
The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft roll out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first time on March 17, 2022.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft roll out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first time on March 17, 2022.
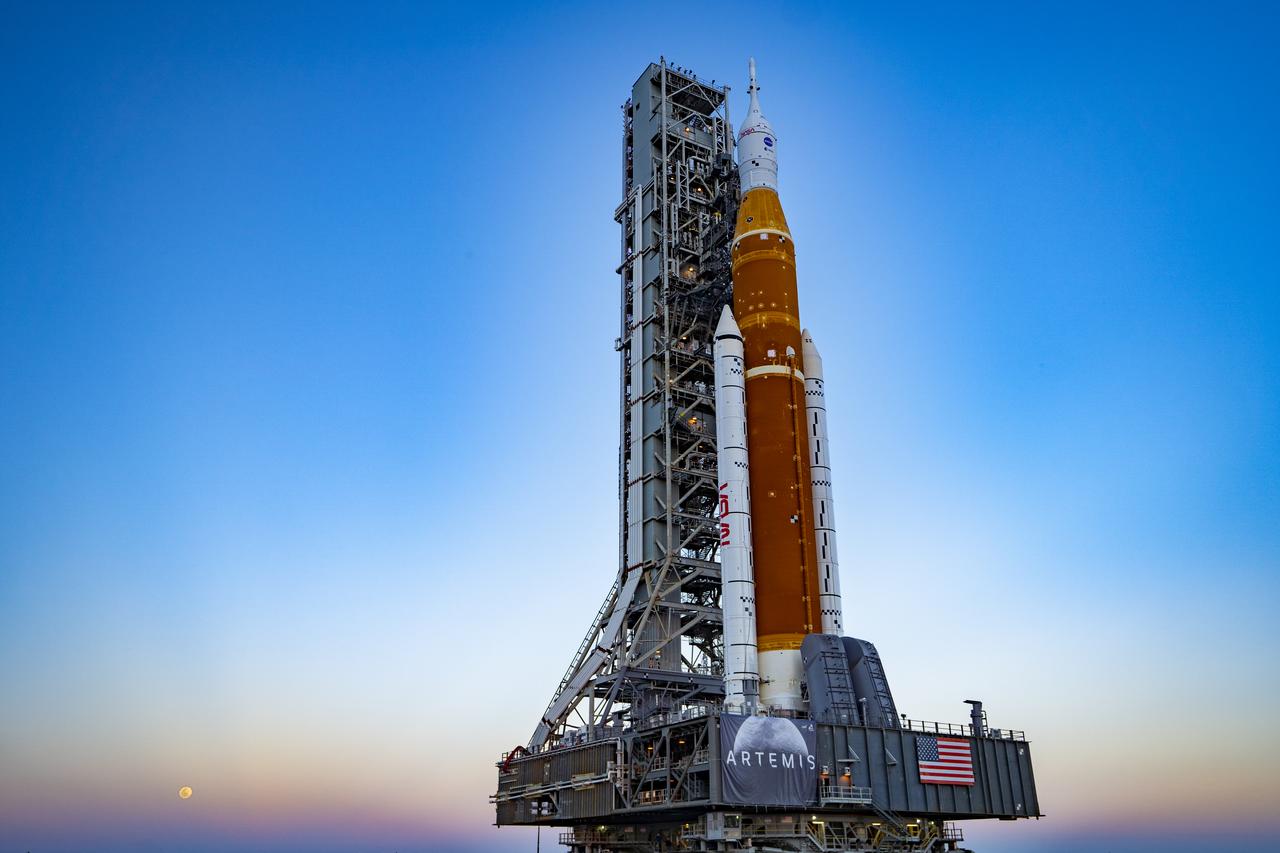

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
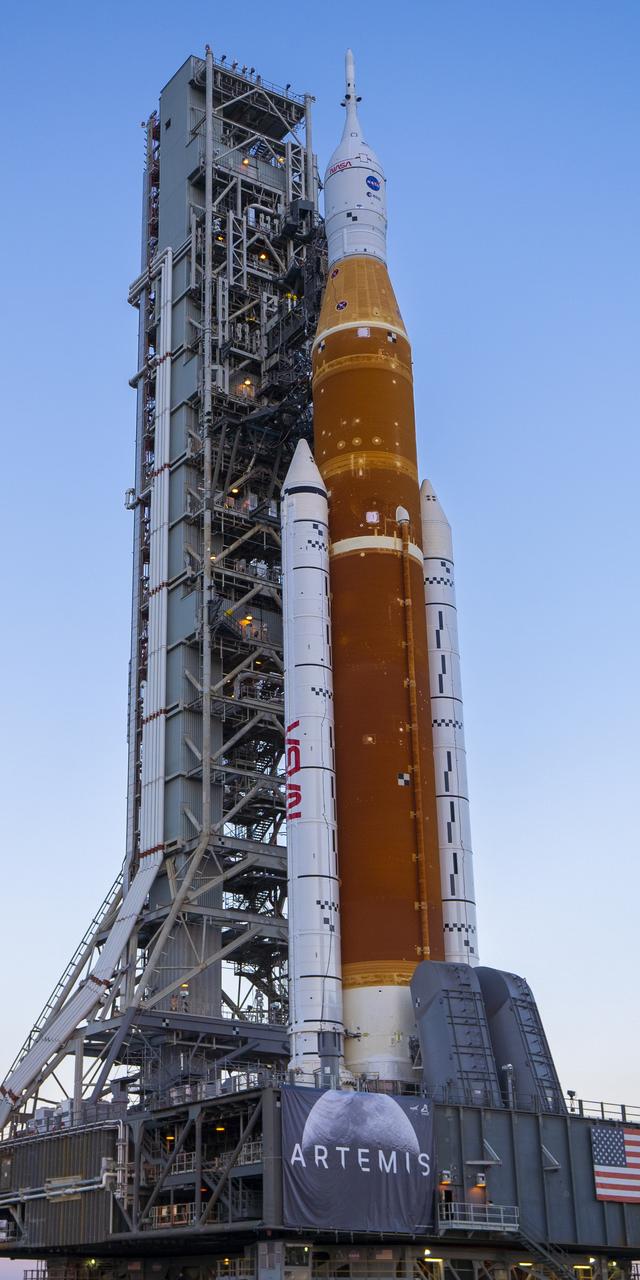

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
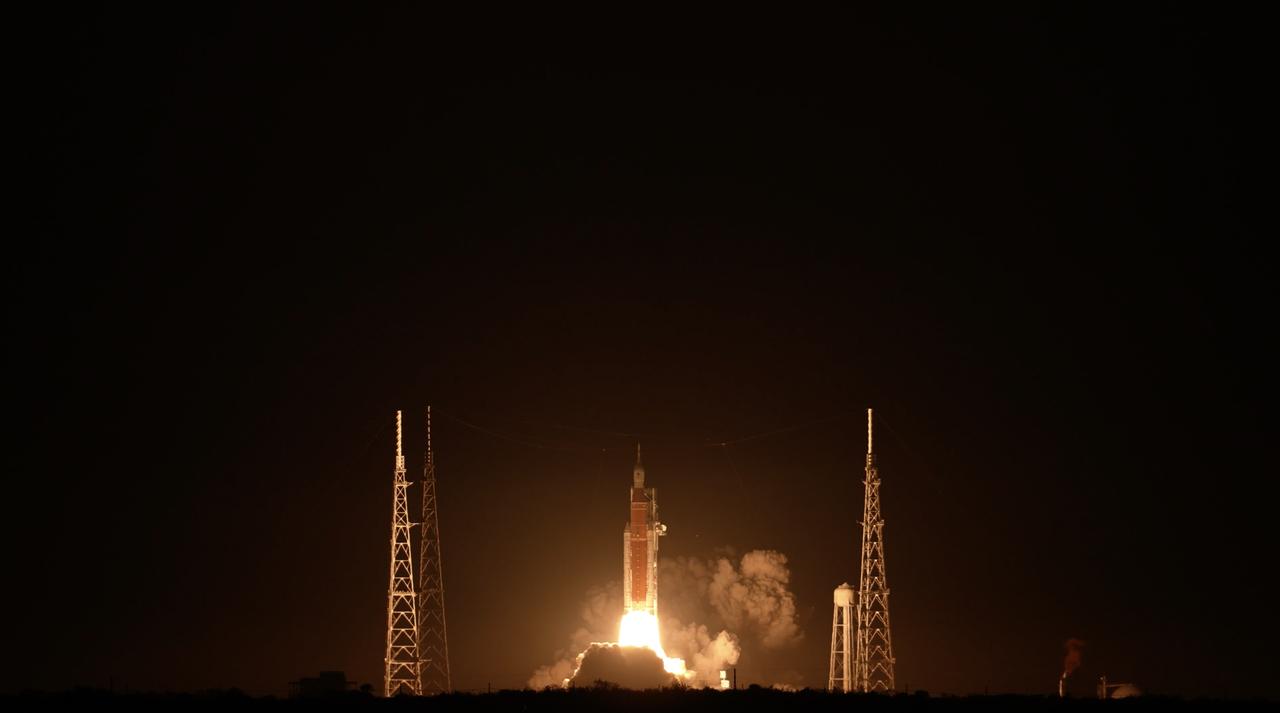

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
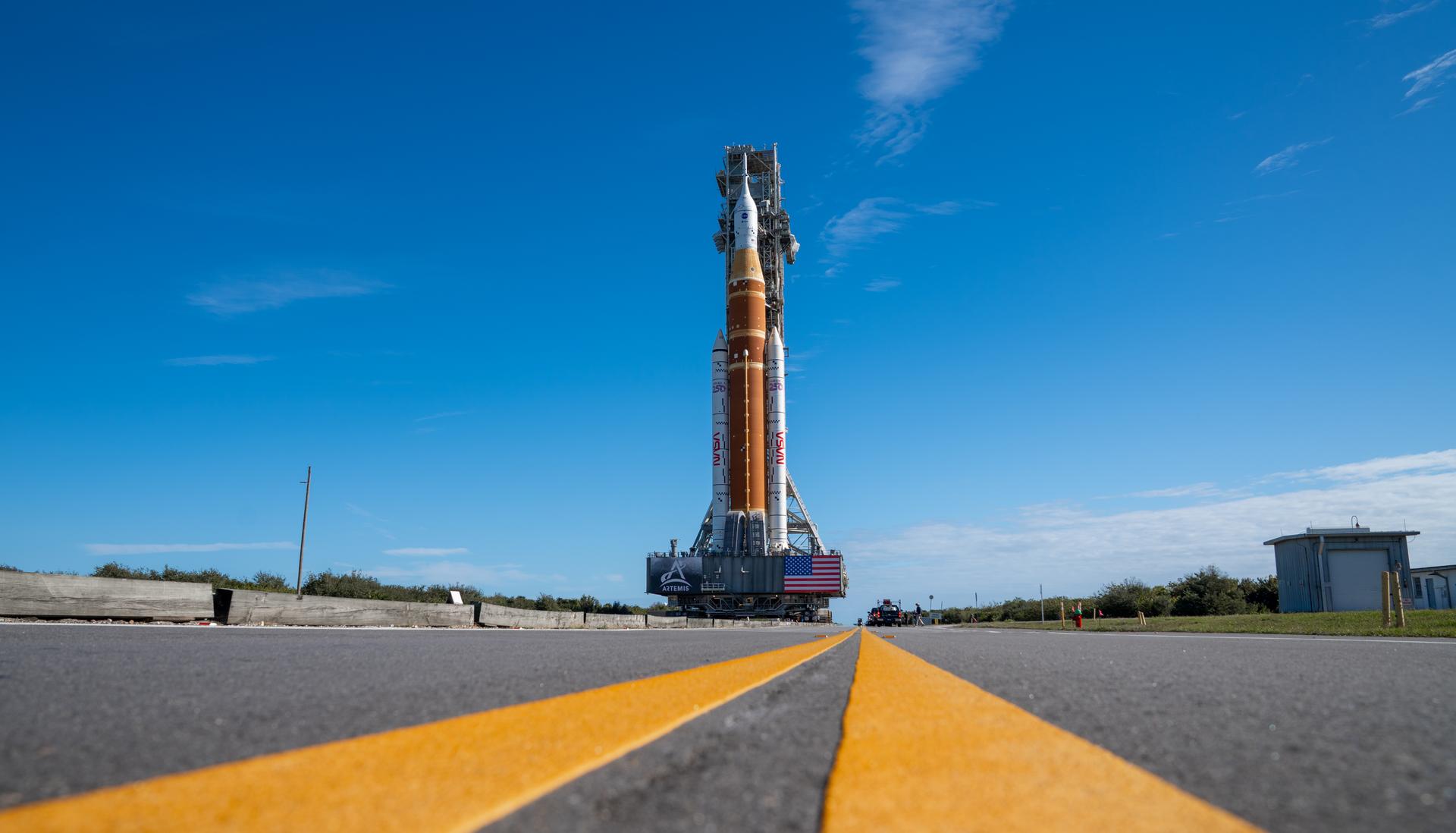

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
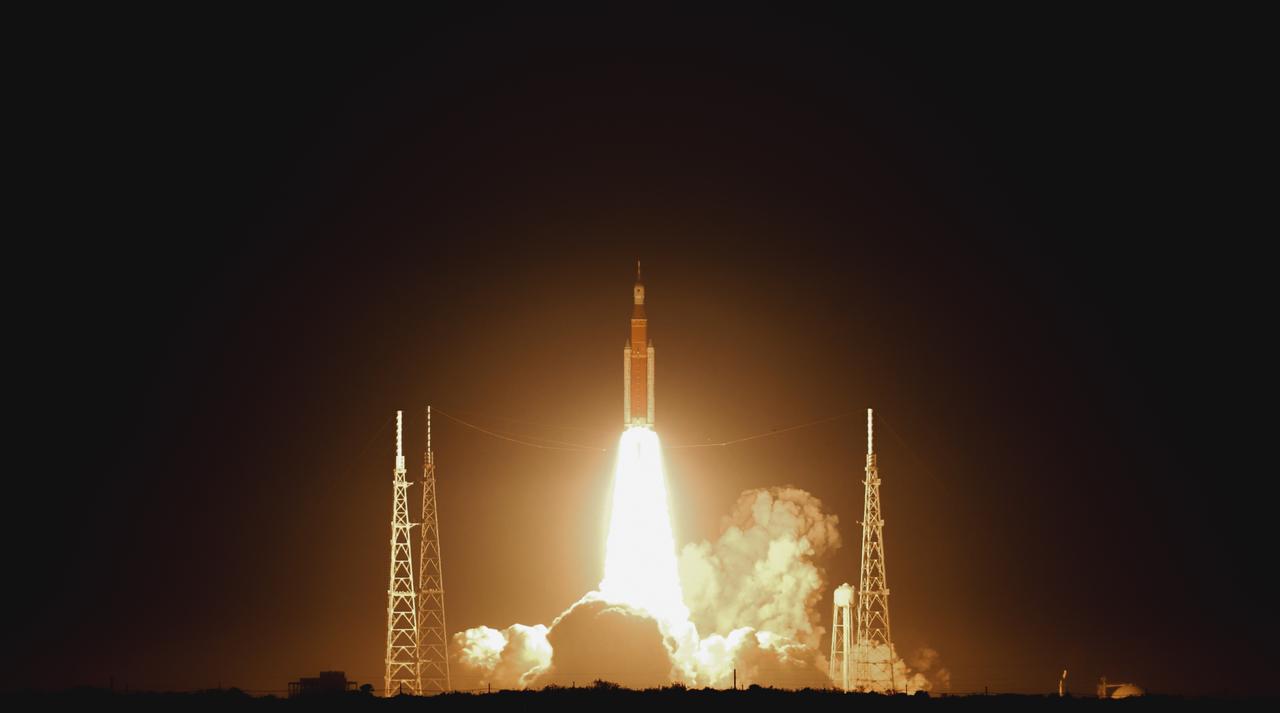

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
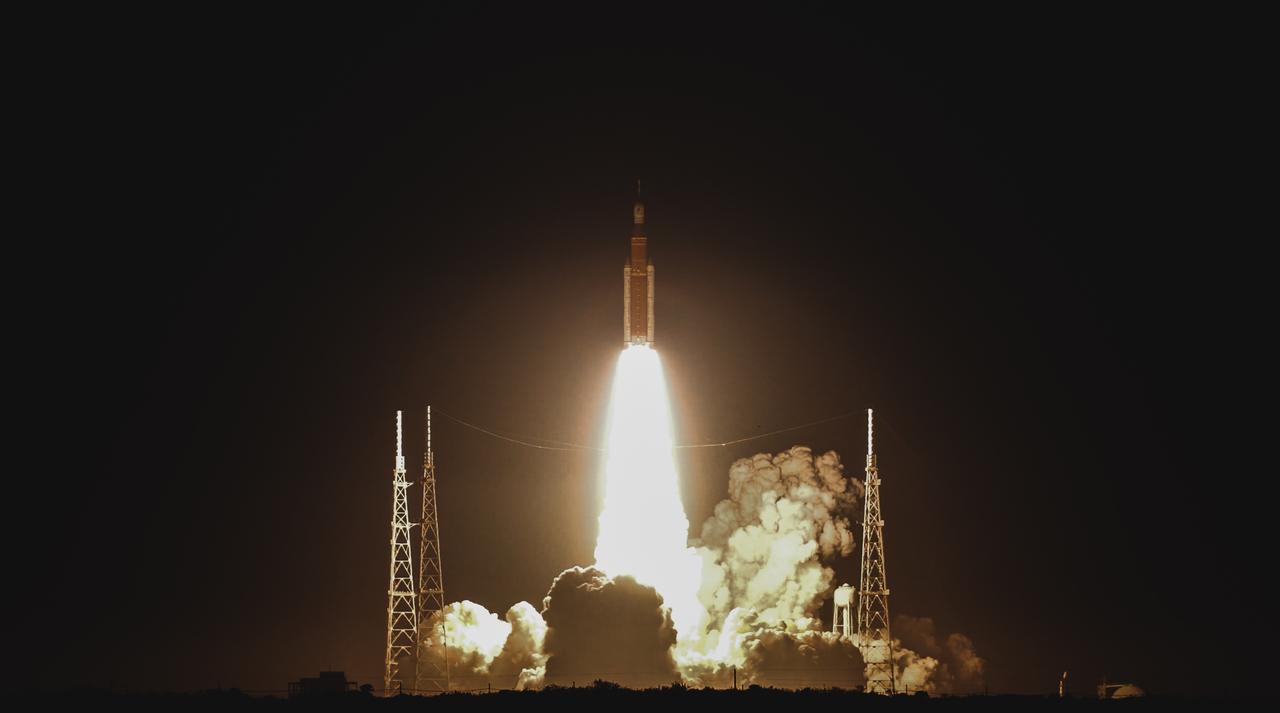

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
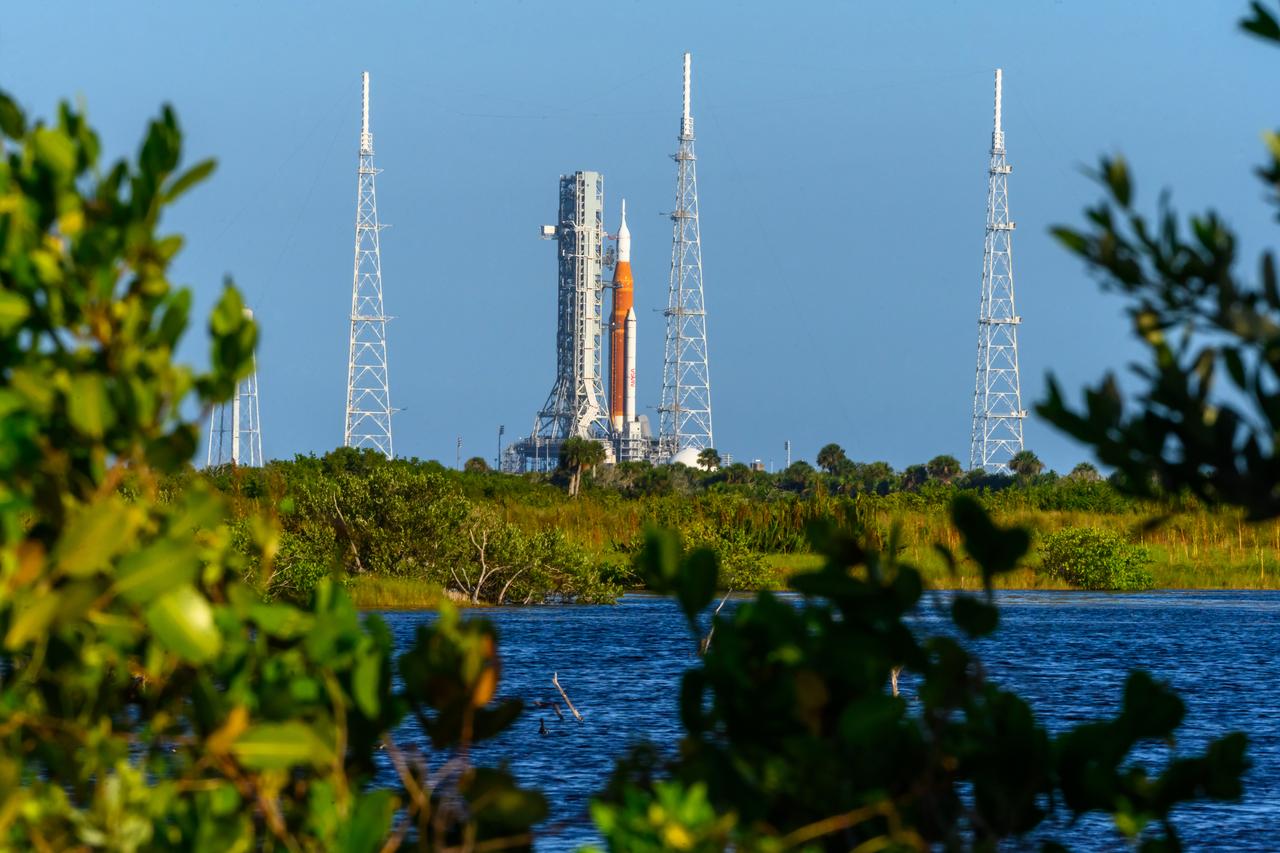

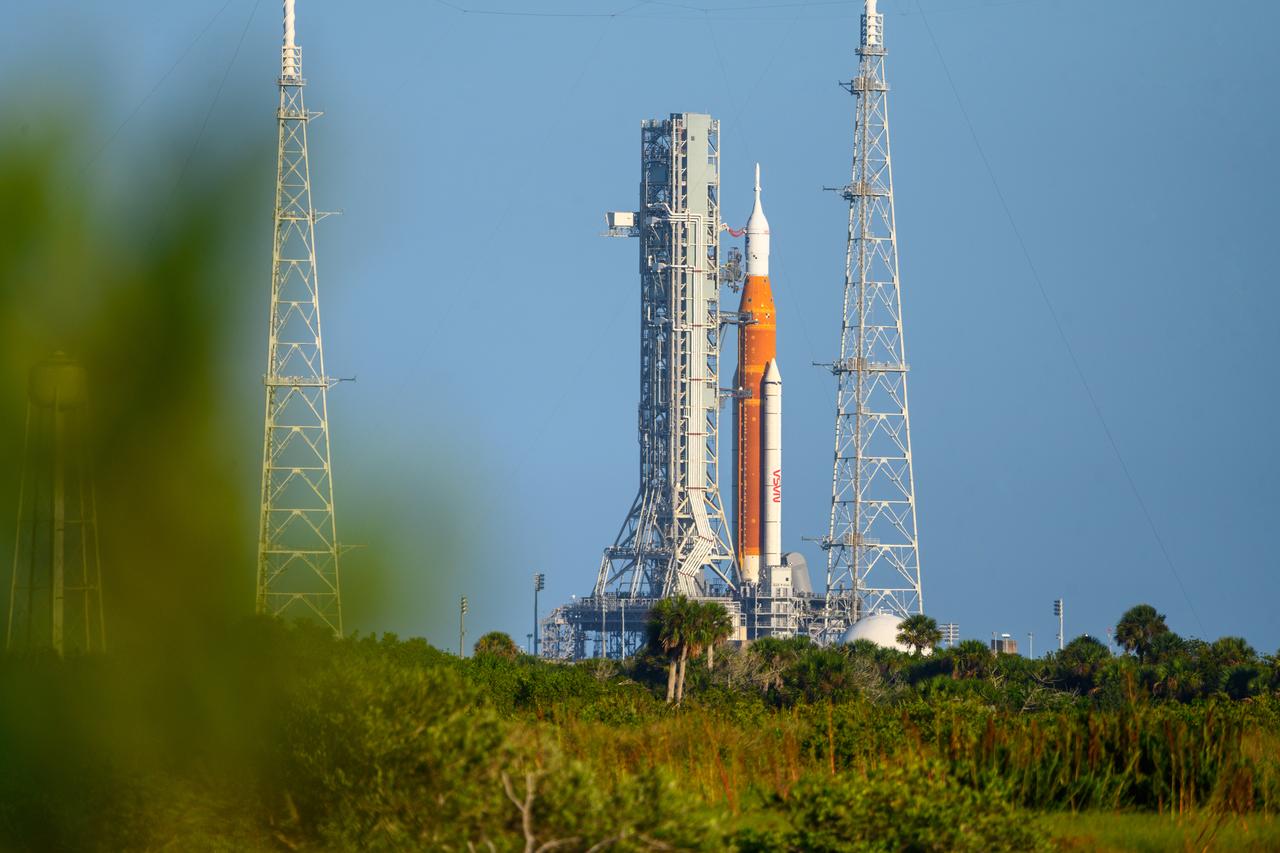
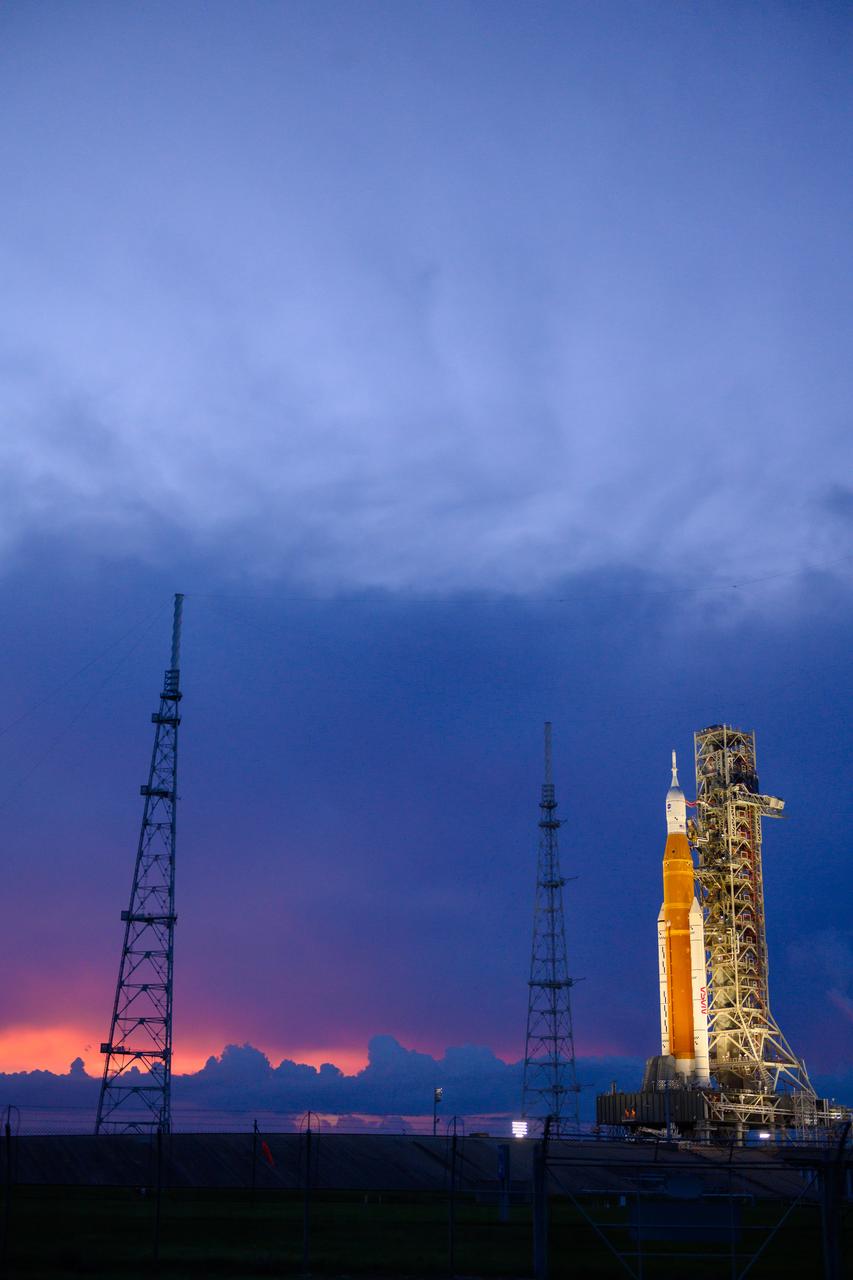
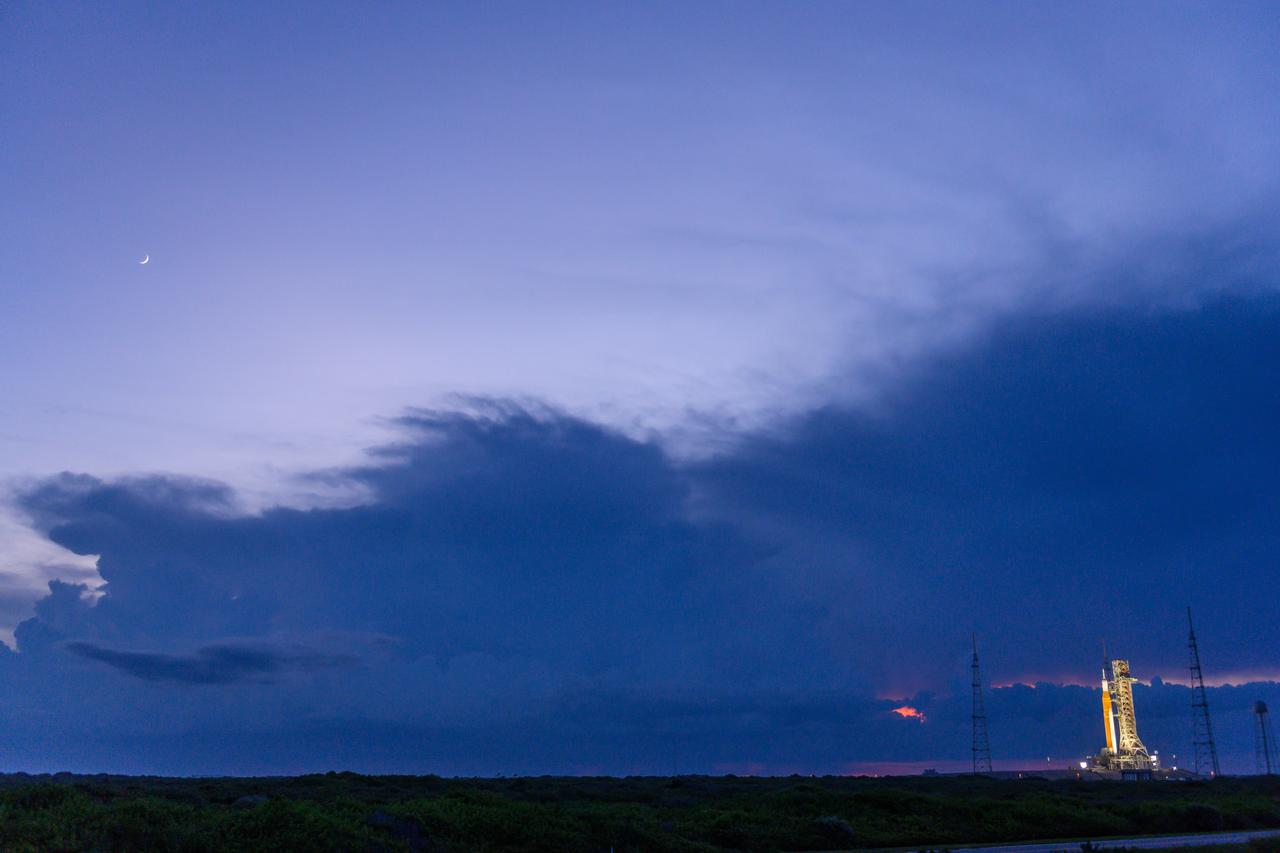
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
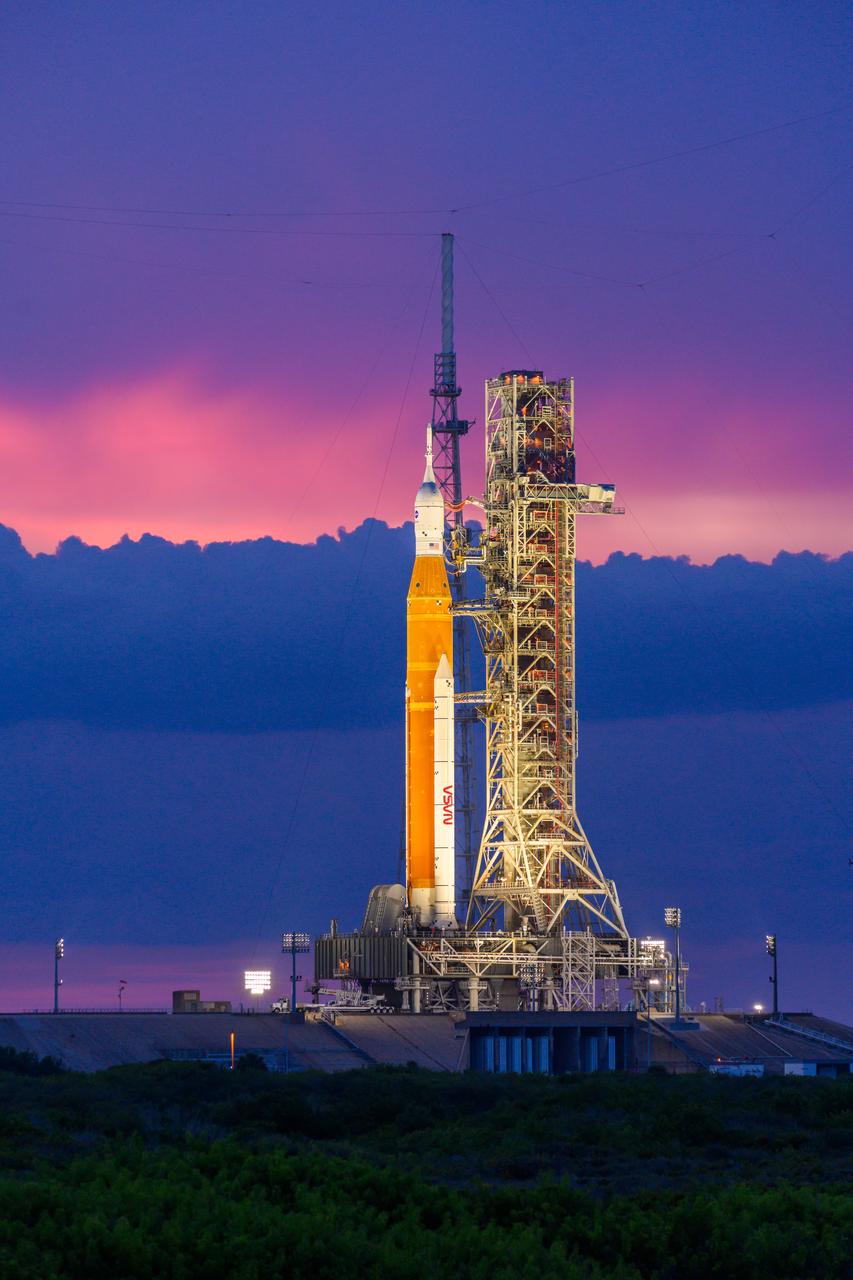

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
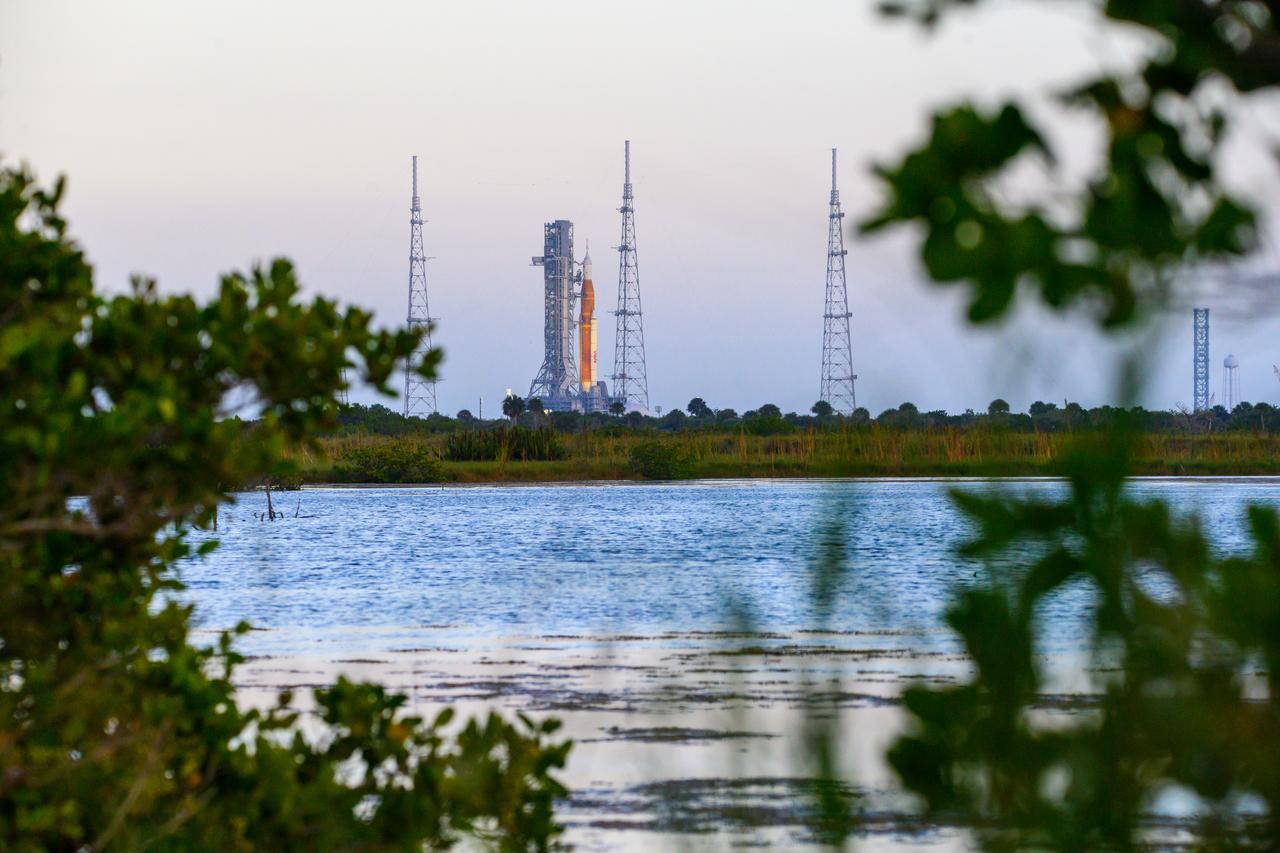

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
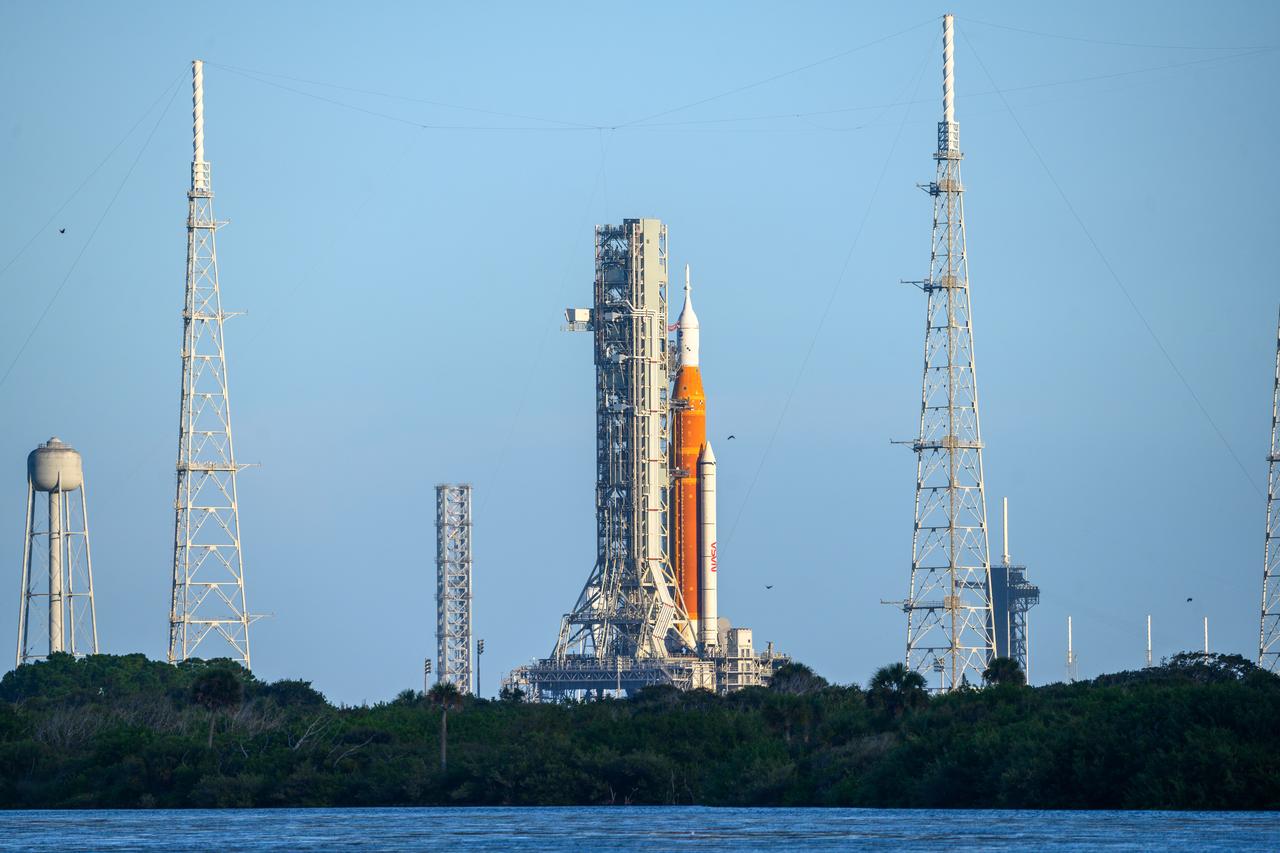

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
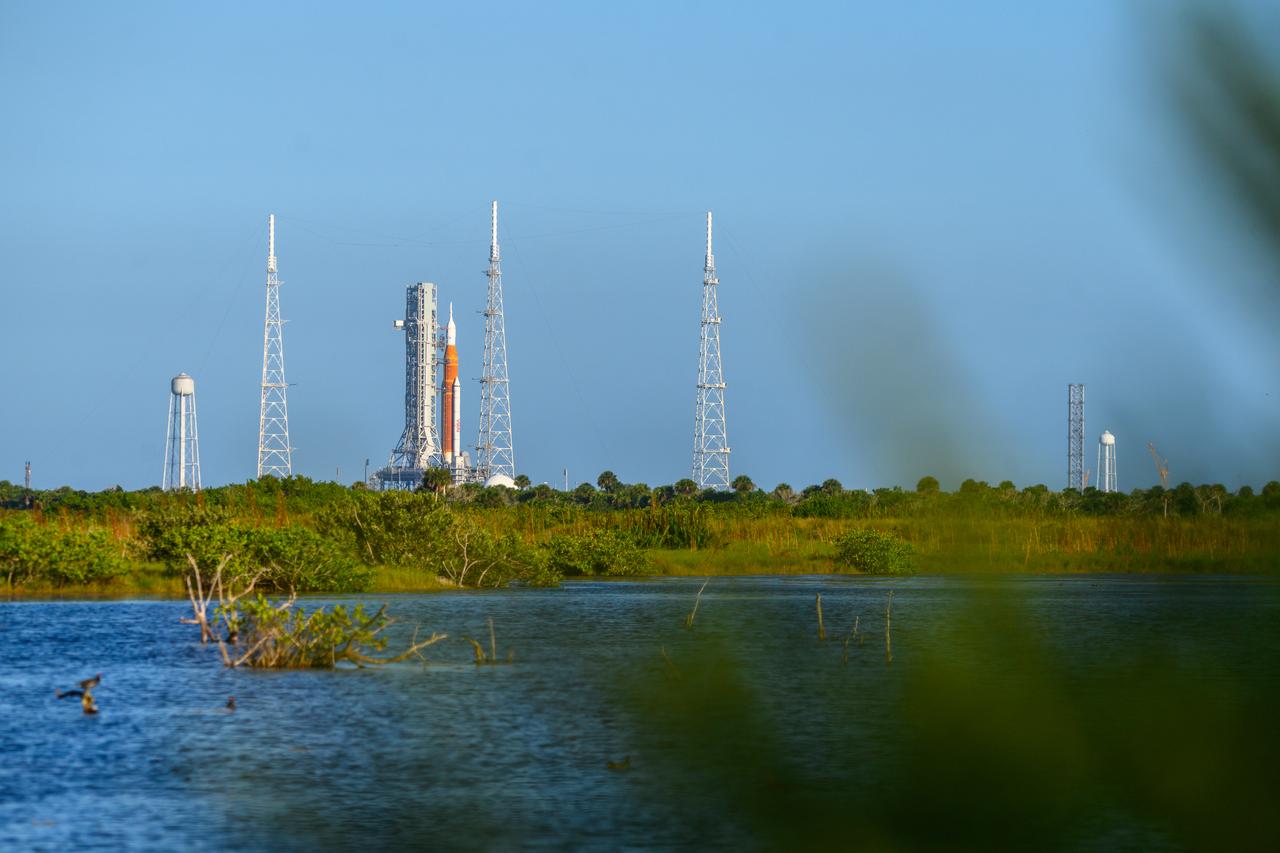

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
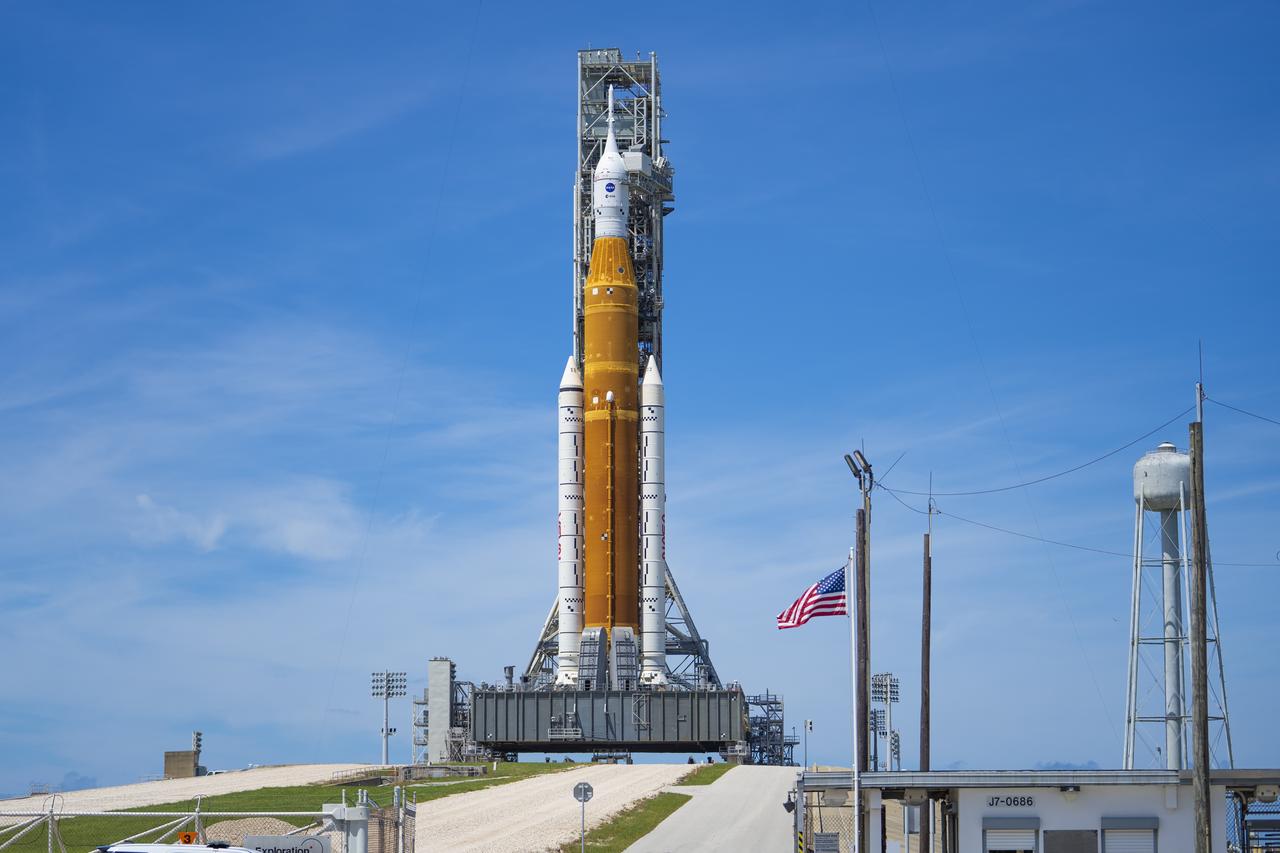

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
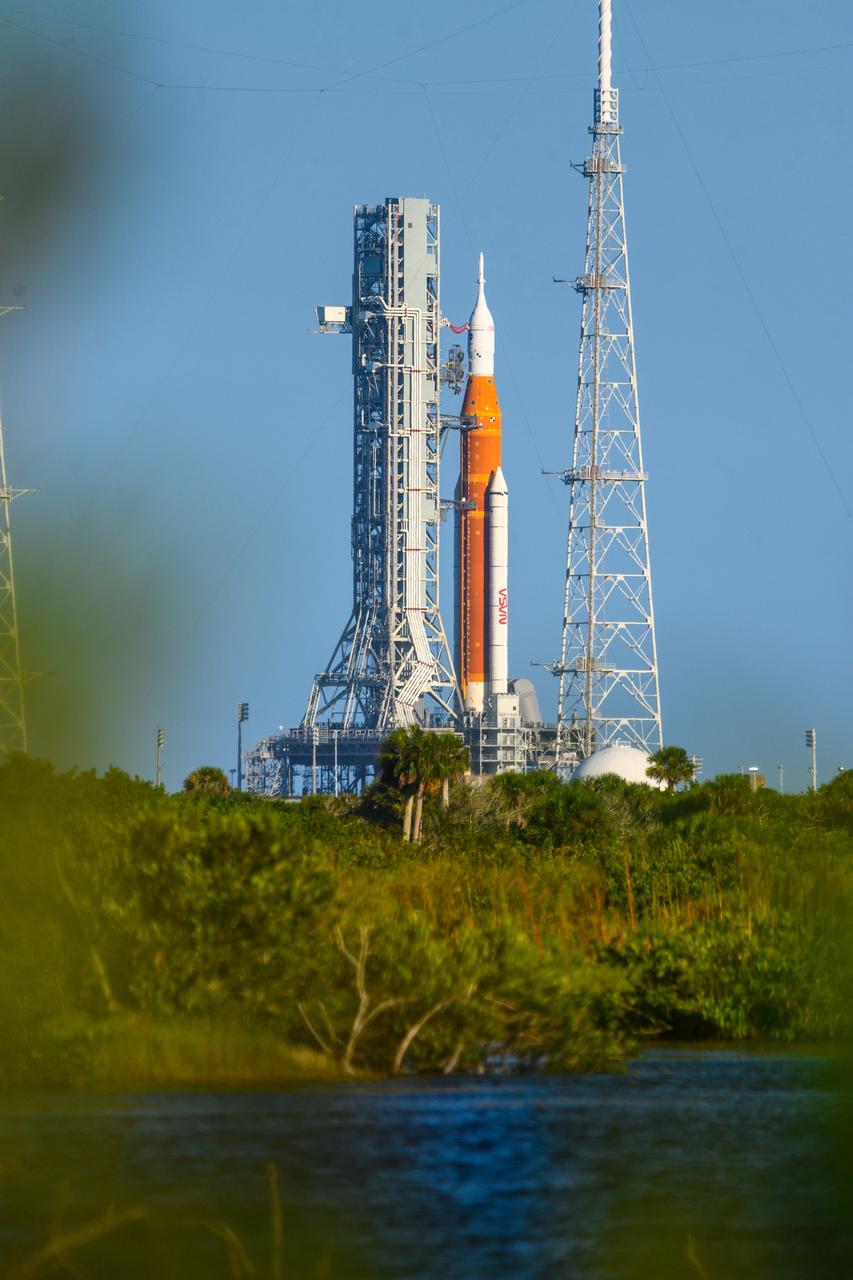

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
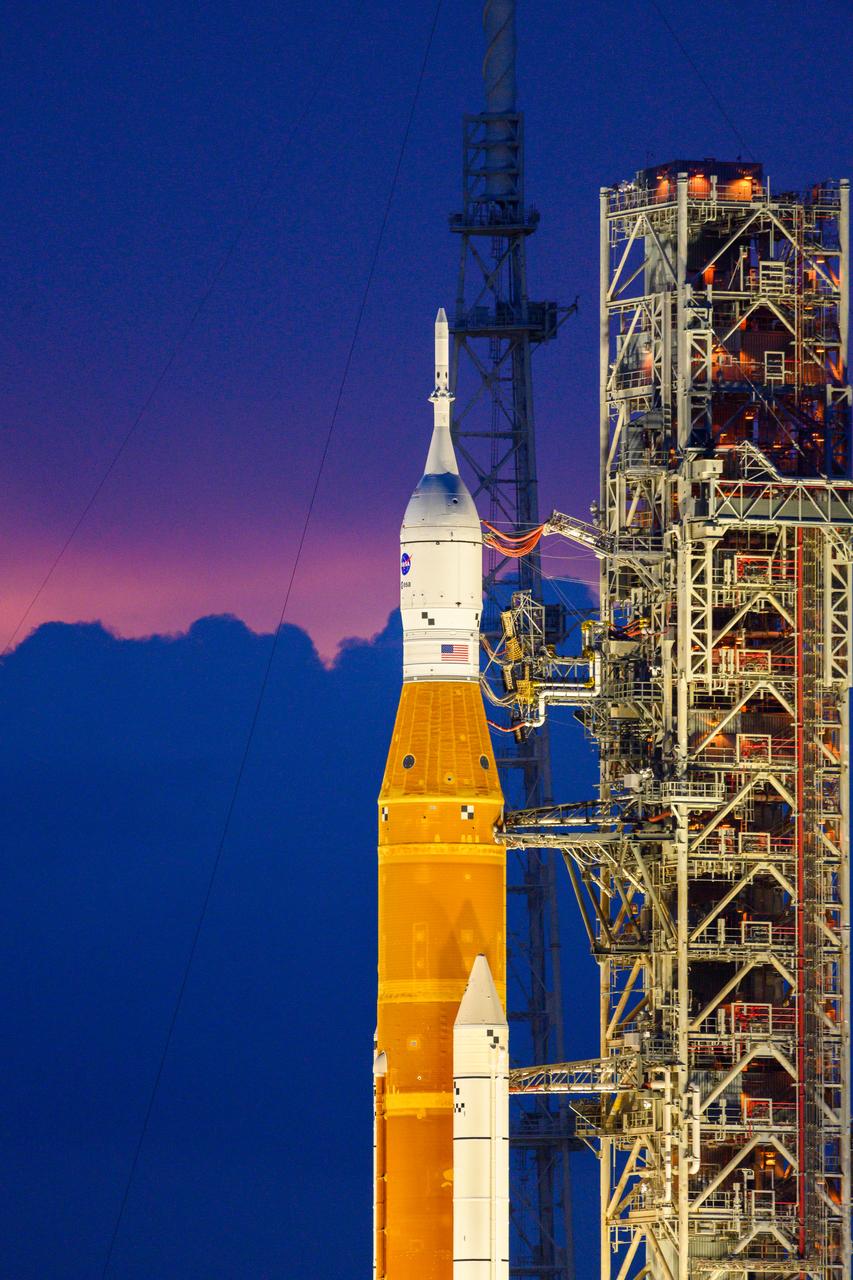

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
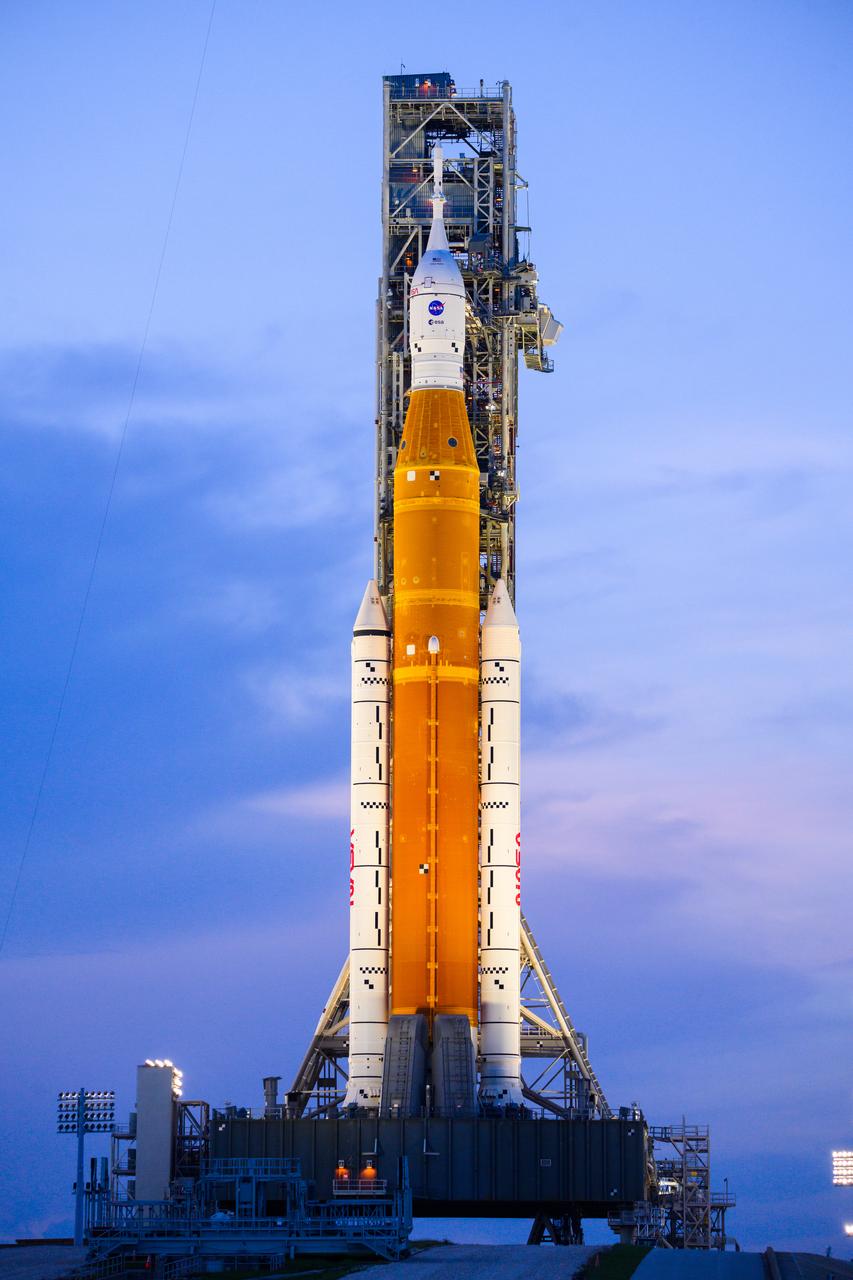

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
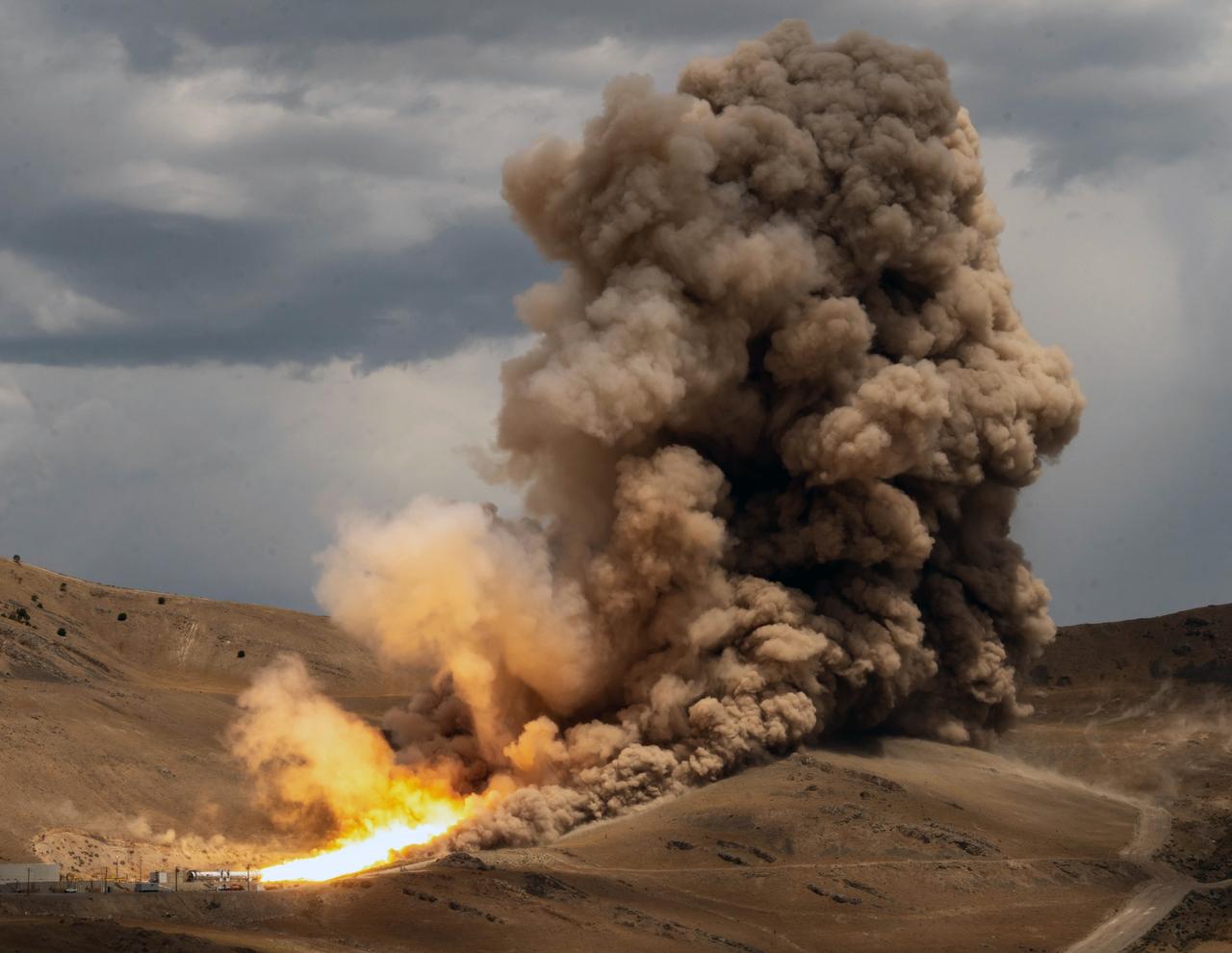

NASA and Northrop Grumman completed a solid rocket booster motor ground test for future flights of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, July 21. The booster motor, called Flight Support Booster-2 (FSB-2), fired for a little over two minutes and produced more than 3.6 million pounds of thrust. Test data will be used to evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters for missions after Artemis III. When SLS launches the Artemis missions to the Moon, its two five-segment solid rocket boosters produce more than 75% of the initial thrust. The SLS boosters are the largest, most powerful boosters ever built for flight. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls
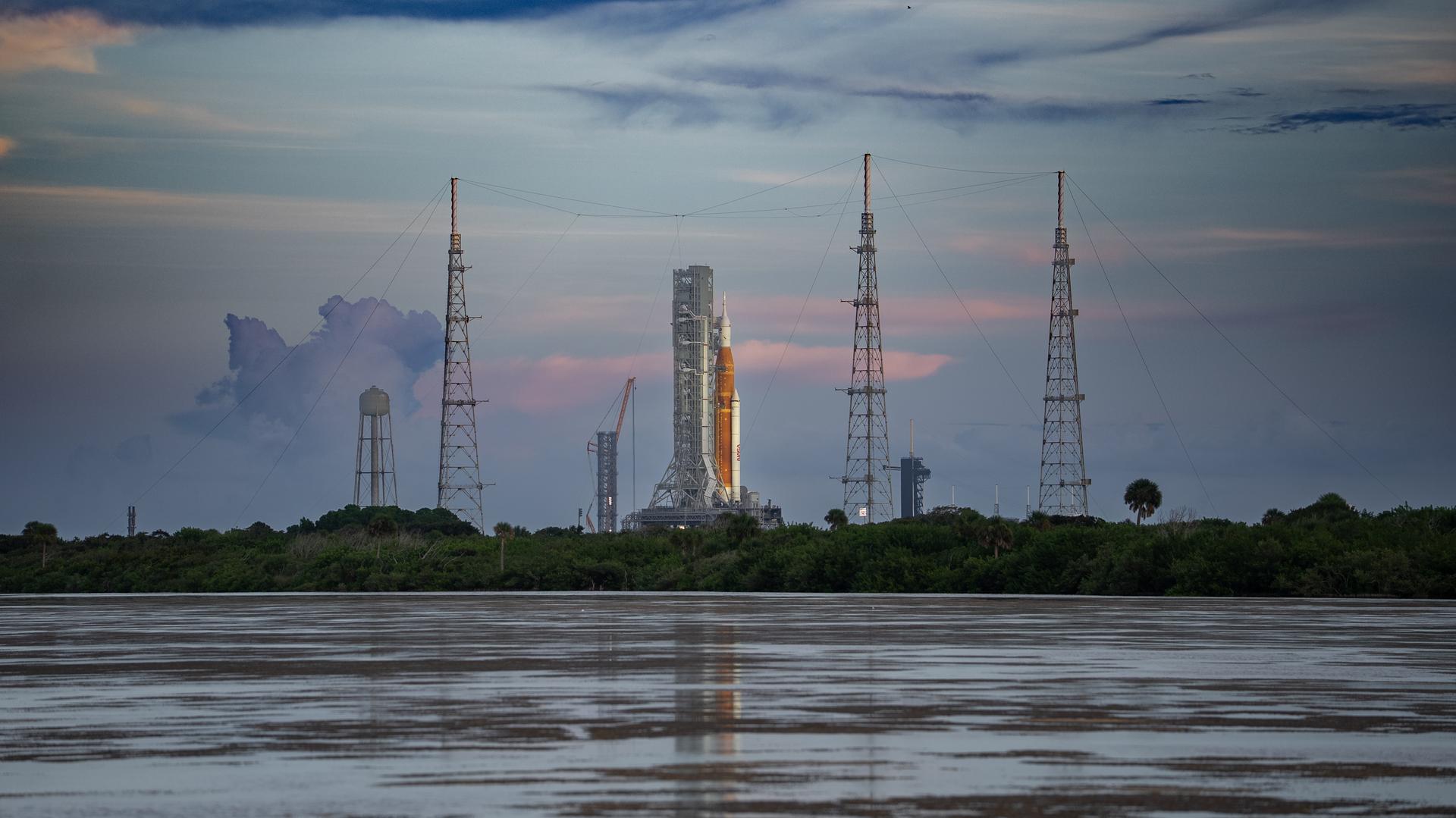

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
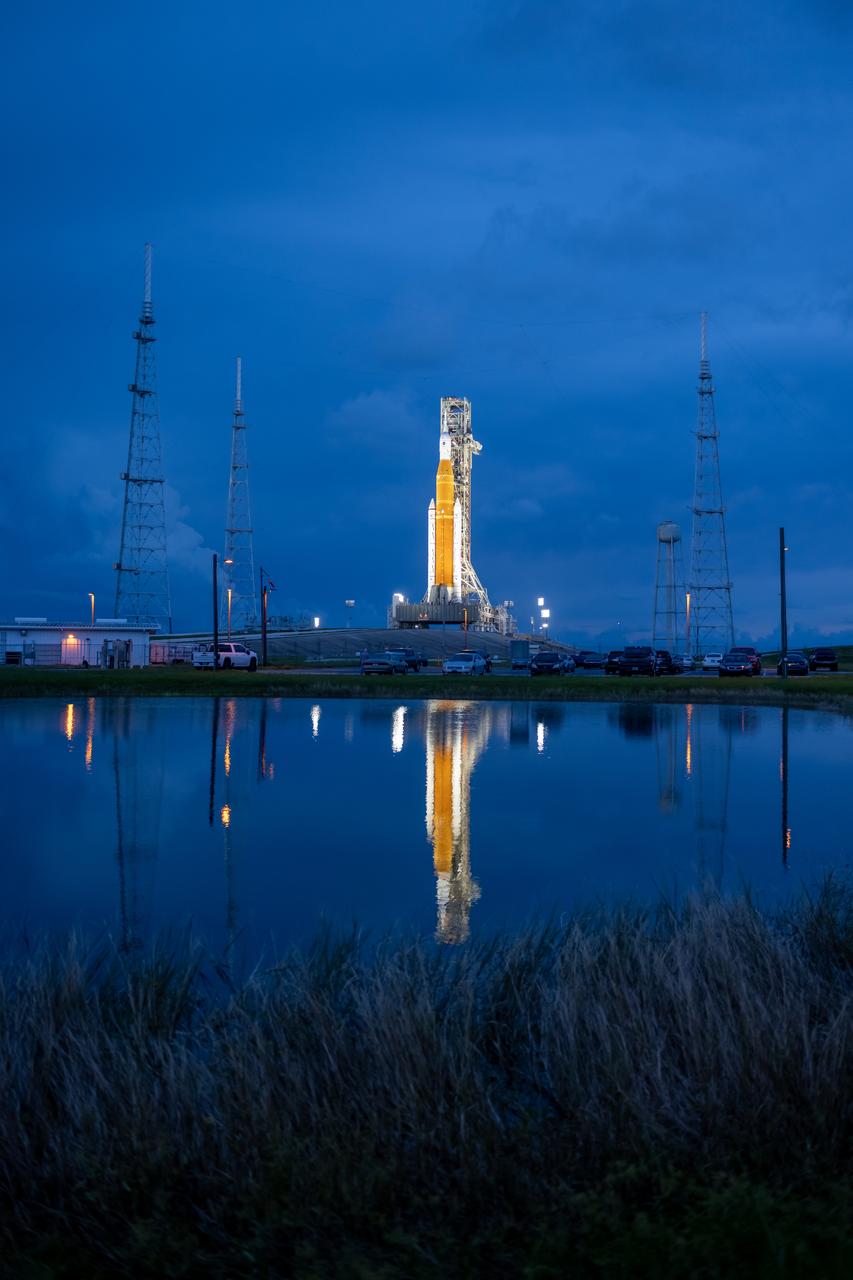

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)
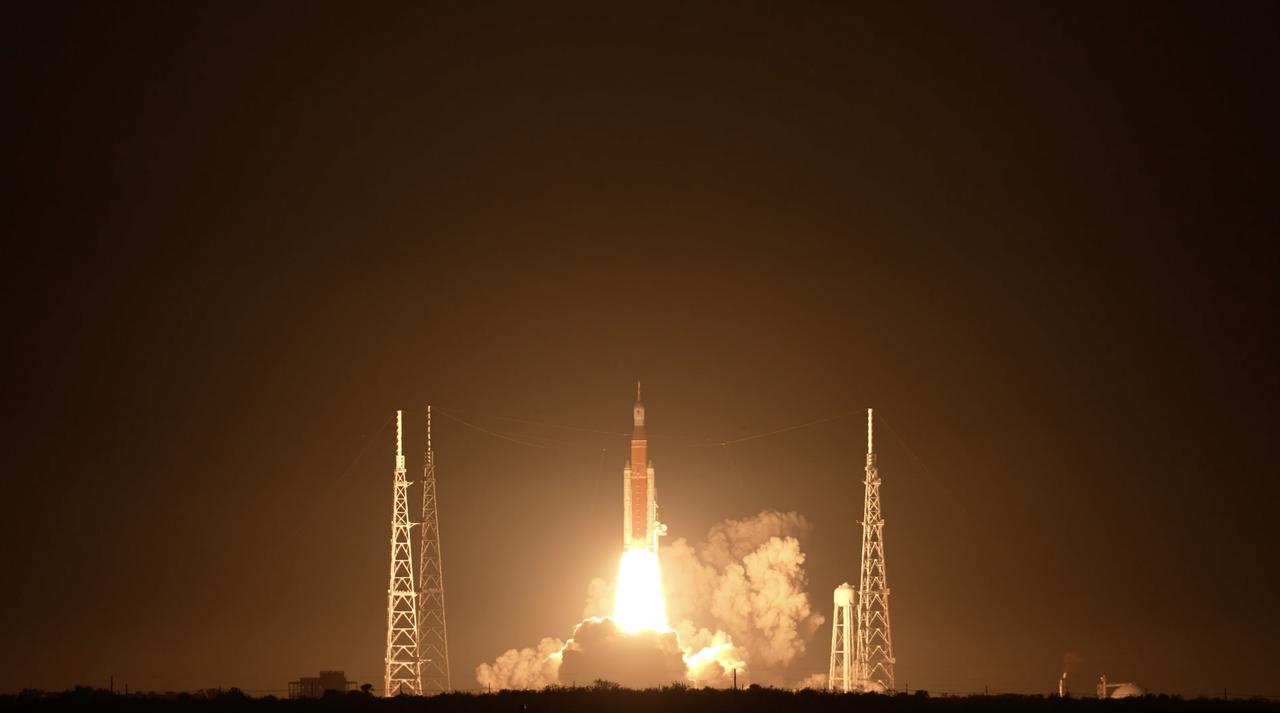

