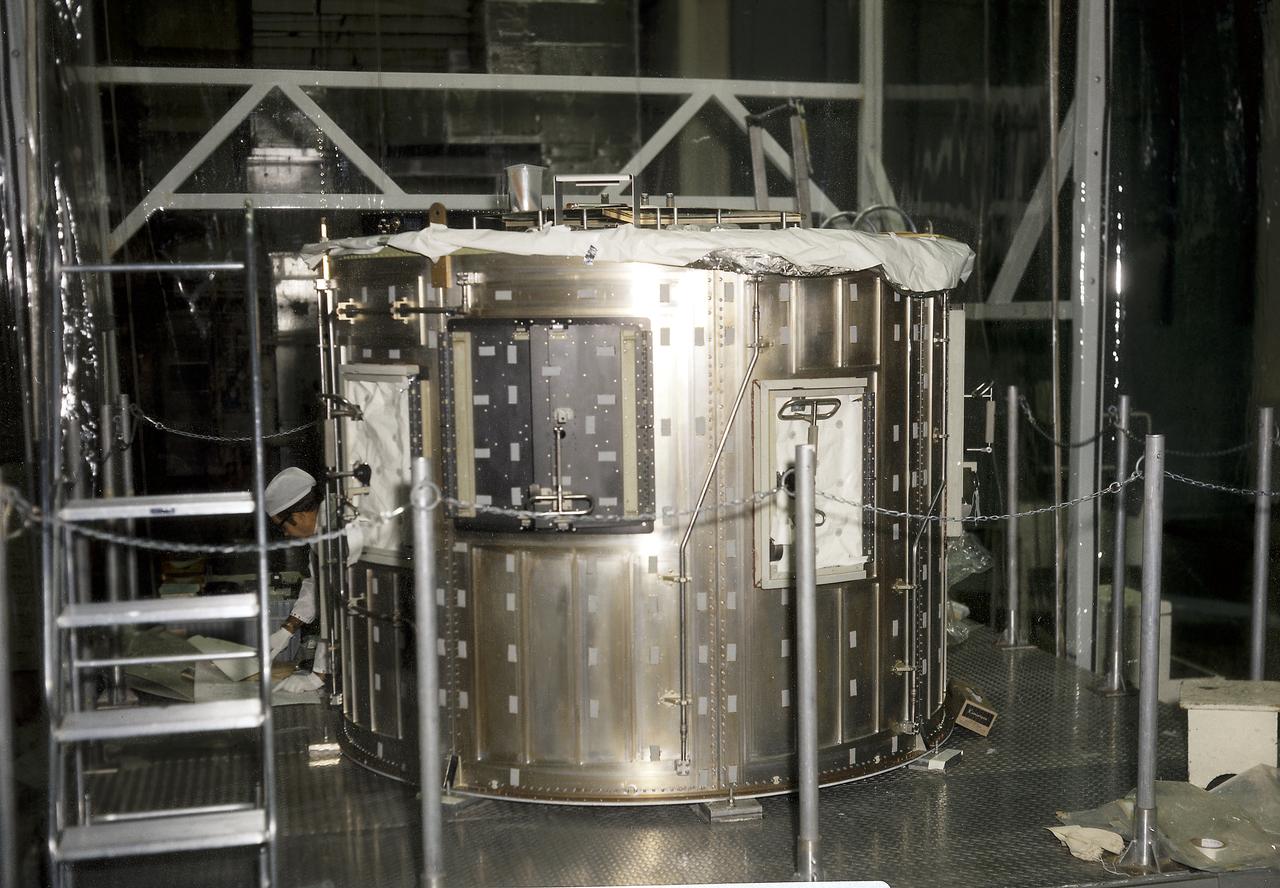
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM consisted of eight scientific instruments as well as a number of smaller experiments. This image is of the ATM flight unit sun end canister in MSFC's building 4755.
