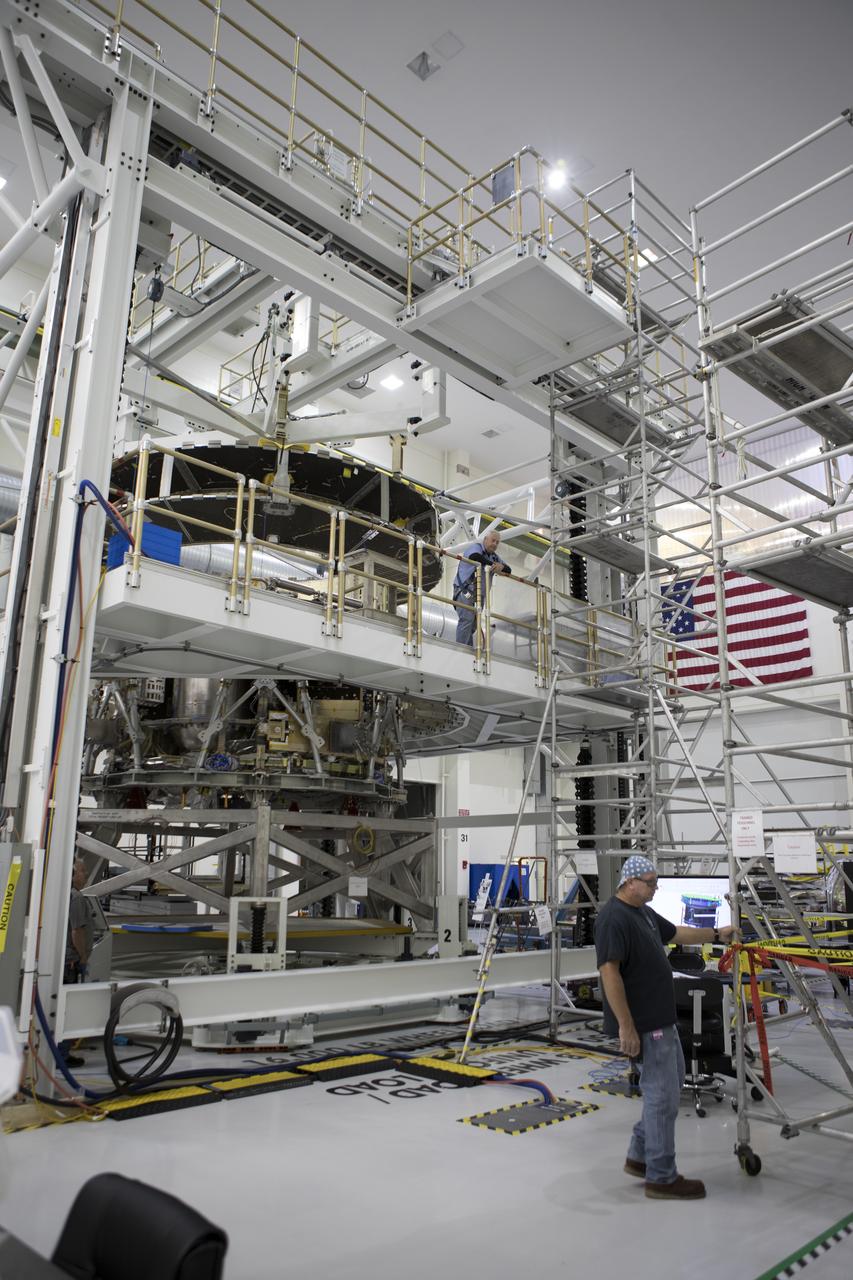

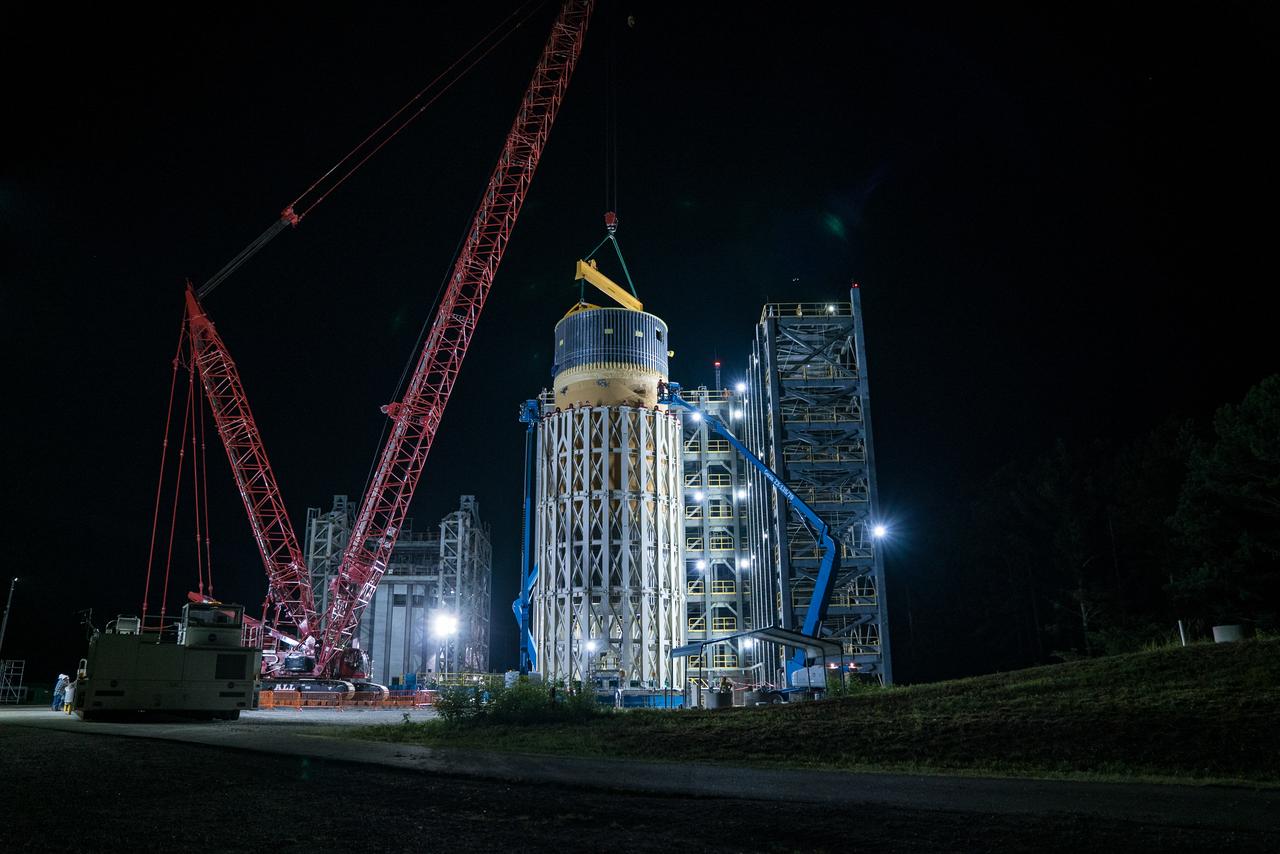
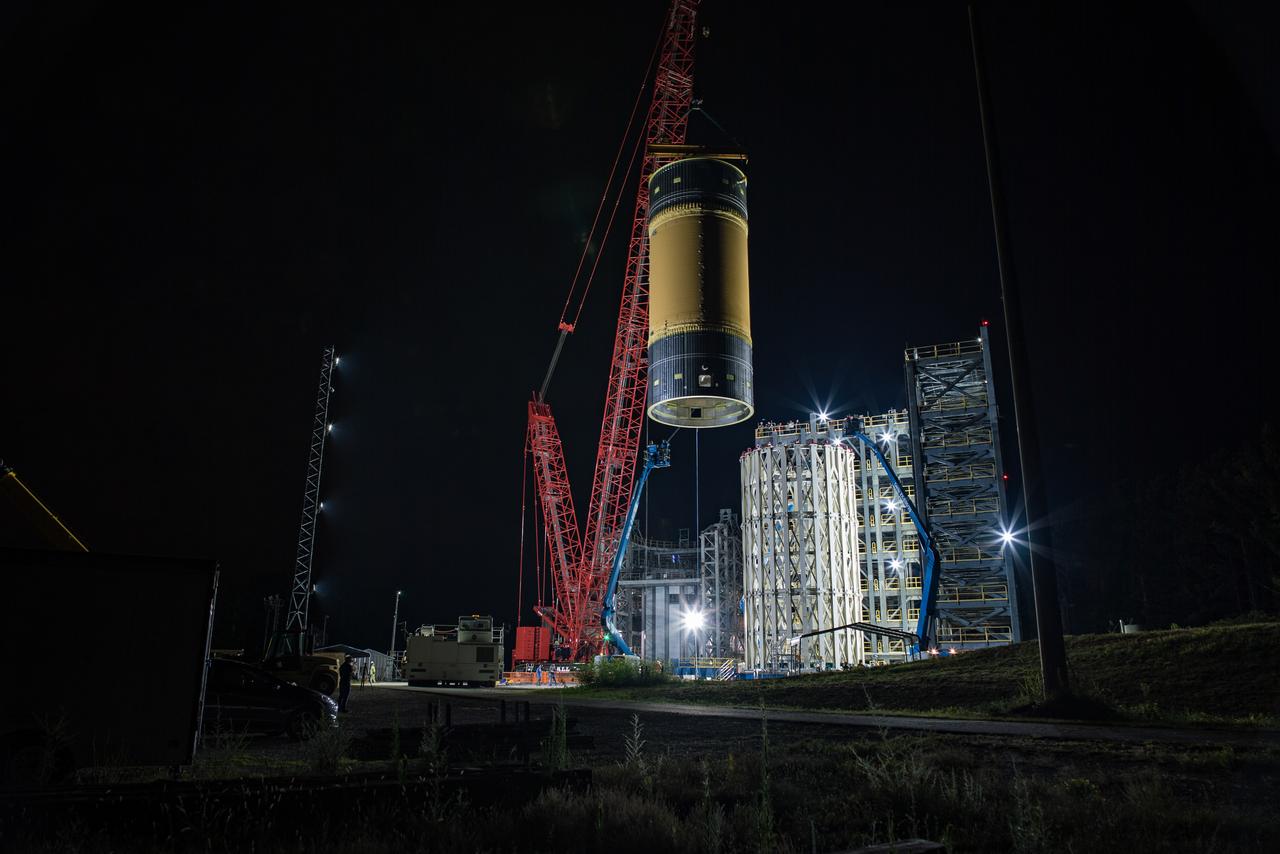
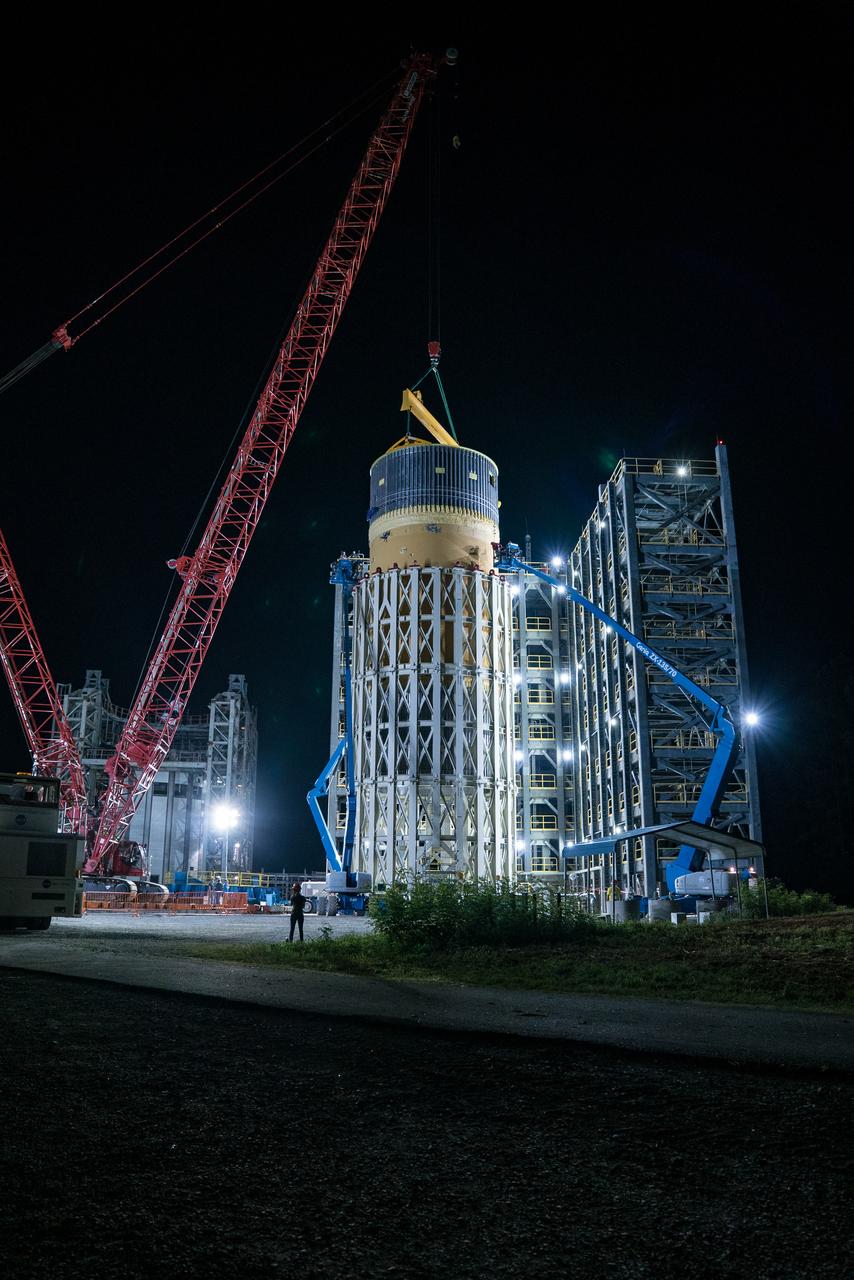
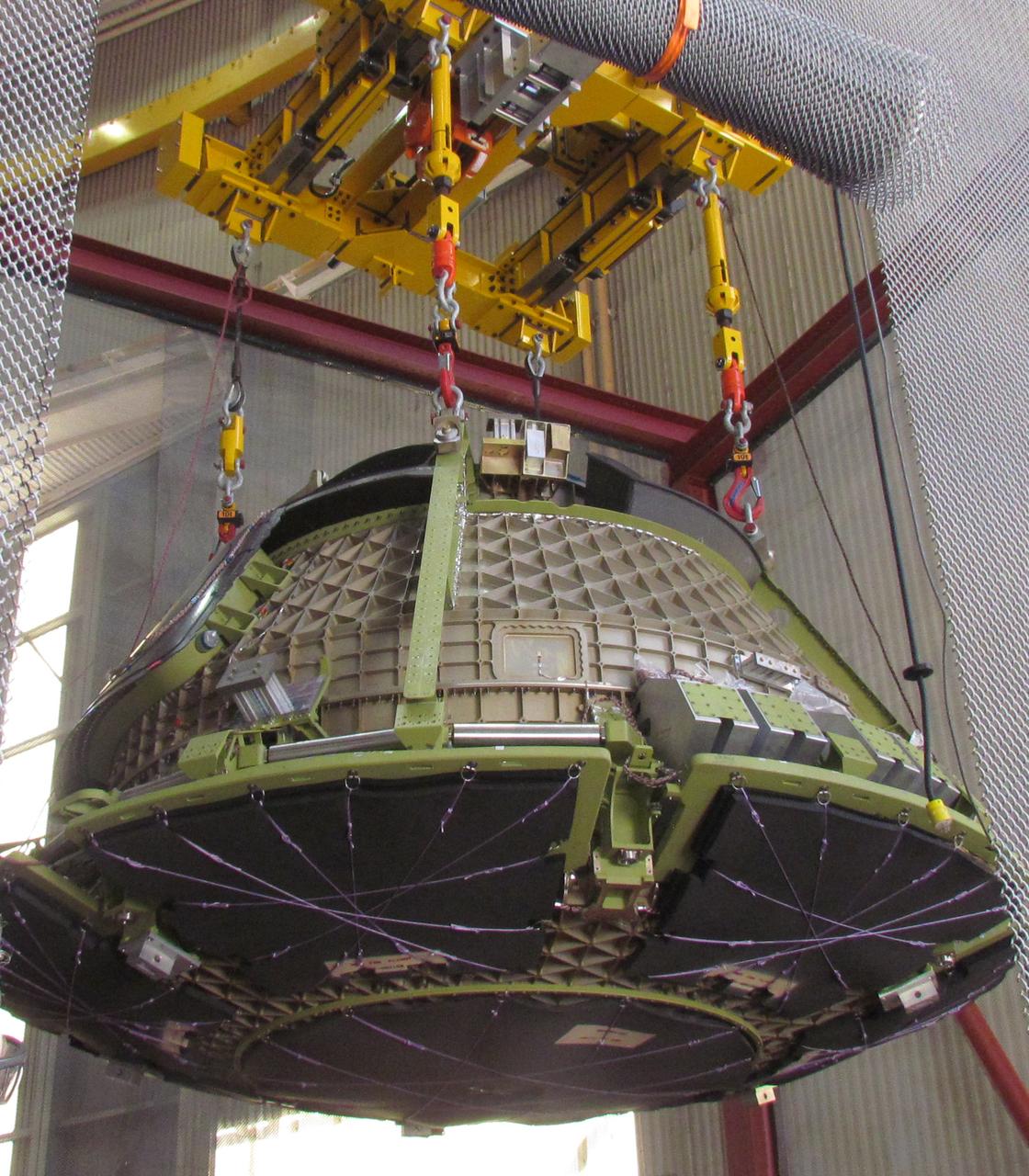
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
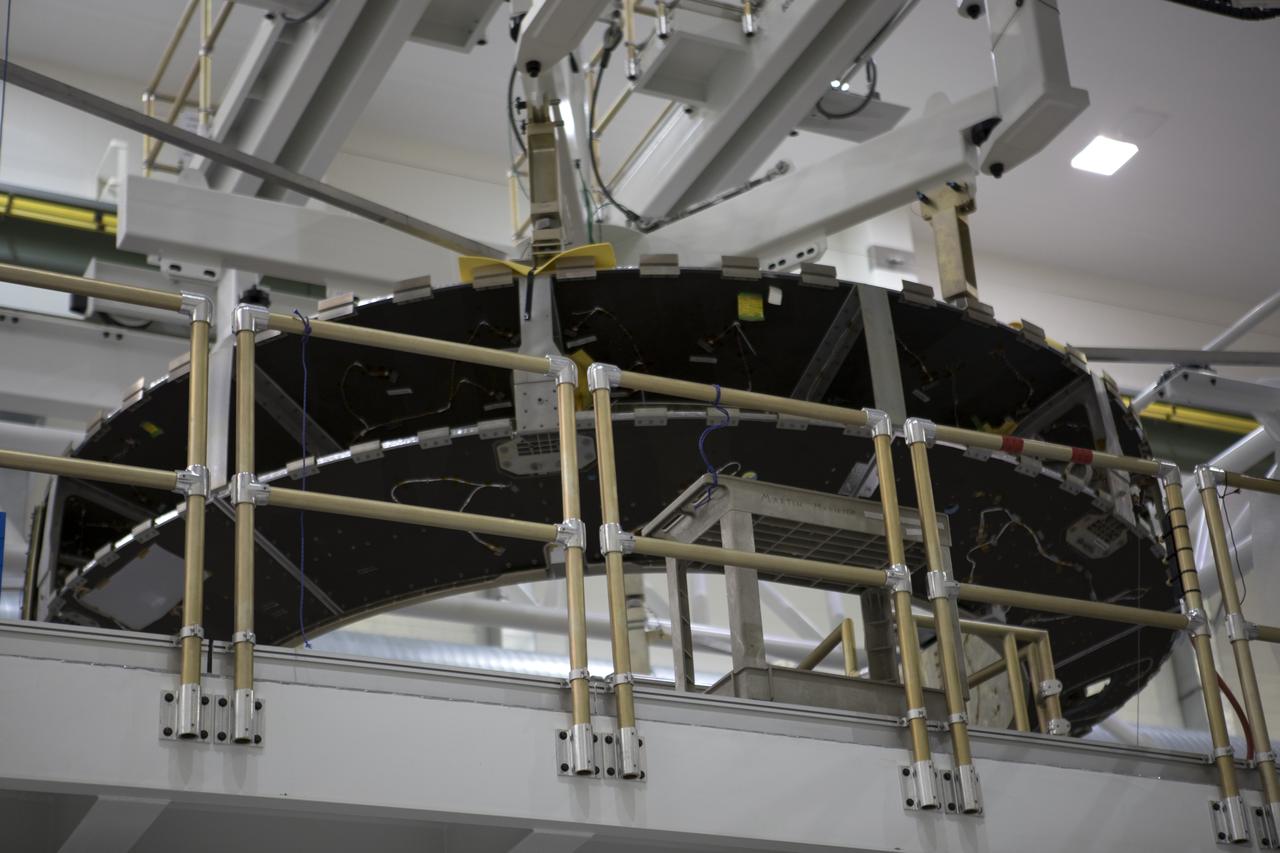

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
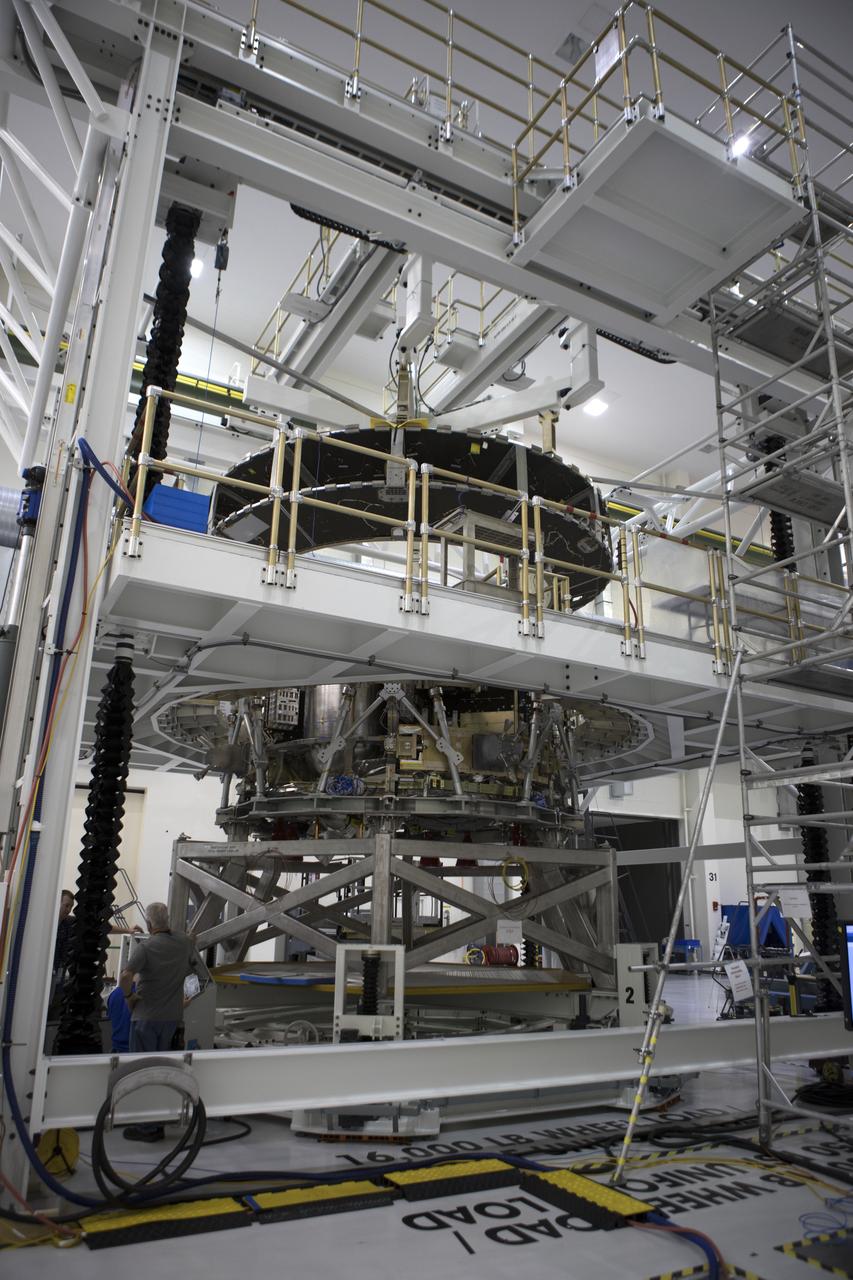

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are underway to lower the Orion crew module adapter structural test article onto the European Space Agency's service module structural test article. After the hardware is attached, the structure will be packed and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1 in 2019.
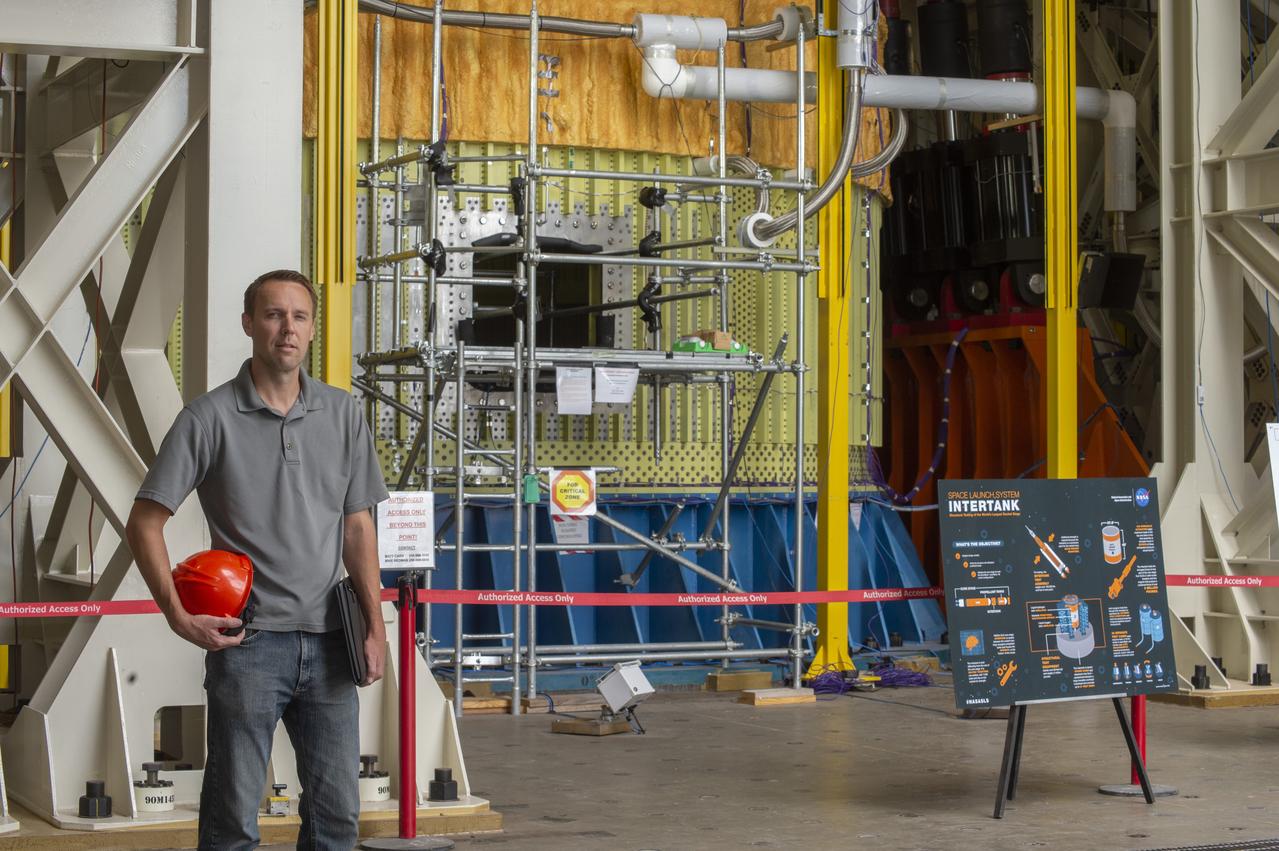

Preston Schmauch, SLS Stages Element Alternate Lead Systems Engineer, oversees testing of the Intertank Structural Test Article (STA), which will push, pull, and bend the STA with millions of pounds of force to prove the SLS Intertank can withstand the immense forces induced by aero, engine, and booster loads during flight.
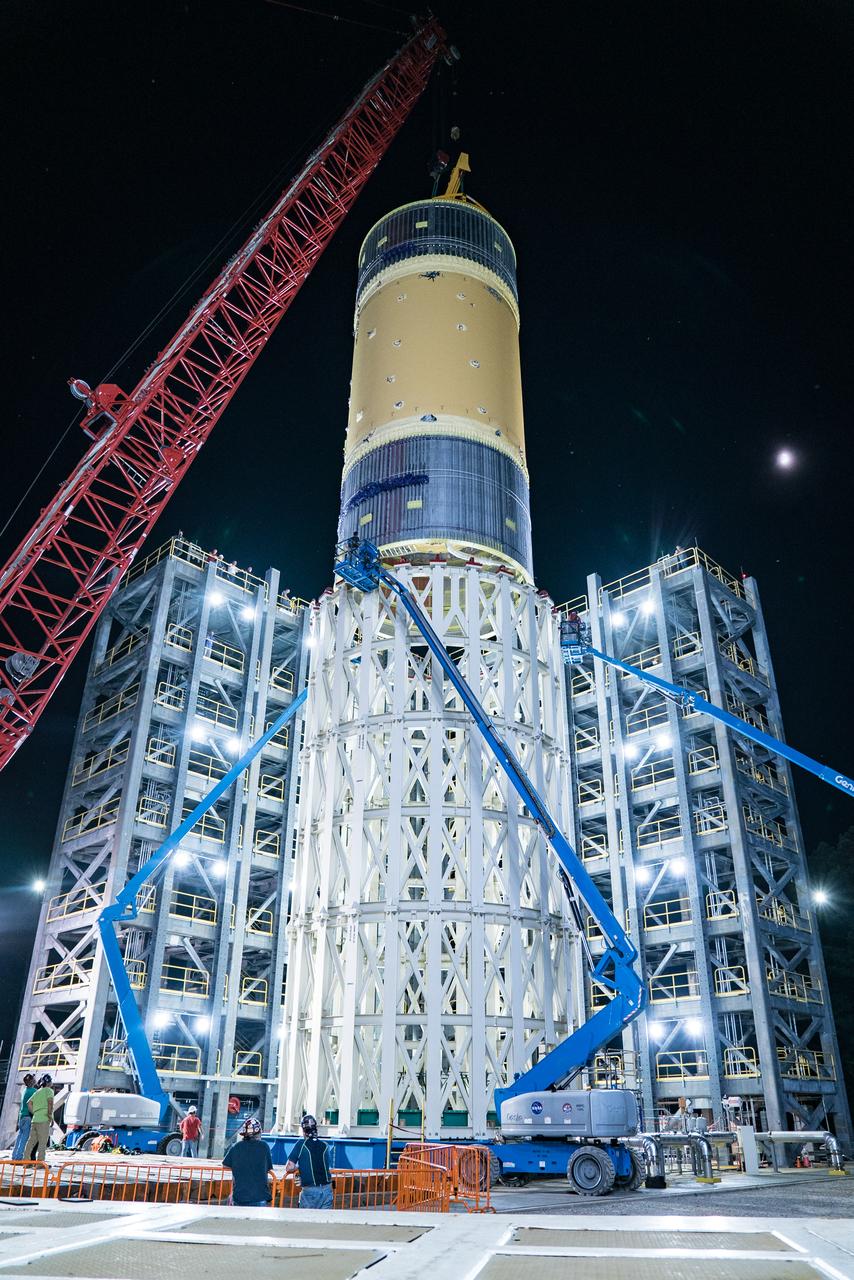

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
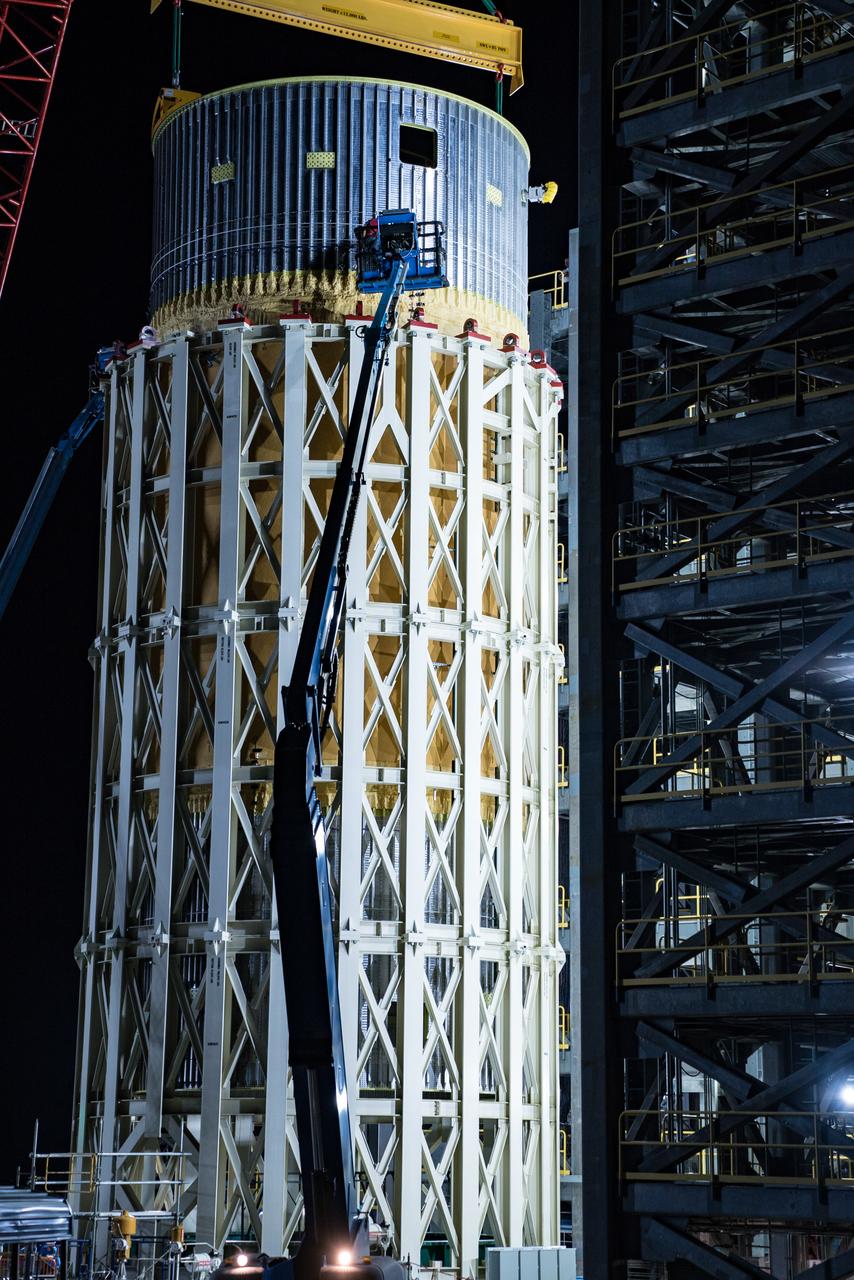

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
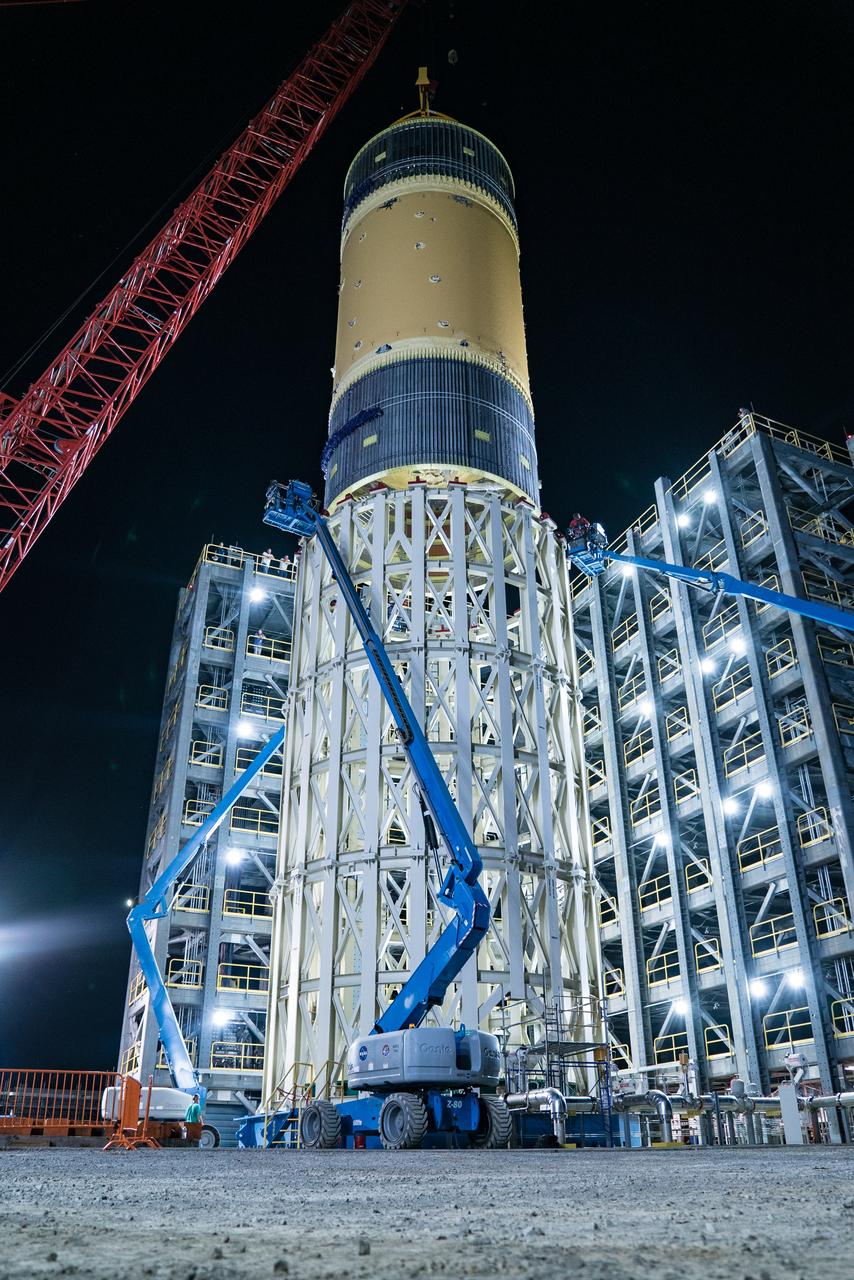

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
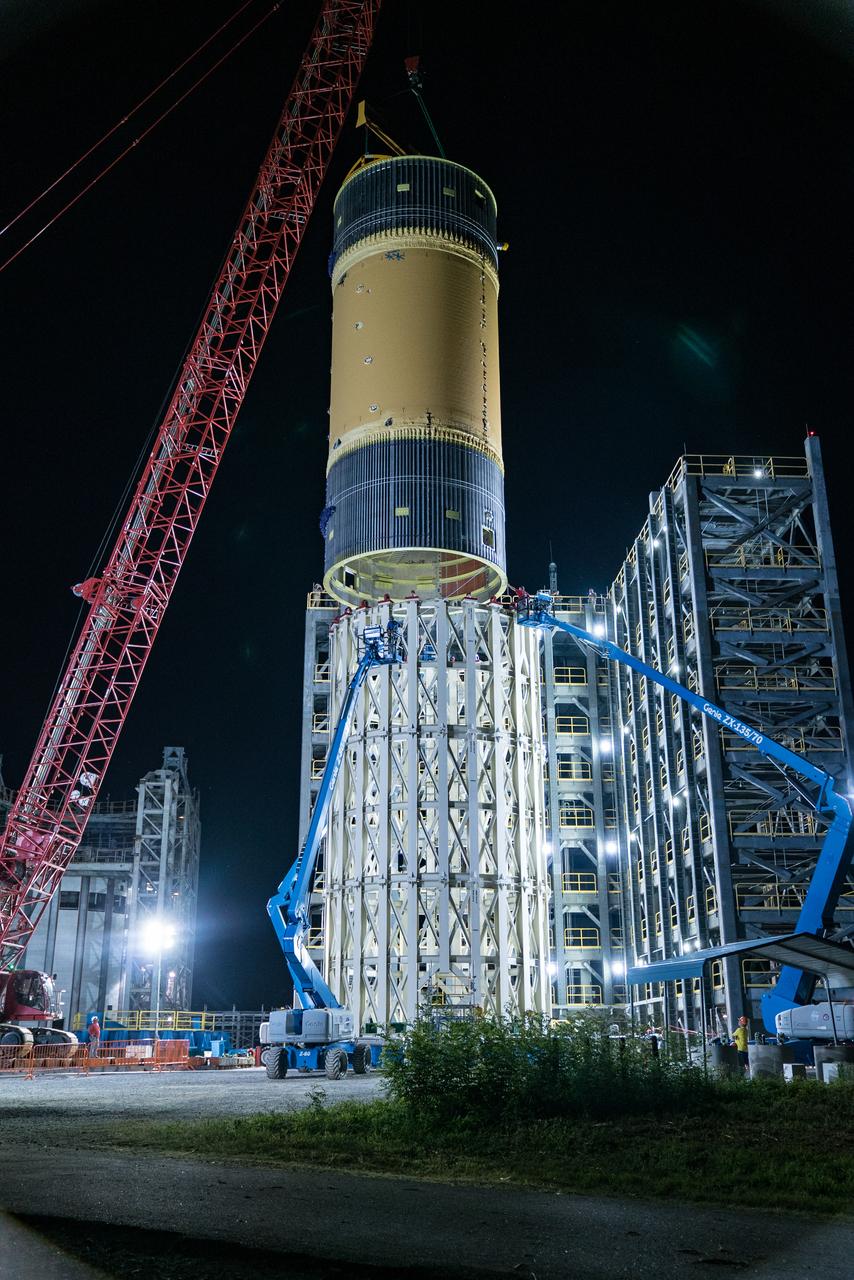