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
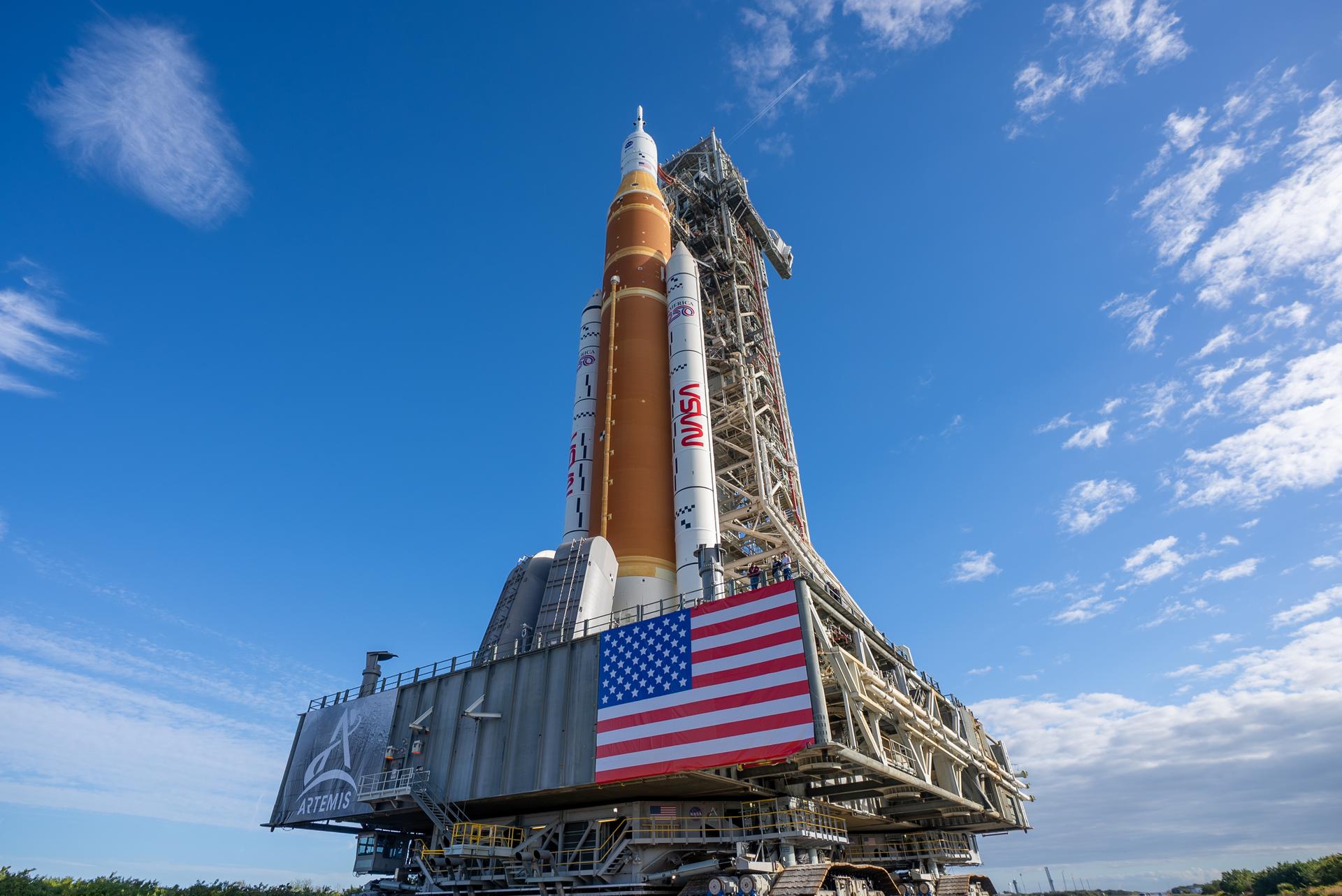

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
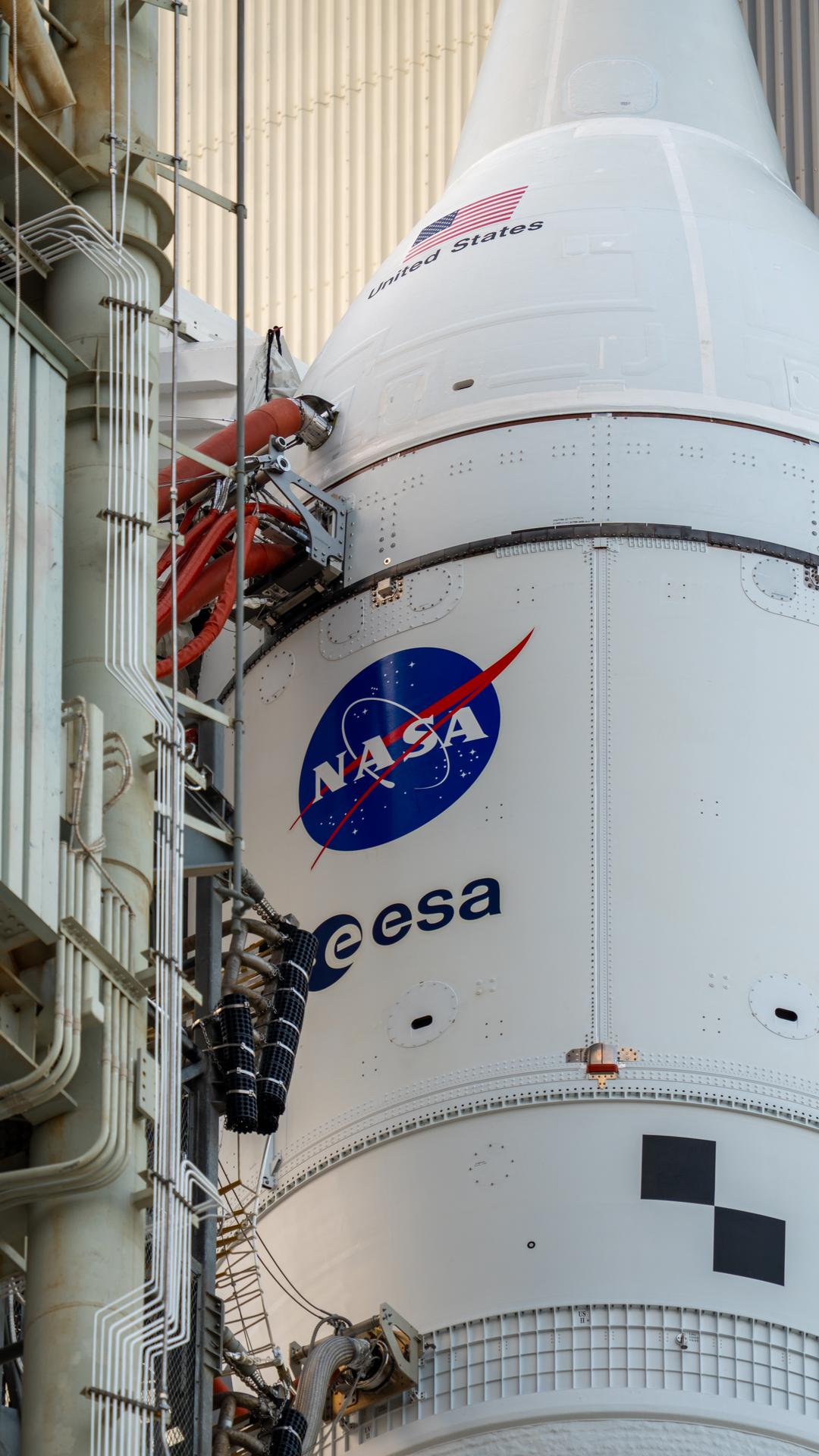

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
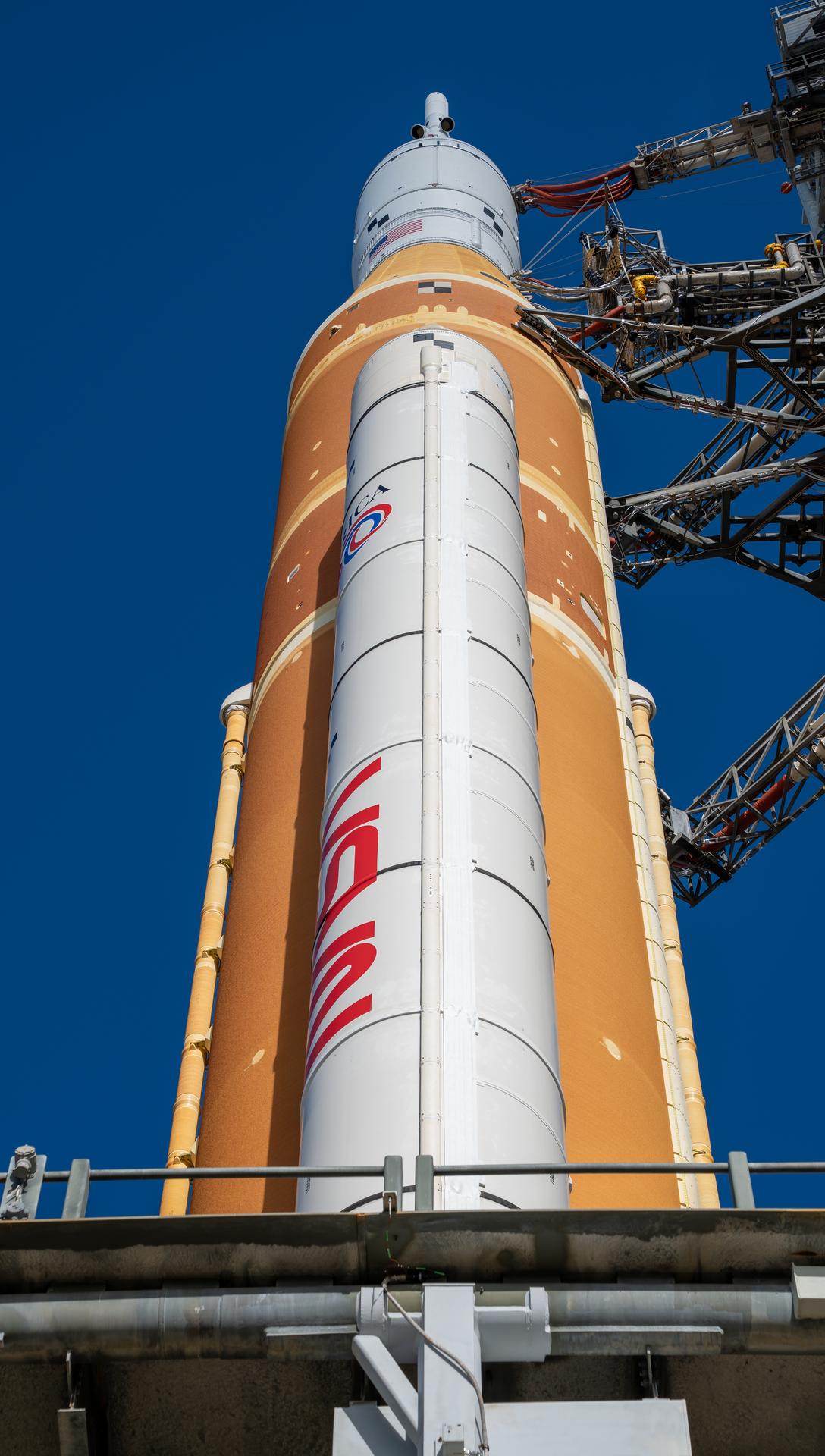

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
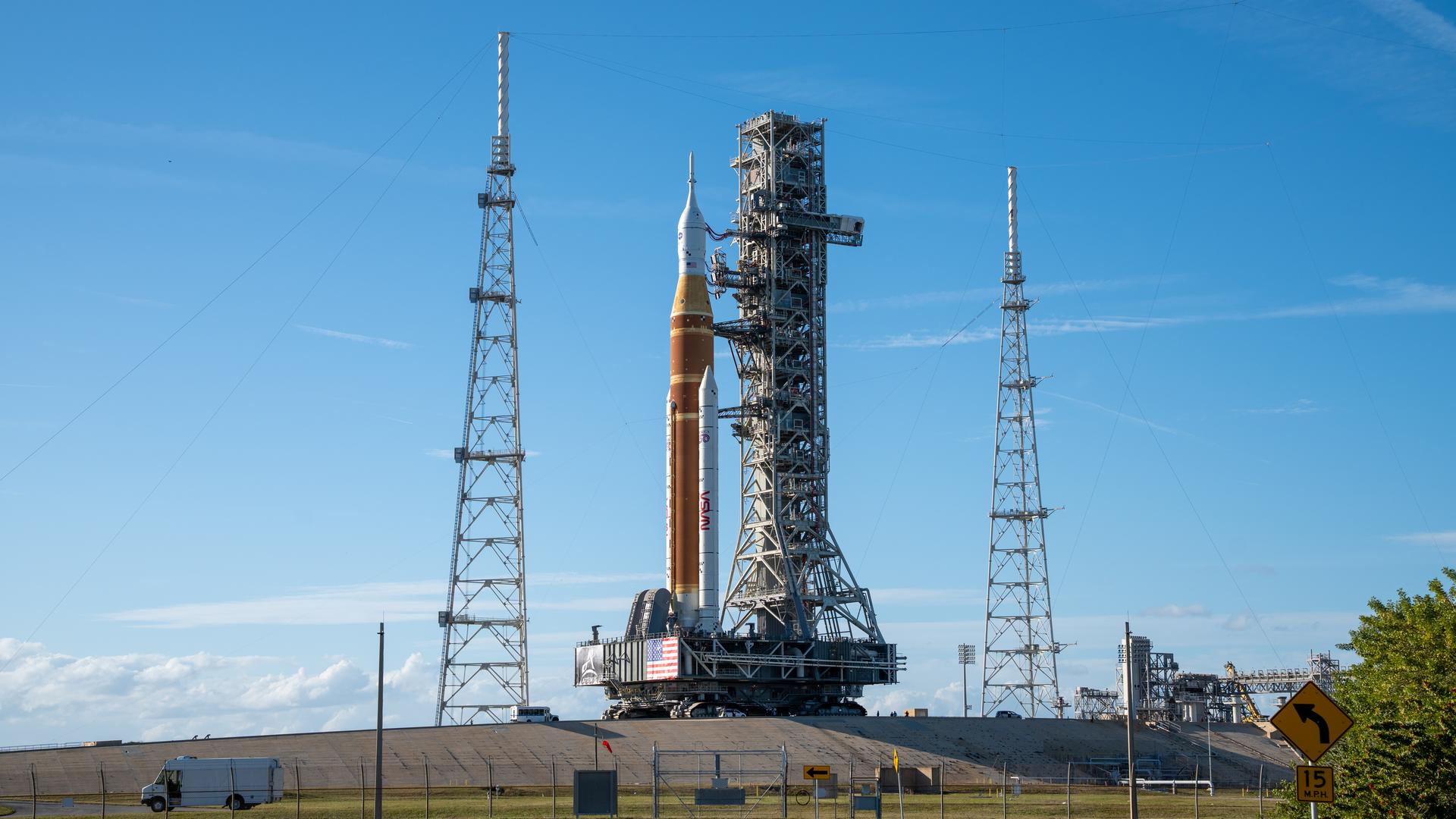

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
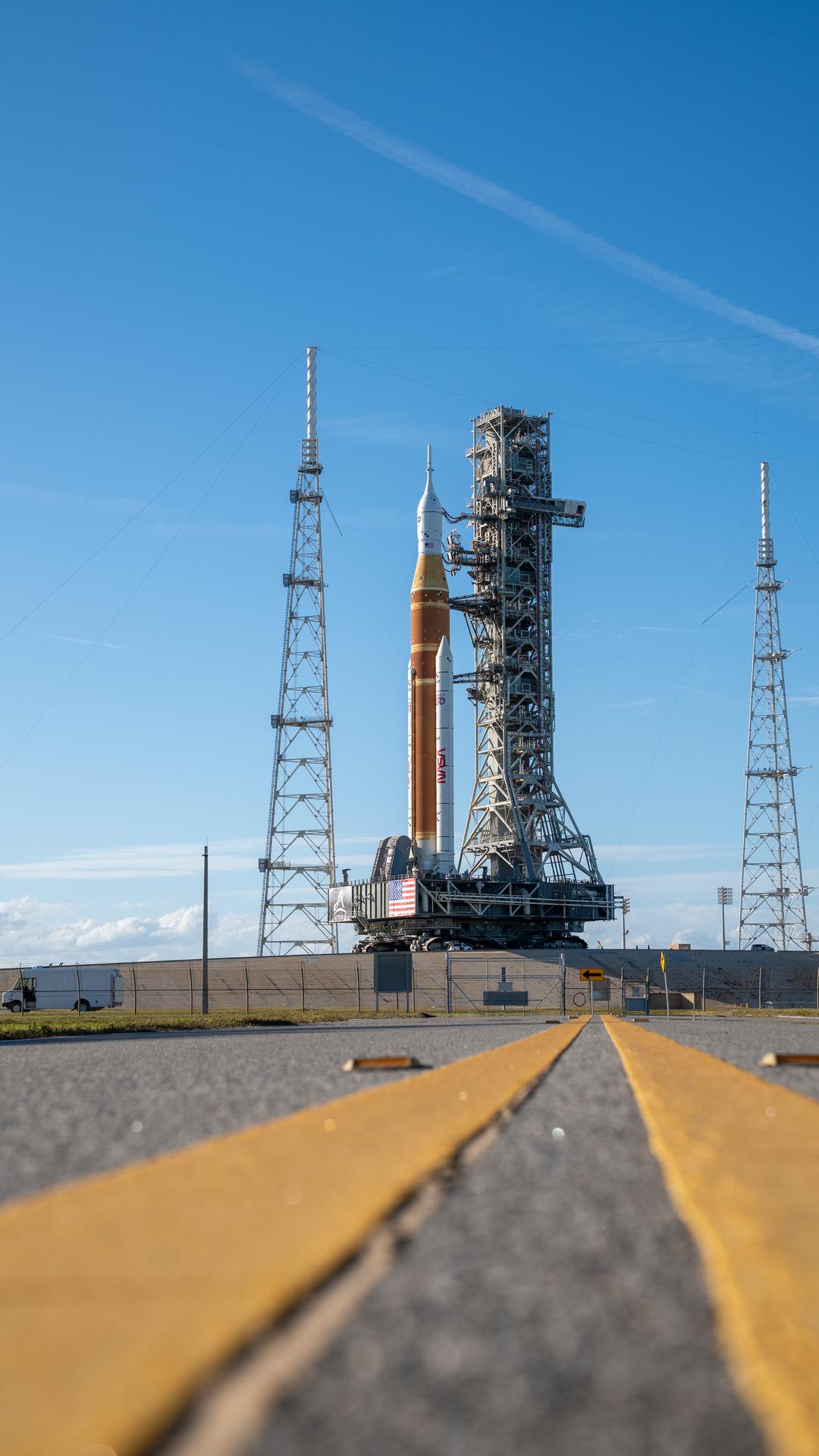

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
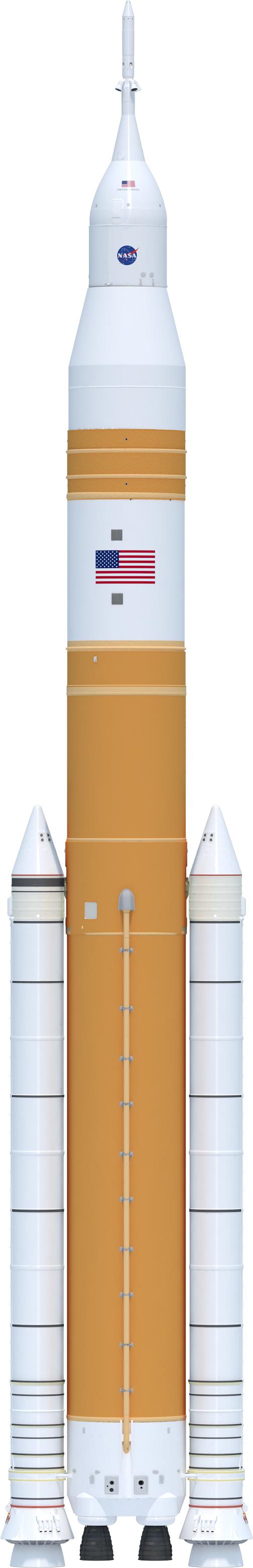

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant outer mold line. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
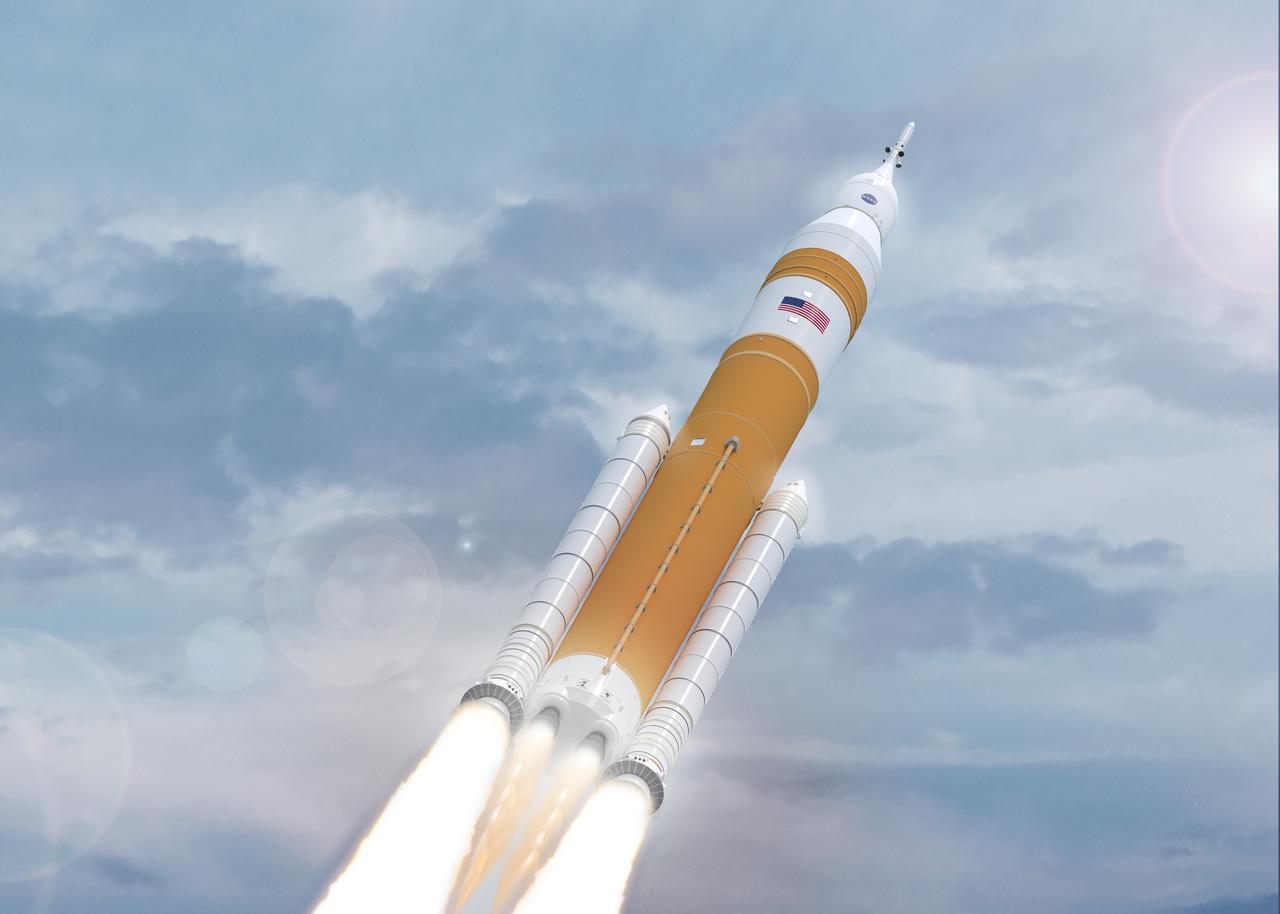

Illustration of evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant in flight. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
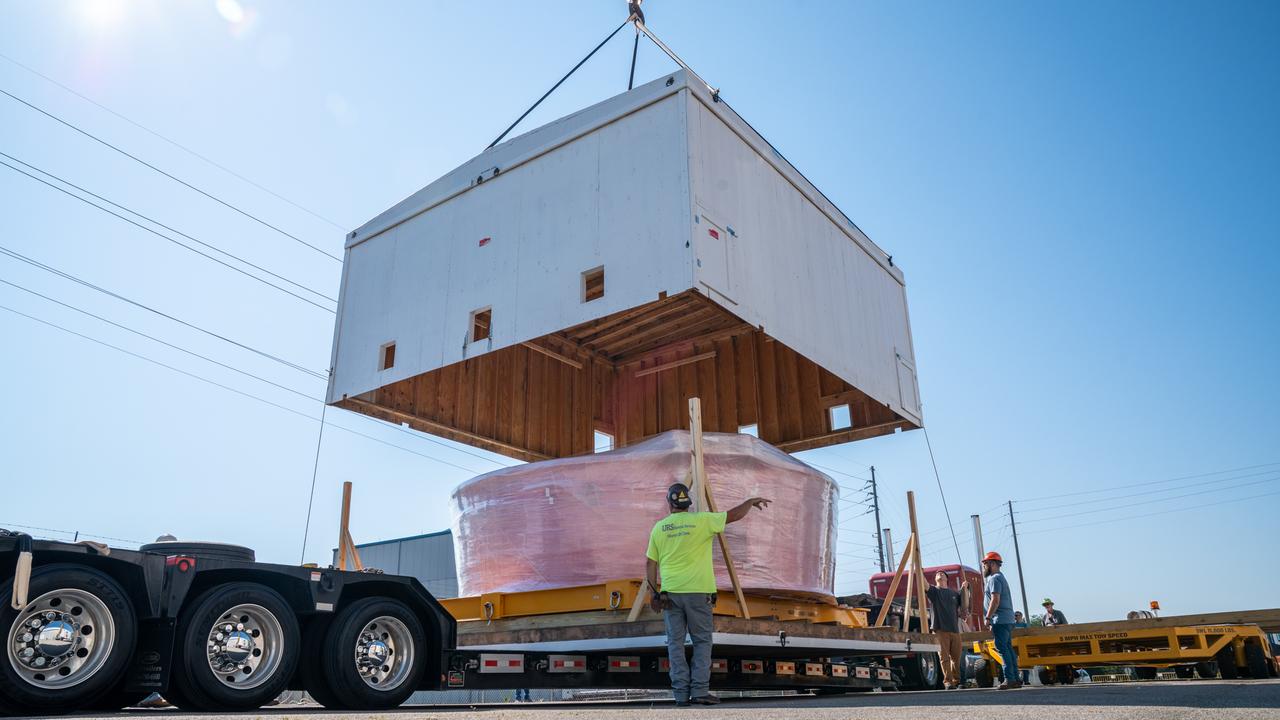

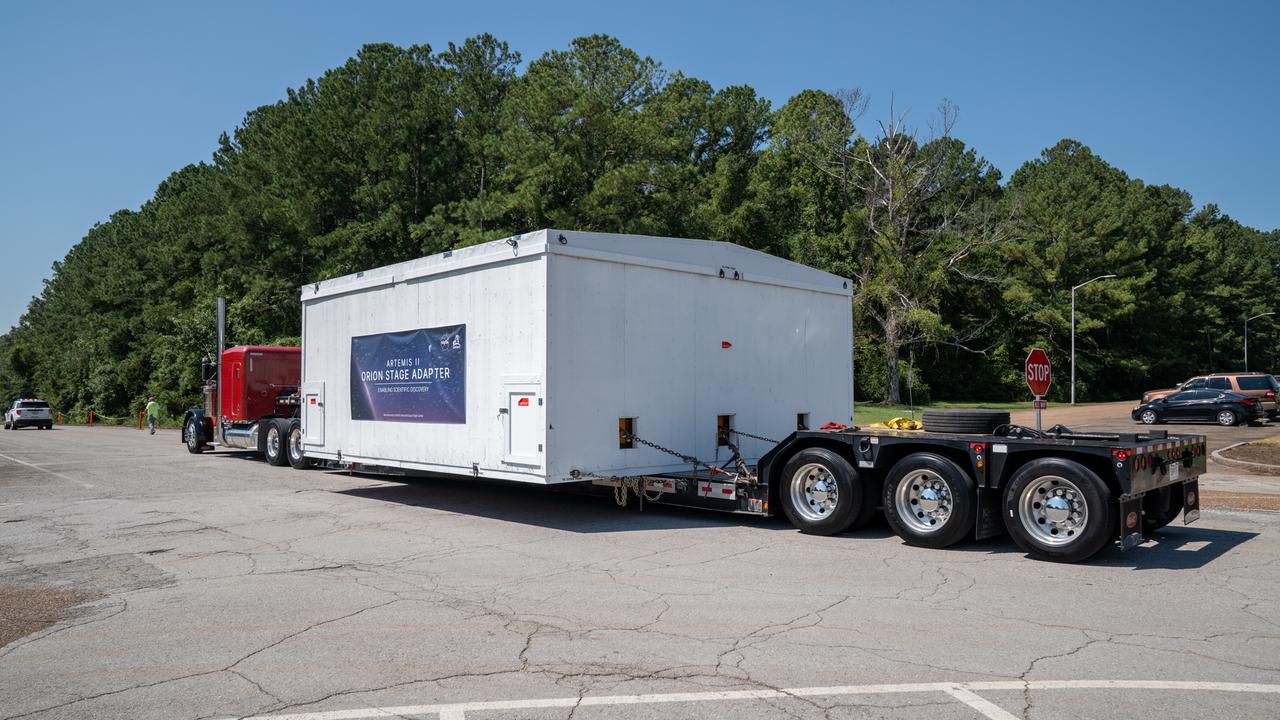
These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