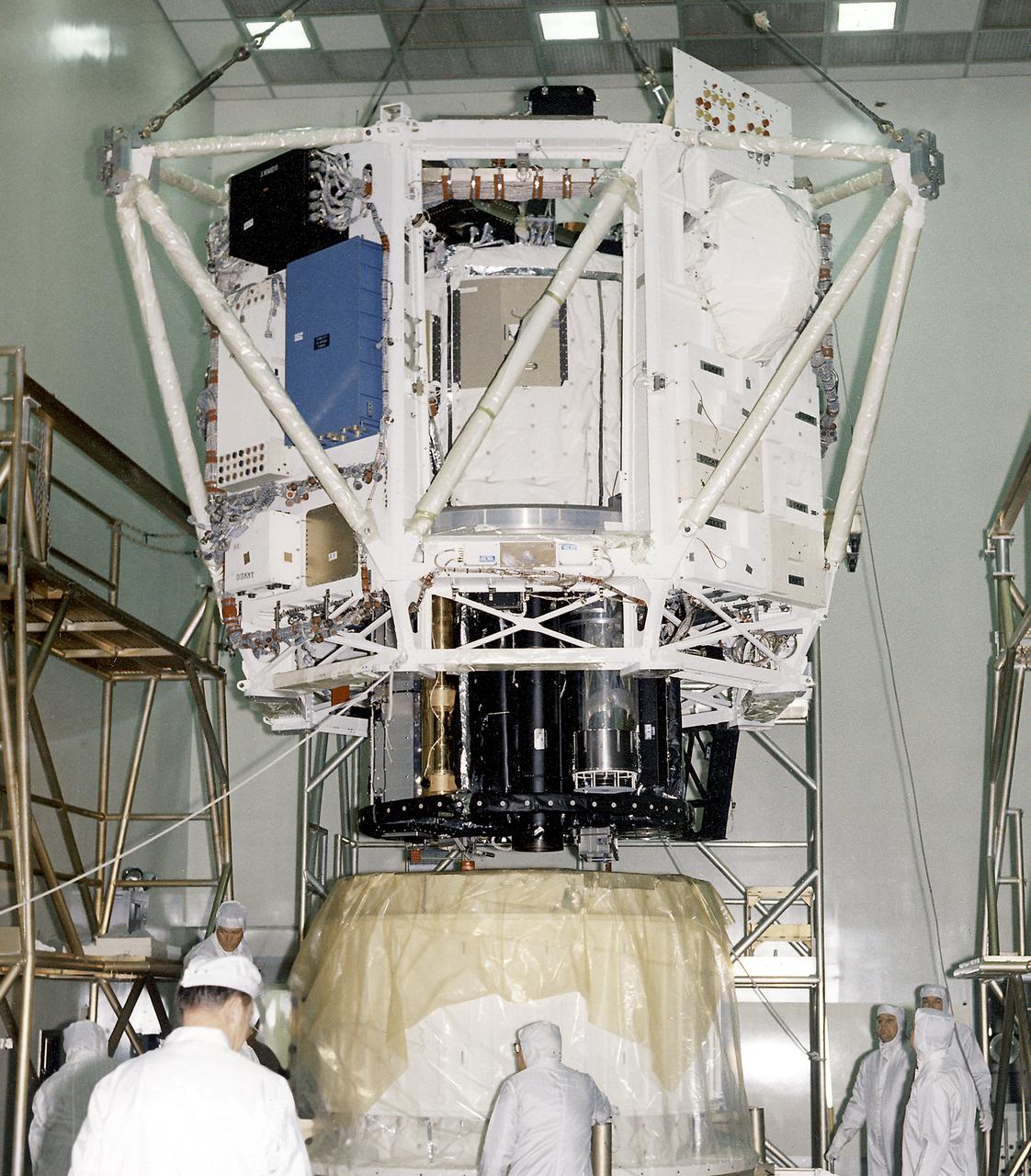
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was one of four major components comprising the Skylab. The ATM housed the first marned scientific telescopes in space. In this photograph, the ATM sun end canister, housing the solar instruments, is being moved to a clean room prior to being mated with the remaining components of the ATM unit.
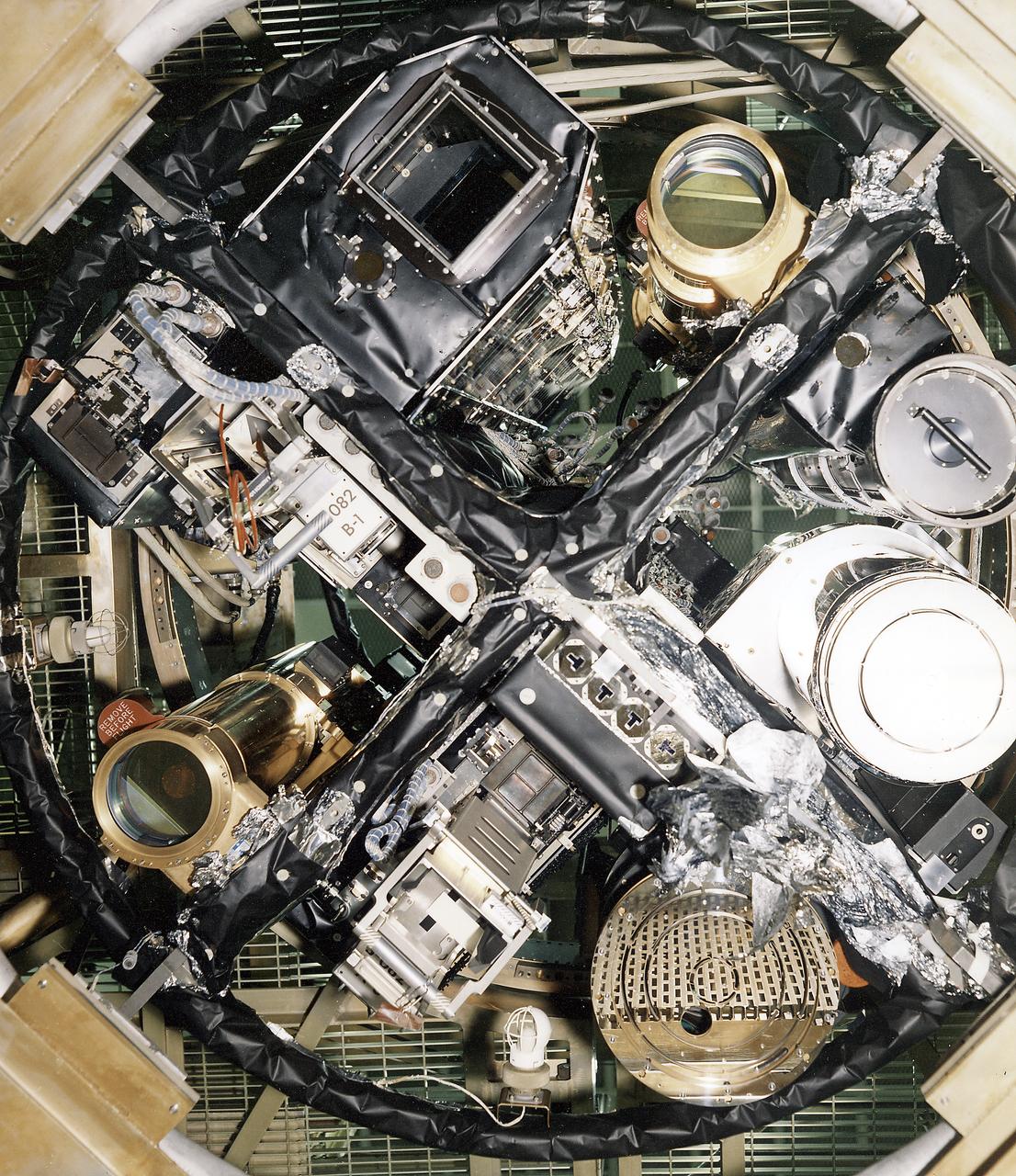
The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and served as the primary scientific instrument unit aboard Skylab (1973-1979). The ATM contained eight complex astronomical instruments designed to observe the Sun over a wide spectrum from visible light to x-rays. This image depicts the sun end and spar of the ATM flight unit showing individual telescopes. All solar telescopes, the fine Sun sensors, and some auxiliary systems are mounted on the spar, a cruciform lightweight perforated metal mounting panel that divides the canister lengthwise into four equal compartments. The spar assembly was nested inside a cylindrical canister that fit into a complex frame named the rack, and was protected by the solar shield.
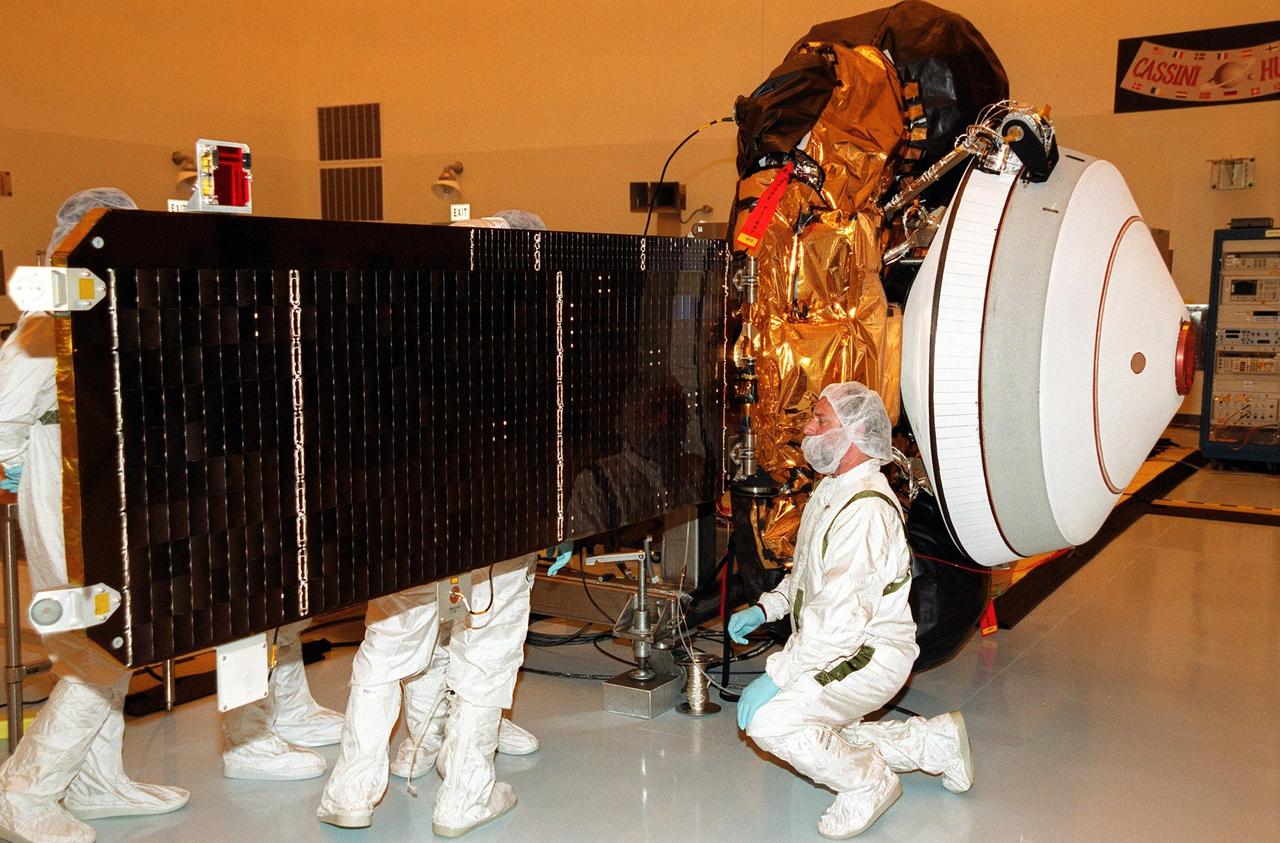

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility check closely the solar arrays on the Genesis spacecraft. Genesis is designed to collect samples of solar wind particles and return them to Earth so that scientists can study the exact composition of the Sun and probe the solar system’s origin. The white object on the end in front of the arrays is the Sample Return Canister backshell, inside of which are the collector arrays. Genesis is scheduled to be launched on a Delta II Lite launch vehicle from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, July 30, at 12:36 p.m. EDT
