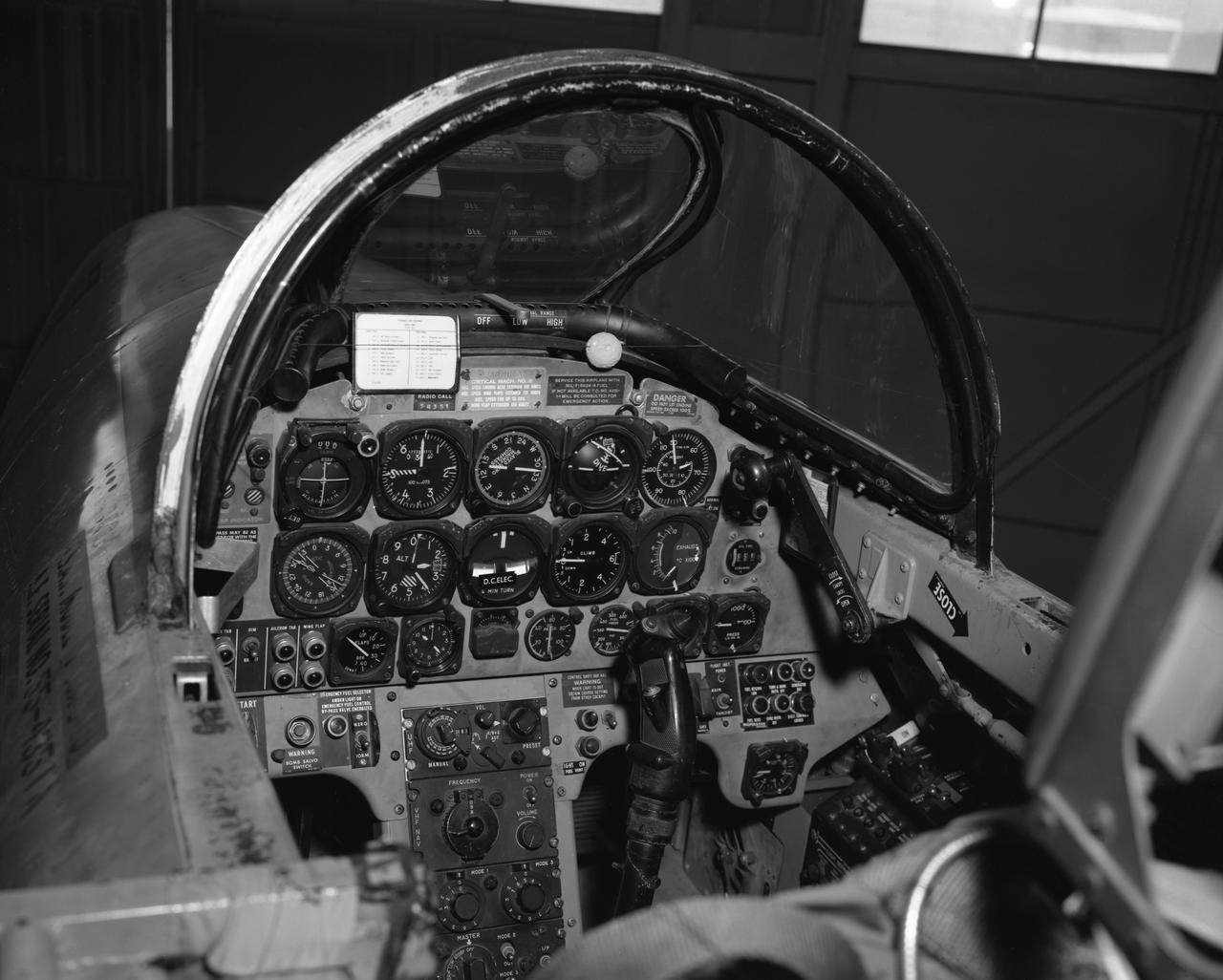

T-33 #351 Cockpit control panel. Feb. 13, 1964
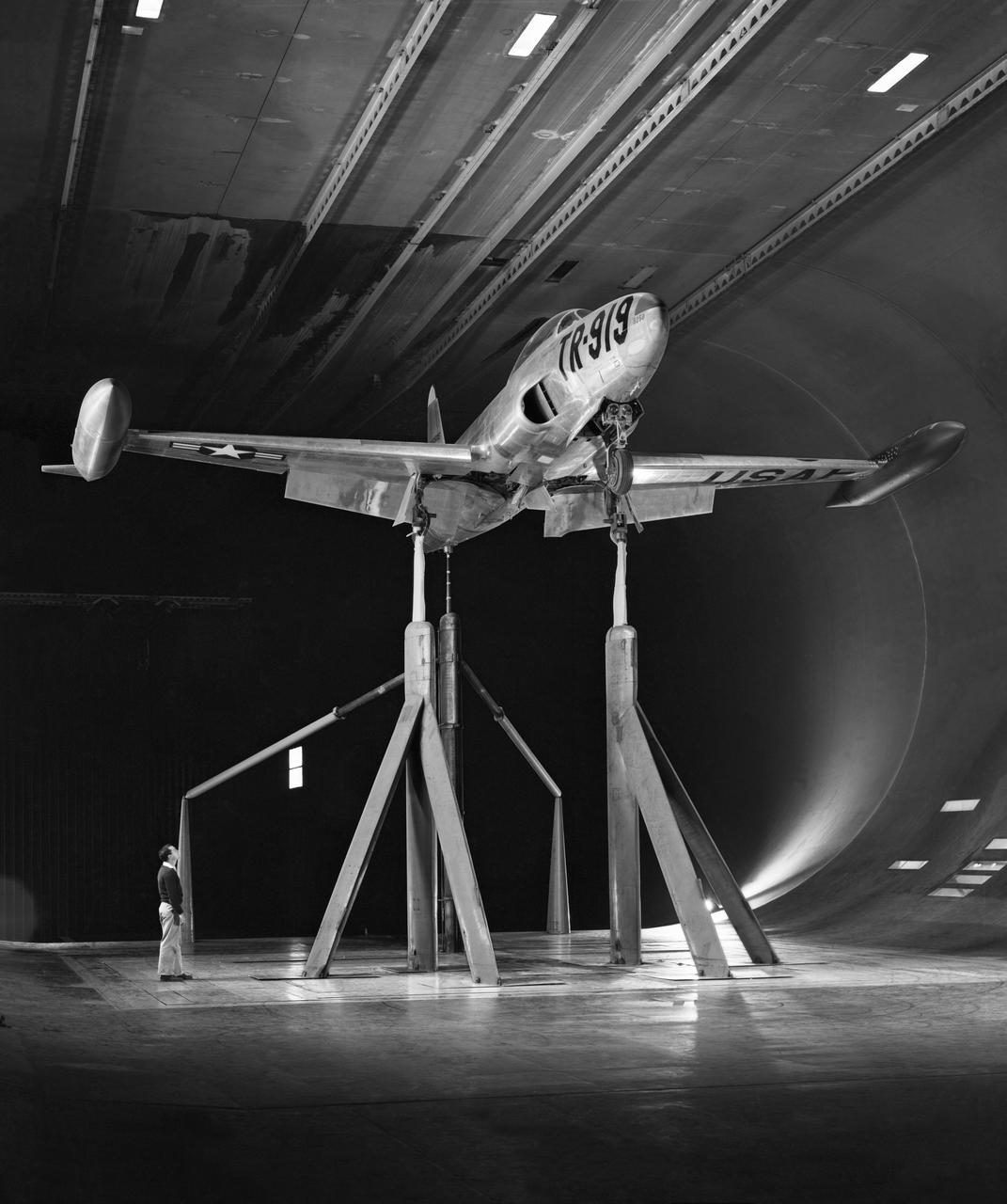

3/4 front view of Wind Tunnel investigation of the Lockheed T-33 modified for area-suction leading-edge and trailing edge flaps in Ames 40x80 foot Wind Tunnel.
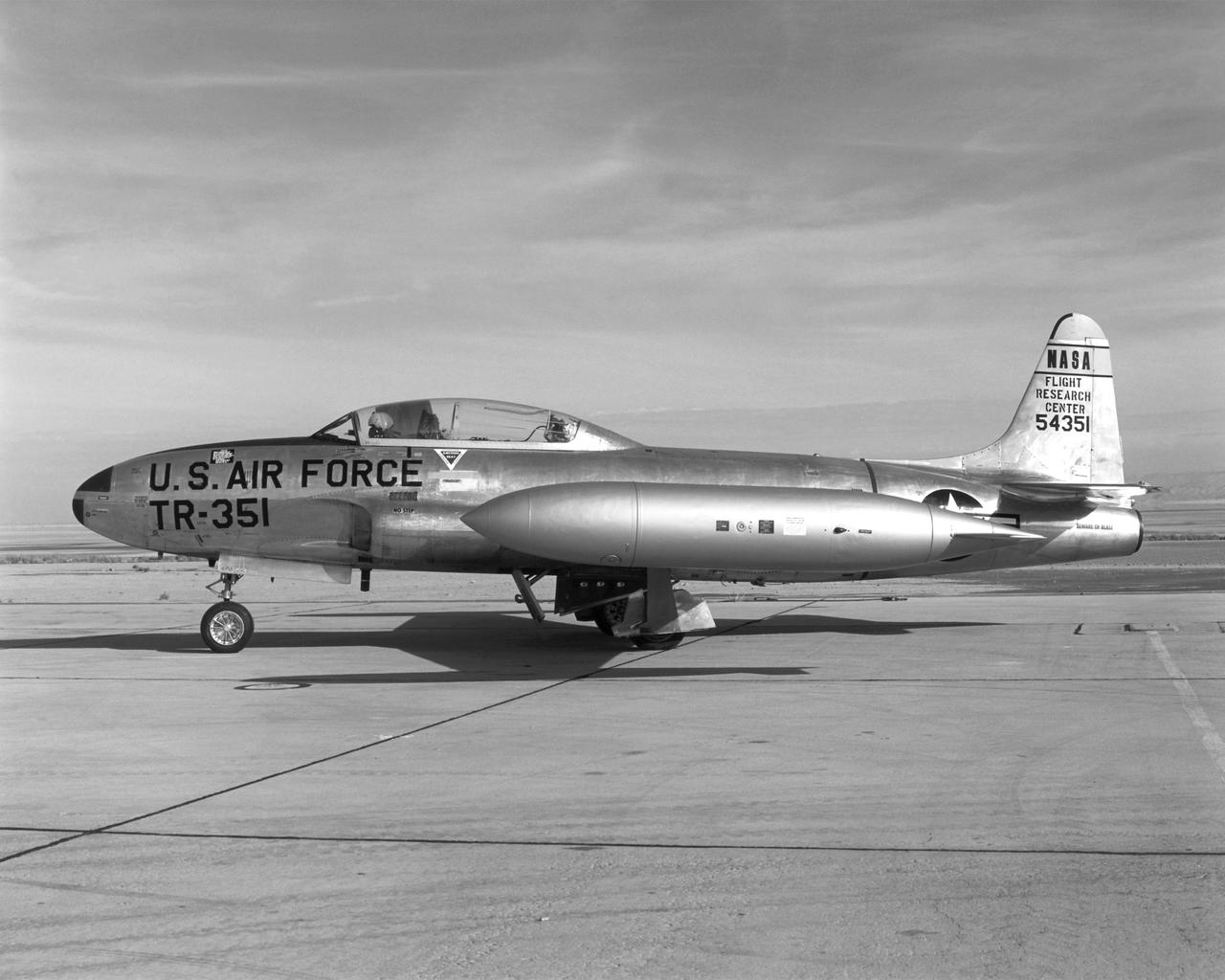

Arrived at NASA FRC January 9, 1963 Departed September 10, 1973 to Redding, California This aircraft, one of four T-33A jet trainers which NASA Dryden used from 1958 to 1973, was used in a monocular vision landing study. The T-33 was the first U.S. Air Force jet trainer, and was originally developed as a two-seat version of the F-80. The T-33 was used by not only the U.S. military, but also by foreign air forces as a trainer, fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft.

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
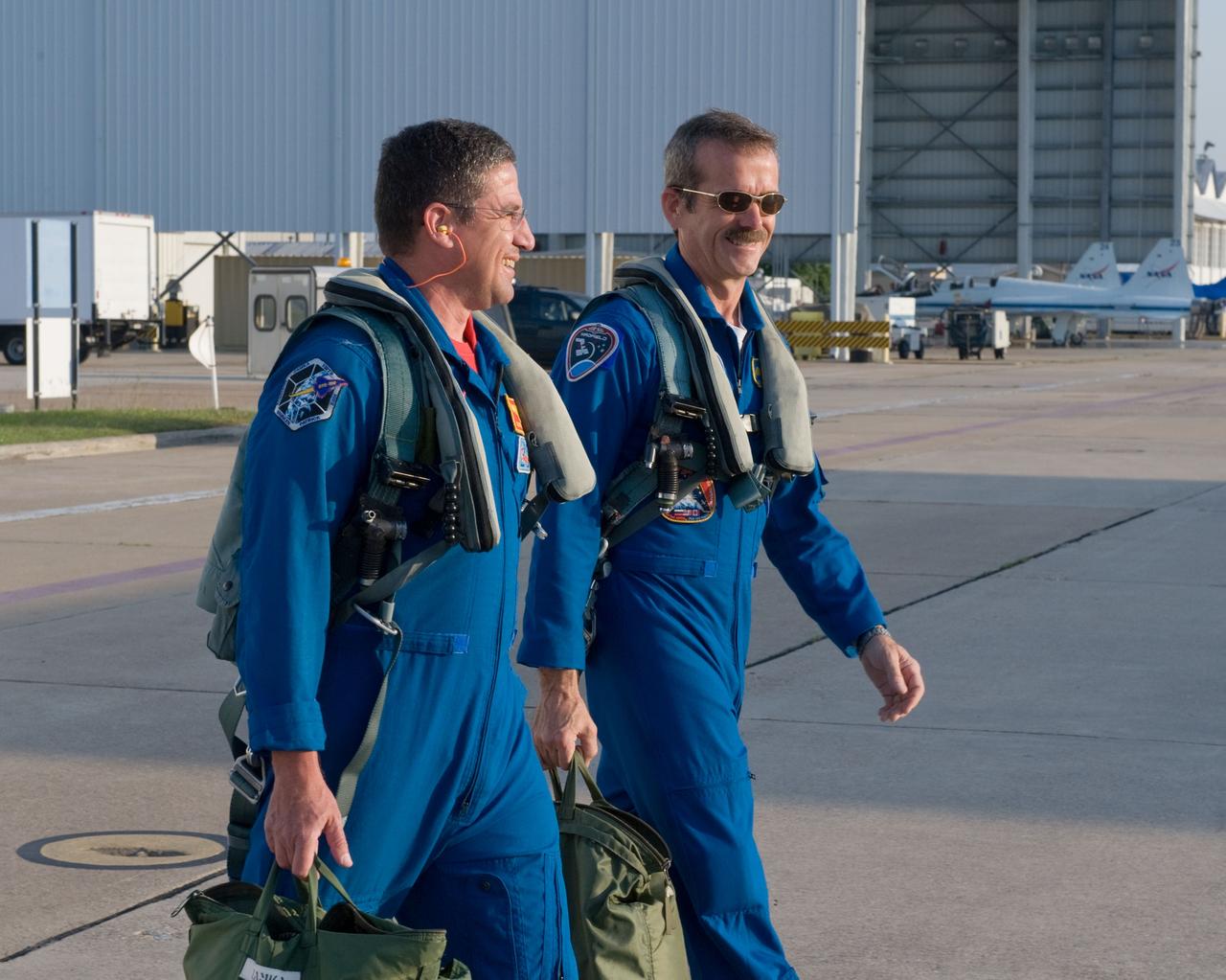

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
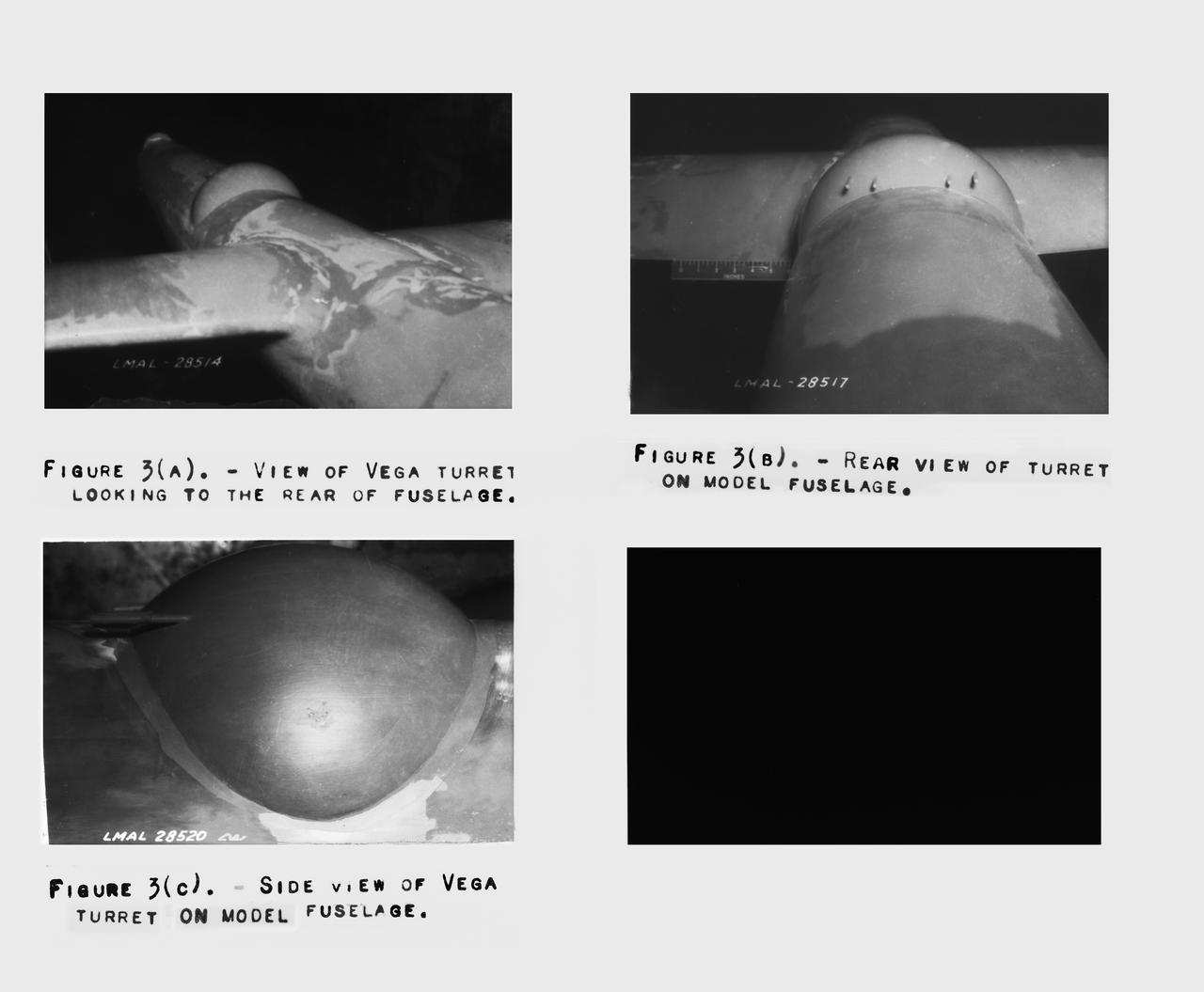
B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
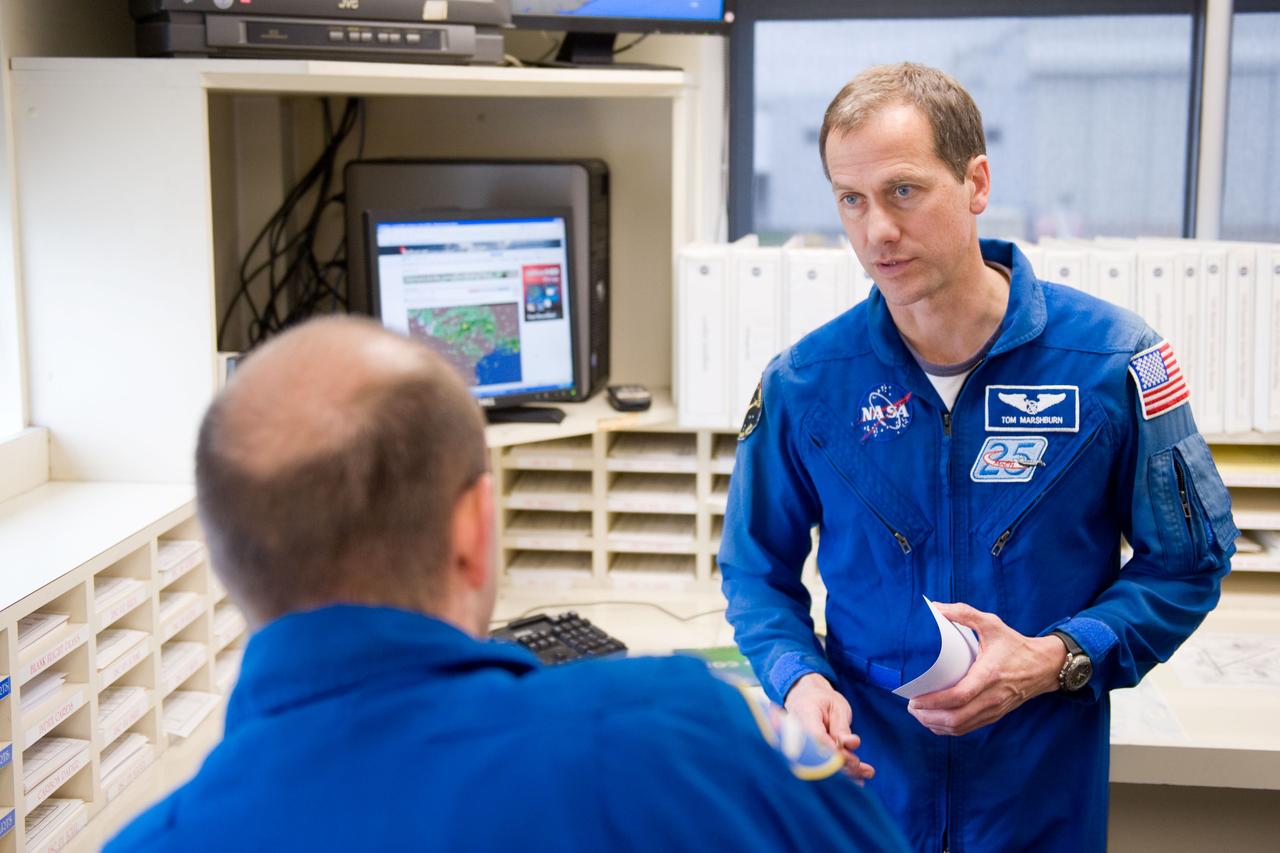

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
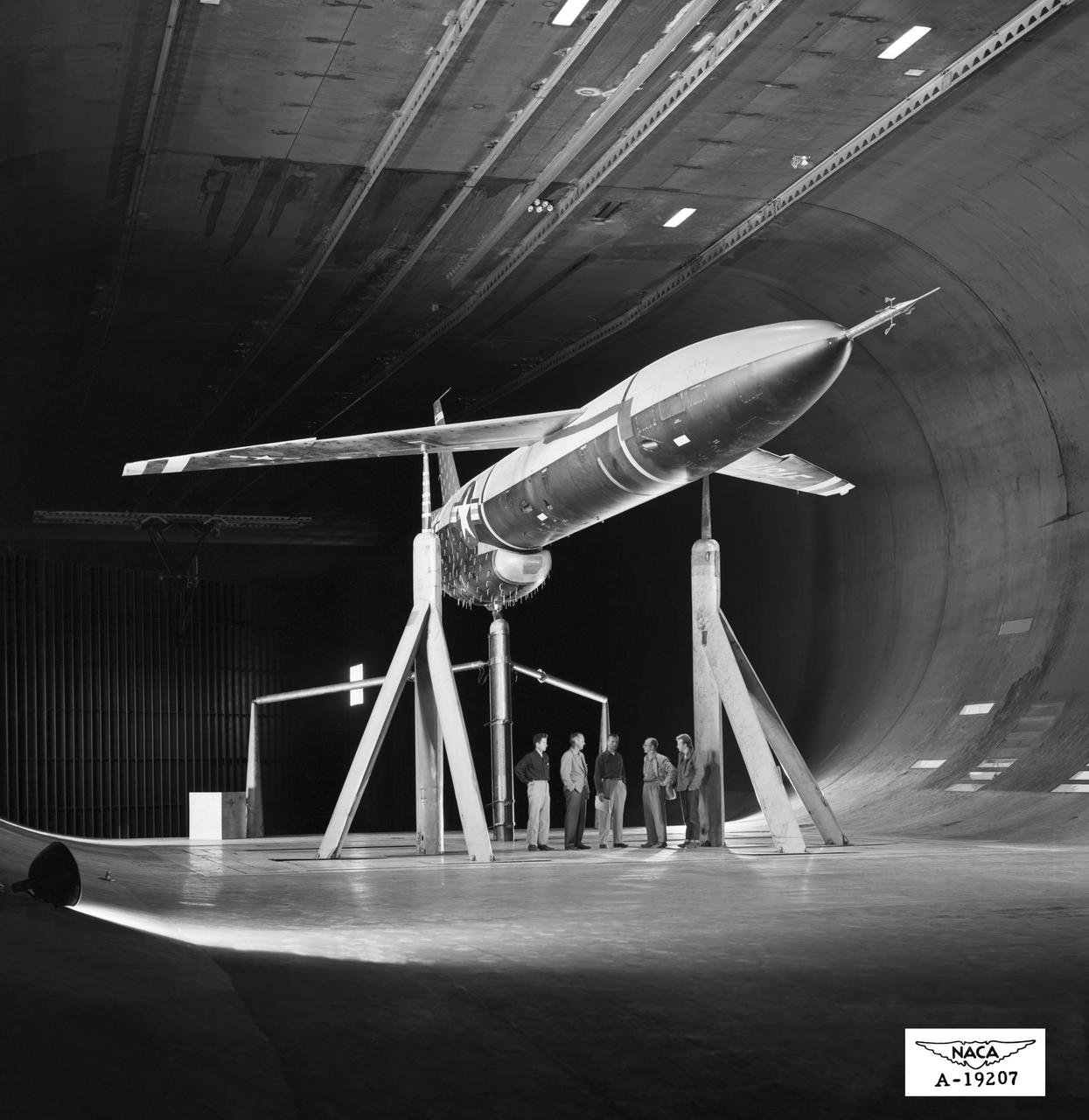

3/4 front view in Ames 40x80 foot Wind Tunnel investigation of the Lockheed T-33 modified for area-suction leading-edge and trailing edge flaps.
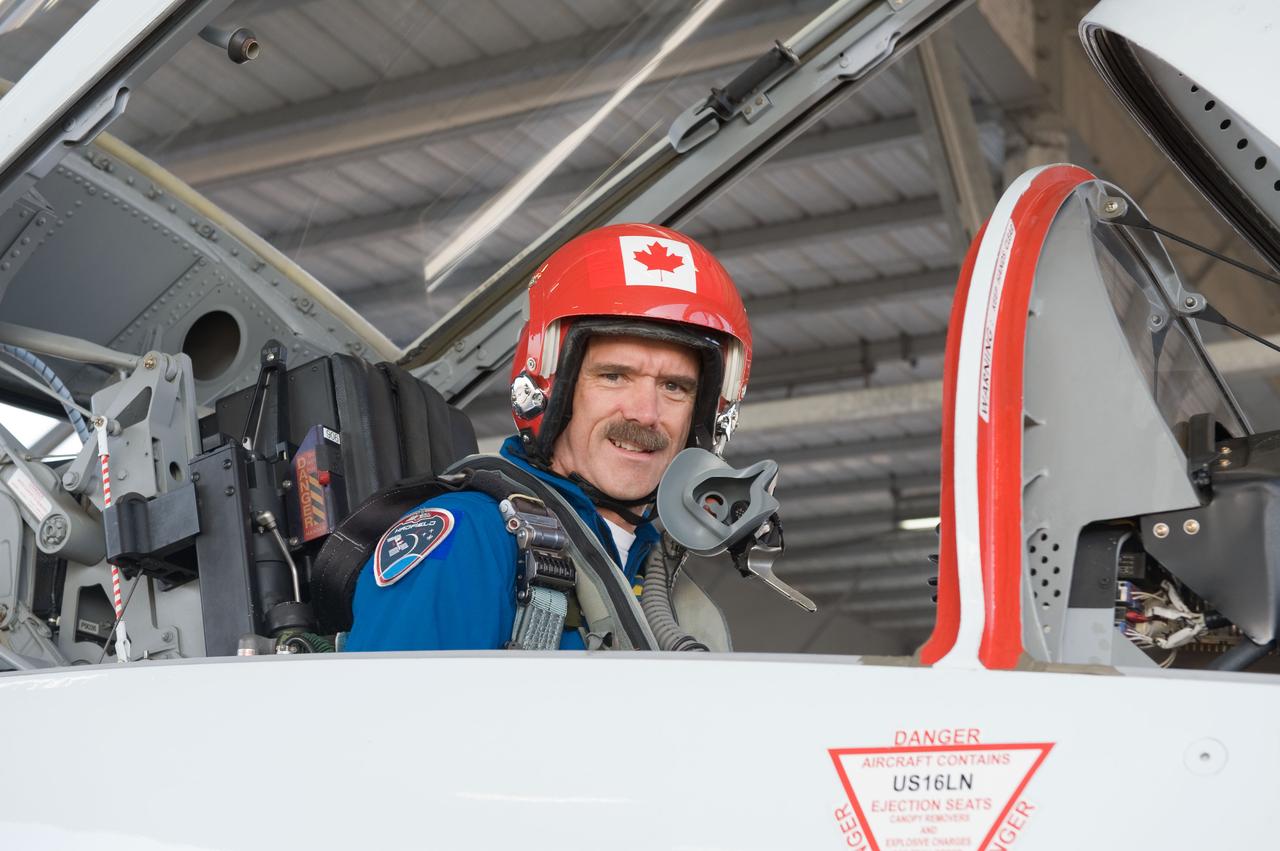

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
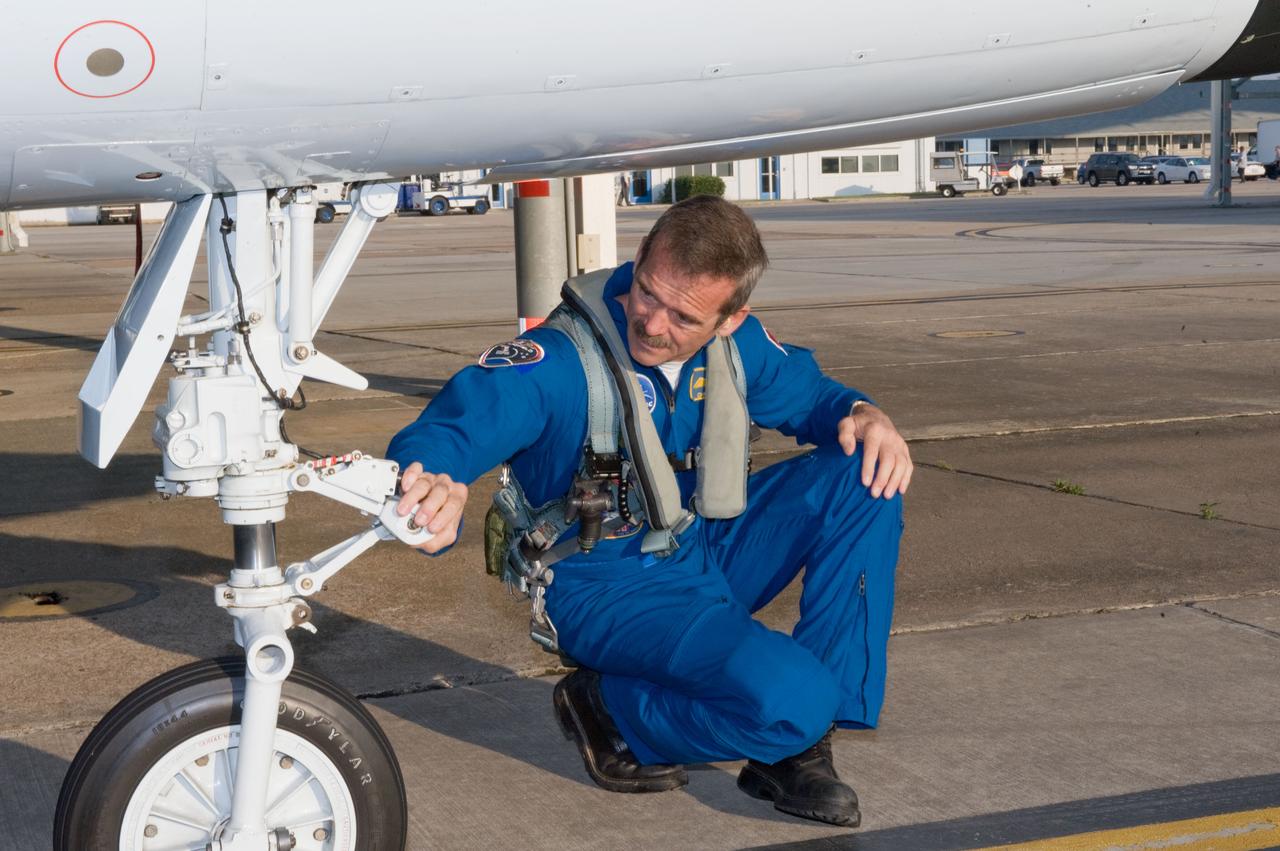

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
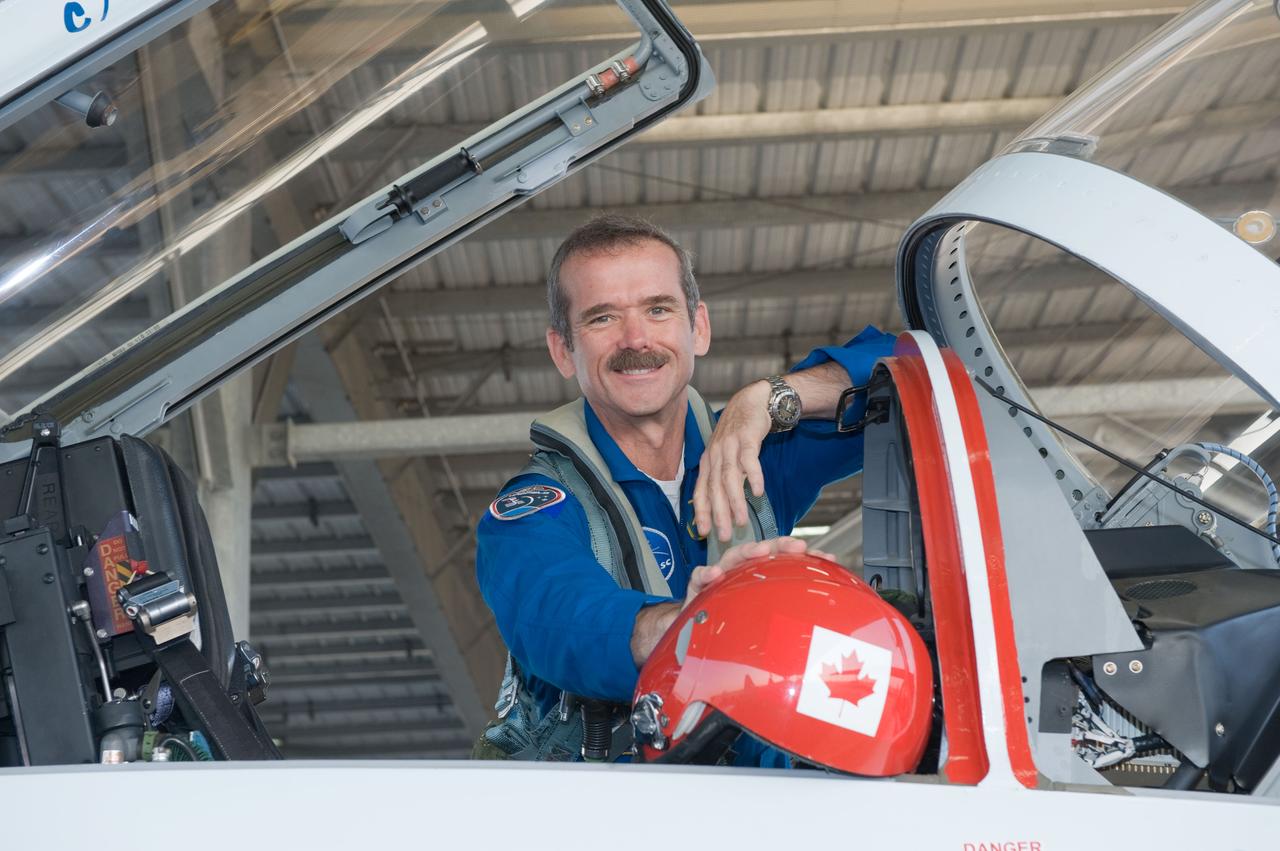

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
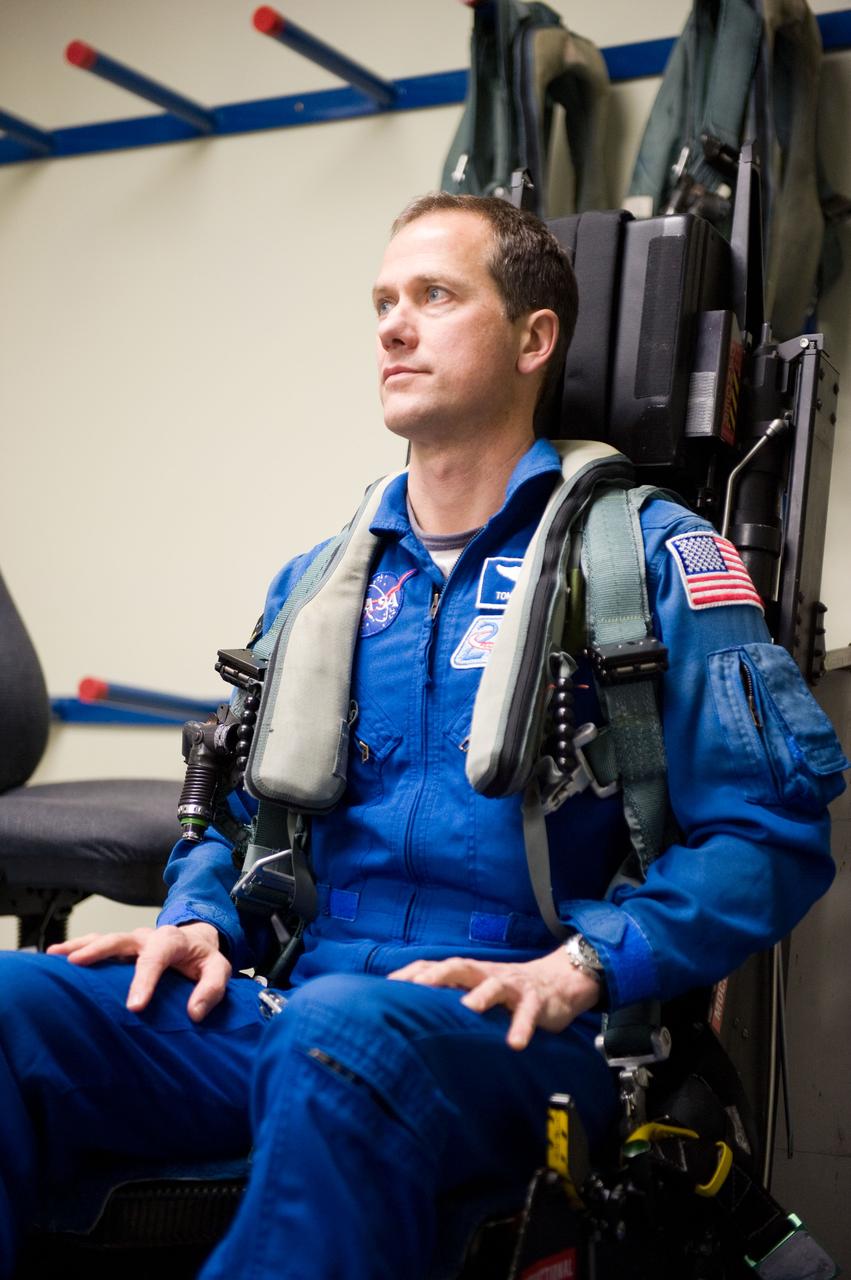

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
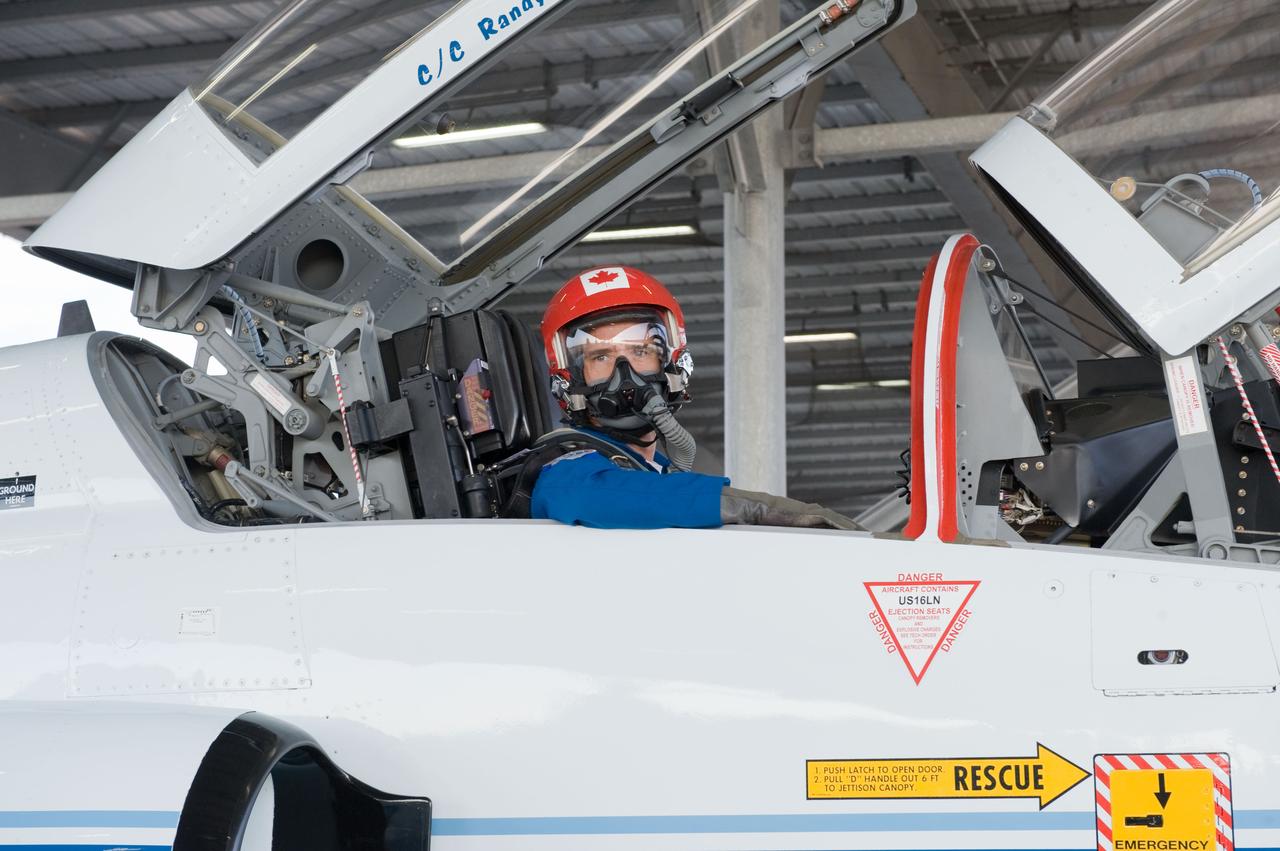

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
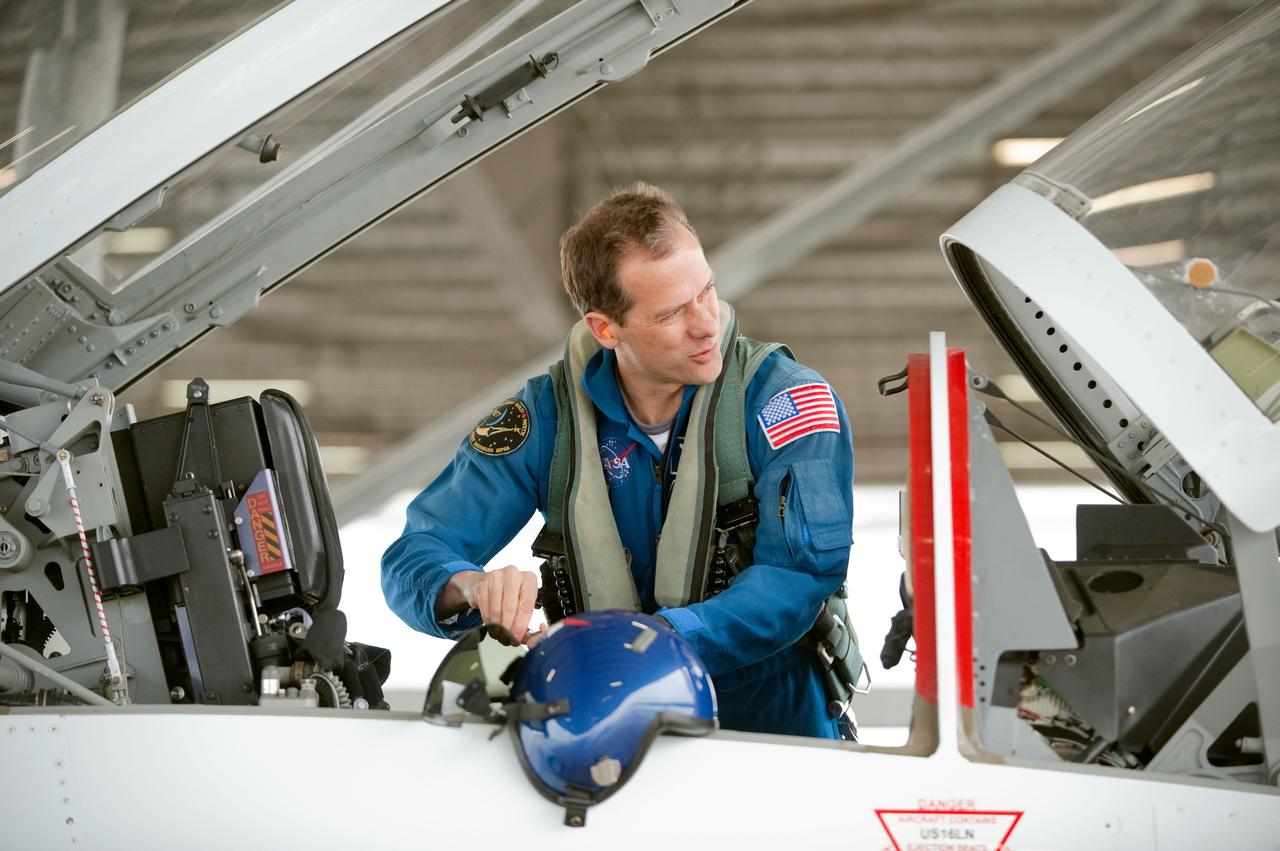

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
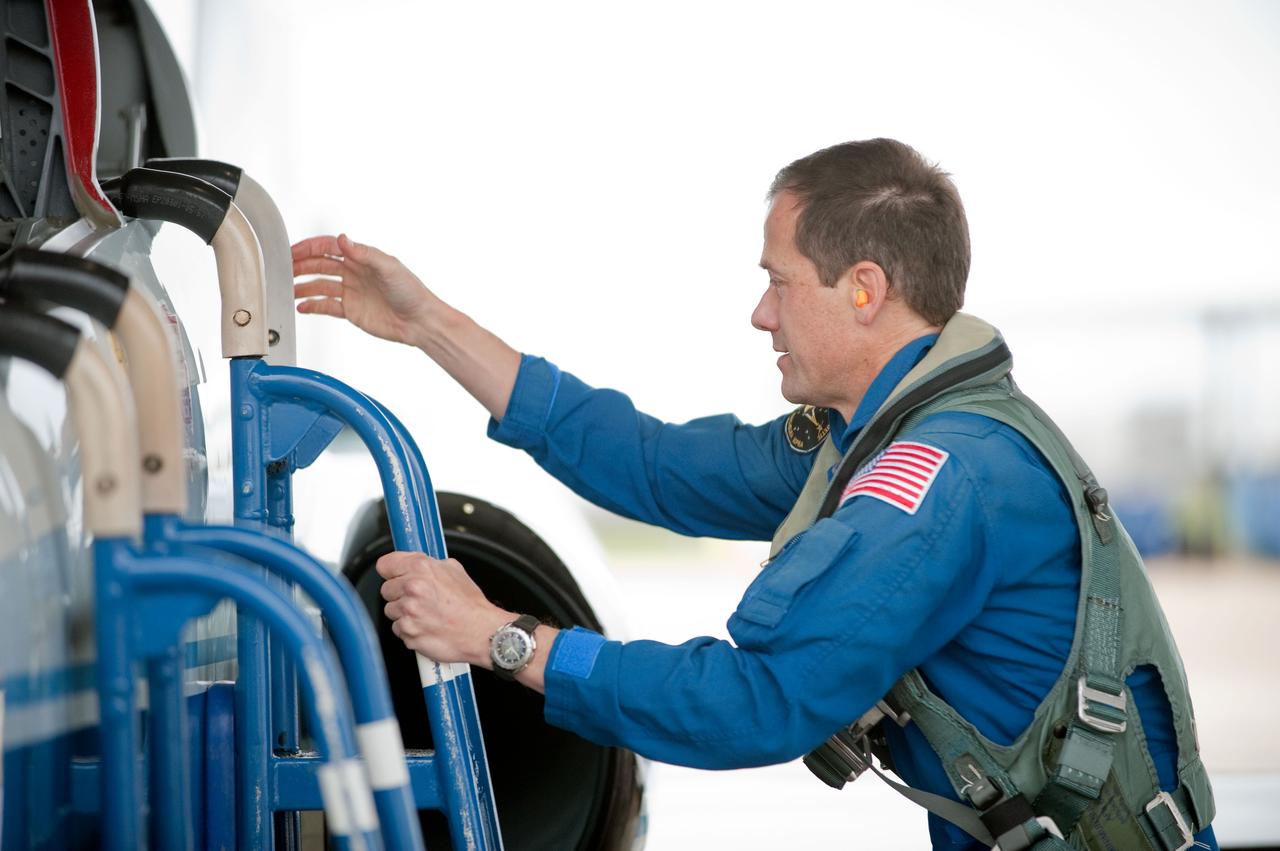

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
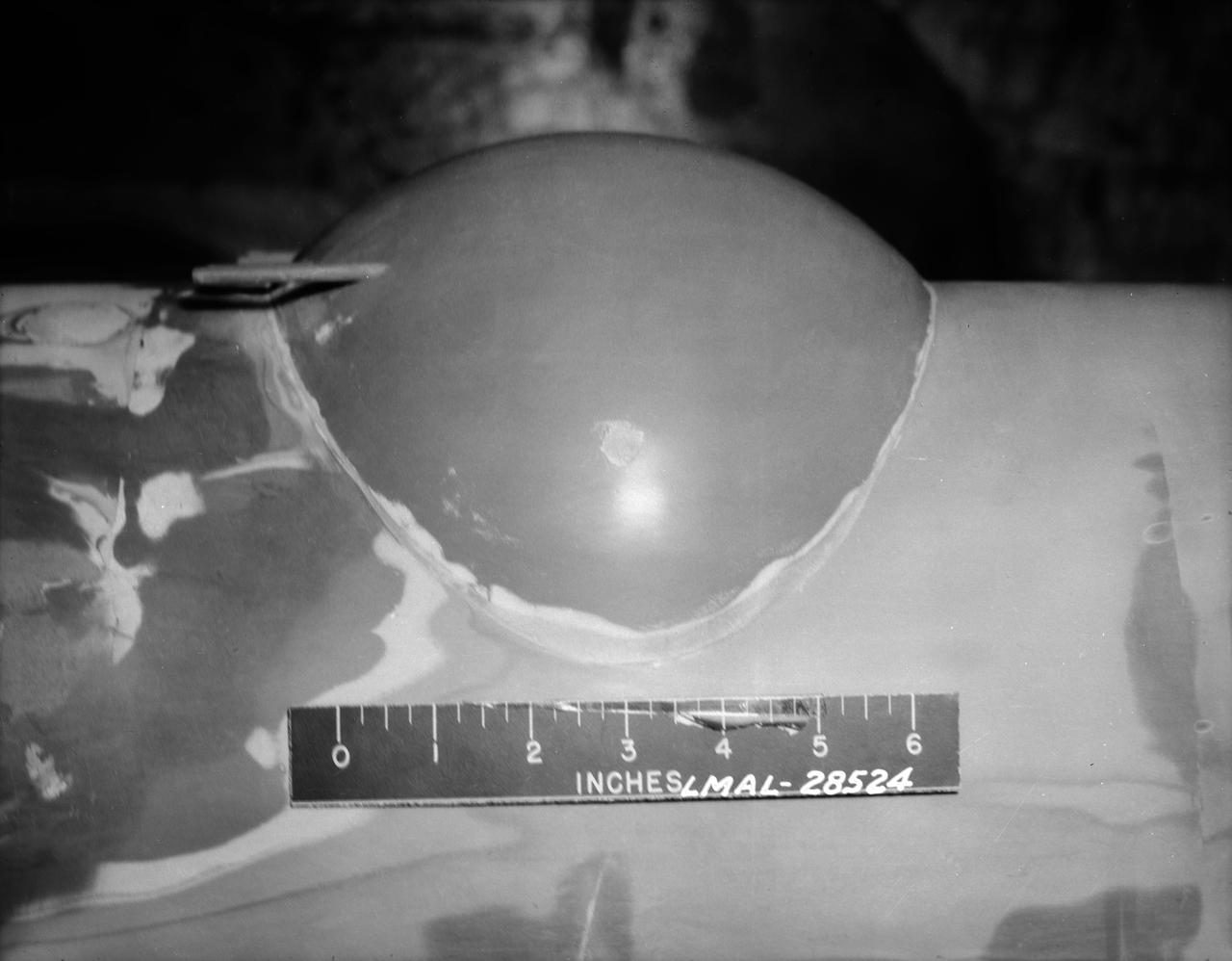
B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
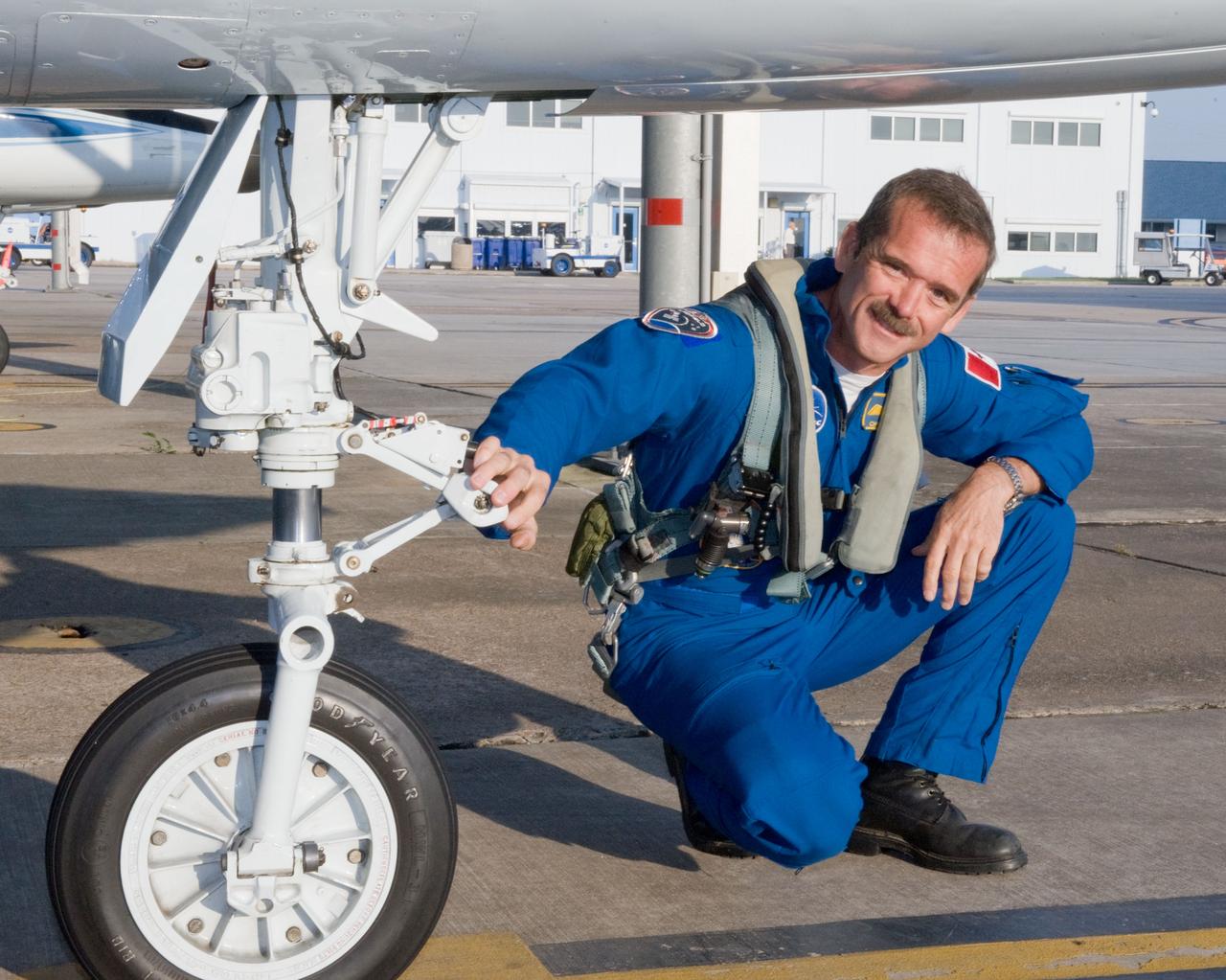

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
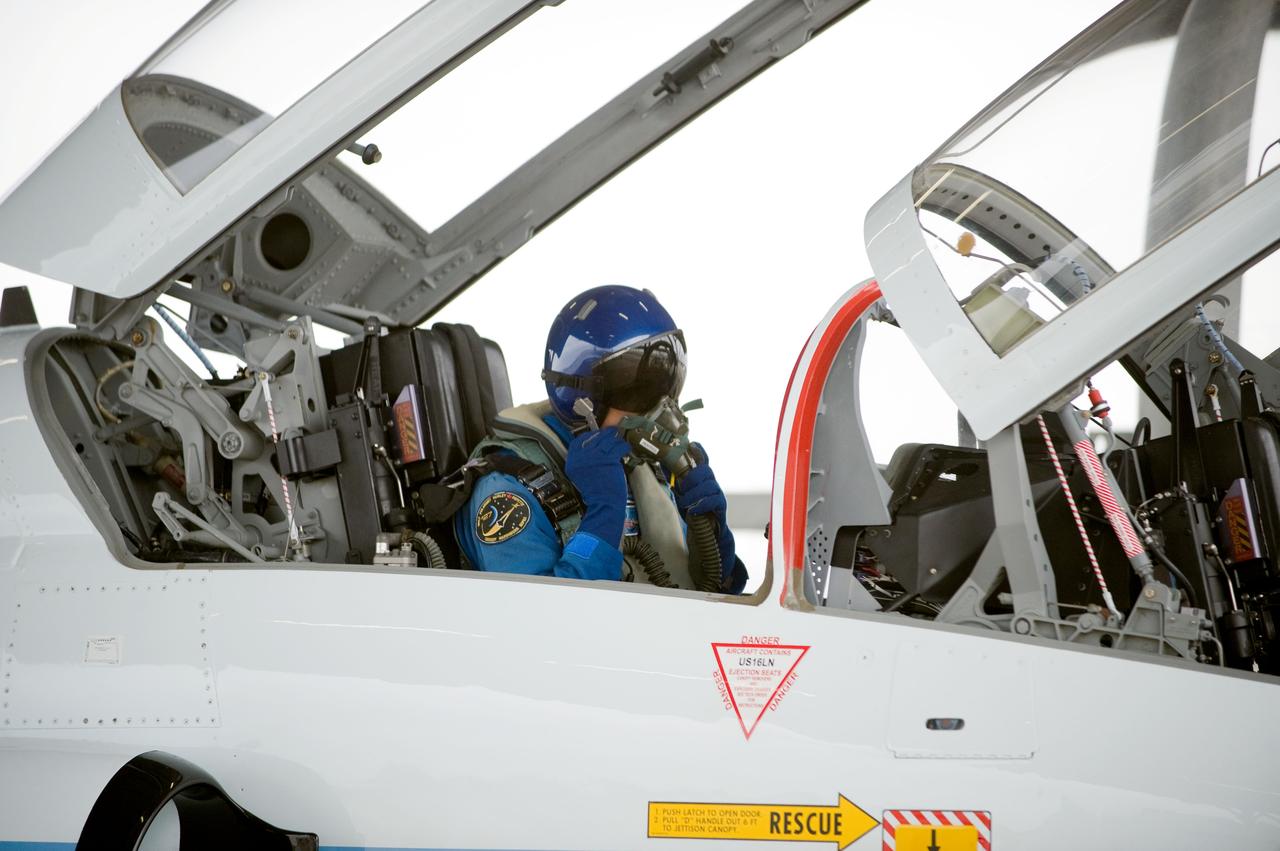

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
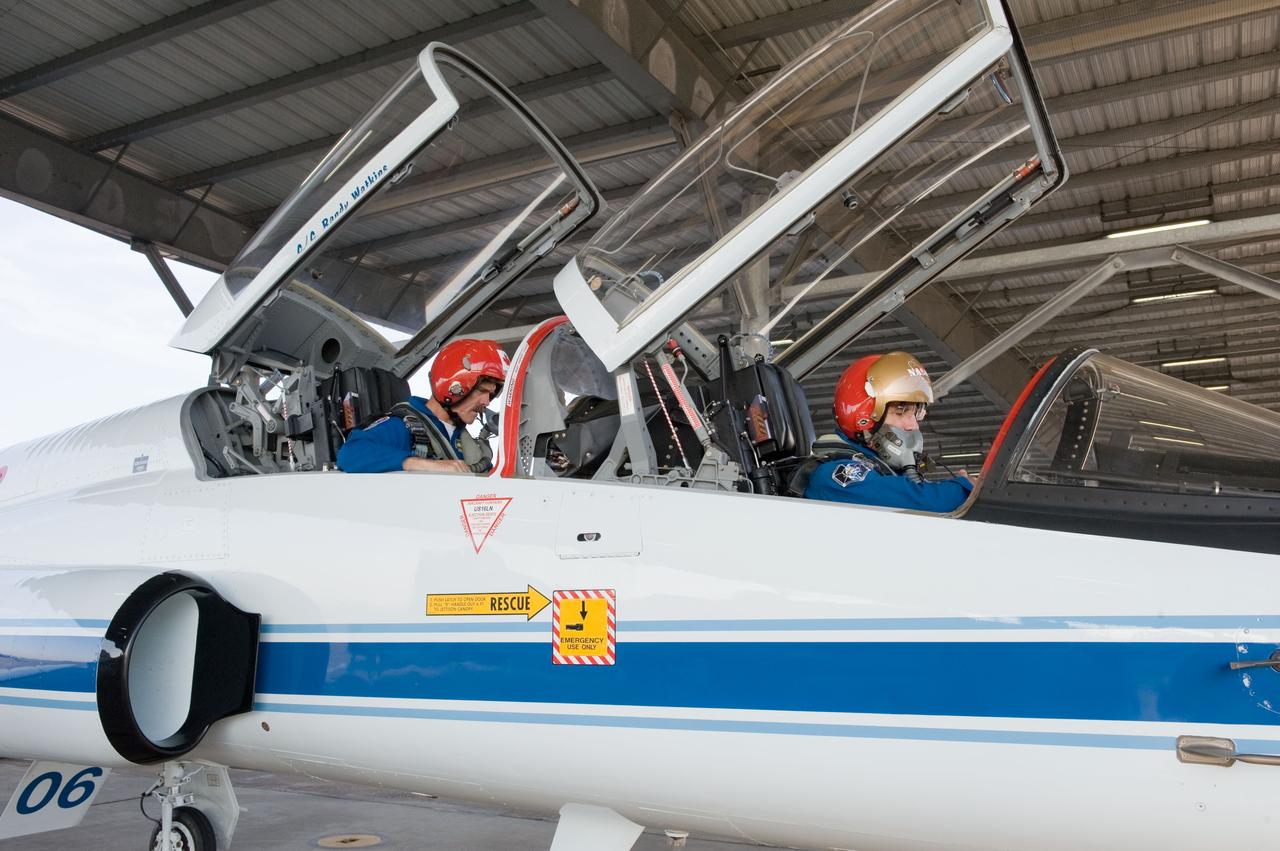

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
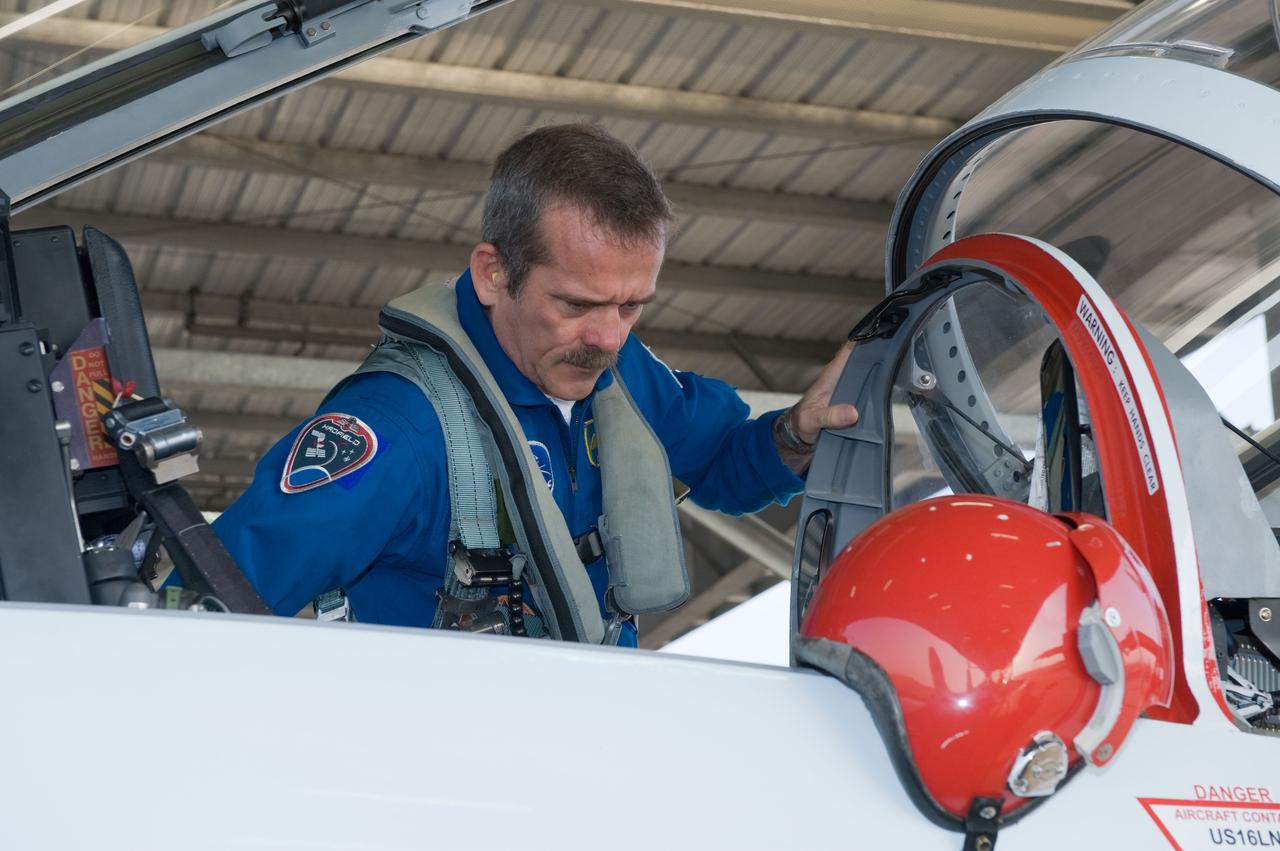

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
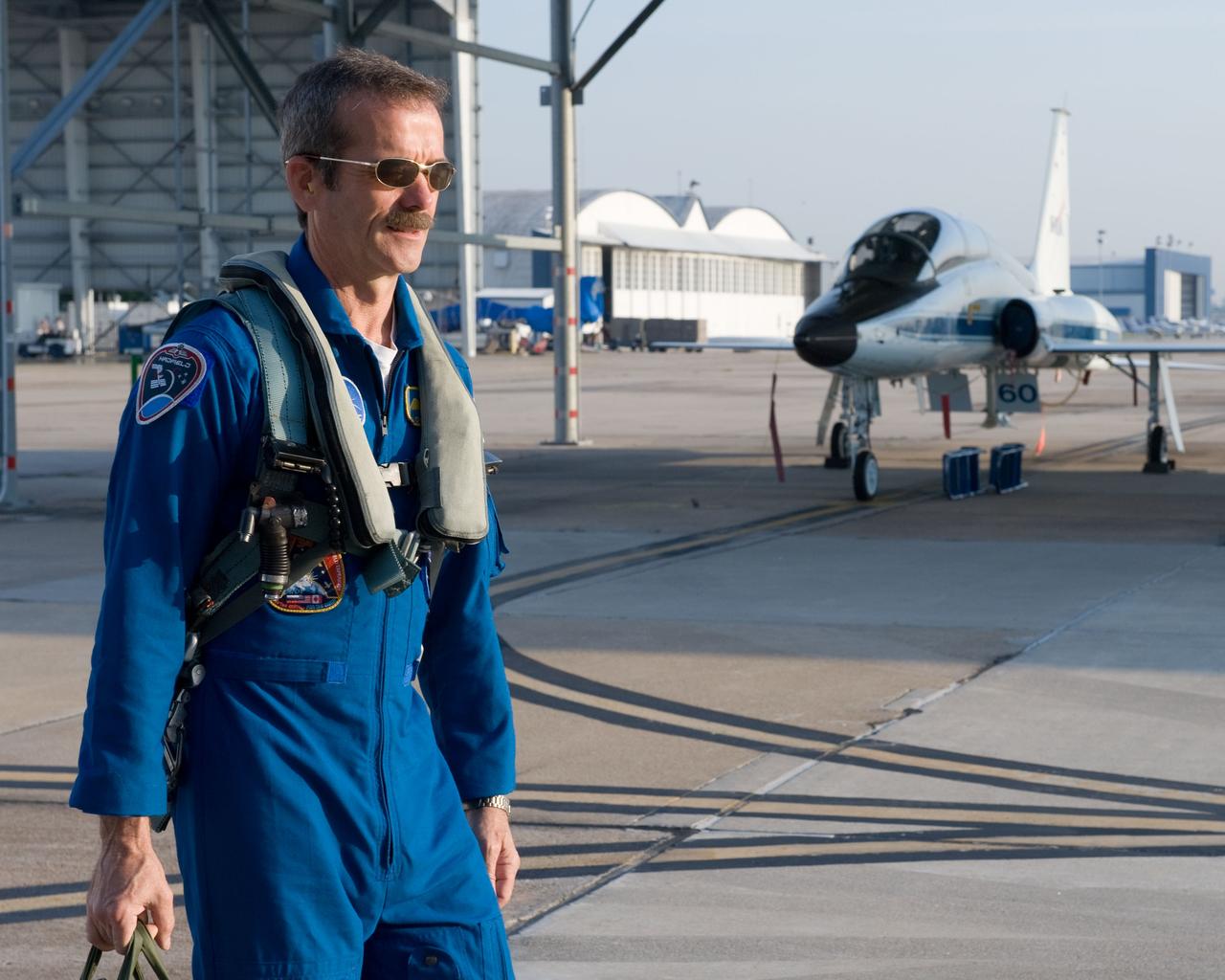

Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Chris Hadfield preparing for a T-38 flight. Photo Date: May 14, 2012. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 276 - Tarmac. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
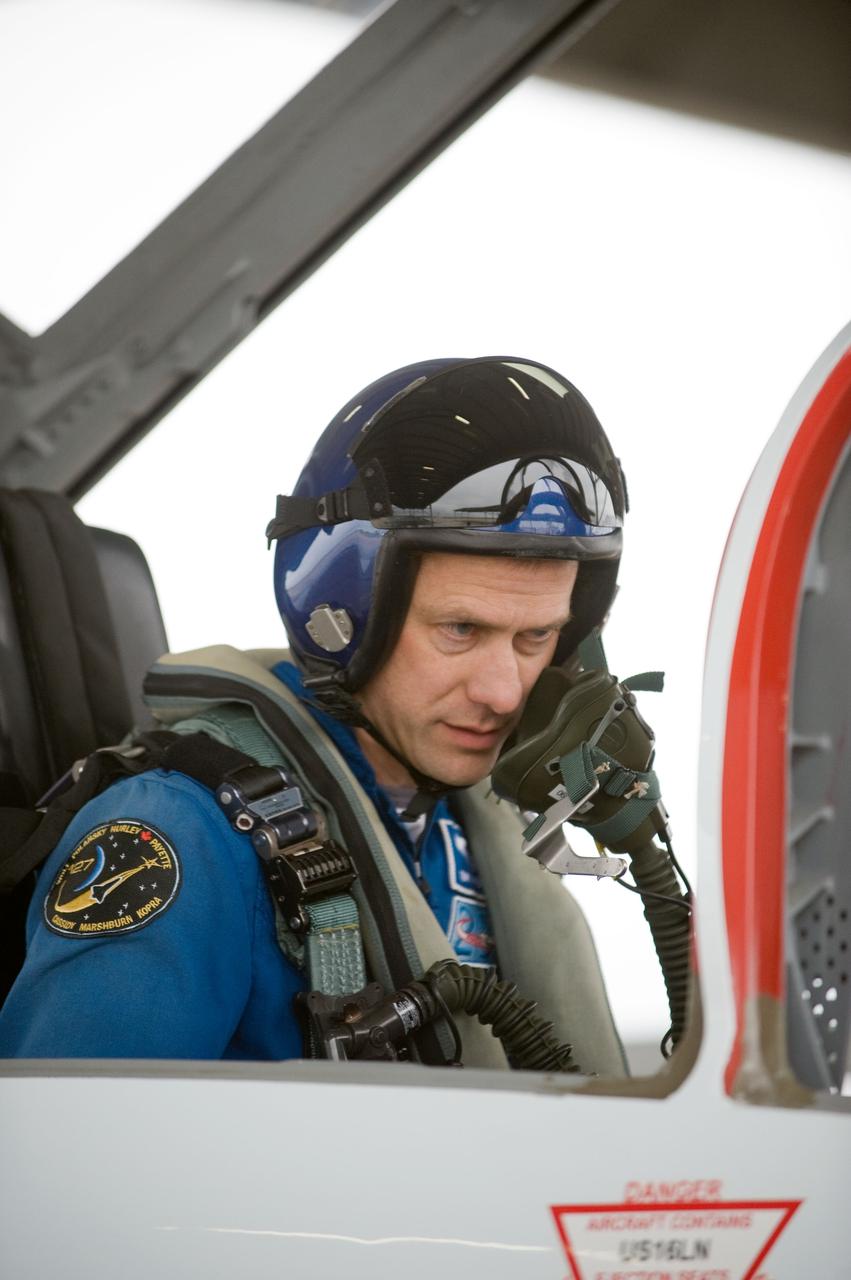

Date: 03-09-12 Location: Ellington Field Subject: Expedition 35 (Soyuz 33S) crew member Tom Marshburn preparing for his T-38 fligh with NASA pilot Thomas Parent. Photographer: James Blair
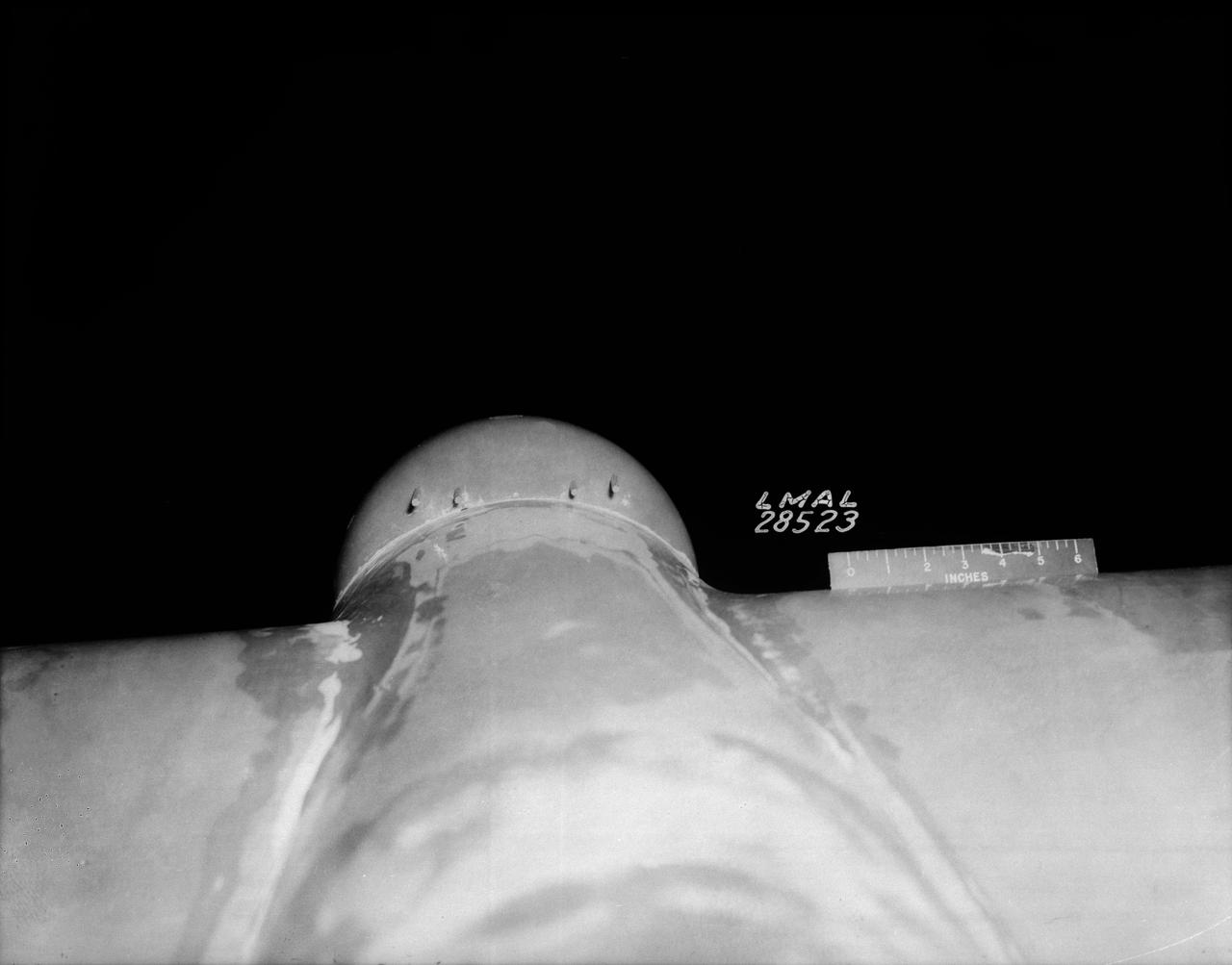

B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
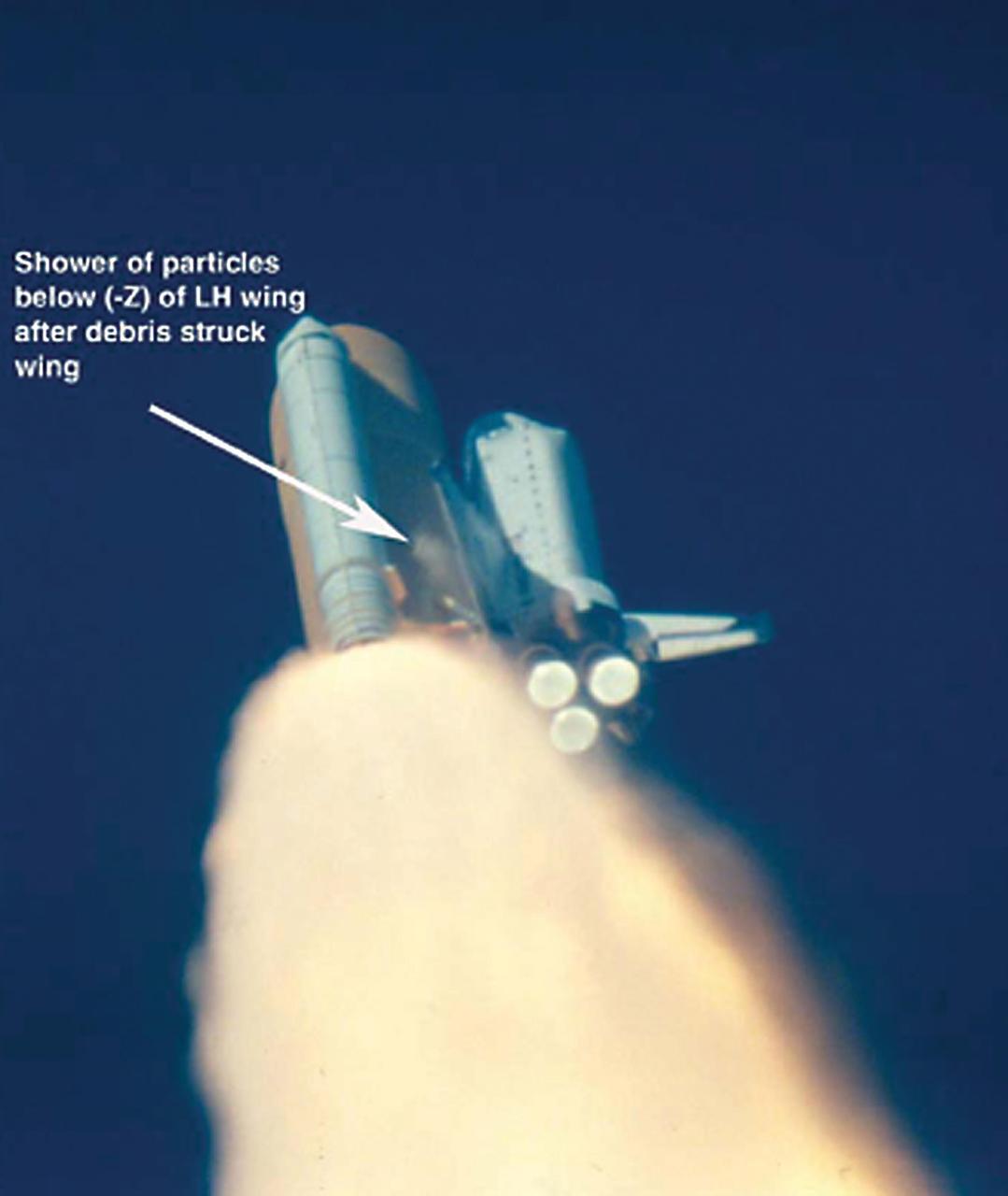
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Approximately 33 seconds after T-0 and liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia, several particles are observed falling away from the -Z portion of the LH solid rocket booster ETA ring. Particles were identified later as probably pieces of the instafoam closeout on the ETA ring.
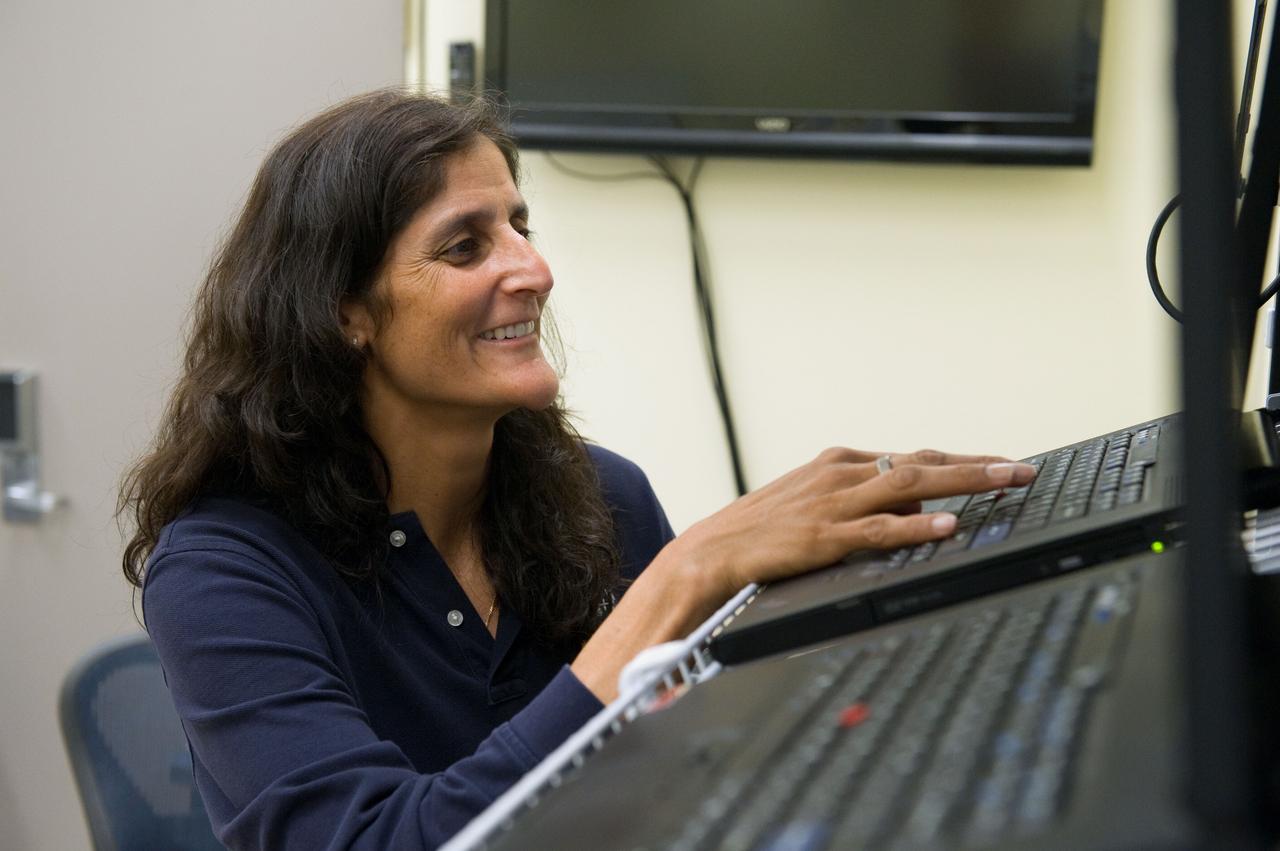

Date: 05-11-12 Location: Bldg 16 Subject: Expedition 32/33 JAXA astronaut Aki Hoshide during MSS PF SSRMS T&C3 training in the Robot Lab with instructor Melanie Miller Photographer: James Blair
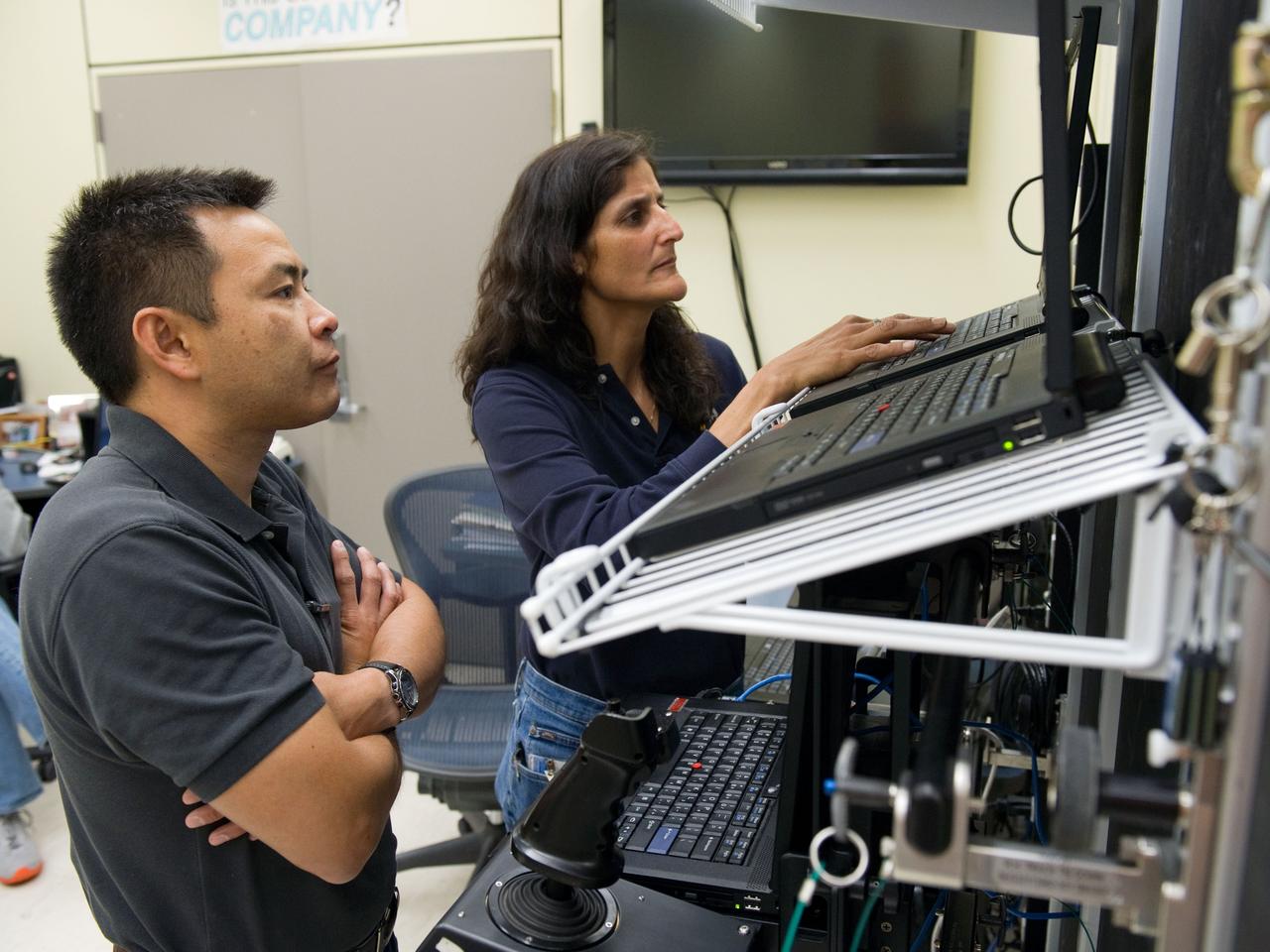

Date: 05-11-12 Location: Bldg 16 Subject: Expedition 32/33 JAXA astronaut Aki Hoshide during MSS PF SSRMS T&C3 training in the Robot Lab with instructor Melanie Miller Photographer: James Blair
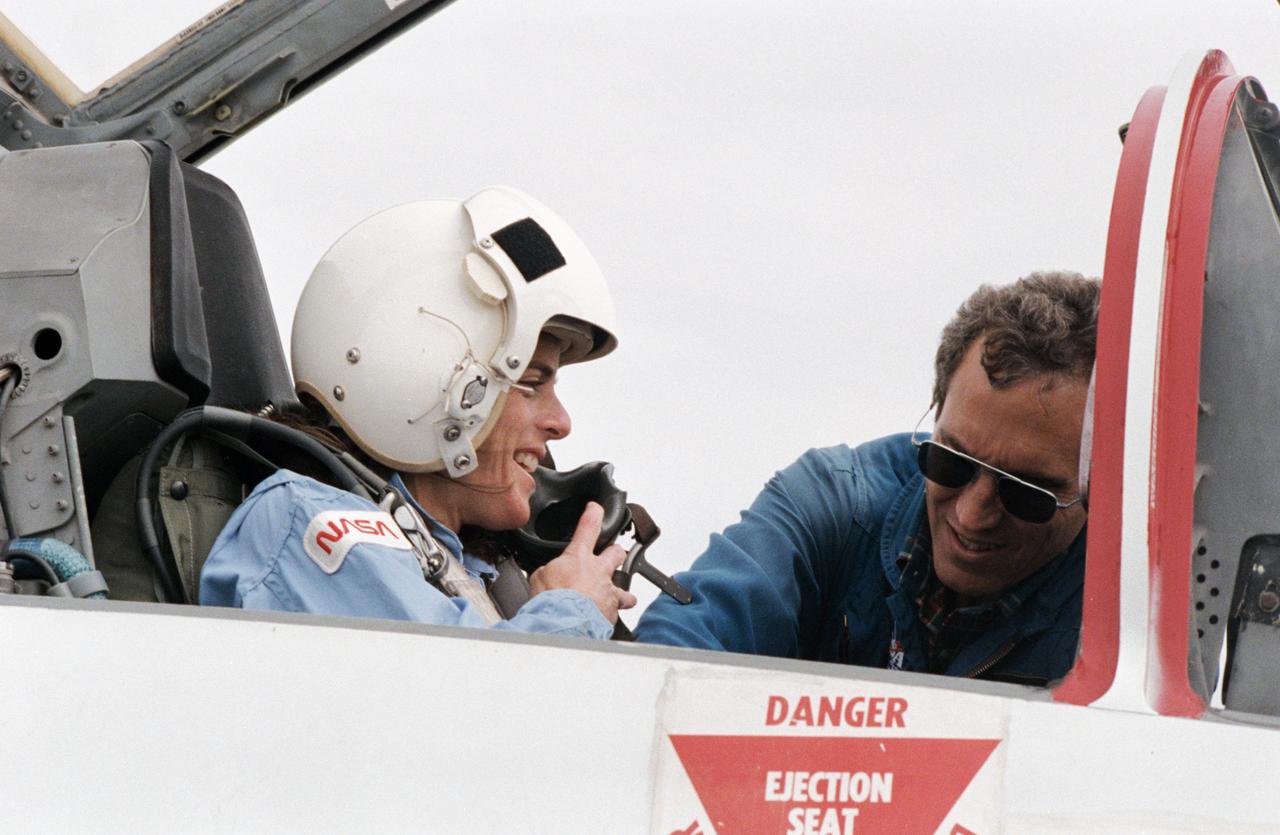

S85-41451 (3 Oct. 1985) --- Barbara Morgan, backup to the Teacher-in-Space participant Christa McAuliffe, prepares for a ride in the rear station of one of NASA's T-38 jet trainers at Ellington Field, near the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The McCall, Idaho teacher is briefed by astronaut Michael J. Smith, 51-L pilot, before departing Ellington Field. Photo credit: NASA
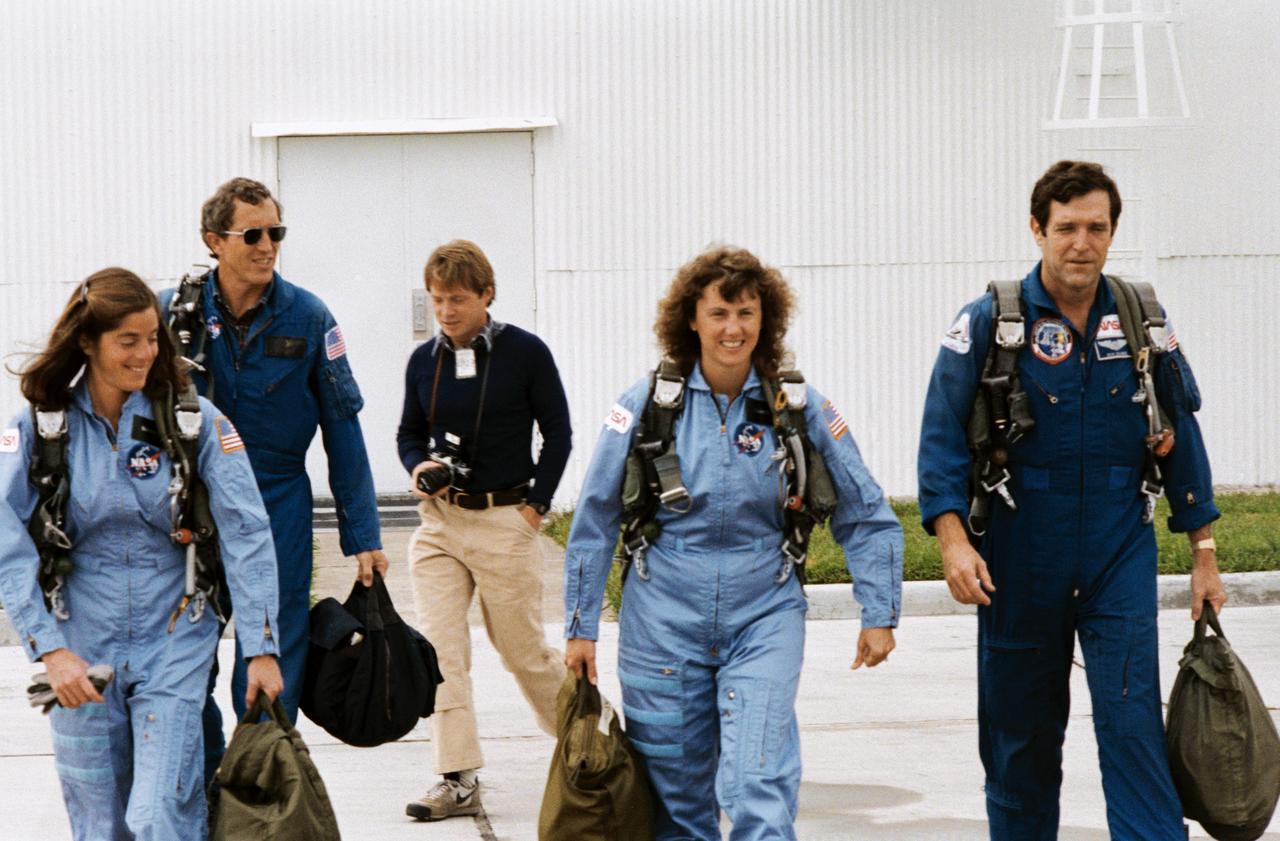

S85-41443 (12 Dec. 1985) --- Assigned STS-51L mission crew members, and a backup, are pictured at Ellington Air Field following brief flights in NASA's T-38 jet trainers. Left to right are Barbara R. Morgan, Michael J. Smith, an unidentified visitor, S. Christa McAuliffe and Francis R. (Dick) Scobee. Morgan is serving as backup, to McAuliffe's payload specialist position, as Teacher-in-Space Project representative on the flight. Scobee and Smith are commander and pilot, respectively, for NASA's 25th STS flight. Photo credit: NASA
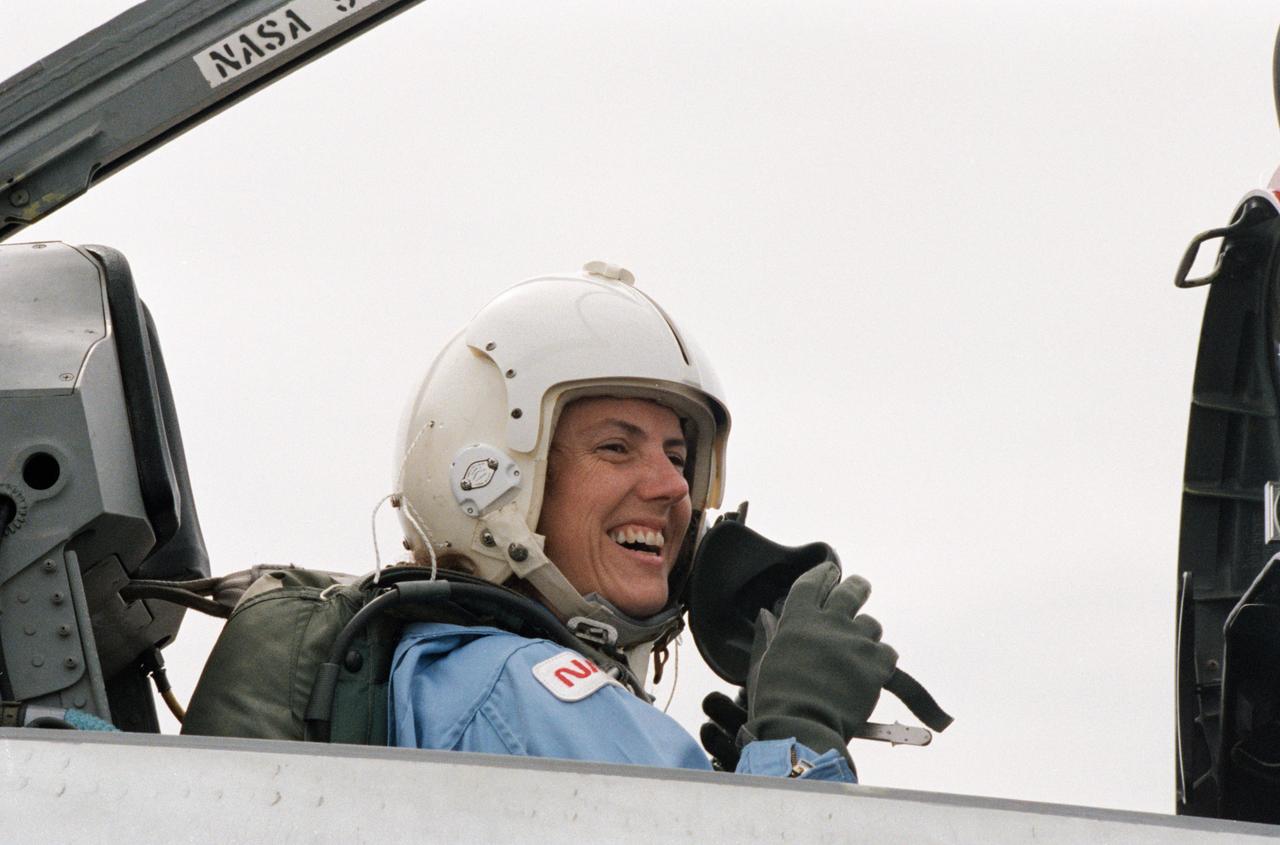

Sharon Christa McAuliffe, the Teacher in Space participant from Concord, New Hampshire, prepares for a ride in the rear station of one of NASA's T-38 jet trainers at Ellington Field near JSC.
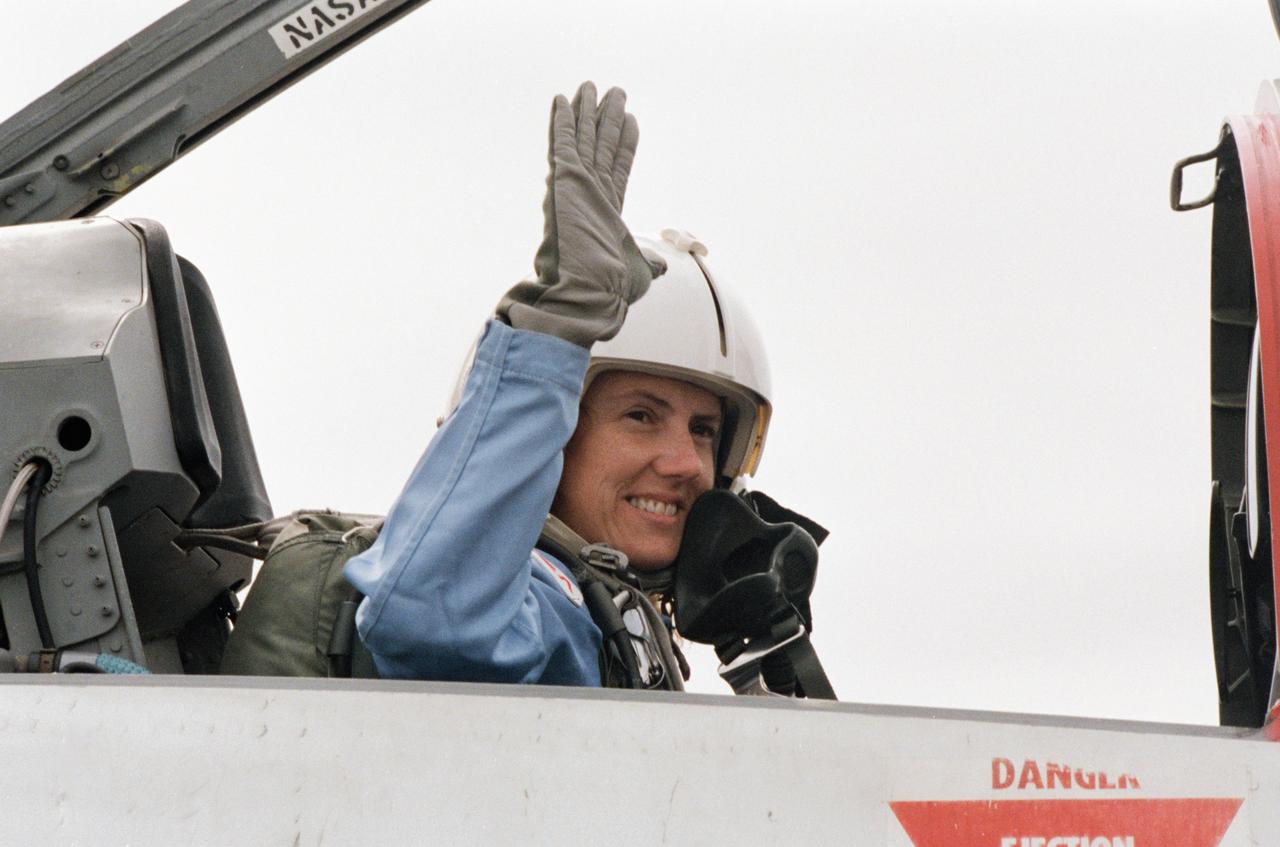

Sharon Christa McAuliffe, the Teacher in Space participant from Concord, New Hampshire, prepares for a ride in the rear station of one of NASA's T-38 jet trainers at Ellington Field near JSC.
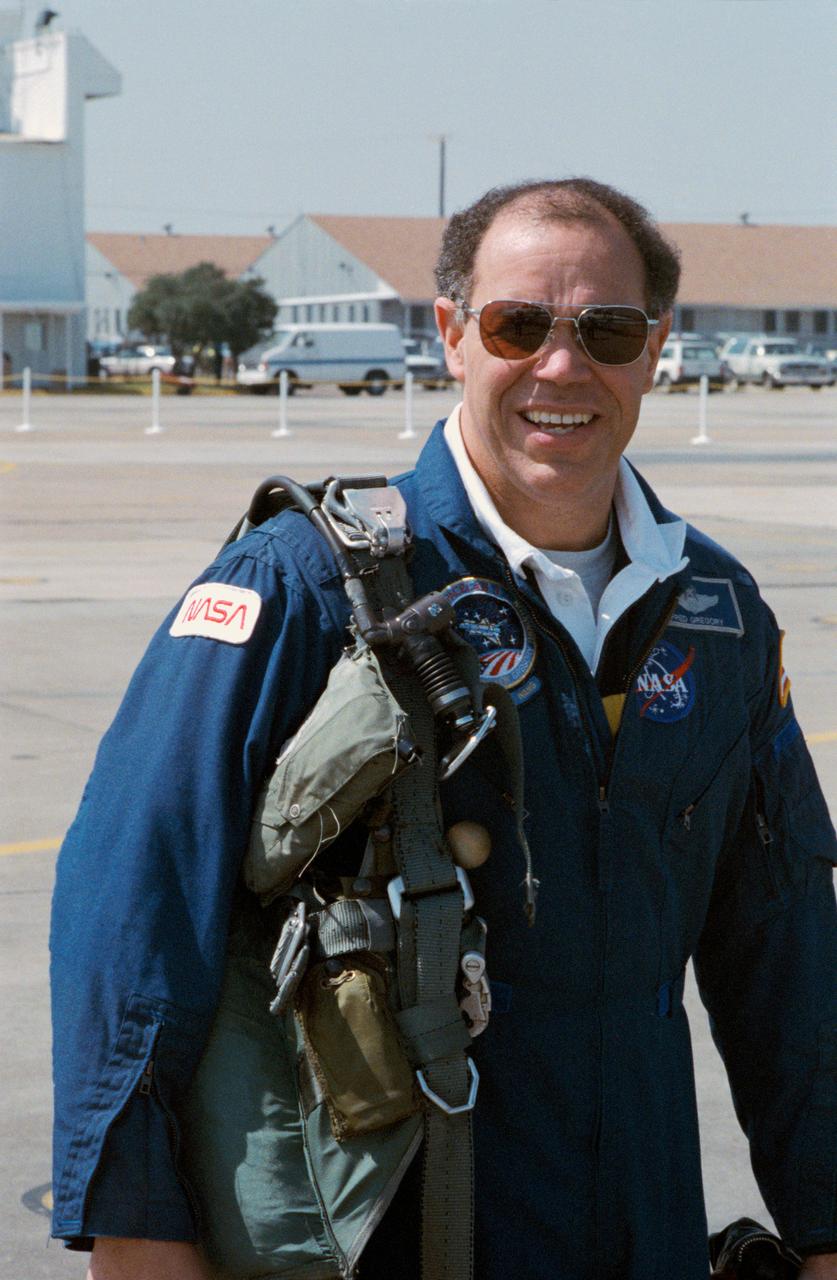

STS029-S-001 (10 March 1989) --- Astronaut Frederick Gregory, STS-33 mission commander, prepares to climb aboard a NASA T-38 jet aircraft. He's part of a group of JSC personnel who, in various NASA aircraft, will accompany the flight crew en route to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch facility. The second post-Challenger flight of Discovery is scheduled for a 8:07 a.m. (EST) launch on March 13, 1989.

Onlookers wearing commemorative t-shirts watch as space shuttle Atlantis rolls to ts new home at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, early Friday, Nov. 2, 2012, in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The spacecraft traveled 125,935,769 miles during 33 spaceflights, including 12 missions to the International Space Station. Its final flight, STS-135, closed out the Space Shuttle Program era with a landing on July 21, 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
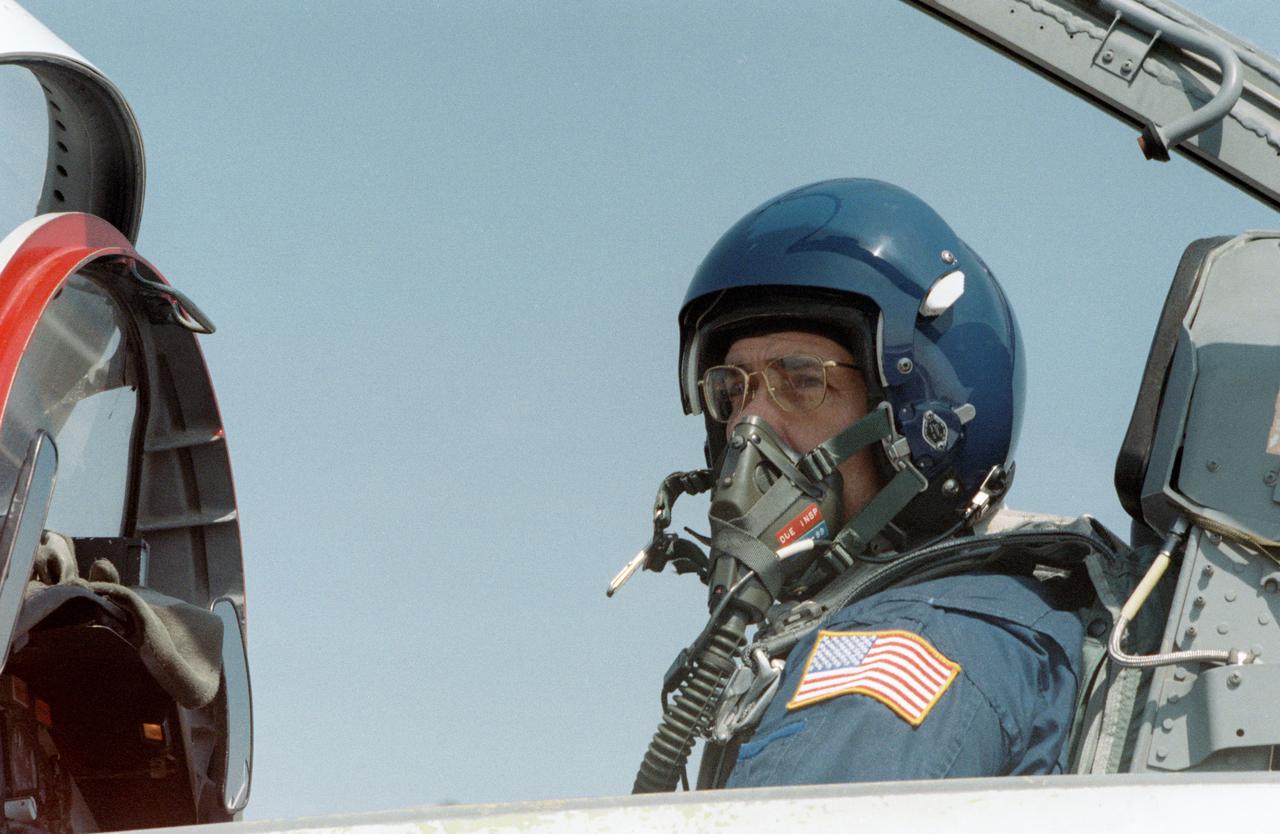

STS029–S-002 (10 March 1989) --- Astronaut Frederick Gregory, STS-33 mission commander, prepares to fly to Florida in a NASA T-38 jet aircraft. He's part of a group of JSC personnel in various NASA aircraft, accompanying the flight crew en route to the Kennedy Space Center launch facility. The second post-Challenger flight of Discovery is scheduled for a 8:07 a.m. (EST) launch on March 13.
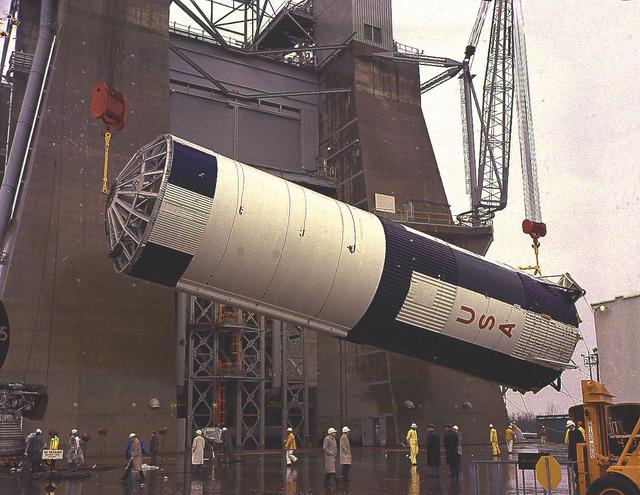

The S-IC-T stage was hoisted into the S-IC Static Test Stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage was a static test vehicle, not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months to prove the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, housed the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that held a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks were cornected by a 26-foot intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
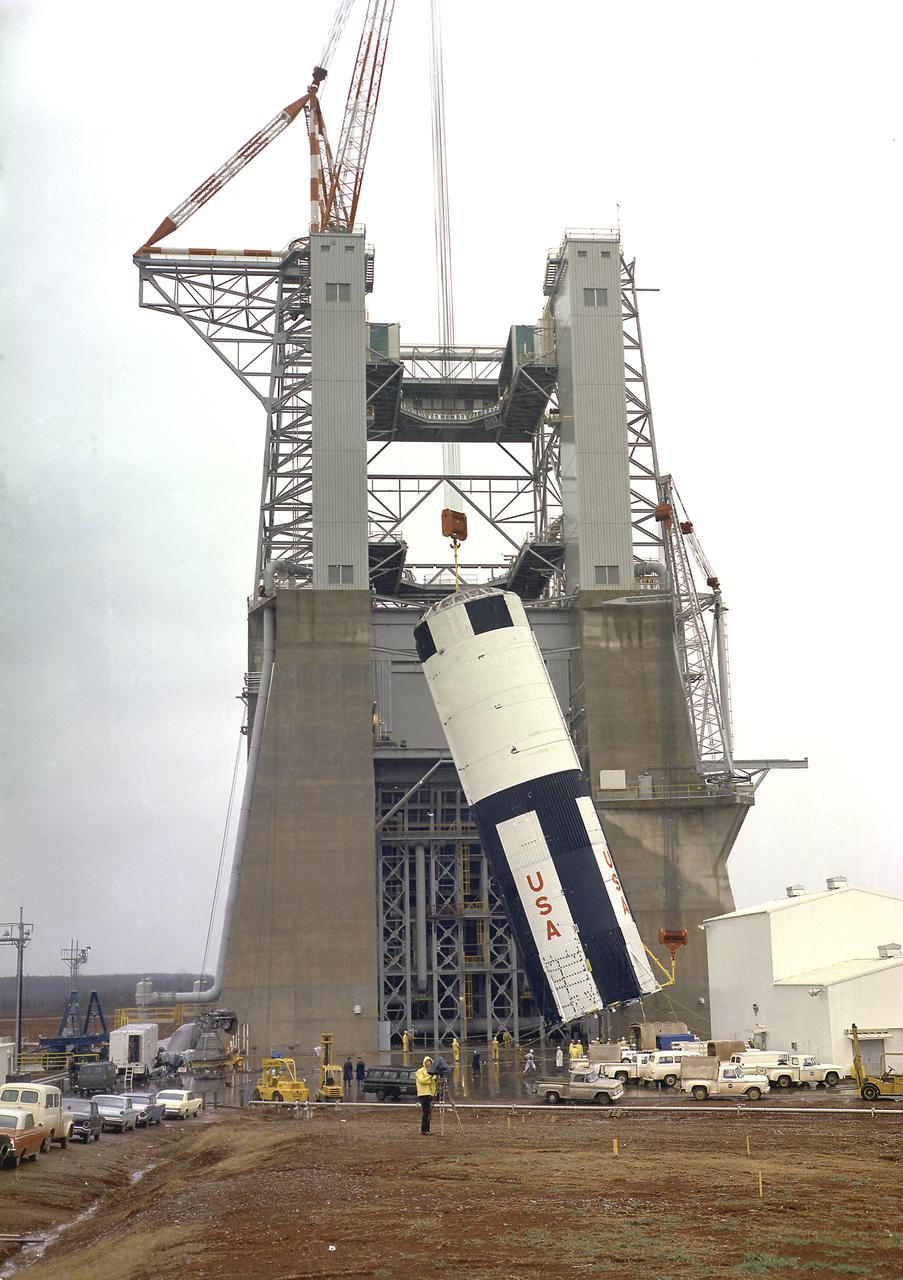

The S-IC-T stage was hoisted into the S-IC static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage was a static test vehicle not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months to prove the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, housed the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that held a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks are cornected by a 26-foot-long intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
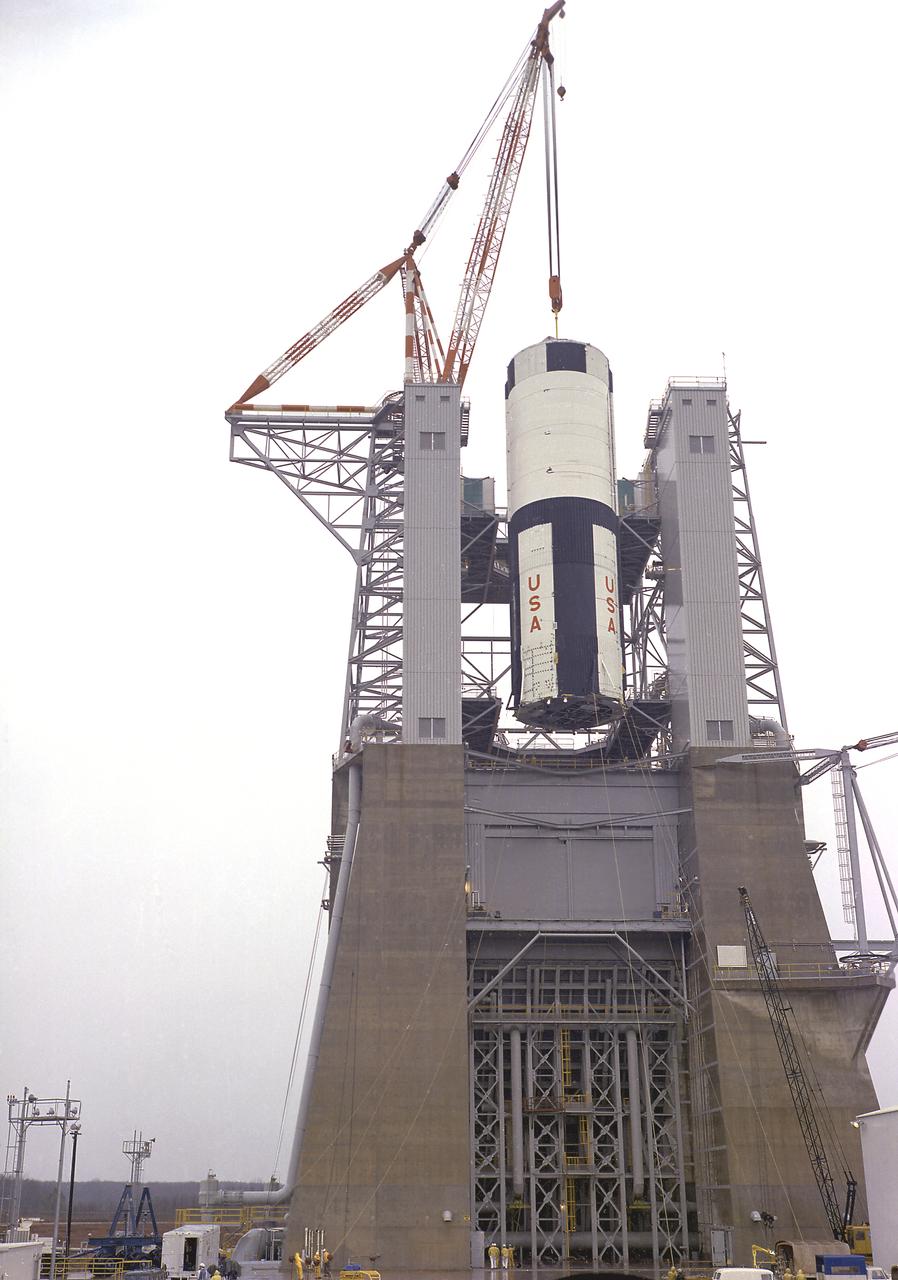

The S-IC-T stage is hoisted into the S-IC static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage is a static test vehicle not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months proving the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, houses the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that hold a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks are cornected by a 26-foot-long intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
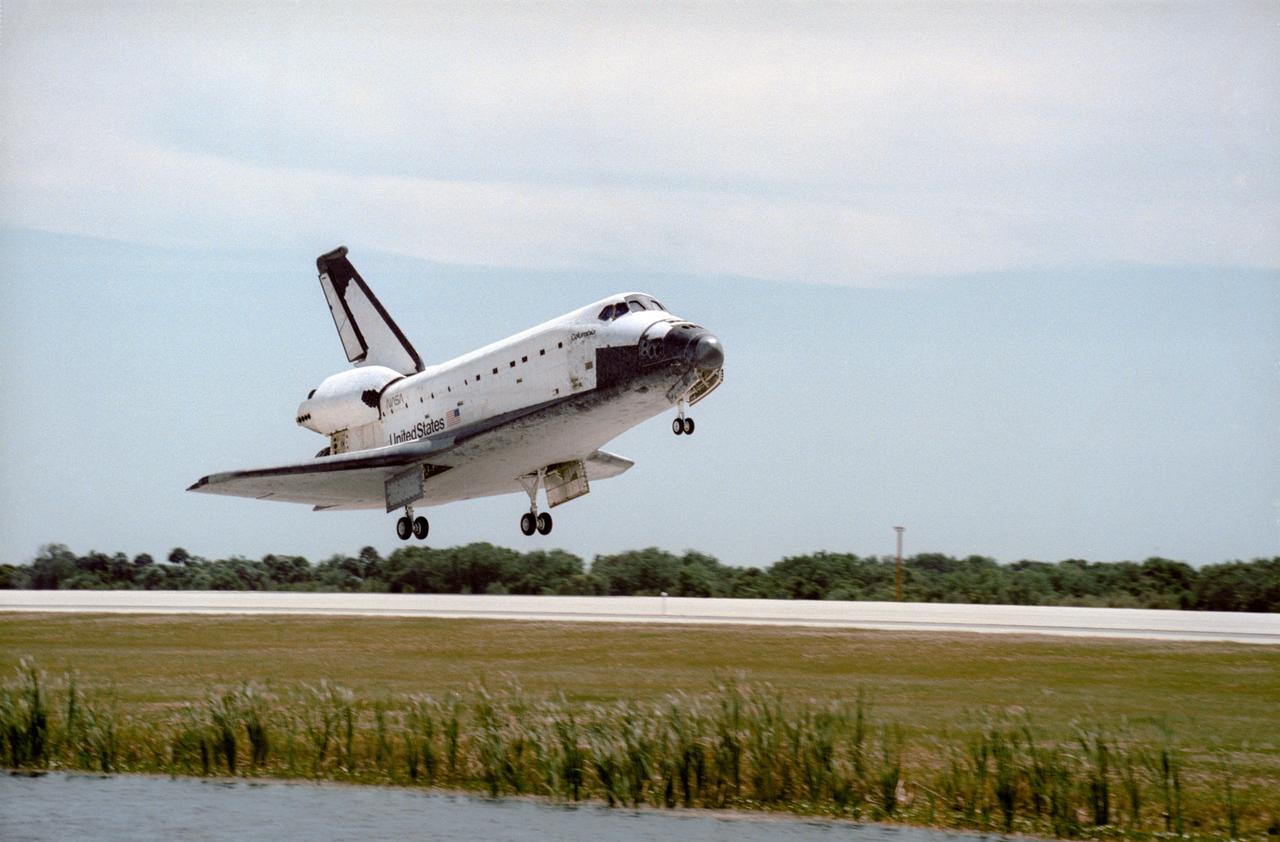

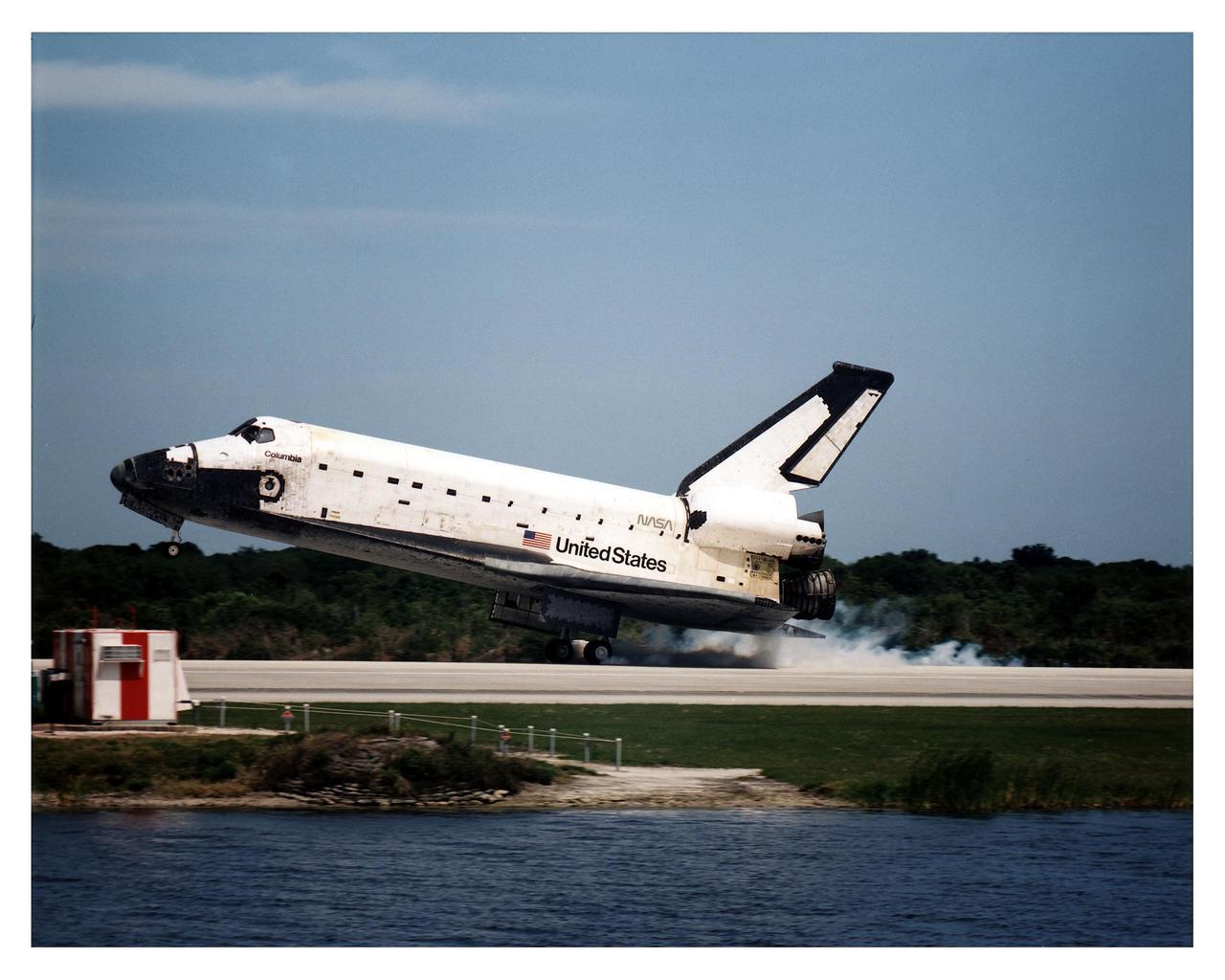
STS083-S-009 (8 April 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Columbia nears touchdown on the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), after completing almost four days of a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit. A problem with one of three fuel cells led to an early landing for the seven-member Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) crew. Touchdown occurred at 1:33:11 p.m. (EDT), April 8, 1997. Onboard Columbia were James D. Halsell, Jr., Susan L. Still, Janice E. Voss, Donald A. Thomas, Michael L. Gernhardt, Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris.
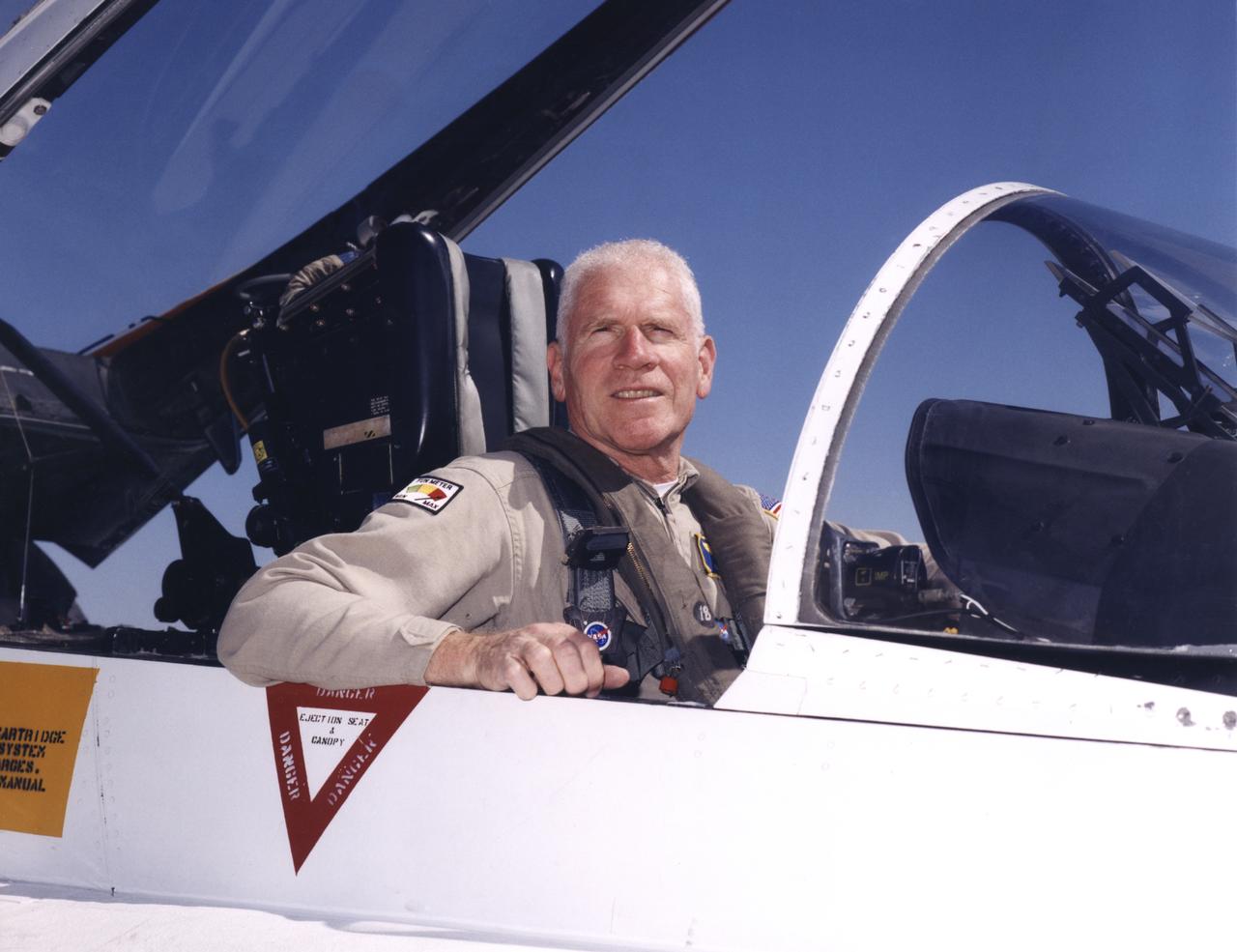

Edwin W. Lewis Jr. is a research pilot in the Airborne Science program, Flight Crew Branch, Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. He currently flies the DC-8, F/A-18, Lear Jet 24, King Air, and T-34C in support of Dryden's flight operations and is mentor pilot for the King Air and the Lear Jet. Prior to accepting this assignment Lewis was a pilot for eight years at NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, flying 10 different aircraft C-130B, DC-8-72, UH-1, SH-3, King Air, Lear 24, T-38A, T-39G and YO-3A in support of NASA flight missions. Lewis also flew the Kuiper Airborne Observatory (a modified civilian version of the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter). He was project pilot for Ames' 747 and T-38 programs. Lewis was born in New York City on May 19, 1936, and began flight training as a Civil Air Patrol cadet in 1951, ultimately earning his commercial pilot's certificate in 1958. He received a bachelor of arts degree in biology from Hobart College, Geneva, N.Y., and entered the U.S. Air Force through the Reserve Officer Training Corps. Following pilot training he was assigned to Moody Air Force Base, Ga., as an instructor pilot, for both the T-33 and T-37 aircraft. He served in Vietnam in 1965 and 1966, where he was a forward air controller, instructor and standardization/evaluation pilot, flying more than 1,000 hours in the O-1 "Bird Dog." Lewis separated from the regular Air Force and joined Pan American World Airways and the 129th Air Commando Group, California Air National Guard (ANG) based in Hayward, California. During his 18-year career with the California ANG he flew the U-6, U-10, C-119, HC-130 aircraft and the HH-3 helicopter. He retired as commander, 129th Air Rescue and Recovery Group, a composite combat rescue group, in the grade of colonel. During his 22 years as an airline pilot, he flew the Boeing 707, 727 and 747. He took early retirement from Pan American in 1989 to become a pilot with NASA.

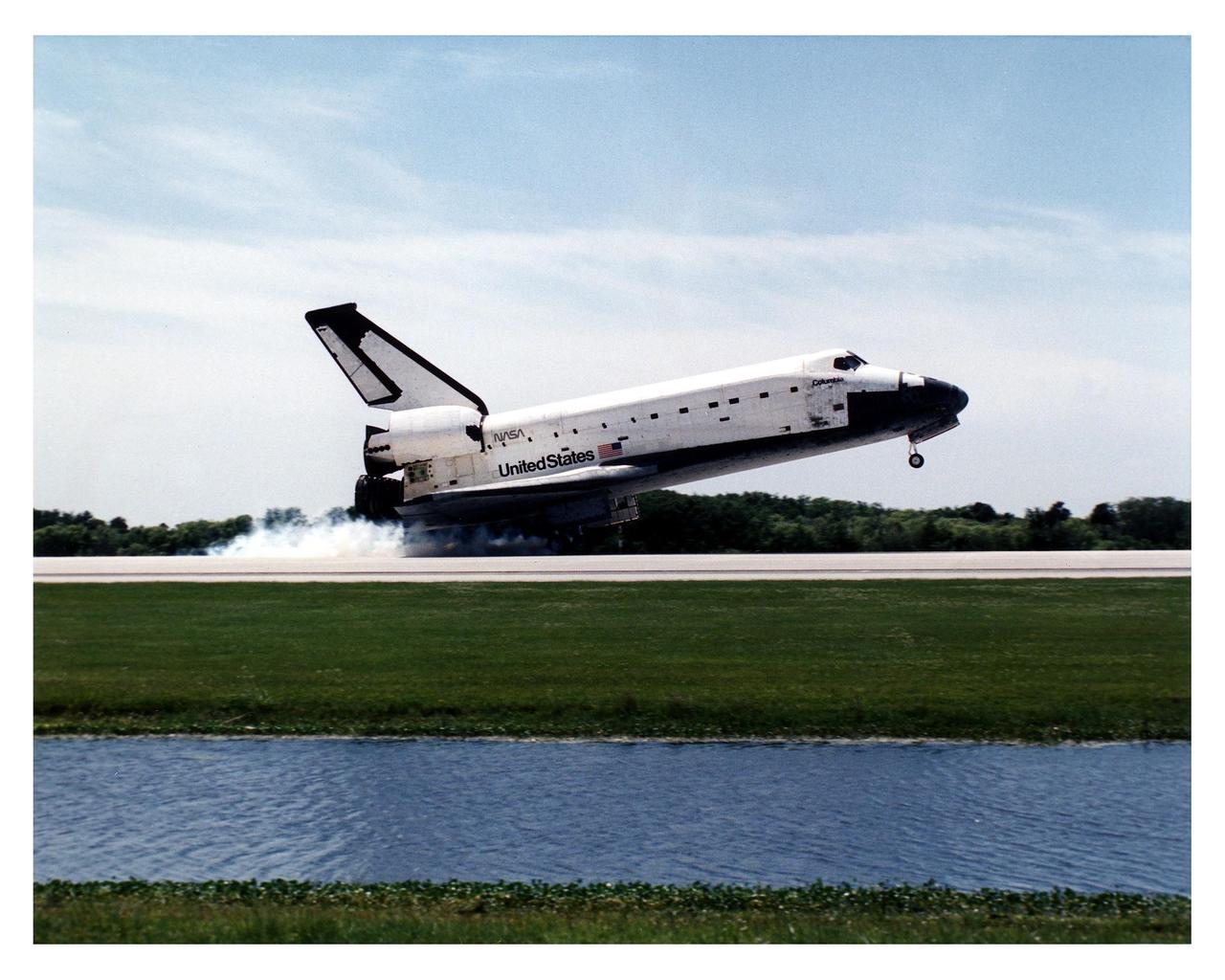
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Columbia hurtles down Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. With main gear touchdown at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to a mechanical problem. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L.Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations
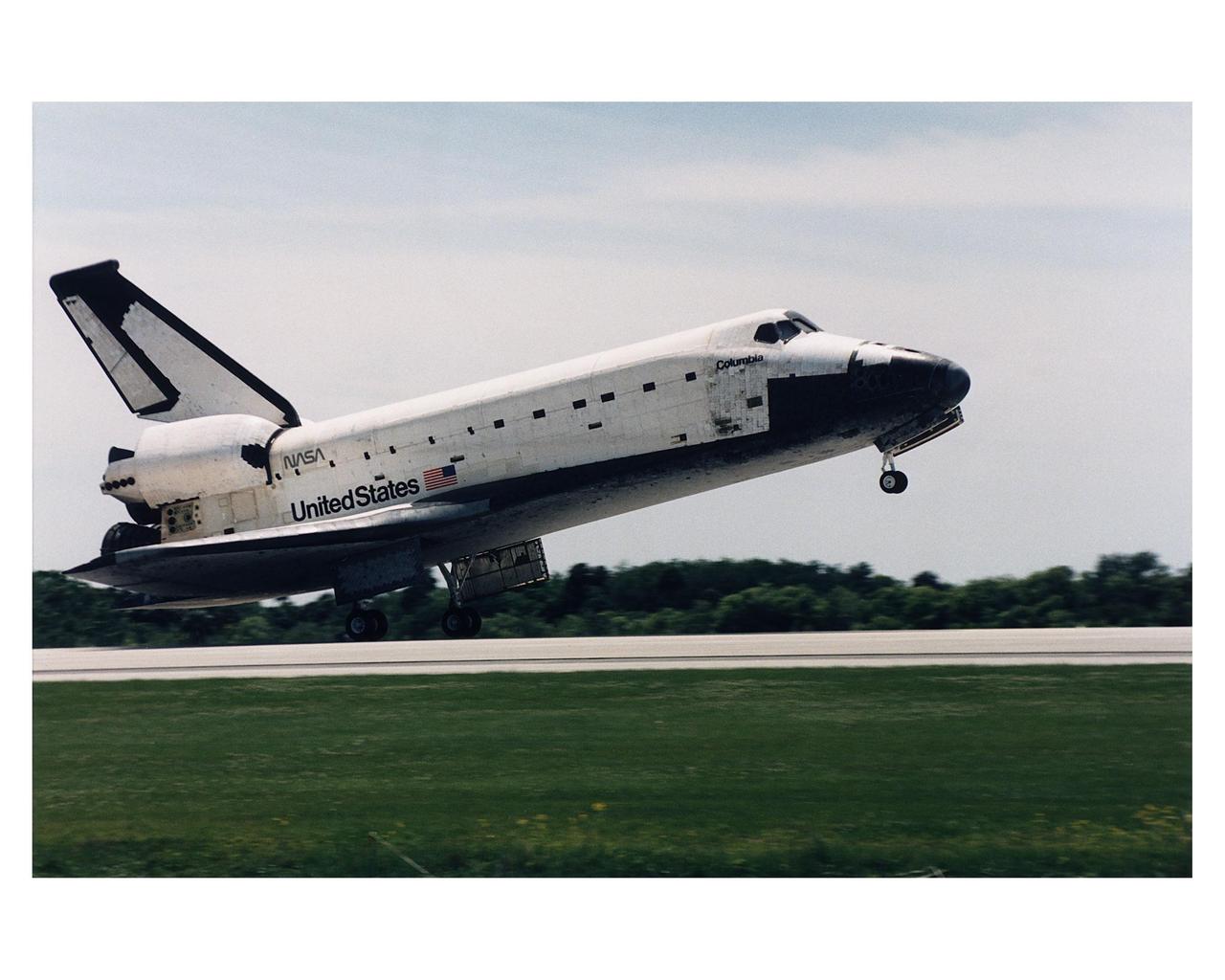

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations
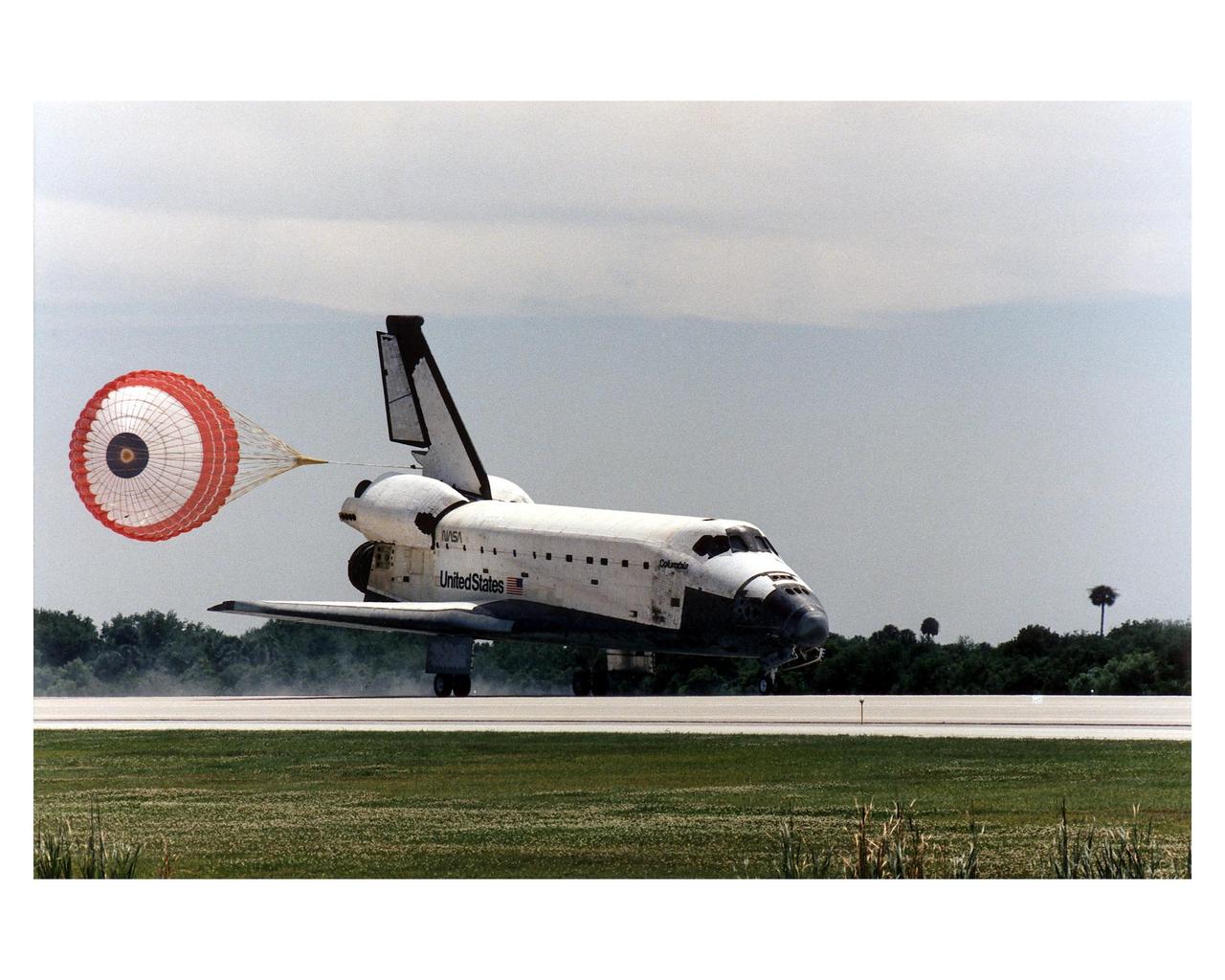

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Columbia hurtles down Runway 33 at KSCþs Shuttle Landing Facility to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. With main gear touchdown at 2:33:11 p.m. EDT, April 8, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to a mechanical problem. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L.Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations
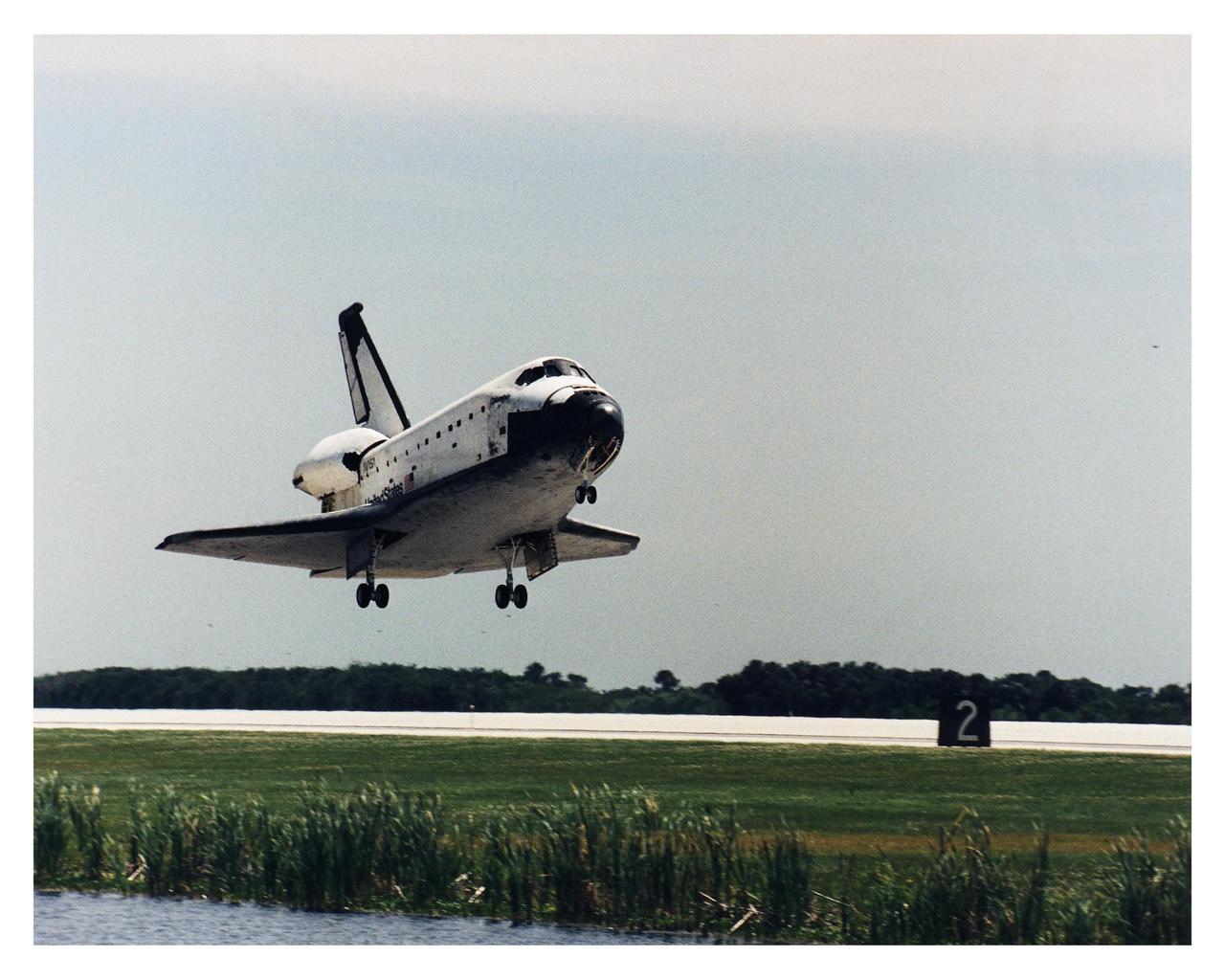

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia prepares to touch down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility at approximately 2:33 p.m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration will be just under four days. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981. Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. flew Columbia to a perfect landing with help from Pilot Susan L. Still. Other crew members are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L.Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. In spite of the abbreviated flight, the crew was able to perform MSL-1 experiments. The Spacelab-module-based experiments were used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station and to conduct combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing investigations
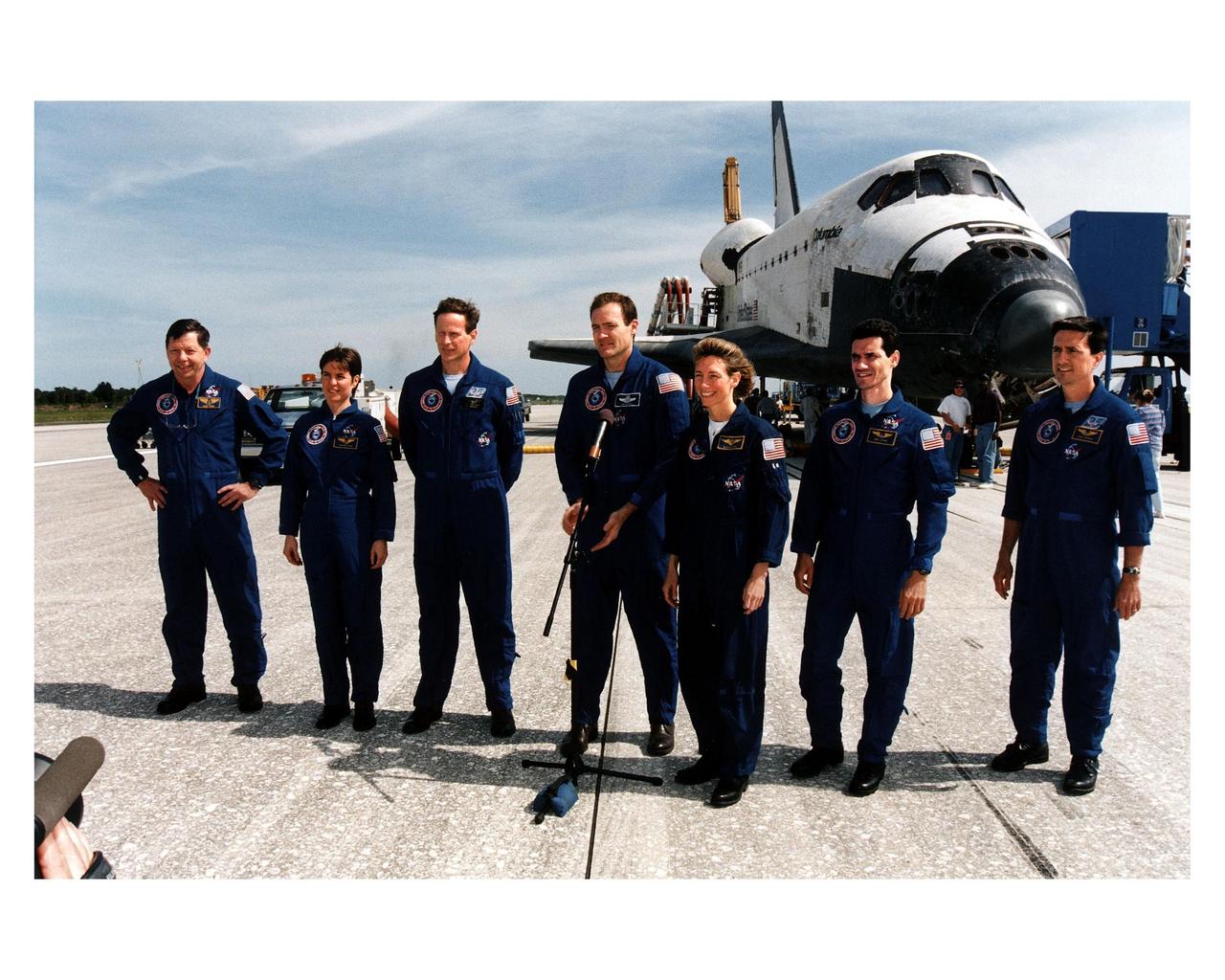

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in the background, STS-83 Mission Commander James D. Halsell (center) gives a post-landing briefing on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Columbia landed at 2:33:11 p. m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. The other flight crew members (from left) are: Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch; Payload Commander Janice Voss; Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt; Pilot Susan L. Still; Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris; and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981
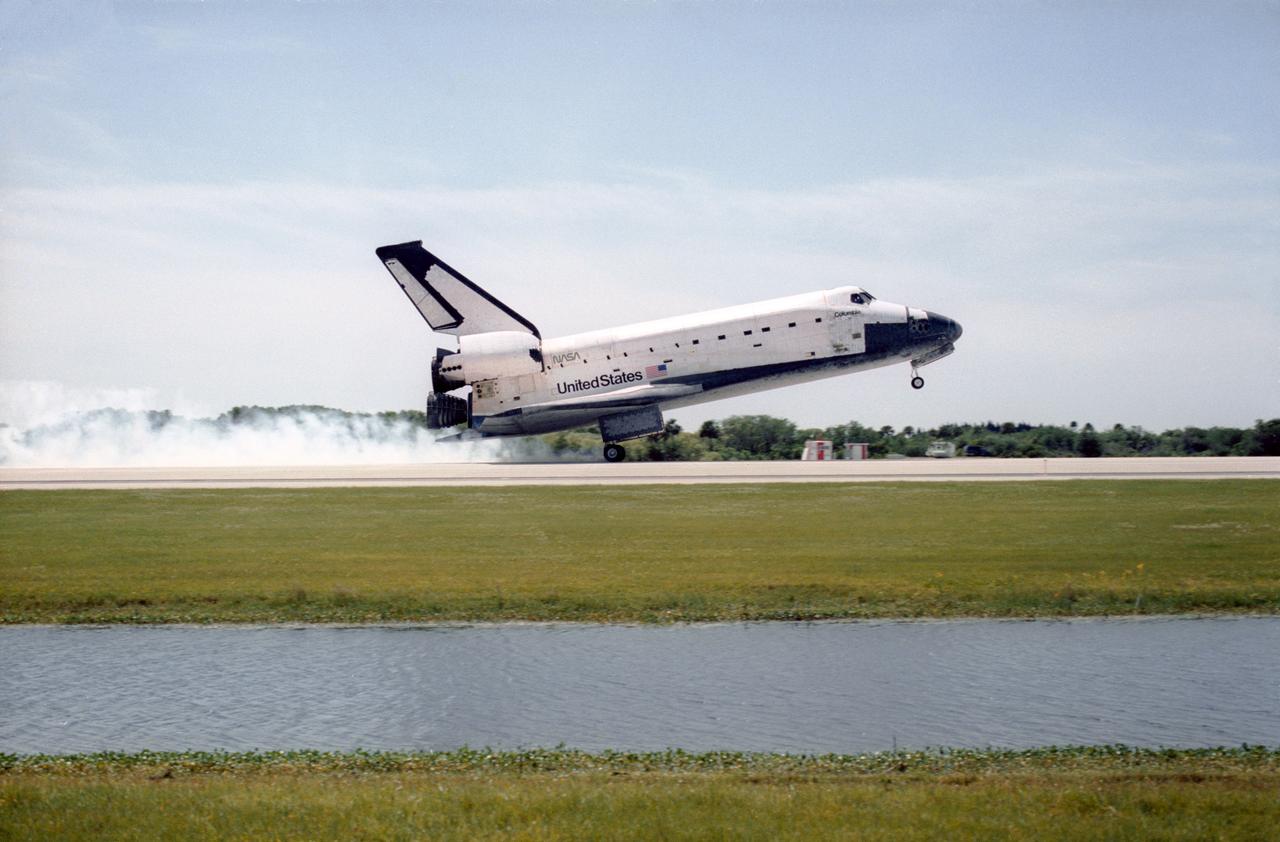

STS083-S-010 (8 April 1997) --- The main landing gear of the Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), after completing almost four days of a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit. A problem with one of three fuel cells led to an early landing for the seven-member Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) crew. Touchdown occurred at 1:33:11 p.m. (EDT), April 8, 1997. Onboard Columbia were James D. Halsell, Jr., Susan L. Still, Janice E. Voss, Donald A. Thomas, Michael L. Gernhardt, Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris.
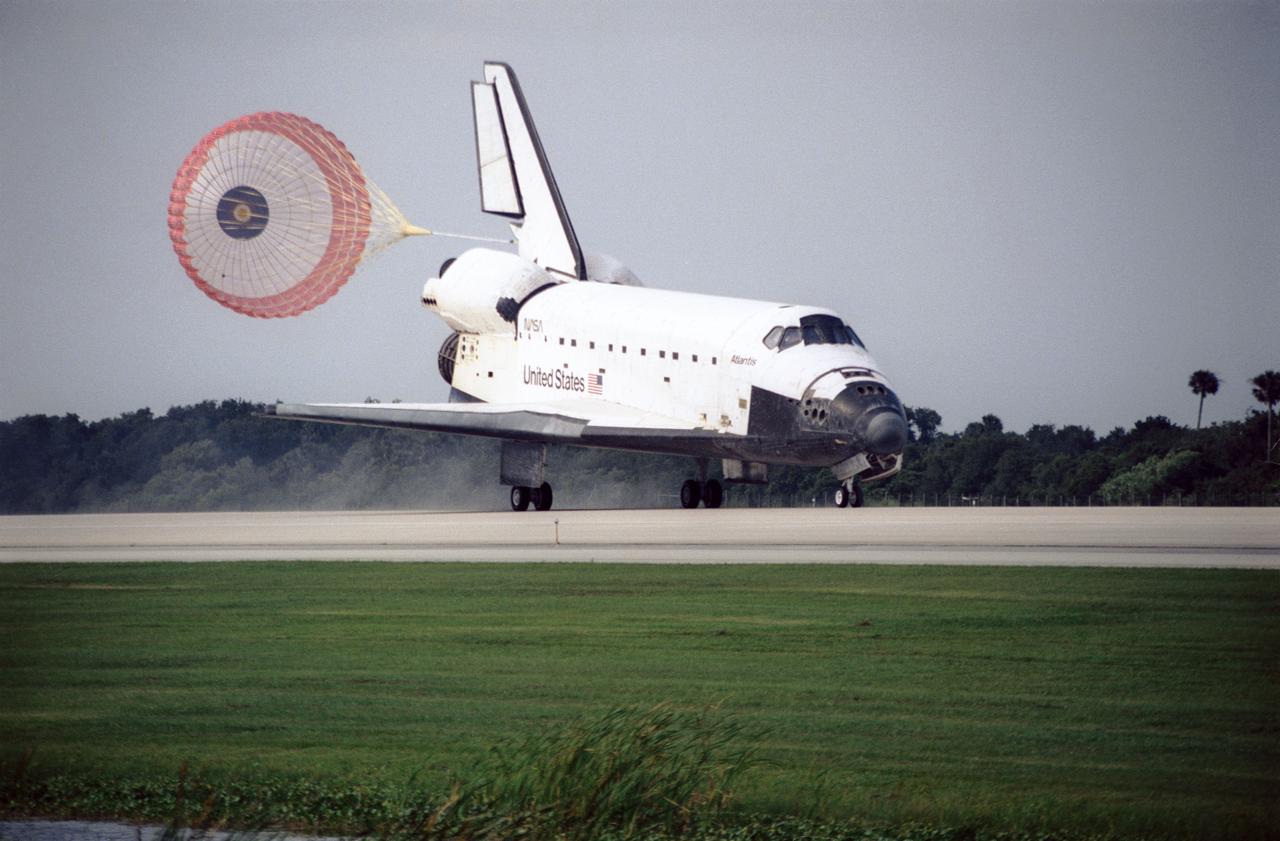

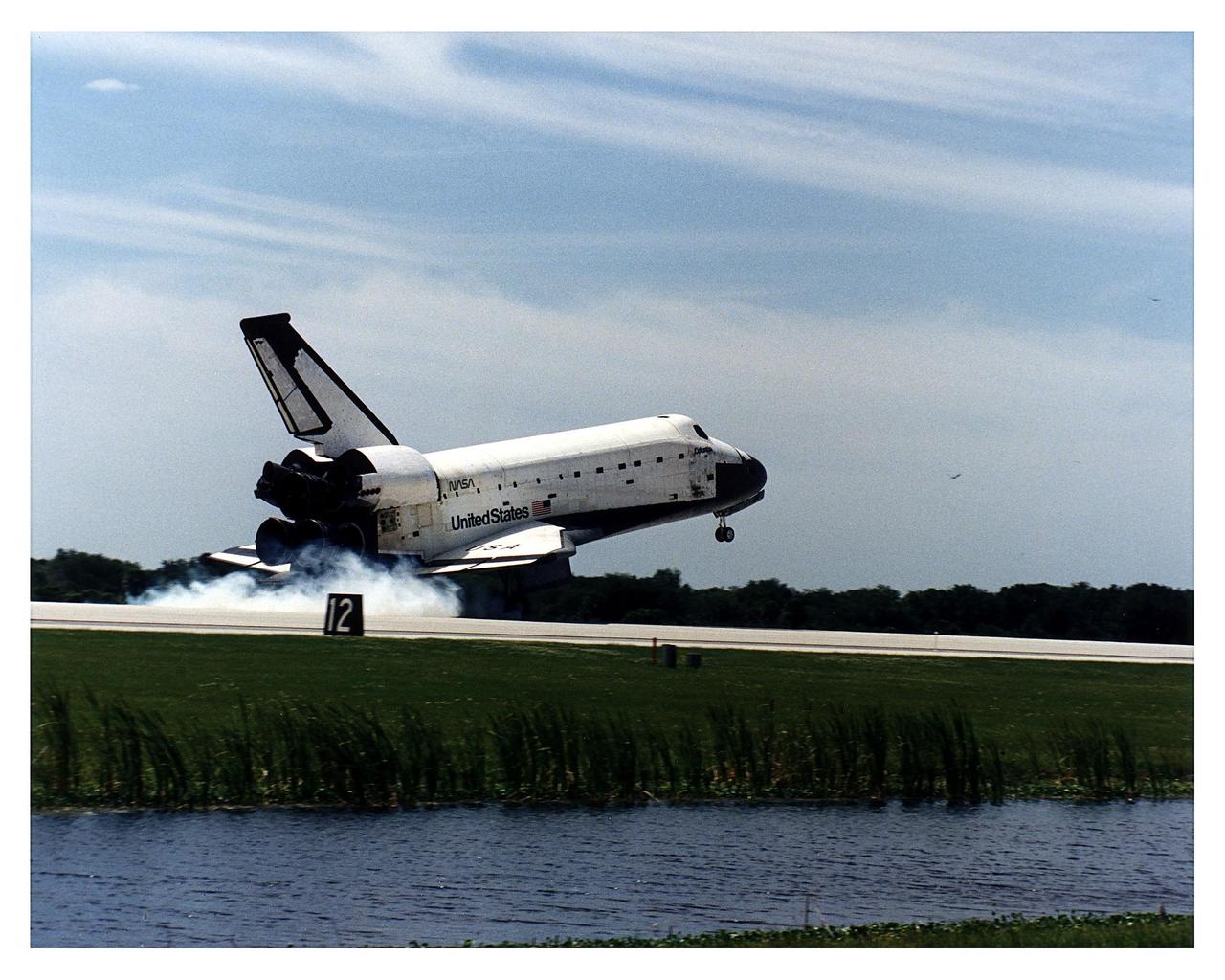
STS084-S-010 (24 May 1997) --- The drag chute on the Space Shuttle Atlantis is deployed as the Space Shuttle touches down on Runway 33 of the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). The landing, at 9:27:44 a.m. (EDT), May 24, 1997, brought to a completion the nine-day mission. This touchdown marked the 37th landing at KSC in the 16-year history of the Space Transportation System (STS) and it also marked the return of astronaut Jerry M. Linenger to Earth following almost four months aboard Russia's Mir Space Station. Onboard for the landing were astronauts Charles J. Precourt, Eileen M. Collins, Jean-Fran?ois Clervoy, Carlos I. Noriega, Edward T. Lu, Linenger and Elena V. Kondakova. Clervoy is with the European Space Agency (ESA) and Kondakova represents the Russian Space Agency (RSA).
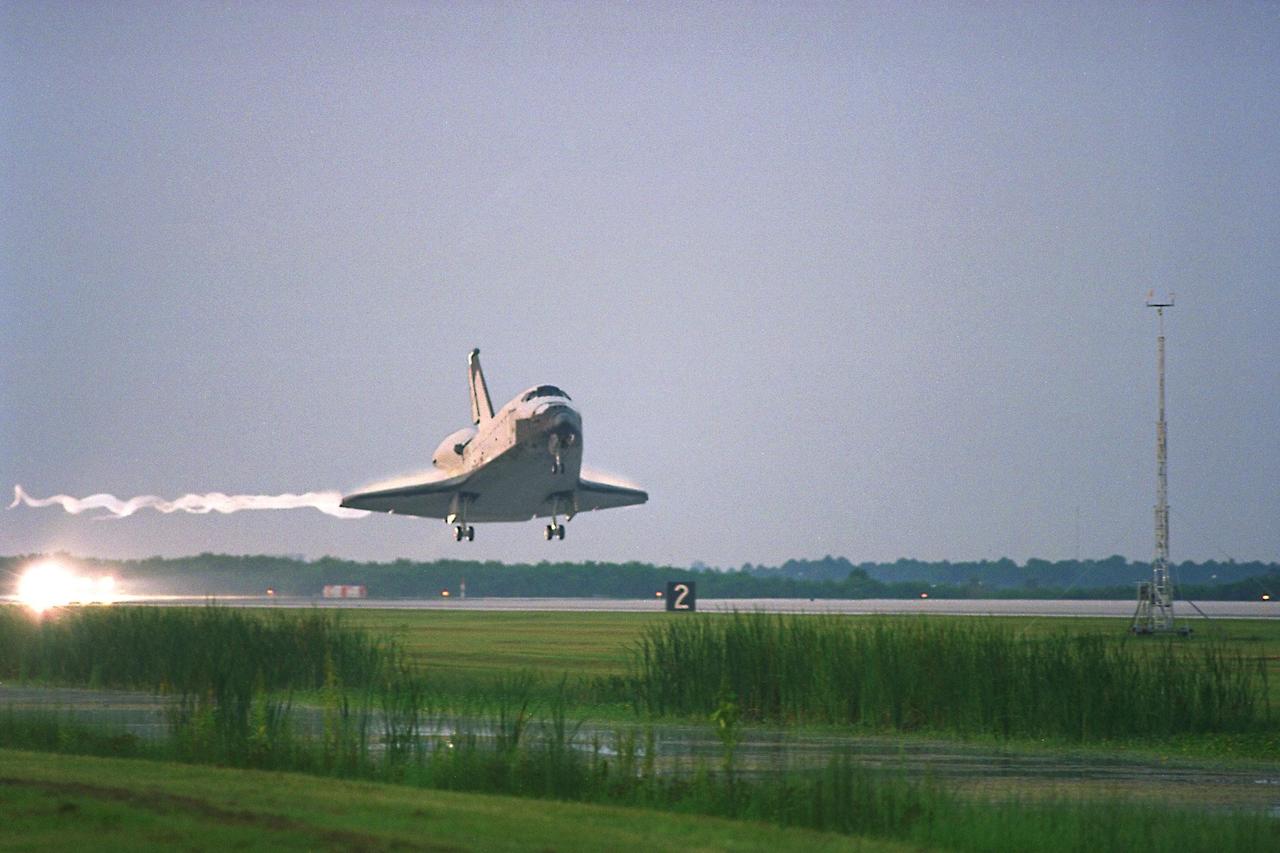

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia glides in for a touchdown on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at approximately 6:46 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K.Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell
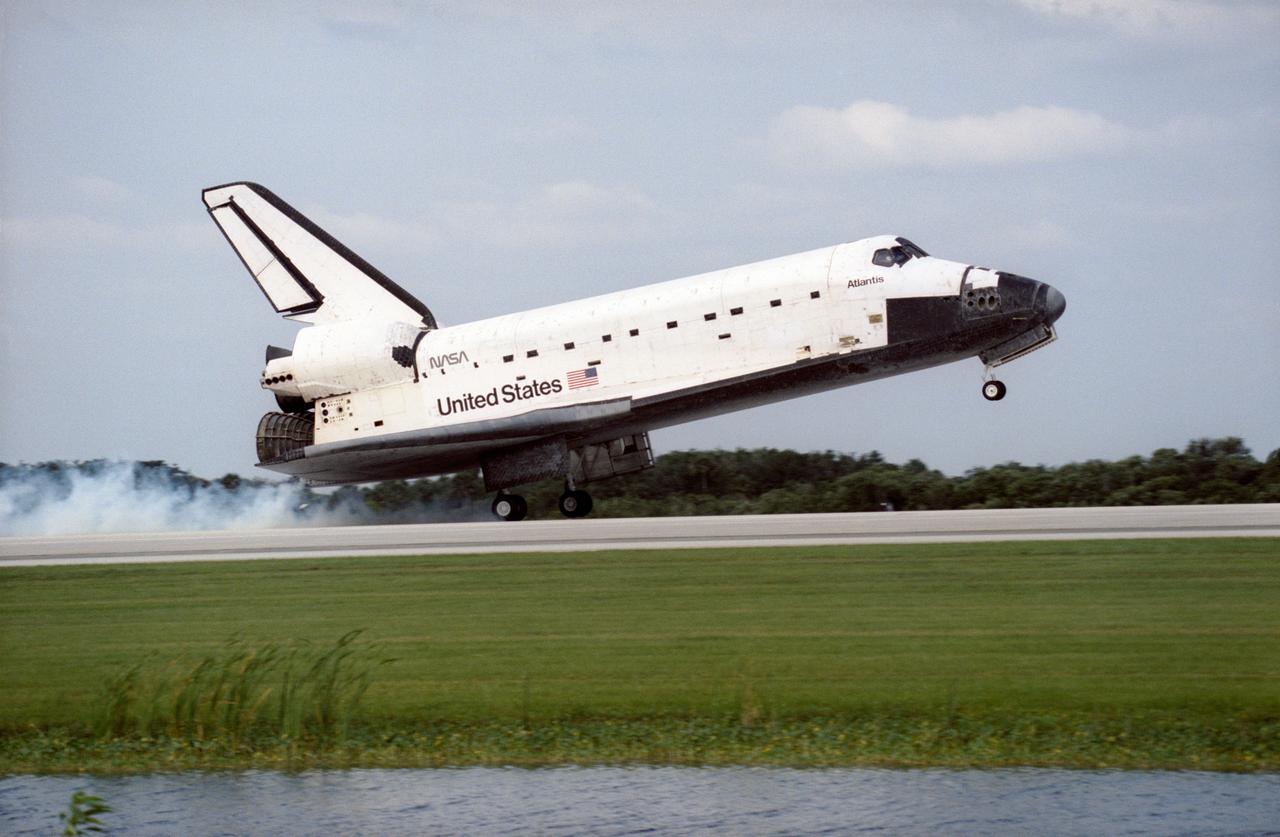

STS084-S-012 (24 May 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 of the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF), bringing to a completion the nine-day mission. Main gear touchdown was at 9:27:44 a.m. (EDT), May 24, 1997. This touchdown marked the 37th landing at KSC in the 16-year history of the Space Transportation System (STS) and it also marked the return of astronaut Jerry M. Linenger to Earth following almost four months aboard Russia's Mir Space Station. Onboard for the landing were astronauts Charles J. Precourt, Eileen M. Collins, Jean-Fran?ois Clervoy, Carlos I. Noriega, Edward T. Lu, Linenger and Elena V. Kondakova. Clervoy is with the European Space Agency (ESA) and Kondakova represents the Russian Space Agency (RSA).
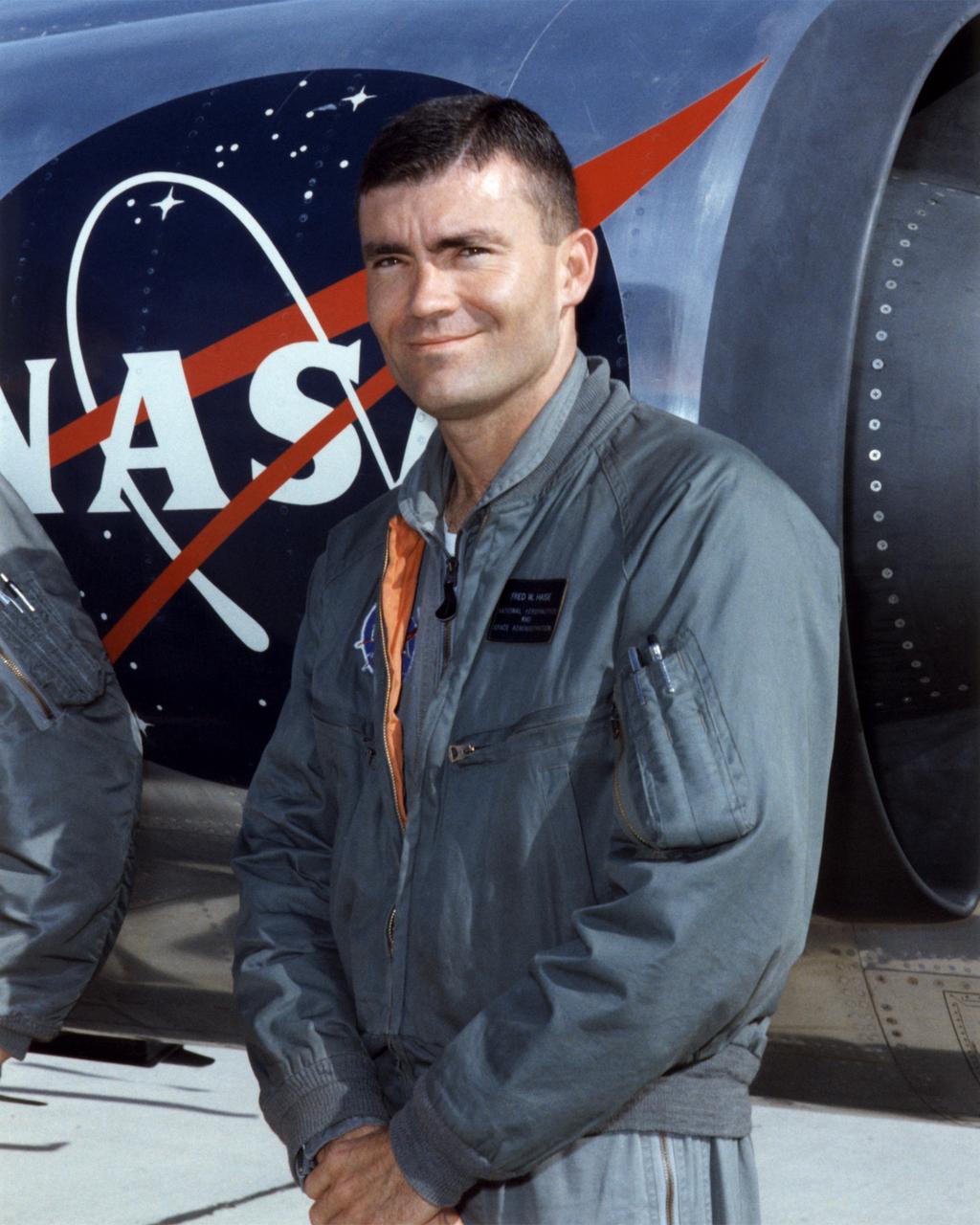

Fred W. Haise Jr. was a research pilot and an astronaut for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration from 1959 to 1979. He began flying at the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio (today the Glenn Research Center), in 1959. He became a research pilot at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC), Edwards, Calif., in 1963, serving NASA in that position for three years until being selected to be an astronaut in 1966 His best-known assignment at the FRC (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center) was as a lifting body pilot. Shortly after flying the M2-F1 on a car tow to about 25 feet on April 22, 1966, he was assigned as an astronaut to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. While at the FRC he had also flown a variety of other research and support aircraft, including the variable-stability T-33A to simulate the M2-F2 heavyweight lifting body, some light aircraft including the Piper PA-30 to evaluate their handling qualities, the Apache helicopter, the Aero Commander, the Cessna 310, the Douglas F5D, the Lockheed F-104 and T-33, the Cessna T-37, and the Douglas C-47. After becoming an astronaut, Haise served as a backup crewmember for the Apollo 8, 11, and 16 missions. He flew on the aborted Apollo 13 lunar mission in 1970, spending 142 hours and 54 minutes in space before returning safely to Earth. In 1977, he was the commander of three free flights of the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise when it flew its Approach and Landing Tests at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Meanwhile, from April 1973 to January 1976, Haise served as the Technical Assistant to the Manager of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Project. In 1979, he left NASA to become the Vice President for Space Programs with the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. He then served as President of Grumman Technical Services, an operating division of Northrop Grumman Corporation, from January 1992 until his retirement. Haise was born in Biloxi, Miss., on November 14, 1933. He underwent flight traini
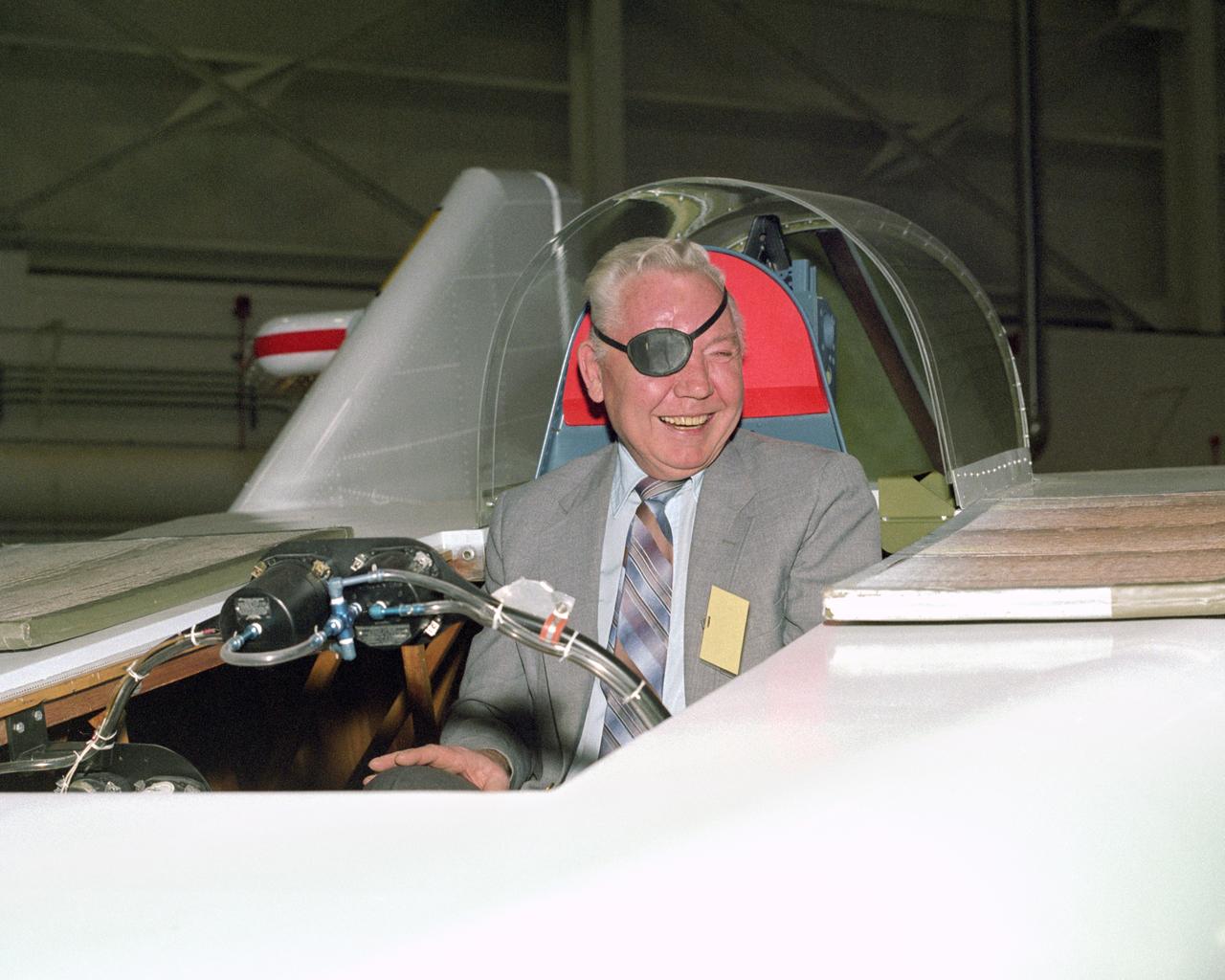

NASA Pilot Bruce Peterson in the cockpit of the restored M2-F1 Lifting Body.
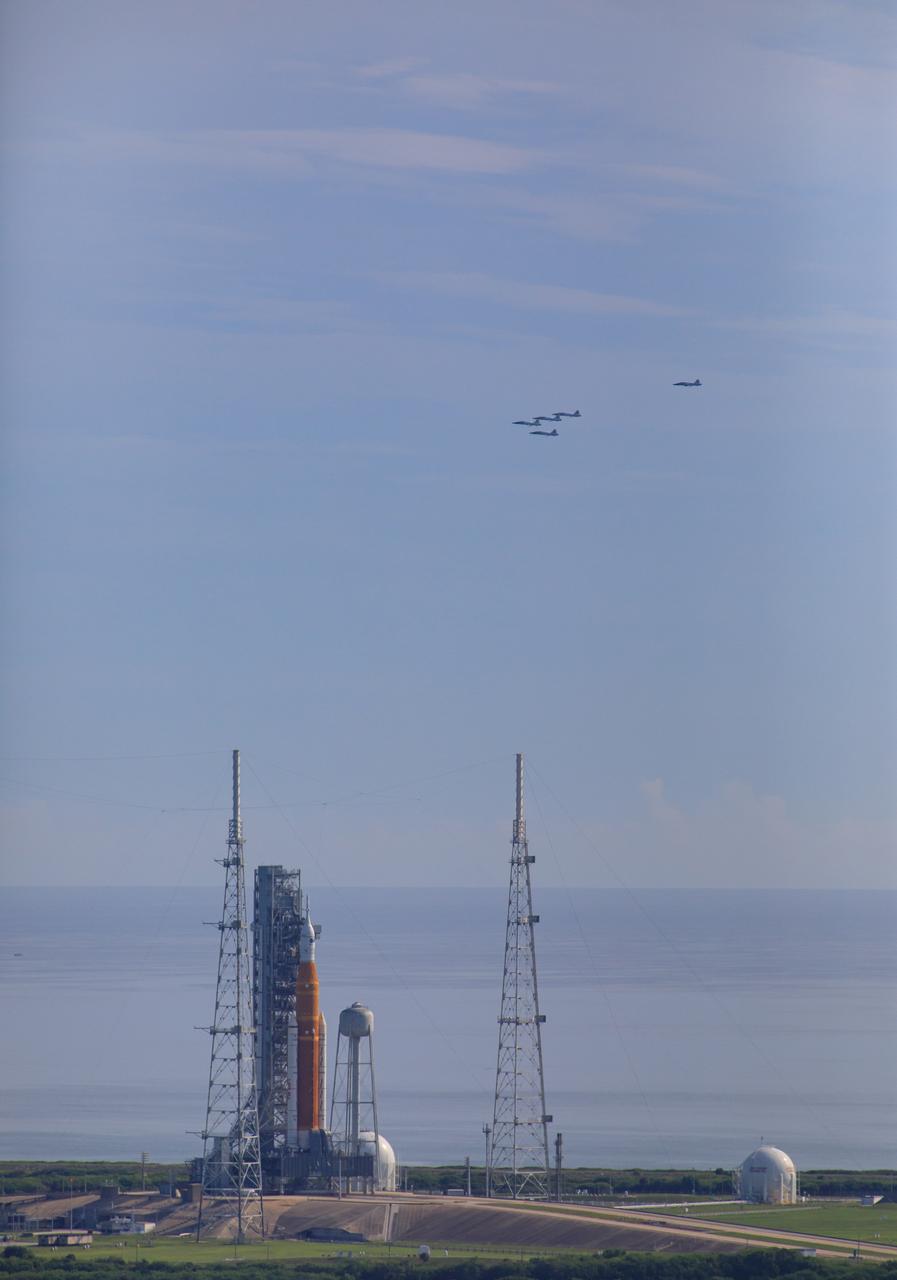

Ahead of NASA’s Artemis I launch, a flight of T-38 supersonic trainer aircraft from the Johnson Space Center Aircraft Operations Division flies in formation over the agency’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft on the pad at Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 23, 2022. Pilots and passengers of the five aircraft include NASA Research Pilot Chris Condon and NASA Astronaut Zena Cardman in the lead plane, followed by NASA astronaut candidate Nicole Ayers and NASA astronaut Christina Koch in the second plane, Canadian Space Agency astronaut Jeremy Hansen and NASA astronaut Drew Morgan in the third plane, NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman and NASA astronaut Joe Acaba in the fourth plane, and NASA astronaut candidate Jack Hathaway and Josh Valcarcel, NASA photographer, in the chase plane. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
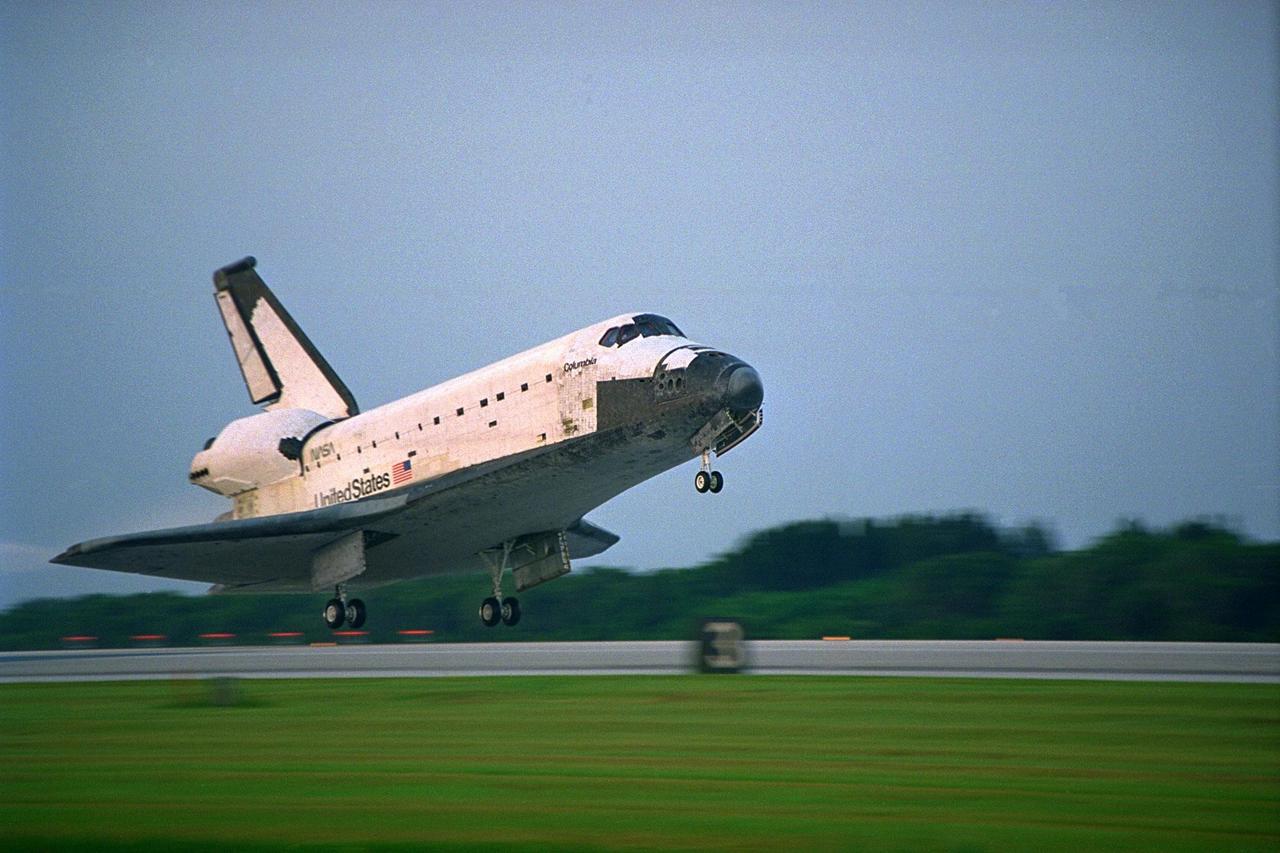

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Framed by the Vehicle Assembly Building at right and the Mate-Demate Device at left, the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia glides onto Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
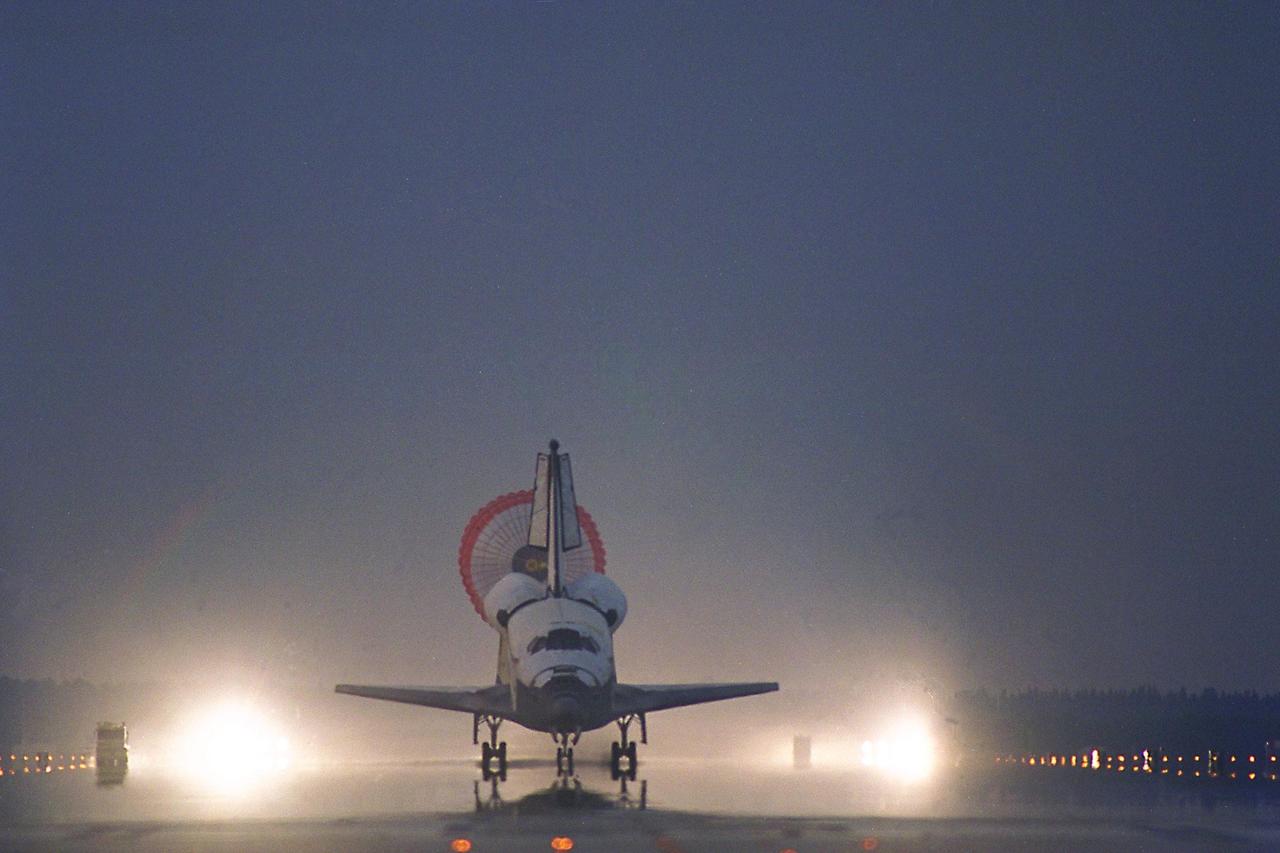

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With its drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt , Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. Mission elapsed time for STS-94 was 15 days,16 hours, 44 seconds. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
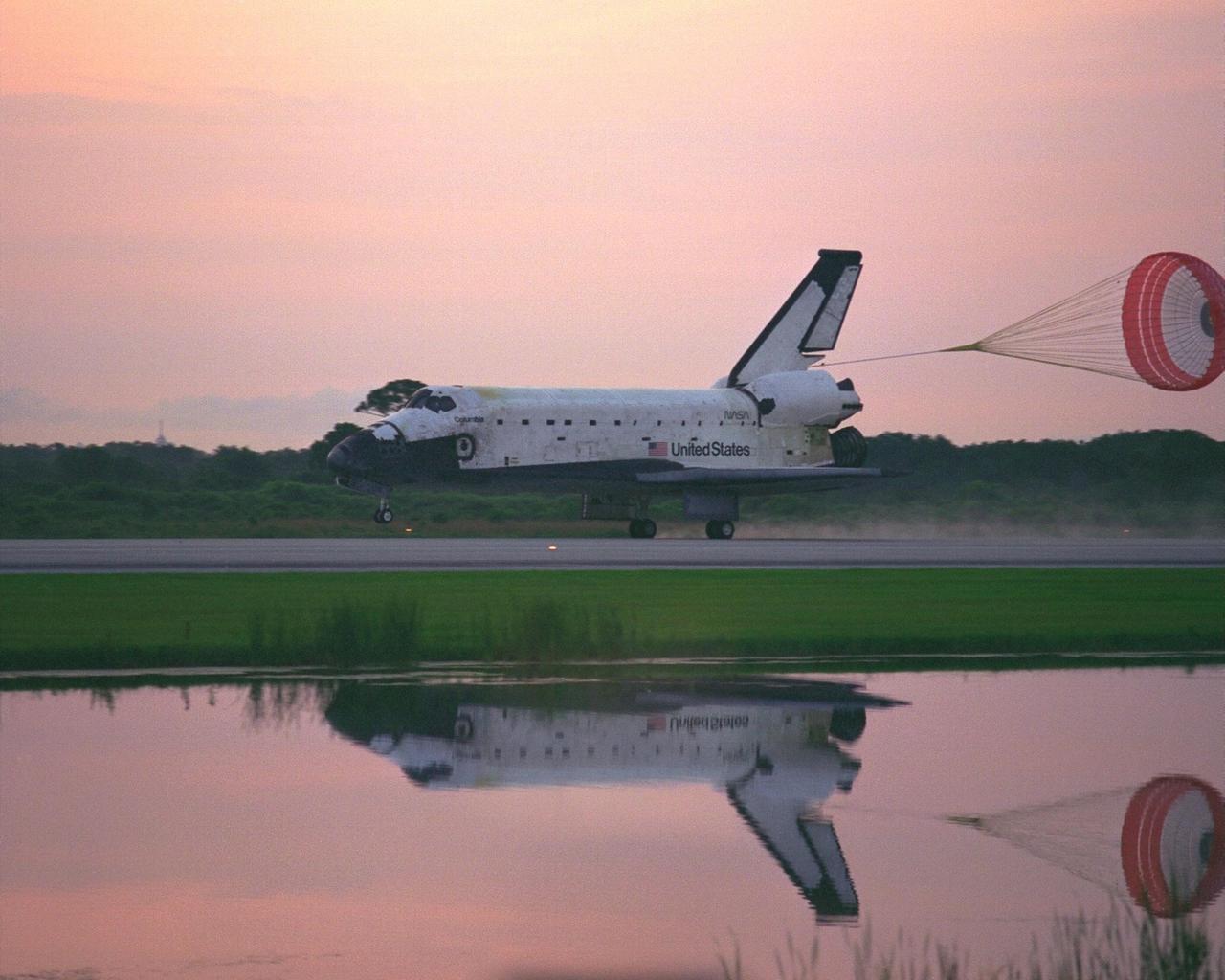

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With its drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt , Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. Mission elapsed time for STS-94 was 15 days,16 hours, 44 seconds. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
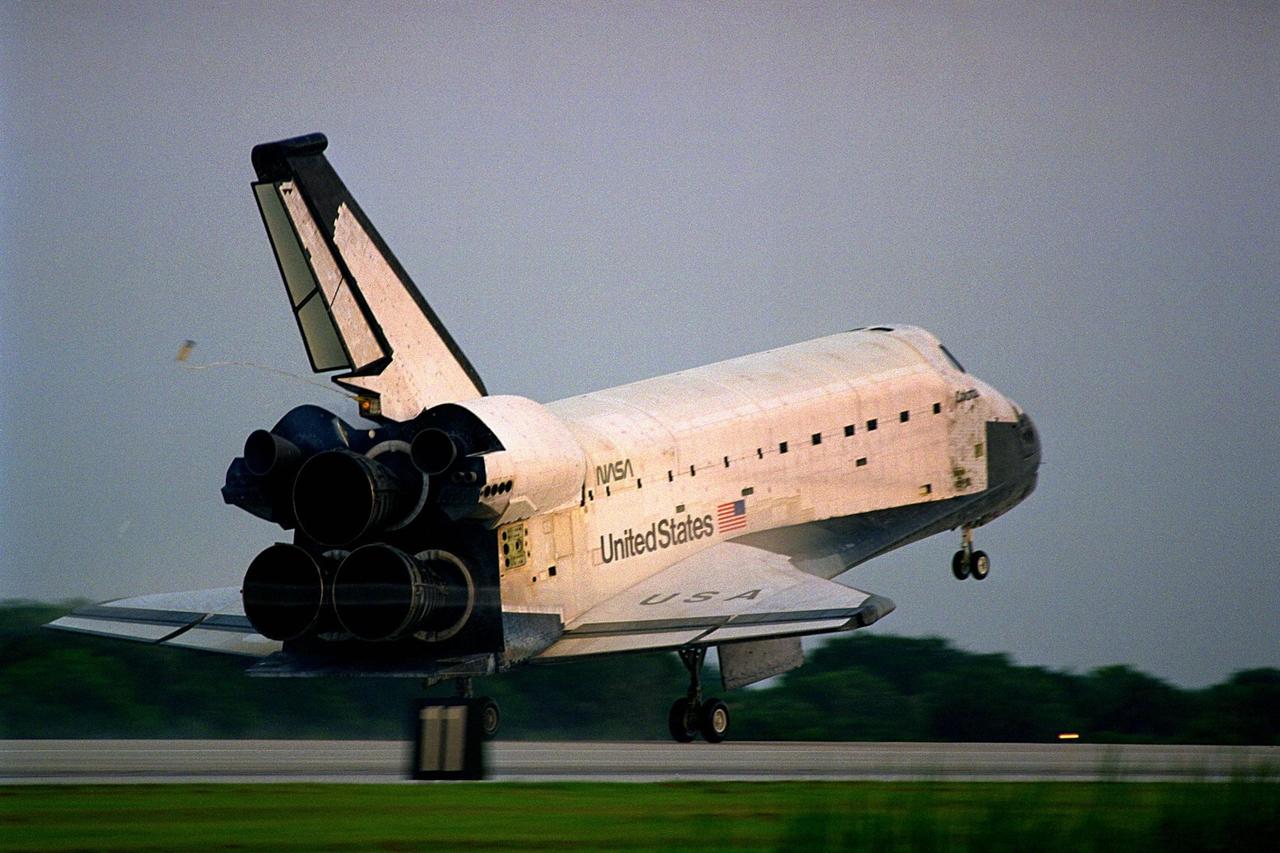

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
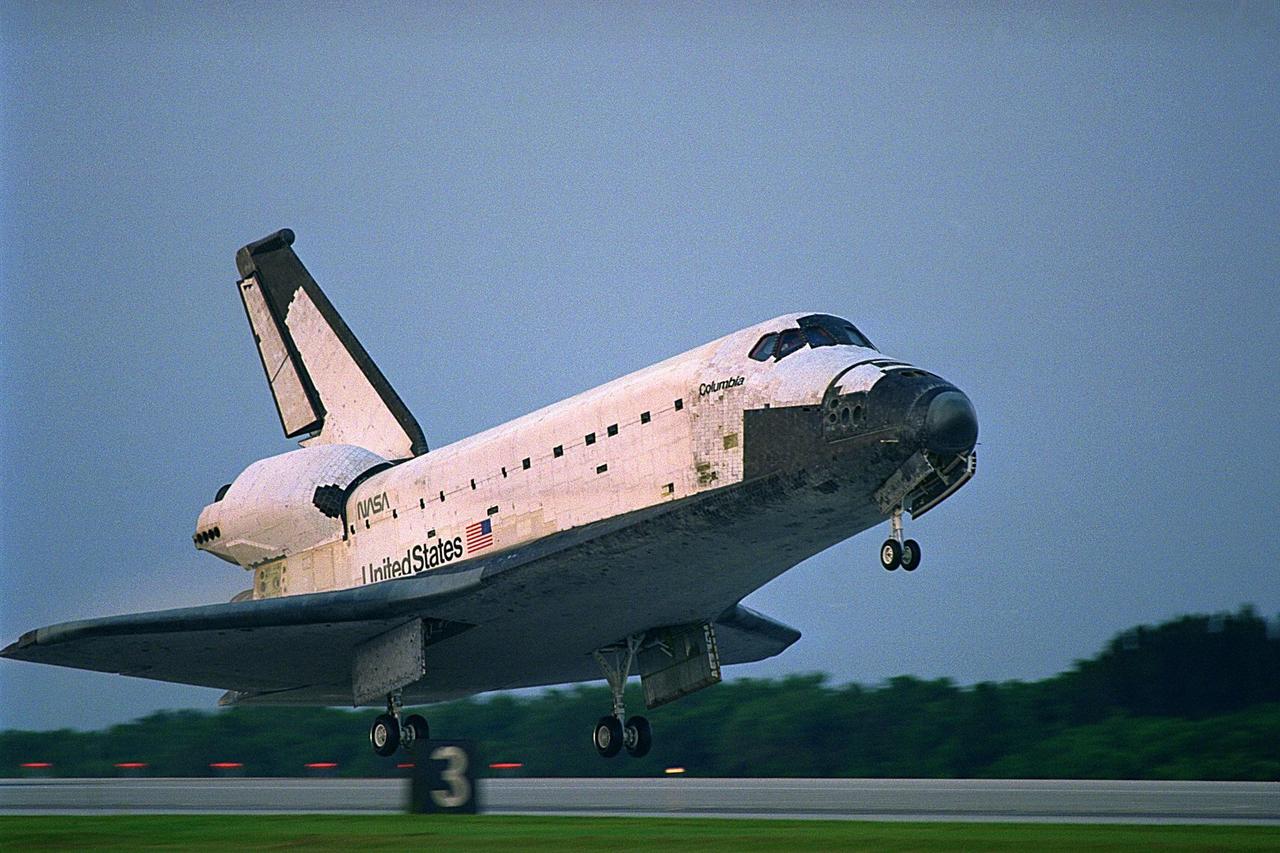

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
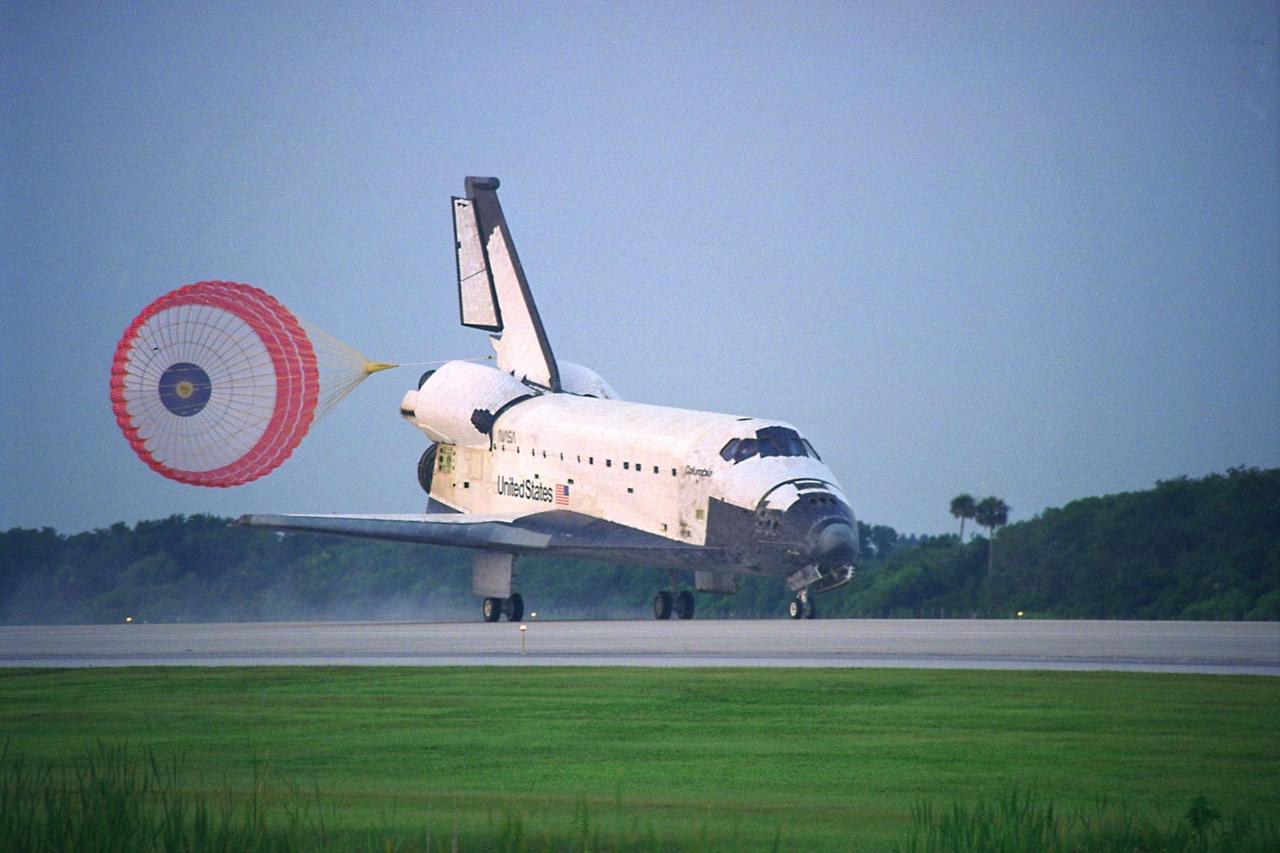

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With its drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt , Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. Mission elapsed time for STS-94 was 15 days,16 hours, 44 seconds. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
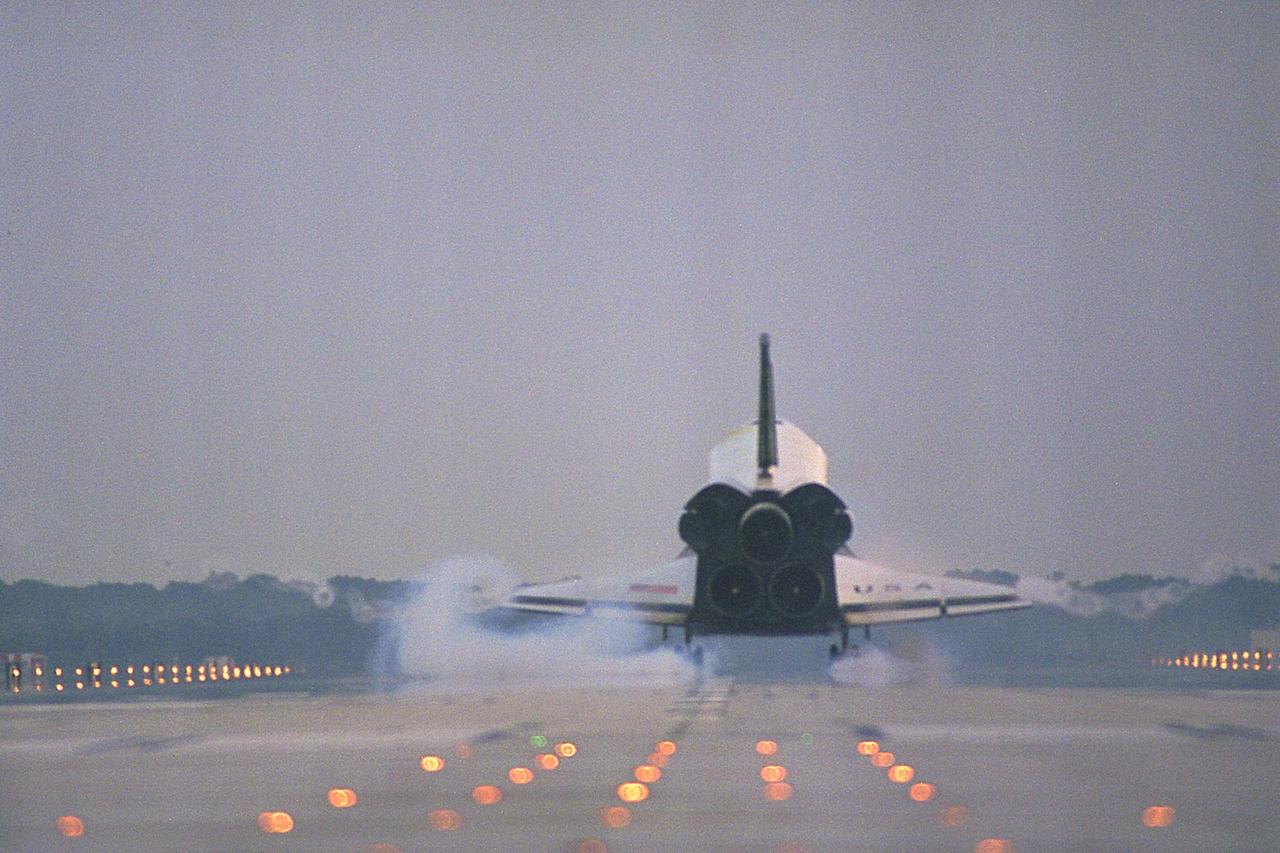

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
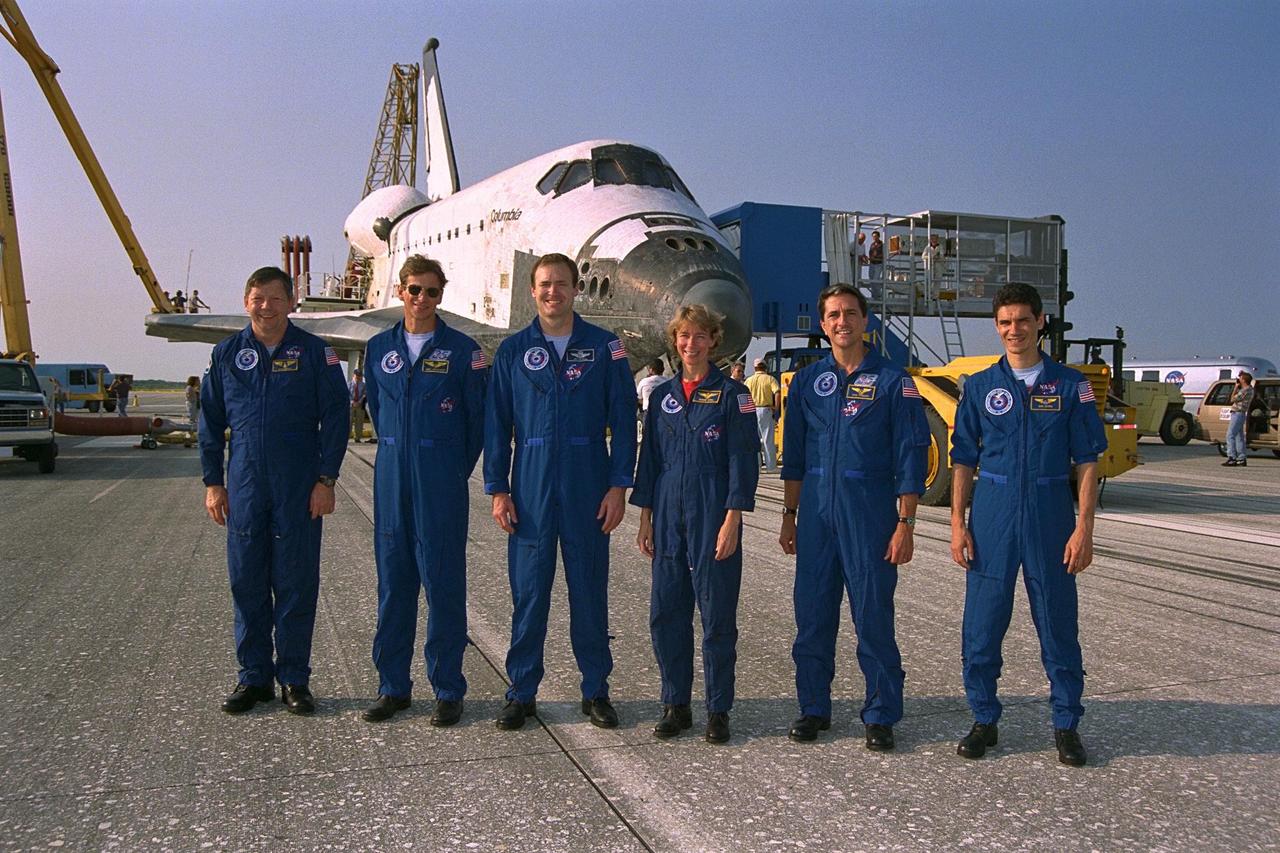

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-94 flight crew poses in front of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia after an end-of-mission landing on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility July 17 to complete the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. They are (from left): Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch; Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt; Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr.; Pilot Susan L. Still; Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris. Not shown is Payload Commander Janice Voss. During the 15-day, 16-hour spaceflight, the MSL-1 Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station; the flight crew also conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission earlier this year that was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell
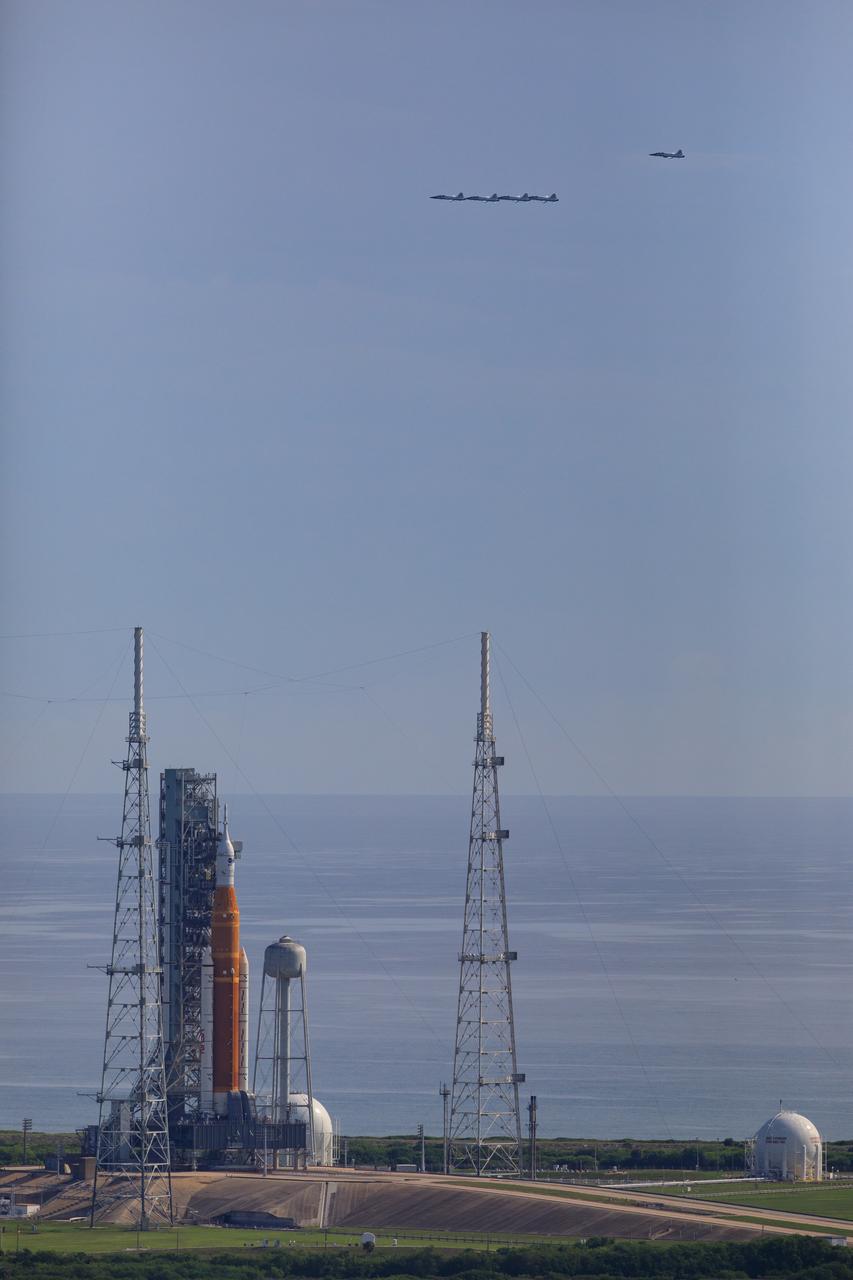

Ahead of NASA’s Artemis I launch, a flight of T-38 supersonic trainer aircraft from the Johnson Space Center Aircraft Operations Division flies in formation over the agency’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft on the pad at Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 23, 2022. Pilots and passengers of the five aircraft include NASA Research Pilot Chris Condon and NASA Astronaut Zena Cardman in the lead plane, followed by NASA astronaut candidate Nicole Ayers and NASA astronaut Christina Koch in the second plane, Canadian Space Agency astronaut Jeremy Hansen and NASA astronaut Drew Morgan in the third plane, NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman and NASA astronaut Joe Acaba in the fourth plane, and NASA astronaut candidate Jack Hathaway and Josh Valcarcel, NASA photographer, in the chase plane. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 8:33 a.m. EDT on Aug. 29, 2022. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With its drag chute deployed, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 6:46:34 a.m. EDT with Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. and Pilot Susan L. Still at the controls to complete the STS-94 mission. Also on board are Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt , Payload Commander Janice Voss, and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. Mission elapsed time for STS-94 was 15 days,16 hours, 44 seconds. During the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the Spacelab module was used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducted combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. This mission was a reflight of the STS-83 mission that lifted off from KSC in April of this year. That space flight was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. This was Columbia’s 11th landing at KSC and the 38th landing at the space center in the history of the Shuttle program
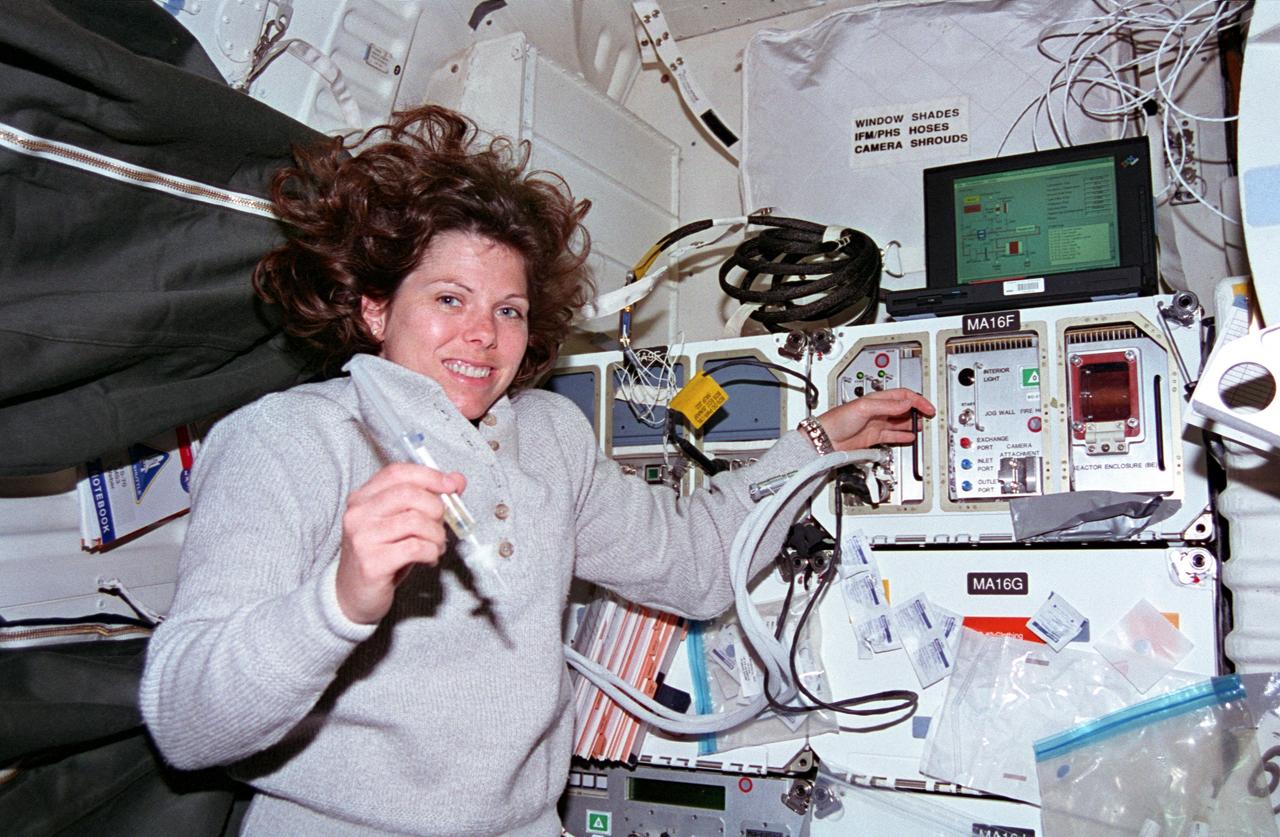

STS070-301-025 (13-22 July 1995) --- Astronaut Mary Ellen Weber works with a syringe related to the Bioreactor Development System (BDS). The almost weightless state of space travel provides life science researchers with the opportunity to grow cells into three-dimensional tissue pieces that are not achievable using conventional tissue culture methods on Earth. At specified times during the STS-70 mission, crew members injected color producing substances to document fluid movement in the reactor, and various-sized beads to estimate the tissue size that could be supported in the Bioreactor. The photo was among NASA's first release of still photography from the STS-70 mission. The mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on July 13, 1995, and ended when Discovery landed on Runway 33 there on July 22, 1995. The crew members were astronauts Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, commander; Kevin R. Kregel, pilot; and Donald A. Thomas, Nancy J. Currie and Weber, all mission specialists.

James Barrilleaux is the assistant chief pilot for ER-2s in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The ER-2s--civilian variants of the military U-2S reconnaissance aircraft--are part of NASA's Airborne Science program. The ER-2s can carry airborne scientific payloads of up to 2,600 pounds to altitudes of about 70,000 feet to investigate such matters as earth resources, celestial phenomena, atmospheric chemistry and dynamics, and oceanic processes. Barrilleaux has held his current position since February 1998. Barrilleaux joined NASA in 1986 as a U-2/ER-2 pilot with NASA's Airborne Science program at Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California. He flew both the U-2C (until 1989) and the ER-2 on a wide variety of missions both domestic and international. Barrilleaux flew high-altitude operations over Antarctica in which scientific instruments aboard the ER-2 defined the cause of ozone depletion over the continent, known as the ozone hole. He has also flown the ER-2 over the North Pole. Barrilleaux served for 20 years in the U.S. Air Force before he joined NASA. He completed pilot training at Reese Air Force Base, Lubbock, Texas, in 1966. He flew 120 combat missions as a F-4 fighter pilot over Laos and North Vietnam in 1970 and 1971. He joined the U-2 program in 1974, becoming the commander of an overseas U-2 operation in 1982. In 1983, he became commander of the squadron responsible for training all U-2 pilots and SR-71 crews located at Beale Air Force Base, Marysville, California. He retired from the Air Force as a lieutenant colonel in 1986. On active duty, he flew the U-2, F-4 Phantom, the T-38, T-37, and the T-33. His decorations included two Distinguished Flying Crosses, 12 Air Medals, two Meritorious Service Medals, and other Air Force and South Vietnamese awards. Barrilleaux earned a bachelor of science degree in chemical engineering from Texas A&M University, College Station, in 1964 and a master of science