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
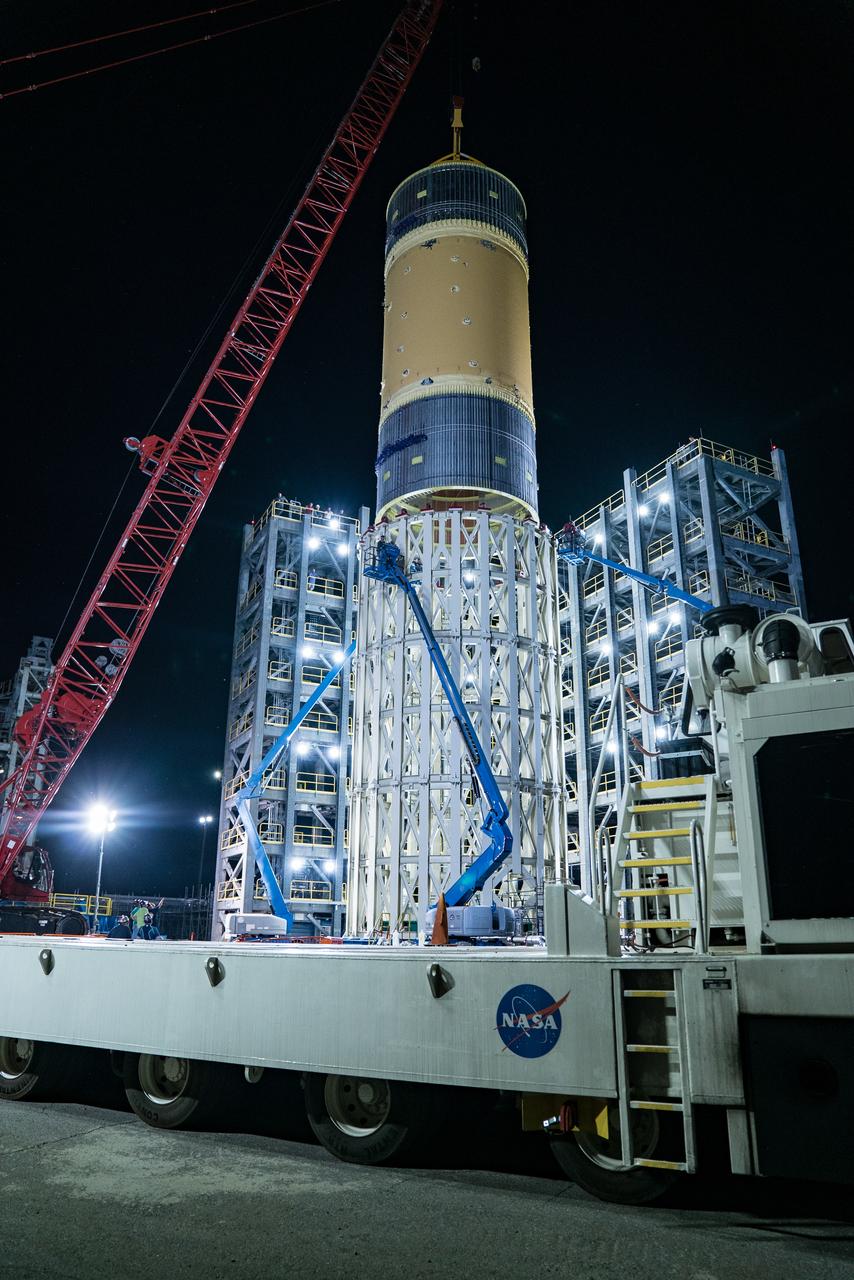

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
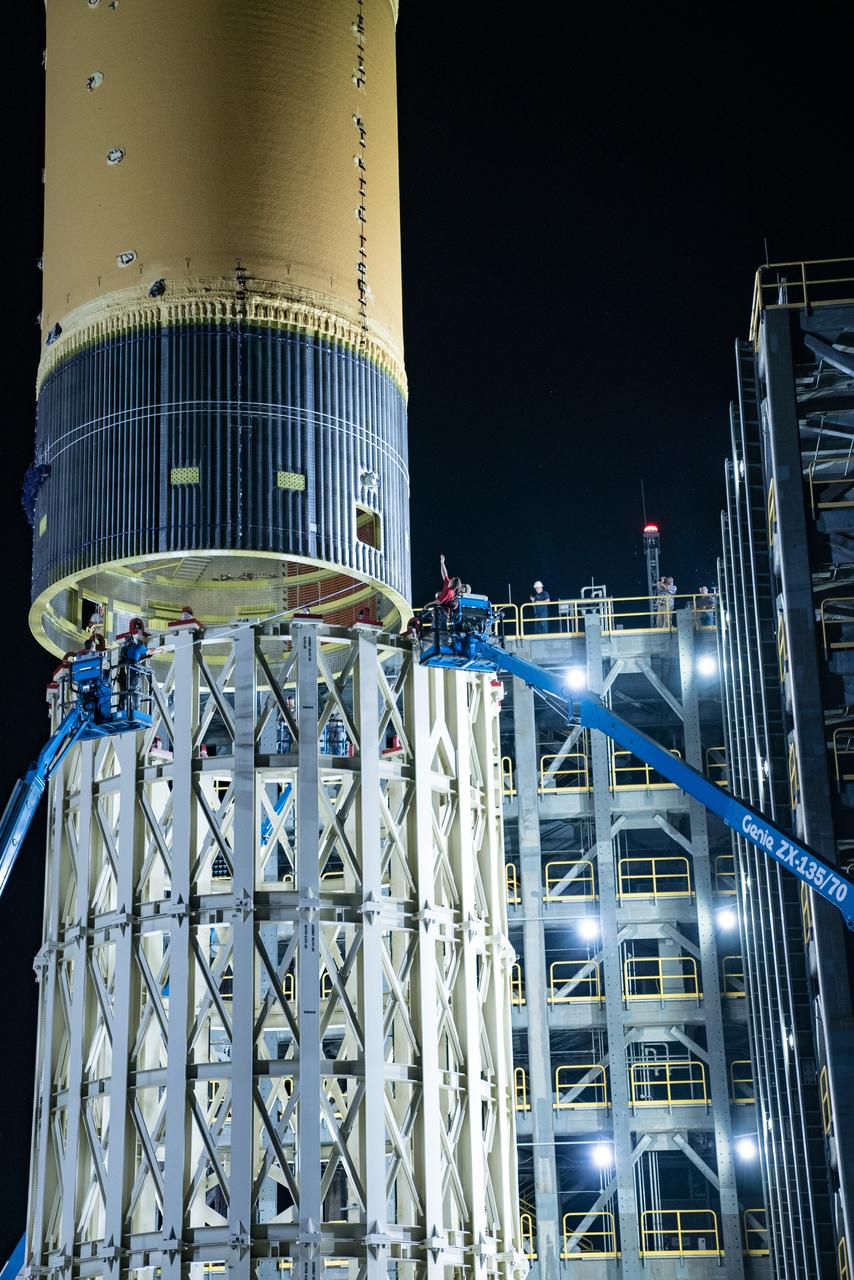

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
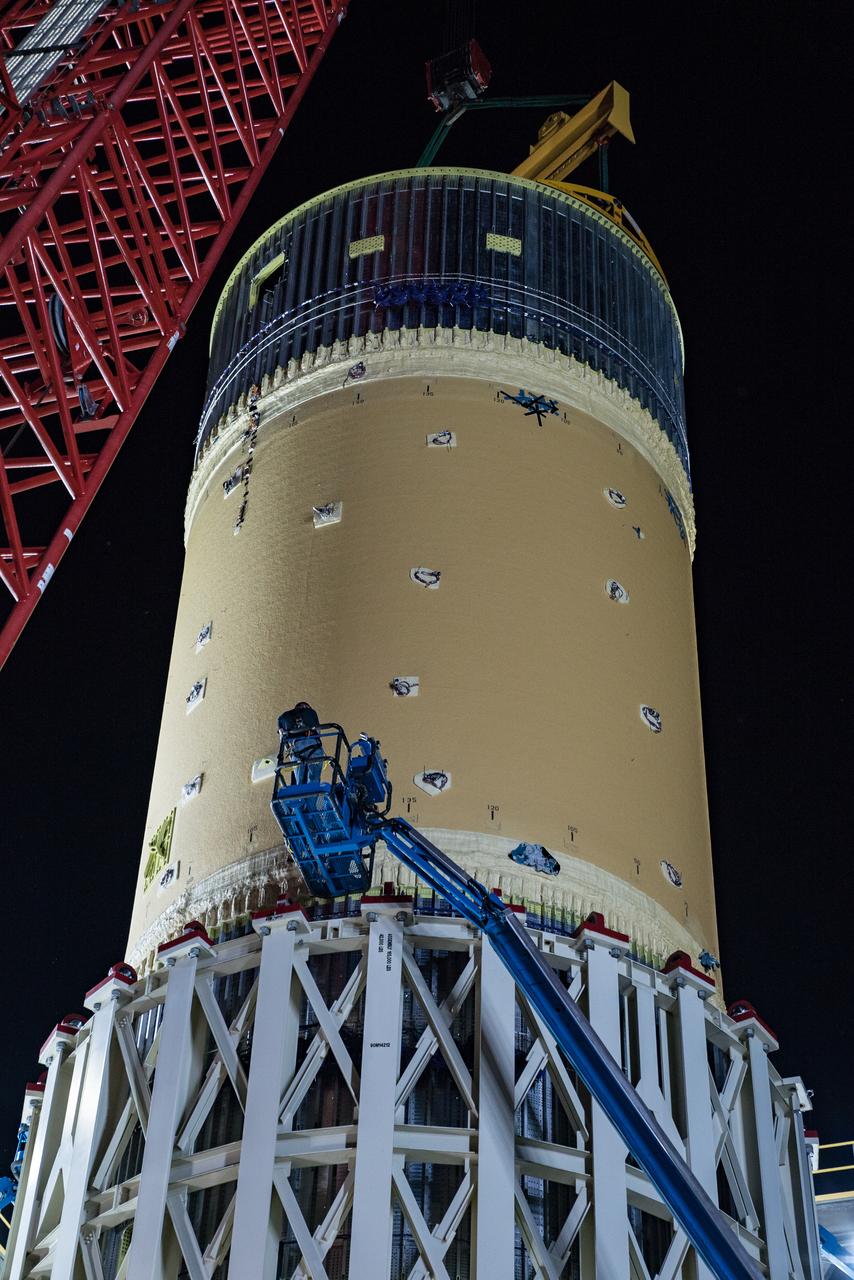

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
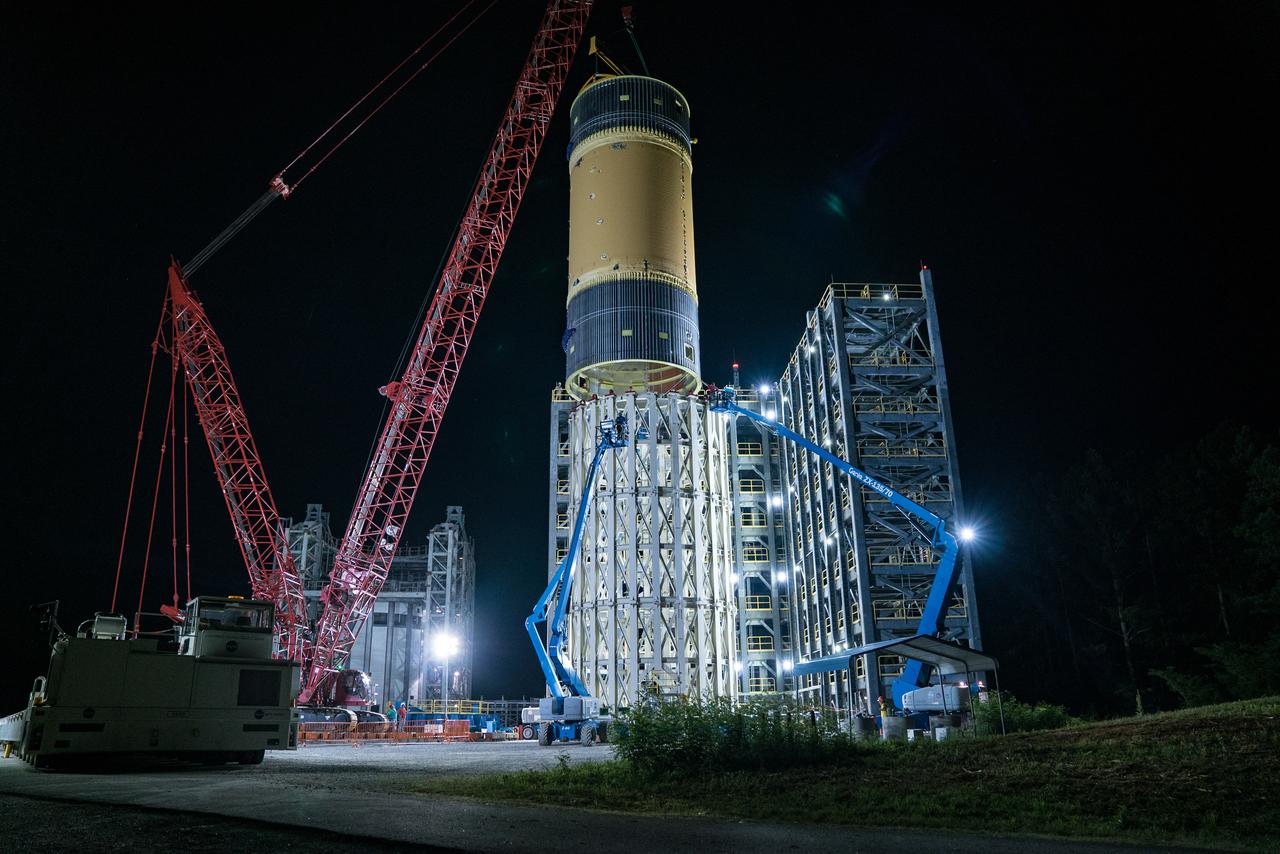

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

FROM RIGHT, KATHRYN GUELDE AND ASHLEY HOLLADAY OF AERIE AEROSPACE LLC IN HUNTSVILLE, INSTALL THE STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE FOR THE FIRST SERIES OF COMPOSITE TESTS FOR THE SHELL BUCKLING KNOCKDOWN FACTOR PROJECT.
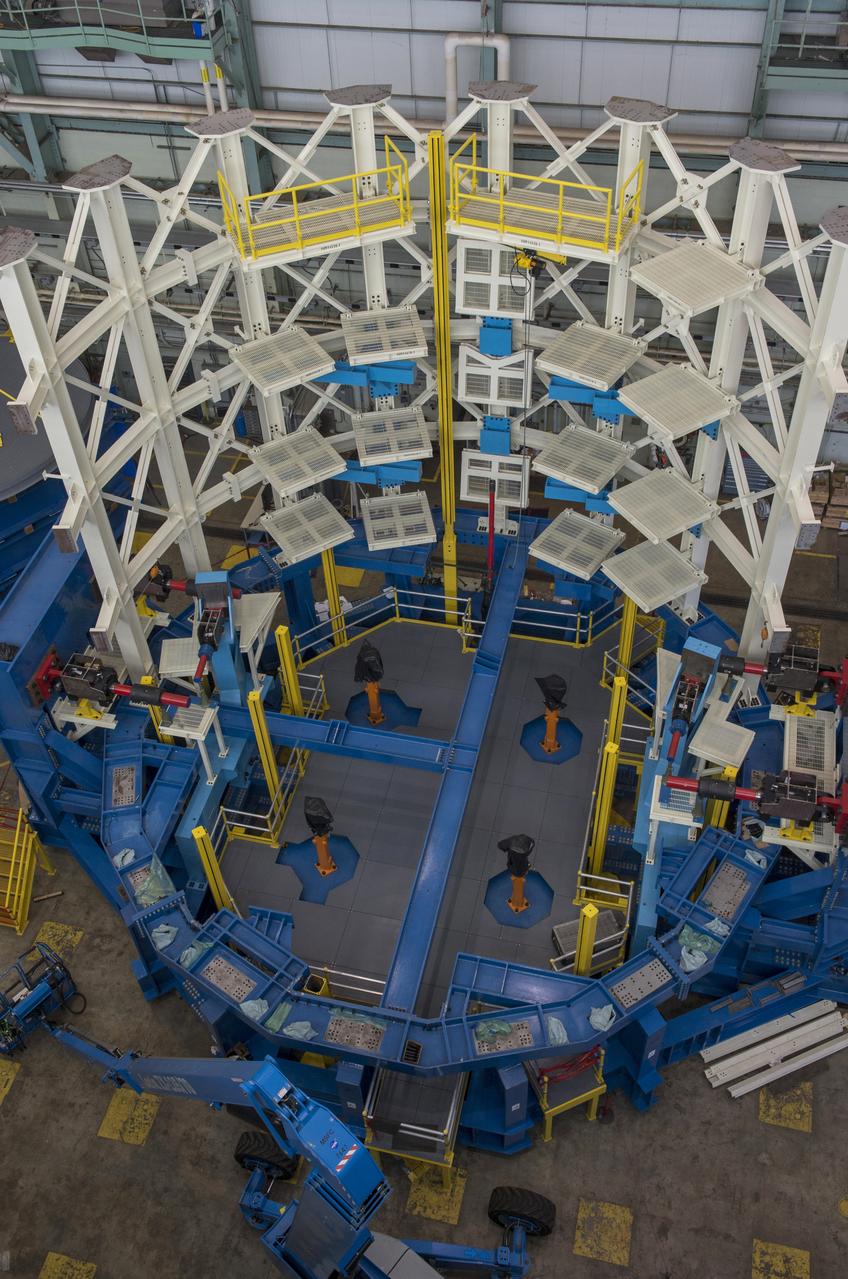

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
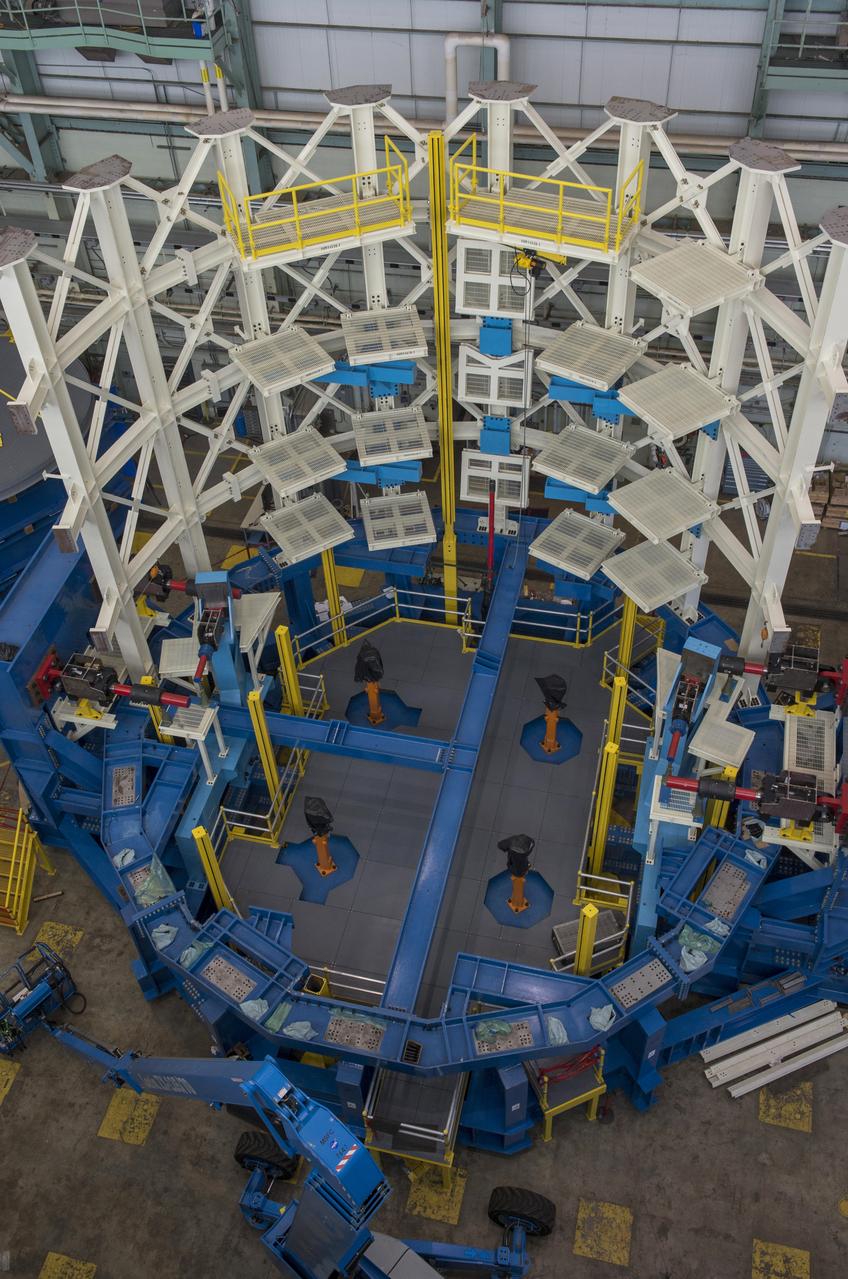

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
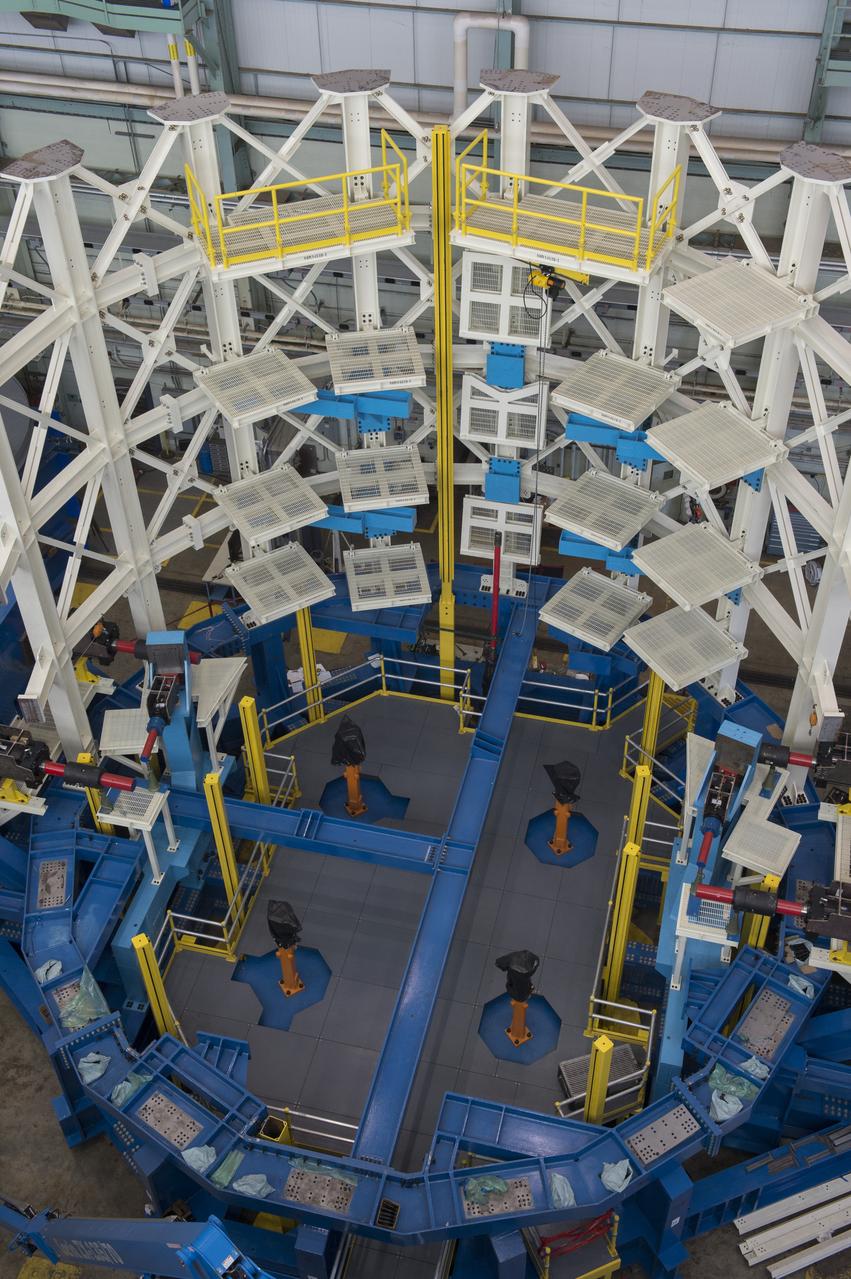

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
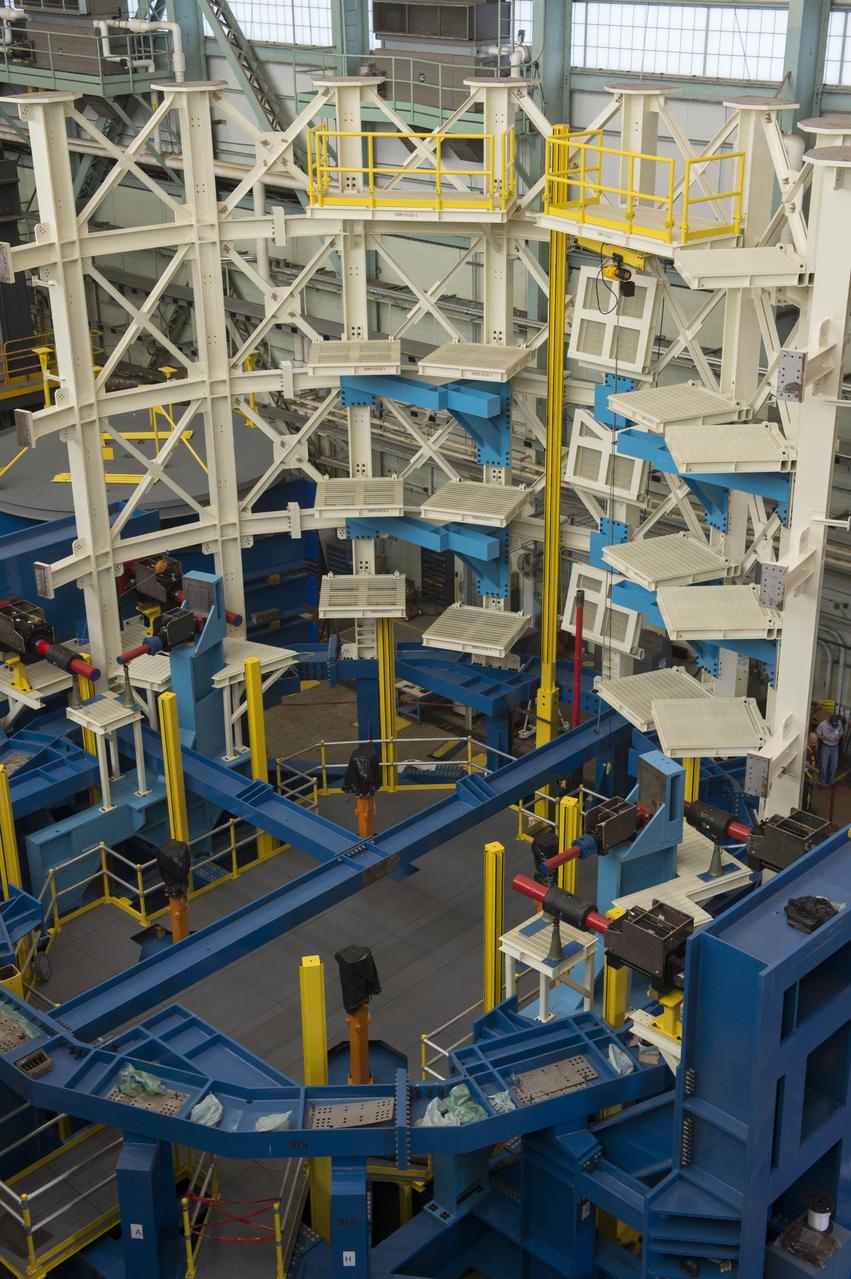

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane is used to lower the container for placement on a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane was used to lower the container onto a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
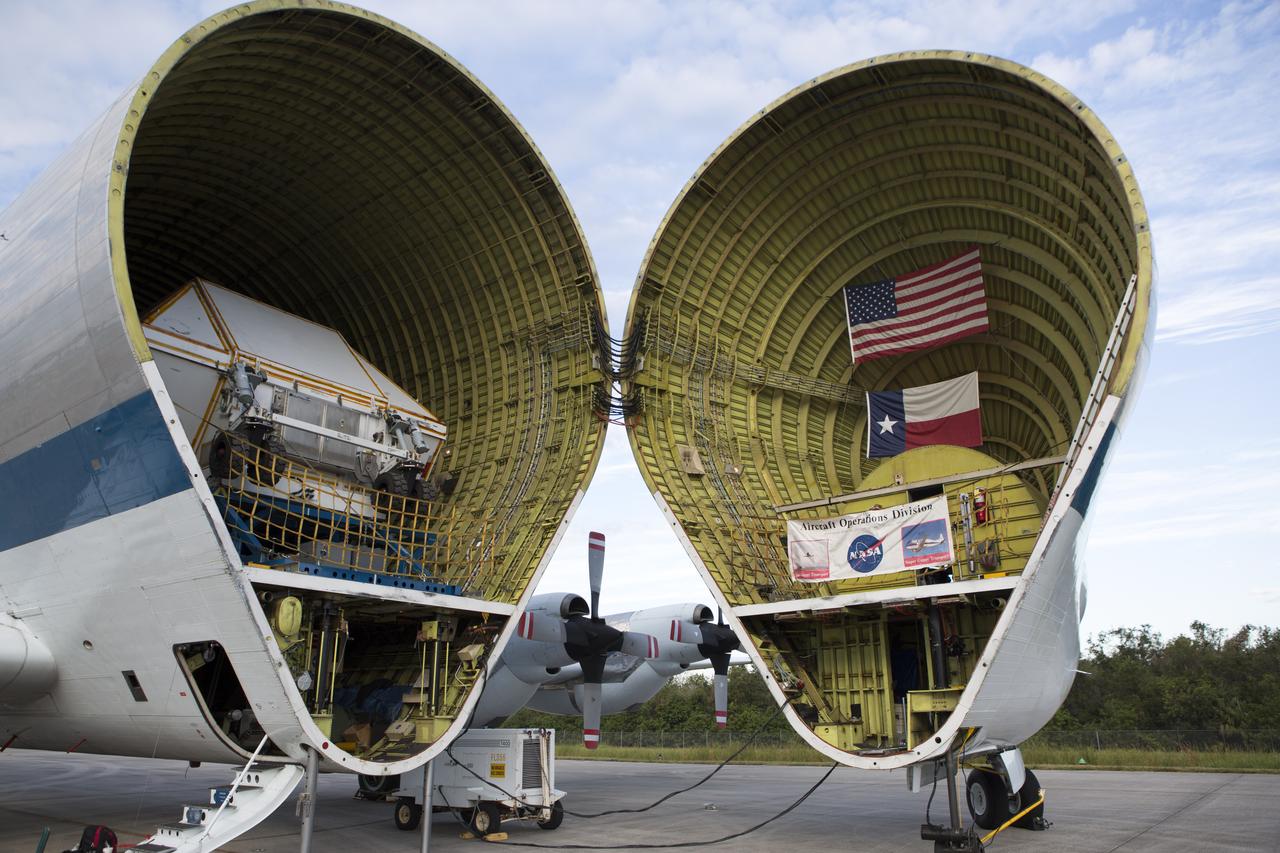

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article, arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft has been opened to reveal the container holding the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
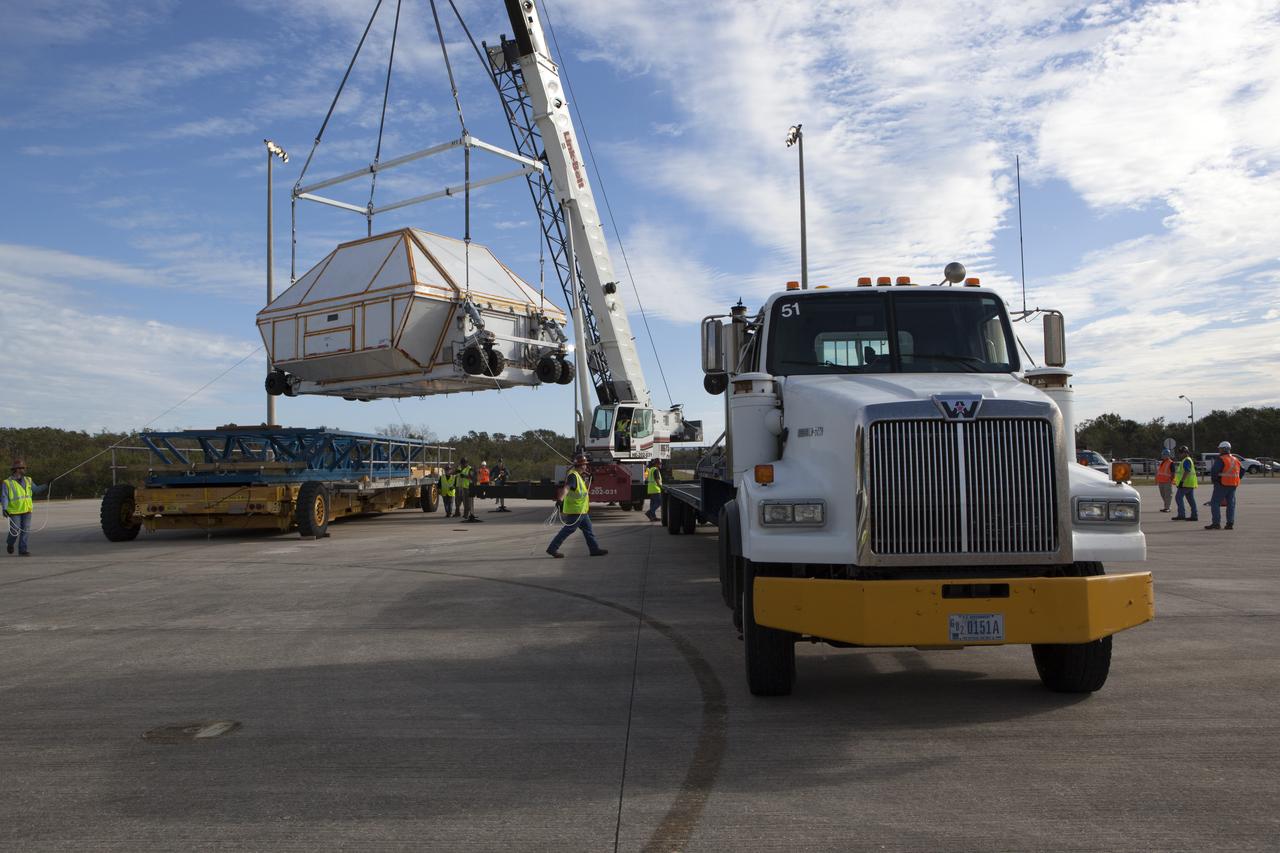

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane has lifted the container for placement on a transporter. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft is being opened to offload the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article, arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The unique aircraft has been opened to reveal the container holding the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrived at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The front of the unique aircraft is being opened to offload the STA. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
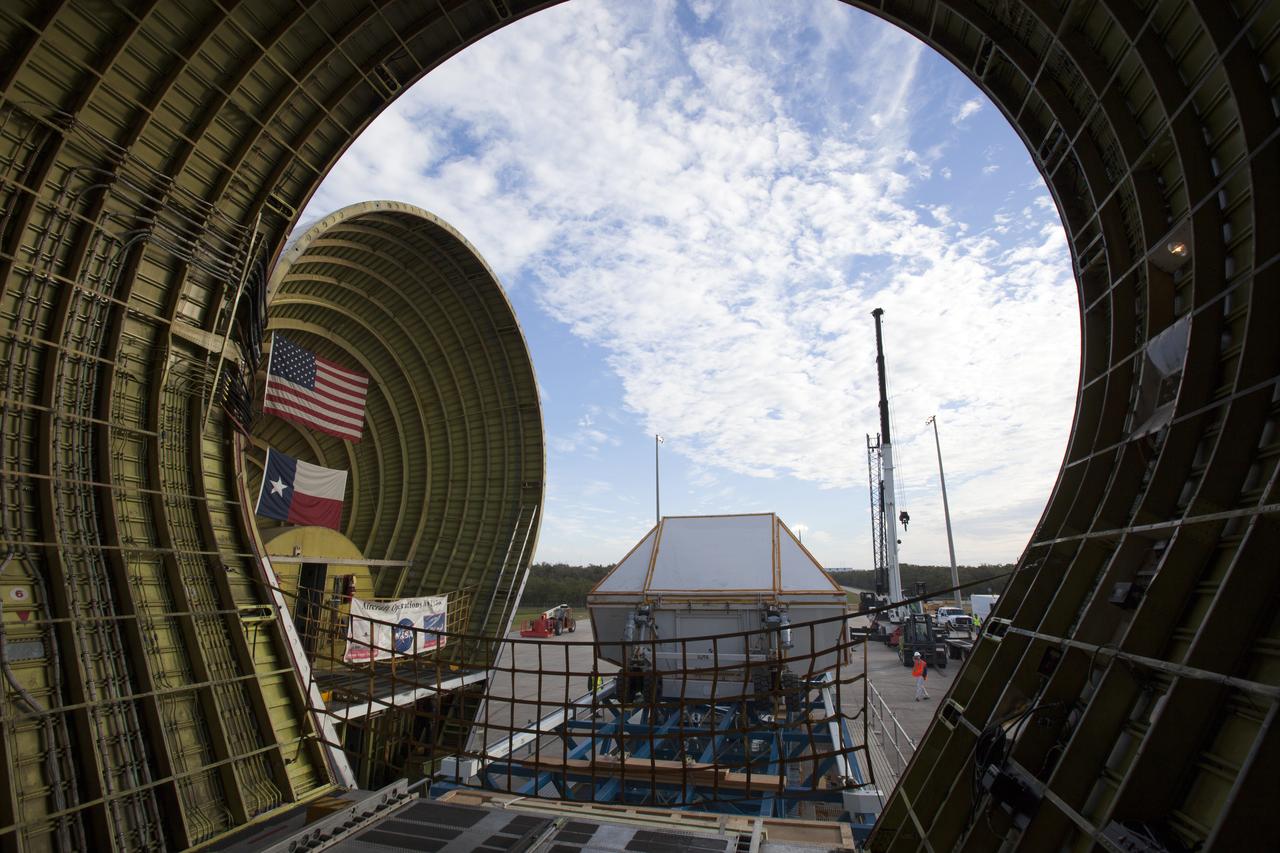

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft has been opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) is being offloaded. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
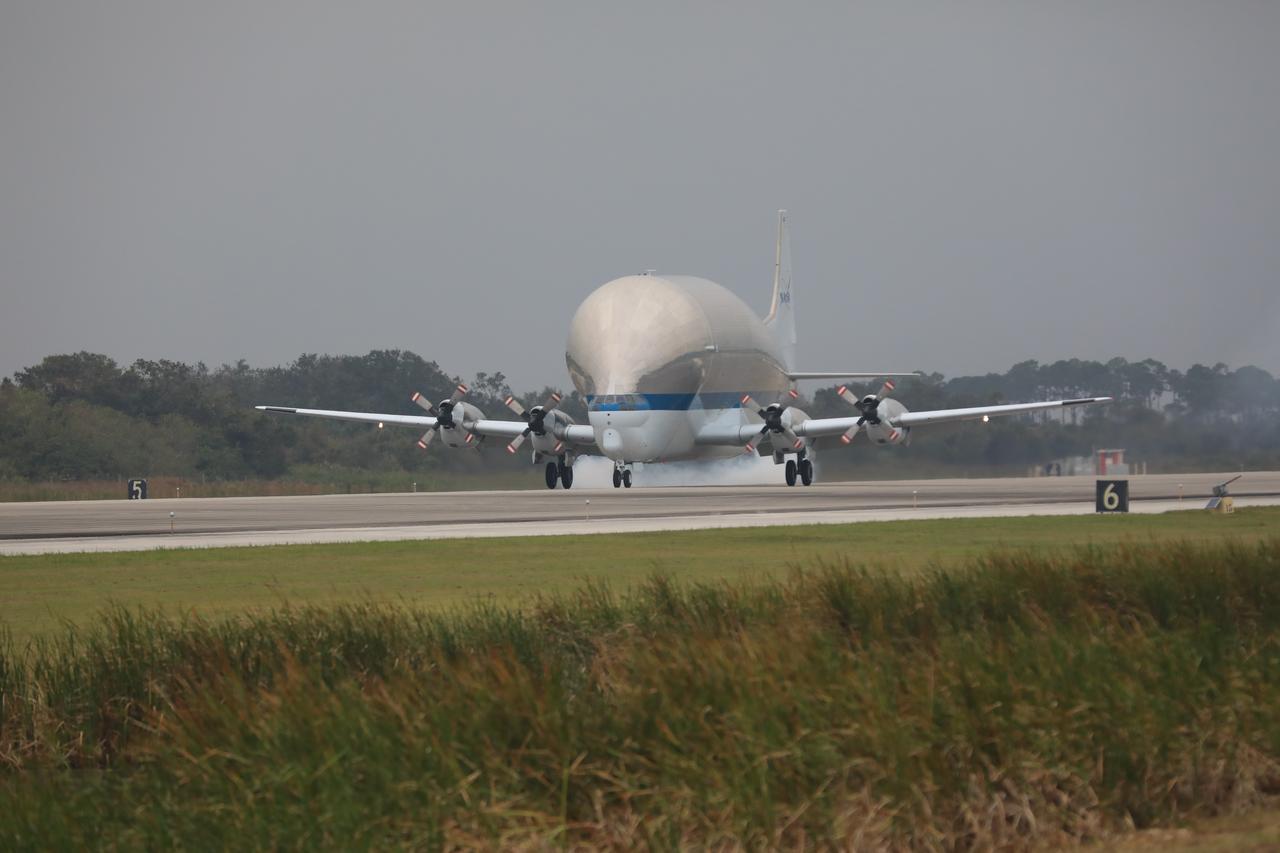

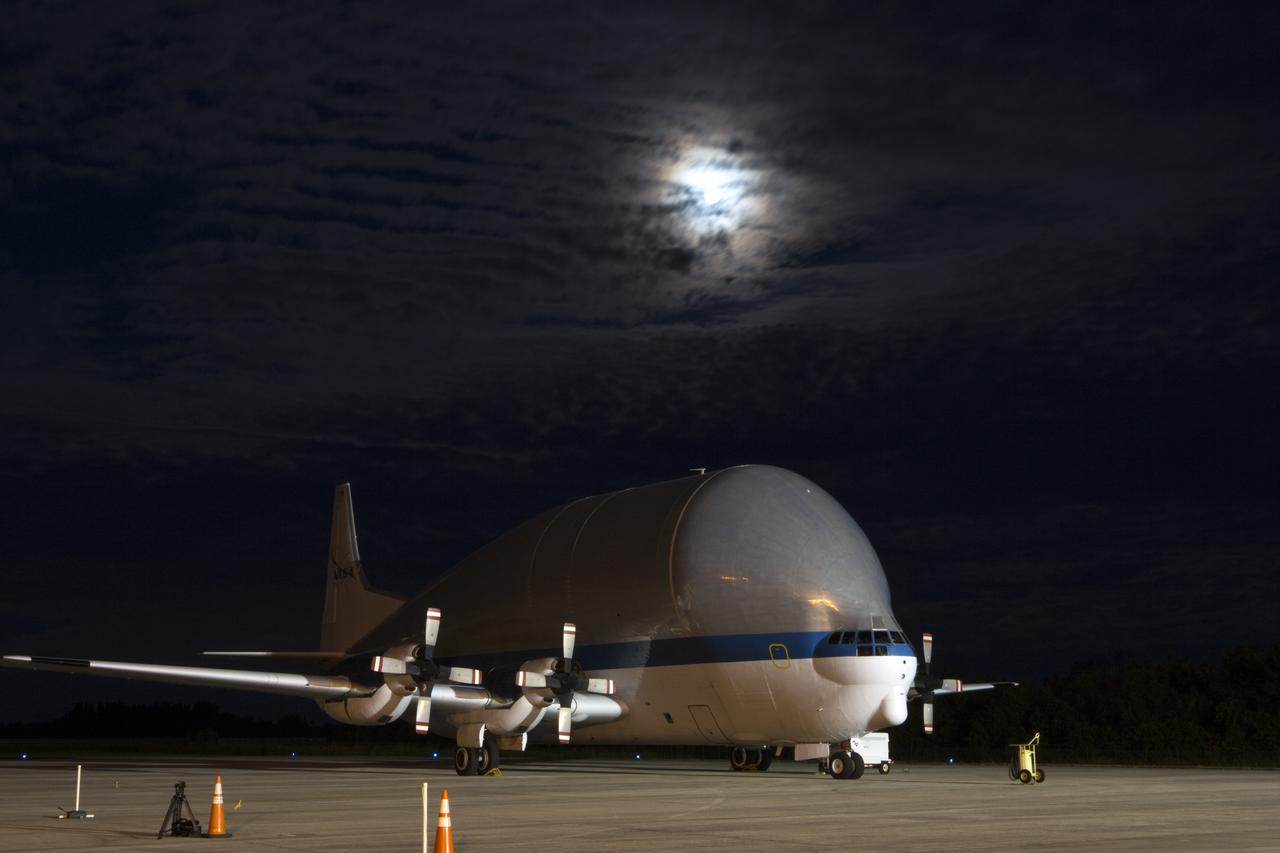
NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
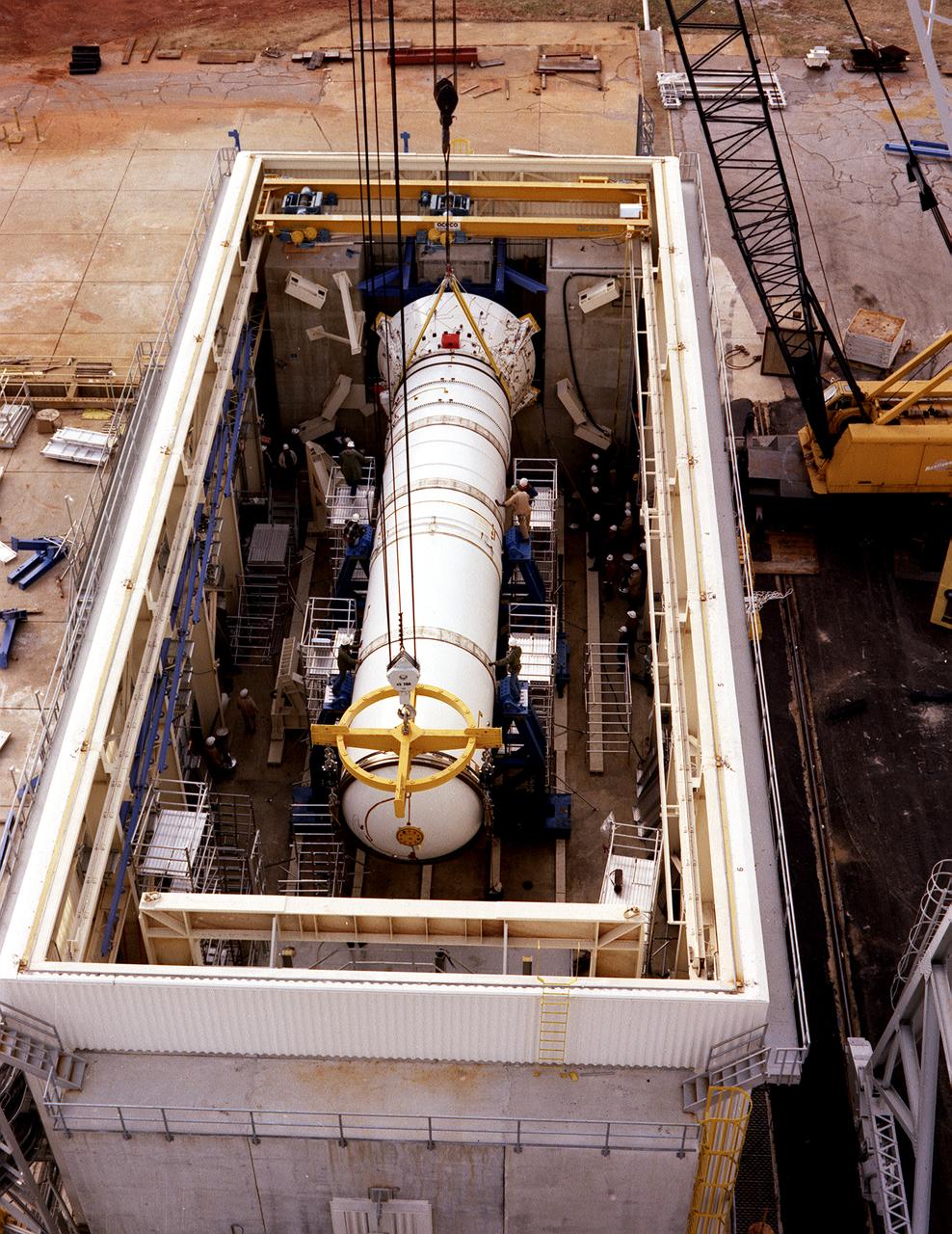
The solid rocket booster (SRB) structural test article is being installed in the Solid Rocket Booster Test Facility for the structural and load verification test at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment.
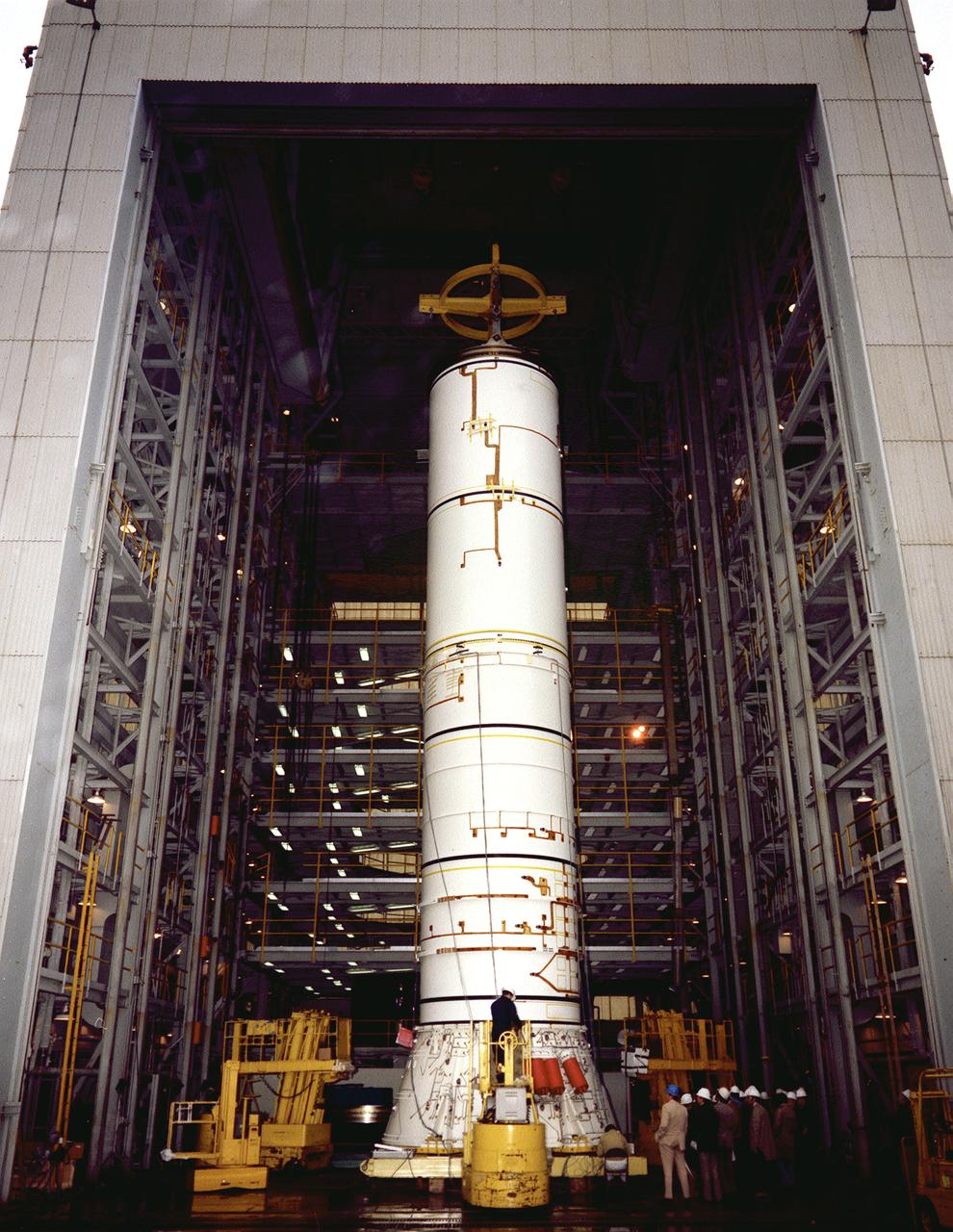

The structural test article to be used in the solid rocket booster (SRB) structural and load verification tests is being assembled in a high bay building of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Shuttle's two SRB's are the largest solids ever built and the first designed for refurbishment and reuse. Standing nearly 150-feet high, the twin boosters provide the majority of thrust for the first two minutes of flight, about 5.8 million pounds, augmenting the Shuttle's main propulsion system during liftoff. The major design drivers for the solid rocket motors (SRM's) were high thrust and reuse. The desired thrust was achieved by using state-of-the-art solid propellant and by using a long cylindrical motor with a specific core design that allows the propellant to burn in a carefully controlled marner. At burnout, the boosters separate from the external tank and drop by parachute to the ocean for recovery and subsequent refurbishment.
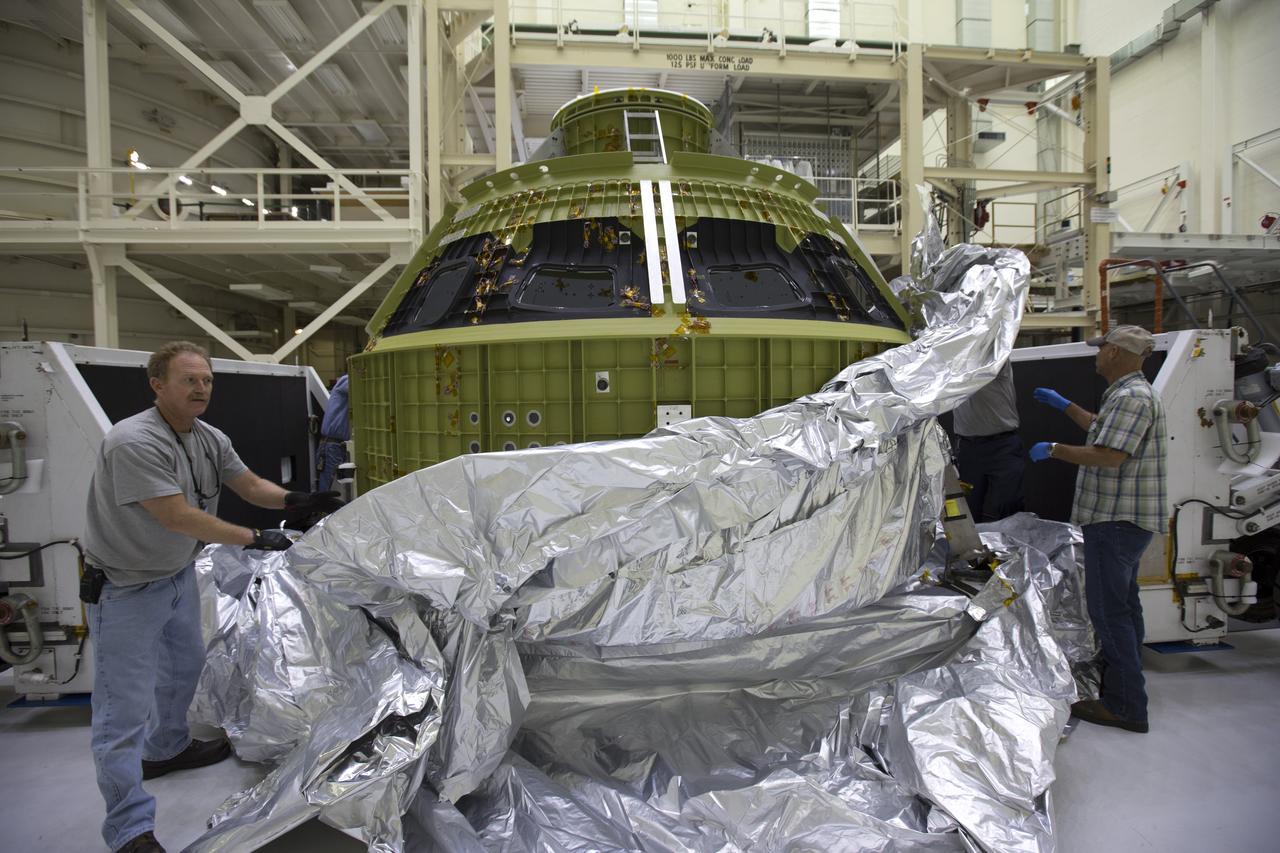

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians remove the protective covering from the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
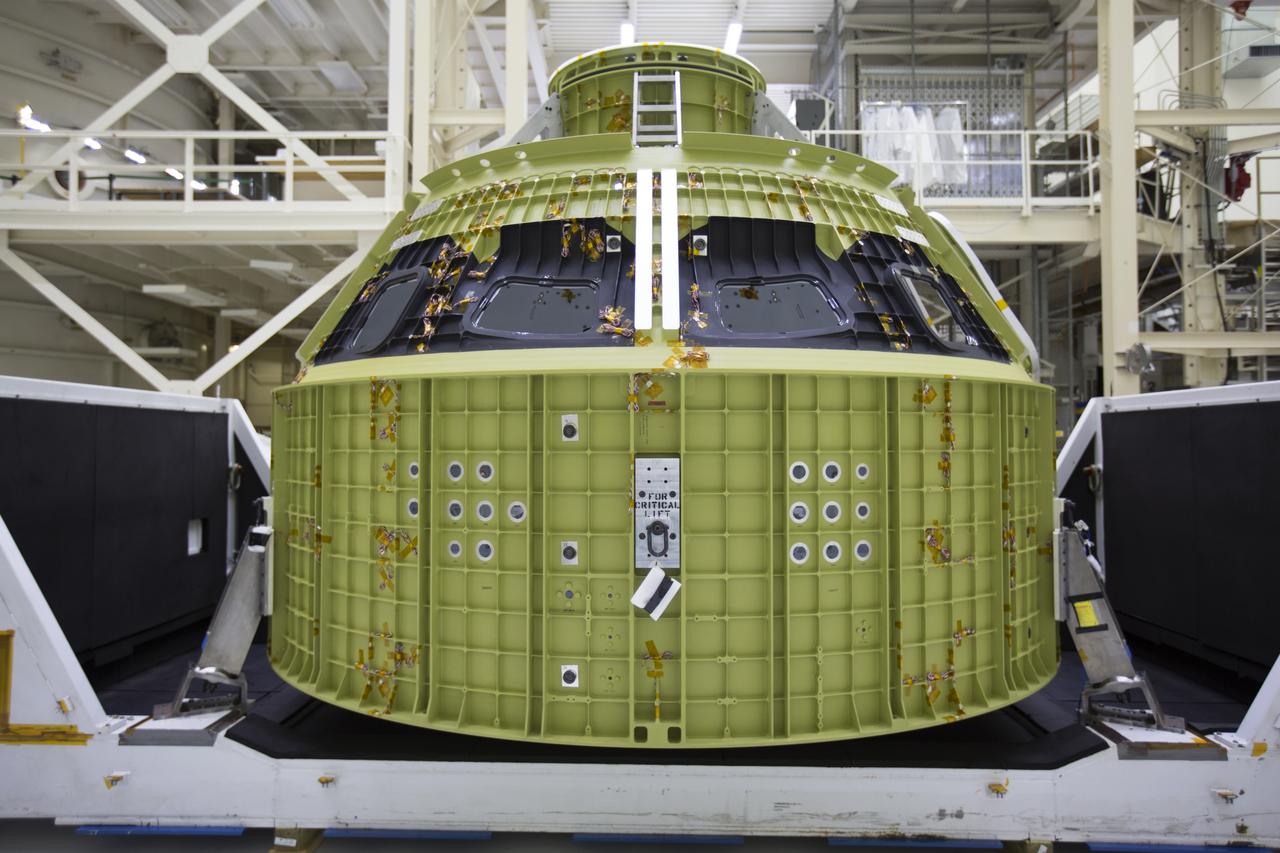

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective covering was removed from the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). It remains secured on the bottom of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
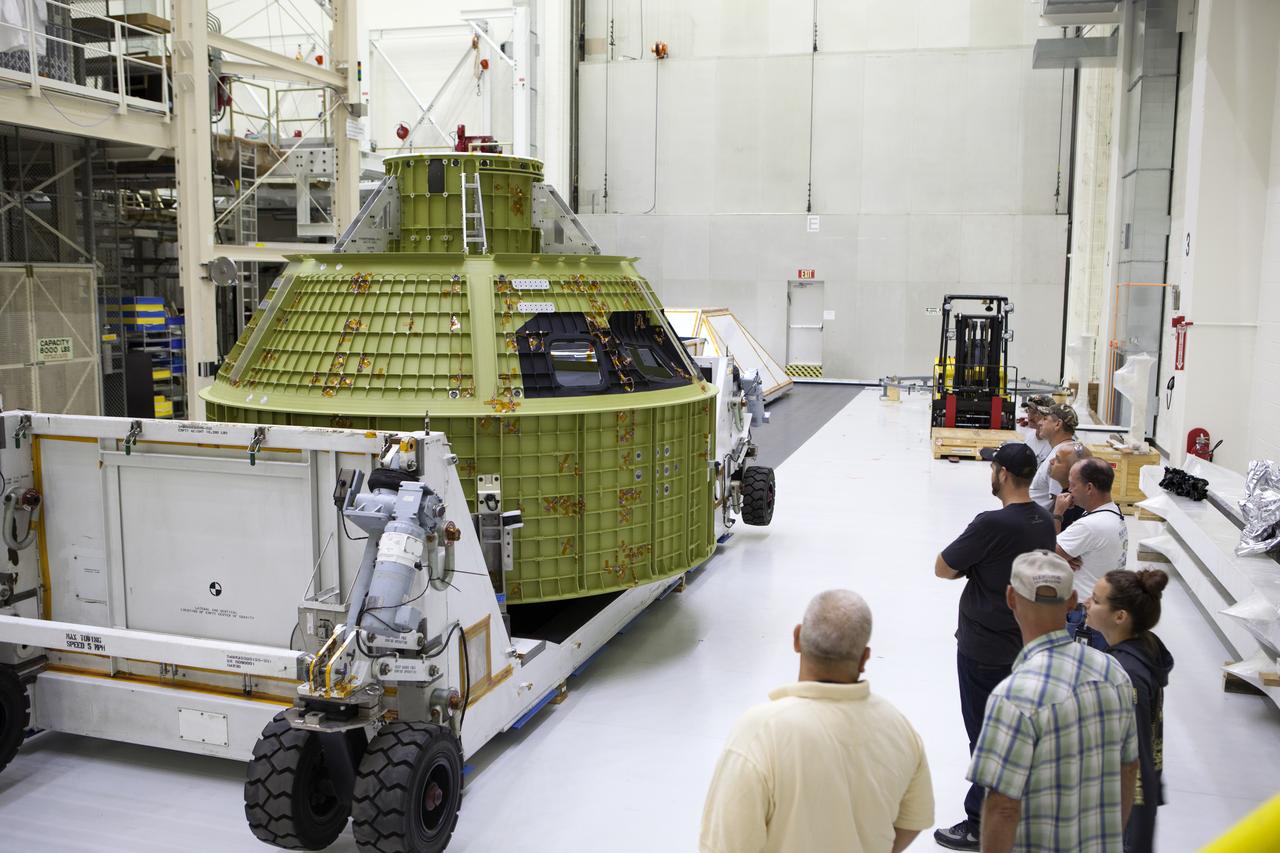

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians with Lockheed Martin look over the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) secured on the bottom of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
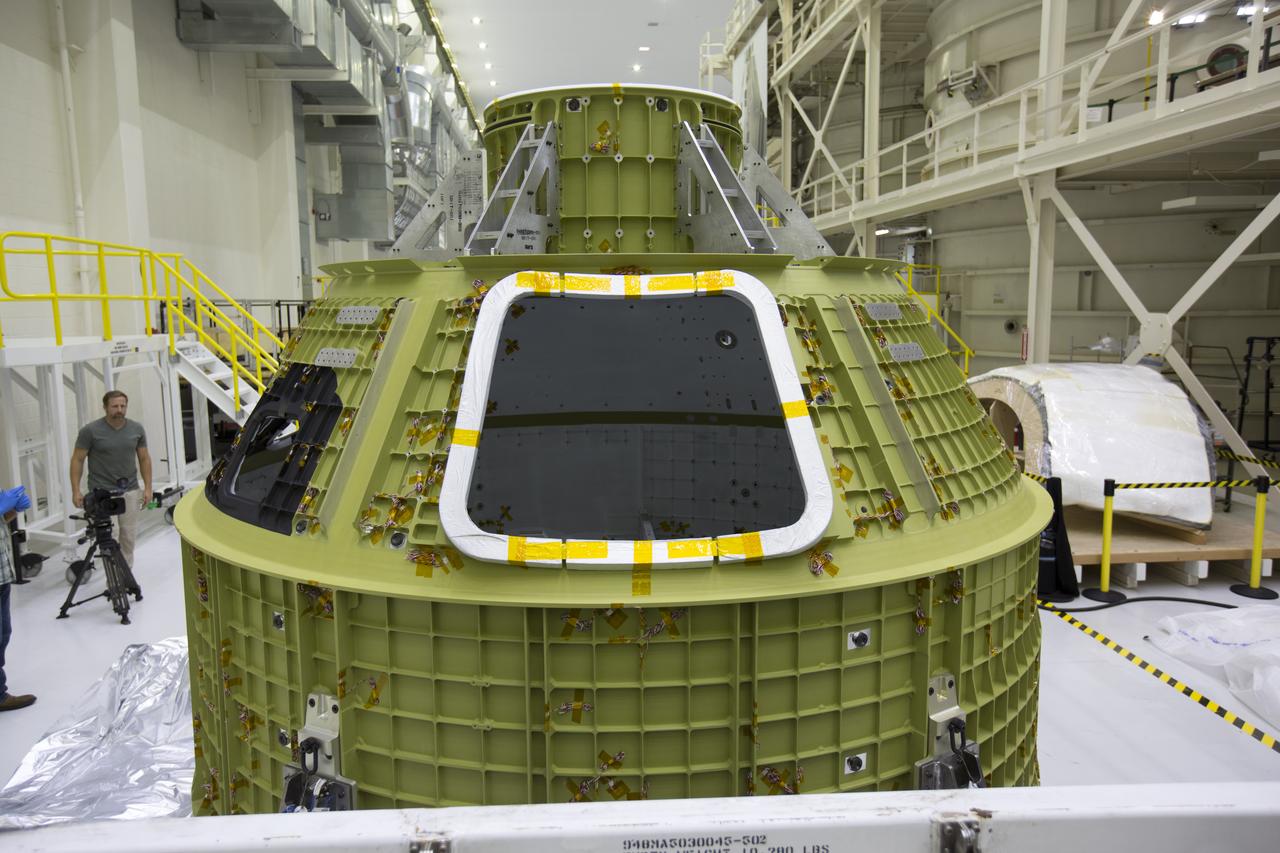

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective covering was removed from the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). It remains secured on the bottom of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
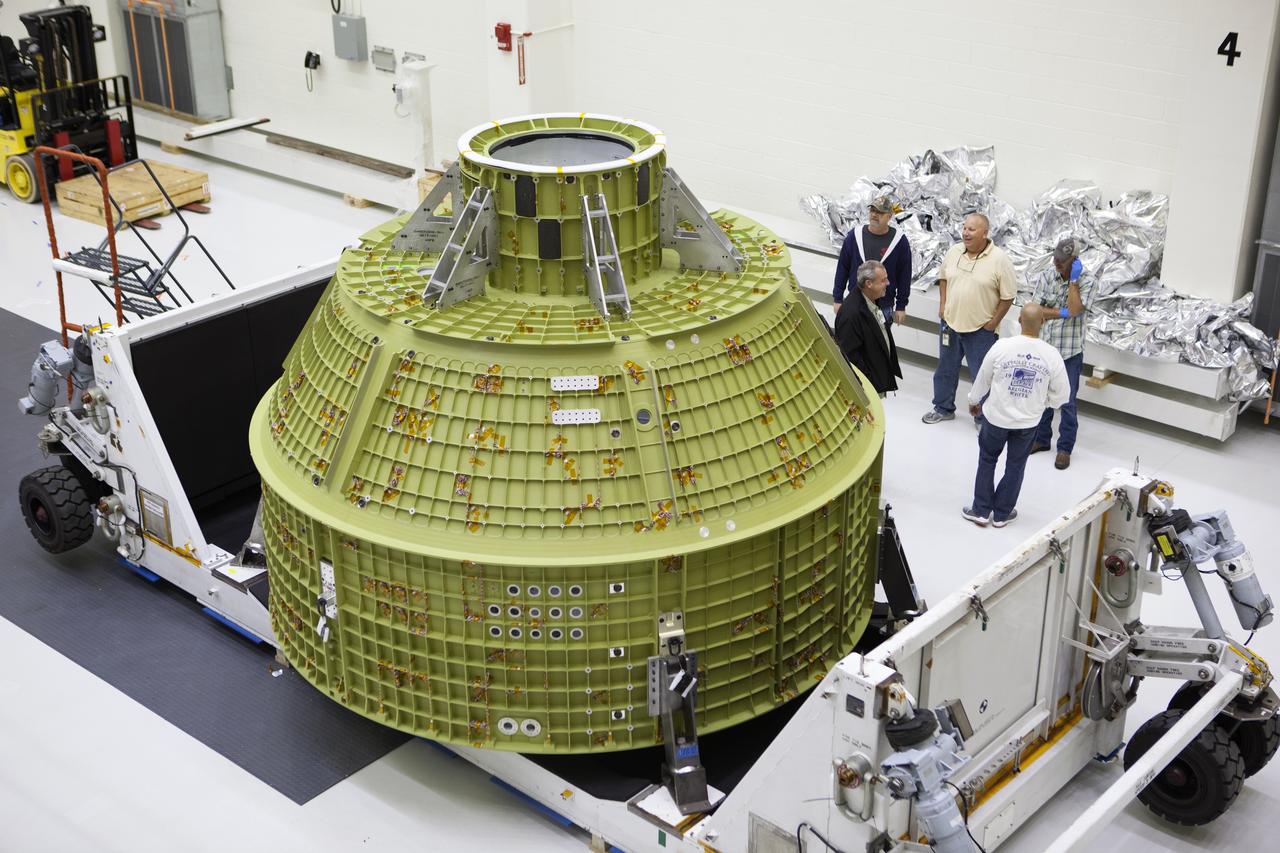

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective covering was removed from the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). It remains secured on the bottom of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
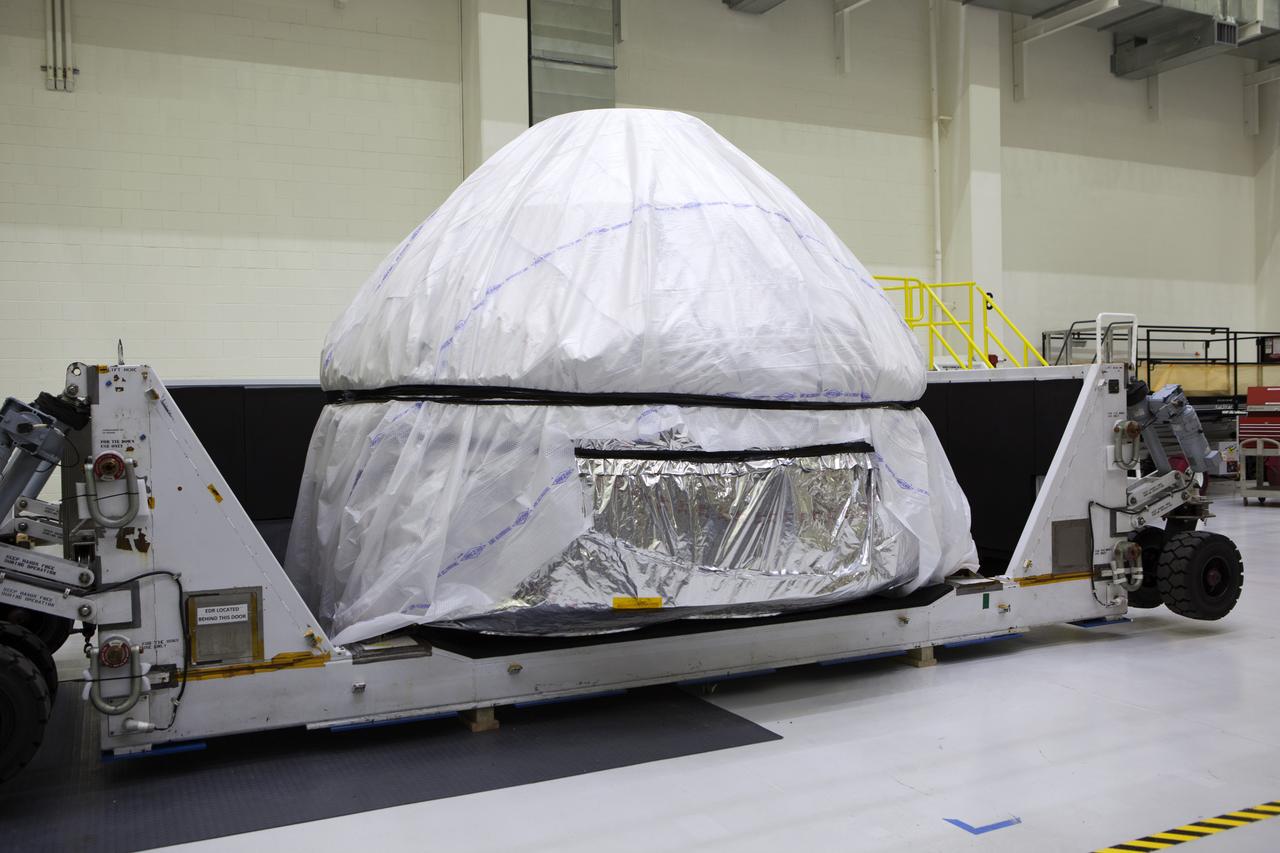

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the cover has been removed from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
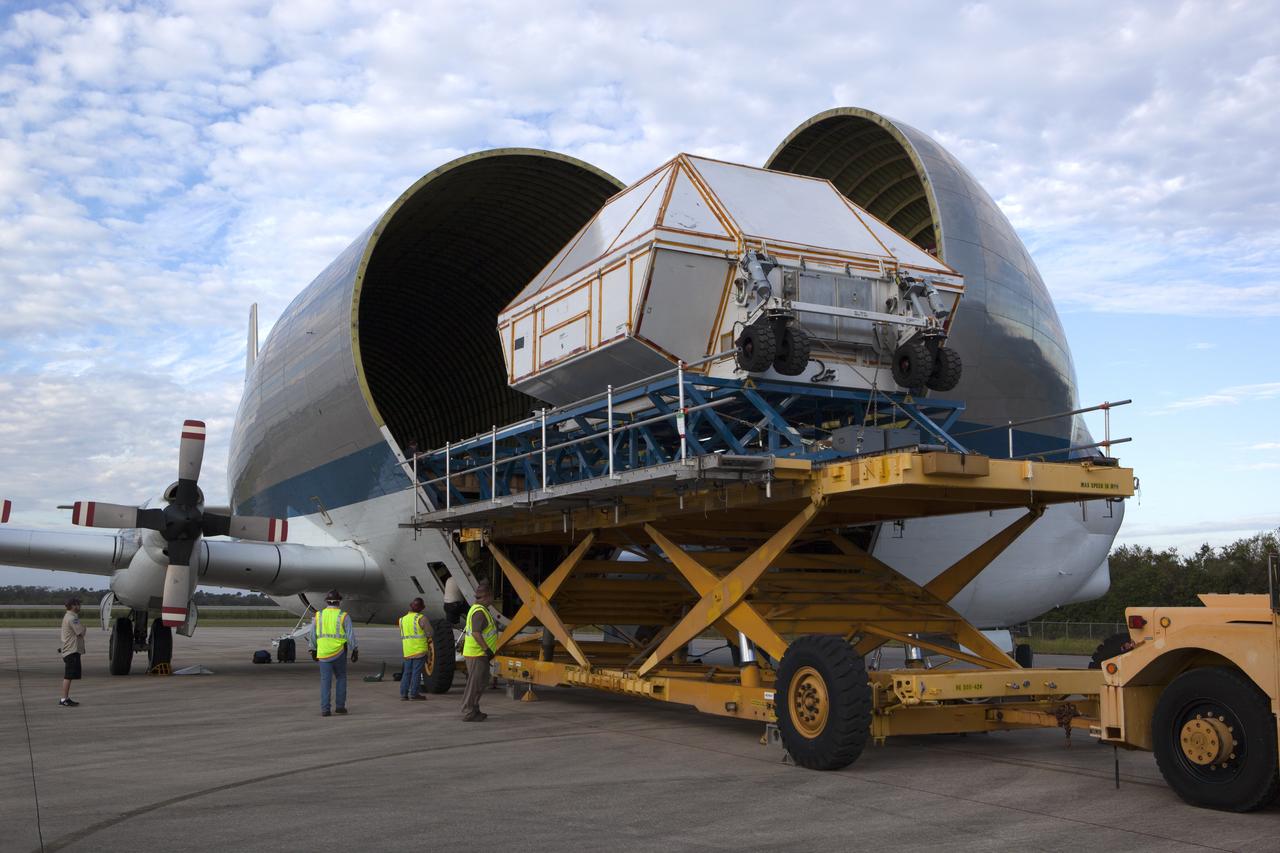

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft has been opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) is being offloaded. The test article will be transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
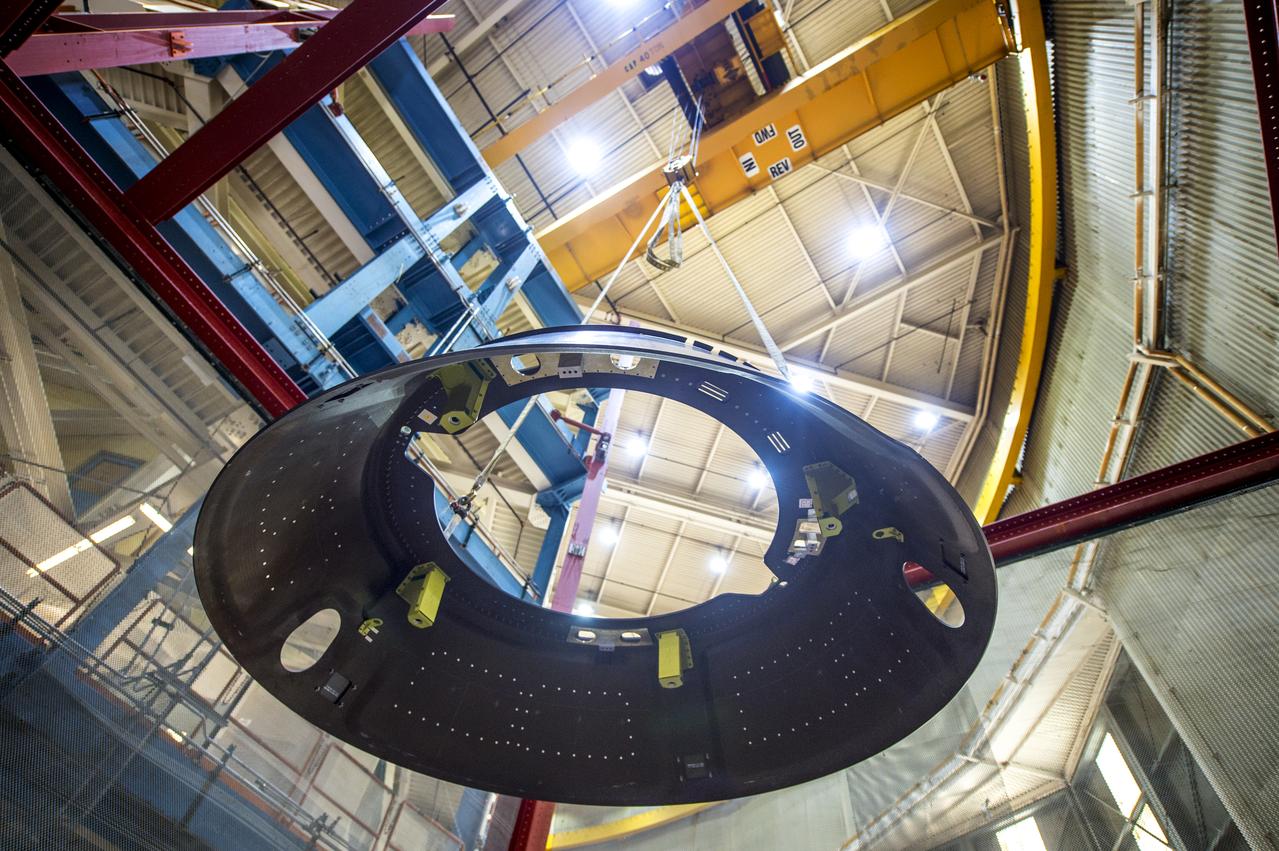

A heat shield is used during separation test activities with Boeing's Starliner structural test article. The test article is undergoing rigorous qualification testing at the company's Huntington Beach Facility in California. Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

Boeing’s Structural Test Article of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the company’s Huntington Beach, California, facilities for evaluations. Built to the specifications of an operational spacecraft, the STA is intended to be evaluated through a series of thorough testing conditions.

Boeing’s Structural Test Article of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the company’s Huntington Beach, California, facilities for evaluations. Built to the specifications of an operational spacecraft, the STA is intended to be evaluated through a series of thorough testing conditions.
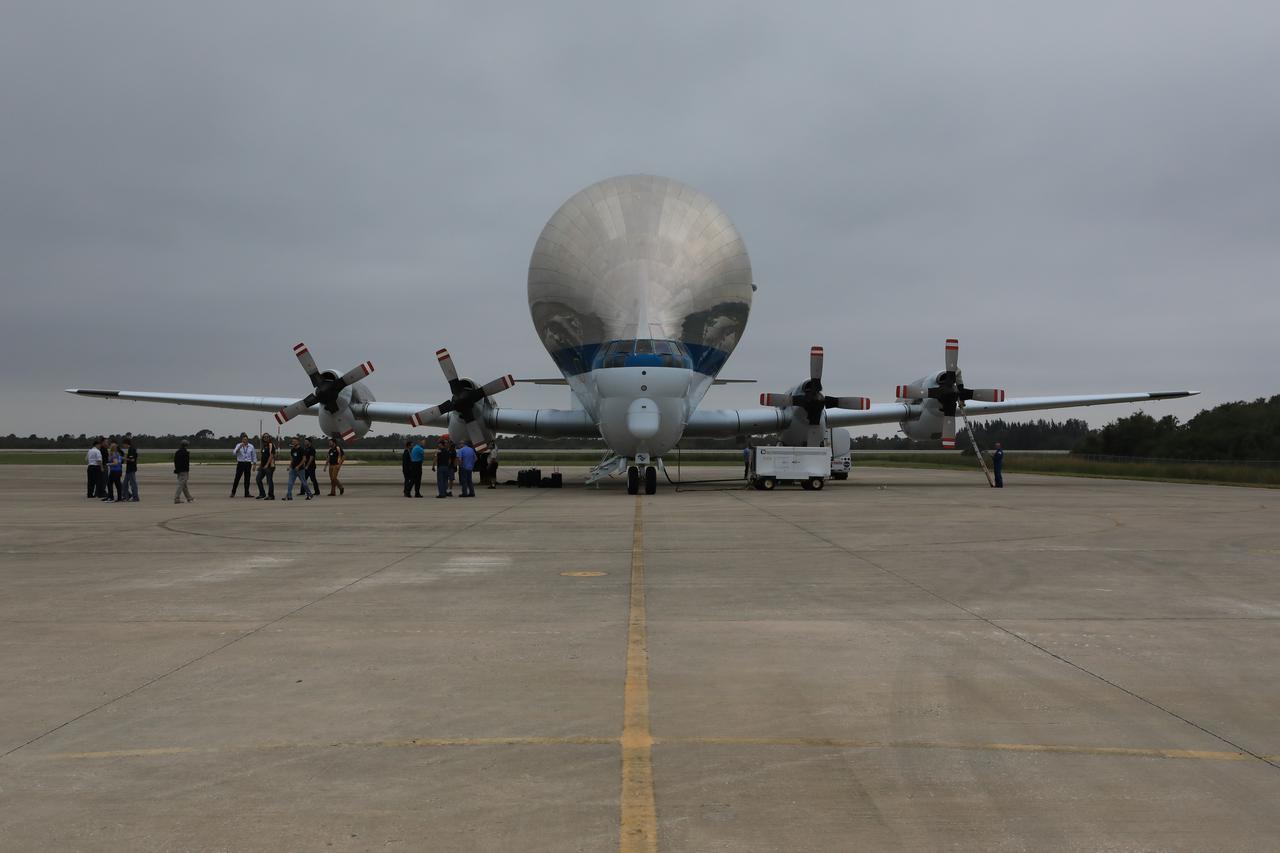

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft arrives on the tarmac after touching down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The guppy is carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
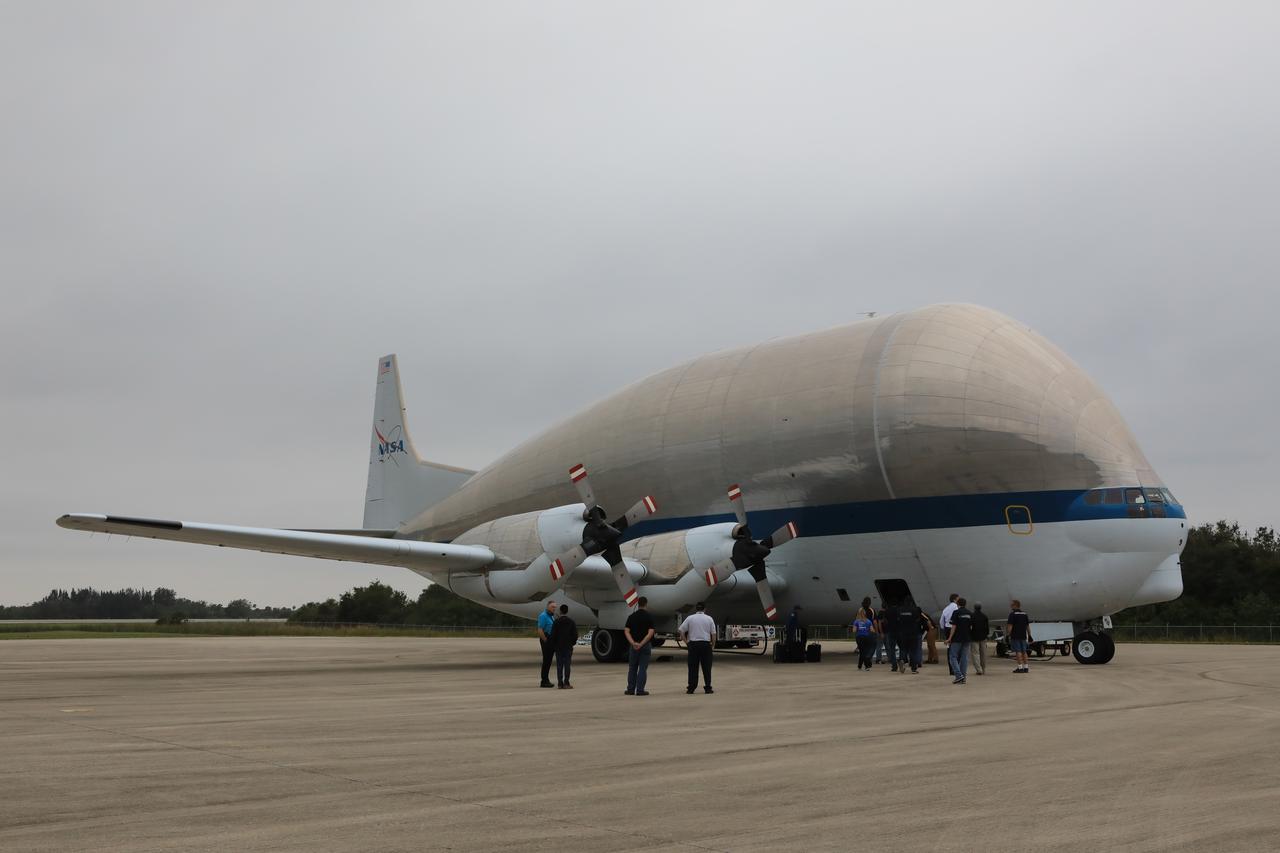

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft arrives on the tarmac after touching down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The guppy is carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
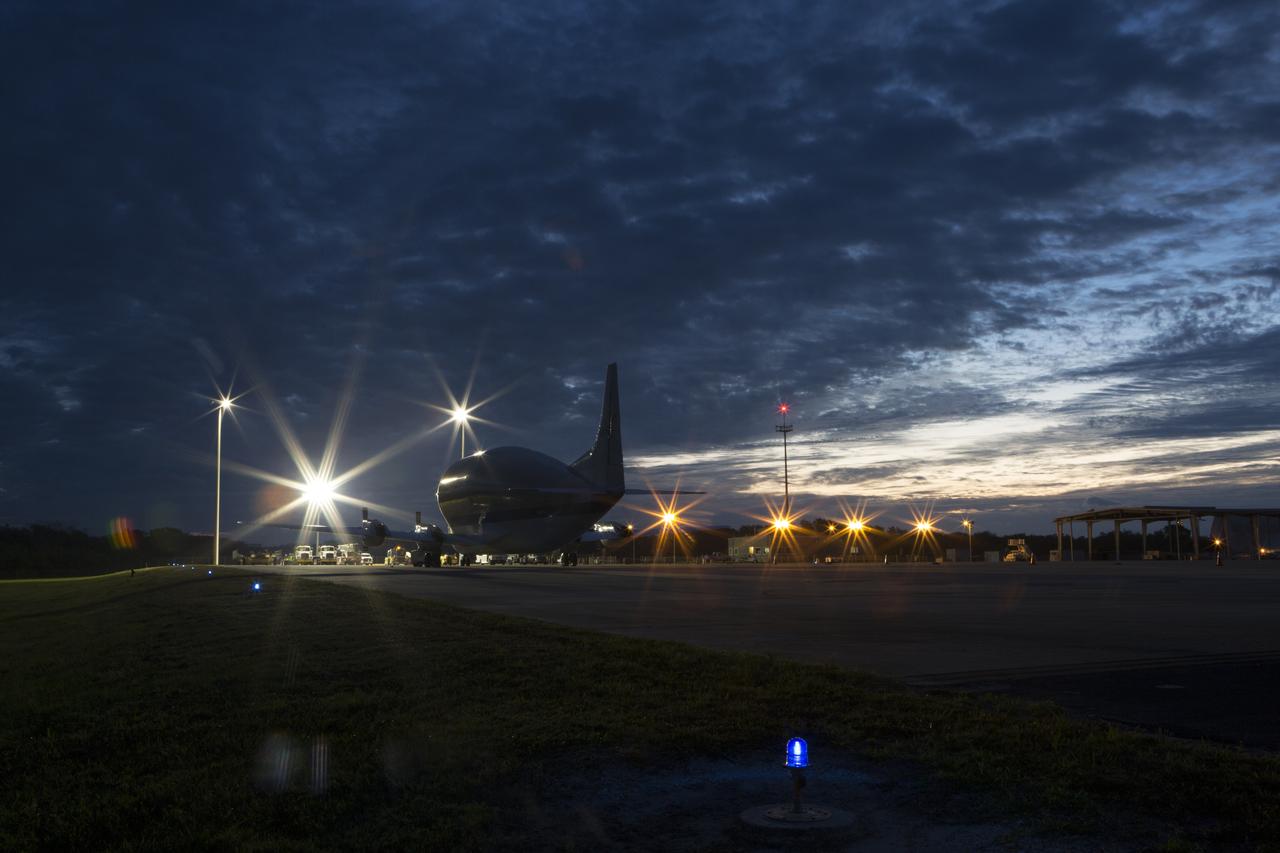

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA), arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The STA will be offloaded and transported to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

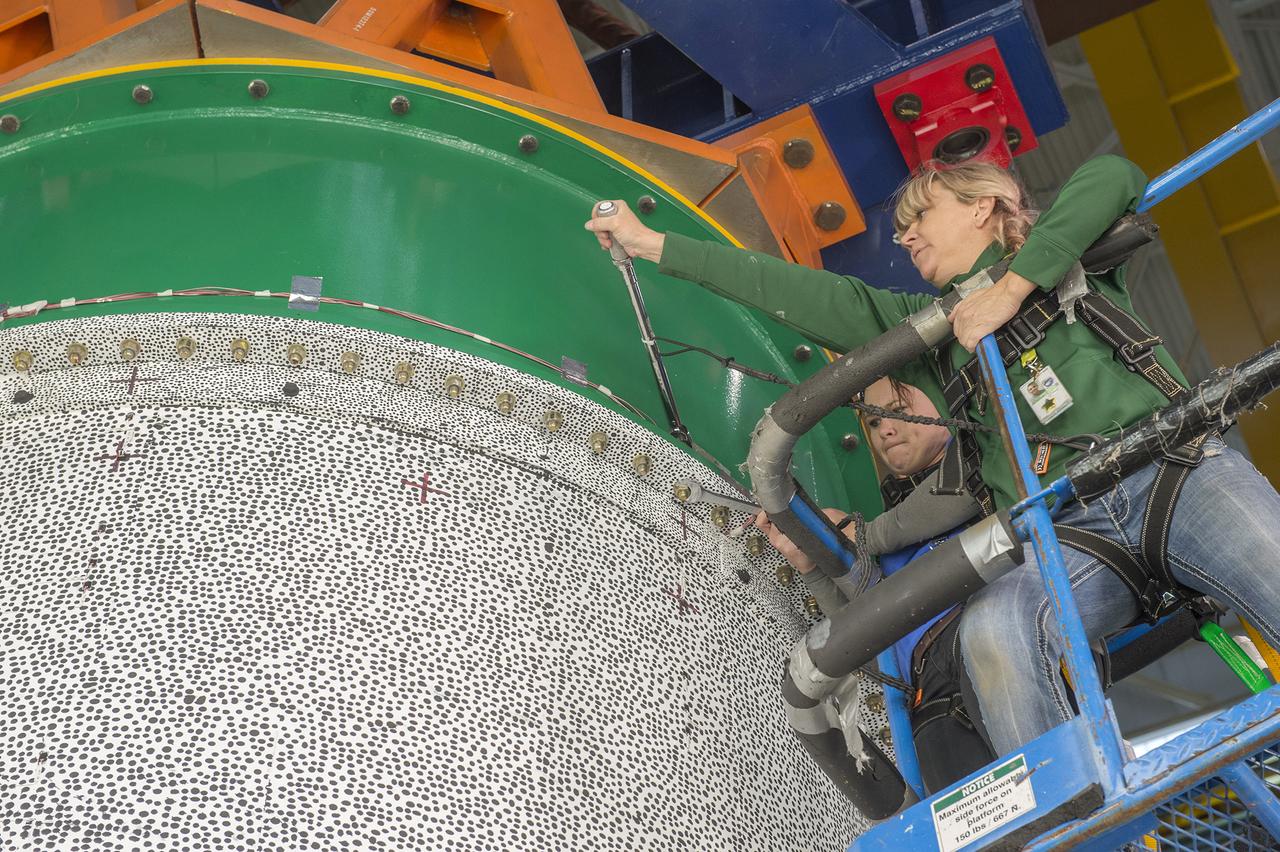
Photos of LaRC team weighting and performing Center of Gravity (CG) measurements of the Structural Test Article (STA) at NASA Langley Research Center.

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) is secured on a test tool called the birdcage. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will undergo further testing in the high bay. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
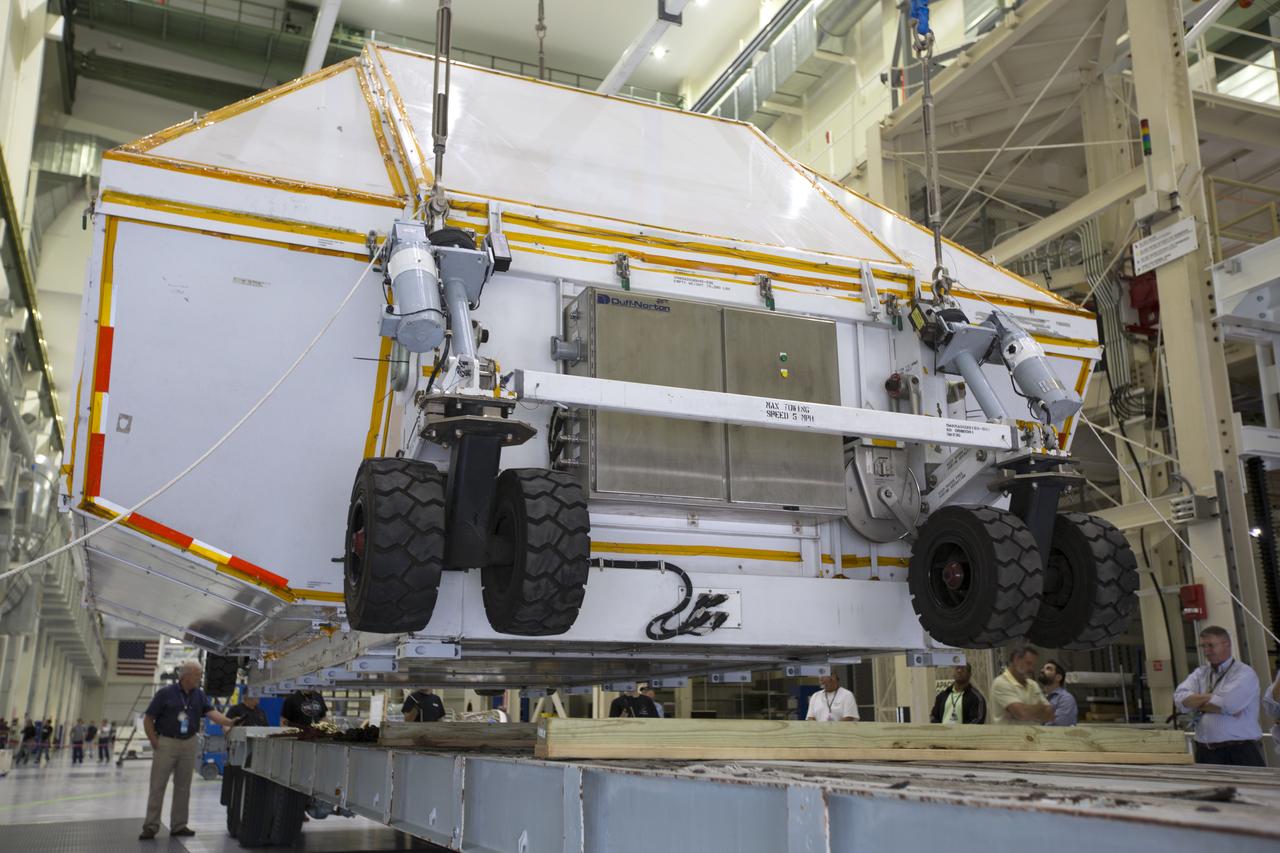

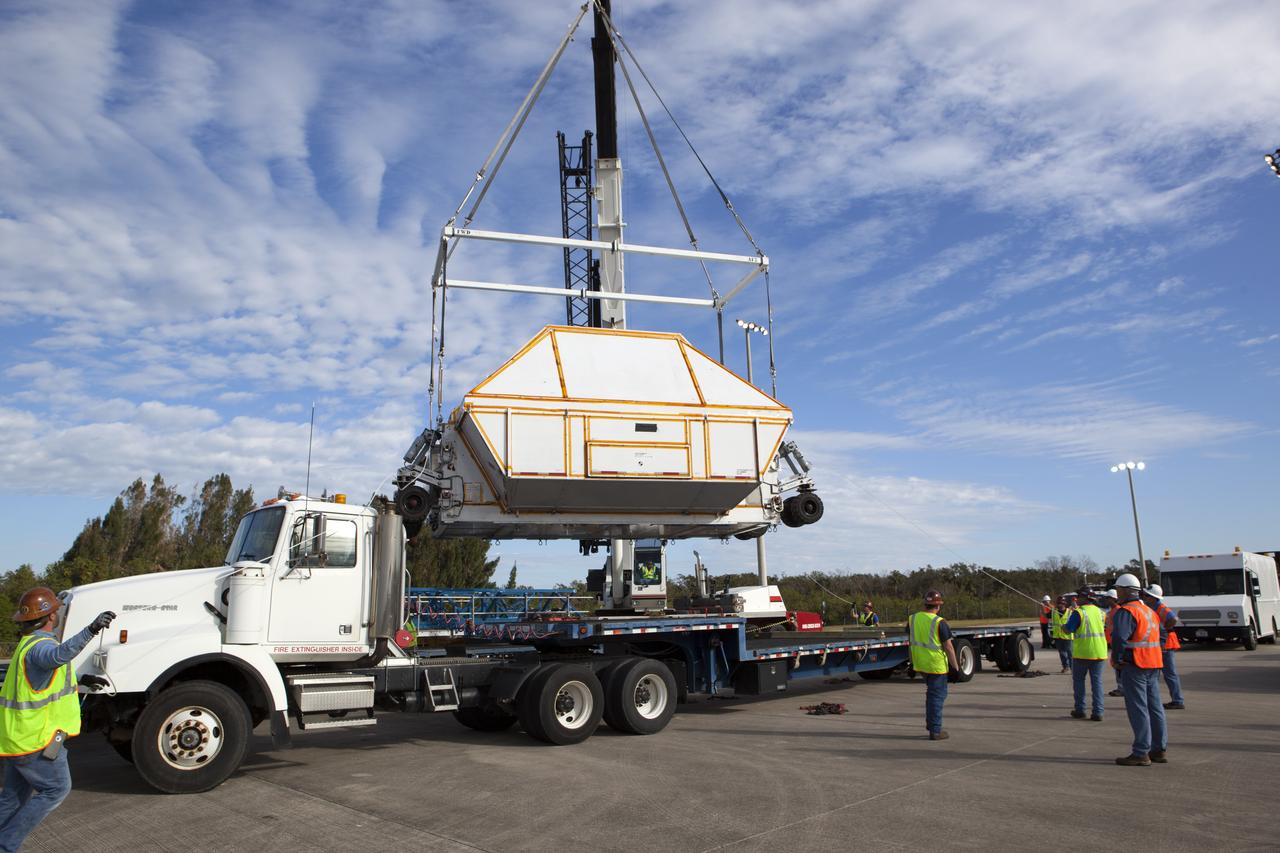
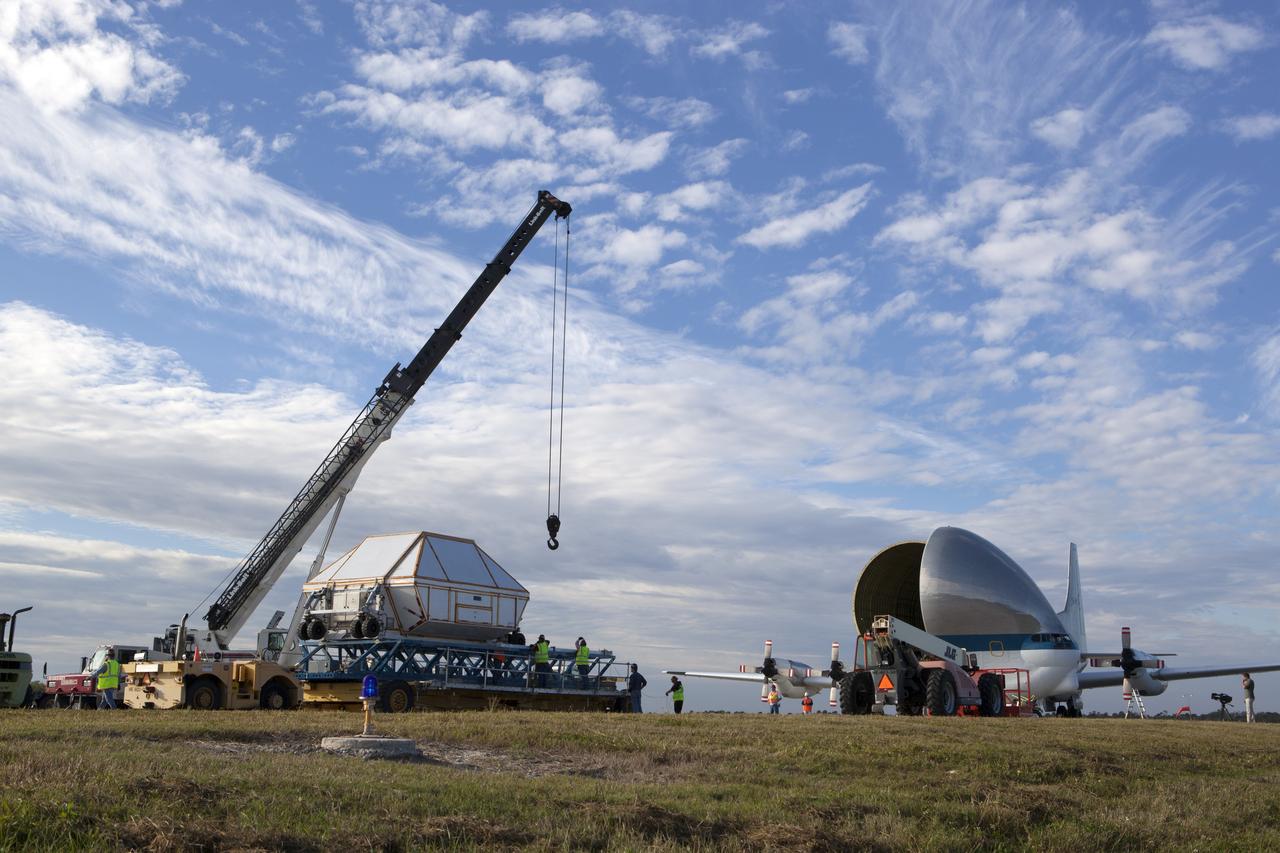
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
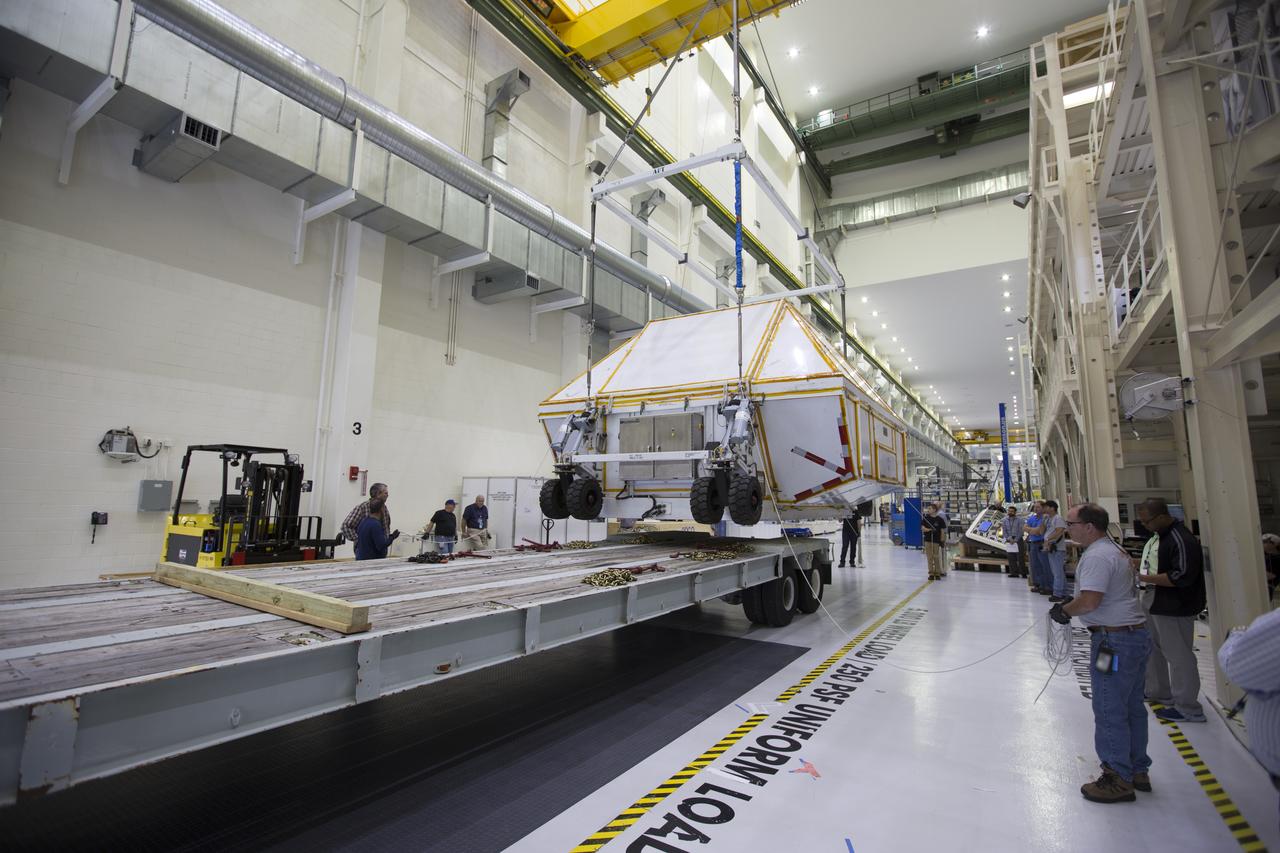

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
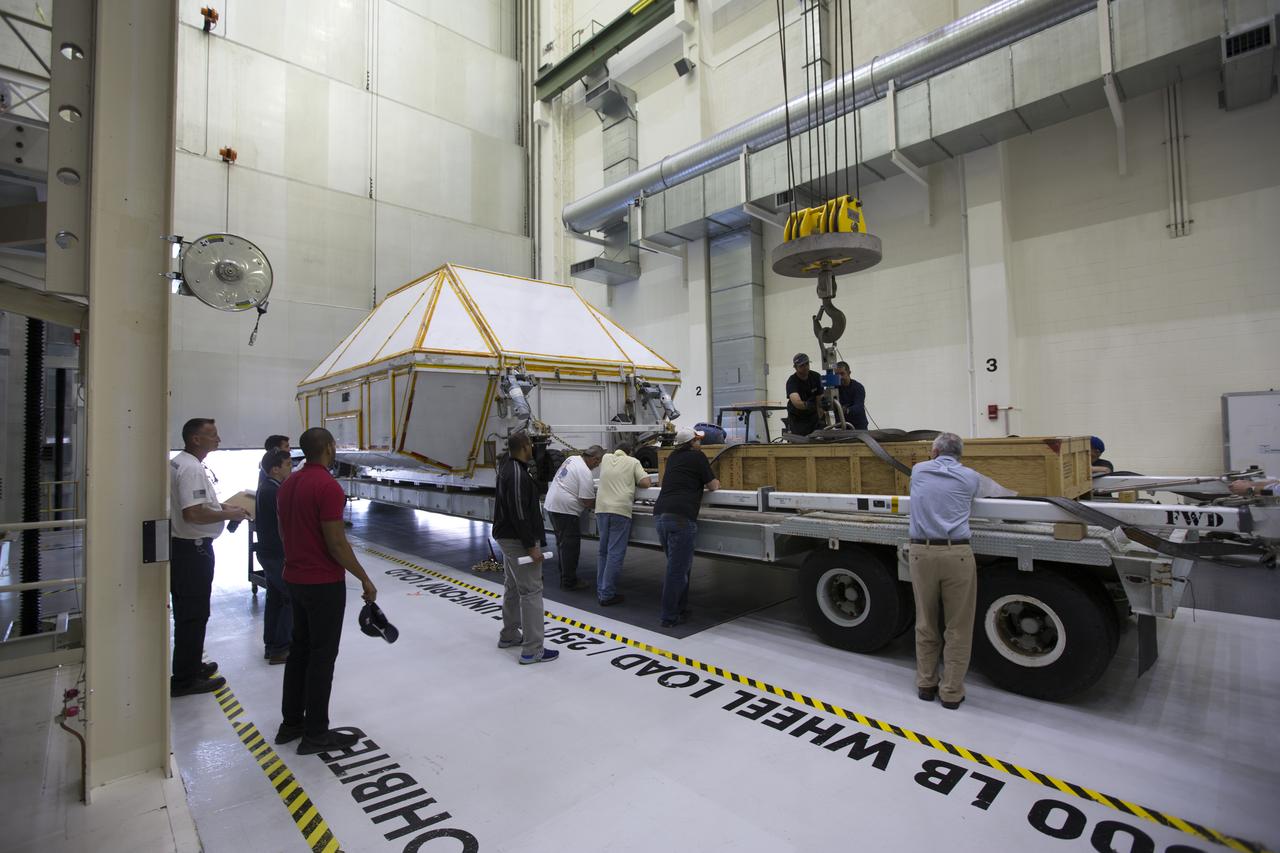

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians secure the transport container with the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
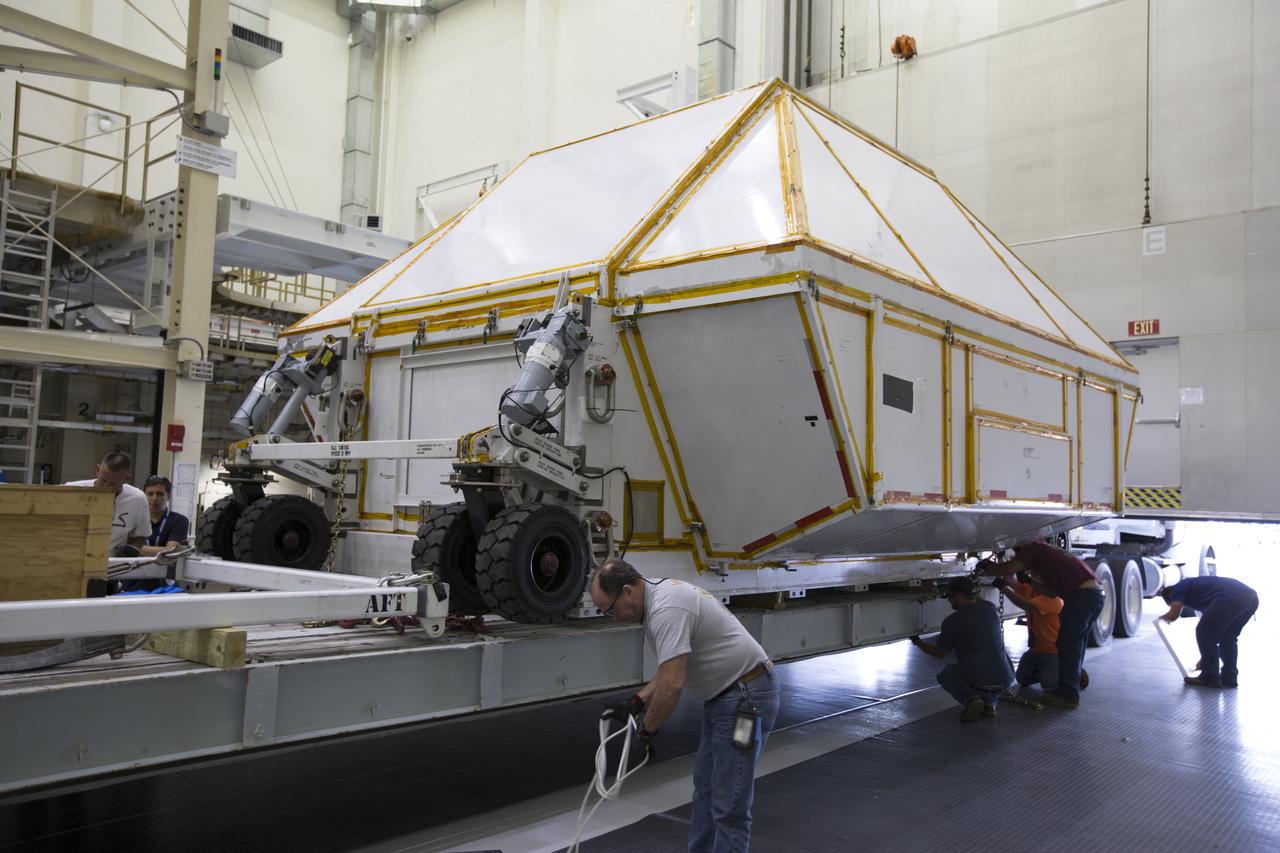

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians secure the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article in its transport container onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
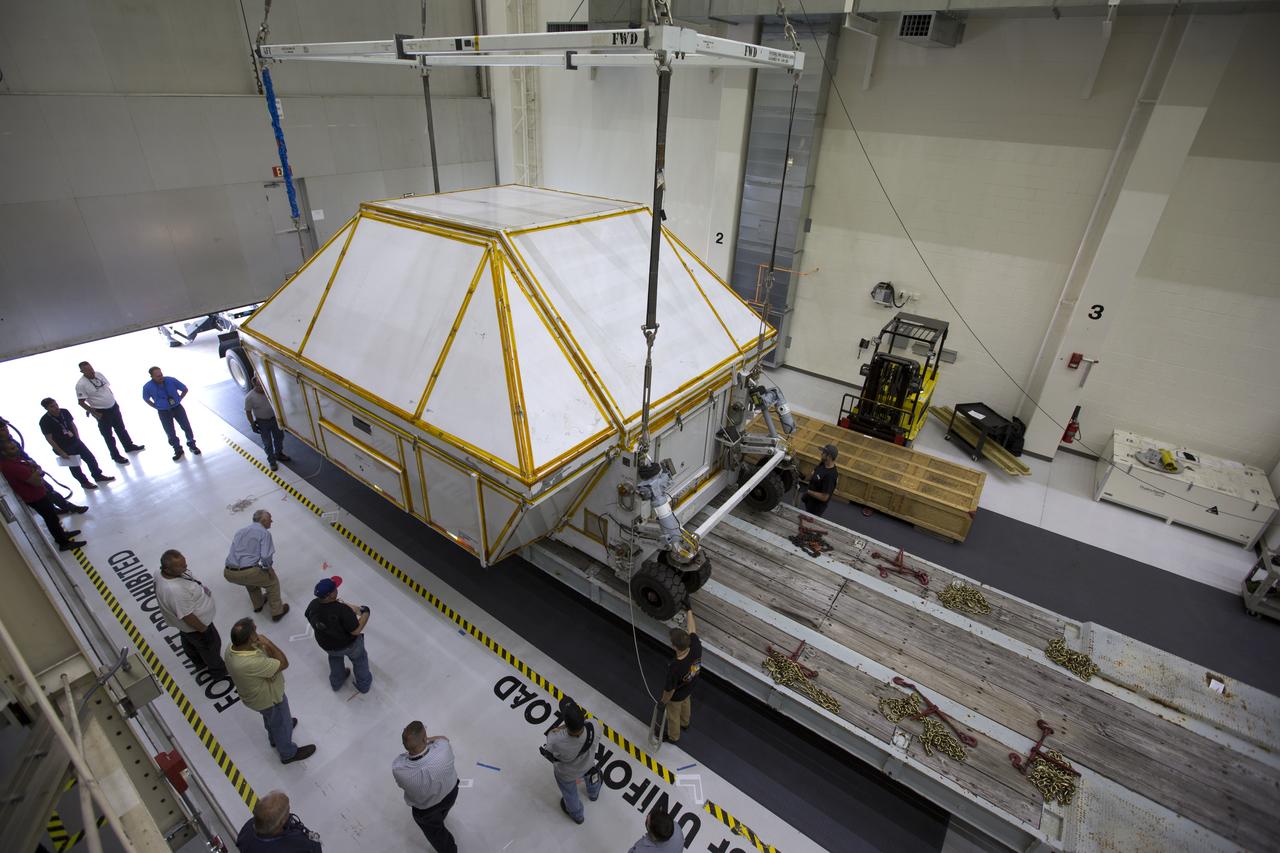

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article inside its transport container, is secured onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
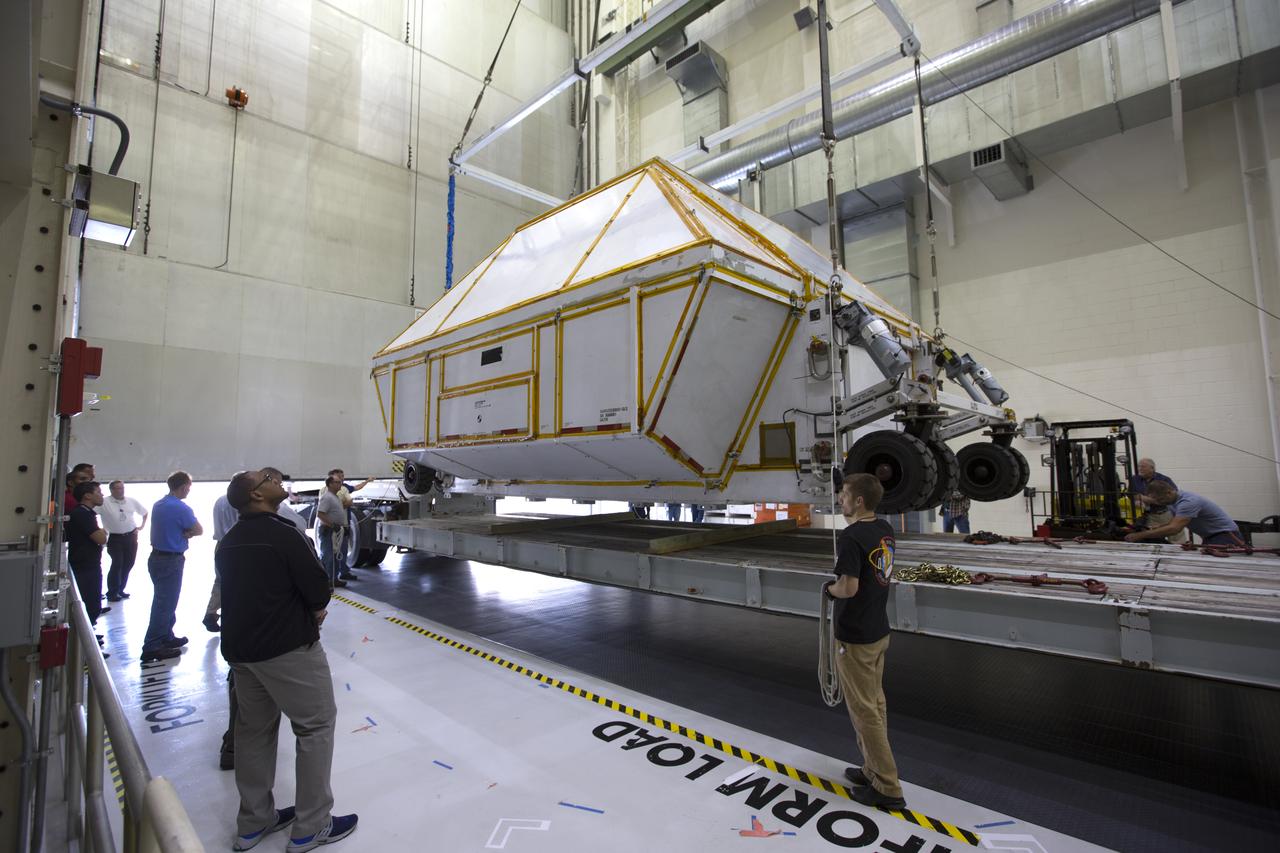

