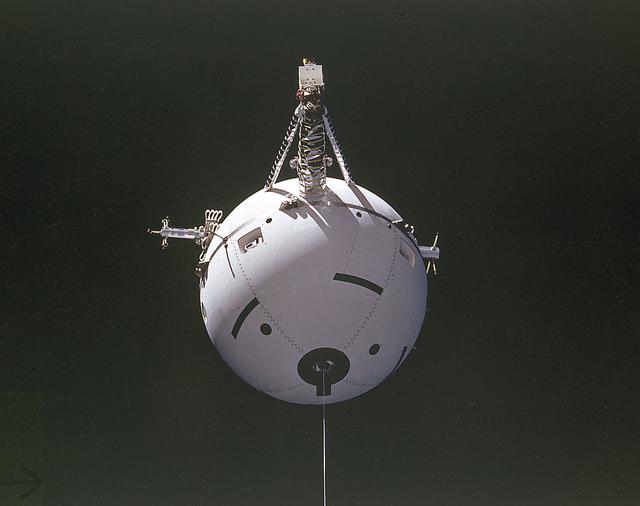

Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) deployment. A cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, the Tethered Satellite System (TSS) made capable the deployment and retrieval of a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
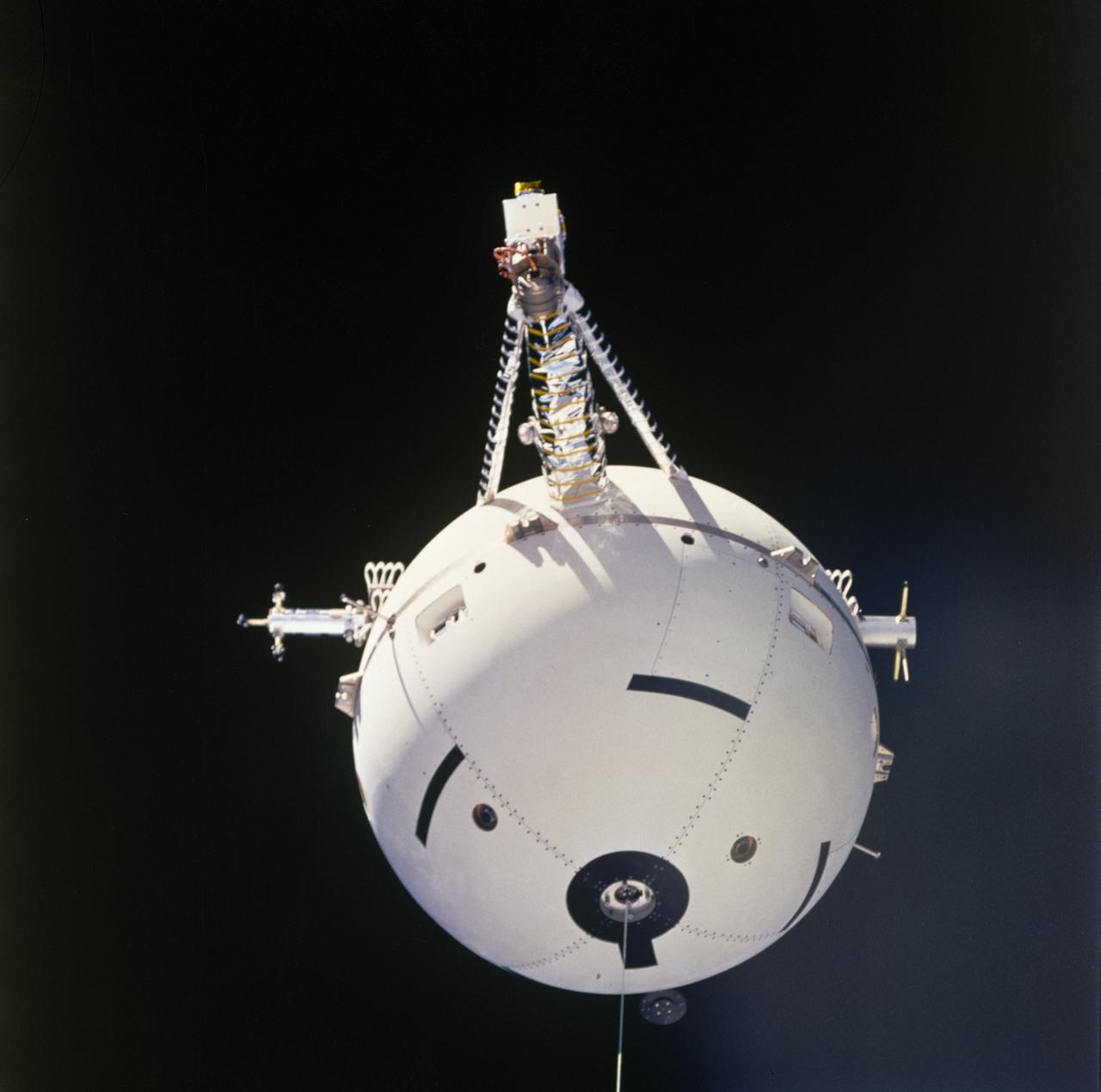

This Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo is a close-up view of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) in orbit above the Shuttle. A cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, the Tethered Satellite System (TSS) made capable the deployment and retrieval of a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
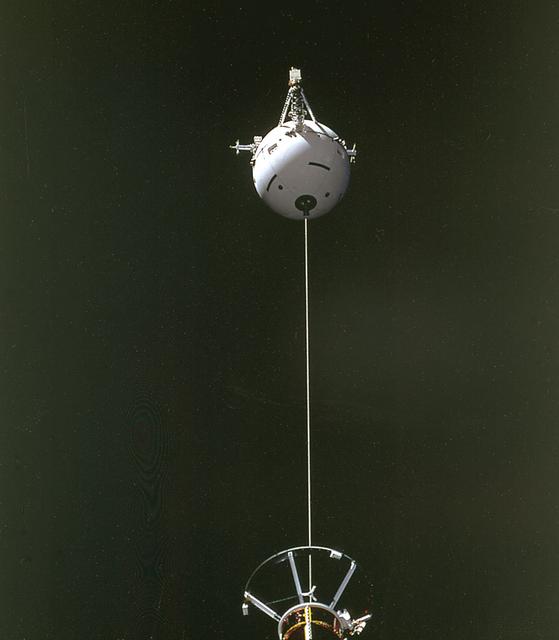

This is a Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) deployment. A cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, the Tethered Satellite System (TSS) made capable the deployment and retrieval of a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
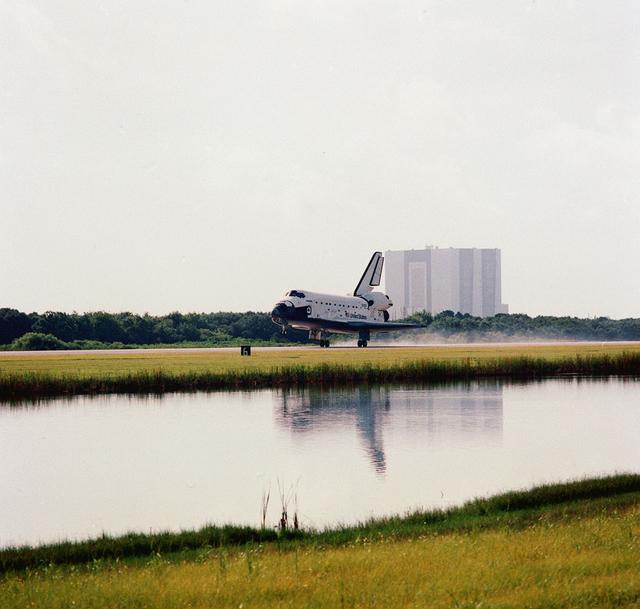

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) touched down at Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility completing an eight day mission of five NASA astronauts and two Europeans. The vehicle assembly building (VAB) can be seen in the background. The STS-46 mission carried and deployed the European Retrievable Carrier (Eureca), and the NASA/ISA Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1), allowing for a new capability for probing the space environment.
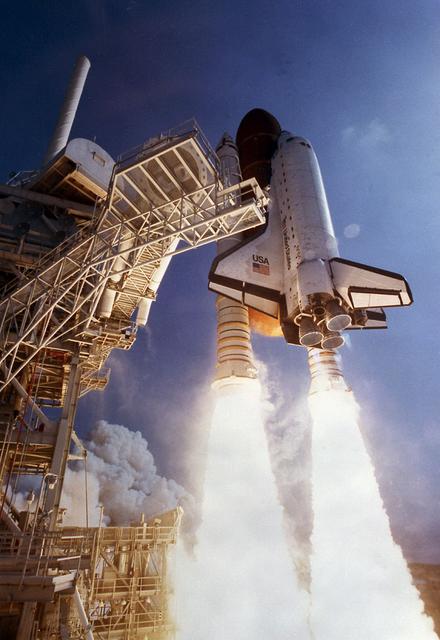

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) breaks free of all earthly constraints and hurdles past the Fixed Service Structure (FSS) and beanie cap which only moments before had been in place above the external tank. The Shuttle Atlantis carried and deployed the European Retrievable Carrier (Eureca). The NASA/ISA Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) was also deployed for the first time, allowing for a new capability for probing the space environment.
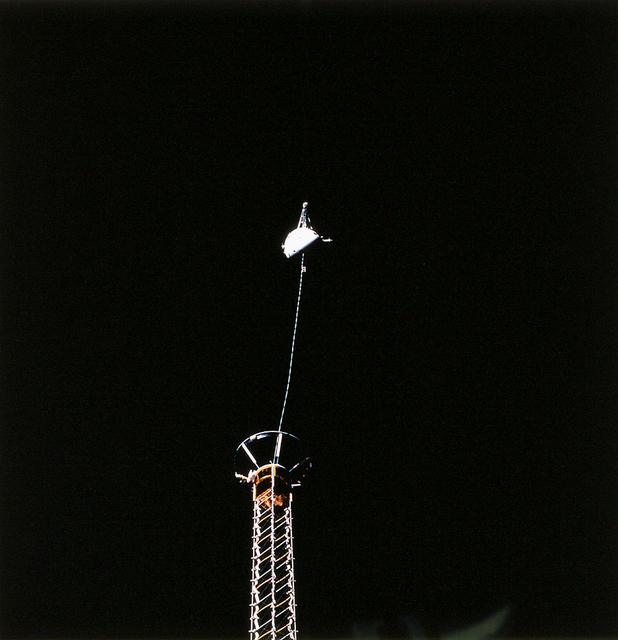

An STS-75 onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System-1 Reflight (TSS-1R) atop its extended boom. The TSS-1R was a reflight of TSS-1, which was flown on the Space Shuttle in July/August, 1992. Building on the knowledge gained on the TSS-1 about tether dynamics, the TSS will circle the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), placing the tether system well within the rarefield, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. The satellite was plarned to be deployed 20.7 kilometers (12.9 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether, generating high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the ionosphere cutting magnetic field lines, would allow scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. In addition, the TSS would increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, such as plasma waves and currents. The tether on the TSS broke as the Satellite was nearing the full extent of its 12.5 mile deployment from the Shuttle. The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, and was managed by scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
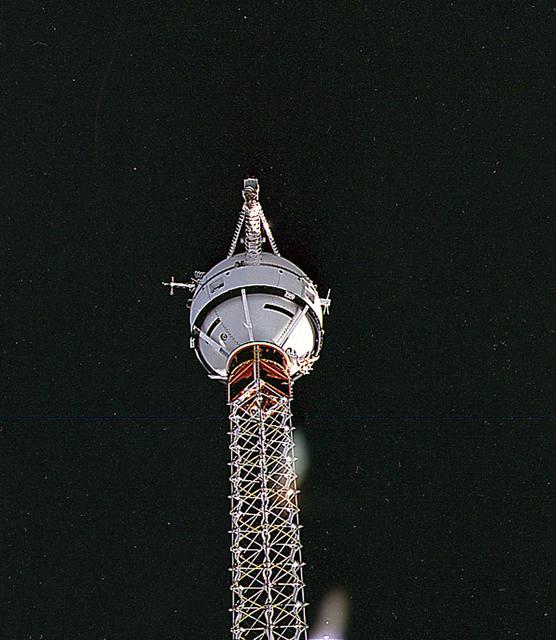

An STS-75 onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System-1 Reflight (TSS-1R) atop its extended boom. The TSS-1R was a reflight of TSS-1, which was flown on the Space Shuttle in July/August, 1992. Building on the knowledge gained on the TSS-1 about tether dynamics, the TSS will circle the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), placing the tether system well within the rarefield, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. The satellite was plarned to be deployed 20.7 kilometers (12.9 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether, generating high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the ionosphere cutting magnetic field lines, would allow scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. In addition, the TSS would increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, such as plasma waves and currents. The tether on the TSS broke as the Satellite was nearing the full extent of its 12.5 mile deployment from the Shuttle. The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, and was managed by scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
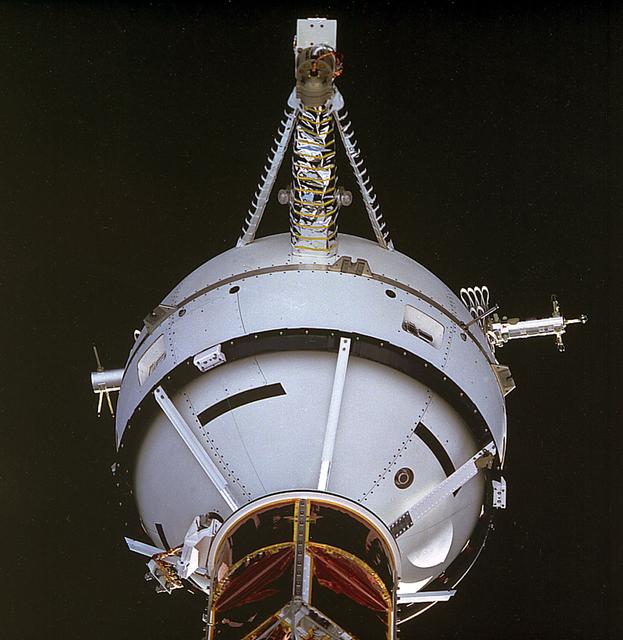

Pictured here is a Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) deployment. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA. Combined efforts resulted in the capability of deploying and retrieving a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100-km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
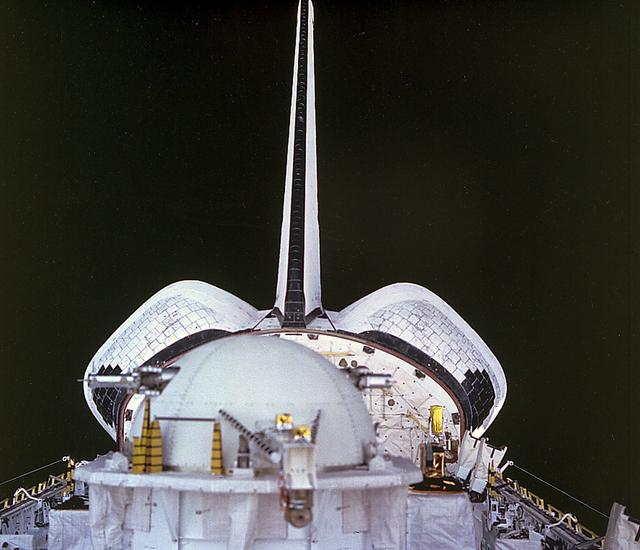
Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) in Orbiter's cargo bay. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA made capable of deploying and retrieving a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
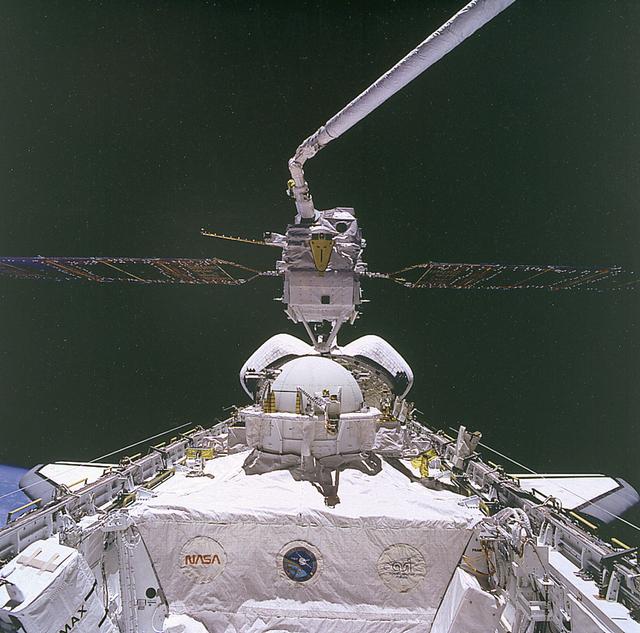

Space Shuttle Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) on deployer boom. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA made capable of deploying and retrieving a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
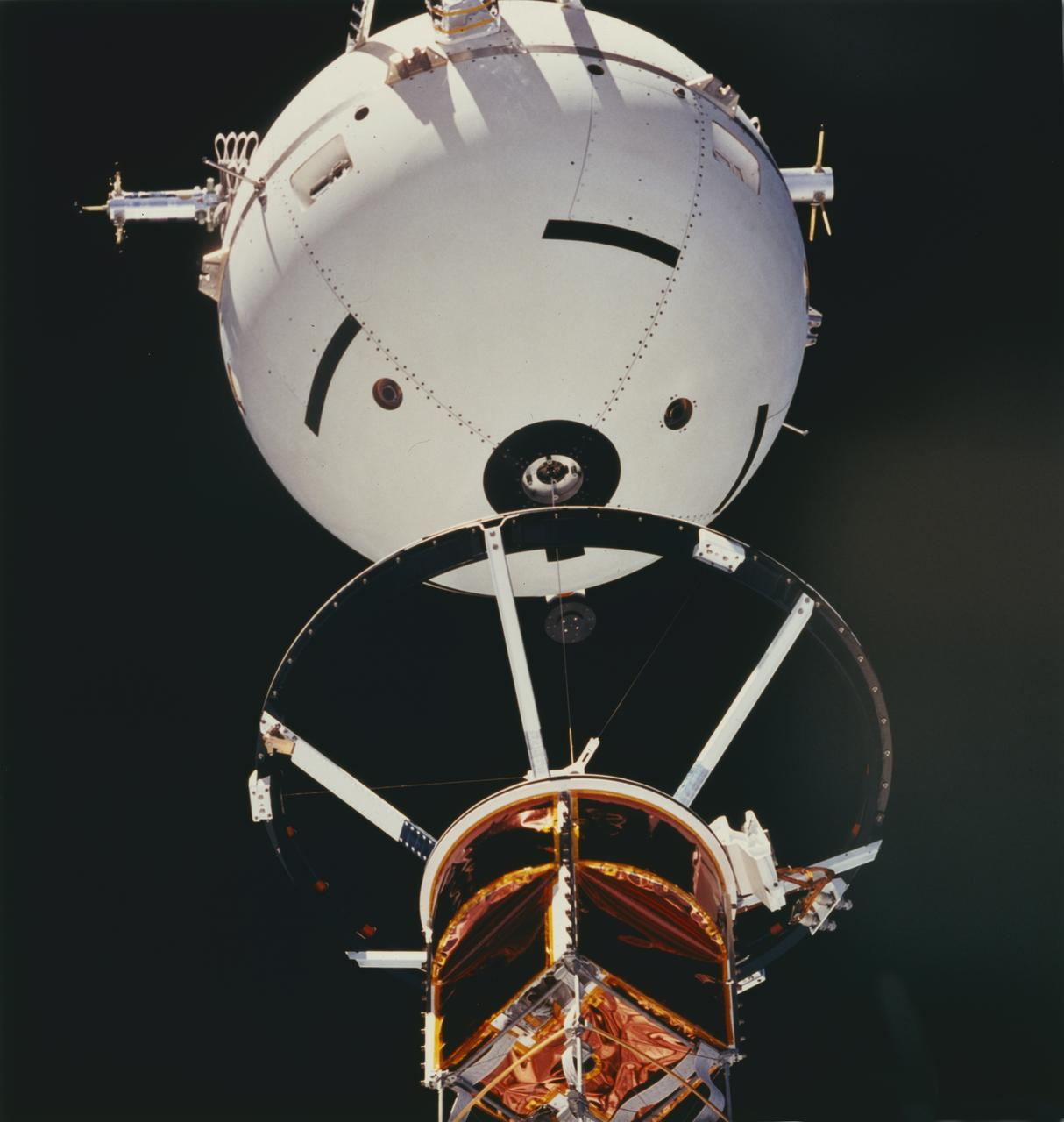

A crewmember aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) used a 70mm handheld camera to capture this medium closeup view of early operations with the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). TSS-1 is being deployed from its boom as it is perched above the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Shuttle circling the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), the TSS-1 will be well within the tenuous, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. There, a satellite attached to the orbiter by a thin conducting cord, or tether, will be reeled from the Shuttle payload bay. On this mission the satellite was plarned to be deployed 20 kilometers (12.5 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether will generate high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the atmosphere allowing scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. These studies will not only increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, but will also help provide an explanation for events witnessed elsewhere in the solar system. The crew of the STS-46 mission were unable to reel the satellite as planned. After several unsuccessful attempts, they were only able to extend the satellite 9.8 kilometers (6.1 miles). The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and NASA.
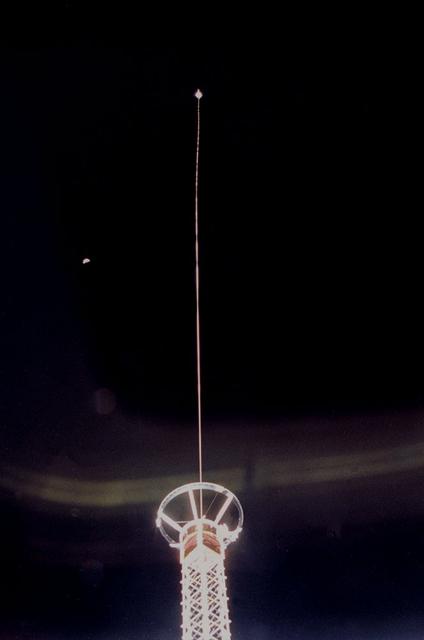

This STS-46 onboard photo is of the Tethered Satellite System-1 (TSS-1) being deployed from its boom as it is perched above the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis. Circling the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), the TSS-1 will be well within the tenuous, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. There, a satellite attached to the orbiter by a thin conducting cord, or tether, will be reeled from the Shuttle payload bay. On this mission the satellite was plarned to be deployed 20 kilometers (12.5 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether will generate high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the atmosphere allowing scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. These studies will not only increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, but will also help provide an explanation for events witnessed elsewhere in the solar system. The crew of the STS-46 mission were unable to reel the satellite as planned. After several unsuccessful attempts, they were only able to extend the satellite 9.8 kilometers (6.1 miles). The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and NASA.

STS046-S-001 (May 1992) --- Designed by the crew members assigned to the flight, the crew patch depicts the space shuttle Atlantis in orbit around Earth, accompanied by major payloads: the European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) and the Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1). In the depiction, EURECA has been activated and released, its antennae and solar arrays deployed, and it is about to start its ten-month scientific mission. The tethered satellite is linked to the orbiter by a 20-kilometer tether. The purple beam emanating from an electron generator in the payload bay spirals around Earth's magnetic field. The TSS mission will study the dynamics and electrodynamics of tethered systems in space and the physics of Earth's ionosphere. Visible on Earth's surface are the United States of America and the thirteen-member countries of the European Space Agency (ESA), in particular, Italy - partner with the United States in the TSS program. The American and Italian flags, as well as the ESA logo, further serve to illustrate the international character of STS-46. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
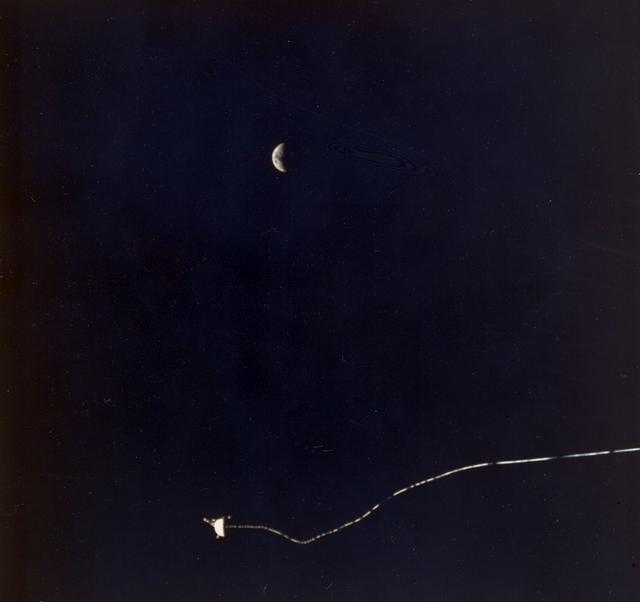
Sharing this scene with a half-moon is the Tethered Satellite System (TSS), in a photo captured onboard the STS-46. Circling Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), the TSS-1 will be well within the tenuous, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. There, a satellite attached to the orbiter by a thin conducting cord, or tether, will be reeled from the Shuttle payload bay. On this mission the satellite was plarned to be deployed 20 kilometers (12.5 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether will generate high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the atmosphere allowing scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. These studies will not only increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, but will also help provide an explanation for events witnessed elsewhere in the solar system. The crew of the STS-46 mission were unable to reel the satellite as planned. After several unsuccessful attempts, they were only able to extend the satellite 9.8 kilometers (6.1 miles). The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and NASA.
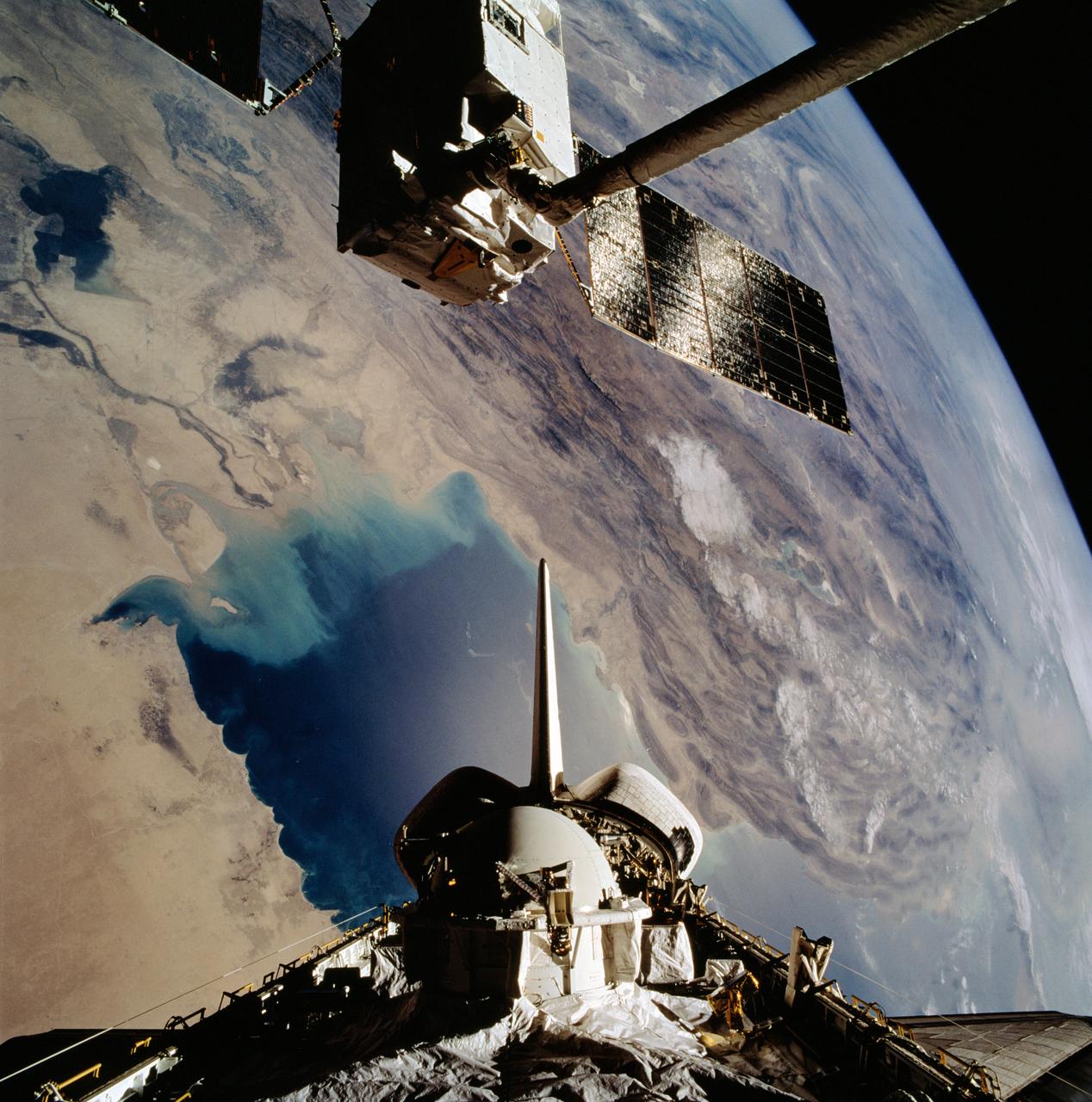

STS046-102-021 (1 Aug 1992) --- The European Space Agency's (ESA) EURECA satellite remains in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) as the Space Shuttle passes over the Persian Gulf. Most of the theater of the recent war is visible in the frame. Parts of Kuwait, Iraq, Iran and Saudi Arabia can be delineated. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) remains stowed in the aft cargo bay of Atlantis.
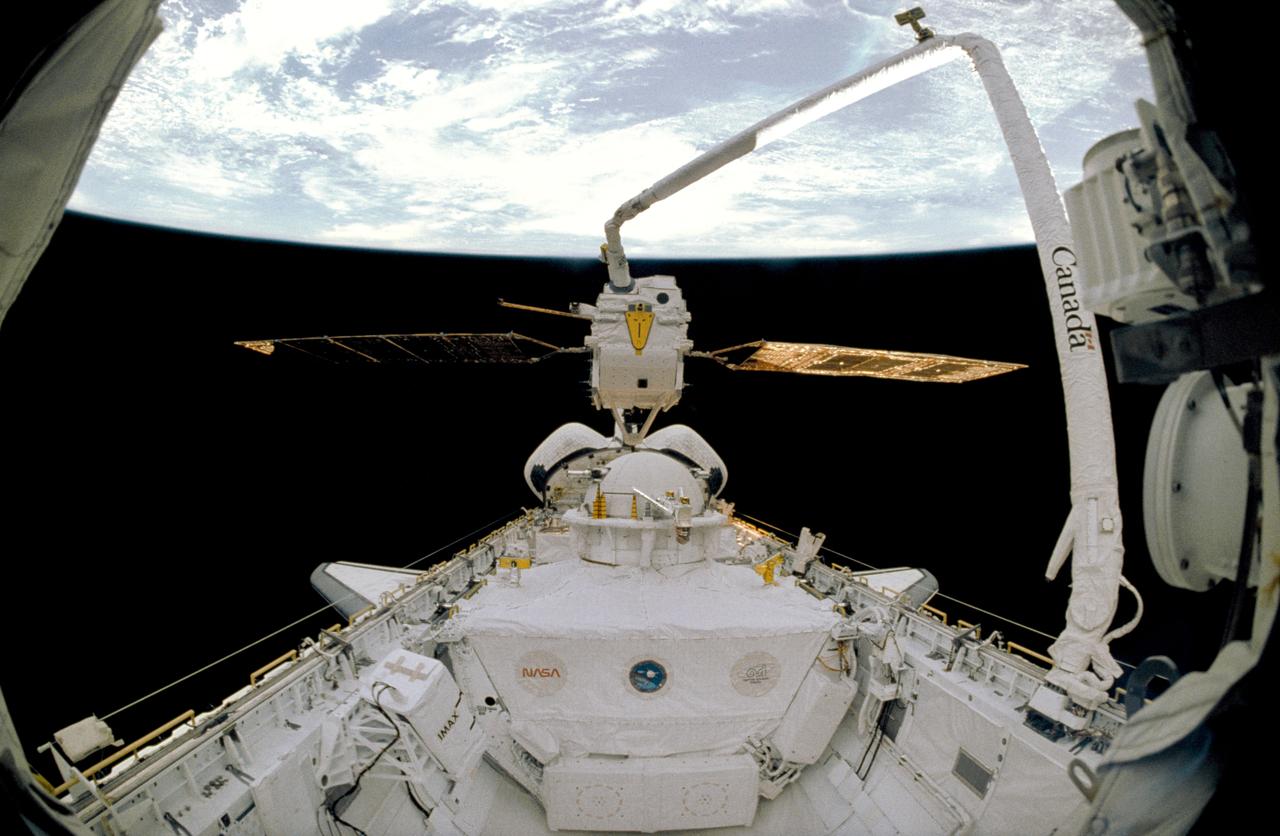

STS046-08-010 (1 Aug 1992) --- The EURECA satellite is hoisted above the Space Shuttle Atlantis' cargo bay by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) during early mission activity aboard the Earth-orbiting Shuttle. A 16mm lens gives this 35mm frame a "fish-eye" effect. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS), center frame, is stowed in the cargo bay, where it awaits extensive operations by the seven-member crew.
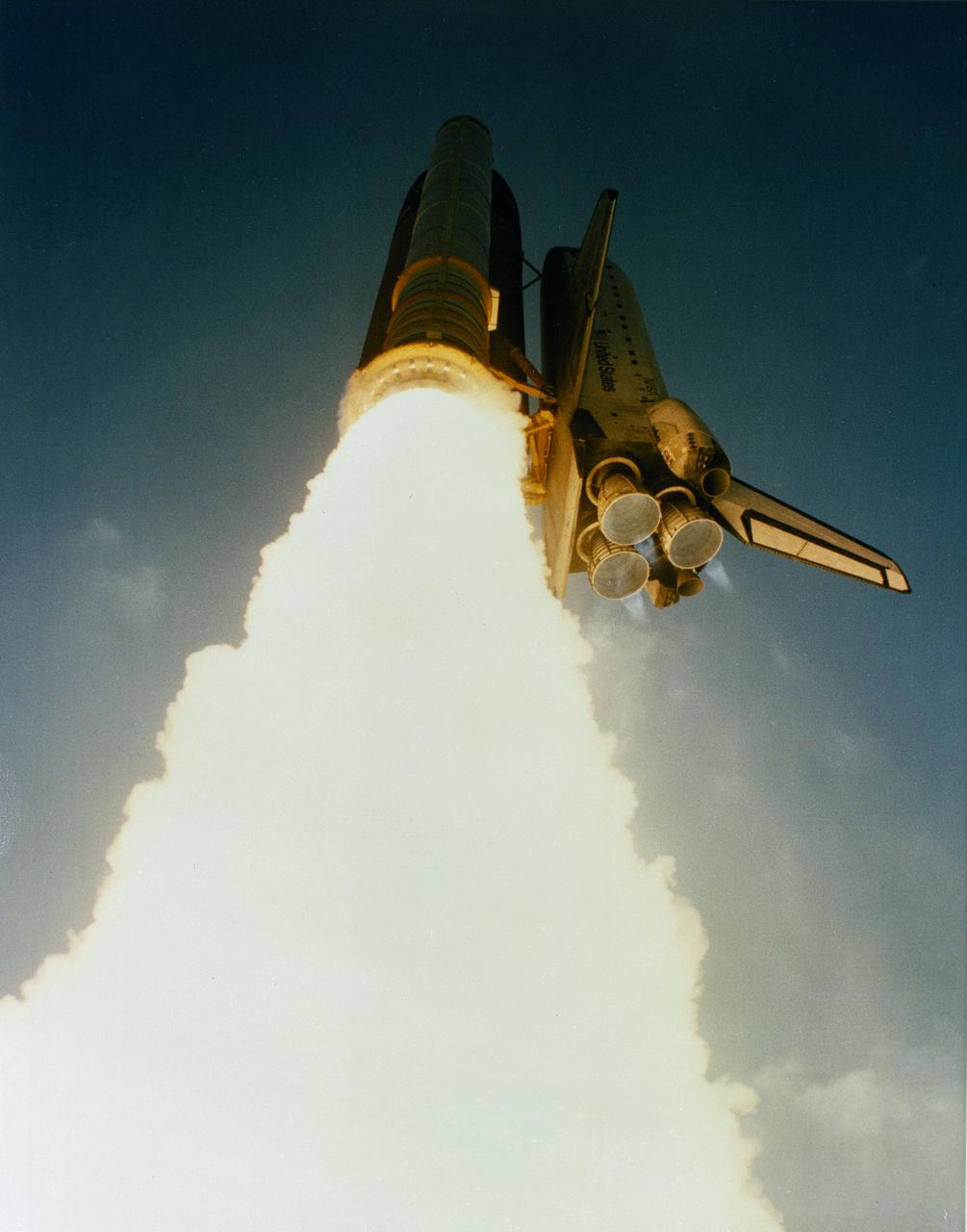

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on July 31, 1992 at 9:56:48 am (EDT), the STS-46 mission’s primary objectives included the deployment of the European Space Agency’s European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) and operation of the joint NASA/Italian Space Agency Tethered Satellite System (TSS). The STS-46 crew of seven included: Loren J. Shriver, commander; Andrew M. Allen, pilot; Jeffrey A. Hoffman, mission specialist 1; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist 2; Claude Nicollier, mission specialist 3; Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist 4; and Franco Malerba, payload specialist 1.
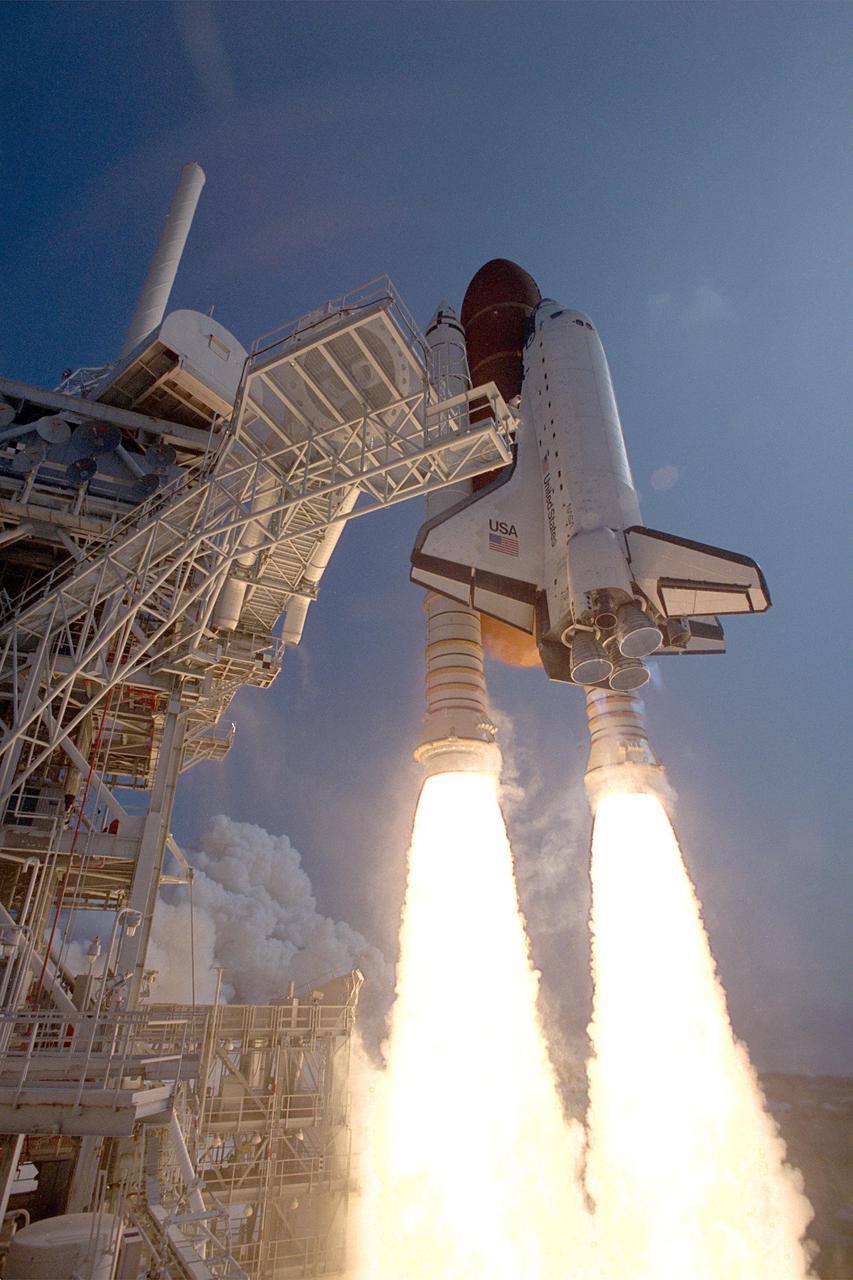

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Atlantis breaks free of all earthly constraints and hurtles past the Fixed Service Structure and 'beanie cap,' which only moments before had been in place above the external tank. STS-46 lifted off at 9:56:48 a.m. EDT, July 31. The Shuttle Atlantis carries Eureca, the European Retrievable Carrier, which is to be put into orbit during this mission. The NASA_Italian Space Agency Tethered Satellite System (TSS-1) will also be deployed for the first time during the STS-46 flight allowing a new capability for probing the space environment.
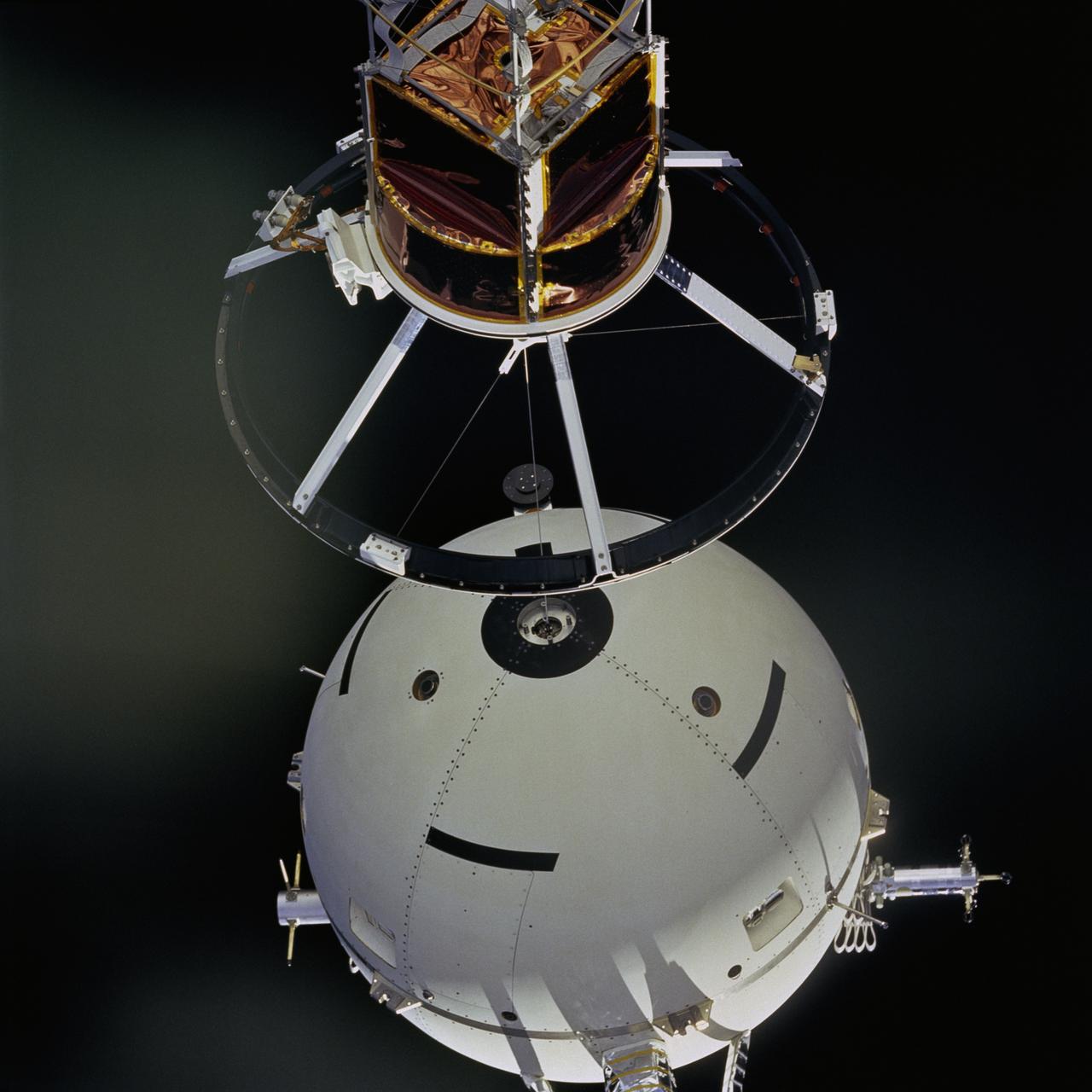

STS046-73-052 (4 Aug 1992) --- A 70mm handheld camera was used by the crew members to capture this medium close-up view of early operations with the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). The sphere can be seen moving away from the ring structure on the boom device in the Space Shuttle Atlantis' cargo bay.