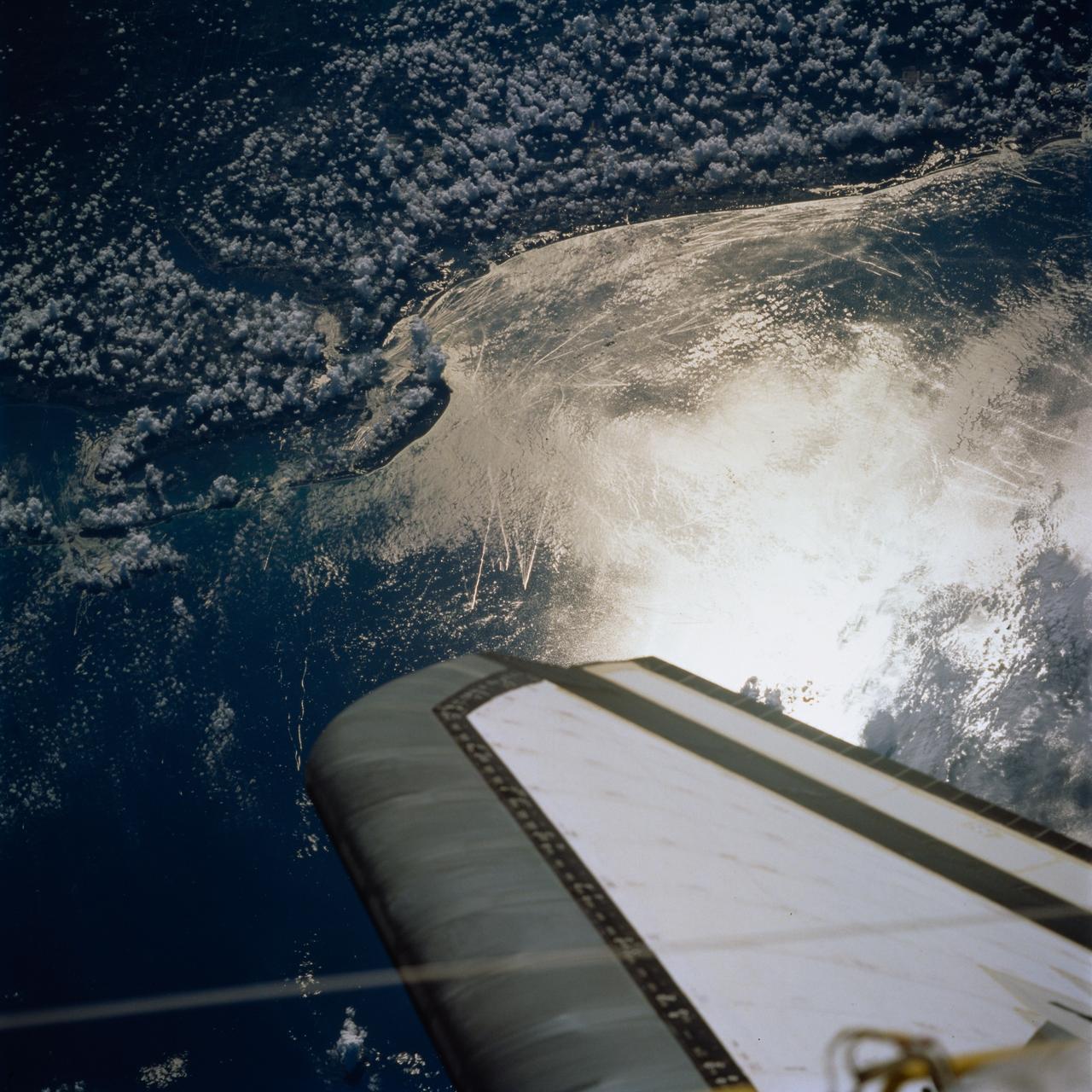

STS077-744-046 (19-29 May 1996) --- This view shows ship wakes off the coast of Fort Myers, Florida. The Sun glint reflecting off the ocean surfaces allowed man-made features to be seen and photographed by the astronaut crew members. When a ship or boat goes through the water it disturbs the surface of the water which causes the Sun?s rays to reflect back differently than the surrounding waters. Photographed on a weekend, this image illustrates how popular recreational boating is around the Fort Myers area.

S69-44464 (July 1969) --- Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong took this series of pictures of the landing site of Apollo 11's Lunar Module (LM) Eagle on the lunar surface. Glare in the middle of the top frames is the result of the Hasselblad being aimed toward the sun.
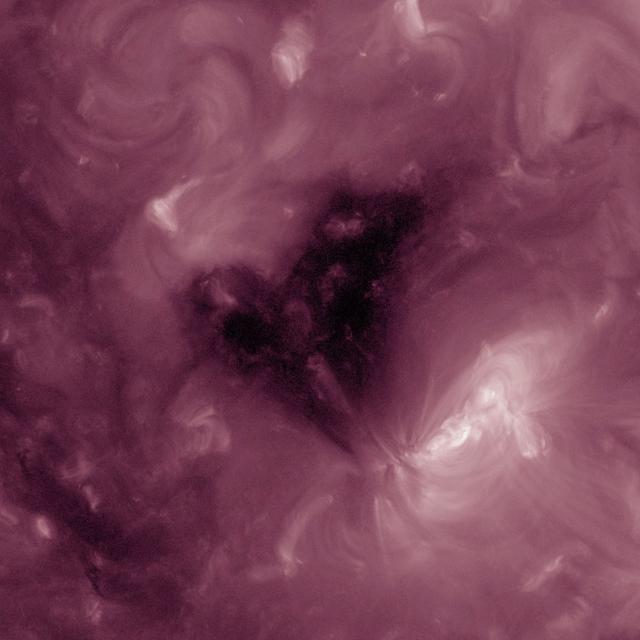
This Solar Dynamics Observatory image of the Sun taken on February 1, 2013 in extreme ultraviolet light captures a heart-shaped dark coronal hole. Coronal holes are areas of the Sun's surface that are the source of open magnetic field lines that head way out into space. They are also the source regions of the fast solar wind, which is characterized by a relatively steady speed of approximately 800 km/s (about 1.8 million mph).
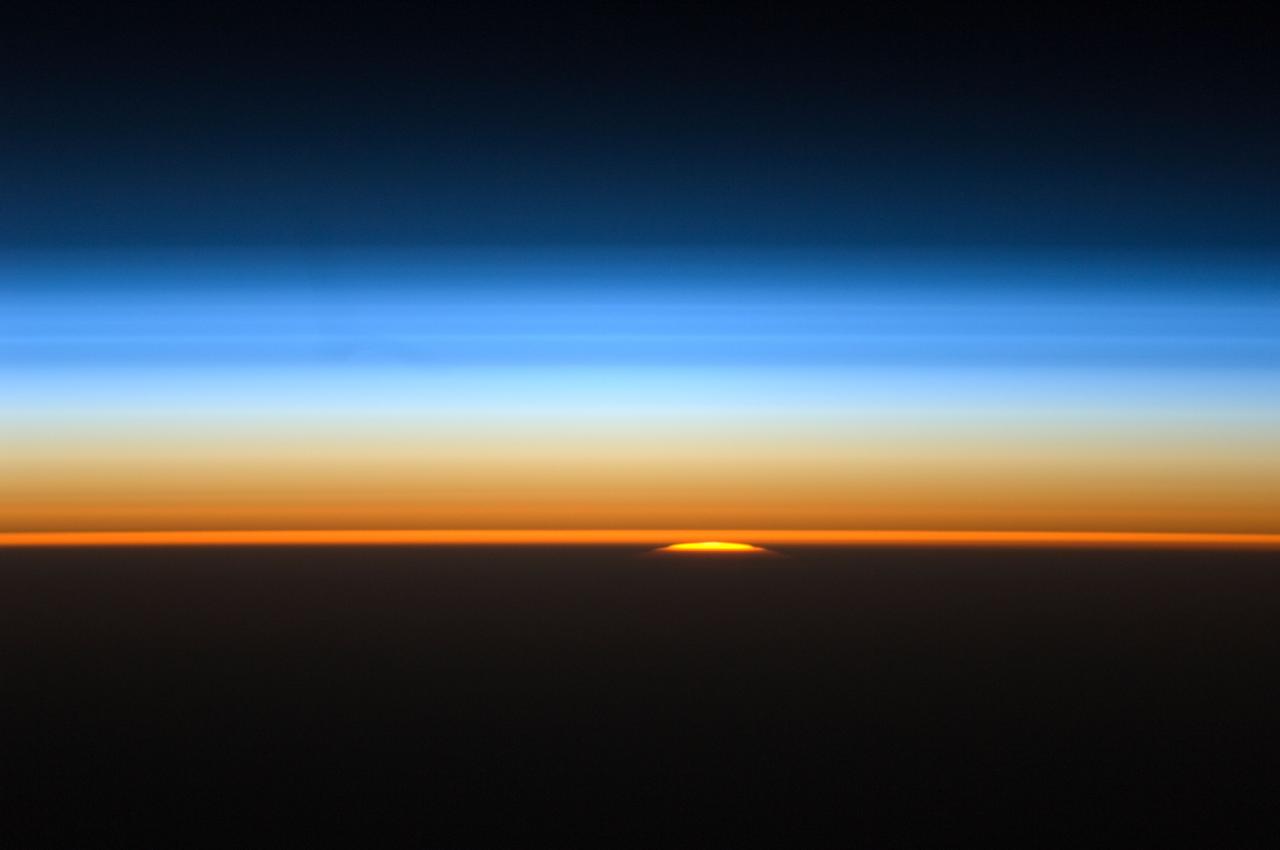

ISS028-E-007274 (11 June 2011) --- This view of the sun peeking over the limb of the Earth was taken by the Expedition 28 crew members aboard the International Space Station while flying parallel to the terminator; the area between daylight and nighttime. This lighting condition occurs in the early summer and late fall for the station's orbit tracks. The rest of the year the orbital outpost passes through the terminator at angles to experience 16 sunrises and sunsets a day. All of the layers of the Earth?s atmosphere are depicted in a beautiful array of color lit by the sun; from near the surface to the darkness of space.
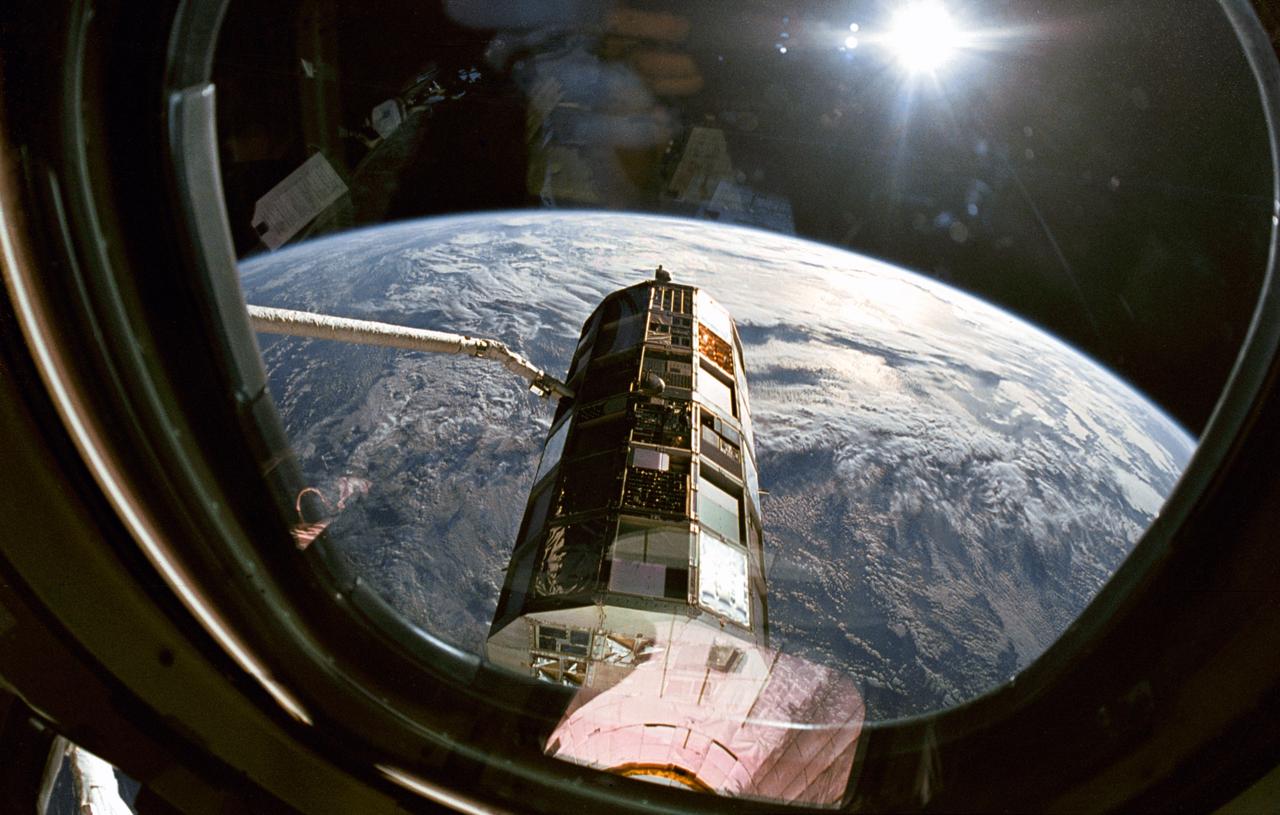

This view taken through overhead window W7 on Columbia's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102's, aft flight deck shows the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) in the grasp of the remote manipulator system (RMS) during STS-32 retrieval activities. Other cameras at eye level were documenting the bus-sized spacecraft at various angles as the RMS manipulated LDEF for a lengthy photo survey. The glaring celestial body in the upper left is the sun with the Earth's surface visible below.

ISS024-E-006136 (16 June 2010) --- Polar mesospheric clouds, illuminated by an orbital sunrise, are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station. Polar mesospheric, or noctilucent (?night shining?), clouds are observed from both Earth?s surface and in orbit by crew members aboard the space station. They are called night-shining clouds as they are usually seen at twilight. Following the setting of the sun below the horizon and darkening of Earth?s surface, these high clouds are still briefly illuminated by sunlight. Occasionally the ISS orbital track becomes nearly parallel to Earth?s day/night terminator for a time, allowing polar mesospheric clouds to be visible to the crew at times other than the usual twilight due to the space station altitude. This unusual photograph shows polar mesospheric clouds illuminated by the rising, rather than setting, sun at center right. Low clouds on the horizon appear yellow and orange, while higher clouds and aerosols are illuminated a brilliant white. Polar mesospheric clouds appear as light blue ribbons extending across the top of the image. These clouds typically occur at high latitudes of both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, and at fairly high altitudes of 76?85 kilometers (near the boundary between the mesosphere and thermosphere atmospheric layers). The ISS was located over the Greek island of Kos in the Aegean Sea (near the southwestern coastline of Turkey) when the image was taken at approximately midnight local time. The orbital complex was tracking northeastward, nearly parallel to the terminator, making it possible to observe an apparent ?sunrise? located almost due north. A similar unusual alignment of the ISS orbit track, terminator position, and seasonal position of Earth?s orbit around the sun allowed for striking imagery of polar mesospheric clouds over the Southern Hemisphere earlier this year.

ISS016-S-001A (February 2007) --- This patch commemorates the sixteenth expeditionary mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The design represents the conjunction of two unique astronomical events: a transit of the ISS across the surface of a full moon, and a nearly complete annular eclipse of the sun. The ISS is shown in its complete configuration, symbolizing the role of this expedition in preparing for the arrival and commissioning of international partner modules and components. The ISS transit across the moon highlights its role in developing the techniques and innovations critical to enable long-duration expeditions to the lunar surface and beyond. The NASA insignia design for shuttle and space station flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced.
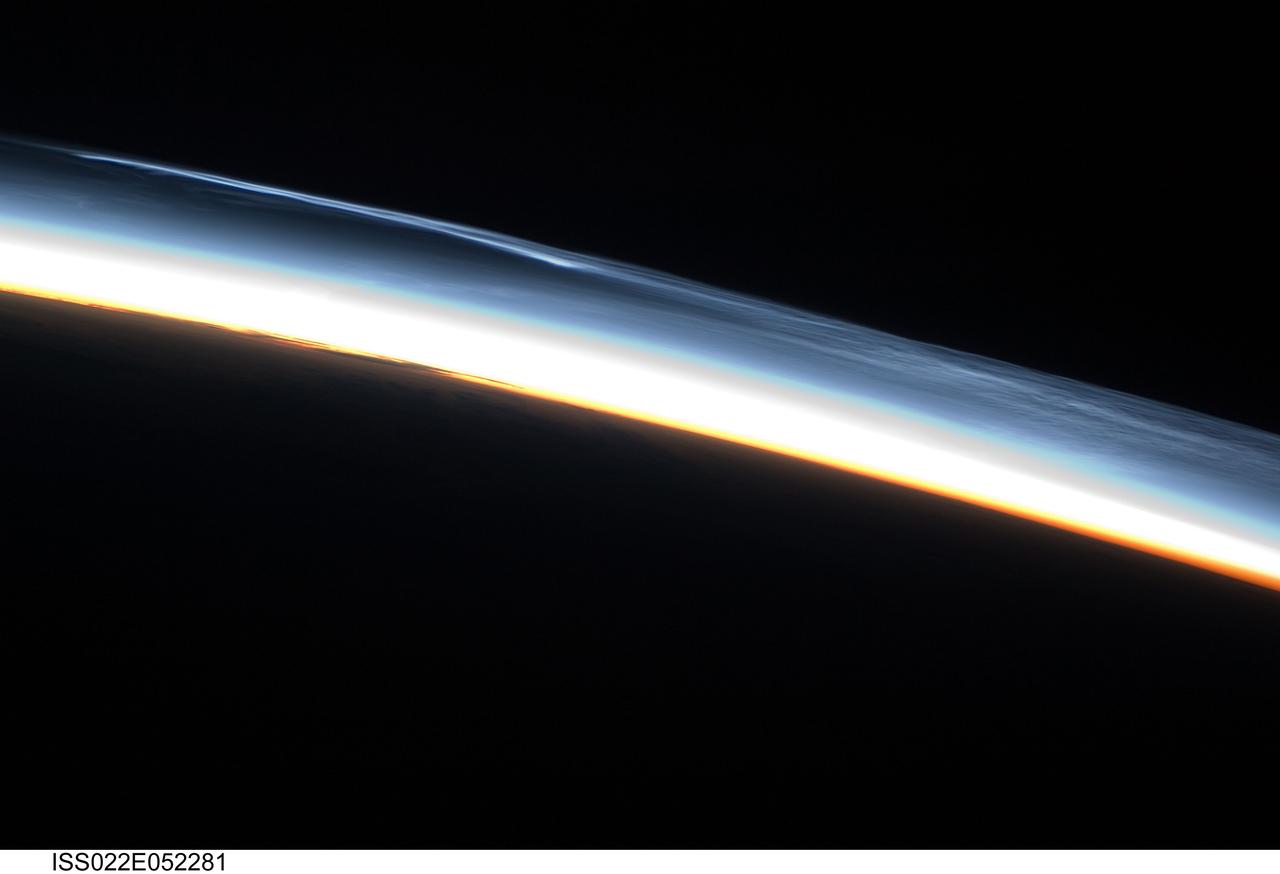

ISS022-E-052281 (30 Jan. 2010) --- Polar mesospheric clouds over the Southern Hemisphere are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. This striking view shows polar mesospheric clouds (PMC) over the polar region of the Southern Hemisphere. These clouds occur over the high latitudes of both northern and southern hemispheres during their respective summer months at very high altitudes of approximately 76?85 kilometers. When present they are visible during twilight, when the clouds are illuminated by the sun while the ground surface below is in darkness. The International Space Station (ISS) orbit extends from latitude 52 North to latitude 52 South; combined with the highly oblique views through Earth?s atmosphere possible with hand-held imagery, the ISS is an ideal platform for documenting these transient, high altitude phenomena. Another NASA mission, the Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere or AIM satellite, is dedicated to the study of PMC and is providing daily information about their formation, distribution, and variability. Polar mesospheric clouds are also known as noctilucent or night-shining clouds ? a property that is clearly visible in this photograph. The PMC exhibit thin, wispy light blue forms that contrast with the darkness of space above (upper right). Lower levels of cloud are strongly illuminated by the sun and appear light orange to white. Clouds closest to Earth?s surface are reddish-orange (center). The image was taken approximately 38 minutes after midnight Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) while the ISS was located over the southern Atlantic Ocean. At this time of year, the sun never sets over Antarctica but rather defines an arc across the local horizon, allowing PMC to be observed near local midnight.

This beautiful Hubble image reveals a young super star cluster known as Westerlund 1, only 15,000 light-years away in our Milky Way neighborhood, yet home to one of the largest stars ever discovered. Stars are classified according to their spectral type, surface temperature, and luminosity. While studying and classifying the cluster’s constituent stars, astronomers discovered that Westerlund 1 is home to an enormous star. Originally named Westerlund 1-26, this monster star is a red supergiant (although sometimes classified as a hypergiant) with a radius over 1,500 times that of our sun. If Westerlund 1-26 were placed where our sun is in our solar system, it would extend out beyond the orbit of Jupiter. Most of Westerlund 1’s stars are thought to have formed in the same burst of activity, meaning that they have similar ages and compositions. The cluster is relatively young in astronomical terms —at around three million years old it is a baby compared to our own sun, which is some 4.6 billion years old. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA
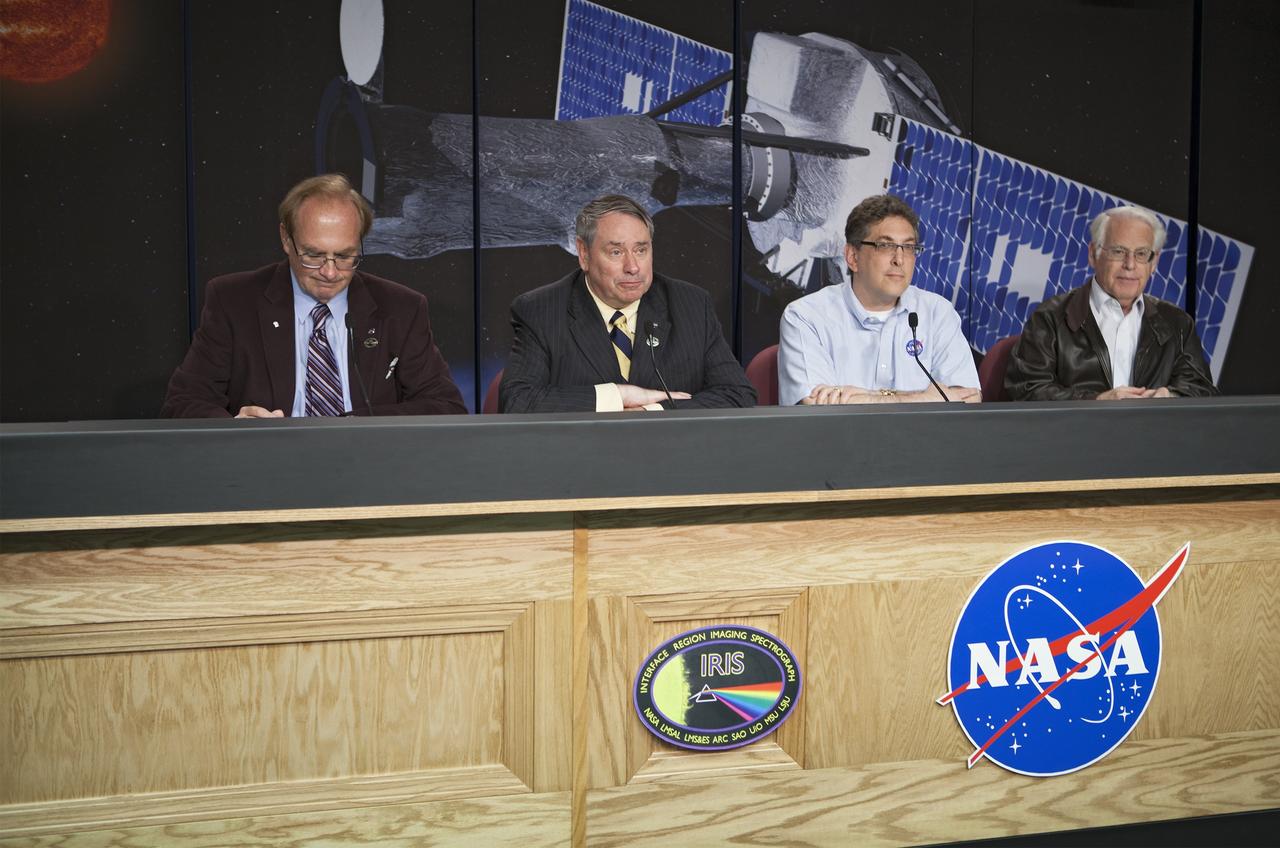

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA hosted a prelaunch mission briefing on the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory scheduled to launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Participating in the news conference are George Diller, NASA Public Affairs, Dr. S. Pete Worden, director of NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif., Jeffrey Newmark, IRIS Program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., and Alan Title, IRIS principal investigator with Lockheed Martin. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper
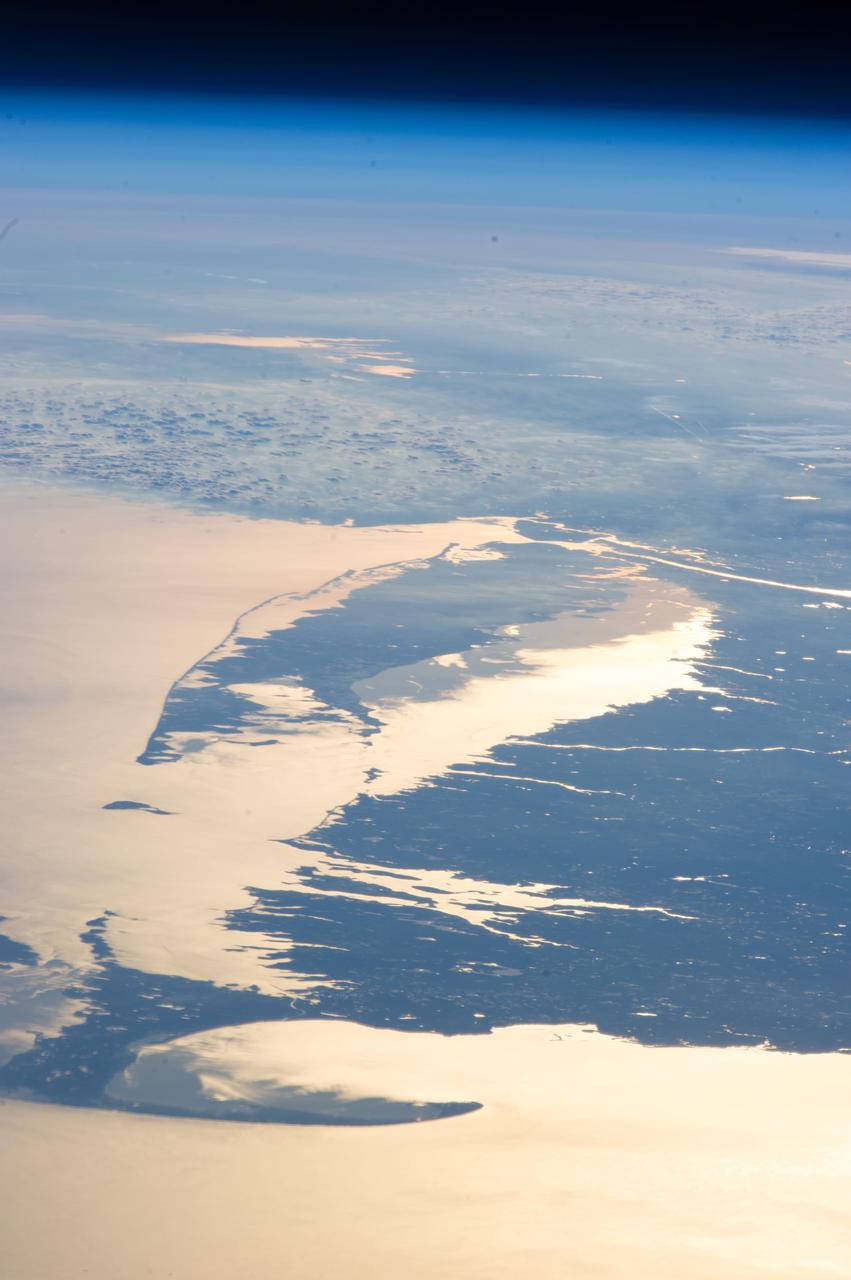

