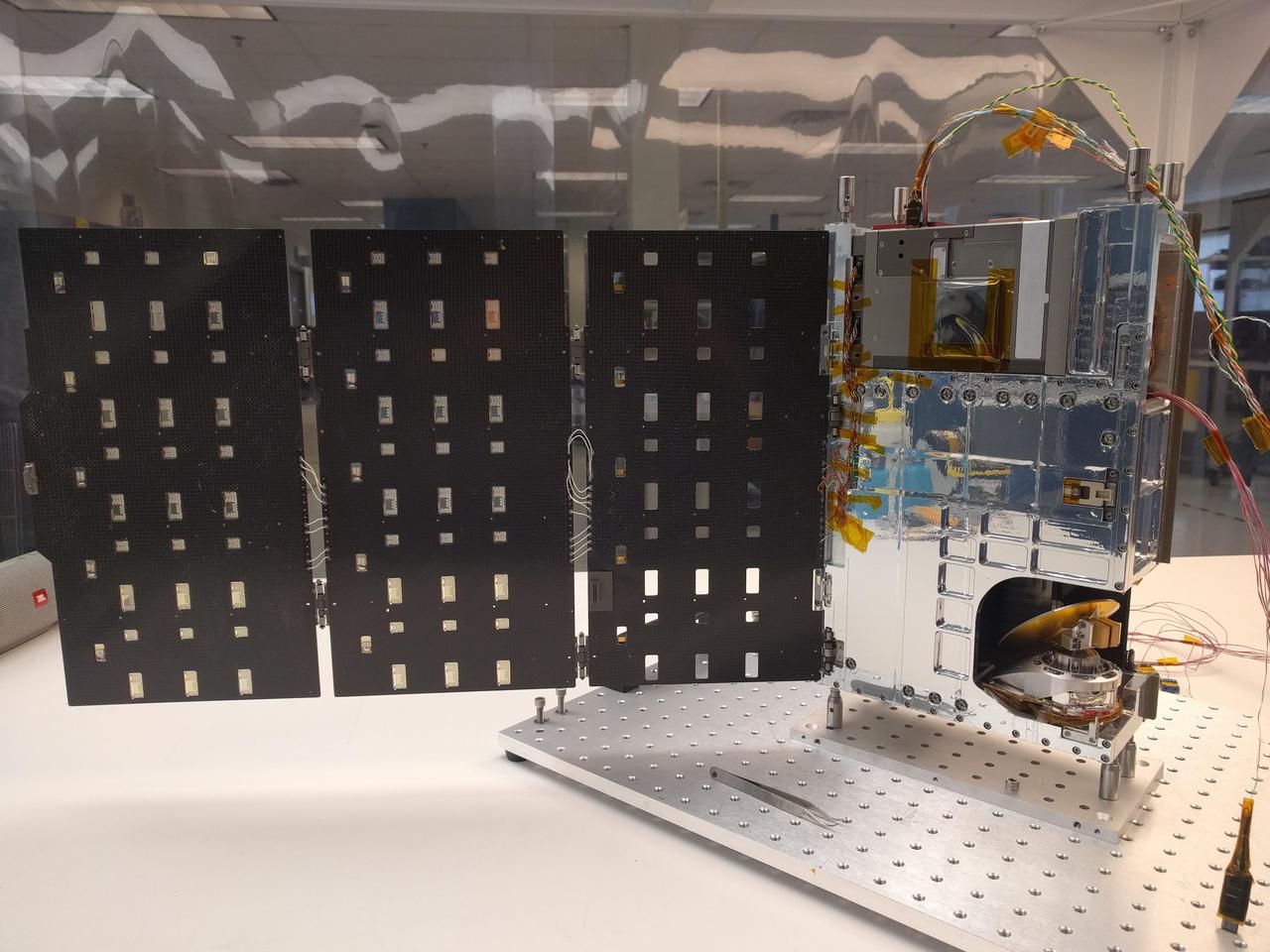
The complete TEMPEST-D spacecraft shown with the solar panels deployed. RainCube, CubeRRT and TEMPEST-D are currently integrated aboard Orbital ATKs Cygnus spacecraft and are awaiting launch on an Antares rocket. After the CubeSats have arrived at the station, they will be deployed into low-Earth orbit and will begin their missions to test these new technologies useful for predicting weather, ensuring data quality, and helping researchers better understand storms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22458
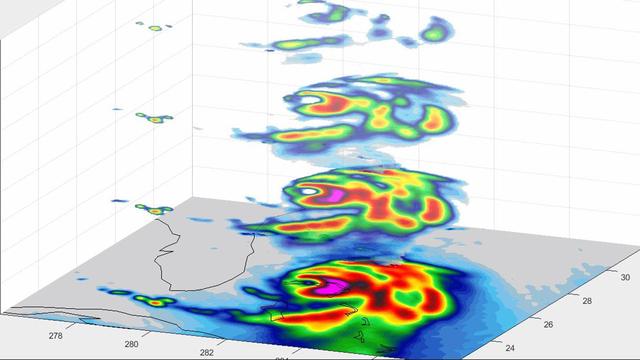
In this animation, TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Florida at 2 a.m. EDT on Sep. 3, 2019 (11 p.m. PDT on Sept. 2, 2019). At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing different depths of the hurricane with areas with heavy rainfall and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors indicate moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow, red and pink areas correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23431
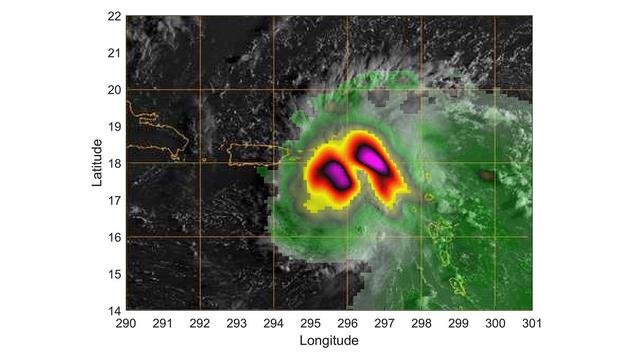
TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Puerto Rico in the early morning hours (local time) of Aug. 28, 2019. At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing areas with strong rain and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors show moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow to pink colors correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23414

The RainCube 6U CubeSat with fully-deployed antenna. RainCube, CubeRRT and TEMPEST-D are currently integrated aboard Orbital ATKs Cygnus spacecraft and are awaiting launch on an Antares rocket. After the CubeSats have arrived at the station, they will be deployed into low-Earth orbit and will begin their missions to test these new technologies useful for predicting weather, ensuring data quality, and helping researchers better understand storms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22457