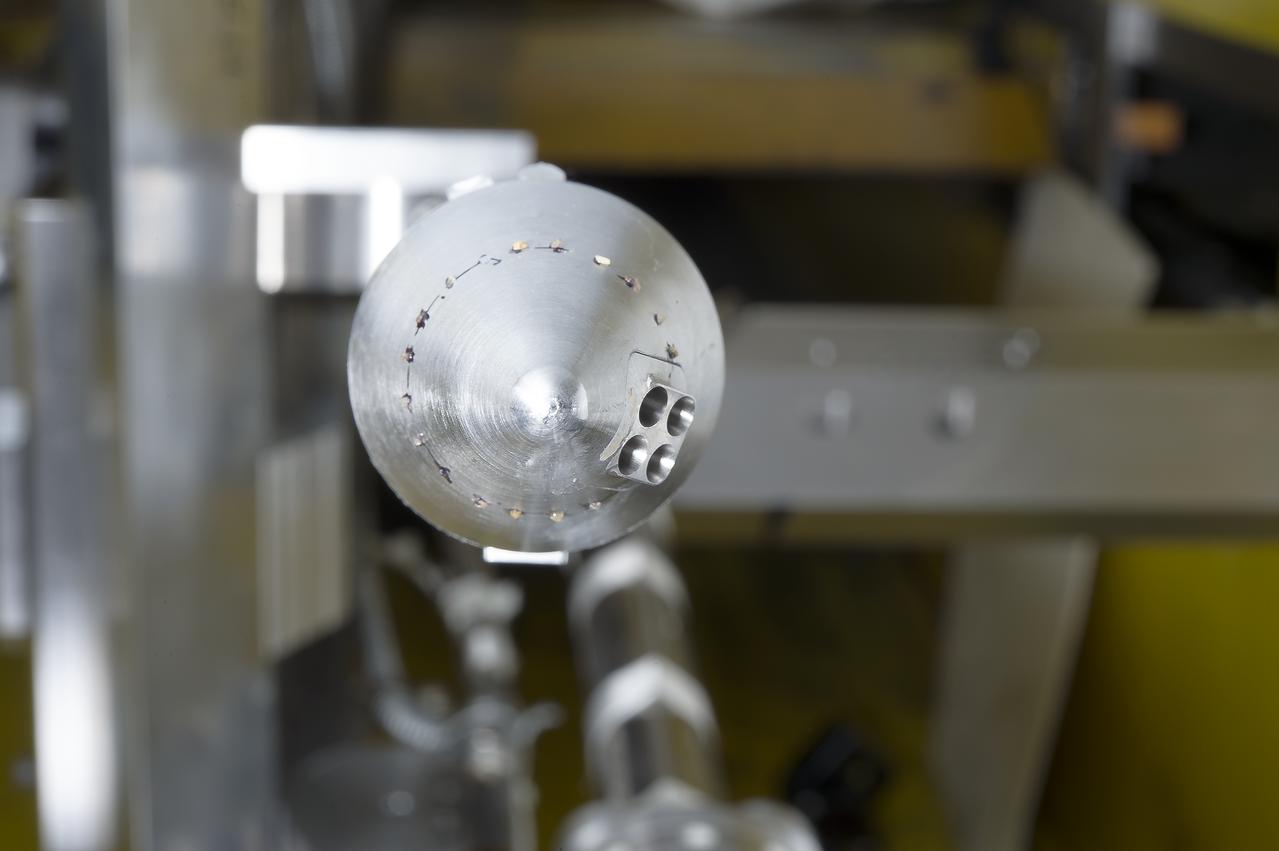
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
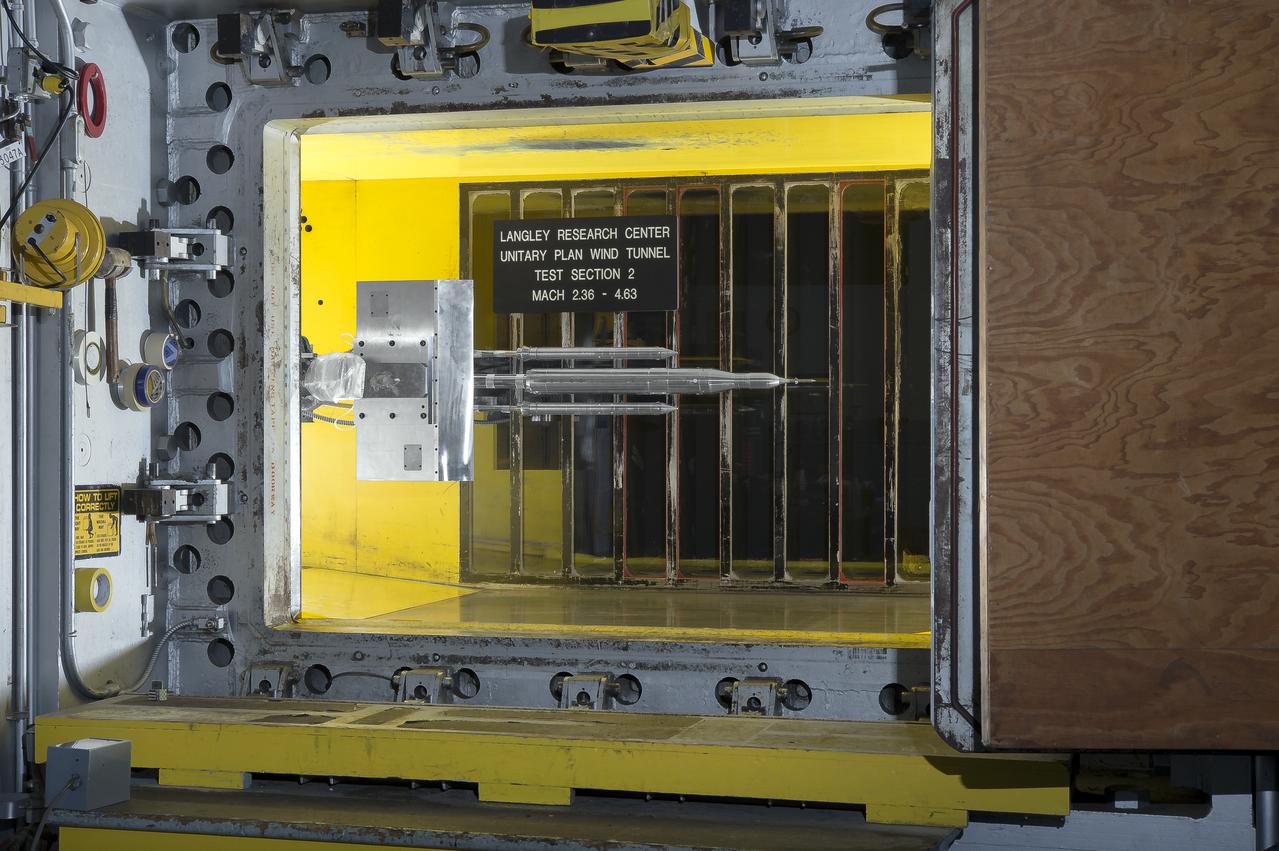
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
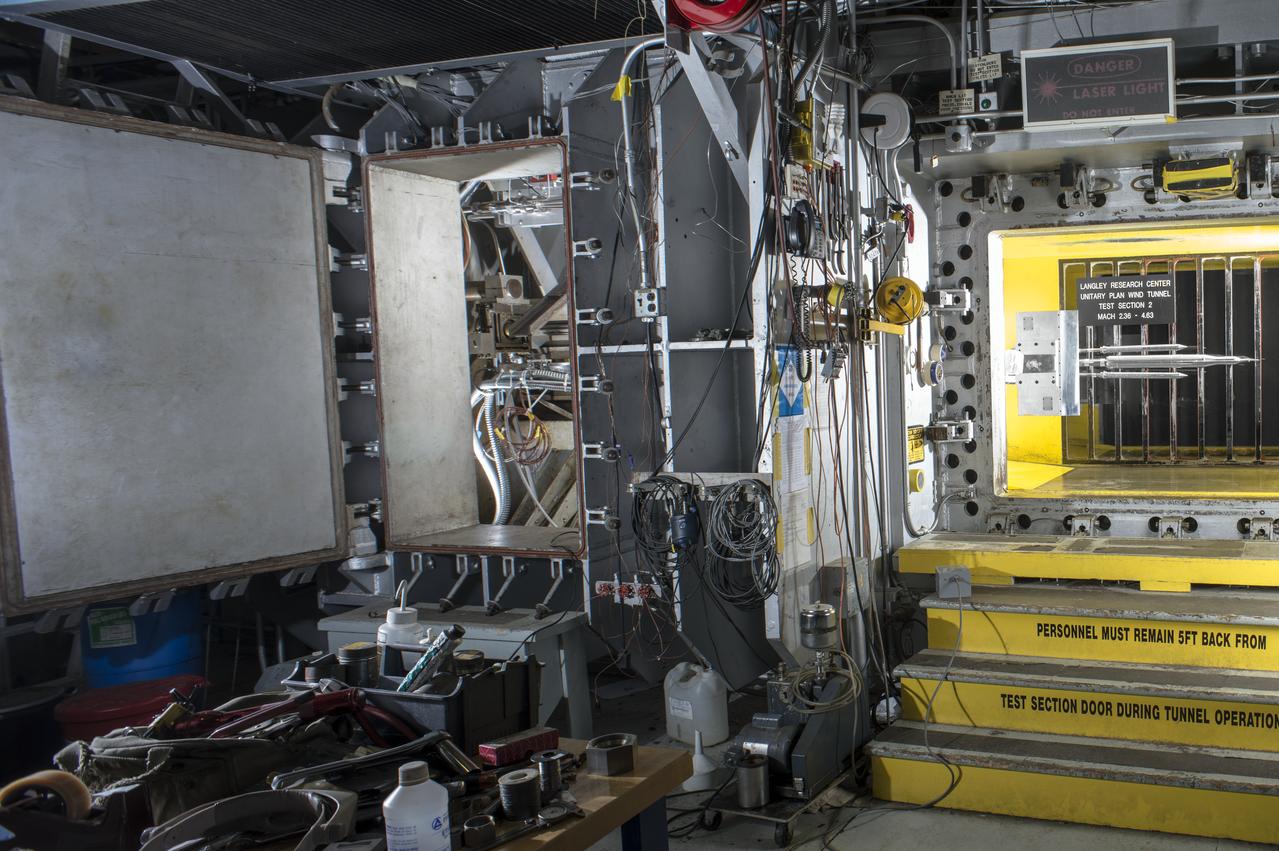
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
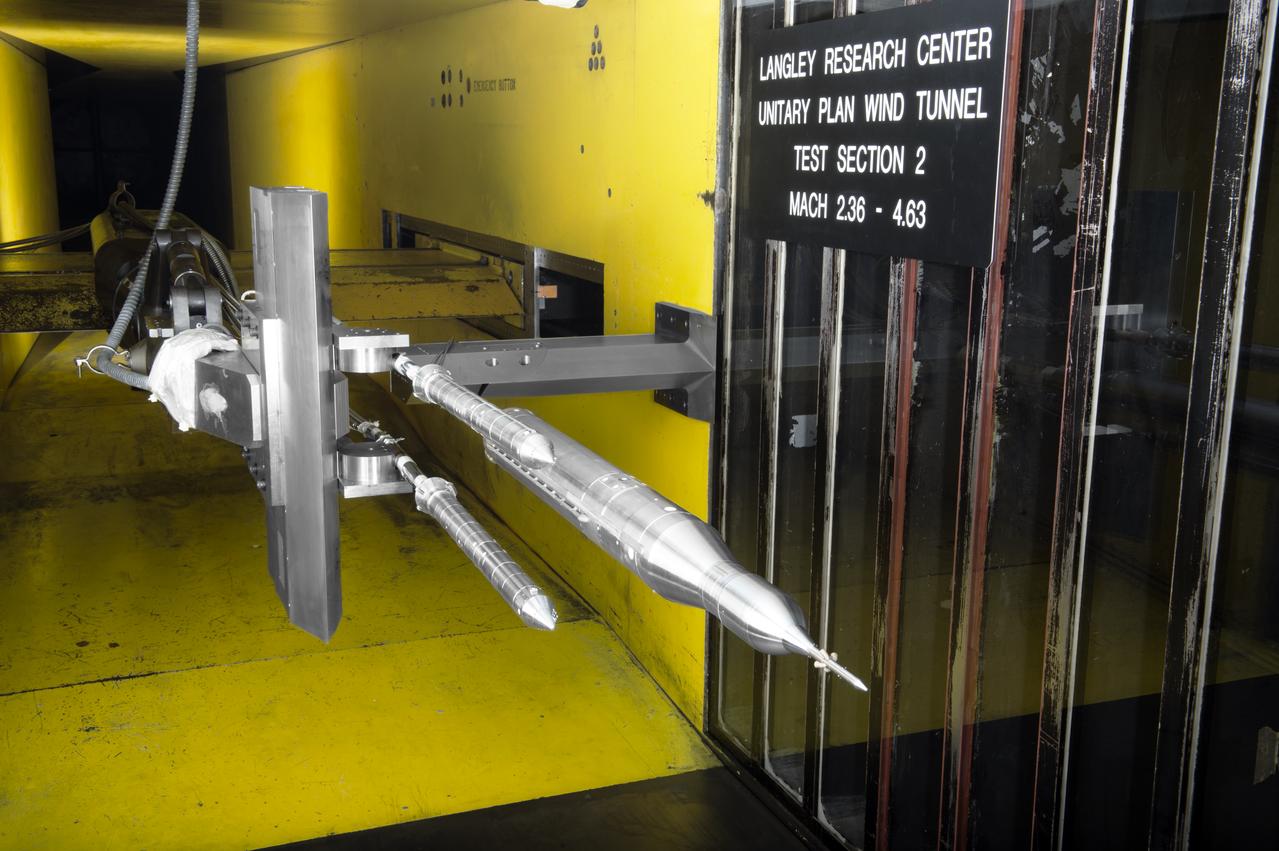
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
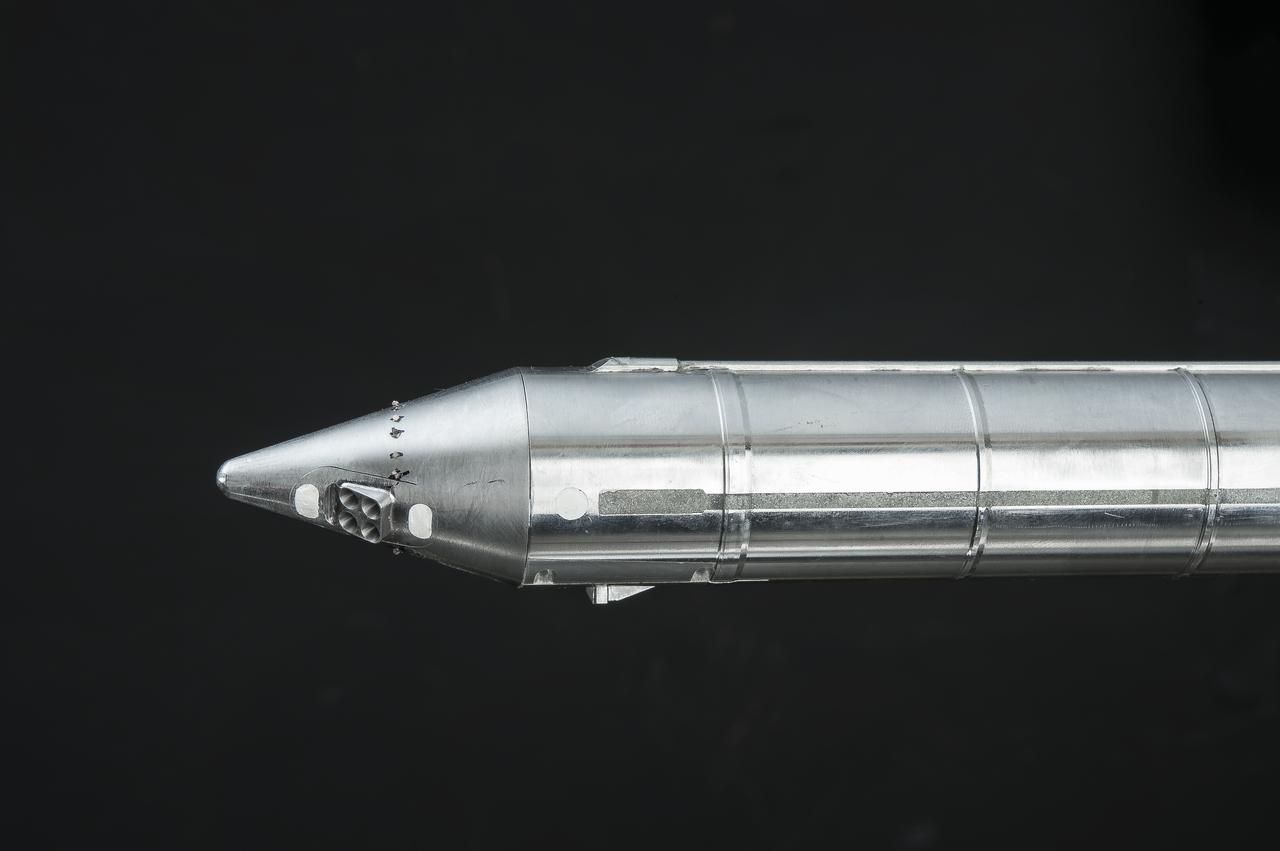

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
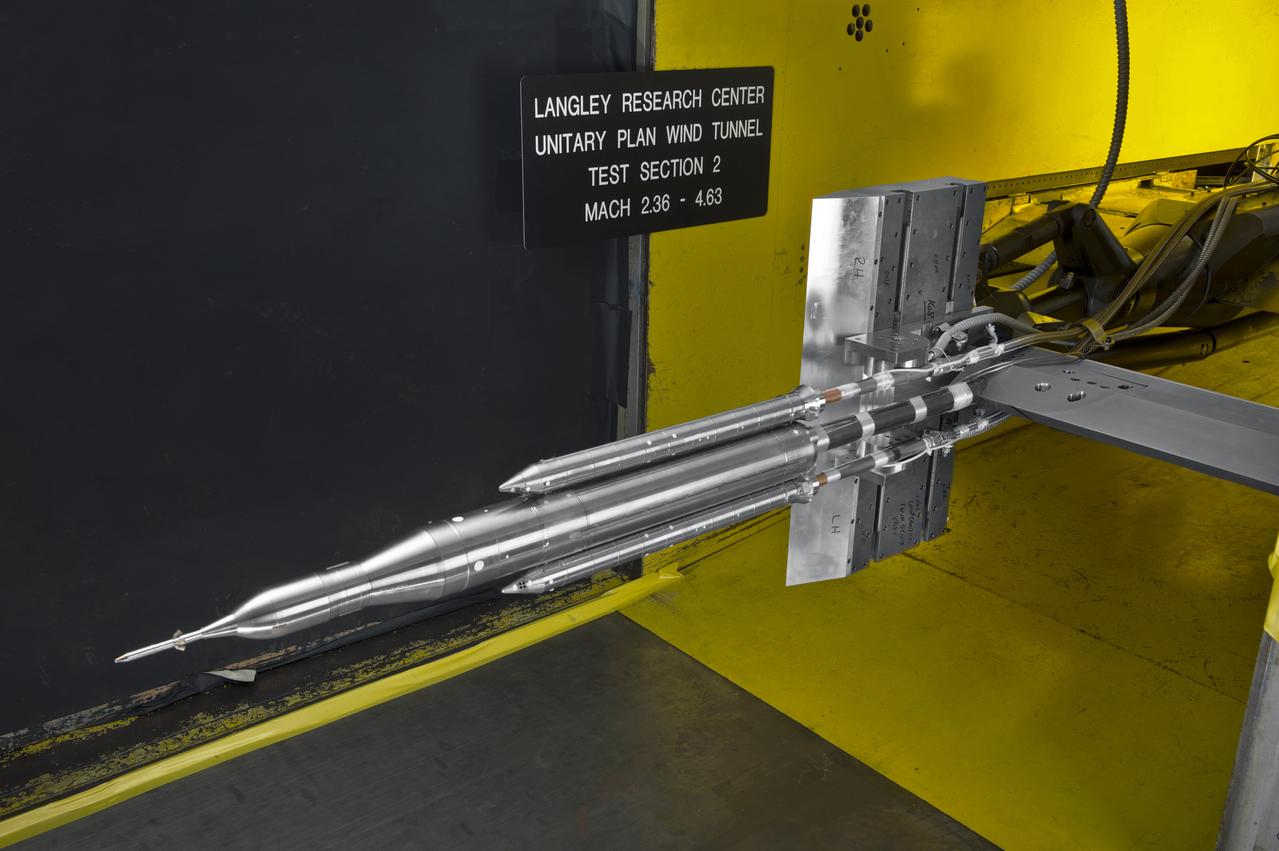
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
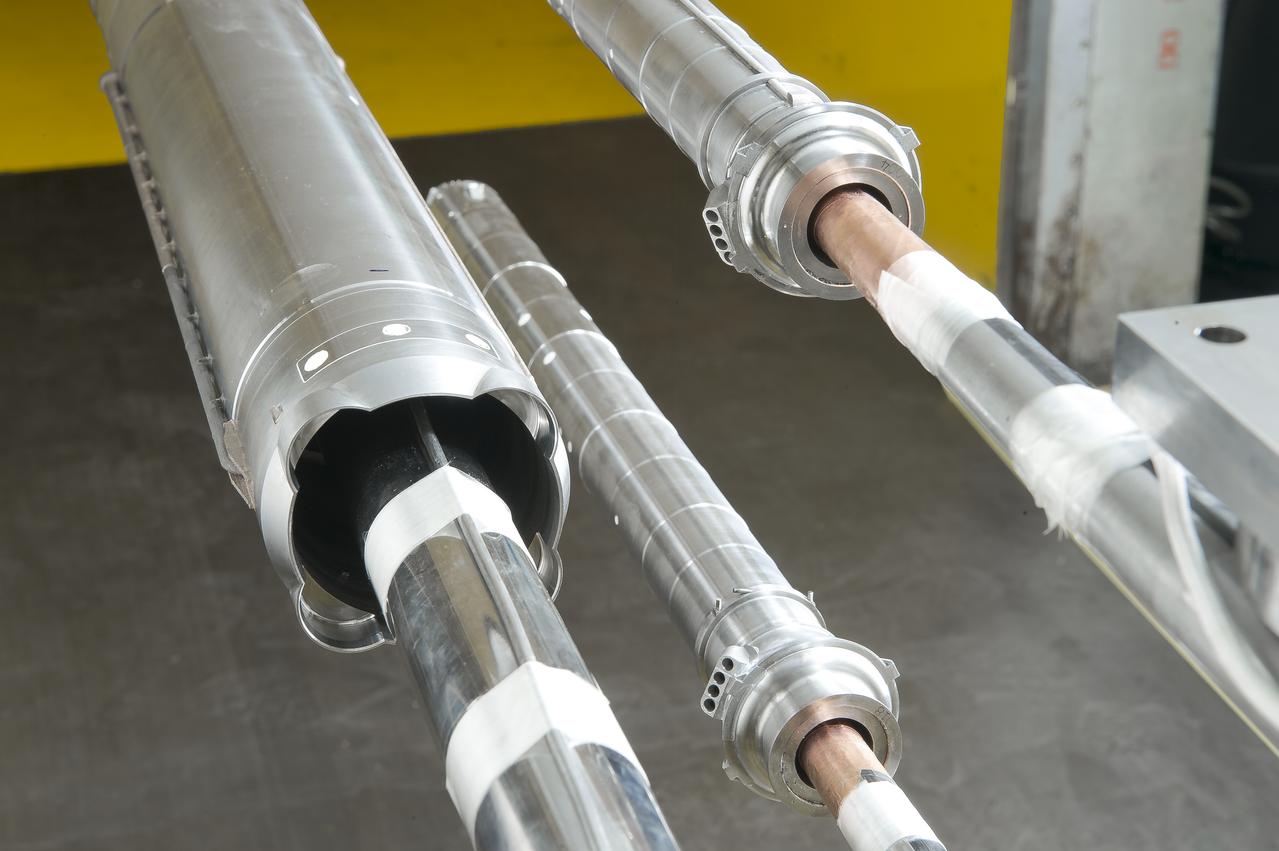

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
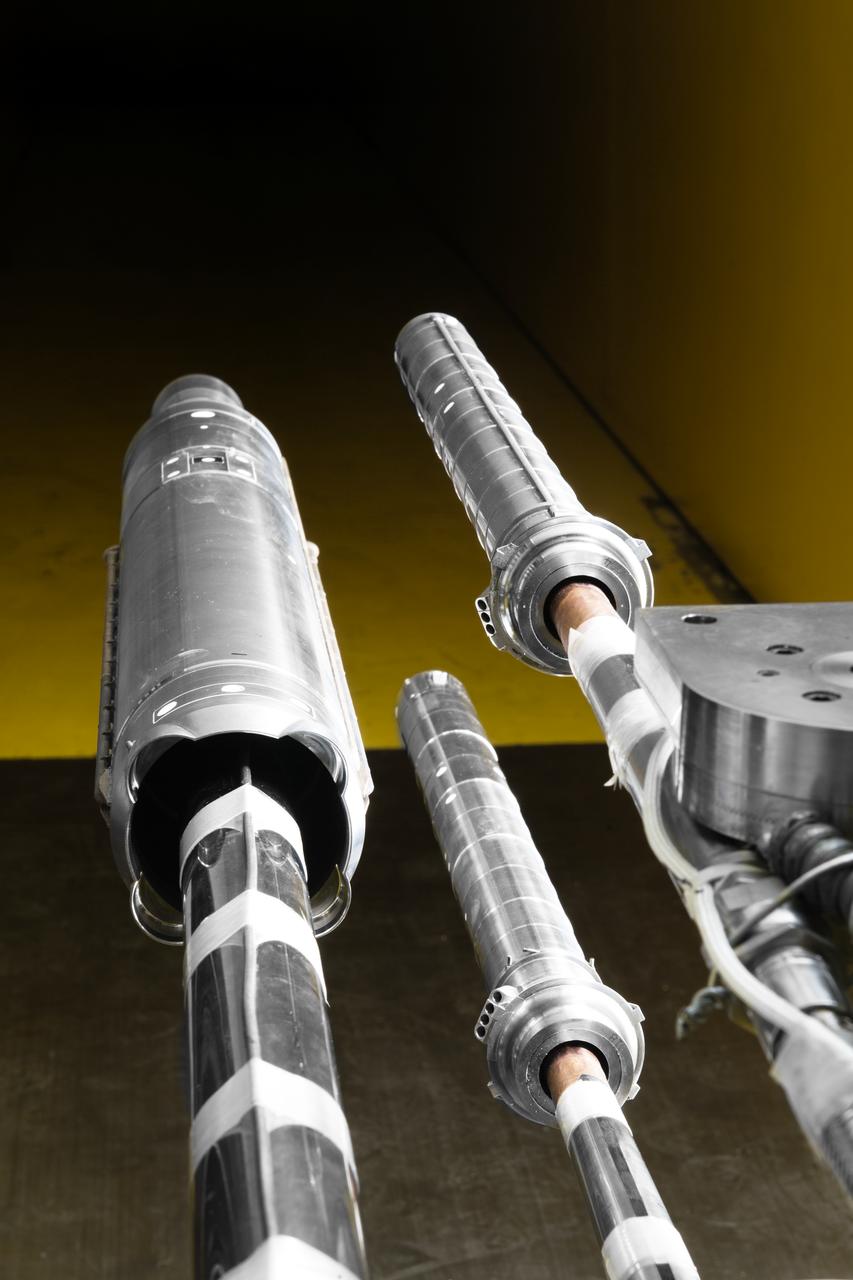

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
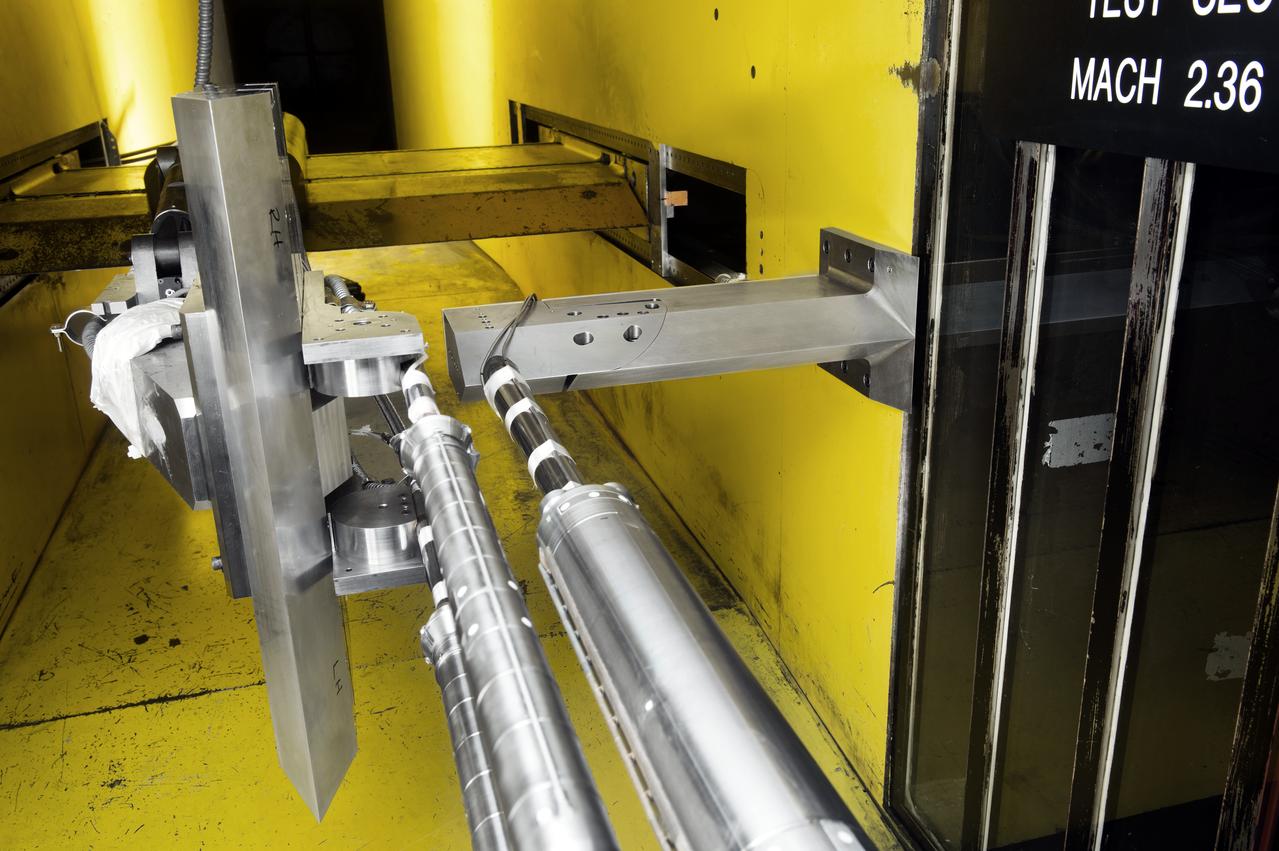

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
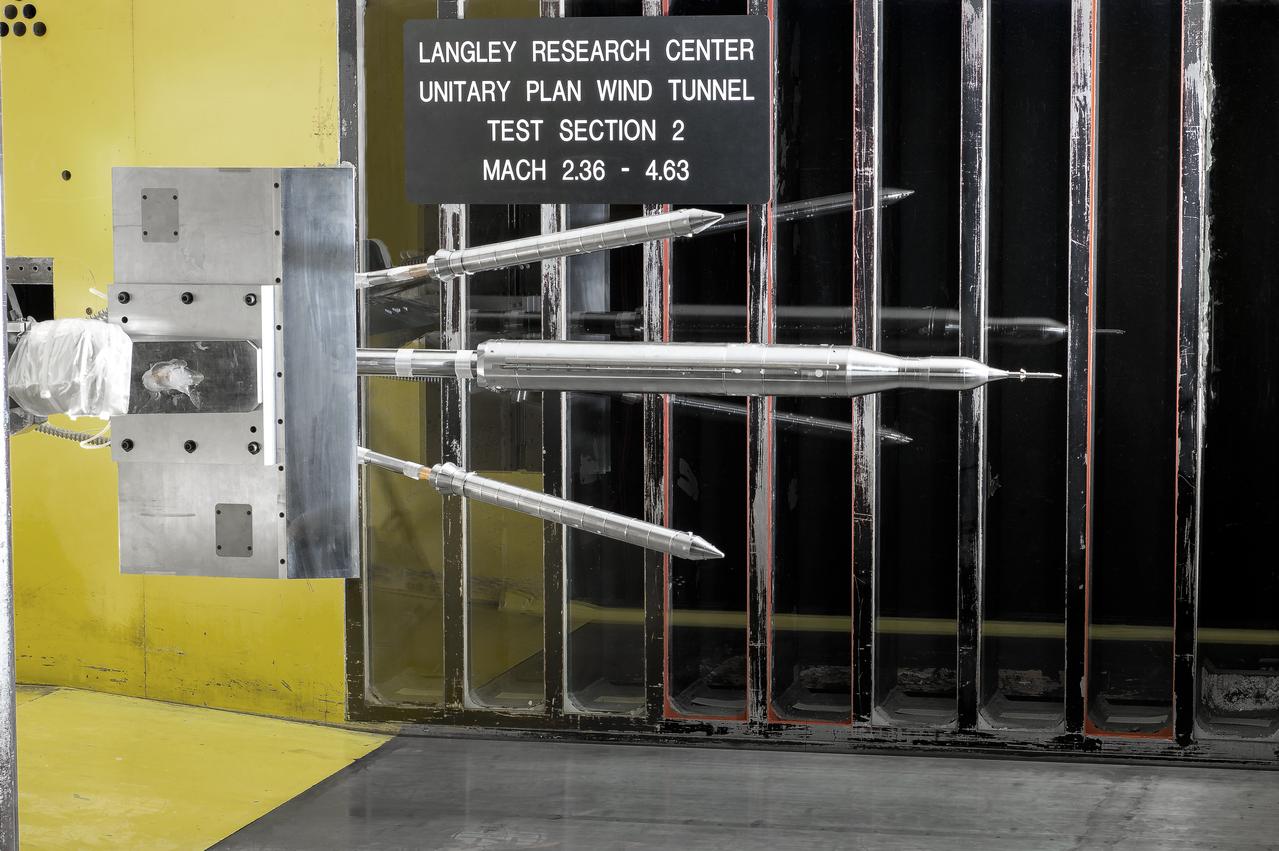

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
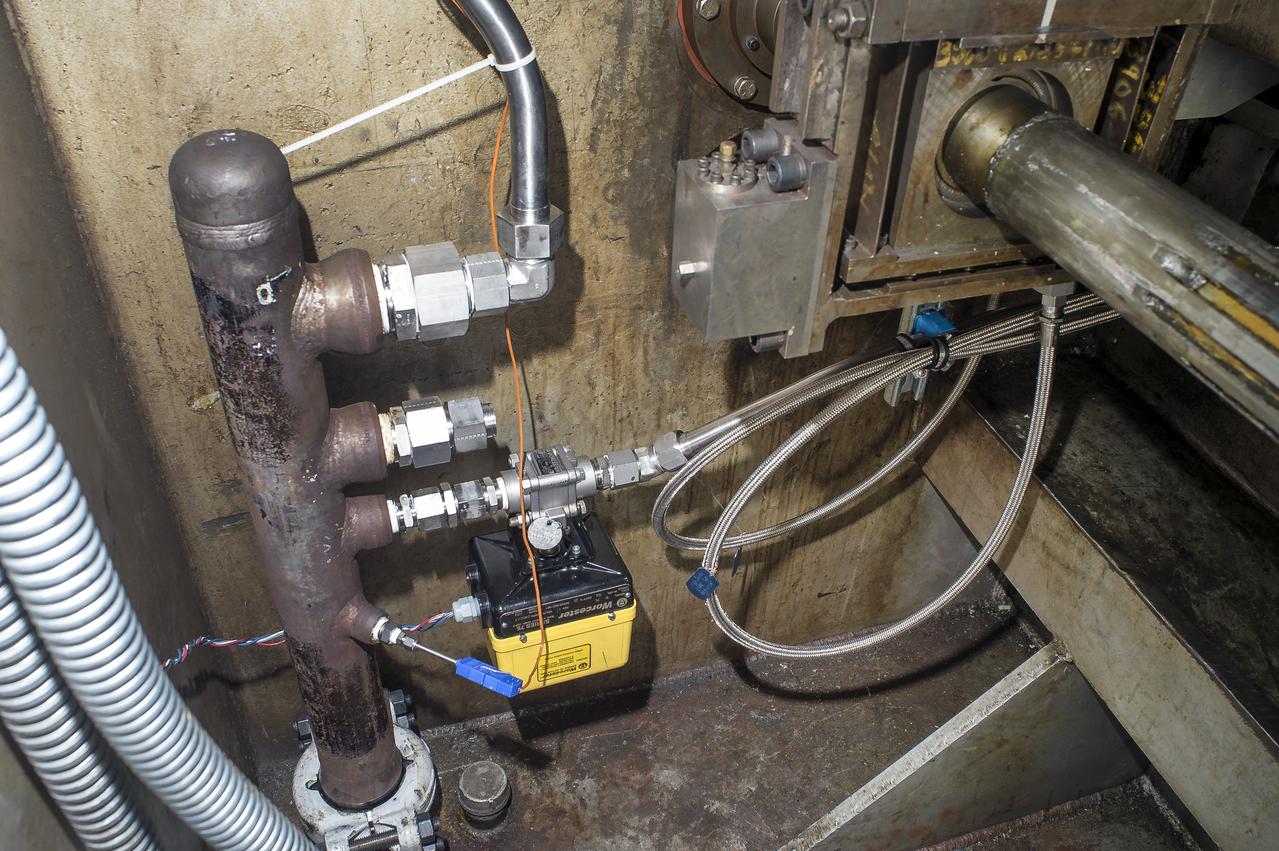

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
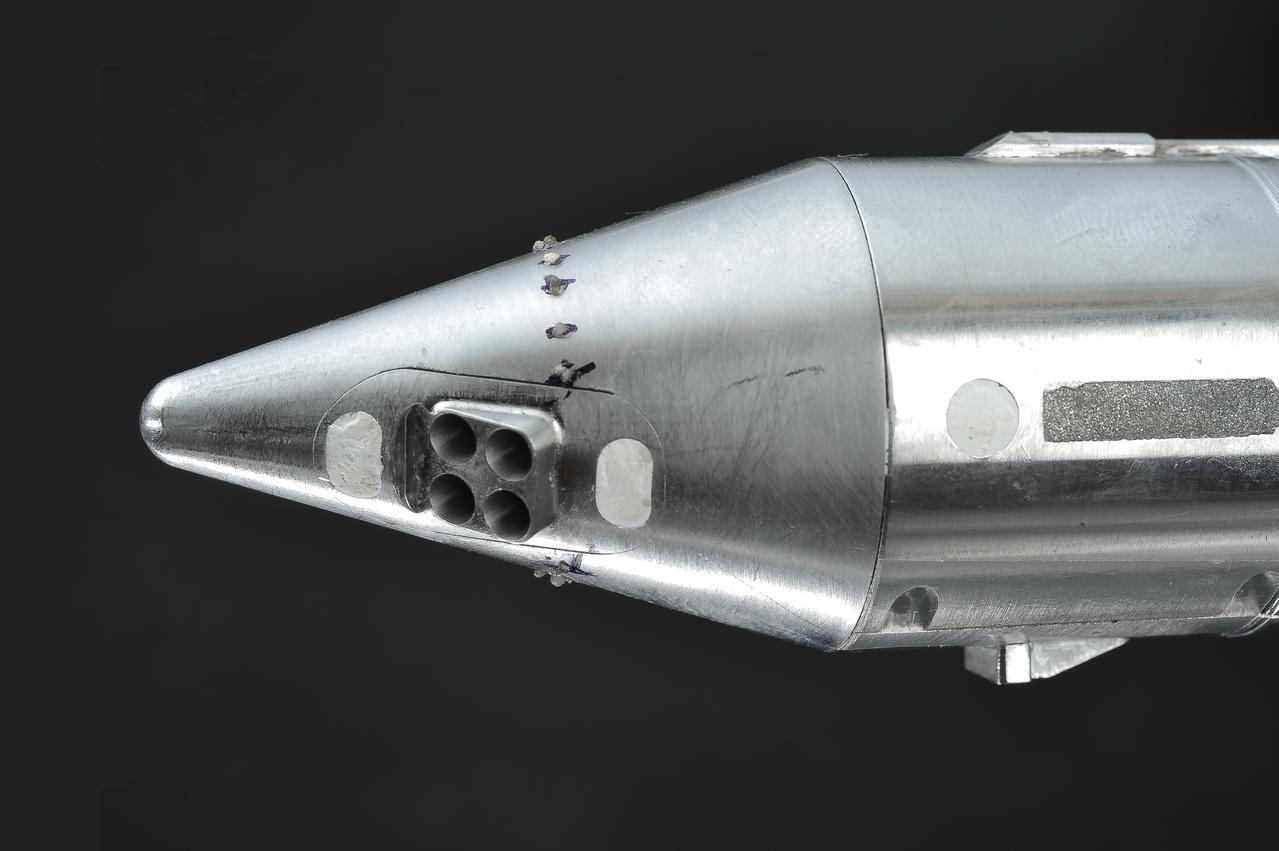

