
AS07-04-1586 (20 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Walter Cunningham, Apollo 7 lunar module pilot, writes with space pen as he is photographed performing flight tasks on the ninth day of the Apollo 7 mission. Note the 70mm Hasselblad camera film magazine just above Cunningham's right hand floating in the weightless (zero gravity) environment of the spacecraft.
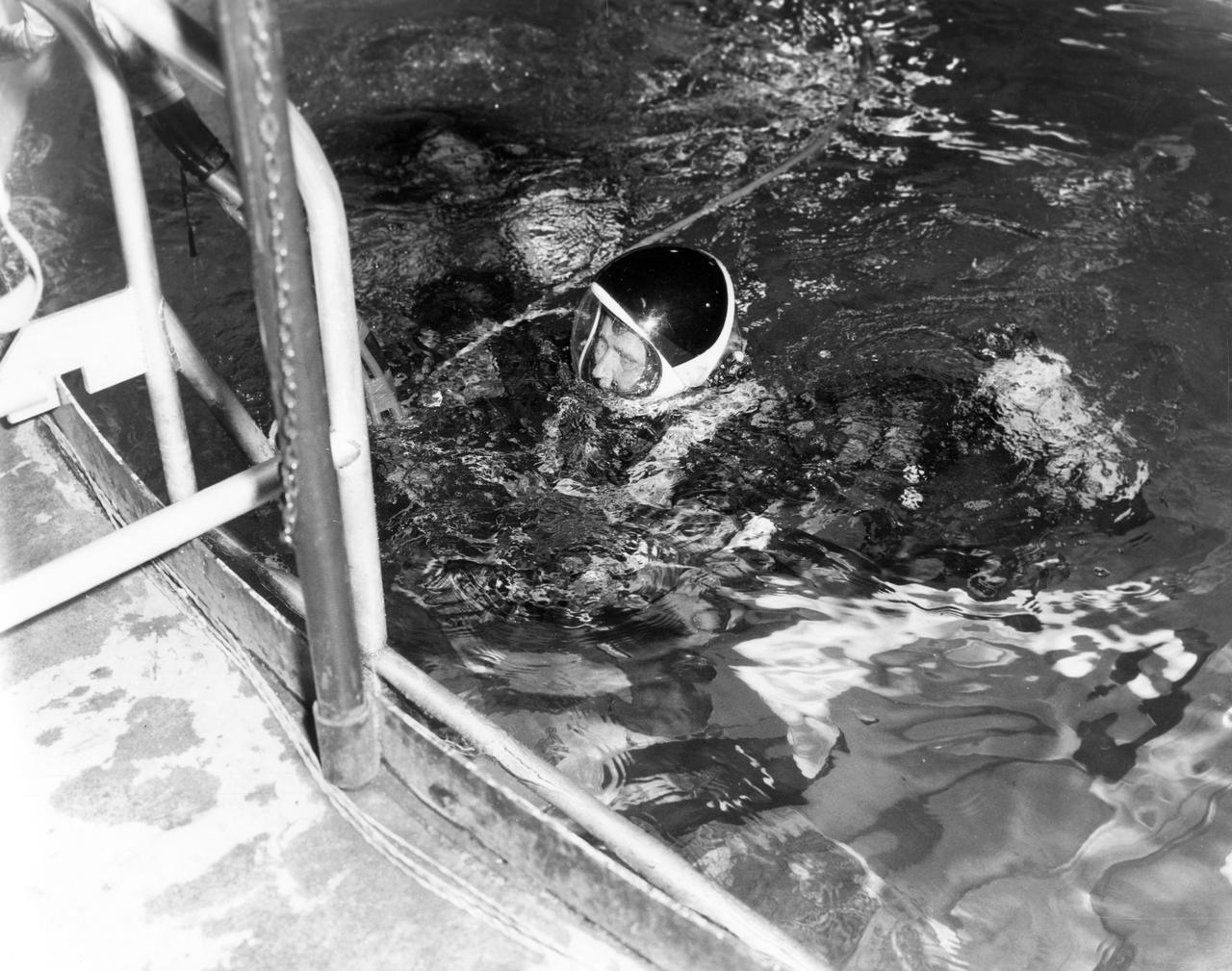

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, submerges after spending some time under water in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, submerges after spending some time under water in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.

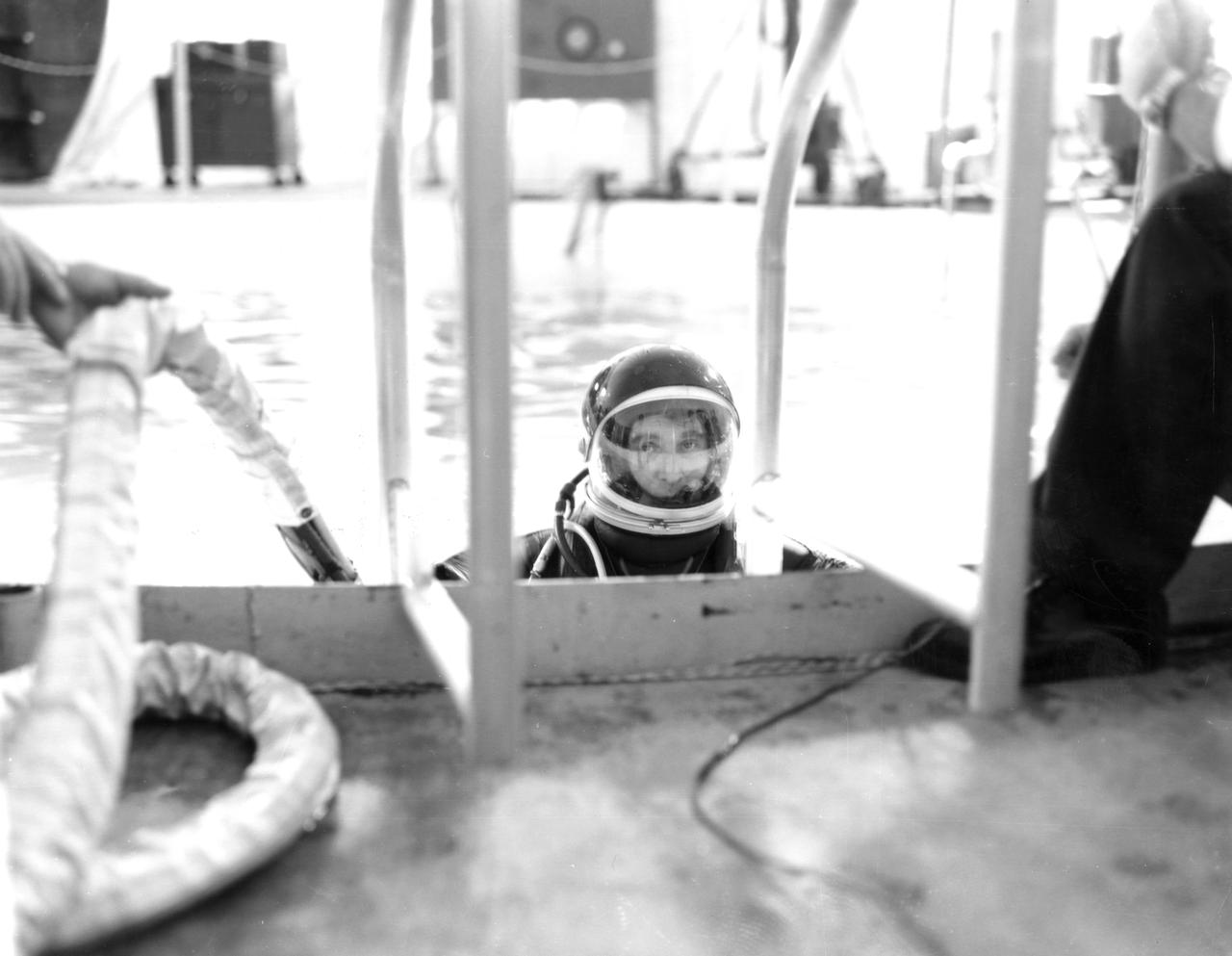
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, is shown fitted with suit and diving equipment as he prepares for a tryout in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.

Dr. von Braun tried out a floating platform in the Marshall Space Flight Center Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory. This was a test rig to help determine how future astronauts will be able to perform maintenance tasks in the weightlessness in space. This photograph is believed to have been taken in 1961.

This chart describes the Skylab student experiment Motor Sensory Performance, proposed by Kathy L. Jackson of Houston, Texas. Her proposal was a very simple but effective test to measure the potential degradation of man's motor-sensory skills while weightless. Without knowing whether or not man can retain a high level of competency in the performance of various tasks after long exposure to weightlessness, this capability could not be fully known. Skylab, with its long-duration missions, provided an ideal testing situation. The experiment Kathy Jackson proposed was similar in application to the tasks involved in docking one spacecraft to another using manual control. It required one of the greatest tests of the motor-sensory capabilities of man. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.
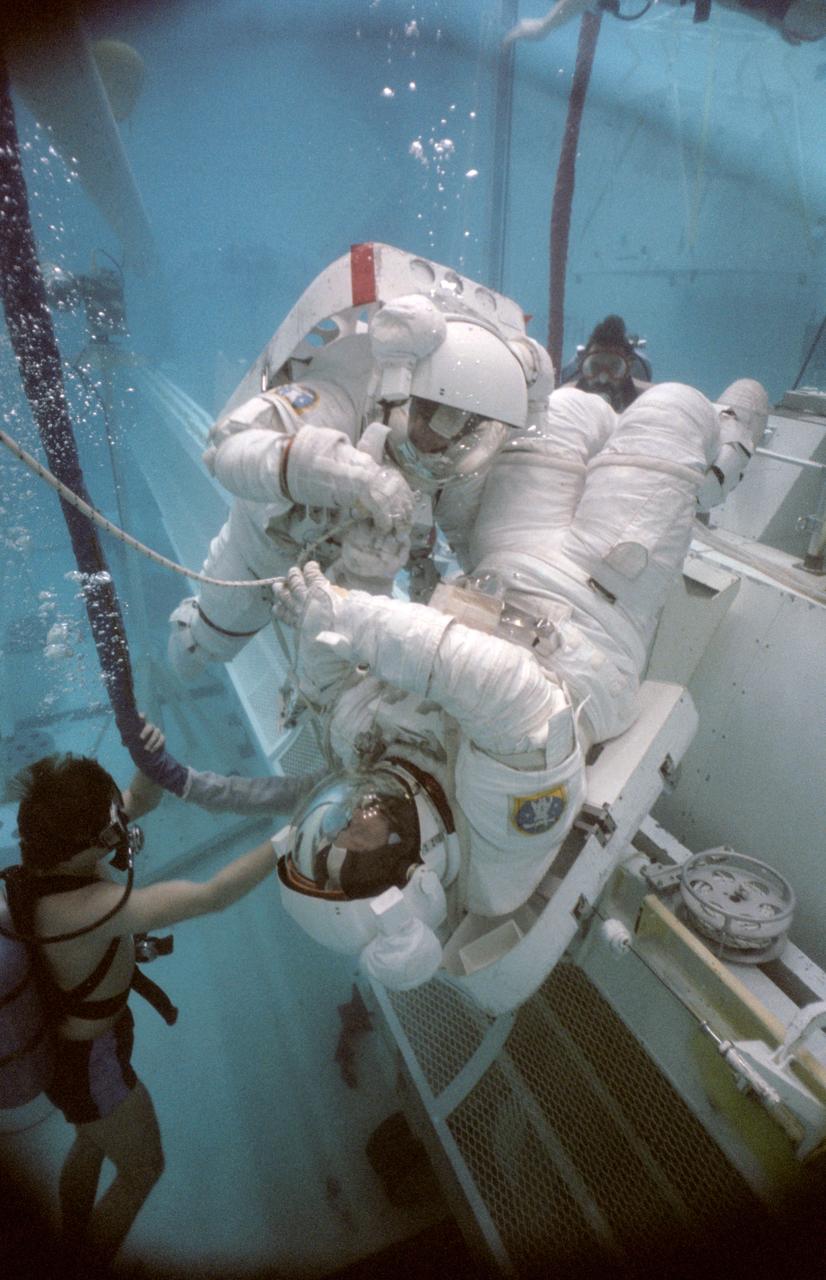

S84-28206 (26 Feb 1984) --- Astronauts Richard M. (Mike) Mullane (with striped suit and PLSS) and Steven A. Hawley participate in and underwater simulation of a 41-D contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). All Shuttle crews, many of which are not scheduled for definite EVAs, possess team members trained to perform in space certain tasks normally done remotely in the event of systems failures. Among those contingent tasks is the manual closing of the payload bay doors. Mullane and Hawley are two of three mission specialists assigned duty on the seven-day 41-D flight. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.

S94-29981 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, awaits his helmet as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
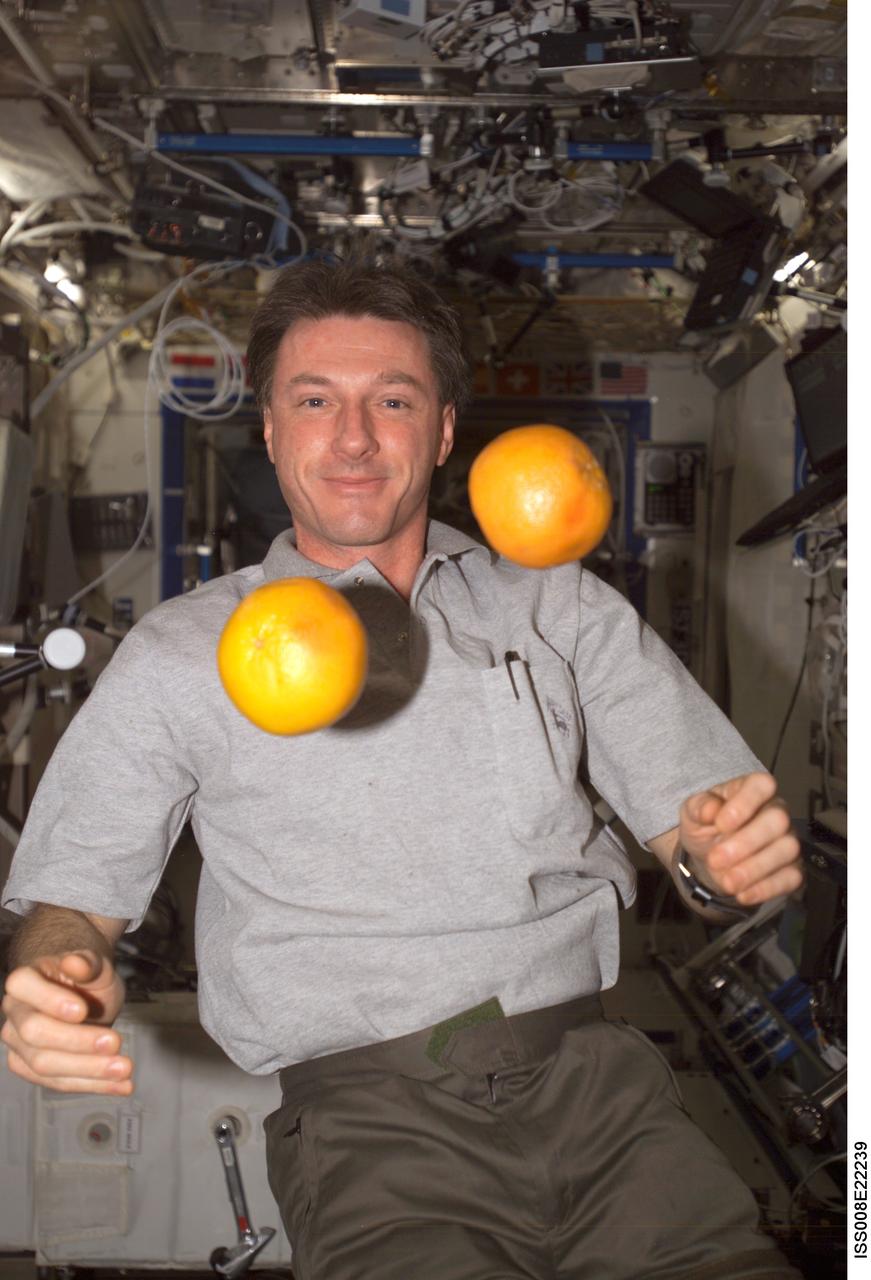

ISS008-E-22239 (22 April 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, “juggles” fresh fruit in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS). The weightless environment of space proves to be an ideal location for some tasks not so easily accomplished in Earth’s gravity.

S94-29978 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
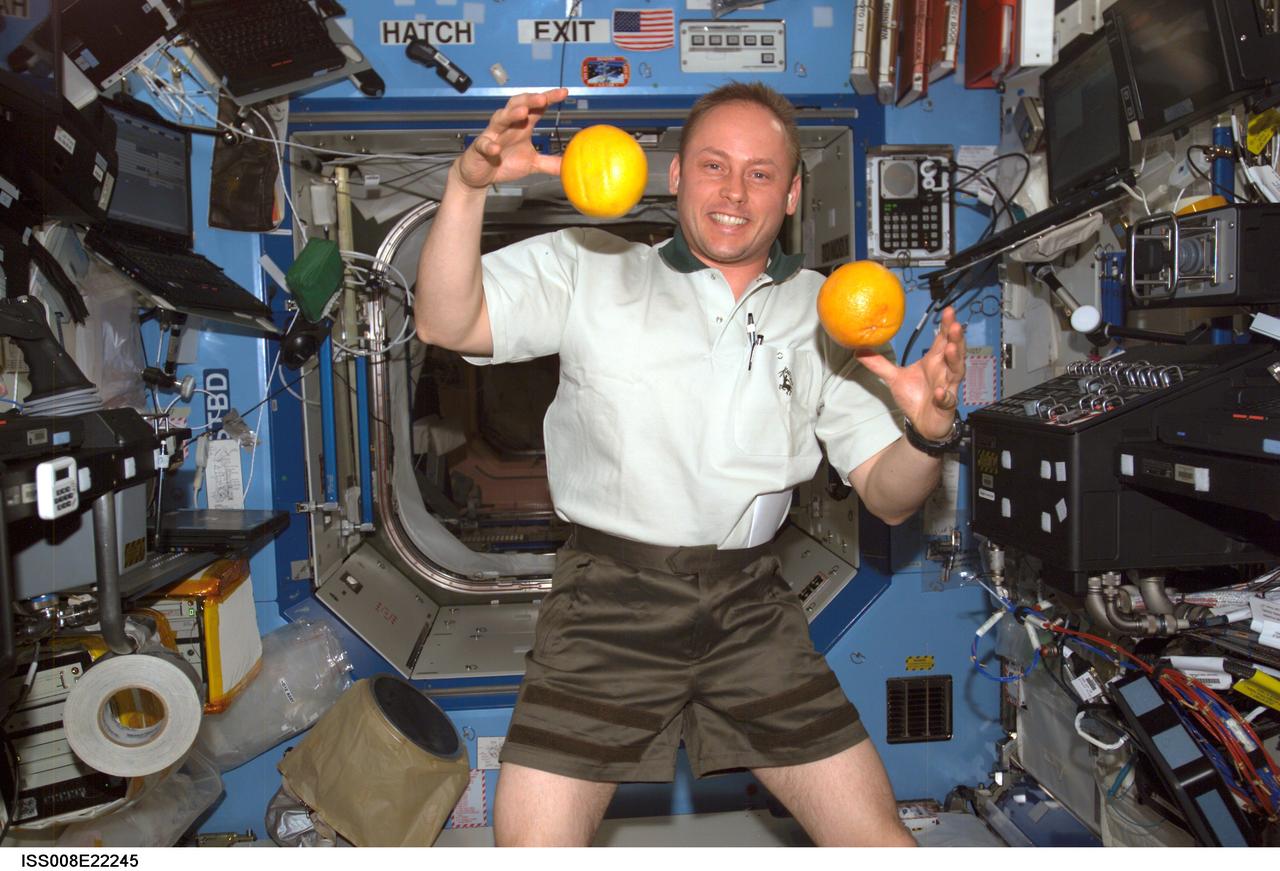

ISS008-E-22245 (22 April 2004) --- Astronaut Edward M. (Mike) Fincke, Expedition 9 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, “juggles” fresh fruit in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS). The weightless environment of space proves to be an ideal location for some tasks not so easily accomplished in Earth’s gravity.
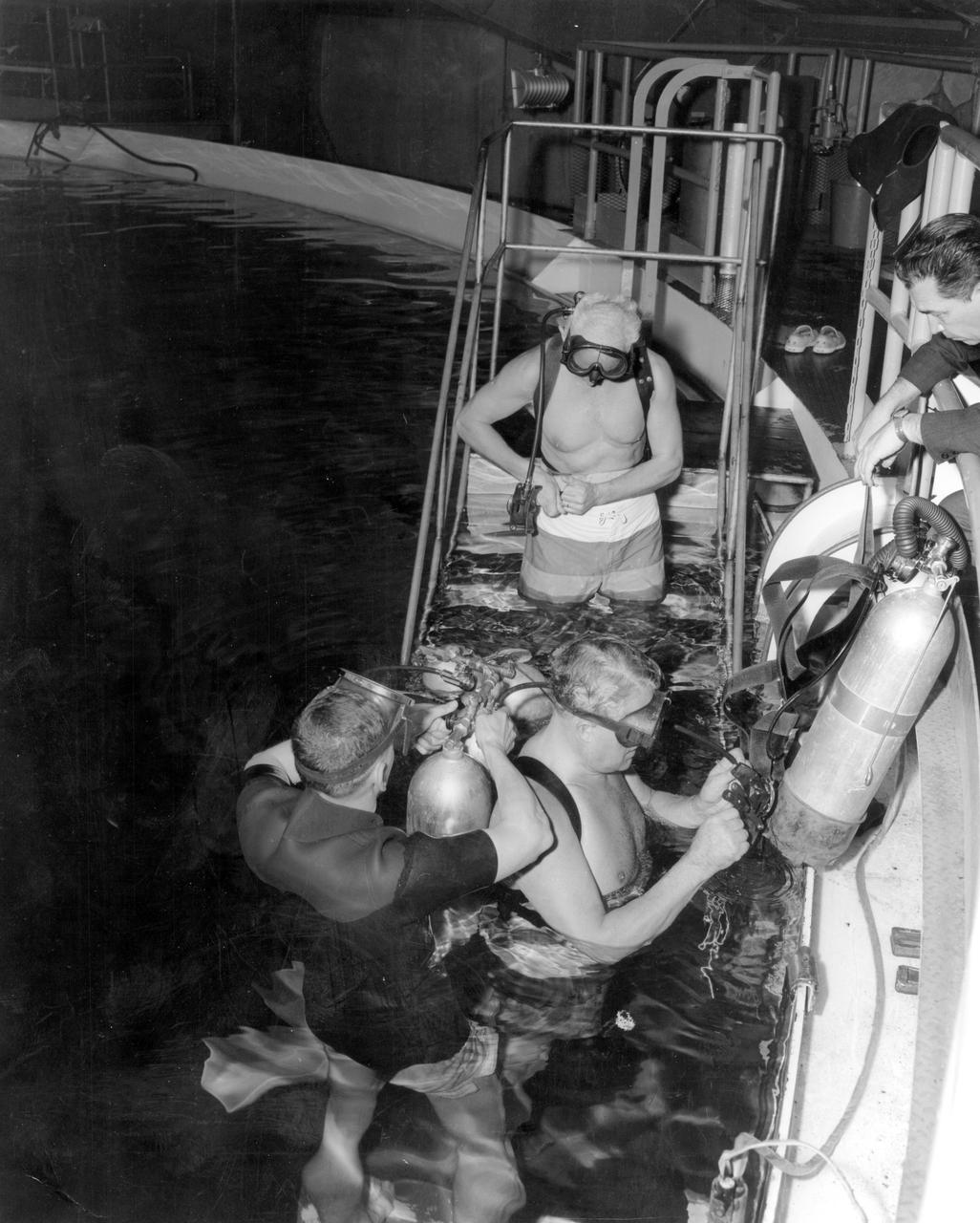

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, Director of Research Projects Office; and Dr. Wernher von Braun, center director, along with others, took a swim in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at MSFC. A safety diver adjusts scuba equipment worn by von Braun, while Stuhlinger adjusts his weight belt prior to entering the tank. In the NBS, subjects were weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition underwater to perform and practice tasks in a simulated weightless condition as would be encountered in space.
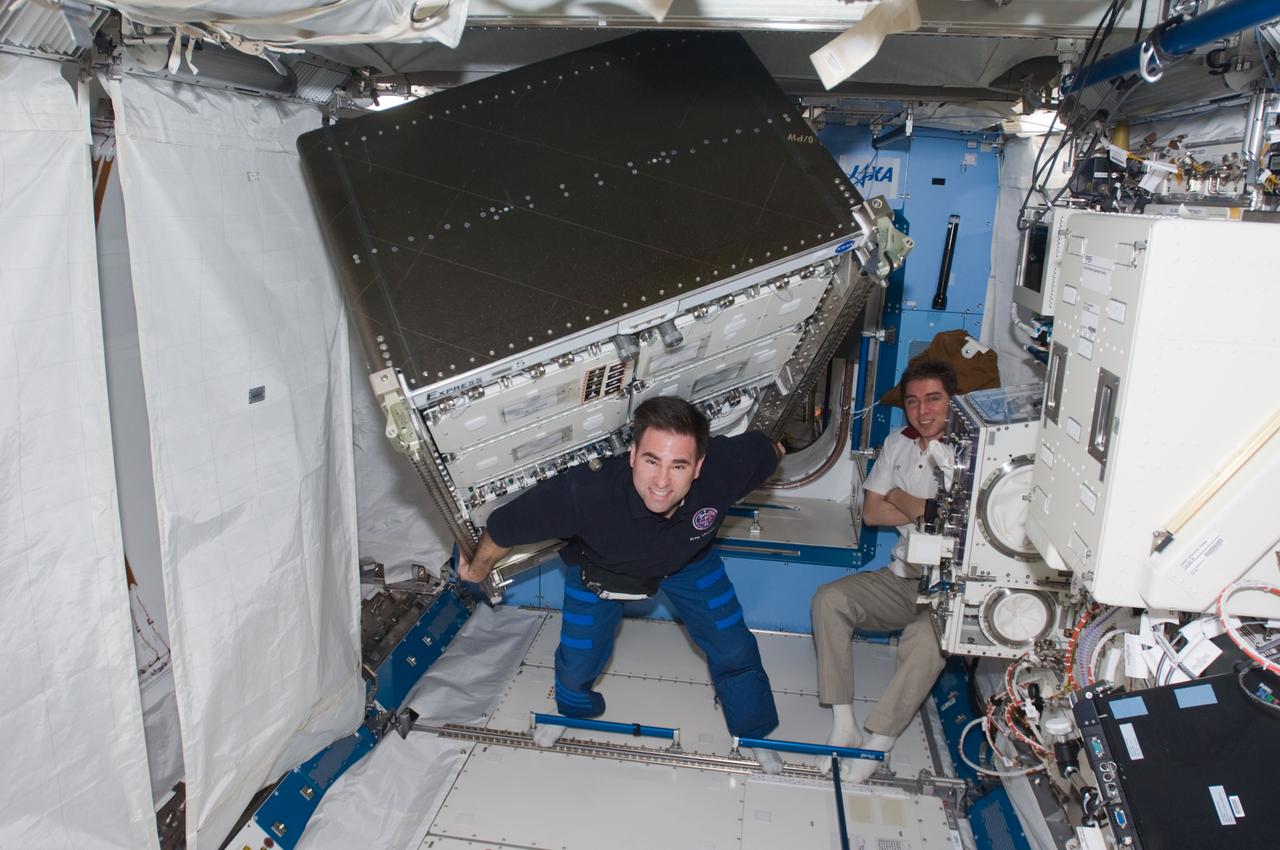

ISS017-E-014091 (26 Aug. 2008) --- Thanks to the weightlessness of space, astronaut Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17 flight engineer, isn't toting the excessive weight load he appears to be in this electronic still photo downlinked by the current inhabitants of the International Space Station. While cosmonaut Sergei Volkov, Expedition 17 commander, looks on, Chamitoff works in the Kibo laboratory to move an experiment rack during a relocation task he and the two Russian crewmembers were sharing.
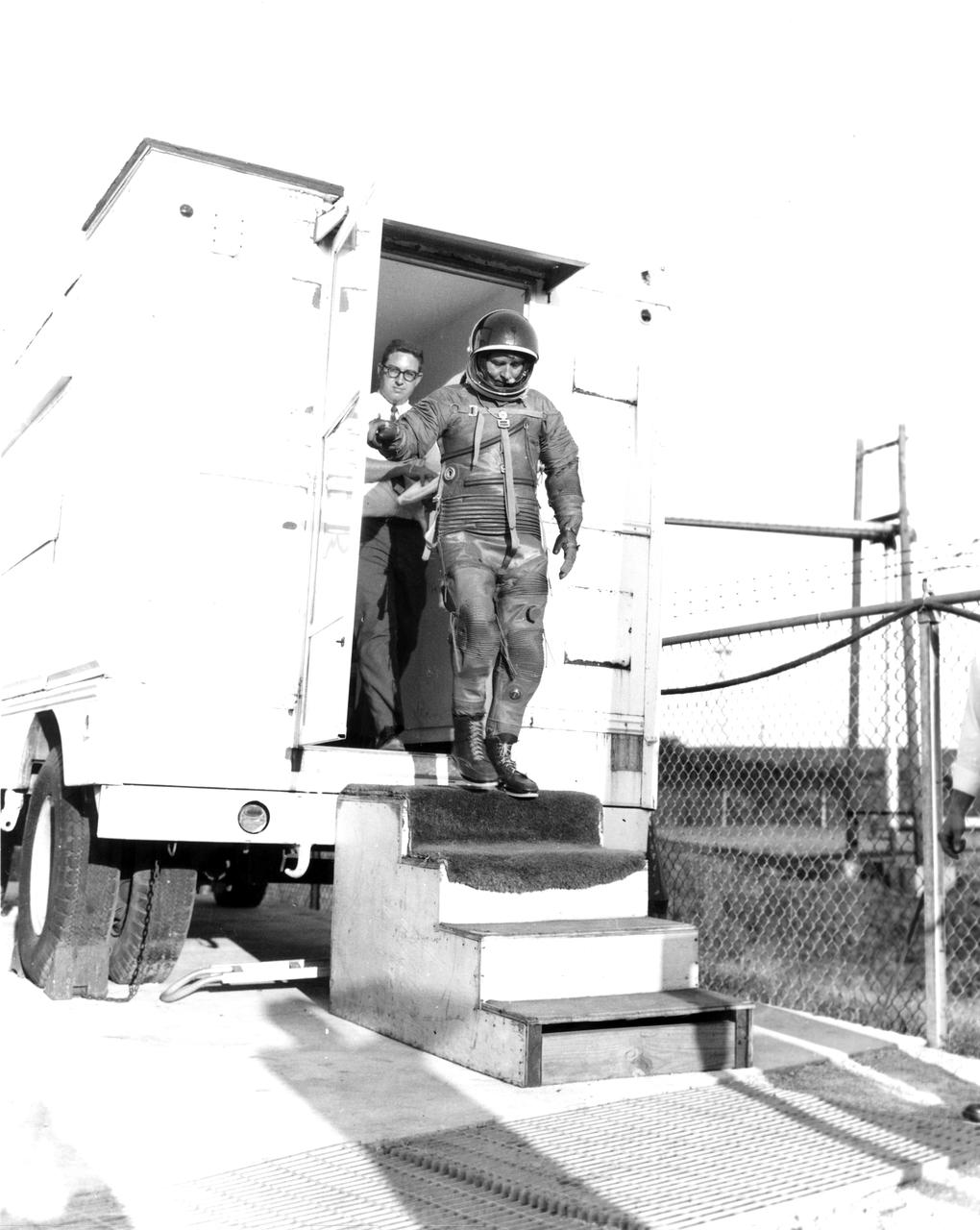

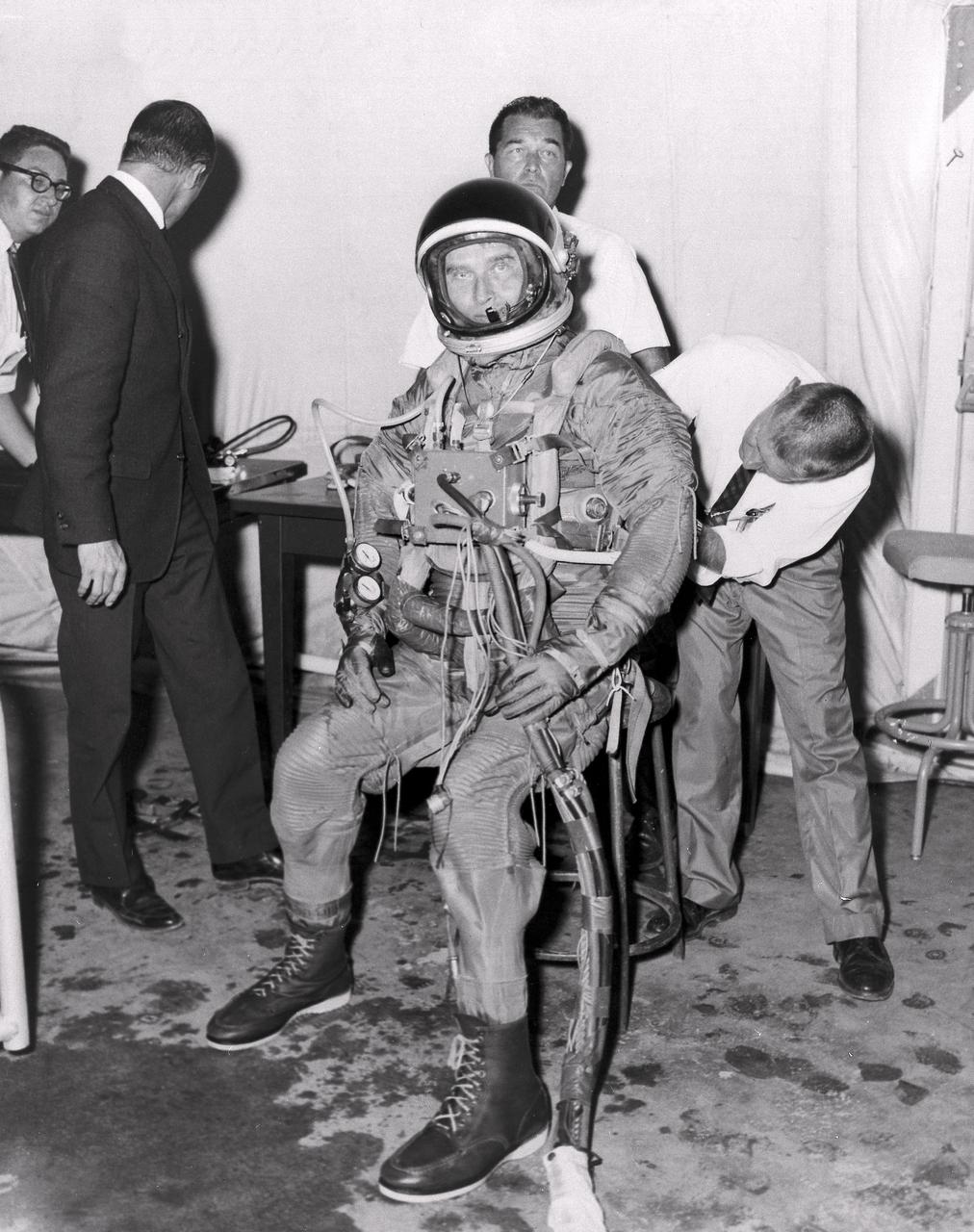
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, is shown leaving the suiting-up van wearing a pressure suit prepared for a tryout in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
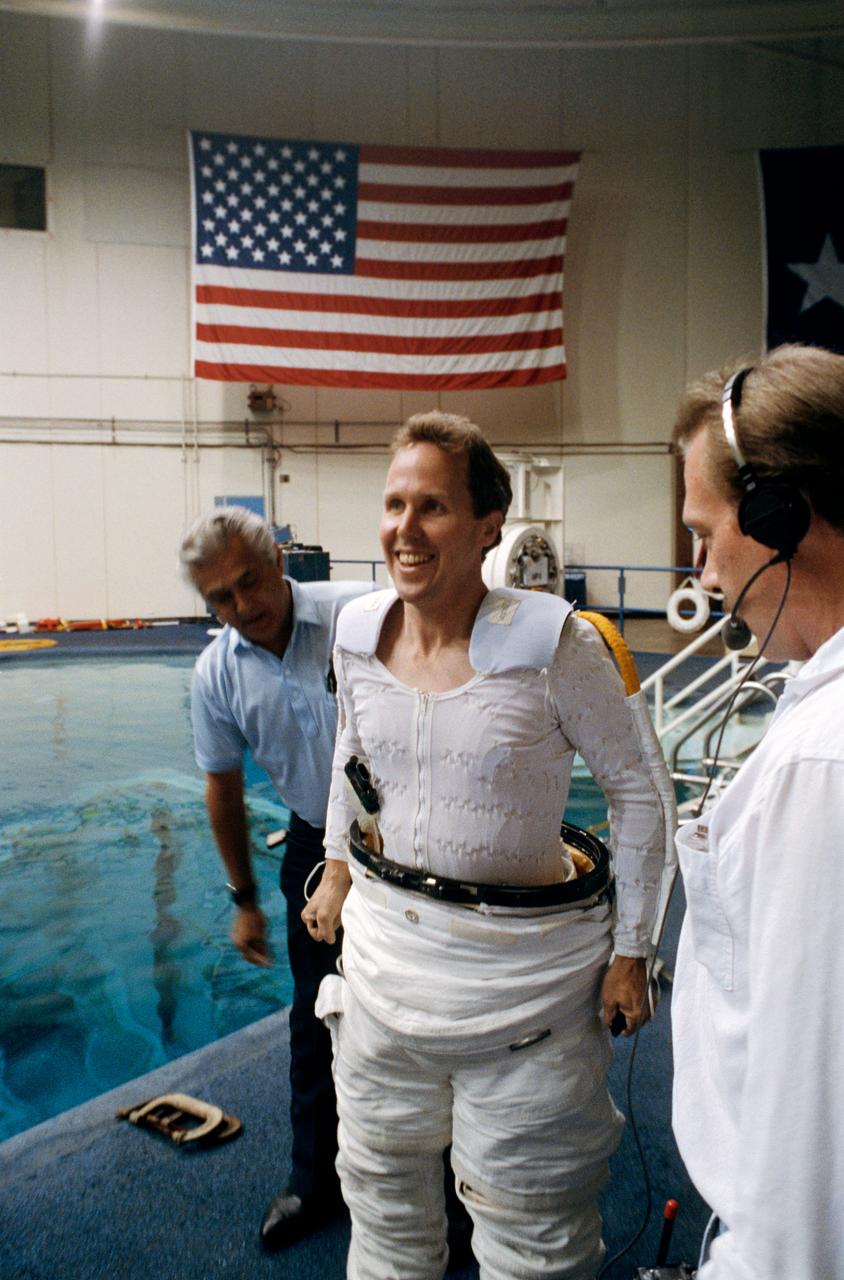

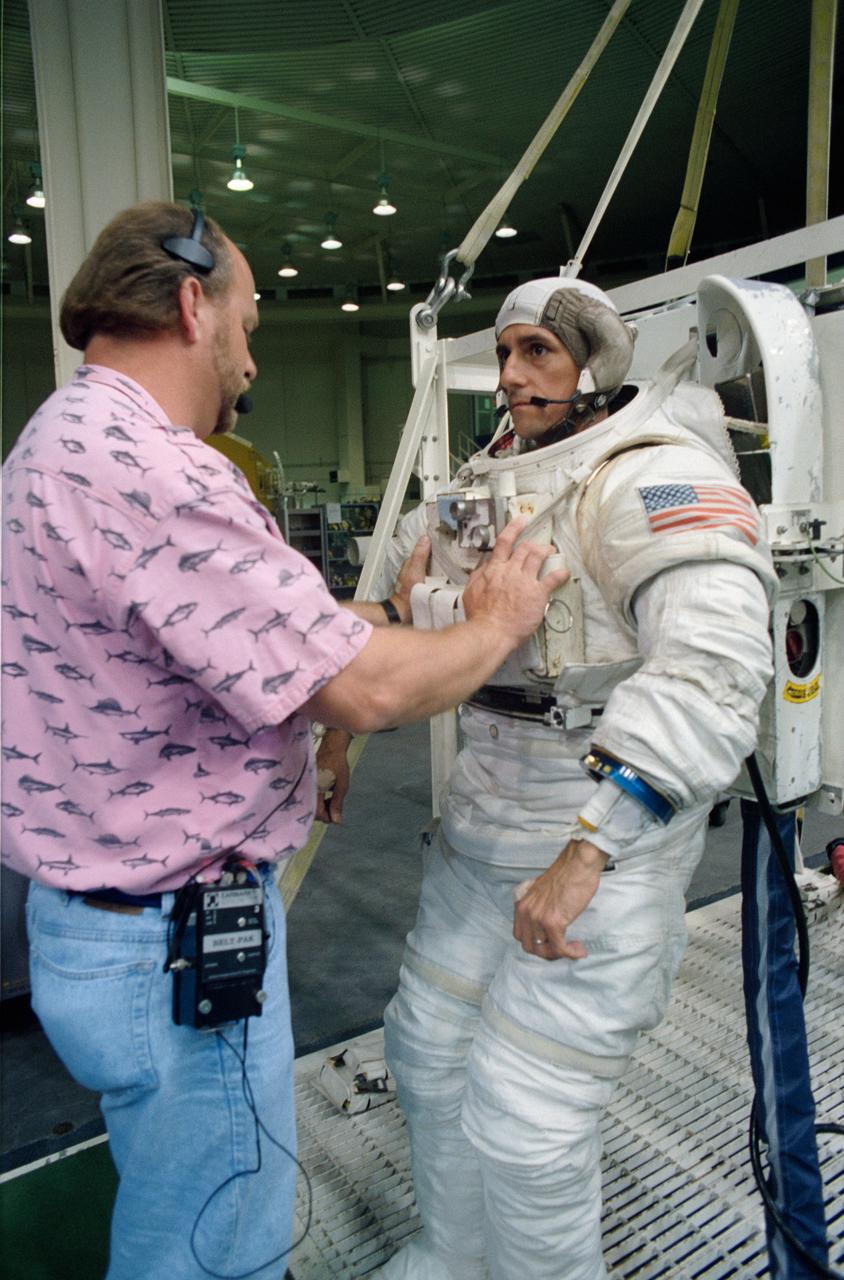
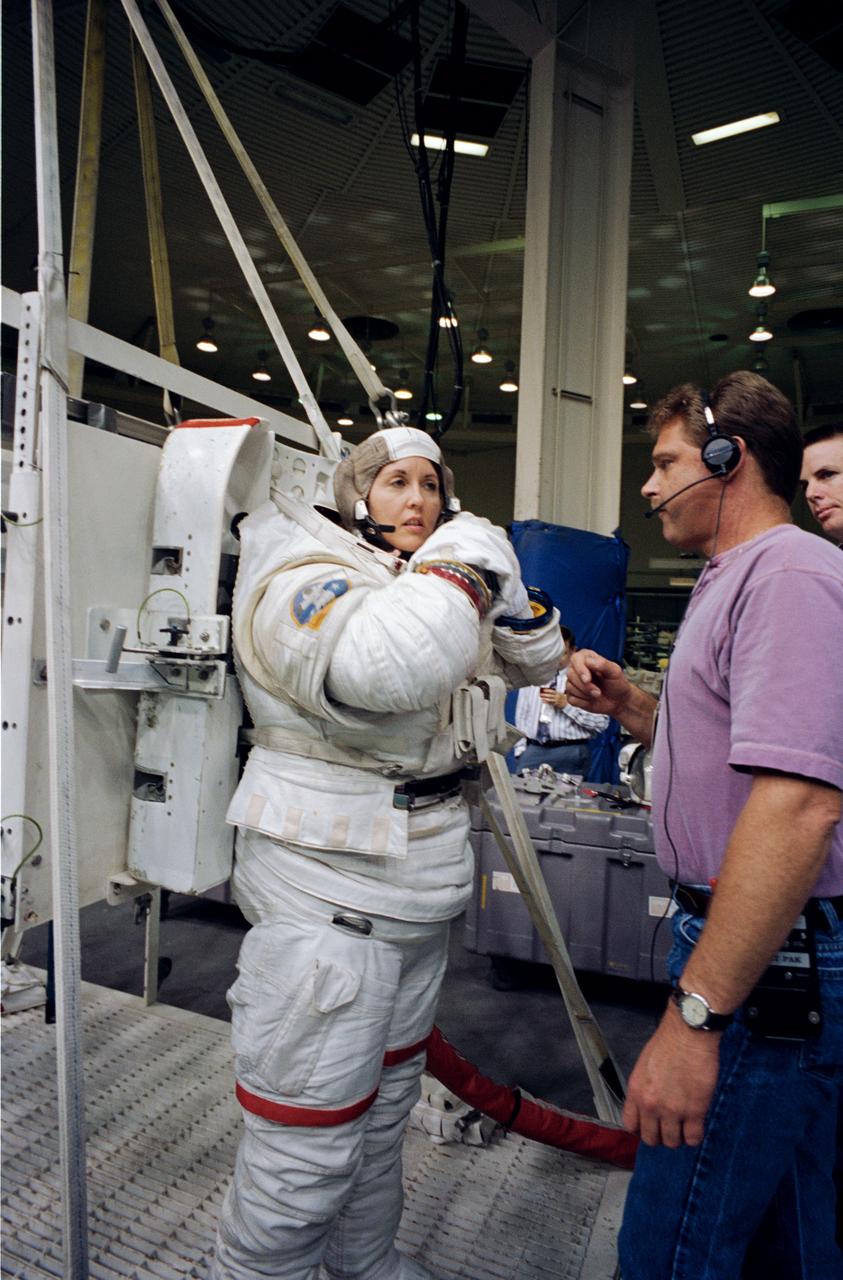
Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, dons a space suit prior to participating in contingency space walk simulations at the JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). Jones is assisted by Frank Hernandez (left) and suit technician Charles Hudson of Hamilton Standard. Jones suit is weighted to that he can achieve a neutrally buoyant state once under water. Extravehicular tasks are not planned for the STS-59 mission, but a number of chores are rehearsed in case of failure of remote systems to perform those jobs.

ISS008-E-22241 (22 April 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, “juggles” fresh fruit in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS). The weightless environment of space proves to be an ideal location for some tasks not so easily accomplished in Earth’s gravity.
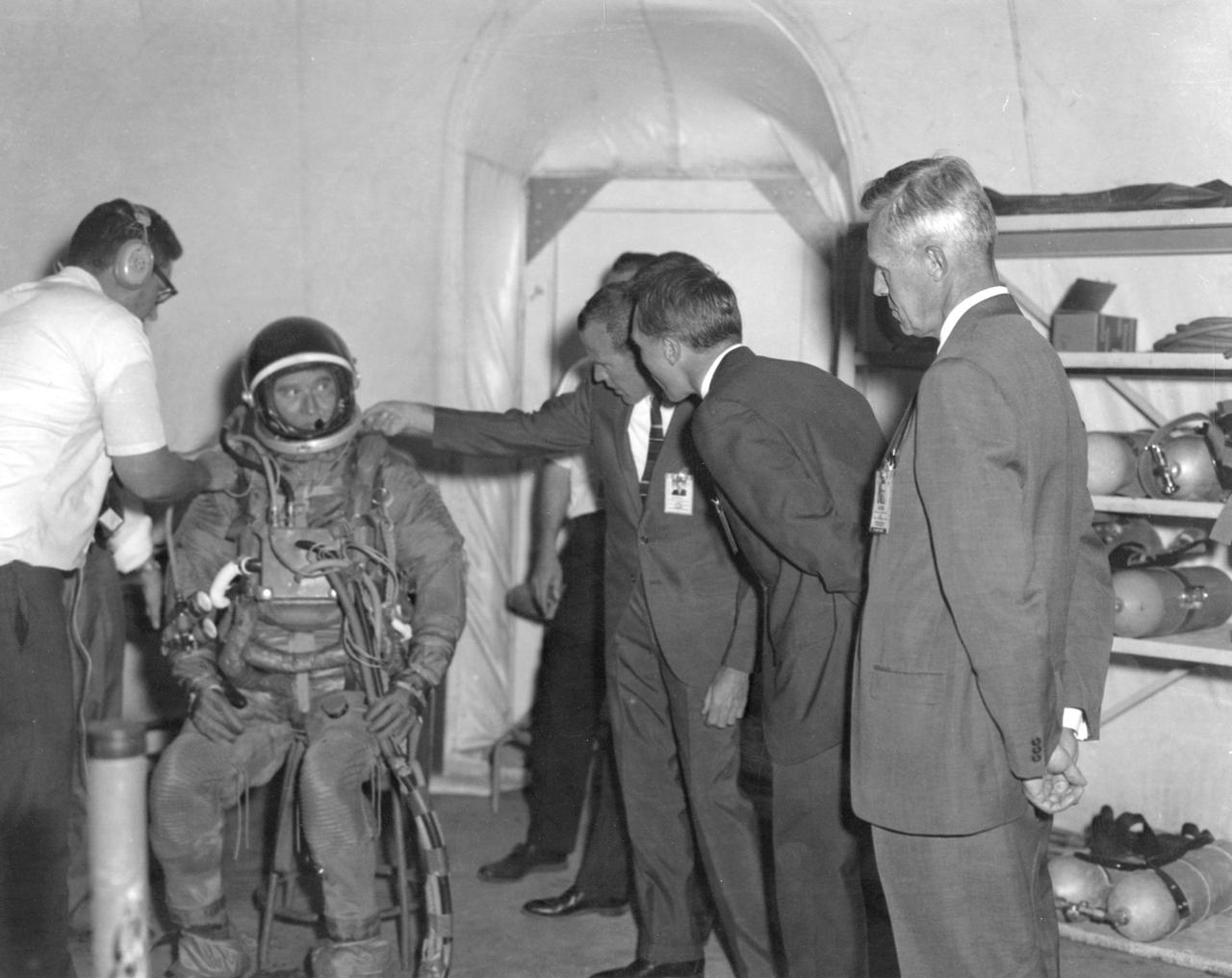

Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper checks the neck ring of a space suit worn by Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun before he submerges into the water of the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Wearing a pressurized suit and weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
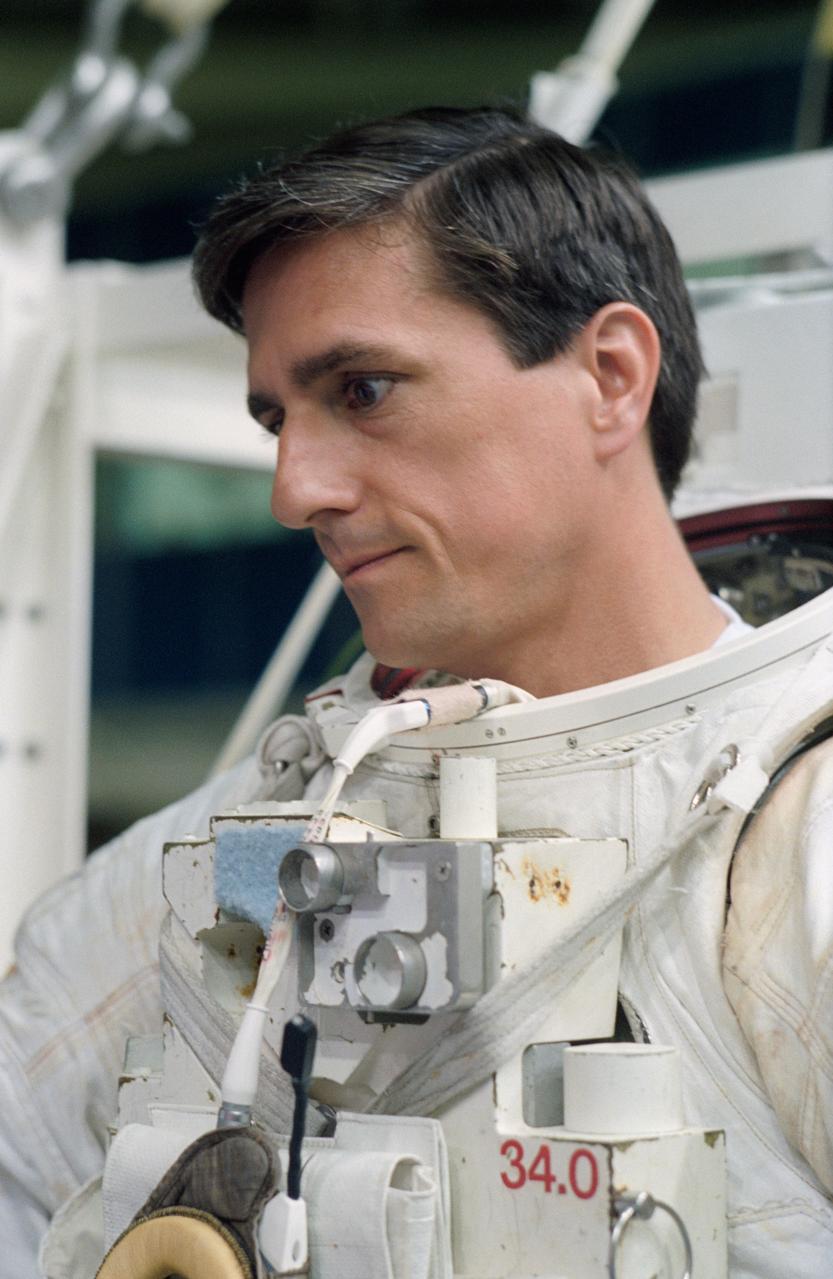

S94-29976 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, awaits his helmet as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
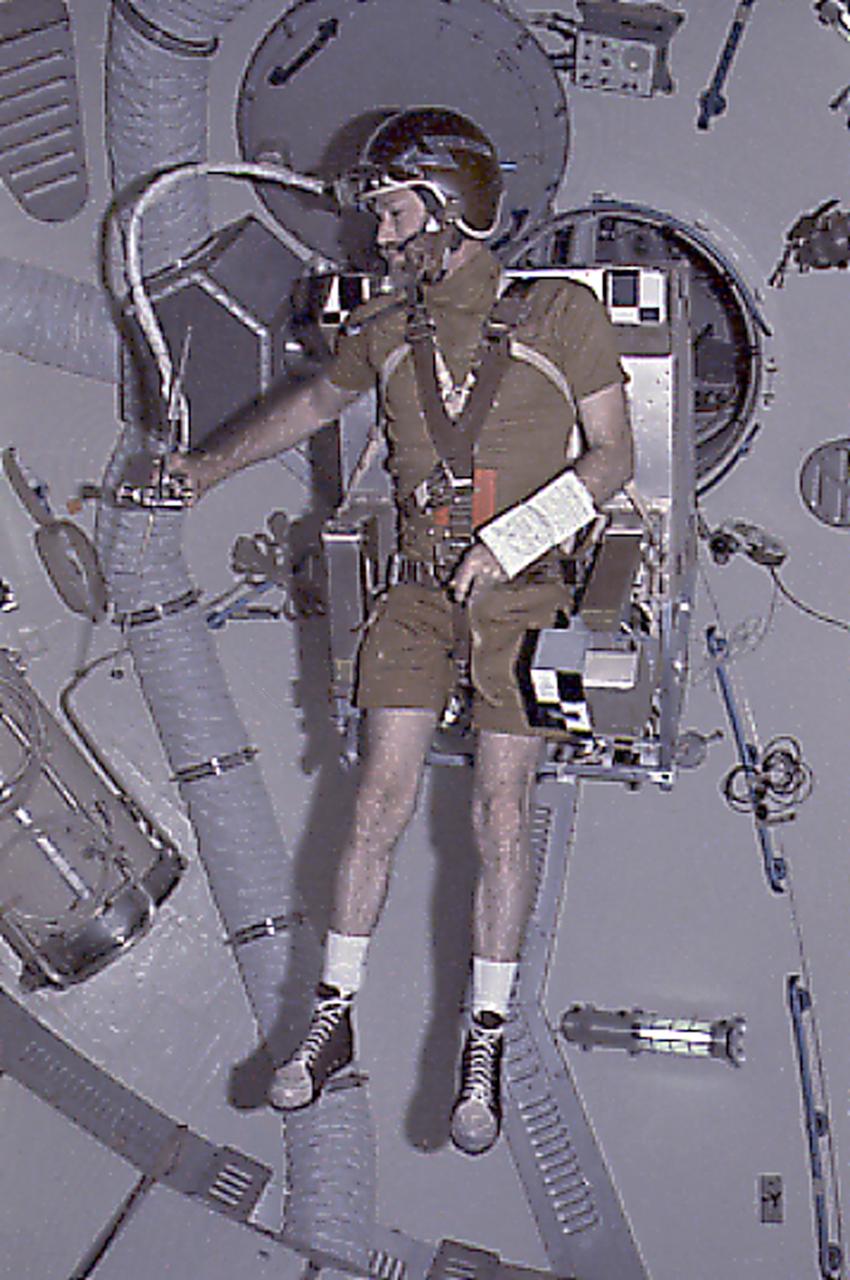
This Skylab-4 onboard photograph depicts Astronaut Gerald Carr testing Astronaut Maneuvering Equipment (M509) by flying it around under weightless conditions in the Orbital Workshop. The M509 experiment was an operational study to evaluate and conduct an in-orbit verification of the utility of various maneuvering techniques to assist astronauts in performing tasks that were representative of future extravehicular activity requirements.

S95-08375 (August 1995) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander for the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission, prepares to go underwater in the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) pool. Thornton was about to rehearse contingency space walk tasks; there is no Extravehicular Activity (EVA) planned for the STS-73 mission.
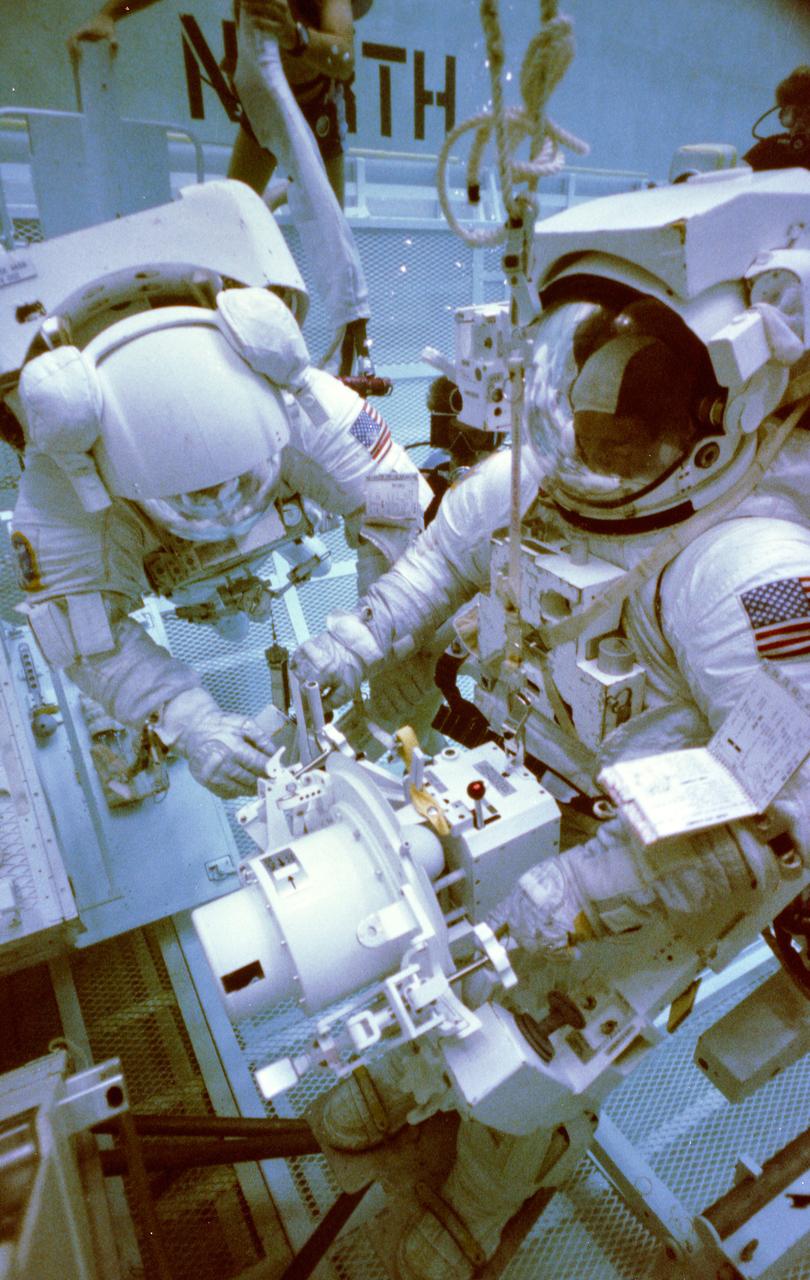
S83-42893 (19 Oct 1983) ---- Astronauts George D. Nelson and James D. van Hoften, two of three STS-41C mission specialists, share an extravehicular activity (EVA) task in this simulation of a Solar Maximum Satellite (SMS) repair visit. The two are making use of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Dr. Nelson is equipped with the manned maneuvering unit (MMU) trainer and he handles the trunion pin attachment device (TPAD), a major tool to be used on the mission. The photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
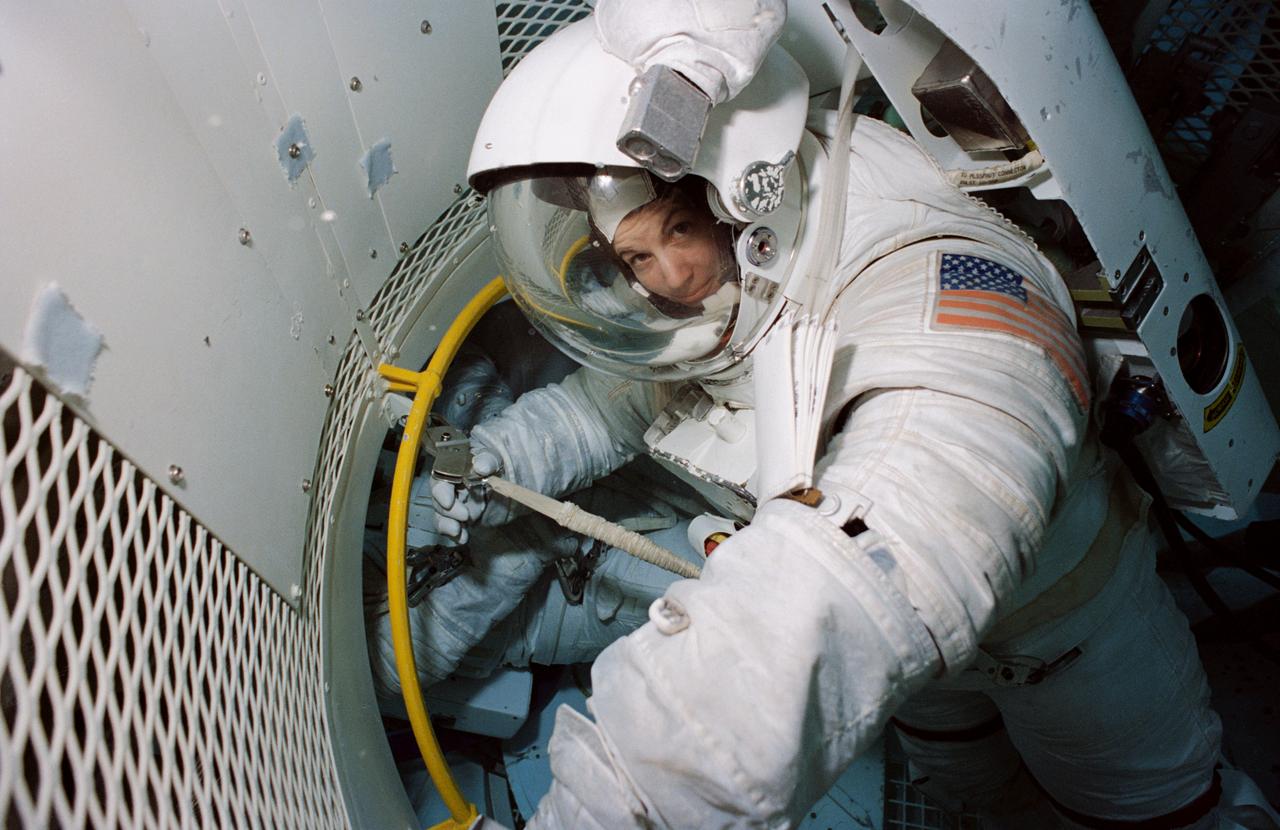

S94-25956 (April 1994) --- Astronaut Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist, wearing a high-fidelity training version of an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), trains for a contingency space walk at the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Coleman has recently been named as one of seven crew members for the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission. The 25-feet deep pool is used to train astronauts for mission specific space walk chores as well as for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) tasks.
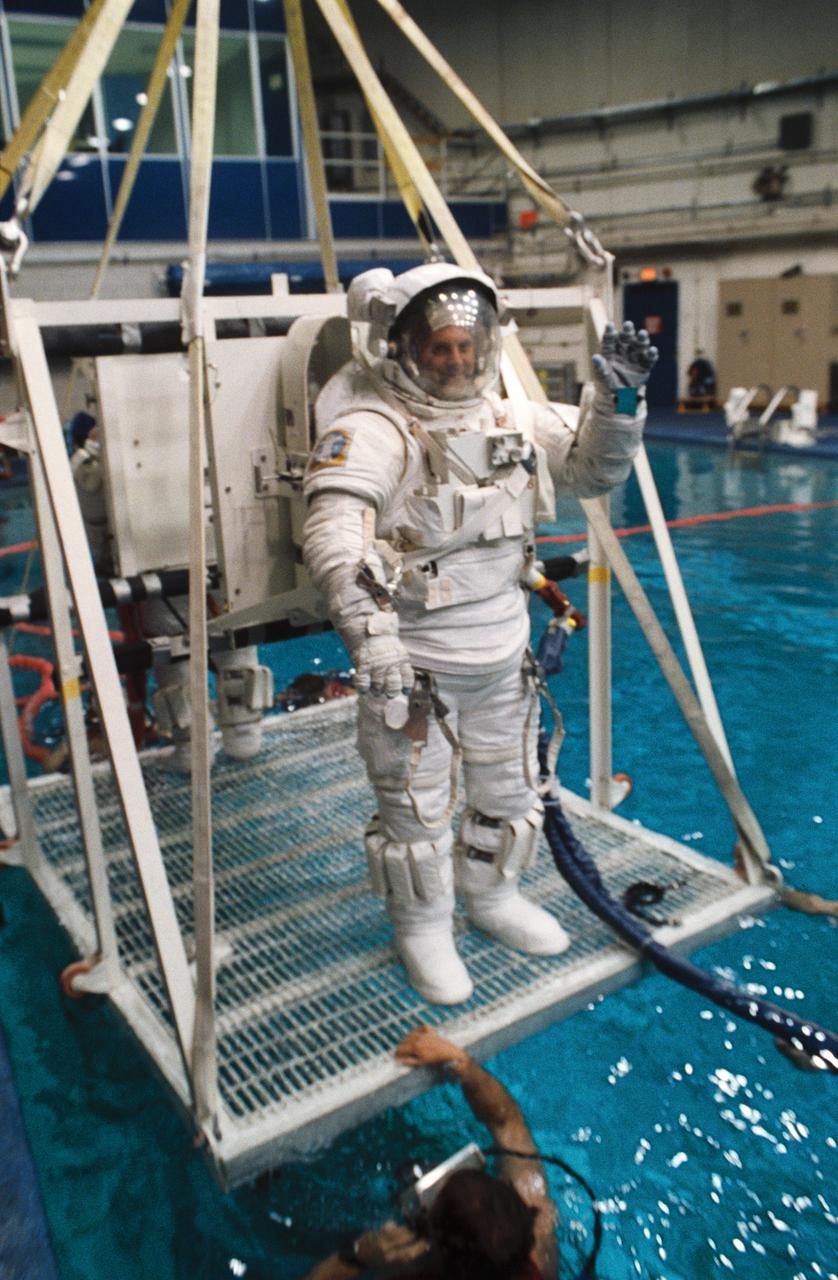

S93-31702 (3 April 1993) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf participates in training for contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. Behind Wolf, sharing the platform with him is astronaut Shannon W. Lucid. For simulation purposes, the two mission specialists were about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.
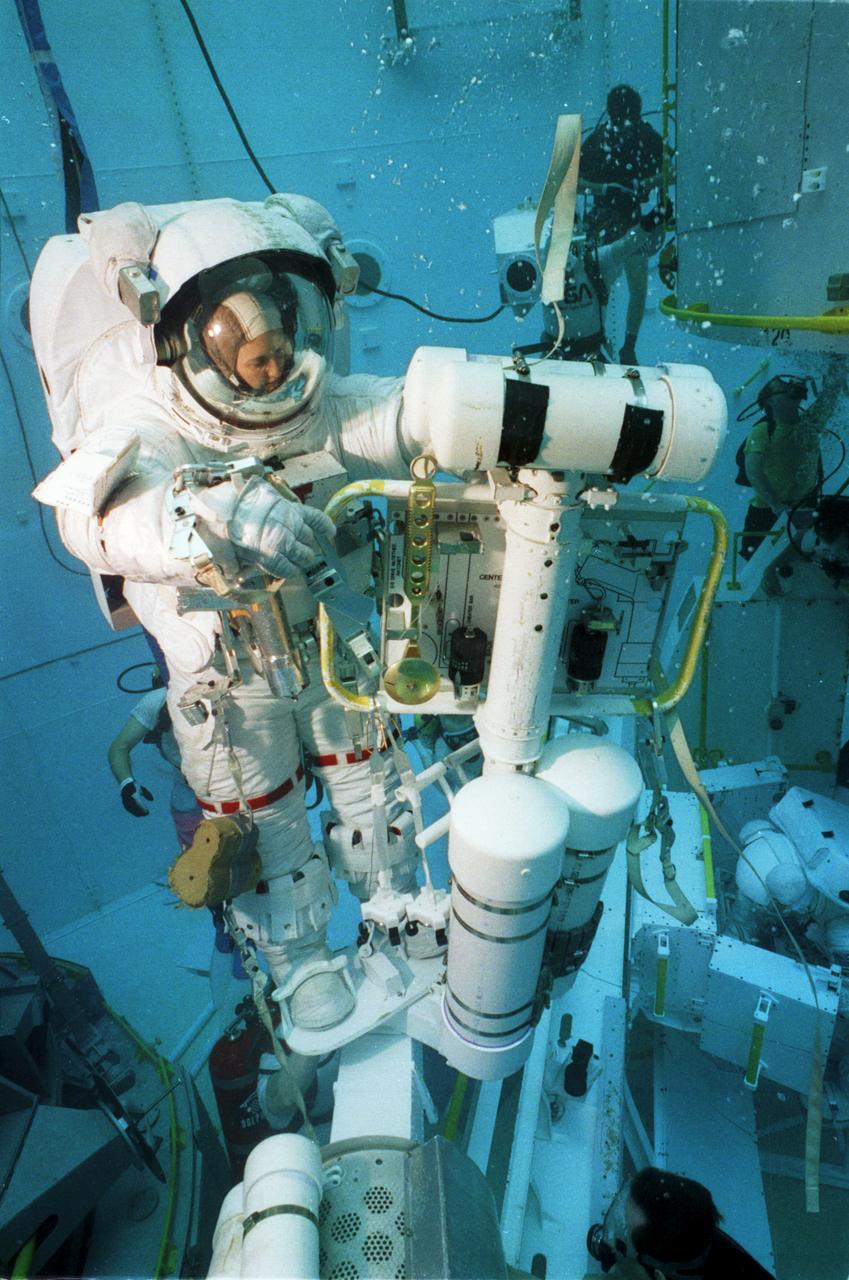
This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist, Kathryn Thornton, was captured under water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neural Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.
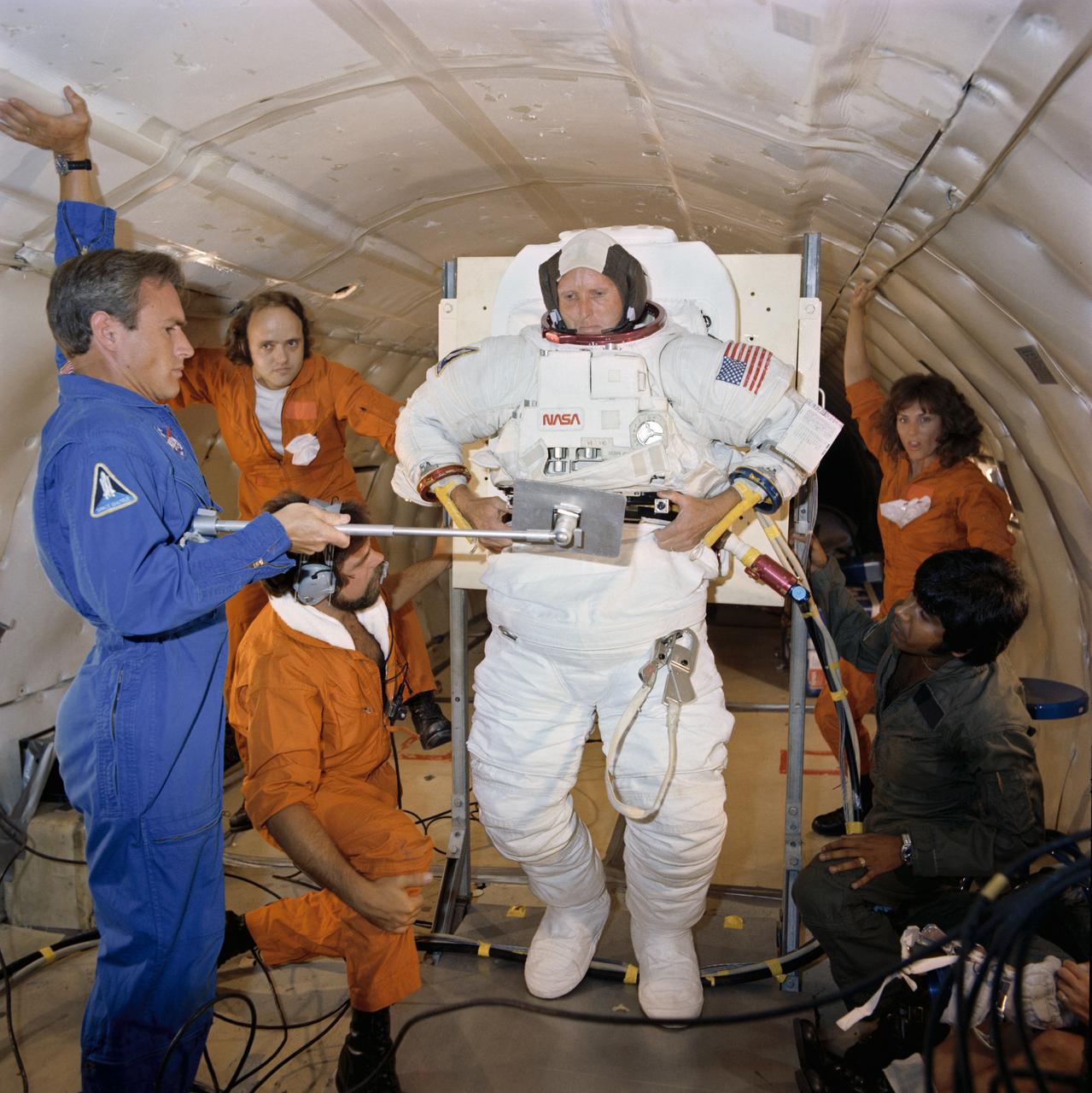

S81-34432 (July 1981) --- Astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, takes part in a suit donning and doffing exercise aboard a KC-135 "zero-gravity" aircraft. Mission specialist/astronaut William F. Fisher holds a mirror to assist Fullerton with hose and cable linkups to his suit. A special parabolic pattern flown by the KC-135 provides short durations of weightlessness. Fullerton's suit is an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), used by astronauts when leaving the shirt-sleeve environment of their shuttle orbiter to go outside and perform tasks in the vacuum of space. There are no such EVA plans on STS-3, but the crewmen are trained in this area in the event of a contingency. Photo credit: NASA

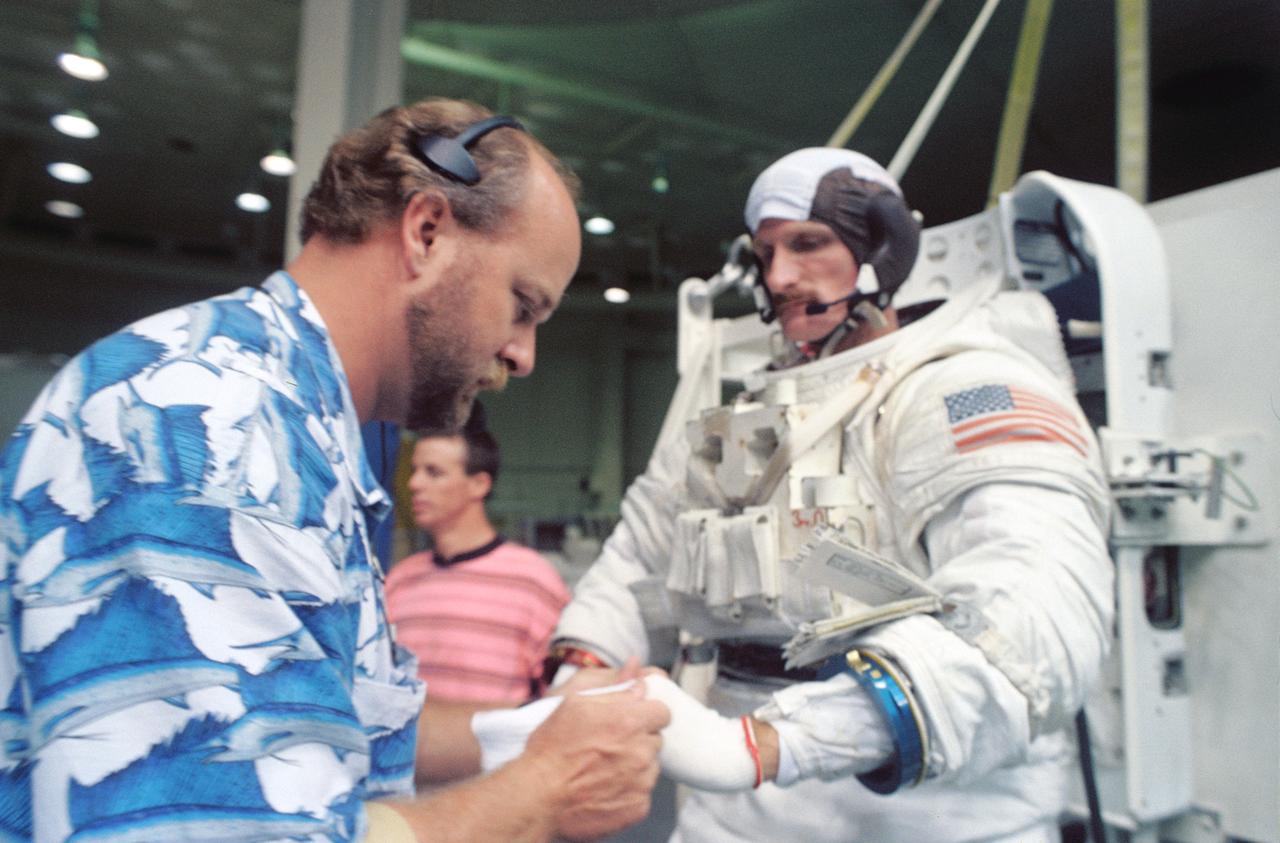
S91-51063 (Dec 1991) --- Partially attired in a special training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, astronaut Bernard J. Harris Jr. is pictured before a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Harris, STS-55 mission specialist, is assisted by Laney Lee. Minutes later, Harris was in a 25-feet deep pool, simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). There is no scheduled EVA for the 1993 flight but each spaceflight crew includes astronauts trained for a variety of contingency tasks that could require exiting the shirt-sleeve environment of a Shuttle's cabin.

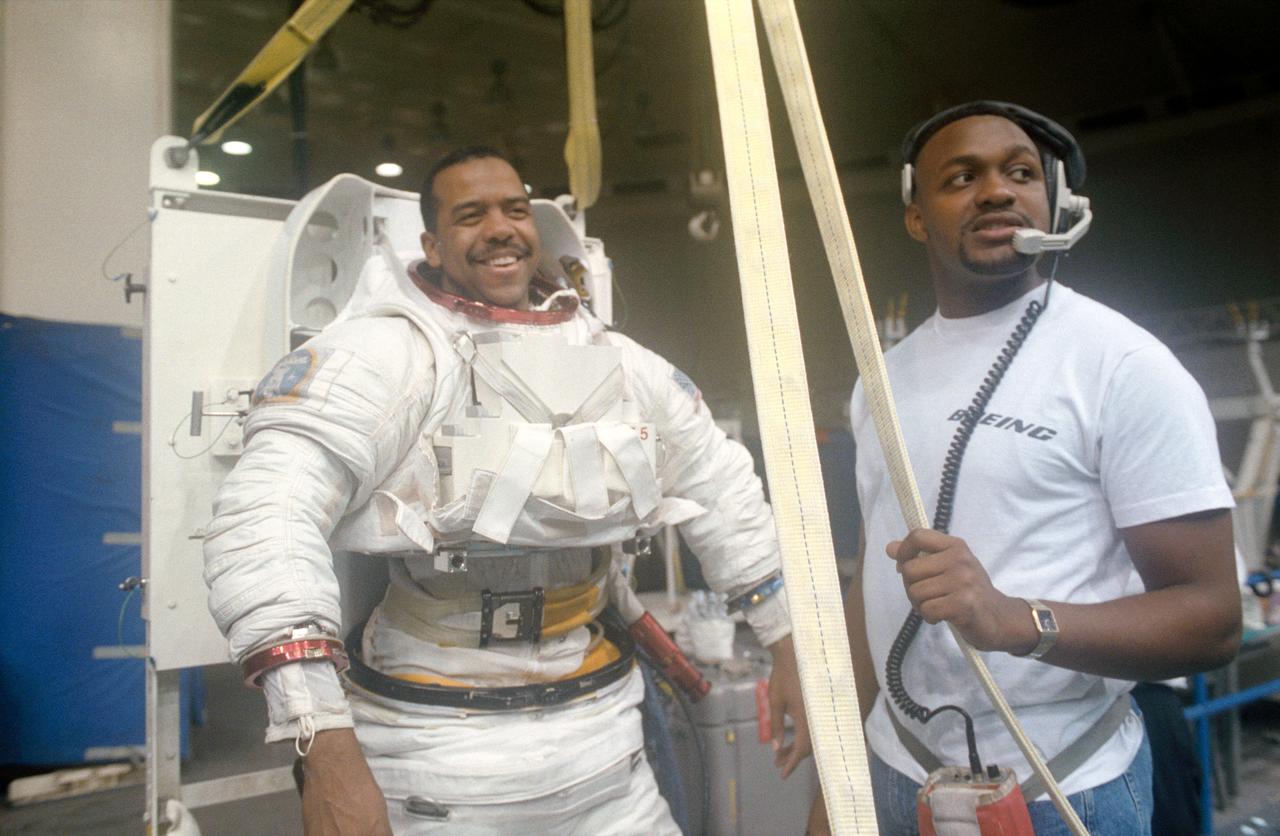
S94-40048 (1 August 1994) --- Astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, is assisted by Boeing suit expert Steve Voyles as he prepares to be submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though no extravehicular activity (EVA) is planned for the mission, at least two astronauts are trained to perform tasks that would require a space walk in the event of failure of remote systems. In November, Tanner will join four other NASA astronauts and a European mission specialist for a week and a half in space aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The flight will support the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
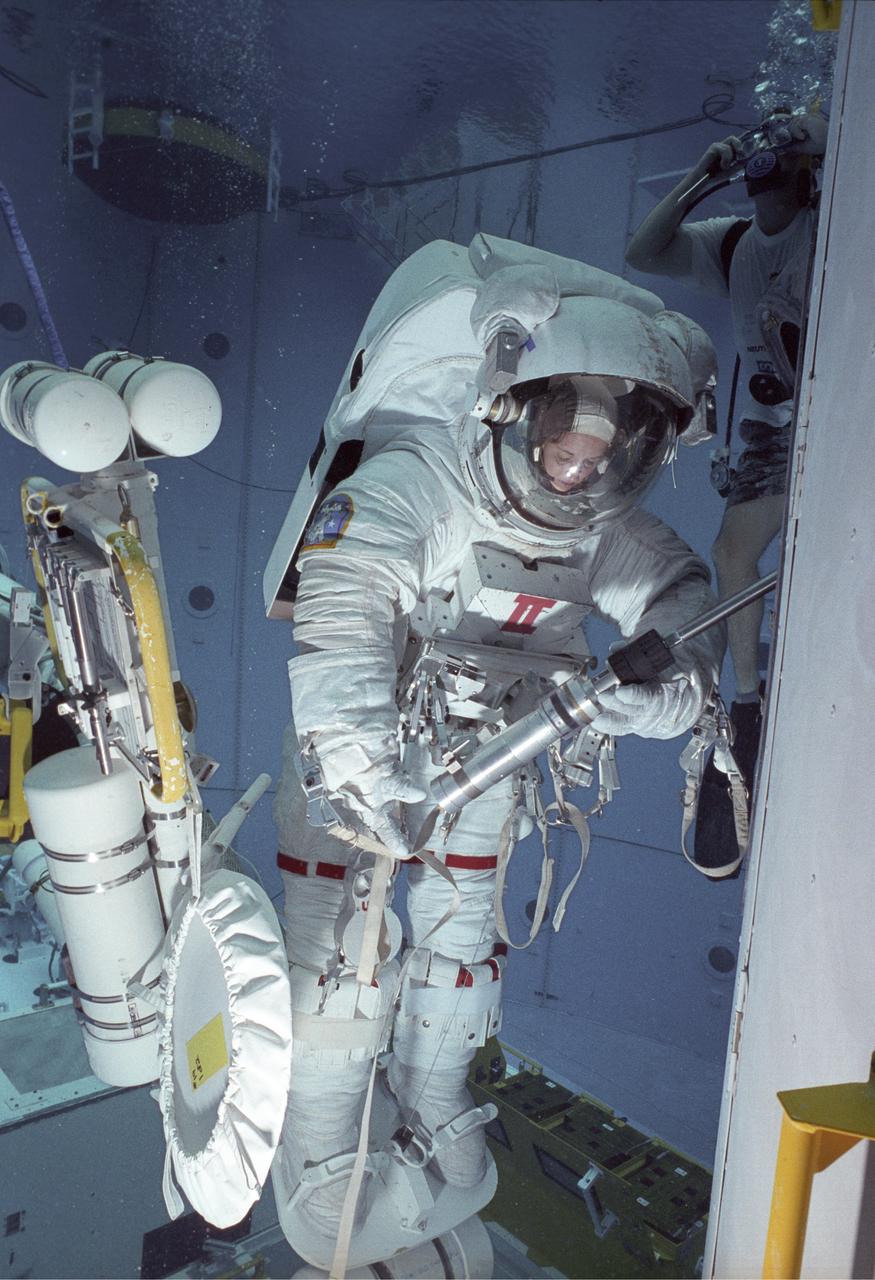

This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist Kathryn Thornton was captured under water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neural Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.
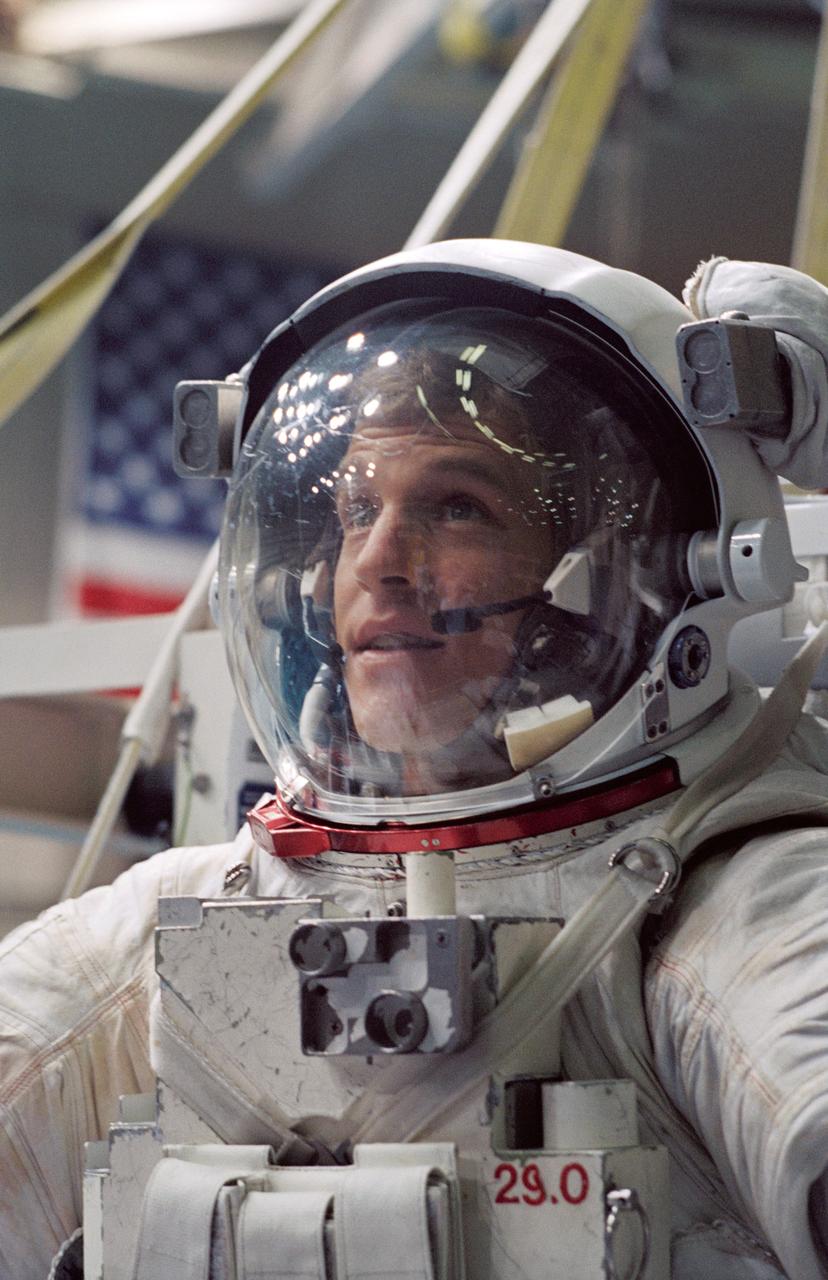

S94-40051 (1 August 1994) --- Attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, mission specialist, prepares to be submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though no extravehicular activity (EVA) is planned for the mission, at least two astronauts are trained to perform tasks that would require a space walk in the event of failure of remote systems. In November, Parazynski will join four other NASA astronauts and a European mission specialist for a week and a half in space aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The flight will support the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.

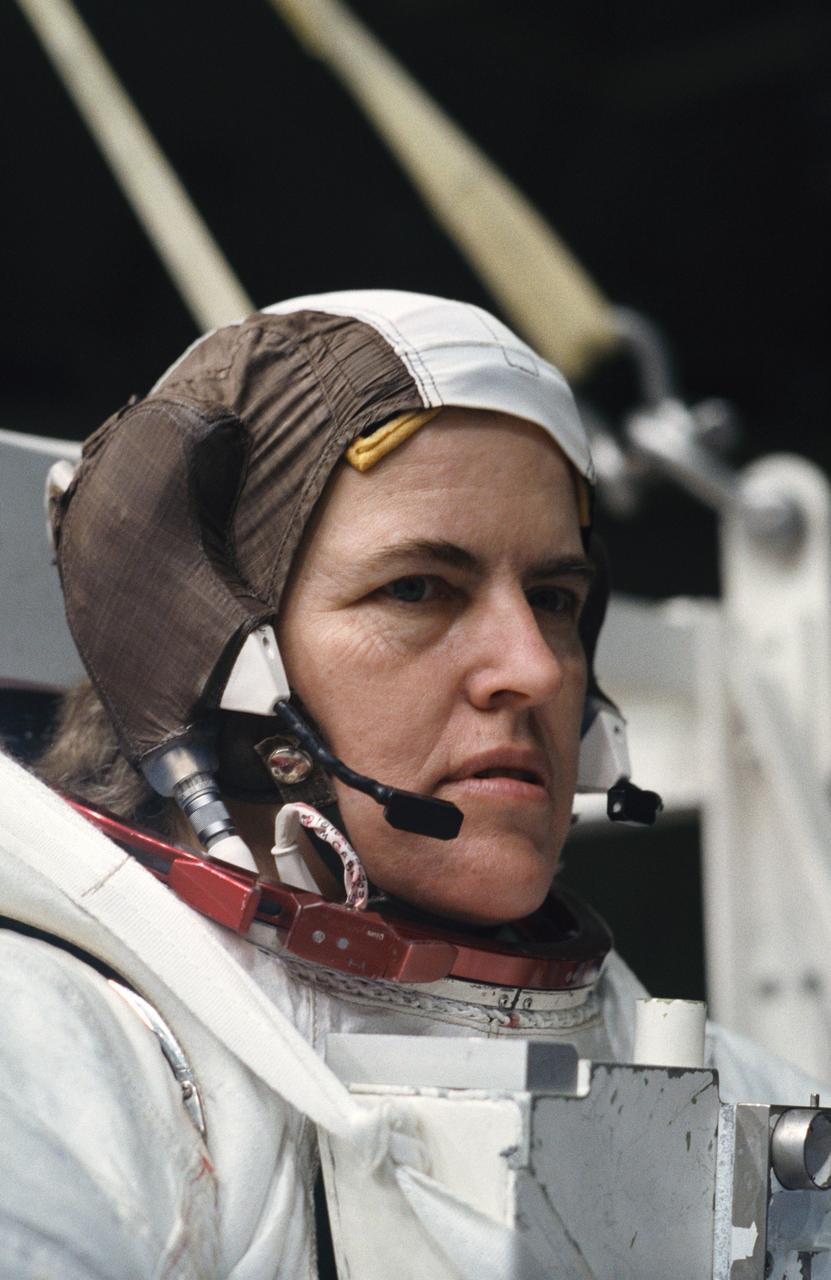
S93-42464 (September 1993) --- Astronaut Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist for STS-73, dons a high-fidelity training version of an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit at the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Coleman, who has recently been named as one of seven crew members for the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission, was about to go underwater in a 25-feet deep pool. The pool is used to train astronauts for mission specific space walk chores as well as for contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) tasks.

S93-31697 (3 April 1993) --- Astronaut Shannon W. Lucid participates in training for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. Behind Lucid, sharing a moveable platform with her, is astronaut David A. Wolf (out of frame). For simulation purposes, the two mission specialists were about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.

S93-31706 (3 April 1993) --- With the aid of technicians and training staffers astronaut David A. Wolf prepares to participate in training for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. Sharing a moveable platform with Wolf was astronaut Shannon W. Lucid (out of frame). For simulation purposes, the two mission specialists were about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.
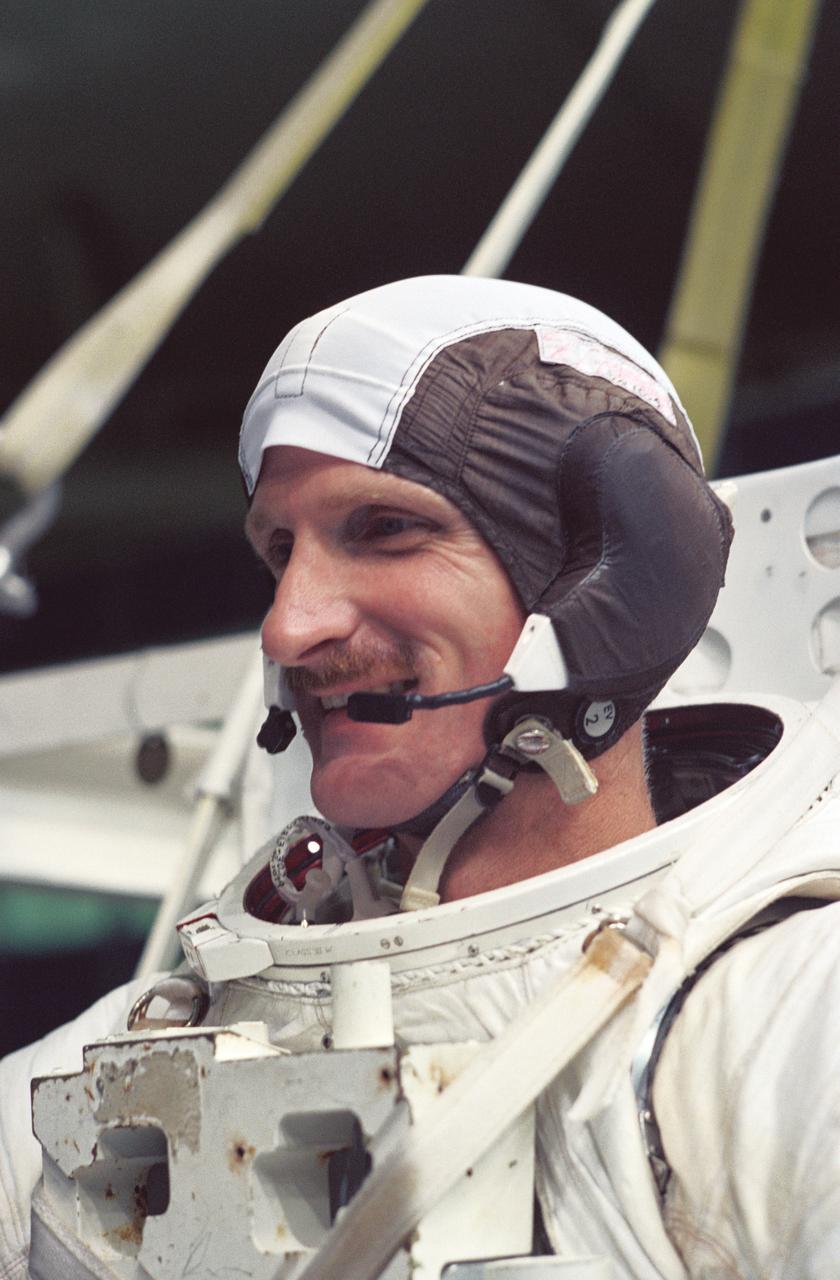

S94-40049 (1 August 1994) --- Attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, prepares to be submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though no extravehicular activity (EVA) is planned for the mission, at least two astronauts are trained to perform tasks that would require a space walk in the event of failure of remote systems. In November, Tanner will join four other NASA astronauts and a European mission specialist for a week and a half in space aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The flight will support the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
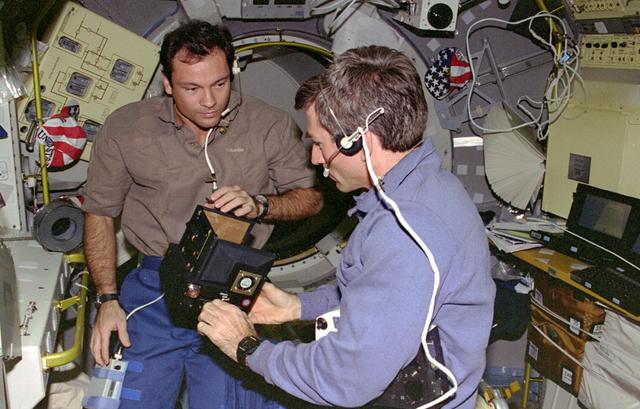

STS073-233-032 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria (left), STS-73 mission specialist, assists payload specialist Fred W. Leslie in an in-flight maintenance task involving the Fiber Support Droplet Combustion (FSDC) experiment. This new Glovebox investigation tests a technique for studying combustion in the weightless environment of space. The two joined five other crew members onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia for 16 days of in-space research in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
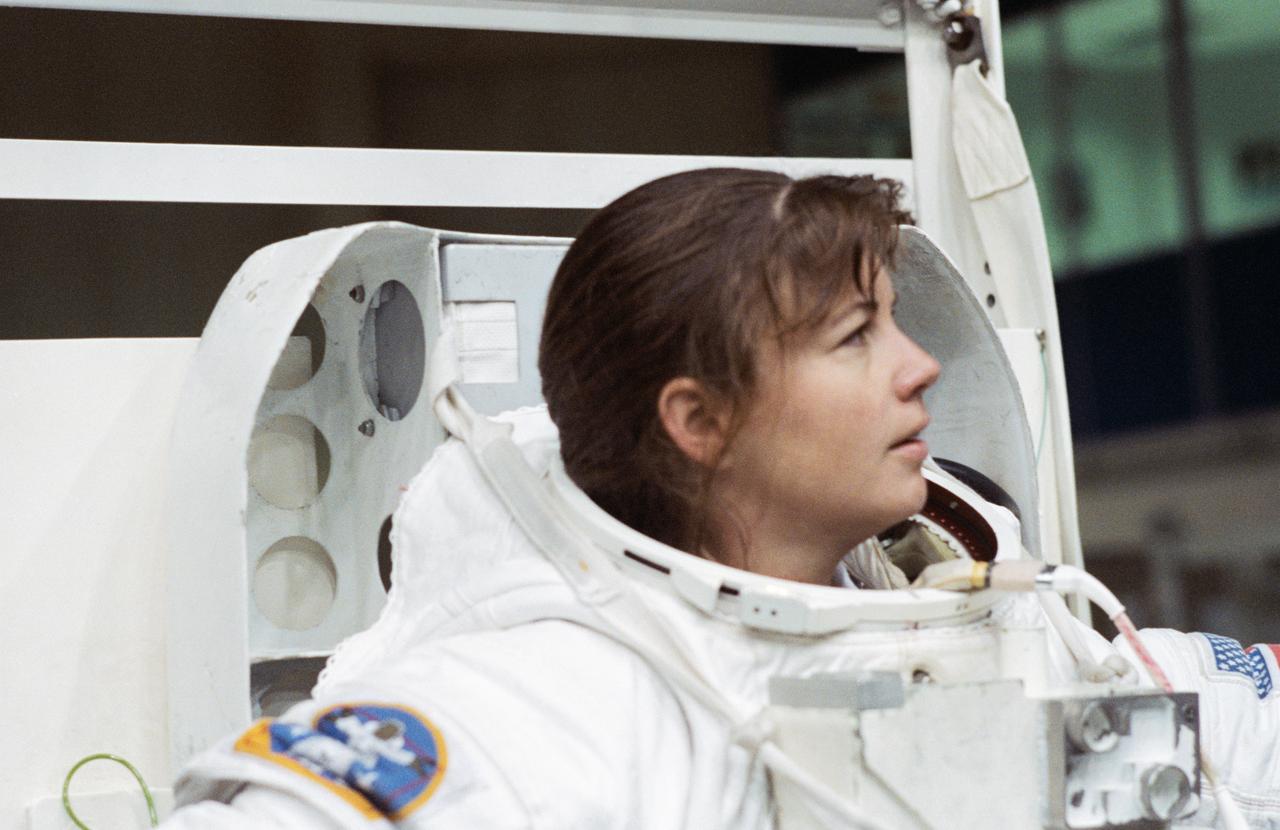

S93-42453 (September 1993) --- Astronaut Catherine G. Coleman, mission specialist for STS-73, is about to don the helmet portion of a high-fidelity training version of an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit at the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Coleman, who has recently been named as one of seven crew members for the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission, was about to go underwater in a 25-feet deep pool. The pool is used to train astronauts for mission specific space walk chores as well as for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) tasks. There is no space walk planned for STS-73.
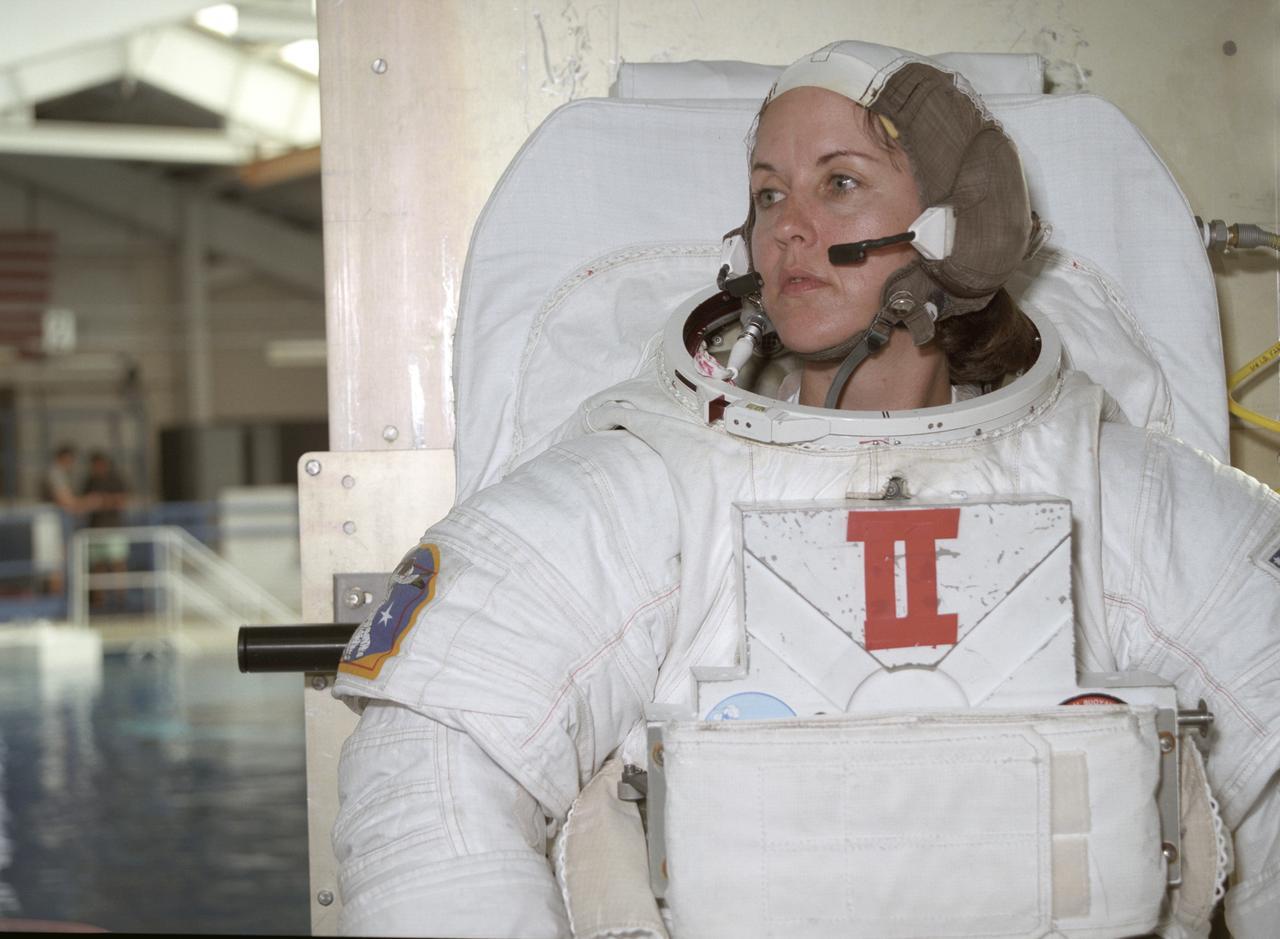

This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist Kathryn Thornton readies herself for submersion into the water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.

S93-43840 (6 Sept 1993) --- Astronaut William S. McArthur, mission specialist, participates in training for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. For simulation purposes, McArthur was about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.

S93-31701 (3 April 1993) --- Displaying the flexibility of his training version of the Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, astronaut David A. Wolf participates in training for contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. Behind Wolf, sharing the platform with him was astronaut Shannon W. Lucid. For simulation purposes, the two mission specialists were about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.

S91-51058 (Dec 1991) --- Partially attired in a special training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, astronaut Bernard A. Harris Jr. is pictured before a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Minutes later the STS-55 mission specialist was in a 25-feet deep pool simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). The platform on which he is standing was used to lower him into the water where, with the aid of weights on his environmentally-controlled pressurized suit, he was able to achieve neutral buoyancy. There is no scheduled EVA for the 1993 flight but each space flight crew includes astronauts trained for a variety of contingency tasks that could require exiting the shirt-sleeve environment of a Shuttle's cabin.

S85-30878 (15 April 1985) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, left, and Astronaut candidate Mark C. Lee rehearse the deployment of two specially designed flyswatter like tools on the end of the orbiter's remote manipulator system (RMS) arm. Their "dry" run of a planned Discovery STS 51-D extravehicular activity (EVA) is actually not so dry, since it is held in a 25 ft. deep pool, part of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment test facility (WET-F). Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman and S. David Griggs, two 51-D mission specialists, have been assigned the task of April 16's EVA. A rendezvous with the troubled Syncom IV (LEASAT) satellite has been scheduled for the day after the EVA, and an attempt will be made by the arm to trip an important lever on the troubled communications satellite.
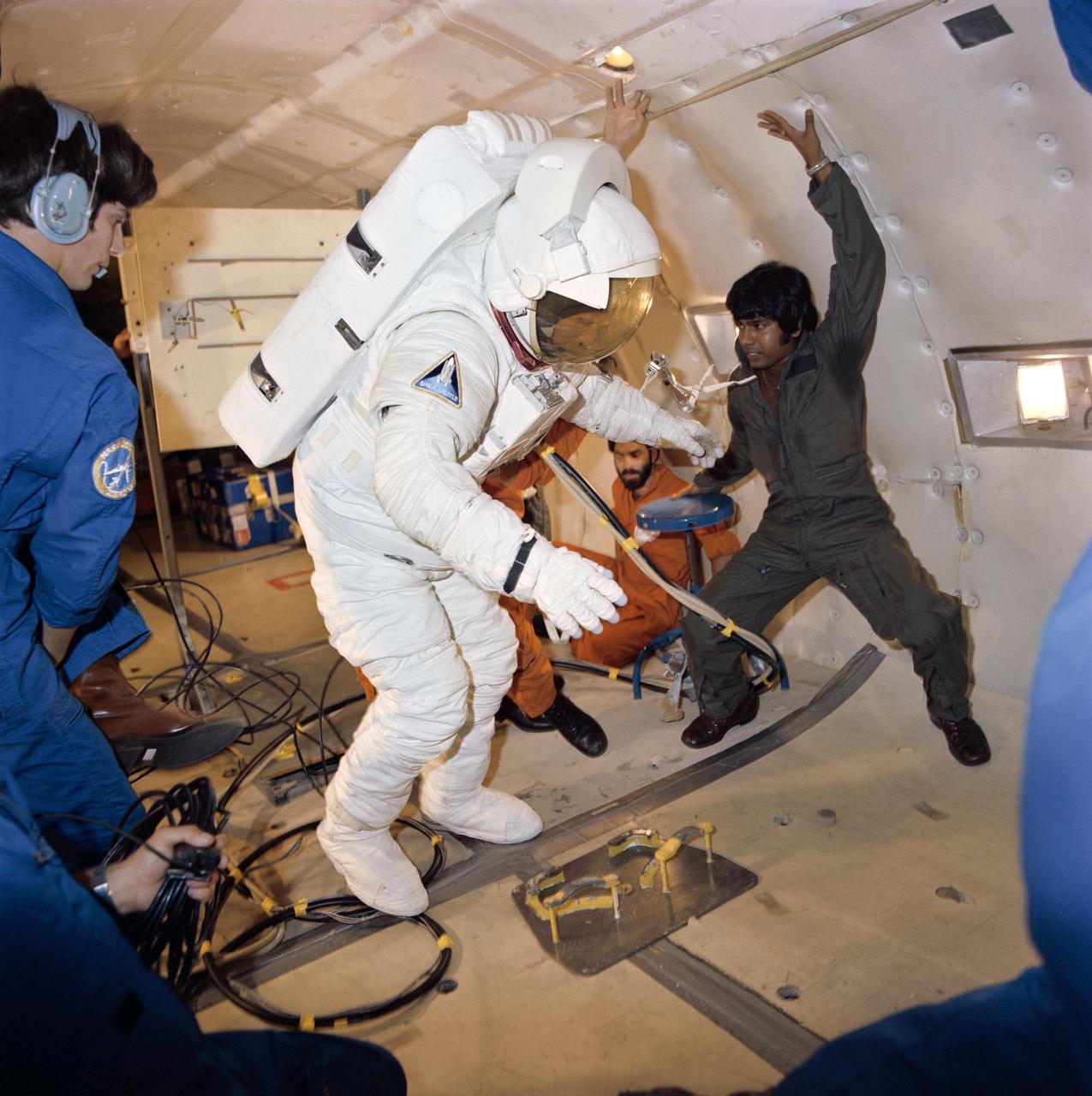

S81-34448 (July 1981) --- Astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, fully suited, gets a preview of what it might be like in space during a flight aboard NASA's KC-135 "zero-gravity" aircraft. A special parabolic pattern flown the aircraft provides short periods of weightlessness. Fullerton's suit is an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), used by astronauts when leaving the shirt-sleeve environment of their shuttle orbiter to go outside perform tasks in space. There are no such EVA plans on STS-3, but crew members are trained in this area in the event of the necessity to perform chores in space that for some reason or other can't be done remotely. The astronaut has just donned his suit during a parabola and now takes the opportunity to float around in the absence of gravity. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27403 (June 1973) --- Engineers at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center examine tools that are being considered for use in freeing the solar array wing of Skylab. The device at center is a cable cutter which is operated by cable. Enhanced television pictures indicate that the wing is being held to the side of the Skylab by a strip of metal from the meteoroid shield. The cable cutter shown here clipped an identical strip of metal in a test at the Marshall Center, requiring 90 pounds of force. The cutter is one of several heads which could be attached to extension rods. Identical tools and rods were carried into orbit by the Skylab 2 crew. At right is the handle end of a rod. White material taped just below the handle is buoyancy packing to make the object weightless when submerged in water. The tools are being tested in underwater EVA tasks in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator. Small object at left is the attachment head for a two-prong "rake" device for use on the end of a pole made up of one, two or more five-foot sections of extension rods. Photo credit: NASA

This illustration is an orbiter cutaway view with callouts. The orbiter is both the brains and heart of the Space Transportation System (STS). About the same size and weight as a DC-9 aircraft, the orbiter contains the pressurized crew compartment (which can normally carry up to seven crew members), the huge cargo bay, and the three main engines mounted on its aft end. There are three levels to the crew cabin. Uppermost is the flight deck where the commander and the pilot control the mission. The middeck is where the gallery, toilet, sleep stations, and storage and experiment lockers are found for the basic needs of weightless daily living. Also located in the middeck is the airlock hatch into the cargo bay and space beyond. It is through this hatch and airlock that astronauts go to don their spacesuits and marned maneuvering units in preparation for extravehicular activities, more popularly known as spacewalks. The Space Shuttle's cargo bay is adaptable to hundreds of tasks. Large enough to accommodate a tour bus (60 x 15 feet or 18.3 x 4.6 meters), the cargo bay carries satellites, spacecraft, and spacelab scientific laboratories to and from Earth orbit. It is also a work station for astronauts to repair satellites, a foundation from which to erect space structures, and a hold for retrieved satellites to be returned to Earth. Thermal tile insulation and blankets (also known as the thermal protection system or TPS) cover the underbelly, bottom of the wings, and other heat-bearing surfaces of the orbiter to protect it during its fiery reentry into the Earth's atmosphere. The Shuttle's 24,000 individual tiles are made primarily of pure-sand silicate fibers, mixed with a ceramic binder. The solid rocket boosters (SRB's) are designed as an in-house Marshall Space Flight Center project, with United Space Boosters as the assembly and refurbishment contractor. The solid rocket motor (SRM) is provided by the Morton Thiokol Corporation.