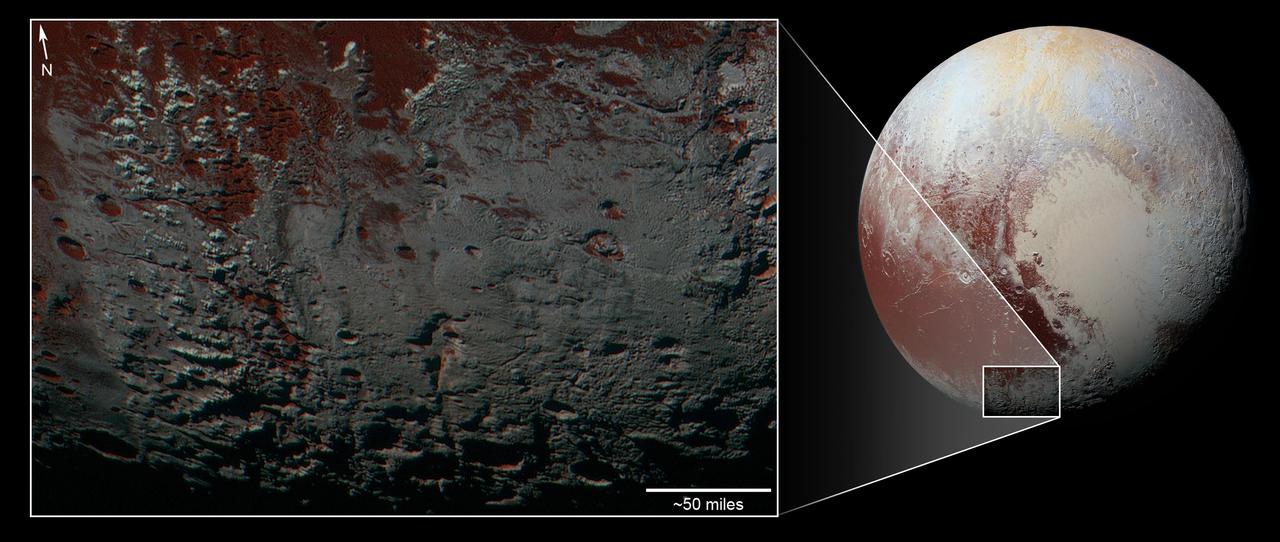

This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleys -- indicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21025
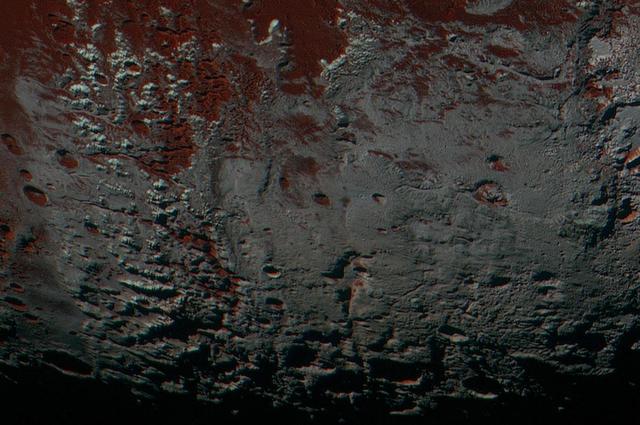
This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleysindicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21026
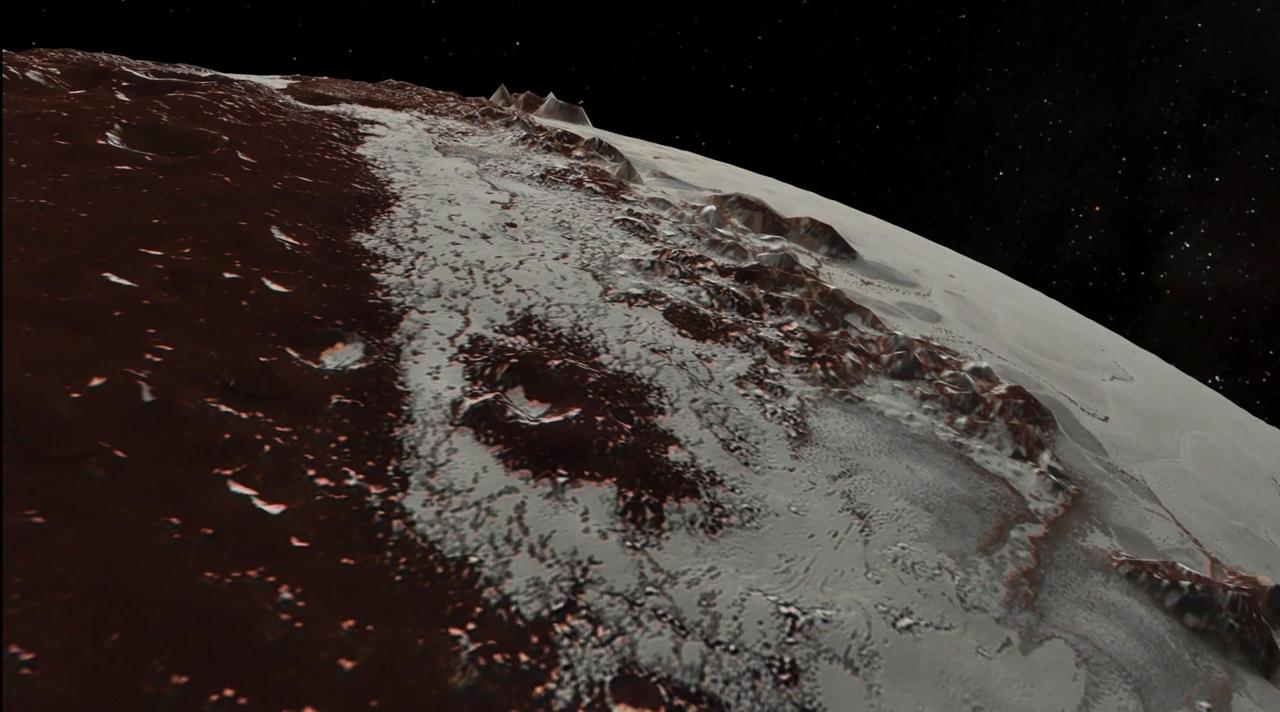

In July 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft sent home the first close-up pictures of Pluto and its moons. Using actual New Horizons data and digital elevation models of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, mission scientists created flyover movies that offer spectacular new perspectives of the many unusual features that were discovered and which have reshaped our views of the Pluto system -- from a vantage point even closer than a ride on New Horizons itself. The dramatic Pluto flyover begins over the highlands to the southwest of the great expanse of nitrogen ice plain informally named Sputnik Planitia. (Note that all feature names in the Pluto system are informal.) The viewer first passes over the western margin of Sputnik, where it borders the dark, cratered terrain of Cthulhu Macula, with the blocky mountain ranges located within the planitia seen on the right. The tour moves north past the rugged and fractured highlands of Voyager Terra and then turns southward over Pioneer Terra, which exhibits deep and wide pits, before concluding over the bladed terrain of Tartarus Dorsa in the far east of the encounter hemisphere. The topographic relief is exaggerated by a factor of 2 to 3 in these movies to emphasize topography; the surface colors have also been enhanced to bring out detail. Digital mapping and rendering were performed by Paul Schenk and John Blackwell of the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston. A video can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21863
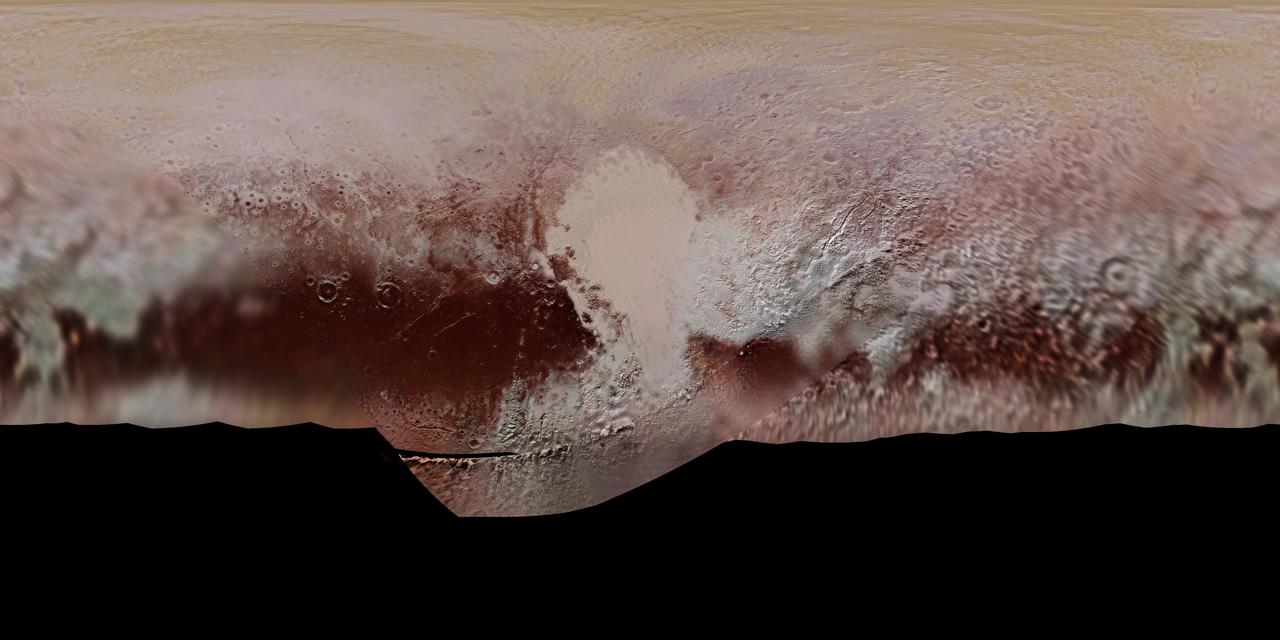
This new, detailed global mosaic color map of Pluto is based on a series of three color filter images obtained by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera aboard New Horizons during the NASA spacecraft's close flyby of Pluto in July 2015. The mosaic shows how Pluto's large-scale color patterns extend beyond the hemisphere facing New Horizons at closest approach- which were imaged at the highest resolution. North is up; Pluto's equator roughly bisects the band of dark red terrains running across the lower third of the map. Pluto's giant, informally named Sputnik Planitia glacier - the left half of Pluto's signature "heart" feature -- is at the center of this map. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11707

What would it be like to actually land on Pluto? This image is one of more than 100 images taken by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft over six weeks of approach and close flyby in the summer of 2015. A video offers a trip down onto the surface of Pluto -- starting with a distant view of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon -- and leading up to an eventual ride in for a "landing" on the shoreline of Pluto's informally named Sputnik Planitia. After a 9.5-year voyage covering more than three billion miles, New Horizons flew through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, coming within 7,800 miles (12,500 kilometers) of Pluto. Carrying powerful telescopic cameras that could spot features smaller than a football field, New Horizons sent back hundreds of images of Pluto and its moons that show how dynamic and fascinating their surfaces are. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11709
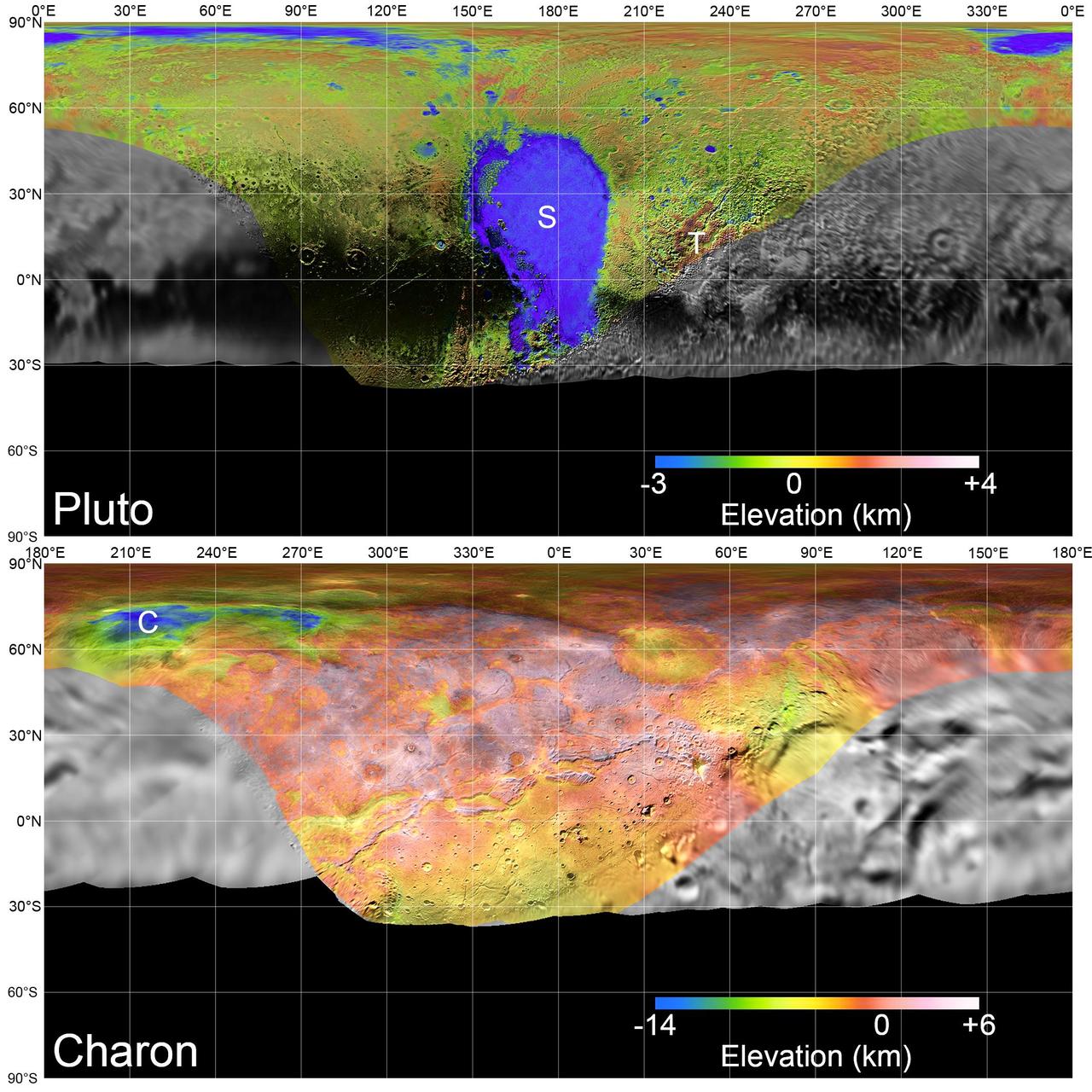
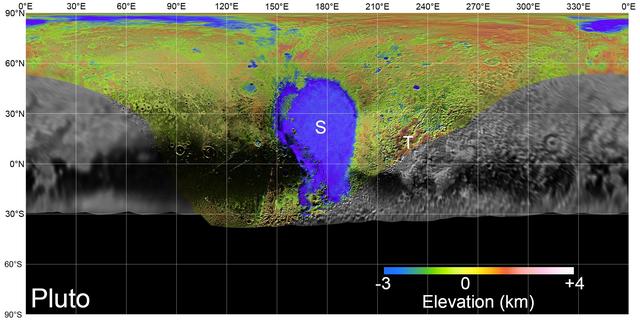
