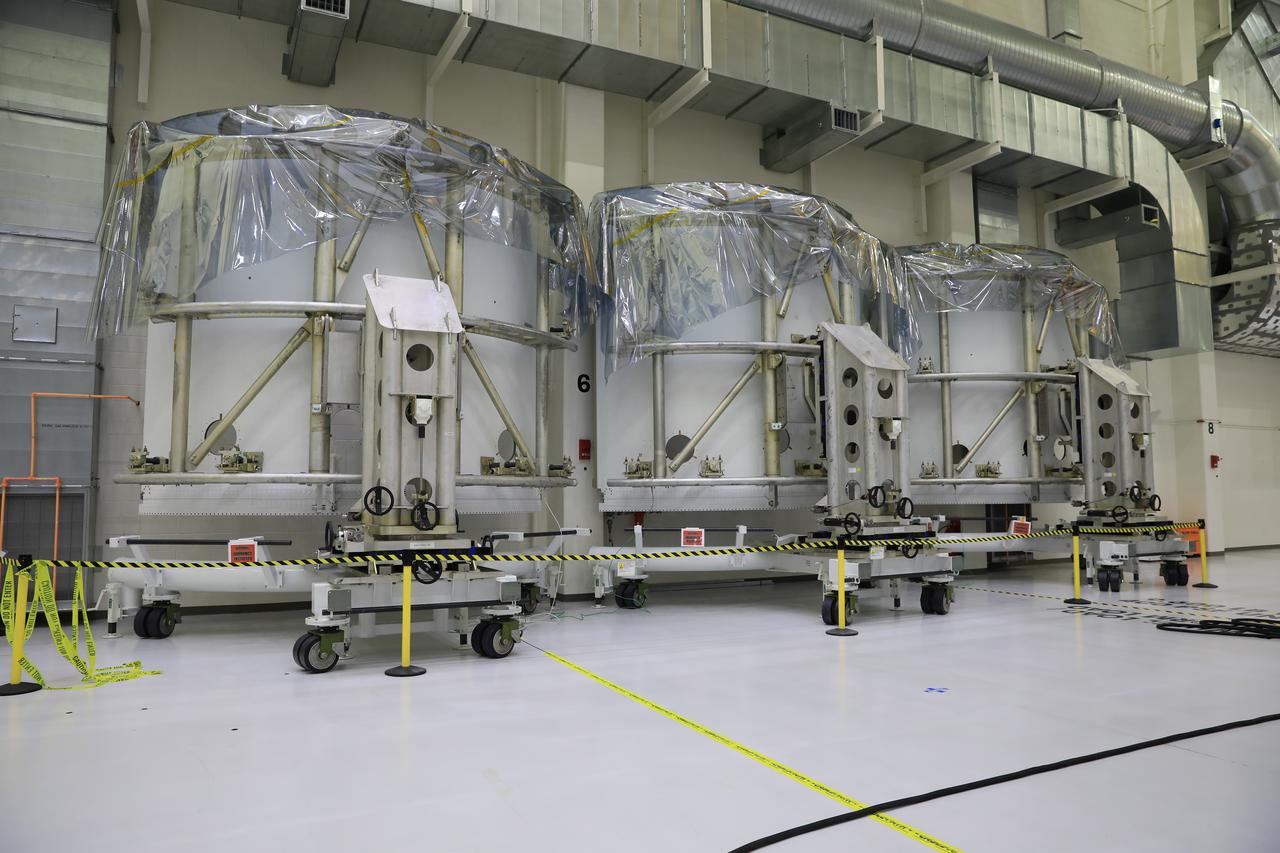

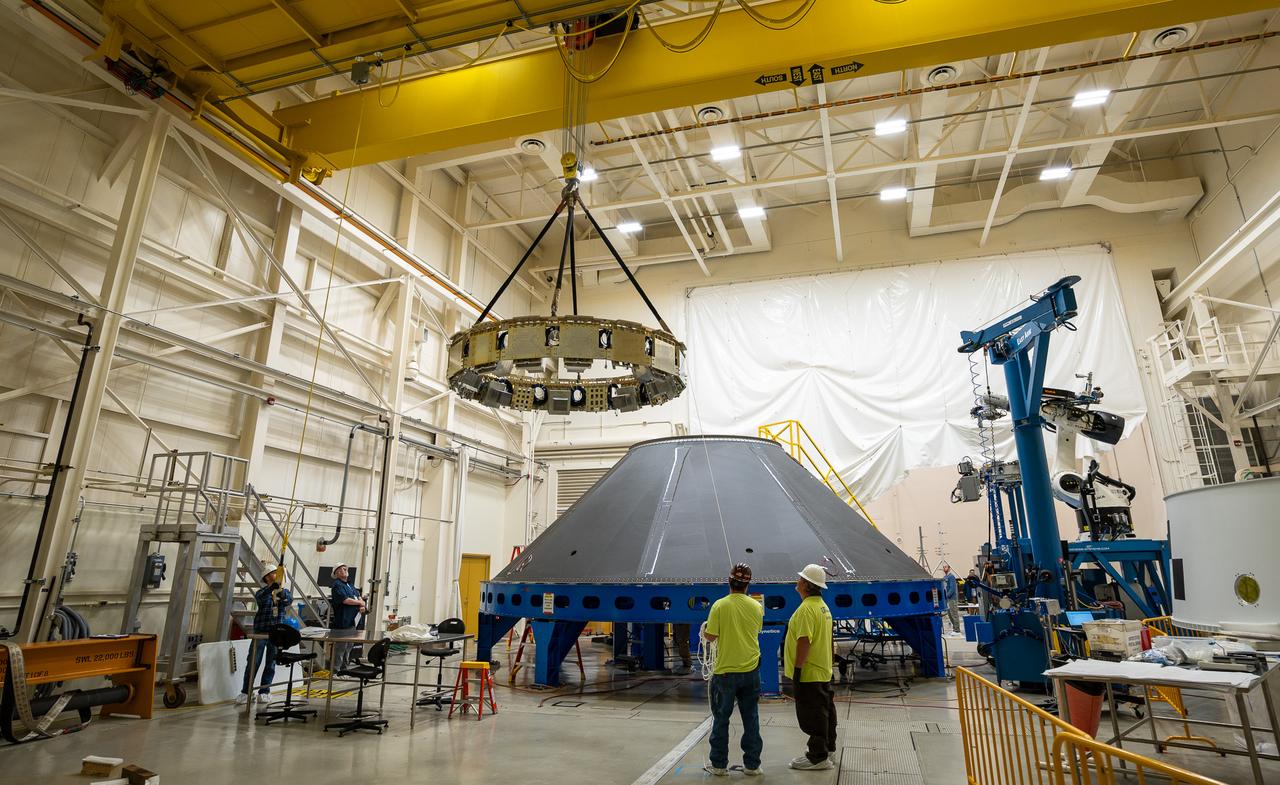
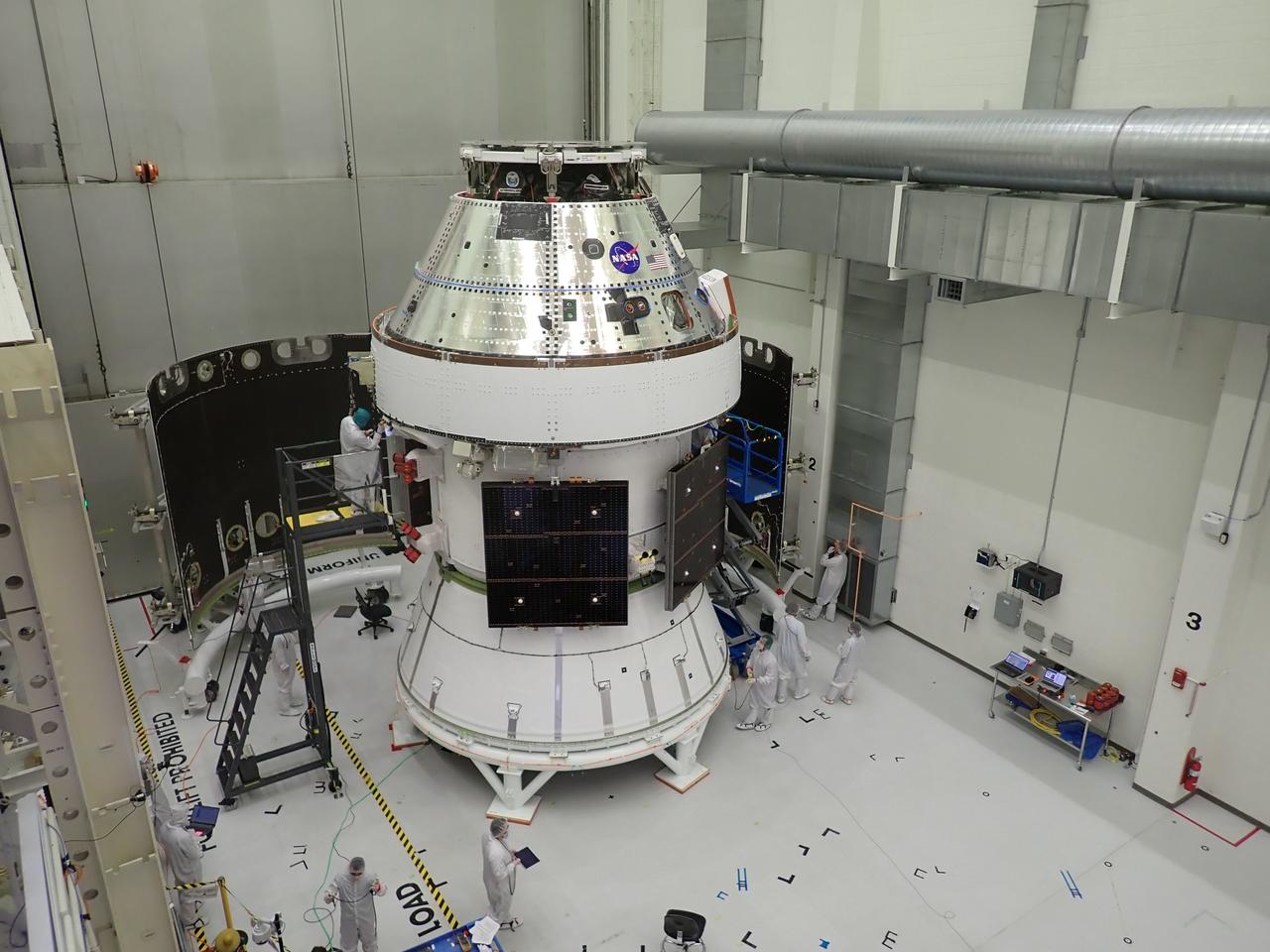
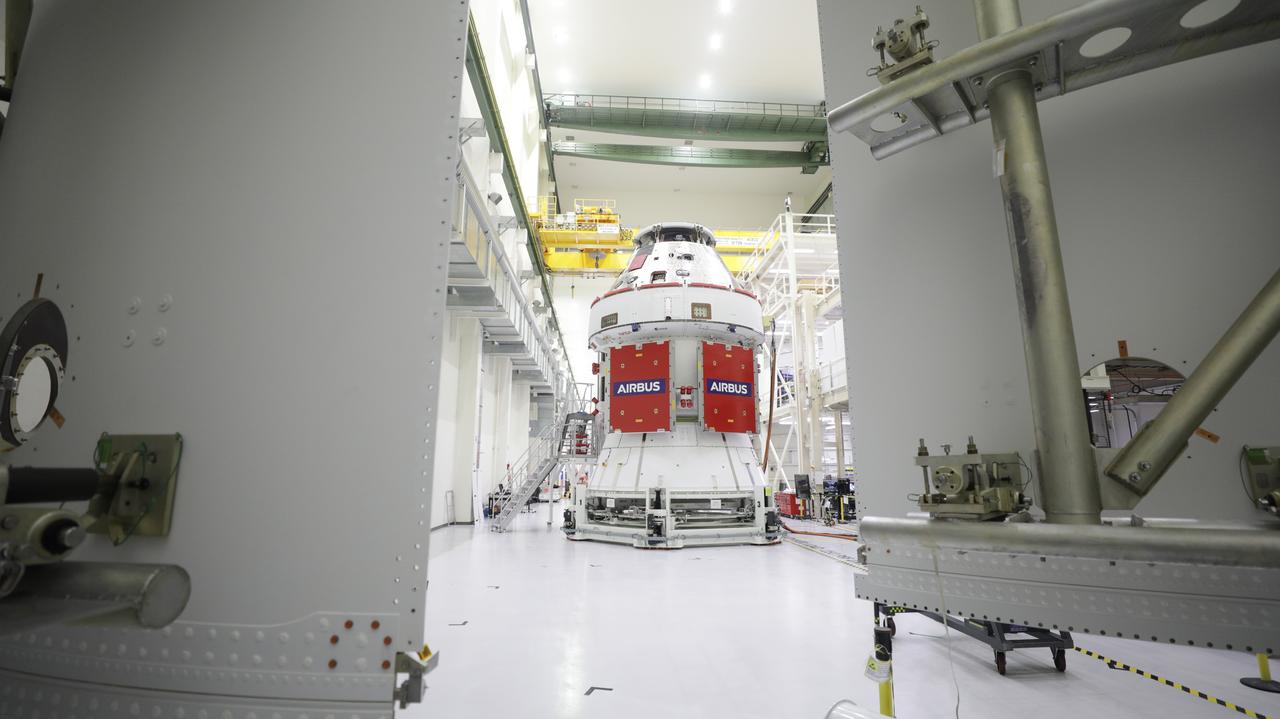
Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
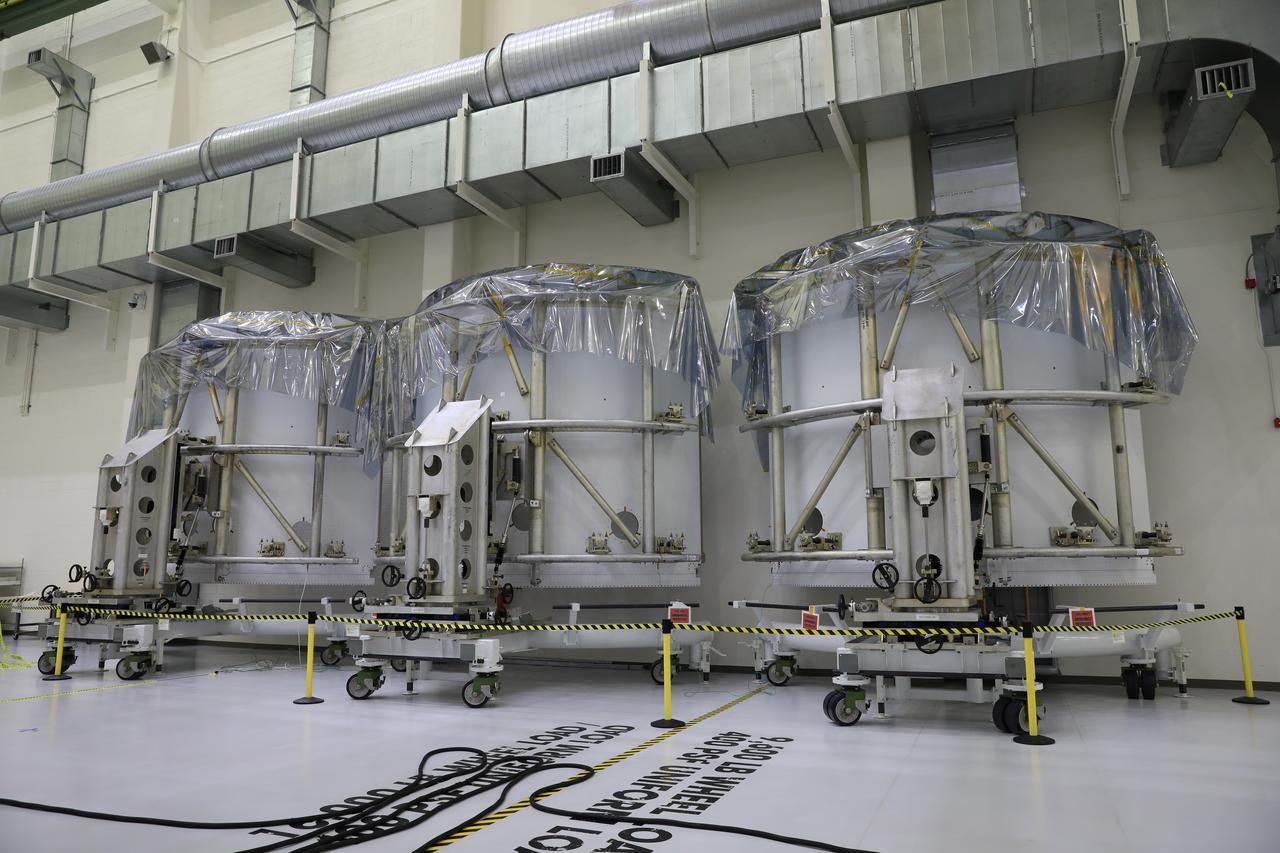

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
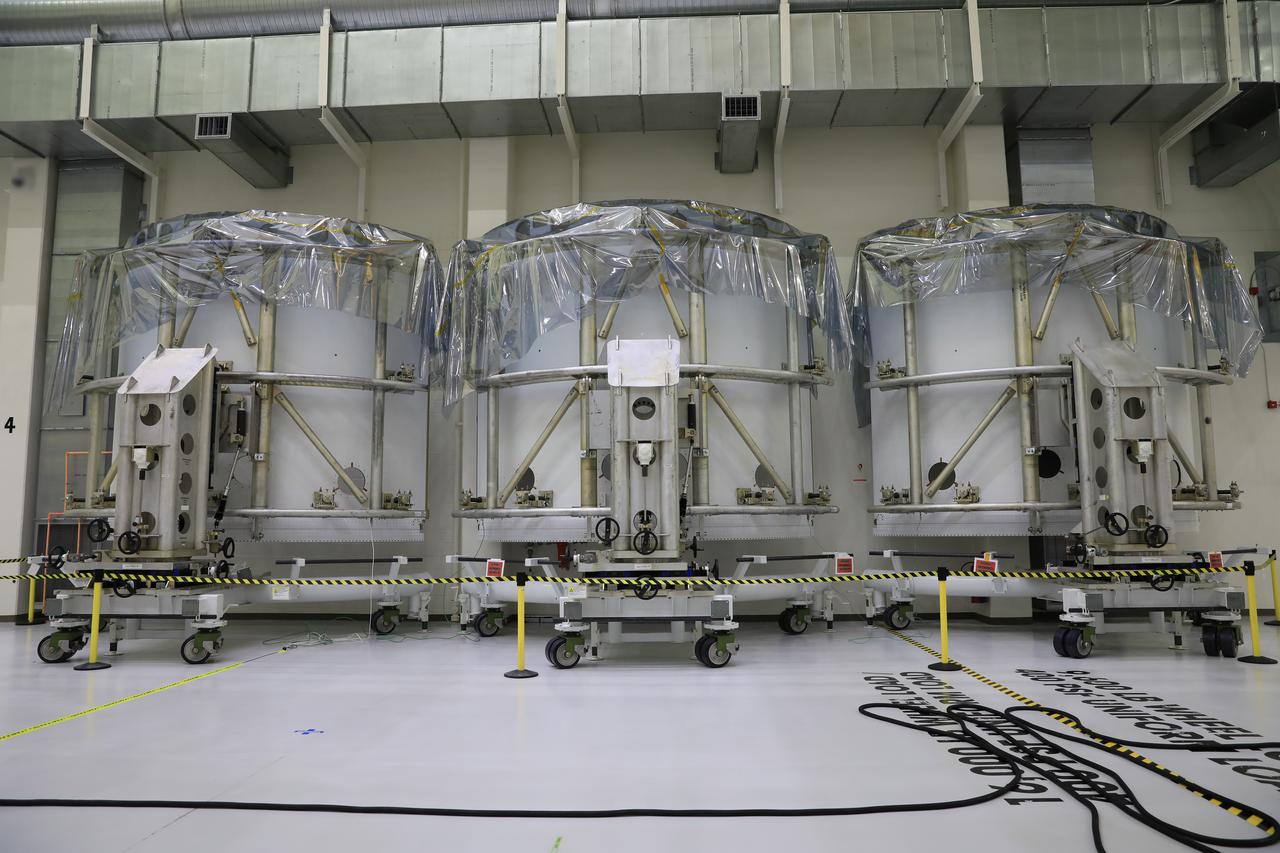

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
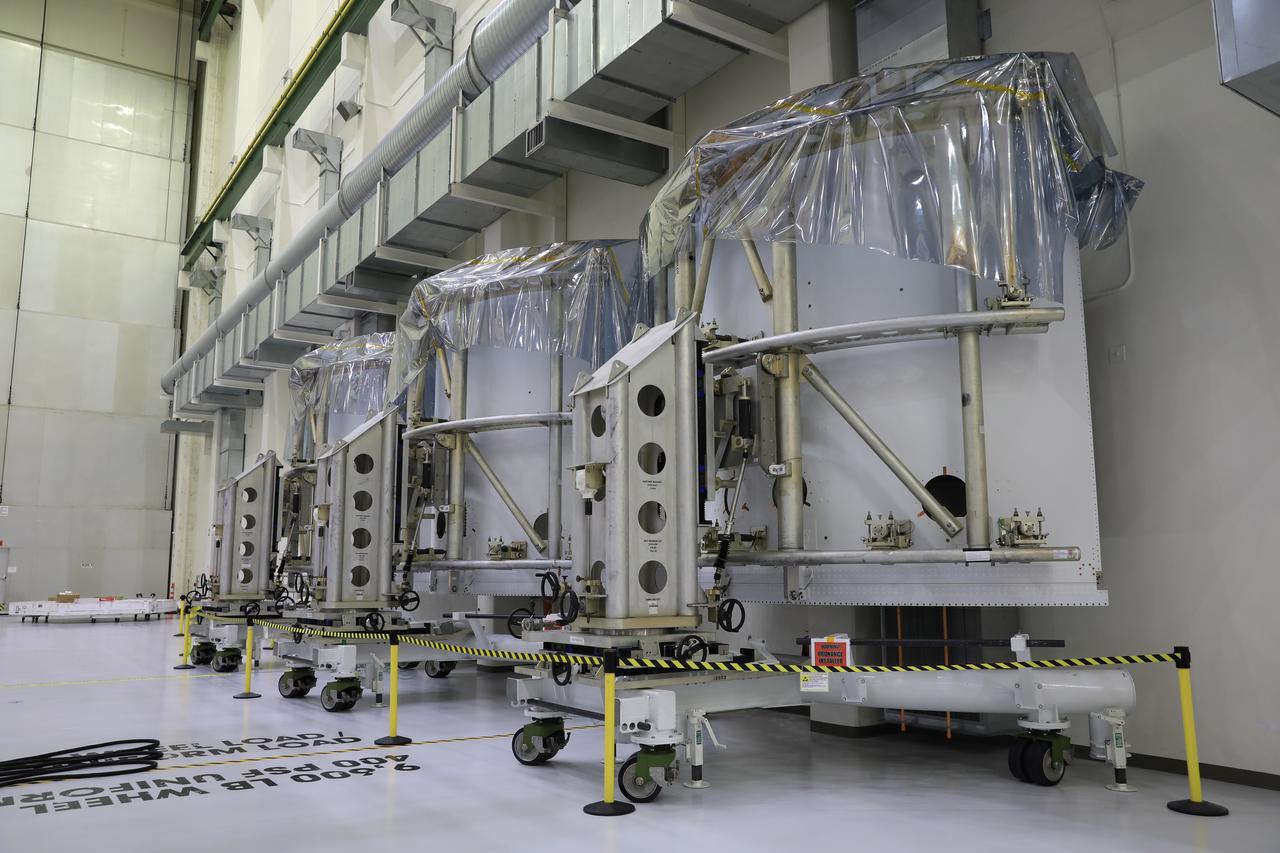

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

ASAP, (Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel), members, Dr. Sandra Magnus, Dr. Donald P. McErlean, Dr. George Nield, Captain Christopher Saindon, Mr. David West, Dr. Patricia Sanders, Ms. Carol Hamilton, Ms. Evette Whatley, Ms. Paula Frankel, view LVSA, (Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter), and Orion Stage Adapter. Members were escorted to buildings 4707 and 4708 by Andrew Schorr, Deputy Manager for Spacecraft/Payload Integration & Evolution Office (SPIE)
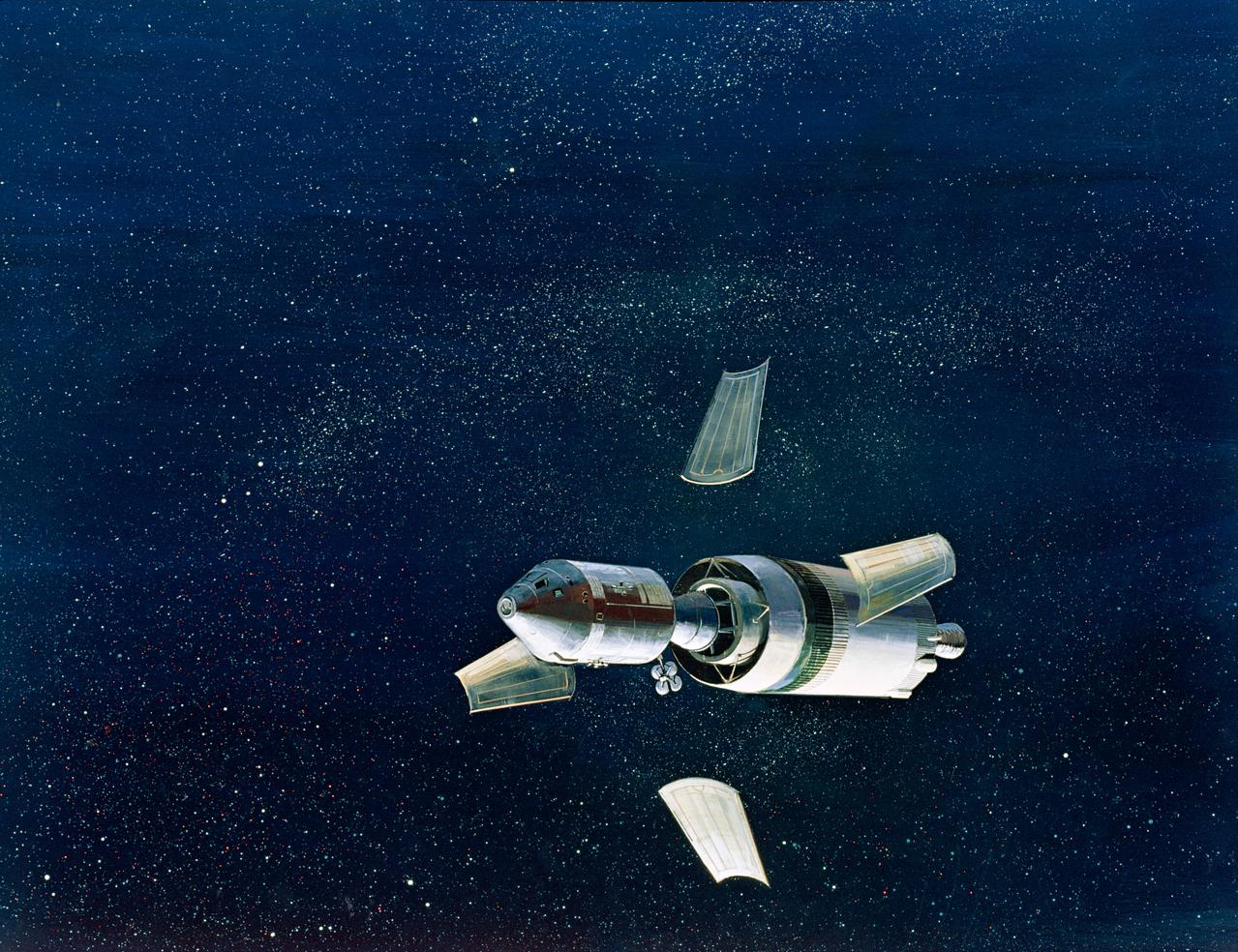
S68-51306 (December 1968) --- North American Rockwell artist's concept illustrating a phase of the scheduled Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. Here, the Apollo 8 spacecraft lunar module adapter (SLA) panels, which have supported the Command and Service Modules, are jettisoned. This is done by astronauts firing the service module reaction control engines. A signal simultaneously deploys and jettisons the panels, separating the spacecraft from the SLA and deploying the high gain (deep space) antenna.
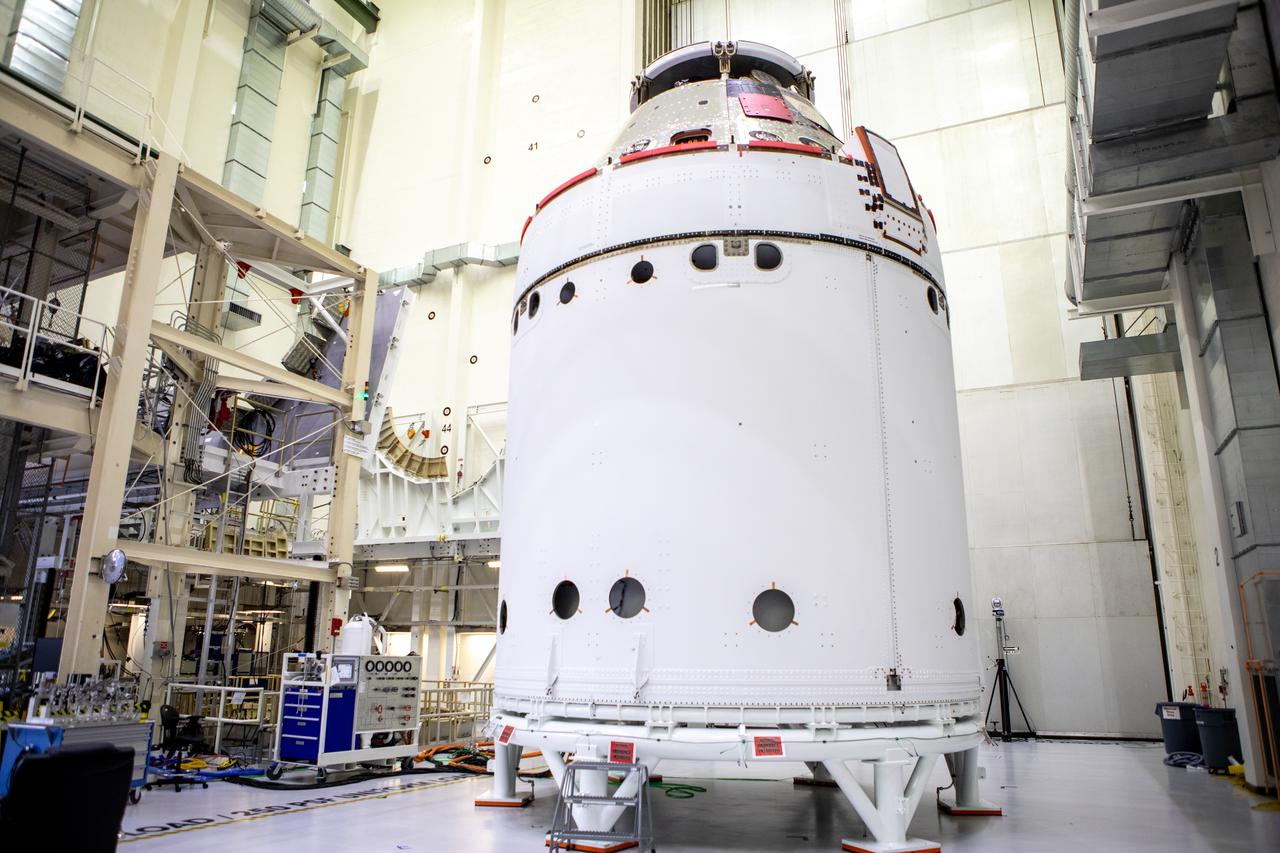
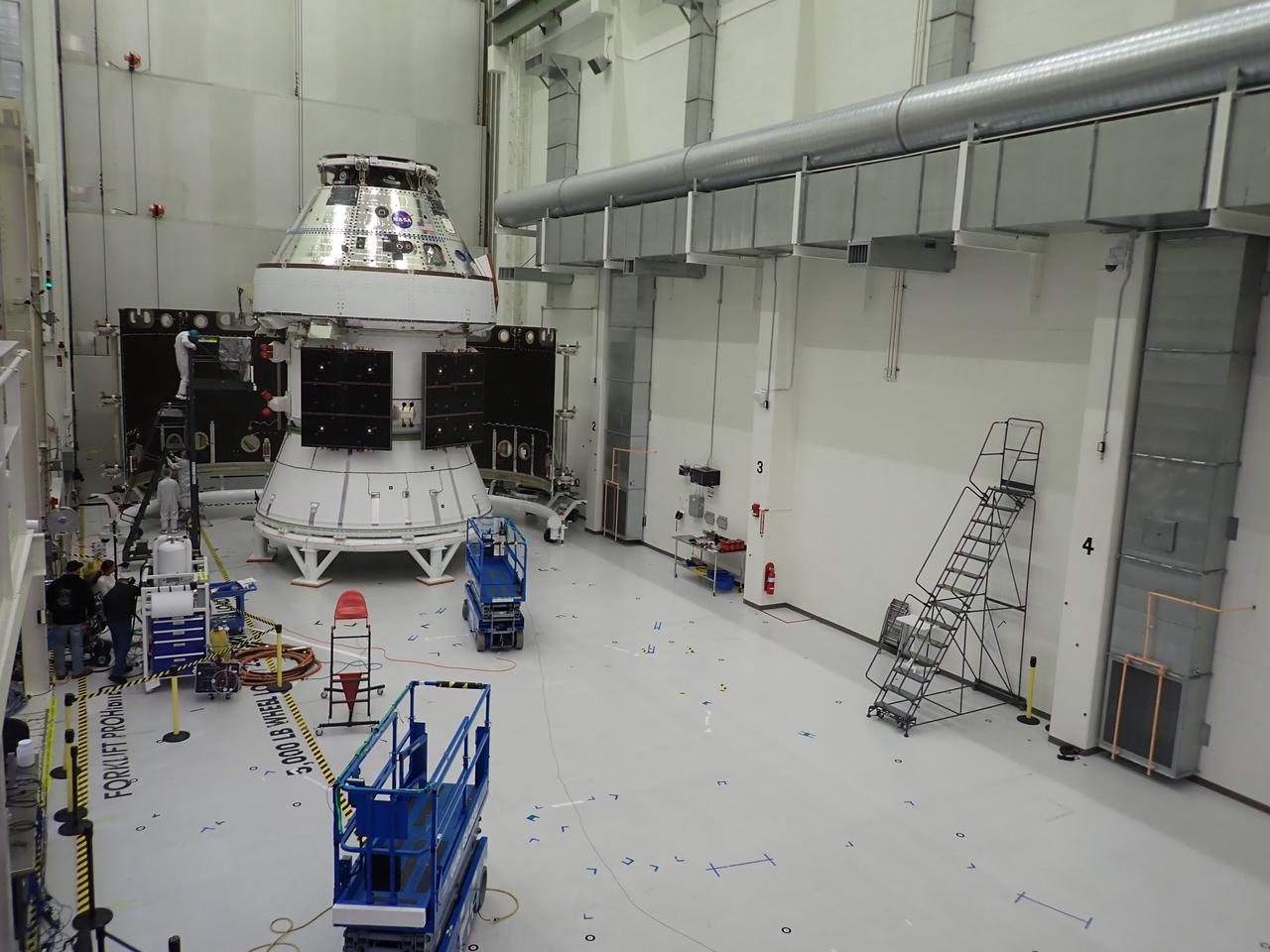
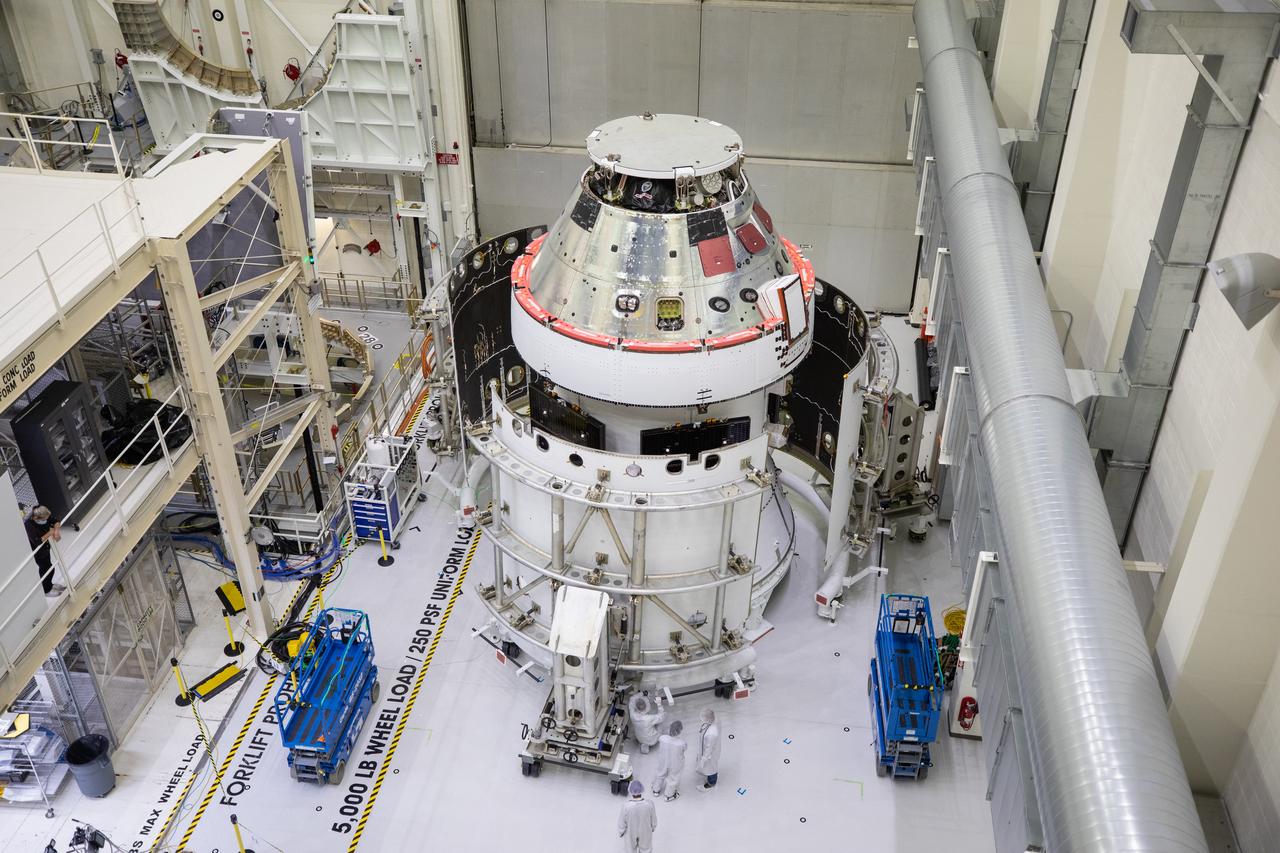
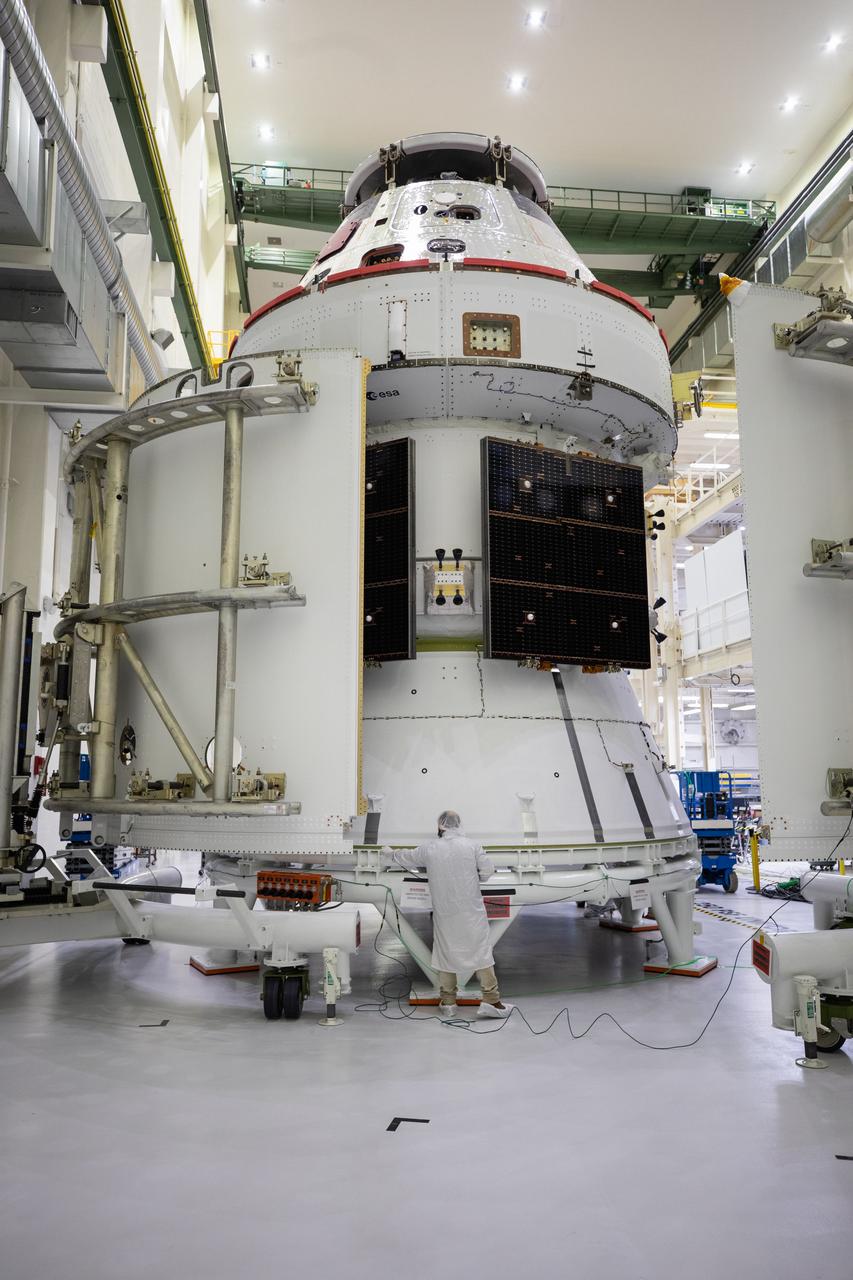
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
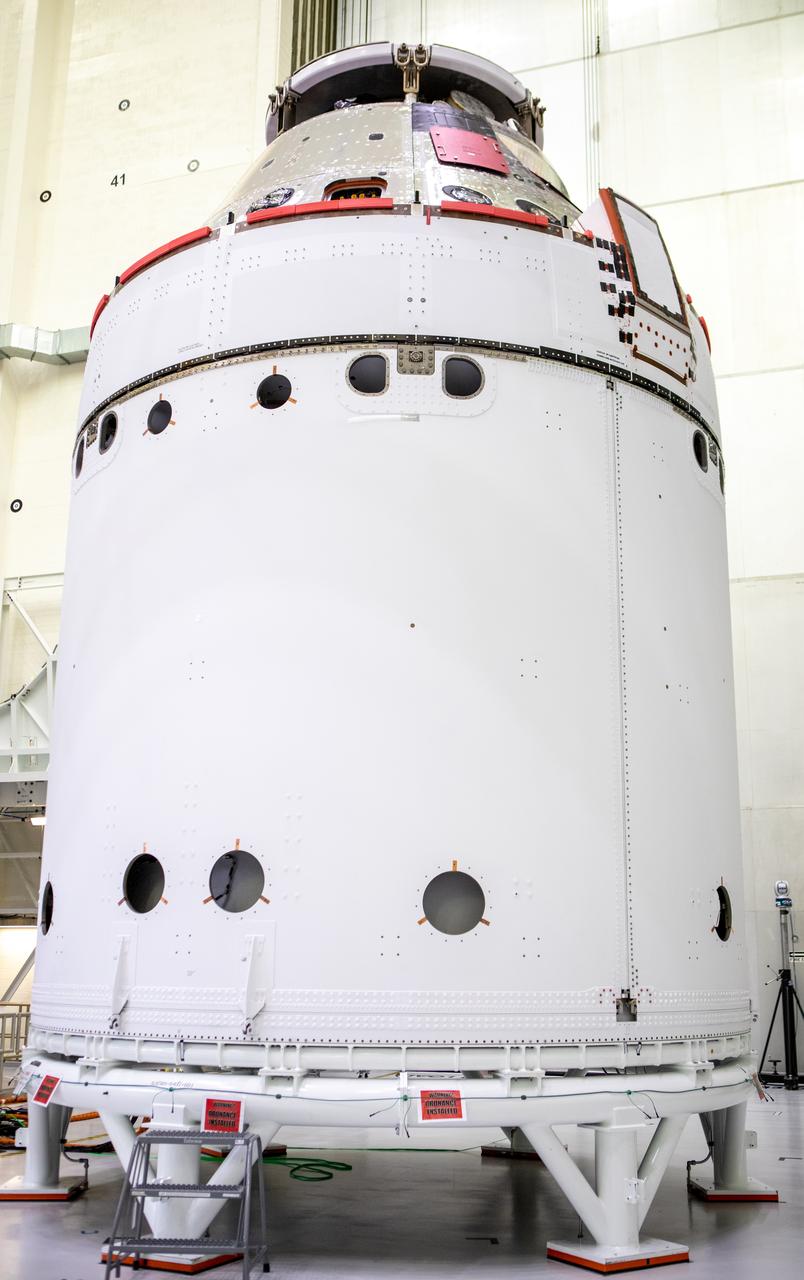
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
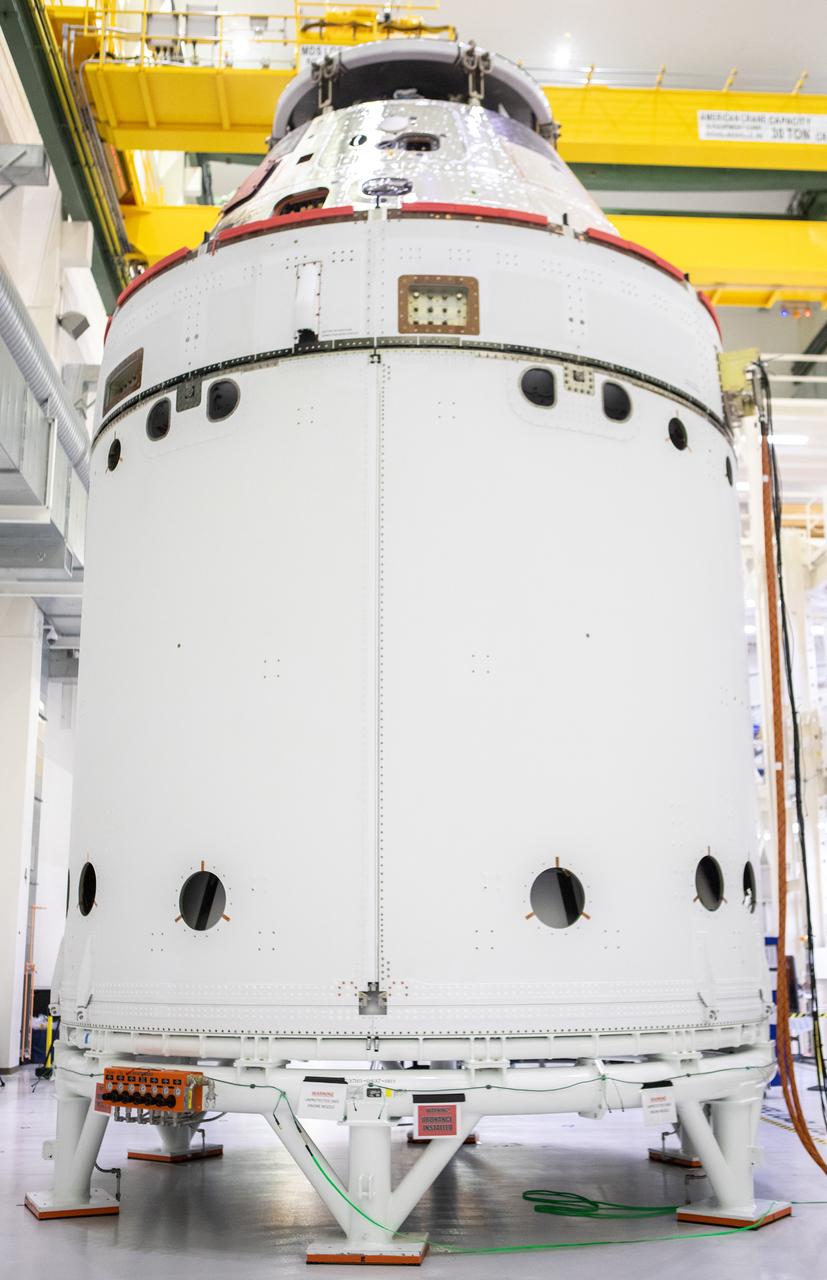

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
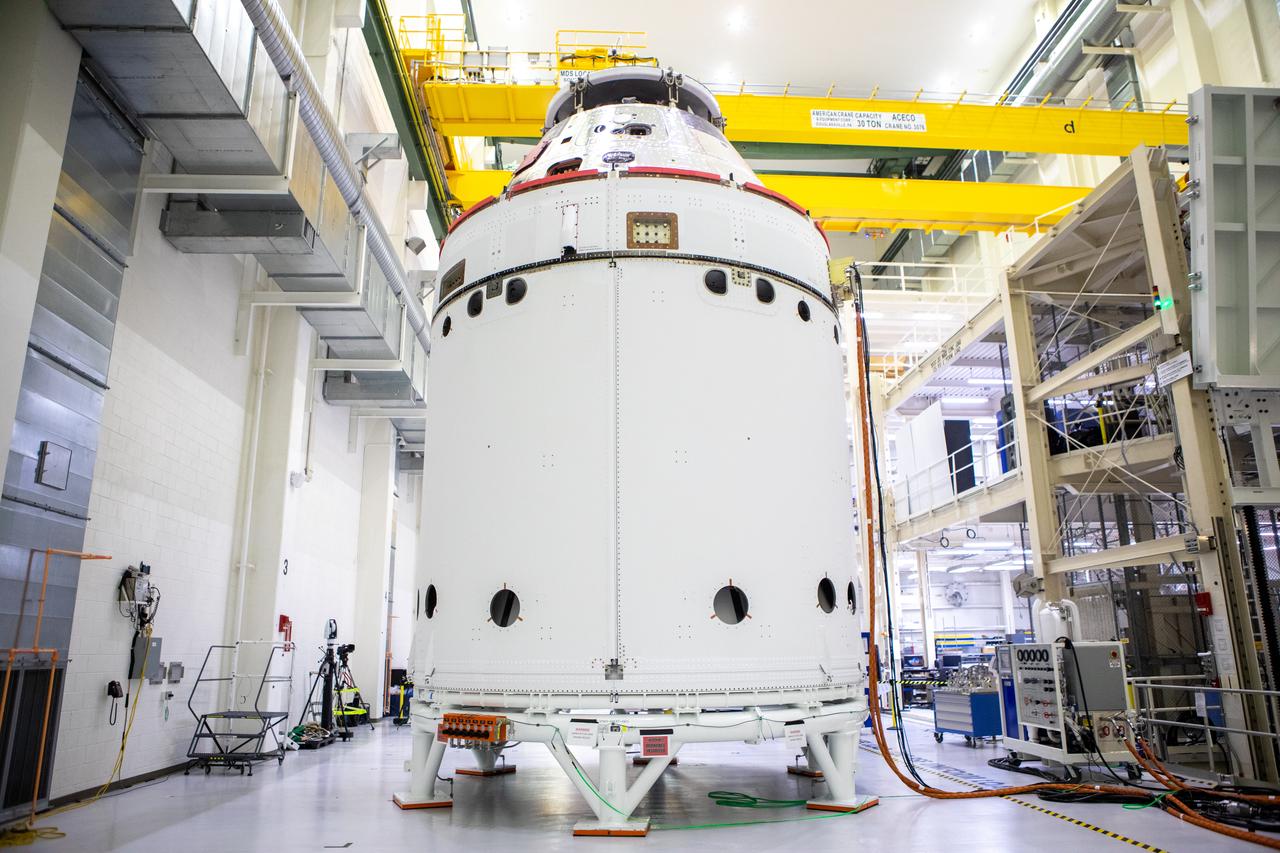

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
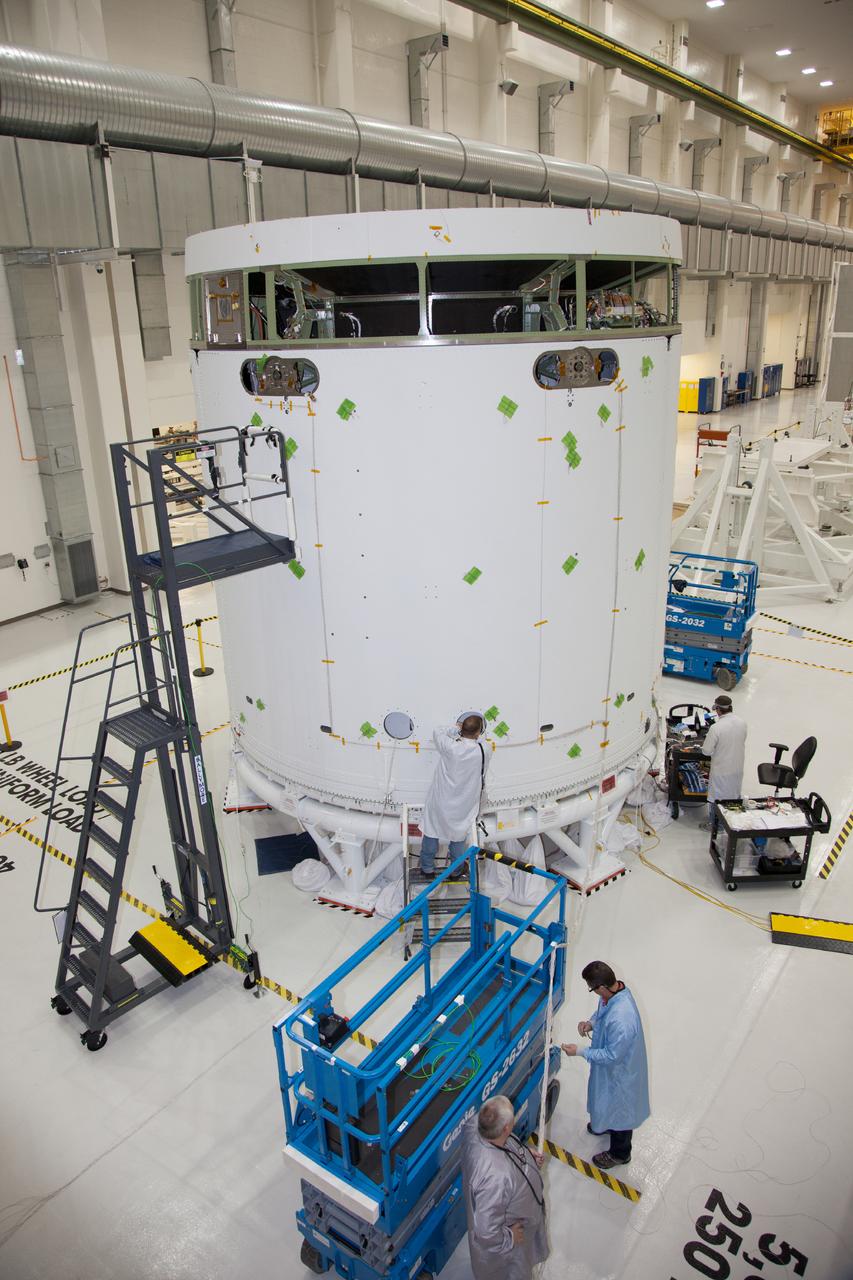

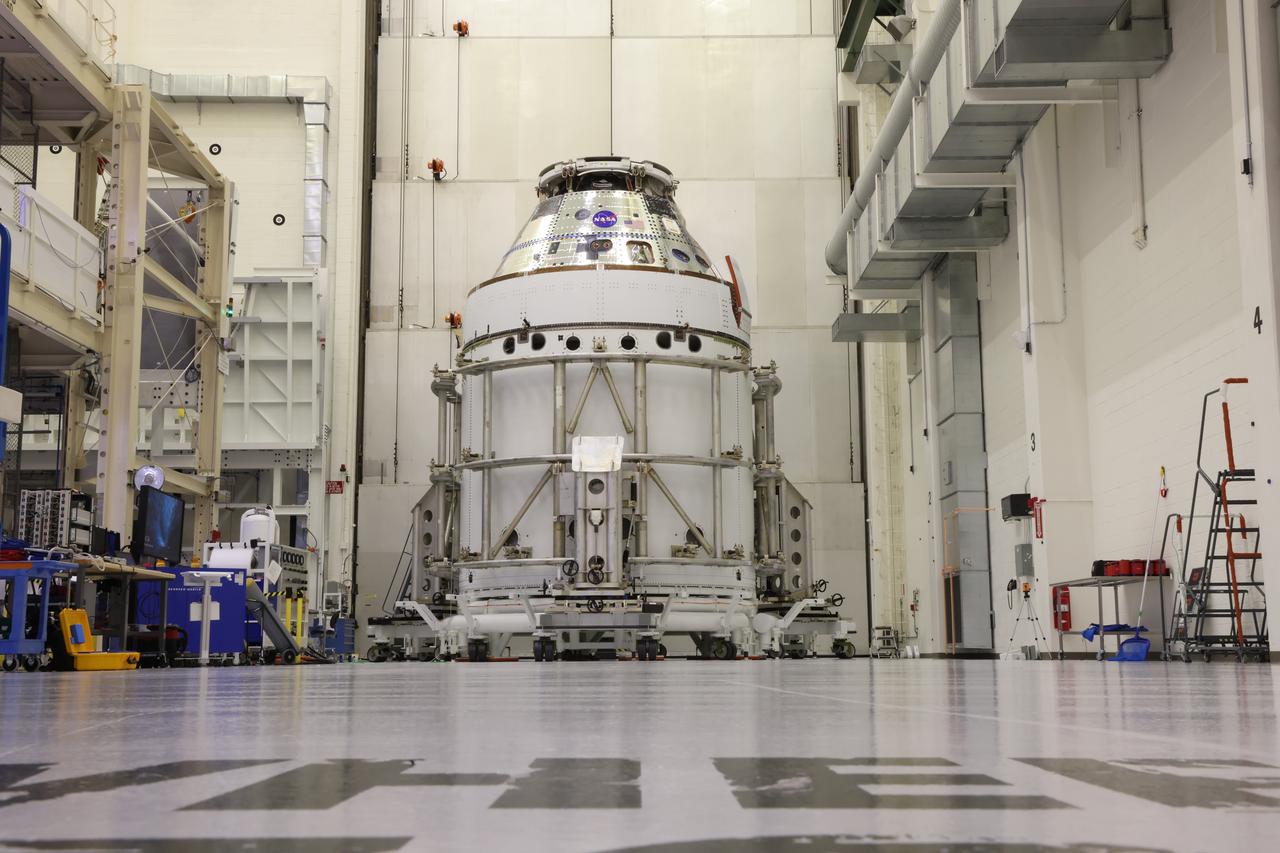
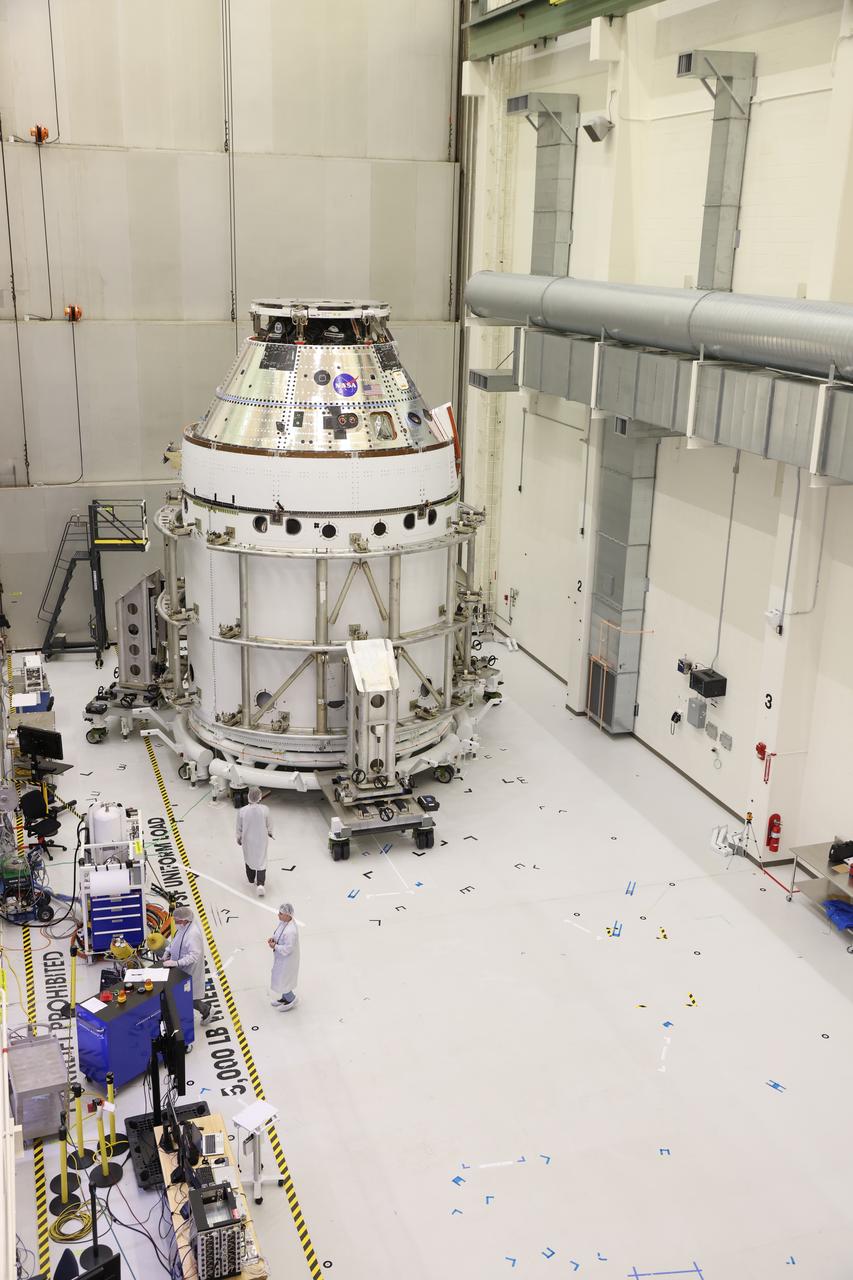
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are installed on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion service module in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy Space Center on Jan. 14 , 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
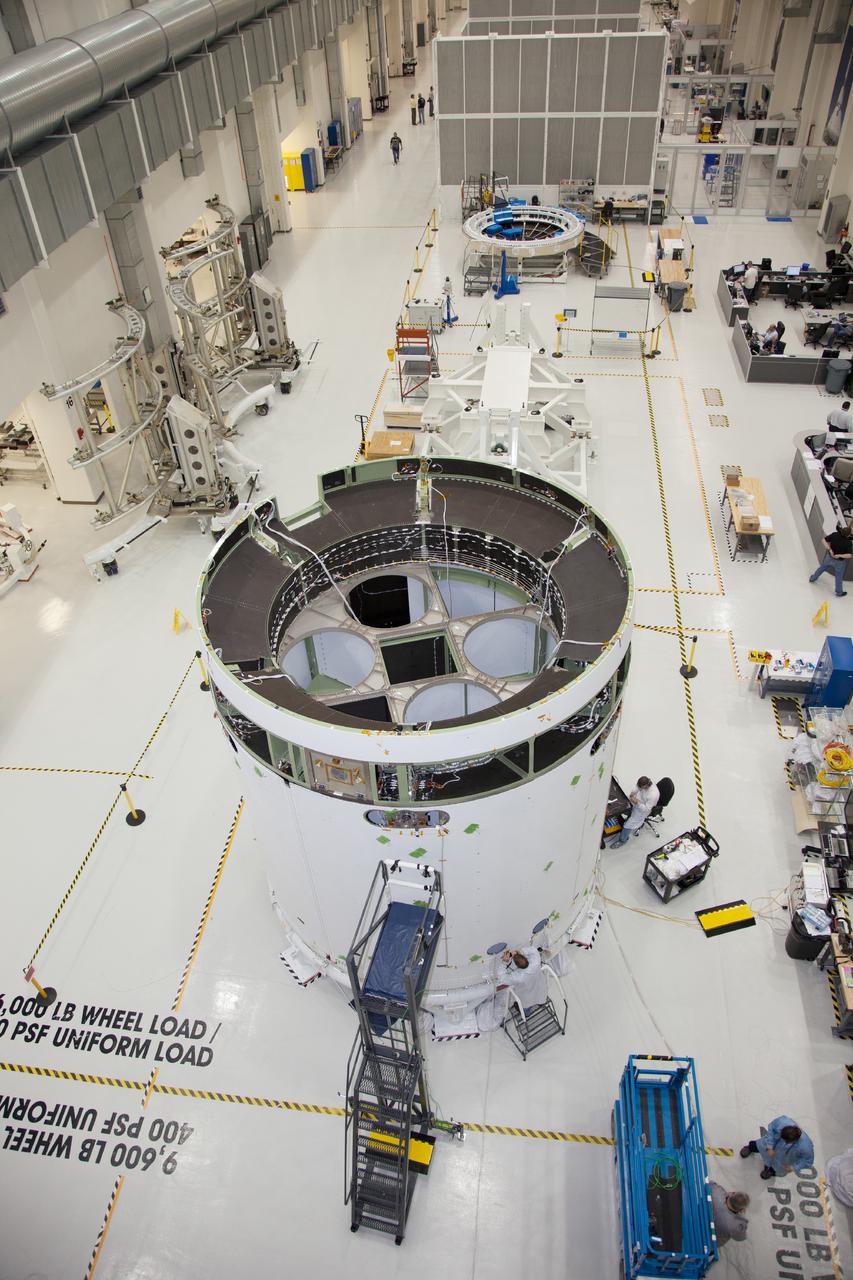

