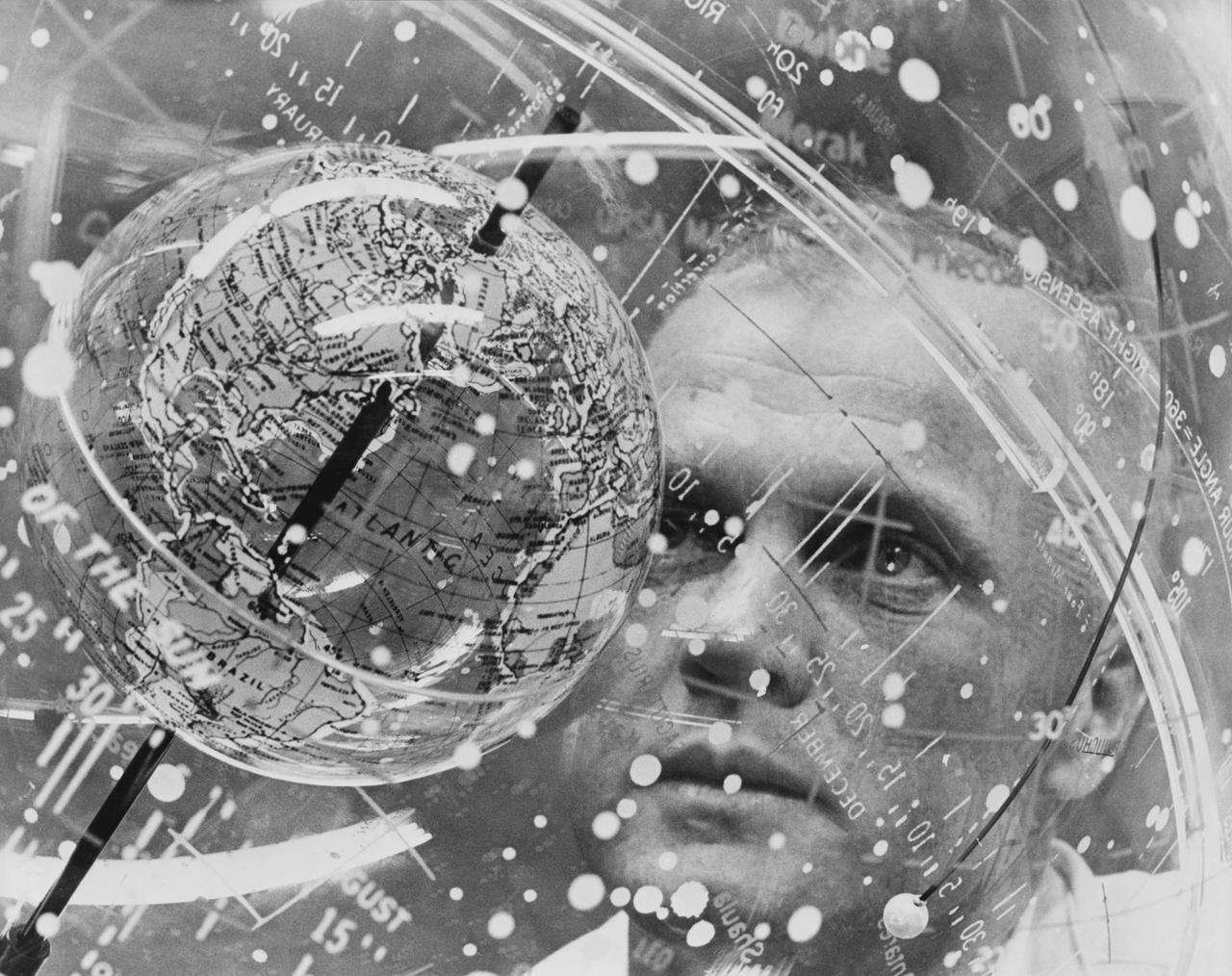

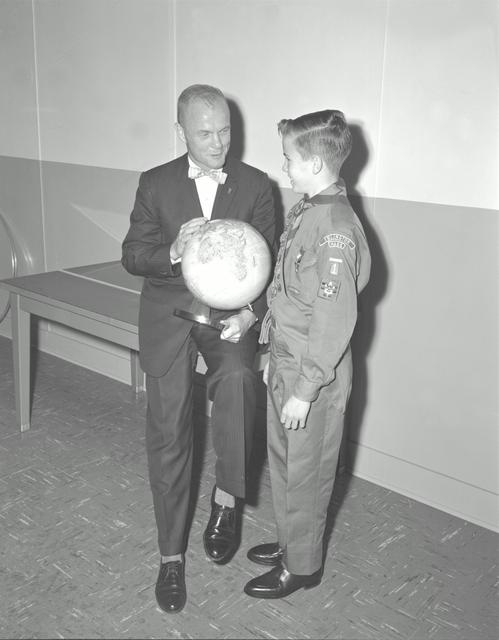
S61-04623 (1961) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. looks into a Celestial Training Device (globe) during training in the Aeromedical Laboratory at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
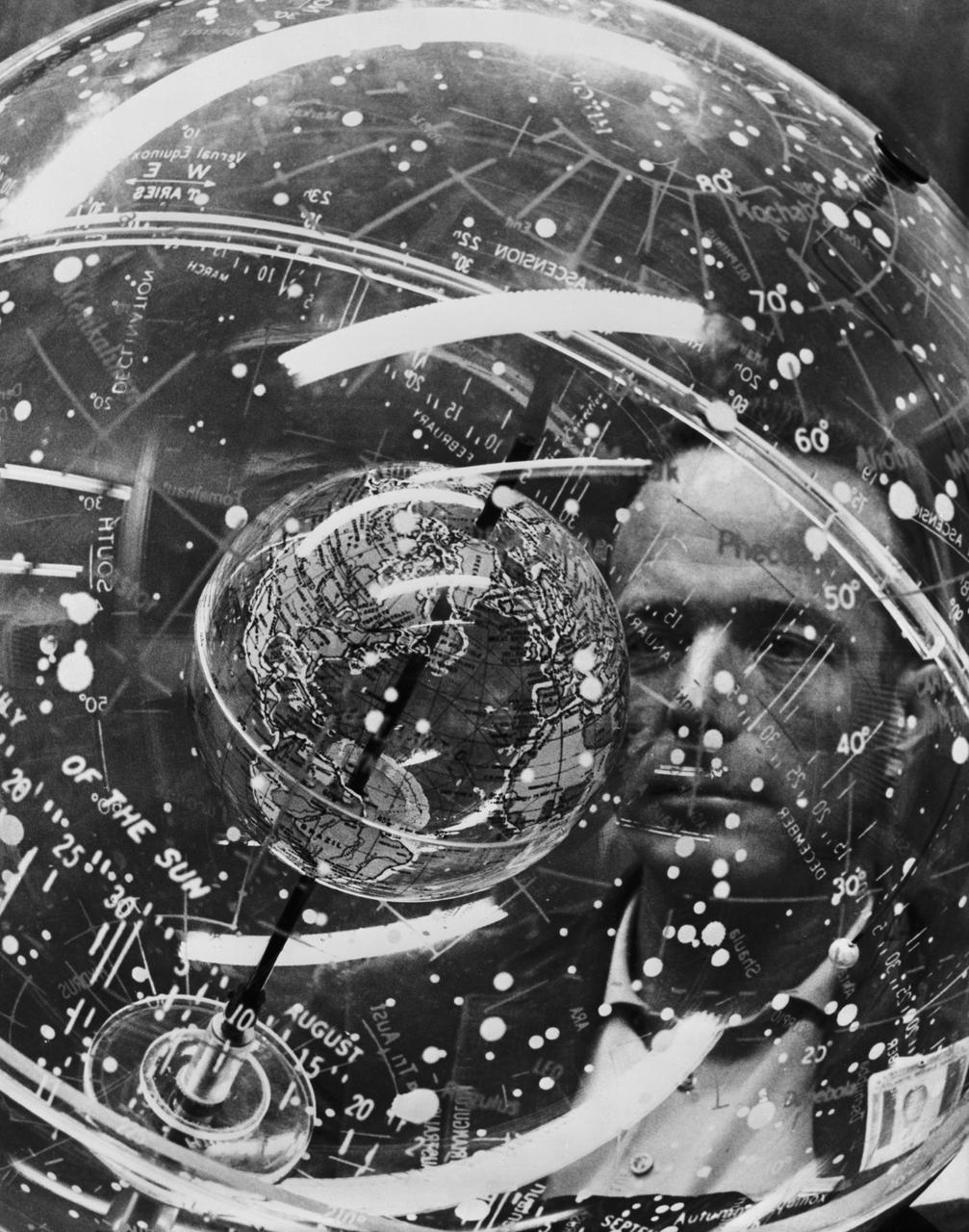

S61-04621 (1961) --- Astronaut M. Scott Carpenter looks into a Celestial Training Device (globe) during training in the Aeromedical Laboratory at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
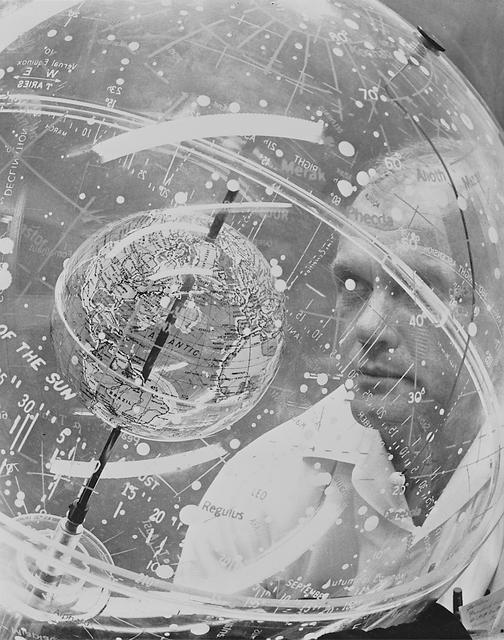

S61-04622 (1961) --- Mercury astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. looks into a Celestial Training Device (globe) during training in the Aeromedical Laboratory at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
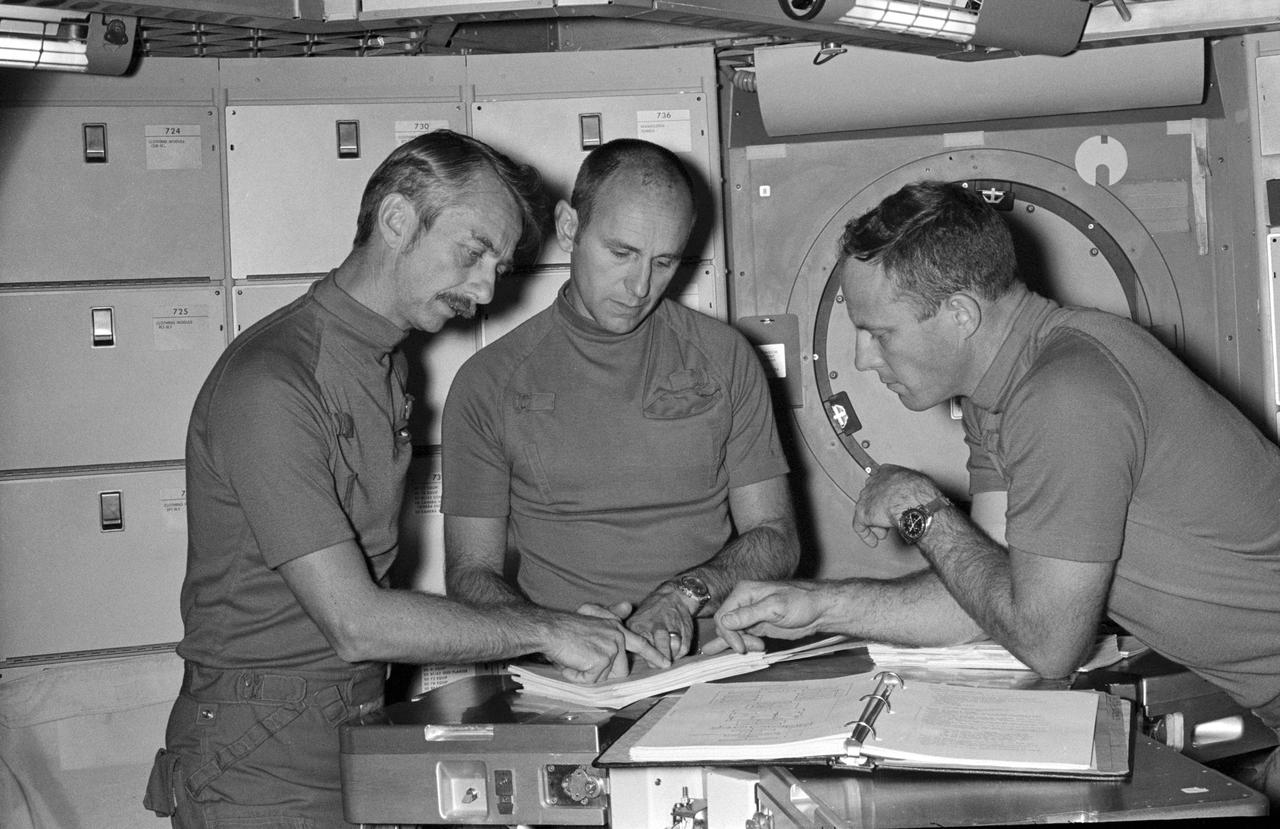

S73-28419 (16 June 1973) --- The three prime crewmen of the Skylab 3 mission check over flight data during a training session in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). They are, from left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; and astronauts Alan L. Bean, commander, and Jack R. Lousma, pilot. The 56-day, second manned Skylab Earth-orbital mission is scheduled for liftoff in the latter part of July 1973. Photo credit: NASA
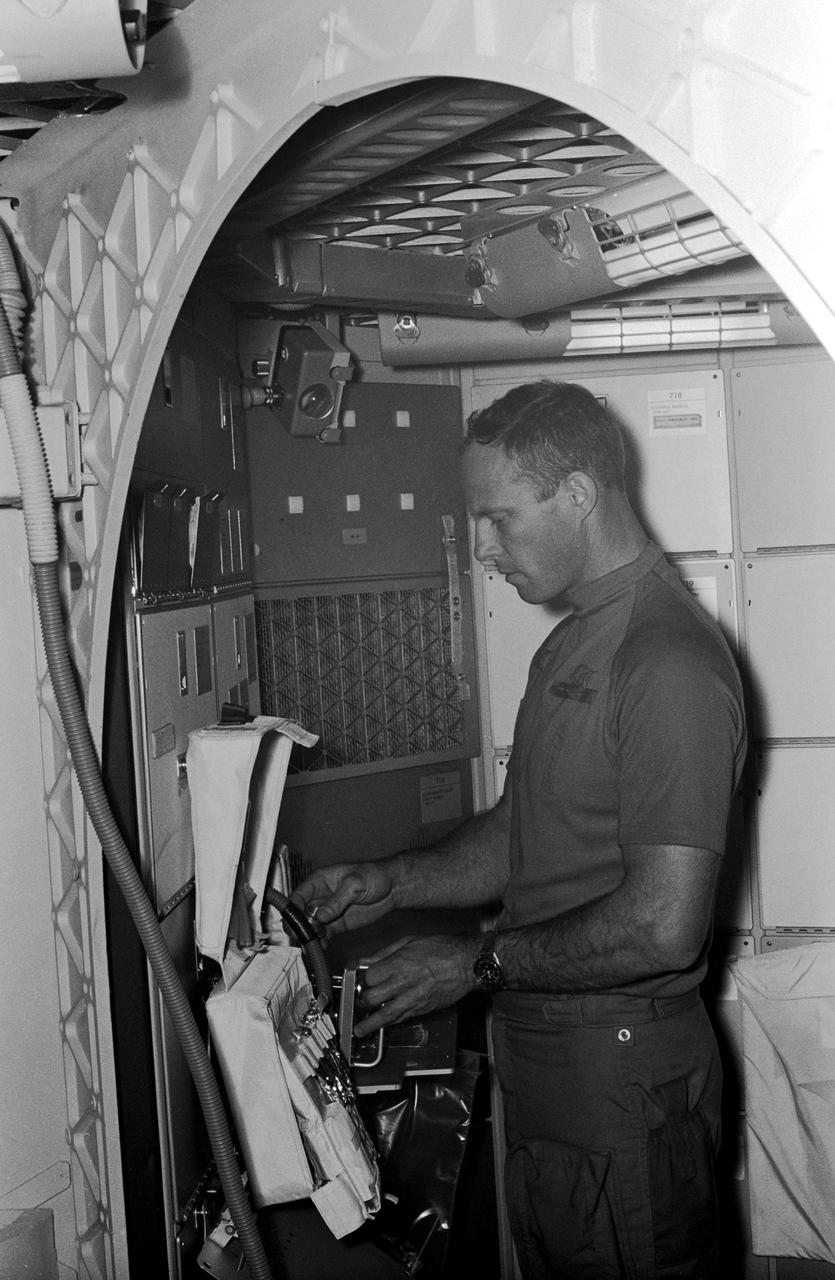

S73-28423 (16 June 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, reaches into a medical kit, part of the Inflight Medical Support System (IMSS), during training for the second manned Skylab Earth-orbital mission. This activity took place in the OWS trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Other Skylab 3 crewmen are astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander, and scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA
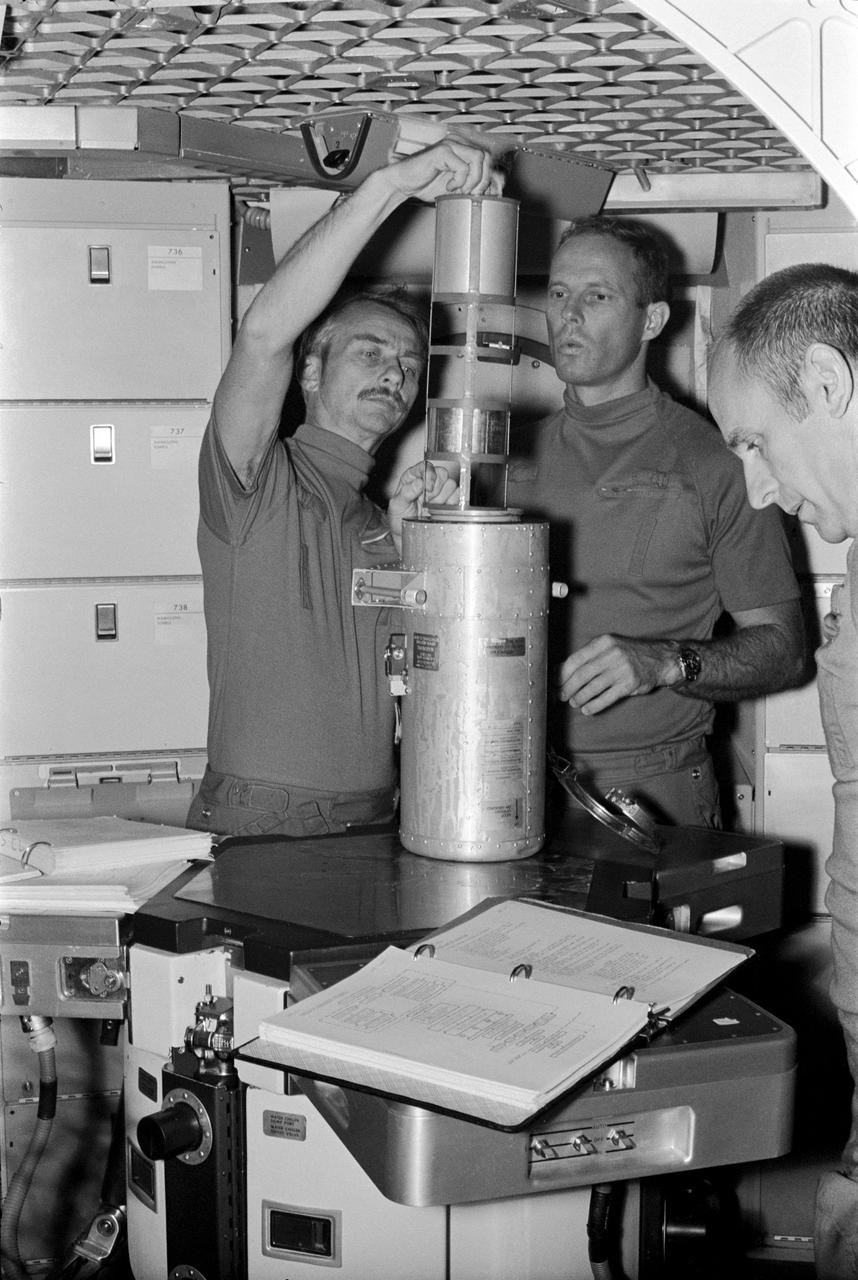

S73-28420 (16 June 1973) --- The three prime crewmen of the Skylab 3 mission check over flight data during a training session in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Skylab 3 crew work with Inflight Medical Support System (IMSS) resupply container atop the food table in the OWS. They are from left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; and astronauts Jack R. Lousma, pilot; and Alan L. Bean, commander. Photo credit: NASA
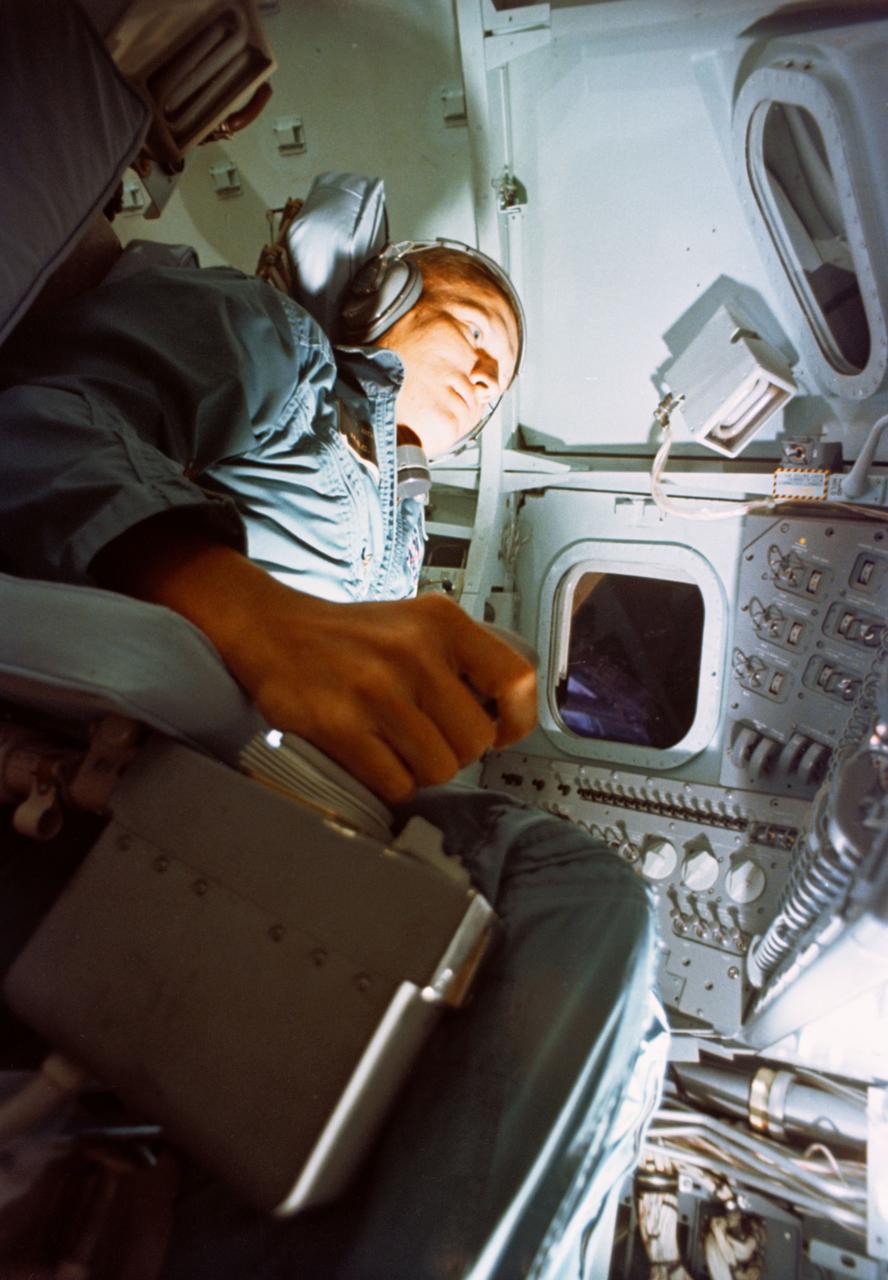

S67-50590 (1867) --- Astronaut Frank Borman, assigned duty as commander of the Apollo 8 mission, participates in a training exercise in the Apollo Mission simulator in the Mission Simulation and training Facility, Building 5, at the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA
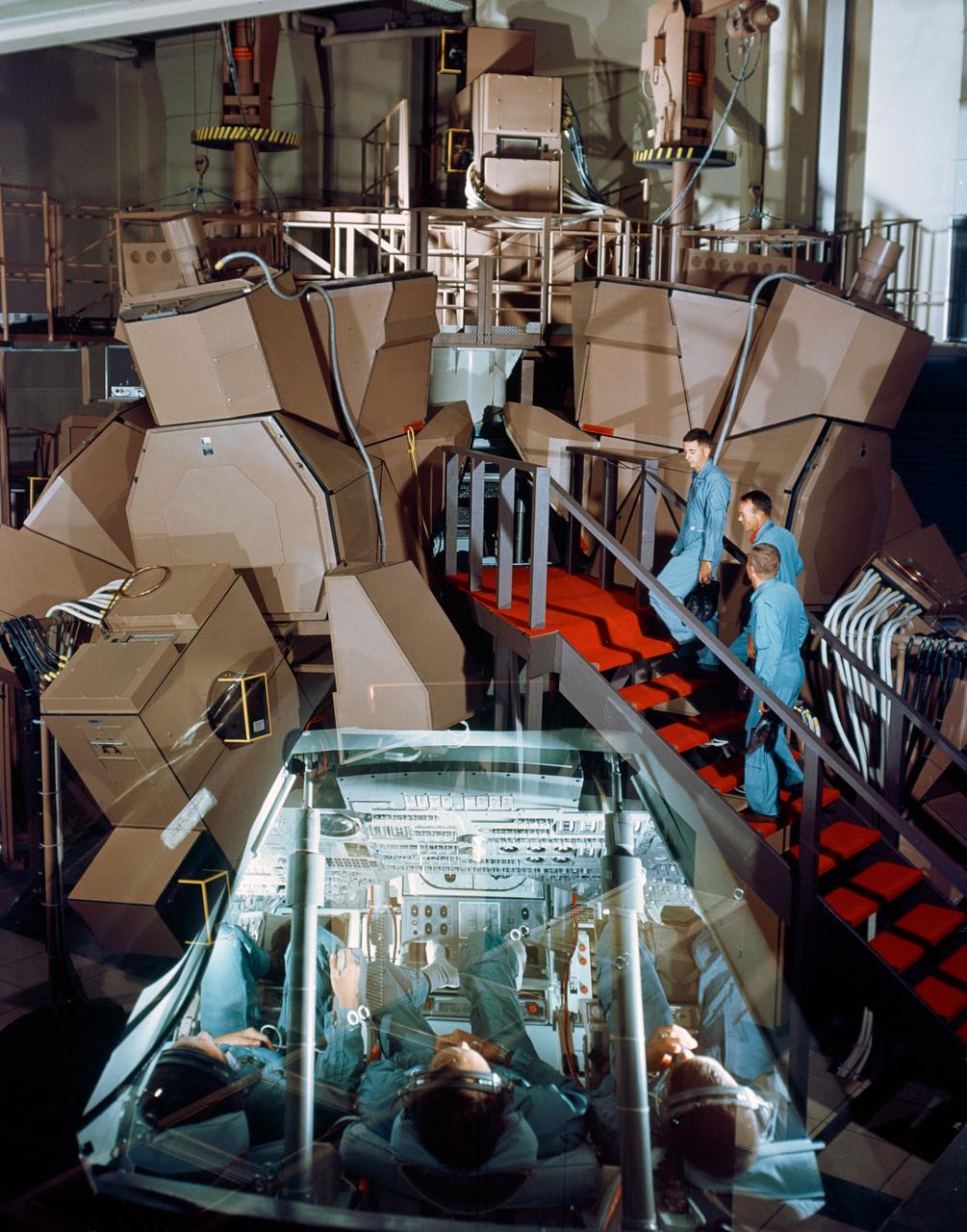

S67-50585 (1967) --- This is an intentional double exposure showing the Apollo Mission Simulator in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Building 5 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. In the exterior view astronauts William A. Anders, Michael Collins, and Frank Borman (reading from top of stairs) are about to enter the simulator. The interior view shows the three astronauts in the simulator. They are (left to right) Borman, Collins, and Anders. Photo credit: NASA

S62-00992 (1961) --- Mercury astronaut John Glenn looks into a Celestial Training Device (globe) during training in the Aeromedical Laboratory at Cape Canaveral, Florida.
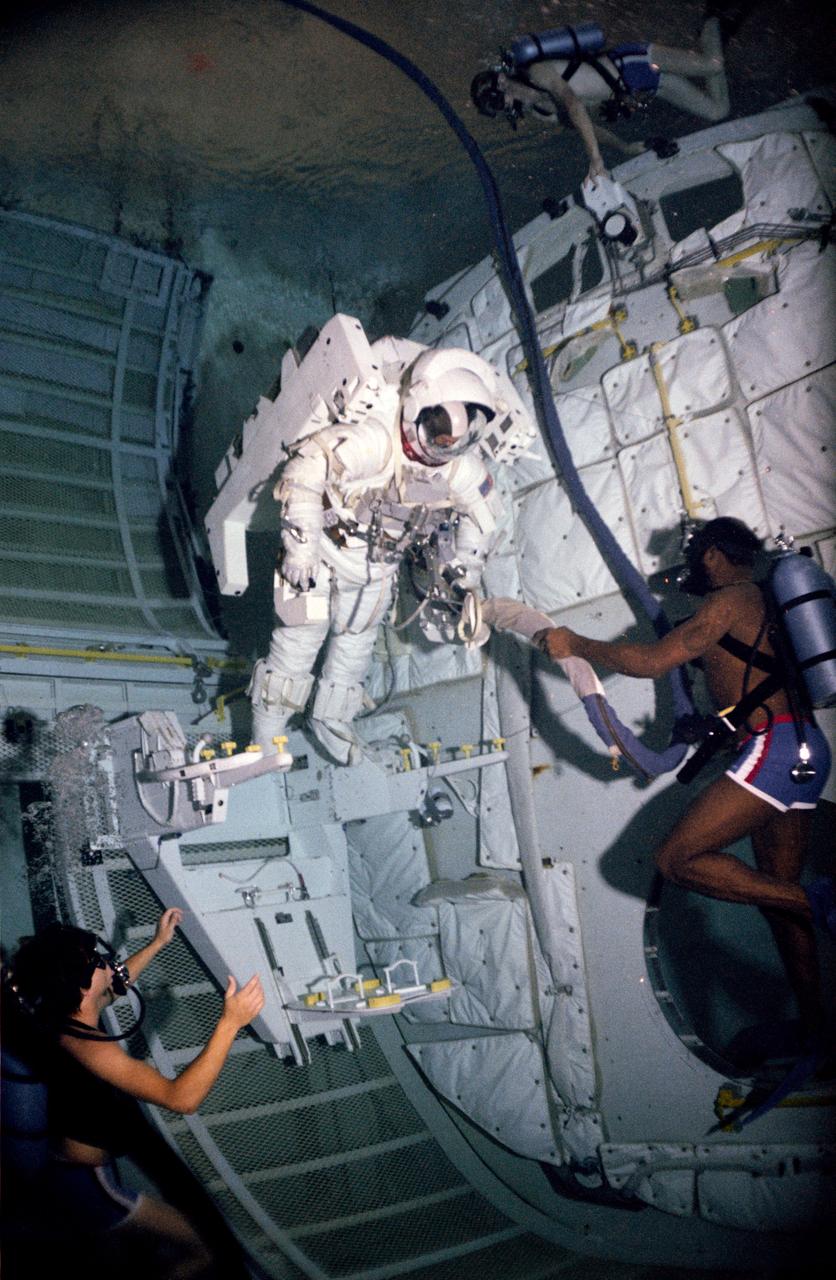

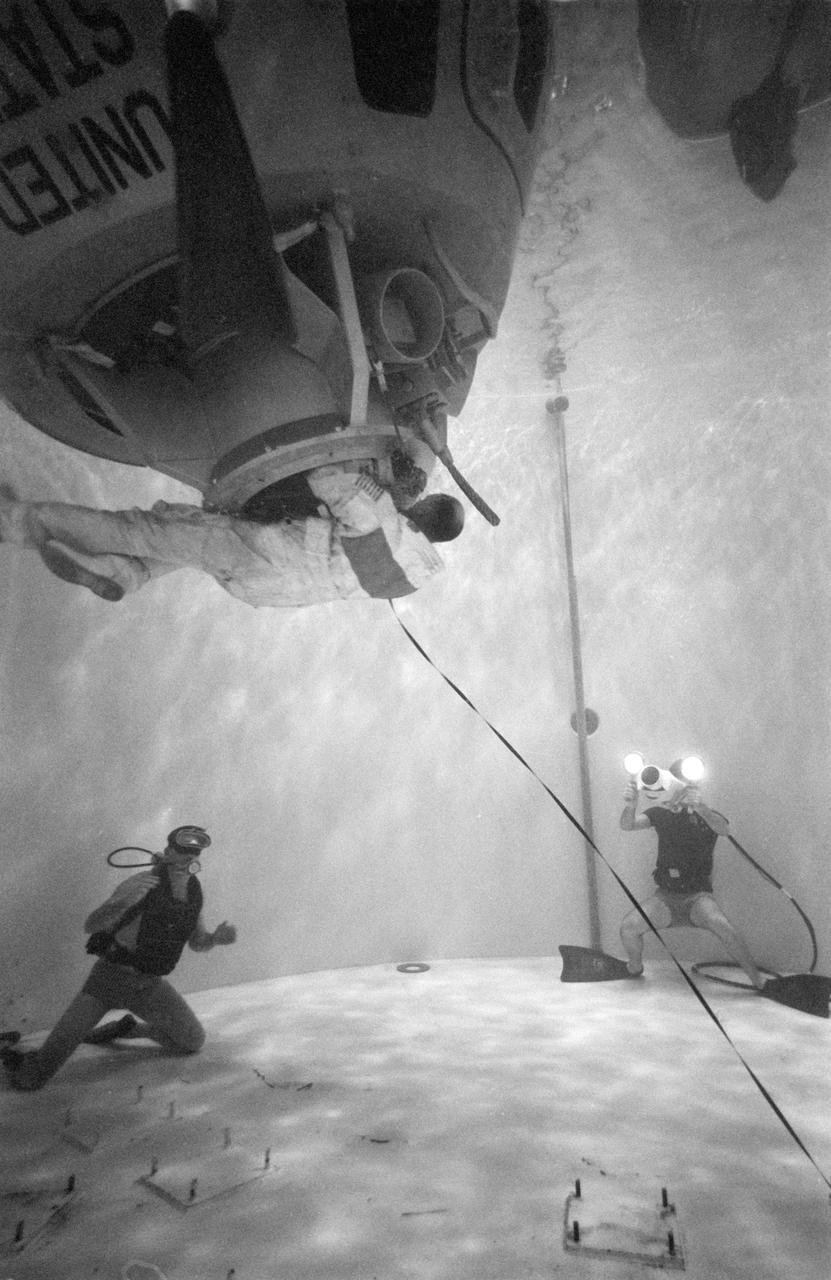
Astronaut Bruce McCandless during an underwater test of the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU) Flight Support Station (FSS) donning and doffing in the Bldg 29 Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). View is of McCandless wearing the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), stepping into the MMU.
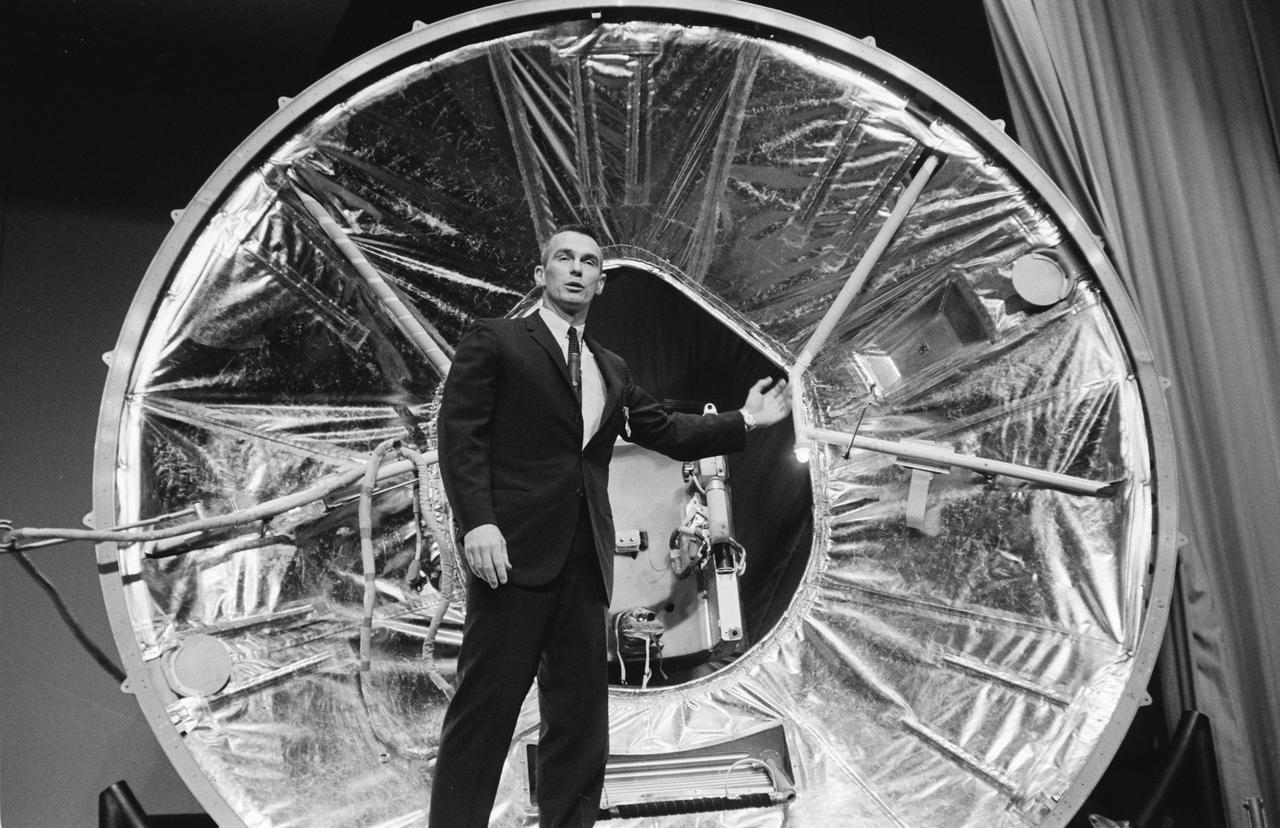

S66-32698 (17 June 1966) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan discusses his Gemini-9A extravehicular activity before a gathering of news media representatives in the MSC auditorium. In the background is an Astronaut Maneuvering Unit (AMU) mock-up mounted in a mock-up of a Gemini spacecraft adapter equipment section. Astronauts Cernan and Thomas P. Stafford completed their three-day mission in space on June 6, 1966. Photo credit: NASA
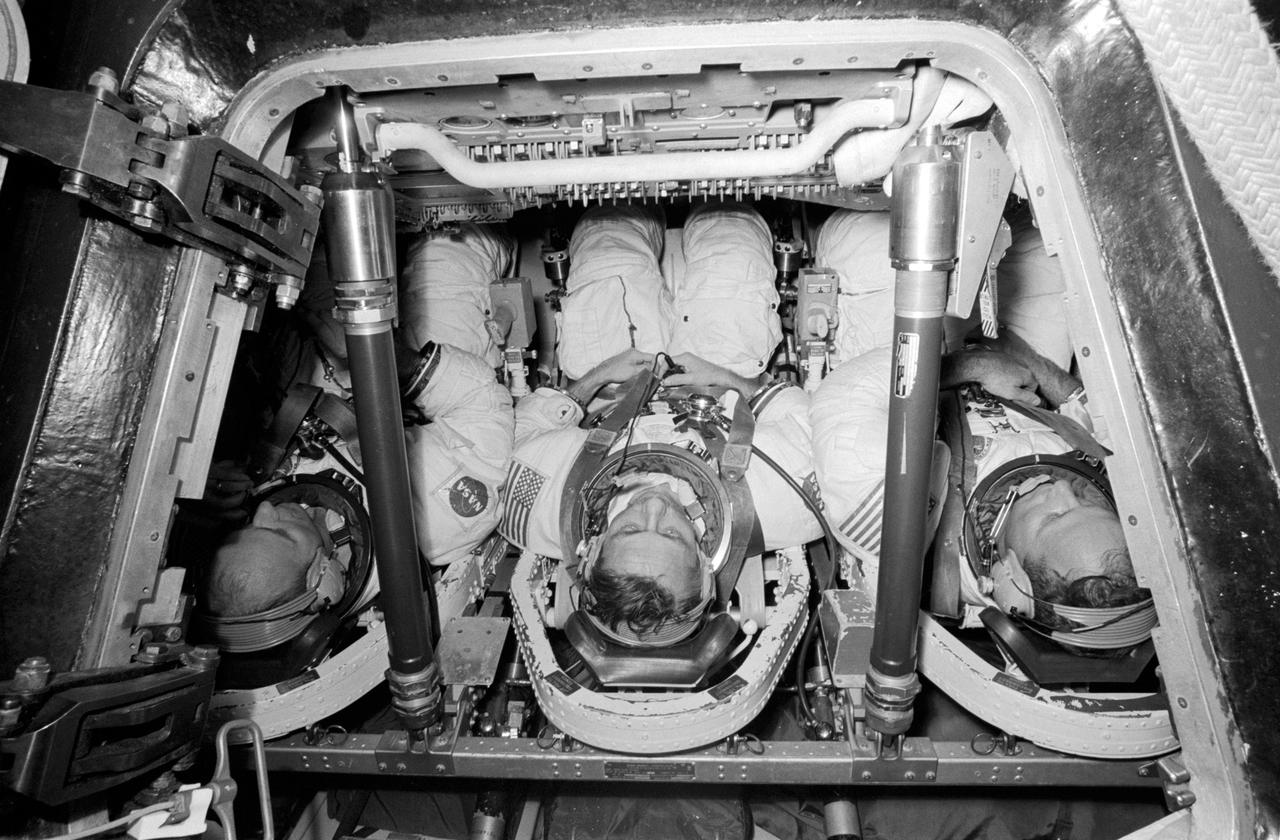
S73-27787 (1 May 1973) --- The three members of the prime crew of the second manned Skylab mission participate in prelaunch training, specifically water egress simulations, at the Johnson Space Center (JSC), Houston. They are, left to right, astronaut Alan J. Bean, commander; scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; and astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot. This training took place in JSC?s Building 220 on May 1, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
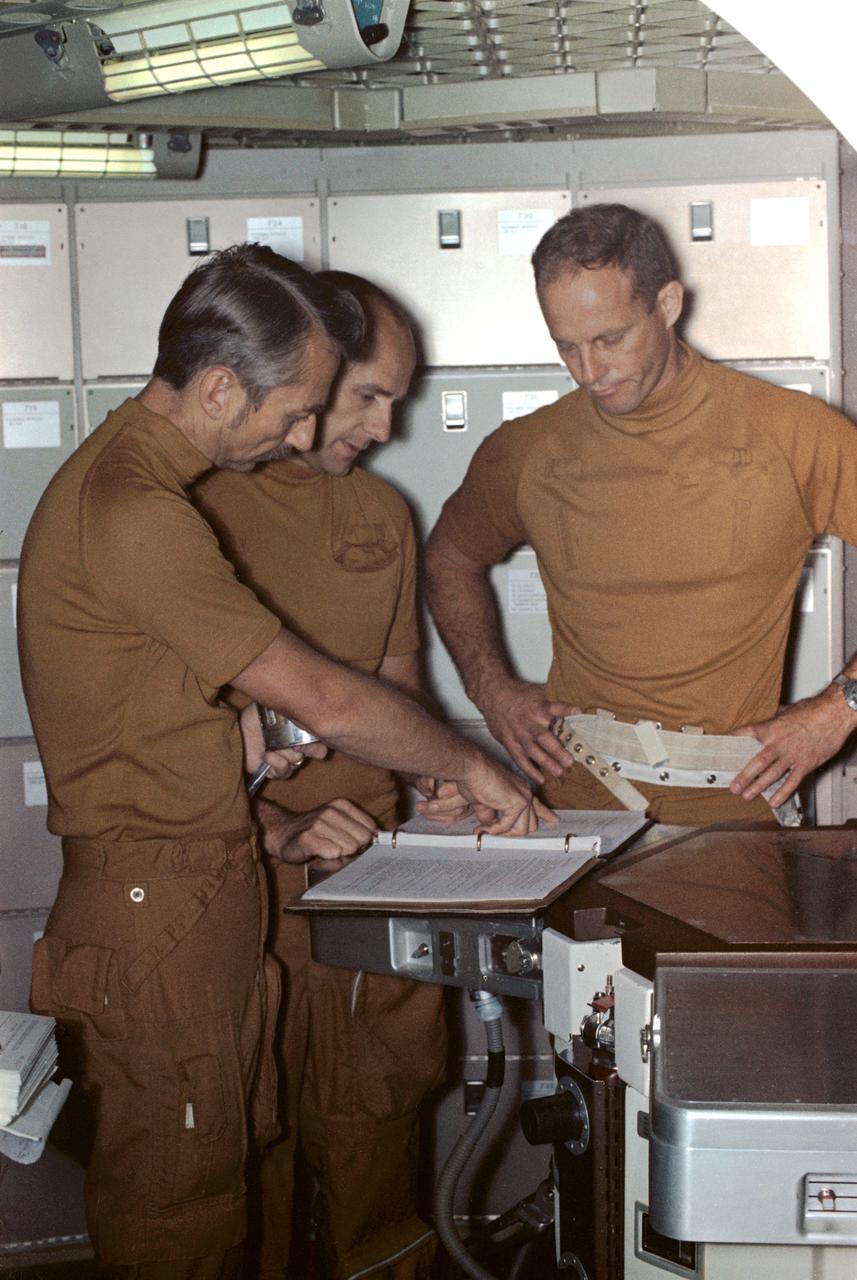

S73-28793 (16 July 1973) --- The three crewmen of the second manned Skylab mission (Skylab 3) go over a checklist during preflight training at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander; and astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot. They are in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop trainer in the Mission Training and Simulation Facility, Building 5, at JSC. Skylab 3 is scheduled as a 59-day mission in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
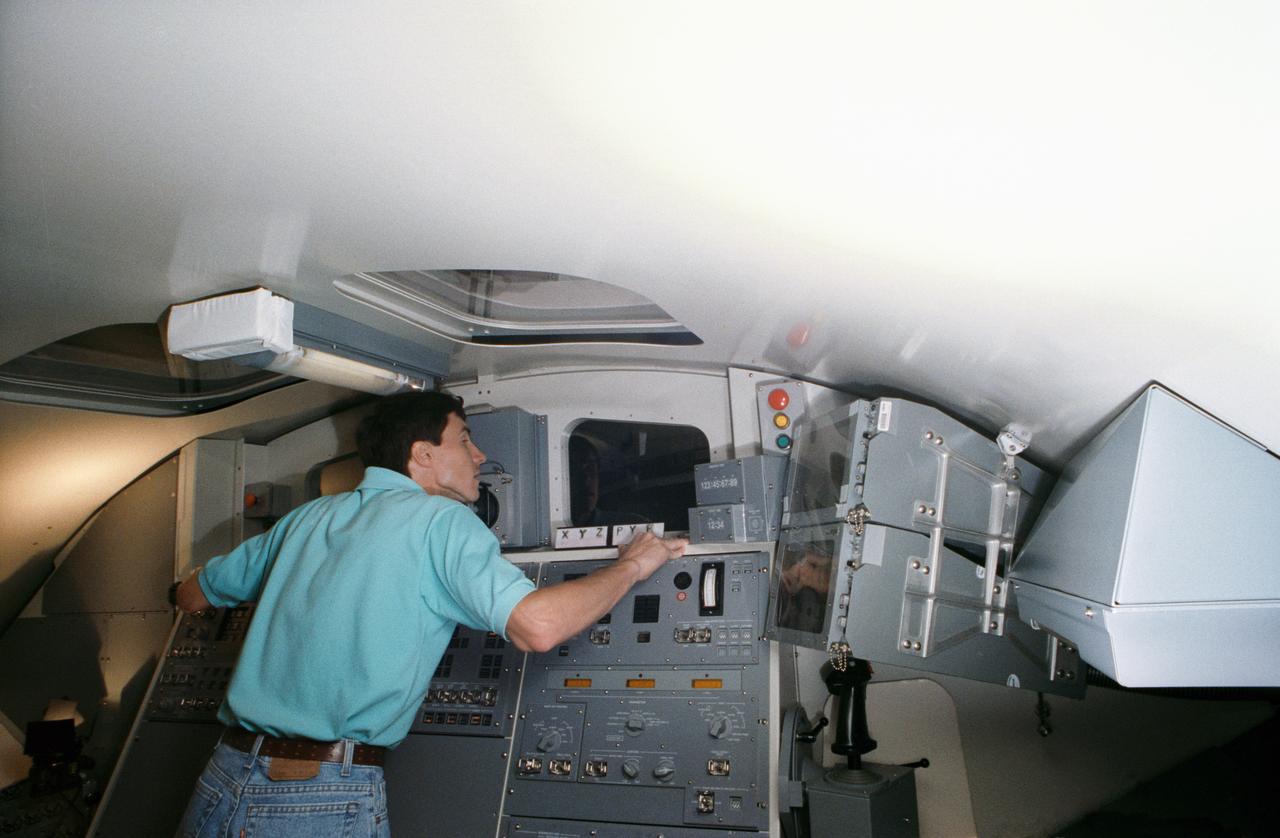

Cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev, STS-60 mission specialist, practices operating the Shuttle's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) during a training exercise at JSC's Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory.
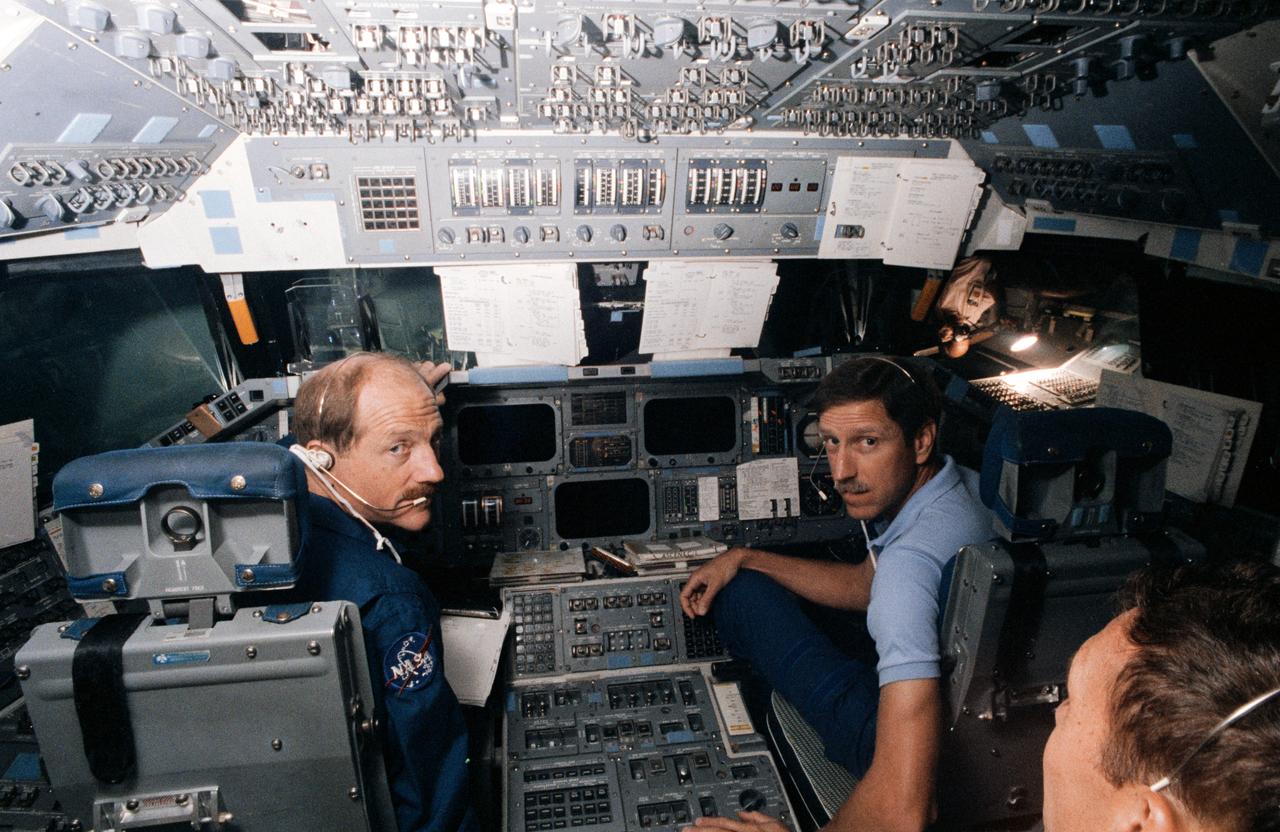

S87-46304 (20 Oct 1987) --- Astronauts Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck, left, STS-26 commander, and Richard O. Covey, pilot, man their respective stations in the Shuttle mission simulator (fixed base) at the Johnson Space Center. A simulation for their anticipated June 1988 flight aboard the space shuttle Discovery began Oct. 20. Astronaut David C. Hilmers, one of three mission specialists for the flight, is partially visible in the foreground.
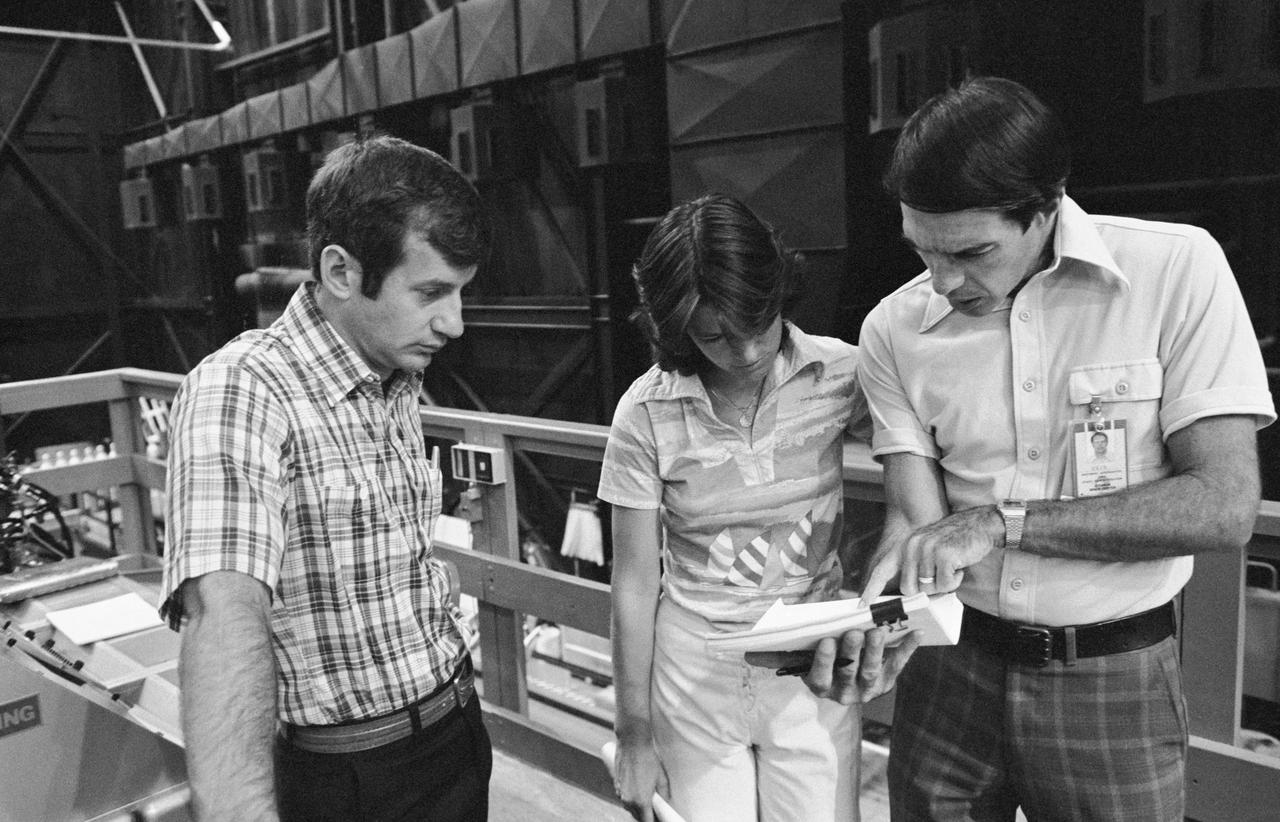

Astronauts Sally Ride and Terry Hart prepare for remote manipulator system (RMS) training for STS-2 in bldg 9A. Views include Ride, Hart and Robert R. Kain of the Flight Activites Branch reviewing procedures for RMS training (34262); Ride and Hart stand beside the RMS control center looking down at the payload bay mock-up (34263).
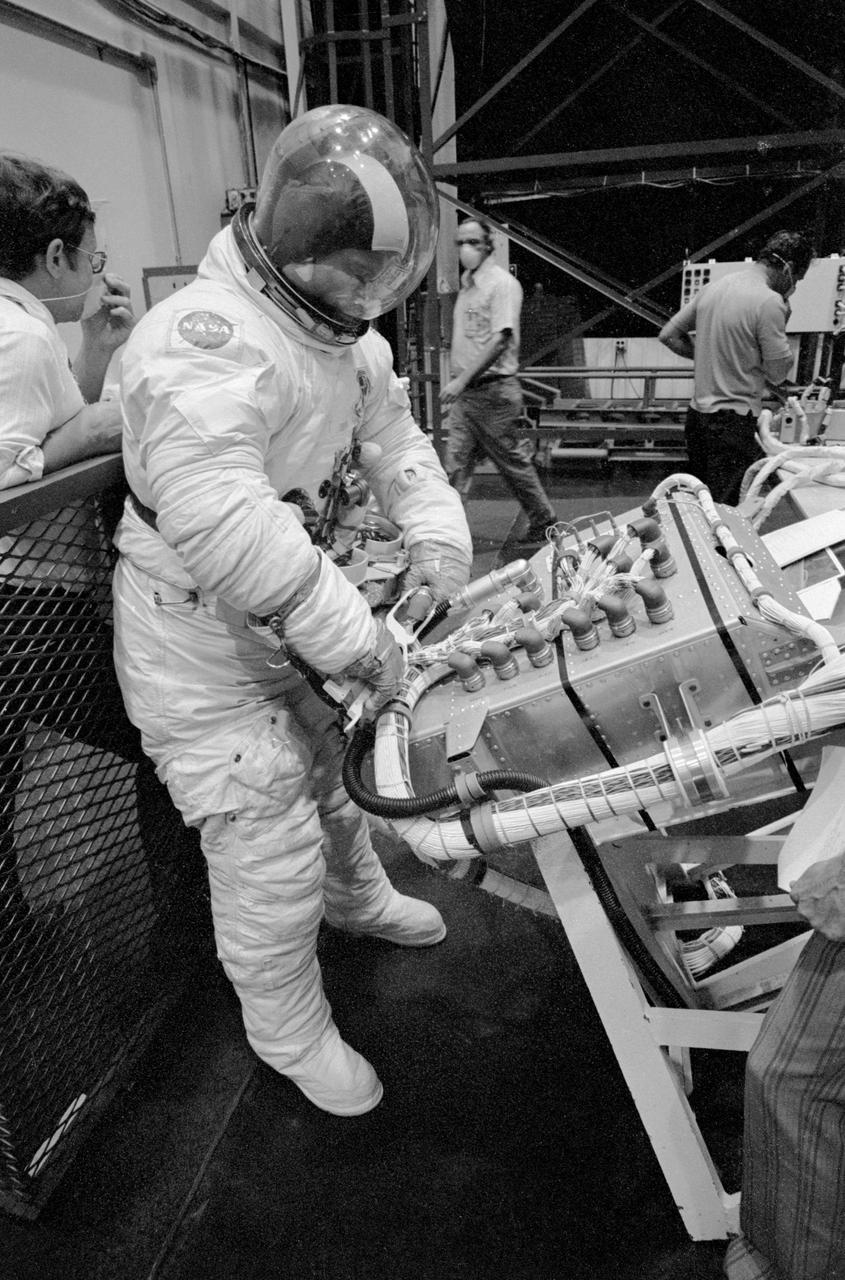

S73-31323 (30 June 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, practices procedures for extravehicular activity (EVA) in his Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit during Skylab 3 prelaunch training at Johnson Space Center. He is working with a mock-up of a trunion plug plate which is on the space station's deployment assembly. Photo credit: NASA
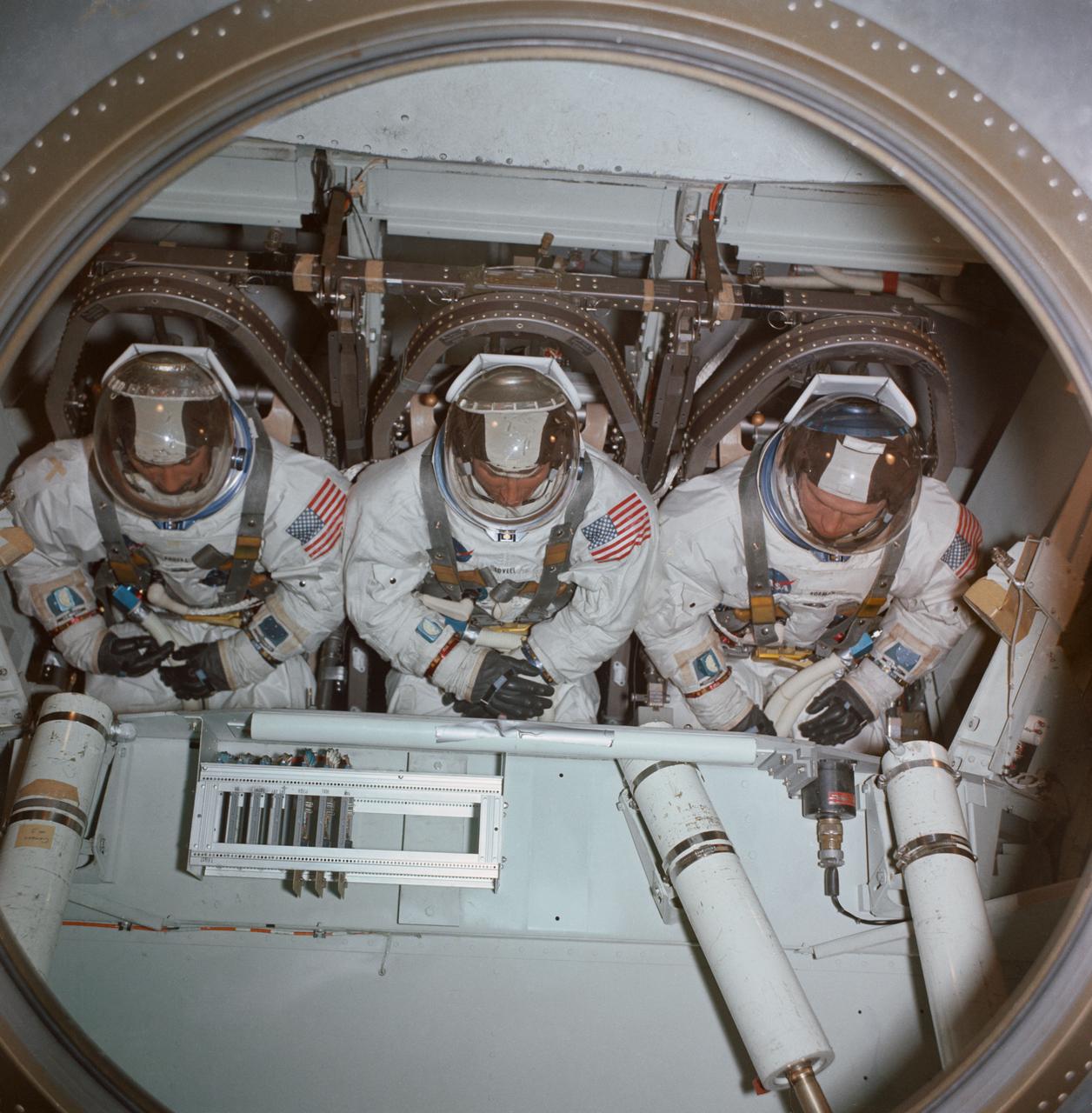

S68-53194 (1 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 8 prime crew inside the centrifuge gondola in Building 29 during centrifuge training in MSC's Flight Acceleration Facility. (View with crew lying on back) Left to right are astronauts William A. Anders, lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. Photo credit: NASA
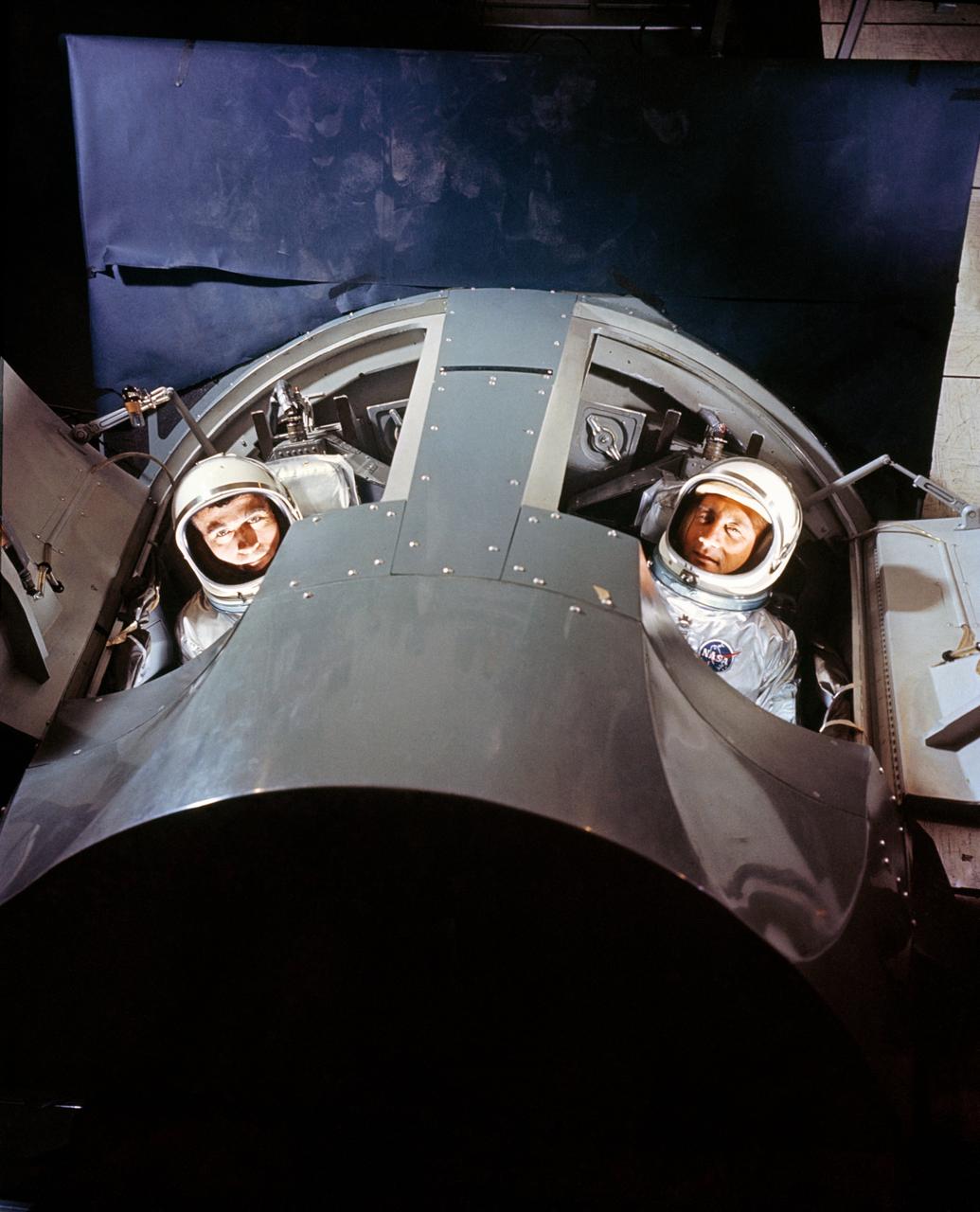
S64-25295 (March 1964) --- Astronauts Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom (right) and John W. Young, prime crew for the first manned Gemini mission (GT-3), are shown inside a Gemini mission simulator at McDonnell Aircraft Corp., St. Louis, MO. The simulator will provide Gemini astronauts and ground crews with realistic mission simulation during intensive training prior to actual launch.
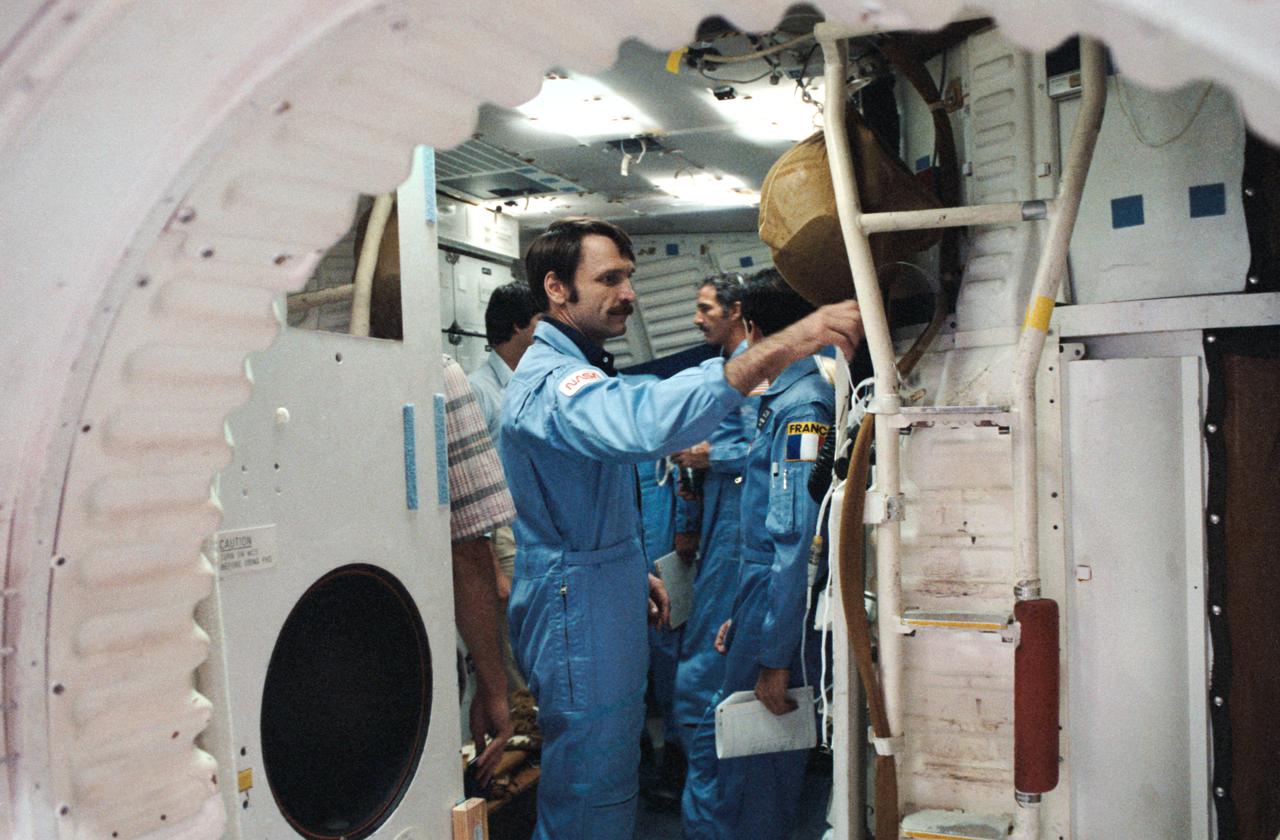

STS 51-E crew is briefed on the Shuttle full fuselage trainer. Astronauts Dave Griggs (foreground), Jean Loup Chretien (behind Griggs) and Jeff Hoffman are being shown the workings of the trainer by flight instructors.
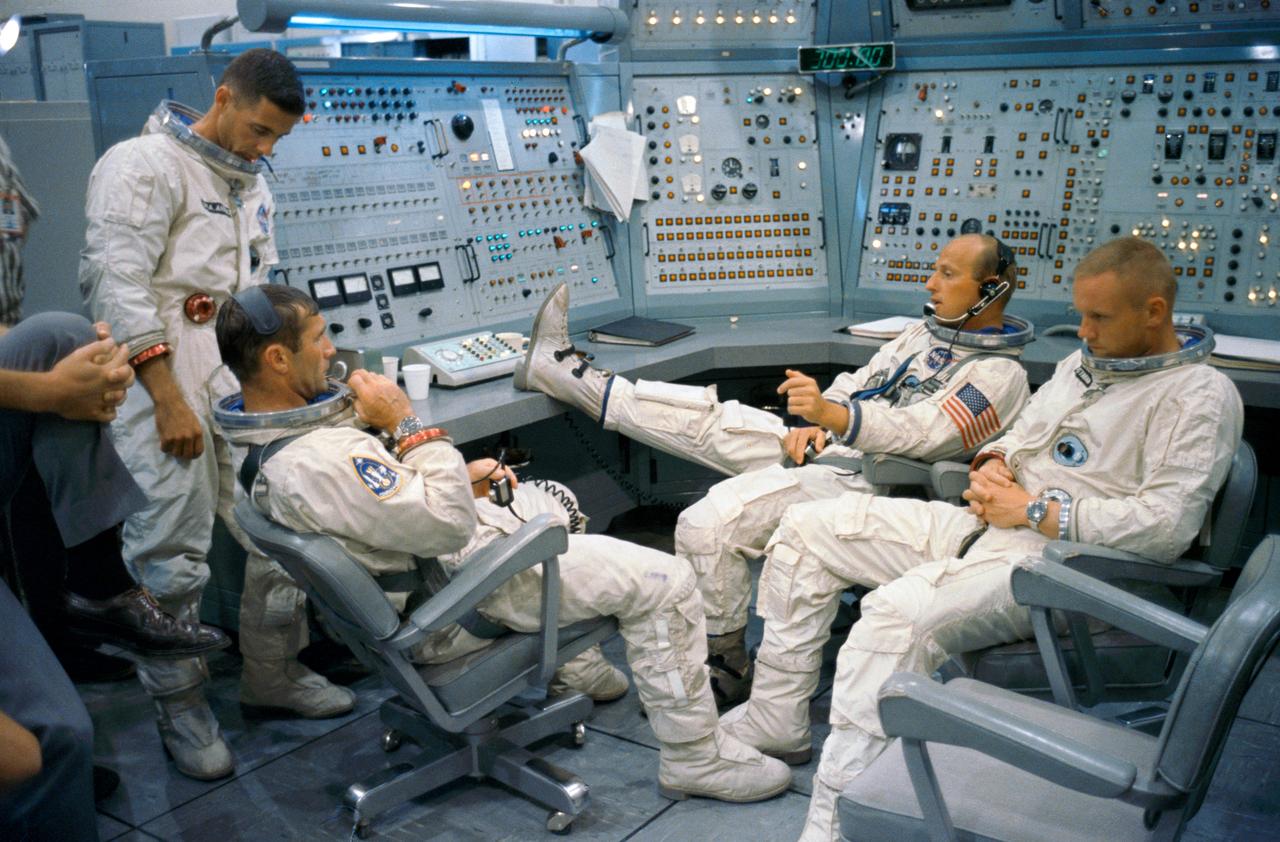

S66-50769 (8 Sept. 1966) --- Gemini-11 prime and backup crews are pictured at the Gemini Mission Simulator at Cape Kennedy, Florida. Left to right are astronauts William A. Anders, backup crew pilot; Richard F. Gordon Jr., prime crew pilot; Charles Conrad Jr. (foot on desk), prime crew command pilot; and Neil A. Armstrong, backup crew command pilot. Photo credit: NASA

S92-29406 (Feb 1992) --- Three mission specialists assigned to the STS-49 flight occupy temporary stations on the "middeck" of a Johnson Space Center (JSC) Shuttle trainer during a rehearsal of Endeavour's launch and entry phases. Left to right are astronauts Thomas D. Akers, Kathryn C. Thornton and Pierre J. Thuot. The three, along with four other NASA astronauts, will be aboard Endeavour in May for a week-long mission during which a satellite will be retrieved and boosted toward a higher orbit and extravehicular activity evaluations for Space Station Freedom assembly techniques will be conducted.
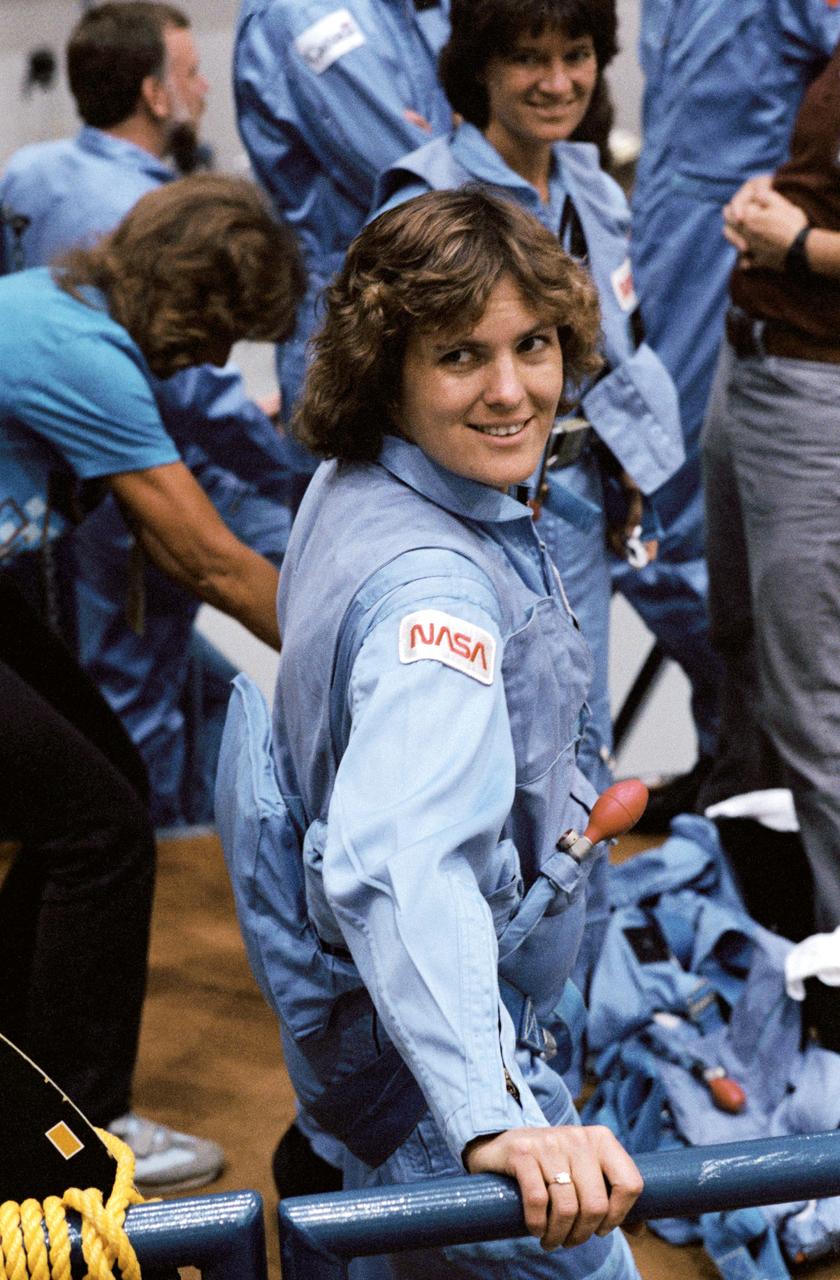

41D-3188 (2 September 1984) --- Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, 41-G mission specialist, joins with other members of the seven-person crew prior to a training session in the Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory at the Johnson Space Center. Dr. Sullivan will be the first American woman to perform an extravehicular activity (EVA) in space when she joins Astronaut David C. Leestma for some outside-the-Challenger duty on October 9. The mission is scheduled for an October 5, 1984 launch.
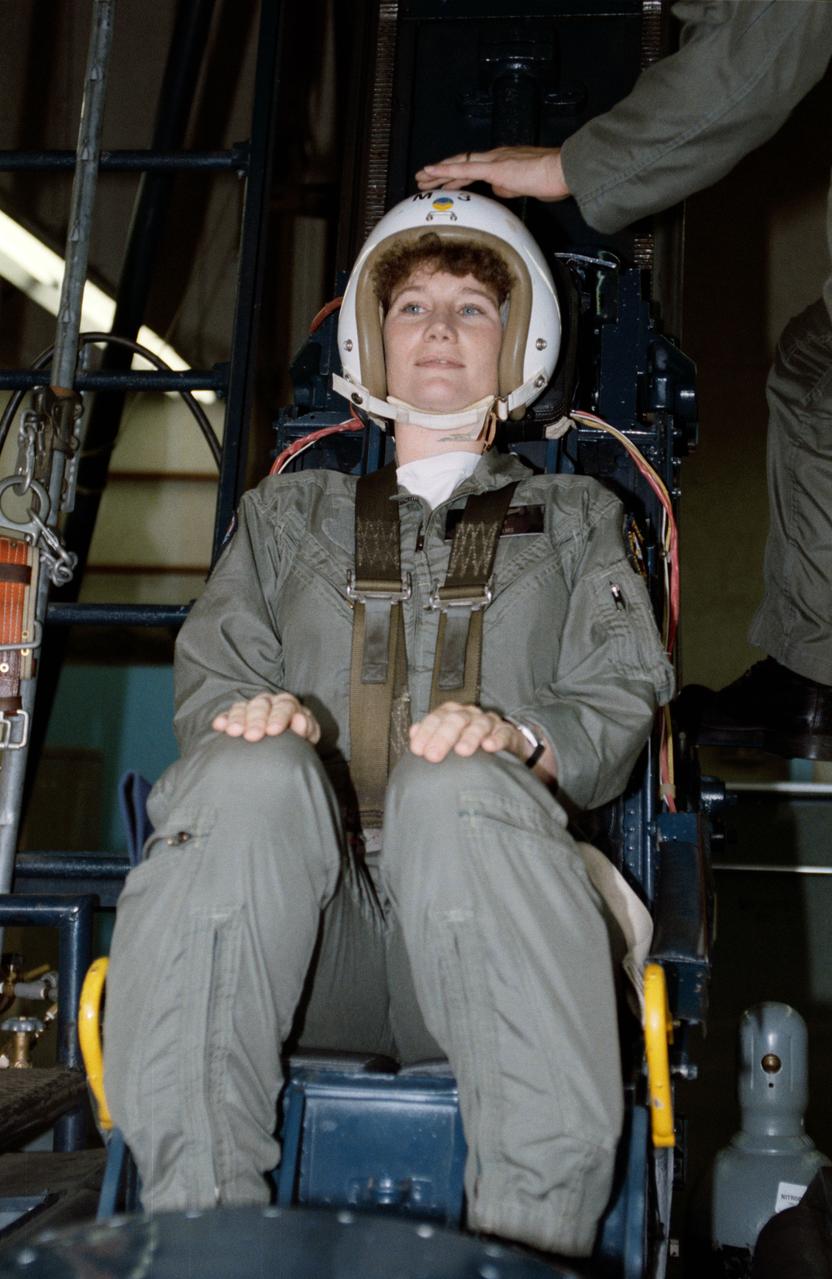

S90-45852 (29-31 July 1990) --- Susan J. Helms, one of 23 astronaut candidates who began a year's training and evaluation in July, participates in one of may sessions at a survival training course at Vance Air Force Base. This portion of the course is designed to familiarize the trainee with the "feel" of emergency ejection from a jet aircraft.
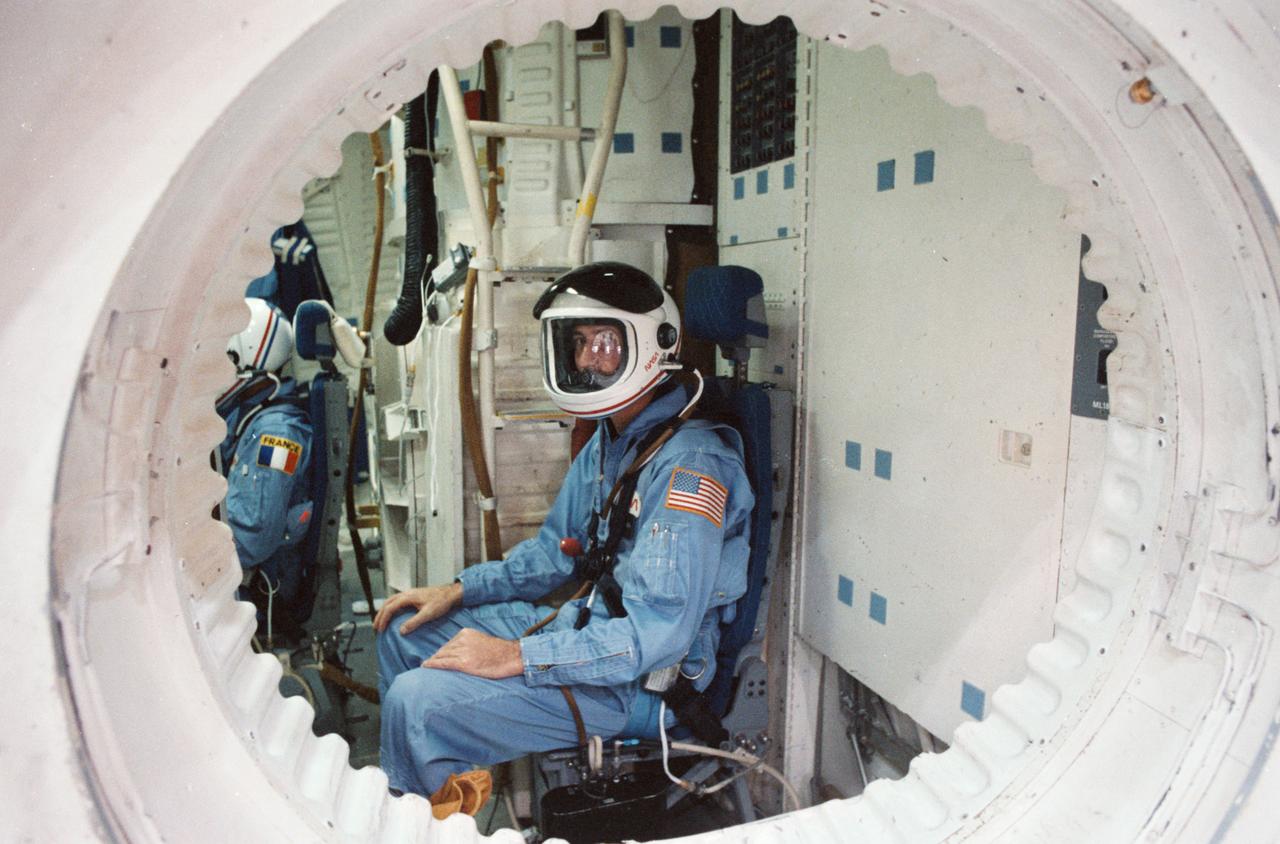

STS 51-E crew is briefed on the Shuttle full fuselage trainer. View of the crewmembers seated at stations inside the cabin was taken from the side hatch.
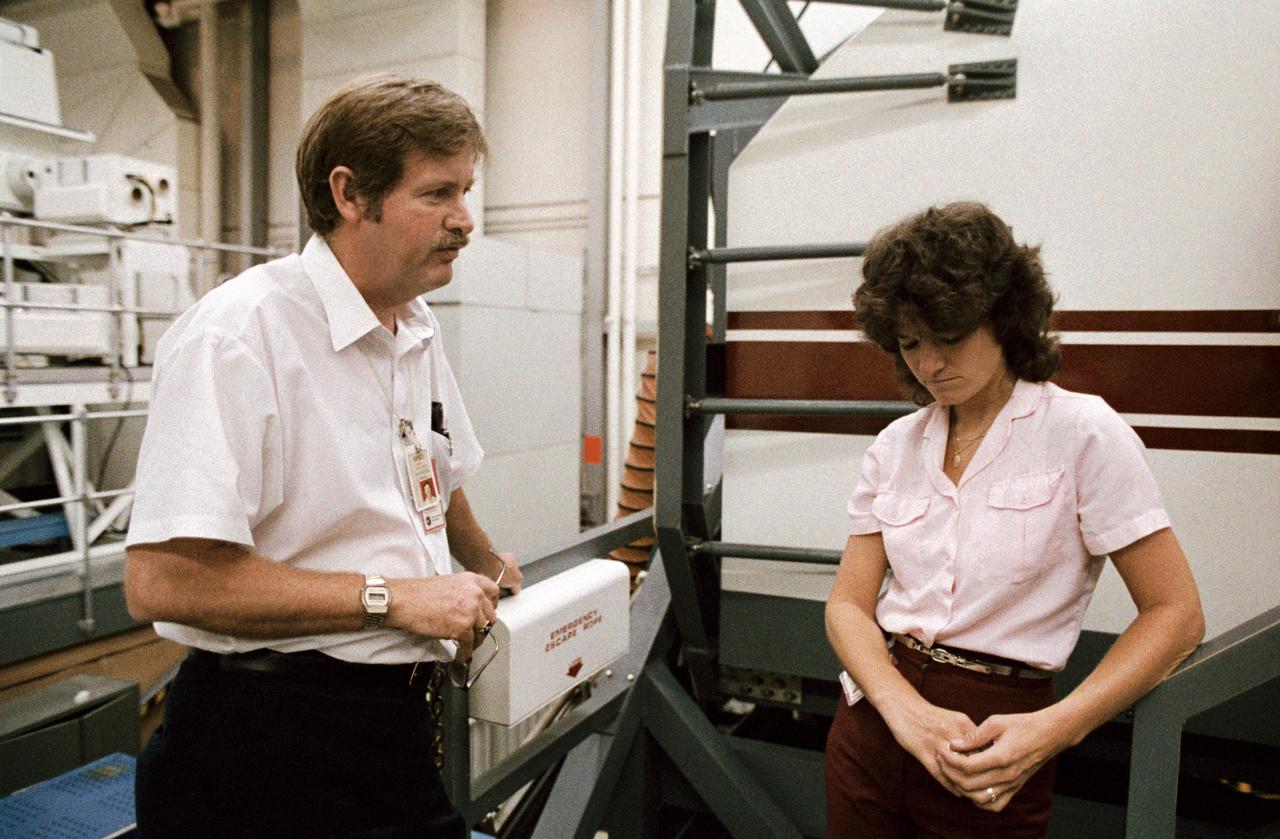

S83-32890 (23 May 1983) --- Astronaut Sally K. Ride, STS-7 mission specialist, stands near the Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) in Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Mission Simulation and Training Facility with suit specialist Alan M. Rochford after simulation of various phases of the upcoming STS-7 flight. Photo credit: NASA
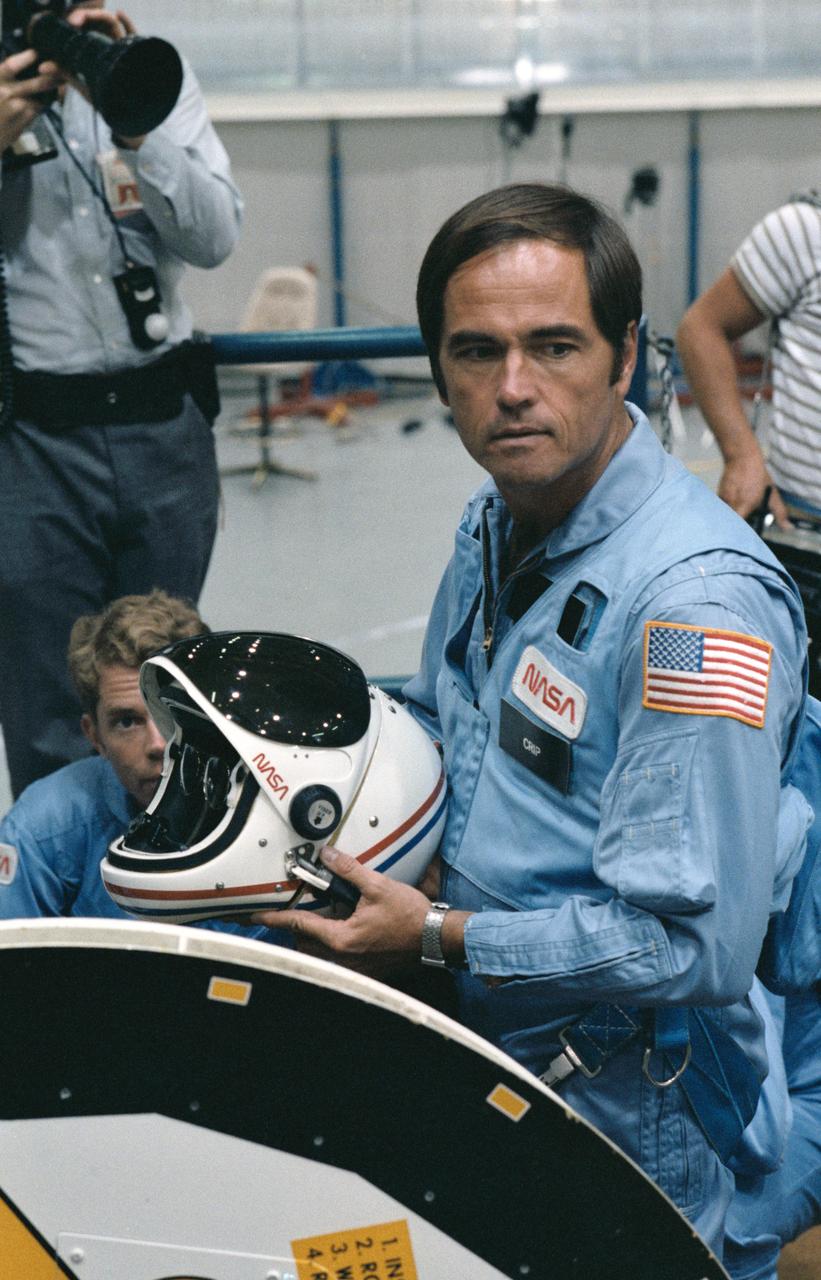

41D-3186 (4 Sept 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, 41-G crew commander, prepares to join his six fellow crewmembers for some training in the mockup and integration laboratory at the Johnson Space Center. Astronaut David C. Leestma, 41-G mission specialist, left, will participate in a scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Challenger's next mission. Today's training is for launch phase procedures.
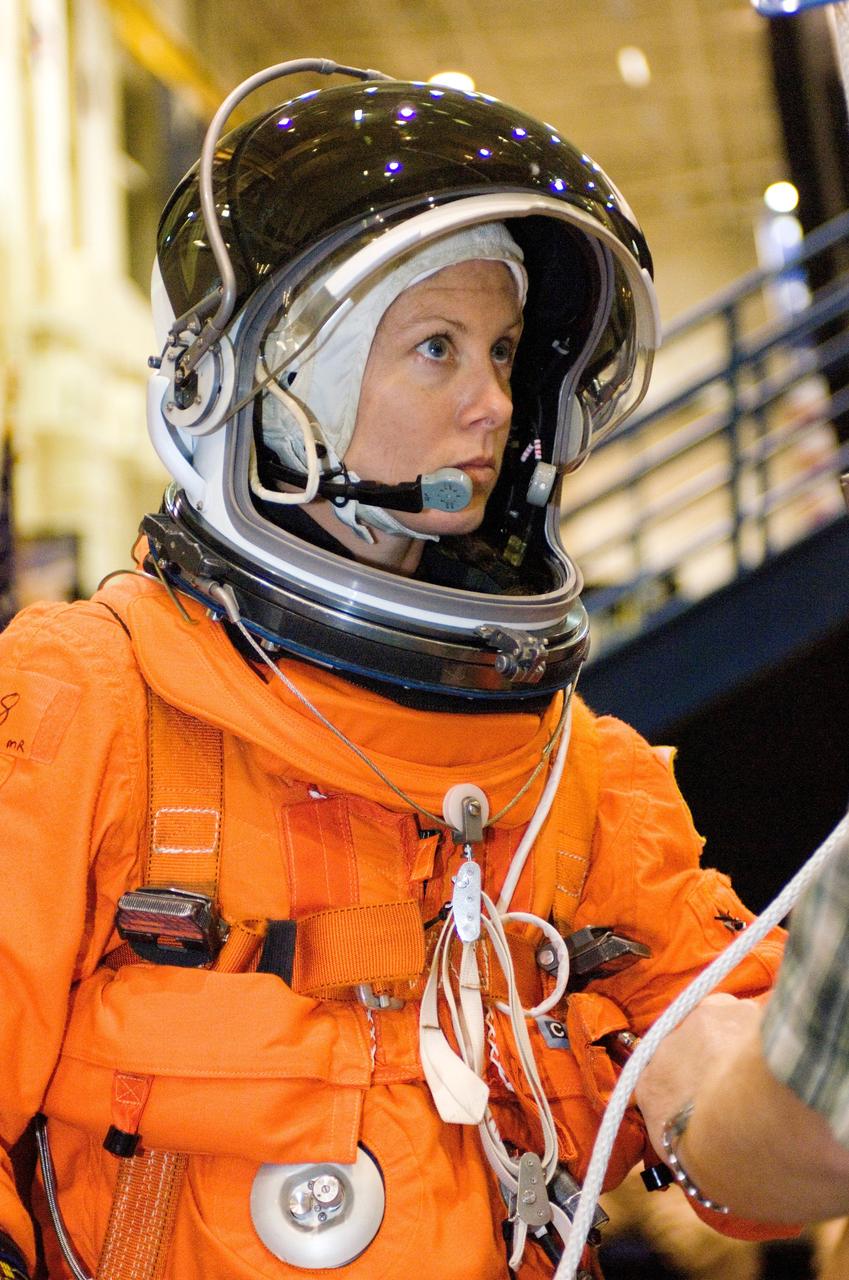

Tracy E. Caldwell, STS-118 astronaut and mission specialist, participates in a training session on the usage of a special device, used to lower oneself from a troubled shuttle, in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Caldwell is wearing a training version of her shuttle launch and entry suit.
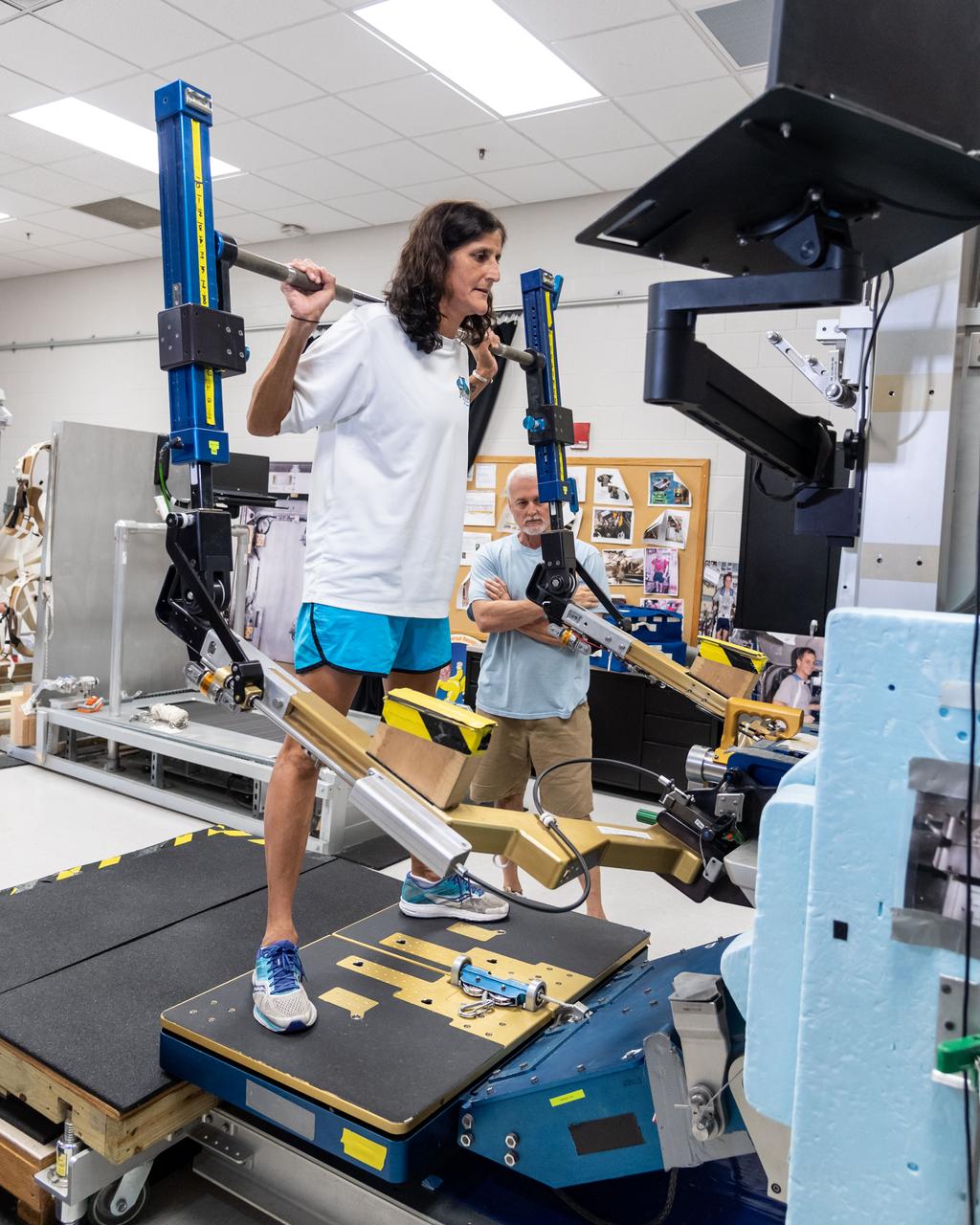

NASA commercial crew astronaut Suni Williams performs physical training on the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Williams is assigned to the Boeing Starliner’s second crewed flight.
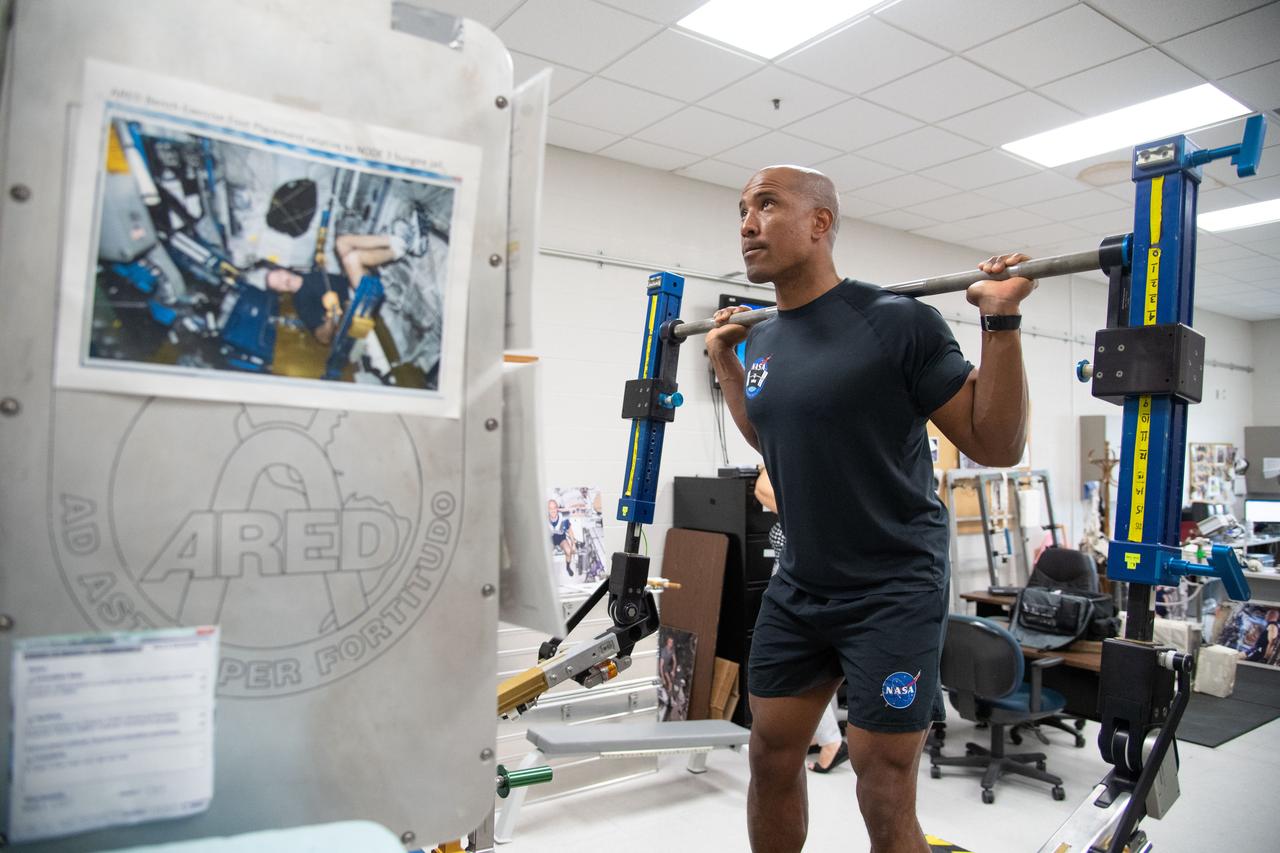

NASA commercial crew astronaut Victor Glover performs physical training on the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Glover is assigned to the SpaceX Crew Dragon’s second crewed flight.
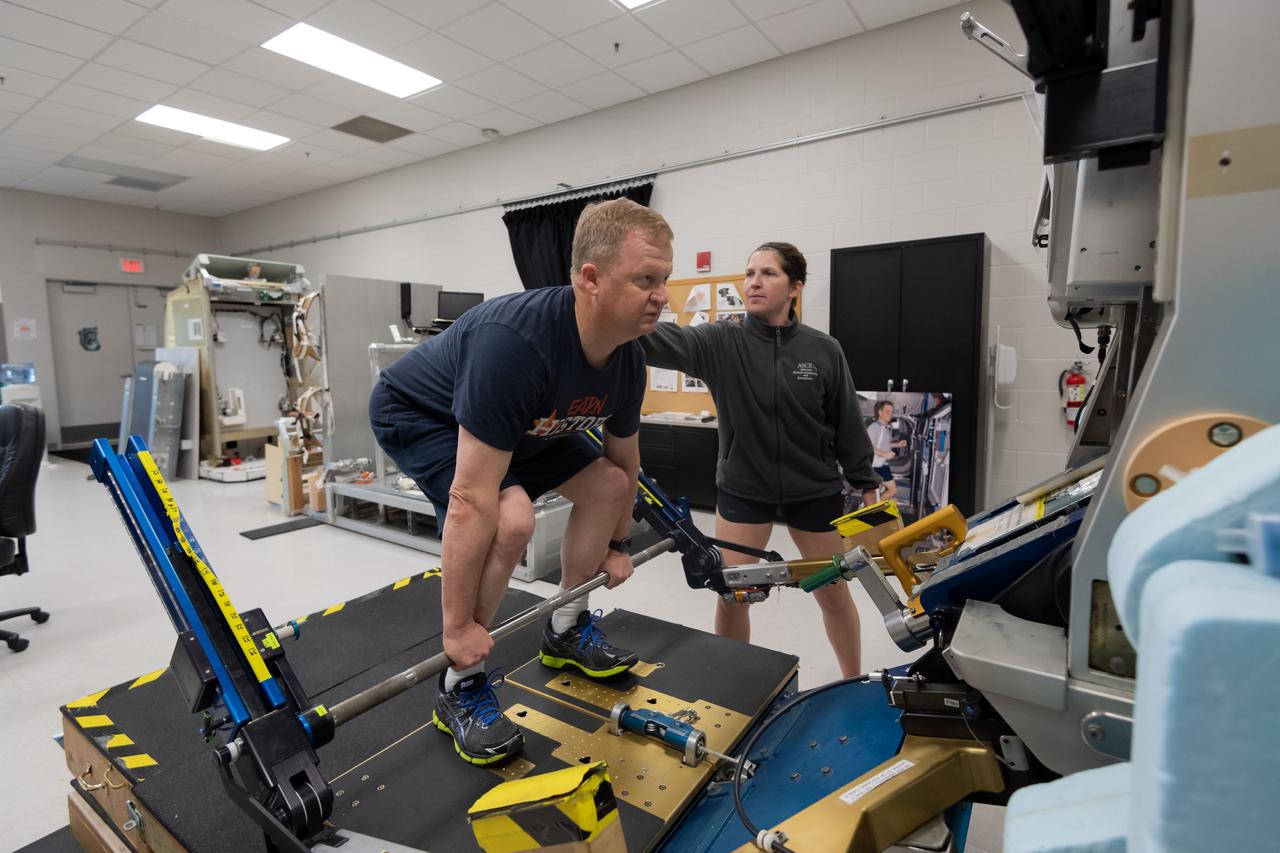

NASA commercial crew astronaut Eric Boe performs physical training on the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Boe is assigned to the Boeing Starliner’s first crewed flight.
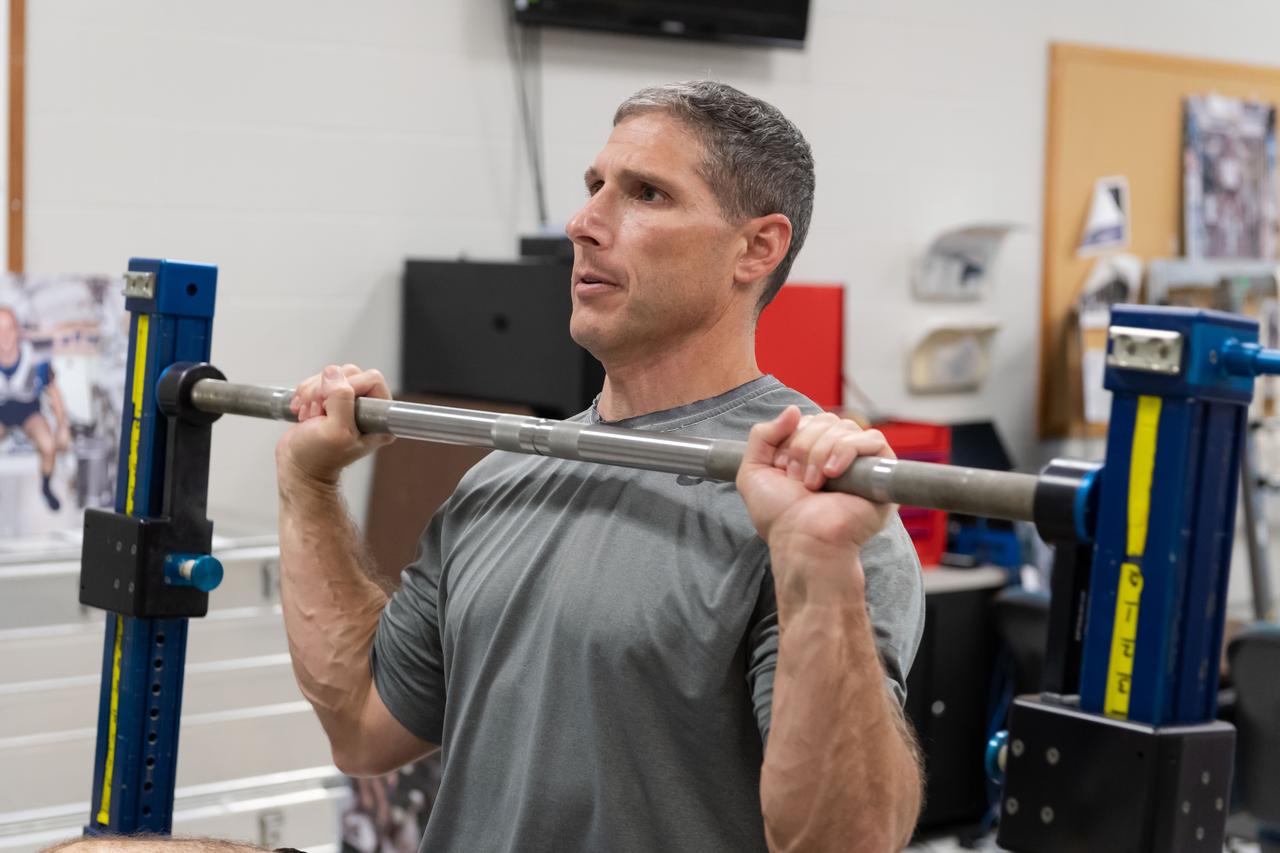

NASA commercial crew astronaut Mike Hopkins performs physical training on the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Hopkins is assigned to the SpaceX Crew Dragon’s second crewed flight.
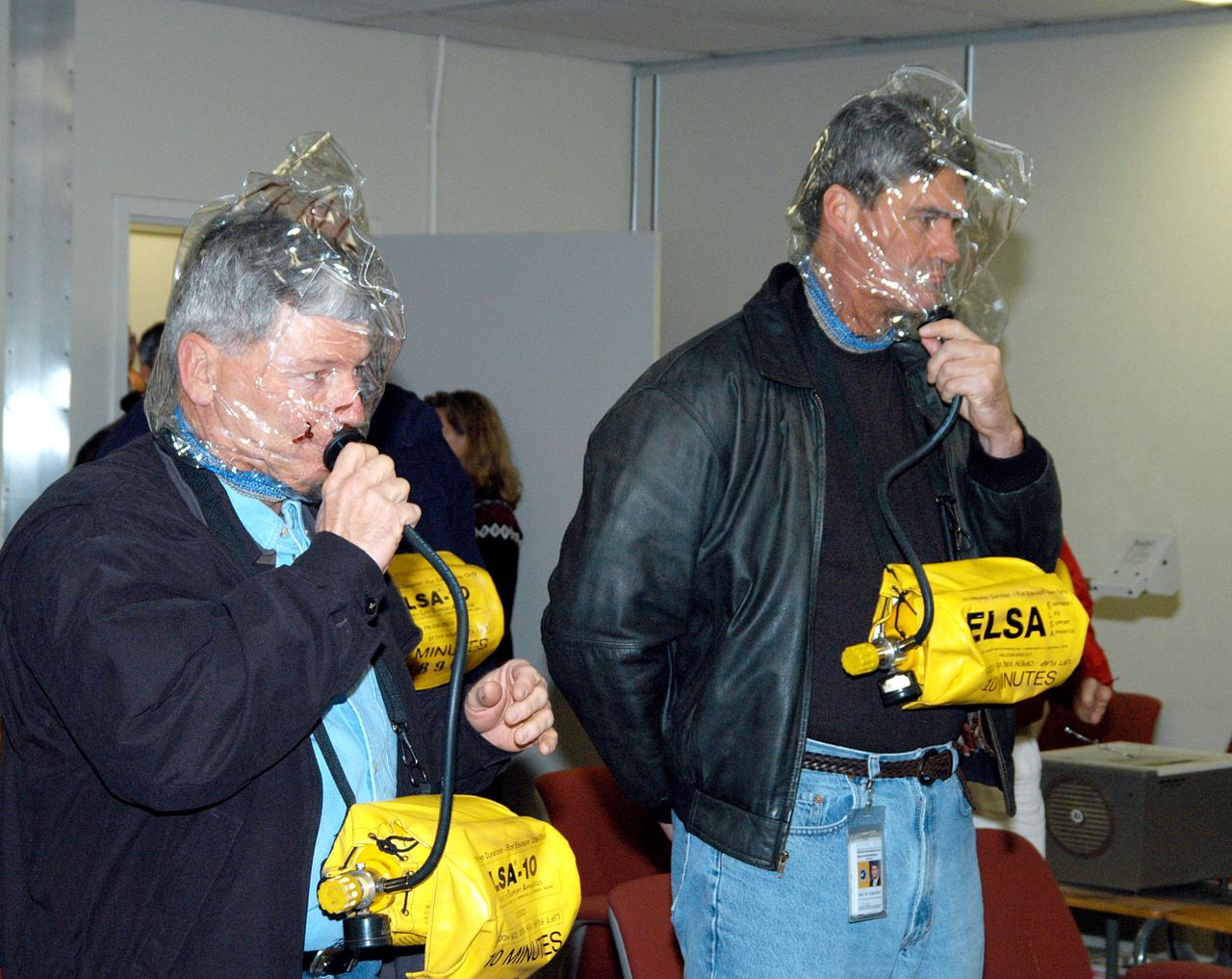

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- From left, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Station and Shuttle Programs Michael Kostelnik and NASA Space Shuttle Program Manager William Parsons each don an Emergency Life Support Apparatus (ELSA) during training on the proper use of the escape devices. NASA and United Space Alliance (USA) Space Shuttle program management are participating in a leadership workday. The day is intended to provide management with an in-depth, hands-on look at Shuttle processing activities at KSC.

41D-3138 (4 Sept 1984)--- Canada's backup payload specialist assists the two 41-G prime payload specialists during a training session in the Johnson Space Center's Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory. Robert Thirsk (without helmet) represents the National Research Council (NRC) and is backup to Marc Garneau (nearest camera), also of the NRC. Paul D. Scully-Power, seated in the other middeck seat for the launch phase, is a civilian oceanographer with the U.S. Navy. The 41-G flight aboard the Challenger is NASA's first to utilize a crew of more than six persons. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
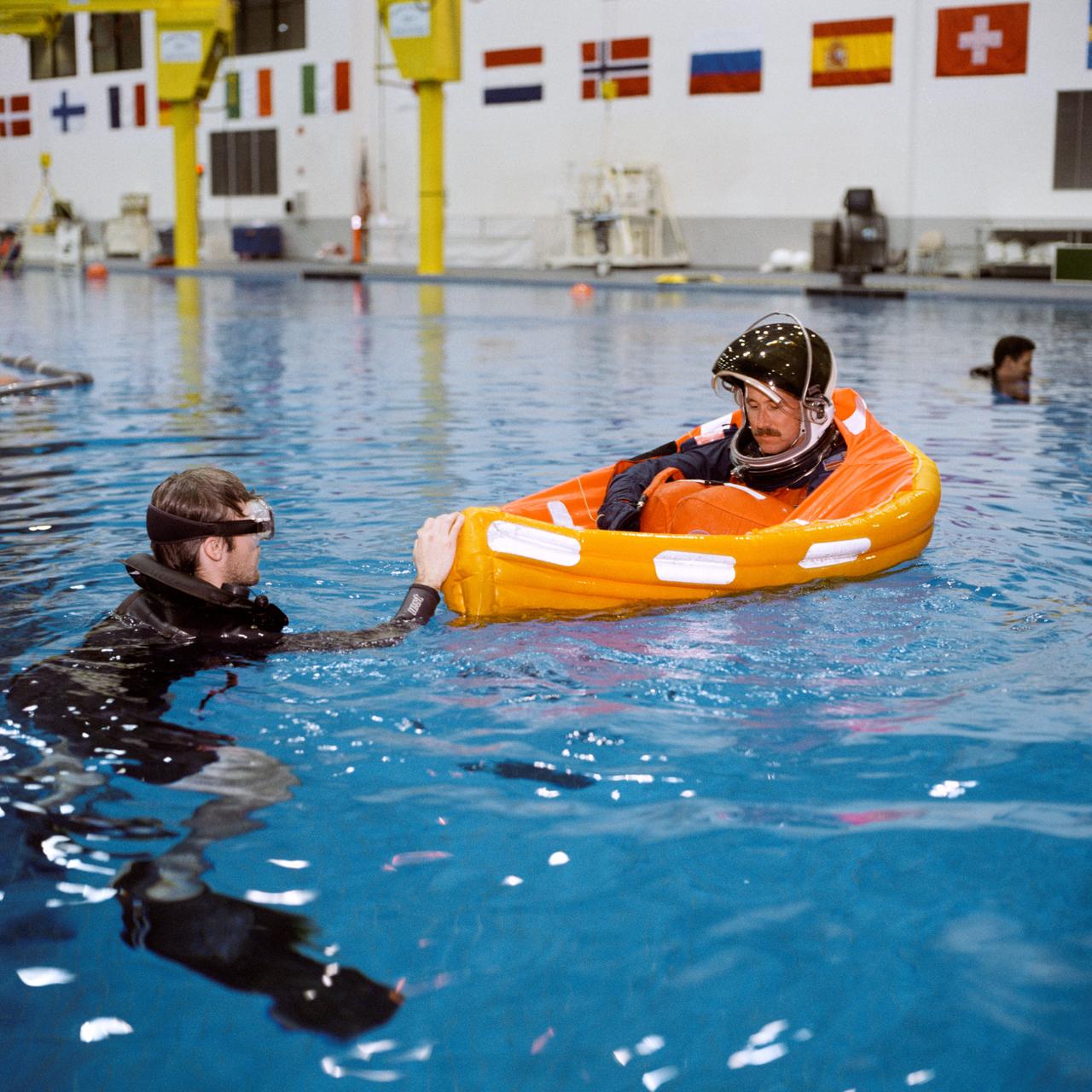

Photographic documentation of the crew of STS-96 conducting bailout training in the Neutral Buoyancy Lab (NBL) pool. Images include: an unidentifiable astronaut in an orange Launch and Entry Suit and helmet being dropped into the pool during training (00580); Mission Specialist (MS) Julie Payette being suspended above the NBL pool prior to being dropped (00581); Julie Payette in her floatation device in the NBL pool (00582-7); Flight Commander Kent Rominger in a blue Launch and Entry Suit (LES) being suspended over the NBL pool prior to being dropped (00589); Mission Specialist (MS) Ellen Ochoa in an orange LES being suspended over the NBL pool prior to being dropped (00590); Pilot Rick D. Husband and MS Daniel T. Barry in floatation devices (00591); closeups of Julie Payette prior to being lifted above the NBL pool (00592-3); MS Tamara E. Jernigan in her floatation device (00594); Julie Payette talking with a NASA employee prior to being raised over the pool (00595); Husband in an orange LES and helmet seated at the poolside talking with a NASA employee (00596); Kominger in his floatation device (00597-8); Barry being assisted with his floatation device at the poolside (00599); Ochoa in her orange LES with helmet talking to NASA personnel at the poolside (00600); Husband in his floatation device operating a transmitter (00601); Rominger splashing Husband (00602); Husband in his floatation device (00603); Barry in an orange LES suspended over the NBL pool prior to being dropped (00604); Ochoa in her floatation device (00605, 00607-8); and Ochoa suspended over the NBL pool with part of her floatation device already inflated (00606).
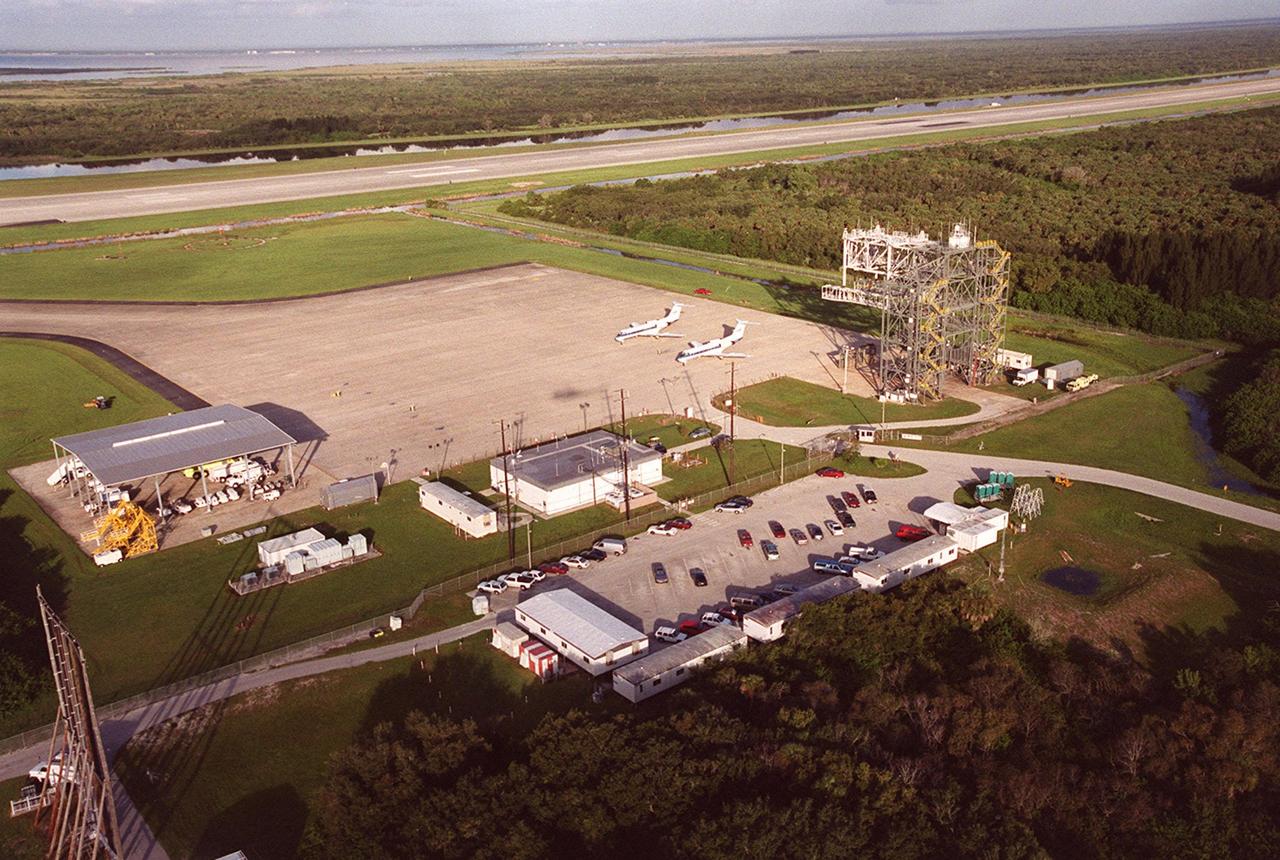

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An aerial view of the Shuttle Landing Facility shows the fuel truck shelter (left), administrative building (center) with parking lot behind it (foreground), two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) parked on the apron and the mate/demate device (right). In the background is the runway. The STAs are Grumman Gulfstream 2 aircraft with converted cockpits that emulate those in the Shuttles for practice landings at the SLF. The mate/demate device is used to lift the orbiter onto or off a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft when it has to be ferried to or from KSC

JSC2000-05556 (3 August 2000) --- Astronaut James M. Kelly, STS-102 pilot, during a session of egress training in the Johnson Space Center's Systems Integration Facility, prepares to use a Sky-genie device to escape from a simulated shuttle in trouble. Crew trainer David Pogue (right) gives the pilot some tips on using the device.
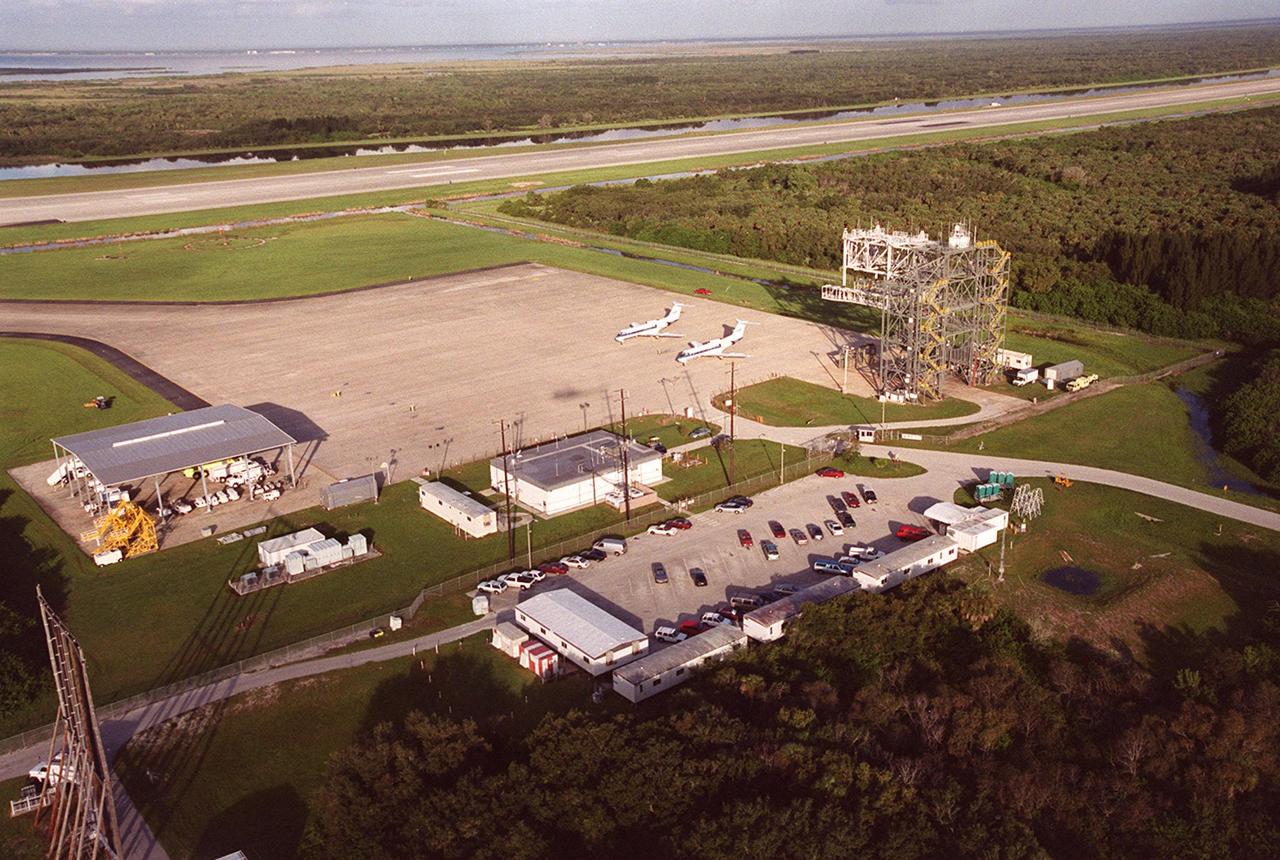

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An aerial view of the Shuttle Landing Facility shows the fuel truck shelter (left), administrative building (center) with parking lot behind it (foreground), two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) parked on the apron and the mate/demate device (right). In the background is the runway. The STAs are Grumman Gulfstream 2 aircraft with converted cockpits that emulate those in the Shuttles for practice landings at the SLF. The mate/demate device is used to lift the orbiter onto or off a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft when it has to be ferried to or from KSC
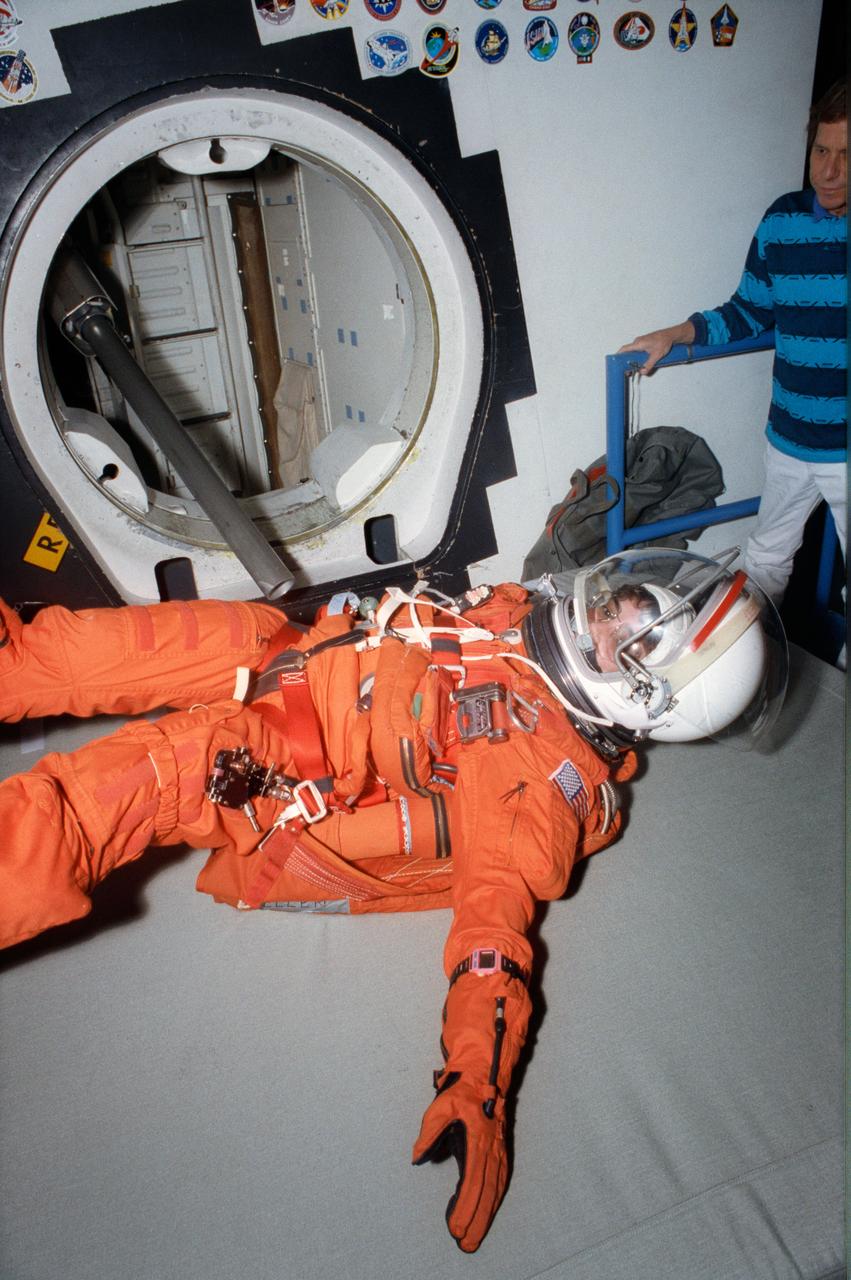

S93-31980 (April 1993) --- Attired in a training version of the Shuttle launch and entry garment, astronaut Nancy J. Sherlock participates in a bailout training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) systems integration facility. Training as a mission specialist for the STS-57 mission, Sherlock was rehearsing using the slide pole escape device. EDITOR'S NOTE: Nancy J. Currie (formerly Sherlock) has been assigned as a mission specialist for the STS-70 mission, scheduled for launch in spring of 1995.
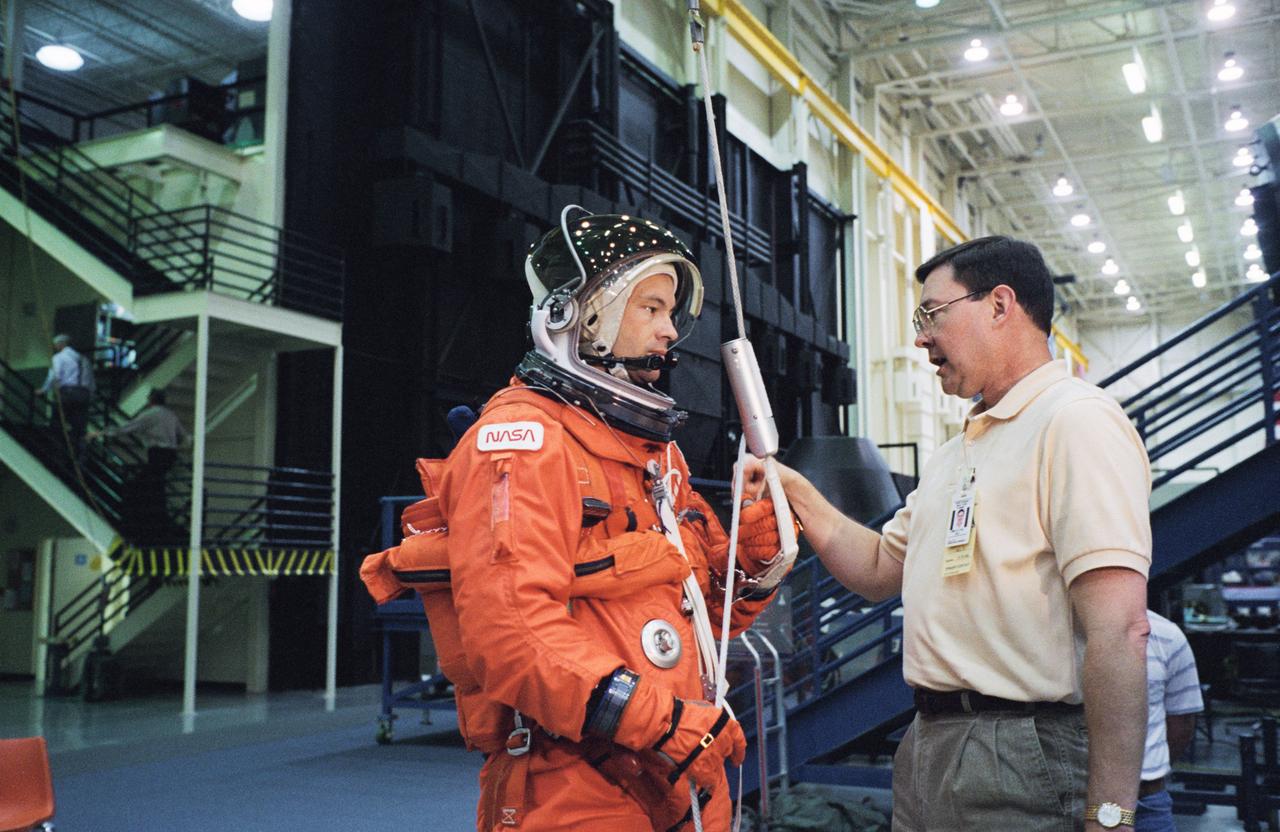

S95-09159 (27 Apr. 1995) --- Attired in a training version of the Shuttle partial pressure launch and entry garment, astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, is briefed on the use of the Sky-genie device by Scott Gill. The briefing was part of an emergency egress training session in the Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Systems Integration Facility. Two high fidelity training facilities in this lab are used to help prepare crew members for emergency procedures and to provide realistic settings for rehearsals of the launch and entry phases.
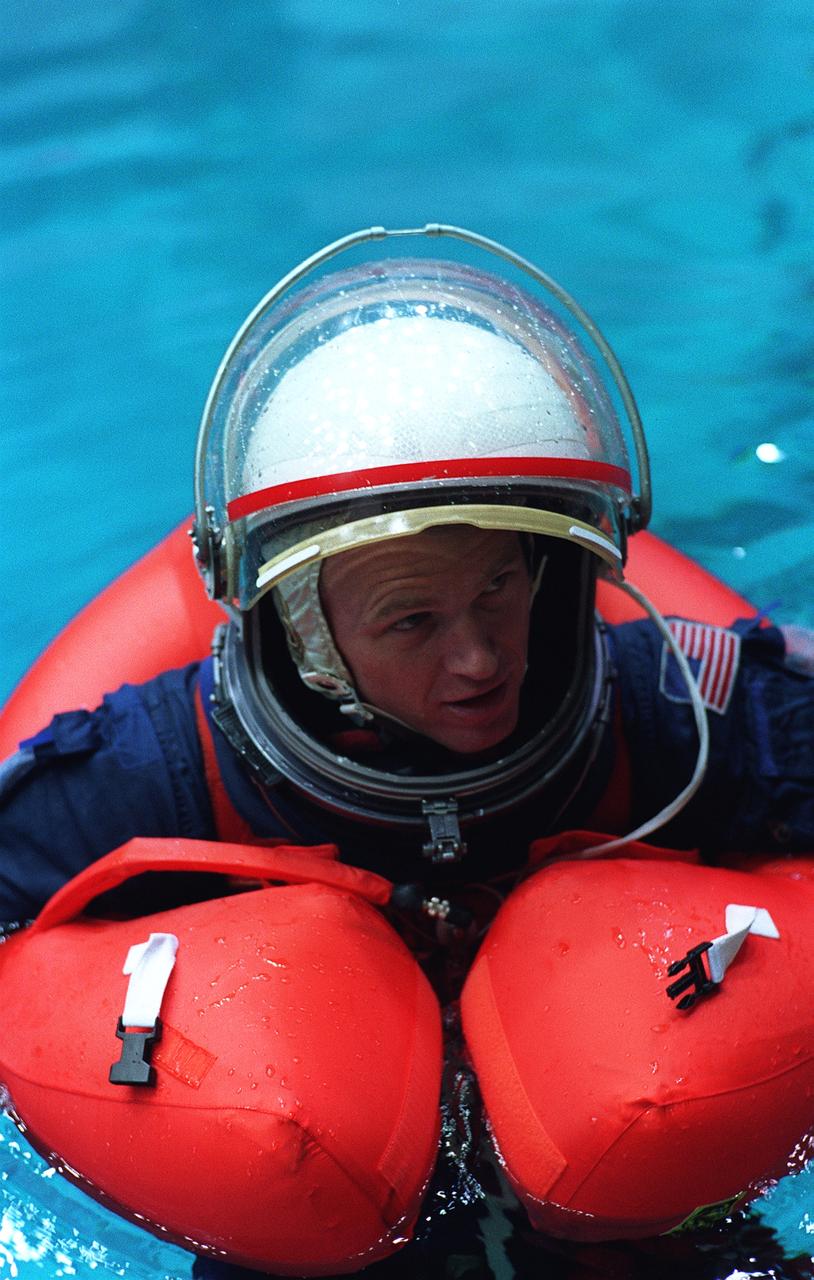

S96-15393 (26 Sept. 1996) --- In the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility, astronaut Brent W. Jett Jr., STS-81 mission specialist, deploys his "Mae West" device to stay afloat during water bailout survival training. Five STS-81 crewmates, out of frame, joined him for the bailout training exercises.
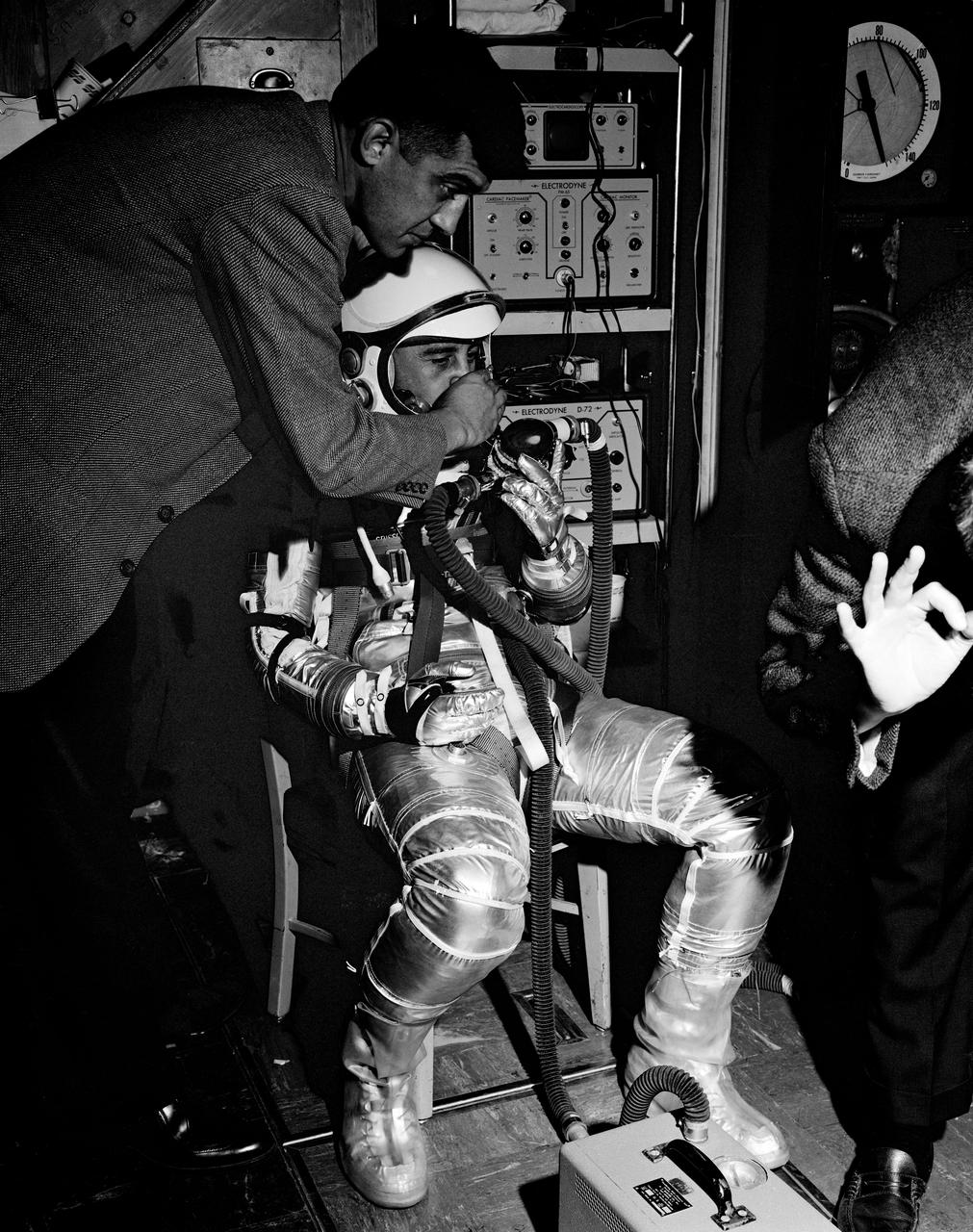

G61-00490 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, wearing the new Mercury pressure suit, is preparing for centrifuge training. He is receiving assistance in adjusting the breathing apparatus which is attached to a data recording device at his feet. Assisting him is Dr. Jackson. Photo credit: NASA

S90-38948 (9 March 1990) --- Astronaut Richard O. Covey, STS-38 commander, is seen in a close-up view during training exercises with a special escape pole. The device was designed and deployed on all active orbiters following the January 1986 Challenger accident.
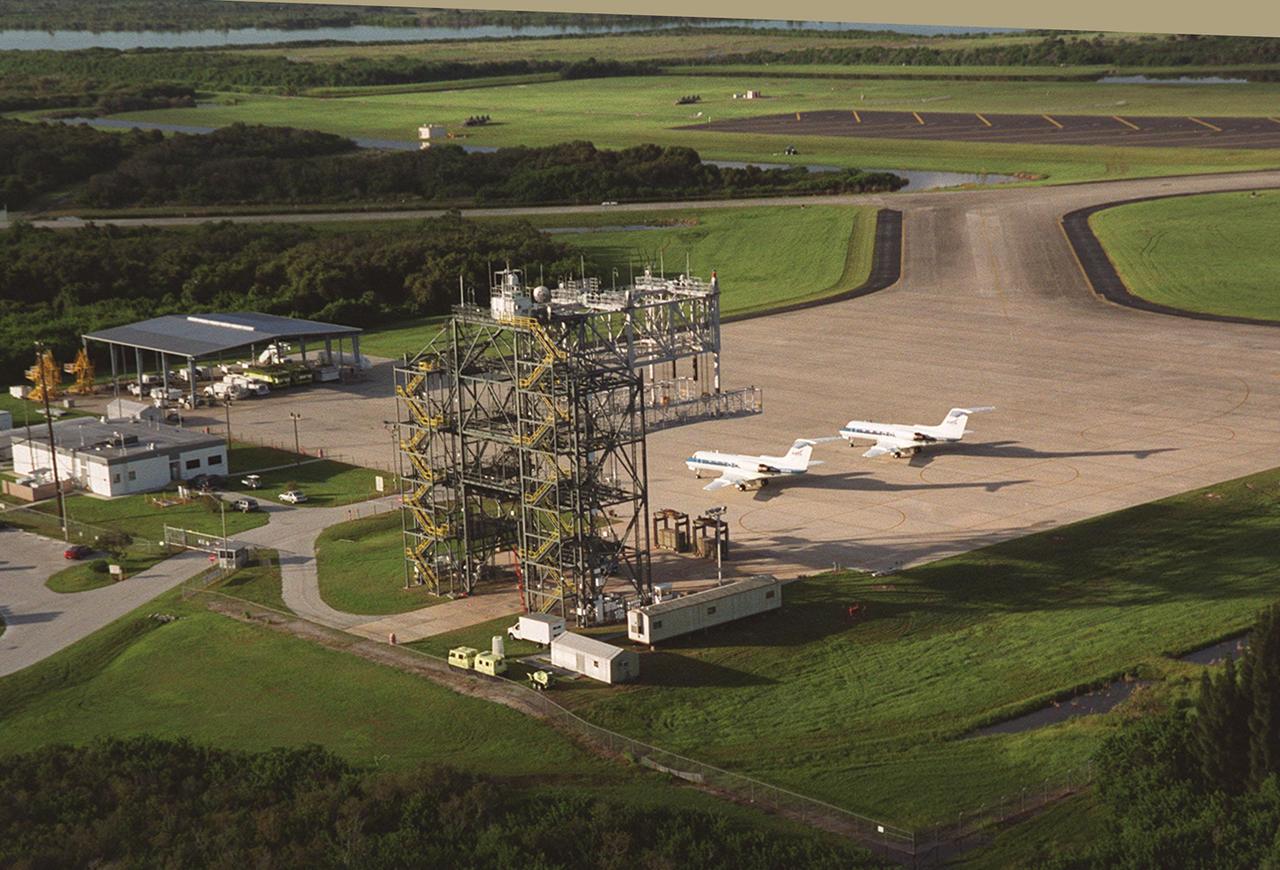

An aerial view of the Shuttle Landing Facility shows the Mate/Demate device in the foreground, with two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) on the ground behind it. Visible in the background is the runway and the taxi way leading from the SLF to the right. The STAs are Grumman Gulfstream 2 aircraft with converted cockpits that emulate those in the Shuttles for practice landings at the SLF.
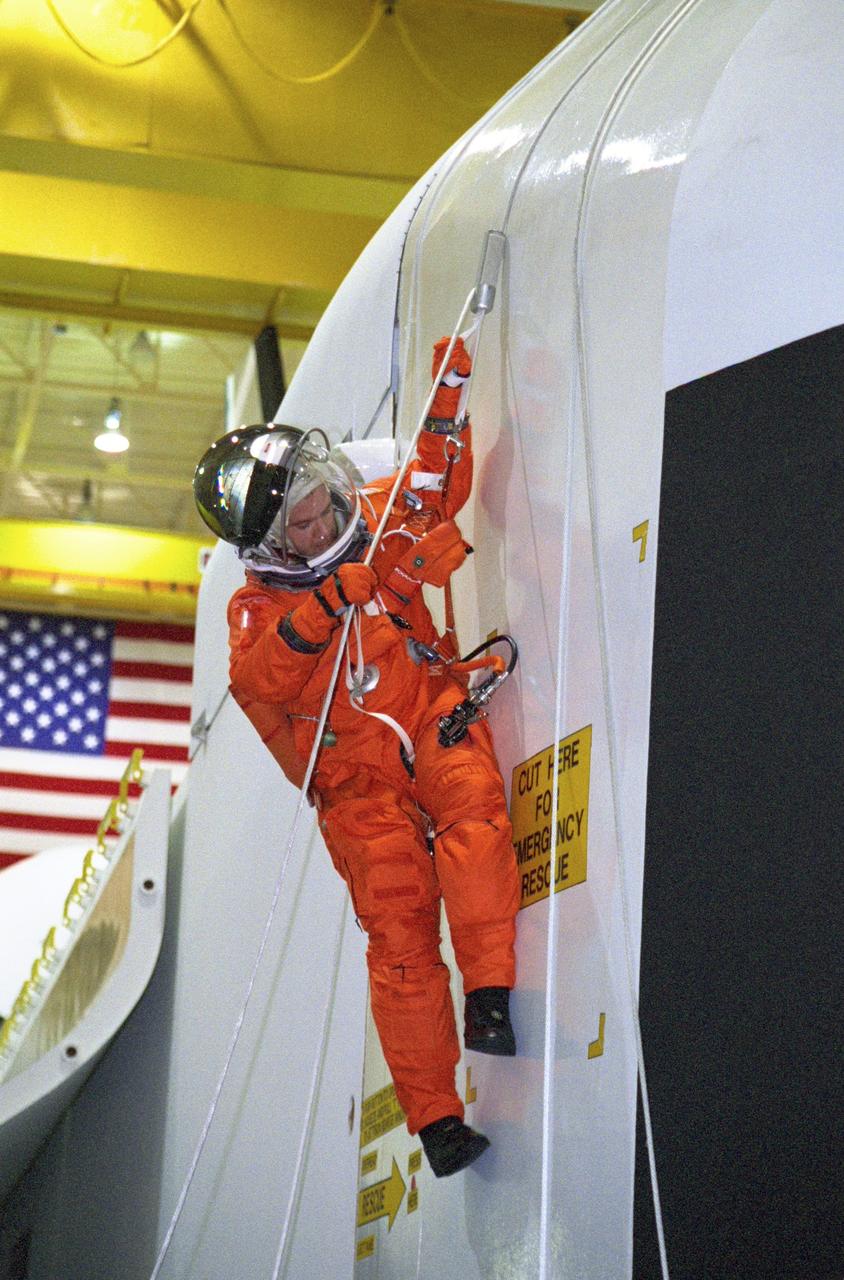

JSC2000-05553 (3 August 2000) --- Astronaut Paul W. Richards, STS-102 mission specialist, during a session of egress training in the Johnson Space Center's Systems Integration Facility, uses a Sky-genie device to escape from a simulated shuttle in trouble. The full fuselage trainer (FFT) is a full scale mockup of a shuttle.
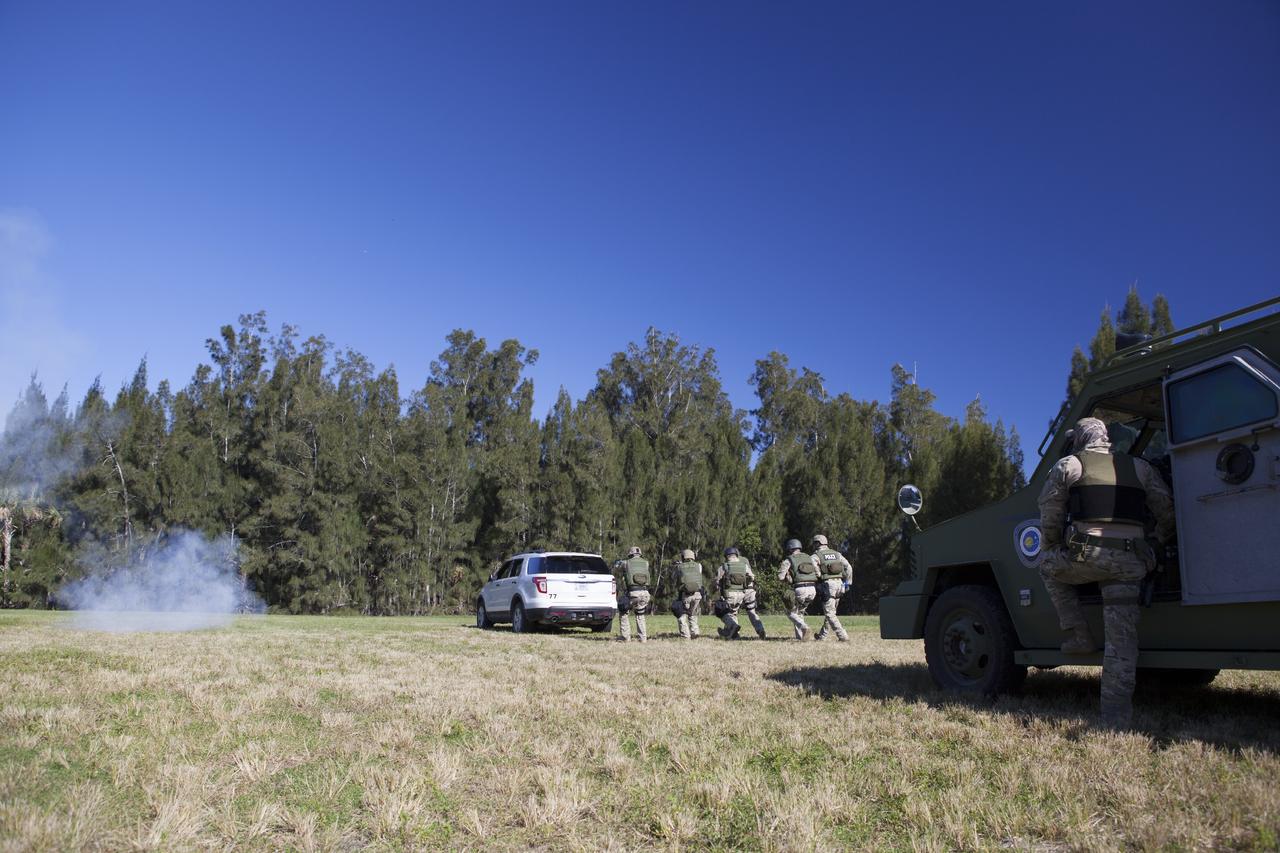

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Protective Services Training Academy at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Emergency Response Team, or ERT, participate in specialized training simulations which includes the use of flash bang diversionary devices. They are wearing full protective gear and carrying non-lethal firearms for the training exercises in order to keep their skills current. Recently, eight members of the ERT competed in the 31st Annual SWAT Roundup International competition in Orlando, Fla., and received recognition by placing in the top five overall. In keeping with NASA’s commitment to safety and security of workforce and assets, the ERT is part of Kennedy’s security team and is trained to respond in the event of an emergency at the center. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
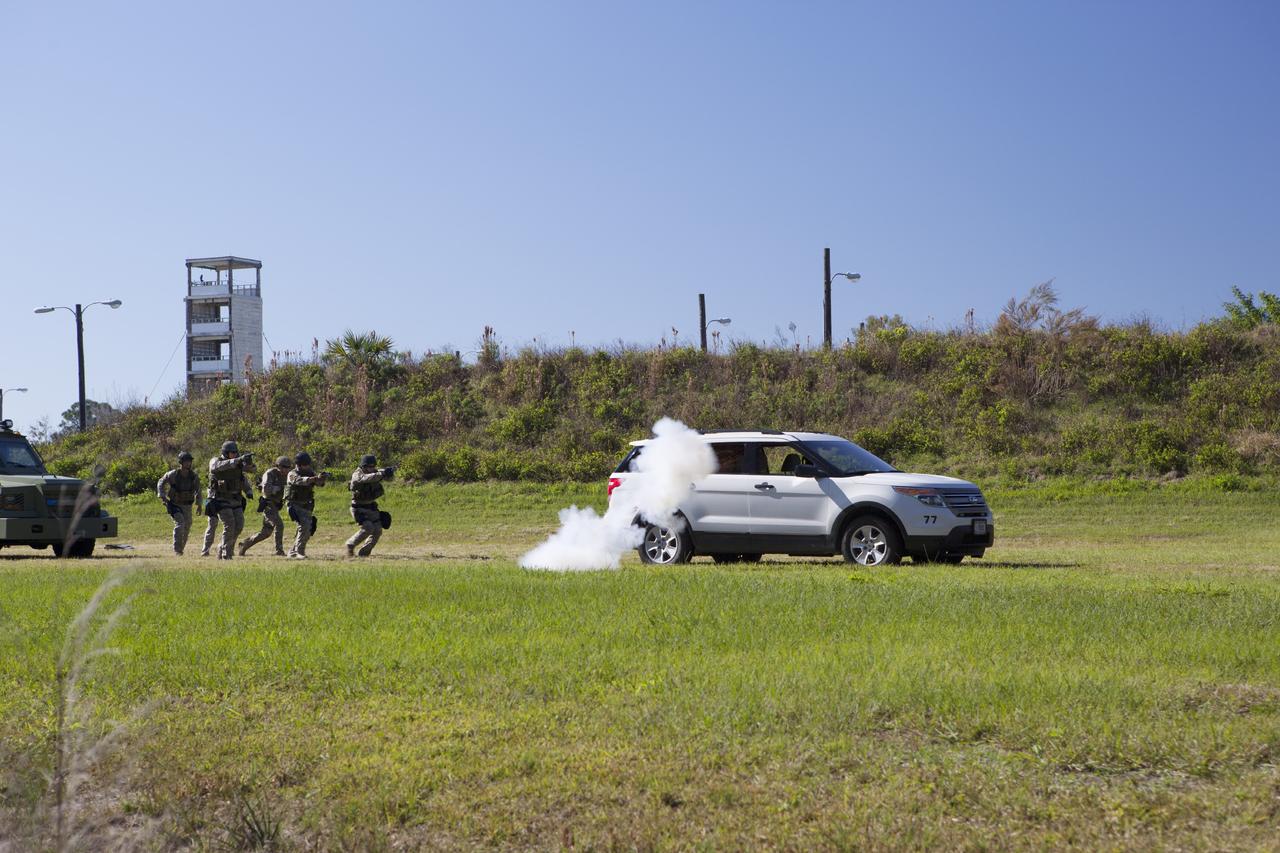

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Protective Services Training Academy at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Emergency Response Team, or ERT, participate in specialized training simulations which includes the use of flash bang diversionary devices. They are wearing full protective gear and carrying non-lethal firearms, for the training exercises in order to keep their skills current. Recently, eight members of the ERT competed in the 31st Annual SWAT Roundup International competition in Orlando, Fla., and received recognition by placing in the top five overall. In keeping with NASA’s commitment to safety and security of workforce and assets, the ERT is part of Kennedy’s security team and is trained to respond in the event of an emergency at the center. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
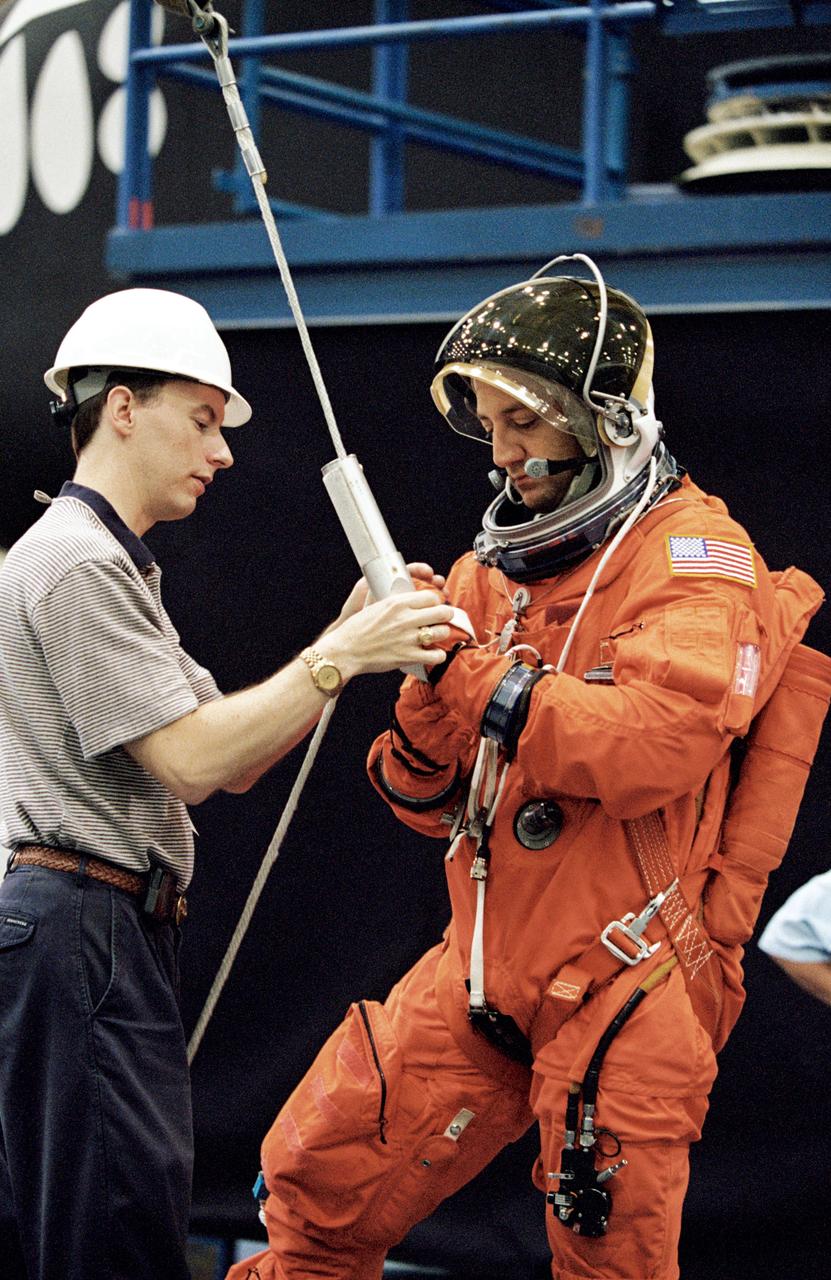

JSC2001-01543 (24 May 2001) --- Astronaut Michael J. Massimino, STS-109 mission specialist, is briefed by United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer David Pogue on the usage of the Sky-genie device, used to lower oneself from a troubled shuttle, in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Massimino is wearing a training version of the full-pressure launch and entry suit. STS-109 will be the 108th shuttle flight and the fourth Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission.
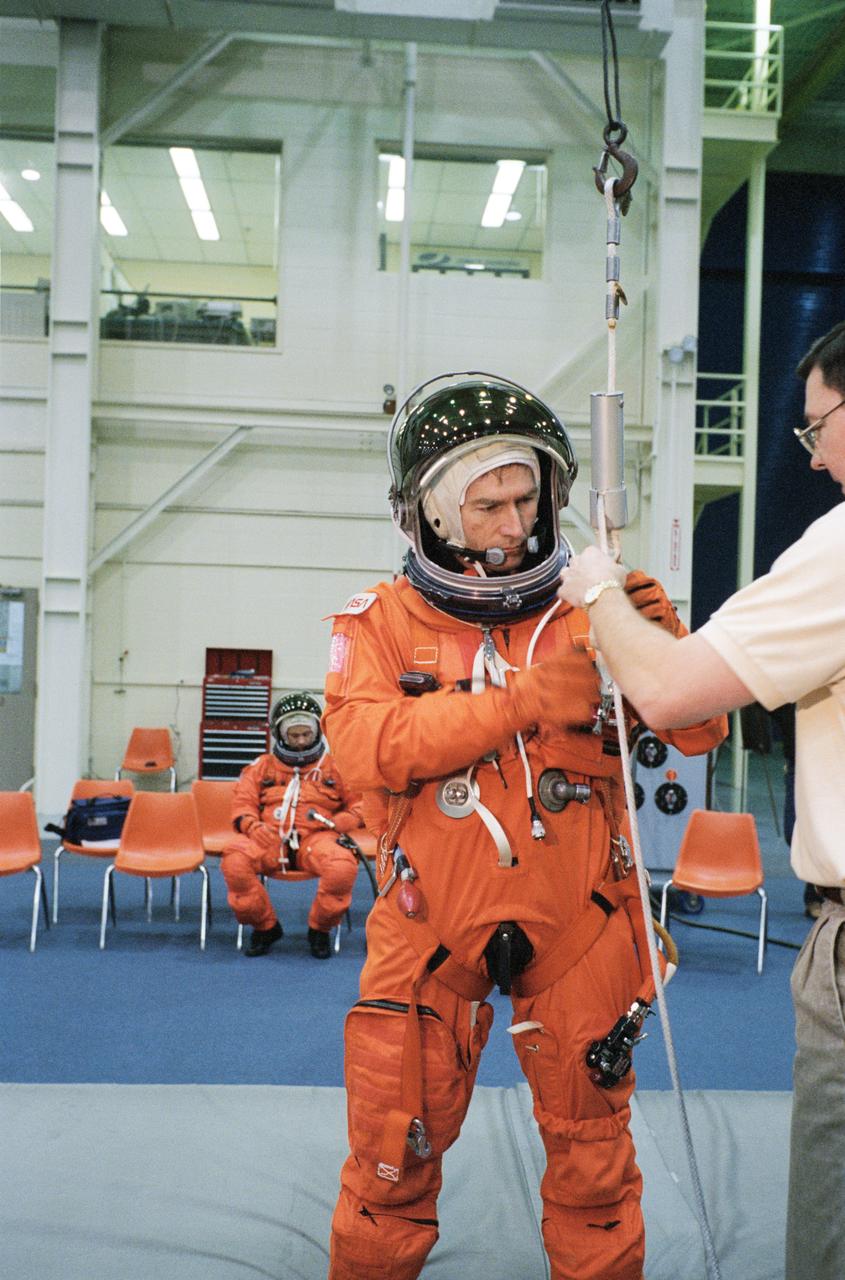

S95-09157 (27 Apr. 1995) --- Payload specialist Fred W. Leslie has just translated from the top of a Shuttle mockup-trainer using a Sky-genie device during emergency egress training with his six STS-73 crew mates. He is assisted here by Scott Gill, a member of the STS-73 training staff. The seven will fly aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia later this year to support the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
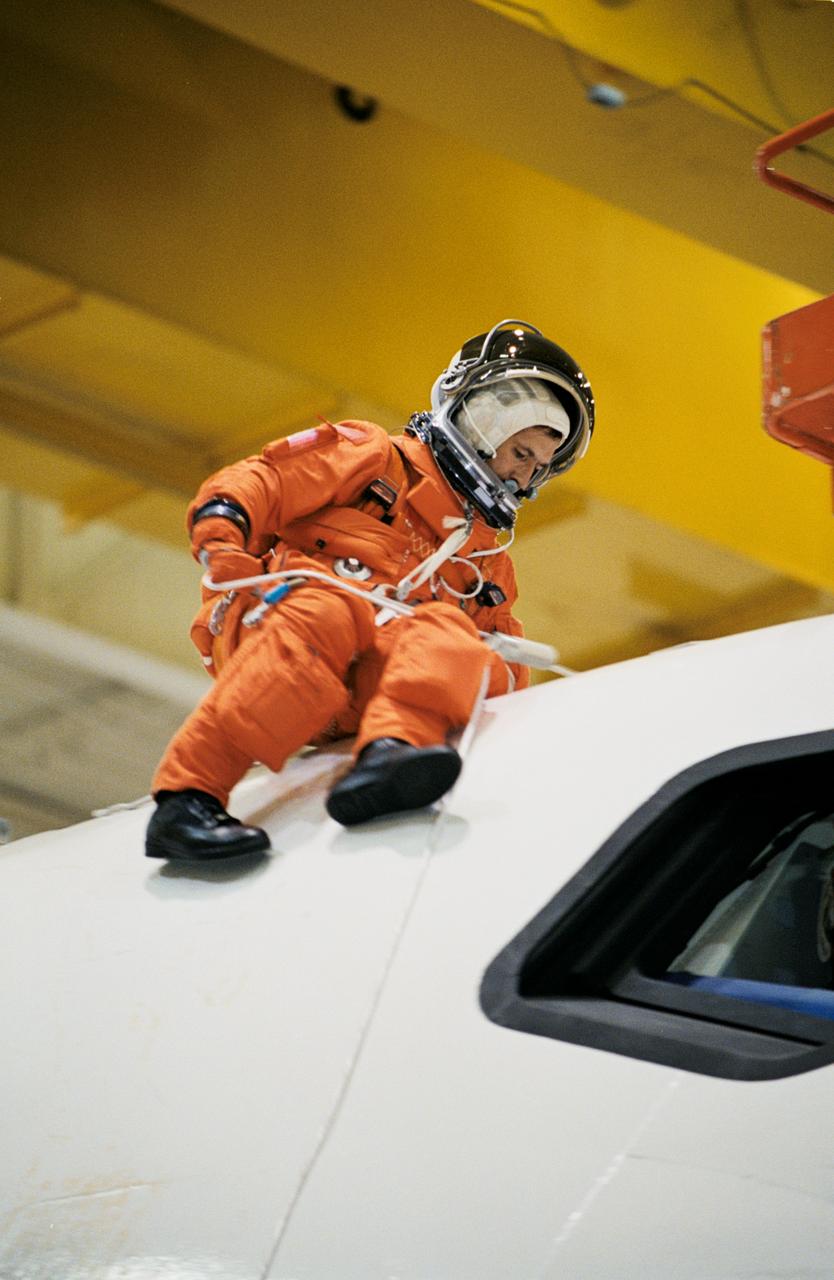

JSC2002-00713 (25 March 2002) --- Astronaut John B. Herrington, STS-113 mission specialist, uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mockup is called the Full Fuselage Trainer (FFT). This exercise trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. Herrington and his crewmates will drop off the Expedition Six crew at the International Space Station (ISS).
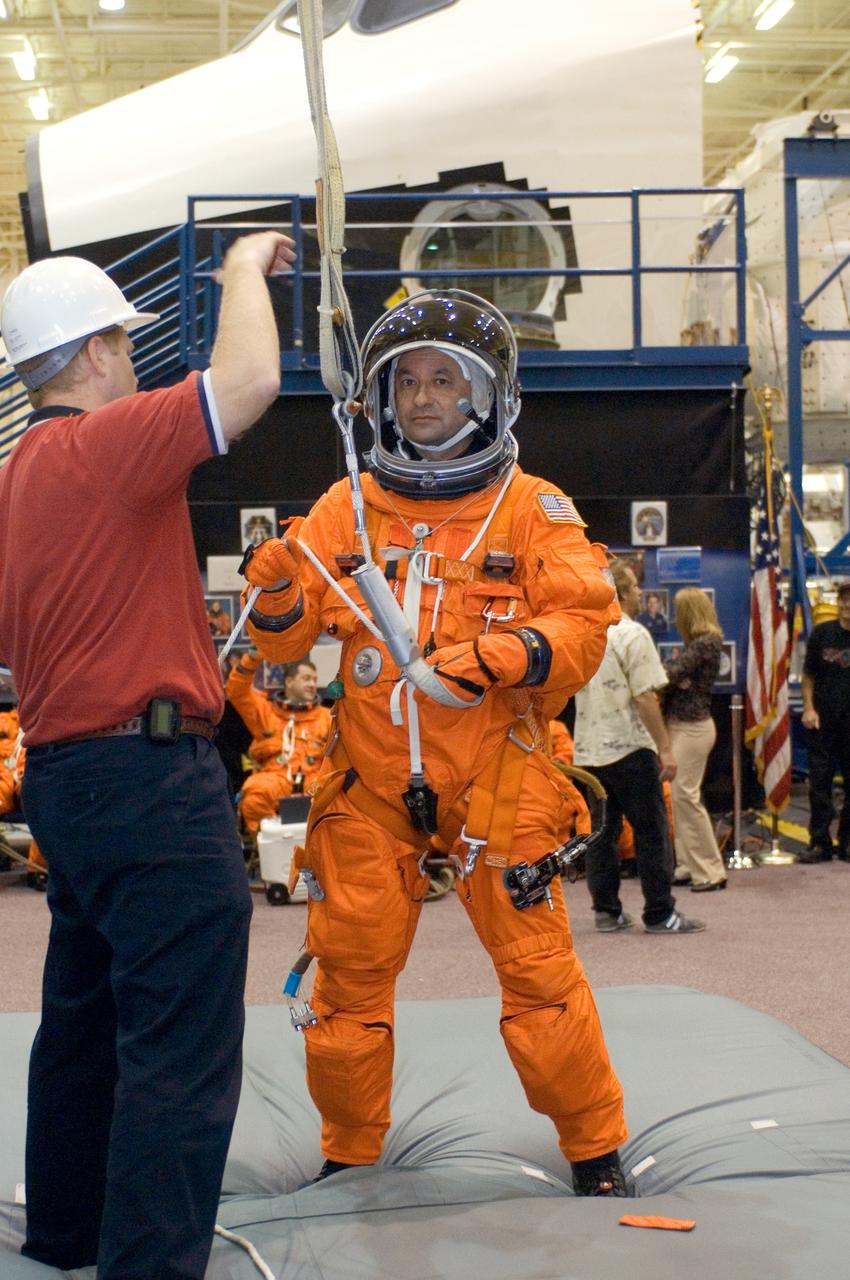

JSC2005-E-32736 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Crew trainer Bob Behrendsen briefs astronaut Mark L. Polansky, STS-116 commander, on the usage of a special pulley device, used to lower oneself from a trouble-plagued shuttle, during a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Polansky is attired in a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
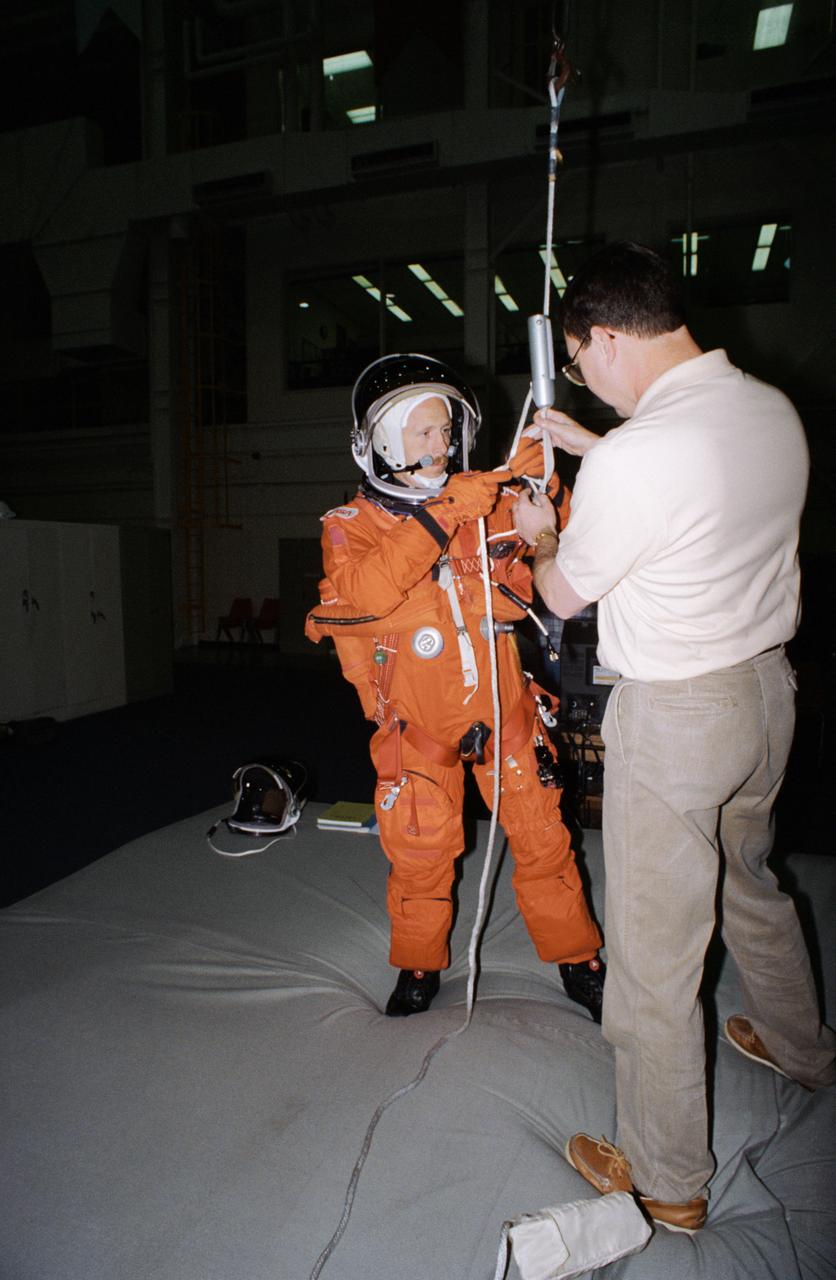

S95-09153 (27 Apr. 1995) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox has just translated from the top of a Shuttle mockup-trainer using a Sky-genie device during emergency egress training with his six STS-73 crew mates. He is assisted here by Scott Gill, a member of the STS-73 training staff. The seven will fly aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia later this year to support the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
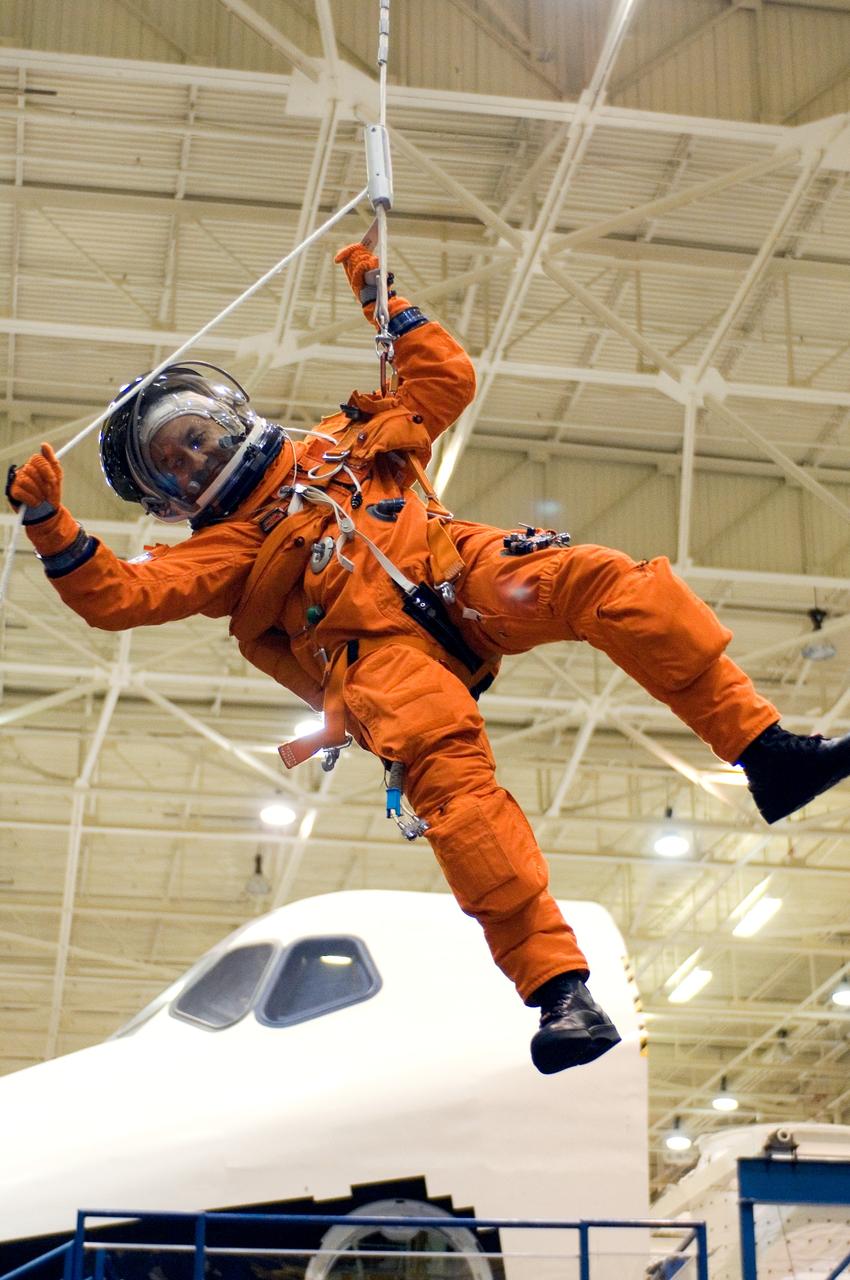

JSC2005-E-32739 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Astronaut Mark L. Polansky, STS-116 commander, uses a special pulley device to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle during a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Polansky is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
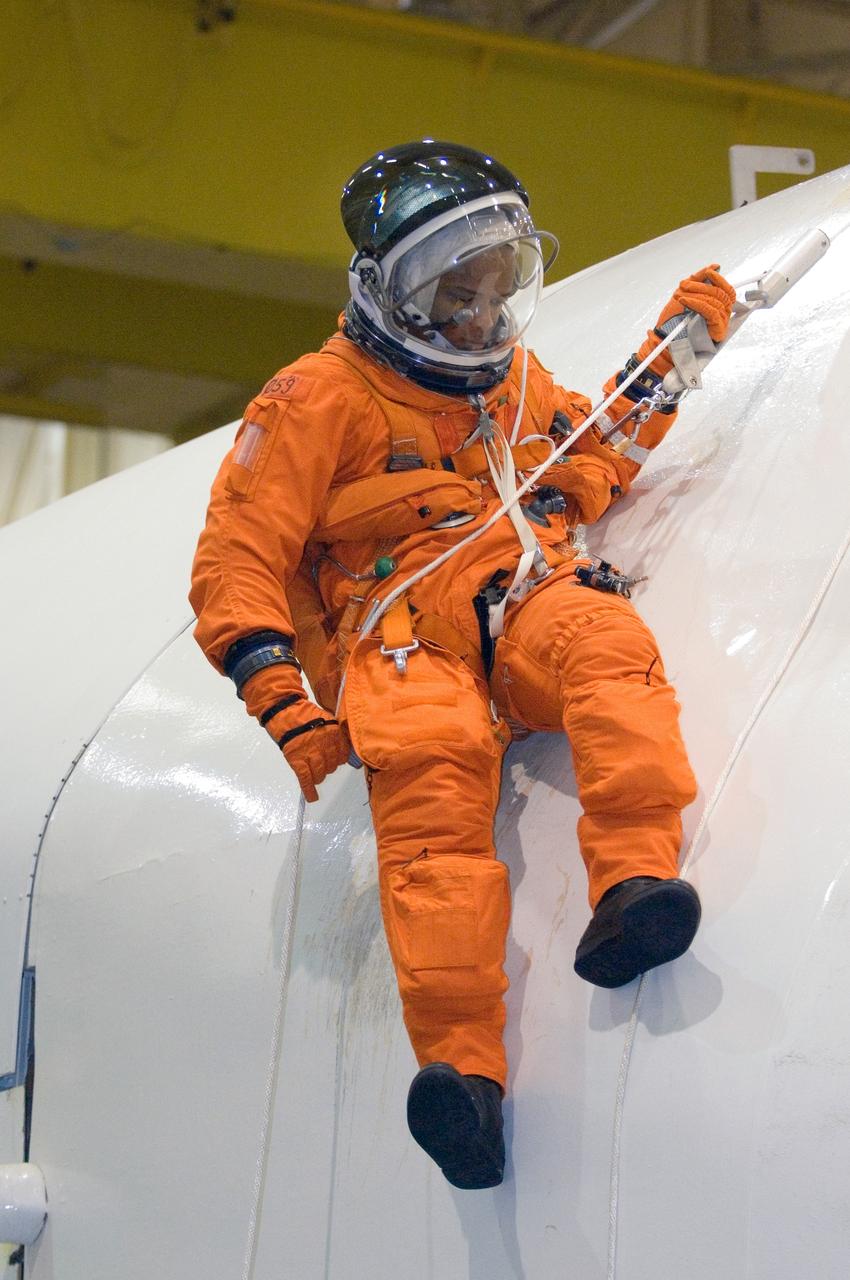

JSC2005-E-32763 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, STS-116 mission specialist, uses a special pulley device to escape from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle during a session of egress training in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at Johnson Space Center. The full fuselage trainer (FFT) is a full-scale mockup of a shuttle. Curbeam is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
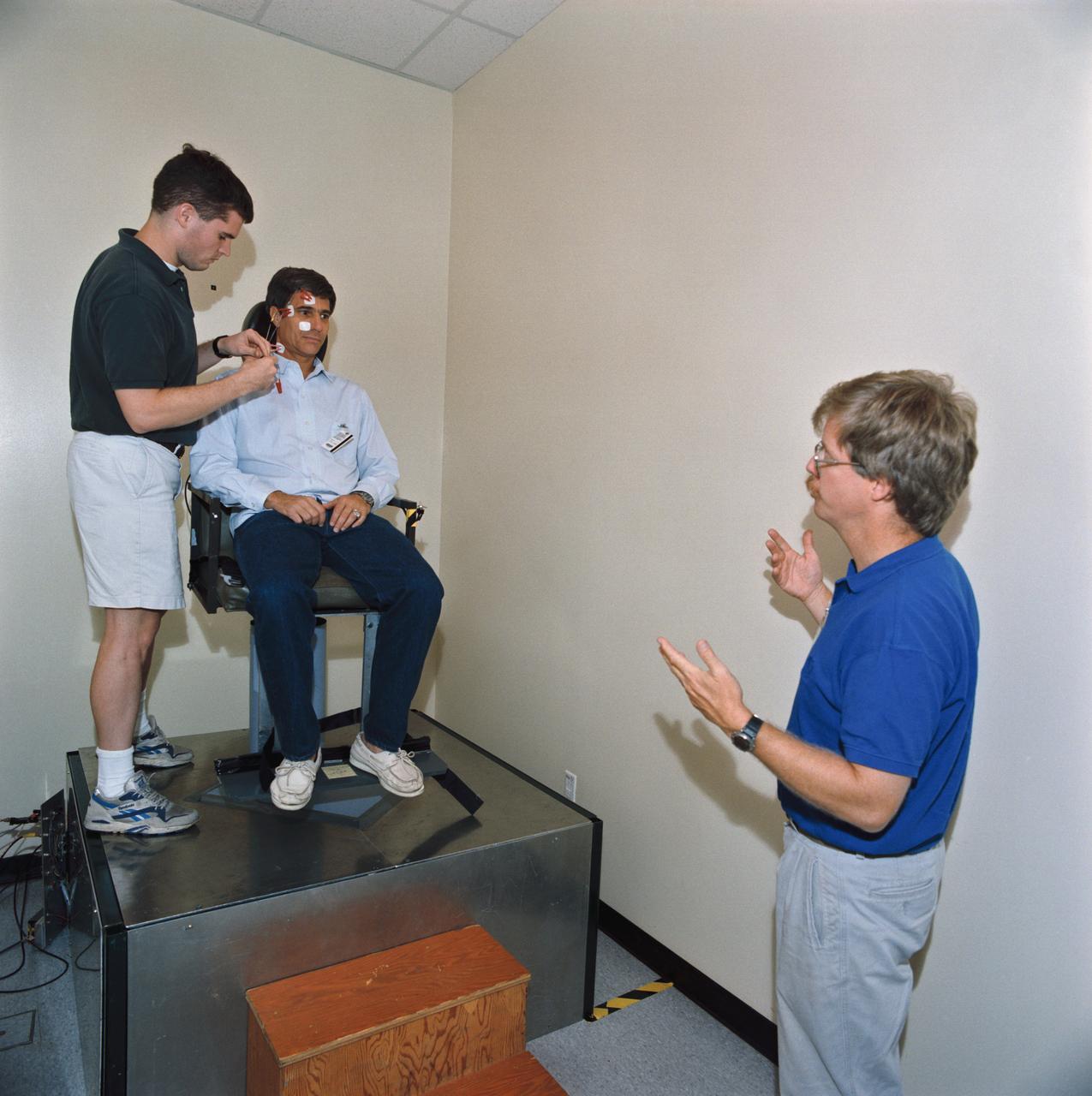
S93-45366 (29 Sept 1993) --- Astronaut John E. Blaha, STS-58 mission commander, sits in a training version of the rotating chair test device. Sensors are attached to Blaha's head and face to record responses to the rotation. Blaha was participating with five other NASA astronauts and a payload specialist for data collection and training in preparation for the two week Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission.
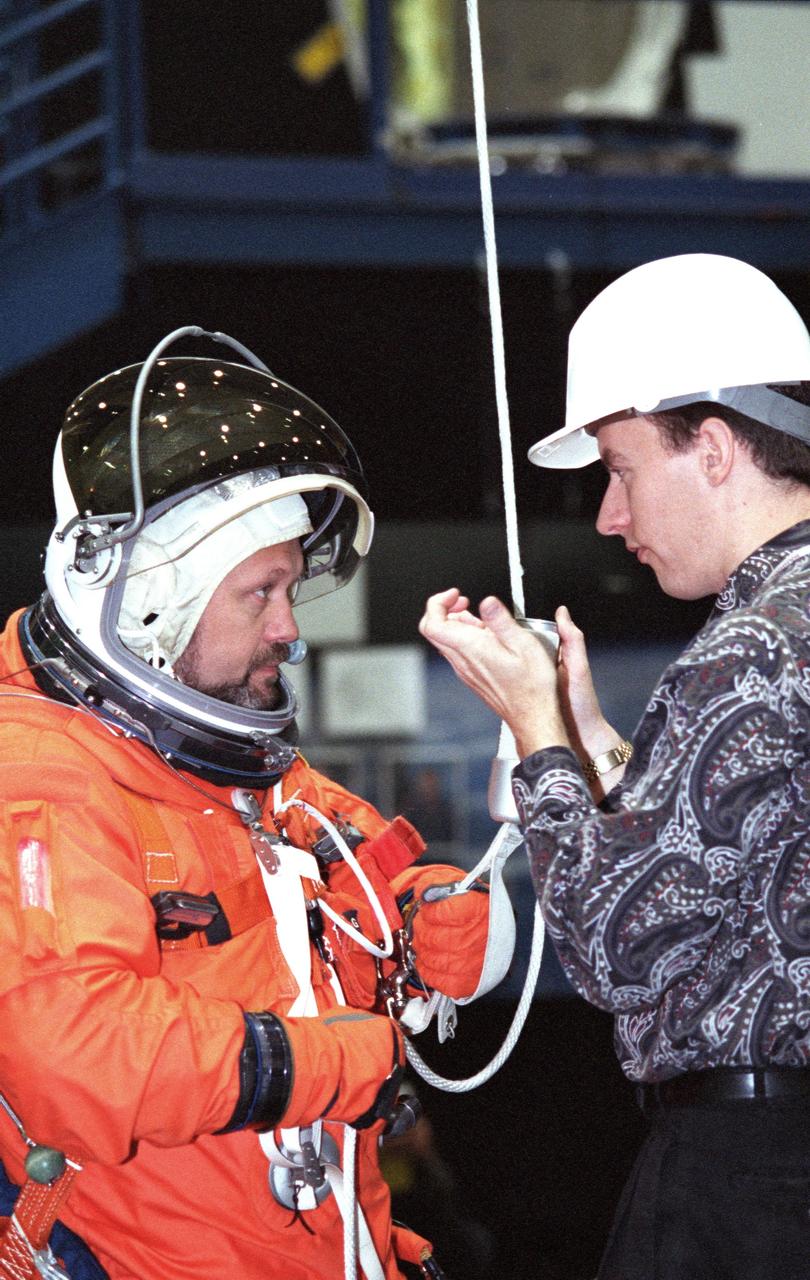

JSC2000-02938 (5 April 2000) --- David Pogue (right), a crew escape equipment trainer, briefs cosmonaut Boris V. Morukov on the usage of a special device that enables the STS-106 mission specialist to rappel from a shuttle in trouble on the ground. A nearby crew-training mockup in the JSC's Systems Integration Facility allowed the Russian Aviation and Space Agency's cosmonaut the opportunity to train for procedures to follow in the event of the need to evacuate a distressed shuttle's cabin while on the ground.
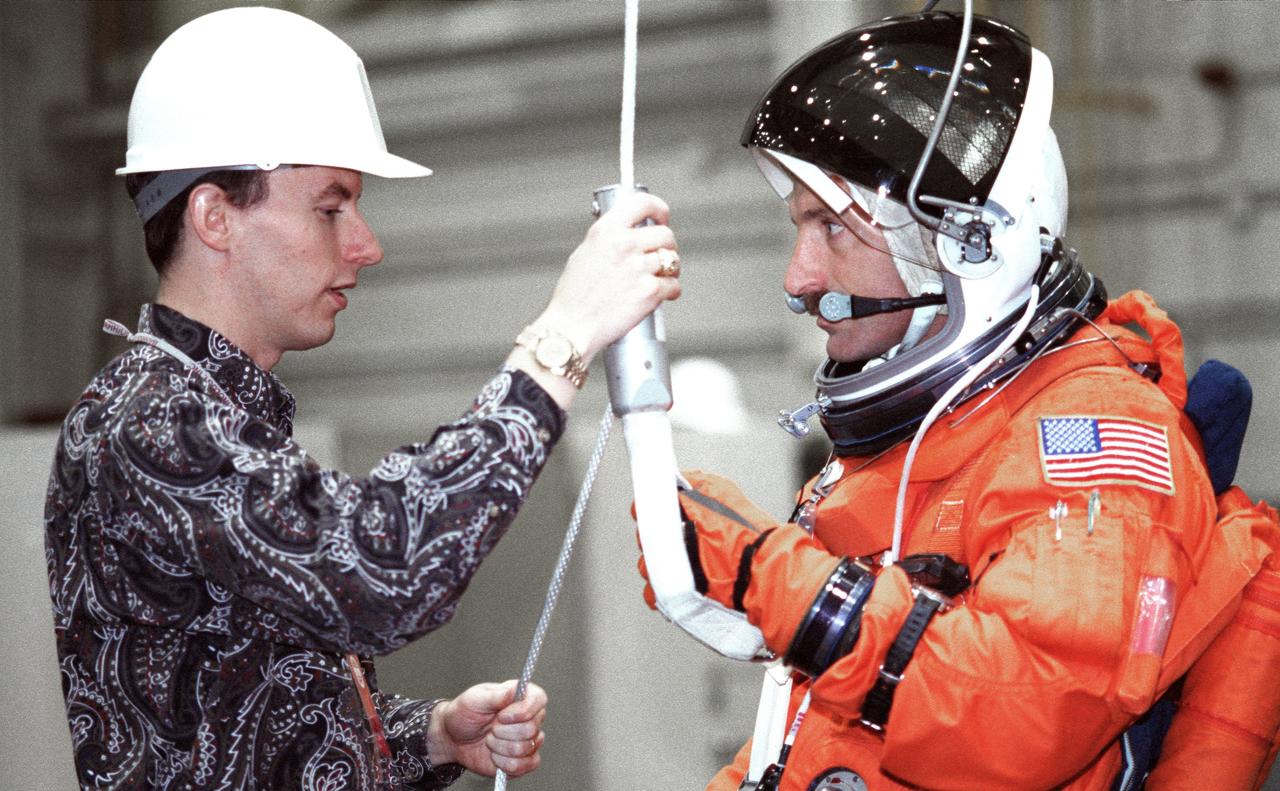

JSC2000-02939 (5 April 2000) --- David Pogue (left), a crew escape equipment trainer, briefs astronaut Daniel C. Burbank on the usage of a special device that enables the mission specialist to rappel from a shuttle in trouble on the ground. A nearby crew-training mockup in the JSC's Systems Integration Facility allowed Burbank and his six crew mates the opportunity to train for procedures to follow in the event of the need to evacuate a distressed shuttle's cabin while on the ground.
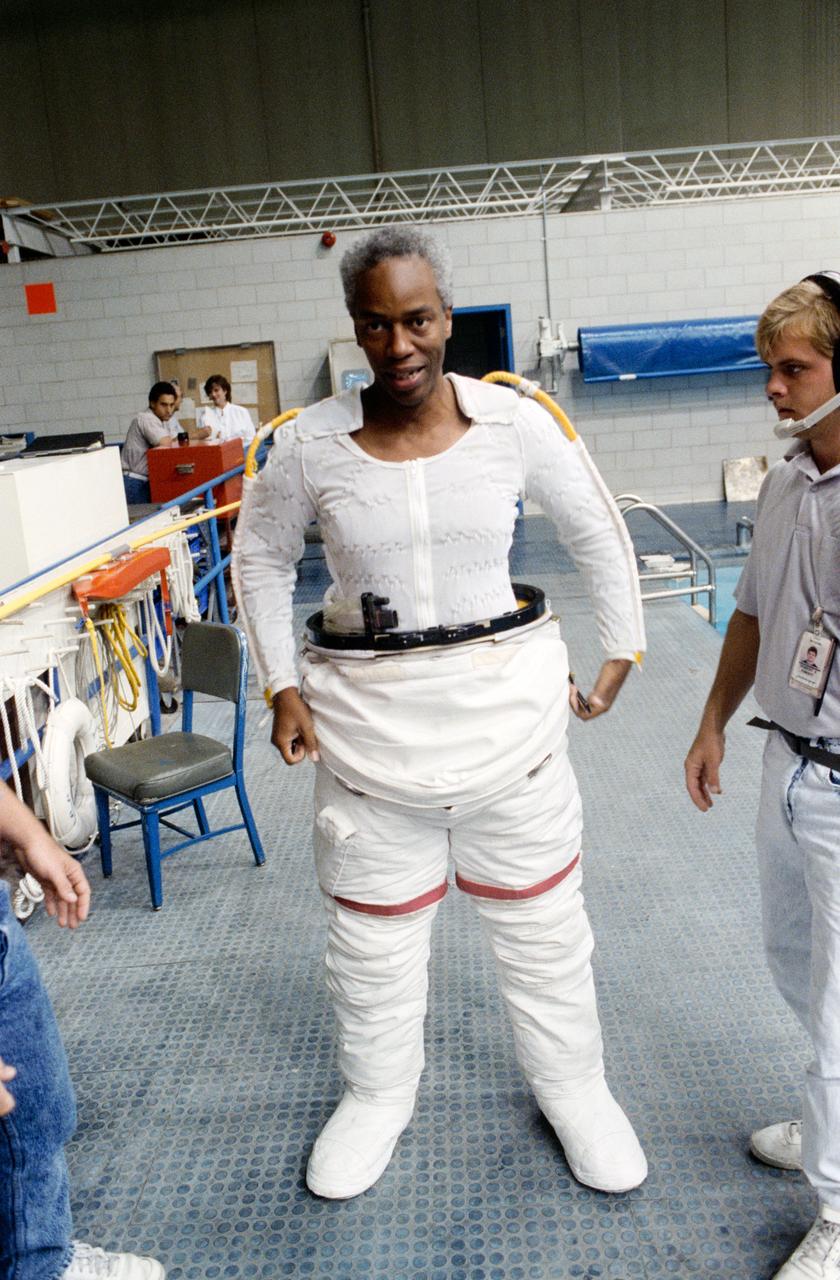

S90-44106 (August 1990) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, mission specialist for STS-39, wearing part of an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to participate in a training session for the scheduled March 1991 spaceflight. Soon after this picture was taken, Bluford was lowered into water by a hoist device for the underwater rehearsal of a contingency EVA. The scene is in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F) which houses a 25-ft. deep pool (visible in right background).
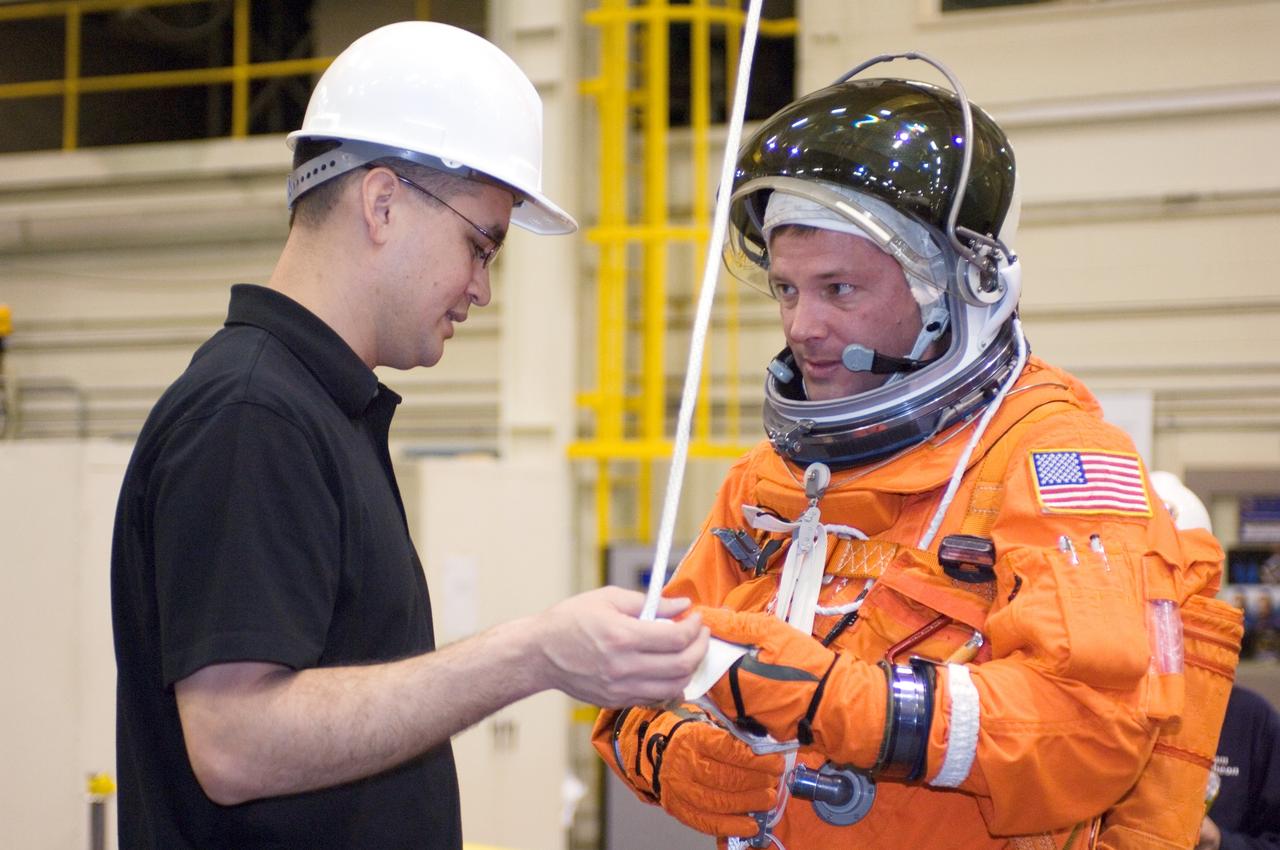

JSC2007-E-18102 (9 April 2007) --- United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer Adam Flagan (left) briefs astronaut Douglas H. Wheelock, STS-120 mission specialist, on the usage of a special pulley device, used to lower oneself from a trouble-plagued shuttle. The briefing came during an emergency egress training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Wheelock is wearing a training version of his shuttle launch and entry suit.
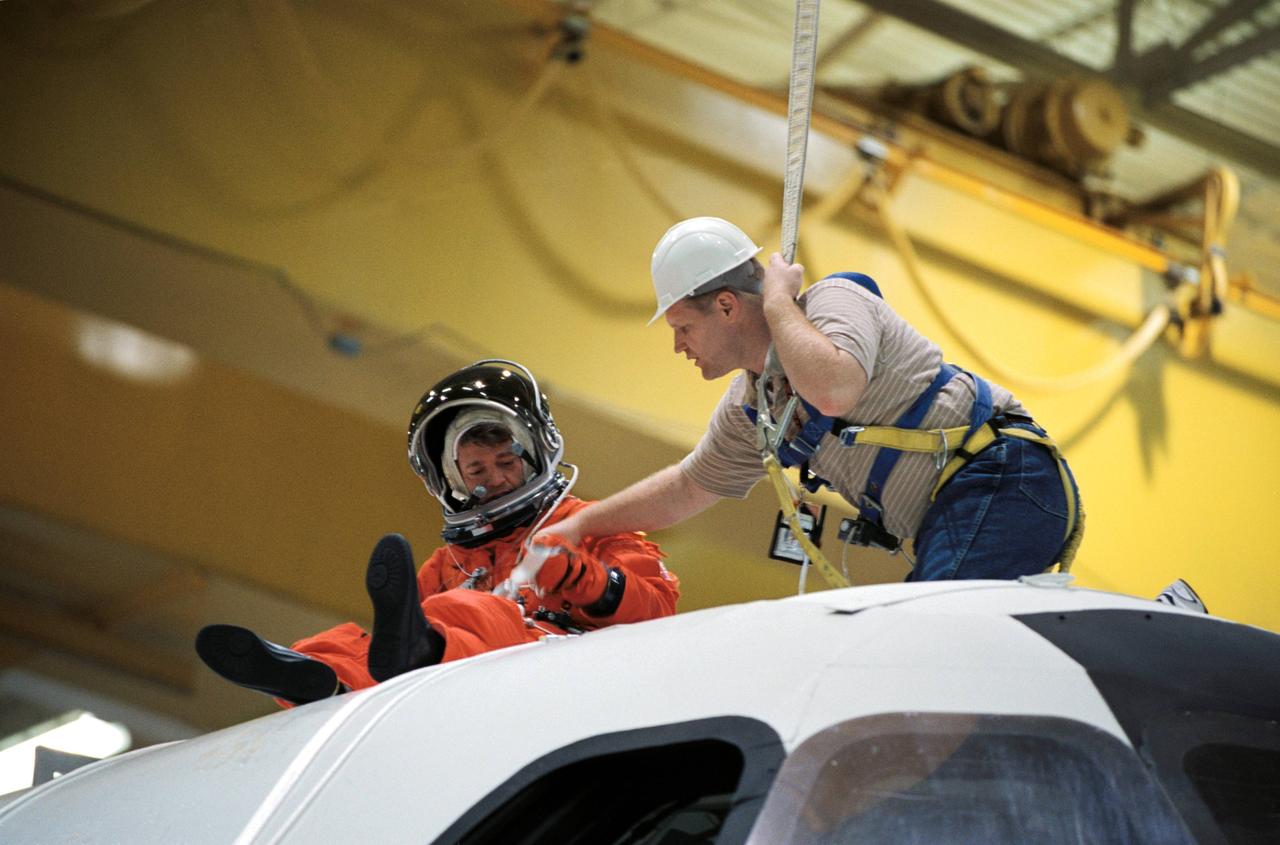

JSC2002-00864 (24 April 2002) --- Astronaut Jeffrey S. Ashby, STS-112 mission commander, uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mockup is called the Full Fuselage Trainer (FFT). This exercise trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer Bob Behrendsen assisted Ashby.
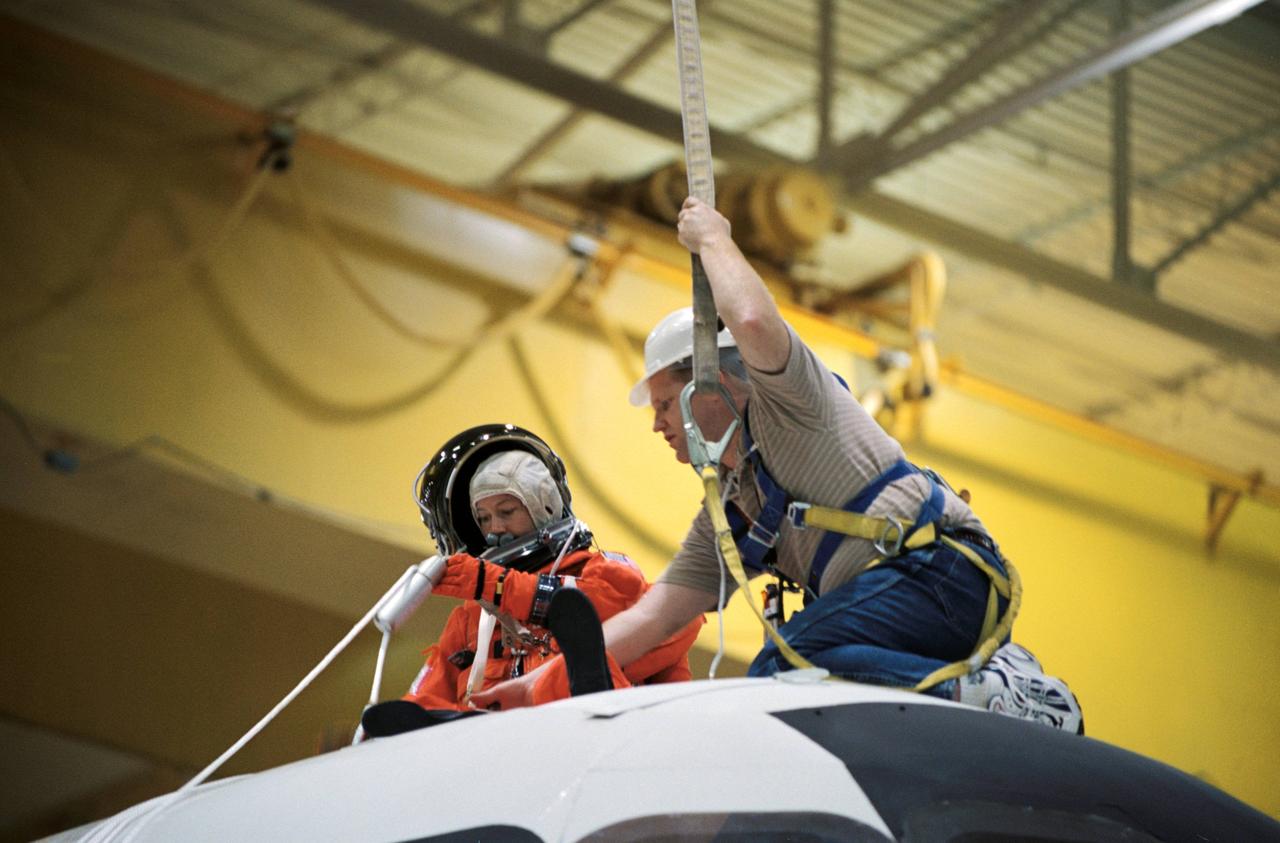

JSC2002-00862 (24 April 2002) --- Astronaut Pamela A. Melroy, STS-112 pilot, uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mockup is called the Full Fuselage Trainer (FFT). This exercise trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer Bob Behrendsen assisted Melroy.
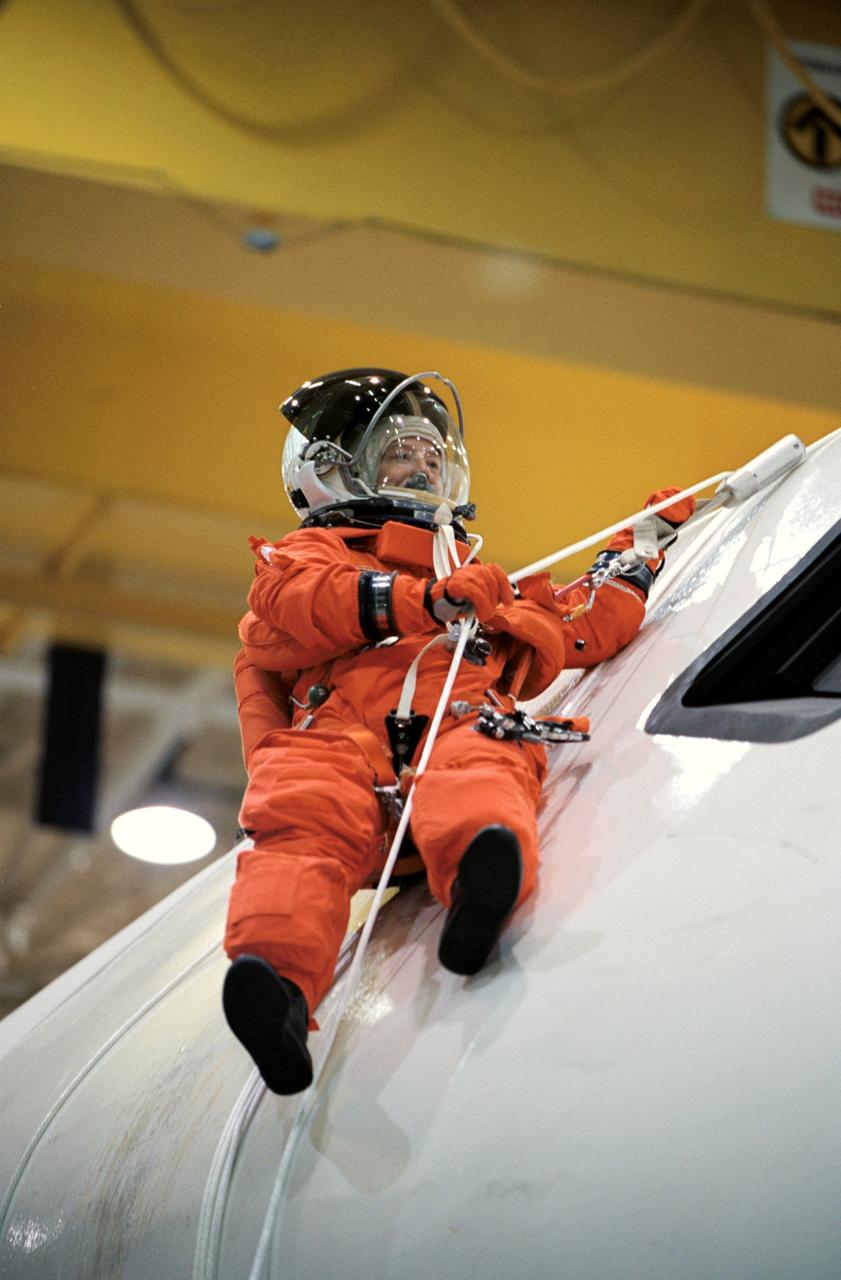

JSC2002-00863 (24 April 2002) --- Astronaut Pamela A. Melroy, STS-112 pilot, uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mockup is called the Full Fuselage Trainer (FFT). This exercise trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground.
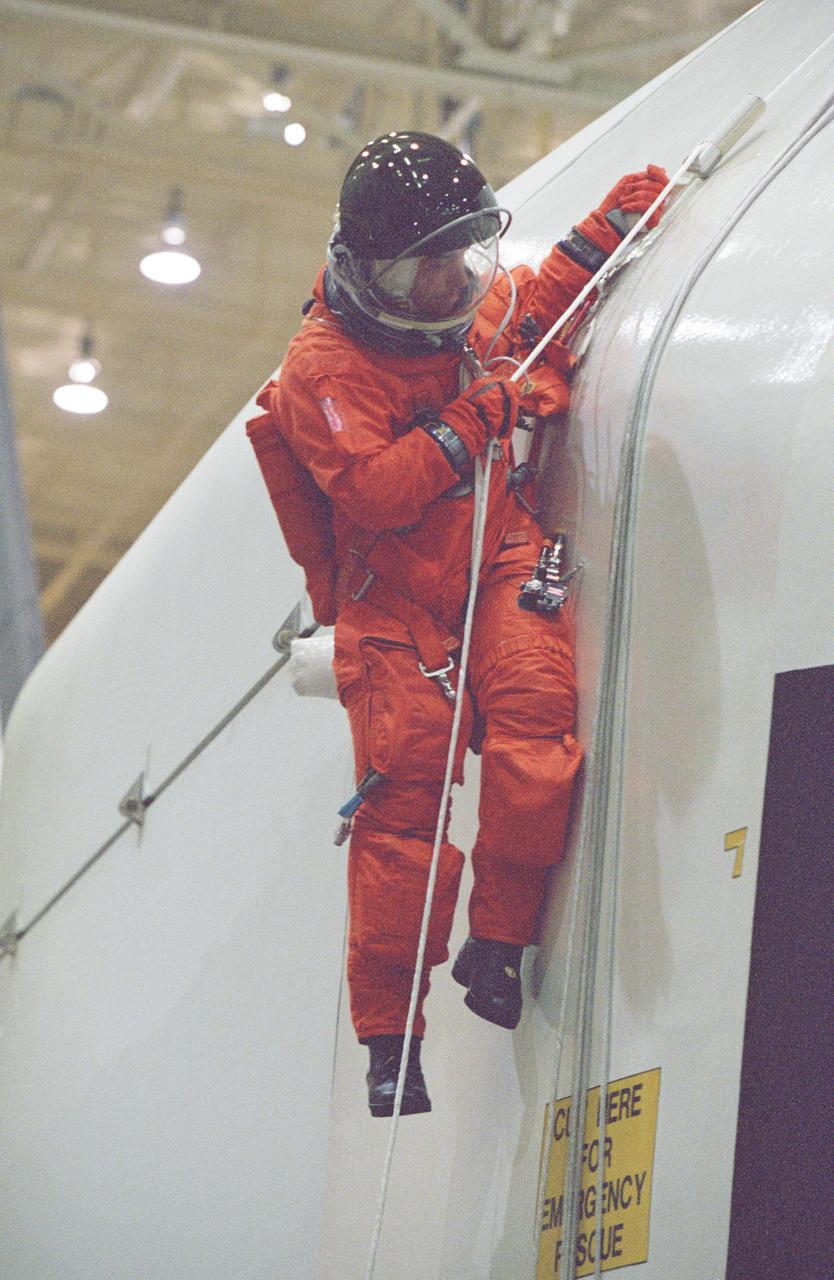

JSC2001-01552 (24 May 2001) --- An unidentified member of the STS-109 crew uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mockup is called the Full Fuselage Trainer (FFT). This exercise trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. STS-109 will be the 108th shuttle flight and the fourth Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission.
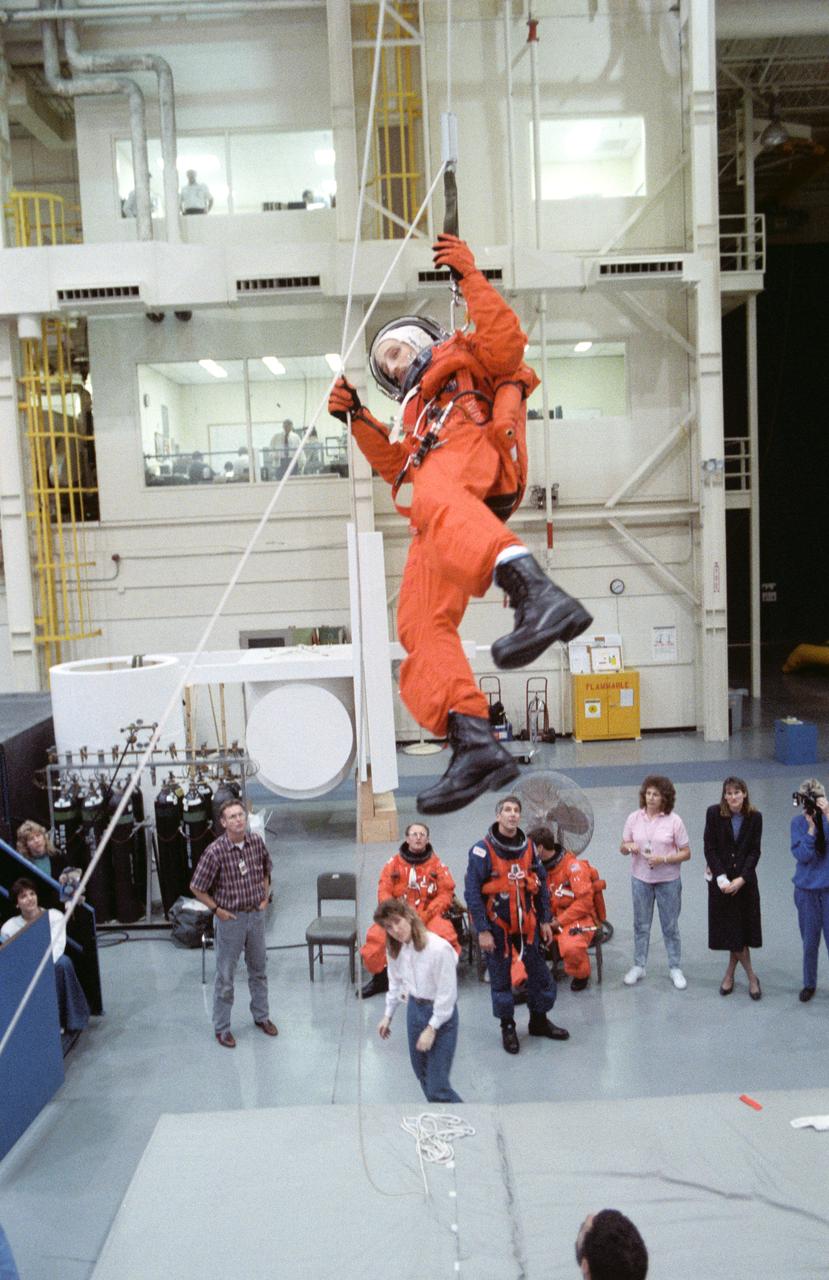

S89-25704 (Feb 1989) --- Astronaut James P. Bagian, STS-29 mission specialist, works his way down to "safety" using a Sky-genie device during emergency egress training for his five-member crew. Three other crewmembers watch in the background and await their turns with the rehearsal. The training took place in the Johnson Space Center's Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory.
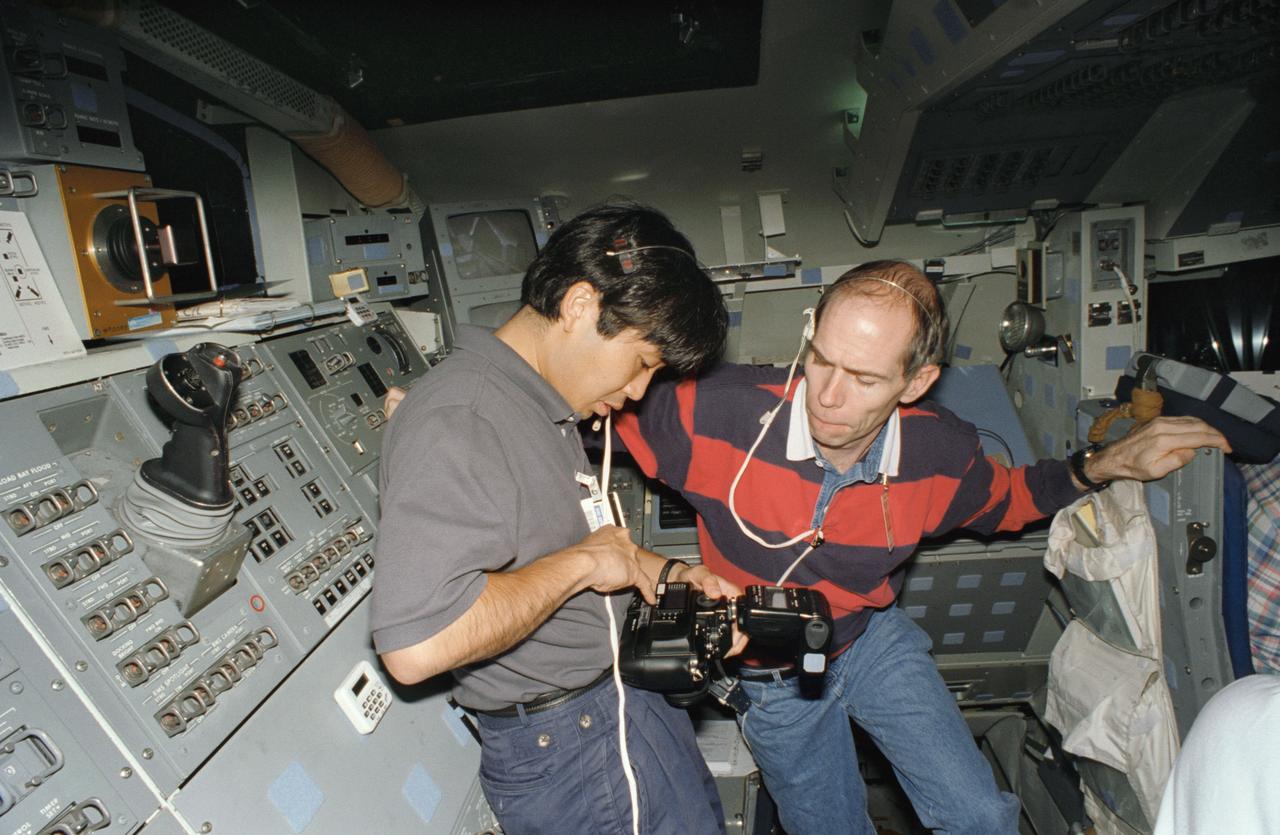

S95-12703 (May 1995) --- Astronauts Koichi Wakata (left) and Daniel T. Barry check the settings on a 35mm camera during an STS-72 training session. Wakata is a mission specialist, representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) and Barry is a United States astronaut assigned as mission specialist for the same mission. The two are on the aft flight deck of the fixed base Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).
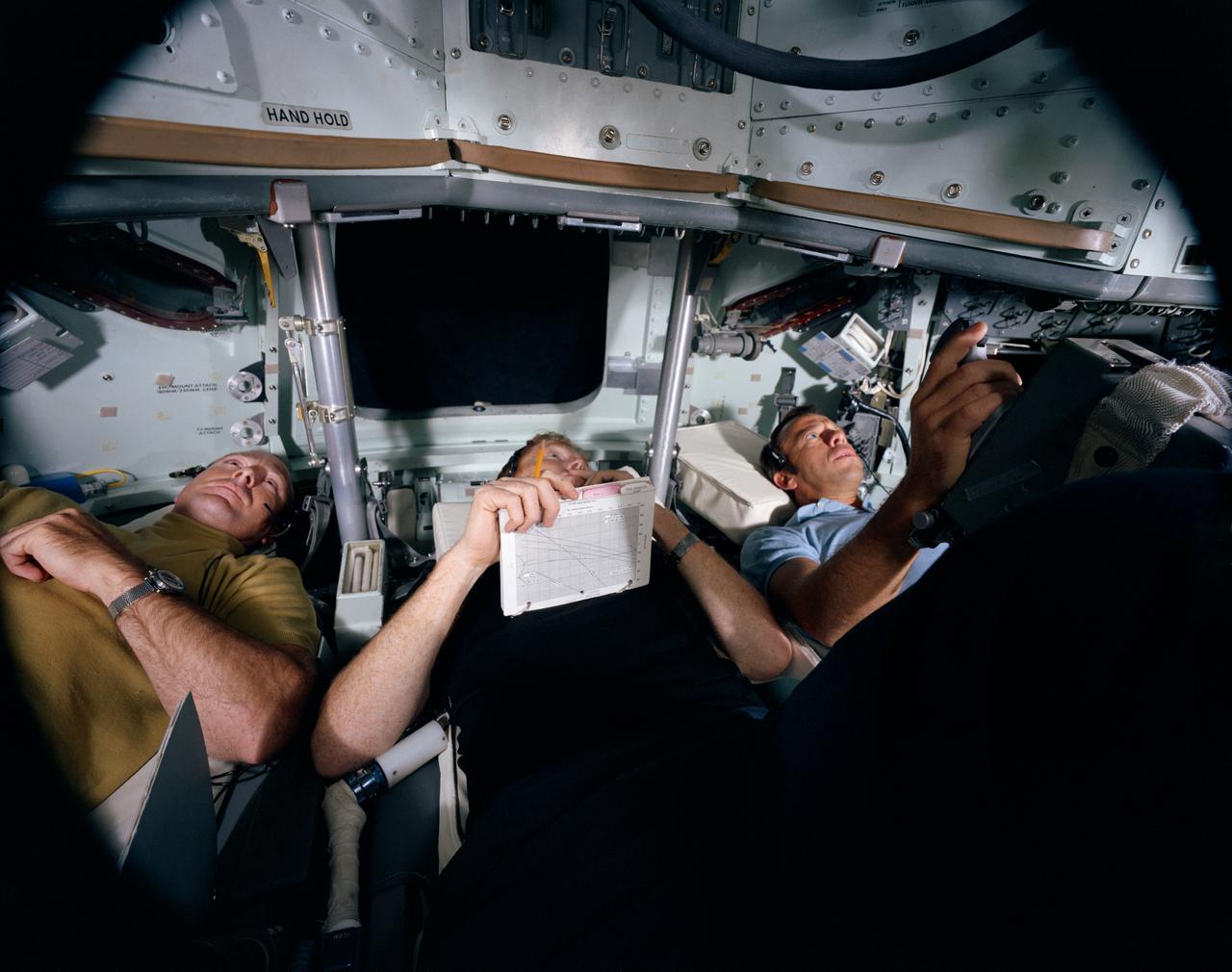

S70-45580 (July 1970) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission participate in Command Module (CM) simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Left to right are astronauts Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander.
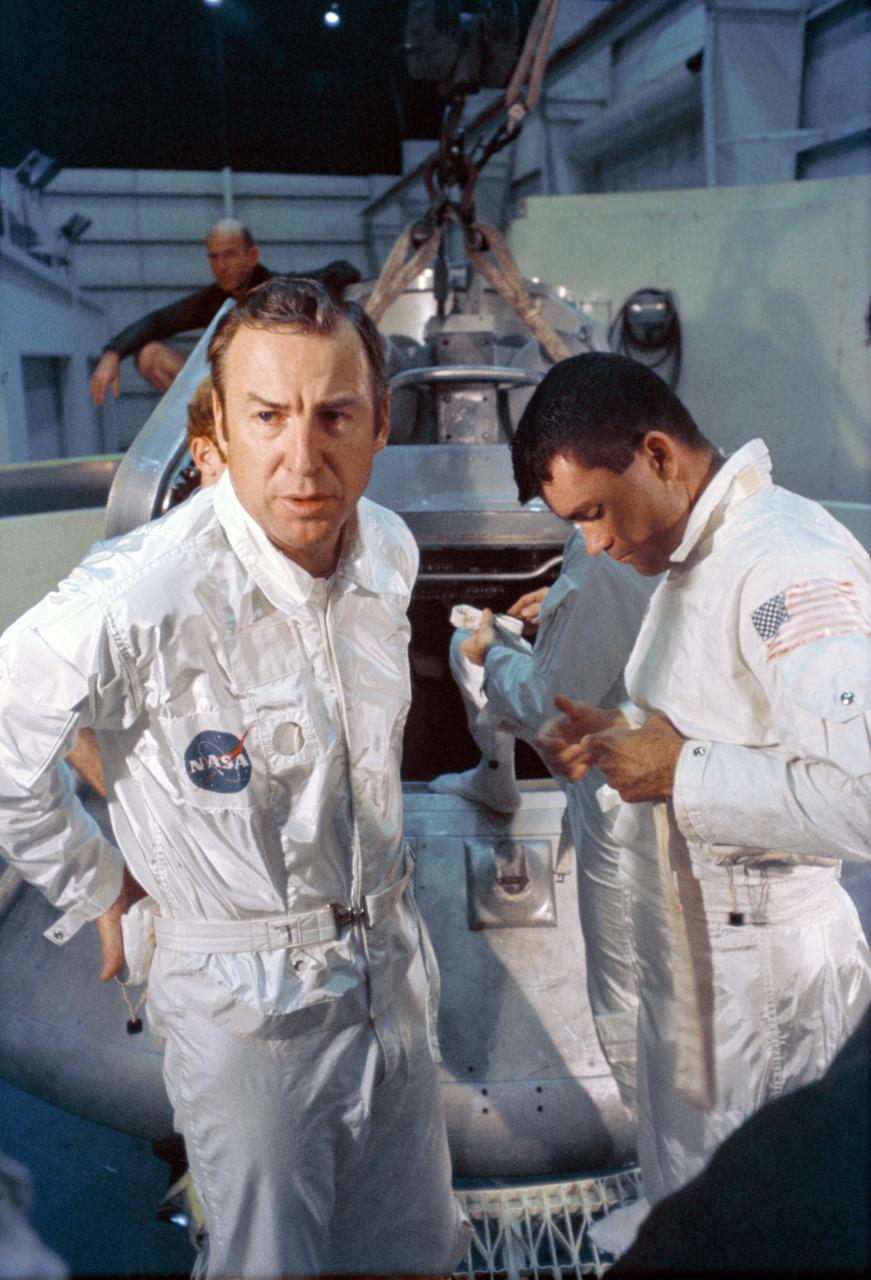

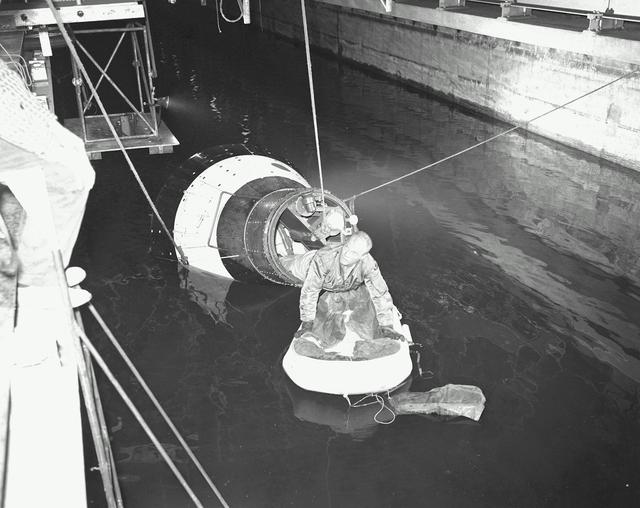
S70-24010 (17 Jan. 1970) --- The three prime crew members of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission stand by to participate in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). They are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (left) commander; Fred W. Haise Jr., (right) lunar module pilot; and Thomas K. Mattingly II (in background, obscured by Haise), command module pilot.
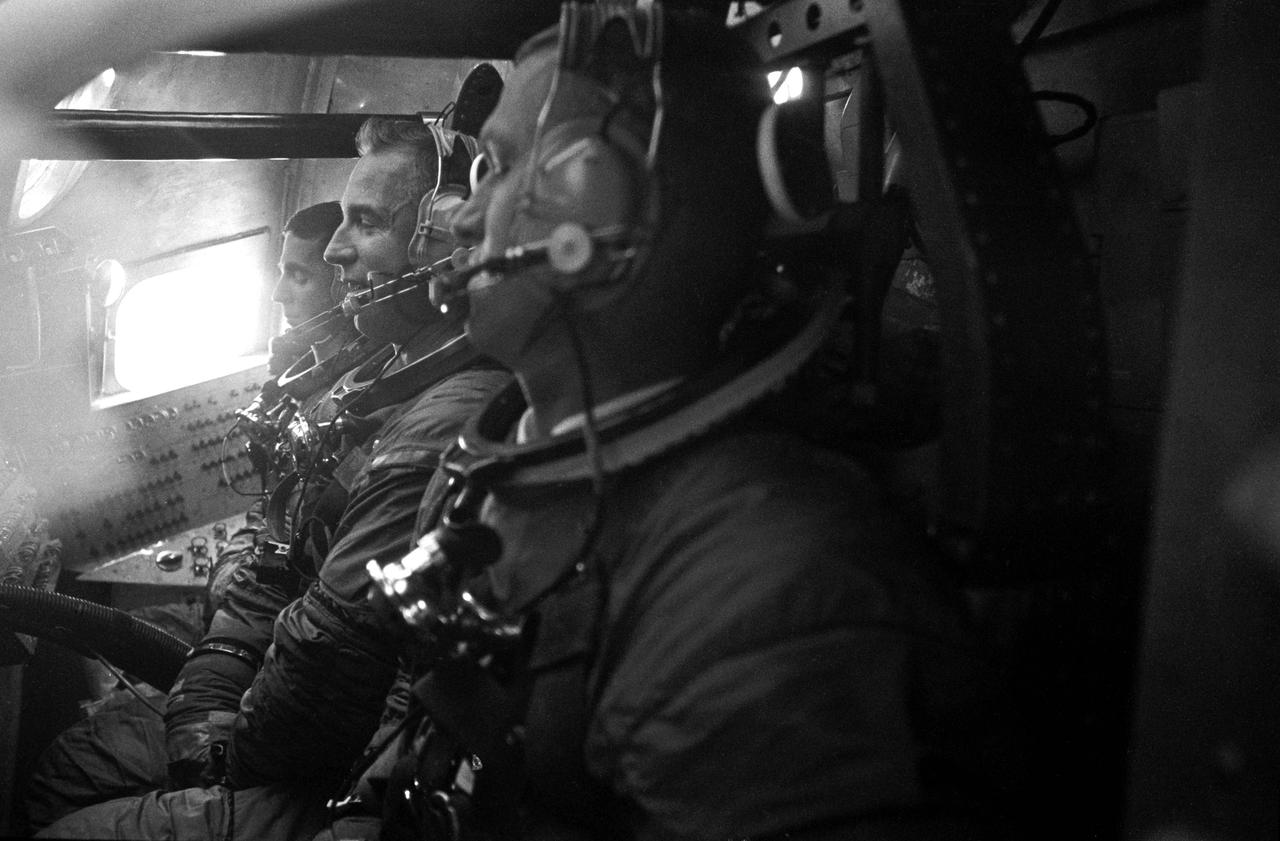

S68-52941 (25 Oct. 1968) --- The Apollo 8 prime crew is seen inside Apollo Boilerplate 1102A during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. From the foreground are astronauts Frank Borman, commander; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and William A. Anders, lunar module pilot. Photo credit: NASA
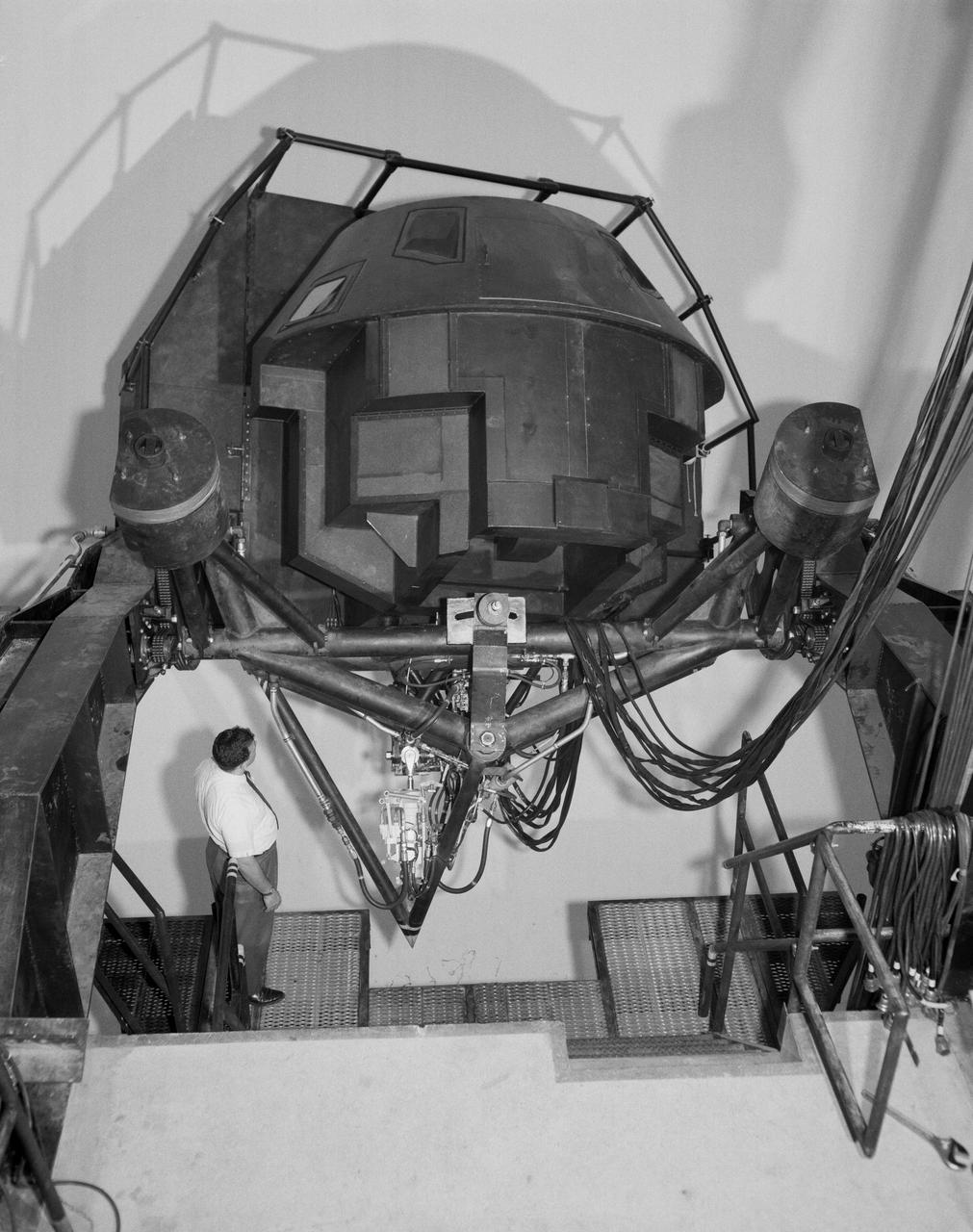
S66-21296 (1967) --- This is a medium exterior view of the Dynamic Crew Procedures Trainer, Command Module configuration, one of the Apollo astronaut training components located in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Building 5, Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA
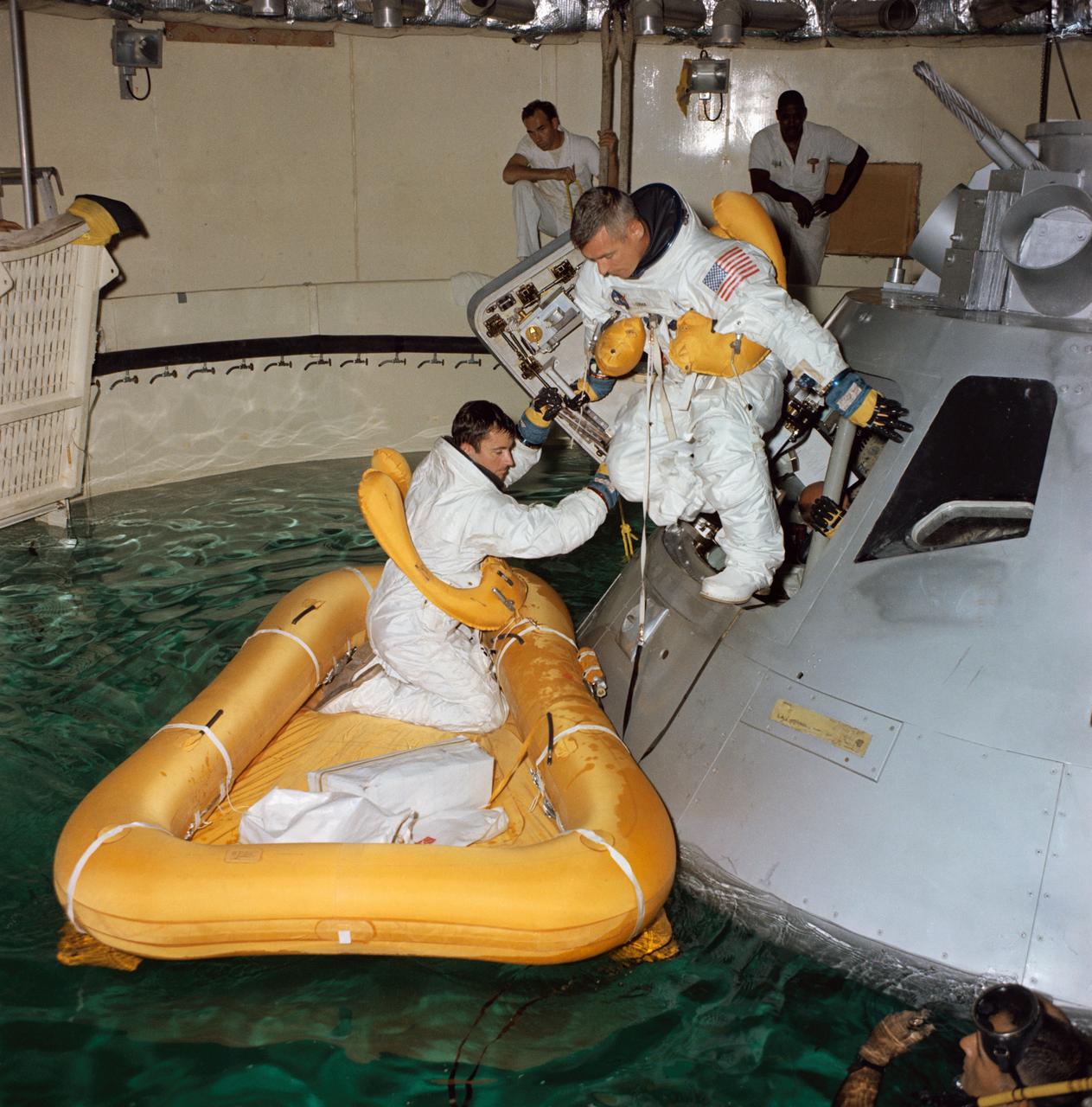

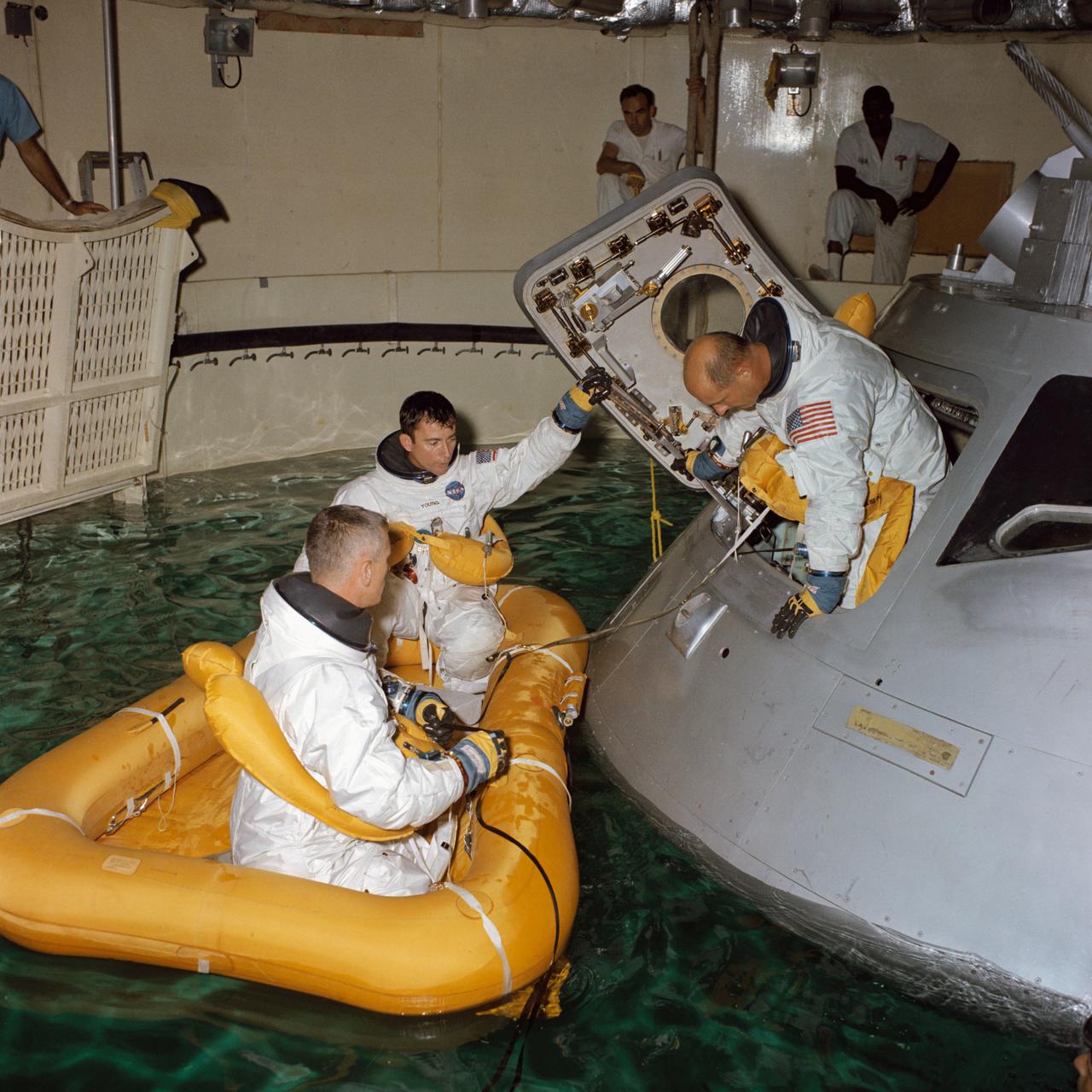
S68-41683 (August 1968) --- Three astronauts participate in Apollo water egress training in a tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Already in life raft is John W. Young. Eugene A. Cernan is egressing the Apollo Command Module trainer. Inside the trainer and almost obscured is Thomas P. Stafford.
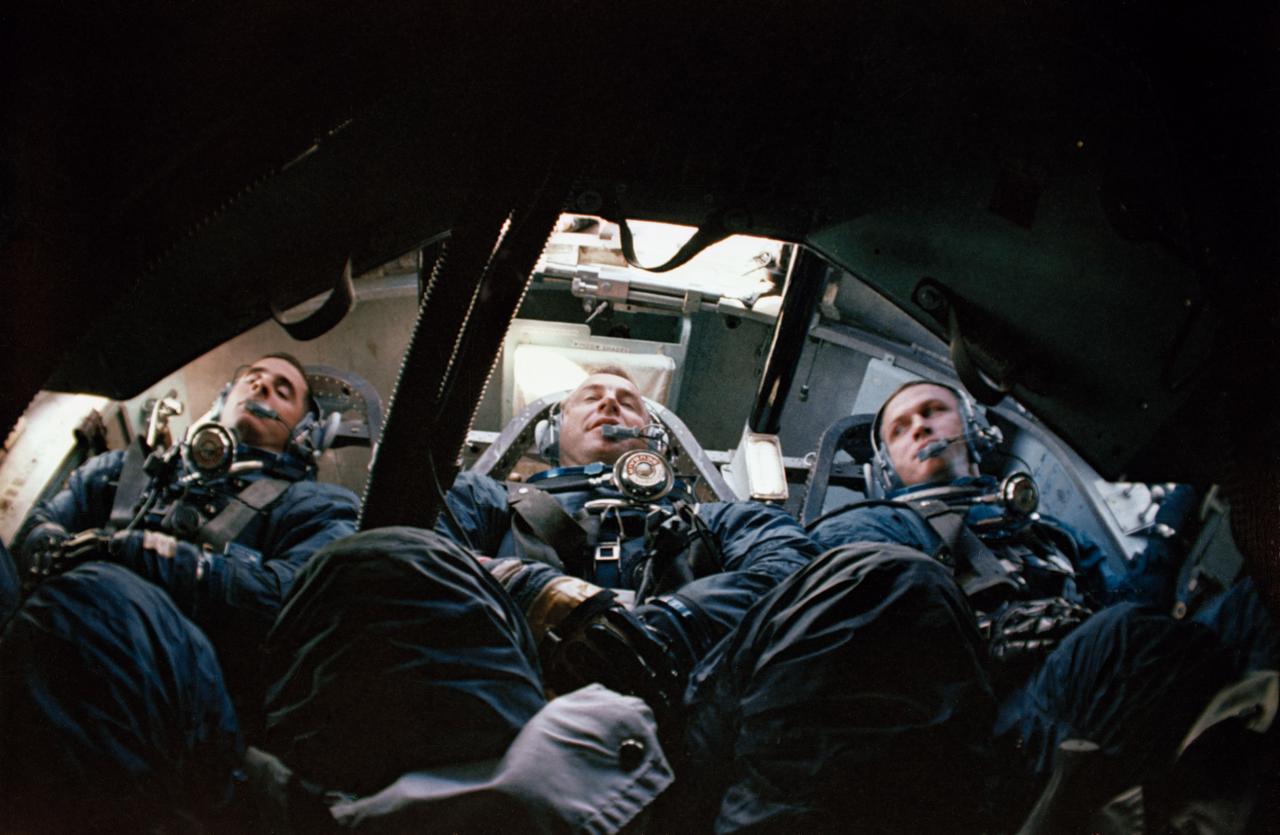

S68-53015 (25 Oct. 1968) --- Astronauts William A. Anders, James A. Lovell Jr., and Frank Borman, (left to right) are seen inside Apollo Boilerplate 1102A during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Borman is Apollo 8 commander; with Lovell serving as command module pilot; and Anders as lunar module pilot. Photo credit: NASA
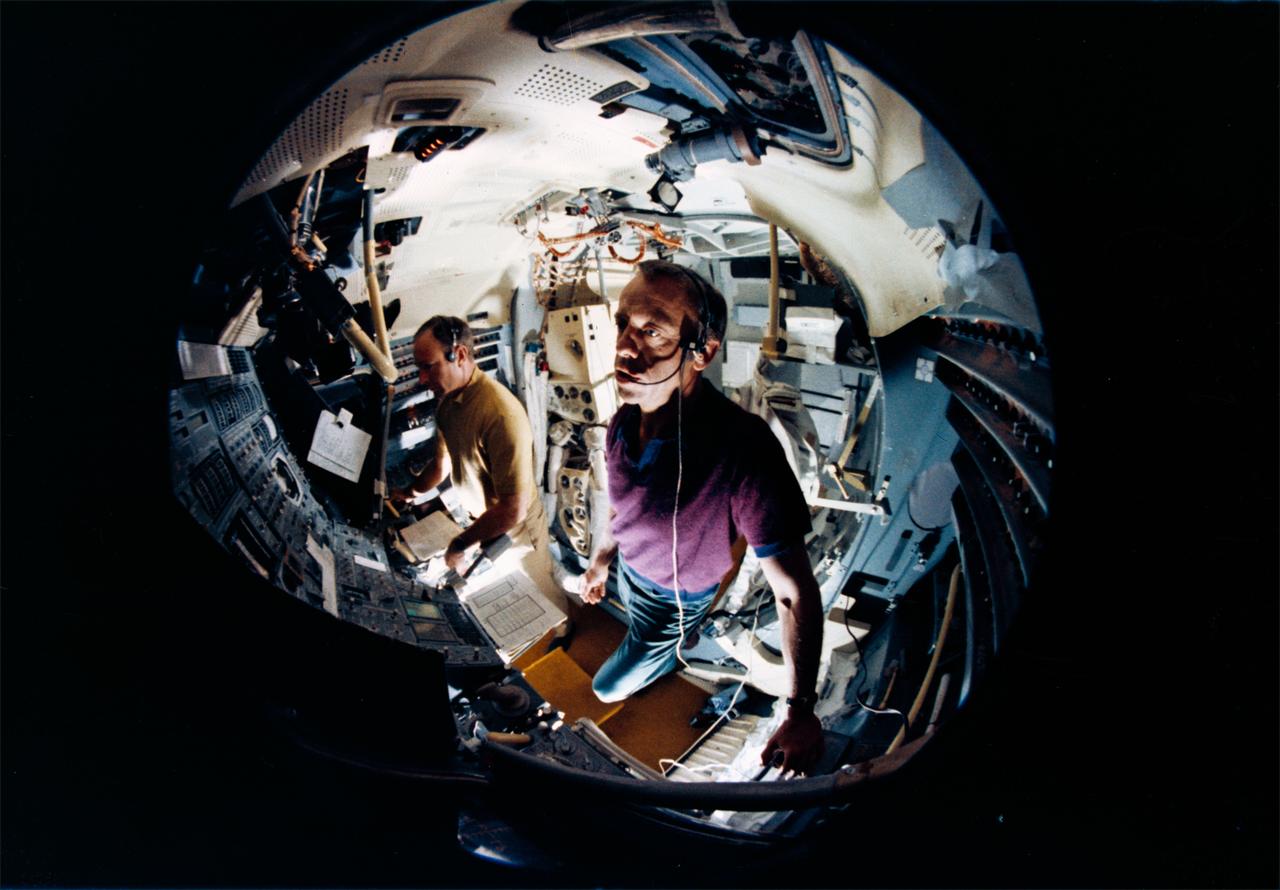

S70-45555 (July 1970) --- A fish-eye lens view showing astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (foreground) and Edgar D. Mitchell in the Apollo lunar module mission simulator at the Kennedy Space Center during preflight training for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Shepard is the Apollo 14 commander; and Mitchell is the lunar module pilot.
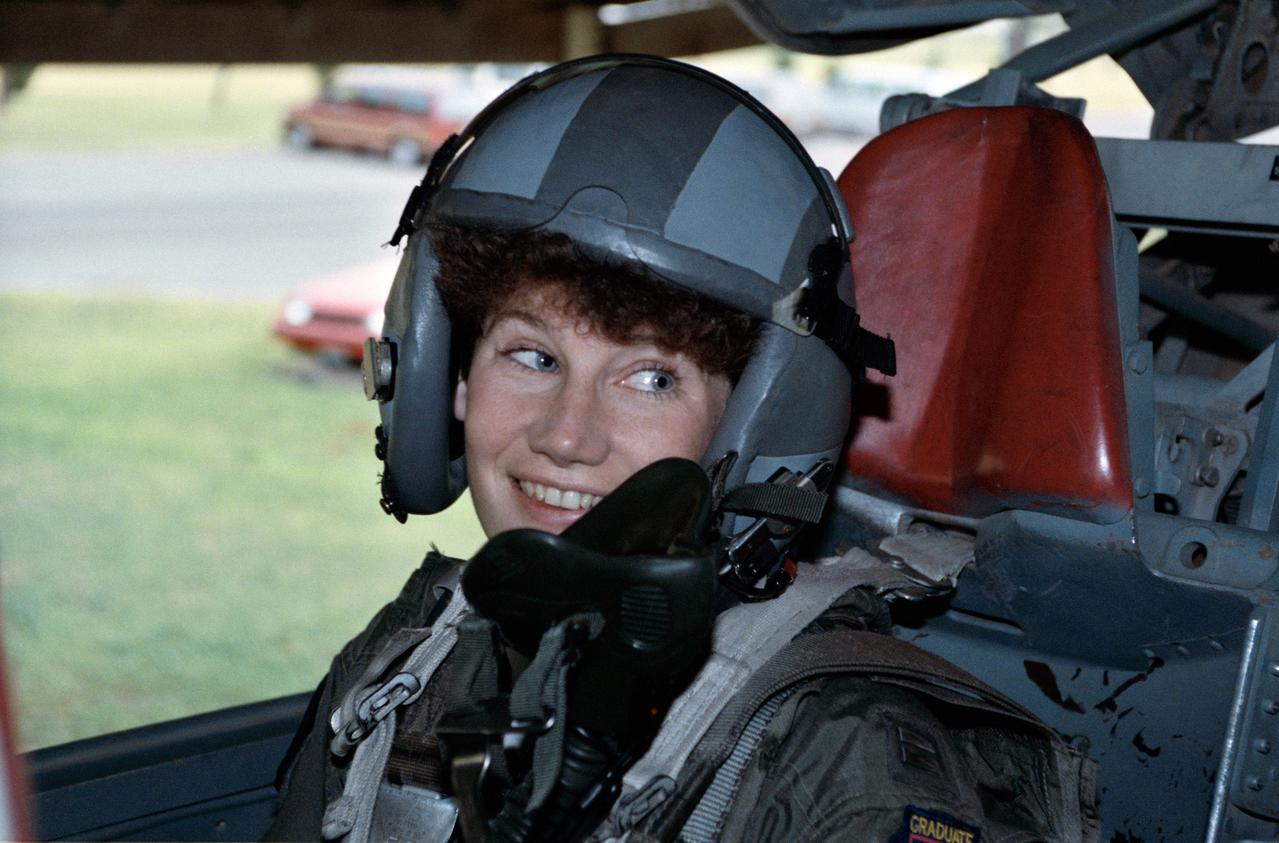

S90-45896 (29-31 July 1990) --- Susan J. Helms, one of the 23 astronaut candidates who began a year's training and evaluation program in July, participates in one of themany sessions at a survival training course at Vance Air Force Base. This portion of the course is designed to familiarize the trainee with procedures to follow in preparation for ejection from a jet aircraft.
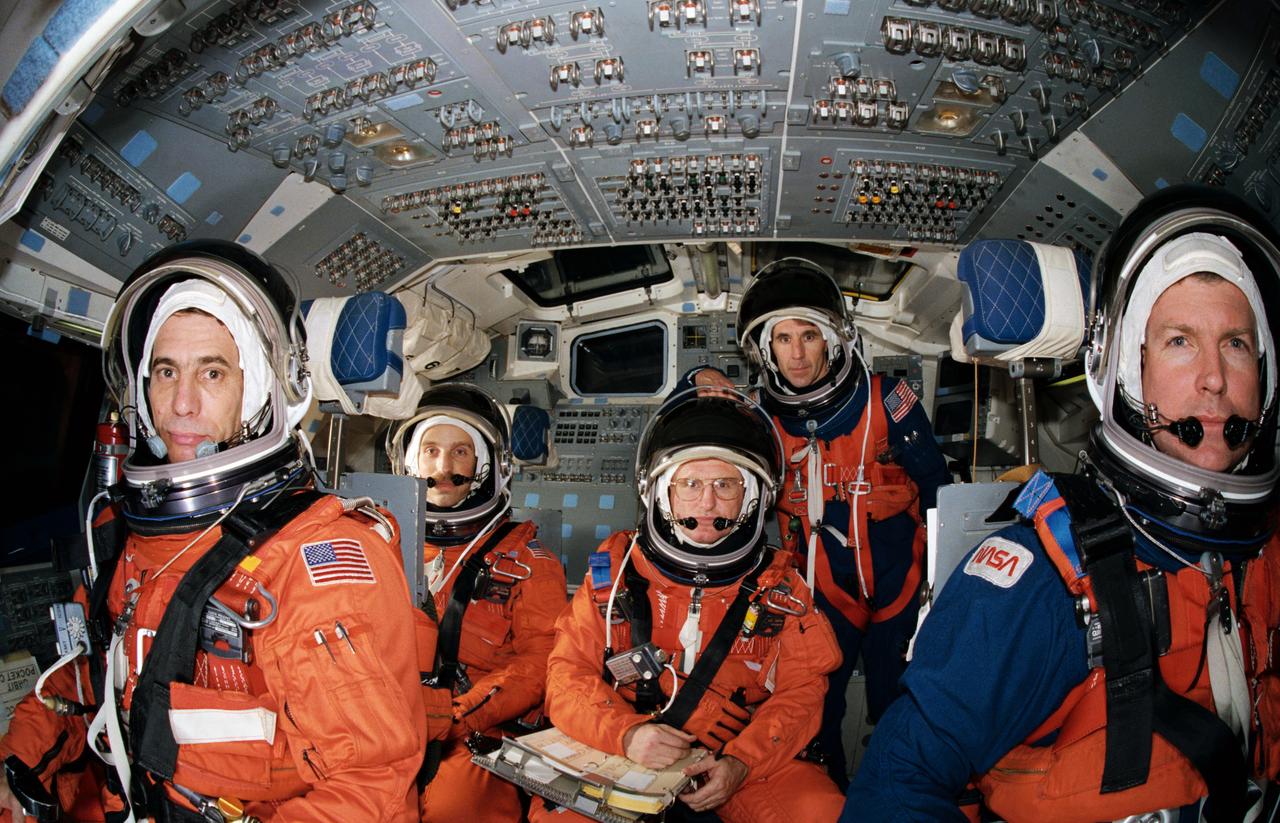

S89-26390 (January 1989) --- The five crew members for STS-29 pause during launch and entry phase rehearsals in the crew compartment trainer at the Johnson Space Center. Four members are in their entry positions and the fifth has been "borrowed" for a moment from the middeck. In front are John E. Blaha (left), pilot, and Michael L. Coats, mission commander. Behind them are James P. Bagian (left), and James F. Buchli, both mission specialists. Robert C. Springer, the third mission specialist, stands here at aft station. He will occupy Discovery's middeck for entry phase, while Bagian will occupy that post for launch. Photo credit: NASA
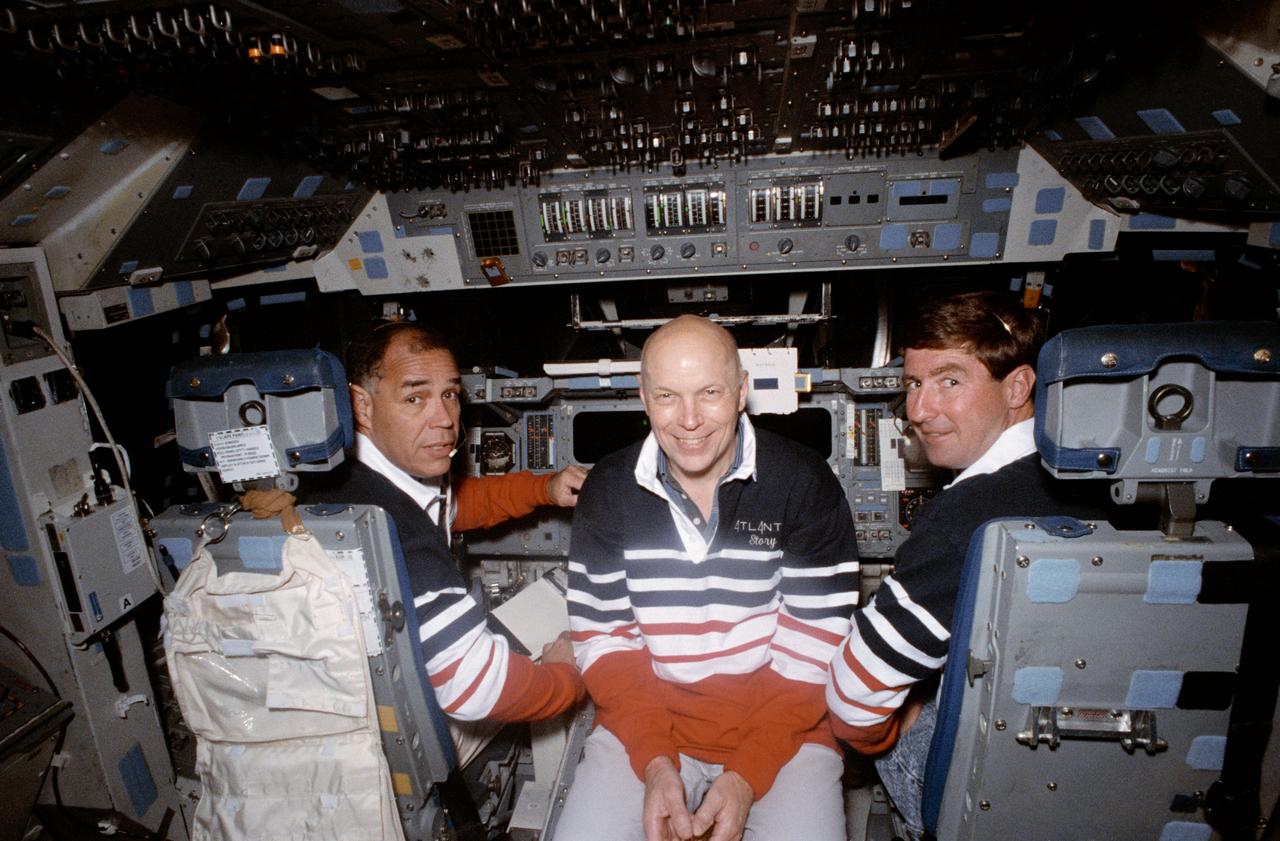

S91-35303 (22 April 1991) --- Astronauts Frederick D. Gregory (left) and Terrence T. Henricks (right), STS-44 commander and pilot, respectively, are joined near their launch and entry stations by F. Story Musgrave, mission specialist. The three pause while rehearsing some of the activities that will be performed during the scheduled ten-day November flight. Musgrave will be in a rear cabin station during launch and entry phases of the flight deck of the fixed-base Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) in the Johnson Space Center's mission simulation and training facility.

S68-41685 (August 1968) --- Three astronauts participate in Apollo water egress training in a tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Egressing the Apollo Command Module trainer is Thomas P. Stafford. Already in life raft are Eugene A. Cernan (in foreground) and John W. Young.
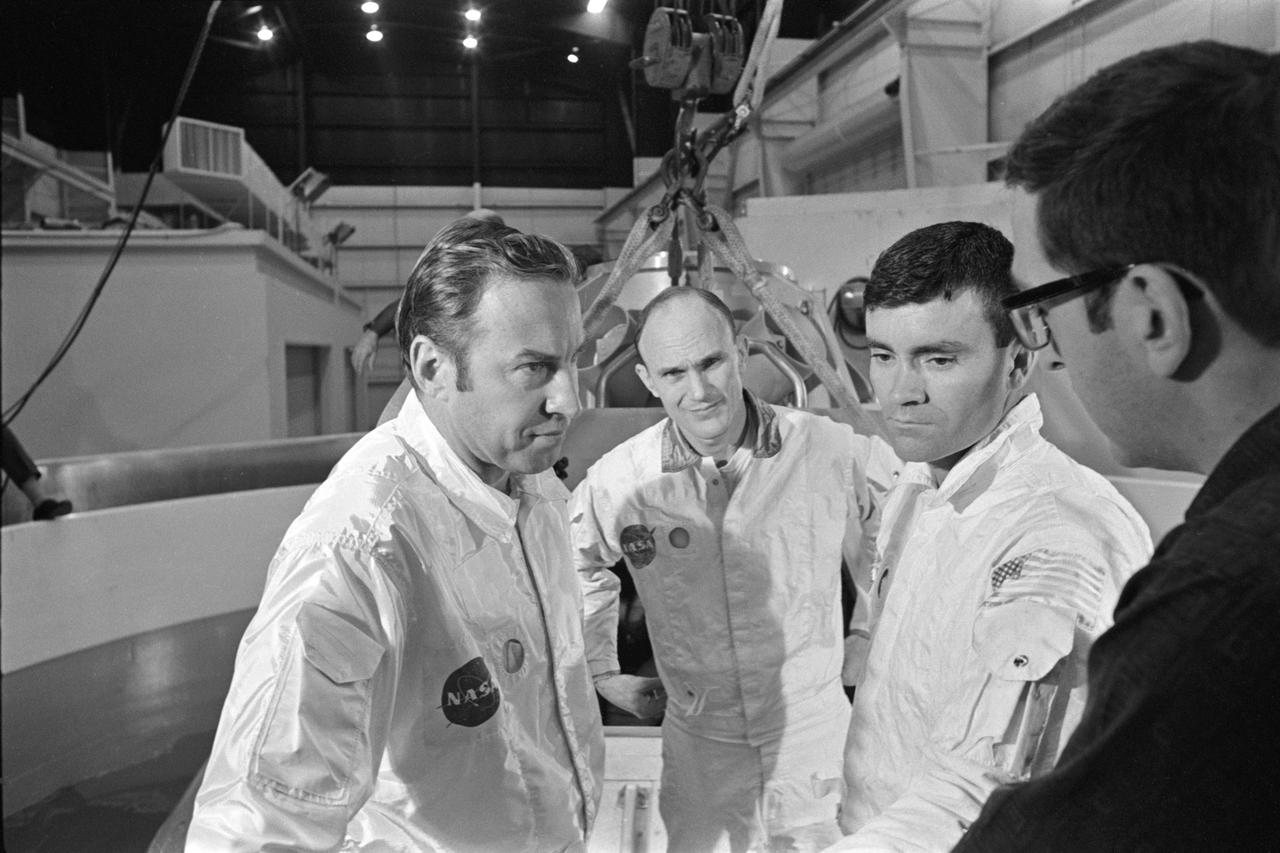

S70-24014 (17 Jan. 1970) --- The three prime crewmen of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission stand by to participate in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center. They were (left to right) astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.

Two payload specialists for the STS 51-D mission get in some training time in the crew compartment trainerat JSC. Charles D. Walker, left, rehearses photography of U.S. Senator E.J. (Jake) Garn in the middeck section of the trainer.

B60-00285 (1960) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., pilot of the Mercury Atlas 6 spaceflight, emerges from an egress trainer during training activity at the Langley Research Center. He is attempting to transfer onto a life raft from the mock-up of the Mercury capsule. Photo credit: NASA

S70-24016 (17 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in water egress training in a water tank in Building 260 at the Manned Spacecraft Center.
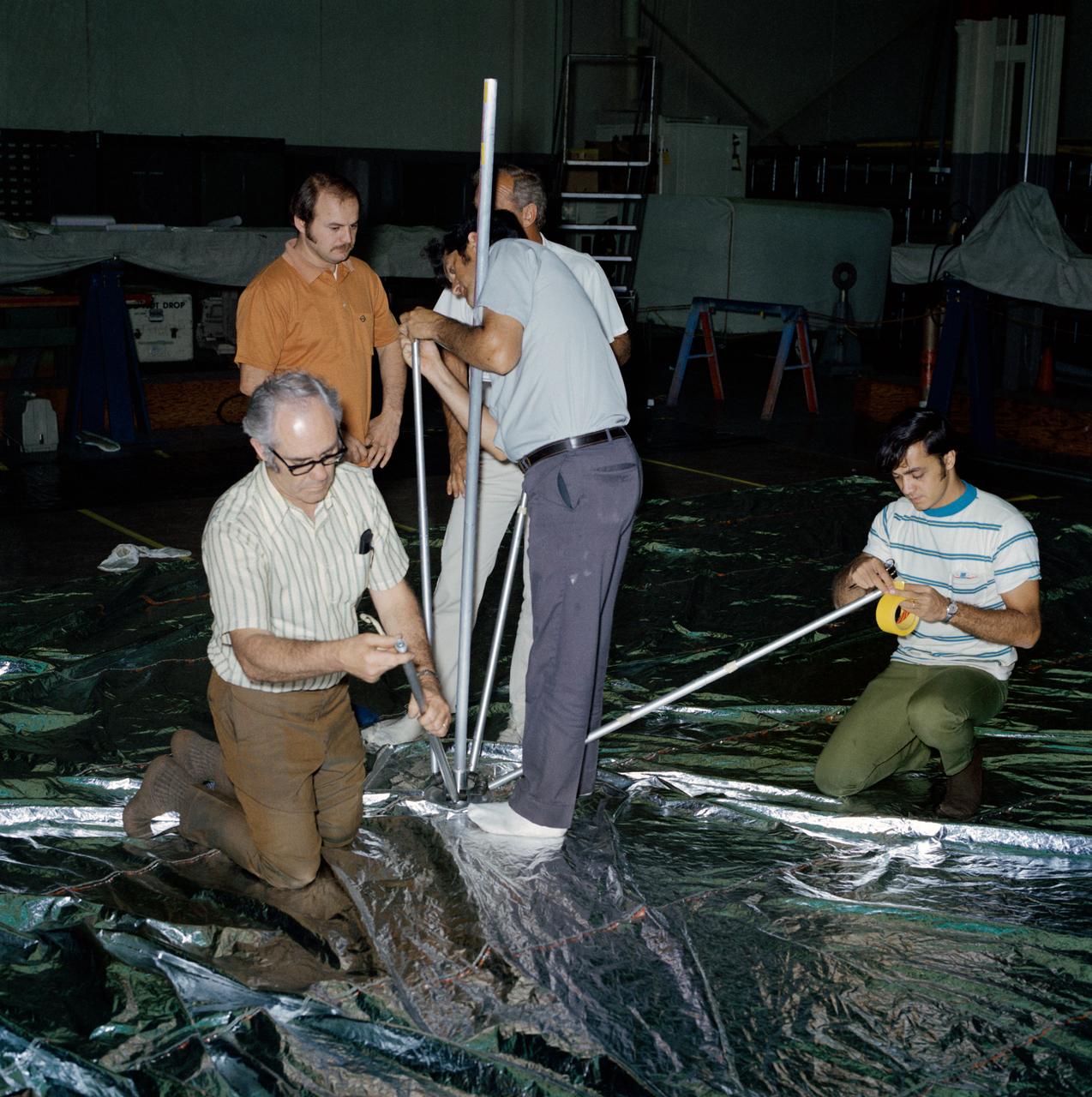

S73-26380 (23 May 1973) --- Technicians in the Technical Services shop in Building 10 work on the fabrication of the umbrella-like mechanical device called the “parasol” during Skylab 2 preflight preparations at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Here, they are attaching the telescoping extension rods to the canopy. The “parasol” is designed to fit into the TO27 experiment photometer canister. The canopy is 24 feet by 22 feet. The sunshade device will be deployed through the solar scientific airlock in the side of the OWS. The “parasol” solar shield is considered the prime possibility for use as the OWS sunshade because it will not require EVA by the Skylab 2 crewmen, because of the operational ease of using it, and because of the simplicity of the device which minimizes crew training. Photo credit: NASA
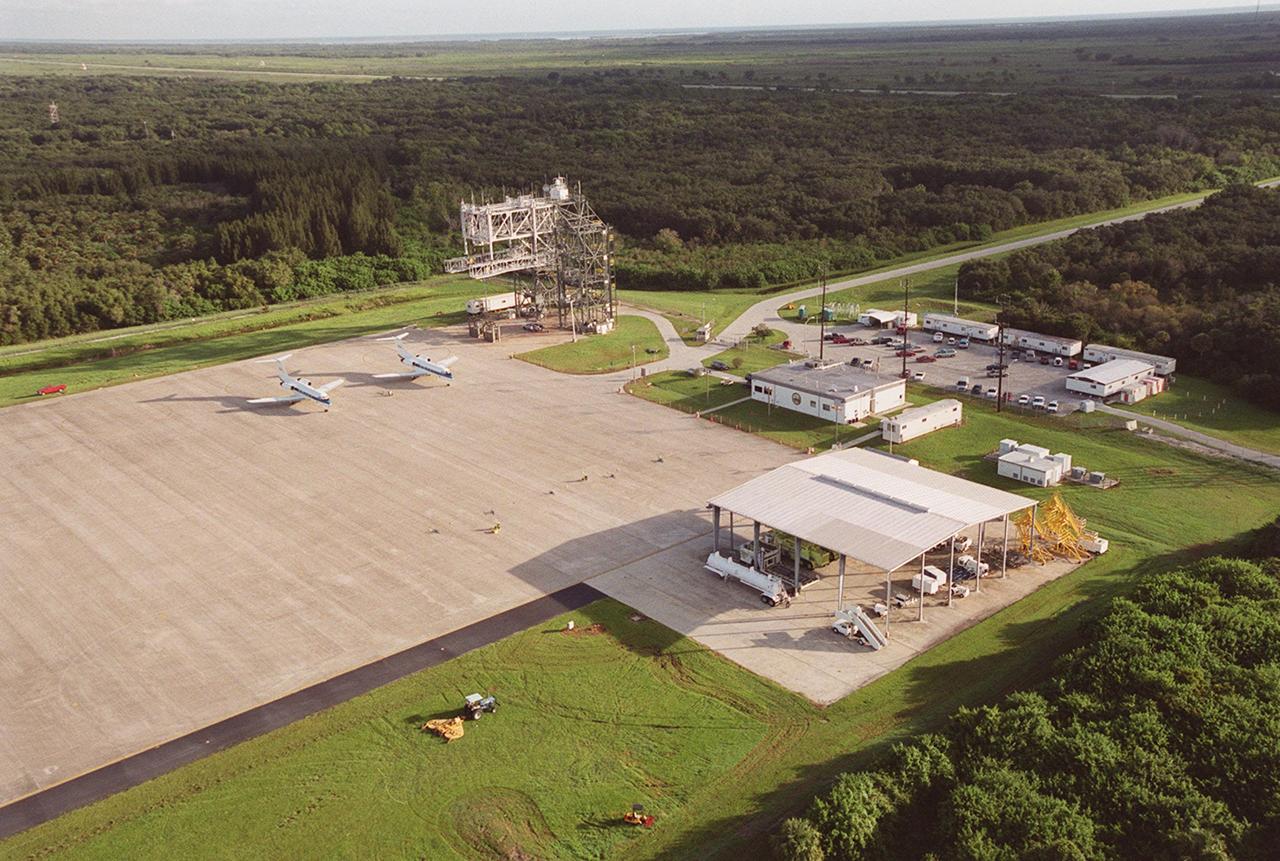

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial view of the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) faces northeast, with the Atlantic Ocean in the distance. In the center is the apron of the SLF with two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) parked there, the mate/demate device behind them, a shelter for fuel trucks (foreground), and an administrative building between. The STAs are Grumman Gulfstream 2 aircraft with converted cockpits that emulate those in the Shuttles for practice landings at the SLF. The mate/demate device is used to lift the orbiter onto or off a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft when it has to be ferried to or from KSC
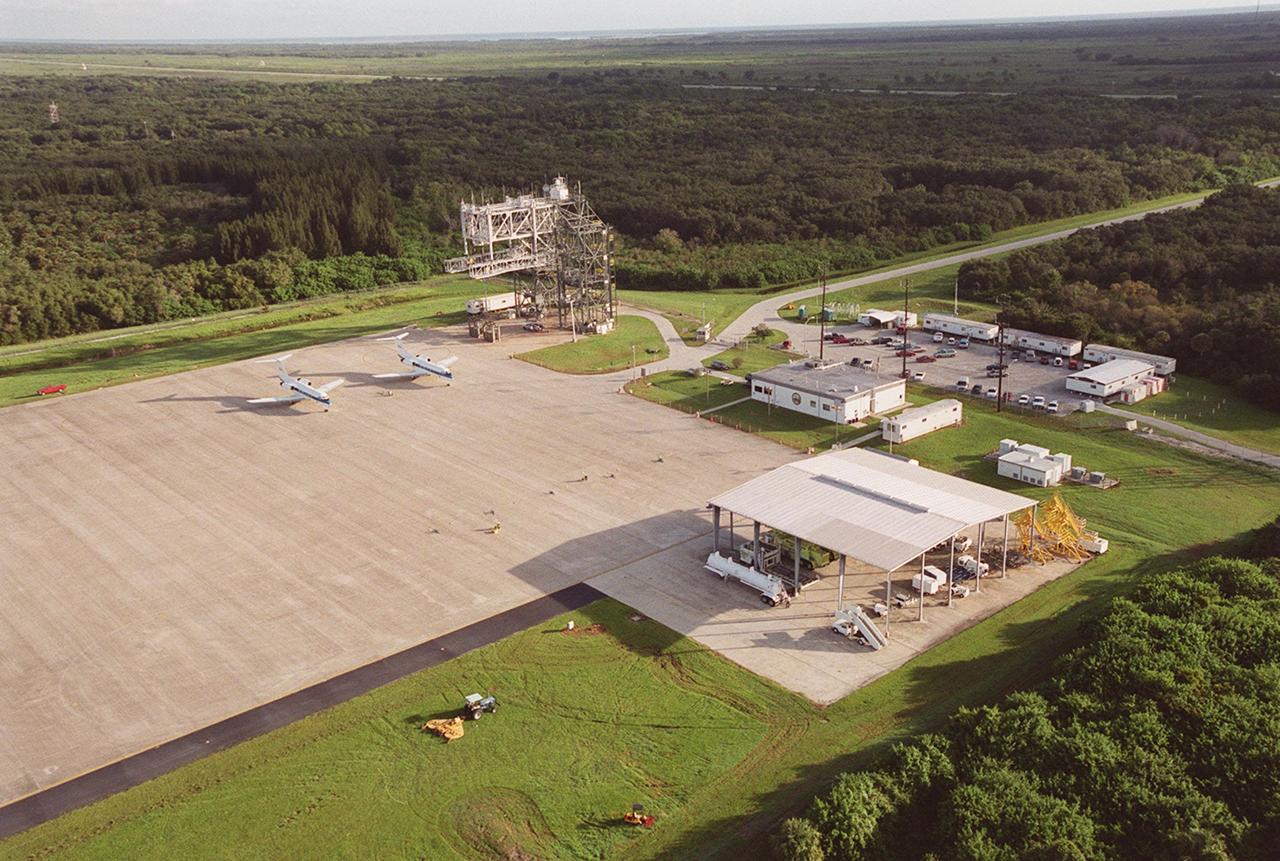

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial view of the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) faces northeast, with the Atlantic Ocean in the distance. In the center is the apron of the SLF with two Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) parked there, the mate/demate device behind them, a shelter for fuel trucks (foreground), and an administrative building between. The STAs are Grumman Gulfstream 2 aircraft with converted cockpits that emulate those in the Shuttles for practice landings at the SLF. The mate/demate device is used to lift the orbiter onto or off a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft when it has to be ferried to or from KSC
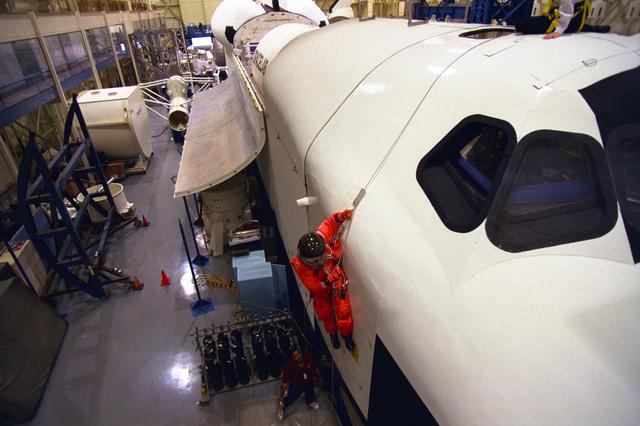

S98-06946 (28 April 1998) --- U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr. (D.-Ohio), uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled Space Shuttle during training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). This training mockup is called The full fuselage trainer (FFT). Glenn has been named as a payload specialist for STS-95, scheduled for launch later this year. This exercise, in the systems integration facility at JSC, trains the crew members for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. Photo Credit: Joe McNally, National Geographic, for NASA
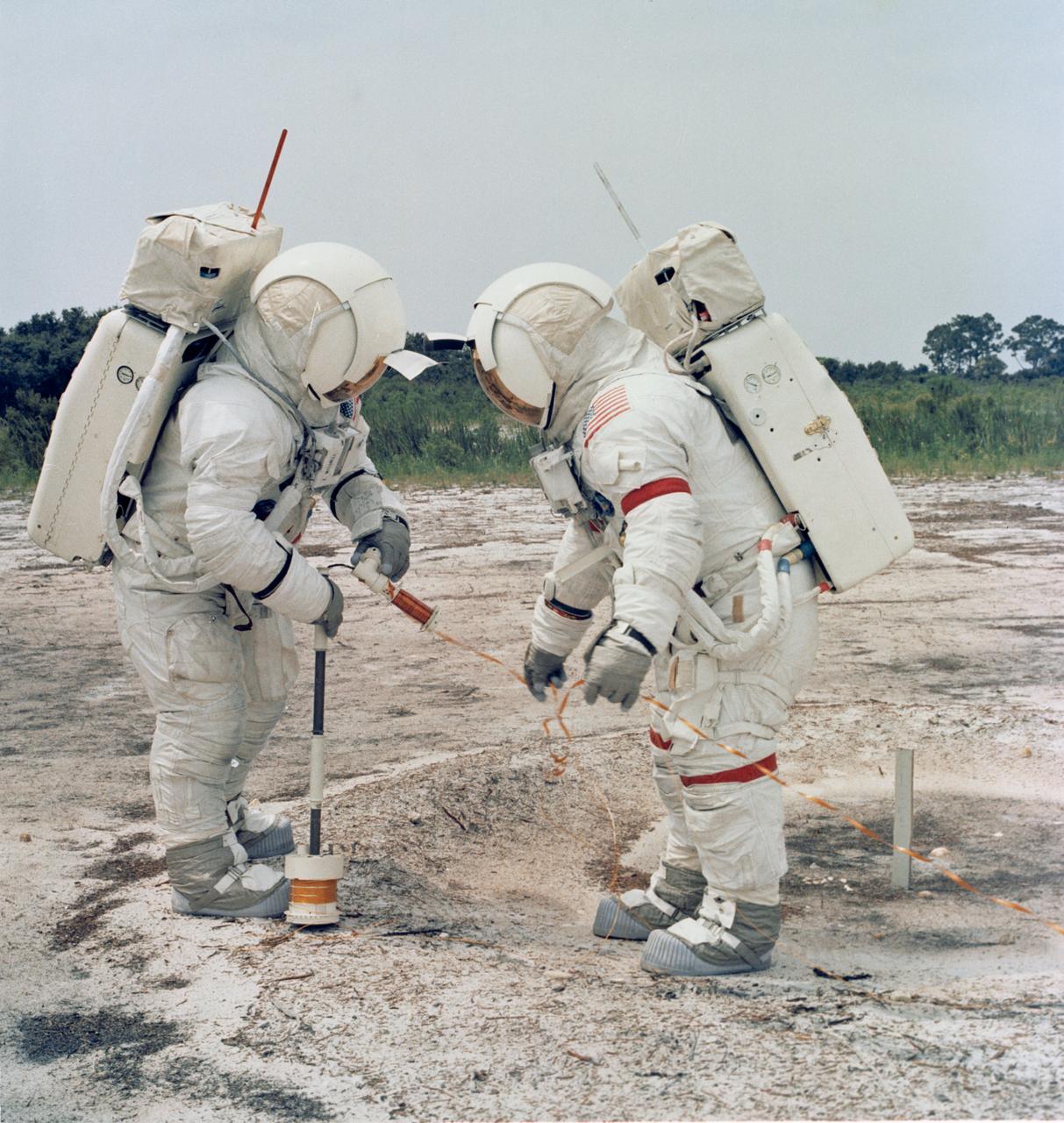

S71-15273 (October 1970) --- Apollo 14 astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander (right); and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, practice using the Active Seismic Experiment (ASE) to set off explosions on the lunar surface and arm a mortar to launch four grenades after they leave. Measurements of the ensuing vibrations of the moon, radioed to Earth, will give scientists new information on the shape, structure and thickness of the outer lunar crust. ASE will be deployed during one of two Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) periods.
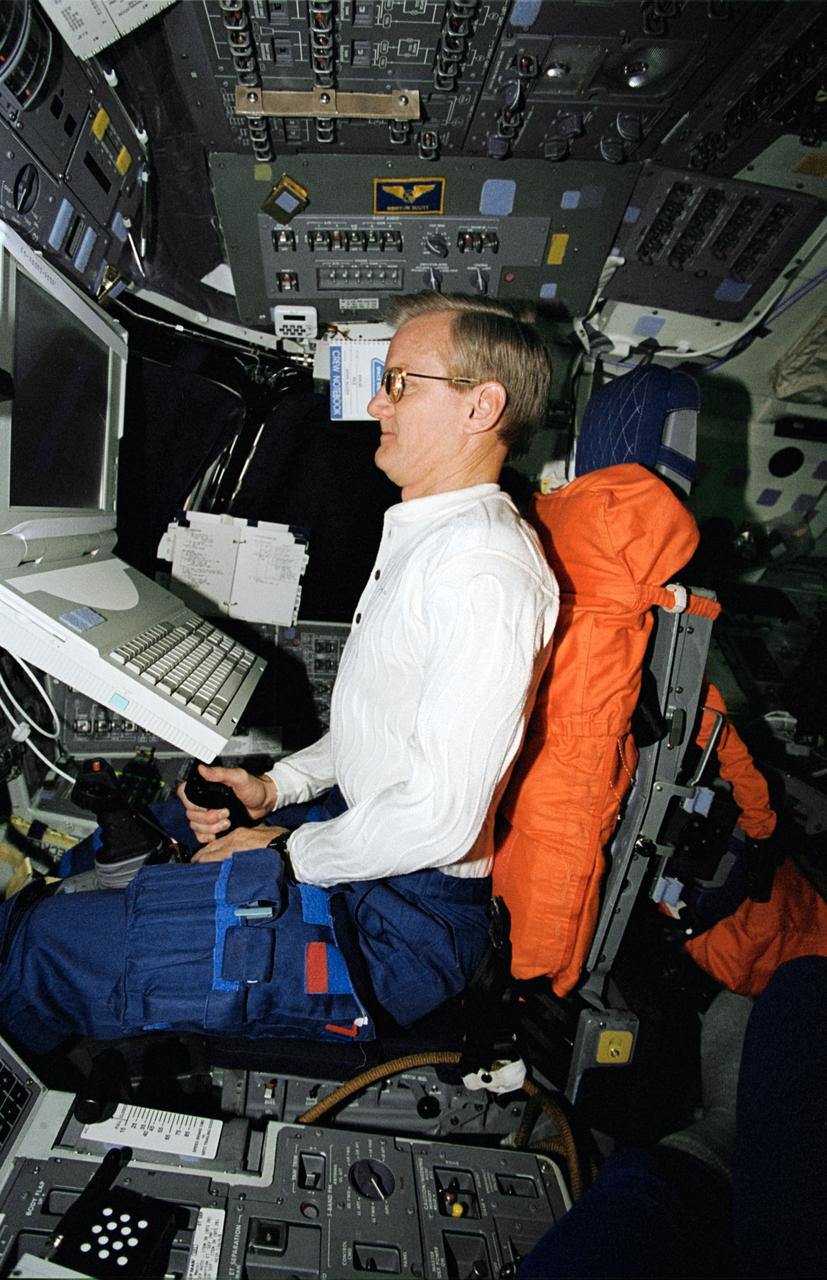

STS062-15-013 (4-18 March 1994) --- Astronaut John H. Casper, mission commander, participates in an experiment that measures the effects of space flight on pilot proficiency. Astronauts Casper and Andrew M. Allen, pilot, continued the testing of the Portable Inflight Landing Operations Trainer (PILOT), which first flew onboard Columbia in October of 1993.
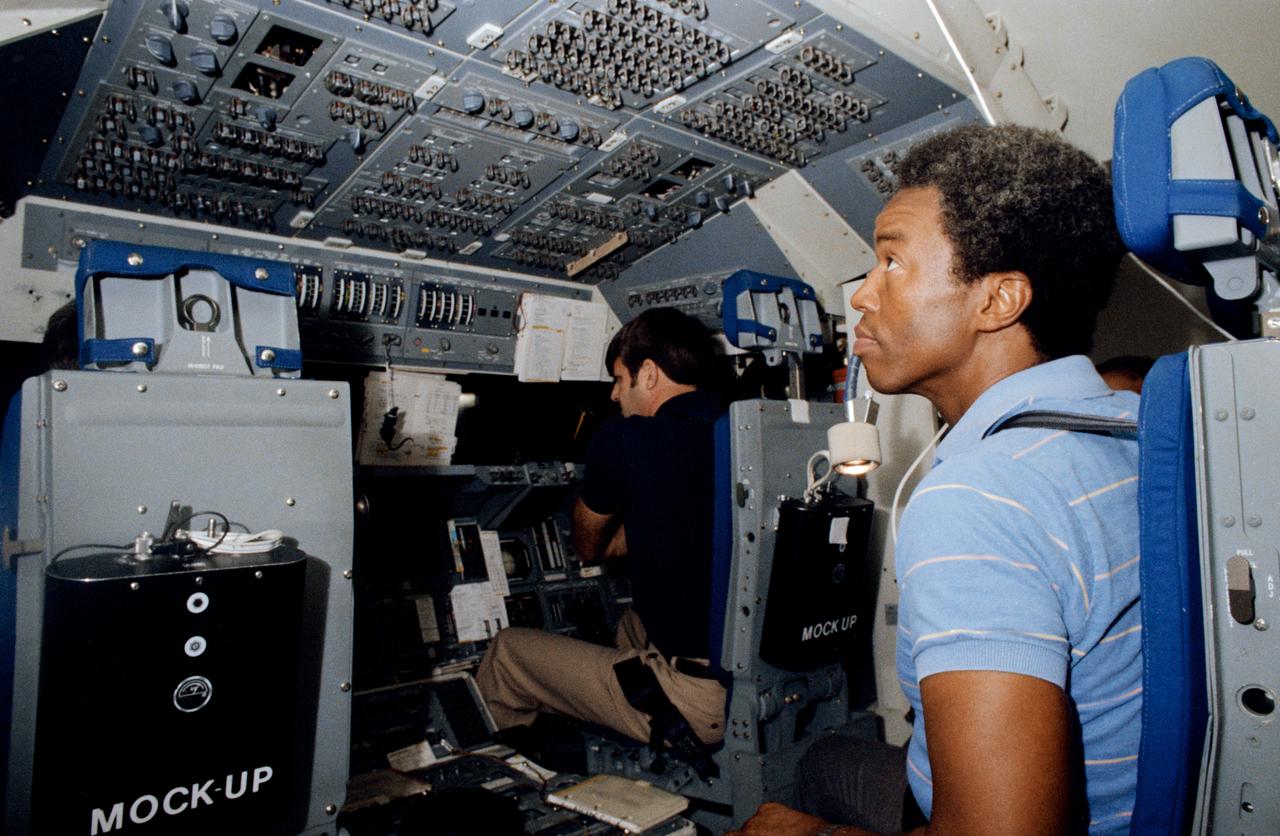

S83-33032 (23 May 1983) --- Astronauts Guion S. Bluford, right, and Daniel C. Brandenstein man their respective Challenger entry and ascent stations in the Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) during a training session for the STS-8 mission. Brandenstein is in the pilot's station, while Bluford, a mission specialist, occupies one of the two aft flight deck seats. Both are wearing civilian clothes for this training exercise. This motion based simulator represents the scene of a great deal of training and simulation activity, leading up to crew preparedness for Space Transportation System (STS) mission. Photo credt: NASA/Otis Imboden, National Geographic
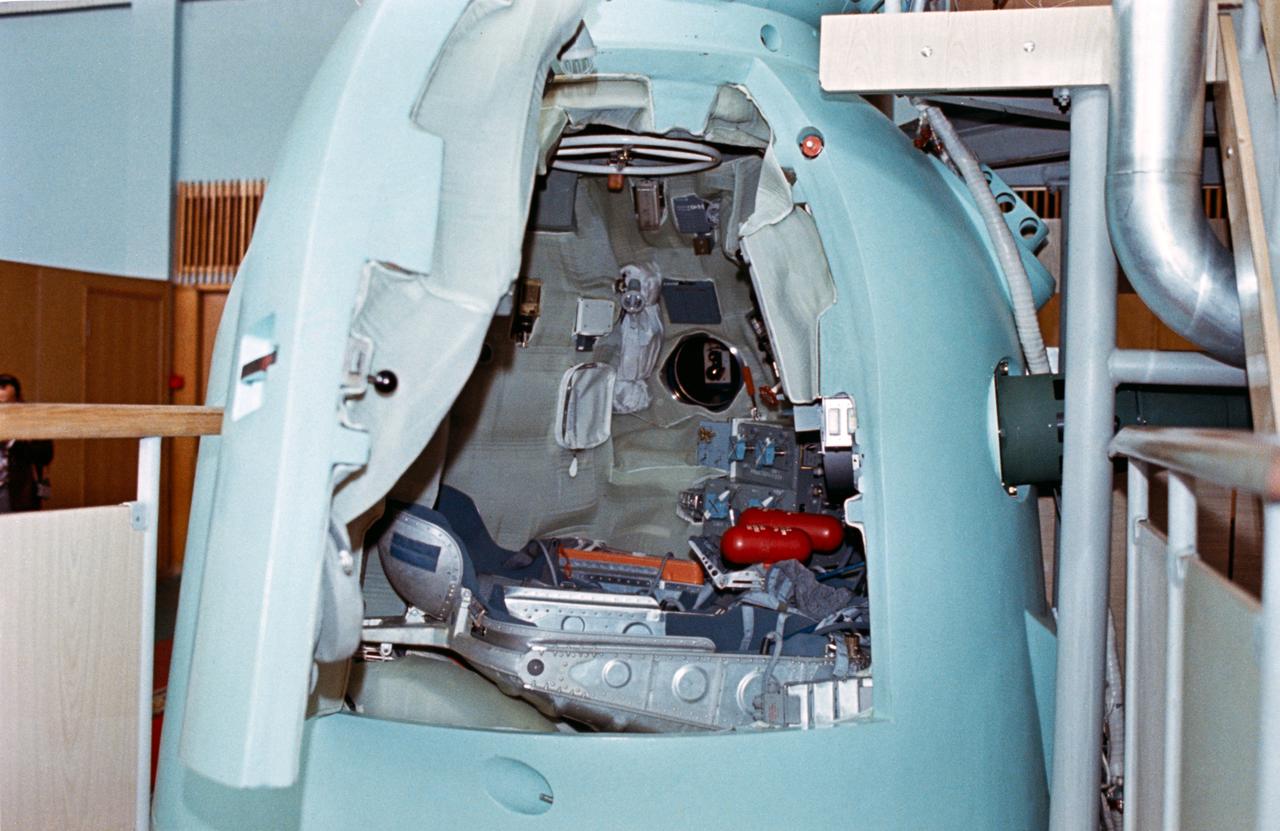
S74-24677 (June 1974) --- A close-up view of the descent vehicle of the Soyuz spacecraft training mock-up on display at the Cosmonuat Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. The open hatch reveals the interior arrangement of the middle section of the Soviet spacecraft. The first (fore) section of the Soyuz is called the orbital module; and the third (aft) section is the instrument-assembly module. The joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975.
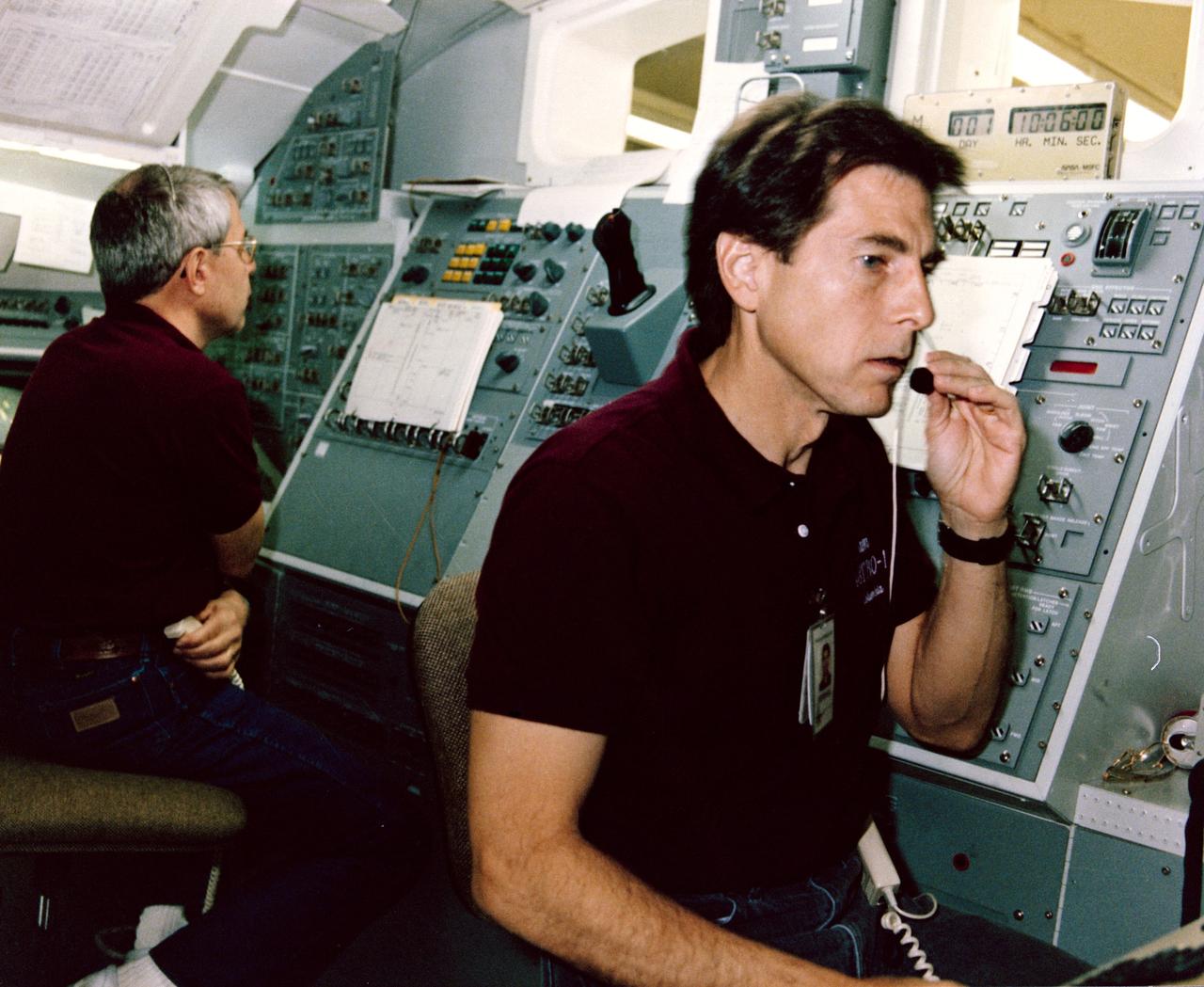

STS-35 Mission Specialist (MS) Robert A.R. Parker (left) and Payload Specialist Samuel T. Durrance practice Astronomy Laboratory 1 (ASTRO-1) experiment procedures in a space shuttle aft flight deck mockup in the Payload Crew Training Complex at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama. For all Spacelab missions, shuttle crew members train regularly in the facility in preparation to operate experiments on their Spacelab missions. The ASTRO-1 crew will operate the ultraviolet telescopes and instrument pointing system (IPS) from Columbia's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102's, aft flight deck. The seven-member ASTRO-1 crew will work around the clock, in 12-hour shifts, to allow the maximum number of observations to be made during their nine or ten days in orbit. In addition to the commander and pilot, the crew consistss of three MSs and two payload specialists. (MSs are career astronauts who are trained in a specialized field. Payload specialists are members of the science investigator teams who were nominated by their peers to operate their experiments on orbit. They are trained and certified for flight by NASA.) View provided by MSFC with alternate number 9005803.
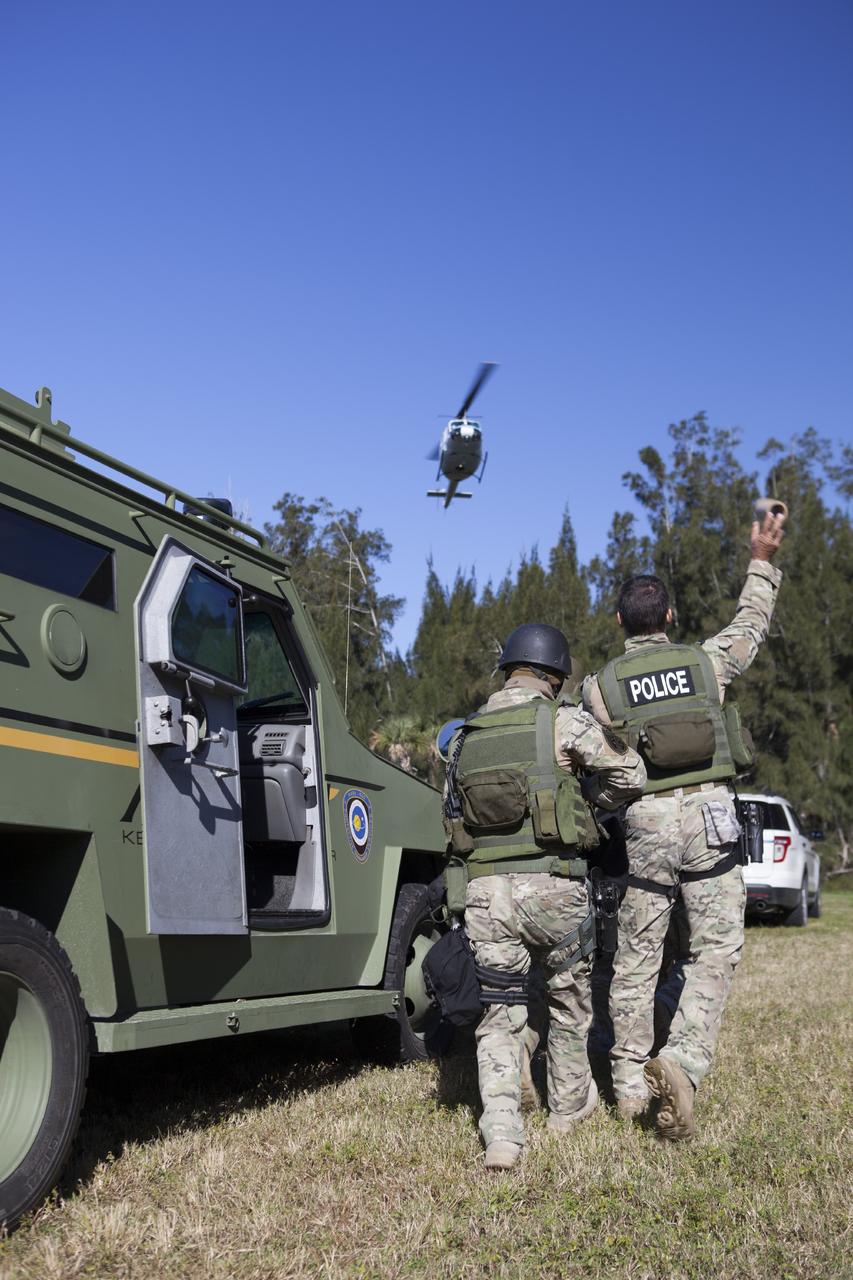

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Protective Services Training Academy at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a member of the Emergency Response Team, or ERT, tosses a flash bang diversionary device during a specialized training simulation as a helicopter hovers above. The ERT members are wearing full protective gear and carrying non-lethal firearms for the training exercises in order to keep their skills current. Recently, eight members of the ERT competed in the 31st Annual SWAT Roundup International competition in Orlando, Fla., and received recognition by placing in the top five overall. In keeping with NASA’s commitment to safety and security of workforce and assets, the ERT is part of Kennedy’s security team and is trained to respond in the event of an emergency at the center. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
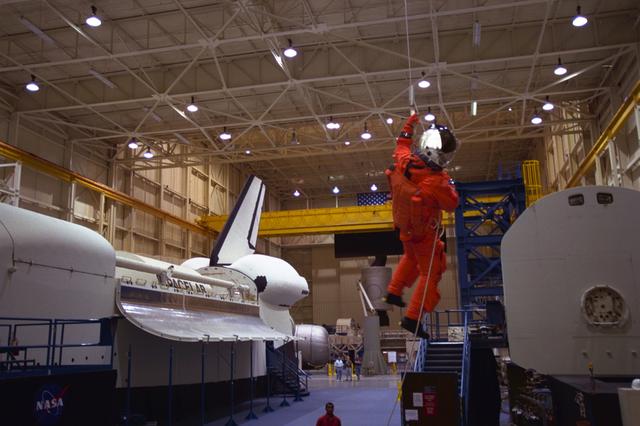

S98-06938 (28 April 1998) --- U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr. (D.-Ohio), uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled Space Shuttle during training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Glenn has been named as a payload specialist for STS-95, scheduled for launch later this year. This exercise, in the systems integration facility at JSC, trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. The full fuselage trainer (FFT) is at left, with the crew compartment trainer (CCT) at right. Photo Credit: Joe McNally, National Geographic, for NASA
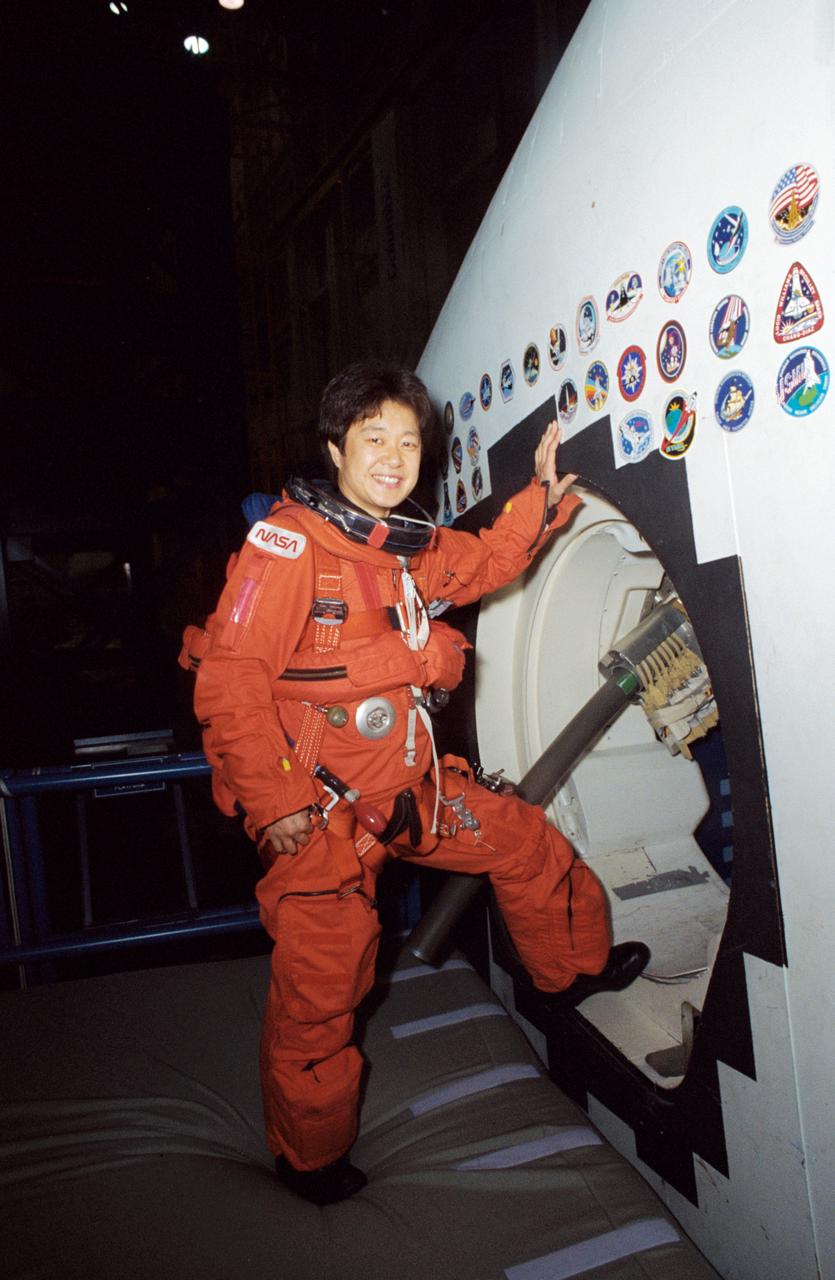

STS-65 Japanese Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai takes a break from training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Wearing a training version of the orange launch and entry suit (LES), Mukai stands at the crew compartment trainer (CCT) side hatch in the Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9NE. Note the crew escape system (CES) pole device extending out the side hatch which would accommodate crewmembers in bailout from a troubled spacecraft. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan and will serve as a payload specialist aboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, during the STS-65 International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) mission.
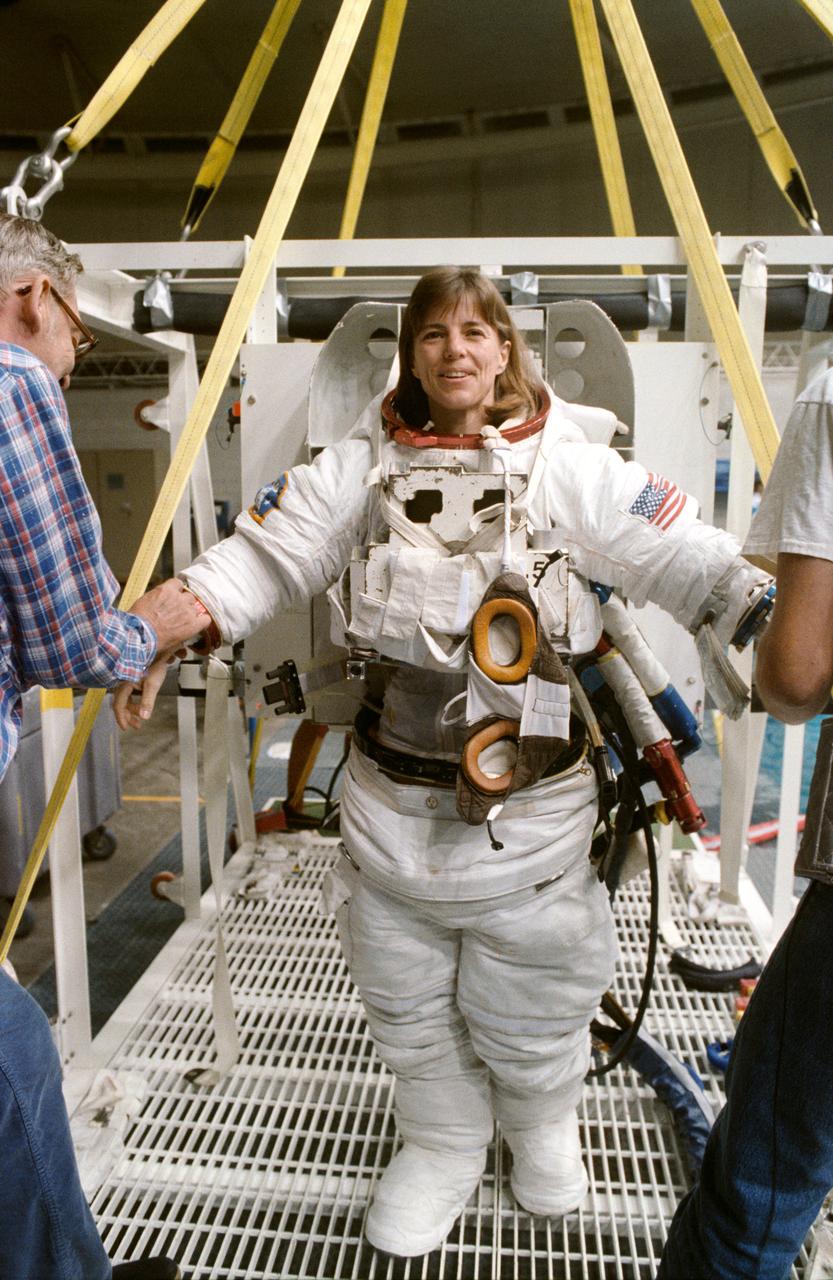

S89-41597 (Nov 1989) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to don gloves and subsequently a helmet and to be lowered by a hoist device for a session of underwater training in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Minutes later, Astronauts Dunbar and G. David Low, mission specialists, were neutrally buoyant in the nearby 25-ft. deep pool simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the scheduled December 1989 STS-32 mission. There are no scheduled EVAs for the crew, whose main missions are to retrieve the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) and to deploy a Syncom satellite.
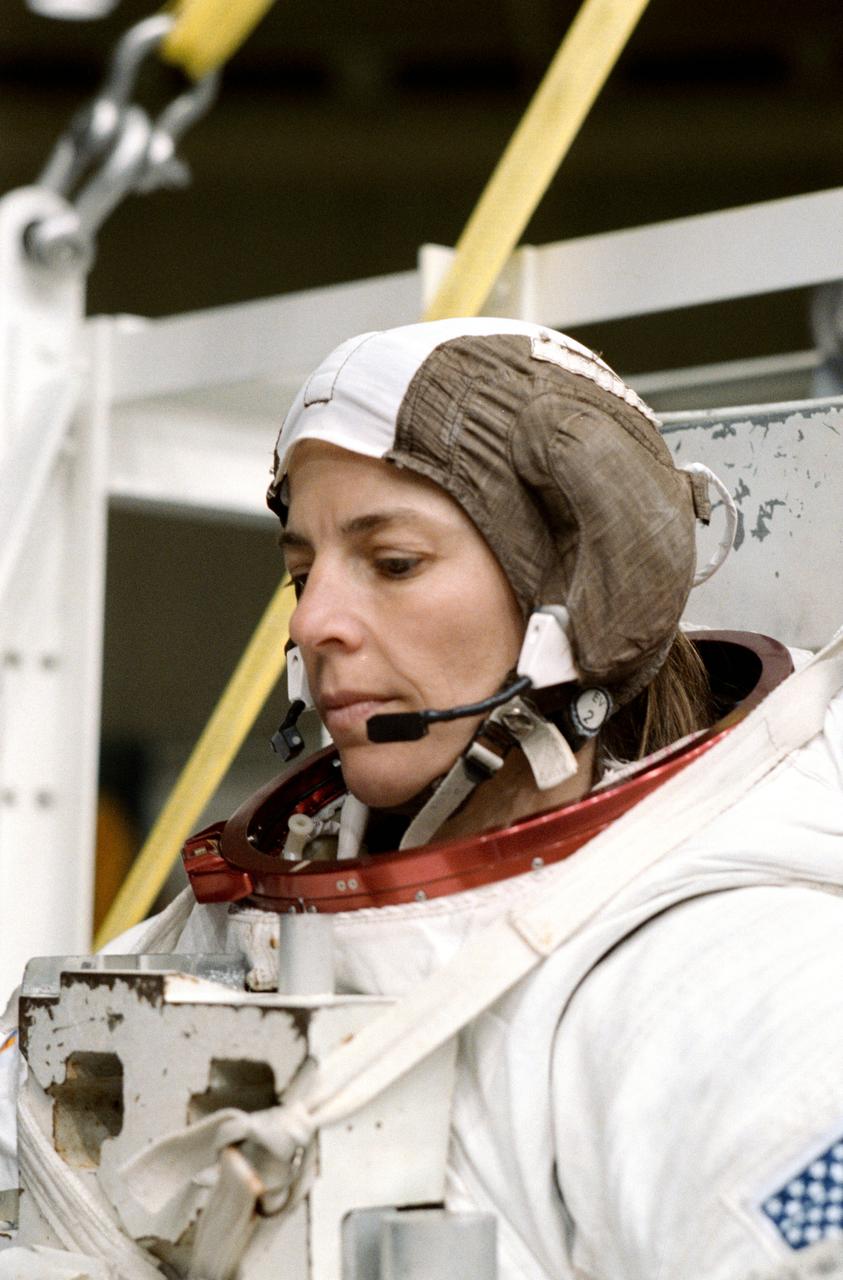

S89-41600 (Nov 1989) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, prepares to don a helmet and be lowered by a hoist device for a session of underwater training in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Minutes later, Astronauts Dunbar and G. David Low, mission specialists, were neutrally buoyant in the nearby 25-ft. deep pool simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the scheduled December 1989 STS-32 mission. There are no scheduled EVAs for the crew, whose main missions are to retrieve the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) and to deploy a Syncom satellite.
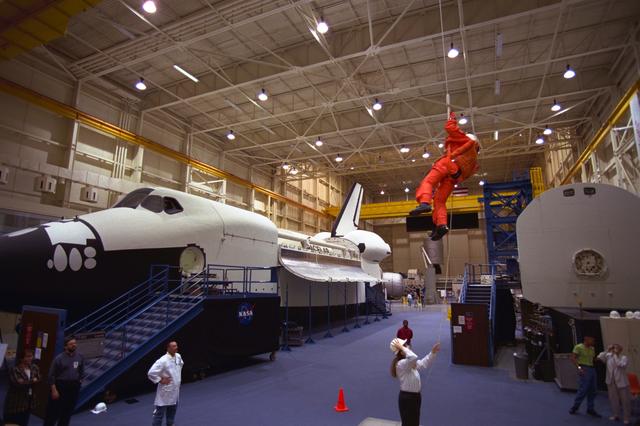

S98-06937 (28 April 1998) --- U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr. (D.-Ohio), uses a device called a Sky genie to simulate rappelling from a troubled Space Shuttle during training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Glenn has been named as a payload specialist for STS-95, scheduled for launch later this year. This exercise, in the systems integration facility at JSC, trains the crewmembers for procedures to follow in egressing a troubled shuttle on the ground. The full fuselage trainer (FFT) is at left, with the crew compartment trainer (CCT) at right. Photo Credit: Joe McNally, National Geographic, for NASA
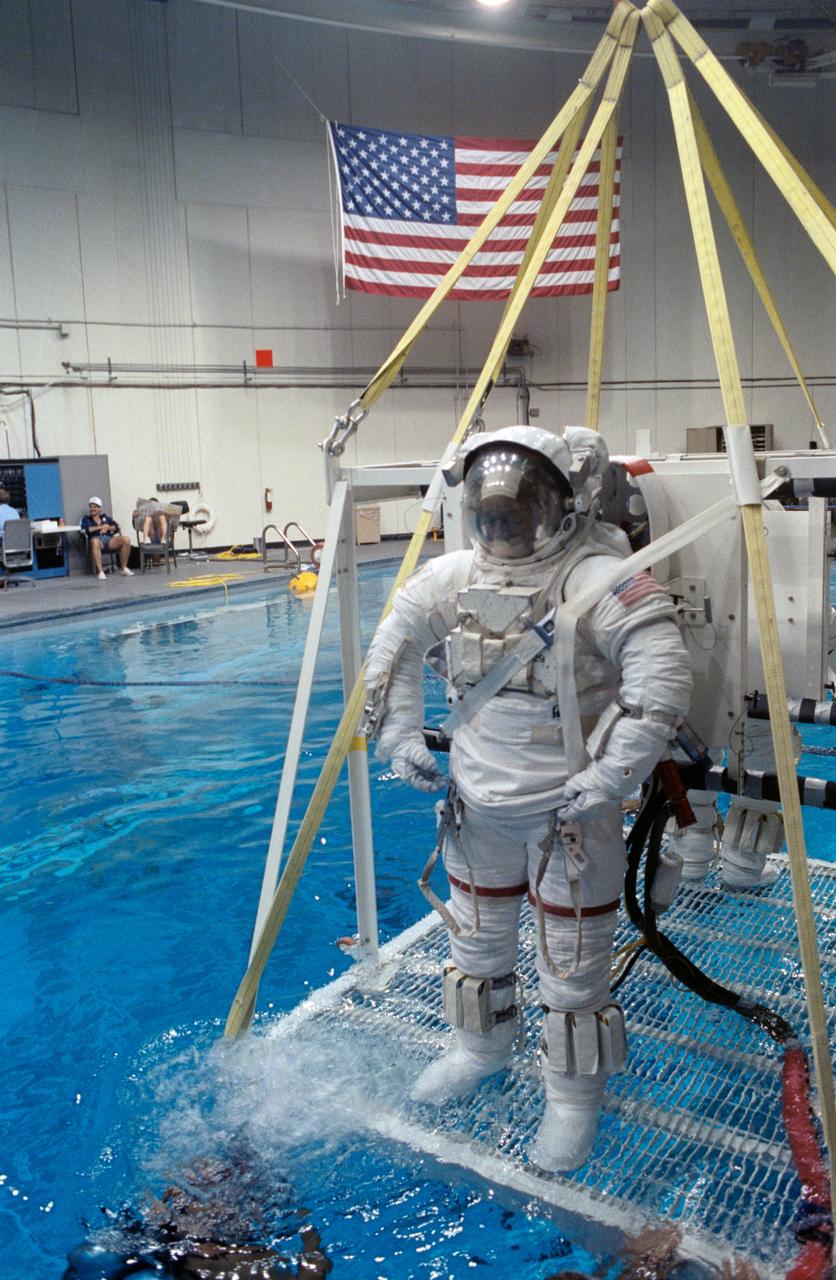

S90-44118 (August 1990) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, mission specialist for STS-39, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, is lowered by a hoist device prior to participating in an underwater rehearsal of a contingency EVA. The scene is in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F) which houses a 25-ft. deep pool (visible in background).
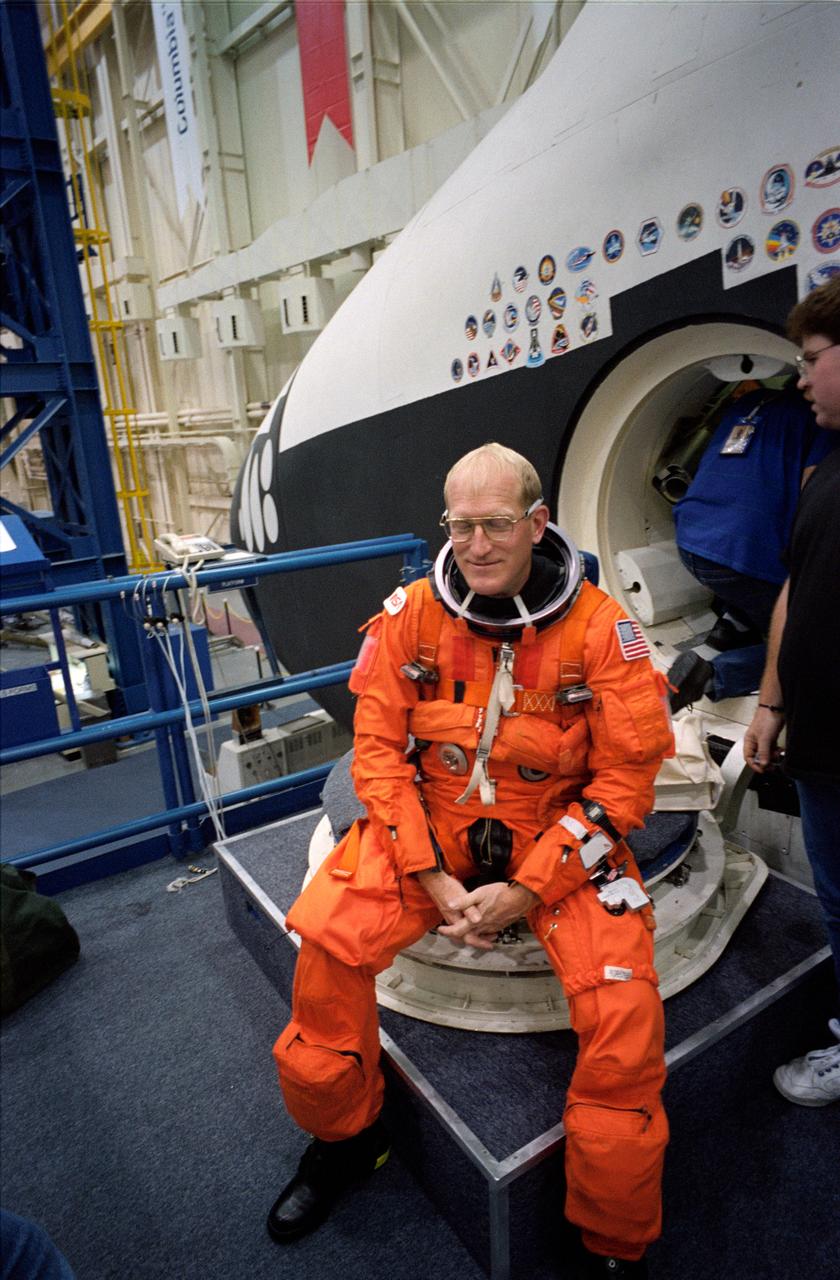

S93-48462 (5 Nov. 1993) --- Astronaut Charles D. (Sam) Gemar, wearing a partial pressure launch and entry suit (LES), takes a break during a training exercise at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The mission specialist and four crew mates rehearsed emergency egress procedures using the escape pole device in the trainer's hatchway (near right center frame).
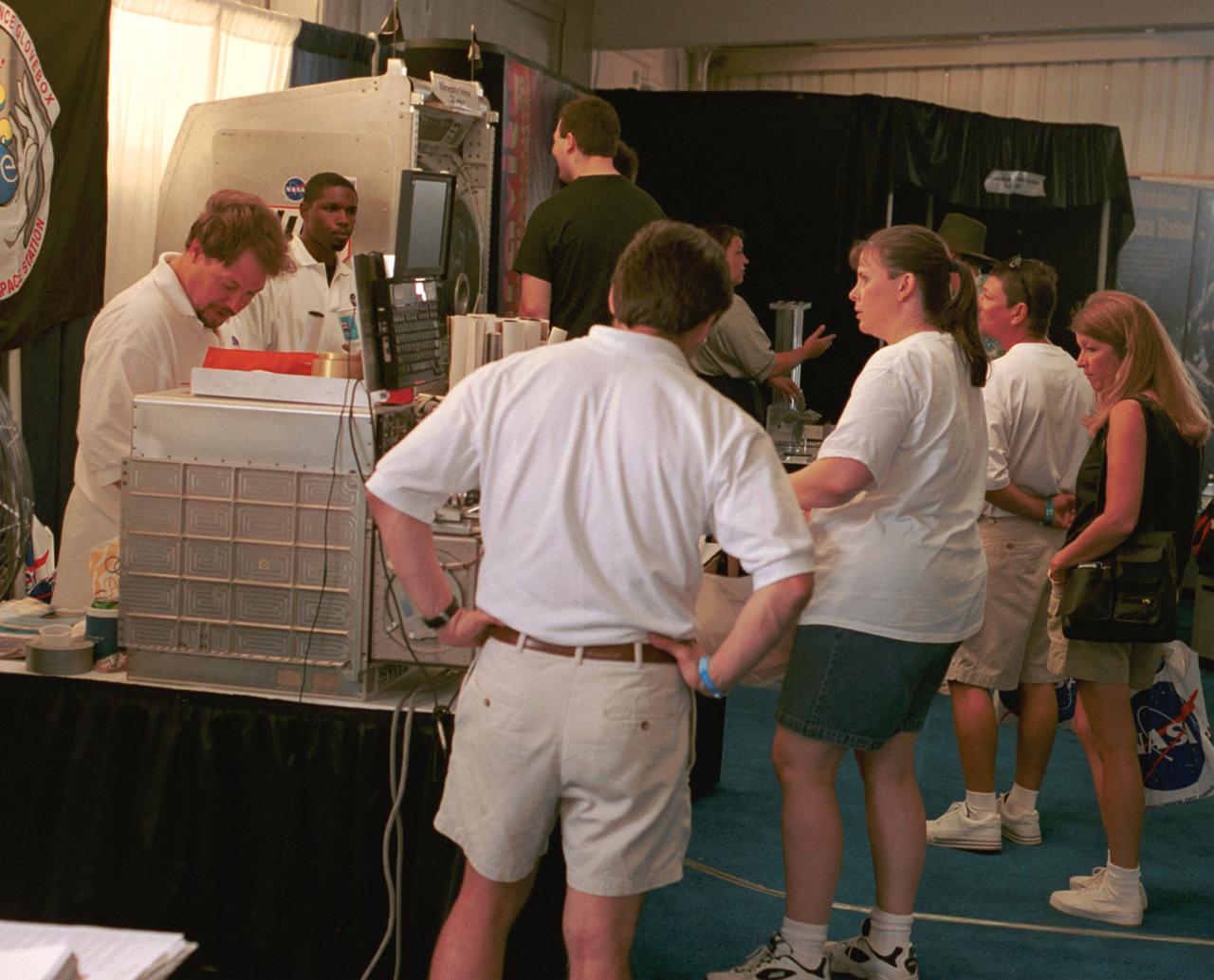

NASA representatives prepare for another day's work answering questions and handing out posters at AirVenture 2000. Part of their demonstrations included a training model of the Middeck Glovebox used aboard the Space Shuttle and Russian Mir Space Station. This and several other devices were used to explain to the public the kinds of research that have been conducted aboard the Space Shuttle and that will continue aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The exhibit was part of the NASA outreach activity at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI.
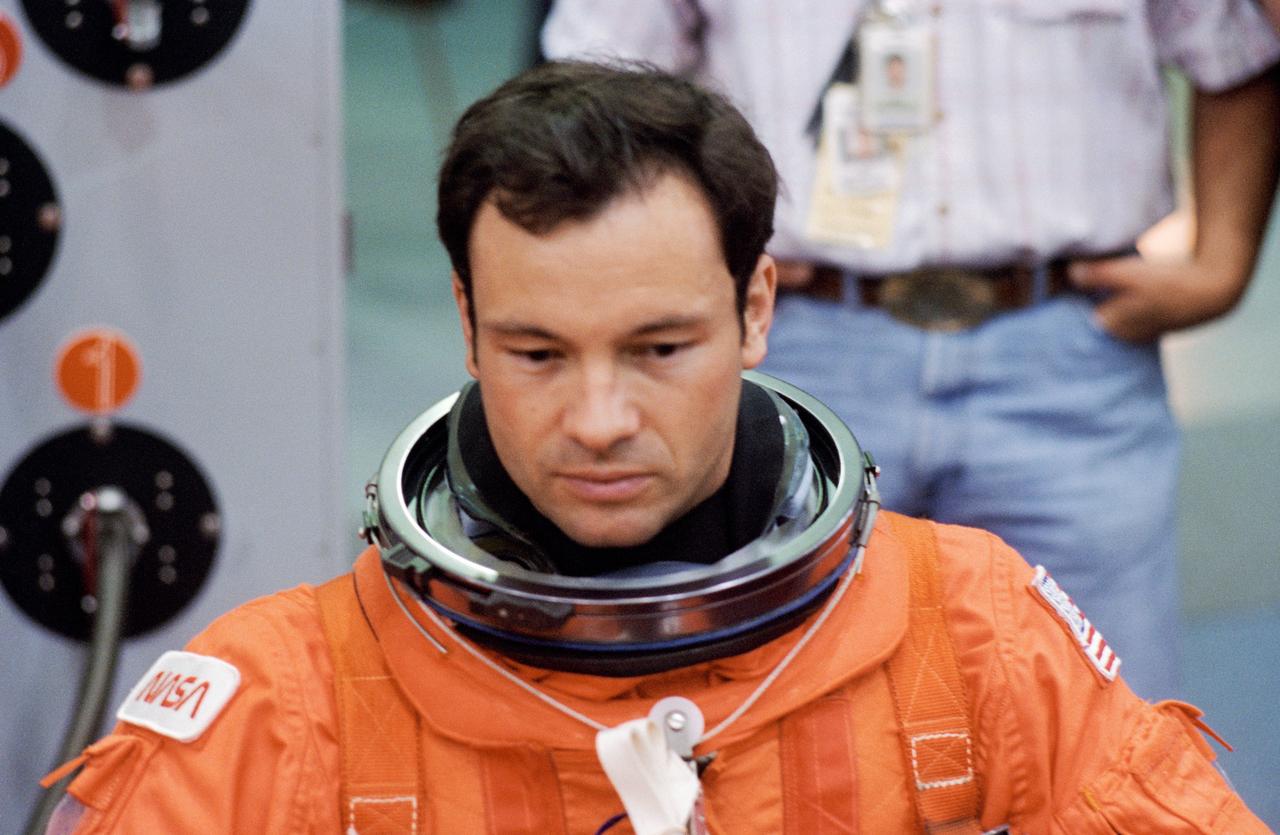

S95-09131 (27 Apr. 1995) --- Astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, mission specialist, watches as one his seven STS-73 crew mates (out of frame) rehearses action necessary in the case of an emergency with the Space Shuttle. The crew mate uses (and Lopez-Alegria later used) a Sky-genie device to rappel from the top of a ?troubled Shuttle? during emergency egress training exercises in the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC).
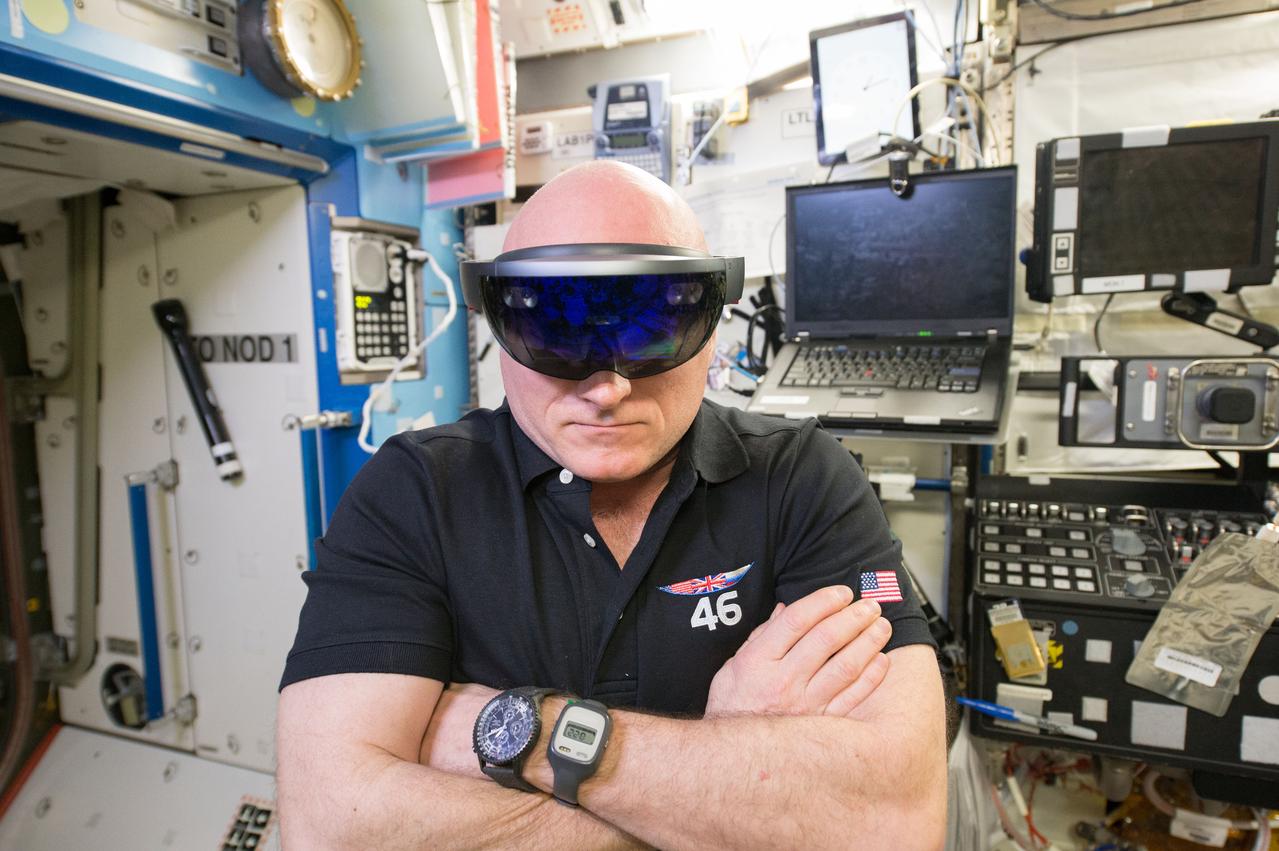

ISS046e043637 (02/20/2016) --- NASA astronaut Scott Kelly tweeted out this image to his followers Feb 20, 2016 with the tag: "This #Saturday morning checked out the @Microsoft #HoloLens aboard @Space_Station! Wow! #YearInSpace ". The device is part of NASA’s project Sidekick which is exploring the use of augmented reality to reduce crew training requirements and increase the efficiency at which astronauts can work in space.