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, secured inside its transport container, is lowered onto a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
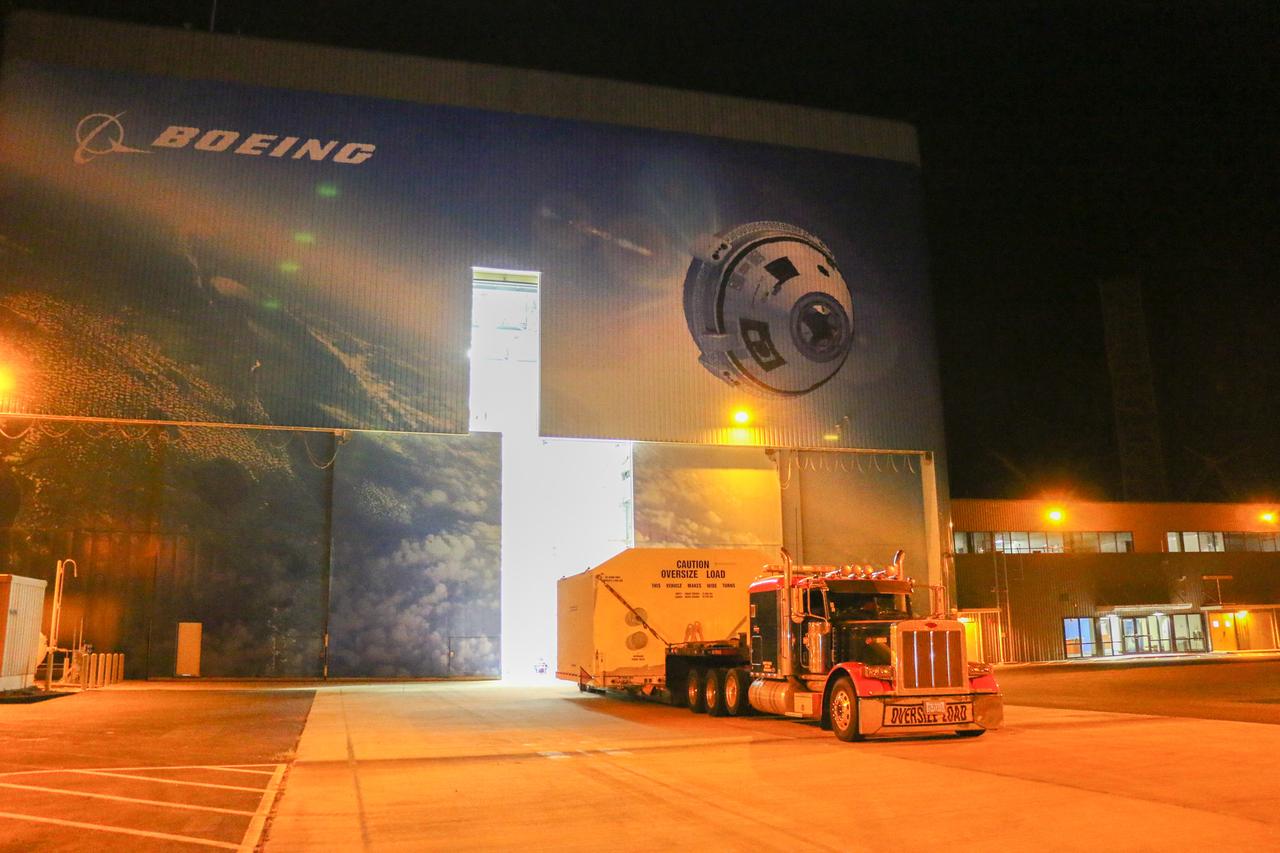

Boeing’s Structural Test Article of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is moved out of the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on its way to Huntington Beach, California, for evaluations. Built to the specifications of an operational spacecraft, the STA is intended to be evaluated through a series of thorough testing conditions.
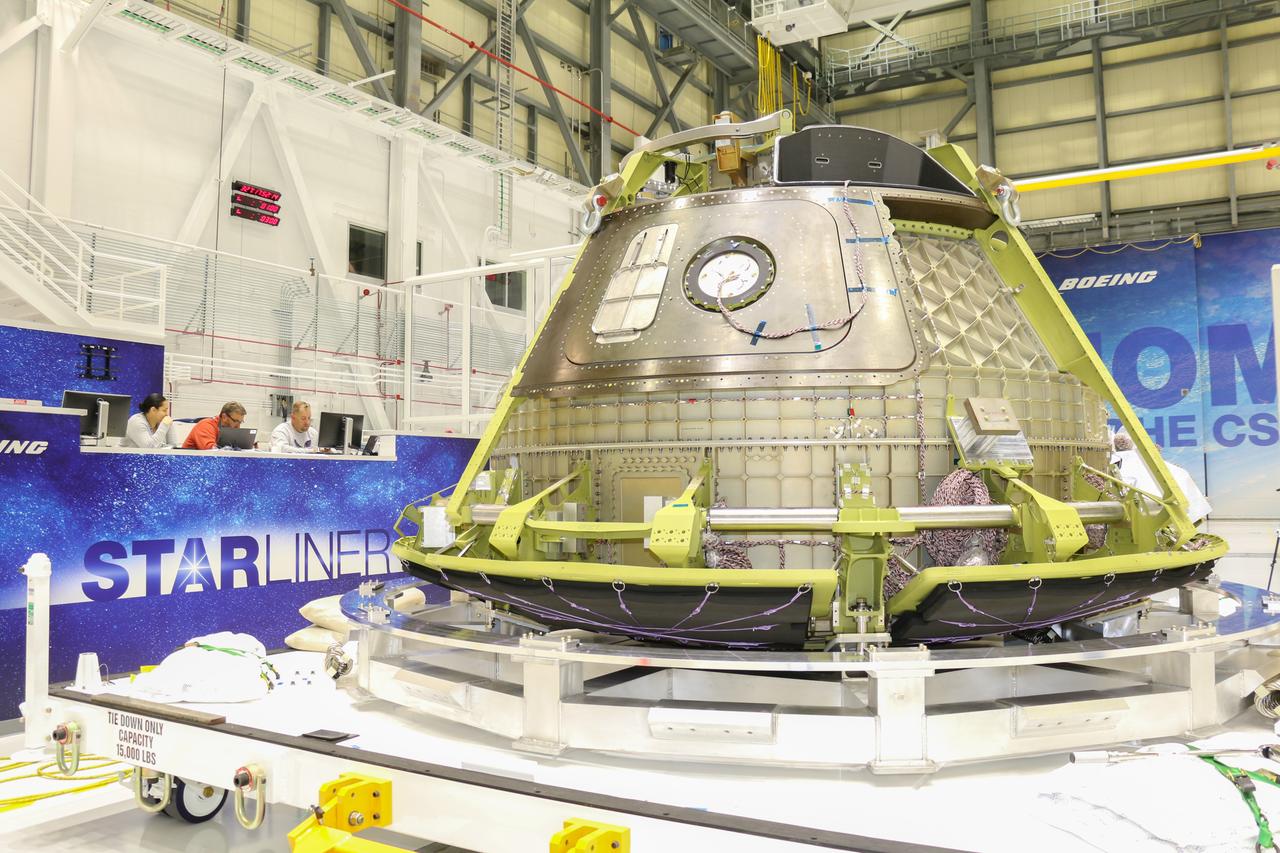

Boeing’s Structural Test Article of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is readied inside the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Built to the specifications of an operational spacecraft, the STA is intended to be evaluated through a series of thorough testing conditions at facilities in Huntington Beach, California.
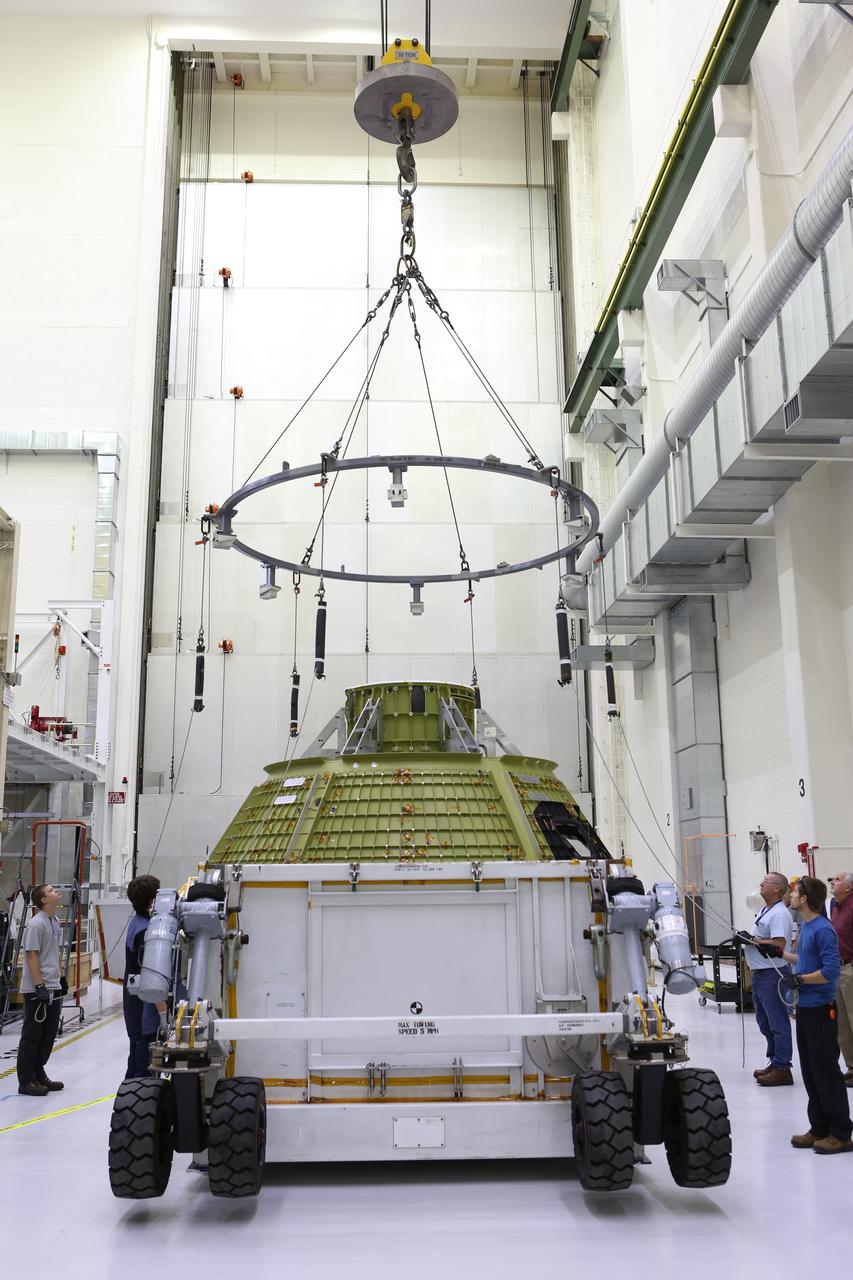

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians prepare to attach lines from a crane to the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be lifted out of its container and moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) onto a test tool called the birdcage. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be secured on the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
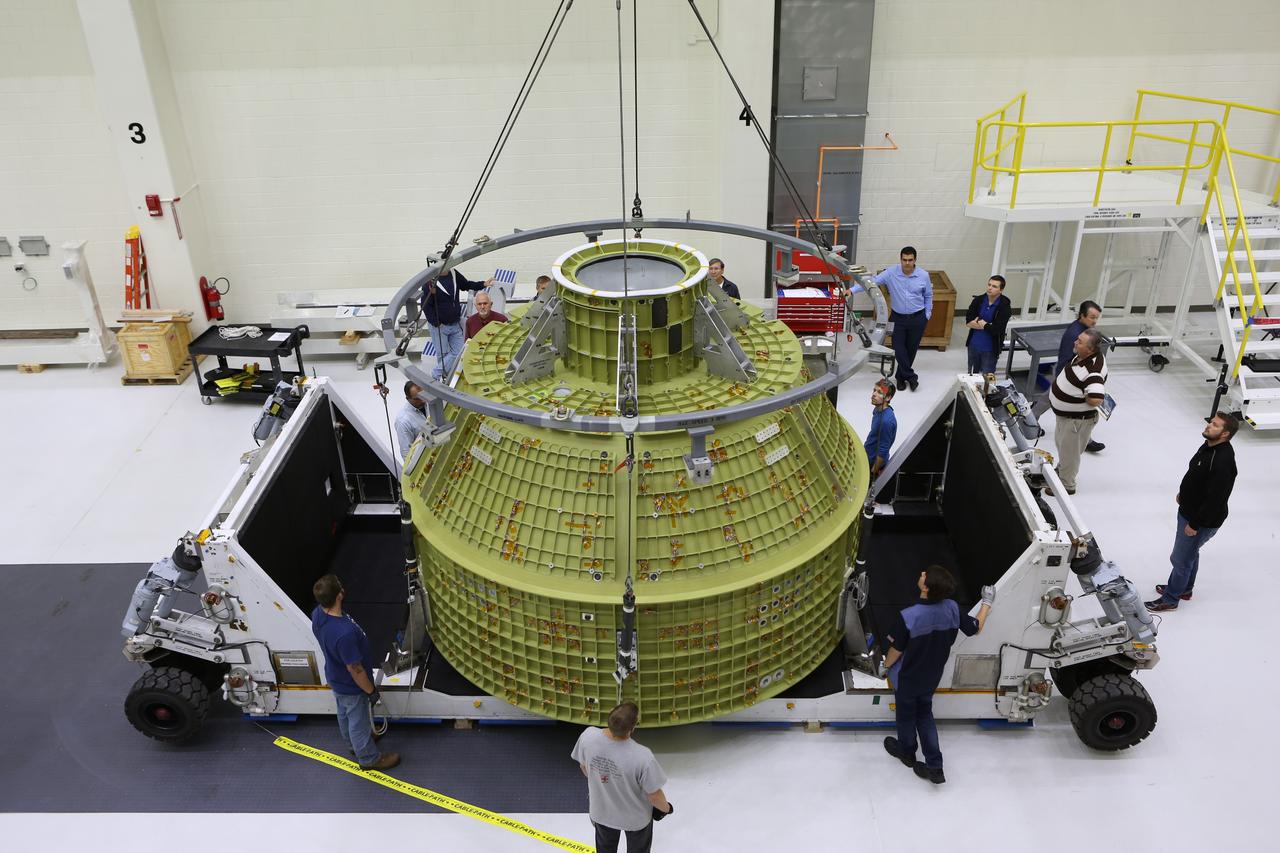

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane begins to lift the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) up from the base of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
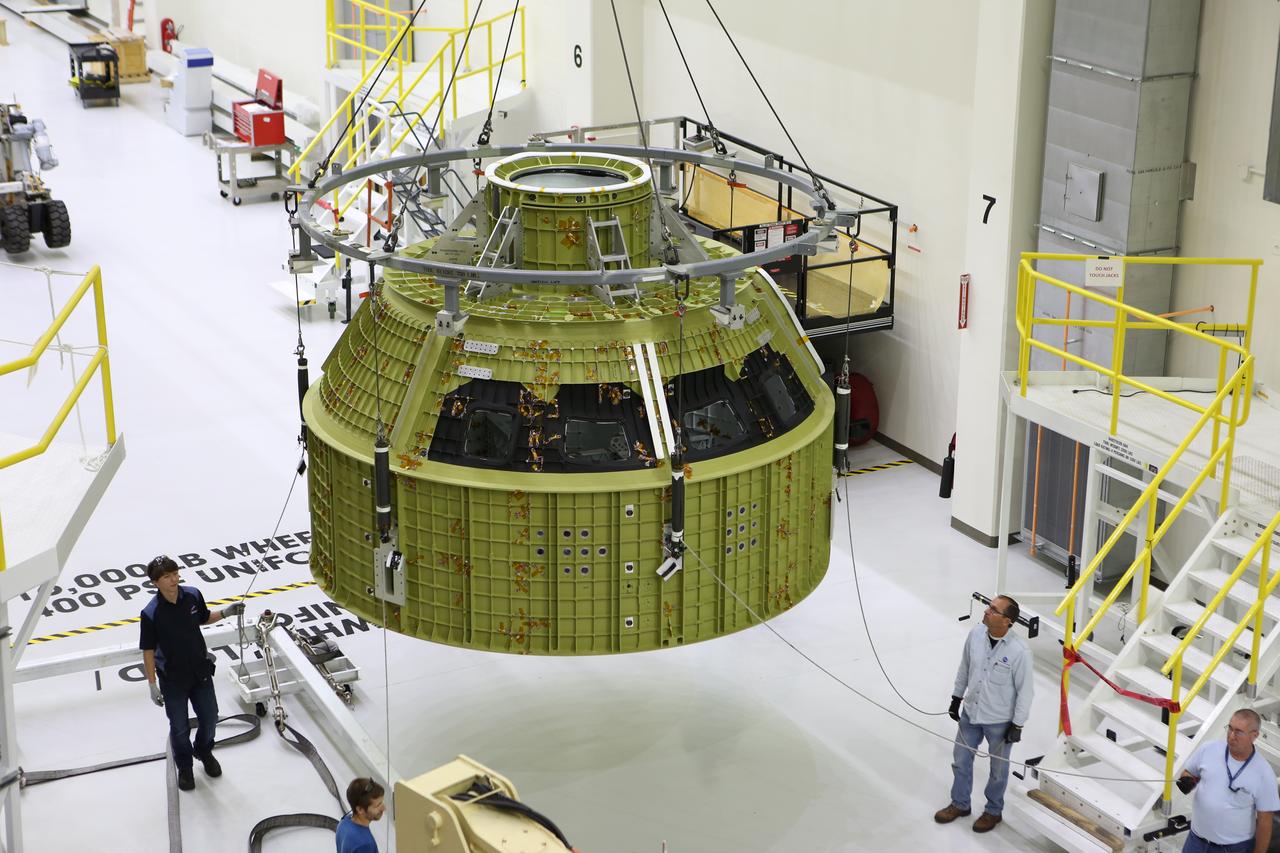

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane moves the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) along the center aisle of the high bay. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
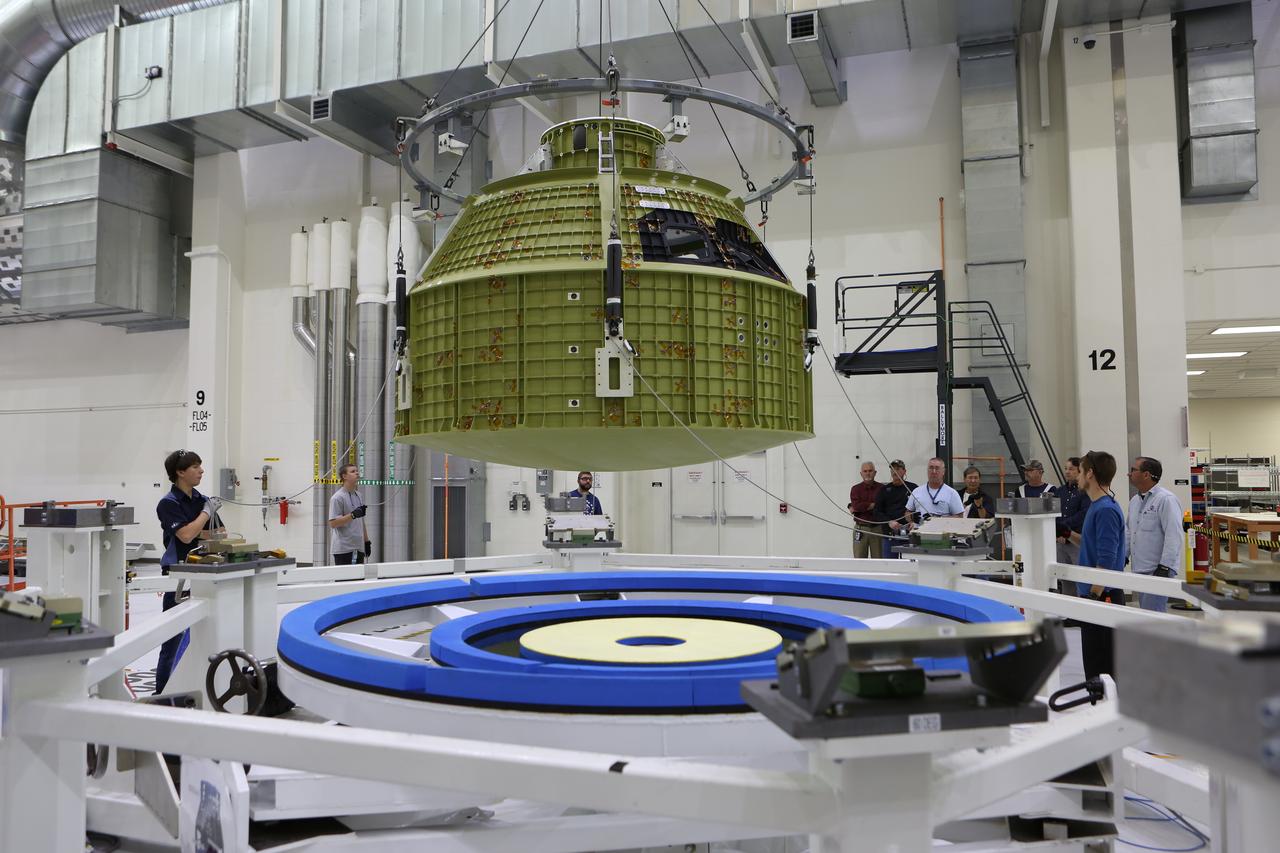

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) toward a test tool called the birdcage. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be secured on the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
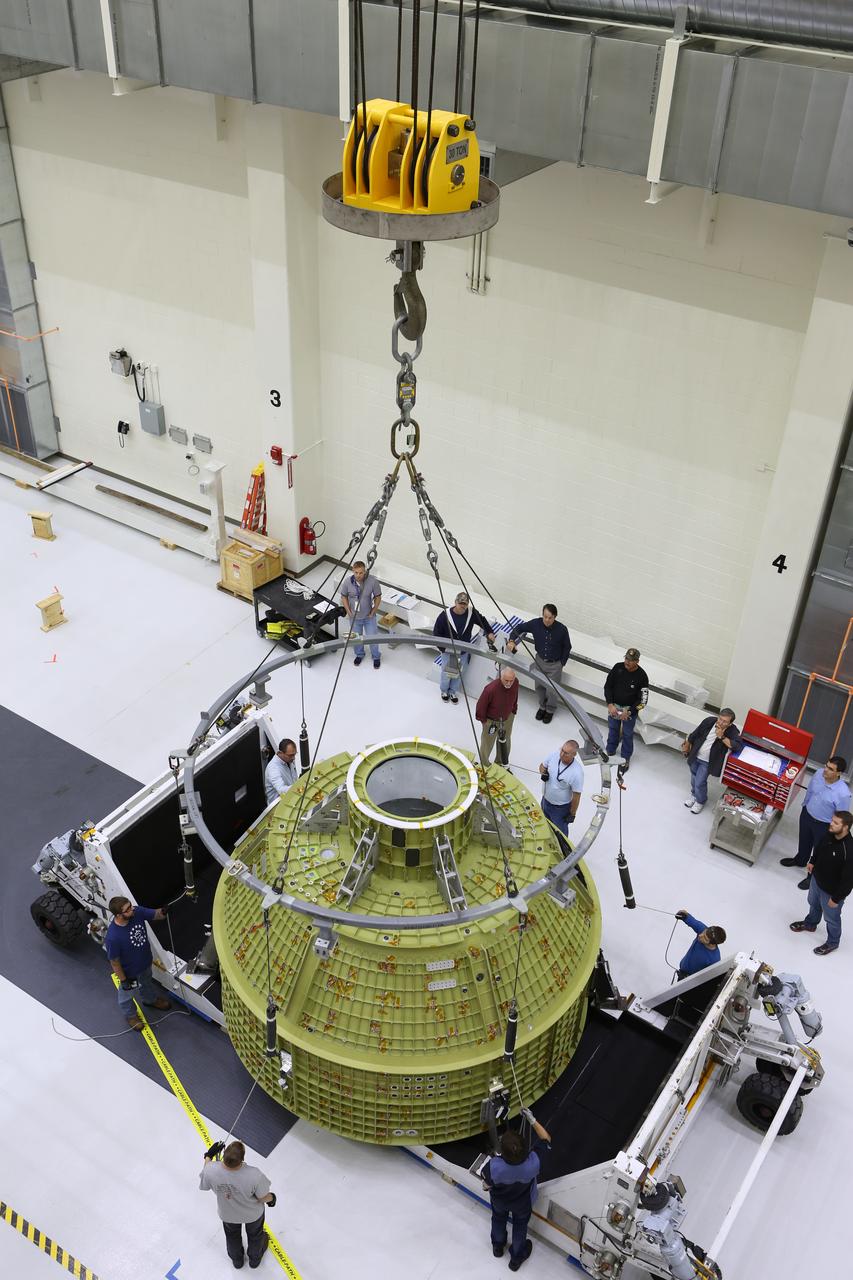

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians attach lines from a crane to the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be lifted out of its container and moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
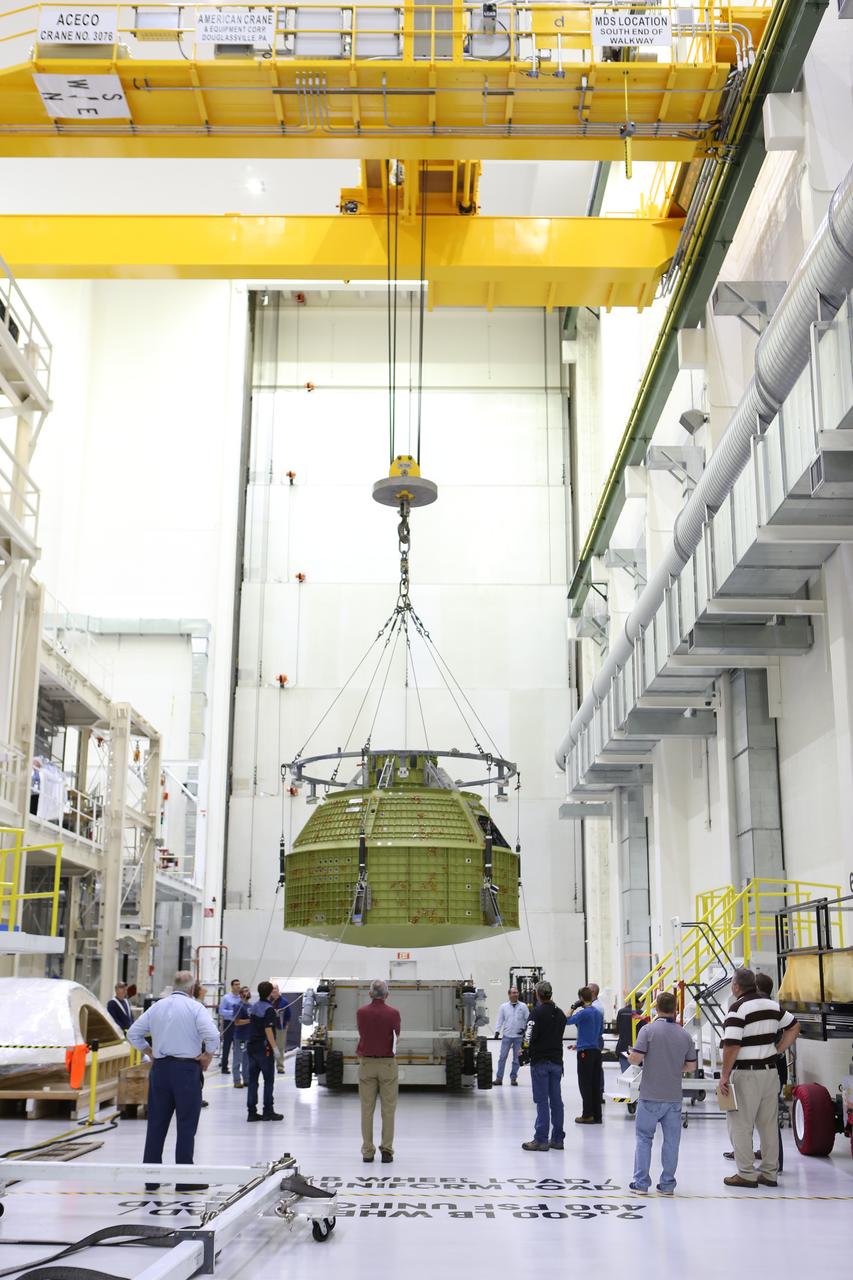

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lifts the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) away from the base of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
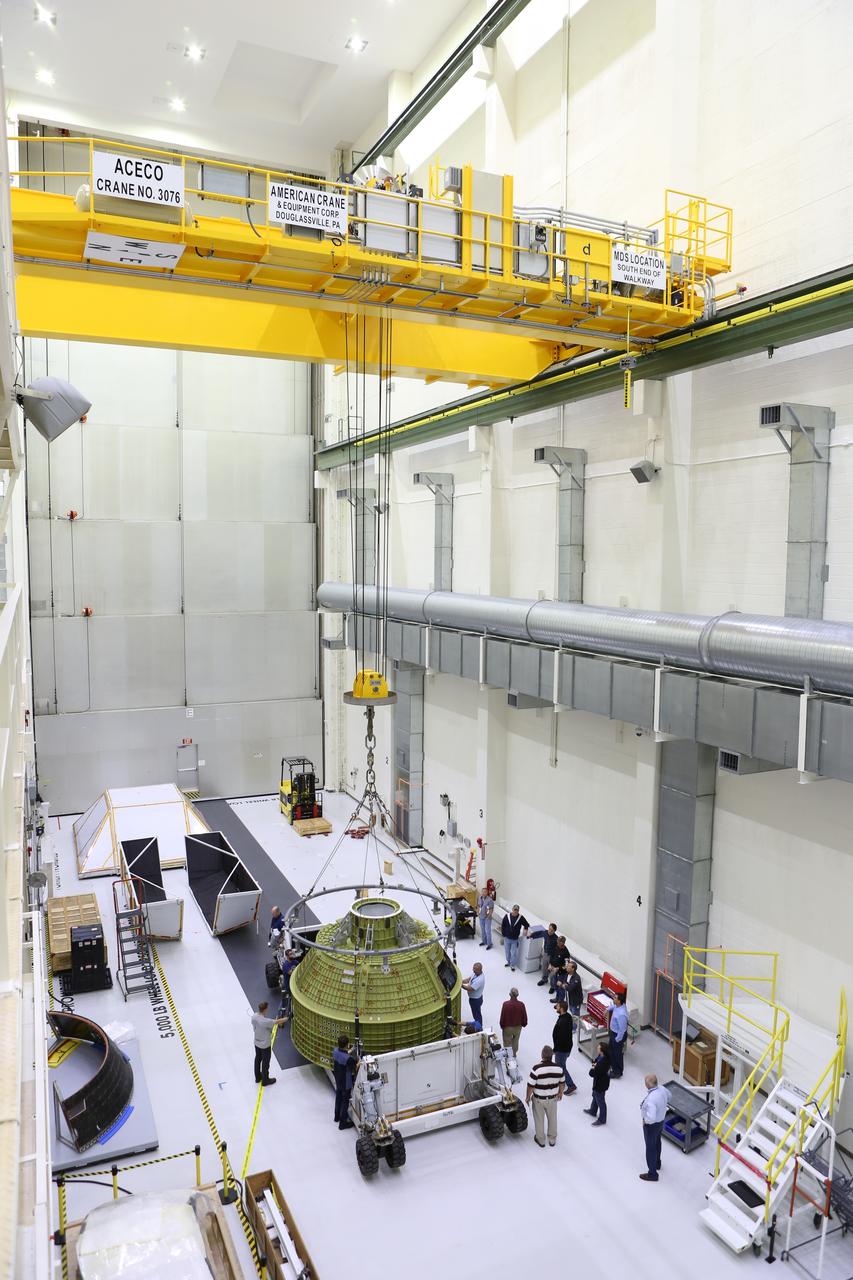

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians attach lines from a crane to the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be lifted out of its container and moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
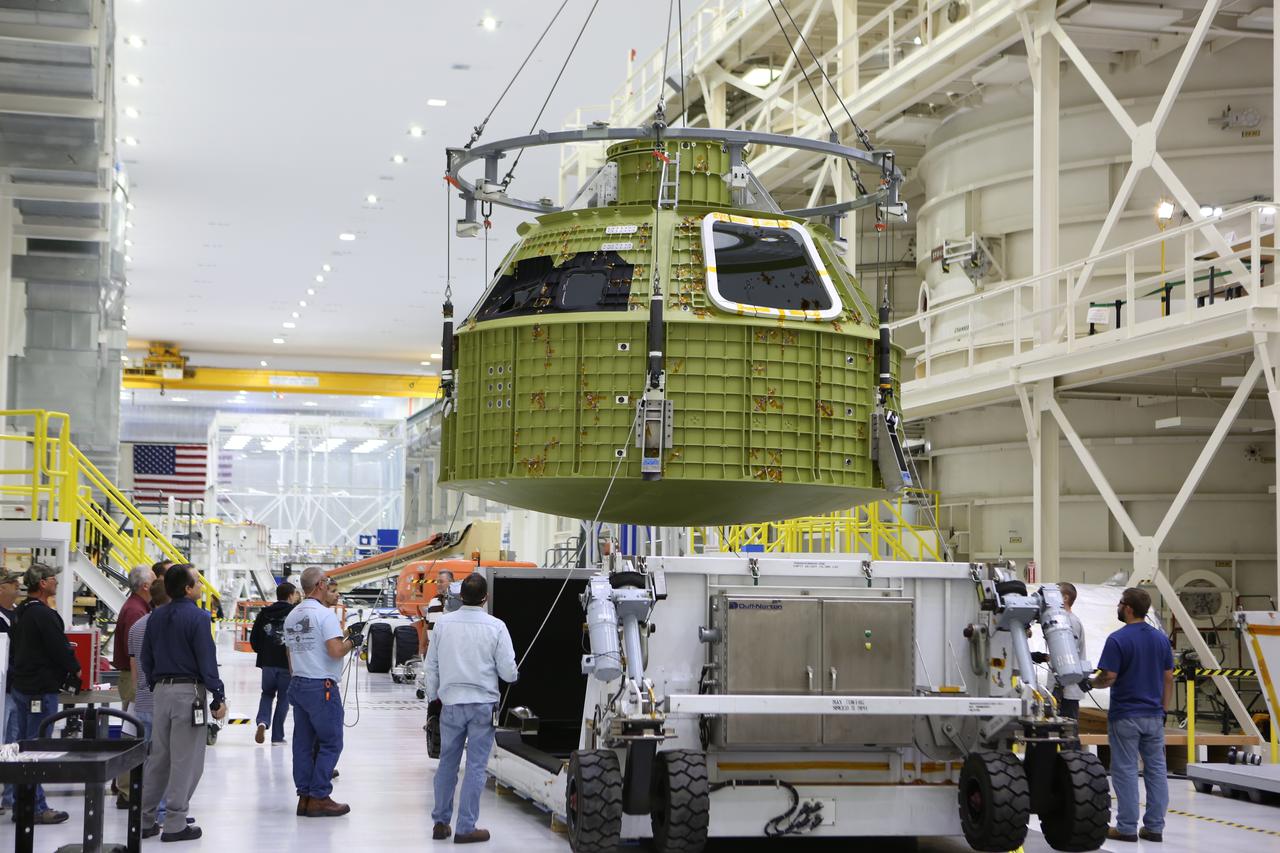

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lifts the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) up from the base of its transport container. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians check the lines attached from a crane to the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be lifted out of its container and moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
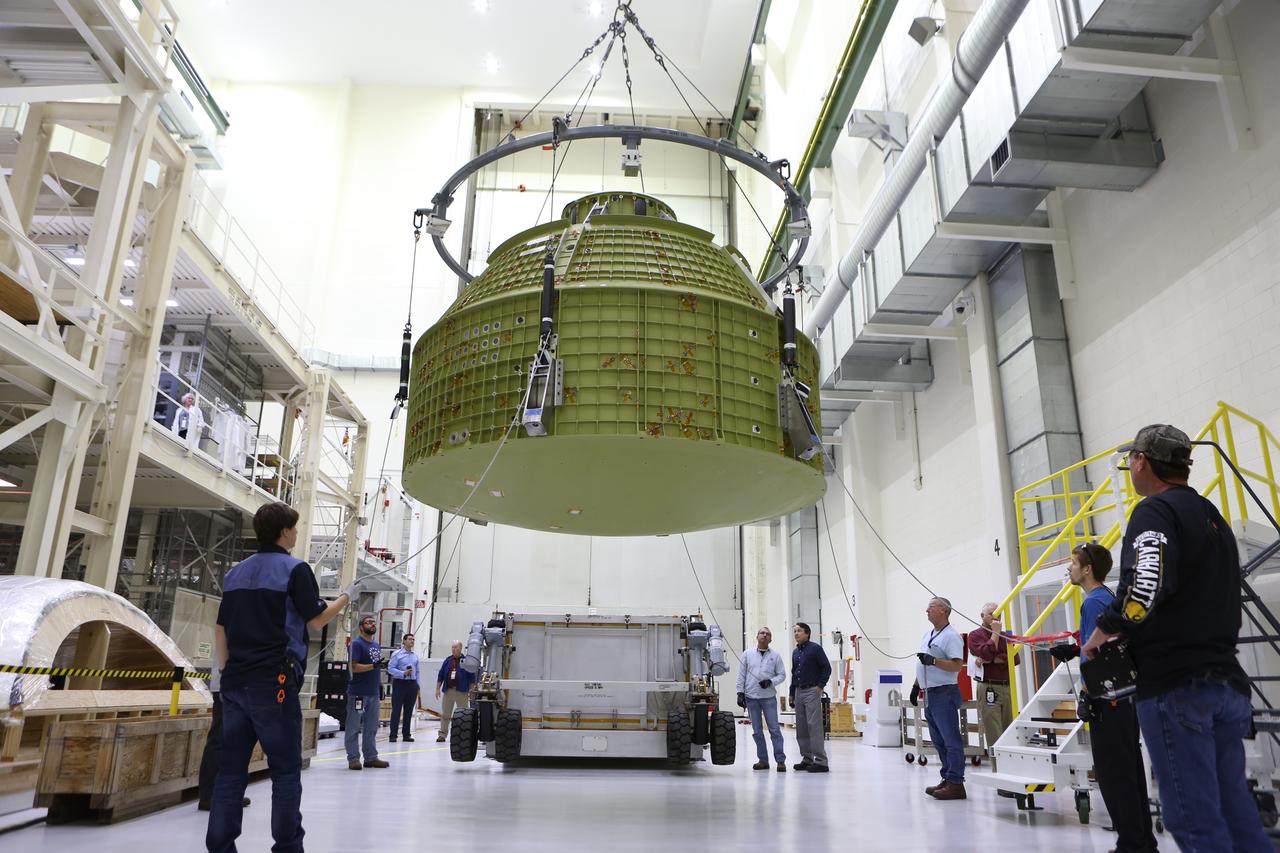

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane moves the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) along the center aisle of the high bay. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved to a test tool called the birdcage for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
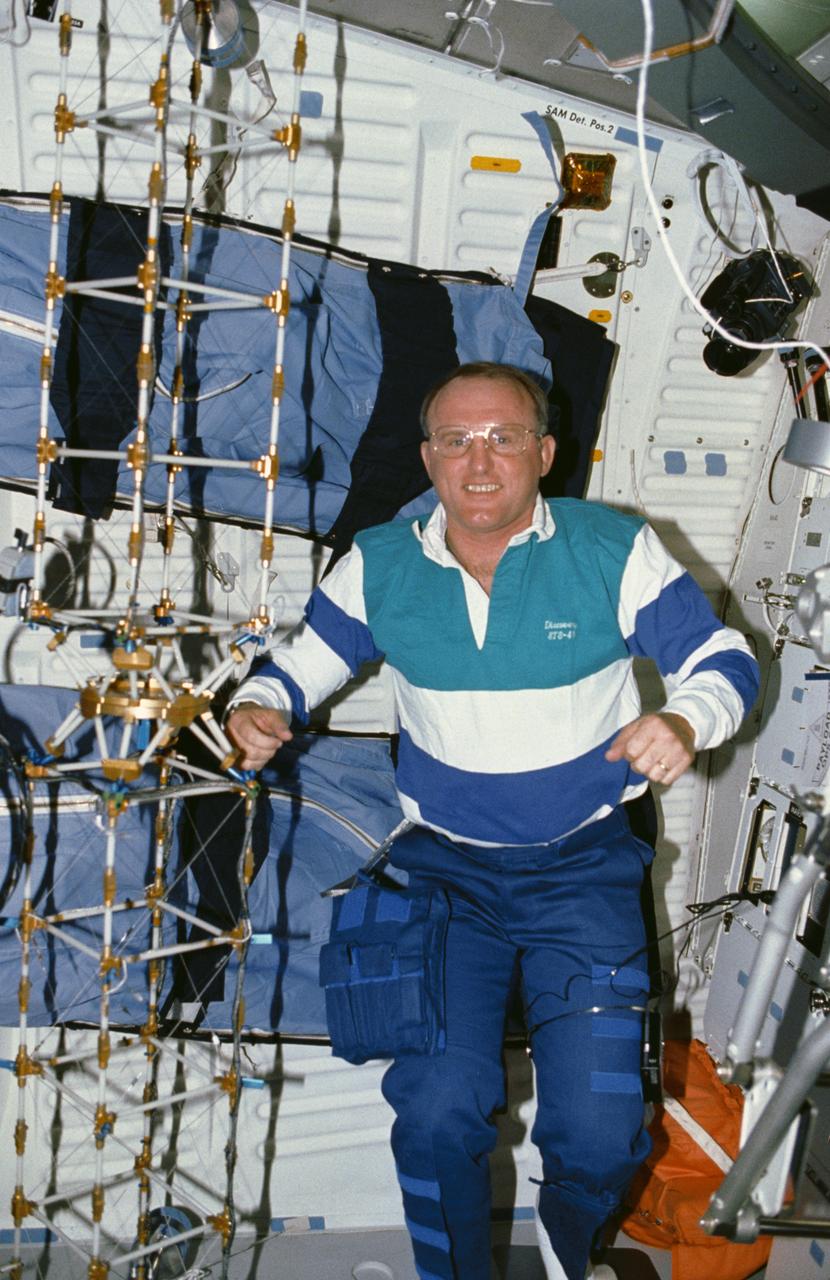

