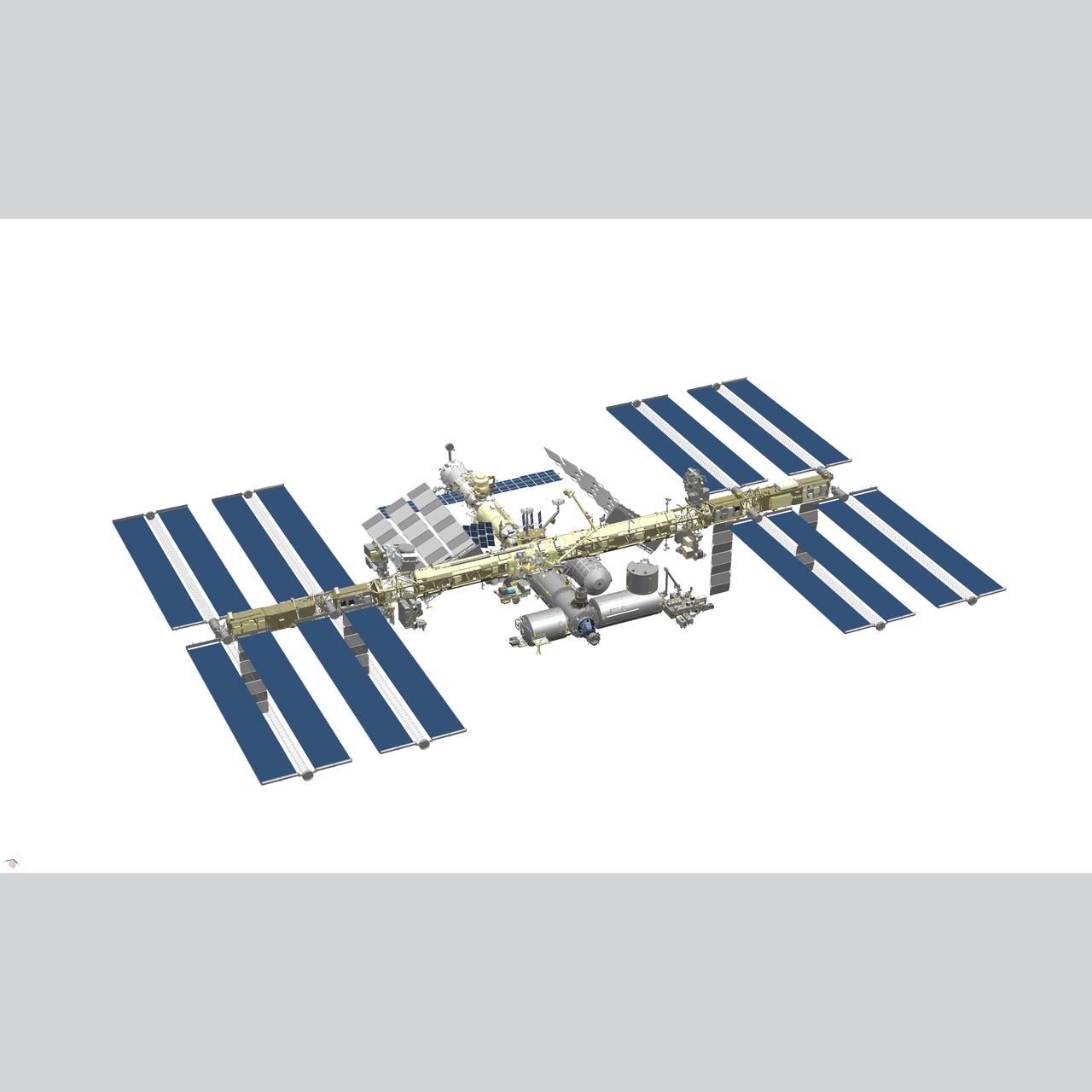
2020 International Space Station Configuration

That No Space Station
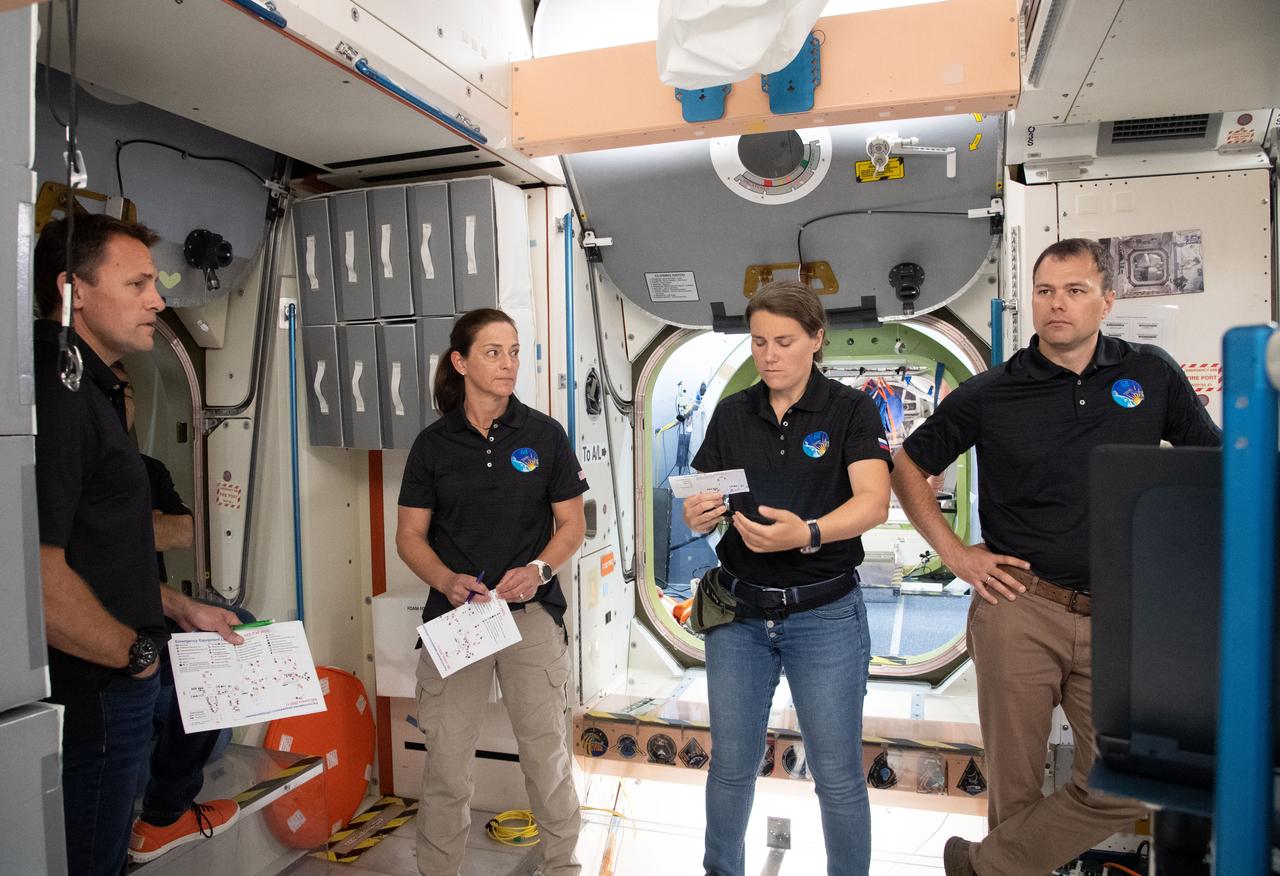

Expedition 68 trains for their upcoming International Space Station mission inside a mockup that models the real orbiting lab at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/James Blair
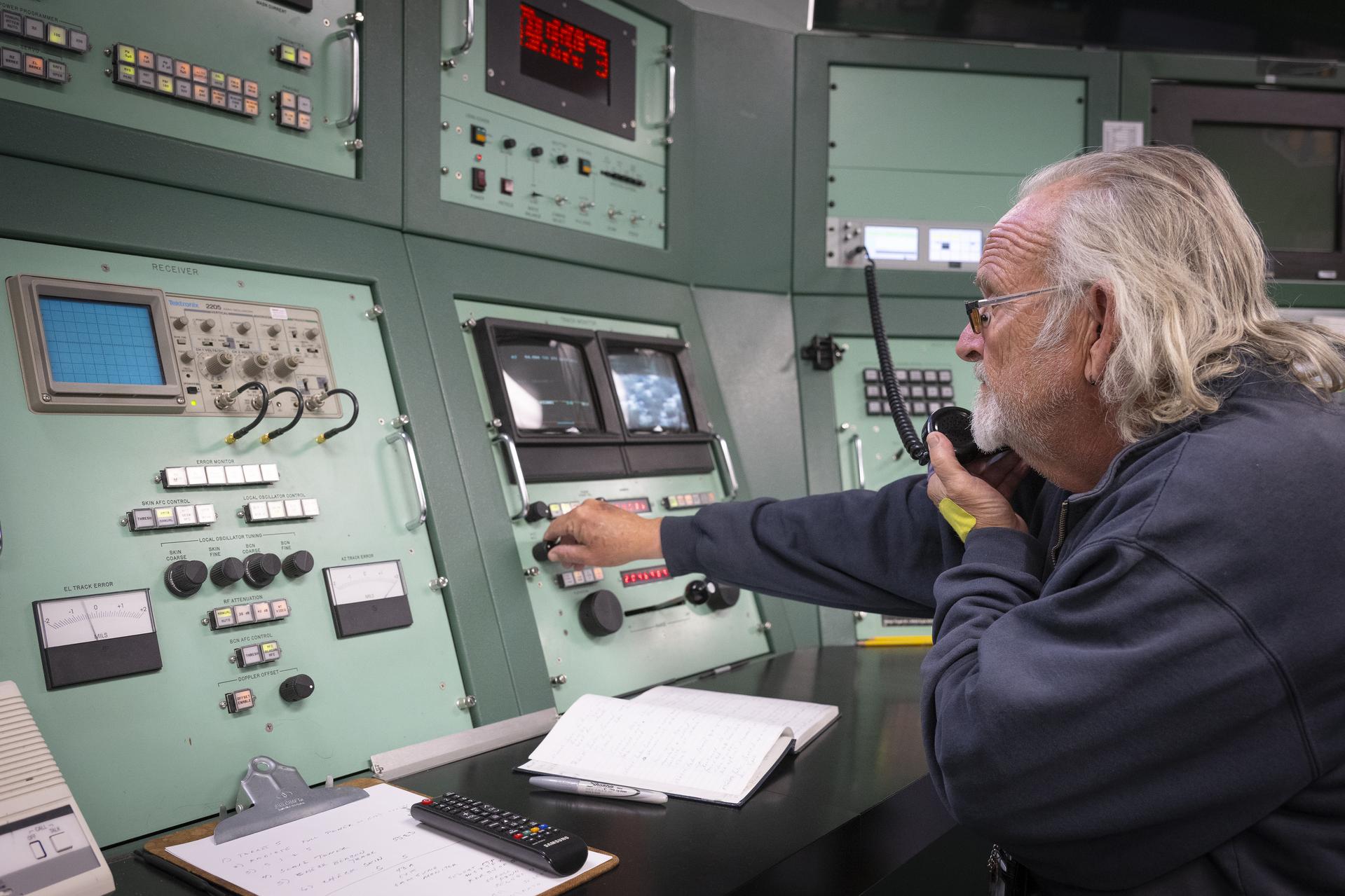

Mission operator Mike Webb sits at one of the radar stations used to track the International Space Station as it passes high above NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on Sept. 30, 2025. Webb is part of the center’s Dryden Aeronautical Test Range, which provides voice and tracking support to the space station.
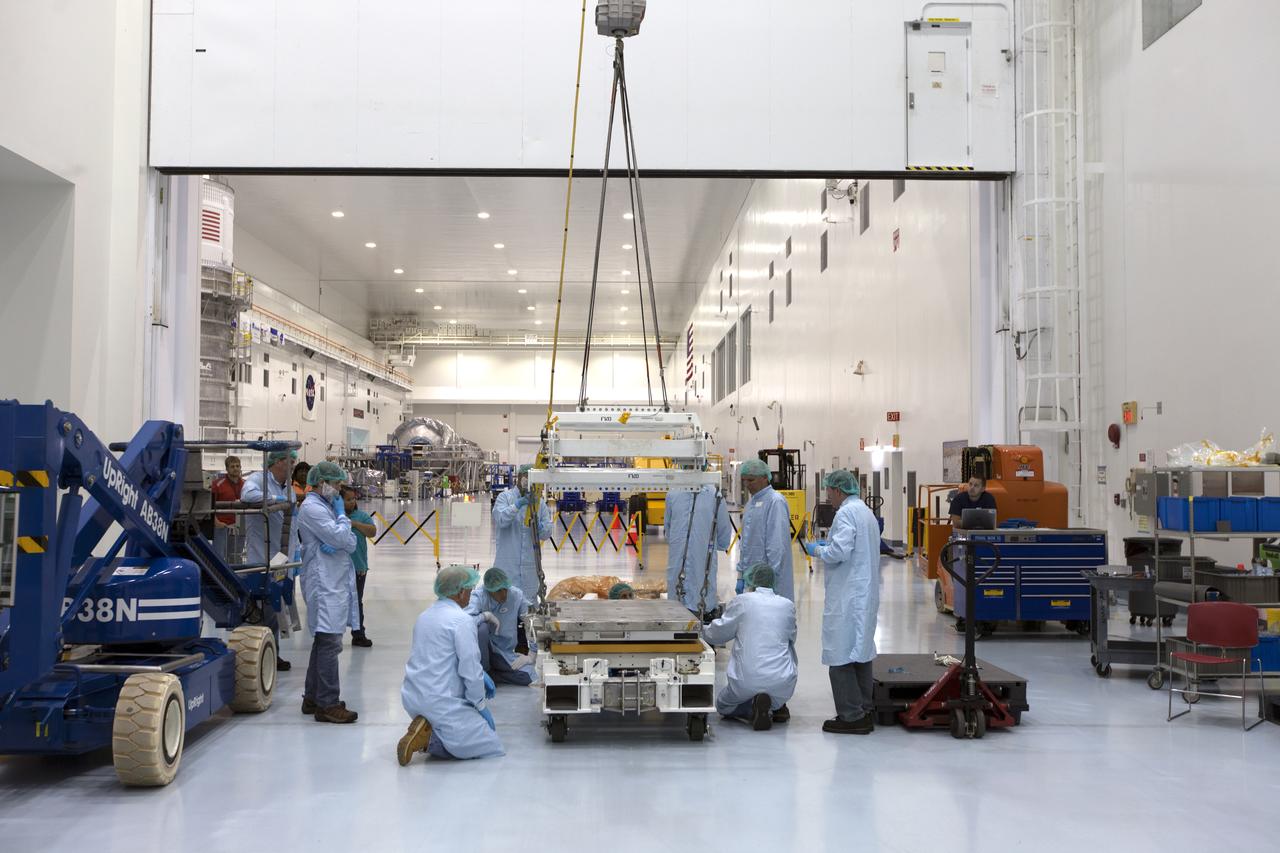

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
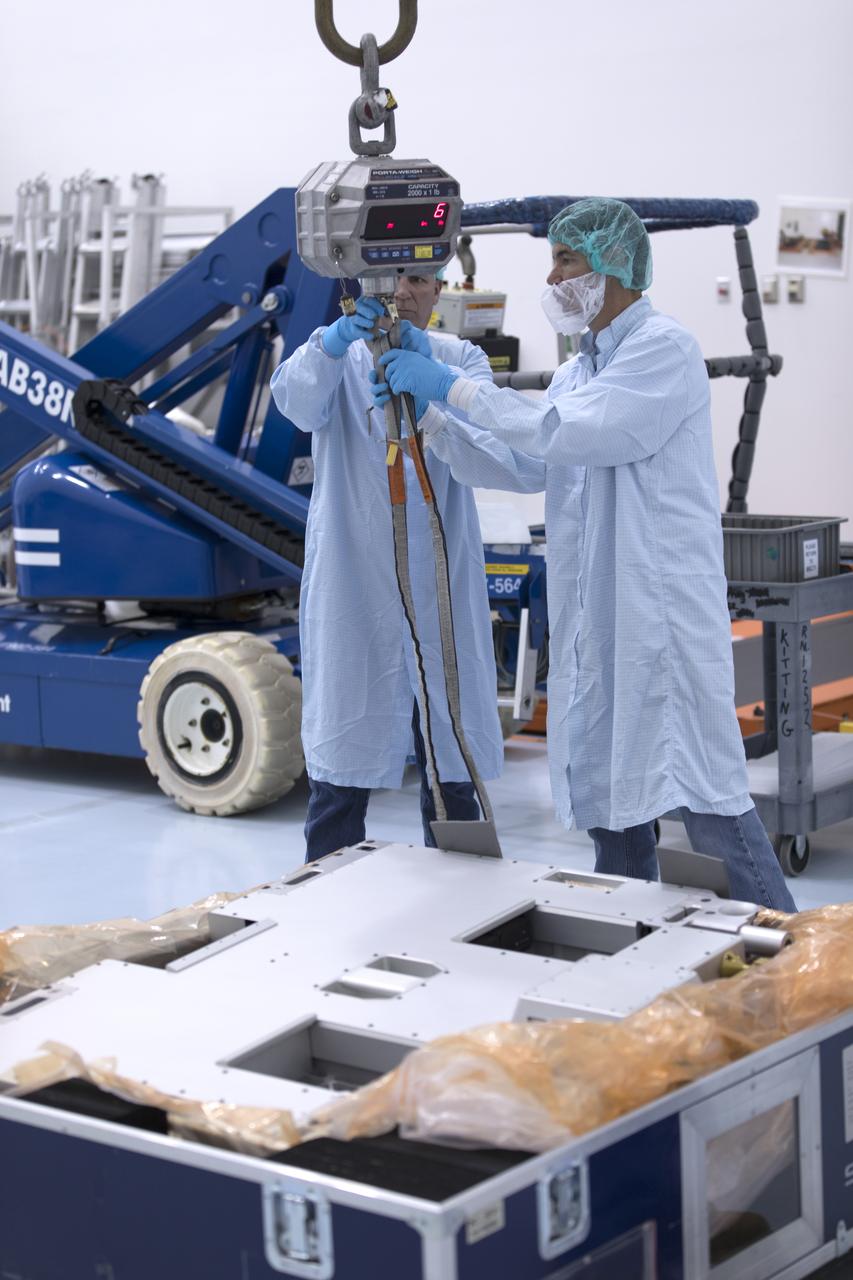

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians work to attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
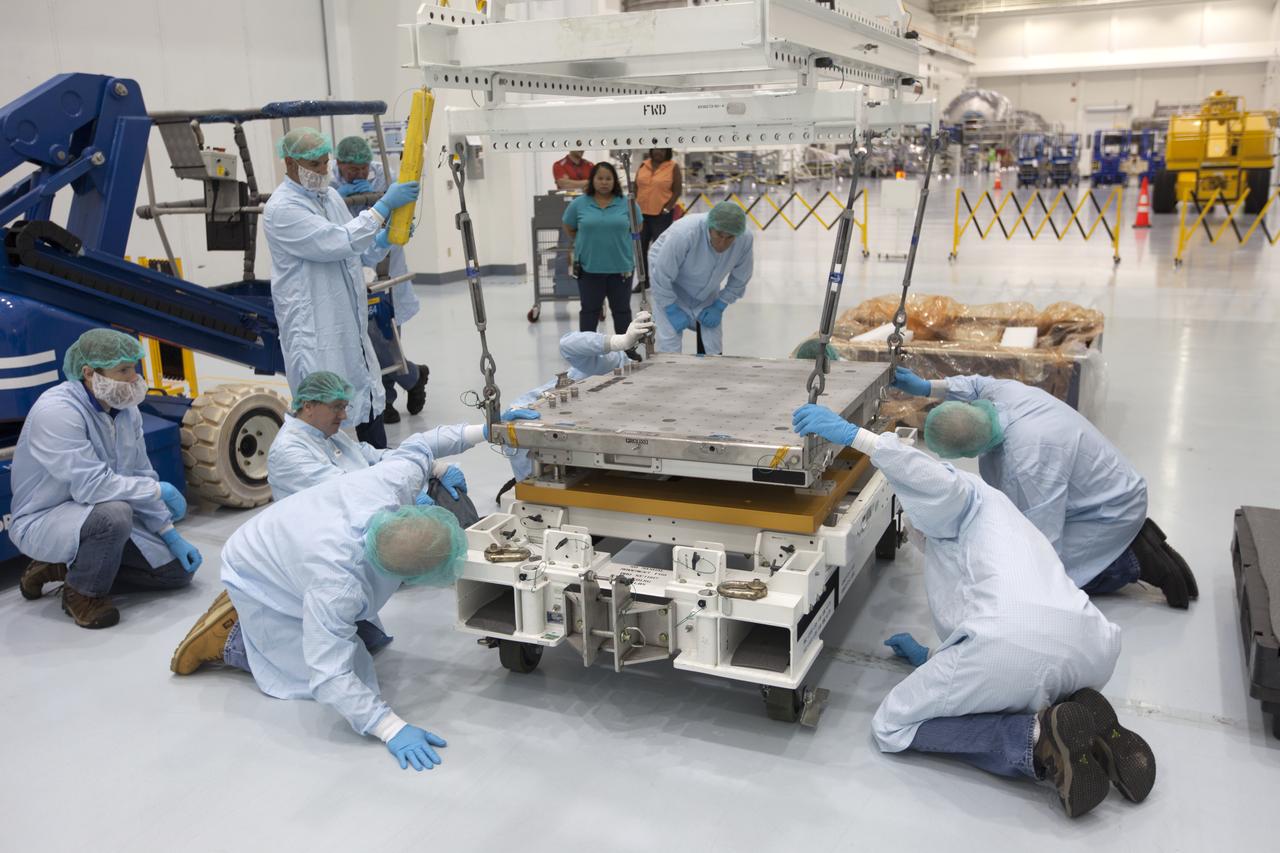

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
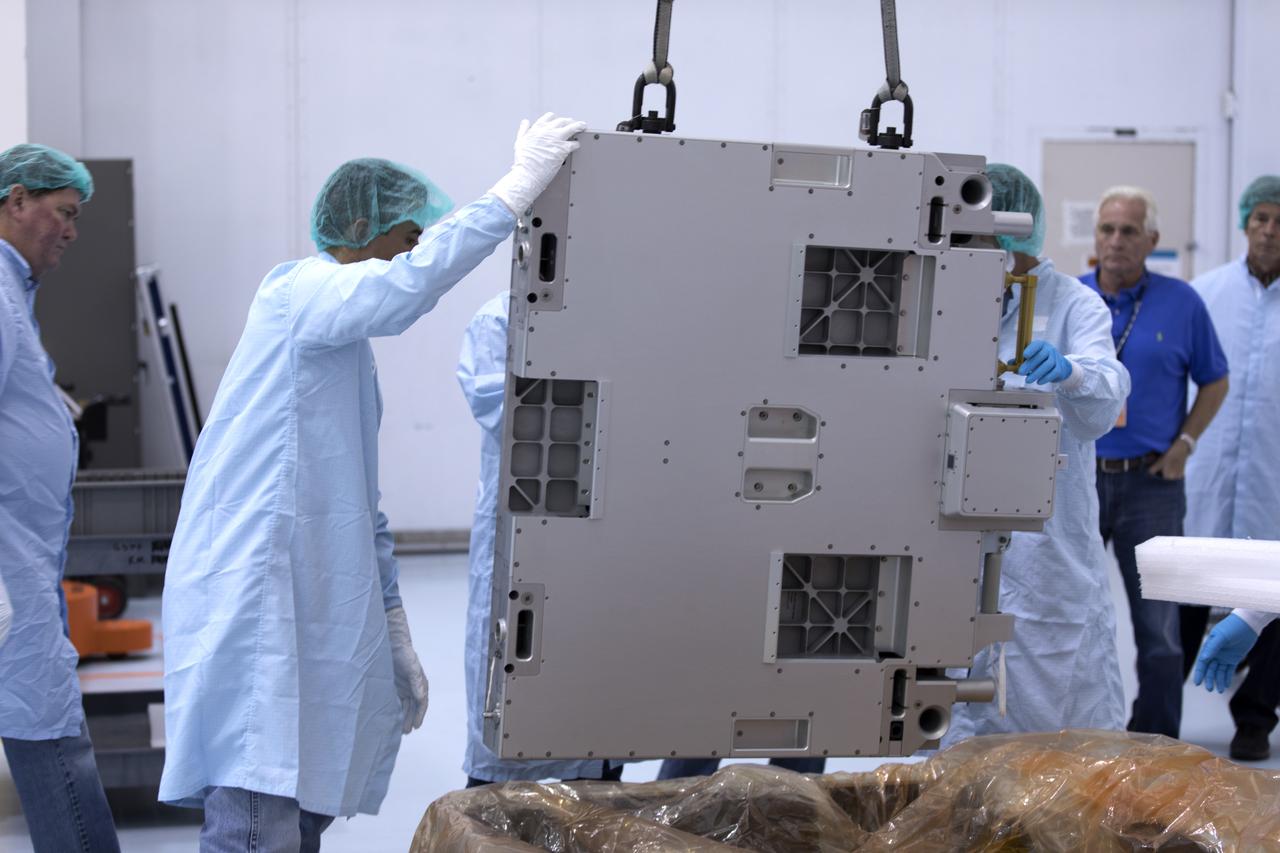

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift MISSE out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
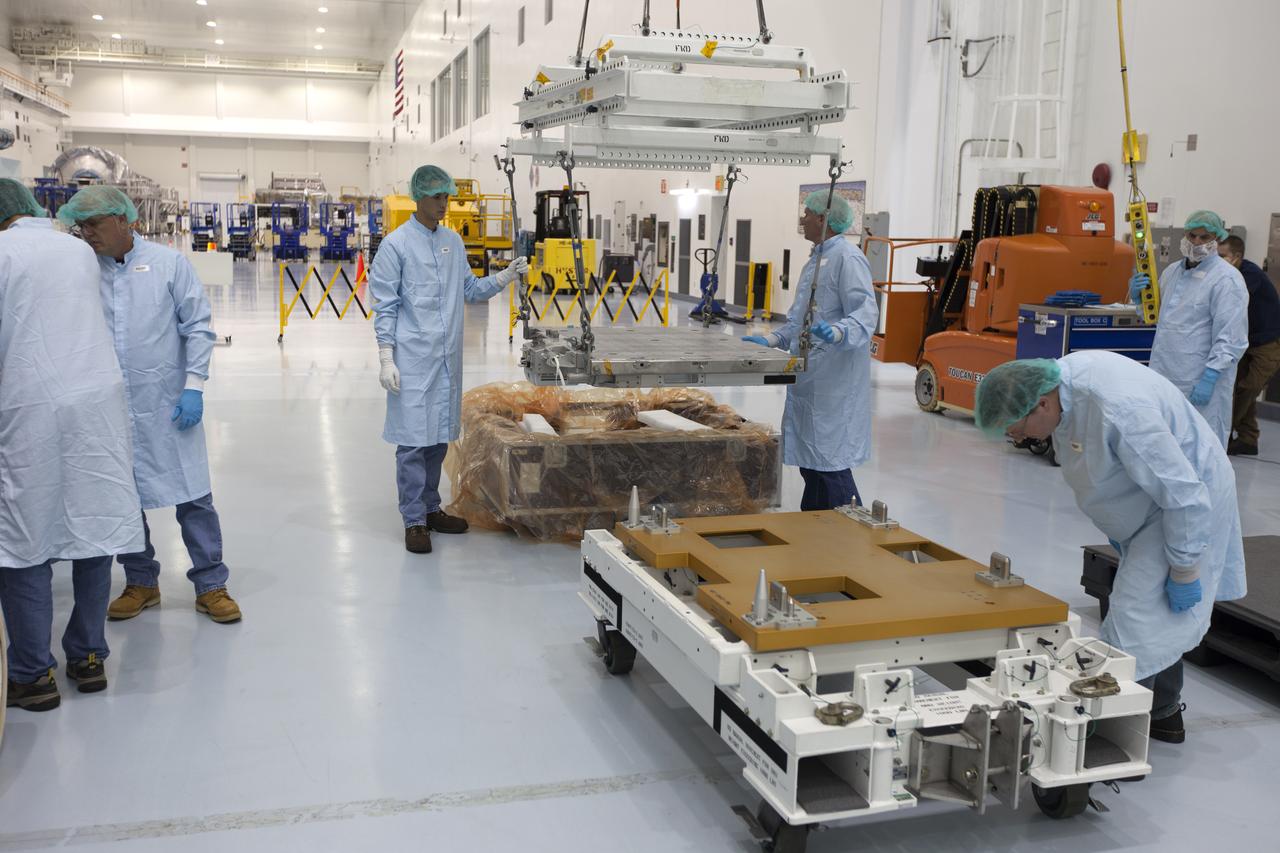

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
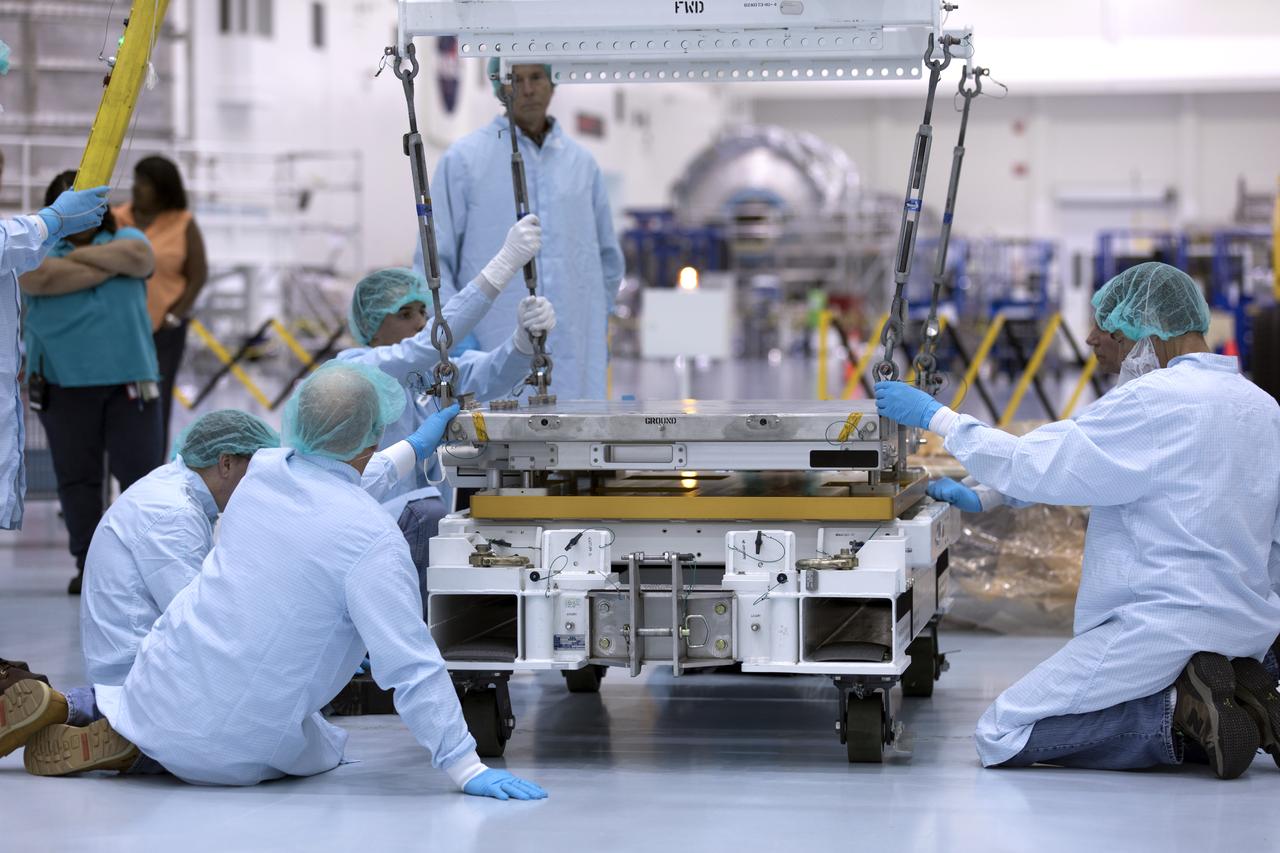

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered and secured onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
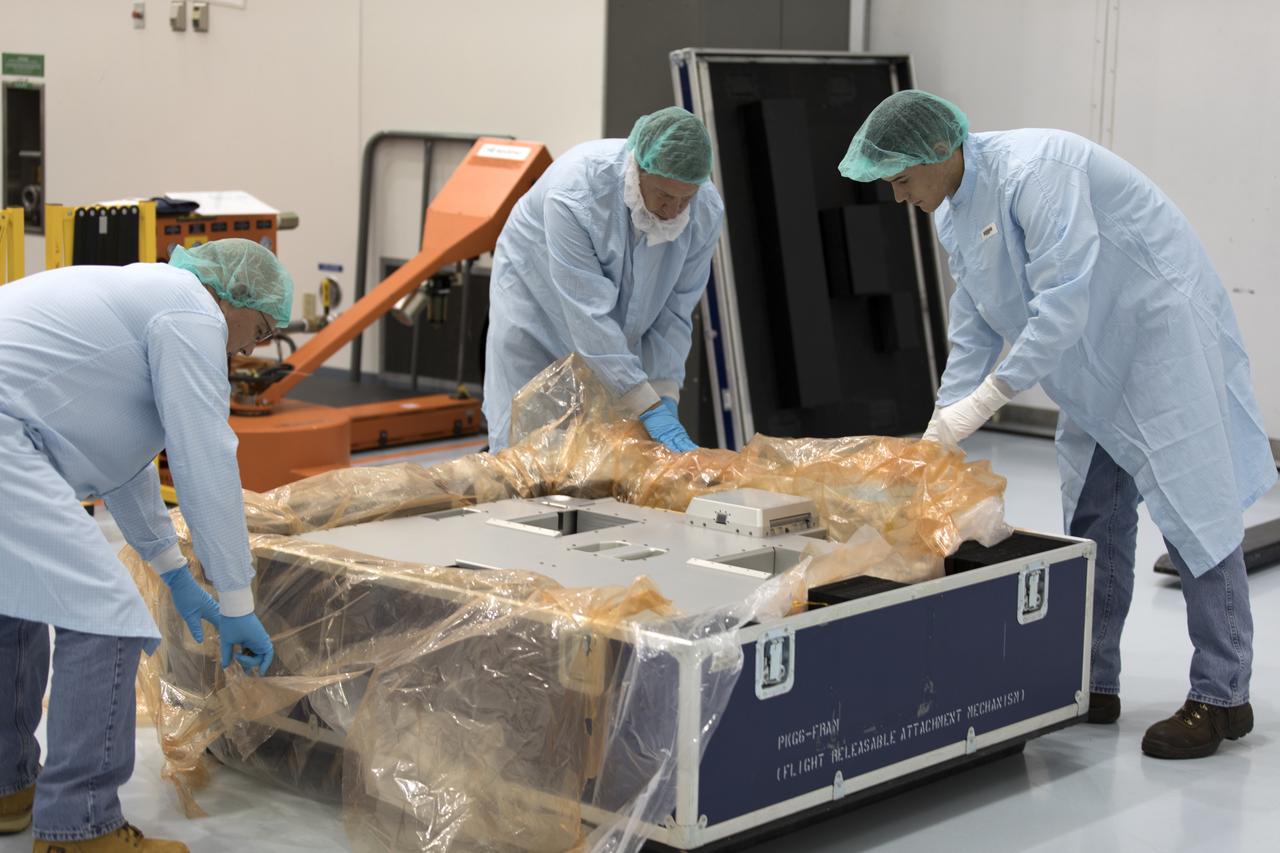

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. MISSE will be unpacked for integration and processing. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
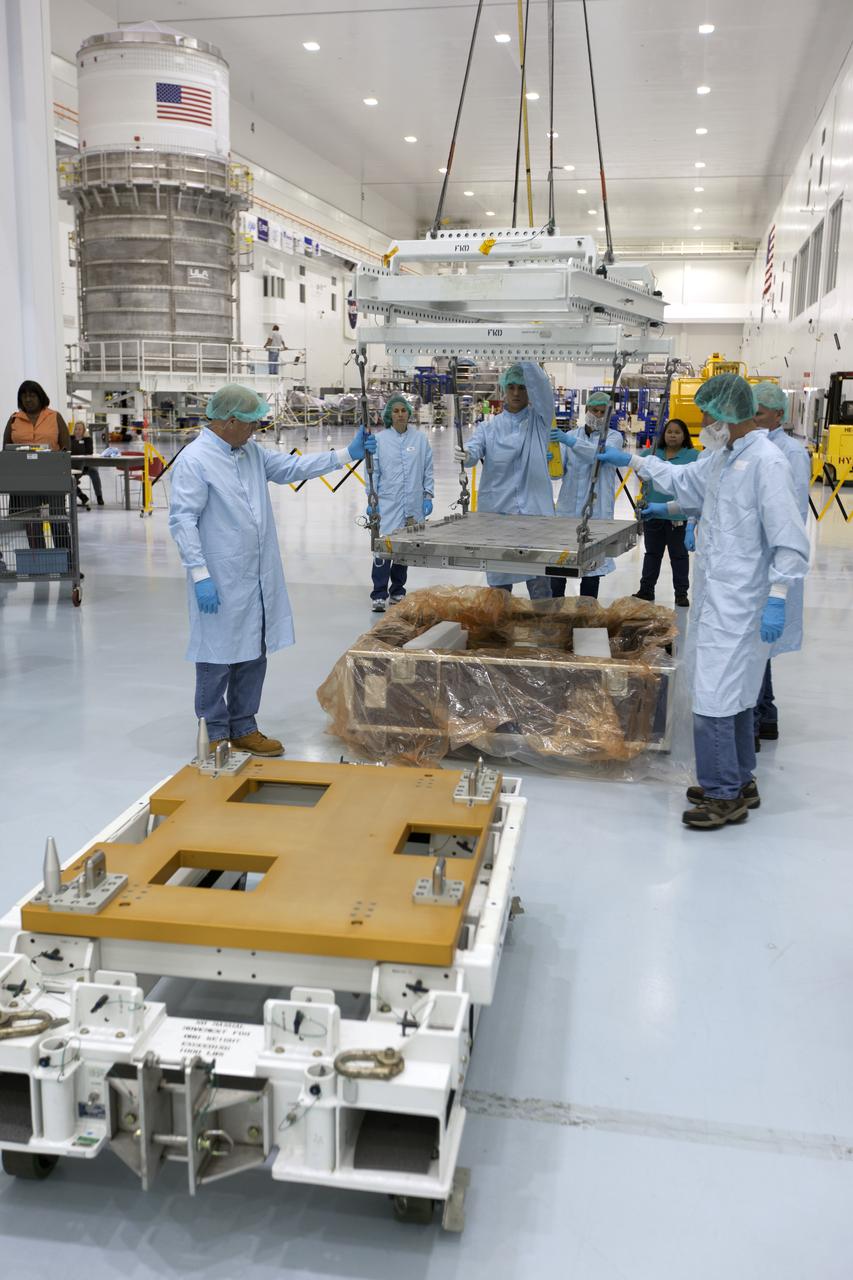

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
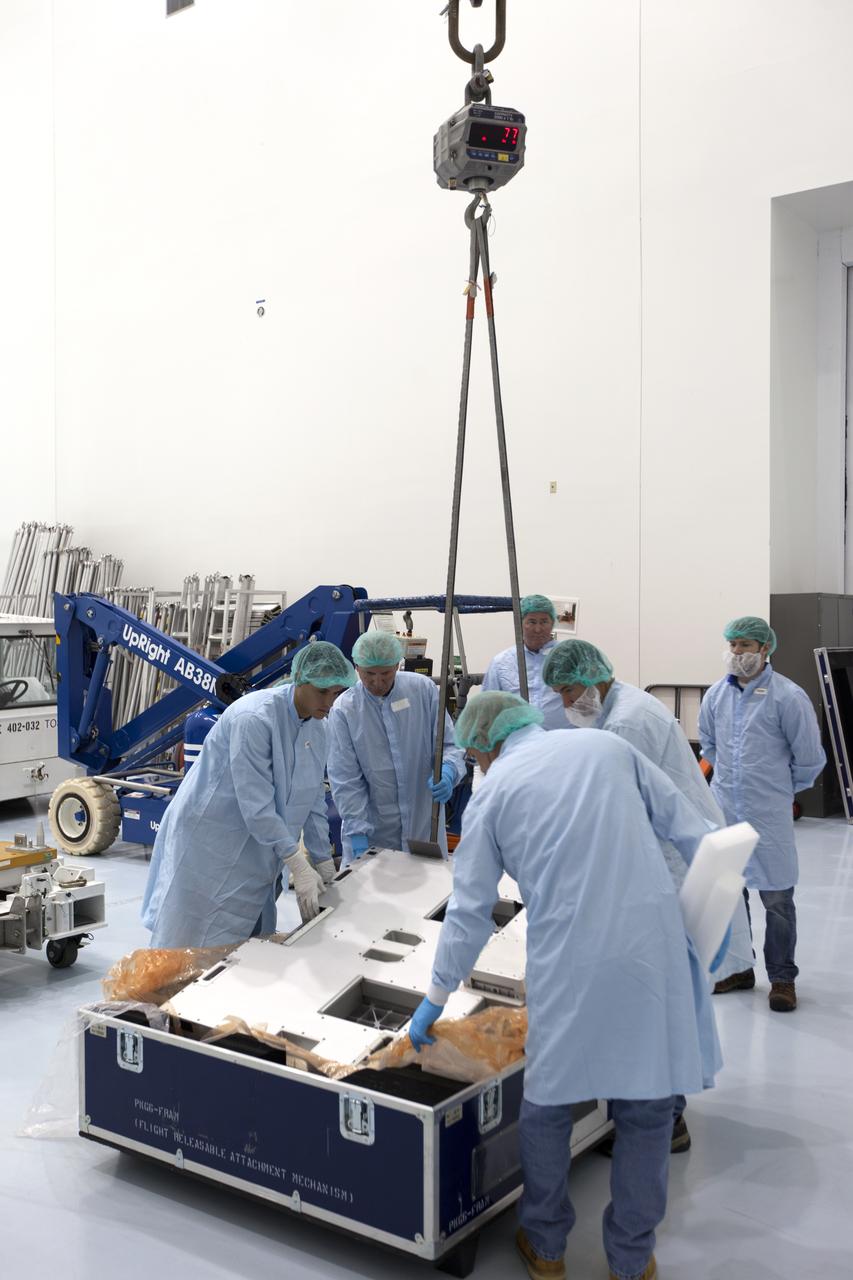

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
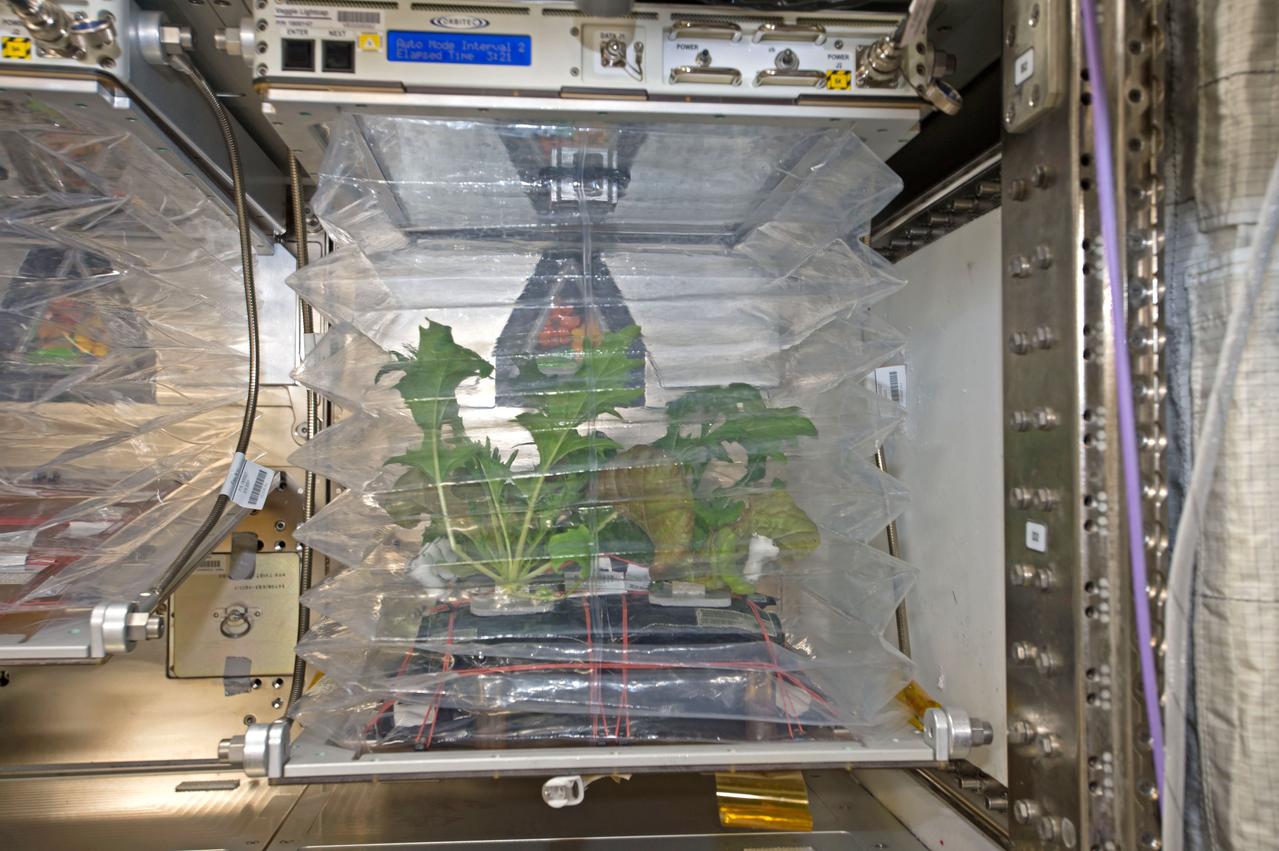

Veg-03D Experiment Onboard the International Space Station. First time three different plant varieties are being grown simultaneously in the Veggie chamber -- Mizuna mustard, Waldmann's green lettuce and Outredgeous Red Romaine lettuce.
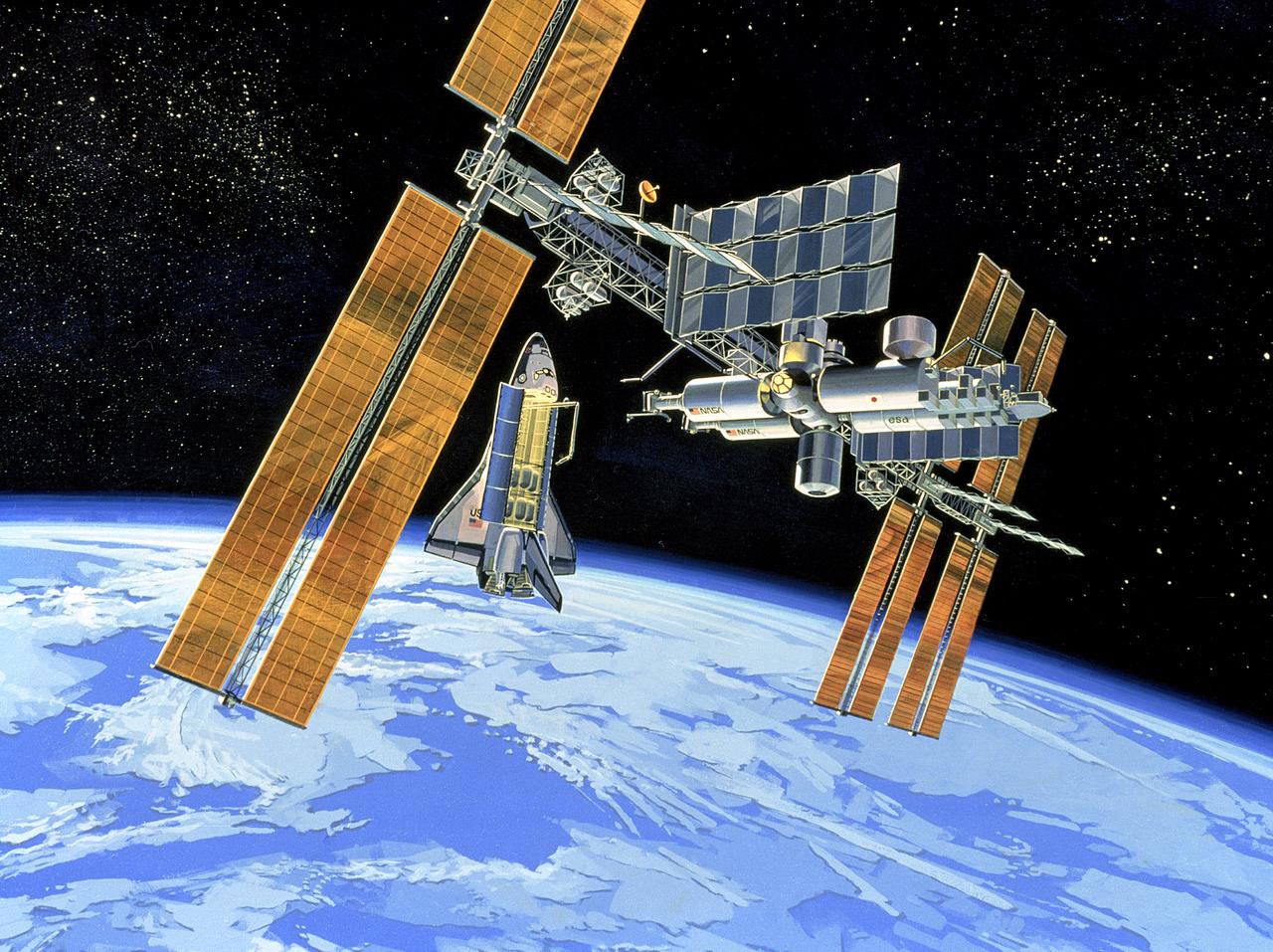

In 1982, the Space Station Task Force was formed, signaling the initiation of the Space Station Freedom Program, and eventually resulting in the Marshall Space Flight Center's responsibilities for Space Station Work Package 1.
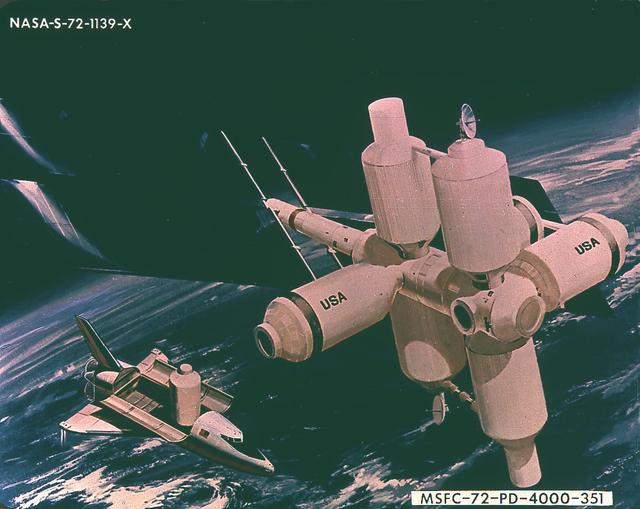
This is an artist's concept of a modular space station. In 1970 the Marshall Space Flight Center arnounced the completion of a study concerning a modular space station that could be launched by the planned-for reusable Space Shuttle. The study envisioned a space station composed of cylindrical sections 14 feet in diameter and of varying lengths joined to form any one of a number of possible shapes. The sections were restricted to 14 feet in diameter and 58 feet in length to be consistent with a shuttle cargo bay size of 15 by 60 feet. Center officials said that the first elements of the space station could be in orbit by about 1978 and could be manned by three or six men. This would be an interim space station with sections that could be added later to form a full 12-man station by the early 1980s.
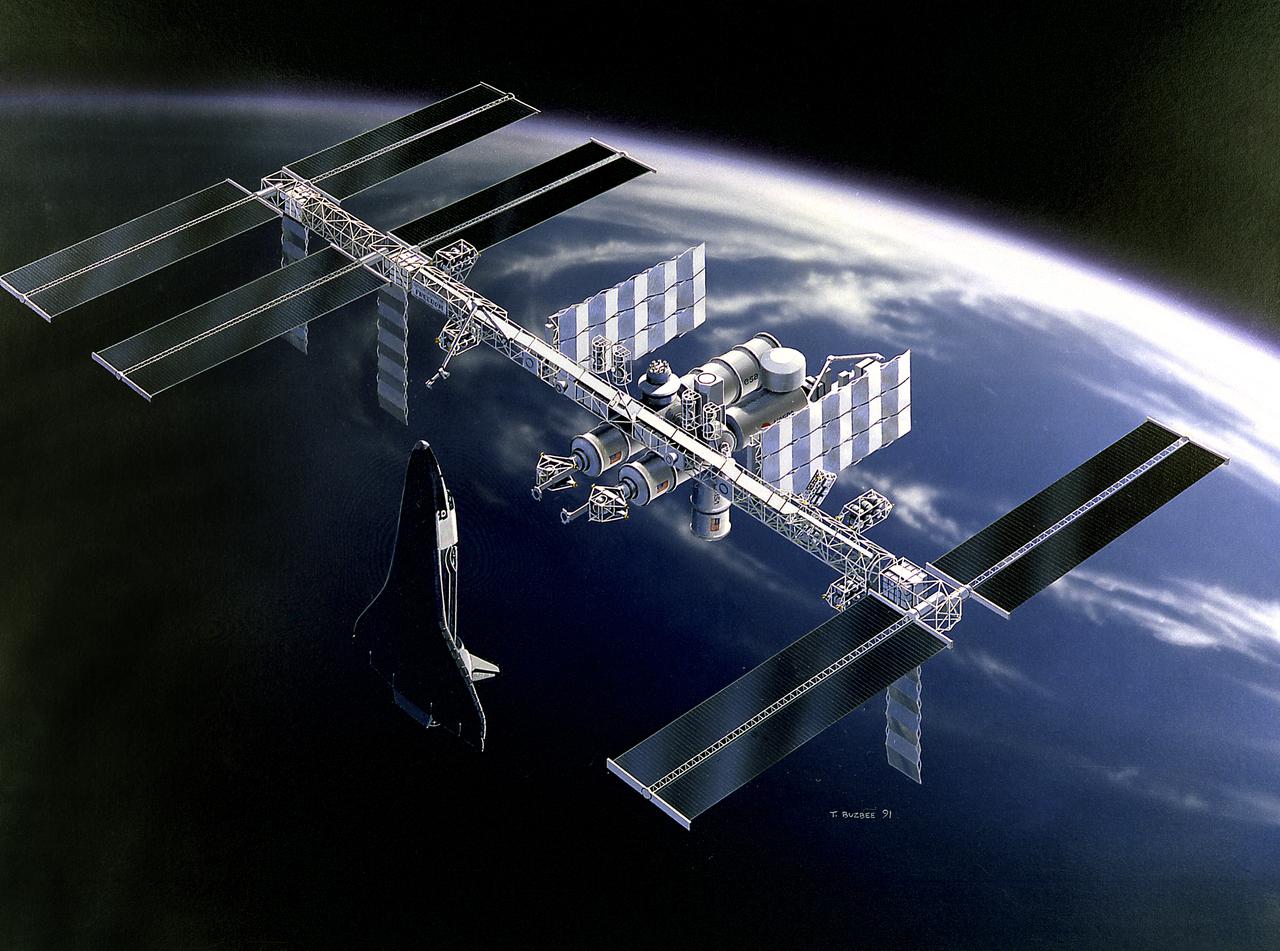
This artist's concept depicts the Space Station Freedom as it would look orbiting the Earth, illustrated by Marshall Space Flight Center artist, Tom Buzbee. Scheduled to be completed in late 1999, this smaller configuration of the Space Station featured a horizontal truss structure that supported U.S., European, and Japanese Laboratory Modules; the U.S. Habitation Module; and three sets of solar arrays. The Space Station Freedom was an international, permanently marned, orbiting base to be assembled in orbit by a series of Space Shuttle missions that were to begin in the mid-1990's.

This artist's concept depicts the Space Station Freedom as it would look orbiting the Earth; illustrated by Marshall Space Flight Center artist, Tom Buzbee. Scheduled to be completed in late 1999, this smaller configuration of the Space Station features a horizontal truss structure that supported U.S., European, and Japanese Laboratory Modules; the U.S. Habitation Module; and three sets of solar arrays. The Space Station Freedom was an international, permanently marned, orbiting base to be assembled in orbit by a series of Space Shuttle missions that were to begin in the mid-1990's.
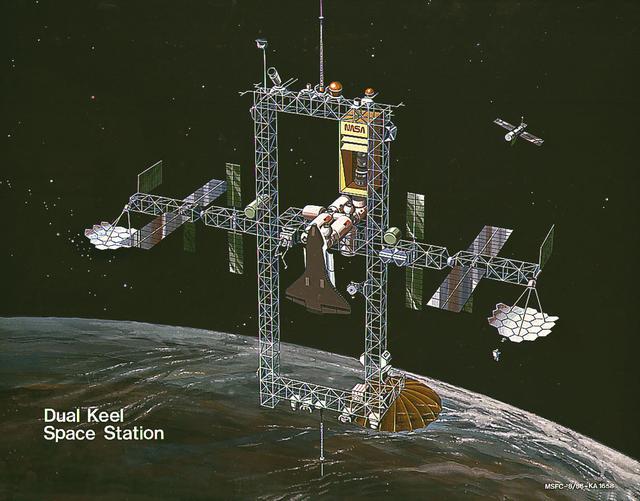

In response to President Reagan's directive to NASA to develop a permanent marned Space Station within a decade, part of the State of the Union message to Congress on January 25, 1984, NASA and the Administration adopted a phased approach to Station development. This approach provided an initial capability at reduced costs, to be followed by an enhanced Space Station capability in the future. This illustration depicts a configuration with enhanced capabilities. It builds on the horizontal boom and module pattern of the revised baseline. This configuration would feature dual keels, two vertical spines 105-meters long joined by upper and lower booms. The structure carrying the modules would become a transverse boom of a basically rectangular structure. The two new booms, 45-meters in length, would provide extensive accommodations for attached payloads, and would offer a wide field of view. Power would be increased significantly, with the addition if a 50-kW solar dynamic power system.
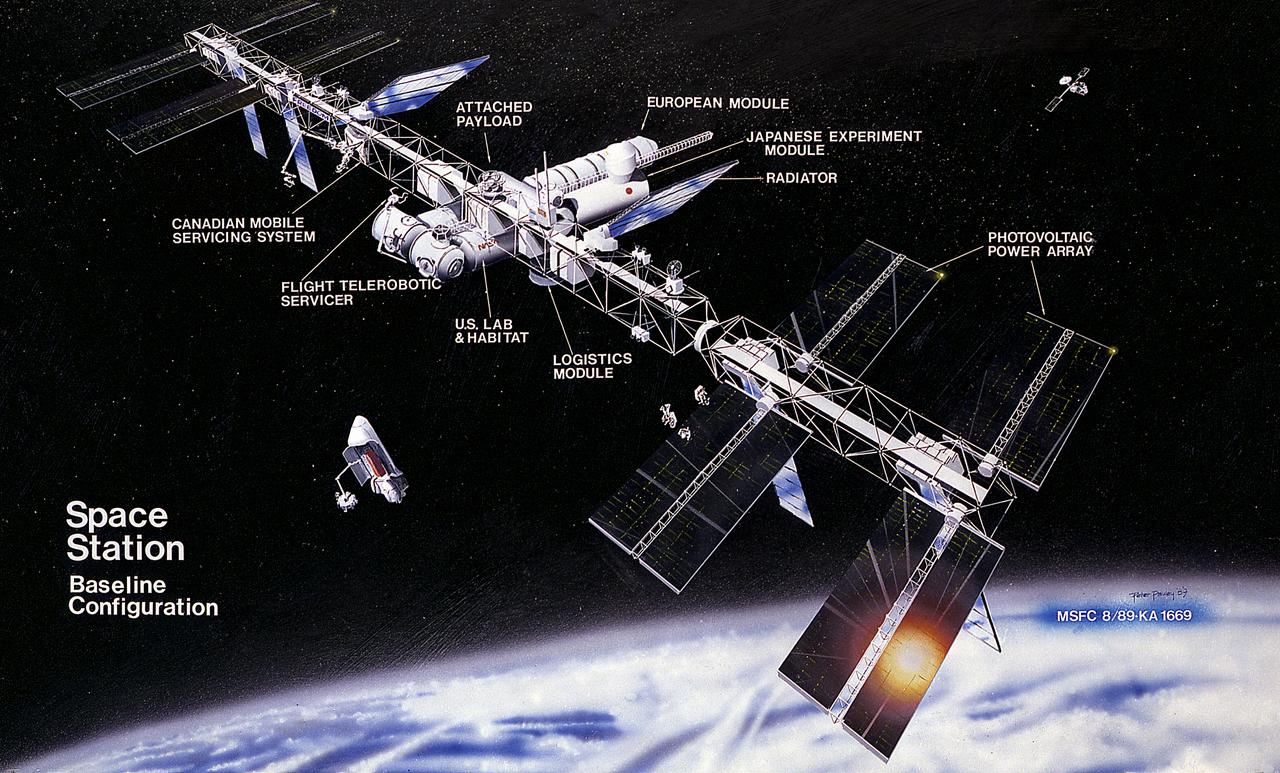
In response to President Reagan's directive to NASA to develop a permanent marned Space Station within a decade, part of the State of the Union message to Congress on January 25, 1984, NASA and the Administration adopted a phased approach to Station development. This approach provided an initial capability at reduced costs, to be followed by an enhanced Space Station capability in the future. This illustration depicts the baseline configuration, which features a 110-meter-long horizontal boom with four pressurized modules attached in the middle. Located at each end are four photovoltaic arrays generating a total of 75-kW of power. Two attachment points for external payloads are provided along this boom. The four pressurized modules include the following: A laboratory and habitation module provided by the United States; two additional laboratories, one each provided by the European Space Agency (ESA) and Japan; and an ESA-provided Man-Tended Free Flyer, a pressurized module capable of operations both attached to and separate from the Space Station core. Canada was expected to provide the first increment of a Mobile Serving System.
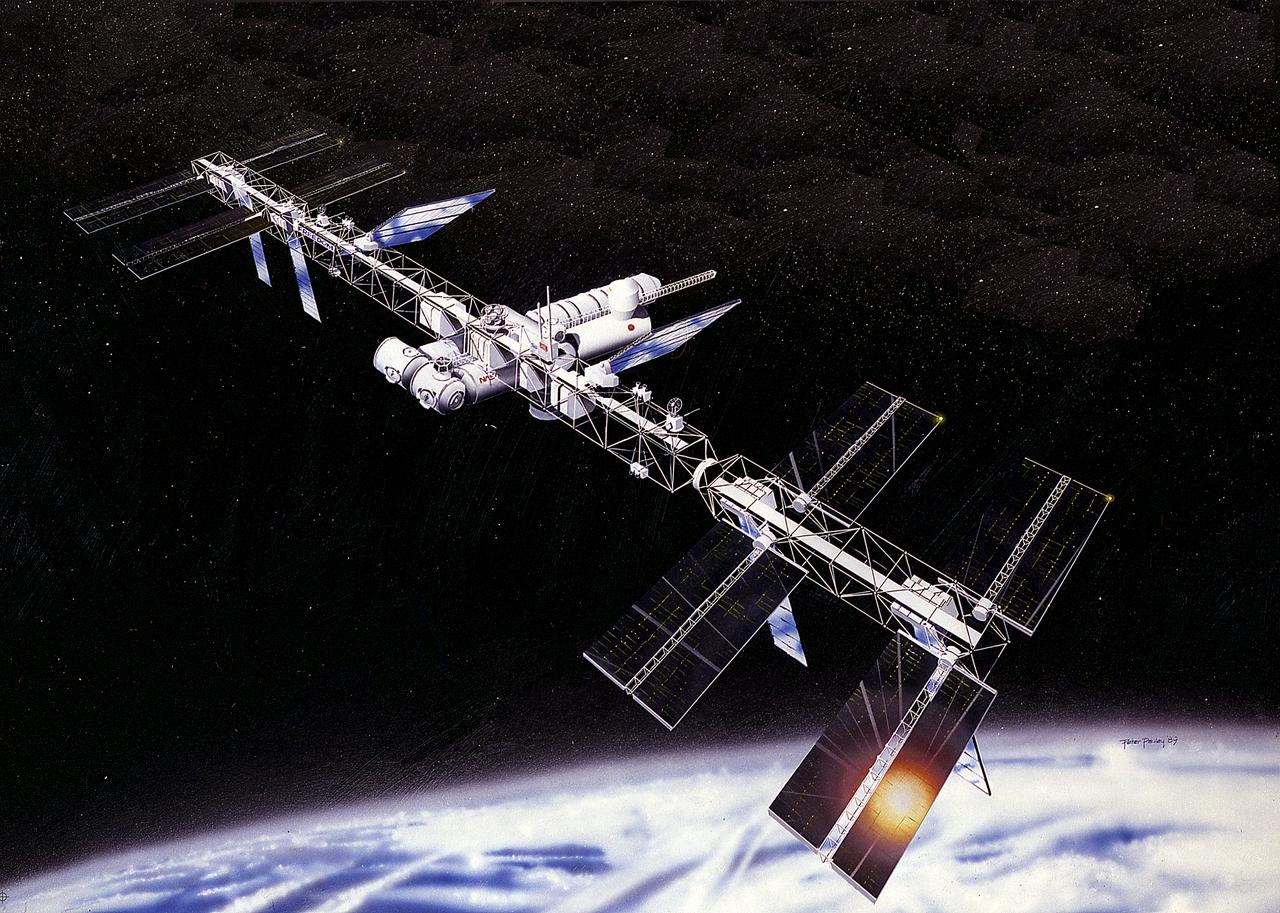
In response to President Reagan's directive to NASA to develop a permanent marned Space Station within a decade, part of the State of the Union message to Congress on January 25, 1984, NASA and the Administration adopted a phased approach to Station development. This approach provided an initial capability at reduced costs, to be followed by an enhanced Space Station capability in the future. This illustration depicts the baseline configuration, which features a 110-meter-long horizontal boom with four pressurized modules attached in the middle. Located at each end are four photovoltaic arrays generating a total of 75-kW of power. Two attachment points for external payloads are provided along this boom. The four pressurized modules include the following: A laboratory and habitation module provided by the United States; two additional laboratories, one each provided by the European Space Agency (ESA) and Japan; and an ESA-provided Man-Tended Free Flyer, a pressurized module capable of operations both attached to and separate from the Space Station core. Canada was expected to provide the first increment of a Mobile Serving System.

This picture illustrates a concept of a 33-Foot-Diameter Space Station Leading to a Space Base. In-house work of the Marshall Space Flight Center, as well as a Phase B contract with the McDornel Douglas Astronautics Company, resulted in a preliminary design for a space station in 1969 and l970. The Marshall-McDonnel Douglas approach envisioned the use of two common modules as the core configuration of a 12-man space station. Each common module was 33 feet in diameter and 40 feet in length and provided the building blocks, not only for the space station, but also for a 50-man space base. Coupled together, the two modules would form a four-deck facility: two decks for laboratories and two decks for operations and living quarters. Zero-gravity would be the normal mode of operation, although the station would have an artificial gravity capability. This general-purpose orbital facility was to provide wide-ranging research capabilities. The design of the facility was driven by the need to accommodate a broad spectrum of activities in support of astronomy, astrophysics, aerospace medicine, biology, materials processing, space physics, and space manufacturing. To serve the needs of Earth observations, the station was to be placed in a 242-nautical-mile orbit at a 55-degree inclination. An Intermediate-21 vehicle (comprised of Saturn S-IC and S-II stages) would have launched the station in 1977.

This is an illustration of the Space Base concept. In-house work of the Marshall Space Flight Center, as well as a Phase B contract with the McDornel Douglas Astronautics Company, resulted in a preliminary design for a space station in 1969 and l970. The Marshall-McDonnel Douglas approach envisioned the use of two common modules as the core configuration of a 12-man space station. Each common module was 33 feet in diameter and 40 feet in length and provided the building blocks, not only for the space station, but also for a 50-man space base. Coupled together, the two modules would form a four-deck facility: two decks for laboratories and two decks for operations and living quarters. Zero-gravity would be the normal mode of operation, although the station would have an artificial-gravity capability. This general-purpose orbital facility was to provide wide-ranging research capabilities. The design of the facility was driven by the need to accommodate a broad spectrum of activities in support of astronomy, astrophysics, aerospace medicine, biology, materials processing, space physics, and space manufacturing. To serve the needs of Earth observations, the station was to be placed in a 242-nautical-mile orbit at a 55-degree inclination. An Intermediate-21 vehicle (comprised of Saturn S-IC and S-II stages) would have launched the station in 1977.

This is a von Braun 1952 space station concept. In a 1952 series of articles written in Collier's, Dr. Wernher von Braun, then Technical Director of the Army Ordnance Guided Missiles Development Group at Redstone Arsenal, wrote of a large wheel-like space station in a 1,075-mile orbit. This station, made of flexible nylon, would be carried into space by a fully reusable three-stage launch vehicle. Once in space, the station's collapsible nylon body would be inflated much like an automobile tire. The 250-foot-wide wheel would rotate to provide artificial gravity, an important consideration at the time because little was known about the effects of prolonged zero-gravity on humans. Von Braun's wheel was slated for a number of important missions: a way station for space exploration, a meteorological observatory and a navigation aid. This concept was illustrated by artist Chesley Bonestell.
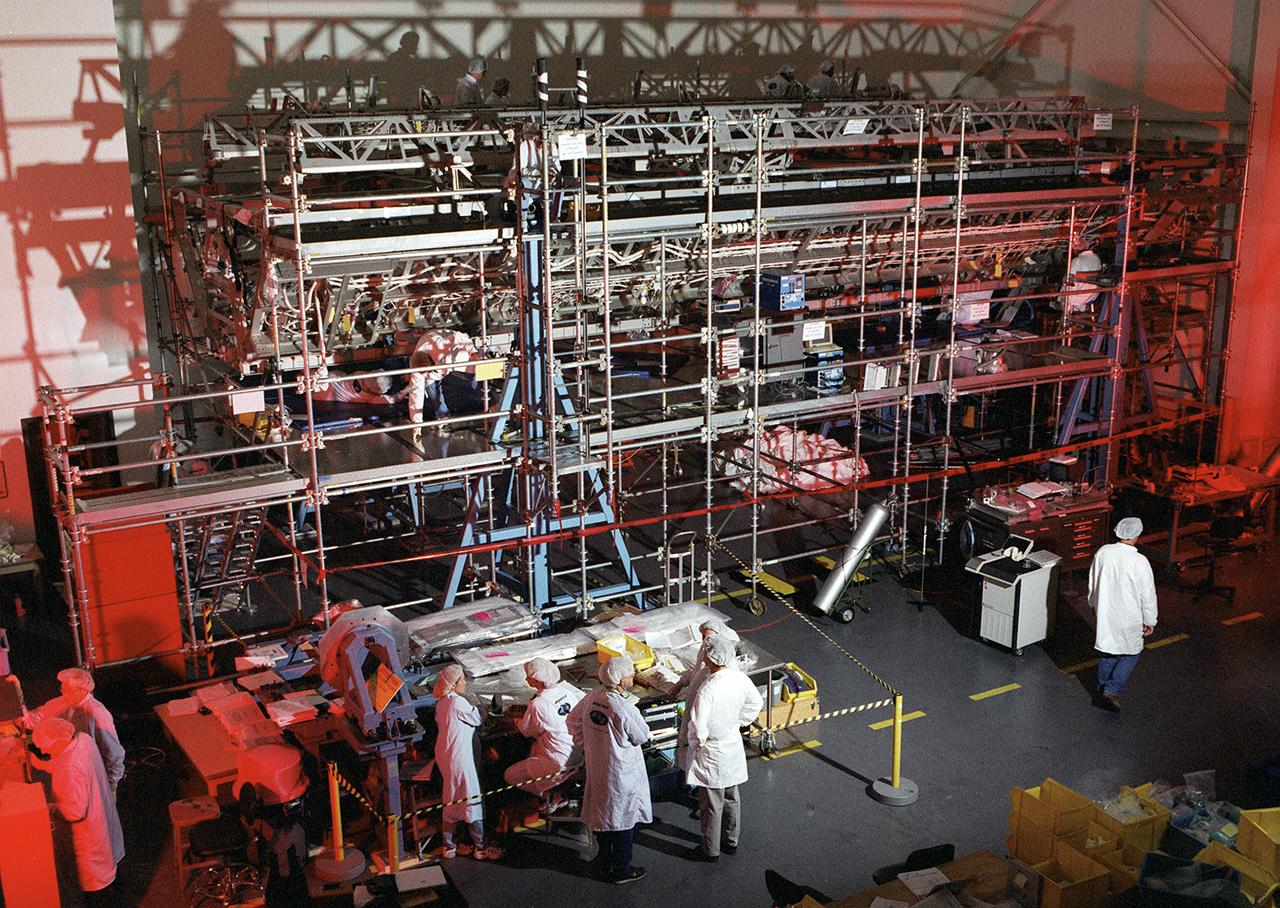

Boeing Company technicians assemble the S-1 truss (starboard side truss) for the International Space Station at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
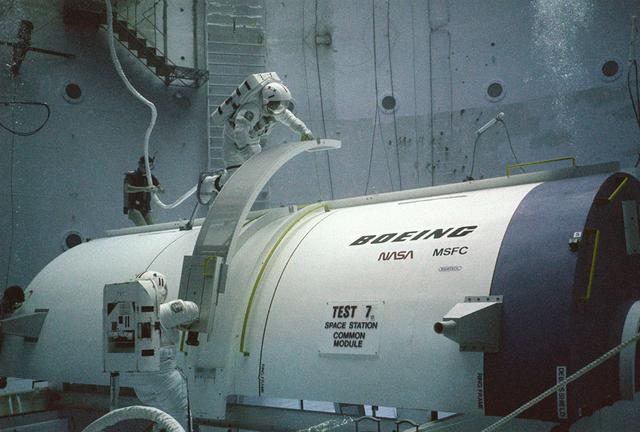

Skylab's success proved that scientific experimentation in a low gravity environment was essential to scientific progress. A more permanent structure was needed to provide this space laboratory. President Ronald Reagan, on January 25, 1984, during his State of the Union address, claimed that the United States should exploit the new frontier of space, and directed NASA to build a permanent marned space station within a decade. The idea was that the space station would not only be used as a laboratory for the advancement of science and medicine, but would also provide a staging area for building a lunar base and manned expeditions to Mars and elsewhere in the solar system. President Reagan invited the international community to join with the United States in this endeavour. NASA and several countries moved forward with this concept. By December 1985, the first phase of the space station was well underway with the design concept for the crew compartments and laboratories. Pictured are two NASA astronauts, at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS), practicing construction techniques they later used to construct the space station after it was deployed.

This artist's digital concept depicts the completely assembled International Space Station (ISS) passing over Florida. As a gateway to permanent human presence in space, the Space Station Program is to expand knowledge benefiting all people and nations. The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide unprecedented undertakings in scientific, technological, and international experimentation. Experiments to be conducted in the ISS include: microgravity research, Earth science, space science, life sciences, space product development, and engineering research and technology. The sixteen countries participating the ISS are: United States, Russian Federation, Canada, Japan, United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, France, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, Denmark, Sweden, Switzerland, and Brazil.

This artist's concept depicts the completely assembled International Space Station (ISS) passing over Florida and the Bahamas. As a gateway to permanent human presence in space, the Space Station Program is to expand knowledge benefiting all people and nations. The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide unprecedented undertakings in scientific, technological, and international experimentation. Experiments to be conducted in the ISS include: microgravity research, Earth science, space science, life sciences, space product development, and engineering research and technology. The sixteen countries participating in the ISS are: United States, Russian Federation, Canada, Japan, United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, France, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, Denmark, Sweden, Switzerland, and Brazil.
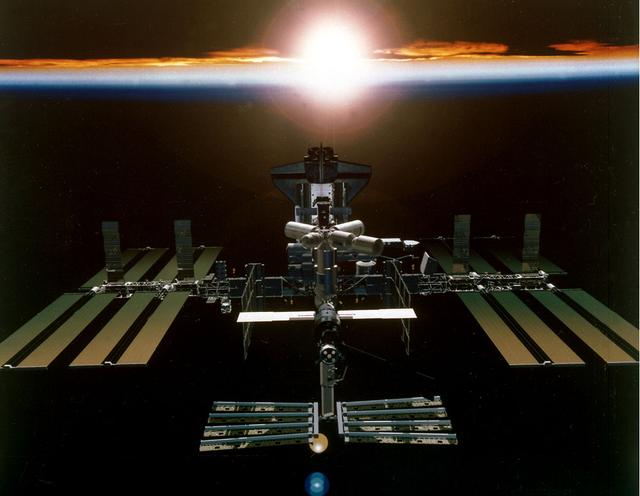

Artist's digital concept of the International Space Station (ISS), a gateway to permanent human presence in space, after all assembly is completed in Year 2003. The Station will be powered by almost an acre of solar panels and have a mass of almost one million pounds. Station modules are being provided by the United States, Russia, Japan, and Europe. Canada is providing a mechanical arm and Canada Hand. Sixteen countries are cooperating to provide a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation.
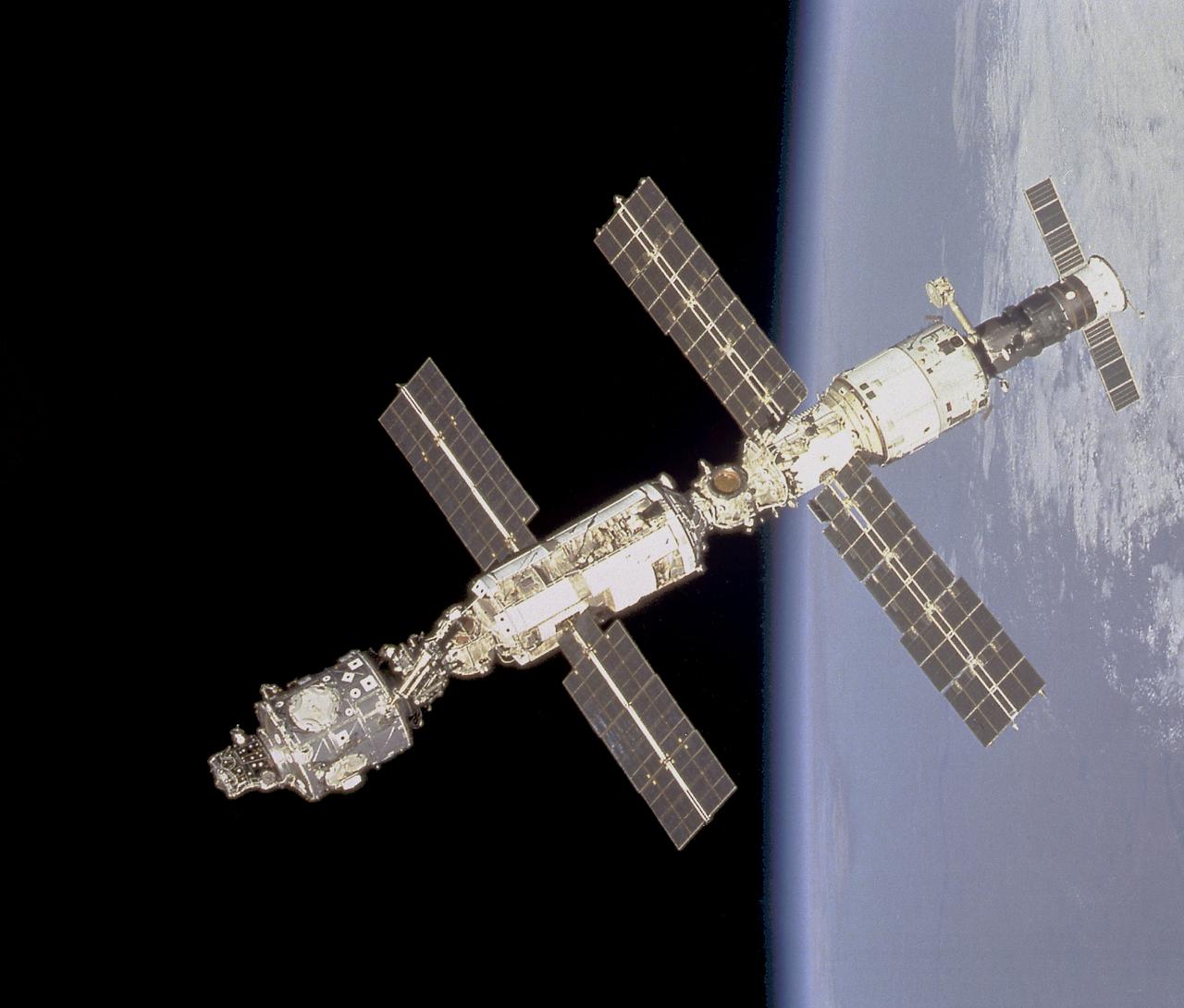
This image of the International Space Station in orbit was taken from the Space Shuttle Endeavour prior to docking. Most of the Station's components are clearly visible in this photograph. They are the Node 1 or Unity Module docked with the Functional Cargo Block or Zarya (top) that is linked to the Zvezda Service Module. The Soyuz spacecraft is at the bottom.

An artist's concept of Phase III of the International Space Station (ISS) with the Shuttle approaching.

Pictured is an artist's concept of the International Space Station (ISS) with solar panels fully deployed. In addition to the use of solar energy, the ISS will employ at least three types of propulsive support systems for its operation. The first type is to reboost the Station to correct orbital altitude to offset the effects of atmospheric and other drag forces. The second function is to maneuver the ISS to avoid collision with oribting bodies (space junk). The third is for attitude control to position the Station in the proper attitude for various experiments, temperature control, reboost, etc. The ISS, a gateway to permanent human presence in space, is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation by cooperation of sixteen countries.

This artist's concept depicts the completely assembled International Space Station (ISS) passing over the Straits of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea. As a gateway to permanent human presence in space, the Space Station Program is to expand knowledge benefiting all people and nations. The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide unprecedented undertakings in scientific, technological, and international experimentation. Experiments to be conducted in the ISS include: microgravity research, Earth science, space science, life sciences, space product development, and engineering research and technology. The sixteen countries participating the ISS are: United States, Russian Federation, Canada, Japan, United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, France, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, Denmark, Sweden, Switzerland, and Brazil.
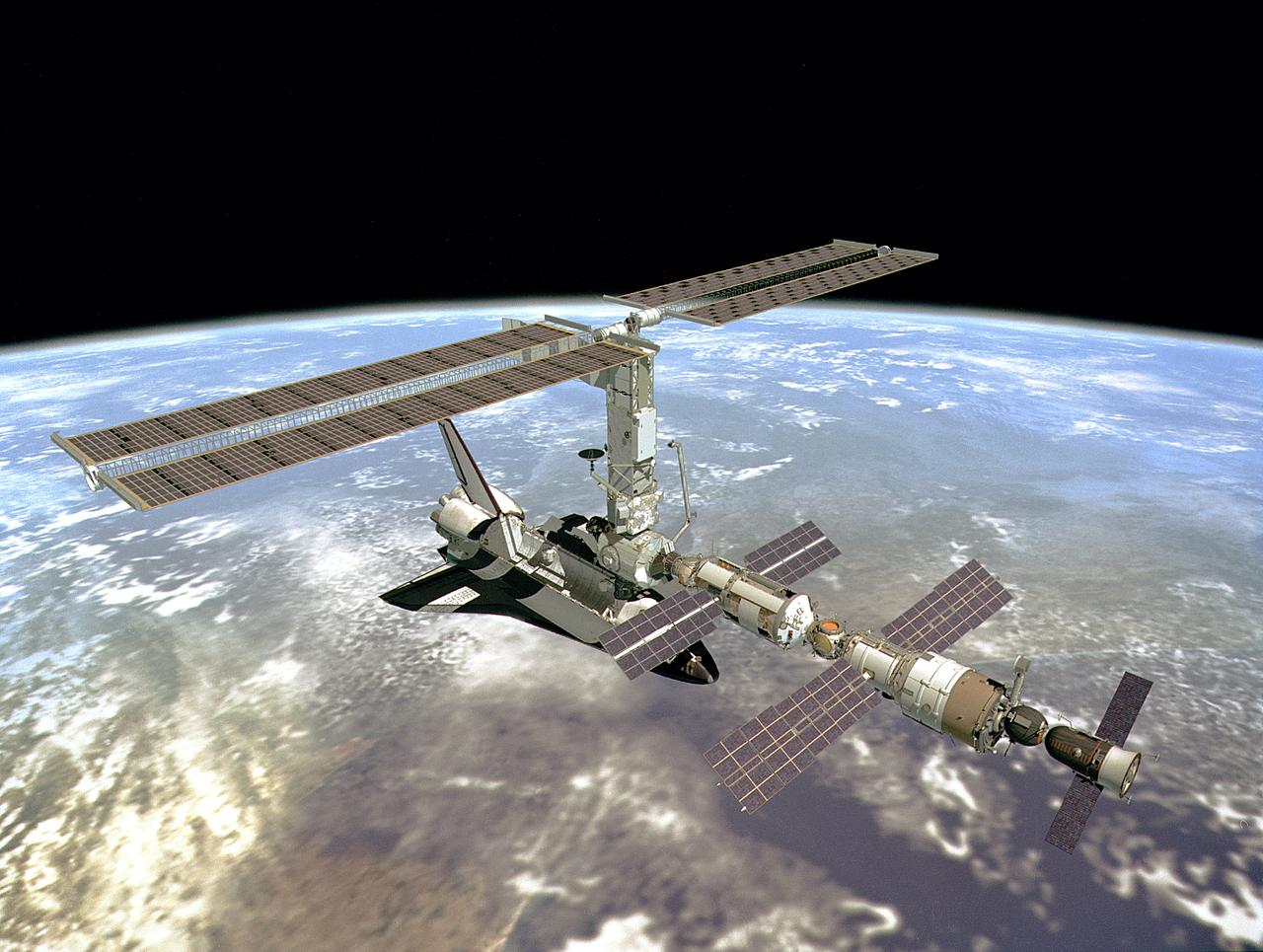

This concept depicts the International Space Station in orbit following its solar array deployment by the crew of the Space Shuttle STS-97 mission.
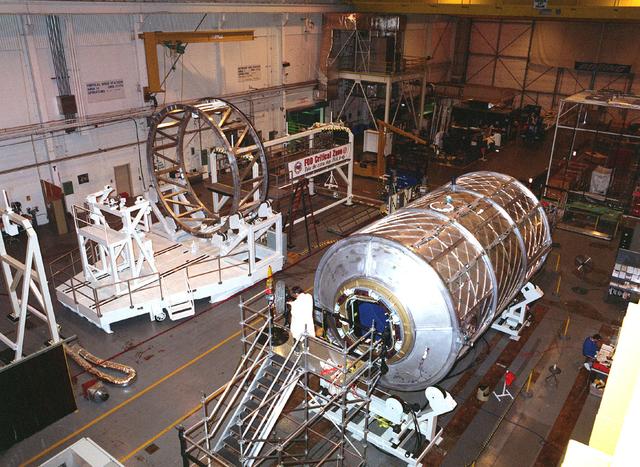

Photograph shows the International Space Station Laboratory Module under fabrication at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), Building 4708 West High Bay. Although management of the U.S. elements for the Station were consolidated in 1994, module and node development continued at MSFC by Boeing Company, the prime contractor for the Space Station.
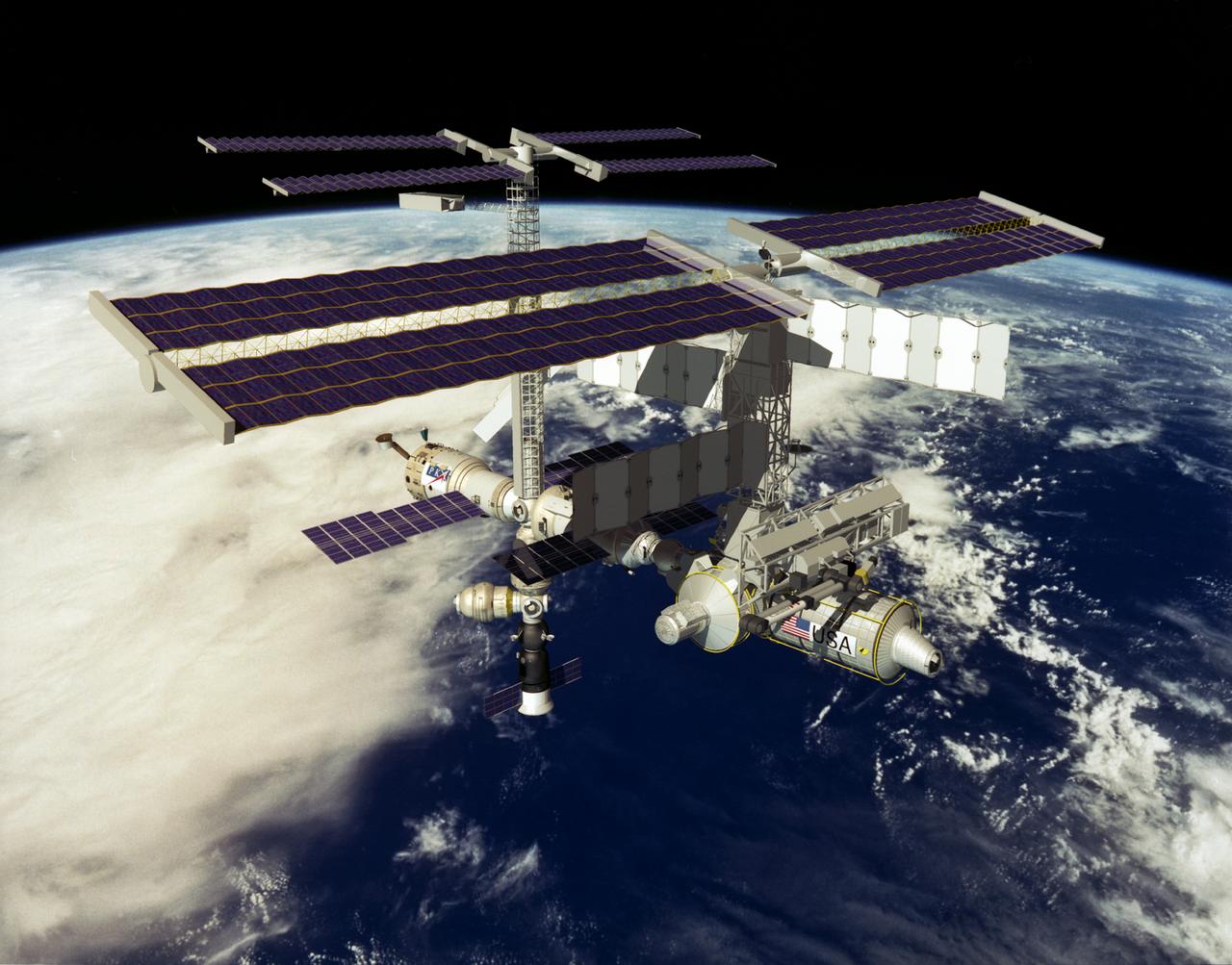

This computer generated scene of the International Space Station (ISS) represents the first addition of hardware following the completion of Phase II. The 8-A Phase shows the addition of the S-9 truss.
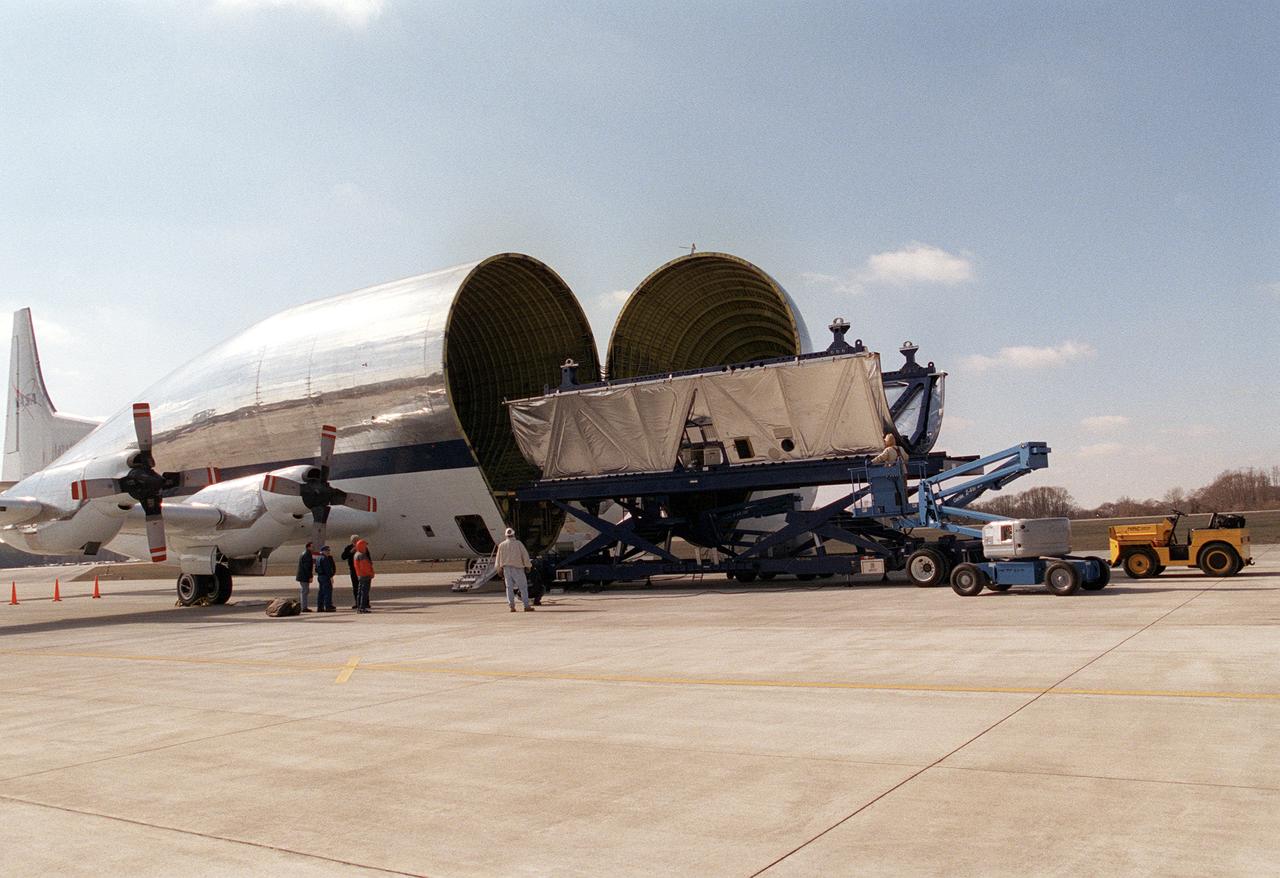

A section of the International Space Station truss assembly arrived at the Marshall Space Flight Center on NASA's Super Guppy cargo plane for structural and design testing as well as installation of critical flight hardware.

Artist's concept of the final configuration of the International Space Station (ISS) Alpha. The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation.
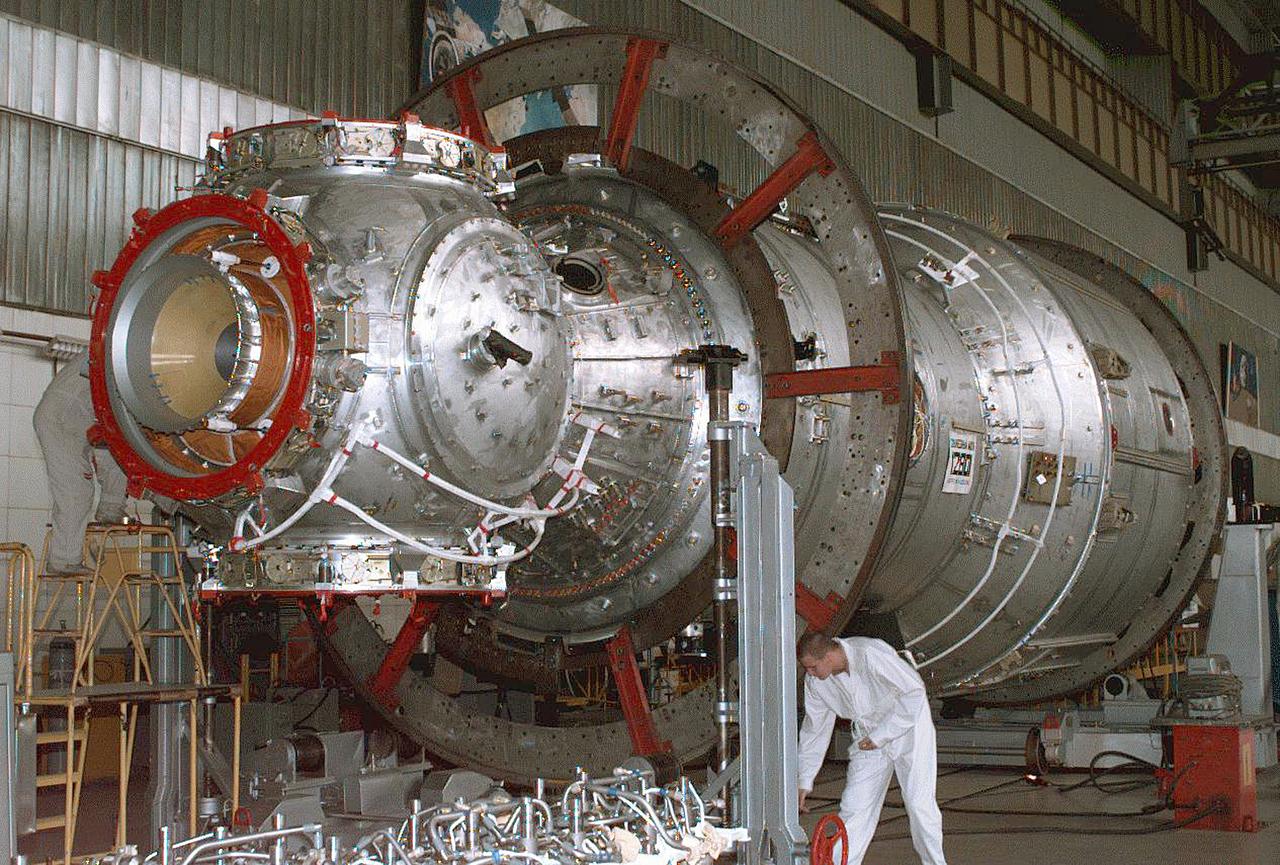
The Zvezda Service Module, the first Russian contribution and third element to the International Space Station (ISS), is shown under construction in the Krunichev State Research and Production Facility (KhSC) in Moscow. Russian technicians work on the module shortly after it completed a pressurization test. In the foreground is the forward portion of the module, including the spherical transfer compartment and its three docking ports. The forward port docked with the cornected Functional Cargo Block, followed by Node 1. Launched via a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000, the Zvezda Service Module serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, life support system, electrical power distribution, data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
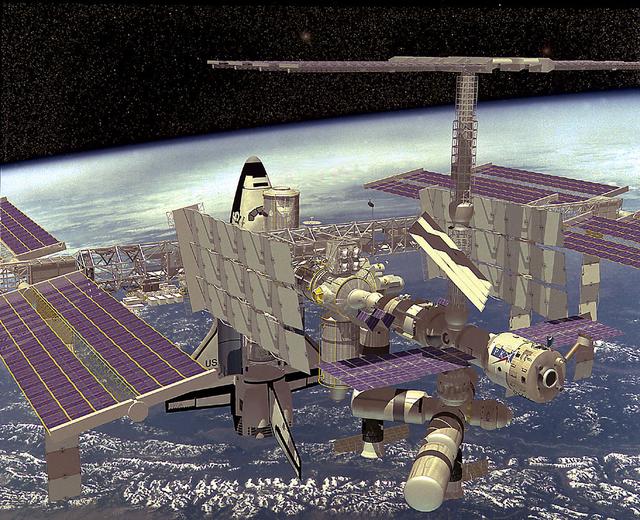

Artist's concept for Phase III of the International Space Station (ISS) as shown here in its completed and fully operational state with elements from the United States, Europe, Canada, Japan, and Russia. Sixteen countries are cooperating to provide a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation.
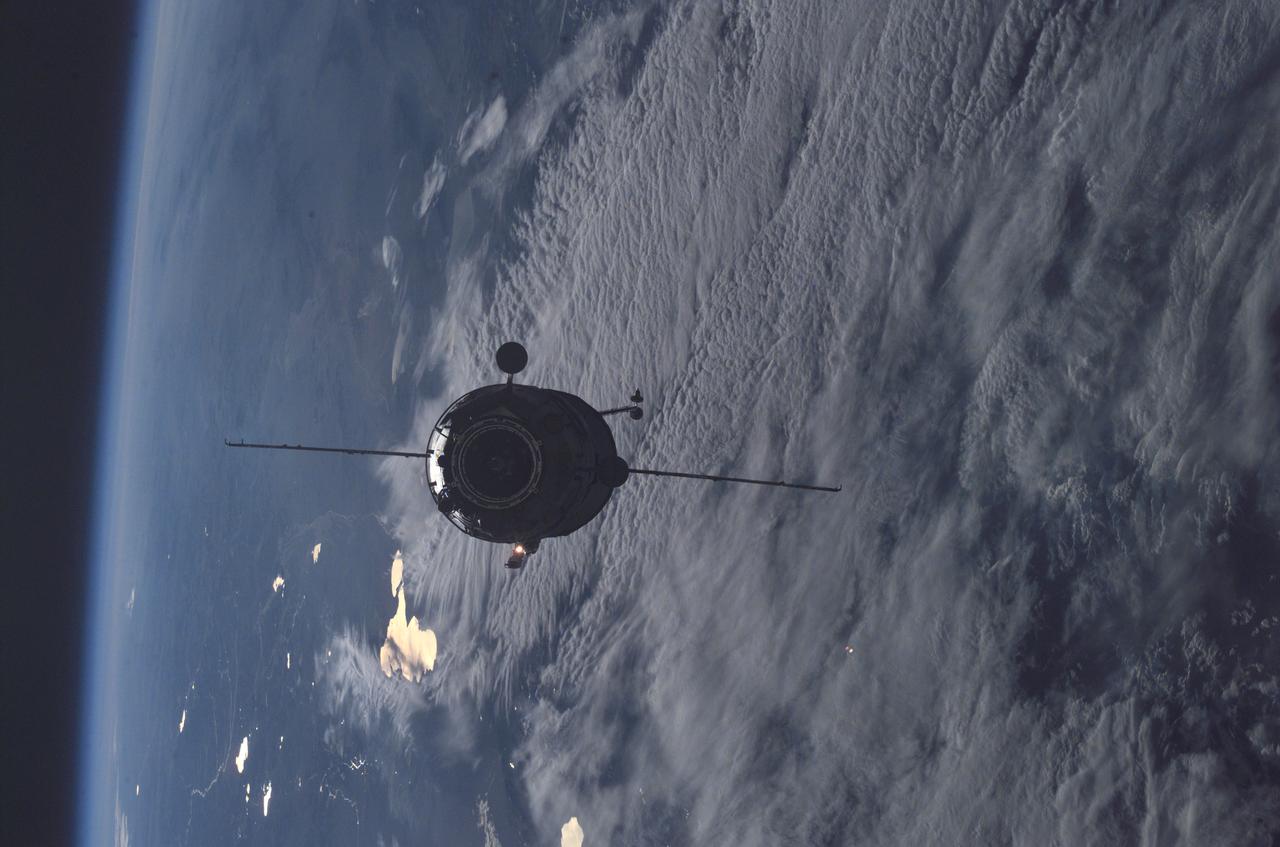

Enroute for docking, the 16-foot-long Russian docking compartment Pirs (the Russian word for pier) approaches the International Space Station (ISS). Pirs will provide a docking port for future Russian Soyuz or Progress craft, as well as an airlock for extravehicular activities. Pirs was launched September 14, 2001 from Baikonur in Russia.

Artist's concept of the International Space Station (ISS) Alpha deployed and operational. This figure also includes the docking procedures for the Space Shuttle (shown with cargo bay open). The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation.

An artist's conception of what the final configuration of the International Space Station (ISS) will look like when it is fully built and deployed. The ISS is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experimentation.

NASA's Earth Dome is seen at Union Station, Monday, April 22, 2013 in Washington. The Earth Dome housed two of NASA's Science Gallery exhibits as part of a NASA-sponsored Earth Day event at Union Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

NASA's Earth Dome is seen at Union Station, Monday, April 22, 2013 in Washington. The Earth Dome housed two of NASA's Science Gallery exhibits as part of a NASA-sponsored Earth Day event at Union Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
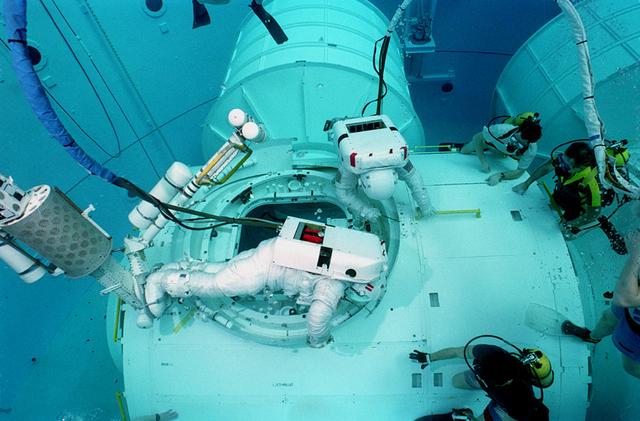
International Space Station testing is conducted in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
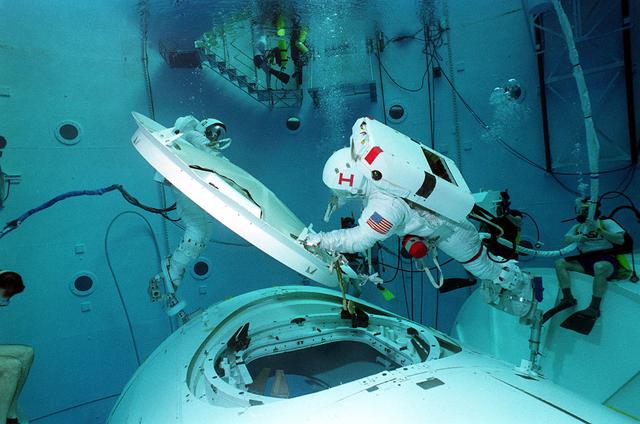

International Space Station testing is conducted in Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
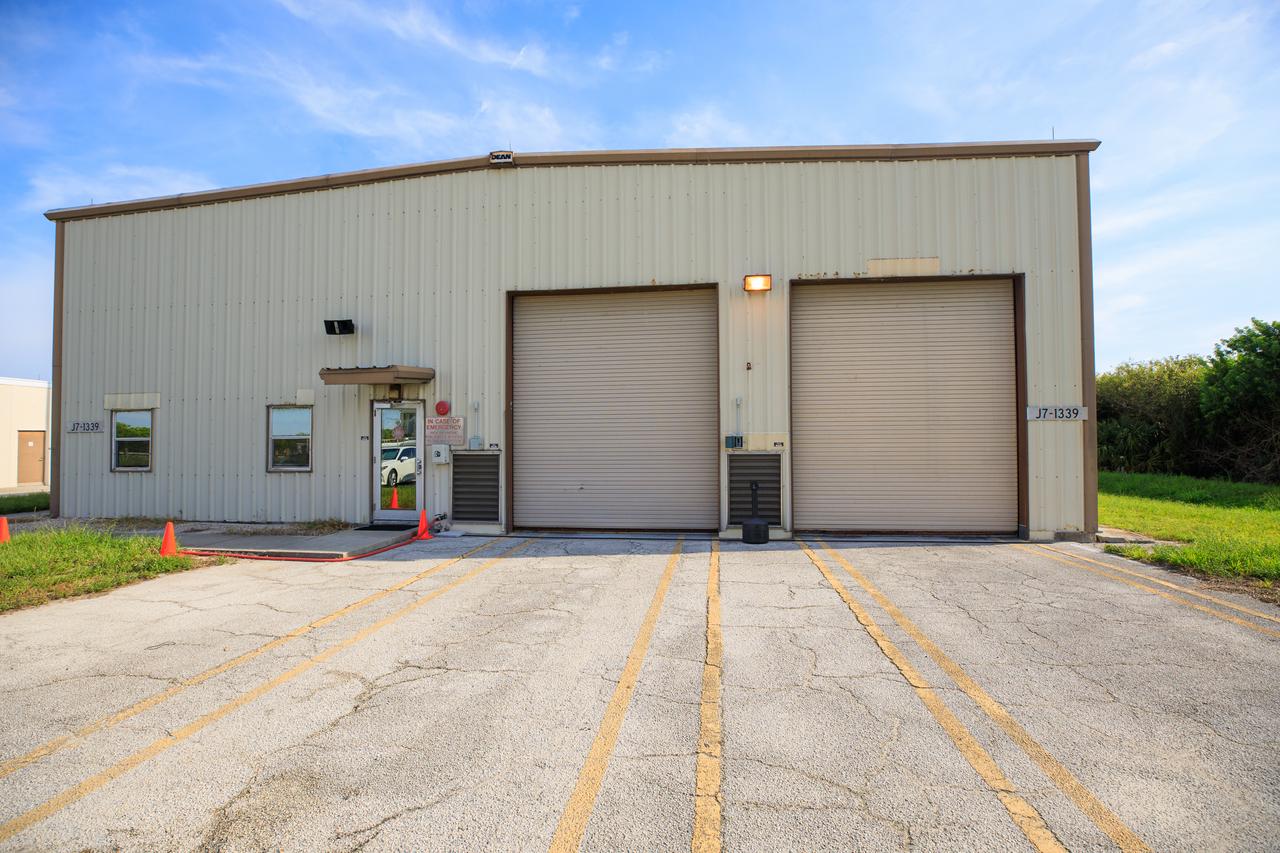

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
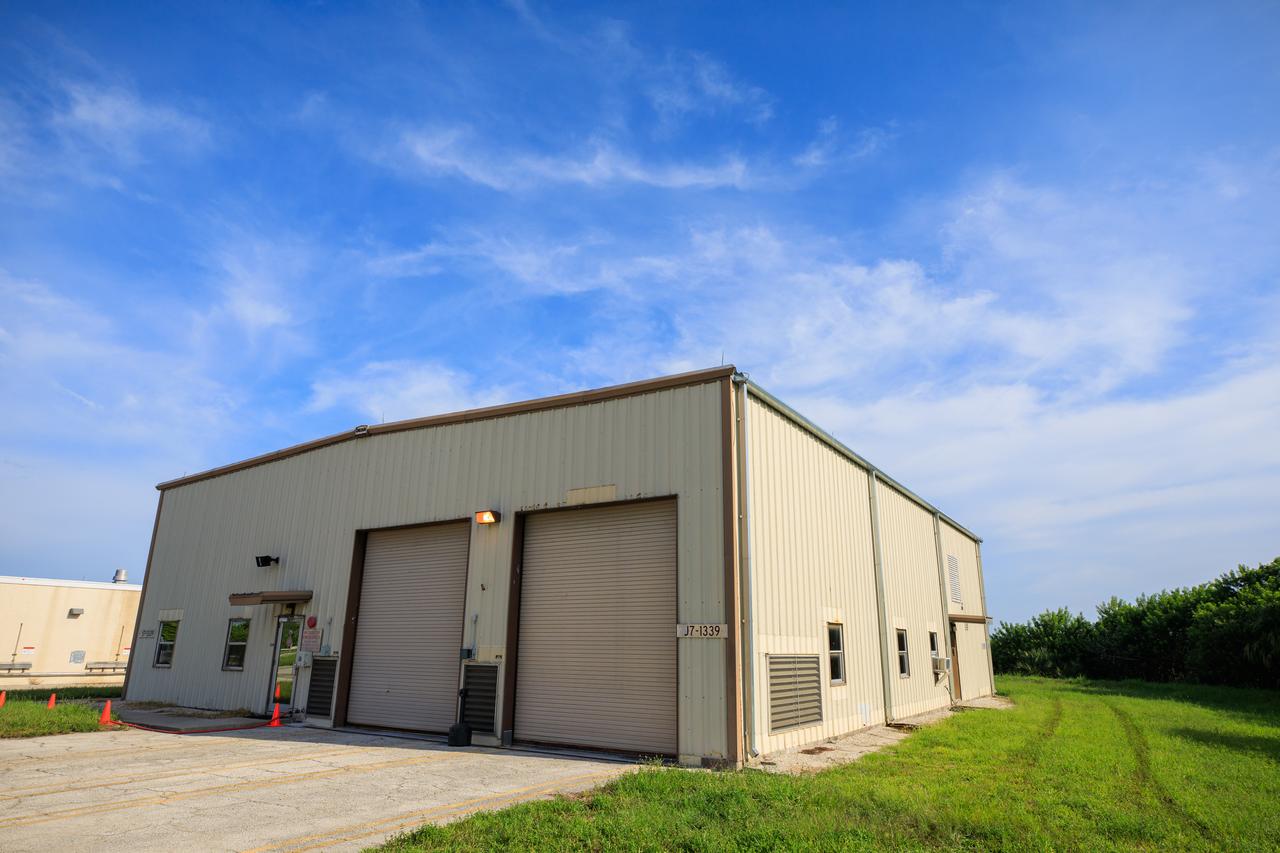

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
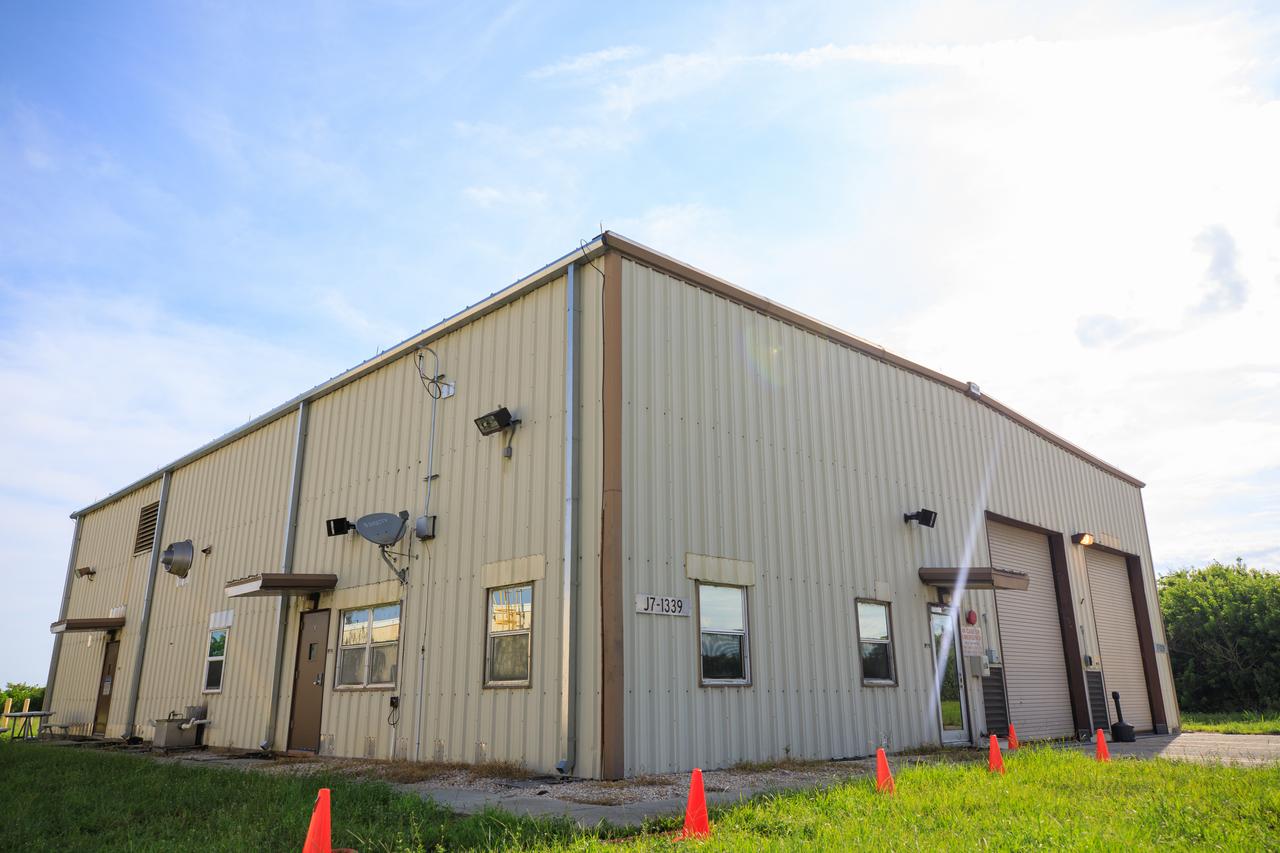

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
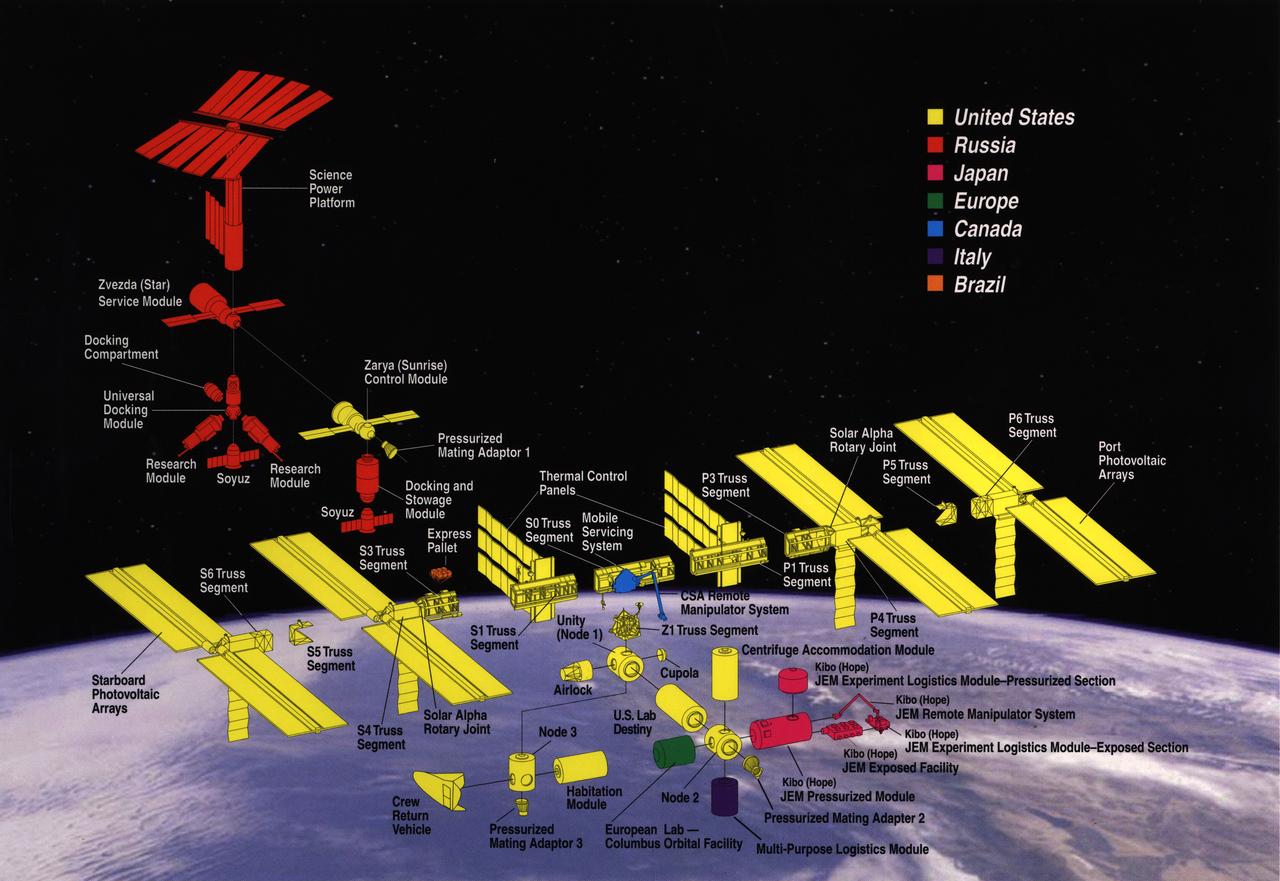
The International Space Station (ISS) is an unparalleled international scientific and technological cooperative venture that will usher in a new era of human space exploration and research and provide benefits to people on Earth. On-Orbit assembly began on November 20, 1998, with the launch of the first ISS component, Zarya, on a Russian Proton rocket. The Space Shuttle followed on December 4, 1998, carrying the U.S.-built Unity cornecting Module. Sixteen nations are participating in the ISS program: the United States, Canada, Japan, Russia, Brazil, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. The ISS will include six laboratories and be four times larger and more capable than any previous space station. The United States provides two laboratories (United States Laboratory and Centrifuge Accommodation Module) and a habitation module. There will be two Russian research modules, one Japanese laboratory, referred to as the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), and one European Space Agency (ESA) laboratory called the Columbus Orbital Facility (COF). The station's internal volume will be roughly equivalent to the passenger cabin volume of two 747 jets. Over five years, a total of more than 40 space flights by at least three different vehicles - the Space Shuttle, the Russian Proton Rocket, and the Russian Soyuz rocket - will bring together more than 100 different station components and the ISS crew. Astronauts will perform many spacewalks and use new robotics and other technologies to assemble ISS components in space.
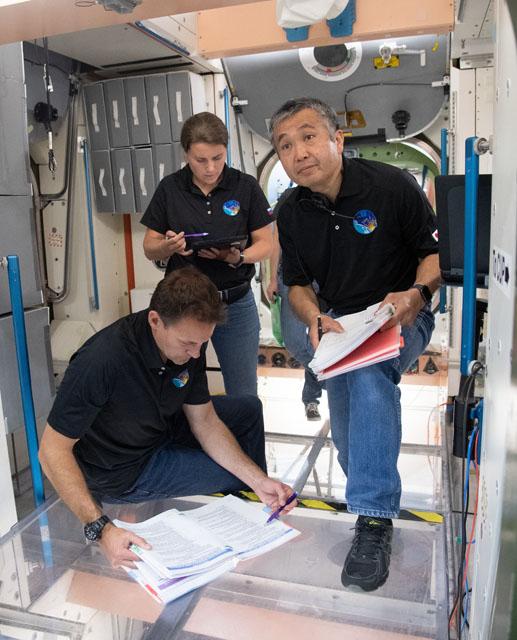

NASA Astronaut Josh Cassada, JAXA astronaut Koichi Wakata, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina train for their upcoming SpaceX Crew-5 mission to the International Space Station inside a mockup facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/James Blair
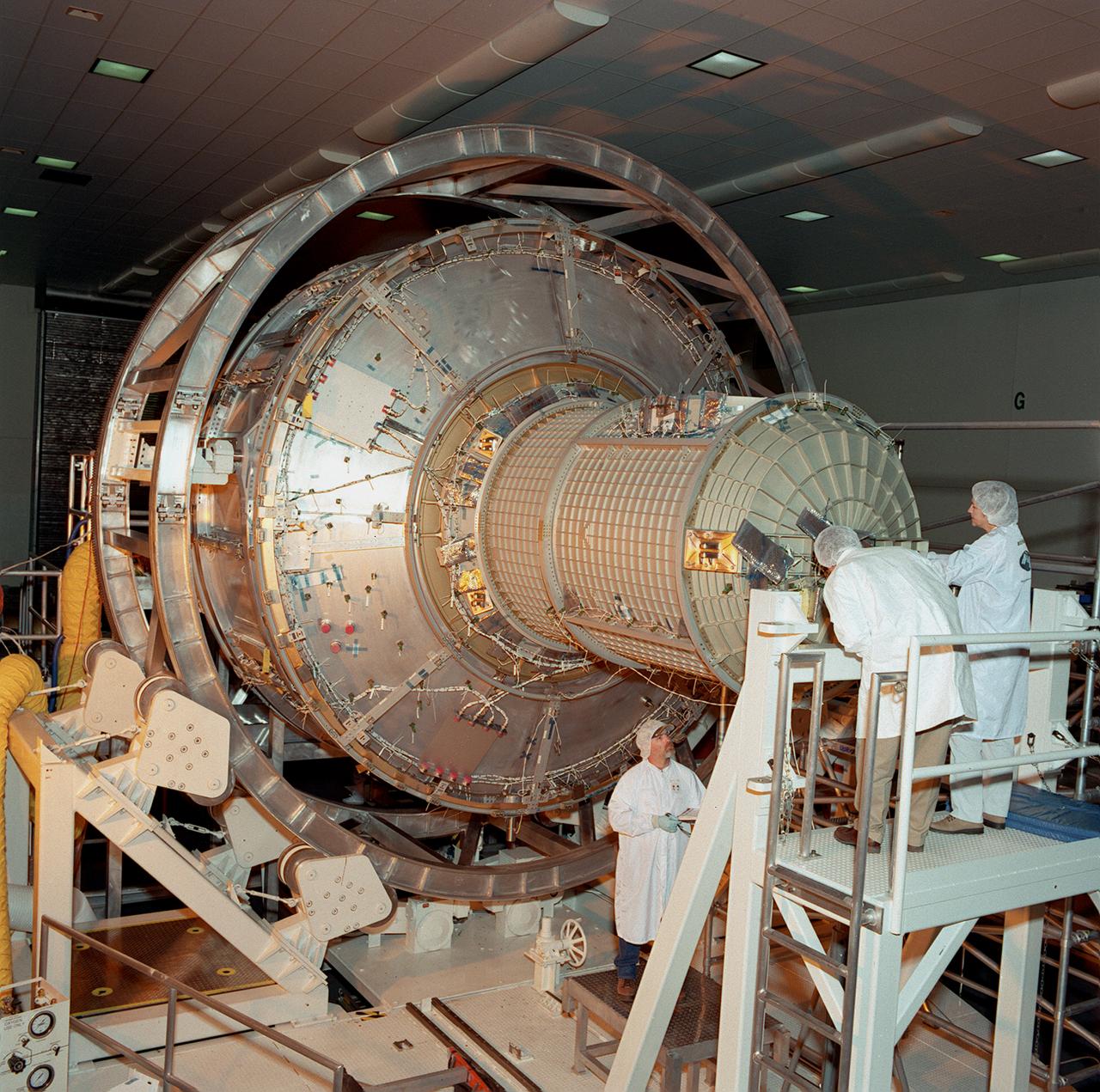

This photograph depicts the International Space Station's (ISS) Joint Airlock Module undergoing exhaustive structural and systems testing in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) prior to shipment to the Kennedy Space Center. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock, on the left, will store spacesuits and associated gear and the narrower crewlock is on the right, from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activity. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.
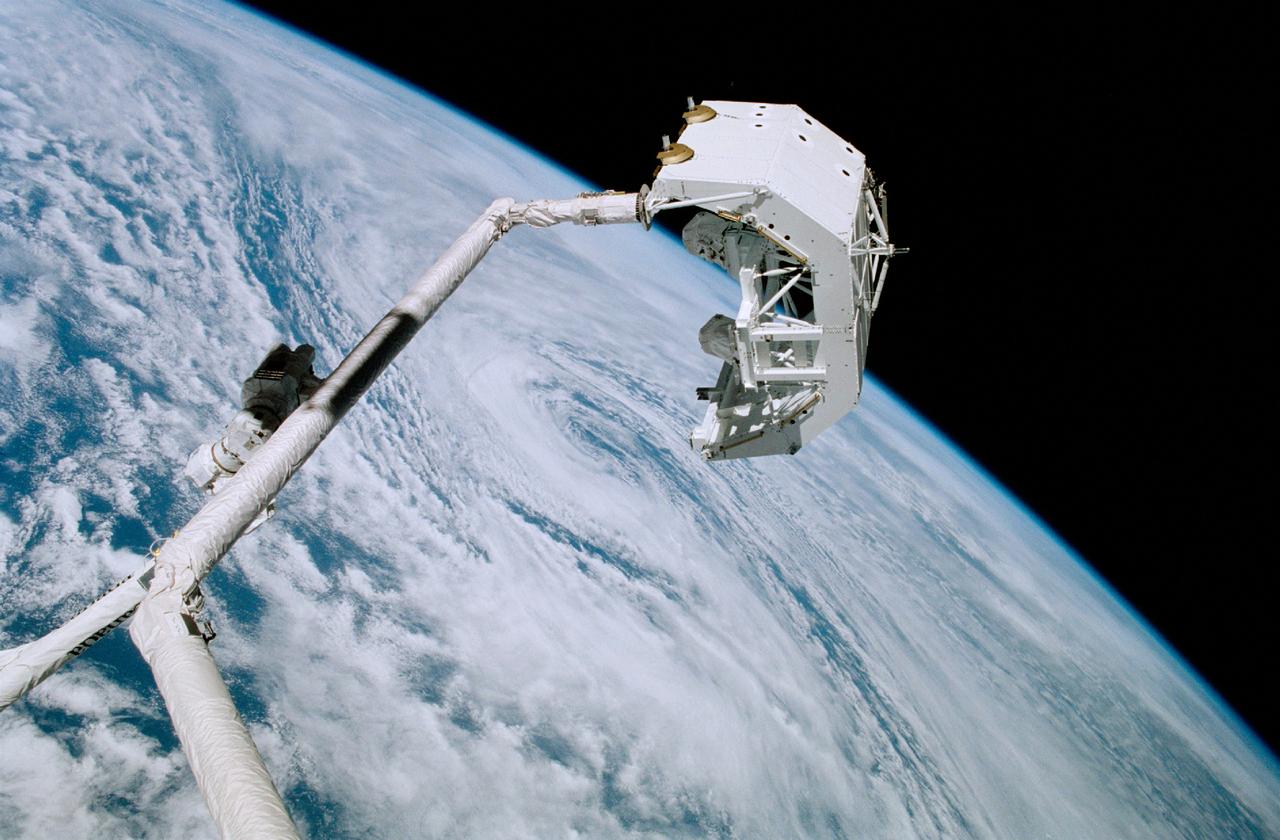

A Canadian "handshake" in space occurred on April 28, 2001, as the Canadian-built space station robotic arm (Canadarm-2) transferred its launch cradle over to Endeavor's robotic arm. Marning the controls from the shuttle's aft flight deck, Canadian Mission Specialist Chris A. Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) was instrumental in the activity. The Spacelab pallet that carried the Canadarm2 robotic arm to the station was developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama.
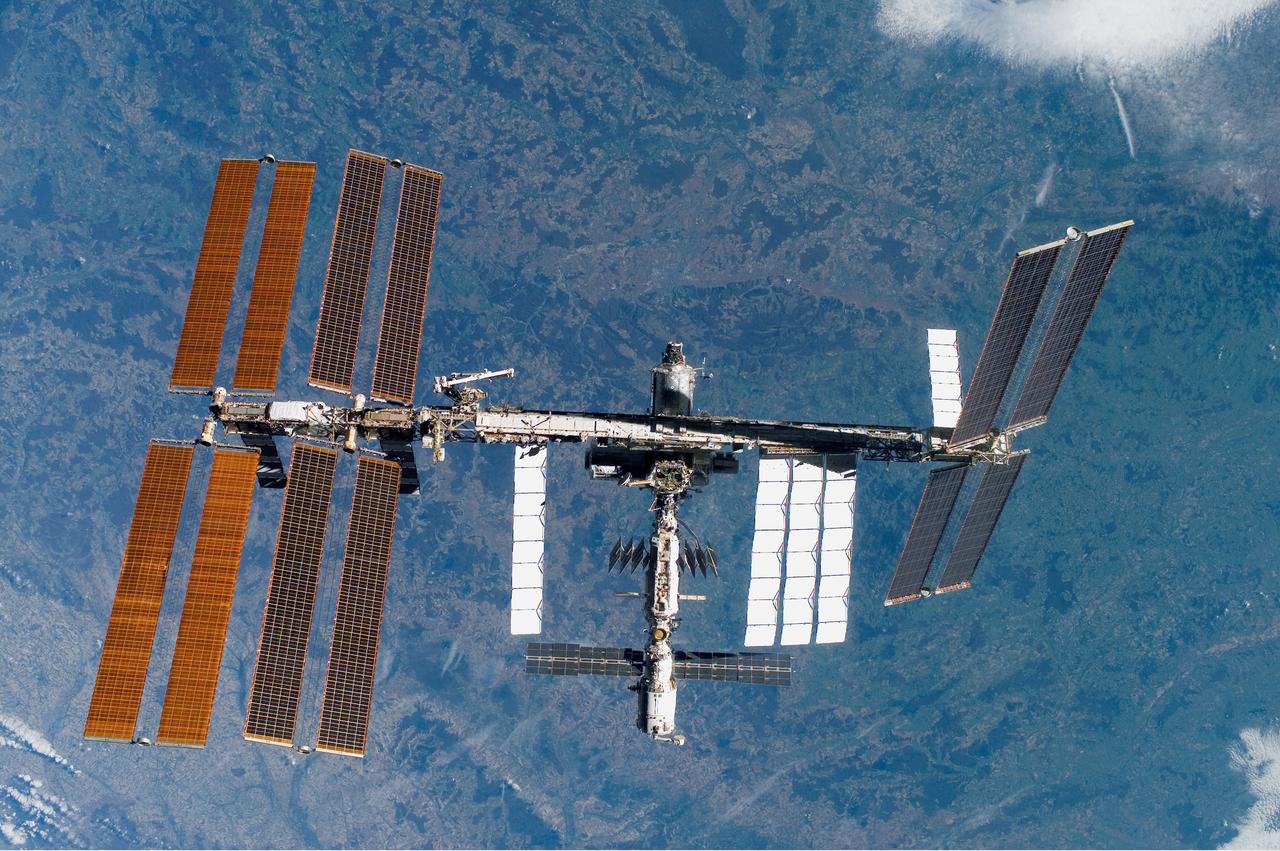

Back dropped by the blueness of Earth is the International Space Station (ISS) as seen from Space Shuttle Discovery as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. The latest configuration of the ISS includes the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, named Harmony, and the P6 truss segment installed over 11 days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station by the STS-120 and Expedition 16 crews. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 4:32 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 5, 2007.
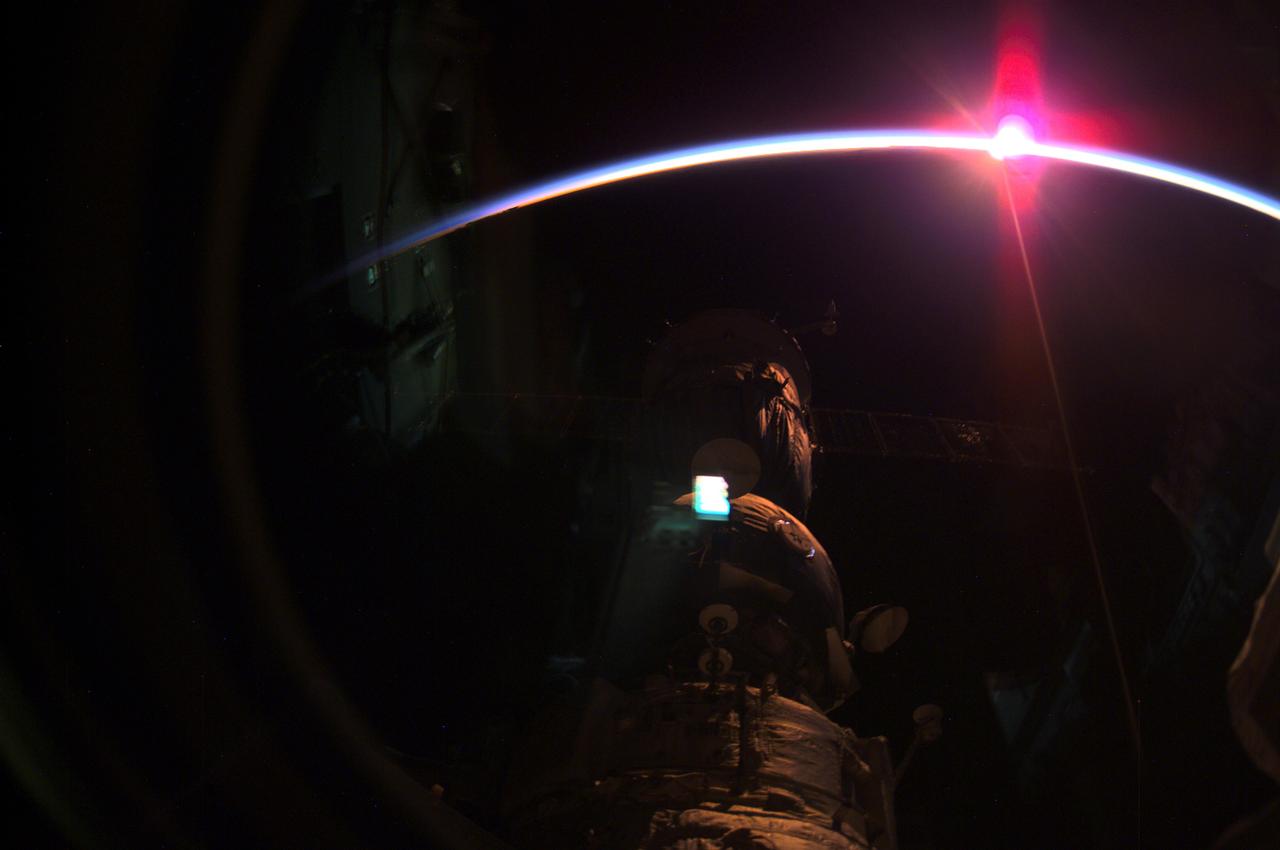

The setting sun and the thin blue airglow line at Earth's horizon was captured by the International Space Station's (ISS) Expedition Three crewmembers with a digital camera. Some of the Station's components are silhouetted in the foreground. The crew was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery STS-105 mission, on August 10, 2001, replacing the Expedition Two crew. After marning the orbiting ISS for 128 consecutive days, the three returned to Earth on December 17, 2001, aboard the STS-108 mission Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour.
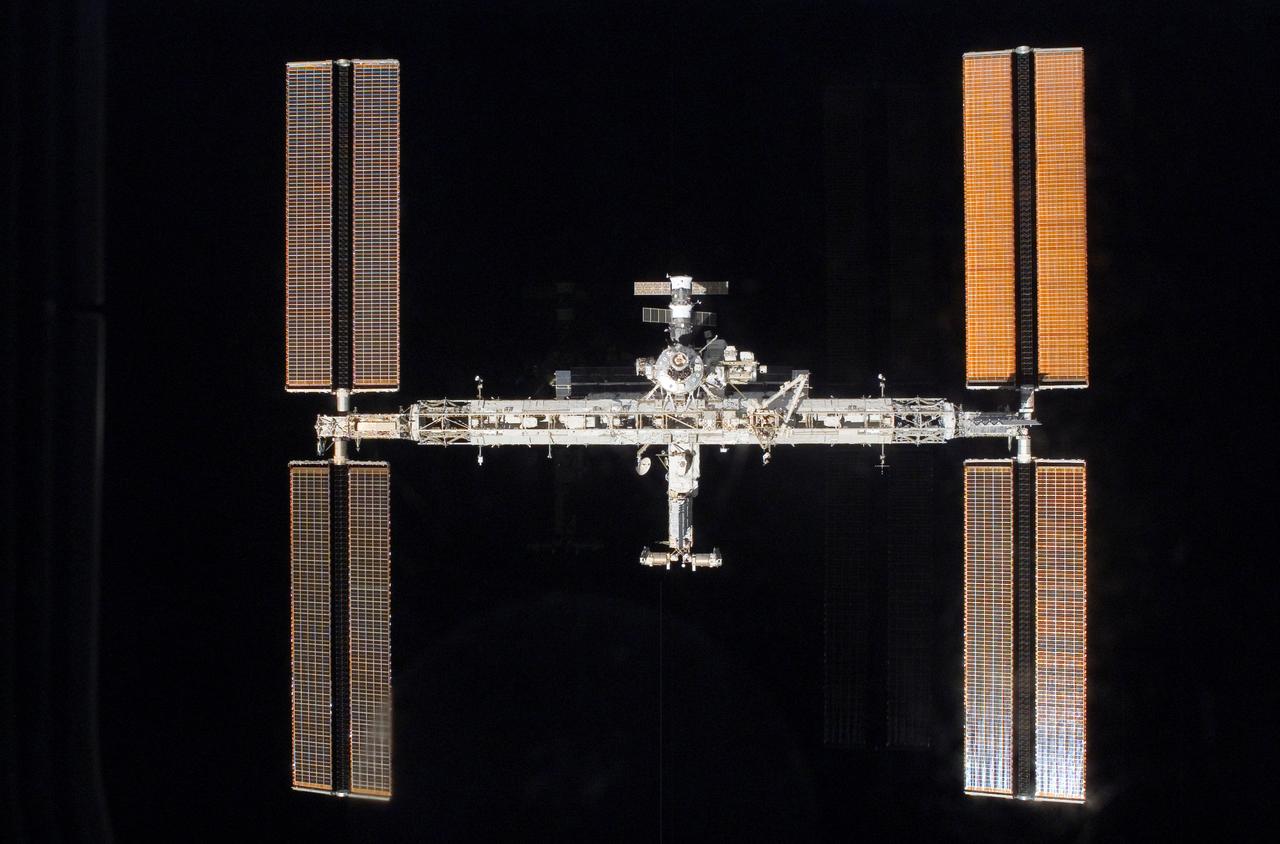
Eight days of construction resumed on the International Space Station (ISS), as STS-117 astronauts and mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the second and third starboard truss segments (S3 and S4). Back dropped by the blackness of space, its newly expanded configuration is revealed as pilot Lee Archambault conducts a fly around upon departure from the station on June 19, 2007.
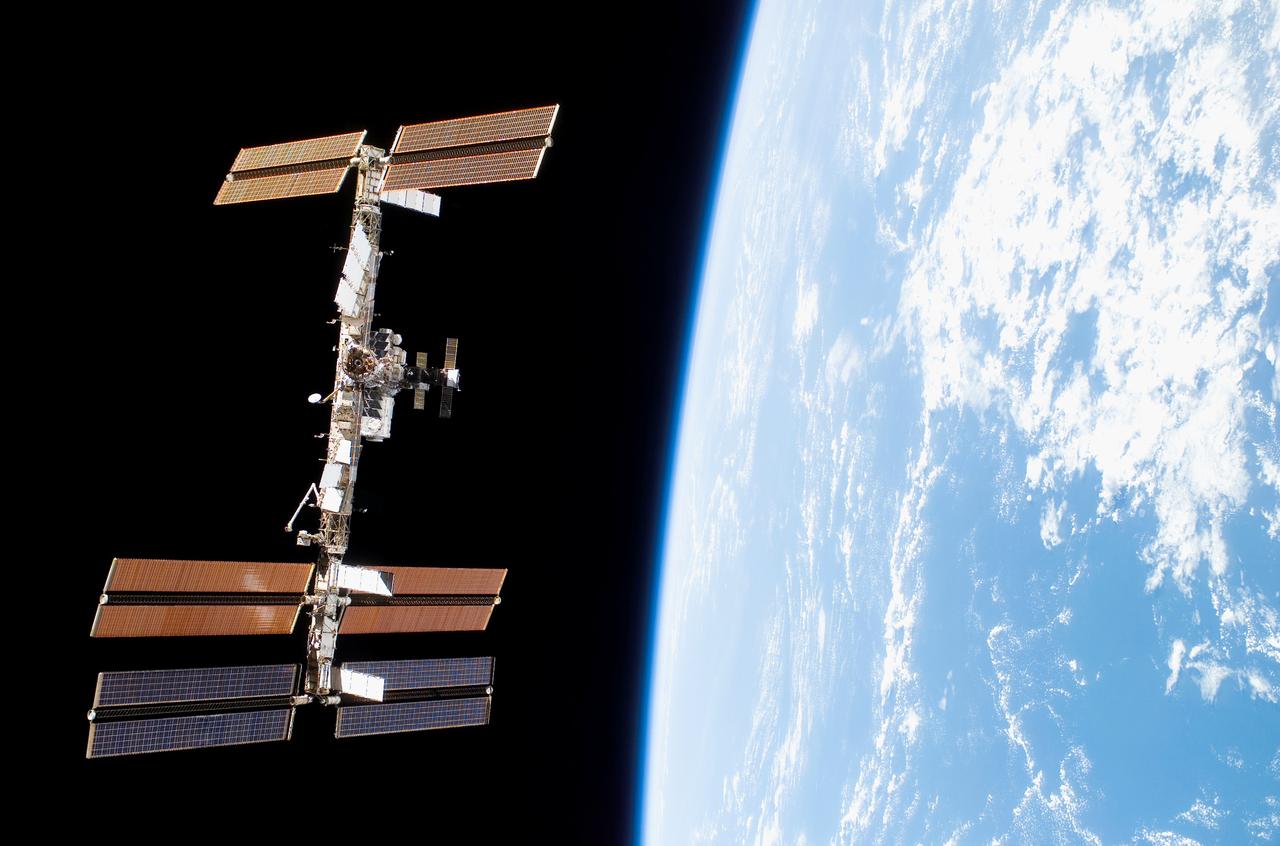

Back dropped by the blackness of space and Earth's horizon is the International Space Station (ISS) as seen from Space Shuttle Discovery as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. The latest configuration of the ISS includes the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, named Harmony, and the P6 truss segment installed over 11 days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station by the STS-120 and Expedition 16 crews. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 4:32 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 5, 2007.
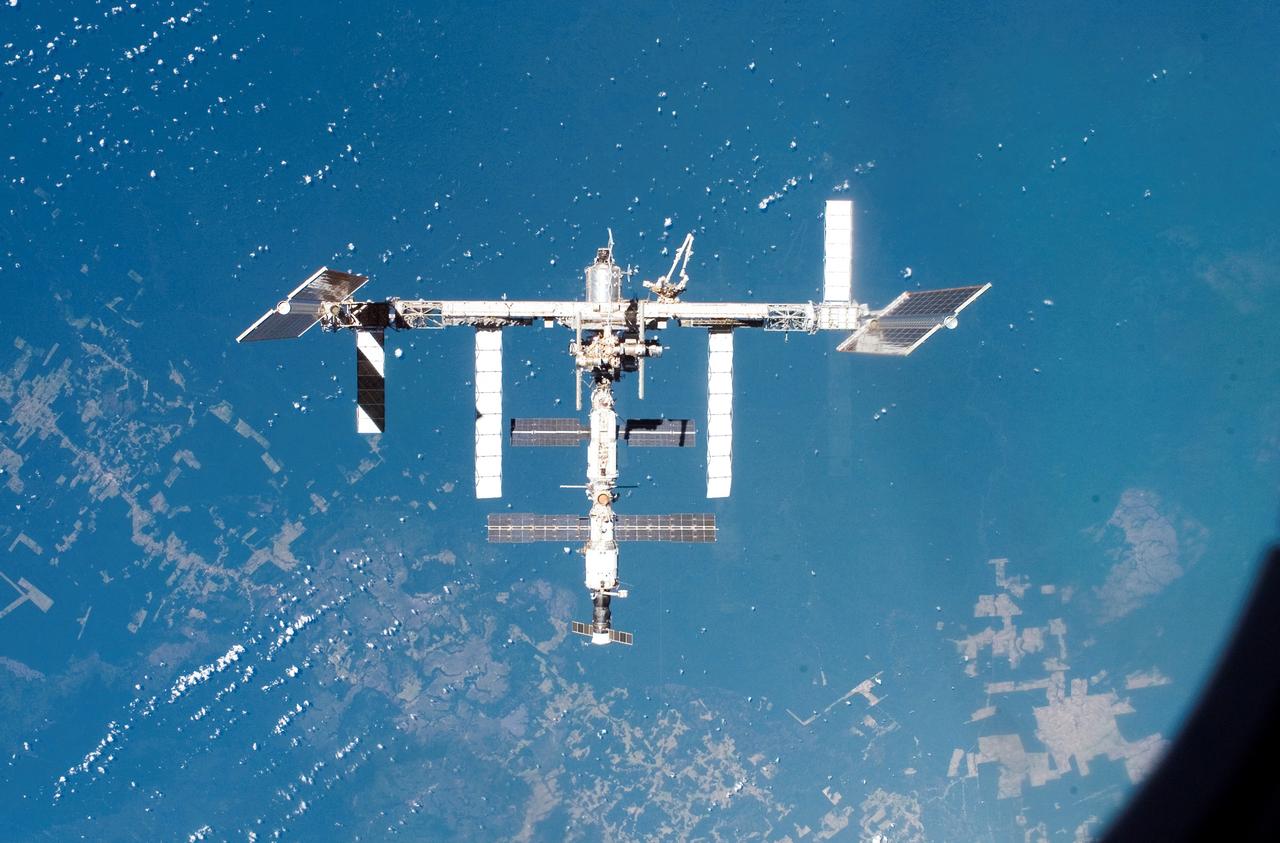

Eight days of construction resumed on the International Space Station (ISS), as STS-117 astronauts and mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the second and third starboard truss segments (S3 and S4). Back dropped by our colorful Earth, its newly expanded configuration is revealed as pilot Lee Archambault conducts a fly around upon departure from the station on June 19, 2007.
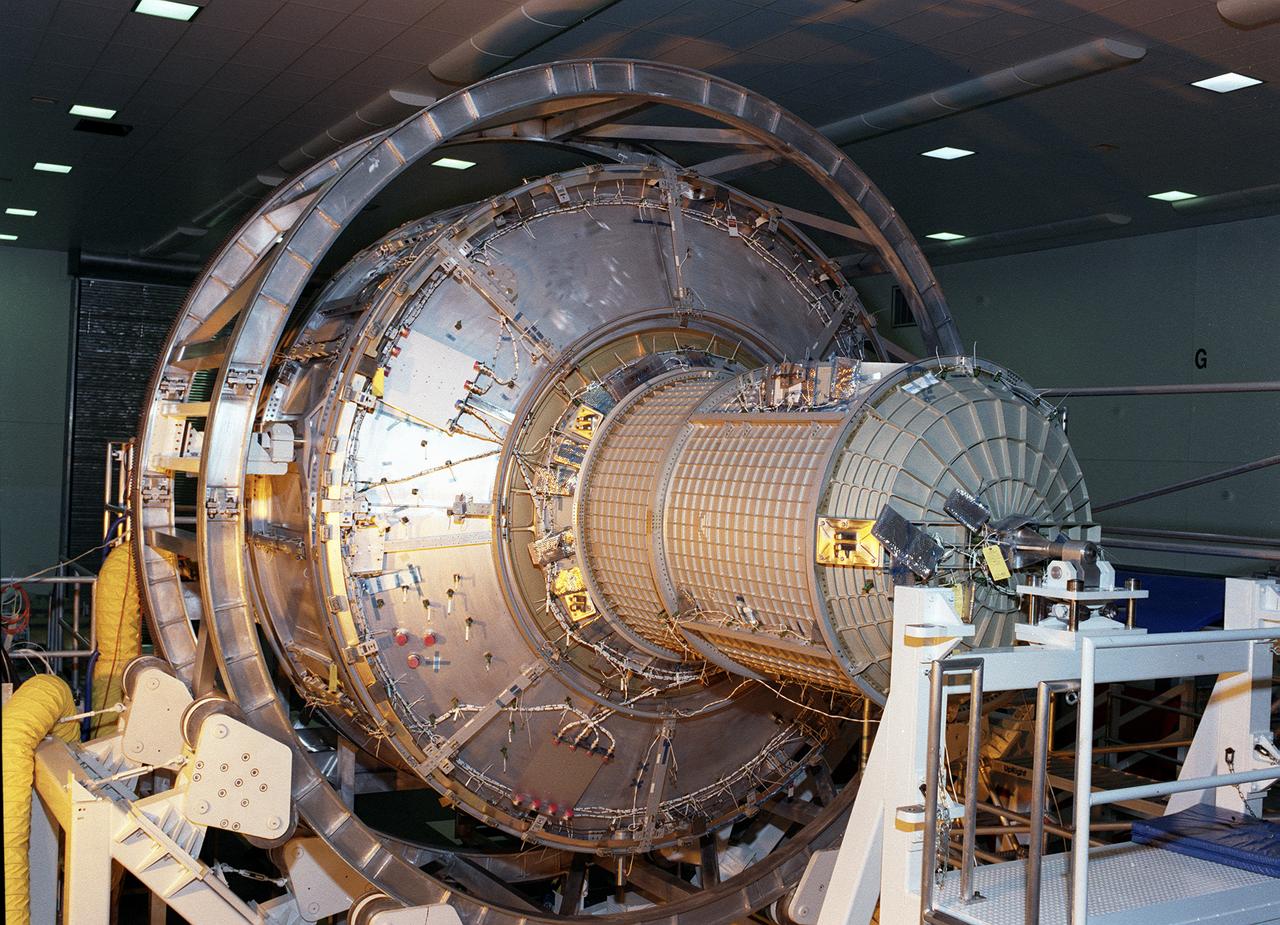
The Joint Airlock Module for the International Space Station (ISS) awaits shipment to the Kennedy Space Center in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock on the left is where crews will change into and out of their spacesuits for extravehicular activities, and store spacesuits, batteries, power tools, and other supplies. The narrower crewlock from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activities, is on the right. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.

This image of the International Space Station (ISS) was photographed by one of the crewmembers of the STS-105 mission from the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery after separating from the ISS. The STS-105 mission was the 11th ISS assembly flight and its goals were the rotation of the ISS Expedition Two crew with Expedition Three crew, and the delivery of supplies utilizing the Italian-built Multipurpose Logistic Module (MPLM) Leonardo. Aboard Leonardo were six resupply stowage racks, four resupply stowage supply platforms, and two new scientific experiment racks, EXPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station) Racks 4 and 5, which added science capabilities to the ISS. Another payload was the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE), which included materials and other types of space exposure experiments mounted on the exterior of the ISS.
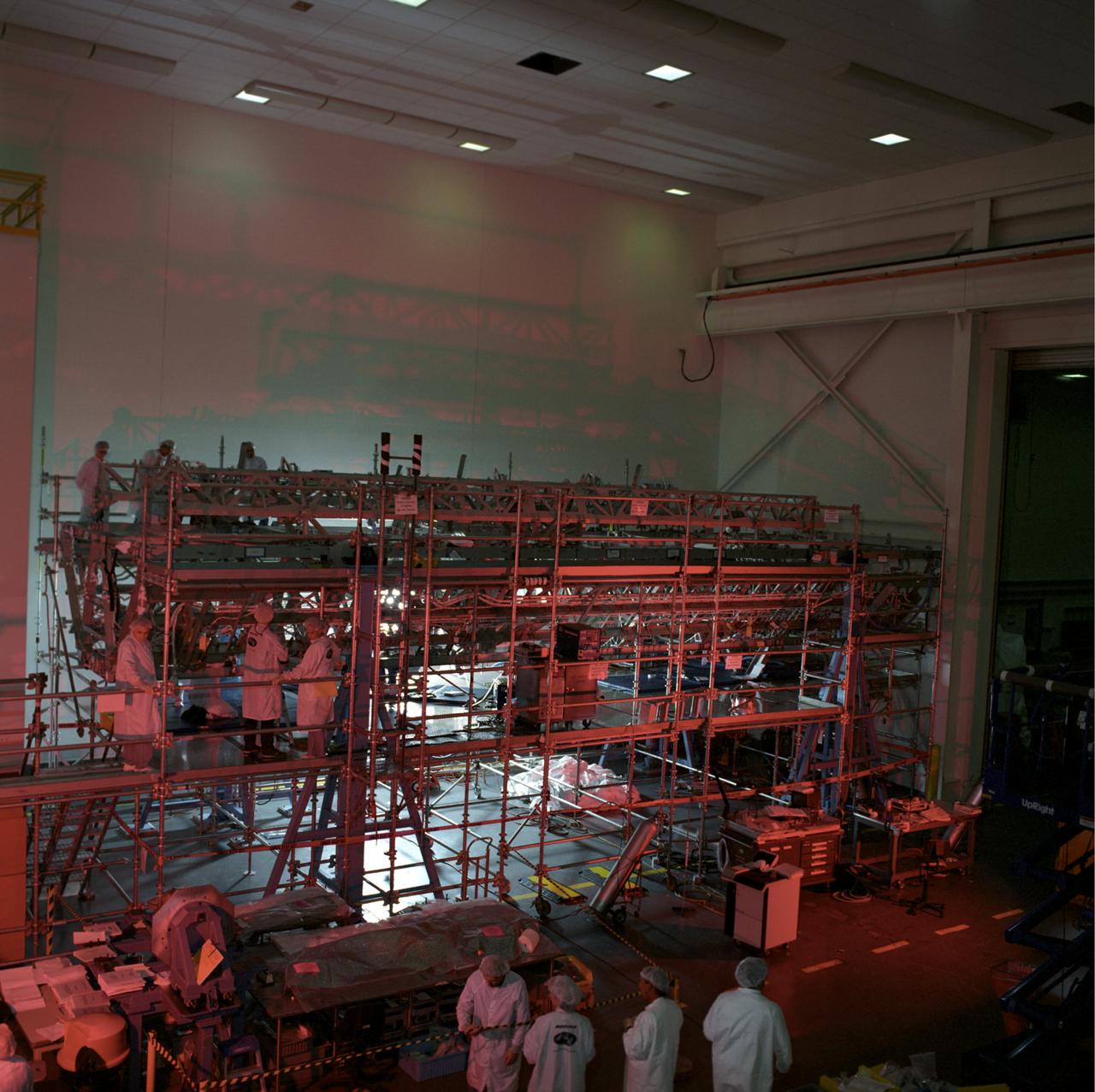

This image shows the Integrated Truss Assembly S-1 (S-One), the Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Truss, for the International Space Station (ISS) undergoing final construction in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. Delivered and installed by the STS-112 mission, the S1 truss, attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss installed by the previous STS-110 mission, flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat rejection radiators. The truss is 45-feet long, 15-feet wide, 10-feet tall, and weighs approximately 32,000 pounds. Manufactured by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, California, the truss primary structure was transferred to the Marshall Space Flight Center in February 1999 for hardware installations and manufacturing acceptance testing.
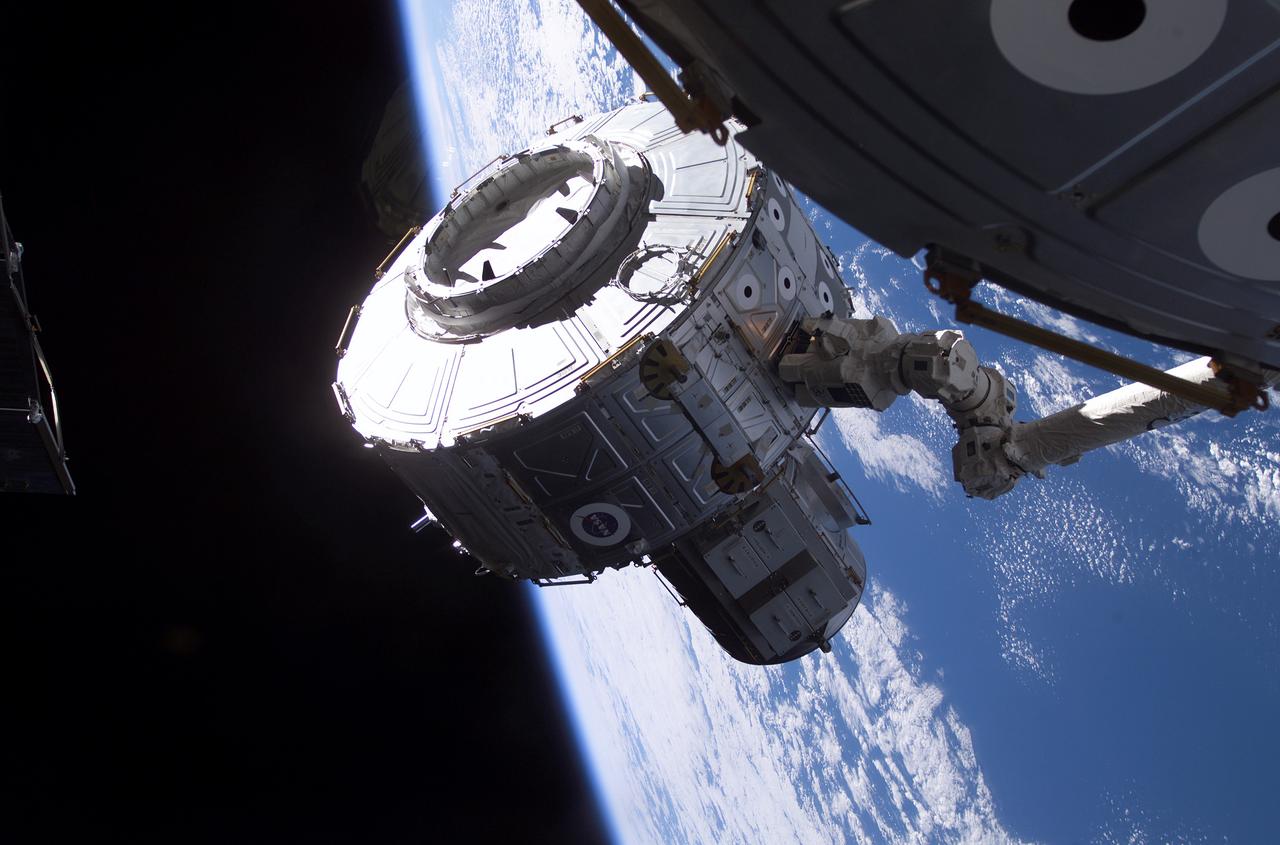

The Quest Airlock is in the process of being installed onto the starboard side of the Unity Node 1 of the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut Susan J. Helms, Expedition Two flight engineer, used controls onboard the station to maneuver the Airlock into place with the Canadarm2, or Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS). The Joint Airlock is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a cornecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the ISS Airlock becomes the primary path for ISS space walk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMUs). In addition, it is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for extravehicular activity (EVA). The Joint Airlock is 20-feet long, 13-feet in diameter and weighs 6.5 tons. It was built at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) by the Space Station prime contractor Boeing. The ISS Airlock has two main components: a crew airlock and an equipment airlock for storing EVA and EVA preflight preps. The Airlock was launched on July 21, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis for the STS-104 mission.
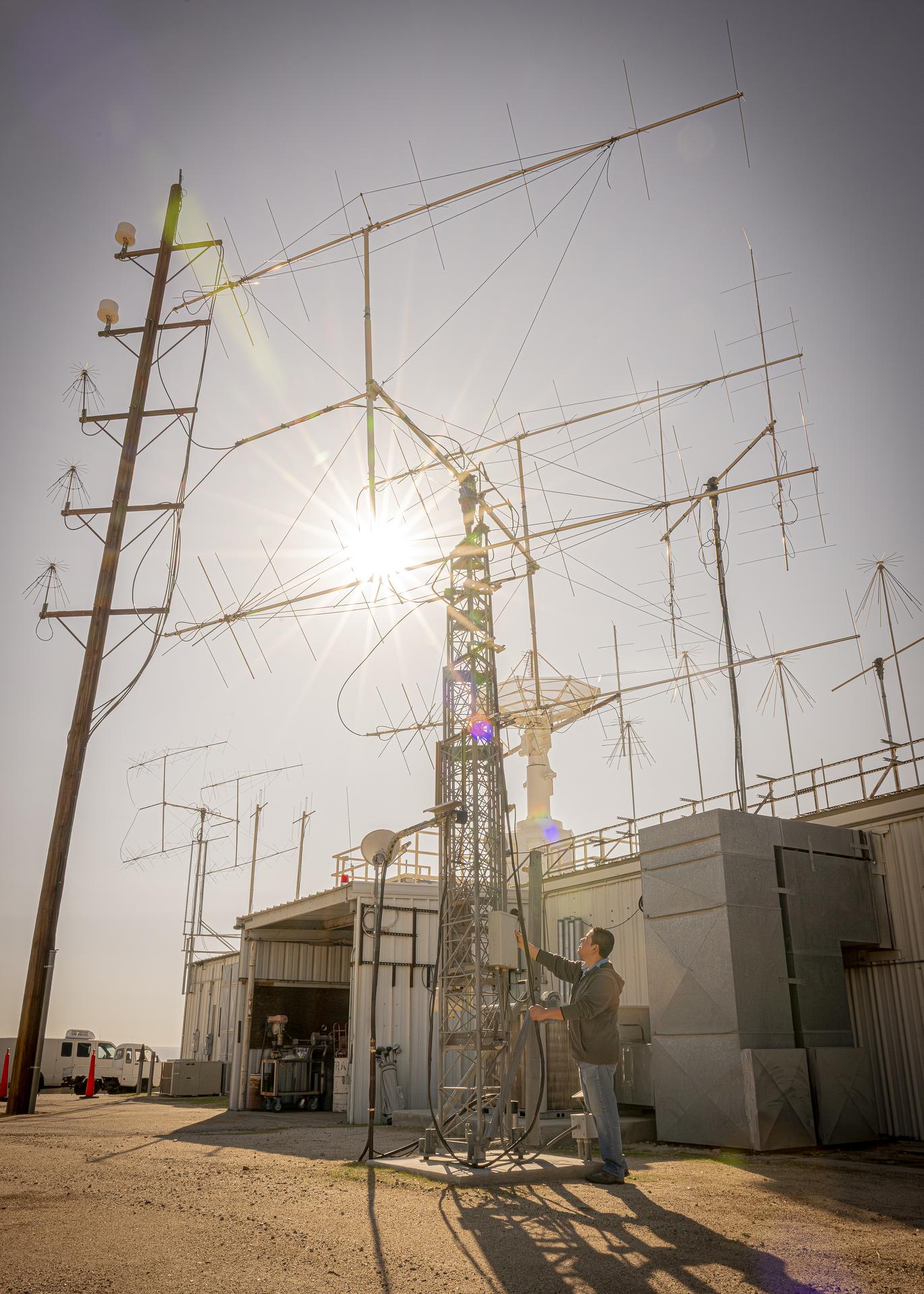

Mission operator Kelvin Menendez watches as antennas rise to track the International Space Station as it passes high above NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on Sept. 30, 2025. Menendez is part of the center’s Dryden Aeronautical Test Range, which provides voice and tracking support to the space station.

A participant at a NASA-sponsored Earth Day event puts together a puzzle of the Earth, Monday, April 22, 2013 at Union Station in Washington. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)

An artist's concept of a fully deployed International Space Station (ISS) Alpha. The ISS-A is a multidisciplinary laboratory, technology test bed, and observatory that will provide an unprecedented undertaking in scientific, technological, and international experiments.
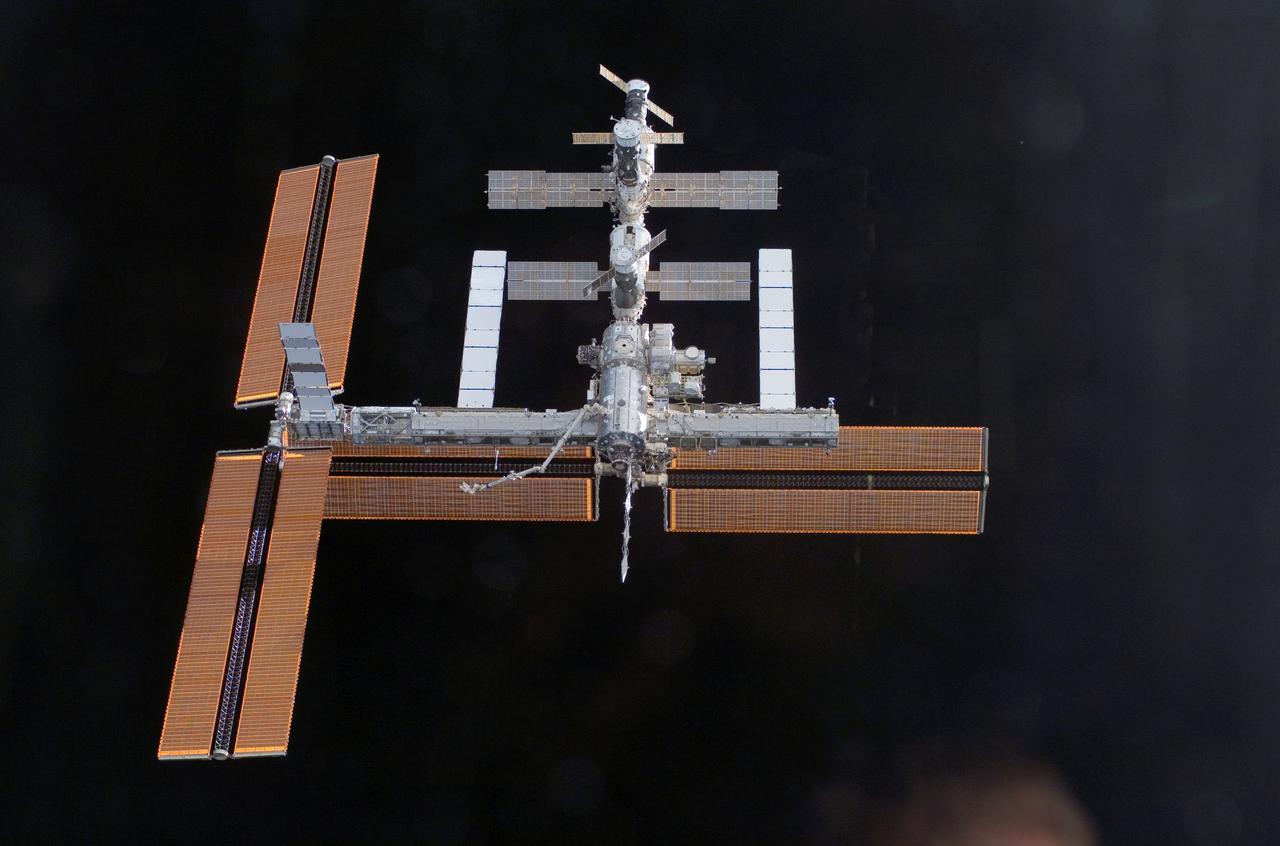
This view of the International Space Station, back dropped against the blackness of space, was taken shortly after the Space Shuttle Atlantis undocked from the orbital outpost at 7:50 a.m. CDT during the STS-115 mission. The unlinking completed after six days, two hours and two minutes of joint operations of the installation of the P3/P4 truss. The new 17 ton truss included batteries, electronics, a giant rotating joint, and sported a second pair of 240-foot solar wings. The new solar arrays will eventually double the onboard power of the Station when their electrical systems are brought online during the next shuttle flight, STS-116.
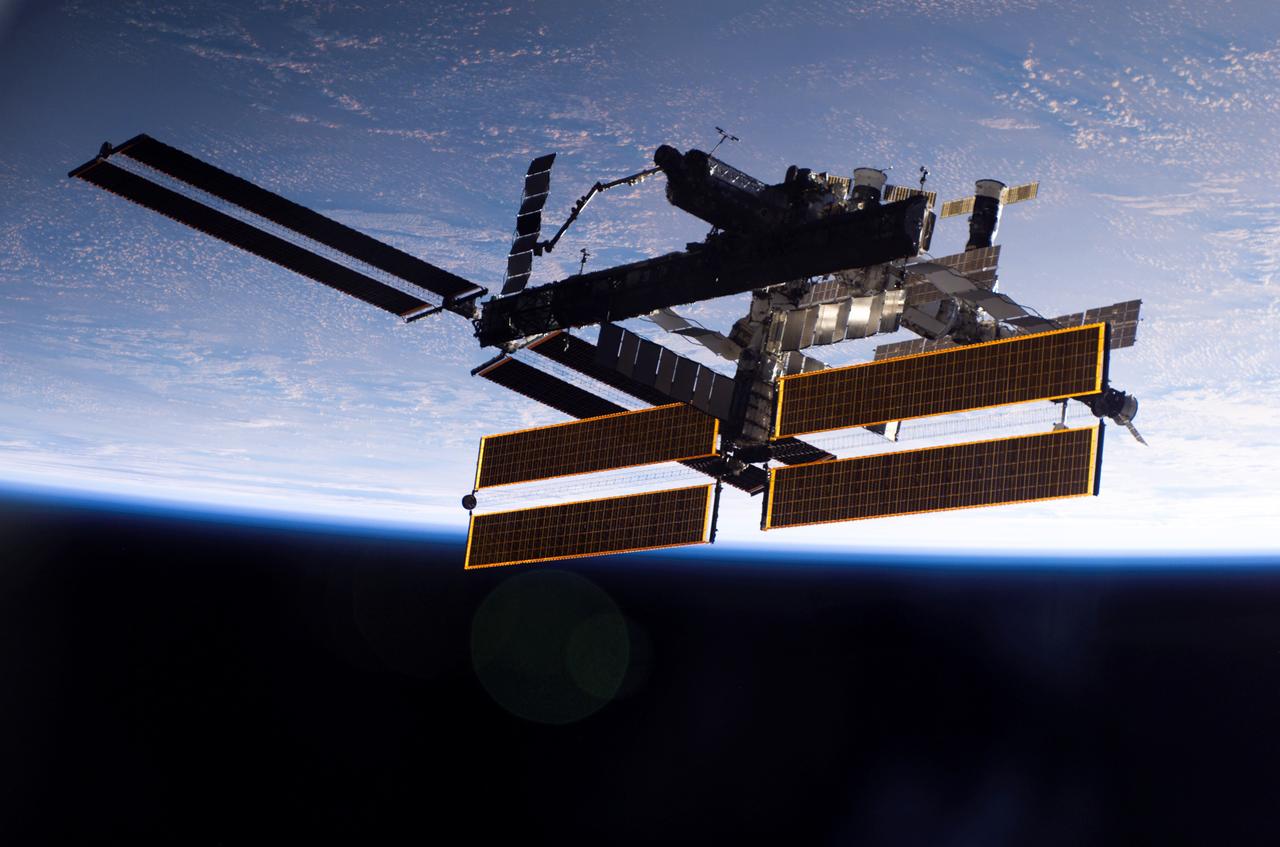

This view of the International Space Station, back dropped against the blackness of space and Earth, was taken shortly after the Space Shuttle Atlantis undocked from the orbital outpost at 7:50 a.m. CDT during the STS-115 mission. The unlinking completed after six days, two hours and two minutes of joint operations of the installation of the P3/P4 truss. The new 17 ton truss included batteries, electronics, a giant rotating joint, and sported a second pair of 240-foot solar wings. The new solar arrays will eventually double the onboard power of the Station when their electrical systems are brought online during the next shuttle flight, STS-116.
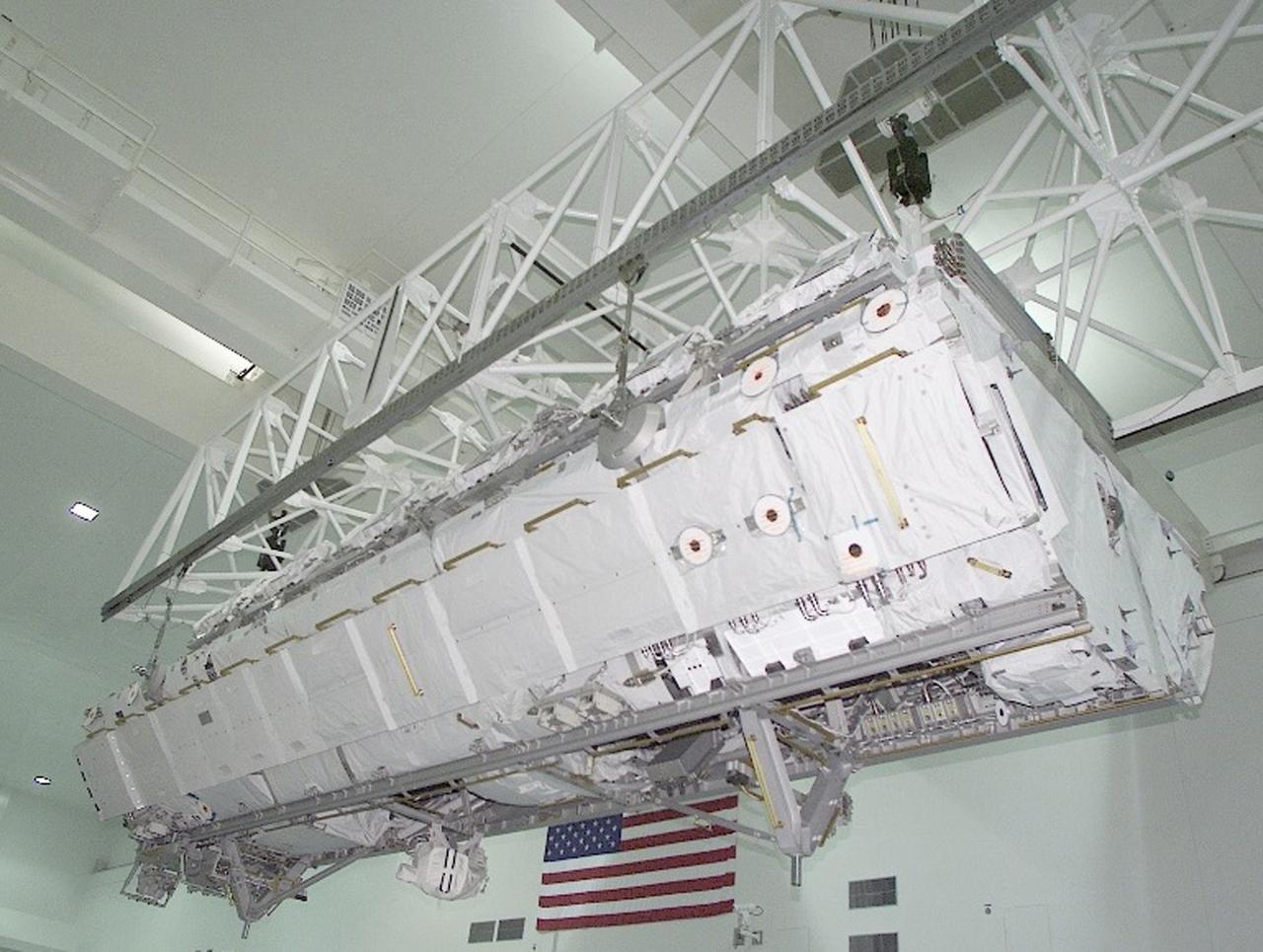

Shown here is the International Space Station (ISS) S1 Truss in preparation for installation in the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis at NASA's Kennedy Space Center )KSC)in Florida. The truss launched October 7, 2002 on the STS-112 mission and will be attached during three spacewalks. Constructed primarily of aluminum, it measures 45 feet long, 15 feet wide, 10 feet tall, and weighs over 27,000 pounds. It is one of nine similar truss segments that, combined, will serve as the Station's main backbone, measuring 356 feet from end to end upon completion. Manufactured by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, California, the truss was flown to the Marshall Space Flight Center, in Huntsville, Alabama where brackets, cable trays, fluid tubing, and other secondary components and outfitting items were added. In Huntsville, it was screened for manufacturing flaws, including pressure and leak checking tubing, and electrical checks for cabling, before being shipped to KSC for final hardware installation and testing. The Space Station's labs, living modules, solar arrays, heat radiators, and other main components will be attached to the truss.
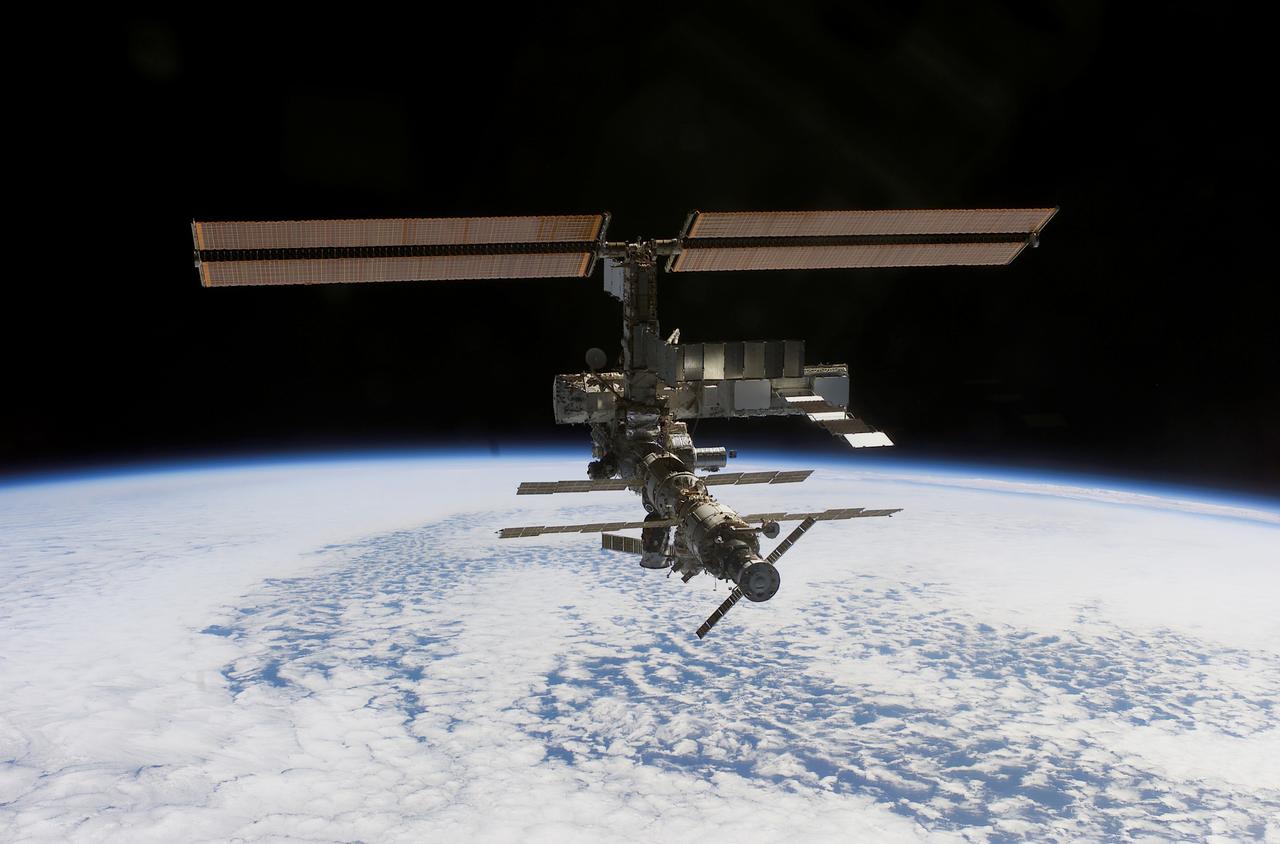

This image of the International Space Station (ISS) was photographed by one of the crewmembers of the STS-112 mission following separation from the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis as the orbiter pulled away from the ISS. The primary payloads of this mission, International Space Station Assembly Mission 9A, were the Integrated Truss Assembly S1 (S-One), the Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Truss, and the Crew Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) cart to the ISS. The S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. The S1 truss was attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss, which was launched on April 8, 2002 aboard the STS-110, and flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat-rejection radiators. The truss is 45-feet long, 15-feet wide, 10-feet tall, and weighs approximately 32,000 pounds. The CETA cart was attached to the Mobil Transporter and will be used by assembly crews on later missions. Manufactured by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, California, the truss primary structure was transferred to the Marshall Space Flight Center in February 1999 for hardware installations and manufacturing acceptance testing. The launch of the STS-112 mission occurred on October 7, 2002, and its 11-day mission ended on October 18, 2002.
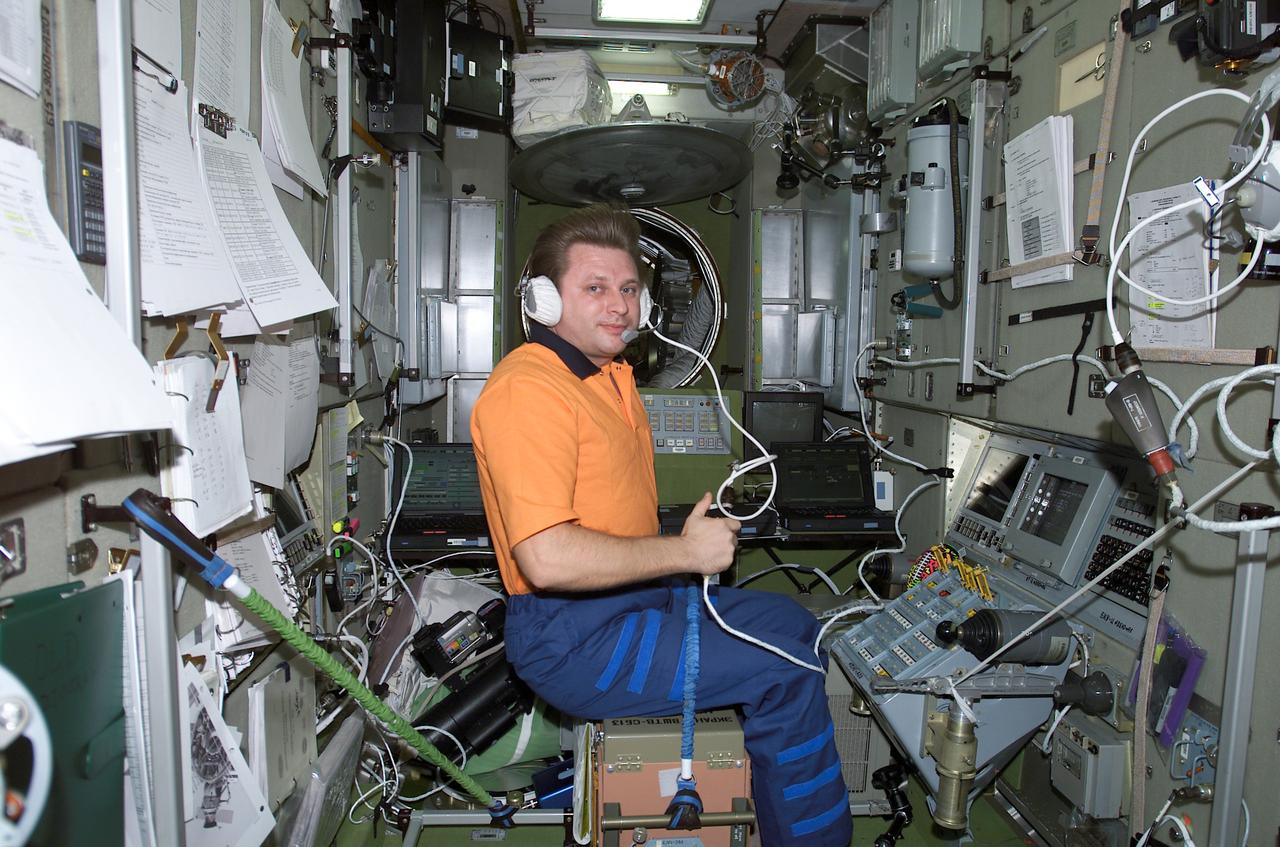

Cosmonaut Yury I. Onufrienko, Expedition Four mission commander, uses a communication system in the Russian Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The Zvezda is linked to the Russian-built Functional Cargo Block (FGB) or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity. The third component of the ISS, Zvezda (Russian word for star), the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
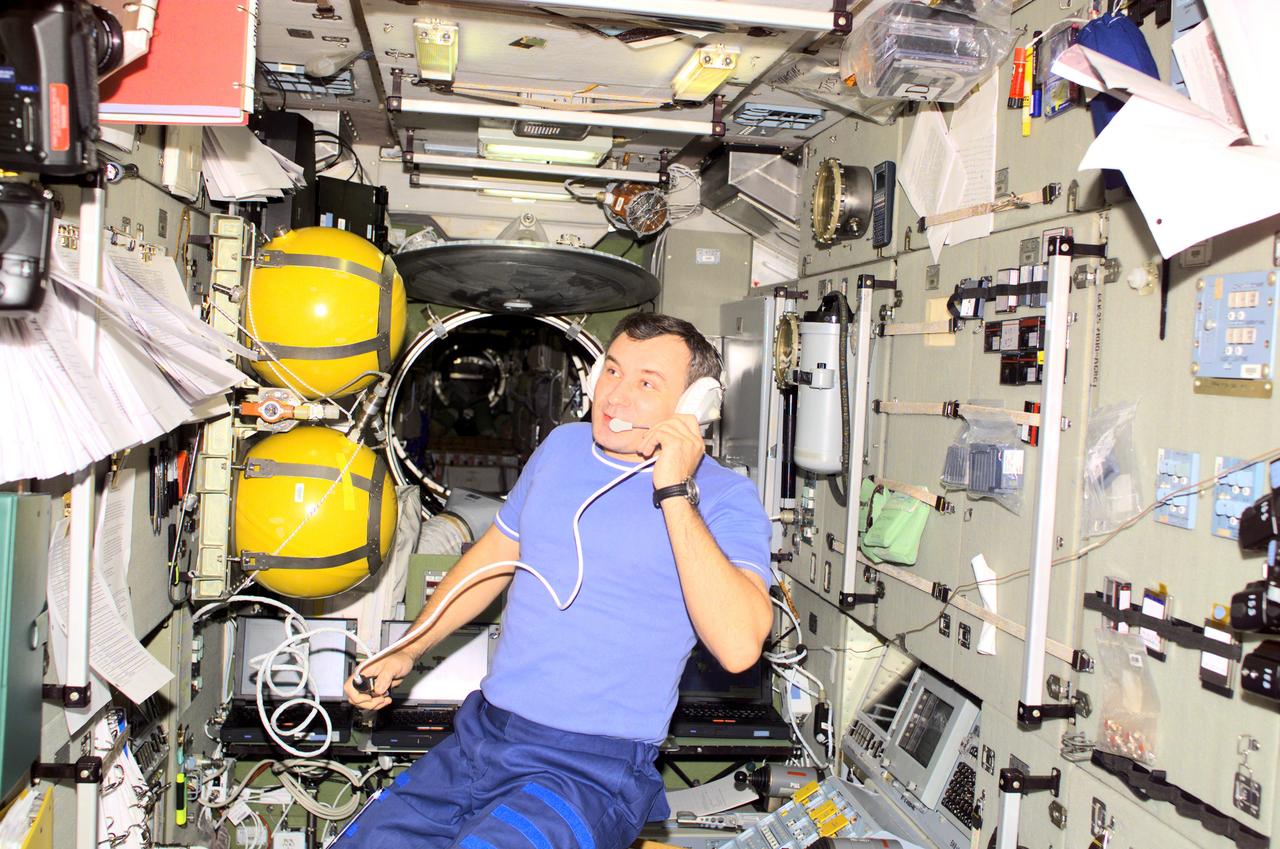

Aboard the International Space Station (ISS), Cosmonaut and Expedition Three flight engineer Vladimir N. Dezhurov, representing Rosaviakosmos, talks with flight controllers from the Zvezda Service Module. Russian-built Zvezda is linked to the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity. The third component of the ISS, Zvezda (Russian word for star), the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.

A participant at NASA's Earth Day Science Gallery Exhibit calculates his carbon footprint at the Carbon Footprint Estimator, Monday, April 22, 2013 at Union Station in Washington. The NASA Science Gallery exhibits are being sponsored by NASA in honor of Earth Day. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
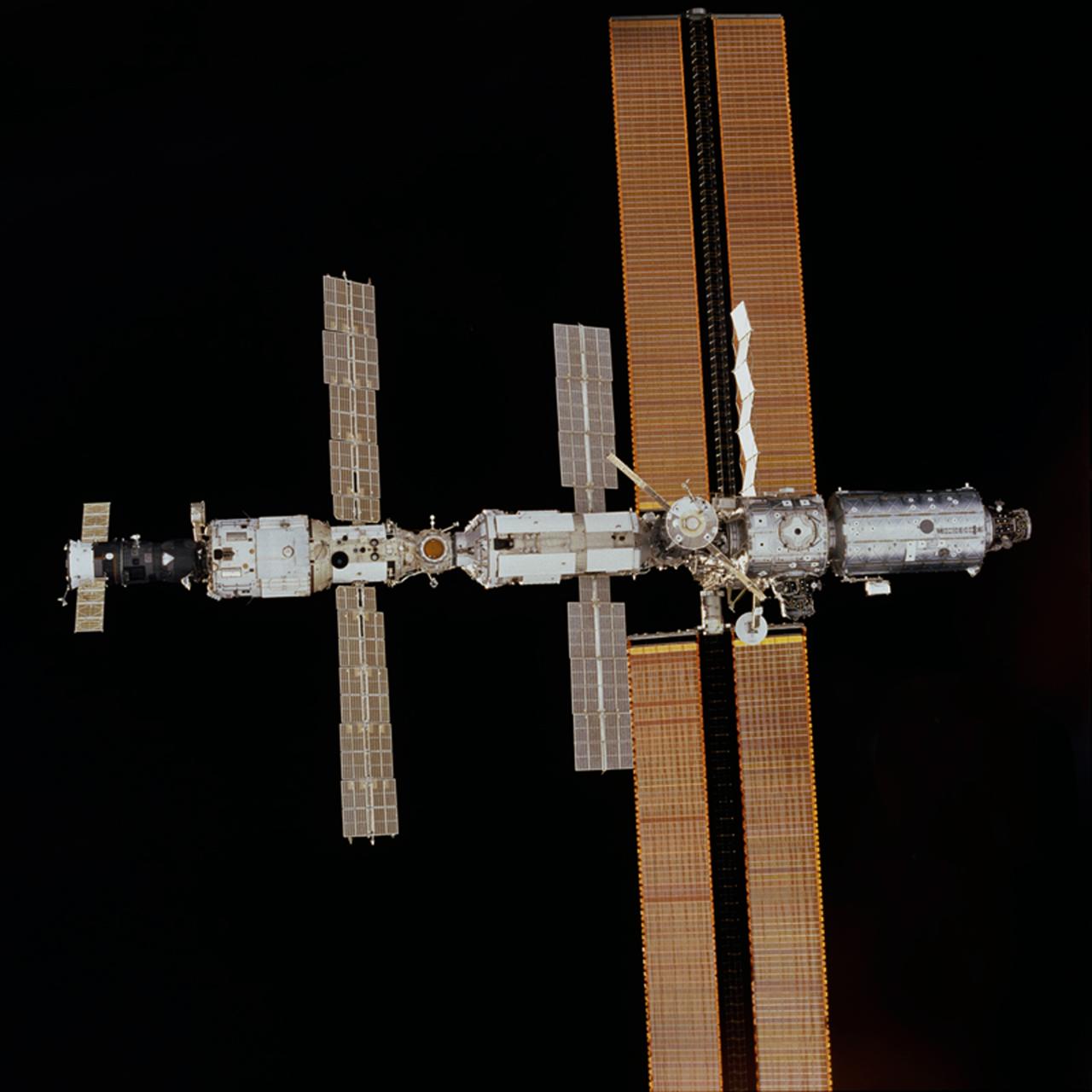
One of the astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery took this photograph, from the aft flight deck of the Discovery, of the International Space Station (ISS) in orbit. The photo was taken after separation of the orbiter Discovery from the ISS after several days of joint activities and an important crew exchange.
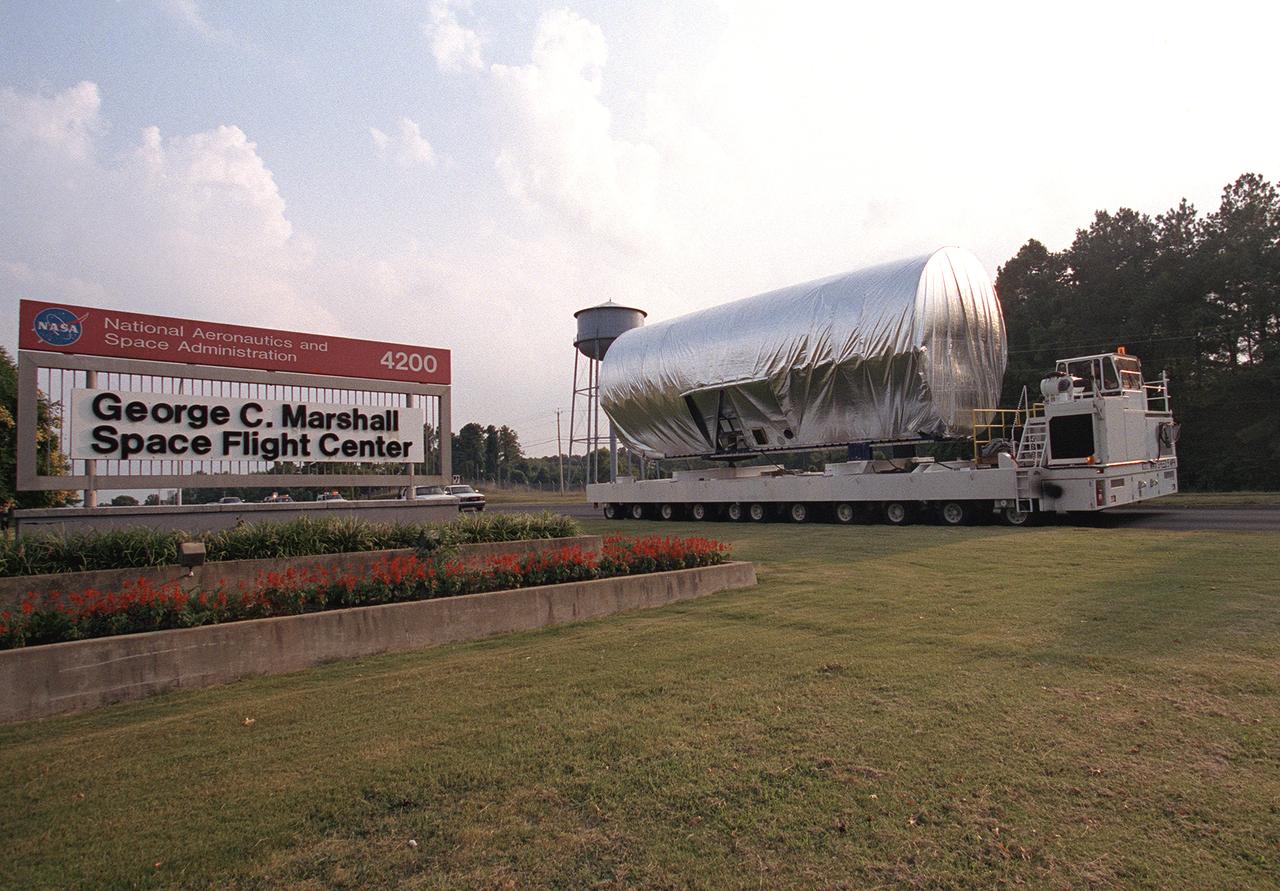

The 45-foot, port-side (P1) truss segment flight article for the International Space Station is being transported to the Redstone Airfield, Marshall Space Flight Center. The truss will be loaded aboard NASA's Super Guppy cargo plane for shipment to the Kennedy Space Center.
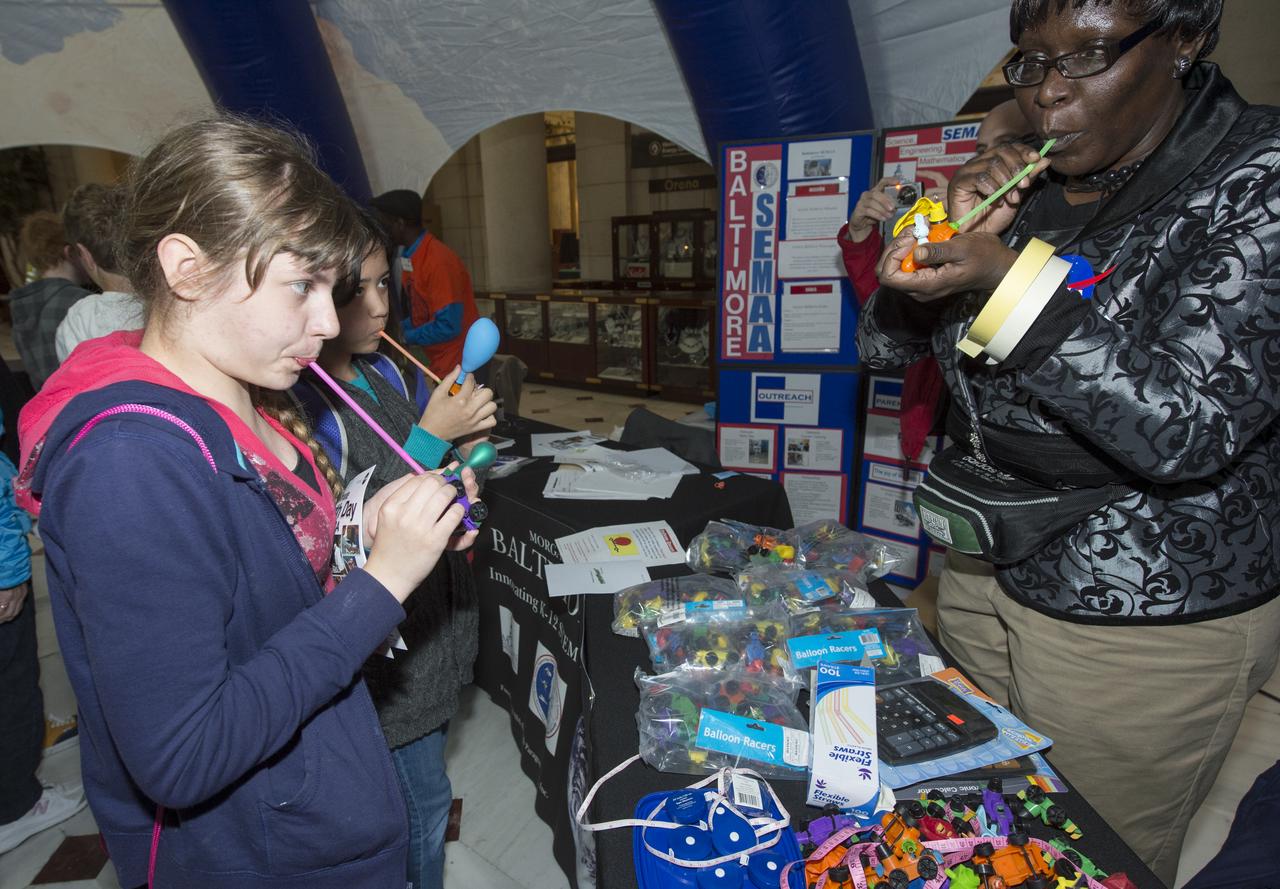

Students assemble balloon race cars and Alka-Seltzer film canister rockets to demonstrate Newton's third Law of motion at the NASA Science Gallery at Union Station, Monday, April 22, 2013 in Washington. The NASA Science Gallery exhibits are being sponsored by NASA in honor of Earth Day. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
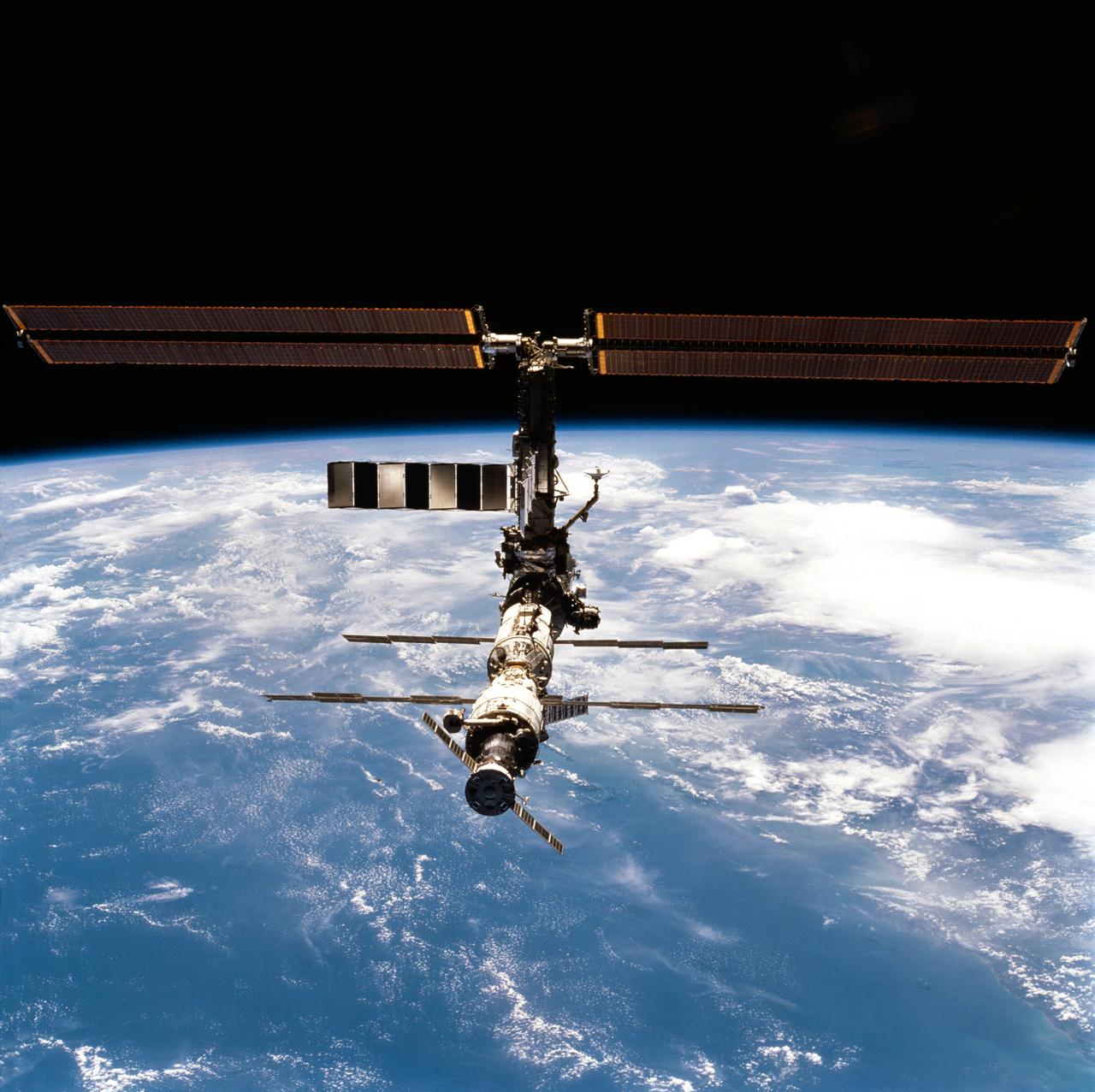

Backdropped against water and clouds, the International Space Station was separated from the Space Shuttle Discovery after several days of joint activities and an important crew exchange. This photograph was taken by one of the crew of this mission from the aft flight deck of Discovery.
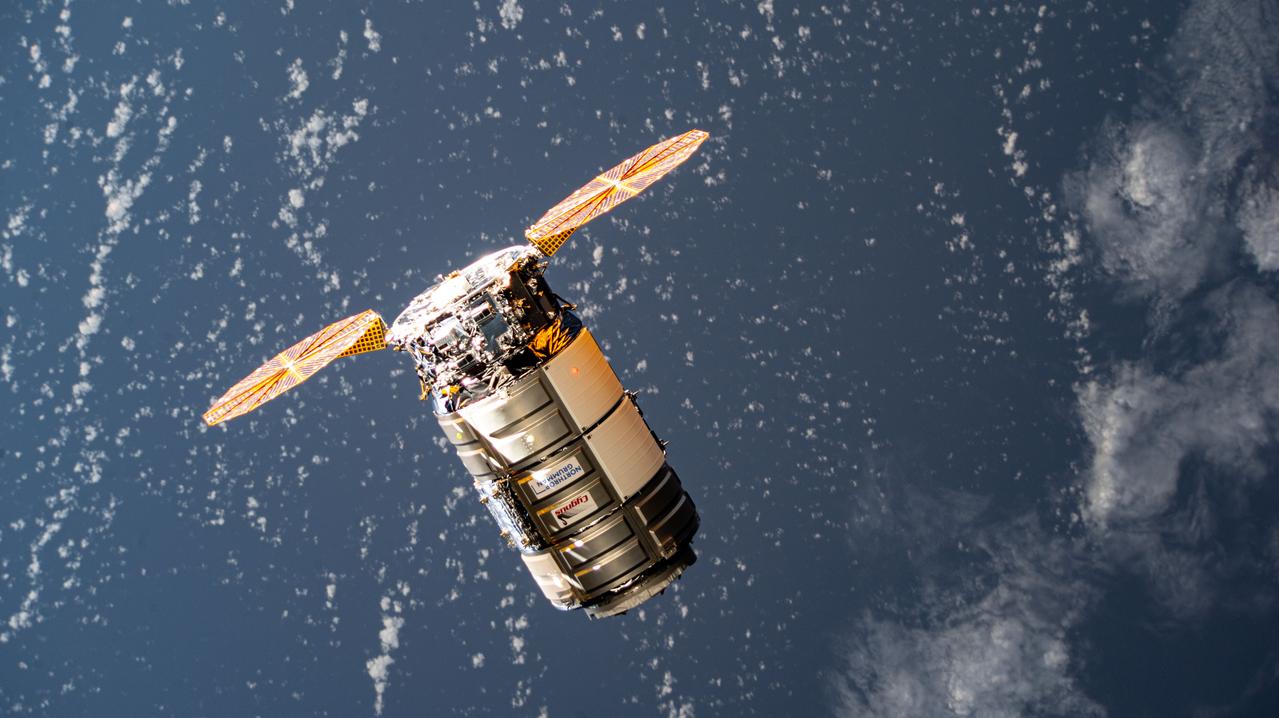

iss071e418230 (Aug. 6, 2024) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus cargo craft, carrying 8,200 pounds of science and supplies, approaches the International Space Station for a capture with the Canadarm2 robotic arm commanded by Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Matthew Dominick of NASA. The maneuver marked the 50th free-flying capture for the Canadarm2 robotic arm.
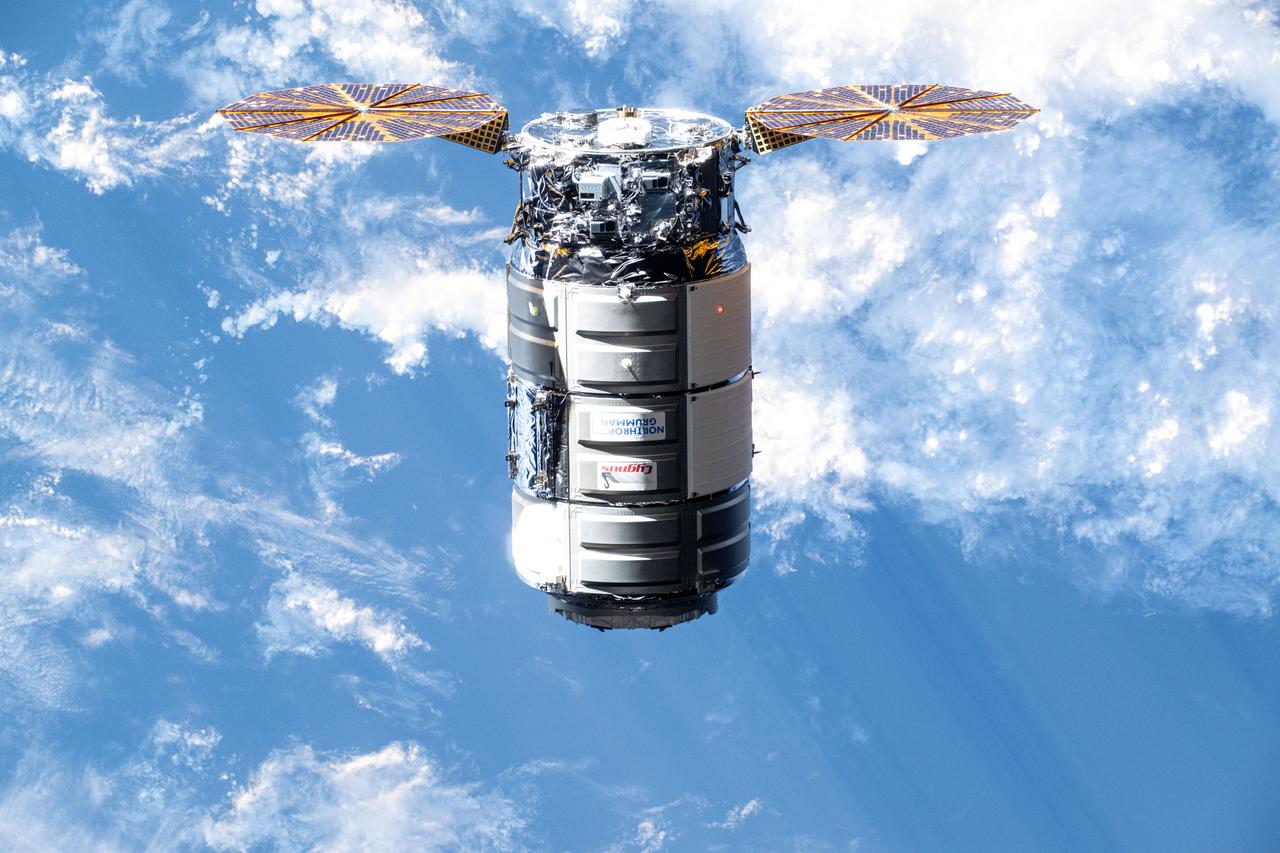

iss071e416851 (Aug. 6, 2024) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus cargo craft, carrying 8,200 pounds of science and supplies, approaches the International Space Station for a capture with the Canadarm2 robotic arm commanded by Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Matthew Dominick of NASA. The maneuver marked the 50th free-flying capture for the Canadarm2 robotic arm.
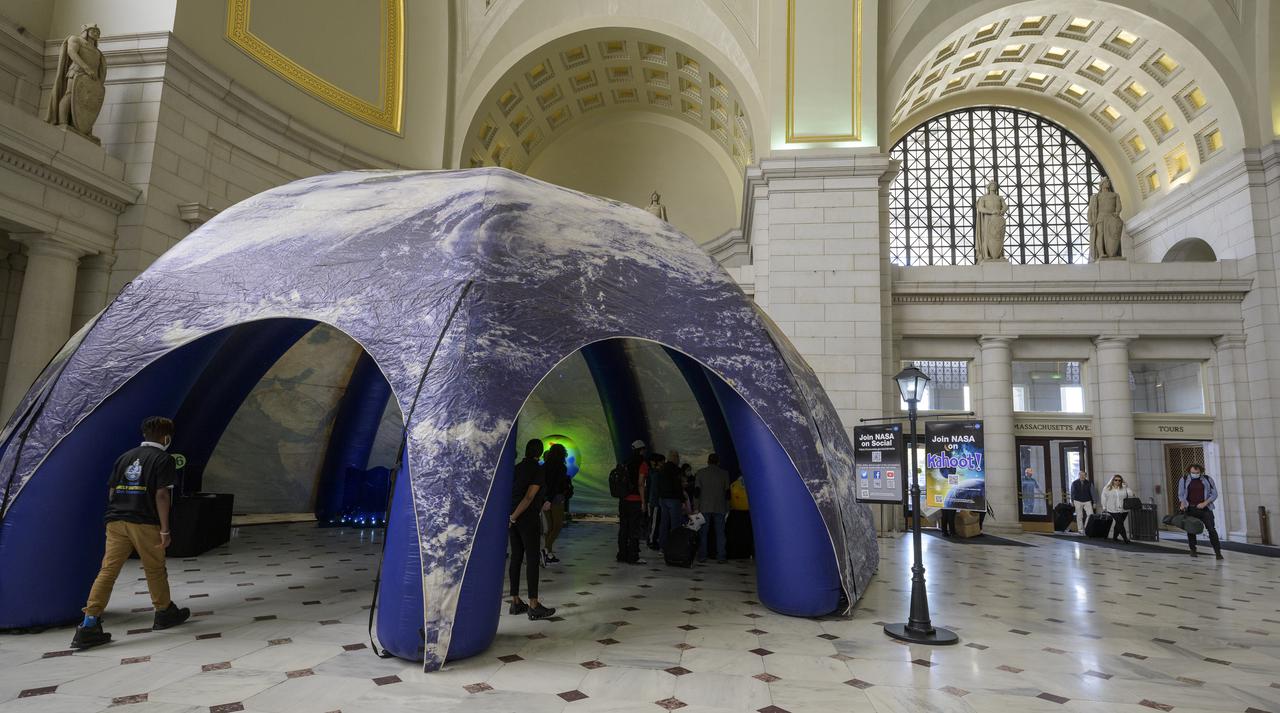

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
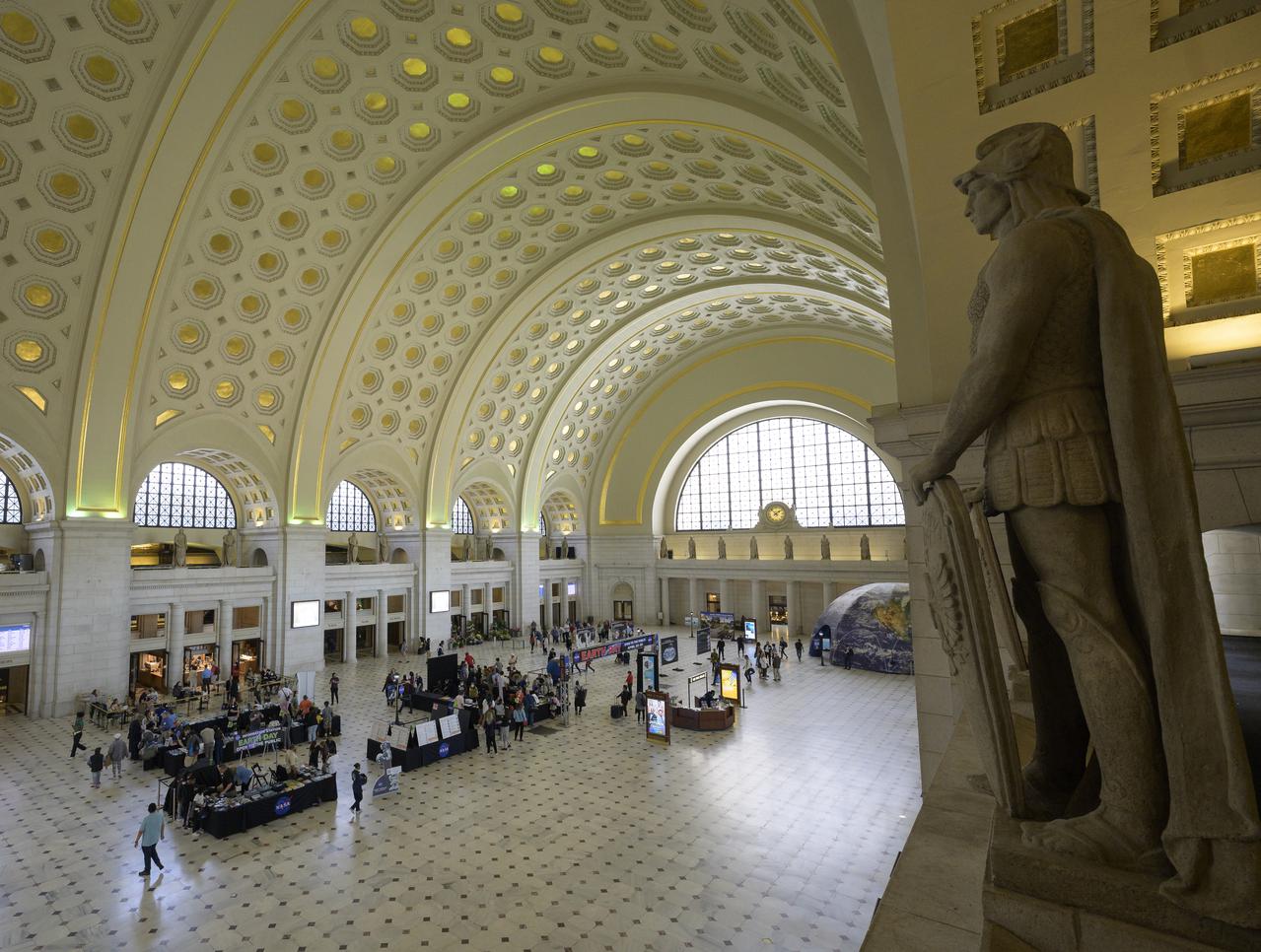

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
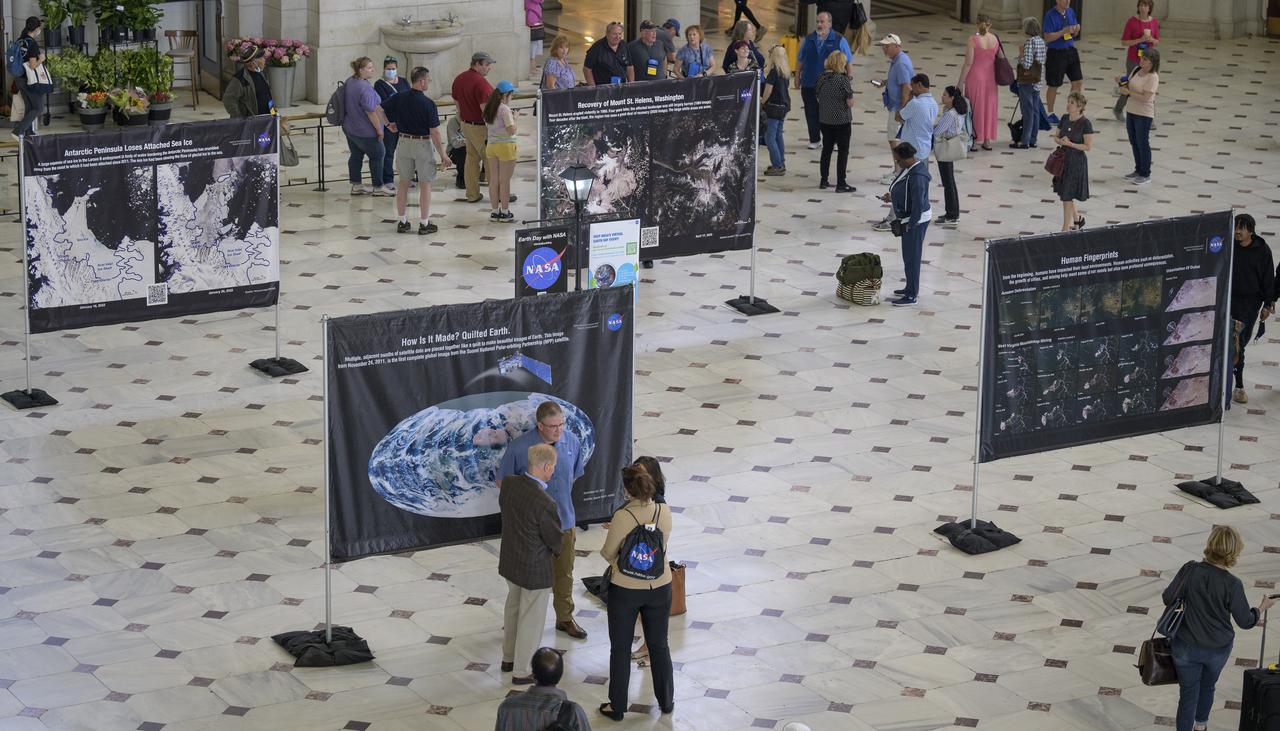

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
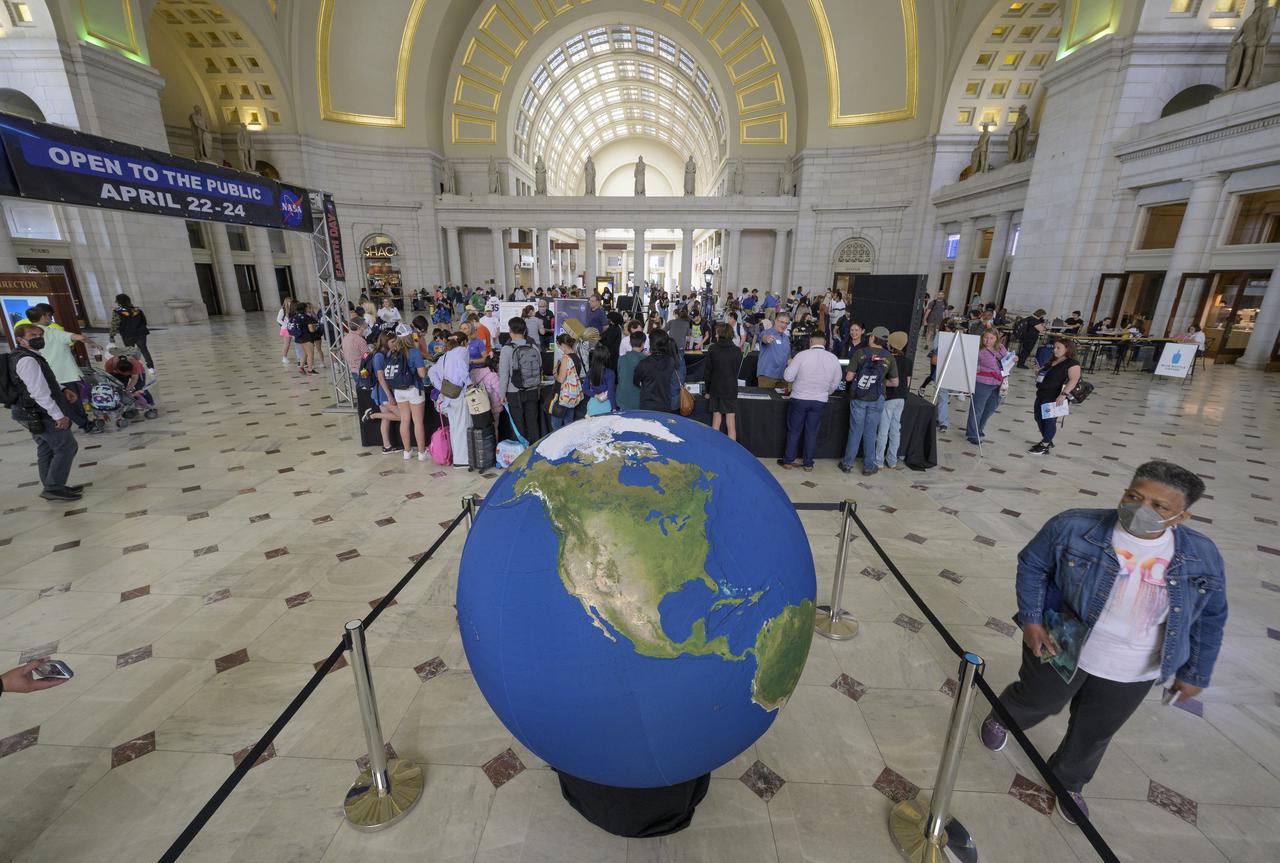

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
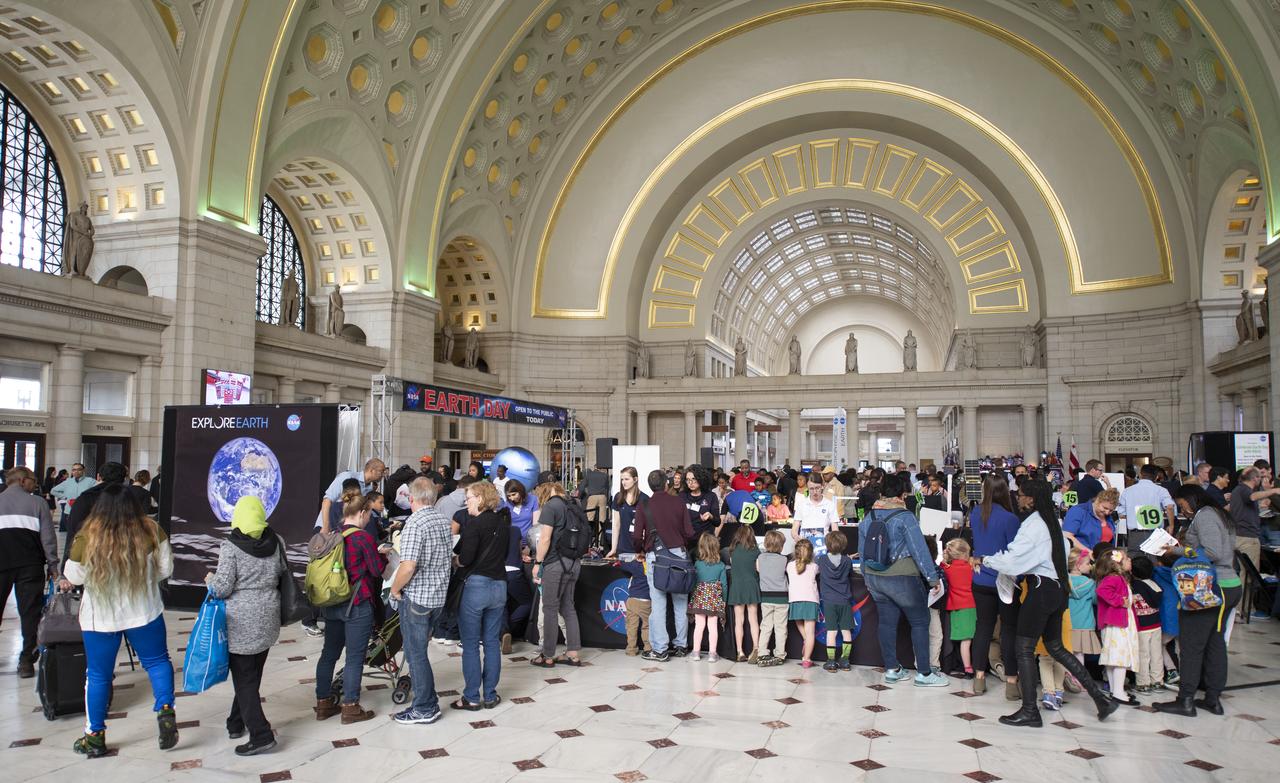

Visitors explore NASA's exhibits at the Earth Day event on Monday, April 22, 2019, at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
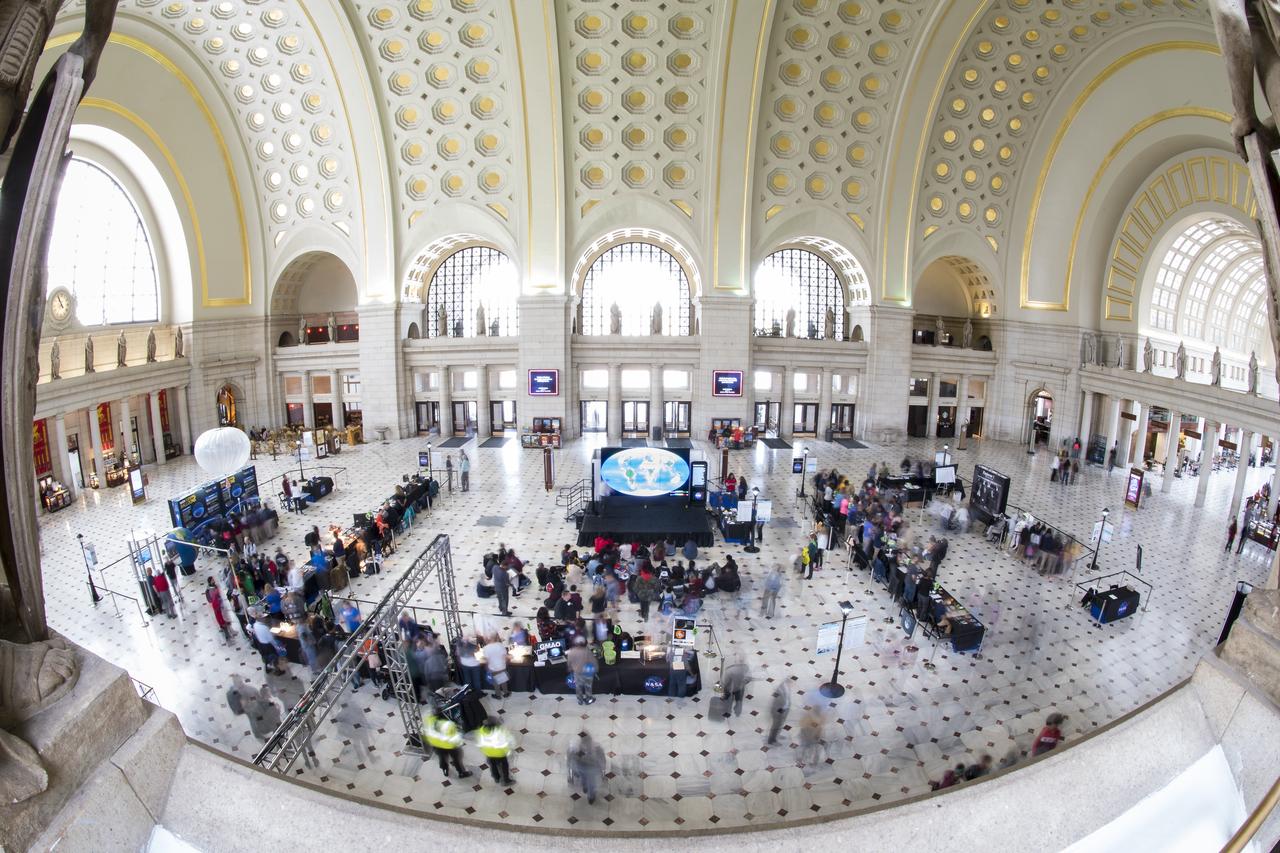

A view of the exhibits at NASA's Earth Day event on Thursday, April 19, 2018 at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
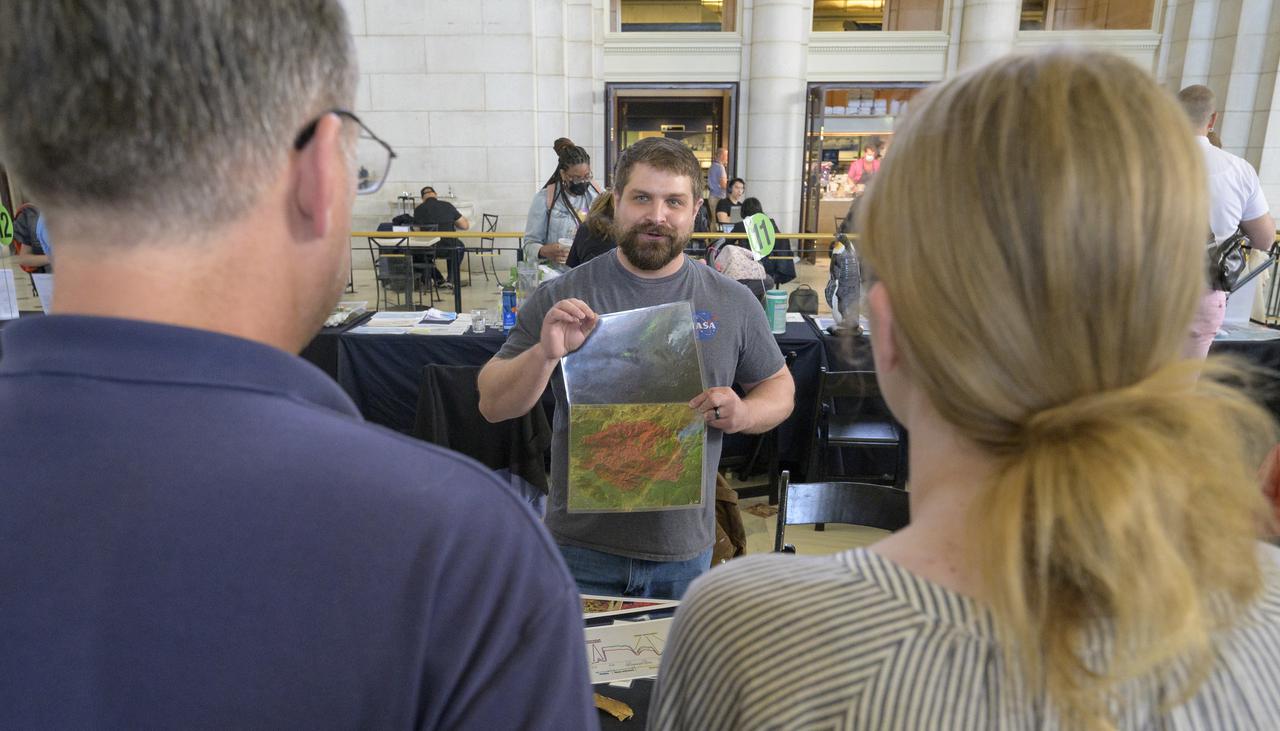

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
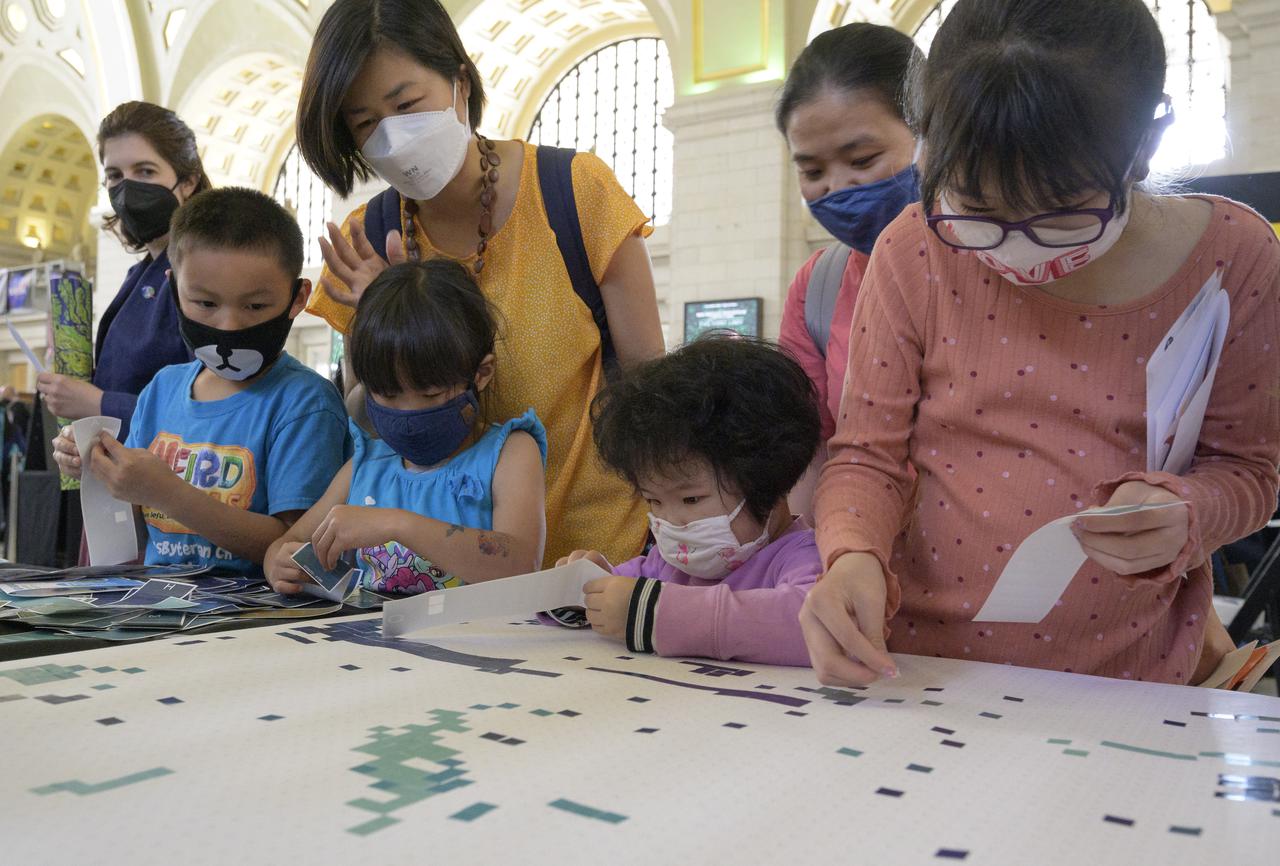

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
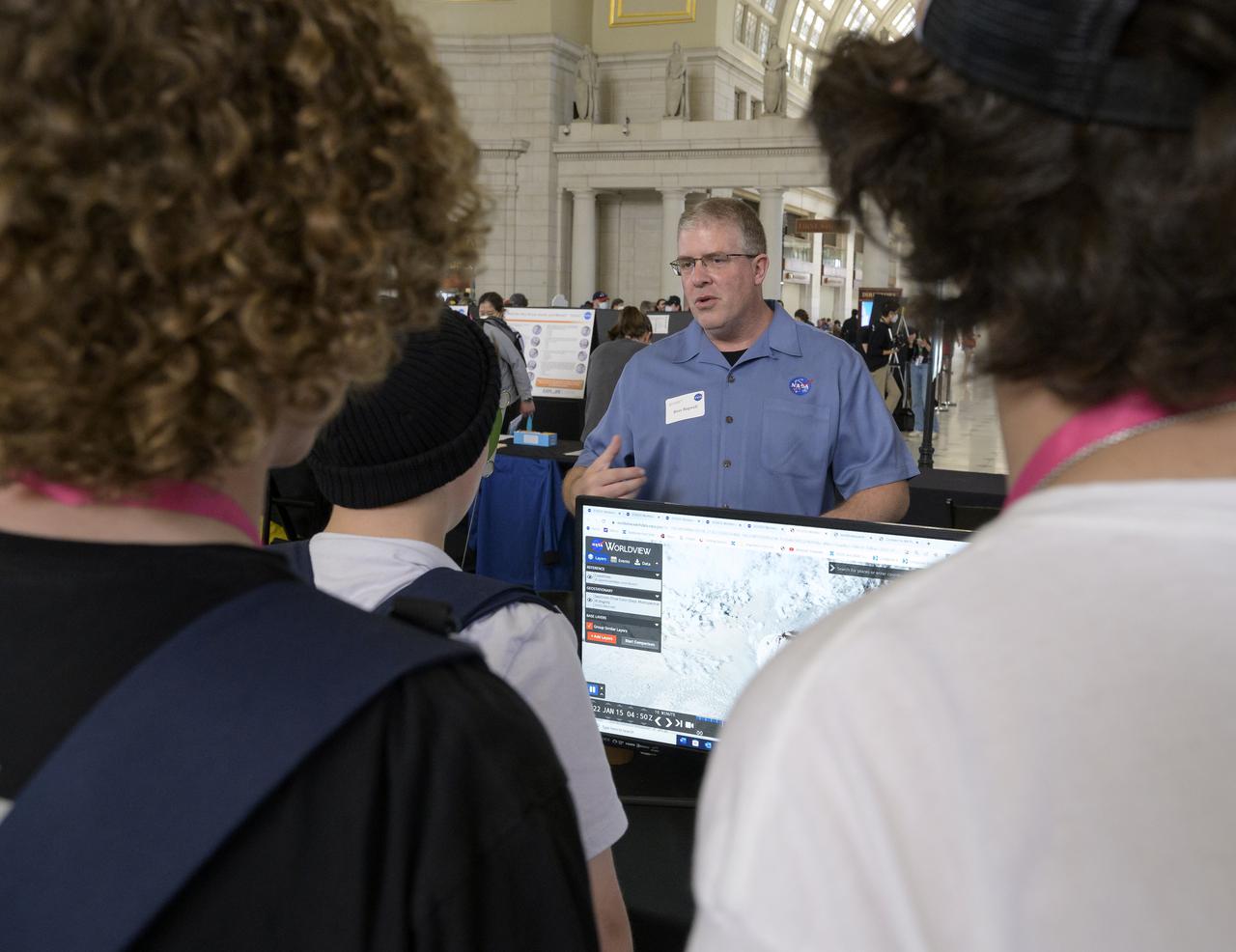

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
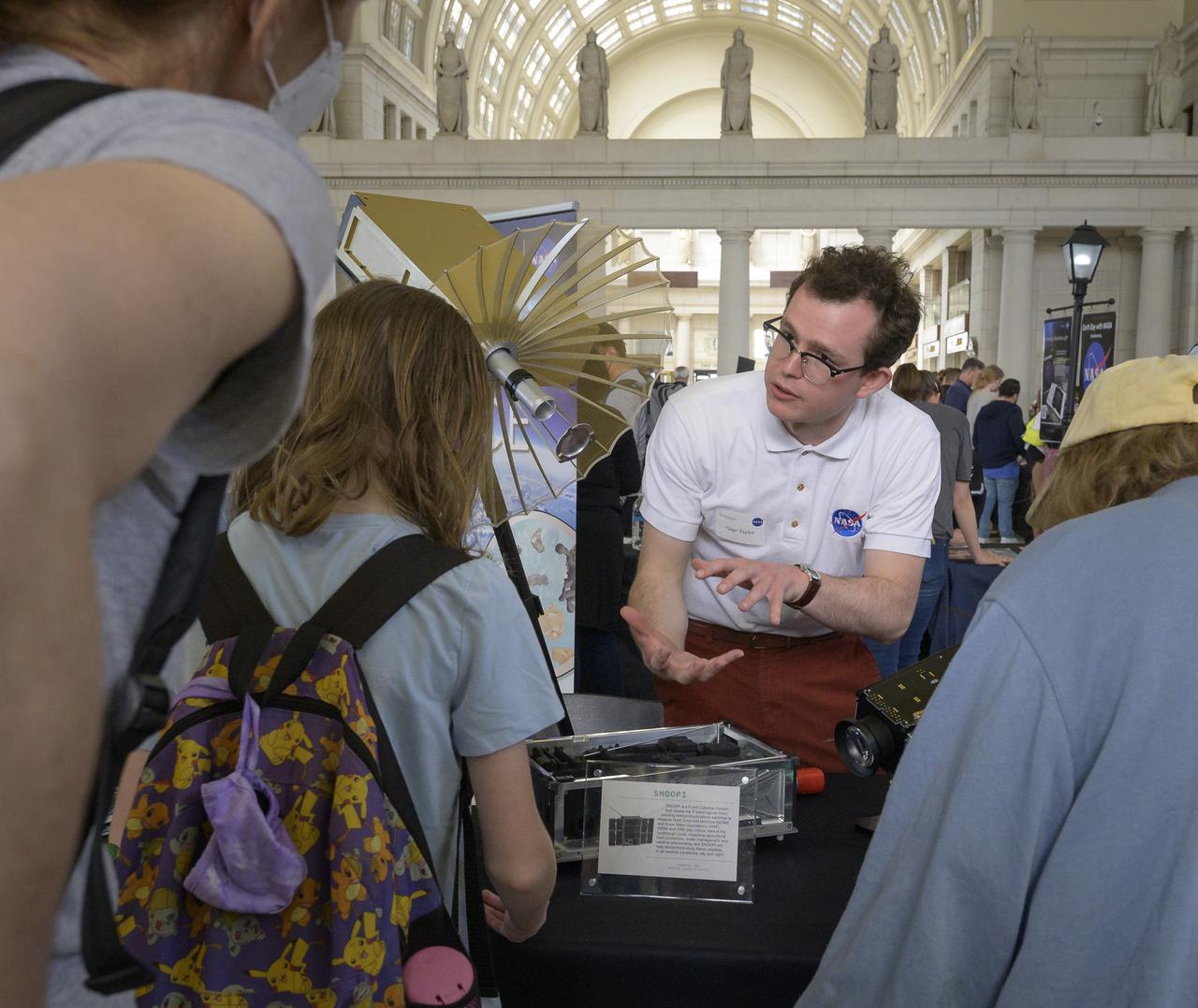

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
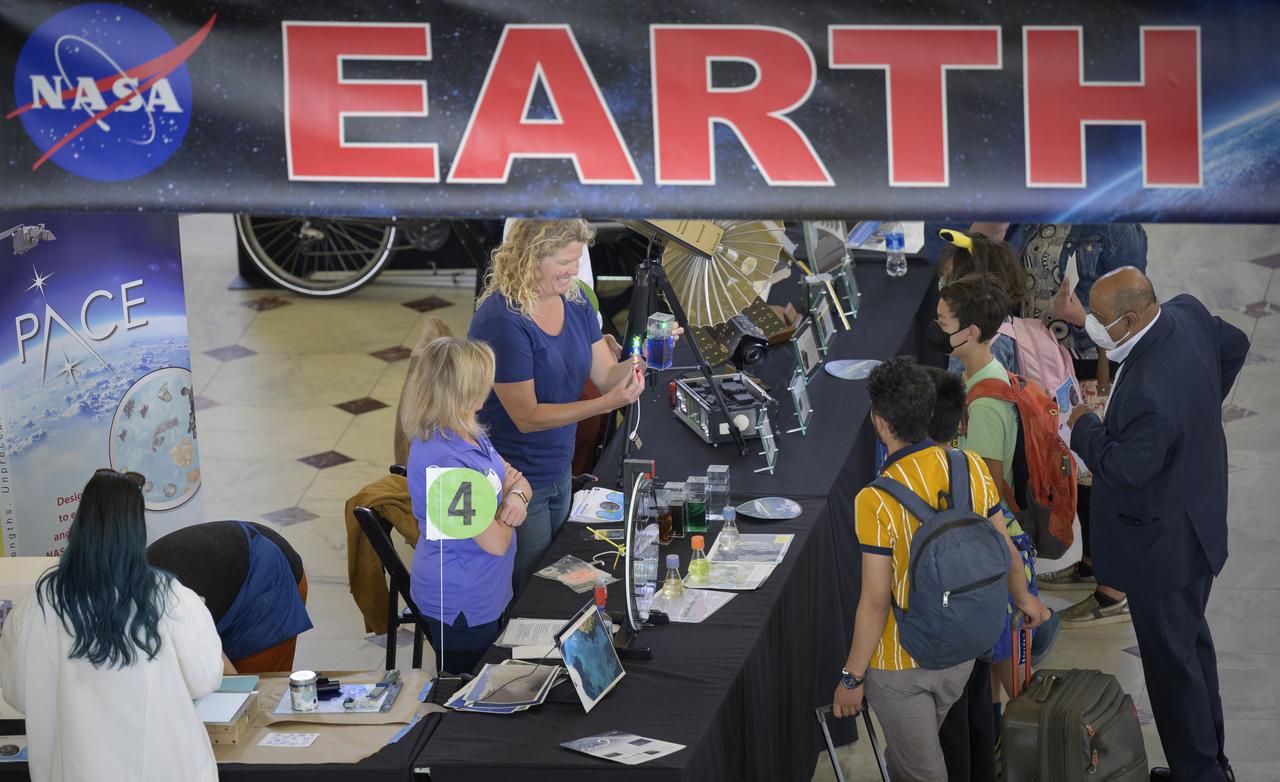

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
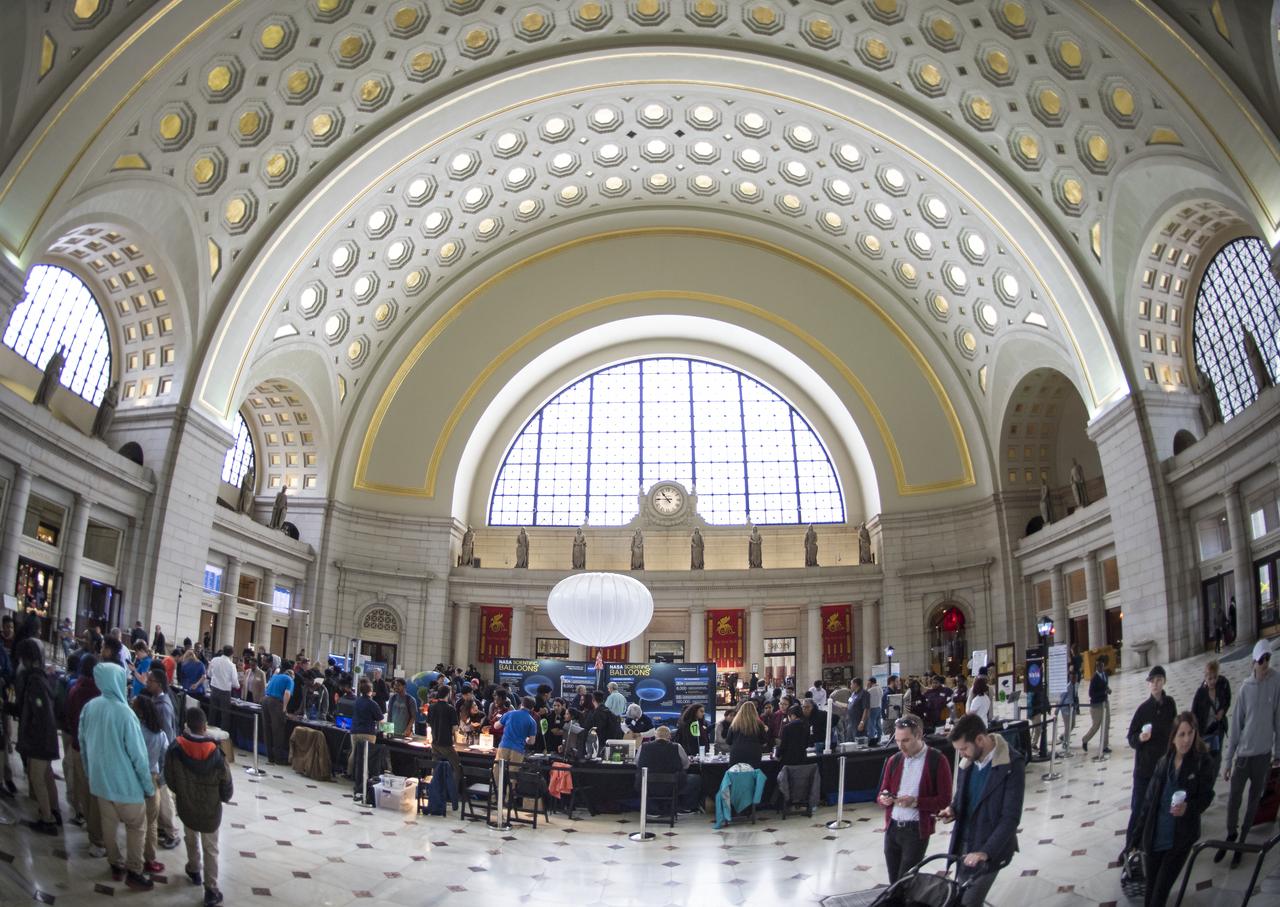

A view of the exhibits at NASA's Earth Day event on Thursday, April 19, 2018 at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
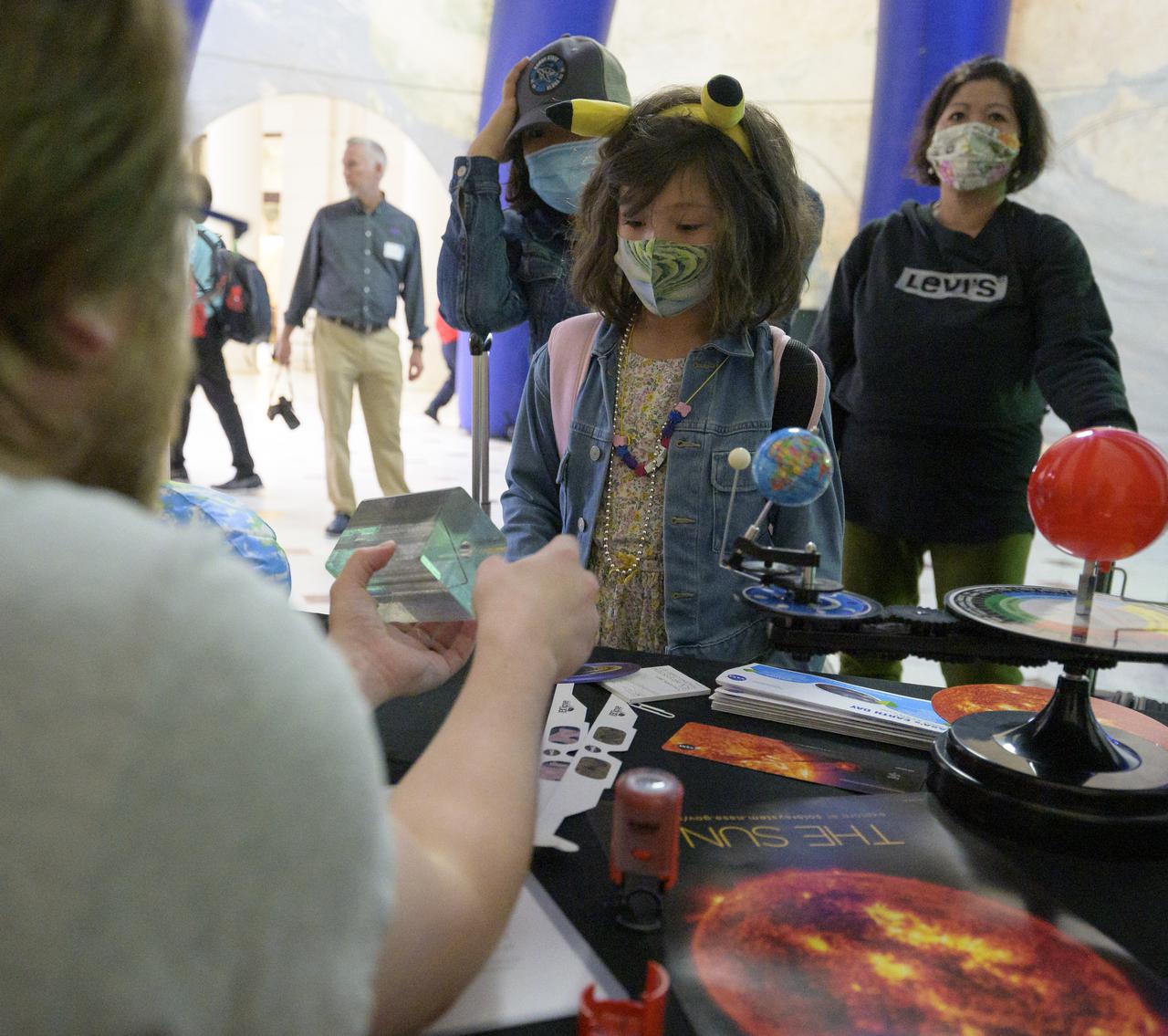

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
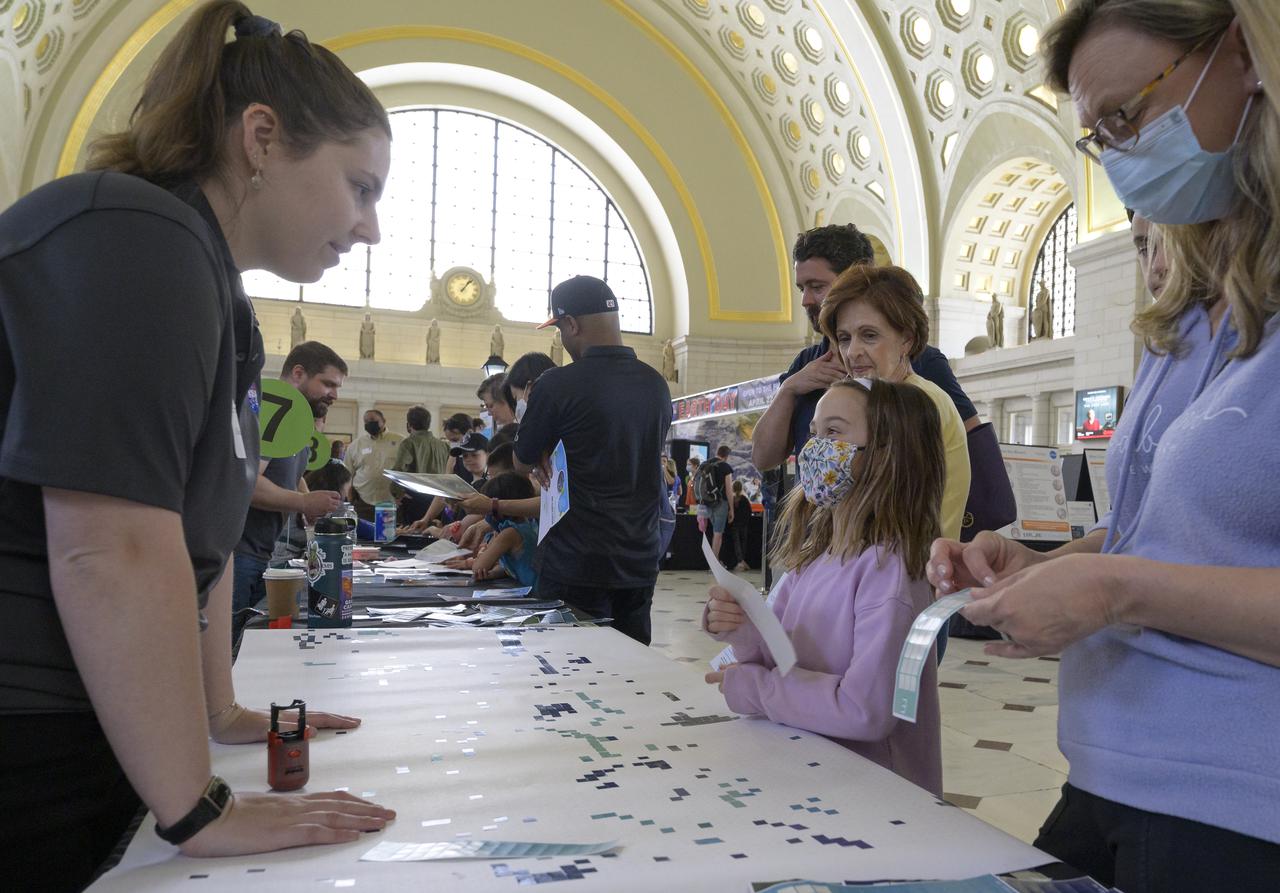

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
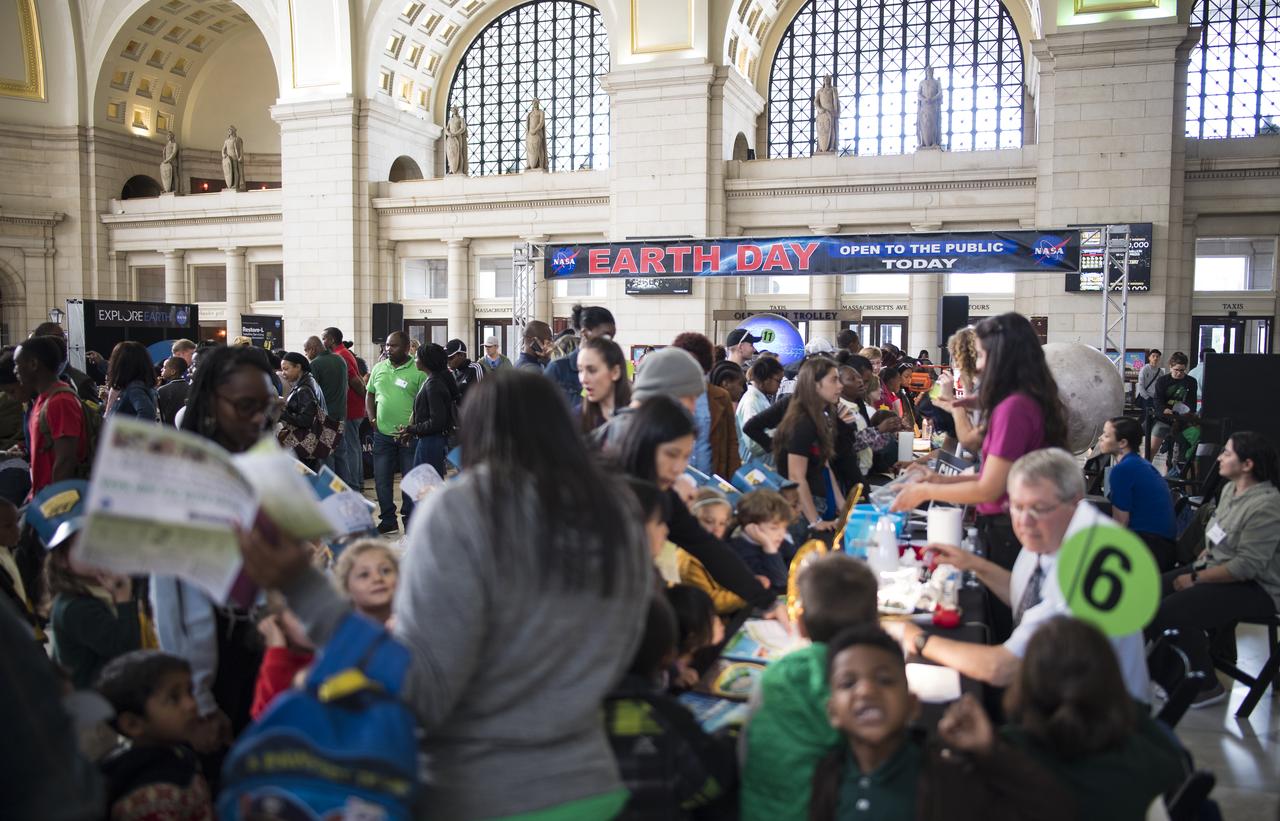

Visitors explore NASA's exhibits at the Earth Day event on Monday, April 22, 2019, at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
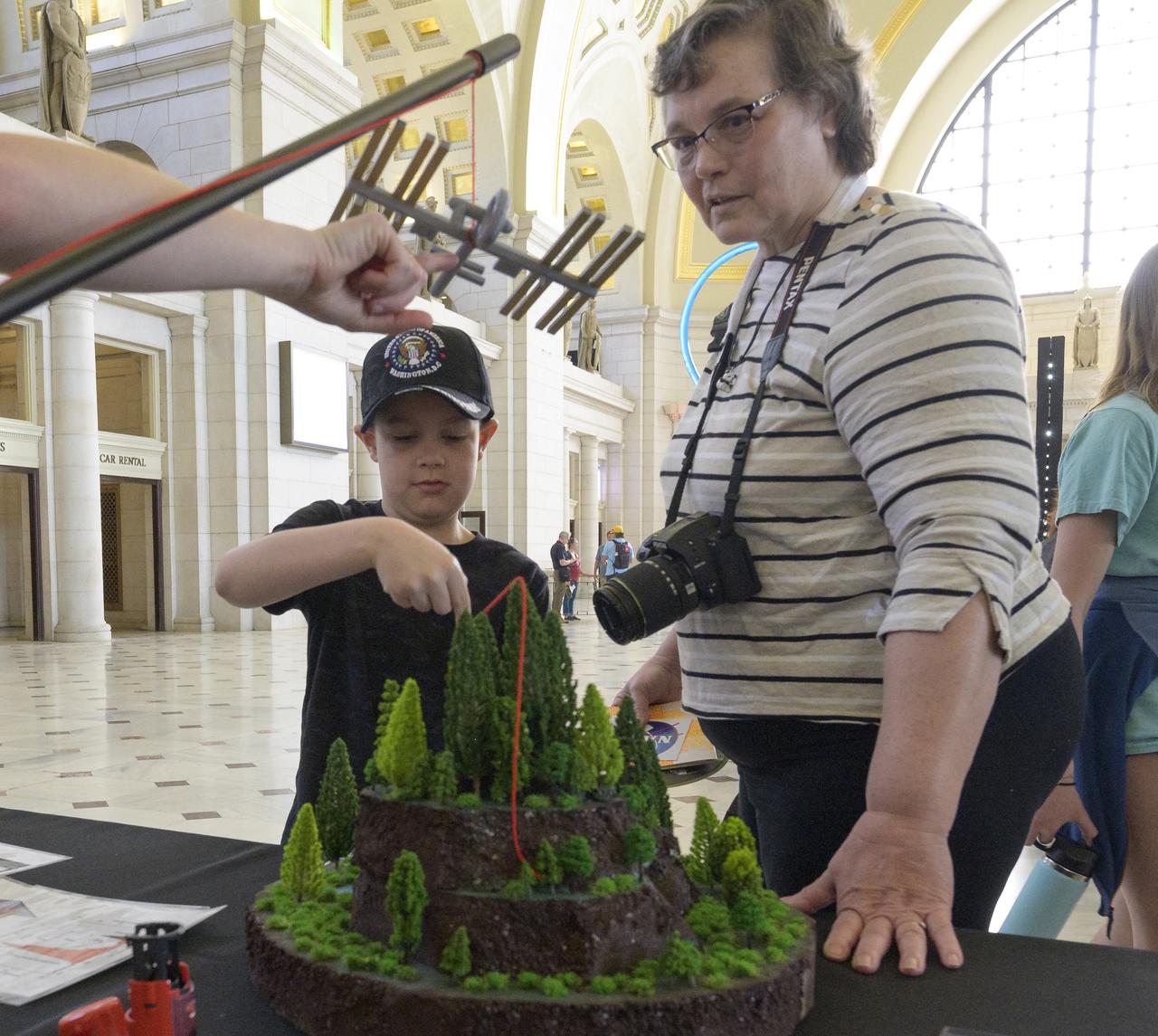

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
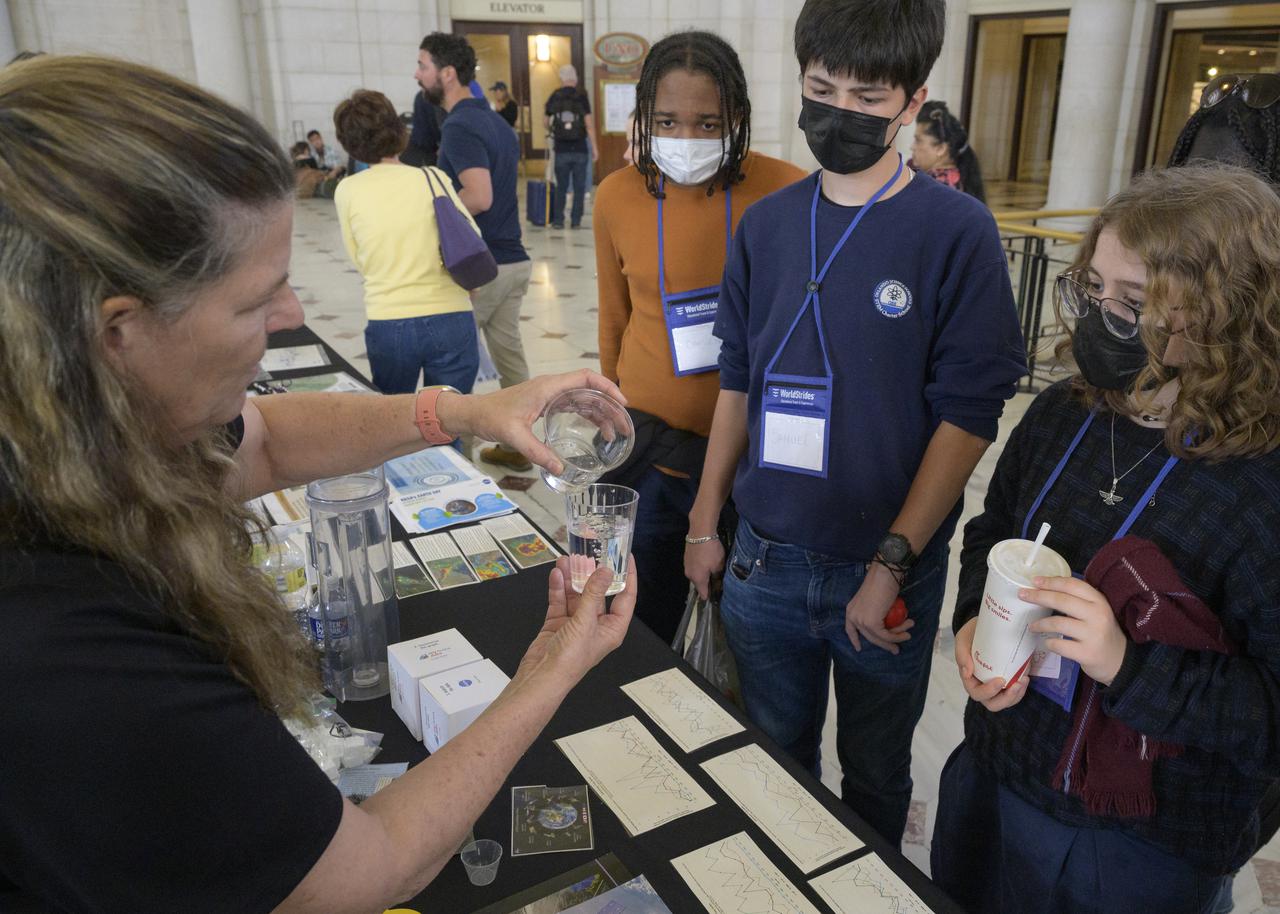

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
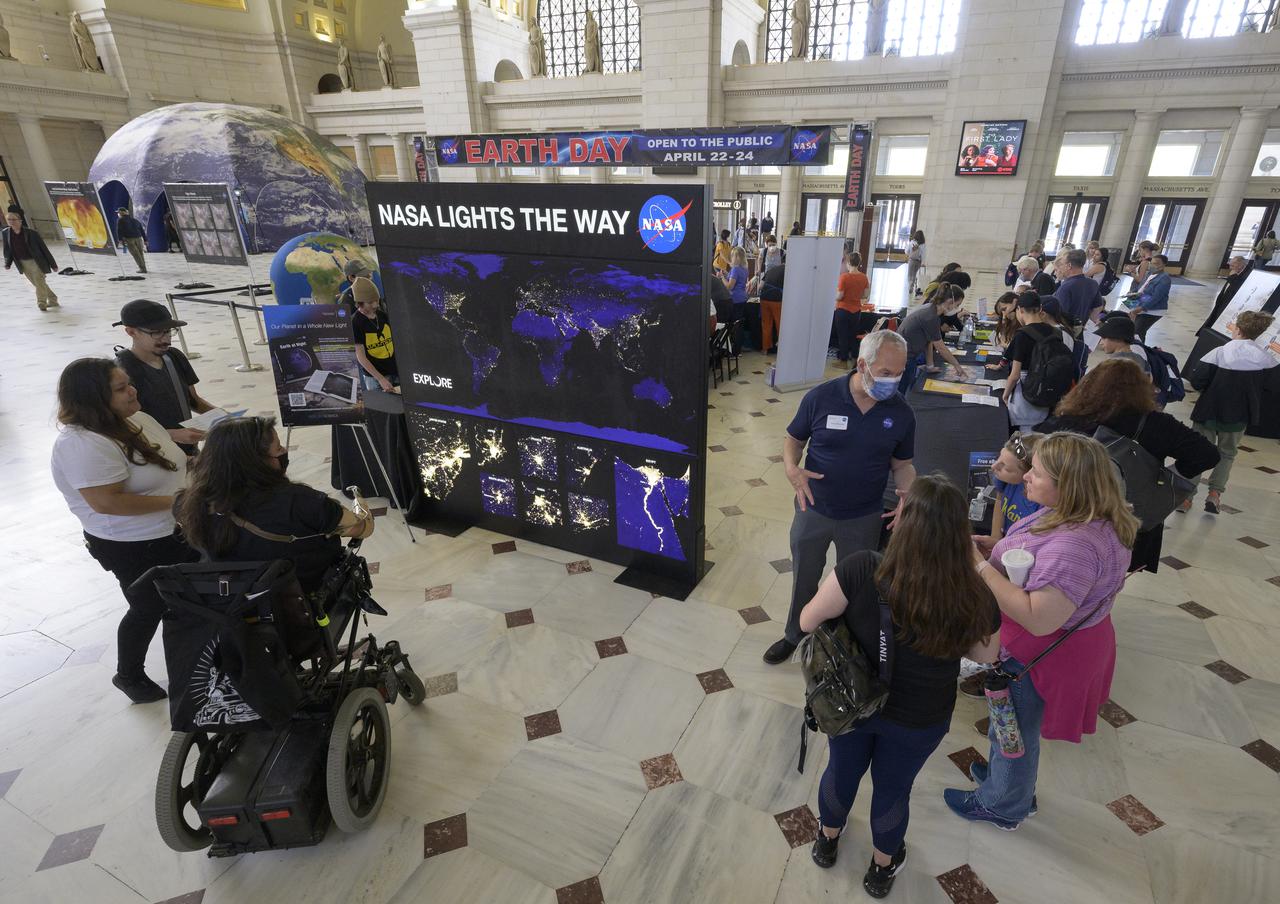

Visitors explore NASA’s hands-on exhibits during Earth Day, Friday, April 22, 2022, at Union Station in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
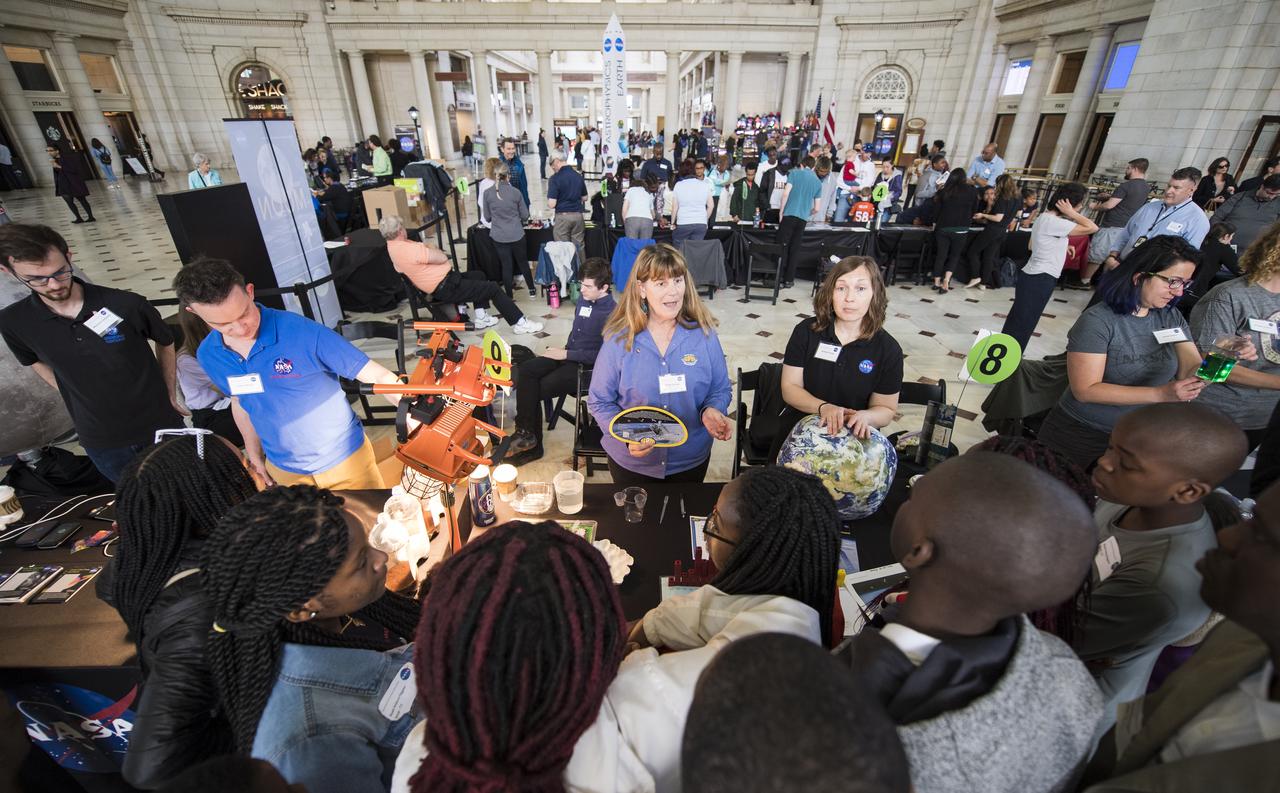

Visitors explore NASA's exhibits at the Earth Day event on Monday, April 22, 2019, at Union Station in Washington, D.C. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)