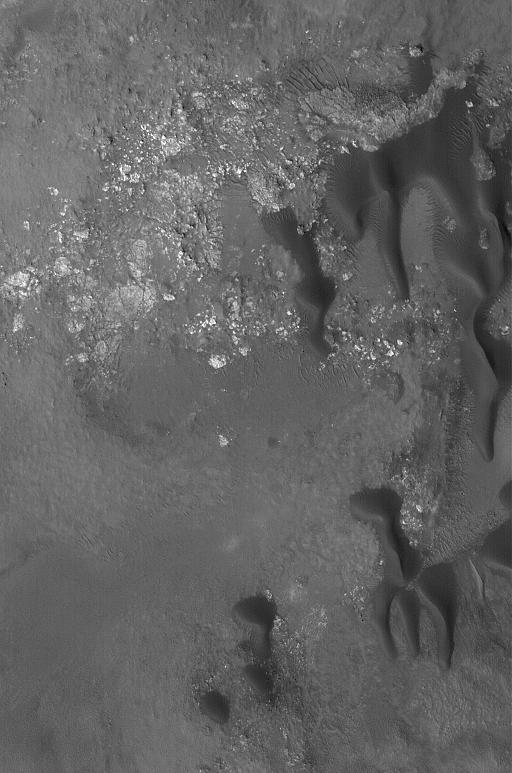

Stokes Crater Dunes
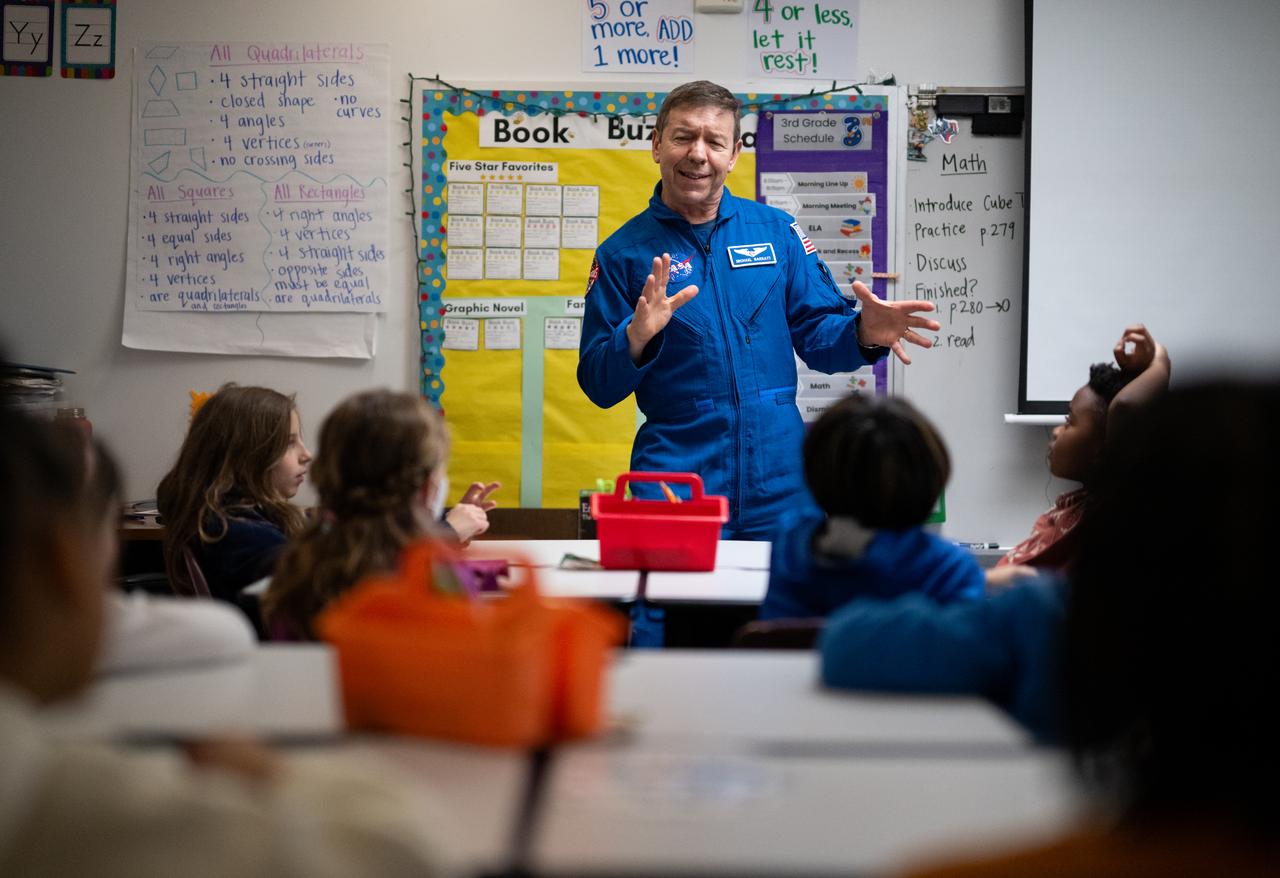

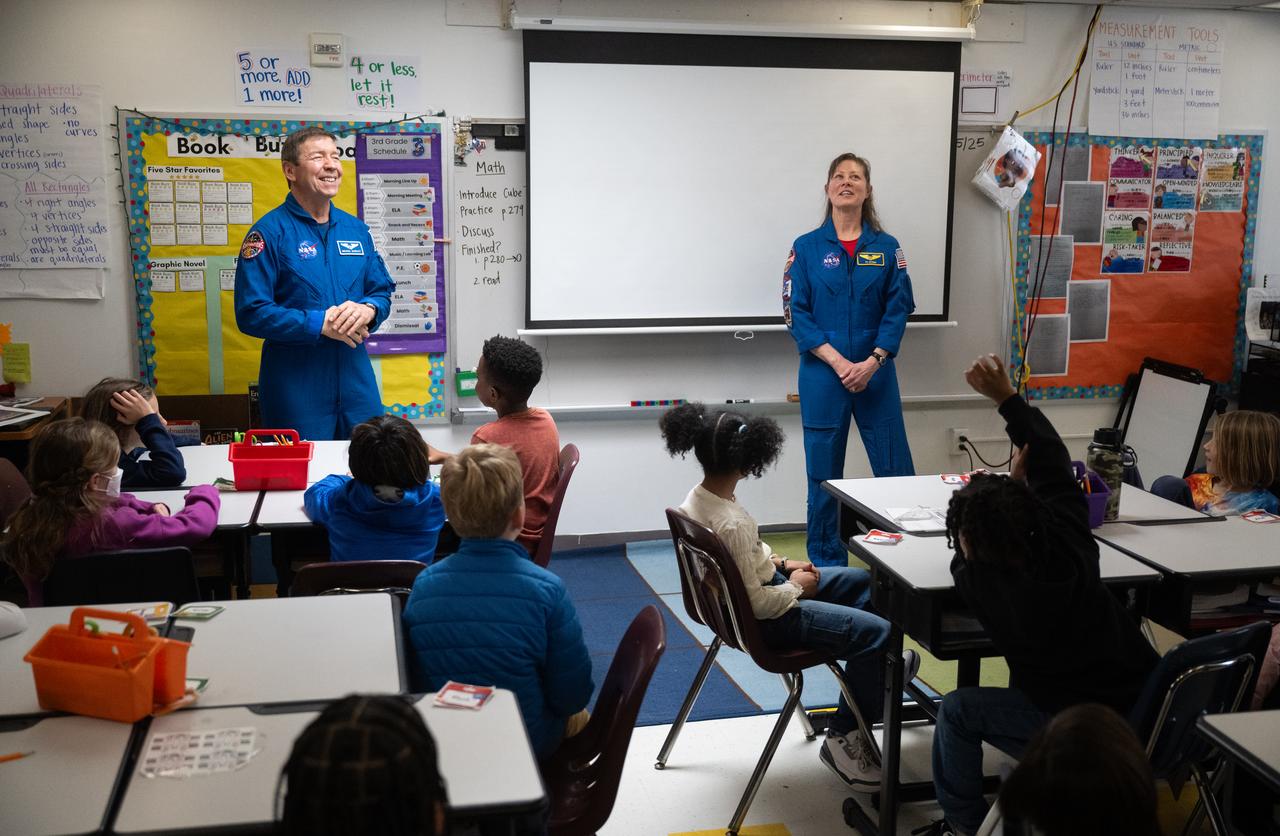
Expedition 71 NASA astronaut Michael Barratt speaks to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025, at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Barratt and fellow crewmates Matthew Dominick, Jeanette Epps, and Tracy Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
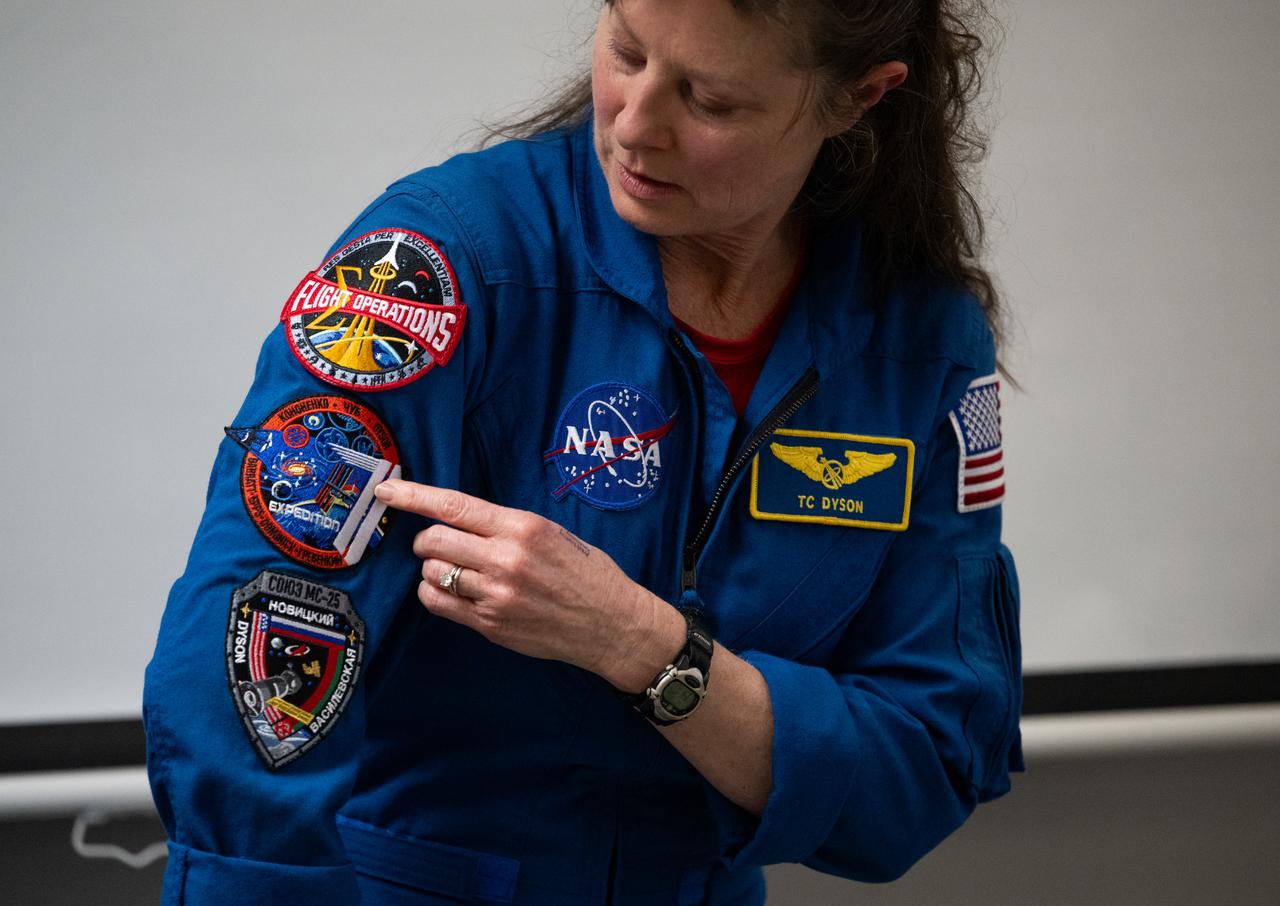

Expedition 71 NASA astronaut Tracy Dyson, points to the Expedition 71 patch on her flight suit as she answers a question from students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Dyson and fellow crewmates Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, and Jeanette Epps served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
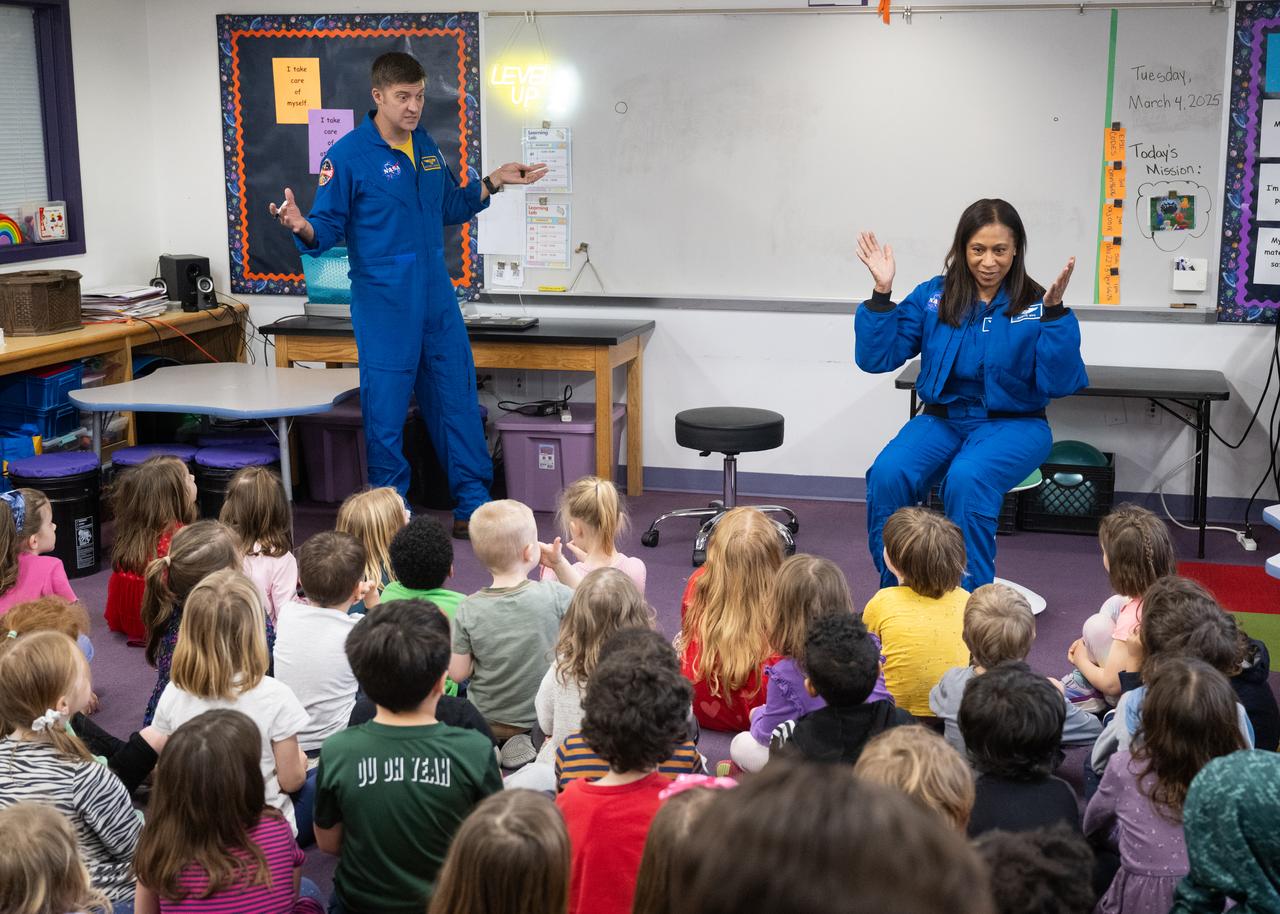

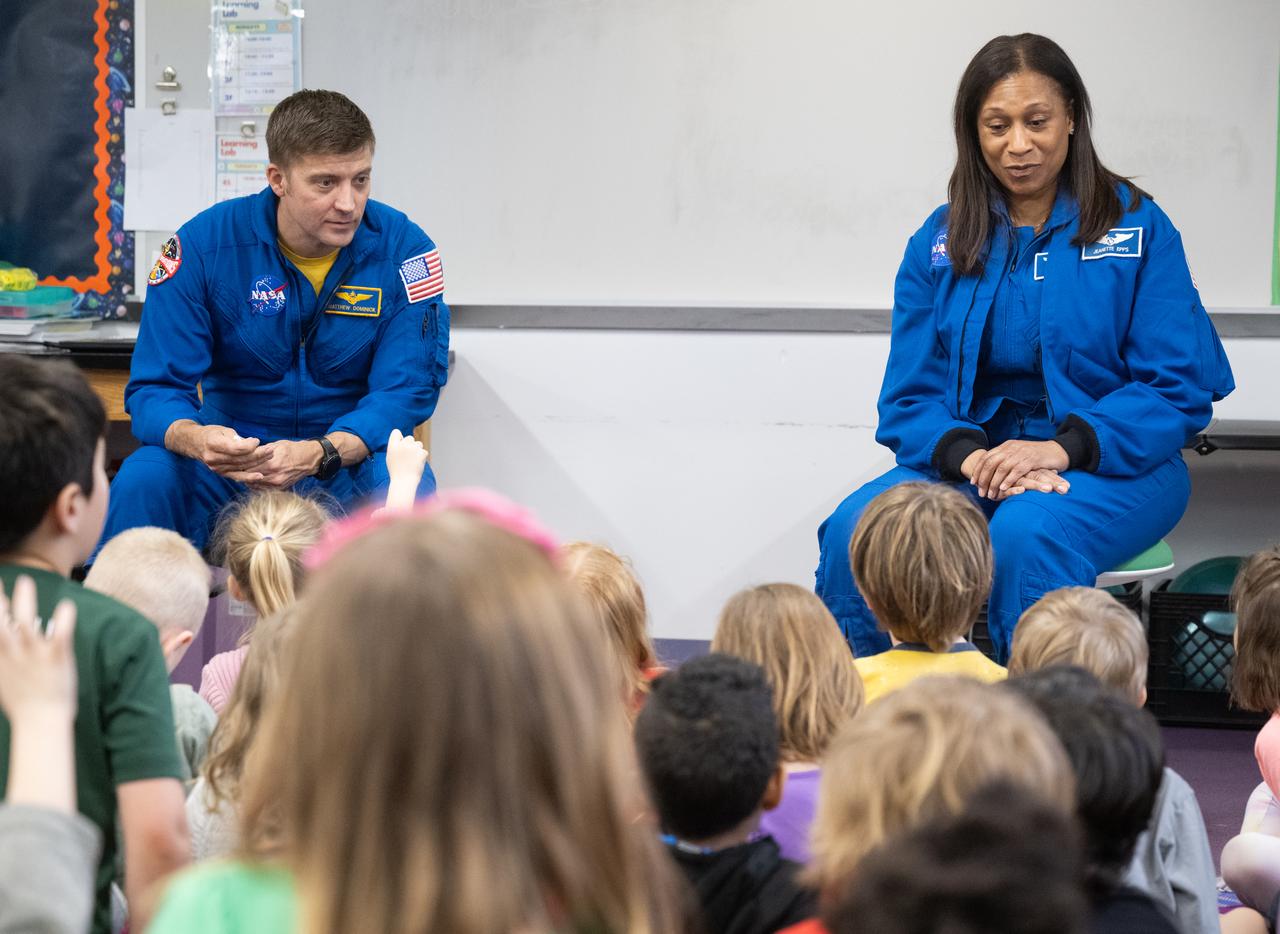
Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, left, and Jeanette Epps, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025, at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Dominick, Epps, and fellow crewmates Michael Barratt and Tracy Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Aya Collins, director of the engagement division of NASA’s Office of Communications, left, and Lisa Frazier, lead for strategic events and engagements in NASA’s Office of Communications, speak to students before introducing Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Jeanette Epps, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Dominick, Epps, and fellow crewmates Michael Barratt and Tracy Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
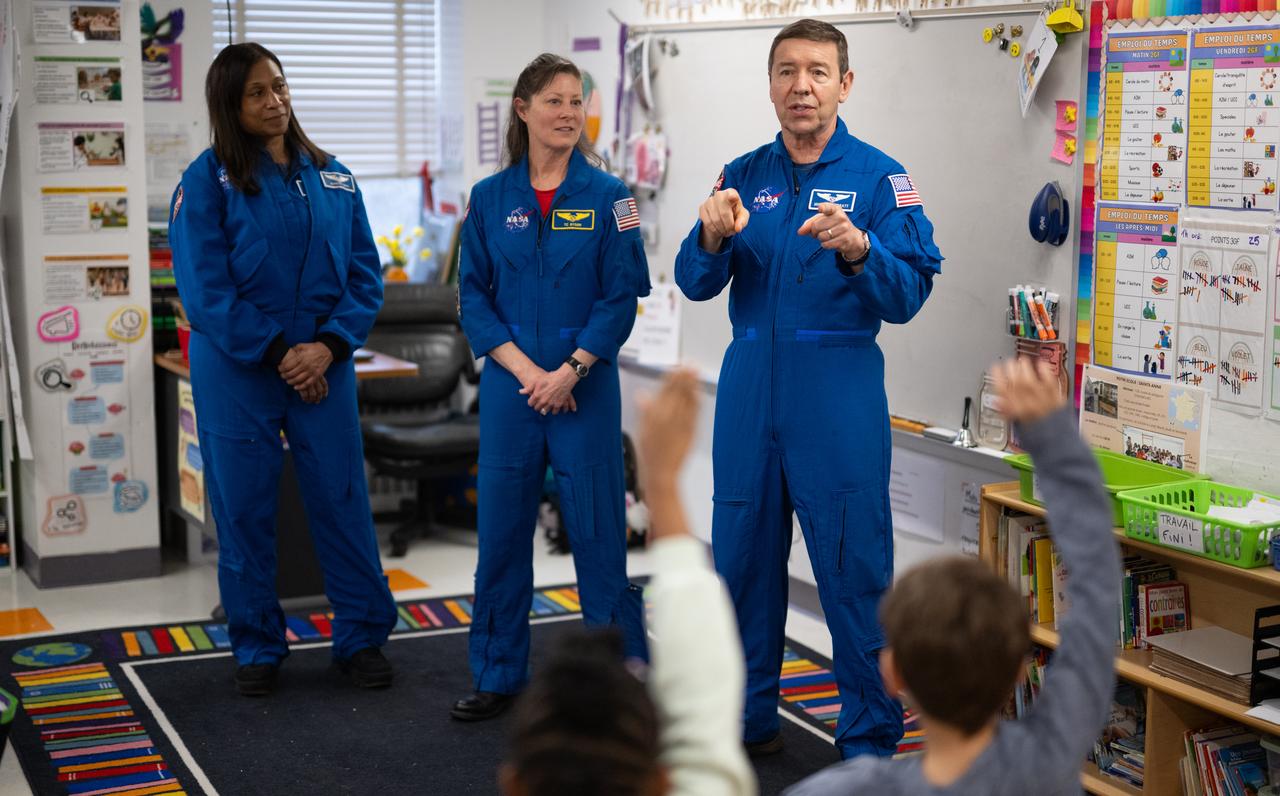

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Jeanette Epps, left, Tracy Dyson, and Michael Barratt, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
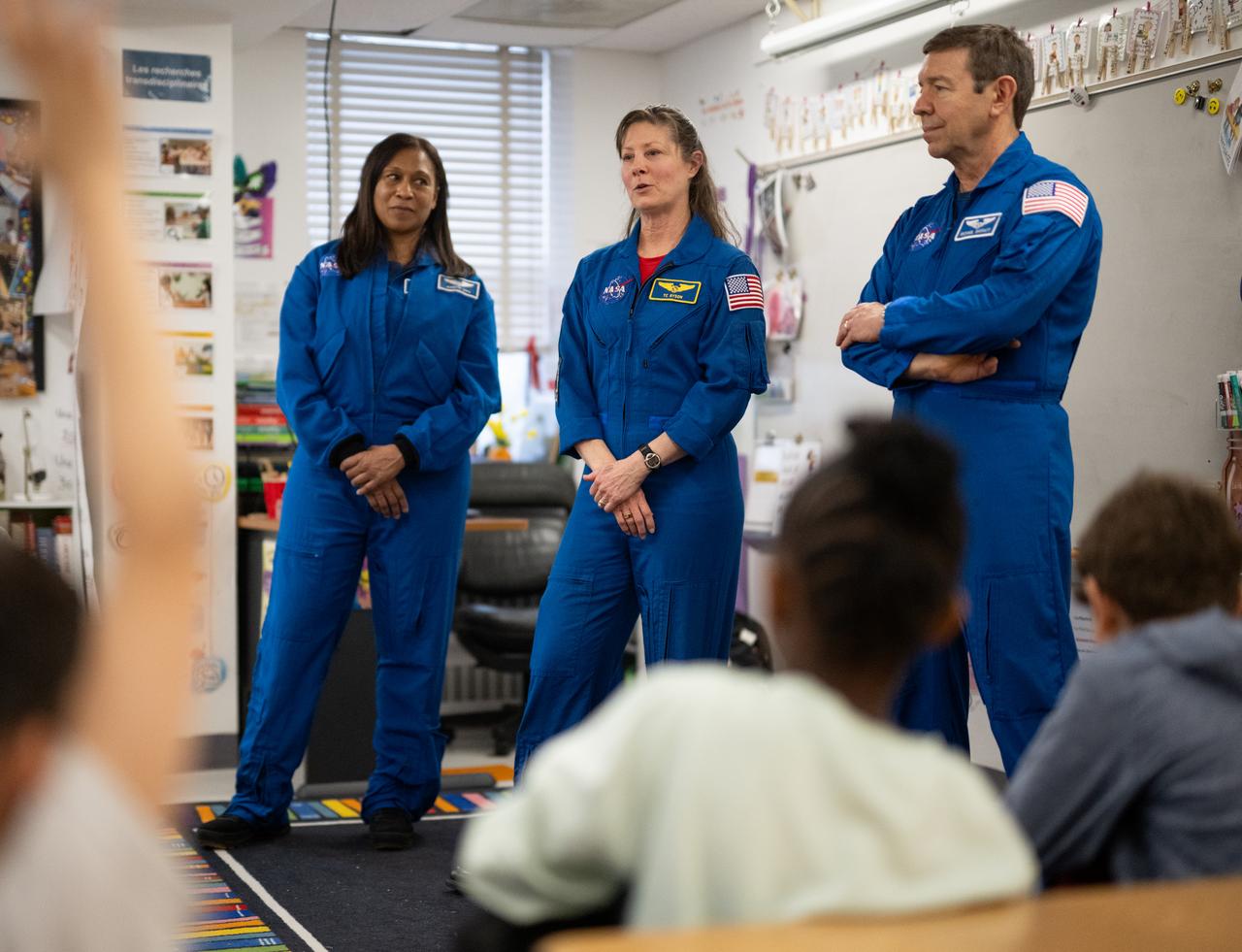

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Jeanette Epps, left, Tracy Dyson, and Michael Barratt, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
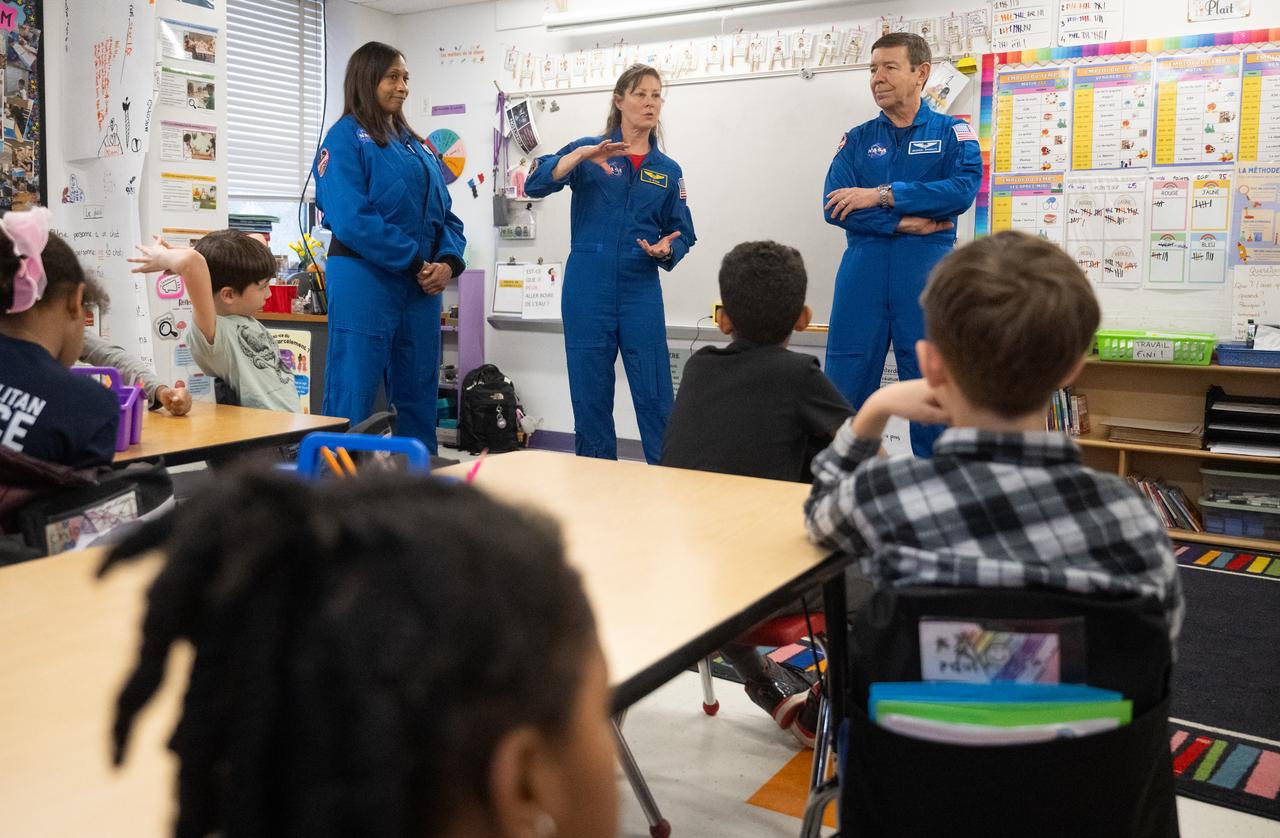

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Jeanette Epps, left, Tracy Dyson, and Michael Barratt, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, left, and Jeanette Epps, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025, at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Dominick, Epps, and fellow crewmates Michael Barratt and Tracy Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
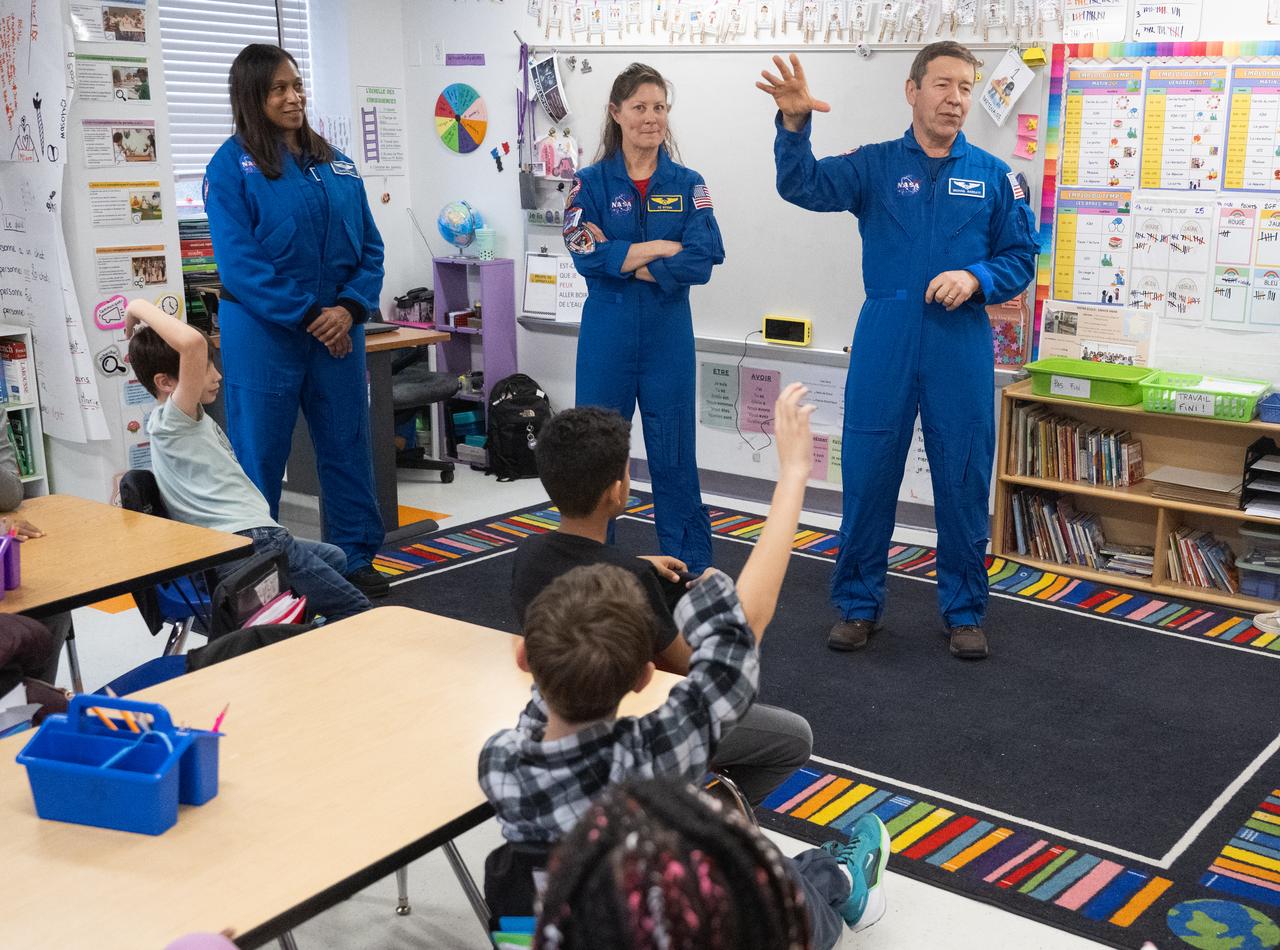

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Jeanette Epps, left, Tracy Dyson, and Michael Barratt, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, left, and Tracy Dyson, speak to students, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at Elsie Whitlow Stokes Community Freedom Public Charter School in Washington. Barratt, Dyson, and fellow crewmates Matthew Dominick and Jeanette Epps served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
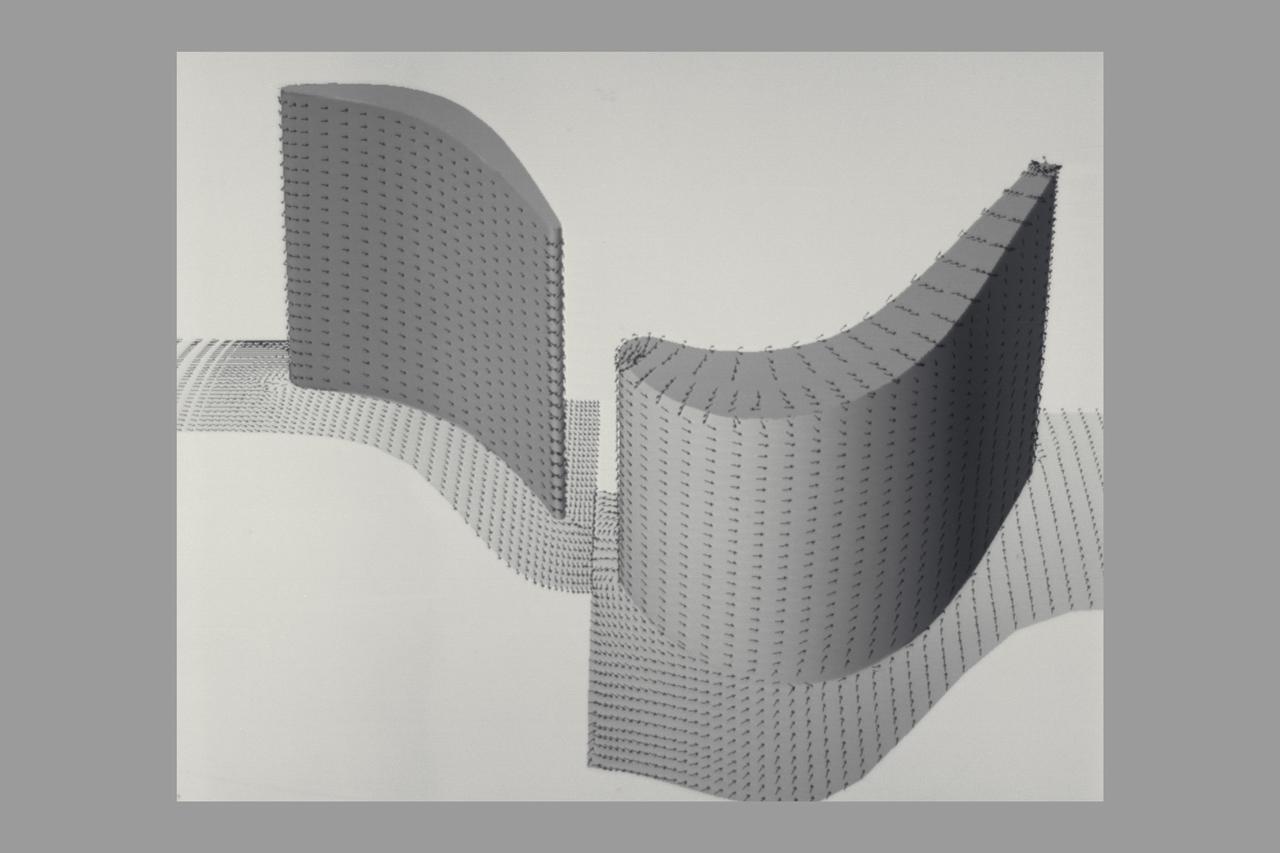
Navier Stokes: Rotor Stator Pressure and Velocity Vectors SSME
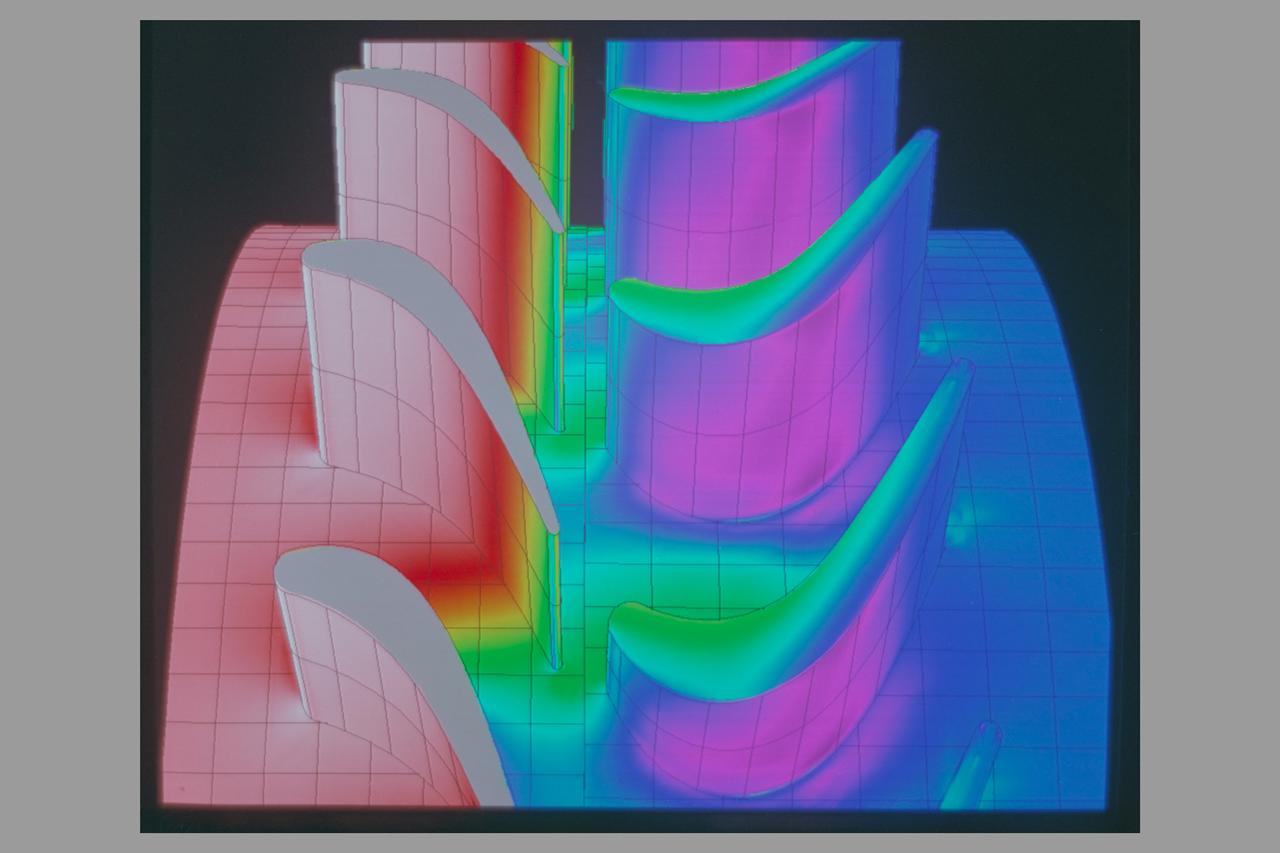
Navier Stokes: Rotor Stator Pressure and Velocity Vectors SSME
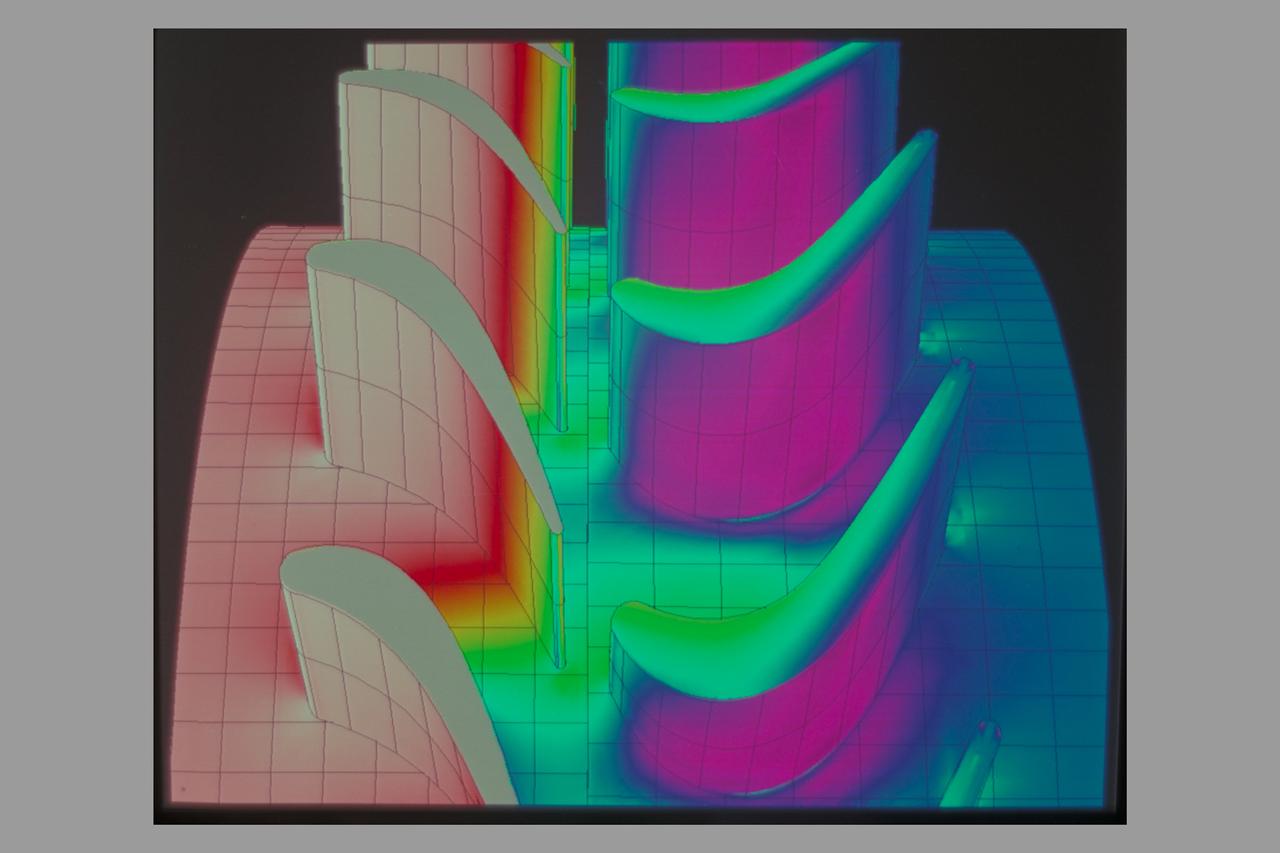
Navier Stokes: Rotor Stator Pressure and Velocity Vectors SSME
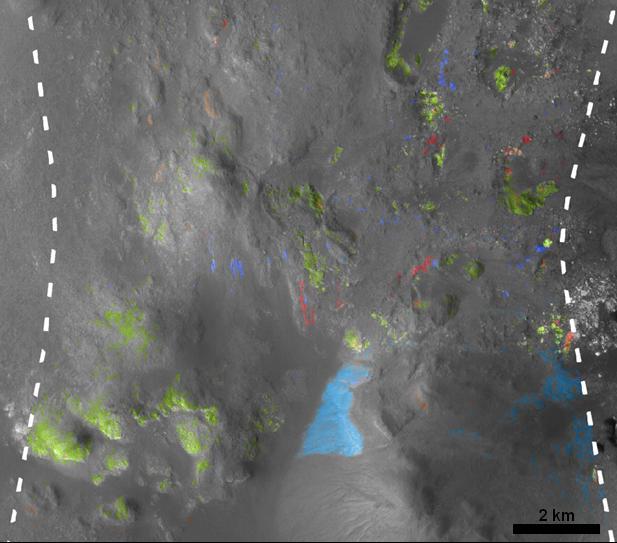

This view of Stokes Crater is a mosaic of images taken by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and ESA Mars Express showing at least one of the nine craters in the northern lowlands of Mars with exposures of hydrated minerals detected from orbit.
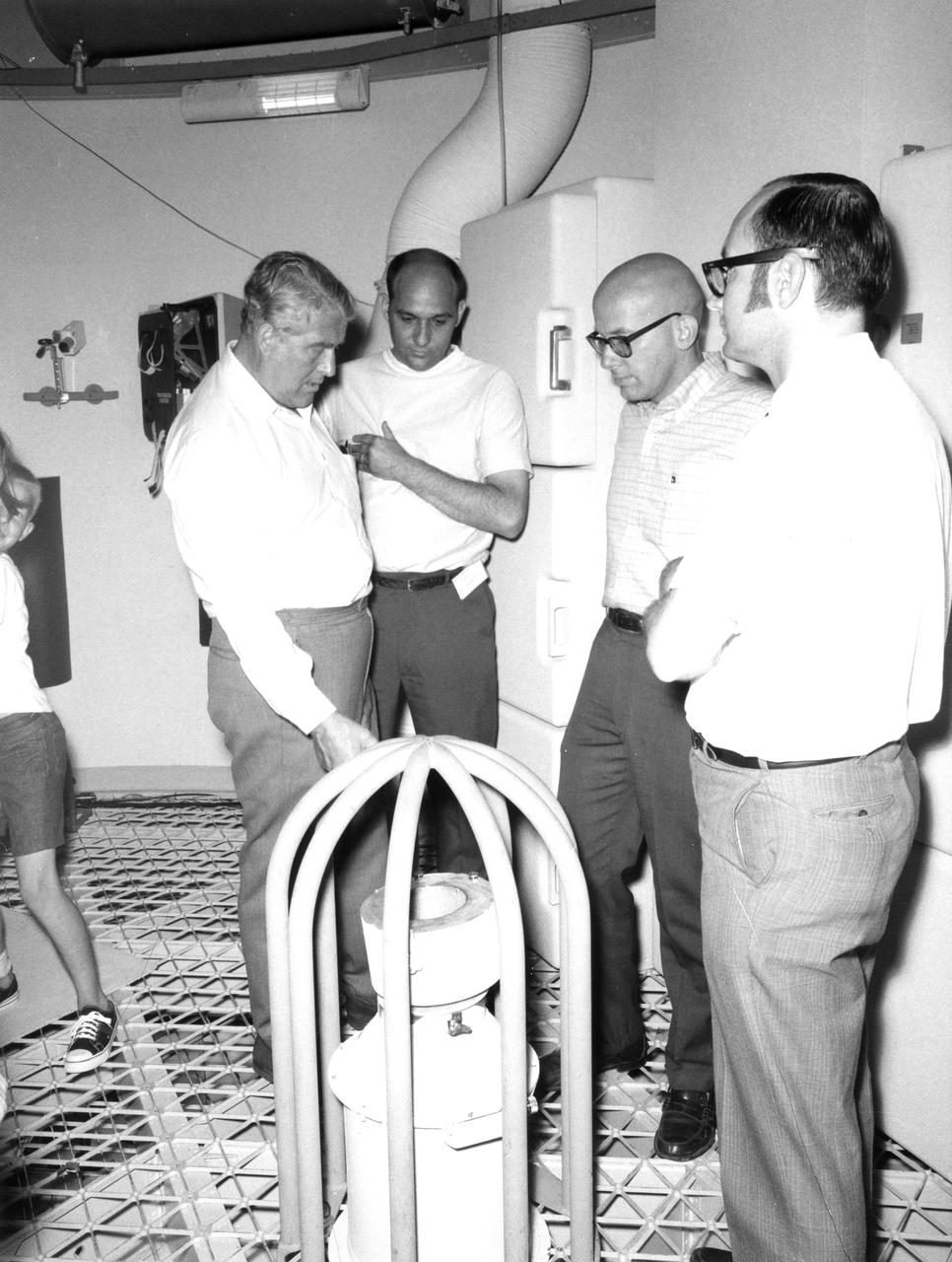

This photograph was taken after Dr. von Braun moved from his post as Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to Deputy Associate Administrator for Planning at NASA Headquarters. On June 27, 1970, he visited the MSFC again during the center’s 10th anniversary to look at a mockup of the spacecraft that would later be known as Skylab. In this photo, he is examining an experiment in the mockup. With von Braun are (left to right): James R. Thompson, Richard T. Heckman, and Jack Stokes of the Center’s Astrionics Laboratory.
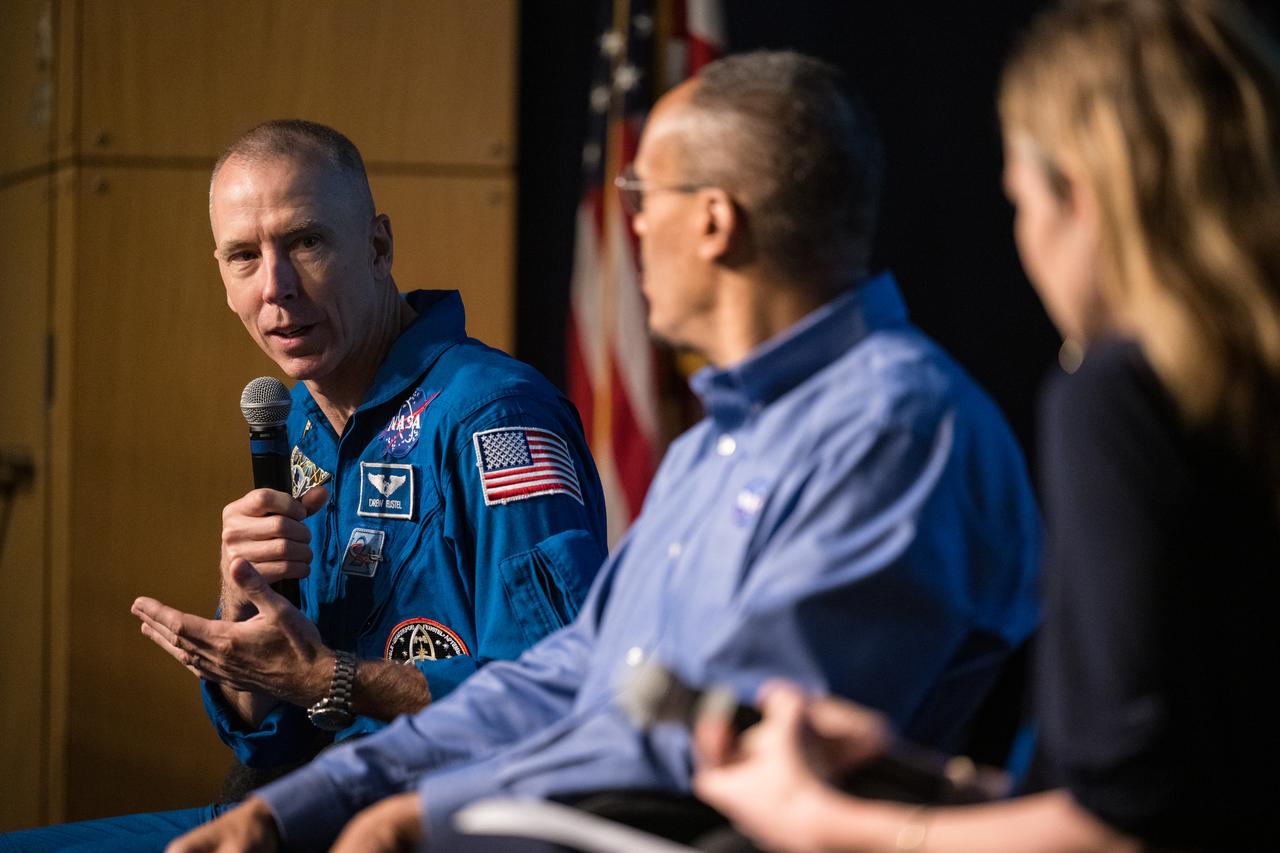

Former astronaut Drew Feustel answers a question from Earth Information Center Lead for NASA, Eleanor Stokes who moderated a question and answer session with him and former astronaut Alvin Drew during the Earth Information Center Student Engagement event at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building, Friday, Sept. 29, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Earth Information Center Lead for NASA, Eleanor Stokes moderates a question and answer session with former astronauts Drew Feustel, left, and Alvin Drew, during the Earth Information Center Student Engagement event at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building, Friday, Sept. 29, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Former astronaut Drew Feustel left, answers a question from an audience member while on a panel with former astronaut Alvin Drew, center, and moderator, Earth Information Center Lead for NASA, Eleanor Stokes, during the Earth Information Center Student Engagement event at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building, Friday, Sept. 29, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
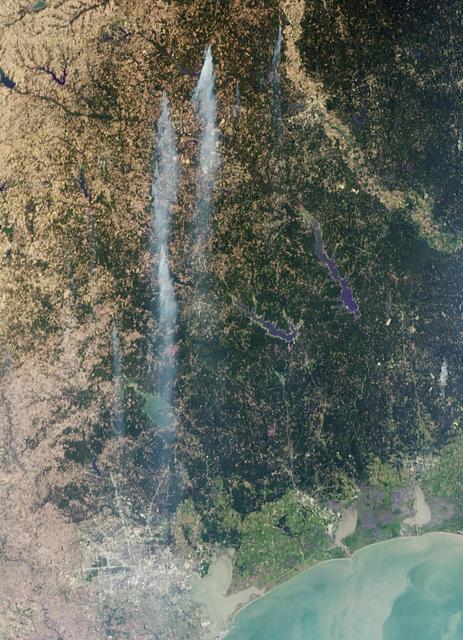

As the remains of Tropical Storm Lee passed over Louisiana on Monday, Sept. 5, 2011, strong, gusty winds on the western side of the storm stoked fires throughout eastern Texas as seen in this image from NASA Terra spacecraft.
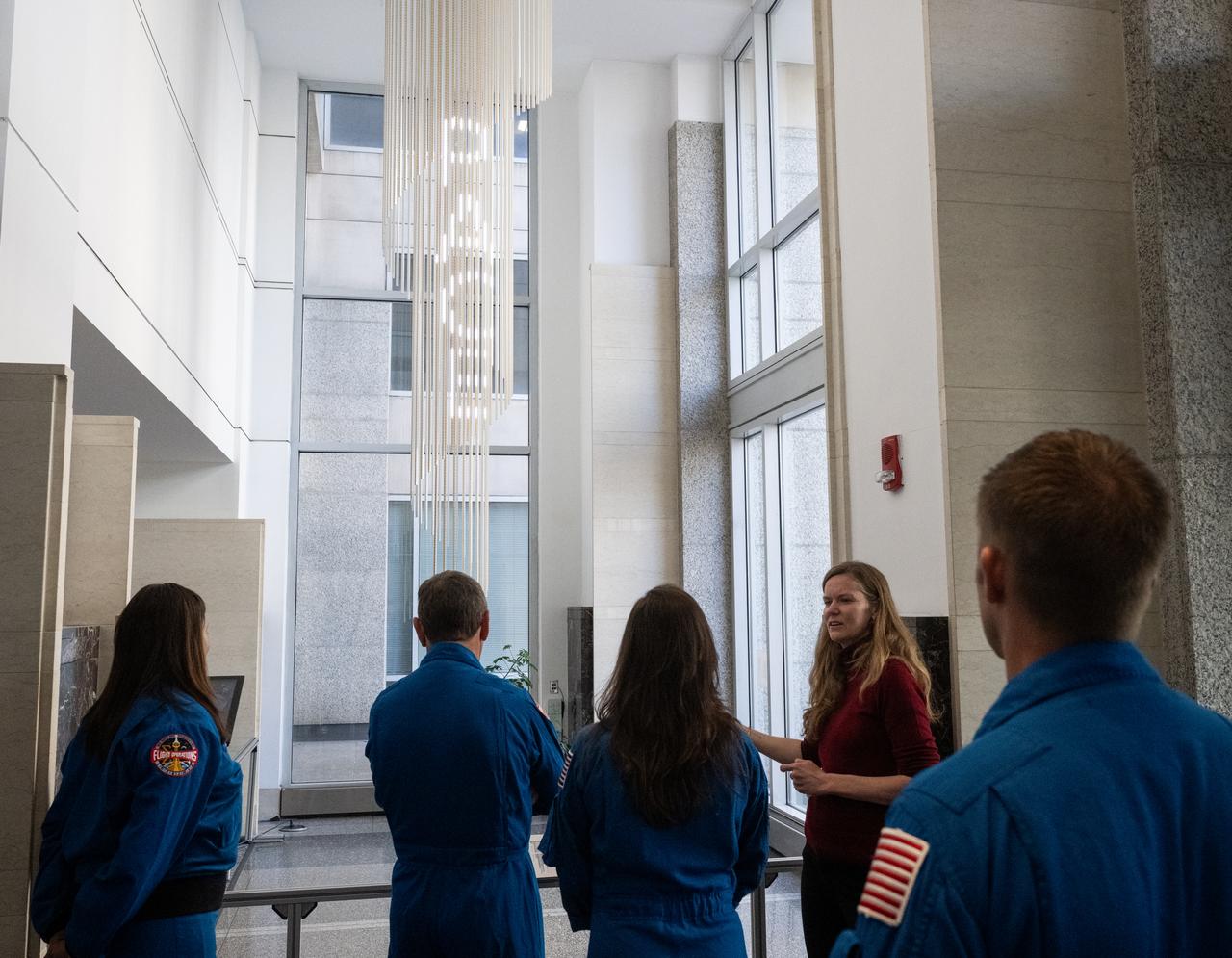

Eleanor Stokes, program manger for NASA’s Earth Information Center, second from right, speaks with Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Jeanette Epps, left, Michael Barratt, Tracy Dyson, and Matthew Dominick during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Monday, March 3, 2025, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Dominick, Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
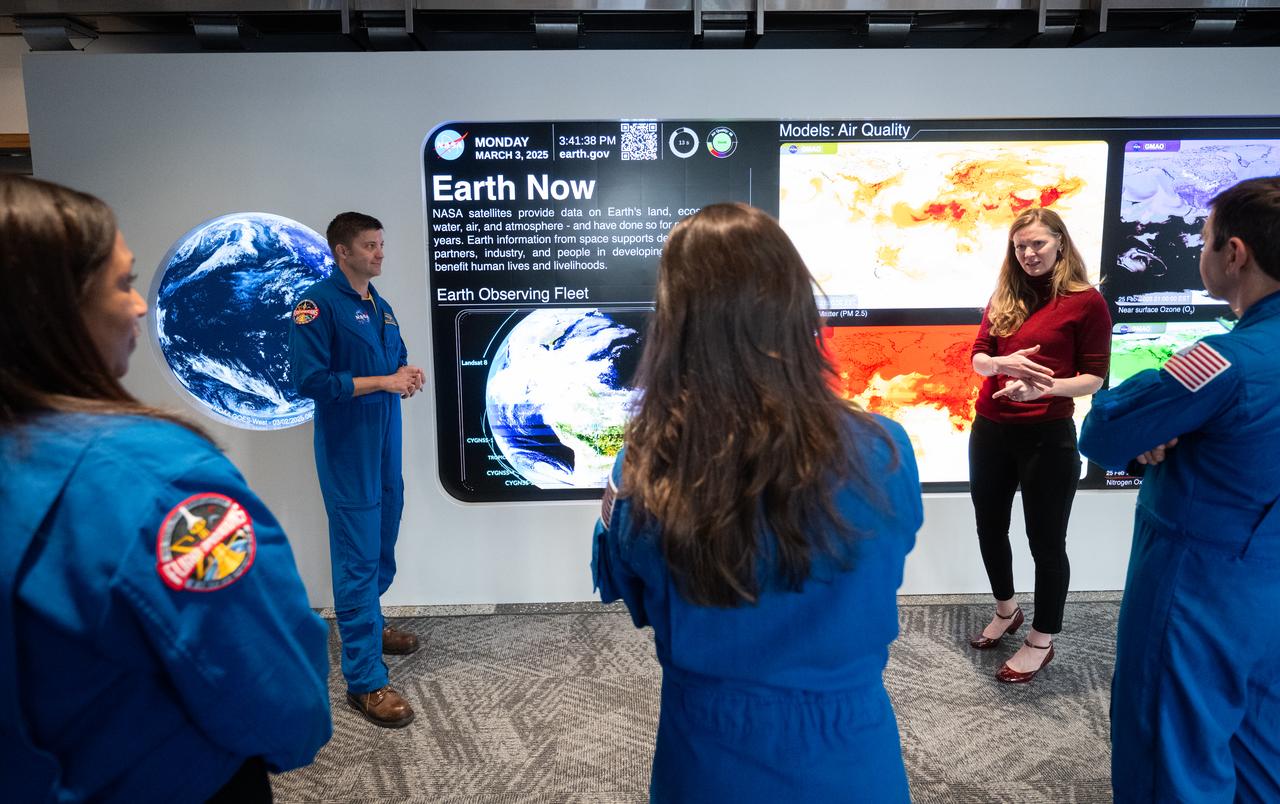

Eleanor Stokes, program manger for NASA’s Earth Information Center, second from right, speaks with Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, Tracy Dyson, Jeanette Epps, and Matthew Dominick during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Monday, March 3, 2025, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Dominick, Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
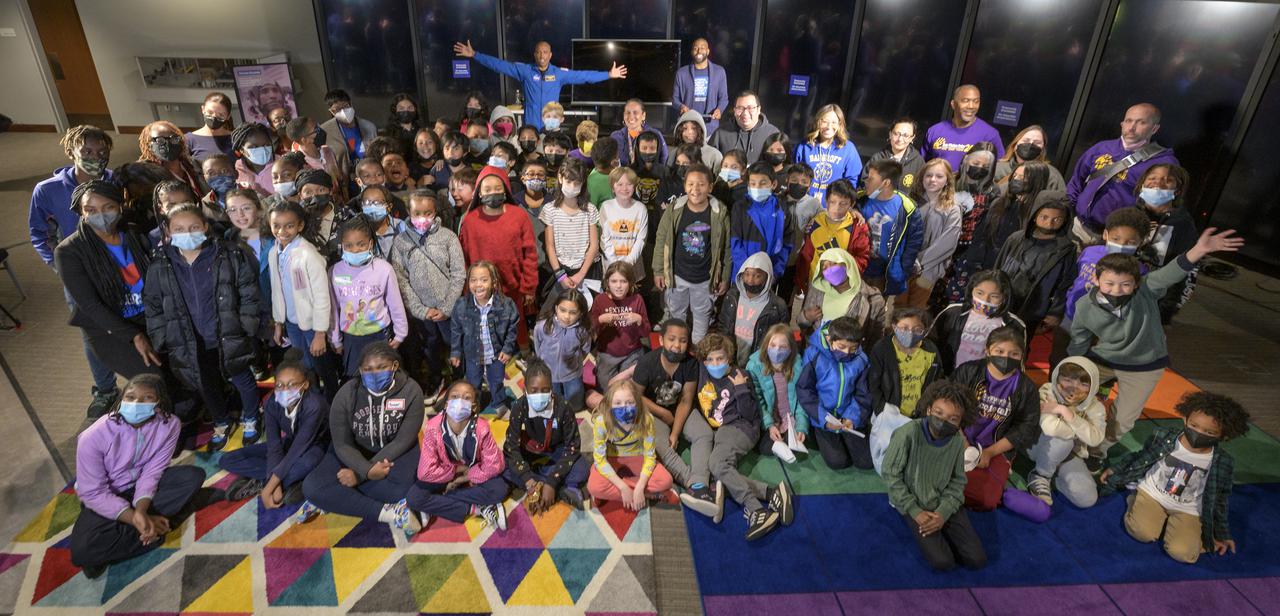

NASA astronaut Victor Glover, back with arms extended, poses for a group photo with school students from Bunker Hill Elementary, Bancroft Elementary, and E.W. Stokes Public Charter School at the conclusion of an educational event, Thursday, April 28, 2022, at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington. Glover most recently served as pilot and second-in-command on the Crew-1 SpaceX Crew Dragon, named Resilience, which landed after a long duration mission aboard the International Space Station, May 2, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
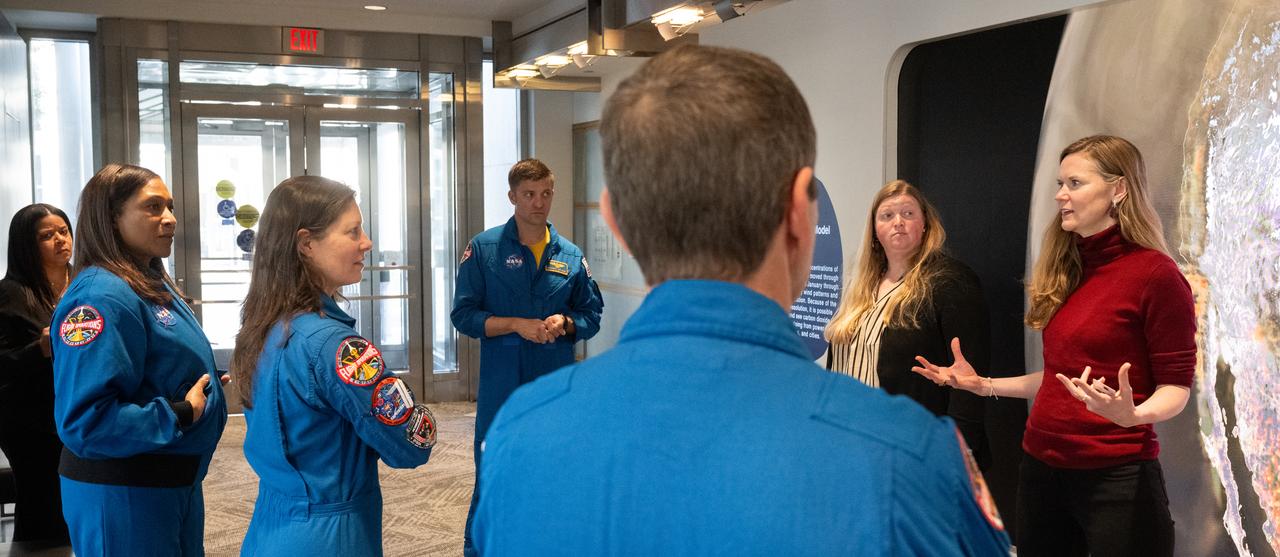

Eleanor Stokes, program manger for NASA’s Earth Information Center, right, and Nicole Ramberg-Pihl, project manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, second from right, speak with Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, Tracy Dyson, Jeanette Epps, and Matthew Dominick during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Monday, March 3, 2025, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Dominick, Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
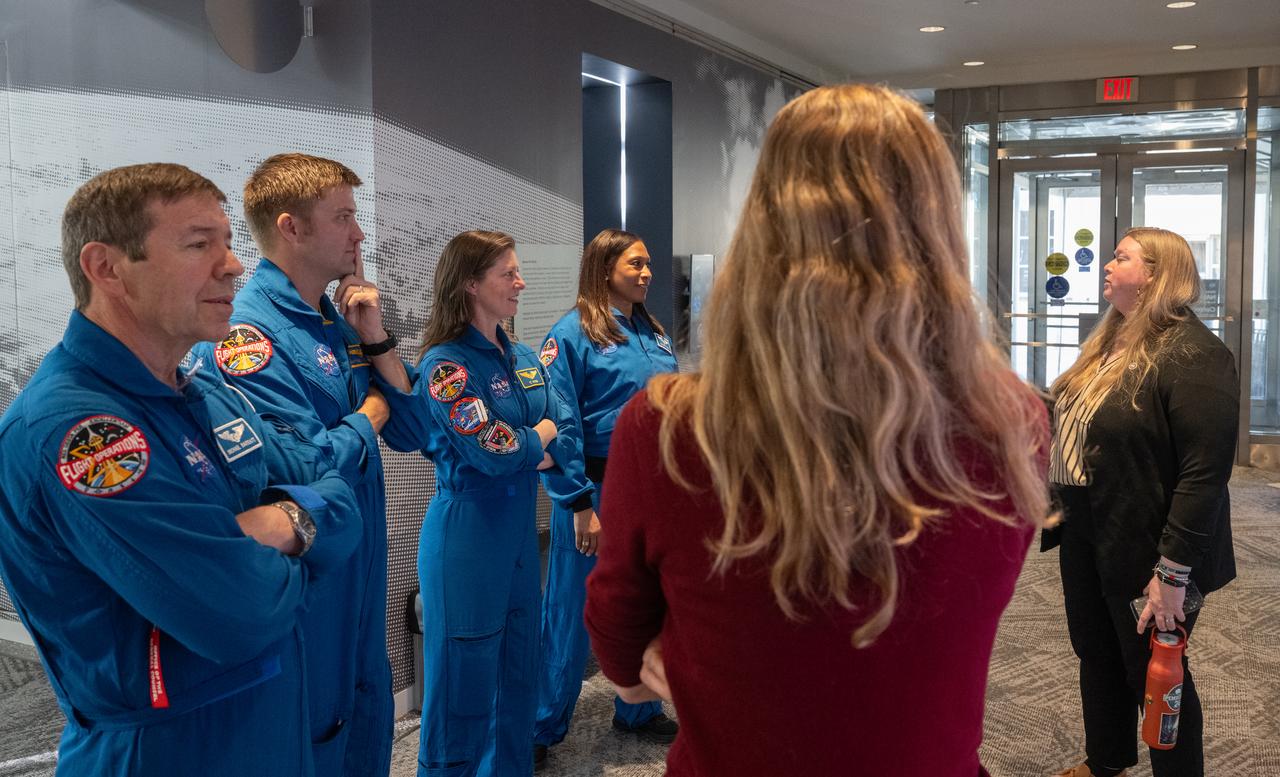

Expedition 71 NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, left, Matthew Dominick, Tracy Dyson, and Jeanette Epps speak with Eleanor Stokes, program manger for NASA’s Earth Information Center, second from right, and Nicole Ramberg-Pihl, project manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, right, during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Monday, March 3, 2025, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Dominick, Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
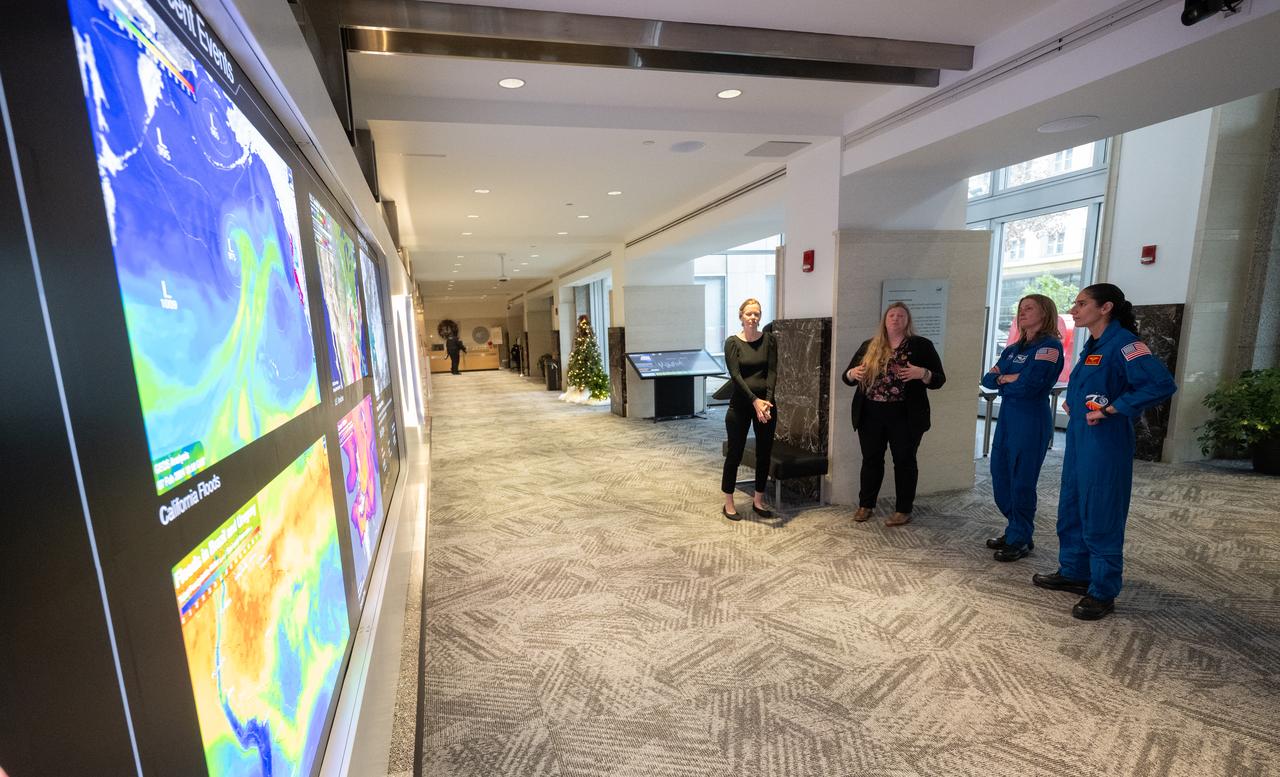

Eleanor Stokes, program manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, left, and Nicole Ramberg-Pihl, project manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, second from left, speak with NASA astronauts Loral O’Hara, second from right, and Jasmin Moghbeli, right, during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Wednesday, Dec. 4, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. O’Hara and Moghbeli spent six months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
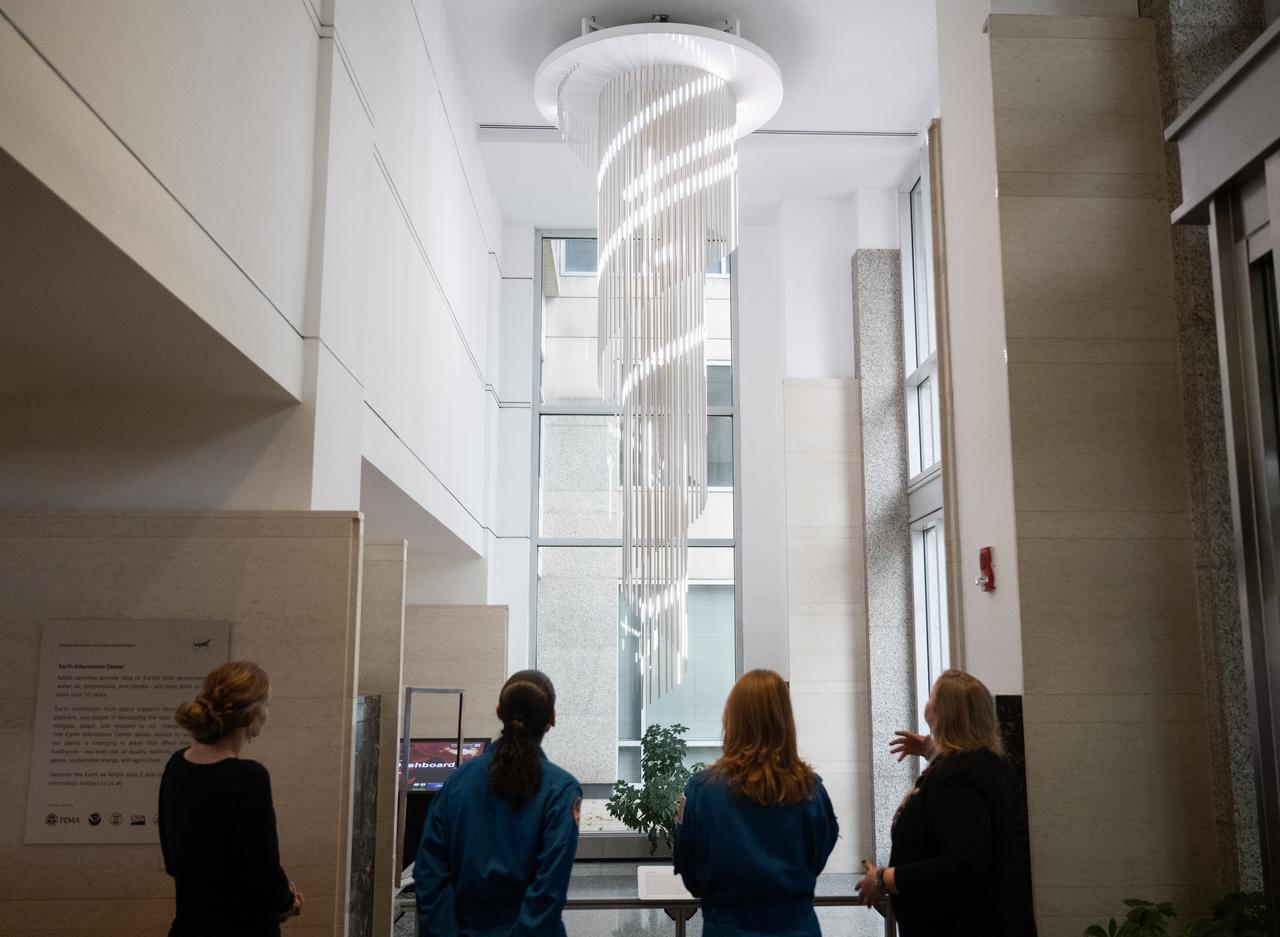

Eleanor Stokes, program manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, left, and Nicole Ramberg-Pihl, project manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, right, speak with NASA astronauts Jasmin Moghbeli, second from left, and Loral O’Hara, second from right, during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Wednesday, Dec. 4, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. O’Hara and Moghbeli spent six months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
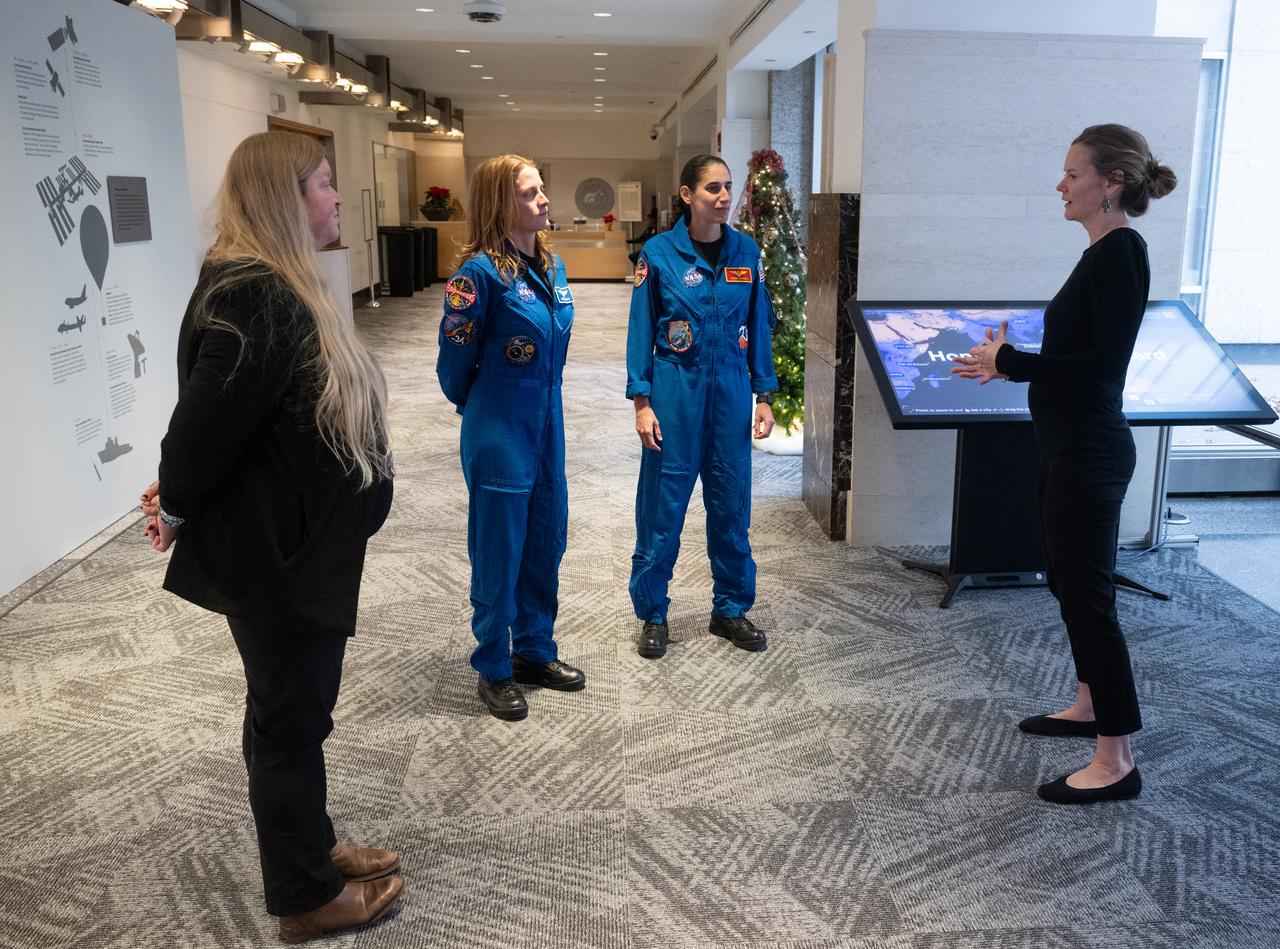

Eleanor Stokes, program manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, right, and Nicole Ramberg-Pihl, project manager for NASA’s Earth Information Center, left, speak with NASA astronauts Loral O’Hara, second from left, and Jasmin Moghbeli, second from right, during a tour of the Earth Information Center, Wednesday, Dec. 4, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. O’Hara and Moghbeli spent six months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
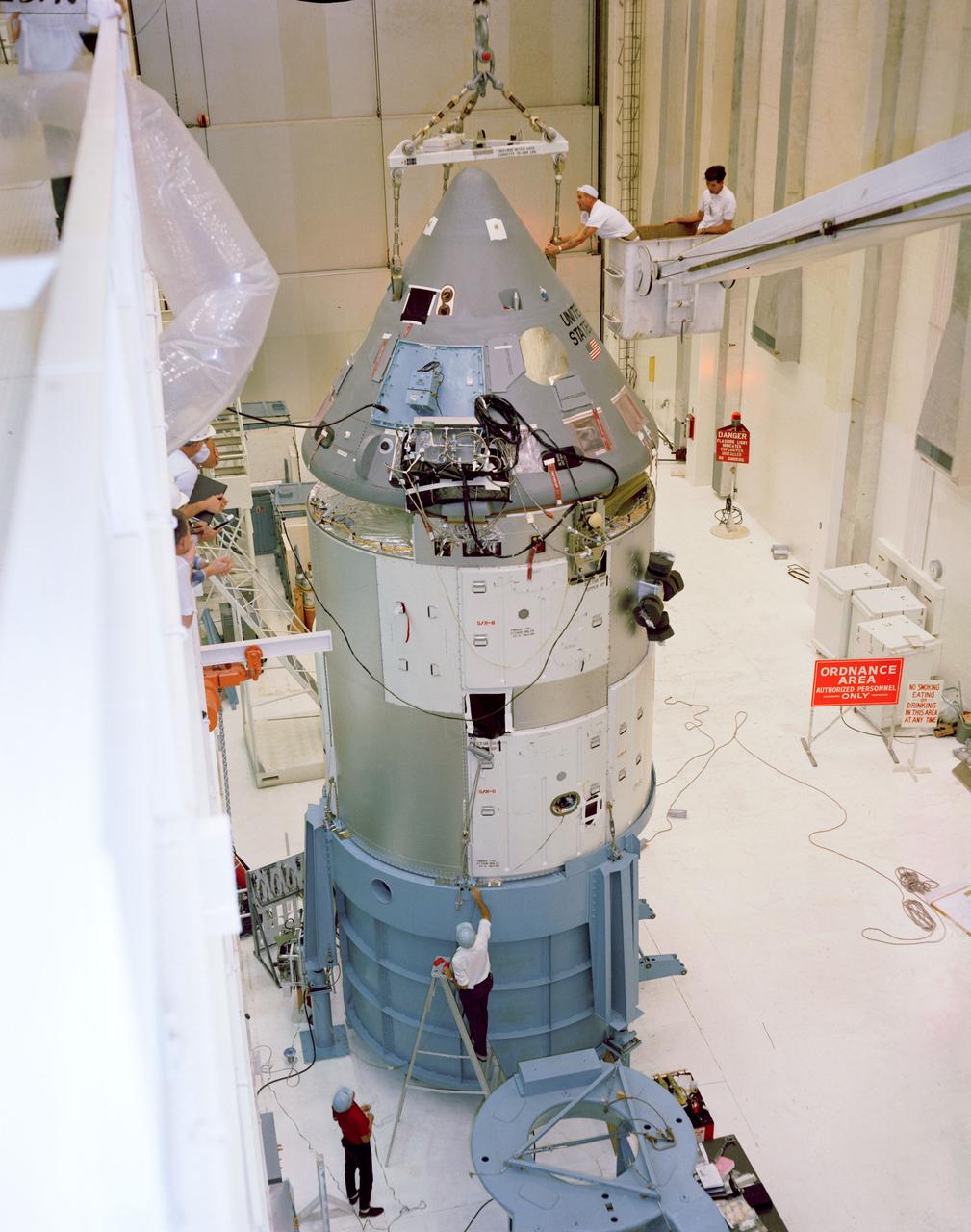

S67-15717 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command/Service Module is moved from H-134 to east stokes for mating to the Saturn Lunar Module Adapter No. 05 in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. S/C 012 will be flown on the Apollo/Saturn 204 mission.
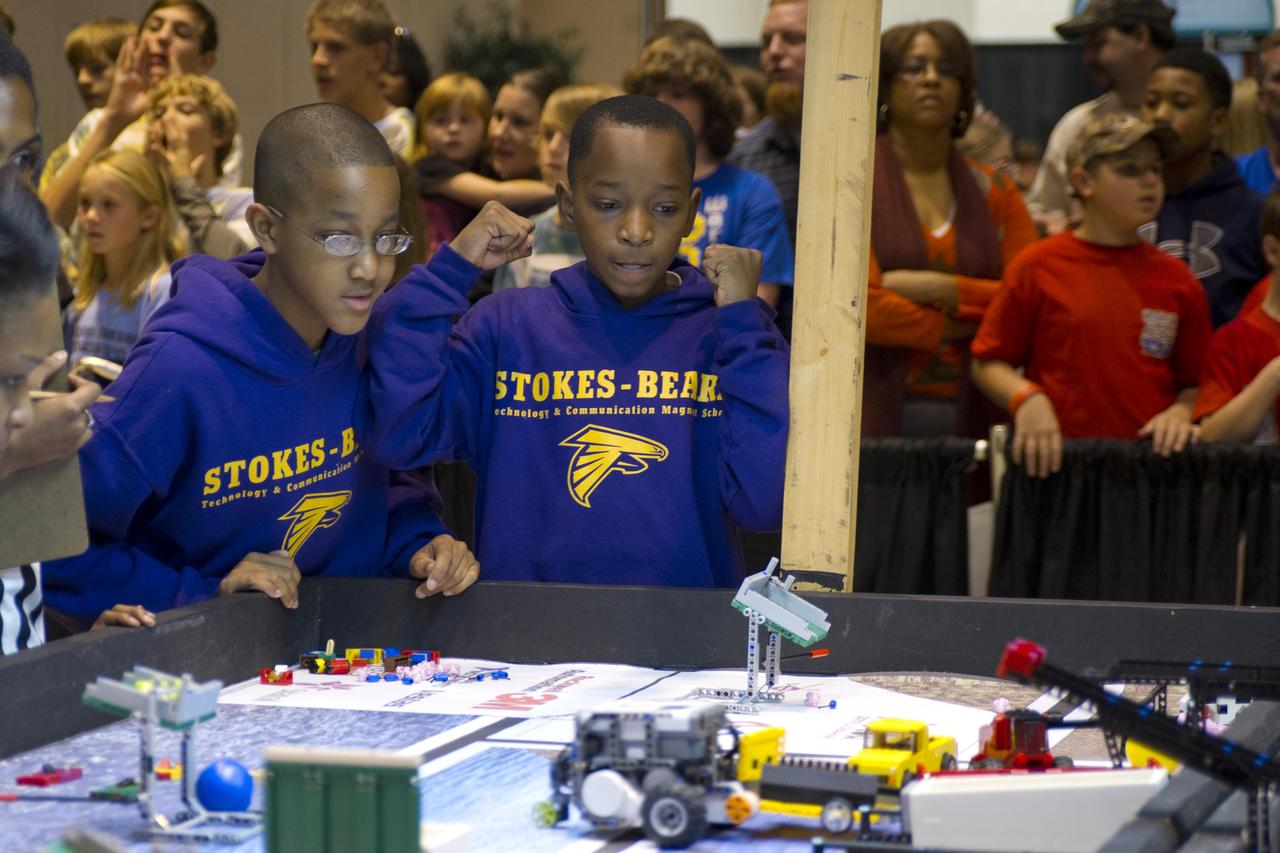

Two 2011 Mississippi FIRST LEGO League competitors from Stokes-Beard Magnet Elementary School in Columbus urge their robots on during the annual tournament Dec. 3. The competition attracted more than 1,000 participants and guests to the Lake Terrace Convention Center in Hattiesburg.
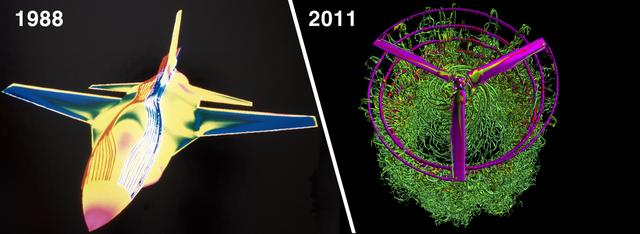
Then and Now: These images illustrate the dramatic improvement in NASA computing power over the last 23 years, and its effect on the number of grid points used for flow simulations. At left, an image from the first full-body Navier-Stokes simulation (1988) of an F-16 fighter jet showing pressure on the aircraft body, and fore-body streamlines at Mach 0.90. This steady-state solution took 25 hours using a single Cray X-MP processor to solve the 500,000 grid-point problem. Investigator: Neal Chaderjian, NASA Ames Research Center At right, a 2011 snapshot from a Navier-Stokes simulation of a V-22 Osprey rotorcraft in hover. The blade vortices interact with the smaller turbulent structures. This very detailed simulation used 660 million grid points, and ran on 1536 processors on the Pleiades supercomputer for 180 hours. Investigator: Neal Chaderjian, NASA Ames Research Center; Image: Tim Sandstrom, NASA Ames Research Center
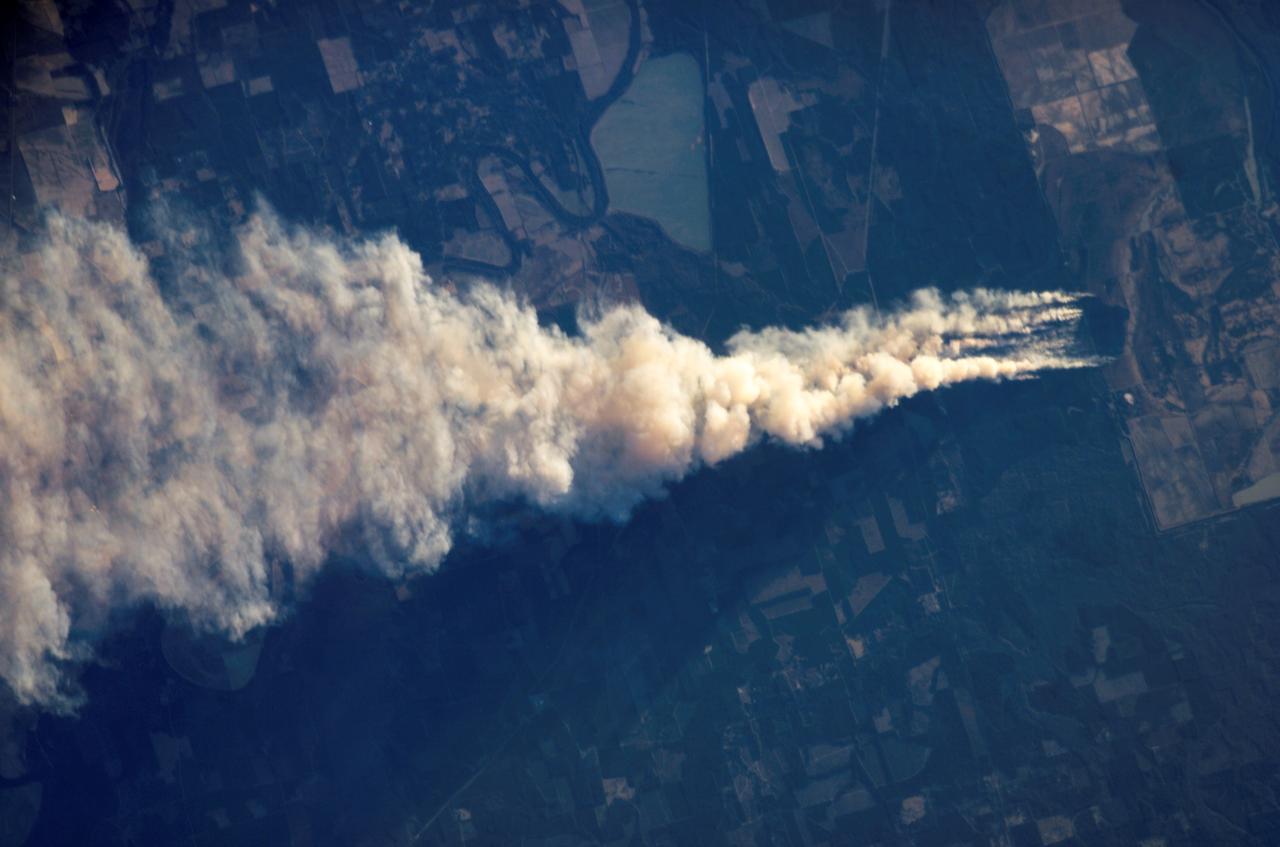

ISS012-E-13692 (2 Jan. 2006) --- A Forest Fire in Ouachita National Wildlife Refuge, Louisiana is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. Dry conditions and high winds have led to numerous recent fire outbreaks throughout much of the southwestern and south-central USA. This image captures the smoke plume from a fire in the Upper Ouachita National Wildlife Refuge in northeastern Louisiana. Drought conditions have persisted for much of the past year, leading to an increased fuel load comprised of dried grasses, shrubs, and trees. The combination of high amounts of dry fuel and frequent high winds has stoked small point fires into widespread brush fires. The fires generating this minimum 25-kilometer smoke plume started at approximately 13:00 hours local time. This image was acquired approximately 3.5 hours later as the station passed over the Texas/Louisiana border to the southwest. The extent of the plume reflects the strong westerly winds that drove the fire eastwards and damaged an estimated 200-300 acres of the wildlife refuge. The striking illumination of the plume is caused by a very low sun angle (angle between the horizon and the Sun directly below the space station), but this also results in generally low illumination of other scene features such as agricultural fields.

NASA astronaut Victor Glover talks with school students at the conclusion of an educational event, Thursday, April 28, 2022, at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington. Glover most recently served as pilot and second-in-command on the Crew-1 SpaceX Crew Dragon, named Resilience, which landed after a long duration mission aboard the International Space Station, May 2, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
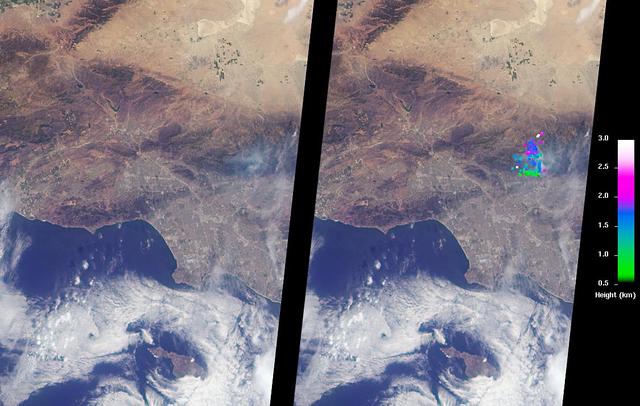
The Los Angeles area is currently suffering the effects of three major wildfires that are blanketing the area with smoke. Over the past few days, Southern California has experienced record-breaking temperatures, topping 110 degrees Fahrenheit in some cities. The heat, in combination with offshore winds, helped to stoke the Sherpa Fire west of Santa Barbara, which has been burning since June 15, 2016. Over the weekend of June 18-19, this fire rapidly expanded in size, forcing freeway closures and evacuations of campgrounds and state beaches. On Monday, June 20, two new fires ignited in the San Gabriel Mountains north of Azusa and Duarte, together dubbed the San Gabriel Complex Fire. They have burned more than 4,900 acres since June 20, sending up plumes of smoke visible to many in the Los Angeles basin and triggering air quality warnings. More than 1,400 personnel have been battling the blazes in the scorching heat, and evacuations were ordered for neighborhoods in the foothills. On June 21, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured this view of the San Gabriel Mountains and Los Angeles Basin from its 46-degree forward-viewing camera, which enhances the visibility of the smoke compared to the more conventional nadir (vertical) view. The width of this image is about 75 miles (120 kilometers) across. Smoke from the San Gabriel Complex Fire is visible at the very right of the image. Stereoscopic analysis of MISR's multiple camera angles is used to compute the height of the smoke plume from the San Gabriel Complex Fire. In the right-hand image, these heights are superimposed on the underlying image. The color scale shows that the plume is not much higher than the surrounding mountains. As a result, much of the smoke is confined to the local area. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20718

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
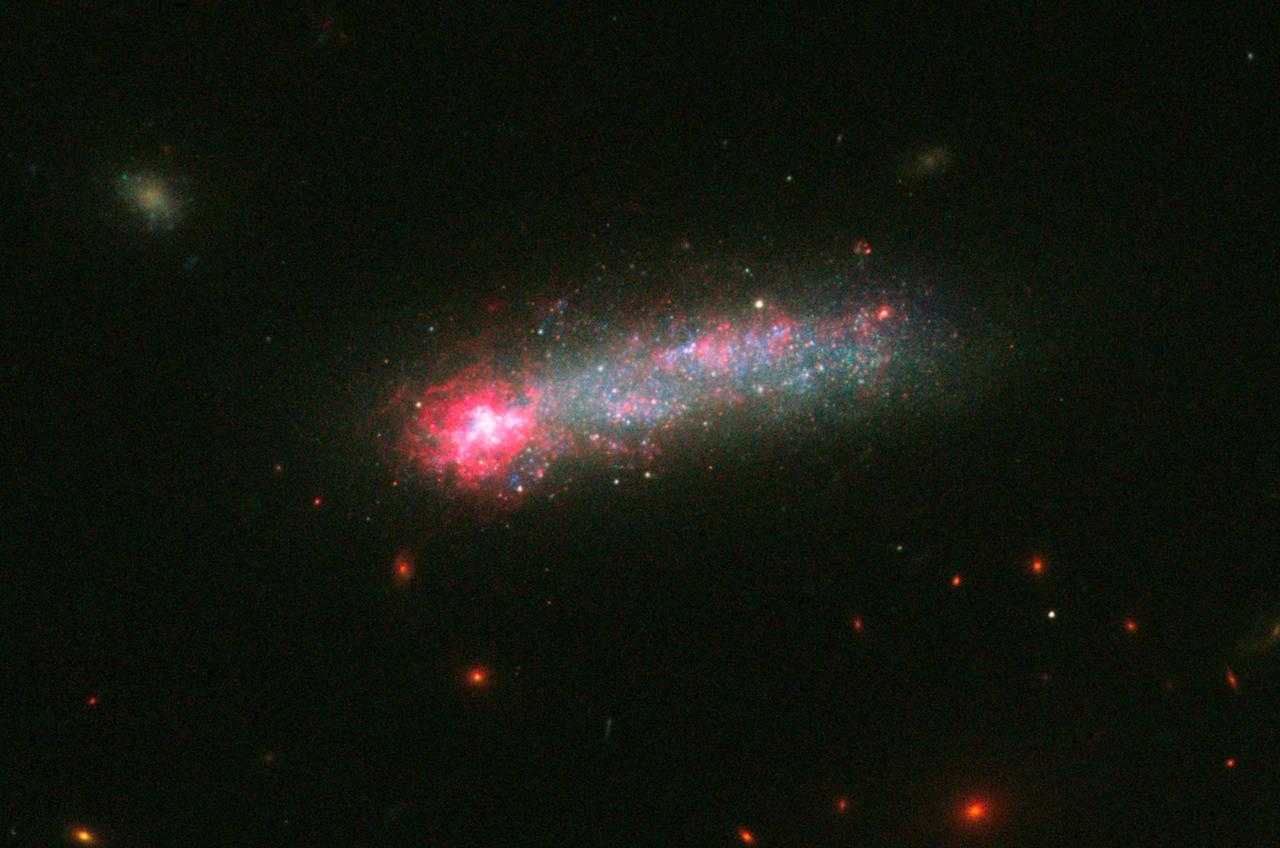

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about Kiso 5639 and Hubble, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2016/23" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2016/23</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> Image credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Elmegreen (Vassar College) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>