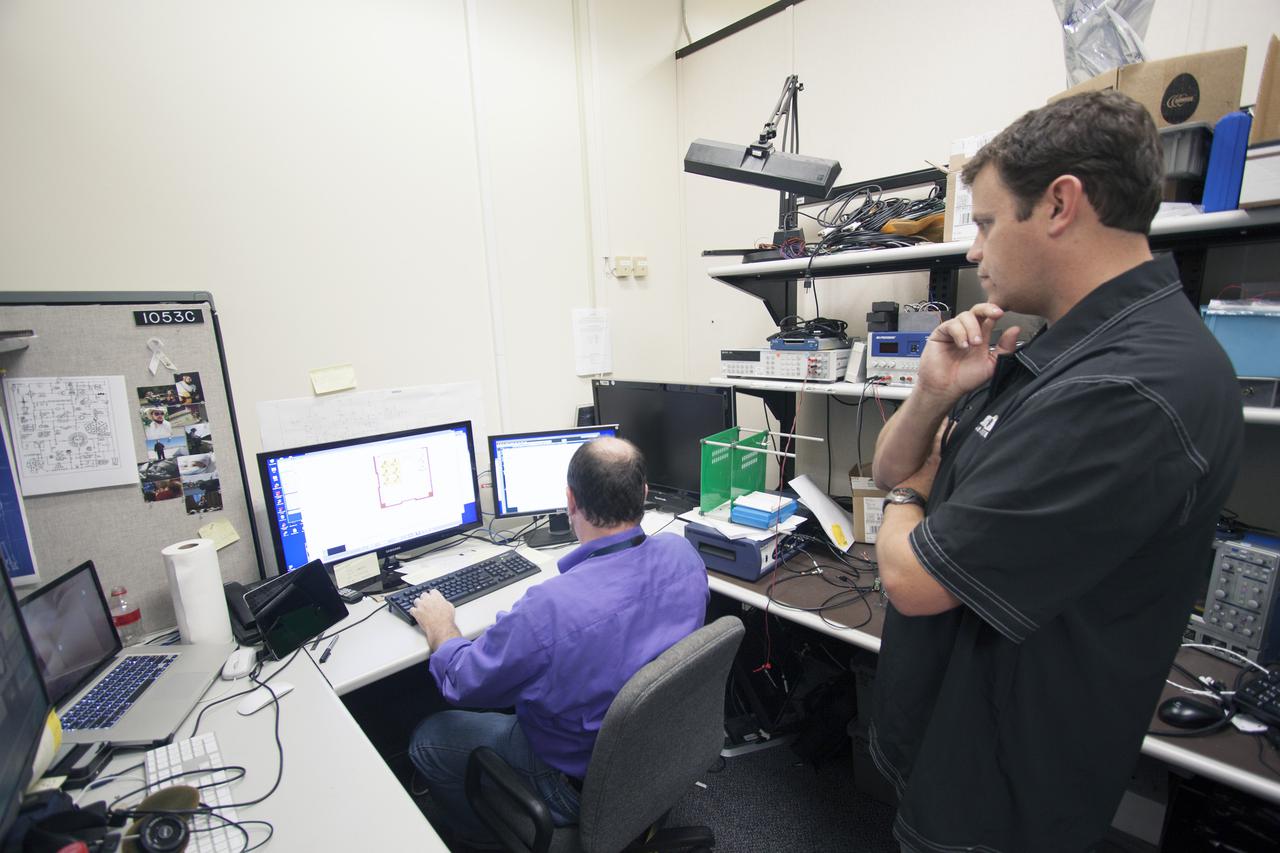

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Shaun Daly, right, and Robert Olsen test elements of a prototype of the StangSat at Kennedy Space Center before final assembly. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Theresa Overcash shows elements of a prototype of the StangSat at Kennedy Space Center to Grace Johnson. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_ Kim Shiflett
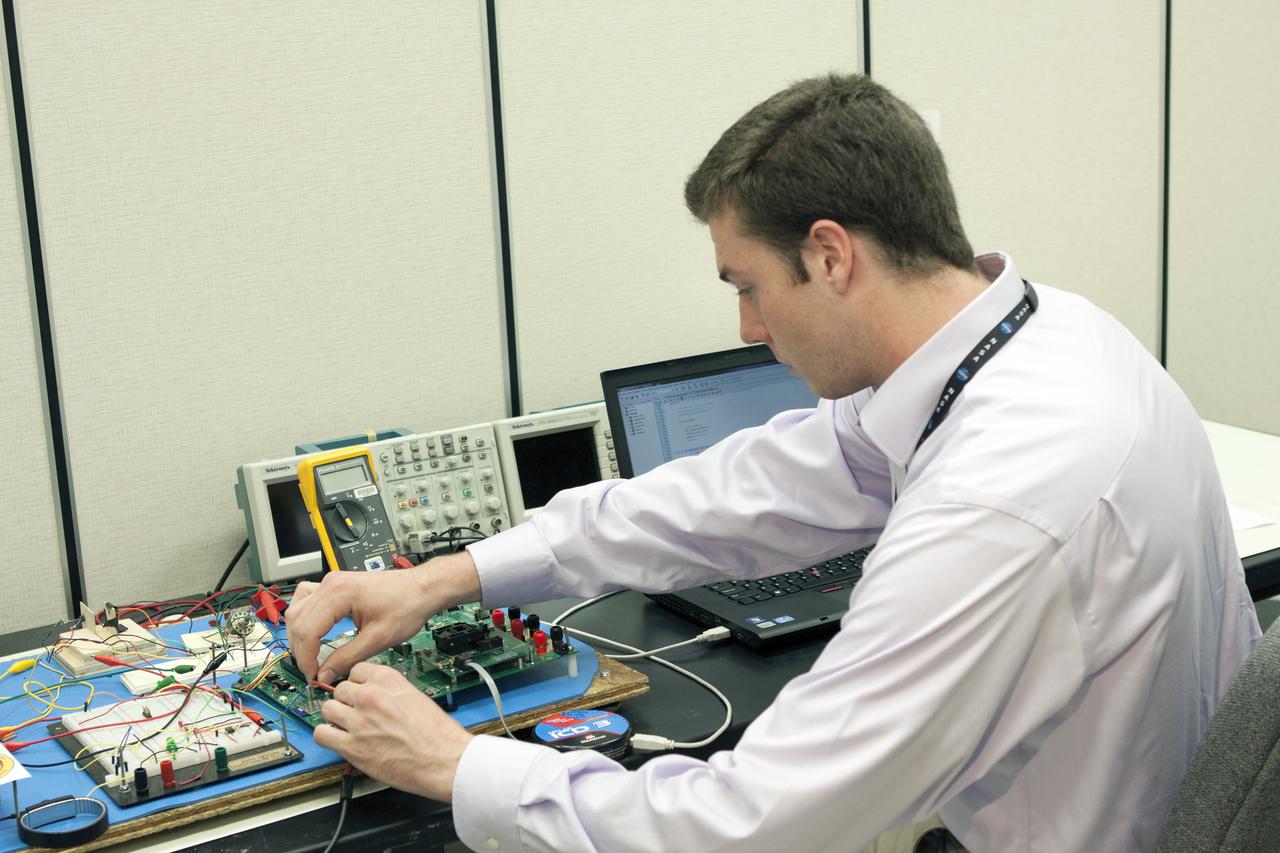

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Benjamin Plotner, an engineering intern, tests elements of a prototype of the StangSat at Kennedy Space Center before final assembly. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
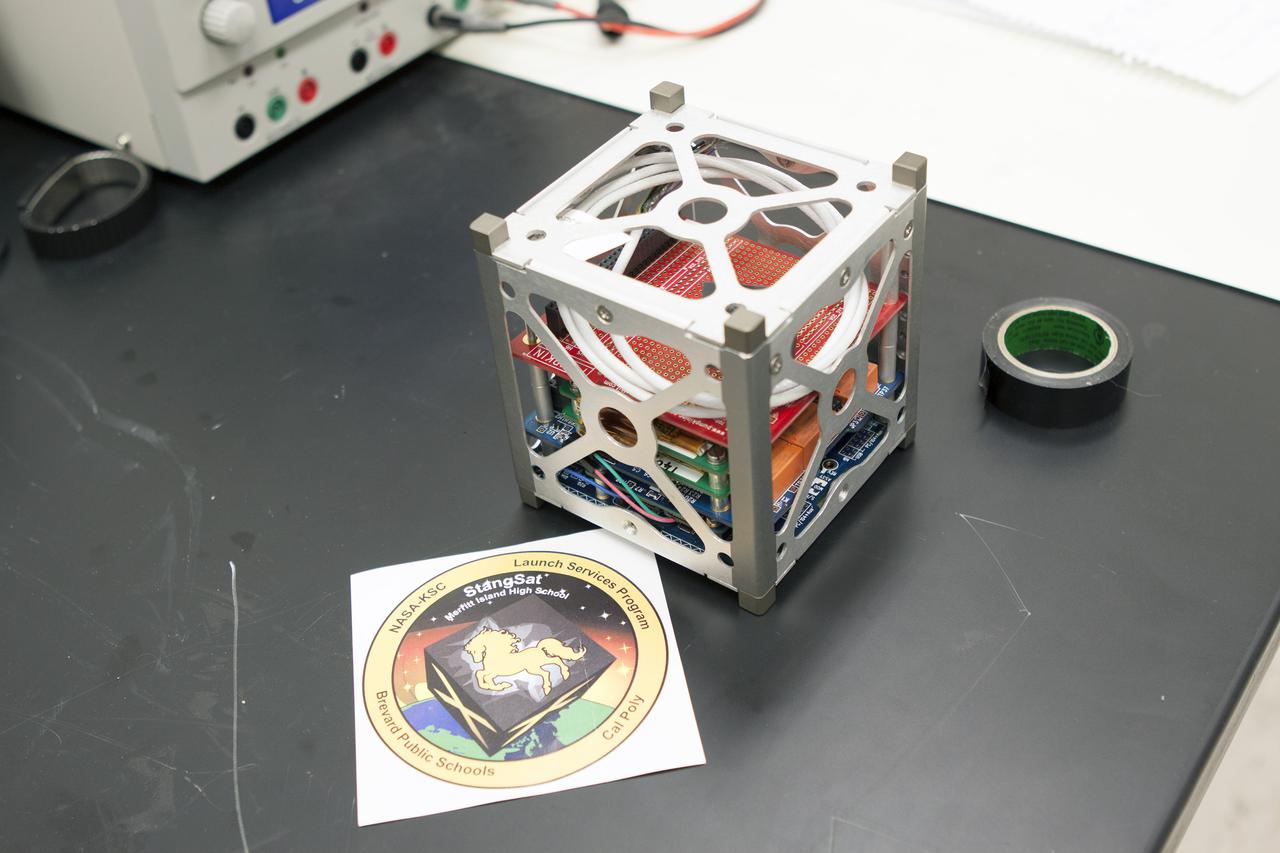
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A prototype of the StangSat undergoes testing at Kennedy Space Center before final assembly. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
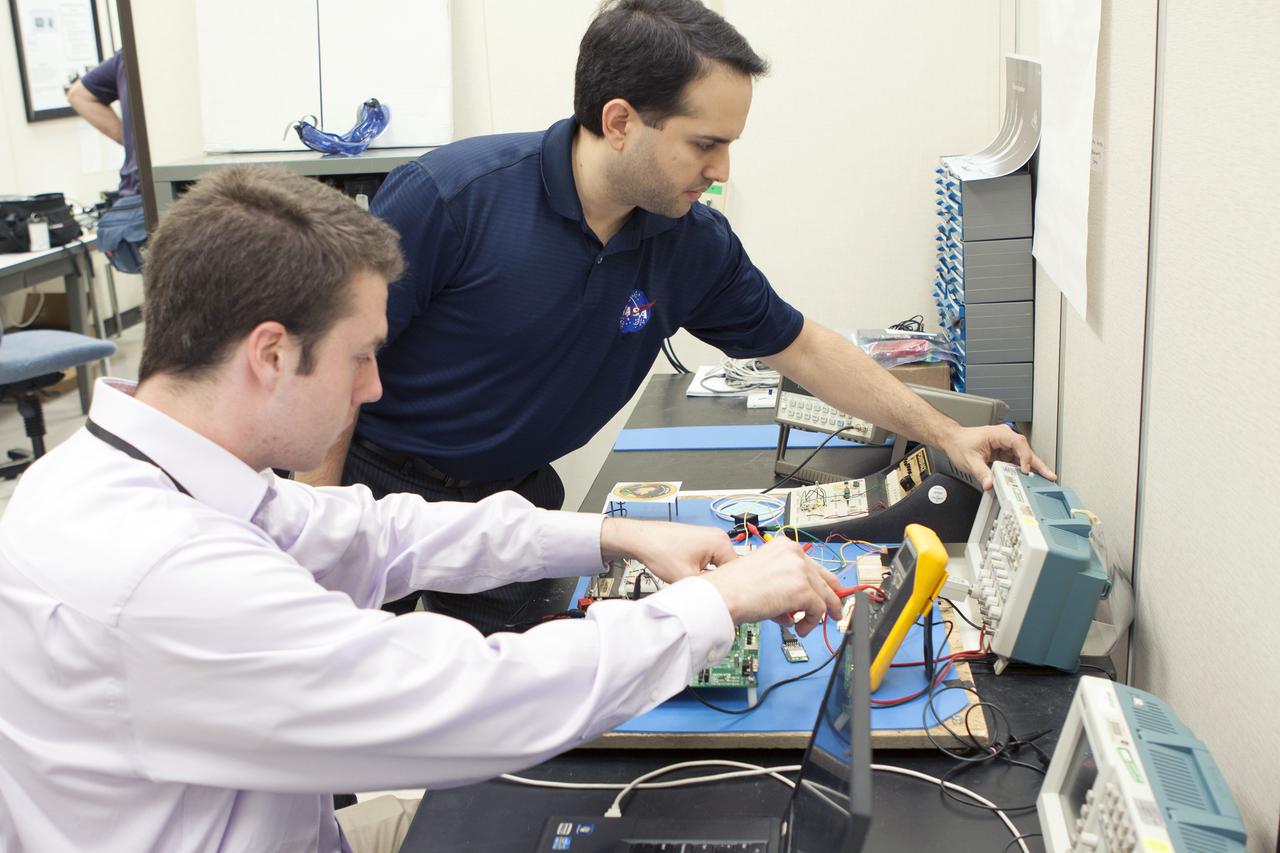

