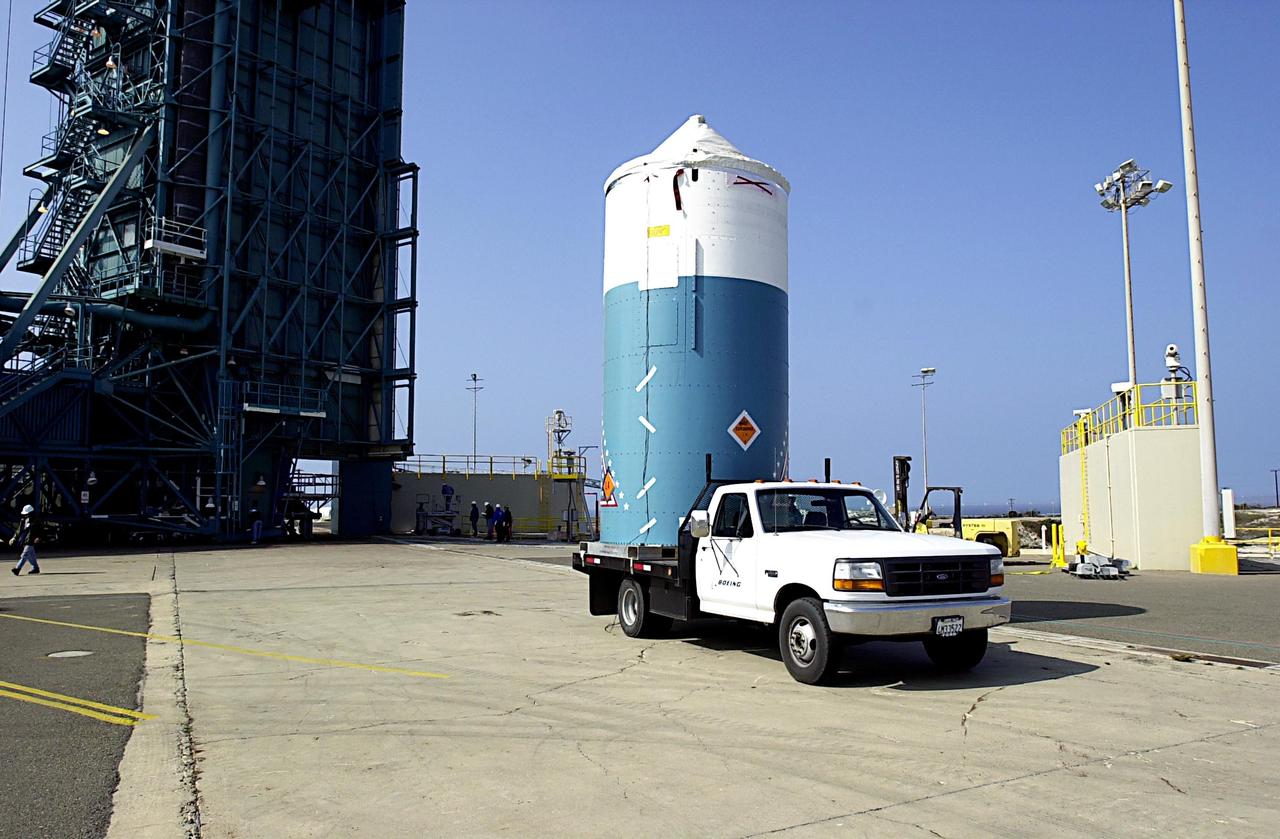

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The interstage of the Delta II rocket arrives at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
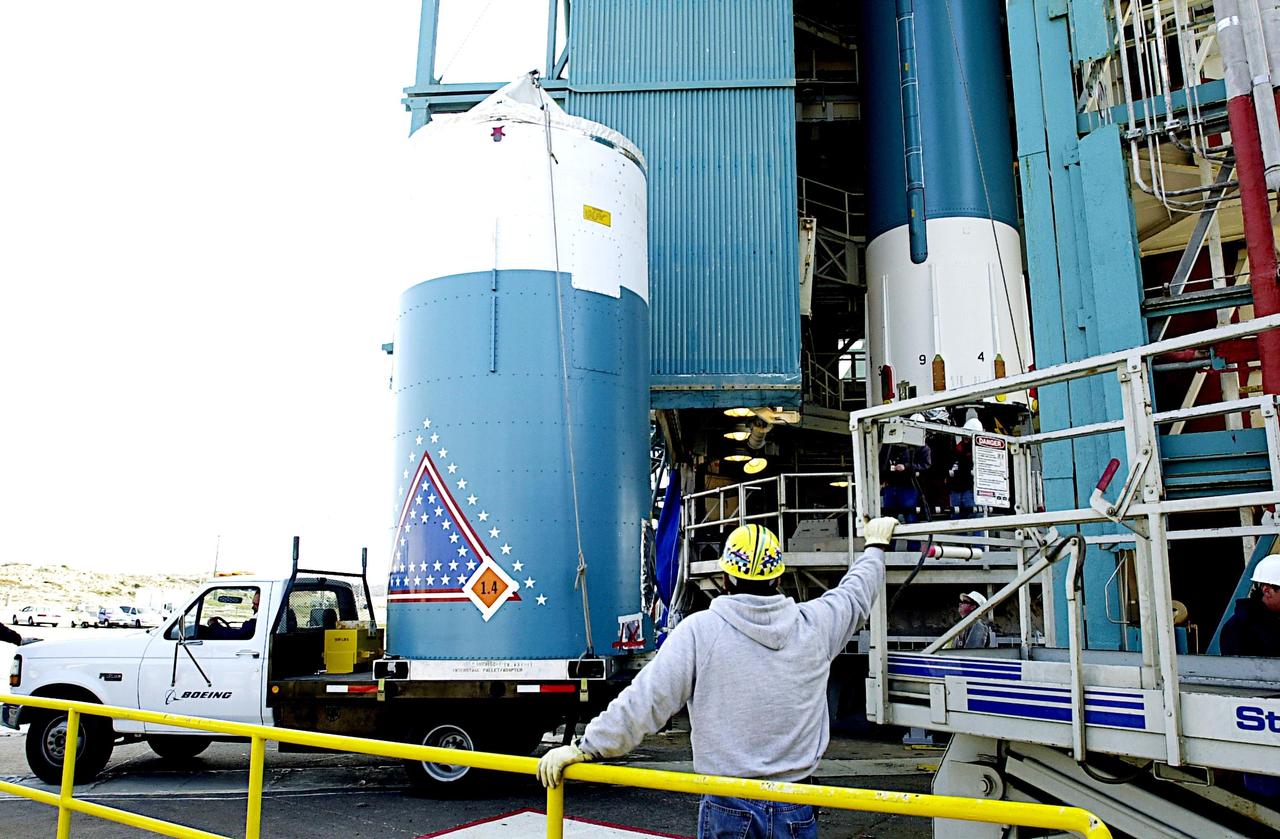

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., the interstage of the Delta II rocket is ready to be lifted up the