
These artist’s concepts show SpaceX’s Starship Human Landing System (HLS) on the Moon. NASA is working with SpaceX to develop Starship HLS to carry astronauts from lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back for Artemis III and Artemis IV as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign. At about 165 feet (50 m), Starship HLS will be about the same height as a 15-story building. An elevator on Starship HLS will be used to transport crew and cargo between the lander and the Moon’s surface.

These artist’s concepts show SpaceX’s Starship Human Landing System (HLS) on the Moon. NASA is working with SpaceX to develop Starship HLS to carry astronauts from lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back for Artemis III and Artemis IV as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign. At about 165 feet (50 m), Starship HLS will be about the same height as a 15-story building. An elevator on Starship HLS will be used to transport crew and cargo between the lander and the Moon’s surface.
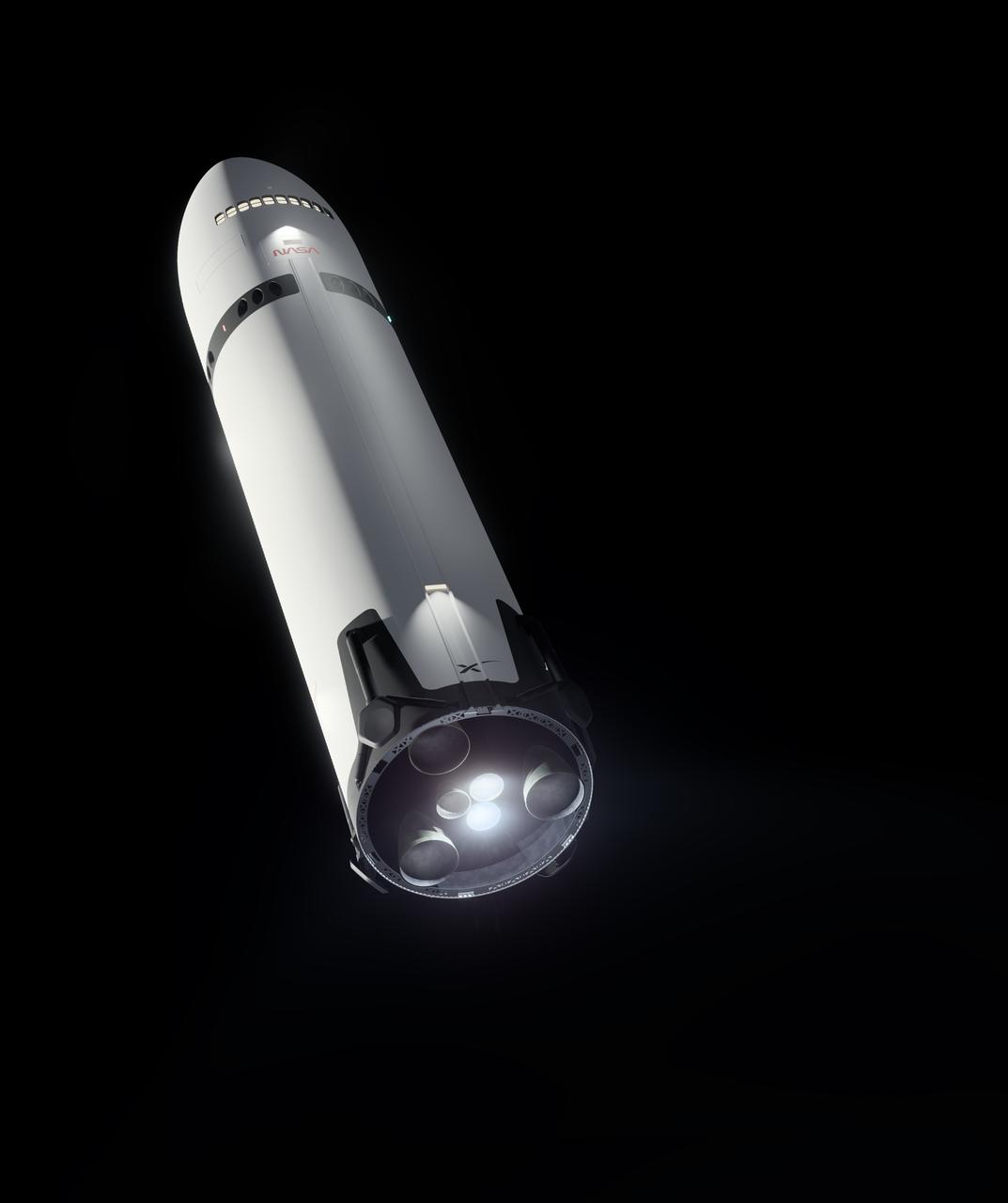

This artist’s concept portrays SpaceX’s Starship Human Landing System (HLS) with two Raptor engines lit, performing a braking burn prior to its Moon landing. The burn will occur after Starship HLS departs low lunar orbit to reduce the lander’s velocity prior to final descent to the lunar surface. NASA is working with SpaceX to develop Starship HLS to carry astronauts from lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back for Artemis III and Artemis IV as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

These artist’s concepts show SpaceX’s Starship Human Landing System (HLS) in operation on its journey to the Moon. Before astronauts launch in NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, SpaceX will launch a storage depot to Earth orbit. For Artemis III and Artemis IV, SpaceX plans to complete propellant loading operations in Earth orbit to send a fully fueled Starship HLS to the Moon. Starship HLS will then dock directly to Orion so that two astronauts can transfer from the spacecraft to the lander to descend to the Moon’s surface, while two others remain in Orion. Beginning with Artemis IV, NASA’s Gateway lunar space station will serve as the crew transfer point. NASA is working with SpaceX to develop Starship HLS to carry astronauts from lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back for Artemis III and Artemis IV as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
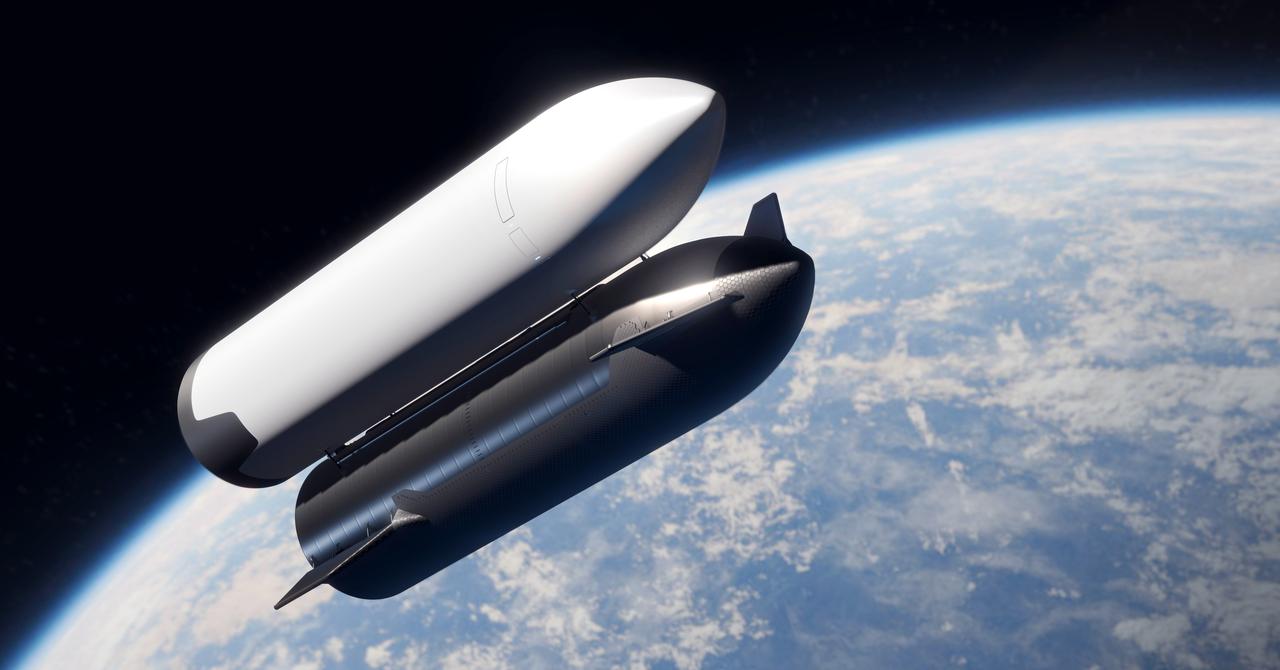