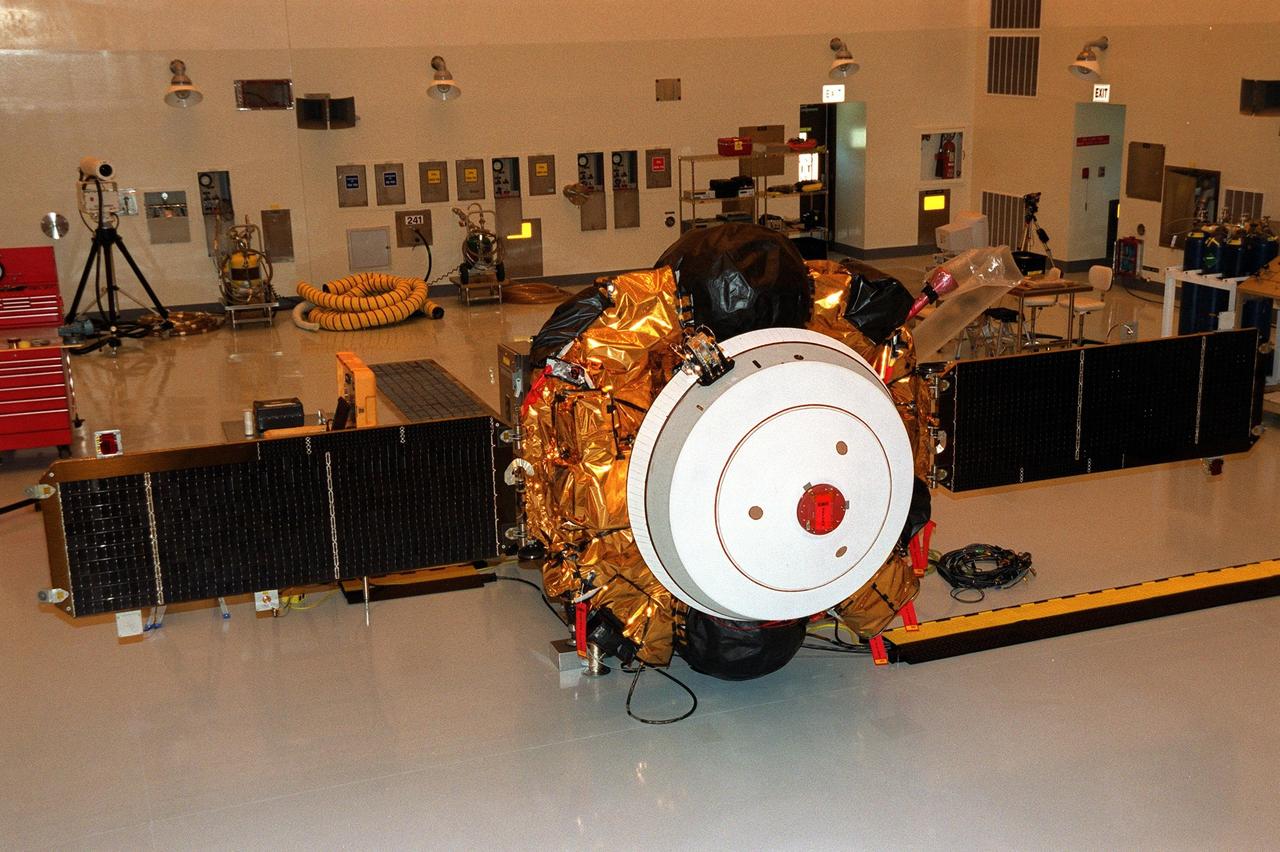

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, both solar arrays on the Genesis spacecraft are deployed. Genesis is designed to collect samples of solar wind particles and return them to Earth so that scientists can study the exact composition of the Sun and probe the solar system’s origin. The white object on the end in front of the arrays is the Sample Return Canister backshell, inside of which are the collector arrays. Genesis is scheduled to be launched on a Delta II Lite launch vehicle from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, July 30, at 12:36 p.m. EDT