tower for mating with the first stage (seen behind it). The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
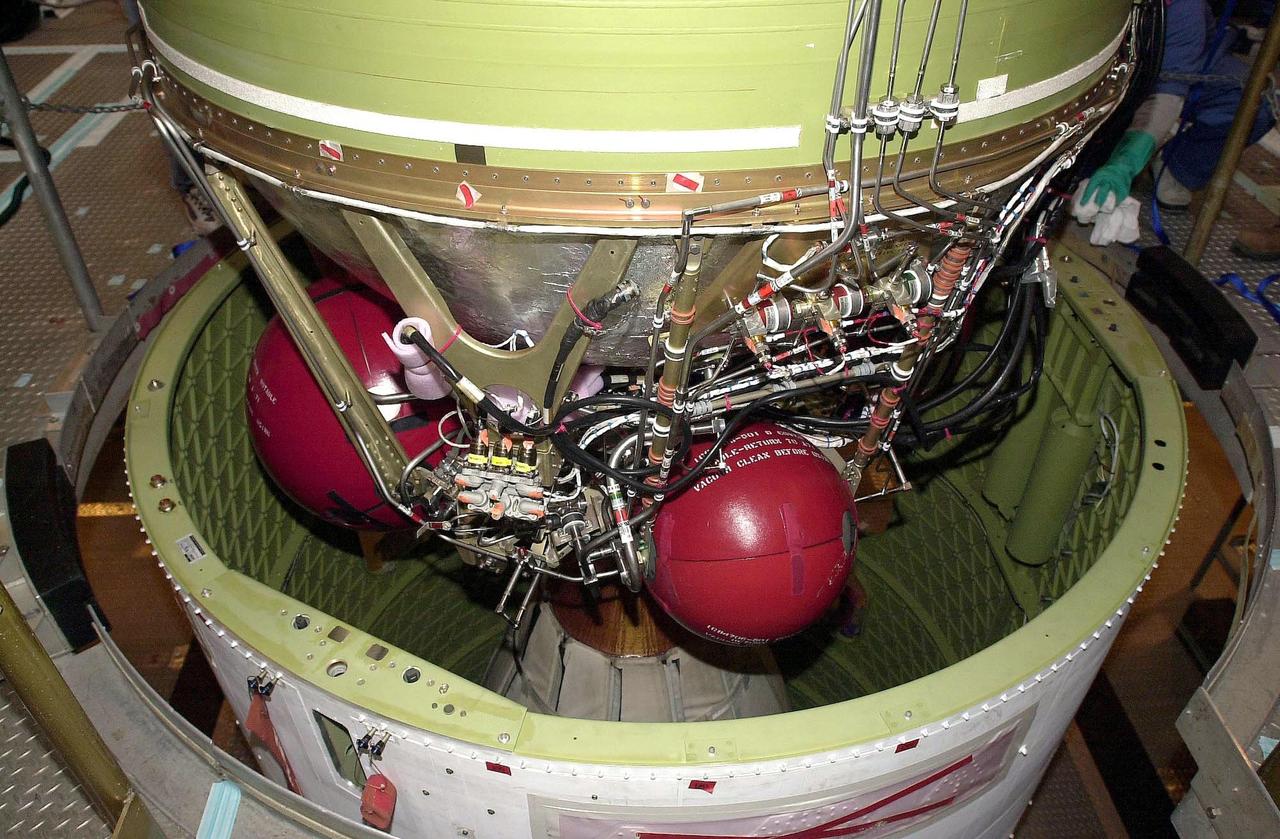
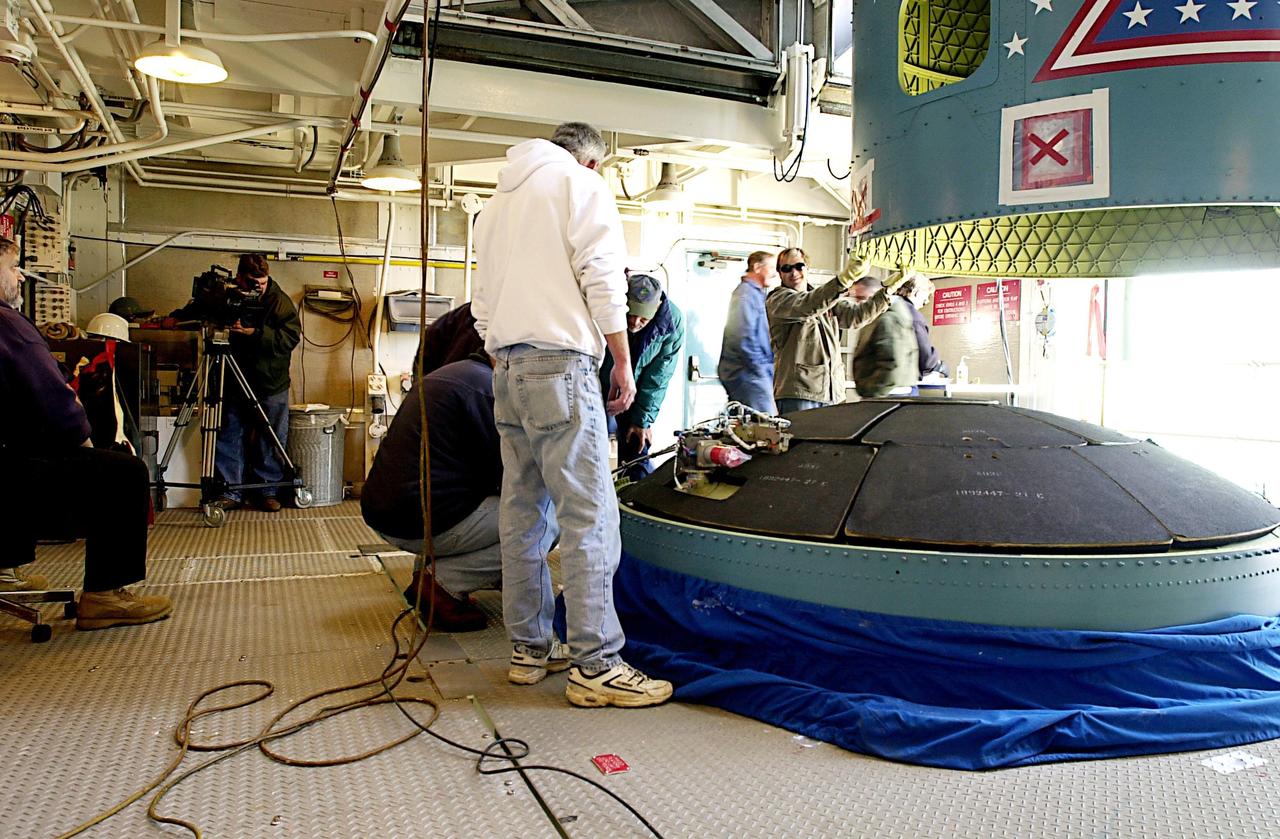
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A second stage is inserted into an interstage atop a Delta II rocket at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat, is