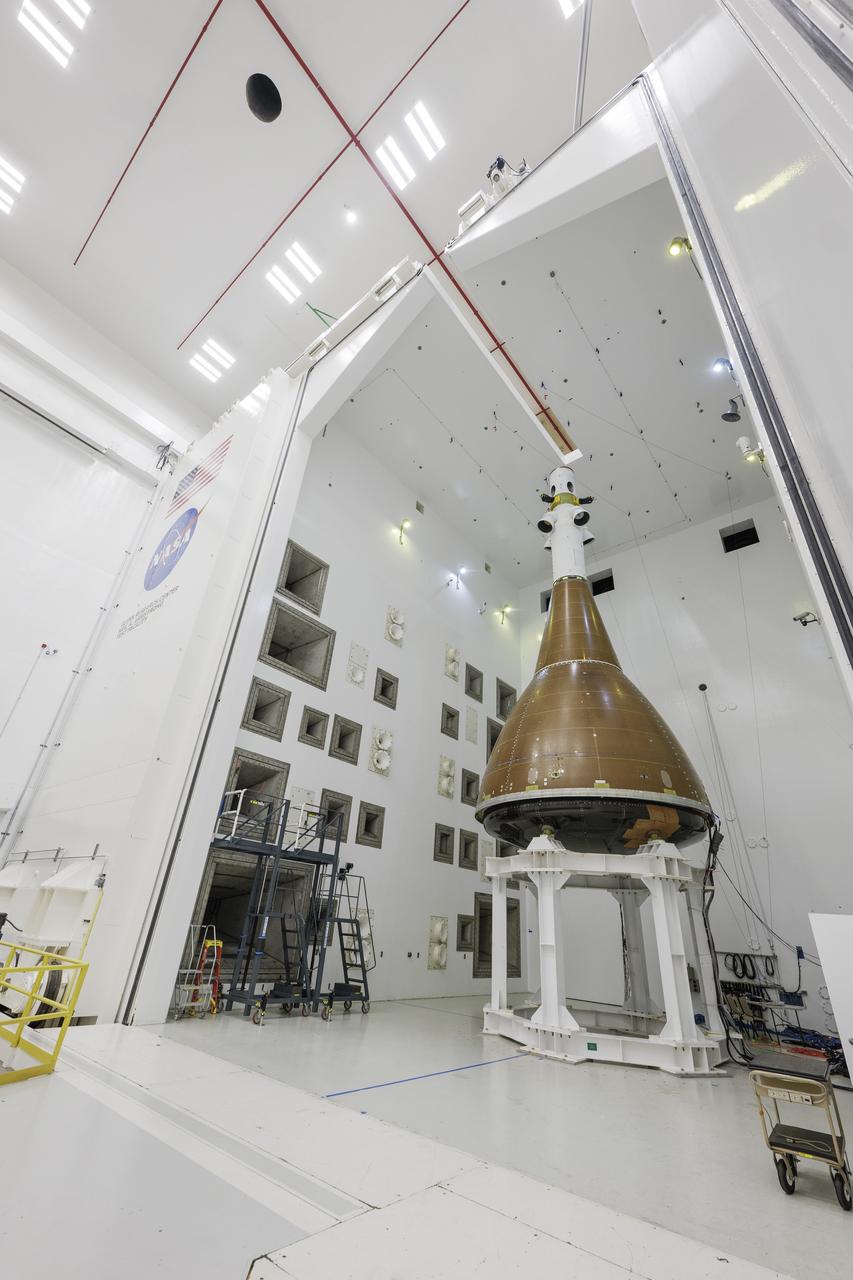

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Photo credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
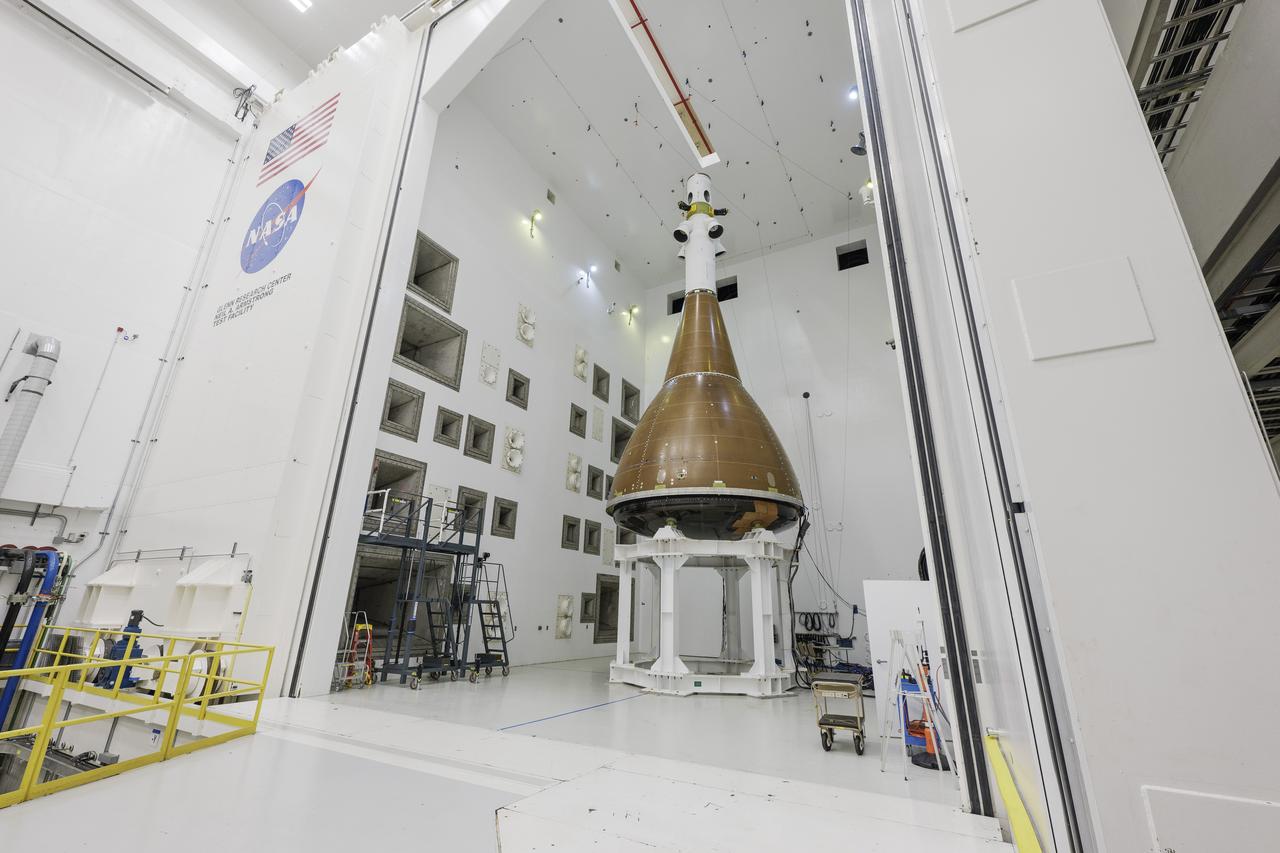

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion.
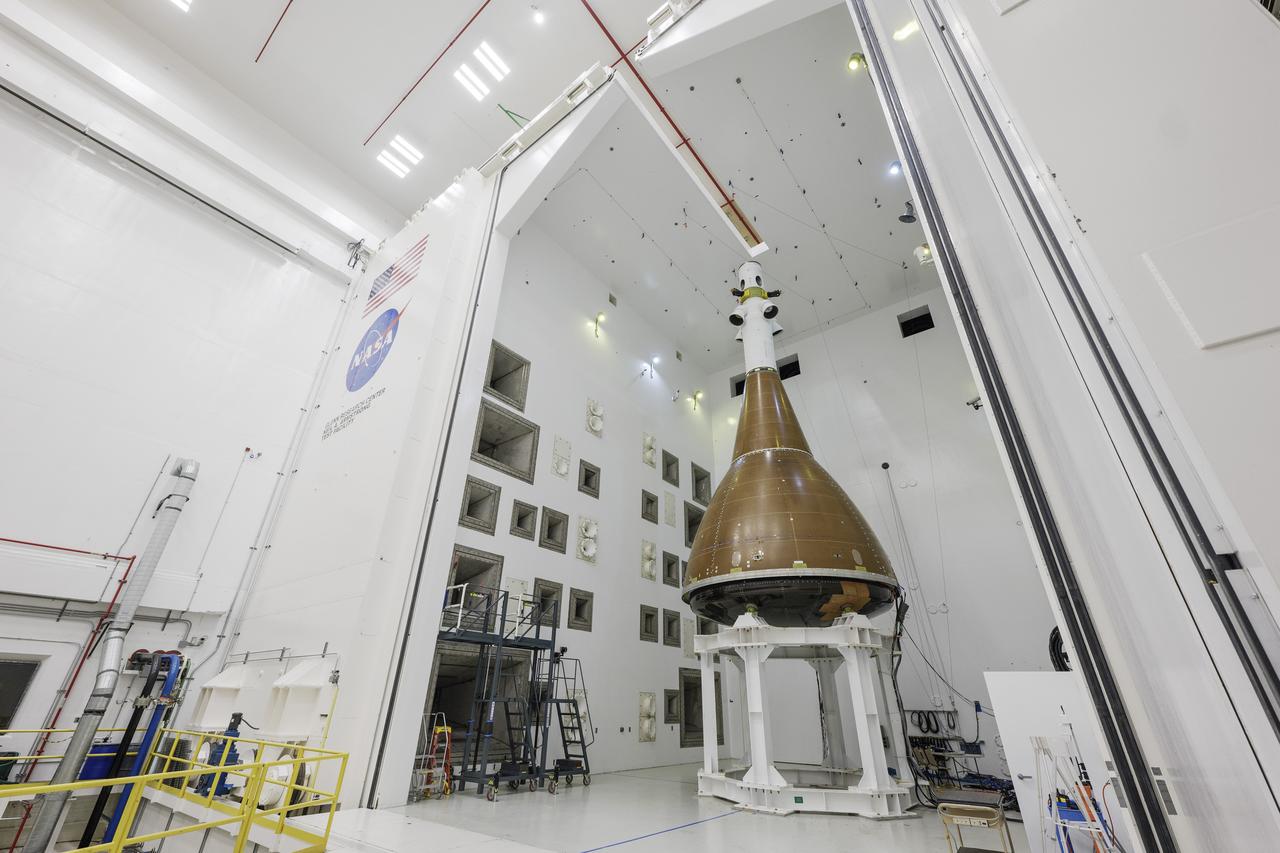

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Photo credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
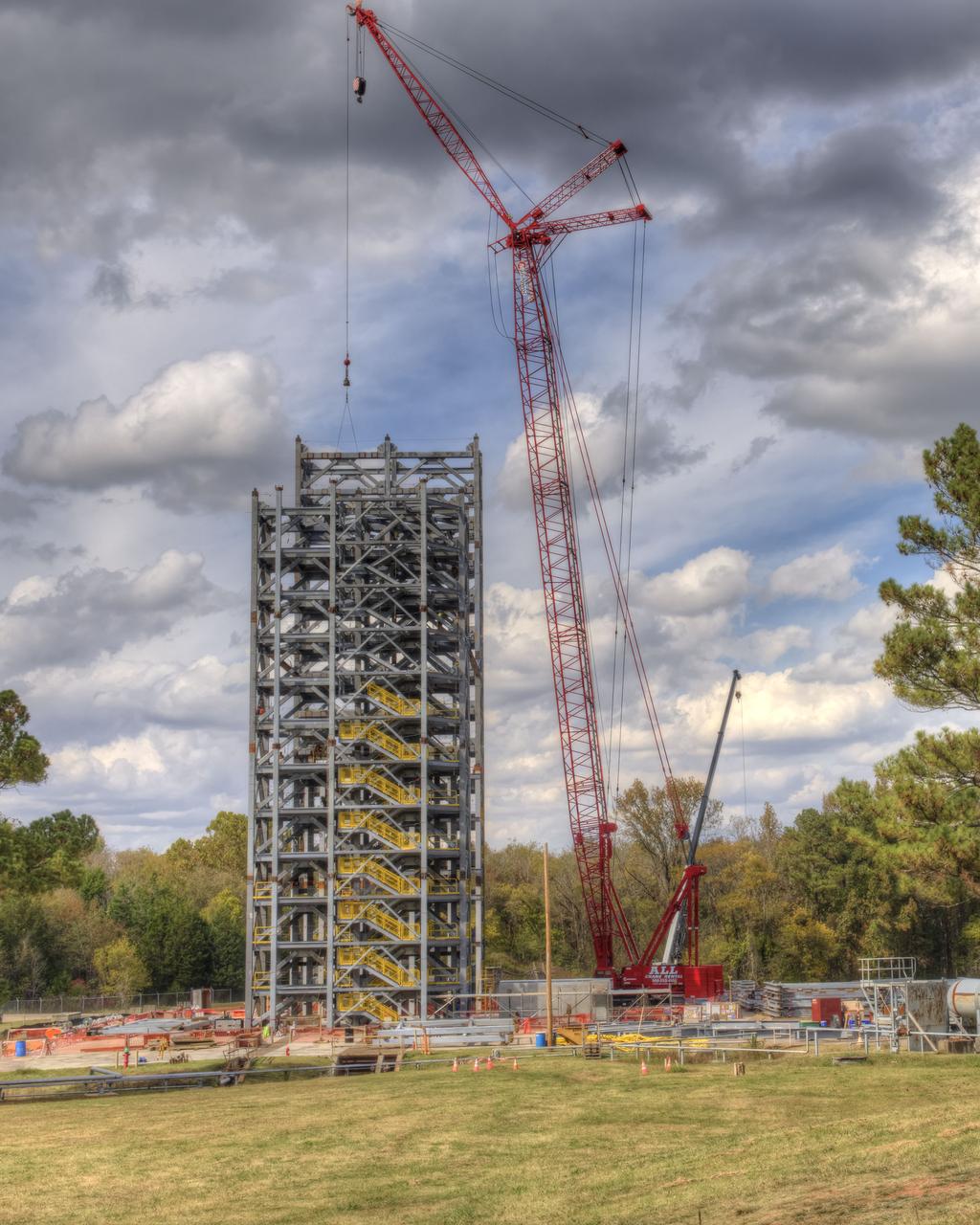

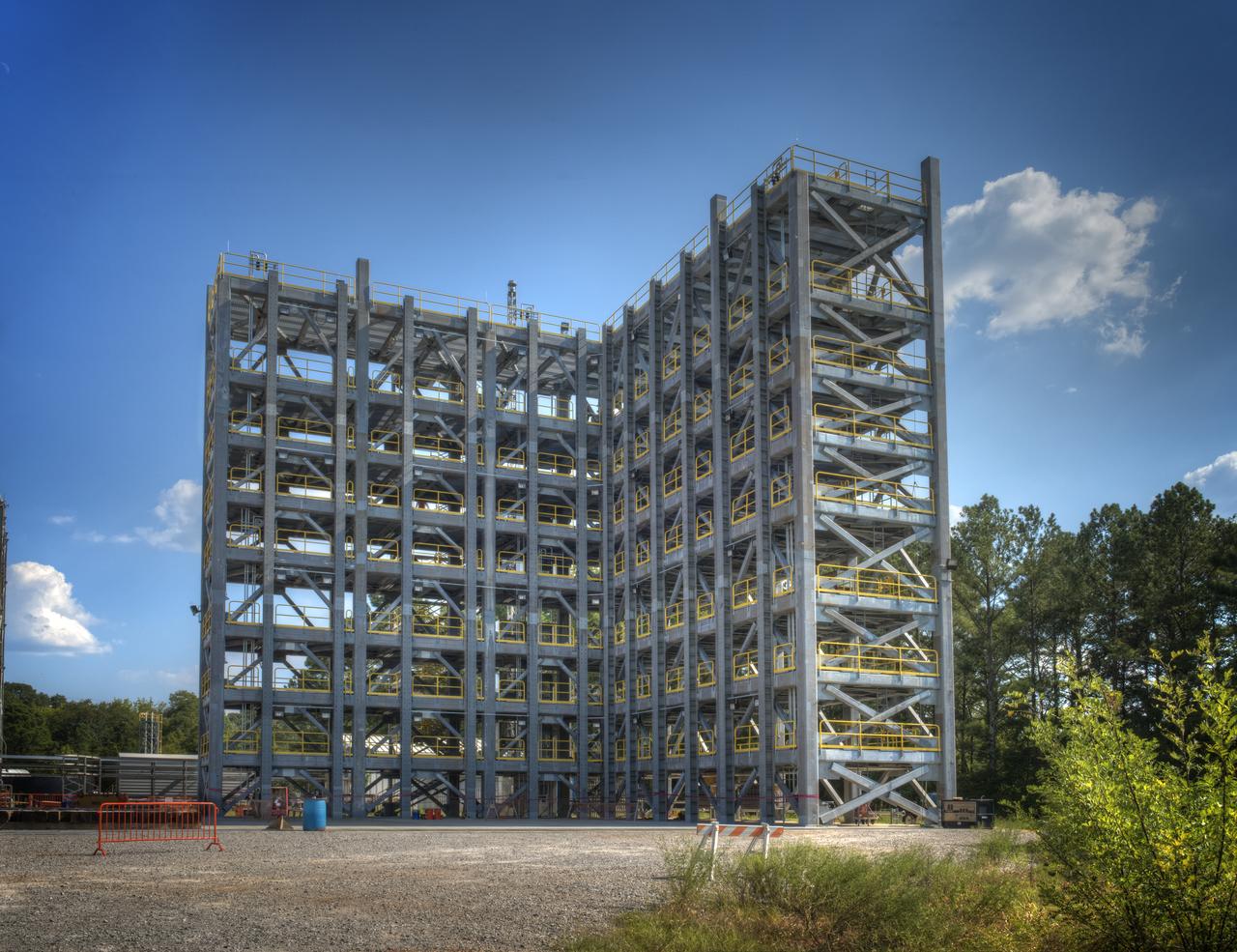
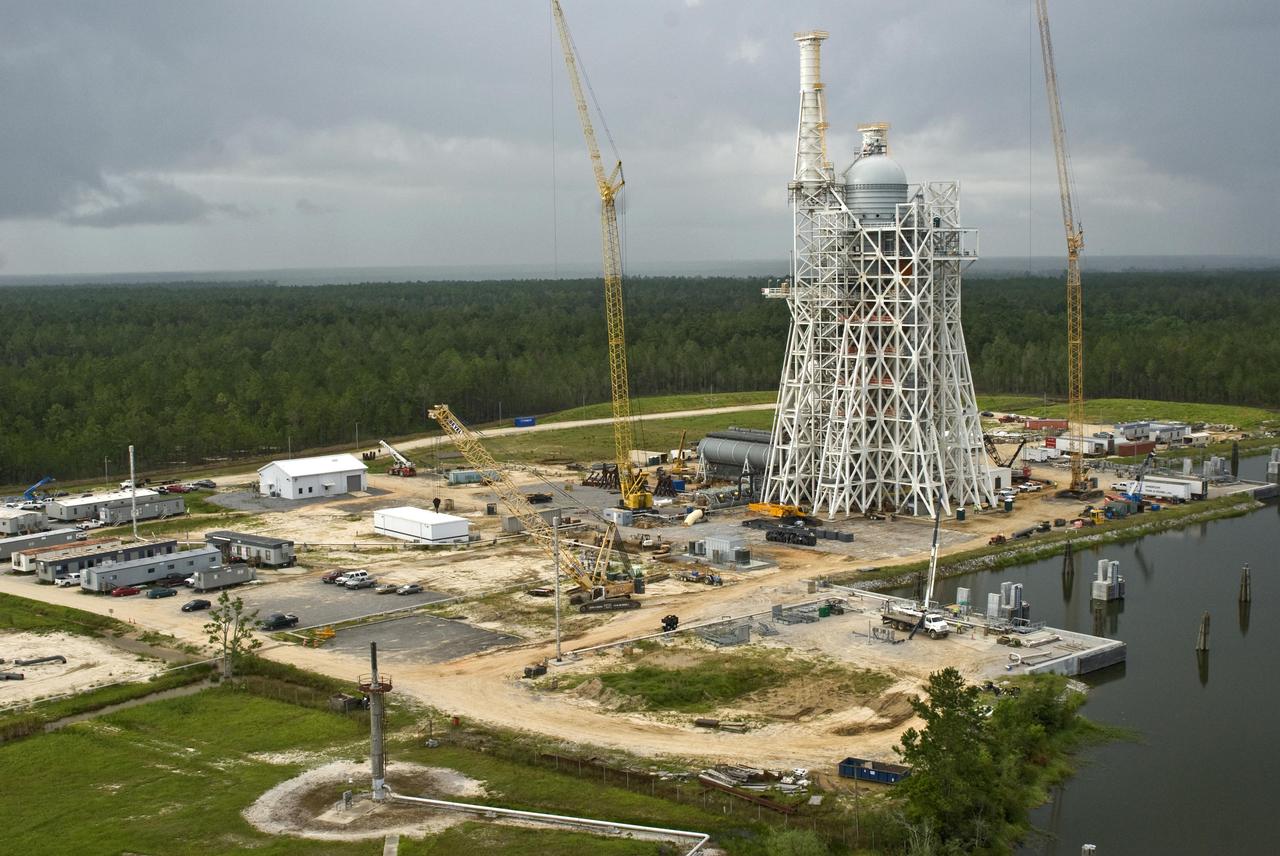
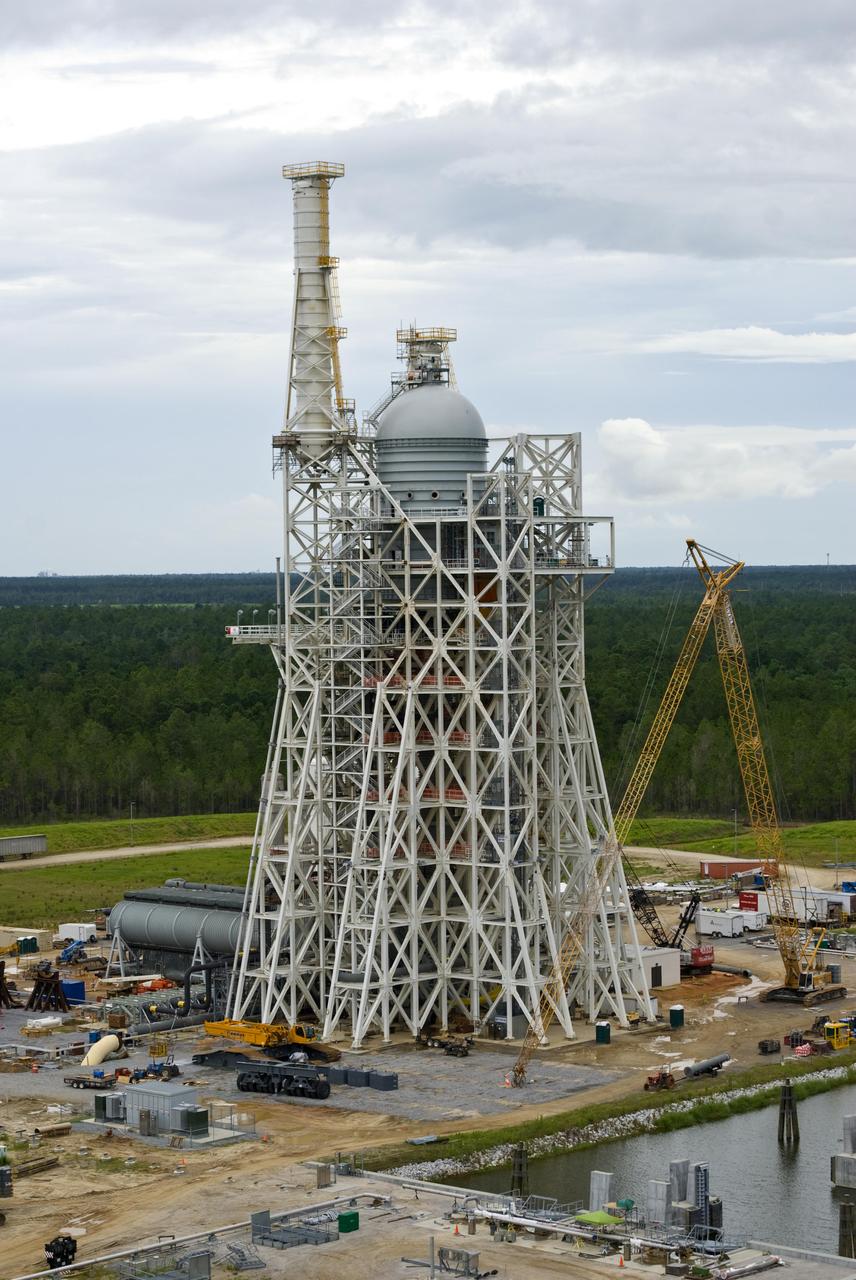
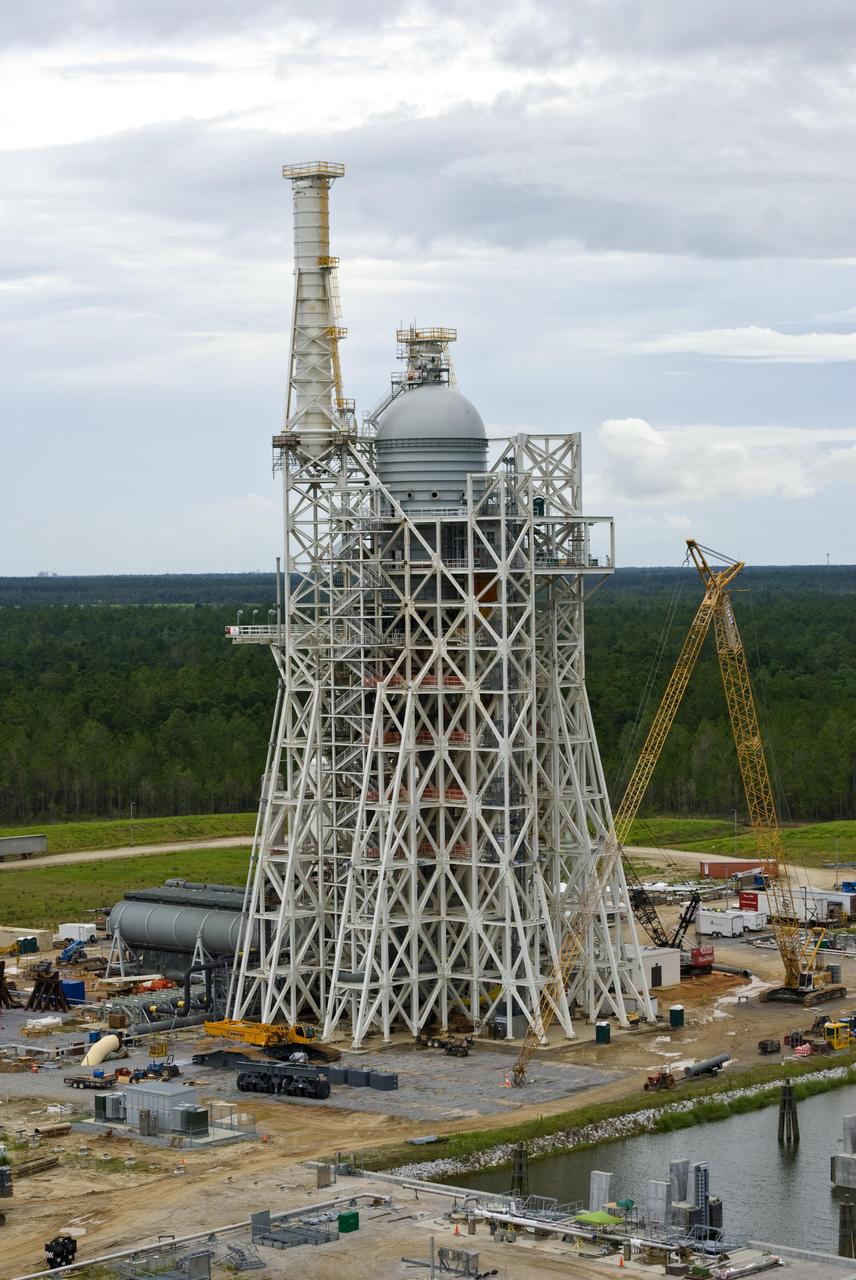
TEST STAND 4693 CONSTRUCTION RISES ABOVE THE TREE LINE. OCTOBER 23, 2015

PLACEMENT OF THE FIRST STEEL GIRDERS FOR THE NEW SLS TEST STAND # 4693
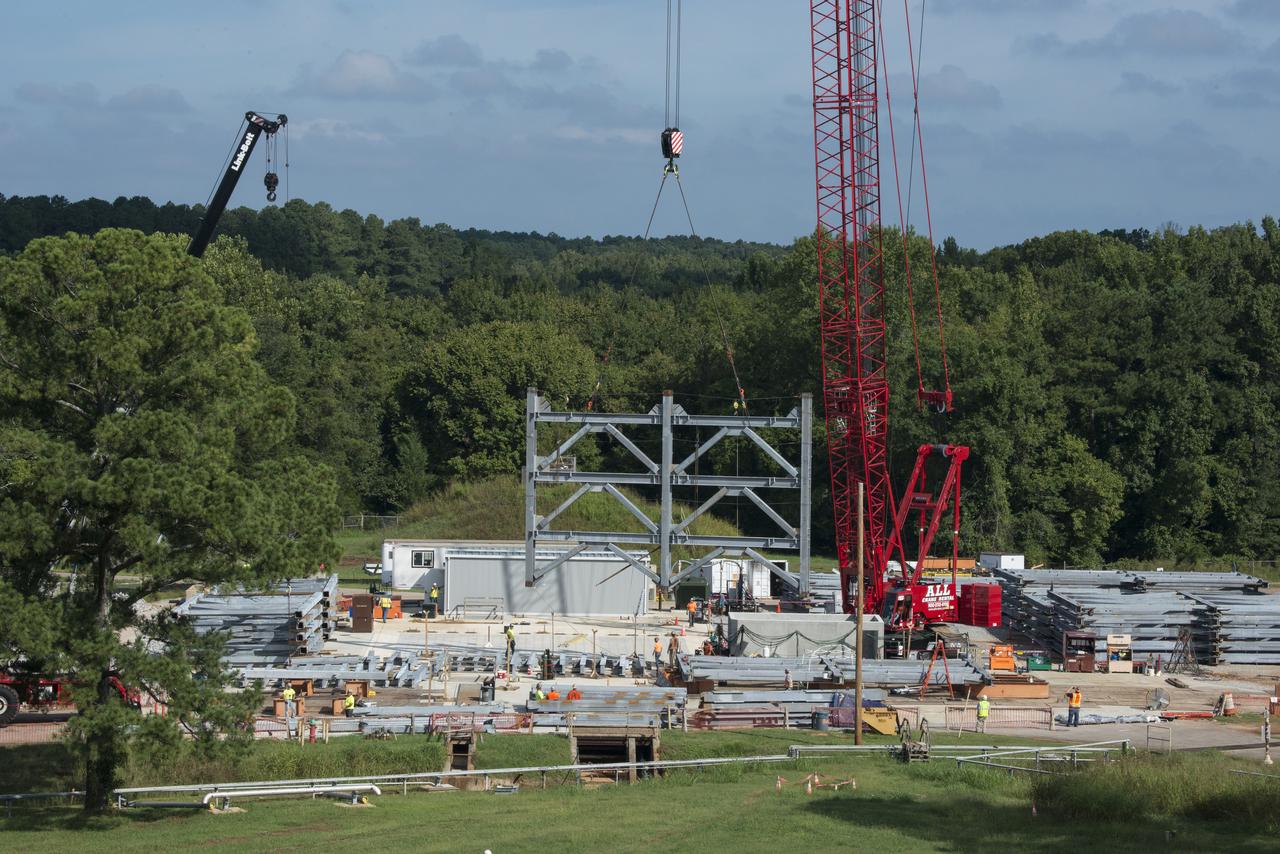

PLACEMENT OF THE FIRST STEEL GIRDERS FOR THE NEW SLS TEST STAND # 4693
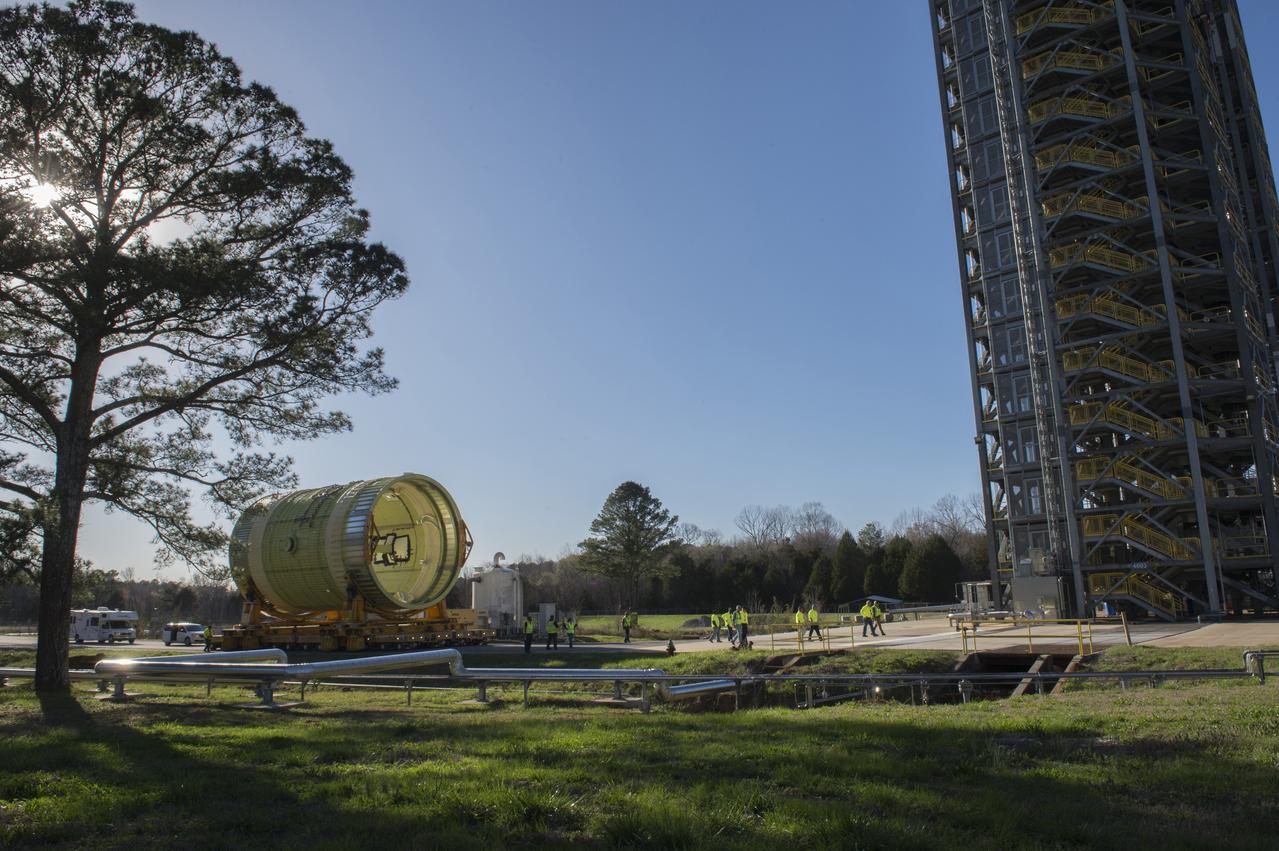

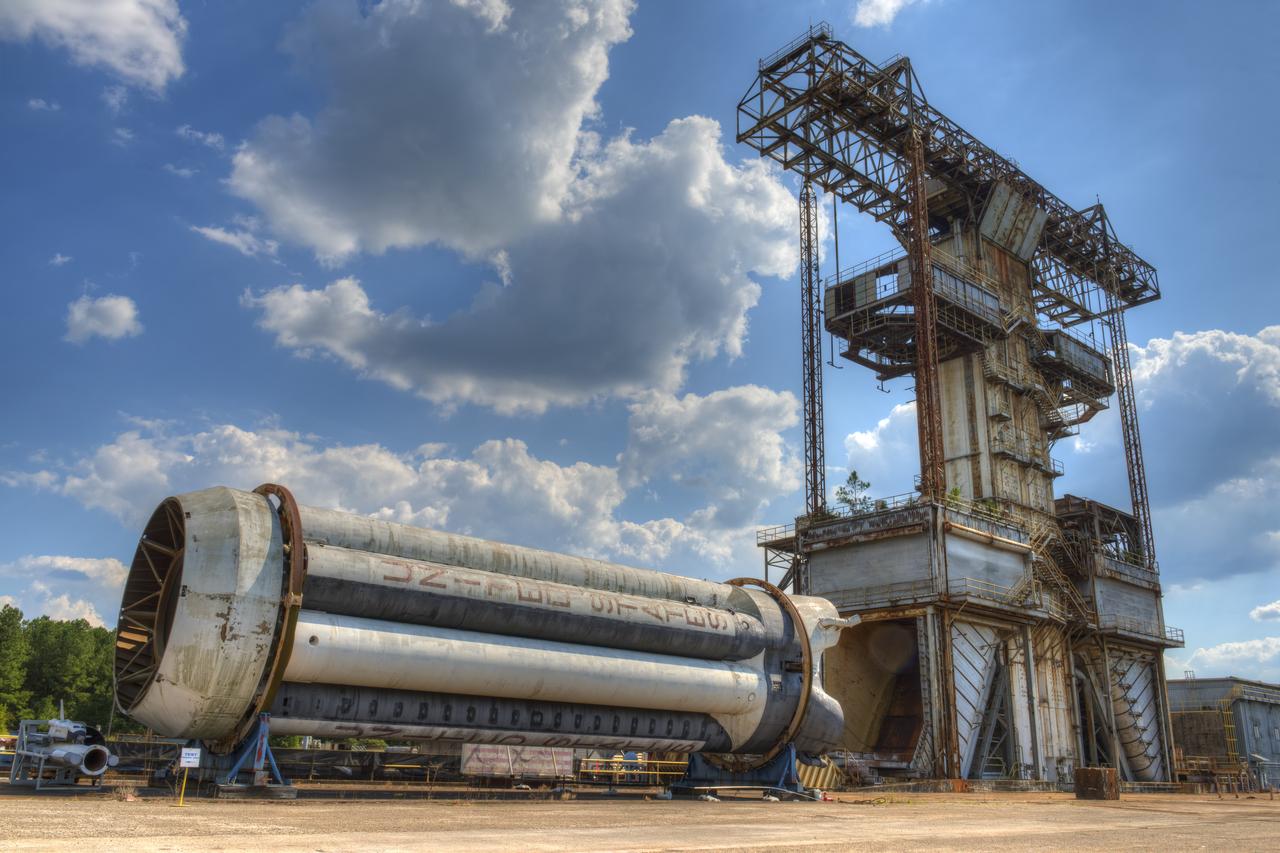
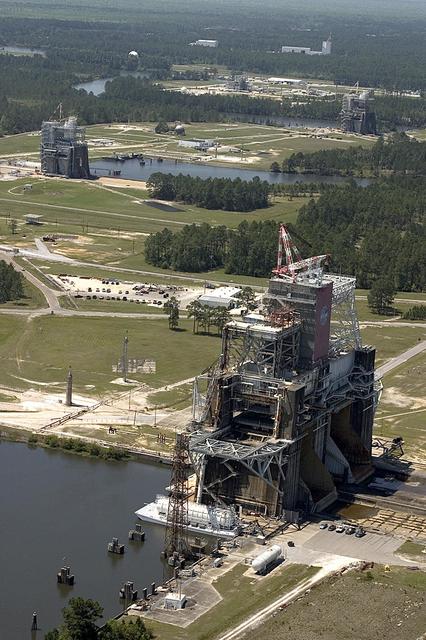
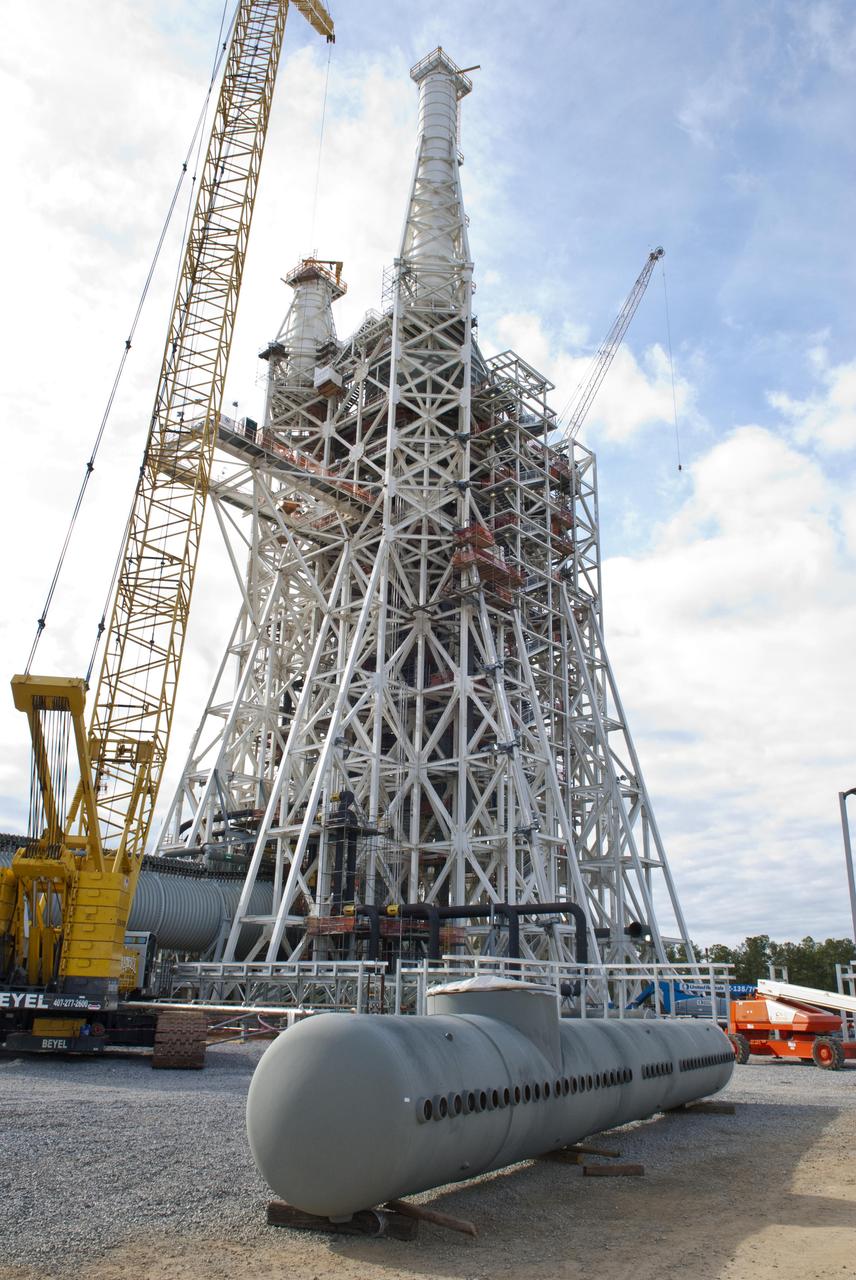
The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing via MSFC West Test Area. STA approaches Test Stand 4693, SLS LH2 test Stand, on way to Bldg. 4619

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html
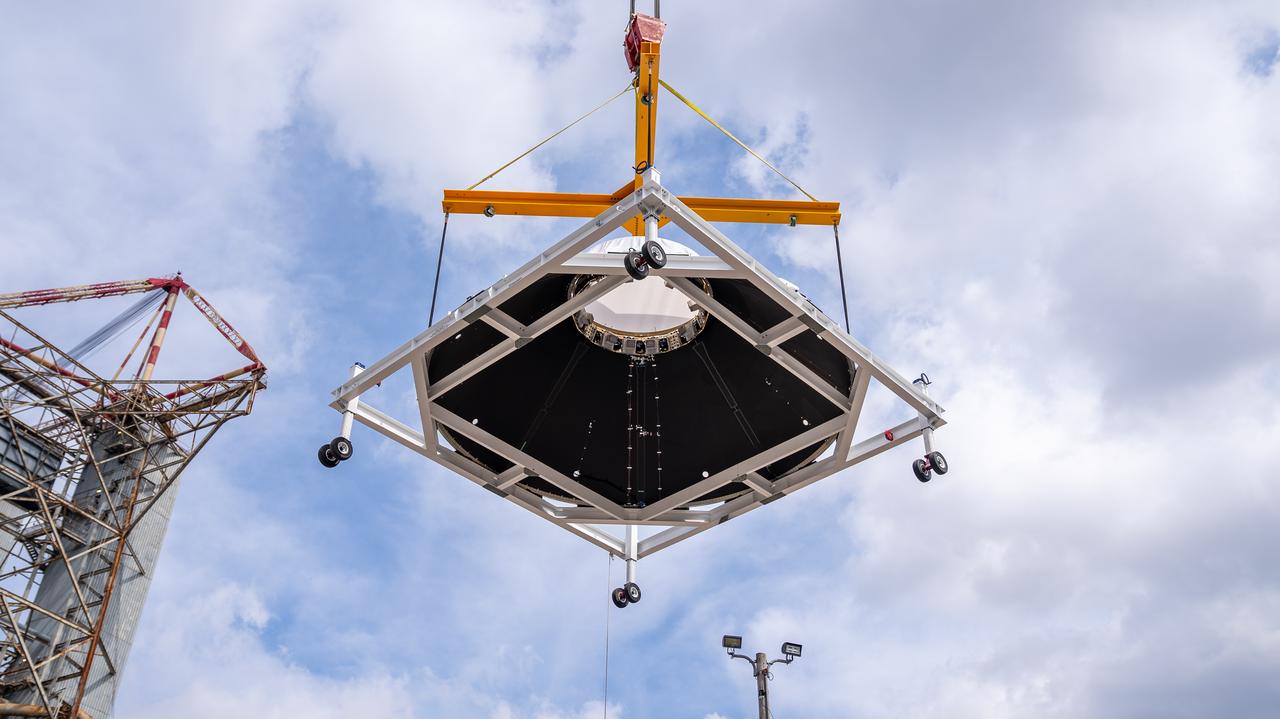

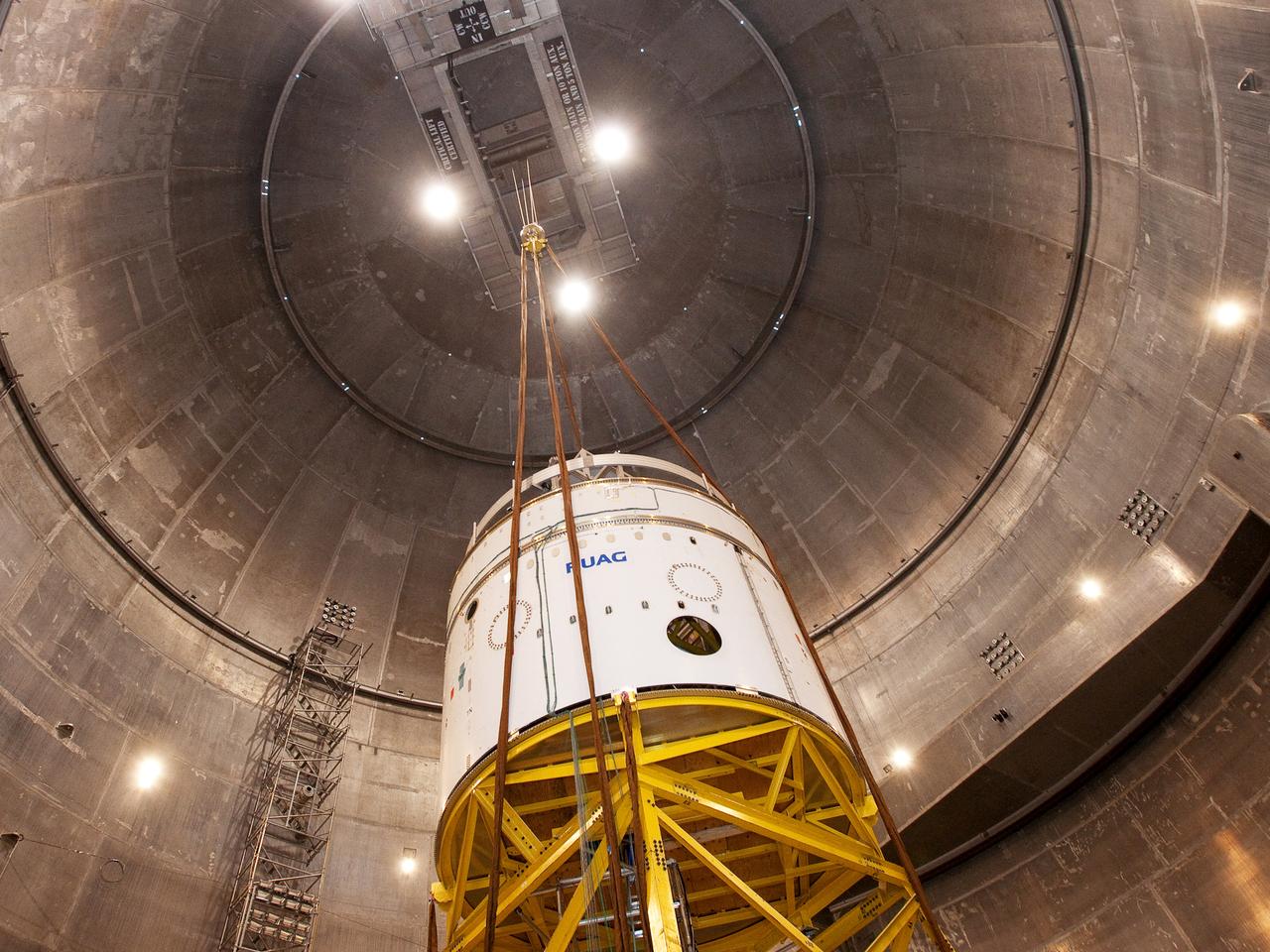
Crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13.
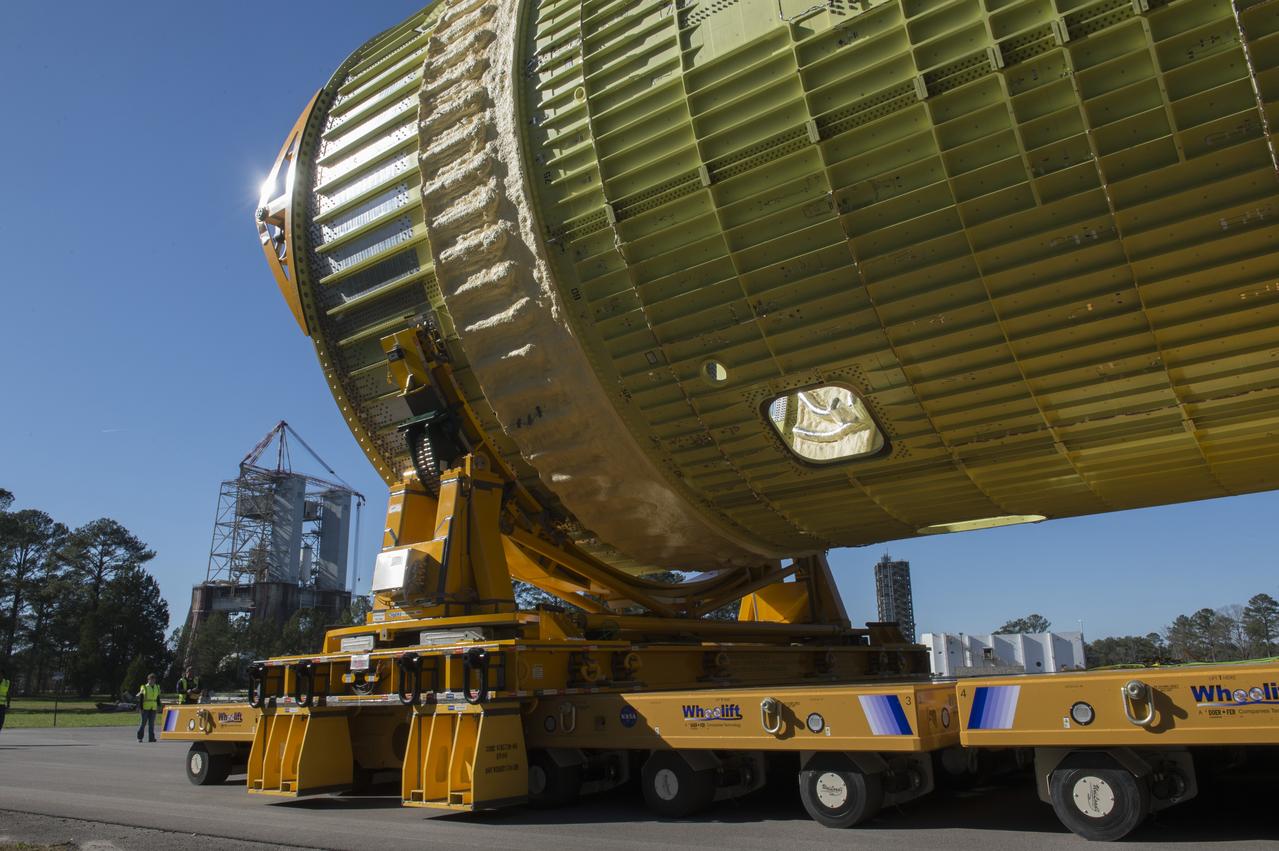

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing via MSFC West Test Area. Historic Saturn 1-C test stand on far left, blockhouse 4670 on far right, SLS LH2 test stand, 4693, in center.

Vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing at Armstrong Test Facility will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Photograph taken on September 11, 2024. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
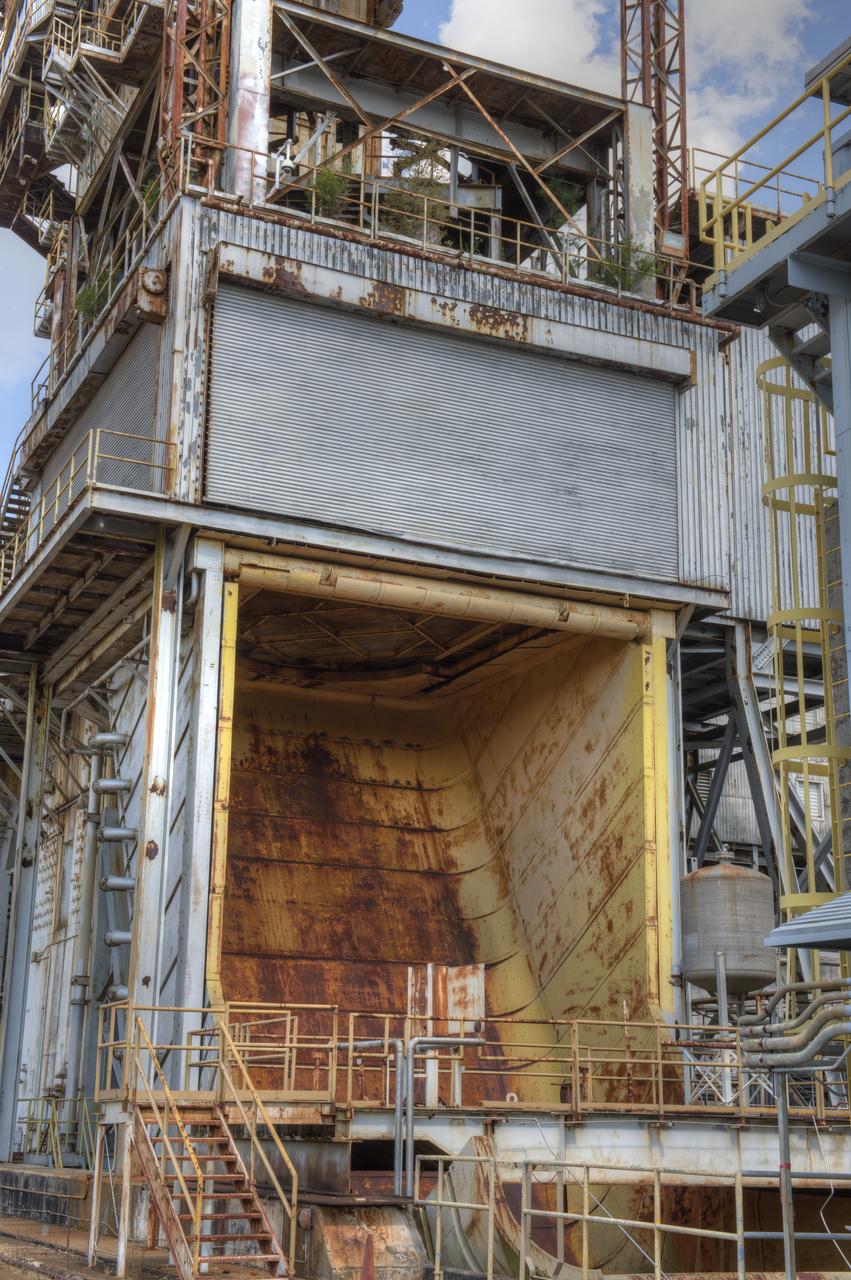

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
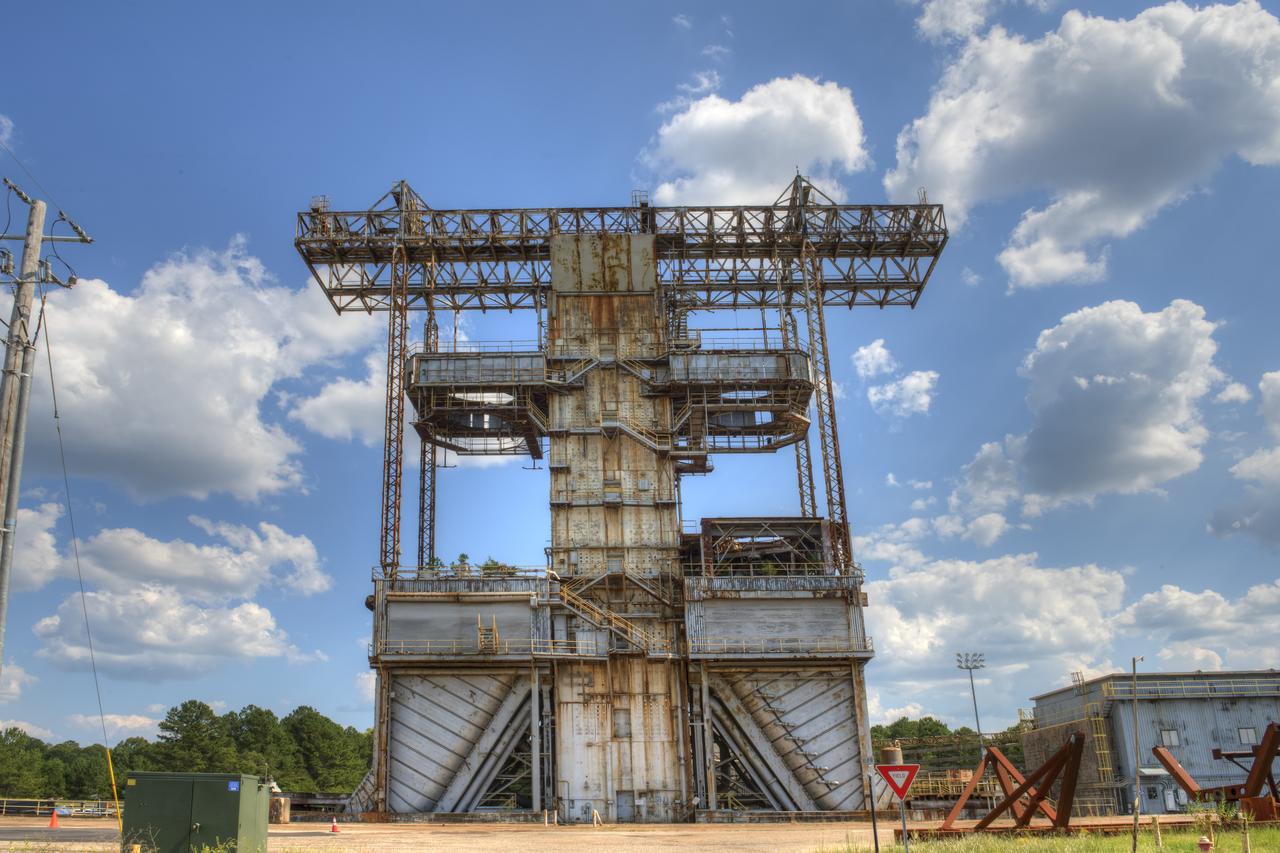

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
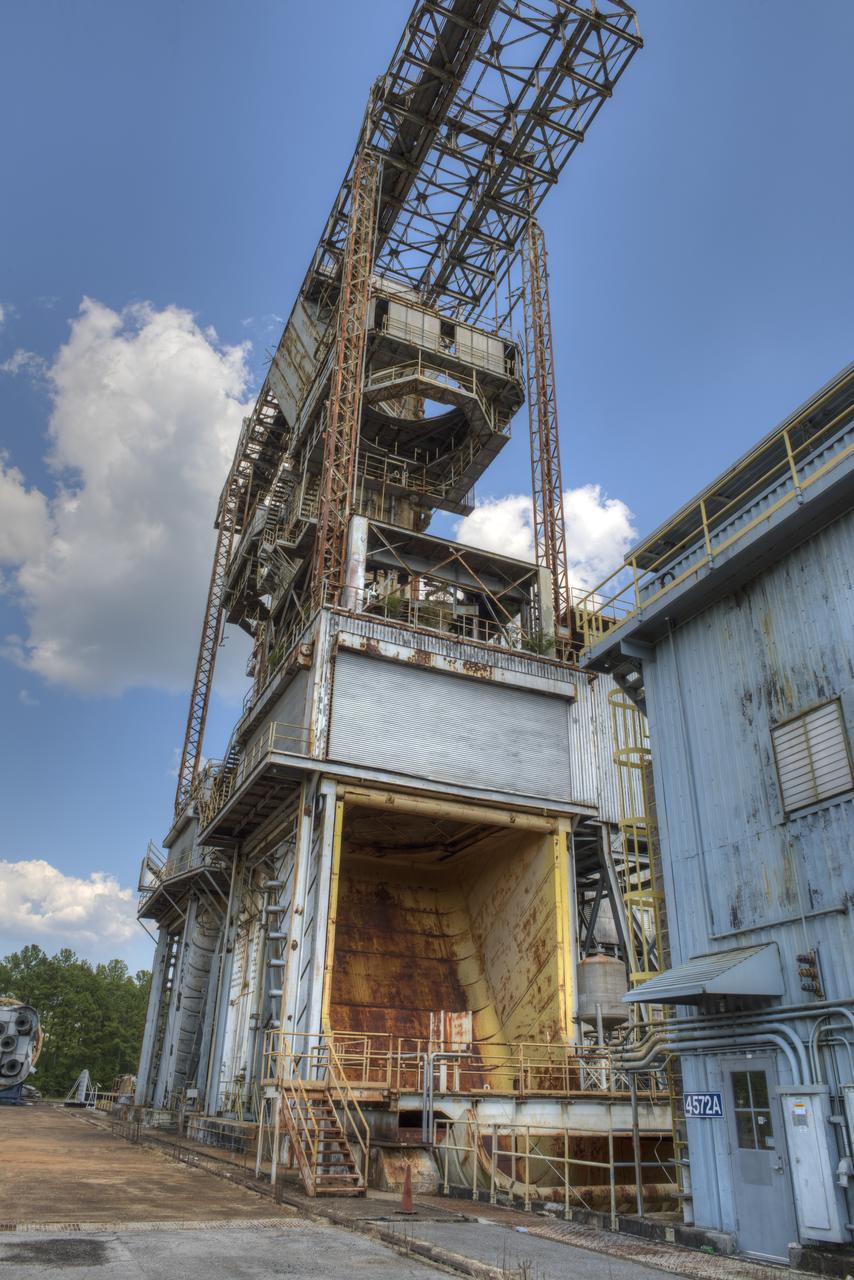

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
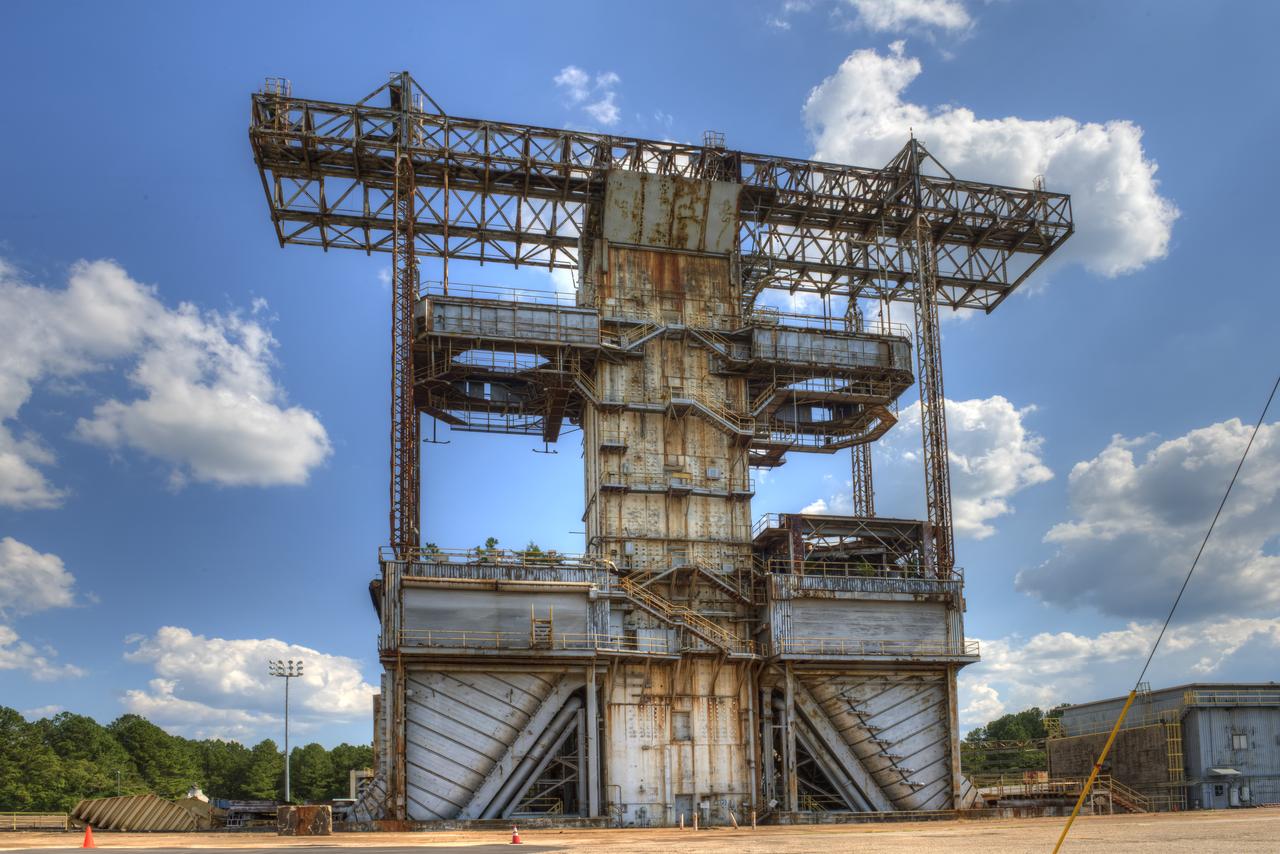

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
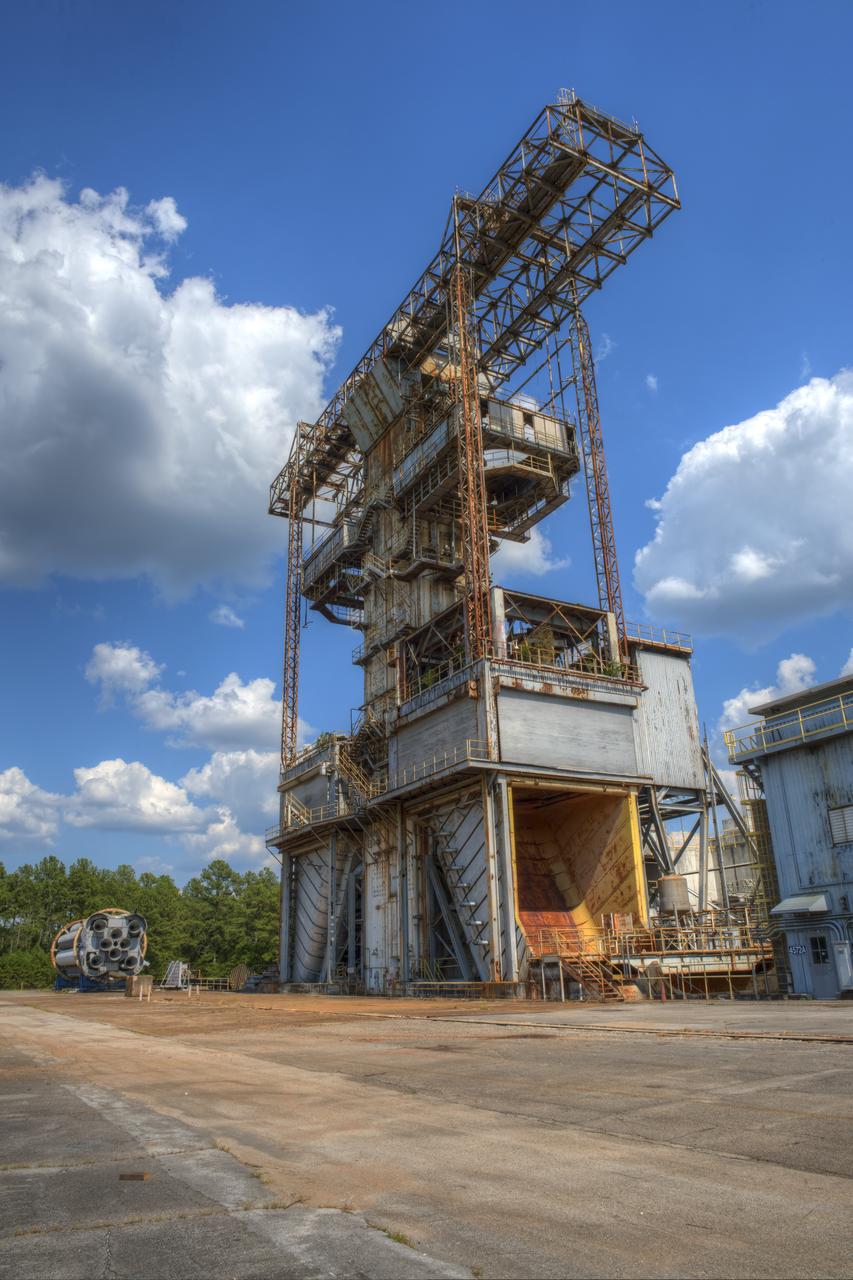

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
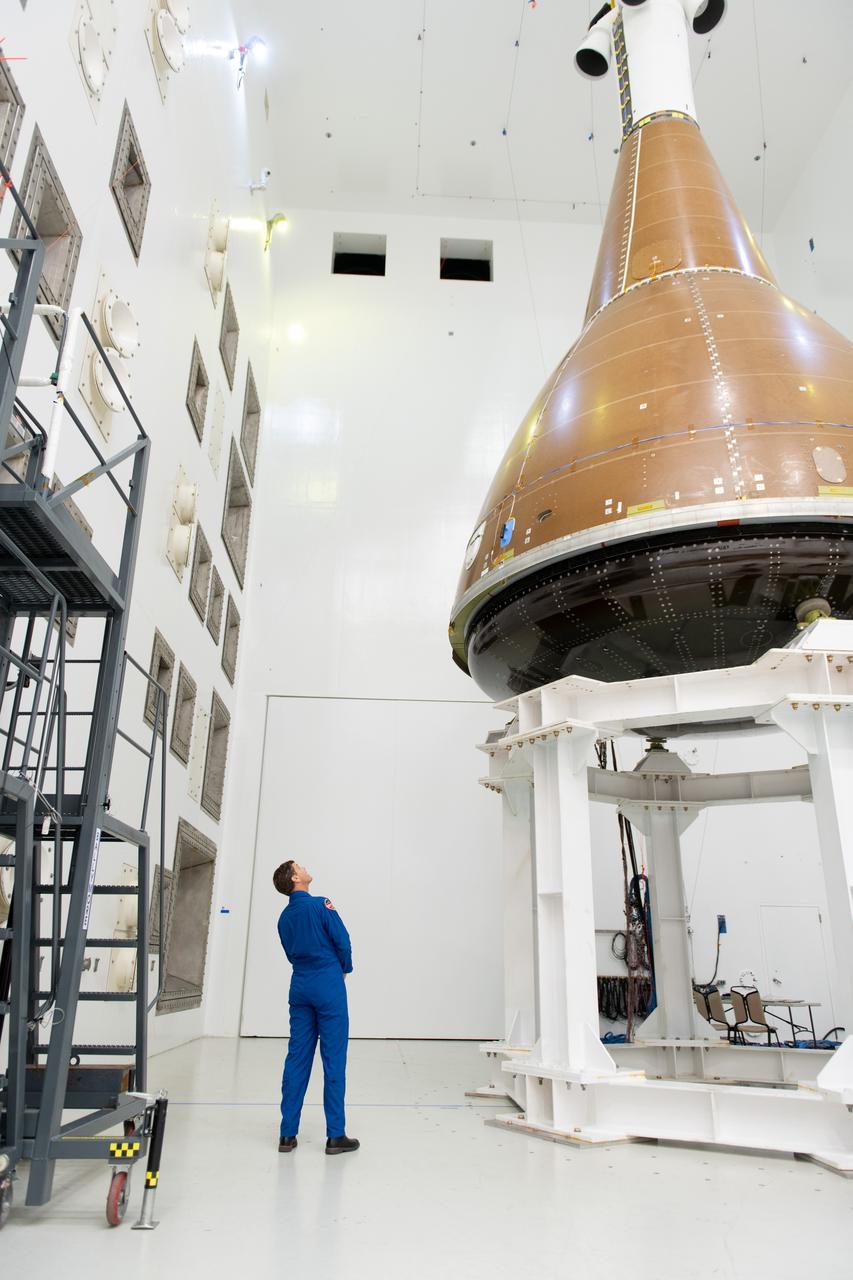

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Commander Reid Wiseman looks up at the Orion capsule during tours on September 11, 2024 of the acoustic lab. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
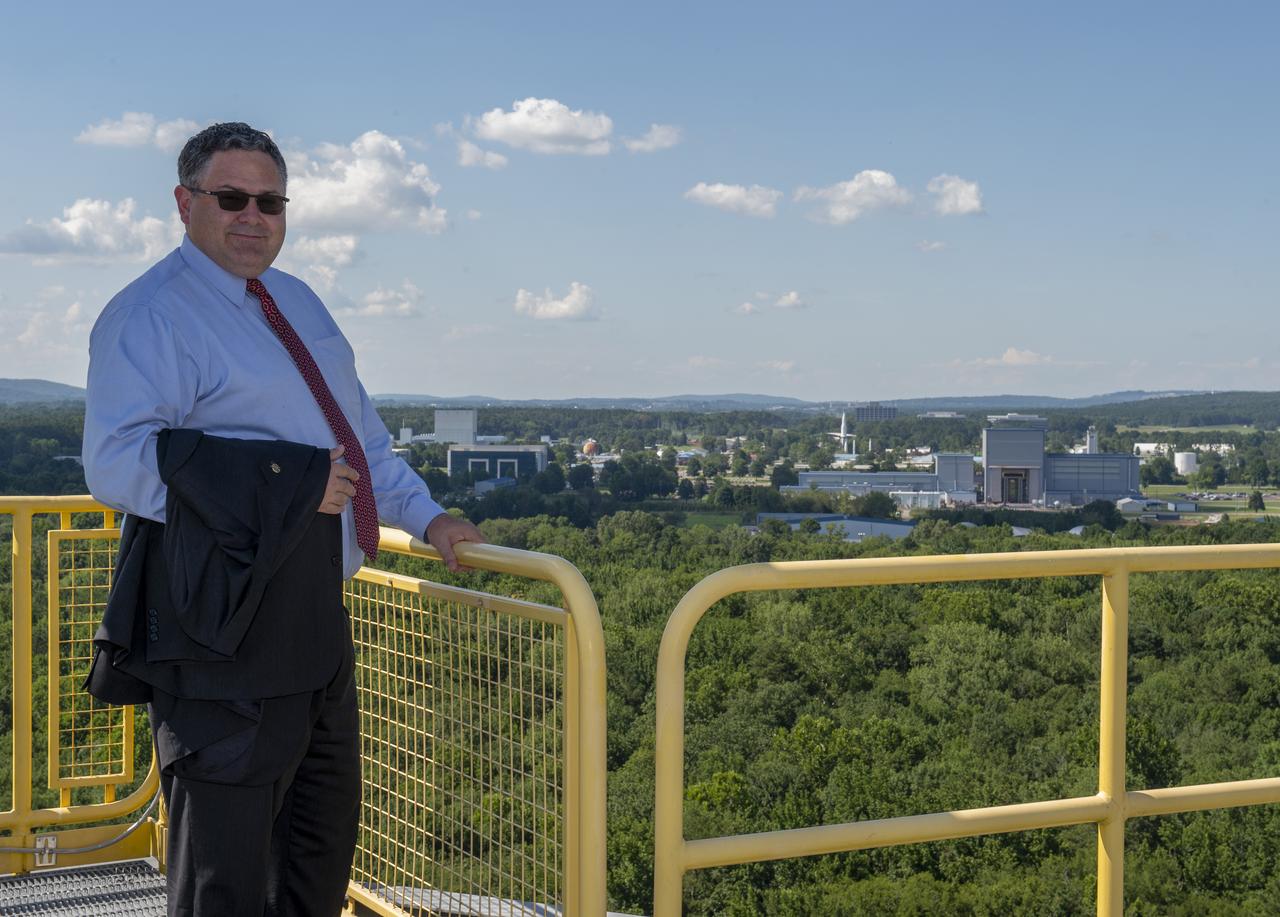

Retiring Marshall Space Flight Center Director Todd May on top of test stand 4693 in MSFC's west test area with MSFC in the background
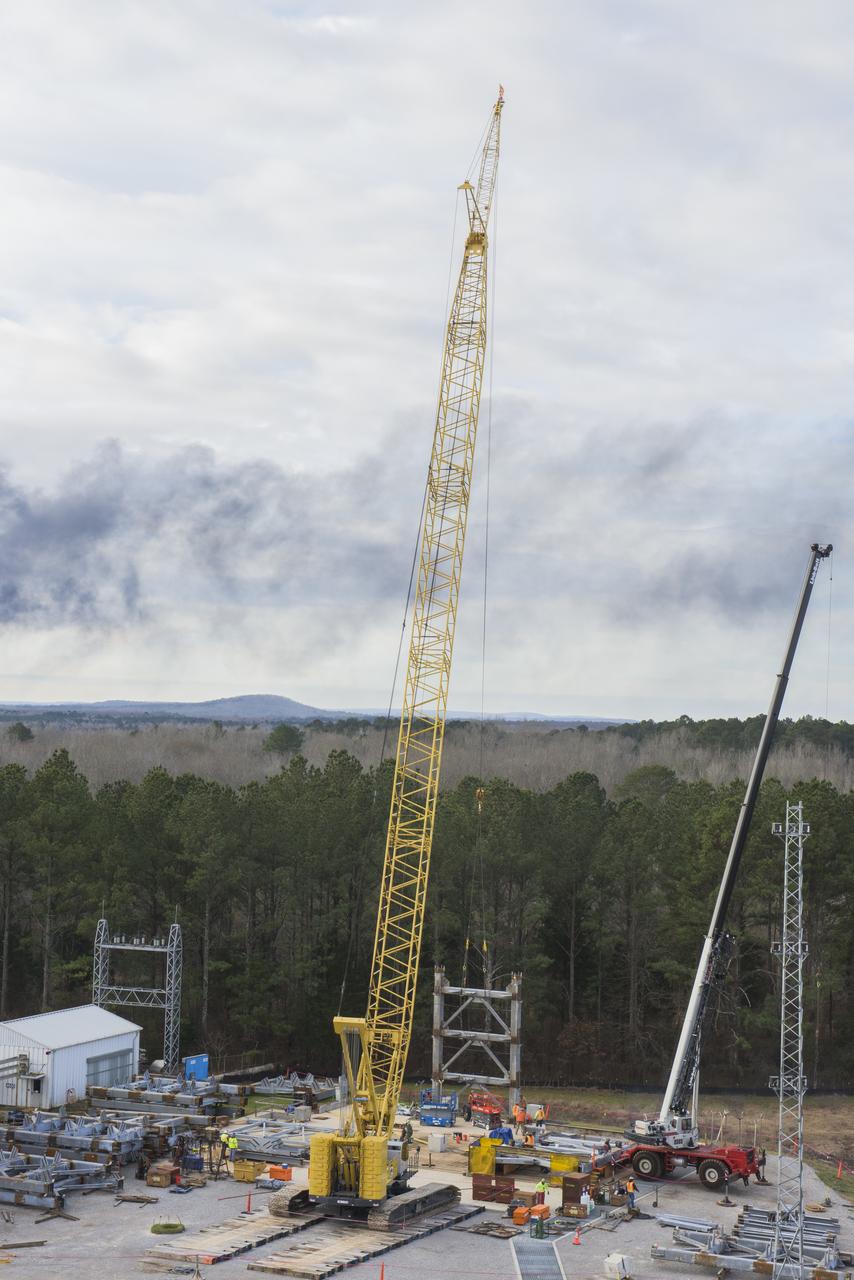

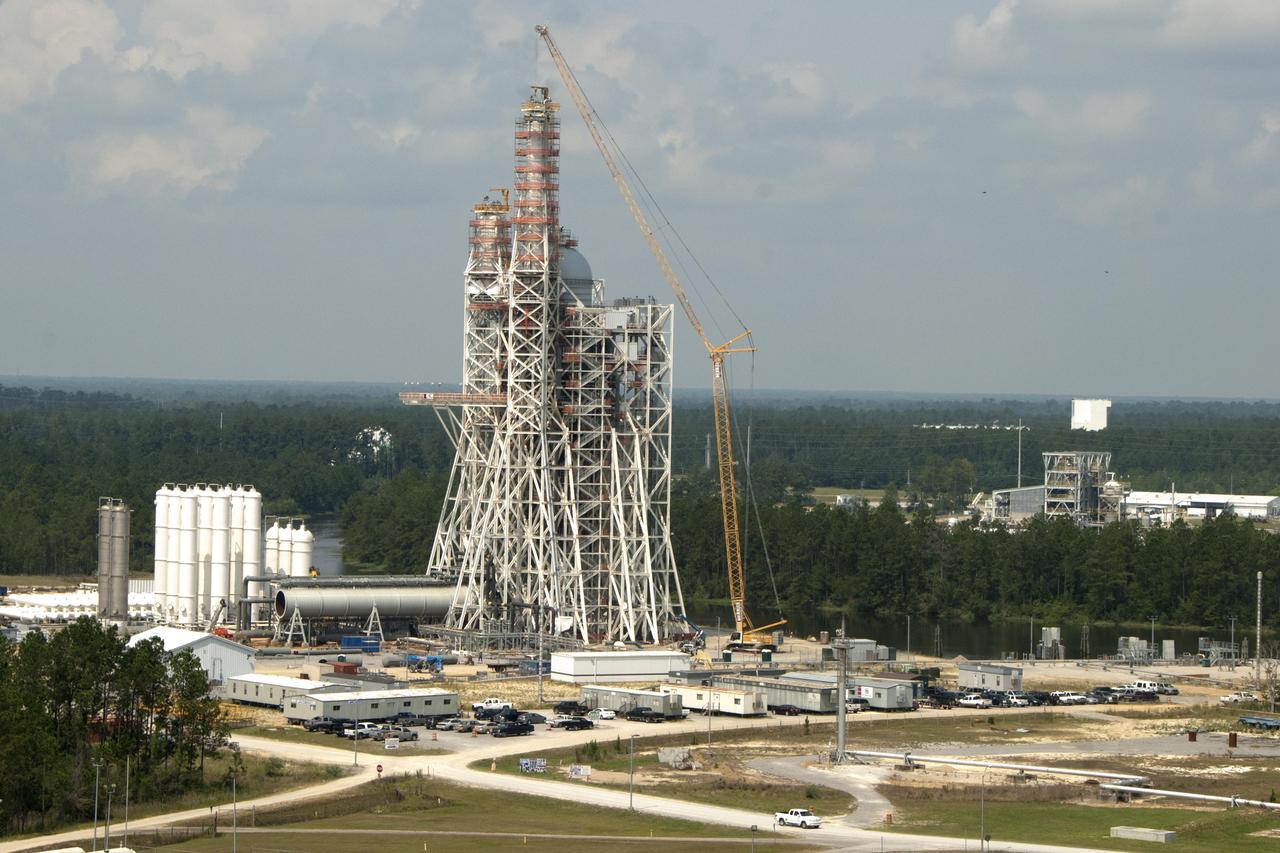
A CRANE MOVES THE FIRST STEEL TIER TO BE BOLTED INTO PLACE ON JAN. 6, FOR WELDING OF A SECOND NEW STRUCTURAL TEST STAND AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA -- CRITICAL TO DEVELOPMENT OF NASA'S SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM. WHEN COMPLETED THIS SUMMER, THE 85-FOOT-TALL TEST STAND 4697 WILL USE HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS TO SUBJECT THE LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AND HARDWARE OF THE MASSIVE SLS CORE STAGE TO THE SAME LOADS AND STRESSES IT WILL ENDURE DURING A LAUNCH. THE STAND IS RISING IN MARSHALL'S WEST TEST AREA, WHERE WORK IS ALSO UNDERWAY ON THE 215-FOOT-TALL TOWERS OF TEST STAND 4693, WHICH WILL CONDUCT SIMILAR STRUCTURAL TESTS ON THE SLS CORE STAGE'S LIQUID HYDROGEN TANK. SLS, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET EVER BUILT, WILL CARRY ASTRONAUTS IN NASA'S ORION SPACECRAFT ON DEEP SPACE MISSIONS, INCLUDING THE JOURNEY TO MARS.
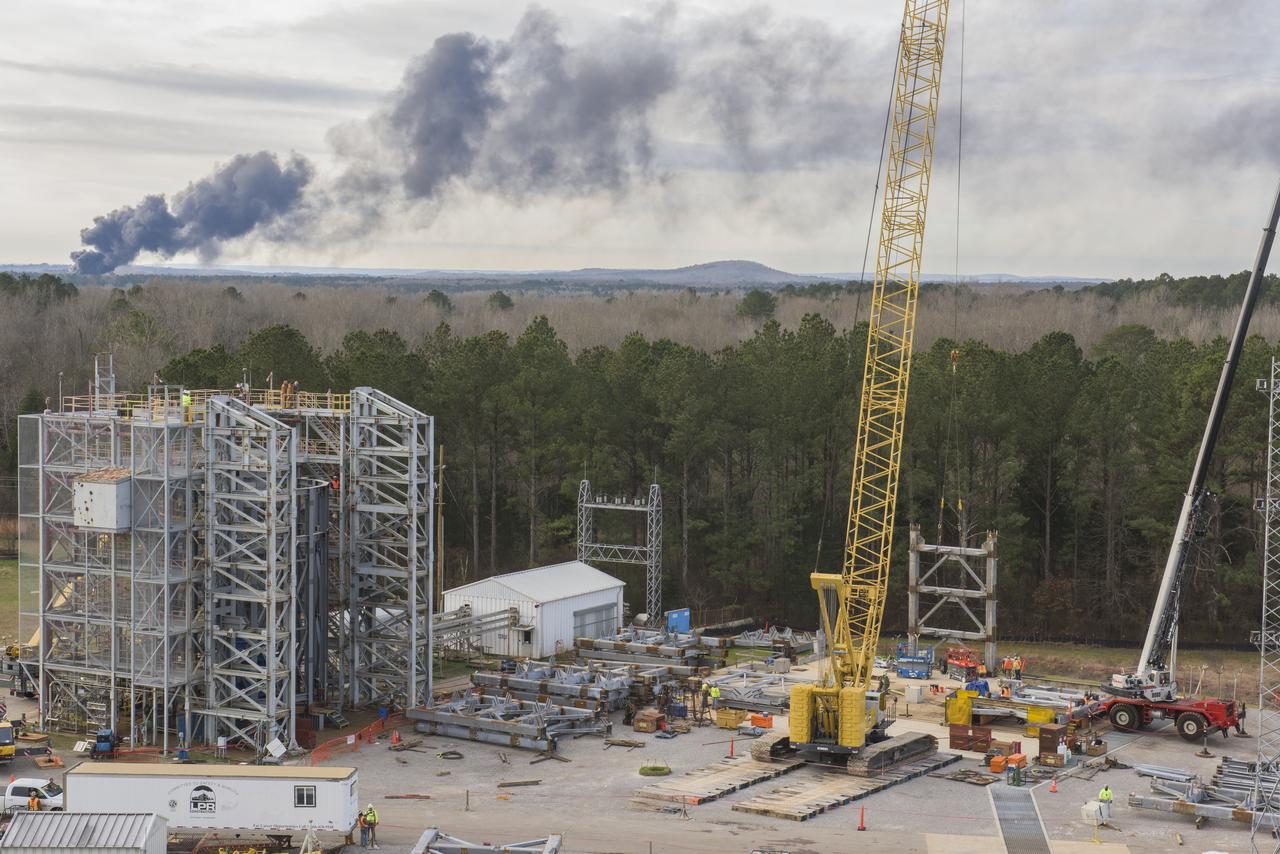

A CRANE MOVES THE FIRST STEEL TIER TO BE BOLTED INTO PLACE ON JAN. 6, FOR WELDING OF A SECOND NEW STRUCTURAL TEST STAND AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA -- CRITICAL TO DEVELOPMENT OF NASA'S SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM. WHEN COMPLETED THIS SUMMER, THE 85-FOOT-TALL TEST STAND 4697 WILL USE HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS TO SUBJECT THE LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AND HARDWARE OF THE MASSIVE SLS CORE STAGE TO THE SAME LOADS AND STRESSES IT WILL ENDURE DURING A LAUNCH. THE STAND IS RISING IN MARSHALL'S WEST TEST AREA, WHERE WORK IS ALSO UNDERWAY ON THE 215-FOOT-TALL TOWERS OF TEST STAND 4693, WHICH WILL CONDUCT SIMILAR STRUCTURAL TESTS ON THE SLS CORE STAGE'S LIQUID HYDROGEN TANK. SLS, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET EVER BUILT, WILL CARRY ASTRONAUTS IN NASA'S ORION SPACECRAFT ON DEEP SPACE MISSIONS, INCLUDING THE JOURNEY TO MARS.
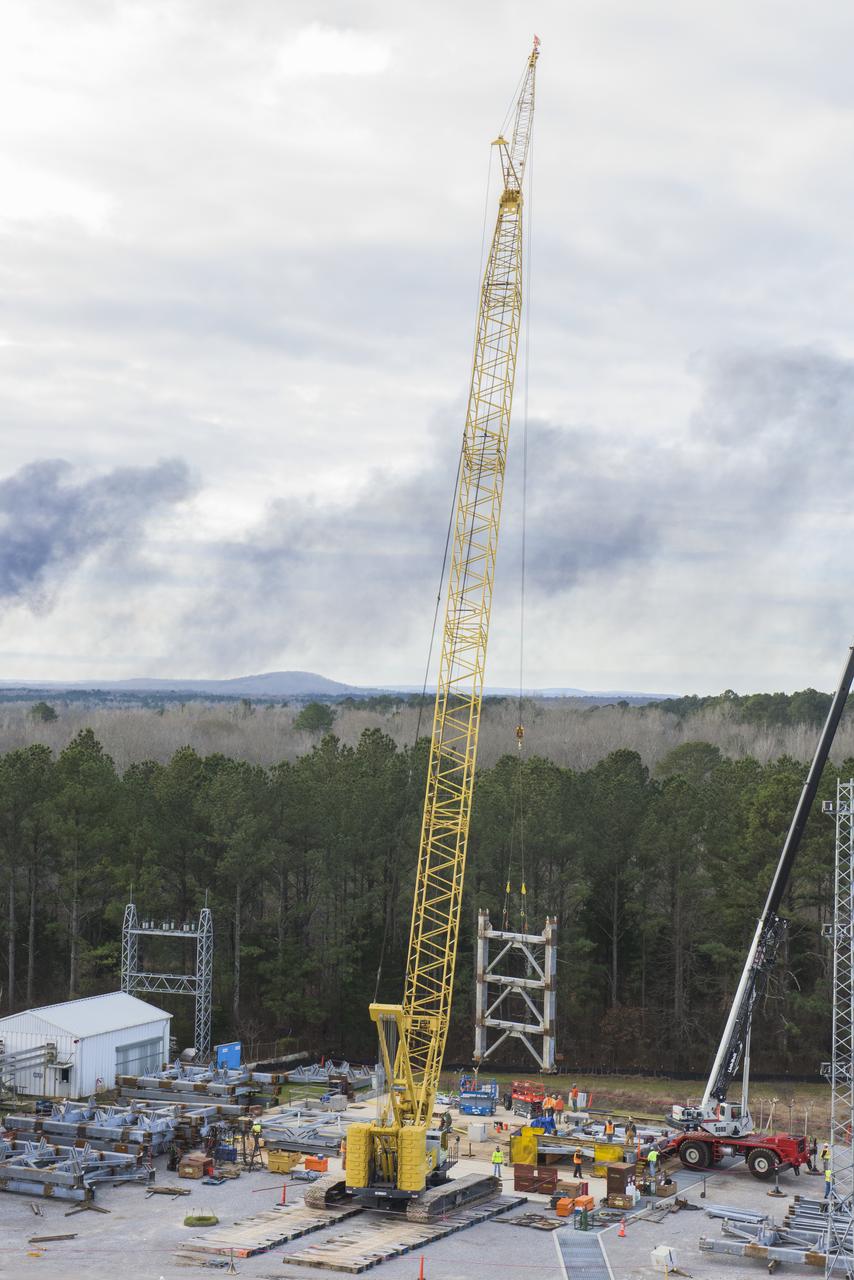

A CRANE MOVES THE FIRST STEEL TIER TO BE BOLTED INTO PLACE ON JAN. 6, FOR WELDING OF A SECOND NEW STRUCTURAL TEST STAND AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA -- CRITICAL TO DEVELOPMENT OF NASA'S SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM. WHEN COMPLETED THIS SUMMER, THE 85-FOOT-TALL TEST STAND 4697 WILL USE HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS TO SUBJECT THE LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AND HARDWARE OF THE MASSIVE SLS CORE STAGE TO THE SAME LOADS AND STRESSES IT WILL ENDURE DURING A LAUNCH. THE STAND IS RISING IN MARSHALL'S WEST TEST AREA, WHERE WORK IS ALSO UNDERWAY ON THE 215-FOOT-TALL TOWERS OF TEST STAND 4693, WHICH WILL CONDUCT SIMILAR STRUCTURAL TESTS ON THE SLS CORE STAGE'S LIQUID HYDROGEN TANK. SLS, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET EVER BUILT, WILL CARRY ASTRONAUTS IN NASA'S ORION SPACECRAFT ON DEEP SPACE MISSIONS, INCLUDING THE JOURNEY TO MARS.
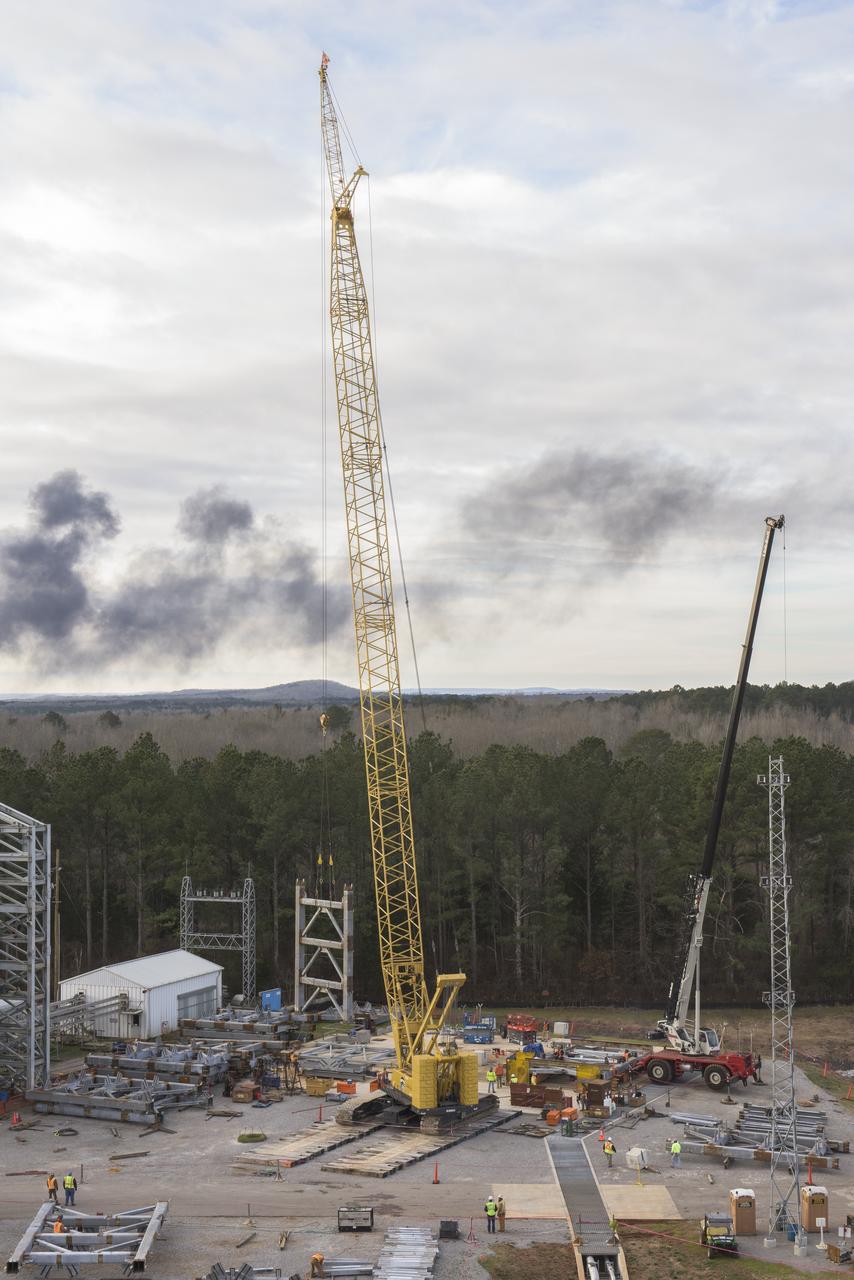

A CRANE MOVES THE FIRST STEEL TIER TO BE BOLTED INTO PLACE ON JAN. 6, FOR WELDING OF A SECOND NEW STRUCTURAL TEST STAND AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA -- CRITICAL TO DEVELOPMENT OF NASA'S SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM. WHEN COMPLETED THIS SUMMER, THE 85-FOOT-TALL TEST STAND 4697 WILL USE HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS TO SUBJECT THE LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AND HARDWARE OF THE MASSIVE SLS CORE STAGE TO THE SAME LOADS AND STRESSES IT WILL ENDURE DURING A LAUNCH. THE STAND IS RISING IN MARSHALL'S WEST TEST AREA, WHERE WORK IS ALSO UNDERWAY ON THE 215-FOOT-TALL TOWERS OF TEST STAND 4693, WHICH WILL CONDUCT SIMILAR STRUCTURAL TESTS ON THE SLS CORE STAGE'S LIQUID HYDROGEN TANK. SLS, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET EVER BUILT, WILL CARRY ASTRONAUTS IN NASA'S ORION SPACECRAFT ON DEEP SPACE MISSIONS, INCLUDING THE JOURNEY TO MARS.
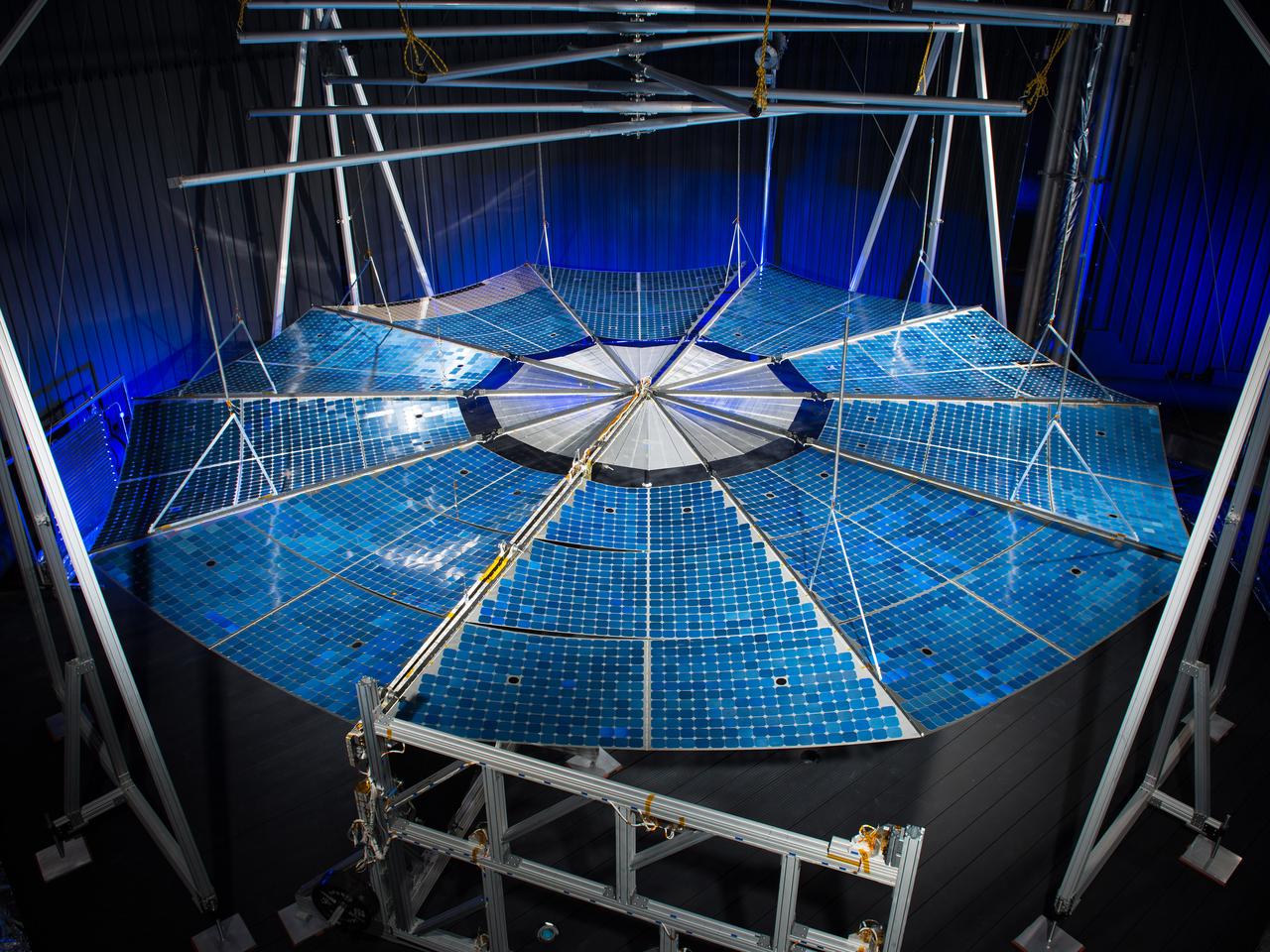
ATK Solar Array Deployment Test at NASA Plum Brook Station Space Power Facility.
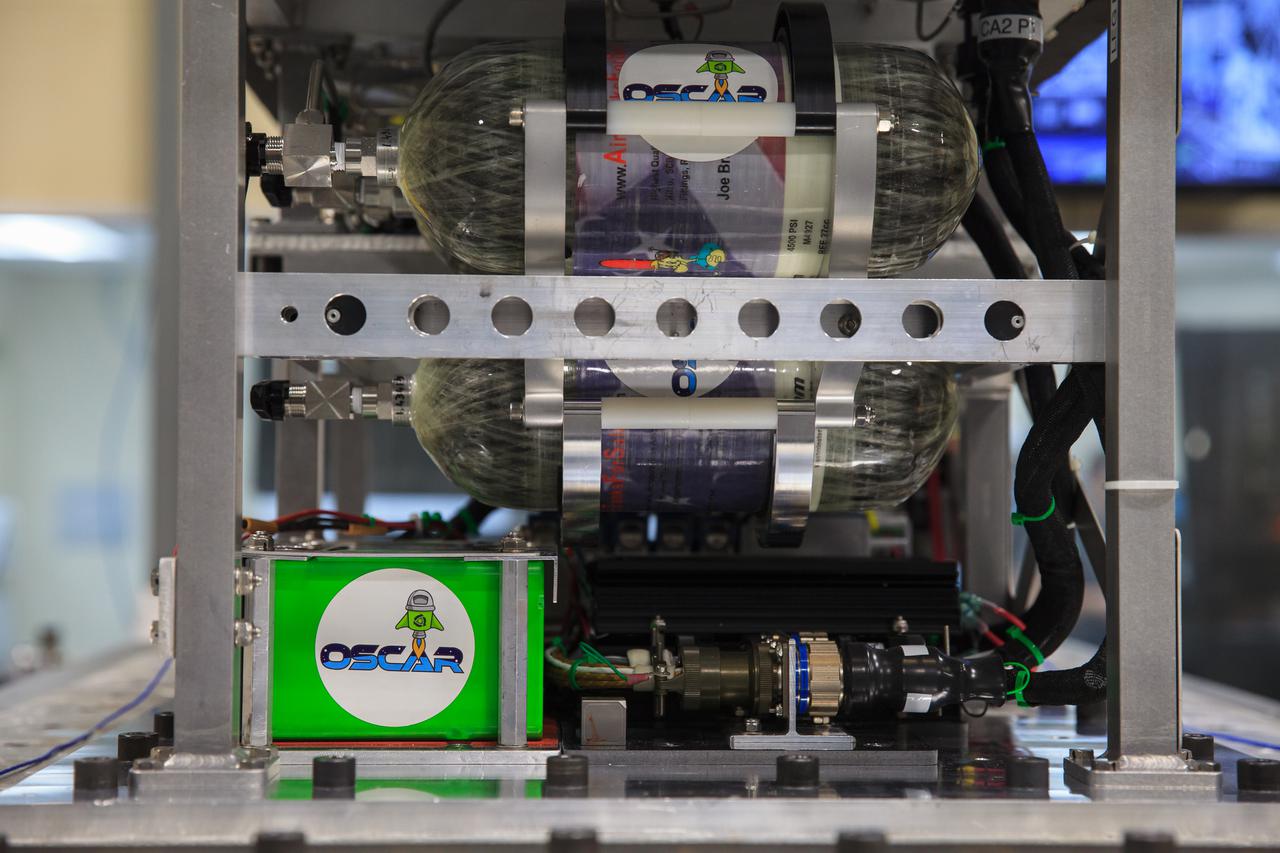
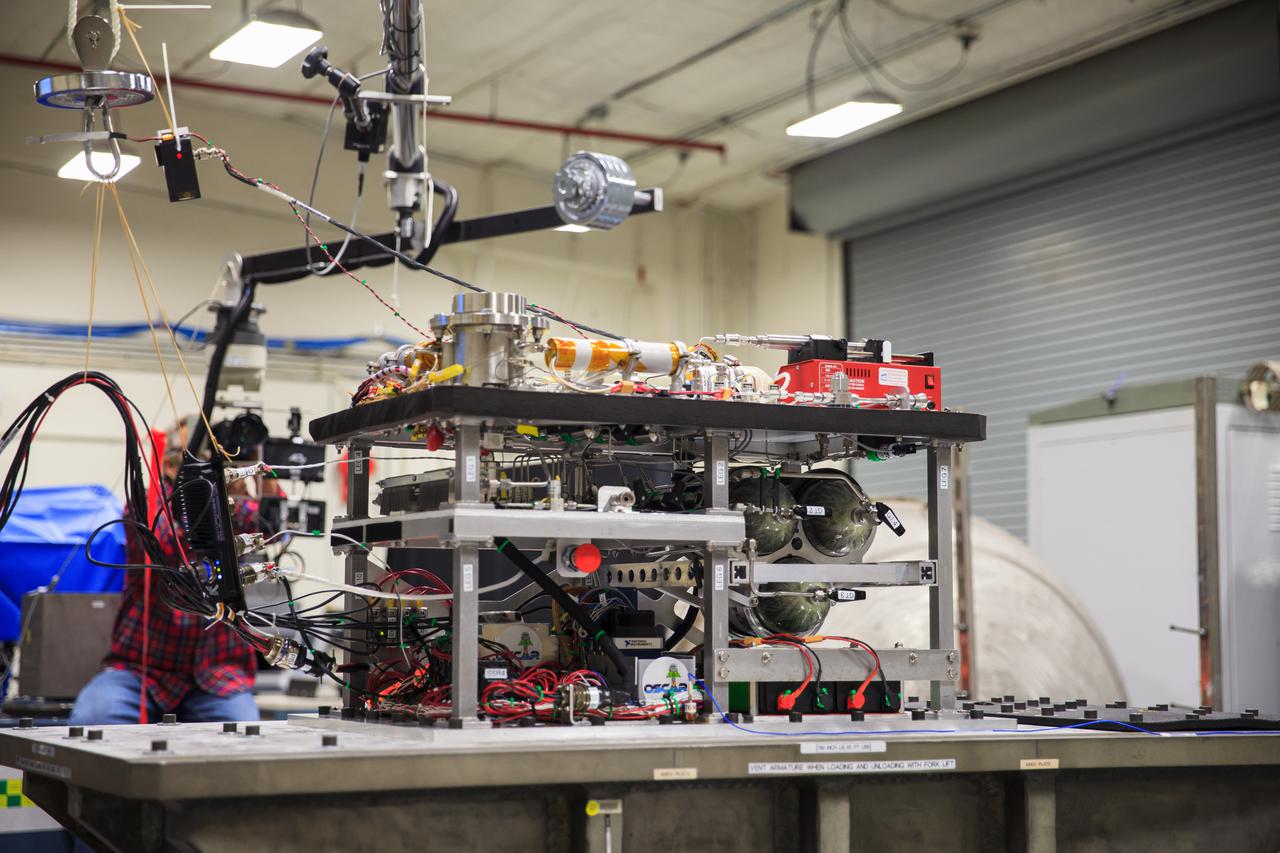
NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
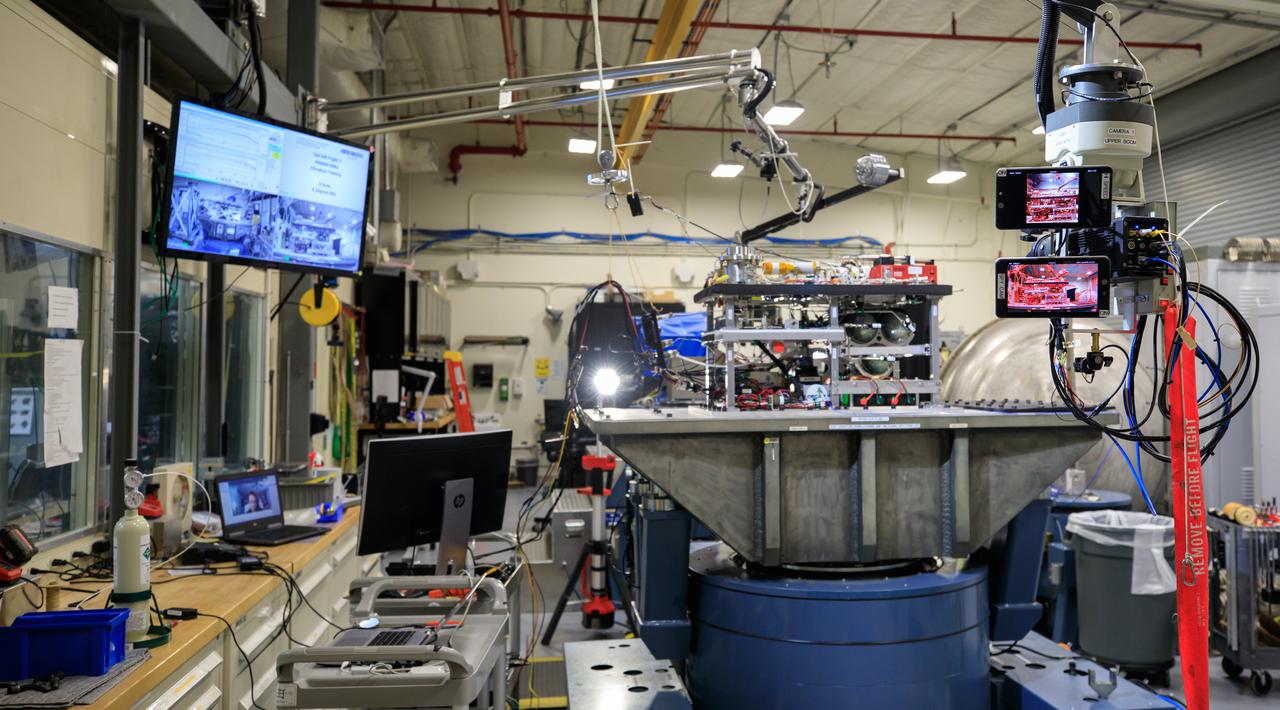

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
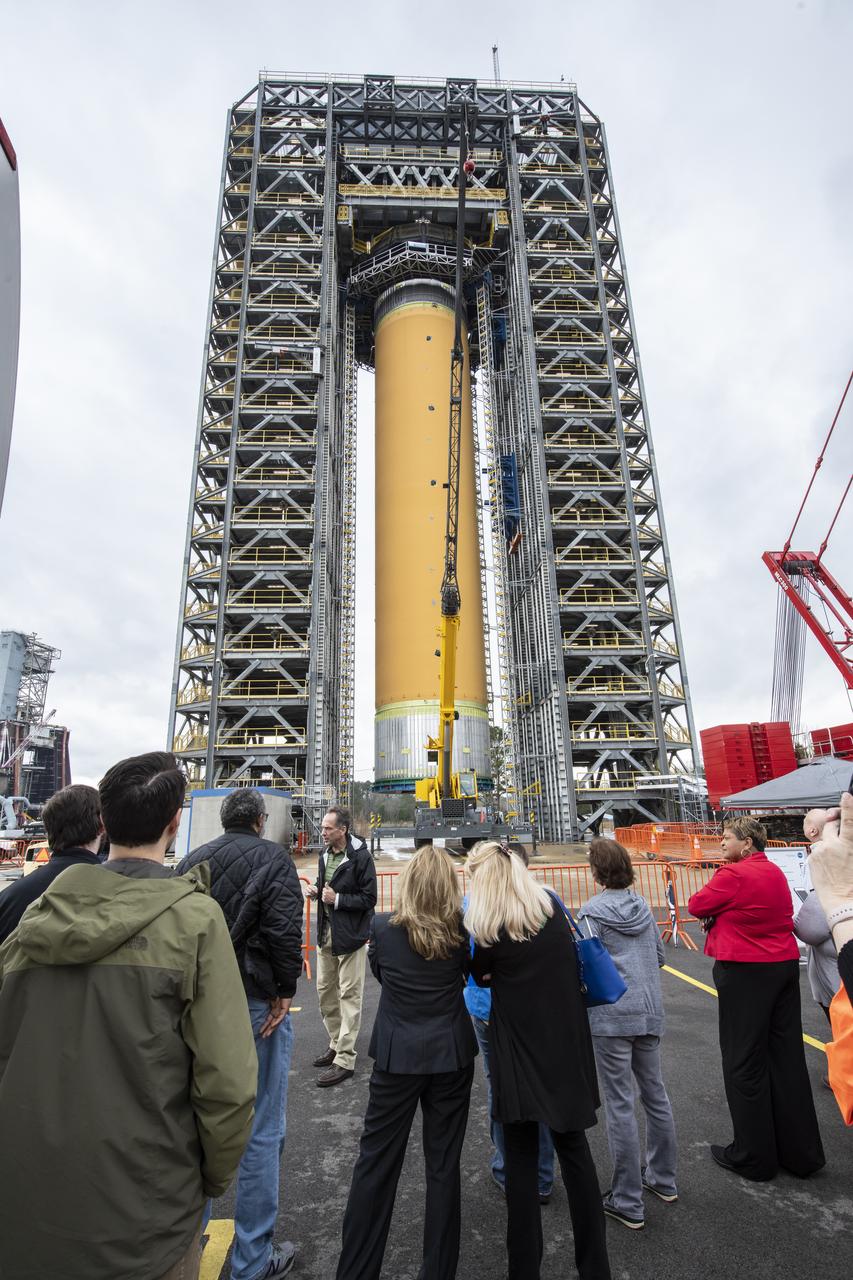

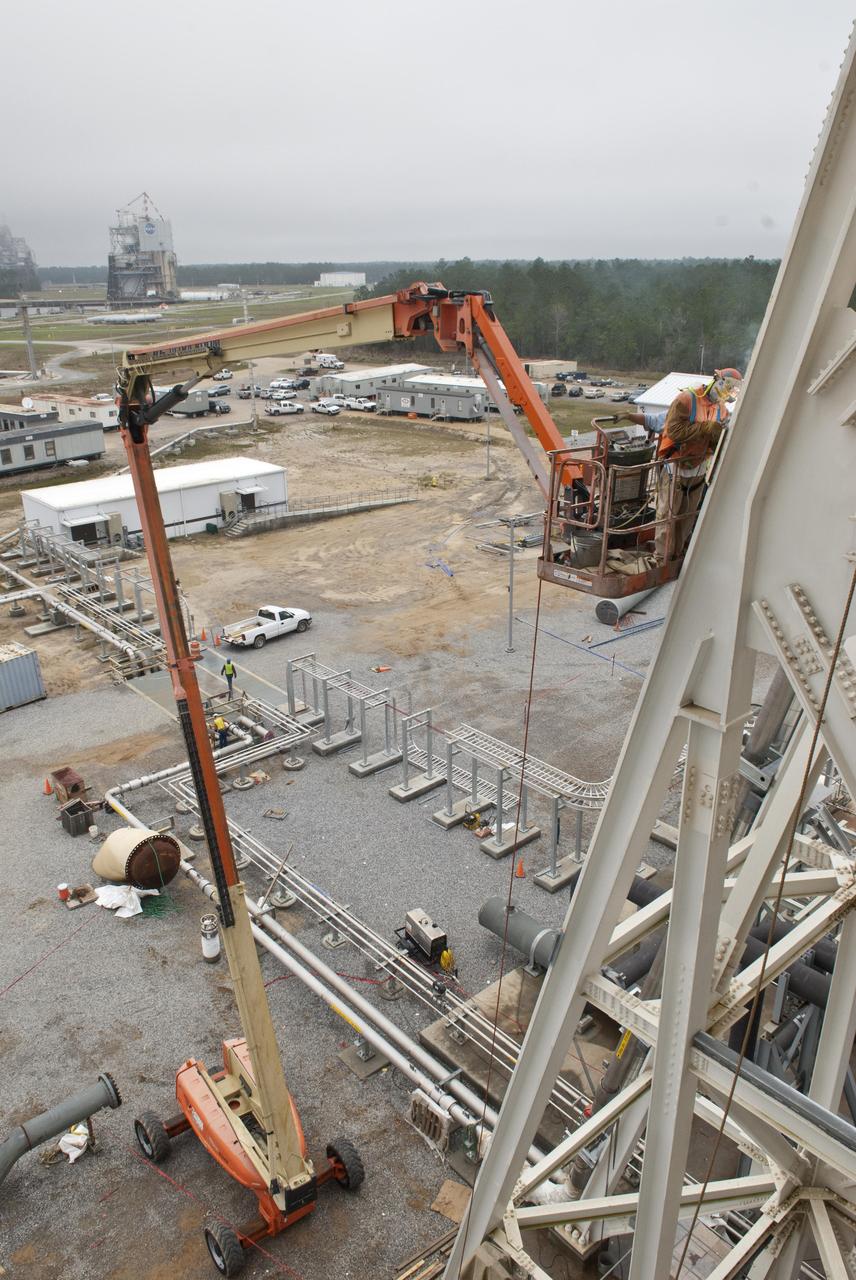
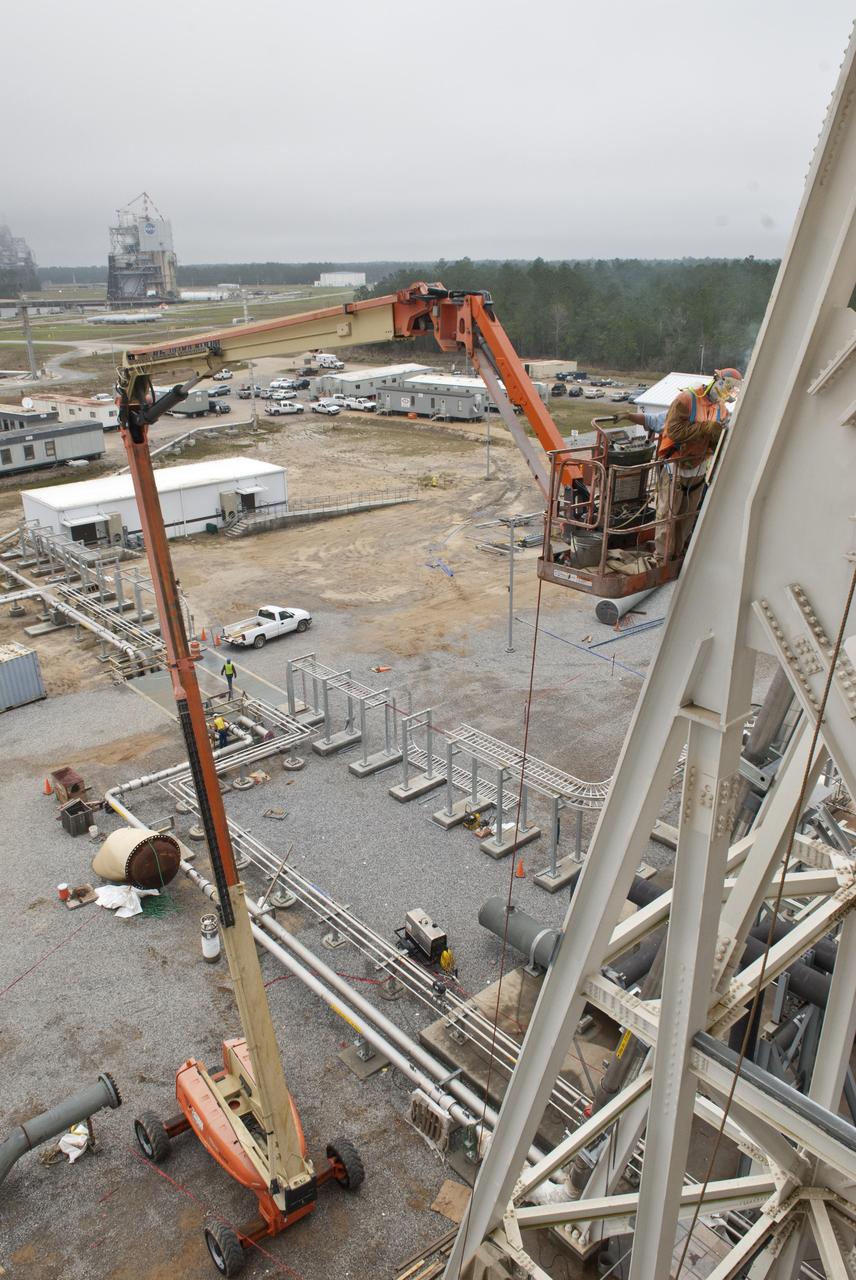
More than 700 NASA Marshall Space Flight Center team members, Boeing employees, Team Redstone participants and local officials filled 17 buses Feb. 6 to view the liquid hydrogen tank structural test article installed in Test Stand 4693 at Marshall. The 149-foot liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is the largest piece of structural test hardware for the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS). At 221 feet tall, Test Stand 4693 is the largest test stand at Marshall -- as well as one of the newest. During testing, dozens of hydraulic cylinders in the test stand will push and pull on the tank to simulate the stresses and loads it will endure during liftoff and flight for lunar missions.
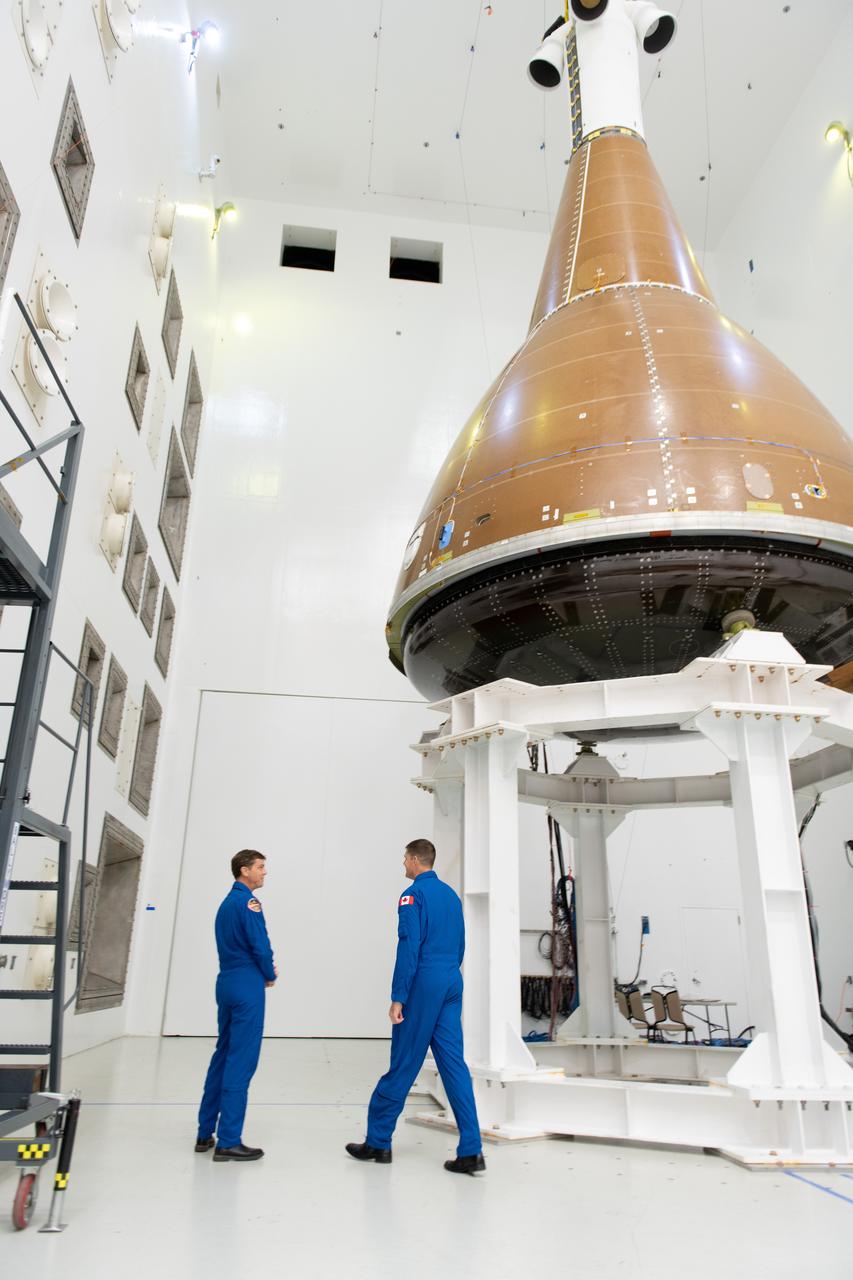

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Commander Reid Wiseman and Mission Specialist Jeremy Hansen look around during tours of the acoustic lab.

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), prepares OSCAR for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
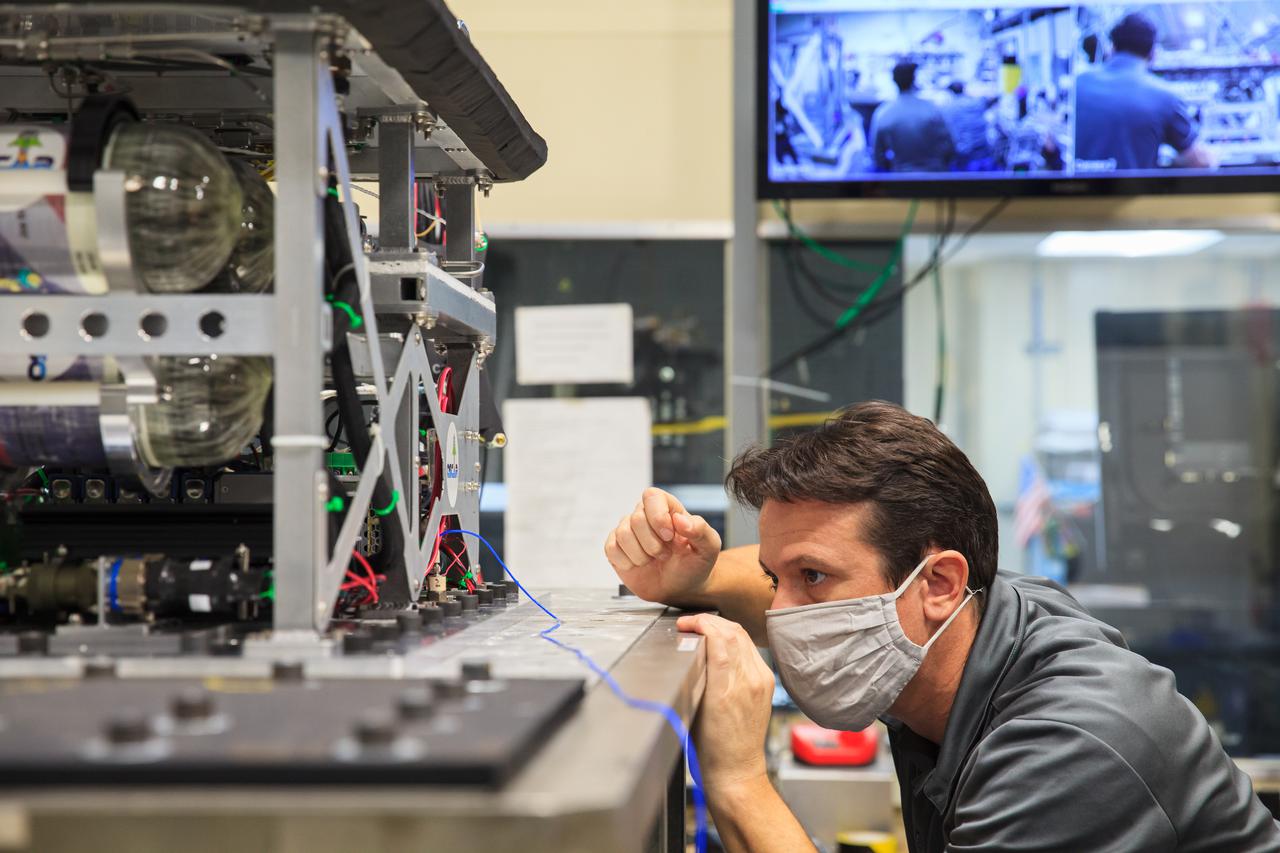

Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
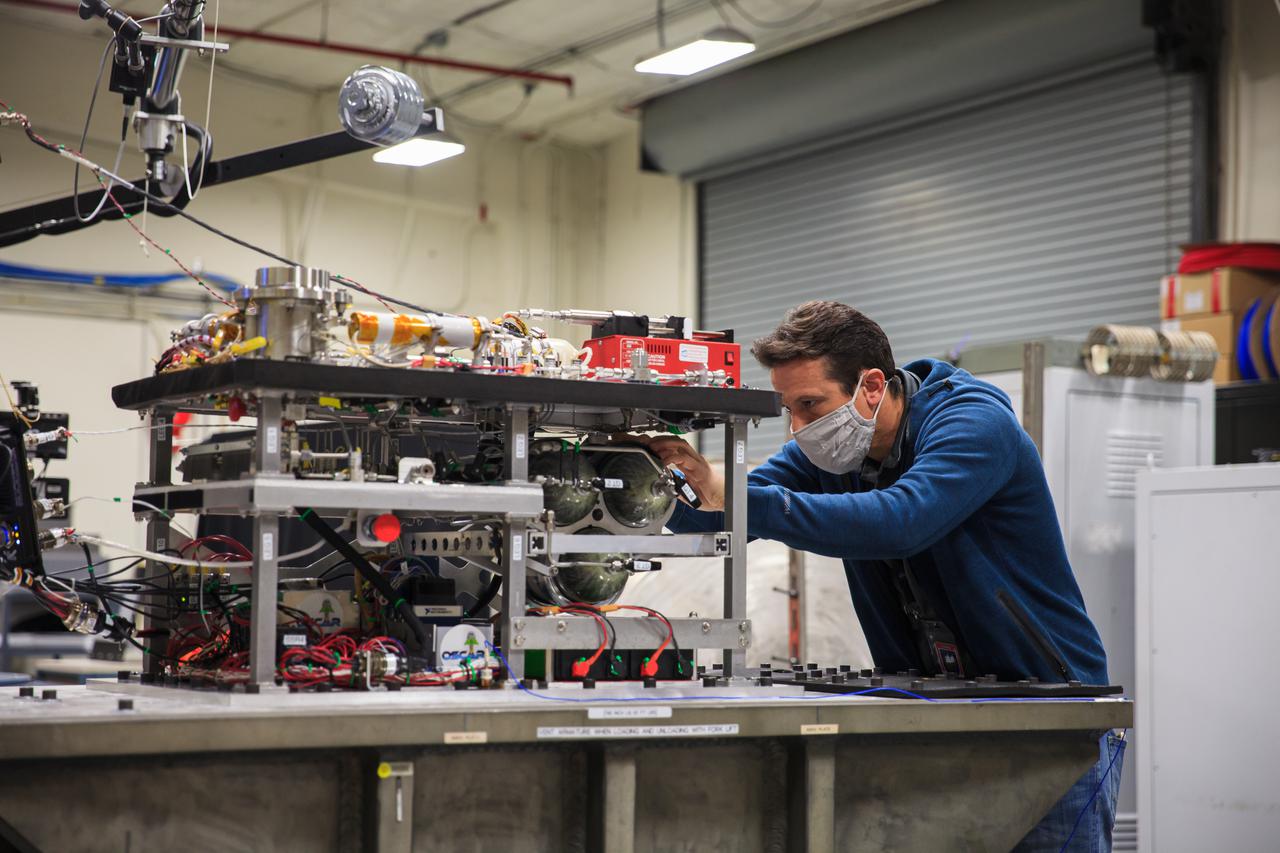

Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
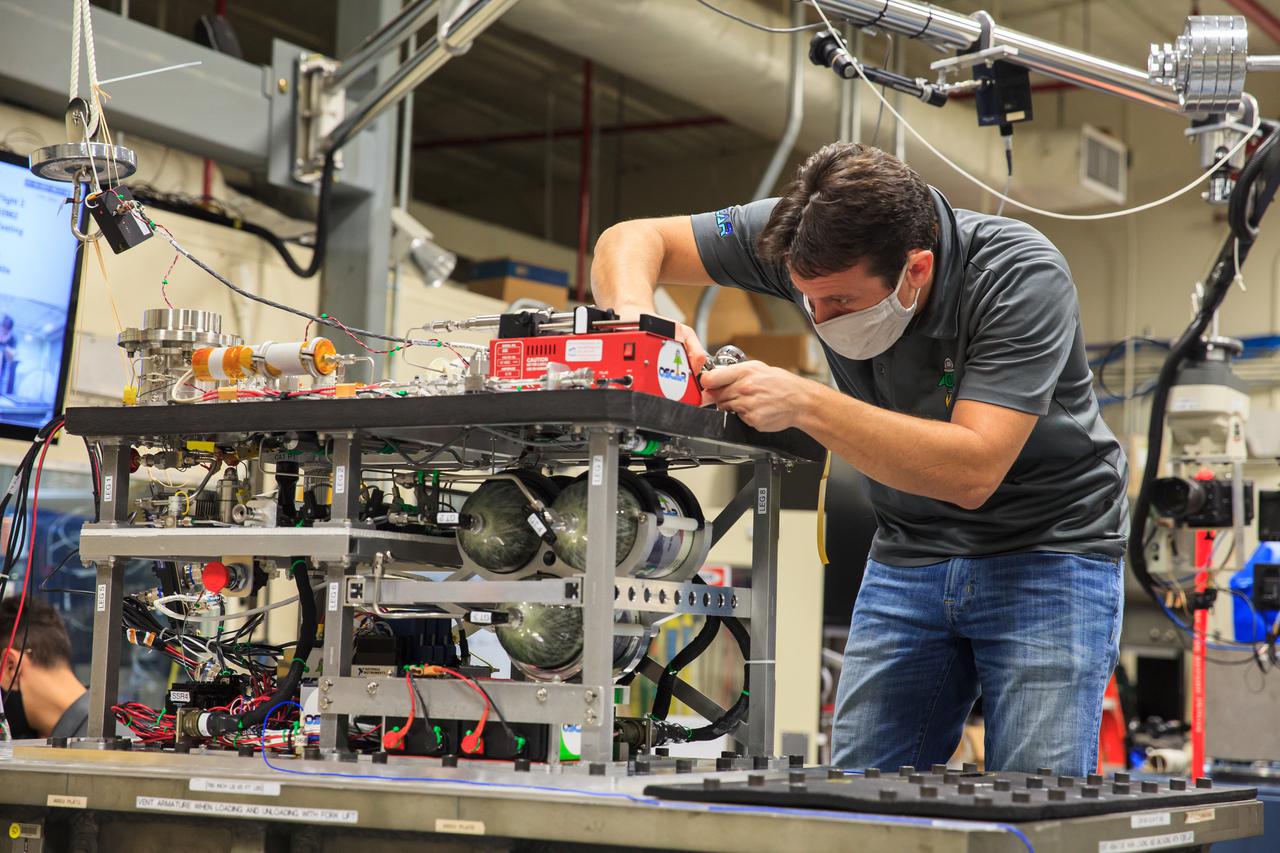
Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for Kennedy Space Center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, prepares NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) for vibration tests inside the Vibration Test Lab at the Florida spaceport on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.

Inside the Vibration Test Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) undergoes vibration testing on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.

TEST STAND 4697 WILL SUBJECT THE 196,000-GALLON CRYOGENIC LIQUID OXYGEN TANK IN THE MASSIVE CORE STAGE OF NASA'S SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM TO THE TREMENDOUS FORCES IT WILL ENDURE IN LAUNCH AND FLIGHT.
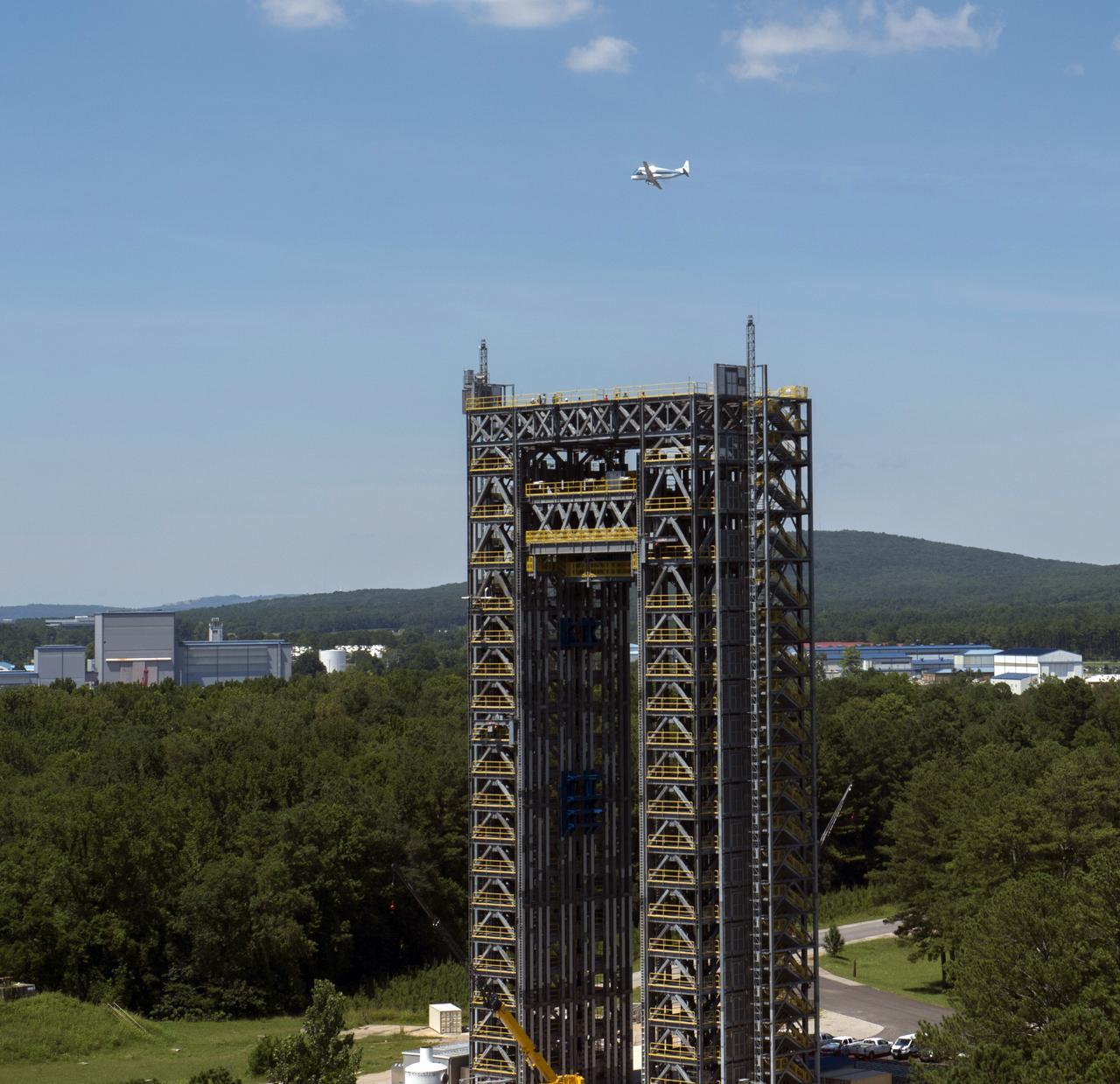

NASA's Super Guppie flies over Marshall Space Flight Center's test stand 4693 in the west test area.
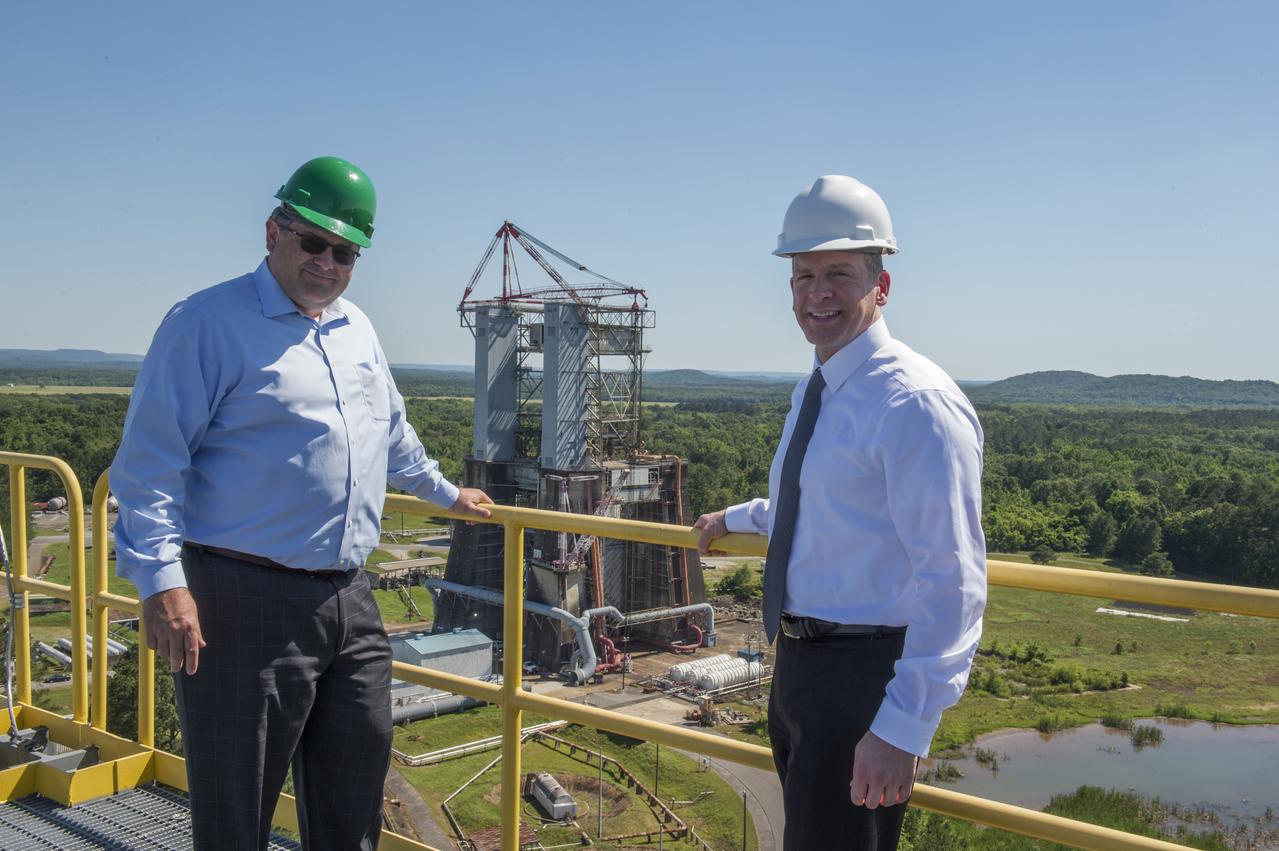

MSFC Director Todd May and FBI Associate Deputy Director Paul Abbate pose atop SLS Test Stand 4693 with historic TTB test stand in background
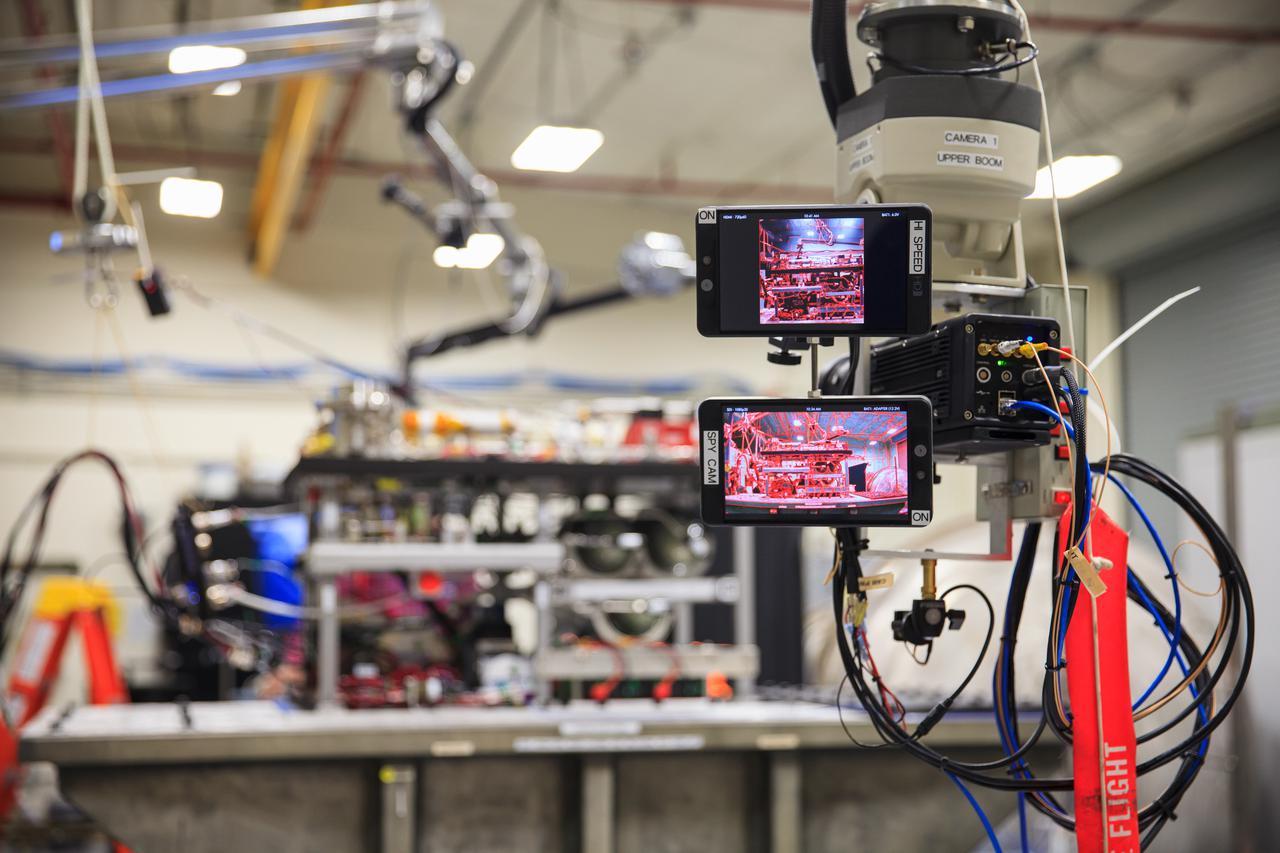

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
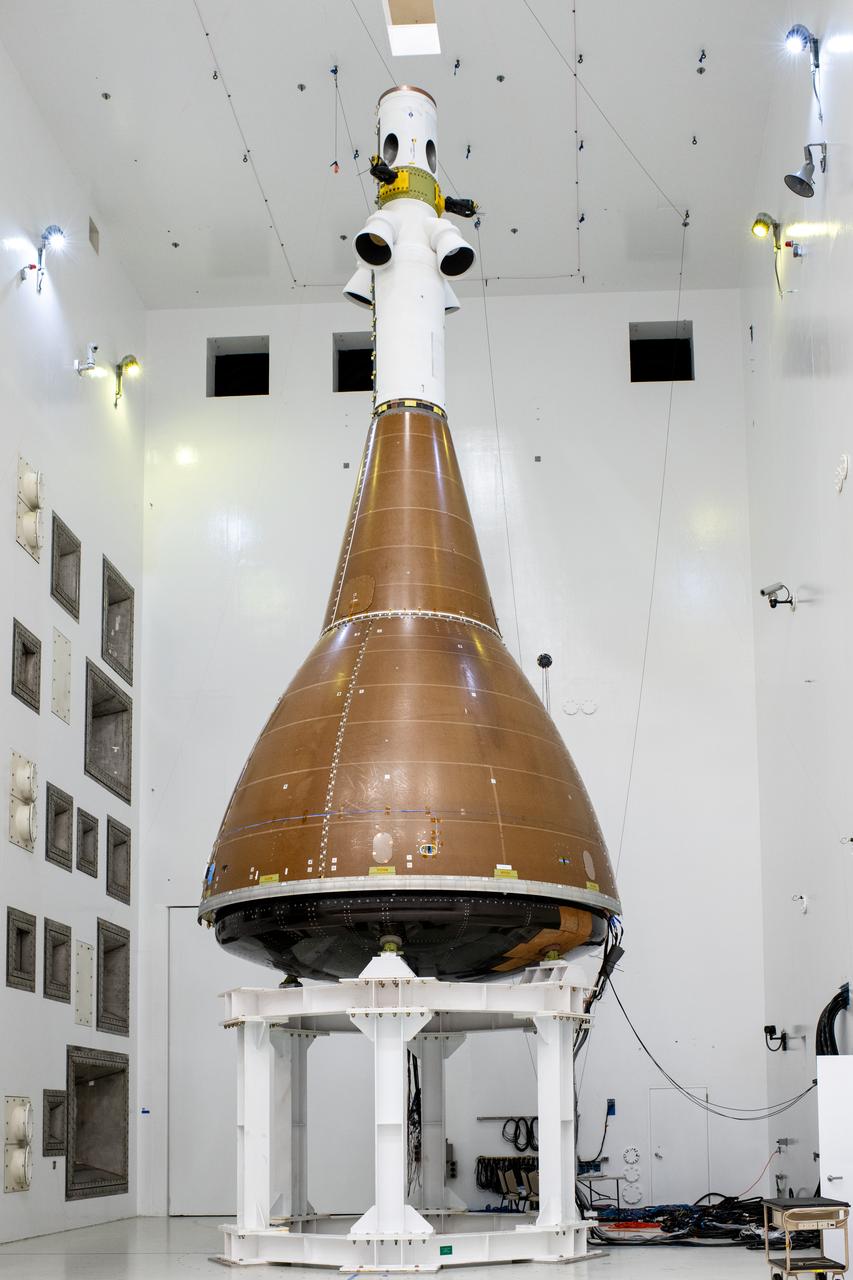

Vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article at Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, OH. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

NASA Glenn conducted a test on the Ariane 5 Payload Fairing at Plum Brook’s Space Power Facility (SPF). The test was to qualify a new horizontal pyrotechnic separation system, which blew the two fairing halves apart and away from the payload during flight.
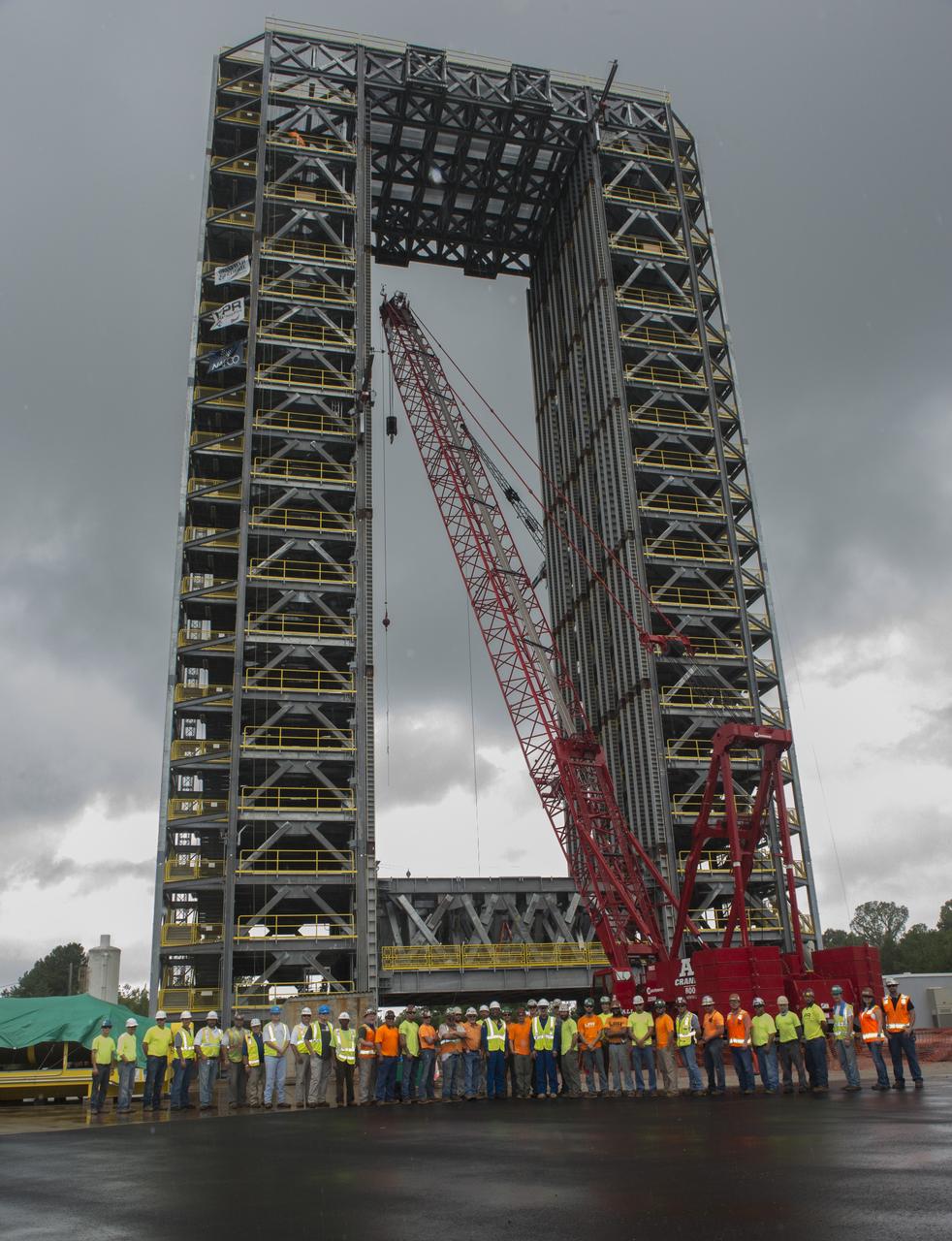

T-38 JETS FLY-OVER TEST STAND 4693 AND ASTRONAUTS DON PETTIT AND VICTOR GLOVER VISIT WITH CONSTRUCTION PERSONNEL.
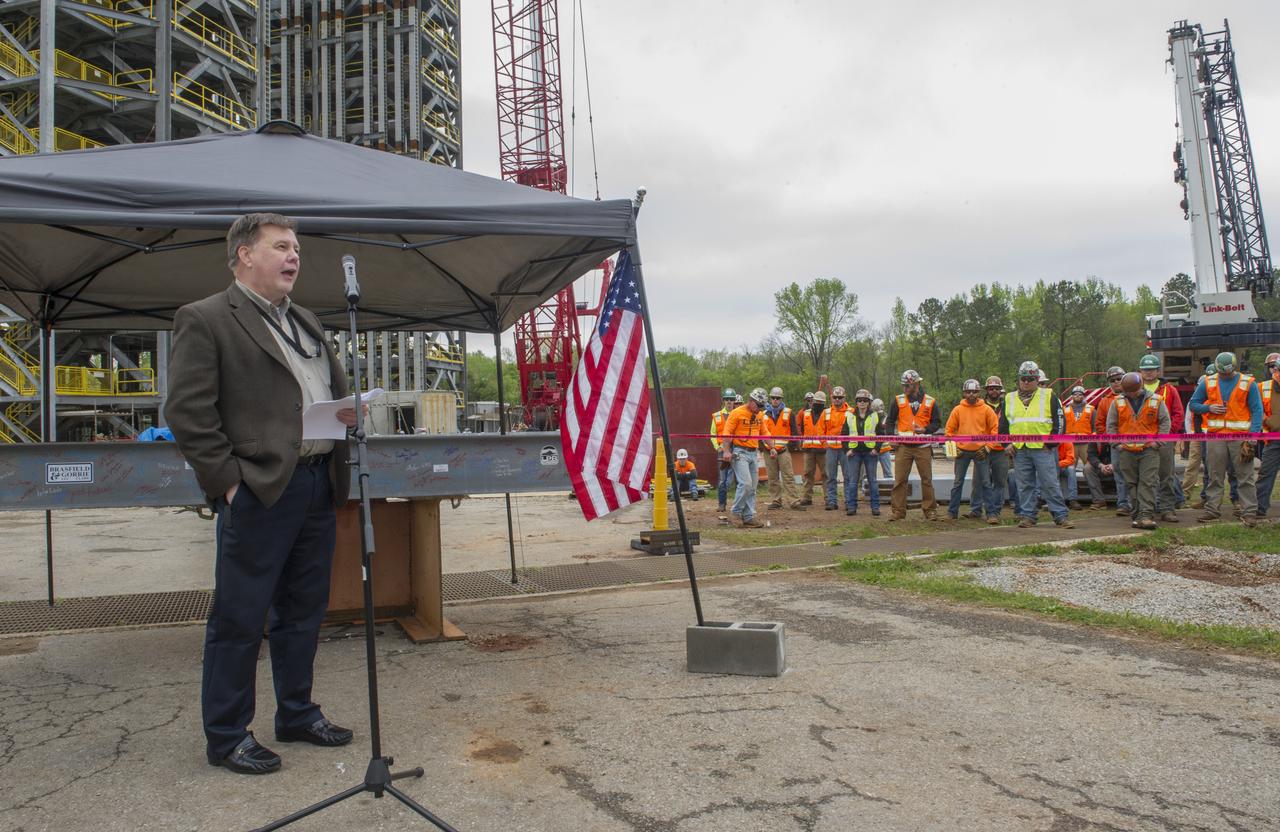

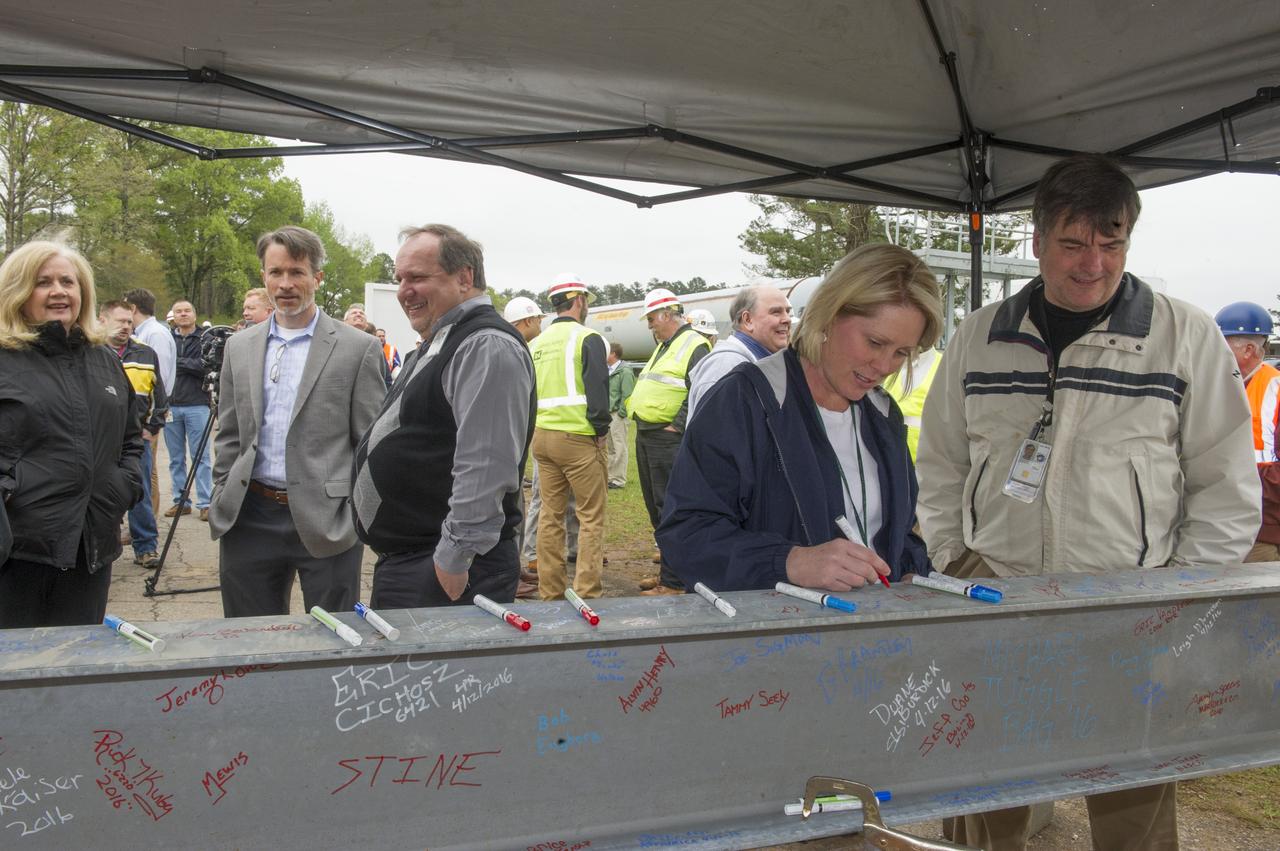
BOB DEVLIN, DEPUTY DIRECTOR OF MARSHALL'S OFFICE OF CENTER OPERATIONS, SPEAKS TO THE CROWD IN FRONT OF A STEEL BEAM DESTINED FOR TEST STAND 4693 DURING THE STRUCTURE'S TOPPING OUT CEREMONY APRIL 12.
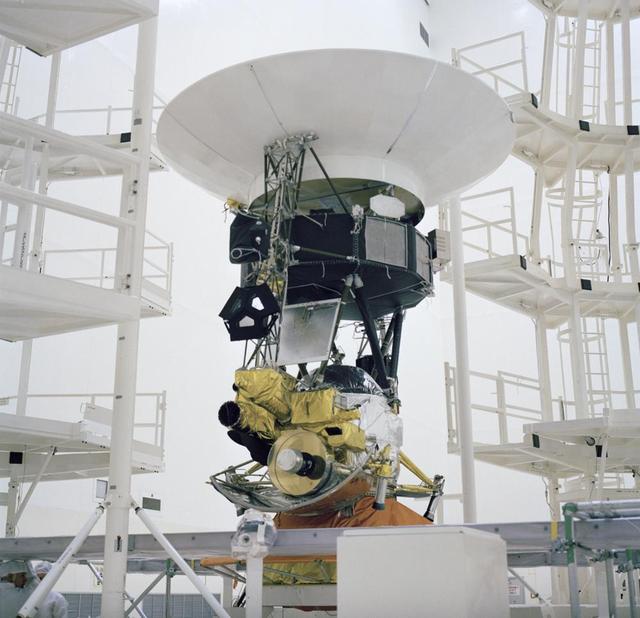

This archival photo shows the encapsulation of the Voyager Development Test Model at NASA's Kennedy Space Center's Eastern Test Range. The picture was taken on October 8, 1976. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21730
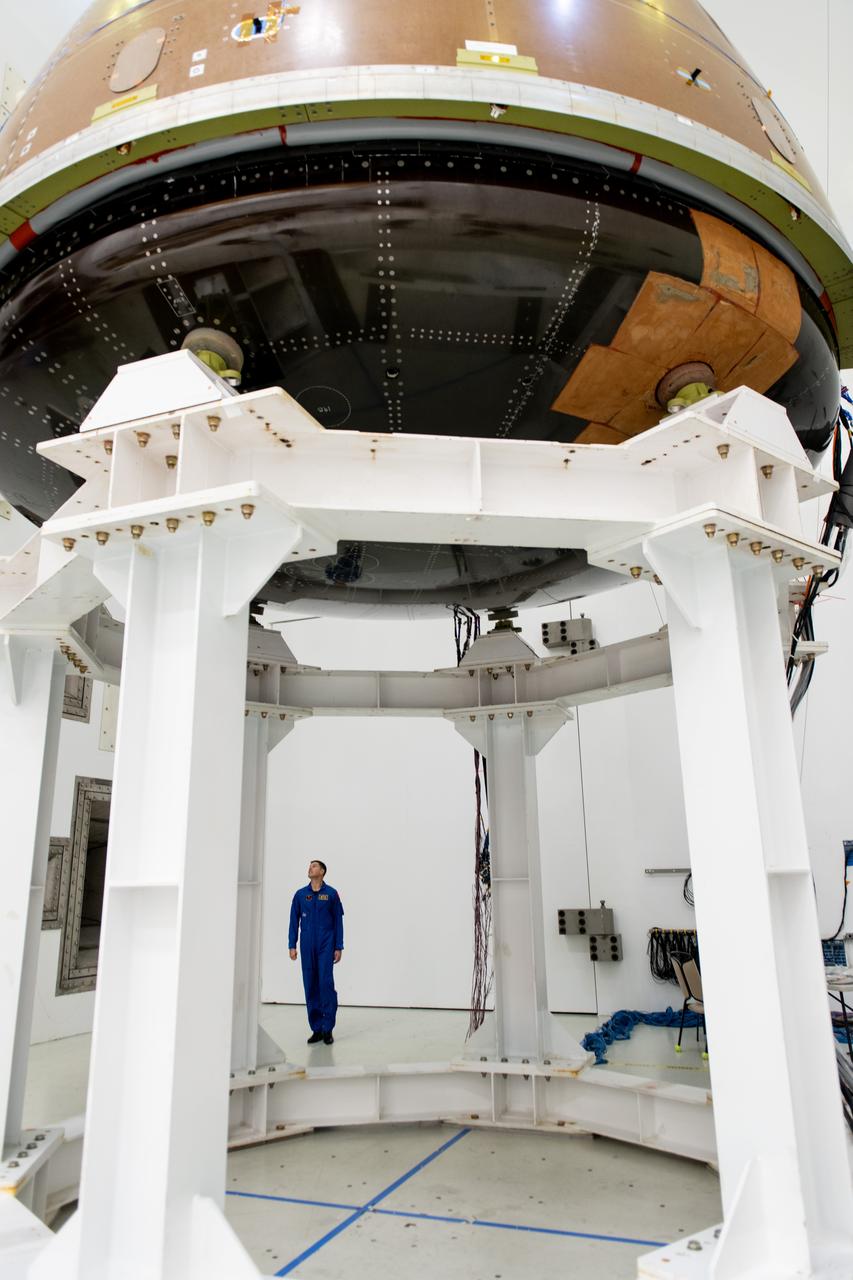

The team at NASA's Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio has begun vibro-acoustic testing on the Orion spacecraft that flew around the Moon on Artemis I, now known as the Environmental Test Article. The testing will help ensure the safety of future crews aboard Orion. Mission Specialis Jeremy Hansen looks up at the Orion capsule during tours of the acoustic lab.
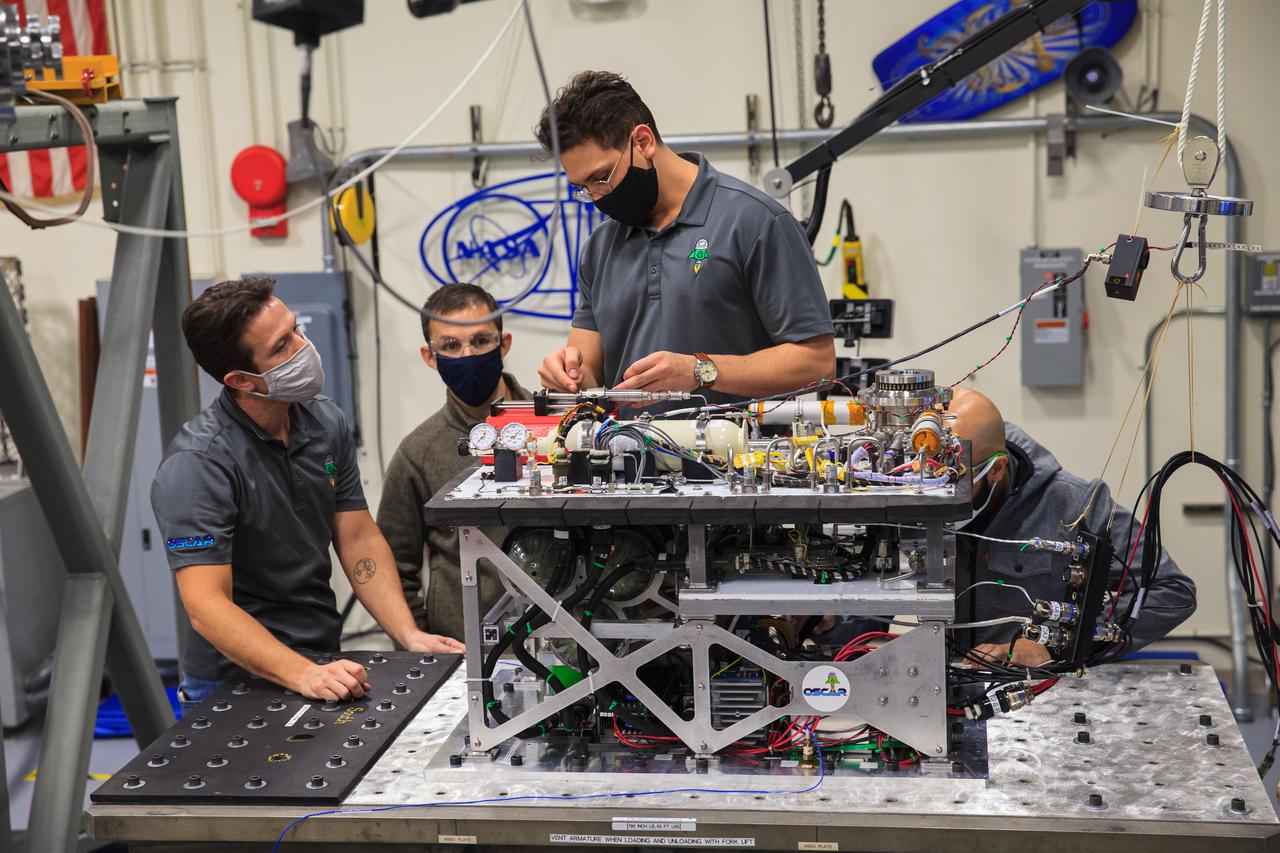
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
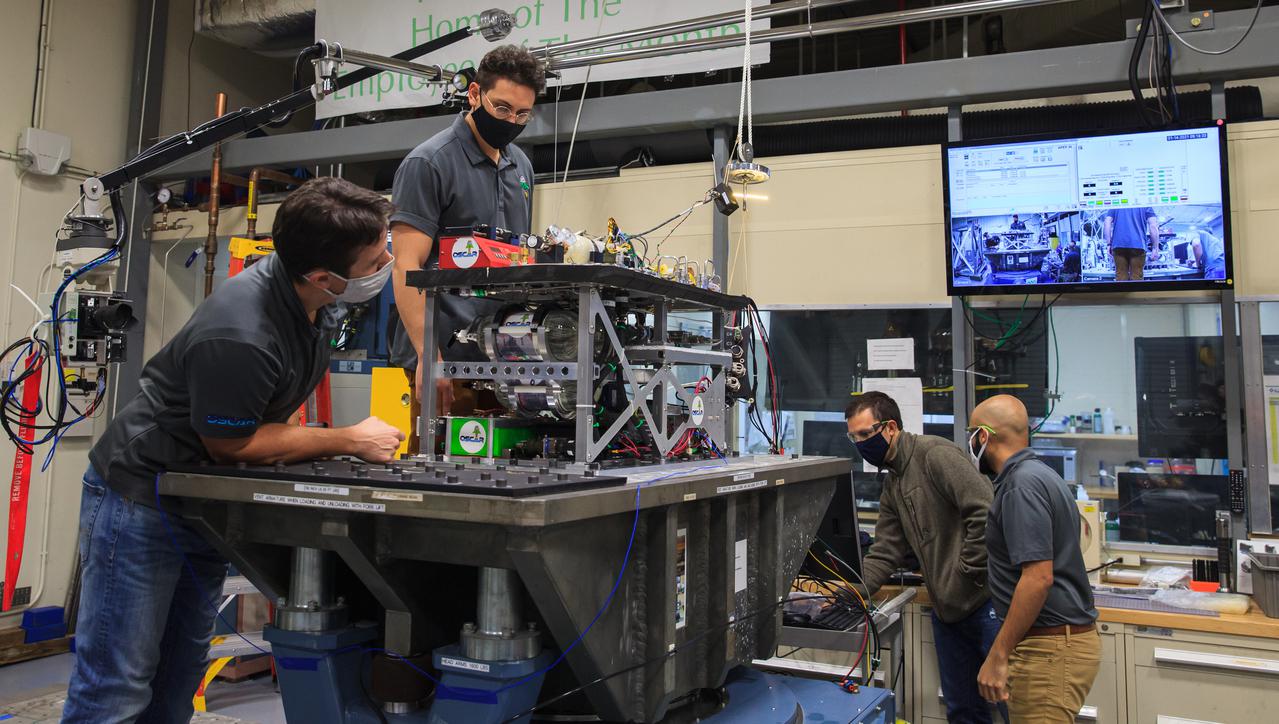
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
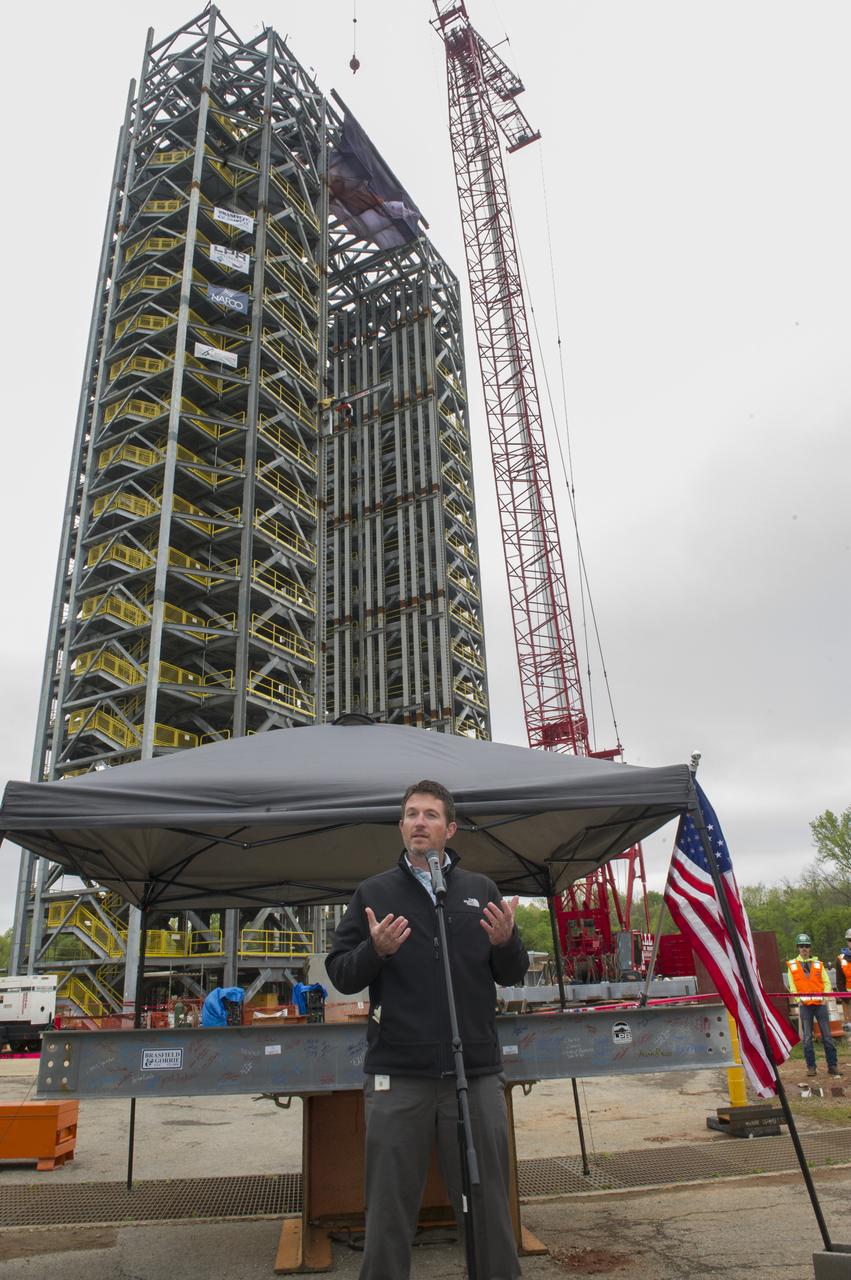

PHIL HENDRIX, SPEAKS TO THE CROWD IN FRONT OF A STEEL BEAM DESTINED FOR TEST STAND 4693 DURING THE STRUCTURE'S TOPPING OUT CEREMONY APRIL 12.
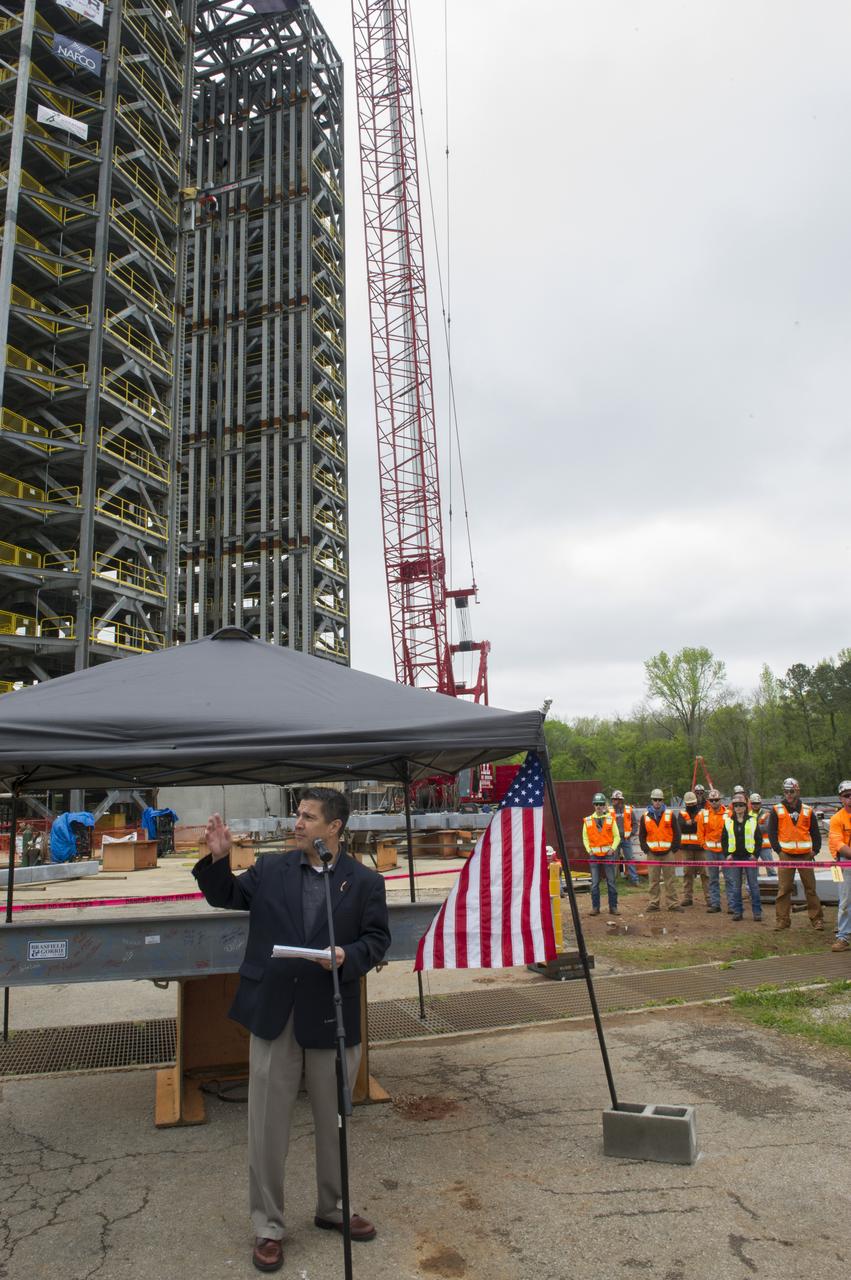

TIM FLORES SPEAKS TO THE CROWD IN FRONT OF A STEEL BEAM DESTINED FOR TEST STAND 4693 DURING THE STRUCTURE'S TOPPING OUT CEREMONY APRIL 12.

SLS INTERTANK TEST ARTICLE IS ATTACHED TO CROSSHEAD OF LOAD TEST ANNEX, BLDG. 4619, AND REMOVED FROM BED OF KMAG TRANSPORTER. Matt Cash conducts tag up meeting before lift of ITA from KMAG transporter
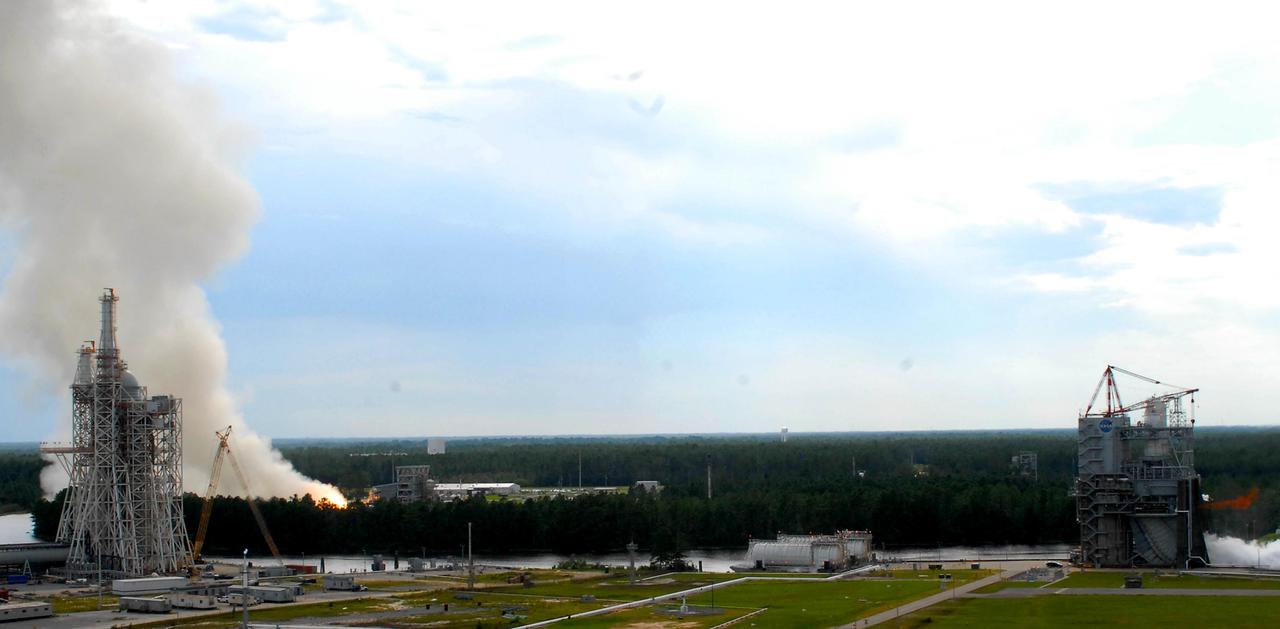

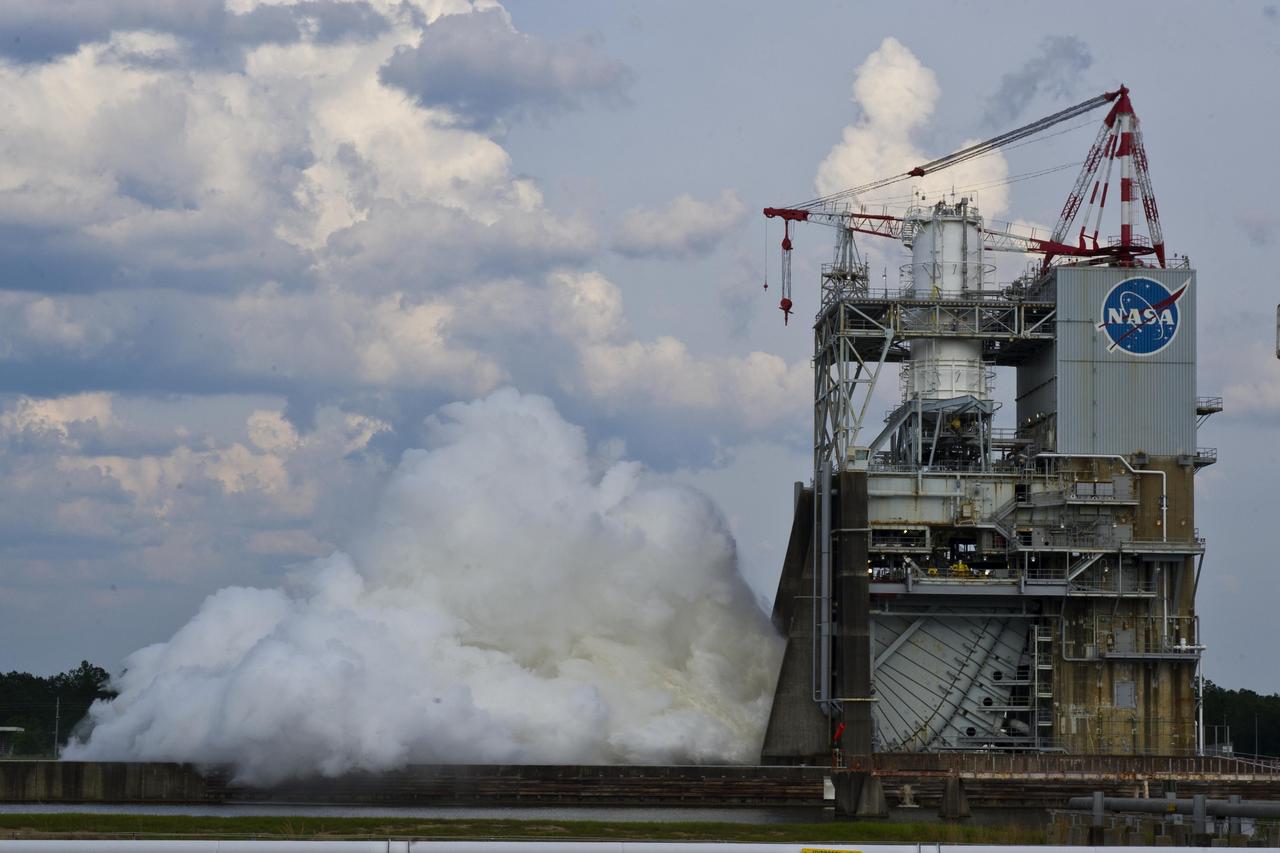
Two large-engine tests were conducted simultaneously for the first time at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16. A plume on the left indicates a test on the facility's E-1 Test Stand. On the right, a finger of fire indicates a test under way on the A-1 Test Stand. In another first, both tests were conducted by female engineers. The image was taken from atop the facility's A-2 Test Stand, offering a panoramic view that includes the new A-3 Test Stand under construction to the left.
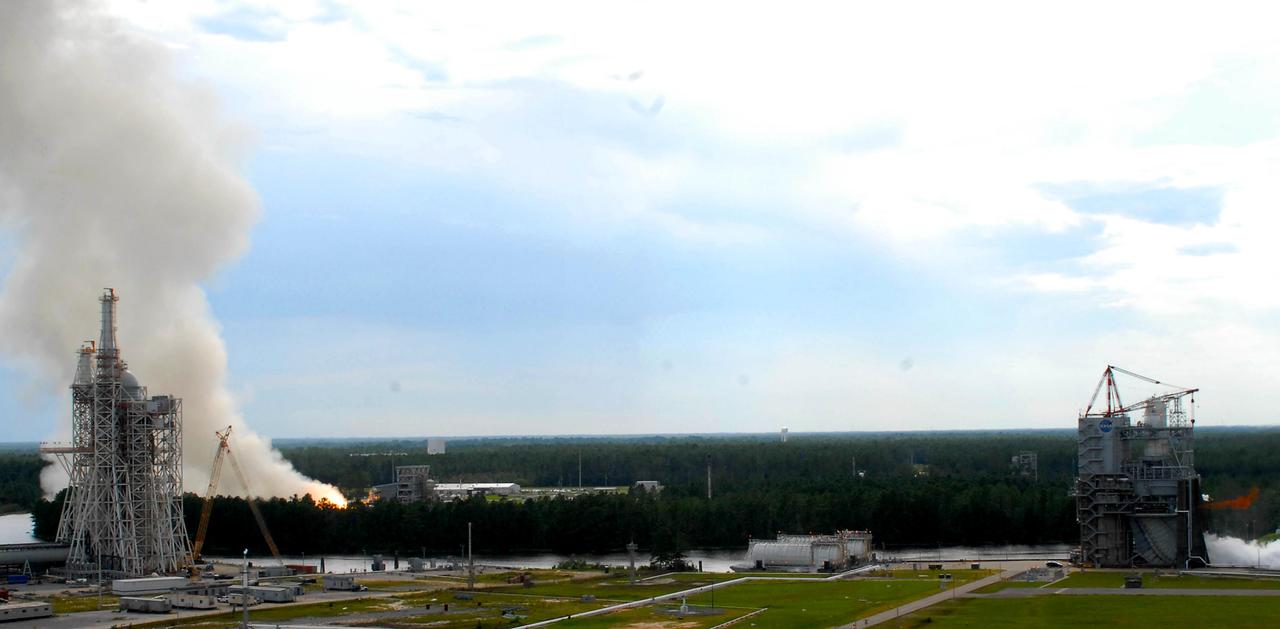

Two large-engine tests were conducted simultaneously for the first time at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16. A plume on the left indicates a test on the facility's E-1 Test Stand. On the right, a finger of fire indicates a test under way on the A-1 Test Stand. In another first, both tests were conducted by female engineers. The image was taken from atop the facility's A-2 Test Stand, offering a panoramic view that includes the new A-3 Test Stand under construction to the left.

This archival photo shows the Voyager Proof Test Model undergoing a mechanical preparation and weight center of gravity test at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, on January 12, 1977. The stack of three white cylinders seen near center is a stand-in for the spacecraft's power generators (called RTGs). Above that, a silvery canister holds the spacecraft's magnetometer in its stowed configuration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21477

This archival photo shows the Voyager Proof Test Model (in the foreground right of center) undergoing a mechanical preparation and weight center of gravity test at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, on January 12, 1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21476
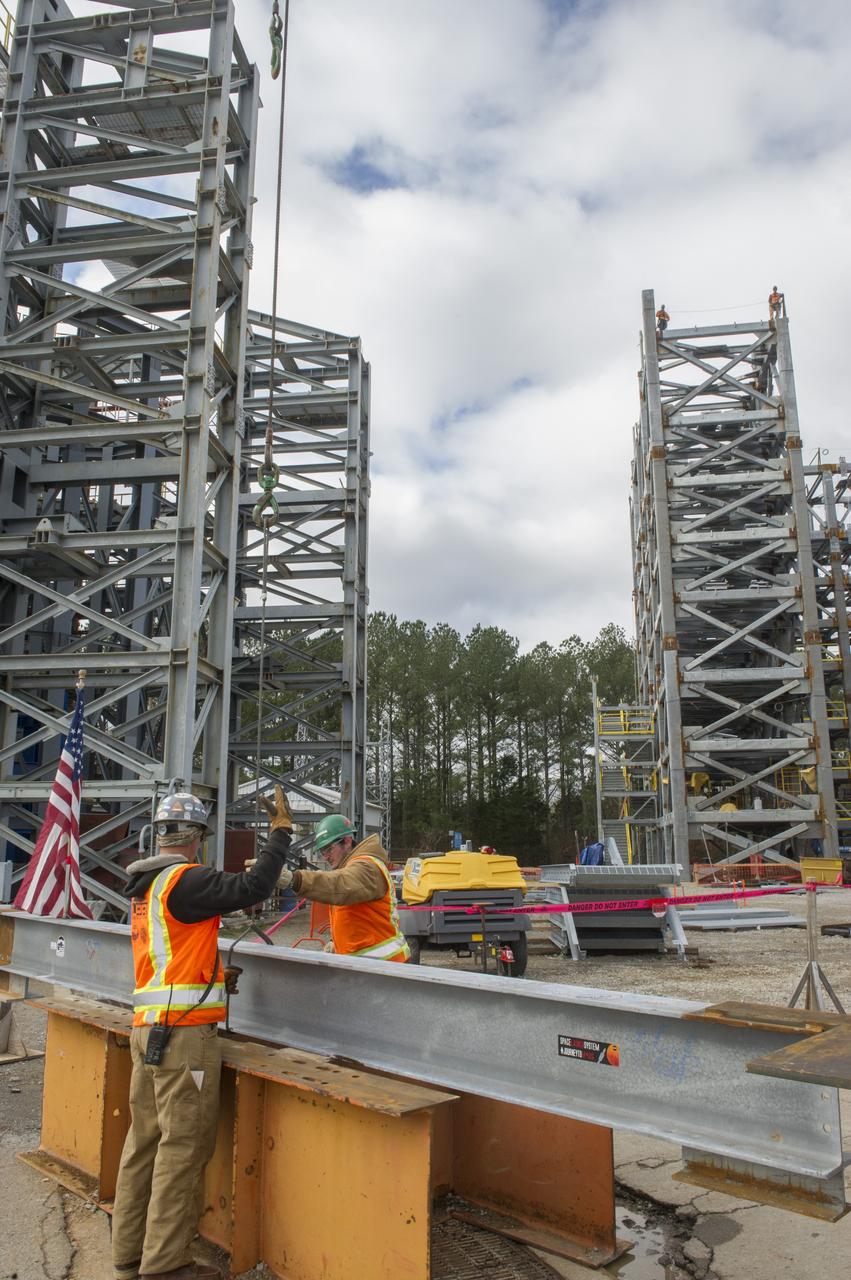

ON MARCH 4, CREW MEMBERS READIED A 900-POUND STEEL BEAM TO "TOP OUT" TEST STAND 4697, WHICH IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION TO TEST THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER.
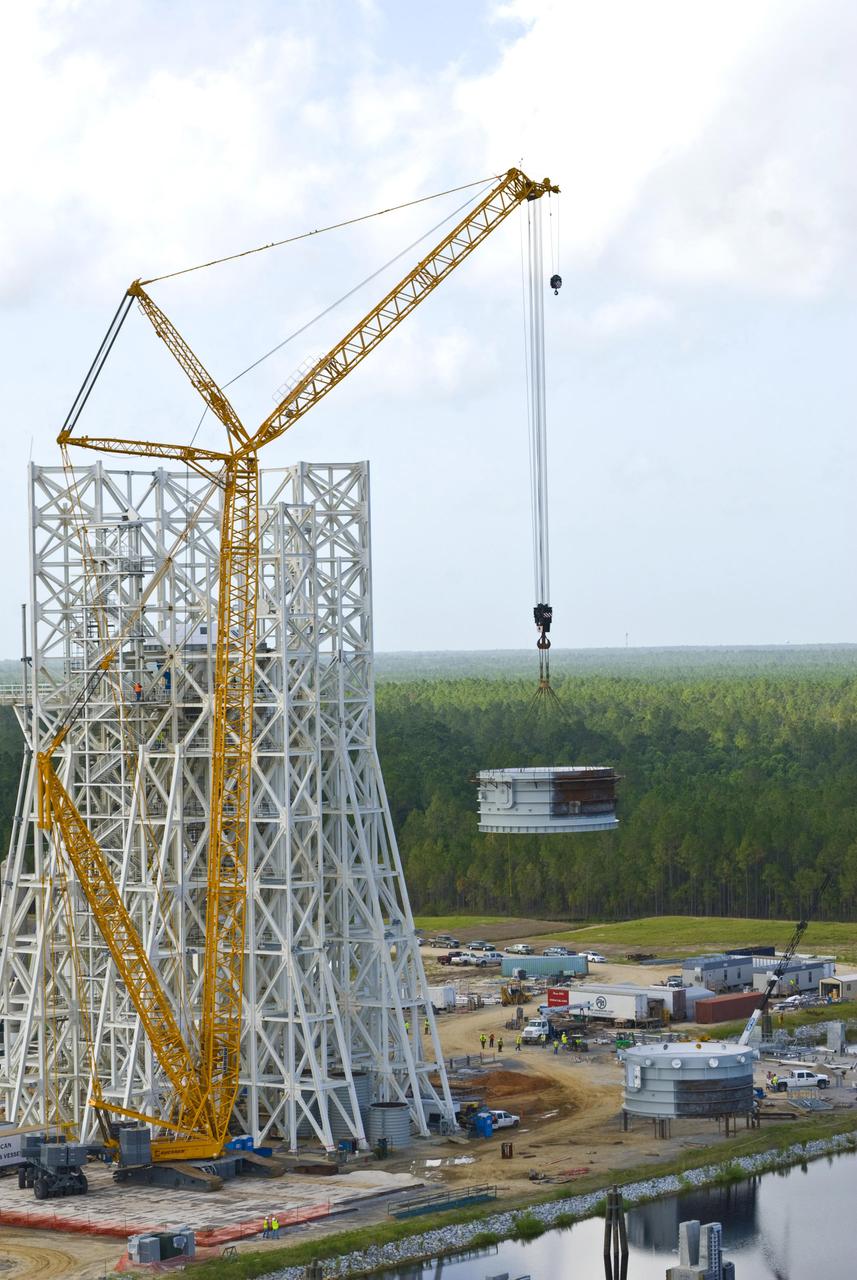

Employees at Stennis Space Center continue work on the A-3 Test Stand. As shown, a section of the test cell is lifted for installation on the stand's structural steel frame. Work on the A-3 Test Stand began in 2007. It is scheduled for activation in 2012.
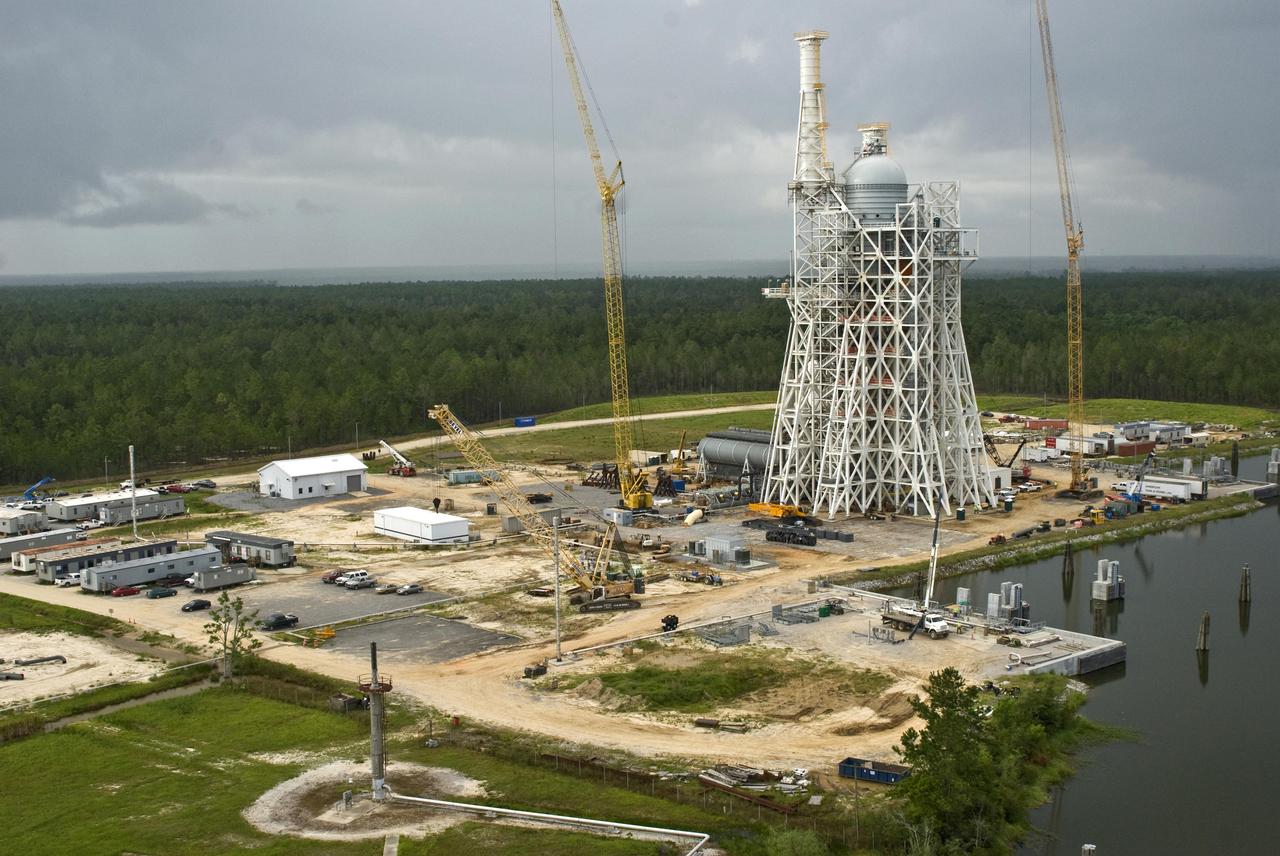

Work continues on the A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. The new stand will allow operators to test next-generation rocket engines at simulated altitudes up to 100,000 feet. The test stand is scheduled for completion and activation in 2013.

Work continues on the A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. The new stand will allow operators to test next-generation rocket engines at simulated altitudes up to 100,000 feet. The test stand is scheduled for completion and activation in 2013.

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA WITH THE SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-) IN FOREGROUND
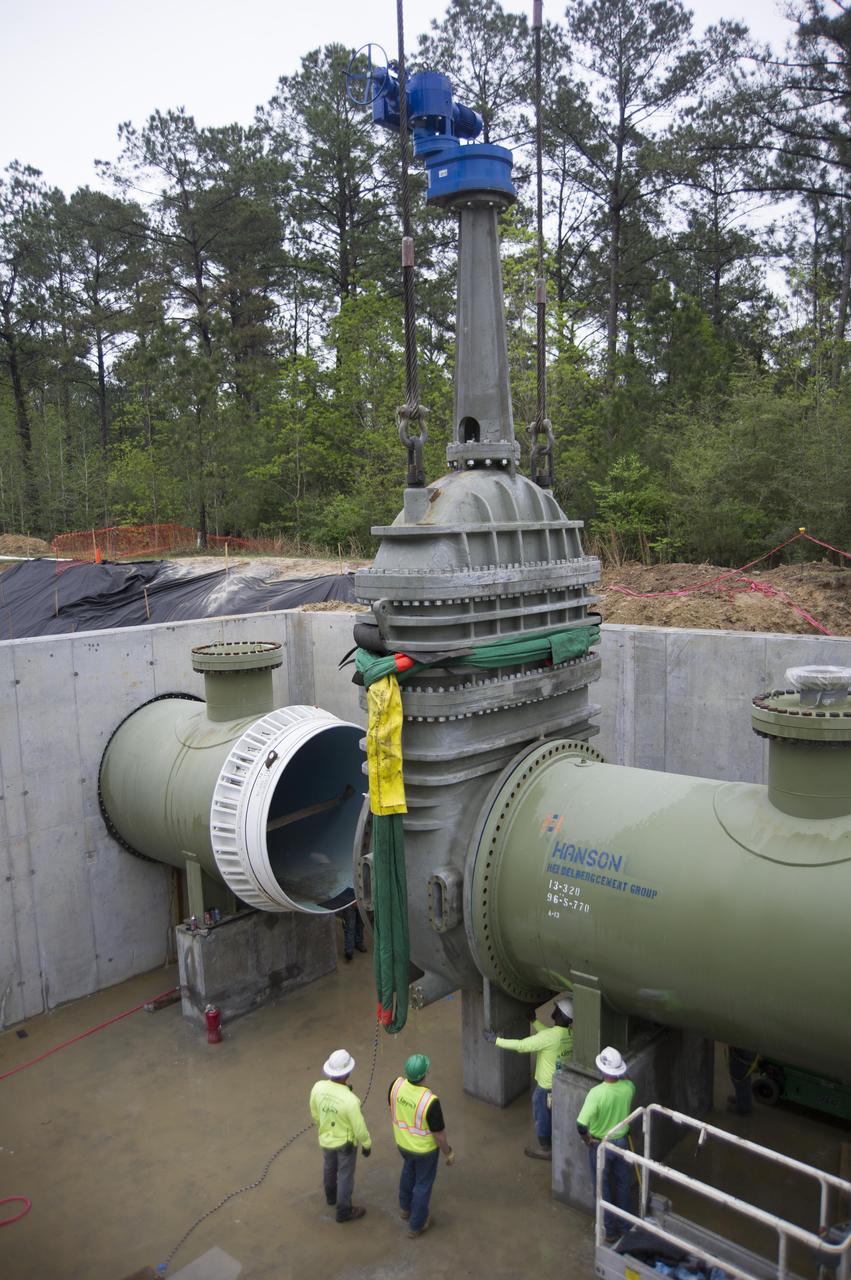

Stennis Space Center employees install a 96-inch valve during a recent upgrade of the high-pressure industrial water system that serves the site’s large rocket engine test stands. The upgraded system has a capacity to flow 335,000 gallons of water a minute, which is a critical element for testing. At Stennis, engines are anchored in place on large test stands and fired just as they are during an actual space flight. The fire and exhaust from the test is redirected out of the stand by a large flame trench. A water deluge system directs thousands of gallons of water needed to cool the exhaust. Water also must be available for fire suppression in the event of a mishap. The new system supports RS-25 engine testing on the A-1 Test Stand, as well as testing of the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis.

HEATHER HANEY SIGNS FINAL BEAM TO BE PLACED ATOP TEST STAND 4693 DURING THE STRUCTURE'S TOPPING OUT CEREMONY
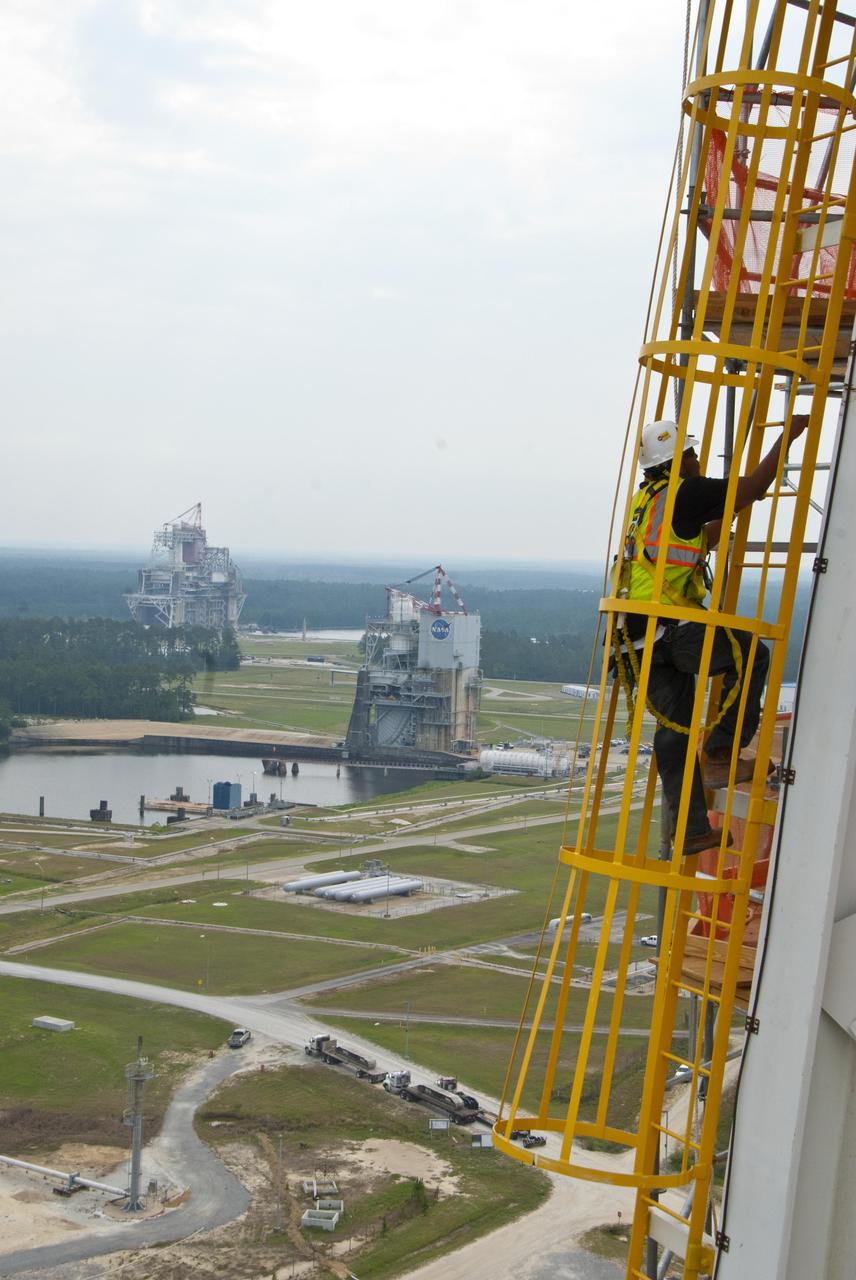

A tethered Stennis Space Center employee climbs an A-3 Test Stand ladder June 8, 2012, against the backdrop of the A-2 and B-1/B-2 stands. The new A-3 Test Stand will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.
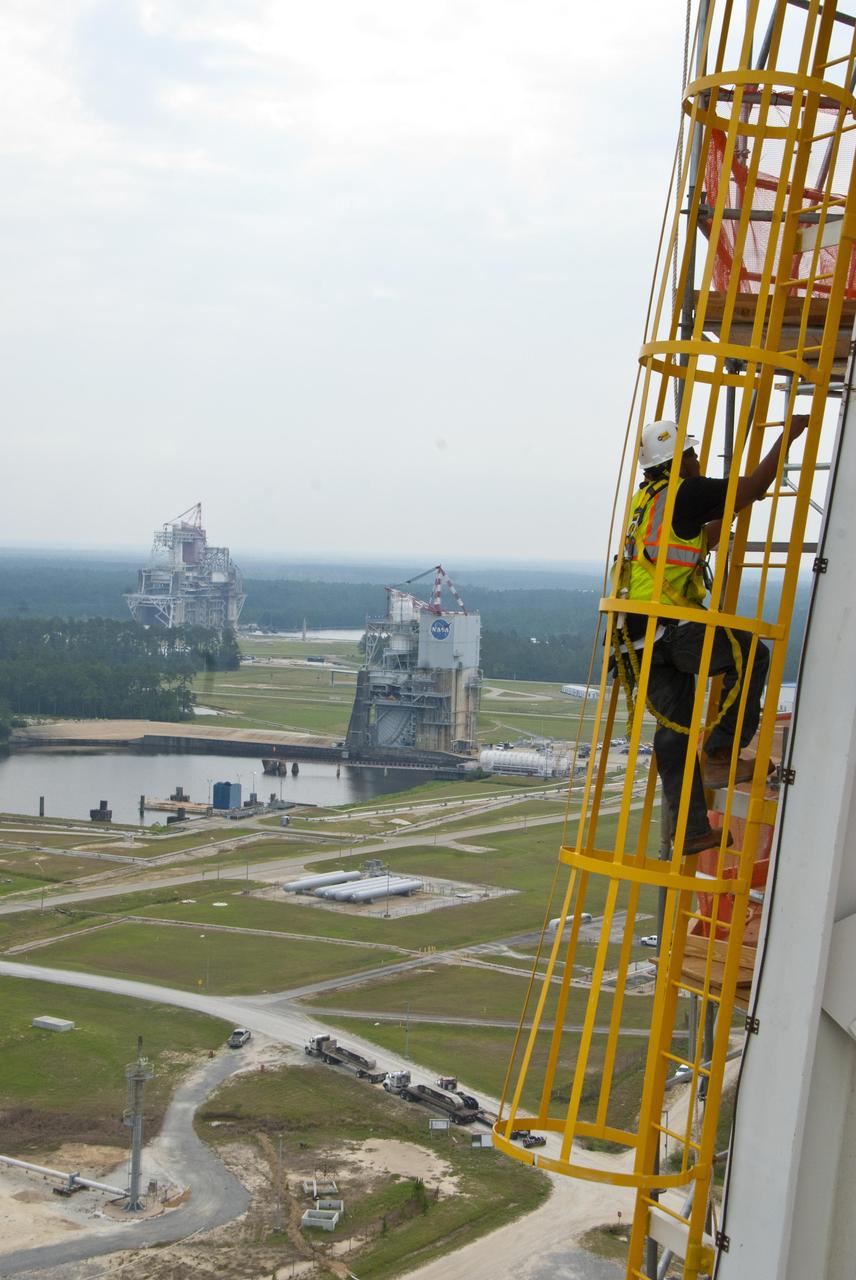

A tethered Stennis Space Center employee climbs an A-3 Test Stand ladded June 8, 2012, against the backdrop of the A-2 and B-1/B-2 stands. The new A-3 Test Stand will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.
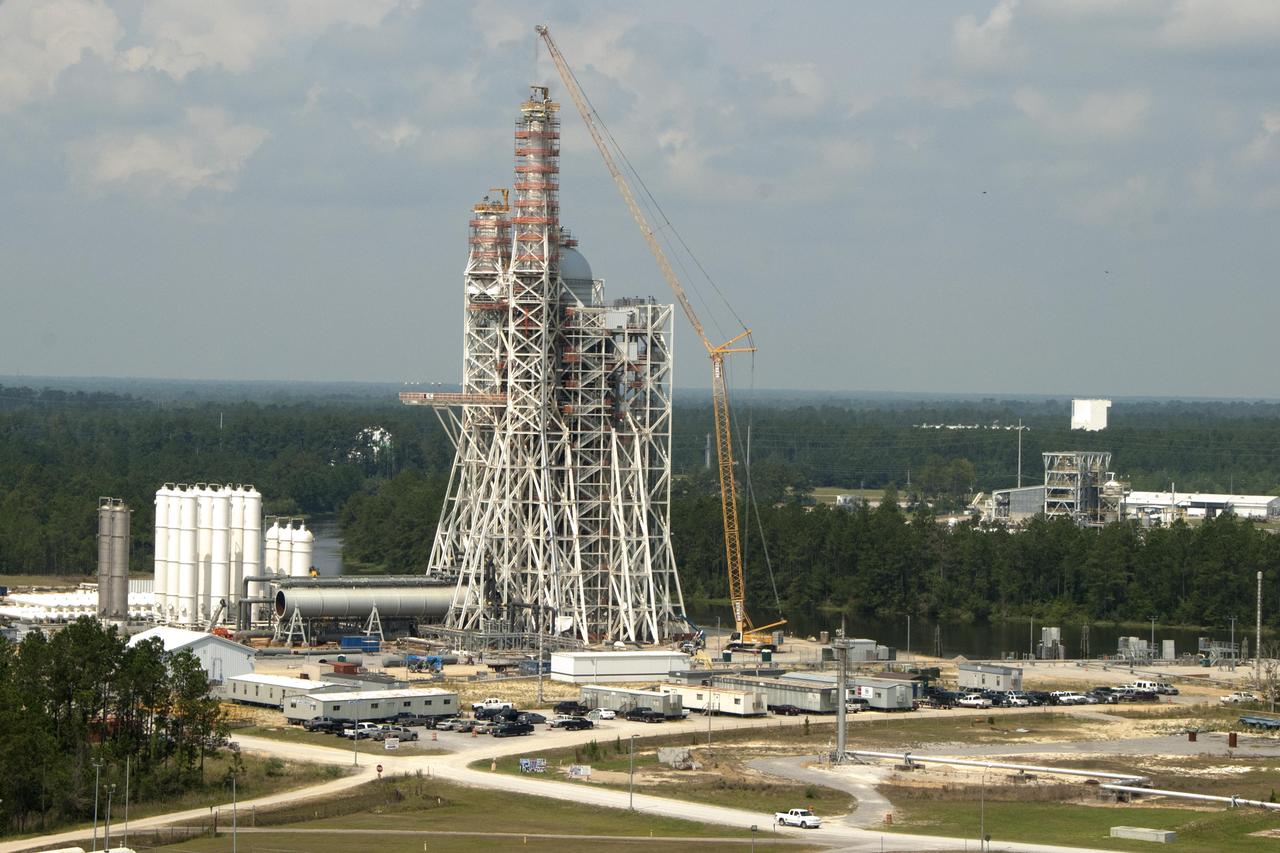

Construction on the new A-3 Test Stand continues at NASA's Stennis Space Center. The stand is the first large test structure built at the NASA facility since the 1960s.
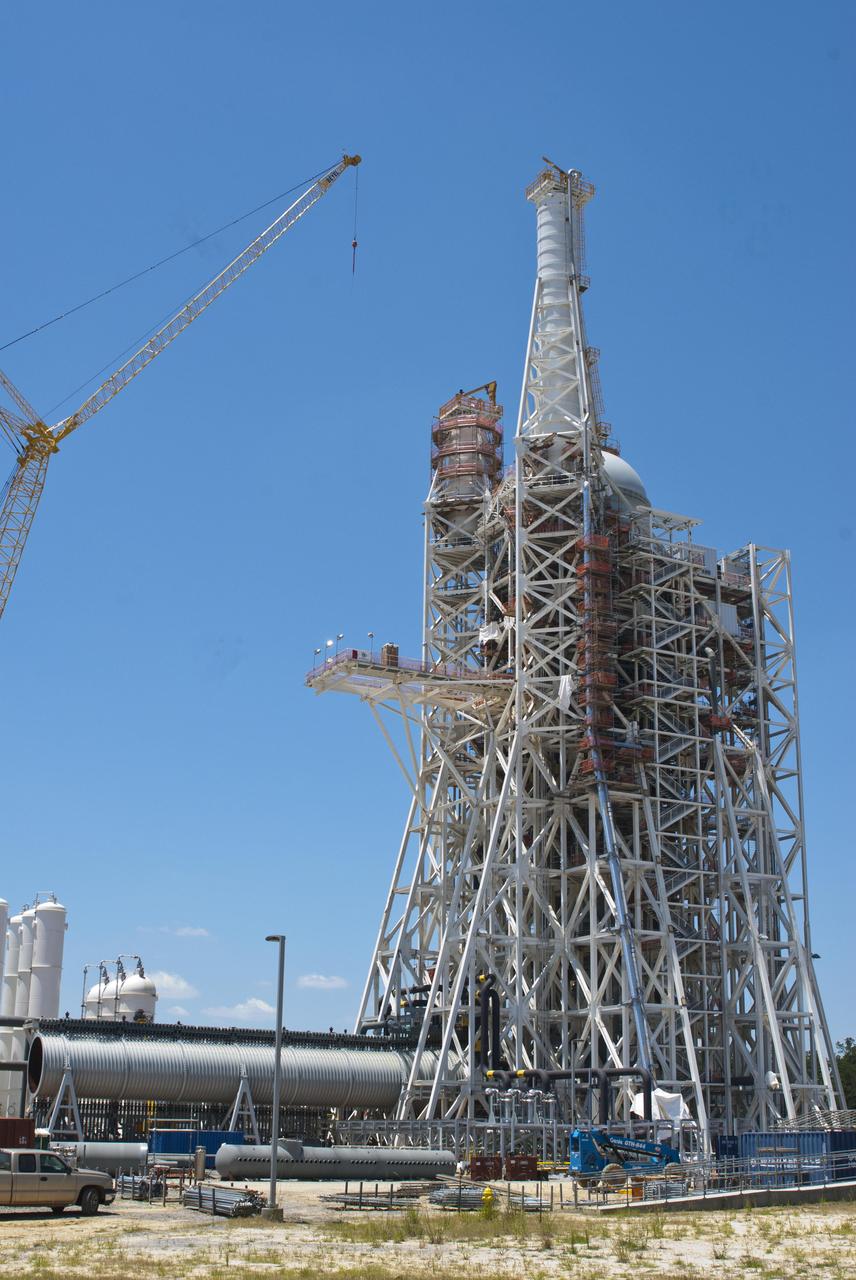

Construction continues on NASA's A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. The stand is the first large test structure built at the south Mississippi facility since the 1960s.

Construction on the new A-3 Test Stand continues at NASA's Stennis Space Center. The stand is the first large test structure built at the NASA facility since the 1960s.

A Stennis Space Center employee works March 2, 2012, to further construction of the A-3 Test Stand, which will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.

A Stennis Space Center employee works March 2, 2012, to further construction of the A-3 Test Stand, which will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html

An aerial photo shows the B-1/B-2 Test Stand (foreground), A-2 Test Stand (middle) and A-1 Test Stand (back). The historic stands have been used to test engines used on every manned Apollo and space shuttle mission.
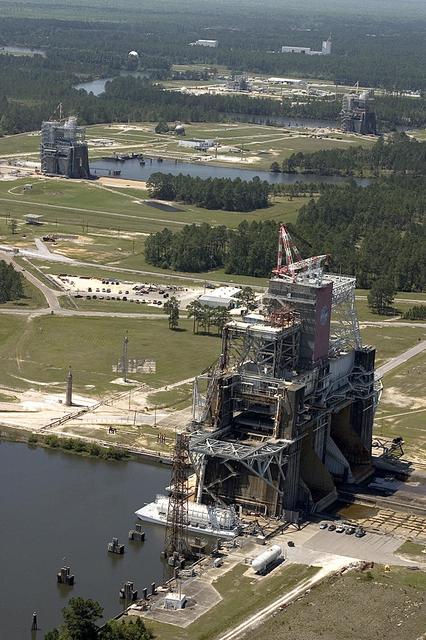

An aerial photo shows the B-1/B-2 Test Stand (foreground), A-2 Test Stand (middle) and A-1 Test Stand (back). The historic stands have been used to test engines used on every manned Apollo and space shuttle mission.
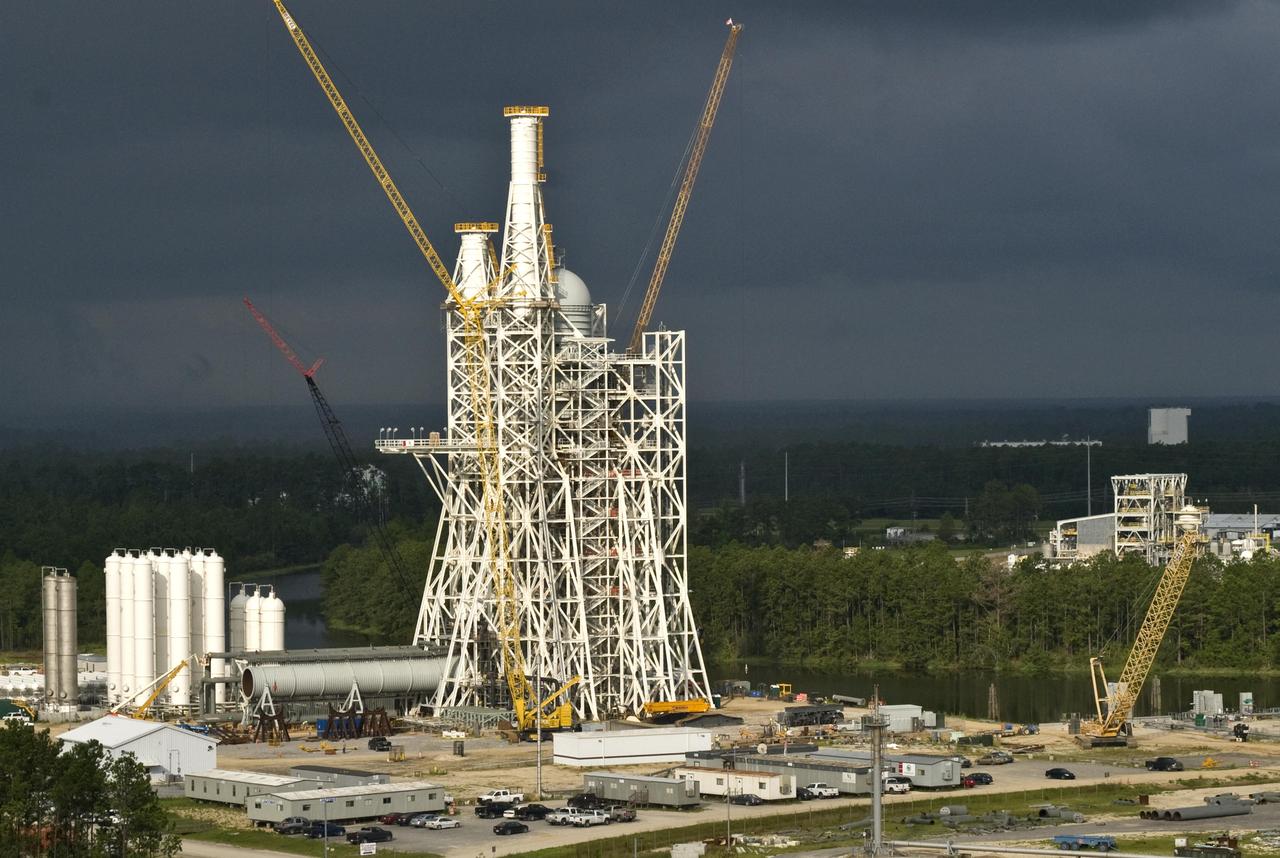

Stennis Space Center employees have installed liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks atop the A-3 Test Stand, raising the structure to its full 300-foot height. The stand is being built to test next-generation rocket engines that could carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space. The A-3 Test Stand is scheduled for completion and activation in 2013.
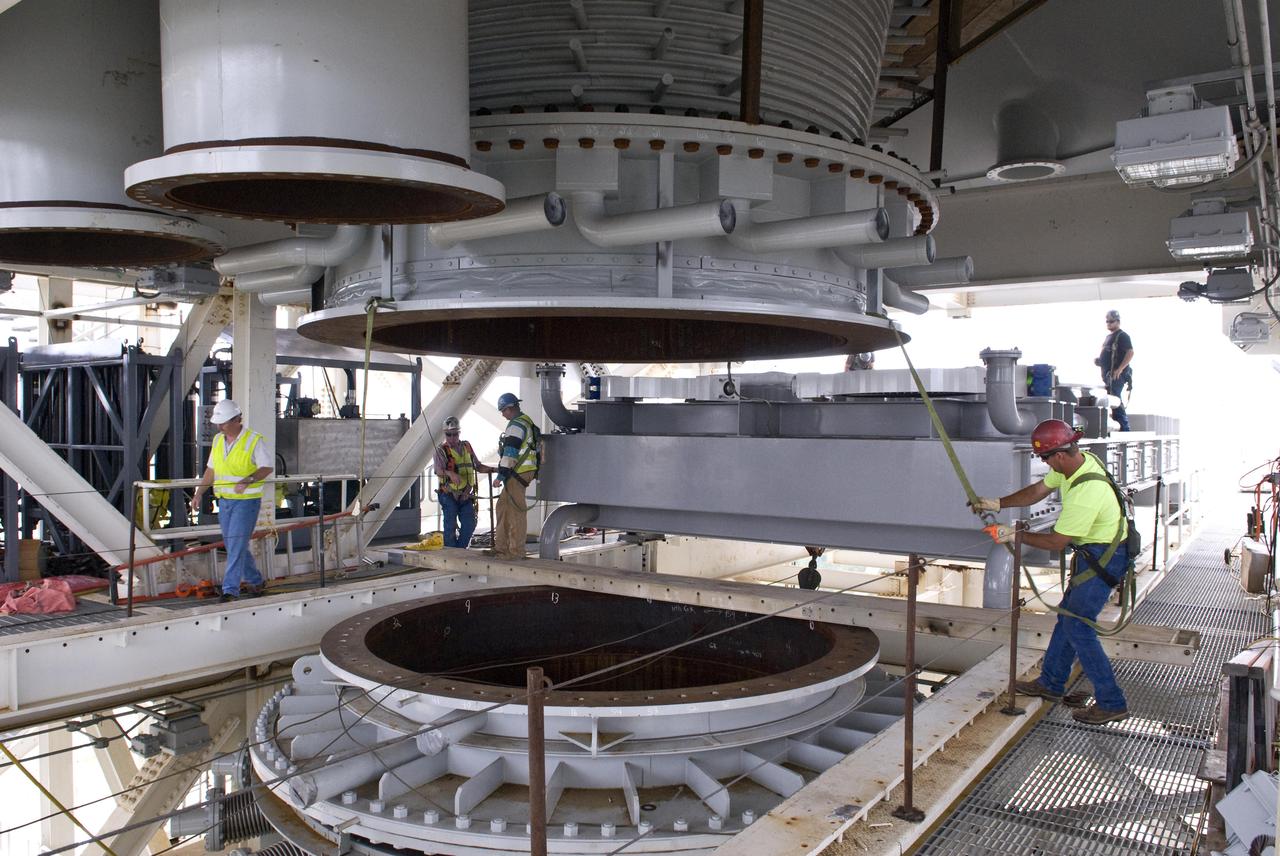

Stennis Space Center employees continue work on the A-3 Test Stand test cell. The stand is being built to test next-generation rocket engines that could carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space.
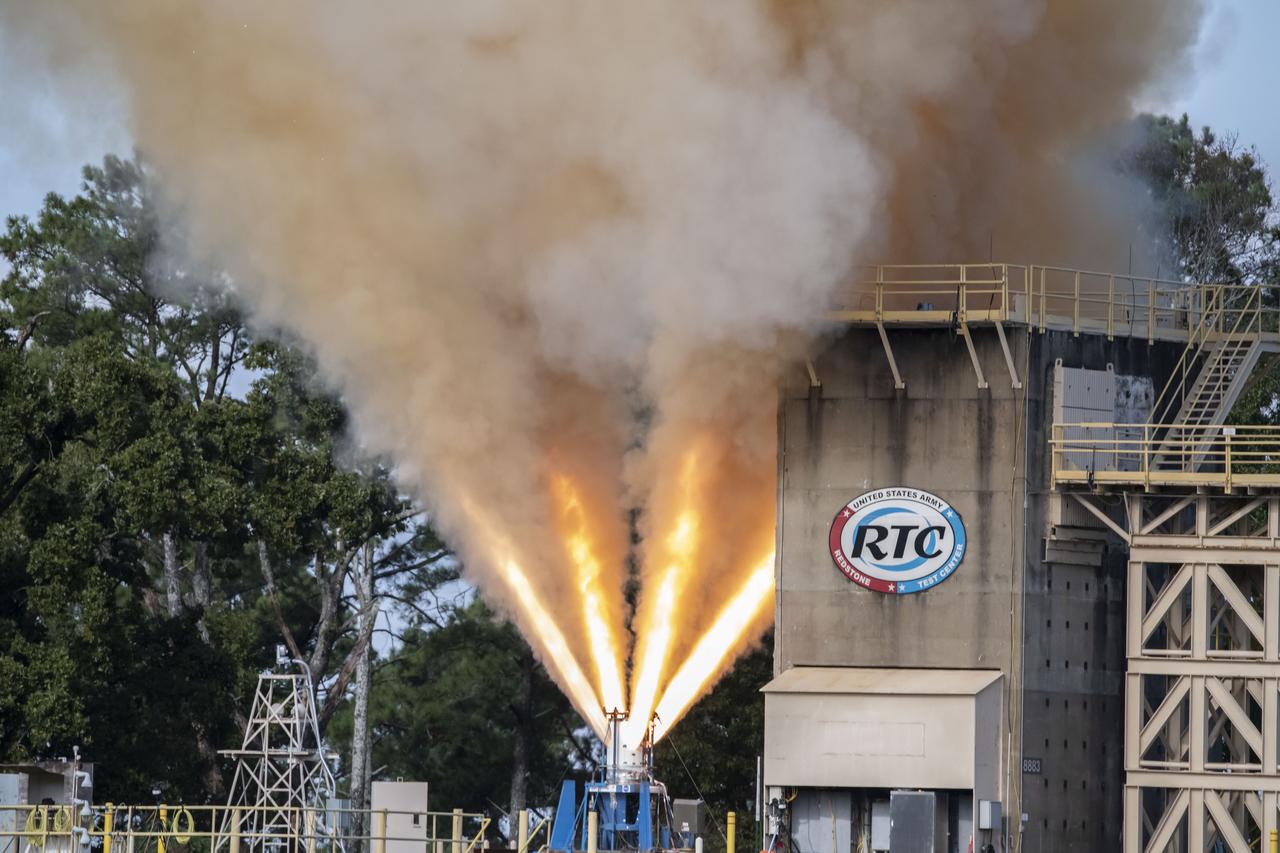

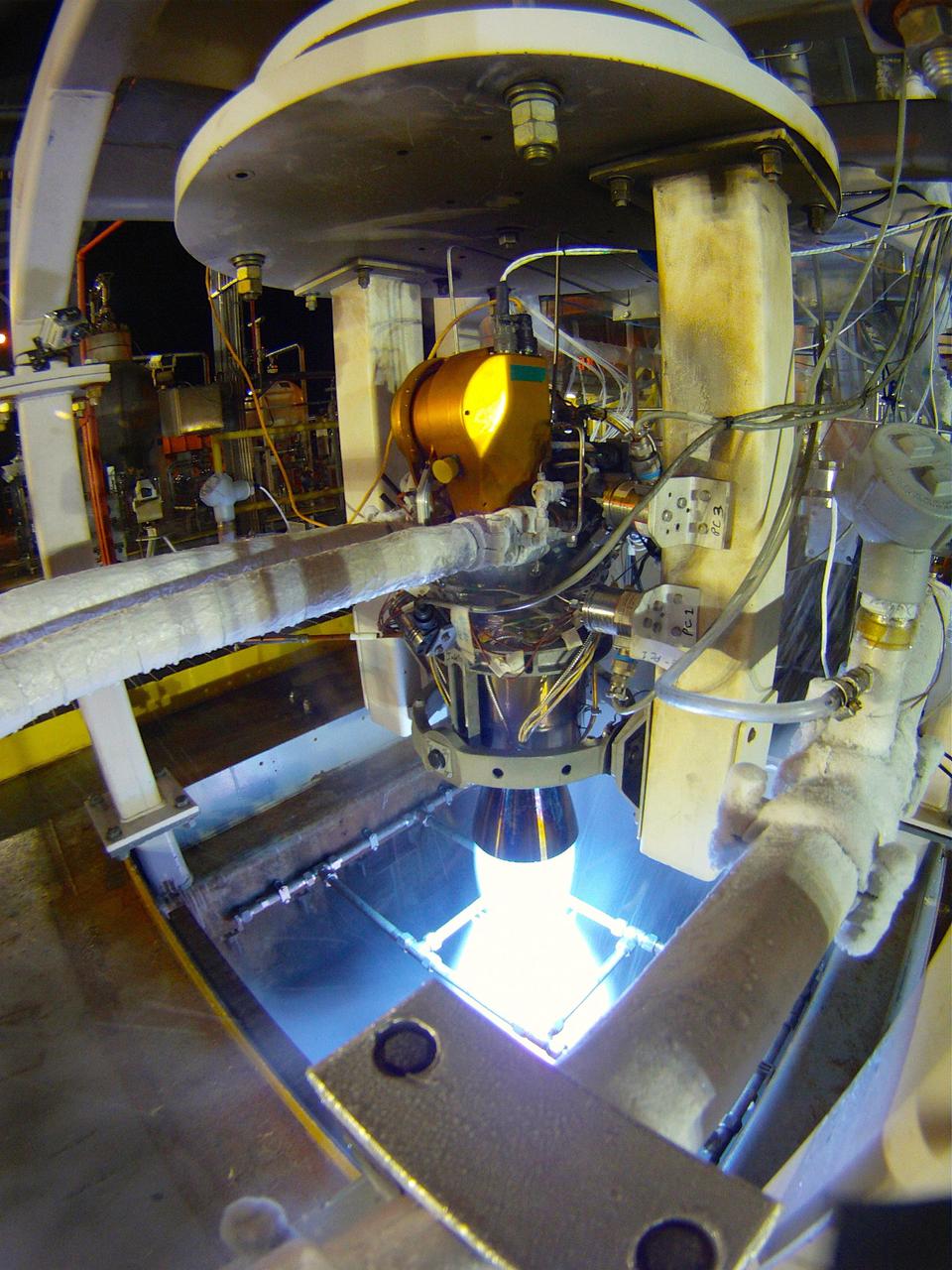
Redstone Test Center hosted the final hot fire test of the Aerojet Rocketdyne Orion Launch Abort System (LAS) at Redstone Arsenal’s test area 5.
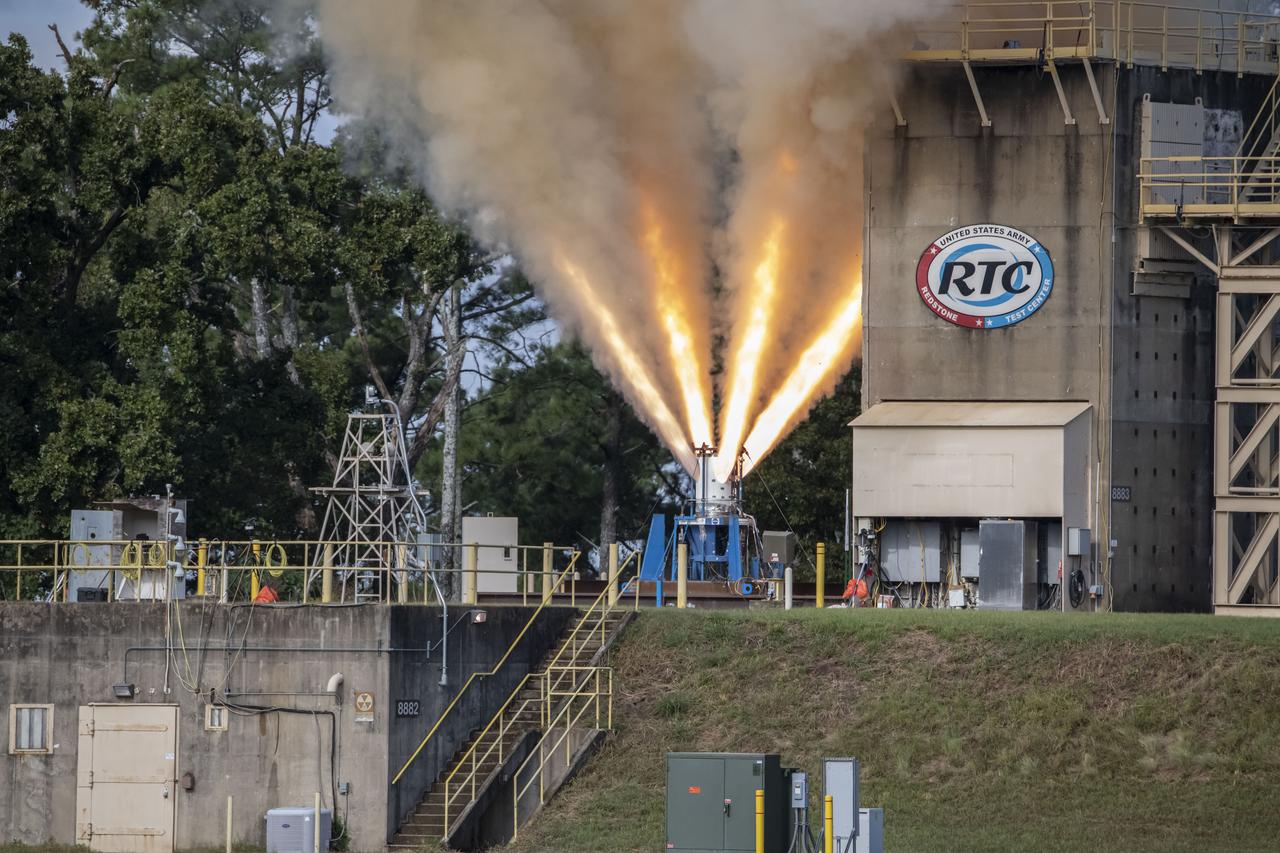

Redstone Test Center hosted the final hot fire test of the Aerojet Rocketdyne Orion Launch Abort System (LAS) at Redstone Arsenal’s test area 5.
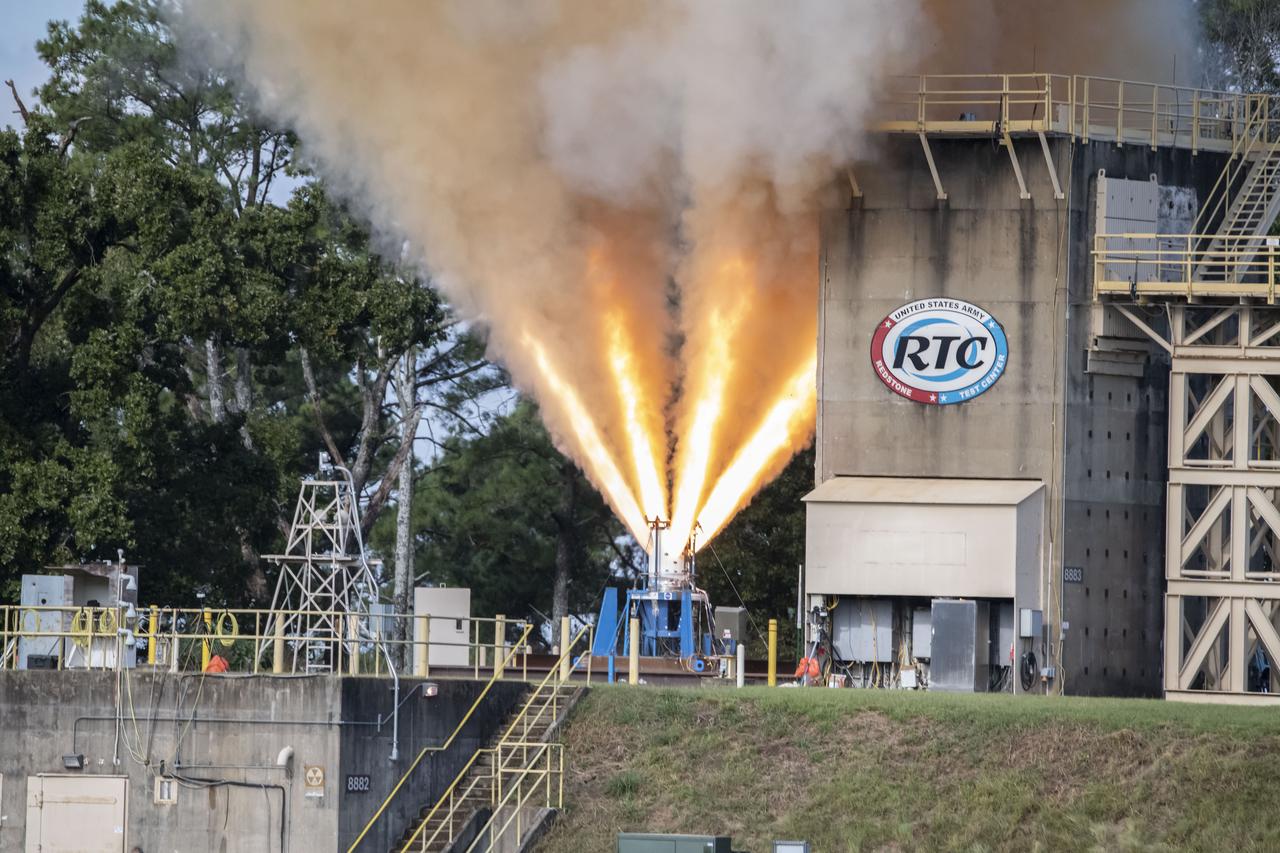

Redstone Test Center hosted the final hot fire test of the Aerojet Rocketdyne Orion Launch Abort System (LAS) at Redstone Arsenal’s test area 5.

Team members check the progress of a liquid nitrogen cold shock test on the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Sept. 15. The cold shock test is used to confirm the test stand's support system can withstand test conditions, when super-cold rocket engine propellant is piped. The A-1 Test Stand is preparing to conduct tests on the powerpack component of the J-2X rocket engine, beginning in early 2012.
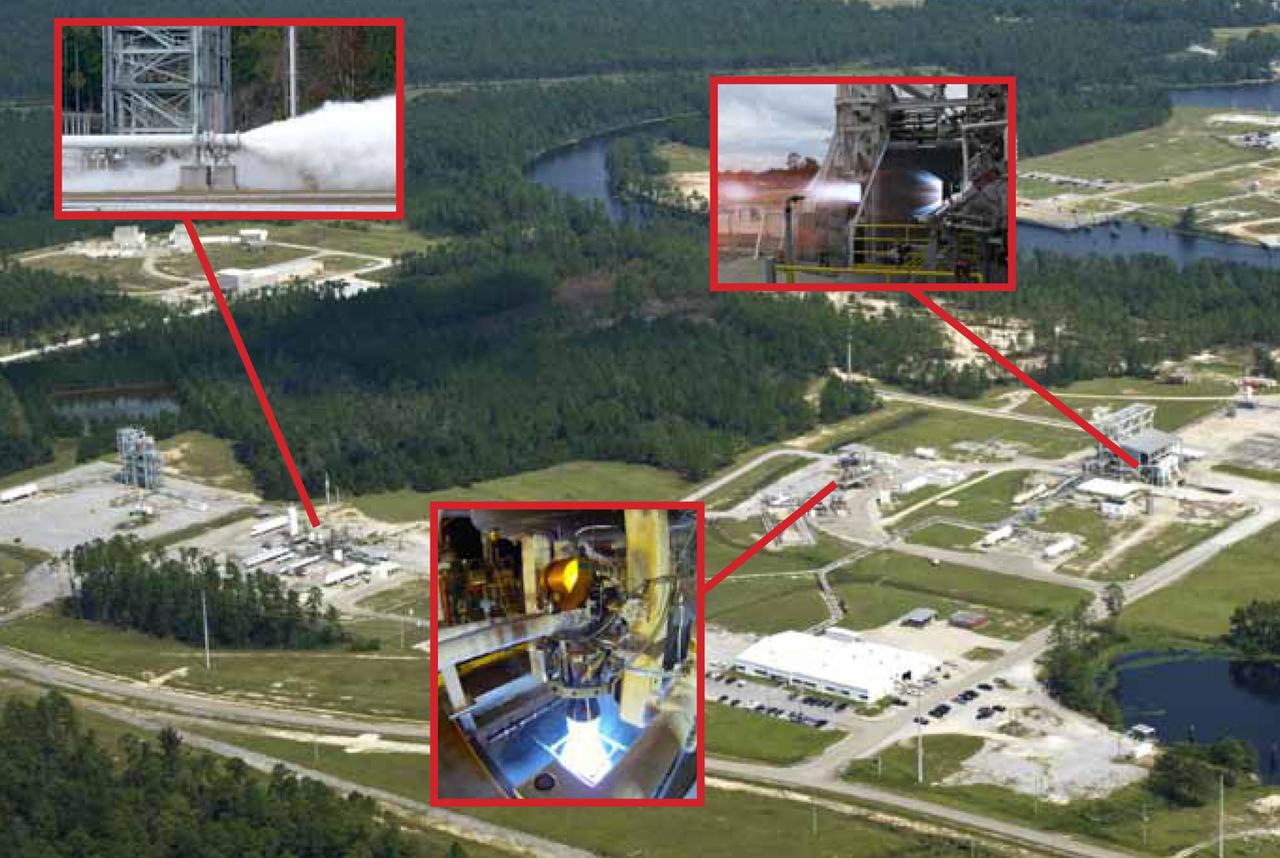

NASA recorded a historic week Nov. 5-9, conducting tests on all three stands in the E Test Complex at John C. Stennis Space Center. Inset images show the types of tests conducted on the E-1 Test Stand (right), the E-2 Test Stand (left) and the E-3 Test Stand (center). The E-1 photo is from an early October test and is provided courtesy of Blue Origin. Other photos are from tests conducted the week of Nov. 5.
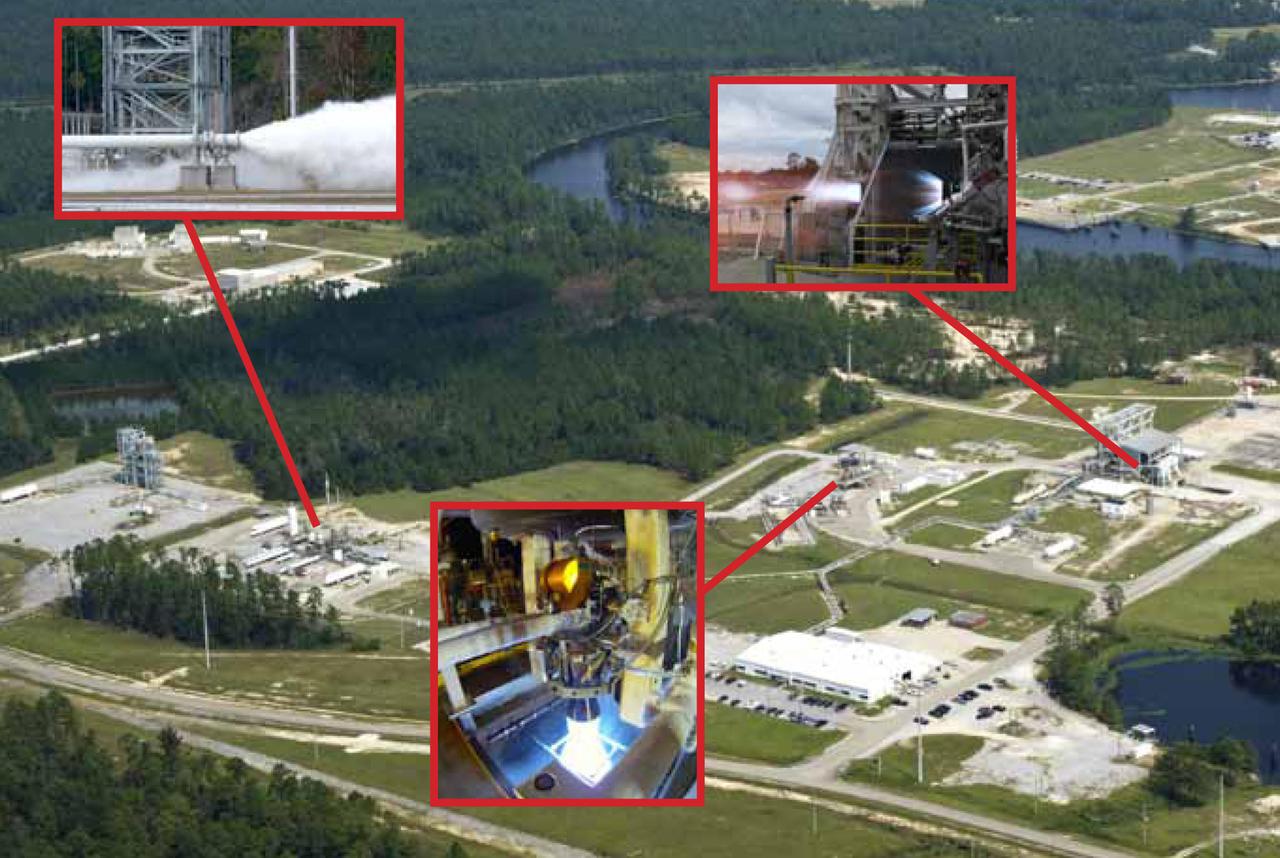

NASA recorded a historic week Nov. 5-9, conducting tests on all three stands in the E Test Complex at John C. Stennis Space Center. Inset images show the types of tests conducted on the E-1 Test Stand (right), the E-2 Test Stand (left) and the E-3 Test Stand (center). The E-1 photo is from an early October test and is provided courtesy of Blue Origin. Other photos are from tests conducted the week of Nov. 5.

NASA conducted a successful seven-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 16, 2012. The J-2X is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.

Rocket engine propellant tanks and cell dome top the A-3 Test Stand under construction at Stennis Space Center. The stand will test next-generation rocket engines that could carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space once more.

Rocket engine propellant tanks and cell dome top the A-3 Test Stand under construction at Stennis Space Center. The stand will test next-generation rocket engines that could carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space once more.
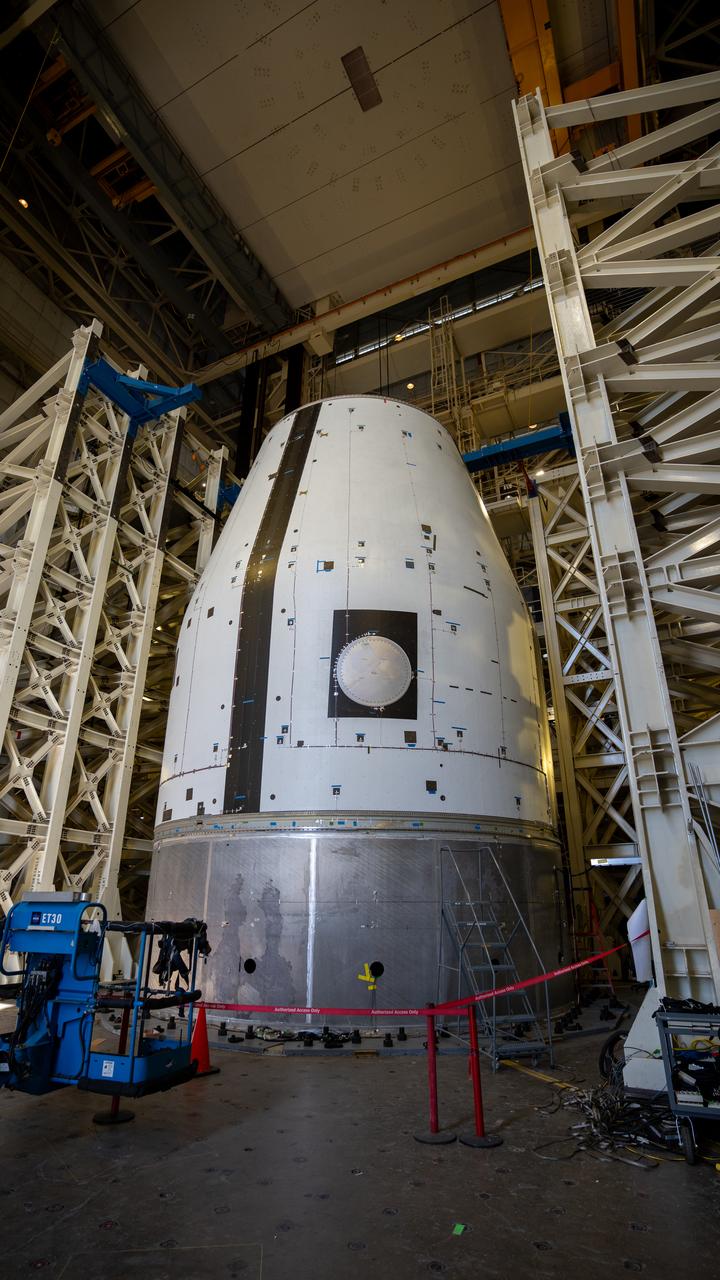

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann presents center director coins to employees following the 'topping out' of the A-3 Test Stand with placement of test cell dome on April 13. The stand is the first large test structure built at Stennis since the 1960s.

A test of NASA's liquid oxygen, liquid methane Project Morpheus engine is conducted Nov. 8 on the E-3 Test Stand at John C. Stennis Space Center. The test was one of 27 conducted in Stennis' E Test Complex the week of Nov. 5. Twenty-seven tests were conducted in a three-day period during the week, on three different rocket engines/components and on three E Complex test stands.

Construction of the A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center continued throughout 2011. The stand is the first large test structure built at Stennis since the 1960s.
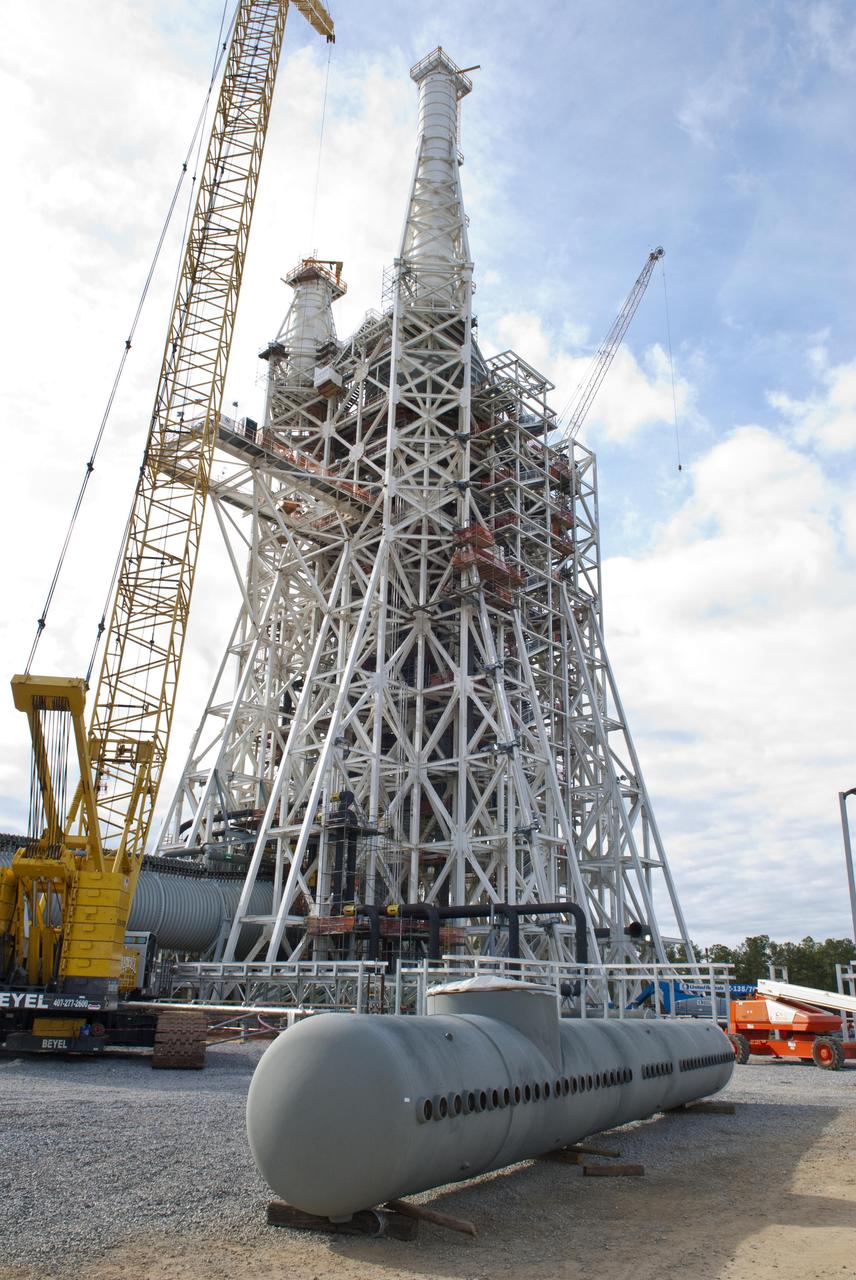

Construction of the A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center continued throughout 2011. The stand is the first large test structure built at Stennis since the 1960s.
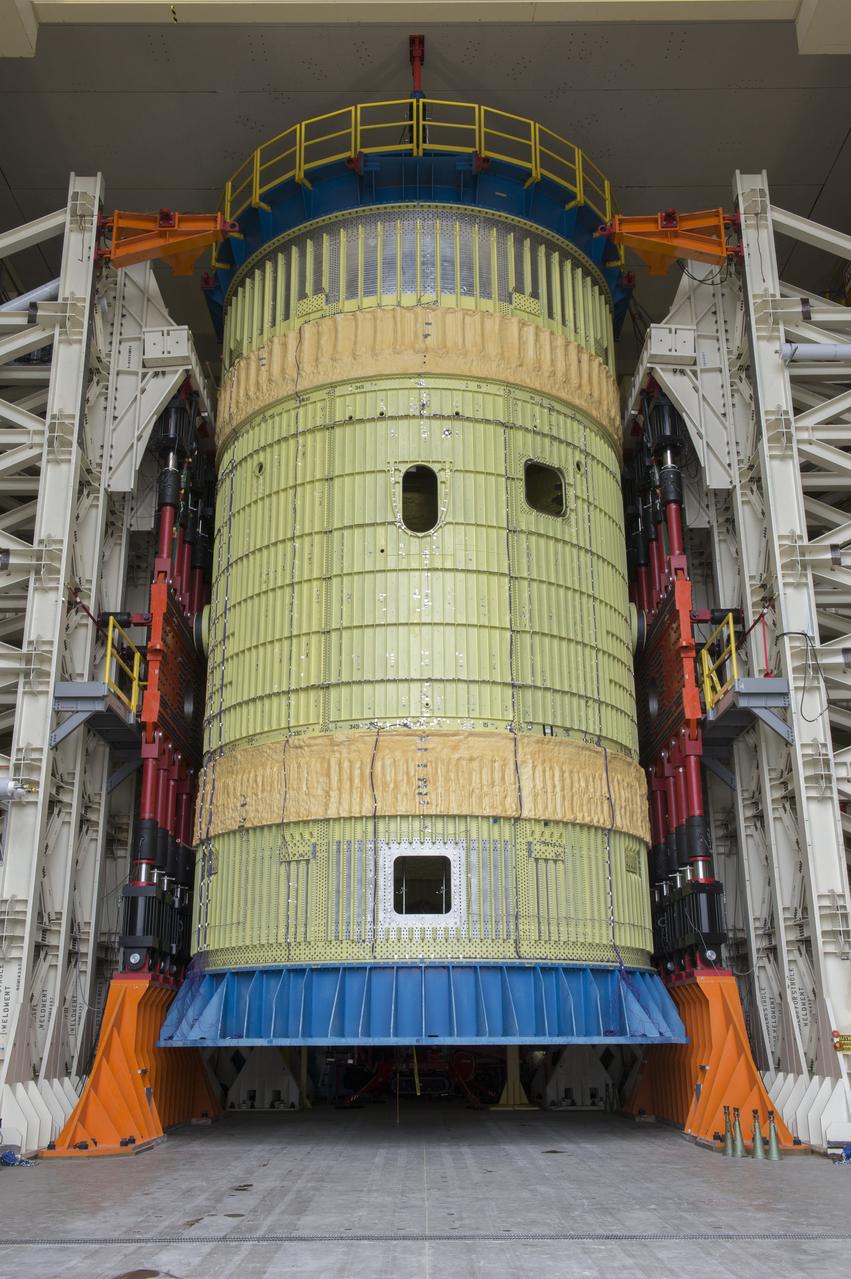

SLS Intertank Test Article, ITA, is attached to crosshead of load test Annex, Bldg. 4619, and removed from bed of KMAG transporter. ITA is suspended from crosshead of Load Test Annex
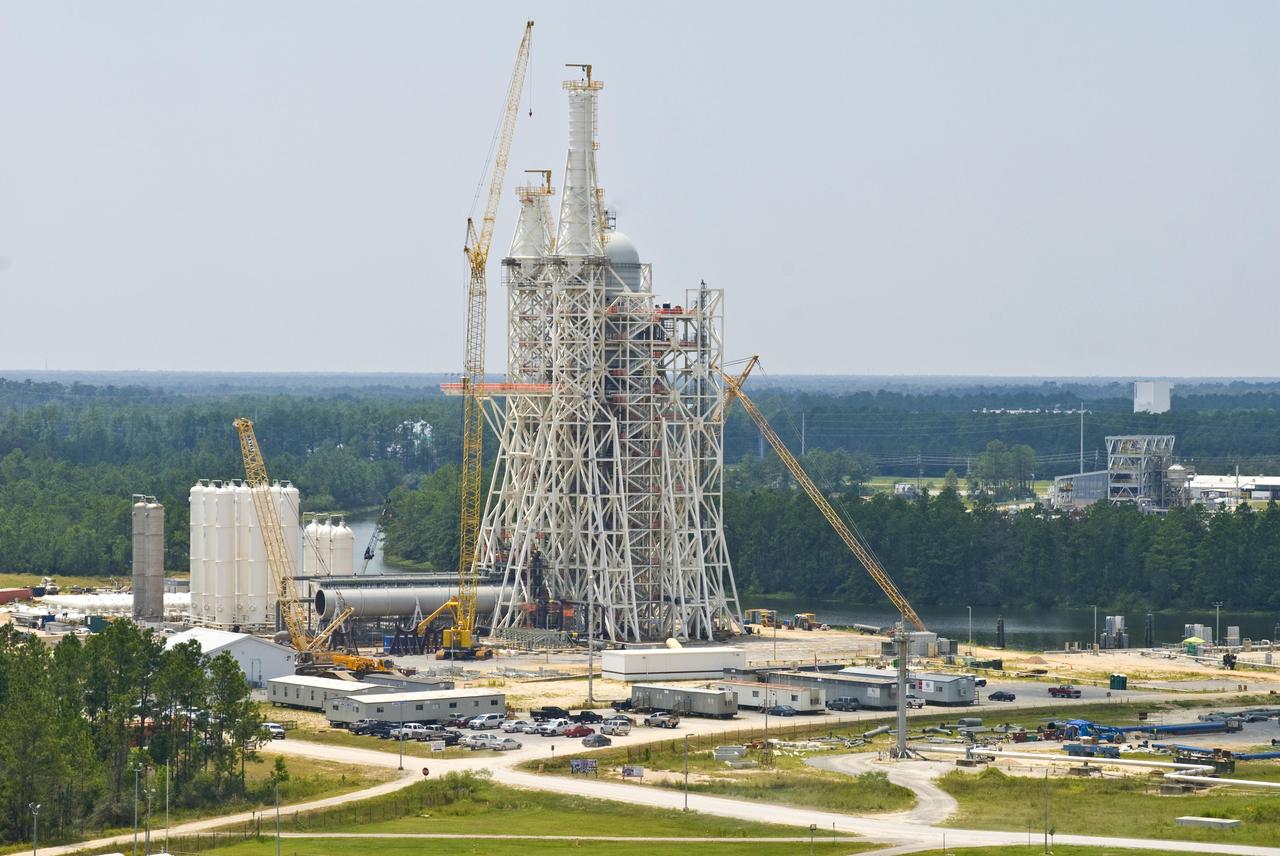

The A-3 Test Stand under construction at Stennis Space Center is set for completion and activation in 2013. It will allow operators to conduct simulated high-altitude testing on the next-generation J-2X rocket engine.
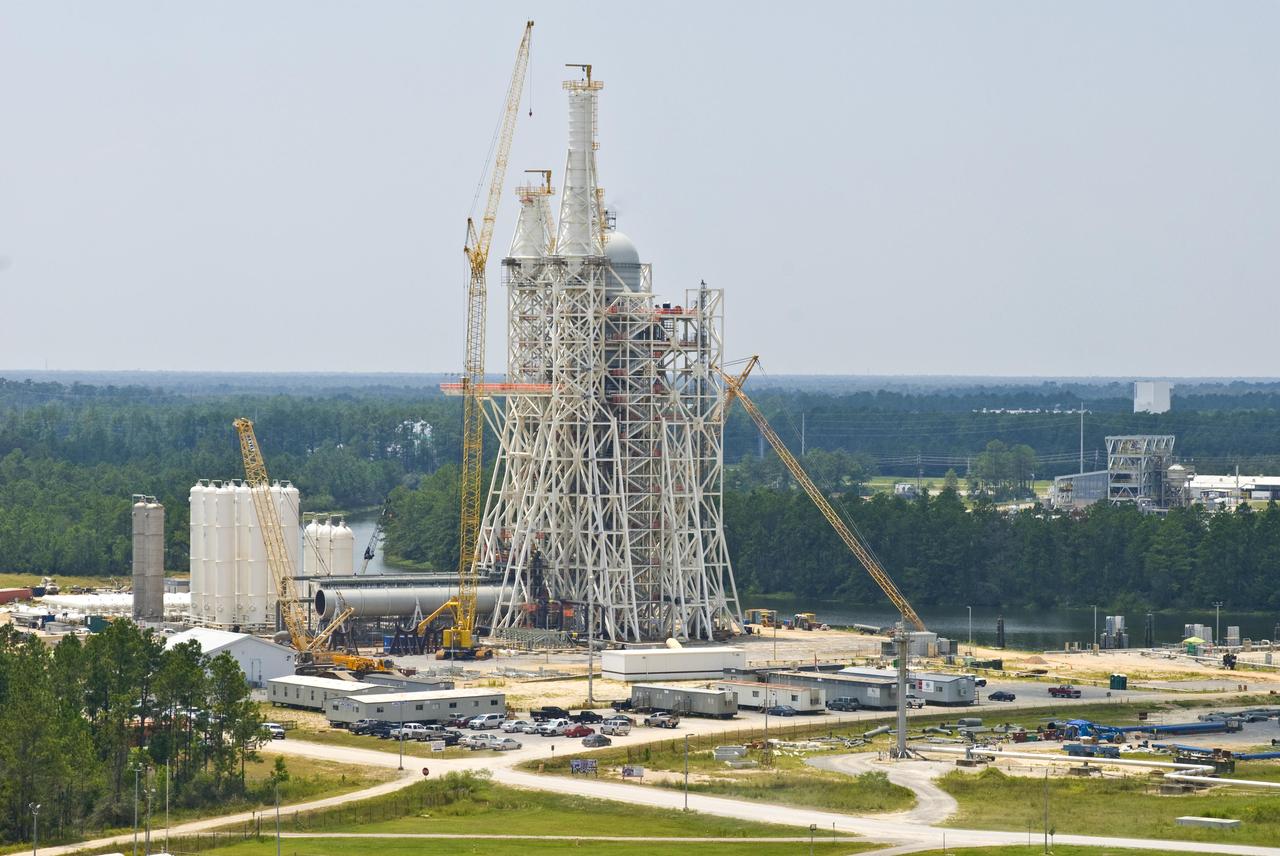

The A-3 Test Stand under construction at Stennis Space Center is set for completion and activation in 2013. It will allow operators to conduct simulated high-altitude testing on the next-generation J-2X rocket engine.
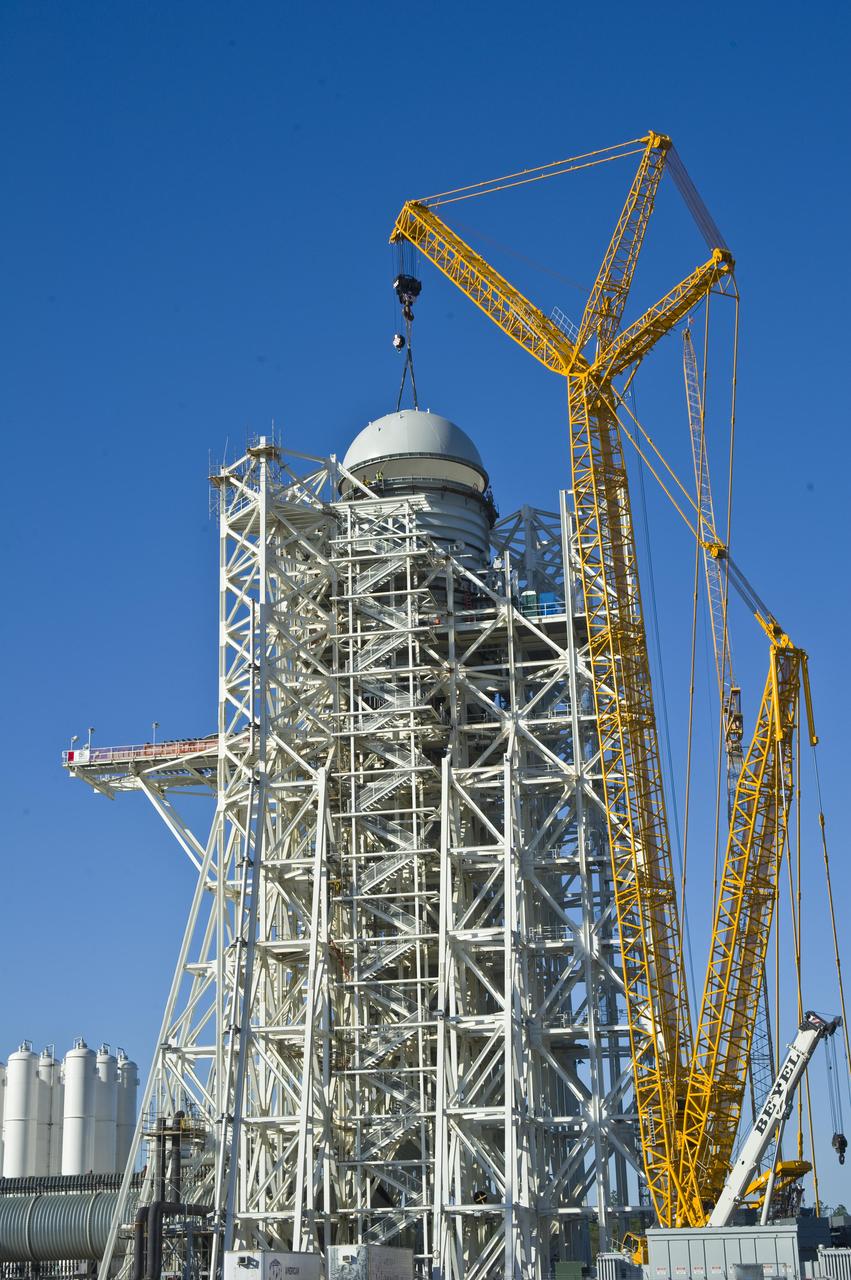

A construction 'topping out' milestone was reached April 13 with placement of the test cell dome atop NASA's new A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. NASA broke ground in 2007 for the new stand, which is being built to provide simulated high-altitude testing for next-generation rocket engines that could carry humans into deep space.
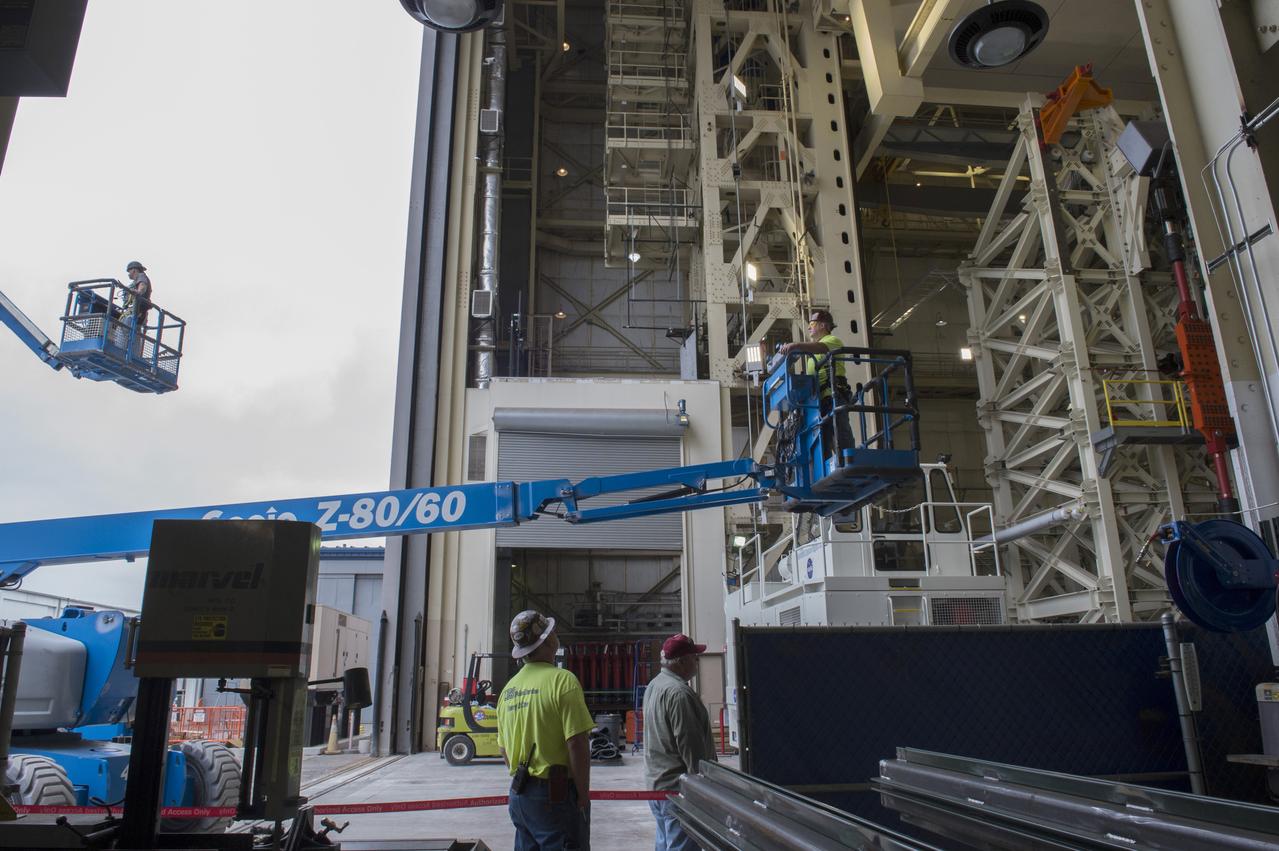

Technicians are removed from SLS Intertank Test Article, ITA, after attaching to crosshead of load test Annex, Bldg. 4619,

NASA engineers tested an Aerojet AJ26 rocket engine on the E-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on June 25, 2012, against the backdrop of the B-1/B-2 Test Stand. The engine will be used by Orbital Sciences Corporation to power commercial cargo flights to the International Space Station.

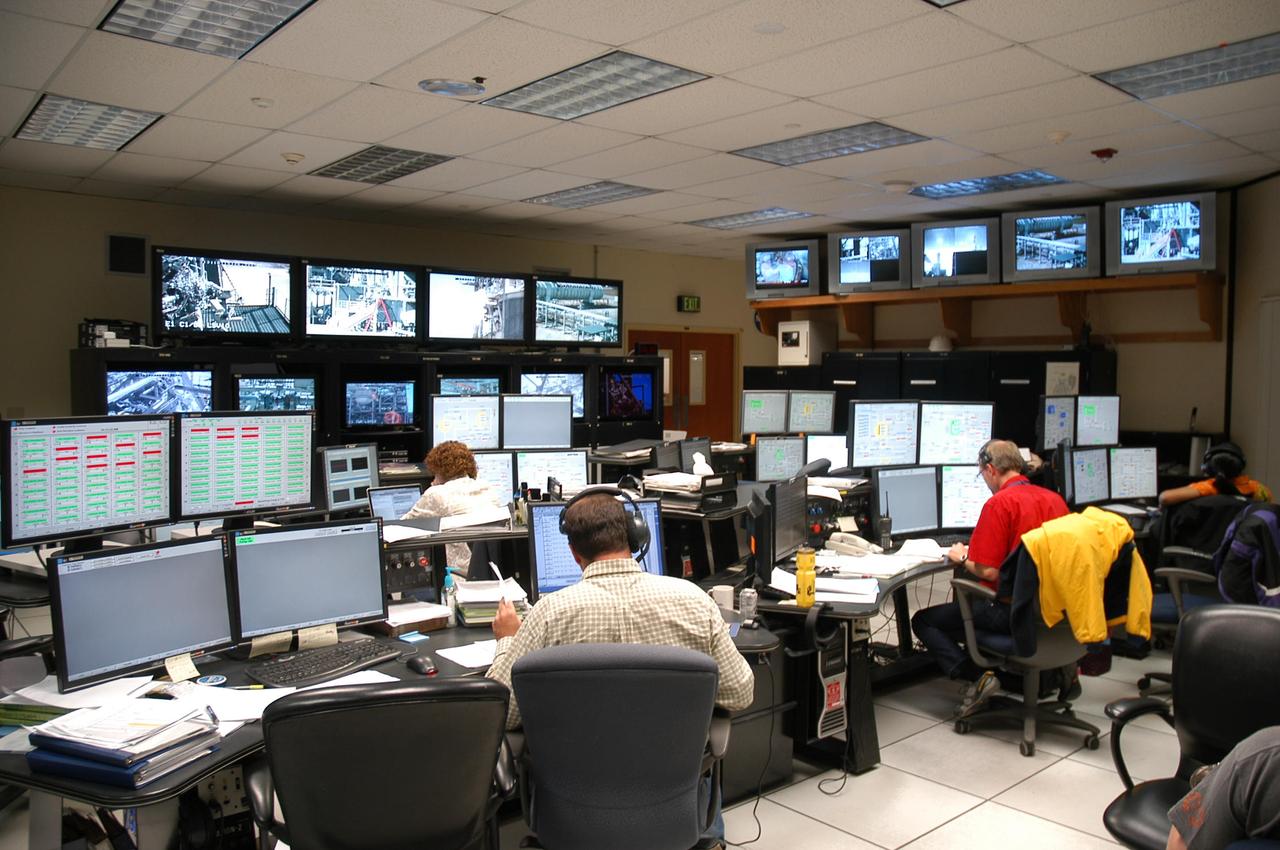
NASA engineer Andy Guymon studies data in the E-3 Test Stand Control Center at John C. Stennis Space Center during testing of NASA's Project Morpheus engine. Nov. 8. The test of the liquid oxygen, liquid methane engine was one of 27 conducted in Stennis' E Test Complex the week of Nov. 5.

Jason Hopper of NASA (front row), Jody Ladner of Lockheed Martin (back row, left) and Chris Mulkey of NASA prepare to test the Blue Origin BE-3 engine thrust chamber in the E-1 Test Stand Control Center at John C. Stennis Space Center on Nov. 8. The test was one of 27 conducted in Stennis' E Test Complex the week of Nov. 5.
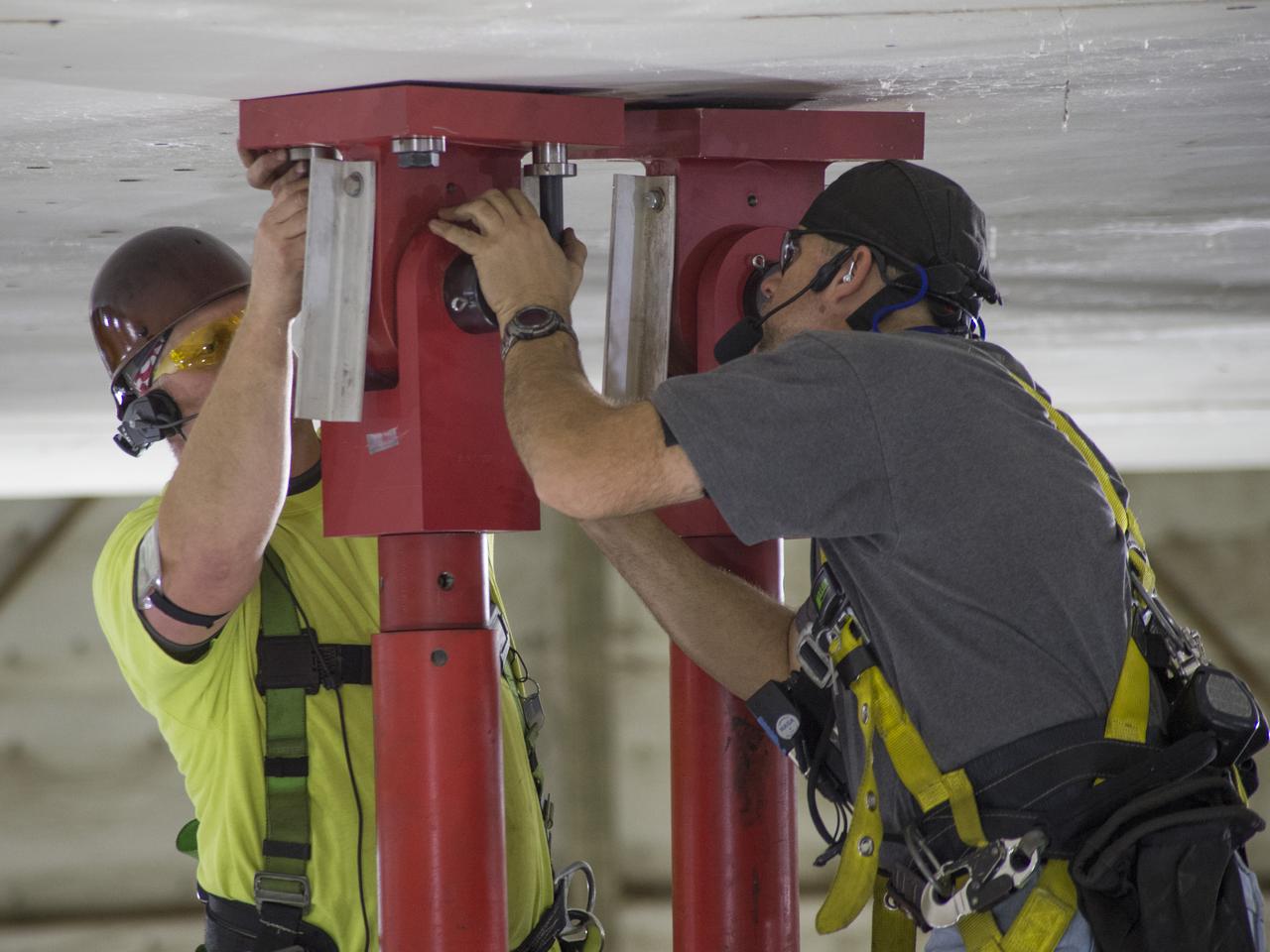

SLS Intertank Test Article, ITA, is attached to crosshead of load test Annex, Bldg. 4619, and removed from bed of KMAG transporter. Rob Ziegler, L, and Roger Myrick, R, of Aerie Aerospace attach load lines to Aft Load Ring of Intertank Test Articlle
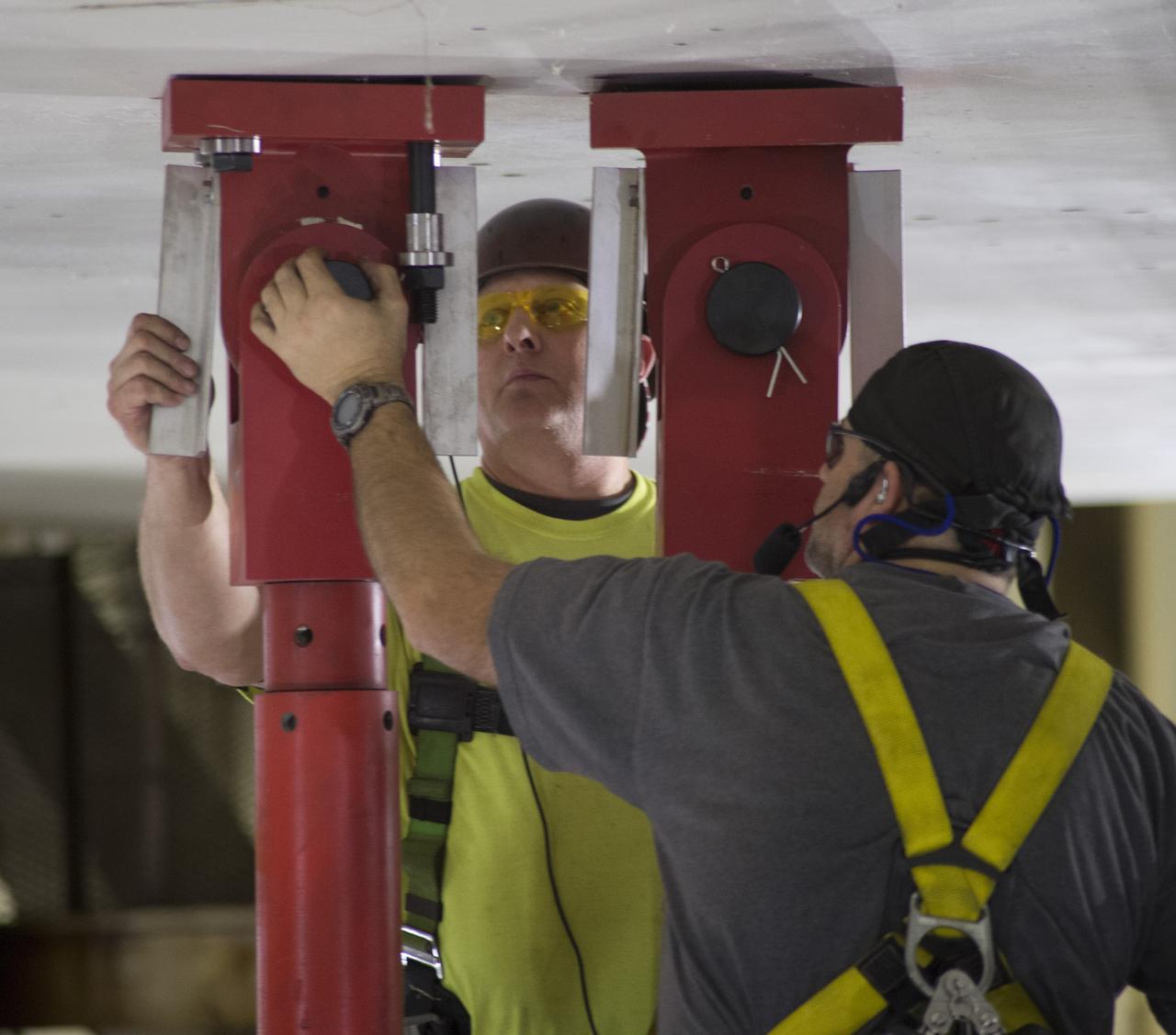

SLS Intertank Test Article, ITA, is attached to crosshead of load test Annex, Bldg. 4619, and removed from bed of KMAG transporter. Rob Ziegler, (L), and Roger Myrick (R), of Aerie Aerospace attach load lines to Aft Load Ring of Intertank Test Article.
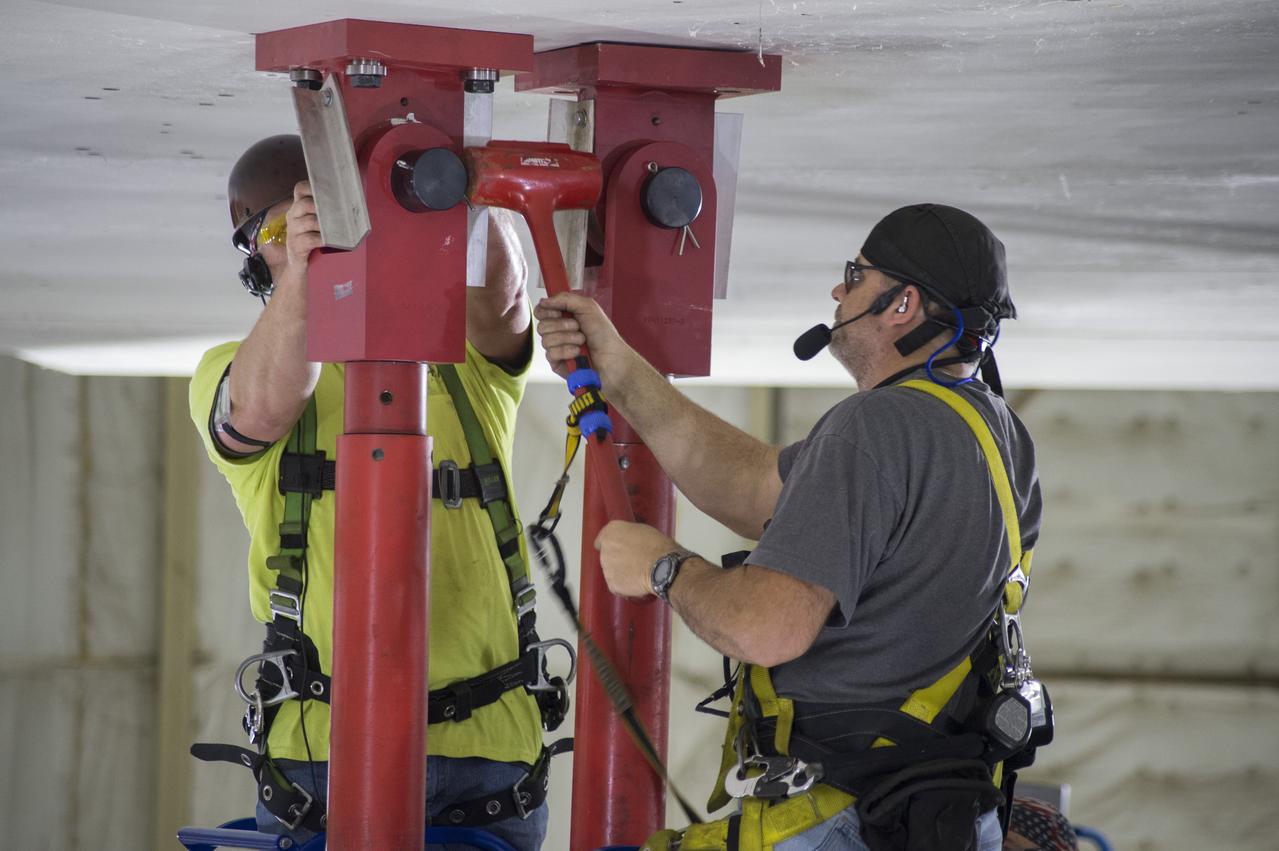

SLS Intertank Test Article, ITA, is attached to crosshead of load test Annex, Bldg. 4619, and removed from bed of KMAG transporter. Rob Ziegler, (L), and Roger Myrick (R), of Aerie Aerospace attach load lines to Aft Load Ring of Intertank Test Article.
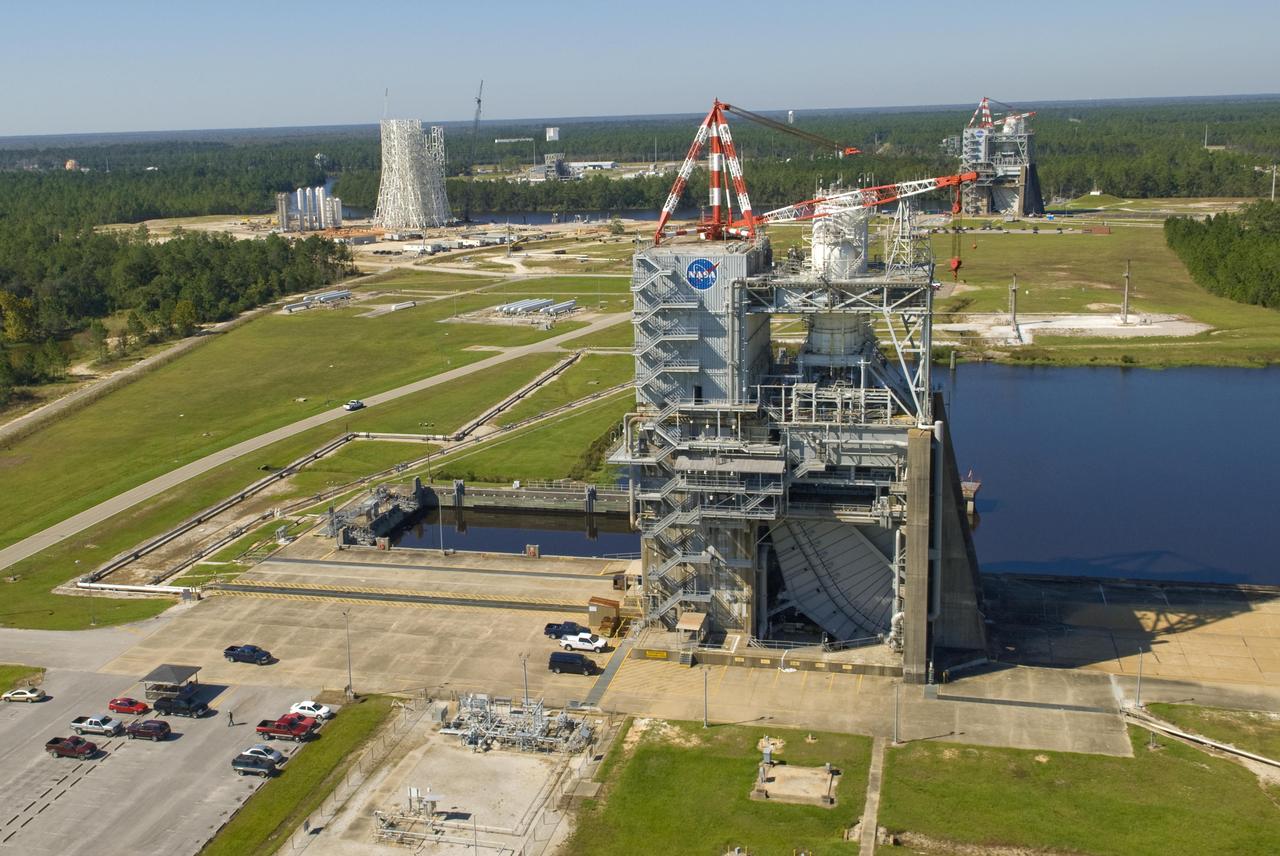

In addition to the historic A-2 Test Stand (foreground) and A-1 Test Stand (back right), construction of a new A-3 Test Stand (back left) is under way at Stennis Space Center. The new stand will allow operators to test next-generation rocket engines at simulated altitudes of 100,000 feet. Such testing is critical for engines that will carry humans into deep space once more.

This archival photo shows the Voyager proof test model, which did not fly in space, in the 25-foot space simulator chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on December 3, 1976. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21735
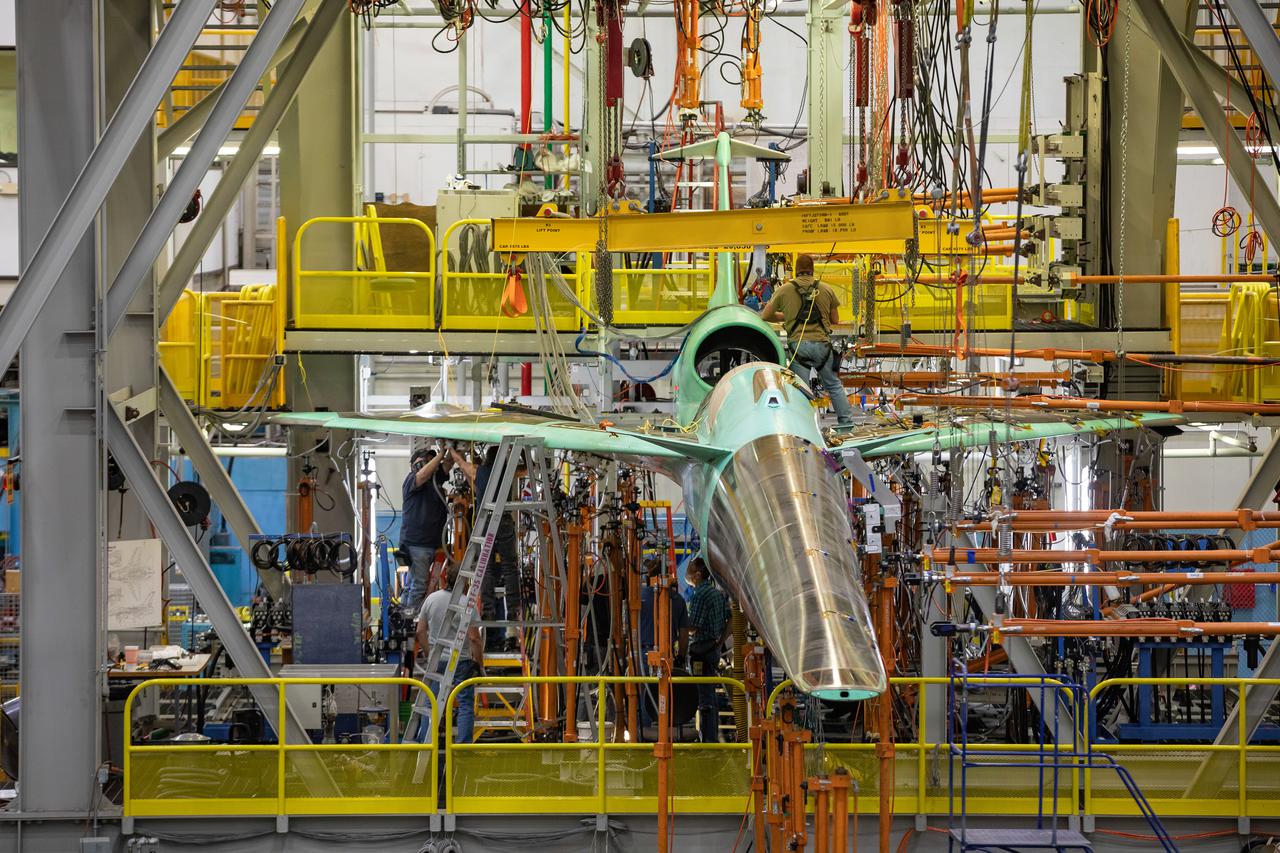

NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology airplane undergoes structural stress tests at a Lockheed Martin facility in Fort Worth, Texas. Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company - Fort Worth - Chris Hanoch Subject: X-59 - Various Angles in Test Fixture FP#: 21-03420 POC: Analiese Smith, Chris Higgins Other info: X-59 in Fort Worth, testing; high angle shots in fixture 1-10-22