STS048-10-023 (16 Sept 1991) --- Astronaut James F. Buchli poses with the structural test article (STA), a model of the space station truss structure. The STA is part of the middeck zero gravity dynamics experiment (MODE). MODE was designed to study the vibration characteristics of the jointed truss structure. The structural test article includes four strain gauges and eleven accelerometers and is vibrated by an actuator. Assembled by crewmembers in the Shuttle orbiter's middeck, the device is about 72 inches long with an 8-inch square cross section.
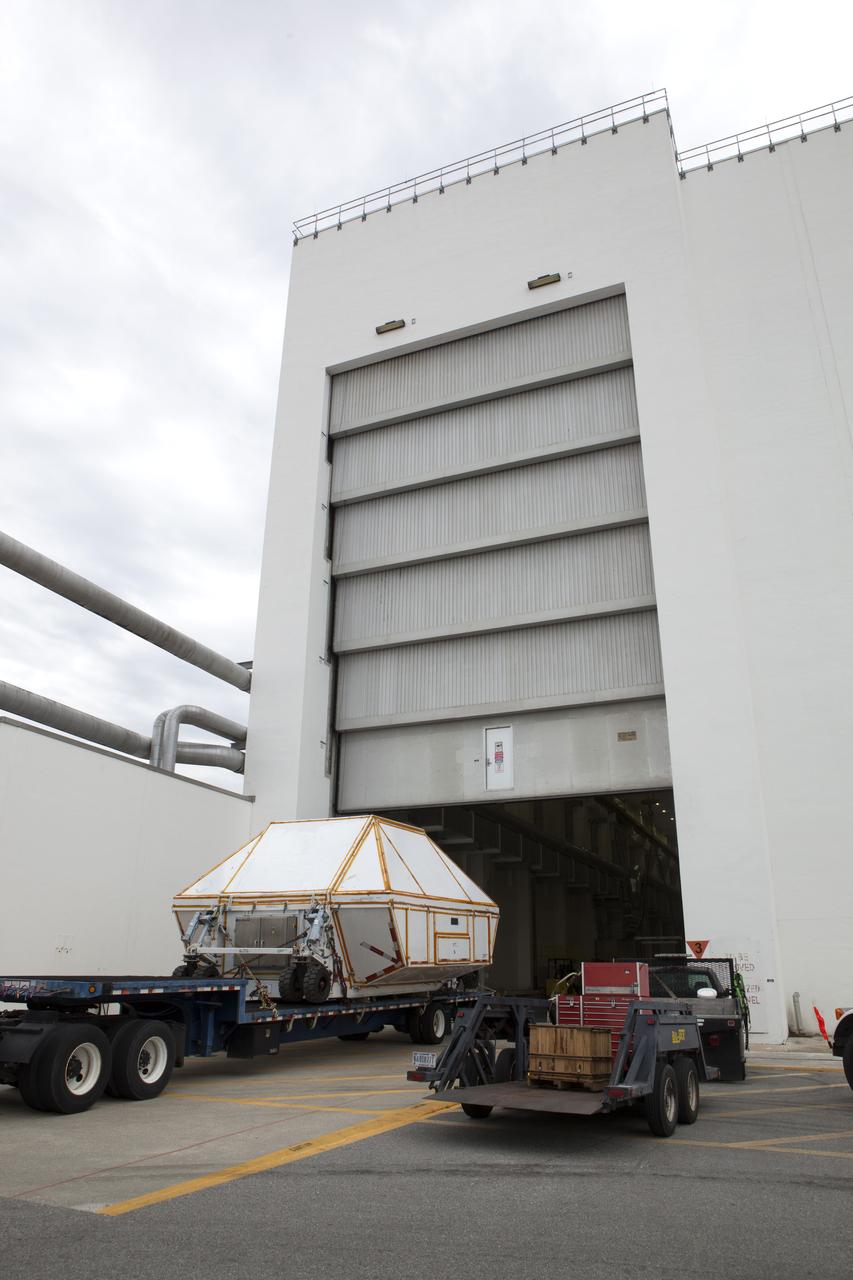

A transporter carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) in its container arrives at the low bay entrance of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
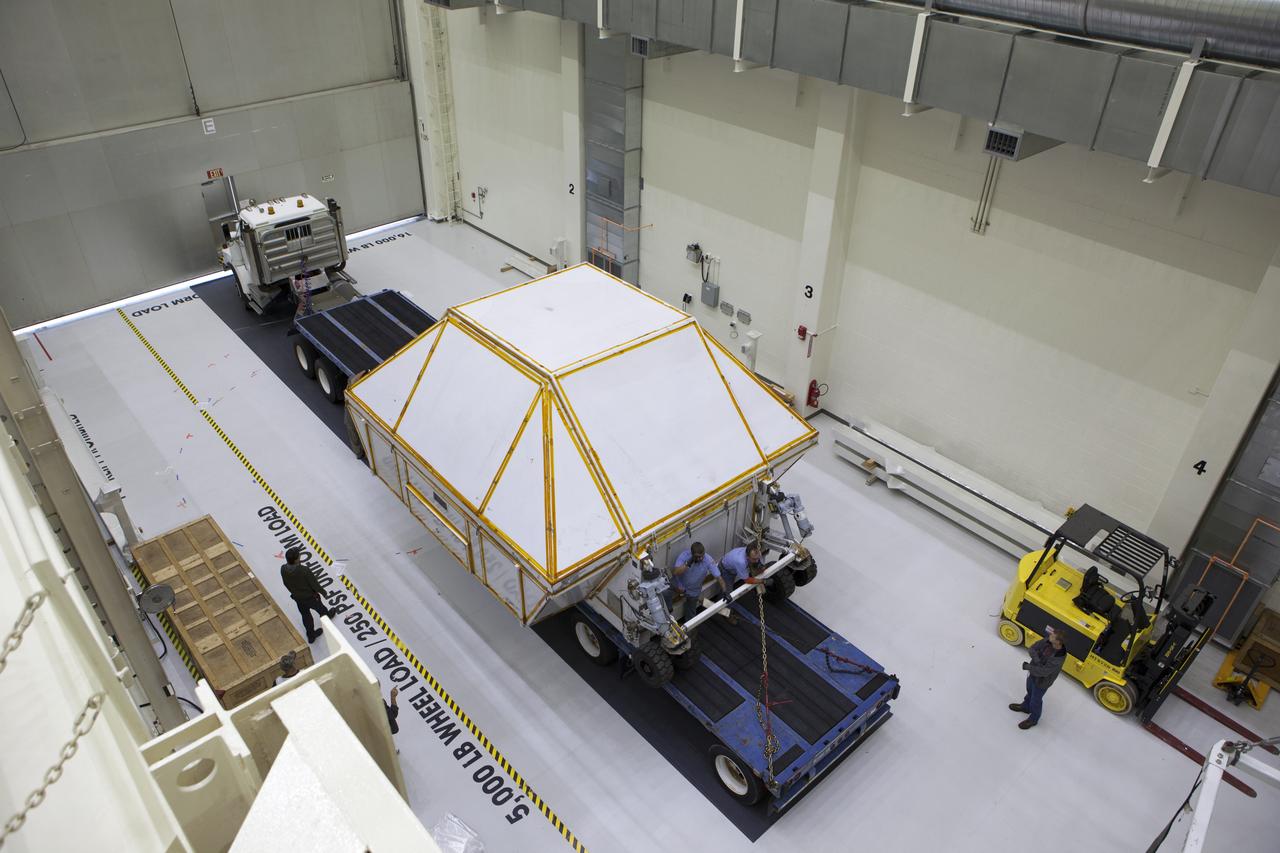

A transporter carrying the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) in its container arrives inside the low bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article will be moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
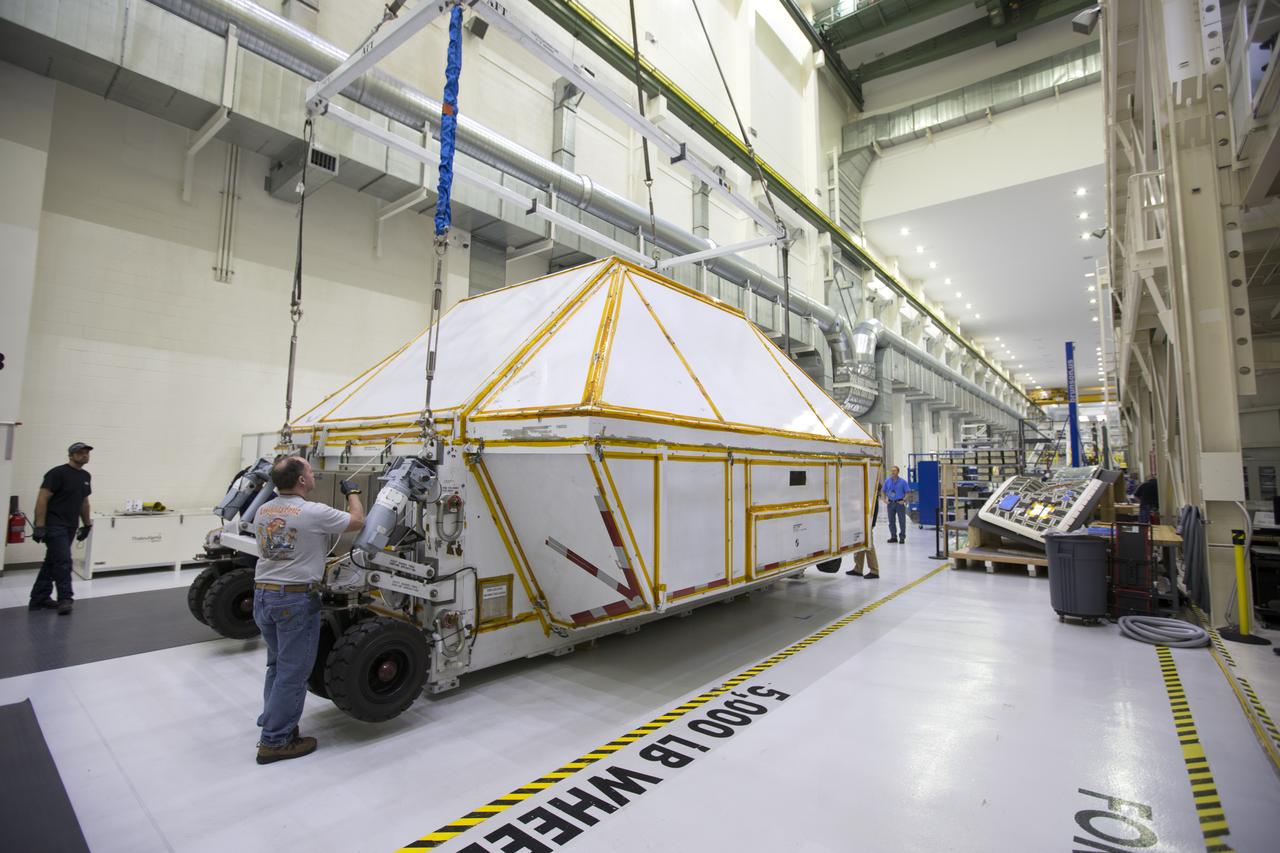

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article is secured inside its transport container. A crane is used to move the container toward a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
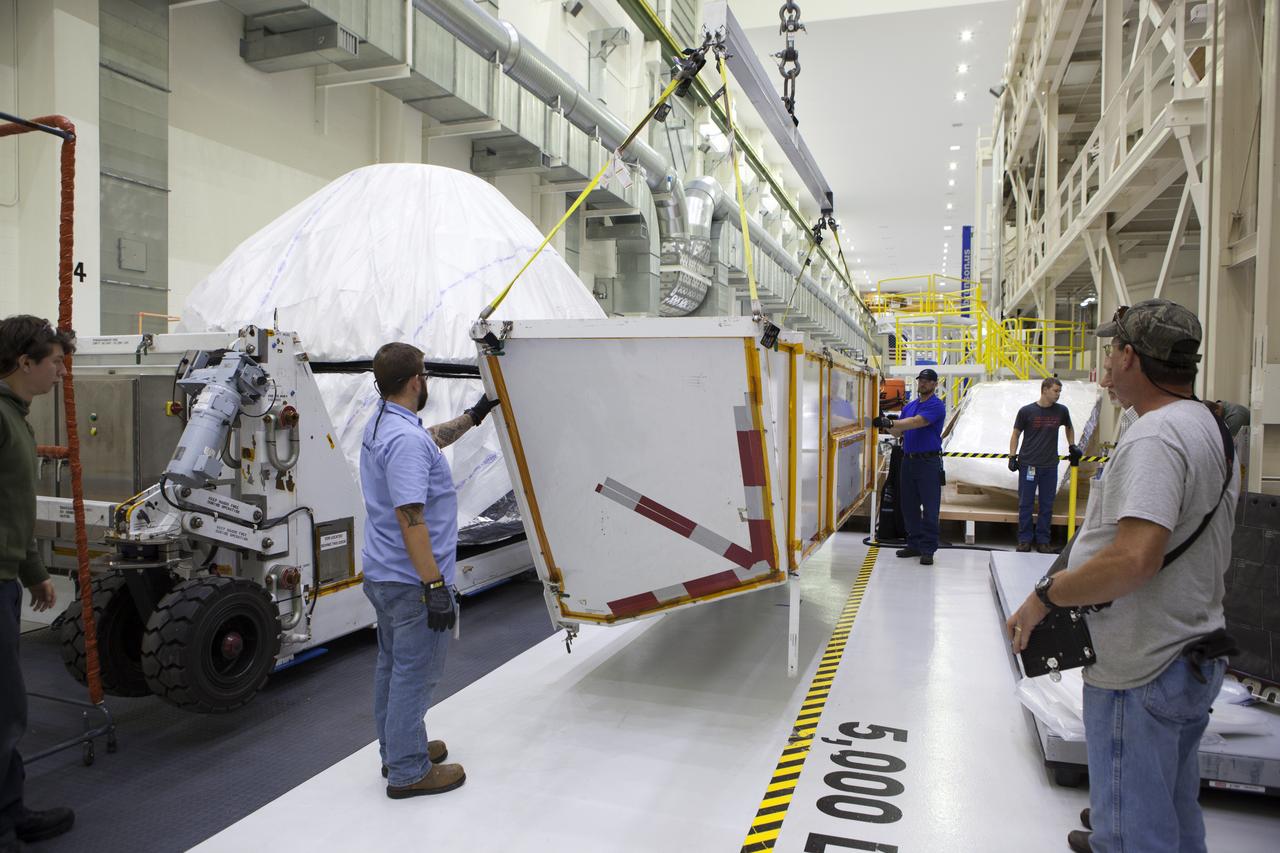

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians with Lockheed Martin assist as a crane lifts the cover away from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
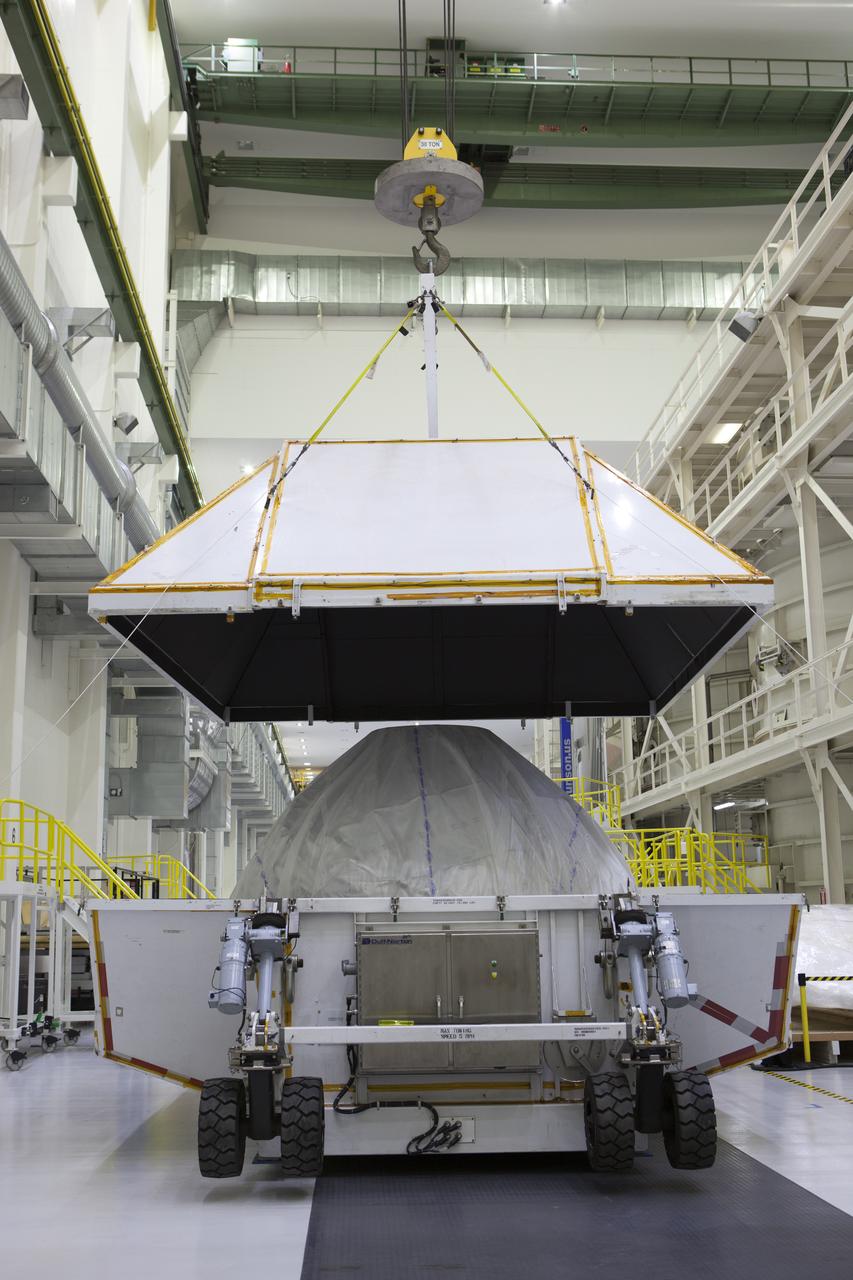

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the cover up from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
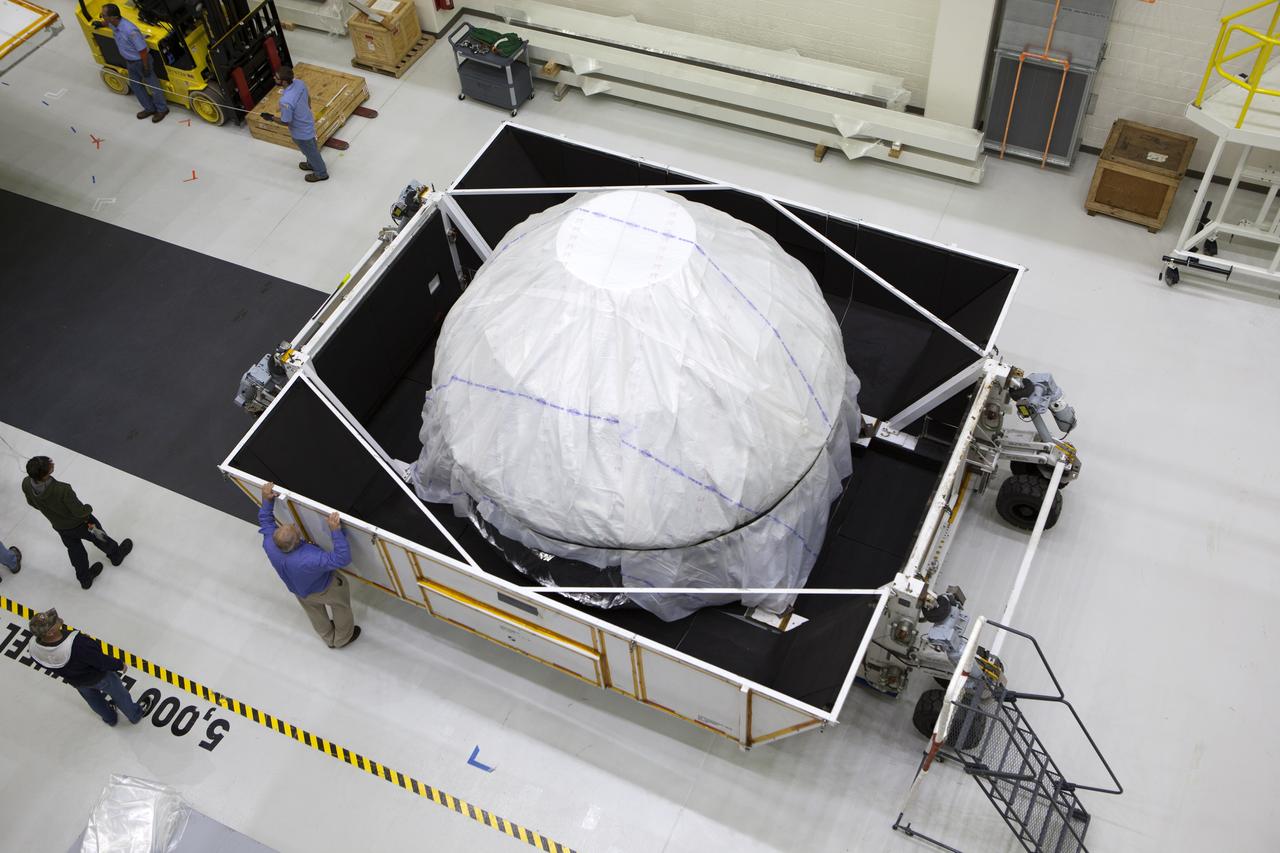

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the cover has been removed from the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA). The STA arrived aboard NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida. The test article was moved inside the facility's high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
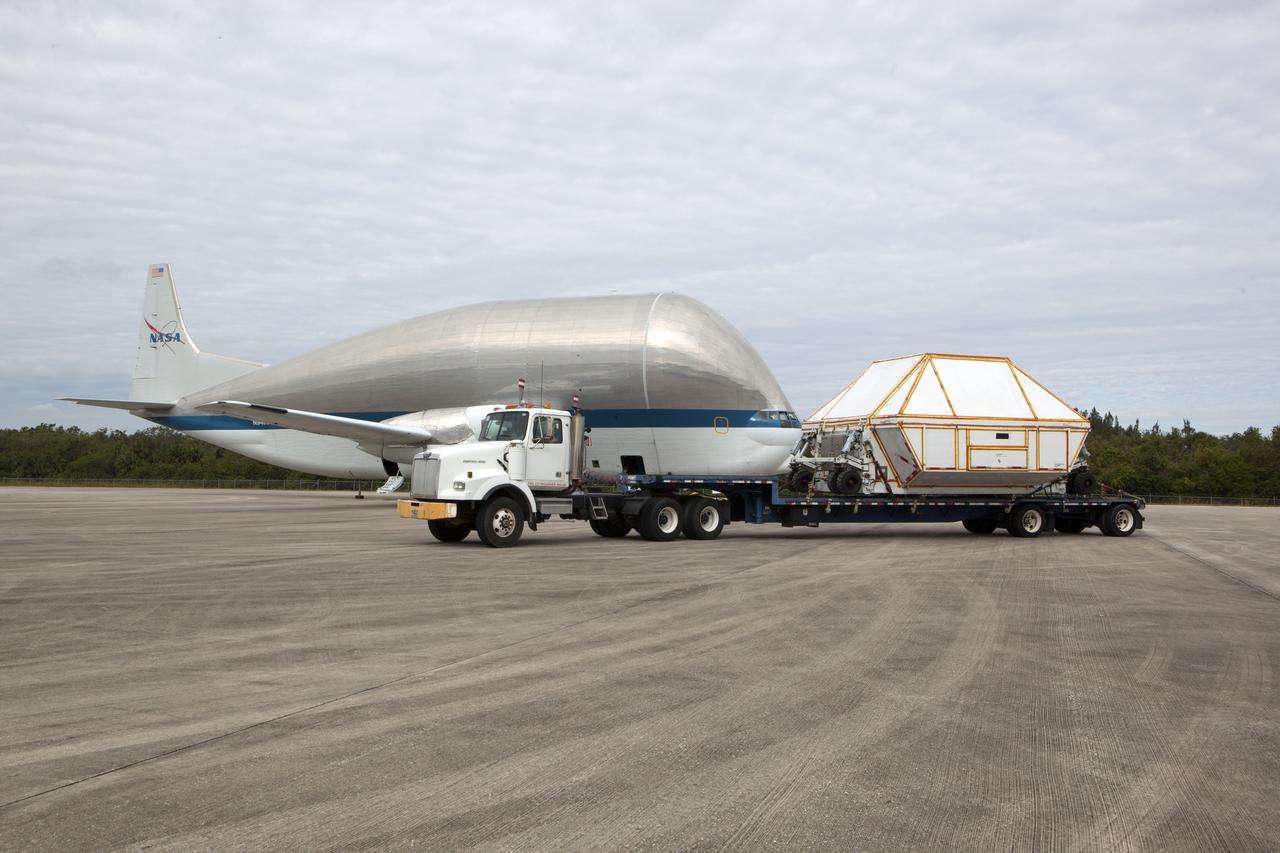

After arriving at the Shuttle Landing Facility operated by Space Florida at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft was opened and the container holding the Orion crew module structural test article (STA) was offloaded. A crane was used to lower the container for placement on a transporter. The Super Guppy has been closed. The test article will be moved to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay for further testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission, in late 2018.
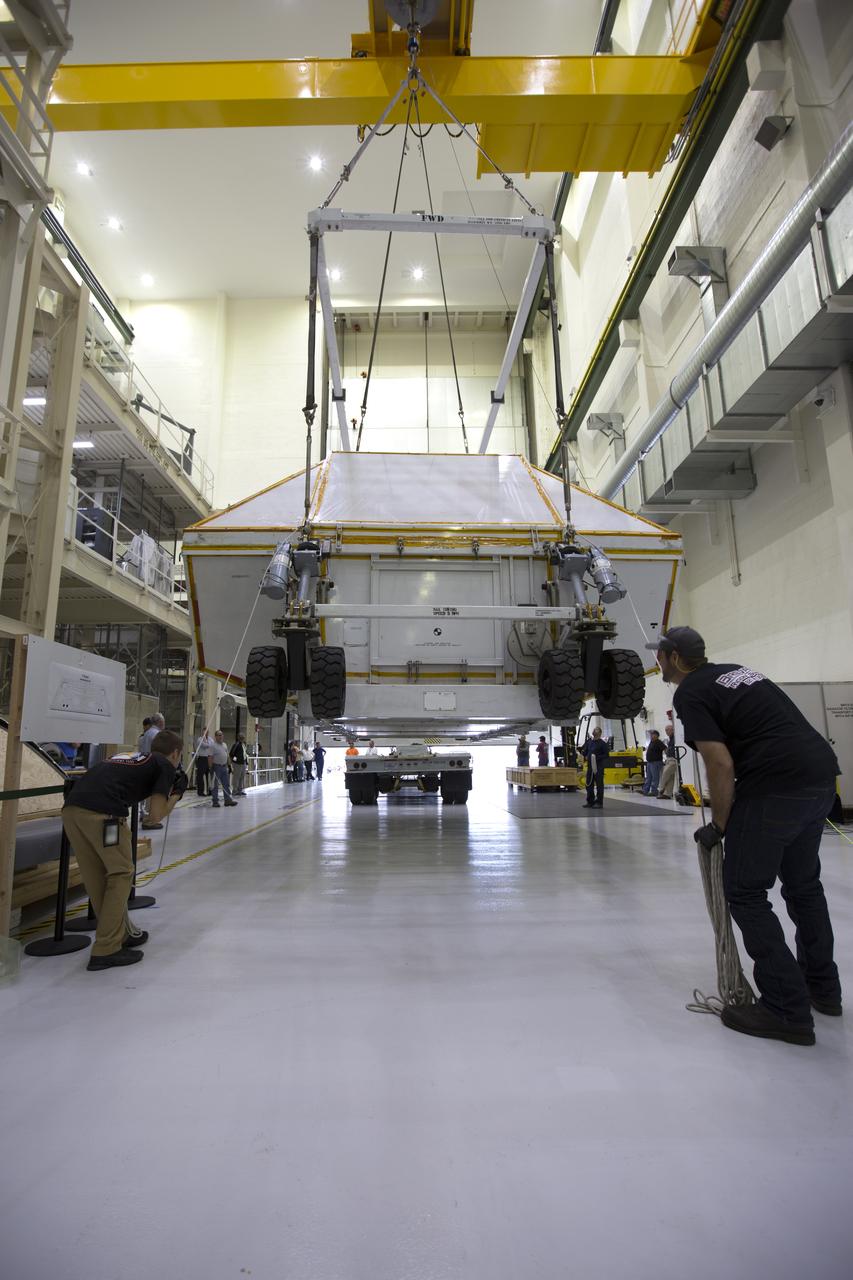

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article is secured inside its transport container. Technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to move the container toward a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
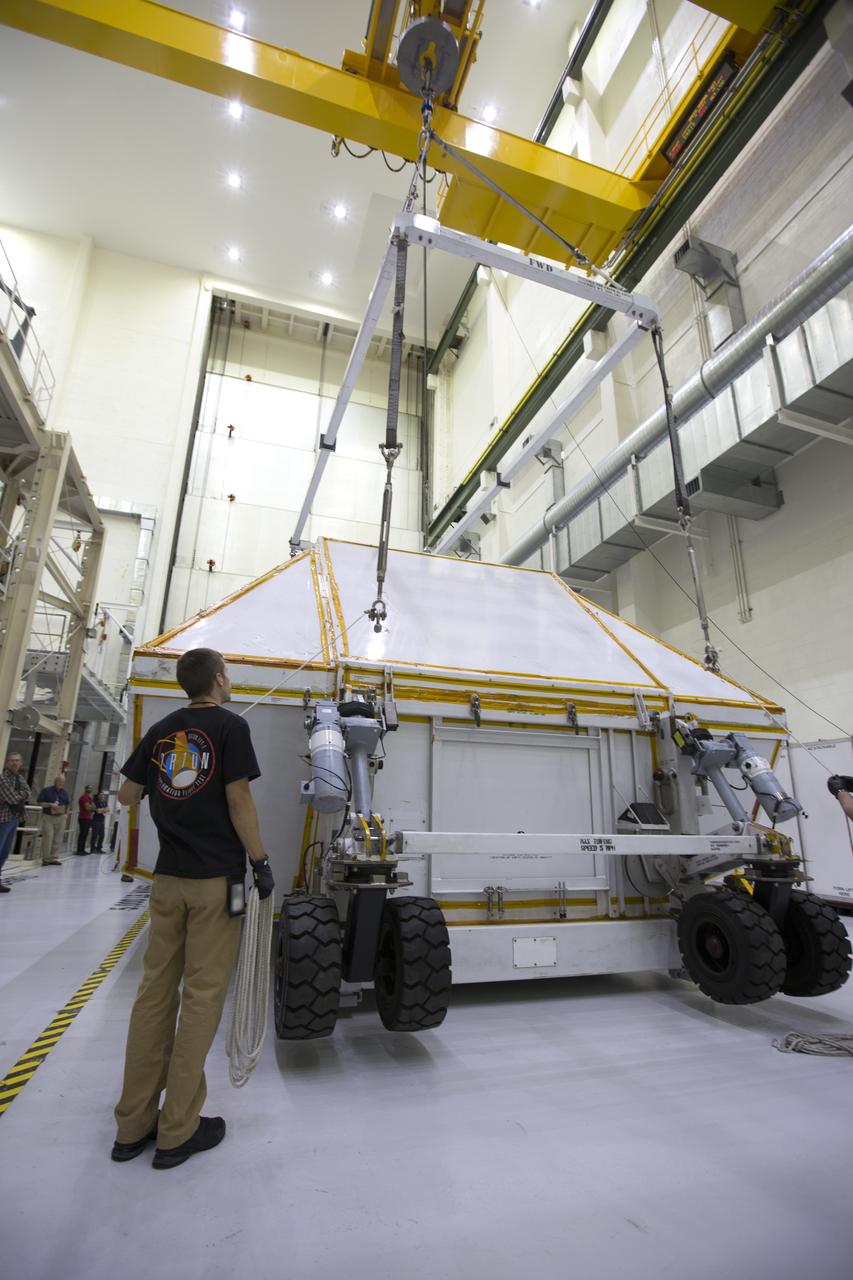

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article is secured inside its transport container. A crane is used to move the container toward a transport vehicle for the move to the Shuttle Landing Facility. The test article will be loaded in NASA's Super Guppy airplane and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
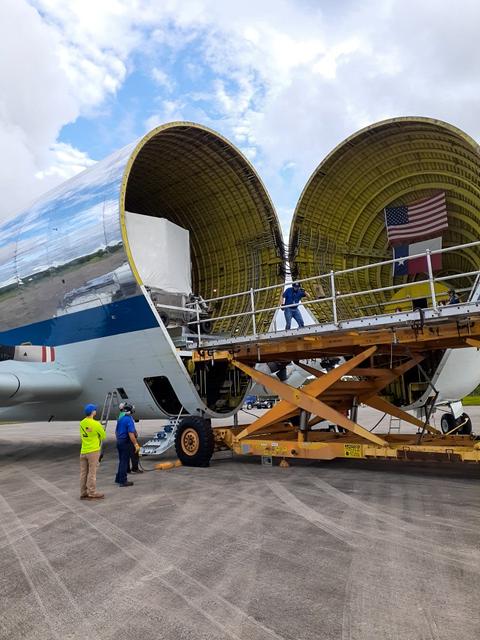

NASA’s Super Guppy arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, carrying the Orion Service Module Structural Test Article (SM-STA). Composed of the European Service Module (ESM) and crew module adapter (CMA), these components mark the completion of the test campaign to certify Orion’s Service Module for Artemis I. The Orion SM-STA is being offloaded for transport to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. Photo credit:
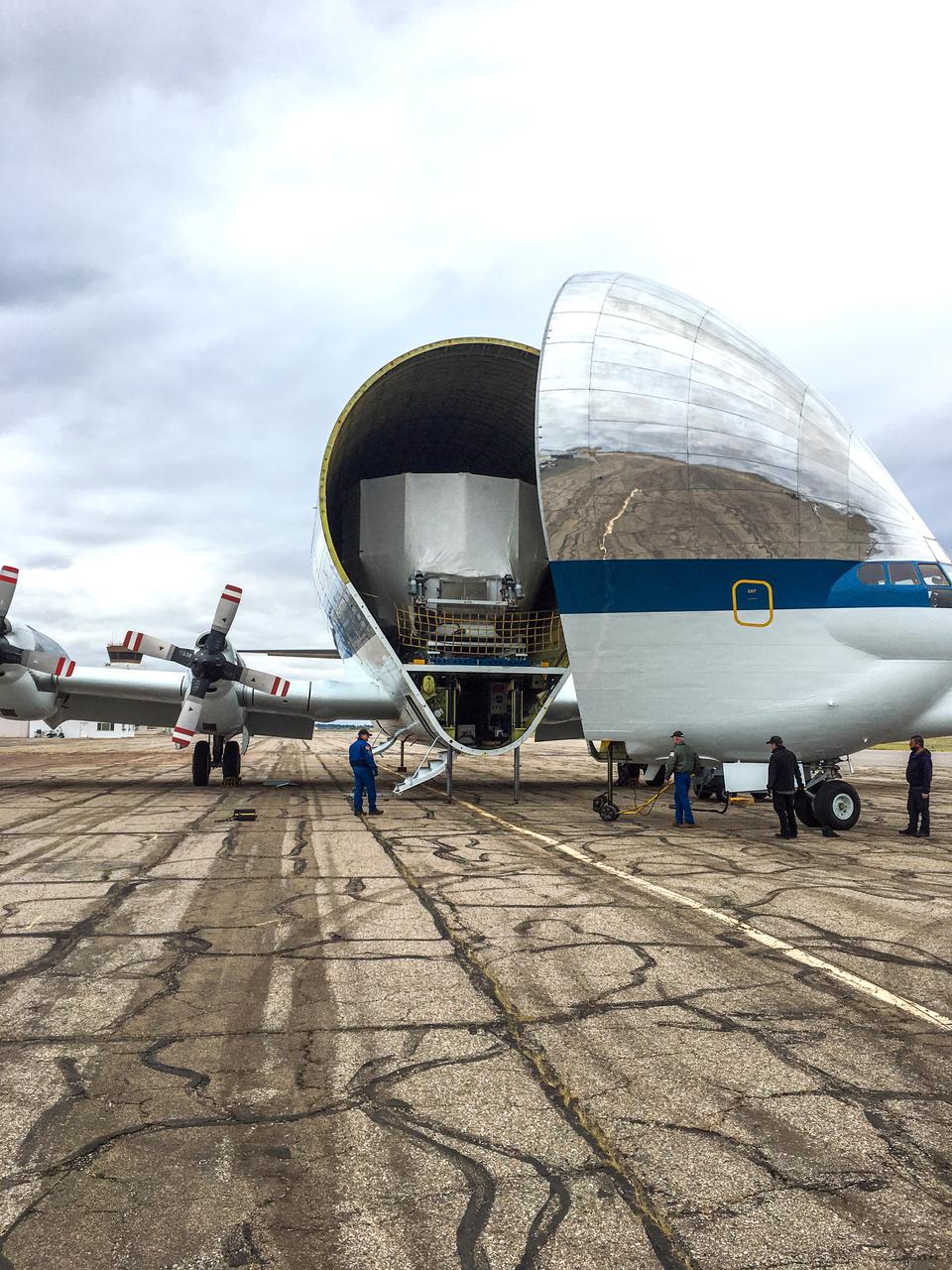

NASA’s Super Guppy arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, carrying the Orion Service Module Structural Test Article (SM-STA). Composed of the European Service Module (ESM) and crew module adapter (CMA), these components mark the completion of the test campaign to certify Orion’s Service Module for Artemis I. The Orion SM-STA is being offloaded for transport to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

NASA’s Super Guppy arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, carrying the Orion Service Module Structural Test Article (SM-STA). Composed of the European Service Module (ESM) and crew module adapter (CMA), these components mark the completion of the test campaign to certify Orion’s Service Module for Artemis I. The Orion SM-STA is being offloaded for transport to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.NASA’s Super Guppy arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, carrying the Orion Service Module Structural Test Article (SM-STA). Composed of the European Service Module (ESM) and crew module adapter (CMA) these components mark the completion of the test campaign to certify Orion’s Service Module for Artemis I. The Orion SM-STA is being offloaded for transport to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
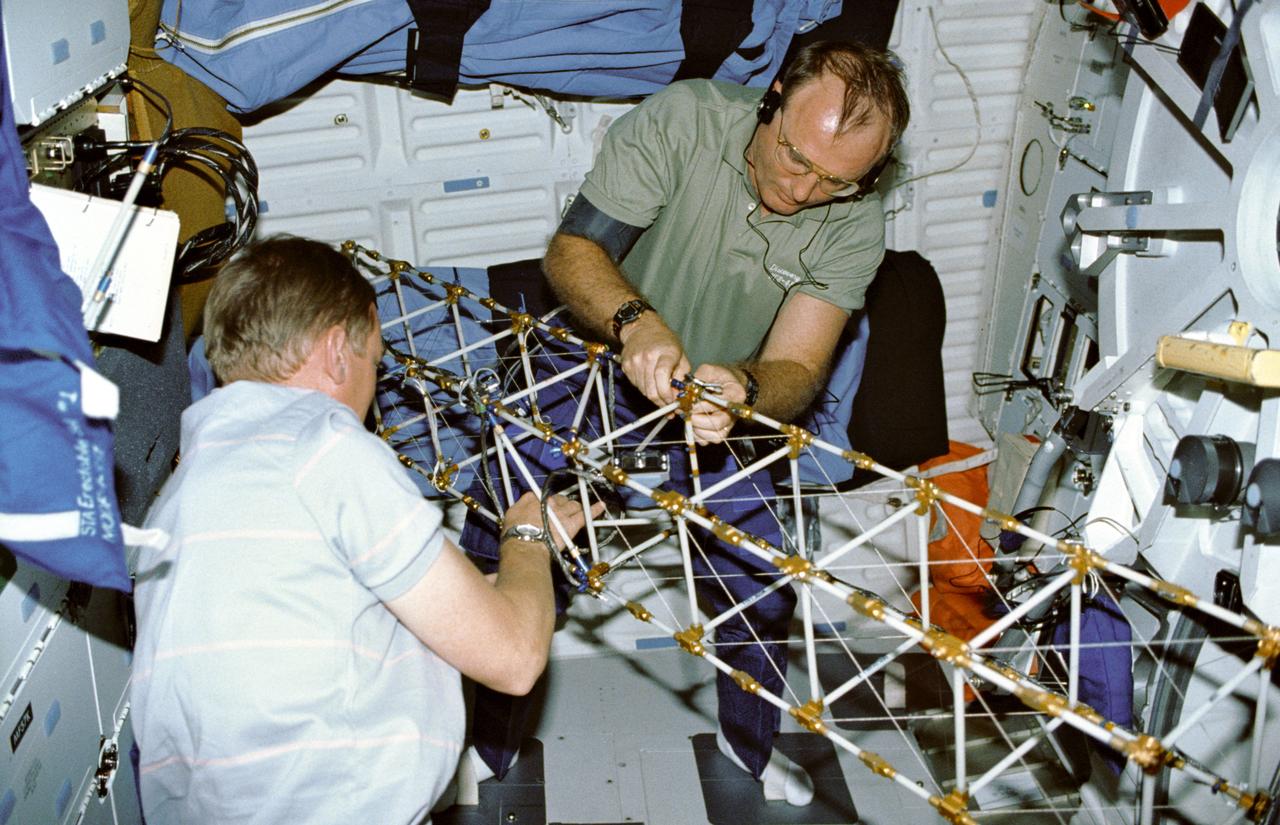

STS048-09-019 (16 Sept 1991) --- Astronauts Mark N. Brown, left, and James F. Buchli work with the structural test article (STA), a model of the space station truss structure. STA is part of the middeck zero gravity dynamics experiment (MODE). MODE was designed to study the vibration characteristics of the jointed truss structure. The structural test article includes four strain gauges and eleven accelerometers and is vibrated by an actuator. Assembled by crewmembers in the Shuttle orbiter's middeck, the device is about 72 inches long with an 8-inch square cross section.