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Benjamin Plotner, an engineering intern, and Kelvin Ruiz test elements of a prototype of the StangSat at Kennedy Space Center before final assembly. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
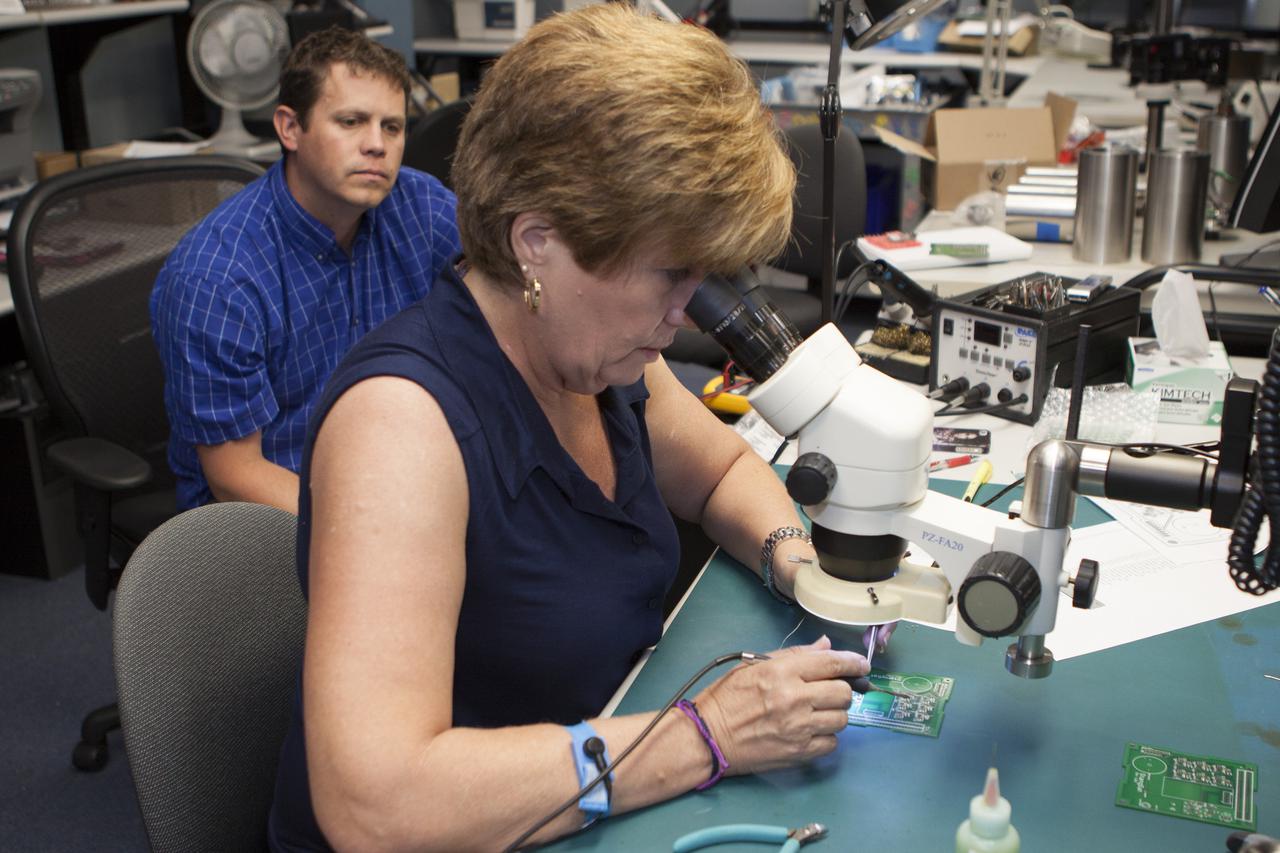

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Theresa Overcash works with elements of a prototype of the StangSat at Kennedy Space Center before final assembly as Shaun Daly looks on. The satellite is a small cube measuring 10 inches on all sides and will be launched on a rocket that will carry it on a suborbital mission in Mojave, Calif. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
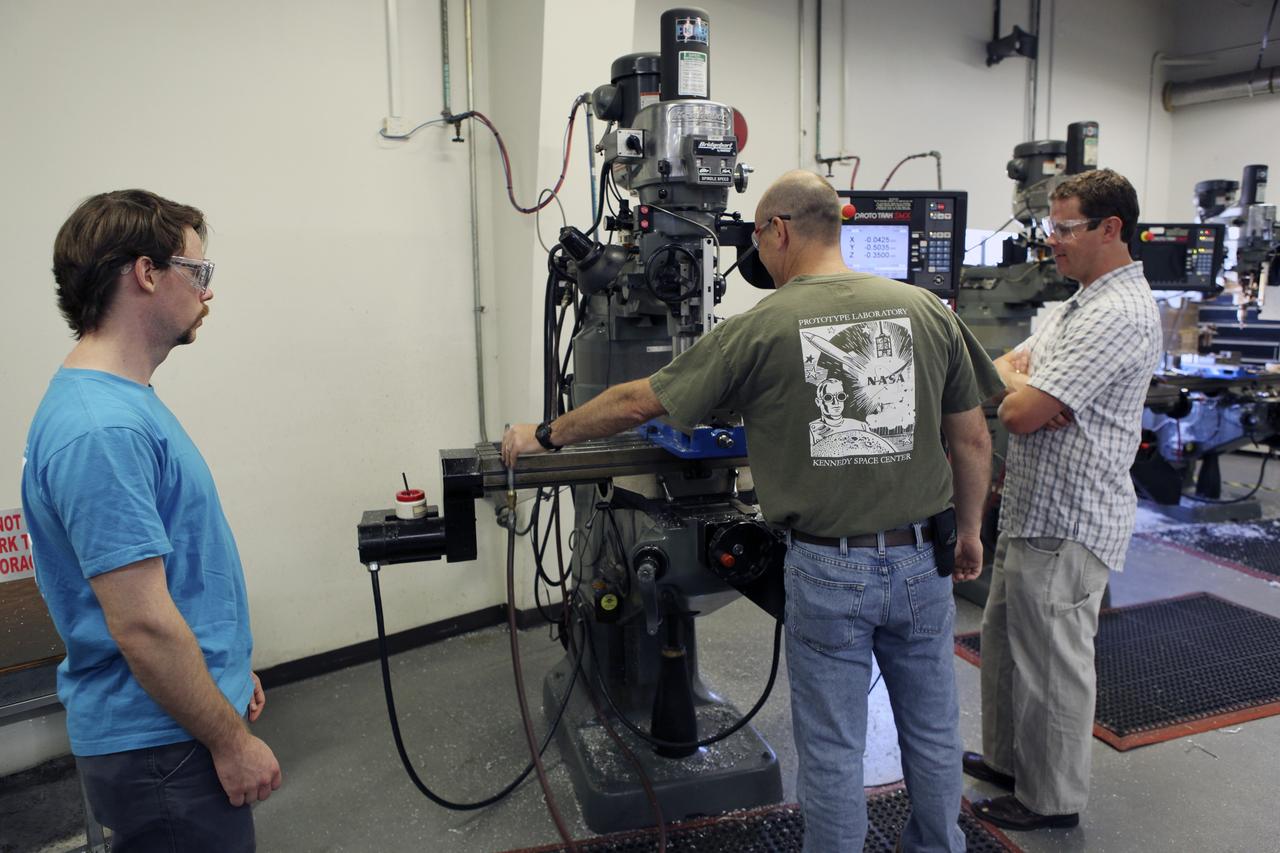

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
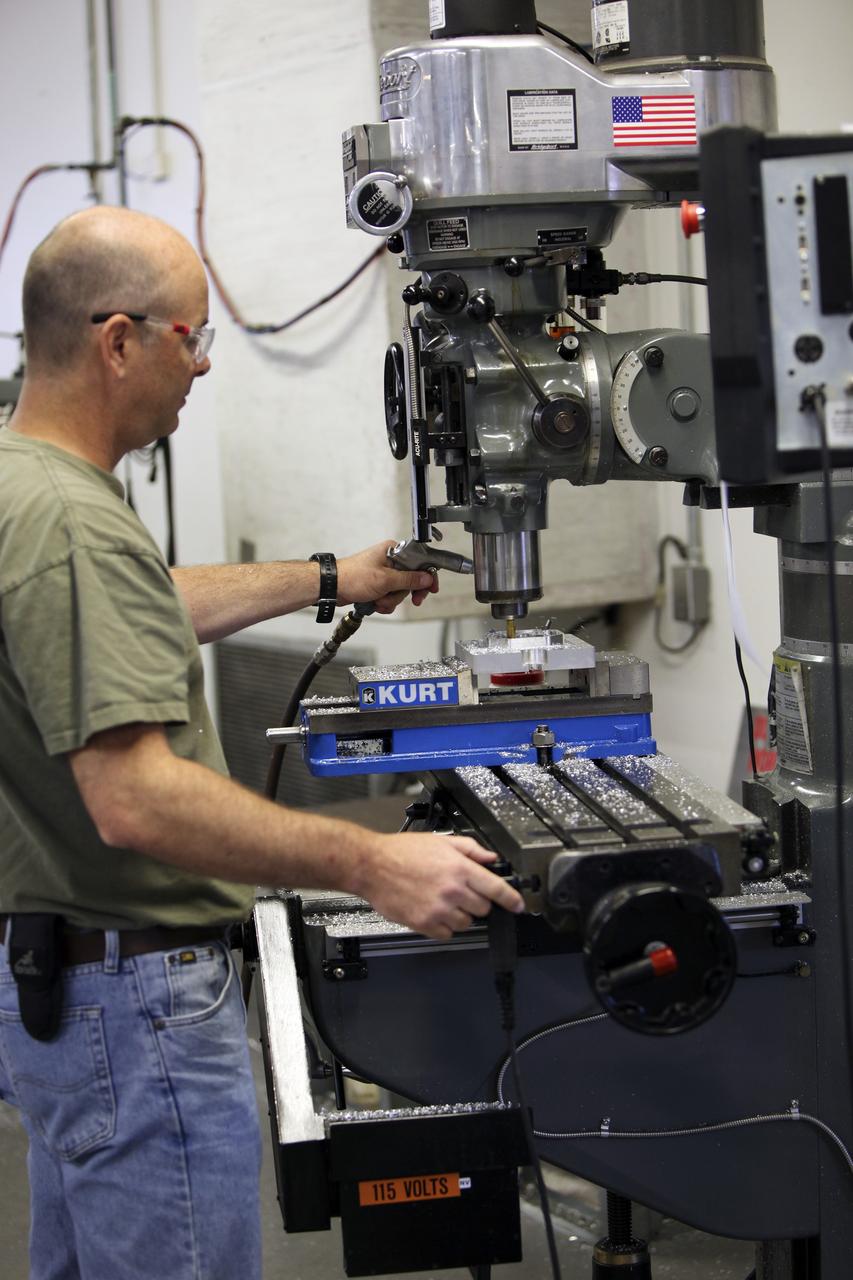

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
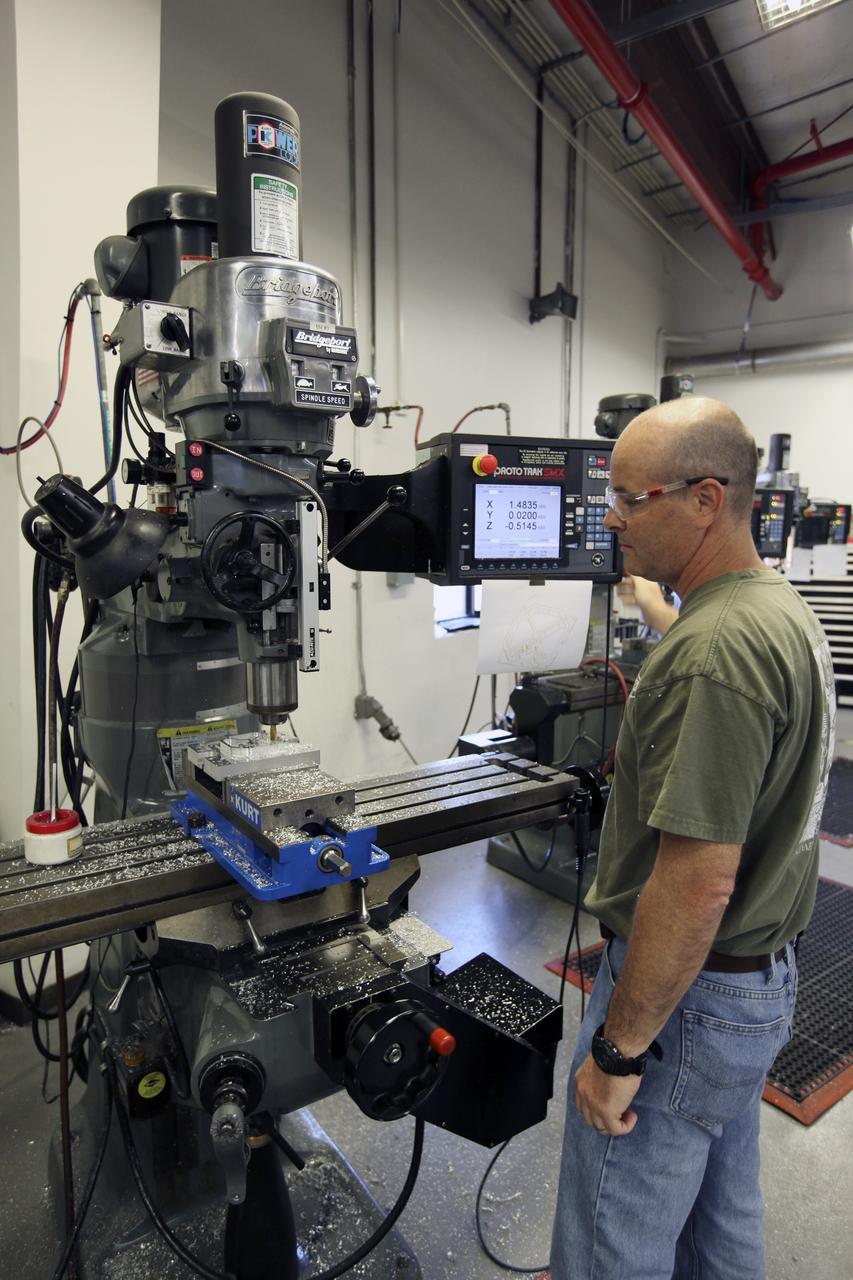

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
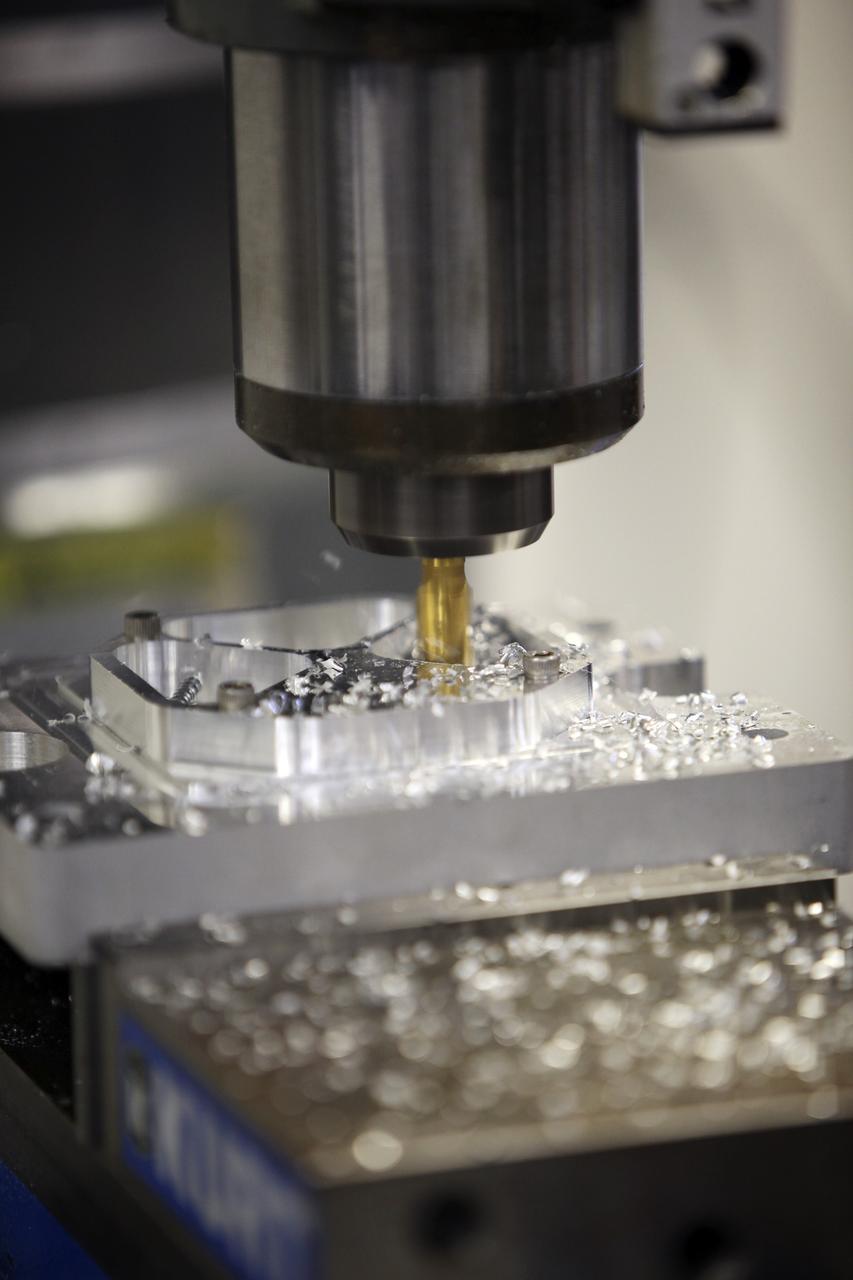