ISS034-E-48455 (14 Feb. 2013) --- Looking out at Earth?s surface from the International Space Station (ISS), astronauts and cosmonauts frequently observe sunglint highlighting both ocean and inland water surfaces. The Atlantic Ocean, including Cape Cod Bay and Buzzards Bay, along the coastlines of Massachusetts and Rhode Island, has a burnished, mirror-like appearance in this image. This is due to sunlight reflected off the water surface back towards the station crew member who took the photo. The peak reflection point is towards the right side of the image, lending the waters of Long Island Sound and the upper Massachusetts coastline an even brighter appearance. Sunglint also illuminates the surface waters of Chesapeake Bay, located over 400 kilometers (250 miles) to the southwest of the tip of Long Island. This suggests that the Sun was low on the horizon due to the observed extent of the sunglint effect. The time of image acquisition, approximately 4:26 p.m. Eastern Standard Time, was about one hour before local sunset. There is little in this image to indicate that the region was still recovering from a major winter storm that dropped almost one meter (three feet) of snow over much of the northeastern USA less than a week earlier. The high viewing angle from the space station also allows Earth?s curvature, or limb, to be seen; blue atmospheric layers gradually fade into the darkness of space across the top part of the image. Low clouds near Cape Cod, Long Island, and further down the Atlantic coastline cast shadows over the water surfaces, reducing the sunglint in some areas.
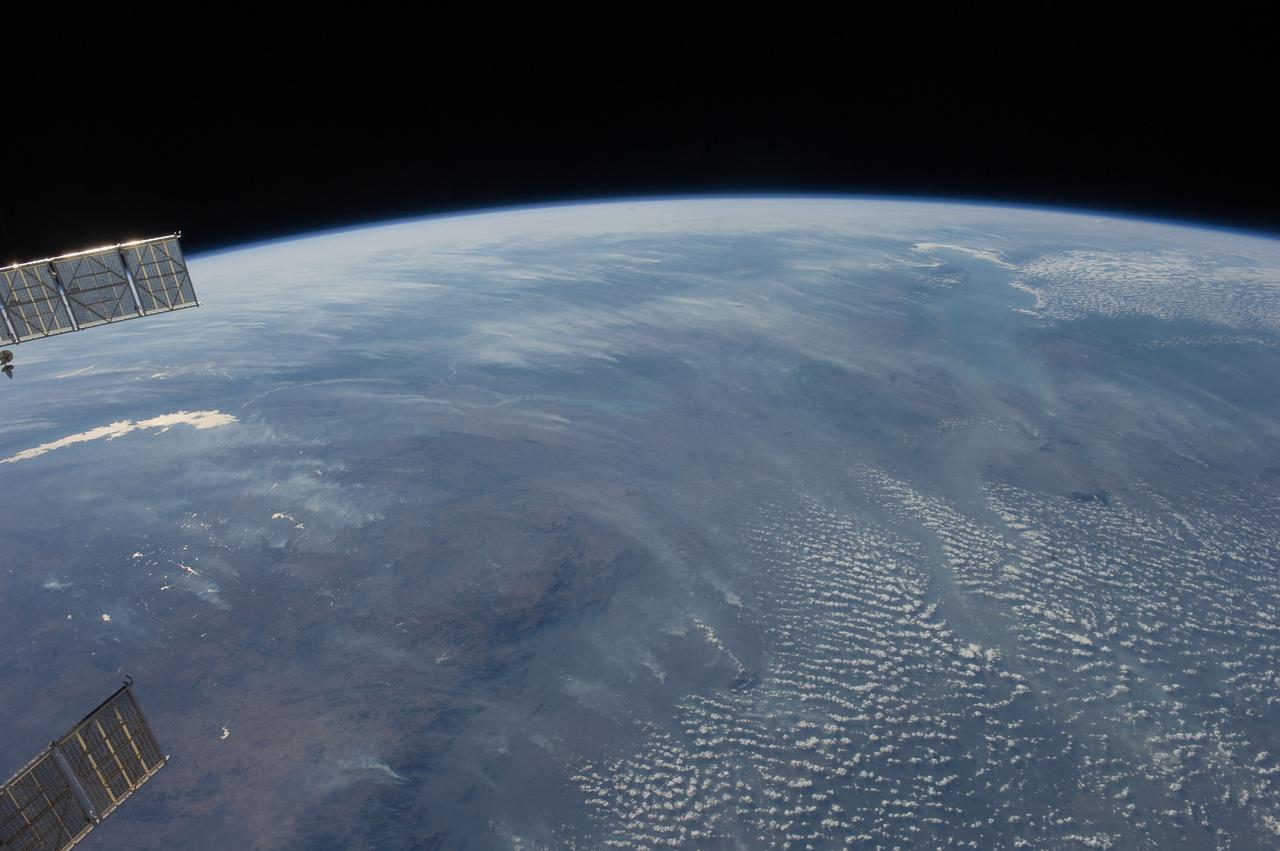

ISS028-E-018675 (23 July 2011) --- Biomass burning in southern Africa is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 28 crew member on the International Space Station. A smoke pall of subcontinental proportions dominates this view of tropical southern Africa. In what has been described as the most fire-prone part of the world, numerous fires give rise to regional smoke palls every dry season. Fires are both natural and set by local people to clear woodland for agricultural fields. This recent, oblique, northwest-looking view taken in July 2011 at the end of the dry season shows the extent of the smoke on the African plateau?from central Zimbabwe (lower left) to northern Malawi more than 1,000 kilometers away (top right)?and in the wide coastal plains of the lower Zambezi River valley of Mozambique (lower right). Here smoke can be seen blowing inland (left to right), channeled up the Zambezi River valley and contributing to the pall on the plateau. The light gray smoke plumes contrast with higher altitude, brighter patchy cloud cover at lower right. The smoke palls obscure much surface detail, so that Lake Malawi, one of Africa?s Great Lakes, is barely visible, as is Lake Cahora Bassa, Africa?s fourth largest reservoir, in the Zambezi valley. The sun?s reflection off its surface (sunglint) makes Lake Kariba most prominent in the view at left. Kariba is the world?s largest artificial reservoir by volume, and is 220 kilometers long, giving a sense of the scale of the view. The steep, shadowed, mid-afternoon faces of the Inyanga Mountains on the Mozambique-Zimbabwe border protrude above the smoke layer at lower left. Solar panels extending from Russian spacecraft docked at the International Space Station are visible in the foreground at left.

This Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) image of the Sun taken on January 20, 2012 in extreme ultraviolet light captures a heart-shaped dark coronal hole. Coronal holes are areas of the Sun's surface that are the source of open magnetic field lines that head way out into space. They are also the source regions of the fast solar wind, which is characterized by a relatively steady speed of approximately 800 km/s (about 1.8 million mph). <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
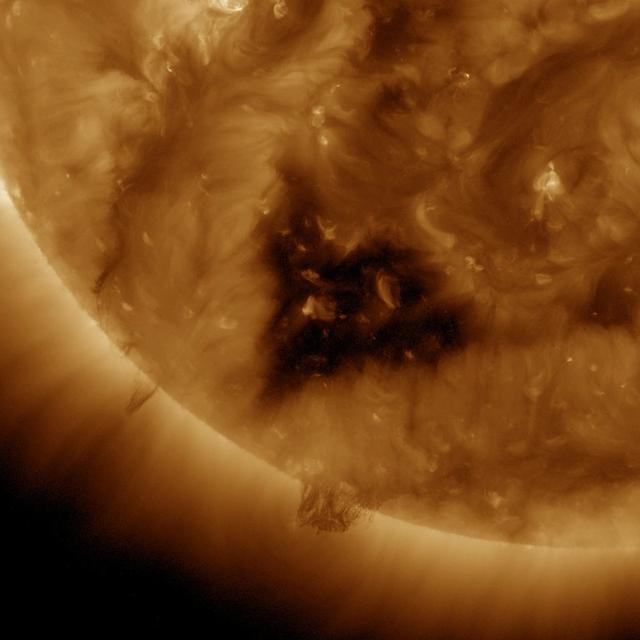

This Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) image of the Sun taken on January 20, 2012 in extreme ultraviolet light captures a heart-shaped dark coronal hole. Coronal holes are areas of the Sun's surface that are the source of open magnetic field lines that head way out into space. They are also the source regions of the fast solar wind, which is characterized by a relatively steady speed of approximately 800 km/s (about 1.8 million mph). <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
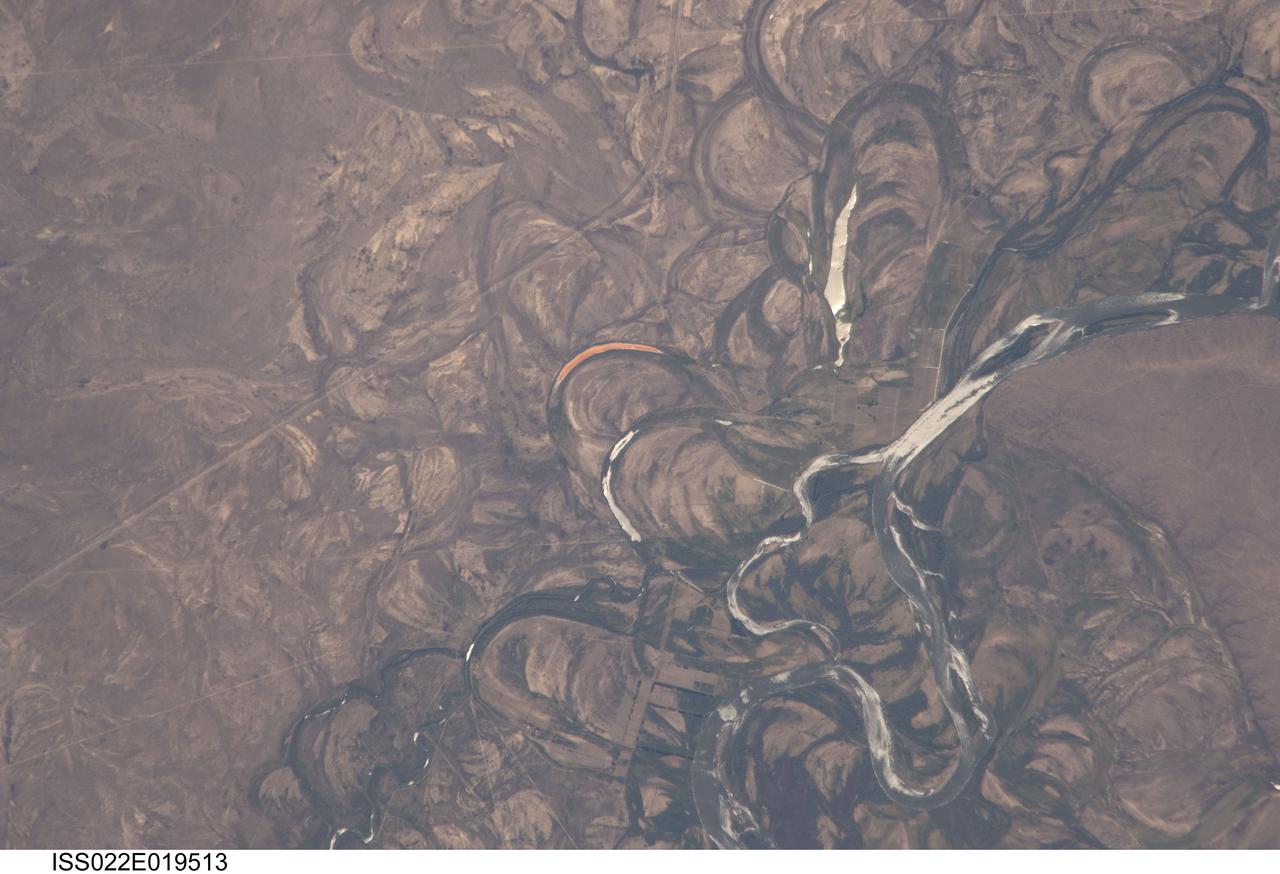

ISS022-E-019513 (4 Jan. 2010) --- The Rio Negro floodplain in Patagonia, Argentina is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. The Rio Negro is recognizable by astronaut crews from orbit as one of the most meandering rivers in South America. This is well illustrated in this view, where the entire river floodplain (approximately 10 kilometers wide) is covered with curved relics of channels known as meander scars. The main channel of the river, flowing south at this point?60 kilometers south of the city of Choele Choel (not shown)?appears in partial sun glint at right. Sun glint occurs when light is reflected off a water surface directly back towards the viewer, imparting a silvery sheen to those areas. When meander scars contain water they are known as oxbow lakes, some of which are also highlighted by sun glint in the image. Meander scars show the numerous past positions of river bends, produced as the river snaked across the plain in the very recent geological past. The Rio Negro is a dramatic example of how mobile a river can be. The orange tint to the water in one of the oxbow lakes (center) could result from orange salt-loving algae. Their appearance here would be unusual since floodplain lakes are usually too fresh for algae blooms. But an explanation may lie in the location of the Rio Negro on the margin of Argentina?s arid Patagonian region with annual rainfall less than 12 inches (300 mm). Evaporation in this cloudless region could be high enough for some lakes to become salty. The Rio Negro flows generally southeast from the Andes Mts. to the Atlantic Ocean. Its floodplain supports the biggest pear- and apple-growing region of Argentina. Rectangular farm boundaries can be seen at bottom center. The river also hosts the world?s longest kayak regatta (653 kilometers), which lasts six days.
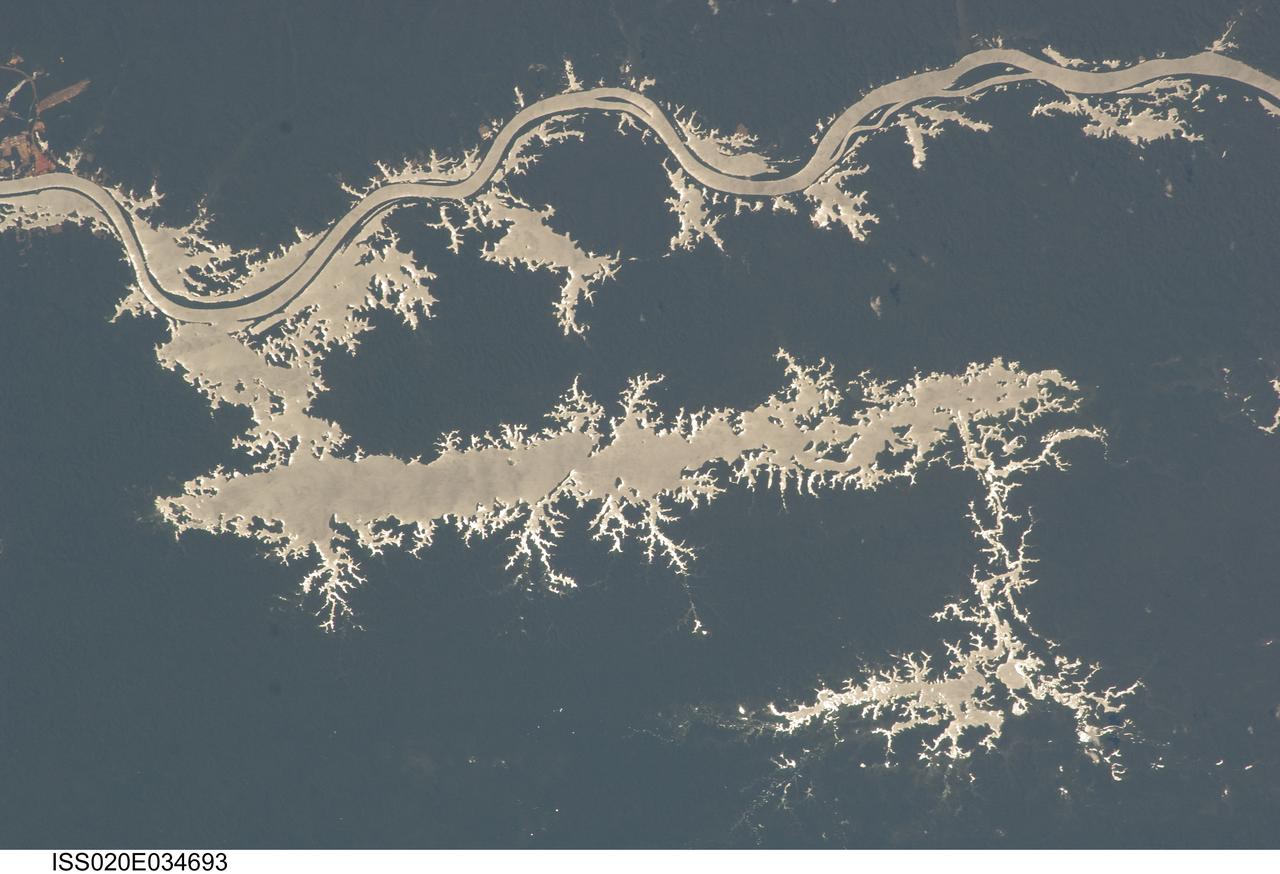

ISS020-E-034693 (25 Aug. 2009) --- Lake Erepecu and Rio Trombetas in Brazil are featured in this sun glint image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member on the International Space Station. The 38 kilometers long Lake Erepecu runs parallel to the lower Rio (river) Trombetas which snakes along the lower half of this photograph. Waterbodies in the Amazon rainforest are often so dark they can be difficult to distinguish. In this image, however, the lake and river stand out from the uniform green of the forest in great detail as a result of sun glint on the water surface. Sun glint is light reflected off of a surface directly back towards the viewer, in this case a crew member onboard the space station. Soil color beneath the forest is red, as shown by airfield clearings near Porto Trombetas (upper left), a river port on the south side of the Trombetas River. The Trombetas flows into the Amazon River from the north about 800 kilometers from the Amazon mouth. Despite being so far from the sea, seagoing ore ships export most of Brazil?s bauxite from Porto Trombetas. Bauxite is the raw material formed in these tropical soils for the production of aluminum (the Trombetas bauxite mine is outside the upper margin of the image). Central Amazonia has many lakes like Erepecu?relatively straight, large waterbodies located just off the main axis of the large rivers. These lakes, as distinct from smaller floodplain lakes next to the large rivers, were created as rivers cut down during the repeated low global sea levels of the recent geological past (according to scientists, related to the ice ages of the last 1.7 million years). River water filled the valleys to form lakes during intervening periods of high sea level. Many larger rivers like the Trombetas and Amazon carried enough sediment to fill their immediate valleys?rivers flowing in unconsolidated sediment produce sinuous courses like those along the upper part of the image?but not enough to fill tributary valleys further from the axis of flow, so that lakes like Erepecu are formed.

This computer animation illustrates how Pluto's moon Nix changes its spin unpredictably as it orbits the "double planet" Pluto-Charon. The view is from the surface of Pluto as the moon circles the Pluto-Charon system. This is a time-lapse view of the moon, compressing four years of motion into two minutes, with one complete orbit of Pluto-Charon every two seconds. (The apparent star movement rate is greatly slowed down for illustration purposes.) The animation is based on dynamical models of spinning bodies in complex gravitational fields — like the field produced by Pluto and Charon's motion about each other. Astronomers used this simulation to try to understand the unpredictable changes in reflected light from Nix as it orbits Pluto-Charon. They also found that Pluto's moon Hydra also undergoes chaotic spin. The football shape of both moons contributes to their wild motion. The consequences are that if you lived on either moon, you could not predict the time or direction the sun would rise the next morning. (The moon is too small for Hubble to resolve surface features, and so the surface textures used here are purely for illustration purposes.) Credit: NASA, ESA, M. Showalter (SETI Institute), and G. Bacon (STScI) Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-s-hubble-finds-pluto-s-moons-tumbling-in-absolute-chaos" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-s-hubble-finds-pluto-s-mo...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion. To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion. Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles. Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons. They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles. The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also helps form the tails. And as they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces, or gravitational stress. In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun. Although they don't actually crash into the solar surface, the sun is able to destroy them anyway. Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group. In fact, close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway. Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it. As clumps of remnants make their way back around the sun, we experience a sharp increase in sungrazing comets, which appears to be going on now. Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011 is the best known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer. And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun. Comet ISON, an upcoming sungrazer with a perihelion of 730,000 miles on November 28, 2013, is not on the Kreutz Path. In fact, ISON's orbit suggests that it may gain enough momentum to escape the solar system entirely, and never return. Before it does so, it will pass within about 40 million miles from Earth on December 26th. More information on this topic available at: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/timeline-of-comet-ison-s-dangerous-journey/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/timeline-of-comet-ison-s-dan...</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

ISS031-E-116058 (13 June 2012) --- Polar mesospheric clouds in the Northern Hemisphere are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 31 crew member on the International Space Station. In both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere, during their respective late spring and early summer seasons, polar mesospheric clouds are at the peak of their visibility. Visible from the ground during twilight, aircraft in flight, and the International Space Station, they typically appear as delicate shining threads against the darkness of space?hence their other name of noctilucent or ?night-shining? clouds. On the same day this image was taken from the space station while it was passing over the night-darkened Tibetan Plateau, polar mesospheric clouds were also visible to aircraft flying above Canada. In addition to this still image, the space station crew took a time-lapse image sequence of polar mesospheric clouds several days earlier (June 5, 2012) while passing over western Asia; this is first such sequence of images of the phenomena taken from orbit. Polar mesospheric clouds form between 76-85 kilometers above the Earth?s surface, when there is sufficient water vapor at these high altitudes to freeze into ice crystals. The clouds are illuminated by the setting sun while the ground surface below is in darkness, lending them their night-shining properties. In addition to the illuminated tracery of polar mesospheric clouds trending across the center of the image, lower layers of the atmosphere are also illuminated; the lowest layer of the atmosphere, the stratosphere, is indicated by dim orange and red tones. While the exact cause of formation of polar mesospheric clouds is still debated?dust from meteors, global warming, and rocket exhaust have all been suggested as contributing factors?recent research suggests that changes in atmospheric gas composition or temperature has caused the clouds to become brighter over time.
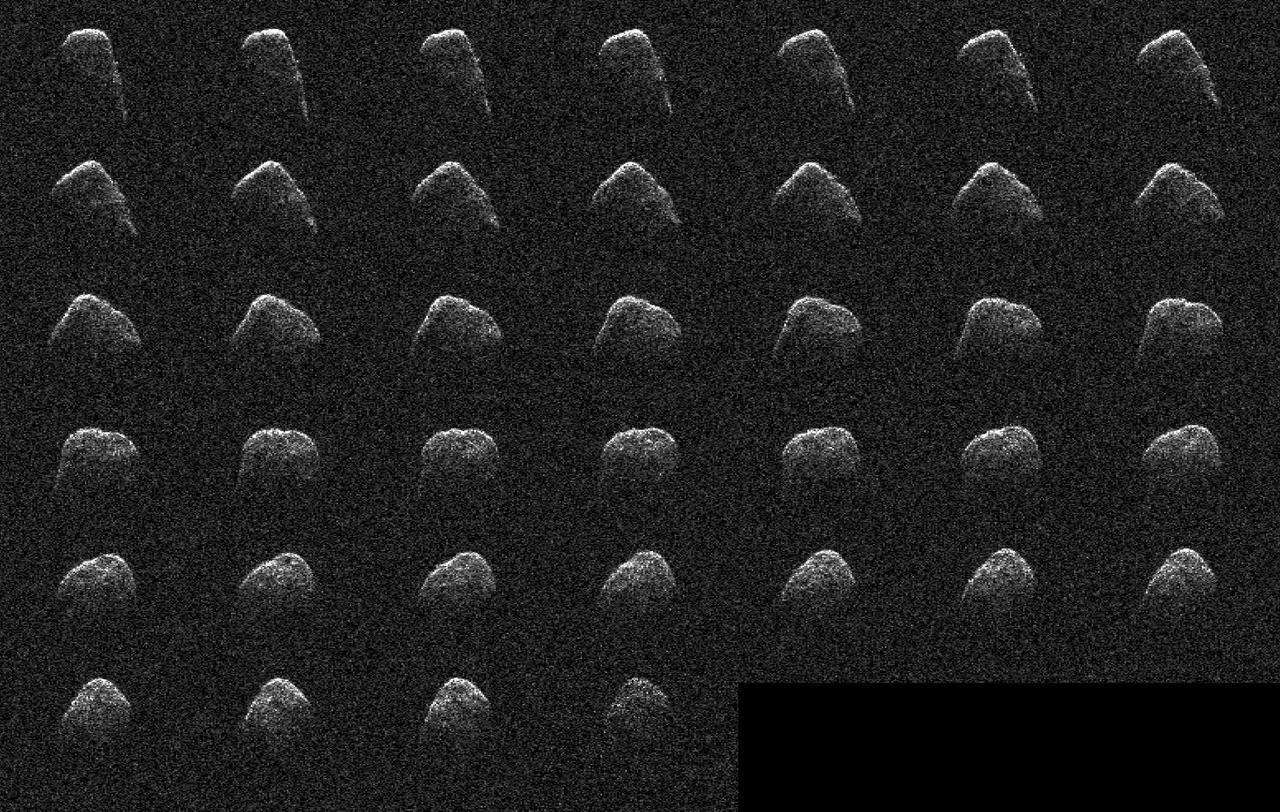
These images and animation represent NASA radar observations of 4660 Nereus on Dec. 10, 2021, before the asteroid's close approach on Dec. 11, when it came within 2.5 million miles (4 million kilometers) of Earth. Using the 70-meter radio antenna at the Deep Space Network's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California, scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory acquired the most detailed radar images of the nearly 1,100-foot-wide (330-meter-wide) near-Earth asteroid since its discovery almost four decades earlier. Nereus' orbit is very well known and the asteroid does not pose a threat to Earth. During the asteroid's close approach, an image resolution of about 12.3 feet (3.75 meters) per pixel was possible, revealing surface features such as potential boulders and craters, plus ridges and other topography. Asteroid Nereus' previous approach in 2002 was near enough to Earth to reveal the asteroid's size and overall shape, but too distant to show surface features. The new observations will also help scientists better understand the asteroid's shape and rotation while providing them new data to further refine its orbital path around the Sun. Nereus belongs to the relatively rare E-type asteroid family that exhibits very unusual radar scattering properties. It's thought that this may be caused by asteroids of this type having particularly rough terrain. Also, E-type asteroids are optically bright, sometimes reflecting as much as 50% of the sunlight that hits their surface. Typical S-type asteroids reflect about 15%, whereas dark C-type asteroids reflect only a few percent. It's thought that E-class asteroids may be the source of very rare Aubrite meteorites and are composed of comparatively bright material. The 2021 close approach was the best opportunity for radar imaging of Nereus until 2060, when the asteroid will approach within 750,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) of Earth, only three times the Earth-Moon distance. At that time, Nereus will be an easy target for small telescopes and possibly even powerful binoculars. Nereus – named after a sea god from Greek mythology – was discovered in 1982 by Eleanor "Glo" Helin as part of the JPL Palomar Planet-Crossing Asteroid Survey. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24566

ISS023-E-035670 (8 May 2010) --- Mingachevir Reservoir, Azerbaijan is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station. This detailed photograph highlights the southern Mingachevir Reservoir located in north-central Azerbaijan. The Mingachevir Reservoir occupies part of the Kura Basin, a topographic depression located between the Greater Caucasus Mountains to the northeast and the Lesser Caucasus Mountains to the southwest. According to scientists, folded layers of relatively young (less than 5.3 million years old) sedimentary rock, explosive volcanic products (ash and tuff), and unconsolidated sediments form the gray hills along the northern and southern shorelines of the reservoir (center and right). Afternoon sun highlights distinctive parallel patterns in the hills that are the result of water and wind erosion of different stratigraphic layers exposed at the surface. The nearby city of Mingachevir (left) is split by the Kur River after it passes through the dam and hydroelectric power station complex at top center. The current city was built in support of the hydroelectric power station constructed as part of the then Soviet Union?s energy infrastructure for the region. Today, Mingachevir is the fourth largest city in Azerbaijan (by population) and has become a cultural and economic center of the country. The reservoir held approximately 15 billion cubic meters of water at the time this image was taken, with a total engineered capacity of 16 billion cubic meters. The width of the reservoir illustrated here is approximately 8 kilometers; a jet flying over the reservoir and its contrail are visible midway between the opposing shorelines.
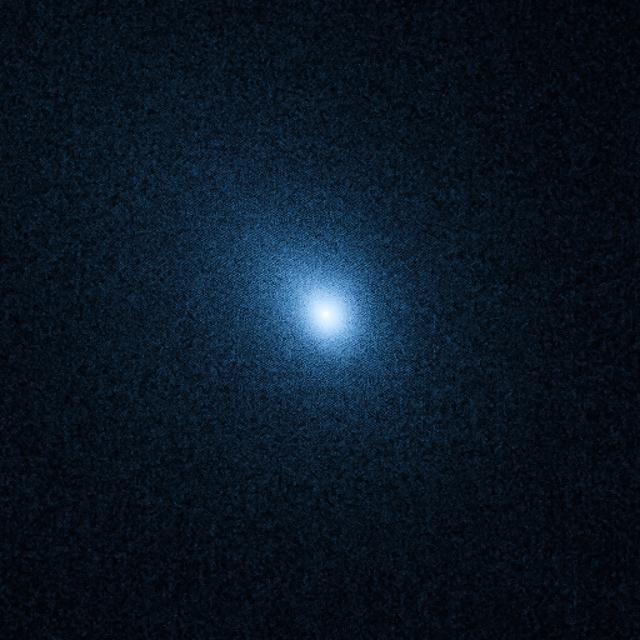

NASA image release October 5, 2010 Hubble Space Telescope observations of comet 103P/Hartley 2, taken on September 25, are helping in the planning for a November 4 flyby of the comet by NASA's Deep Impact eXtended Investigation (DIXI) spacecraft. Analysis of the new Hubble data shows that the nucleus has a diameter of approximately 0.93 miles (1.5 km), which is consistent with previous estimates. The comet is in a highly active state, as it approaches the Sun. The Hubble data show that the coma is remarkably uniform, with no evidence for the types of outgassing jets seen from most "Jupiter Family" comets, of which Hartley 2 is a member. Jets can be produced when the dust emanates from a few specific icy regions, while most of the surface is covered with relatively inert, meteoritic-like material. In stark contrast, the activity from Hartley 2's nucleus appears to be more uniformly distributed over its entire surface, perhaps indicating a relatively "young" surface that hasn't yet been crusted over. Hubble's spectrographs - the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) and the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) -- are expected to provide unique information about the comet's chemical composition that might not be obtainable any other way, including measurements by DIXI. The Hubble team is specifically searching for emissions from carbon monoxide (CO) and diatomic sulfur (S2). These molecules have been seen in other comets but have not yet been detected in 103P/Hartley 2. 103P/Hartley has an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit in Siding Spring, Australia. The comet will pass within 11 million miles of Earth (about 45 times the distance to the Moon) on October 20. During that time the comet may be visible to the naked eye as a 5th magnitude "fuzzy star" in the constellation Auriga. Credit: NASA, ESA, and H. Weaver (The Johns Hopkins University/Applied Physics Lab) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>