a 661-pound satellite carrying the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer, or CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11, 2003, between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
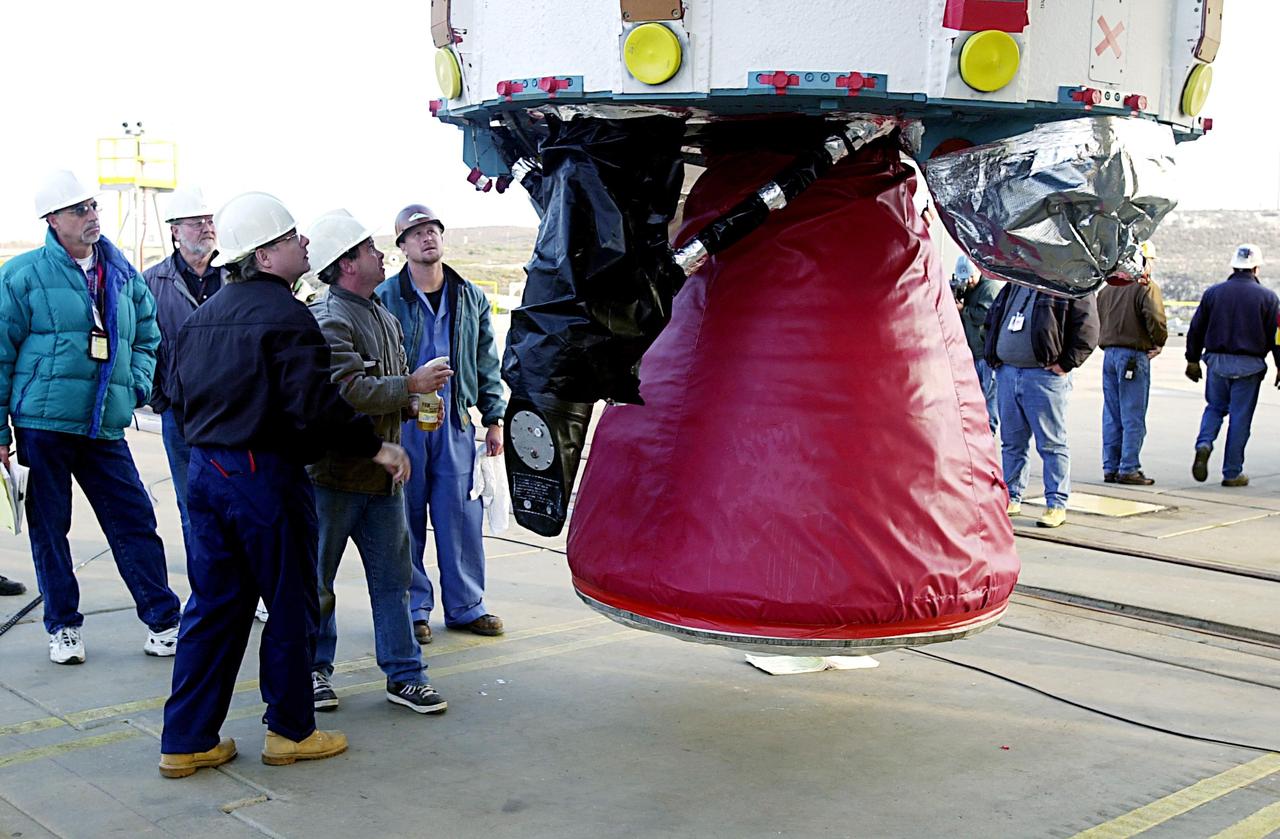

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With the transporter moved from below, the