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
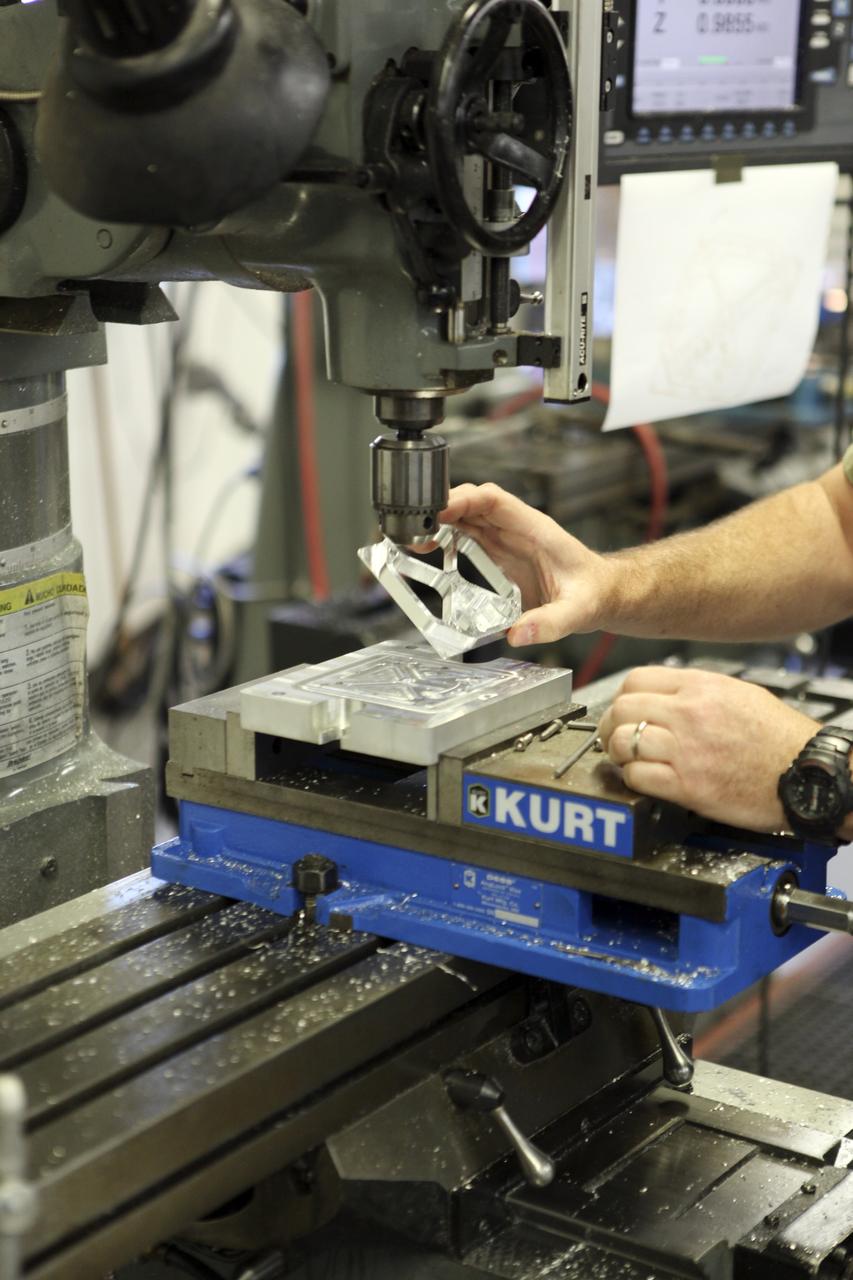

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
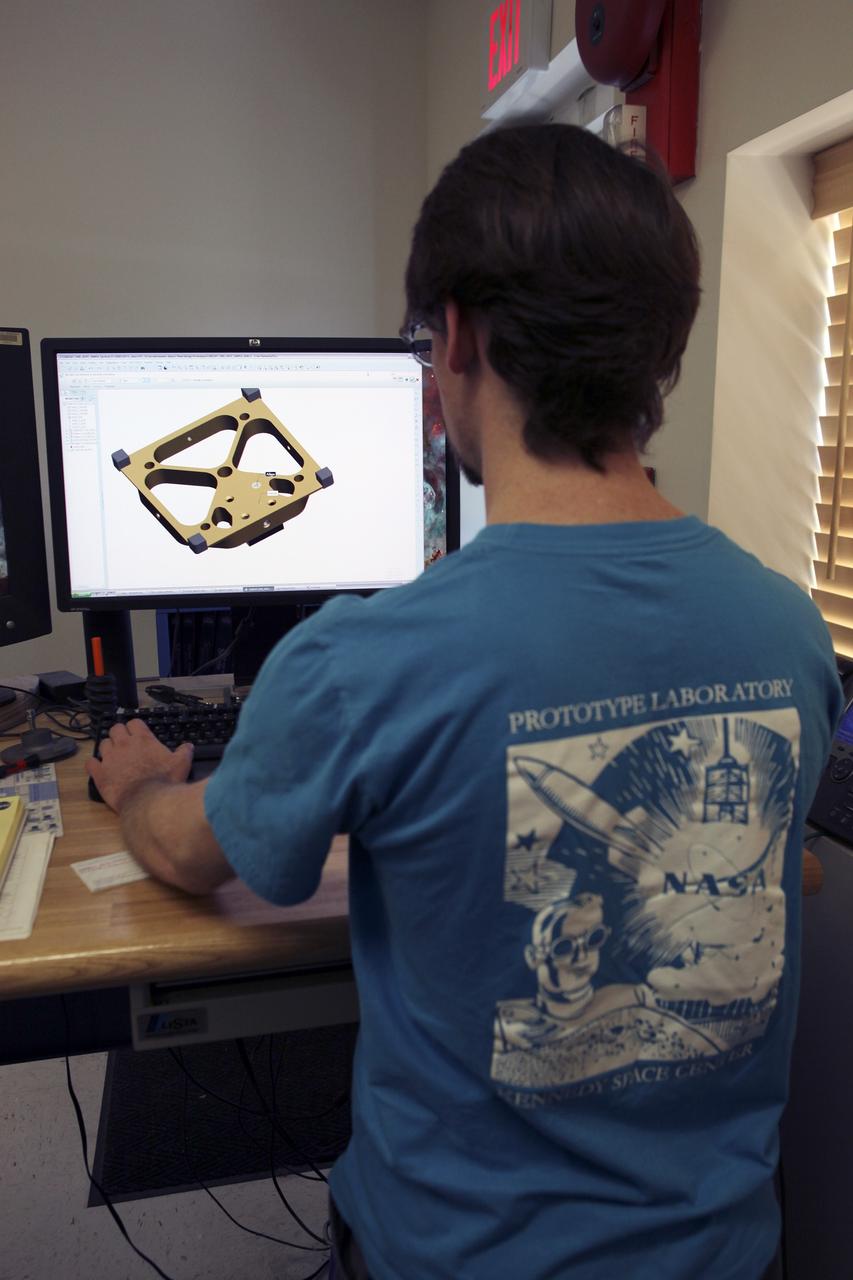

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A component is machined for a cubesat that is being assembled for launch in June. The component, being machined at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida will hold accelerometers for the StangSat, which is a project whose development includes students from Merritt Island High School in Florida. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and collect other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
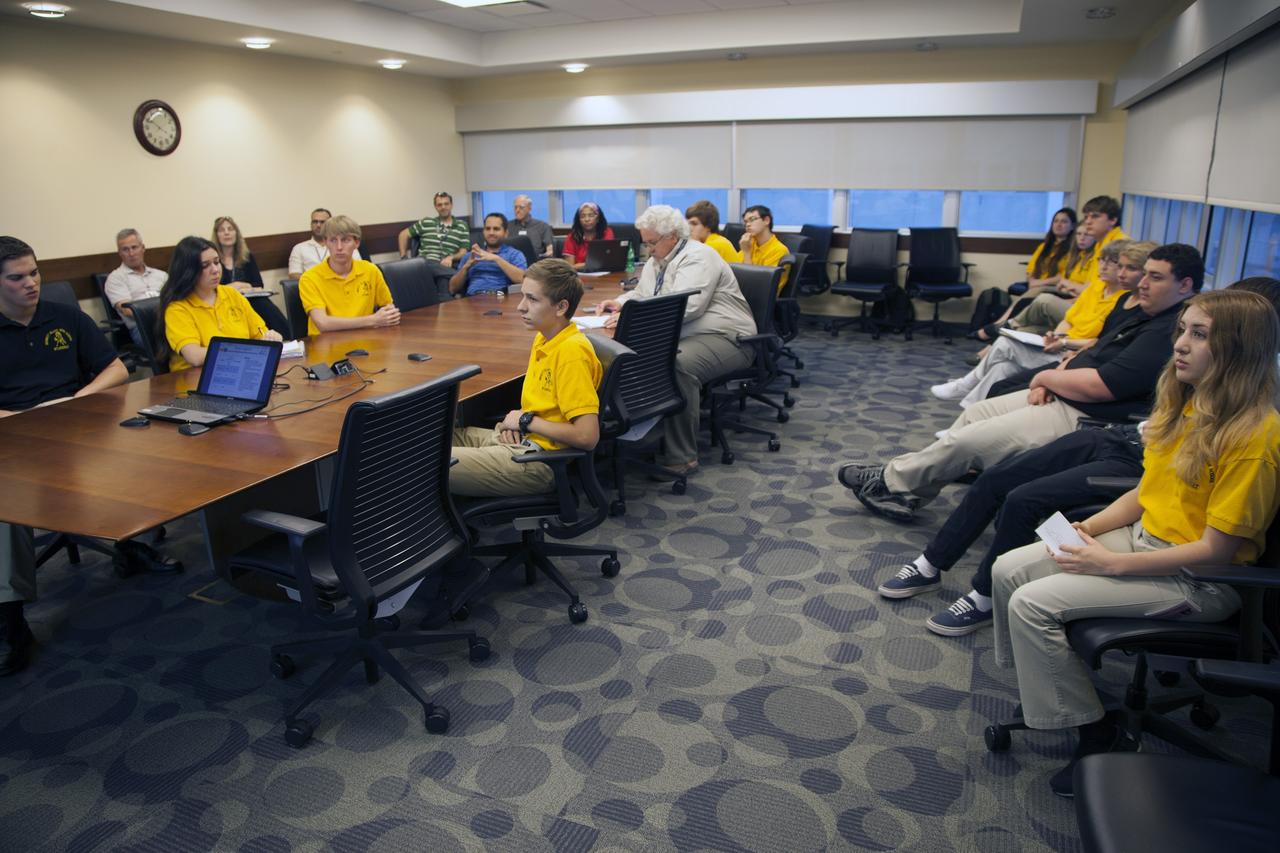

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students and their NASA mentors participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
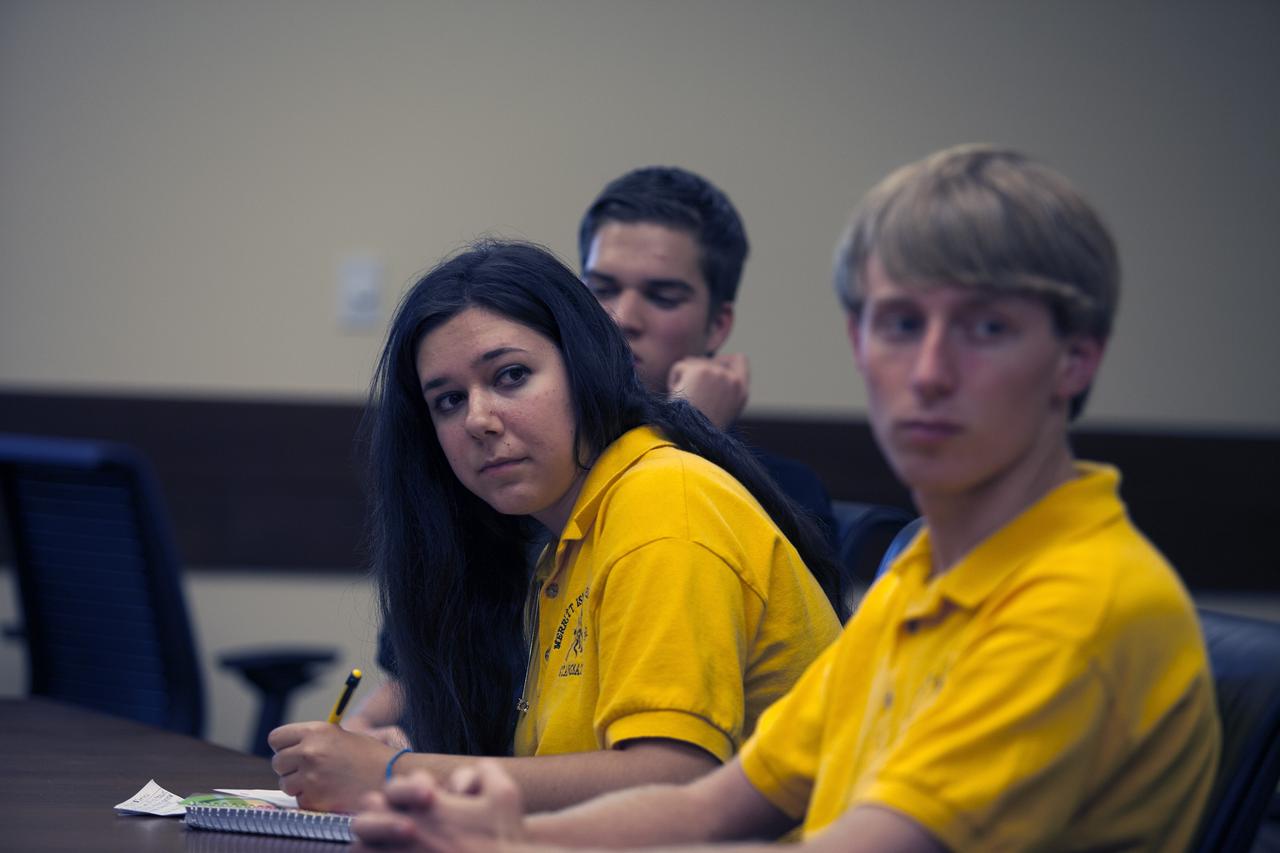