These artist’s concepts show SpaceX’s Starship Human Landing System (HLS) in operation on its journey to the Moon. Before astronauts launch in NASA’s Orion spacecraft atop the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, SpaceX will launch a storage depot to Earth orbit. For Artemis III and Artemis IV, SpaceX plans to complete propellant loading operations in Earth orbit to send a fully fueled Starship HLS to the Moon. Starship HLS will then dock directly to Orion so that two astronauts can transfer from the spacecraft to the lander to descend to the Moon’s surface, while two others remain in Orion. Beginning with Artemis IV, NASA’s Gateway lunar space station will serve as the crew transfer point. NASA is working with SpaceX to develop Starship HLS to carry astronauts from lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back for Artemis III and Artemis IV as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
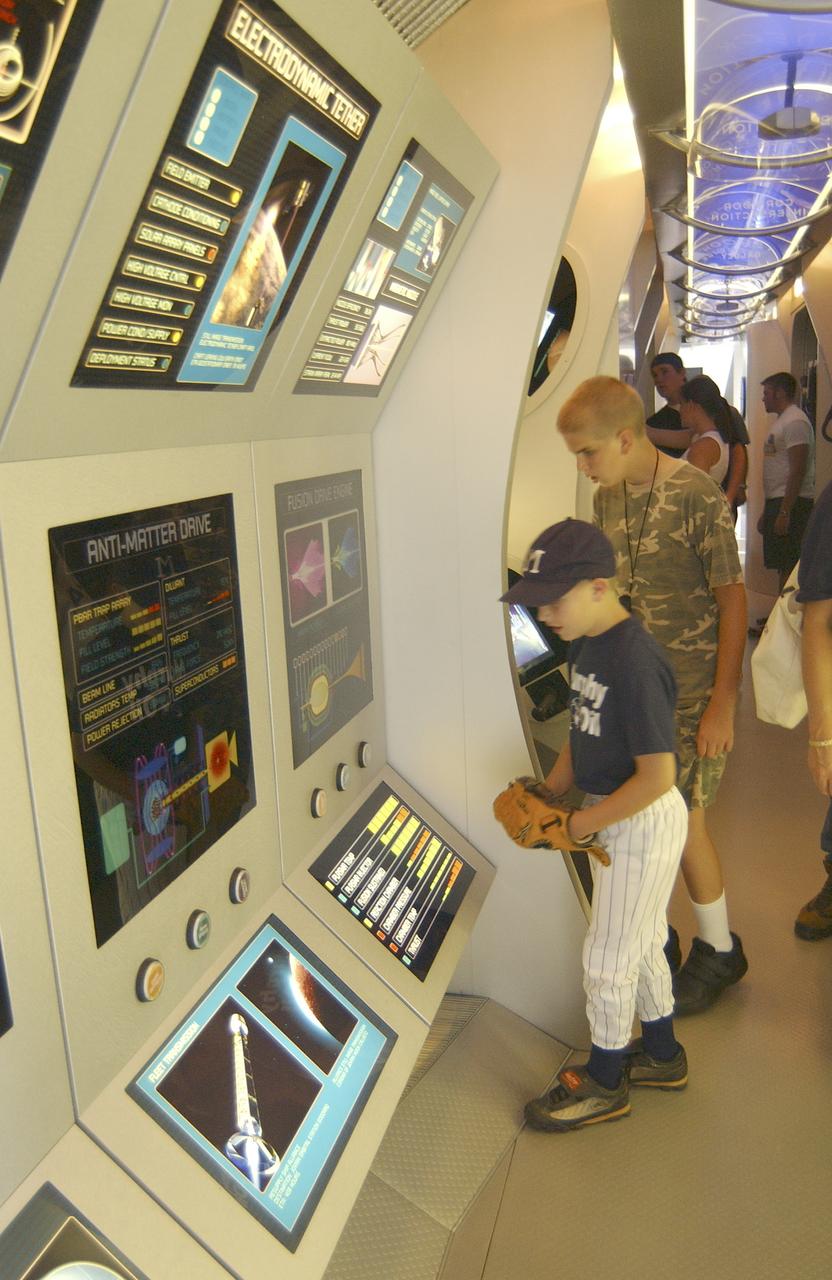

This photograph shows onlookers viewing displays within the Starship 2040 exhibit on display at Joe Davis Stadium in Huntsville, Alabama. Developed by the Space Transportation Directorate at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Starship 2040 exhibit is housed in a 48-ft (14.6-m) tractor and trailer rig, permitting it to travel around the Nation, demonstrating NASA's vision of what commercial spaceflight might be like 40 years from now. All the irnovations suggested aboard the exhibit (automated vehicle health monitoring systems, high-energy propulsion drive, navigational aids, and emergency and safety systems) are based on concepts and technologies now being studied at NASA Centers and partner institutions around the Nation. NASA is the Nation's premier agency for development of the space transportation system, including future-generation reusable launch vehicles. Such systems, the keys to a "real" Starship 2040, require revolutionary advances in critical aerospace technologies, from thermal, magnetic, chemical, and propellantless propulsion systems to new energy sources such as space solar power or antimatter propulsion. These and other advances are now being studied, developed, and tested at NASA field centers and partner institutions all over the Nation.
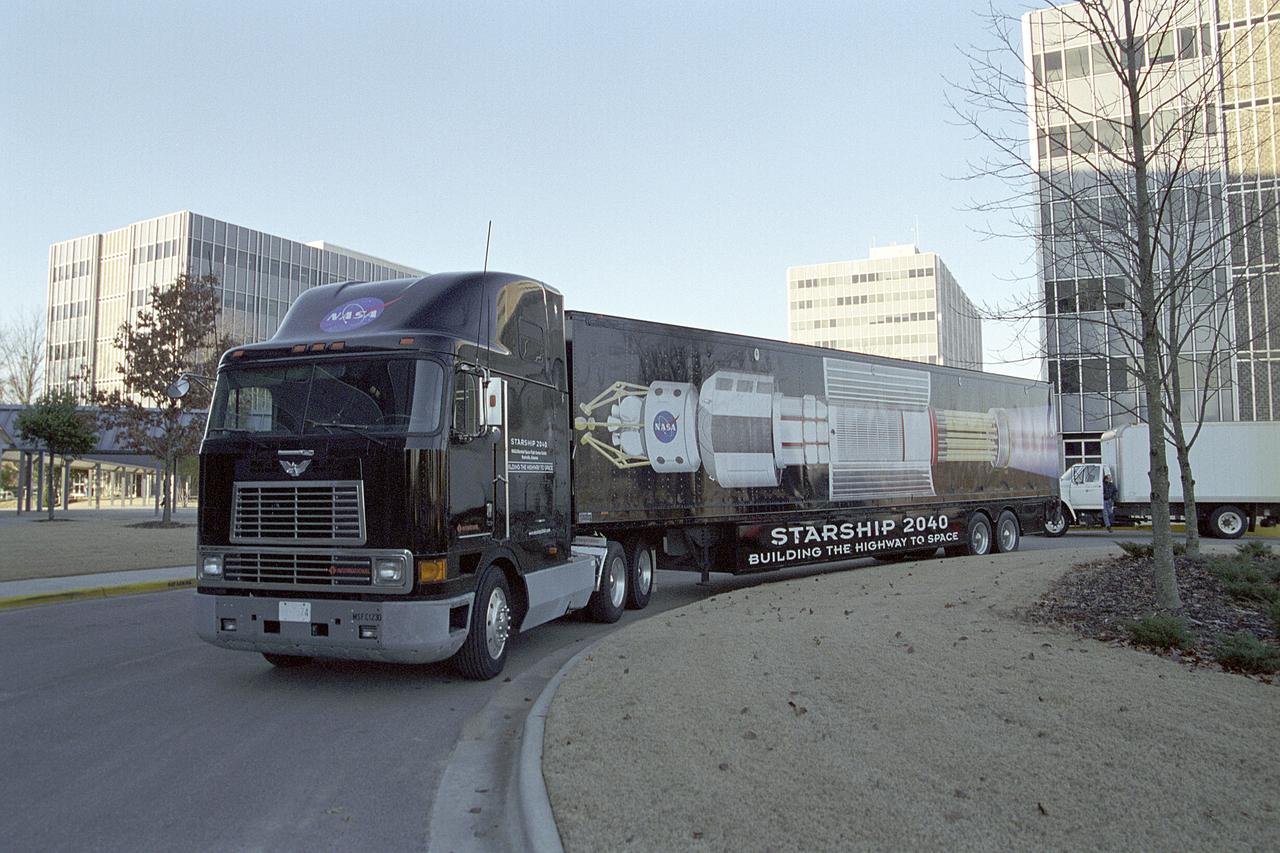

This photograph shows the Starship 2040 leaving the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for the exhibit site. Developed by the Space Transportation Directorate at MSFC, the Starship 2040 exhibit is housed in a 48-ft (14.6-m) tractor and trailer rig, permitting it to travel around the Nation, demonstrating NASA's vision of what commercial spaceflight might be like 40 years from now. All the irnovations suggested aboard the exhibit, automated vehicle health monitoring systems, high-energy propulsion drive, navigational aids and emergency and safety systems, are based on concepts and technologies now being studied at NASA Centers and partner institutions around the Nation. NASA is the nation's premier agency for development of the space transportation system, including future-generation reusable launch vehicles. Such systems, the keys to a "real" Starship 2040, require revolutionary advances in critical aerospace technologies, from thermal, magnetic, chemical, and propellantless propulsion systems to new energy sources such as space solar power or antimatter propulsion. These and other advances are now being studied, developed, and tested at NASA field centers and partner institutions all over the Nation.
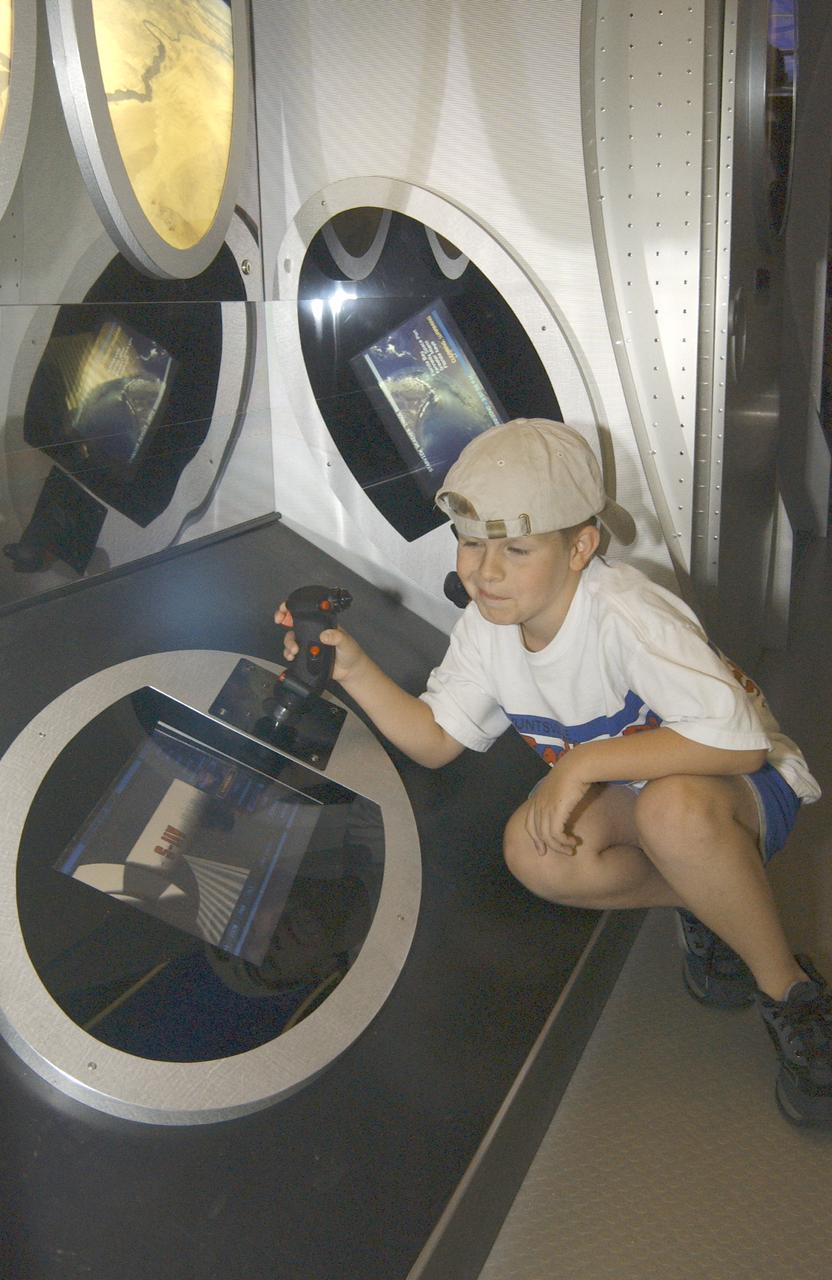