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
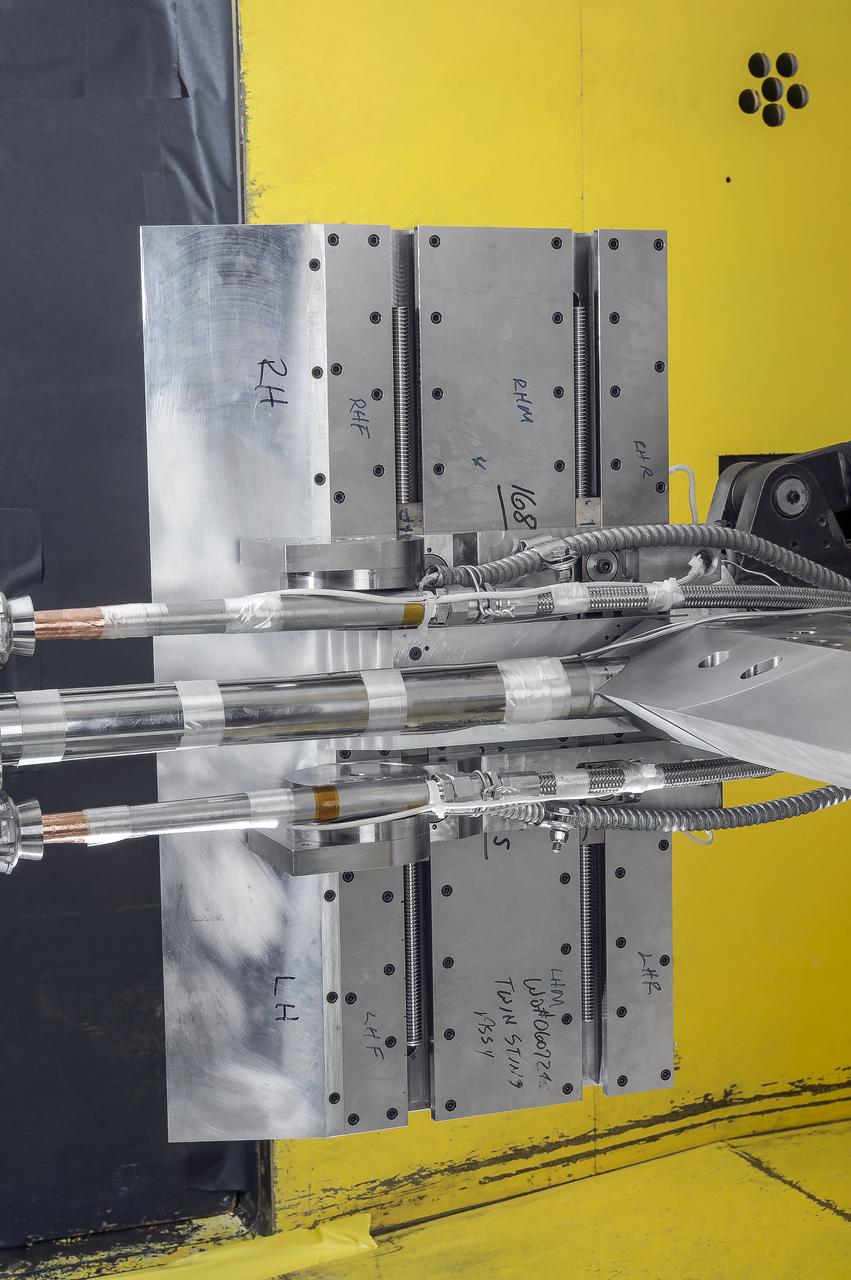

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
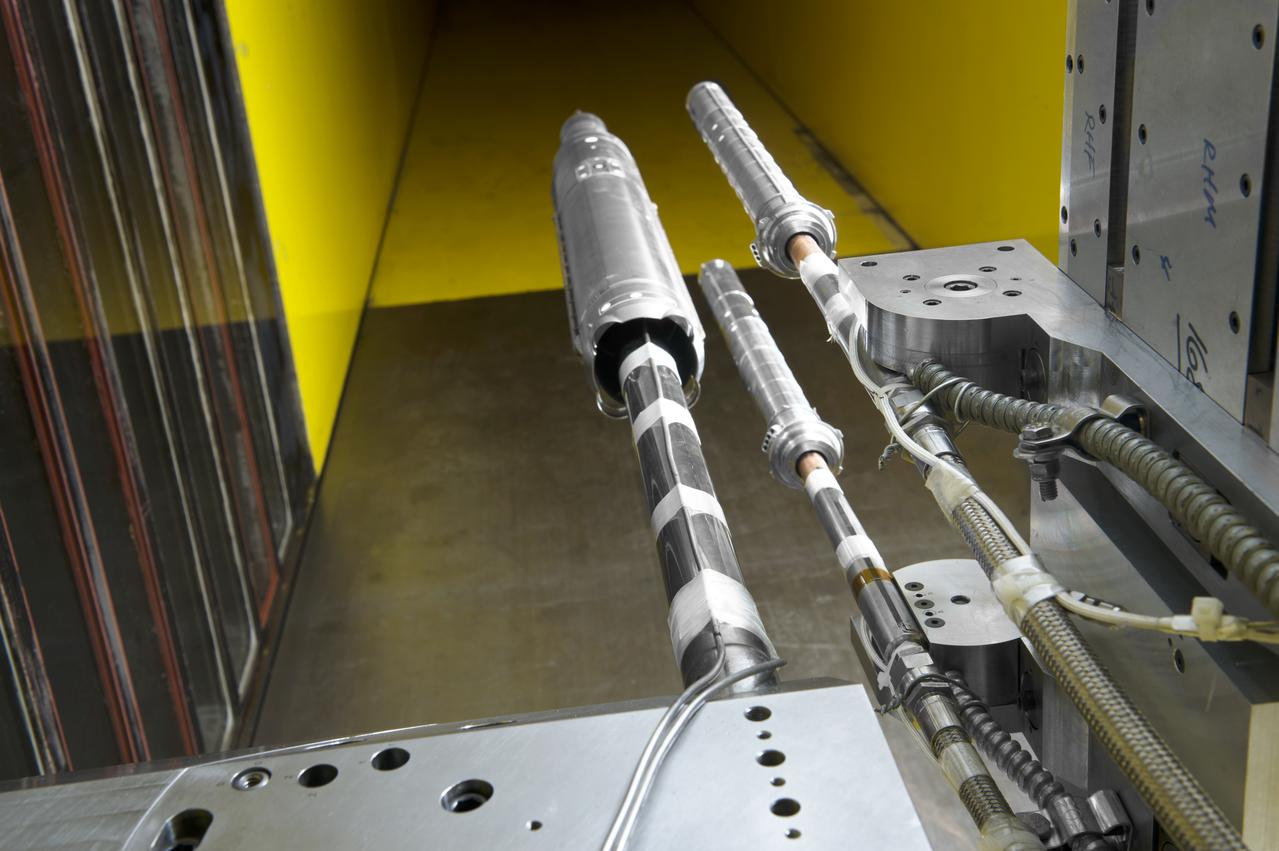

Stage Separation Test of the Space Launch System(SLS) in the Langley Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT). The model used High Pressure air blown through the solid rocket boosters. (SRB) to simulate the booster separation motors (BSM) firing.
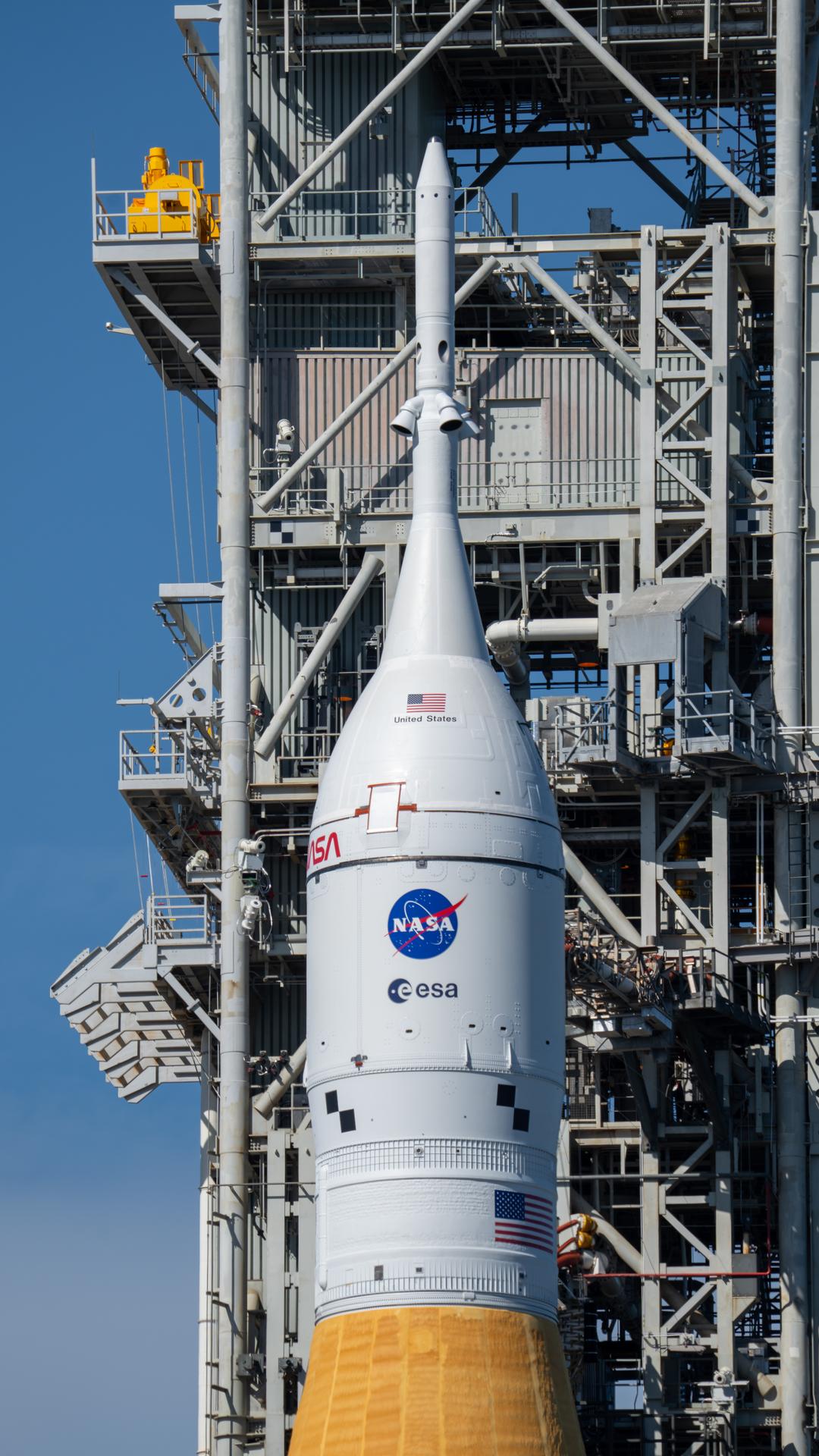

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
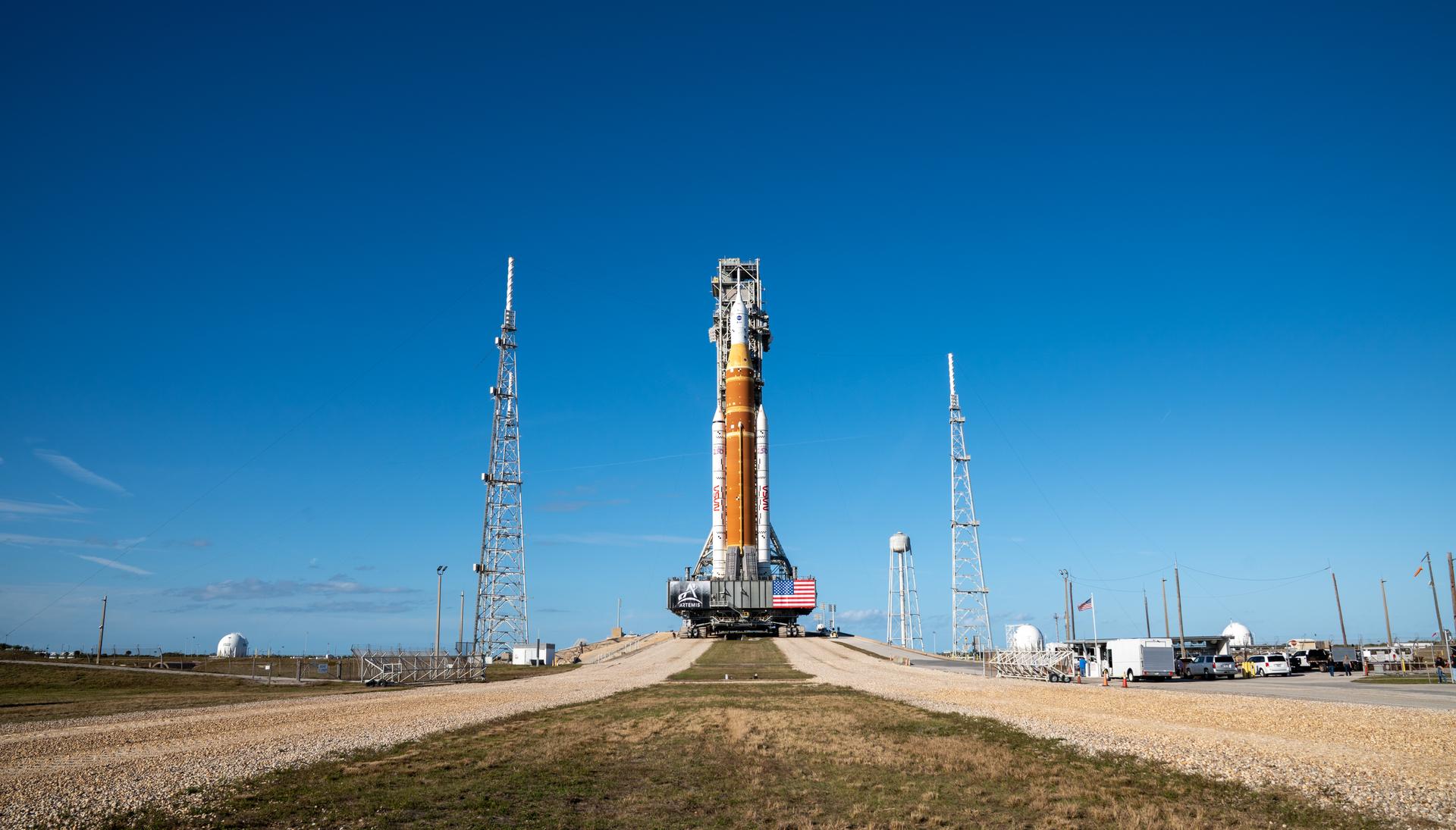

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
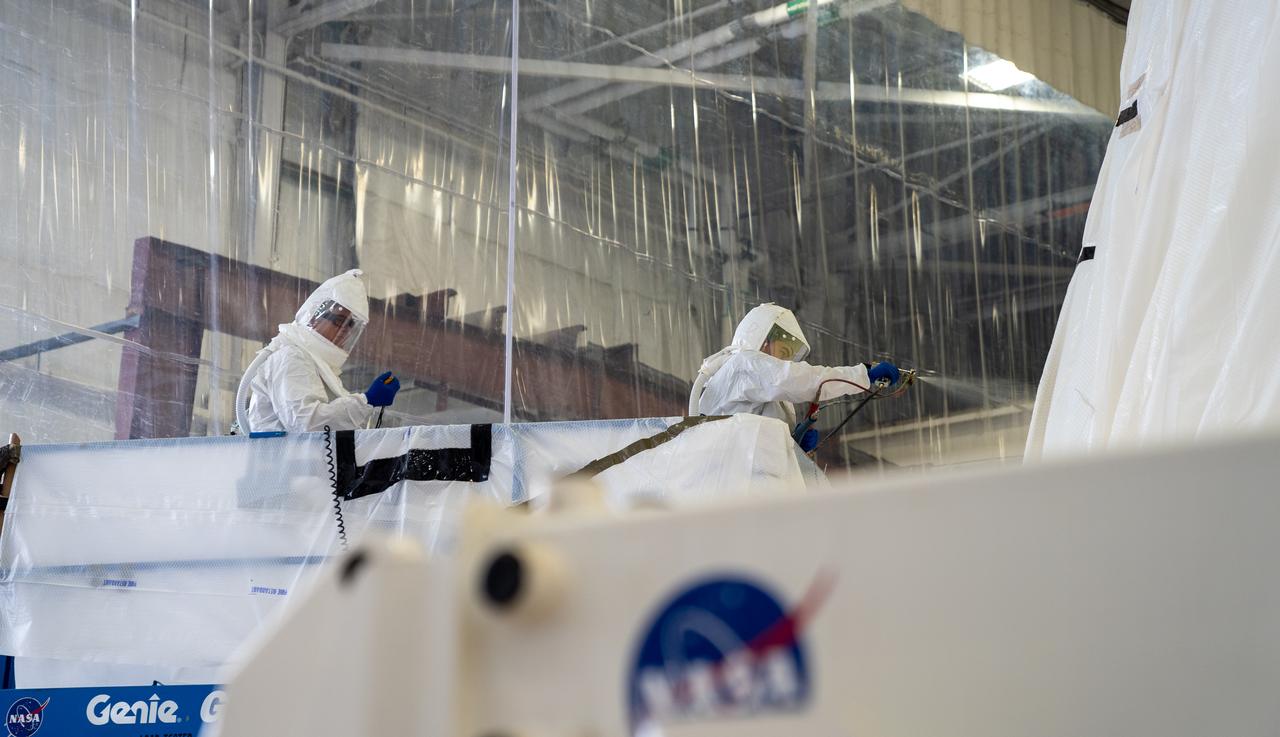

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
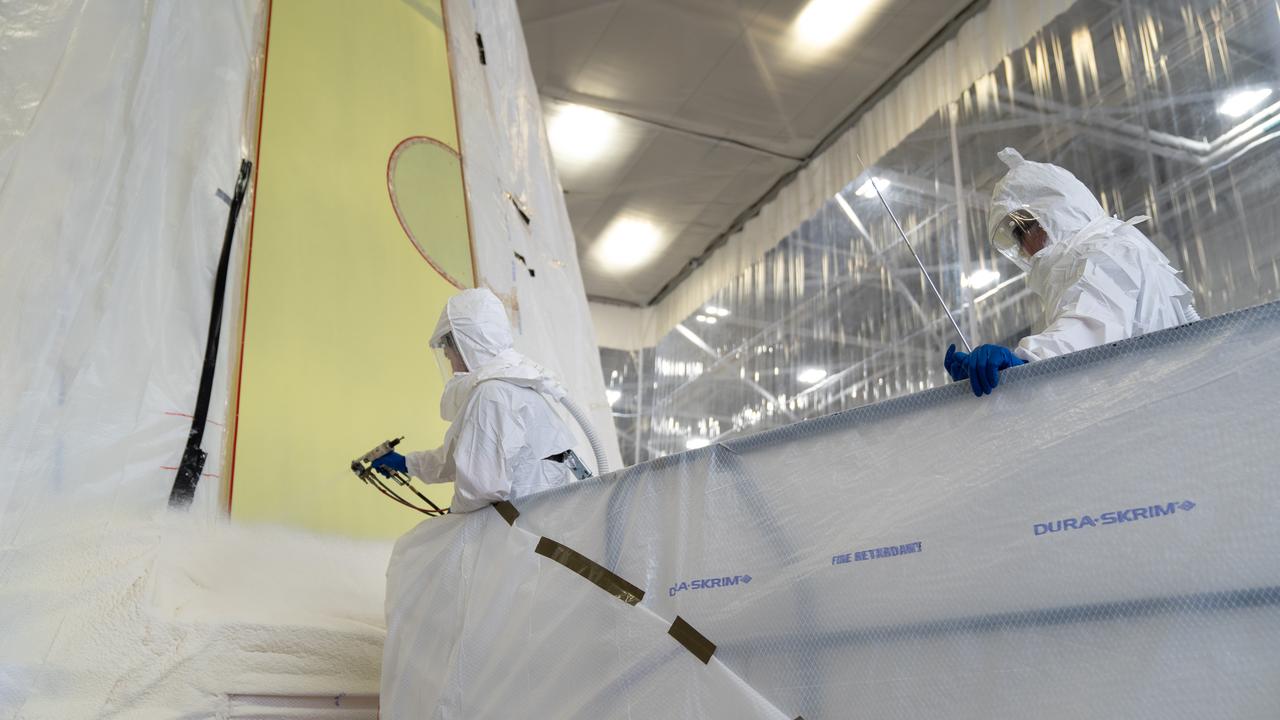

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
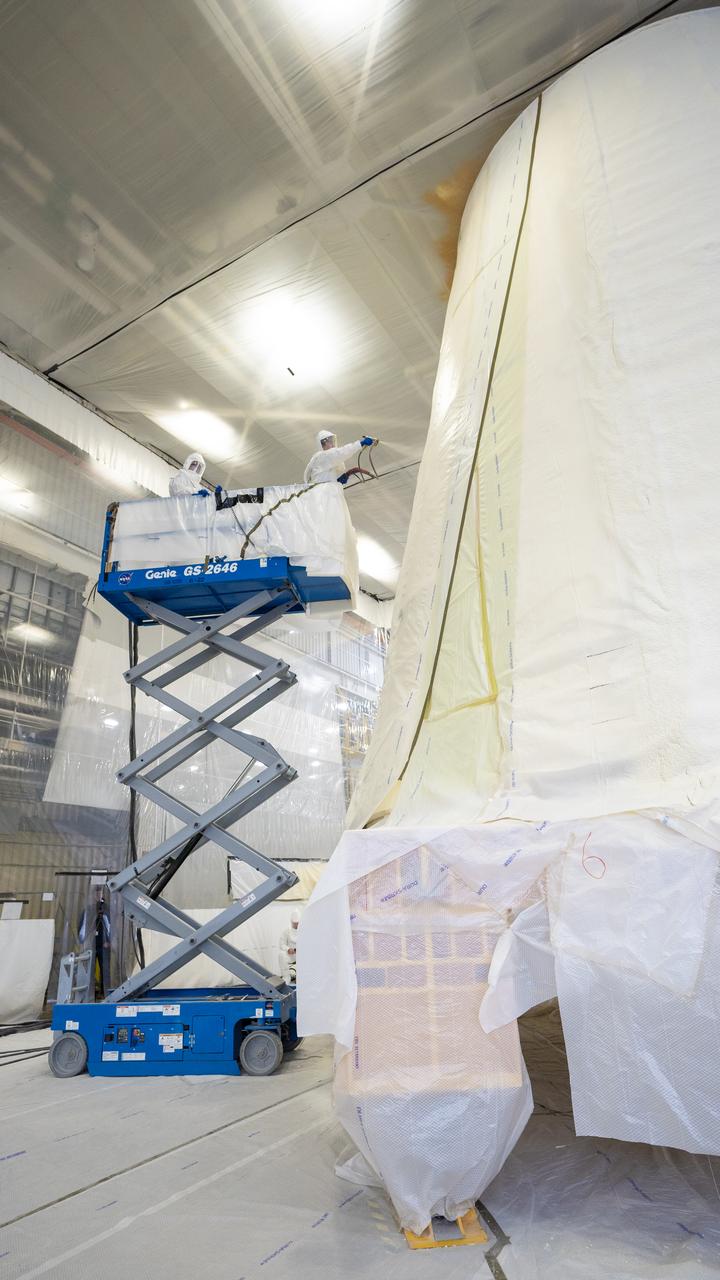

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
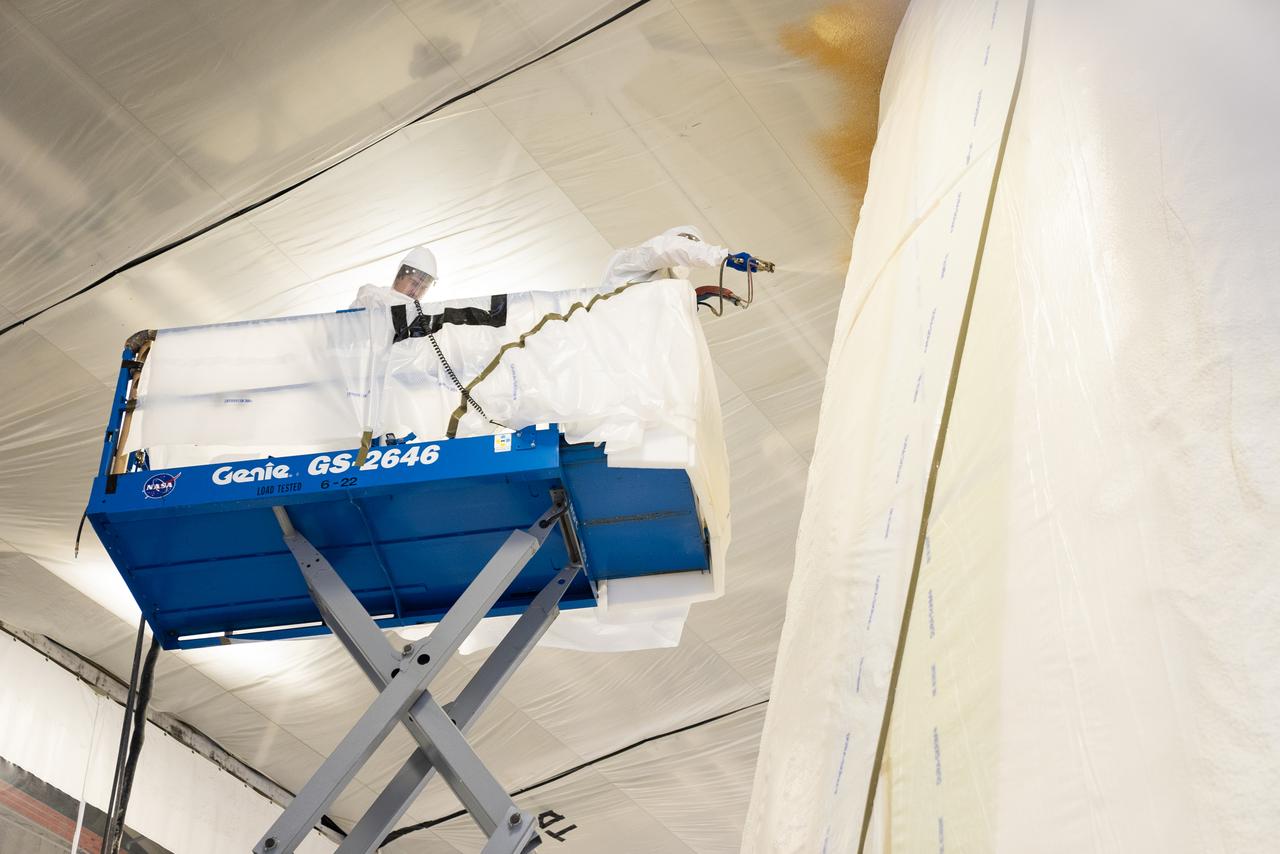

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

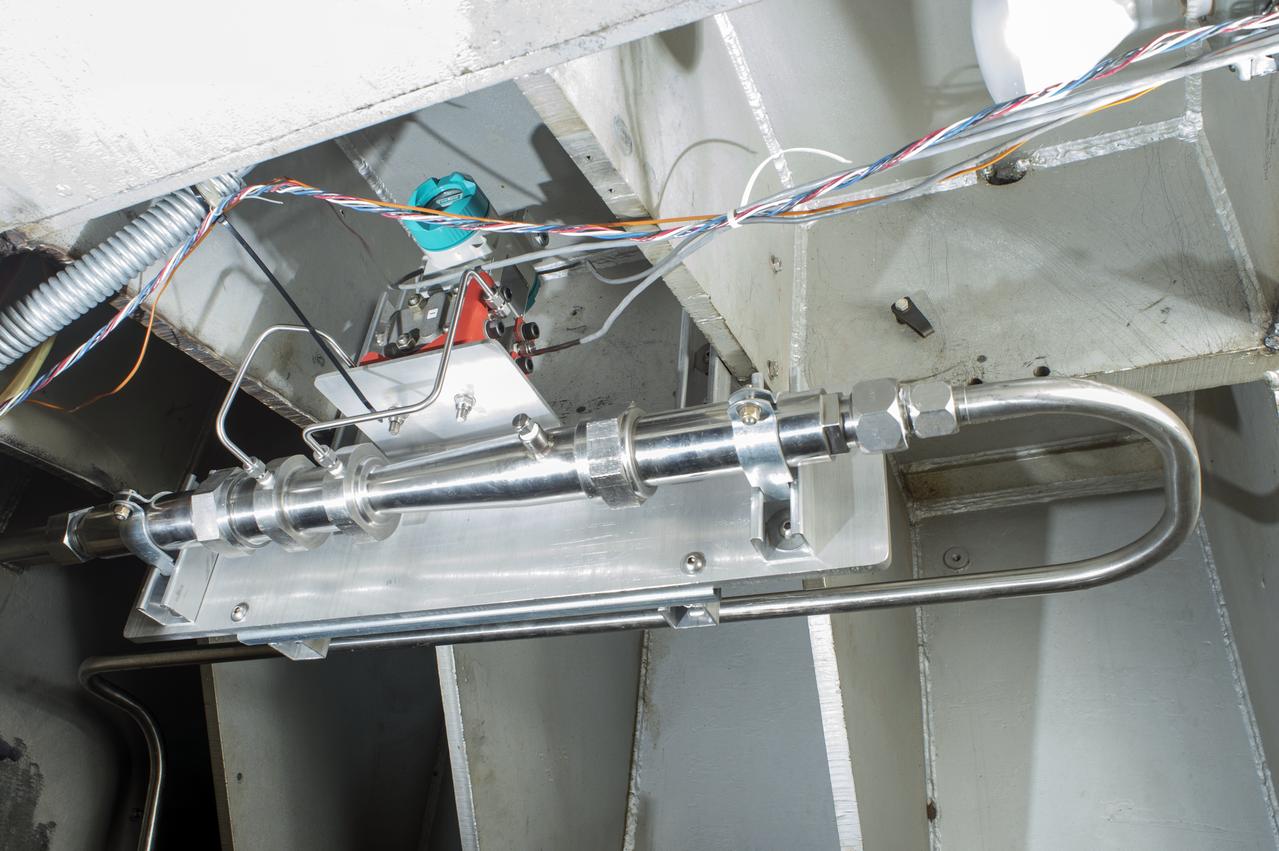
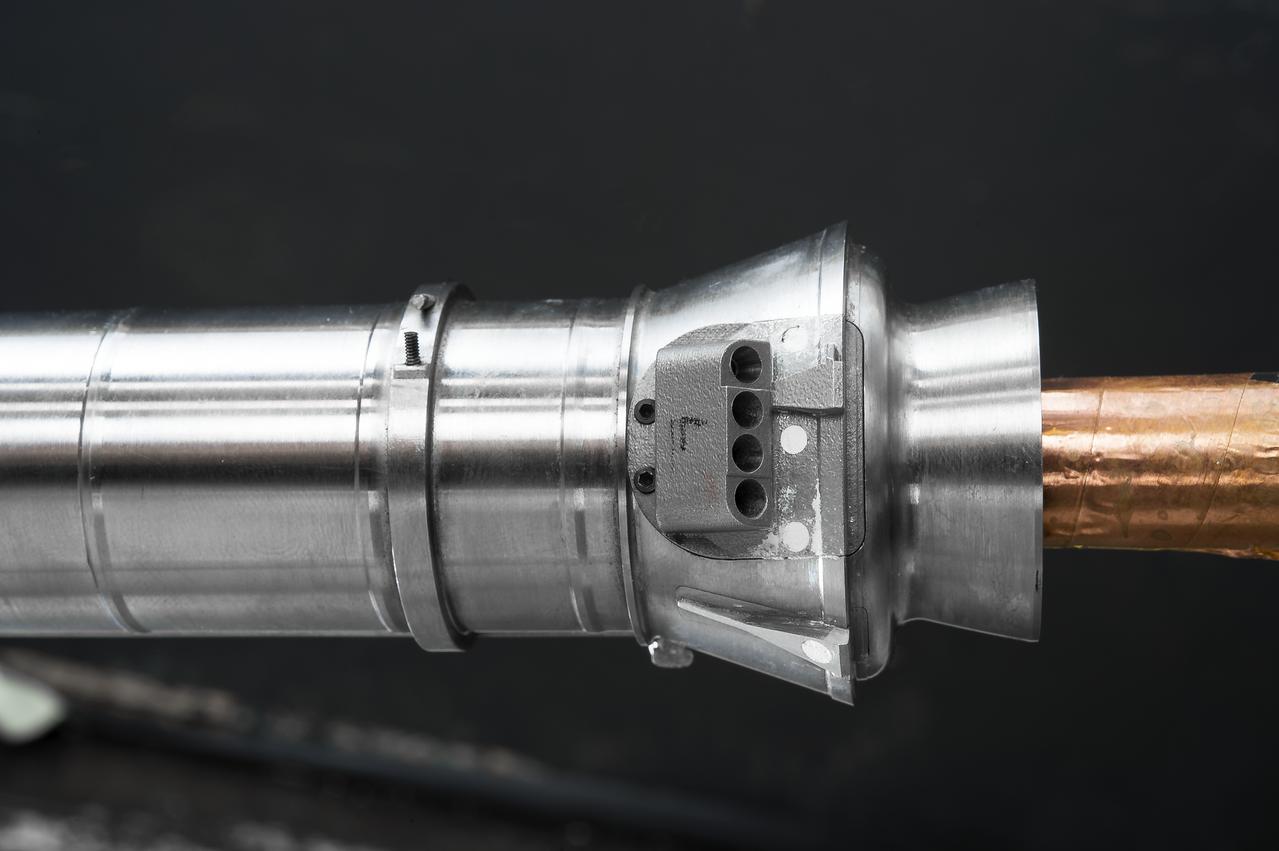
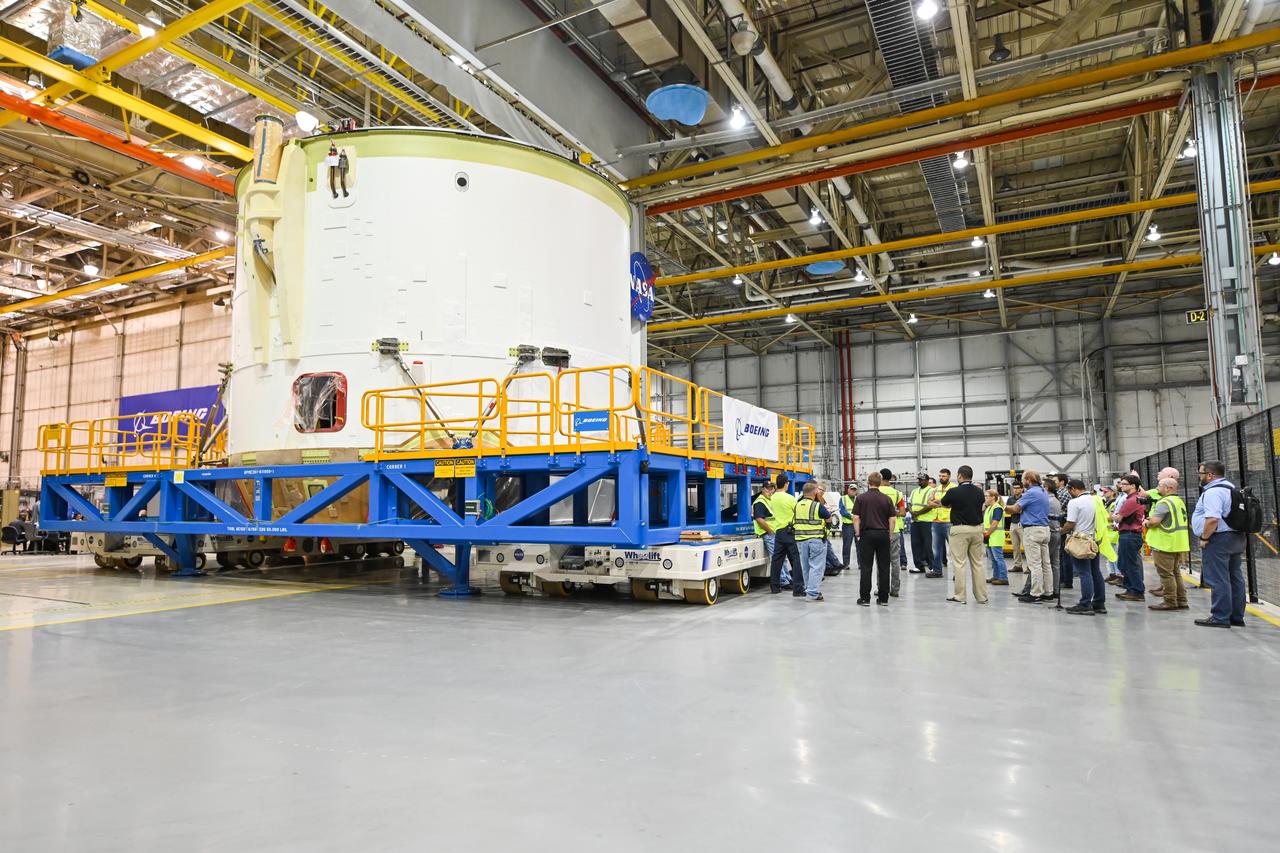
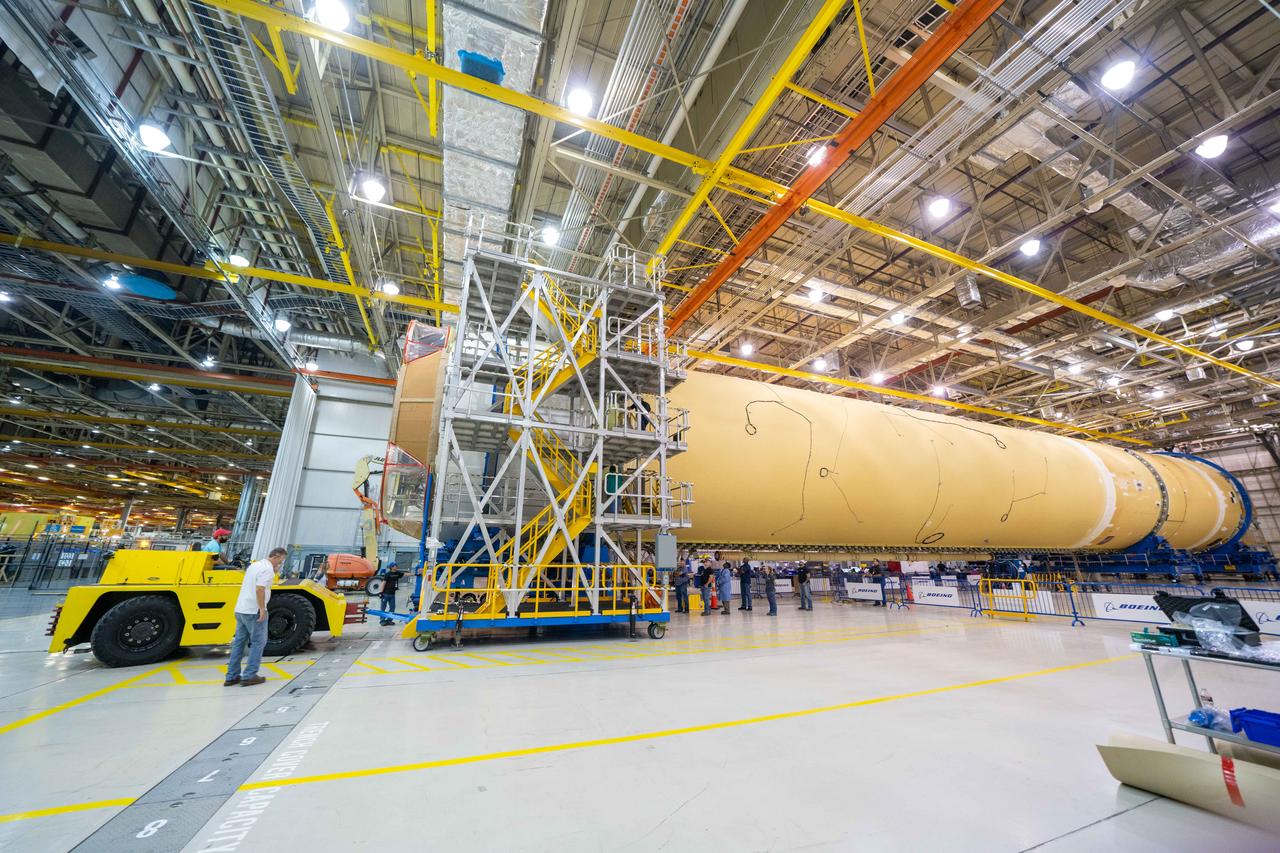
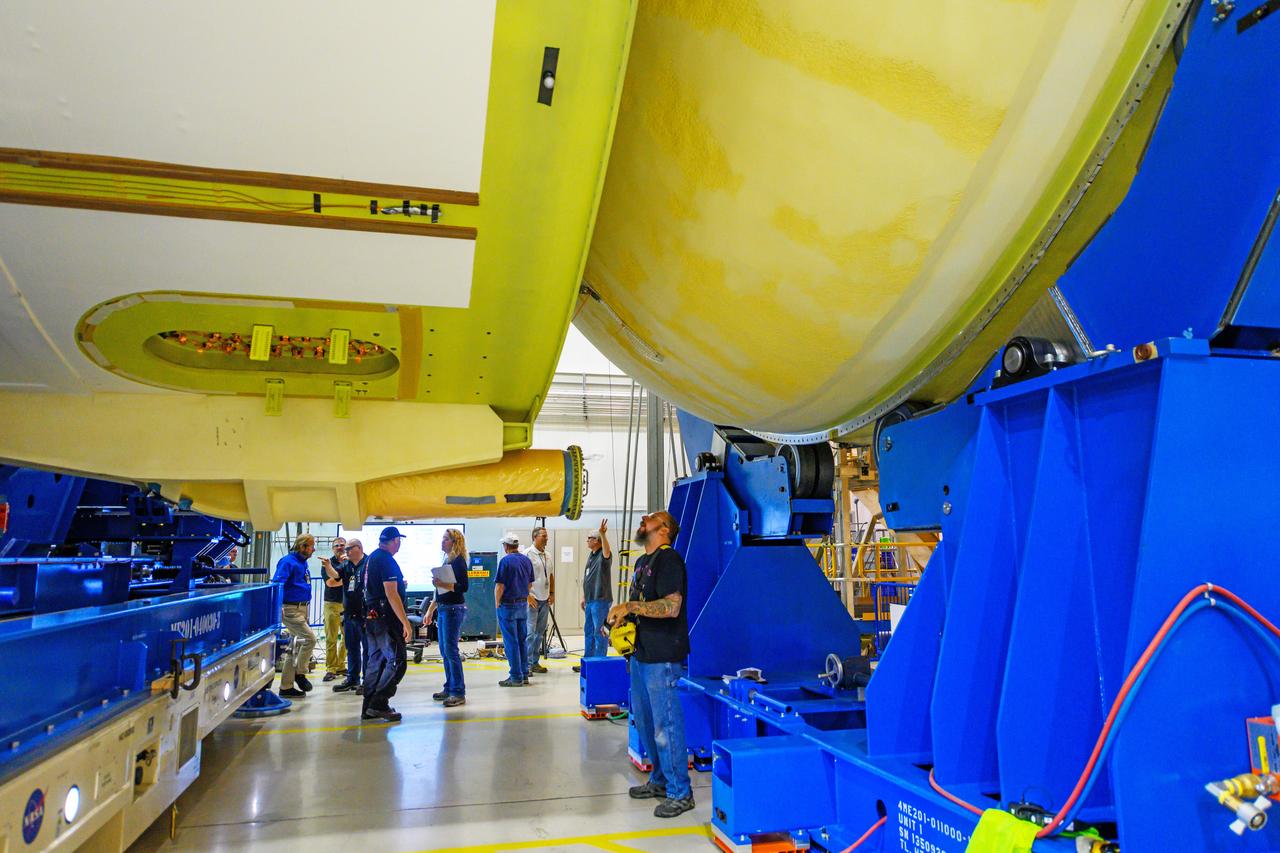
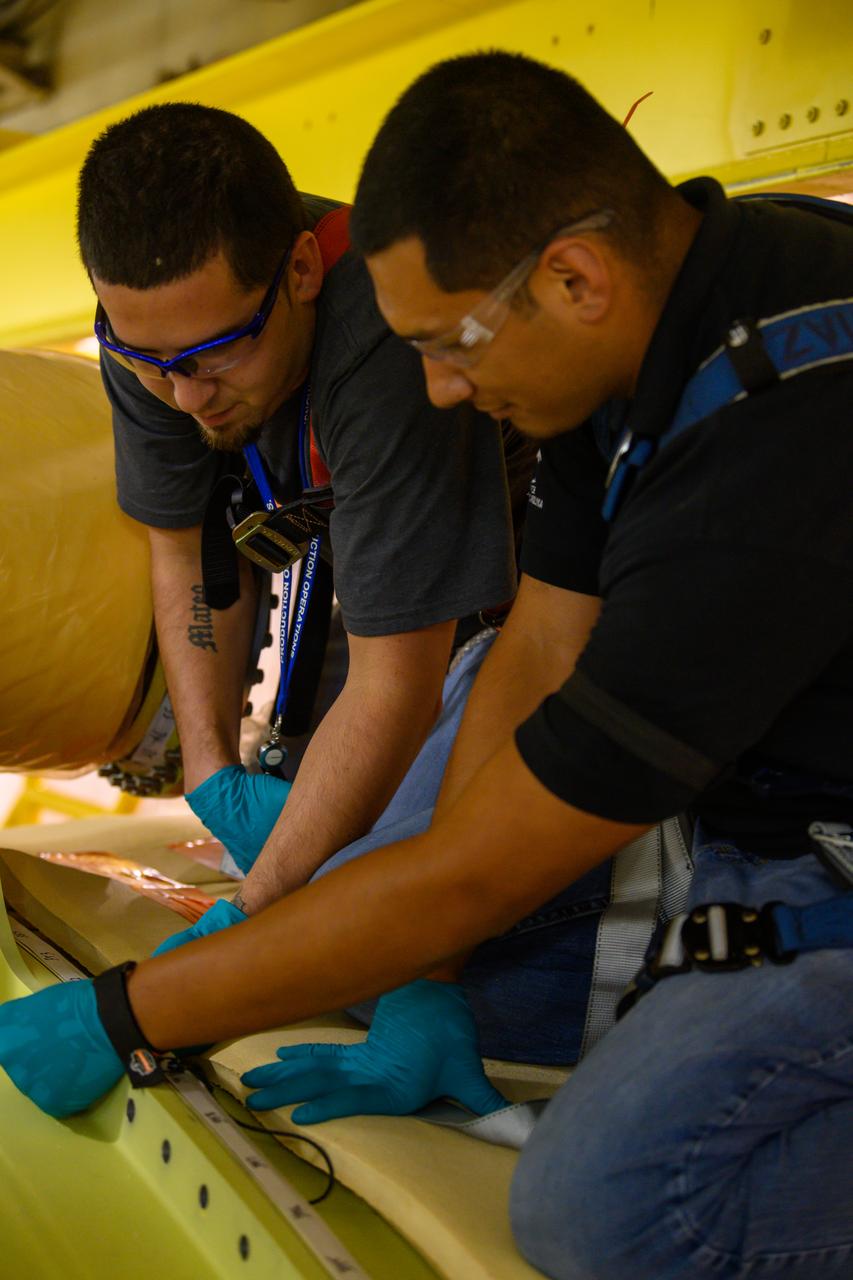
NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

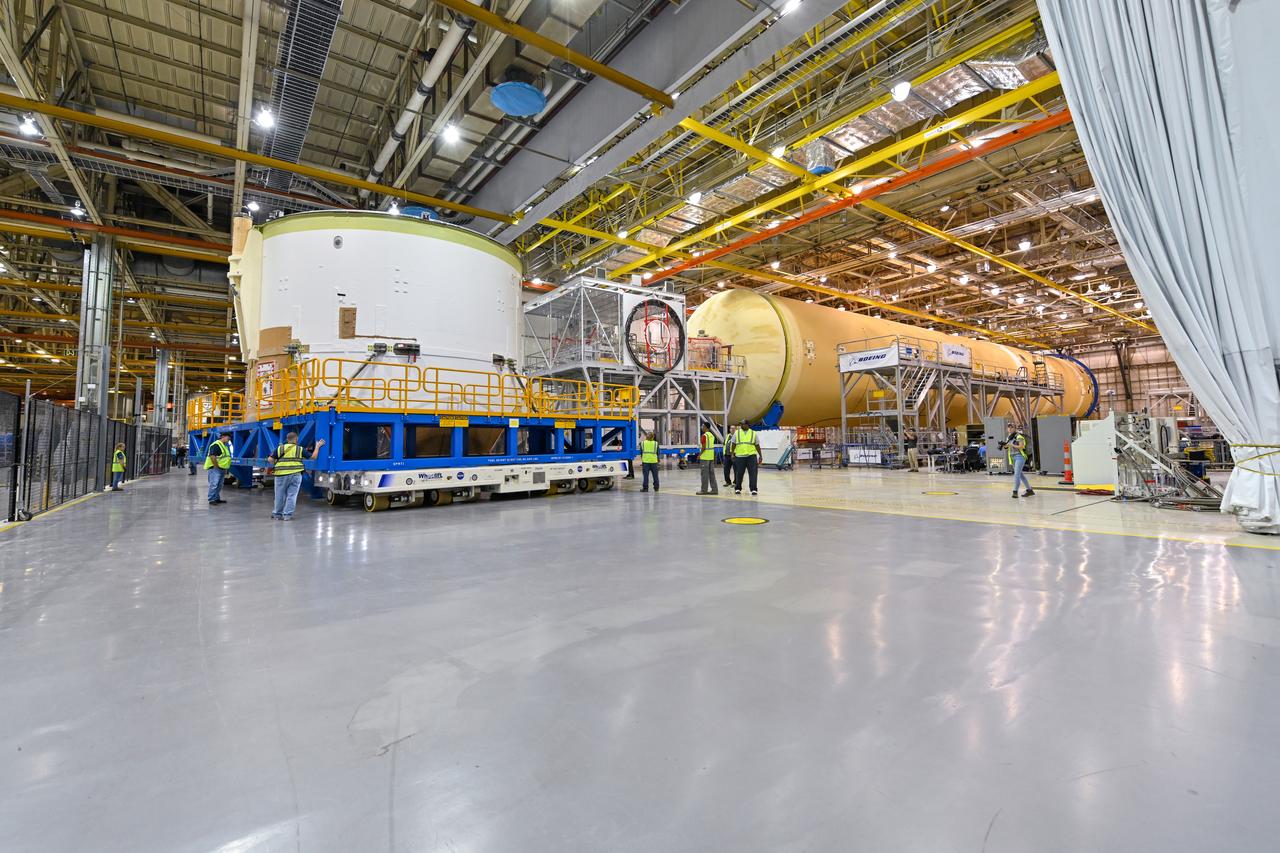
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

NASA finished assembling and joining the main structural components for the largest rocket stage the agency has built since the Saturn V that sent Apollo astronauts to the Moon. Engineers at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans connected the last of the five sections of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage Sept. 19. The stage will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I, the first flight SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The engine section is located at the bottom of the 212-foot-tall stage and houses the four RS-25 engines. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
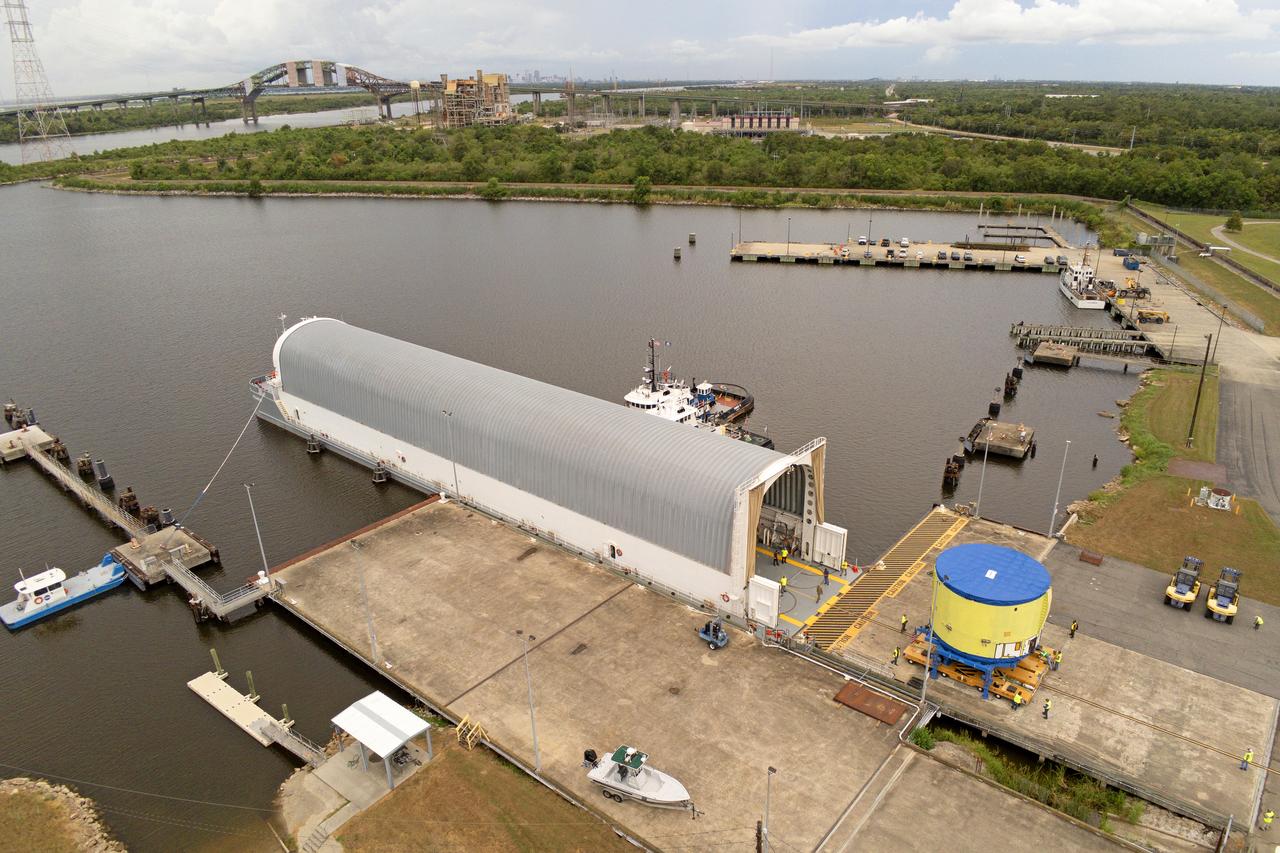

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
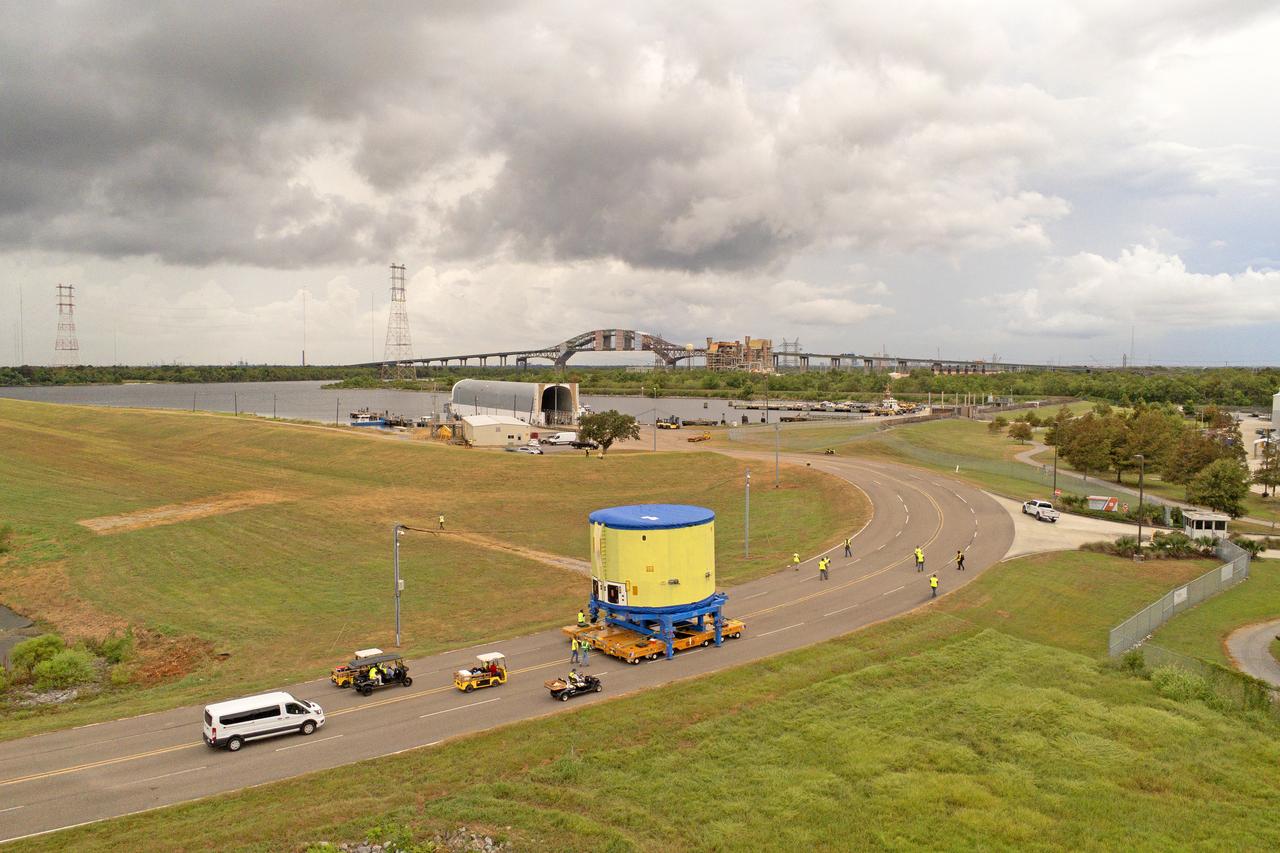

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
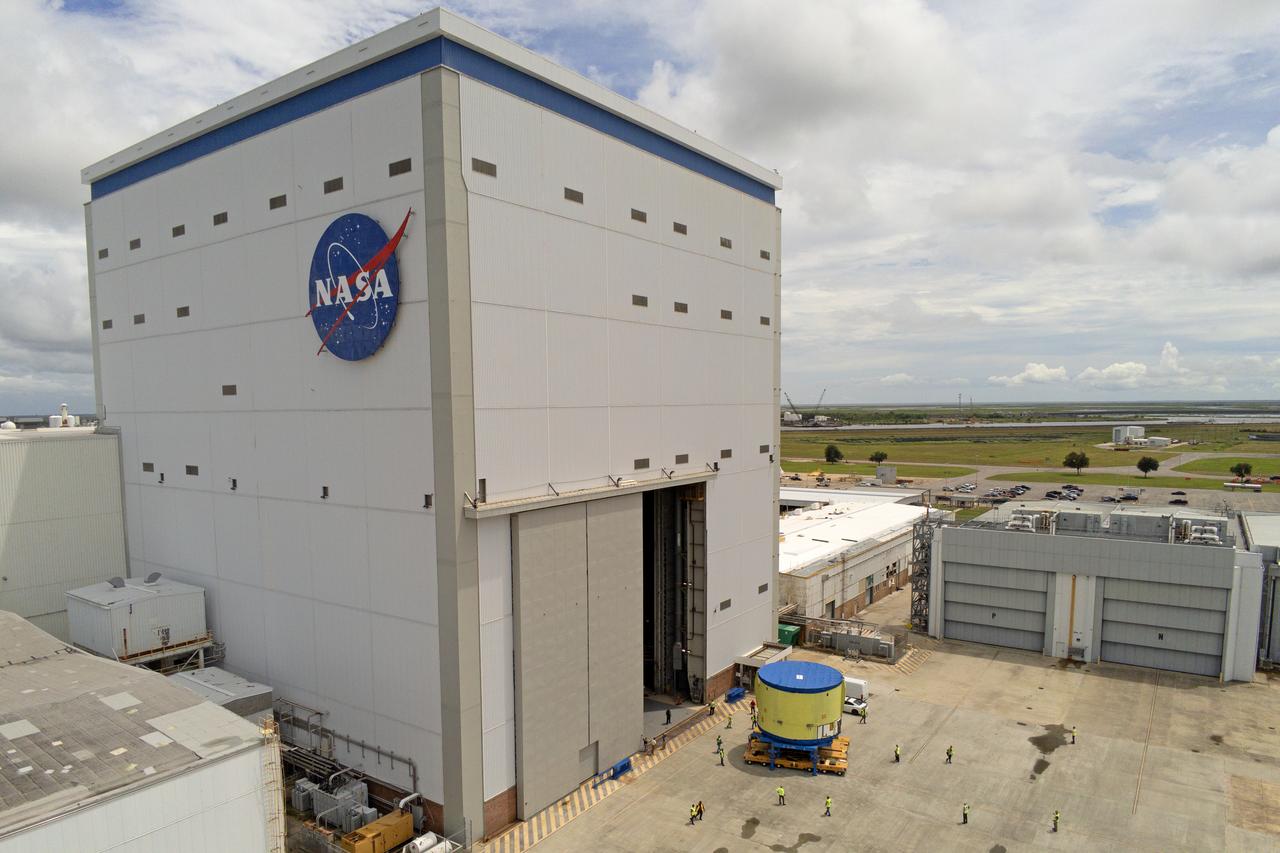

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
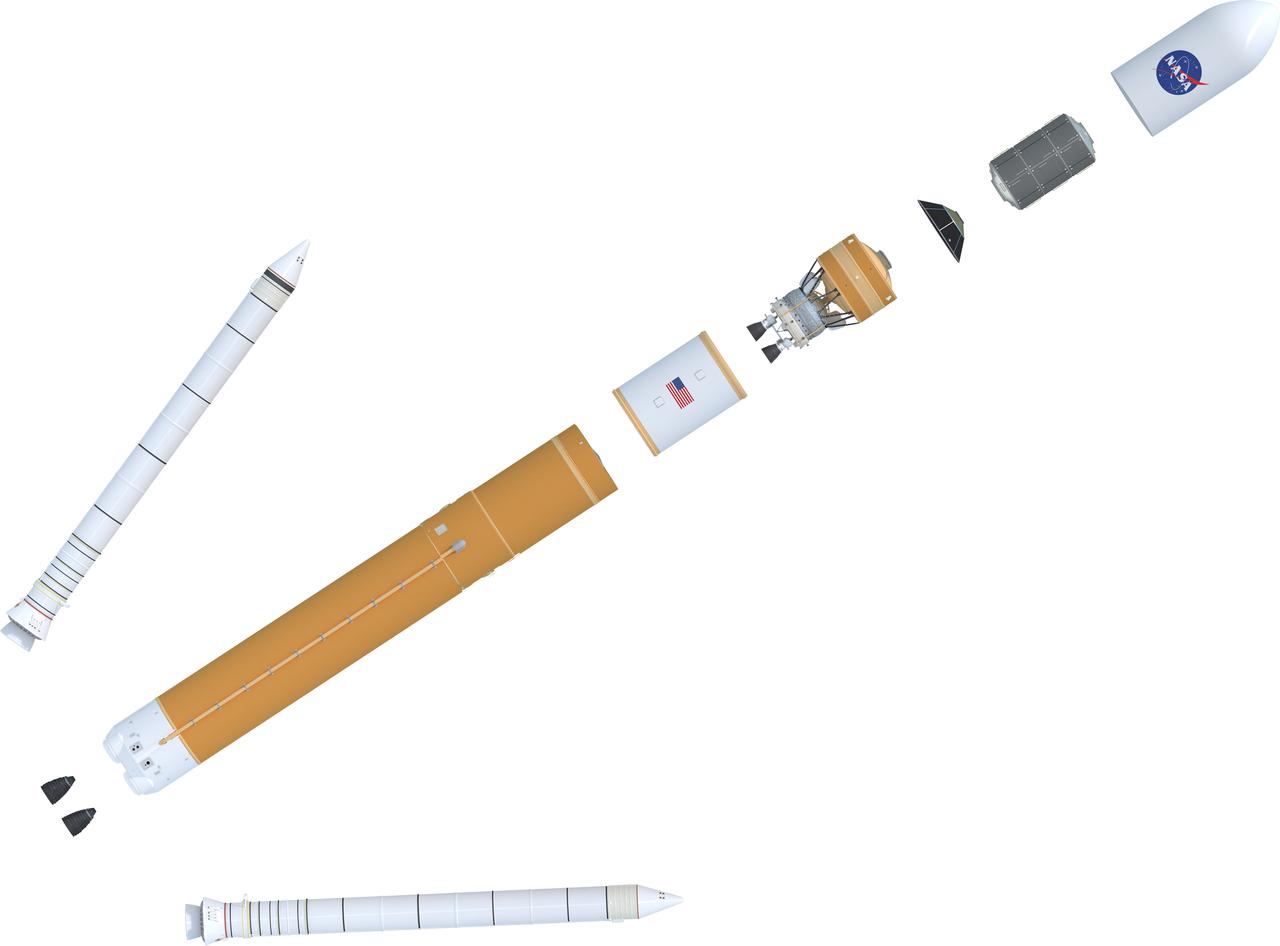
Expanded view illustration of elements of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
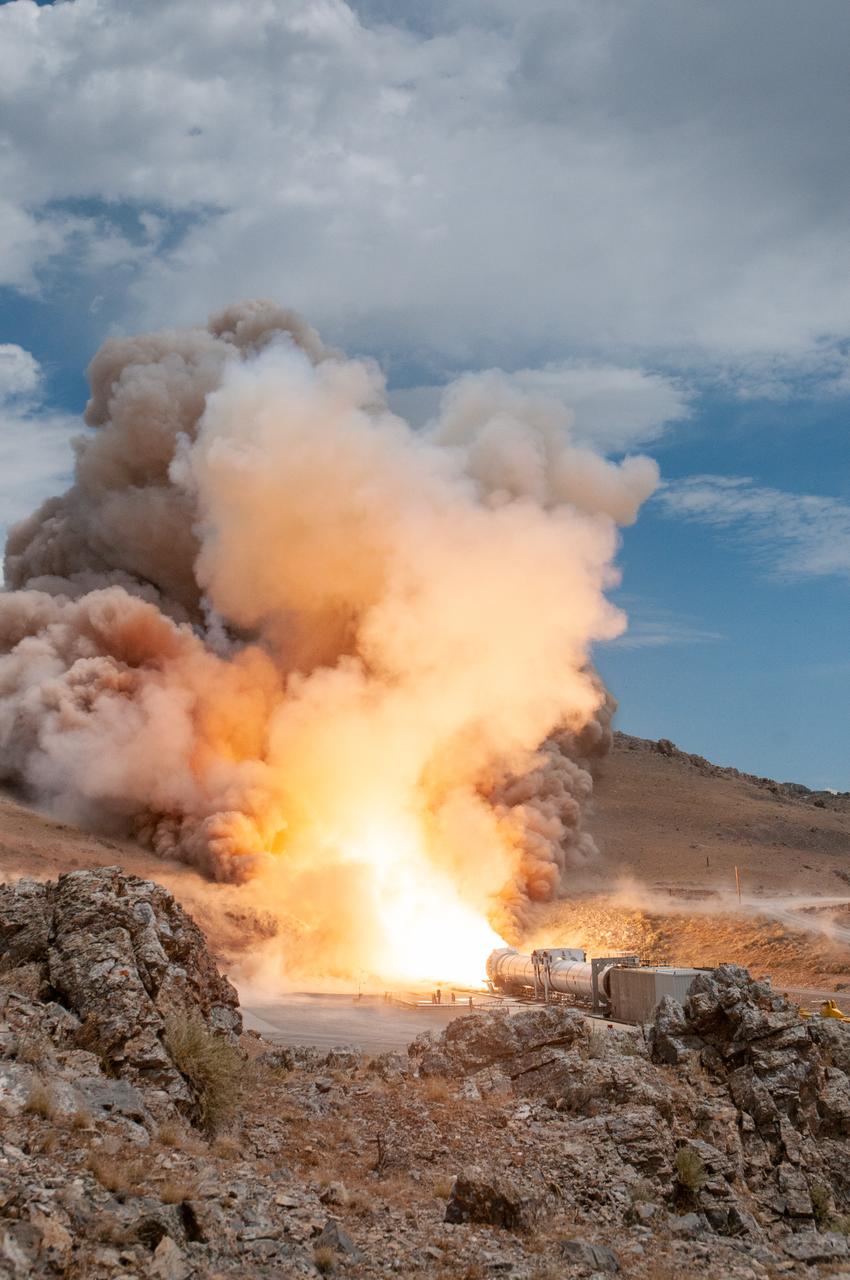

NASA and Northrop Grumman completed a solid rocket booster motor ground test for future flights of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, July 21. The booster motor, called Flight Support Booster-2 (FSB-2), fired for a little over two minutes and produced more than 3.6 million pounds of thrust. Test data will be used to evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters for missions after Artemis III. When SLS launches the Artemis missions to the Moon, its two five-segment solid rocket boosters produce more than 75% of the initial thrust. The SLS boosters are the largest, most powerful boosters ever built for flight. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls
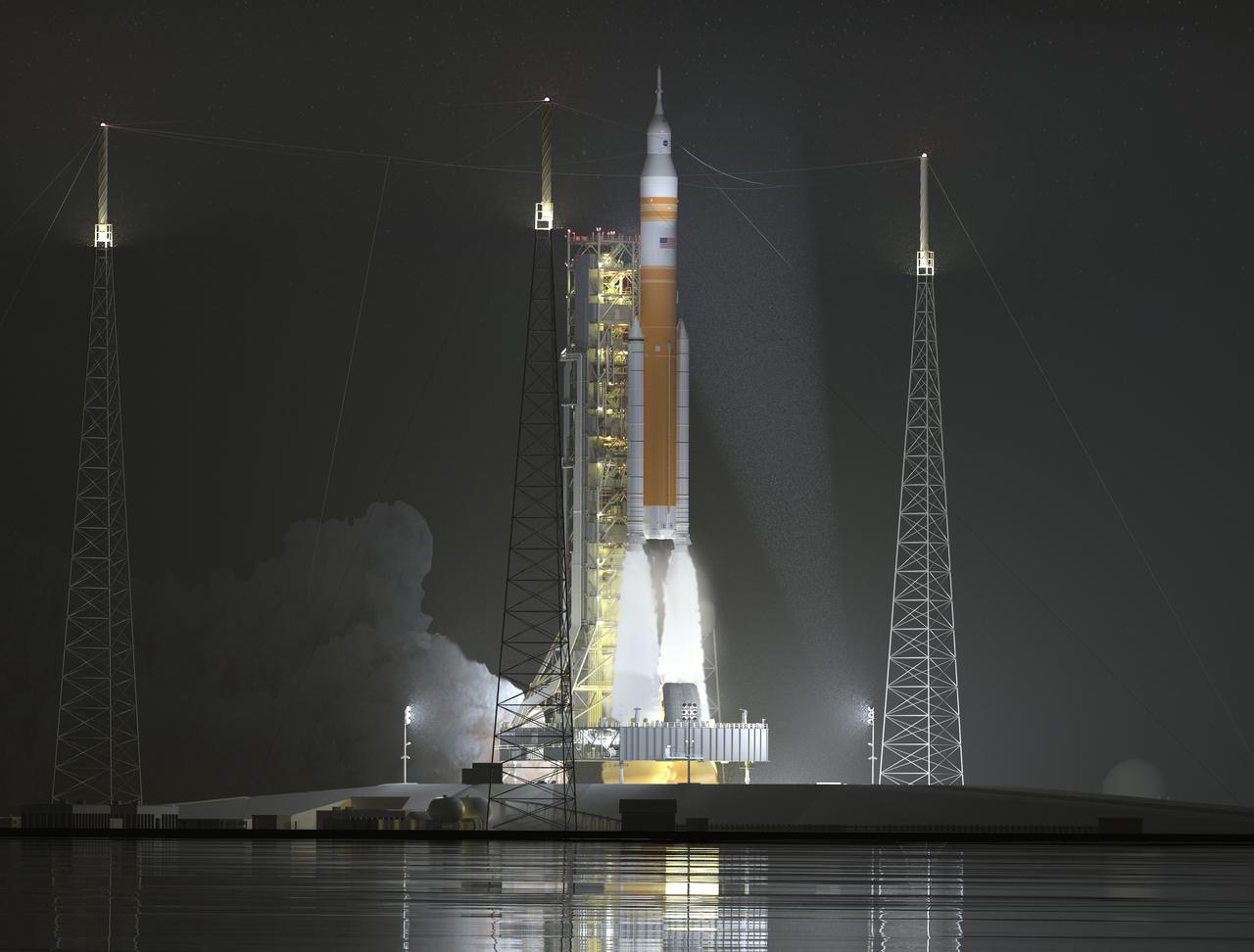

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant night launch. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA) In album: B1B_Crew_SLS
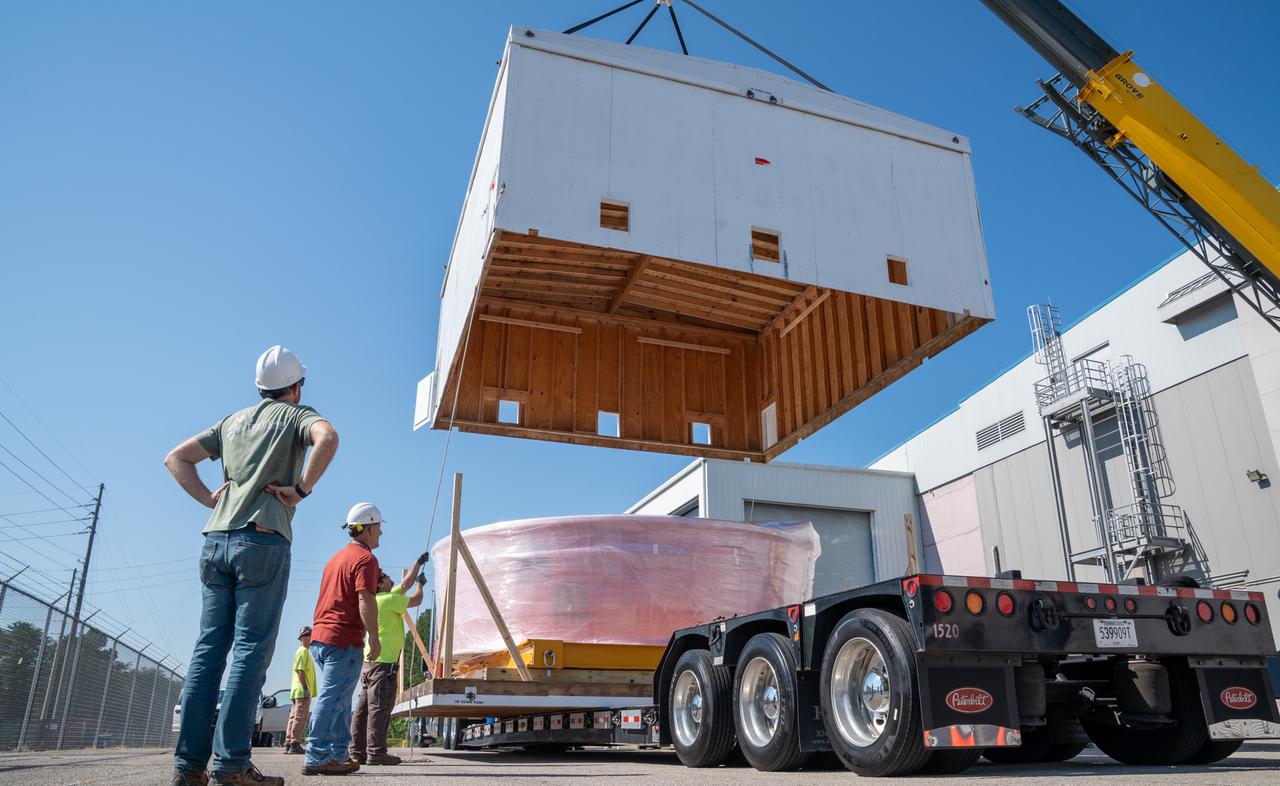

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
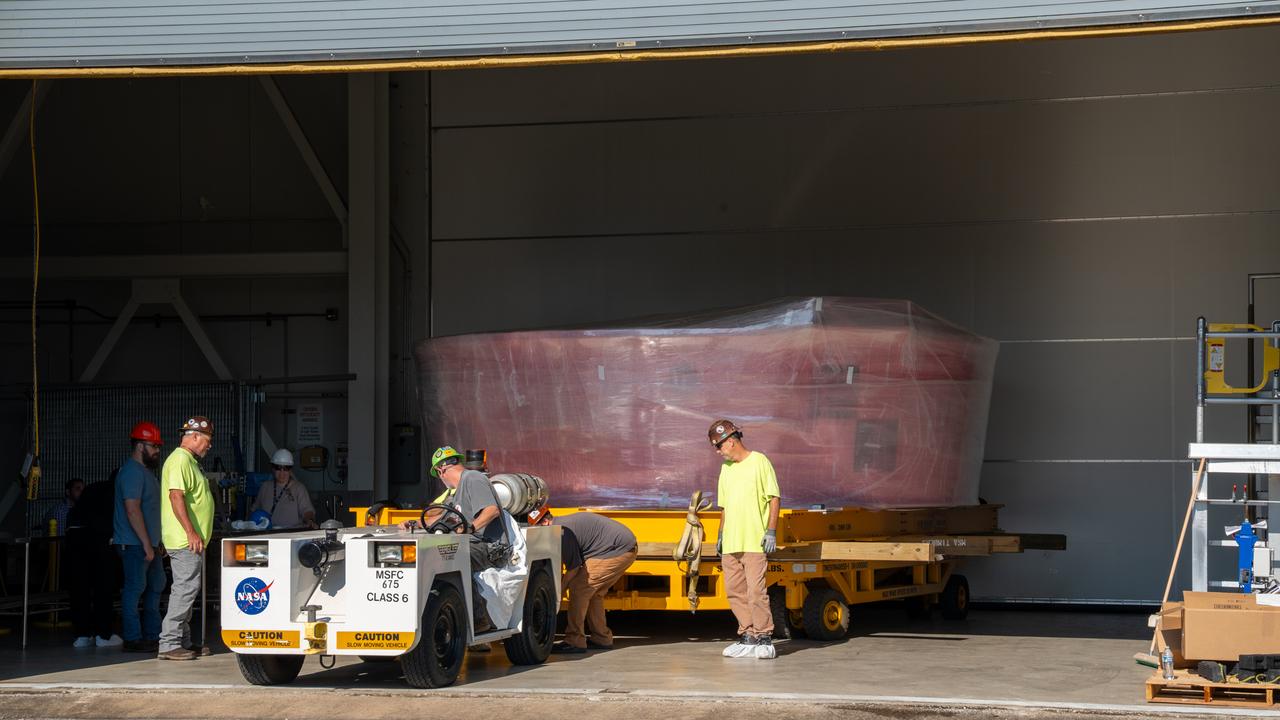

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
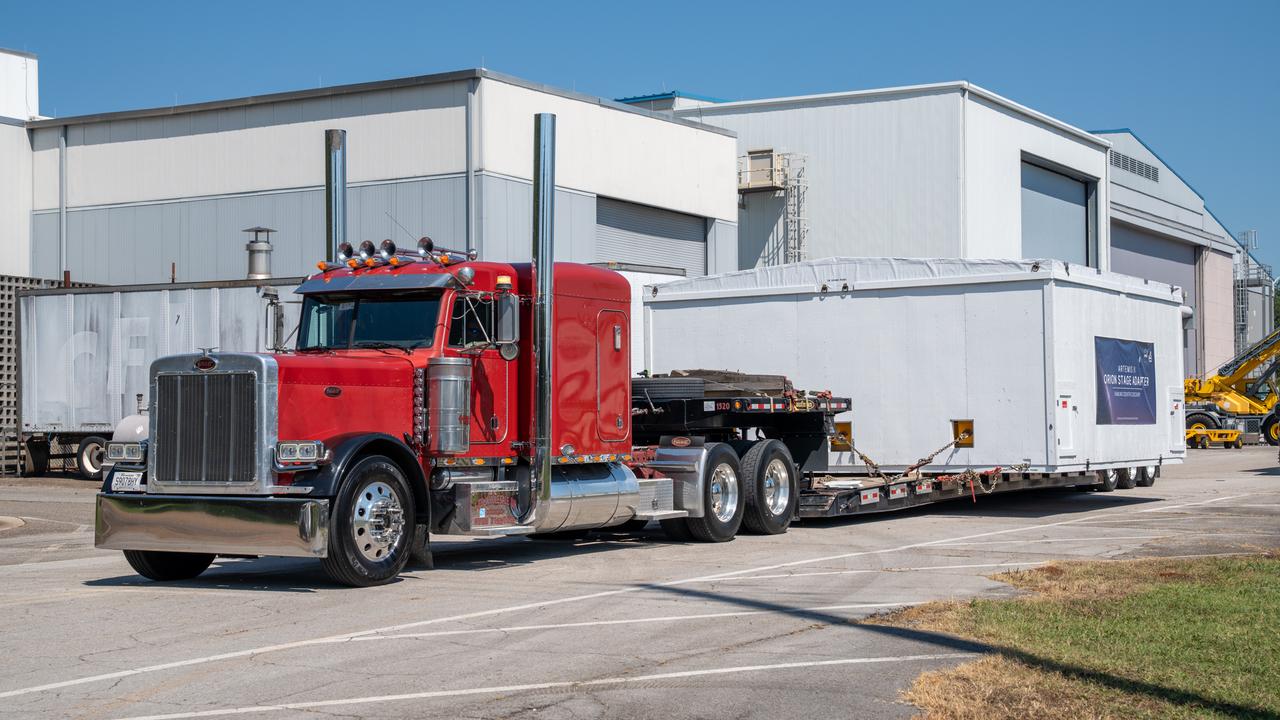

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
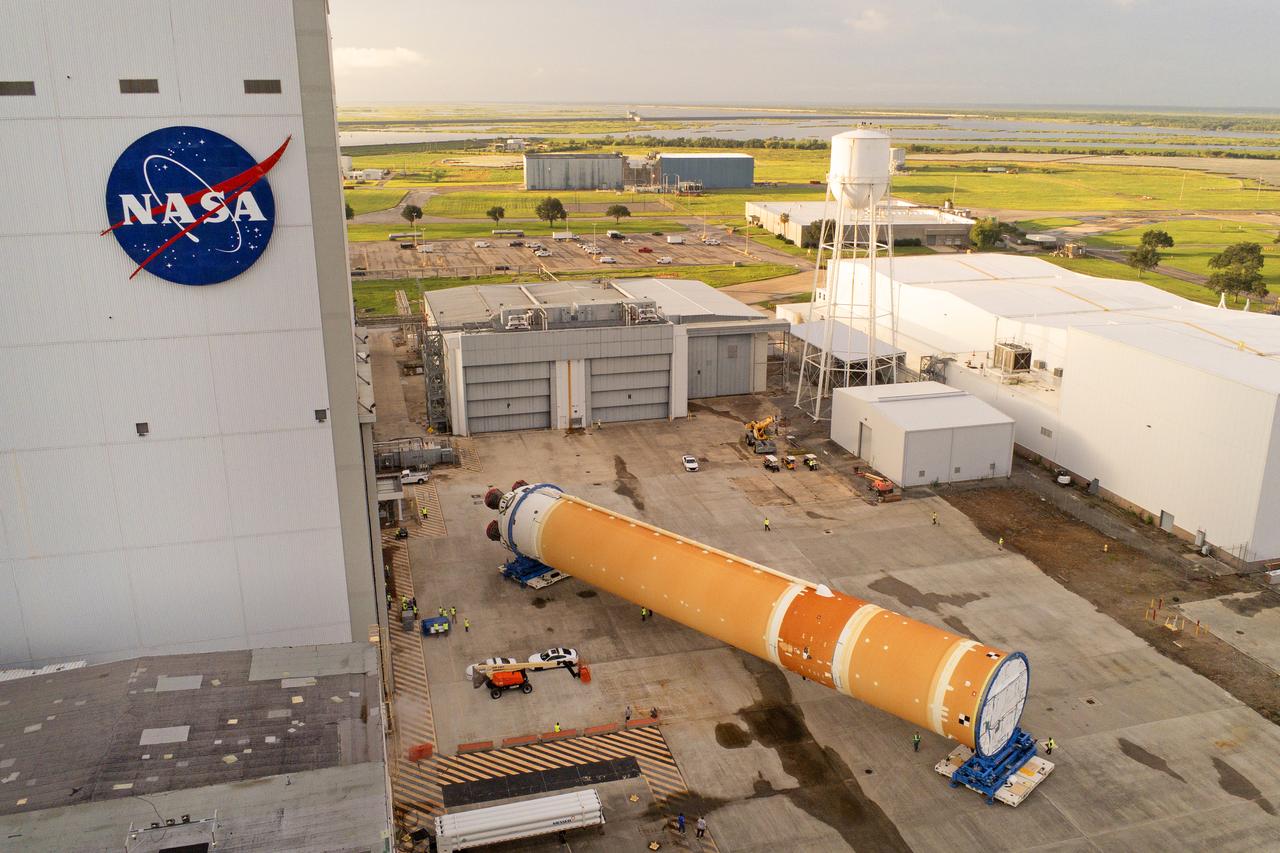

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
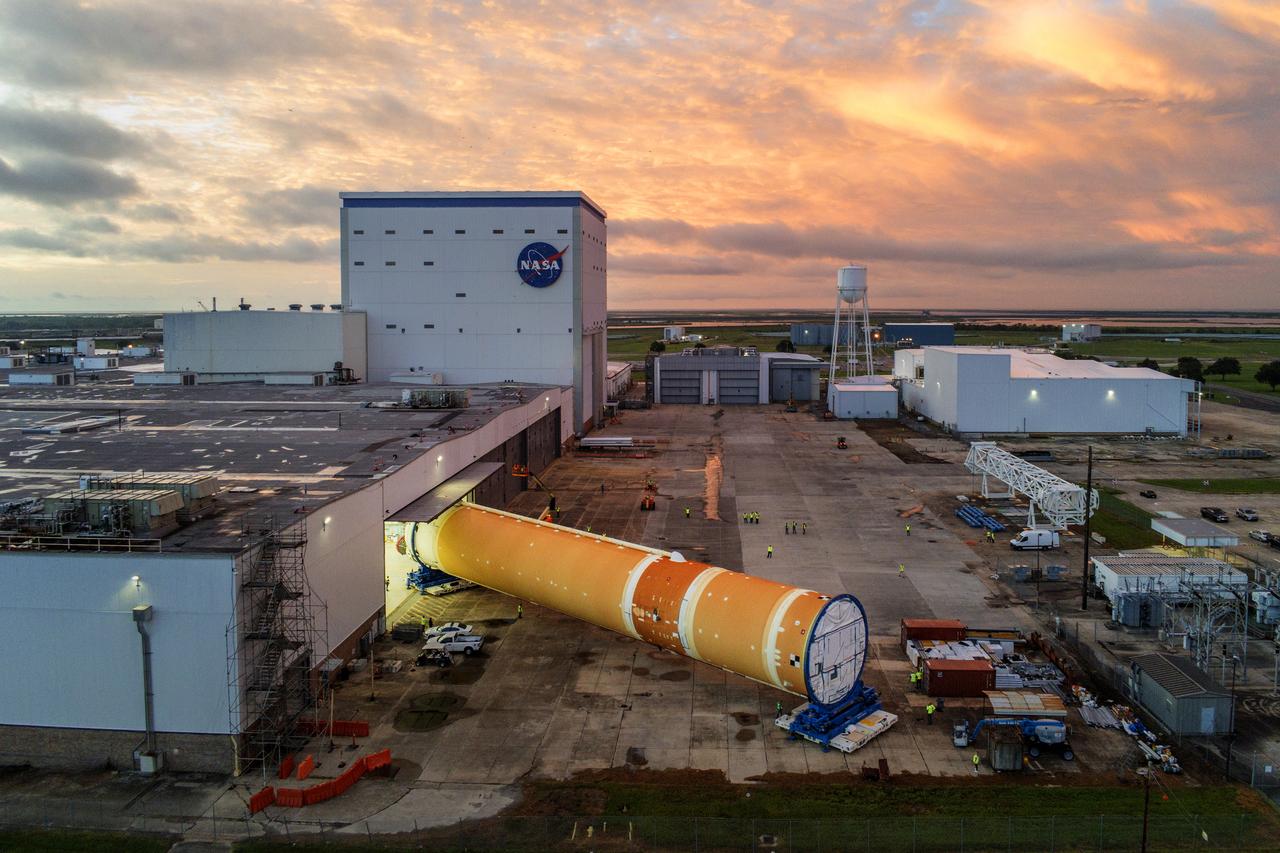

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
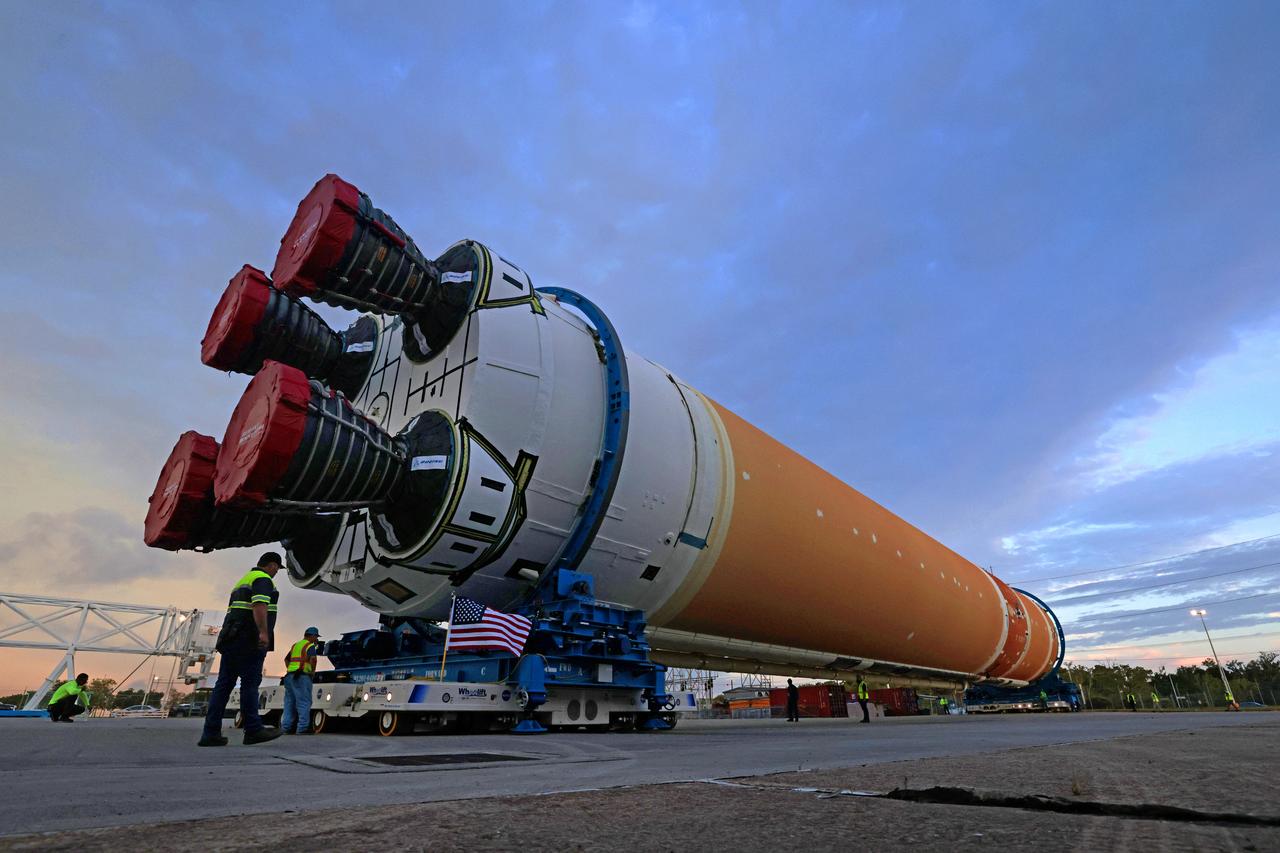

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
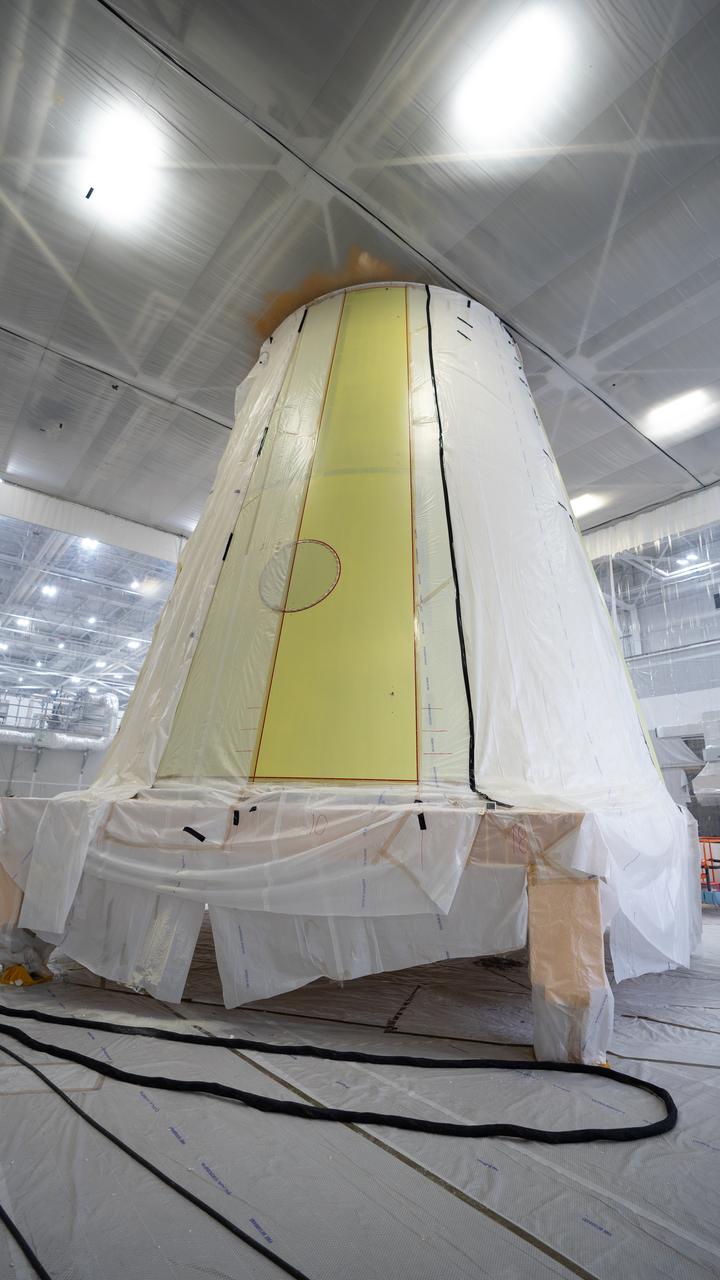

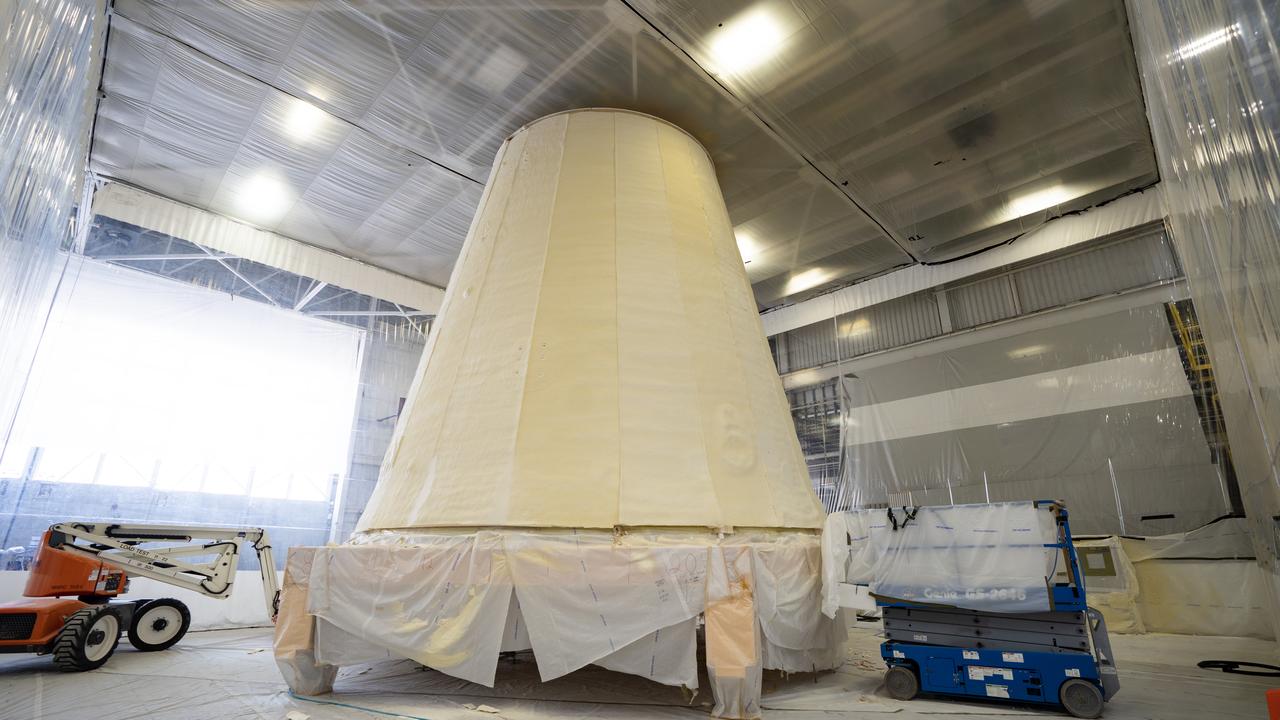
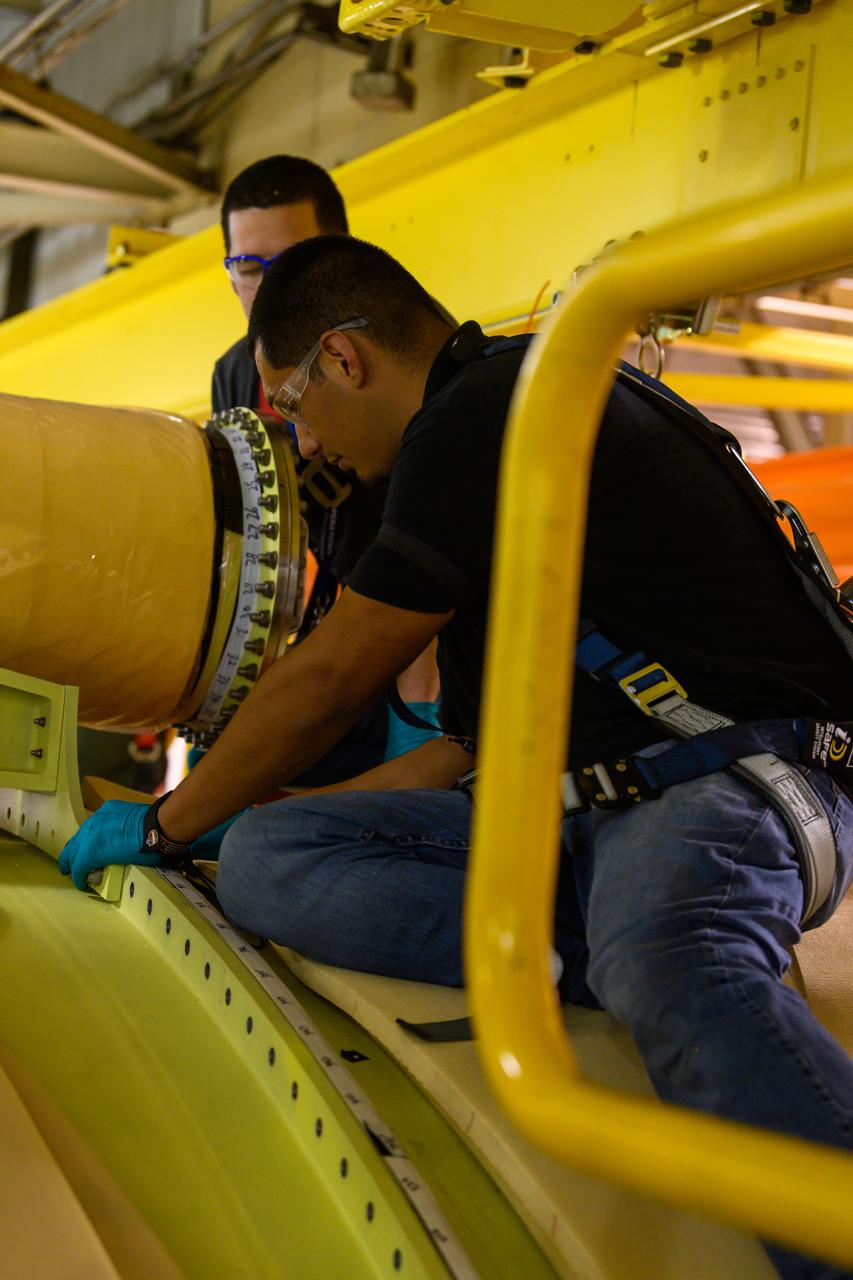
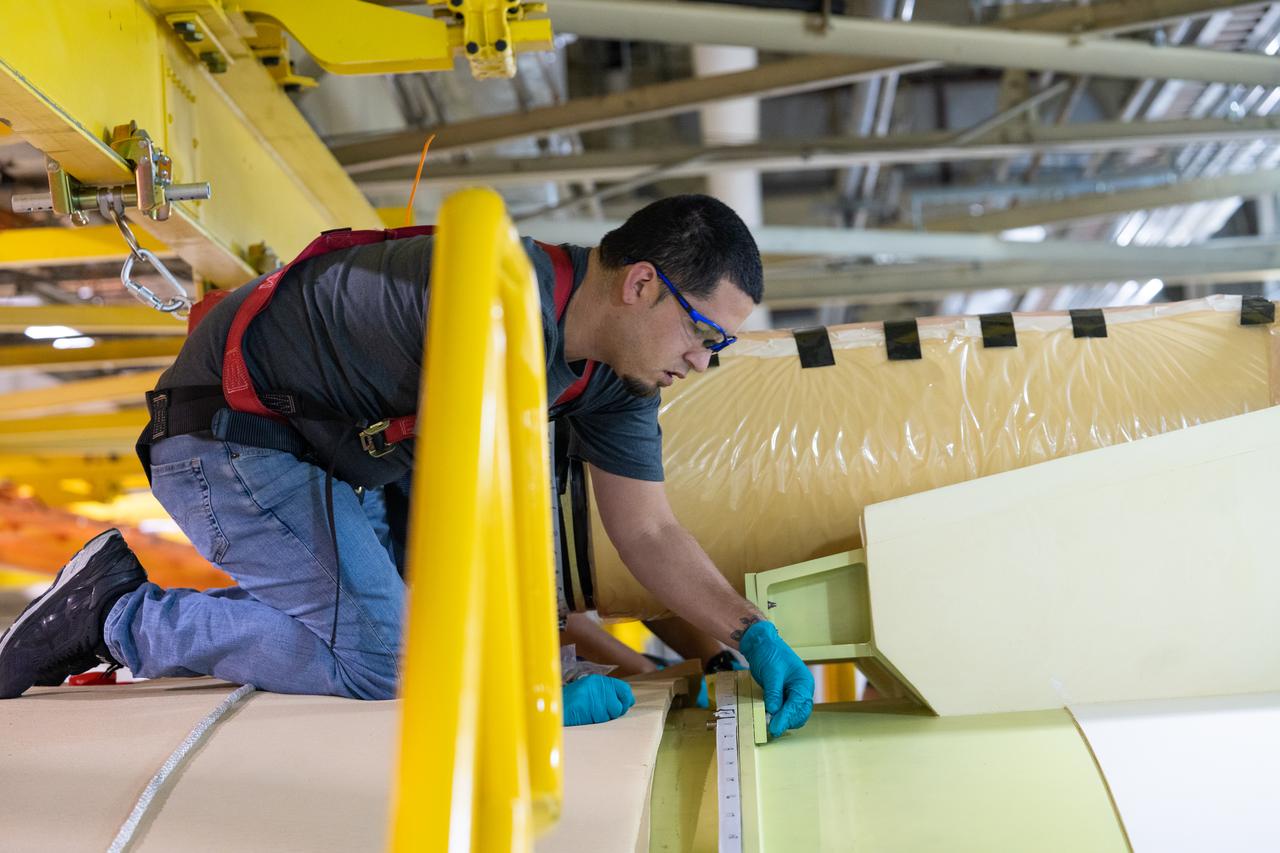
These photos show the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III before technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, applied the thermal protection system to it. Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discover and inspire the Artemis Generation. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
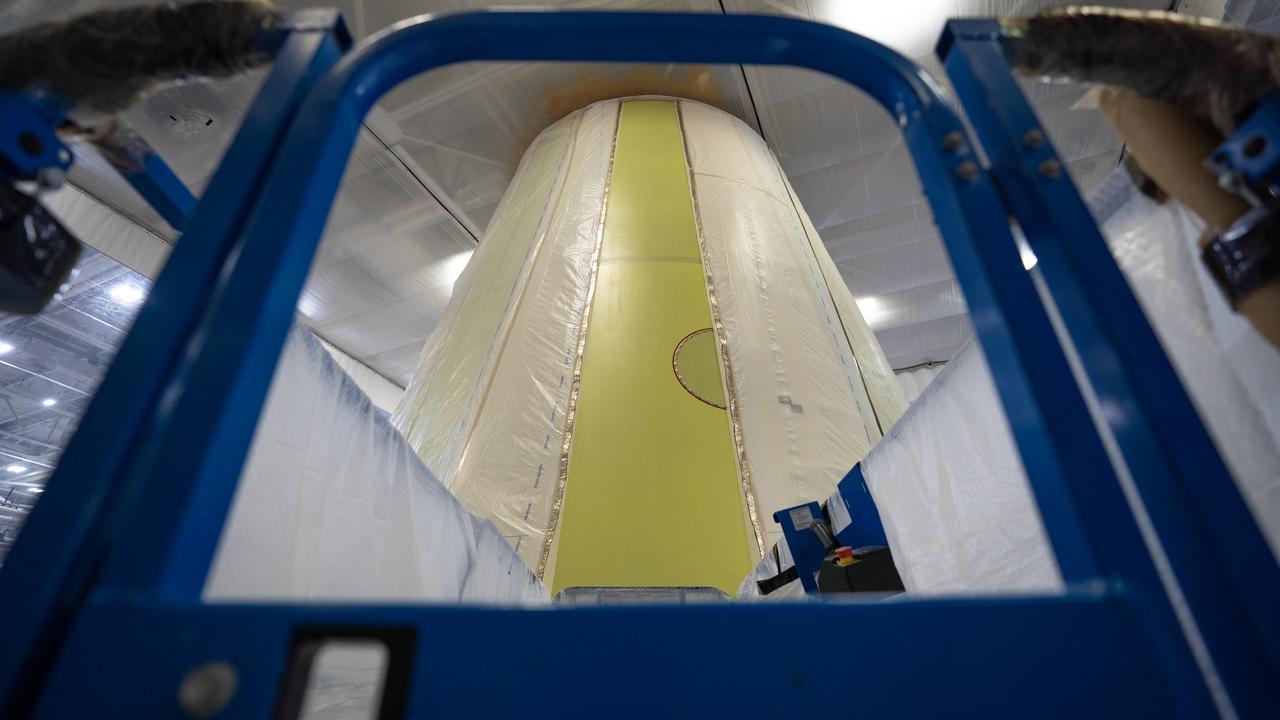
These photos show the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III before technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, applied the thermal protection system to it. Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discover and inspire the Artemis Generation. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
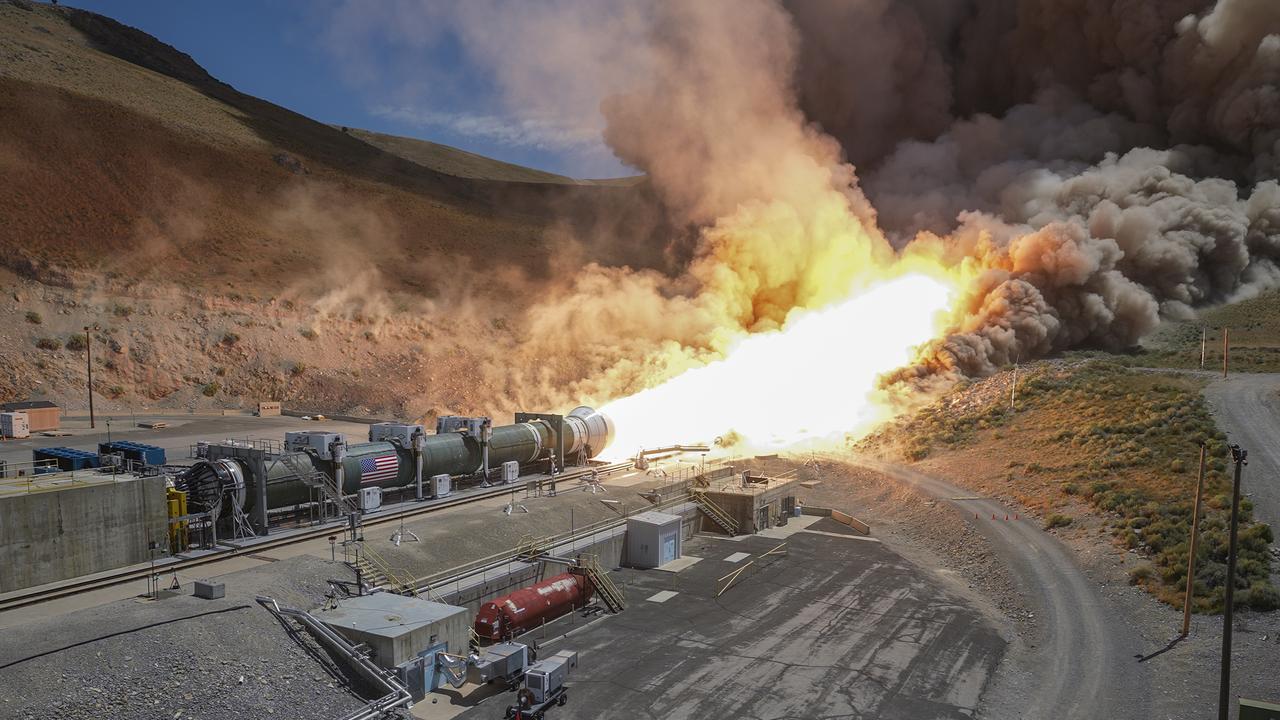

Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. Teams from NASA and Northrop Grumman fire a ground-based version of a booster for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket June 26. Secured horizontally in a test stand at Northrop Grumman’s test facility in Promontory, Utah, the single five-segment booster motor fired for more than two minutes and produced 3.9 million pounds of thrust. The booster for this test, known as Demonstration Motor-1 (DM-1), is the result of the Booster Obsolescence Life Extension (BOLE) project. This test was the first full-scale ground test of a new five-segment solid rocket motor. During the test, there was an abnormal event approximately 15 seconds before the end of the motor firing. Despite this event, NASA achieved several of the test’s primary objectives and received valuable data on technical risks identified ahead of the test. Testing this evolved booster for the SLS will help evaluate improvements and new materials in the boosters. The BOLE effort was launched to transition to a more efficient, lower cost commercial solution for the boosters for the SLS rocket. Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will send astronauts to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and to build the foundation for the first crewed missions to Mars – for the benefit of all. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
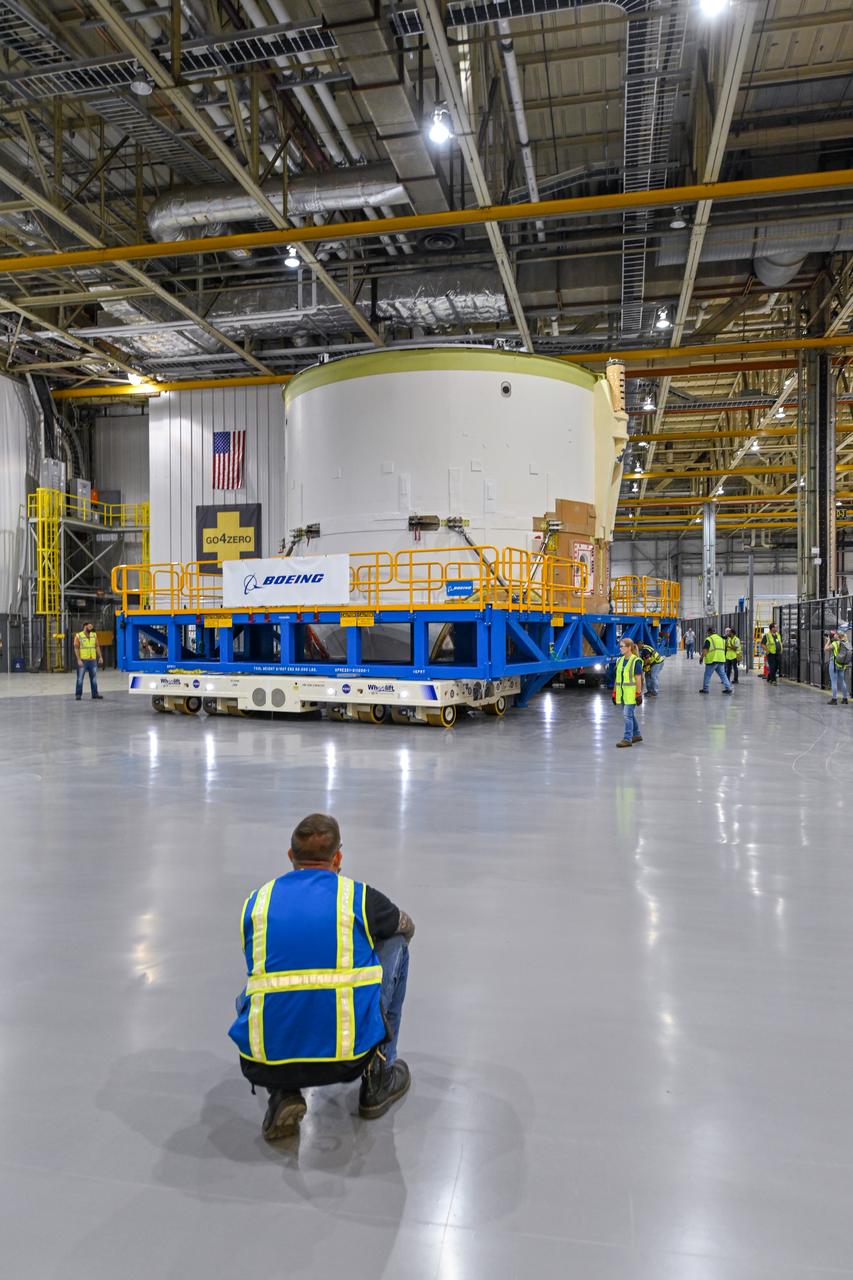

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
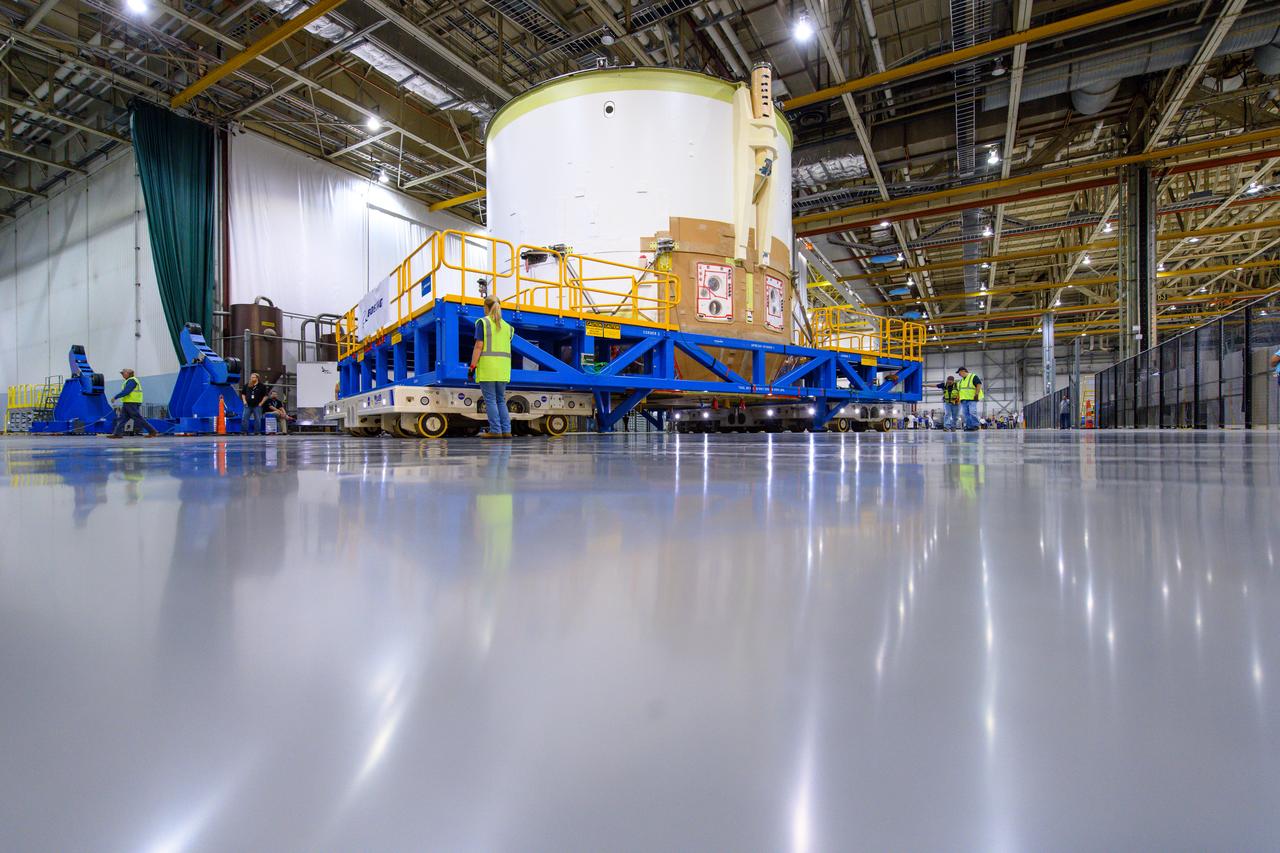

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Seen here, is a nighttime rendering of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant positioned on the mobile launcher. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
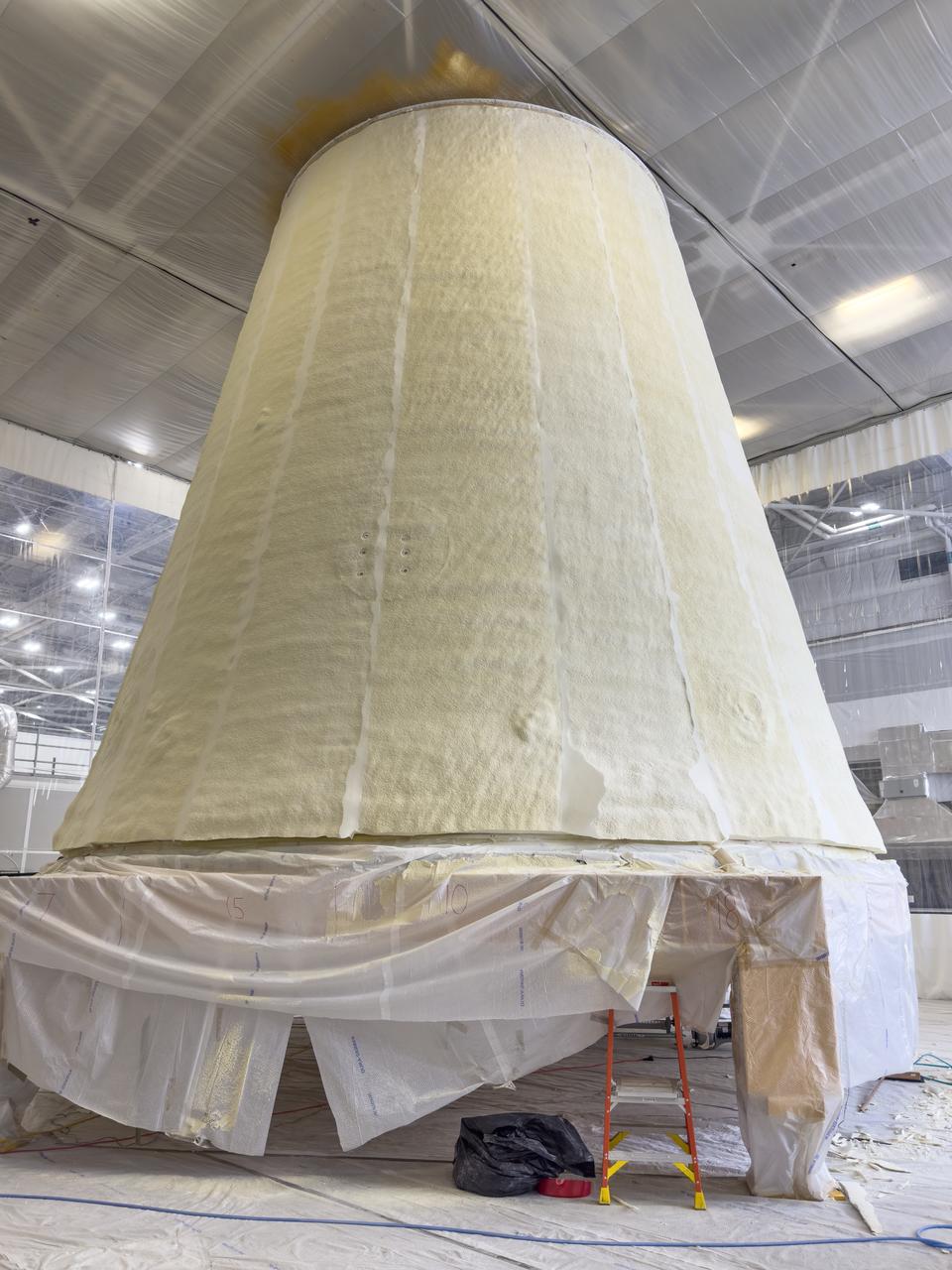

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
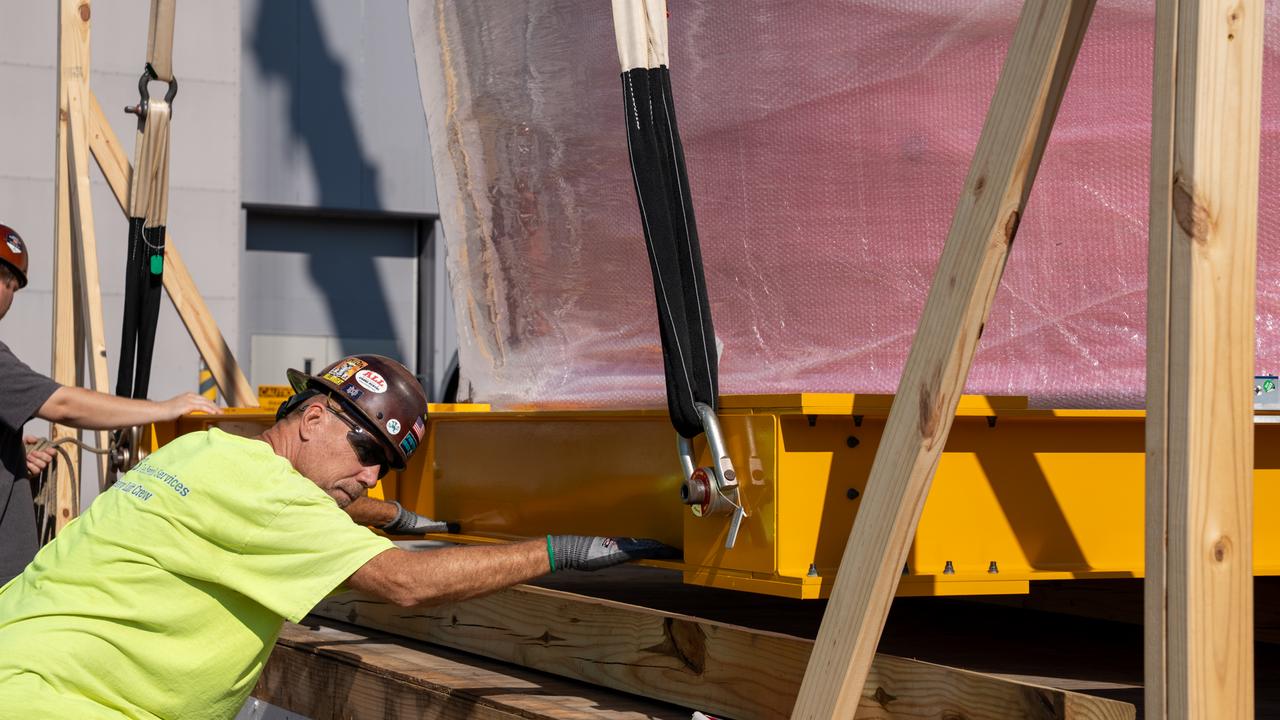

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
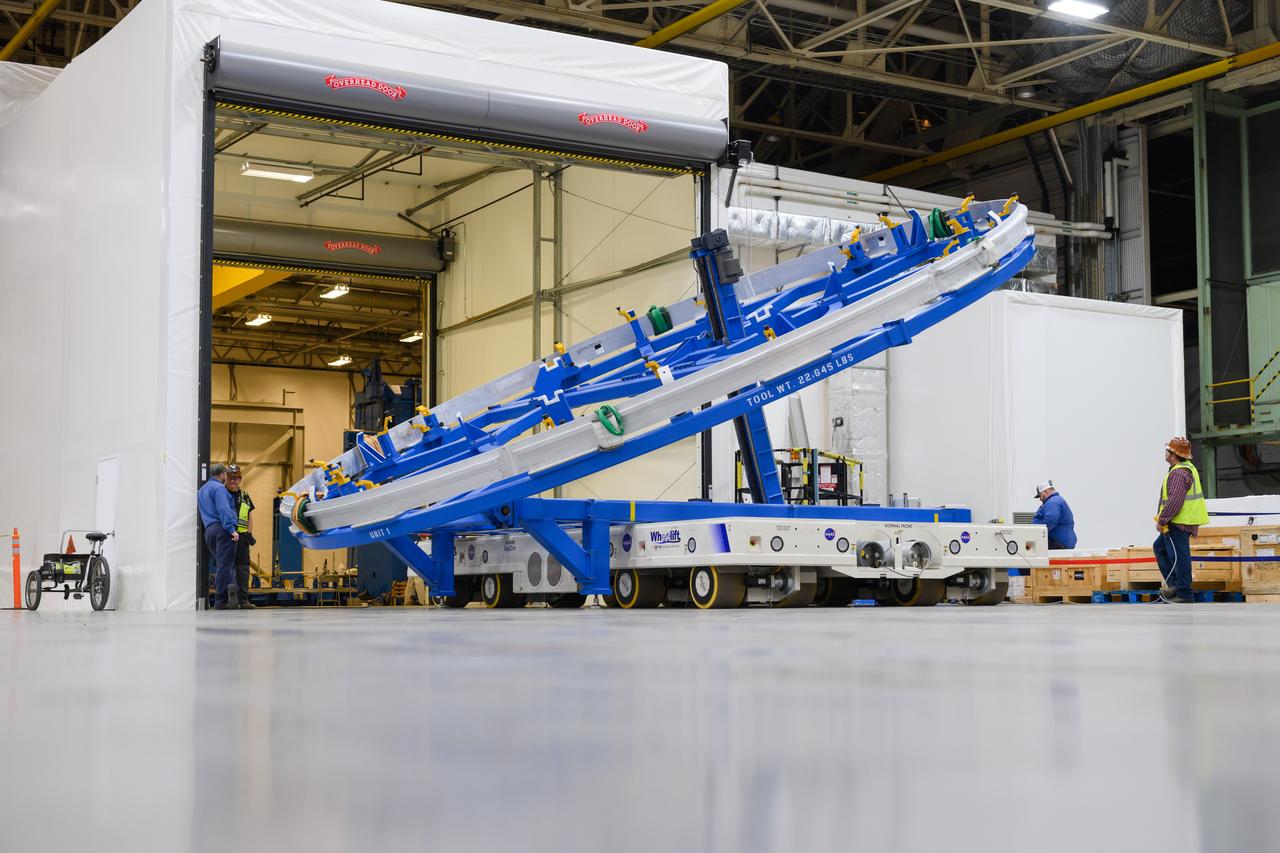

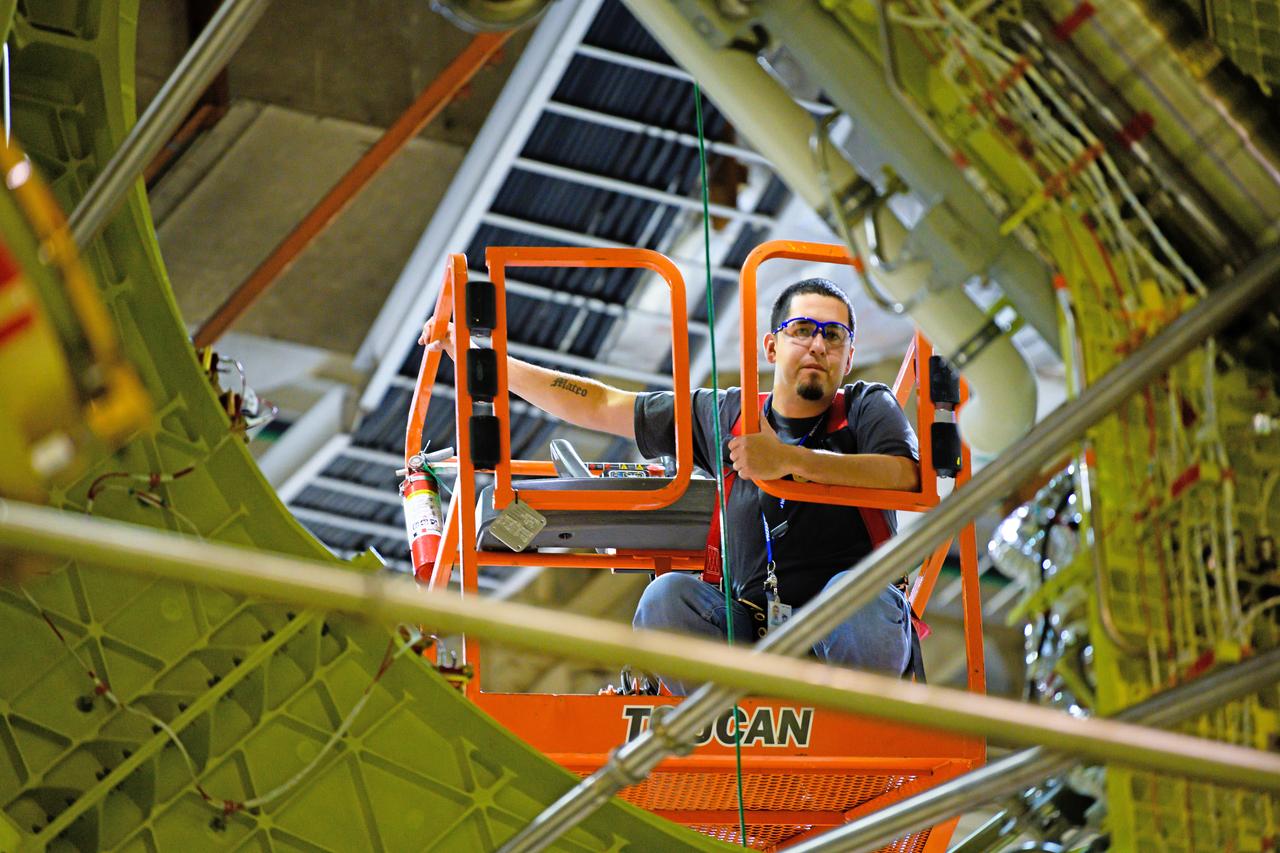
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
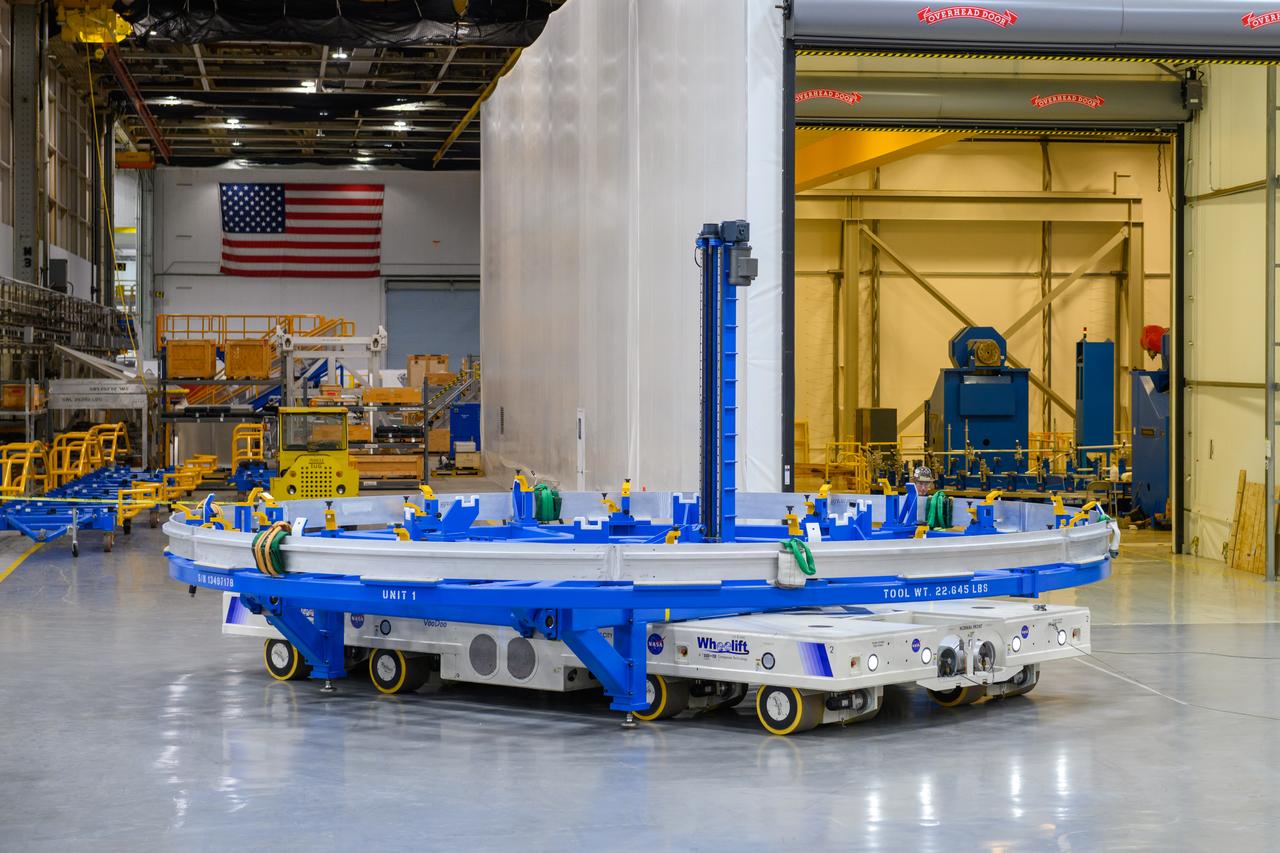

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
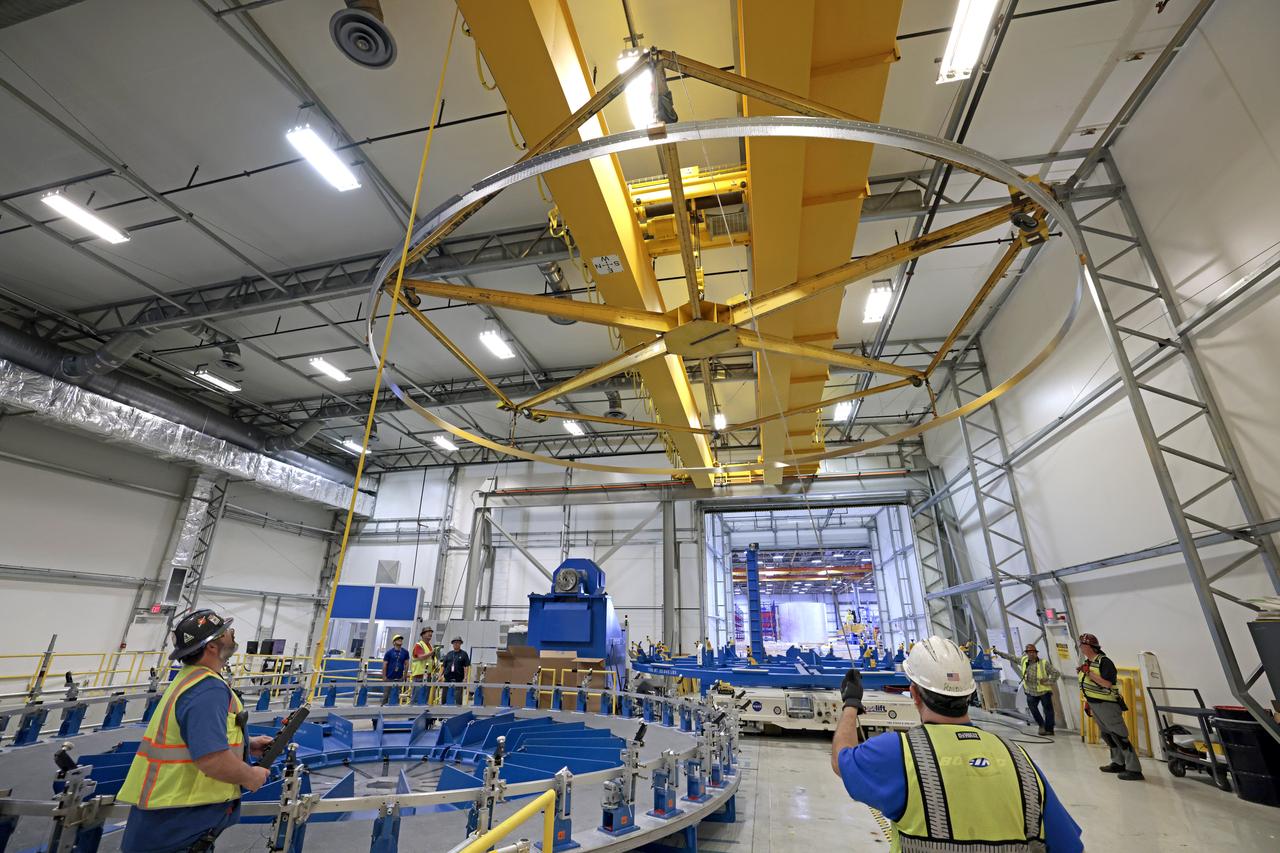

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
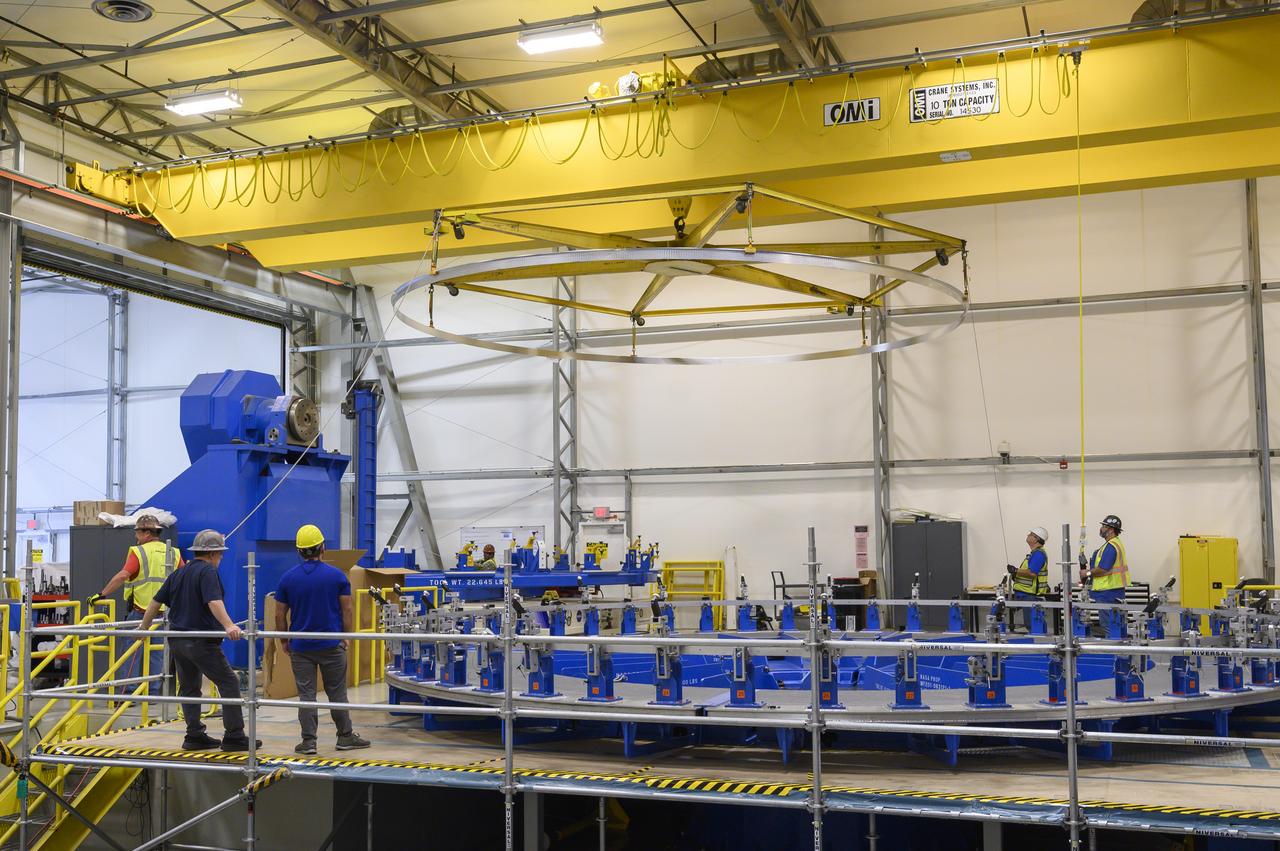

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
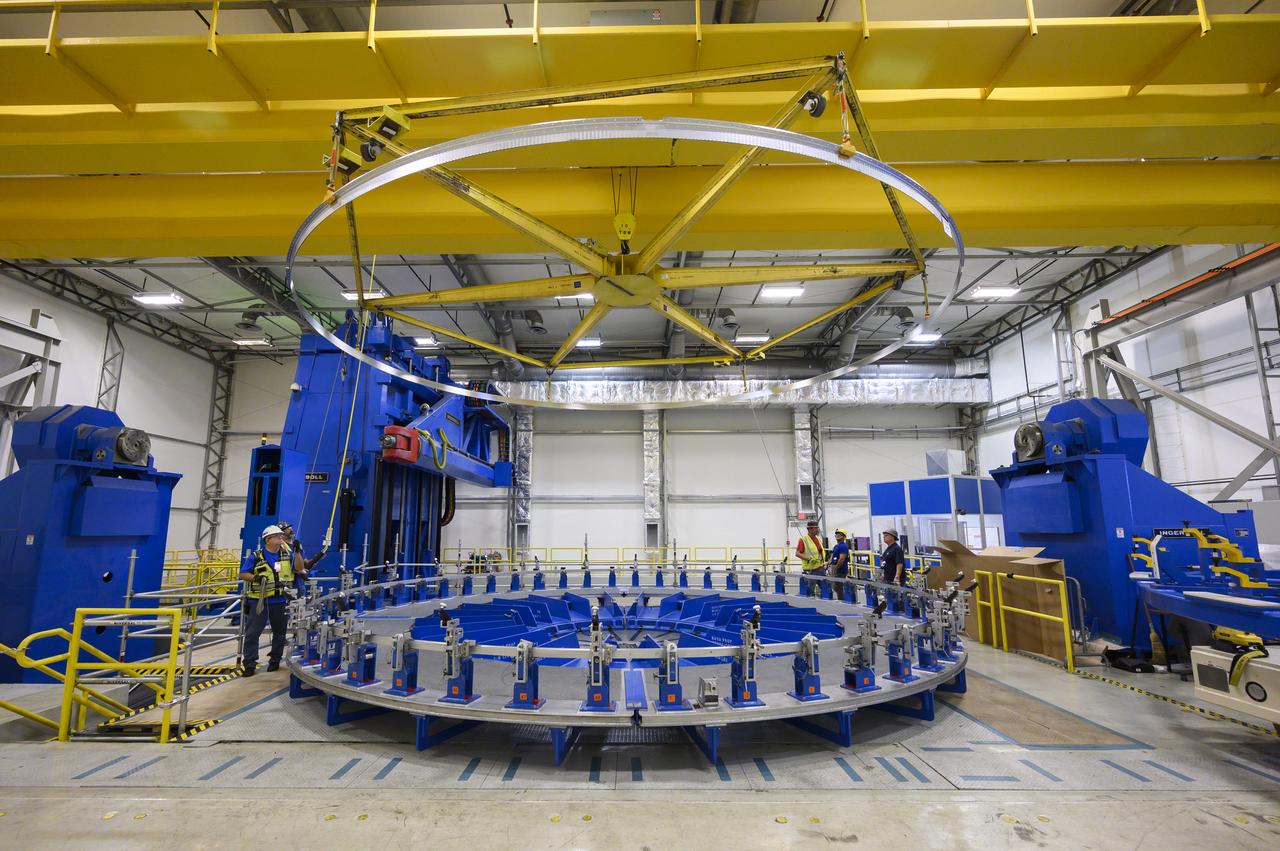

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.