Global mosaics of Pluto and Charon projected at 300 meters (985 feet) per pixel that have been assembled from most of the highest resolution images obtained by the Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) onboard New Horizons. Transparent, colorized stereo topography data generated for the encounter hemispheres of Pluto and Charon have been overlain on the mosaics. Terrain south of about 30°S on Pluto and Charon was in darkness leading up to and during the flyby, so is shown in black. "S" and "T" respectively indicate Sputnik Planitia and Tartarus Dorsa on Pluto, and "C" indicates Caleuche Chasma on Charon. All feature names on Pluto and Charon are informal. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21862

Scientists on NASA's New Horizons mission have discovered what looks like a giant bite-mark on the planet's surface. In this image, north is up. The southern portion of the left inset above shows the cratered plateau uplands informally named Vega Terra (note that all feature names are informal). This terrain is separated from the young, nearly uncratered, mottled plains of Piri Planitia in the center of the image by a generally north-facing jagged scarp called Piri Rupes. The scarp breaks up into isolated mesas in several places. Cutting diagonally across Piri Planitia is the long extensional fault of Inanna Fossa, which stretches eastward 370 miles (600 kilometers) from here to the western edge of the great nitrogen ice plains of Sputnik Planum. Compositional data from the New Horizons spacecraft's Ralph/Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA) instrument, shown in the right inset, indicate that the plateau uplands south of Piri Rupes are rich in methane ice (shown in false color as purple). Scientists speculate that sublimation of methane may be causing the plateau material to erode along the face of the scarp cliffs, causing them to retreat south and leave the plains of Piri Planitia in their wake. Compositional data also show that the surface of Piri Planitia is more enriched in water ice (shown in false color as blue) than the plateau uplands, which may indicate that Piri Planitia's surface is made of water ice bedrock, on top of which the layer of retreating methane ice had been sitting. Because the surface of Pluto is so cold, the water ice behaves like rock and is immobile. The light/dark mottled pattern of Piri Planitia in the left inset is reflected in the composition map, with the lighter areas corresponding to areas richer in methane – these may be remnants of methane that have not yet sublimated away entirely. The inset at left shows about 650 feet (200 meters) per pixel; the image measures approximately 280 miles (450 kilometers) long by 255 miles (410 kilometers) wide. It was obtained by New Horizons at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before the spacecraft's closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015.The LEISA data at right was gathered when the spacecraft was about 29,000 miles (47,000 kilometers) from Pluto; best resolution is 1.7 miles (2.7 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20531
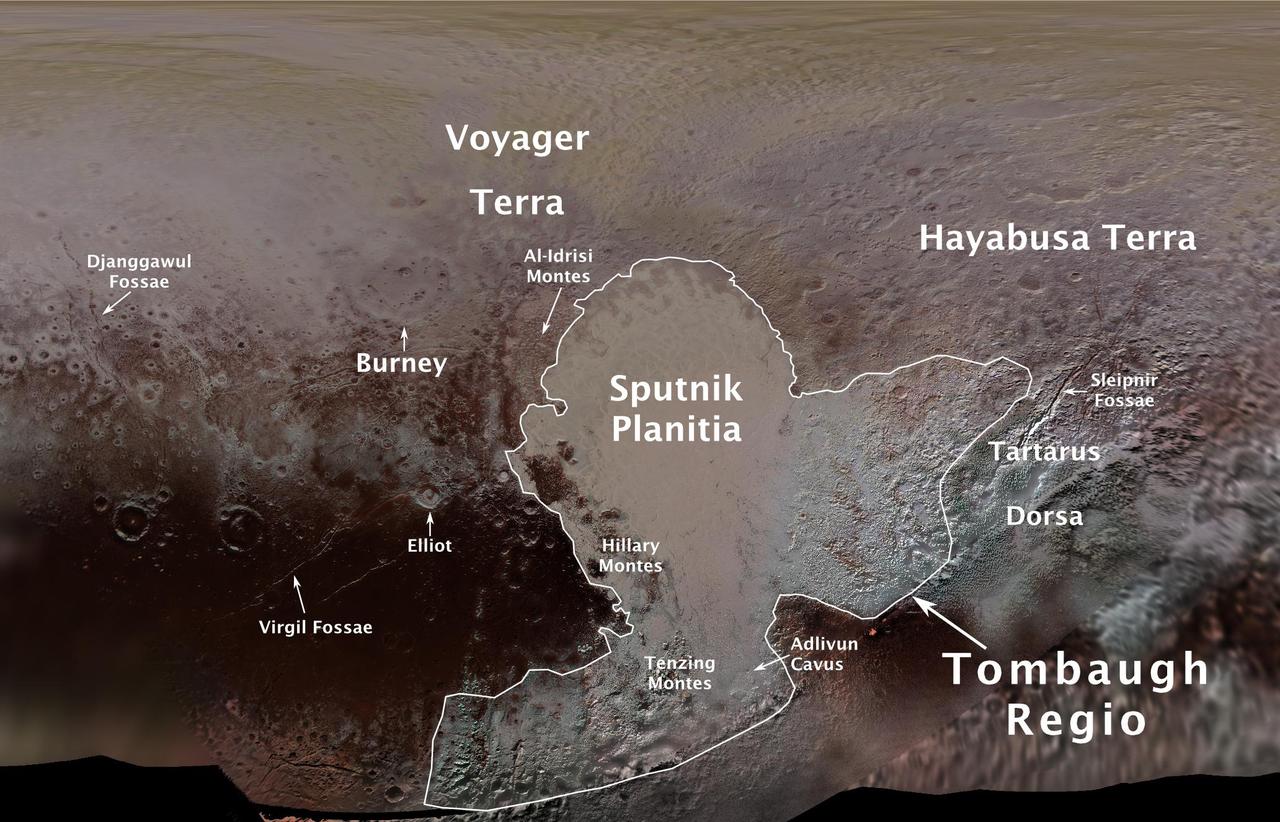
The International Astronomical Union (IAU), the internationally recognized authority for naming celestial bodies and their surface features, approved names of 14 surface features on Pluto in August 2017. The names were proposed by NASA's New Horizons team following the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moons by the New Horizons spacecraft in 2015. The names, listed below, pay homage to the underworld mythology, pioneering space missions, historic pioneers who crossed new horizons in exploration, and scientists and engineers associated with Pluto and the Kuiper Belt. Tombaugh Regio honors Clyde Tombaugh (1906-1997), the U.S. astronomer who discovered Pluto in 1930 from Lowell Observatory in Arizona. Burney crater honors Venetia Burney (1918-2009), who as an 11-year-old schoolgirl suggested the name "Pluto" for Clyde Tombaugh's newly discovered planet. Later in life she taught mathematics and economics. Sputnik Planitia is a large plain named for Sputnik 1, the first space satellite, launched by the Soviet Union in 1957. Tenzing Montes and Hillary Montes are mountain ranges honoring Tenzing Norgay (1914-1986) and Sir Edmund Hillary (1919-2008), the Indian/Nepali Sherpa and New Zealand mountaineer were the first to reach the summit of Mount Everest and return safely. Al-Idrisi Montes honors Ash-Sharif al-Idrisi (1100-1165/66), a noted Arab mapmaker and geographer whose landmark work of medieval geography is sometimes translated as "The Pleasure of Him Who Longs to Cross the Horizons.†Djanggawul Fossae defines a network of long, narrow depressions named for the Djanggawuls, three ancestral beings in indigenous Australian mythology who traveled between the island of the dead and Australia, creating the landscape and filling it with vegetation. Sleipnir Fossa is named for the powerful, eight-legged horse of Norse mythology that carried the god Odin into the underworld. Virgil Fossae honors Virgil, one of the greatest Roman poets and Dante's fictional guide through hell and purgatory in the Divine Comedy. Adlivun Cavus is a deep depression named for Adlivun, the underworld in Inuit mythology. Hayabusa Terra is a large land mass saluting the Japanese spacecraft and mission (2003-2010) that performed the first asteroid sample return. Voyager Terra honors the pair of NASA spacecraft, launched in 1977, that performed the first "grand tour" of all four giant planets. The Voyager spacecraft are now probing the boundary between the Sun and interstellar space. Tartarus Dorsa is a ridge named for Tartarus, the deepest, darkest pit of the underworld in Greek mythology. Elliot crater recognizes James Elliot (1943-2011), an MIT researcher who pioneered the use of stellar occultations to study the solar system -- leading to discoveries such as the rings of Uranus and the first detection of Pluto's thin atmosphere. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21944
On July 14, 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft made its historic flight through the Pluto system. This detailed, high-quality global mosaic of Pluto was assembled from nearly all of the highest-resolution images obtained by the Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) on New Horizons. The mosaic is the most detailed and comprehensive global view yet of Pluto's surface using New Horizons data. It includes topography data of the hemisphere visible to New Horizons during the spacecraft's closest approach. The topography is derived from digital stereo-image mapping tools that measure the parallax -- or the difference in the apparent relative positions -- of features on the surface obtained at different viewing angles during the encounter. Scientists use these parallax displacements of high and low terrain to estimate landform heights. The global mosaic has been overlain with transparent, colorized topography data wherever on the surface stereo data is available. Terrain south of about 30°S was in darkness leading up to and during the flyby, so is shown in black. Examples of large-scale topographic features on Pluto include the vast expanse of very flat, low-elevation nitrogen ice plains of Sputnik Planitia ("P") -- note that all feature names in the Pluto system are informal -- and, on the eastern edge of the encounter hemisphere, the aligned, high-elevation ridges of Tartarus Dorsa ("T") that host the enigmatic bladed terrain, mountains, possible cryovolcanos, canyons, craters and more. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21861