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts with NASA engineers in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A student representing a team from Merritt Island High School presents their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
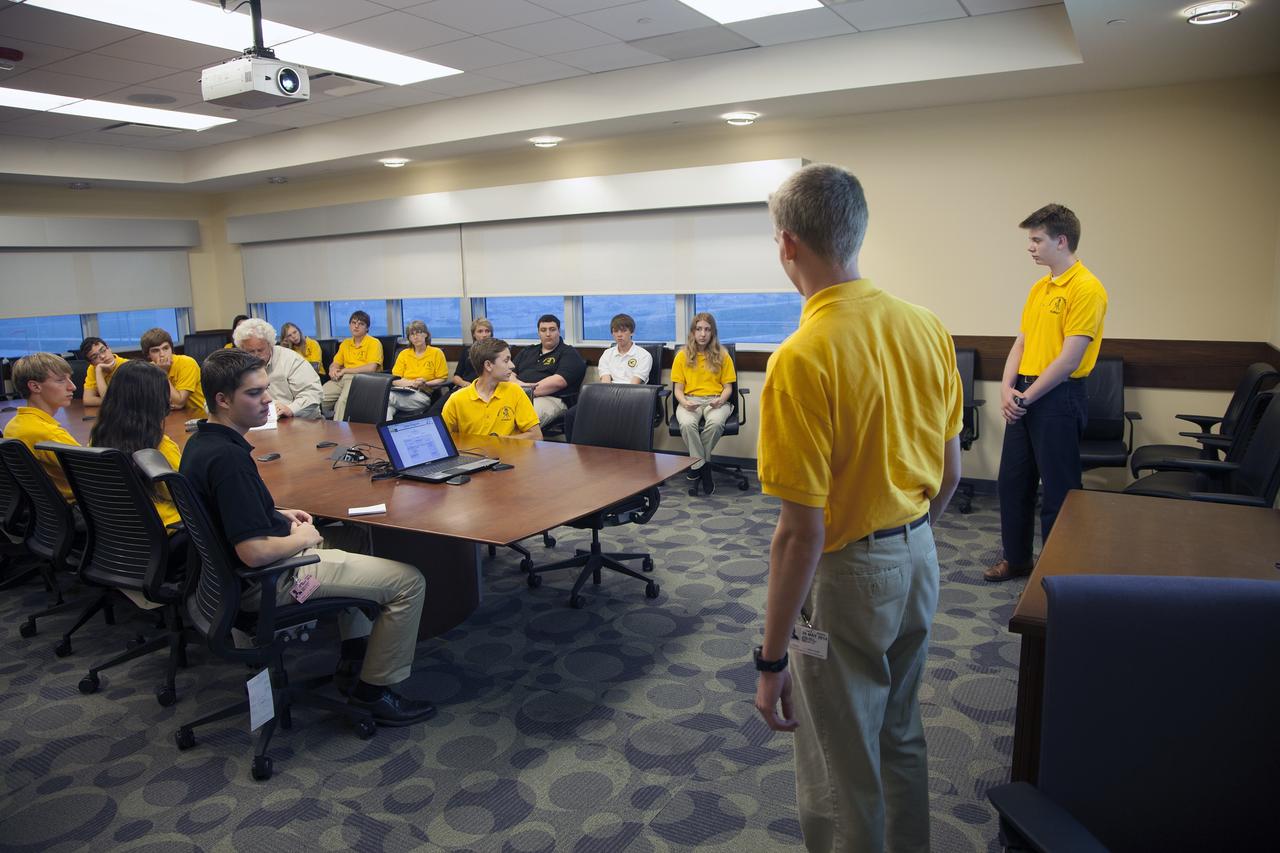

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students representing a team from Merritt Island High School present their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
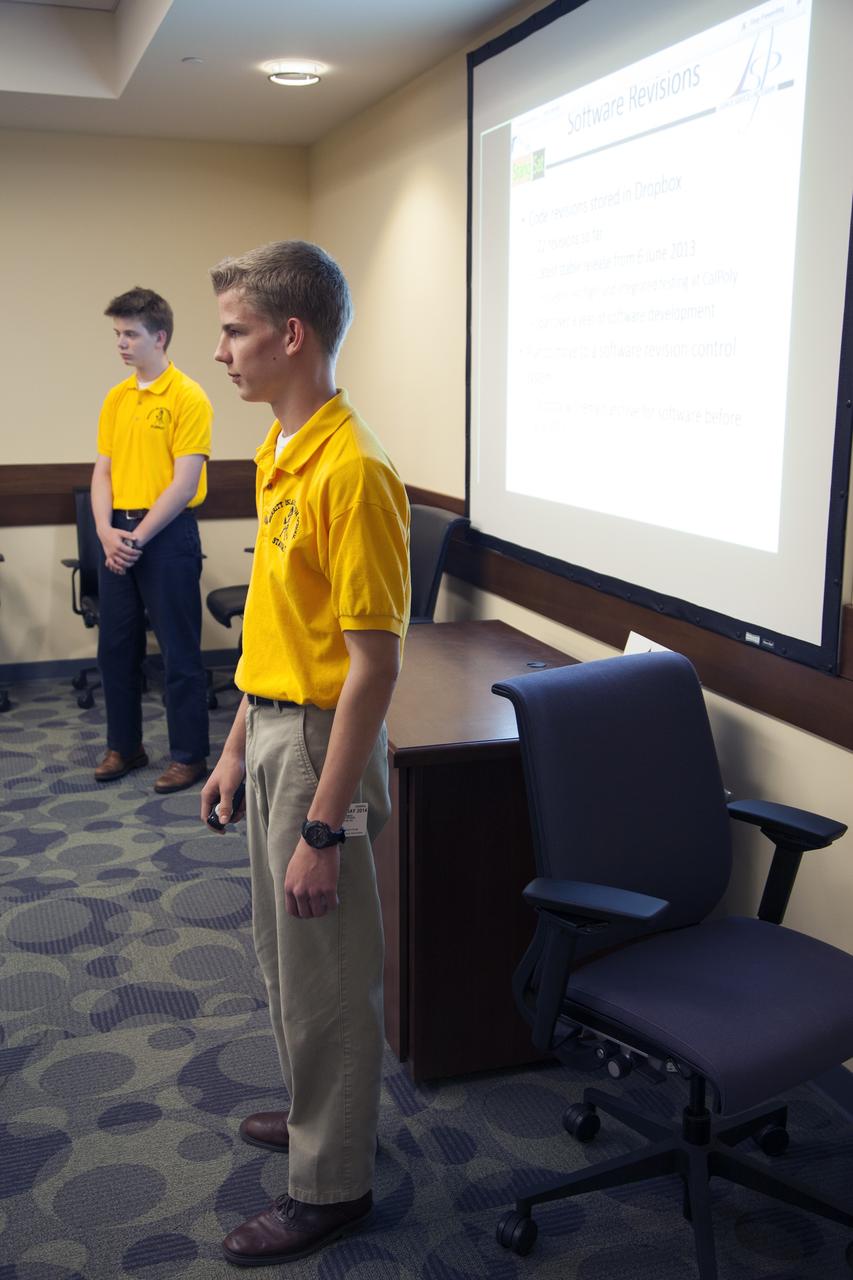

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students representing a team from Merritt Island High School present their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
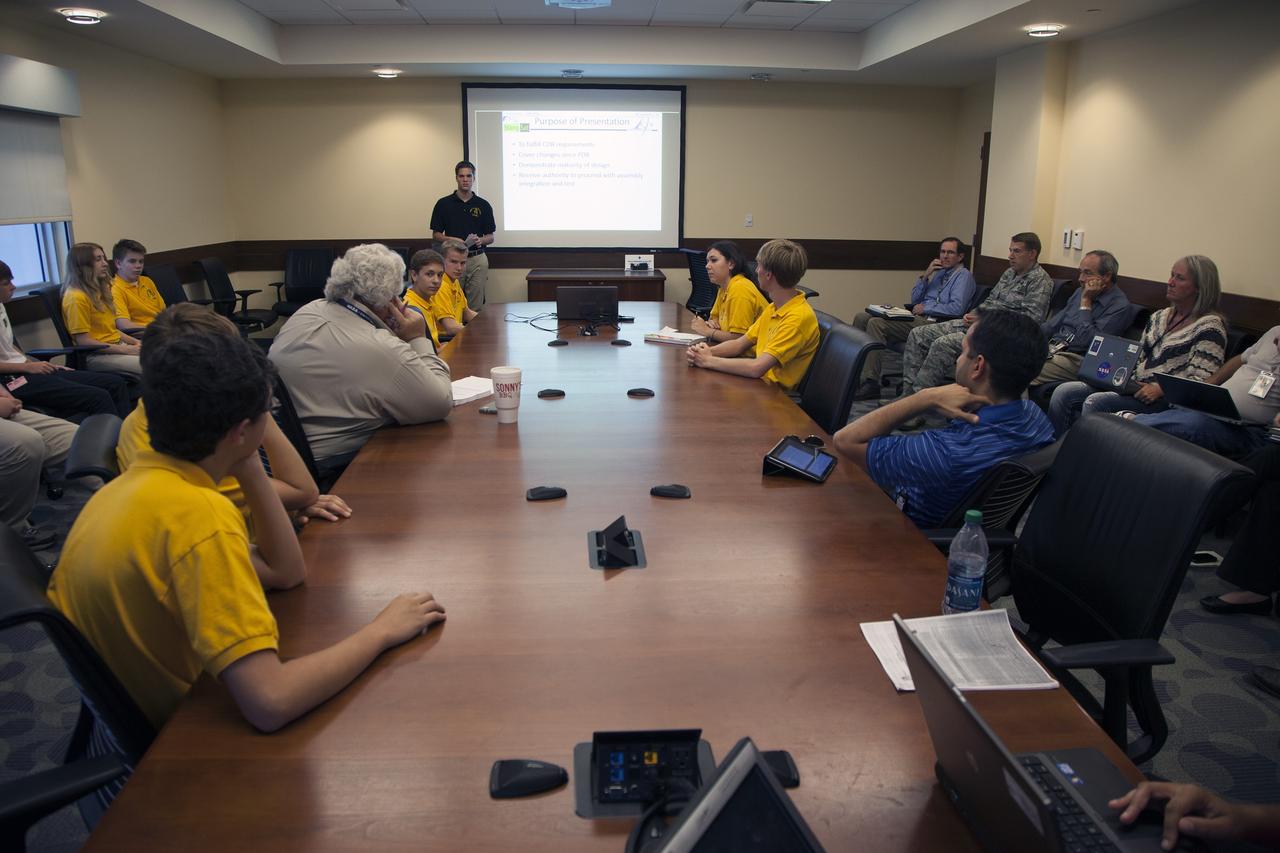

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A student representing a team from Merritt Island High School presents their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
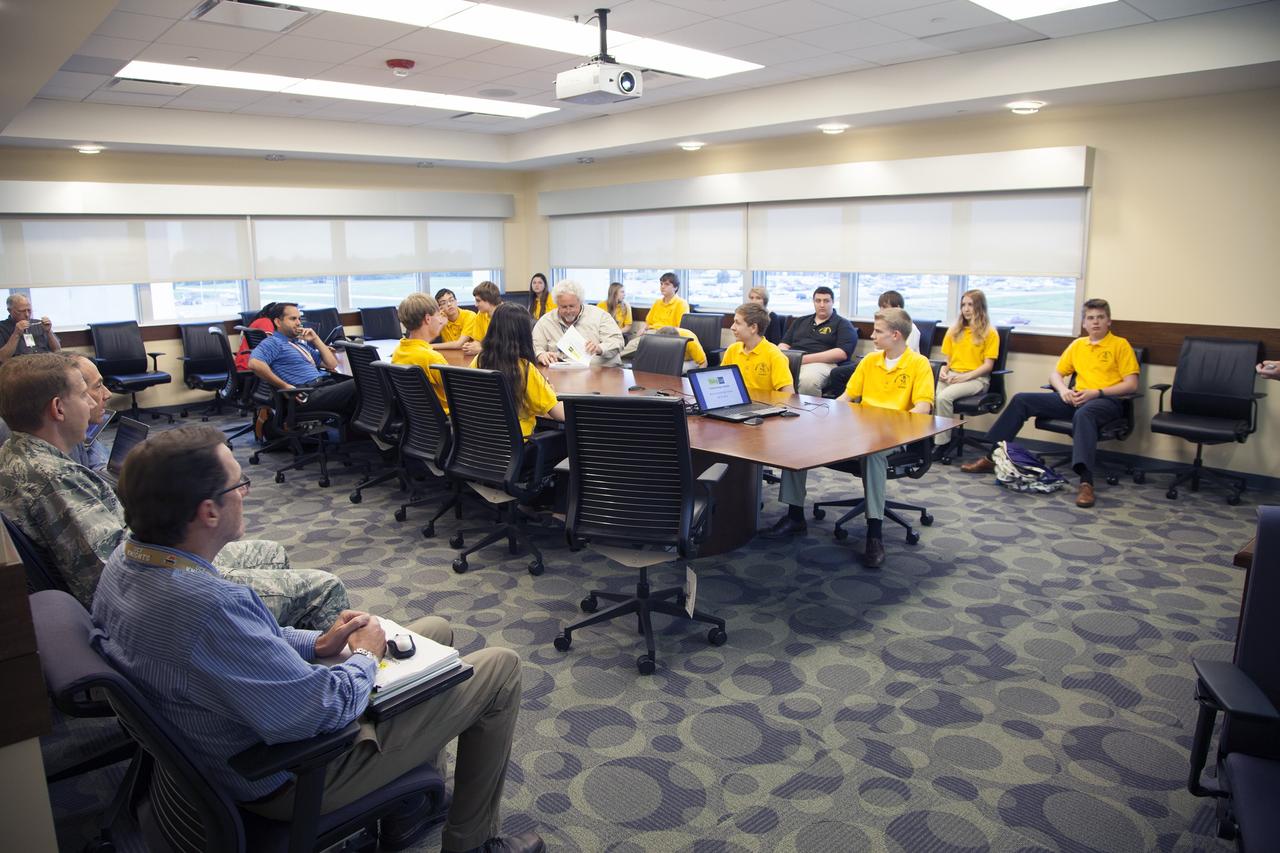

