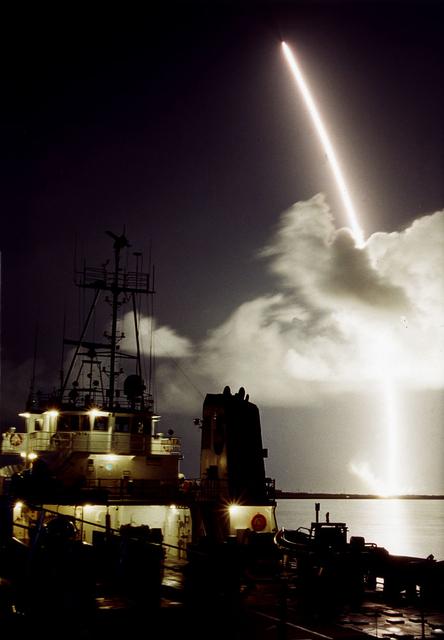

The 7-year journey to Saturn began with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/ Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe. After a 2.2-billion mile journey that included two swingbys of Venus and one of the Earth to gain additional velocity, the two-story tall spacecraft will arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The orbiter will circle the planet for 4 years, its compliment of 12 scientific instruments gathering data about Saturn's atmosphere, rings and magnetosphere and conducting close-up observations of Saturnian moons. Huygens, with a separate suite of 6 science instruments, will separate from Cassini to fly on a ballistic trajectory toward Titan, the only celestial body besides Earth to have an atmosphere rich in nitrogen. Scientists are eager to study further this chemical similarity in hopes of learning more about the origins of our own planet Earth. Huygens will provide the first direct sampling of Titan's atmospheric chemistry and the first detailed photographs of its surface. The Cassini mission is an International effort involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI).
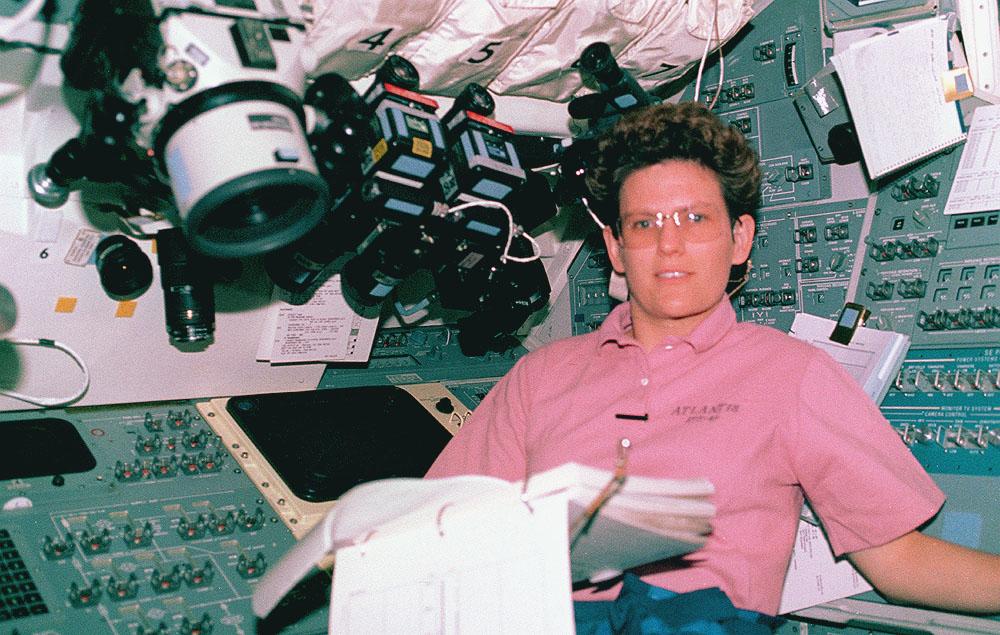
Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-45) onboard photo of Mission Specialist Kathryn Sullivan working in the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (Atlas-1) module. Atlas-1 flew in a series of Spacelab flights that measured long term variability in the total energy radiated by the Sun and determined the variability in the solar spectrum.
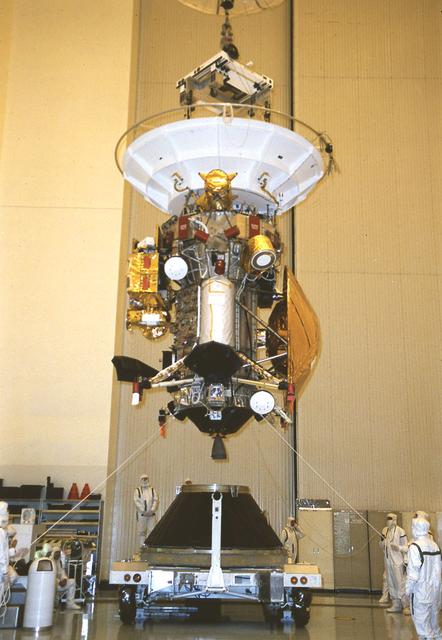

Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify the pressure relief device bellow's integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electrical power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on it seven year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four year mission at Saturn.
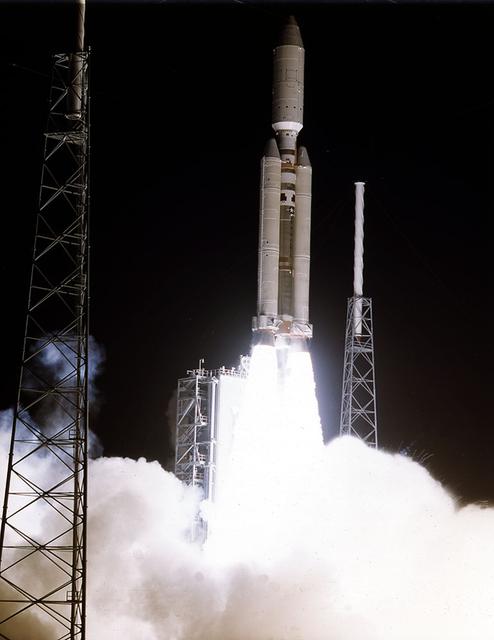

The 7-year journey to Saturn began with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe. After a 2.2-billion mile journey that included two swingbys of Venus and one of Earth to gain additional velocity, the two-story tall spacecraft will arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The orbiter will circle the planet for 4 years, its compliment of 12 scientific instruments gathering data about Saturn's atmosphere, rings and magnetosphere, and conducting close-up observations of the Saturnian moons. Huygens, with a separate suite of 6 science instruments, will separate from Cassini to fly on a ballistic trajectory toward Titan, the only celestial body besides Earth to have an atmosphere rich in nitrogen. Scientists are eager to study further this chemical similarity in hopes of learning more about the origins of our own planet Earth. Huygens will provide the first direct sampling of Titan's atmospheric chemistry and the first detailed photographs of its surface. The Cassini mission is an international effort involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI).
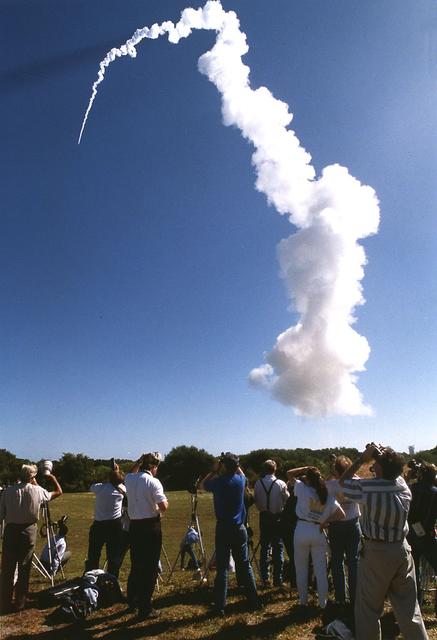

The journey back to Mars begins with a liftoff of the Mars Global Surveyor atop a Delta II 7925A expendable launch vehicle from the Cape Canaveral Air Station. After an approximate 10-month interplanetary odyssey, the spacecraft will arrive at Mars and begin a 4-month aerobreaking phase, an irnovative technique first demonstrated during the Magellan mission to Venus, to achieve a mapping orbit. It will take about 2 Earth years for Surveyor to circle above most of the planet, its suite of sophisticated remote-sensing instruments building a comprehensive global portrait of Mars by mapping its topography, magnetism, mineral composition and atmosphere. Among the locations the Surveyor will pass over are the landing sites where the two U.S. Viking landers have stood since 1975 as silent monuments to the most recent successful U.S. missions to Mars. The Global Surveyor is the first of a trio of spacecraft being launched to Mars; next is Russia's Mars `96 spacecraft, followed by the U.S.'s Mars Pathfinder.

Signage points the way to NASA exhibits at the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 held at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
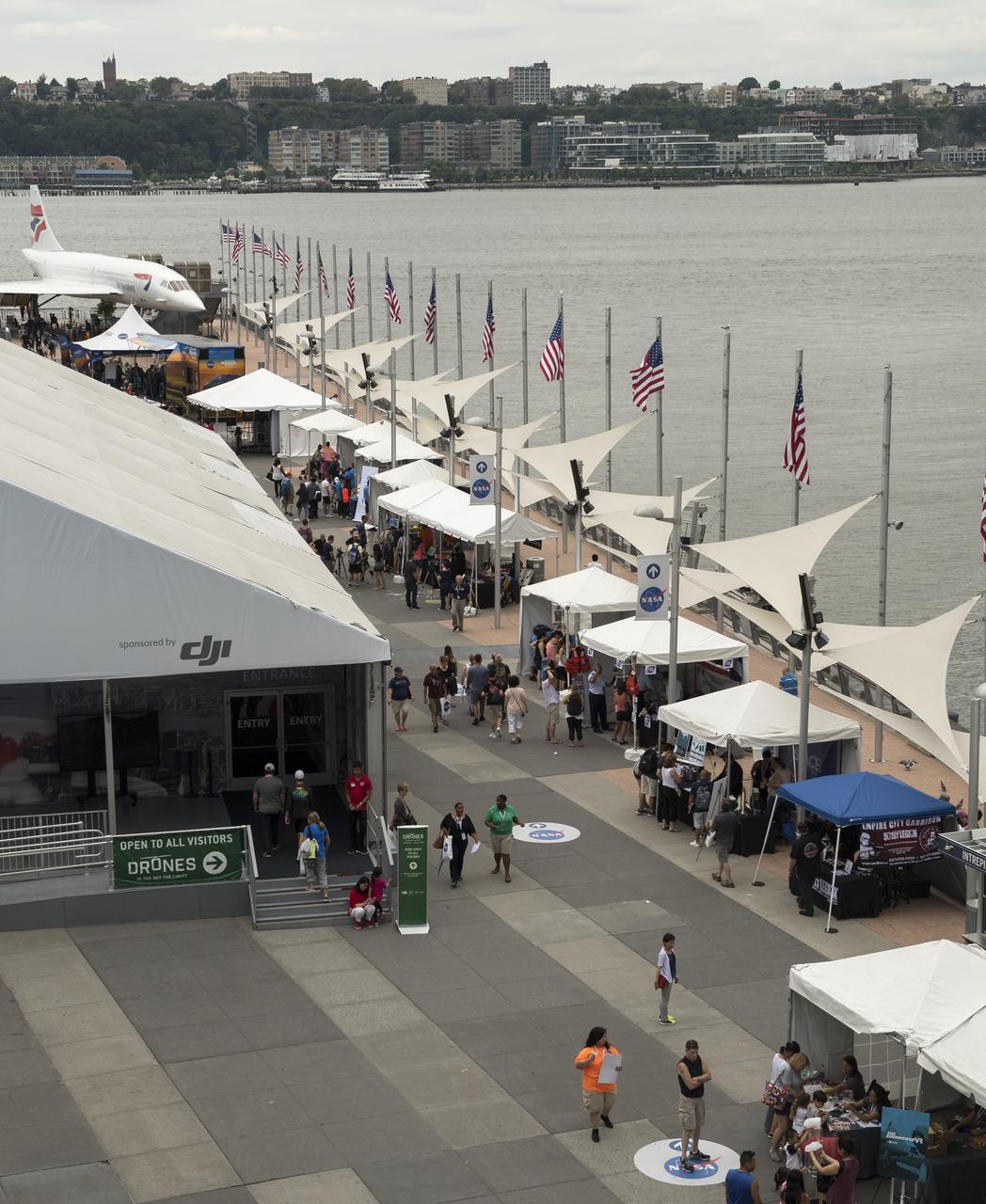

NASA exhibits line Pier 86 during the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 held at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
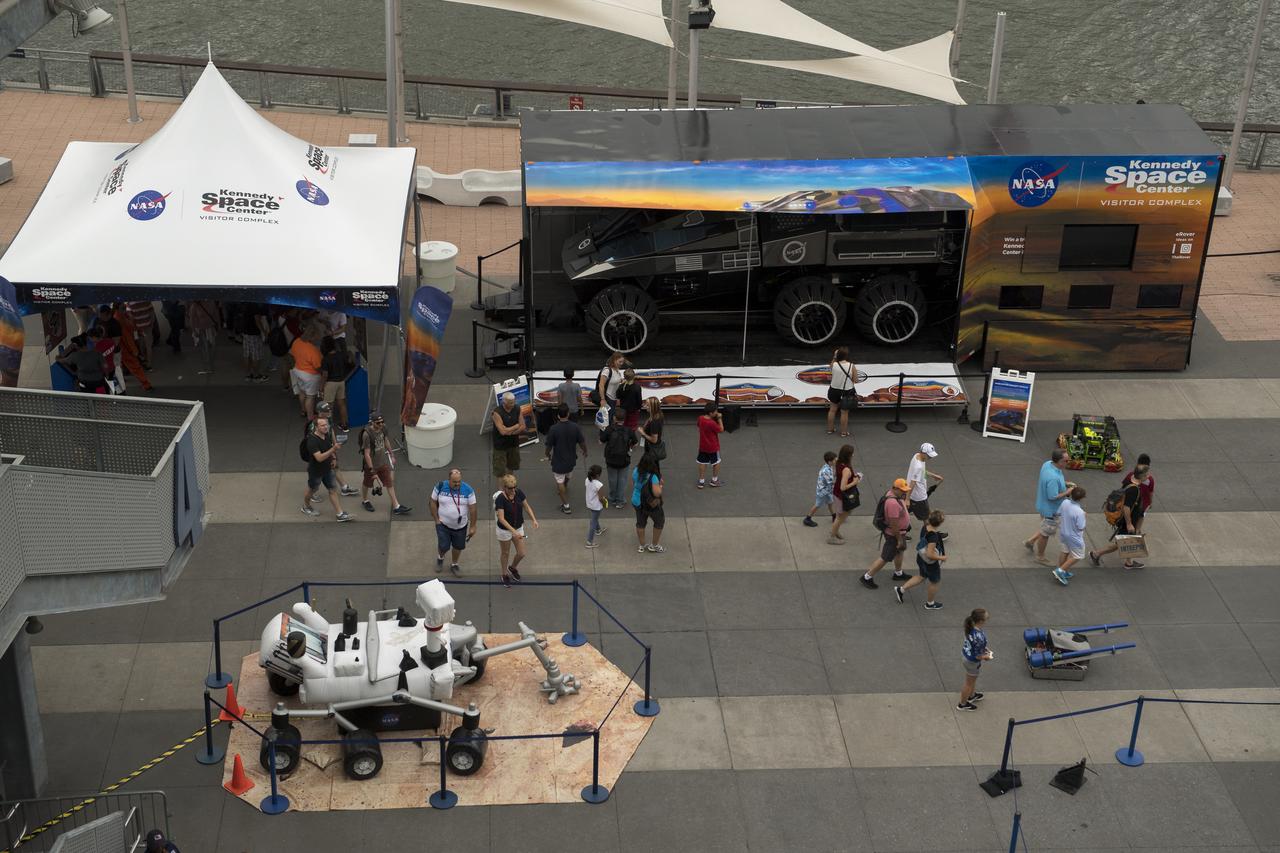

NASA exhibits line Pier 86 during the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 held at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
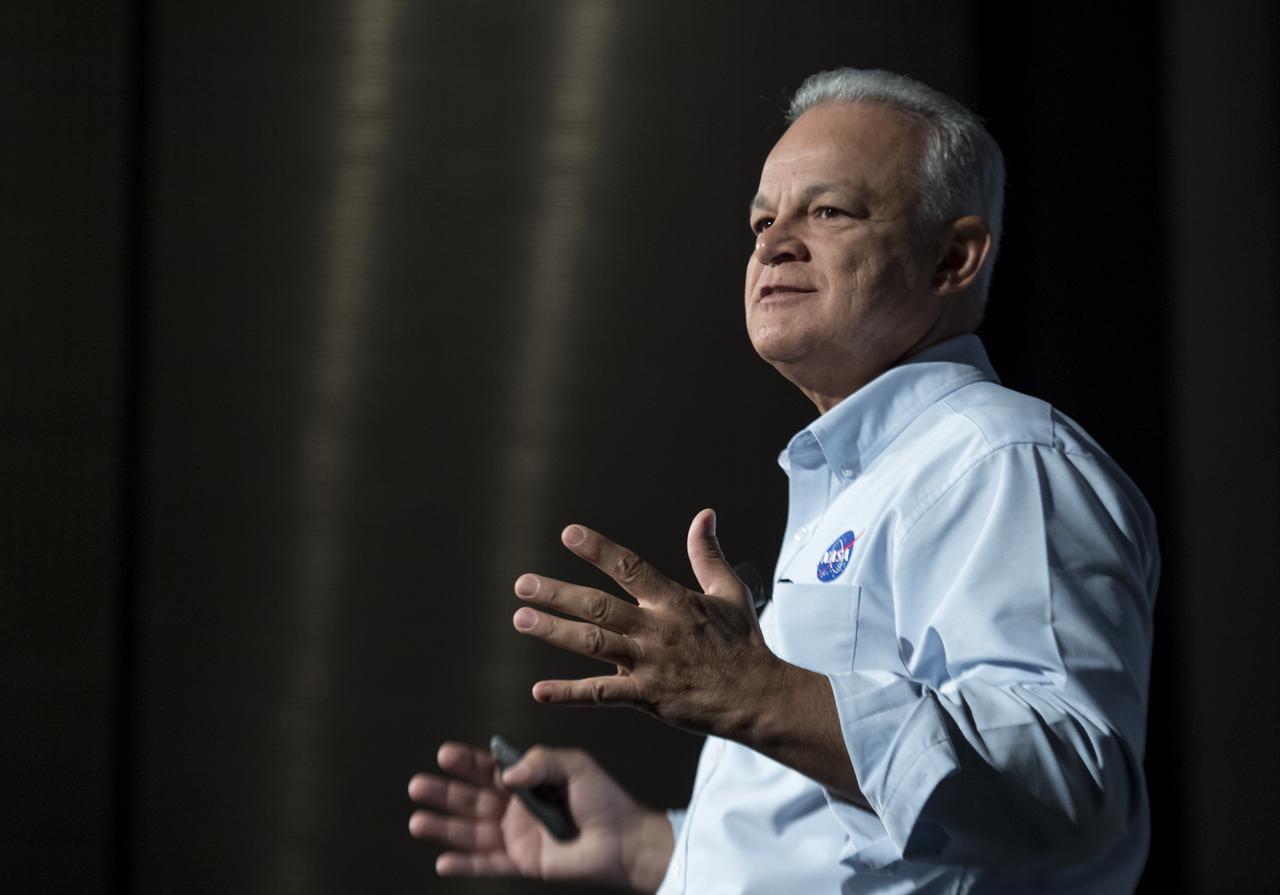

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
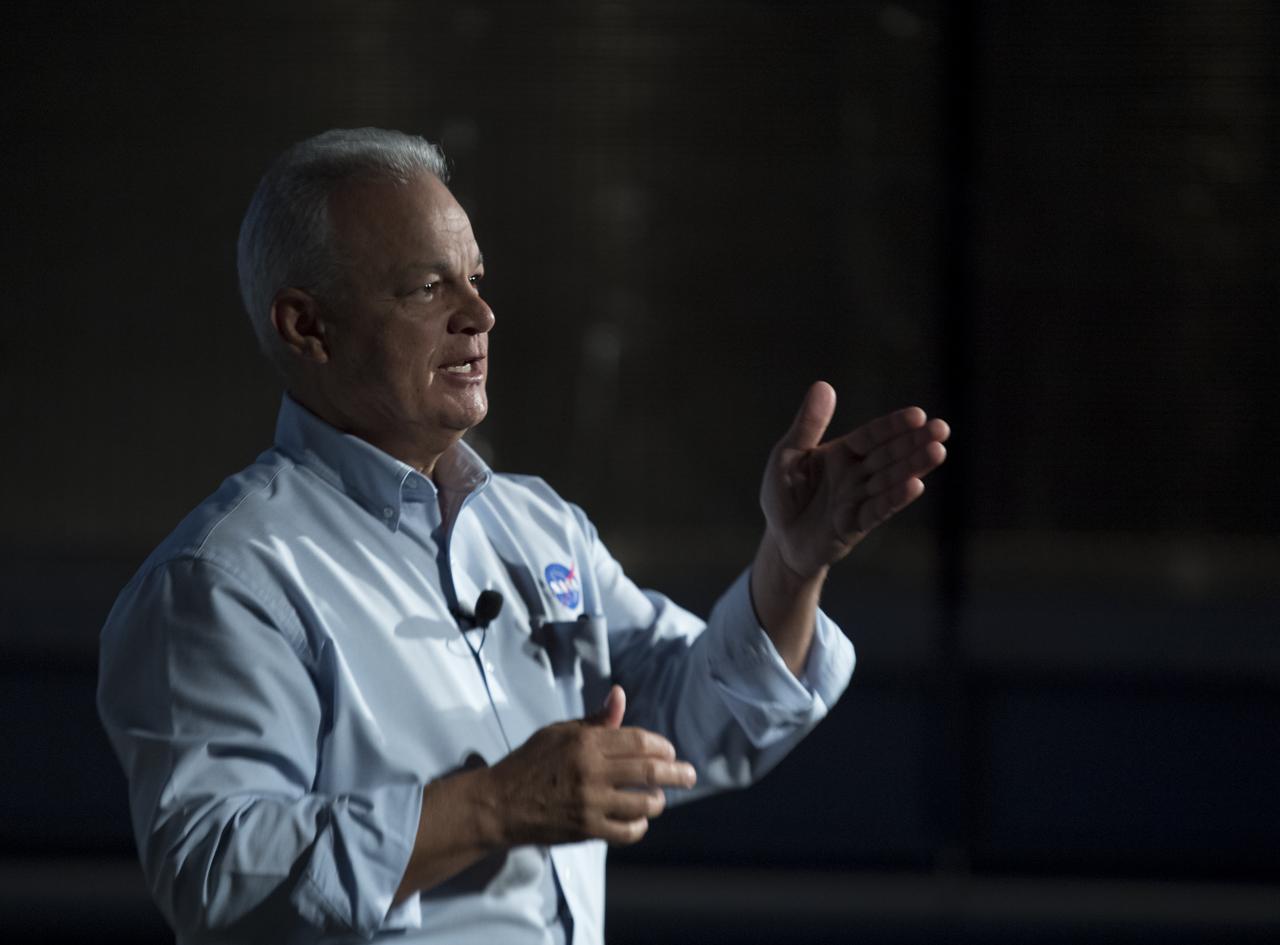

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
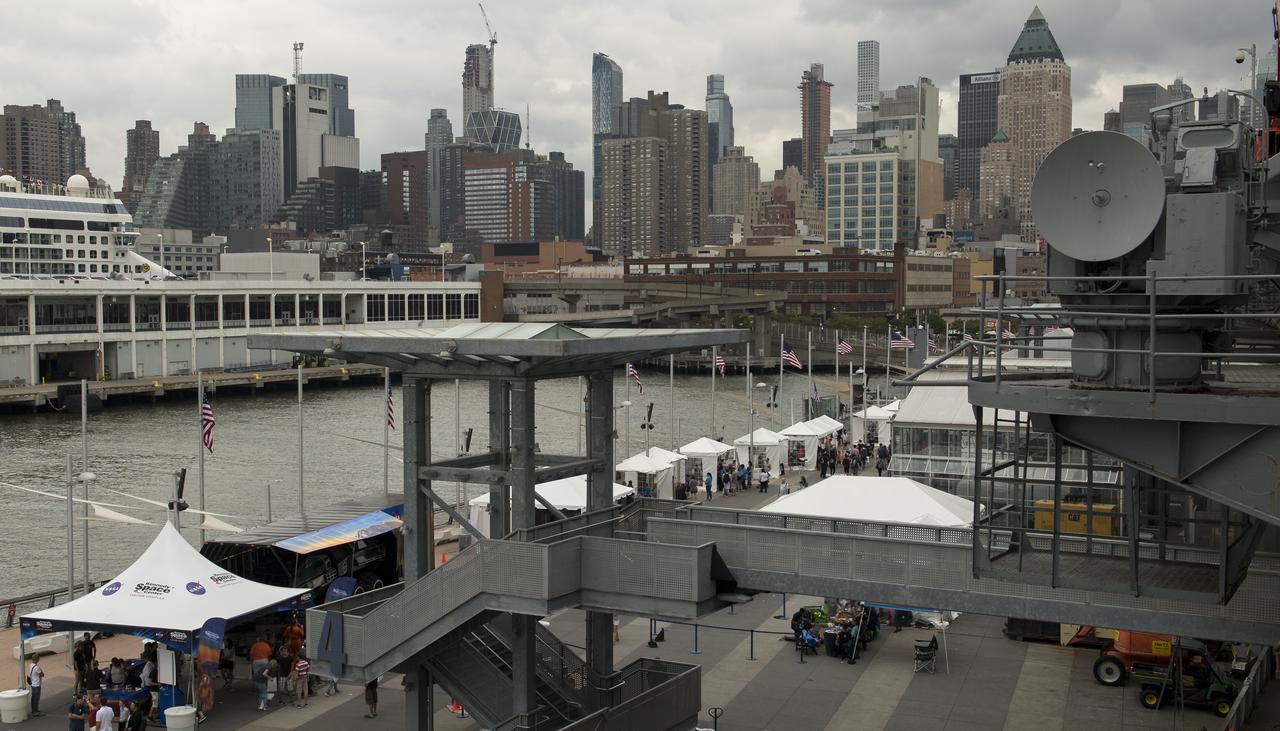

NASA exhibits under white tents line Pier 86 during the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 held at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
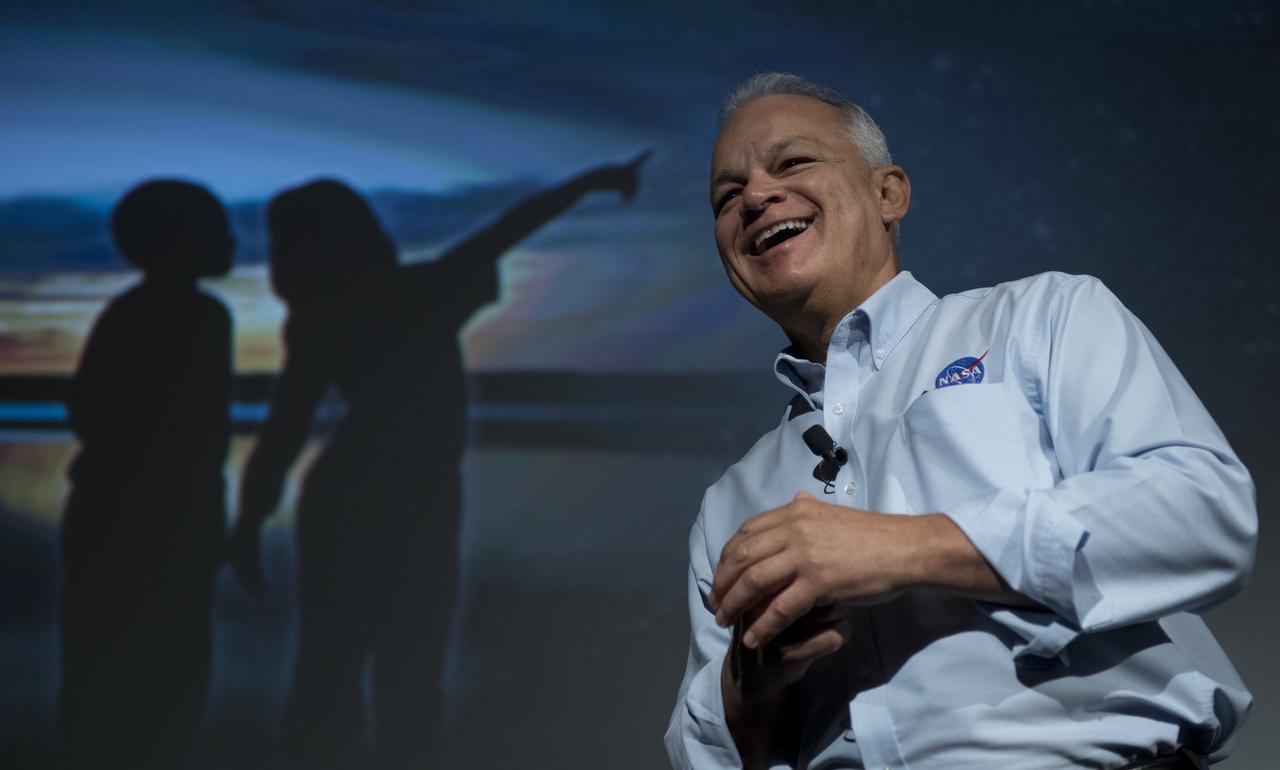

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
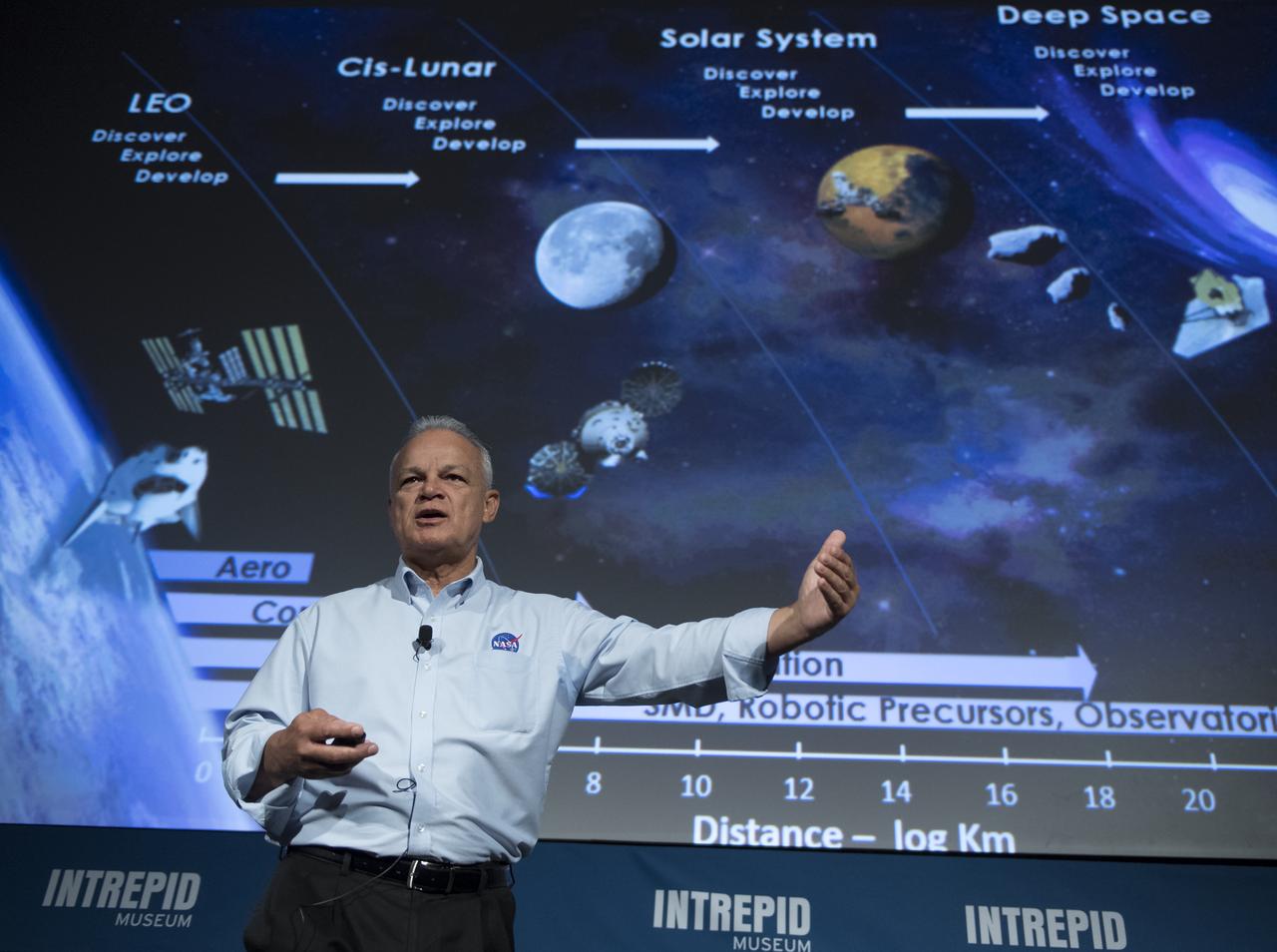
NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
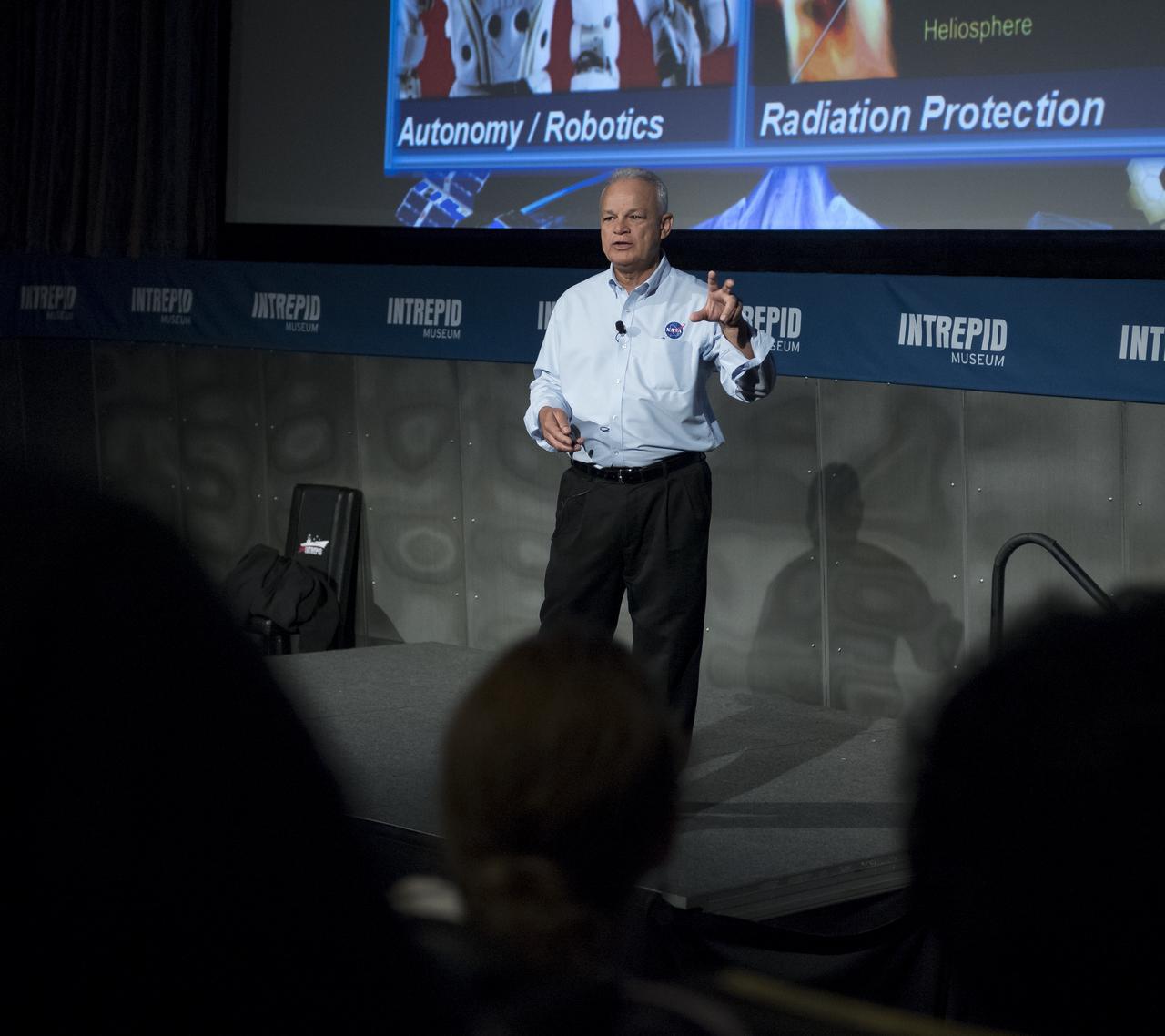

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
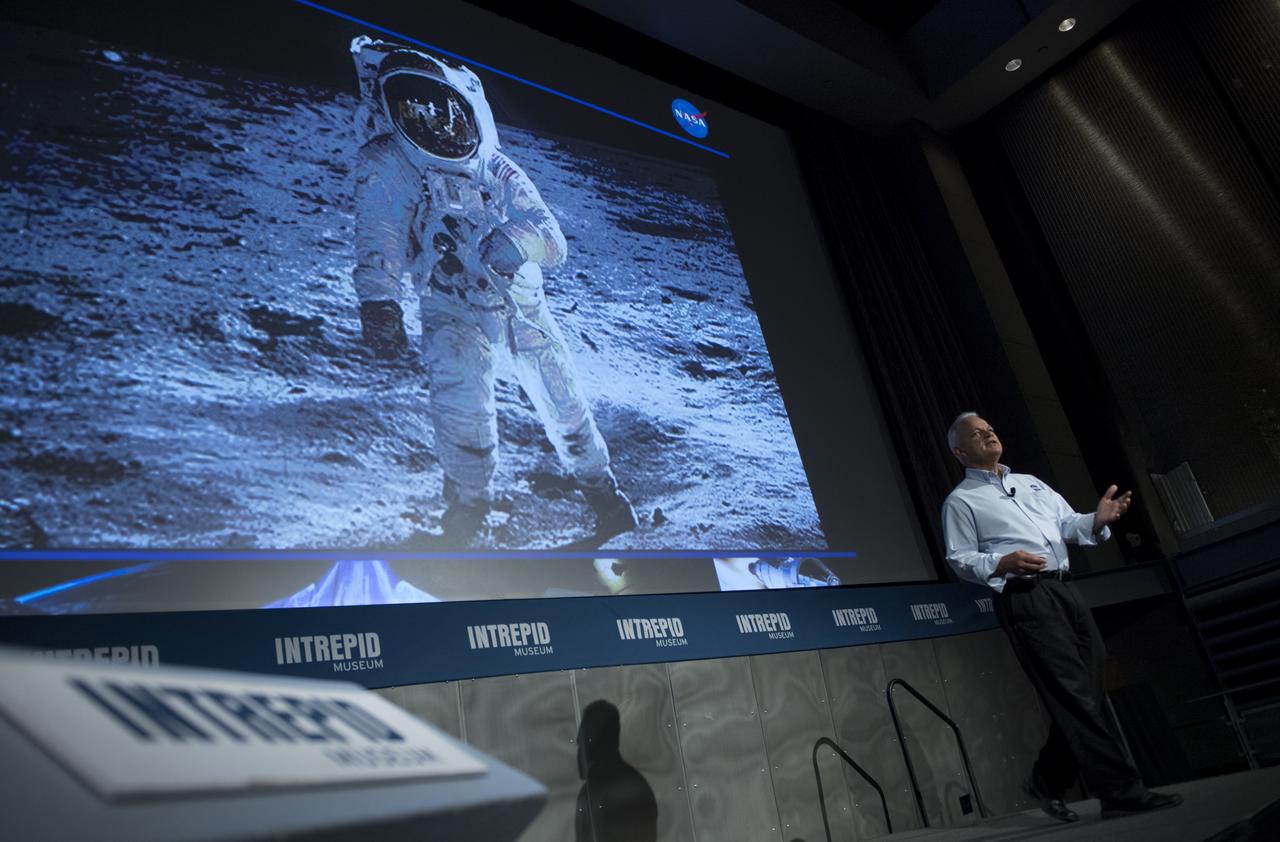

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier gives a talk to teachers attending a professional development workshop held in tandem with the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An inflatable scale model of the SLS rocket is seen on Pier 86 during the Intrepid Space & Science Festival, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 held at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. The week-long festival featured talks, films and cutting-edge displays showcasing NASA technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
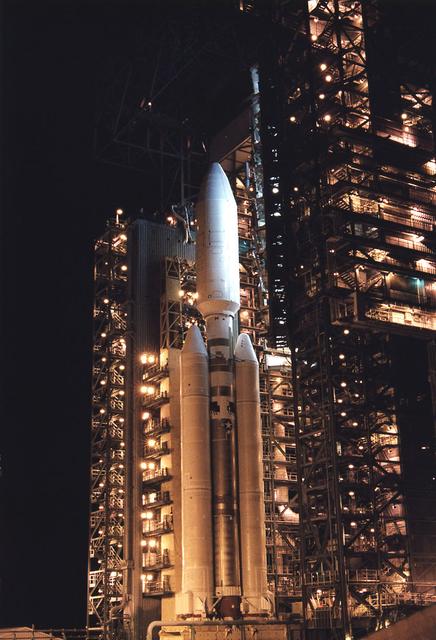

At Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station, the Mobile Service Tower is being rolled away from the Titan IVB/Centaur launch vehicle carrying the Cassini spacecraft, completing a major countdown milestone. This is the second launch attempt for the Saturn-bound mission. A a first try was scrubbed primarily due to concerns about upper level wind conditions.
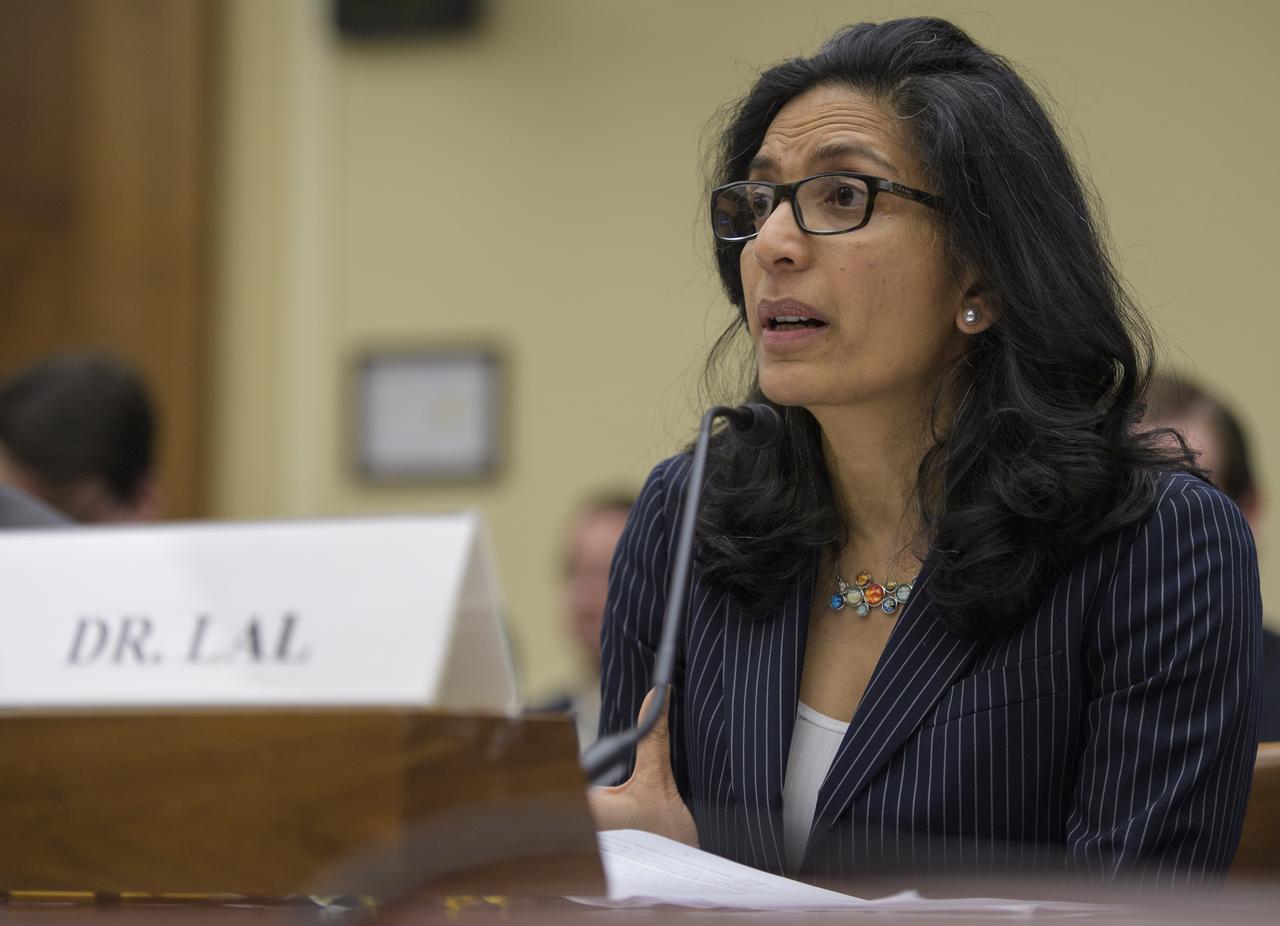

Dr. Bhavya Lal, a researcher at the Institute for Defense Analysis's Science and Technology Policy Institute, testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
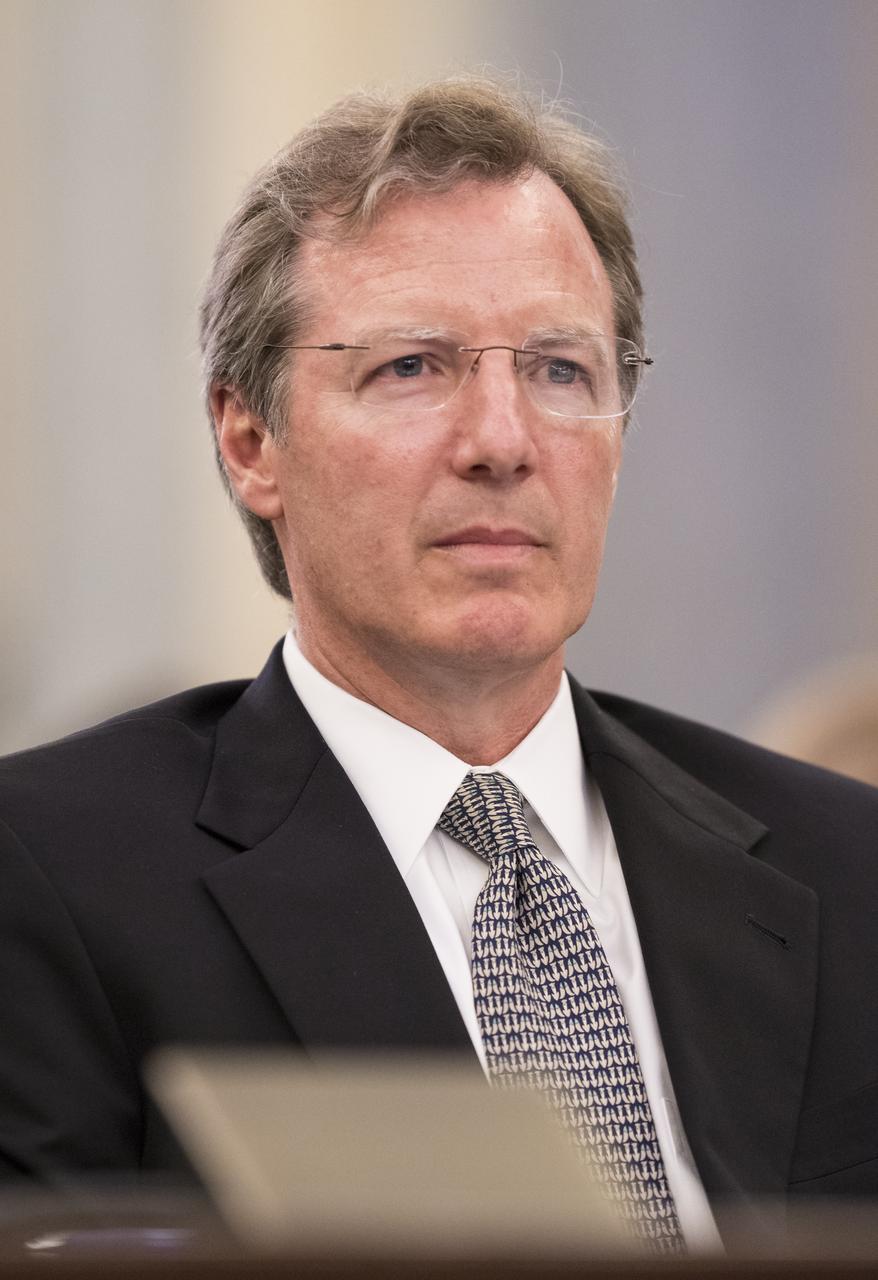

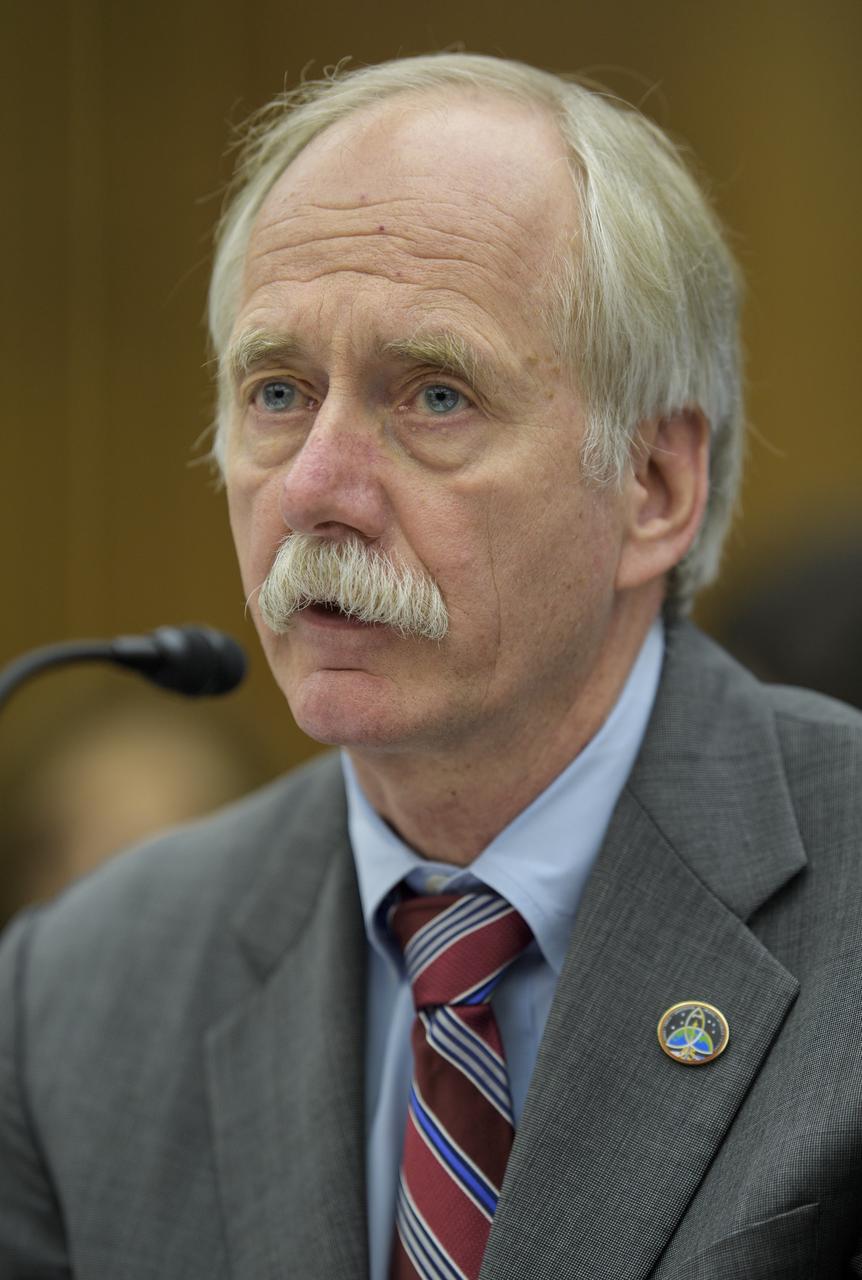
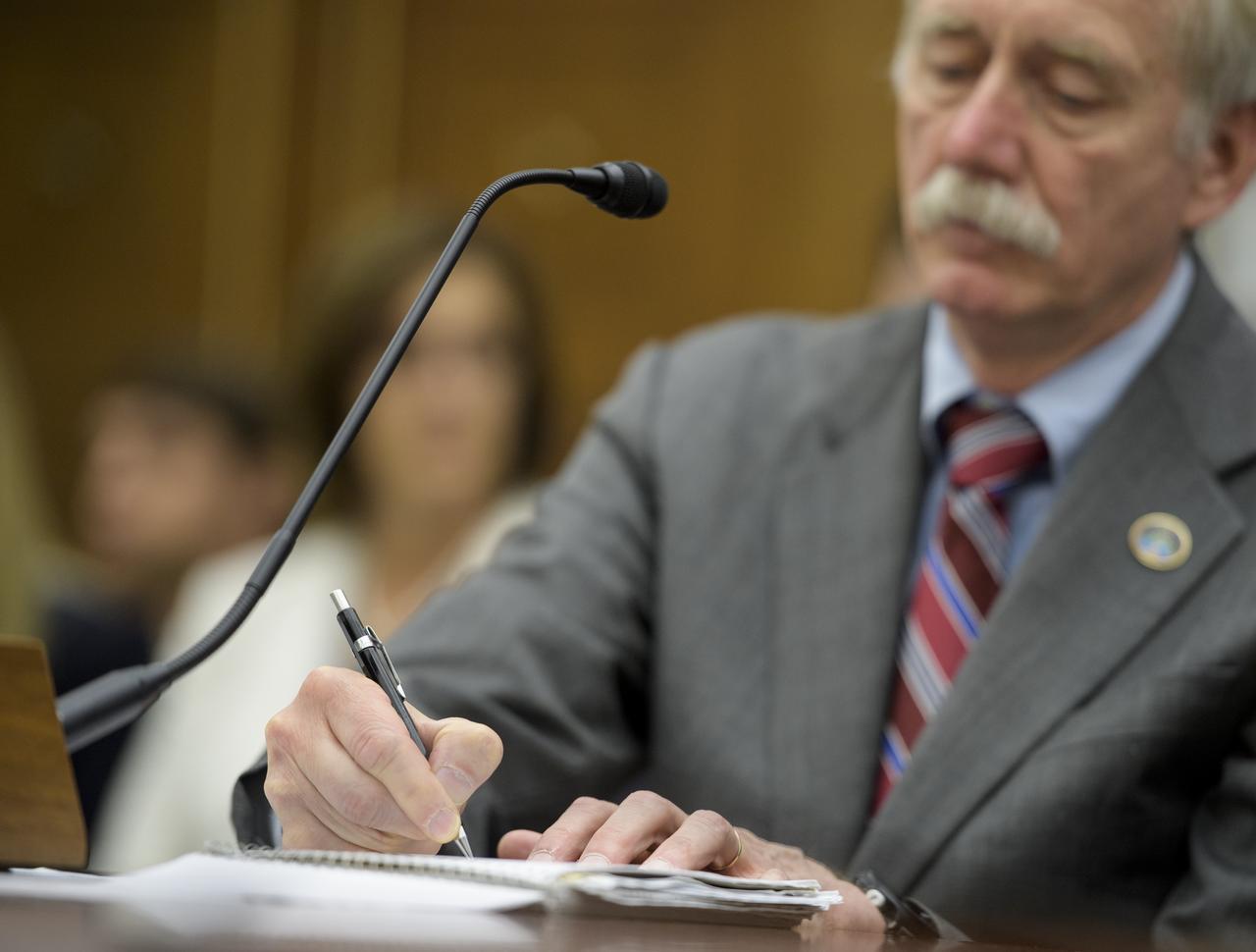
NASA Inspector General Paul Martin is seen during a Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
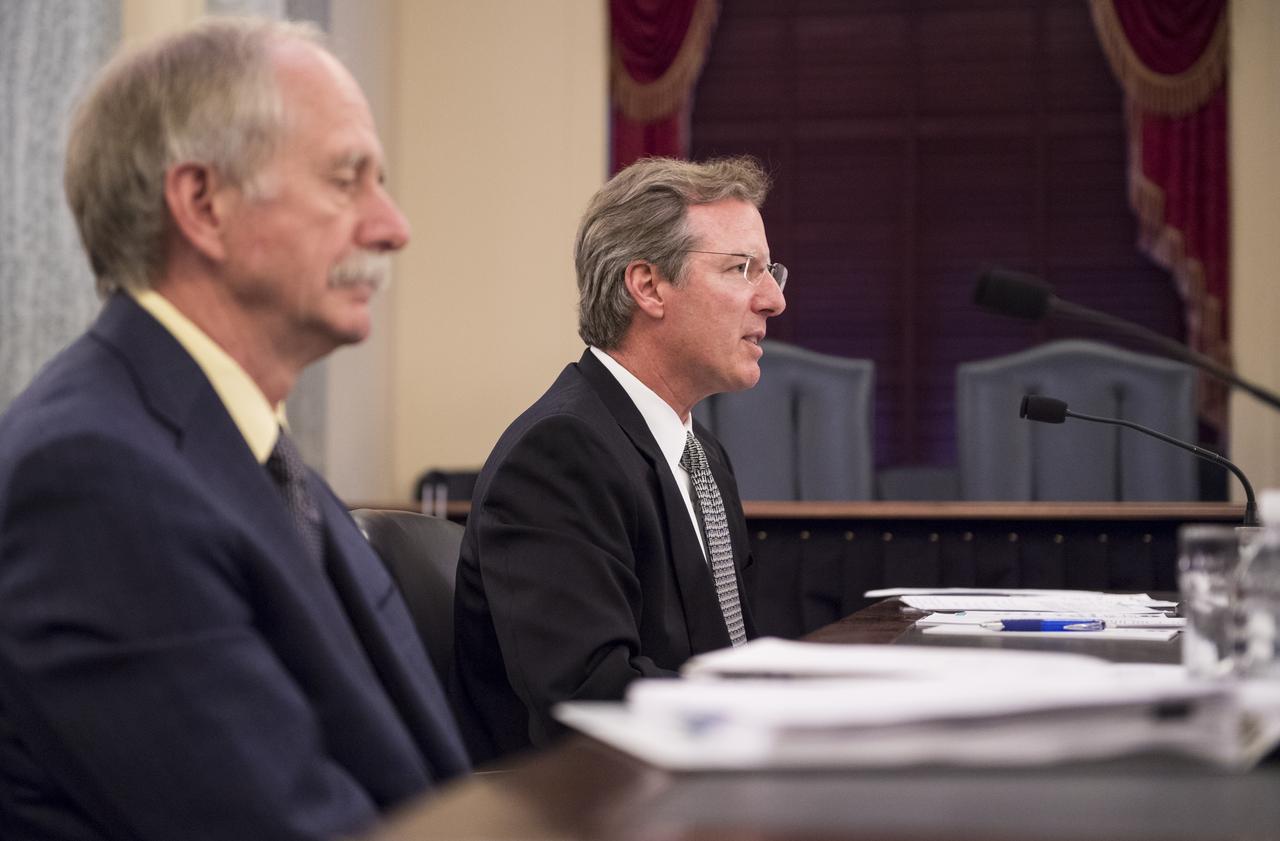

