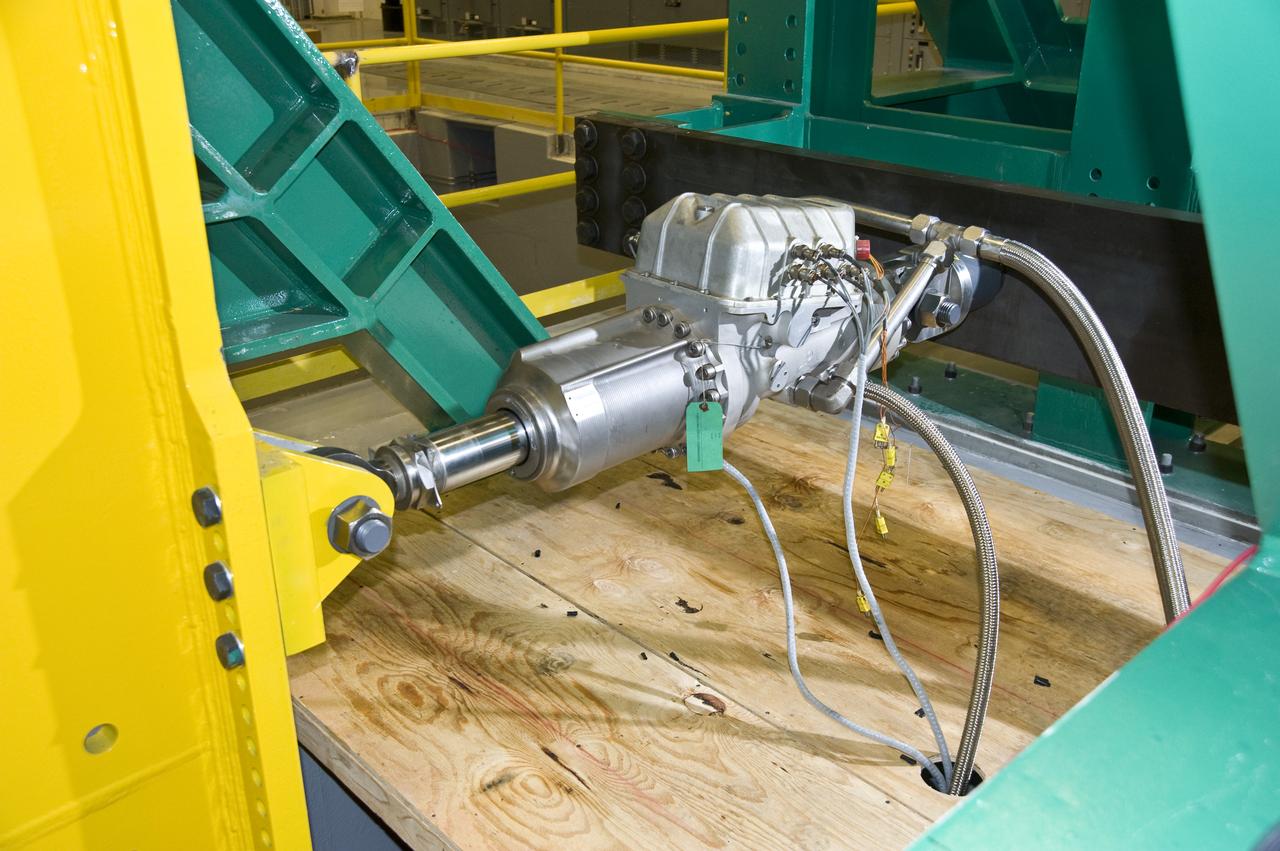

THRUST VECTOR CONTROL (TVC) TEST LAB TEST ACTUATOR
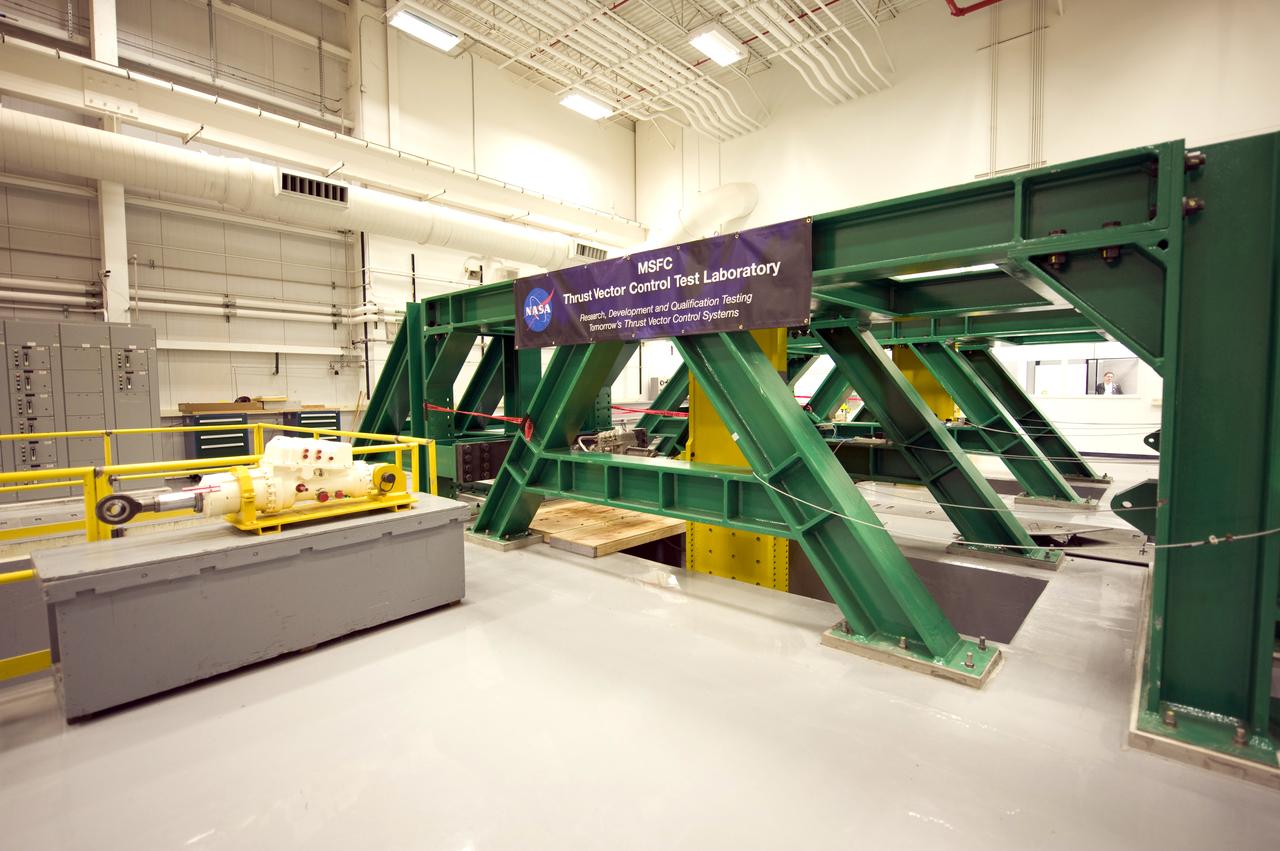

THRUST VECTOR CONTROL (TVC) TEST LAB INERTIAL LOAD SIMULATORS

Testing of the Ascent Thrust Vector Control System in support of the Ares 1-X program at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This image is extracted from a high definition video file and is the highest resolution available
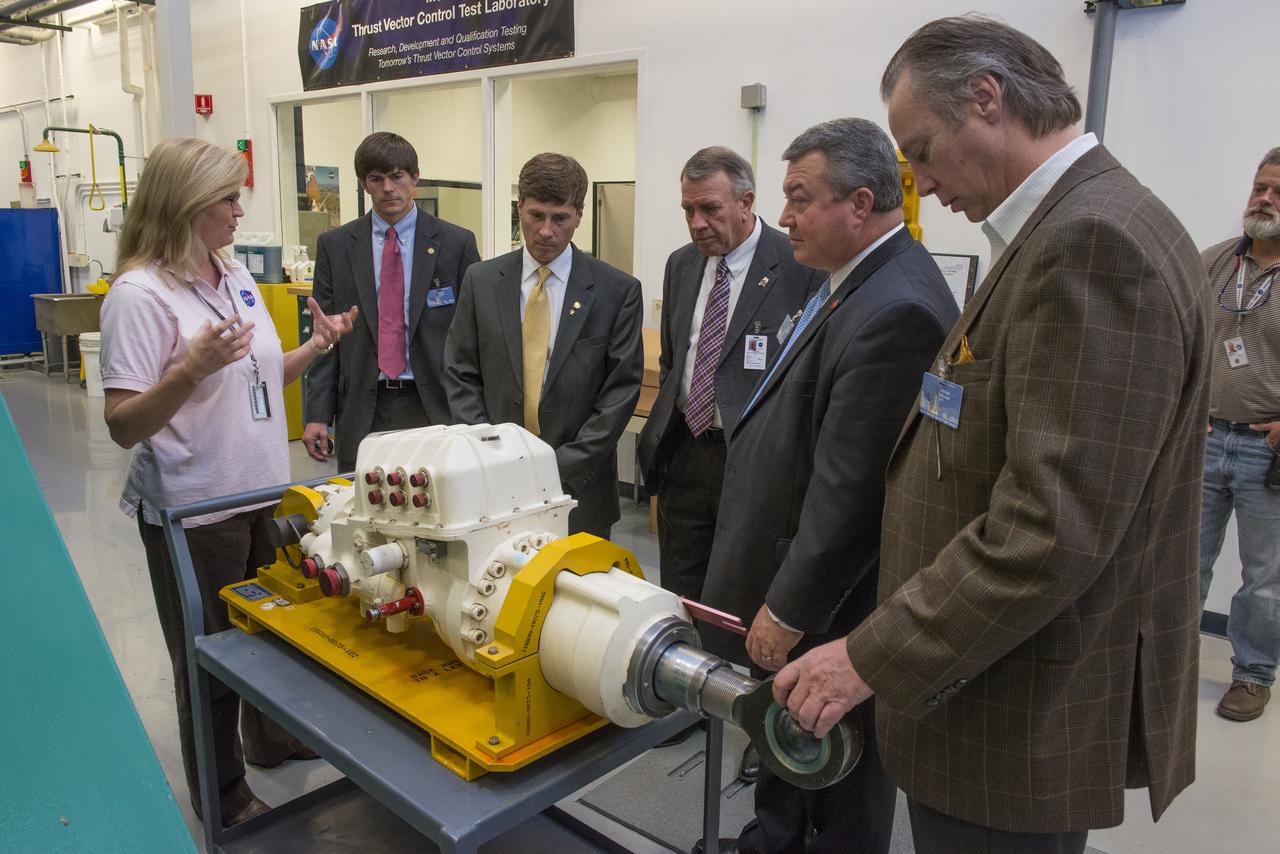

LISA BATES PROVIDES AN OVERVIEW OF THRUST VECTOR CONTROL TO STATE SENATOR BILL HOLTZCLAW, REPRESENTATIVE MAC MCCUTCHEON, GREG CANFIELD OF THE ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE, GOVERNOR BENTLEY’S CHIEF OF STAFF, DAVID PERRY, AND LT. GOVERNOR STRANGES CHIEF OF STAFF, STEVE PELHAM.

LISA BATES PROVIDES AN OVERVIEW OF THRUST VECTOR CONTROL TO STATE SENATOR BILL HOLTZCLAW, REPRESENTATIVE MAC MCCUTCHEON, GREG CANFIELD OF THE ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE, GOVERNOR BENTLEY’S CHIEF OF STAFF, DAVID PERRY, AND LT. GOVERNOR STRANGES CHIEF OF STAFF, STEVE PELHAM
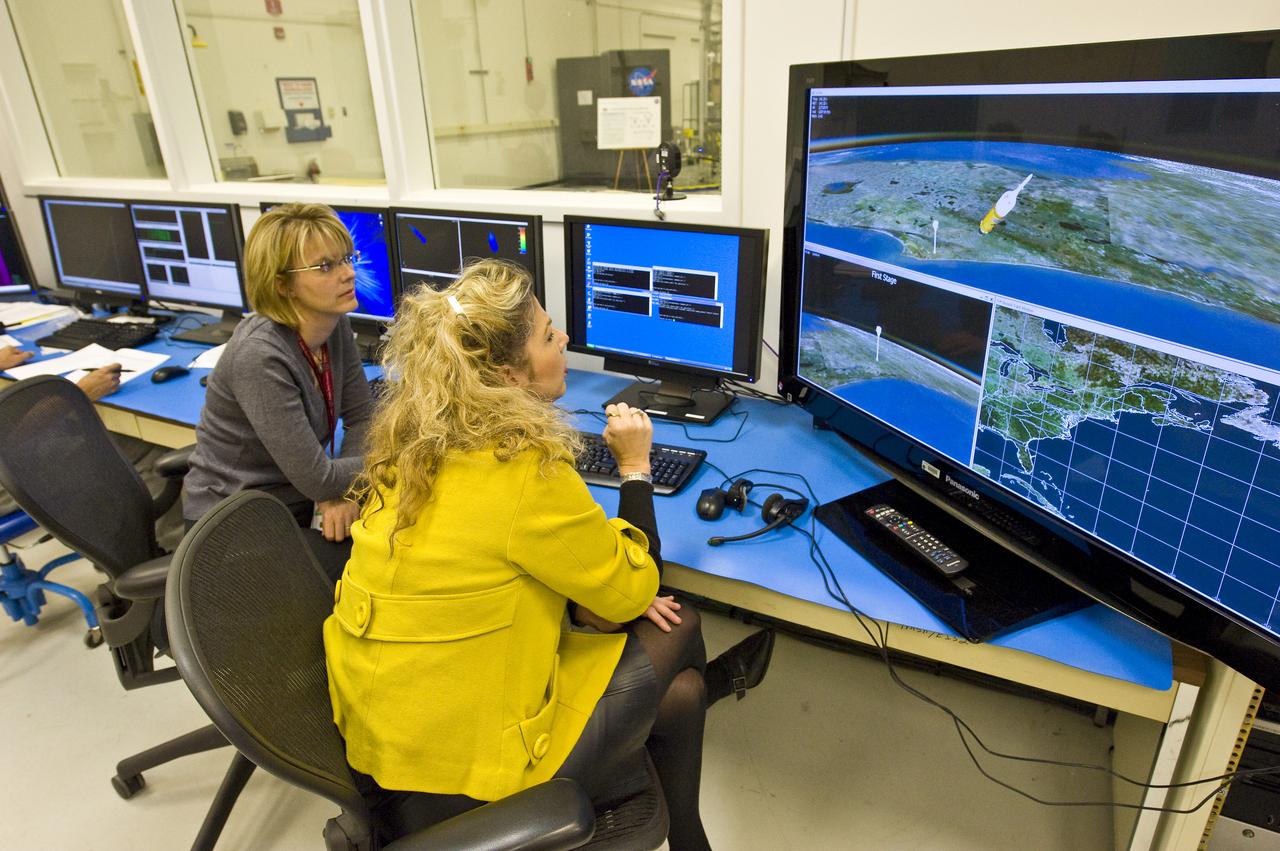

TVC TEST LAB/HARDWARE IN THE LOOP FACILITY FLIGHT SIMULATION CONTROL ROOM
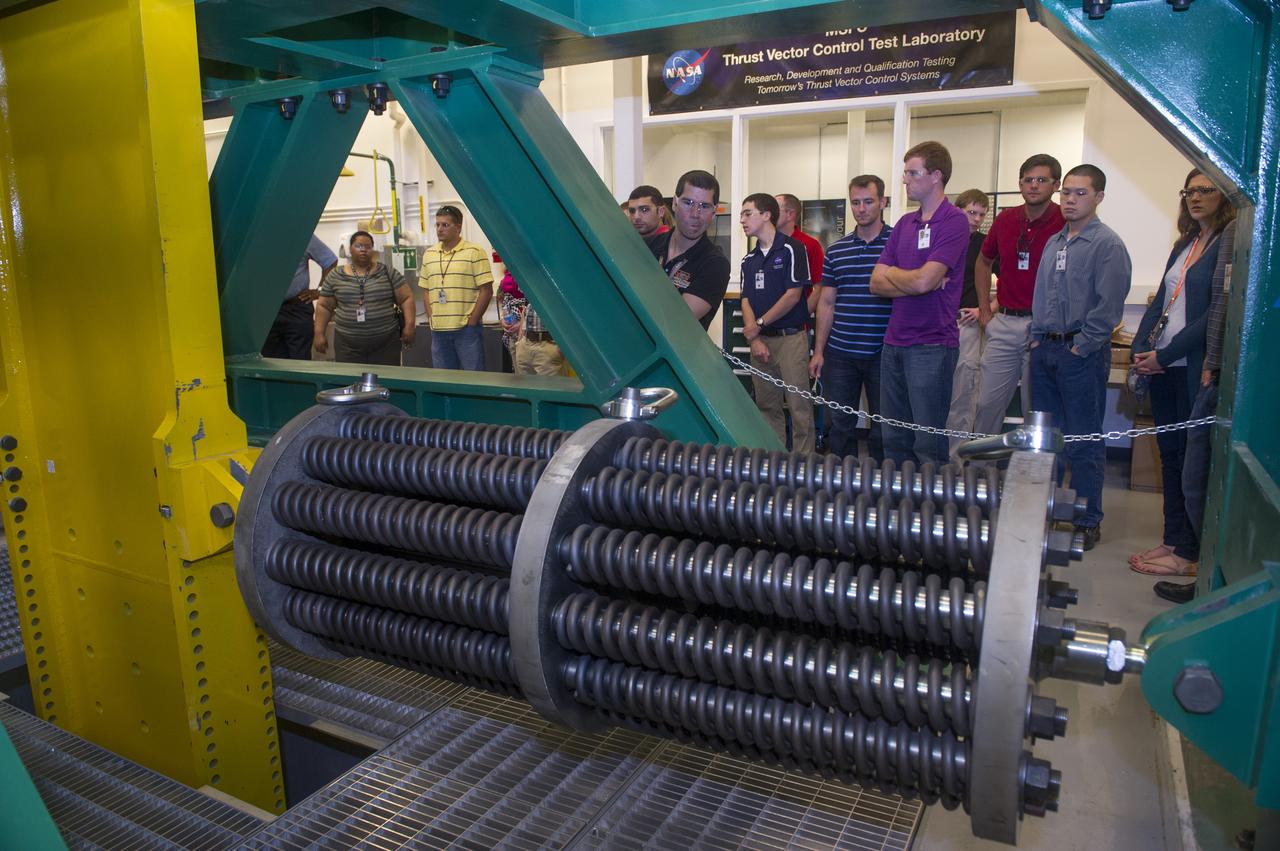

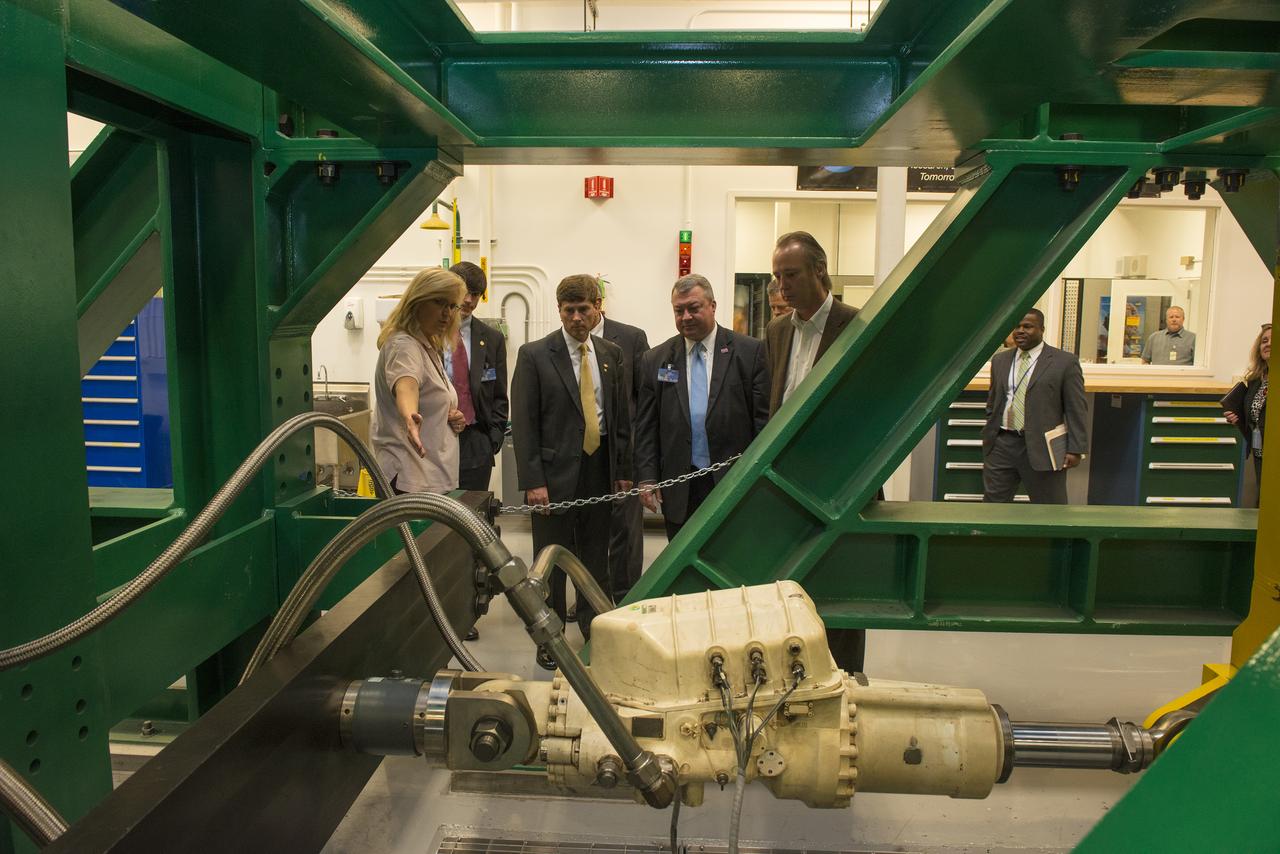
MIRANDA HOLTON GIVES OVERVIEW OF THRUST VECTOR CONTROL LAB
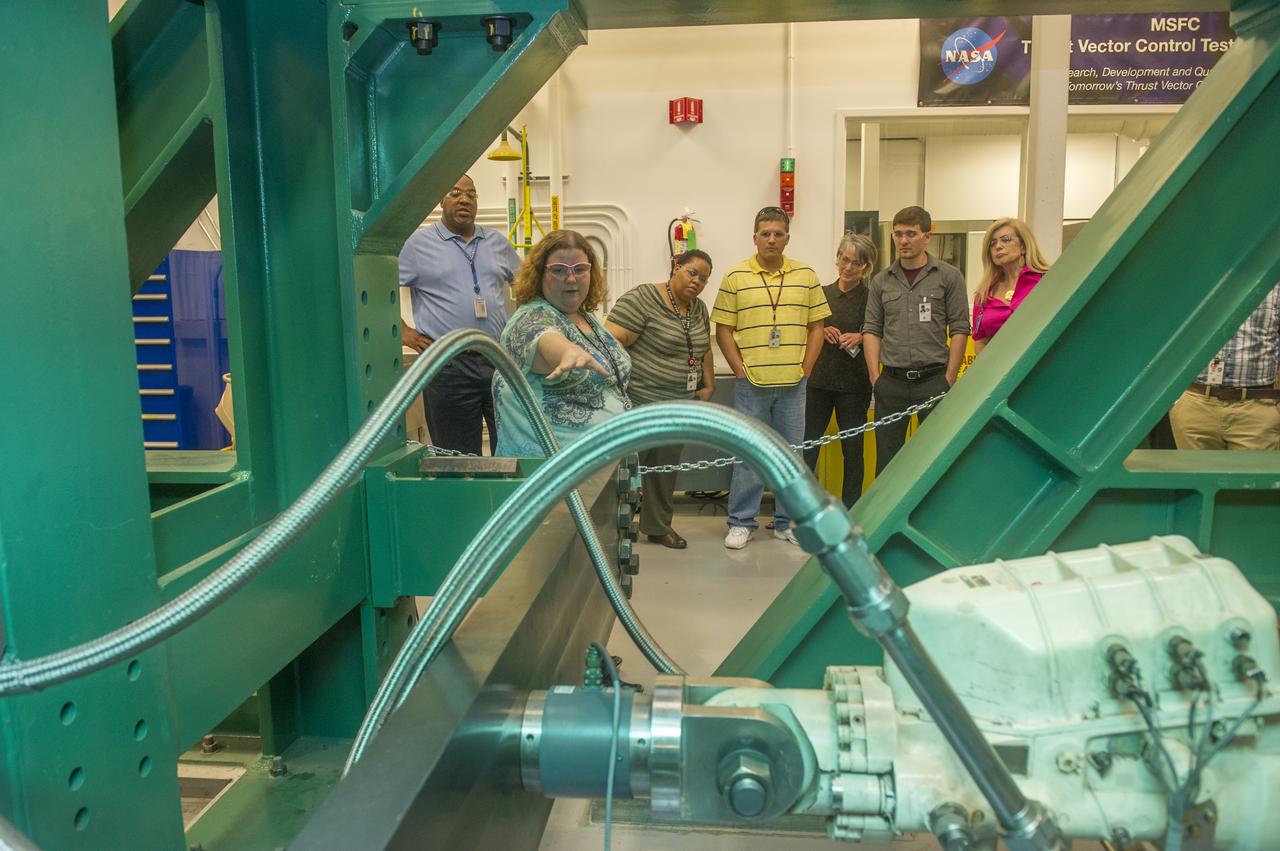

MIRANDA HOLTON GIVES OVERVIEW OF THRUST VECTOR CONTROL LAB
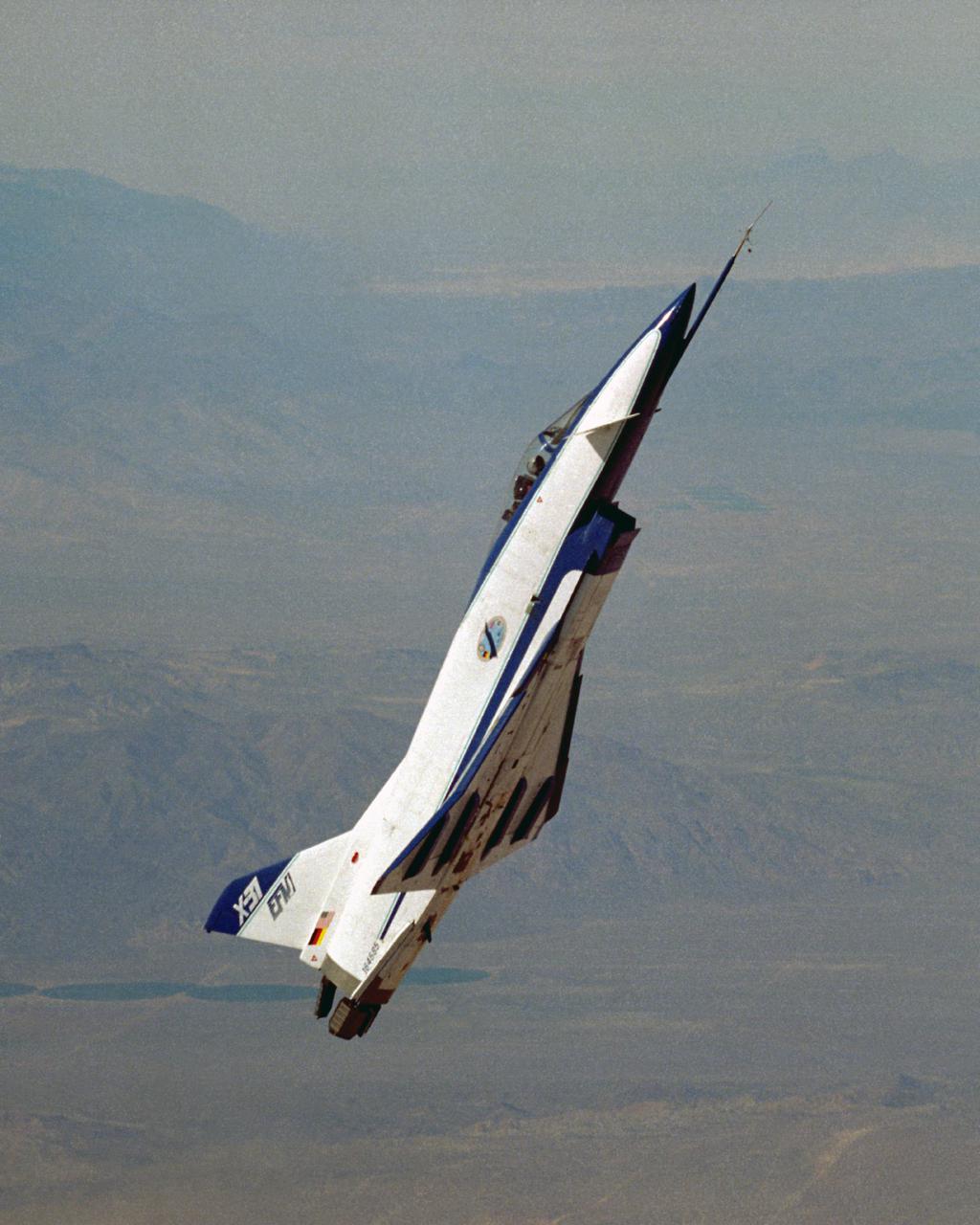

The X-31, the world’s first international X-plane, demonstrates controlled flight at high alpha courtesy of its canards and thrust vectoring paddles in the exhaust stream.

THE 2013 ASTRONAUT CANDIDATE CLASS VISITED THE THRUST VECTOR CONTROL TEST LAB AT MARSHALL'S PROPULSION RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT LABORATORY WHERE ENGINEERS ARE DEVELOPING AND TESTING THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM'S GUIDANCE, NAVIGATION AND CONTROL SOFTWARE AND AVIONICS HARDWARE.
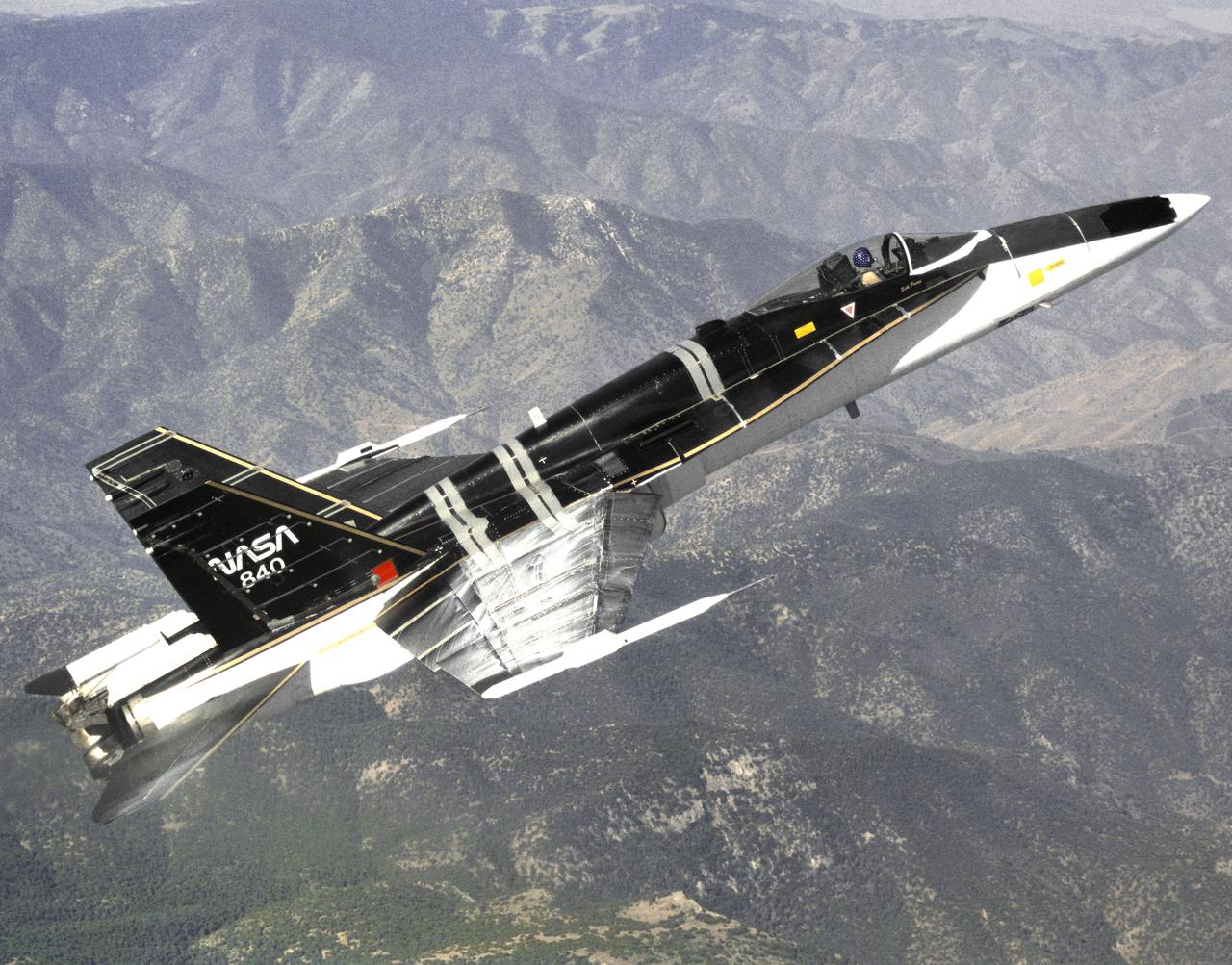

The modified F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV) carries out air flow studies on a flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Using oil, researchers were able to track the air flow across the wing at different speeds and angles of attack. A thrust vectoring system had been installed on the engines' exhaust nozzles for the high angle of attack research program. The thrust vectoring system, linked to the aircraft's flight control system, moves a set of three paddles on each engine to redirect thrust for directional control and increased maneuverability at angles of attack at up to 70 degrees.
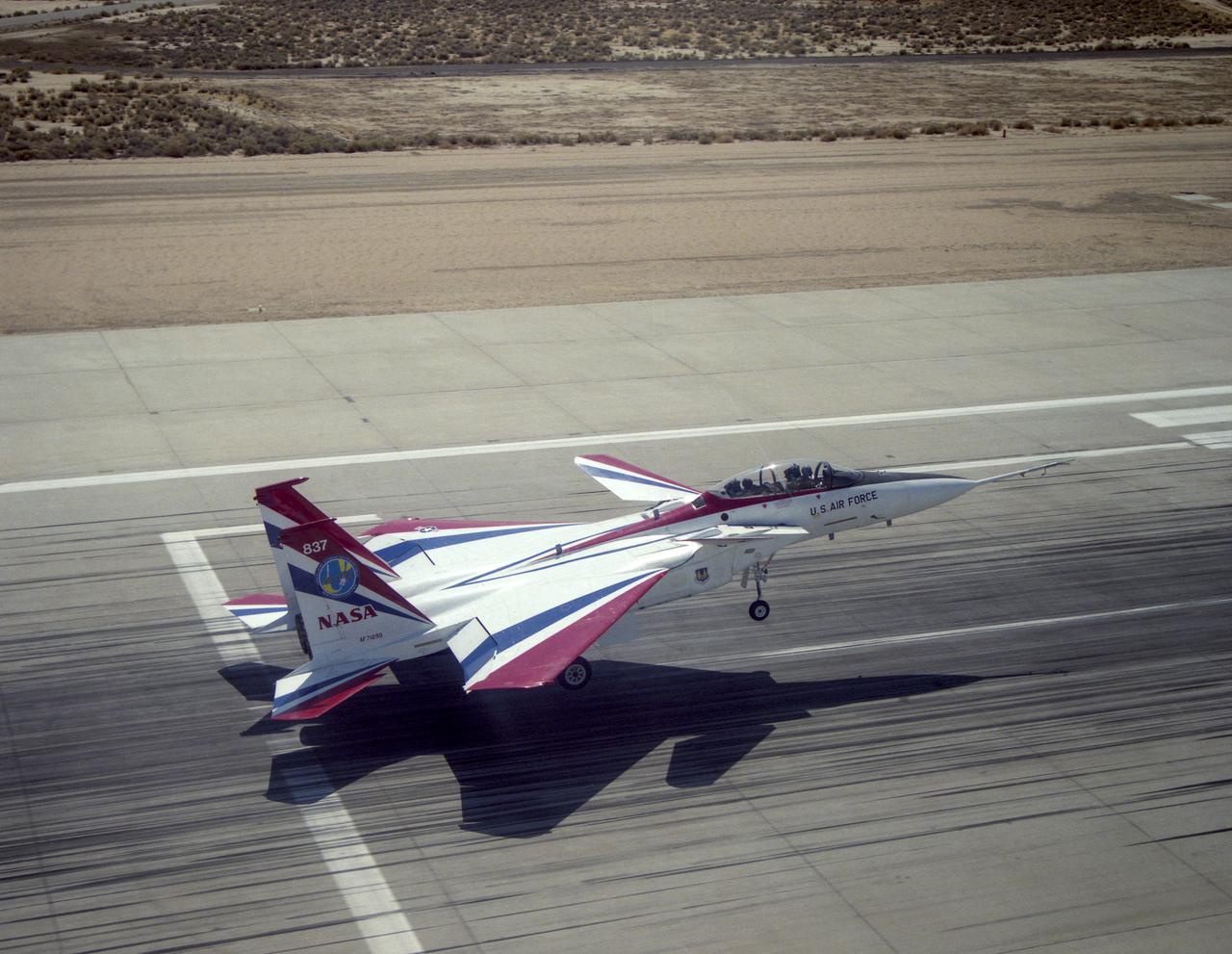

The F-15 Advanced Controls Technology for Integrated Vehicles, the first pre-production F-15B, shows its canards. Less obvious are the multi-axis thrust vectoring exhaust nozzles.
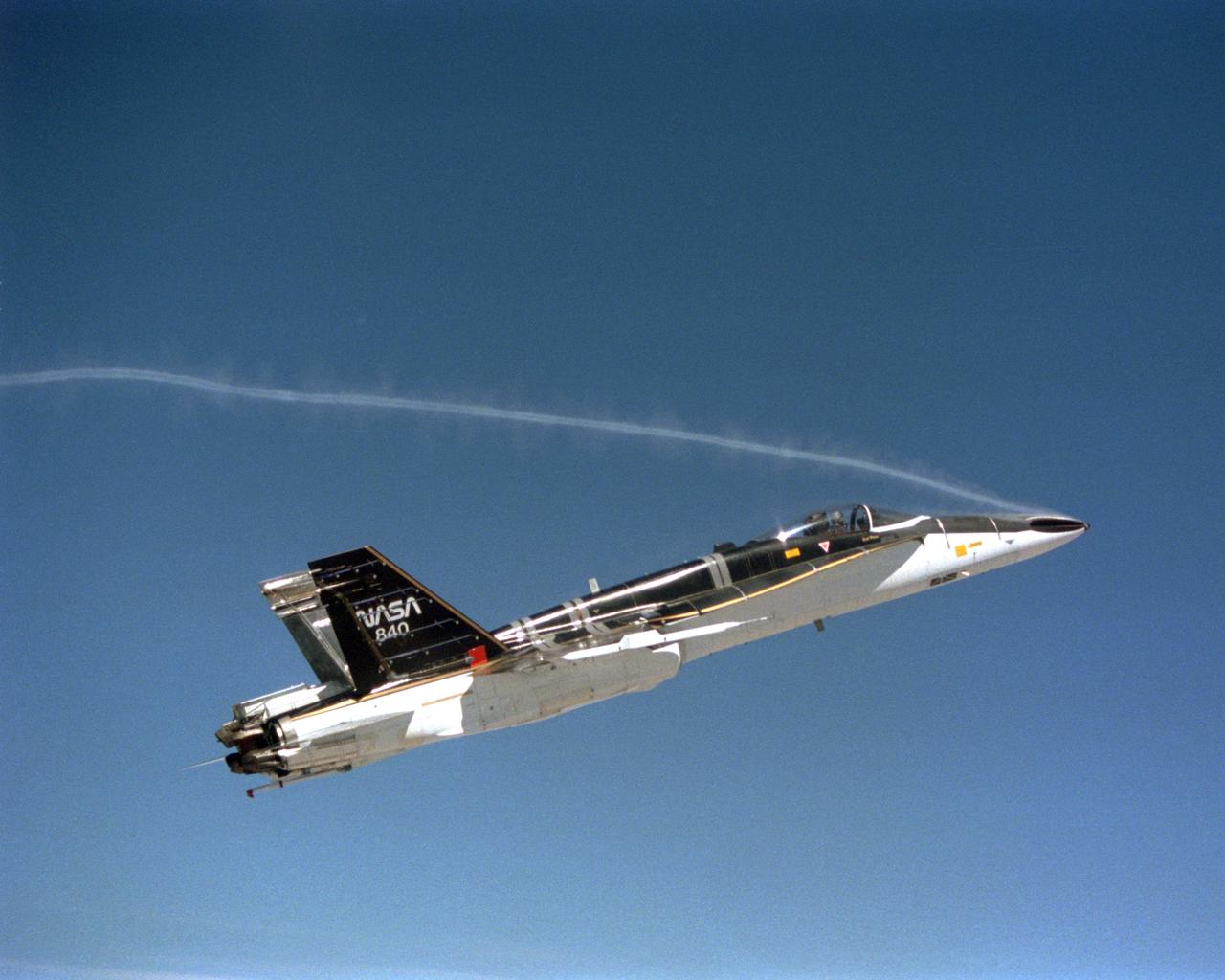

During the final phase of tests with the HARV, Dryden technicians installed nose strakes, which were panels that fitted flush against the sides of the forward nose. When the HARV was at a high alpha, the aerodynamics of the nose caused a loss of directional stability. Extending one or both of the strakes results in strong side forces that, in turn, generated yaw control. This approach, along with the aircraft's Thrust Vectoring Control system, proved to be stability under flight conditions in which conventional surfaces, such as the vertical tails, were ineffective.

F-15B ACTIVE in flight
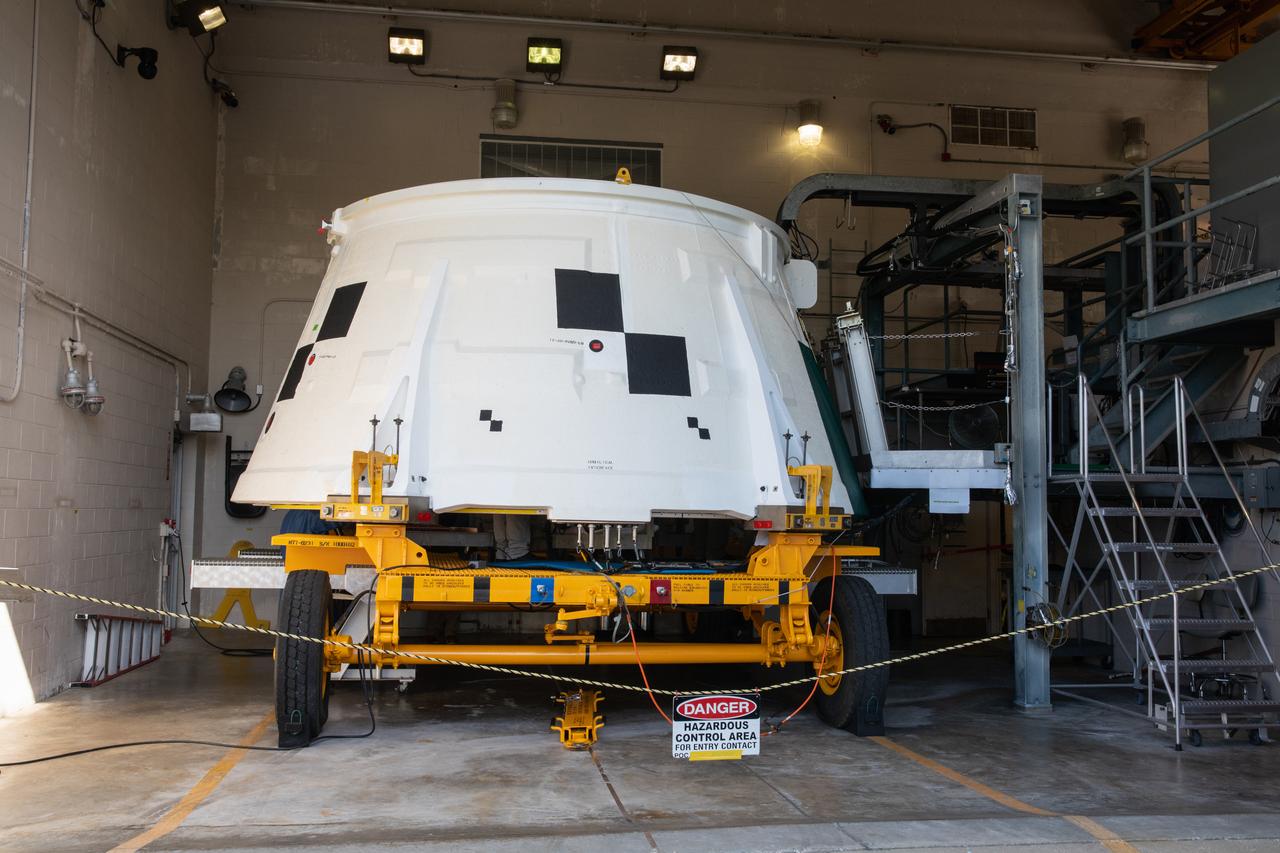

The aft skirt for one of the Space Launch System’s (SLS) two solid rocket boosters is inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 16, 2019. Segments of the boosters are being inspected and prepared for Artemis I, the agency’s first uncrewed flight of Orion atop the SLS. The aft skirts contain the thrust vector control system that steers the booster’s nozzles based on commands from the booster avionics during launch.
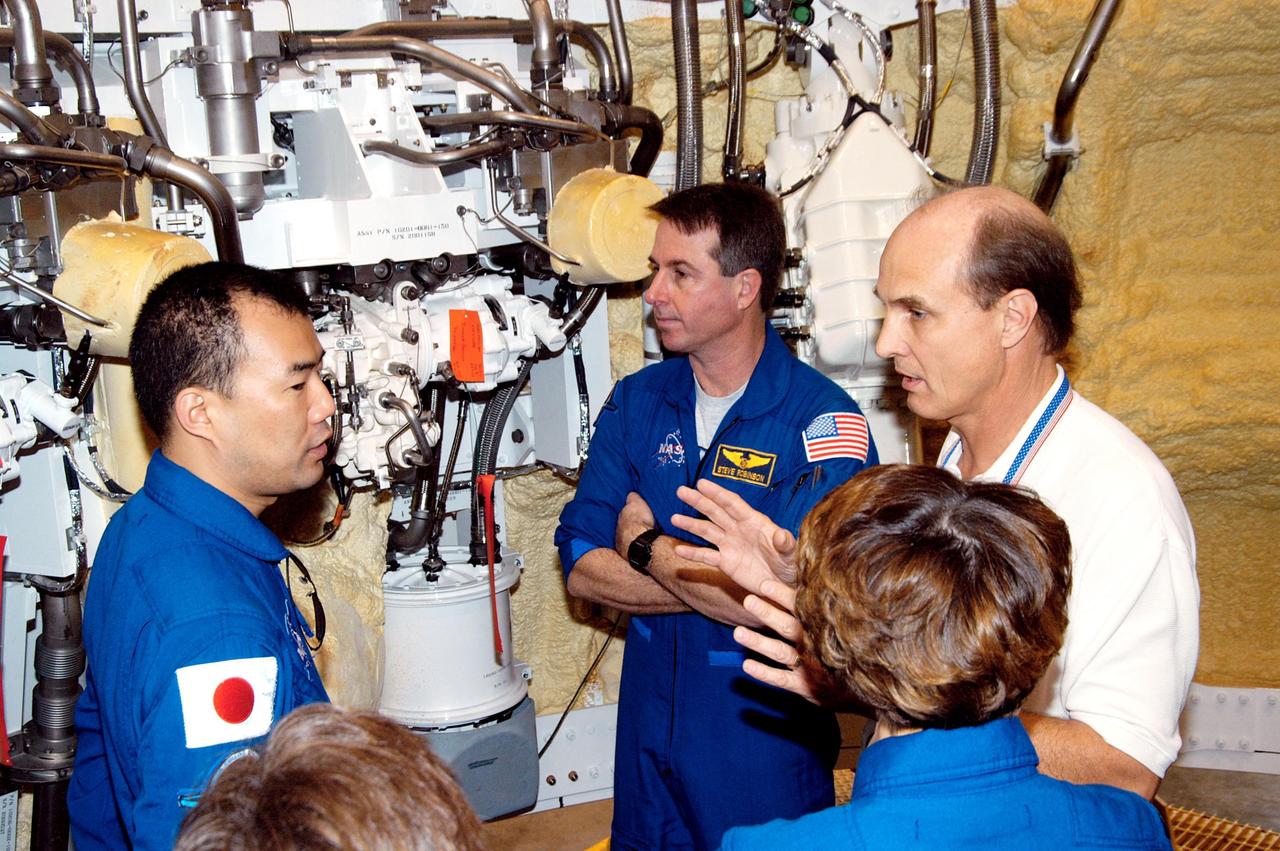

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, STS-114 Mission Specialists Soichi Noguchi (left), Stephen Robinson (center) and Commander Eileen Collins (back to camera) are briefed by Bob Dougert, manager of Test Engineering and Operations, on the thrust vector control system in solid rocket boosters. The crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
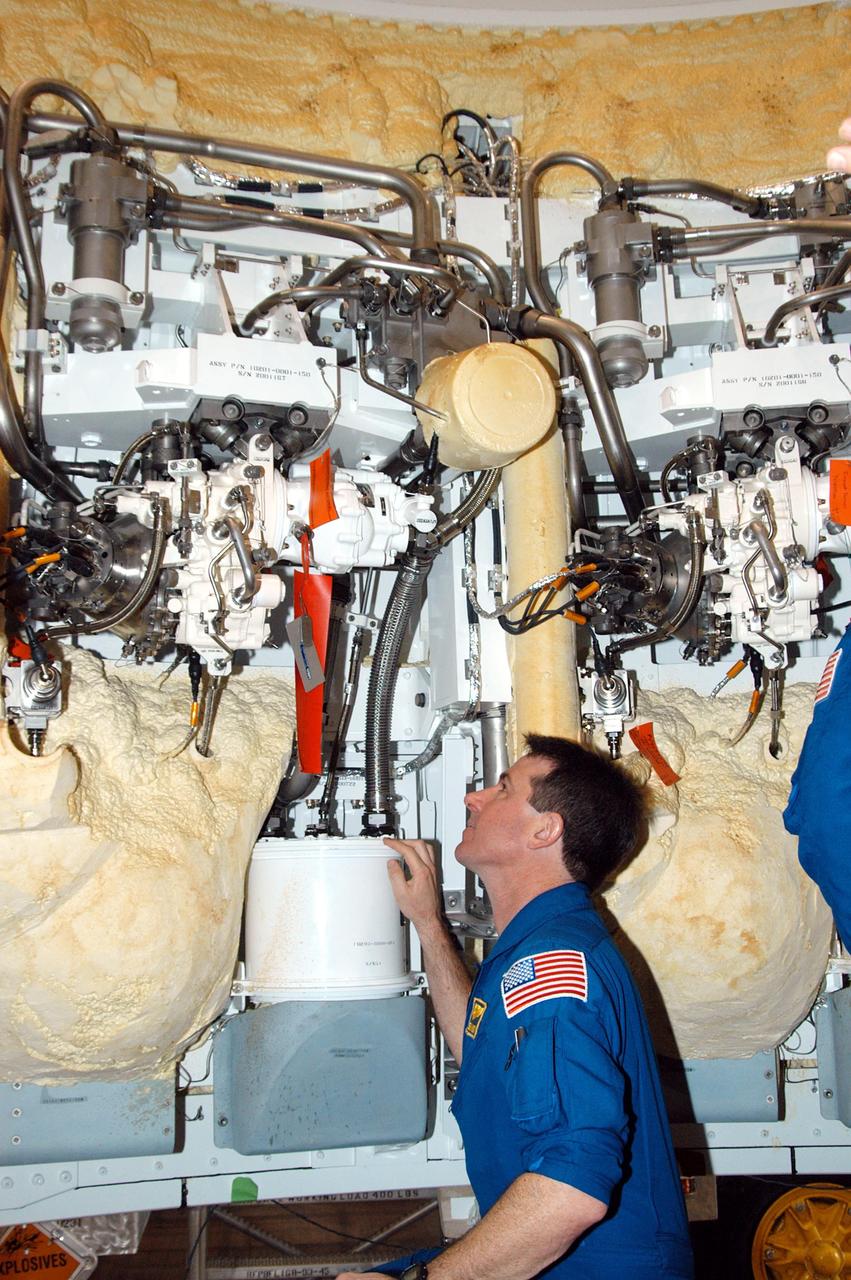

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, STS-114 Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson looks at part of the thrust vector control system in a segment of a solid rocket booster. The crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
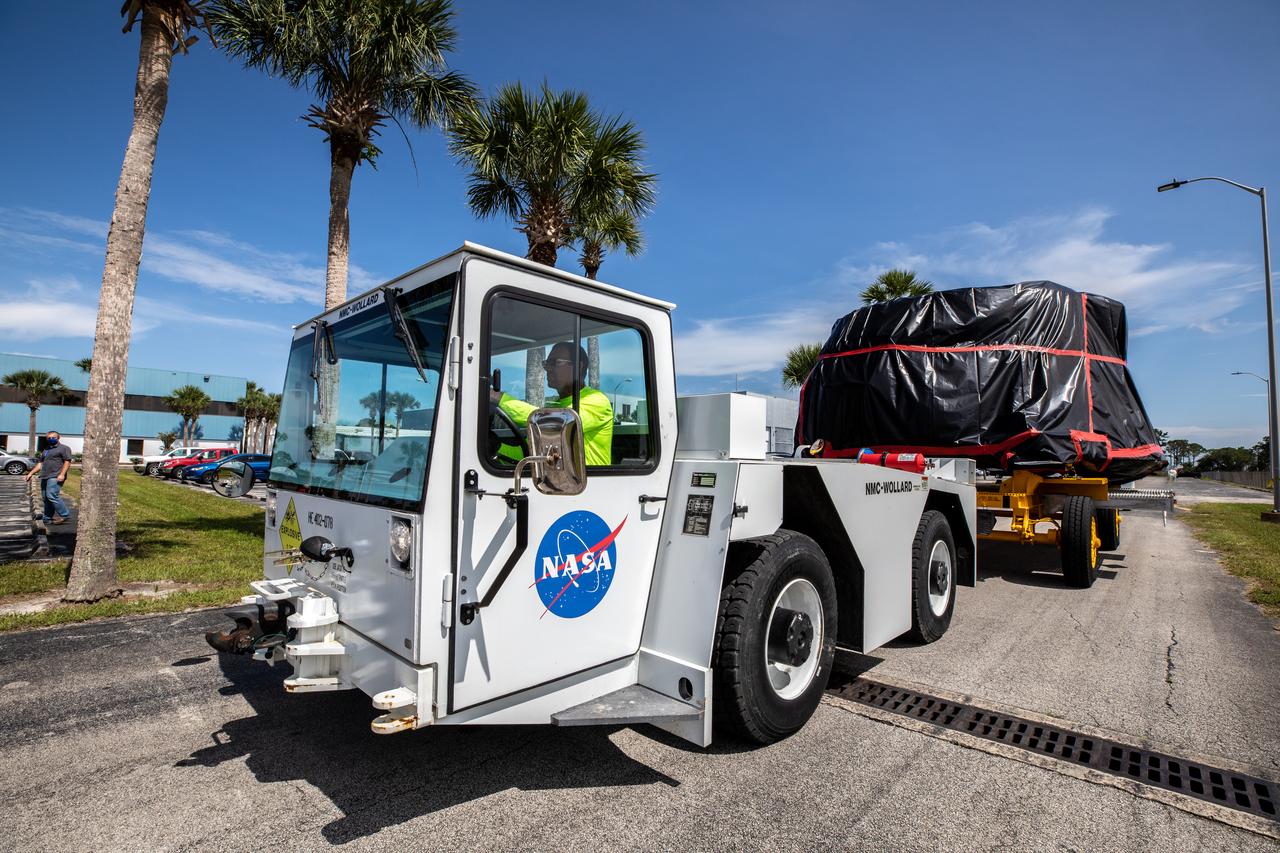

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
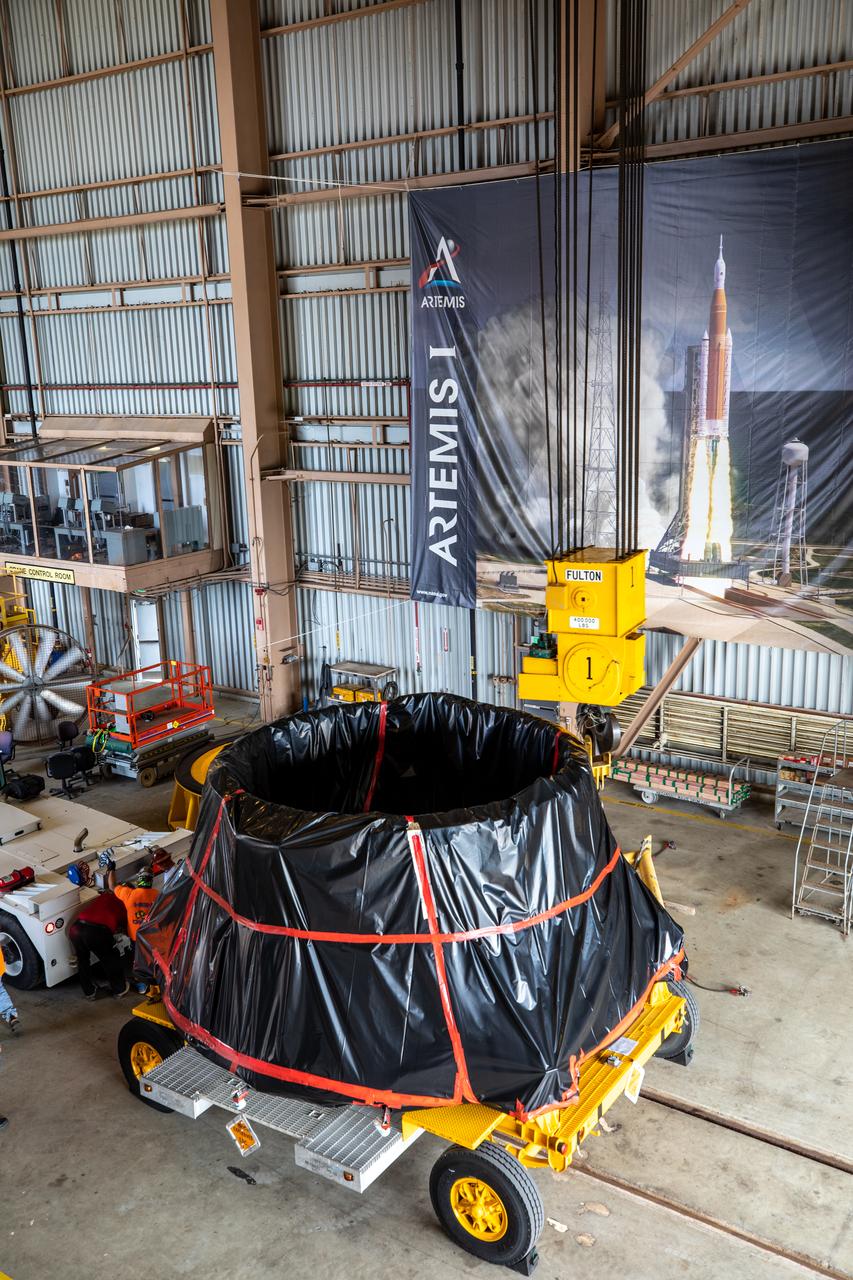

The first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters is moved into the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
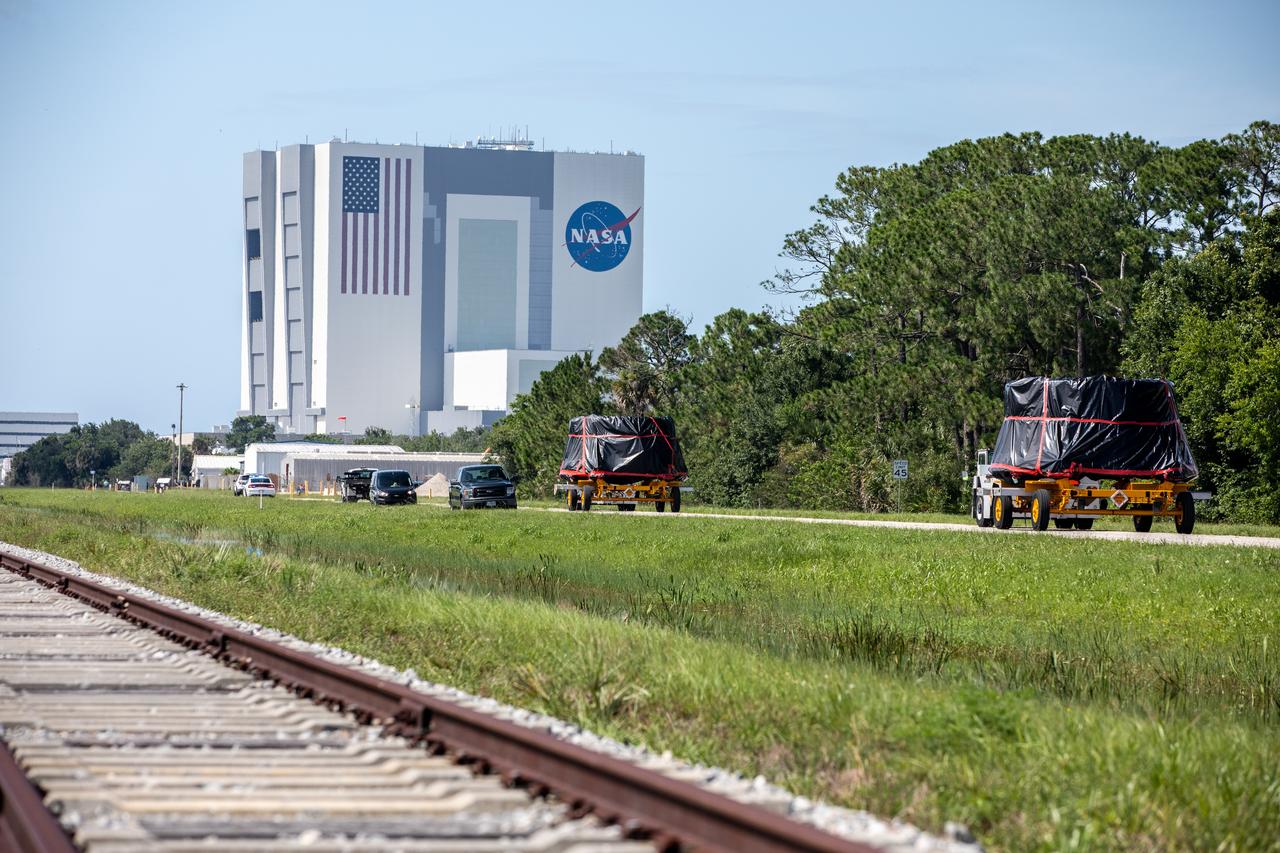

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
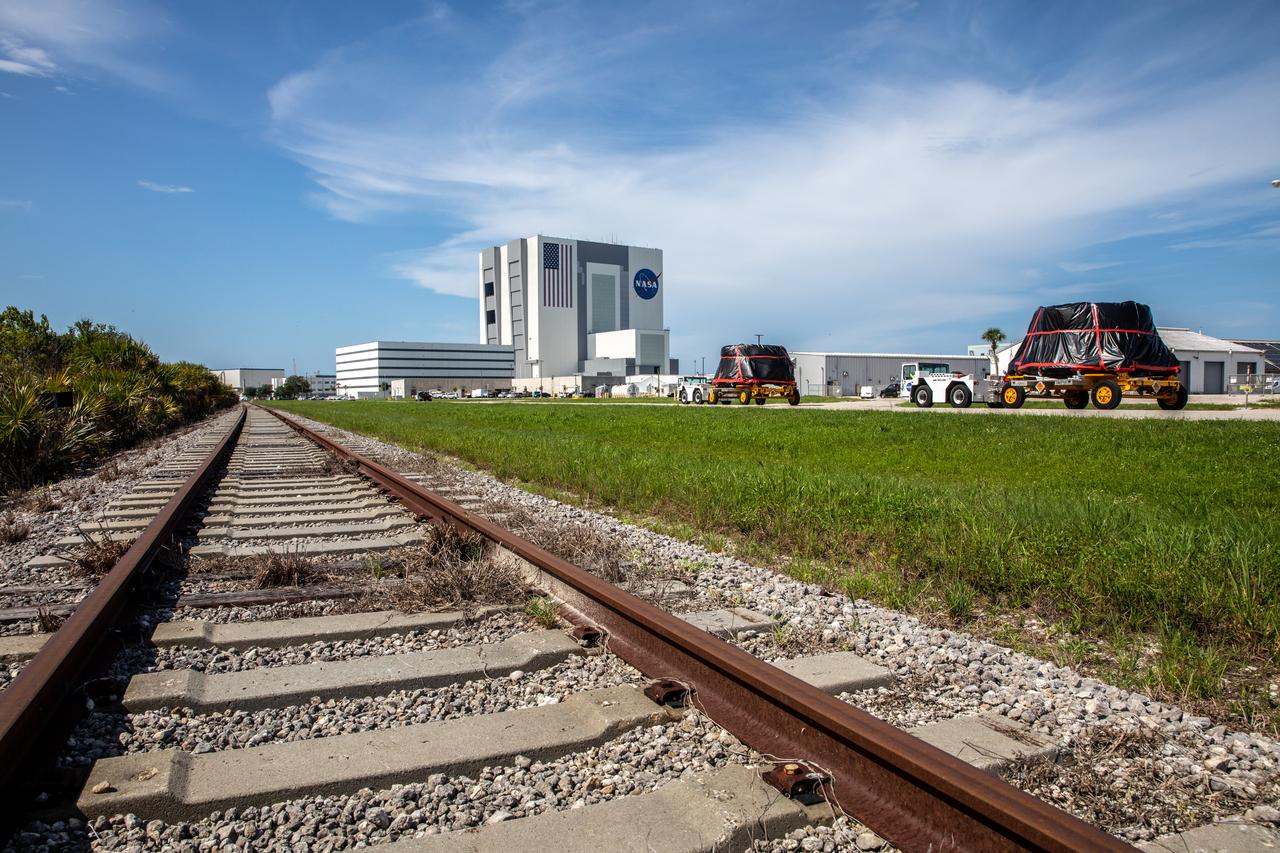

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
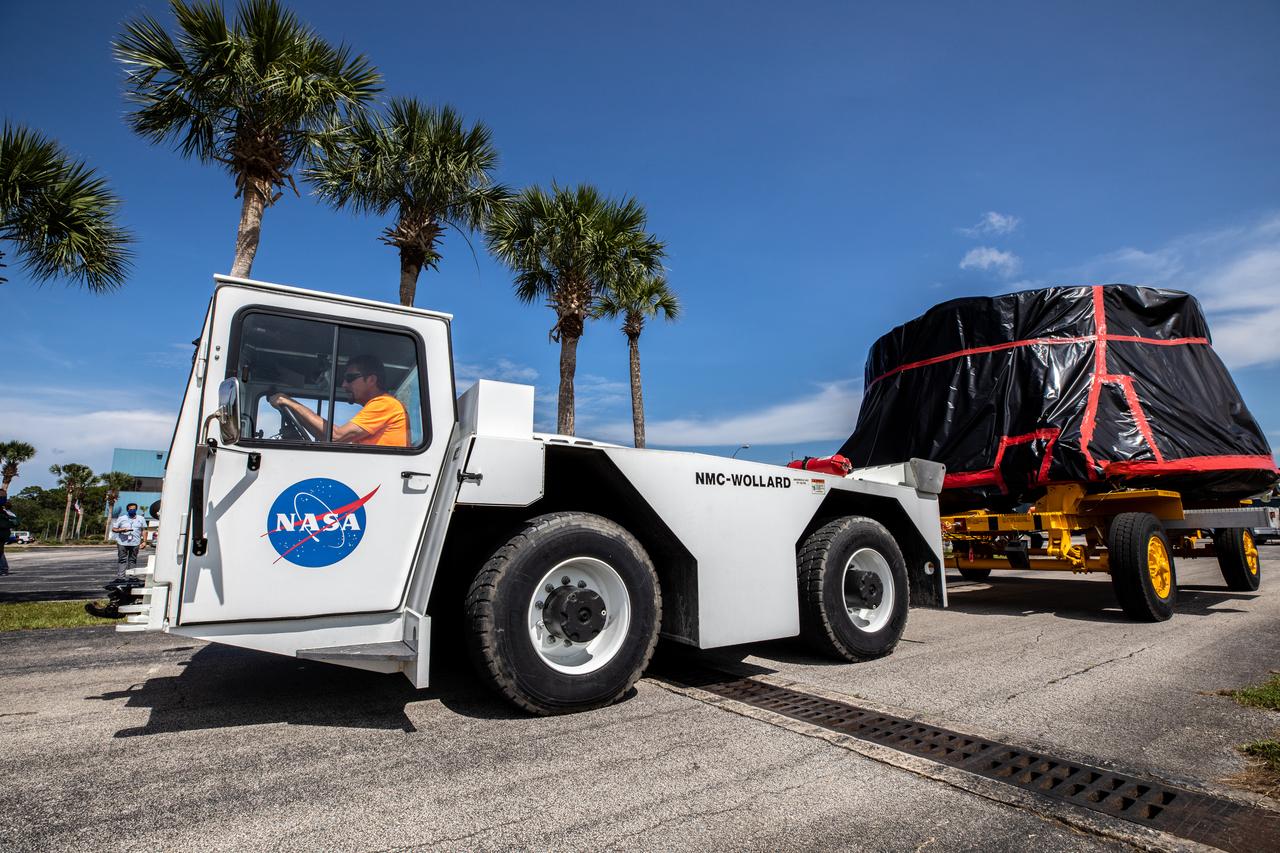

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
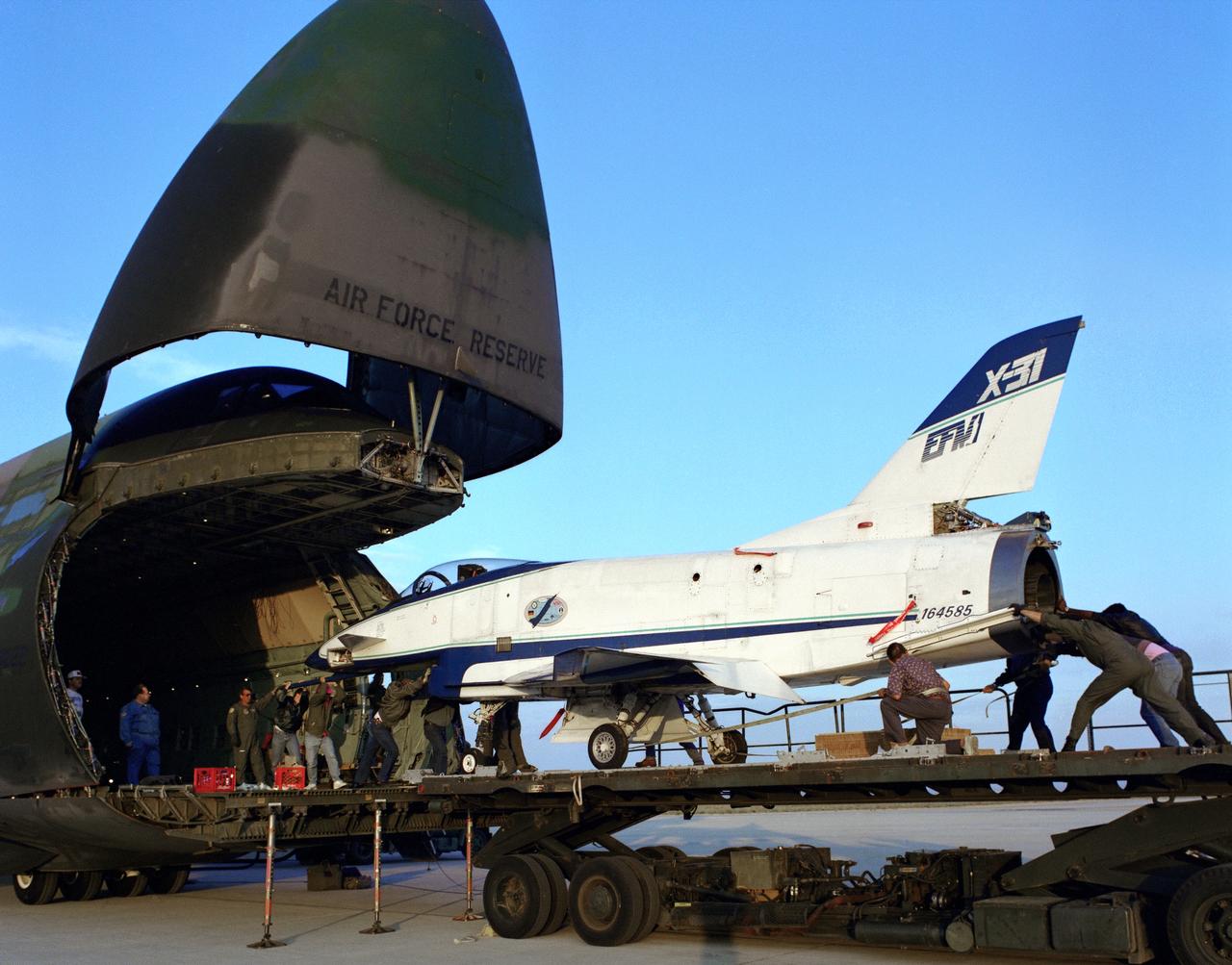

The X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, begins rolling aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport which ferried it on May 22, 1995 to Europe where it was flown in the Paris Air Show in June 1995. To fit in the C-5 the right wing of the X-31 had to be removed. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack.

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
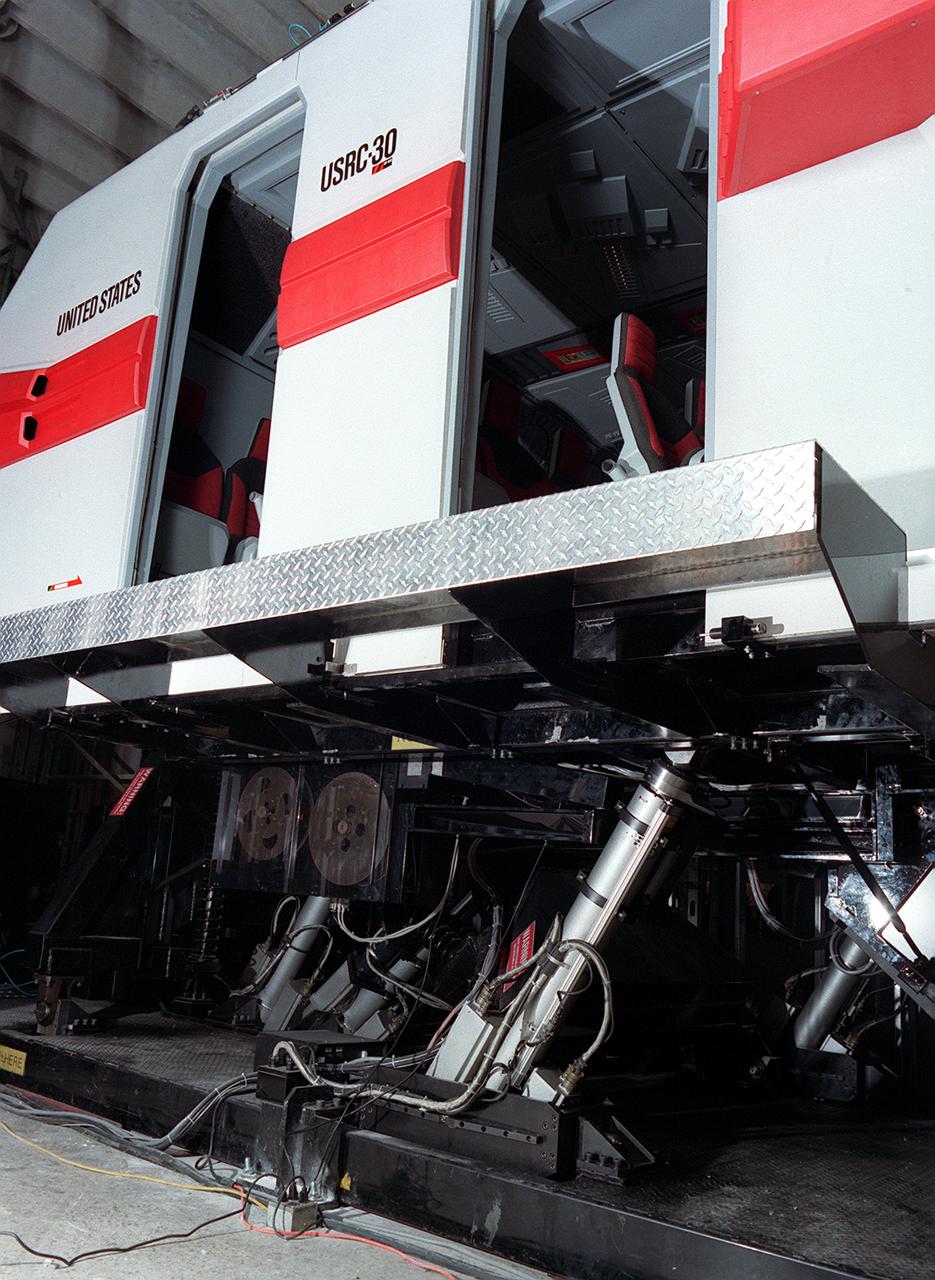

The development of the electric space actuator represents an unusual case of space technology transfer wherein the product was commercialized before it was used for the intended space purpose. MOOG, which supplies the thrust vector control hydraulic actuators for the Space Shuttle and brake actuators for the Space Orbiter, initiated development of electric actuators for aerospace and industrial use in the early 1980s. NASA used the technology to develop an electric replacement for the Space Shuttle main engine TVC actuator. An electric actuator is used to take passengers on a realistic flight to Jupiter at the US Space and Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama.
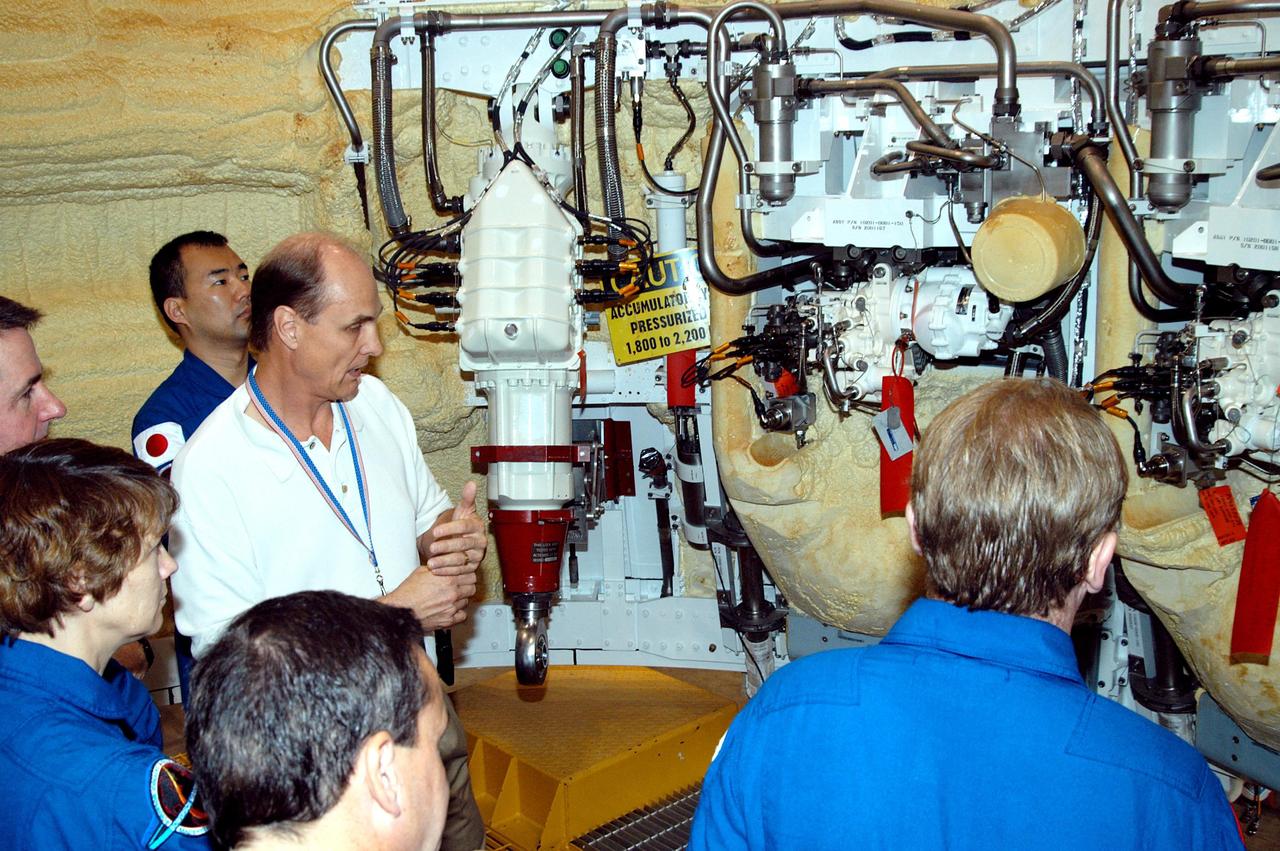
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, Bob Dougert, manager of Test Engineering and Operations, explains the thrust vector control system to the STS-114 crew. Counterclockwise from upper left are Mission Specialists Soichi Noguchi and Stephen Robinson, Commander Eileen Collins, and Mission Specialists Charles Camarda and Andrew Thomas. The crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
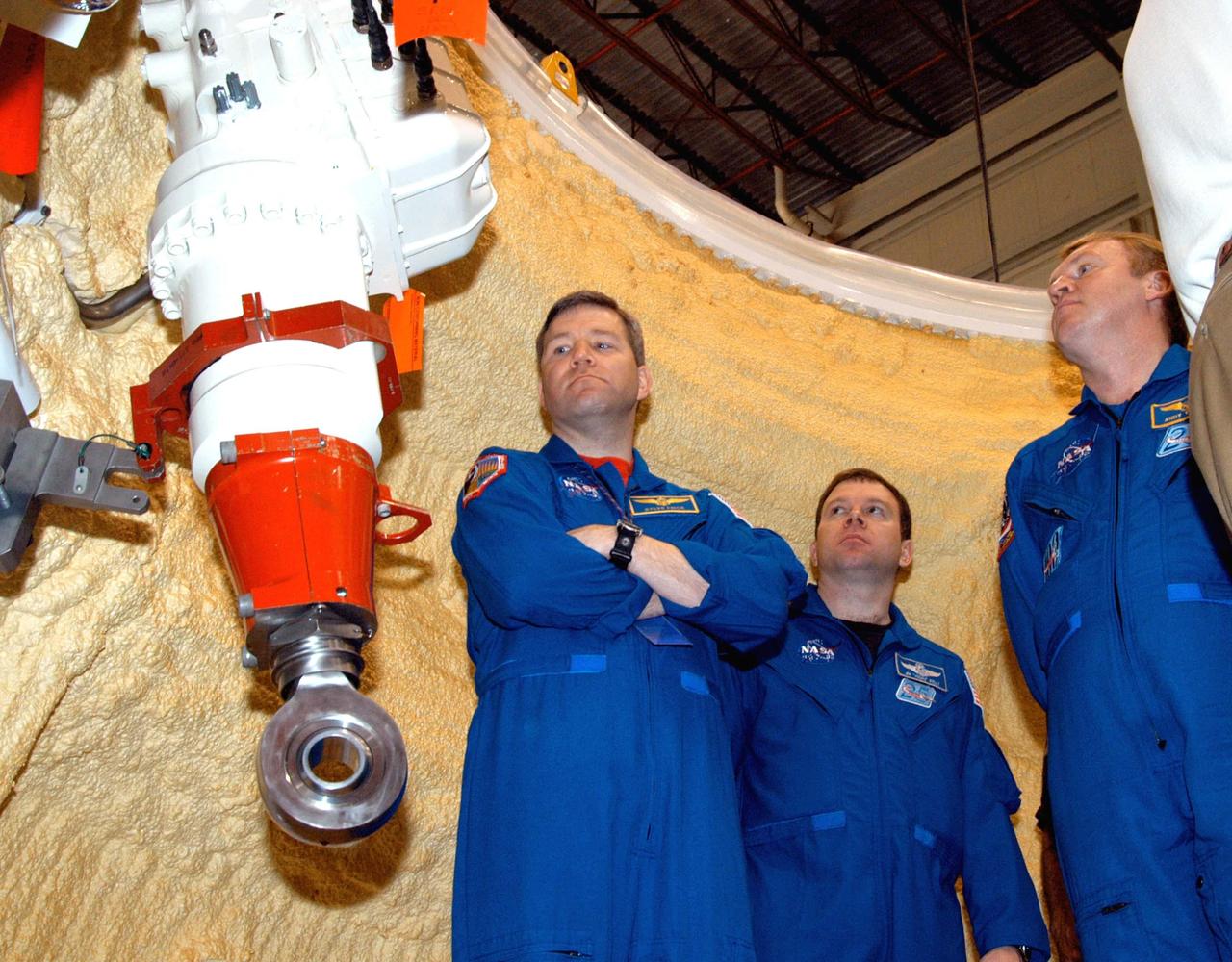

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, members of the STS-114 crew get a close look at an actuator, part of the thrust vector control system, in a segment of a solid rocket booster. Behind them is the yellow foam insulation. At left is astronaut Steven Frick; in the center is STS-114 Pilot James Kelly and, at right, is Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas. The crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
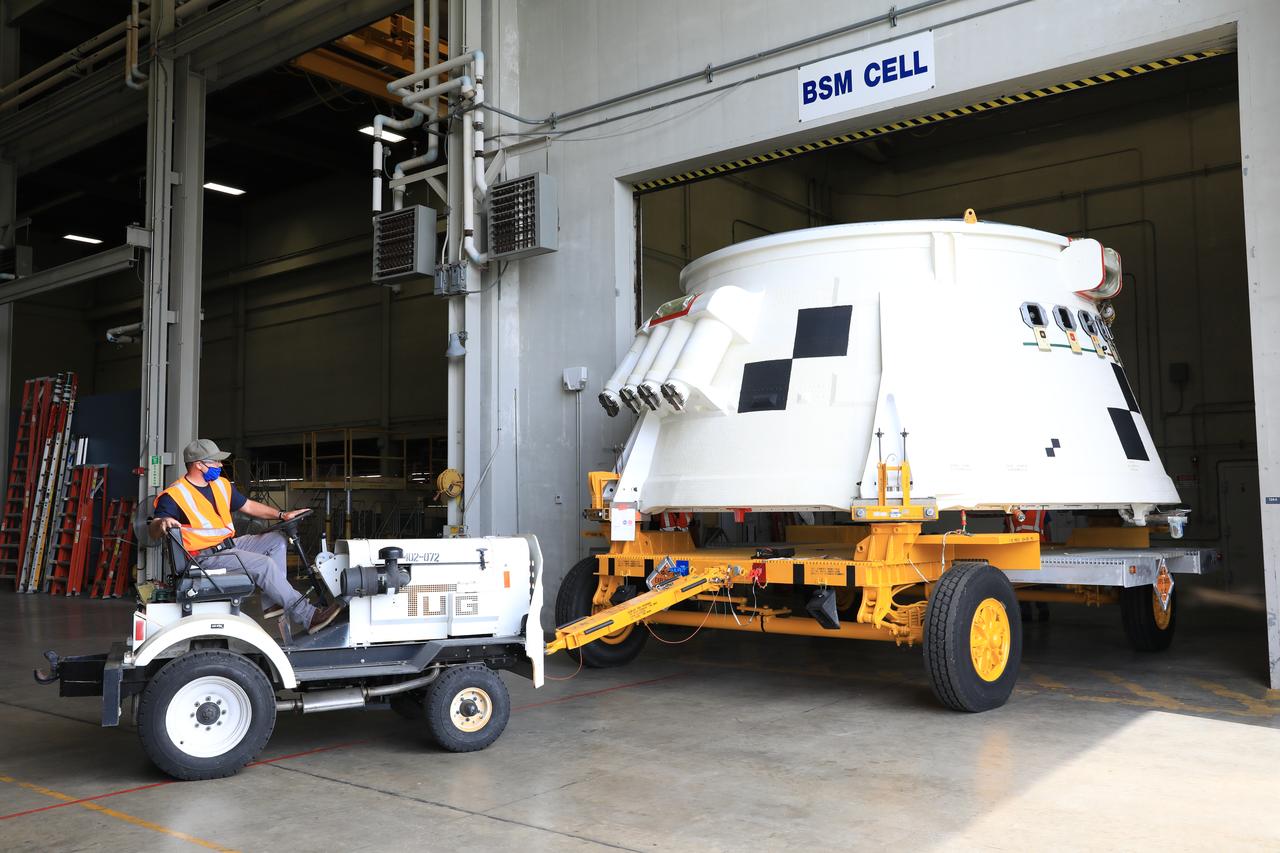

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
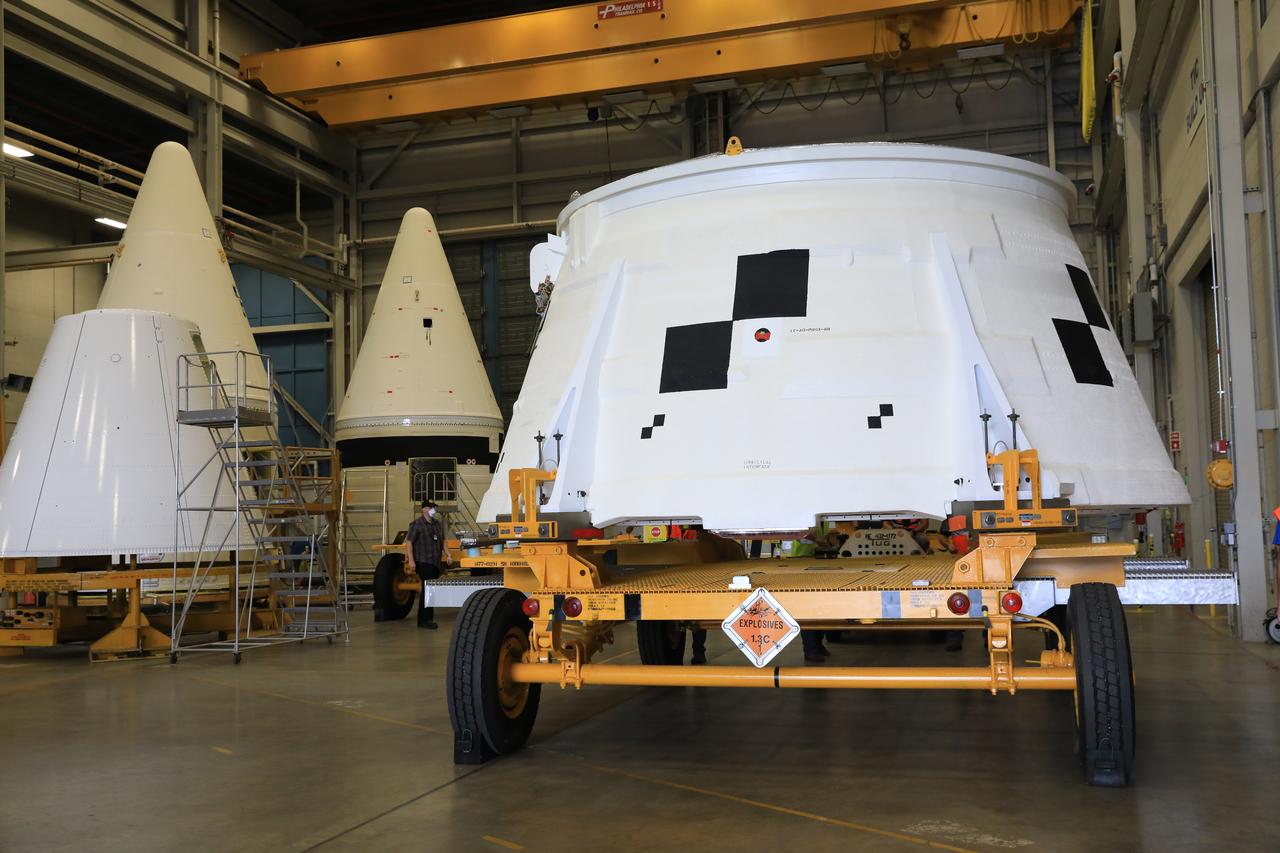

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved out of their test cells and are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at right is the right aft skirt. In view at left are the two Artemis I forward assemblies. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
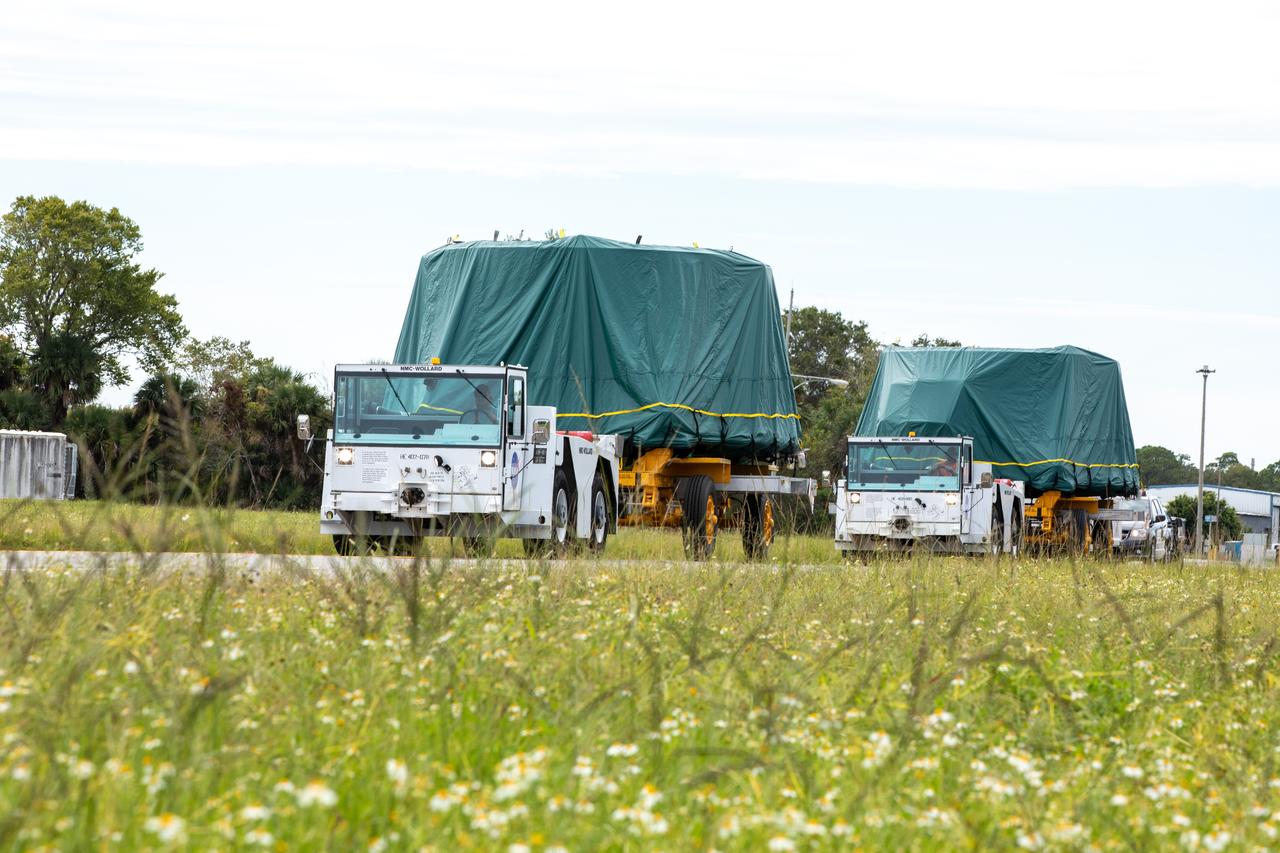

The Artemis II aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 25, 2023. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman and house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Artemis II astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Jeremy Hansen will launch from Kennedy, traveling around the Moon on the first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems.
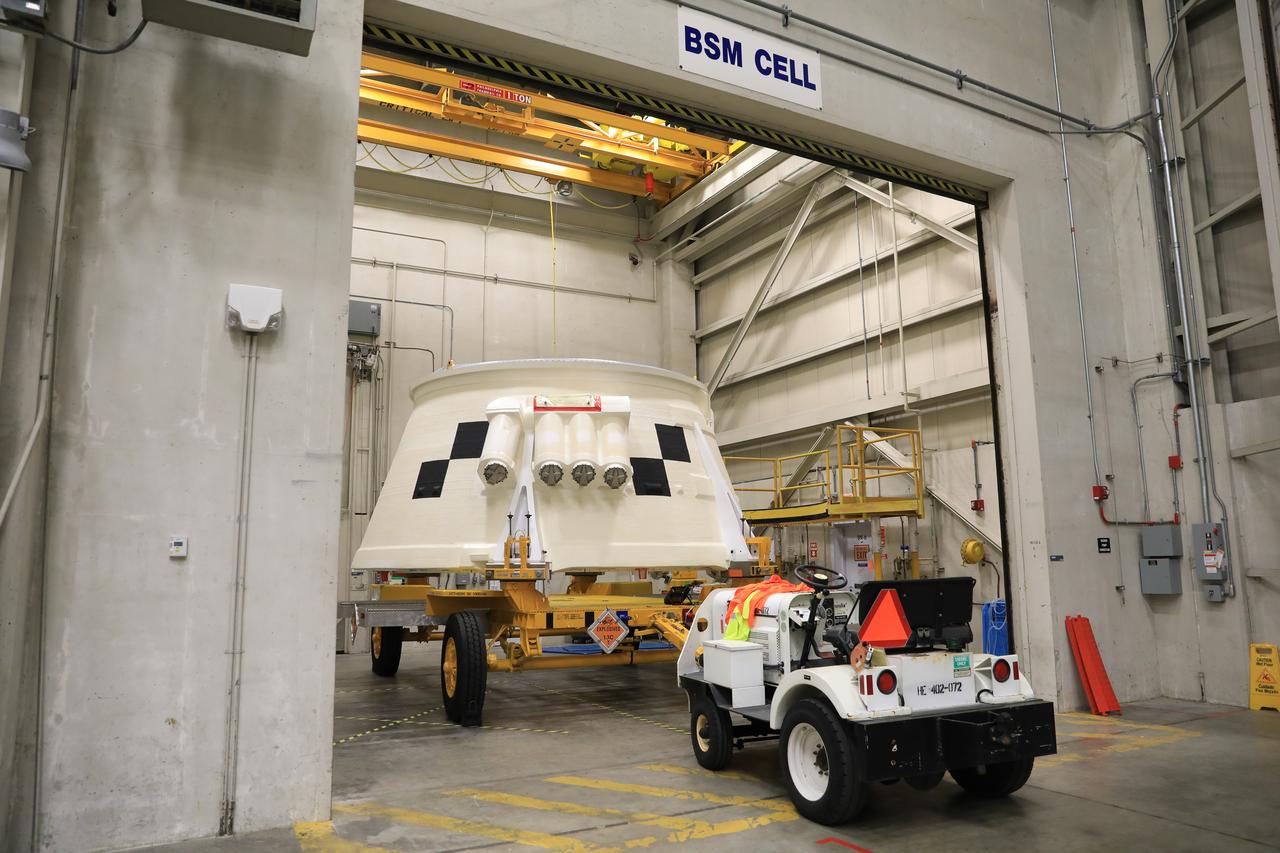

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle in a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
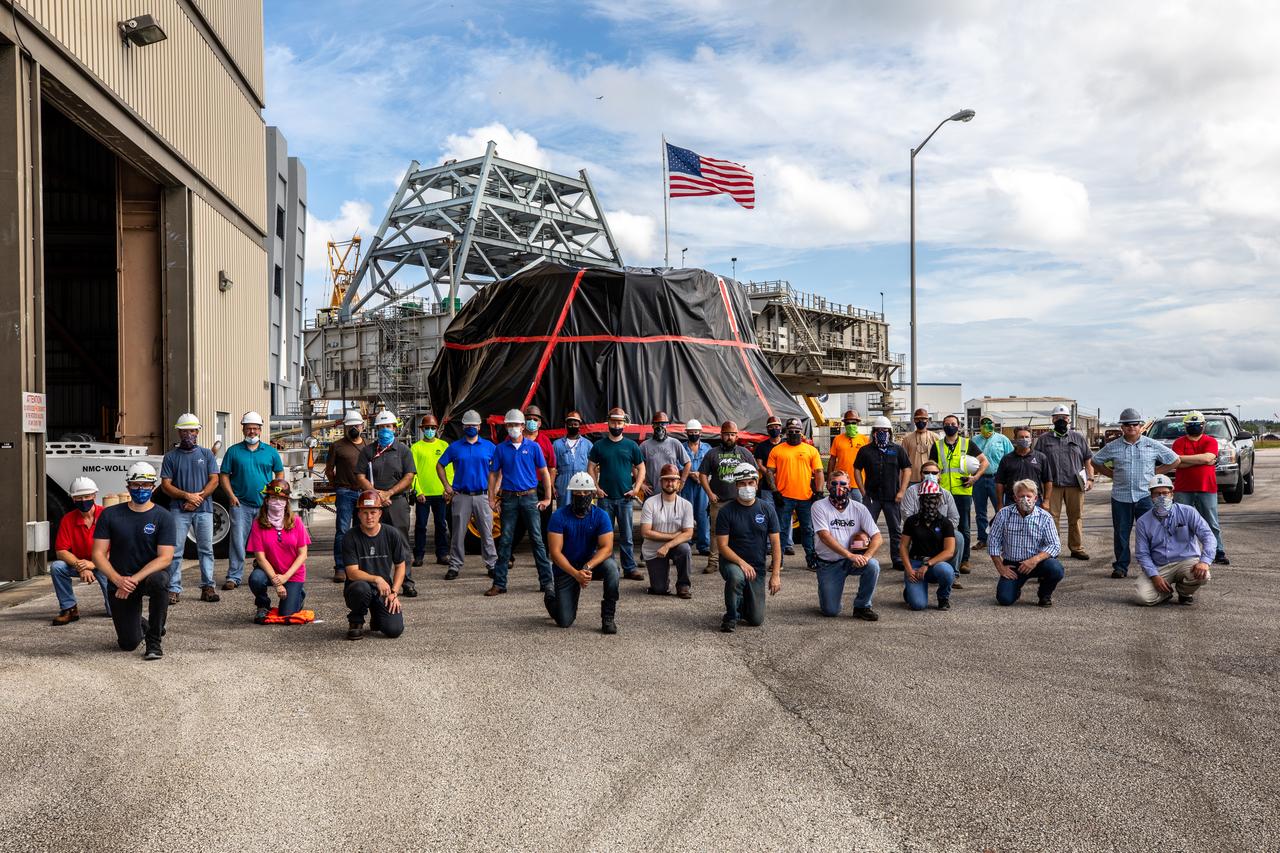

Exploration Ground Systems workers gather in front of the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020, to mark the arrival of the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters. The aft skirts were moved from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
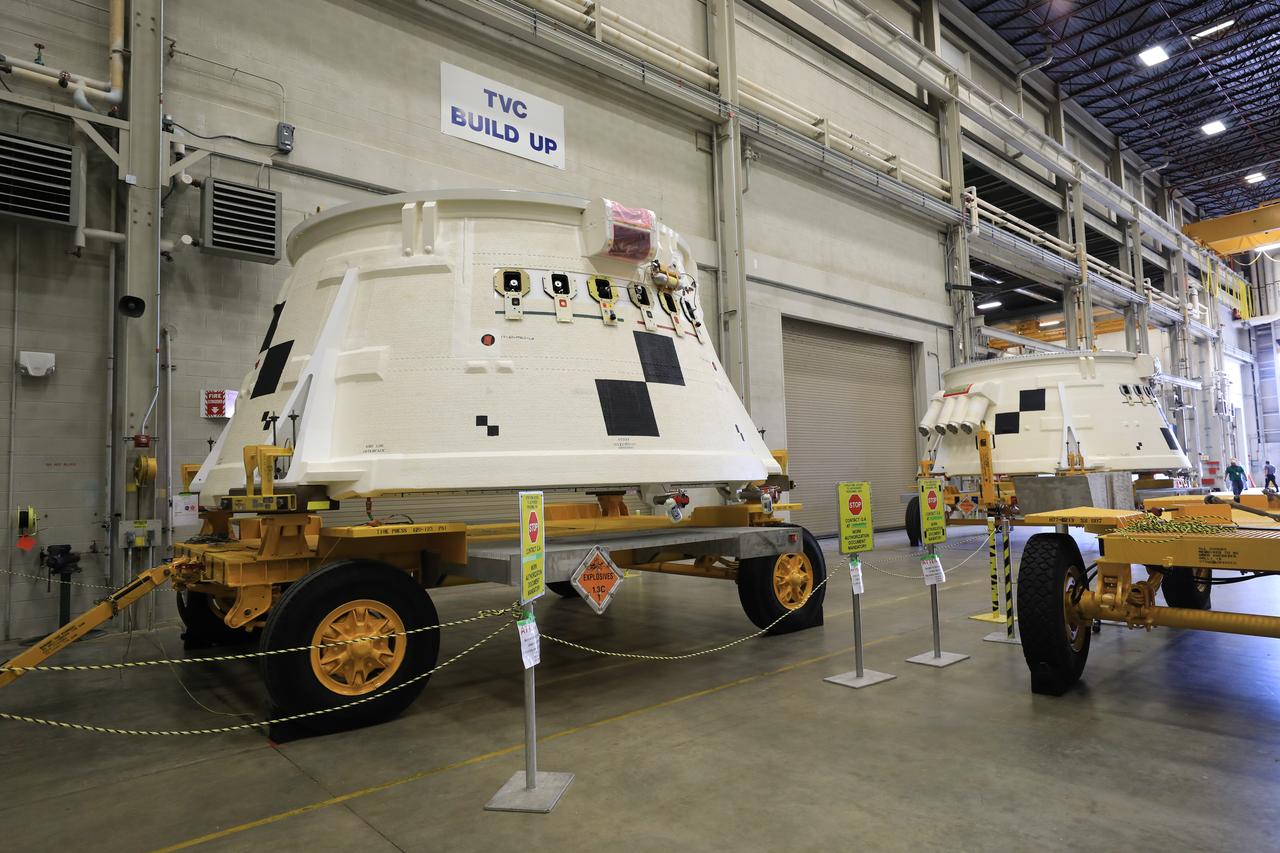

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly, and at far right is the right aft skirt assembly. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
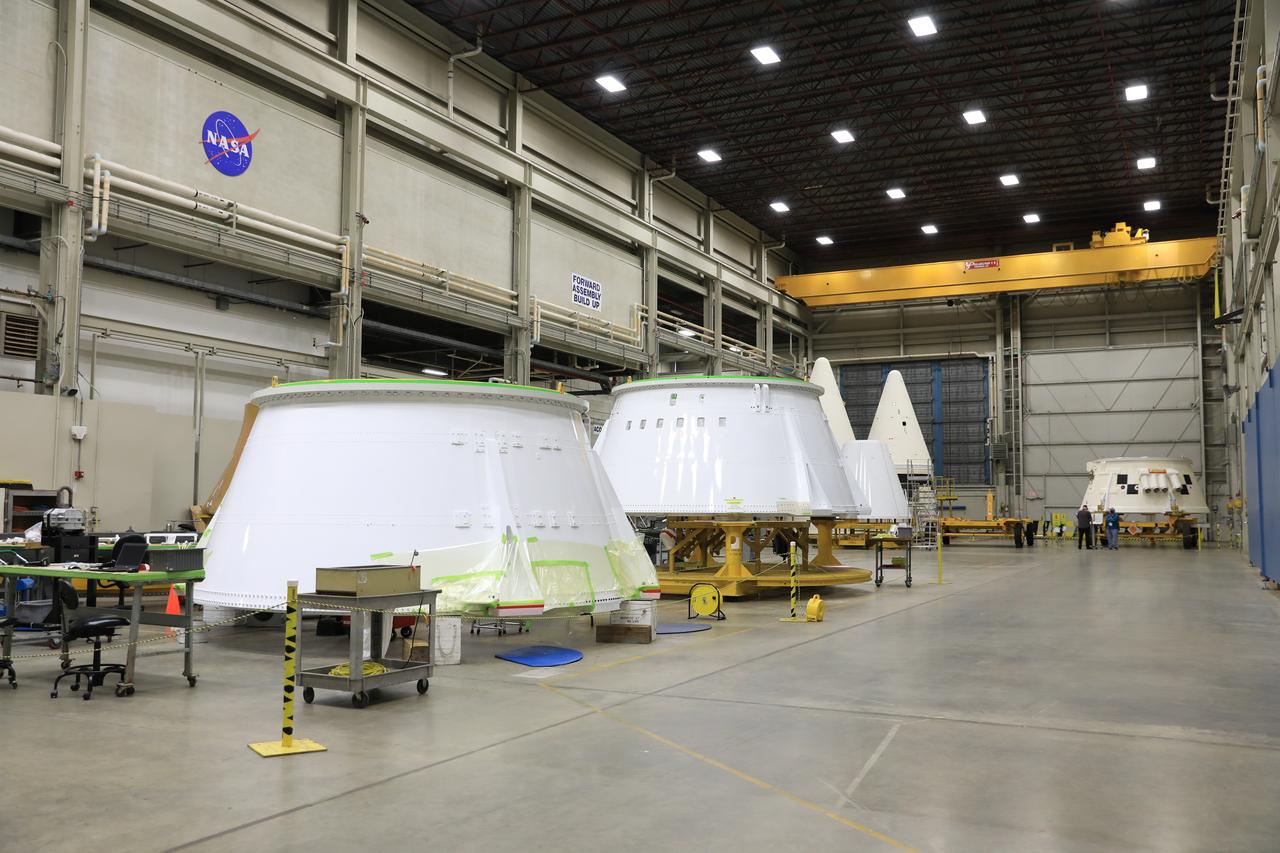

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis II aft skirt structures for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are in view at left. Behind them are the two Artemis I forward assemblies. At far right, in the distance, is the right aft skirt assembly. In the BFF, the two aft skirt assemblies are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
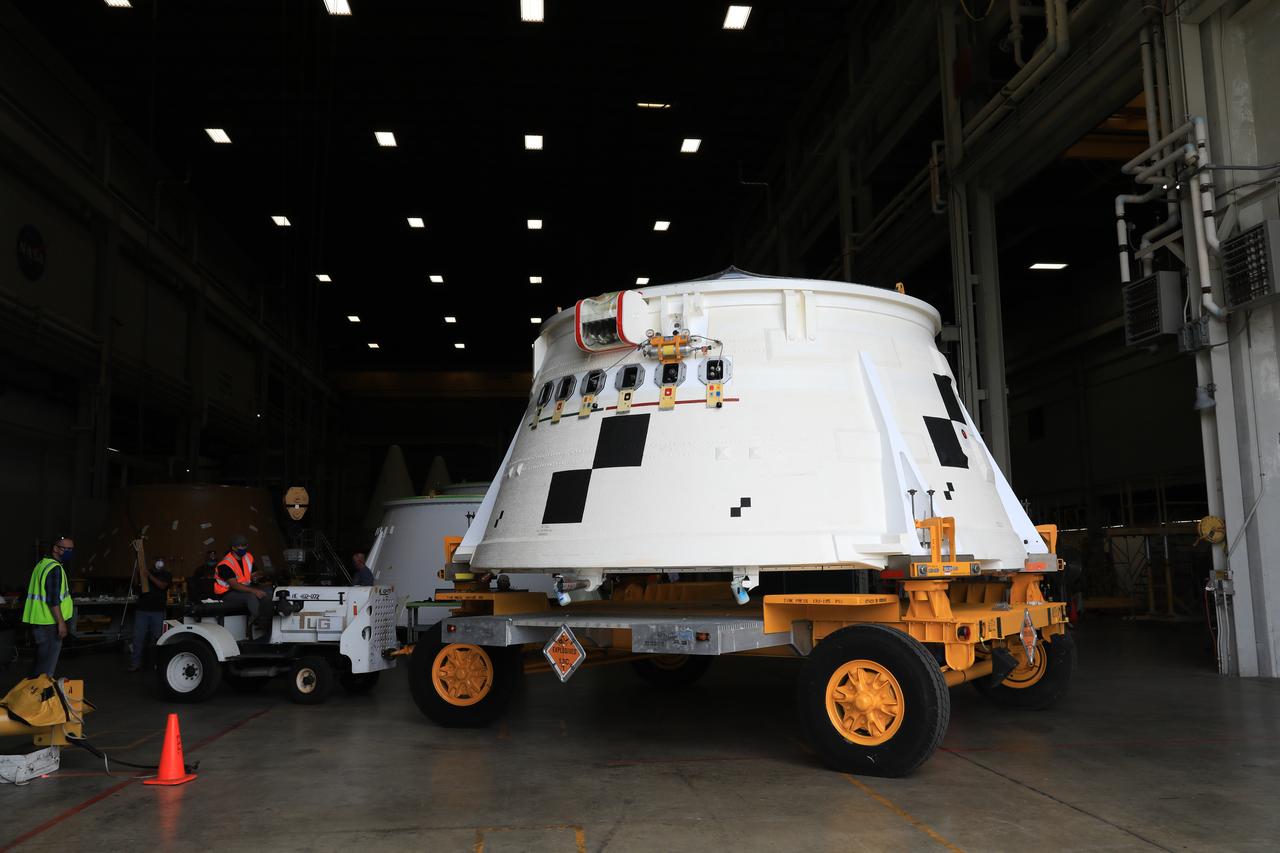

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly. Behind it to the right is the right aft skirt assembly. Also in view at far right, are the Artemis I forward assemblies, with the left assembly in front and the right assembly behind it. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
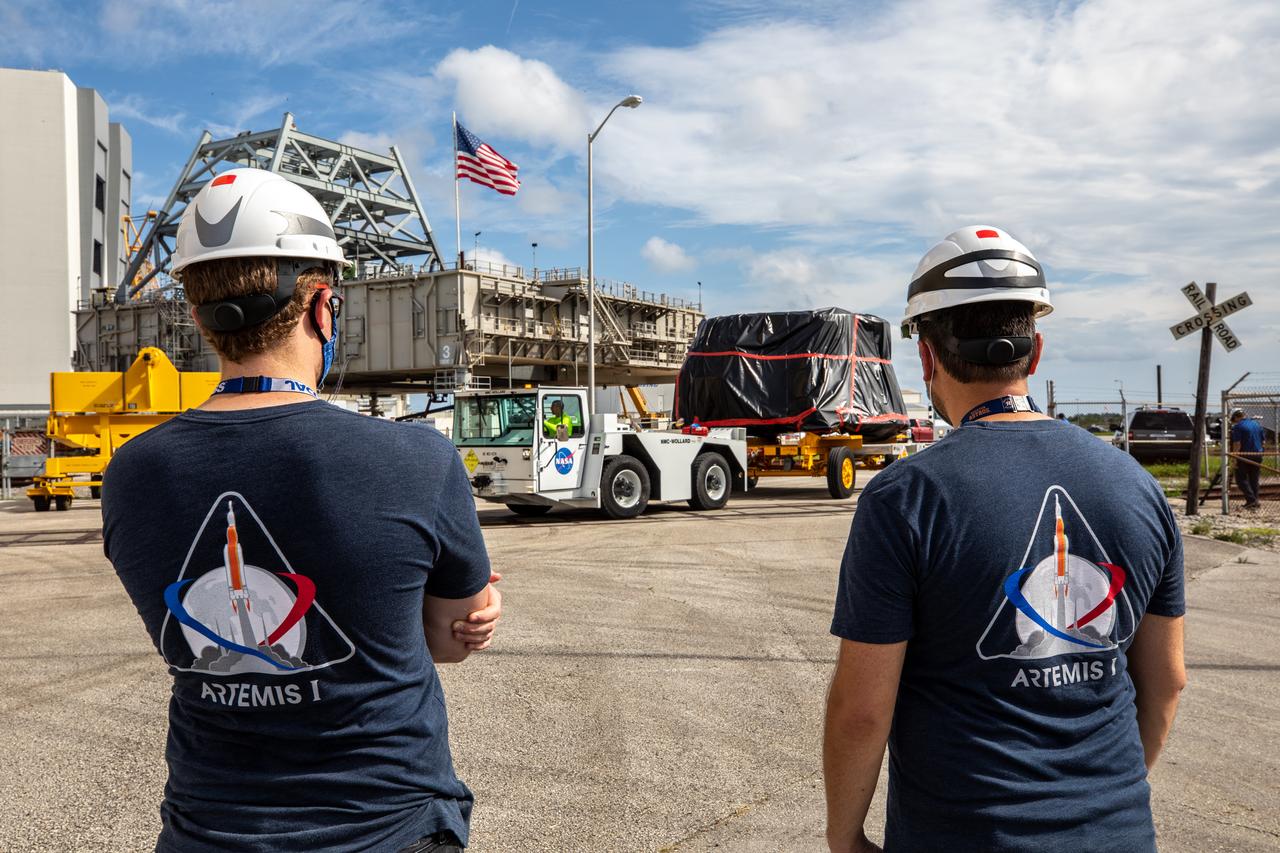

Exploration Ground Systems workers watch as the first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses a railroad track on its way to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
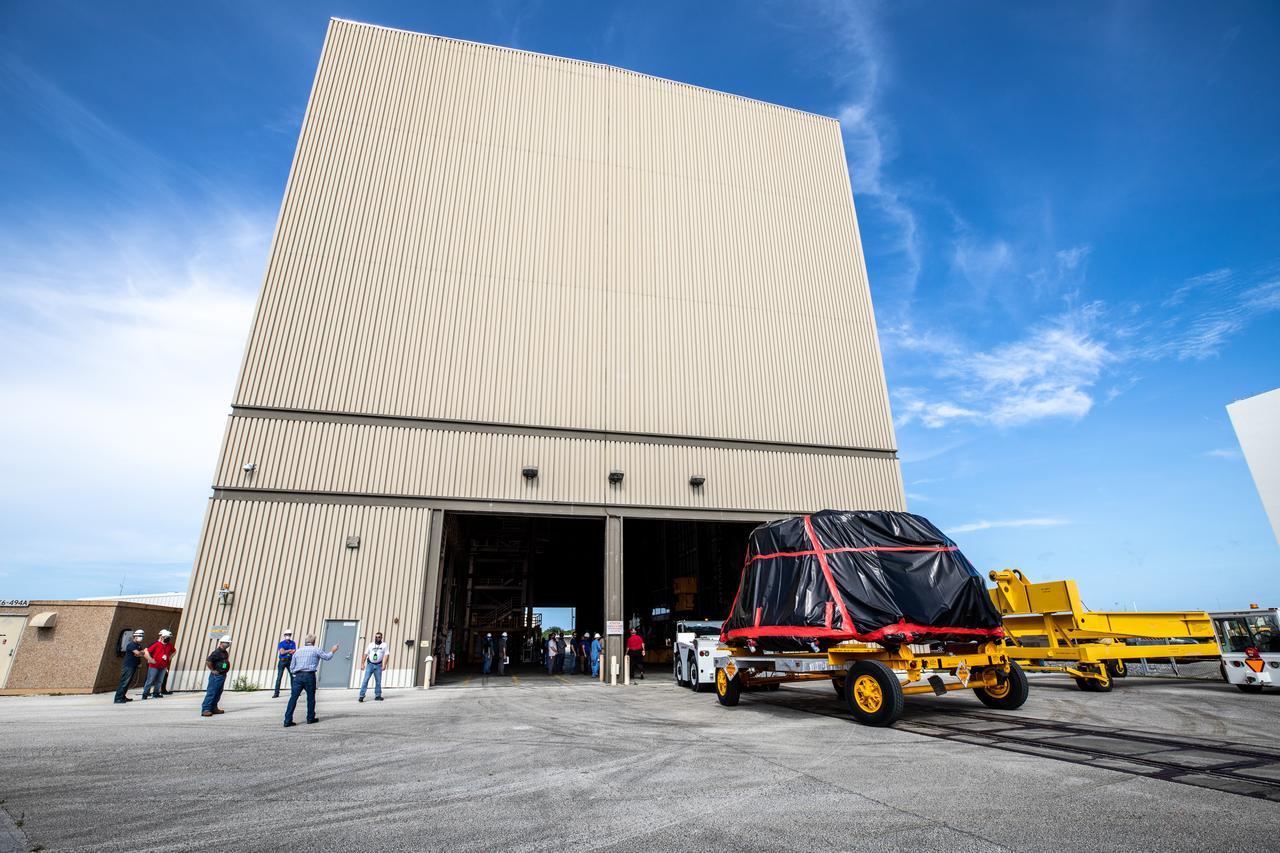

The first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
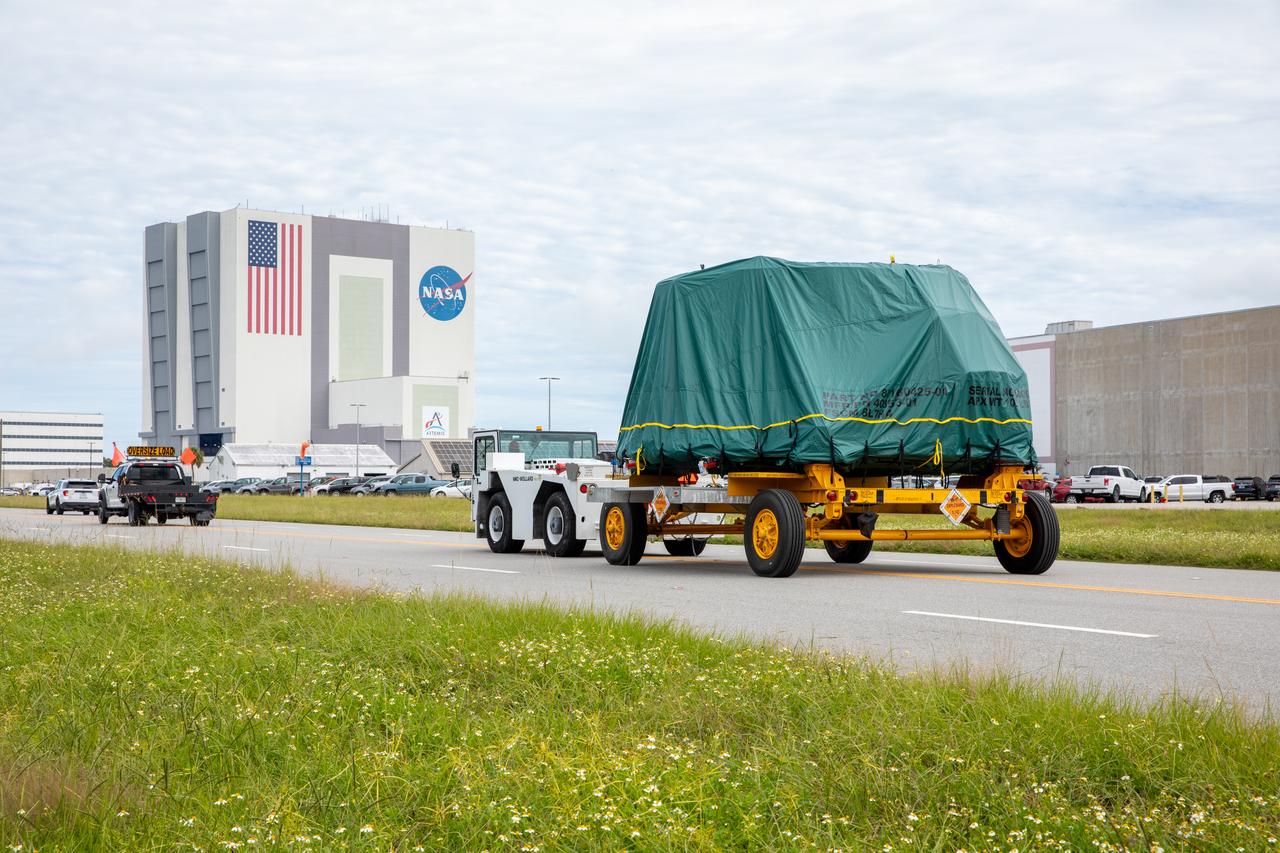

One of two Artemis II aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters is transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 25, 2023. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman and house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Artemis II astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Jeremy Hansen will launch from Kennedy, traveling around the Moon on the first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems.

One of two Artemis II aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses railroad tracks on its way from the Booster Fabrication Facility to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 25, 2023. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman and house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Artemis II astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Jeremy Hansen will launch from Kennedy, traveling around the Moon on the first crewed mission under Artemis that will test all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems.

The Artemis I aft skirts for the NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved along the road to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. In the background is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The aft skirts will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the VAB. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

Outlined with gold stripes are the hinged nose strakes, modifications made to NASA's F-18 HARV (High Alpha Research Vehicle) at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Actuated Nose Strakes for Enhanced Rolling (ANSER) were installed to fly the third and final phase in the HARV flight test project. Normally folded flush, the units -- four feet long and six inches wide -- can be opened independently to interact with the nose vortices to produce large side forces for control. Early wind tunnel tests indicated that the strakes would be as effective in yaw control at high angles of attack as rudders are at lower angles. Testing involved evaluation of the strakes by themselves as well as combined with the aircraft's Thrust Vectoring System. The strakes were designed by NASA's Langley Research Center, then installed and flight tested at Dryden.
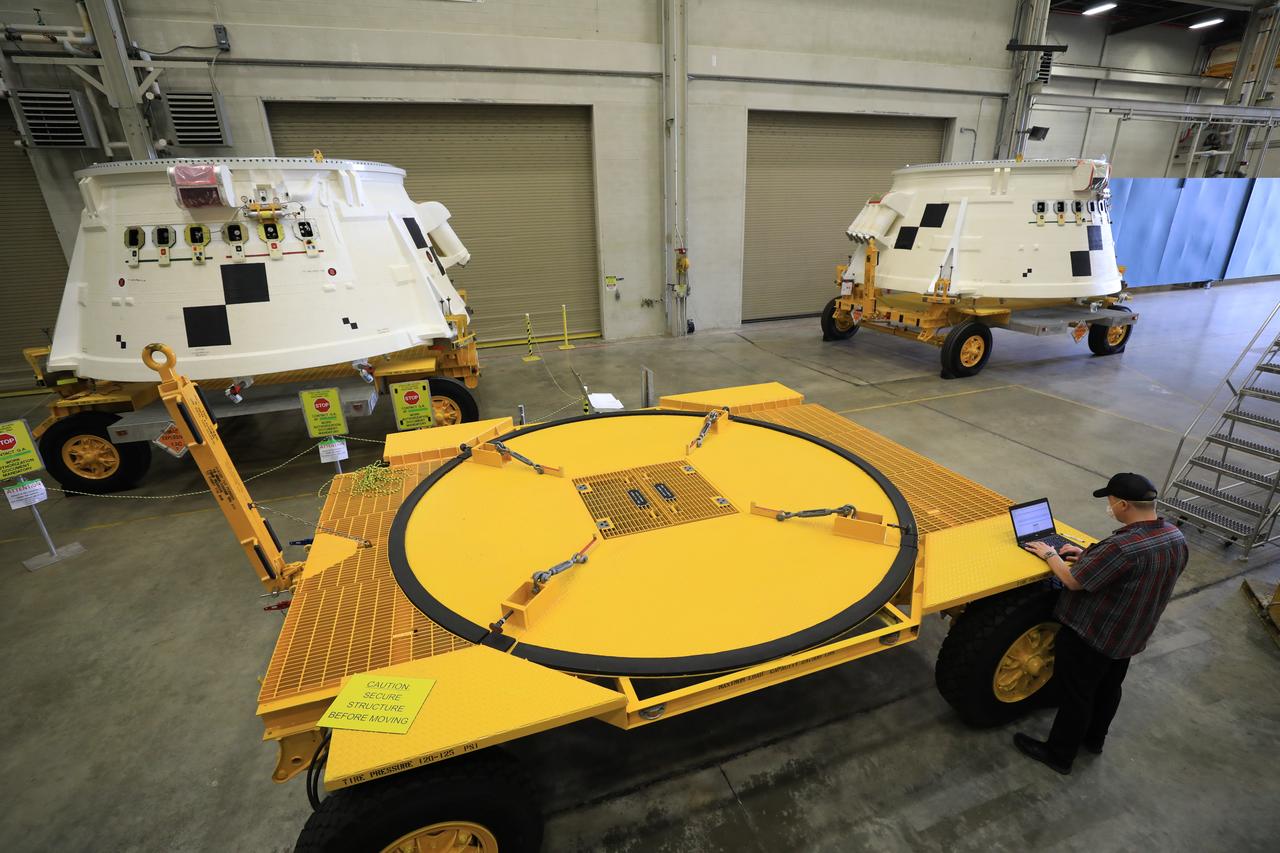

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view at left is the left aft skirt assembly, and at right is the right aft skirt assembly. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
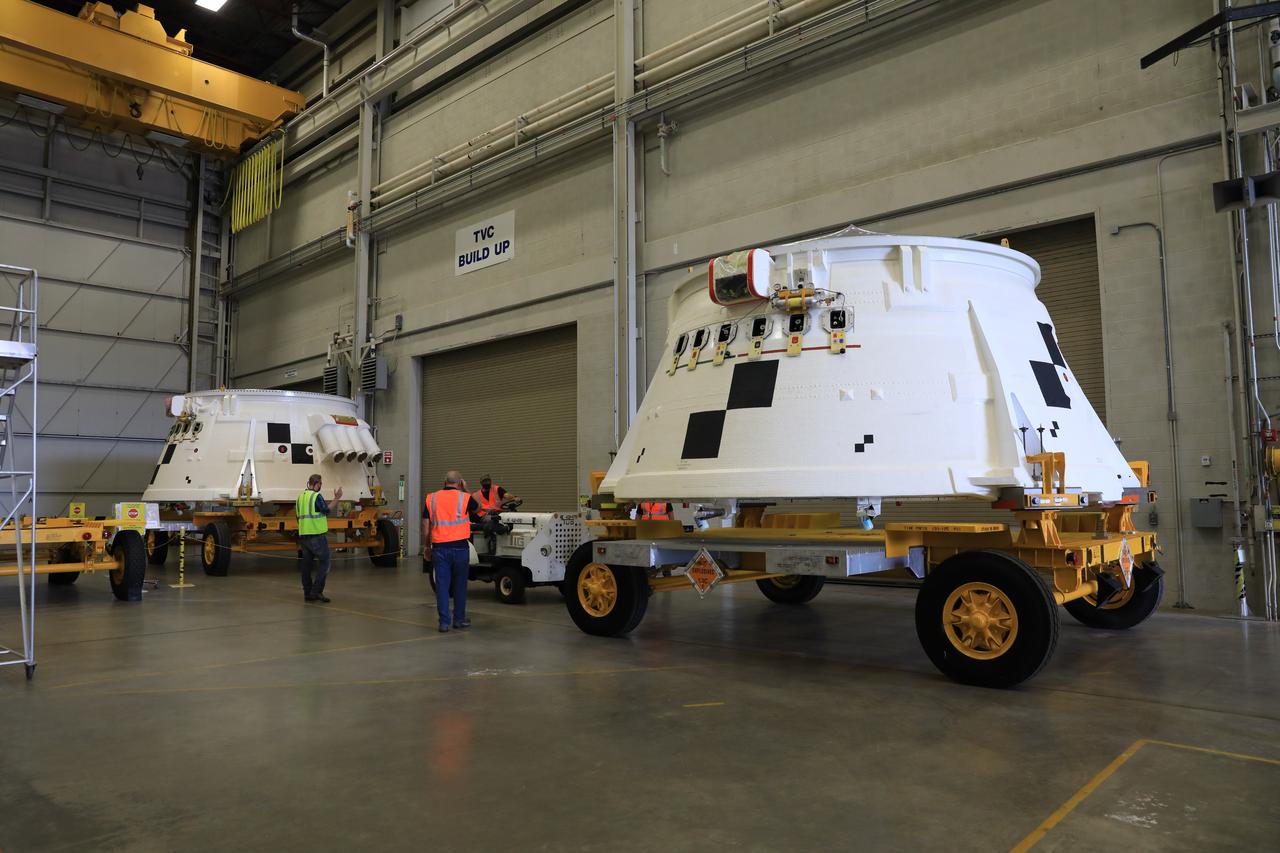

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are moved out of their test cells and are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
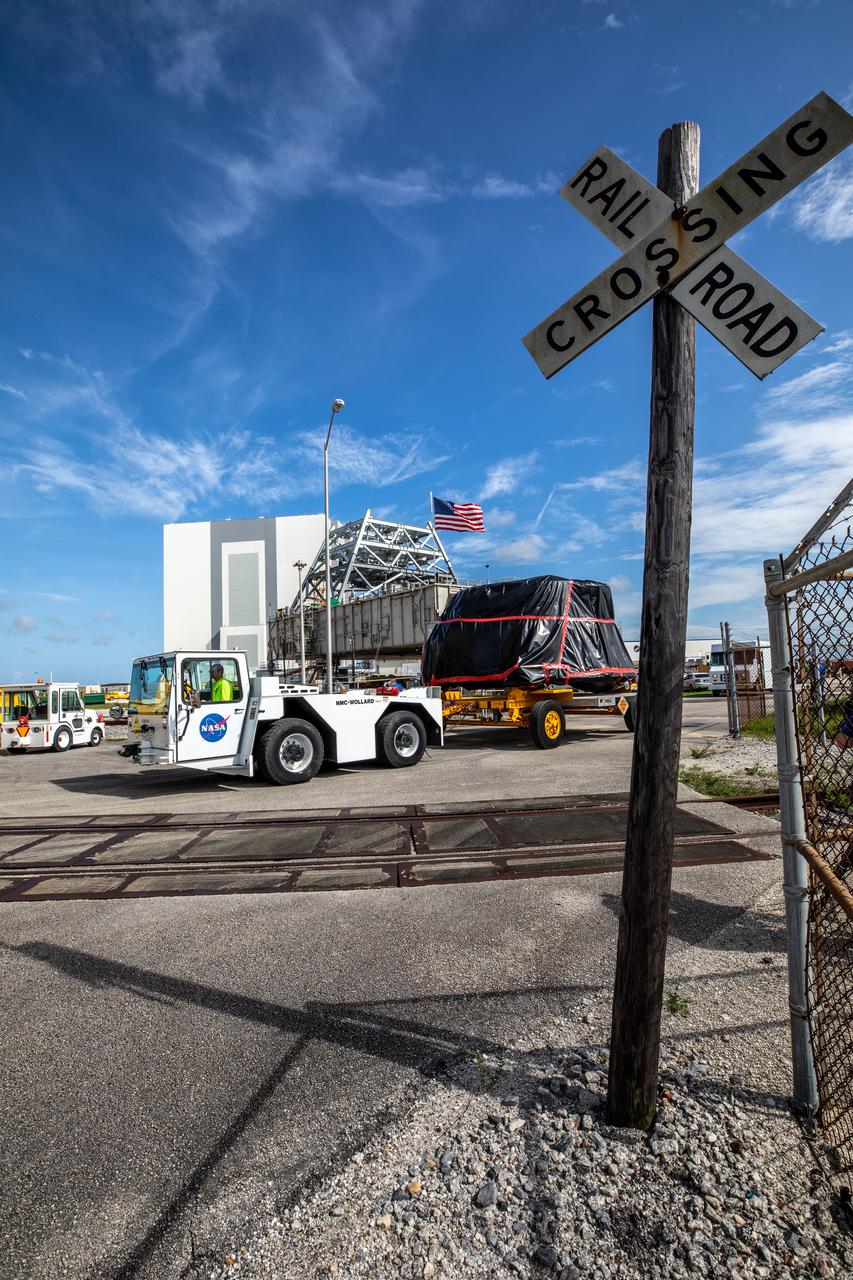

One of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses a railroad track on its way to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
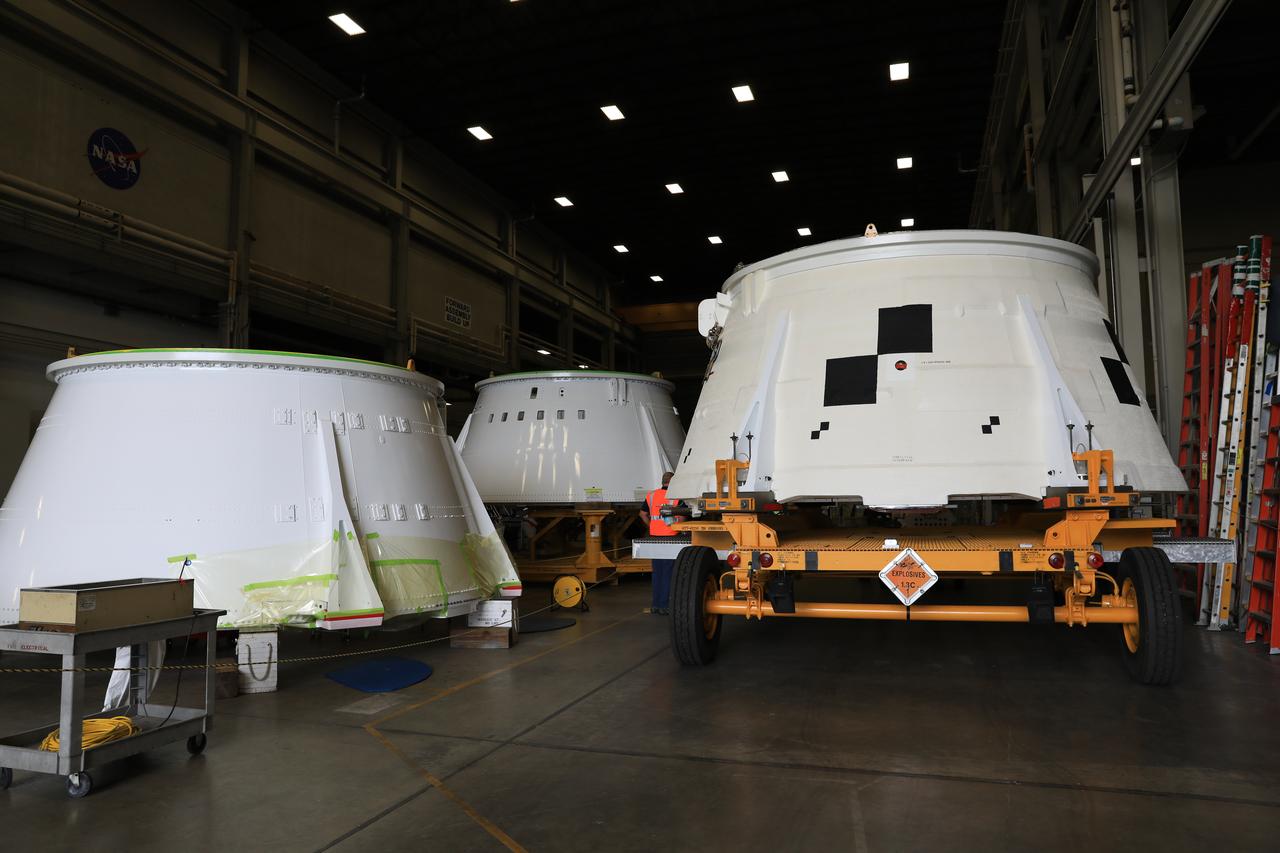

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are being readied for their move to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 9, 2020. In view, the left aft skirt assembly is attached to a move vehicle and moved out of a test cell. The Artemis II aft skirt structures are in view at left. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
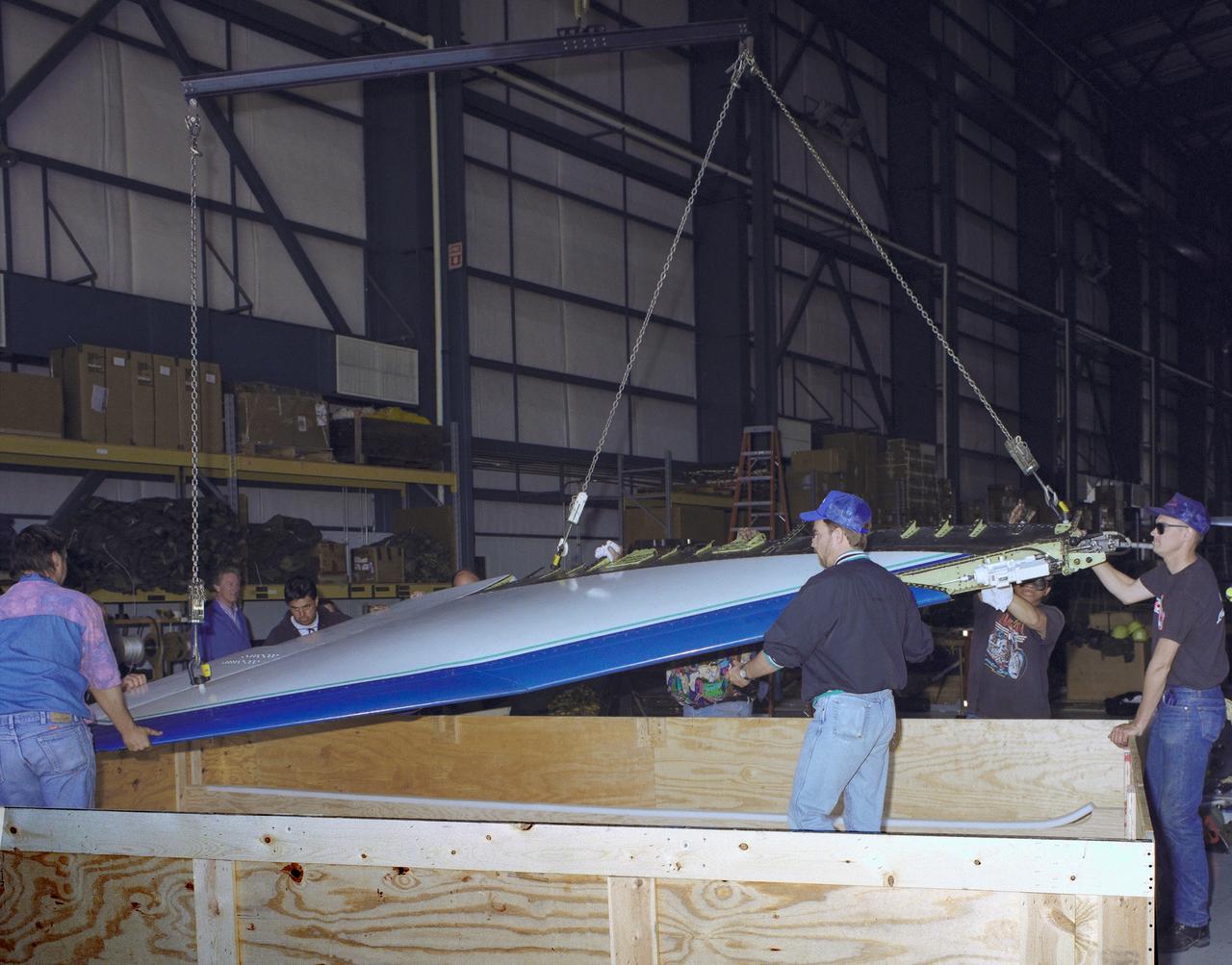

The right wing of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator Aircraft is seen here being put into a shipping container May 18, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, by U.S. and German members of the program. To fit inside an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport, which was used to ferry the X-31 to Europe on May 22, 1995, the right wing had to be removed. Manching, Germany, was used as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for participation in the Paris Air Show. At the air show on June 11 through the 18th, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in an Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995, and off loaded at Dryden the 27th. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
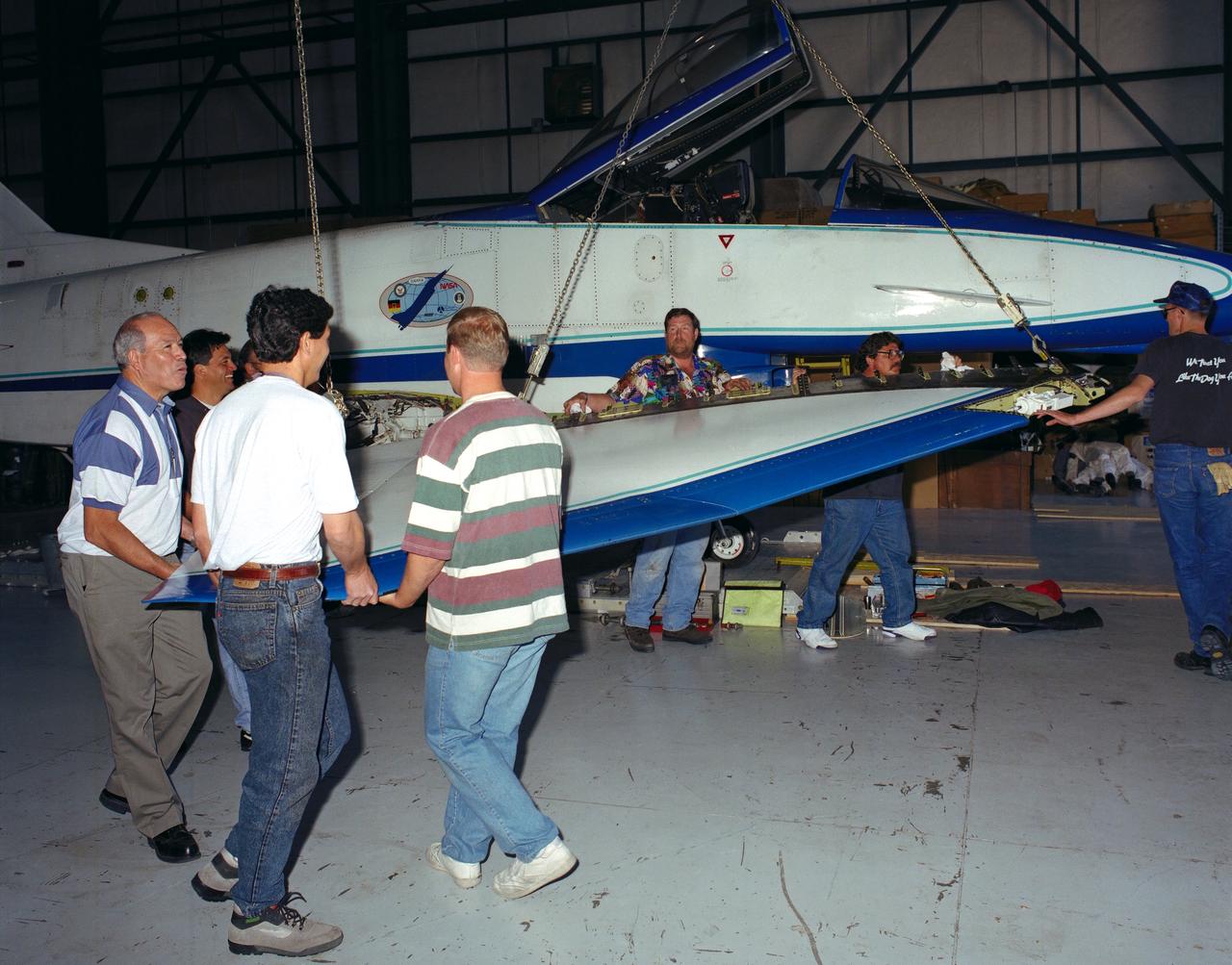

U.S. and German personnel of the X-31 Enhanced Fighter Maneuverability Technology Demonstrator aircraft program removing the right wing of the aircraft, which was ferried from Edwards Air Force Base, California, to Europe on May 22, 1995 aboard an Air Force Reserve C-5 transport. The X-31, based at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center was ferried to Europe and flown in the Paris Air Show in June. The wing of the X-31 was removed on May 18, 1995, to allow the aircraft to fit inside the C-5 fuselage. Officials of the X-31 project used Manching, Germany, as a staging base to prepare the aircraft for the flight demonstration. At the air show, the X-31 demonstrated the value of using thrust vectoring (directing engine exhaust flow) coupled with advanced flight control systems to provide controlled flight at very high angles of attack. The aircraft arrived back at Edwards in a Air Force Reserve C-5 on June 25, 1995 and off loaded at Dryden June 27. The X-31 aircraft was developed jointly by Rockwell International's North American Aircraft Division (now part of Boeing) and Daimler-Benz Aerospace (formerly Messerschmitt-Bolkow-Blohm), under sponsorship by the U.S. Department of Defense and the German Federal Ministry of Defense.
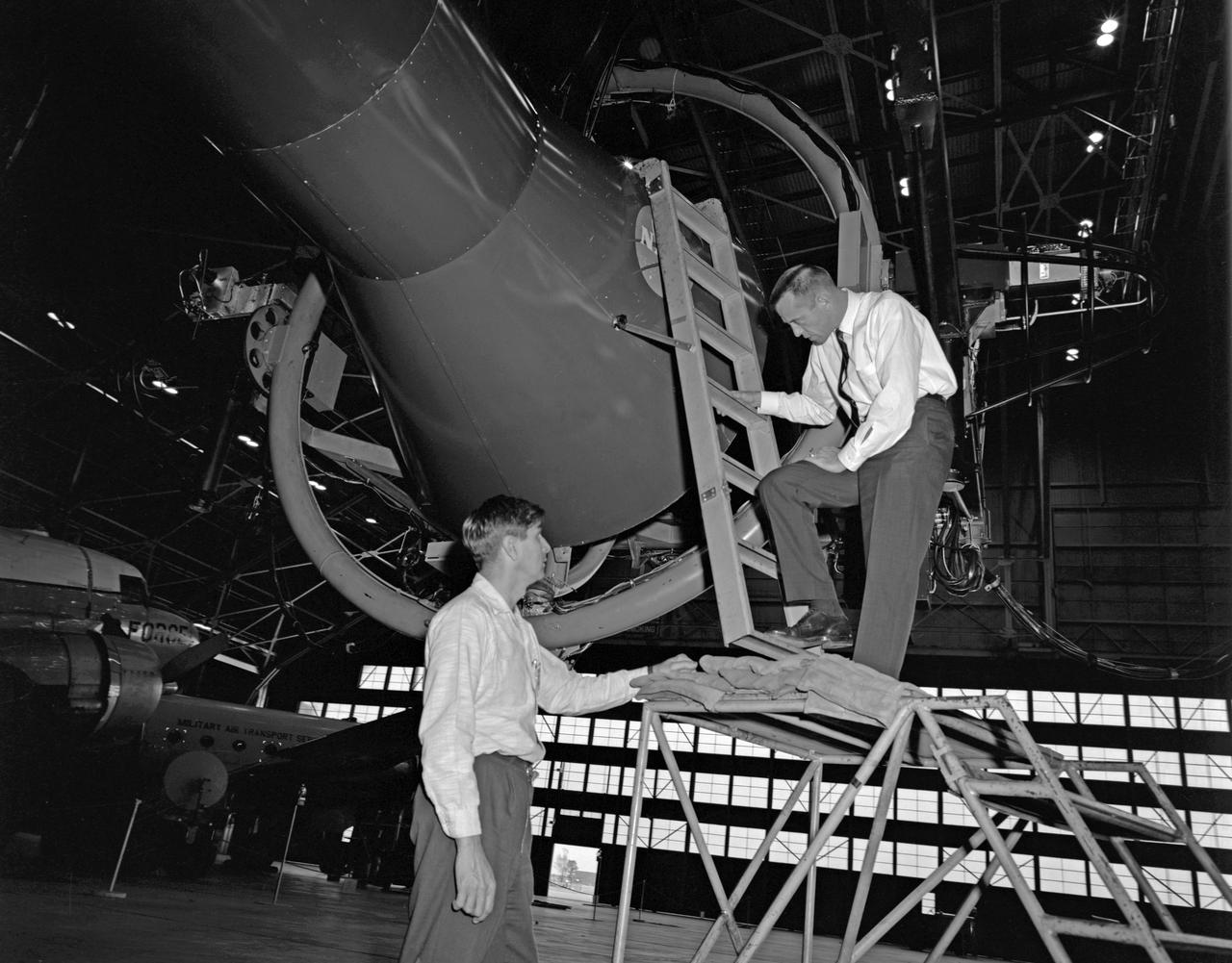

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.
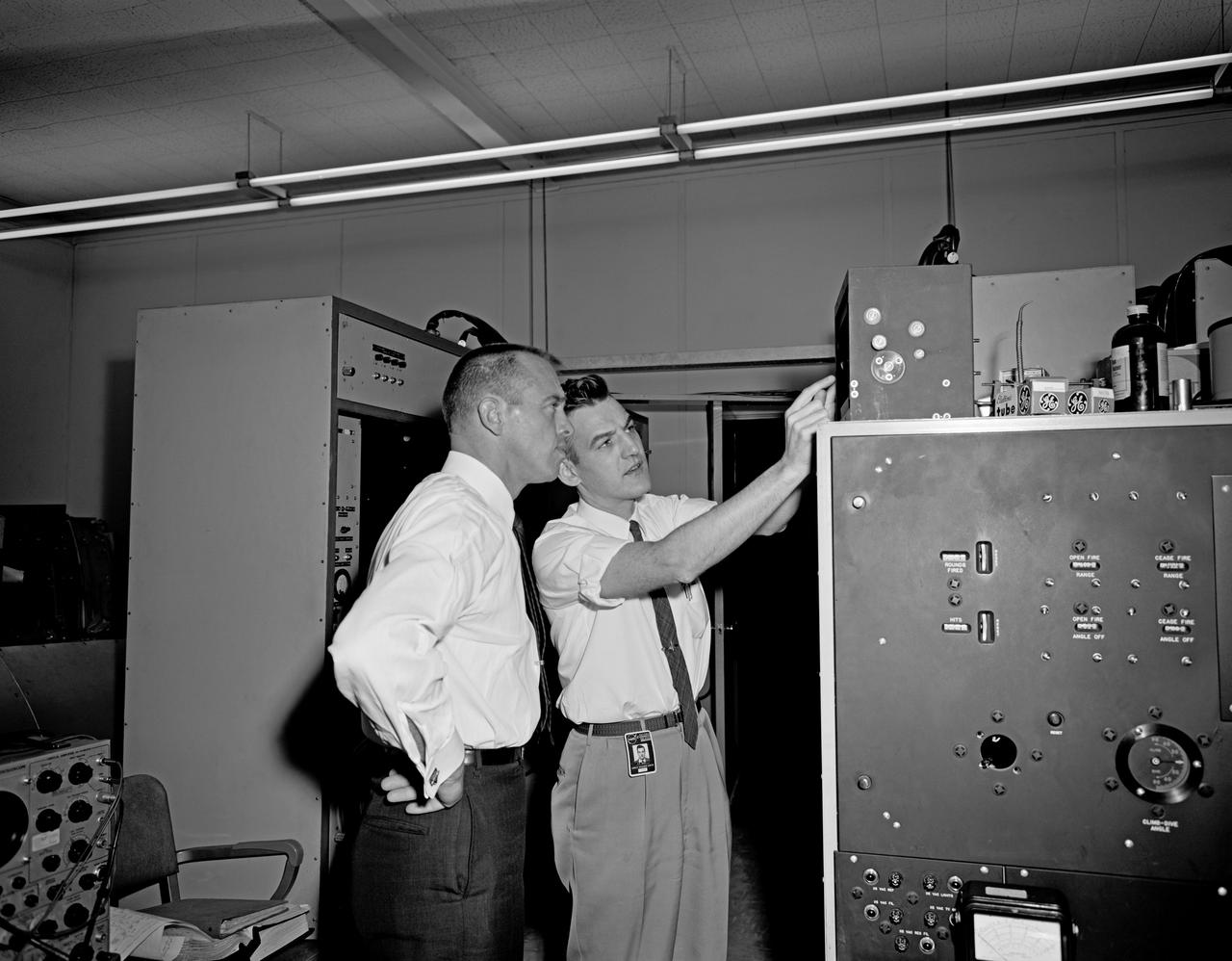

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.