first stage of the Delta II rocket is suspended in air waiting to be lifted up the tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
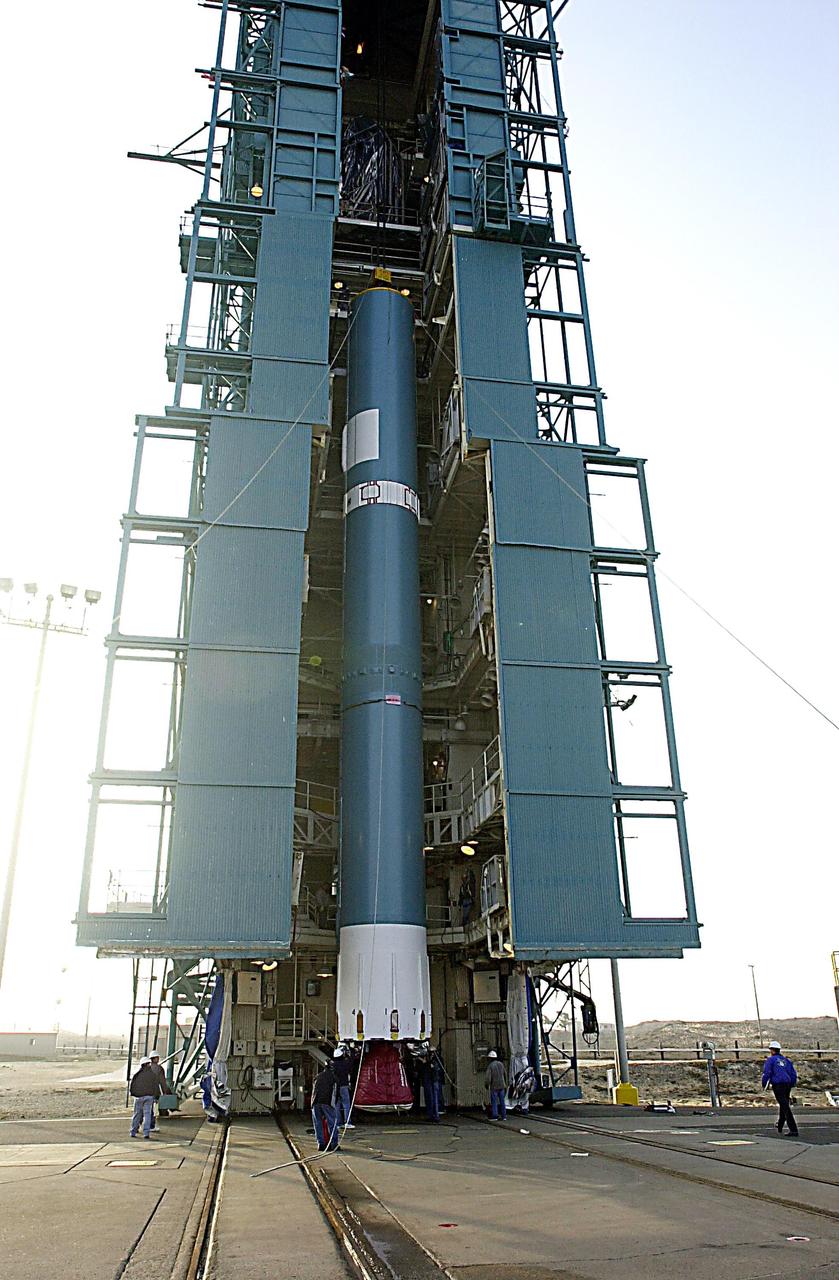

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first stage of the Delta II rocket is ready to be lifted up the tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
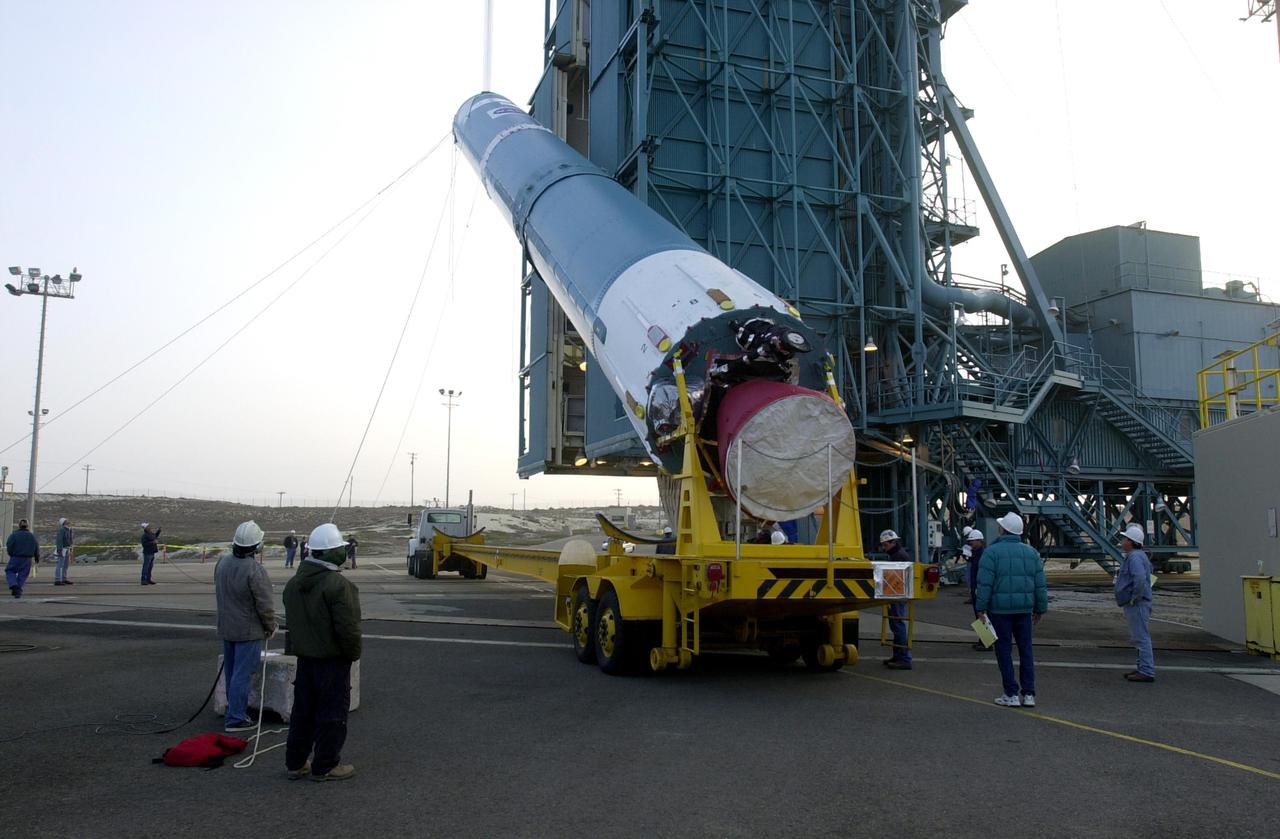

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., watch as the first stage of the Delta II rocket is raised to a vertical position. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
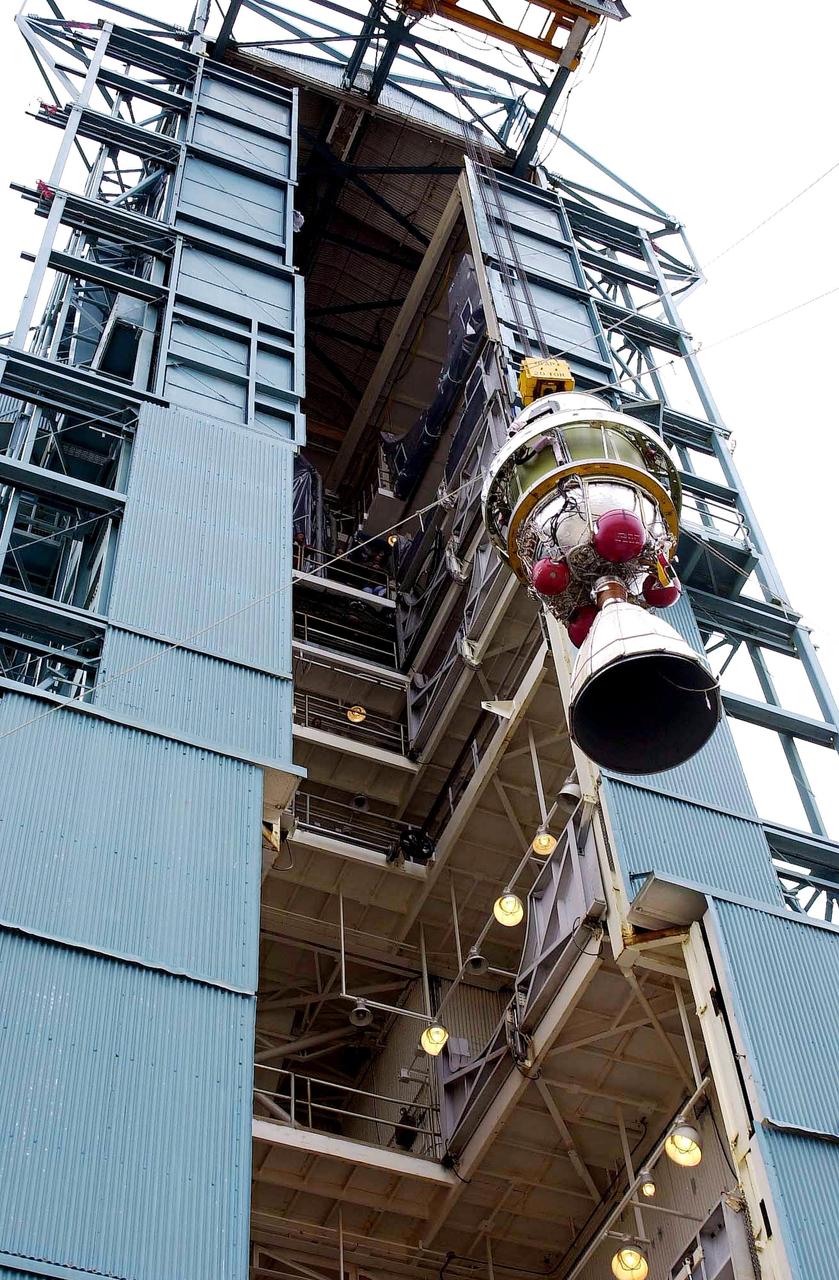

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A second stage is lifted at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., for placement atop a Delta II rocket. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat, is a 661-pound satellite carrying the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer, or CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11, 2003, between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
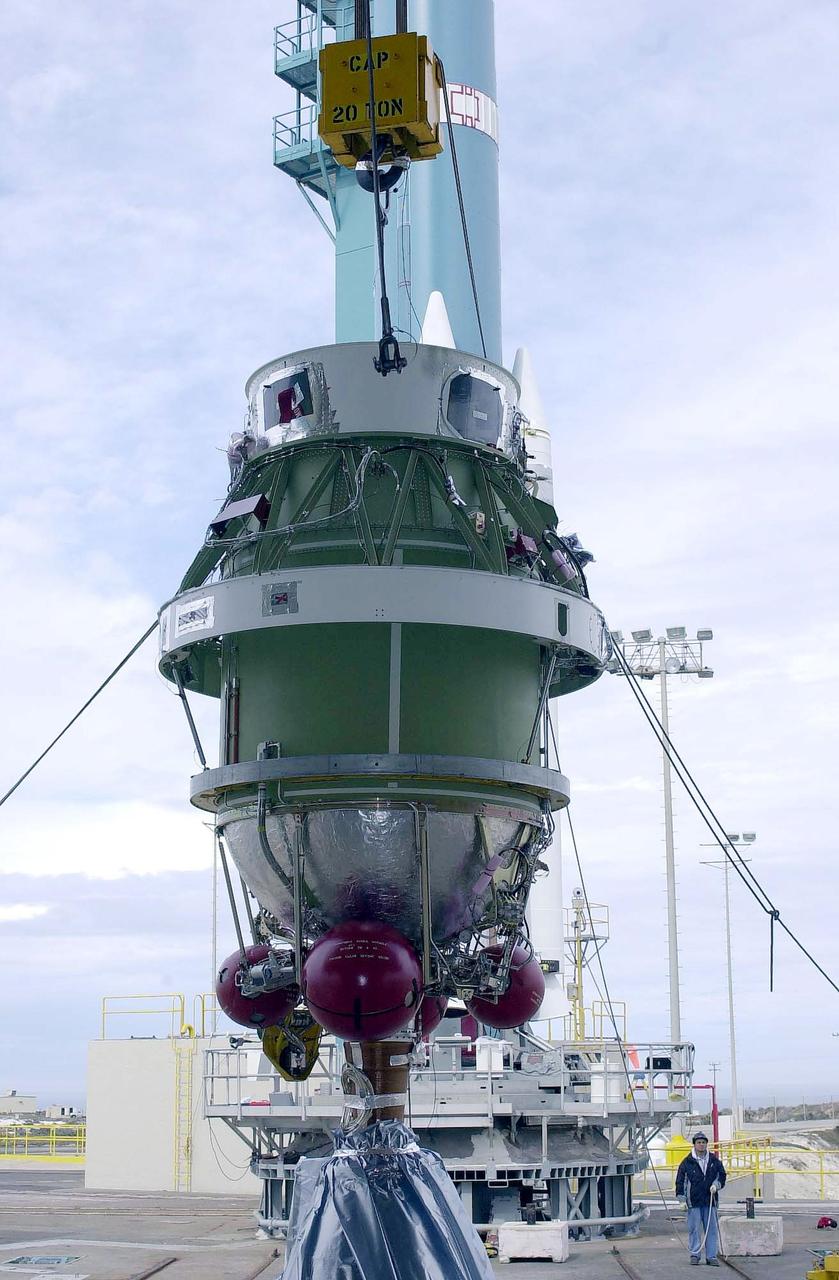

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A second stage is lifted at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., for placement on a Delta II rocket The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat, is a 661-pound satellite carrying the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer, or CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11, 2003, between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
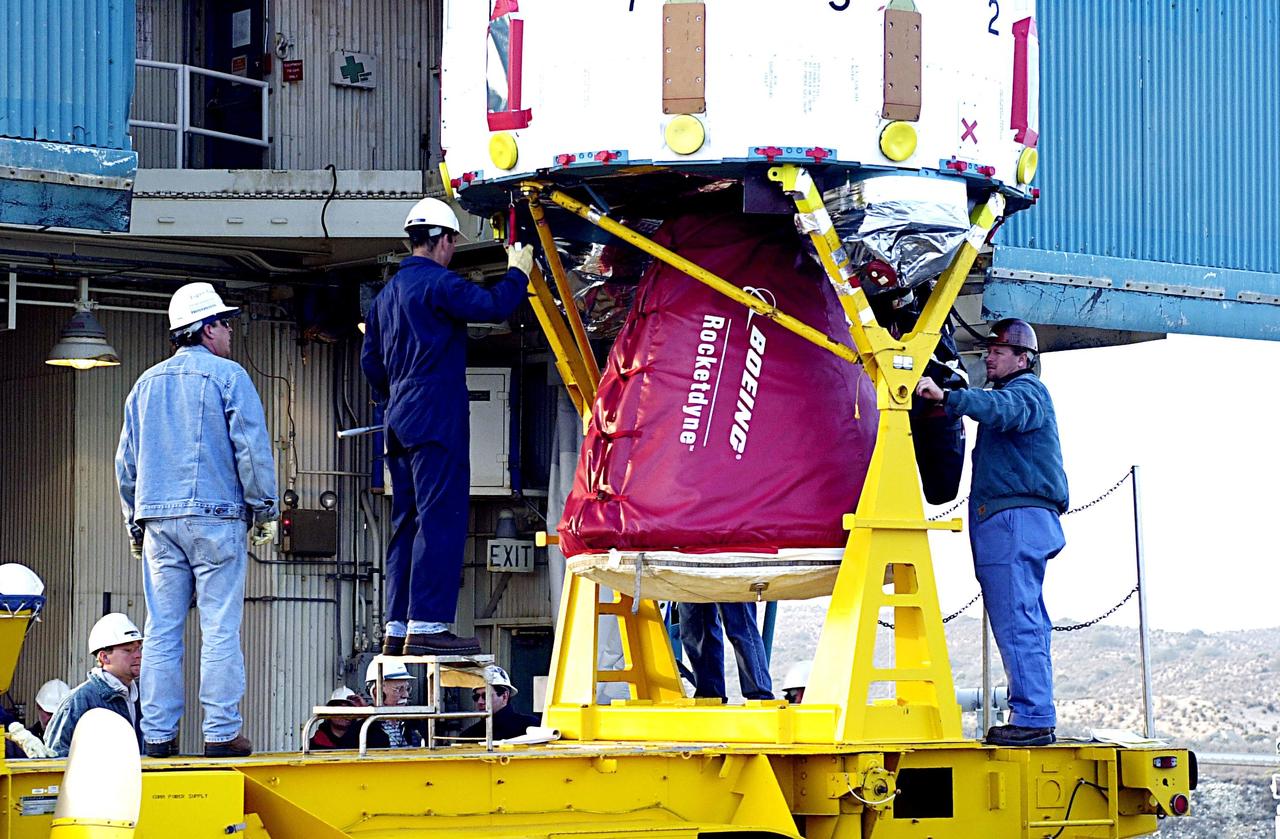

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers check the lower end of the first stage of the Delta II rocket before it is lifted up the tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.