This photograph shows Justin Varnadore, son of a Marshall TV employee, at the controls of one of the many displays within the Starship 2040 exhibit on display at Joe Davis Stadium in Huntsville, Alabama. Developed by the Space Transportation Directorate at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Starship 2040 exhibit is housed in a 48-ft (14.6-m) tractor and trailer rig, permitting it to travel around the Nation, demonstrating NASA's vision of what commercial spaceflight might be like 40 years from now. All the irnovations suggested aboard the exhibit (automated vehicle health monitoring systems, high-energy propulsion drive, navigational aids, and emergency and safety systems) are based on concepts and technologies now being studied at NASA Centers and partner institutions around the Nation. NASA is the Nation's premier agency for development of the space transportation system, including future-generation reusable launch vehicles. Such systems, the keys to a "real" Starship 2040, require revolutionary advances in critical aerospace technologies, from thermal, magnetic, chemical, and propellantless propulsion systems to new energy sources such as space solar power or antimatter propulsion. These and other advances are now being studied, developed, and tested at NASA field centers and partner institutions all over the Nation.
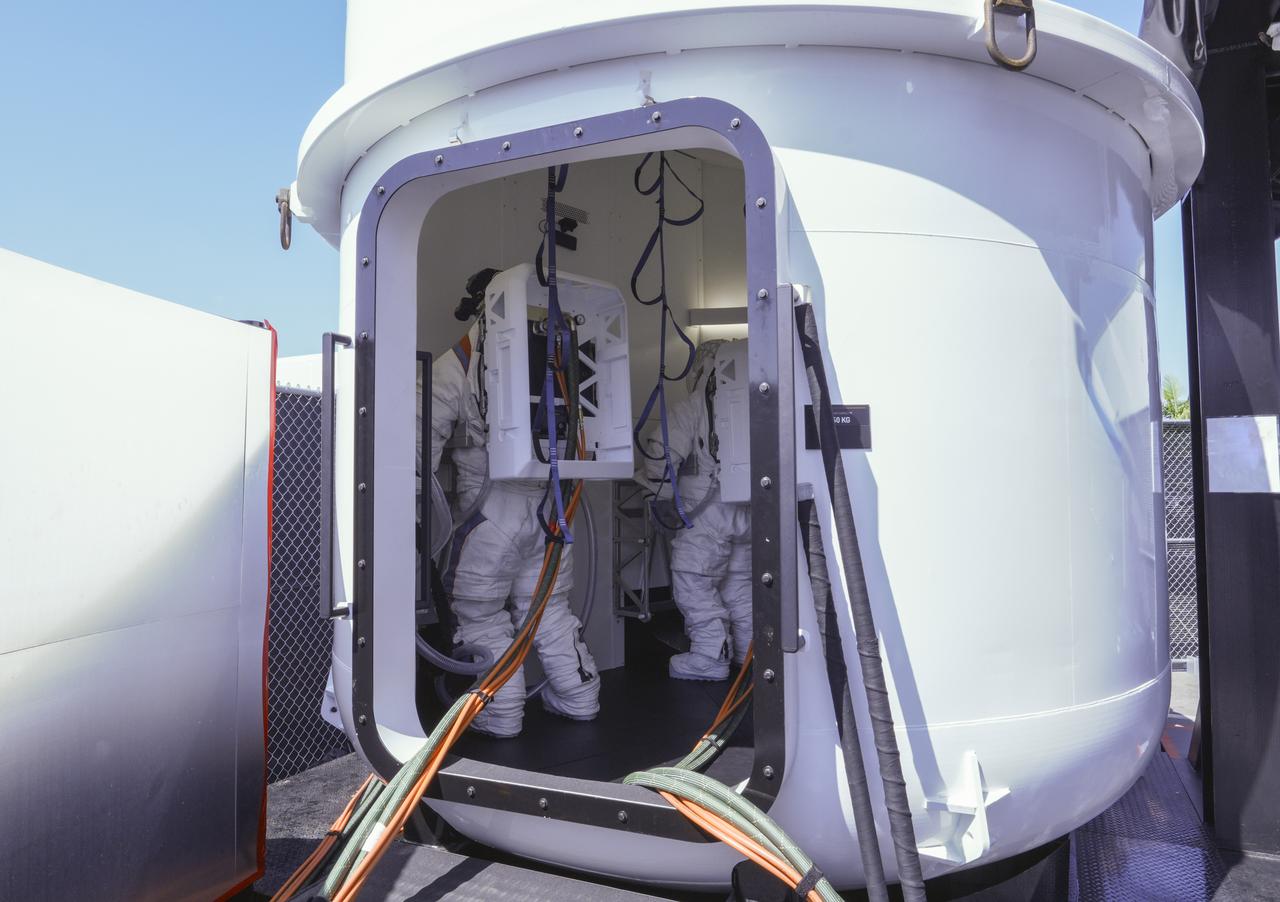

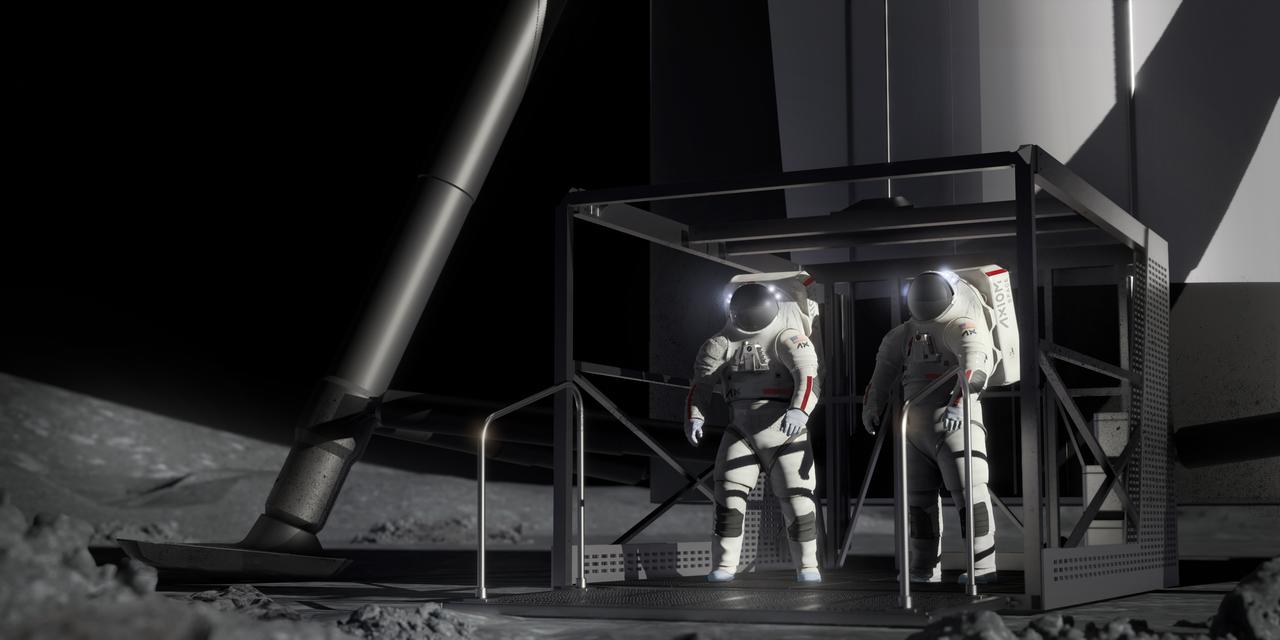
NASA astronaut Doug “Wheels” Wheelock and Axiom Space astronaut Peggy Whitson were fully suited while conducting mission-like maneuvers in the full-scale build of the Starship human landing system’s airlock which will be located inside Starship under the crew cabin. Image Credit: SpaceX
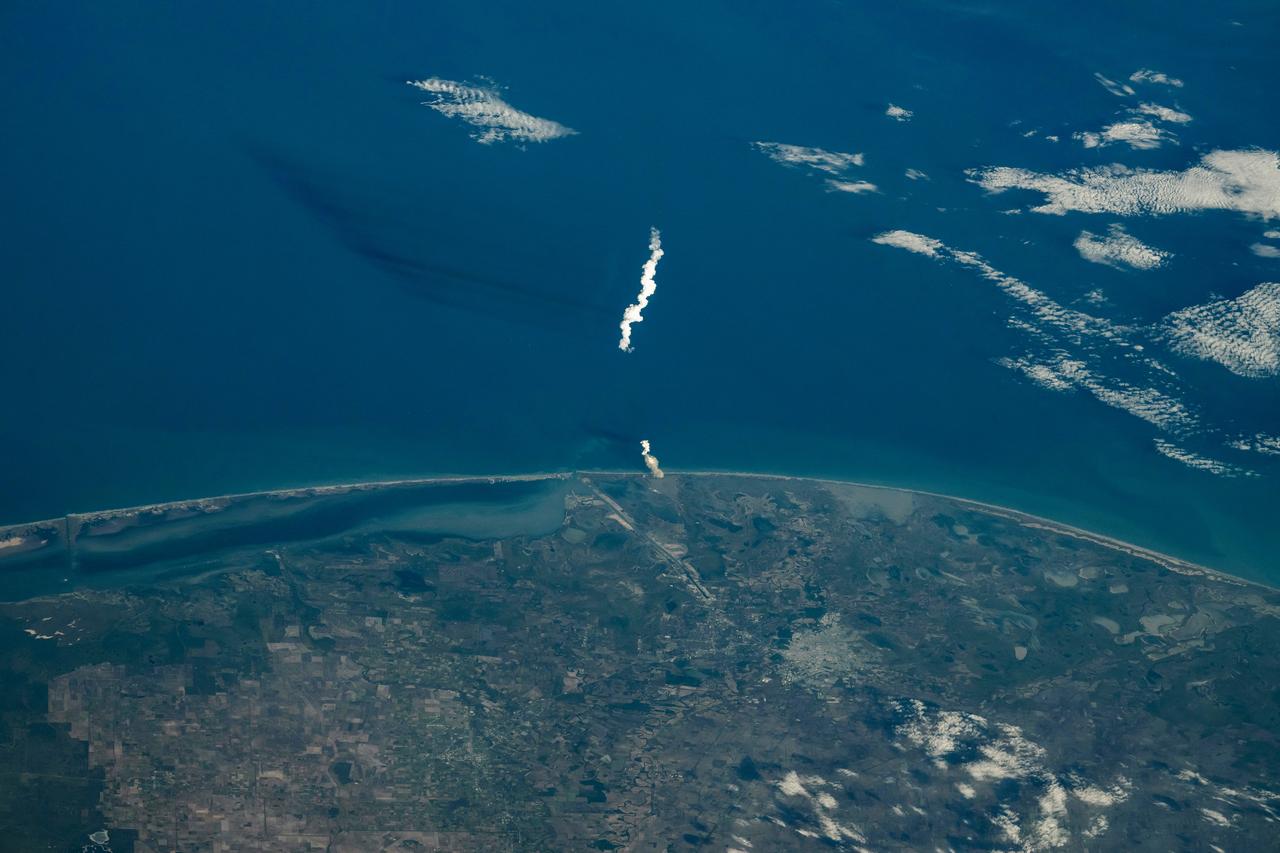

iss072e220043 (Nov. 19, 2024) --- The plume from the SpaceX Starship 6 rocket can be seen after launching on its sixth flight test from the company's Starbase site in Boca Chica, Texas. Credit: Don Pettit/NASA
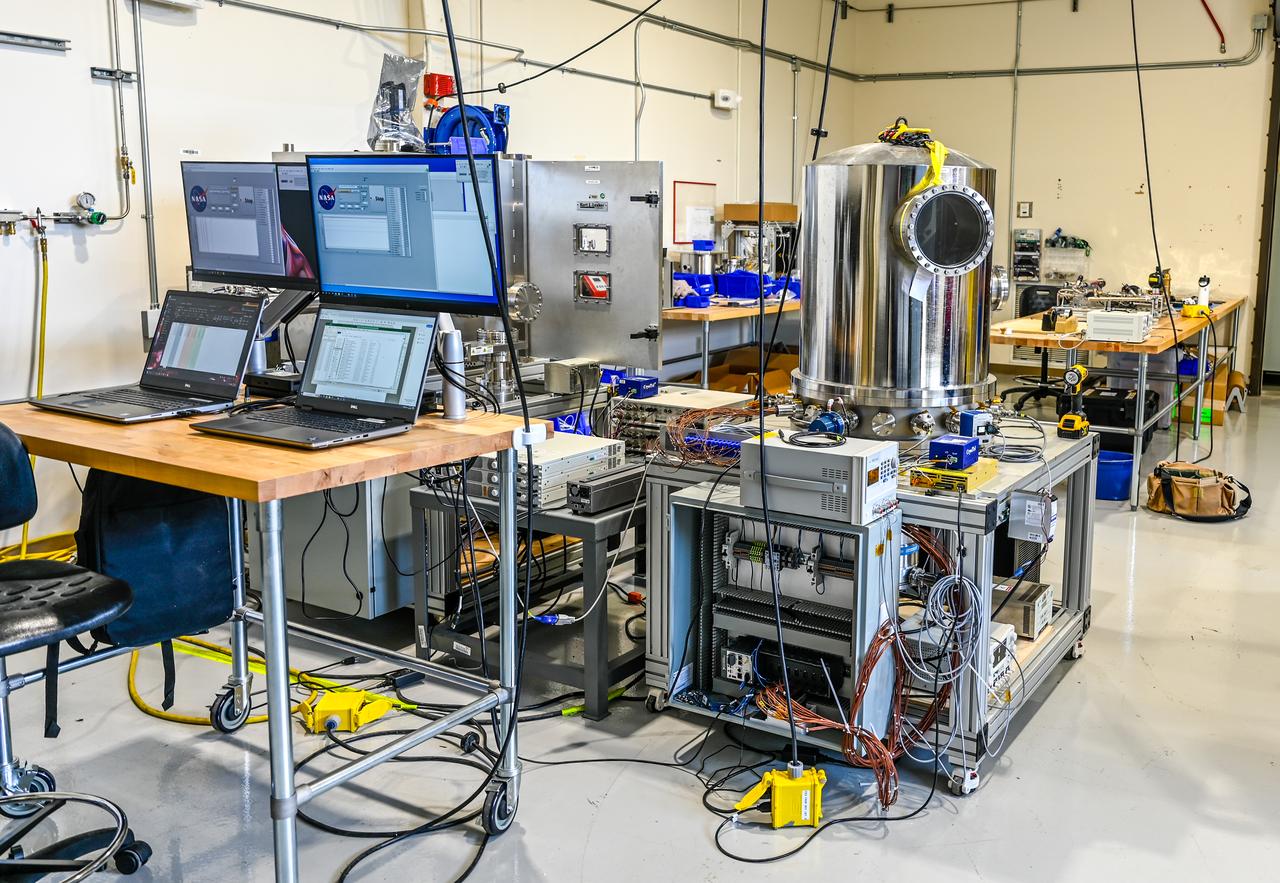

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
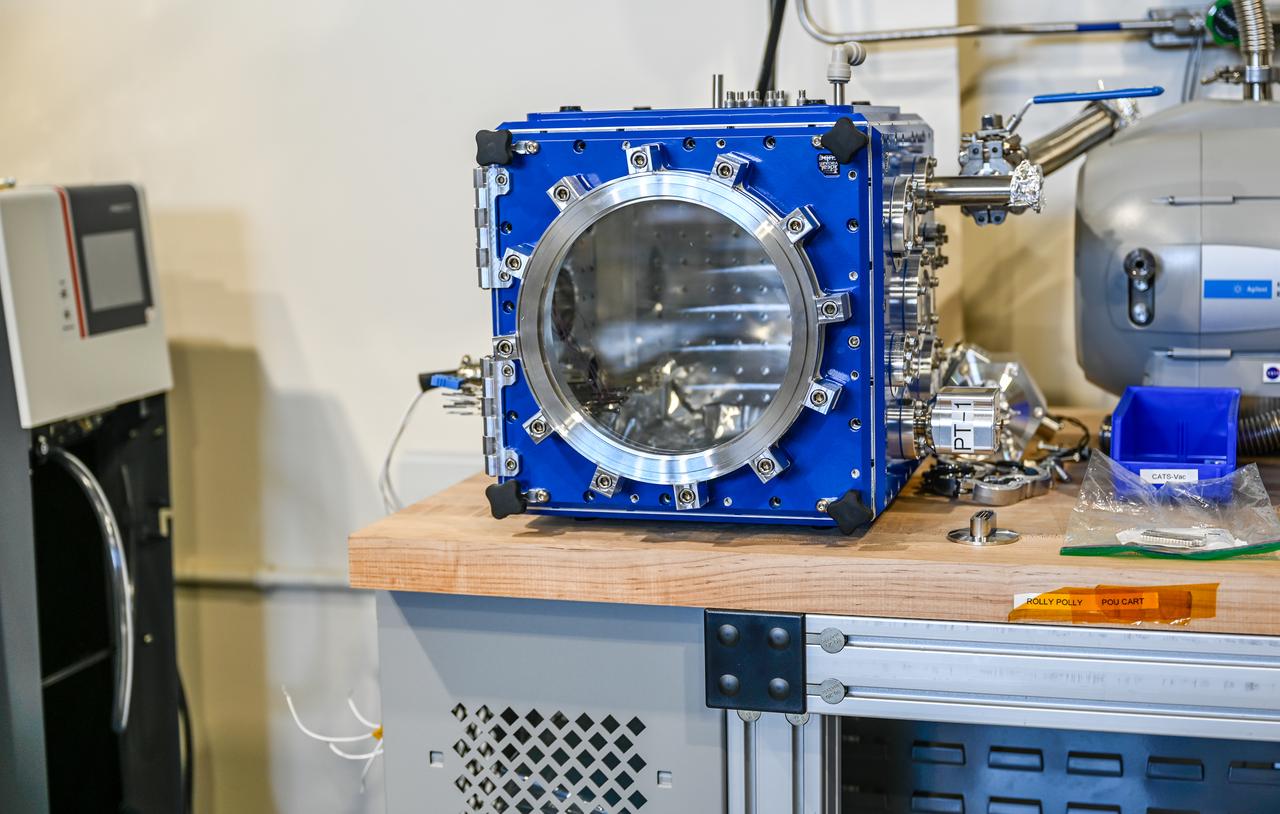
These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
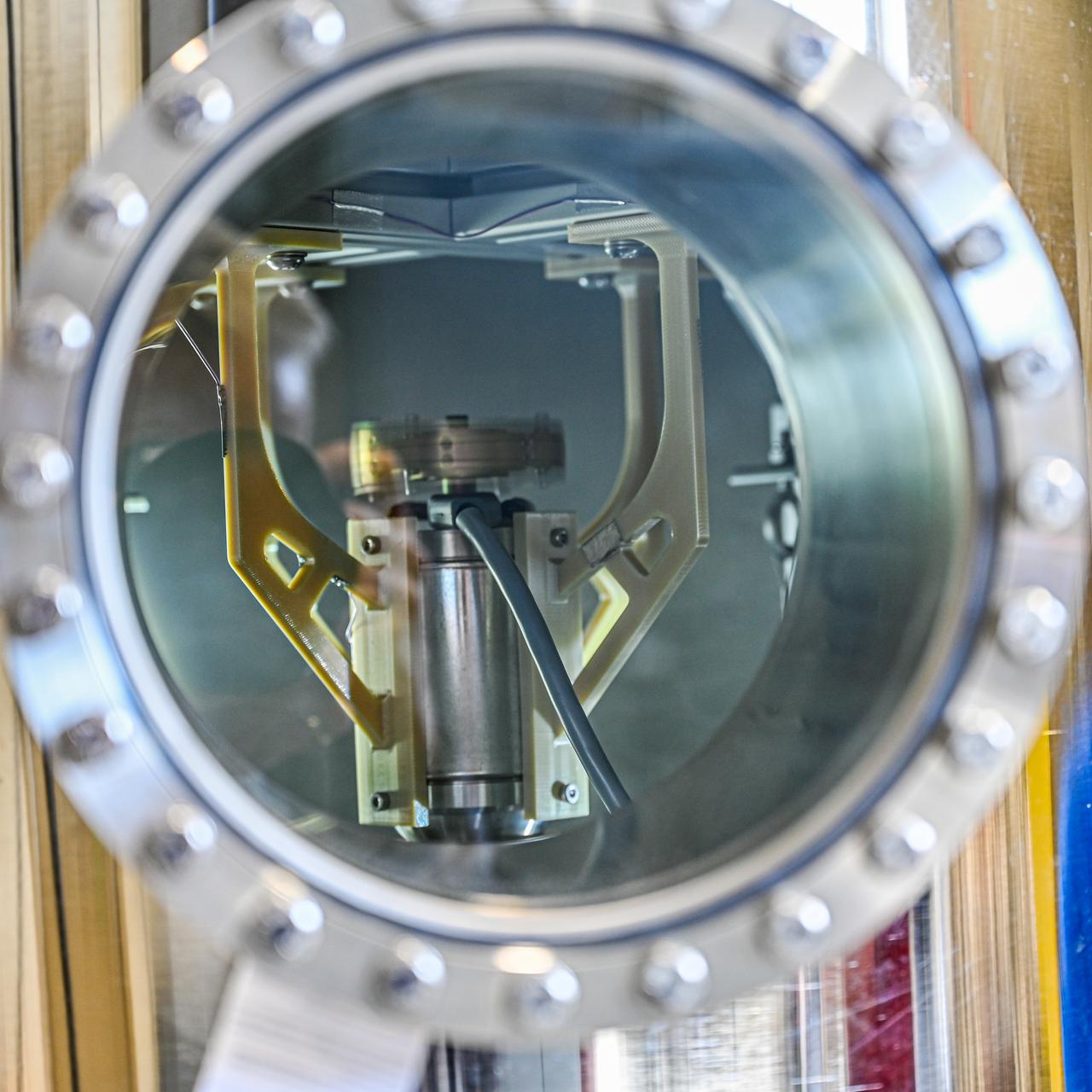
These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
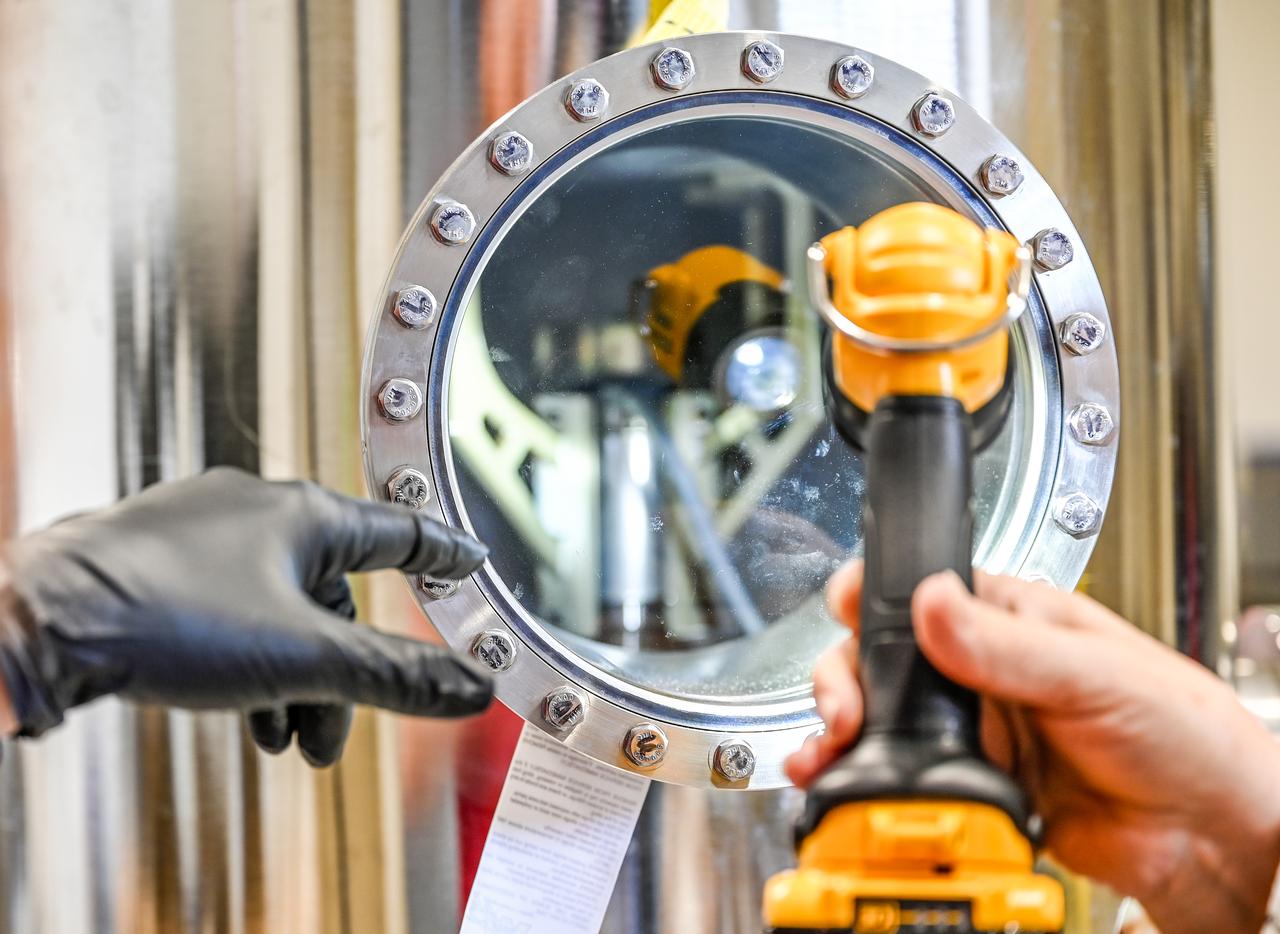

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
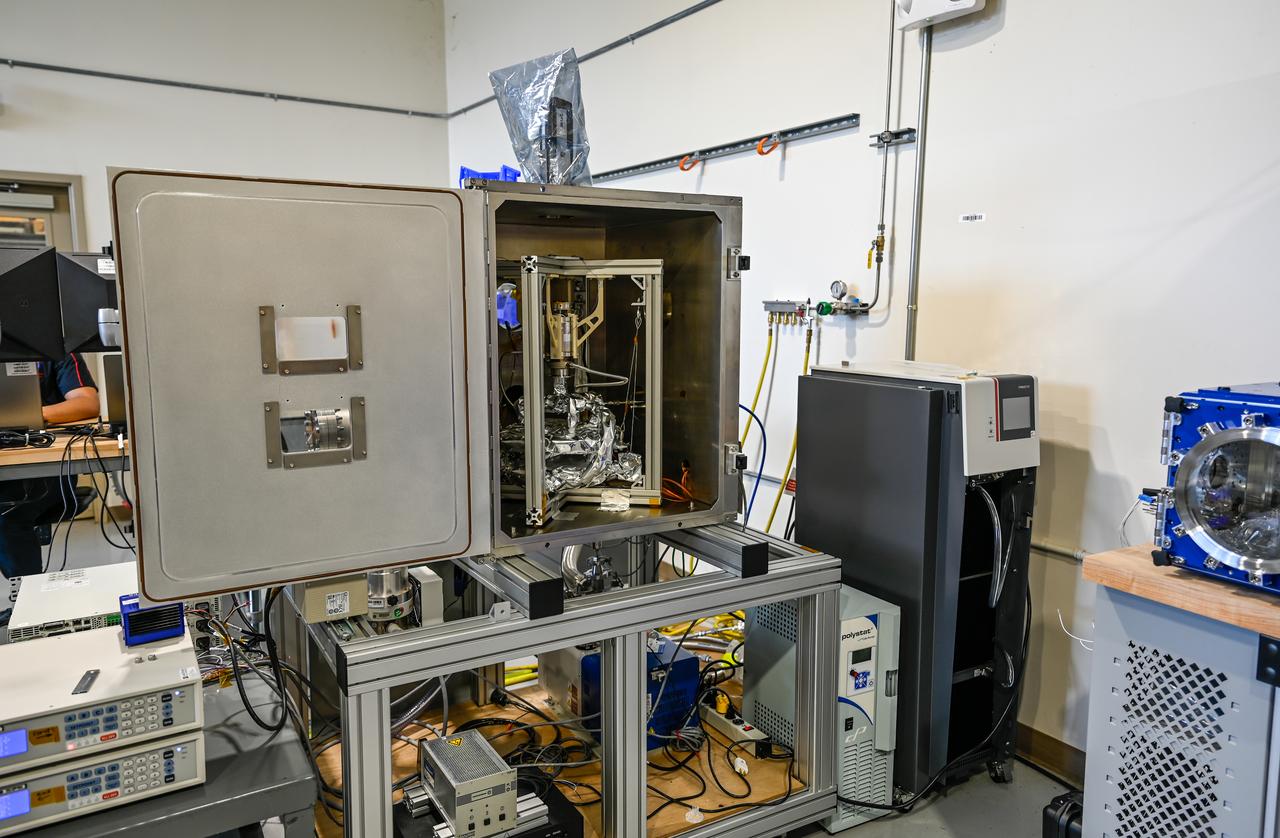

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
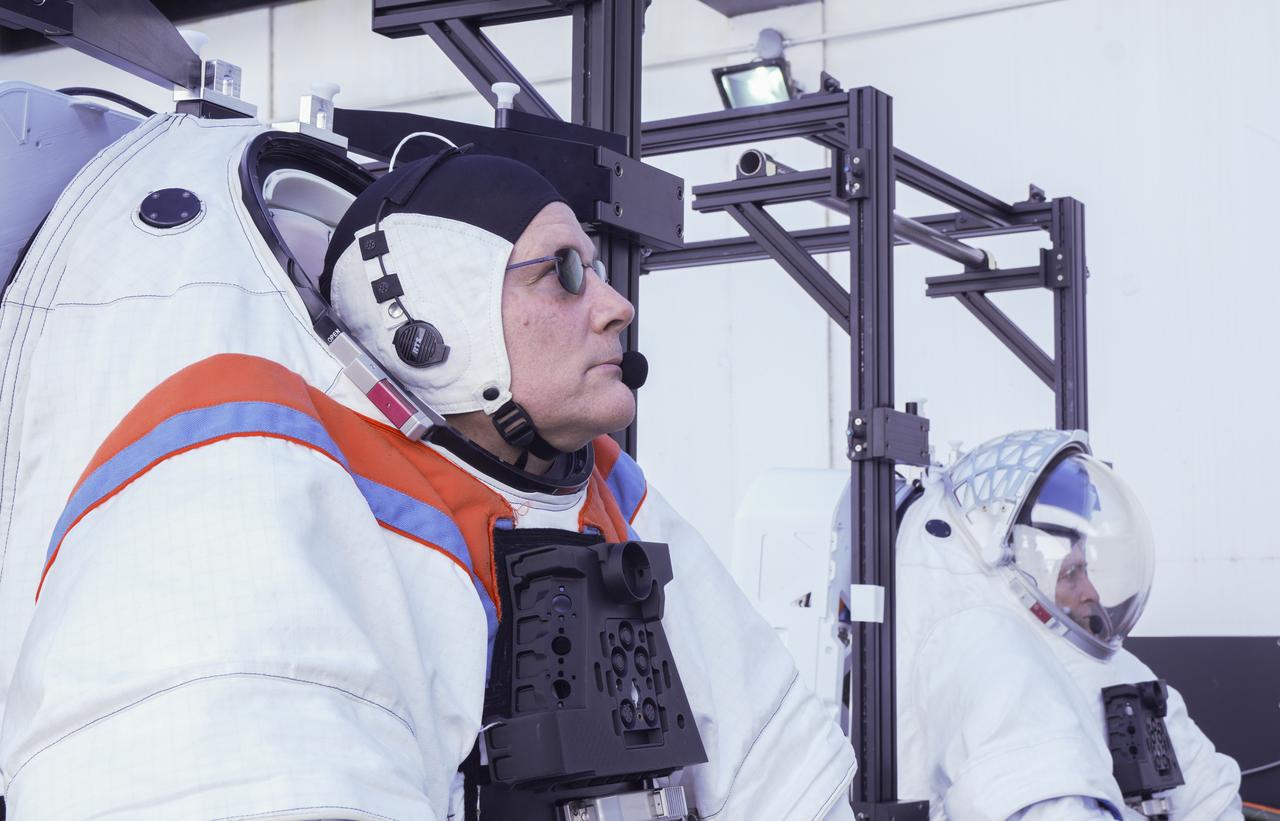

NASA astronaut Doug “Wheels” Wheelock and Axiom Space astronaut Peggy Whitson prepare for a test of full-scale mockups of spacesuits developed by Axiom Space and SpaceX’s Starship human landing system developed for NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image Credit: SpaceX
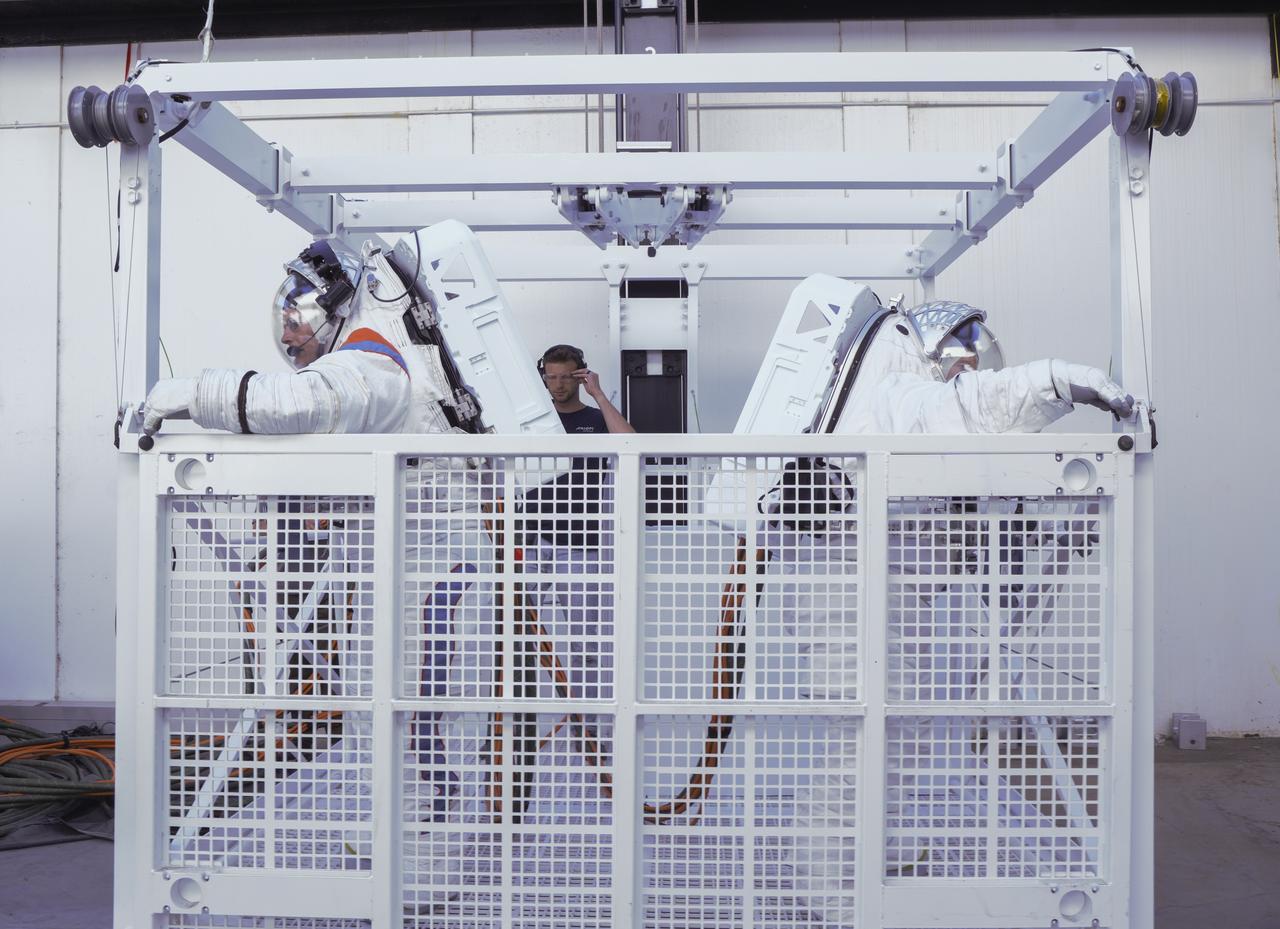

NASA astronaut Doug "Wheels" Wheelock and Axiom Space astronaut Peggy Whitson were able to test the agility of the spacesuits by conducting movements and tasks similar to those necessary during lunar surface exploration on Artemis missions, such as operating the full-scale mockup of Starship’s elevator gate. Image Credit: SpaceX
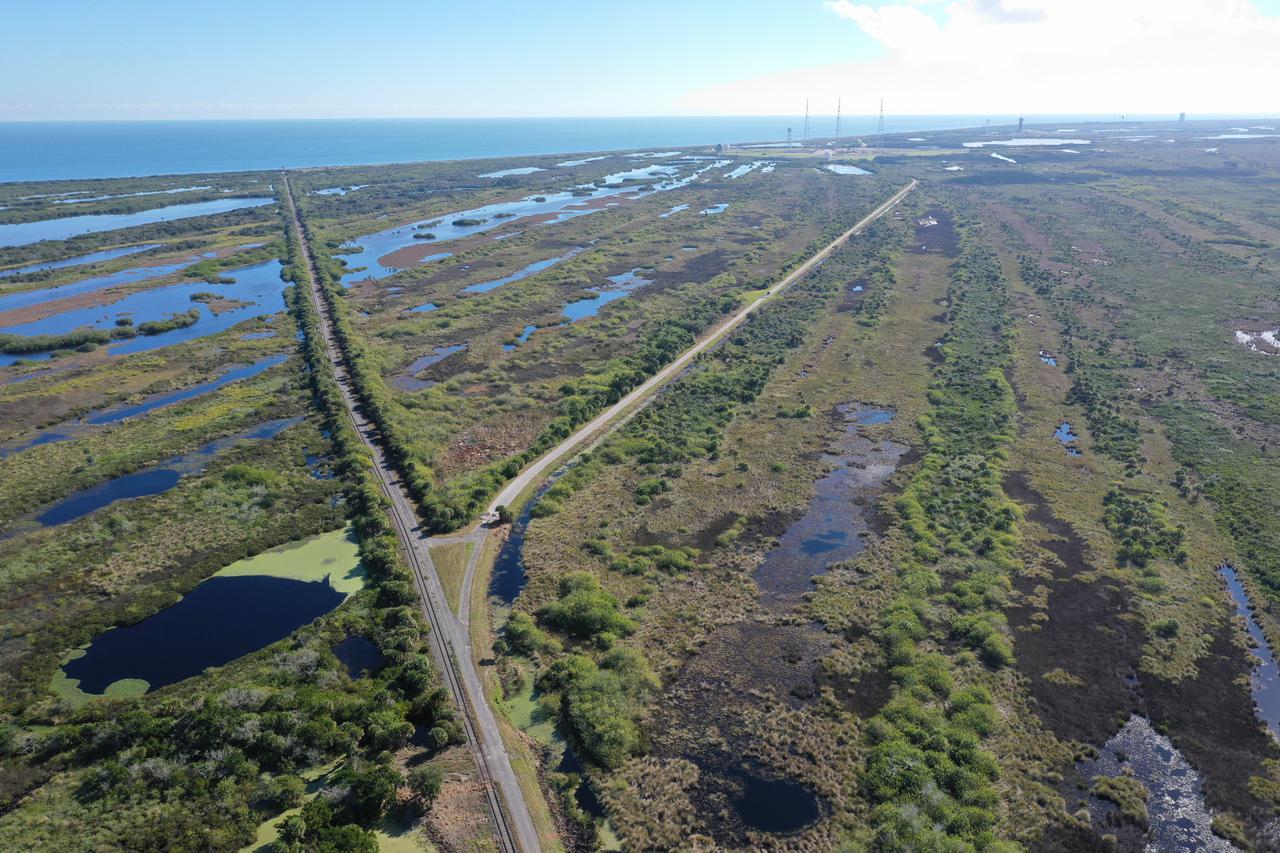

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
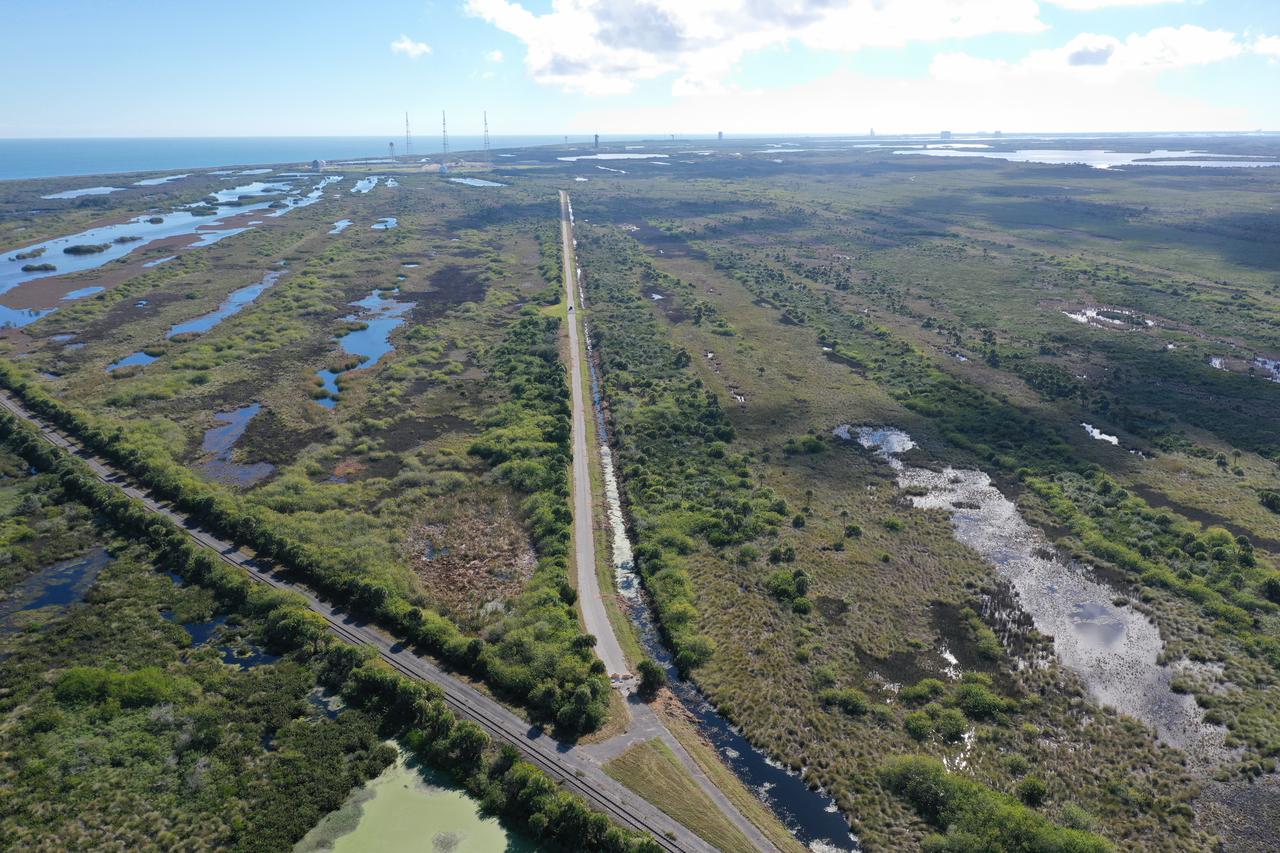

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
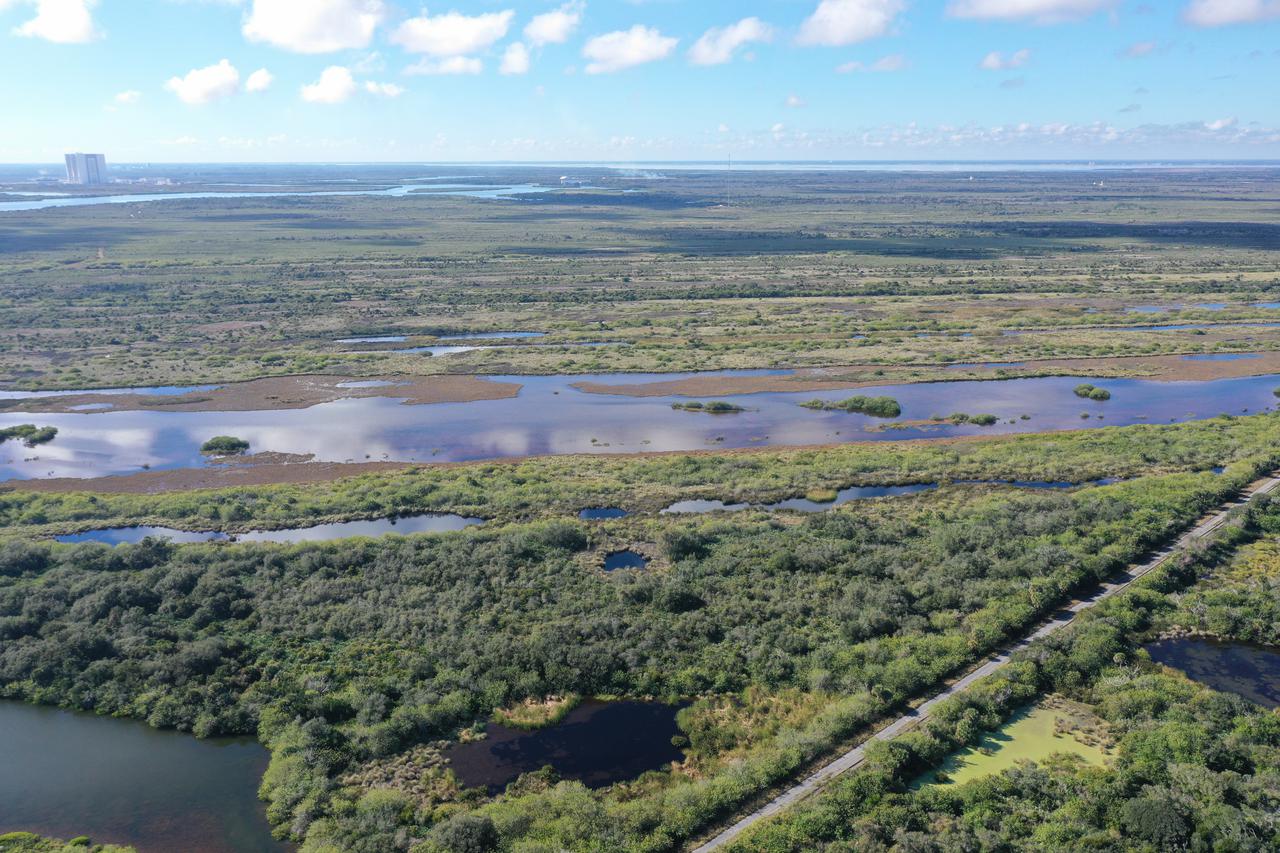

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
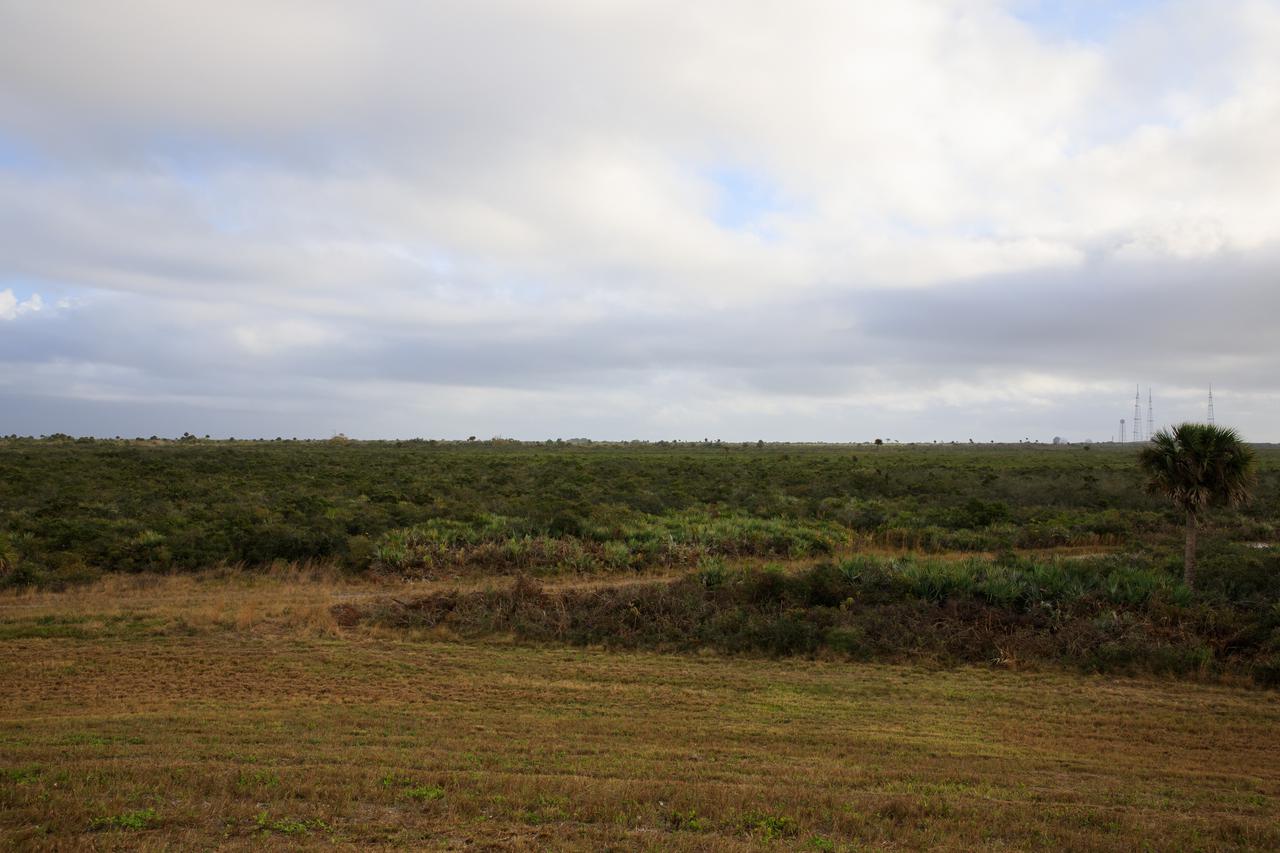

A view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 20, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
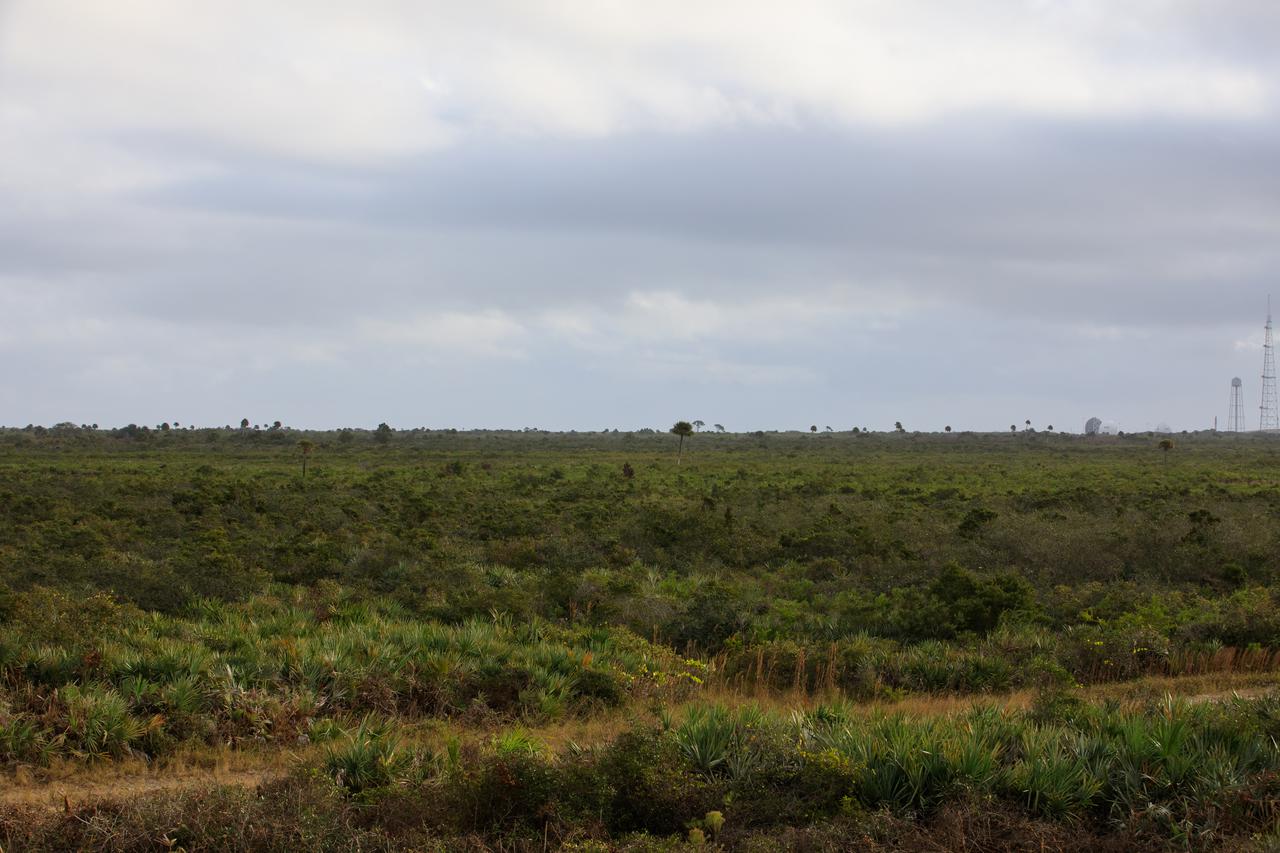

A view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 20, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
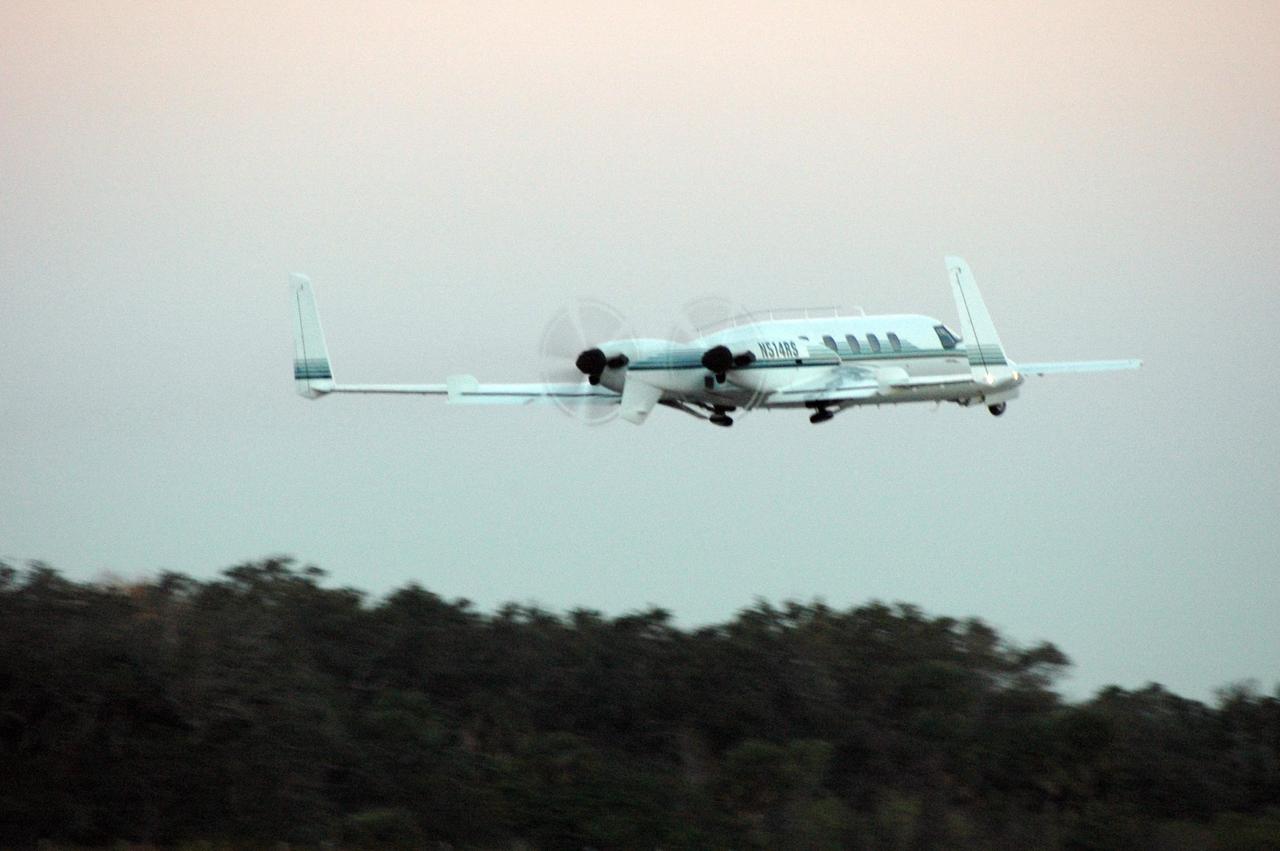

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beechcraft Starship aircraft precedes the takeoff of the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer from NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Photographers on board the Beachcraft will capture the historic event from the air. Pilot Steve Fossett is attempting a record-breaking solo flight, non-stop without refueling, to surpass the current record for the longest flight of any aircraft. This is the second attempt in two days after a fuel leak was detected Feb. 7. The actual launch time was 7:22 a.m. Feb. 8.

Just in time for the 50th anniversary of the TV series "Star Trek," which first aired September 8th,1966, this infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope may remind fans of the historic show. Just as one might see the shapes of animals or other objects in clouds -- a phenomenon called pareidolia -- iconic starships from the series may seem to emerge in these nebulae./ With a little scrutiny (see Figure 1), you may see hints of the saucer and hull of the original USS Enterprise, captained by James T. Kirk, as if it were emerging from a dark nebula. To the left, its "Next Generation" successor, Jean-Luc Picard's Enterprise-D, flies off in the opposite direction. Astronomically speaking, the region pictured here falls within the disk of our Milky Way galaxy, and displays two regions of star formation that are hidden behind a haze of dust when viewed in visible light. Spitzer's ability to peer deeper into dust clouds has revealed a myriad of stellar birthplaces like these, which are officially known only by their catalog numbers, IRAS 19340+2016 and IRAS19343+2026. Trekkies, however, may prefer using the more familiar designations NCC-1701 and NCC-1701-D. This image was assembled using data from Spitzer's biggest surveys of the Milky Way, called GLIMPSE and MIPSGAL. Light with a wavelength of 3.5 microns is shown in blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns in red. The green colors highlight organic molecules in the dust clouds, illuminated by starlight. Red colors are related to thermal radiation emitted from the very hottest areas of dust. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20917