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students and their NASA mentors participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
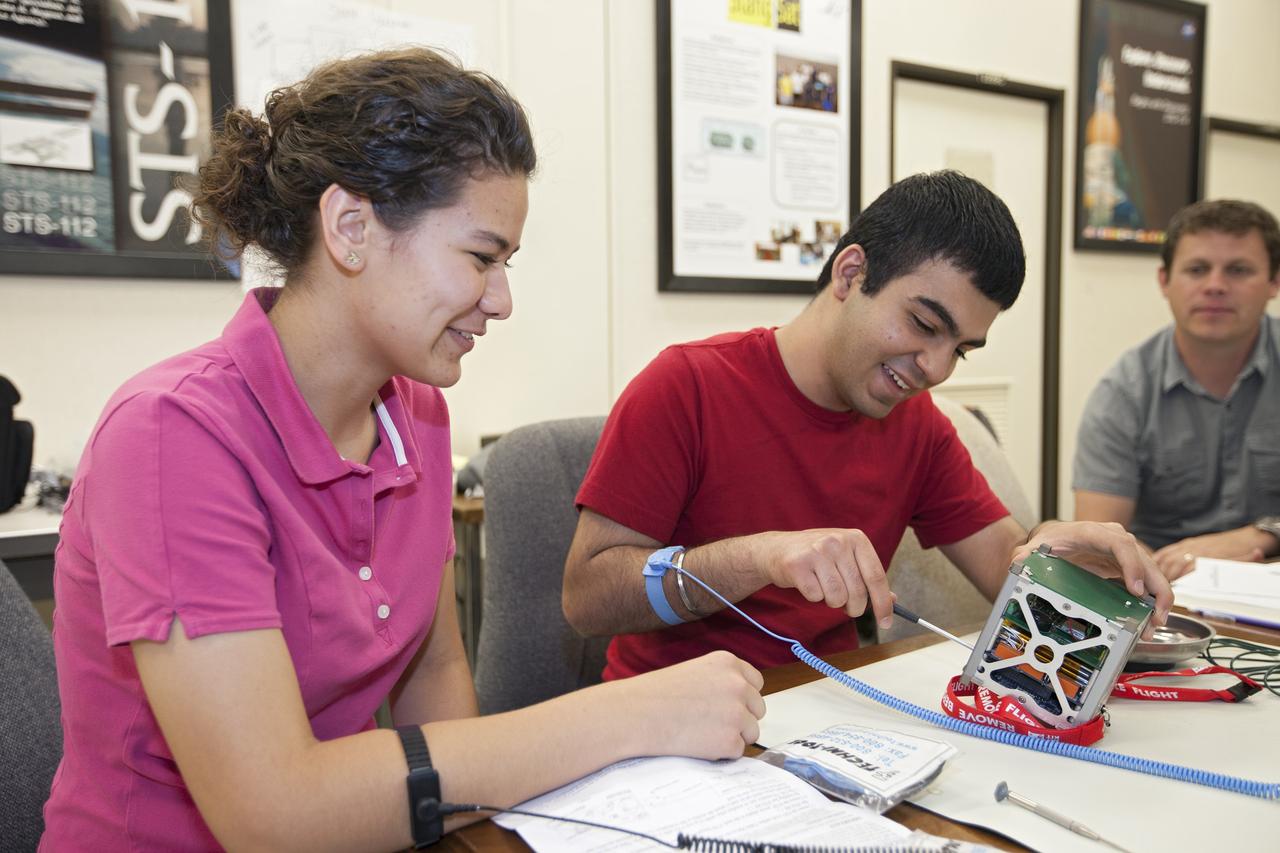

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students from Merritt Island High School in Florida perform integration tests a cubesat called StangSat they will fly on a suborbital mission in the summer. The satellite will work inside a small rocket to measure vibration and other data during launch. NASA engineers are acting as mentors for the project and some of the space agency's labs at Kennedy Space Center, including this one inside the Operations and Checkout Building, are being used by the teams. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
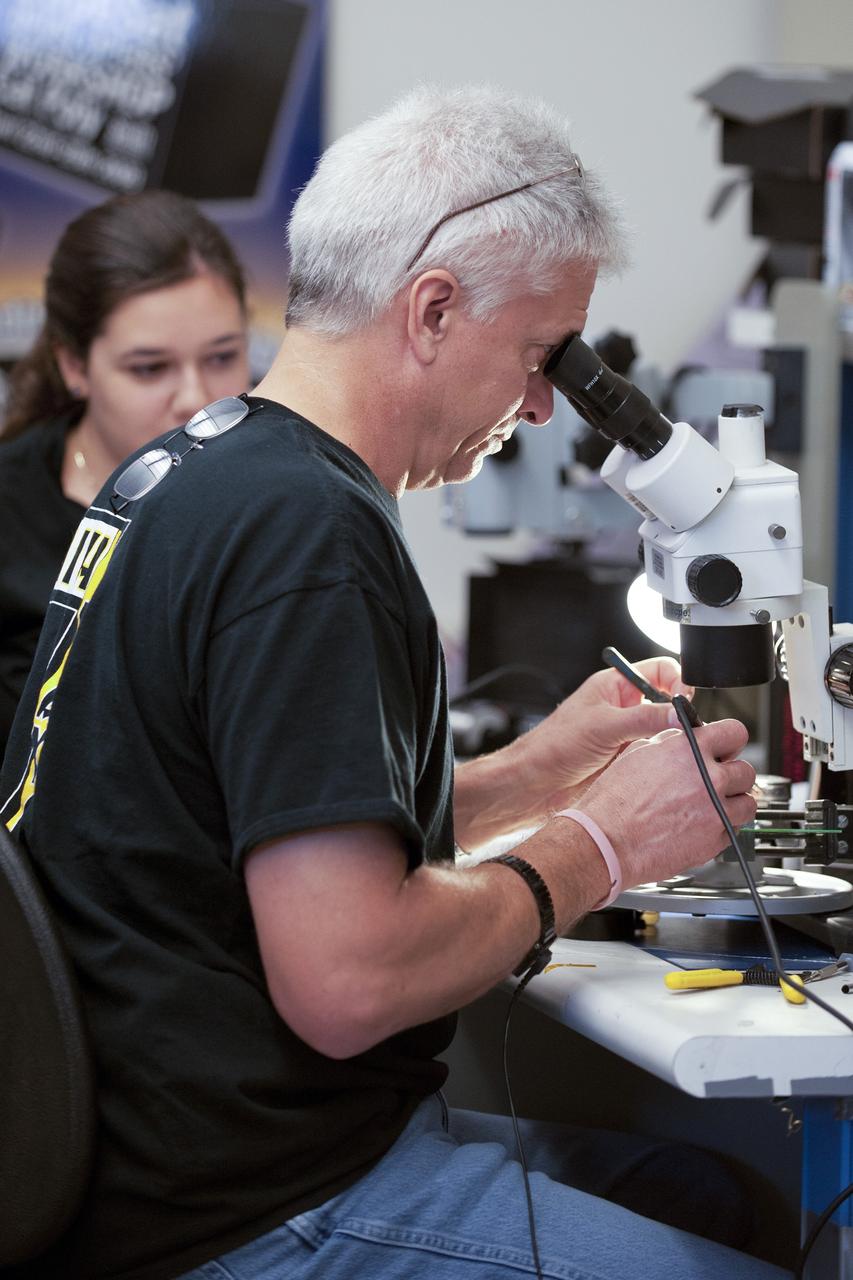

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Jim Kinney, a NASA mentor for the student launch team of the StangSat, works inside the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the StangSat will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen the design before it is carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
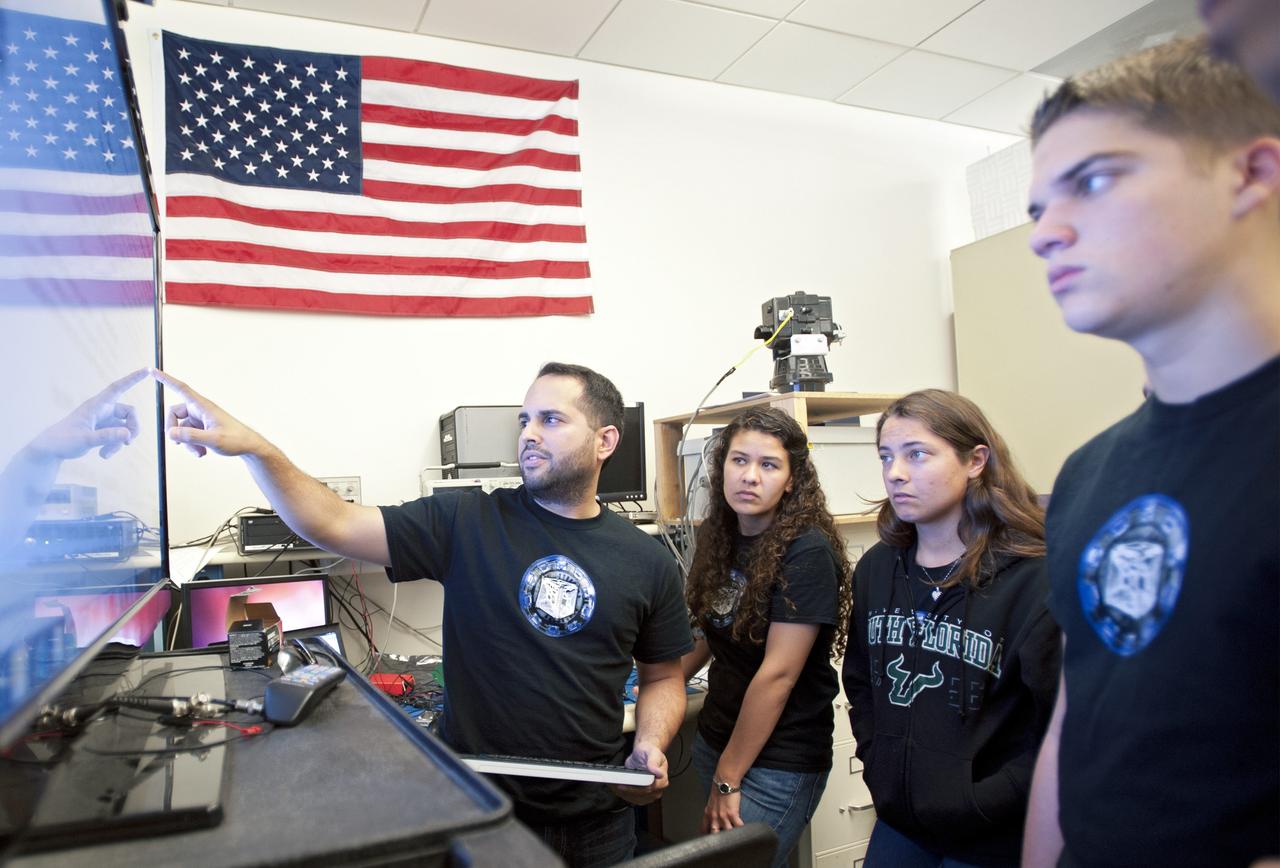

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – NASA mentors and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
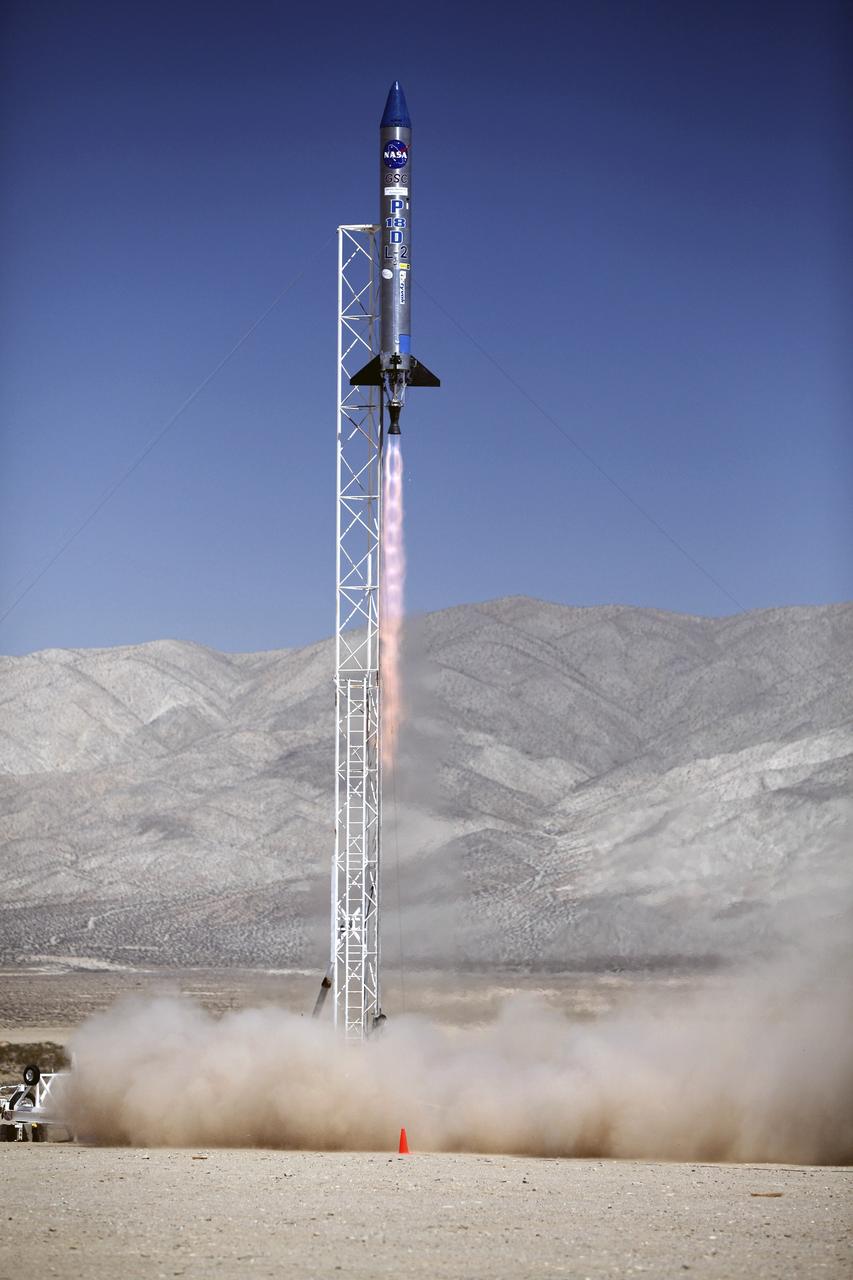