NASA Inspector General Paul Martin testifies during a Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" held on Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
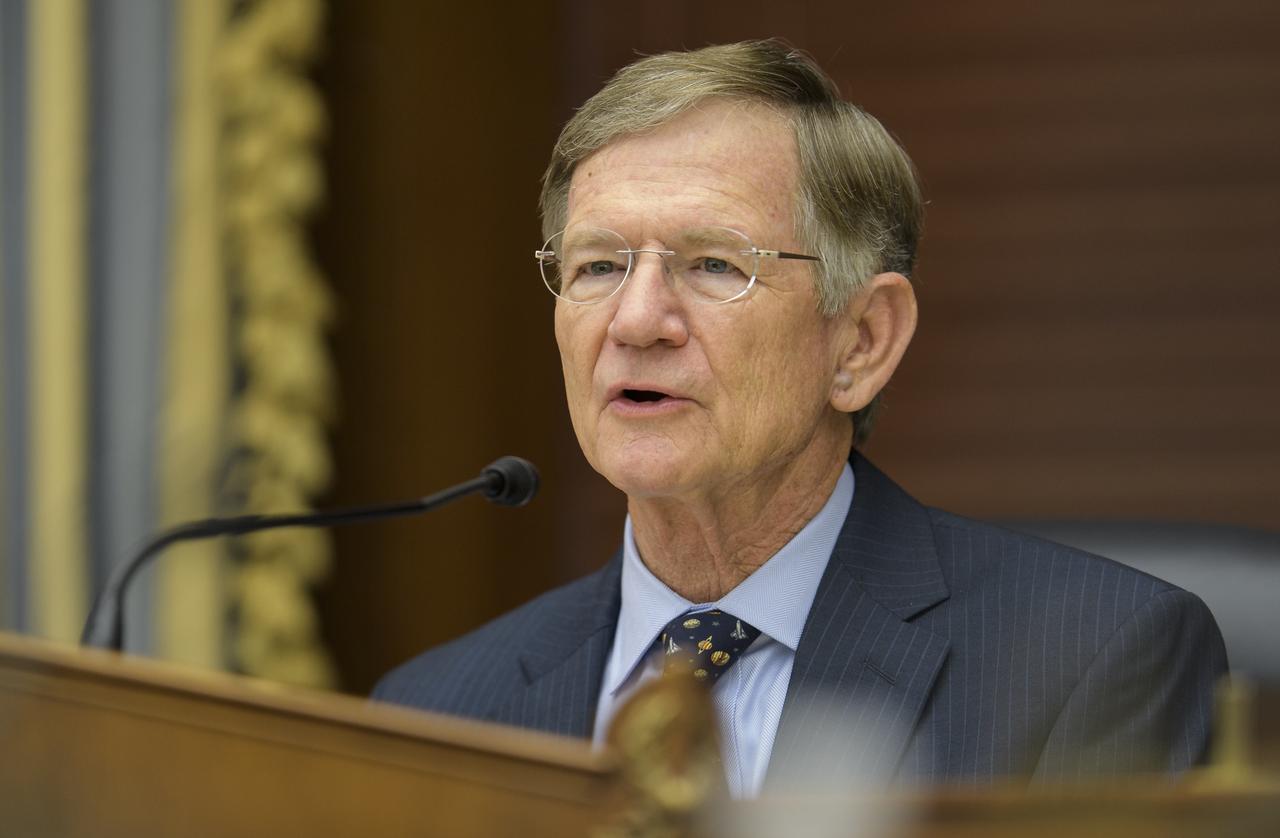

Rep. Lamar Smith, R-Texas, chairman of the House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, delivers his opening statement during a hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier is seen prior to the start of a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology Hearing titles "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
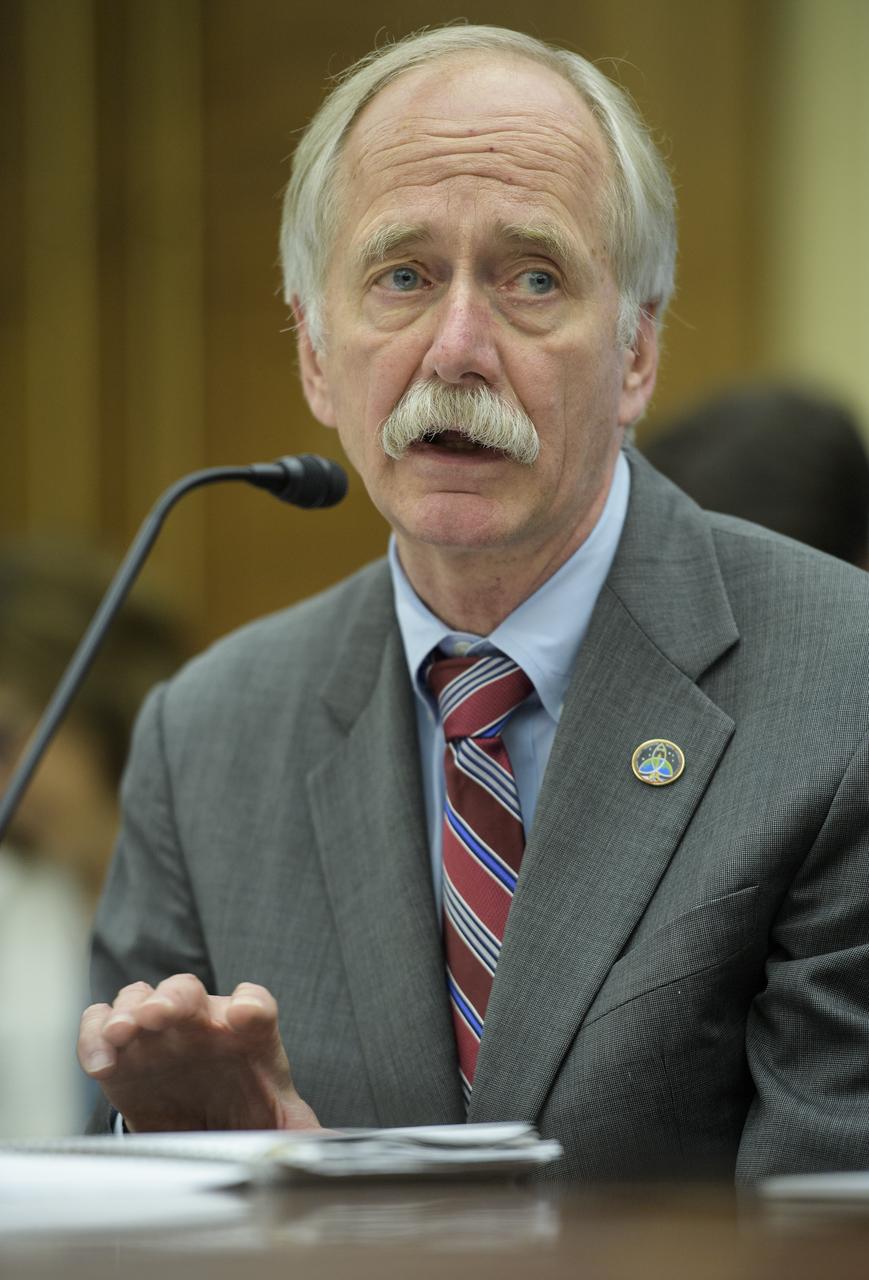

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
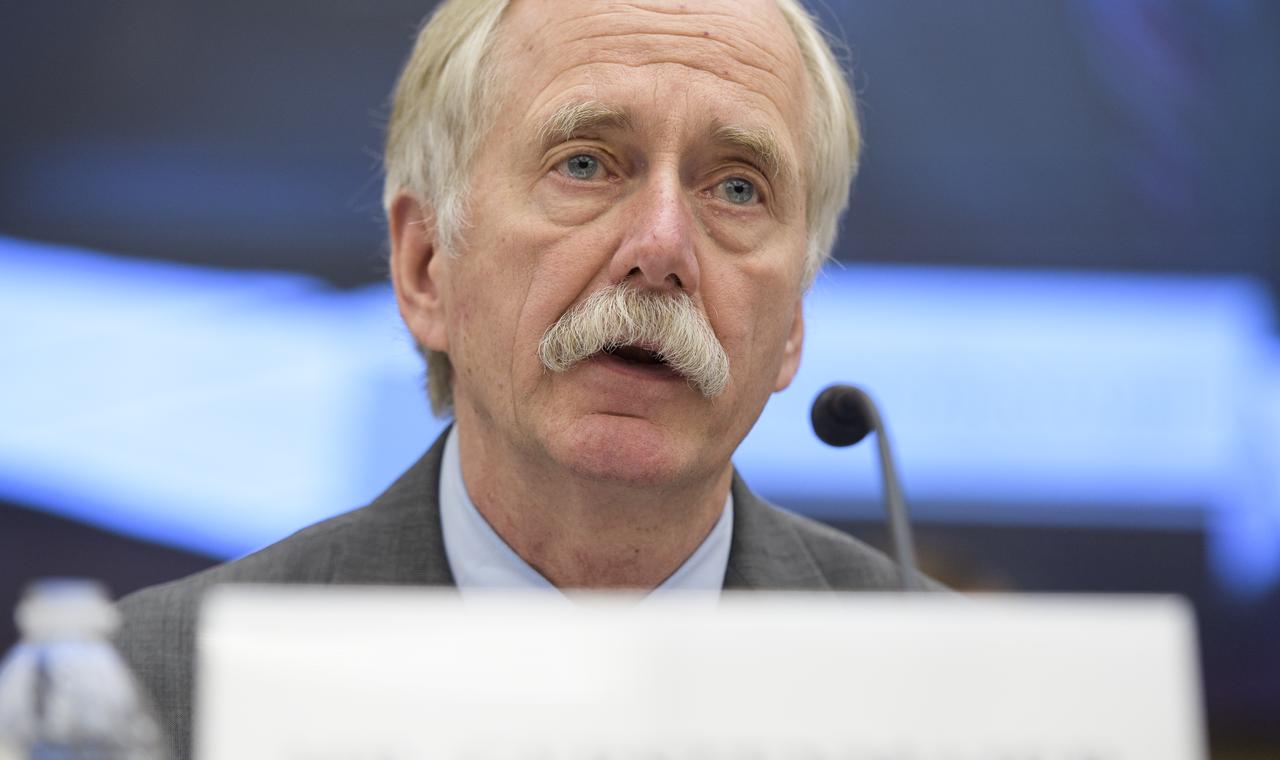

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
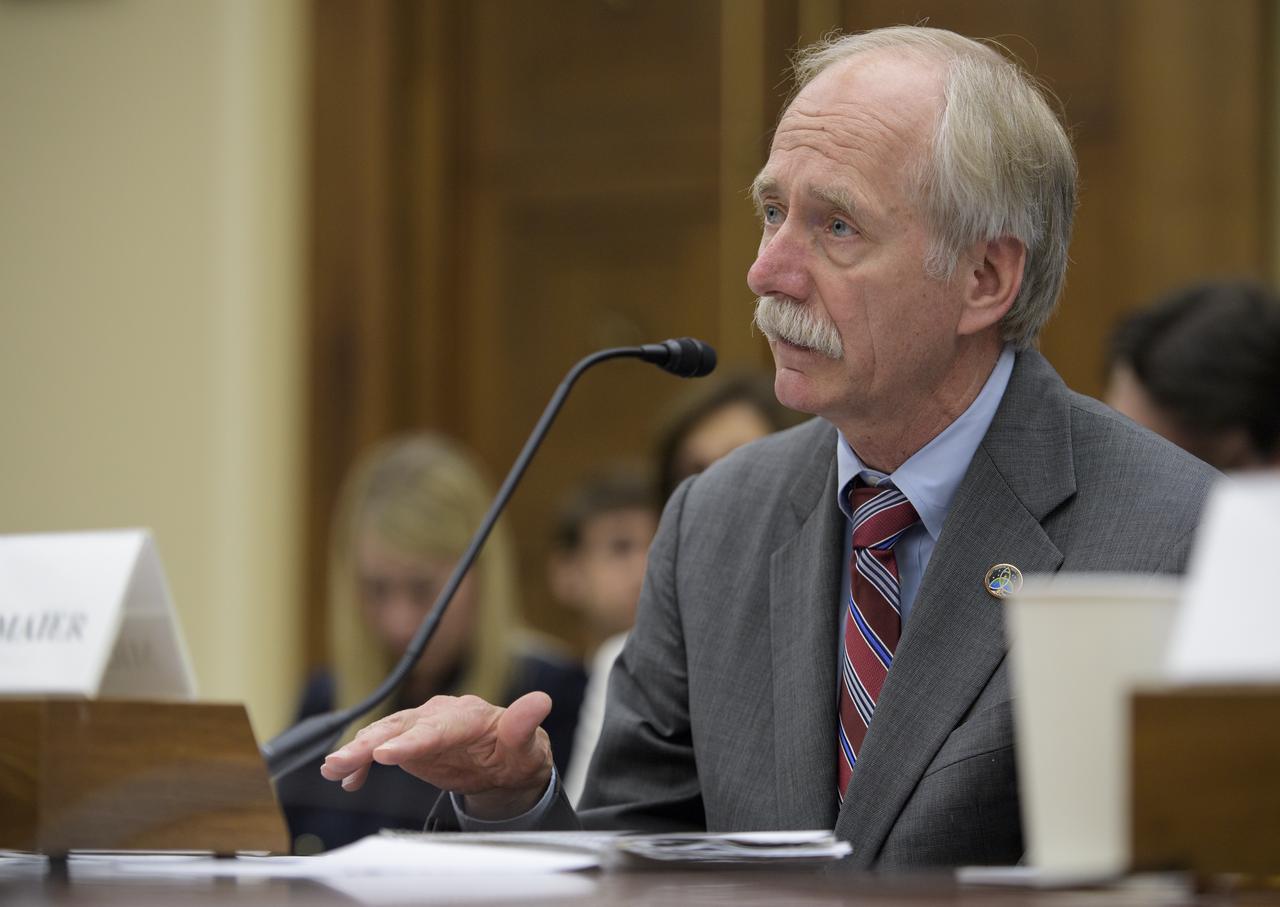

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
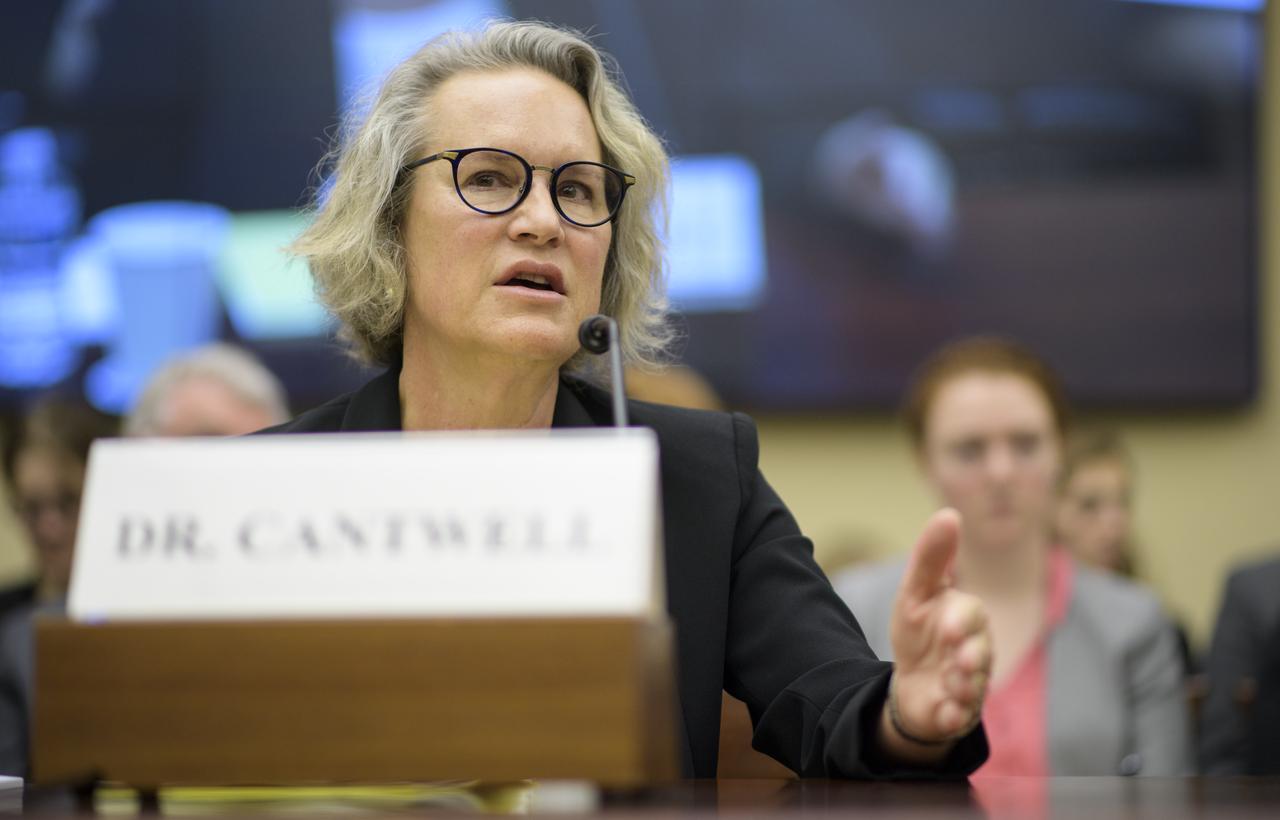

Elizabeth Cantwell, chief executive officer at the Arizona State University Research Enterprise, testifies during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
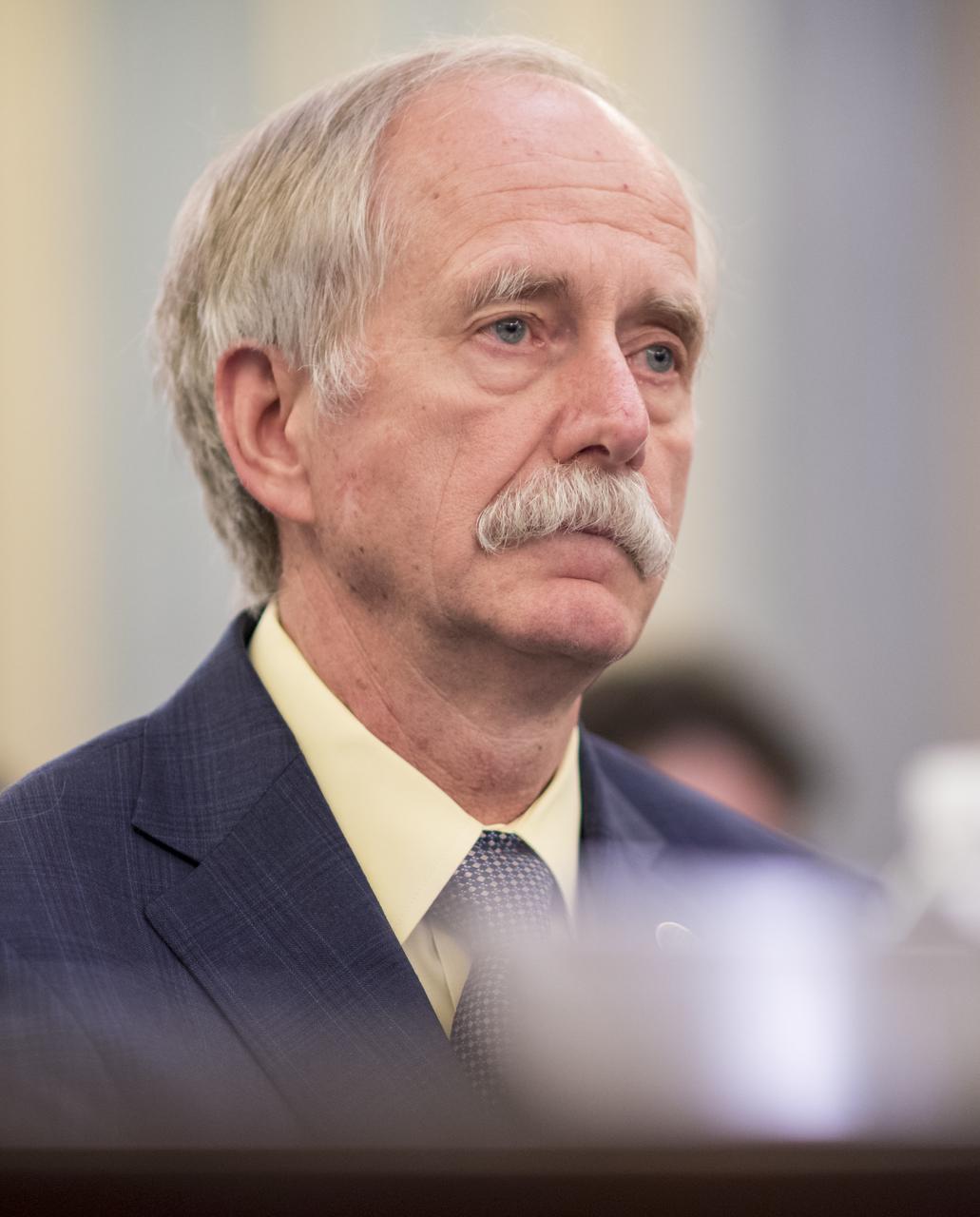

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" held on Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
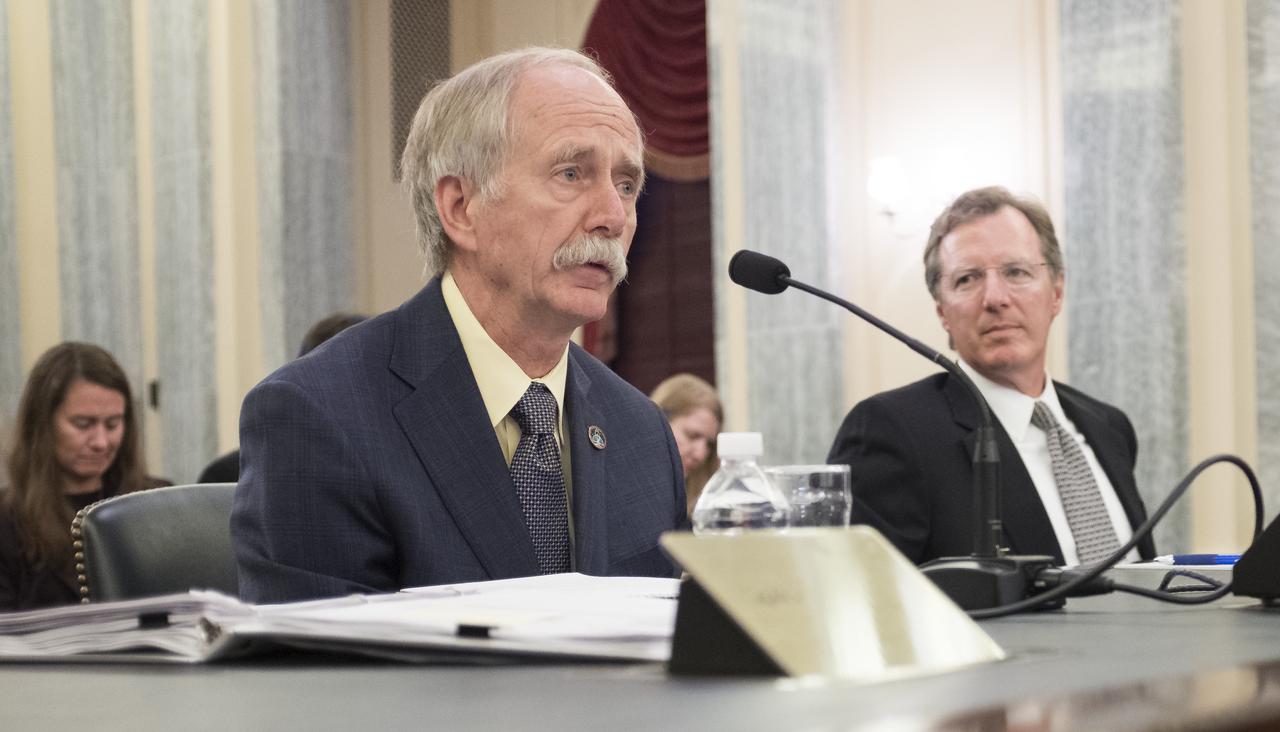

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" held on Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
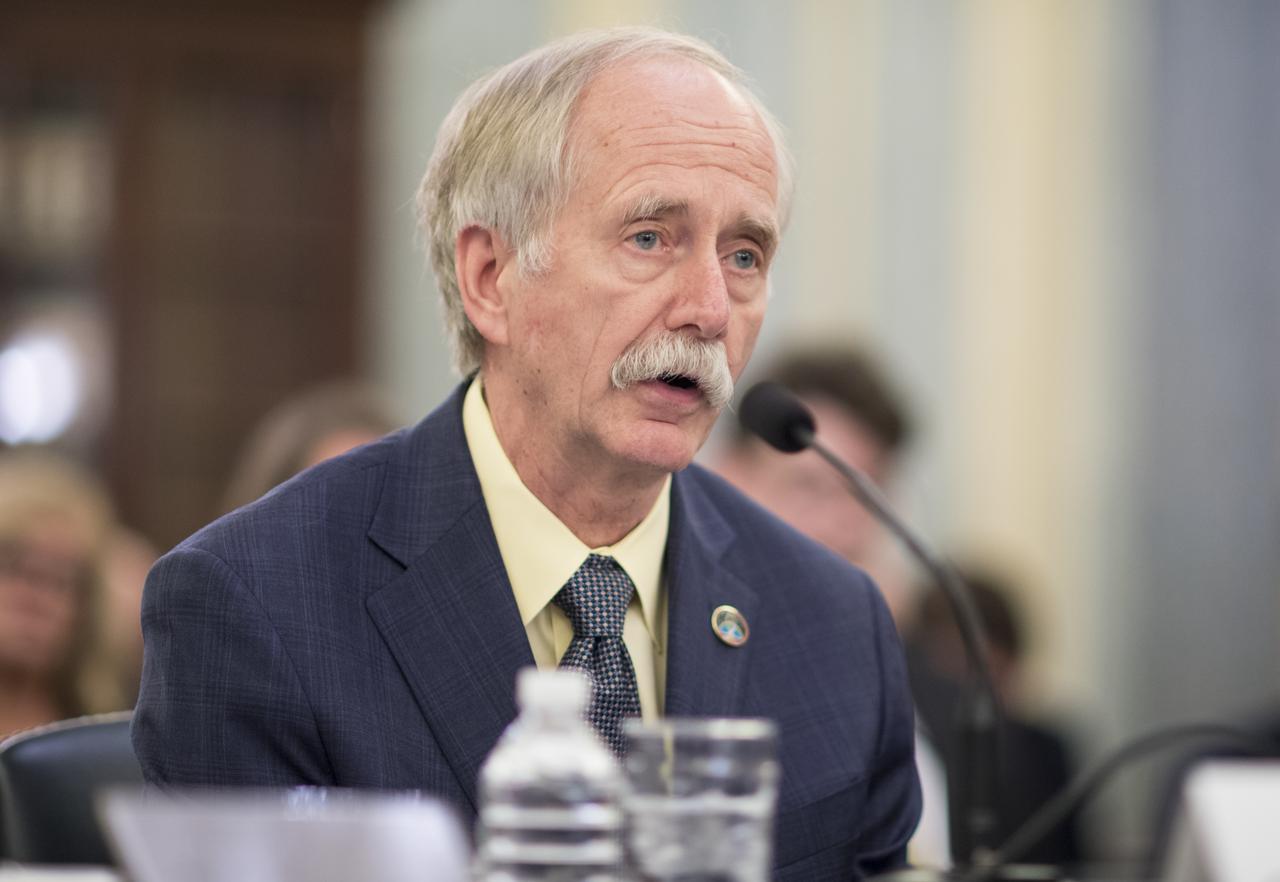

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier testifies during a Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" held on Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
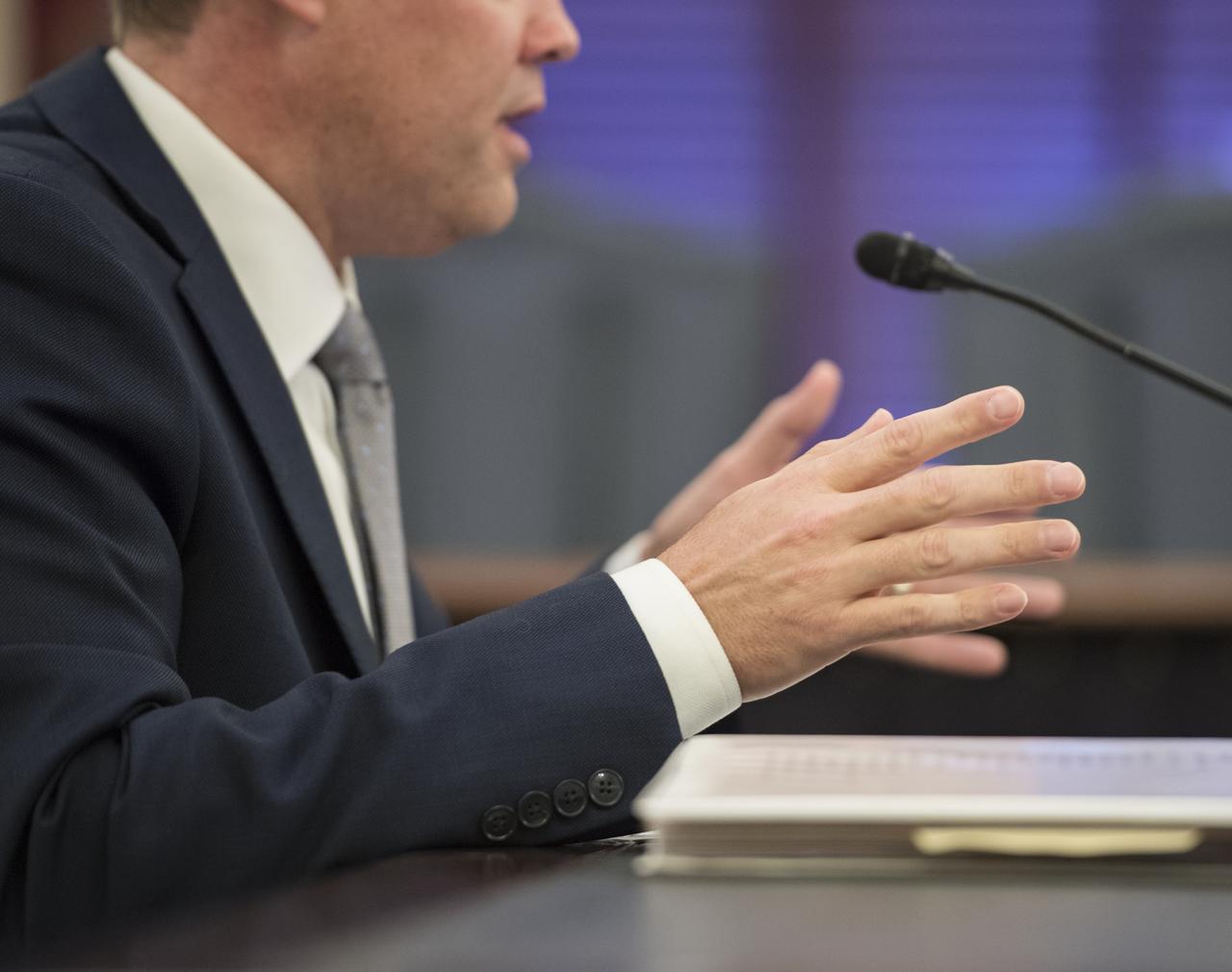

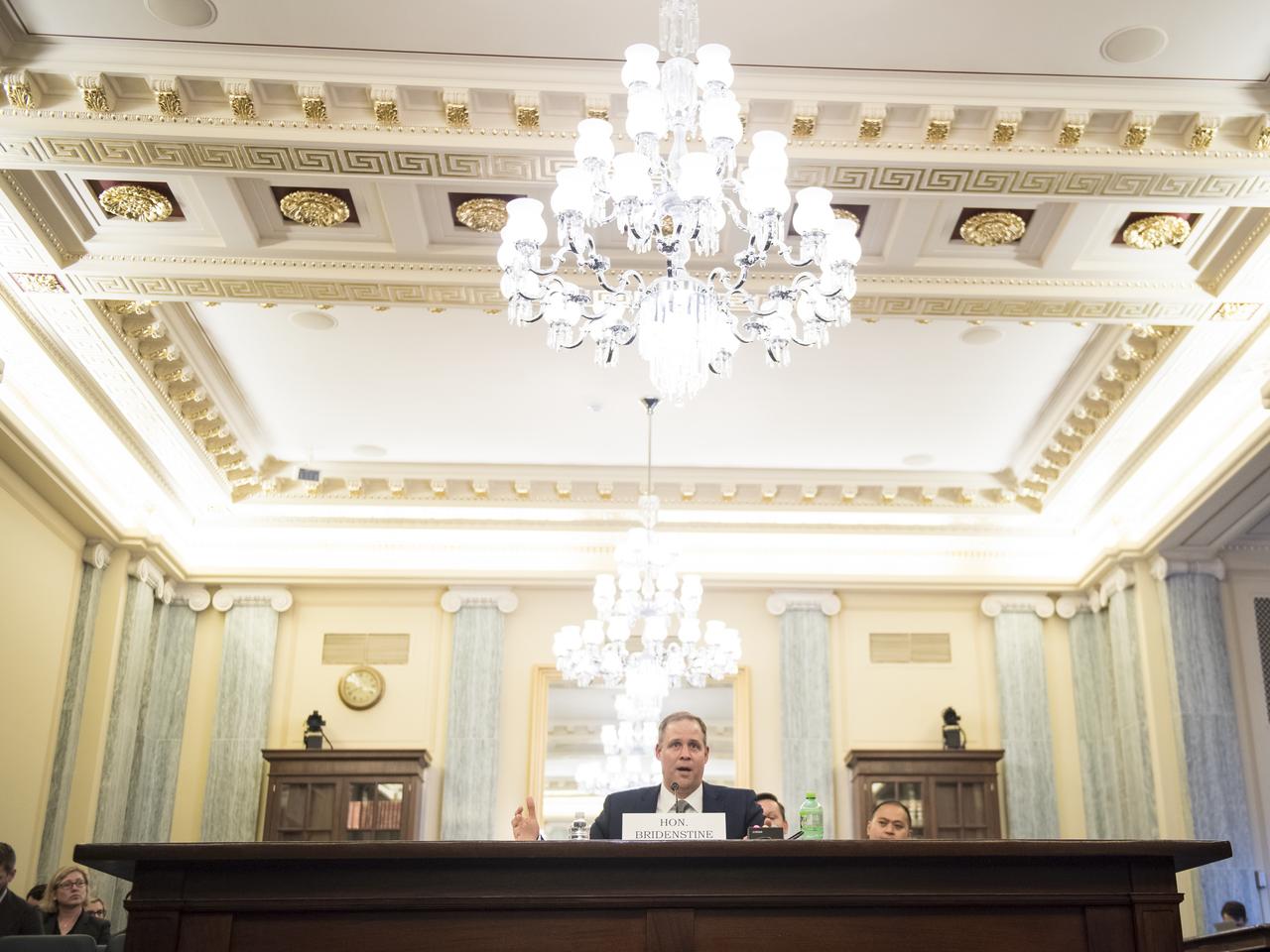
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
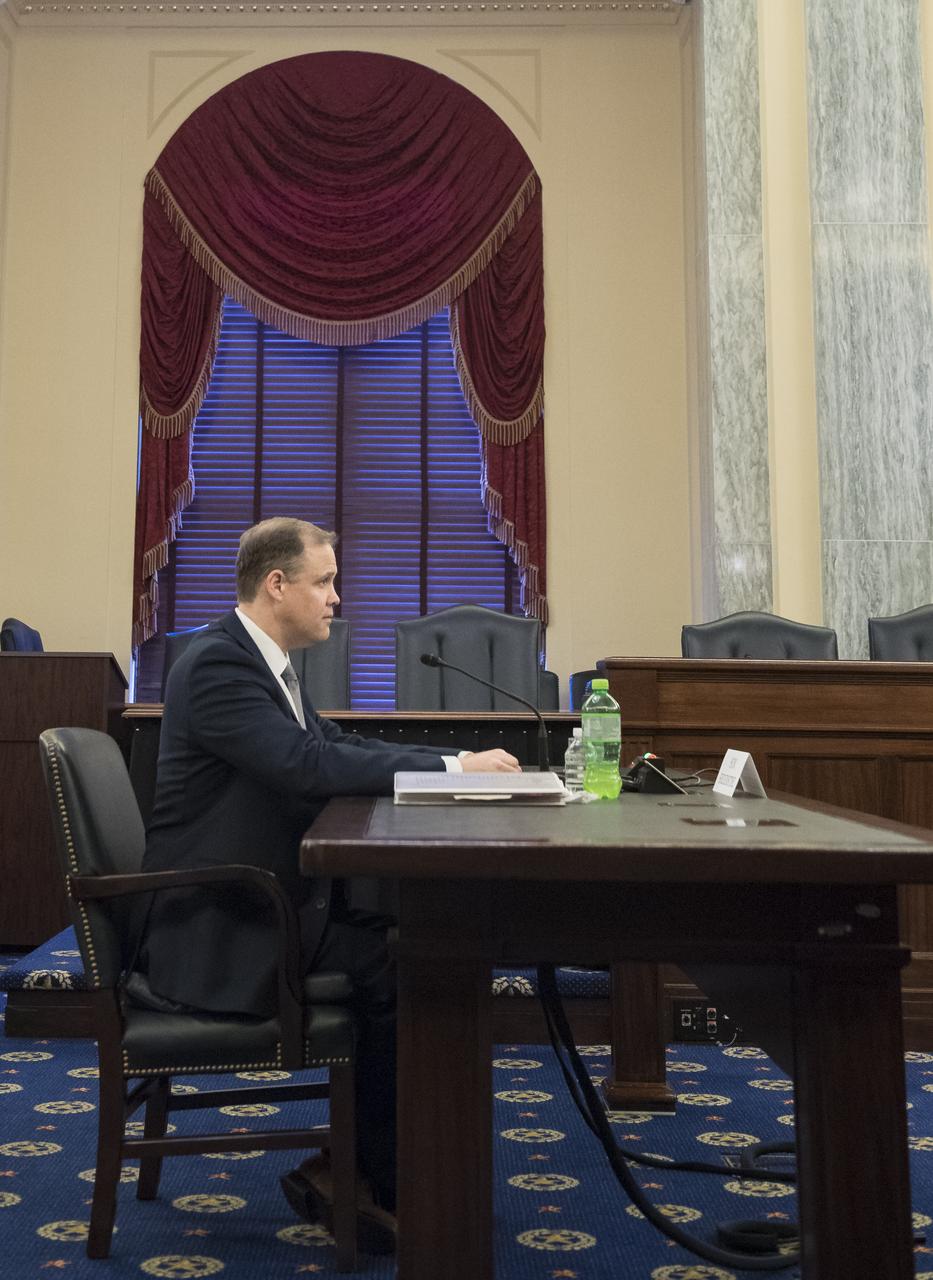
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
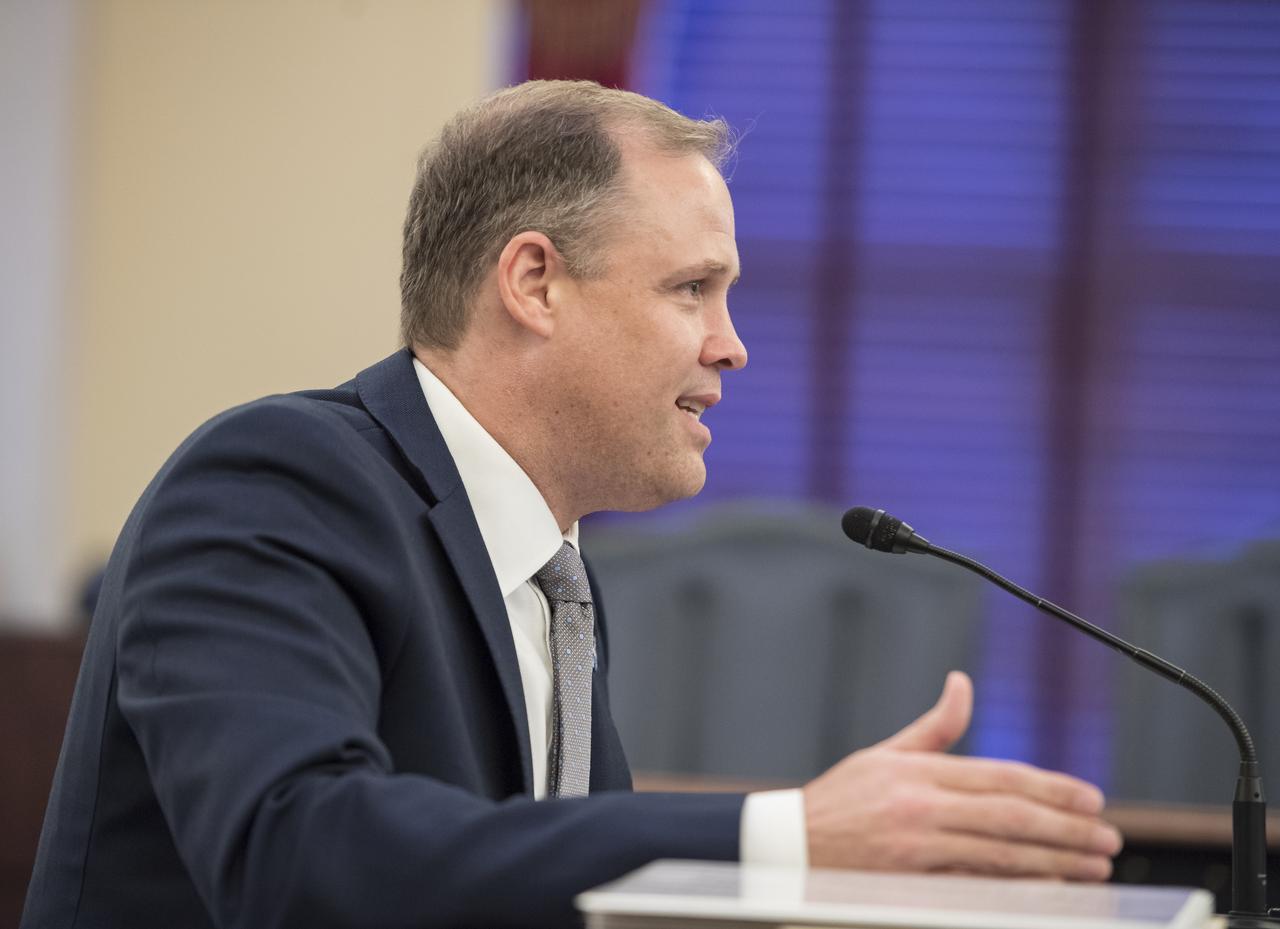

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
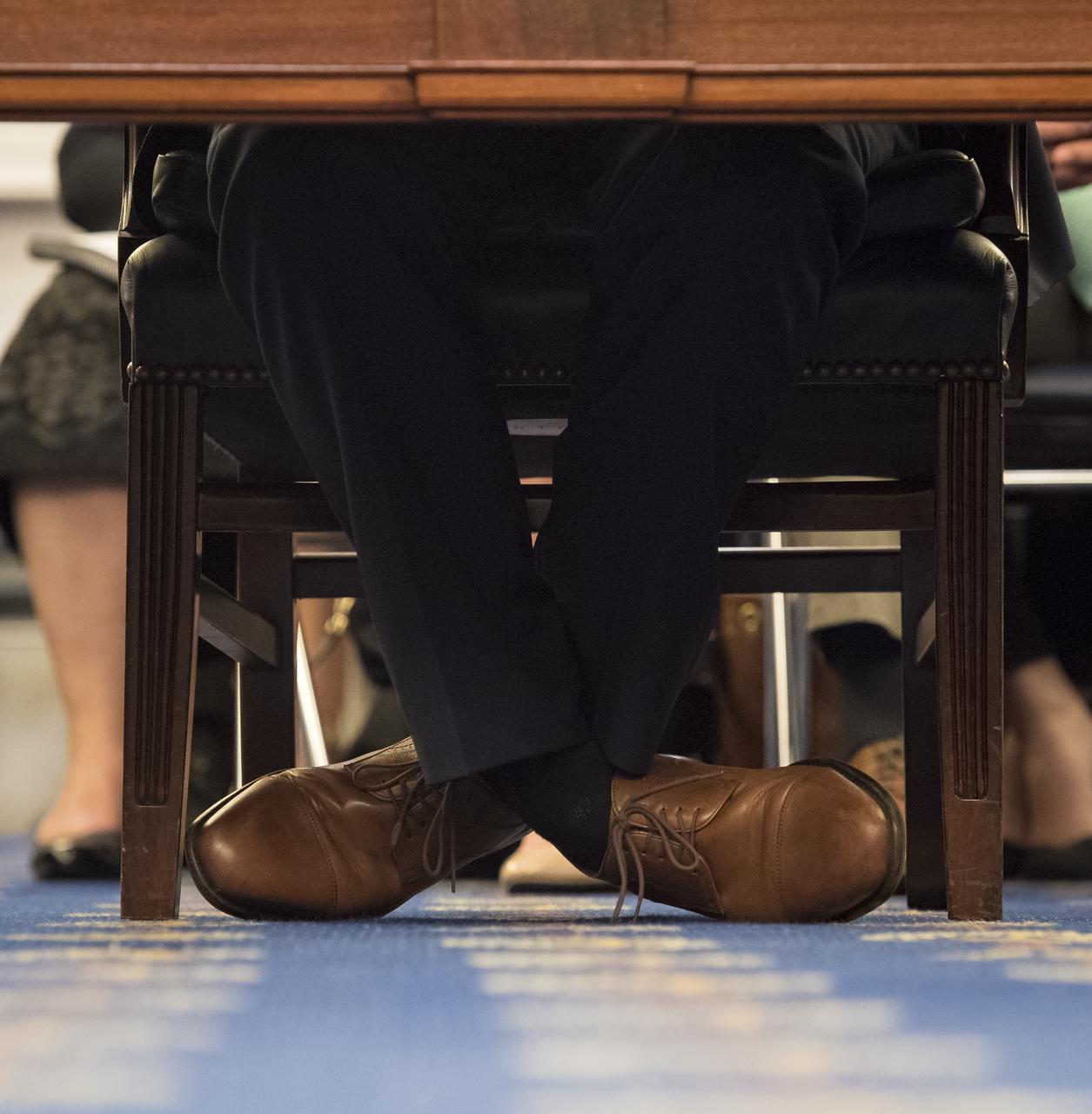

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine's shoes are seen while testifying during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
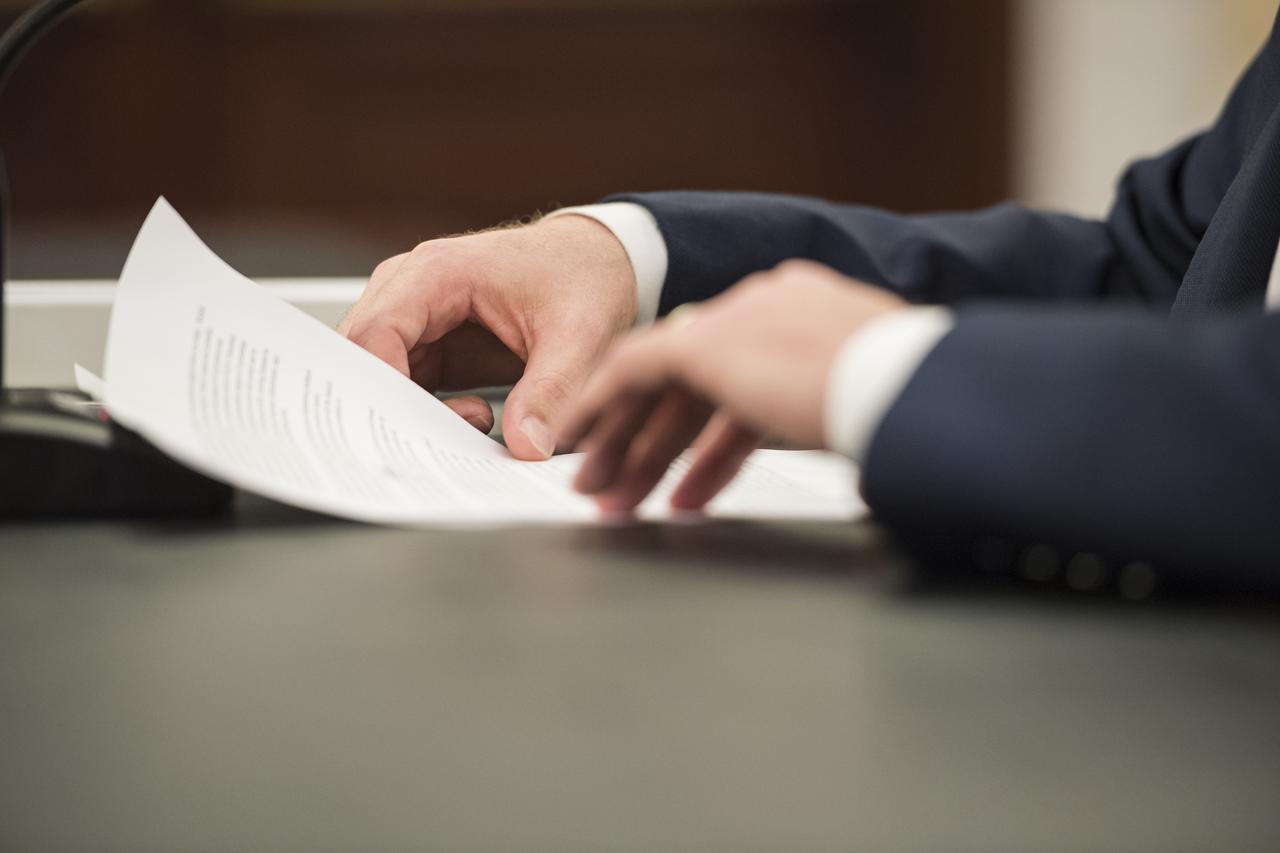

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gestures with a bottle of water while testifying during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
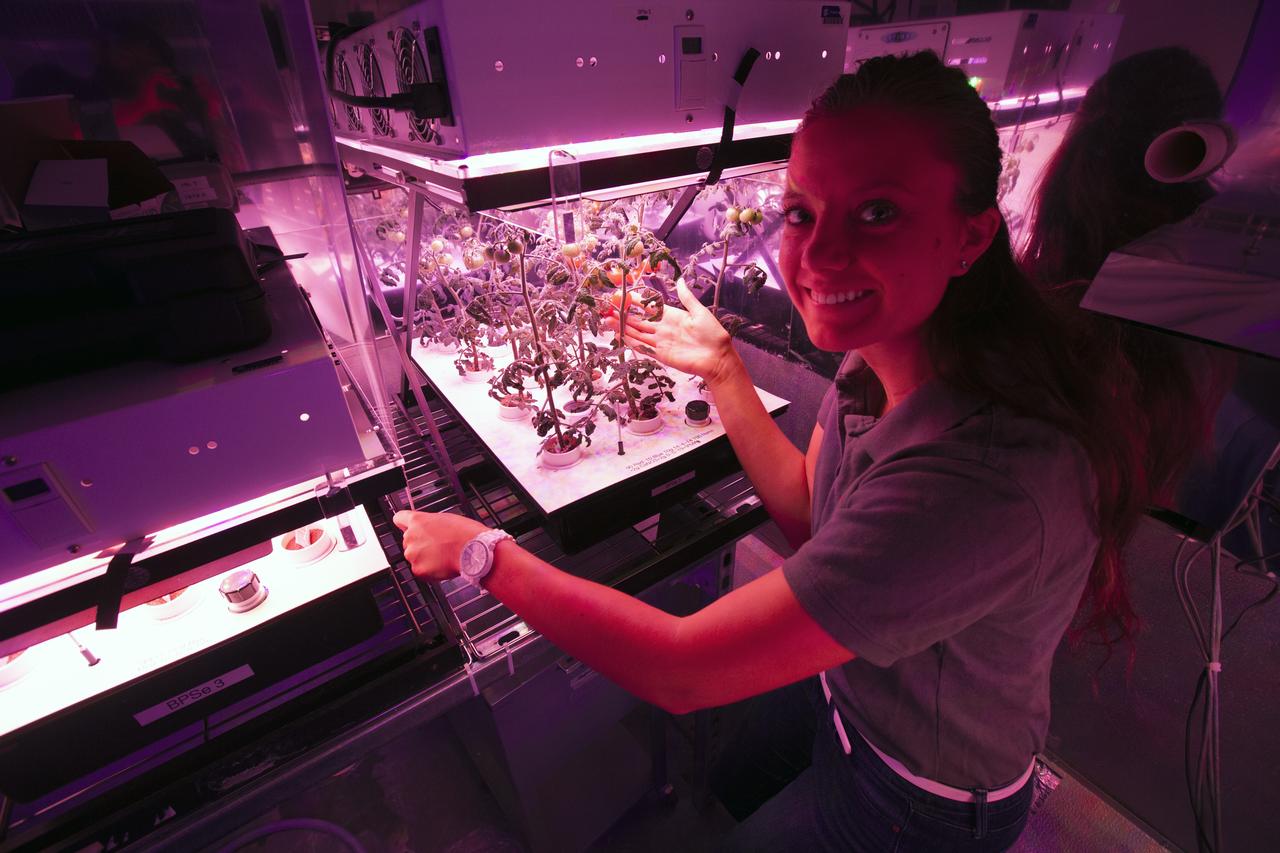
In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns such as Ayla Grandpre are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. Grandpre is majoring in computer science and chemistry at Rocky Mountain College in Billings, Montana. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
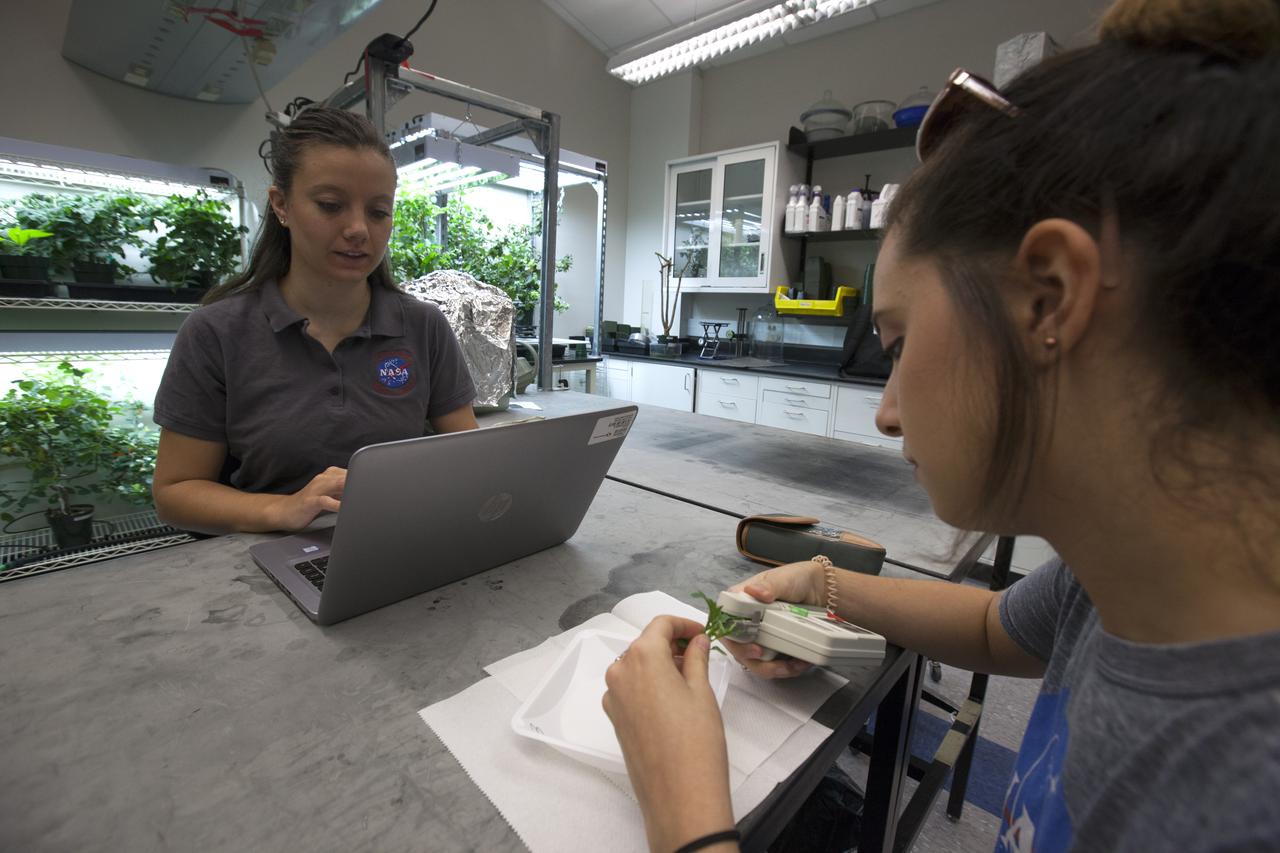

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns such as Ayla Grandpre, left, and Payton Barnwell are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. Grandpre is pursuing a degree in computer science and chemistry at Rocky Mountain College in Billings, Montana. Barnwell is a mechanical engineering and nanotechnology major at Florida Polytechnic University. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.

Sen. Ted Cruz, R-Texas, chairman of the Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness speaks during a hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives," Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
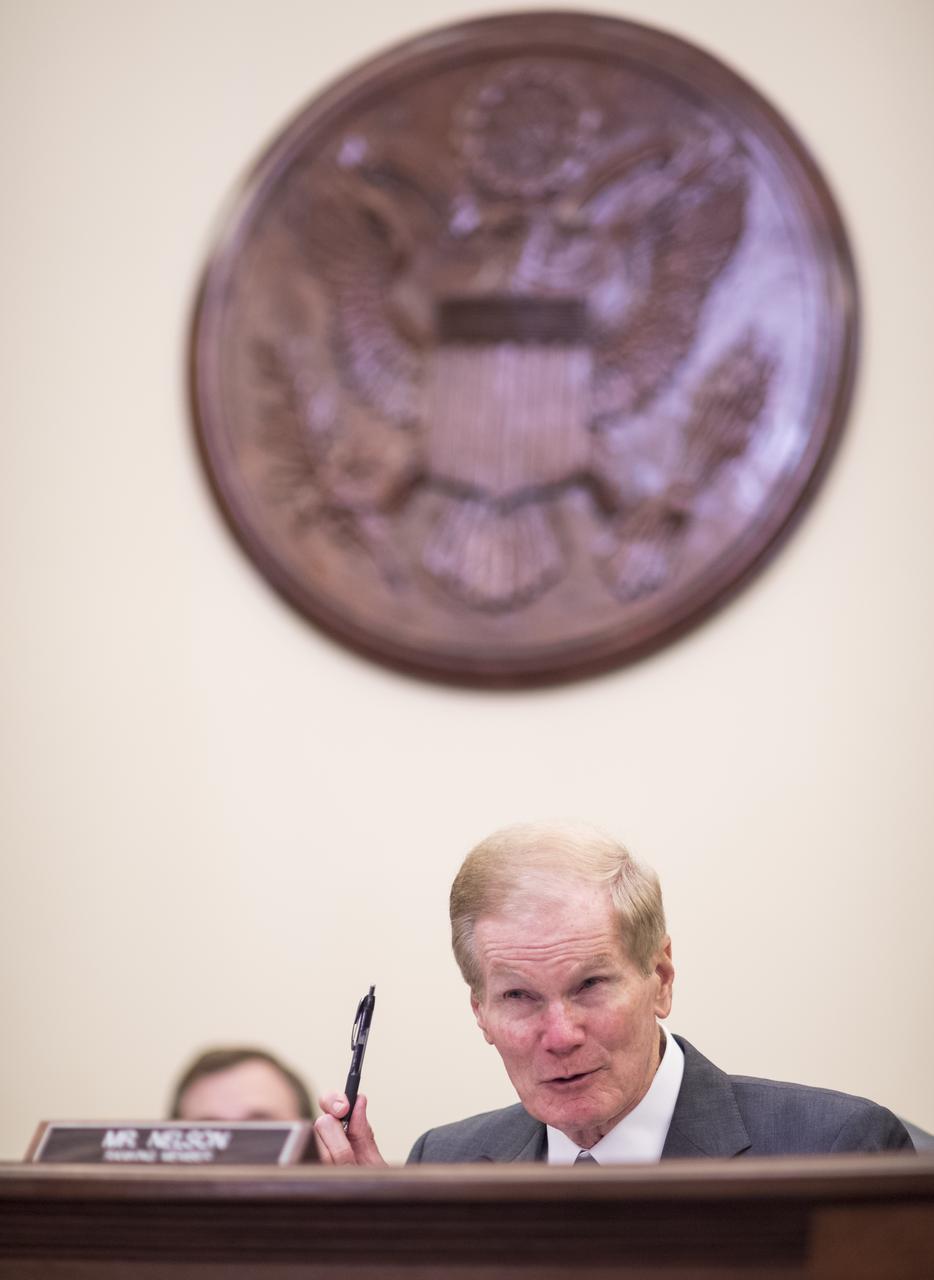

Sen. Bill Nelson, D-Fla., ranking member of the Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness speaks during a hearing titled "Examining the Future of the International Space Station: Administration Perspectives" held on Wednesday, May 16, 2018 in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier, left, Dr. Bhavya Lal, a researcher at the Institute for Defense Analysis's Science and Technology Policy Institute, center, and Dr. Elizabeth Cantwell, chief executive officer at the Arizona State University Research Enterprise, right, listen as Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, is seen on screen as he delivers an opening statement during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier, left, Dr. Bhavya Lal, a researcher at the Institute for Defense Analysis's Science and Technology Policy Institute, center, and Dr. Elizabeth Cantwell, chief executive officer at the Arizona State University Research Enterprise, right, listen as Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, is seen on screen as he delivers an opening statement during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
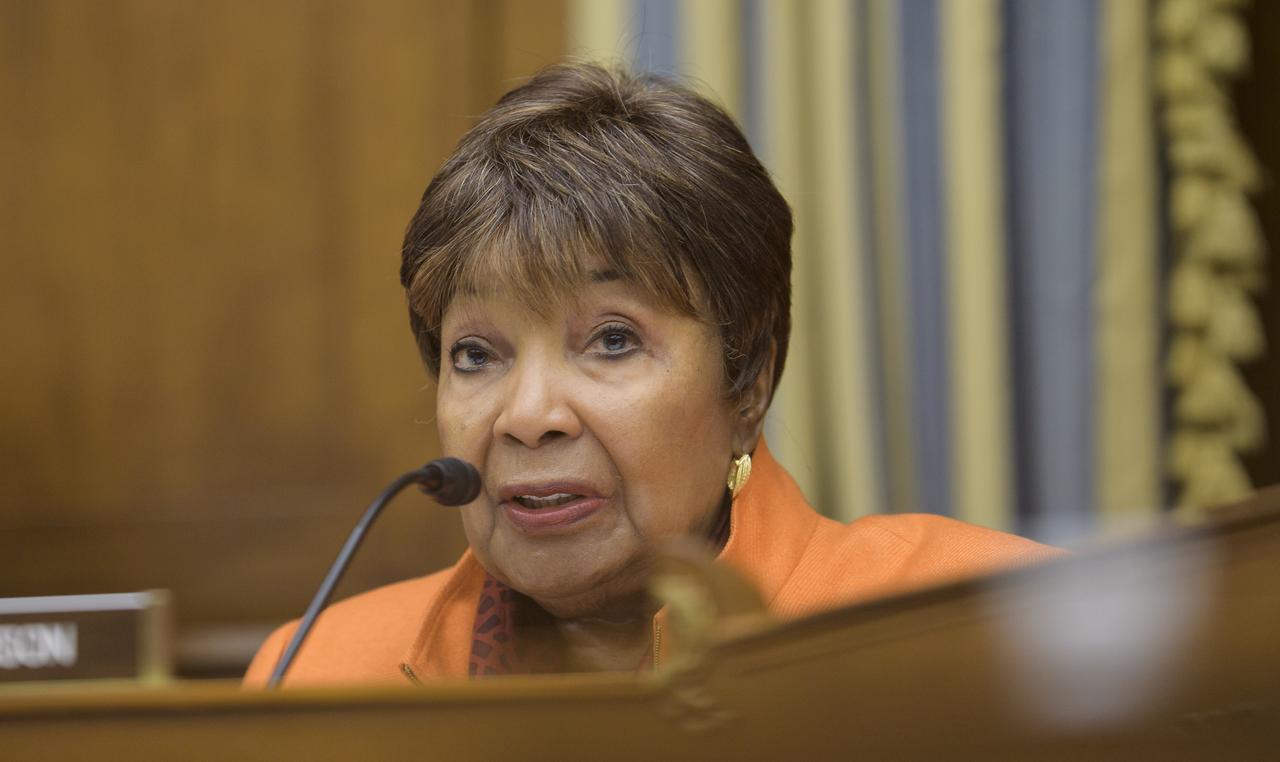

Rep. Eddie Bernice Johnson, D-Texas, ranking member of the House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology delivers her opening statement during a hearing titled "America's Human Presence in Low-Earth Orbit" on Thursday, May 17, 2018 in the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
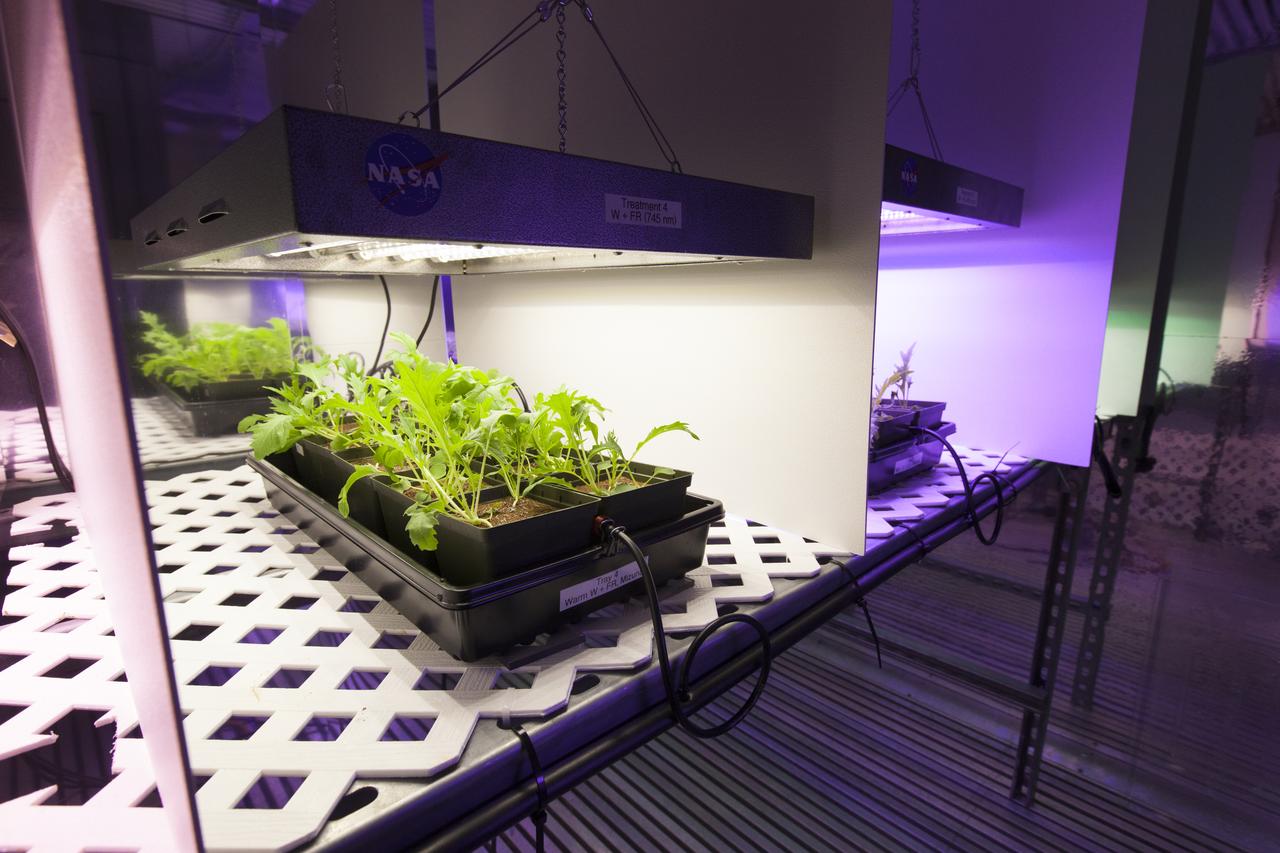

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
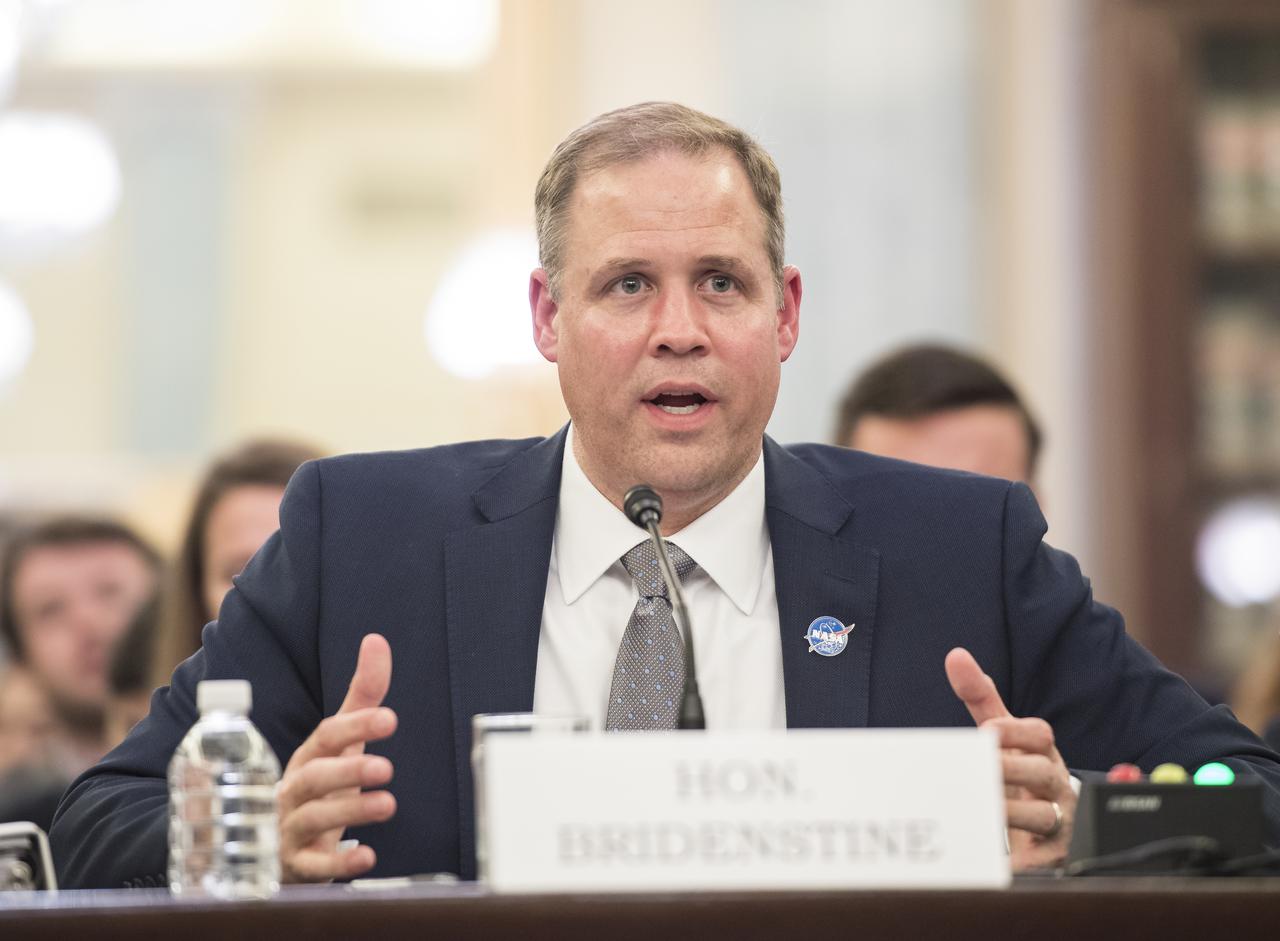

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine testifies during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier, moderates a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture" with NASA James Webb Space Telescope systems engineer Mike Menzel, SpaceX Director of space operations and former NASA astronaut Garret Reisman, Honeybee Robotics co-founder and chairman Stephen Gorevan, and former NASA astronaut Mike Massimino, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
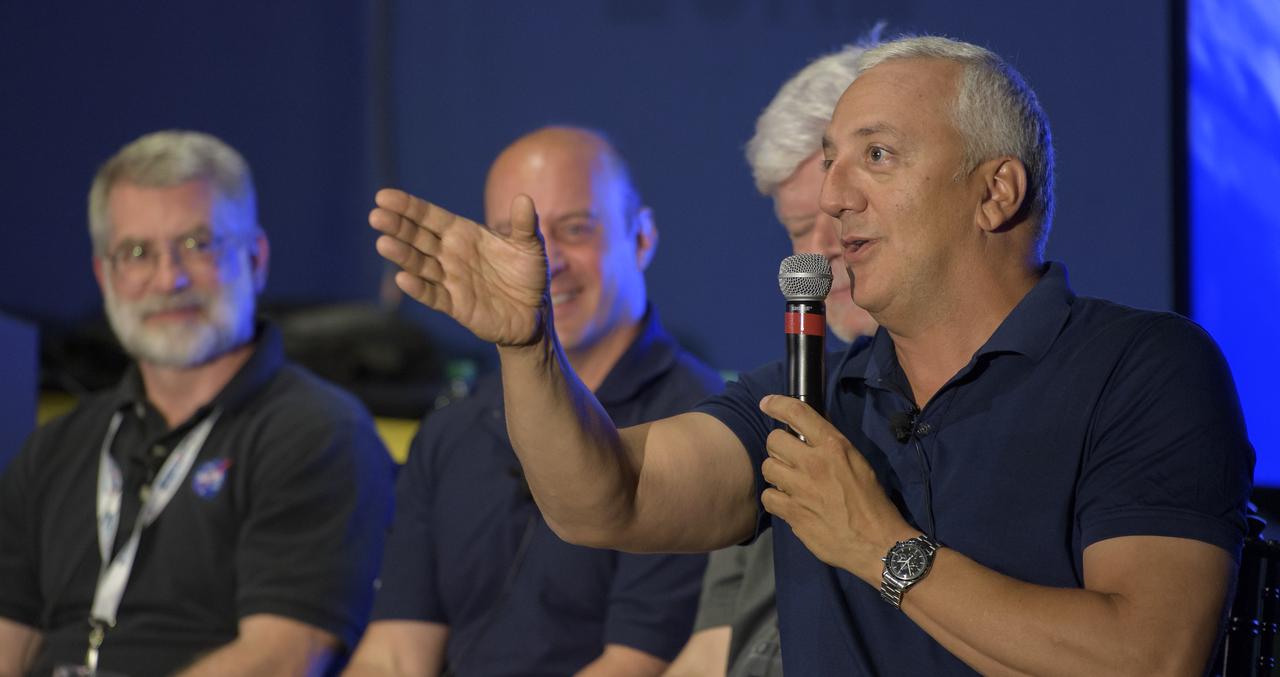

Former NASA astronaut Mike Massimino participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
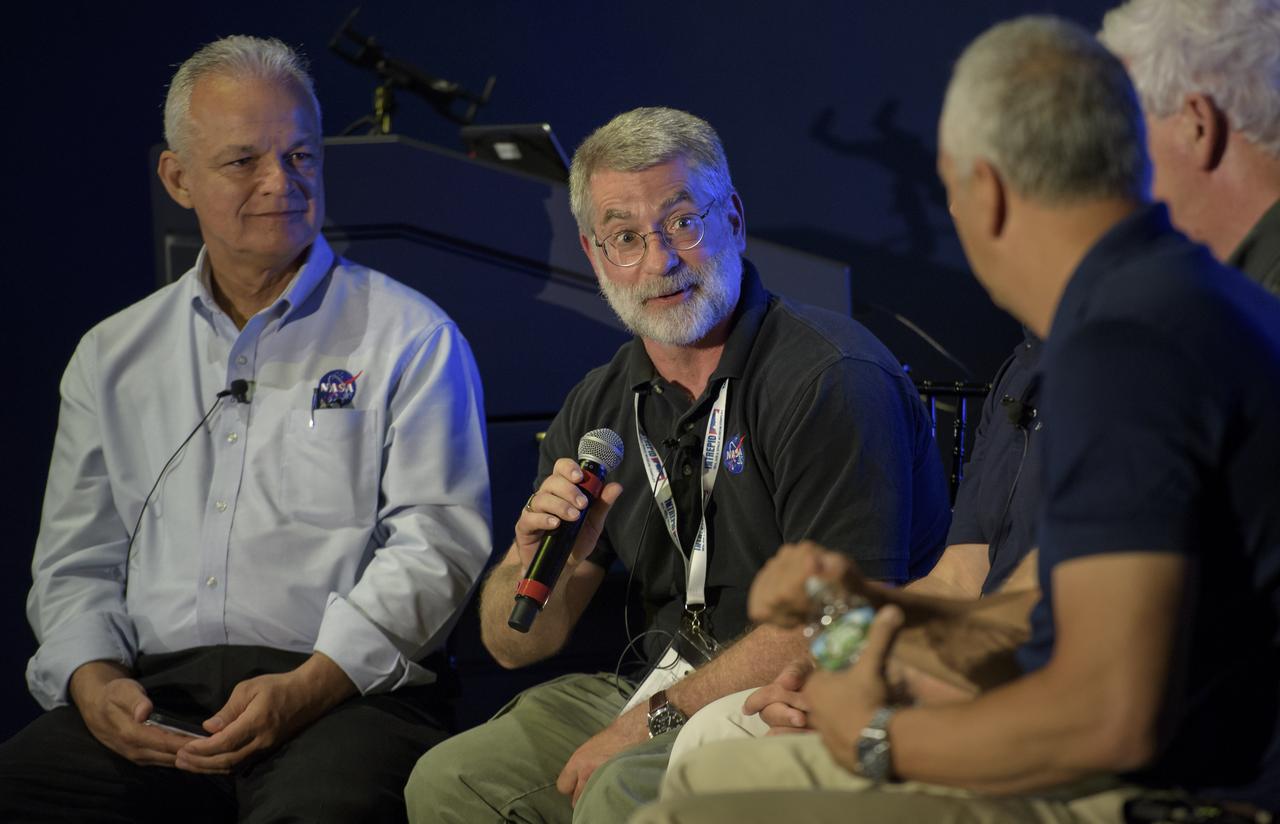

NASA James Webb Space Telescope systems engineer Mike Menzel, center, participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

SpaceX Director of space operations and former NASA astronaut Garret Reisman participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Former NASA astronaut Mike Massimino participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Honeybee Robotics co-founder and chairman Stephen Gorevan participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope systems engineer Mike Menzel, participates in a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture", Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, seen on a television monitor, testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

House Science, Space, and Technology Committee Ranking Member Zoe Lofgren, D-CA, gives opening remarks during a hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

House Science, Space, and Technology Committee Chairman Frank Lucas, R-Okla., gives opening remarks during a hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson testifies during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing regarding the NASA Fiscal Year 2025 budget, Tuesday, April 30, 2024, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
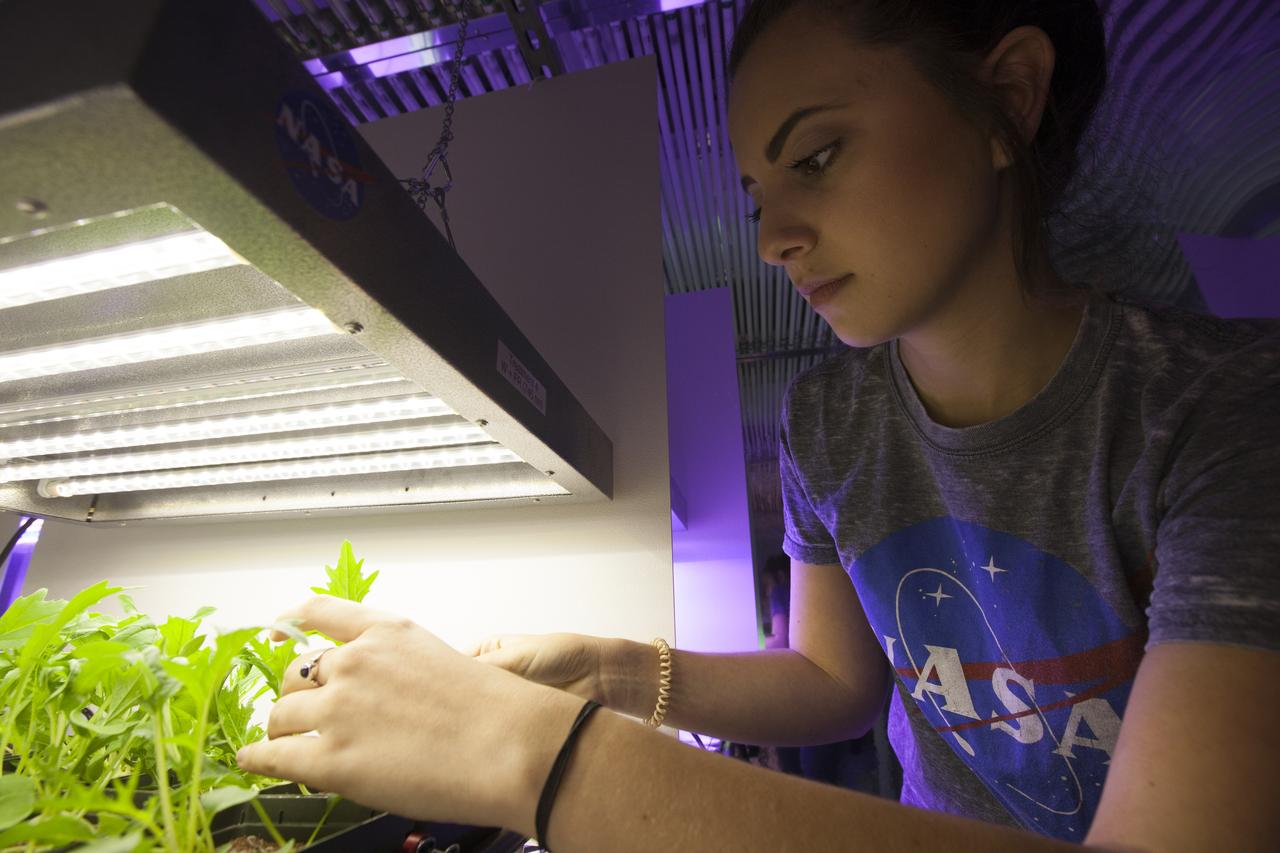

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns such as Payton Barnwell are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. Barnwell is a mechanical engineering and nanotechnology major at Florida Polytechnic University. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
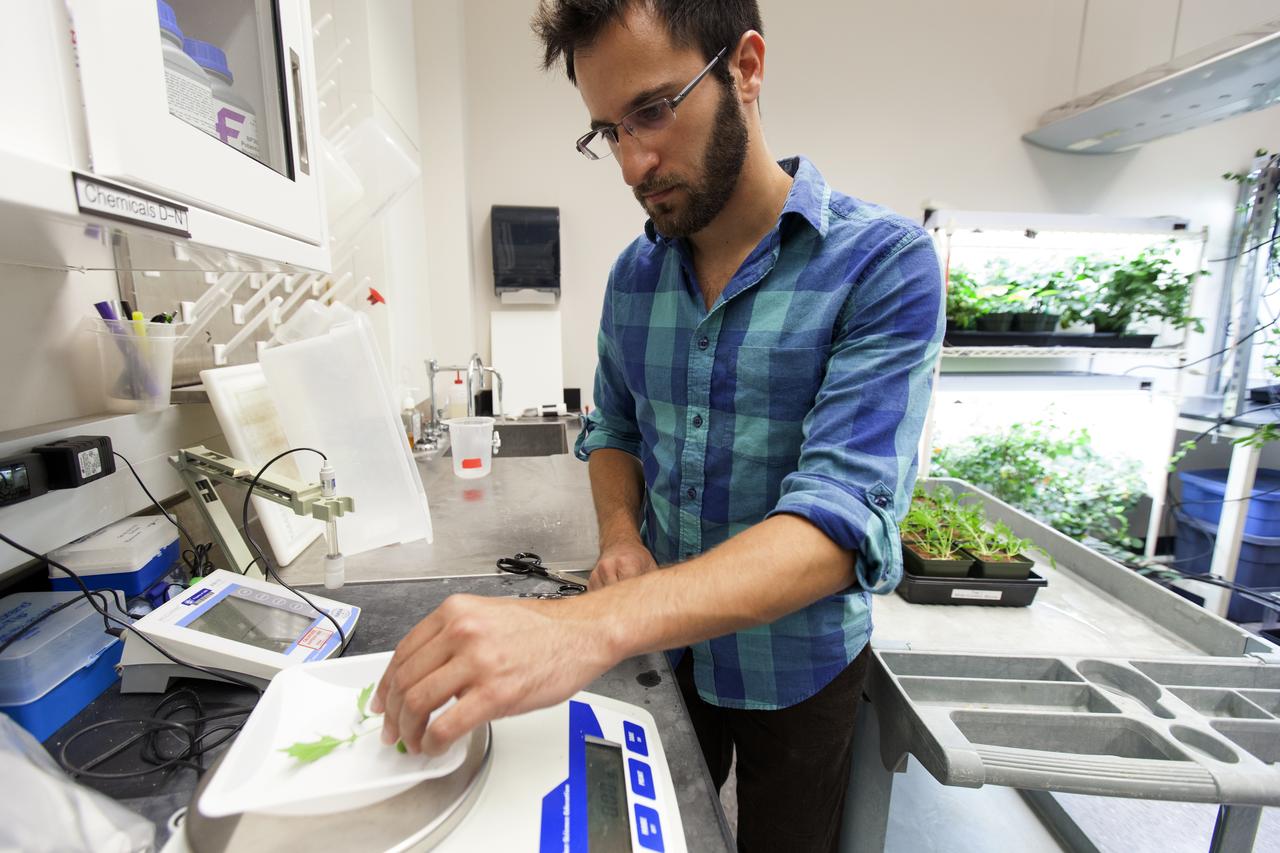

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns such as Alex Litvin are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. Litvin is pursuing doctorate in horticulture at Iowa State University. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
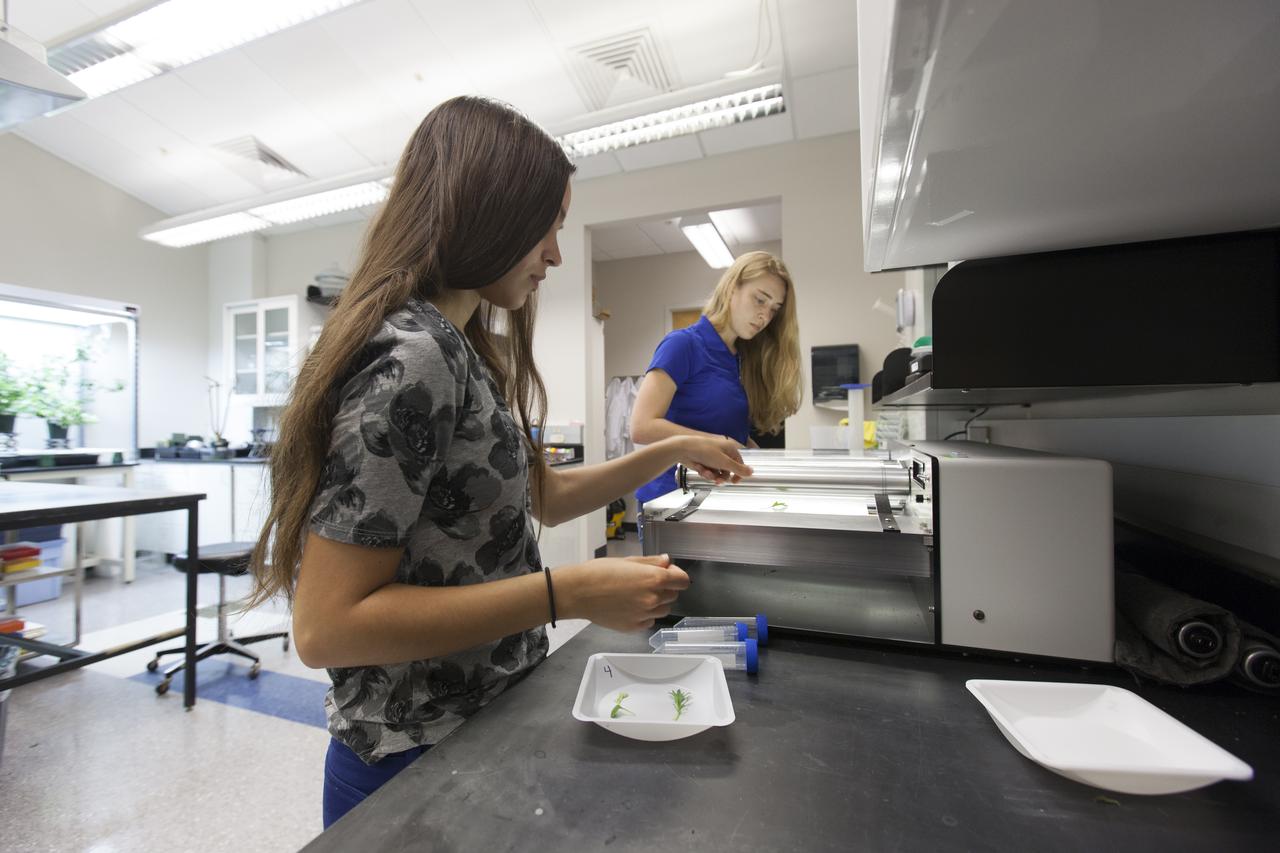

In the Space Life Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns such as Emma Boehm, left, and Jessica Scotten are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of plant growth research for food production in space. Boehm is pursuing a degree in ecology and evolution at the University of Minnesota. Scotten is majoring in microbiology at Oregon State University. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
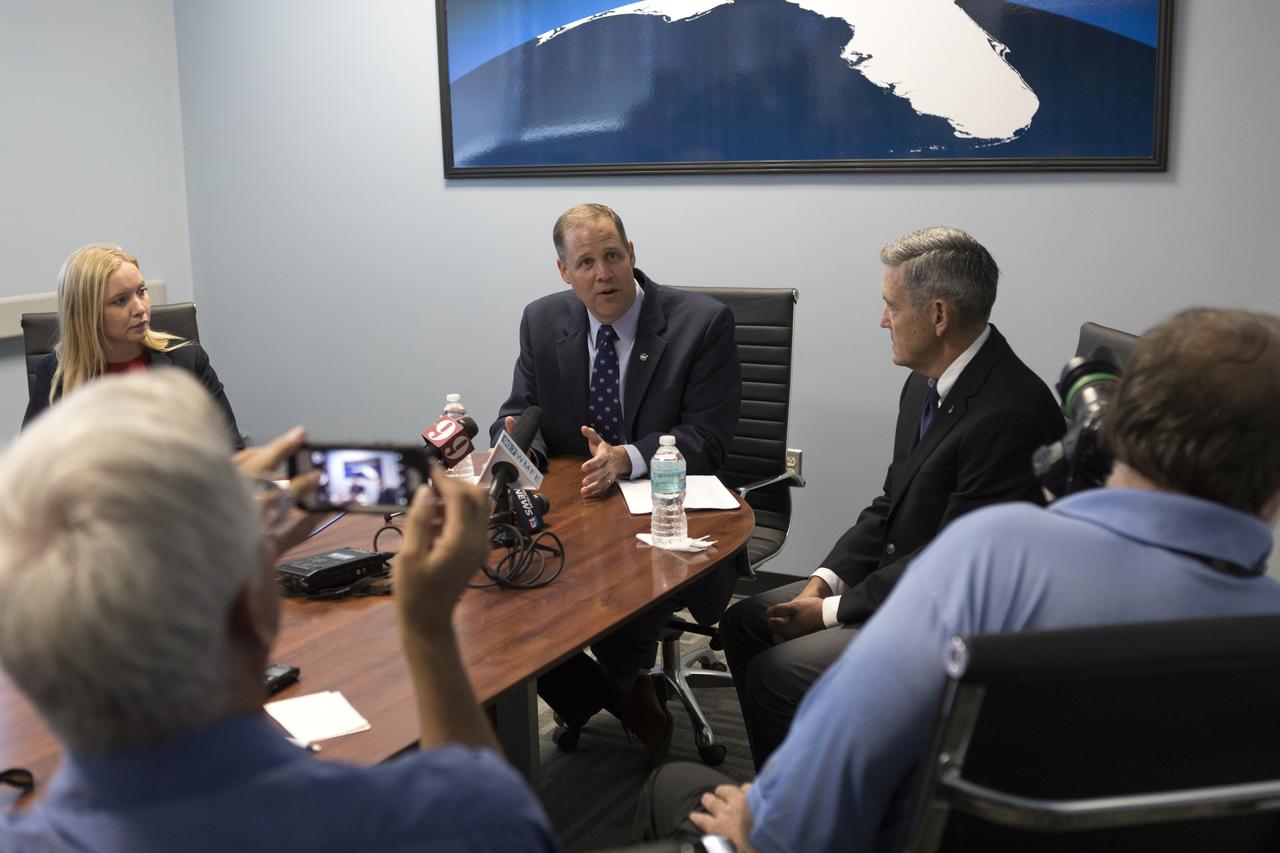

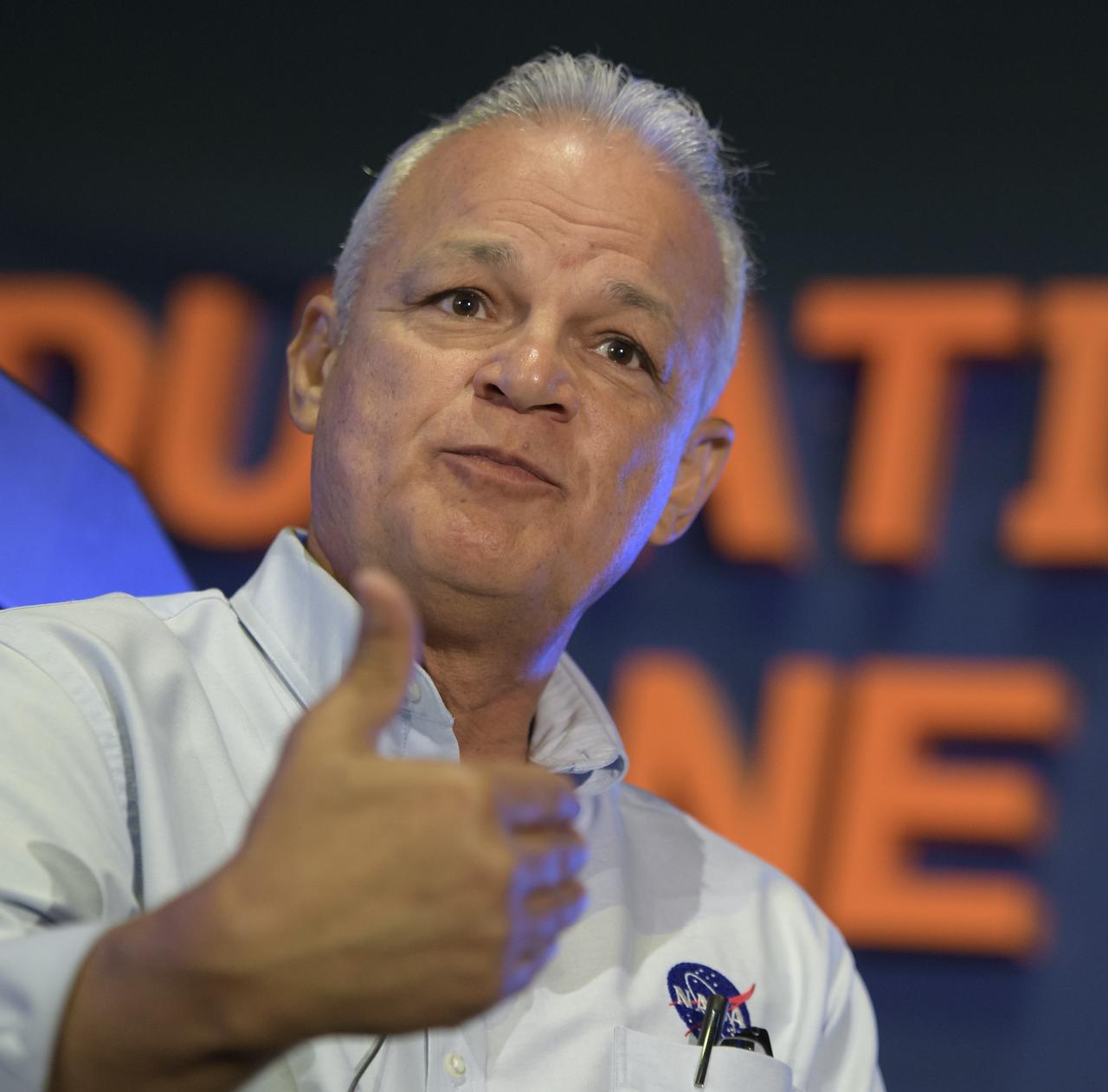
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, talks with members of the local media in a conference room inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory during his tour of Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 7, 2018. Seated at right is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. The administrator toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.
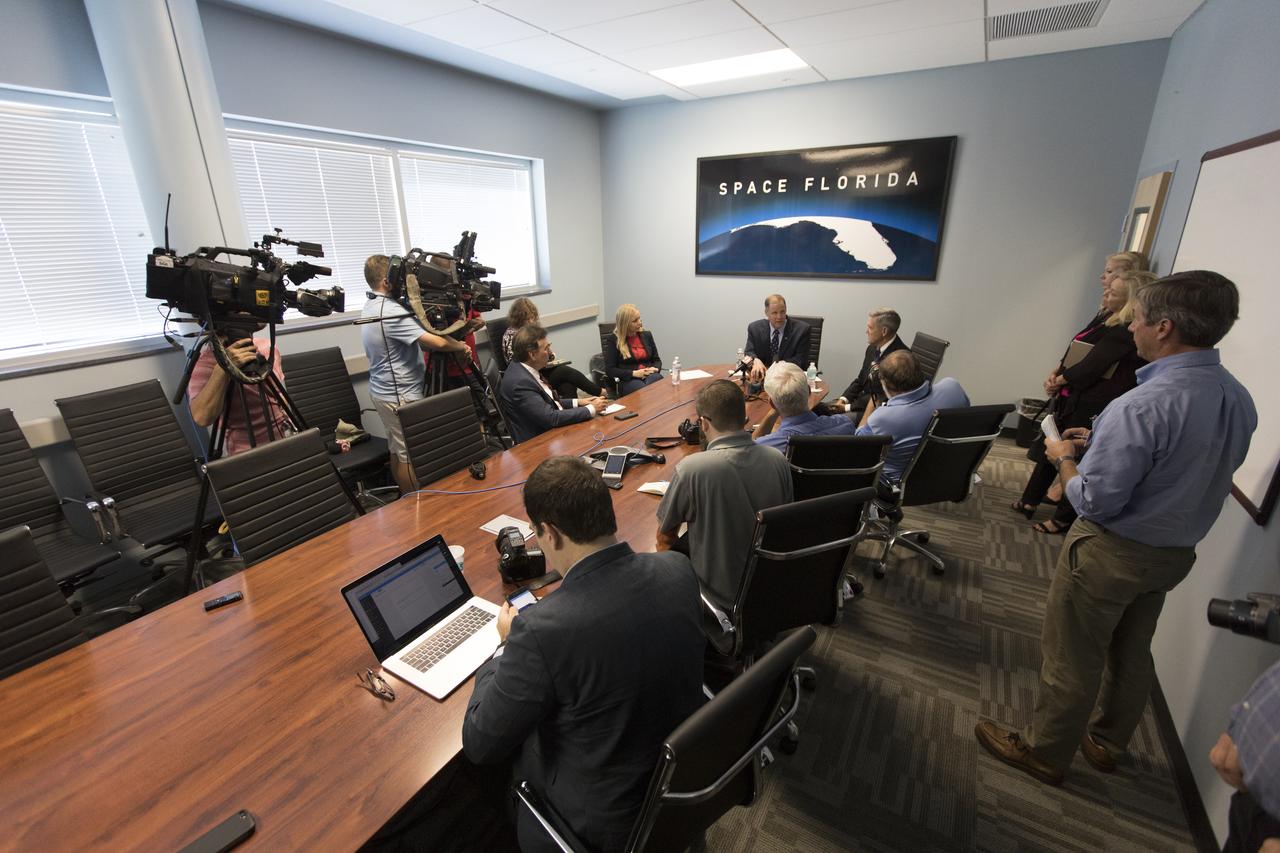

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, seated, far end of the table, center, talks with members of the local media in a conference room inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory during his tour of Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 7, 2018. Seated next to him is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. The administrator toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, right, speaks with Chairman Ted Cruz, R-Texas after testifying at a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
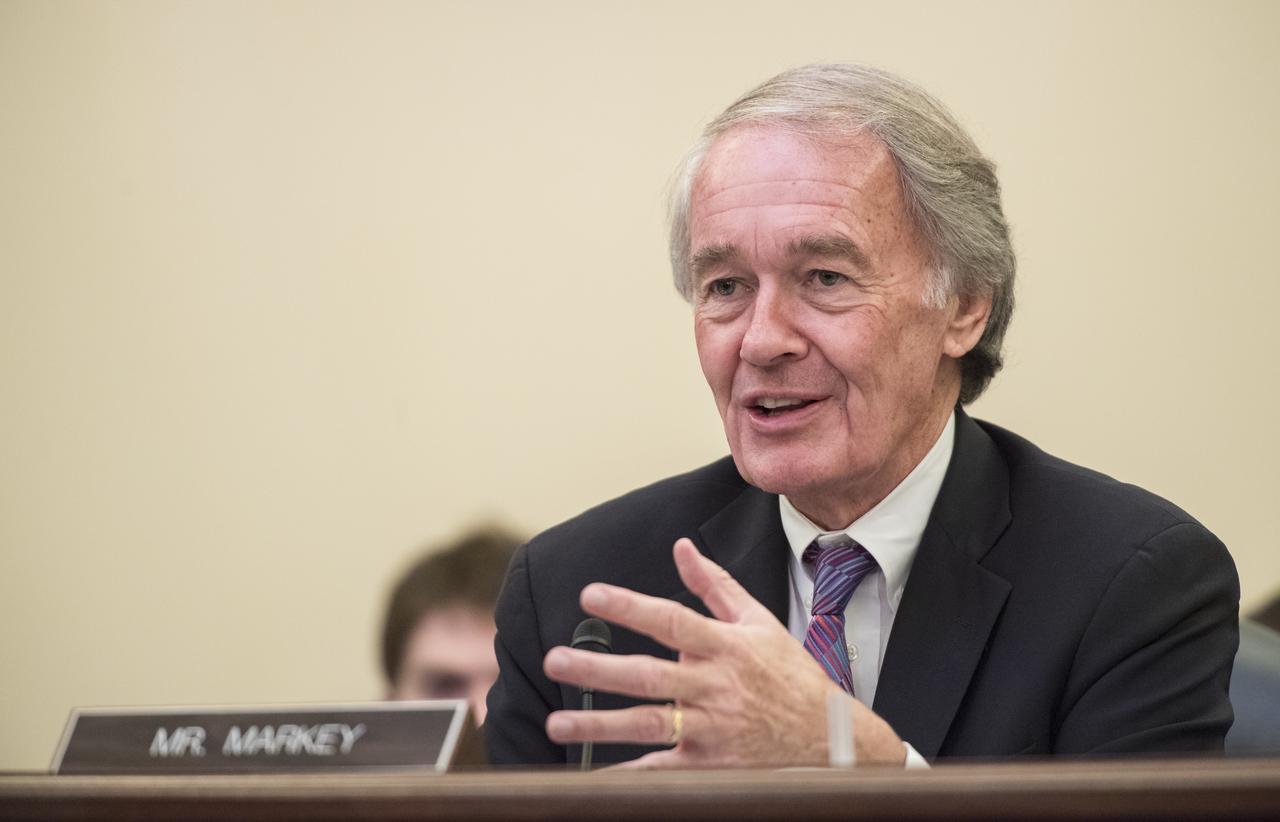

Senator Ed Markey, D-Mass, asks NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine a question during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
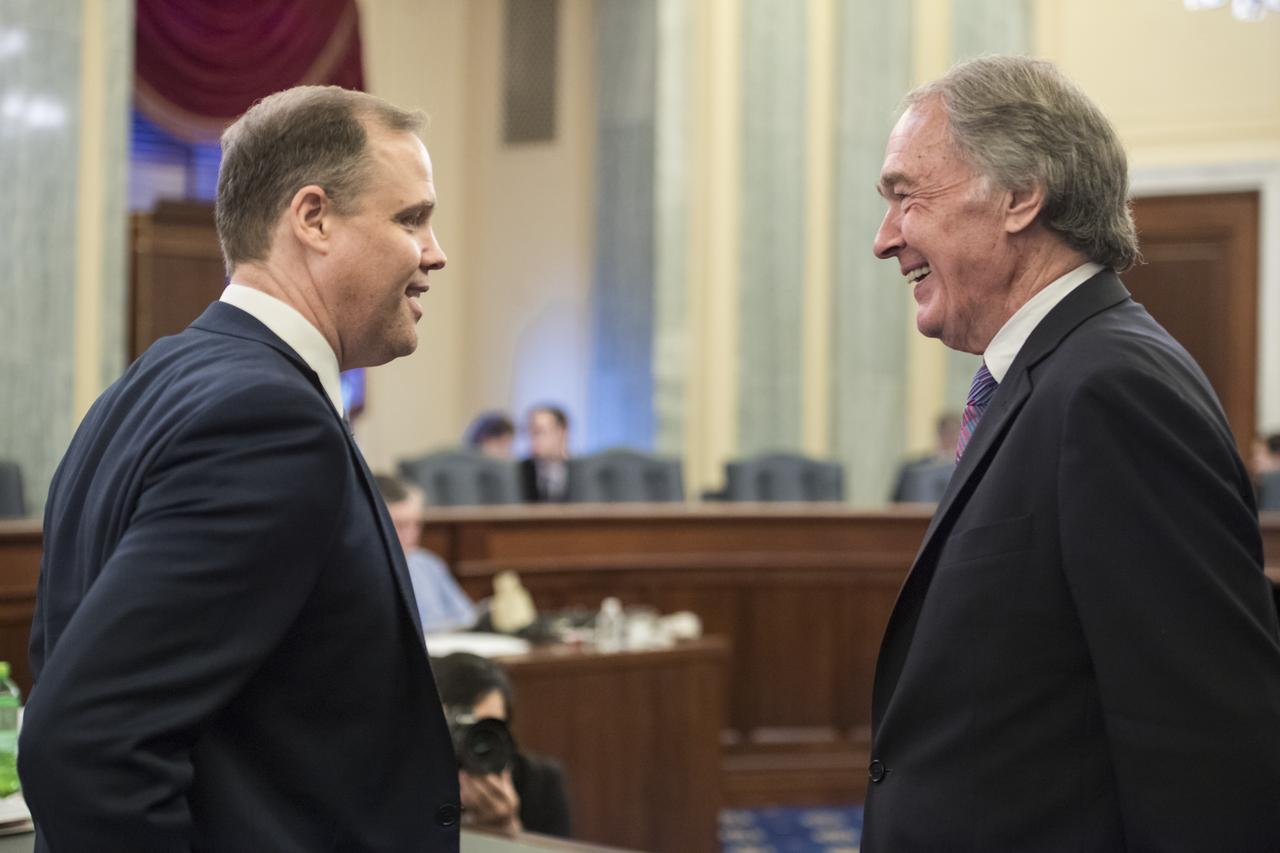

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, speaks with Senator Ed Markey, D-Mass, before testifying at a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
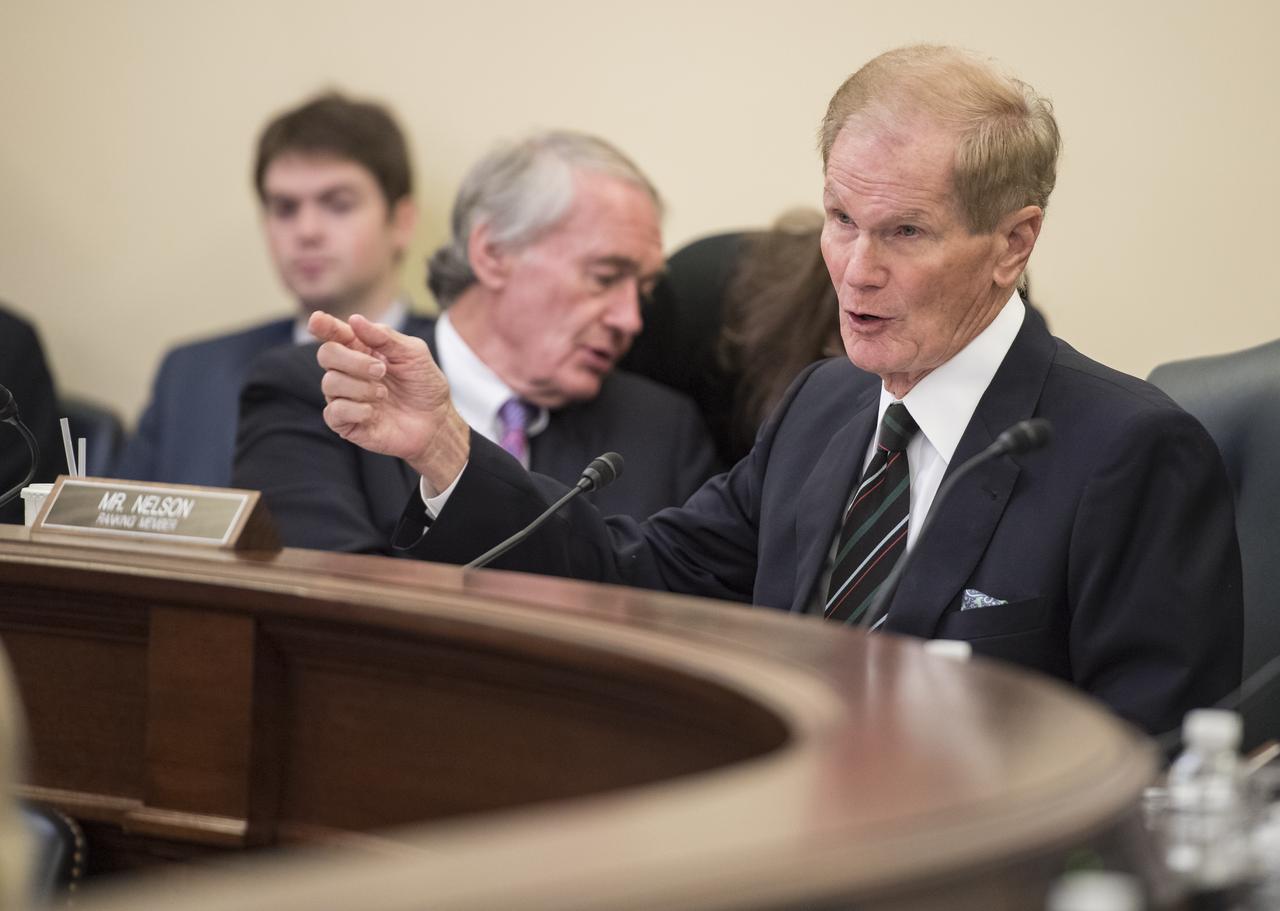

Senator Bill Nelson, D-Fla, asks NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine a question during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Chairman Ted Cruz, R-Texas, asks NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine a question during a Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness hearing titled, "Global Space Race: Ensuring the United States Remains the Leader in Space," Wednesday, September 26, 2018 at the Russell Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). This image of a sunspot, taken by Hinode, is a prime example of what the spacecraft can offer.
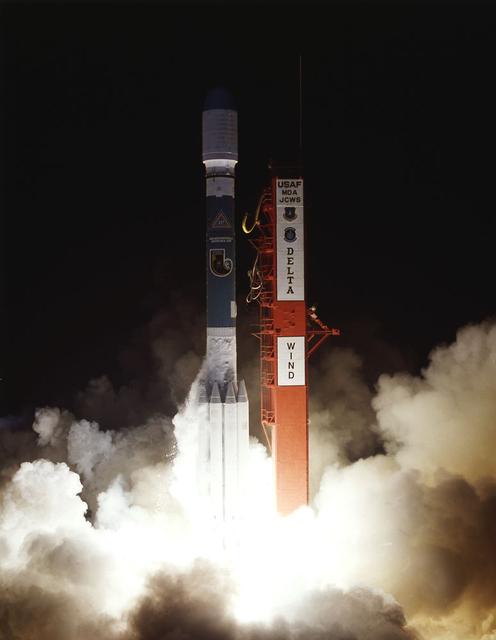

An international effort to learn more about the complex interaction between the Earth and Sun took another step forward with the launch of WIND spacecraft from Kennedy Space Center (KSC). WIND spacecraft is studded with eight scientific instruments - six US, one French, and one - the first Russian instrument to fly on a US spacecraft - that collected data about the influence of the solar wind on the Earth and its atmosphere. WIND is part of the Global Geospace Science (GGS) initiative, the US contribution to NASA's International Solar Terrestrial Physics (ISTP) program.
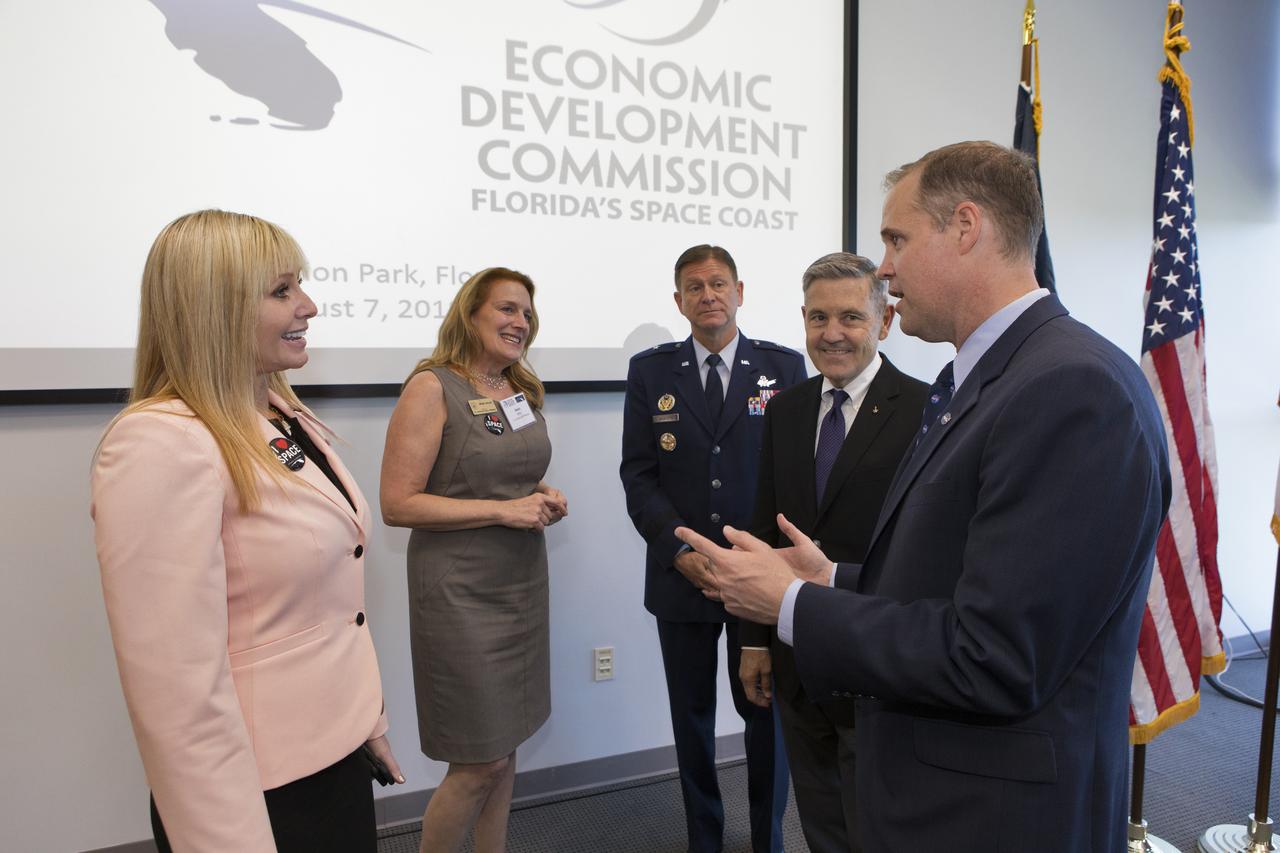

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, far right, talks with participants of an Economic Development Commission roundtable discussion hosted by Space Florida at the Space Life Sciences Laboratory on Aug. 7, 2018, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view next to Bridenstine is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, and Brigadier General Wayne Monteith, commander, 45th Space Wing, and director, Eastern Range, at Patrick Air Force Base in Florida. The administrator also toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, facing away from the camera, participates in an Economic Development Commission roundtable discussion hosted by Space Florida at the Space Life Sciences Laboratory on Aug. 7, 2018, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At right is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. The administrator also toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.
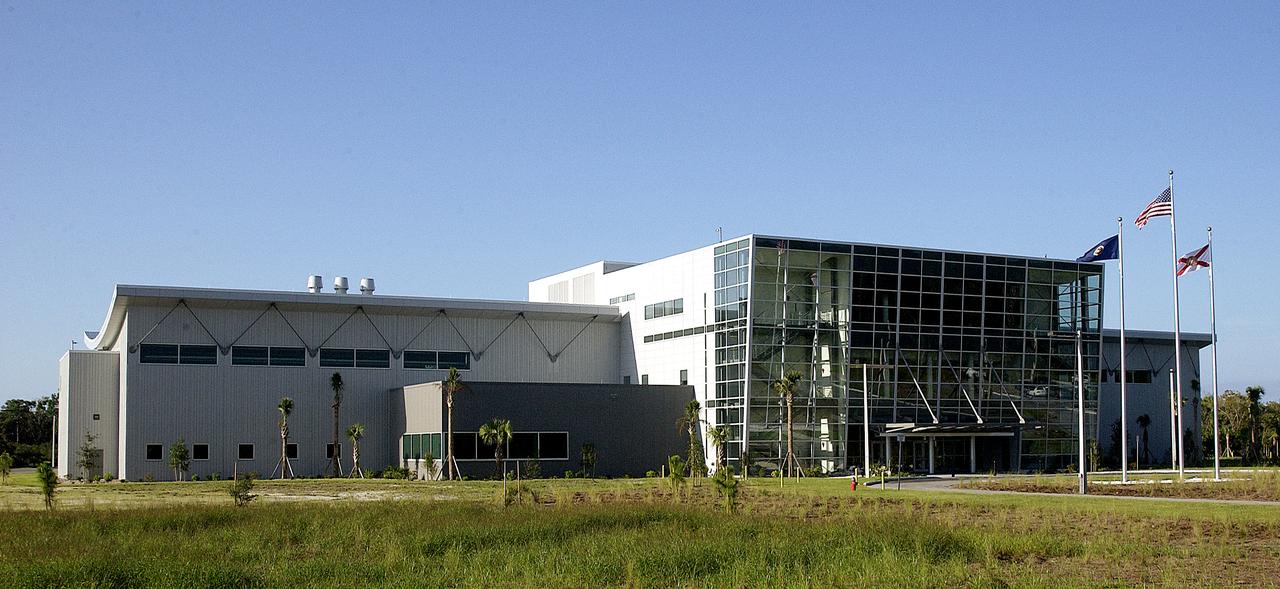

The Space Life Sciences Lab (SLSL), formerly known as the Space Experiment Research and Processing Laboratory (SERPL), is a state-of-the-art facility built for ISS biotechnology research. Developed as a partnership between NASA-KSC and the State of Florida, NASA’s life sciences contractor is the primary tenant of the facility, leasing space to conduct flight experiment processing and NASA-sponsored research. About 20 percent of the facility will be available for use by Florida’s university researchers through the Florida Space Research Institute.
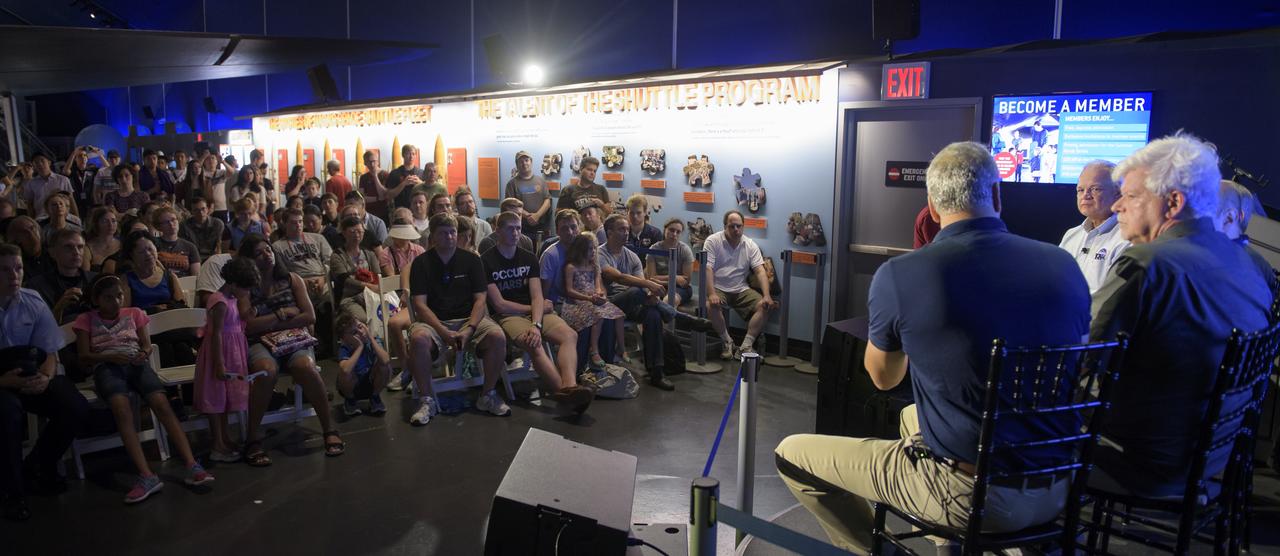

Audience members, seated under the wing of the space shuttle Enterprise, listen as NASA Acting Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier, moderates a panel discussion titled "The Big Picture" with NASA James Webb Space Telescope systems engineer Mike Menzel, SpaceX Director of space operations and former NASA astronaut Garret Reisman, Honeybee Robotics co-founder and chairman Stephen Gorevan, and former NASA astronaut Mike Massimino, Saturday, Aug. 5, 2017 at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York City. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Miria Finckenor, a researcher at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, shows off the 15th Materials International Space Station Experiment, or MISSE, an external science payload berthed on the International Space Station since 2001
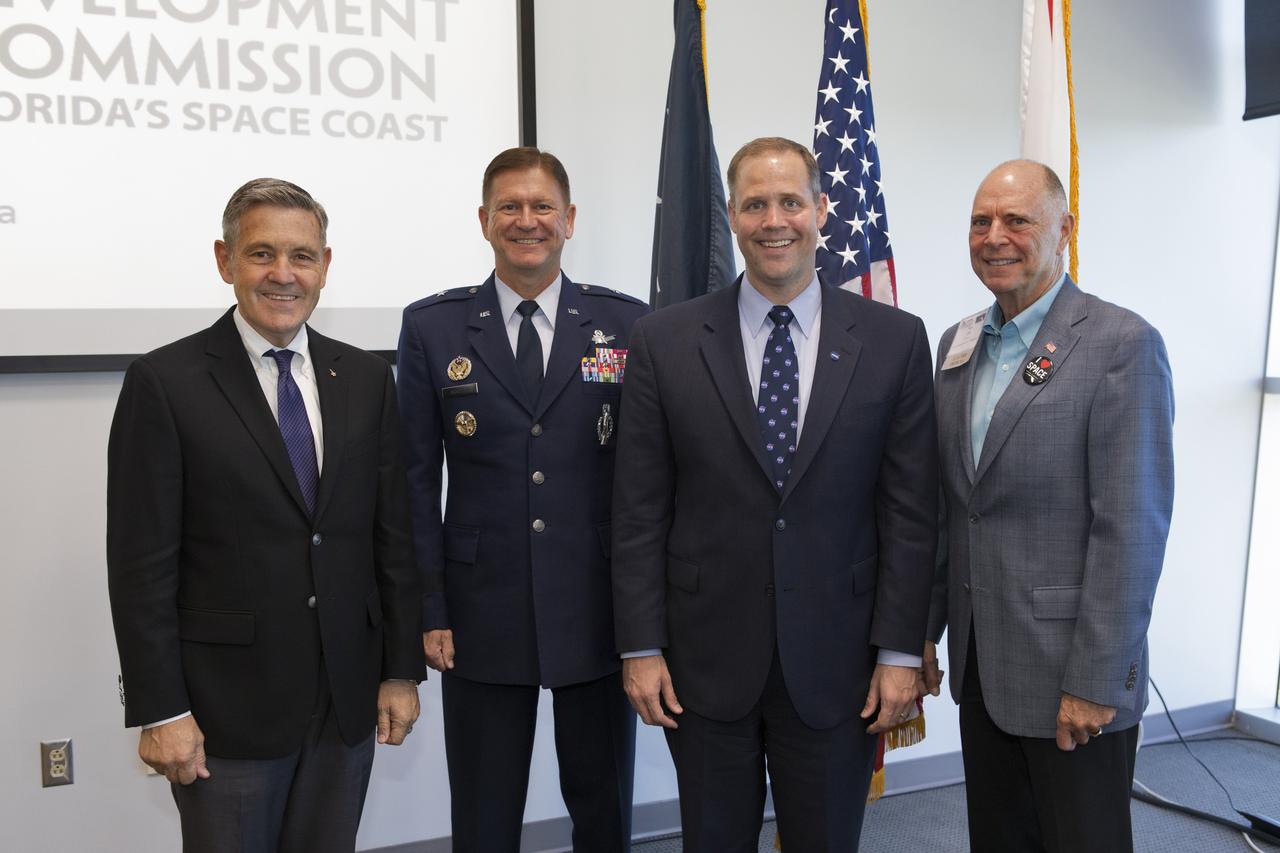

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from right, participates in an Economic Development Commission roundtable discussion hosted by Space Florida at the Space Life Sciences Laboratory on Aug. 7, 2018, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. With him, from left, are Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana; Brigadier General Wayne Monteith, commander, 45th Space Wing, and director, Eastern Range, Patrick Air Force Base in Florida; and U.S. Rep. Bill Posey. The administrator also toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.
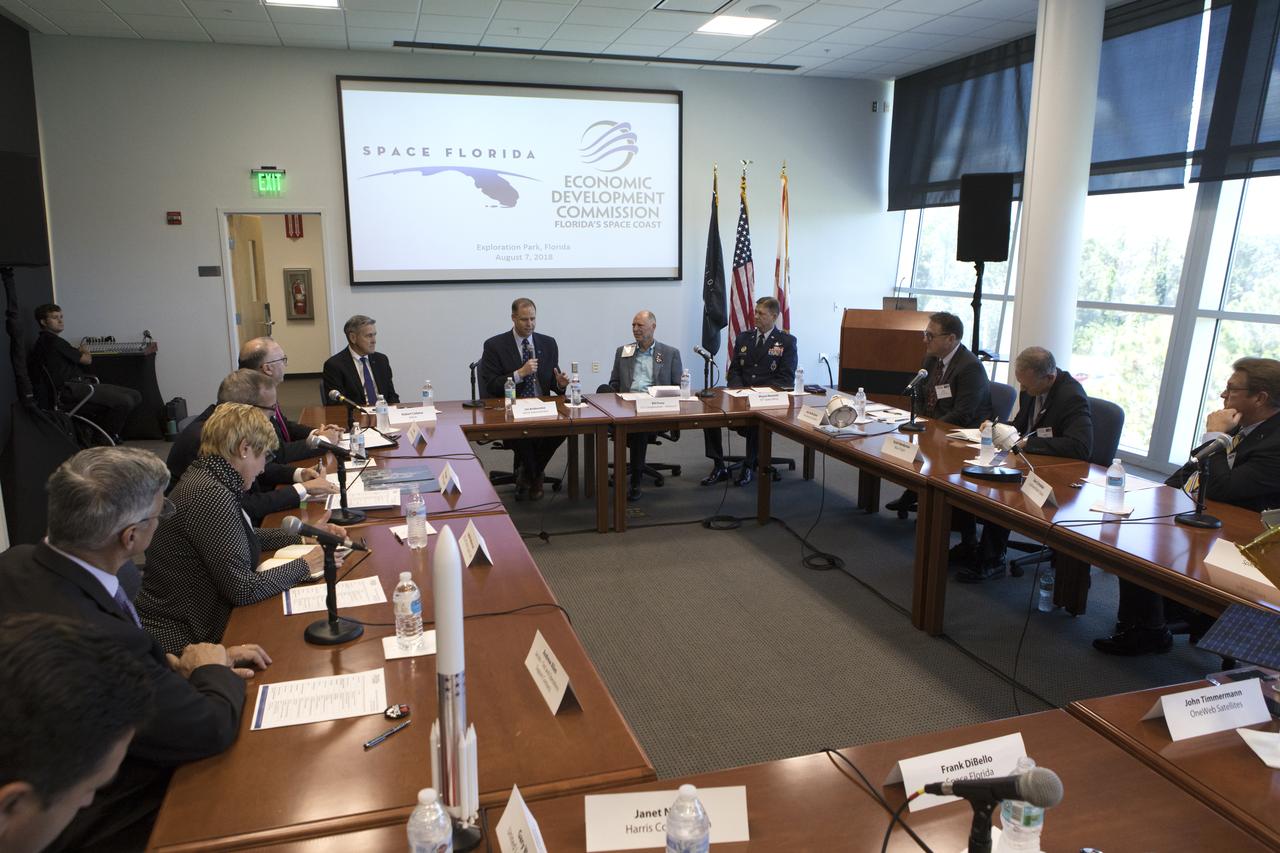

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, seated at the far table, center, participates in an Economic Development Commission roundtable discussion hosted by Space Florida at the Space Life Sciences Laboratory on Aug. 7, 2018, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seated at left is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. Seated at right is U.S. Rep. Bill Posey, and Brigadier General Wayne Monteith, commander, 45th Space Wing, and director, Eastern Range, Patrick Air Force Base in Florida. The administrator also toured Kennedy facilities and received updates on various center accomplishments.
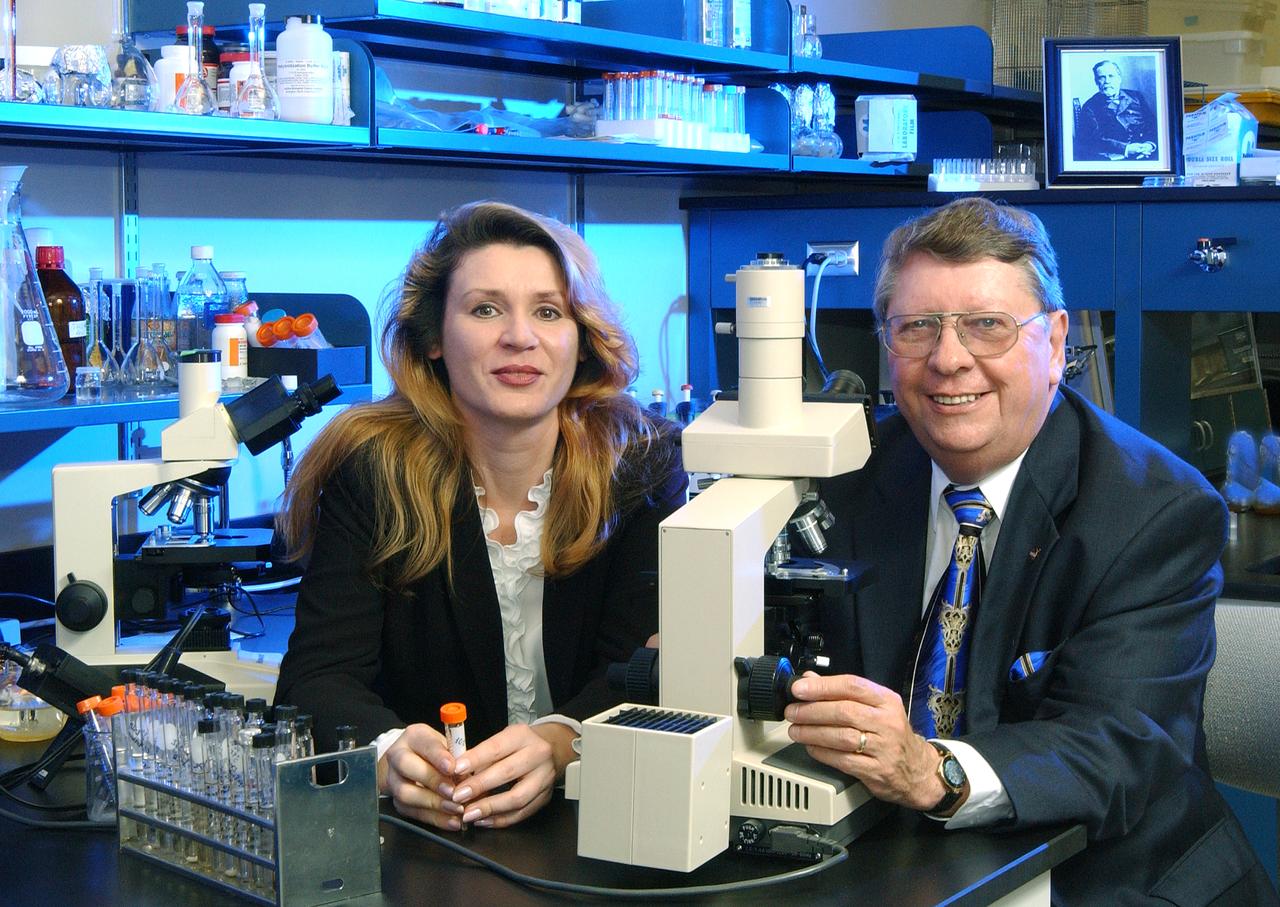

Microbiologist Dr. Elena V. Pikuta, and Astrobiologist Richard Hoover culture extremophiles, microorganisms that can live in extreme environments, in the astrobiology laboratory at the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama. The scientists recently discovered a new species of extremophiles, Spirochaeta Americana. The species was found in Northern California's Mono Lake, an alkaline, briny oxygen-limited lake in a closed volcanic crater that Hoover believes may offer new clues to help identify sites to research for potential life on Mars. Hoover is an astrobiologist at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), and Pikuta is a microbiologist with the Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomy Research Laboratory at the University of Alabama in Huntsville. The NSSTC is a partnership with MSFC, Alabama universities, industry, research institutes, and federal agencies.
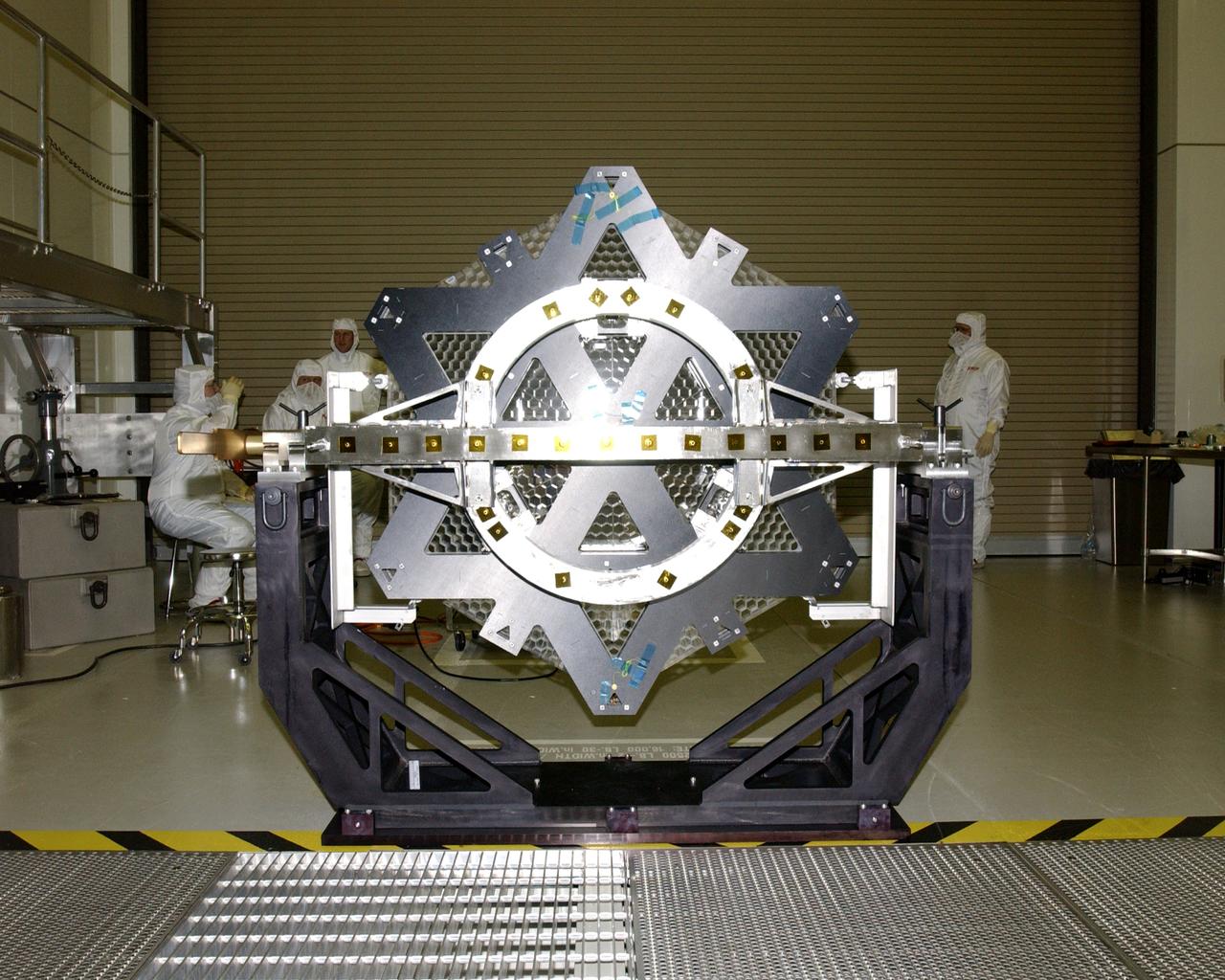
This photo (rear view) is of one of many segments of the Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
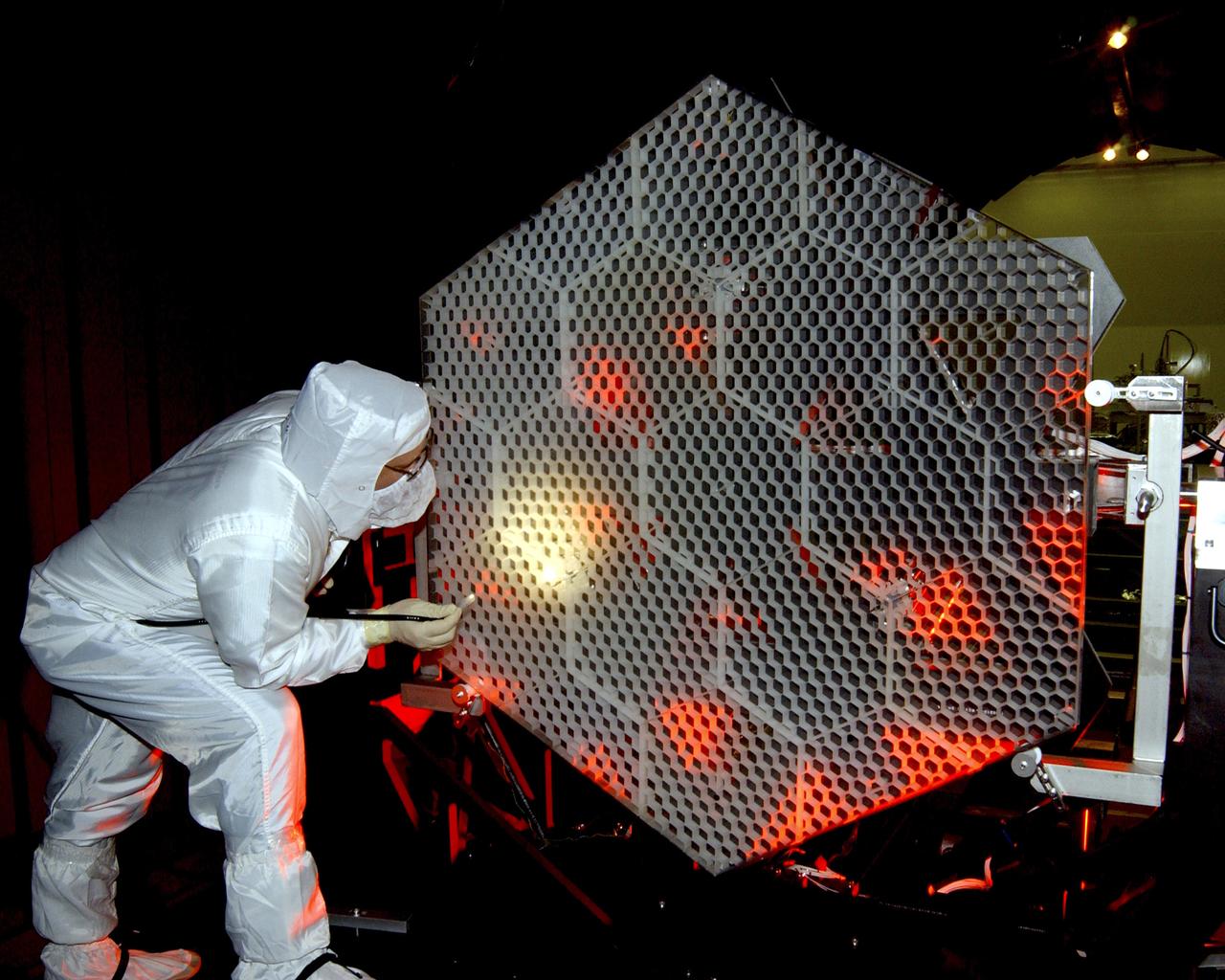

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, an MSFC employee is inspecting one of many segments of the mirror assembly for flaws. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
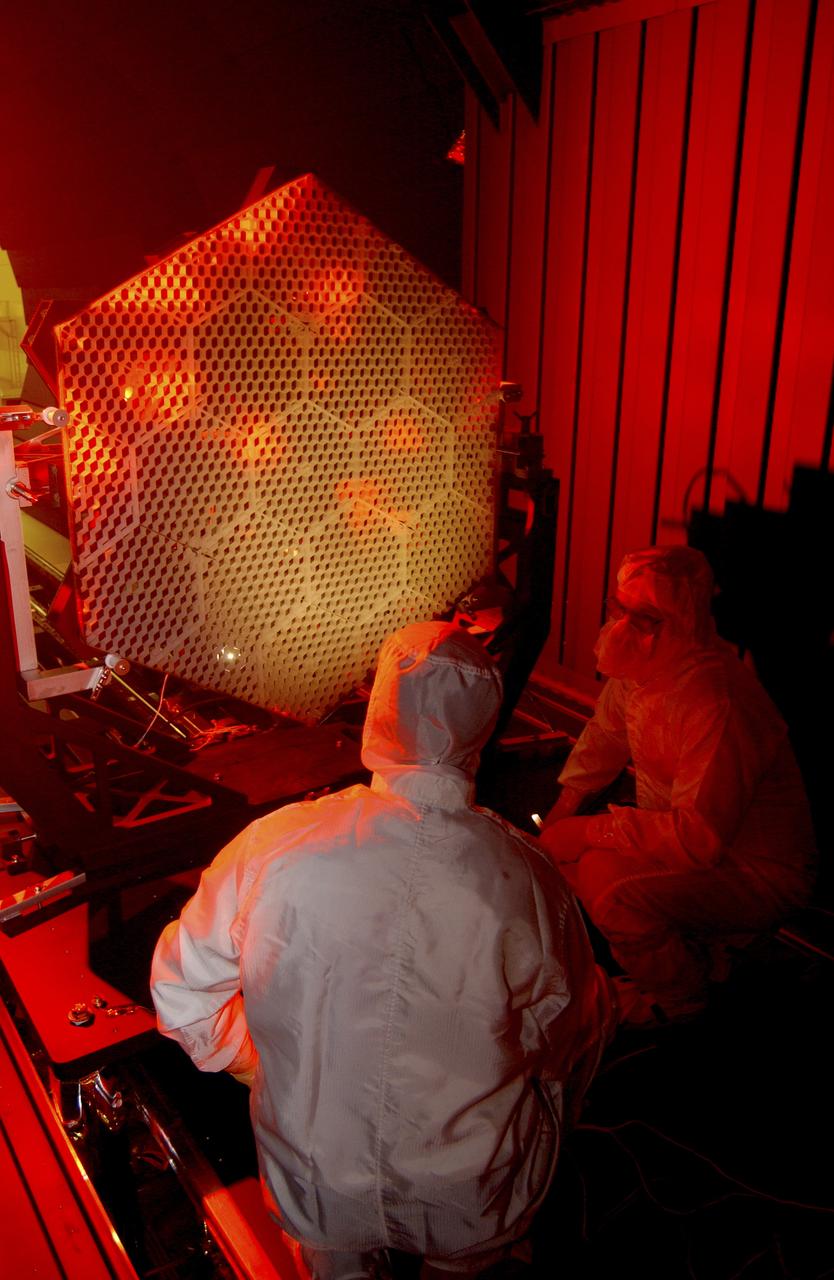

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, one of many segments of the mirror assembly is being set up inside the 24-ft vacuum chamber where it will undergo x-ray calibration tests. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
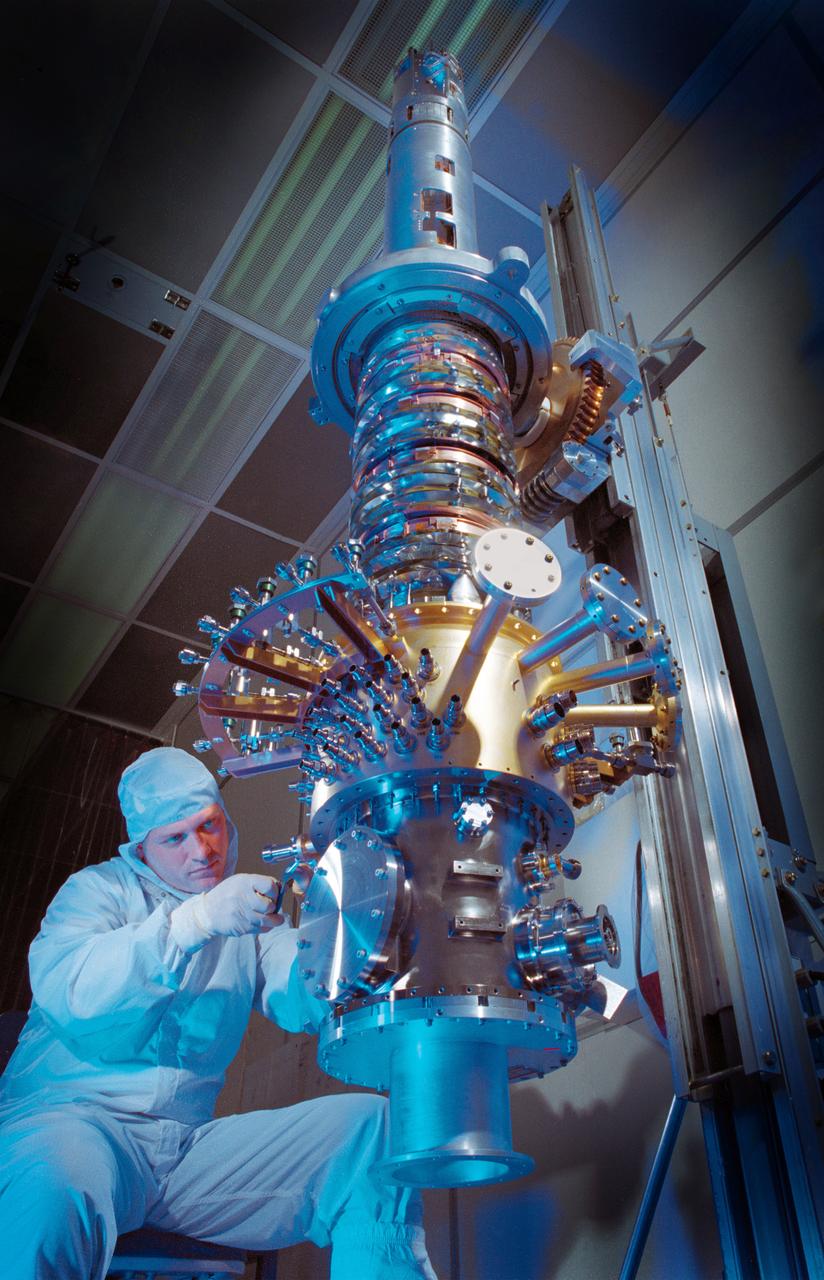

In this photo, the Gravity Probe B (GP-B) space vehicle is being assembled at the Sunnyvale, California location of the Lockheed Martin Corporation. The GP-B is the relativity experiment developed at Stanford University to test two extraordinary predictions of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity. The experiment will measure, very precisely, the expected tiny changes in the direction of the spin axes of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at a 400-mile altitude. So free are the gyroscopes from disturbance that they will provide an almost perfect space-time reference system. They will measure how space and time are very slightly warped by the presence of the Earth, and, more profoundly, how the Earth’s rotation very slightly drags space-time around with it. These effects, though small for the Earth, have far-reaching implications for the nature of matter and the structure of the Universe. GP-B is among the most thoroughly researched programs ever undertaken by NASA. This is the story of a scientific quest in which physicists and engineers have collaborated closely over many years. Inspired by their quest, they have invented a whole range of technologies that are already enlivening other branches of science and engineering. Launched April 20, 2004 , the GP-B program was managed for NASA by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Development of the GP-B is the responsibility of Stanford University along with major subcontractor Lockheed Martin Corporation. (Image credit to Russ Underwood, Lockheed Martin Corporation).
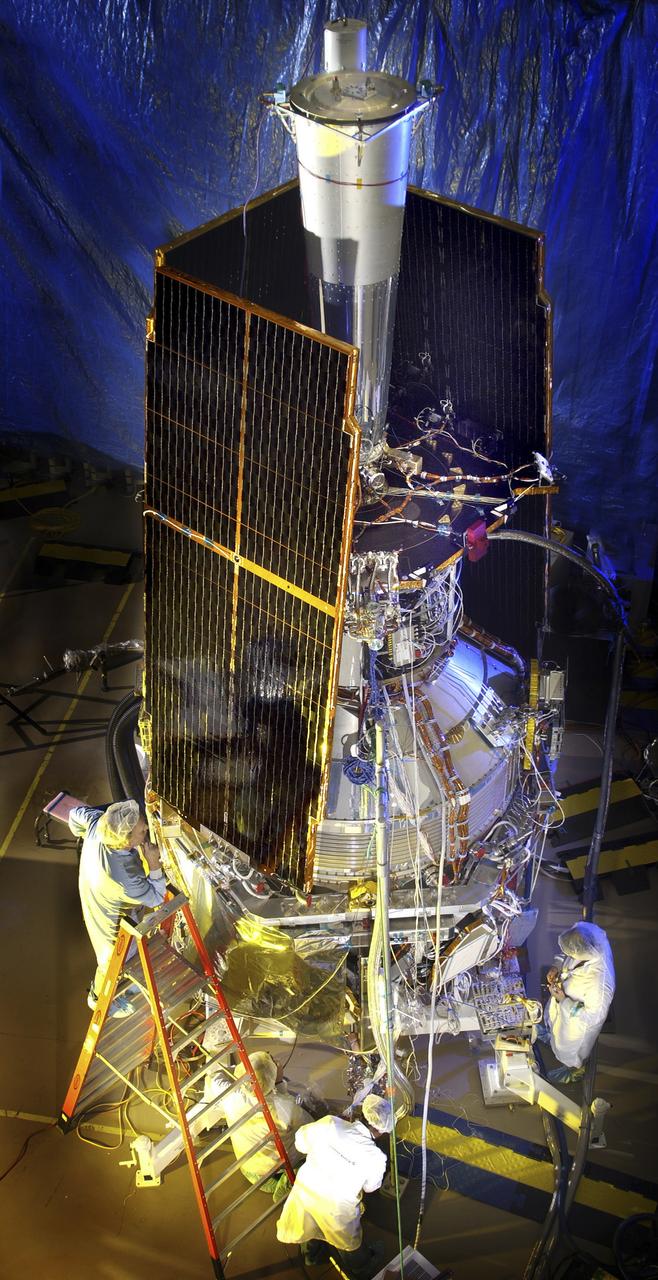

In this photo, the Gravity Probe B (GP-B) space vehicle is completed during the solar array installation. The GP-B is the relativity experiment developed at Stanford University to test two extraordinary predictions of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity. The experiment will measure, very precisely, the expected tiny changes in the direction of the spin axes of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at a 400-mile altitude. So free are the gyroscopes from disturbance that they will provide an almost perfect space-time reference system. They will measure how space and time are very slightly warped by the presence of the Earth, and, more profoundly, how the Earth’s rotation very slightly drags space-time around with it. These effects, though small for the Earth, have far-reaching implications for the nature of matter and the structure of the Universe. GP-B is among the most thoroughly researched programs ever undertaken by NASA. This is the story of a scientific quest in which physicists and engineers have collaborated closely over many years. Inspired by their quest, they have invented a whole range of technologies that are already enlivening other branches of science and engineering. GP-B is scheduled for launch in April 2004 and managed for NASA by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Development of the GP-B is the responsibility of Stanford University along with major subcontractor Lockheed Martin Corporation. (Image credit to Russ Underwood, Lockheed Martin Corporation).
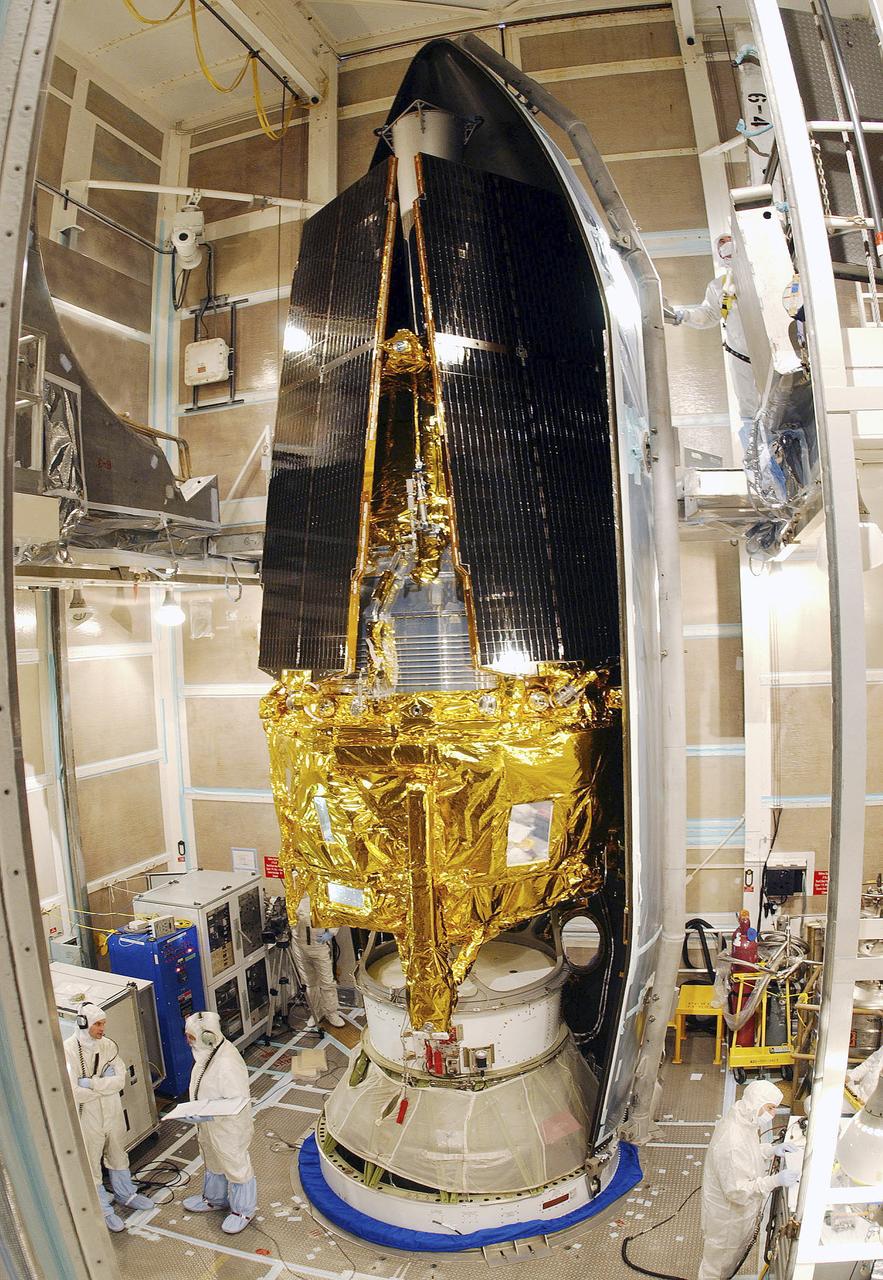

In this photo, the Gravity Probe B (GP-B) space vehicle is being encapsulated atop the Delta II launch vehicle. The GP-B is the relativity experiment developed at Stanford University to test two extraordinary predictions of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity. The experiment will measure, very precisely, the expected tiny changes in the direction of the spin axes of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at a 400-mile altitude. So free are the gyroscopes from disturbance that they will provide an almost perfect space-time reference system. They will measure how space and time are very slightly warped by the presence of the Earth, and, more profoundly, how the Earth’s rotation very slightly drags space-time around with it. These effects, though small for the Earth, have far-reaching implications for the nature of matter and the structure of the Universe. GP-B is among the most thoroughly researched programs ever undertaken by NASA. This is the story of a scientific quest in which physicists and engineers have collaborated closely over many years. Inspired by their quest, they have invented a whole range of technologies that are already enlivening other branches of science and engineering. Launched April 20, 2004 , the GP-B program was managed for NASA by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Development of the GP-B is the responsibility of Stanford University along with major subcontractor Lockheed Martin Corporation. (Image credit to Russ Underwood, Lockheed Martin Corporation).