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are installed on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion service module in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy Space Center on Jan. 14 , 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
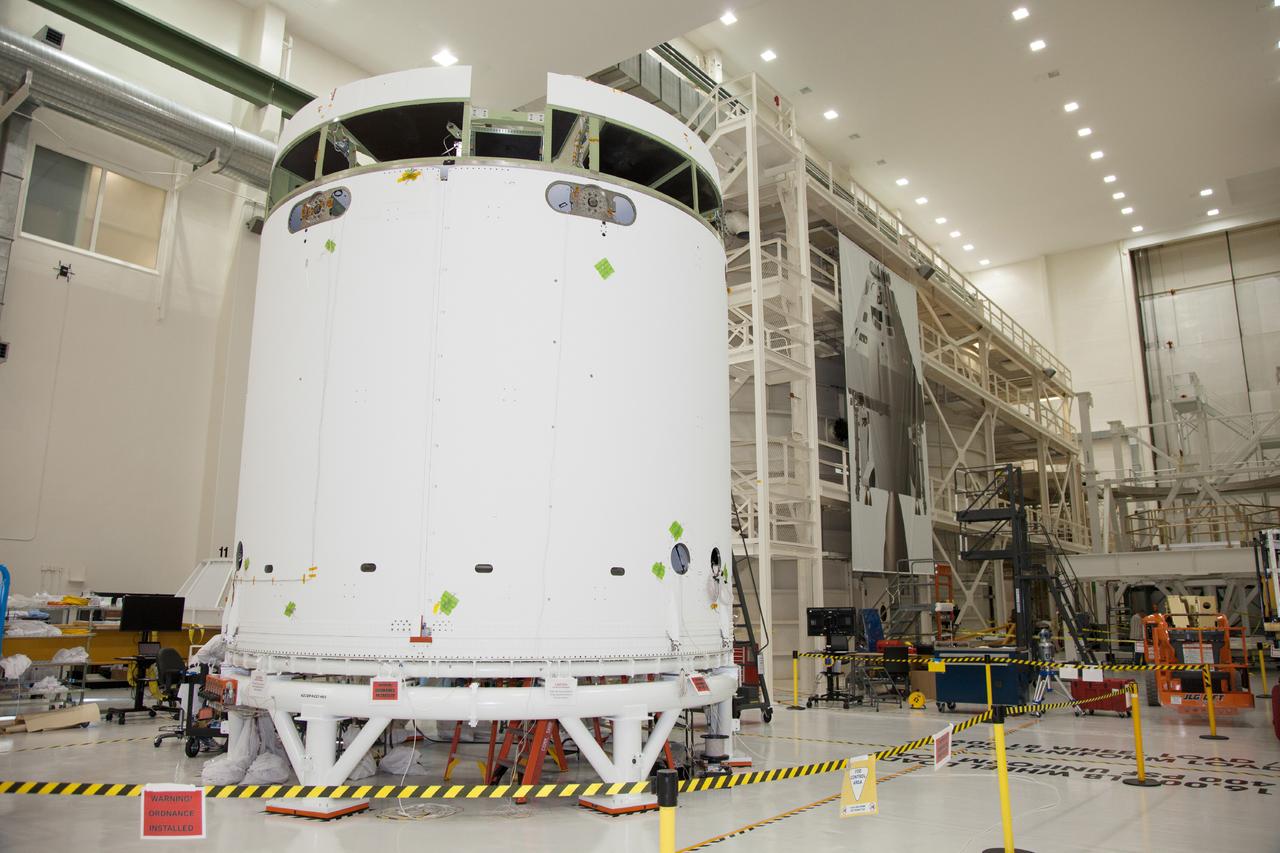

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are installed on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion service module in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy Space Center on Jan. 14 , 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are installed on the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion service module in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at Kennedy Space Center on Jan. 14 , 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
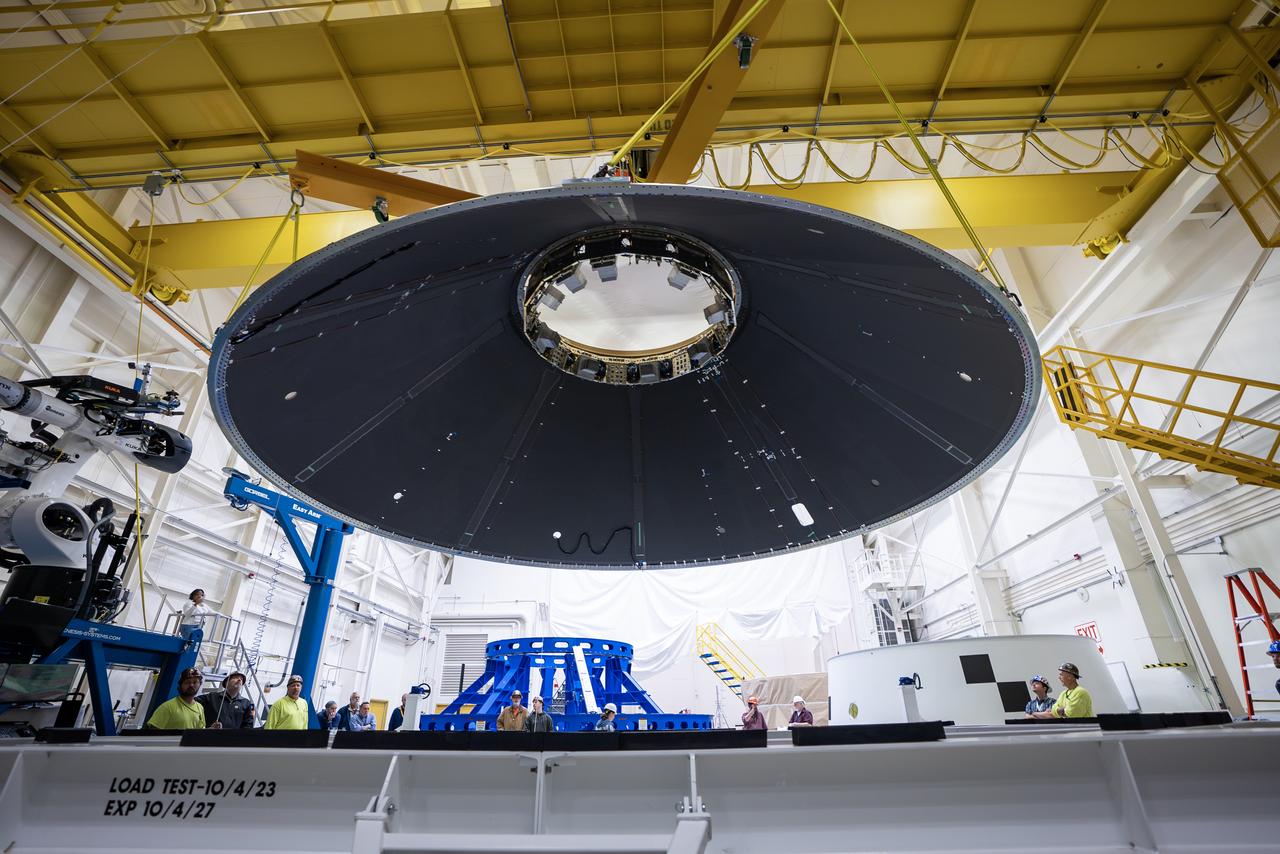

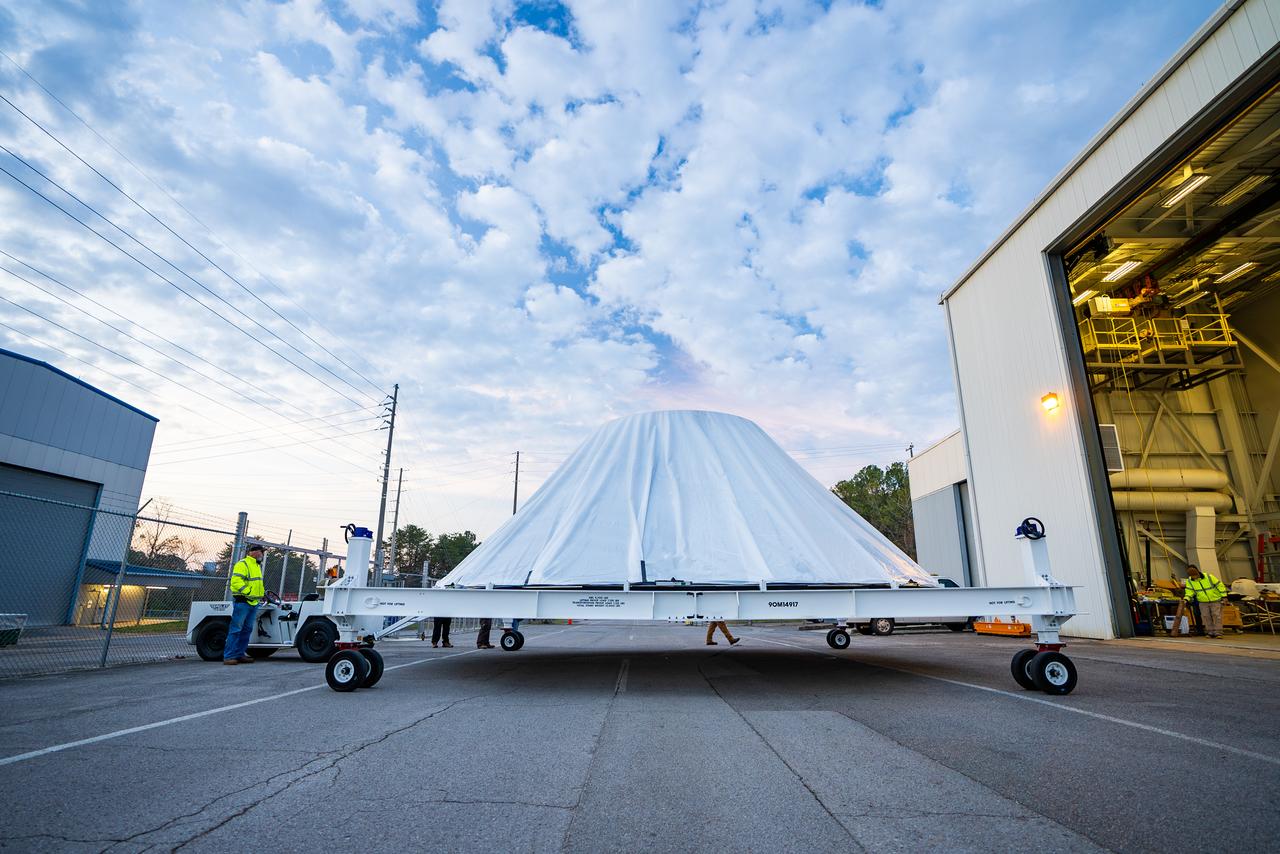
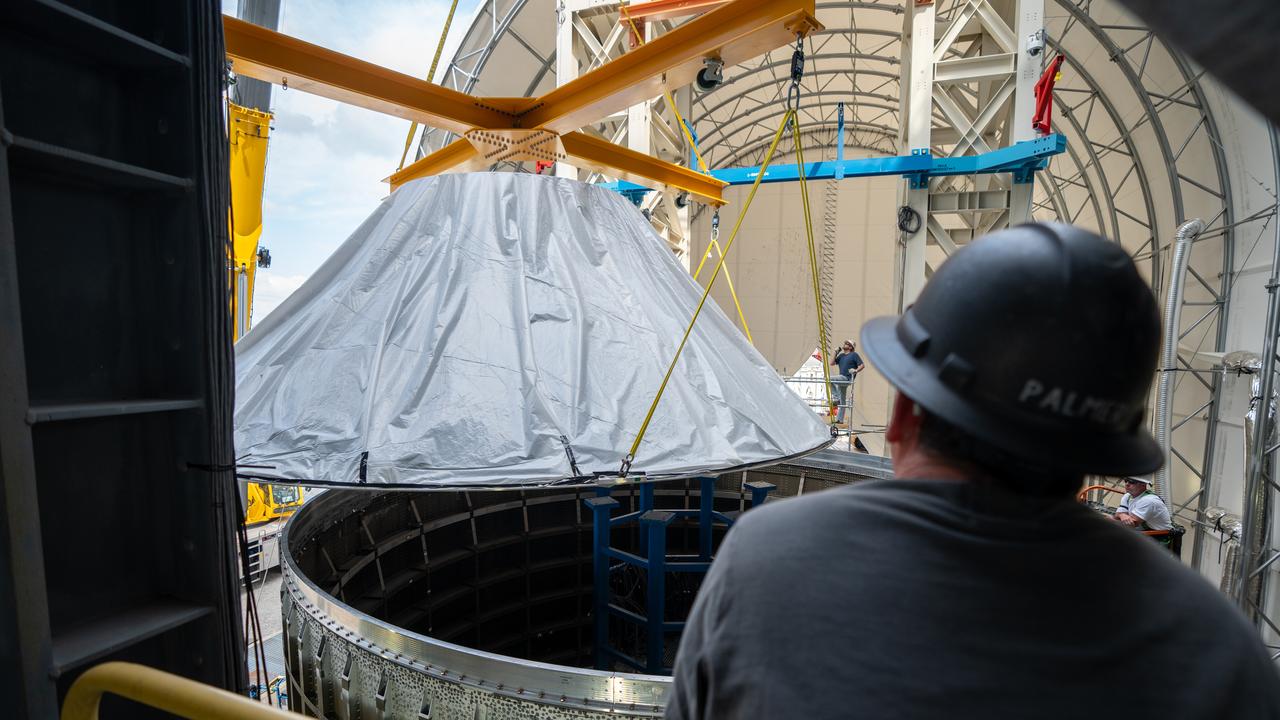
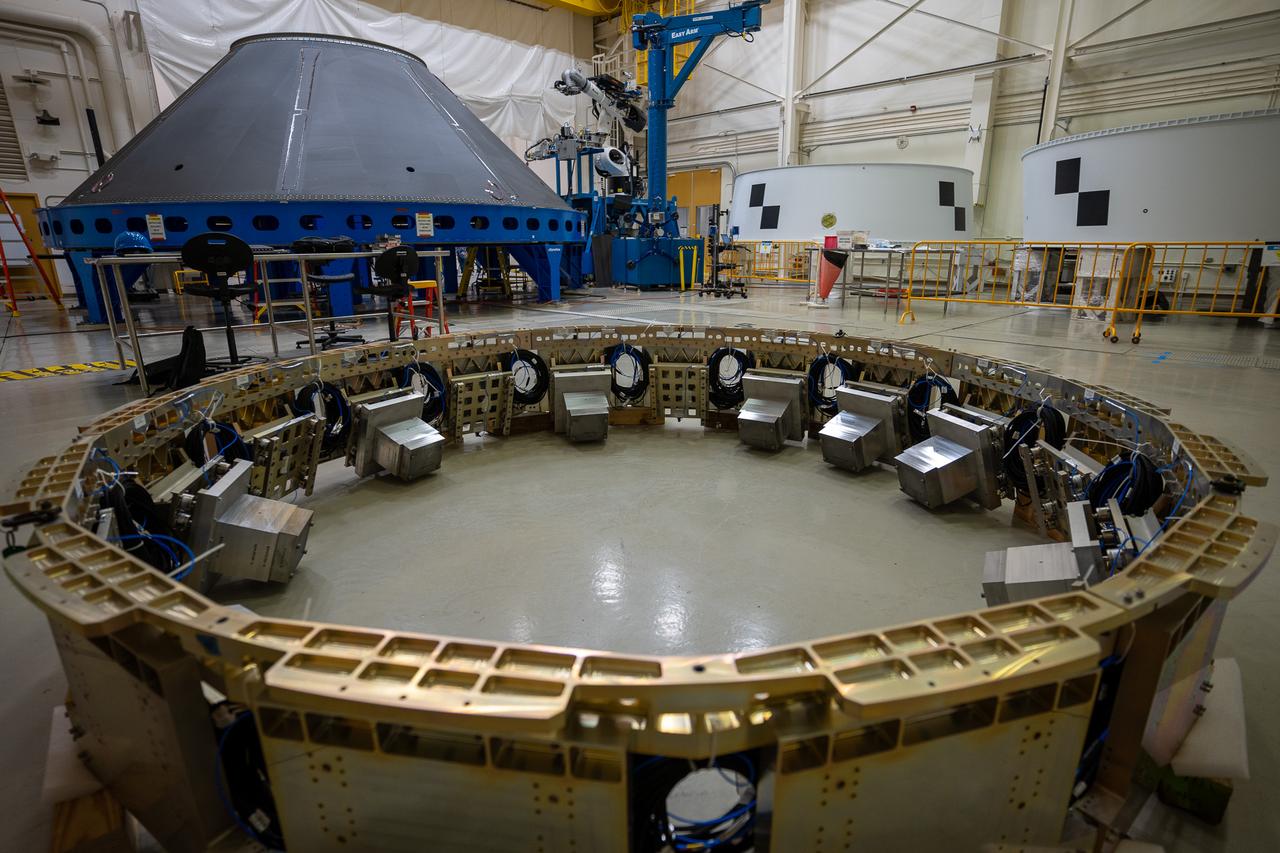
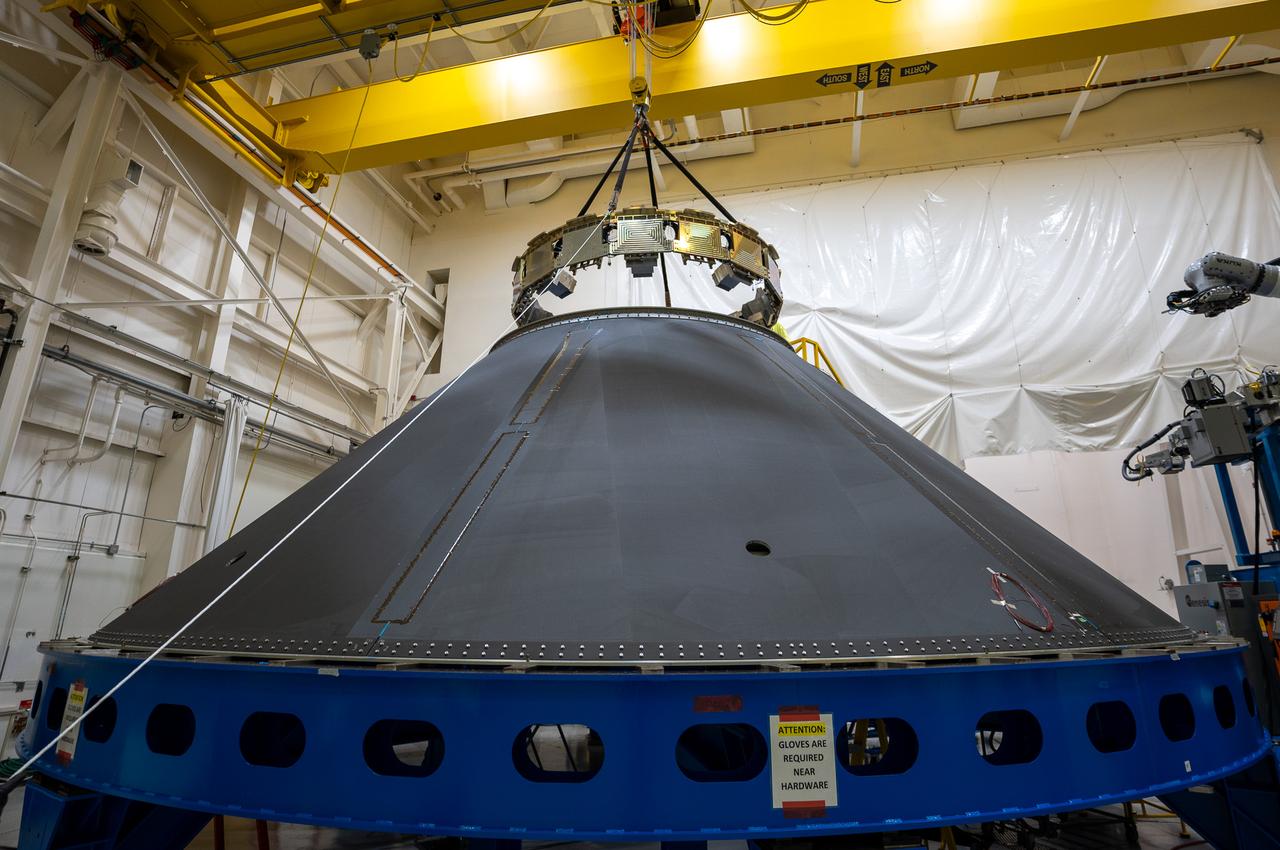
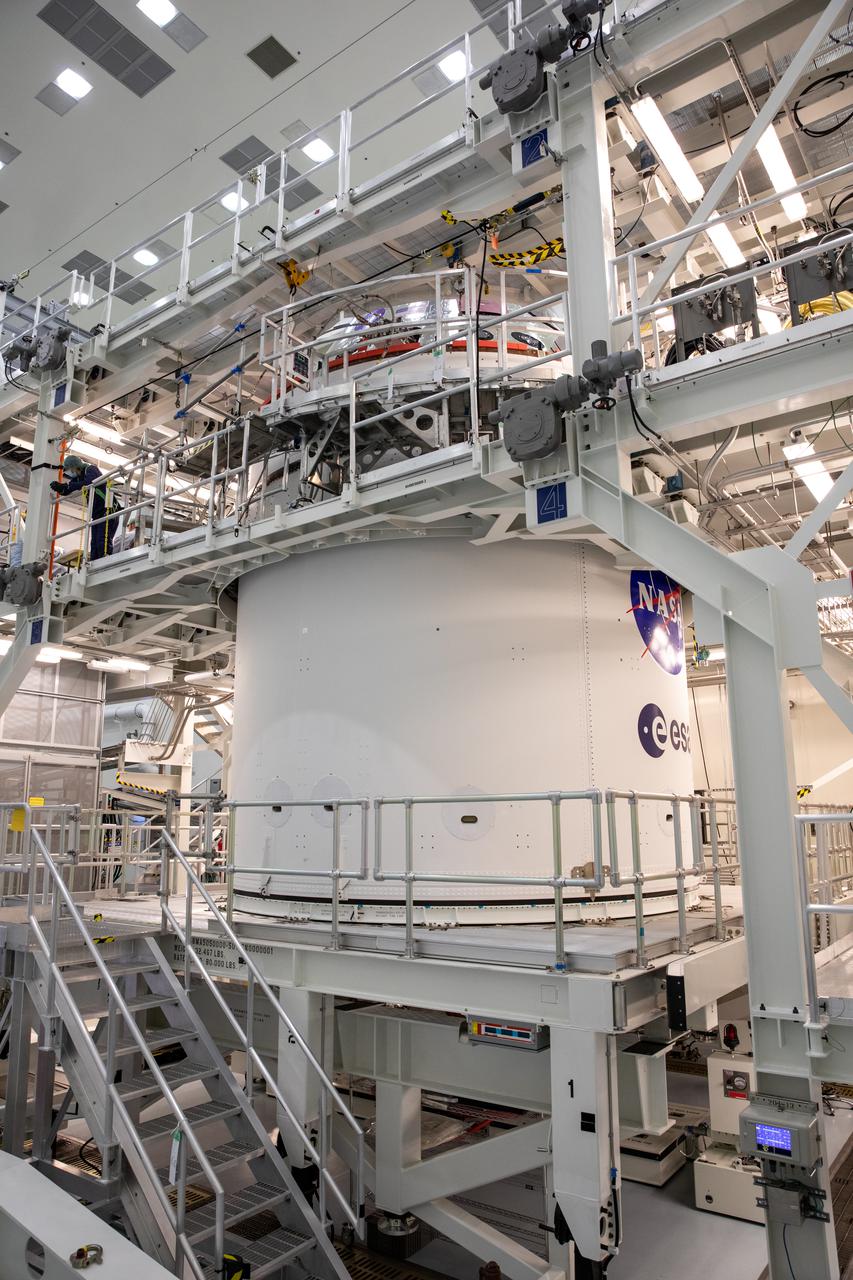
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
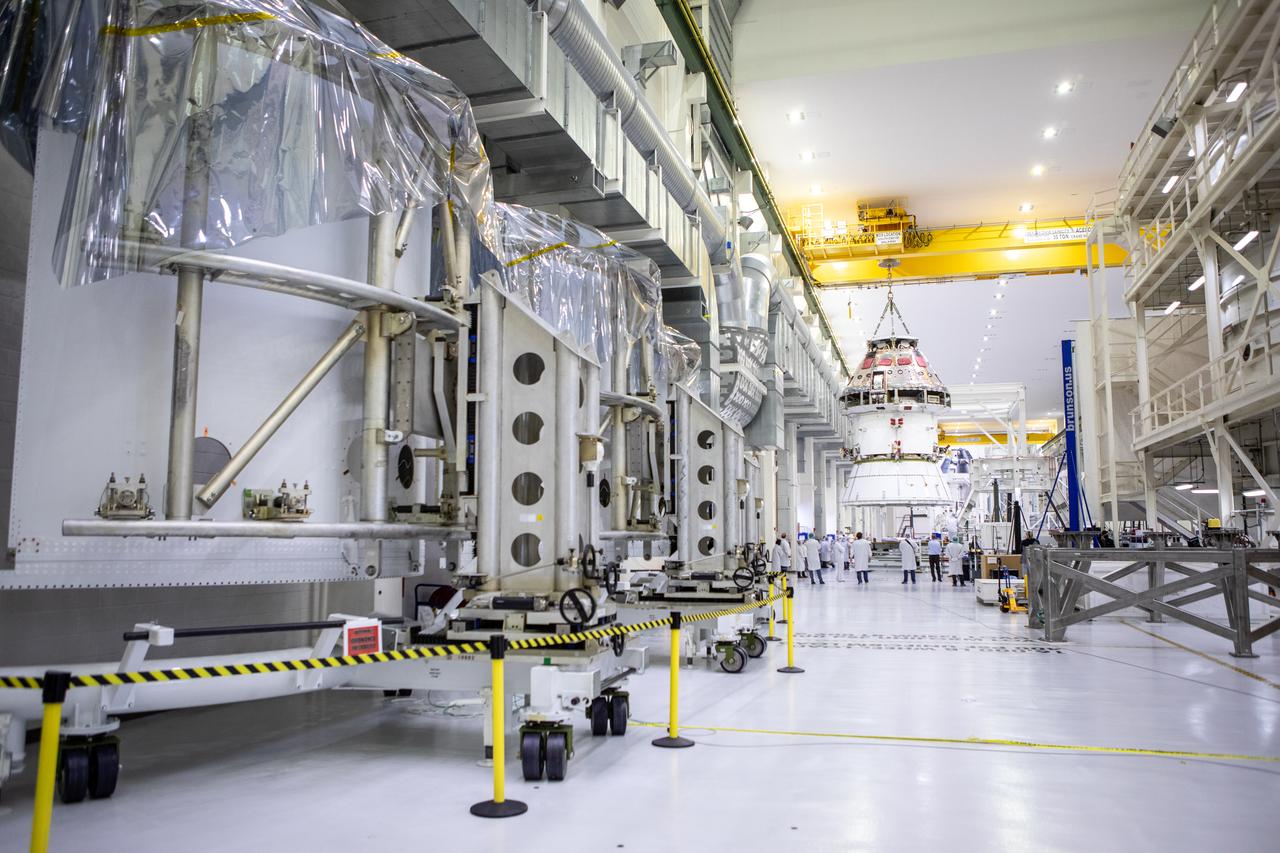

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). In view at left in the foreground are the Spacecraft Adapter Jettison Fairing panels that will protect Orion’s service module from the environment around it during the ascent. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
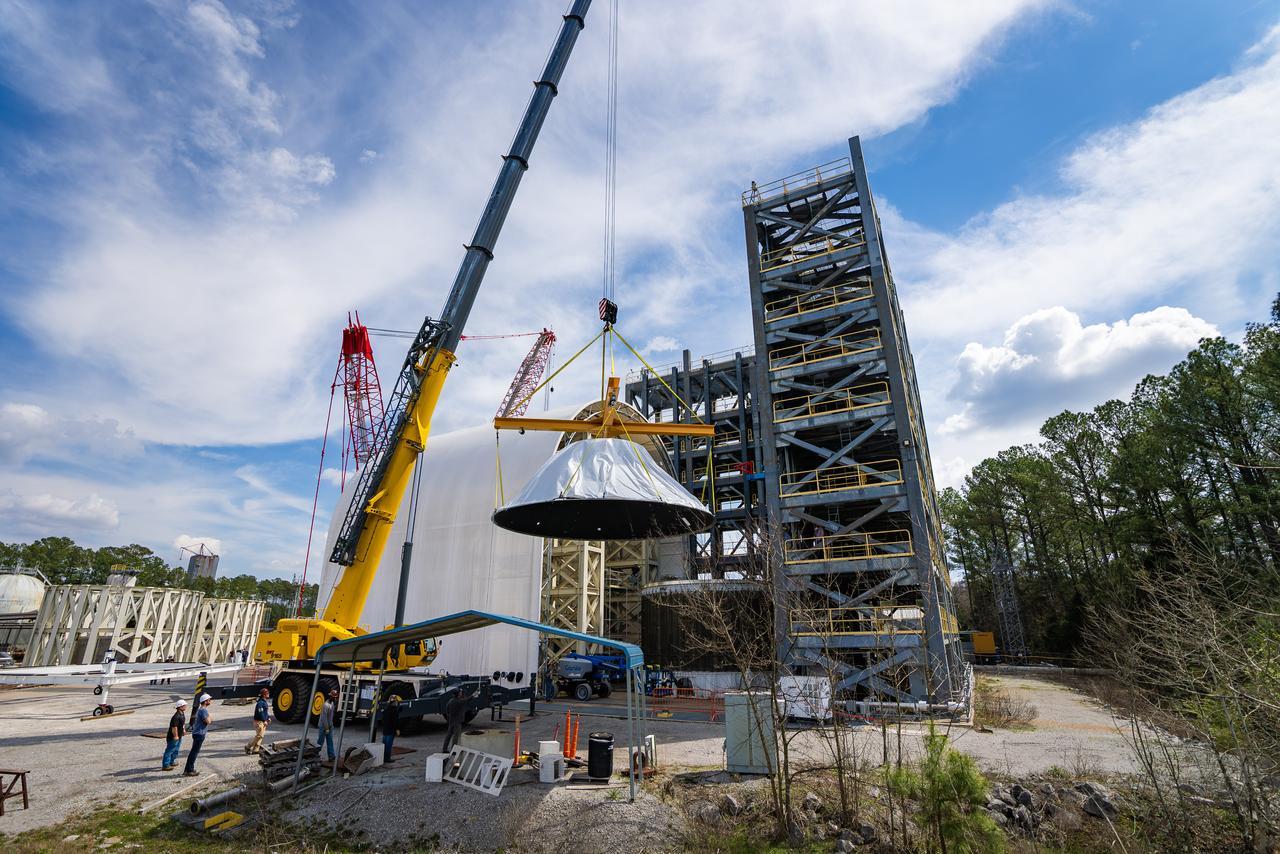

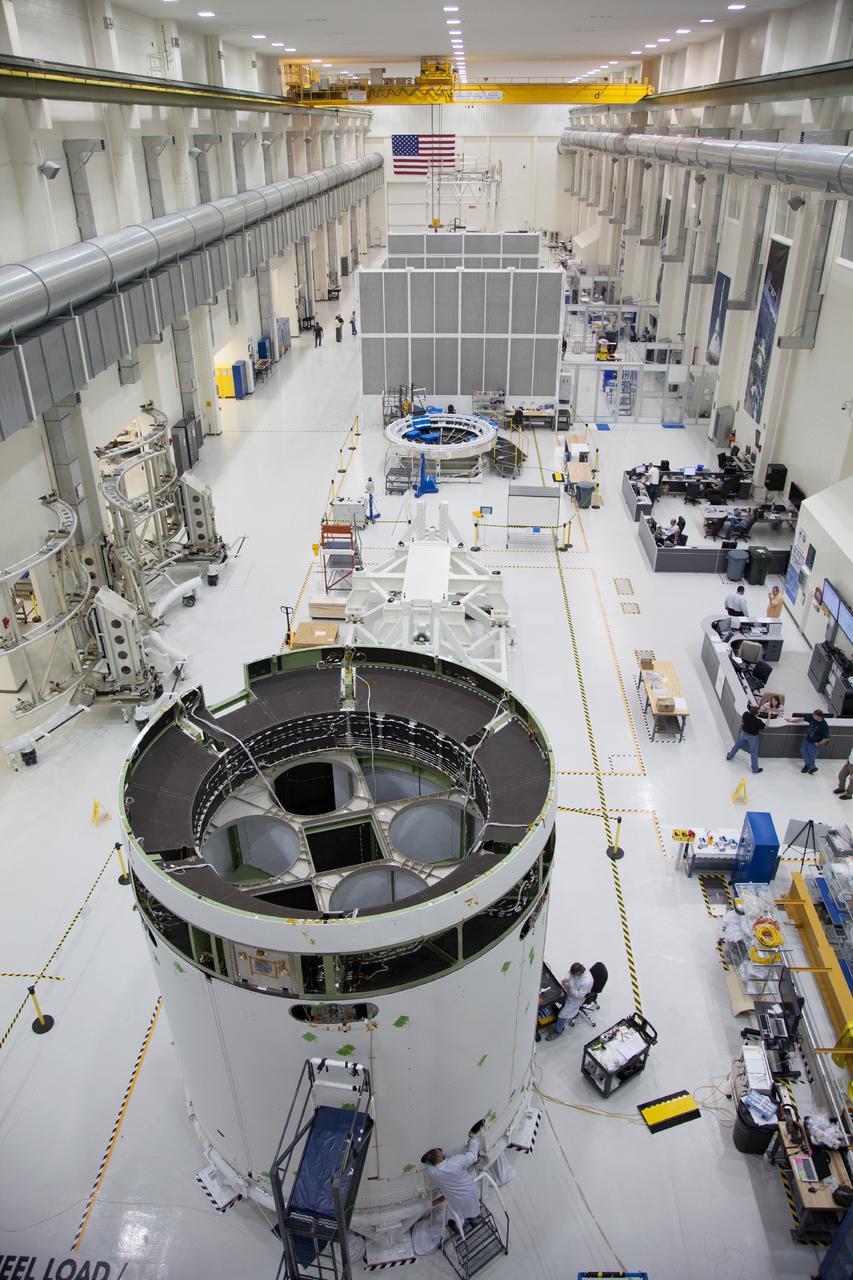
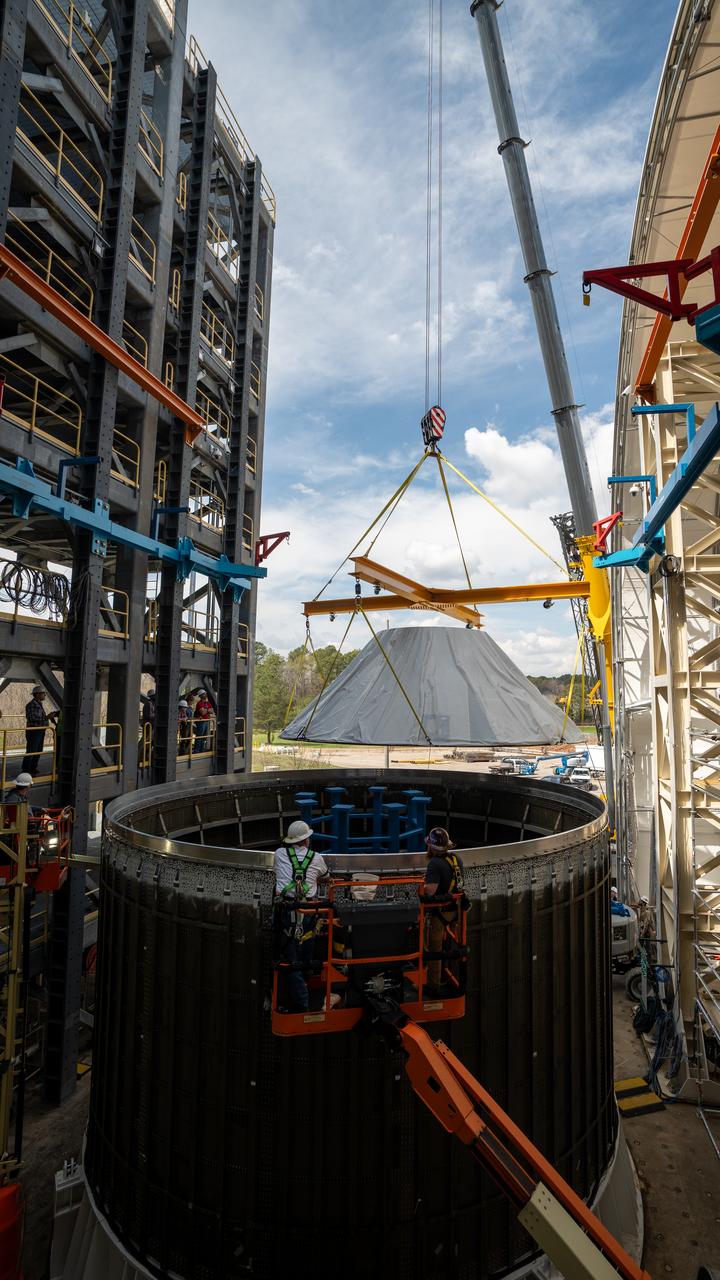
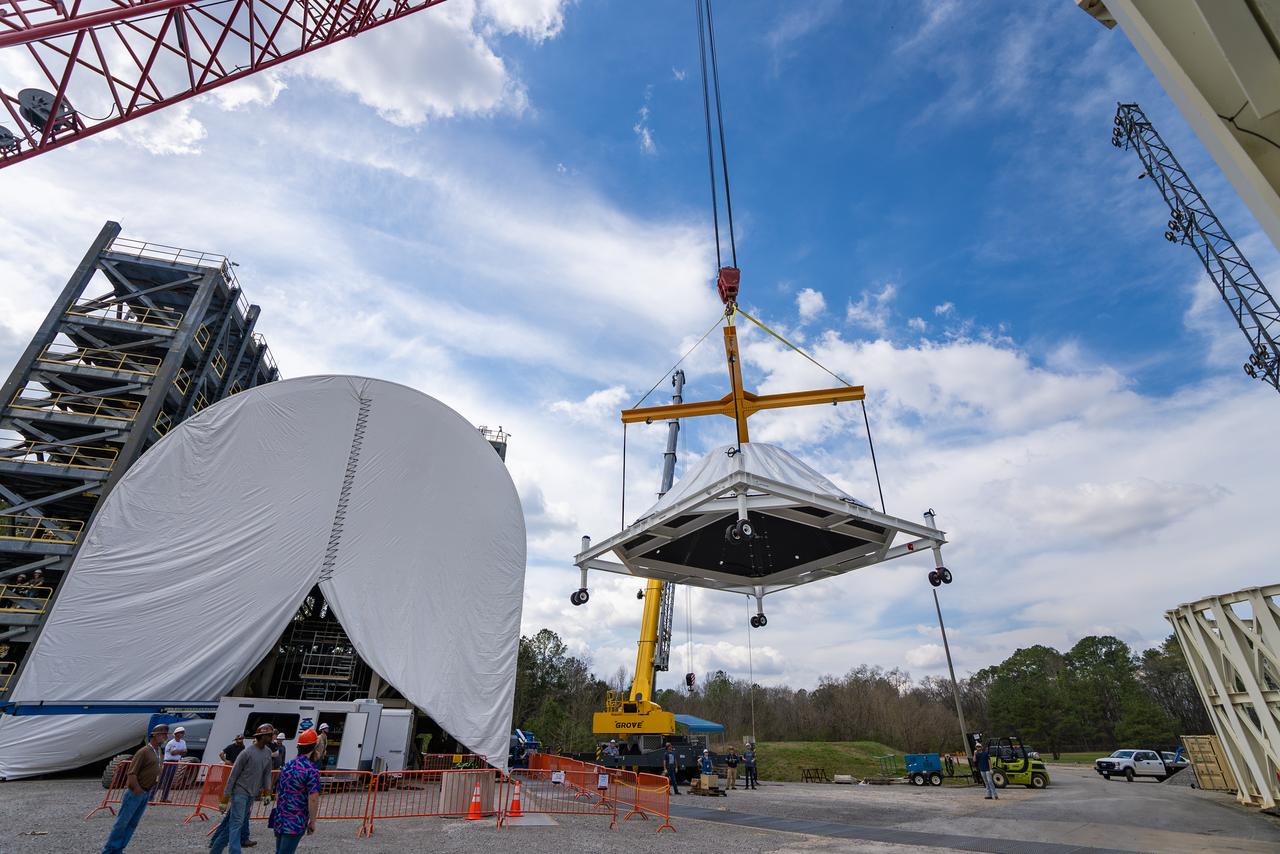
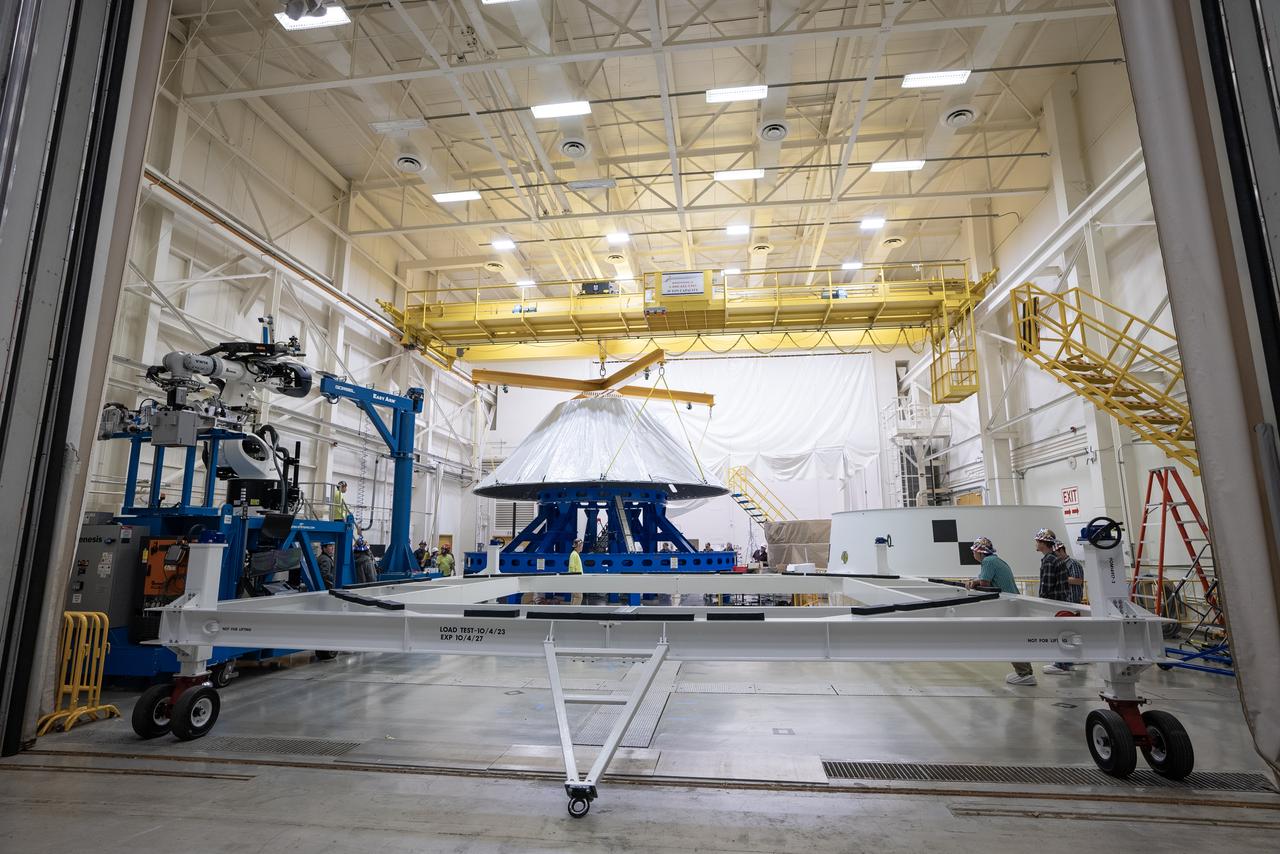
These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
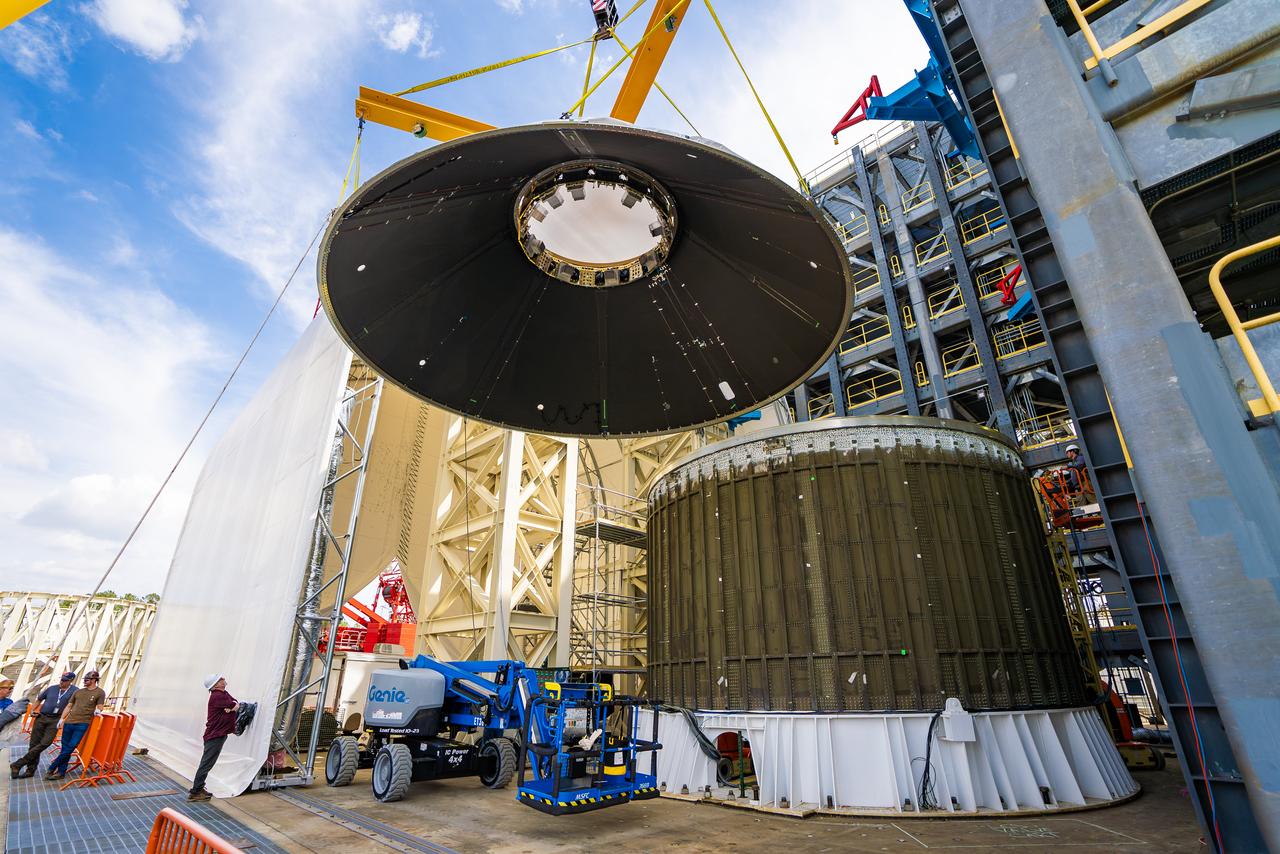

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
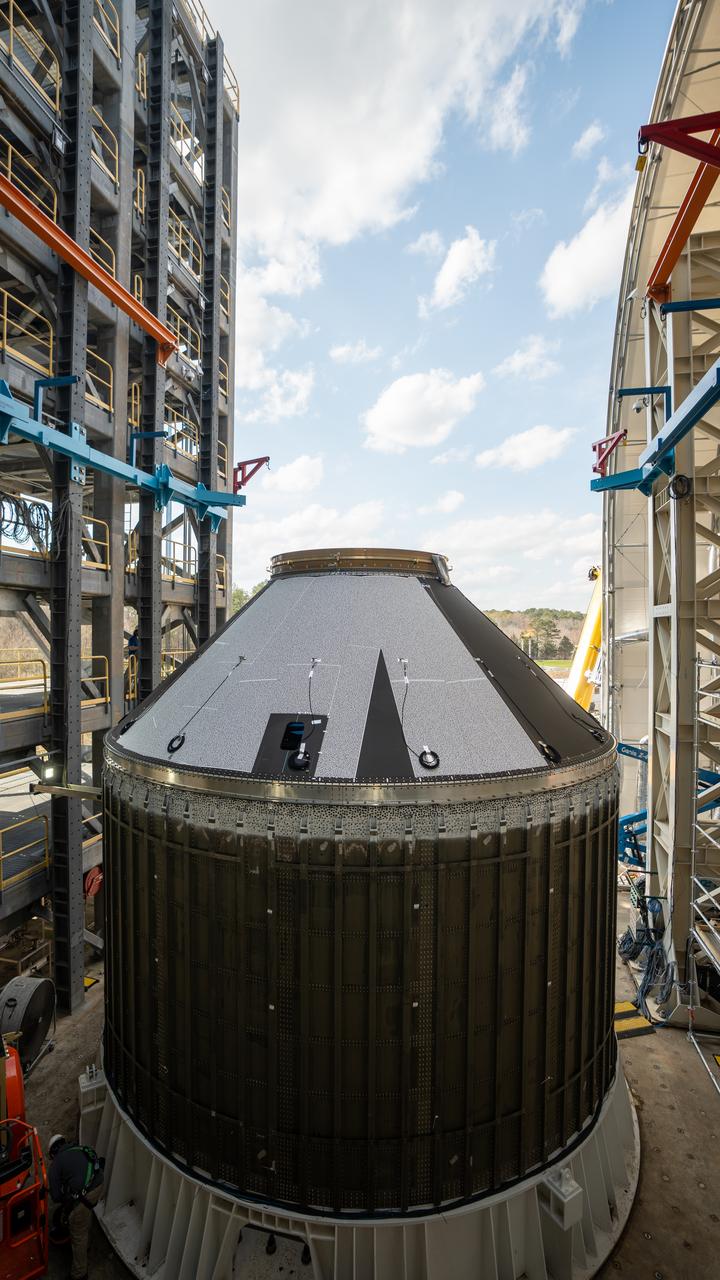

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
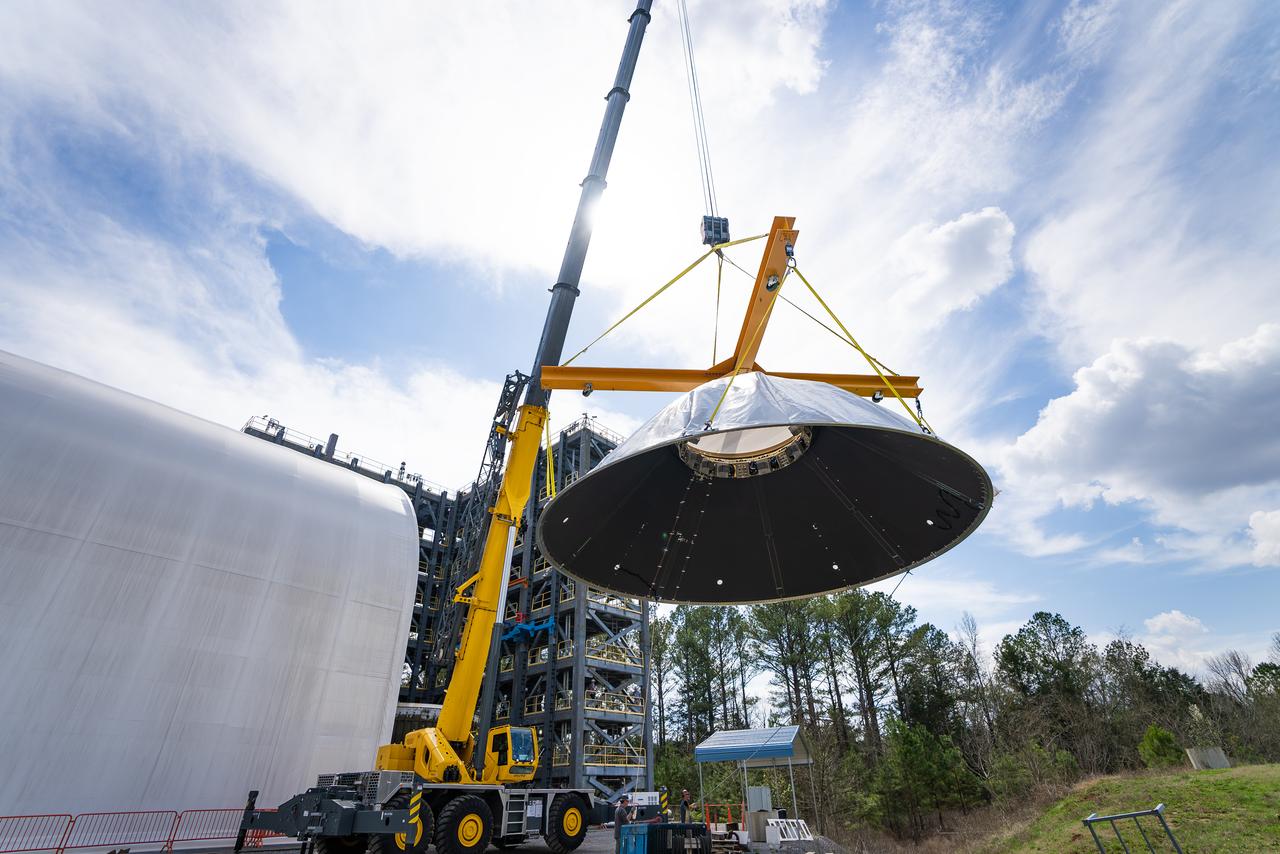

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
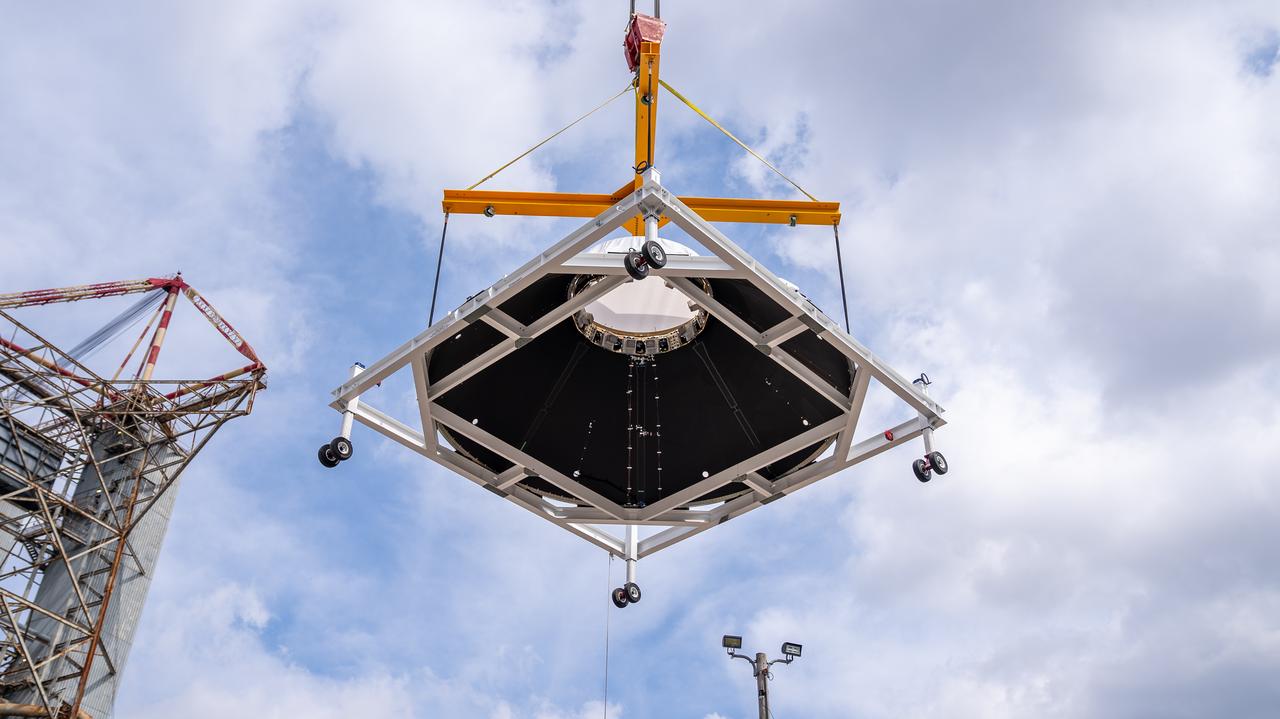

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
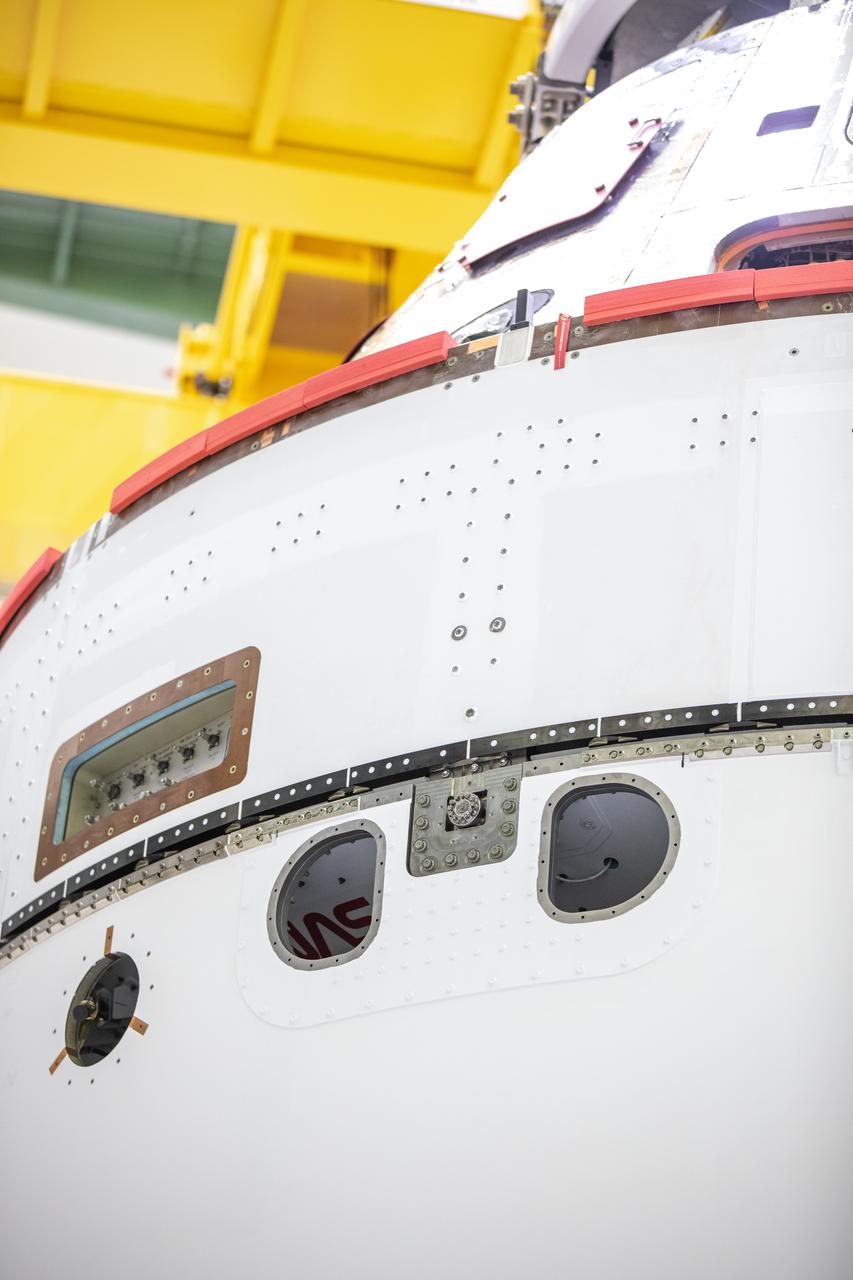

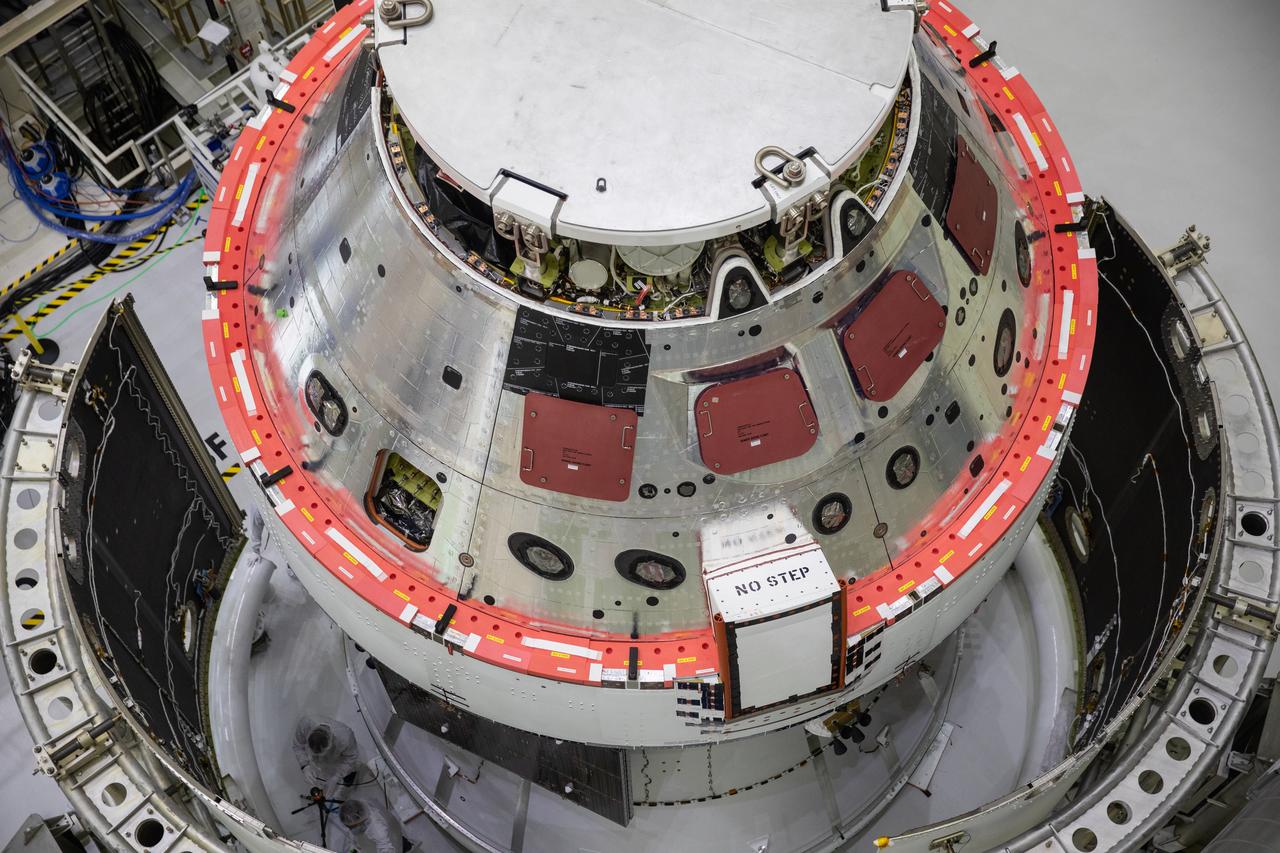
A close-up view of the Orion’s crew module adapter with the spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels secured in place shows a peak of the iconic NASA worm insignia on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
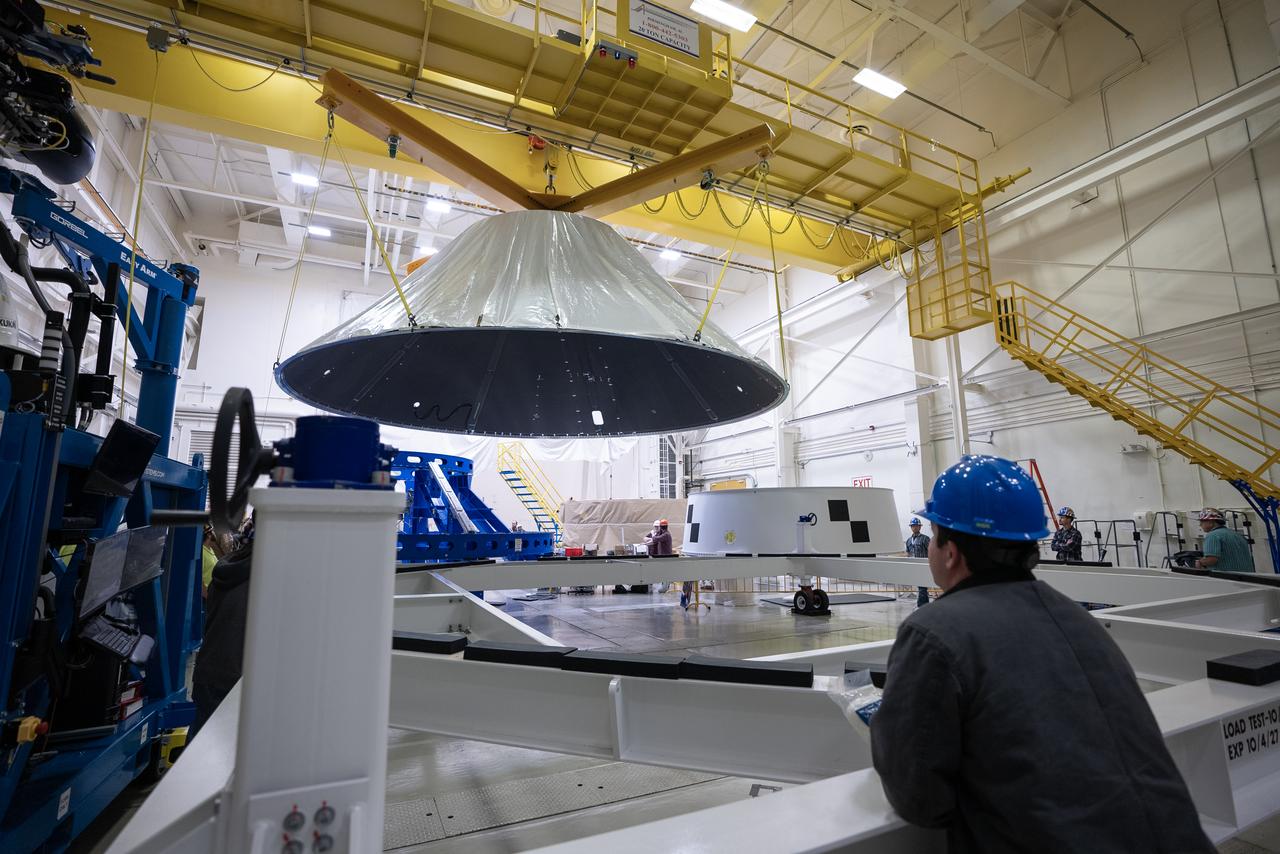

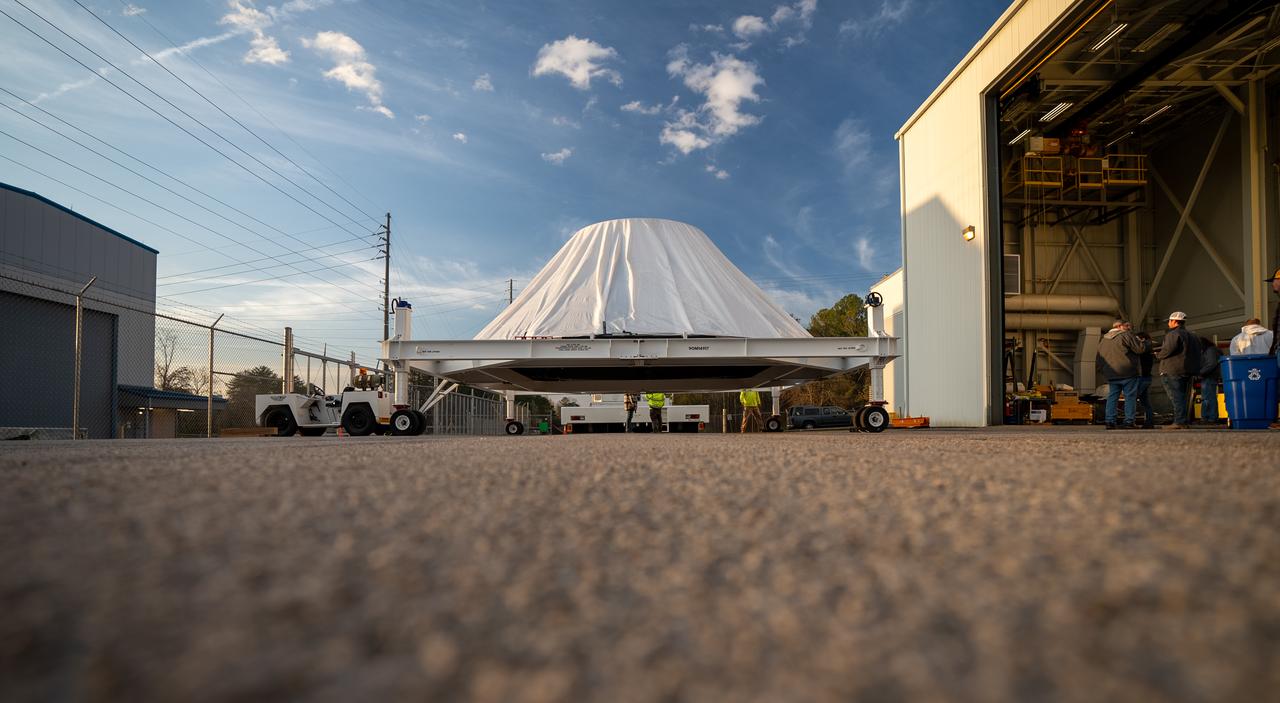
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
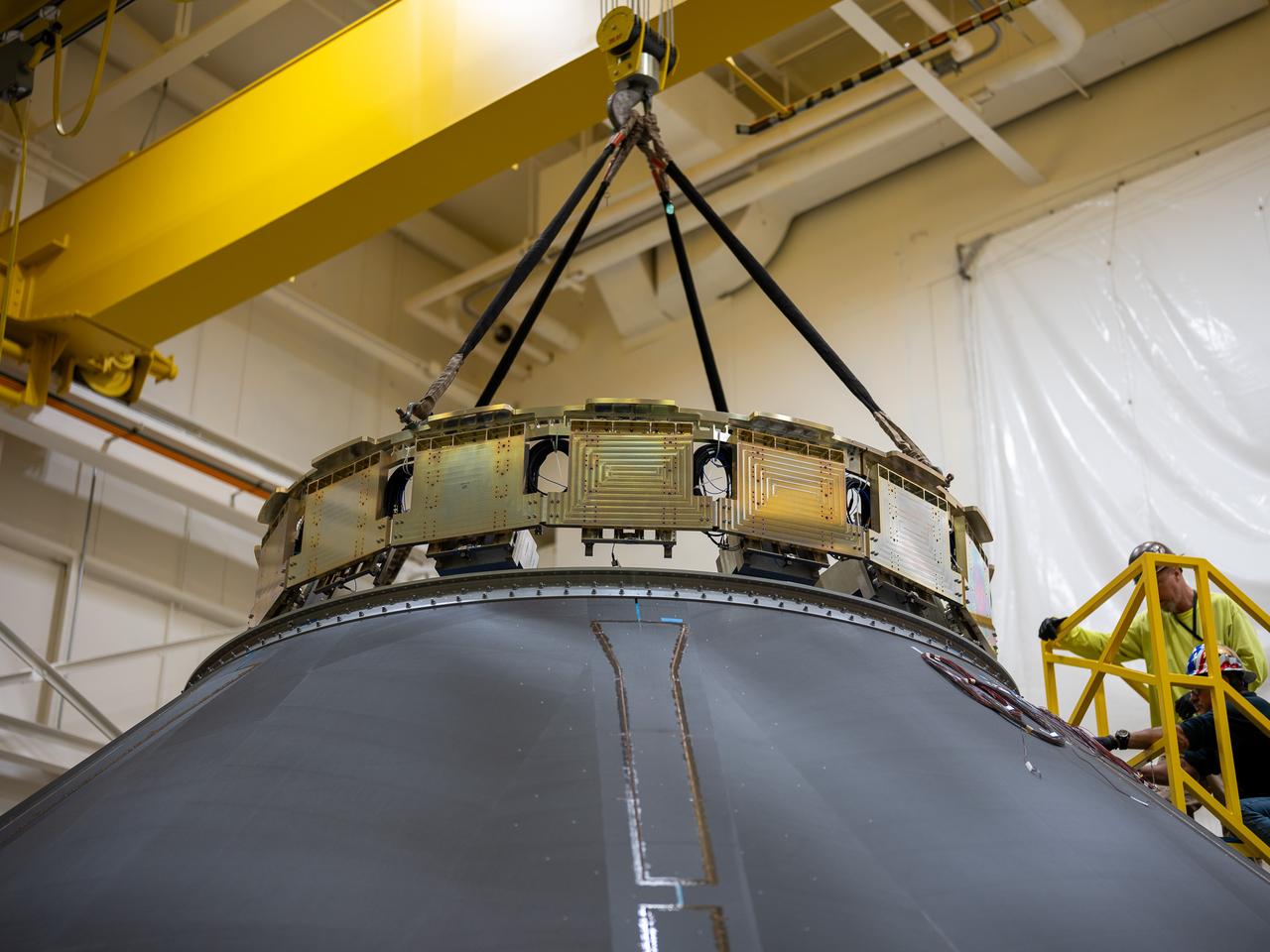

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
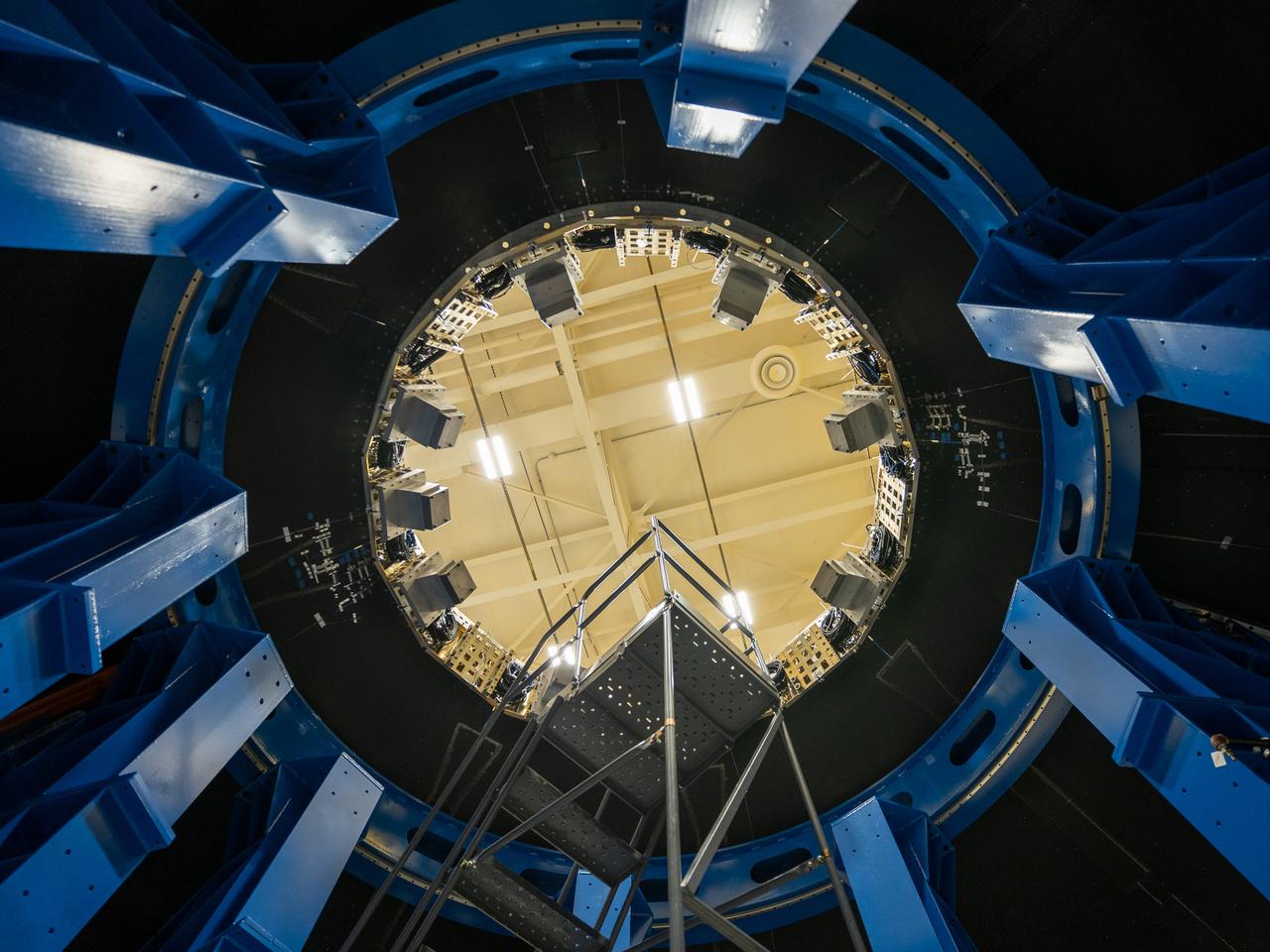

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
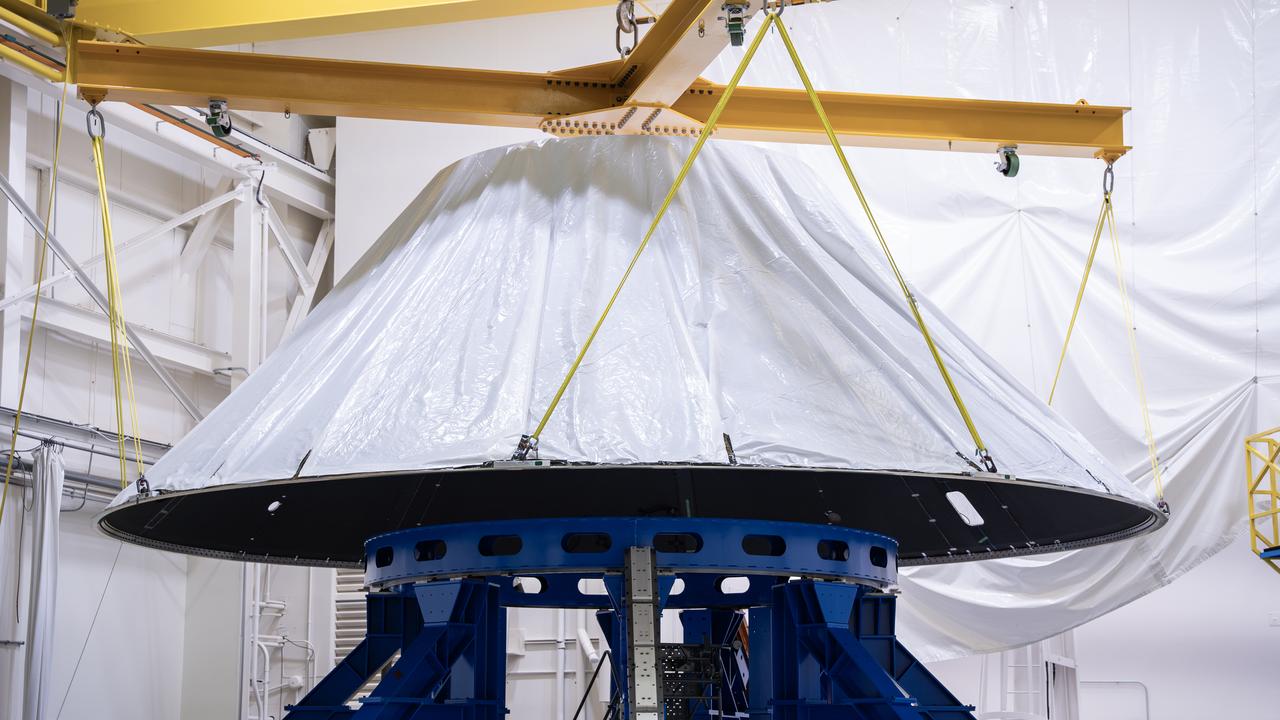

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
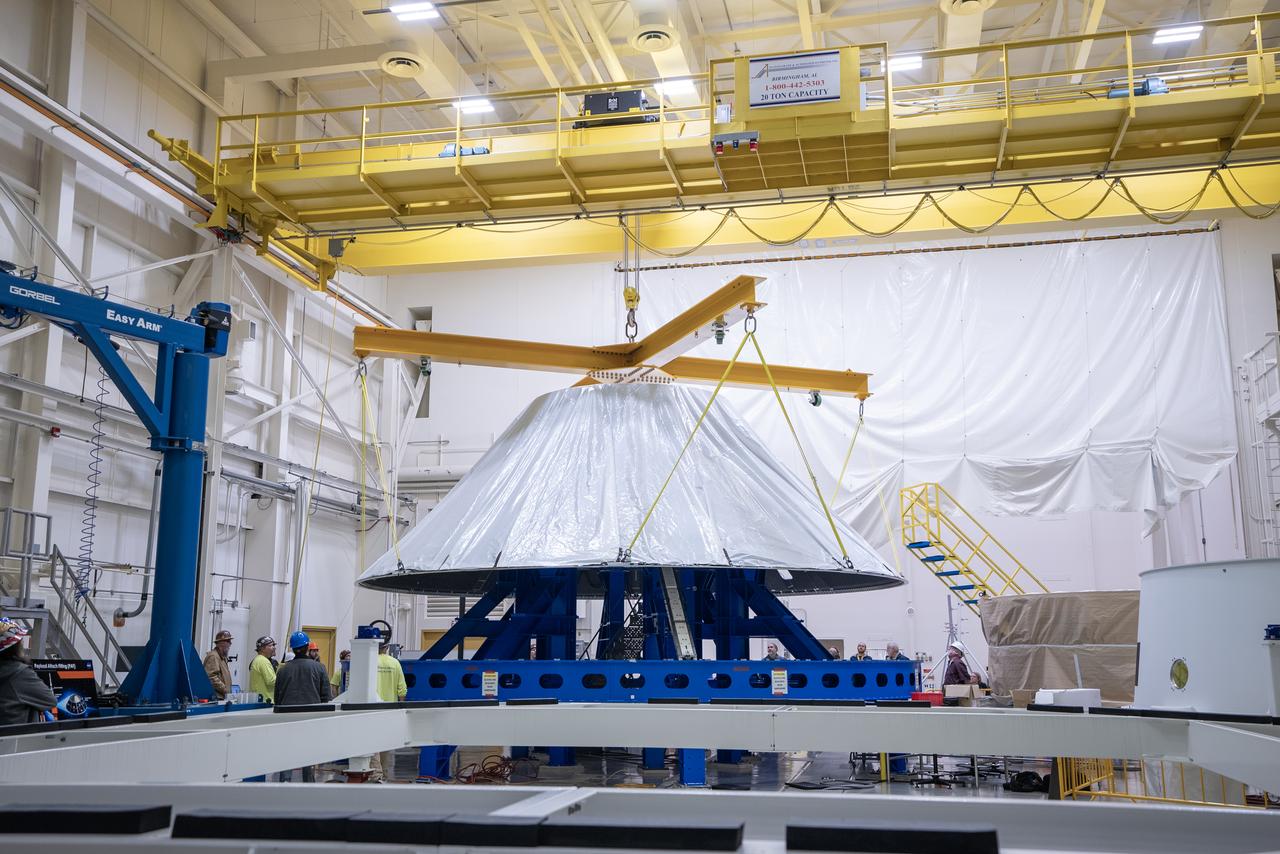

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
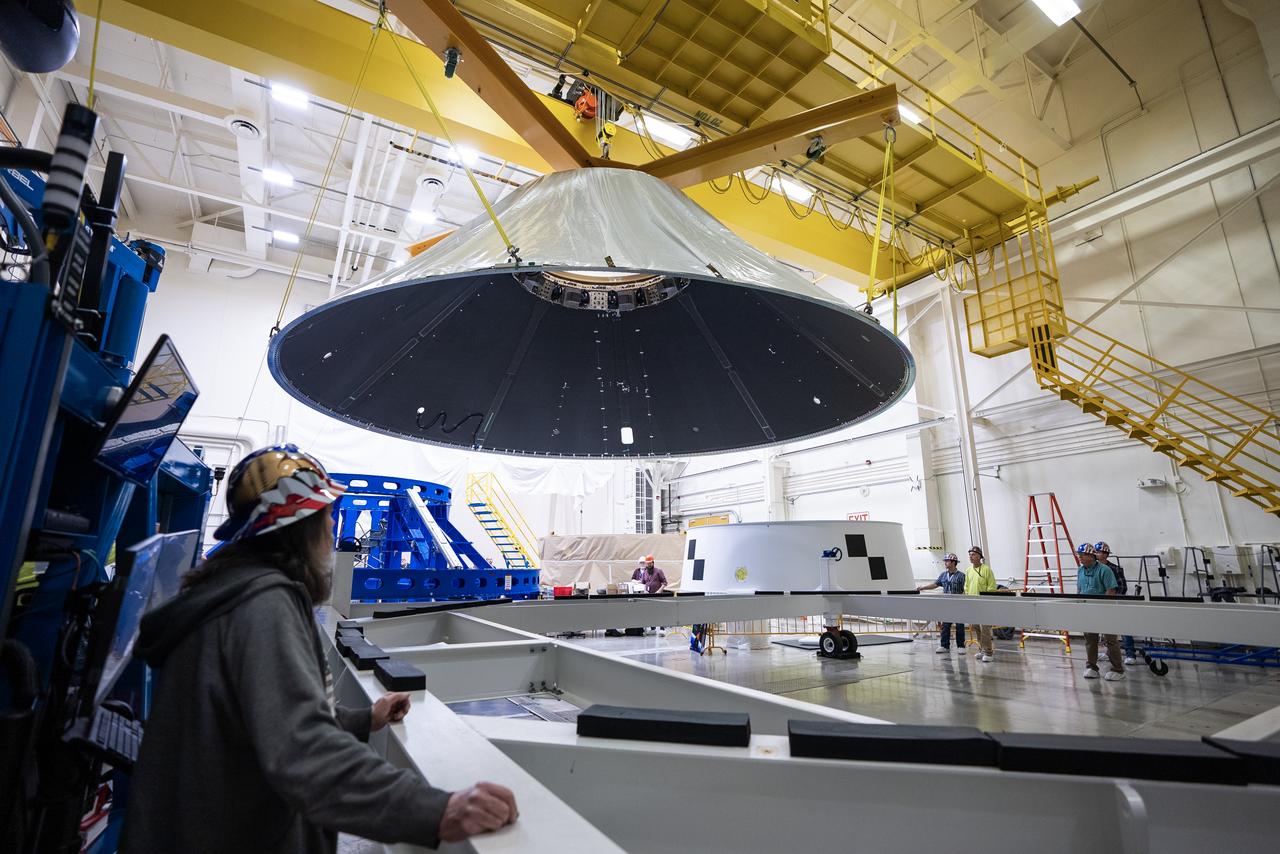

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
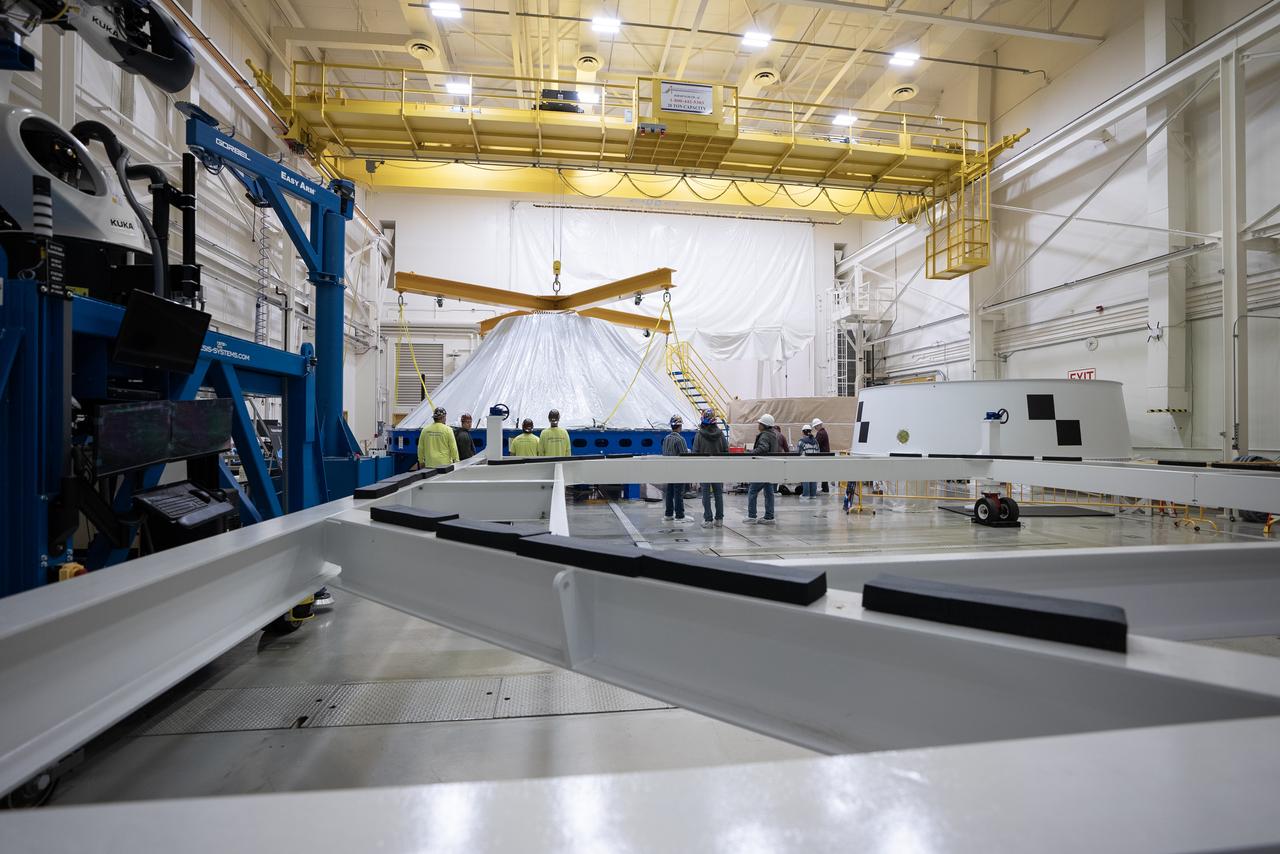

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
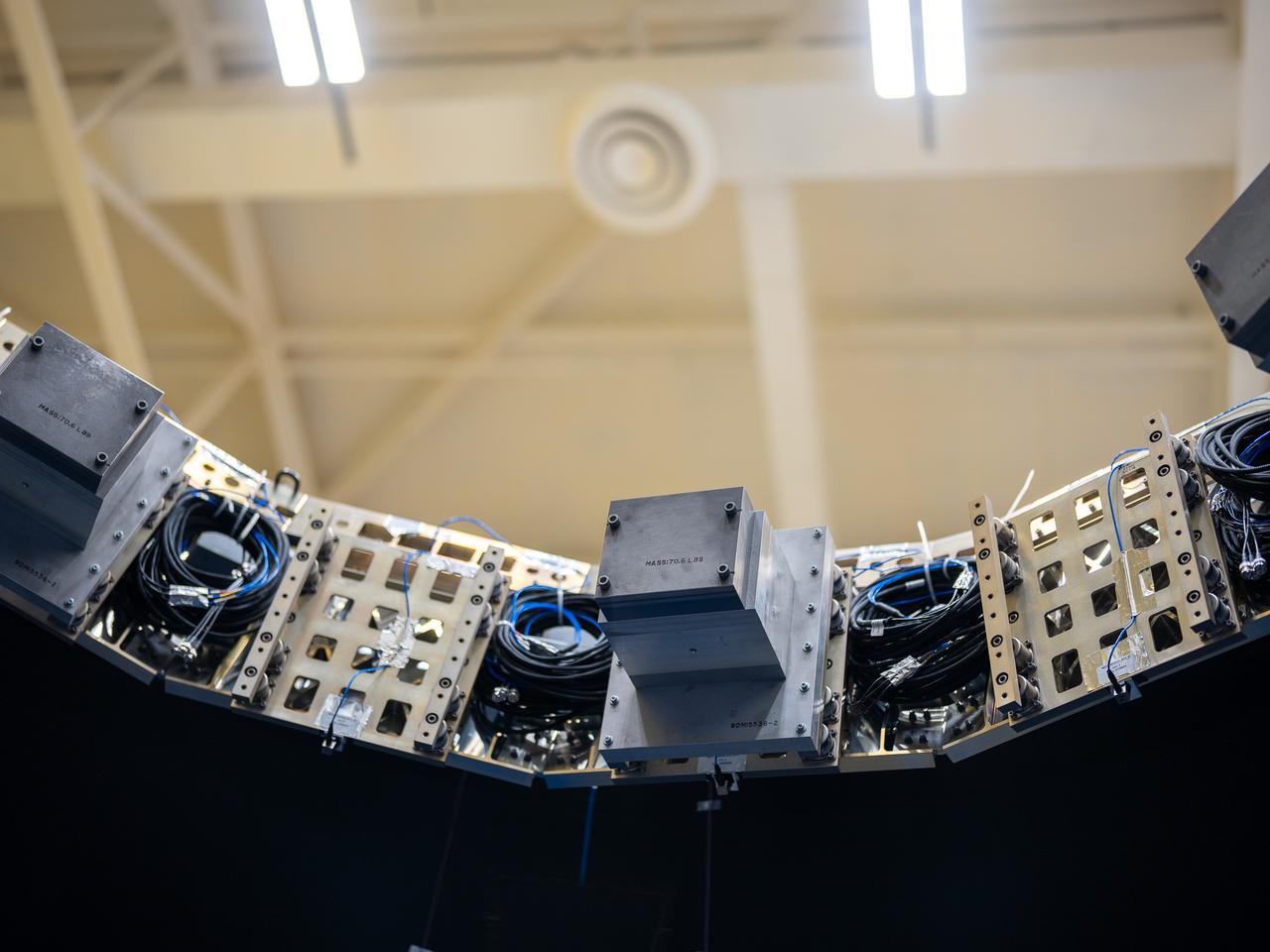
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
Izeal Battle, ASRC technician, is shown in the foreground with the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion (not in view) are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
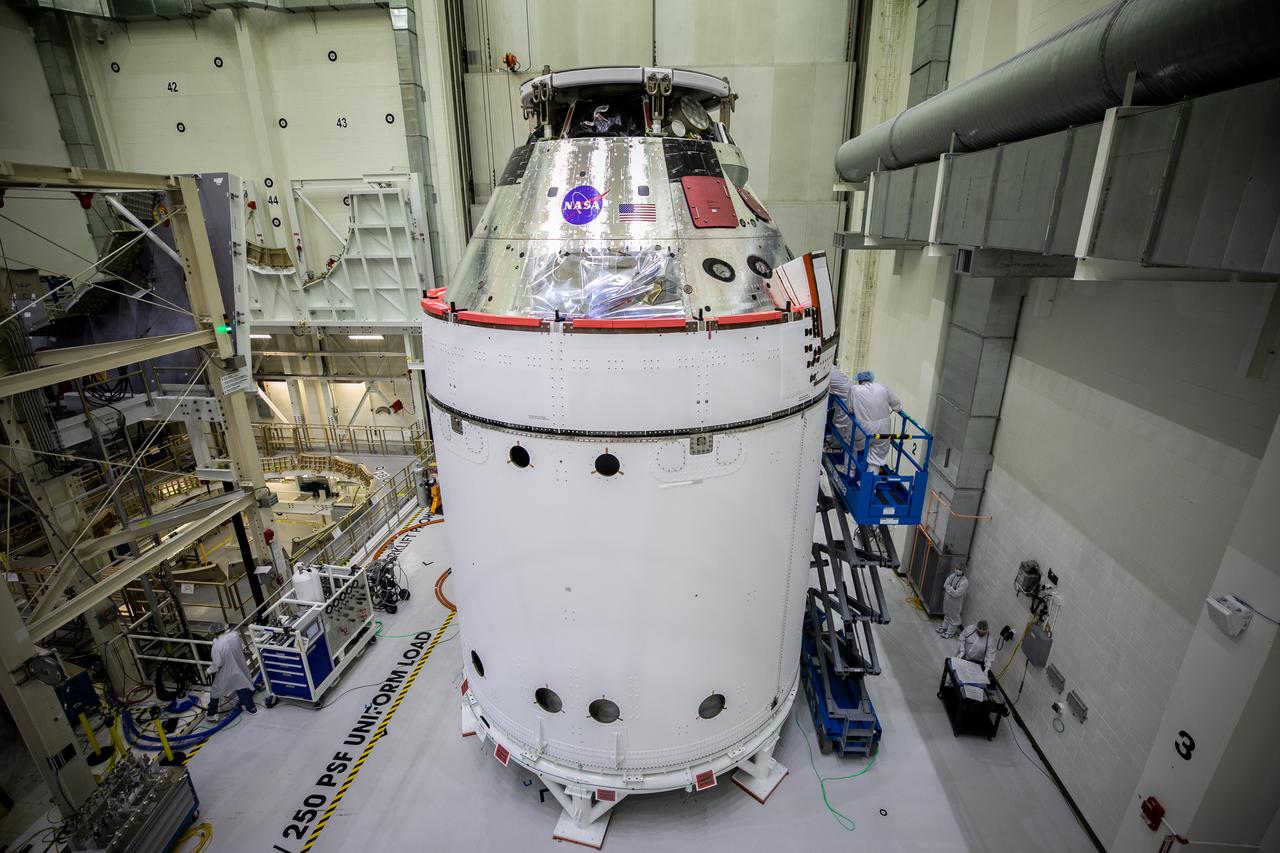

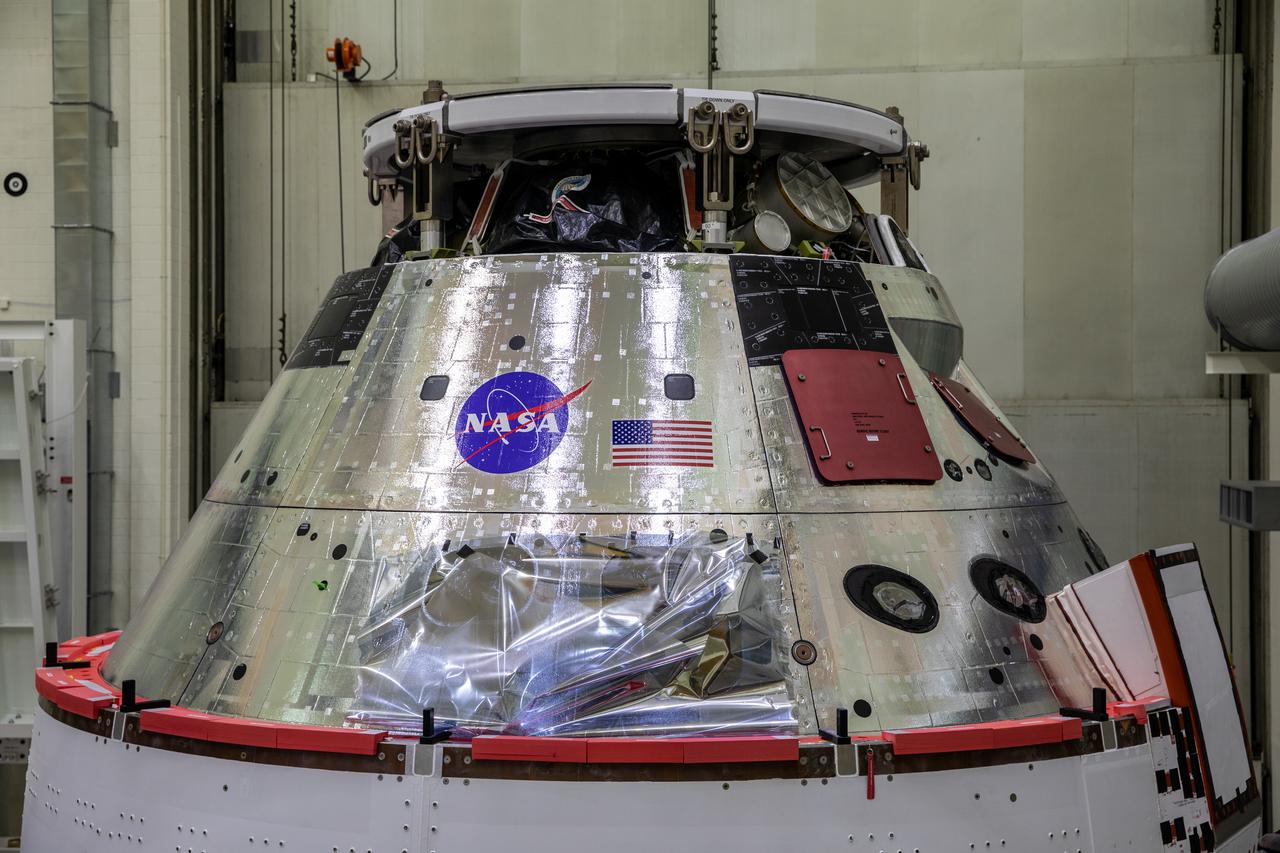
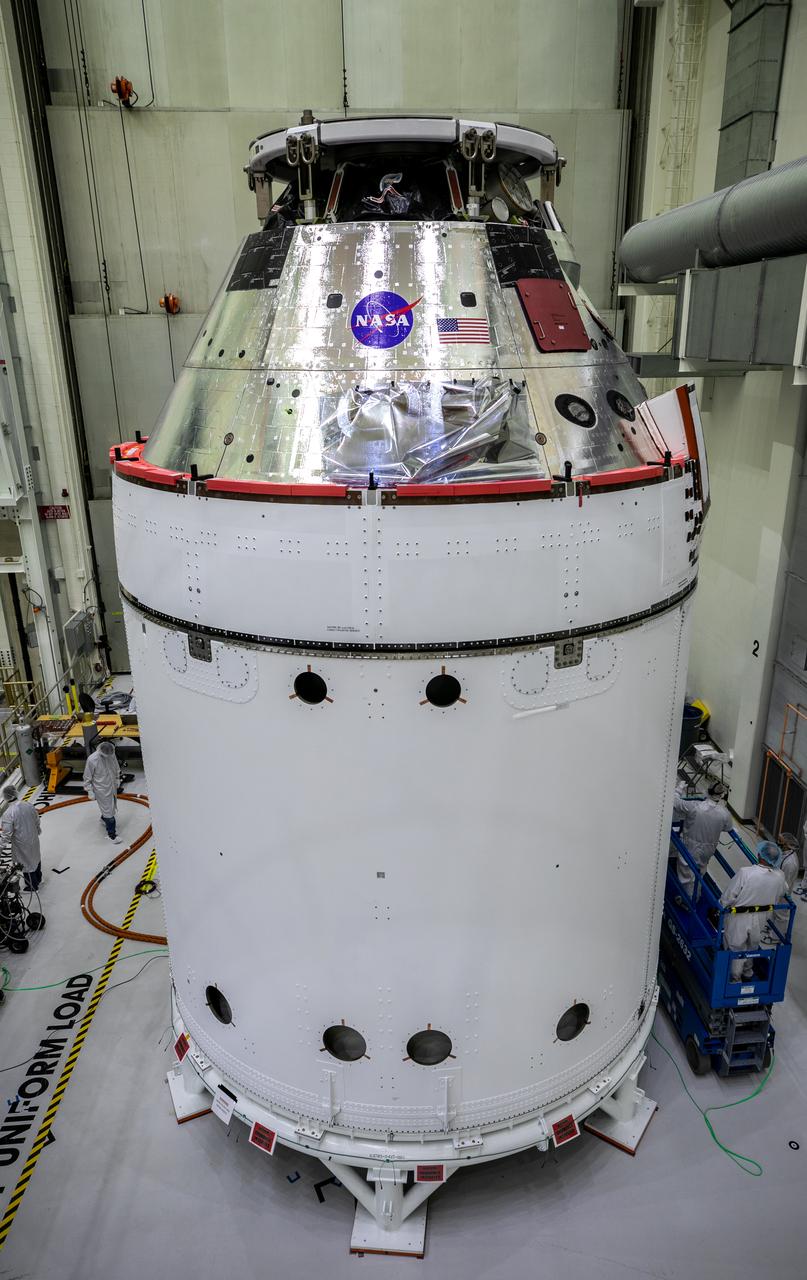
The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in view inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Oct. 28, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Todd Biddle, ASRC technician, is shown in the foreground with the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission behind him inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2020. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and American Fag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shawn Corwin, at left, ASRC technician, Shawn Corwin, at left, points to the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2020. At right is Eric Nolan, ASRC technician. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and American Flag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
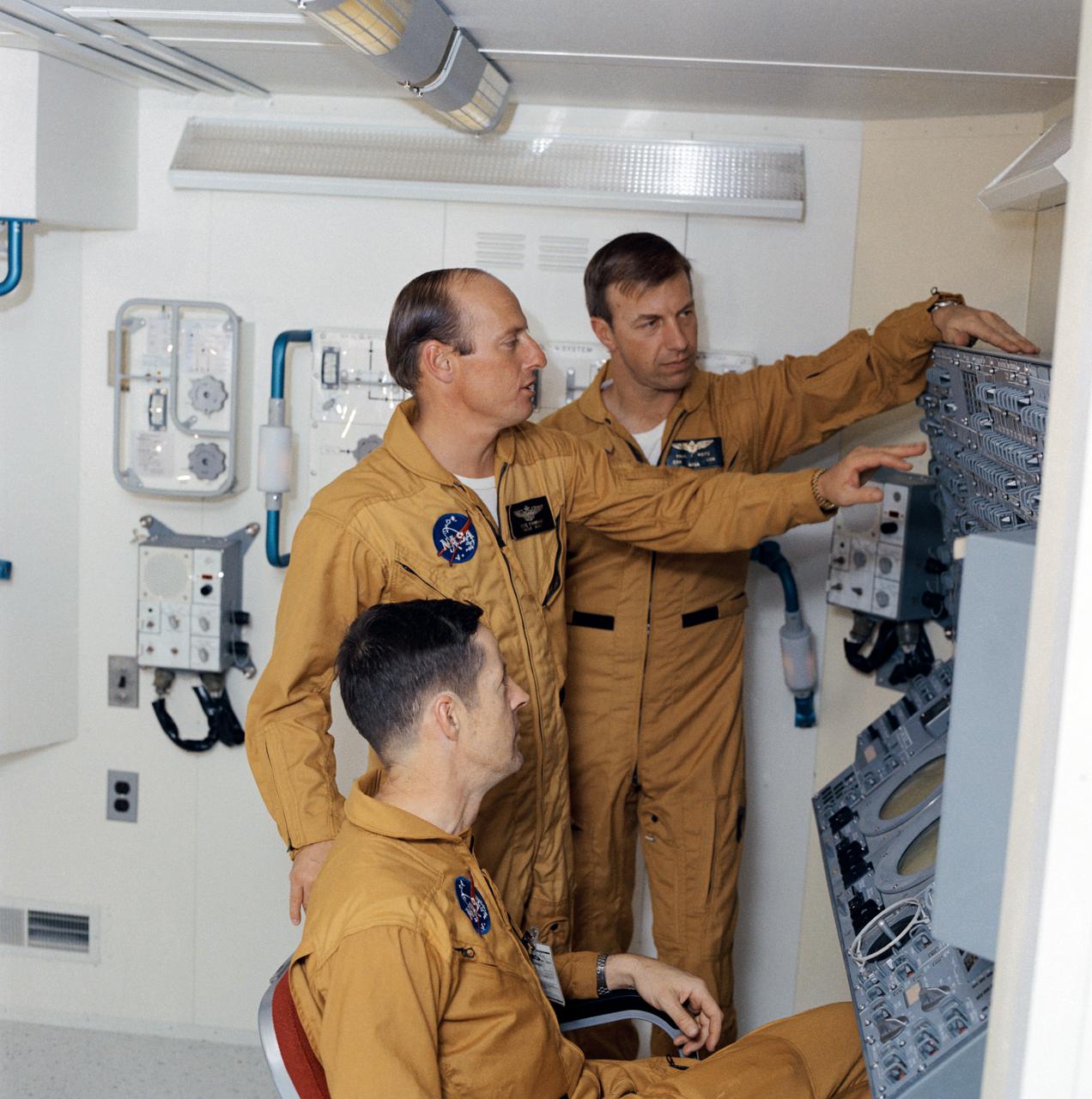

S72-17509 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
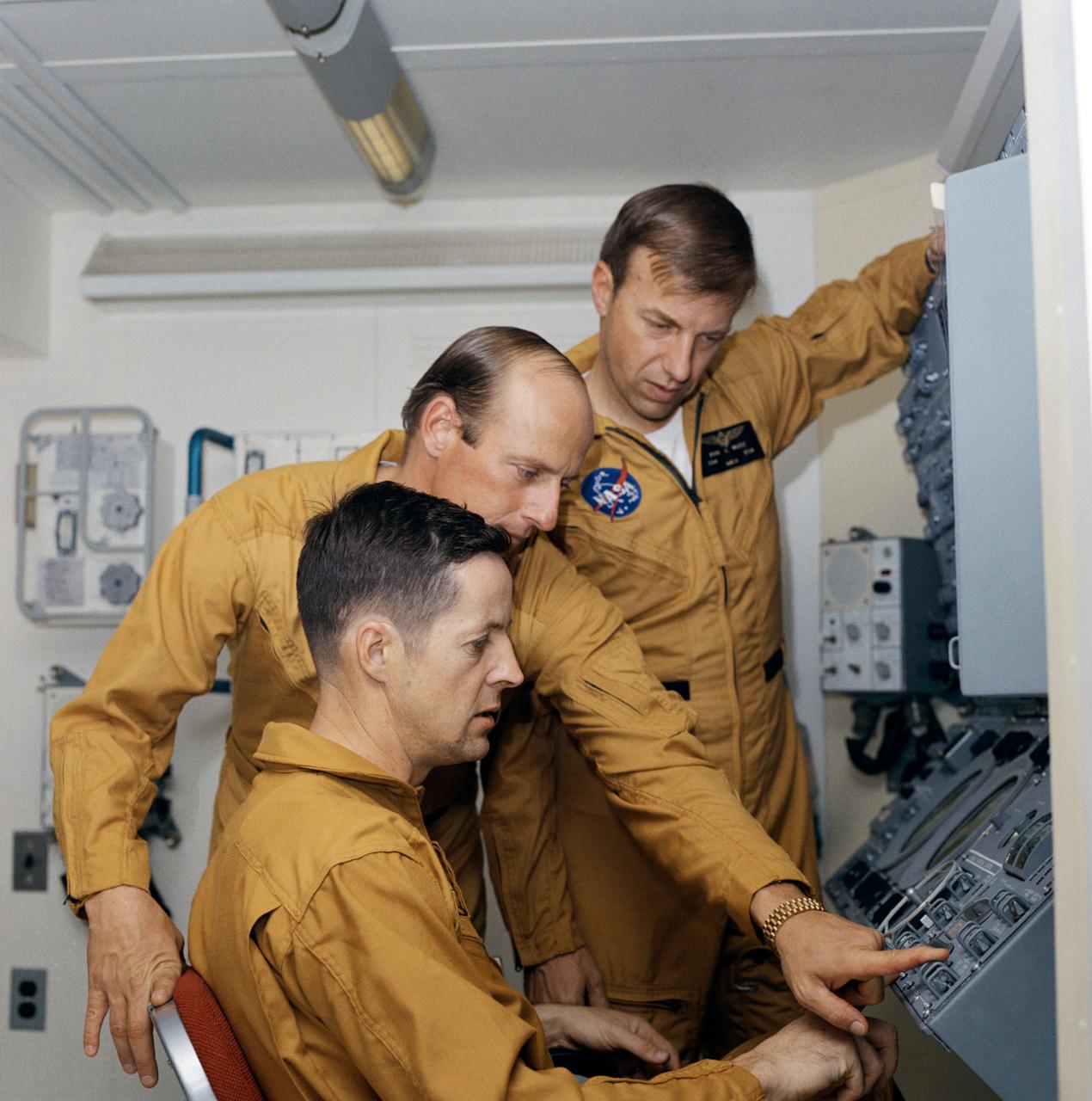

S72-17512 (19 Jan. 1972) --- These three men are the crewmen for the first manned Skylab mission. They are astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, standing left; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, seated; and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. They were photographed and interviewed during an "open house" press day in the realistic atmosphere of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The control and display panel for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) is at right. Photo credit: NASA
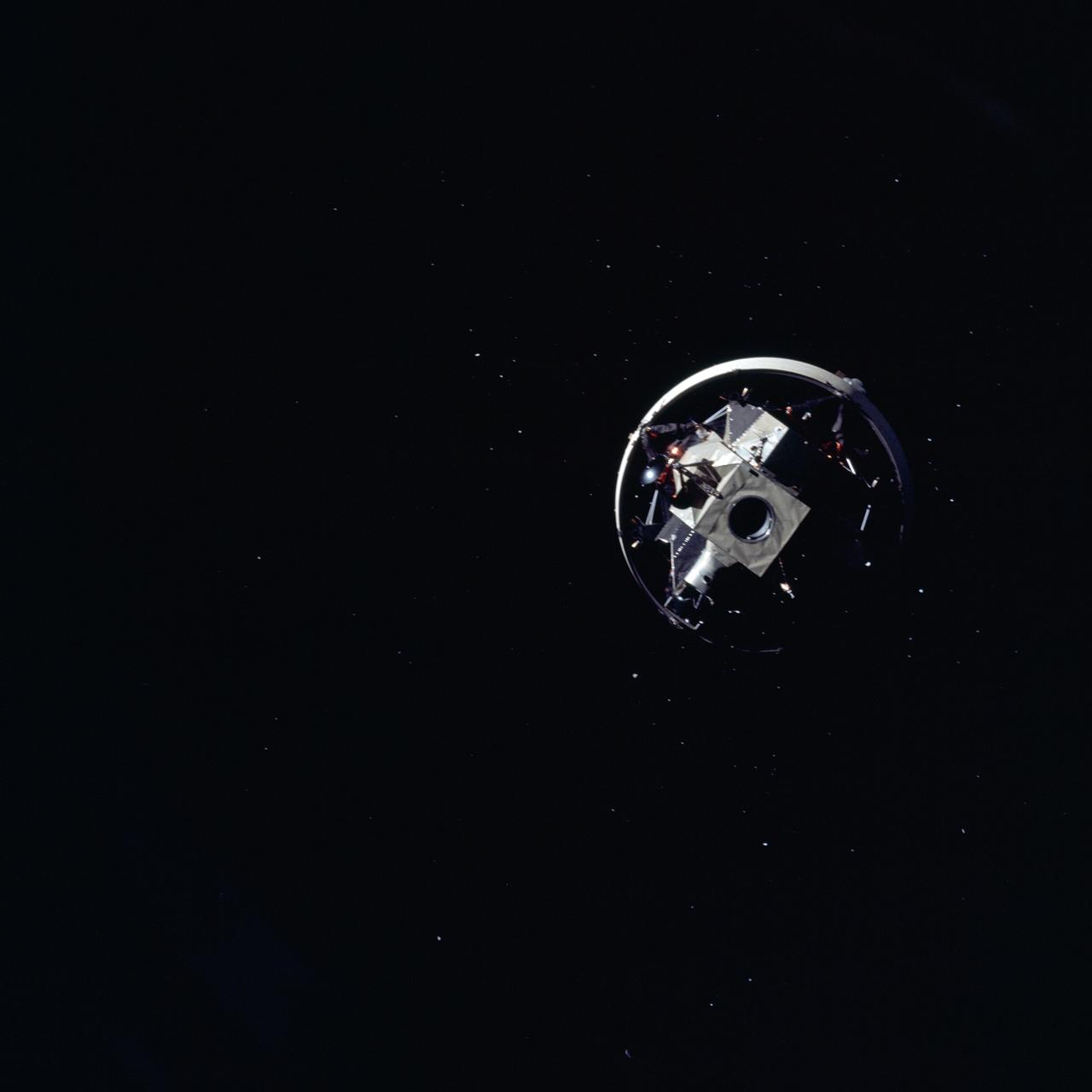

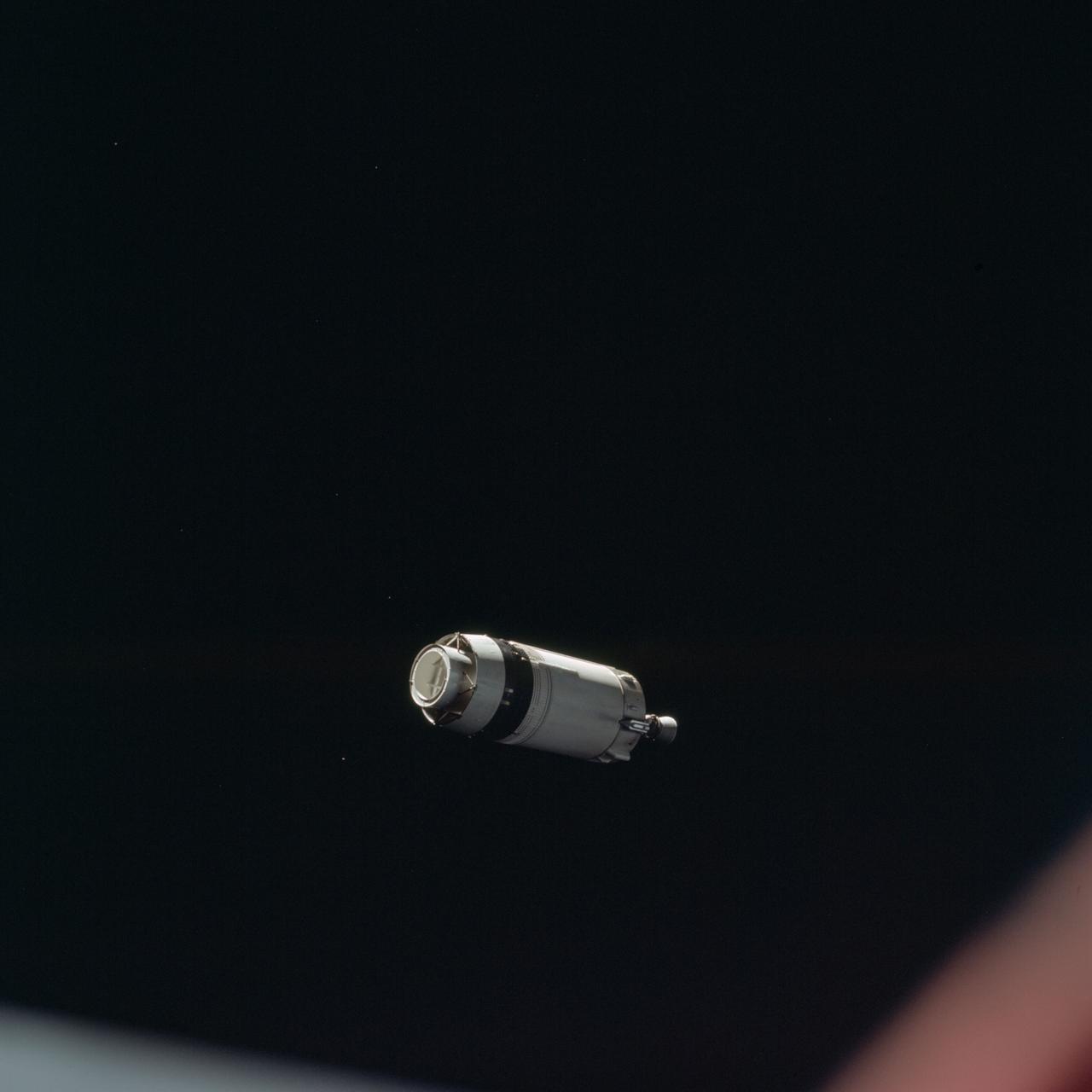
AS12-50-7328 (14 Nov. 1969) --- Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is pictured as seen from Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the first day of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. This photograph was taken following CSM separation from LM/S-IVB and prior to Lunar Module extraction from the S-IVB stage. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned.

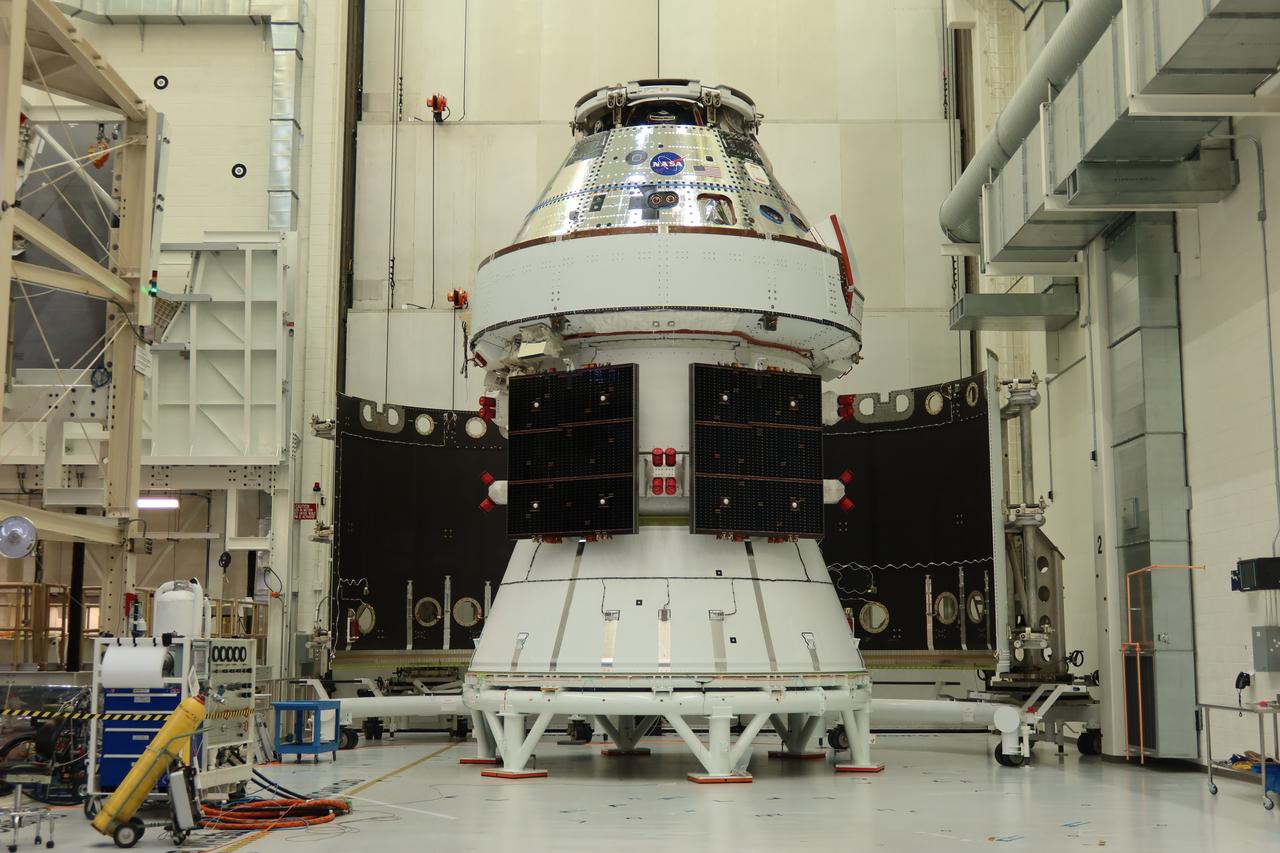
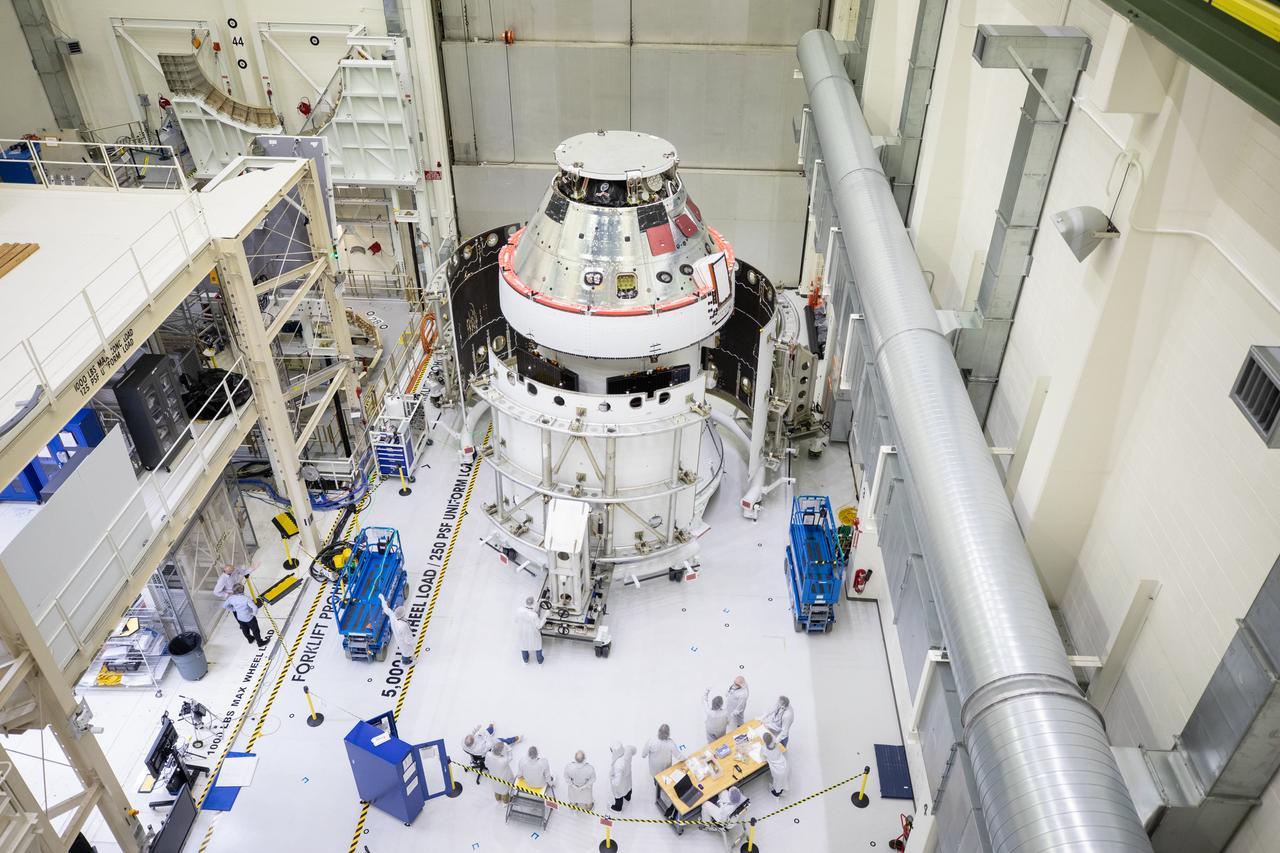
The Artemis II Orion spacecraft sits in the transfer aisle in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following successful installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings on Wednesday, March 19, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, as well as help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

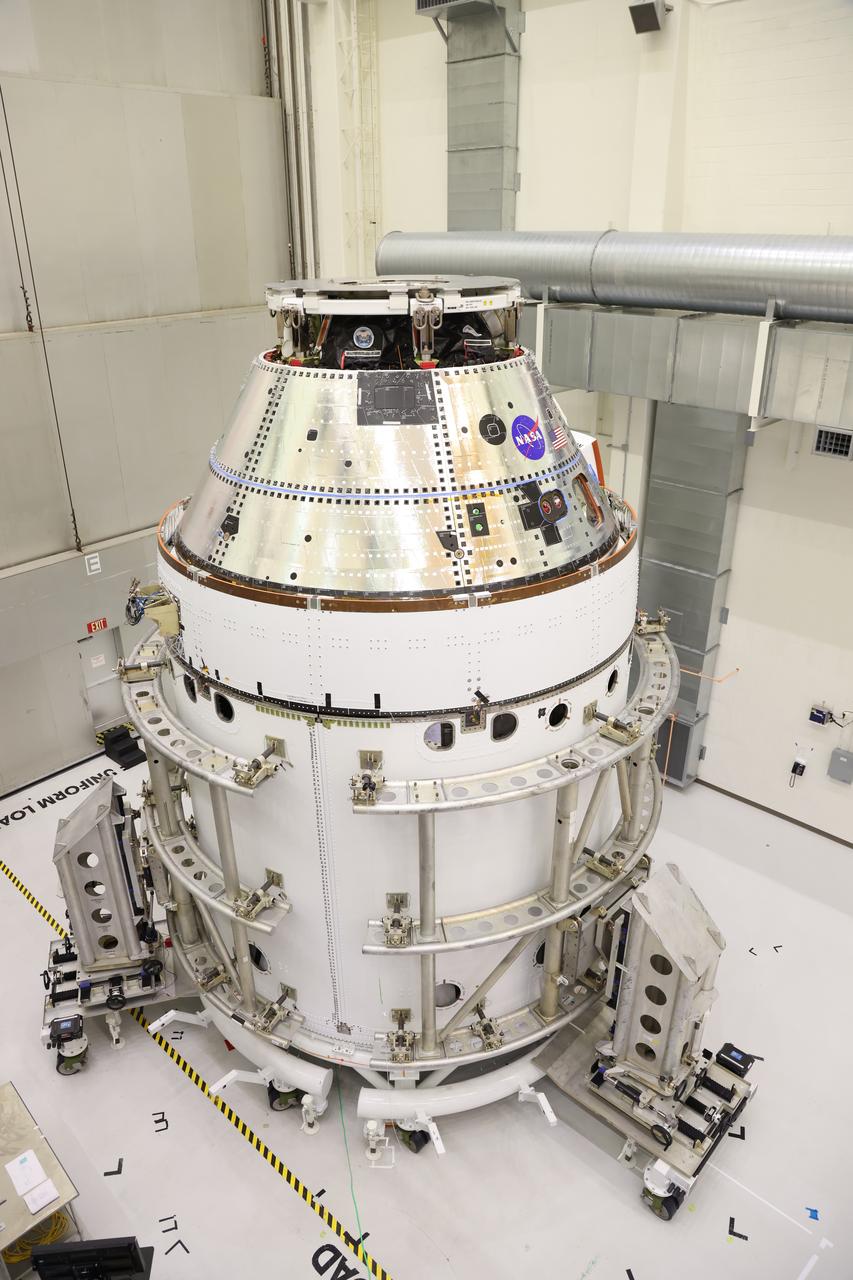
The Artemis II Orion spacecraft sits in the transfer aisle in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for the installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, plus help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

Technicians with Lockheed Martin prepare the Artemis II Orion spacecraft for the installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, plus help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft sits in the transfer aisle in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following successful installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings on Wednesday, March 19, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, as well as help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

Technicians with Lockheed Martin prepare the Artemis II Orion spacecraft for the installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, plus help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

Technicians with Lockheed Martin prepare the Artemis II Orion spacecraft for the installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, plus help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft sits in the transfer aisle in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following successful installation of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairings on Wednesday, March 19, 2025. The fairings encapsulate the service module and protect the solar array wings, shielding them from the heat, wind, and acoustics of launch and ascent, as well as help redistribute the load between Orion and the massive thrust of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during liftoff and ascent. Once the spacecraft is above the atmosphere, the three fairing panels will separate from the service module reducing the mass of the spacecraft.

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
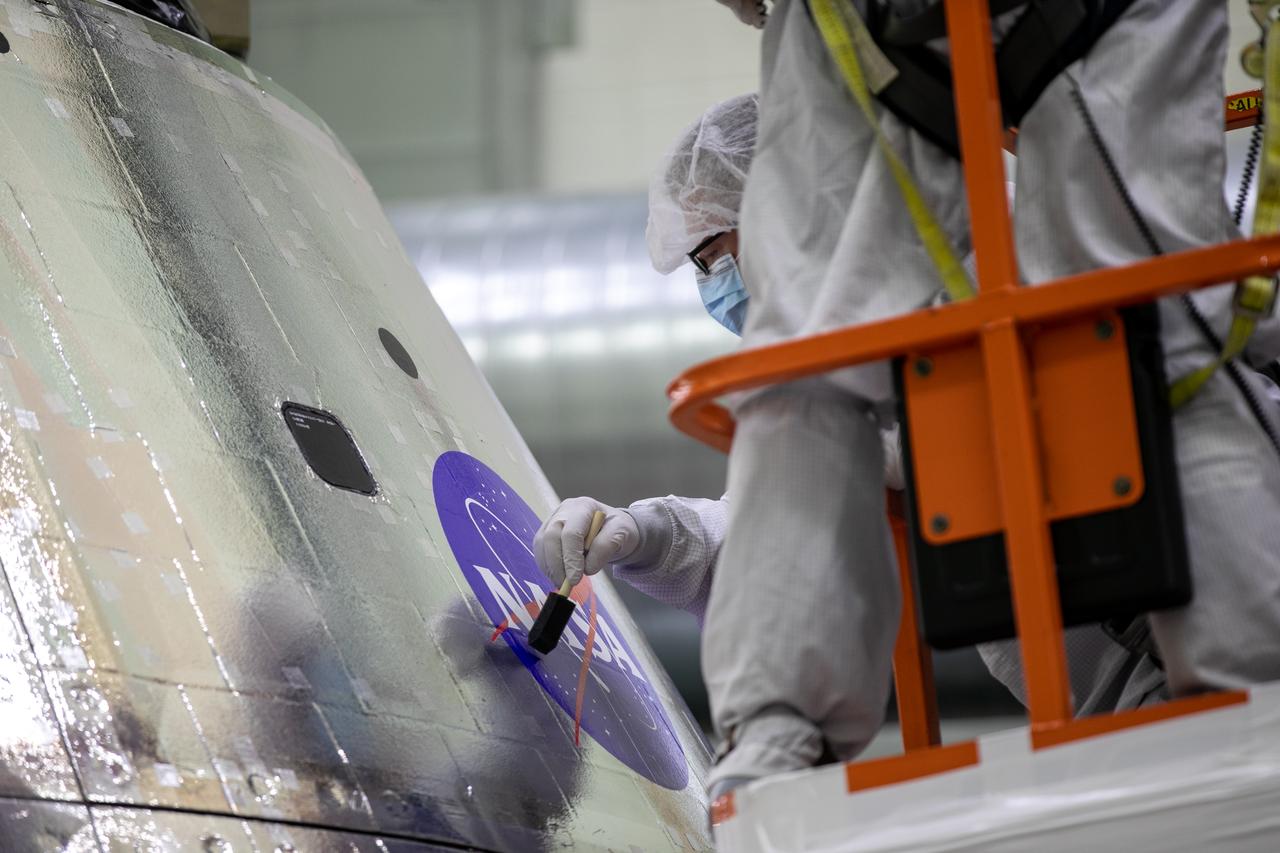

Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, paints a clear adhesive over the NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” on the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The American Flag also has been added. Attached below Orion (not in view) are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
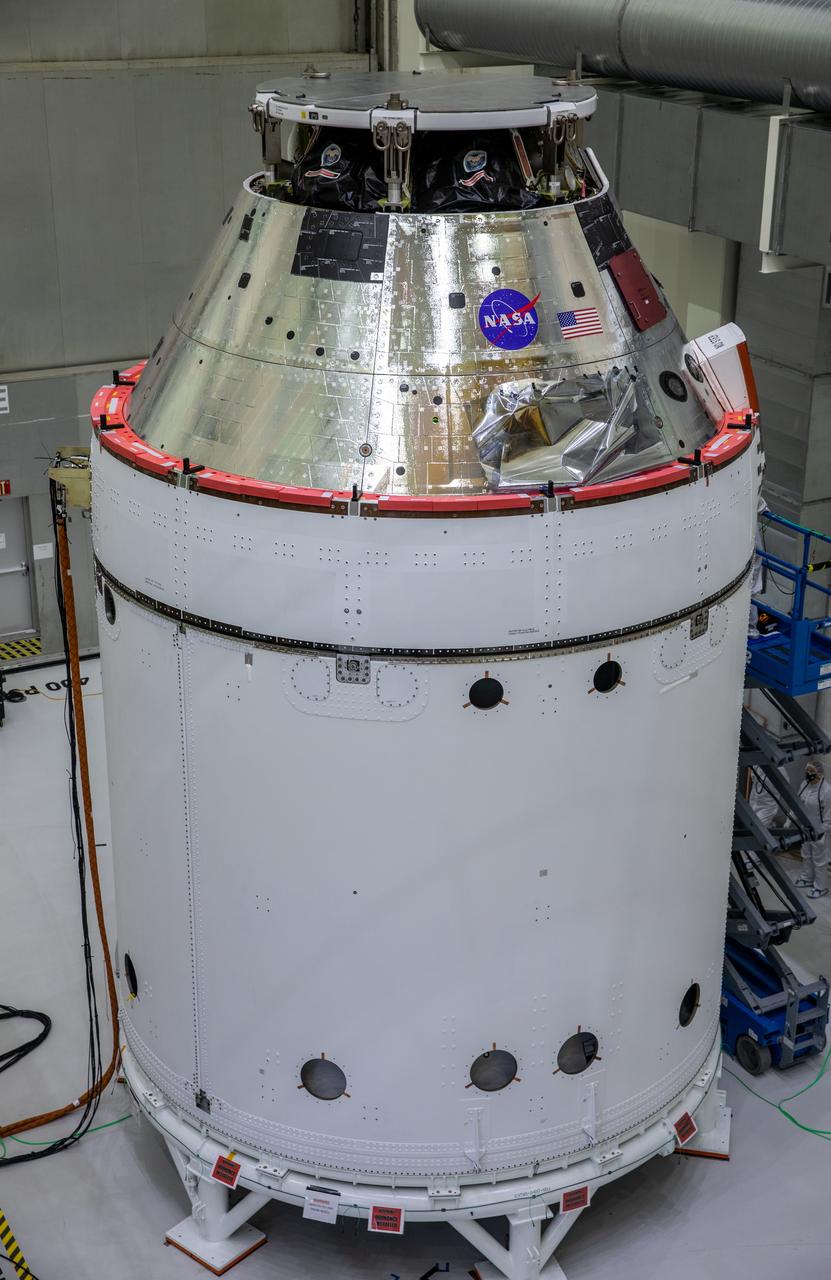

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
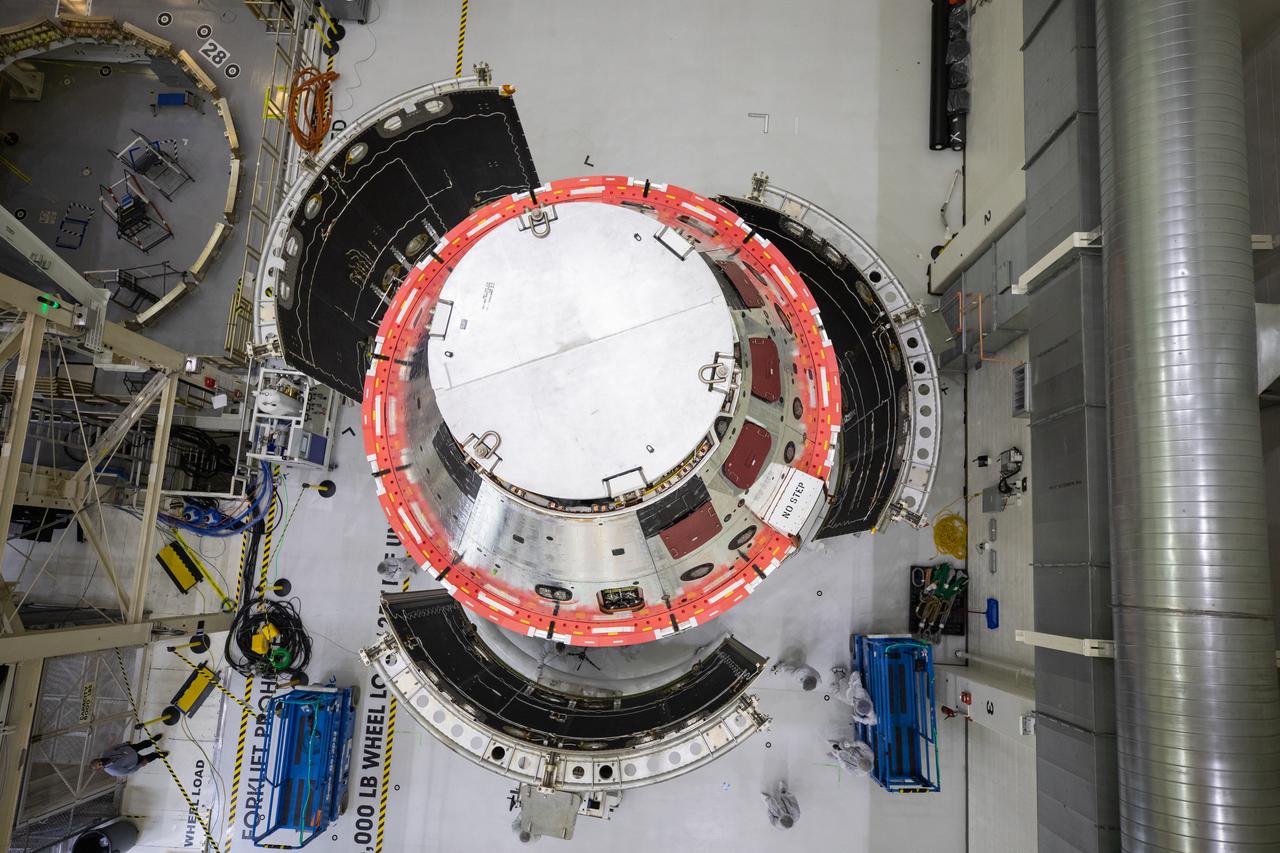
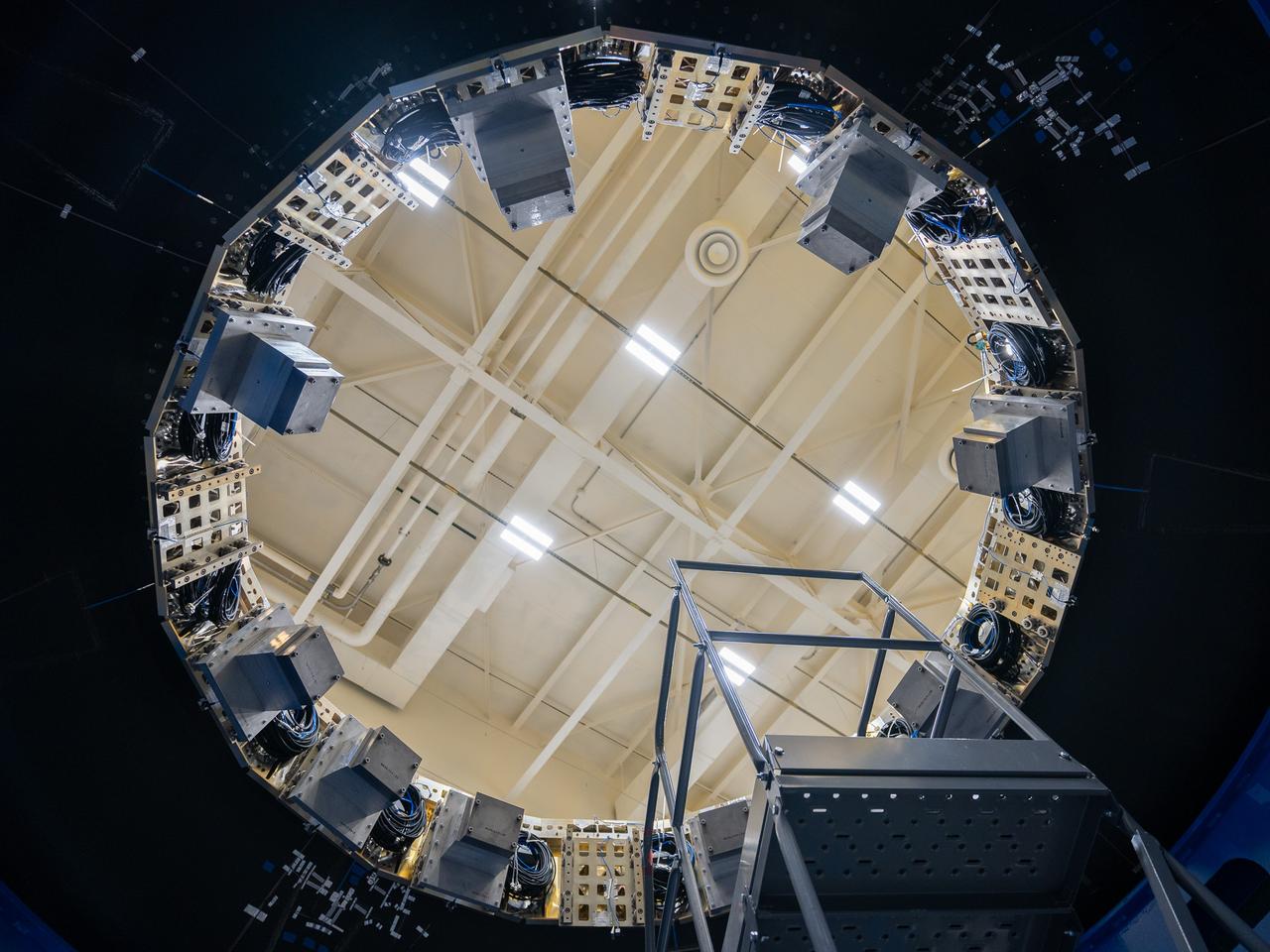
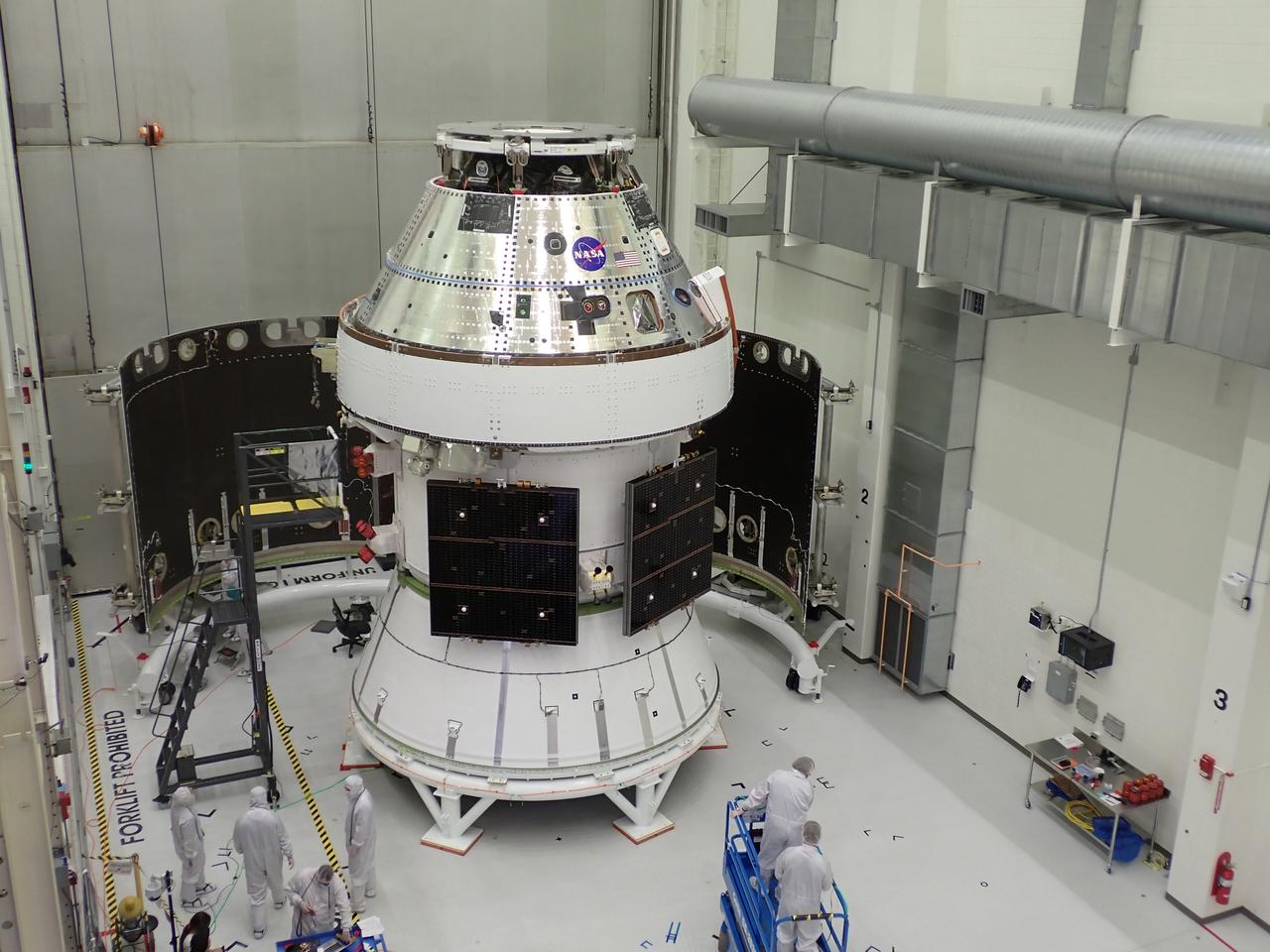
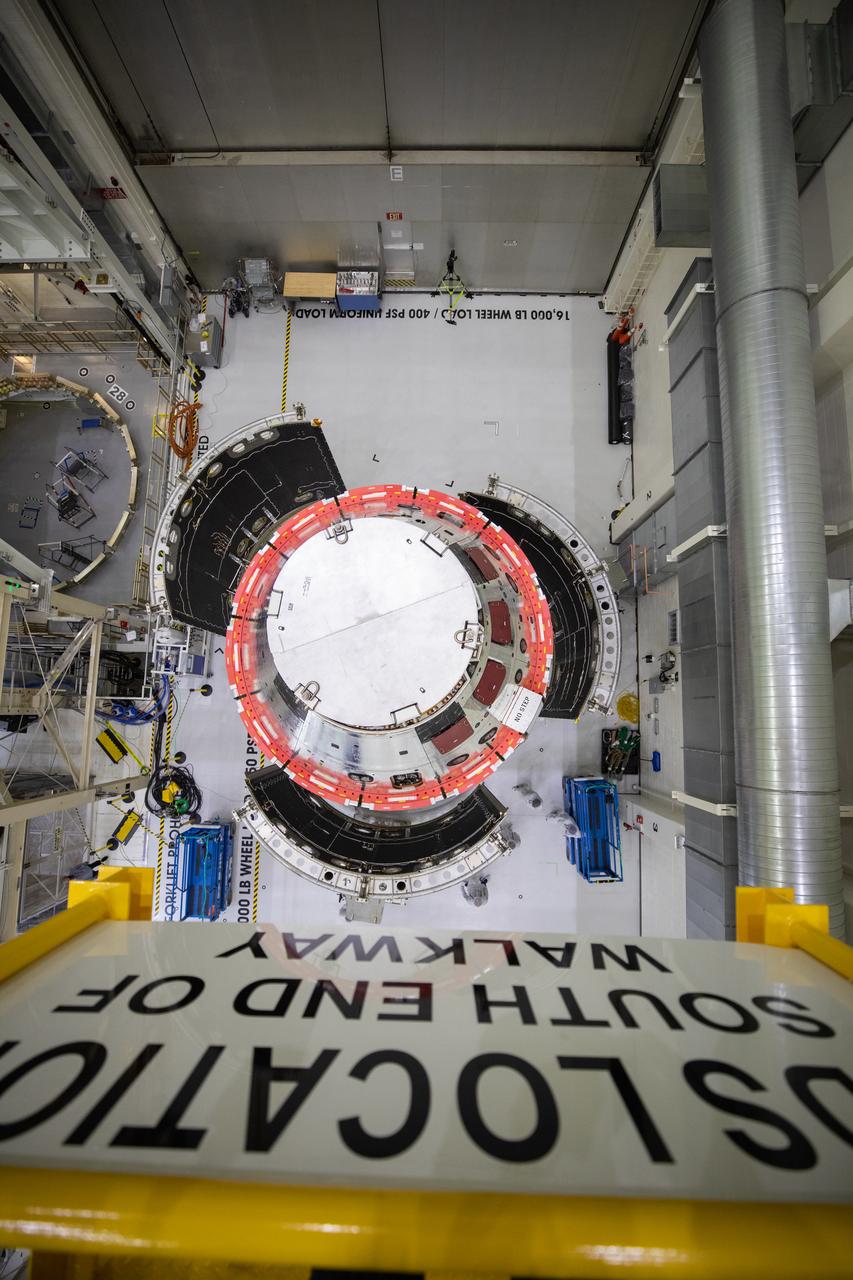
Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
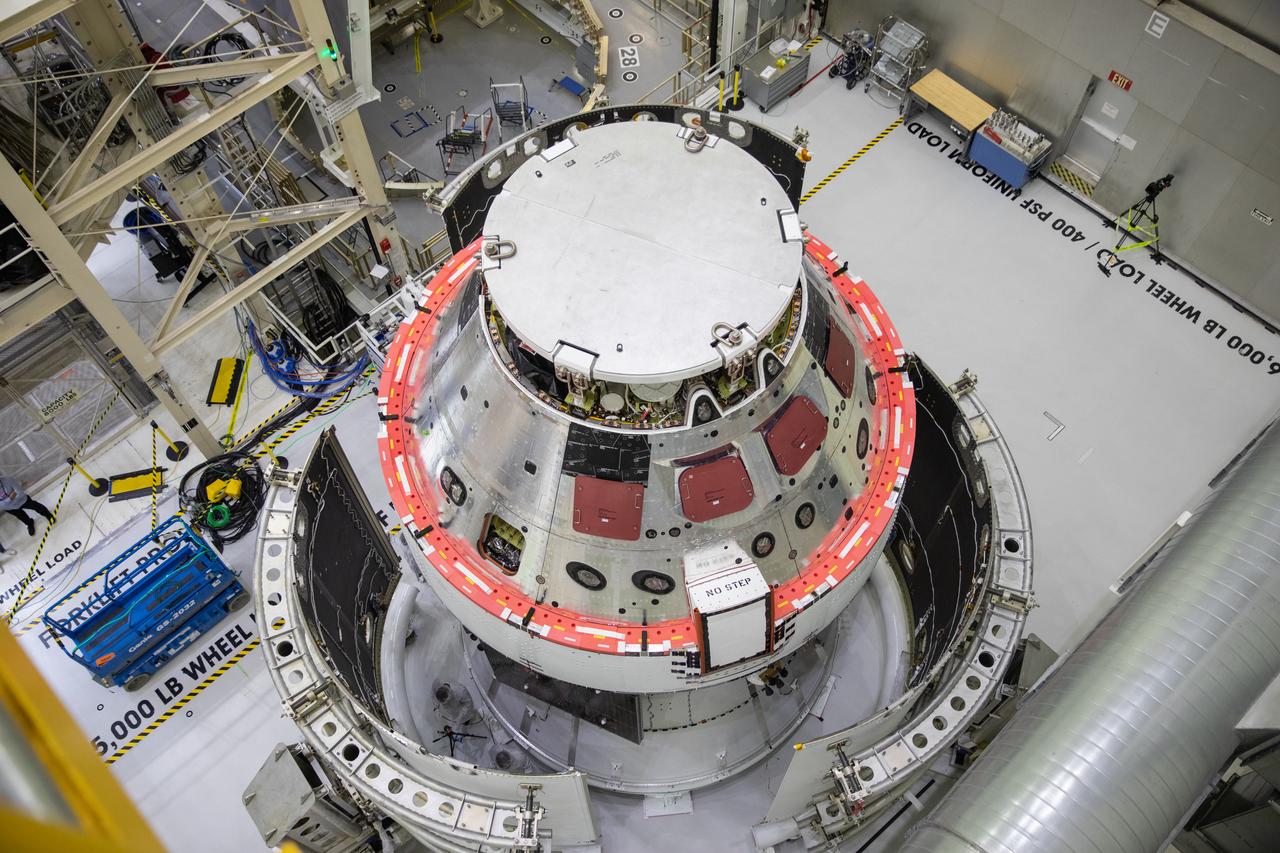
Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
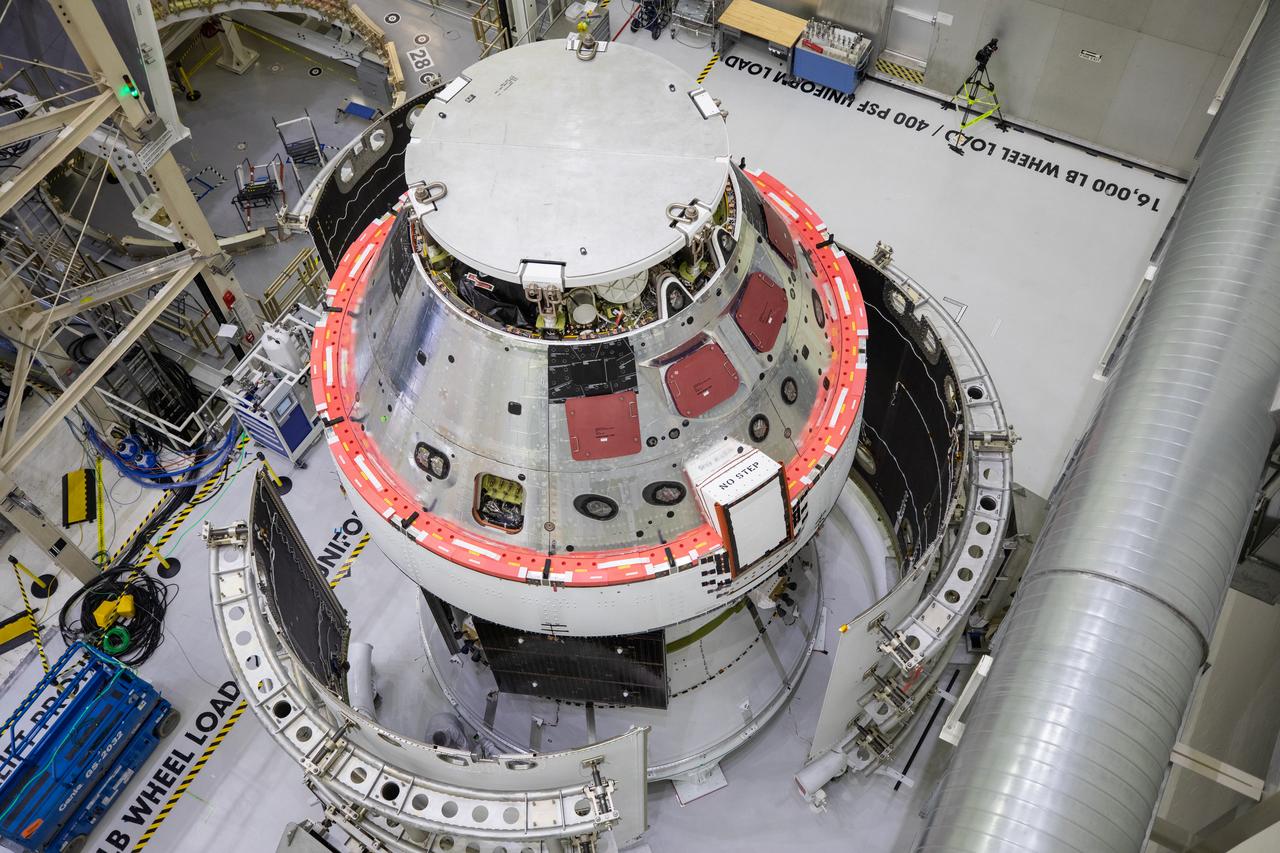
Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
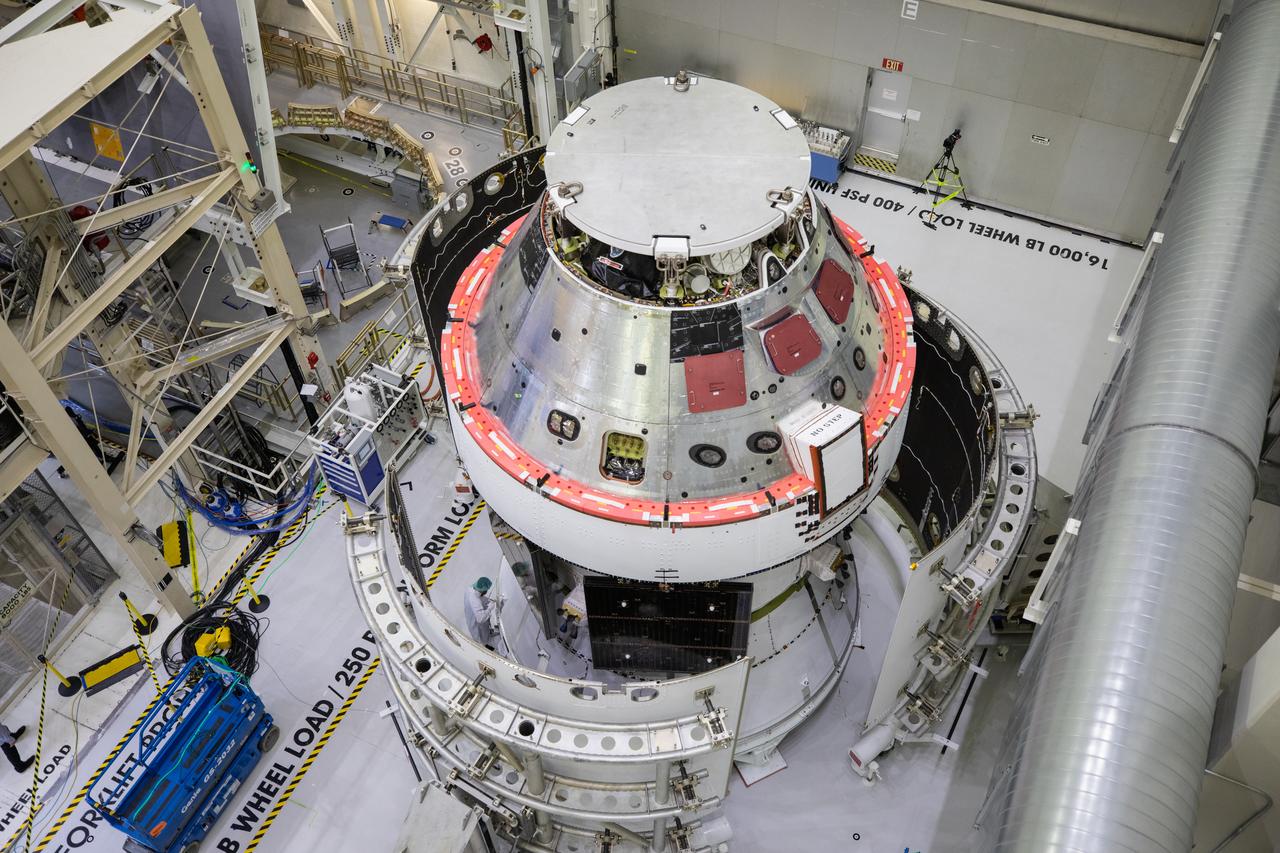
Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
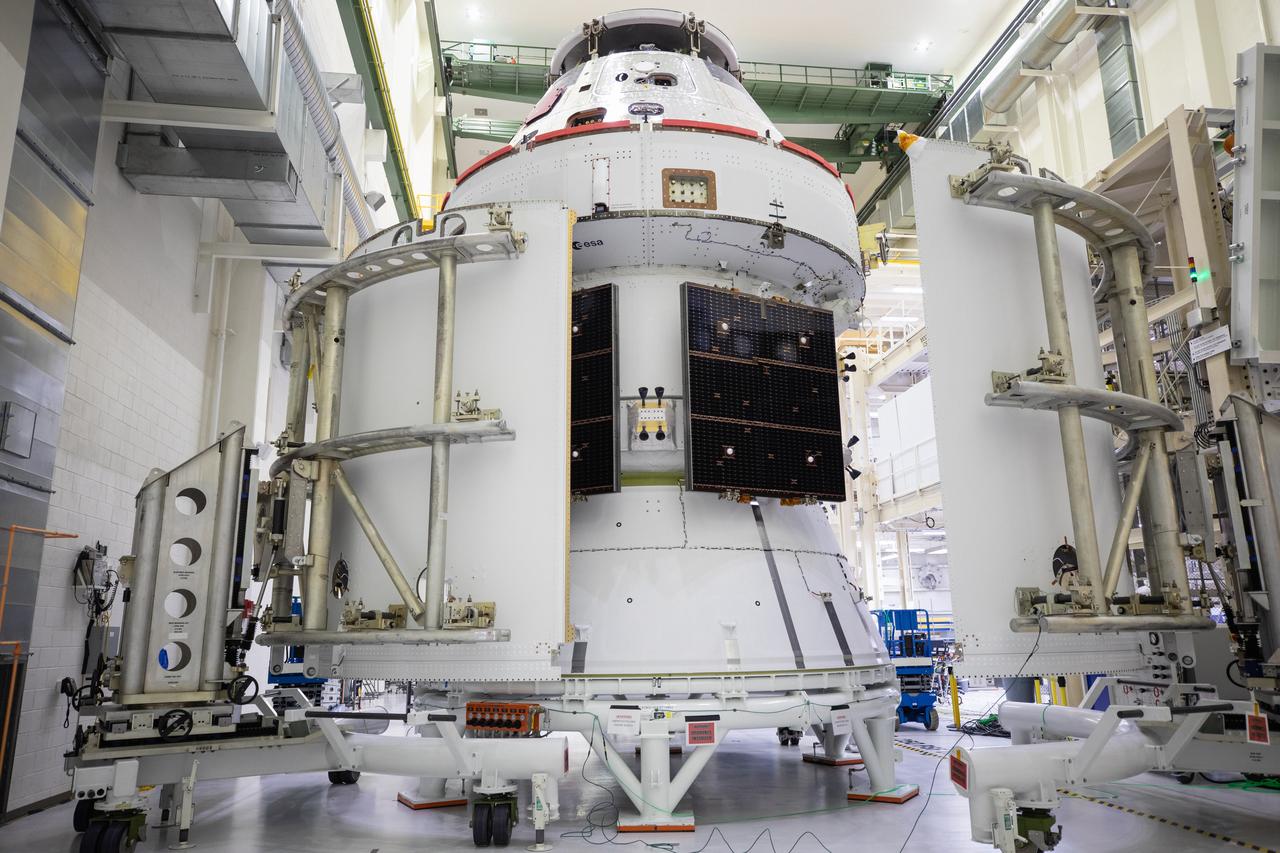

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
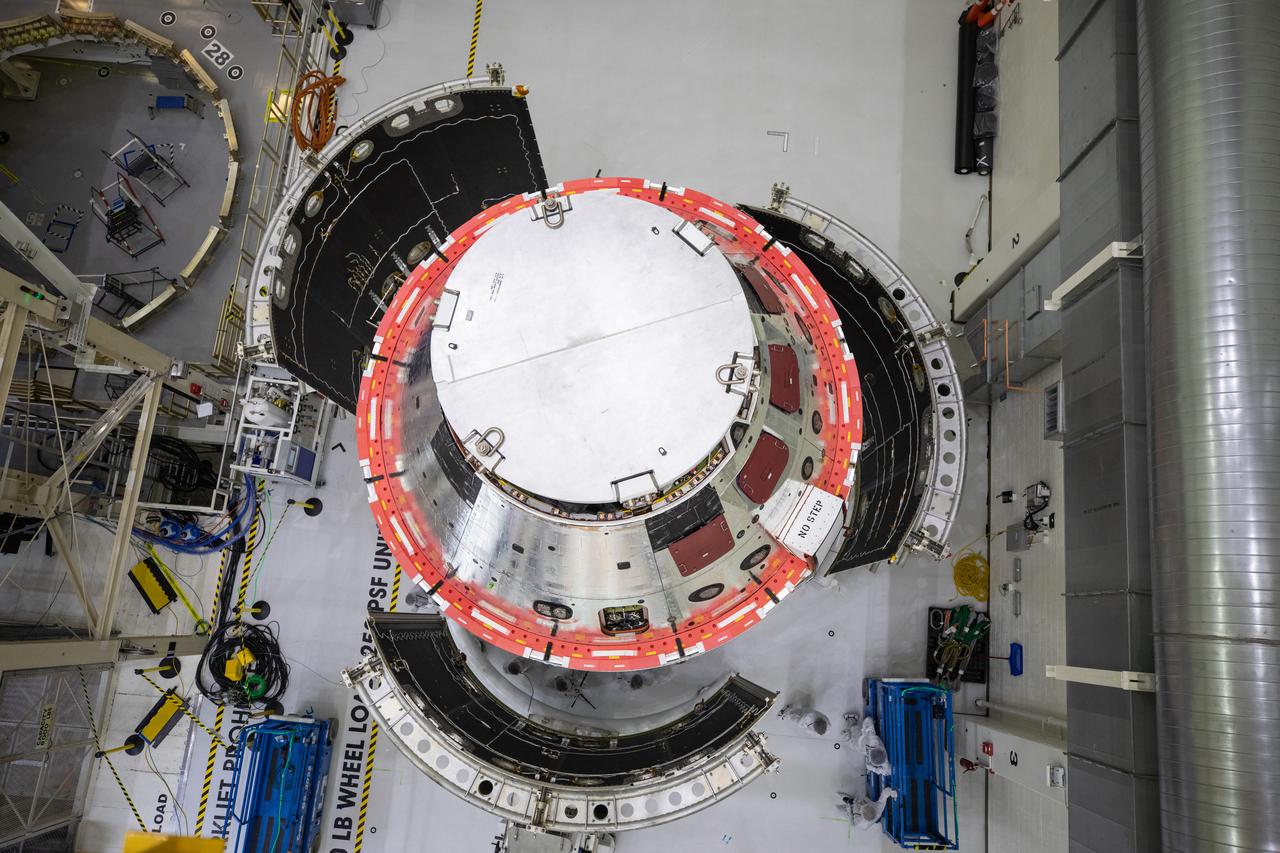
Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shown is an overhead view of three spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels fitted onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 13, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. Once secured, they will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
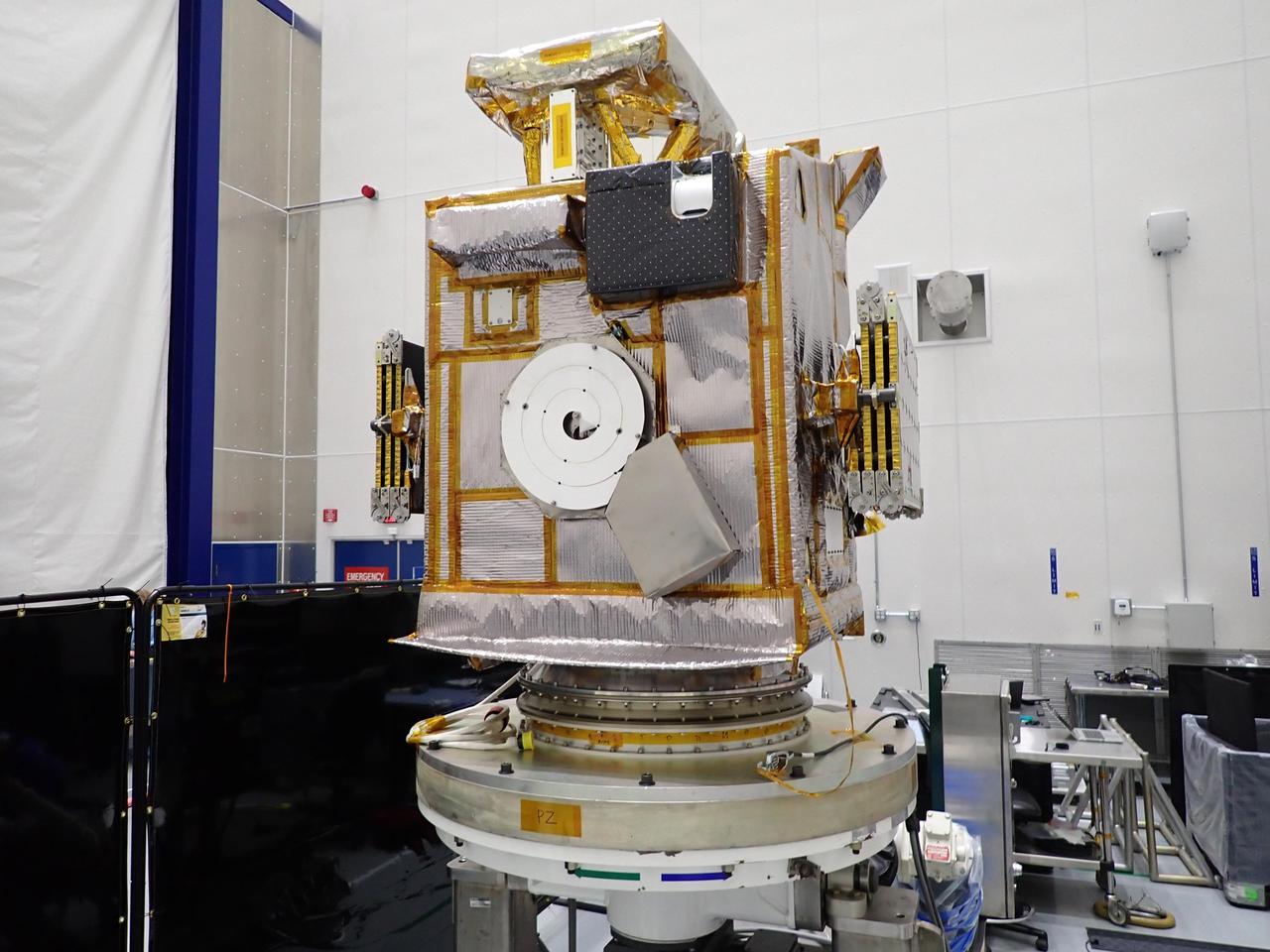

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer sits on its rotation fixture after being fueled and prior to being installed to the EELV Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) ring at SpaceX's payload processing facility in NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in early February 2025. The ESPA ring is an adaptor used for launching secondary payloads on launch vehicles. Figure A shows the spacecraft mounted horizontally, in its launch configuration, to the ESPA ring. The mission's two science instruments are visible. The High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) is the angular structure atop the spacecraft; the Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM) is the black square on the upper right of the front facing panel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26460
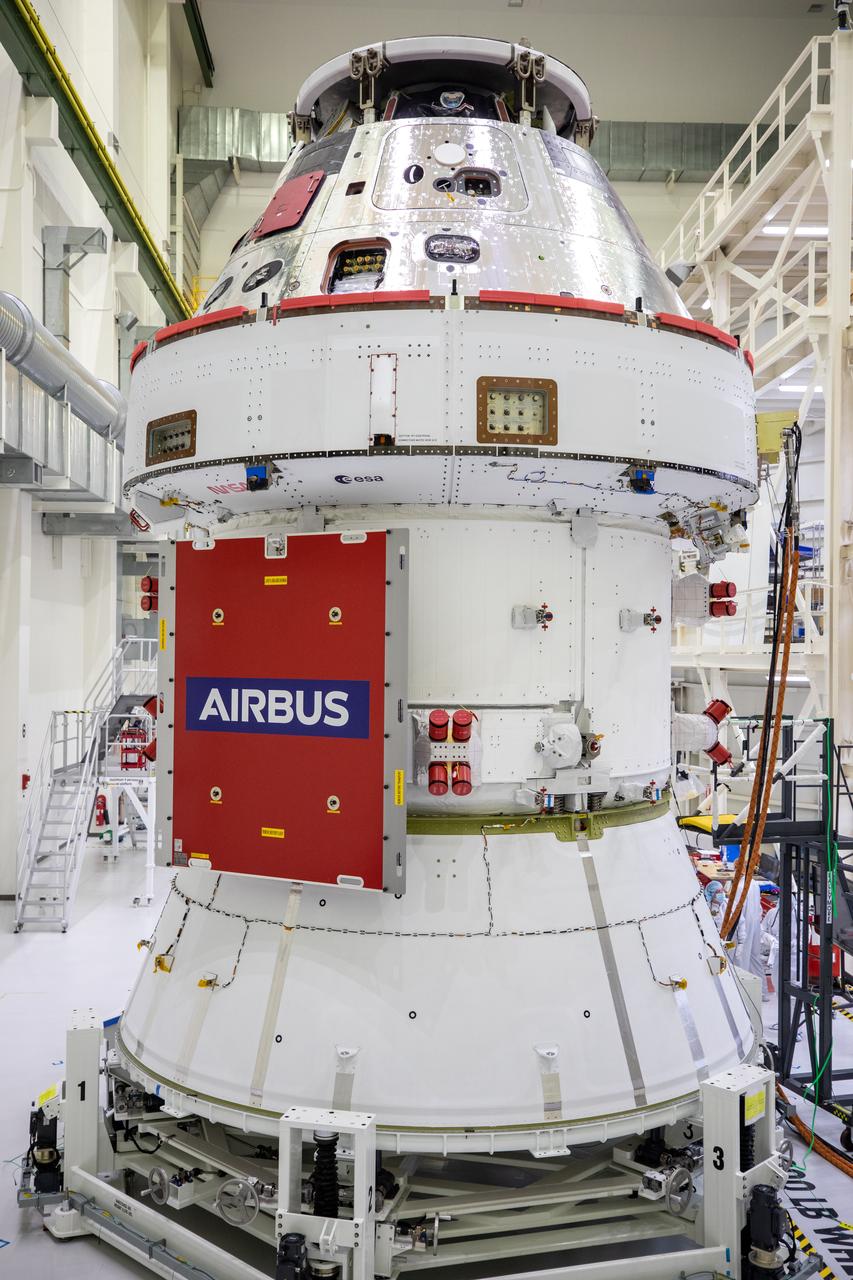

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays shown on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
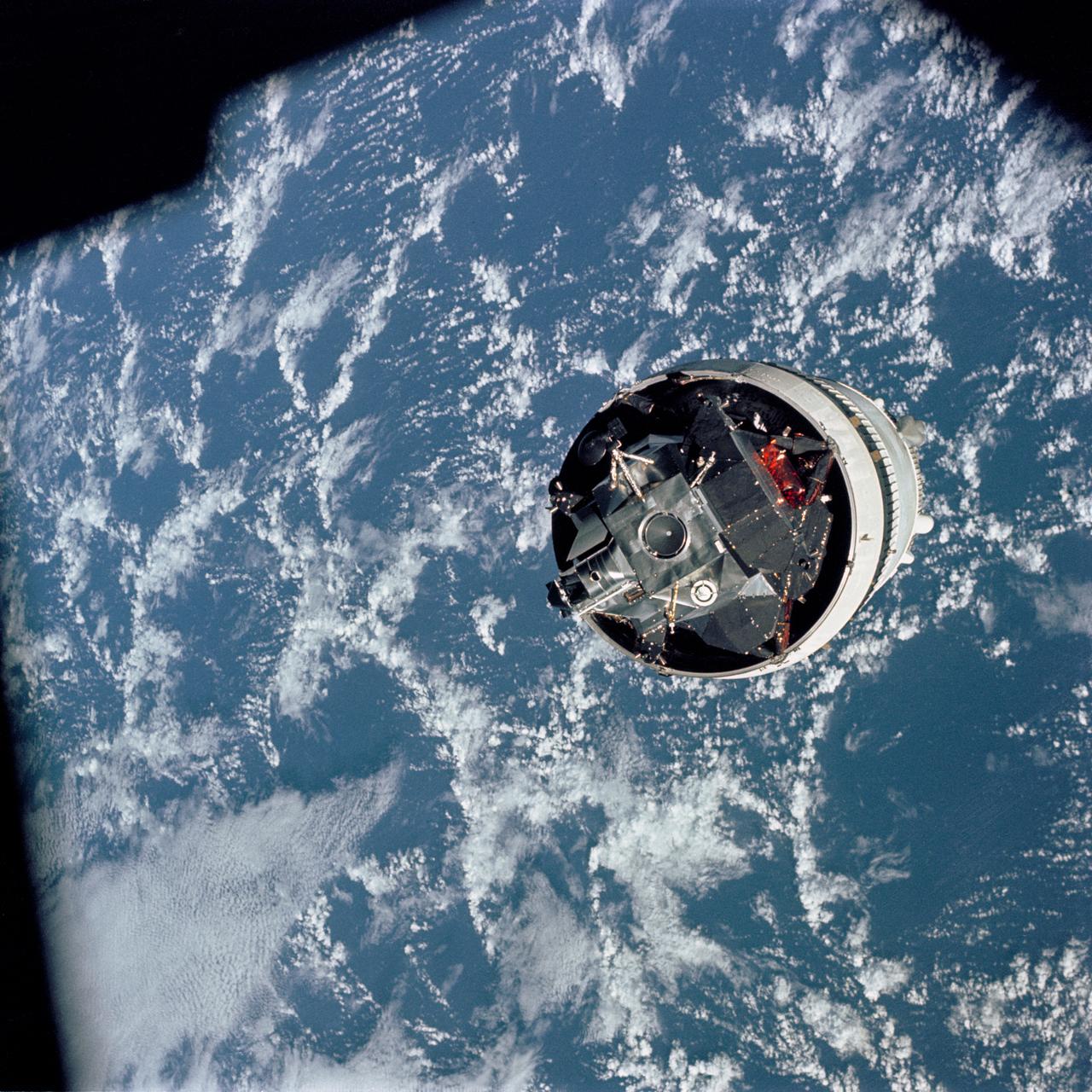
The Lunar Module (LM) 3 "Spider",still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage,is photographed from the Command/Service Module (CSM) "Gumdrop" on the first day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. This picture was taken following CSM/LM-S-IVB separation,and prior to LM extraction from the S-IVB. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned. Film magazine was A,film type was SO-368 Ektachrome with 0.460 - 0.710 micrometers film / filter transmittance response and haze filter, 80mm lens.

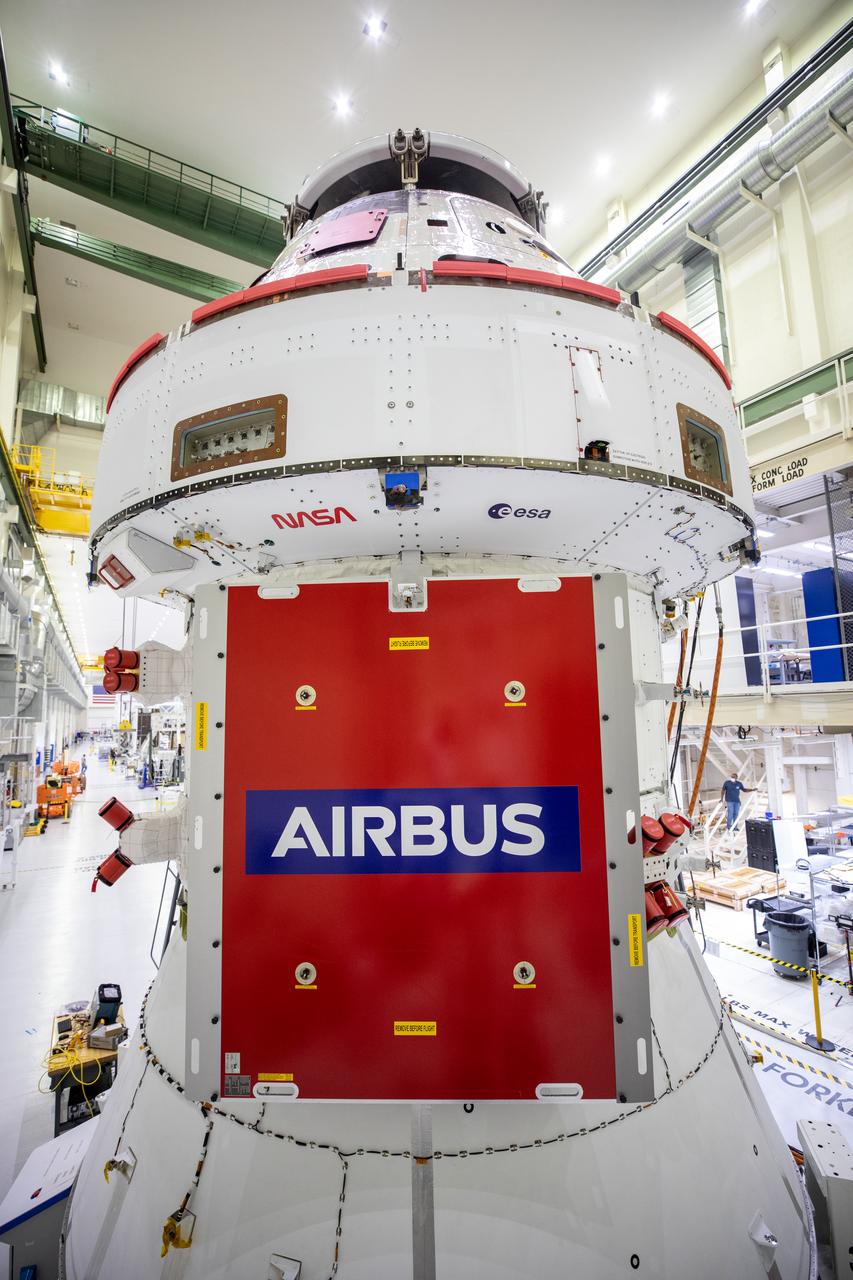
Artemis I extends NASA and ESA’s (European Space Agency) strong international partnership beyond low-Earth orbit to lunar exploration with Orion on Artemis missions, as the ESA logo joins the historic NASA “meatball” insignia on the Artemis I spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels that protect the service module during launch. Orion is currently stationed at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, where it will undergo fueling and servicing by NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs Technology teams in preparation for the upcoming flight test with the Space Launch System rocket under the agency’s Artemis program.
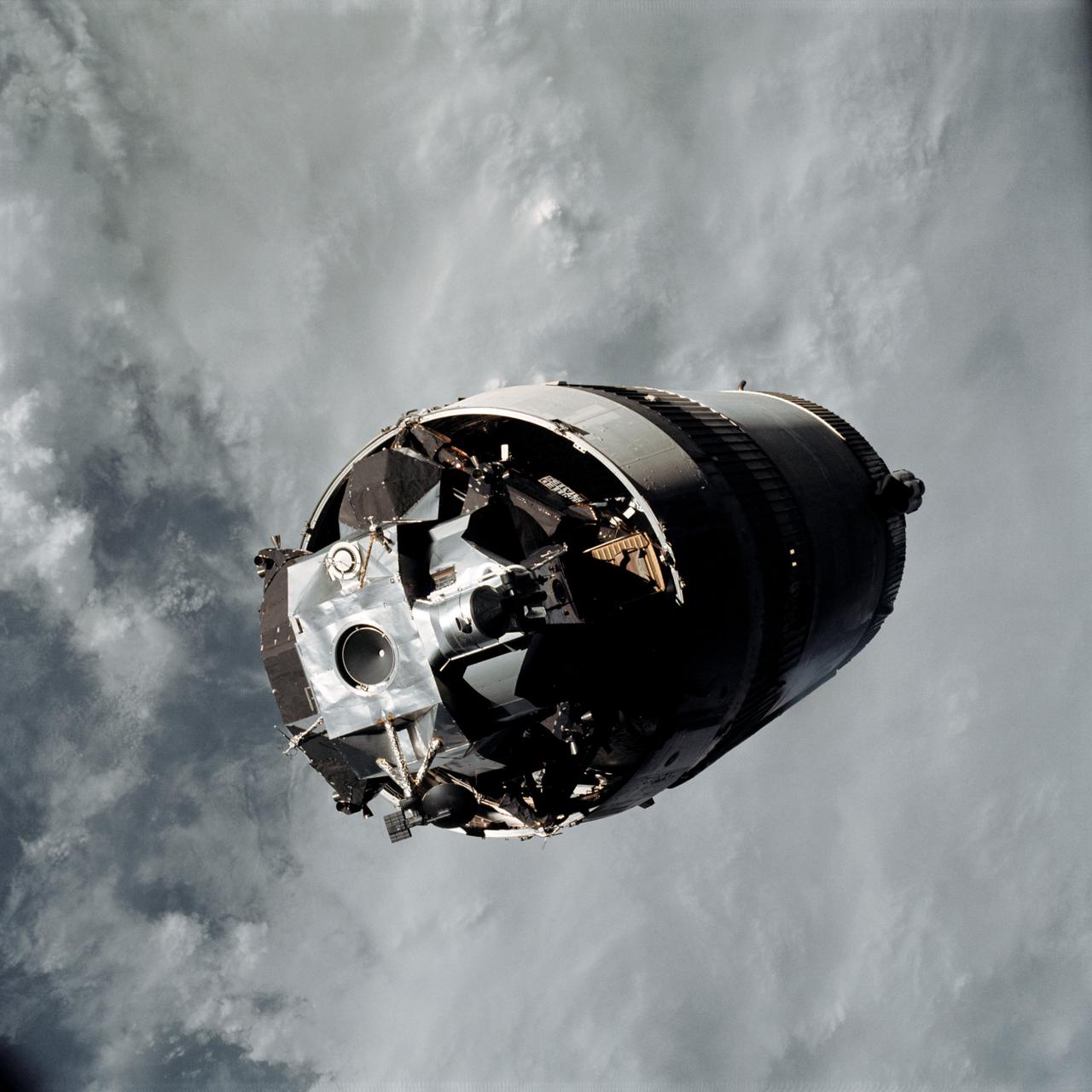

AS09-19-2919 (3 March 1969) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Spider", still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Gumdrop" on the first day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. This picture was taken following CSM/LM-S-IVB separation and prior to LM extraction from the S-IVB. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned. Inside the Command Module were astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.

Artemis I extends NASA and ESA’s (European Space Agency) strong international partnership beyond low-Earth orbit to lunar exploration with Orion on Artemis issions, as the the ESA logo joins the historic NASA “meatball” insignia on the Artemis I spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels that protect the service module during launch. Orion is currently stationed at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, where it will undergo fueling and servicing by NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs Technology teams in preparation for the upcoming flight test with the Space Launch System rocket under the agency’s Artemis program.

Two of the four solar array wings are shown from behind the spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels after being installed on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2020, work begins to install four solar array wings on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

AS08-16-2584 (21 Dec. 1968) --- This is a photograph taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking back at the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage from which the spacecraft had just separated following trans-lunar injection. Attached to the S-IVB is the Lunar Module Test Article (LTA) which simulated the mass of a Lunar Module (LM) on the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. The 29-feet panels of the Spacecraft LM Adapter which enclosed the LTA during launch have already been jettisoned and are out of view. Sunlight reflected from small particles shows the "firefly" phenomenon which was reported by astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. during the first Earth-orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) of the Mercury Program.
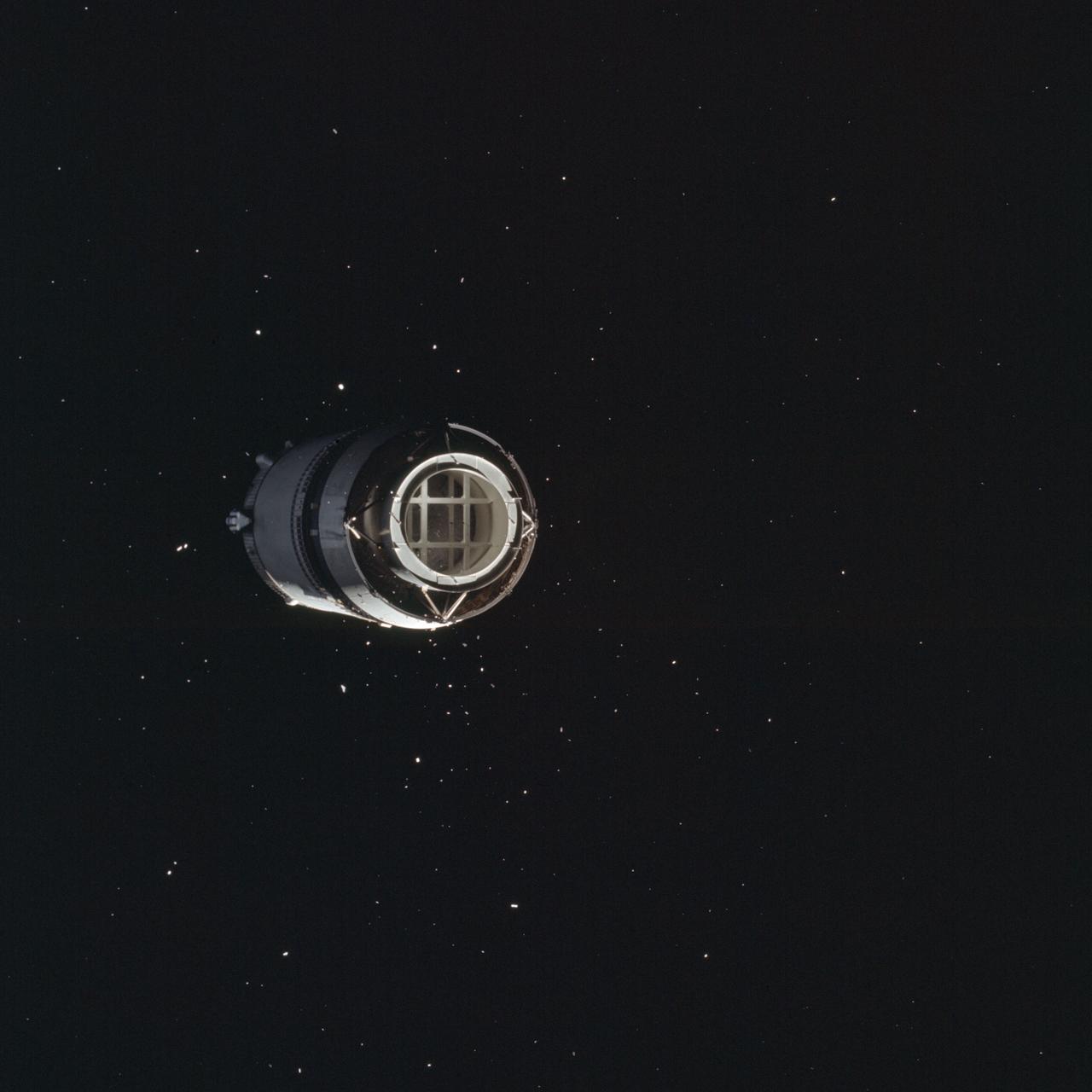

AS08-16-2583 (21 Dec. 1968) --- This is a photograph taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking back at the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage from which the spacecraft had just separated following trans-lunar injection. Attached to the S-IVB is the Lunar Module Test Article (LTA) which simulated the mass of a Lunar Module (LM) on the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. The 29-feet panels of the Spacecraft LM Adapter which enclosed the LTA during launch have already been jettisoned and are out of view. Sunlight reflected from small particles shows the "firefly" phenomenon which was reported by astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. during the first Earth-orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) of the Mercury Program.
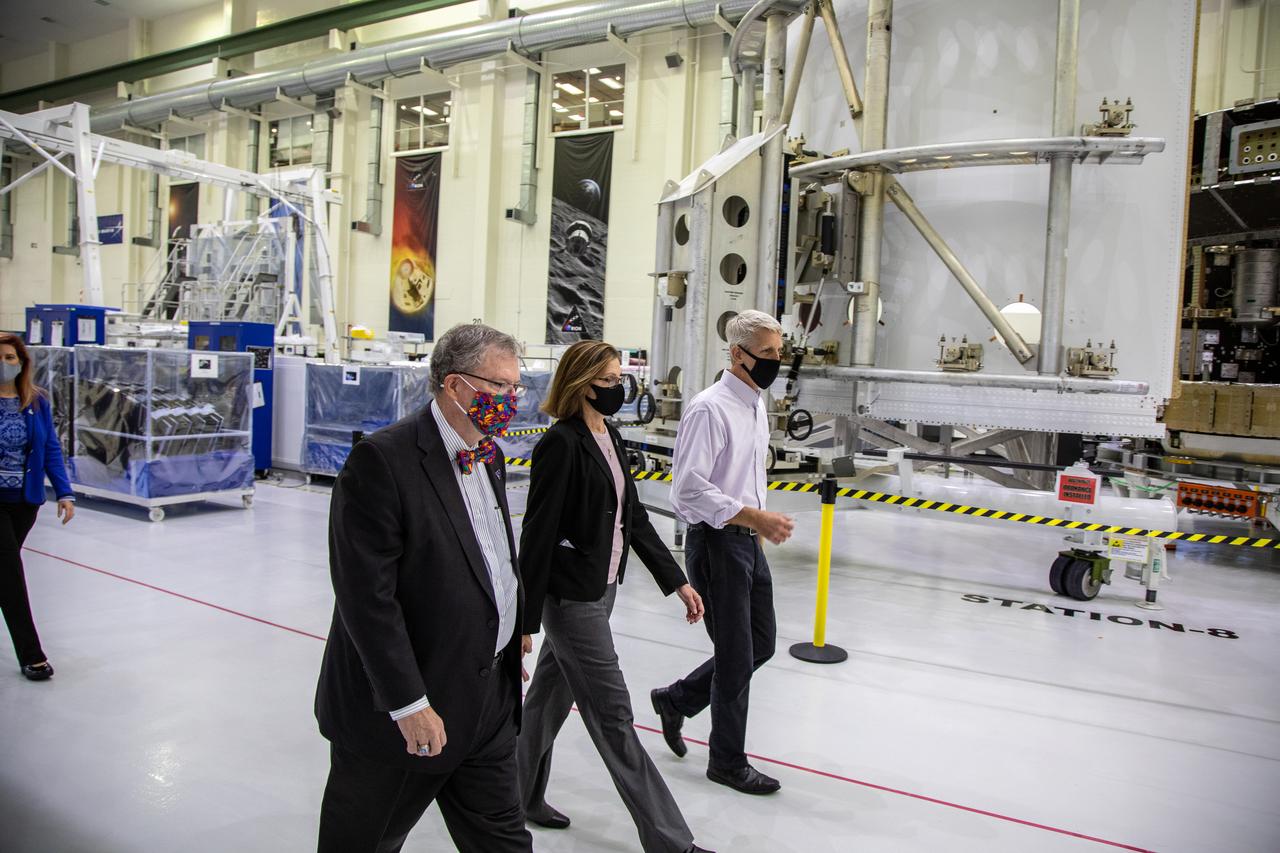
Catherine Koerner, in the center, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tours the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her, at left is Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager; and at right is Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager. Koerner viewed the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions. They are shown with one of the space adapter jettison fairing panels that will be installed on Orion for the Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
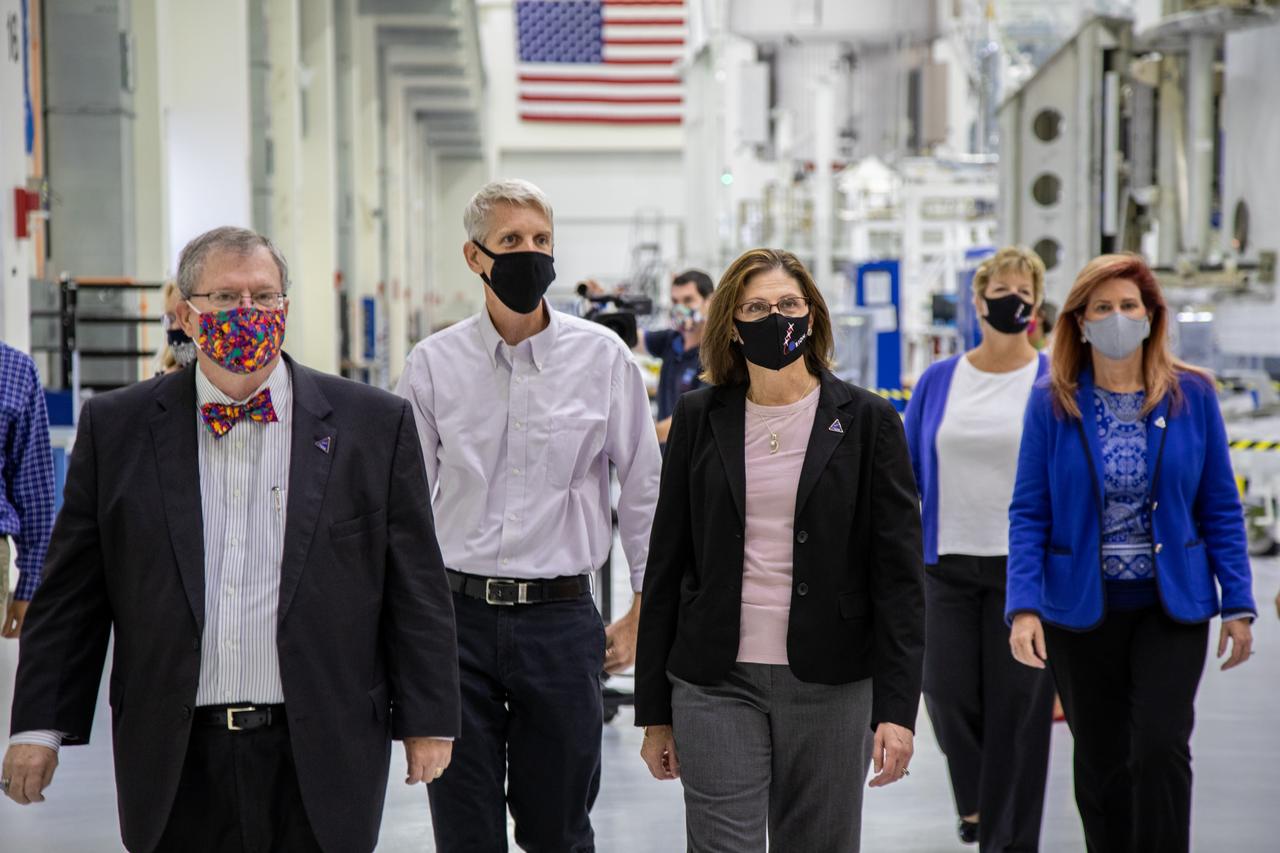

Catherine Koerner, in the center, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tour the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager; Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; and Kelly DeFazio, Lockheed Martin vehicle production director on the Orion Production Operations Contract. Koerner viewed Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions. In view in the background, at right, is one of three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels to be installed on the spacecraft. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.