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
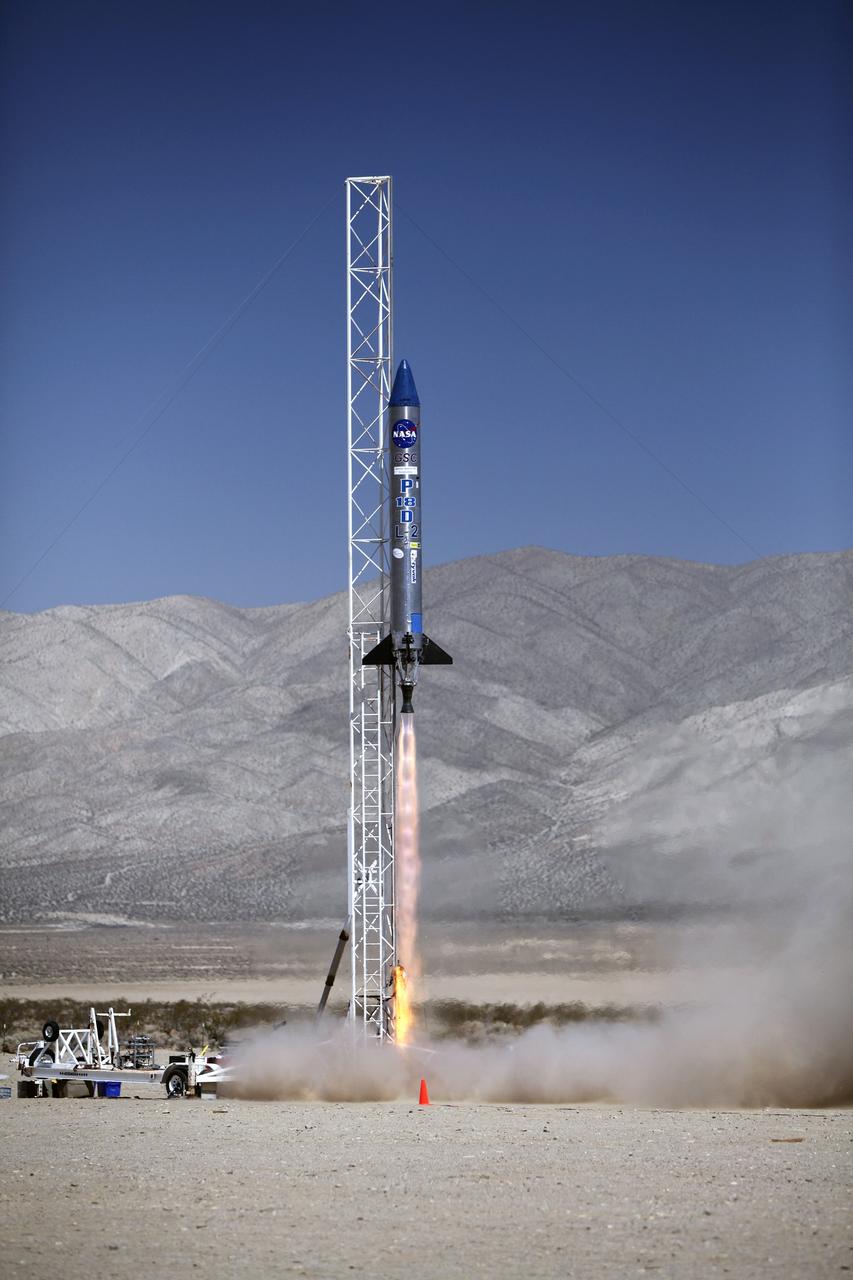

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
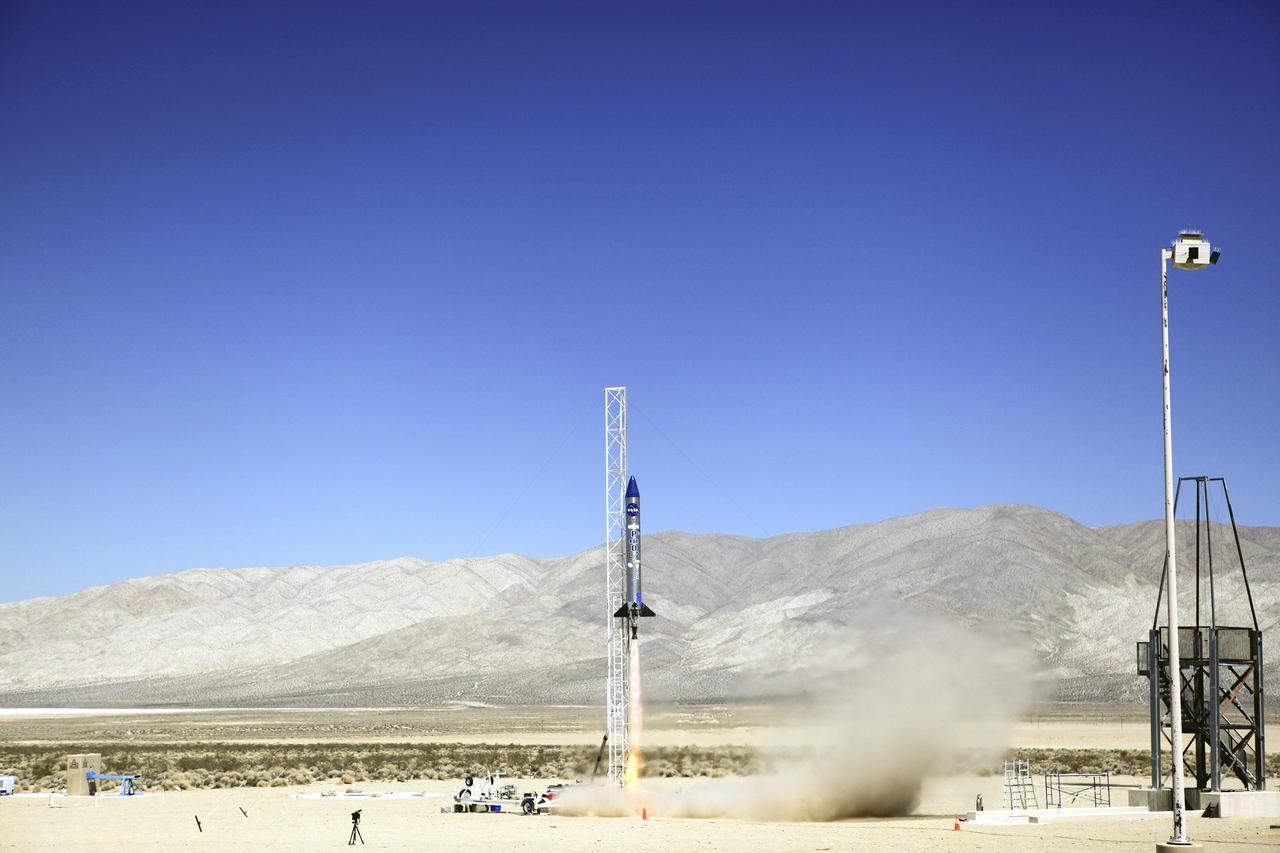

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
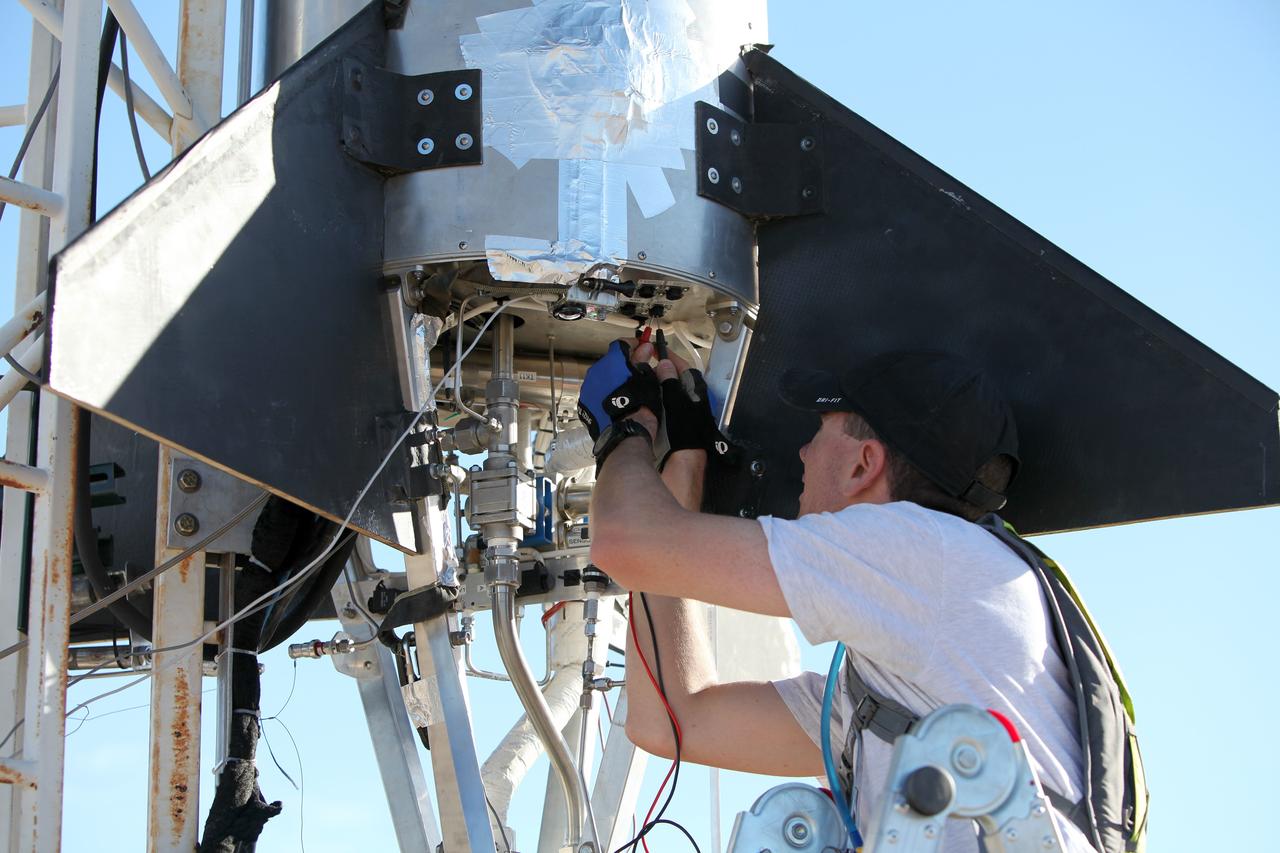

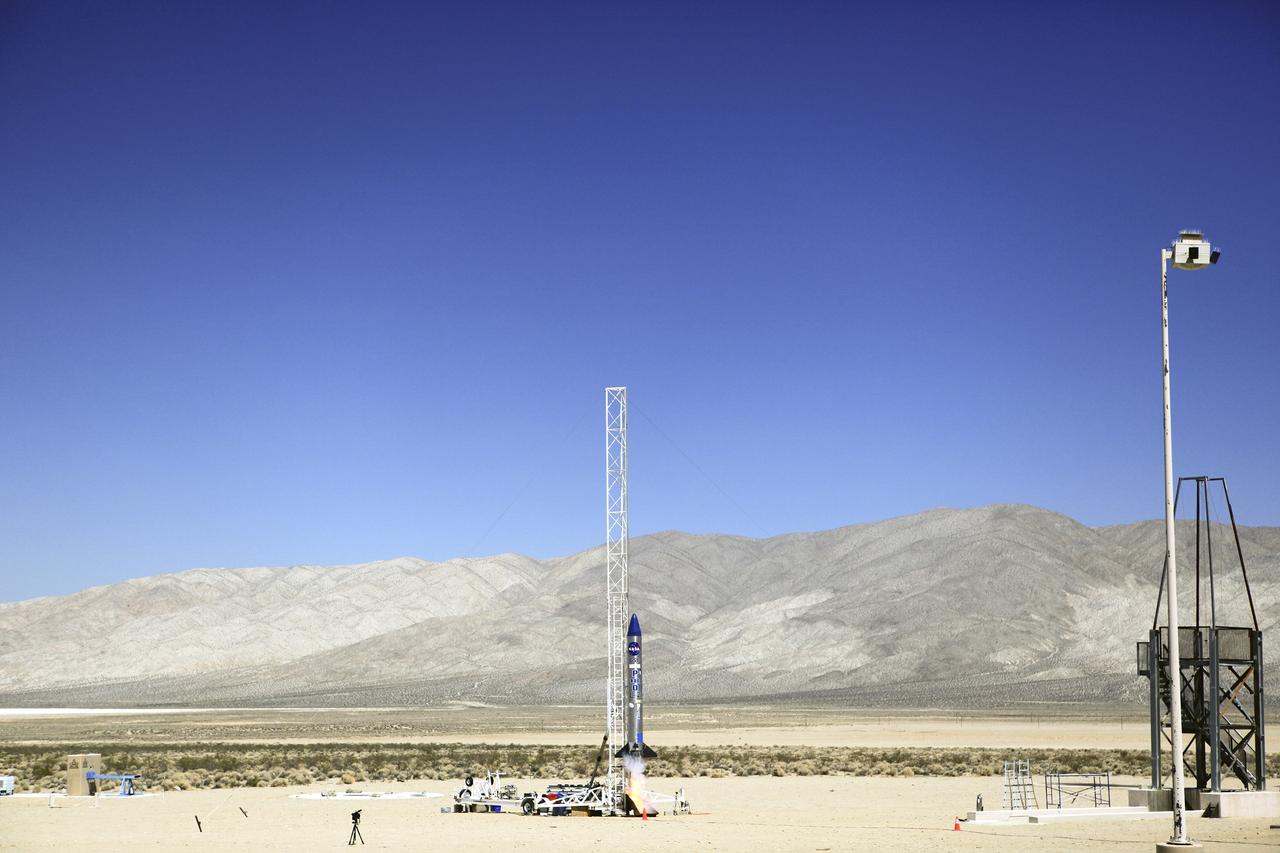
MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, final checkouts are completed on the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
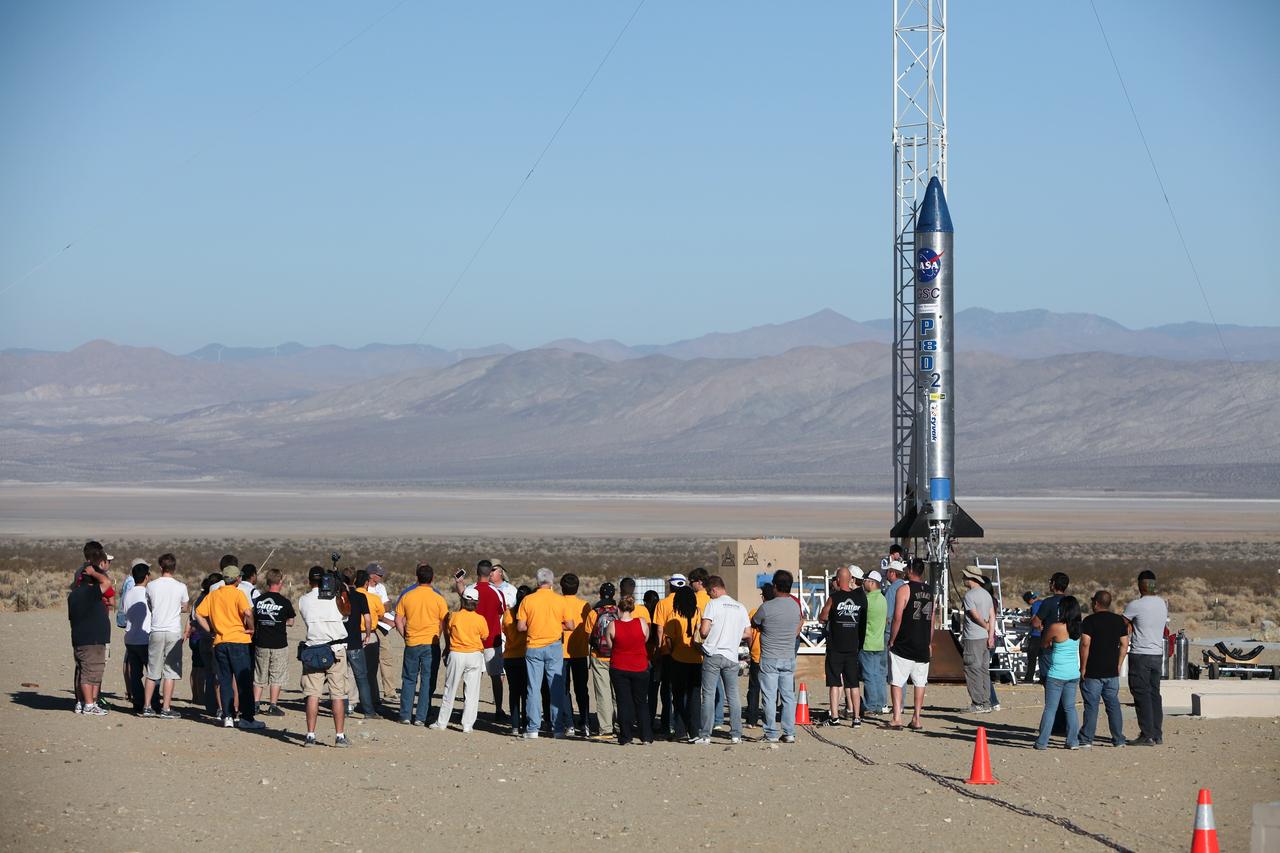

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers participate in a pre-launch briefing before the lift off of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled to launch the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
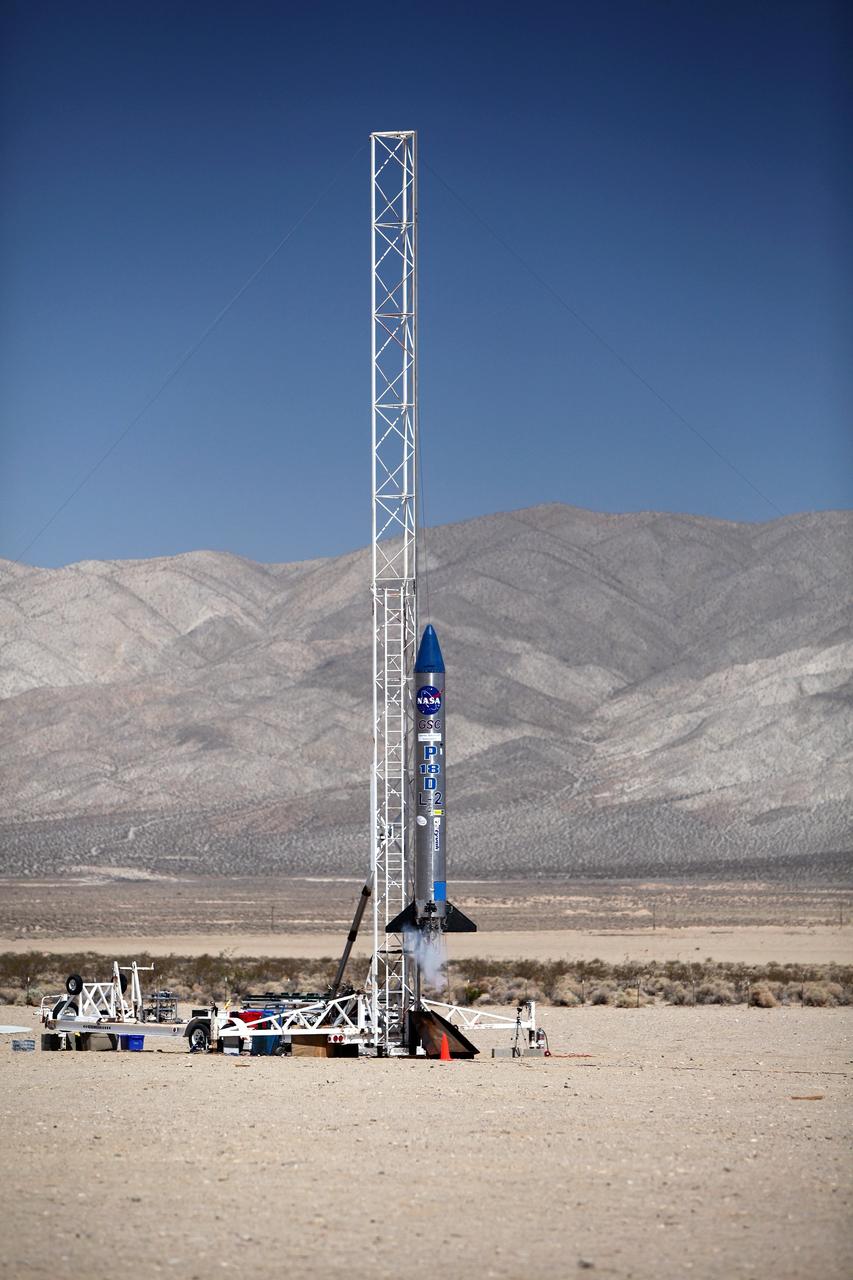

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the ignition sequence begins on the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The vehicle is carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
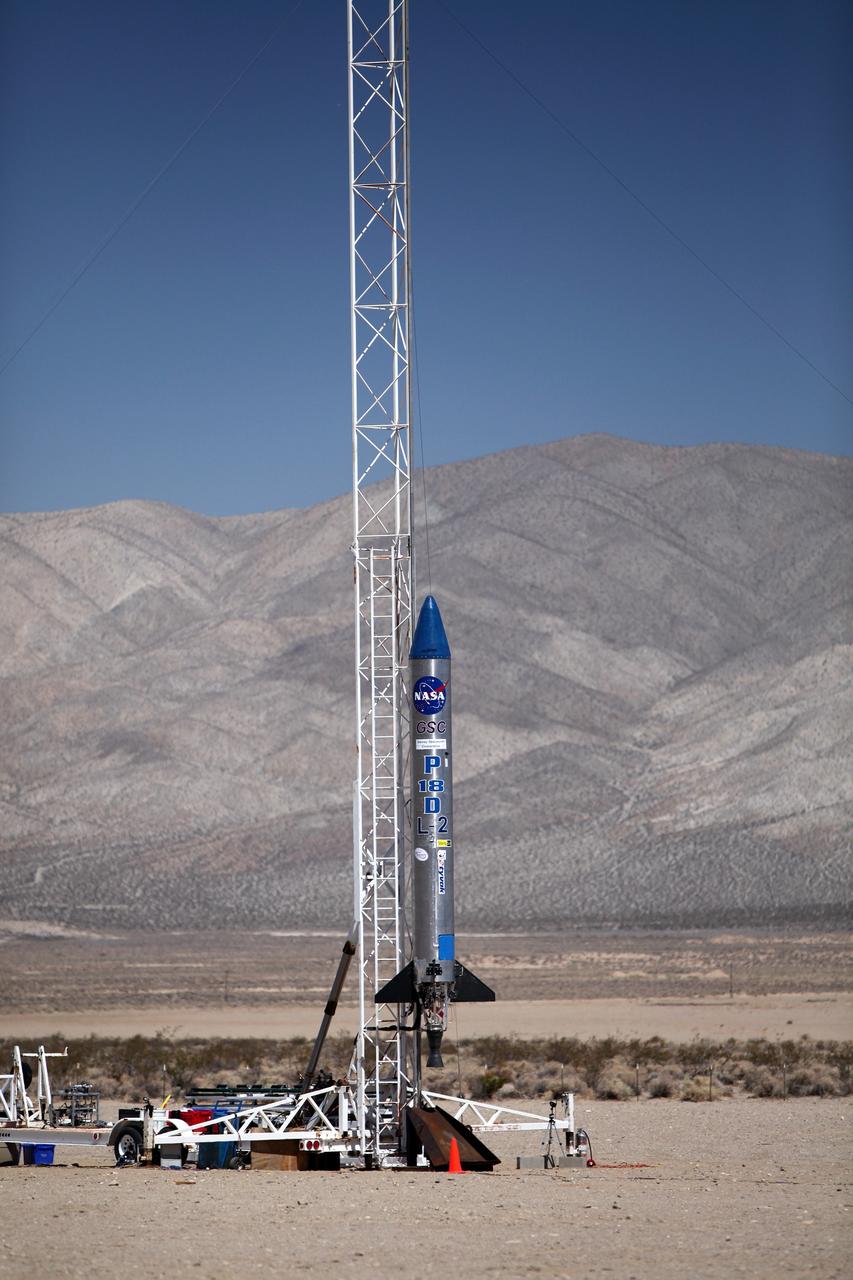

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket is positioned for launch with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Members of the student launch team for the StangSat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
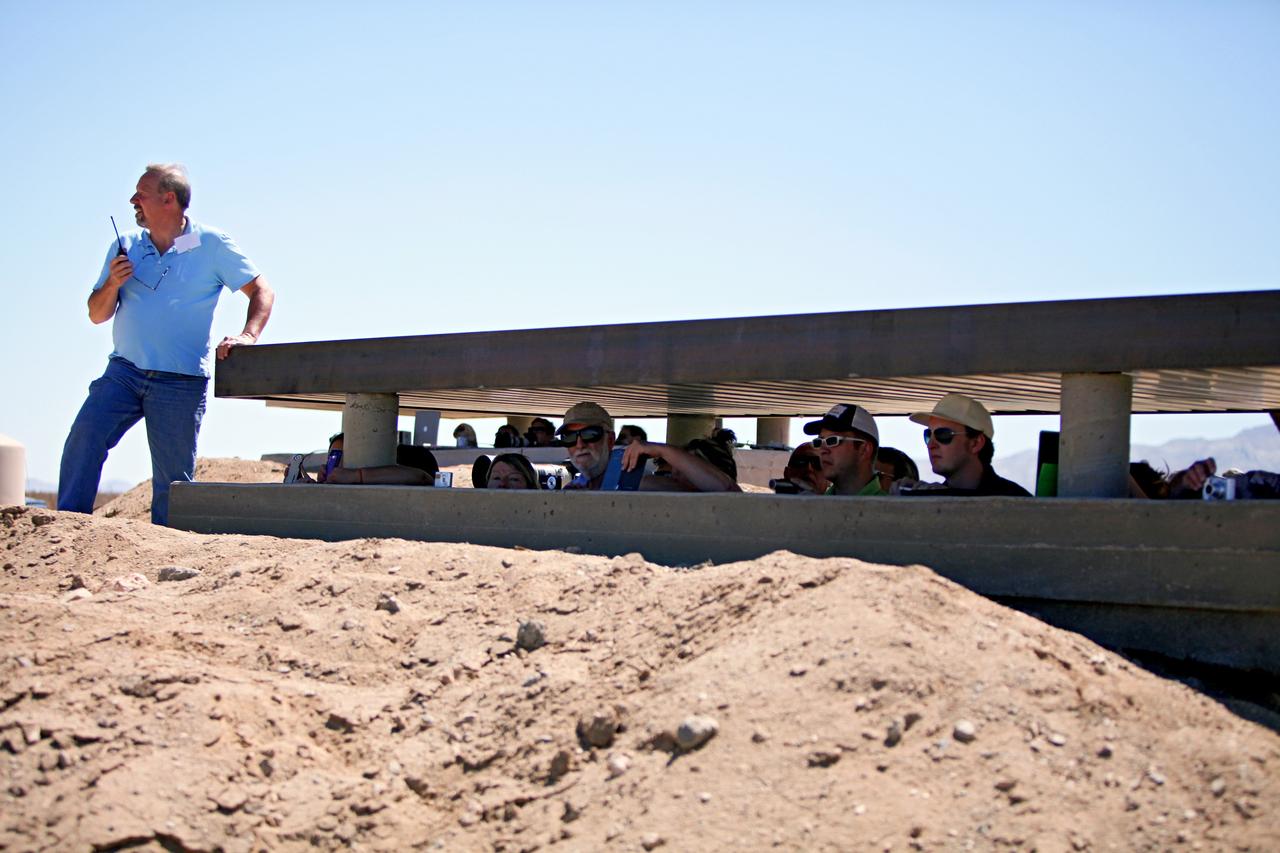

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, Kevin Baxter, a range representative of the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site, ensures all is ready for launch of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket with the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
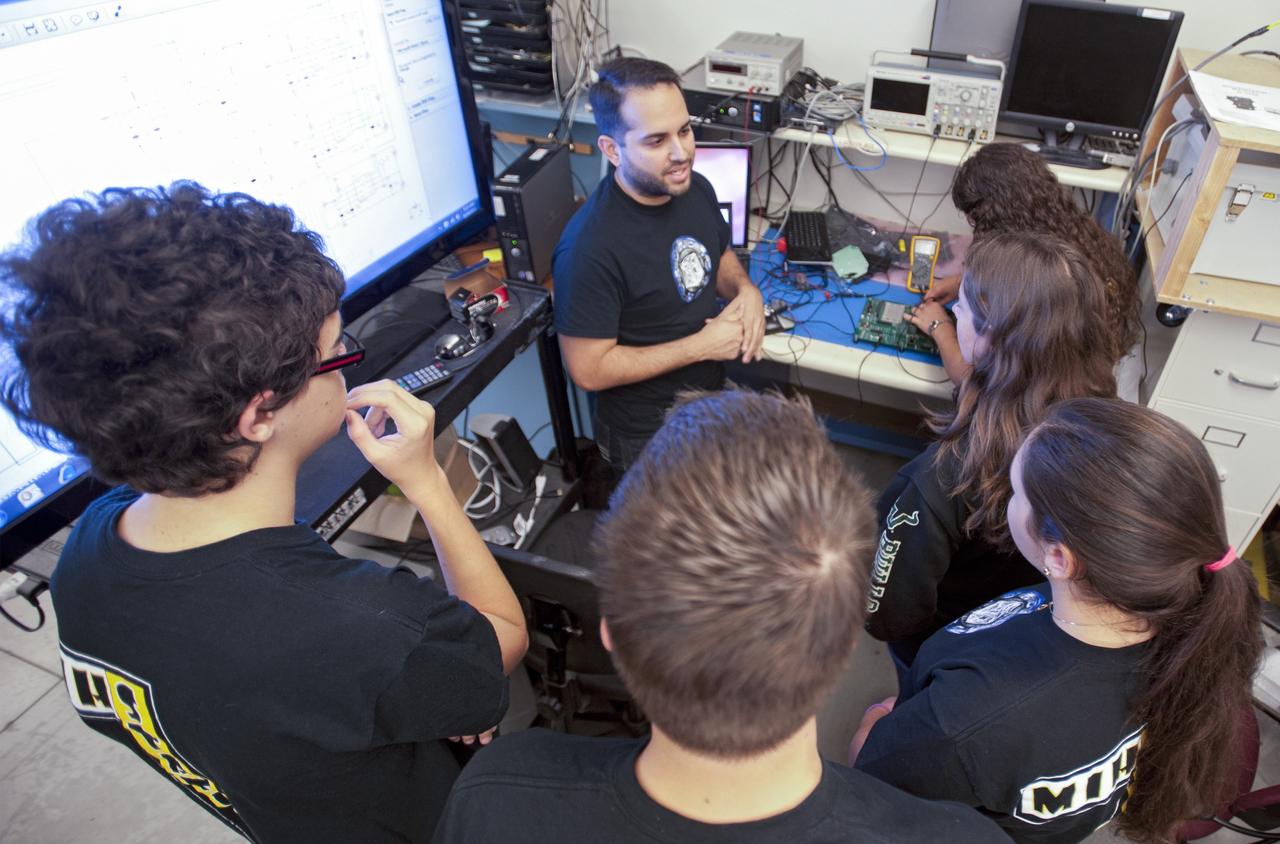

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – NASA mentors and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Kevin Ruiz, a NASA mentor, and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
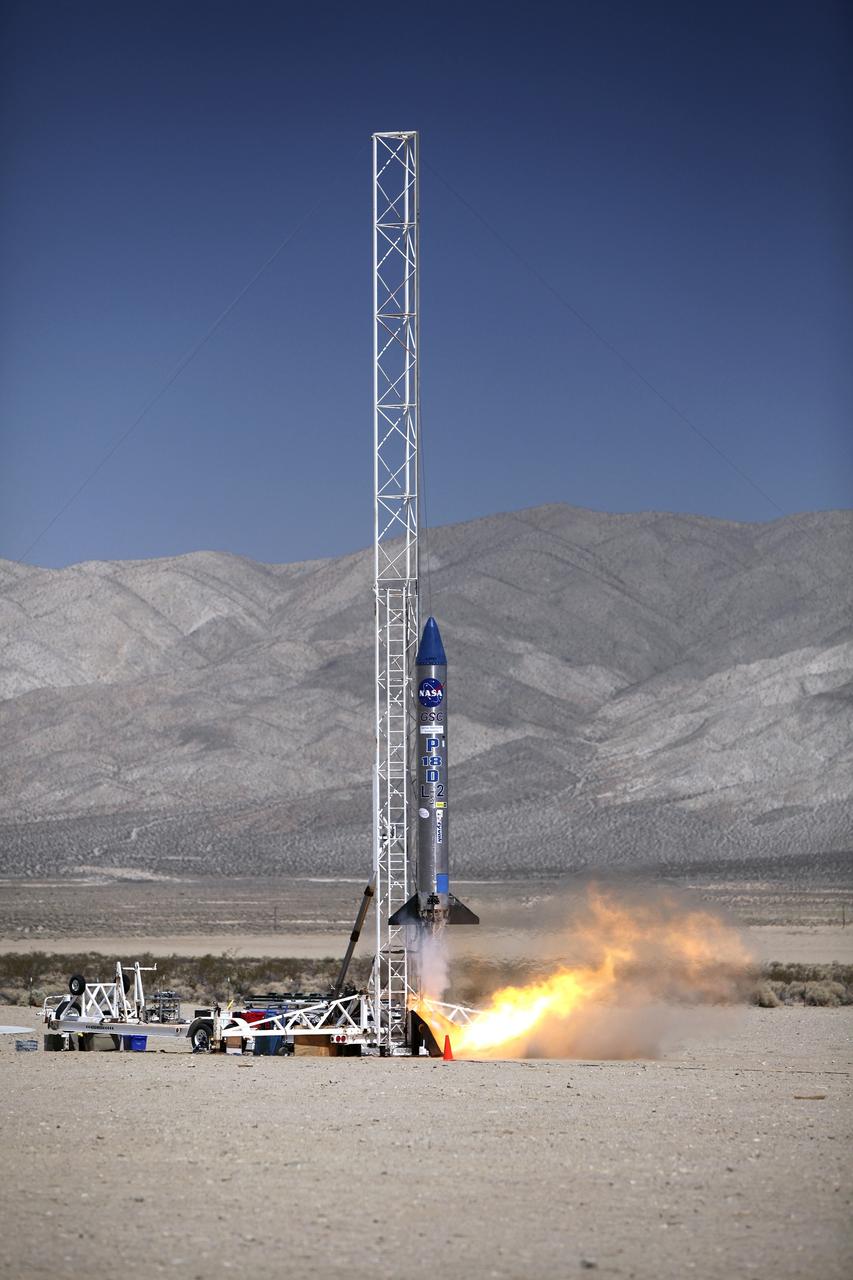

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket lifts off at 10:52 a.m. PDT carrying the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket carried four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Members of the student launch team for the StangSat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
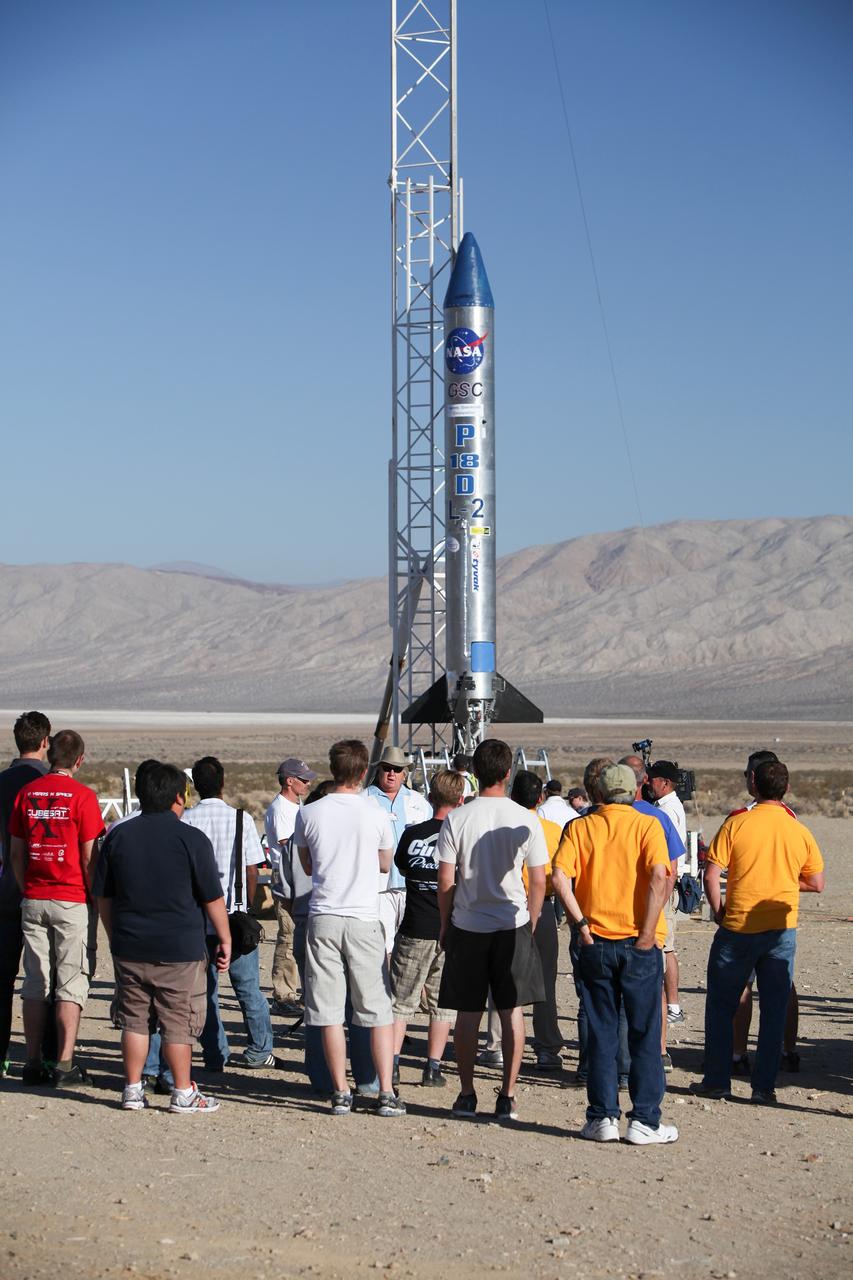

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, students and engineers participate in a pre-launch briefing before the lift off of the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket. The rocket is scheduled to launch the RUBICS-1 payload on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. The rocket will carry four satellites made from four-inch cube sections. The rocket reached a peak altitude of about 9,000 feet, however the parachute deployed prematurely and the vehicle continued on its trajectory, coasting and tumbling to a hard landing on its side. In spite of the rough ride, all four CubeSats were recovered. PhoneSat and RUBICS received data in flight, but sustained structural damage. CP-9 and StangSat fared better, and their teams are working to recover as much information as possible. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites were designed to record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. The results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
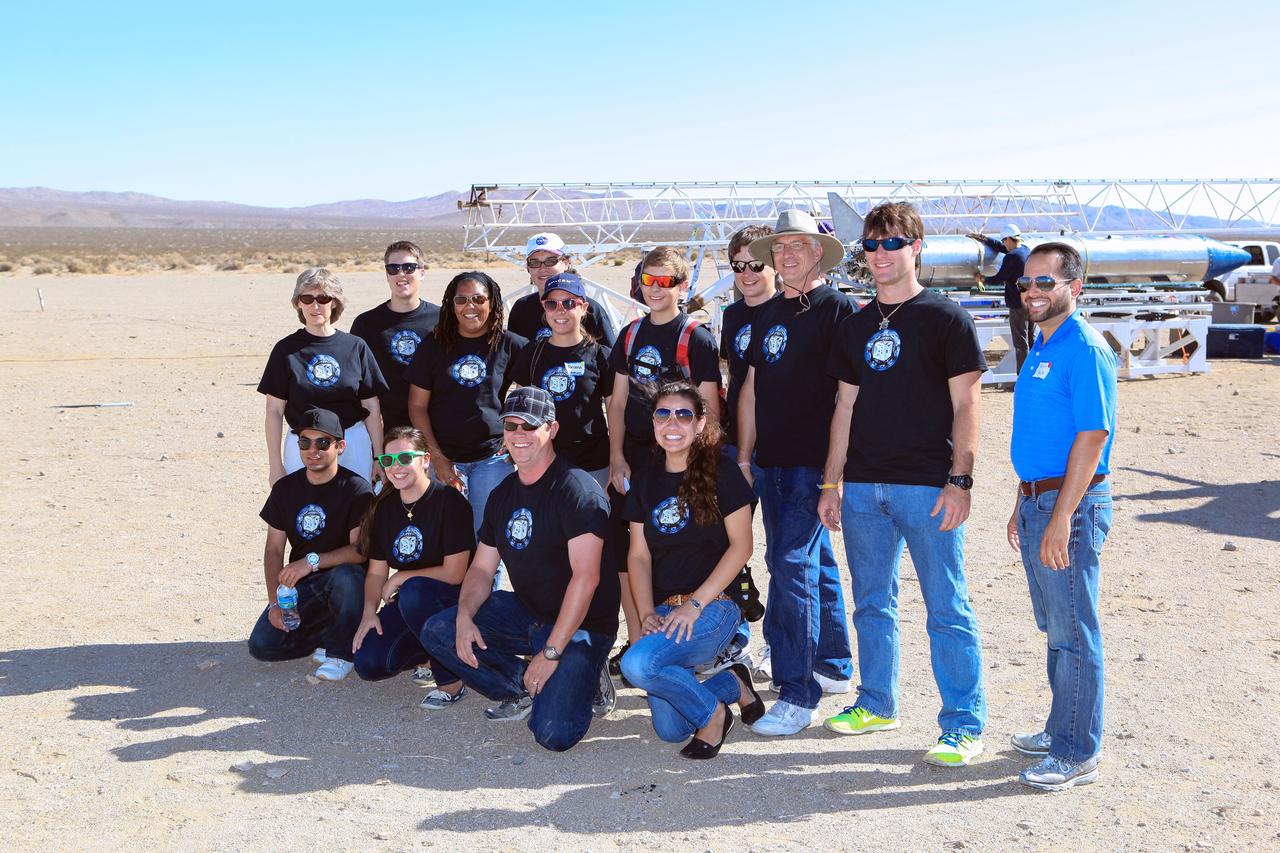

MOJAVE DESERT, Calif. – In the Mojave Desert in California, a student StangSat Team of students from Merritt Island High School in Florida posed for a pre-launch photograph as the Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket, in the background, was being prepared for flight at the Friends of Amateur Rocketry launch site. Kneeling from left to right, are: Gurkirat Kainth, Megan Mackool, NASA mentor Shaun Daly and Maurisa Orona. Standing from left to right, are: teacher sponsor Tracey Beatovich, Brian Robusto, NASA Education program manager Grace Johnson, Nathan Stephens, Briana Luthman, Jackson Kinney, Steven Krygier, NASA mentor Jim Kinney, Joshua Zirkle and NASA mentor Kelvin Ruiz. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
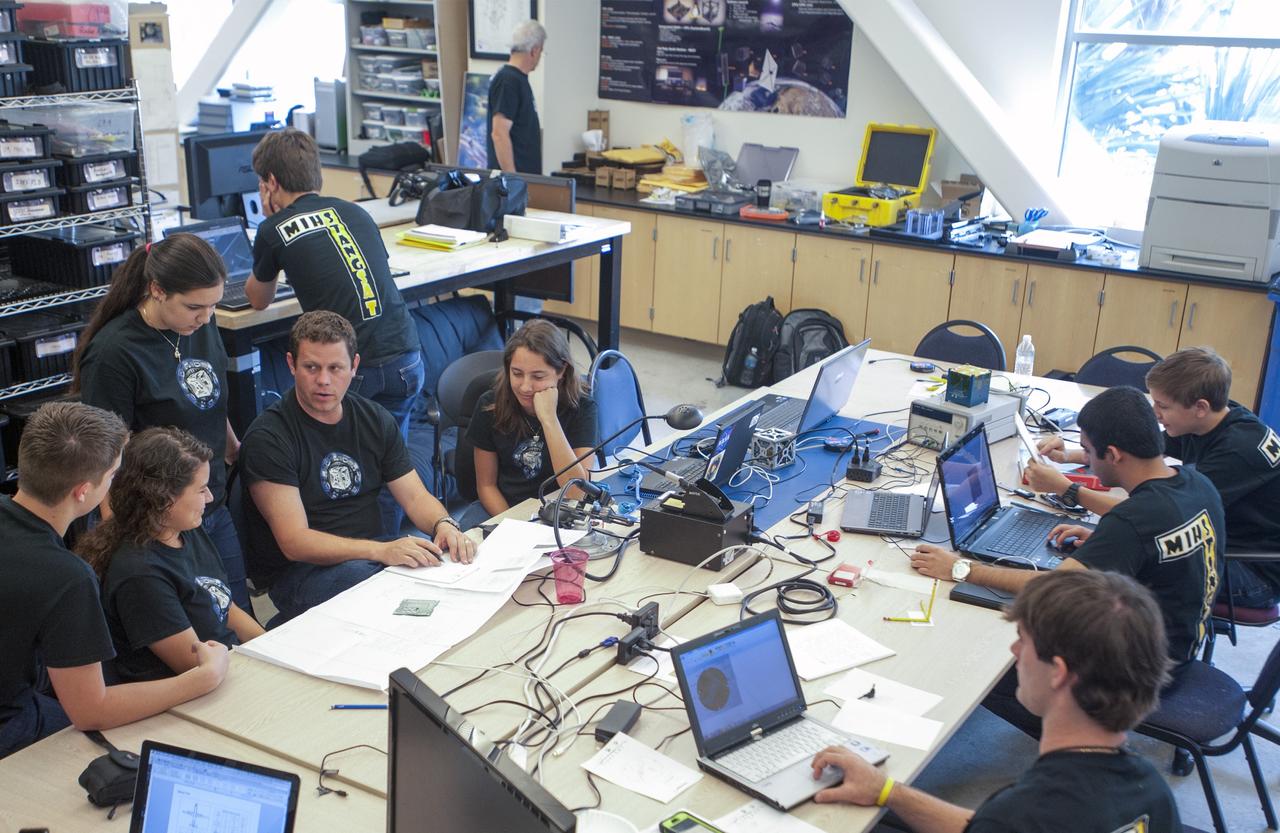

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – NASA mentors and the student launch team for the StangSat and Polysat go through final checks in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payloads, which include sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cubes, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Collectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi PeoplesCollectively known as CubeSats, the satellites will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. They will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. A new, lightweight carrier is also being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis