
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket is lifted up the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket nears the top of the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket arrives at the top of the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket is halfway up the launch tower . The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
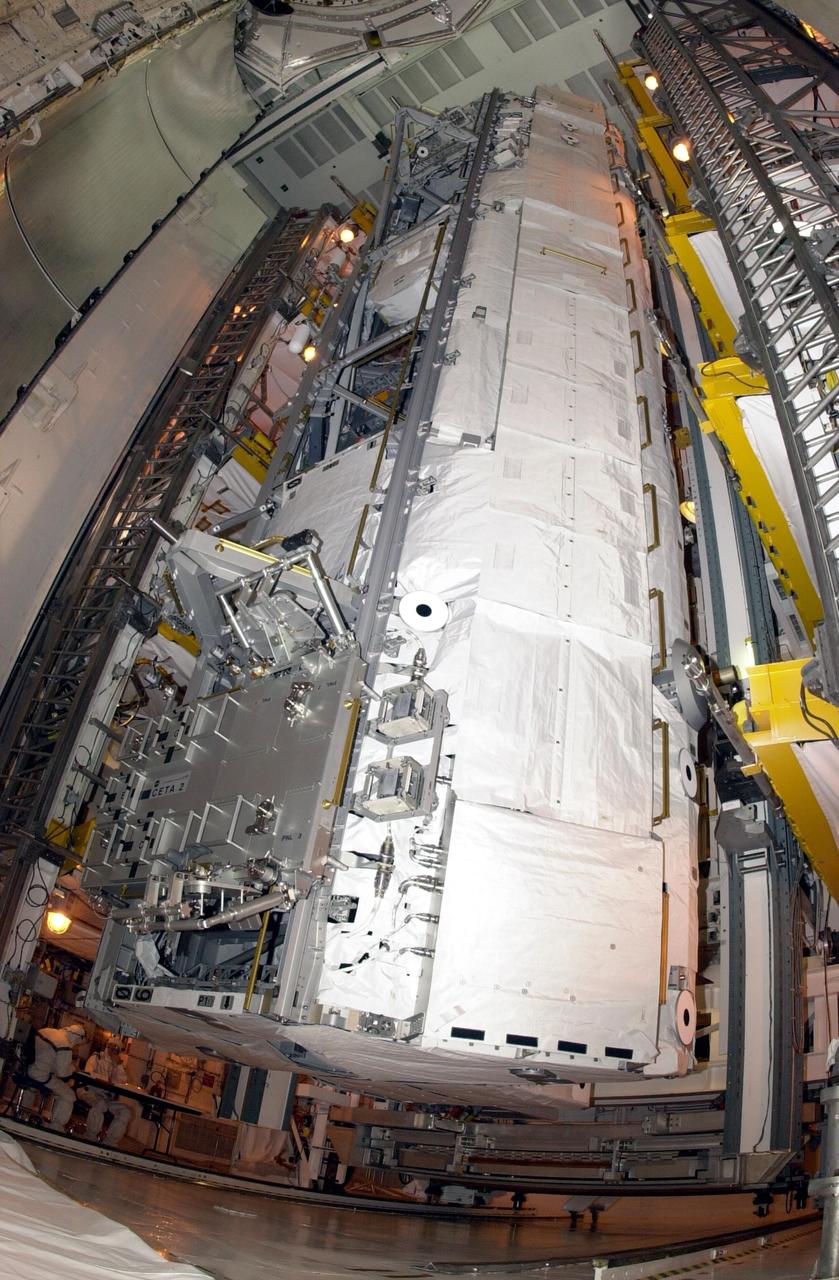
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - From the Payload Changeout Room on Launch Pad 39A, the P1 truss payload, plus the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) cart B, are moved into the payload bay of Space Shuttle Endeavour. Scheduled to launch Nov. 10 on mission STS-113, Endeavour will make the 16th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. The mission will also deliver the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return Expedition 5 to Earth.
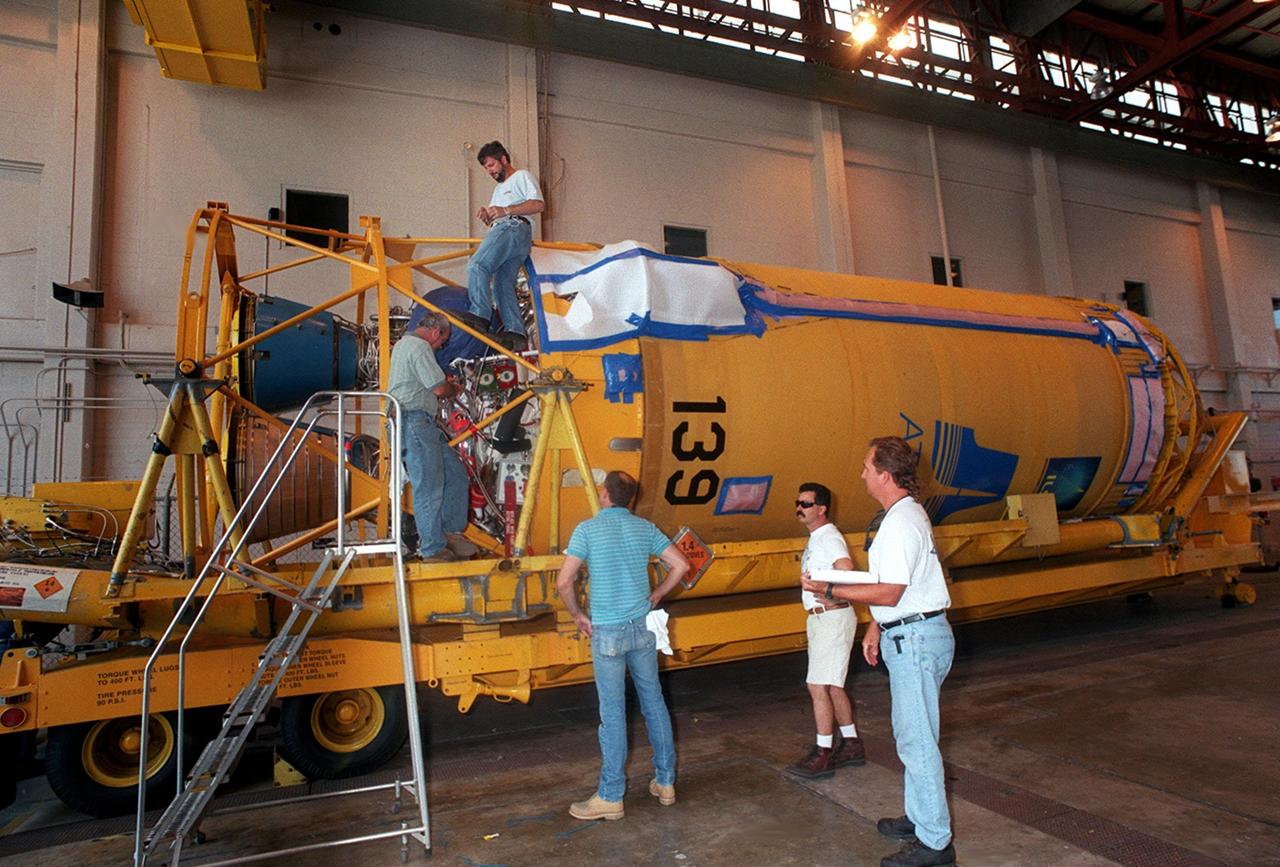

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
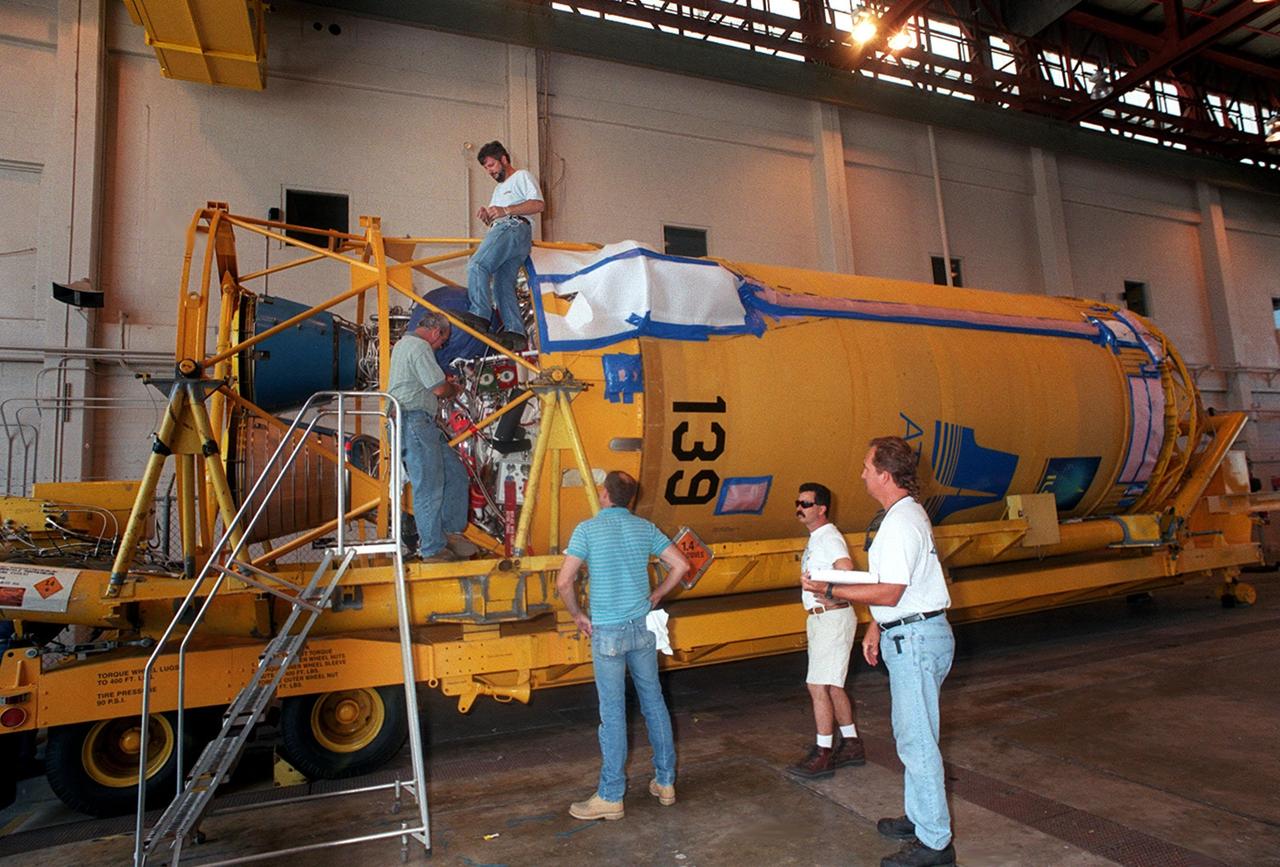

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
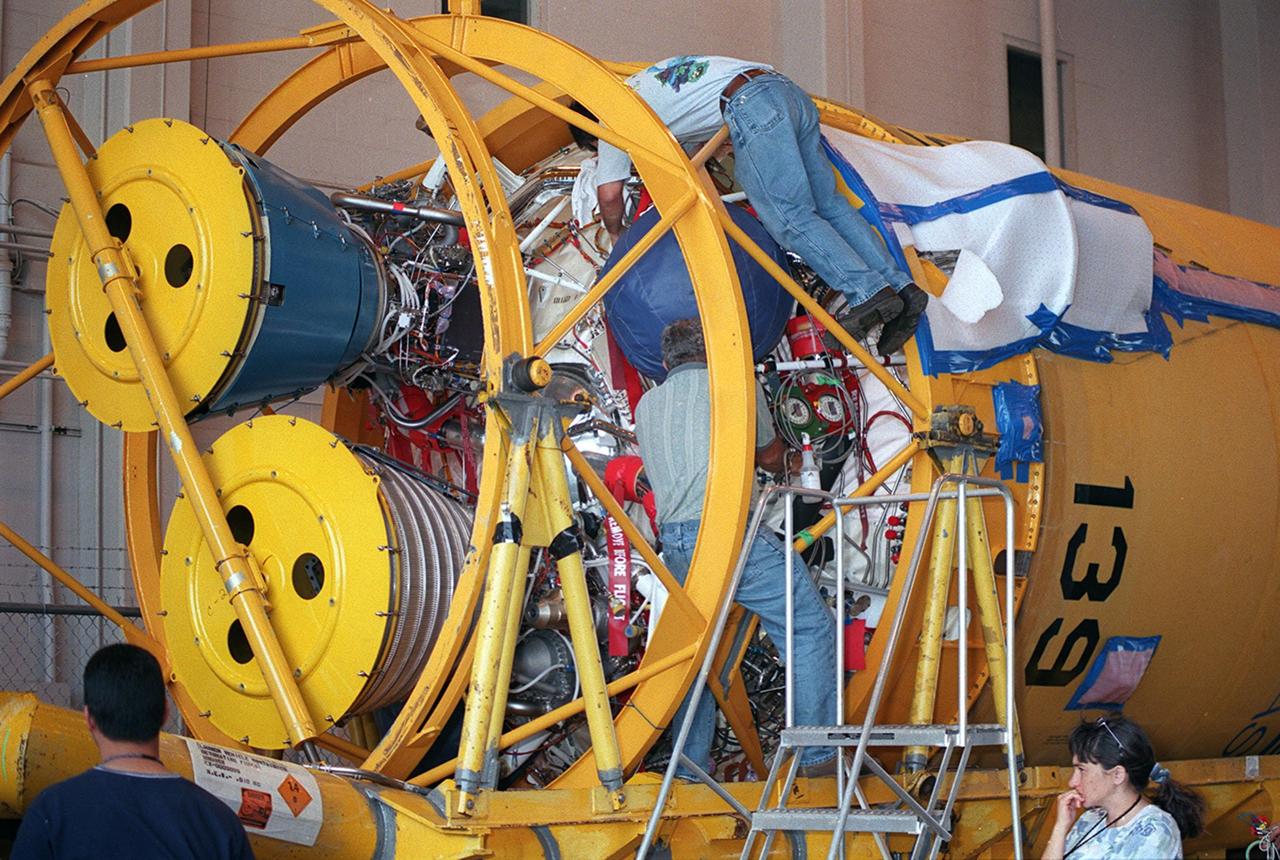

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
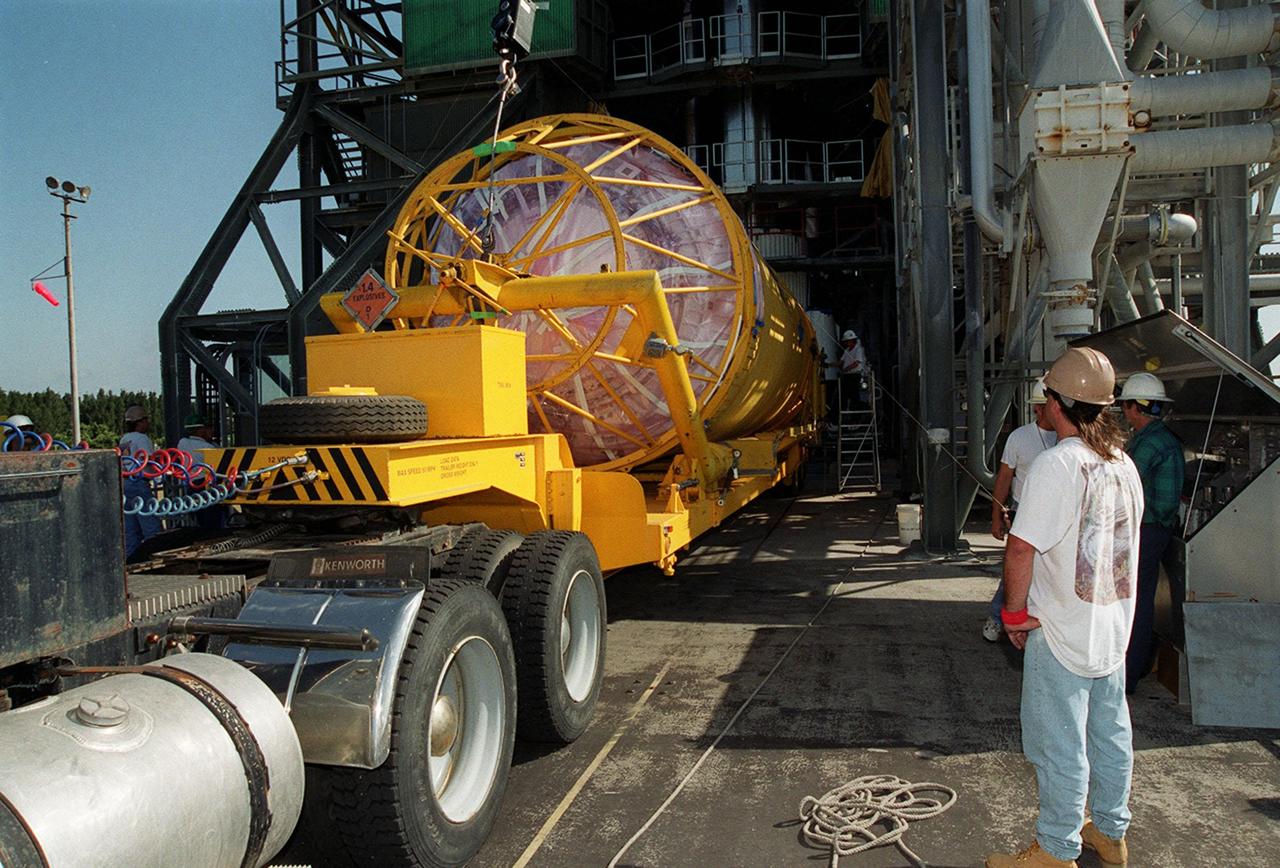

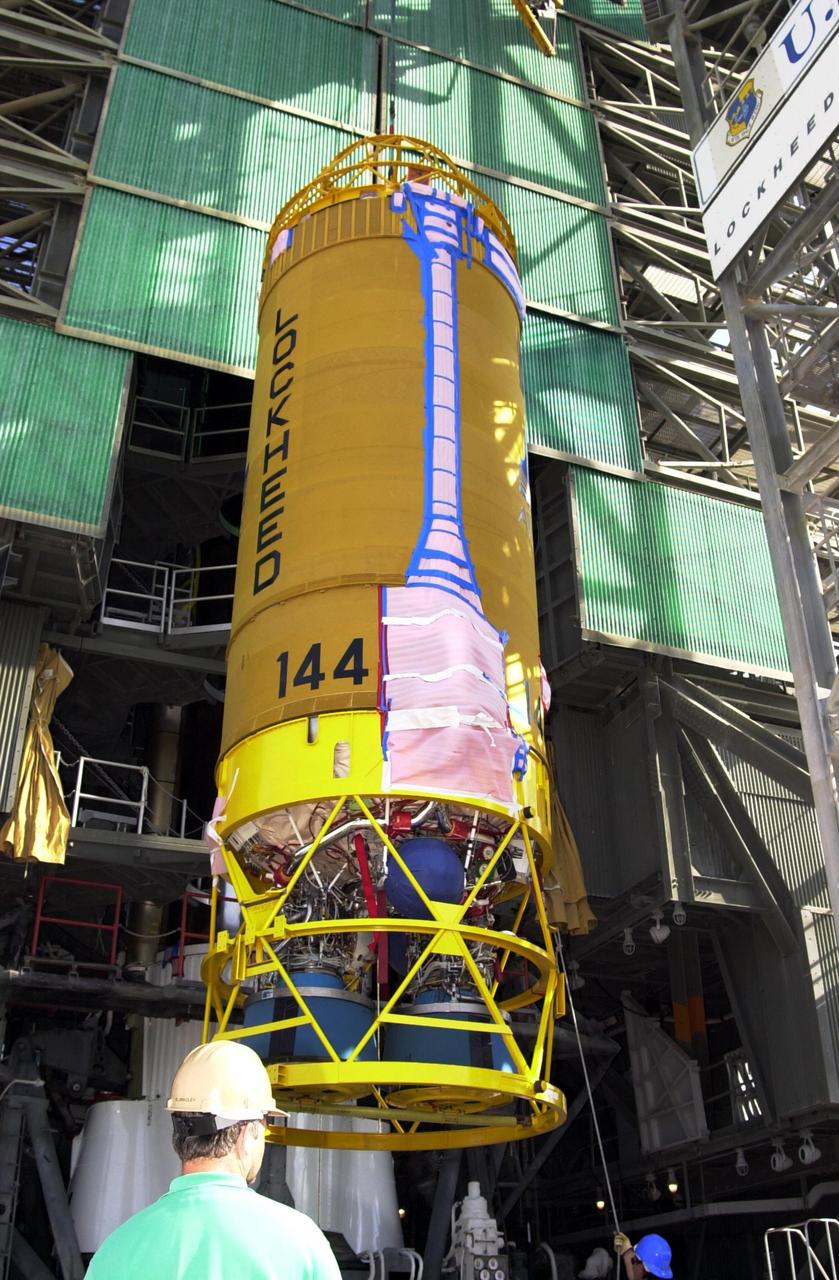
At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Centaur rocket arrives for mating with the Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Centaur upper stage is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
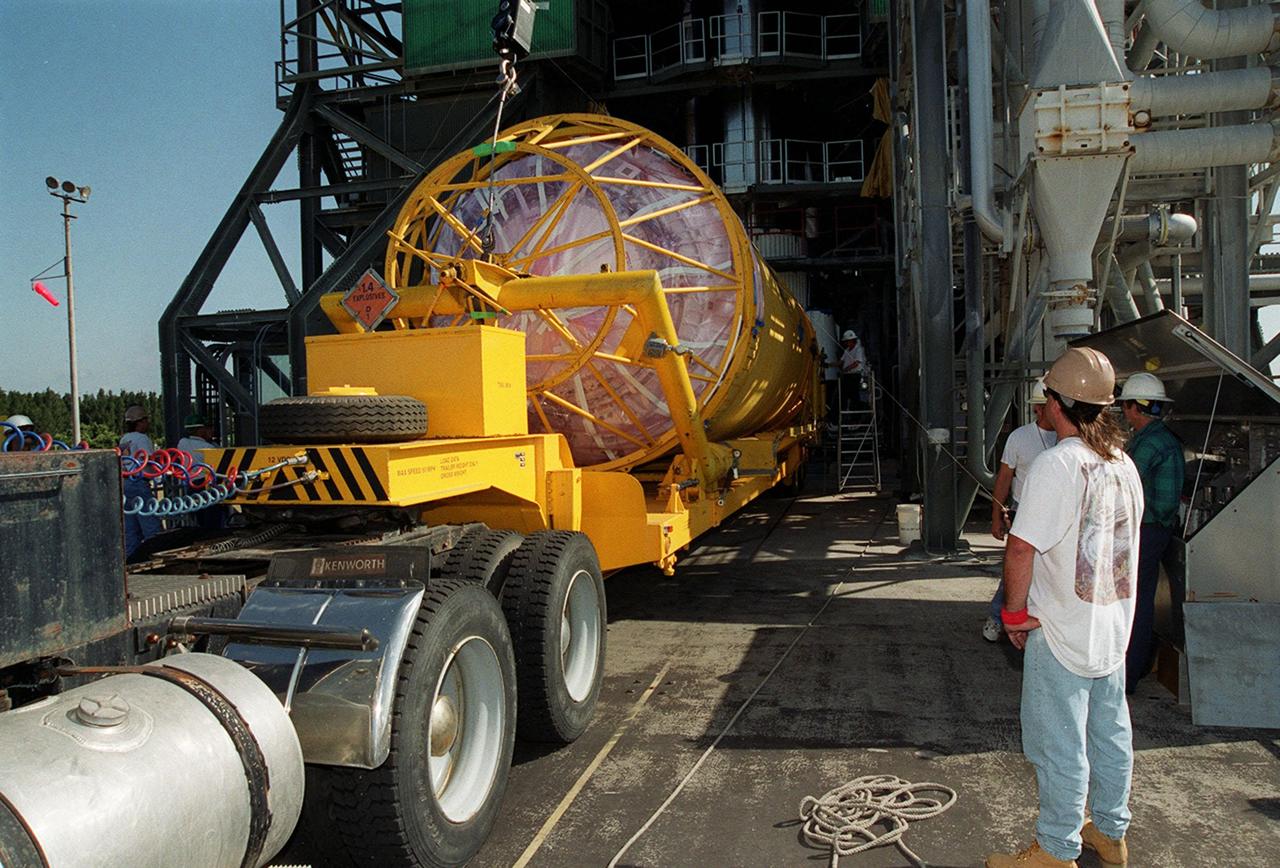

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Centaur rocket arrives for mating with the Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Centaur upper stage is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
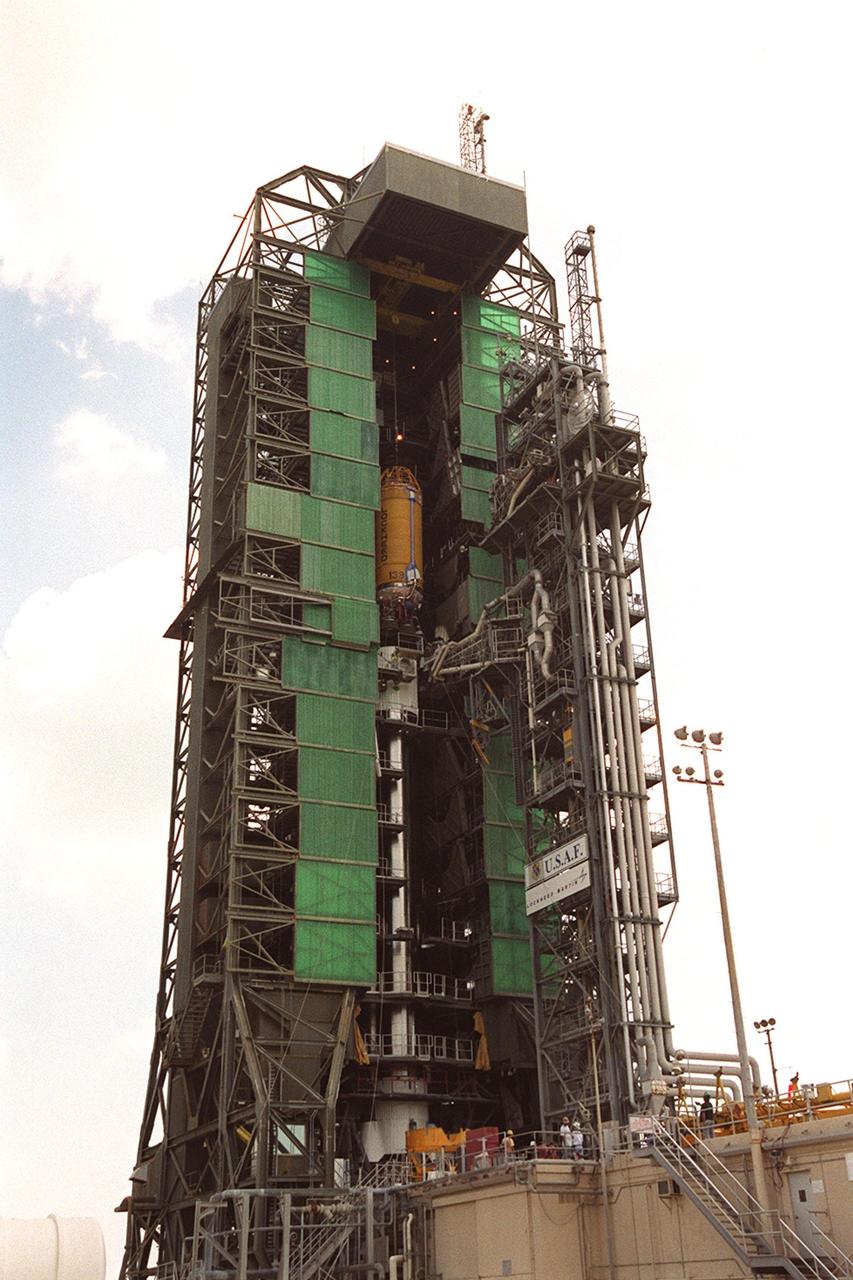

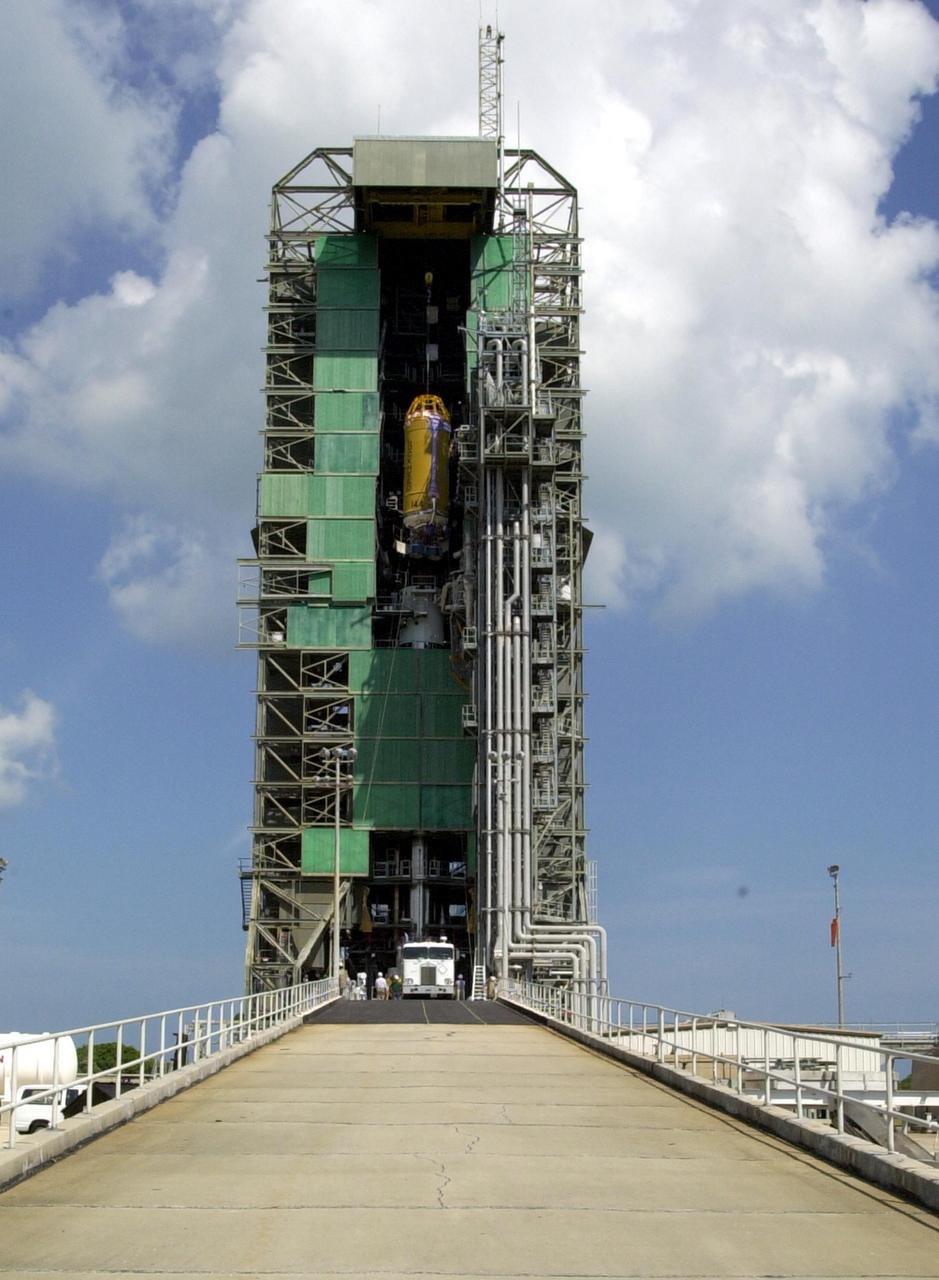
In this long view of the launch tower at Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the upper stage Centaur rocket can be seen as it rises up the tower to be mated to the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already there. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit

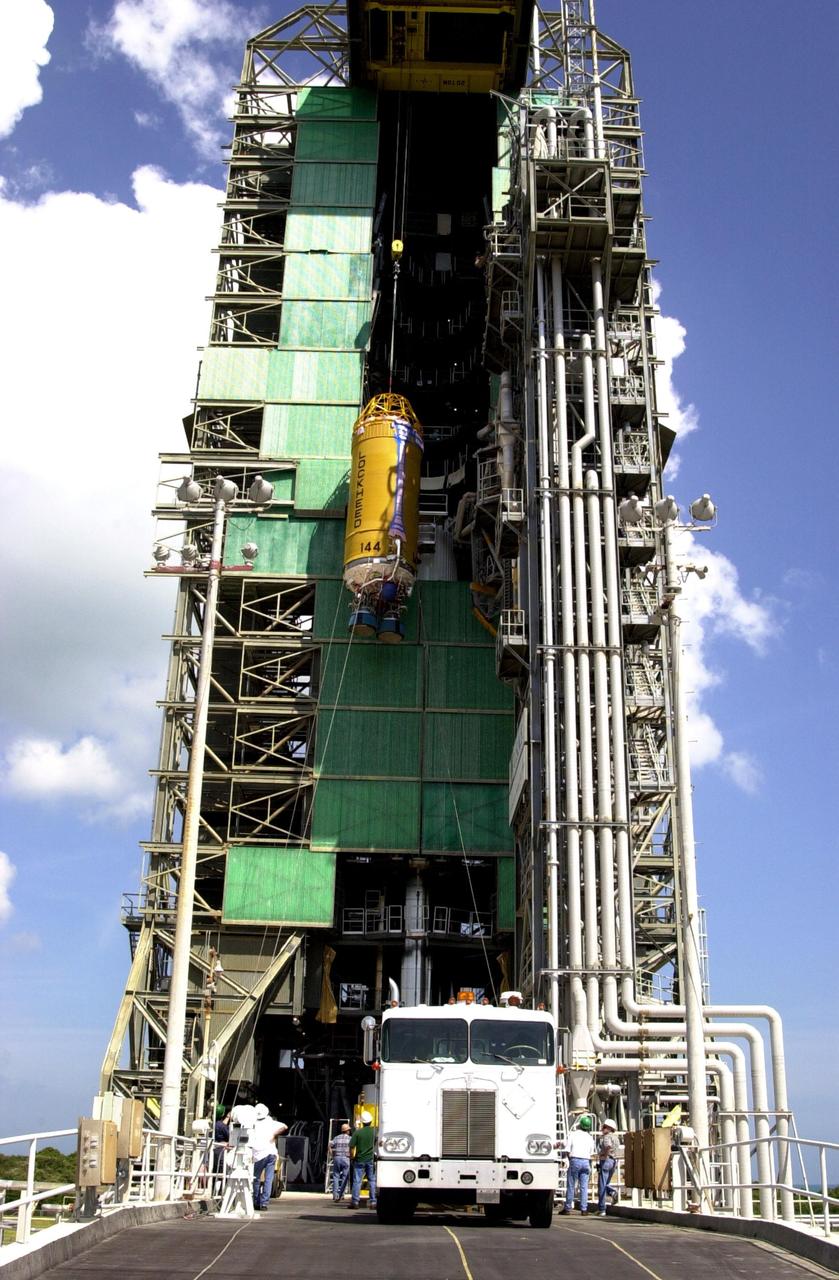
At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers guide the ascent of a Centaur rocket up the launch tower where it will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
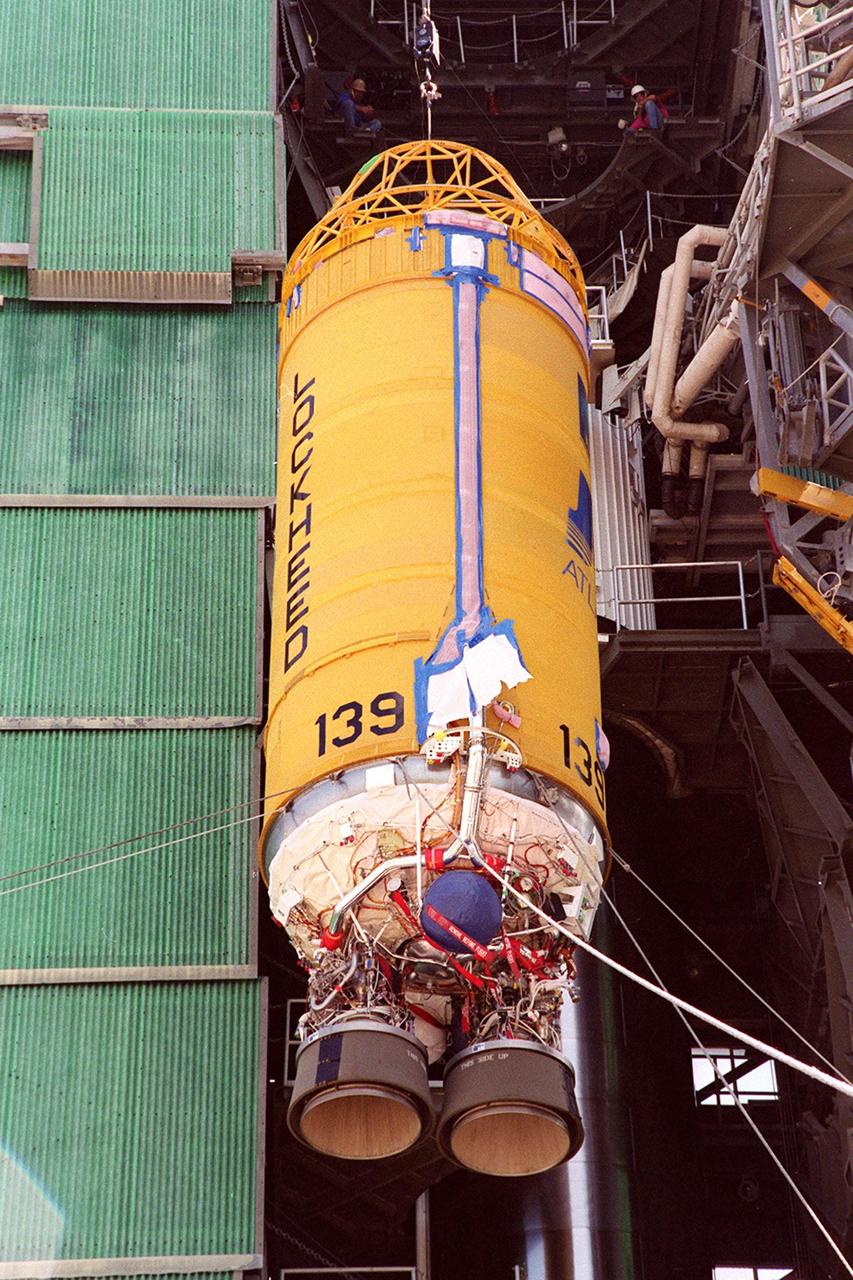

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lines help guide the ascent of a Centaur rocket up the launch tower where it will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
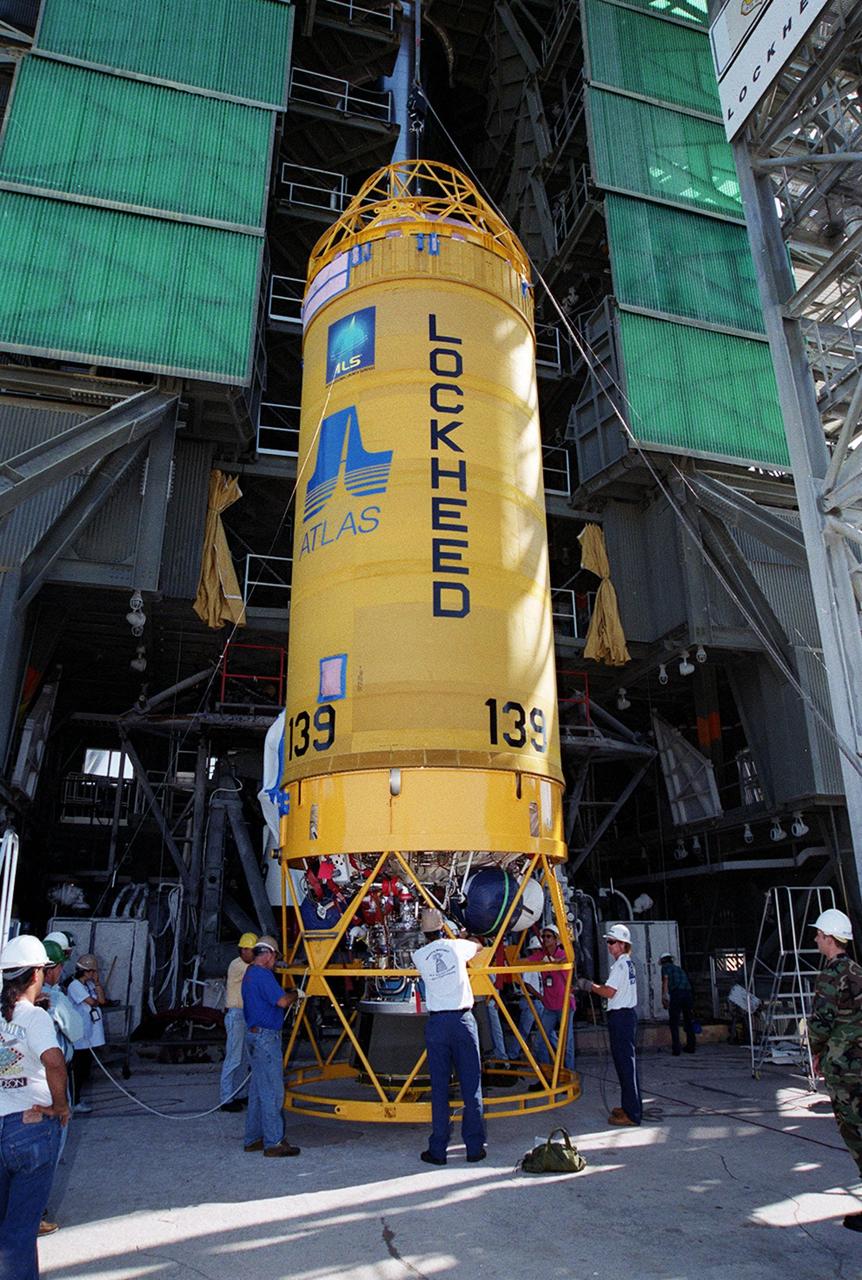

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check out a Centaur rocket for its lift up the launch tower to be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
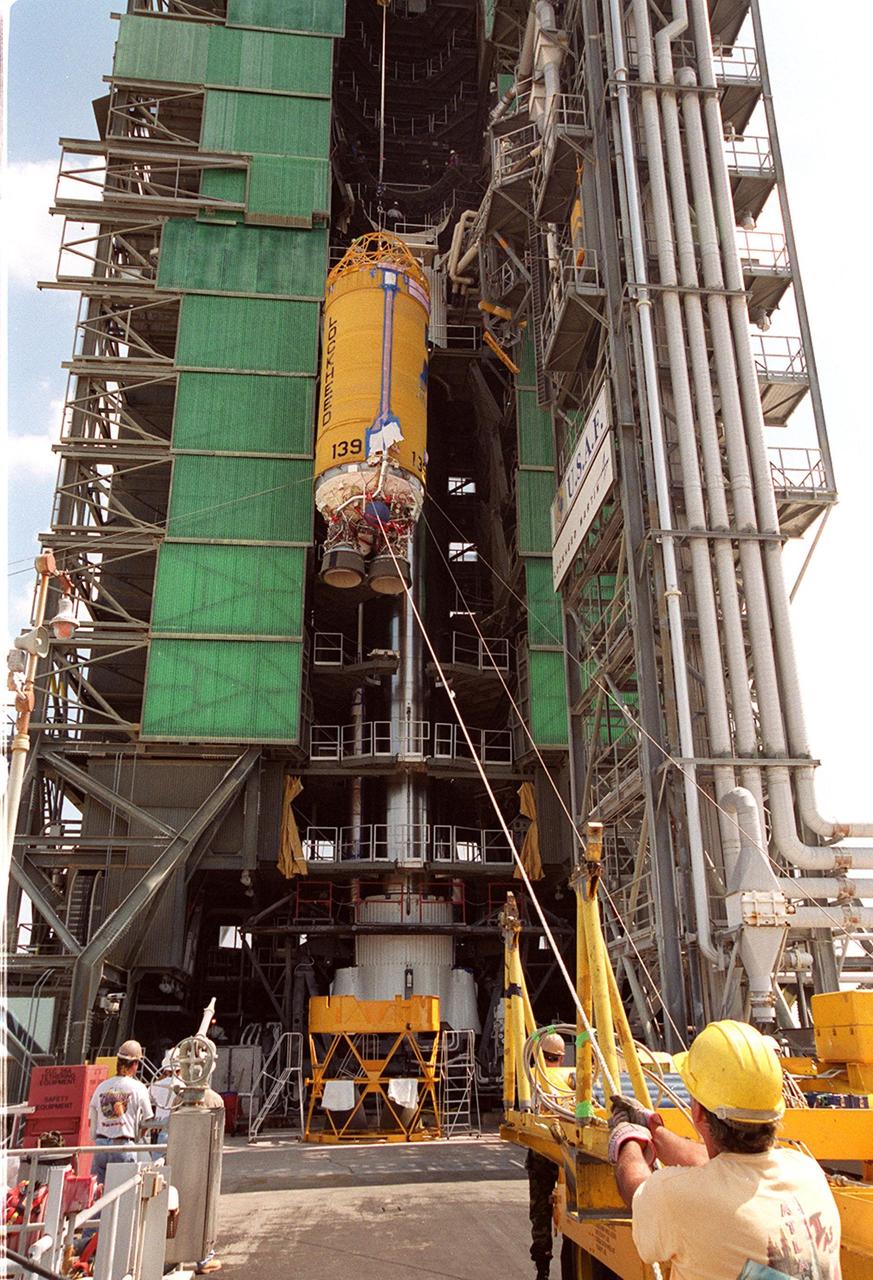

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers guide the ascent of a Centaur rocket up the launch tower where it will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
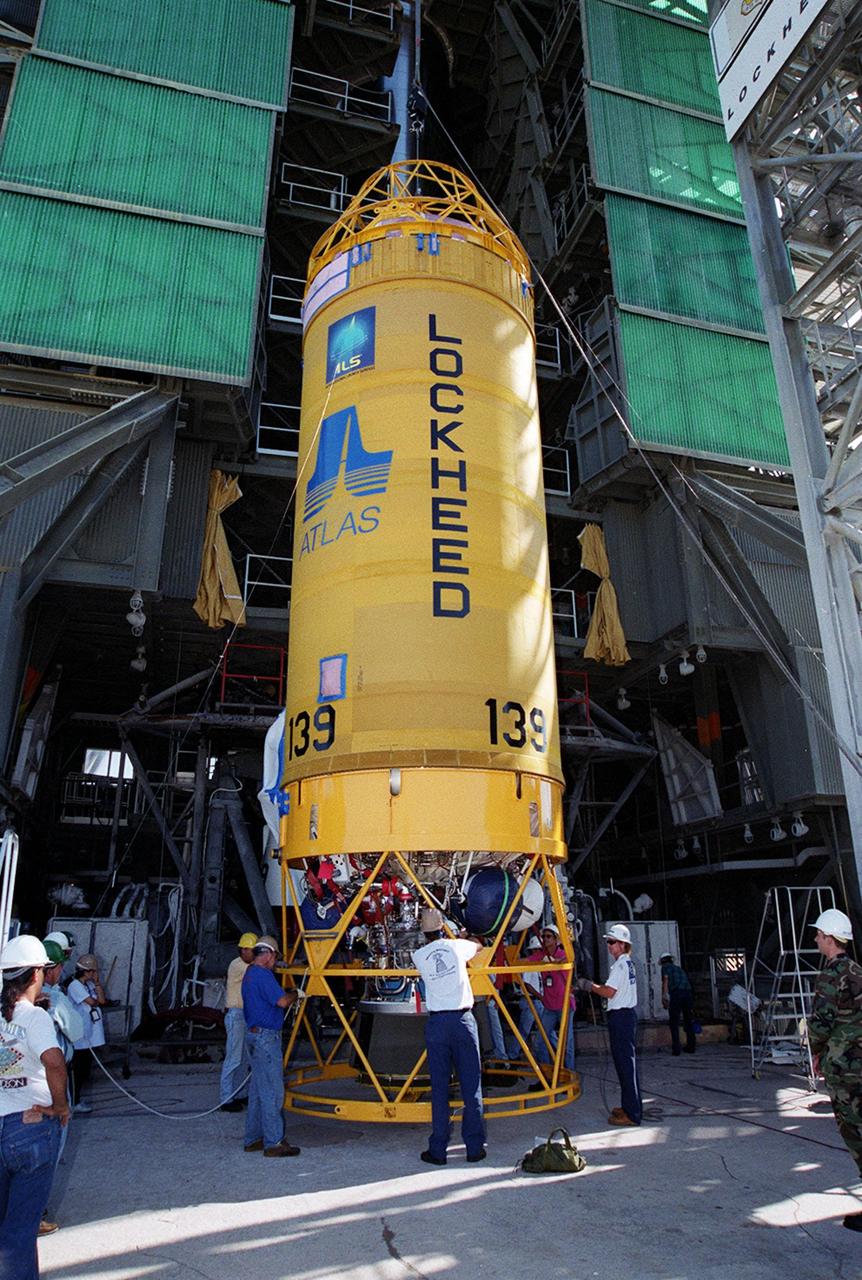

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check out a Centaur rocket for its lift up the launch tower to be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
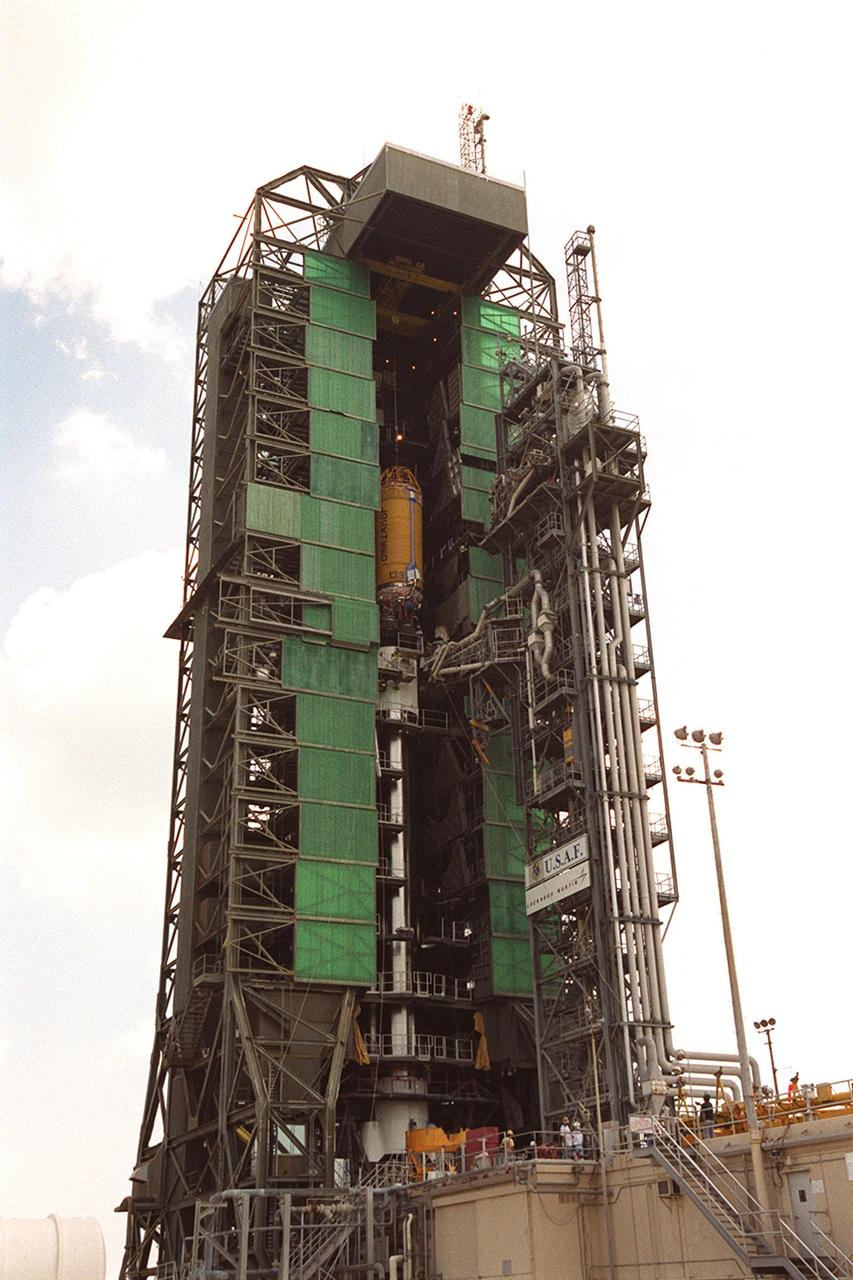

In this long view of the launch tower at Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the upper stage Centaur rocket can be seen as it rises up the tower to be mated to the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already there. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
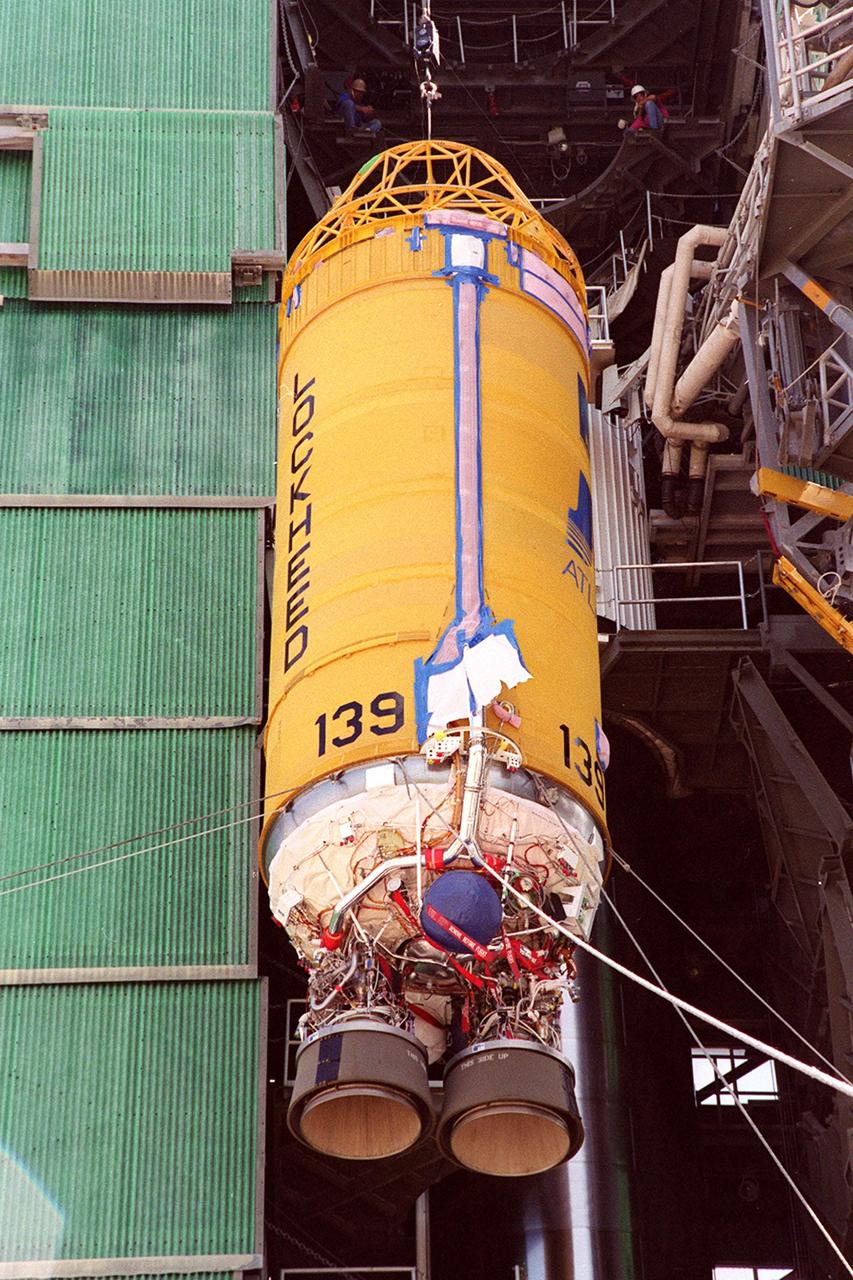

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lines help guide the ascent of a Centaur rocket up the launch tower where it will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
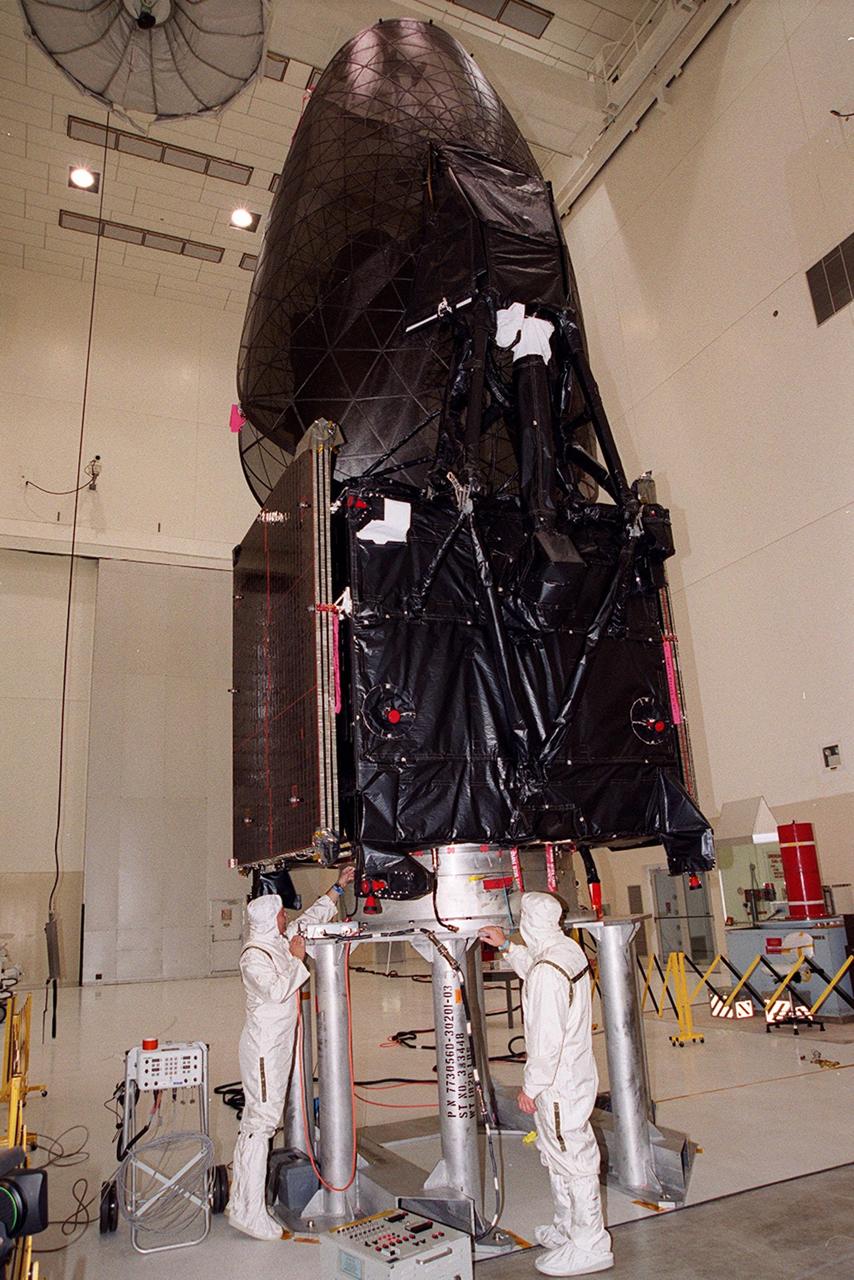

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) conduct electrical testing on the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
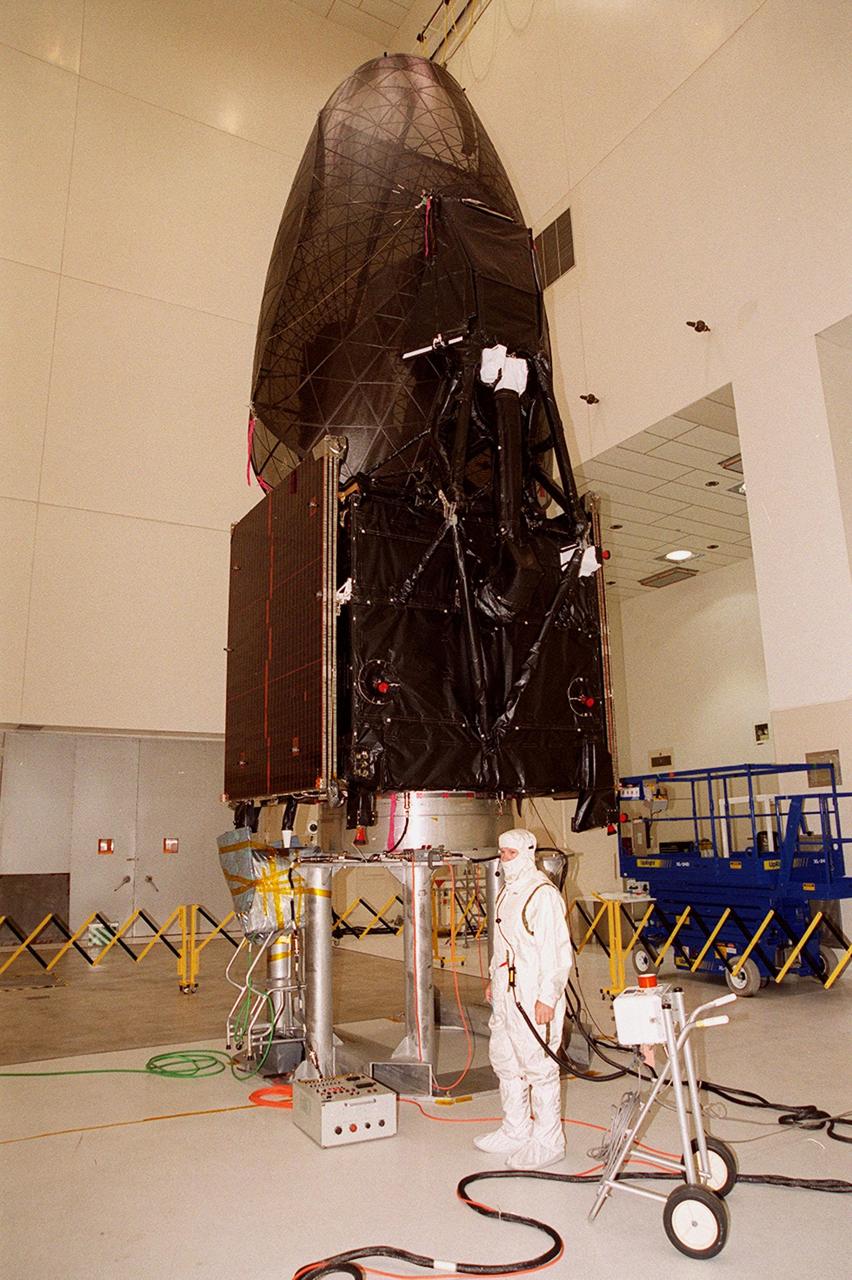

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits on a workstand in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) in order to undergo electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
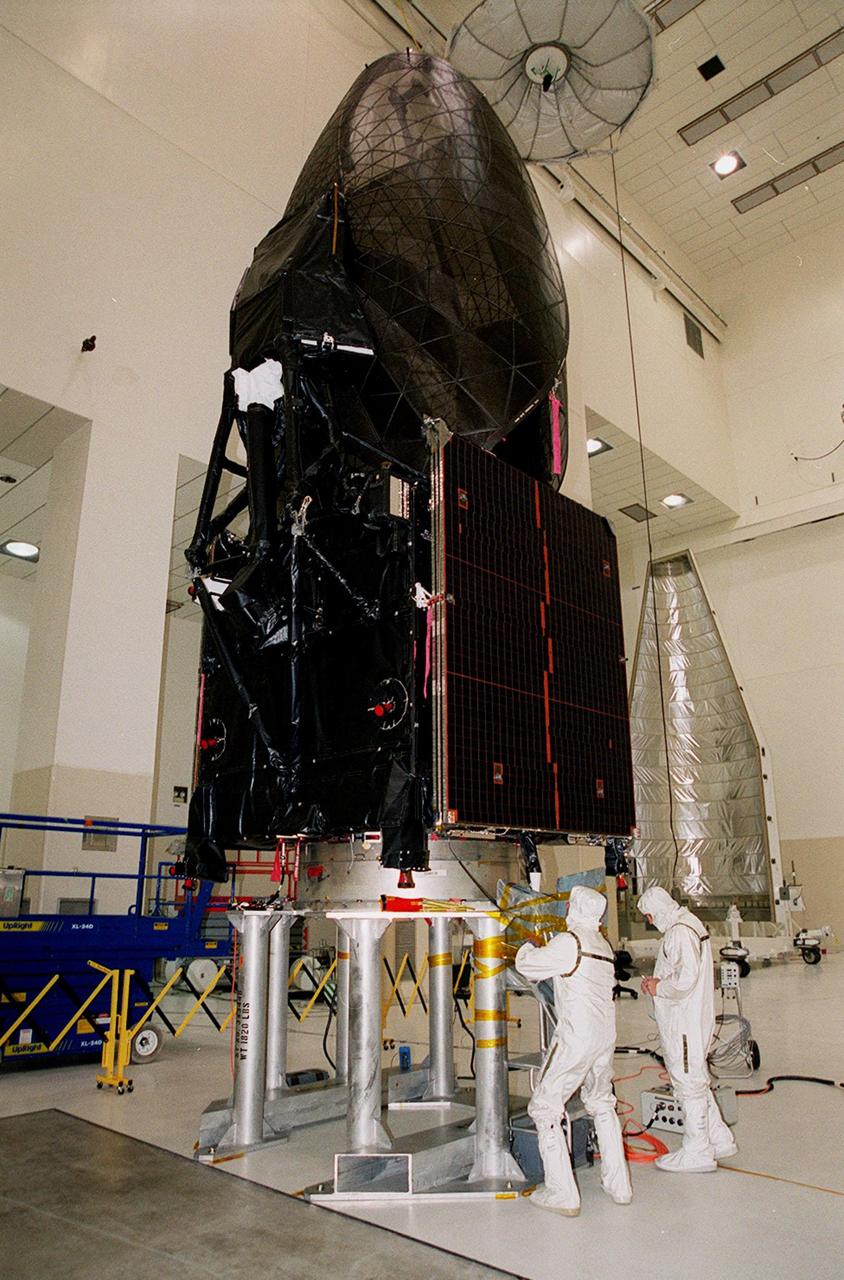

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) prepare the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them for electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
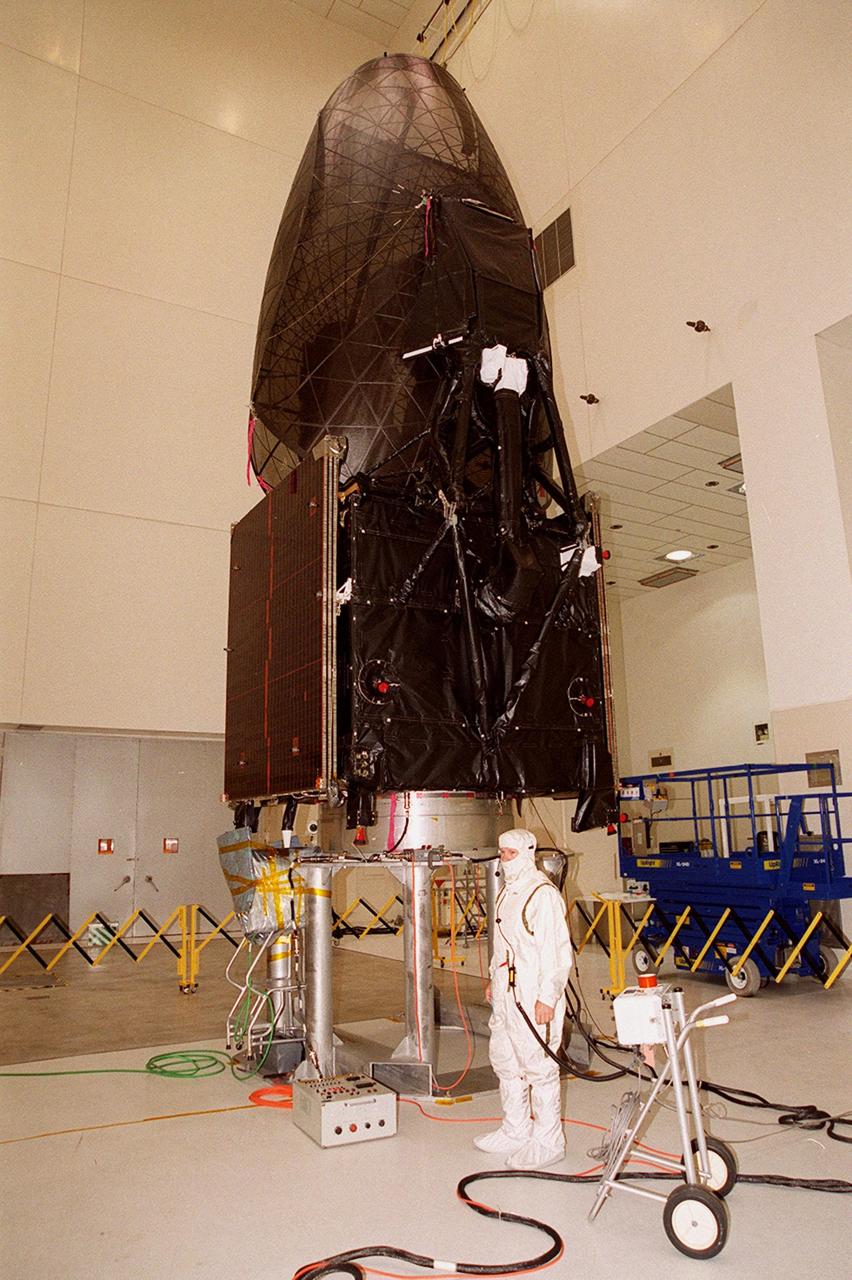

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits on a workstand in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) in order to undergo electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) prepare the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them for electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
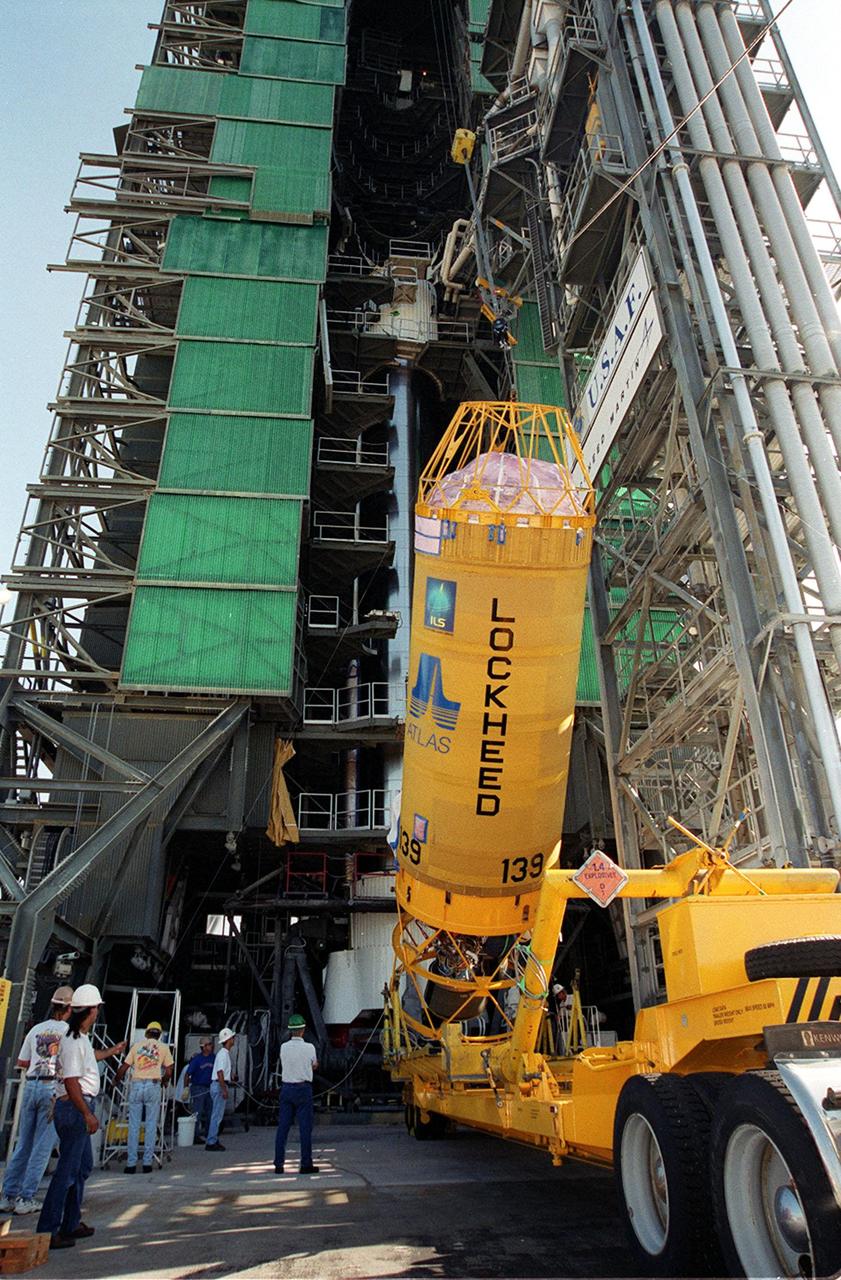

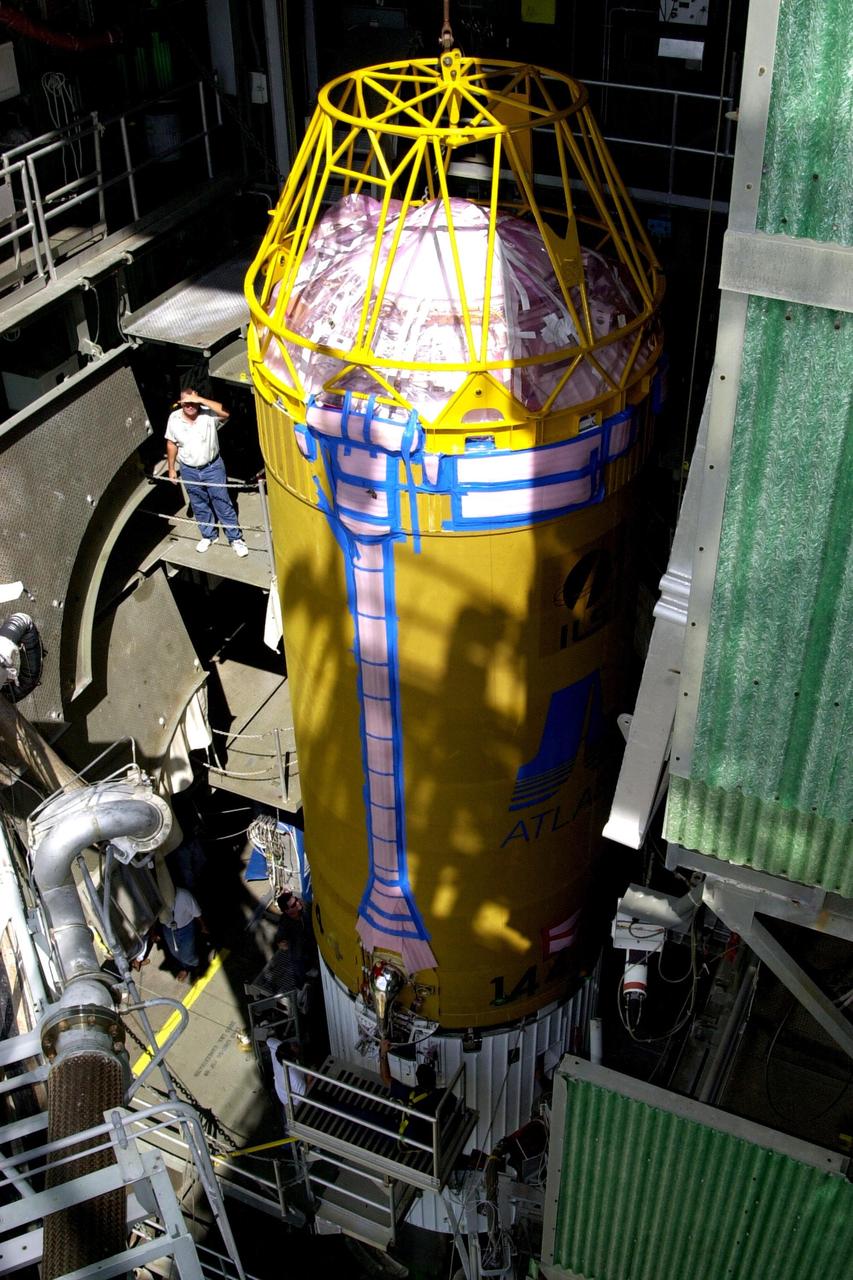
At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position before lifting it up the launch tower. It will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket, already in the tower, to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
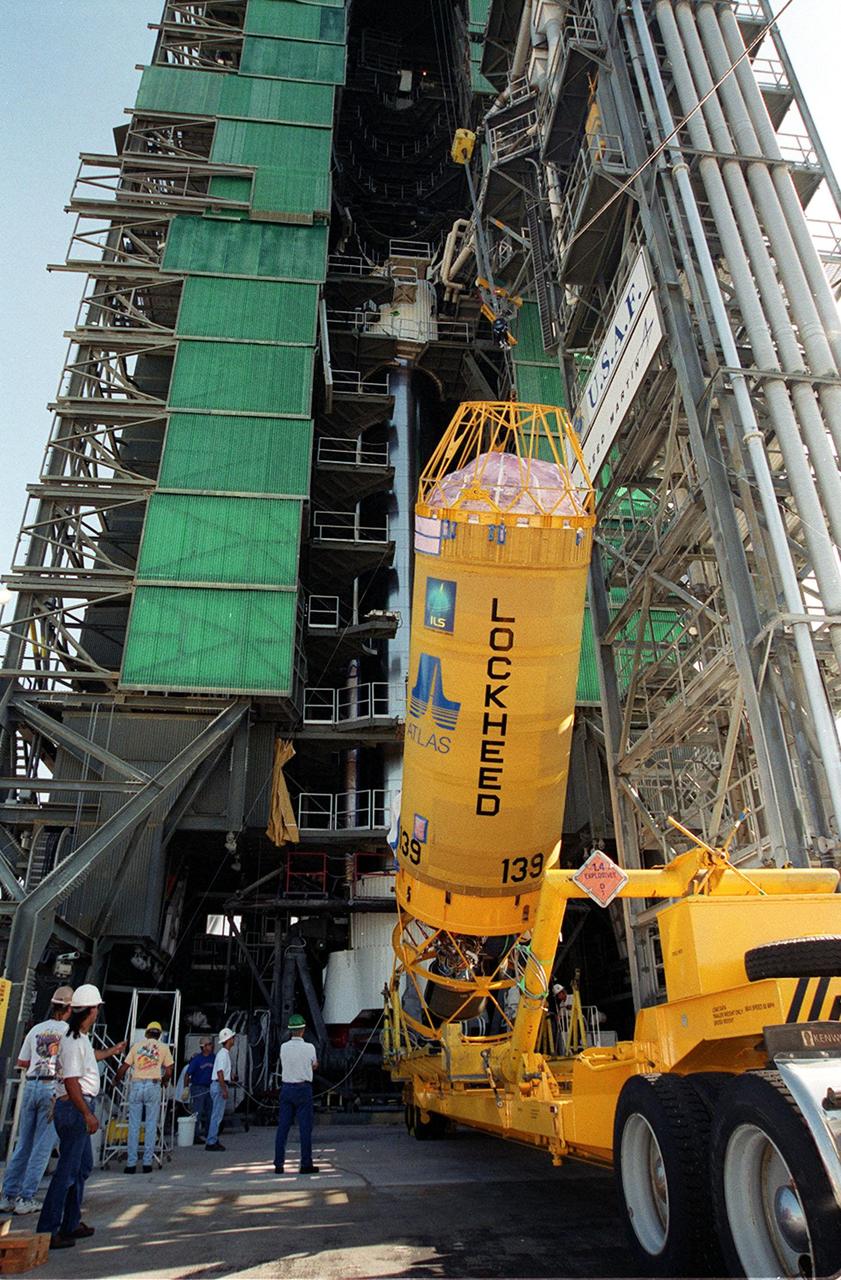

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position before lifting it up the launch tower. It will be mated with the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket, already in the tower, to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
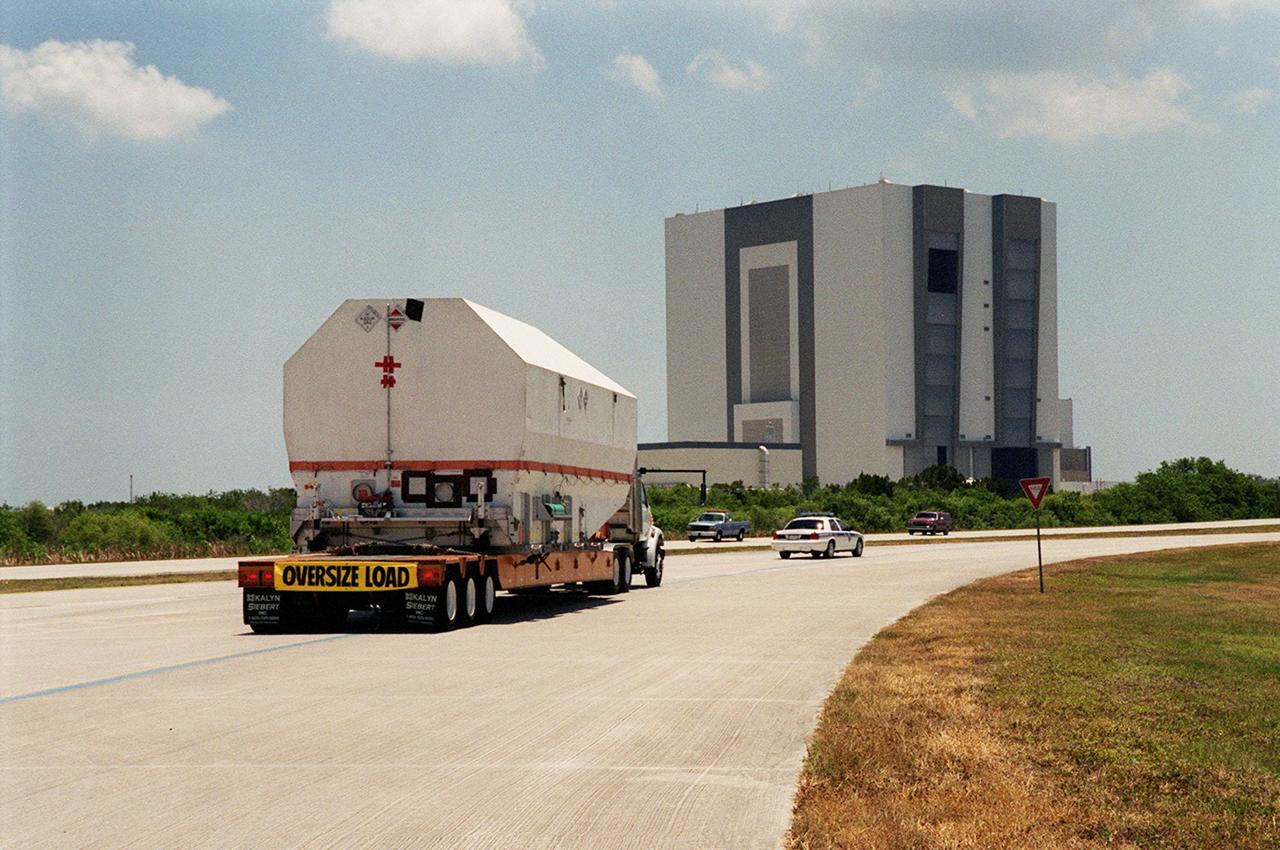

After its arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is transported past the Vehicle Assembly Building (in the background) to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
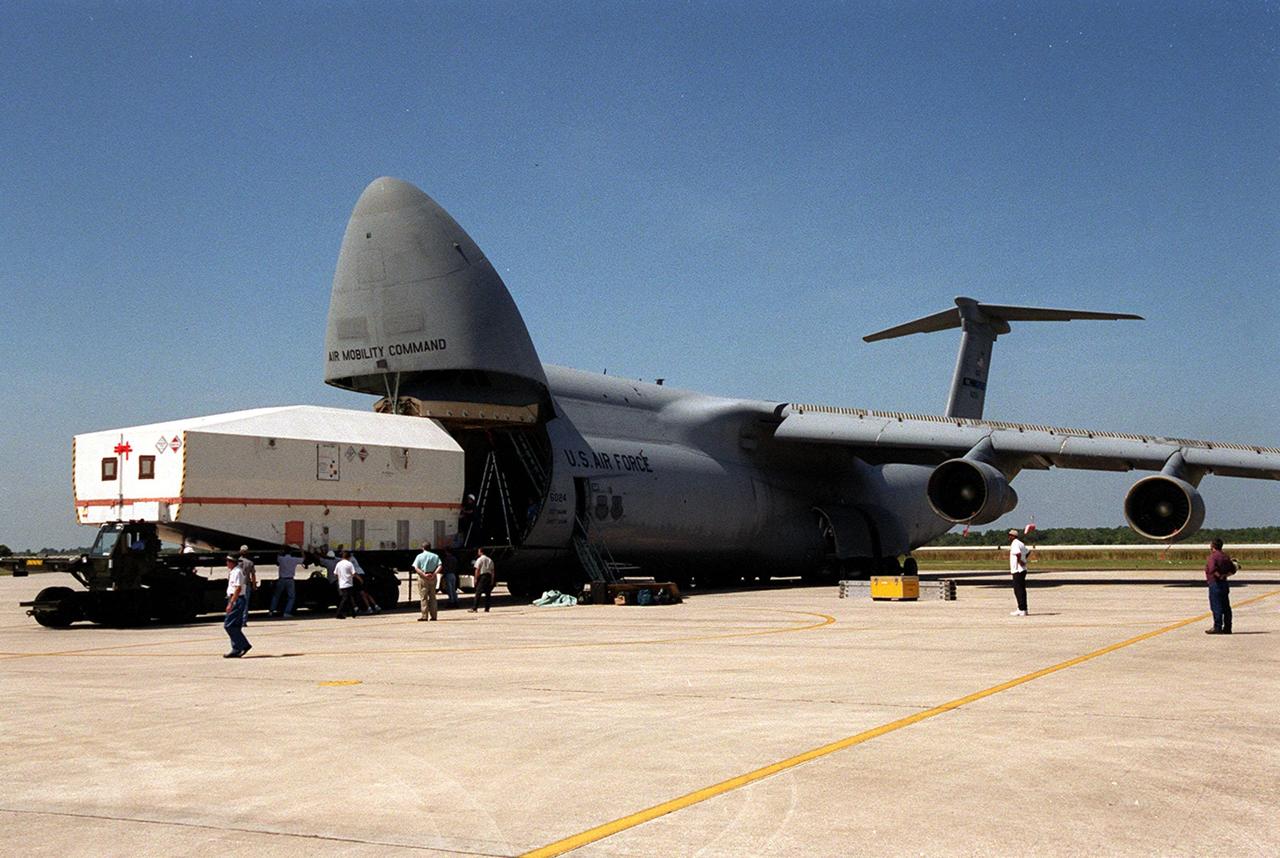

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is offloaded from an air cargo plane. It will be taken to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket

The logo for the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is predominantly displayed on the fairing that will encapsulate the satellite for launch. The fairing is in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) where TDRS is undergoing testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit

The logo for the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is predominantly displayed on the fairing that will encapsulate the satellite for launch. The fairing is in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) where TDRS is undergoing testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
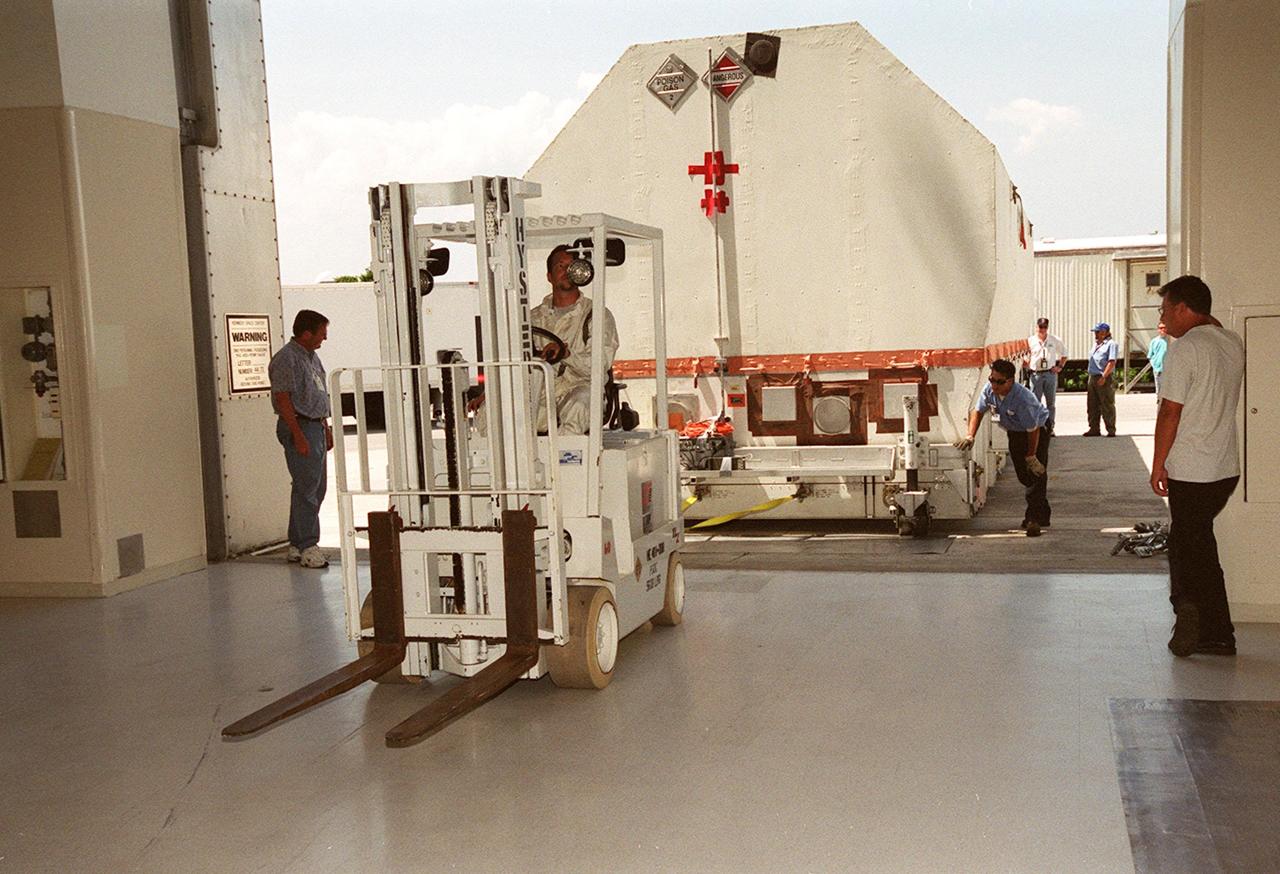

The crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is pulled inside the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) after its arrival at KSC. The TDRS will undergo testing in the SAEF-2. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
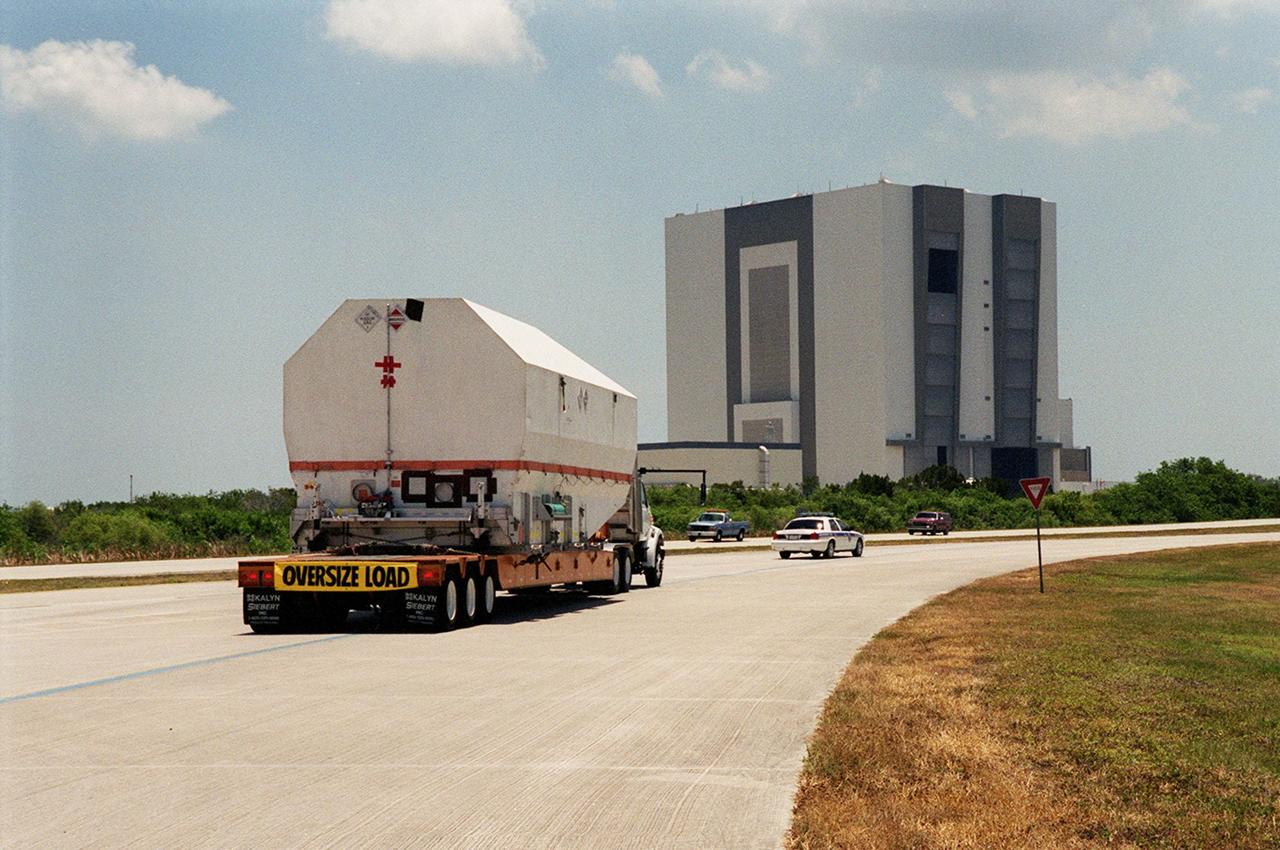

After its arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is transported past the Vehicle Assembly Building (in the background) to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
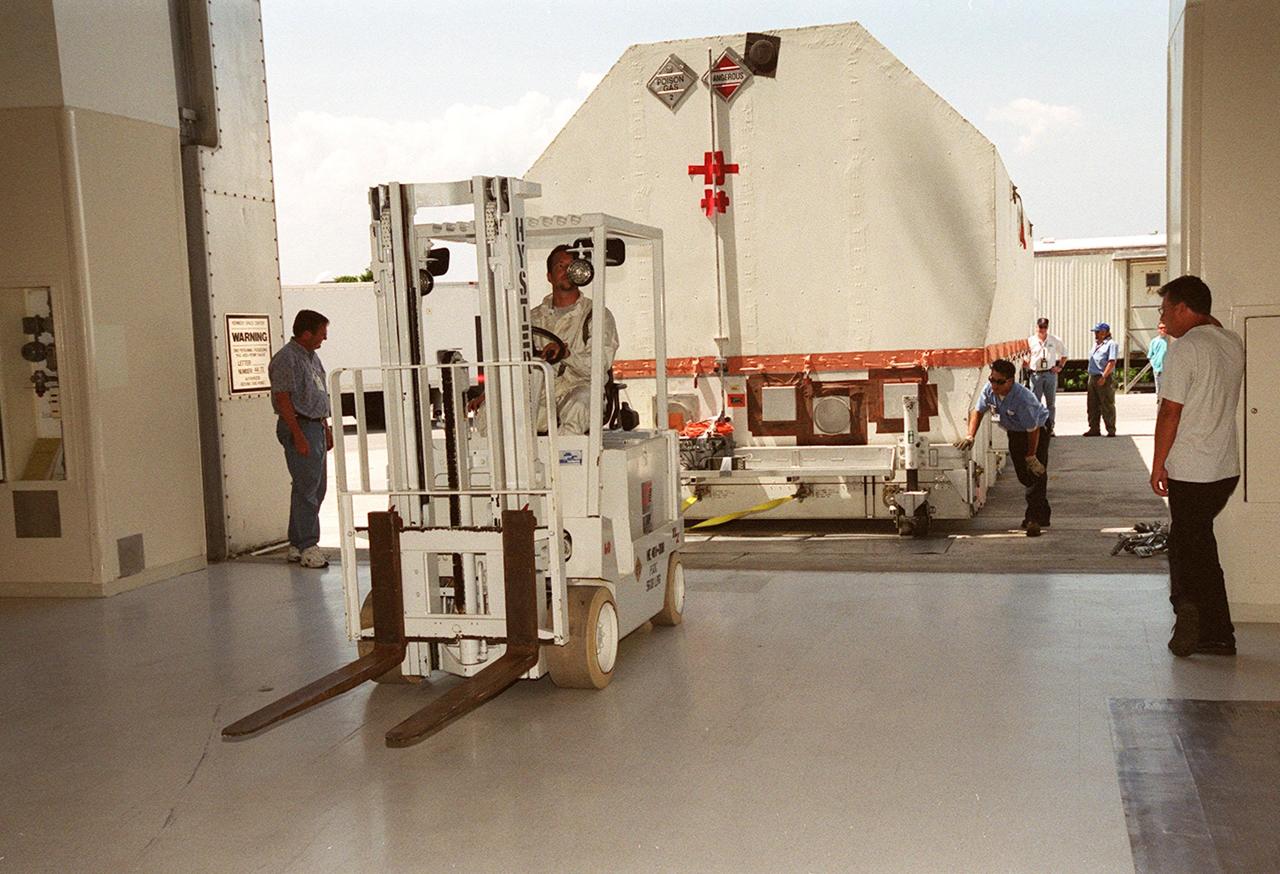

The crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is pulled inside the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) after its arrival at KSC. The TDRS will undergo testing in the SAEF-2. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
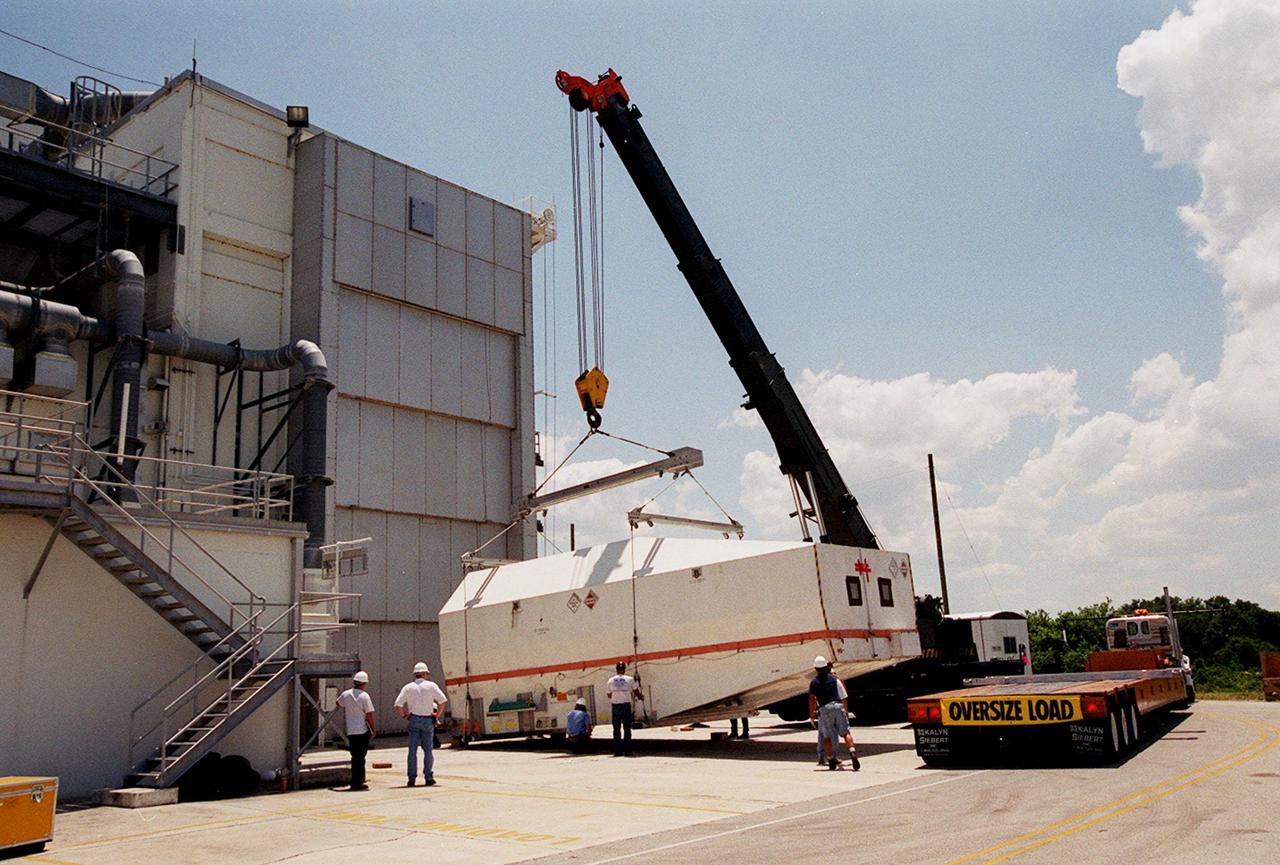

At the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2), a crane lowers the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) onto the ground. It was transported to SAEF-2 on the truckbed at right. The TDRS will undergo testing in SAEF-2. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
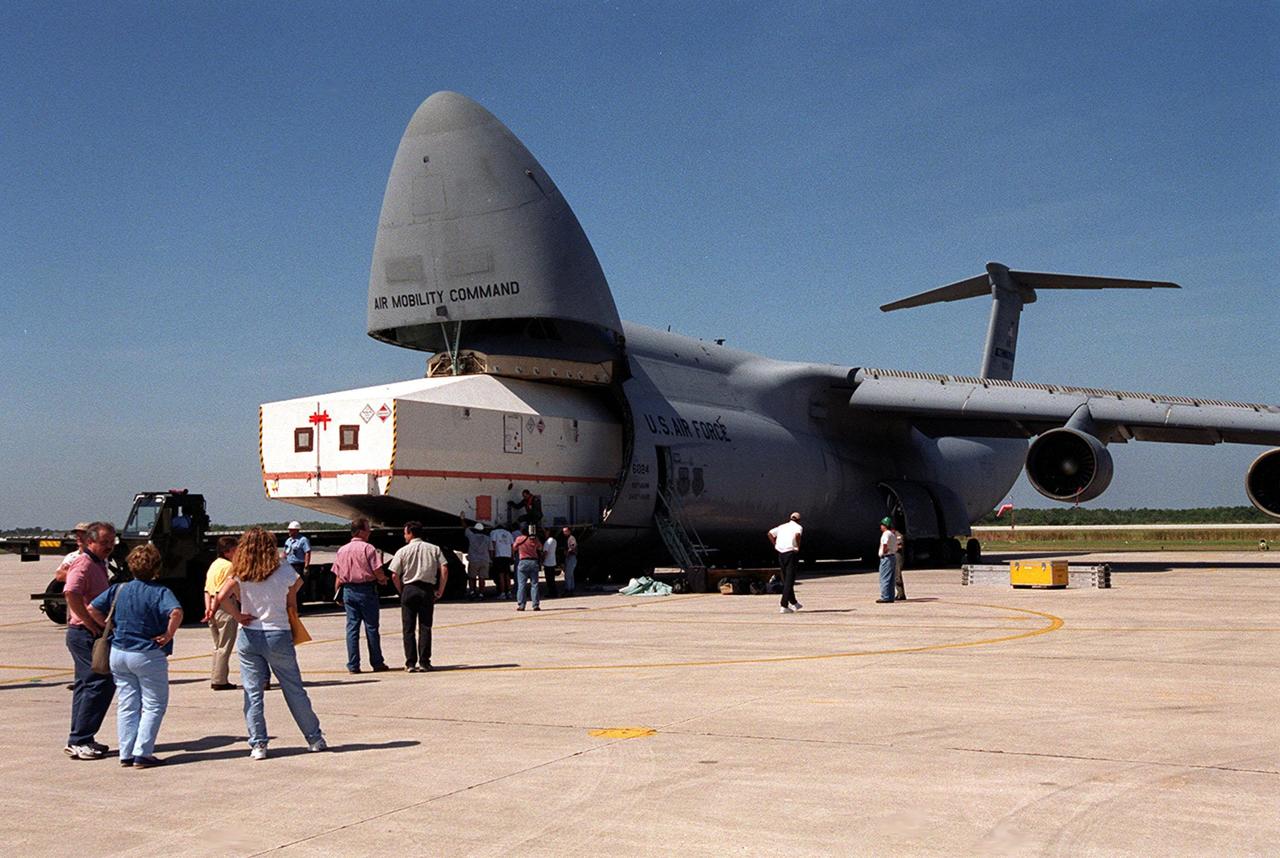

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is offloaded from an air cargo plane. It will be taken to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket
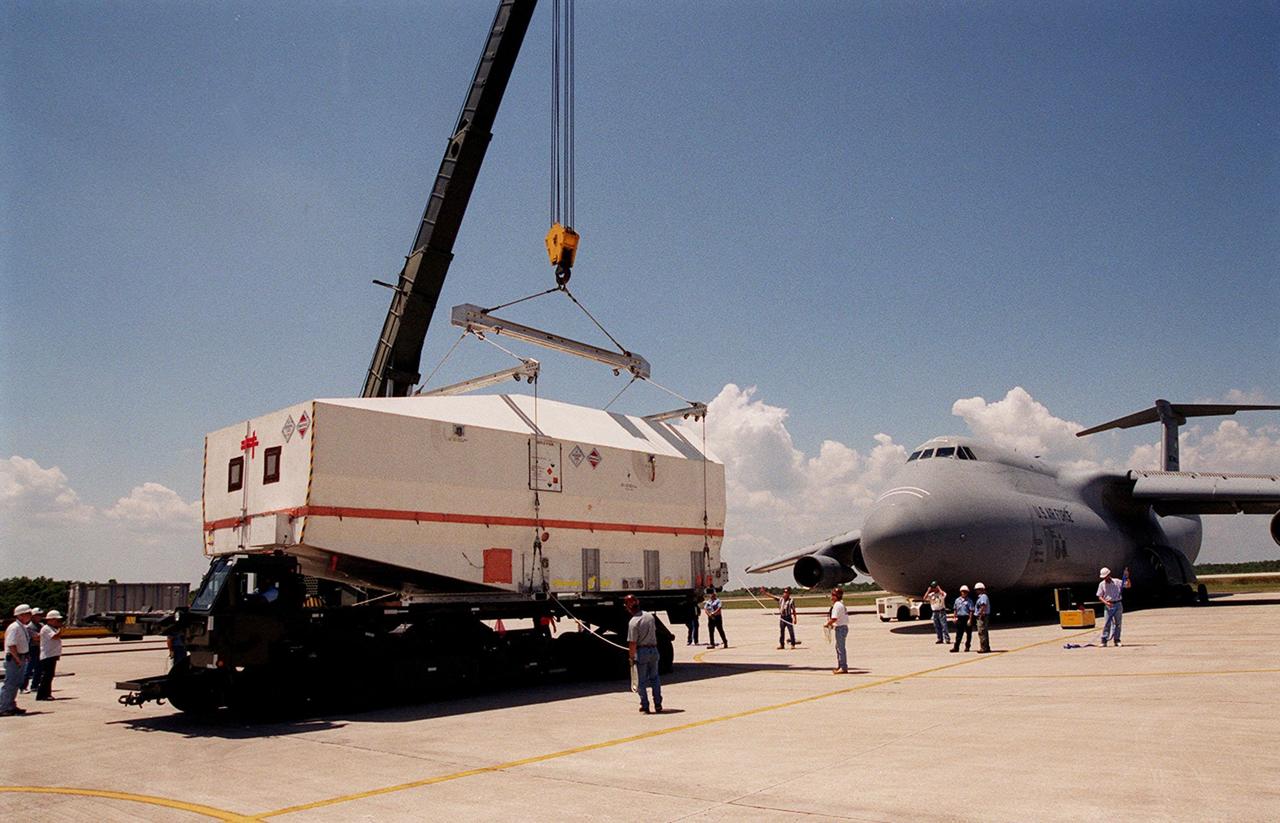

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the crated Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) is placed onto a transporter for its move to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) for testing. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket