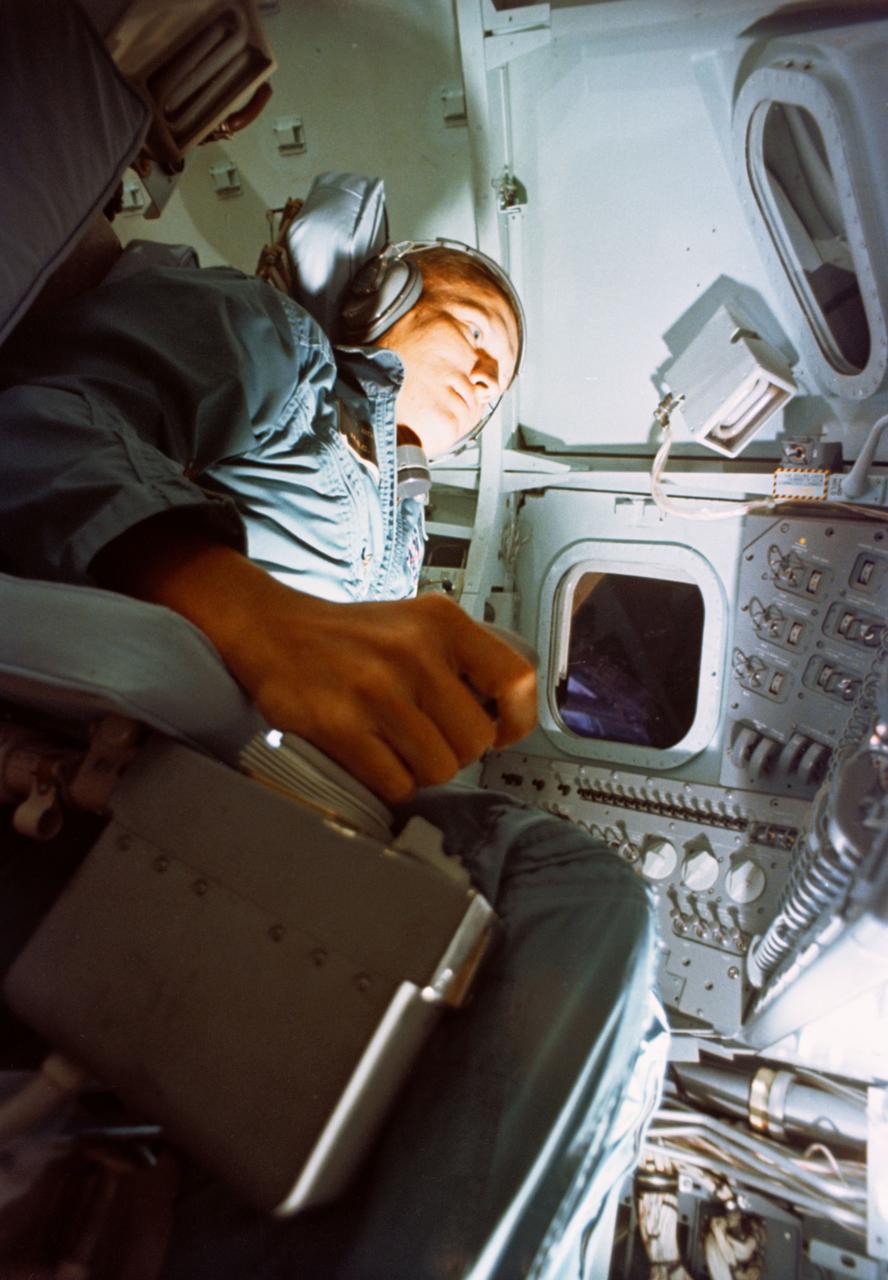

S67-50590 (1867) --- Astronaut Frank Borman, assigned duty as commander of the Apollo 8 mission, participates in a training exercise in the Apollo Mission simulator in the Mission Simulation and training Facility, Building 5, at the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA

NASA astronaut candidate Jasmin Moghbeli poses for a portrait in the Systems Engineering Simulator, a real-time, crew-in-the-loop engineering simulator for the space station and advanced spaceflight programs, Tuesday, July 9, 2019 at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
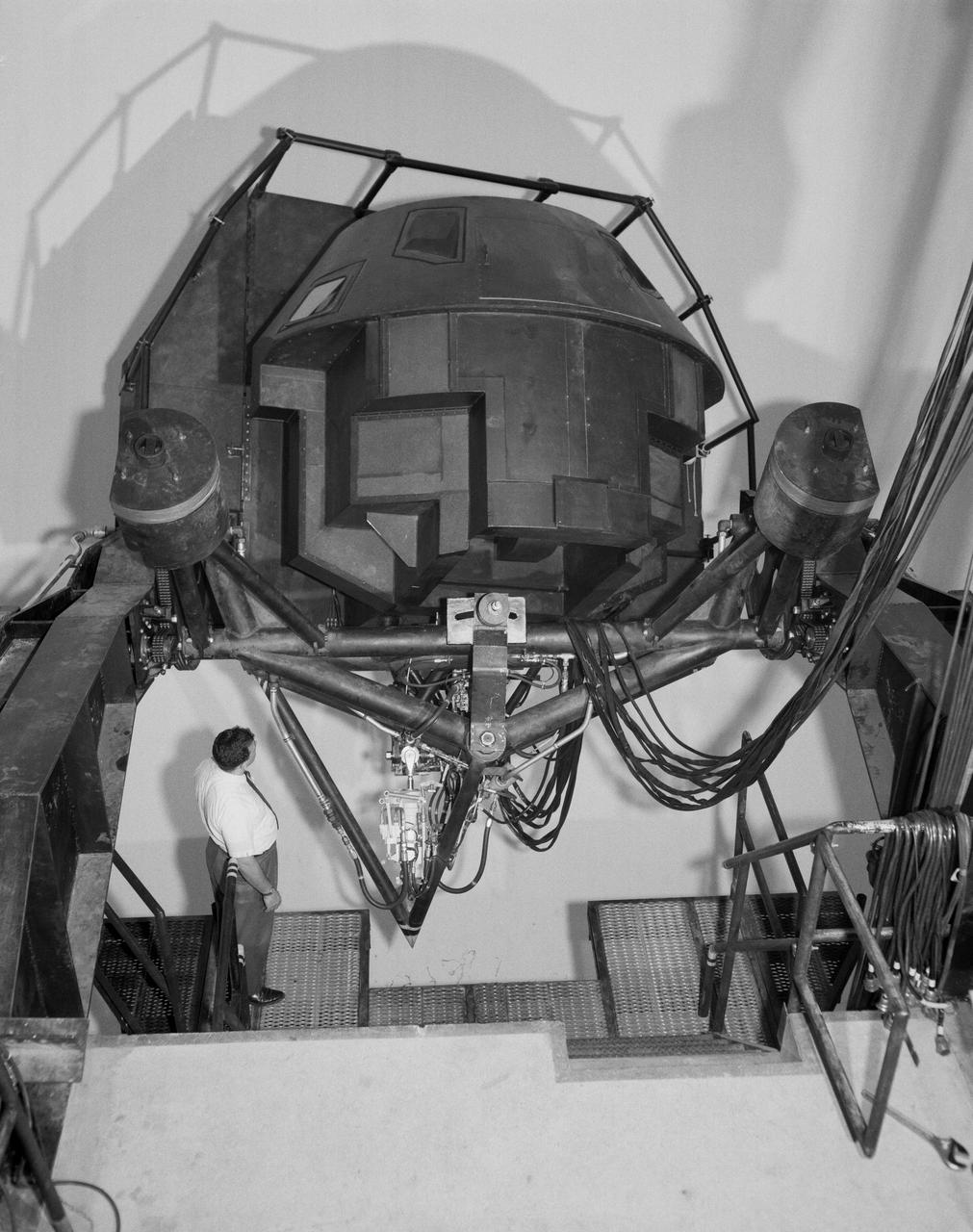
S66-21296 (1967) --- This is a medium exterior view of the Dynamic Crew Procedures Trainer, Command Module configuration, one of the Apollo astronaut training components located in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Building 5, Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA
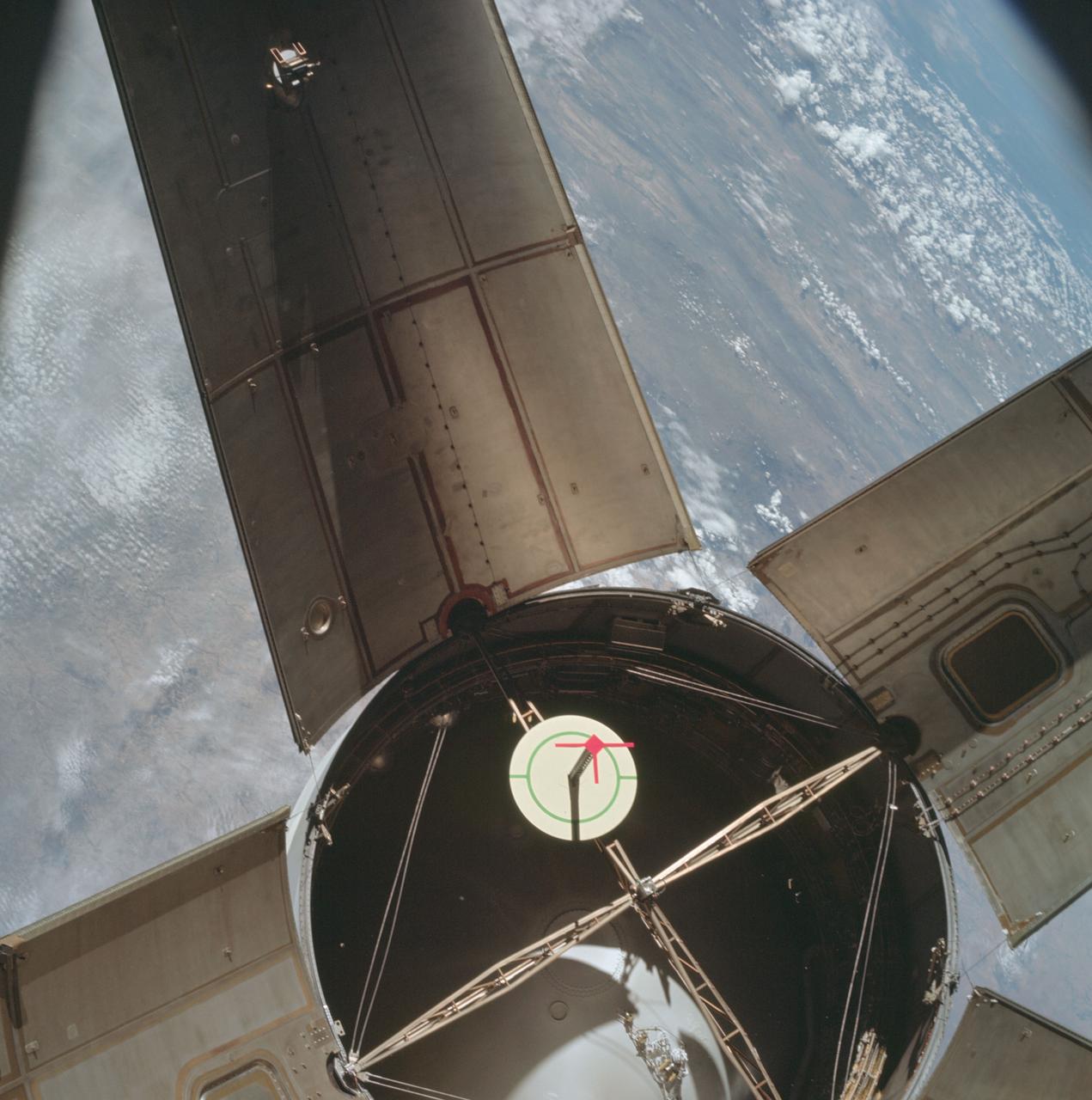

AS07-03-1535 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers at an altitude of 126 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of three hours, 11 minutes. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions. The spacecraft is directly over Odessa-Midland, Texas. The view between the two panels (area of large puffy clouds) extends southwest across Texas into the Mexican State of Chihuahua. The distance between the Apollo 7 spacecraft and the S-IVB is approximately 50 feet.
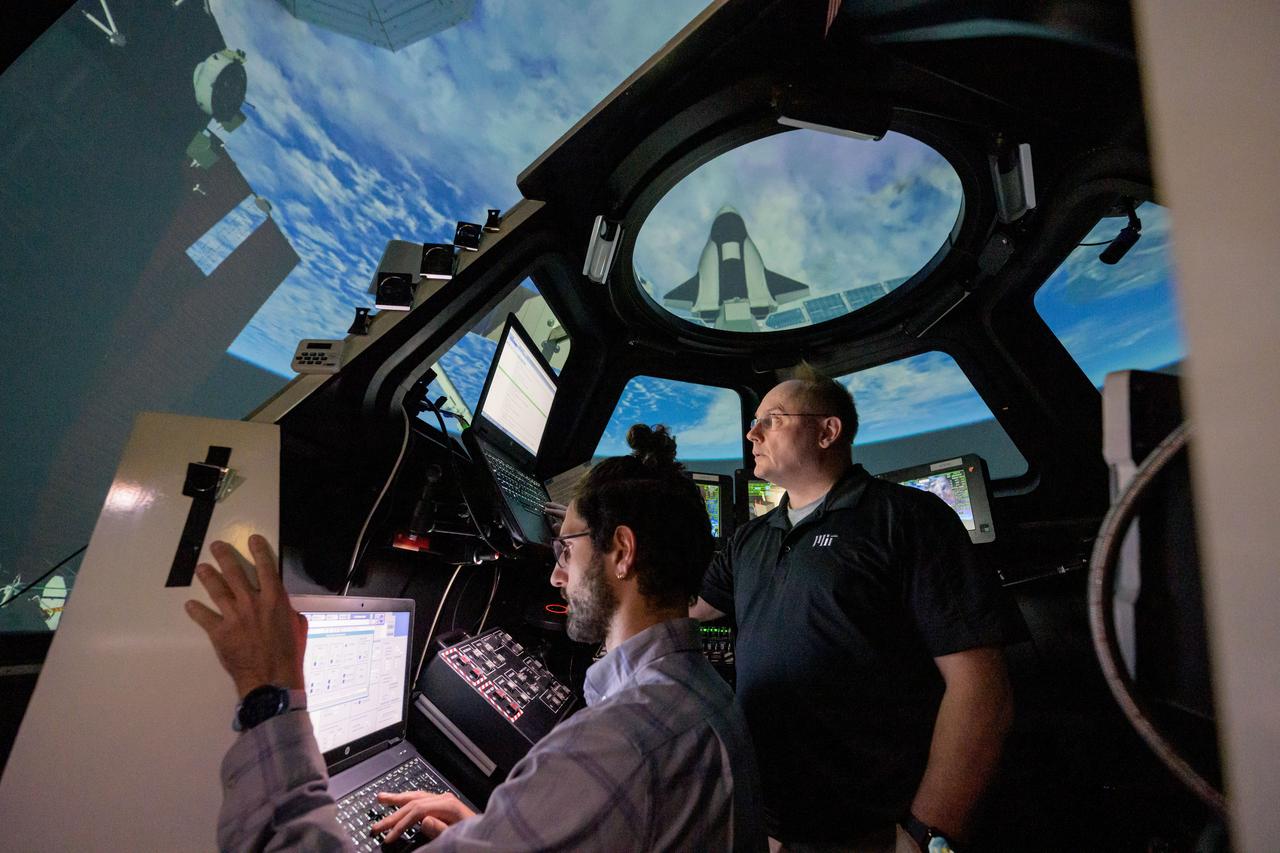

jsc2025e003643 (Jan. 28, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Mike Fincke (right) works with his trainers in a simulator to brush up on berthing Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser and other space station robotics skills at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.
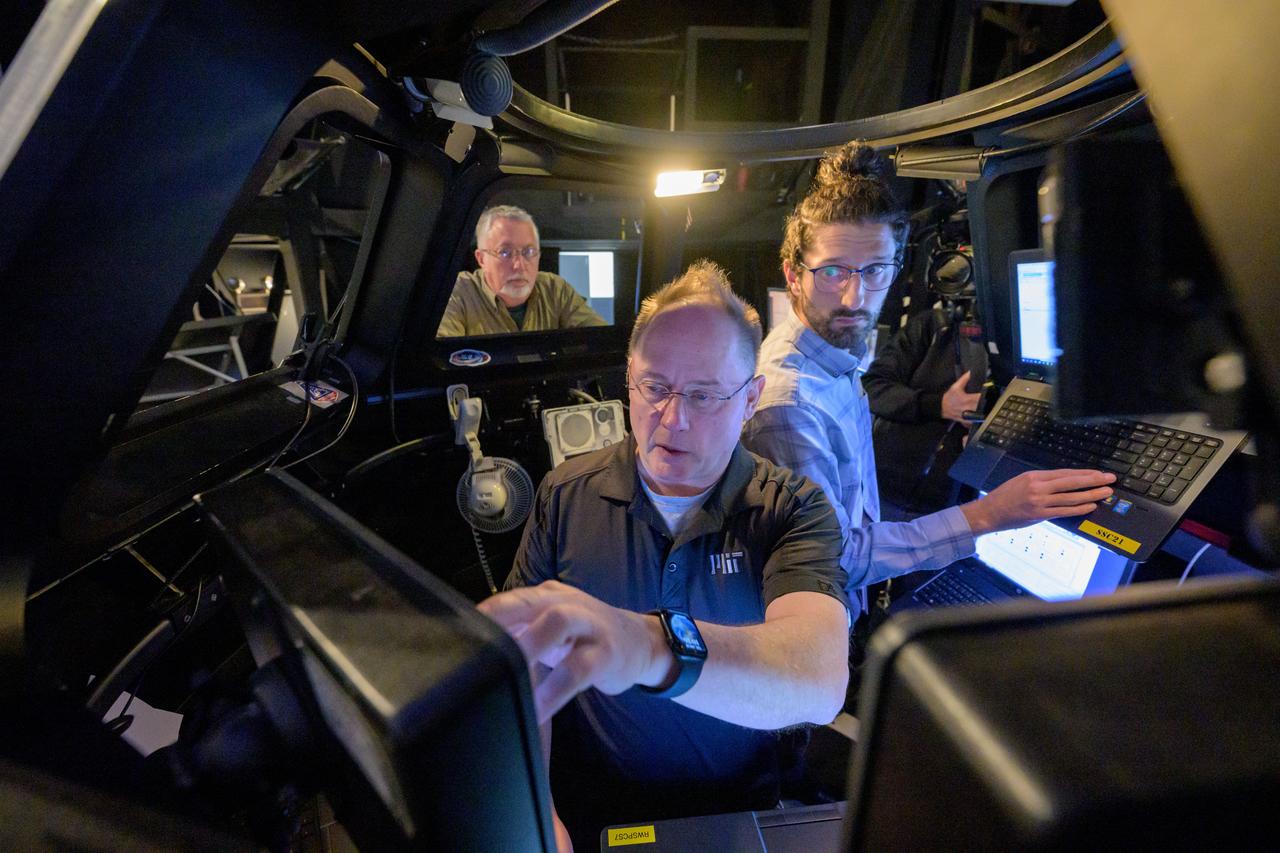

jsc2025e003631 (Jan. 28, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Mike Fincke (center) works with his trainers in a simulator to brush up on berthing Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser and other space station robotics skills at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
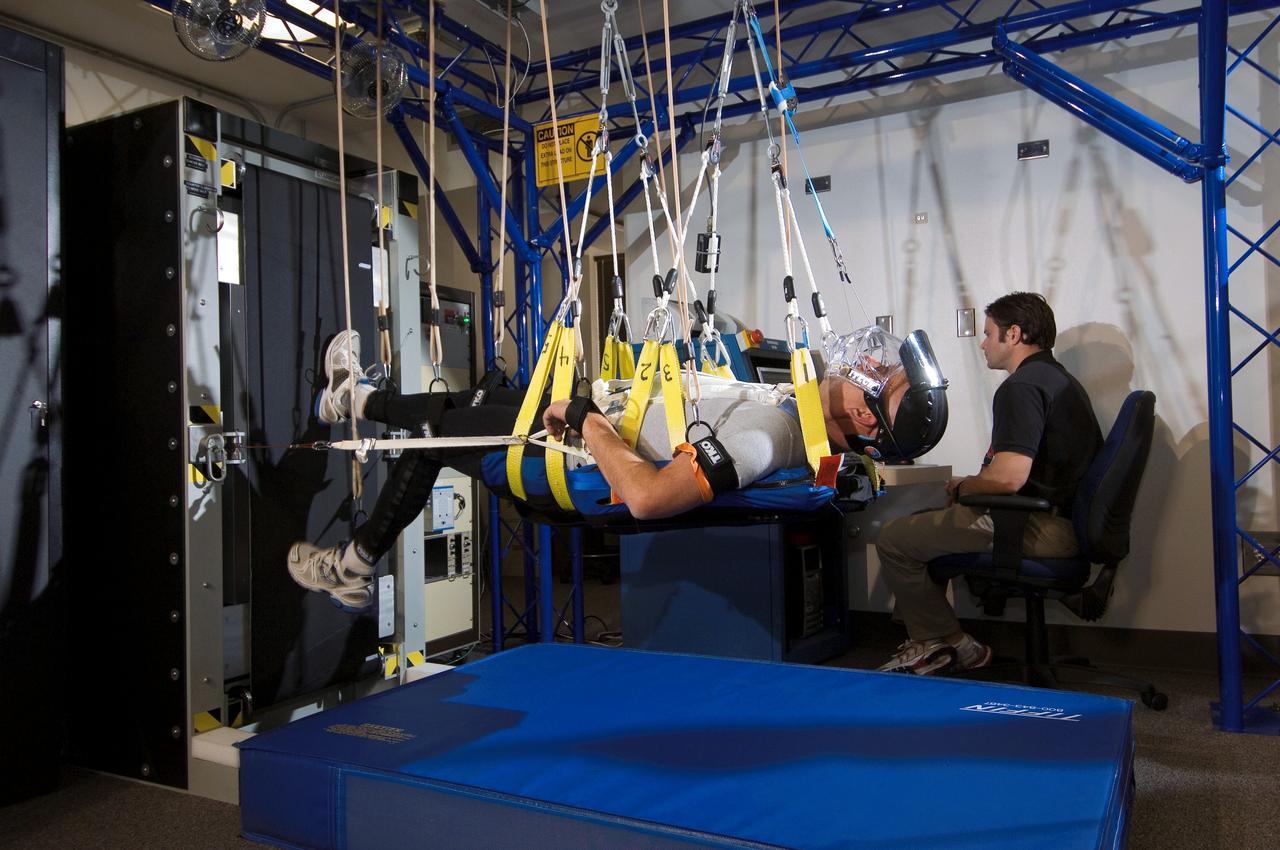

JSC2008-E-004100 (11 Jan. 2008) --- John Byard, Wyle Research and Test Operations Safety Officer, runs on the Standalone Zero Gravity Locomotion Simulator (sZLS) at the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) at Galveston, Texas. James Brent Crowell, right, Wyle exercise physiologist, serves as the operator of the device.
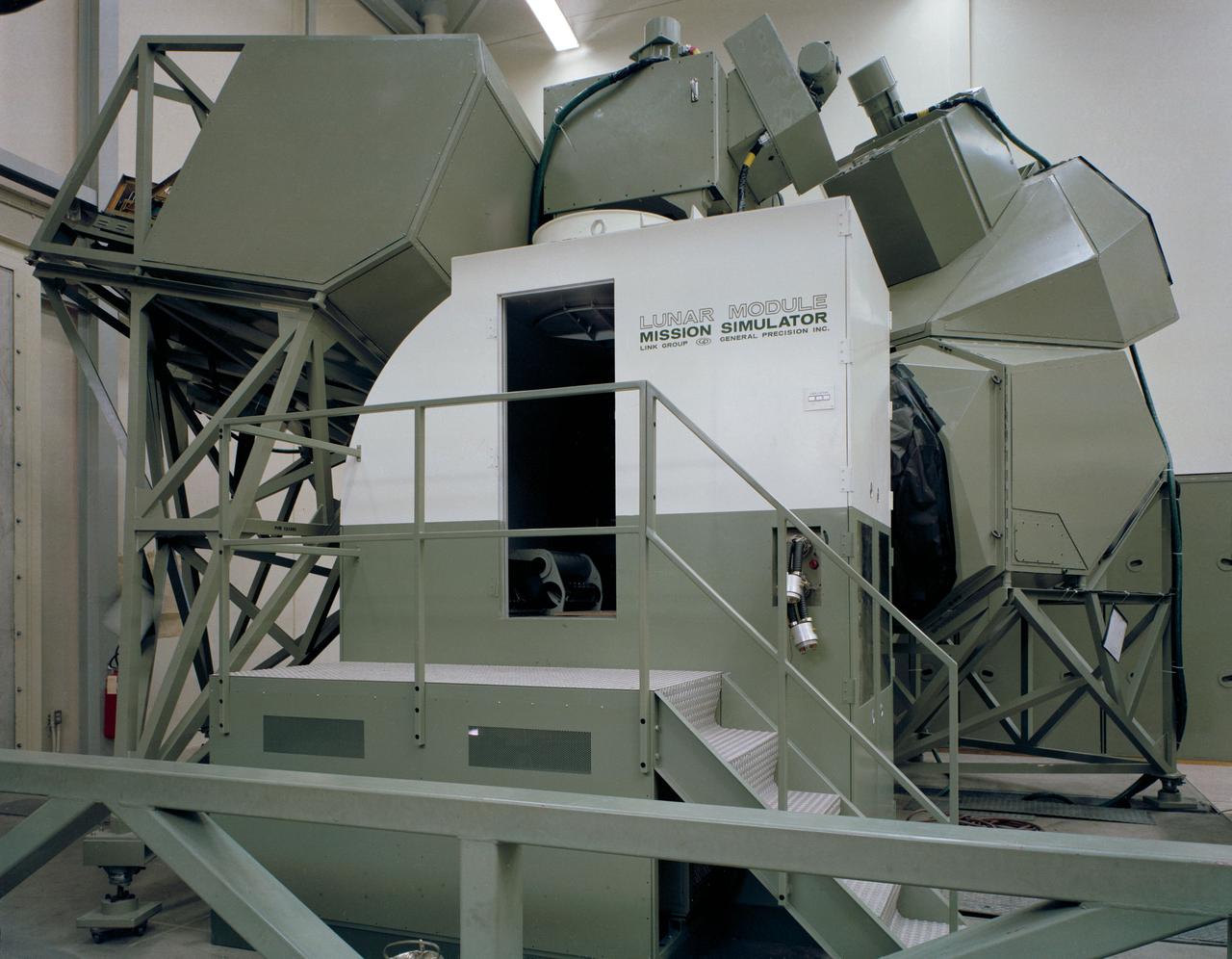

S67-15795 (1967) --- Overall view of the Lunar Module Mission Simulator, Bldg. 5, Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA

This is a photograph that was made on October 14, 1964 of Dr. von Braun while he toured the Marned Spacecraft Center, now the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. He is shown inspecting a Gemini-Agena Docking Simulator.
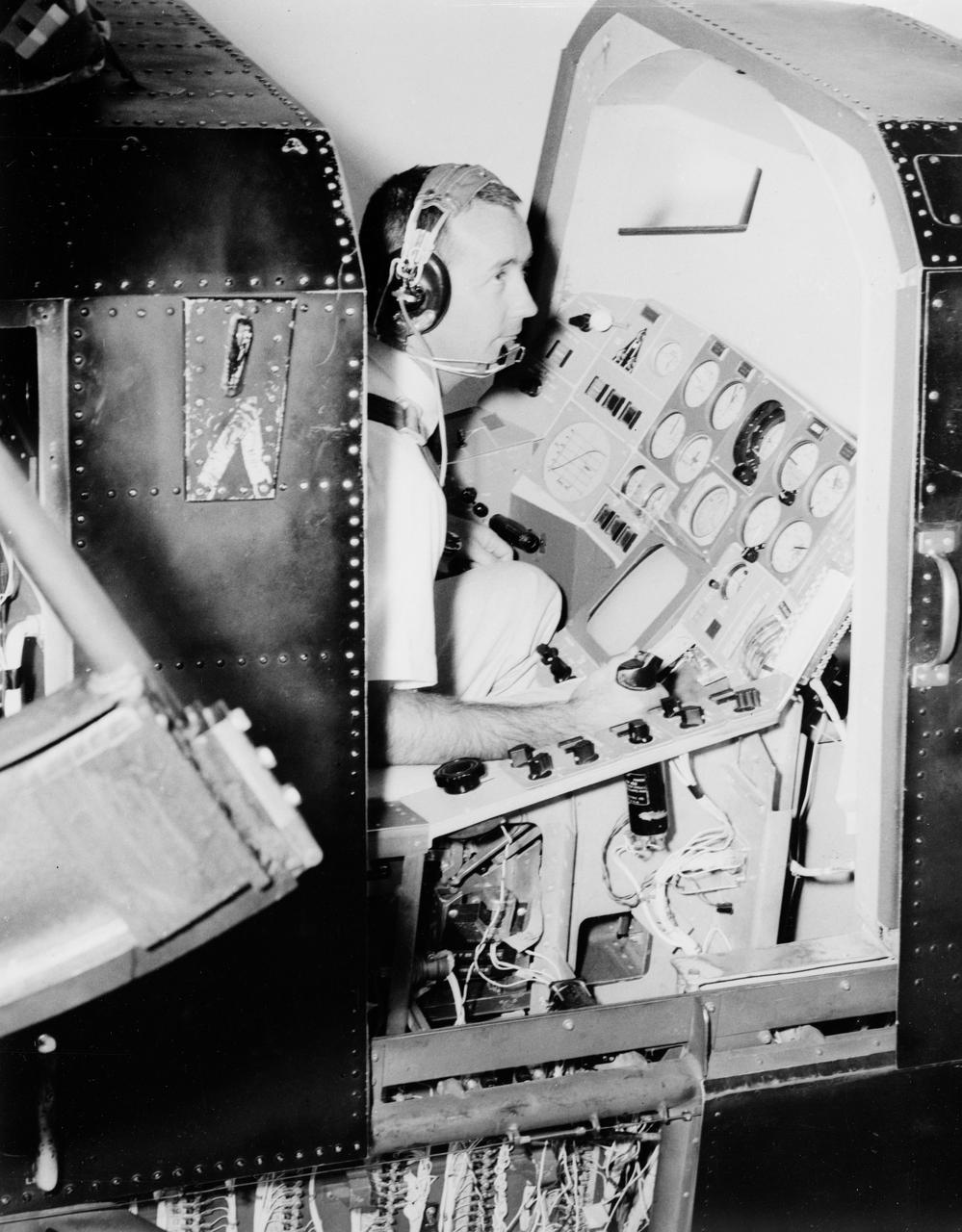
S65-19472 (10 May 1965) --- Astronaut James A. McDivitt is shown in the gondola of a realistic manned spaceflight simulator developed by the Astronautics Division of Ling-Temco-Vought in Dallas, Texas.
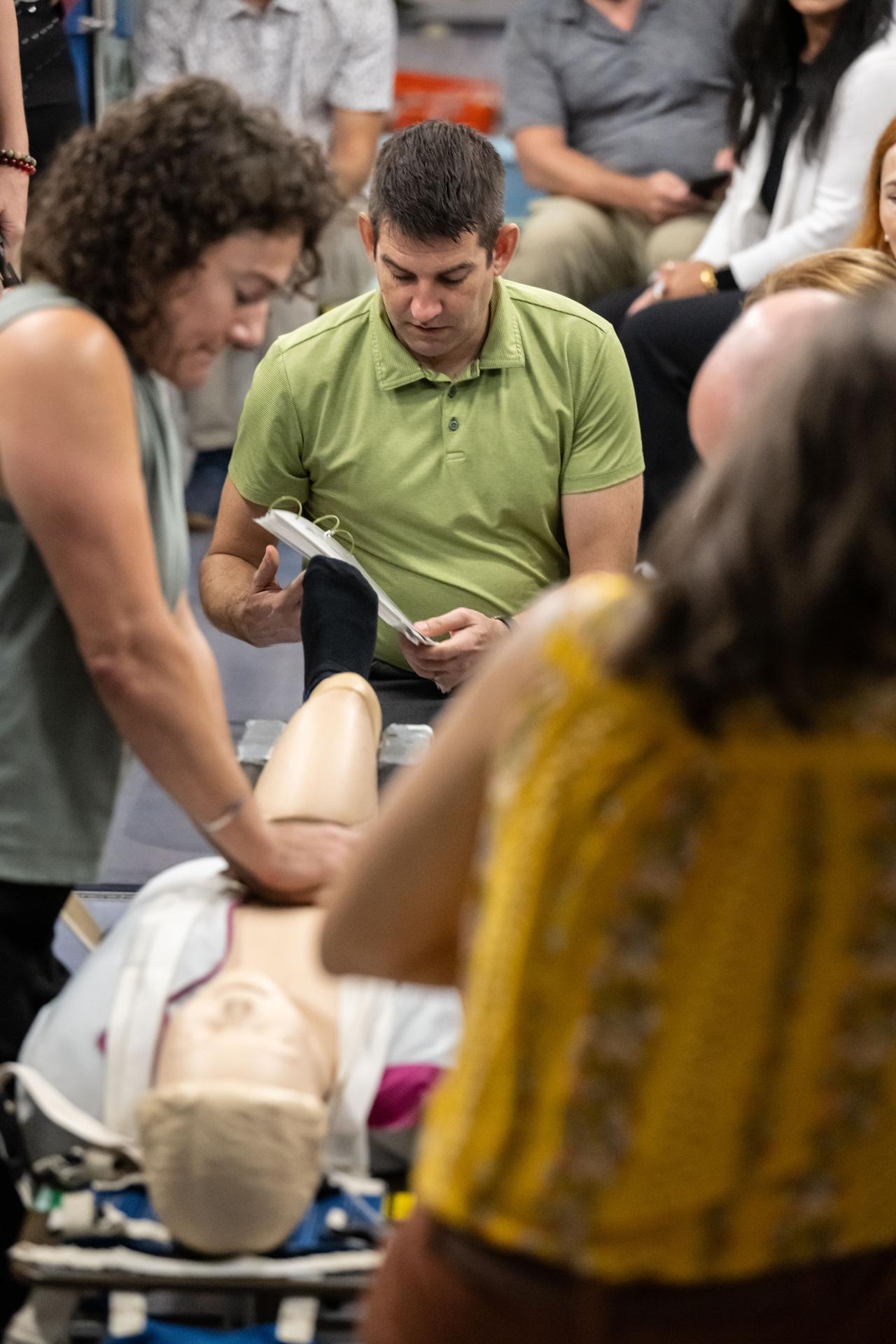
jsc2025e070045 (Aug. 21, 2025) --- NASA's SpaceX Crew-12 members Jessica Meir and Jack Hathaway, both NASA astronauts, practice cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) during a medical emergency simulation as part of their training for mission to the International Space Station. Surrounding Meir and Hathaway are various training support personnel at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
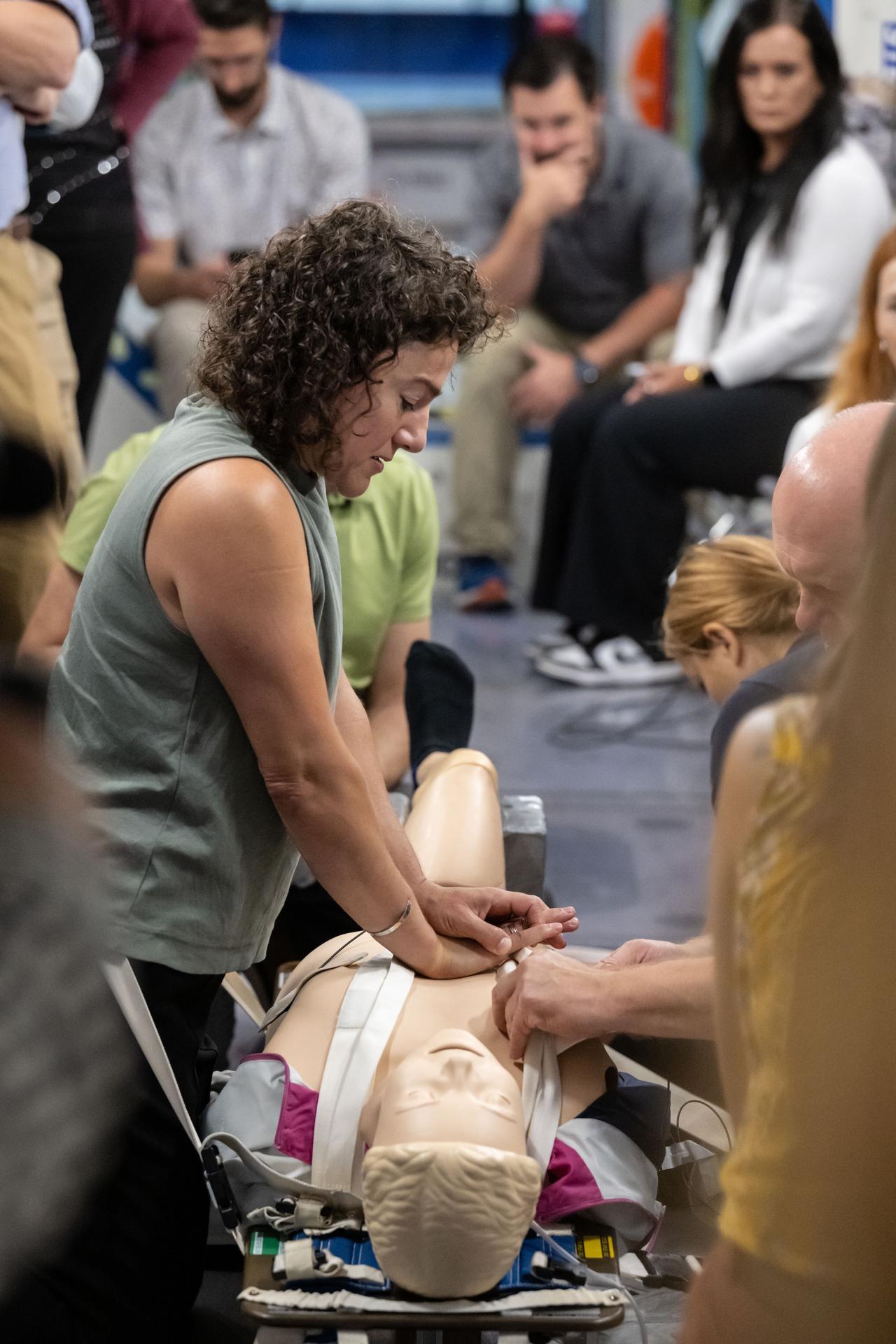
jsc2025e070047 (Aug. 21, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Jessica Meir practices cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) during a medical emergency simulation as part of her training for NASA's SpaceX Crew-12 mission to the International Space Station. Surrounding Meir are various training support personnel at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Bill Stafford

jsc2025e070056 (Aug. 21, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Jack Hathaway reviews cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques during a medical emergency simulation as part of his training for NASA's SpaceX Crew-12 mission to the International Space Station. Surrounding Hathaway are various training support personnel at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Bill Stafford
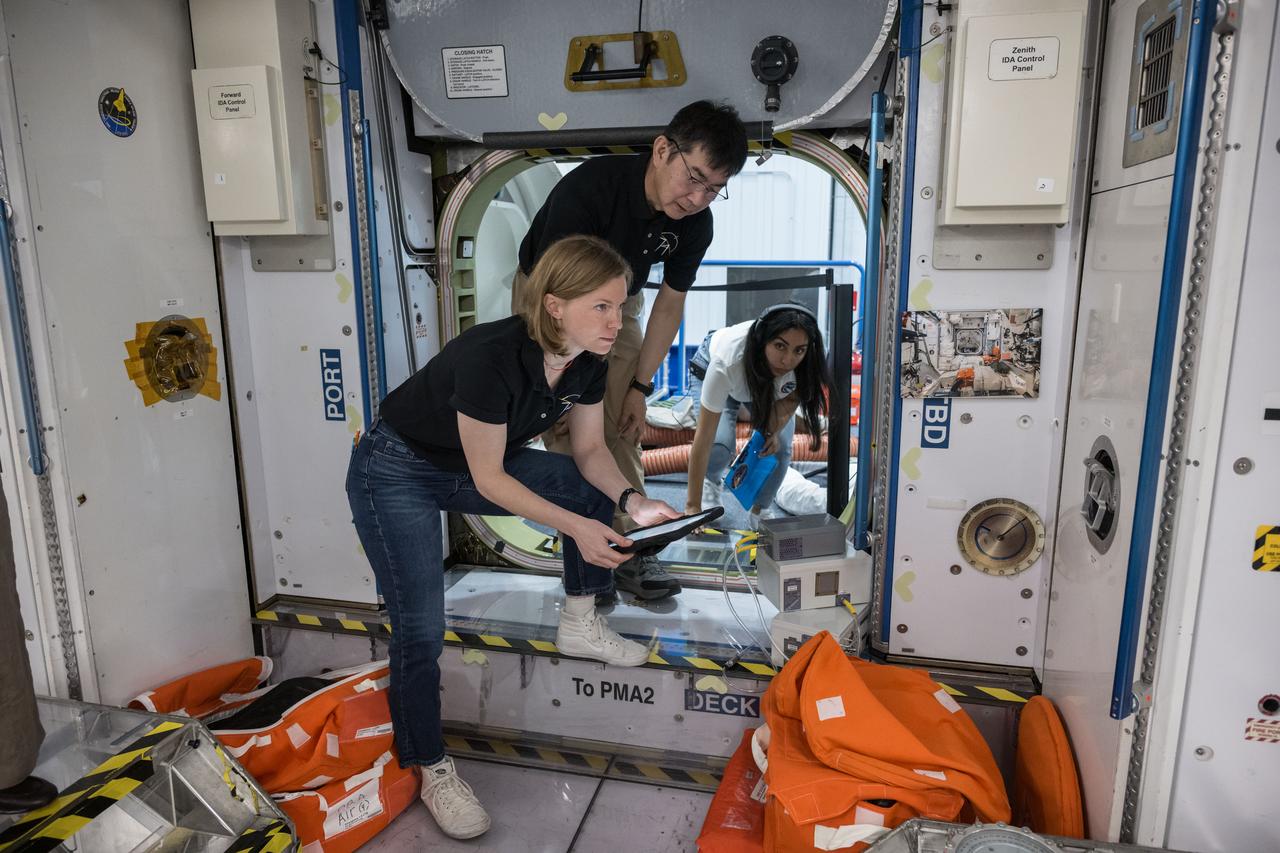

jsc2025e045063 (May 14, 2025) --- NASA astronaut Zena Cardman (front) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Kimiya Yui participate in a training simulation inside a mockup at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, along with their Expedition 74 crewmates (not shown). Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
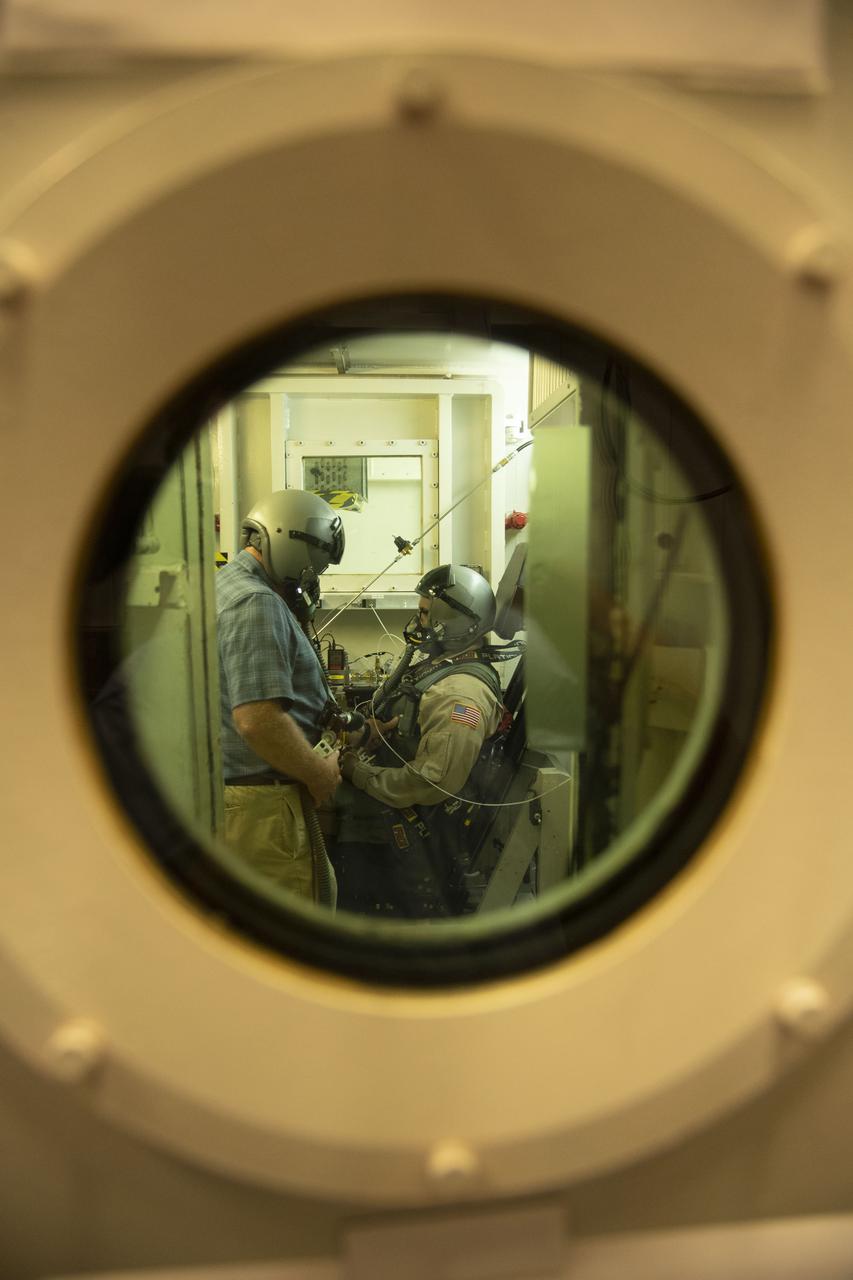

The low pressure (hypobaric) chamber at KBR’s facility in San Antonio, Texas, simulates very high altitudes by reducing the air pressure inside of the chamber. The subject inside the chamber experiences the reduced pressure conditions that exist at higher altitudes, in this case altitudes up to 60,000 feet.
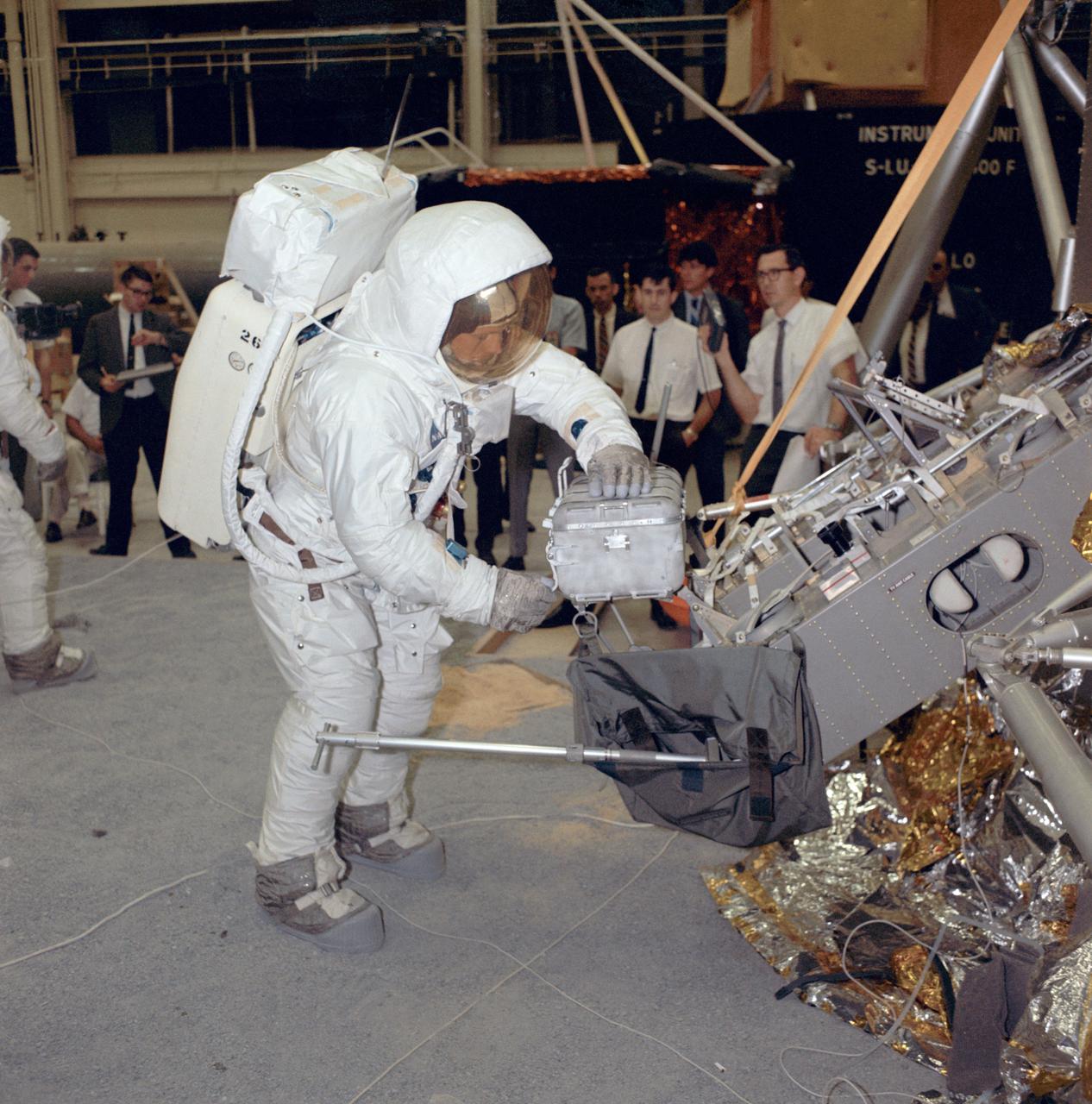

Apollo 11 commander Neil Armstrong works with an Apollo Lunar Sample Return Container during a two-and-a-half-hour lunar surface simulation training exercise. The image was taken on Apr. 18, 1969, in Building 9 at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. The sample tubes carried by NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover are destined to carry the first samples in history from another planet back to Earth. Future scientists will use these carefully selected representatives of Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust), to look for evidence of potential microbial life present in Mars' ancient past and to answer other key questions about Mars and its history. Perseverance will land at Mars' Jezero Crater on Feb. 18, 2021. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24297
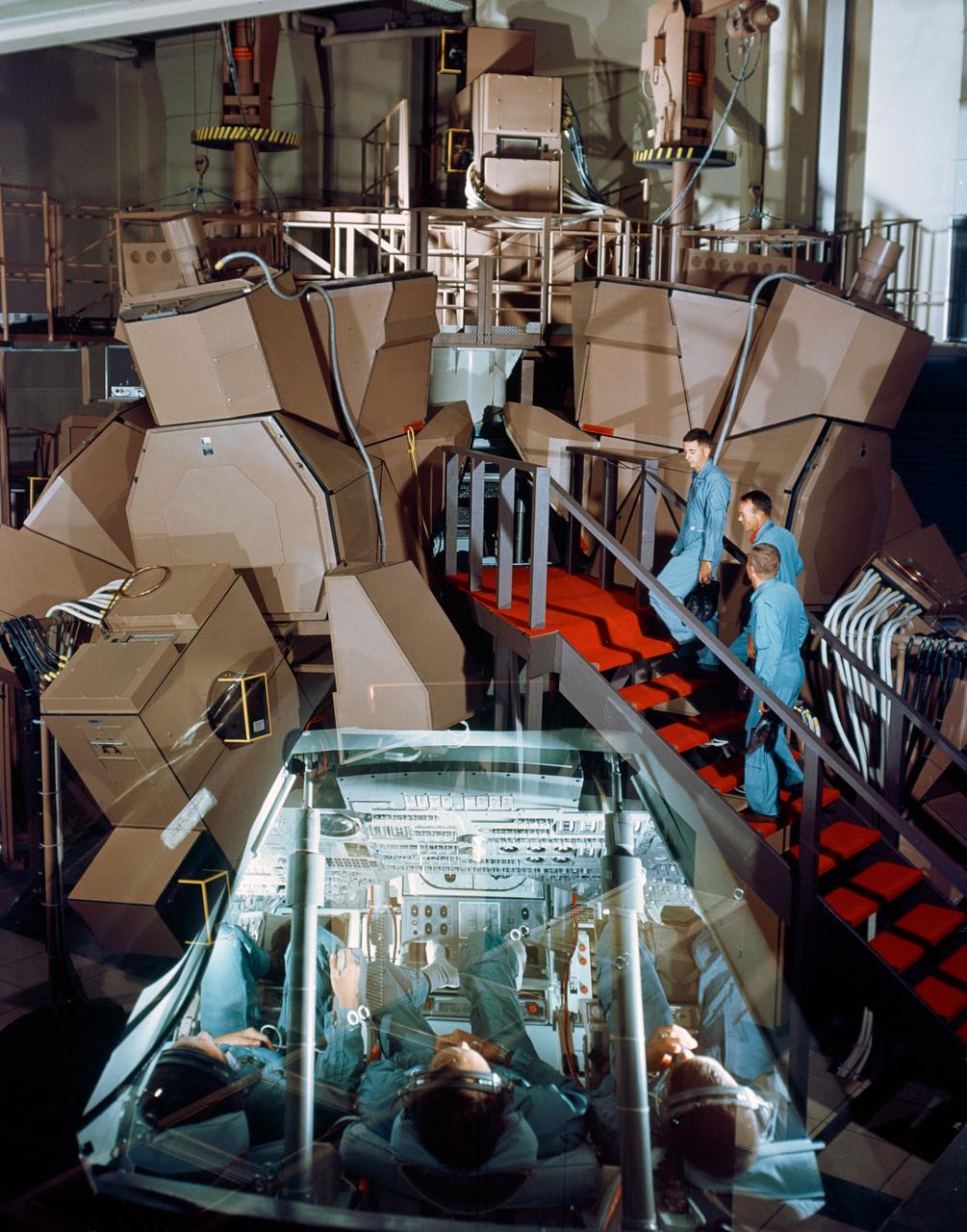

S67-50585 (1967) --- This is an intentional double exposure showing the Apollo Mission Simulator in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Building 5 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. In the exterior view astronauts William A. Anders, Michael Collins, and Frank Borman (reading from top of stairs) are about to enter the simulator. The interior view shows the three astronauts in the simulator. They are (left to right) Borman, Collins, and Anders. Photo credit: NASA
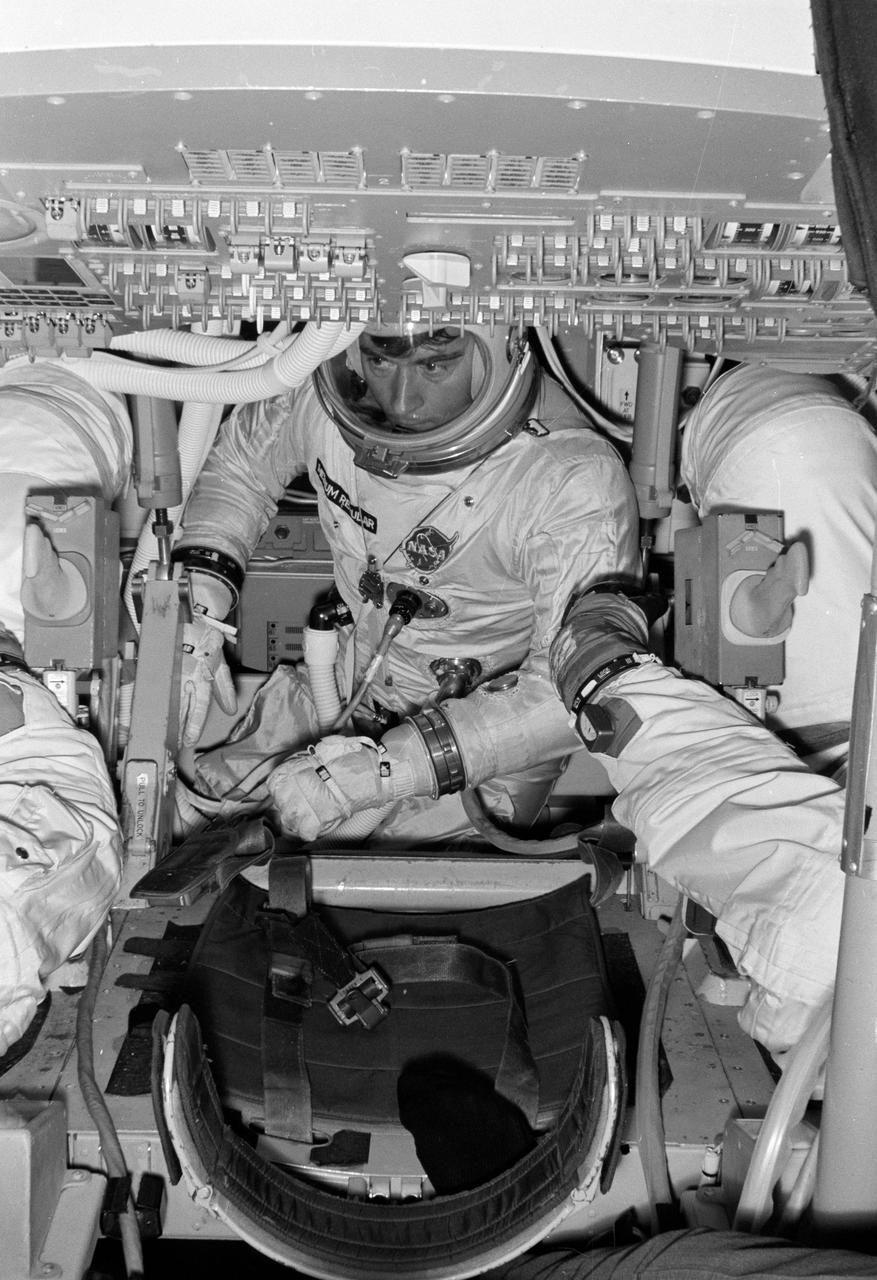

S68-15979 (15 Jan. 1968) --- Astronaut John W. Young, command module pilot, inside the Command Module Simulator in Building 5 during an Apollo Simulation. Out of view are astronaut Thomas P. Stafford (on the left), commander; and astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (on the right), lunar module pilot.
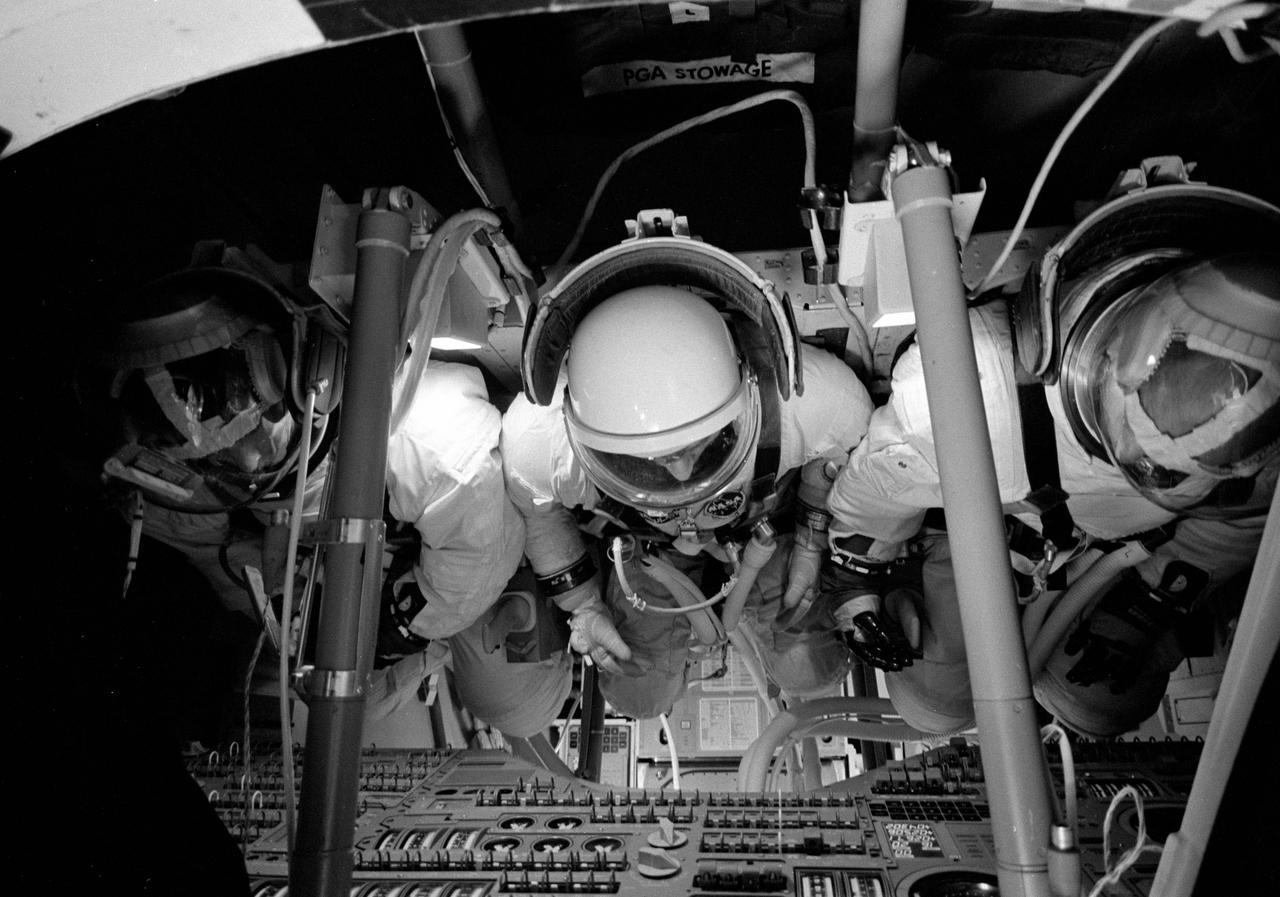

S68-15952 (15 Jan. 1968) --- Three astronauts inside the Command Module Simulator in Building 5 during an Apollo Simulation. Left to right, are astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.

Weather Instrumentation Engineer Nick O’Connor works with the Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. It will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.

Weather Instrumentation Engineer Nick O’Connor works with the Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. It will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.

Weather Instrumentation Engineer Nick O’Connor works with the Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. It will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.

COLOR 13 SEPTEMBER 1996 S96-14353 JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS STS-81 TRAINING VIEW --- In the Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F), astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, STS-81 mission specialist, prepares for an underwater simulation of a contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Linenger, attired in a training version will utilize the nearby 25-feet deep pool, in which he will be able to achieve a neutrally buoyant state.

jsc2025e045913 (May 14, 2025) --- From left to right: Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Platonov, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Zena Cardman, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Kimiya Yui pose for a photo after participating in a training simulation inside a mockup at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
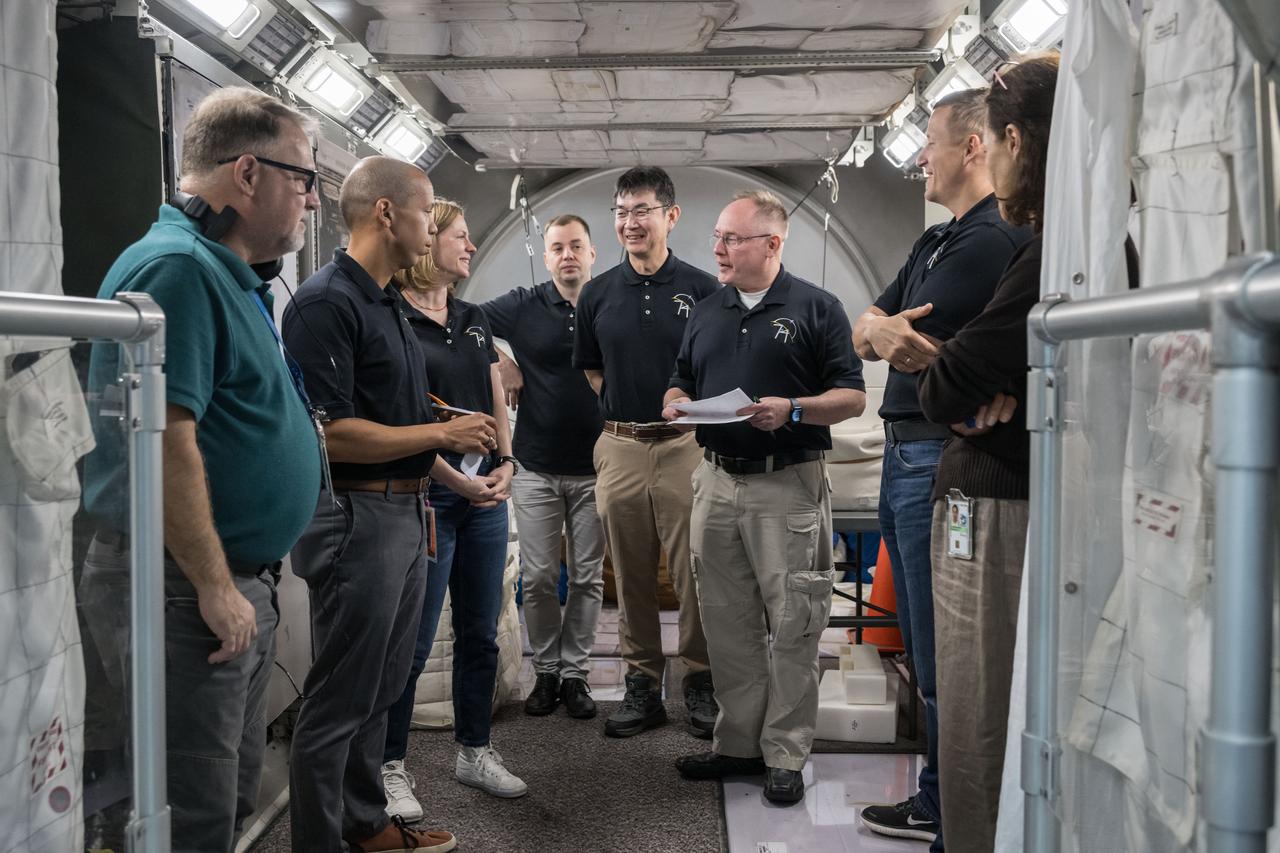

jsc2025e045053 (May 14, 2025) --- The International Space Station’s Expedition 74 crew, including NASA astronauts Zena Cardman, Mike Fincke, and Chris Williams, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Kimiya Yui, and Roscosmos Cosmonauts Oleg Platonov and Sergey Kud-Sverchokov participate in a training simulation inside a mockup at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
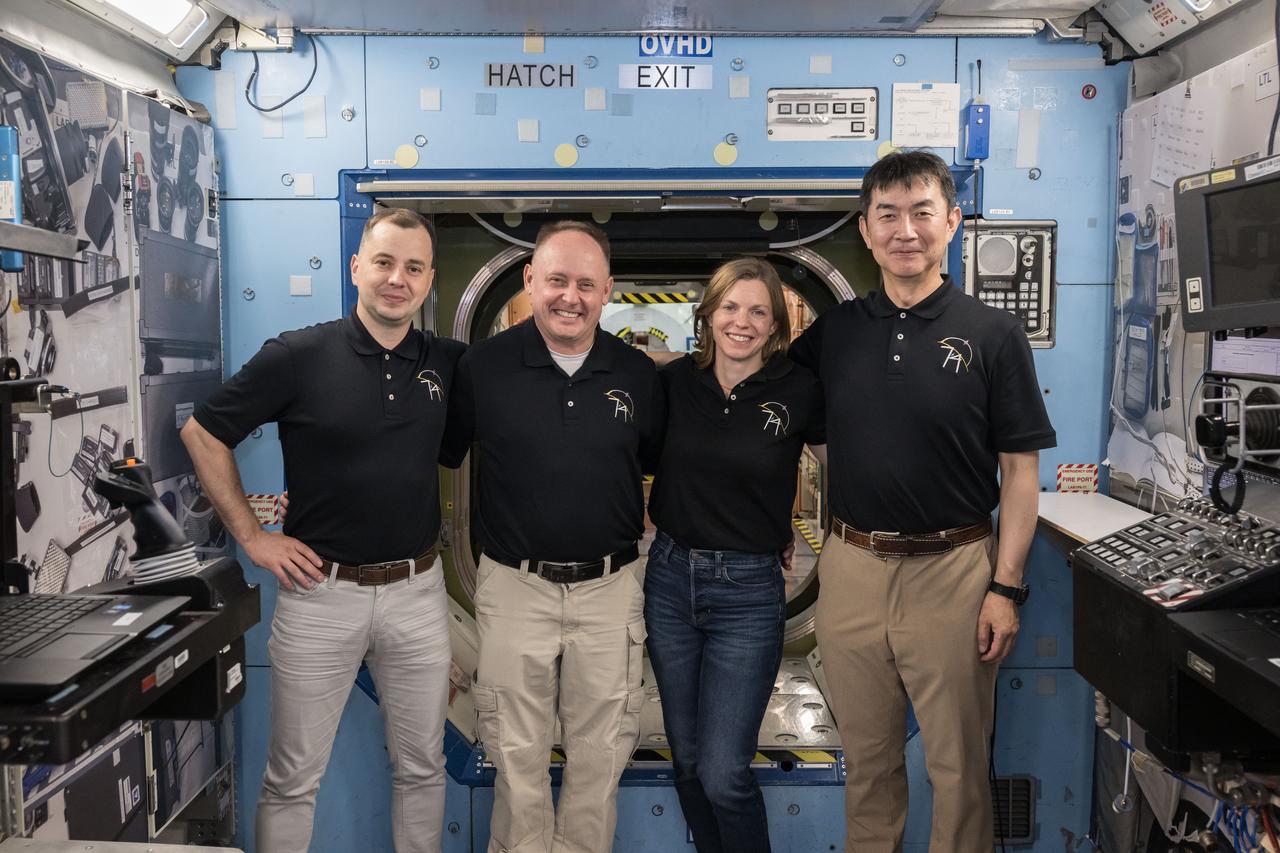
jsc2025e045914 (May 14, 2025) --- From left to right: Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Platonov, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Zena Cardman, and JAXA astronaut (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kimiya Yui pose for a photo after participating in a training simulation inside a mockup at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
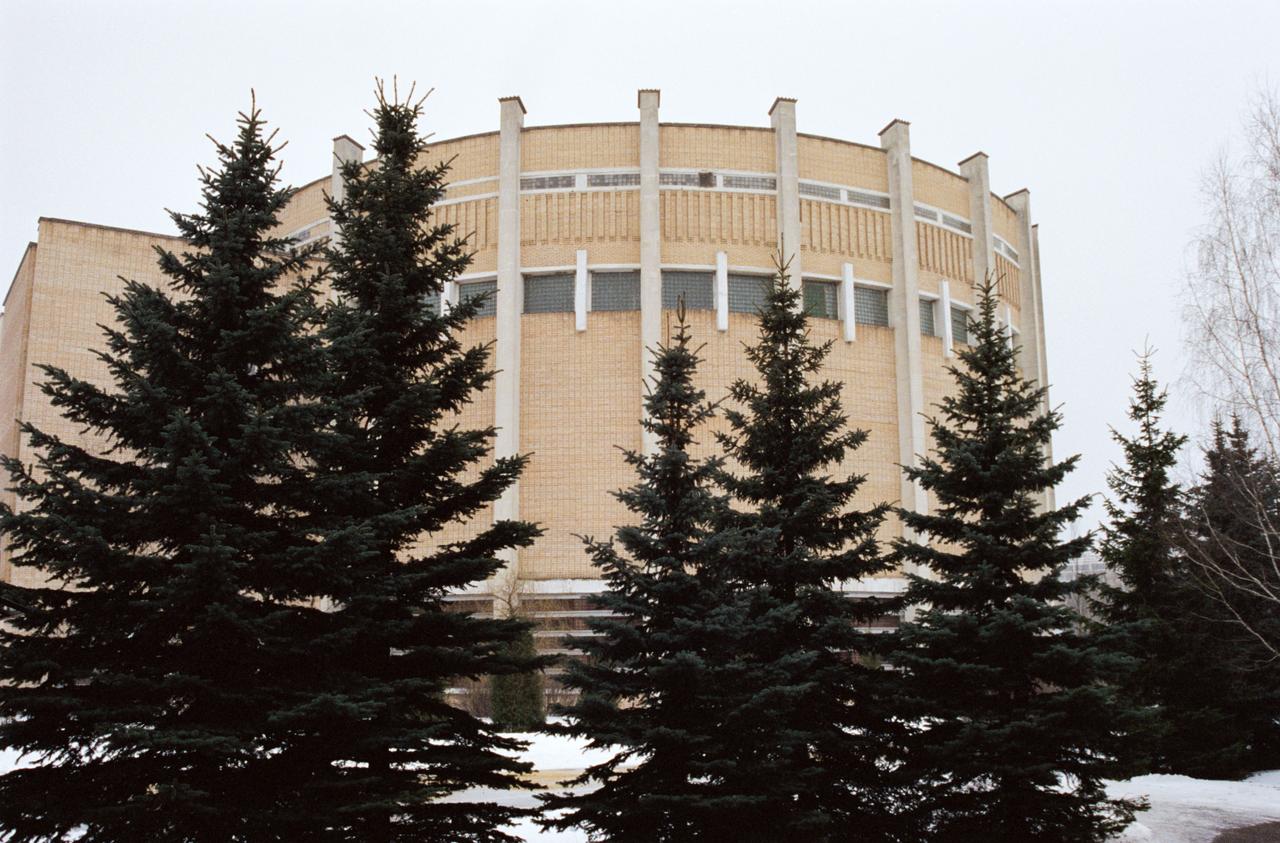

S95-04319 (22 Feb 1995) --- The neutral buoyancy facility at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia, is used for underwater training for missions aboard the Russian Mir Space Station. The facility is similar to NASA's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas, and the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama.
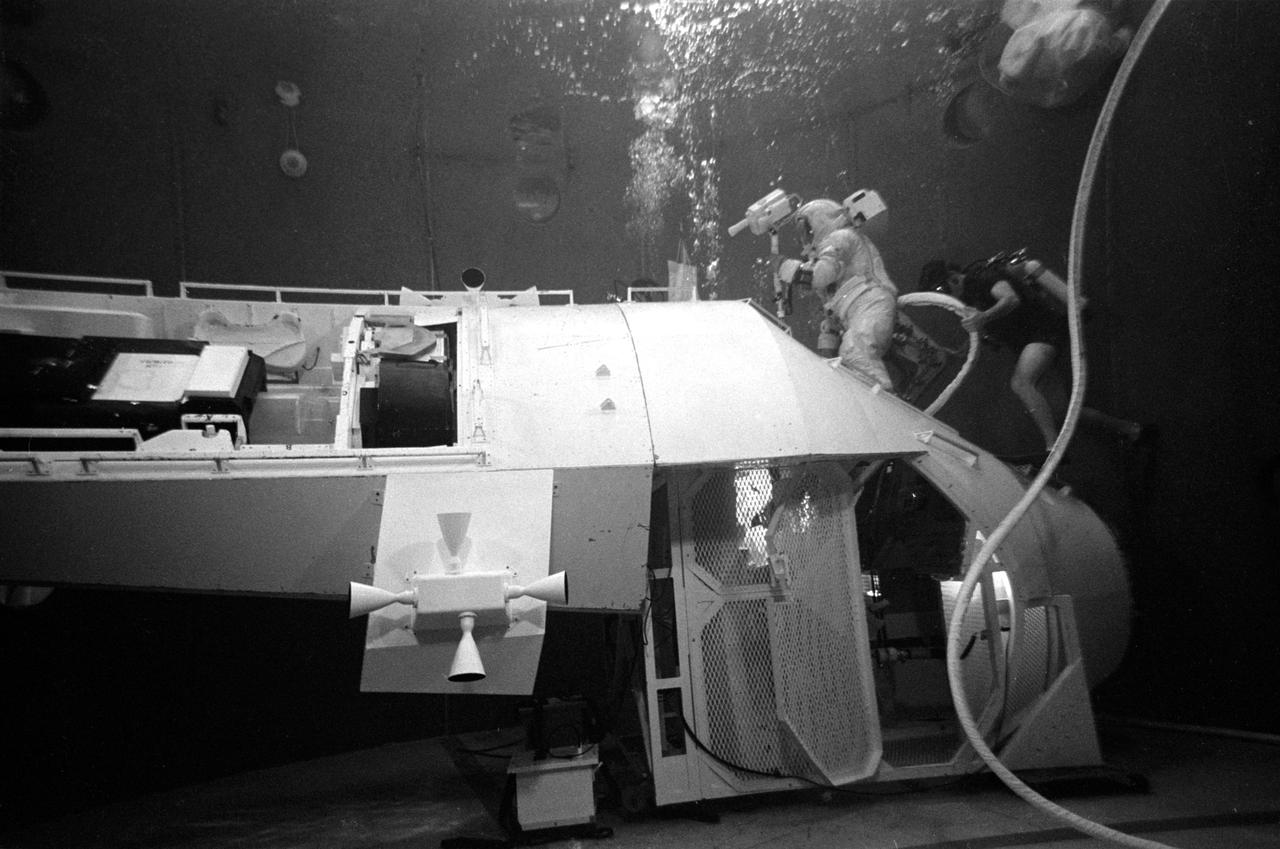
S71-58148 (1 Dec. 1971) --- Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot of the planned Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, participates in extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations in the water facility tank in Building 5 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), Houston, Texas, during training preparations for the forthcoming mission. Mattingly is scheduled to perform EVA during the trans-Earth journey of the Apollo 16 mission.
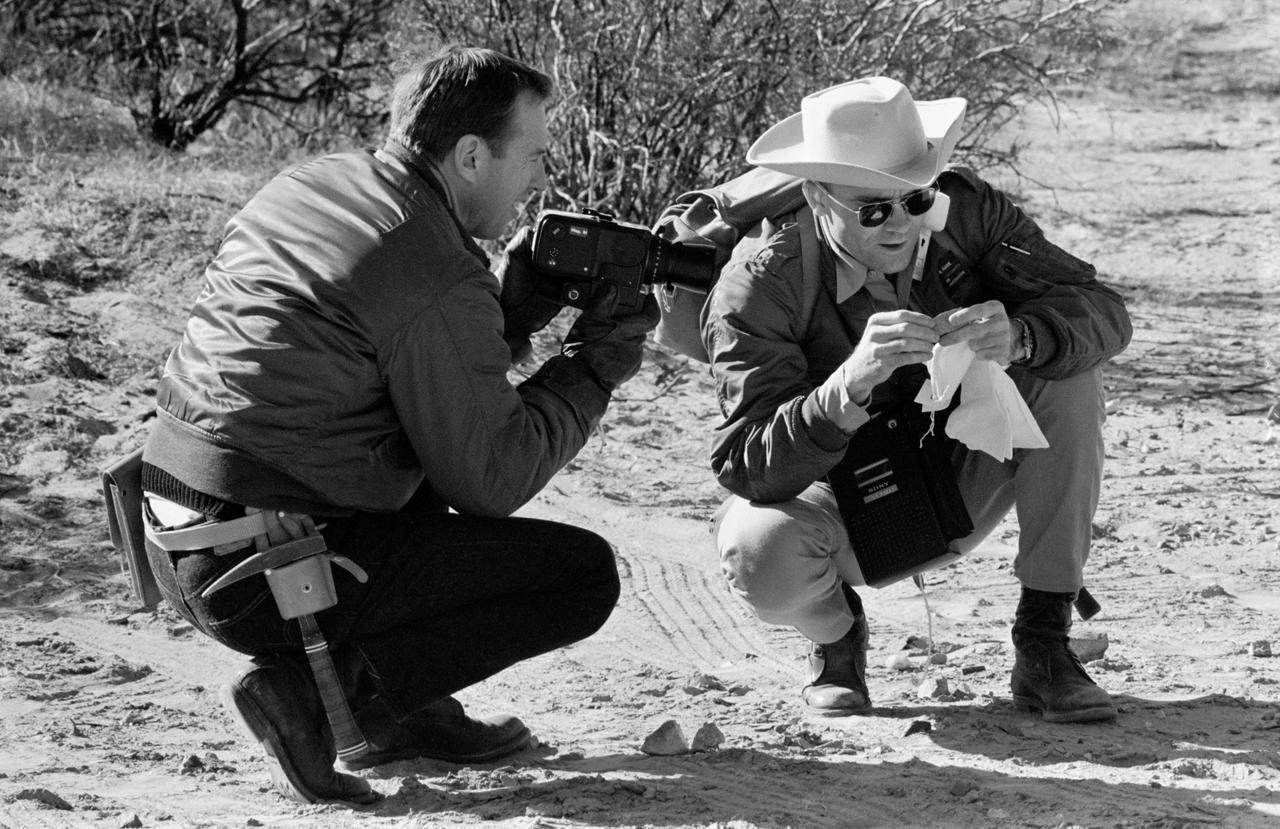

S69-25199 (25 Feb. 1969) --- Two Apollo 11 astronauts study a rock specimen during a geological field trip to the Quitman Mountains area near the Fort Quitman ruins in far west Texas. On the left is James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 11 backup crew commander; and on the right is Fred W. Haise Jr., backup crew lunar module pilot. Lovell holds a camera which was used in simulating taking pictures of actual lunar samples on the surface of the Moon.
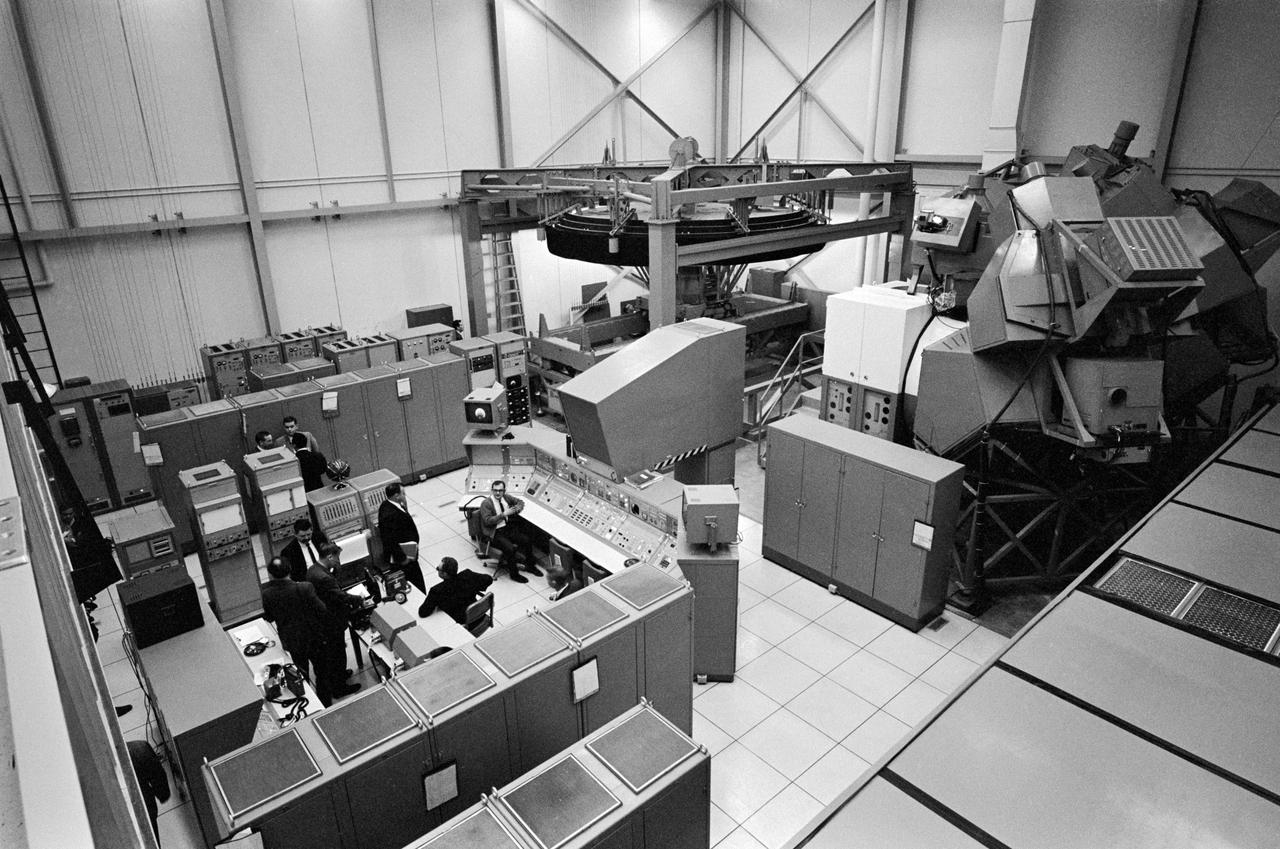

Overall view of the Lunar Module Mission Simulator, an astronaut training facility located in bldg 5.
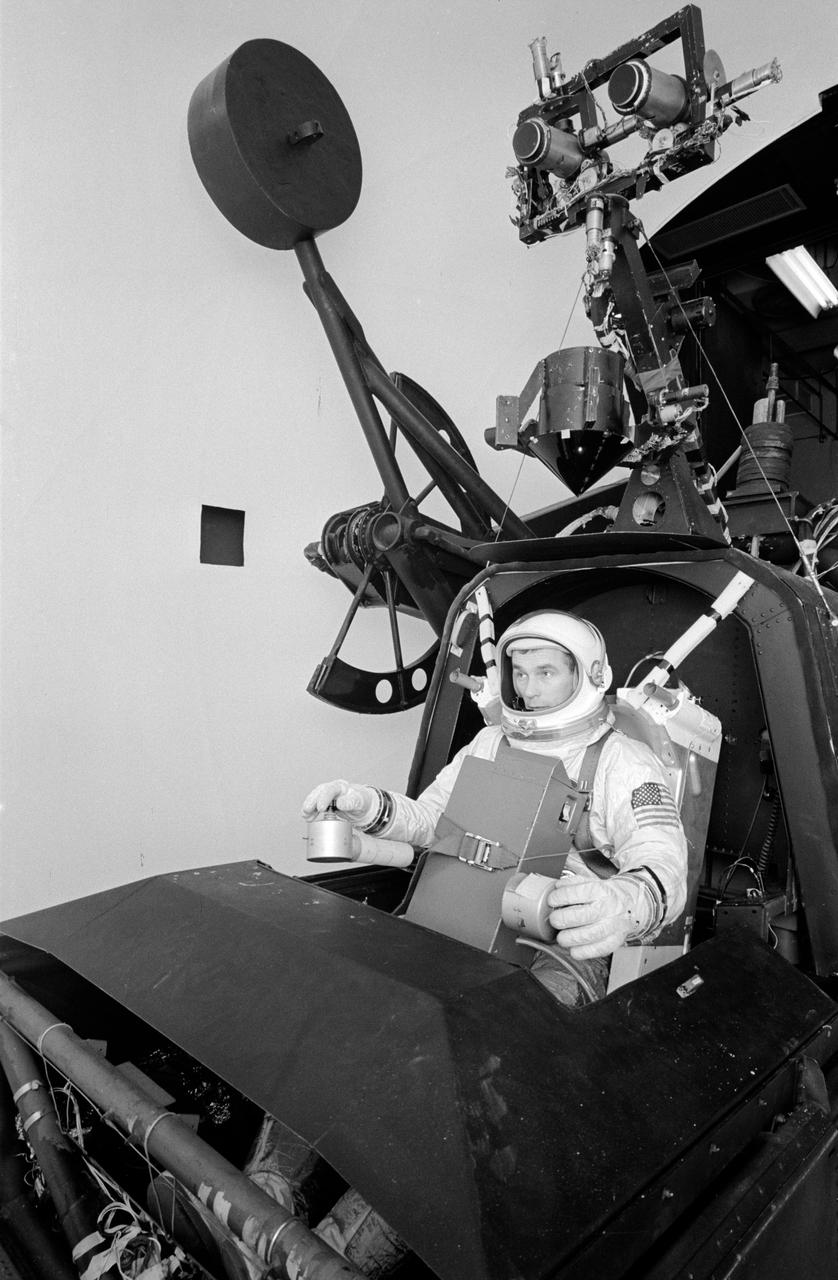

S66-27990 (March 1966) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, pilot for the Gemini-9 spaceflight, works out procedures for his historic space excursion in a unique manned Aerospace Flight Simulator at LTV Corp. at Dallas, Texas. The LTV simulator is used frequently by NASA astronauts for a variety of space programs maneuvers to provide many of the sensations and visual scenes of actual spaceflight. Controlled through a complex of computers, the device makes it possible for the astronauts to work out procedures, solve problems and simulate missions in real time with great accuracy. The astronaut rides in a spacecraft-like gondola which moves in roll, pitch and yaw in response to his controls and accurate computer inputs. The simulator's usual spacecraft displays and canopy have been removed and AMU backpack complete with control electronics installed. The astronaut makes his simulated flight in an inflated pressure suit and with the NASA-developed Extravehicular Life Support system chest pack which will be used in the Gemini flight. Photo credit: NASA
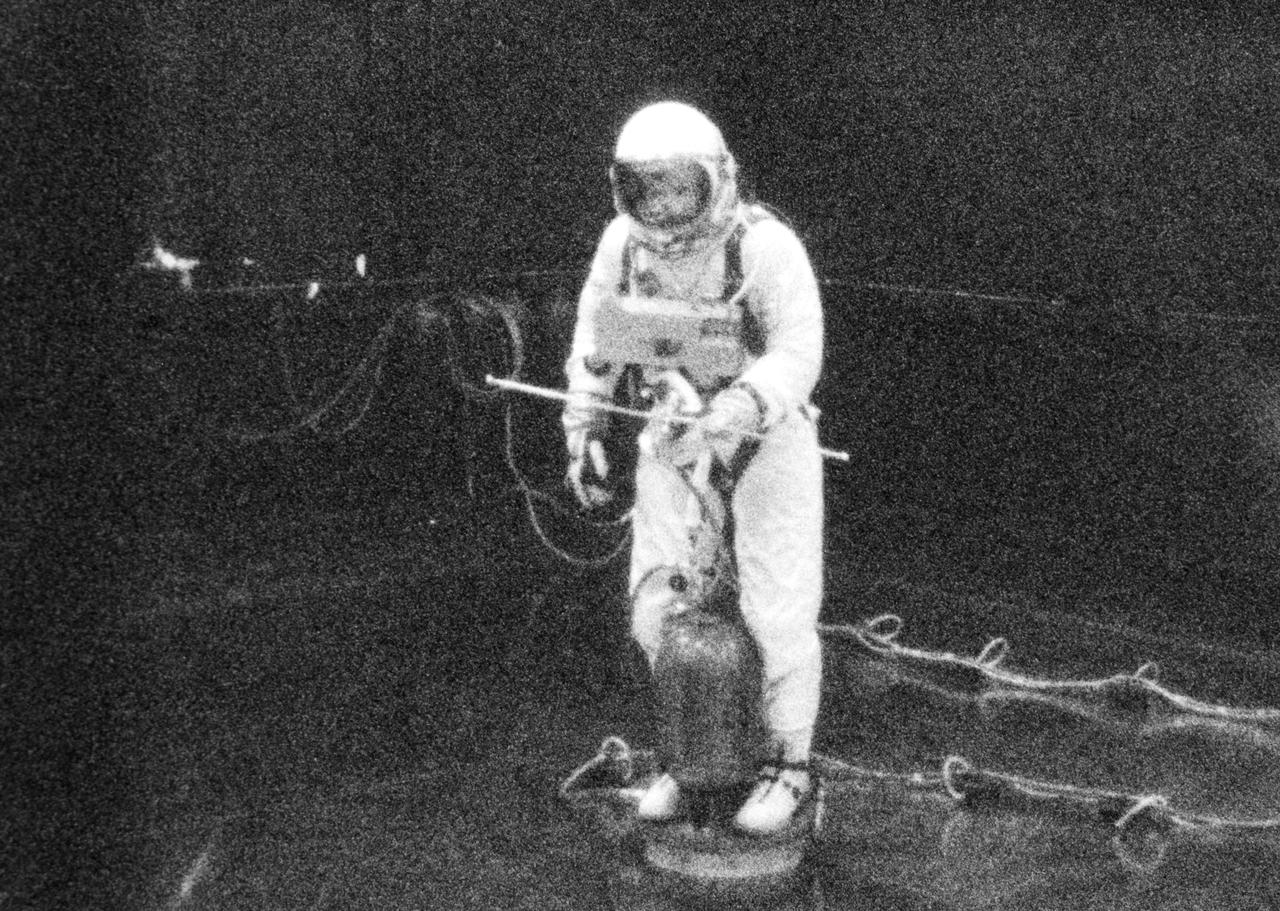

S65-19504 (28 May 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew, is pictured during an extravehicular exercise in the Building 4 laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. White is controlling about the yaw (vertical) axis while translating. He stands on a Balance Extravehicular Training Aircraft which is separated from the level steel floor by a .001th-inch cushion of air. In his right hand White holds a zero-gravity integral propulsion unit which is a self-maneuvering device used by an astronaut in a zero-gravity environment. This condition is simulated in this training exercise. White's spacesuit is pressurized to create a realistic training condition. The simulated umbilical line is floated on air with the aid of eleven small air pads.
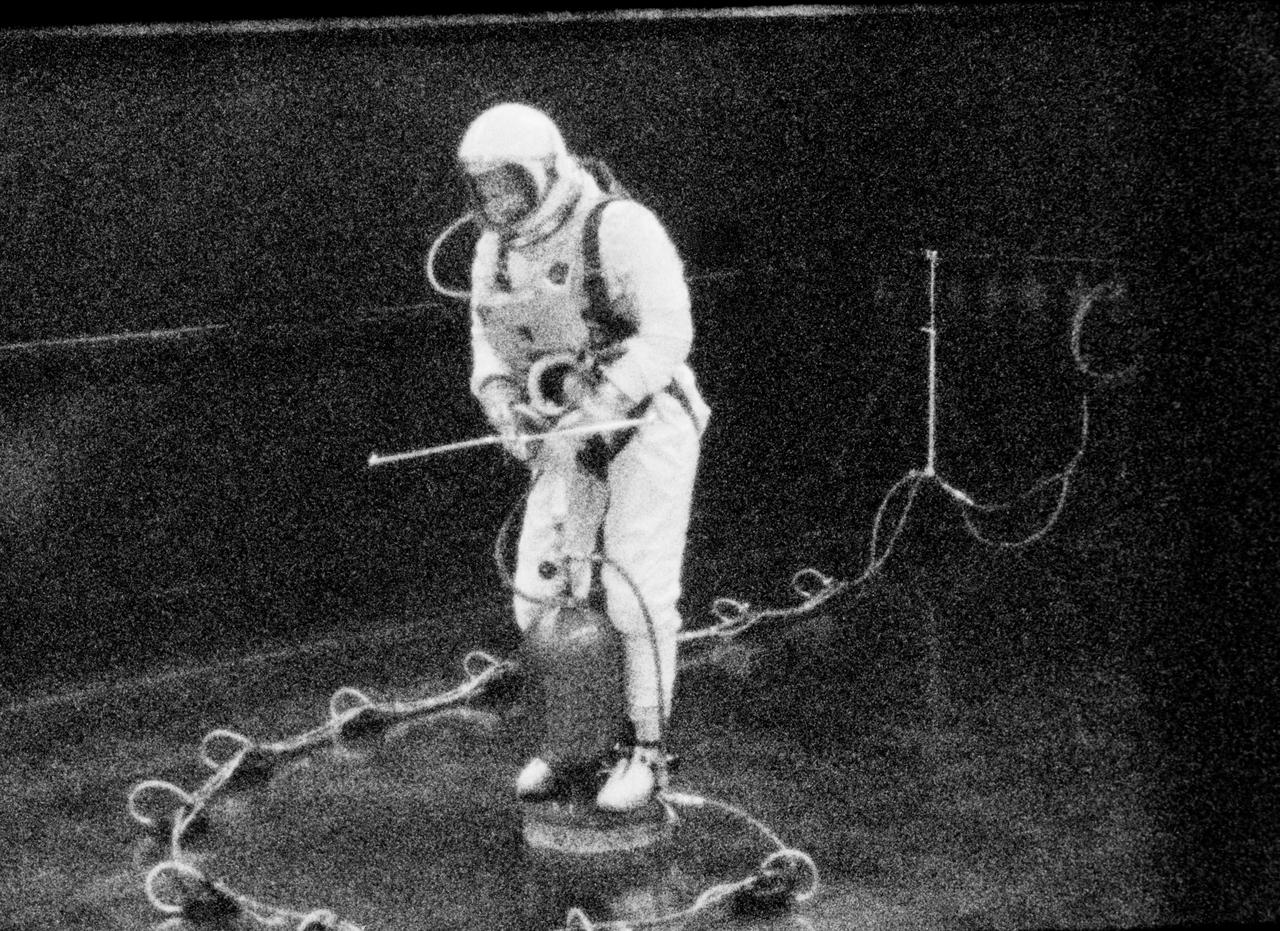
S65-19505 (28 May 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew, is pictured during an extravehicular exercise in the Building 4 laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas. White is controlling about the yaw (vertical) axis while translating. He stands on a Balance Extravehicular Training Aircraft which is separated from the level steel floor by a .001th-inch cushion of air. In his right hand White holds a zero-gravity integral propulsion unit which is a self-maneuvering device used by an astronaut in a zero-gravity environment. This condition is simulated in this training exercise. White's spacesuit is pressurized to create a realistic training condition. The simulated umbilical line is floated on air with the aid of eleven small air pads.

Weather Instrumentation Technician Gavin Oglesby, left, and Weather Instrumentation Engineer Nick O’Connor work with the Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. It will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.

Weather Instrumentation Technician Gavin Oglesby, left, and Weather Instrumentation Engineer Nick O’Connor work with the Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. It will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
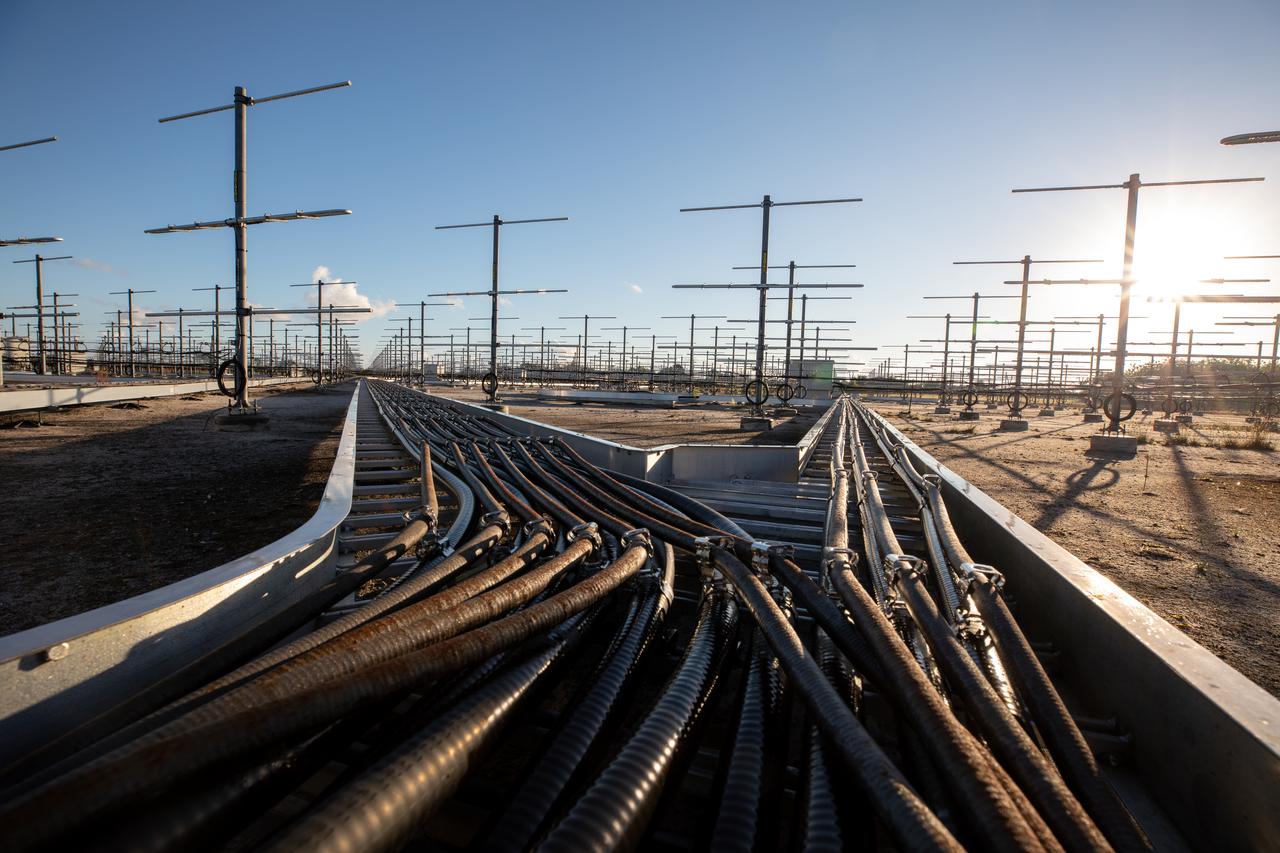

The Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler, located on five acres near the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is shown during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler consists of 640 antennae and delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. The instrument will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
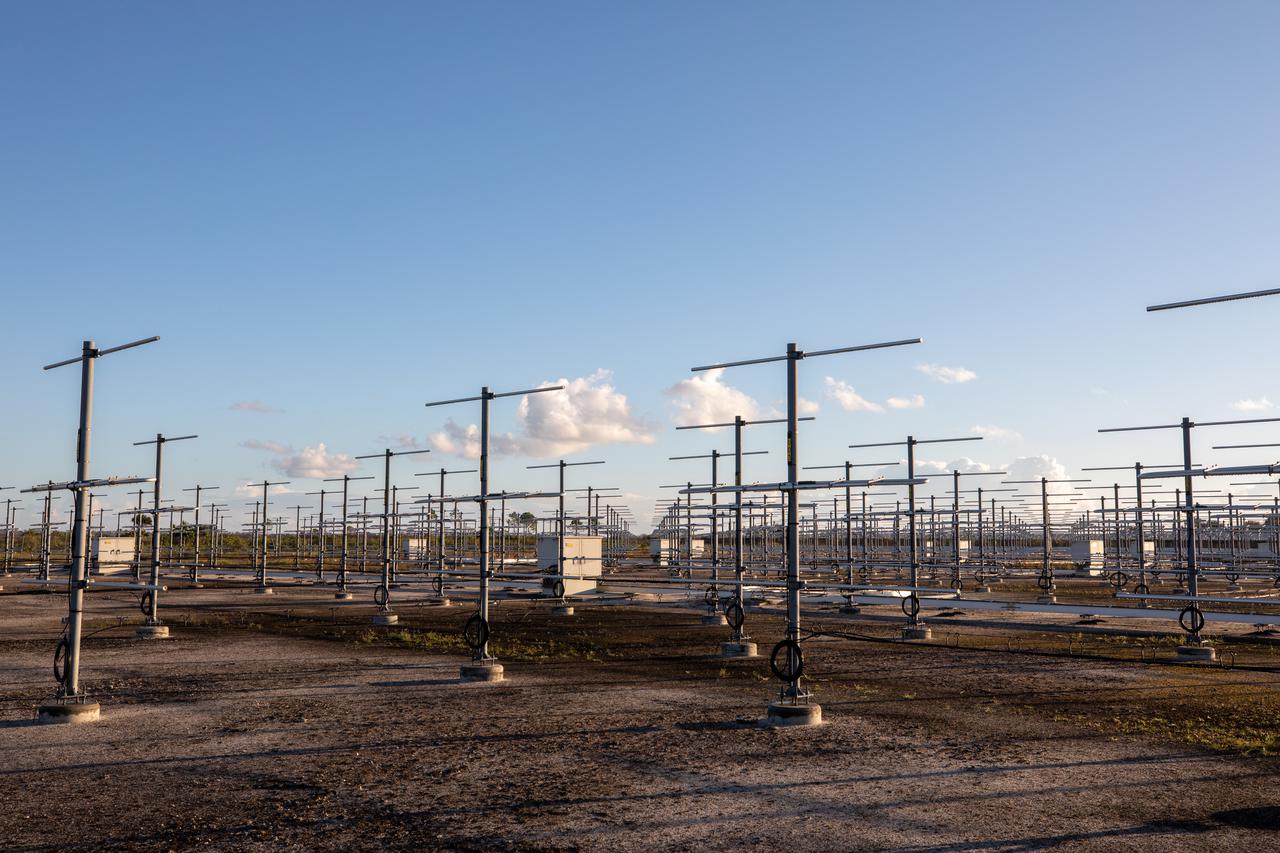

The Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler, located on five acres near the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is shown during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler consists of 640 antennae and delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. The instrument will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
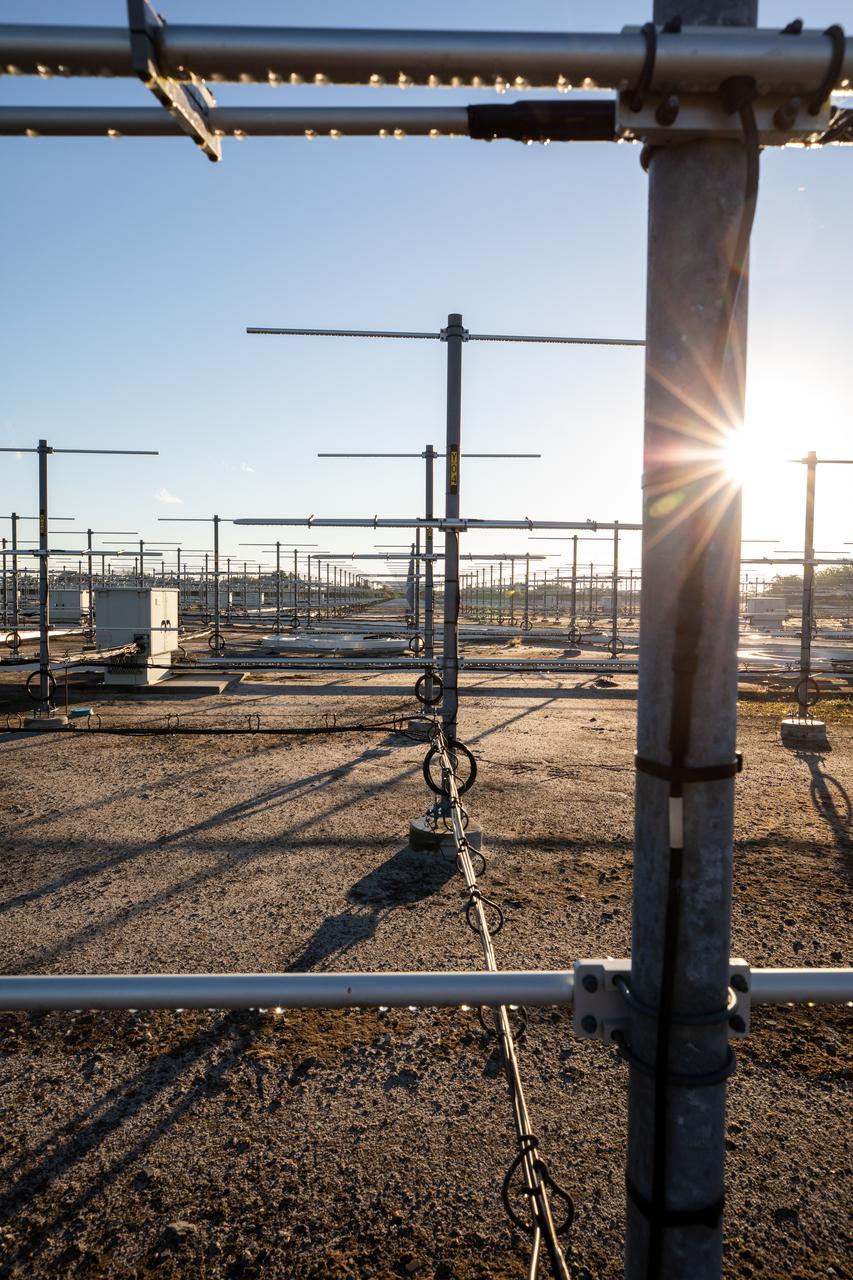

The Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler, located on five acres near the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is shown during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The simulation involved teams from Kennedy, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. The radar wind profiler consists of 640 antennae and delivers data – from 6,000 to 62,000 feet – every five minutes. The instrument will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
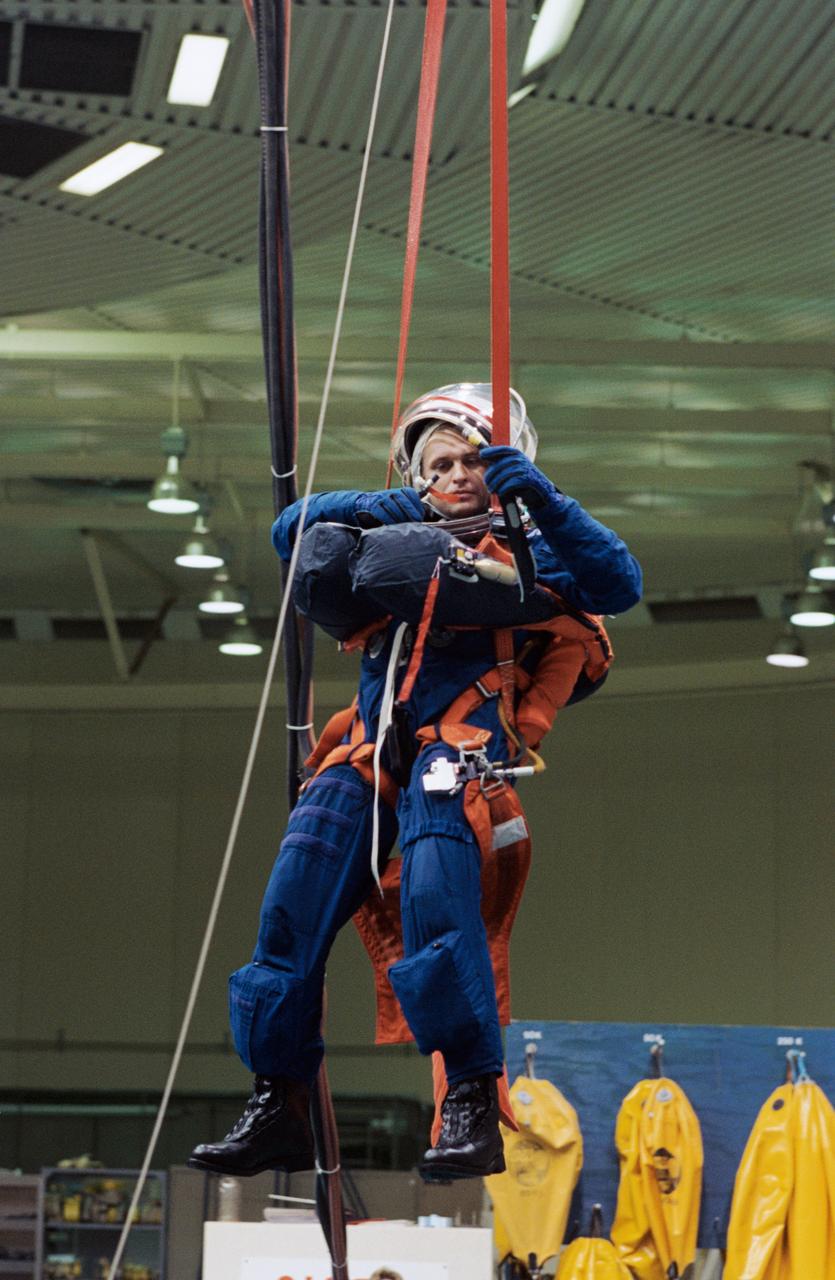

S94-47232 (13 Oct 1994) --- Cosmonaut Yuriy I. Onufriyenko (right), in the United States to participate in training for joint Russia-United States space missions, simulates a parachute drop into water. The training took place in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) because it contains a 25-feet-deep pool. Onufriyenko, a Mir reserve team member, and a number of other cosmonauts and astronauts participating in the joint program were in Houston, Texas to prepare for upcoming missions which involve crewmembers from the two nations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepared three test articles that will be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles were flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
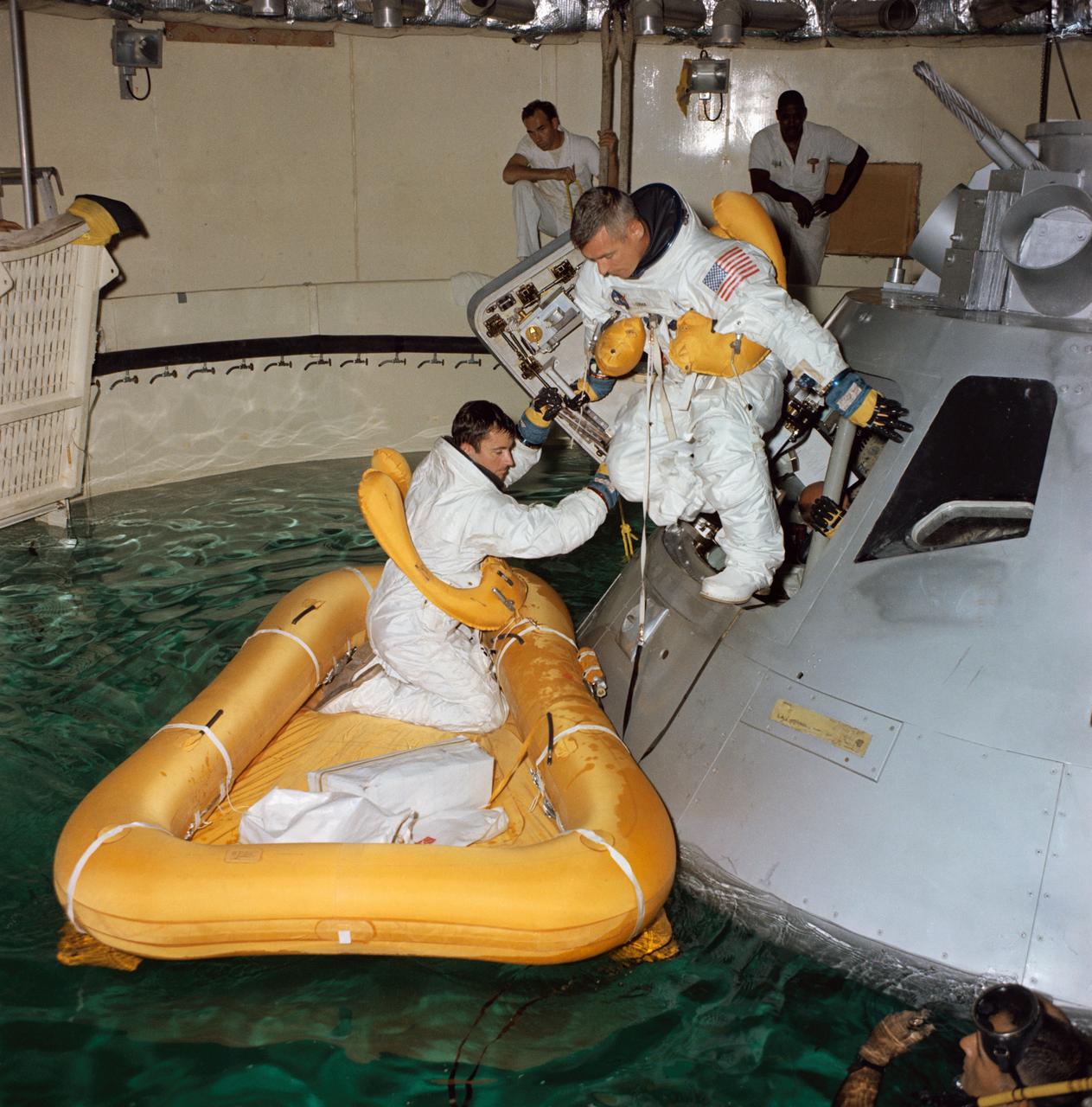

S68-41683 (August 1968) --- Three astronauts participate in Apollo water egress training in a tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Already in life raft is John W. Young. Eugene A. Cernan is egressing the Apollo Command Module trainer. Inside the trainer and almost obscured is Thomas P. Stafford.
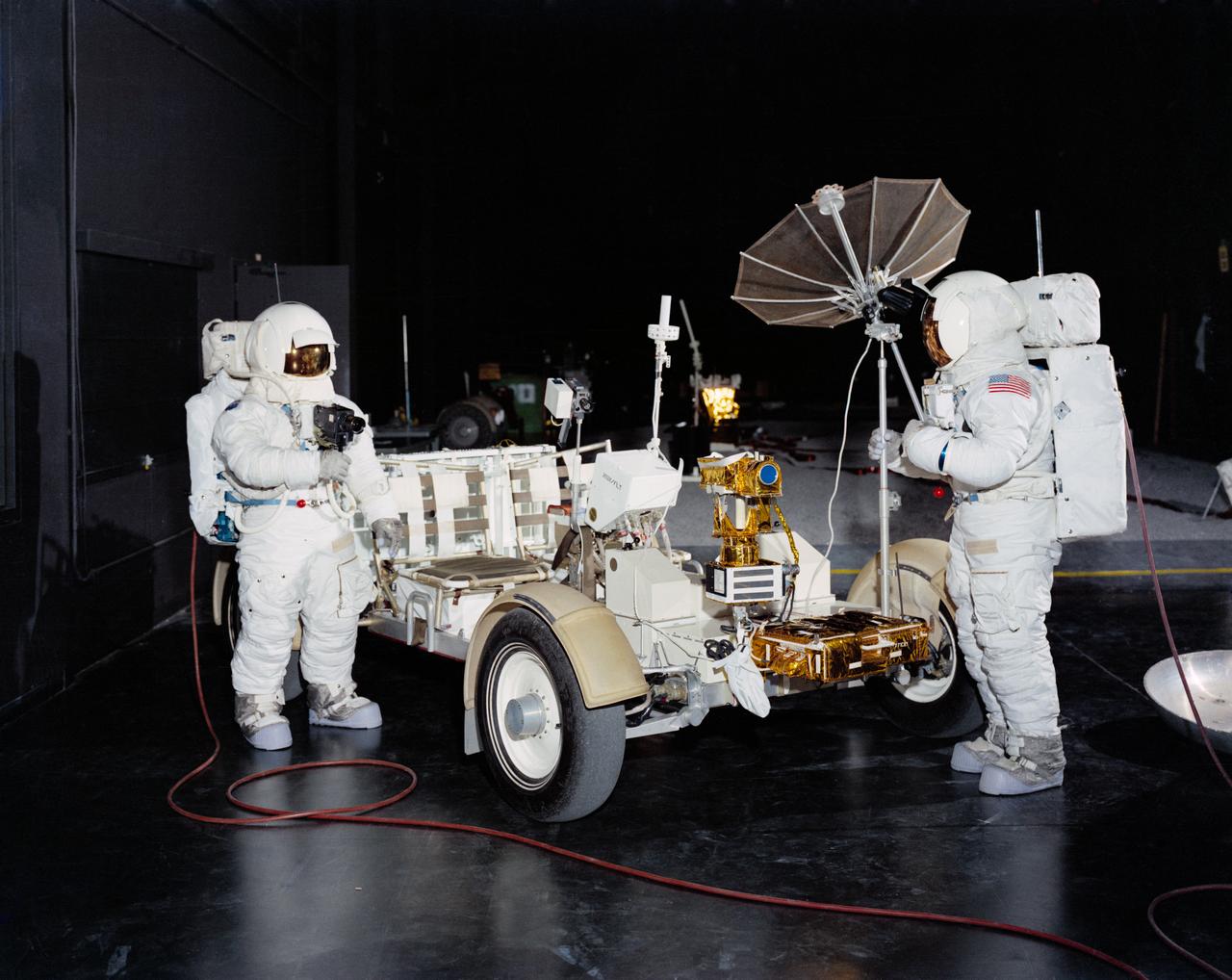

S71-16722 (January 1971) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission are shown with the Lunar Roving Vehicle "one G" trainer in Building 5, Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Manned Spacecraft Center. Astronaut David R. Scott (on right) is the Apollo 15 commander; and astronaut James B. Irwin is the lunar module pilot. A Lunar Roving Vehicle similar to this trainer will be used by Scott and Irwin during their Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity.
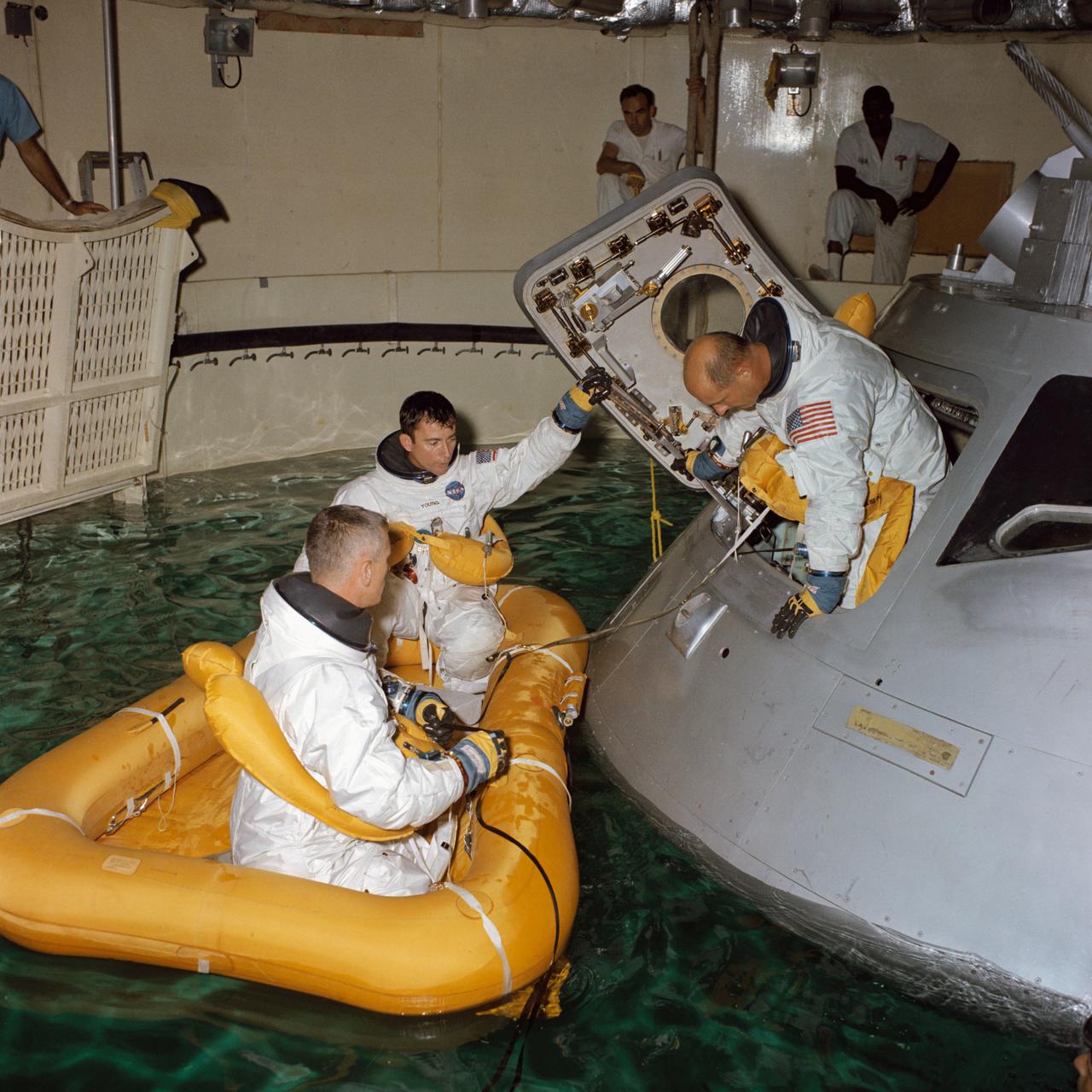

S68-41685 (August 1968) --- Three astronauts participate in Apollo water egress training in a tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Egressing the Apollo Command Module trainer is Thomas P. Stafford. Already in life raft are Eugene A. Cernan (in foreground) and John W. Young.
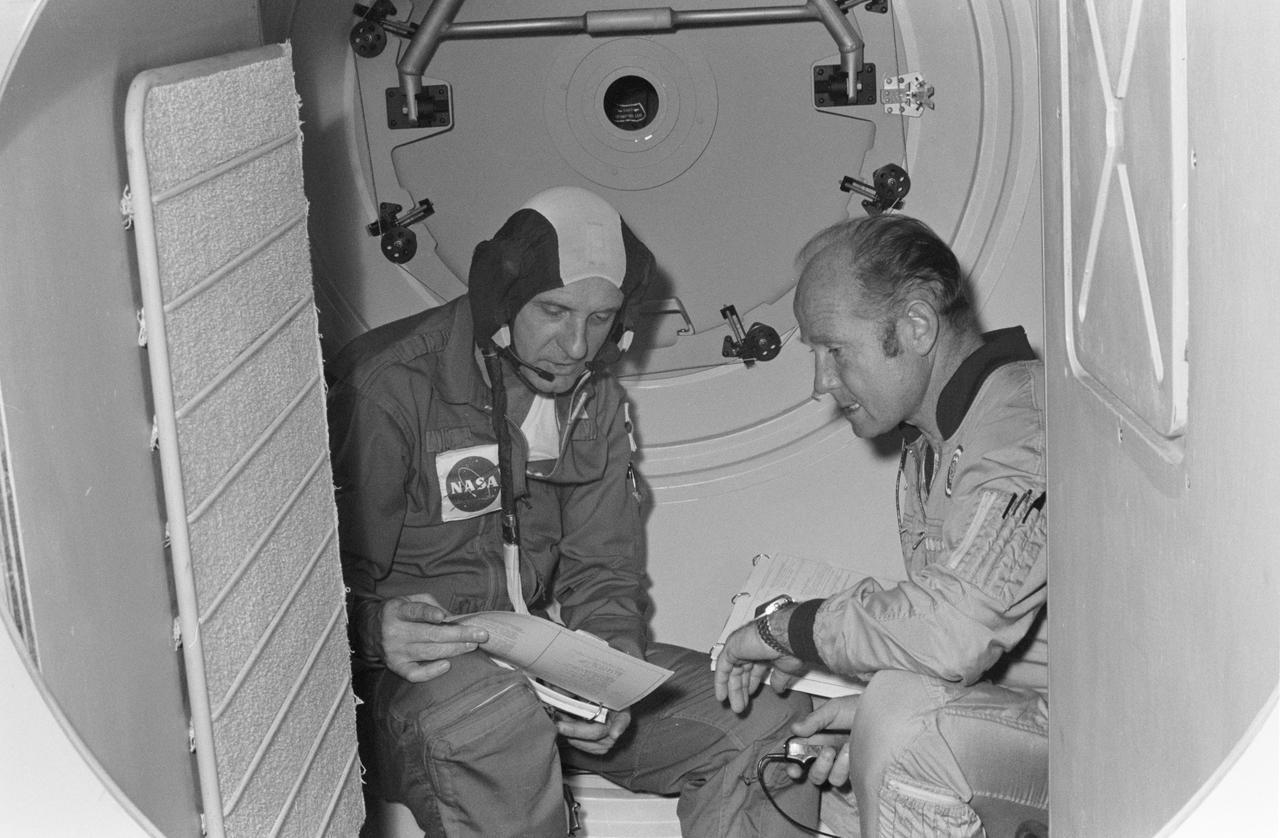

S74-29041 (September 1974) --- The commanders of the American astronaut and Soviet cosmonaut crews for the joint U.S.?USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission compare notes in a Soyuz spacecraft?s orbital module mock-up in Building 35 at the Johnson Space Center during a training and simulation exercise. They are Aleksey A. Leonov, right, and Thomas P. Stafford. The hatchway in the background leads to the Docking Module. The prime crewmen, along with backup crewmen, are training in both the U.S. and USSR for the joint mission scheduled for the summer of 1975.
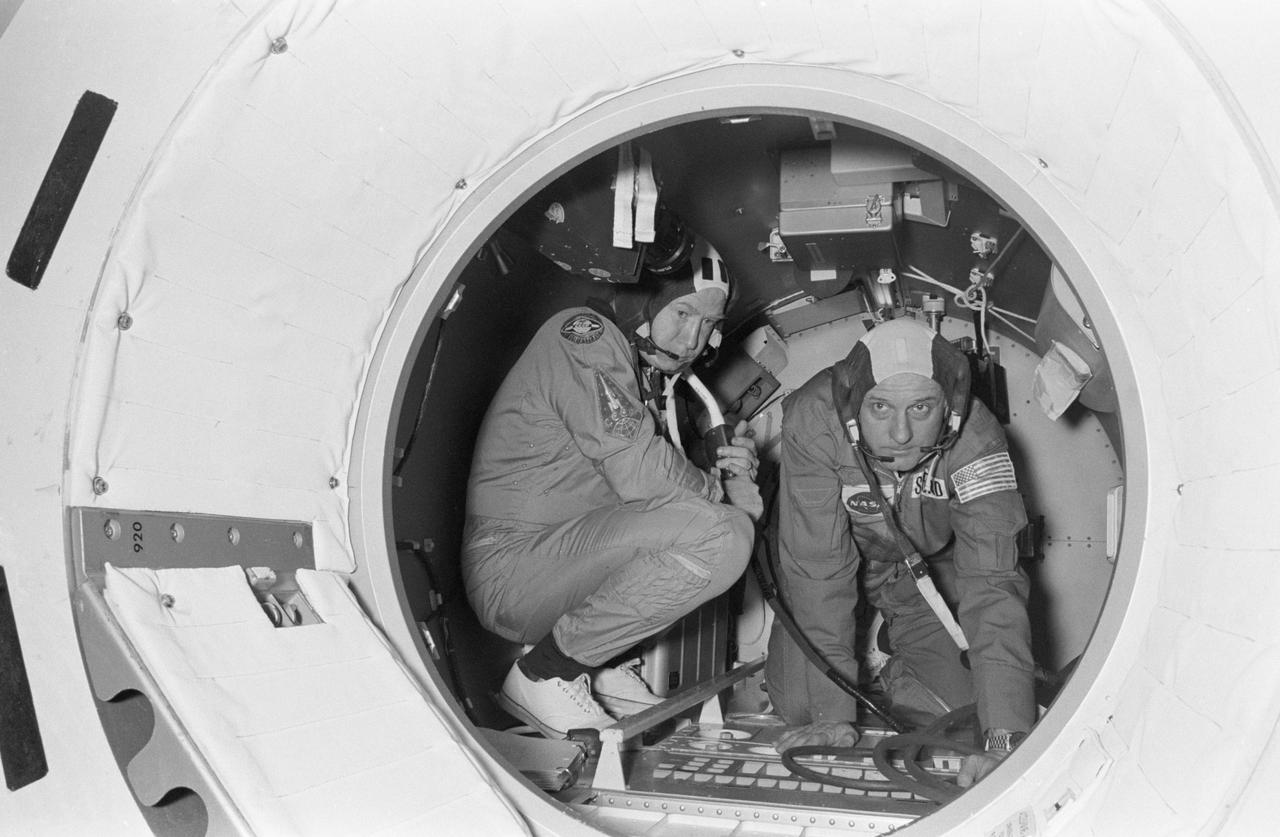

S75-21945 (24 Feb. 1975) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (left) and astronaut Thomas P. Stafford take part in Apollo-Soyuz Test Project joint crew training in Building 35 at NASA's Johnson Space Center. They are commanders of their respective prime crews. The training session simulated the activities of the second day in Earth orbit. Stafford and Leonov are in the Docking Module mock-up.
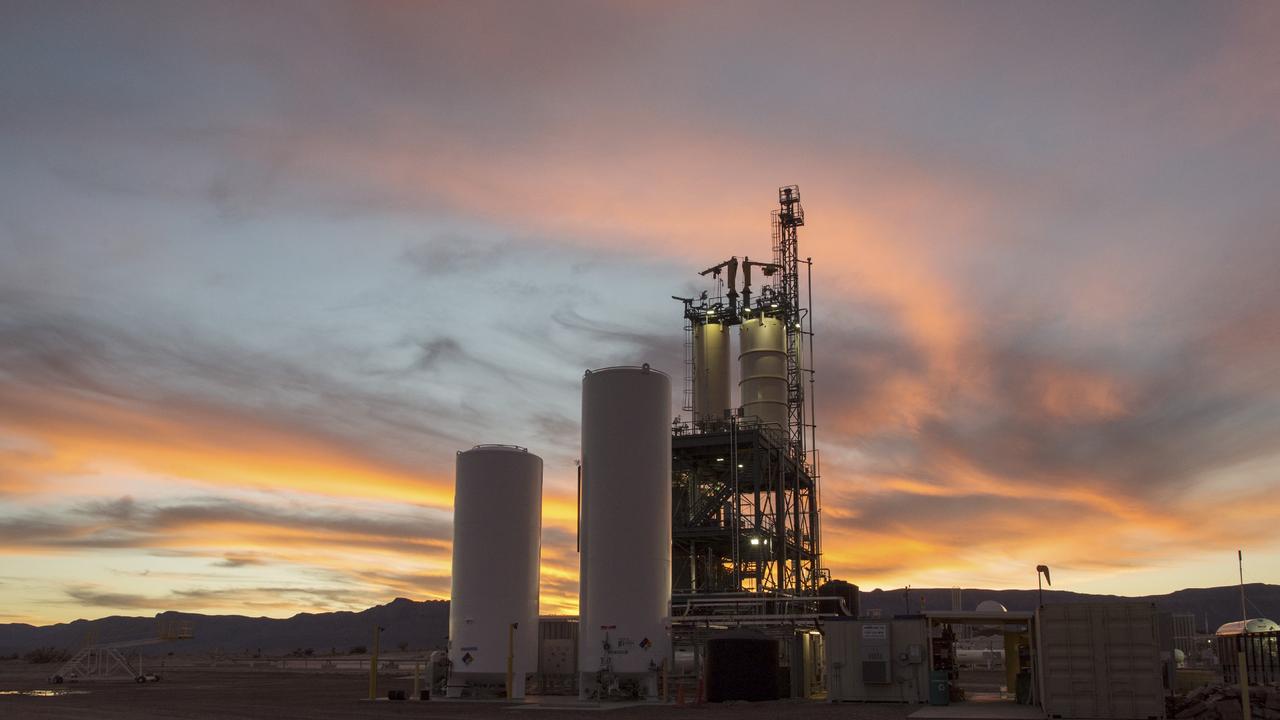

VAN HORN, Texas – The sun sets over a test stand at Blue Origin’s West Texas facility. The company used this test stand to fire its powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine, the BE-3, on Nov. 20. The BE-3 fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
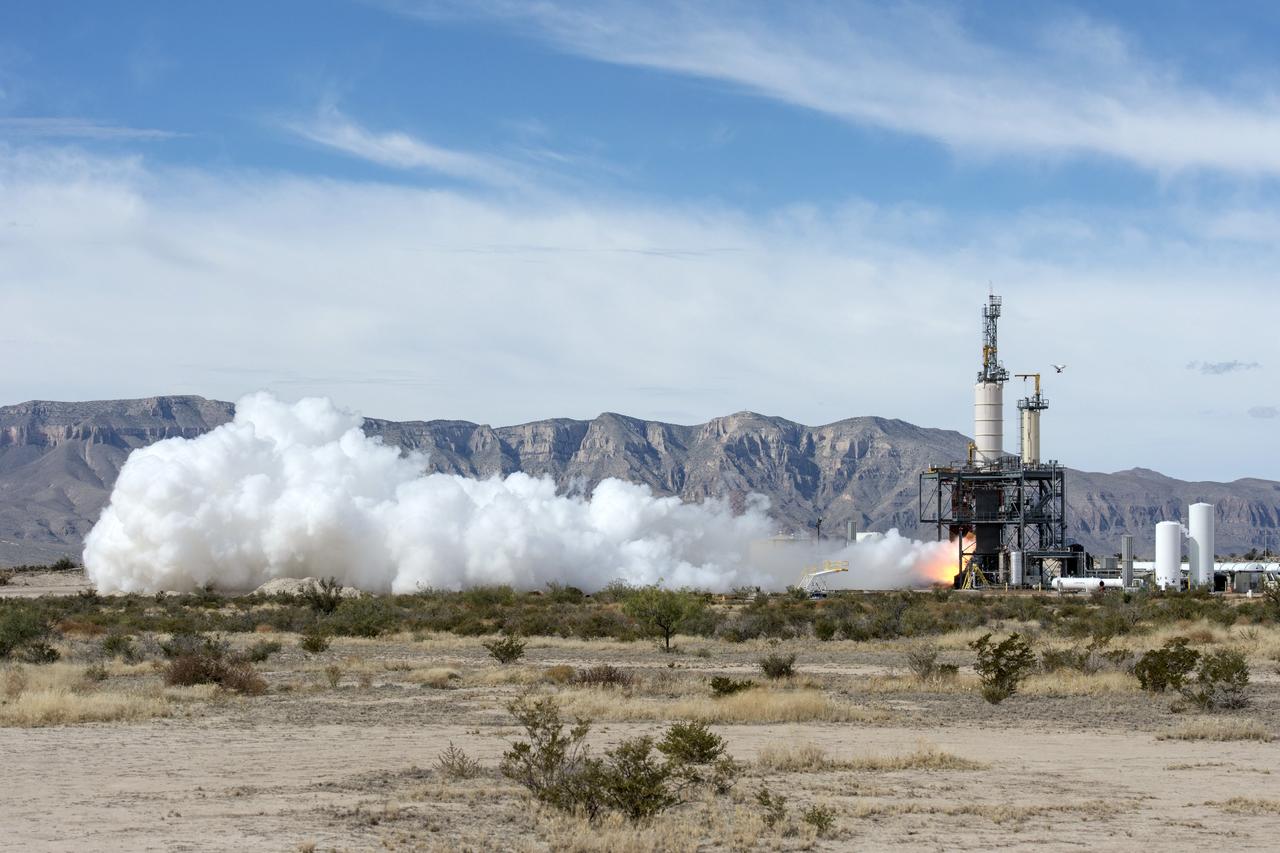

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin test fires a powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine at the company's West Texas facility. During the test, the BE-3 engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
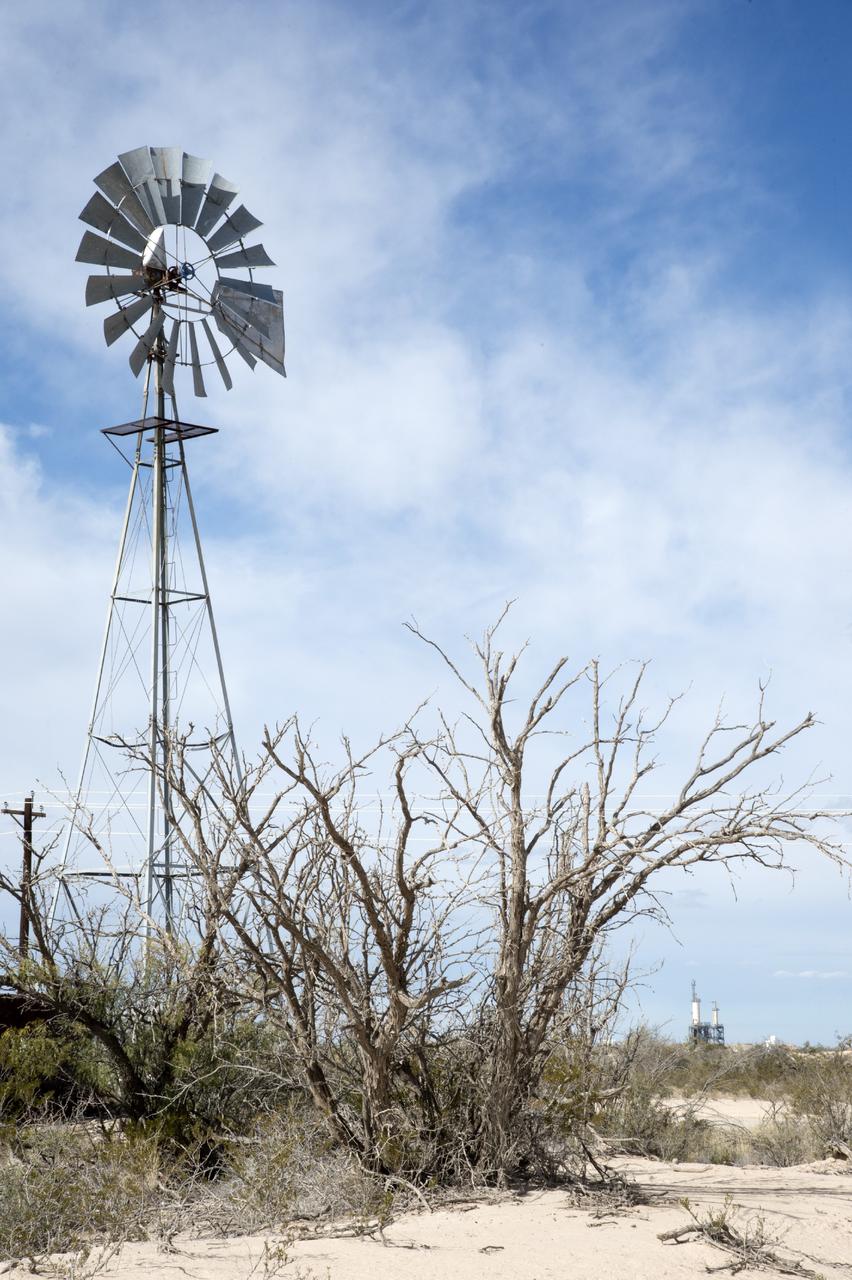

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s test stand, back right, is framed by a wind mill at the company’s West Texas facility. The company used this test stand to fire its powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine, the BE-3. The engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
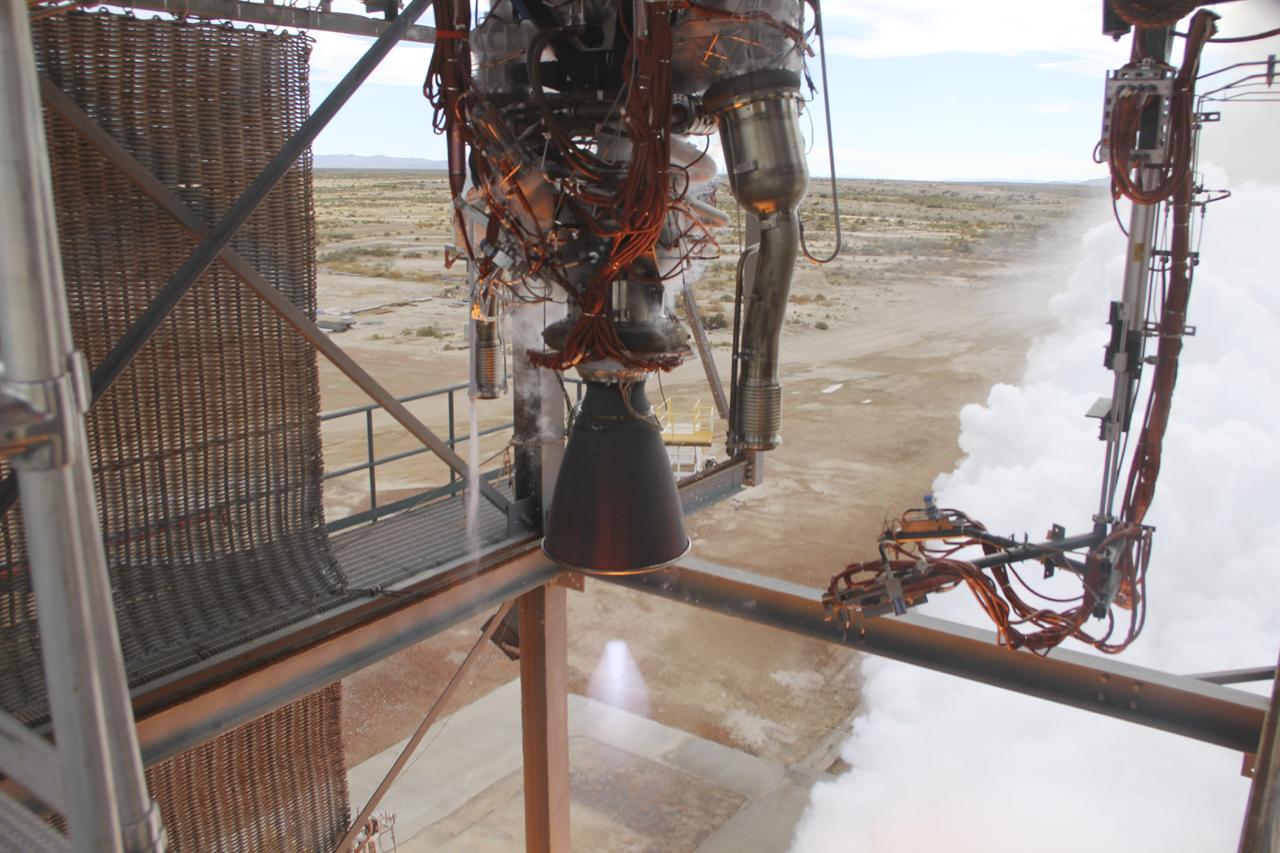
VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin test fires a powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine at the company's West Texas facility. During the test, the BE-3 engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Blue Origin

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A United Space Alliance employee prepares a test article that will be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepare test articles to be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
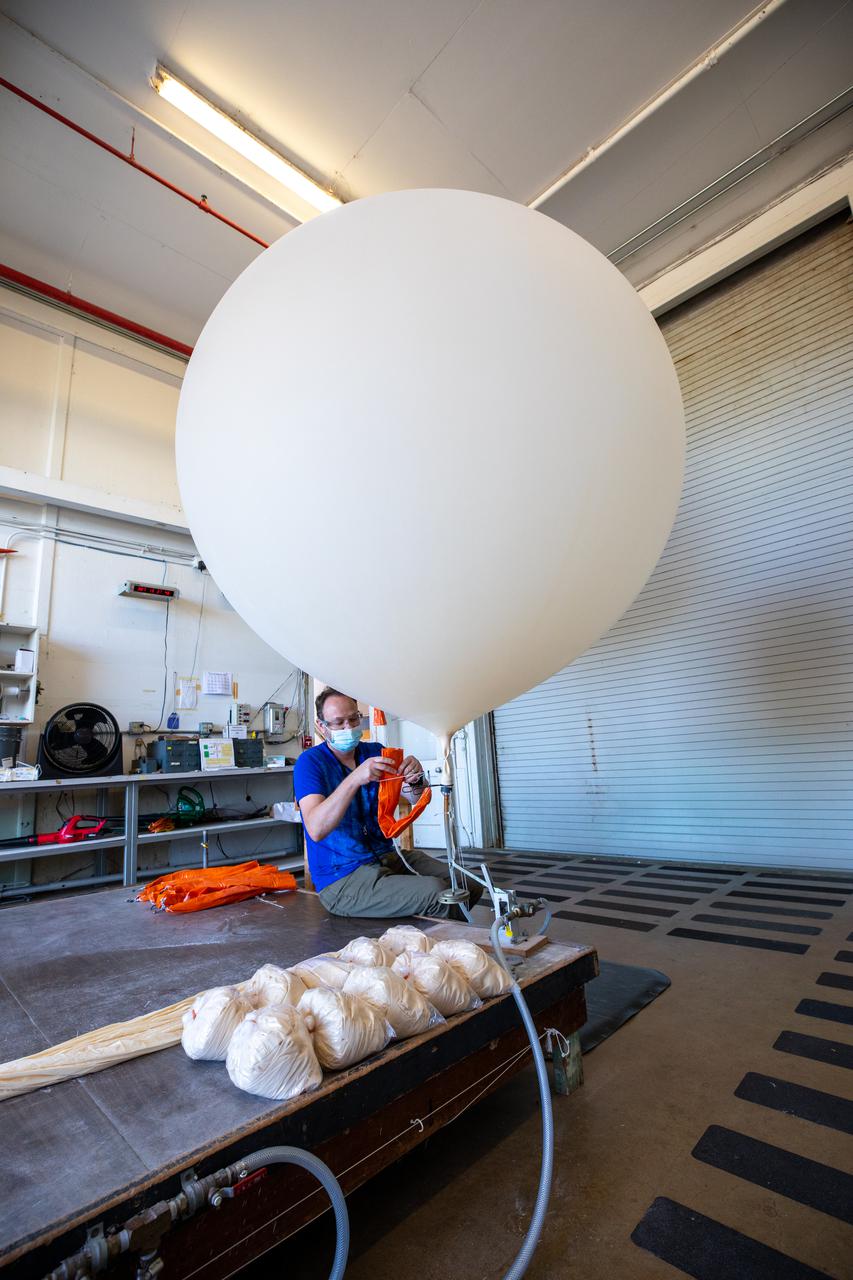

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer prepares weather balloons for release at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station in preparation for an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
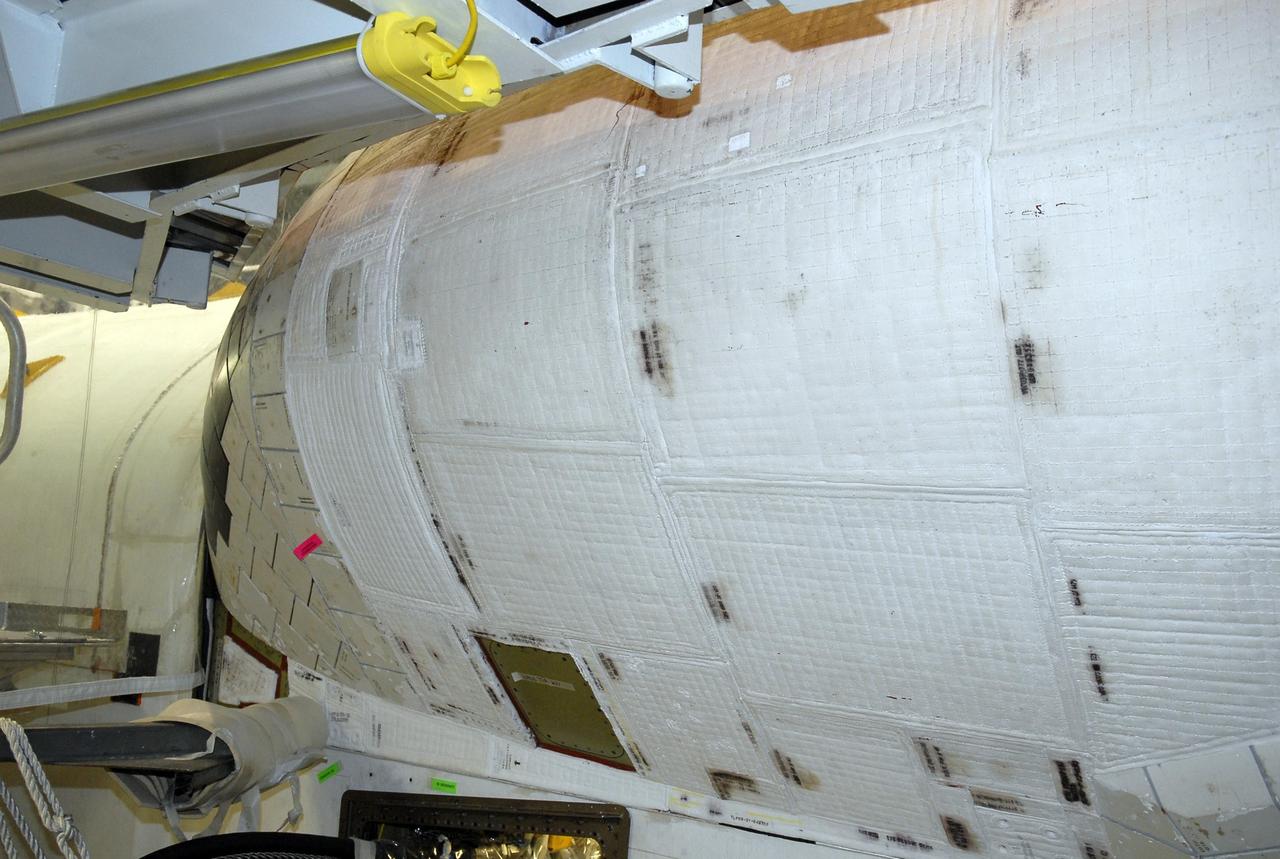

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Another view of the area of orbiter Endeavour's orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod where the tear occurred on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles were flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
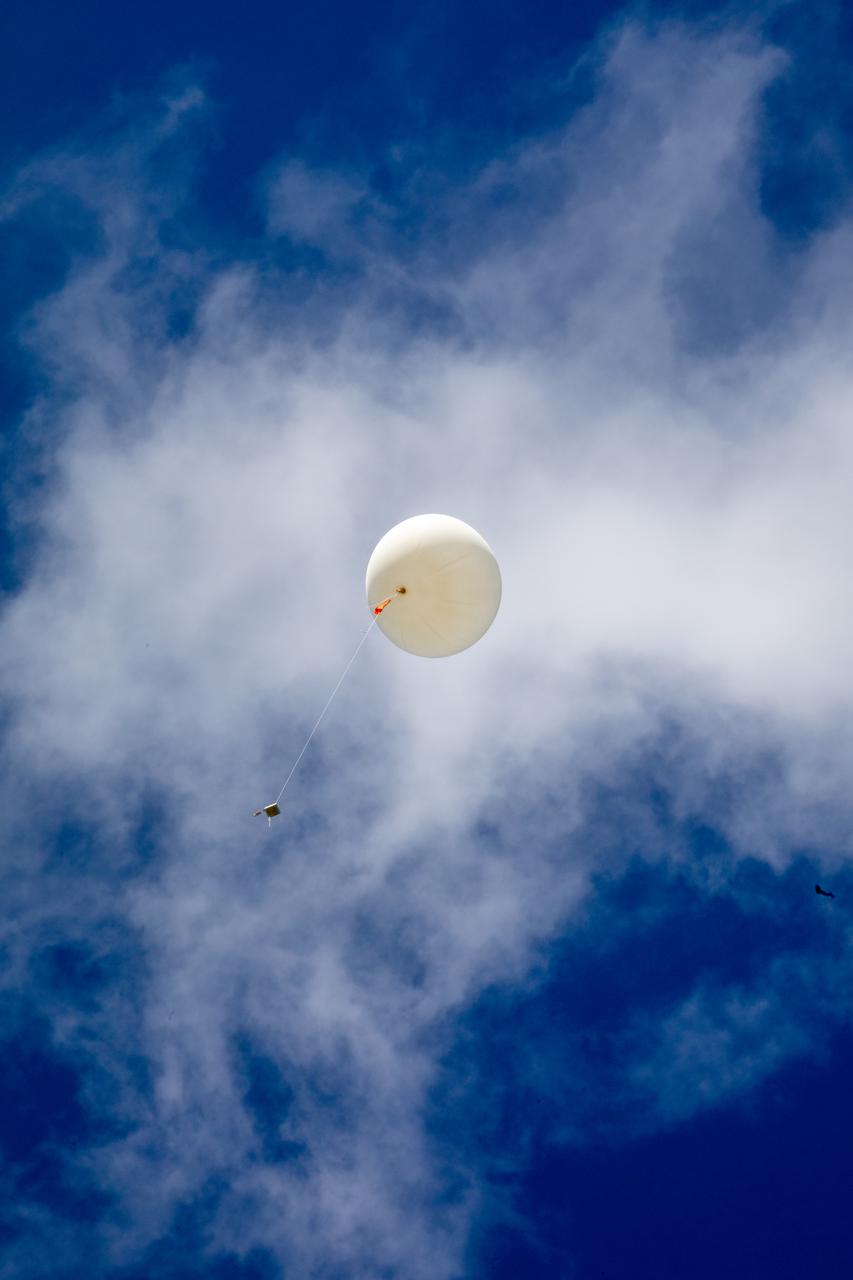

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer releases a weather balloon at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
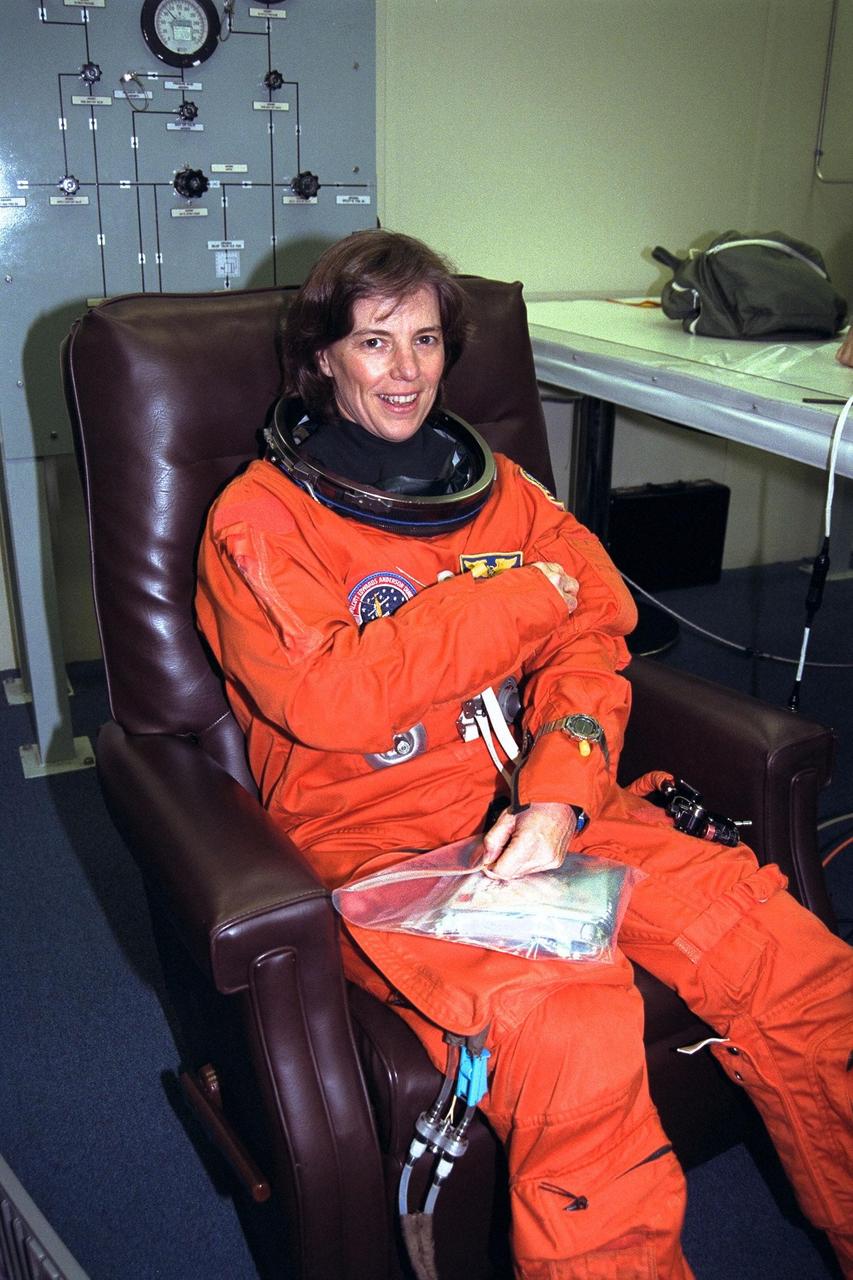

STS-89 Mission Specialist Bonnie Dunbar, Ph.D., smiles as she completes the donning of her launch/entry suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. Dr. Dunbar completed her doctorate at the University of Houston in Texas. Her multi-disciplinary dissertation (materials science and physiology) involved evaluating the effects of simulated space flight on bone strength and fracture toughness. She and six fellow crew members will shortly depart the O&C and head for Launch Pad 39A, where the Space Shuttle Endeavour will lift off during a launch window that opens at 9:43 p.m. EST, Jan. 22. STS-89 is the eighth of nine planned missions to dock the Space Shuttle with Russia's Mir space station
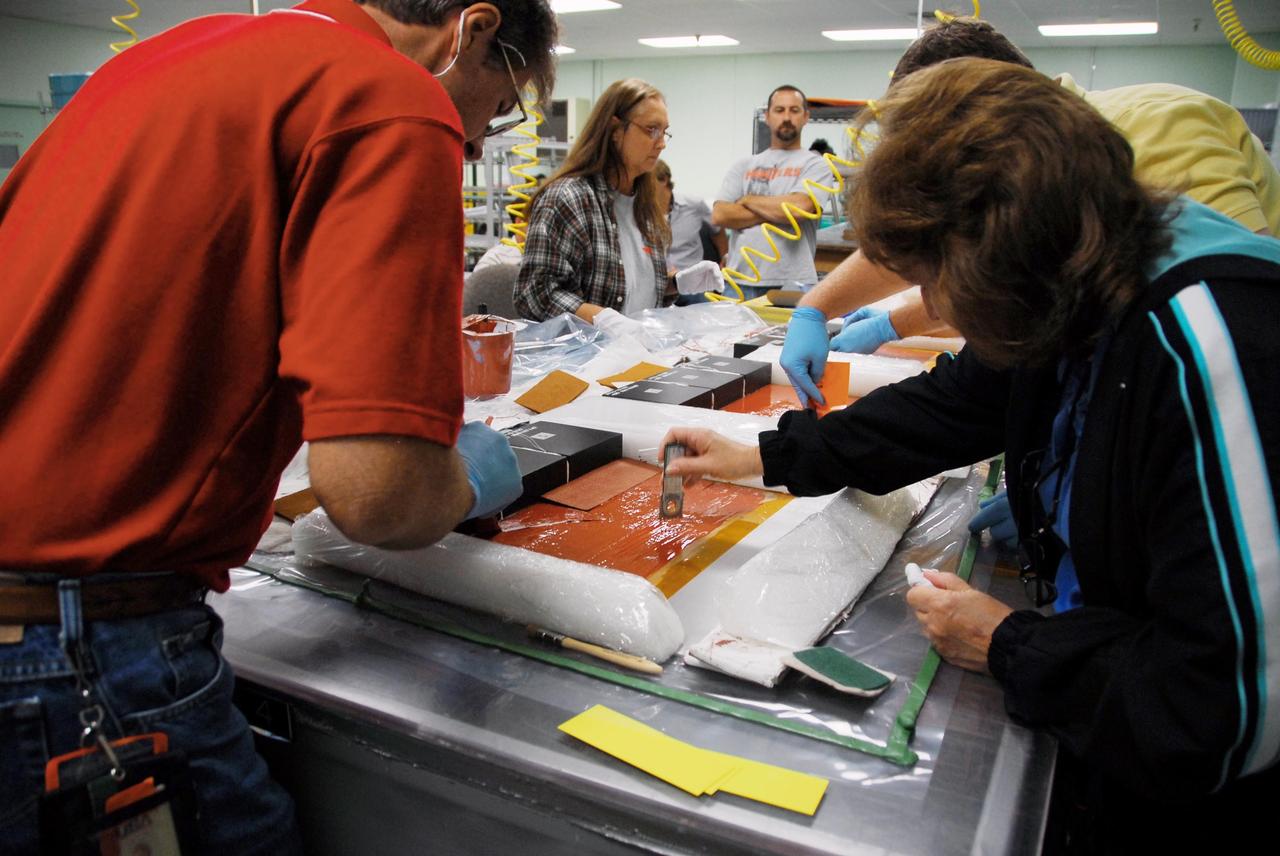

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepare test articles to be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
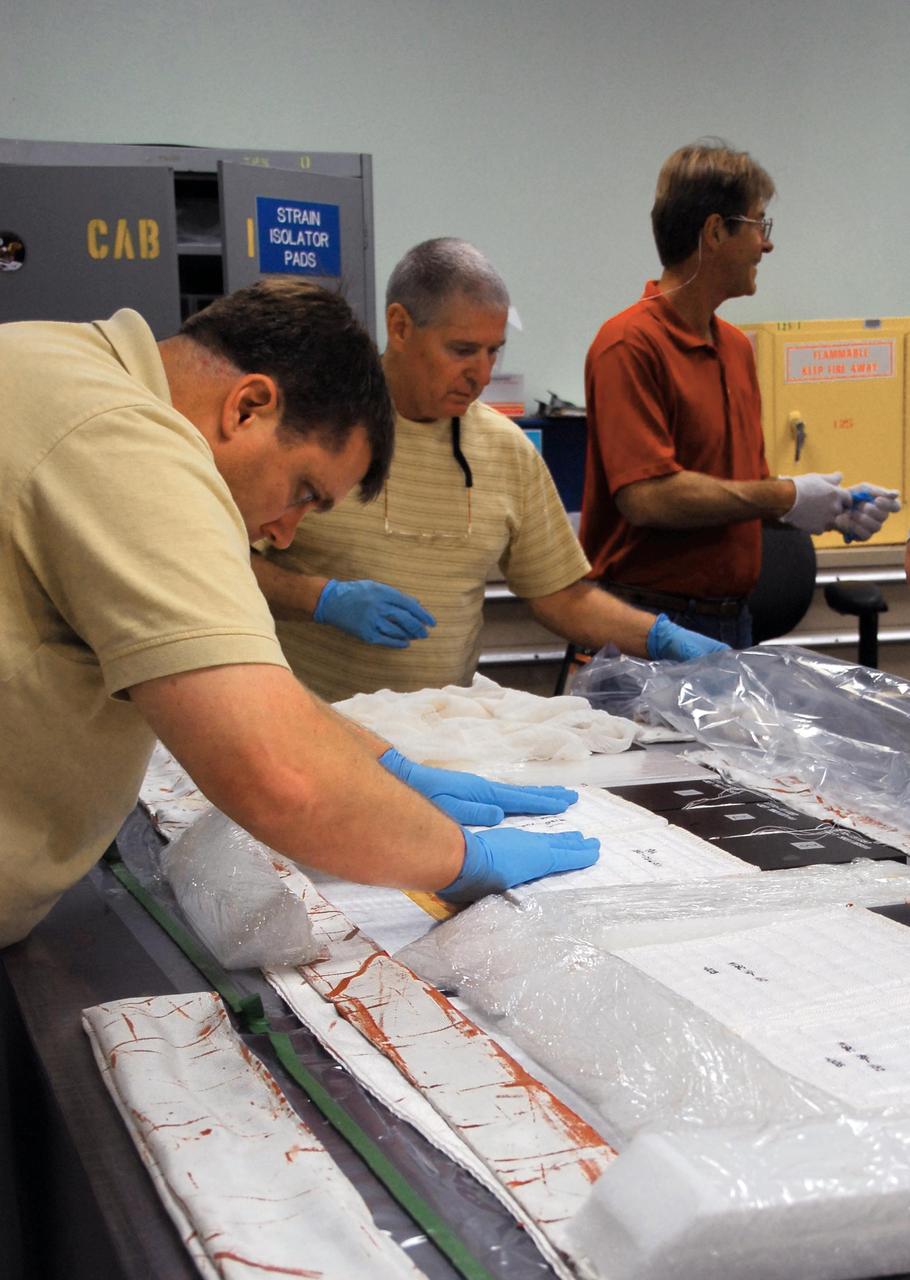

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepare test articles to be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
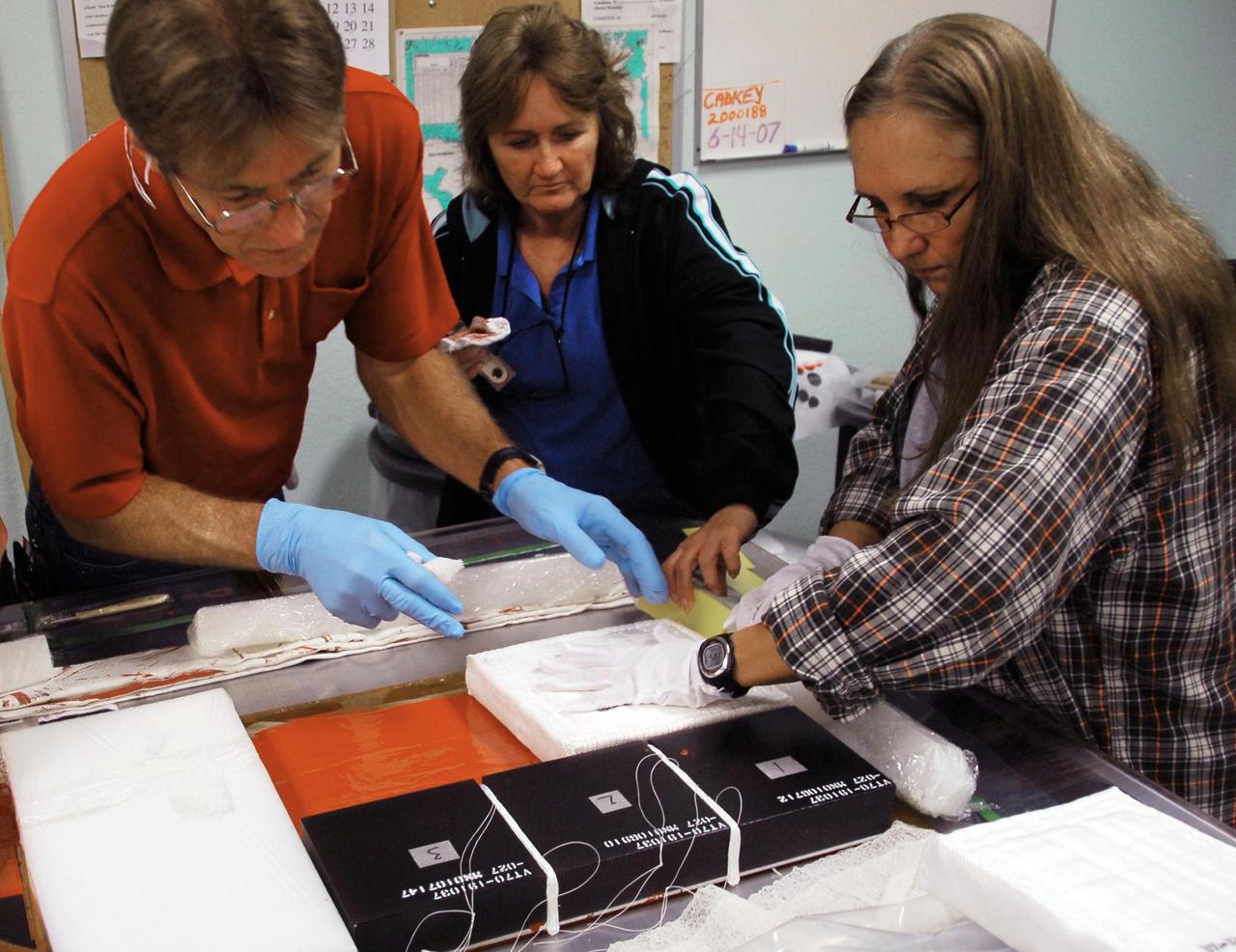

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepare test articles to be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer prepares weather balloons for release at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station in preparation for an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
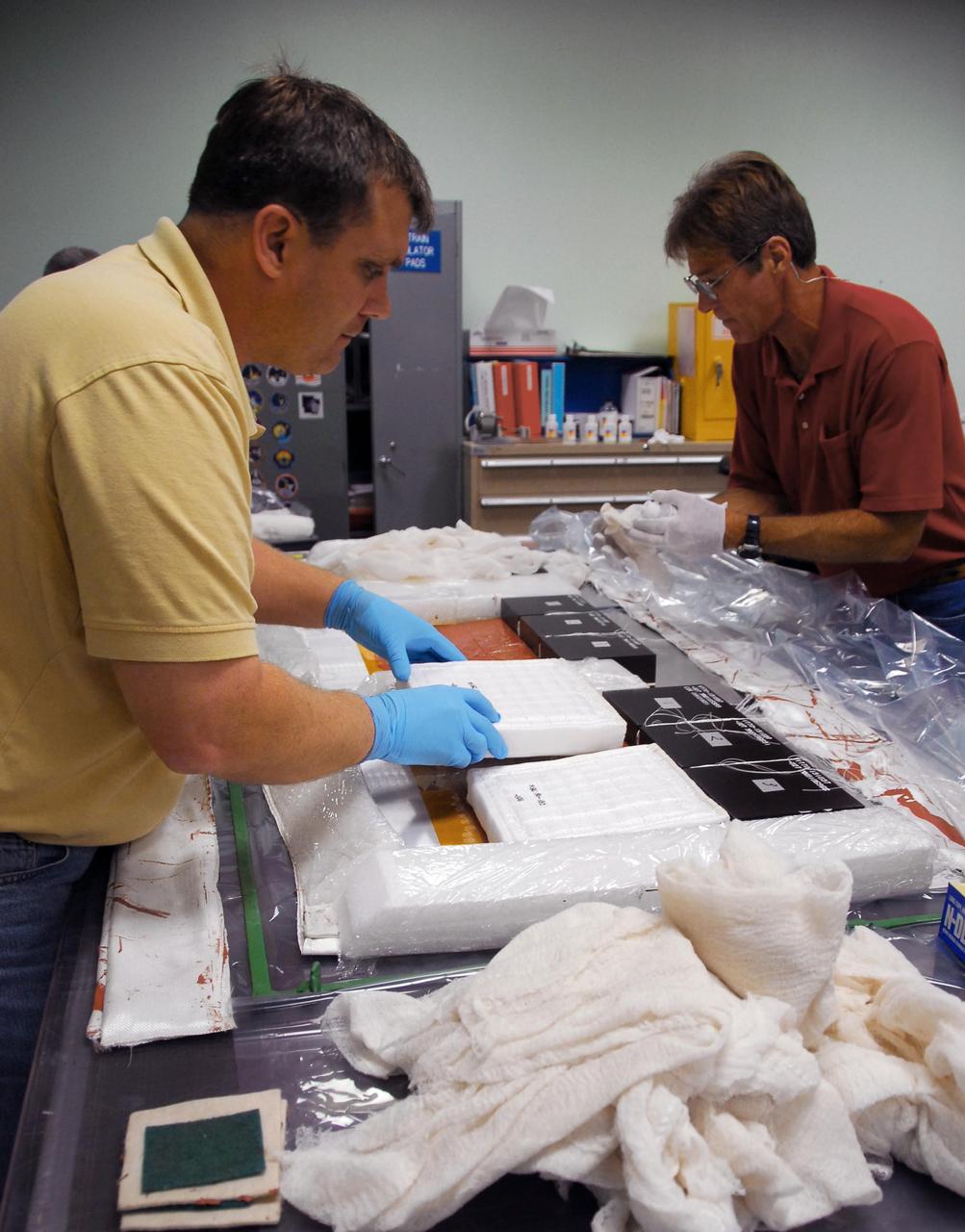

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance employees prepare test articles to be used in wind tunnel testing by NASA to collect data for analysis of the detached Flexible Insulation Blanket, or FIB, on Atlantis. A tear occurred in an area of the OMS pod on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles will be flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
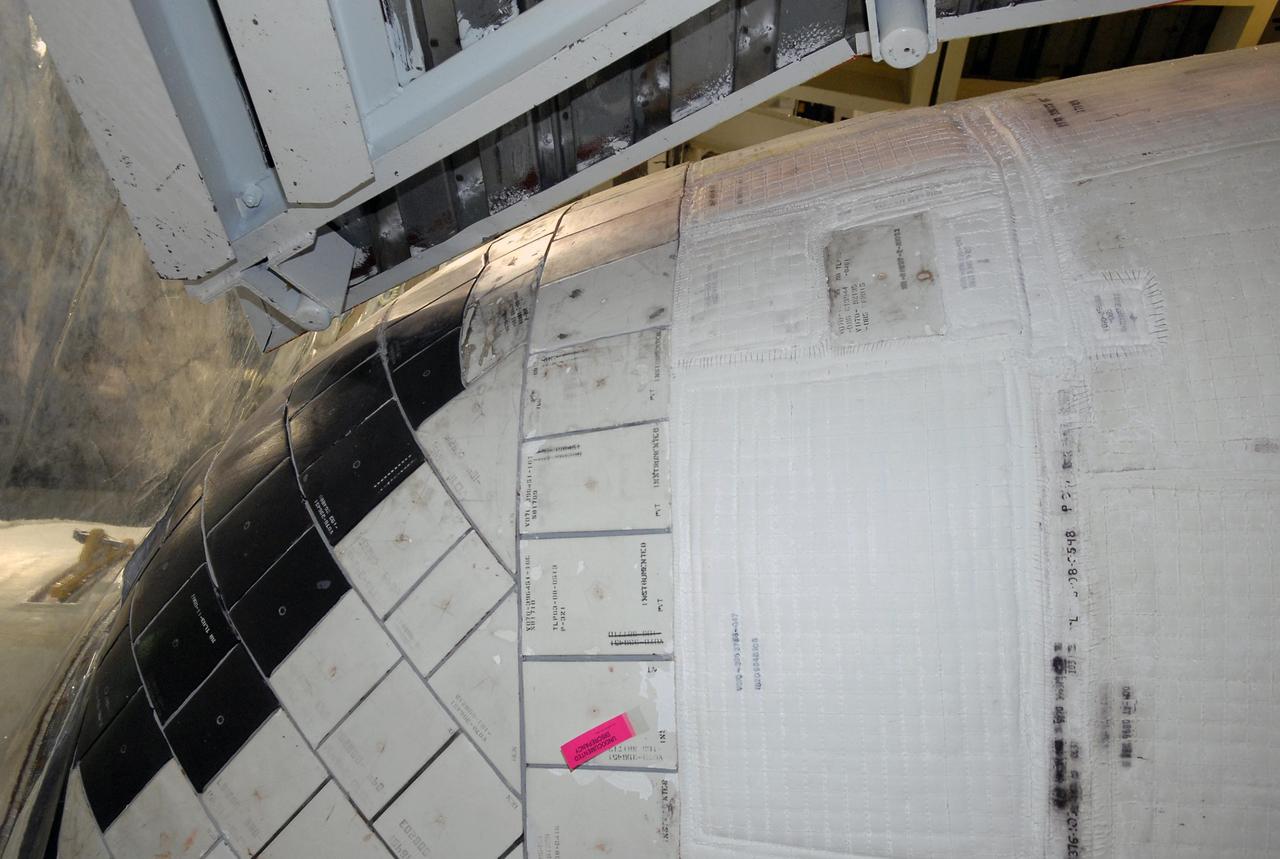
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Another view of the area of orbiter Endeavour's orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod where the tear occurred on Atlantis during launch of mission STS-117 on June 8, 2007. Repair is under consideration following testing at KSC and Houston. The test articles each feature three tiles (Low Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation, or LRSI) affixed next to two FIB blankets, simulating the thermal protection system set-up on Atlantis' OMS pod in the vicinity of the in-flight anomaly. These test articles were flown to Texas the morning of June 14. The TPS team at KSC has also provided a total of 22 FIB samples for other testing and analysis. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
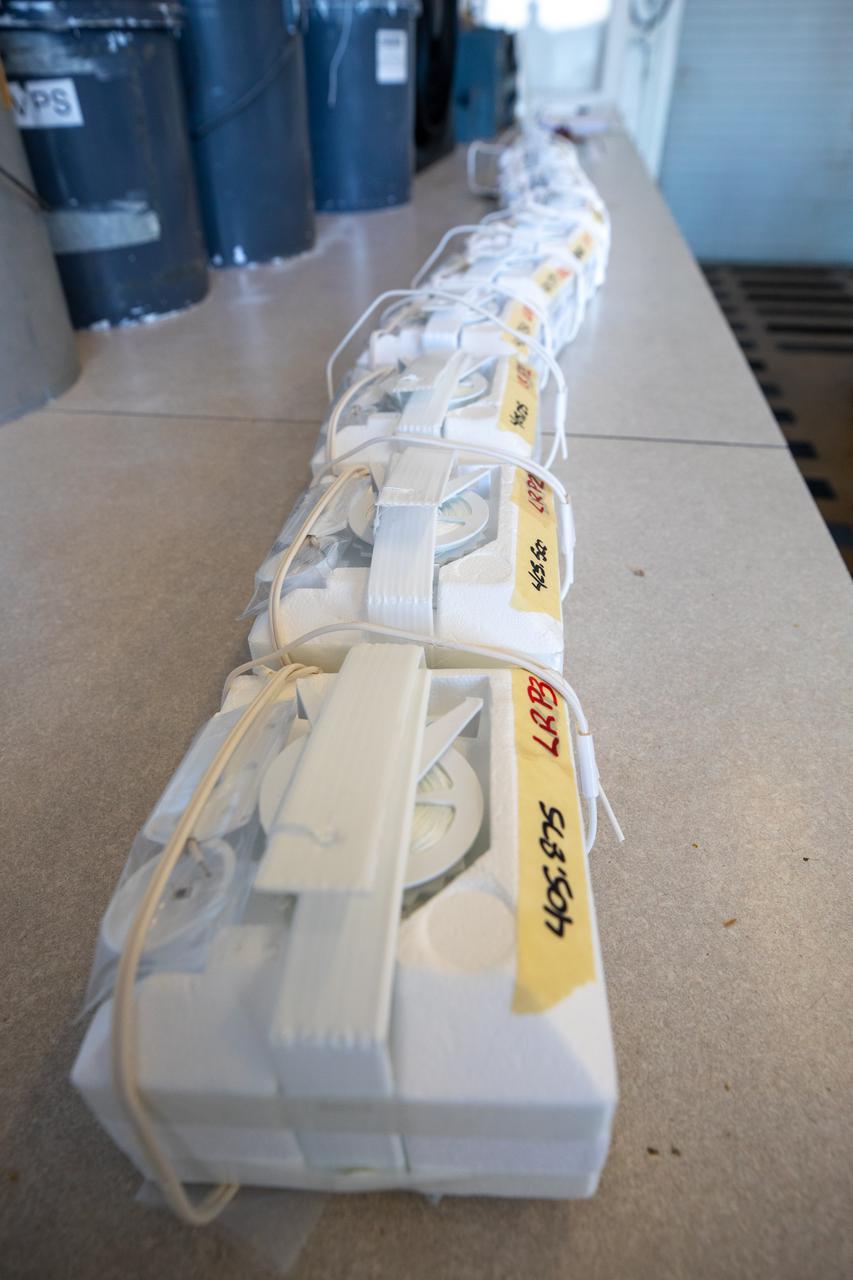

Weather balloons are lined up prior to release at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station in preparation for an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
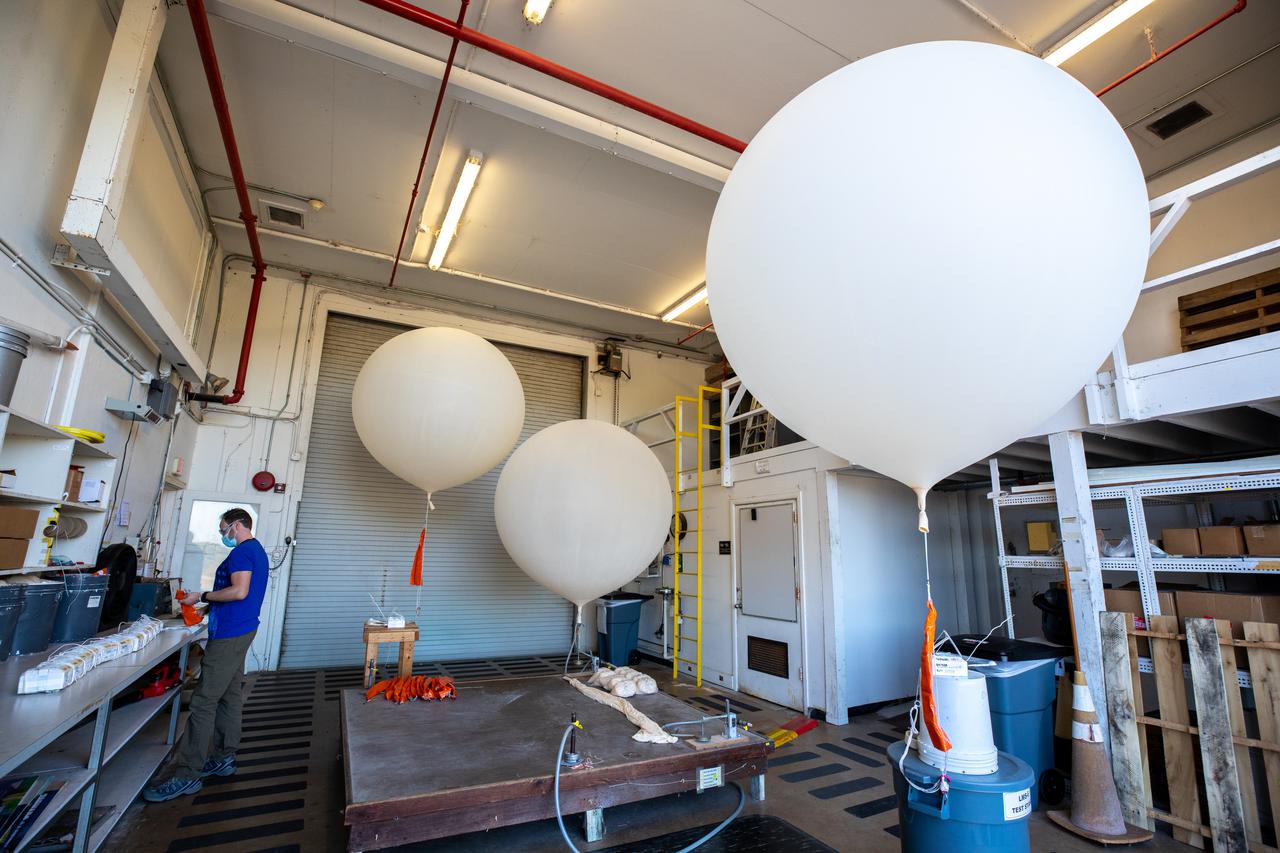

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer prepares weather balloons for release at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station in preparation for an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer releases a weather balloon at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
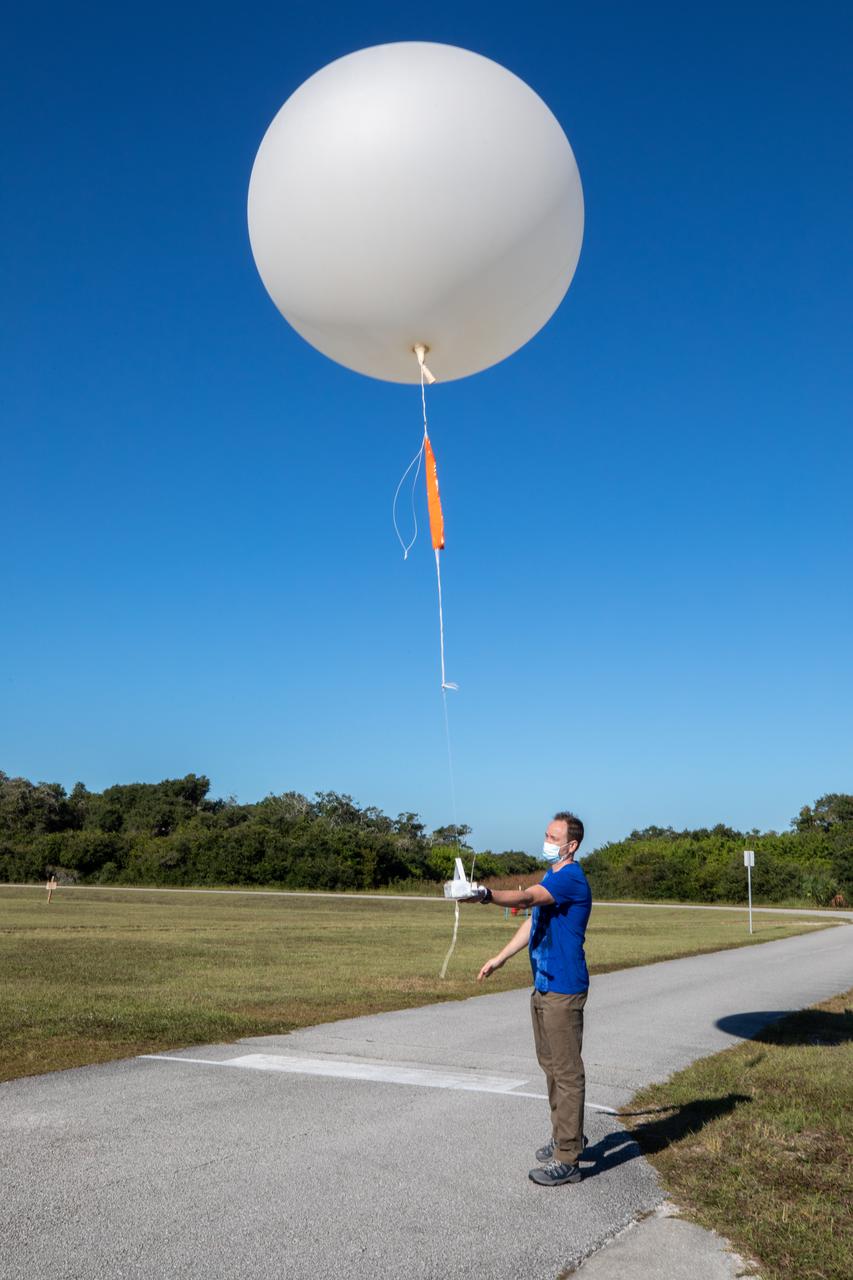

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer releases a weather balloon at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
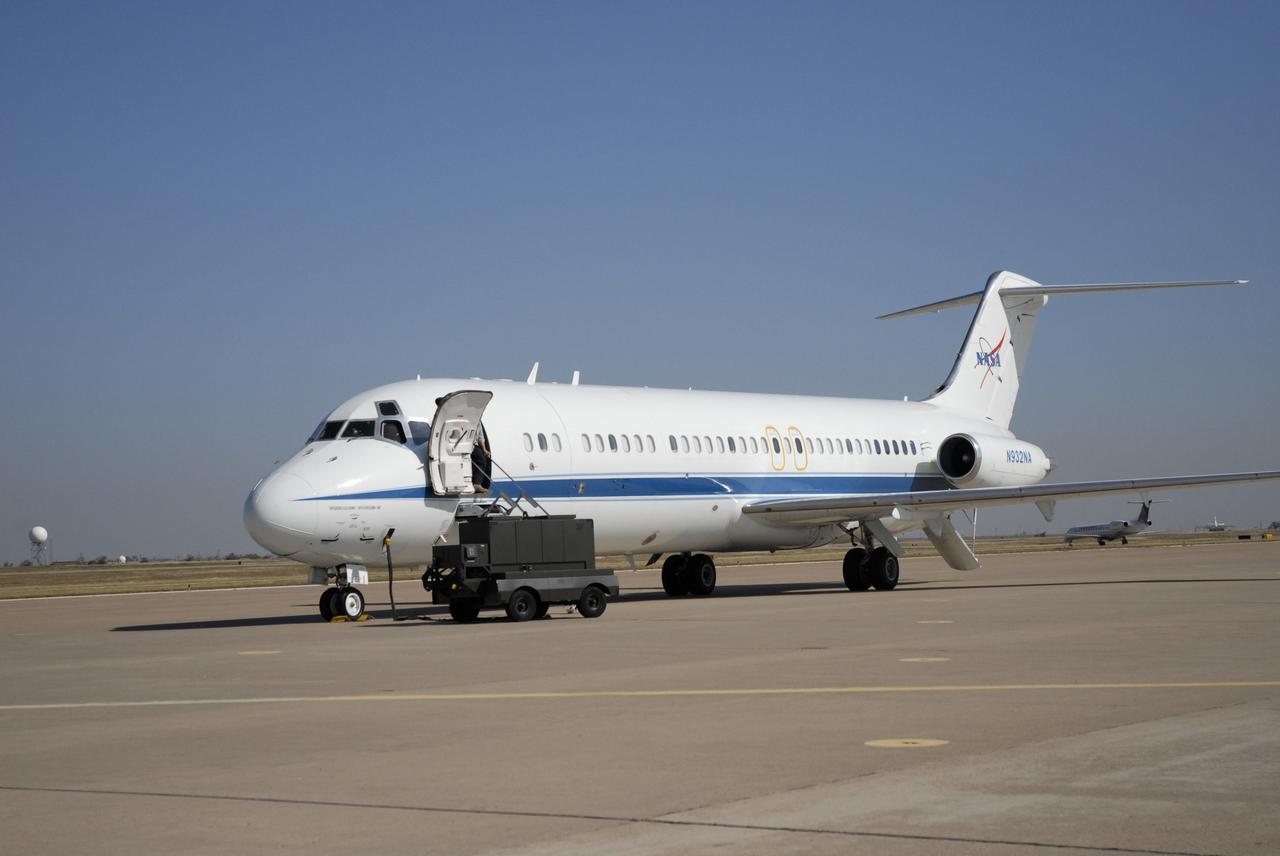

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's C-9 aircraft, also known as the Weightless Wonder VI, lands for refueling at the Rick Husband Amarillo International Airport in Texas on its way to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The C-9, normally used to train astronauts by simulating zero gravity, was used as the support aircraft on space shuttle Discovery's ferry flight from Edwards Air Force Base in California. Discovery landed at Edwards Sept. 11 concluding its STS-128 mission to the International Space Station. The shuttle delivered more than 7 tons of supplies, science racks and equipment, as well as additional environmental hardware to sustain six crew members on the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Mary Ann Chevalier

Meteorological Data Specialist Michael Boyer prepares to release a weather balloon at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Weather Station during an Artemis I weather simulation on Nov. 3, 2021. The event involved teams from CCSFS, Kennedy Space Center, Johnson Space Center in Texas, and Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Weather balloons provided data below 6,000 feet and above 62,000 feet, while Kennedy’s Tropospheric Doppler Radar Wind Profiler delivered data from 6,000 to 62,000 feet. The radar wind profiler will be used as the primary upper level wind instrument for NASA’s Artemis missions, including Artemis I, the first launch of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft on a flight beyond the Moon.
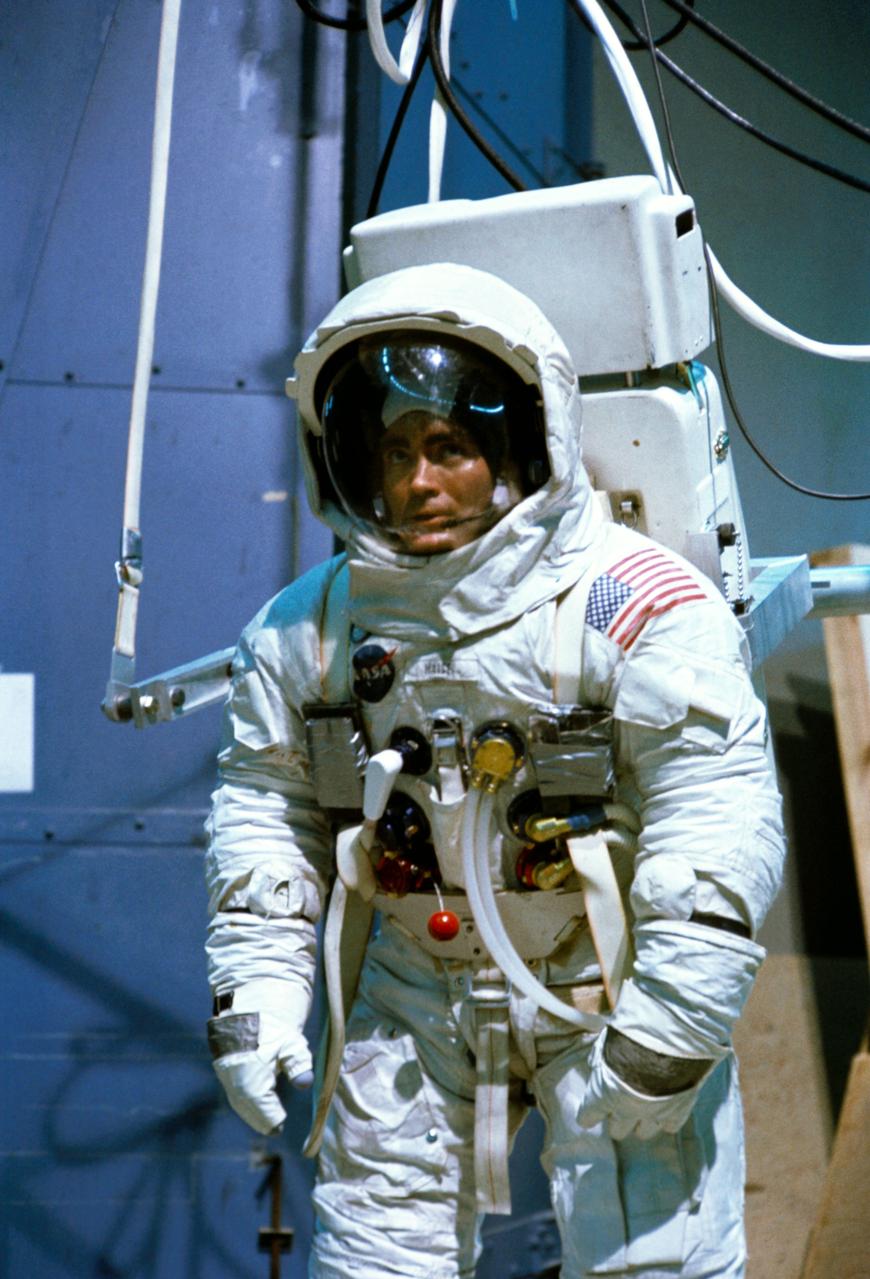

S70-24012 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface simulation training at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise is attached to a Six Degrees of Freedom Simulator.
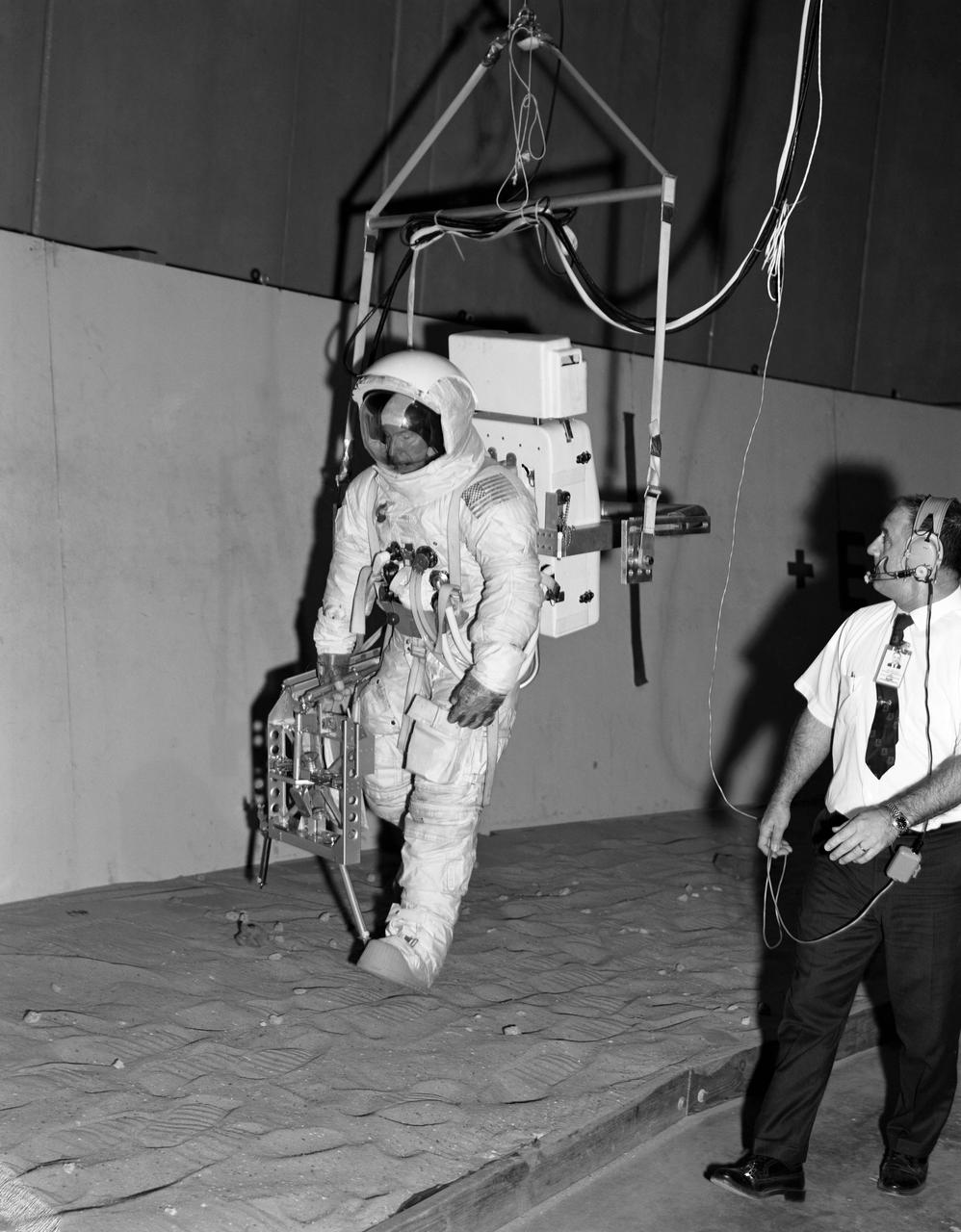

S70-28229 (16 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface simulation training at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Lovell is attached to a Six Degrees of Freedom Simulator. He is carrying an Apollo Lunar Hand Tools carrier in his right hand.

Astronaut John W. Young, Apollo 16 prime crew commander (right), takes a drive in the One-G Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) trainer in the Lunar Topgraphic Simulation area at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). He is accompanied by John Omstead, with General Electric, MSC.
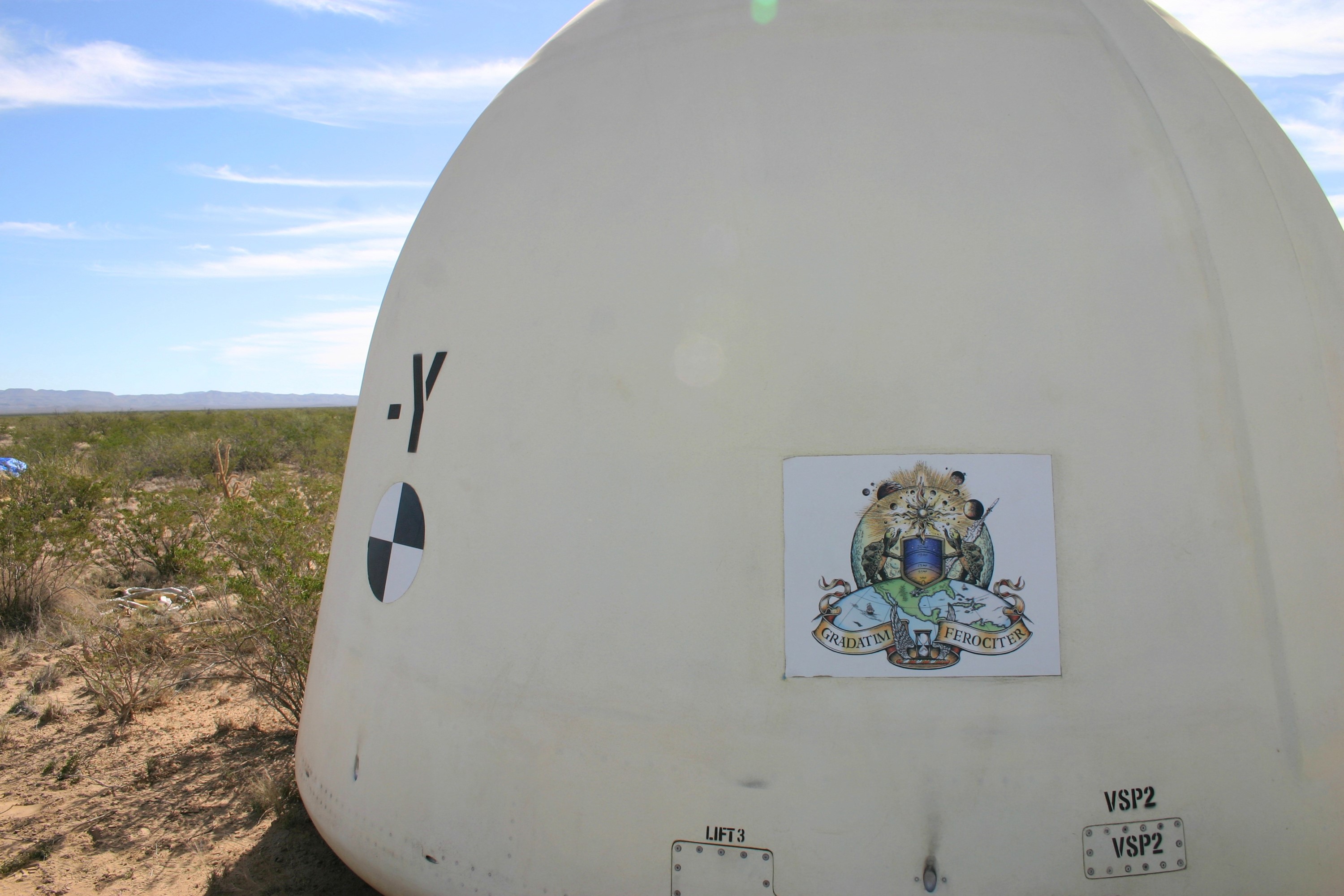

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s New Shepard crew capsule touched down 1,630 feet from the its simulated propulsion module launch pad at the company's West Texas launch site, completing a successful test of its New Shepard crew capsule escape system. The pusher escape system was designed and developed by Blue Origin to allow crew escape in the event of an emergency during any phase of ascent for its suborbital New Shepard system. As part of an incremental development program, the results of this test will shape the design of the escape system for the company's orbital biconic-shaped Space Vehicle. The system is expected to enable full reusability of the launch vehicle, which is different from NASA's previous launch escape systems that would pull a spacecraft away from its rocket before reaching orbit. The test was part of Blue Origin's work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2). Through initiatives like CCDev2, NASA is fostering the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit. After the capability is matured and available to the government and other customers, NASA could contract to purchase commercial services to meet its station crew transportation needs. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Blue Origin
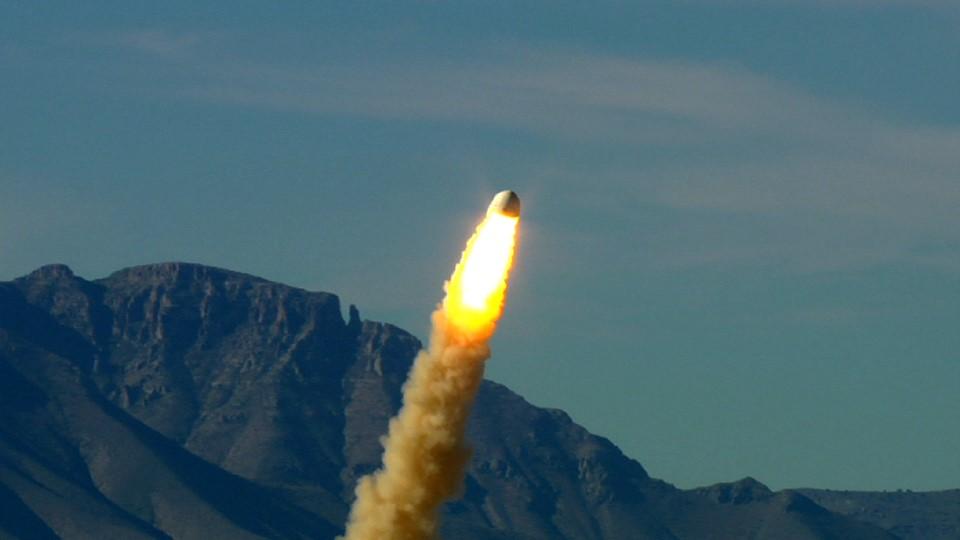

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s pusher escape system rockets its New Shepard crew capsule away from a simulated propulsion module launch pad at the company's West Texas launch site, demonstrating a key safety system for both suborbital and orbital flights. The pad escape test took the company's suborbital crew capsule to an altitude of 2,307 feet during the flight test before descending safely by parachute to a soft landing 1,630 feet away. The pusher escape system was designed and developed by Blue Origin to allow crew escape in the event of an emergency during any phase of ascent for its suborbital New Shepard system. As part of an incremental development program, the results of this test will shape the design of the escape system for the company's orbital biconic-shaped Space Vehicle. The system is expected to enable full reusability of the launch vehicle, which is different from NASA's previous launch escape systems that would pull a spacecraft away from its rocket before reaching orbit. The test was part of Blue Origin's work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2). Through initiatives like CCDev2, NASA is fostering the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit. After the capability is matured and available to the government and other customers, NASA could contract to purchase commercial services to meet its station crew transportation needs. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Blue Origin
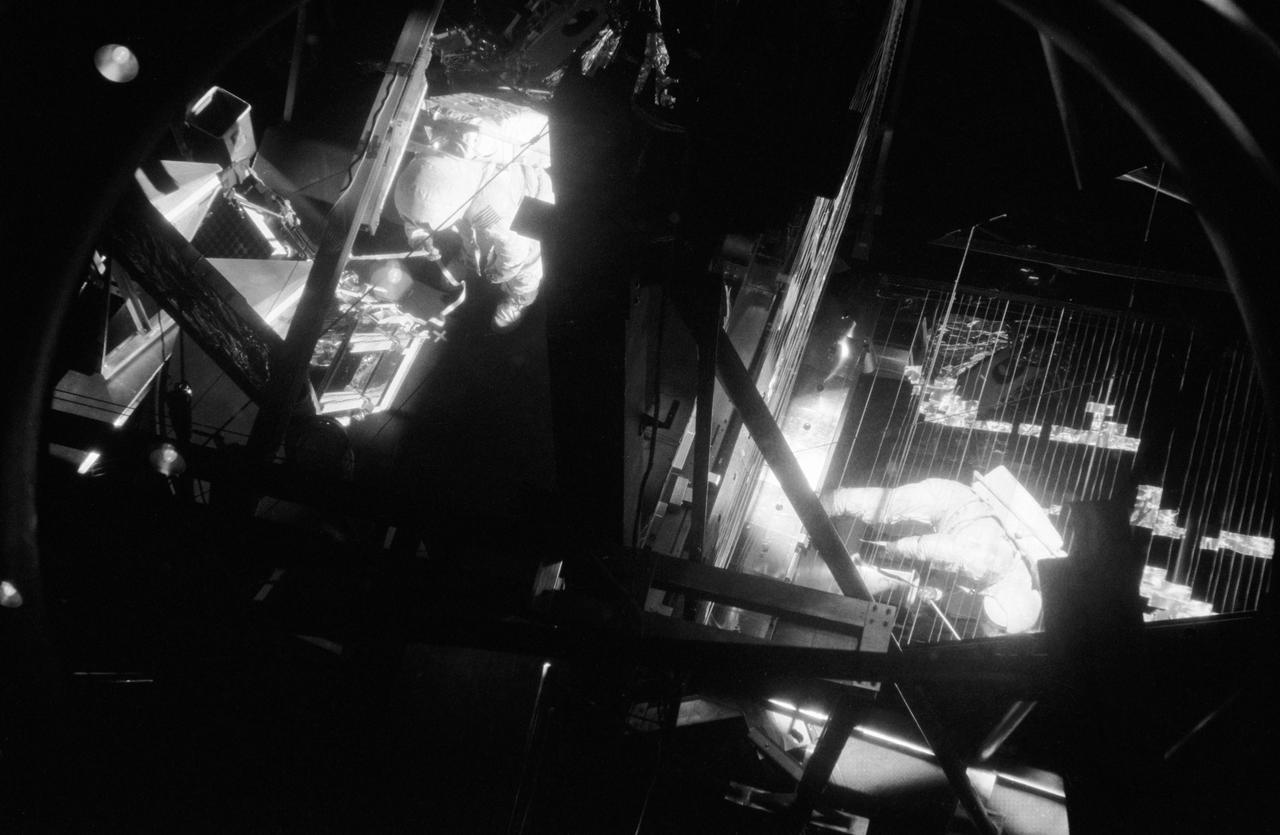

Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, is photographed during thermovacuum training in Chamber B of the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory, Building 32, Manned Spacecraft Center. He is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit. The training simulated lunar surface vacuum and thermal conditions during astronaut operations outside the Lunar Module on the moon's surface. The mirror was used to reflect solar light.

Fred W. Haise Jr. was a research pilot and an astronaut for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration from 1959 to 1979. He began flying at the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio (today the Glenn Research Center), in 1959. He became a research pilot at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC), Edwards, Calif., in 1963, serving NASA in that position for three years until being selected to be an astronaut in 1966 His best-known assignment at the FRC (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center) was as a lifting body pilot. Shortly after flying the M2-F1 on a car tow to about 25 feet on April 22, 1966, he was assigned as an astronaut to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. While at the FRC he had also flown a variety of other research and support aircraft, including the variable-stability T-33A to simulate the M2-F2 heavyweight lifting body, some light aircraft including the Piper PA-30 to evaluate their handling qualities, the Apache helicopter, the Aero Commander, the Cessna 310, the Douglas F5D, the Lockheed F-104 and T-33, the Cessna T-37, and the Douglas C-47. After becoming an astronaut, Haise served as a backup crewmember for the Apollo 8, 11, and 16 missions. He flew on the aborted Apollo 13 lunar mission in 1970, spending 142 hours and 54 minutes in space before returning safely to Earth. In 1977, he was the commander of three free flights of the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise when it flew its Approach and Landing Tests at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Meanwhile, from April 1973 to January 1976, Haise served as the Technical Assistant to the Manager of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Project. In 1979, he left NASA to become the Vice President for Space Programs with the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. He then served as President of Grumman Technical Services, an operating division of Northrop Grumman Corporation, from January 1992 until his retirement. Haise was born in Biloxi, Miss., on November 14, 1933. He underwent flight traini