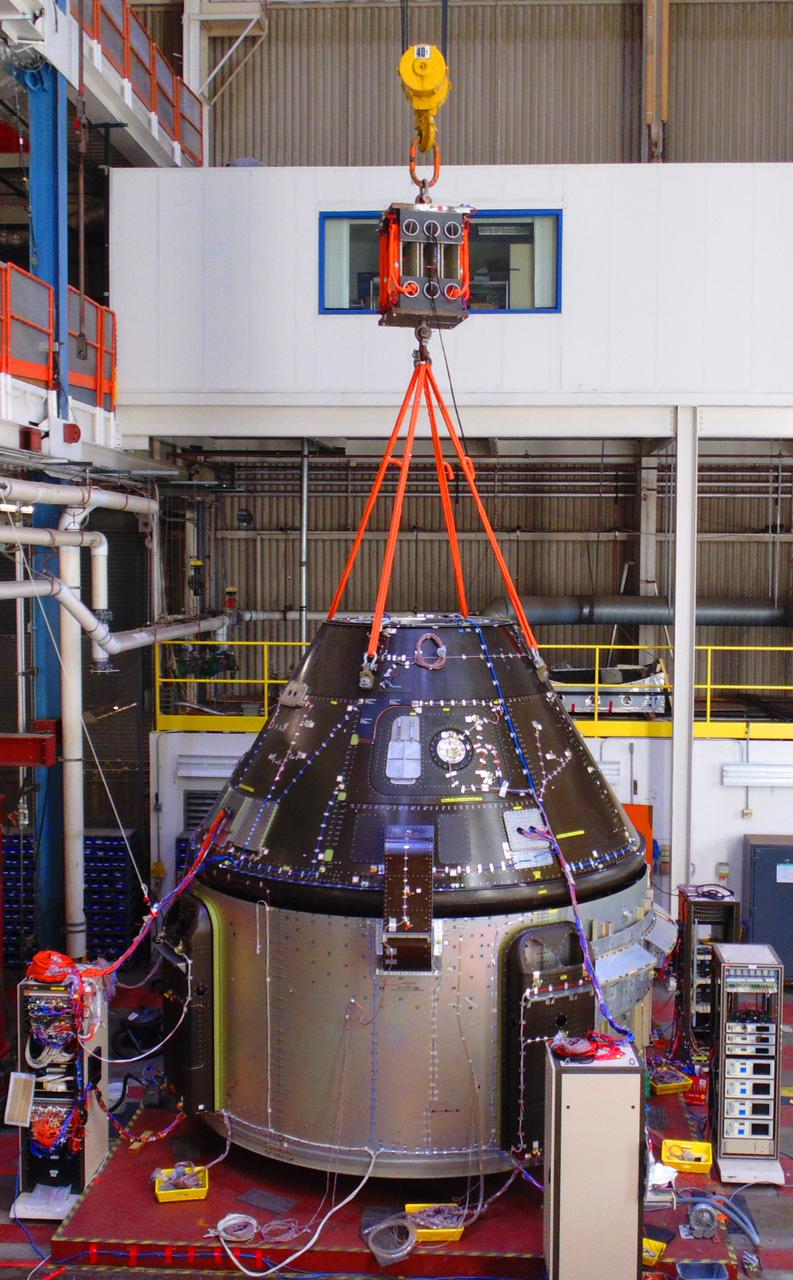
The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the module, secured on a stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
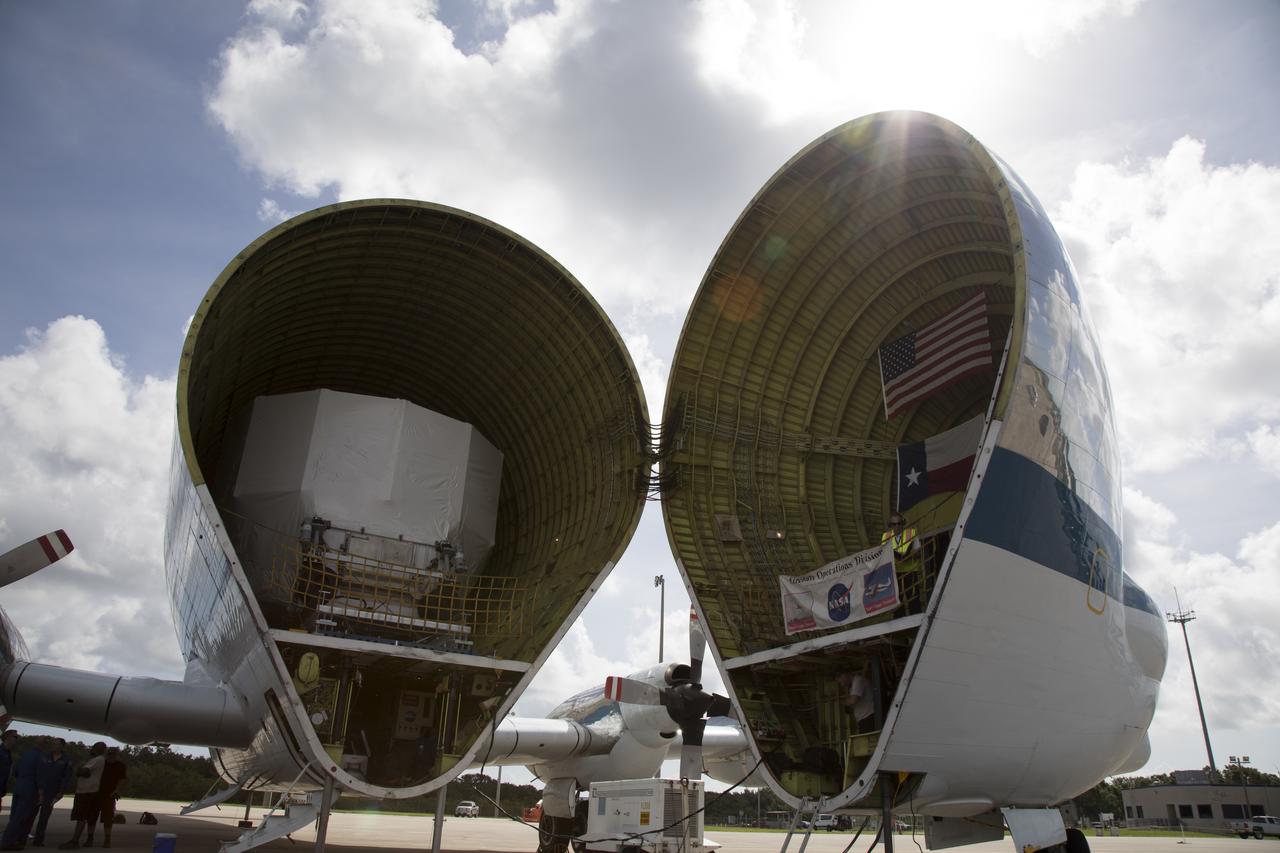

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is secured inside NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. The module will be shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
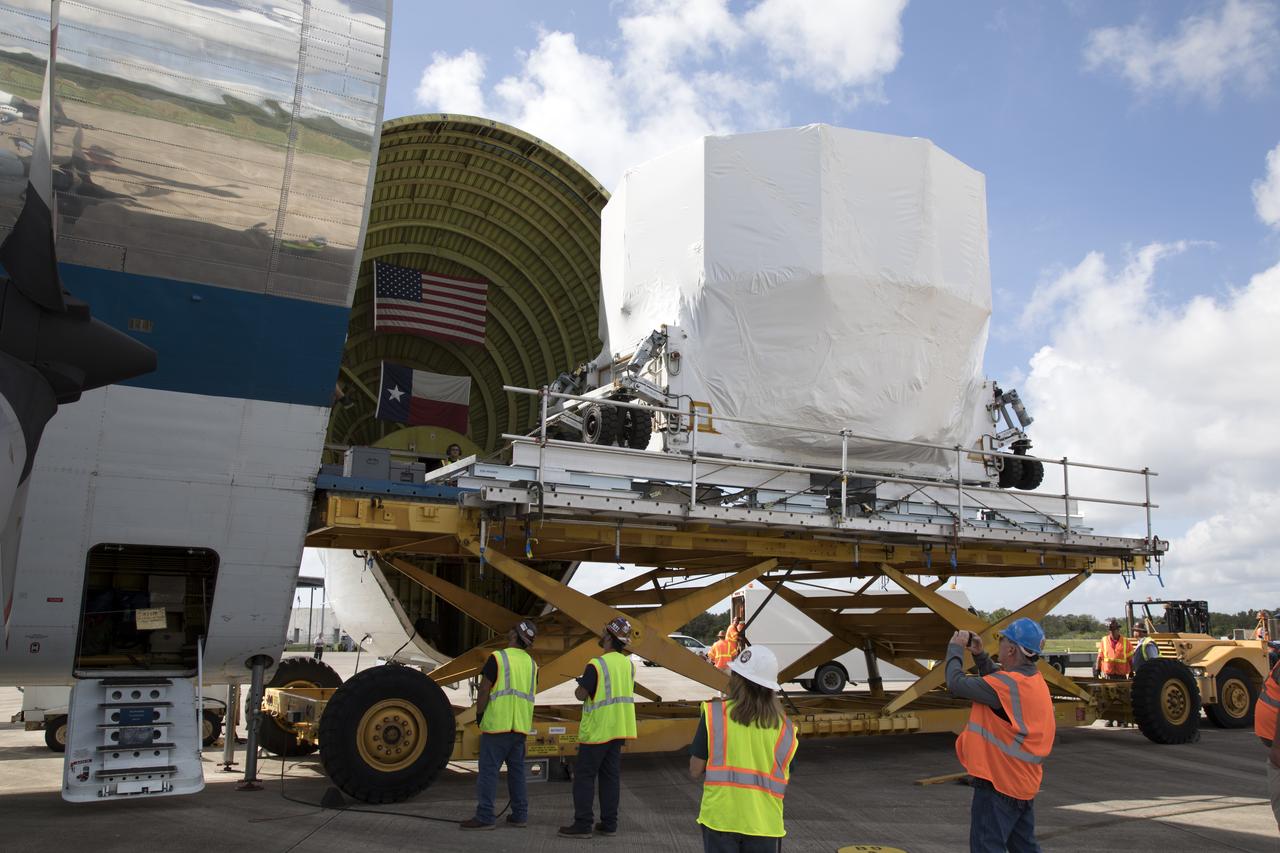

At Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility in Florida, workers prepare to move the Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, inside NASA's Super Guppy aircraft. The module will be secured inside the aircraft and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
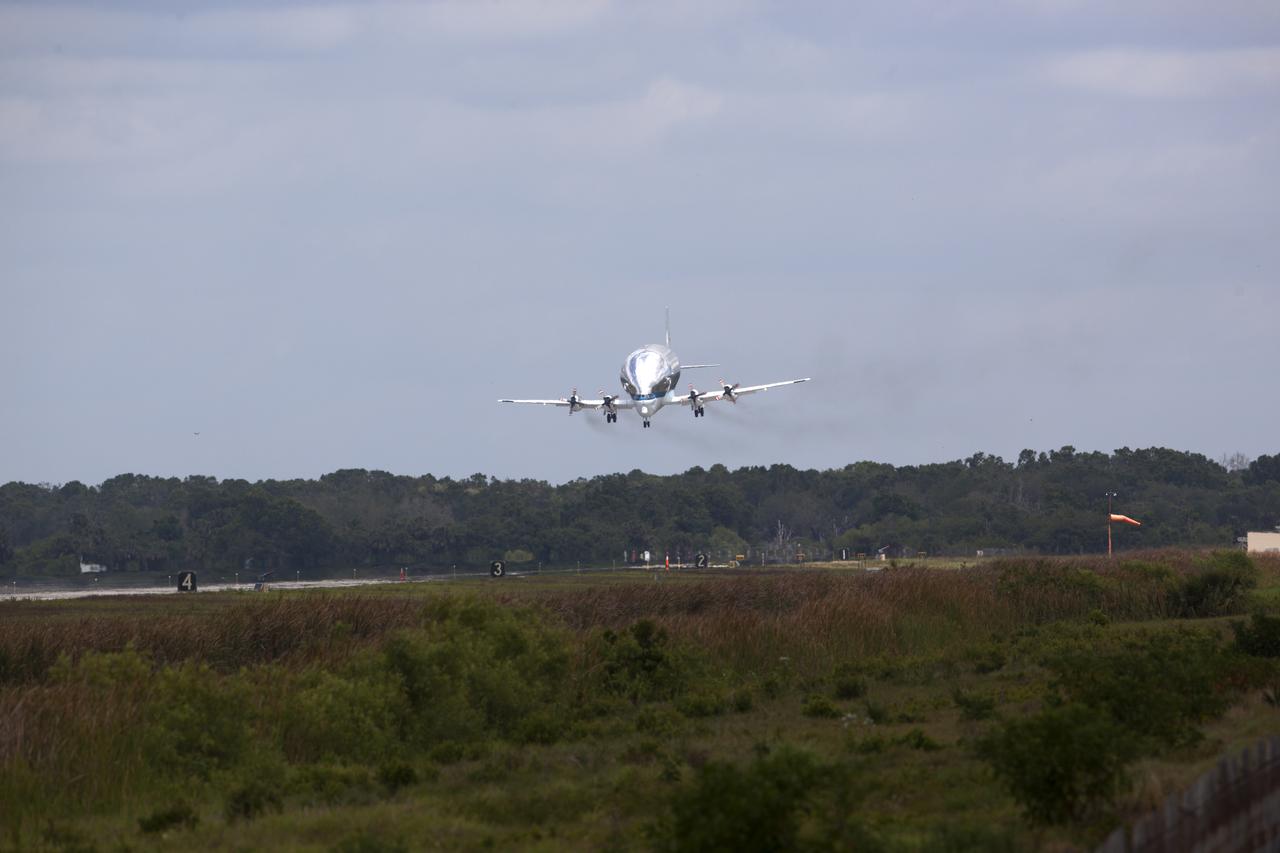

NASA's Super Guppy airplane descends toward the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article will be loaded in the Super Guppy and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
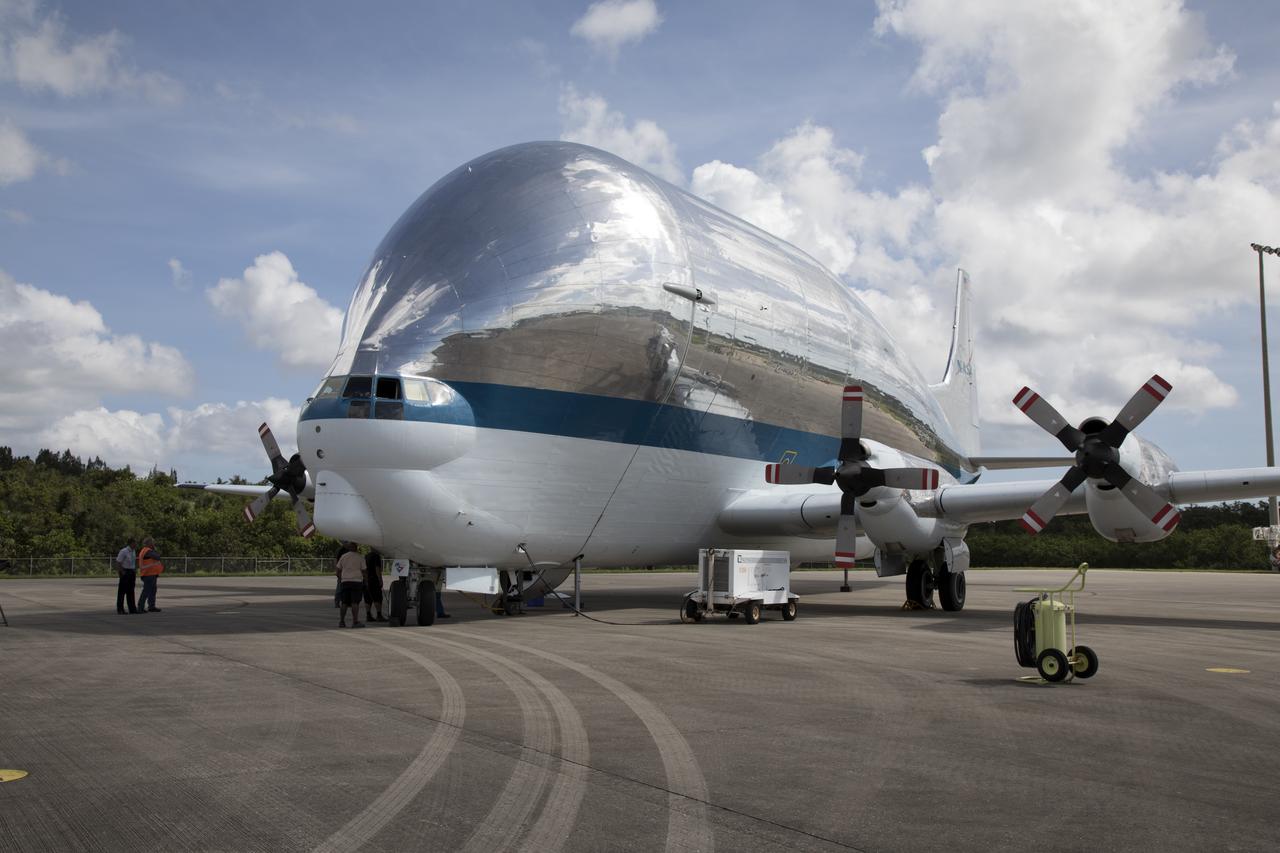

NASA's Super Guppy aircraft has arrived on the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility, managed and operated by Space Florida, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, will be loaded into the Guppy for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
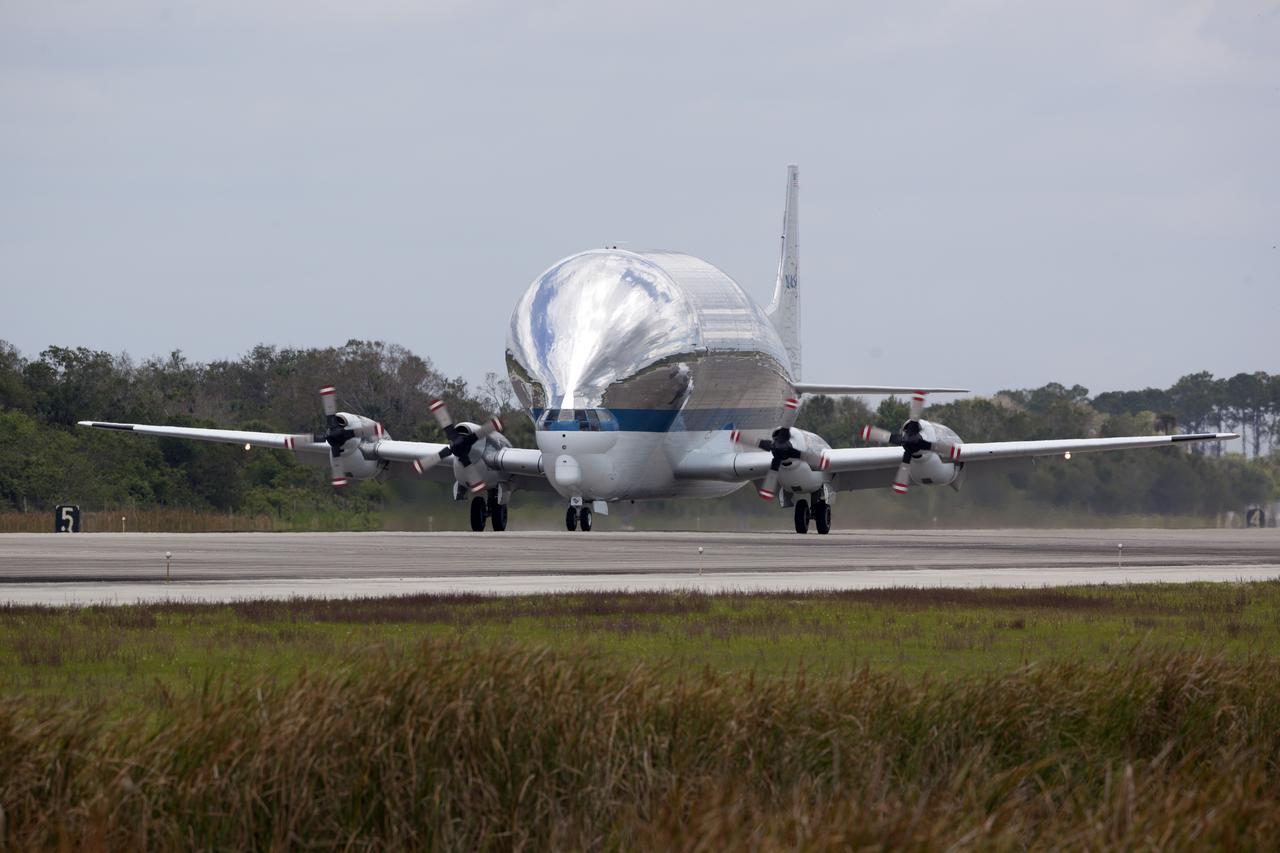

NASA's Super Guppy airplane touches down on the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article will be loaded in the Super Guppy and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
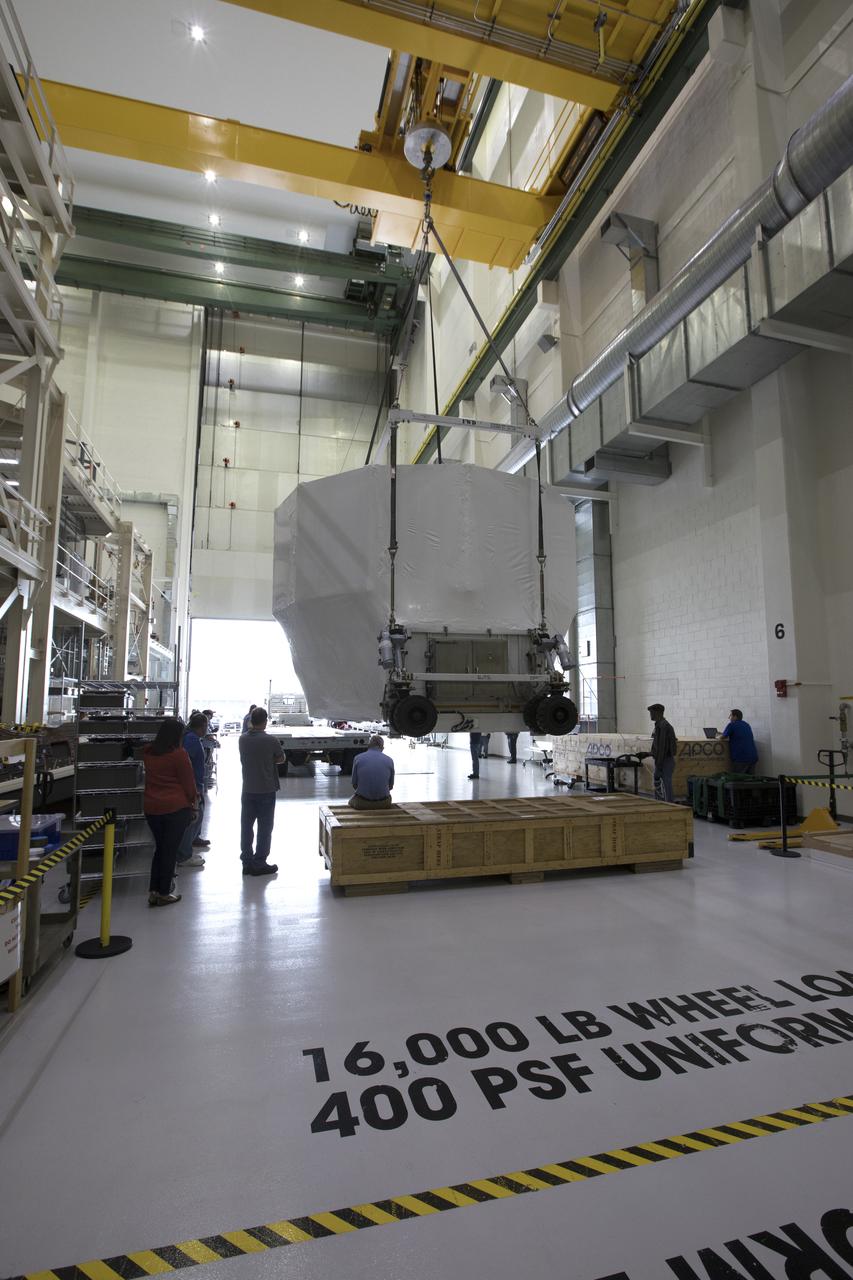

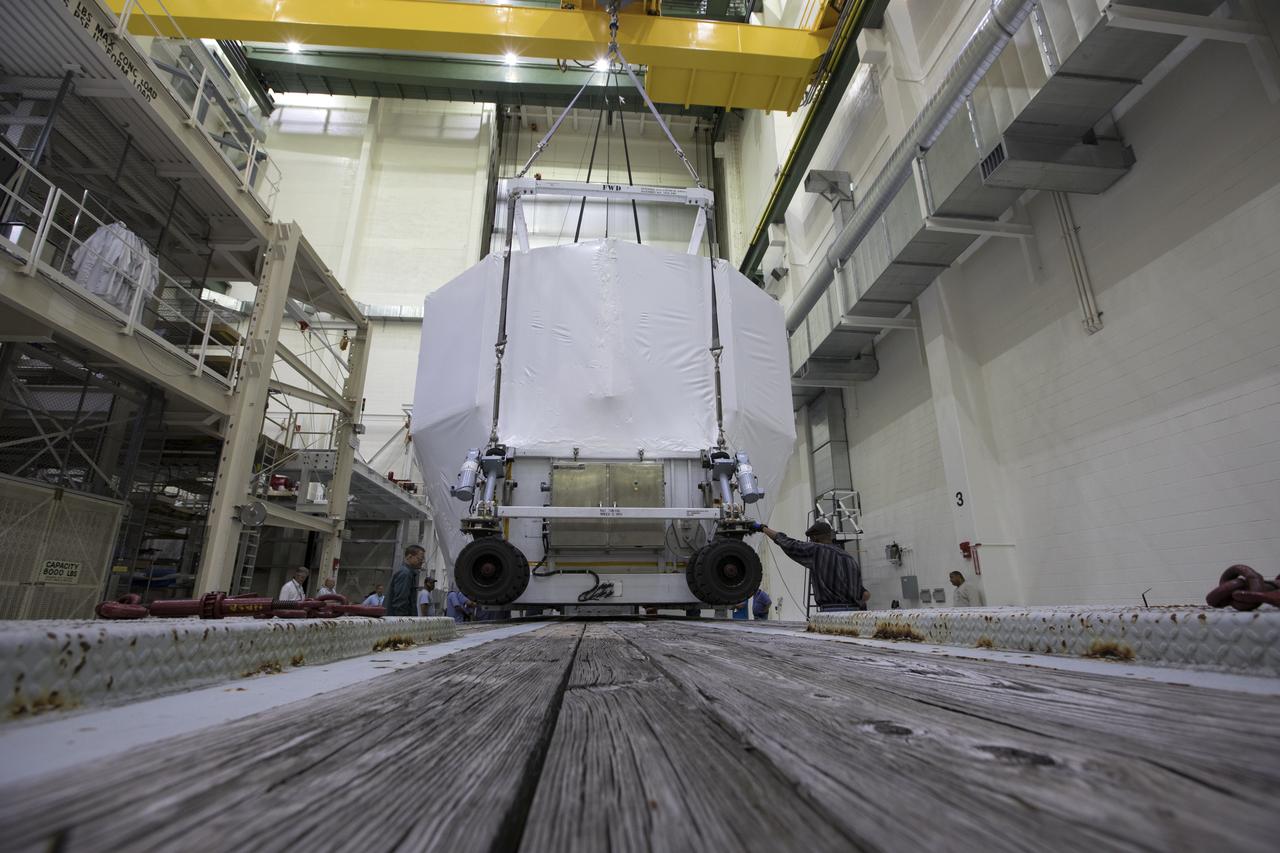
The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the module, secured on a stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
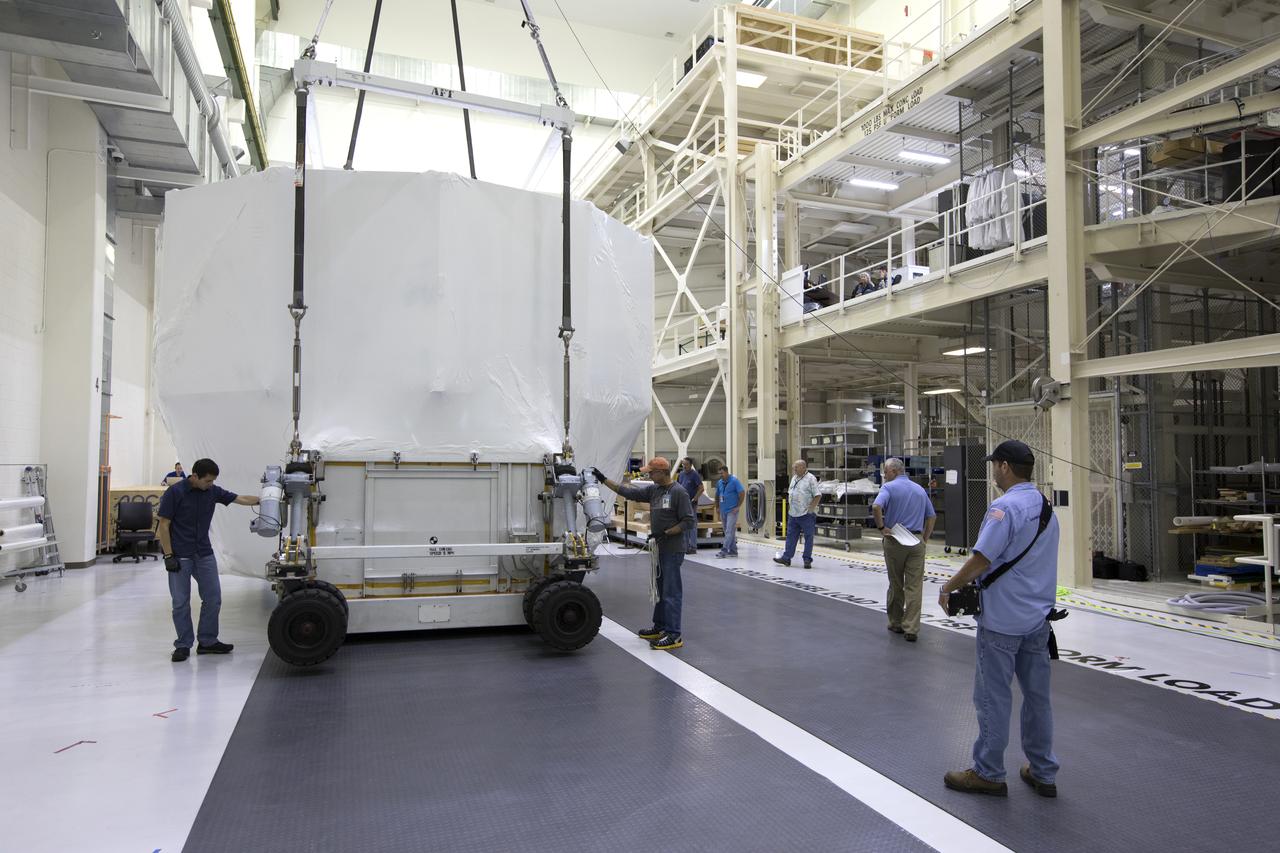

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure the protective covering around the module and a crane lifts the module, secured on stand, for the move to the transport truck. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
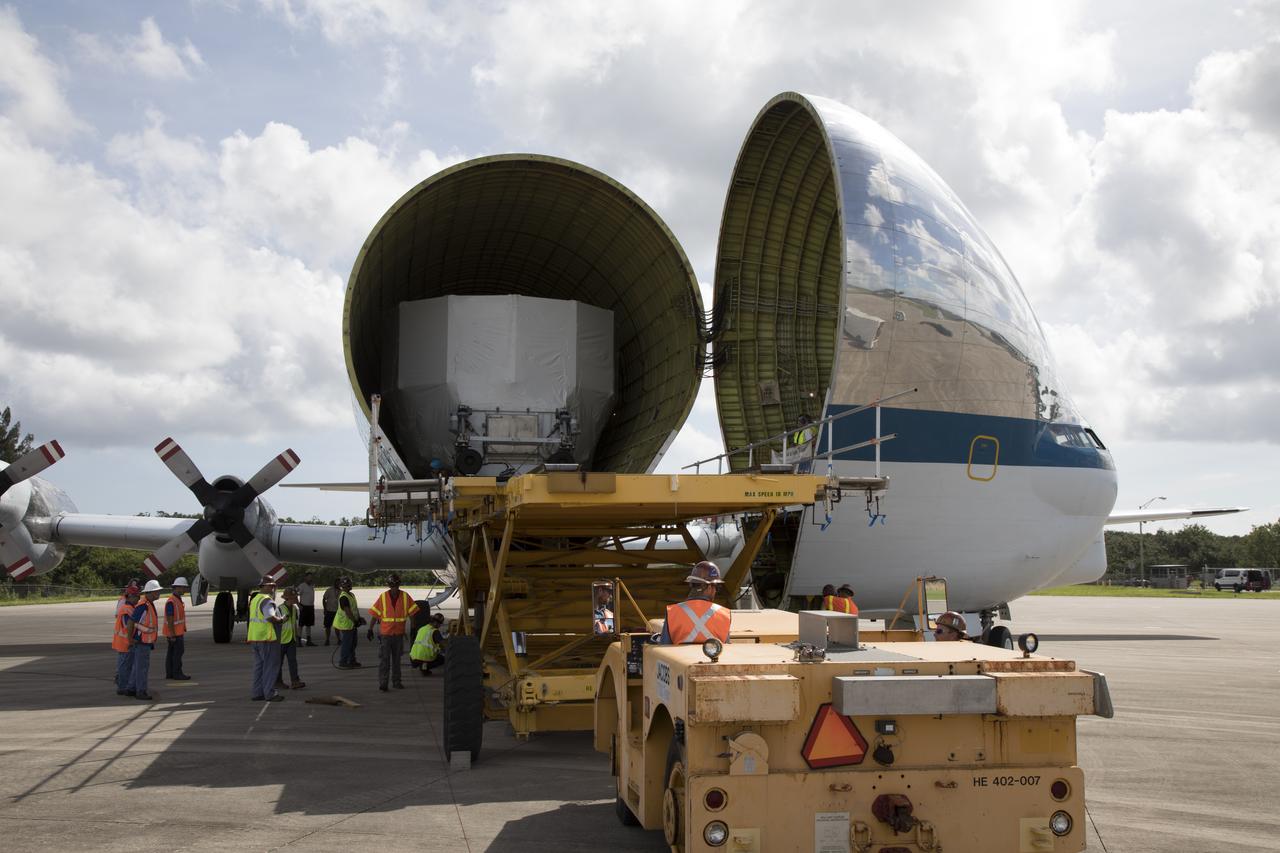

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is moved inside NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. The module will be secured inside the aircraft and shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
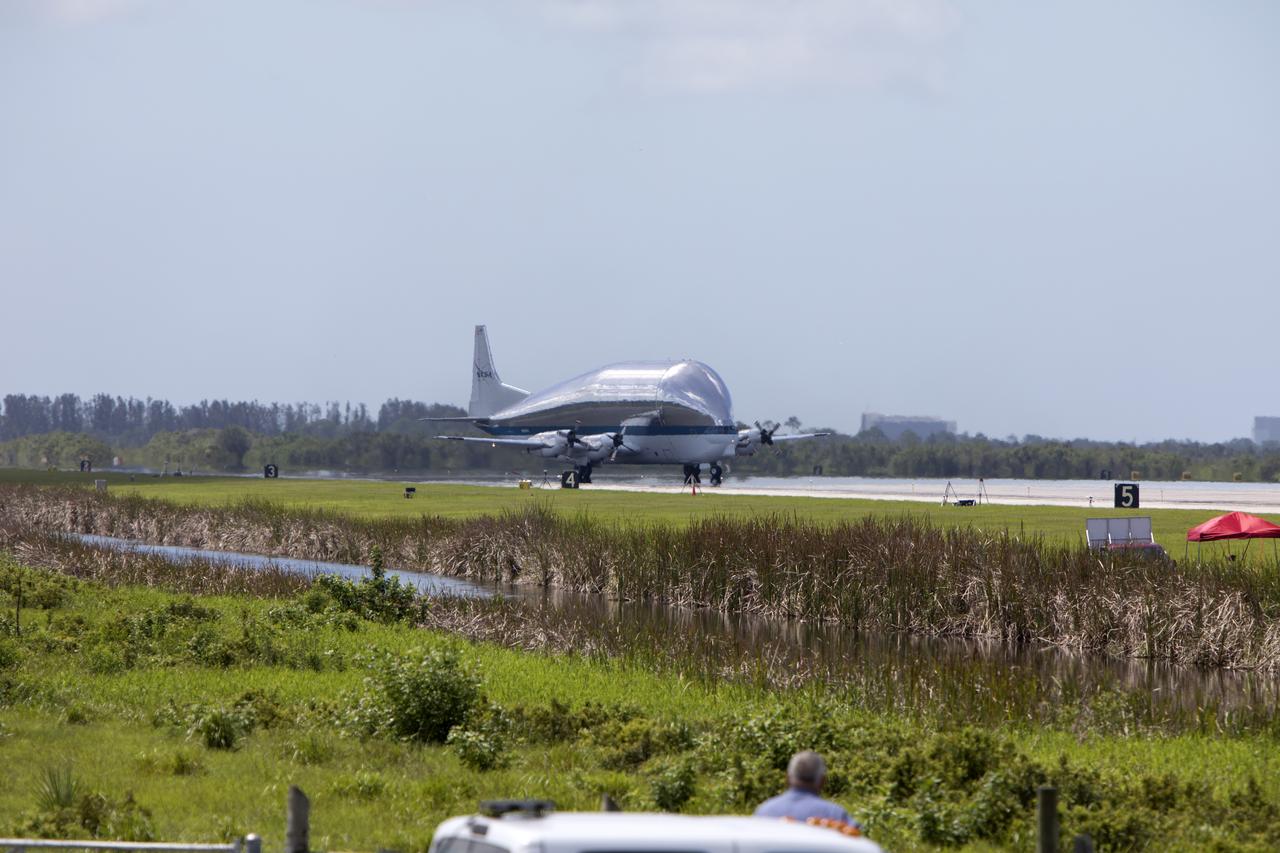

NASA's Super Guppy aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility, managed and operated by Space Florida, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, will be loaded into the Guppy for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
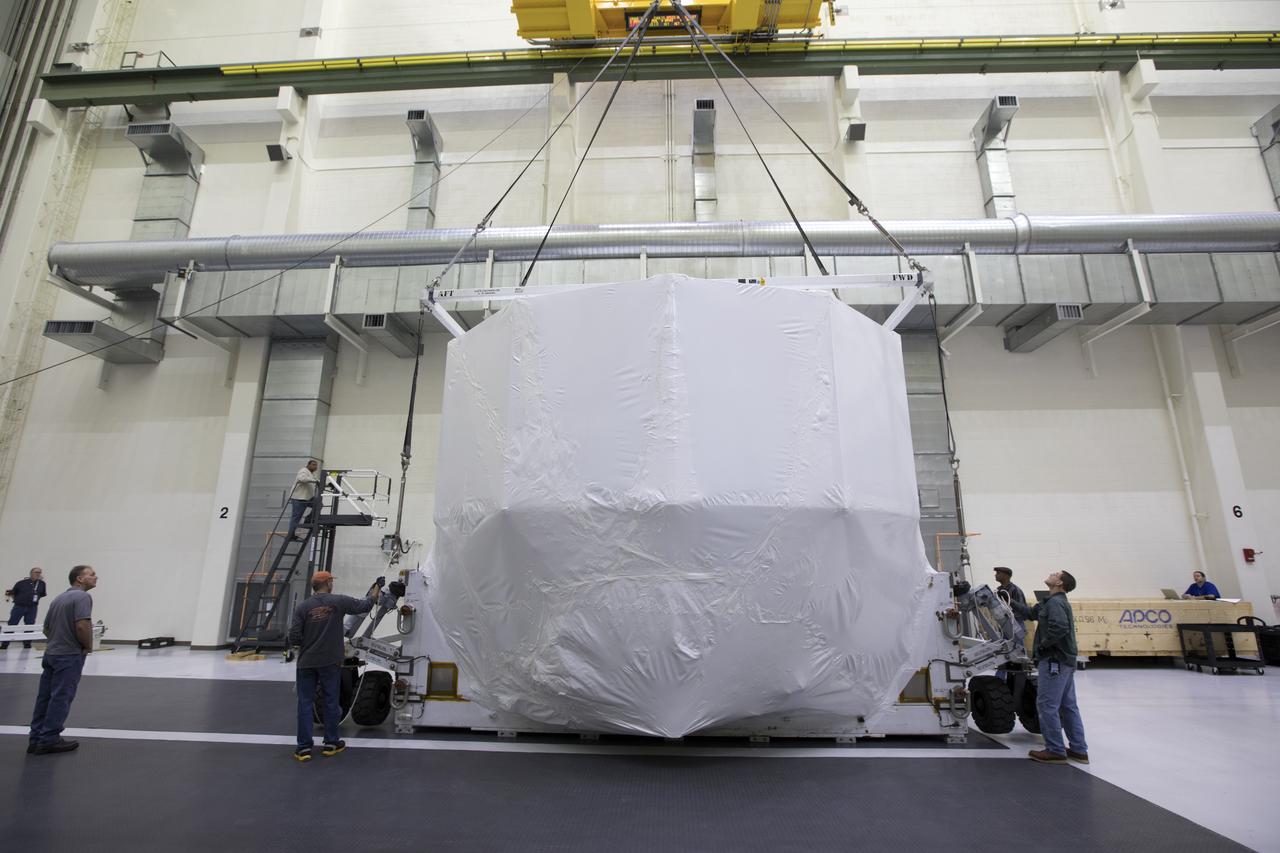

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is prepared for shipment to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure the protective covering around the module and a crane is used to lower it onto a stand. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
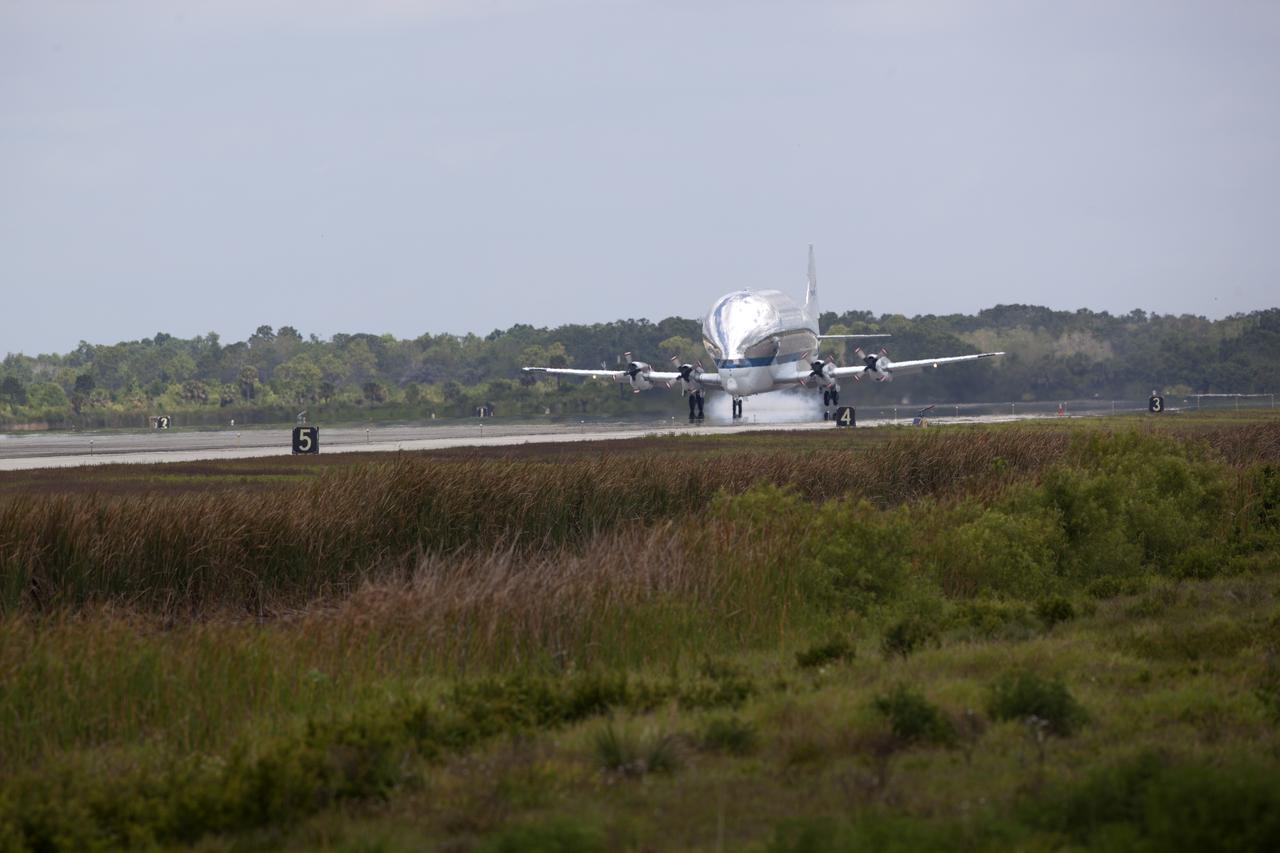

NASA's Super Guppy airplane touches down on the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article will be loaded in the Super Guppy and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
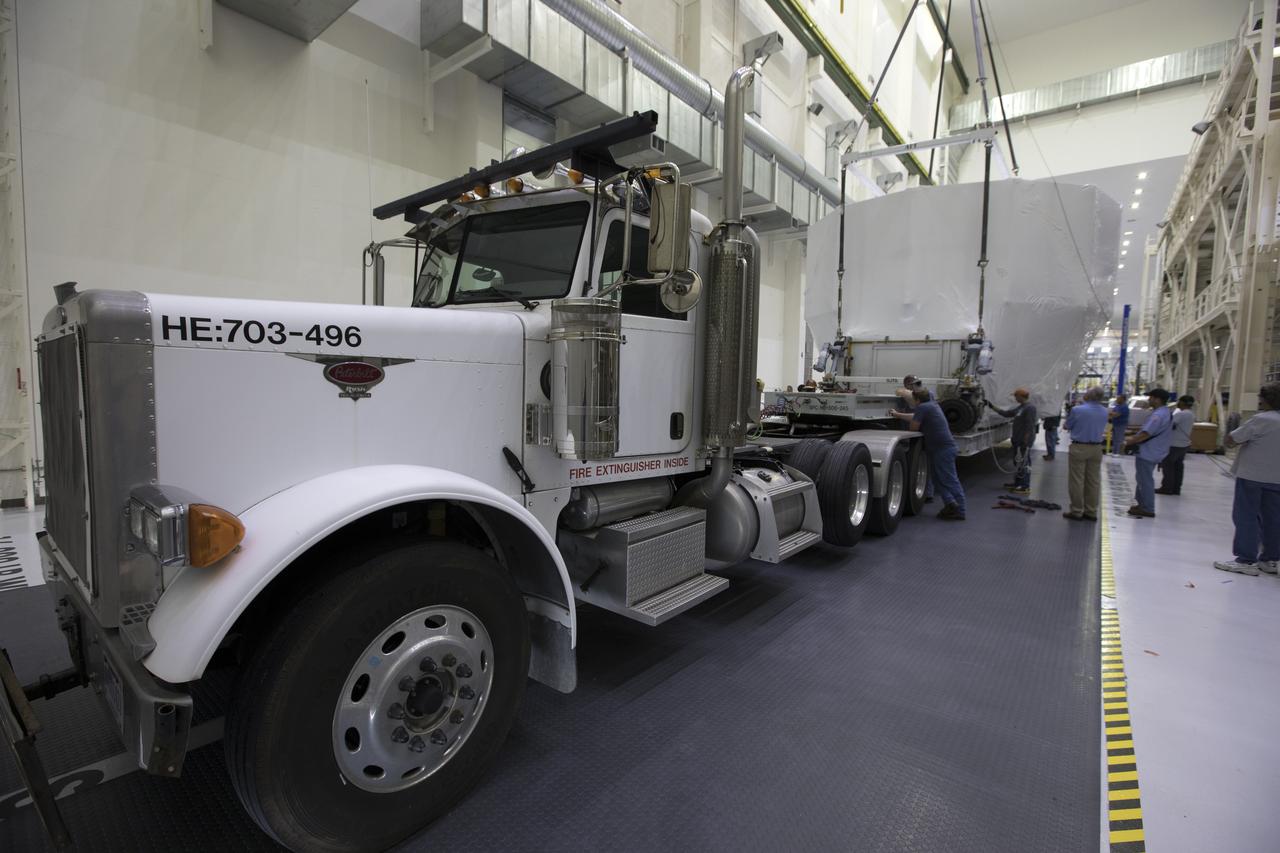

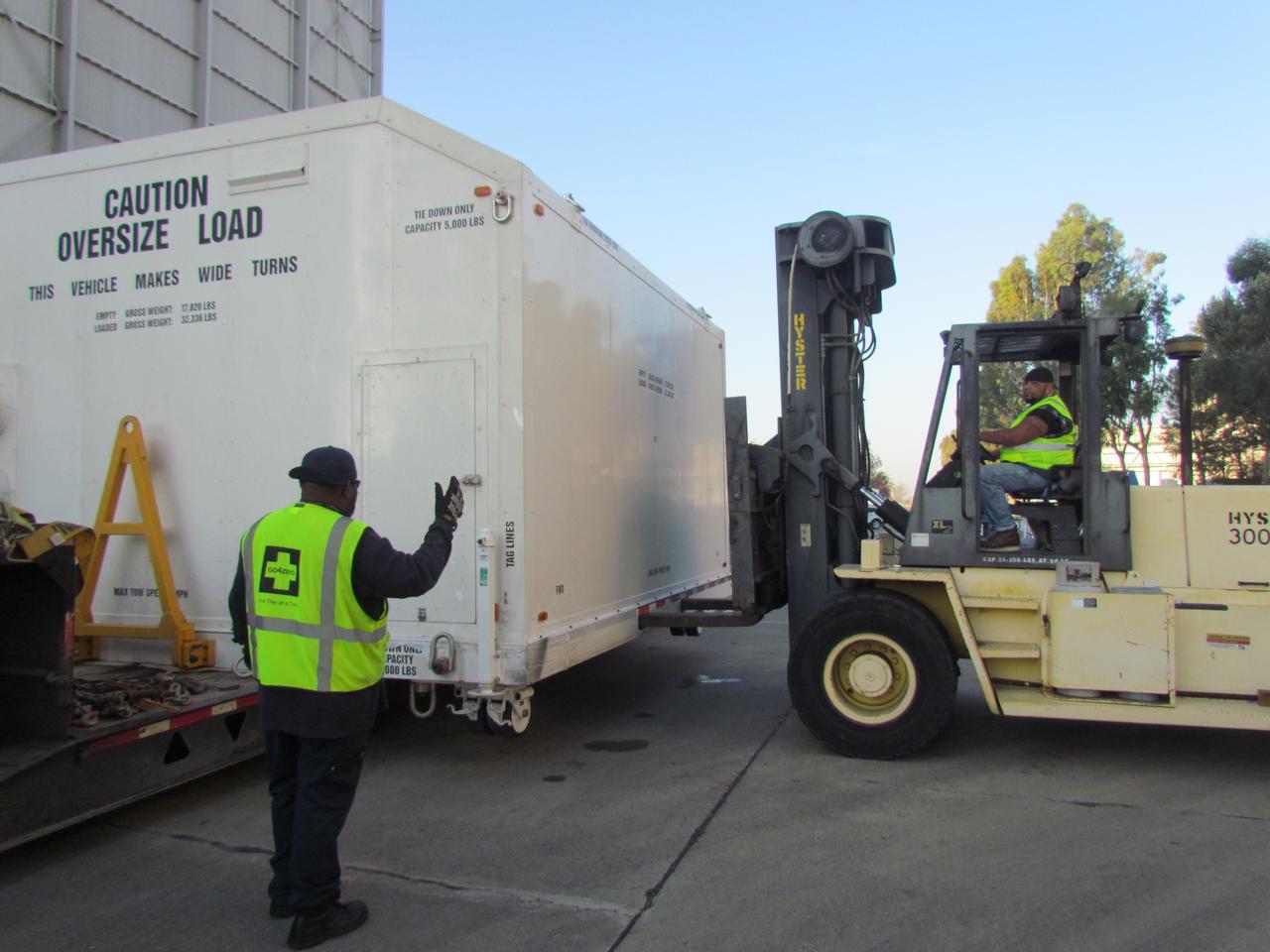
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, the Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is secured on the flatbed of a transport truck. The service module will be shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
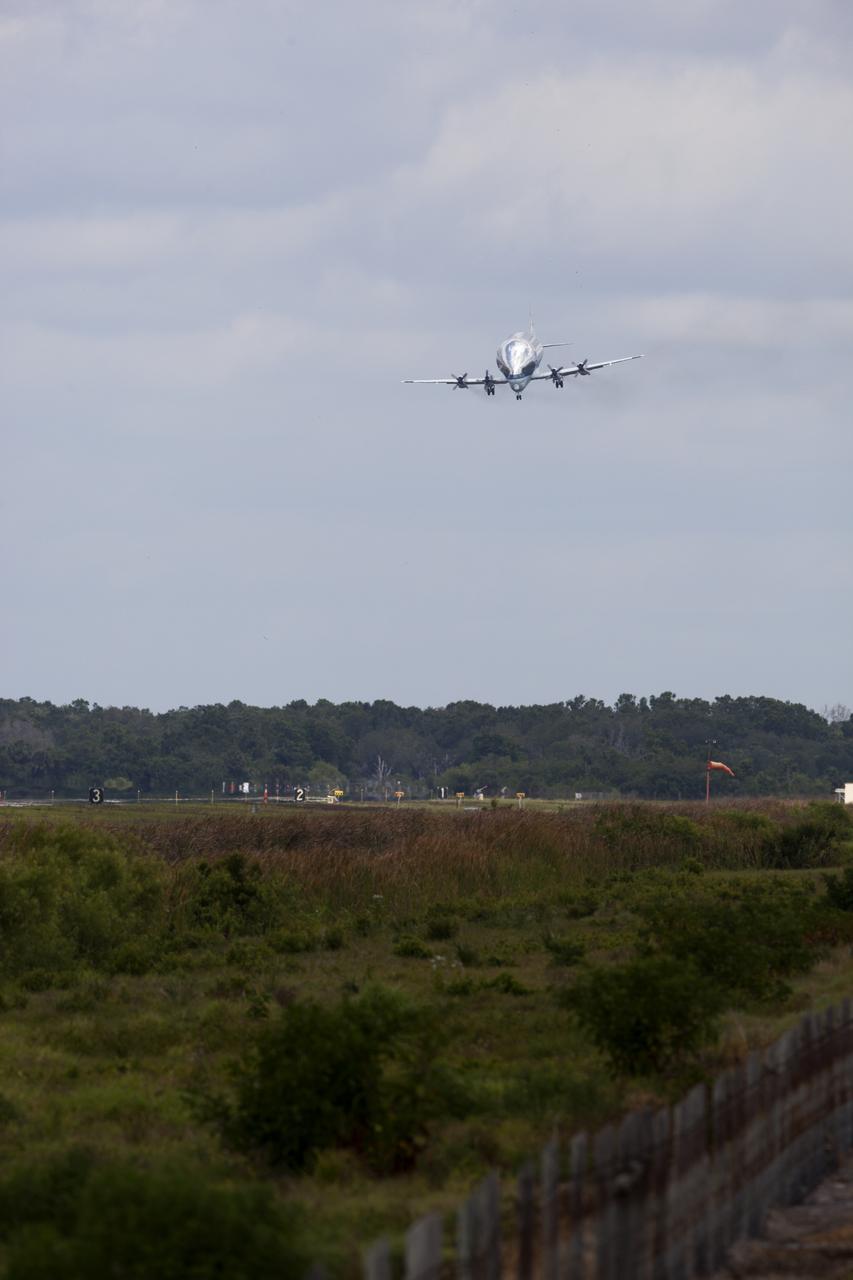

NASA's Super Guppy airplane descends toward the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article will be loaded in the Super Guppy and transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
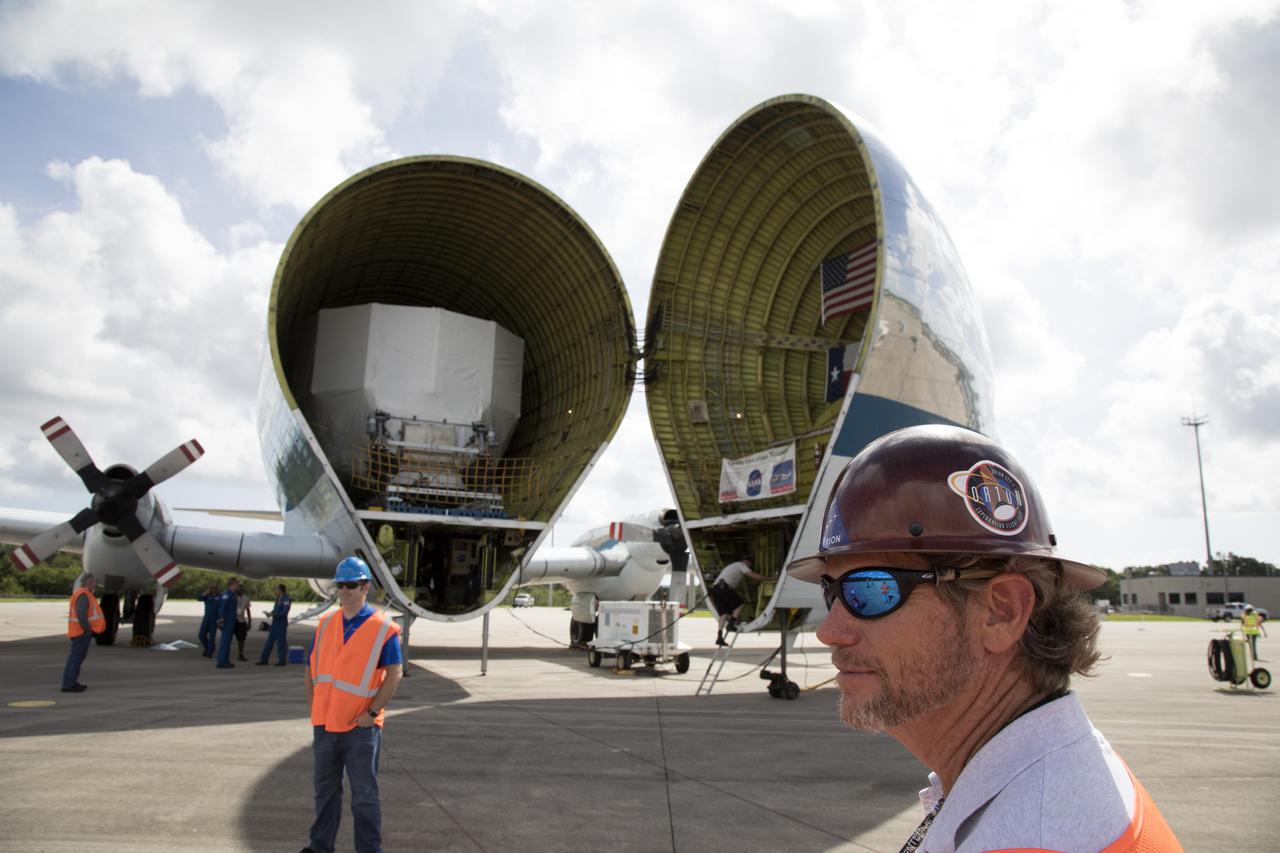

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is secured inside NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. The module will be shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.
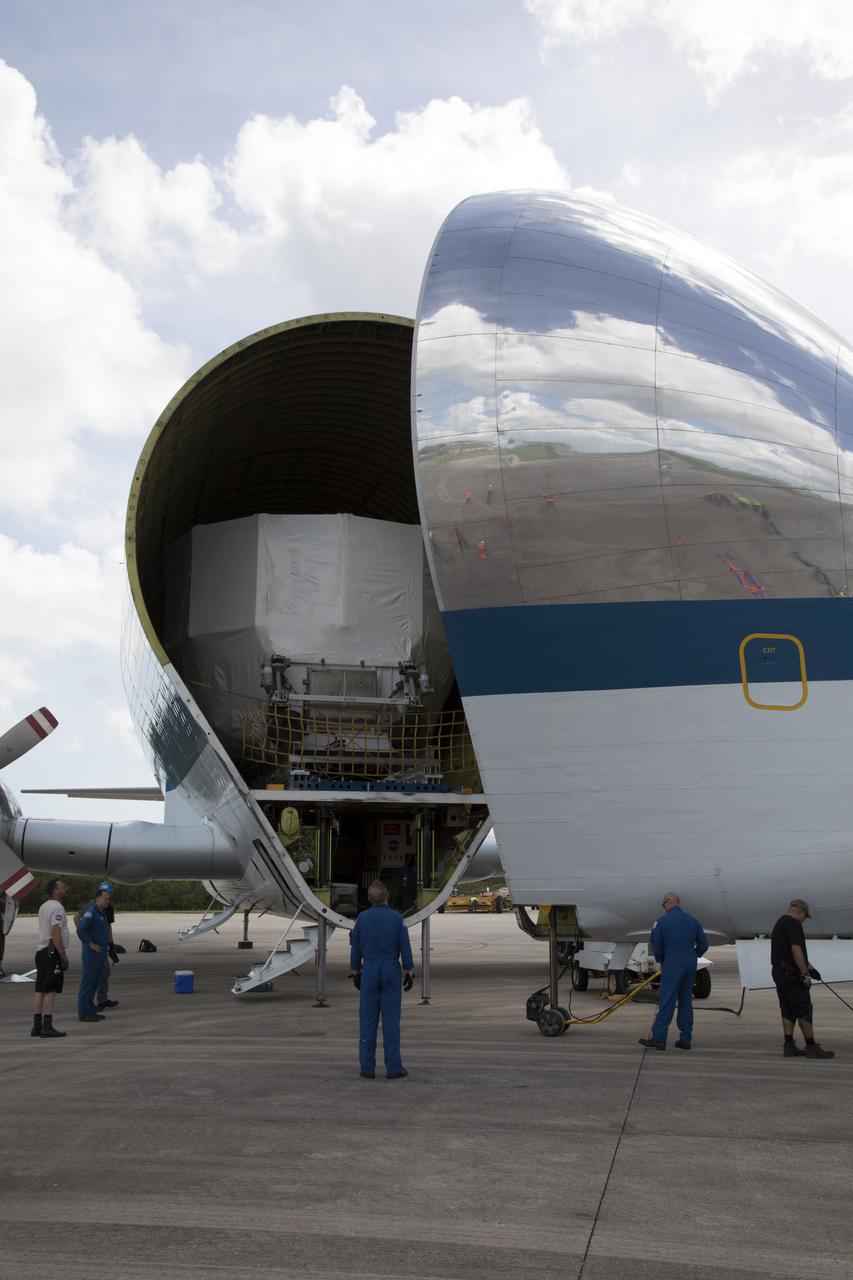

The Orion service module structural test article for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), built by the European Space Agency, is secured inside NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. The module will be shipped to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility to undergo testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on EM-1 in 2019.

A Starliner structural test article at Boeing's Huntington Beach Facility in California, where the spacecraft, including the service module and other hardware of the Atlas V upper stage, are undergoing rigorous qualification testing, including tests like shock, separation and vibration. Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner will launch on the Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
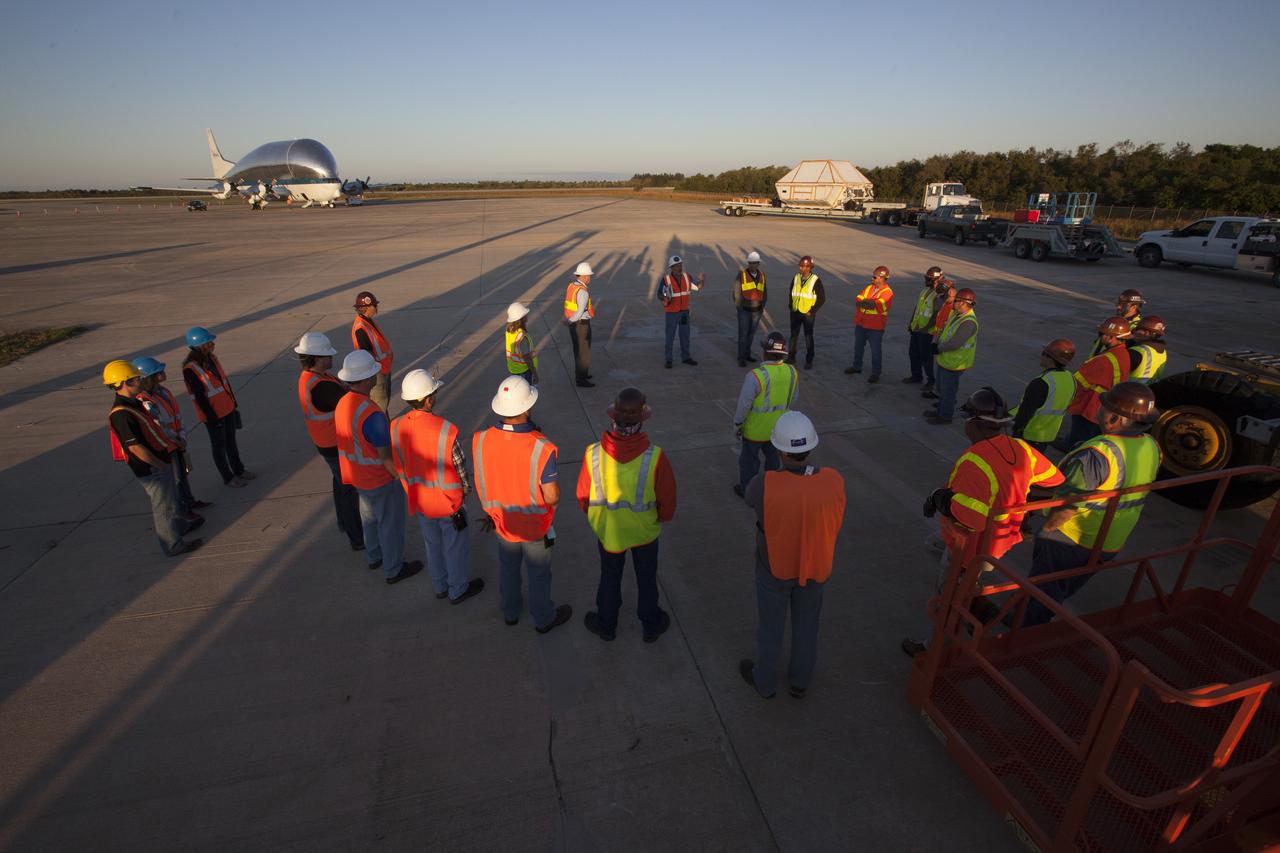

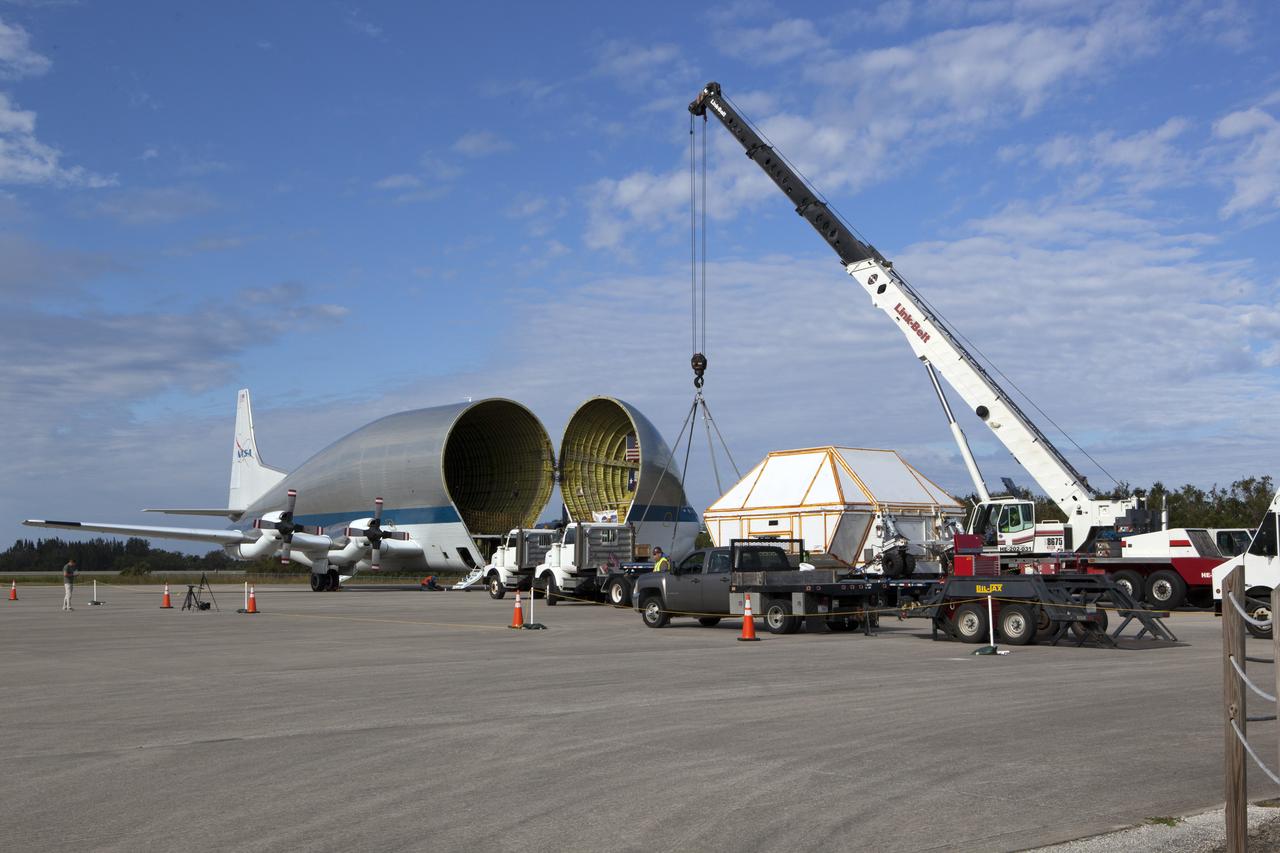
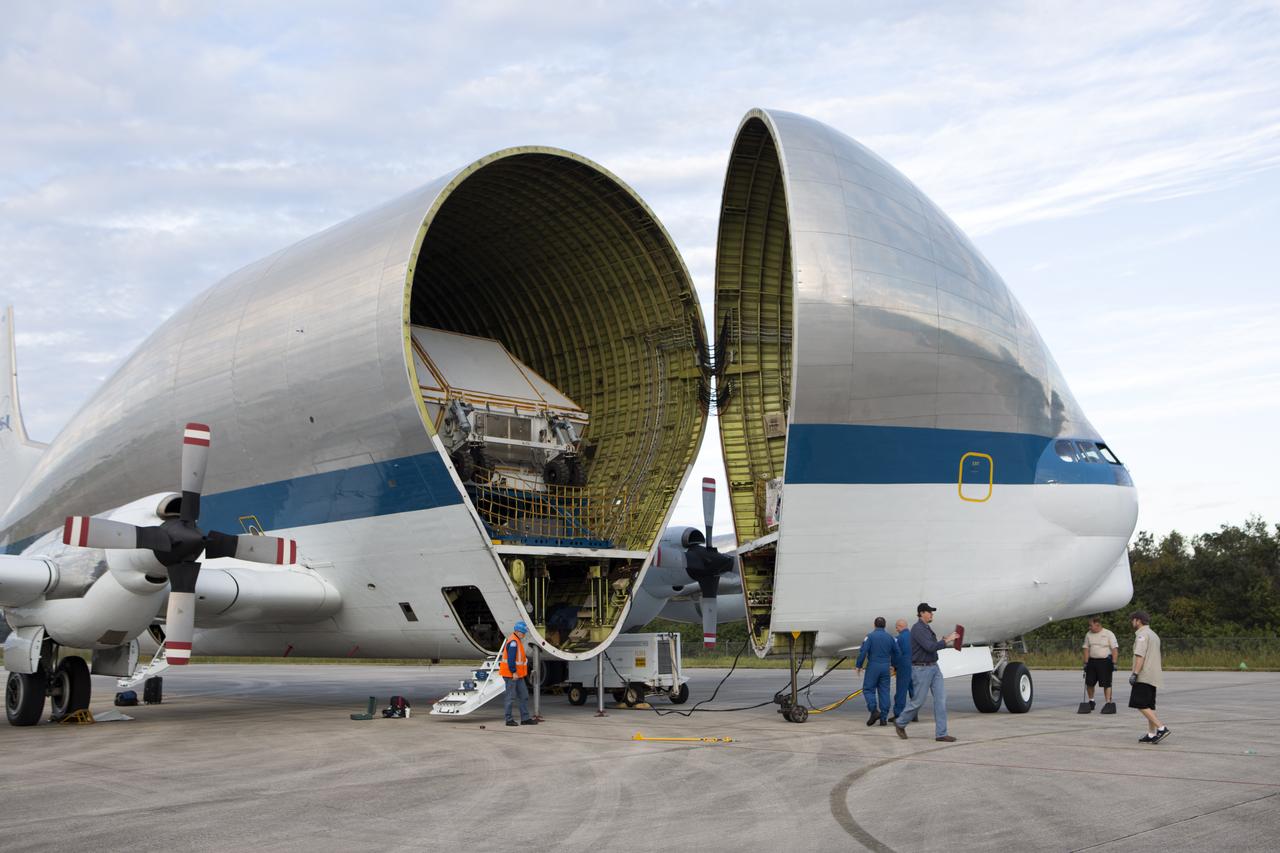
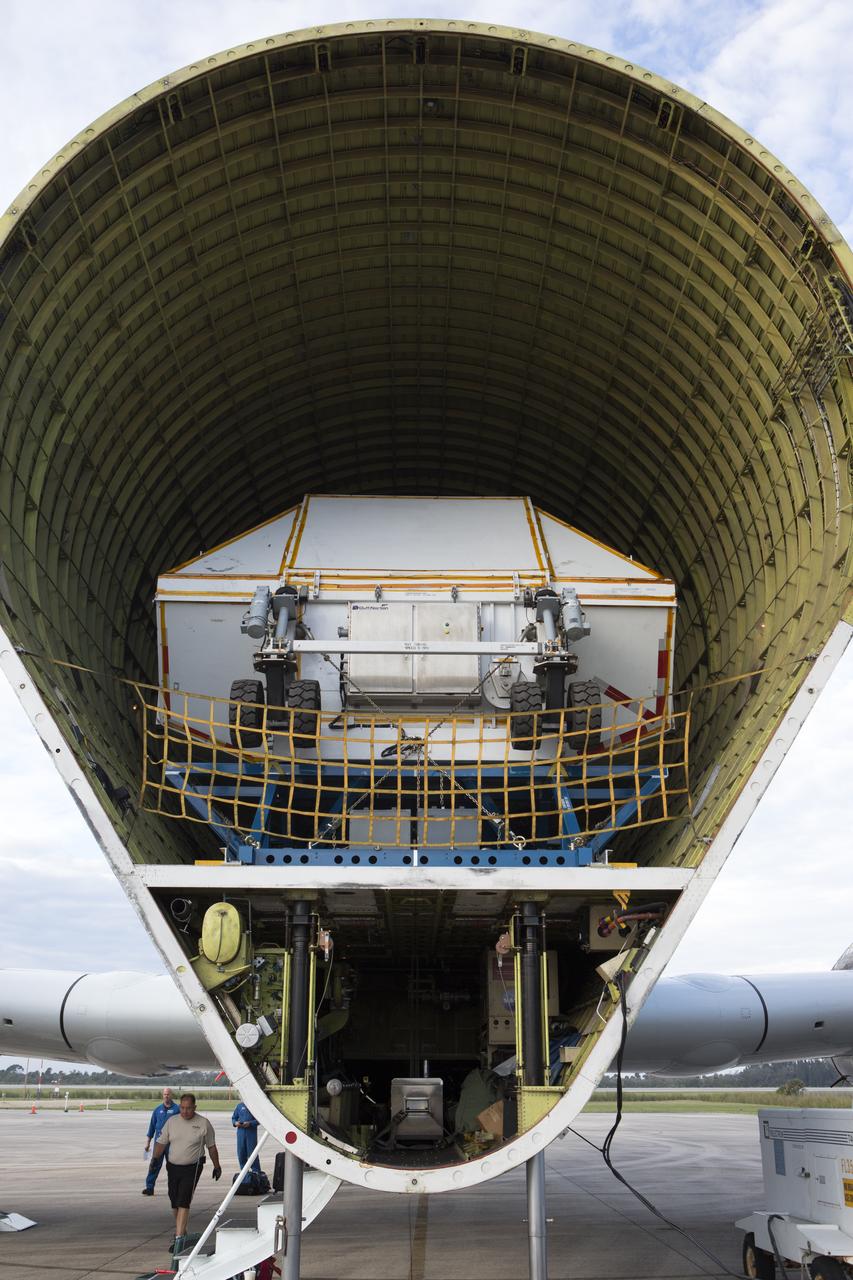
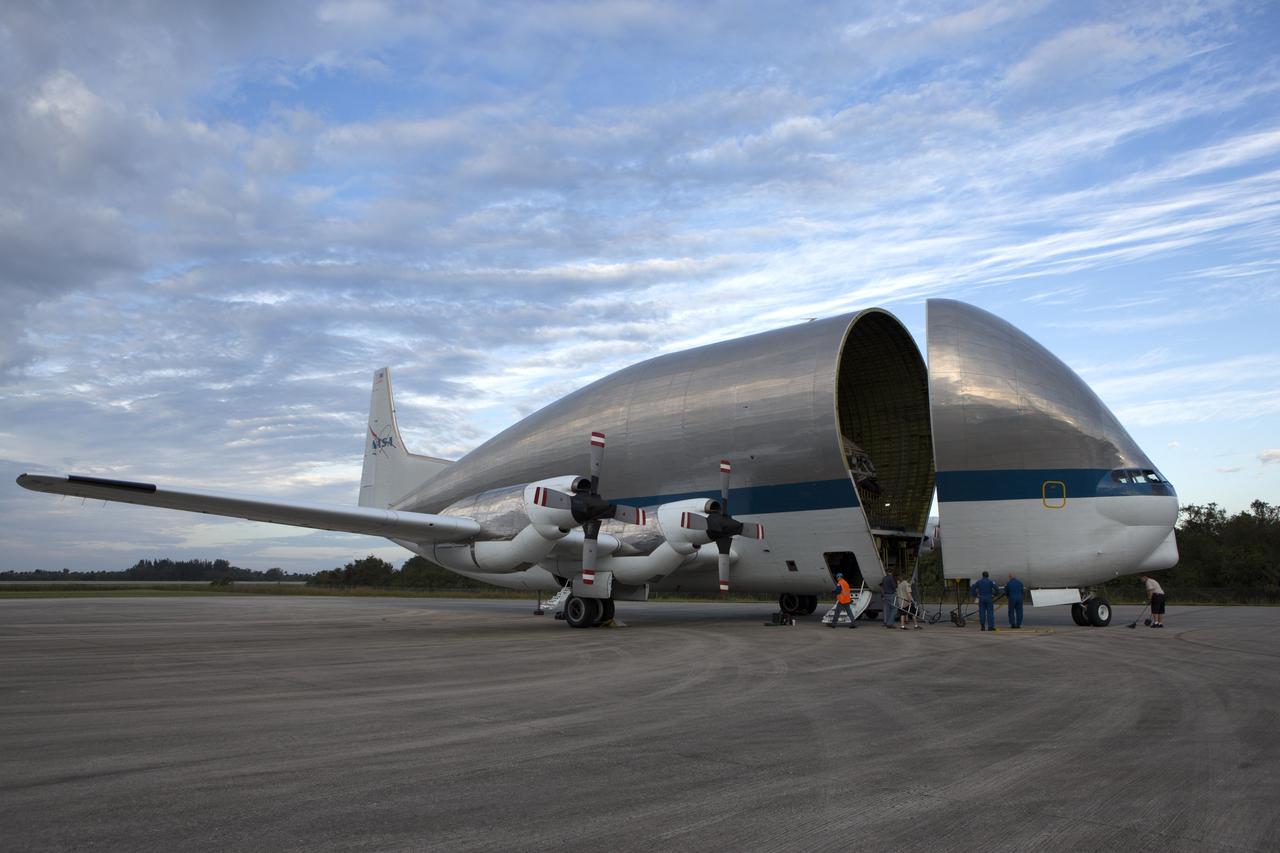
On the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA and contractor workers review procedures before beginning loading of the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article in its transport container into NASA's Super Guppy aircraft. The test article will be transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.
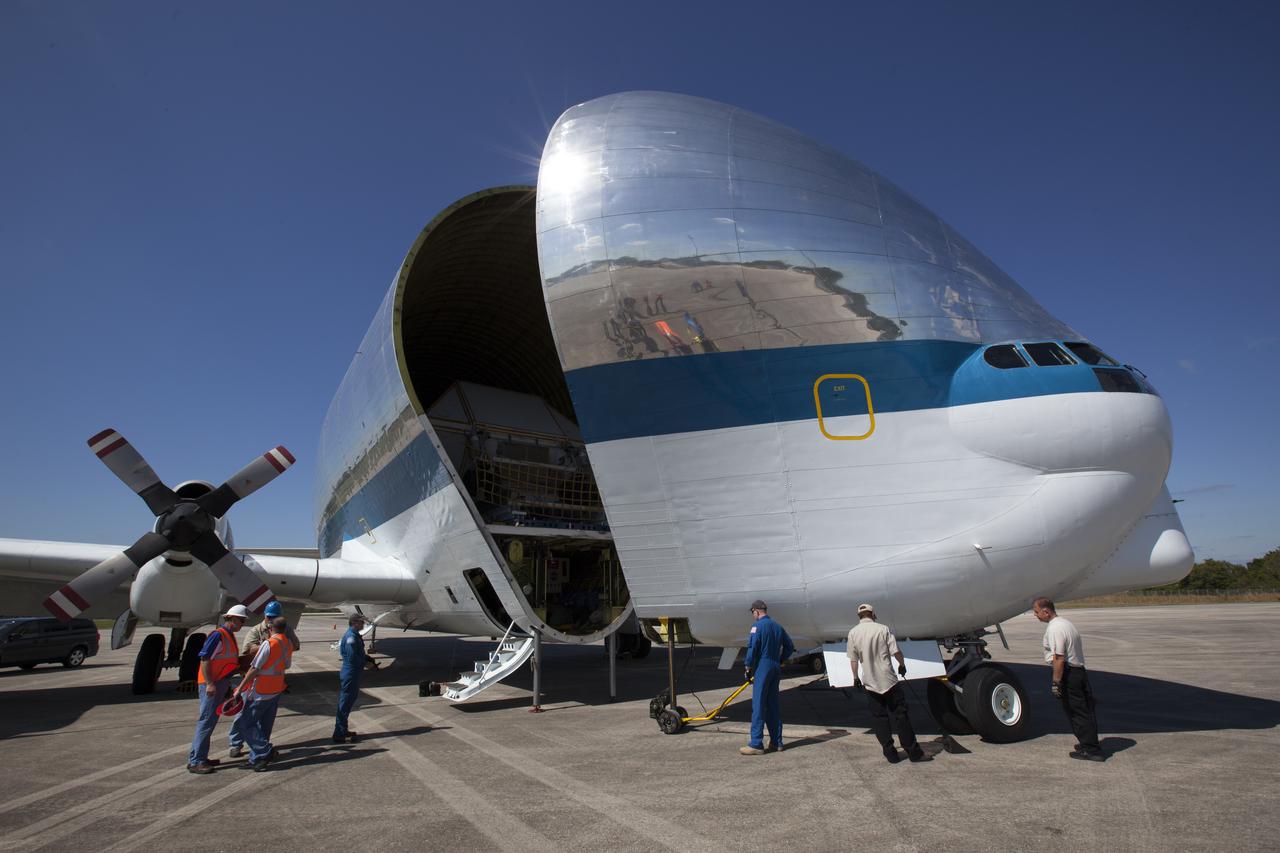

On the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Super Guppy aircraft closes after the Orion Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) structural test article, in its transport container, is secured inside. The test article will be transported to Lockheed Martin's Denver facility for testing. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket on EM-1, its first deep space mission.