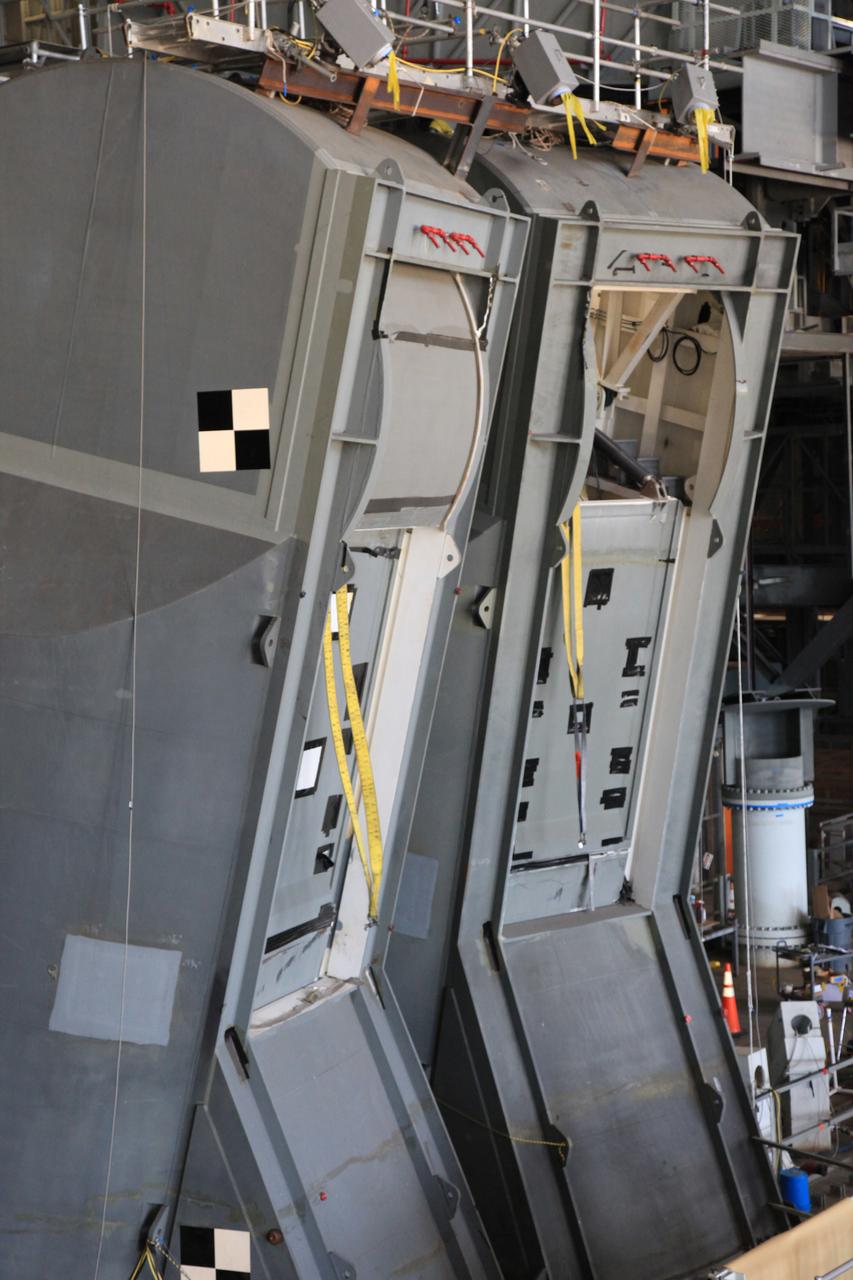

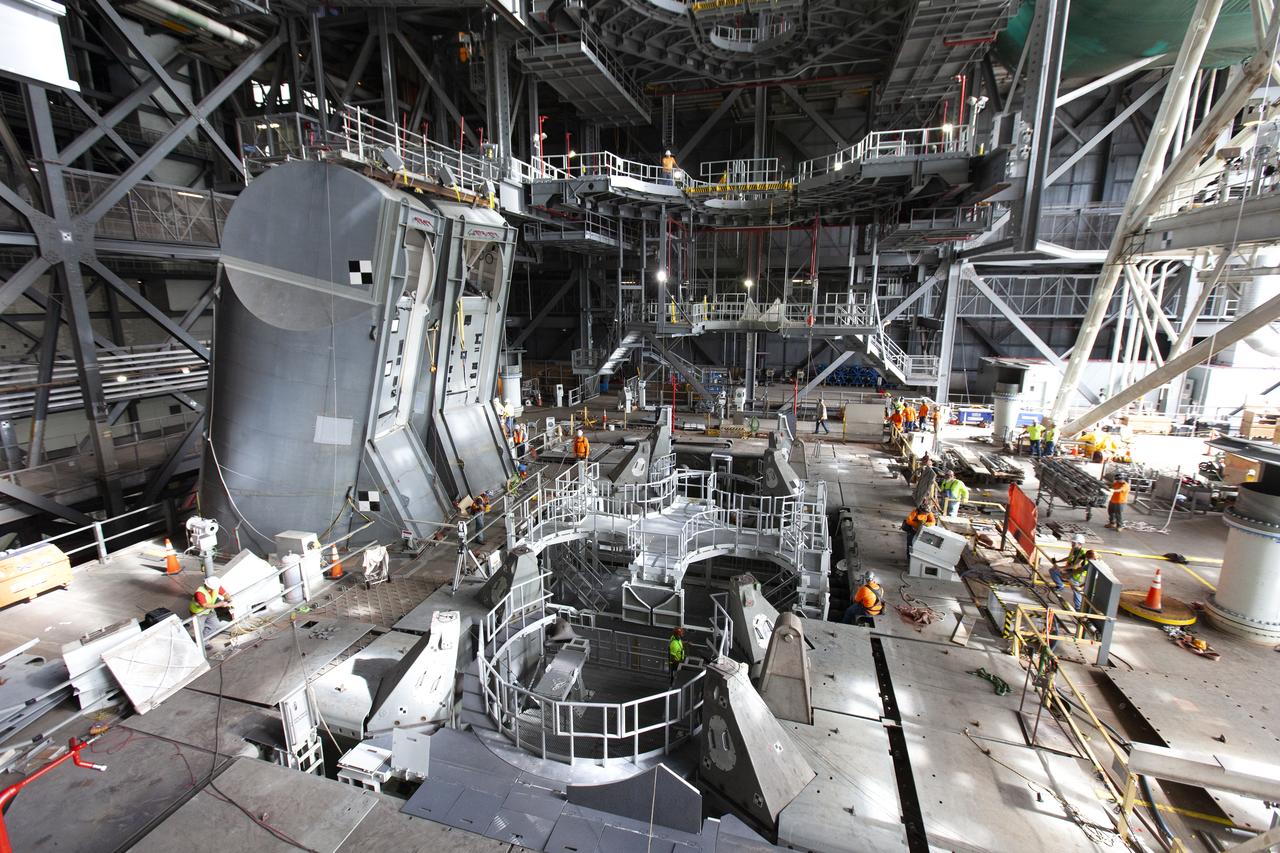
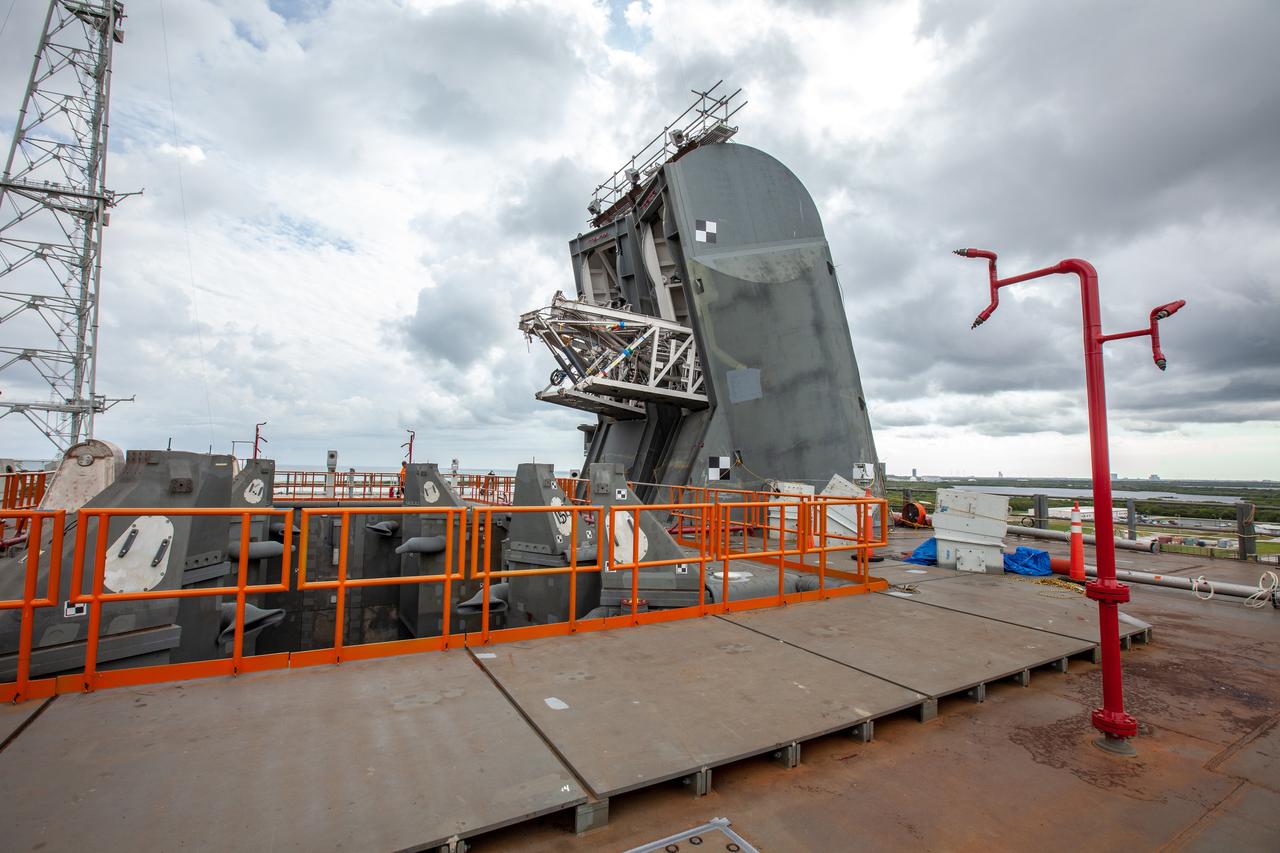
Preparations are underway to conduct a drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
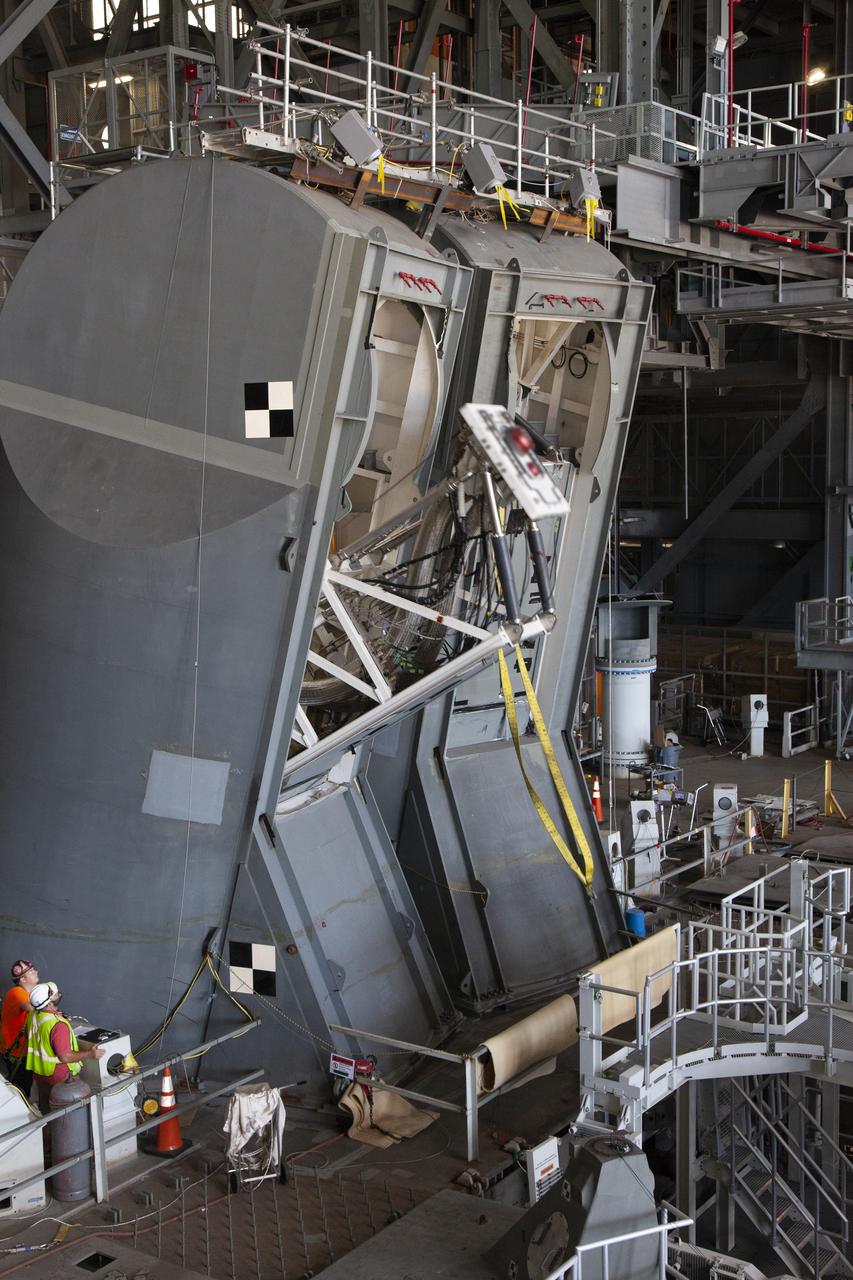

A drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is underway on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
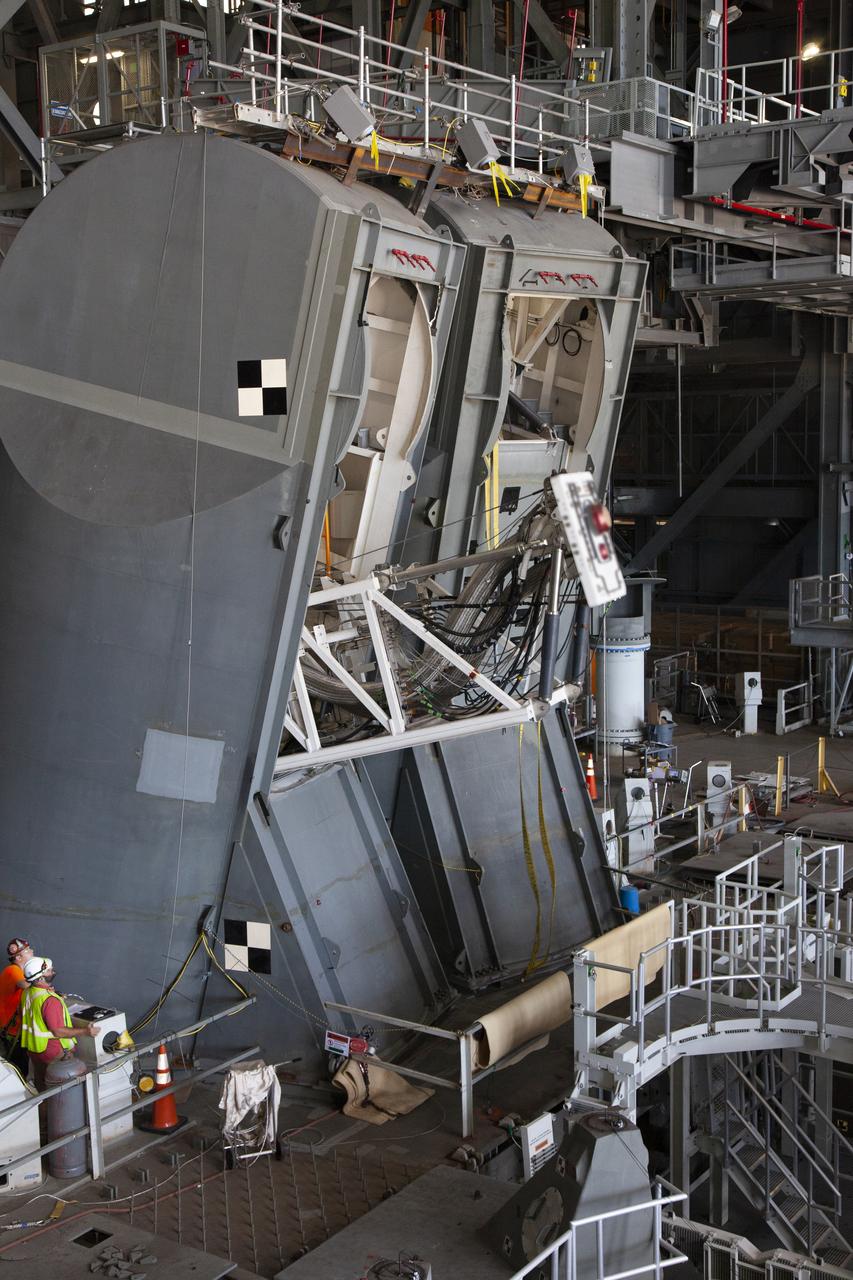

A drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is underway on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
Preparations are underway to conduct a drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.

A crane is attached to the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
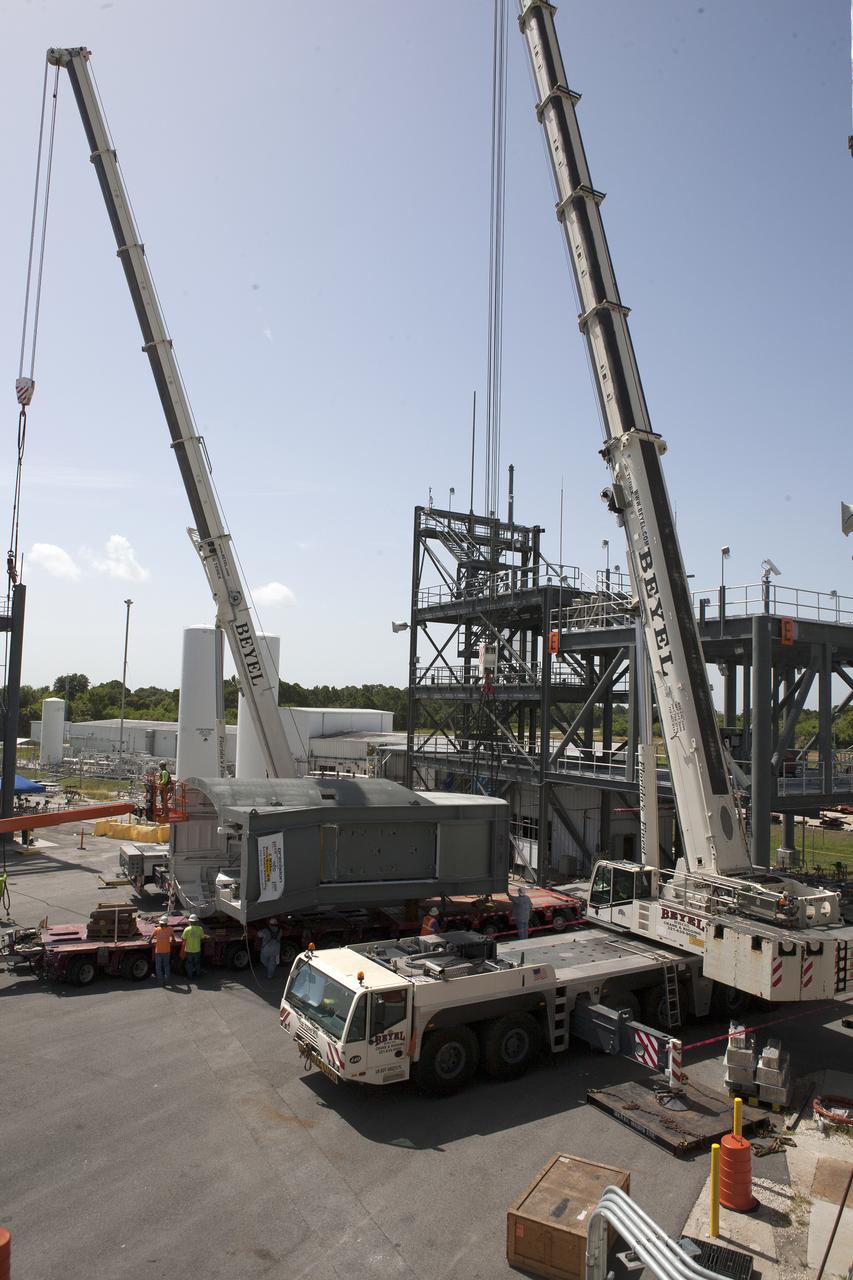

A crane is prepared to help lift the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
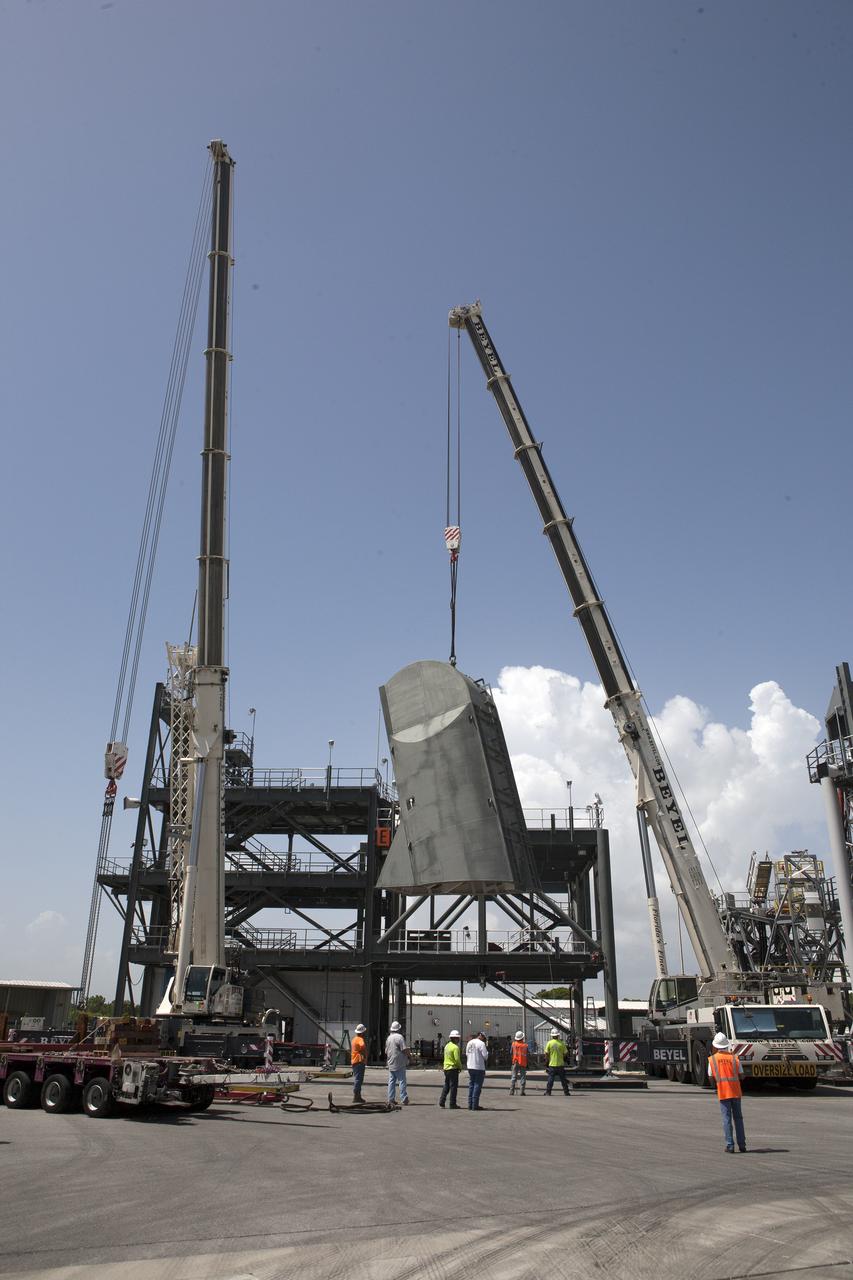

A crane lifts the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) up for placement on a test stand at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
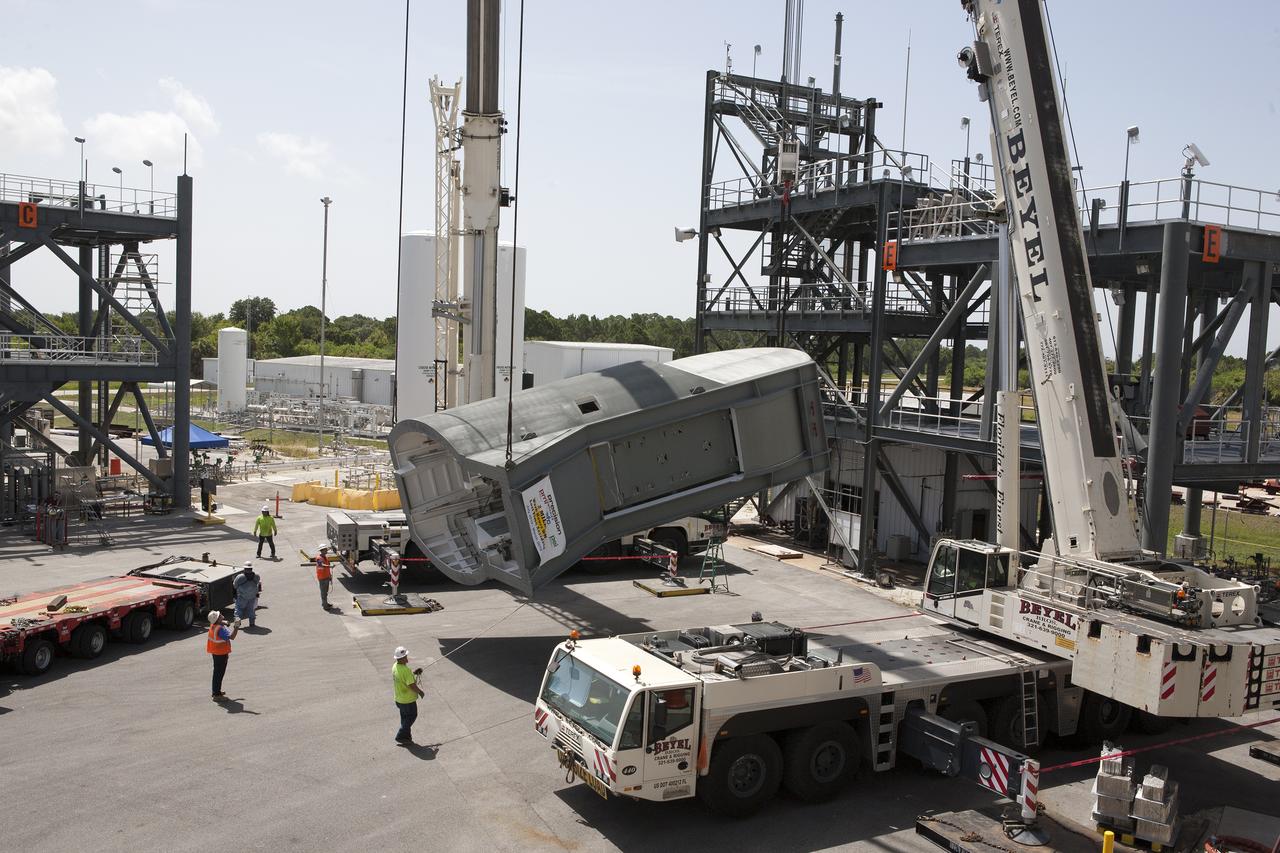

Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) away from the flatbed of the transport truck at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
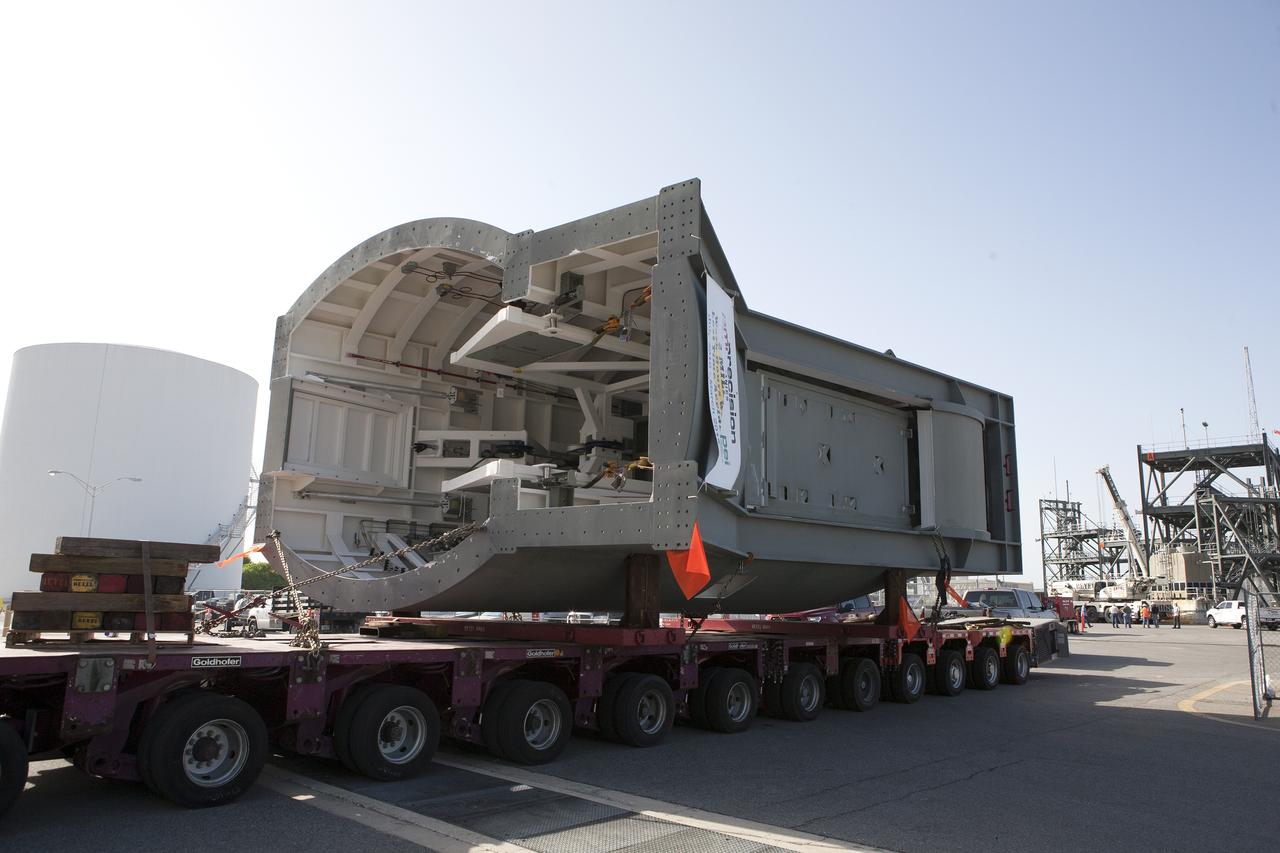

A heavy-lift transport truck arrives at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, with the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS). Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.

A crane lowers the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) onto a test stand at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
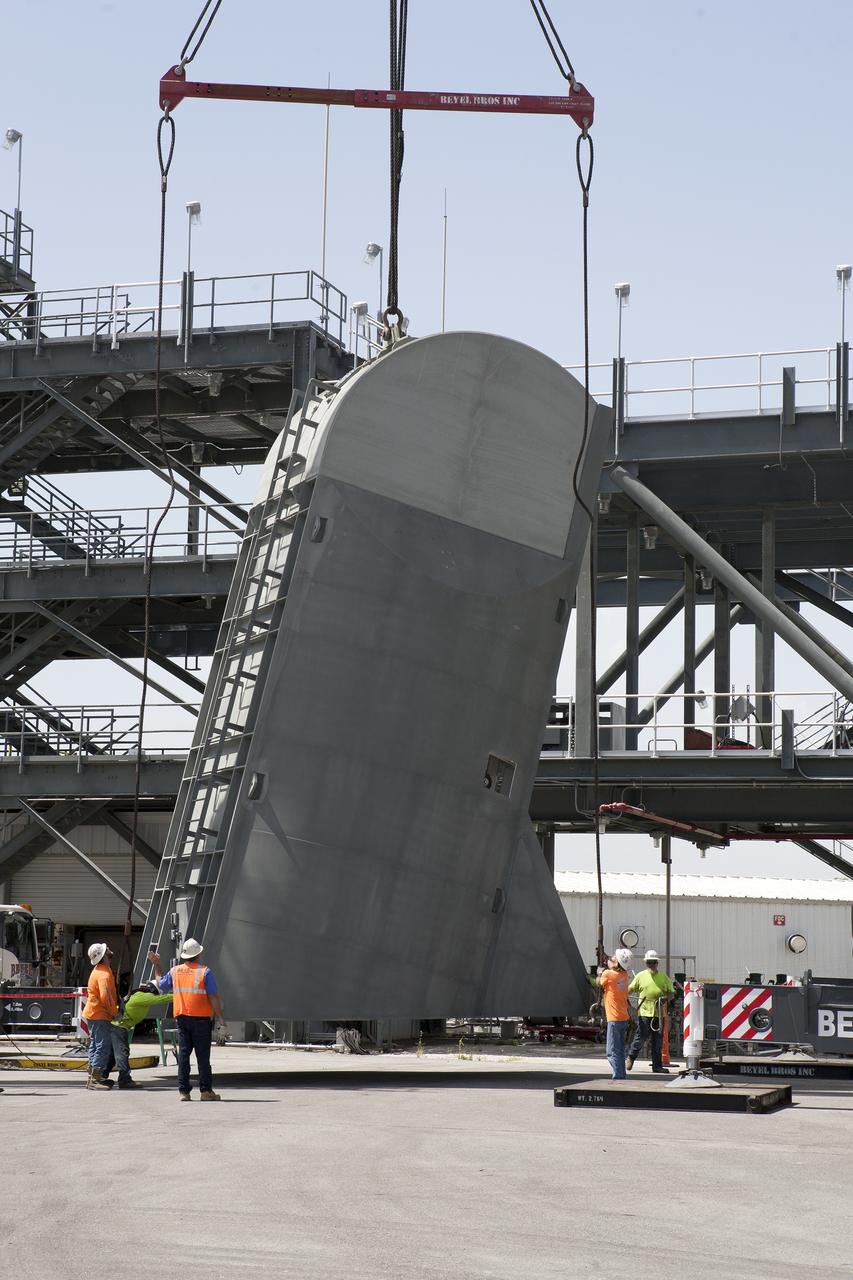

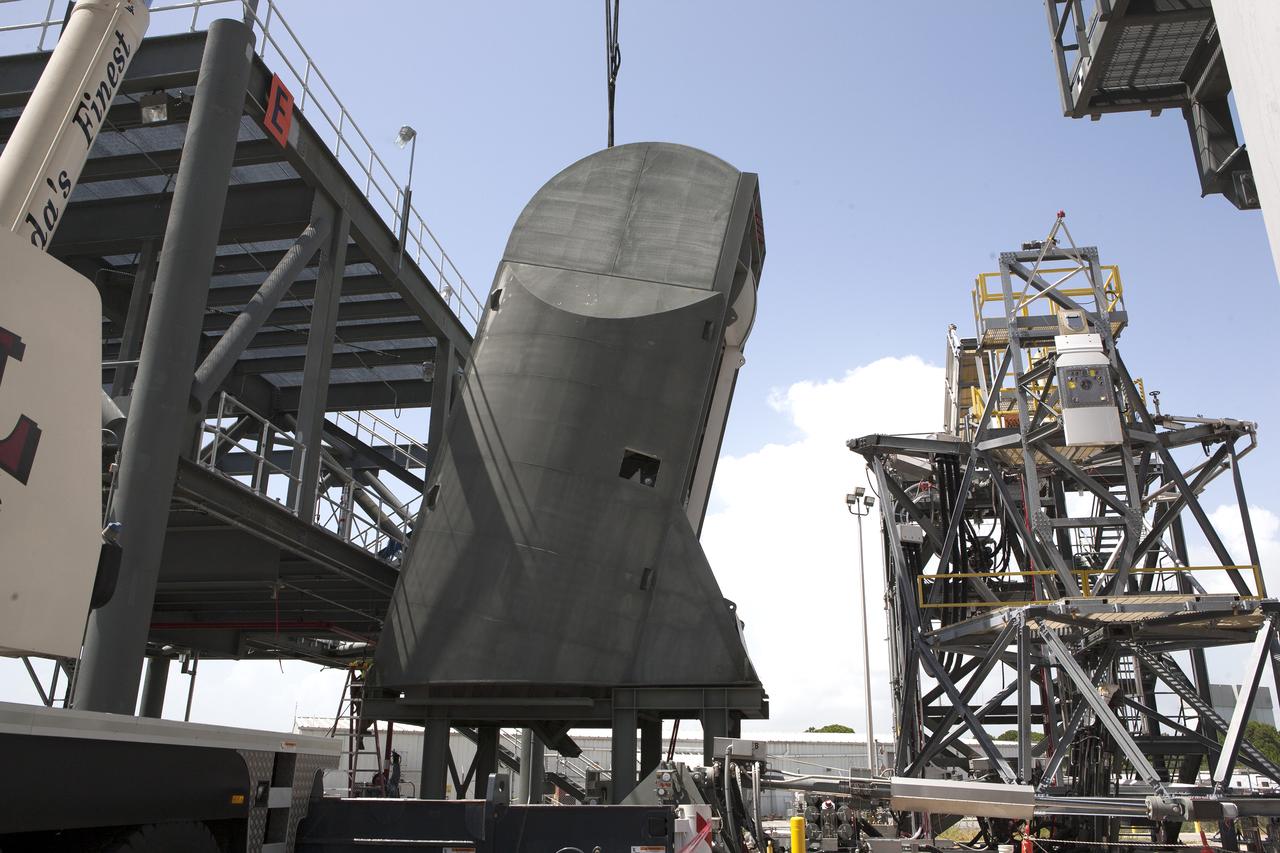
Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) into the vertical position at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
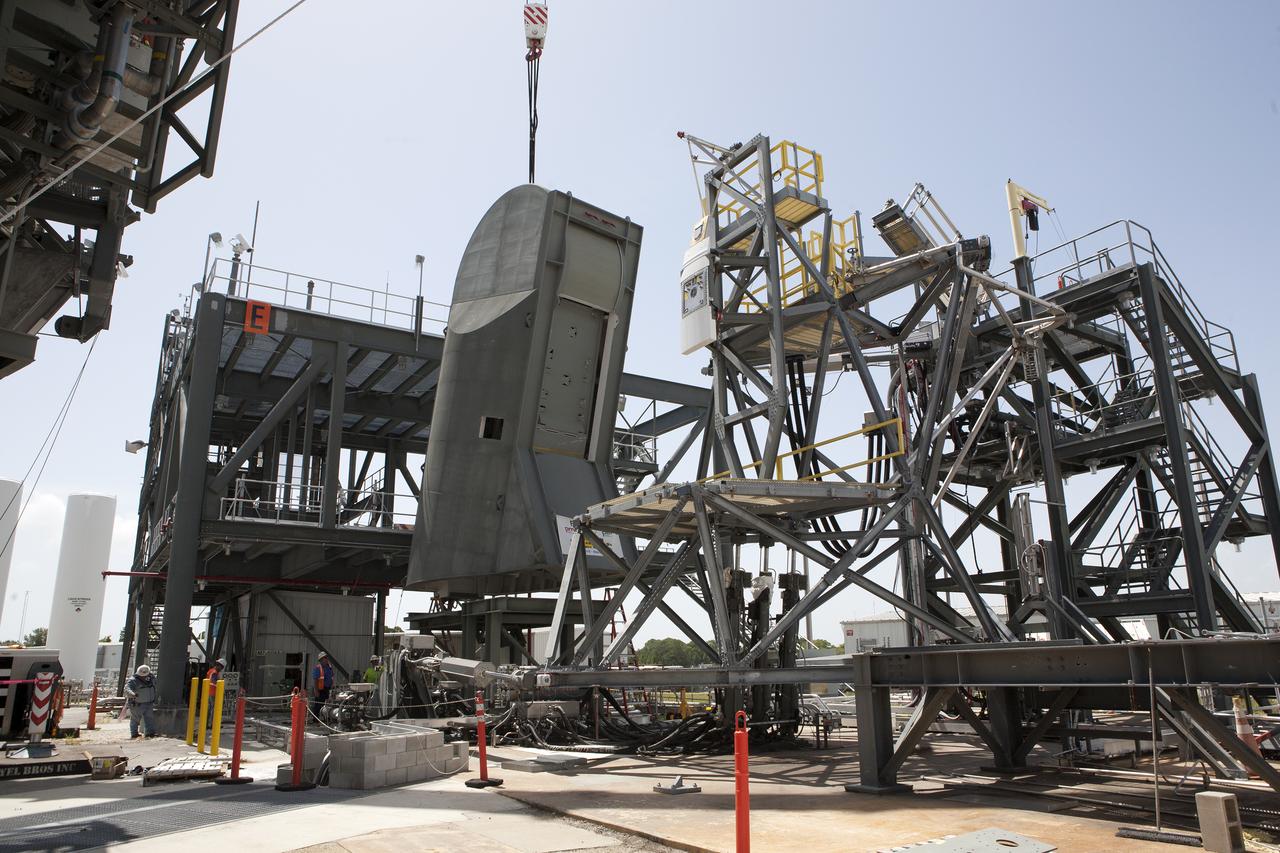

Technician monitors the progress as a crane lowers the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) onto a test stand at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.

Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift the first Tail Service Mast Umbilical (TSMU) up from the flatbed of the transport truck at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two TSMUs will provide liquid propellants and power to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage engine. Both TSMUs will connect to the zero-level deck on the mobile launcher, providing fuel and electricity to the SLS rocket before it launches on Exploration Mission 1. The TSMU will undergo testing and validation at the LETF to verify it is functioning properly. The center’s Engineering Directorate and the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program are overseeing processing and testing of the umbilicals.
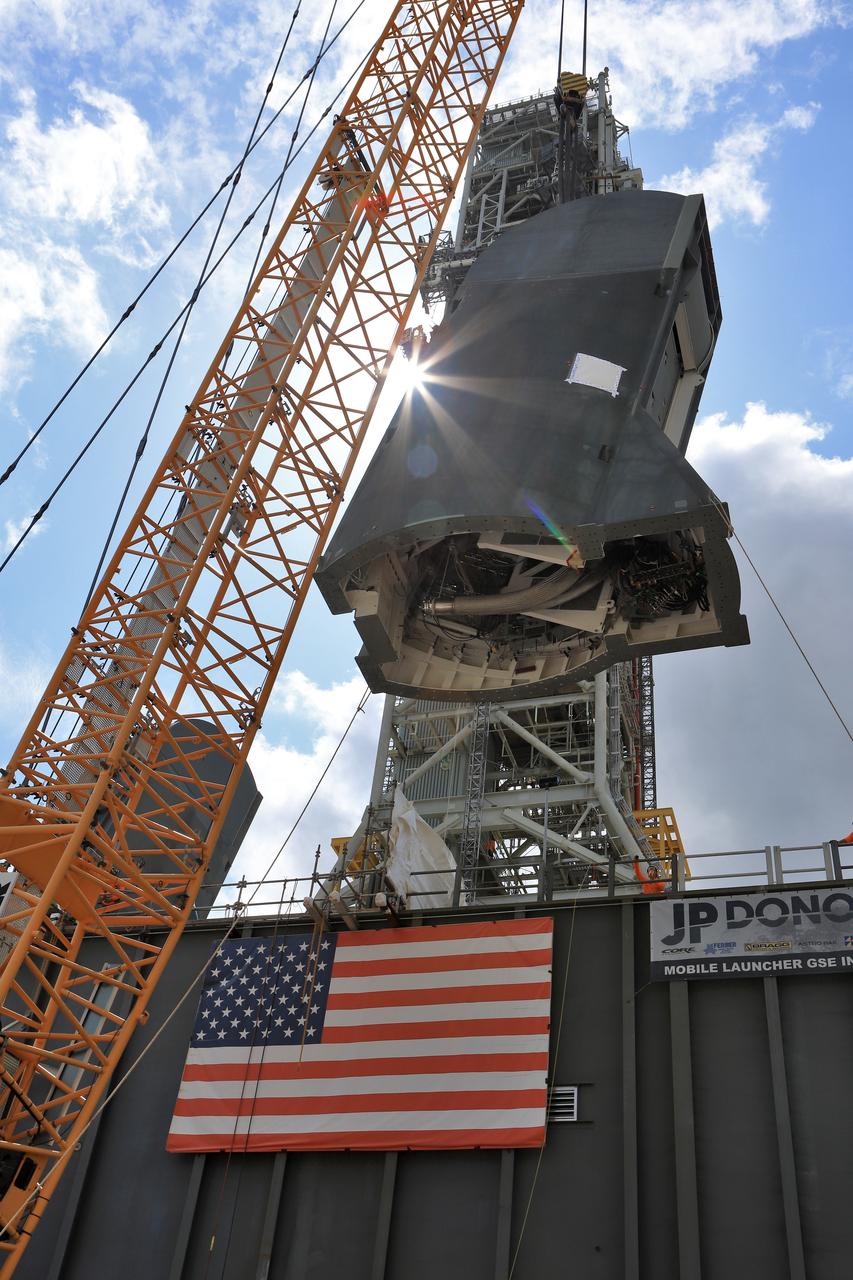

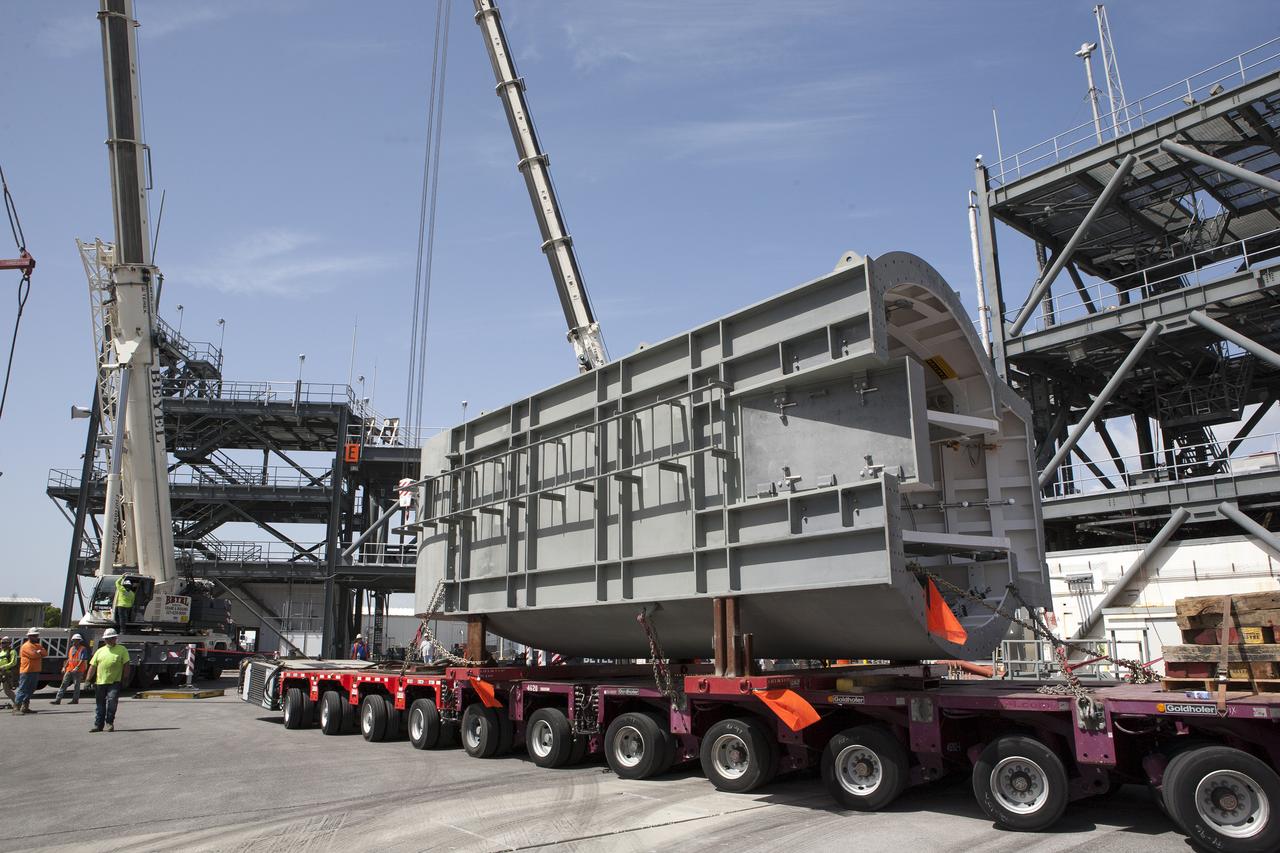
The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

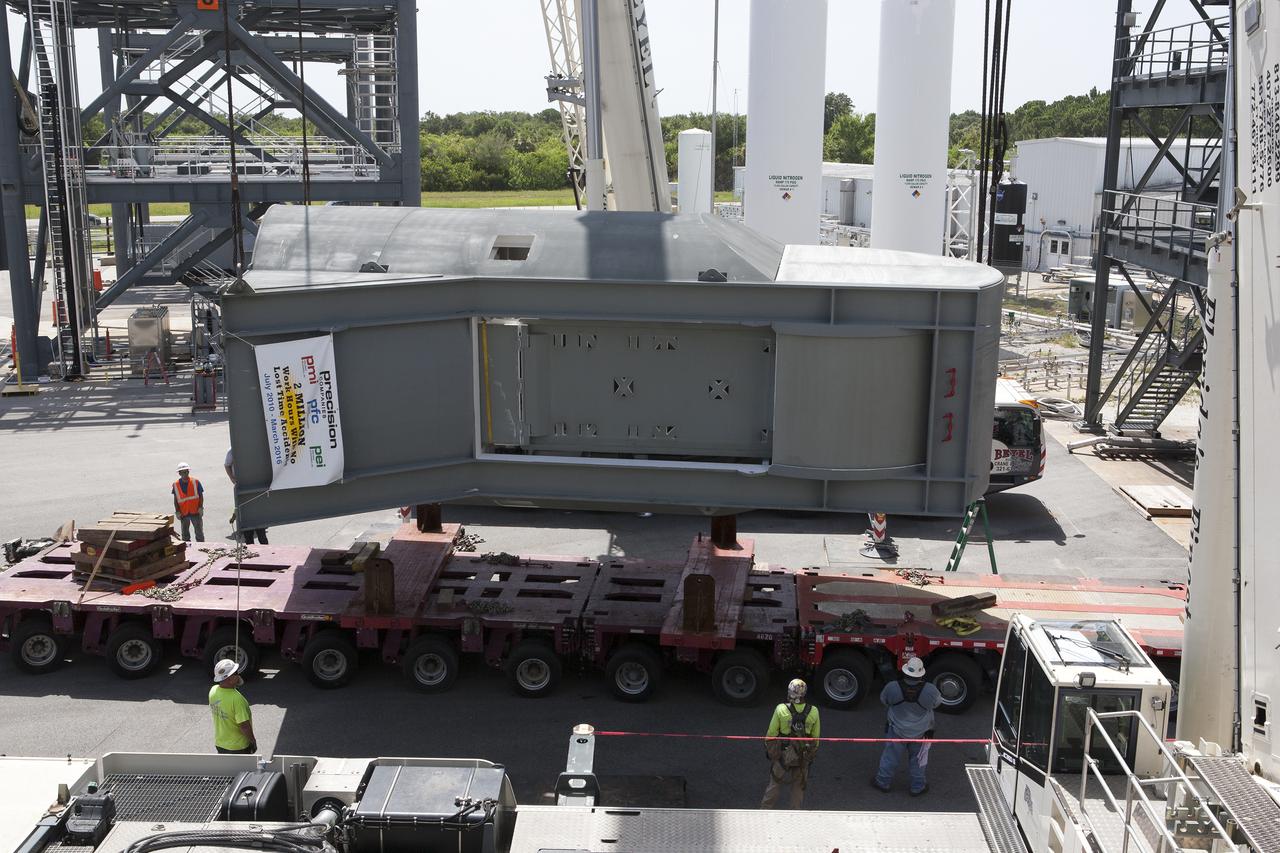
A crane is used to lift up the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
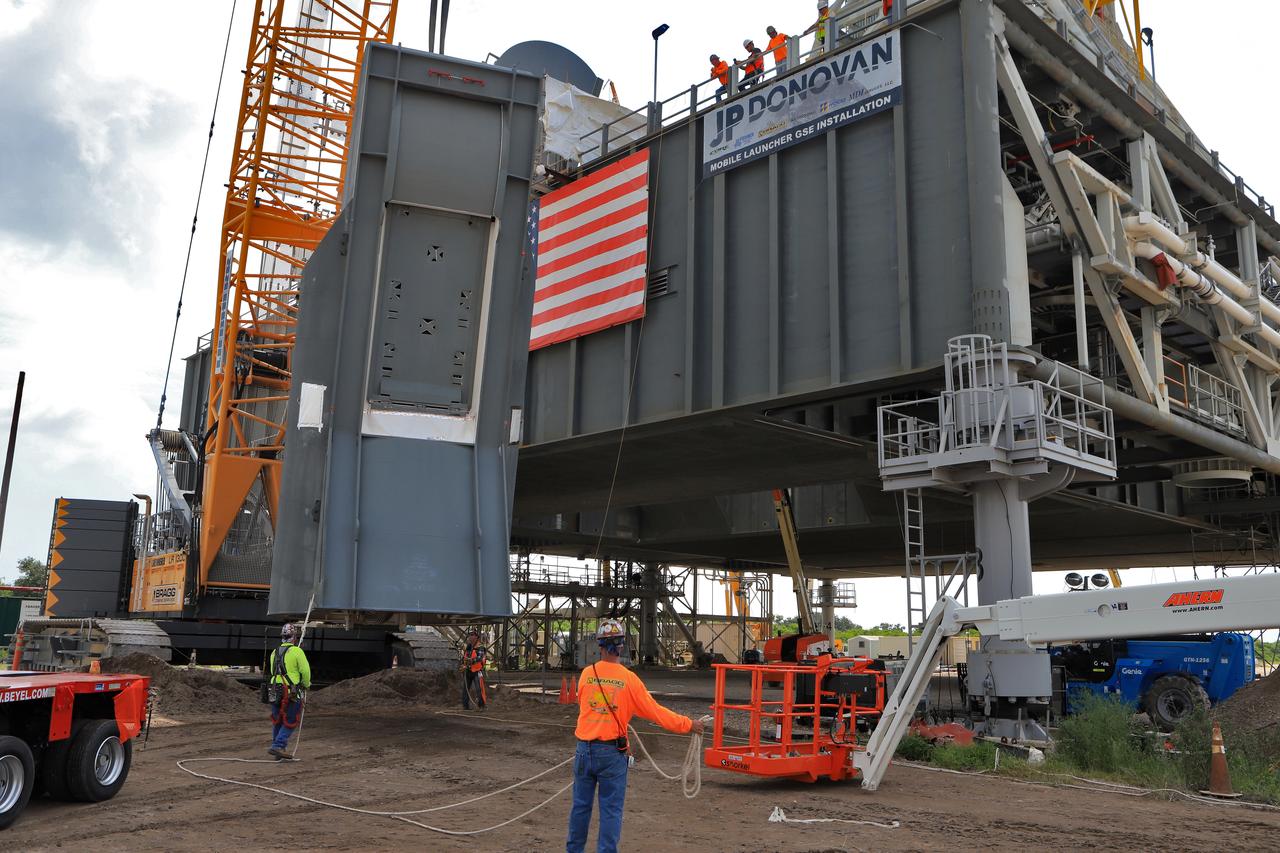

Construction workers with JP Donovan assist as a crane lifts the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals up for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

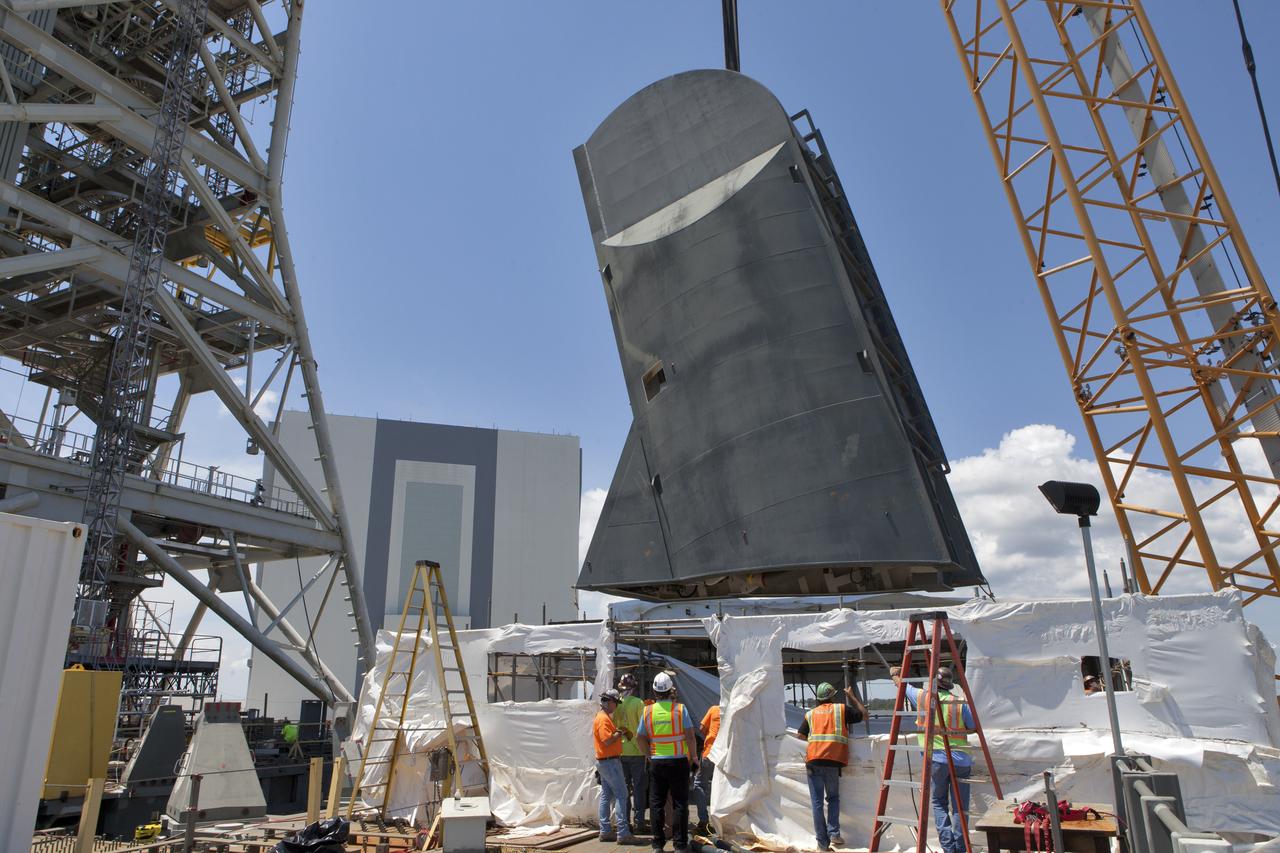
The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
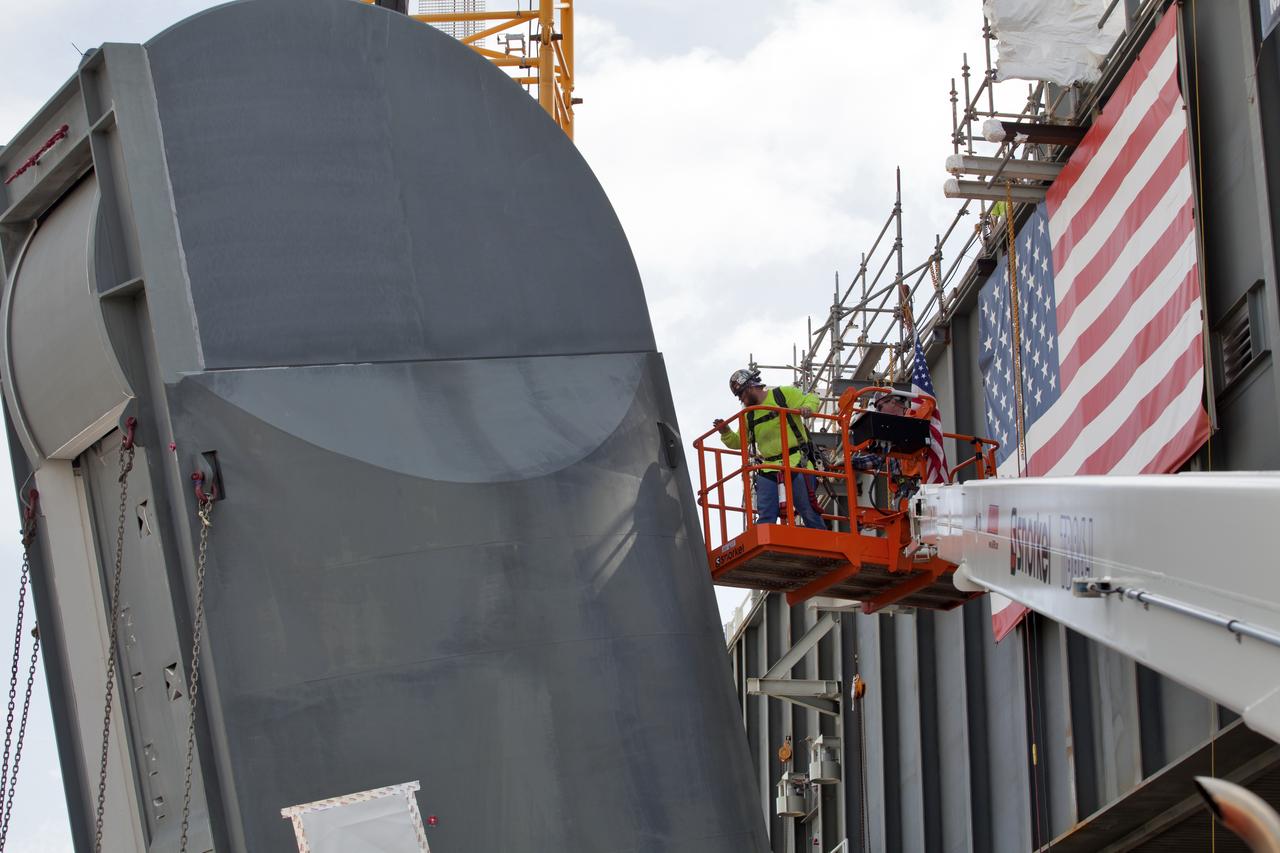

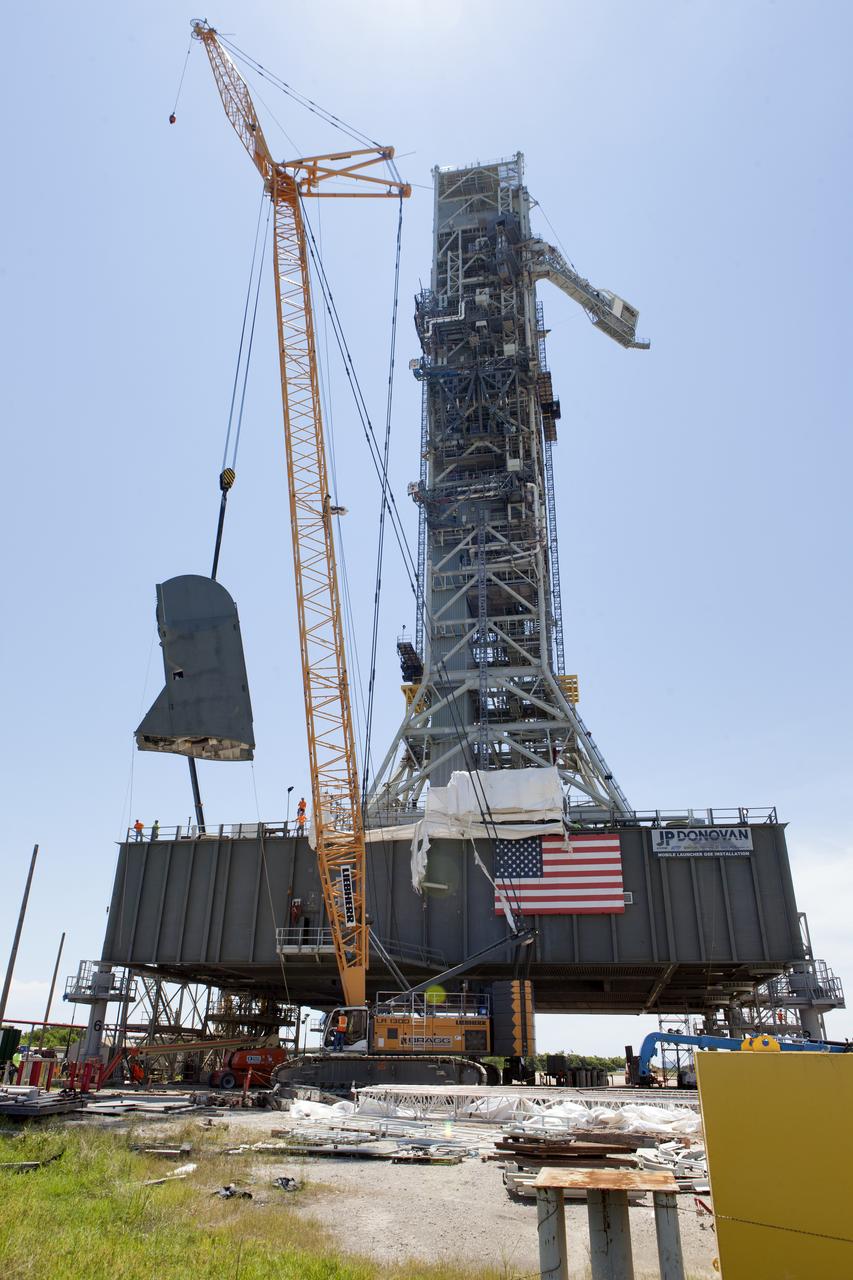
Preparations are underway to install the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

The first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lowered onto the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
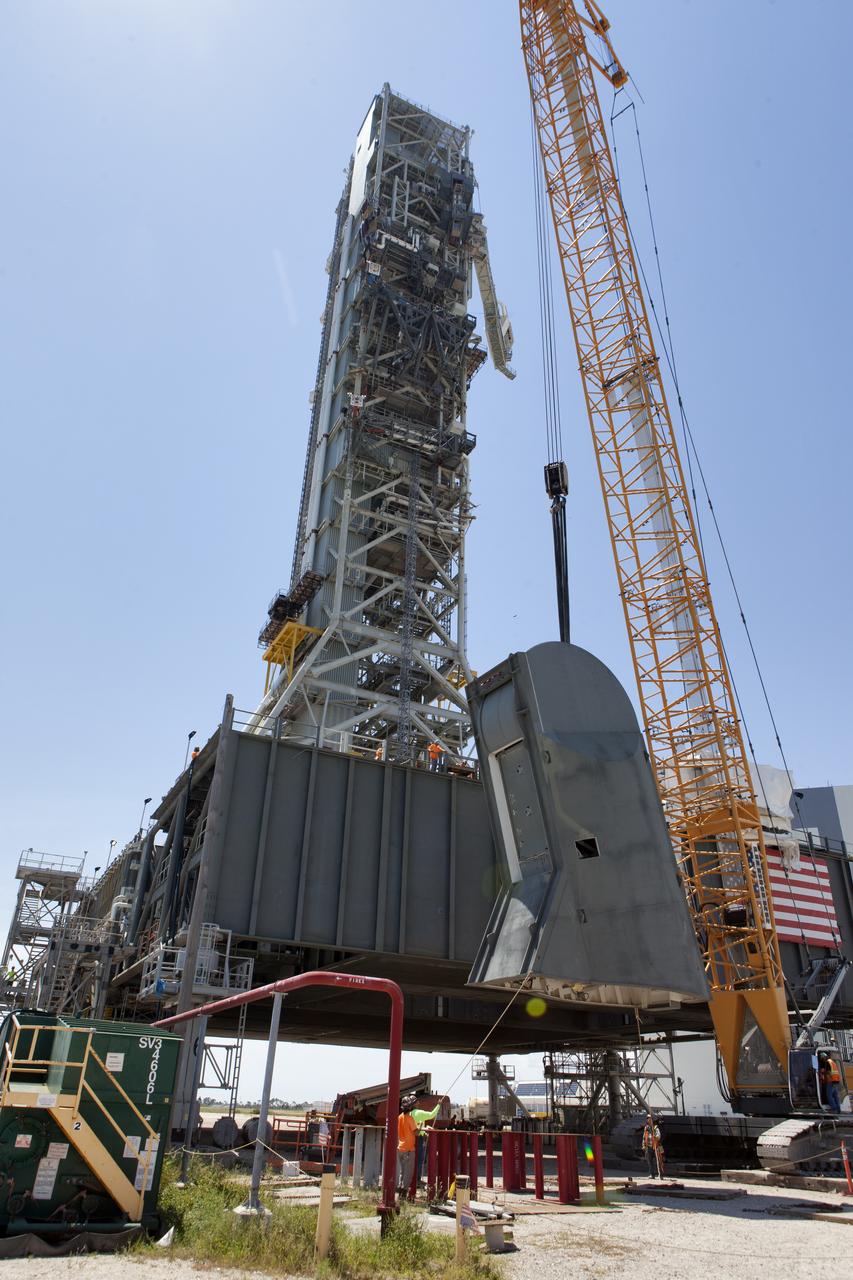

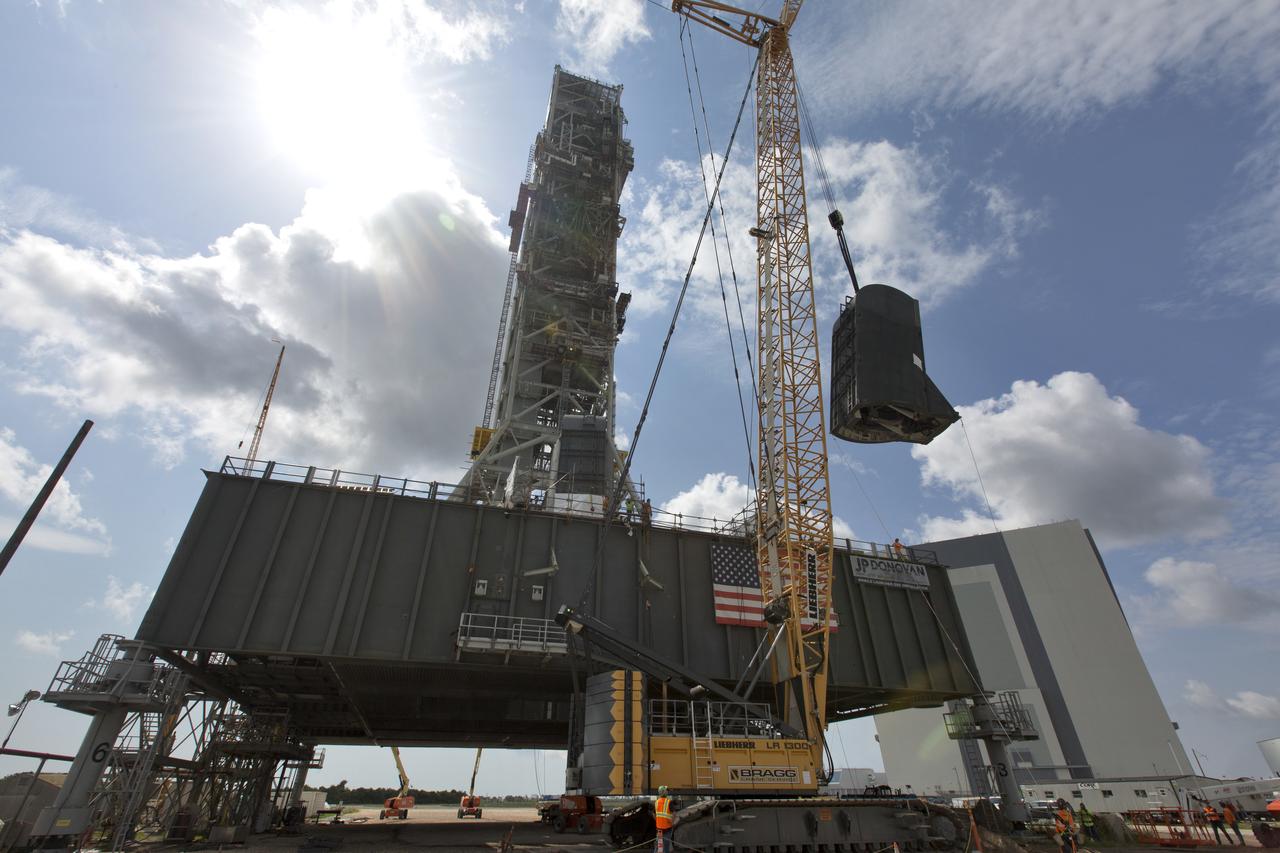
The first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted up for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

Construction workers with JP Donovan monitor operations as a crane is used to lower the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
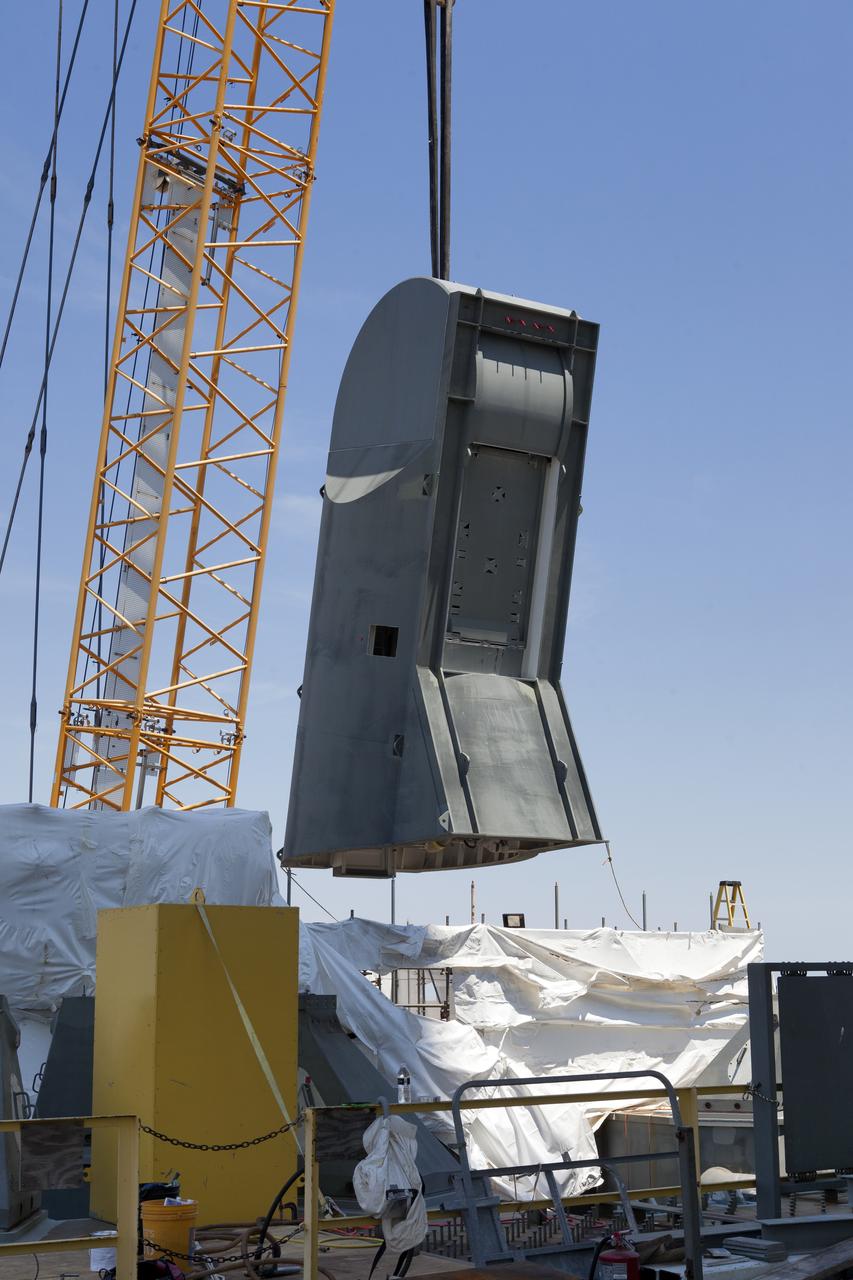

A crane is used to lift up the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
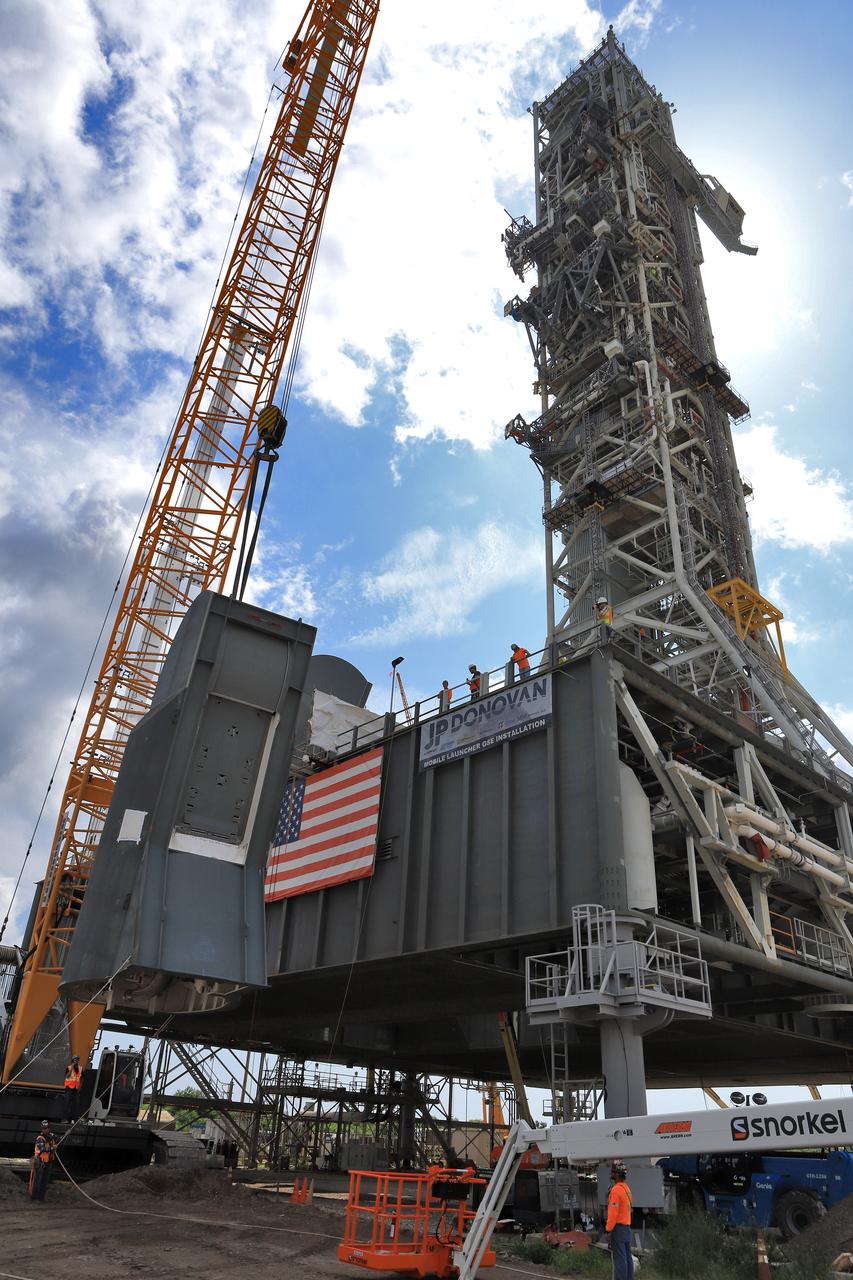

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
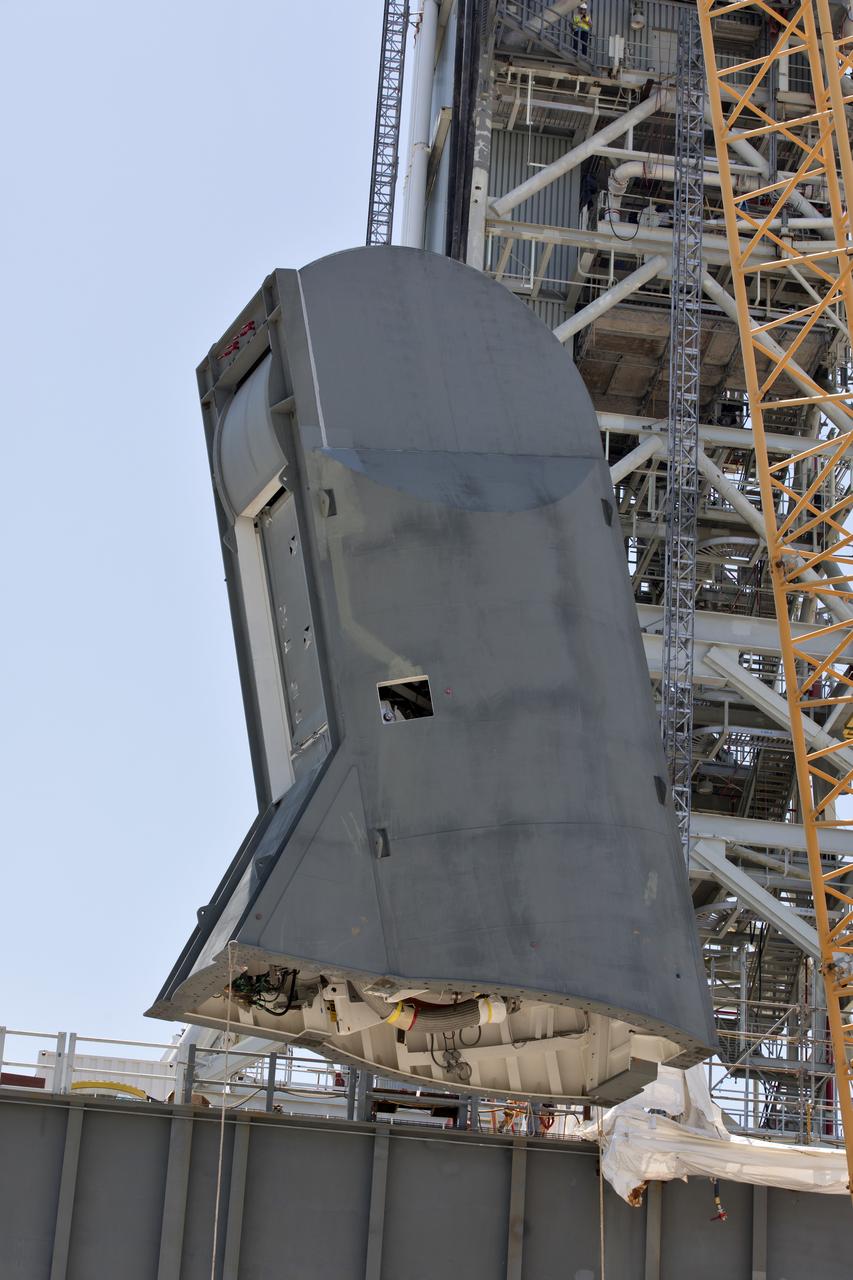

The first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted up for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
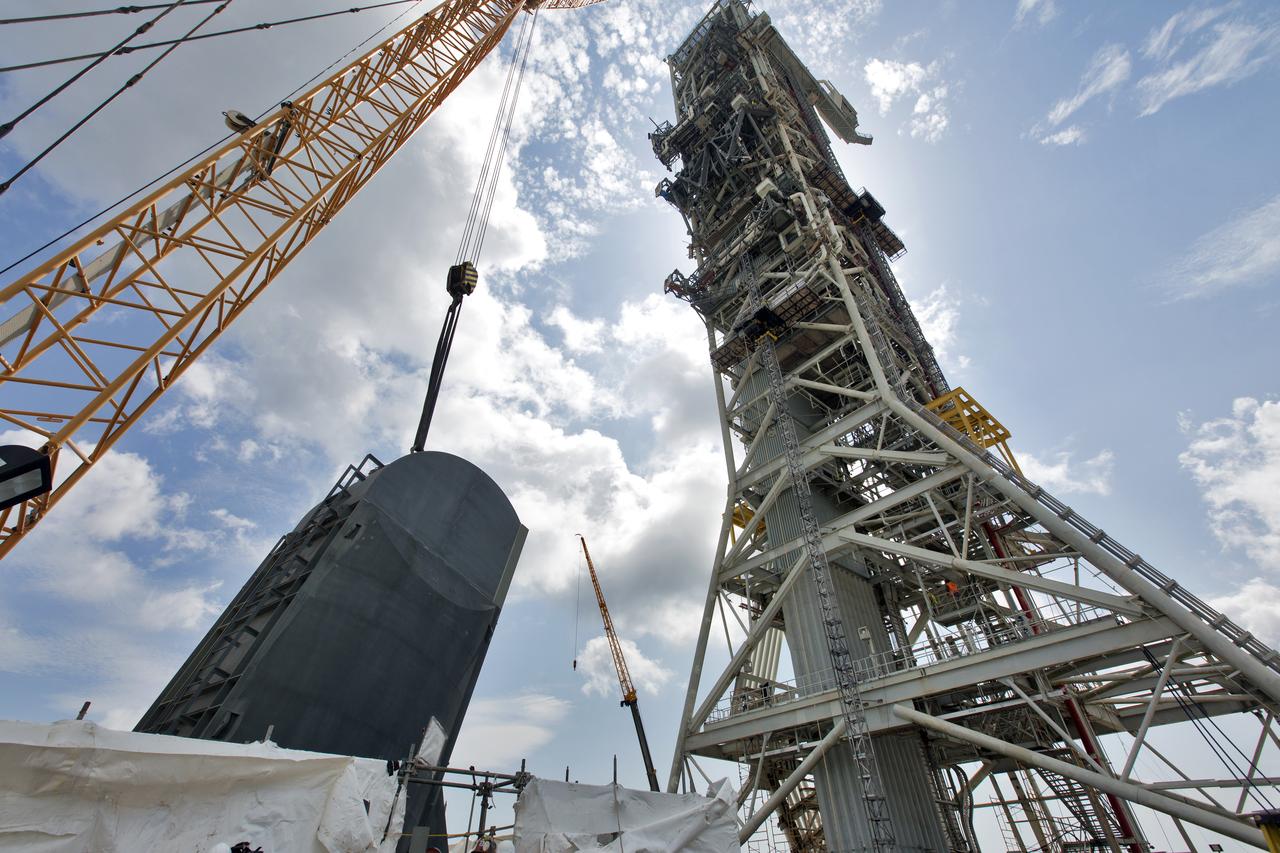

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lowered by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
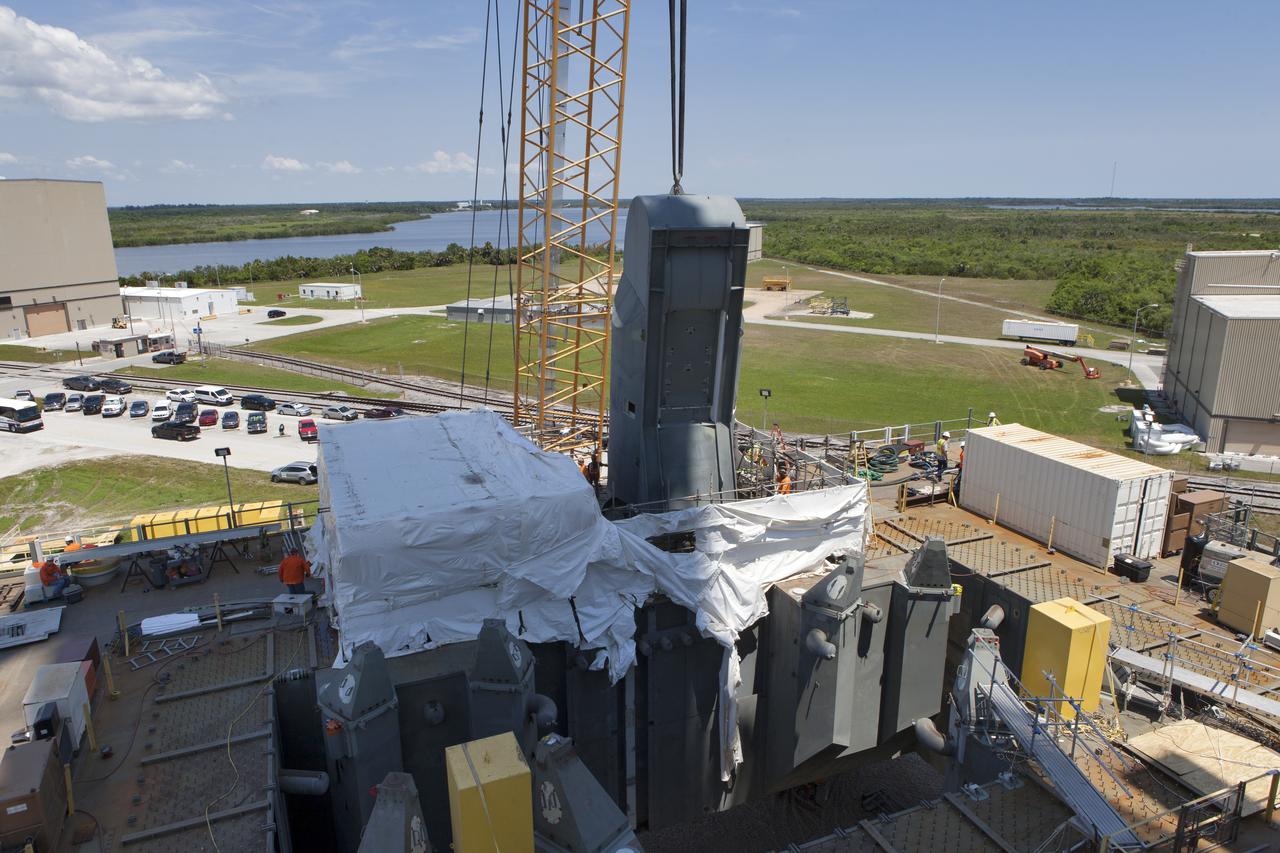

A crane is used to lower the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
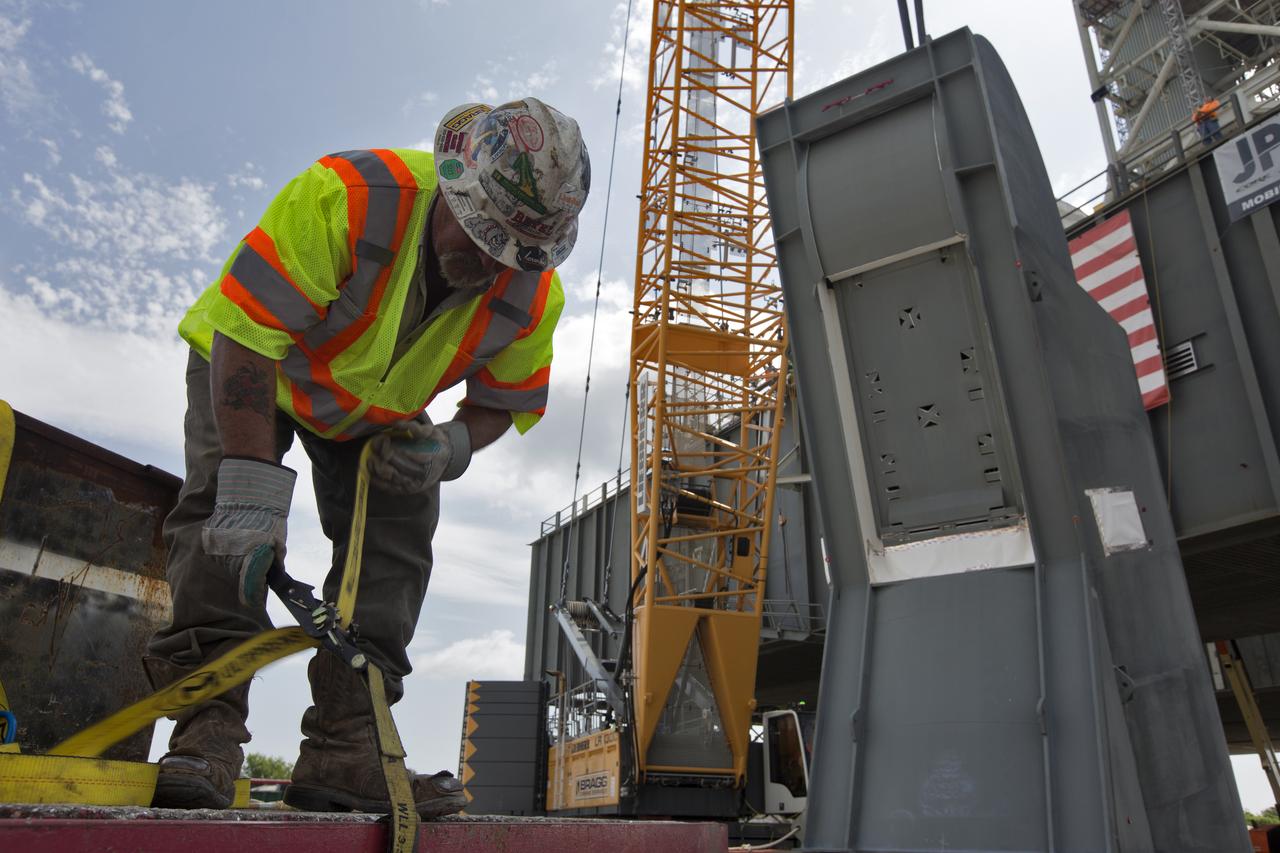

A JP Donovan construction worker makes preparations for lifting of the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
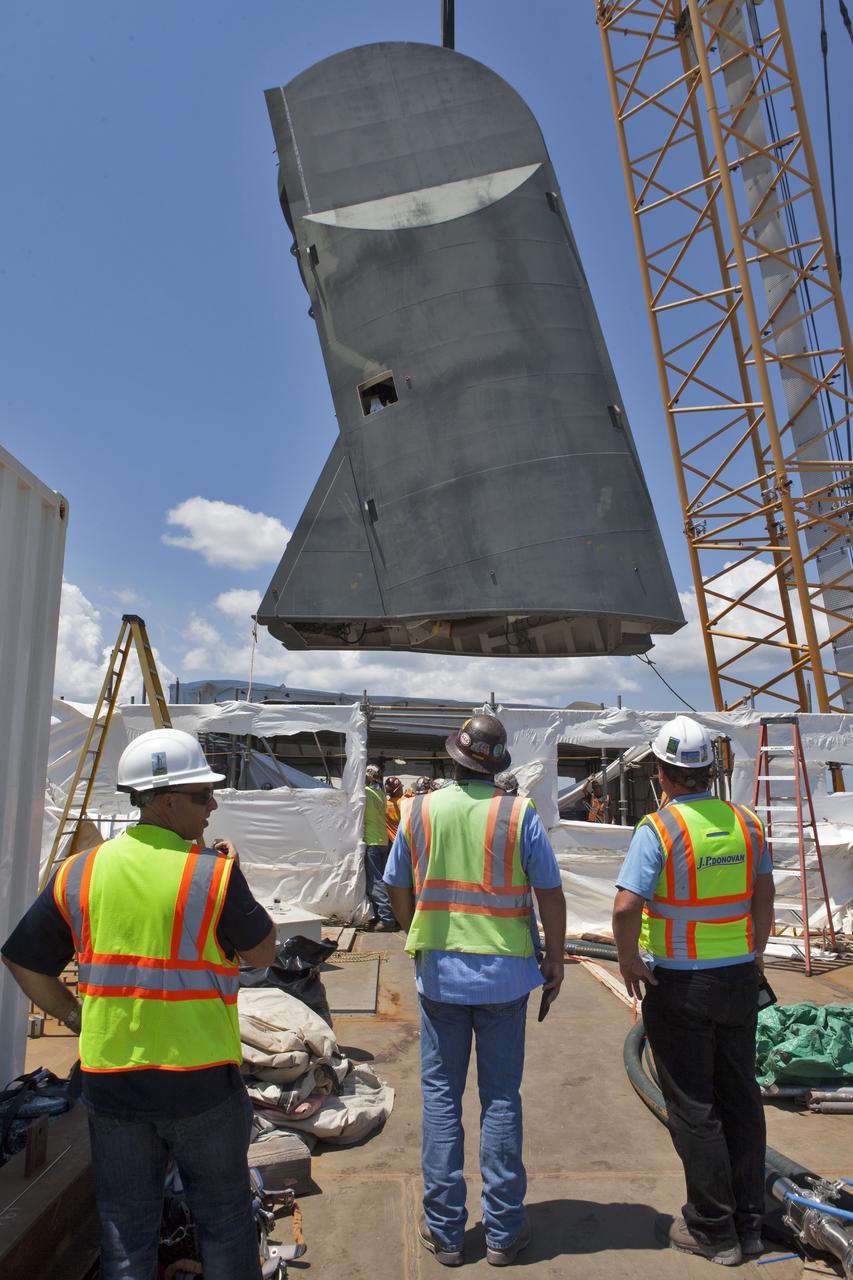

Construction workers with JP Donovan monitor operations as a crane is used to lower the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
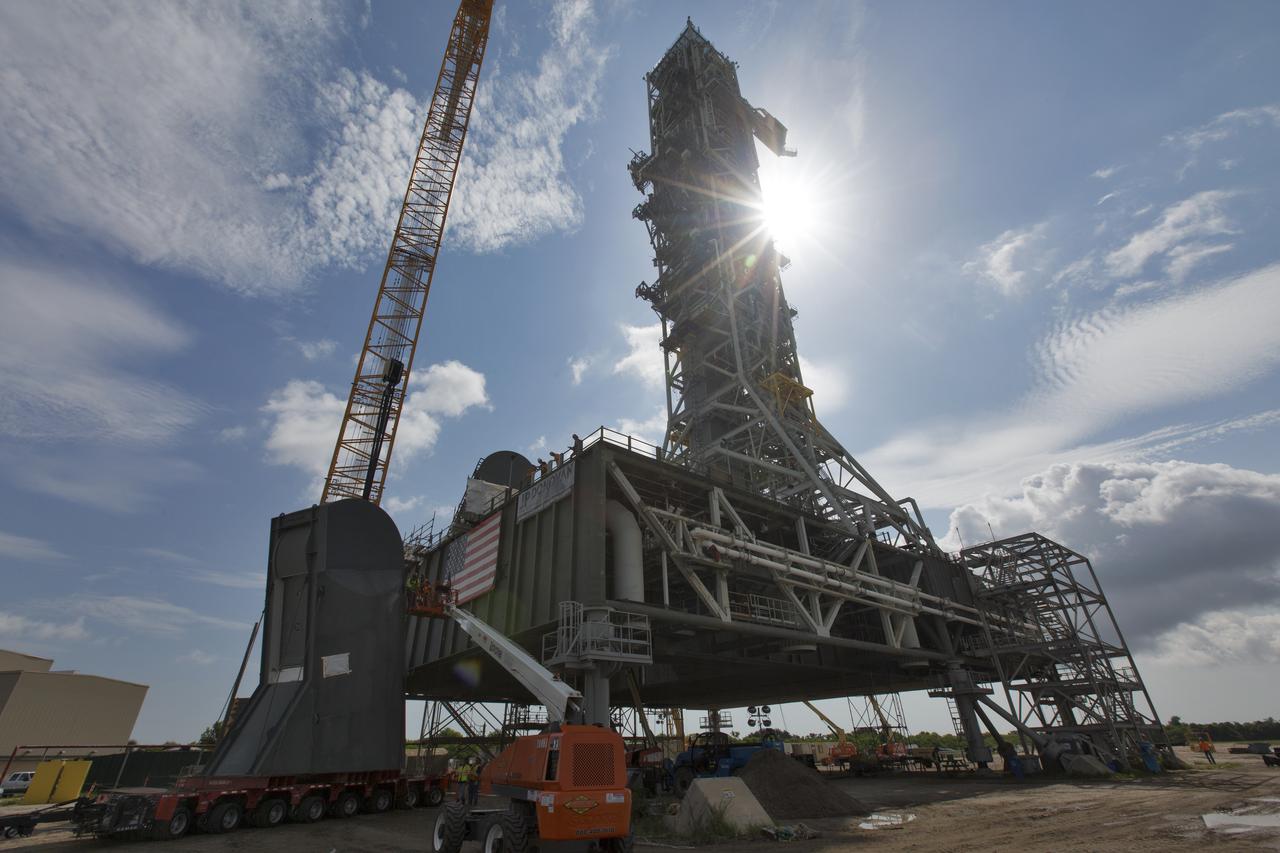

Preparations are underway to install the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
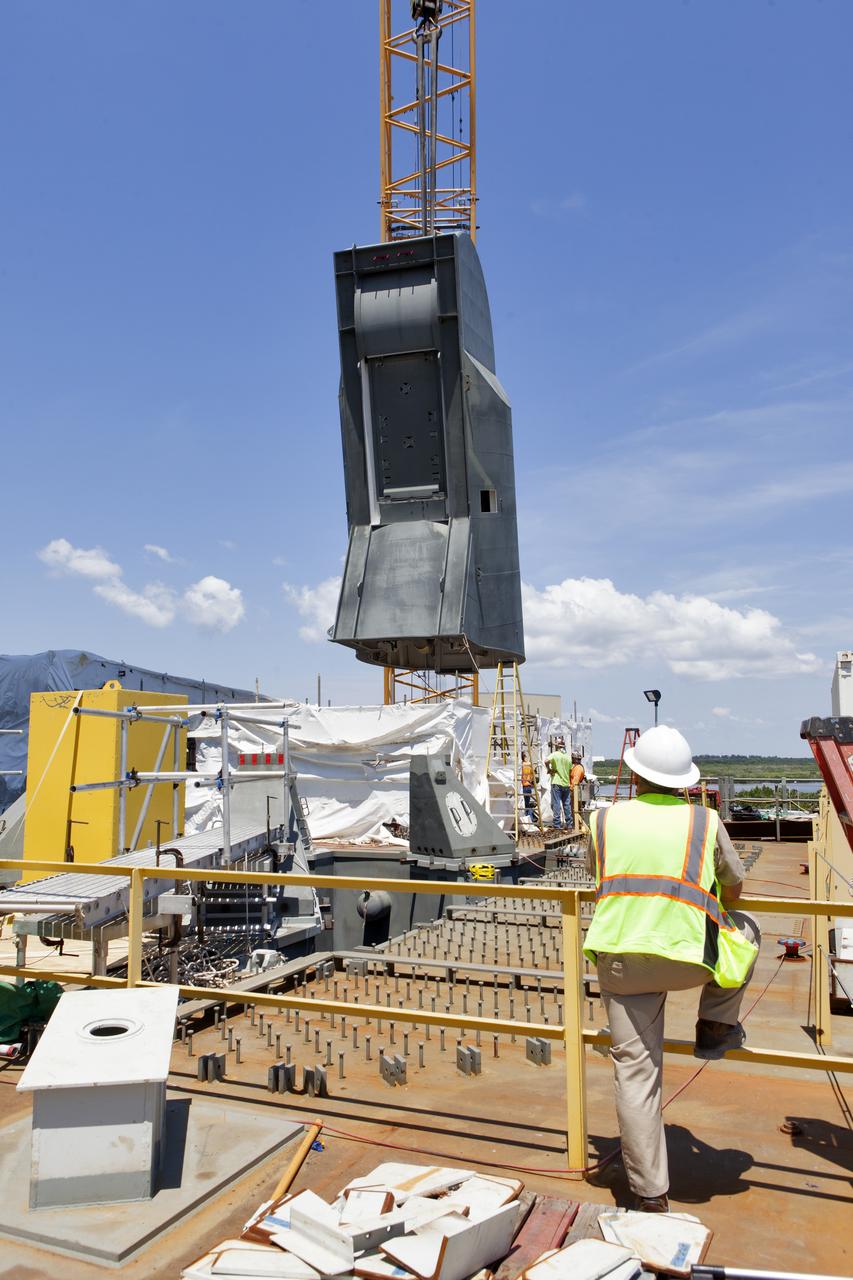

A crane is used to lower the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

The first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted up for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

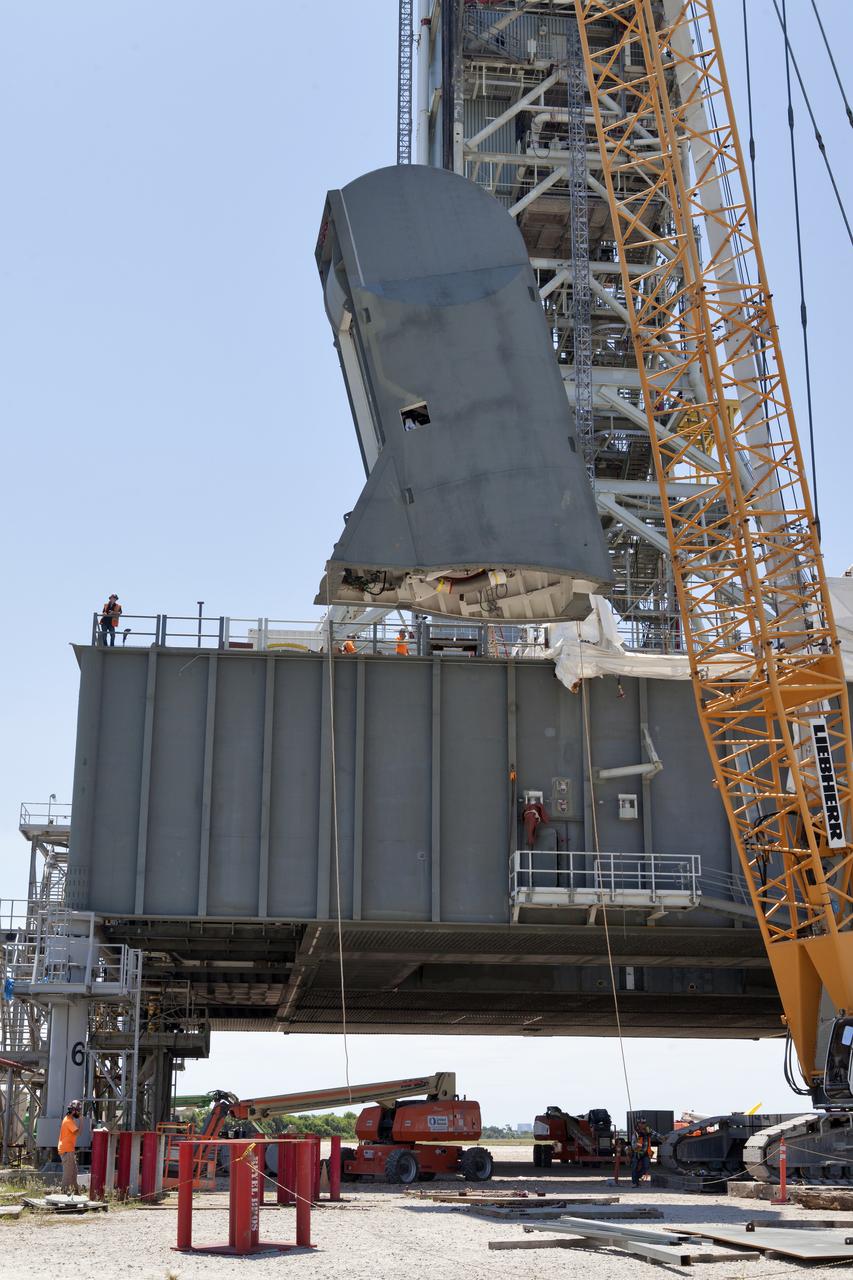
The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

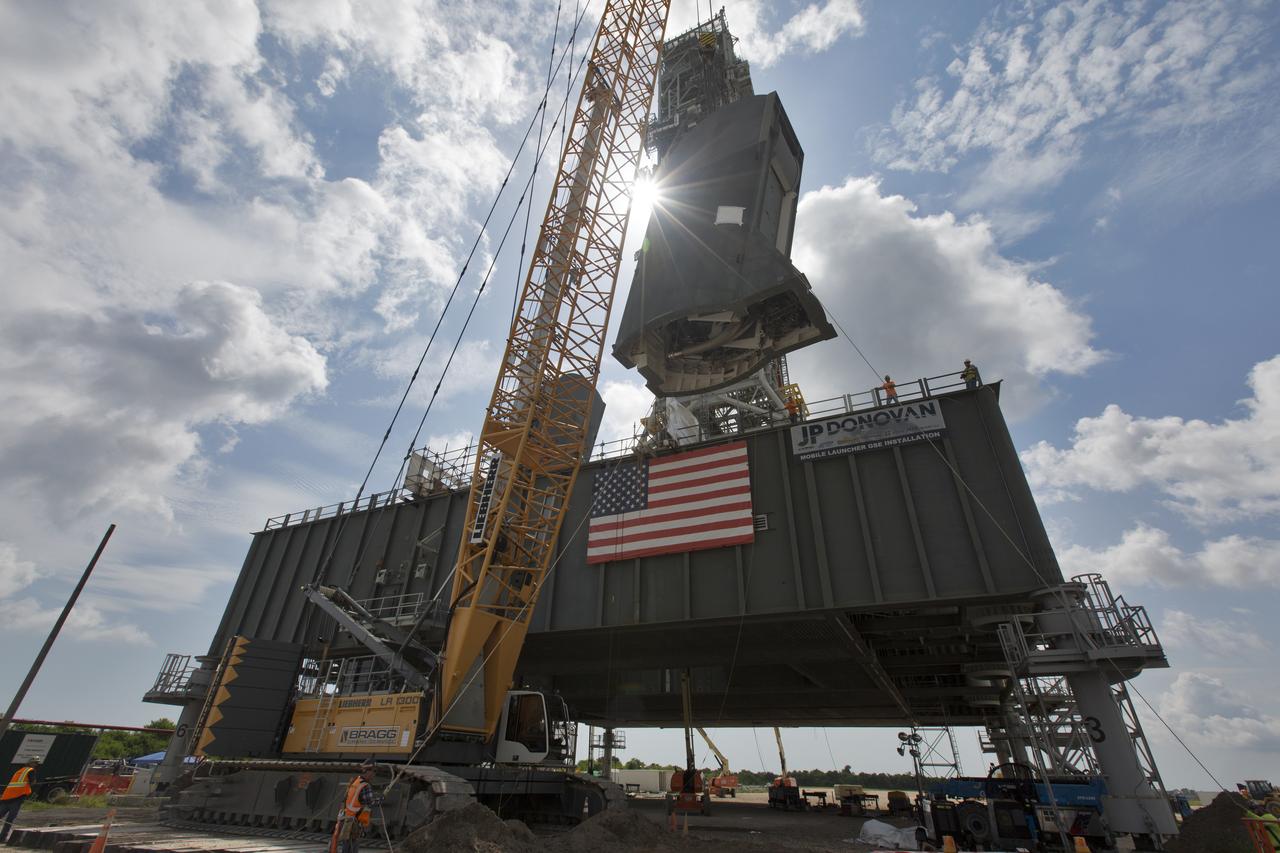
The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
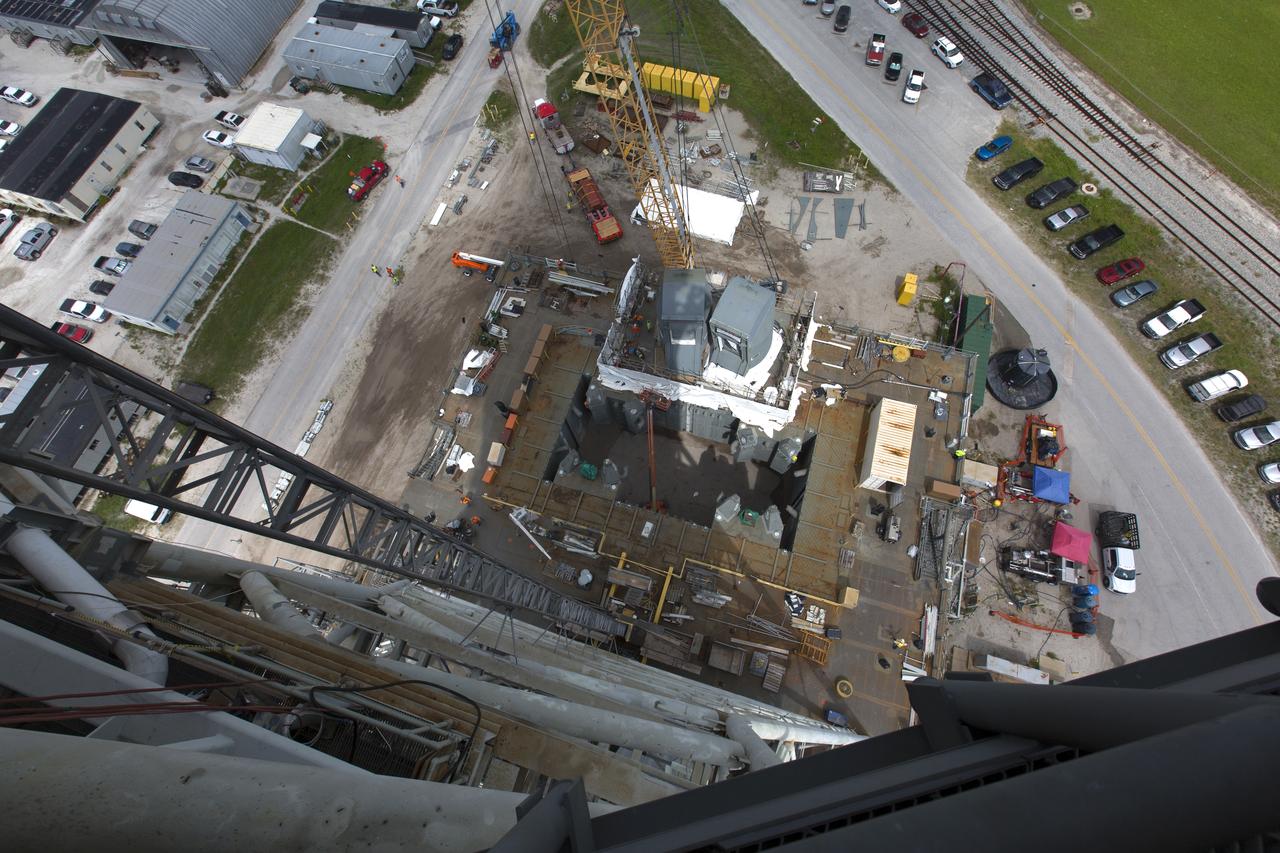

In this view from high above on the mobile launcher tower, a crane is used to lower the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
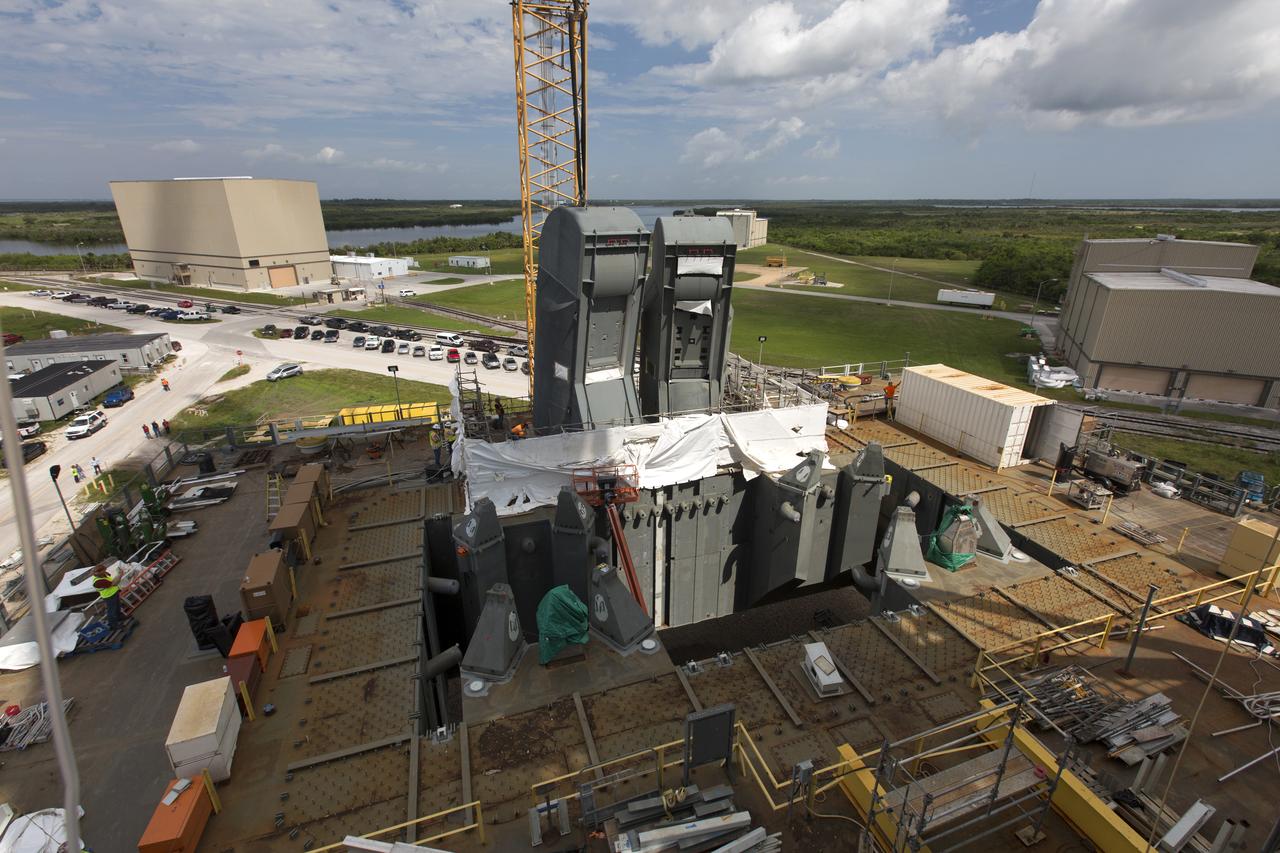

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
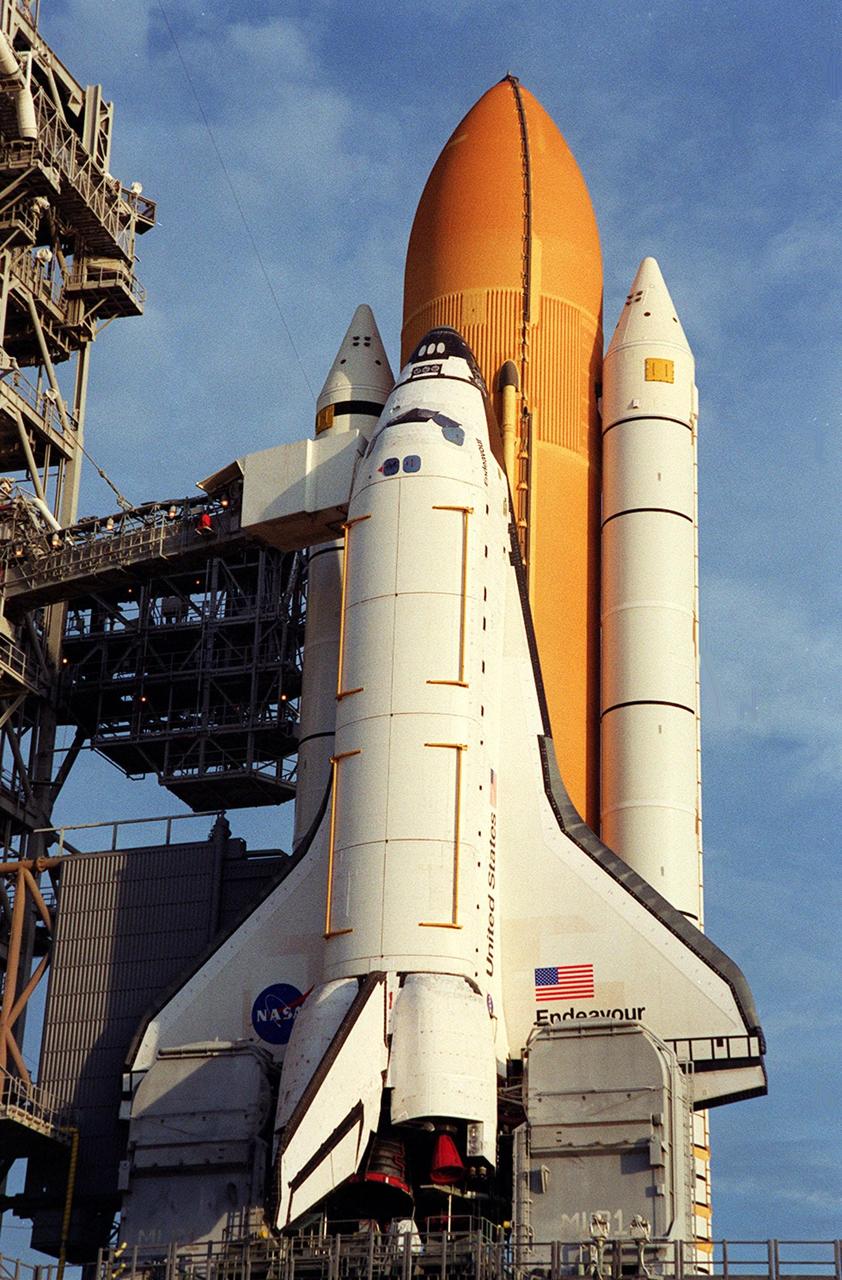

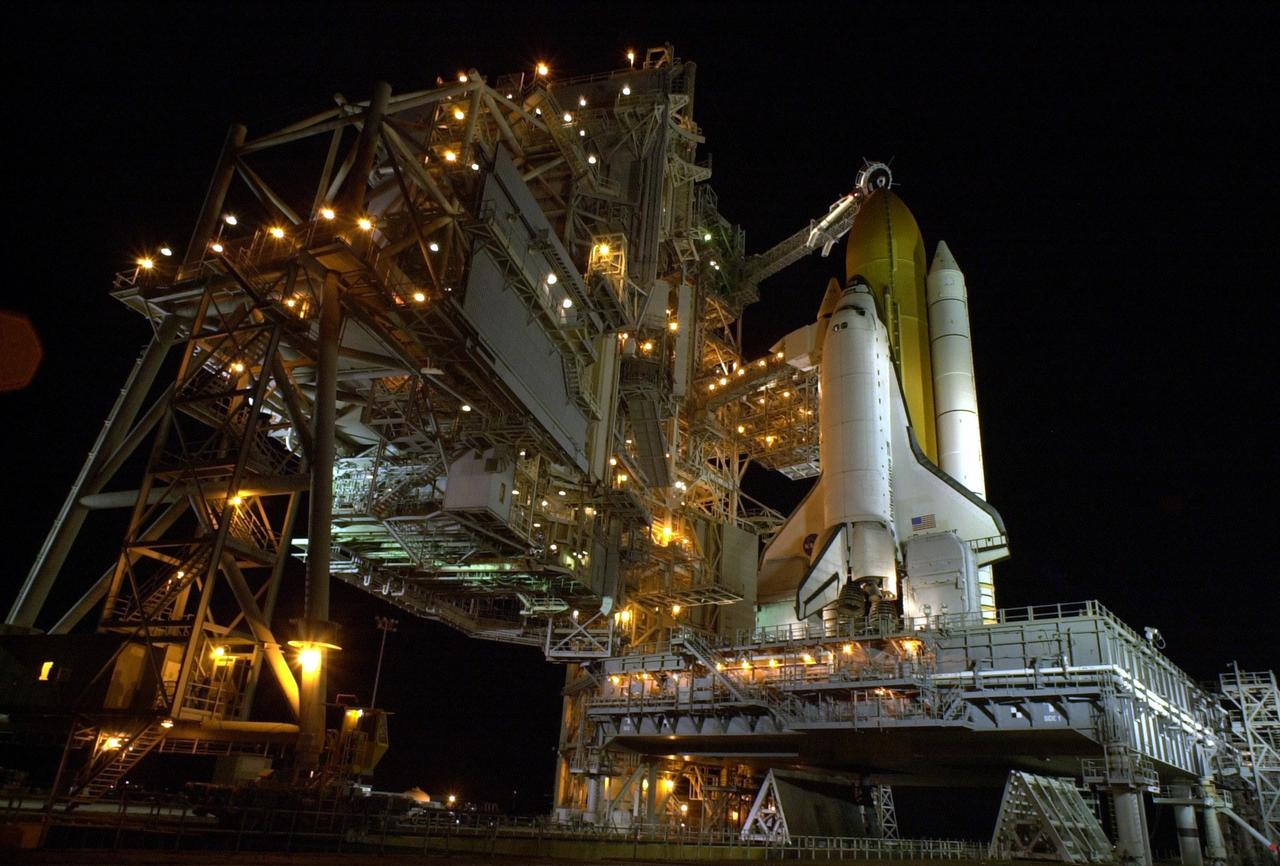
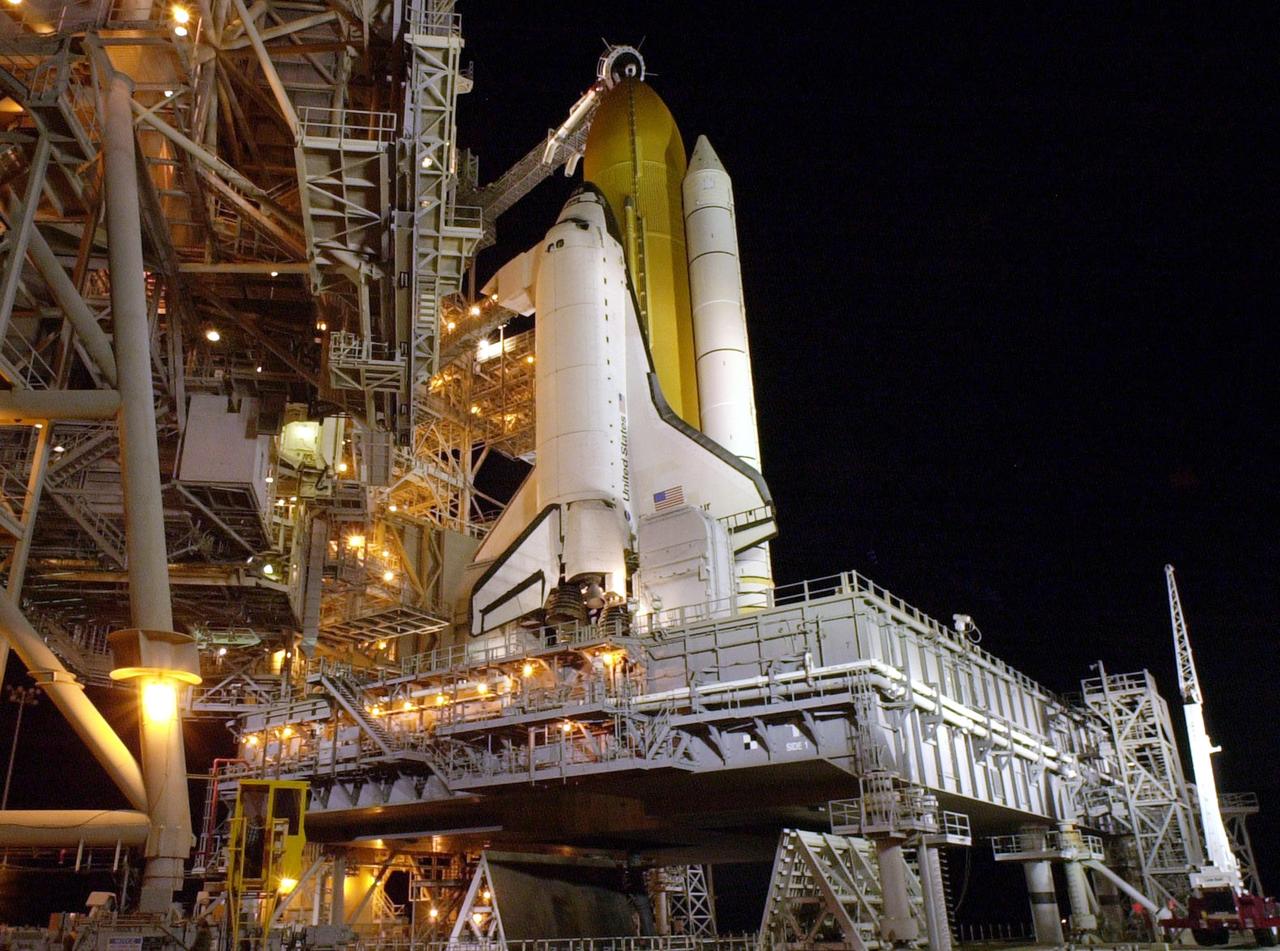
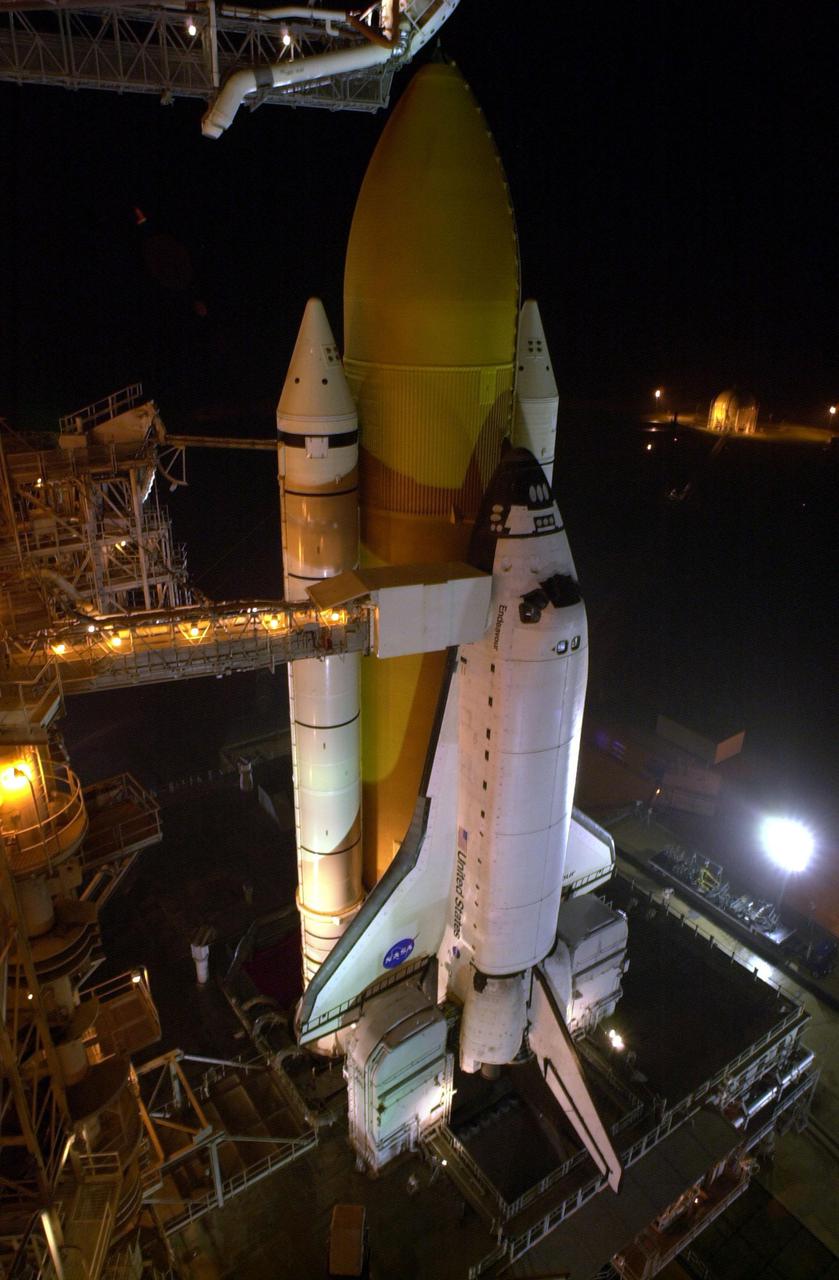
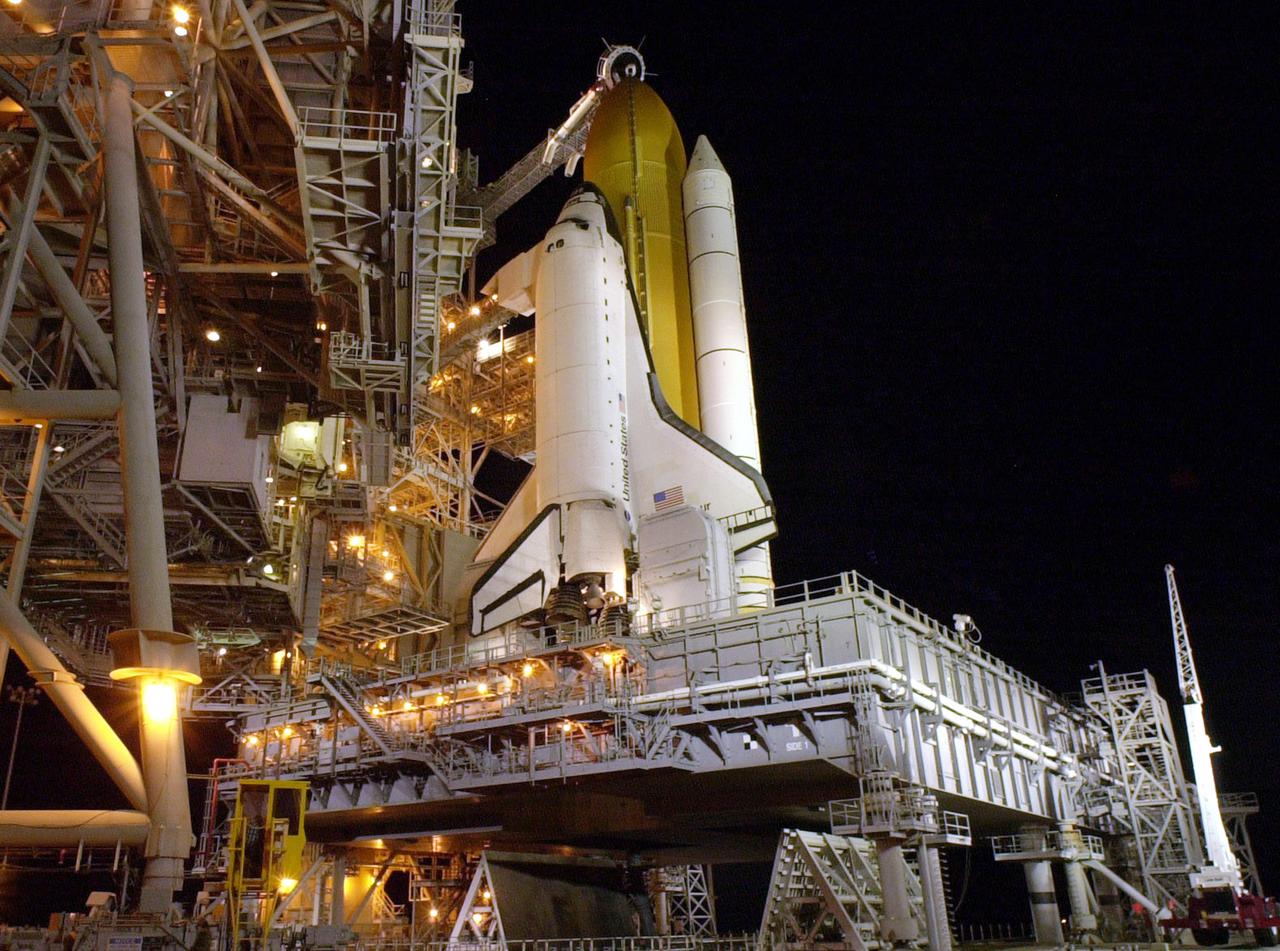
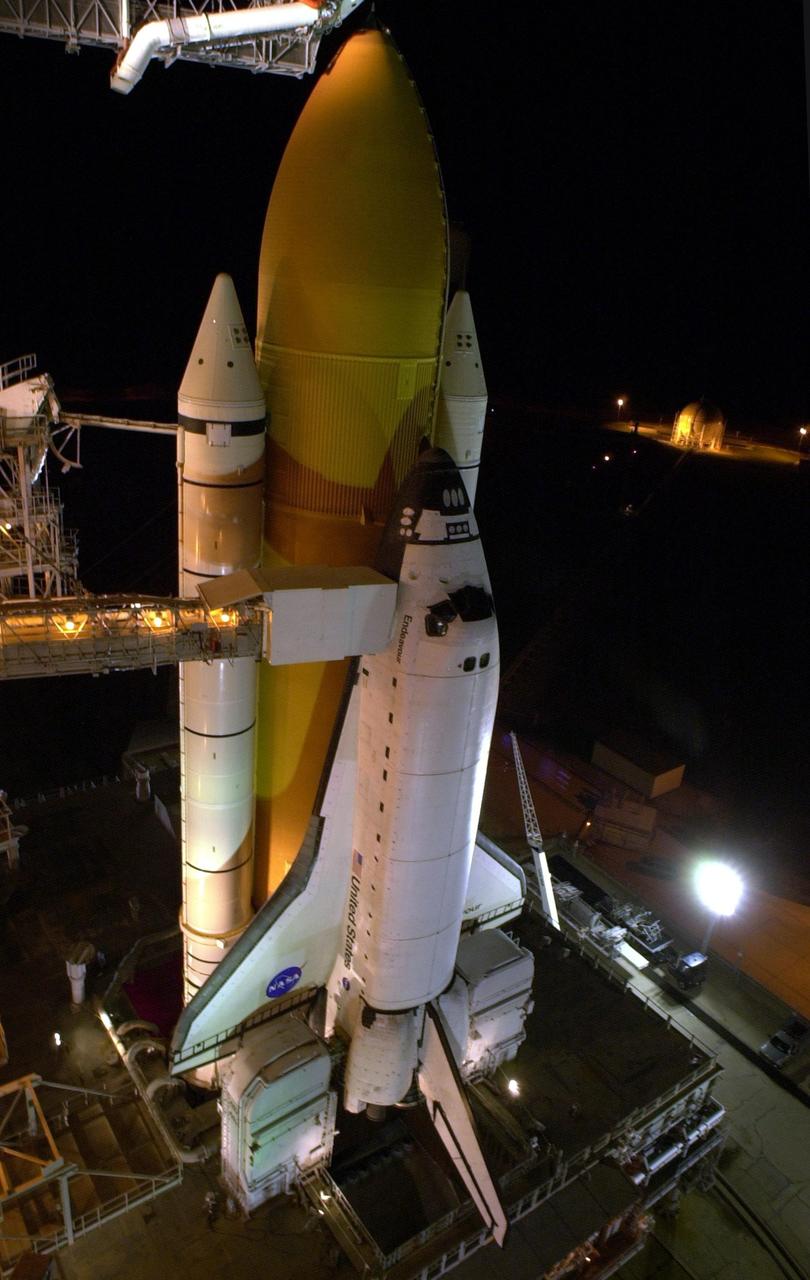
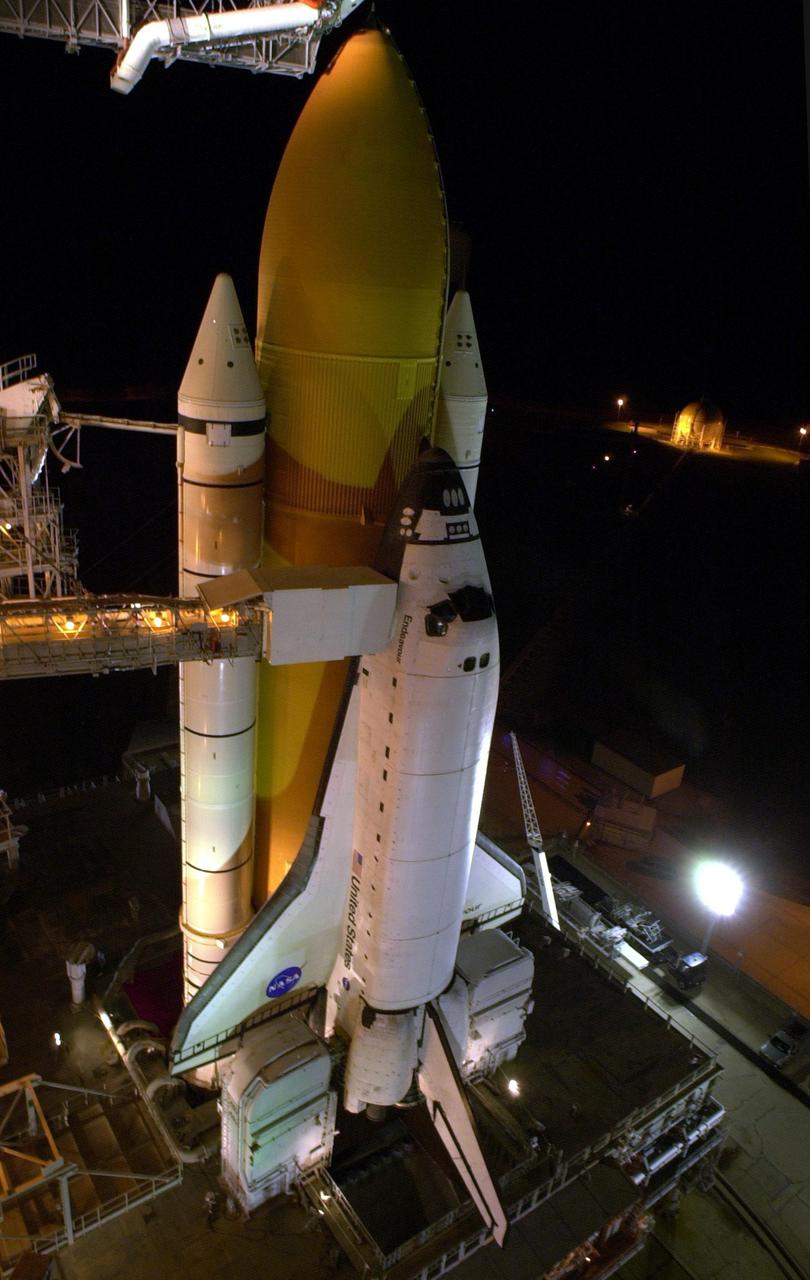
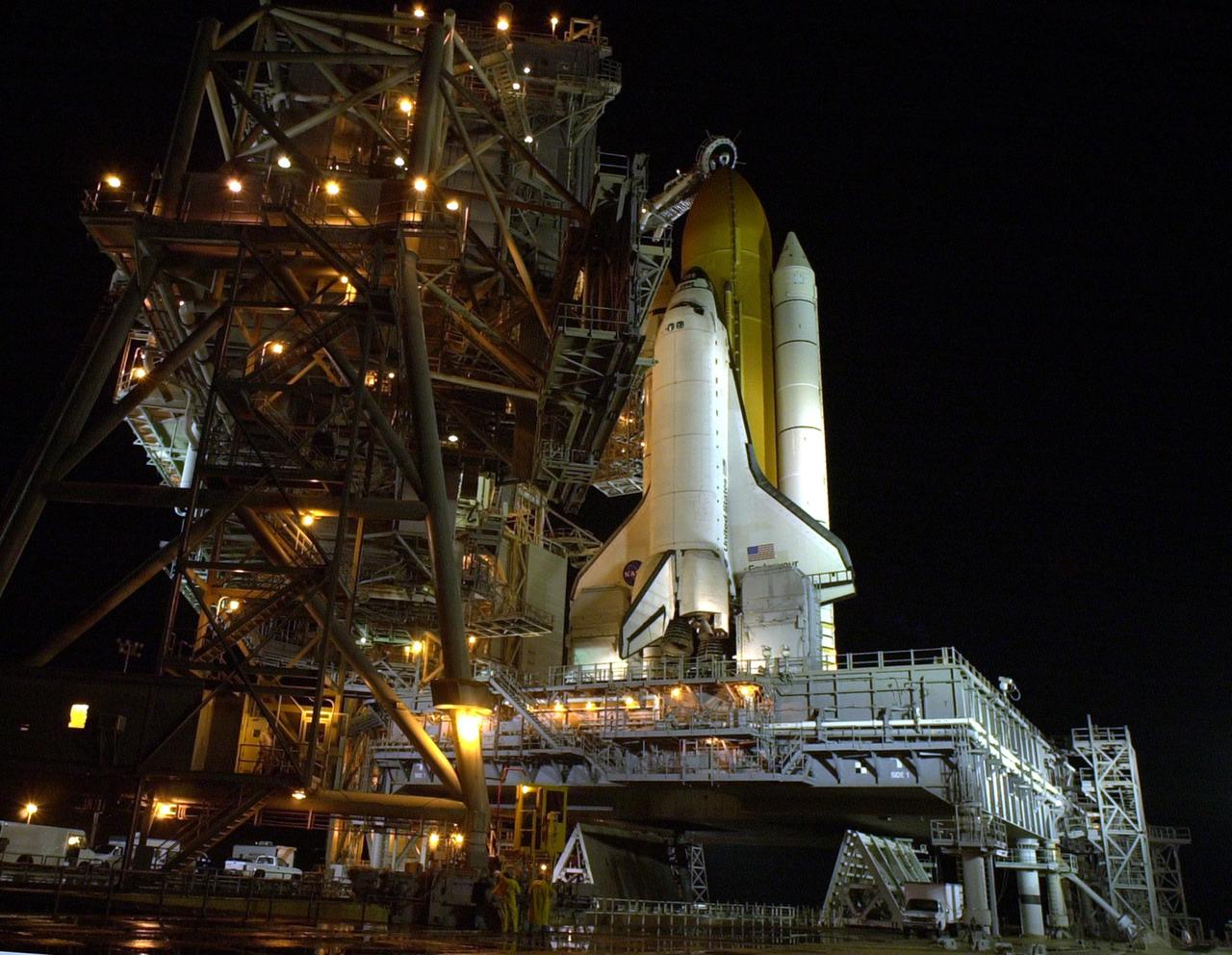
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour waits on Launch Pad 39B for launch on mission STS-97. Behind it are the orange external tank flanked by two solid rocket boosters. On either side of Endeavour’s tail are the tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. The masts also protect the ground half of those umbilicals from the harsh launch environment. At launch, the masts rotate backward, triggering a compressed-gas thruster and causing a protective hood to move into place and completely seal the structure from the main engine exhaust. At the end of the orbiter access arm, near the nose of Endeavour, is the White Room, an environmental chamber that provides both entrance to the orbiter and emergency egress, if needed. The arm remains extended until 7 minutes, 24 seconds before launch. The arm extends from the Fixed Service Structure. In the center of Endeavour are the payload bay doors. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
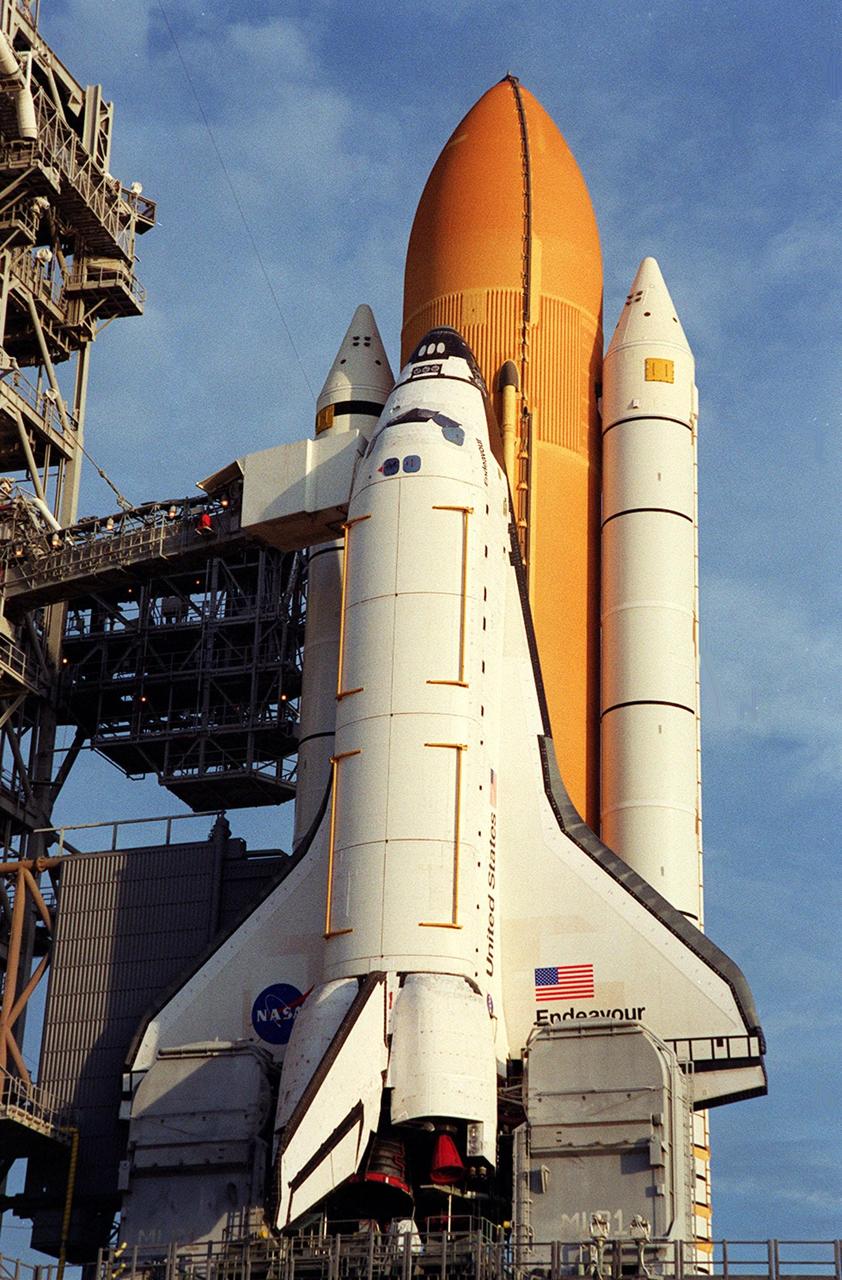

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour waits on Launch Pad 39B for launch on mission STS-97. Behind it are the orange external tank flanked by two solid rocket boosters. On either side of Endeavour’s tail are the tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. The masts also protect the ground half of those umbilicals from the harsh launch environment. At launch, the masts rotate backward, triggering a compressed-gas thruster and causing a protective hood to move into place and completely seal the structure from the main engine exhaust. At the end of the orbiter access arm, near the nose of Endeavour, is the White Room, an environmental chamber that provides both entrance to the orbiter and emergency egress, if needed. The arm remains extended until 7 minutes, 24 seconds before launch. The arm extends from the Fixed Service Structure. In the center of Endeavour are the payload bay doors. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST

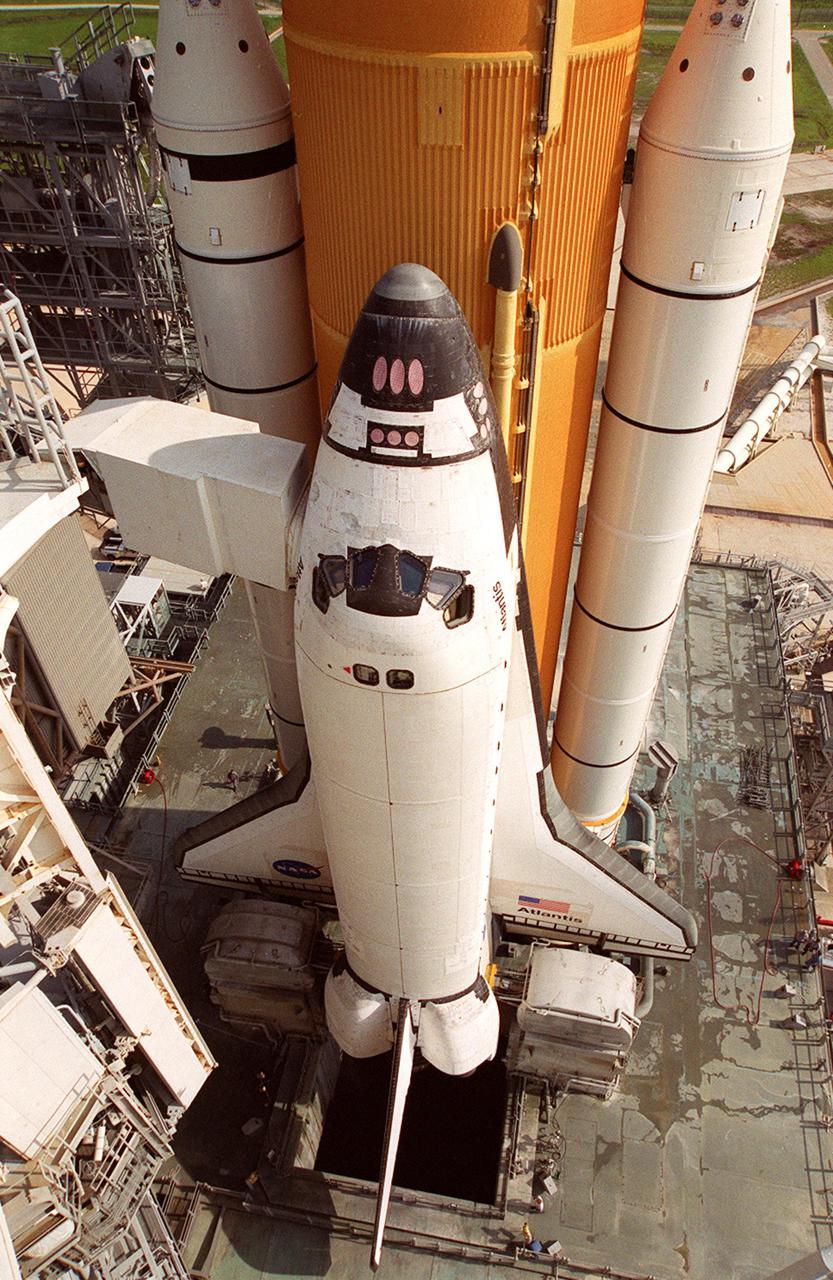
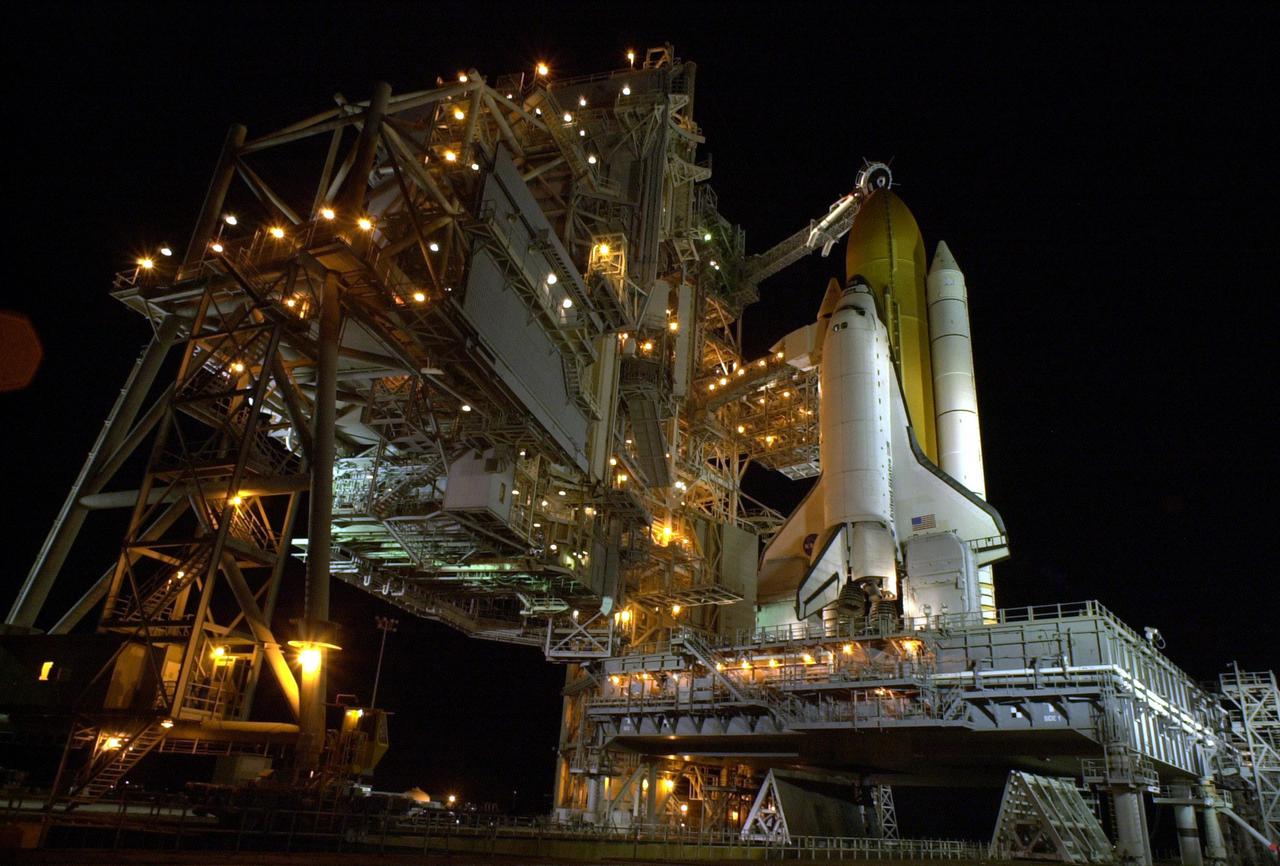
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers clean the mobile launcher platform on which sits Space Shuttle Atlantis. They are standing in front of one of two tail service masts on either side of the Shuttle, in front of each wing. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This view from above Space Shuttle Atlantis reduces the workers below to appearing like ants. Seen below the Shuttle is the opening over the exhaust hole containing flame detectors. On either side of the Atlantis, in front of the wings, are two tail service masts. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour stands ready for launch after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen are the twin solid rocket boosters flanking the orange external tank. Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. Below Endeavour is the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour stands ready for launch after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen are the twin solid rocket boosters flanking the orange external tank. Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. Below Endeavour is the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

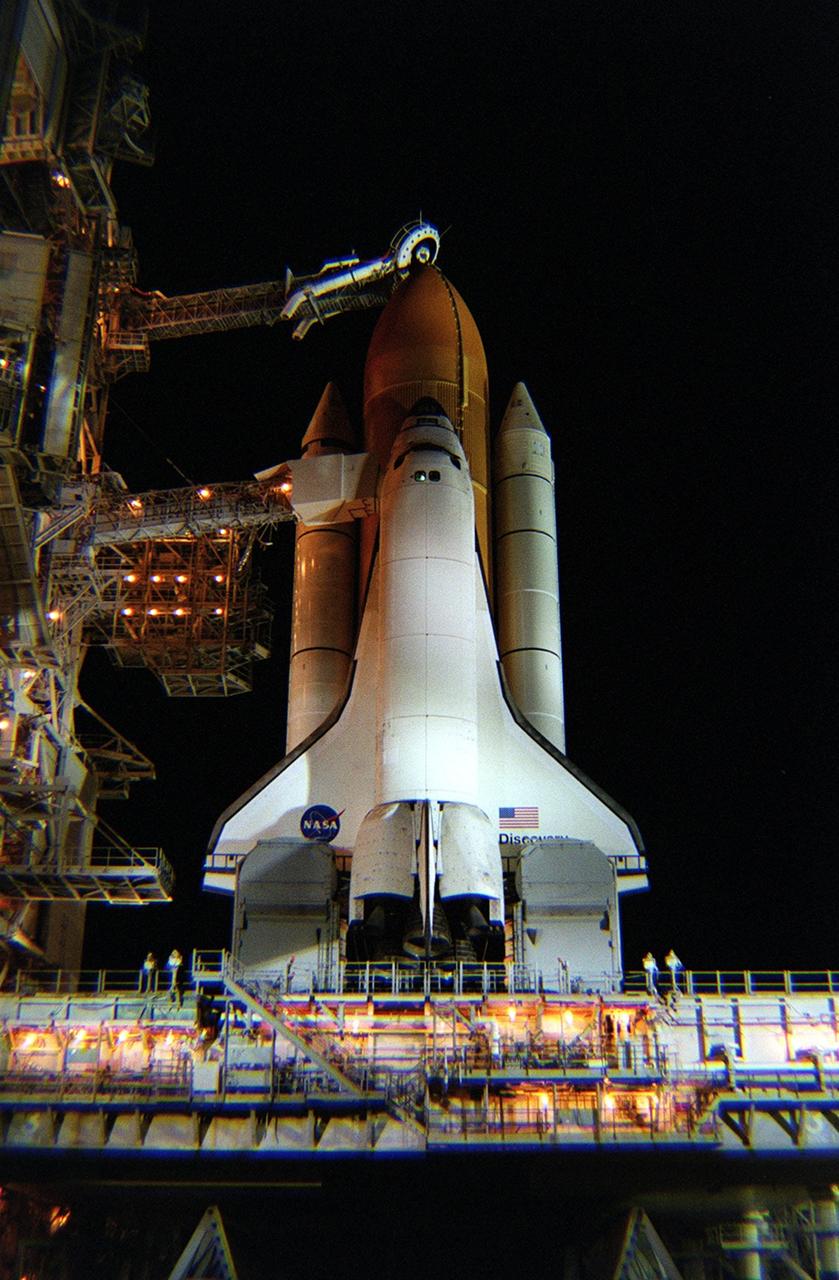
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery shines on Launch Pad 39B after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Situated above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. Extended out from the Fixed Service Structure (left) to the orbiter is the orbiter access arm with an environmentally controlled chamber, known as the White Room, at the end of the arm. The White Room provides entrance for the astronaut crew into the orbiter. On either side of the tail and main engines are the tail service masts. Rising 31 feet above the Mobile Launcher Platform, the tail masts provide umbilical connections for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen lines to fuel the external tank from storage tanks adjacent to the launch pad. Discovery carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Launch on mission STS-102 is scheduled March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery shines on Launch Pad 39B after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Situated above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. Extended out from the Fixed Service Structure (left) to the orbiter is the orbiter access arm with an environmentally controlled chamber, known as the White Room, at the end of the arm. The White Room provides entrance for the astronaut crew into the orbiter. On either side of the tail and main engines are the tail service masts. Rising 31 feet above the Mobile Launcher Platform, the tail masts provide umbilical connections for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen lines to fuel the external tank from storage tanks adjacent to the launch pad. Discovery carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Launch on mission STS-102 is scheduled March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST

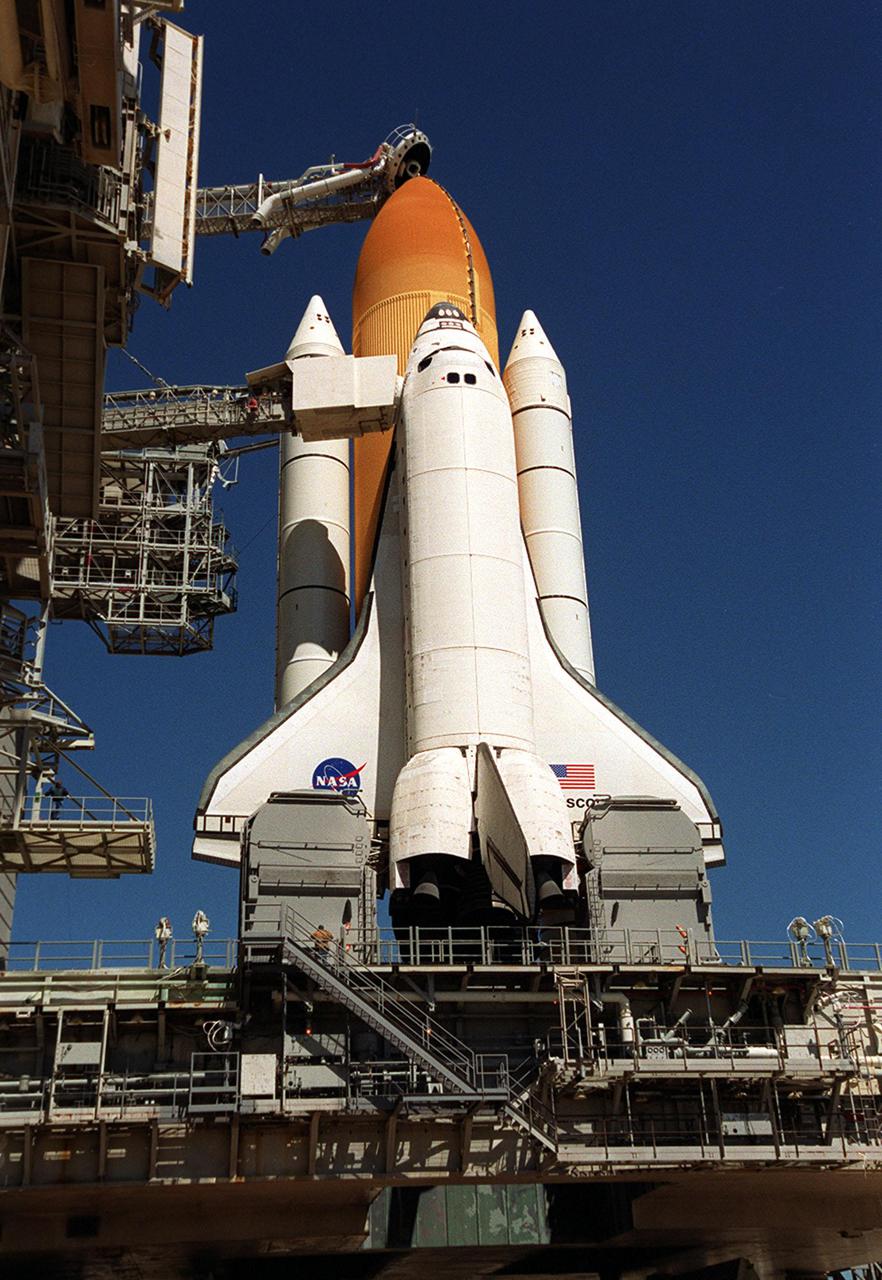
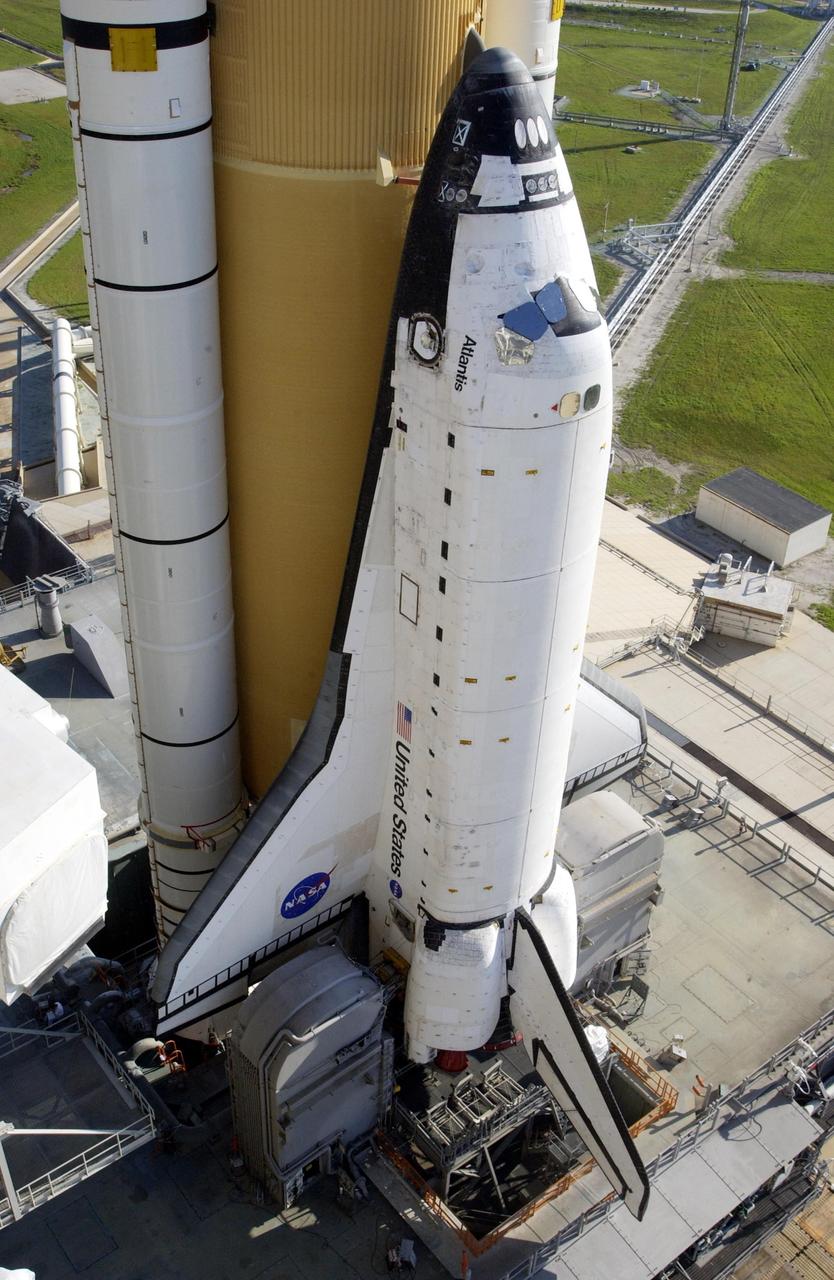
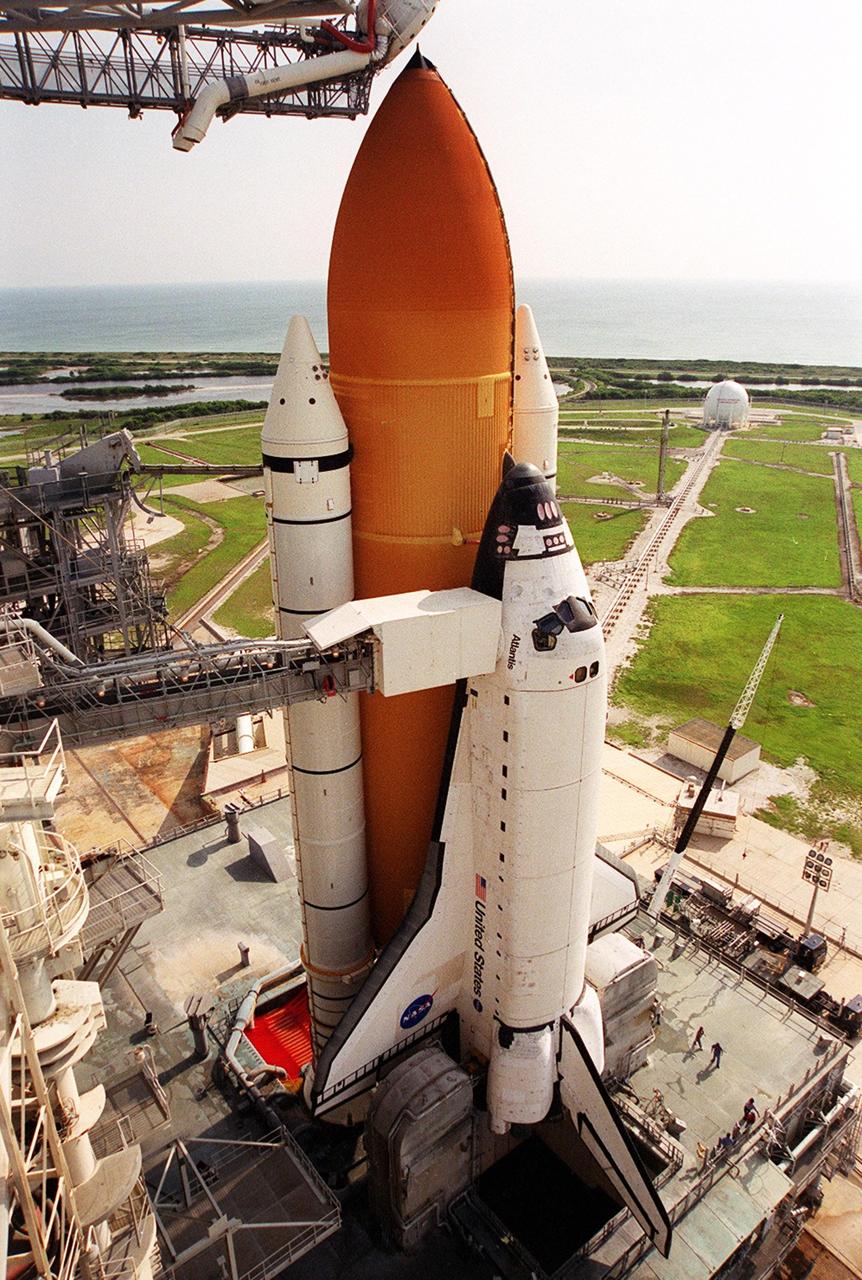
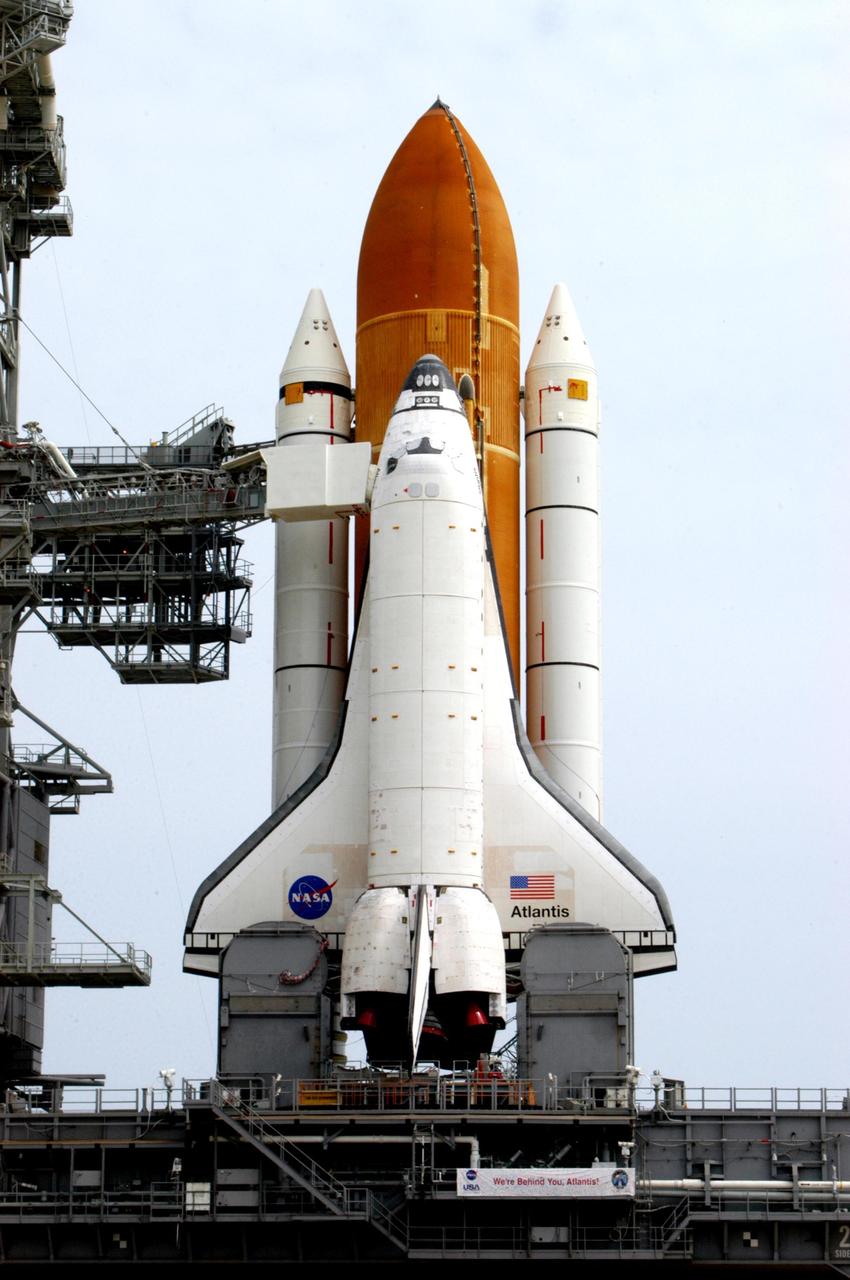
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis is hard down on the launch pad after its mid-day rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Part of the Fixed Service Structure is at left. On either side of the tail of Atlantis are the tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis is scheduled for launch April 4 on mission STS-110, which will install the S0 truss, the framework that eventually will hold the power and cooling systems needed for future international research laboratories on the International Space Station. The Canadarm2 robotic arm will be used exclusively to hoist the 13-ton truss from the payload bay to the Station. The S0 truss will be the first major U.S. component launched to the Station since the addition of the Quest airlock in July 2001. The four spacewalks planned for the construction will all originate from the airlock. The mission will be Atlantis' 25th trip to space

This closeup reveals Space Shuttle Atlantis after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Below Atlantis, on either side of the tail, are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program

This closeup reveals Space Shuttle Atlantis after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Below Atlantis, on either side of the tail, are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
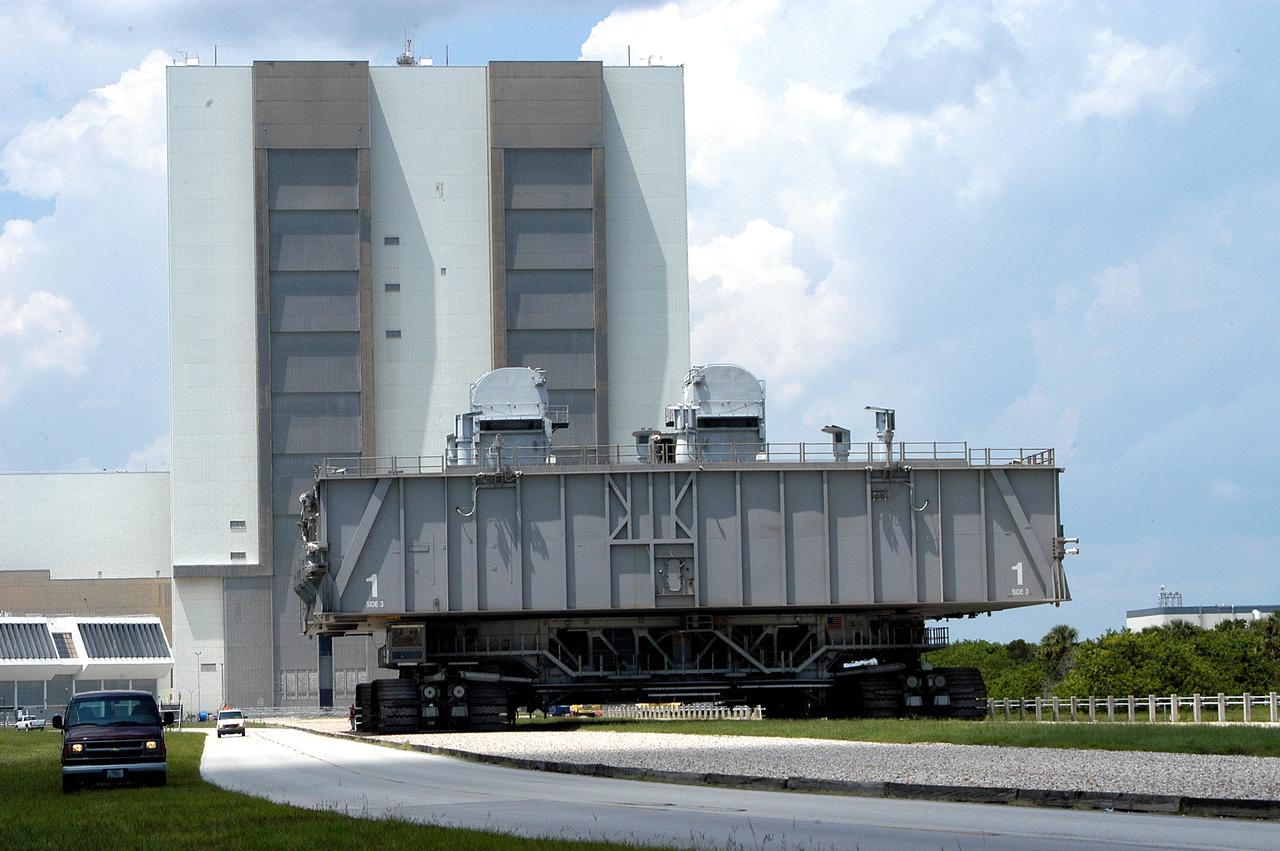

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Crawler-transporter (CT) number 2, moves away from the Vehicle Assembly Building with a Mobile Launcher Platform (MLP) on top on a test run to the launch pad. The CT recently underwent modifications to the cab. The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
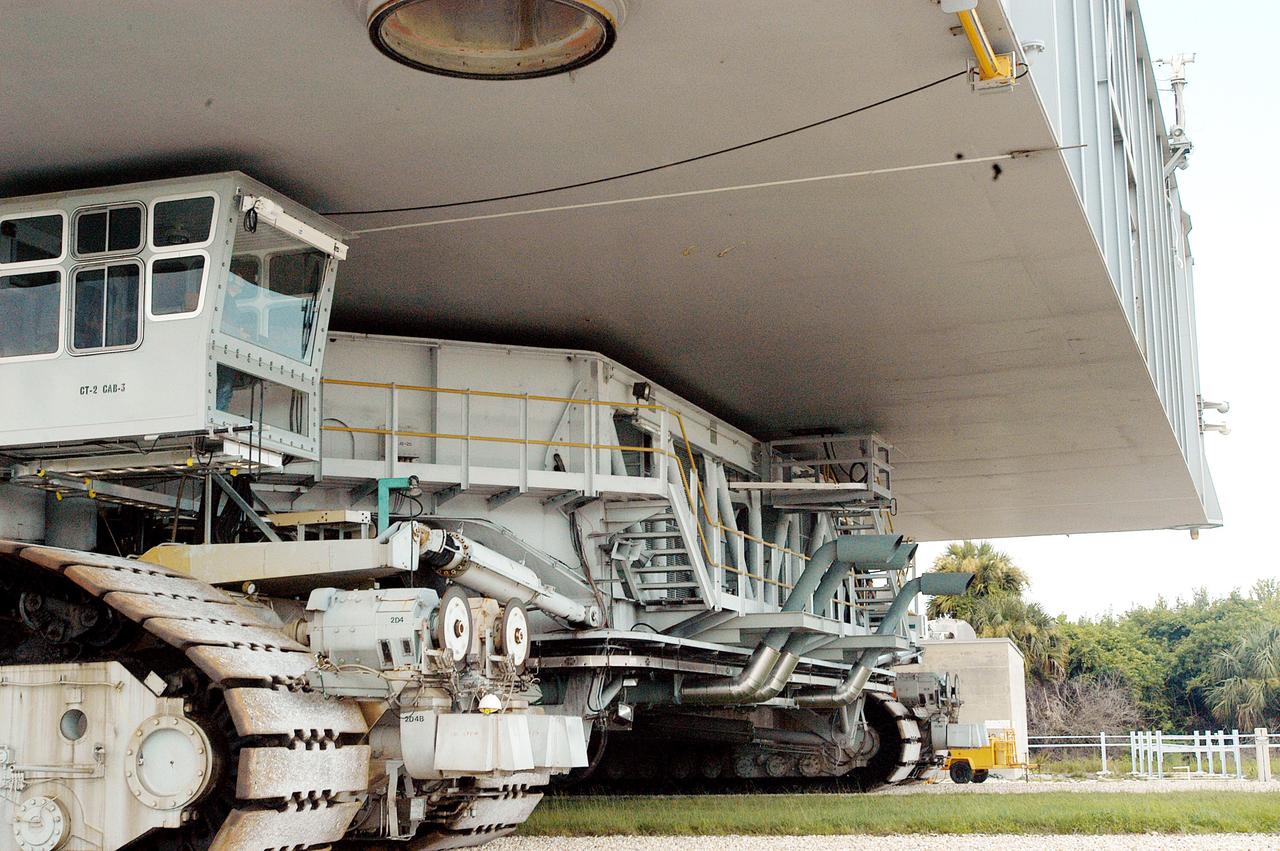

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup of crawler-transporter (CT) number 2 shows the cab, at left, that recently underwent modifications. The CT is transporting a Mobile Launch Platform (MLP) on a test run to the pad. The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
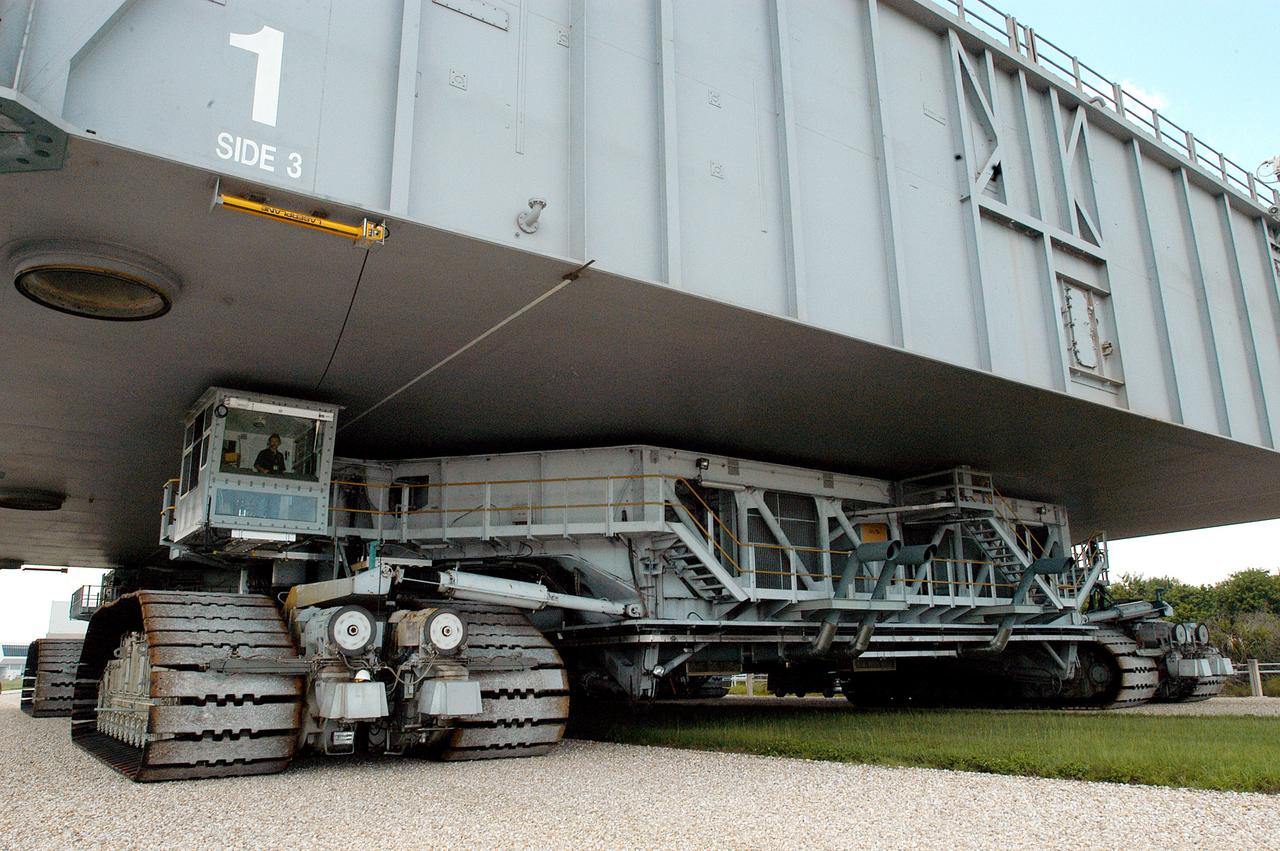

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup of crawler-transporter (CT) number 2 shows the cab (left, above the tracks) that recently underwent modifications. The CT is transporting a Mobile Launch Platform (MLP) on a test run to the pad. The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup of crawler-transportation (CT) number 2 shows the new muffler system on the vehicle. The CT also recently underwent modifications to the cab. The CT is transporting a Mobile Launch Platform (MLP). The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
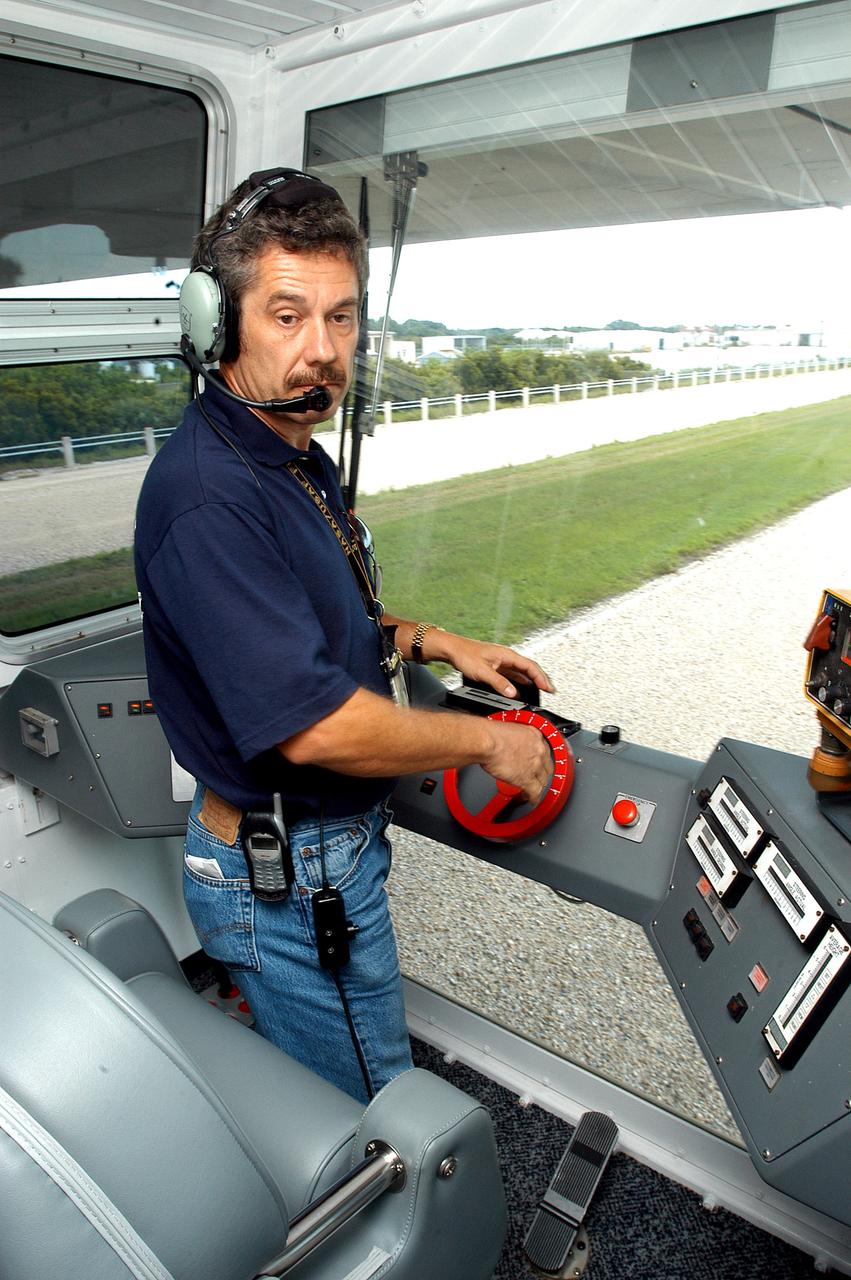

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the cab of crawler-transporter (CT) number 2, driver Sam Dove, with United Space Alliance, operates the vehicle on a test run to the launch pad. The CT recently underwent modifications to the cab. The CT is transporting a Mobile Launch Platform (MLP). The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
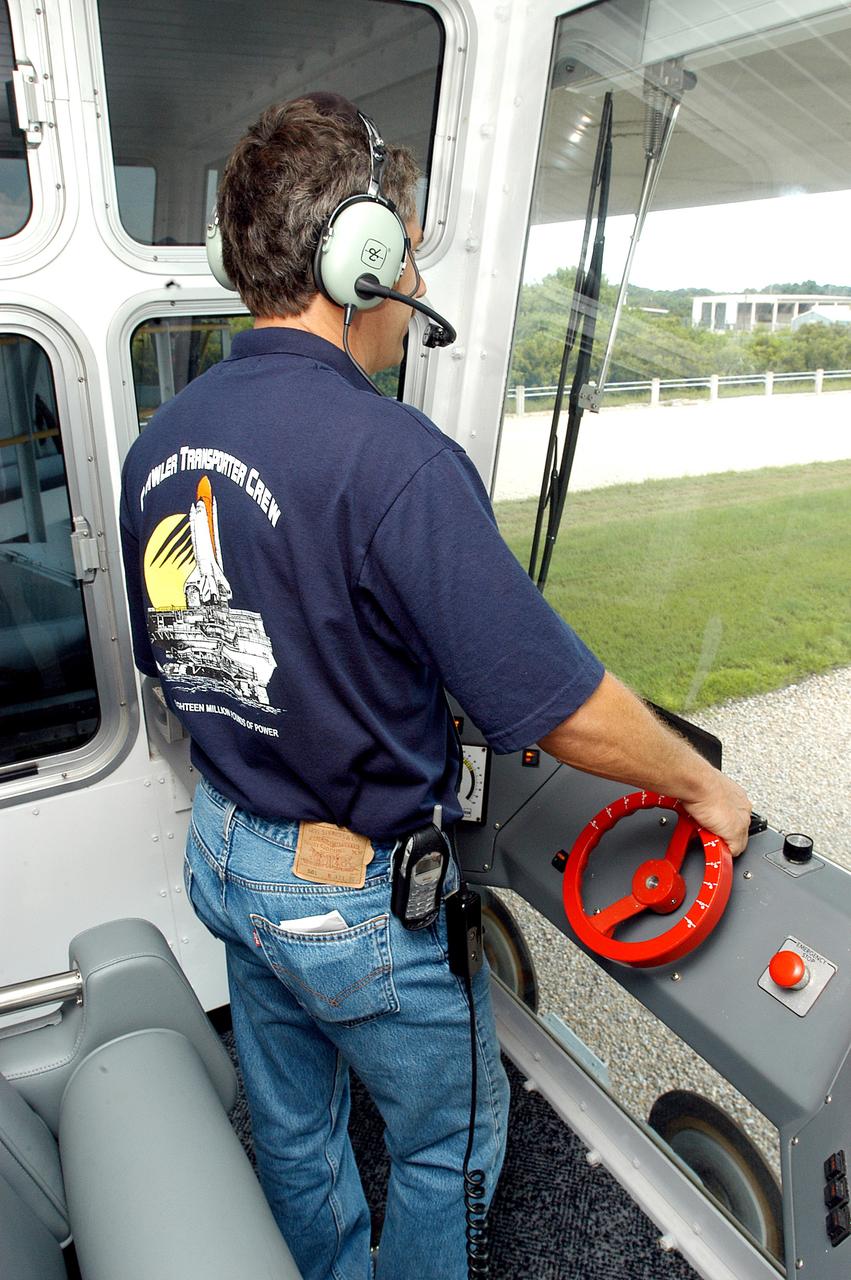

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the cab of crawler-transporter (CT) number 2, driver Sam Dove, with United Space Alliance, operates the vehicle on a test run to the launch pad. The CT recently underwent modifications to the cab. The CT is transporting a Mobile Launch Platform (MLP). The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
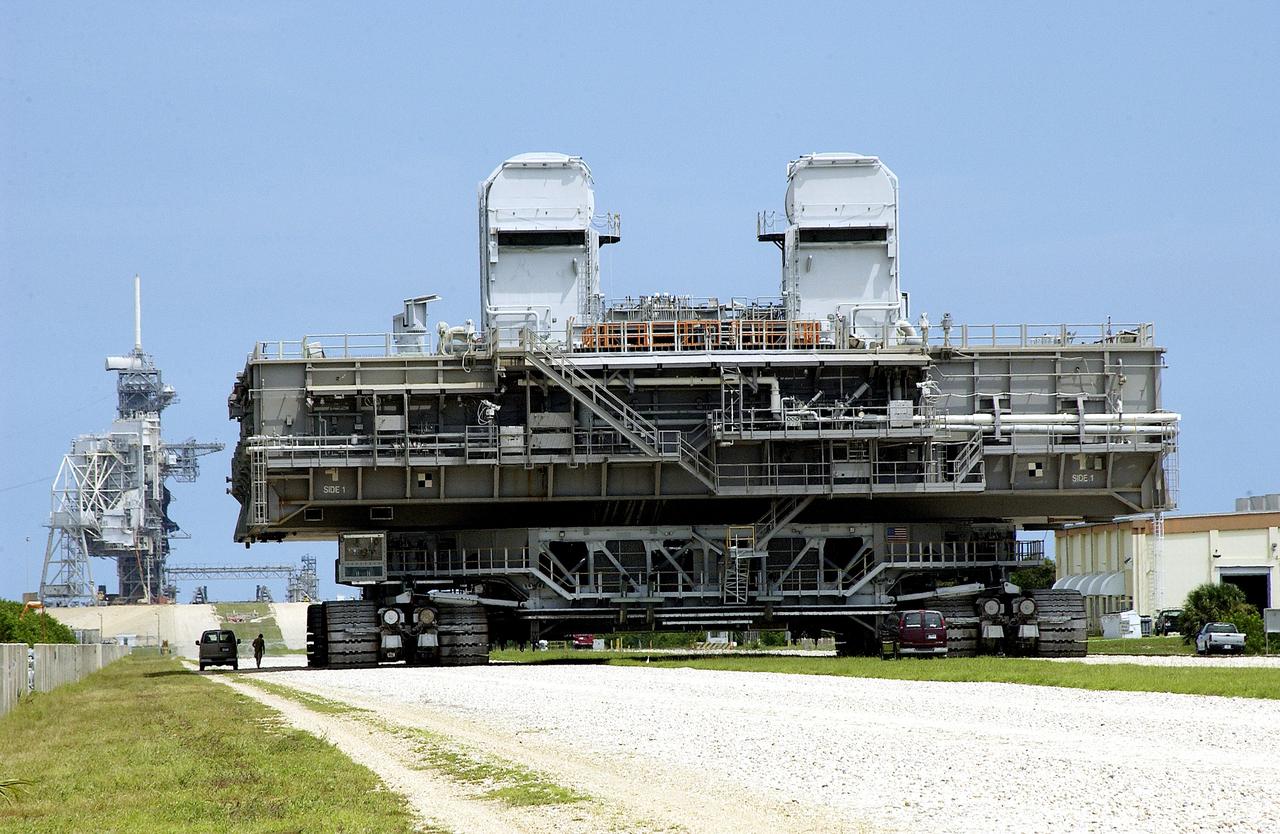

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Crawler-transporter (CT) number 2 nears the launch pad with a Mobile Launcher Platform (MLP) on top. After recent modifications to the cab and muffler system, the CT was taken on a test run. The CT moves Space Shuttle vehicles, situated on the MLP, between the VAB and launch pad. Moving on four double-tracked crawlers, the CT uses a laser guidance system and a leveling system for the journey that keeps the top of a Space Shuttle vertical within plus- or minus-10 minutes of arc. The system enables the CT-MLP-Shuttle to negotiate the ramp leading to the launch pads and keep the load level. Unloaded, the CT weighs 6 million pounds. Seen on top of the MLP are two tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals.
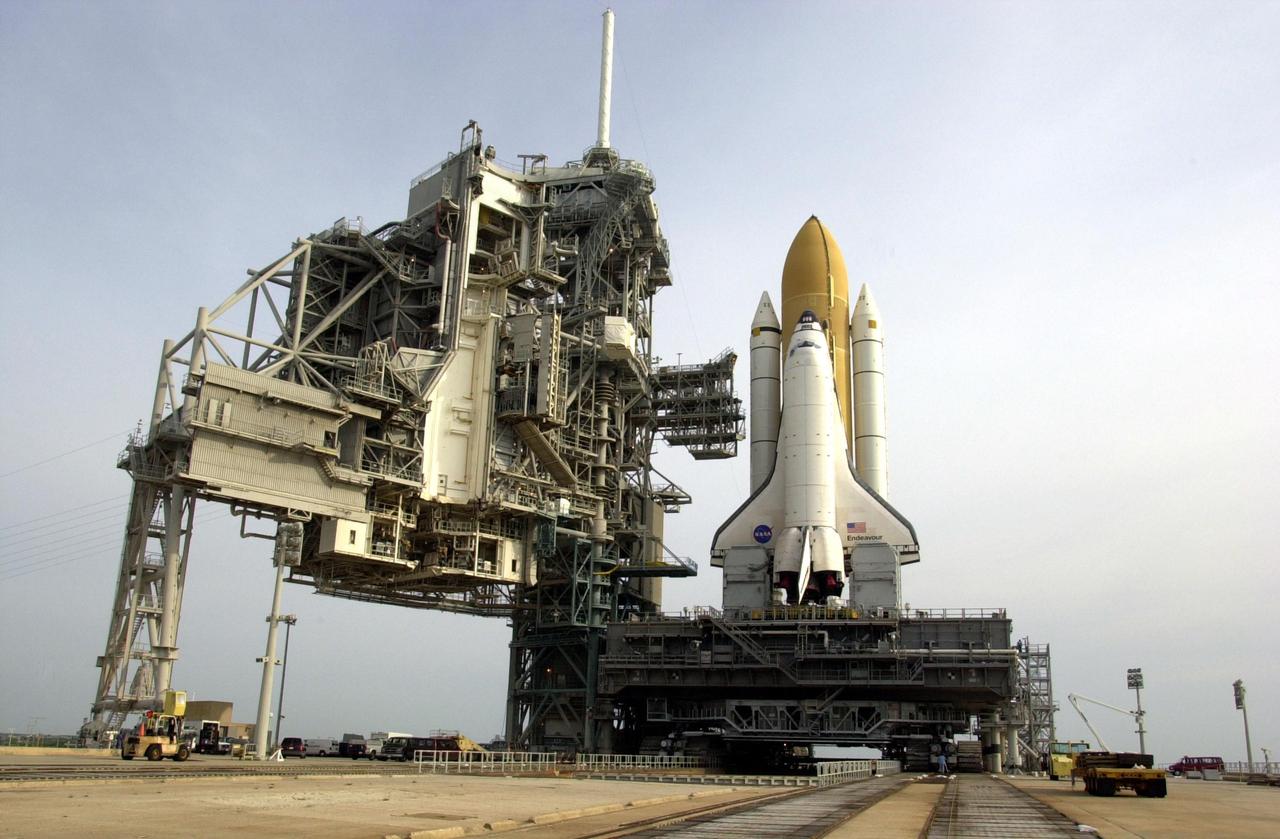

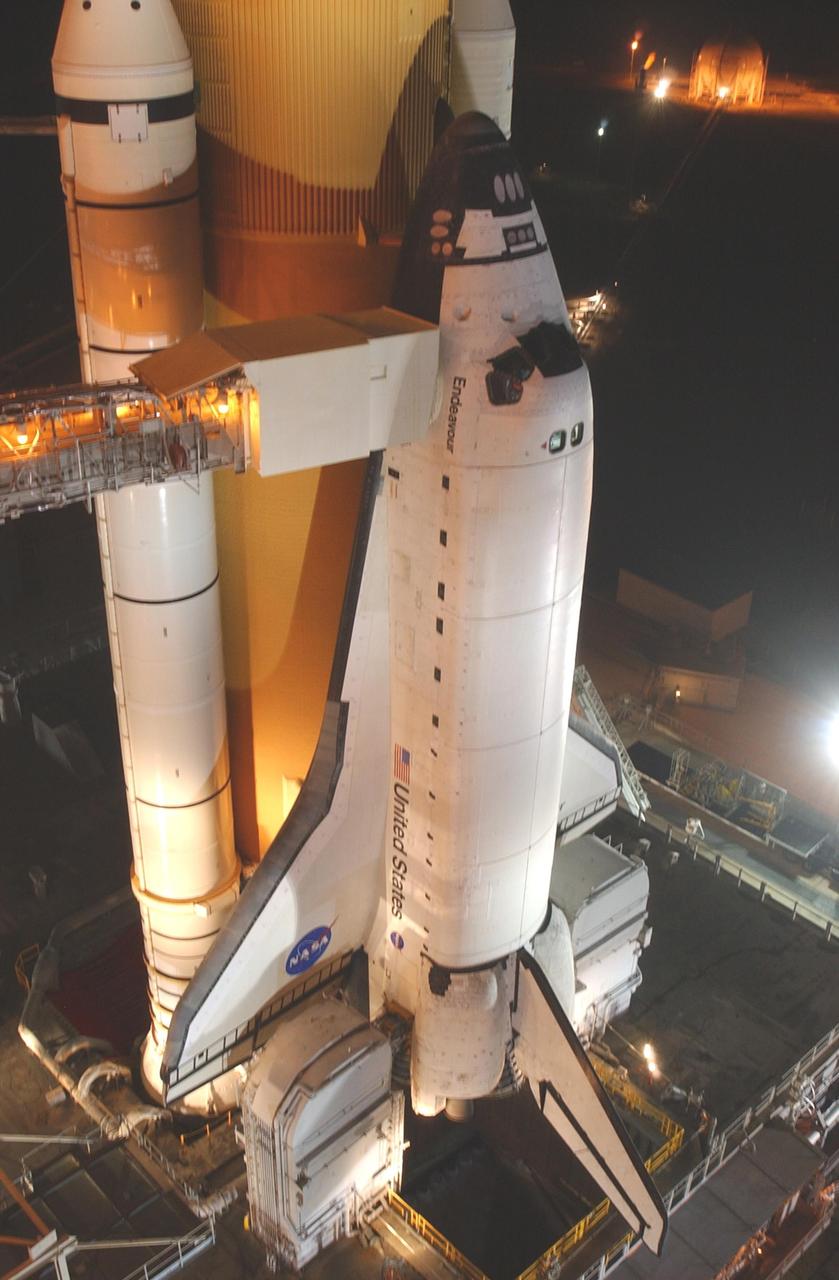
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour rests on Launch Pad 39A after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle comprises the orbiter, in front, and the taller orange external tank behind it flanked by twin solid rocket boosters. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform that straddles the flame trench below. On either side of Endeavour's tail and main engines are the tail service masts that support the fluid,, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxyen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. At left is the open Rotating Service Structure and the Fixed Service Structure to its right, with its 80-foot lightning mast on top. Mission STS-111 is designated UF-2, the 14th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Endeavour's payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and Mobile Base System. The mission also will swap resident crews on the Station, carrying the Expedition 5 crew and returning to Earth Expedition 4. Liftoff of Endeavour is scheduled between 4 and 8 p.m. May 30, 2002
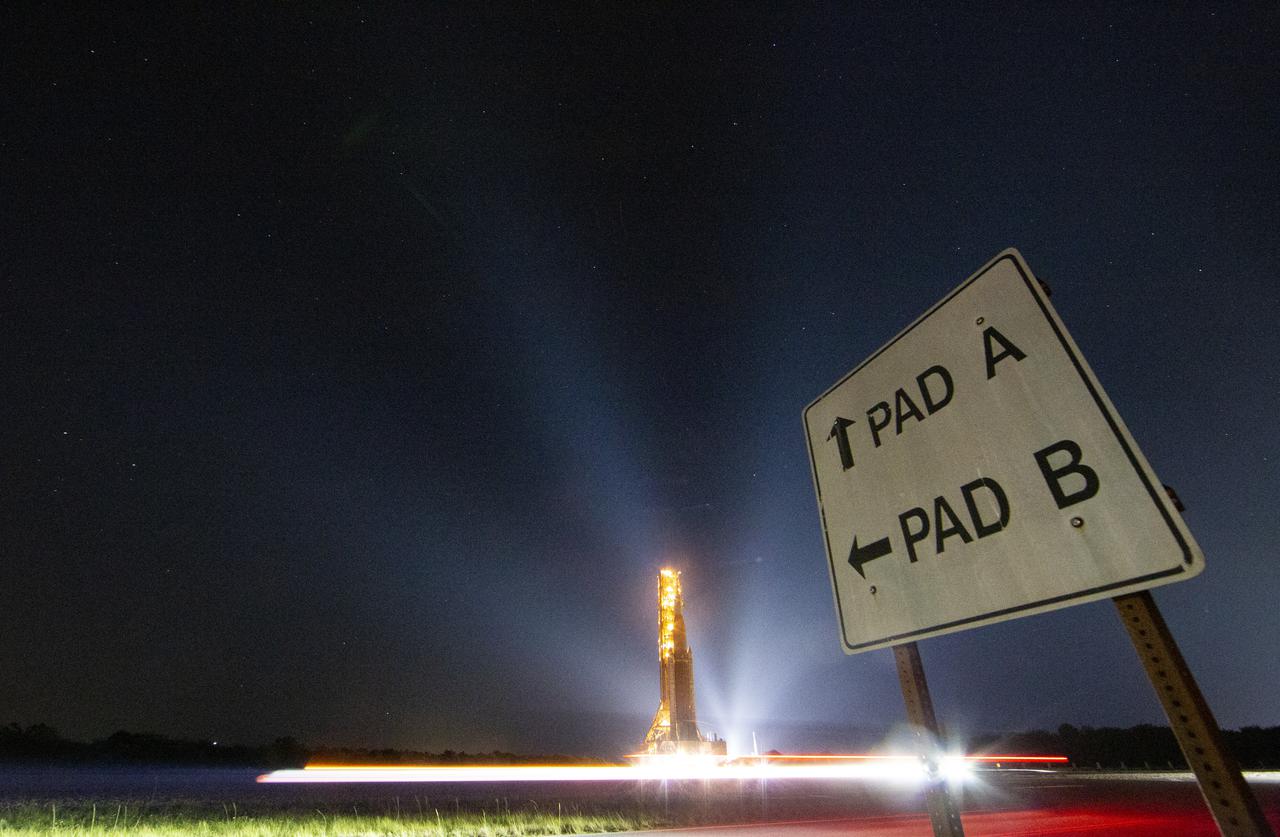

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop a mobile launcher as it rolls back to the Vehicle Assembly Building, Tuesday, April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, teams will work on replacing a faulty upper stage check valve and a small leak within the tail service mast umbilical ground plate housing on the mobile launcher while the supplier for the gaseous nitrogen makes upgrades to their pipeline configuration to support Artemis I testing and launch. Following completion, teams will return to the launch pad to complete the next wet dress rehearsal attempt. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
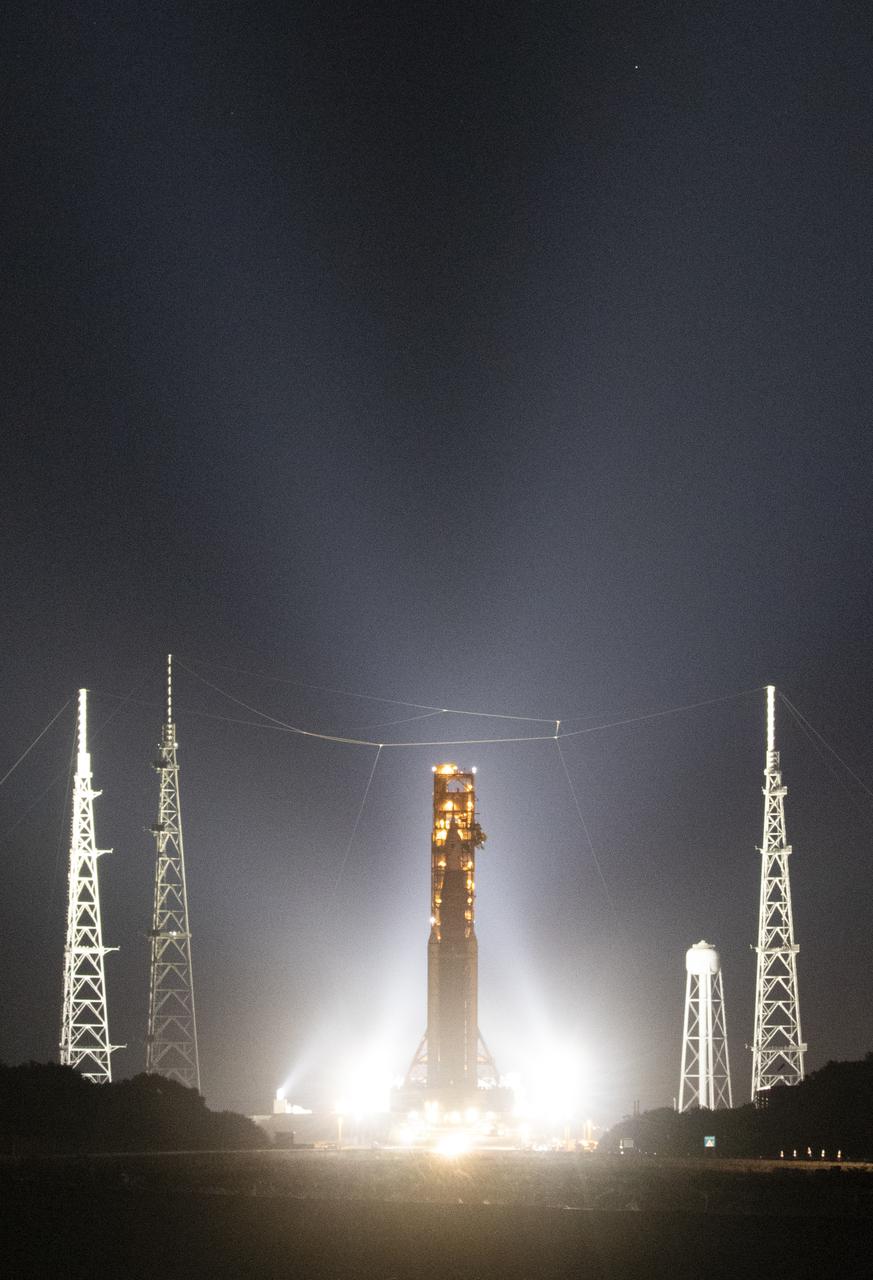

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop a mobile launcher as it rolls back to the Vehicle Assembly Building, Monday, April 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, teams will work on replacing a faulty upper stage check valve and a small leak within the tail service mast umbilical ground plate housing on the mobile launcher while the supplier for the gaseous nitrogen makes upgrades to their pipeline configuration to support Artemis I testing and launch. Following completion, teams will return to the launch pad to complete the next wet dress rehearsal attempt. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
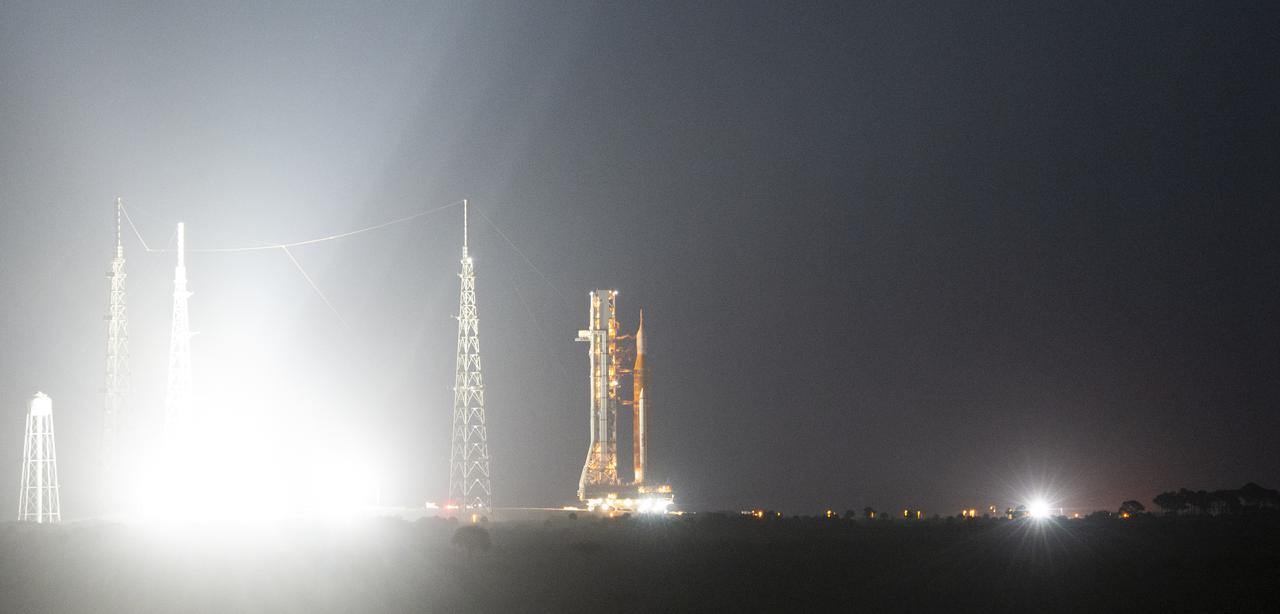

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop a mobile launcher as it rolls back to the Vehicle Assembly Building, Monday, April 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, teams will work on replacing a faulty upper stage check valve and a small leak within the tail service mast umbilical ground plate housing on the mobile launcher while the supplier for the gaseous nitrogen makes upgrades to their pipeline configuration to support Artemis I testing and launch. Following completion, teams will return to the launch pad to complete the next wet dress rehearsal attempt. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
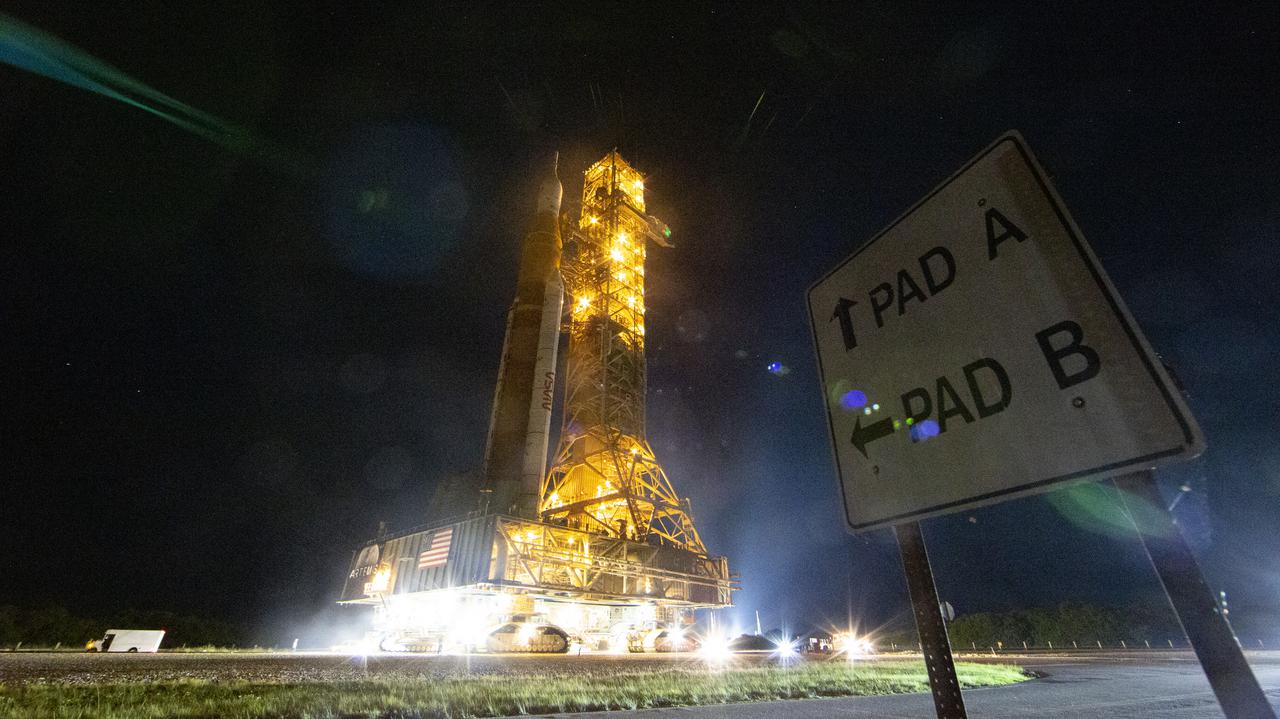

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop a mobile launcher as it rolls back to the Vehicle Assembly Building, Tuesday, April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, teams will work on replacing a faulty upper stage check valve and a small leak within the tail service mast umbilical ground plate housing on the mobile launcher while the supplier for the gaseous nitrogen makes upgrades to their pipeline configuration to support Artemis I testing and launch. Following completion, teams will return to the launch pad to complete the next wet dress rehearsal attempt. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B rolls away from Space Shuttle Endeavour atop the Mobile Launcher Platform. The Space Shuttle comprises the orbiter and an external tank flanked by twin solid rocket boosters. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." On either side of the orbiter's tail and main engines are two tail masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. . Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After an early morning rollout, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on the launch pad. Visible near the tail are the tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. After being stacked with its solid rocket boosters and external tank, Atlantis began its rollout to Launch Pad 39B at 2:27 a.m. EDT in preparation for launch to the International Space Station. The Shuttle arrived at the Pad and was hard down at 9:38 a.m. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Oct. 2 for mission STS-112, the 15th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis will carry the S1 Integrated Truss Structure, which will be attached to the central truss segment, the S0 truss, during the mission.
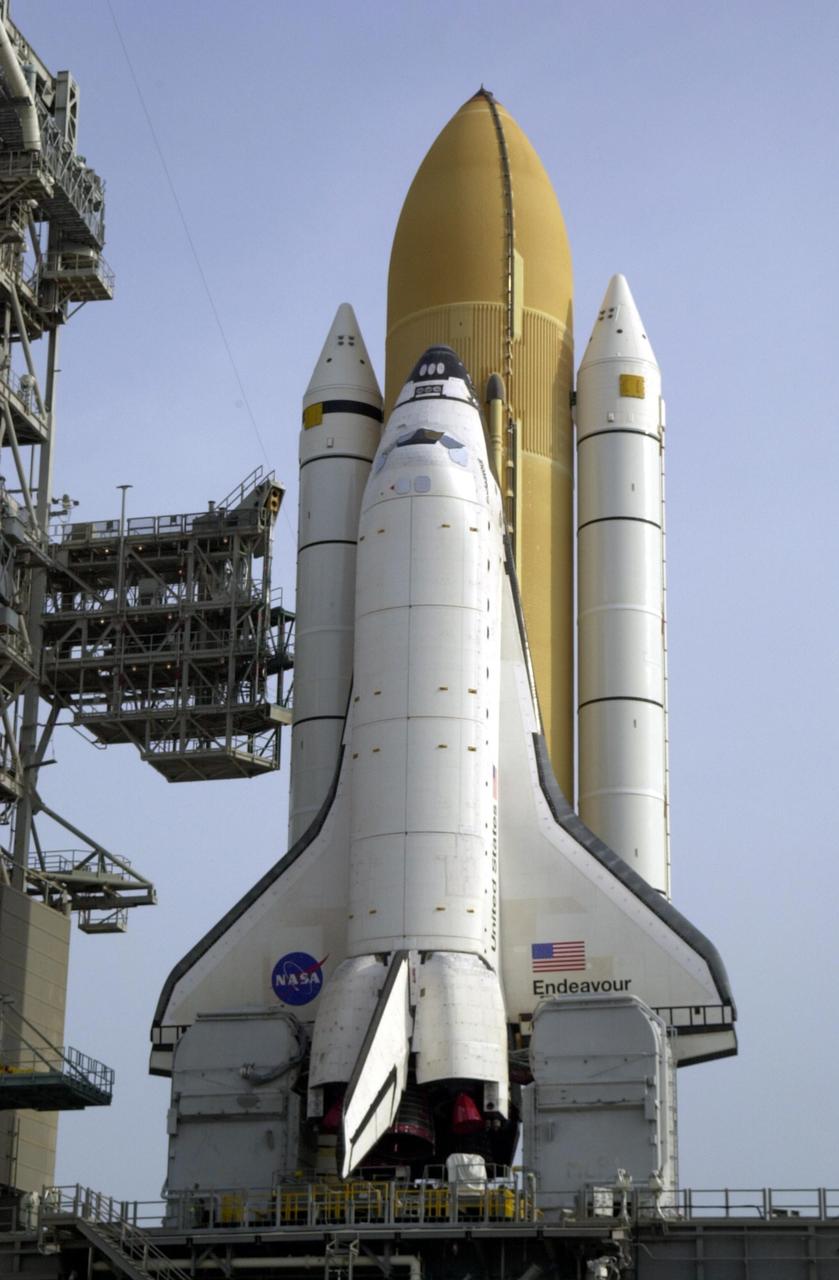

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour rests on Launch Pad 39A after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle comprises the orbiter, in front, and the taller orange external tank behind it flanked by twin solid rocket boosters. On either side of Endeavour's tail and main engines are the tail service masts that support the fluid,, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxyen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Mission STS-111 is designated UF-2, the 14th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Endeavour's payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and Mobile Base System. The mission also will swap resident crews on the Station, carrying the Expedition 5 crew and returning to Earth Expedition 4. Liftoff of Endeavour is scheduled between 4 and 8 p.m. May 30, 2002

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready for final launch preparations. The orbiter access arm is extended to the orbiter to allow entry into Atlantis. The White Room at the end is the point of entry, and is an environmentally controlled room where the Shuttle crew have final adjustments made to their launch and entry suits. At the lower end of Atlantis are the tail service masts, in front of either wing. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Viewed in the background is the Atlantic Ocean. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload
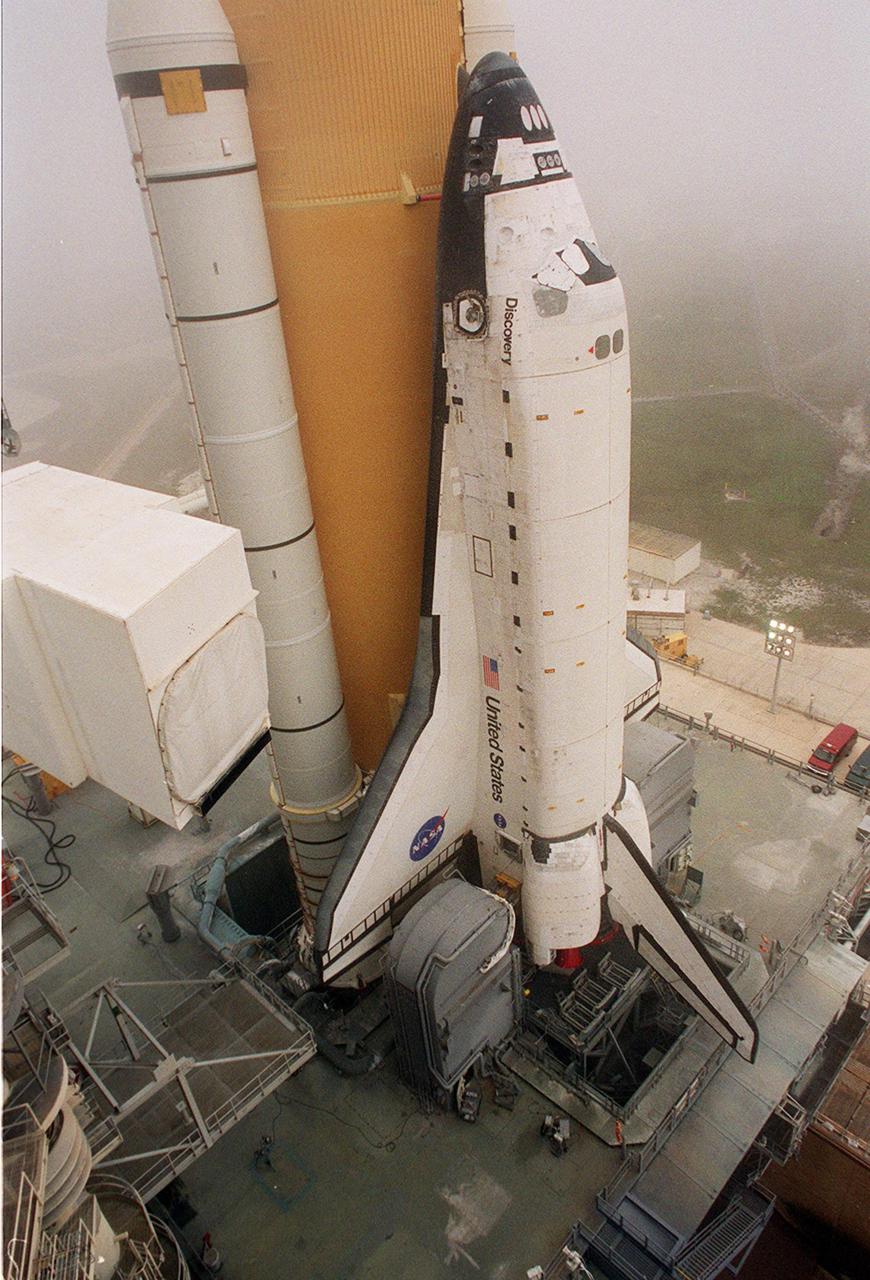

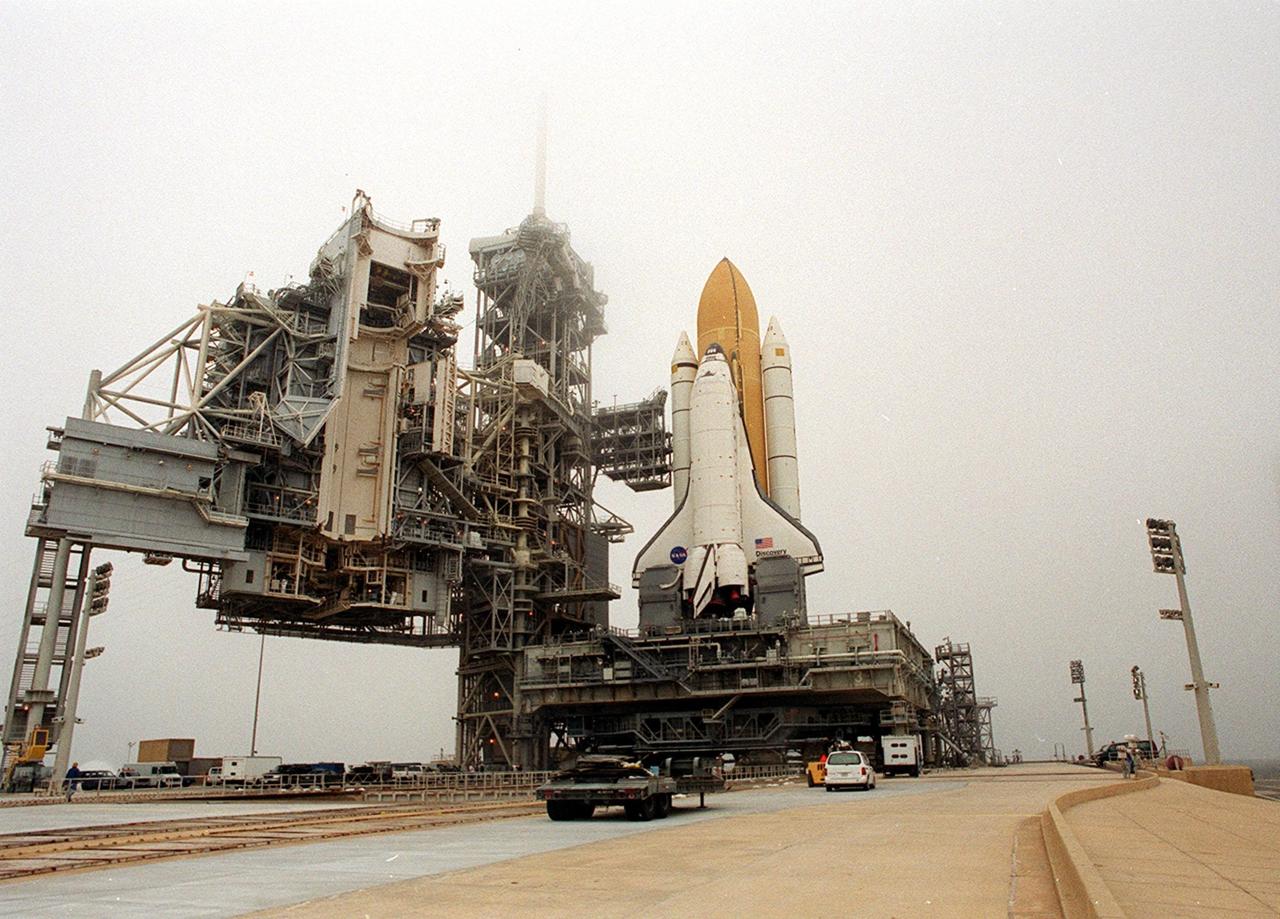
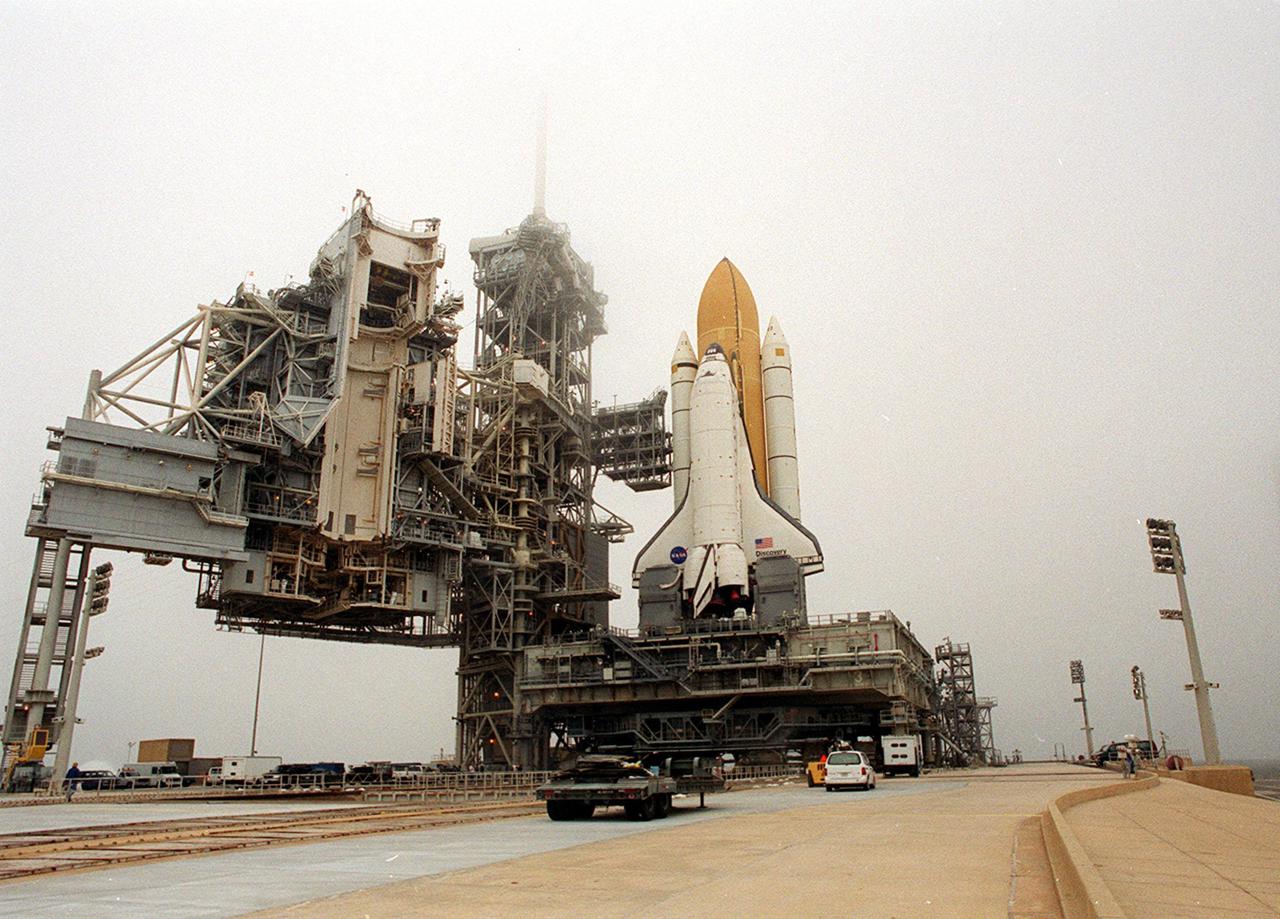
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
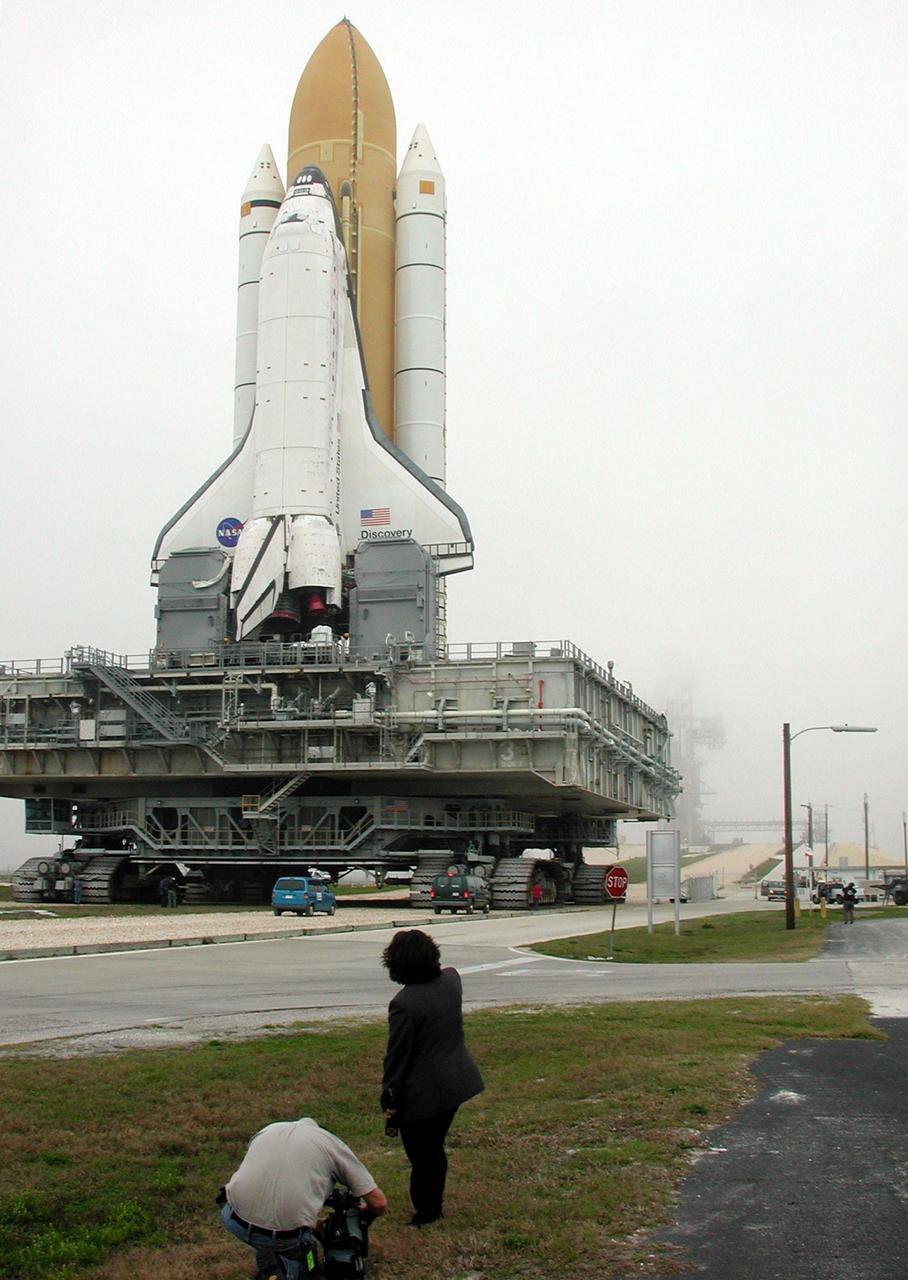

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This closeup shows Space Shuttle Discovery as it travels to Launch Pad 39B. Underneath Discovery is the Mobile Launcher Platform, a two-story movable launch base. Part of the MPLM is the tail service mast, seen here at the bottom of the wind and next to the Shuttle’s main engines. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
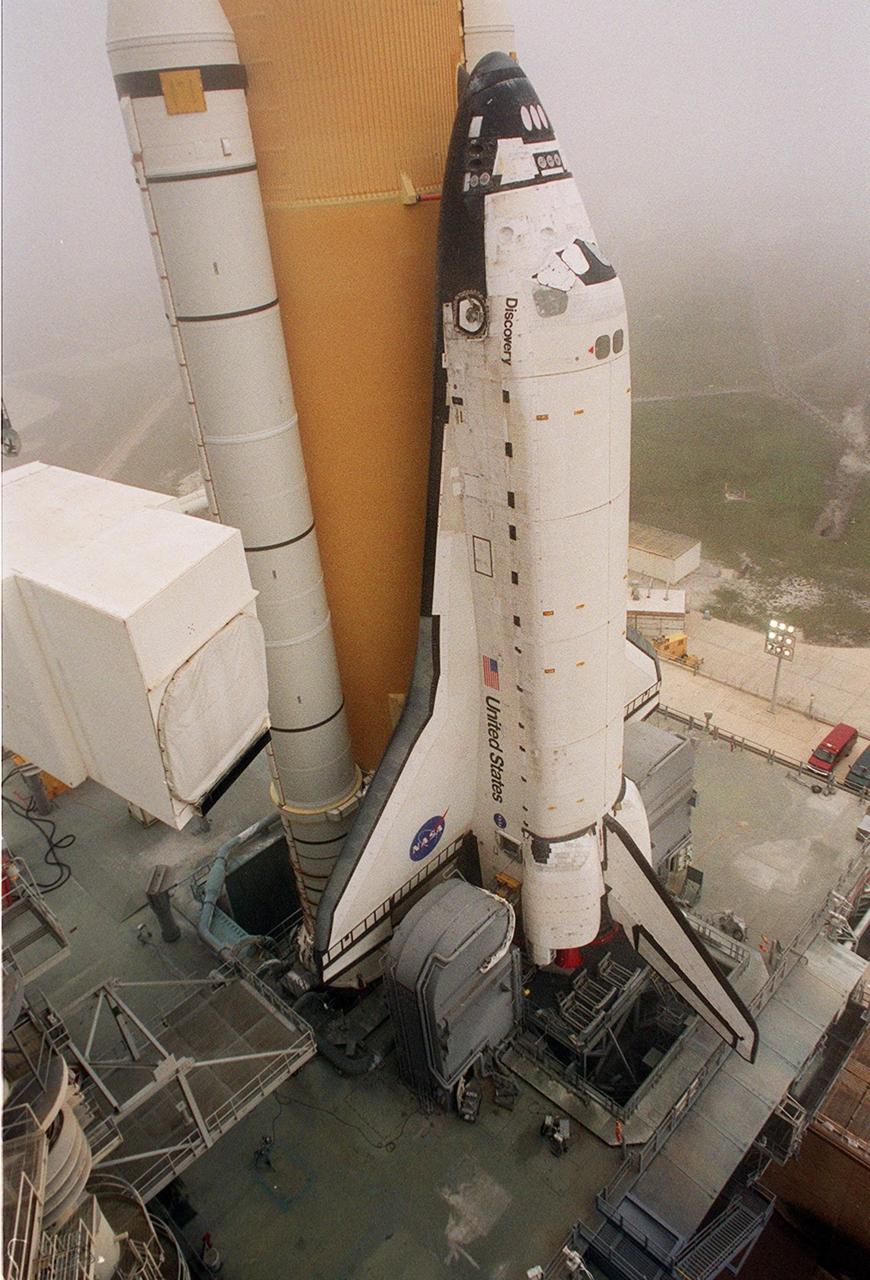

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
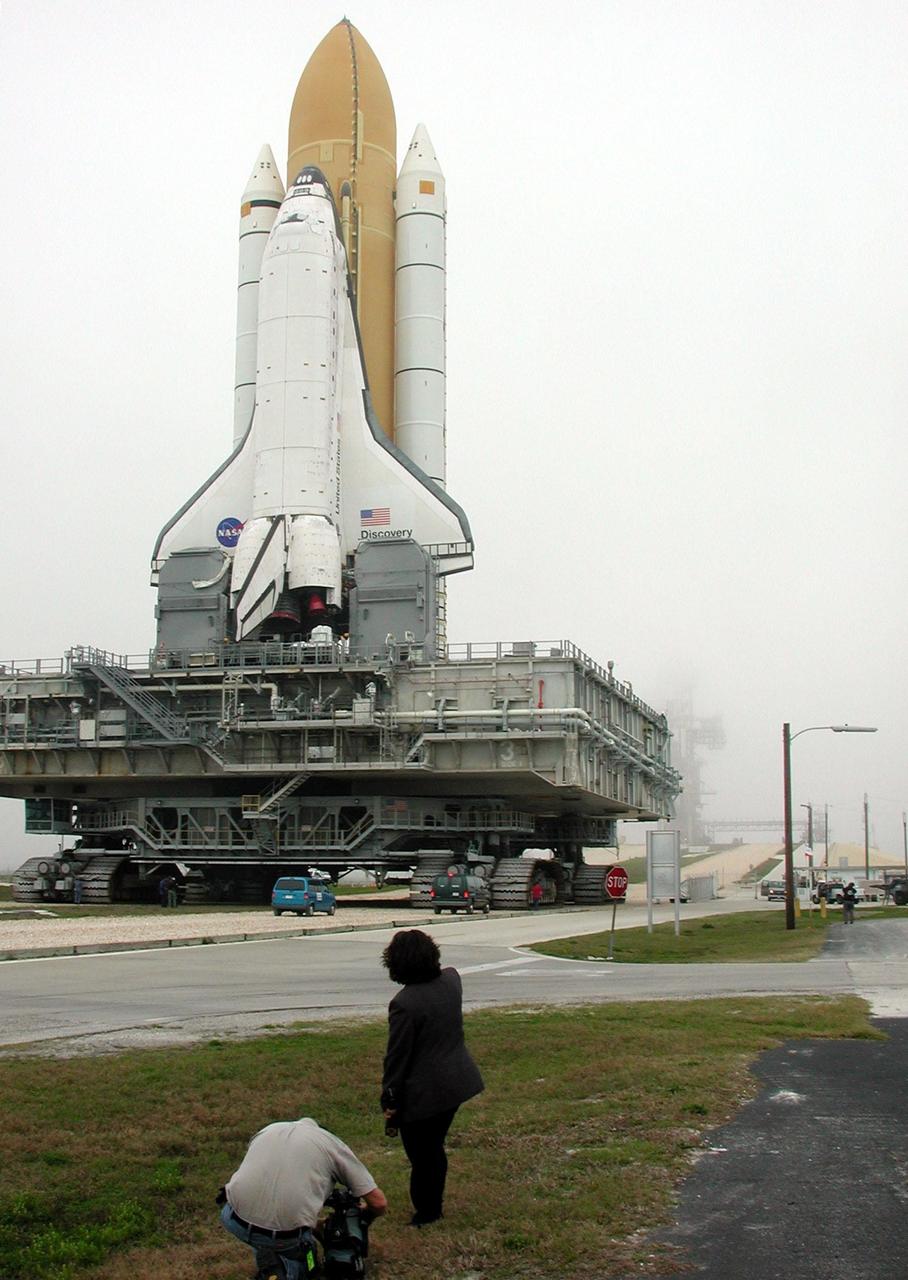

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This closeup shows Space Shuttle Discovery as it travels to Launch Pad 39B. Underneath Discovery is the Mobile Launcher Platform, a two-story movable launch base. Part of the MPLM is the tail service mast, seen here at the bottom of the wind and next to the Shuttle’s main engines. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
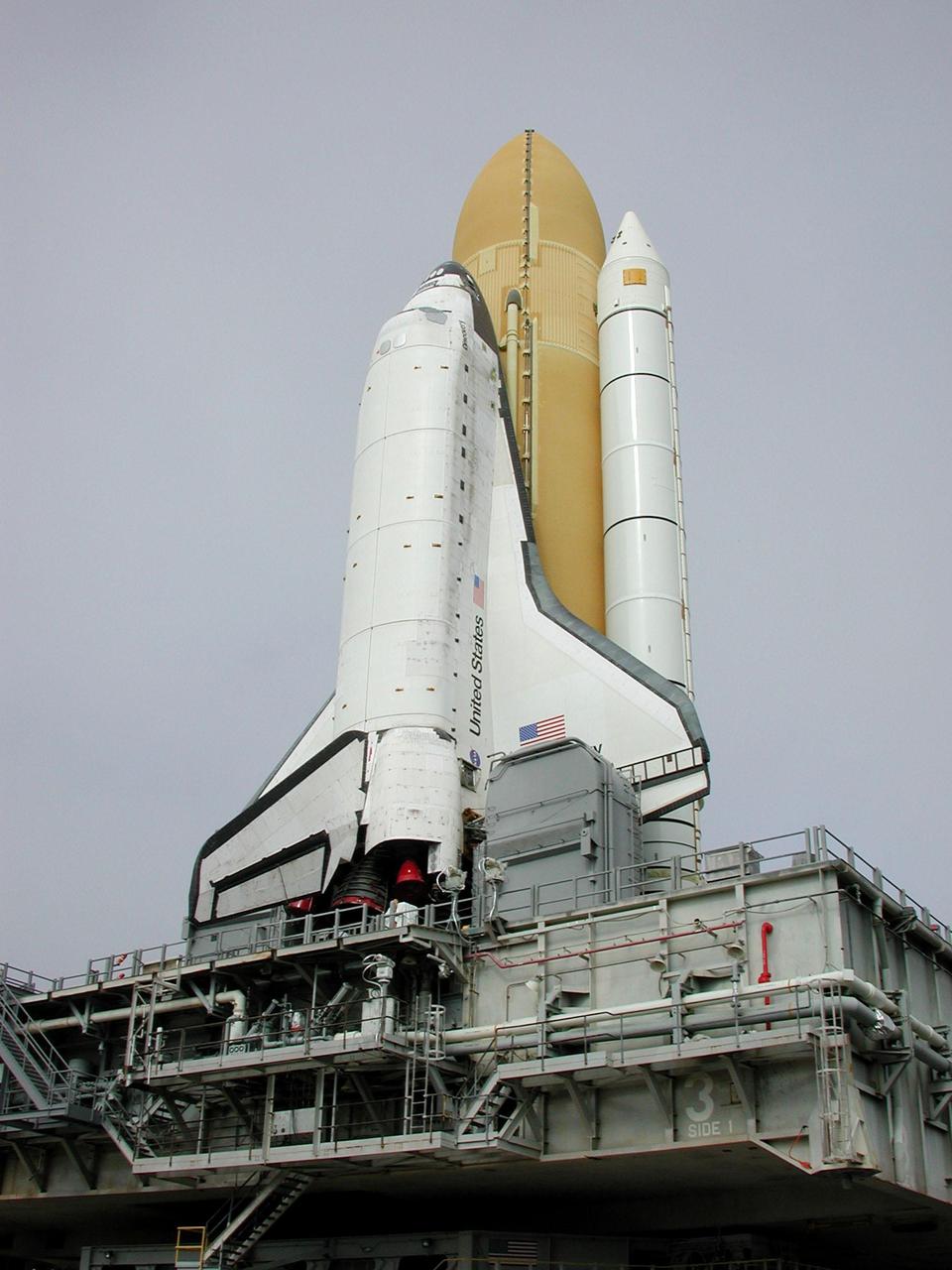

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This closeup shows Space Shuttle Discovery as it travels to Launch Pad 39B. Underneath Discovery is the Mobile Launcher Platform, a two-story movable launch base. Part of the MPLM is the tail service mast, seen here at the bottom of the wind and next to the Shuttle’s main engines. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
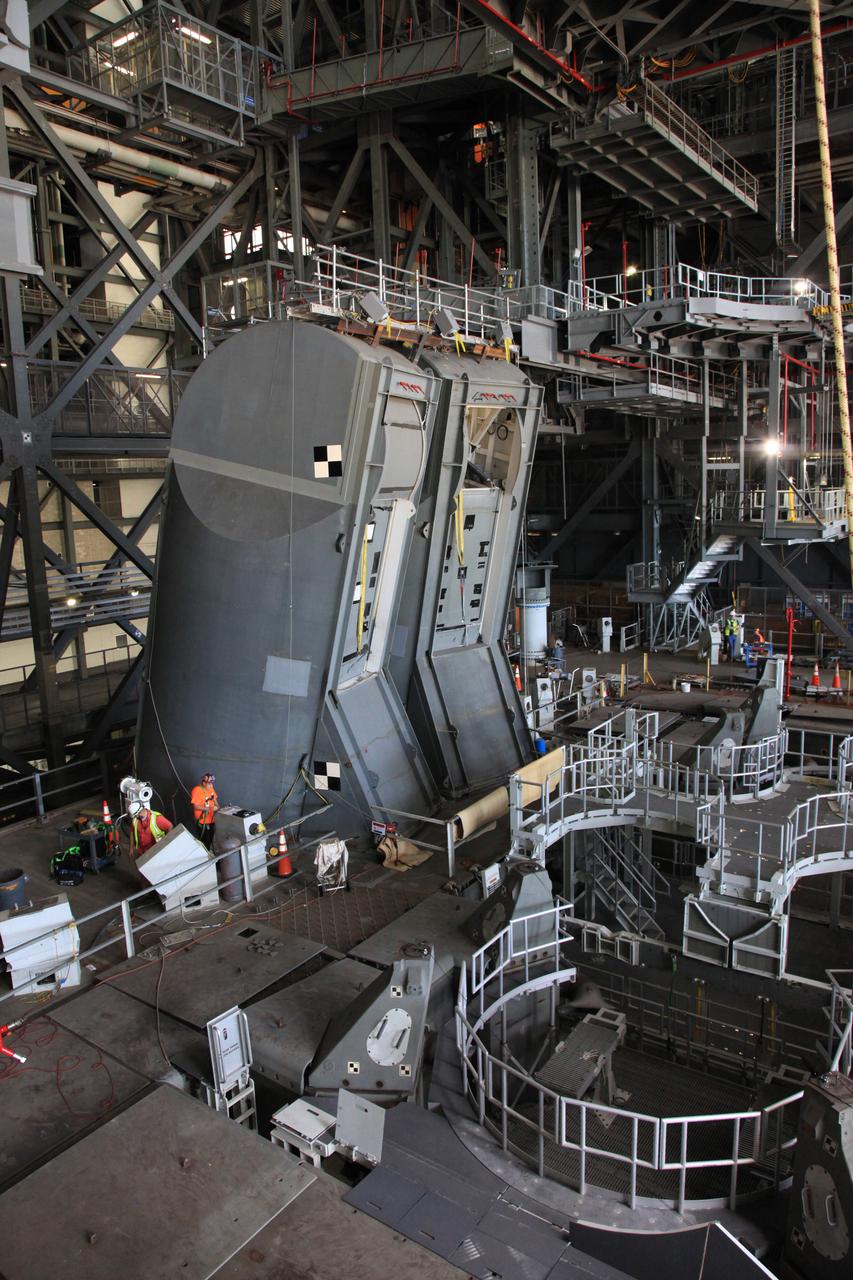
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. In view at left are the two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals. They will provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the SLS core stage engine section. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Rain on the ground around Space Shuttle Endeavour on Launch Pad 39B reflects the many lights illluminating the Rotating Service Structure (at left), Fixed Service Structure and Shuttle. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching from the FSS to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
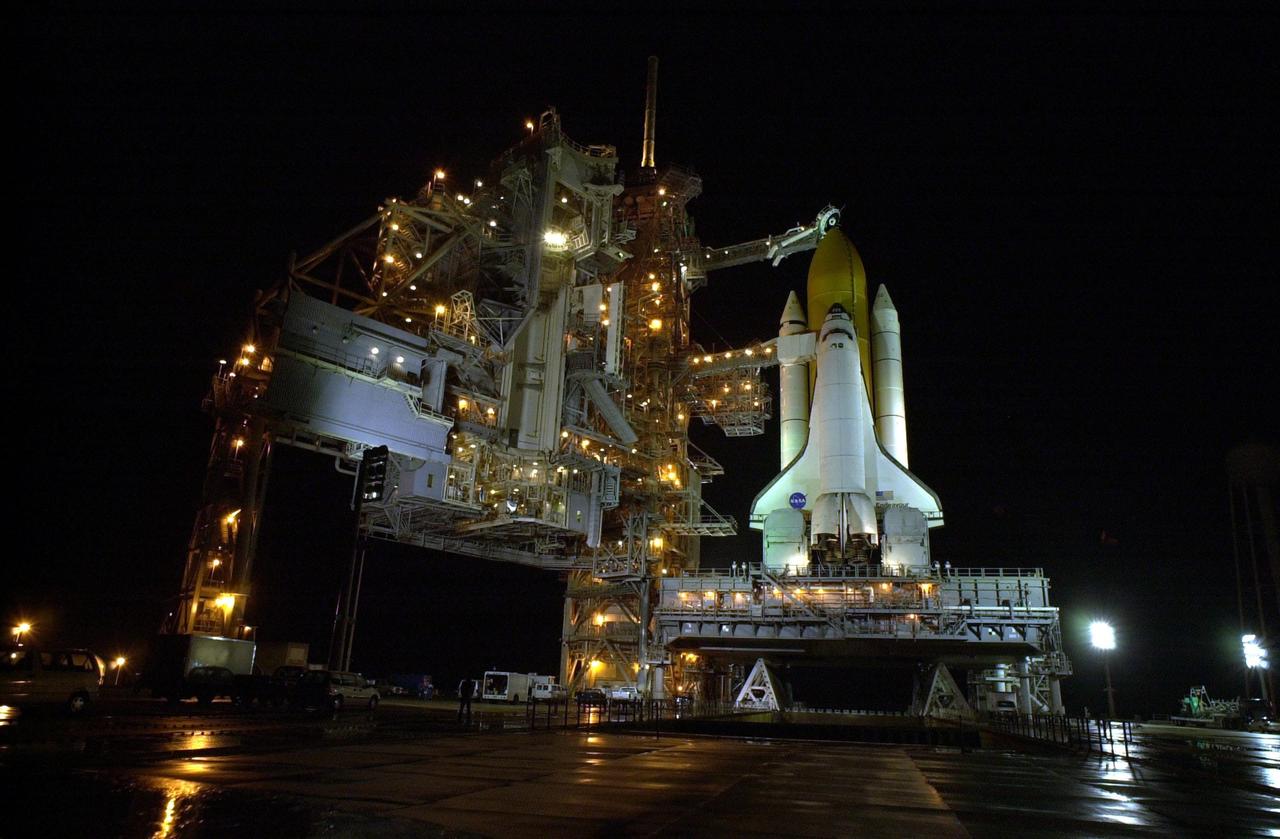

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Rain on the ground around Space Shuttle Endeavour on Launch Pad 39B reflects the many lights illluminating the Rotating Service Structure (at left), Fixed Service Structure and Shuttle. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching from the FSS to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
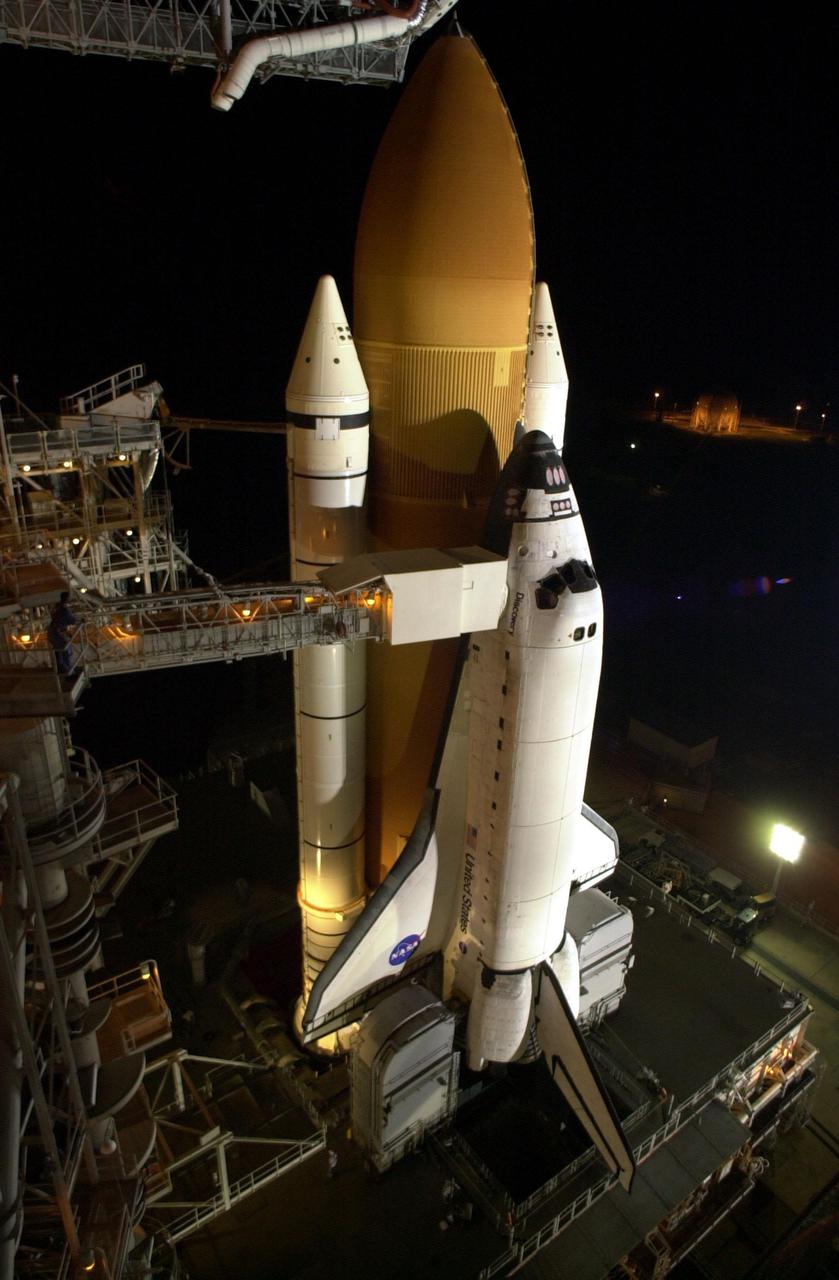

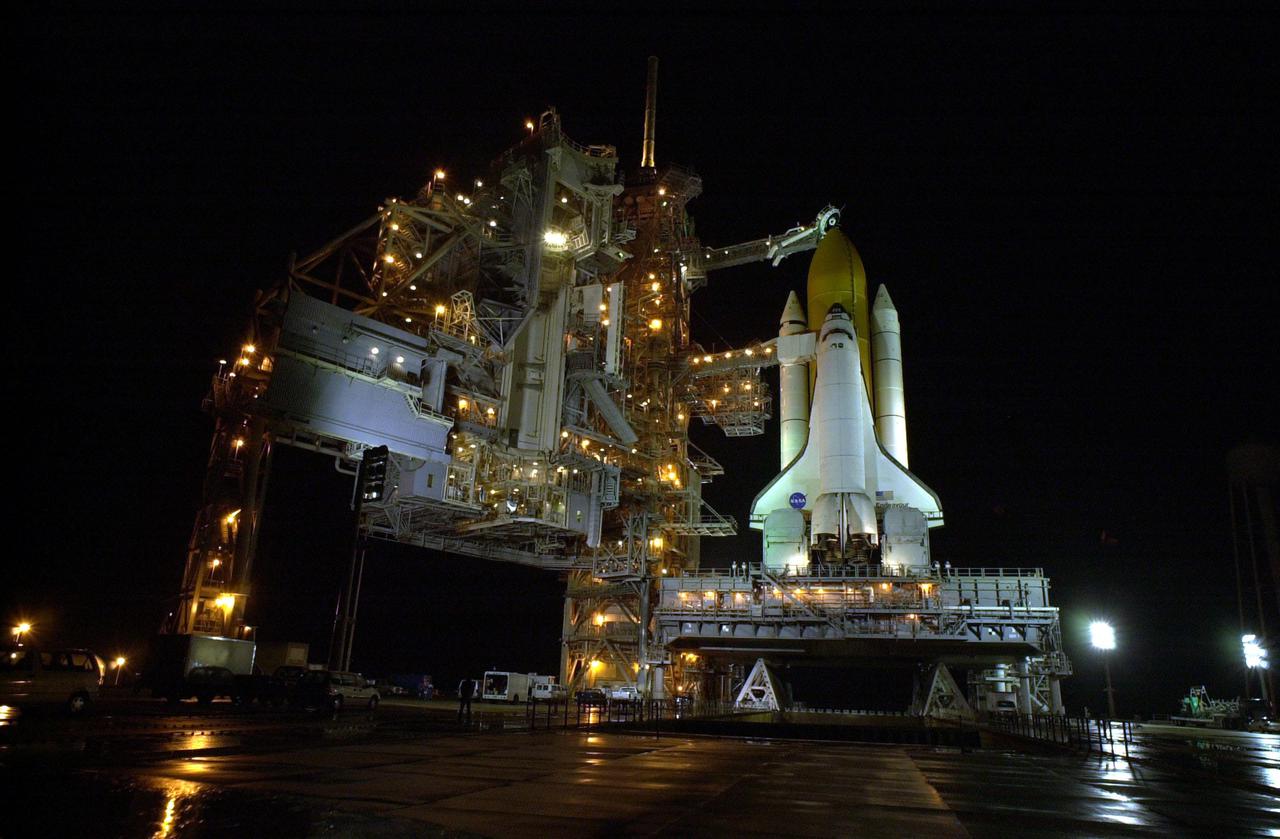
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery is bathed in light after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure in preparation for launch on mission STS-105. The Shuttle comprises the two solid rocket boosters, external tank and orbiter, all of which are secured on the mobile launcher platform beneath them. Extending toward Discovery from the fixed service structure at left is the orbiter access arm. At the end of the arm is the White Room, an environmental chamber that mates with the orbiter and allows personnel to enter the crew compartment. Below, on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. On mission STS-105, Discovery will be transporting the Expedition Three crew and several payloads and scientific experiments to the ISS, including the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS) tank. The EAS, which will support the thermal control subsystems until a permanent system is activated, will be attached to the Station during two spacewalks. The three-member Expedition Two crew will be returning to Earth aboard Discovery after a five-month stay on the Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:38 p.m. EDT Aug. 9
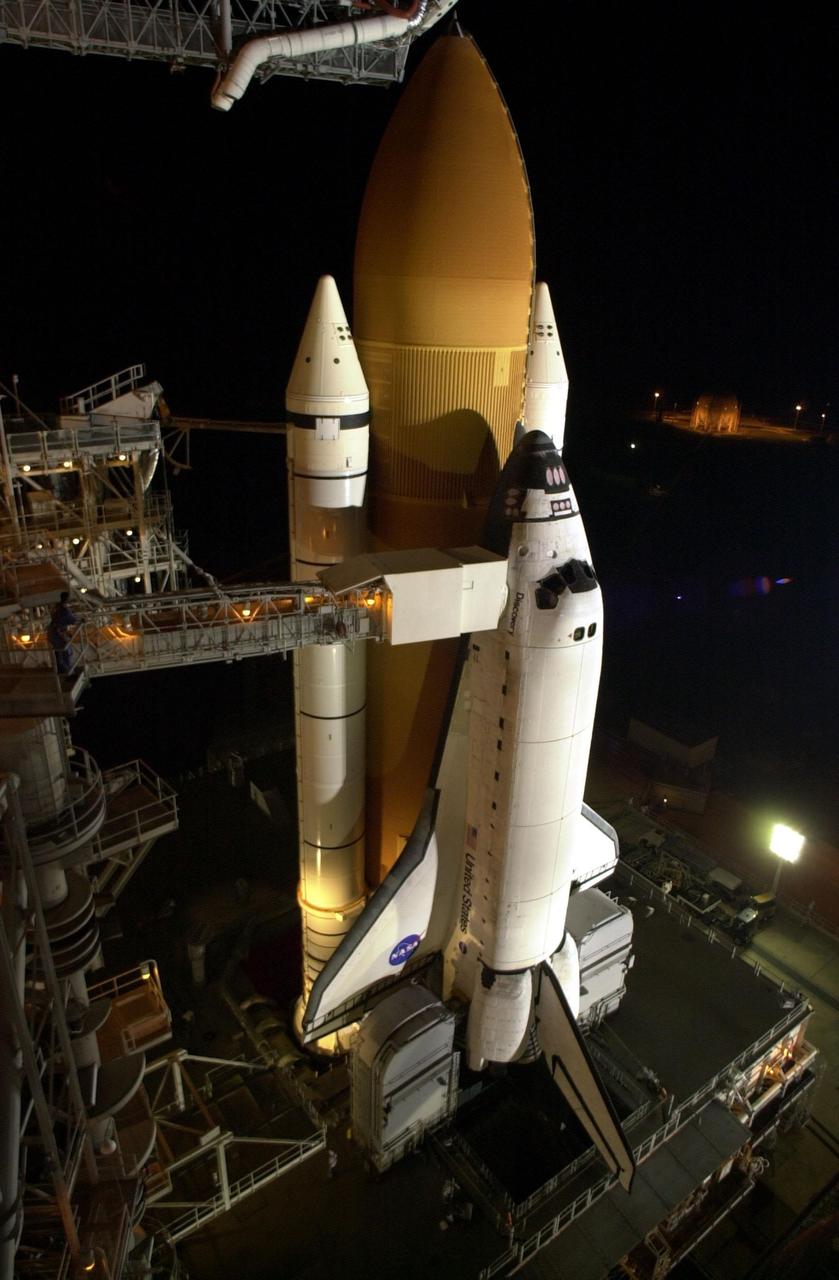

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery is bathed in light after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure in preparation for launch on mission STS-105. The Shuttle comprises the two solid rocket boosters, external tank and orbiter, all of which are secured on the mobile launcher platform beneath them. Extending toward Discovery from the fixed service structure at left is the orbiter access arm. At the end of the arm is the White Room, an environmental chamber that mates with the orbiter and allows personnel to enter the crew compartment. Below, on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. On mission STS-105, Discovery will be transporting the Expedition Three crew and several payloads and scientific experiments to the ISS, including the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS) tank. The EAS, which will support the thermal control subsystems until a permanent system is activated, will be attached to the Station during two spacewalks. The three-member Expedition Two crew will be returning to Earth aboard Discovery after a five-month stay on the Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:38 p.m. EDT Aug. 9
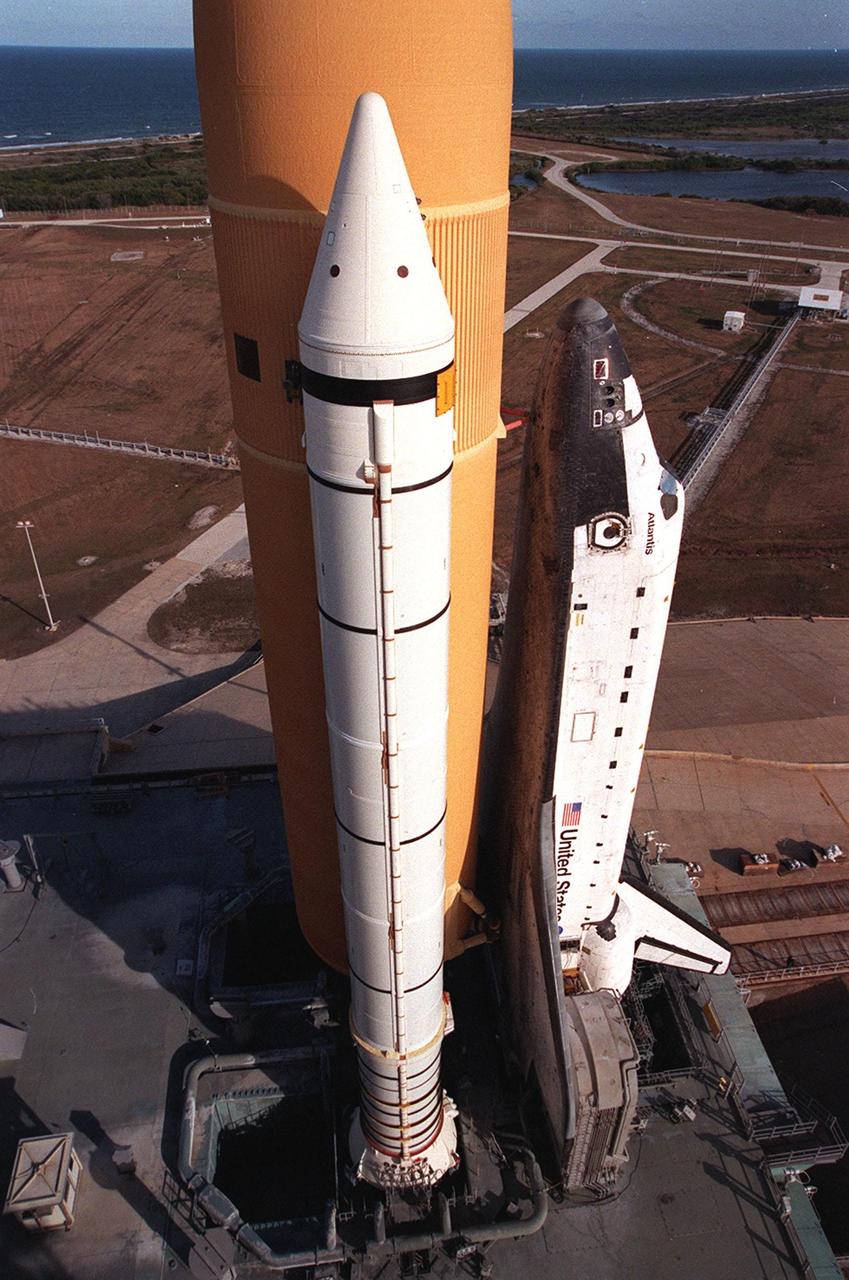

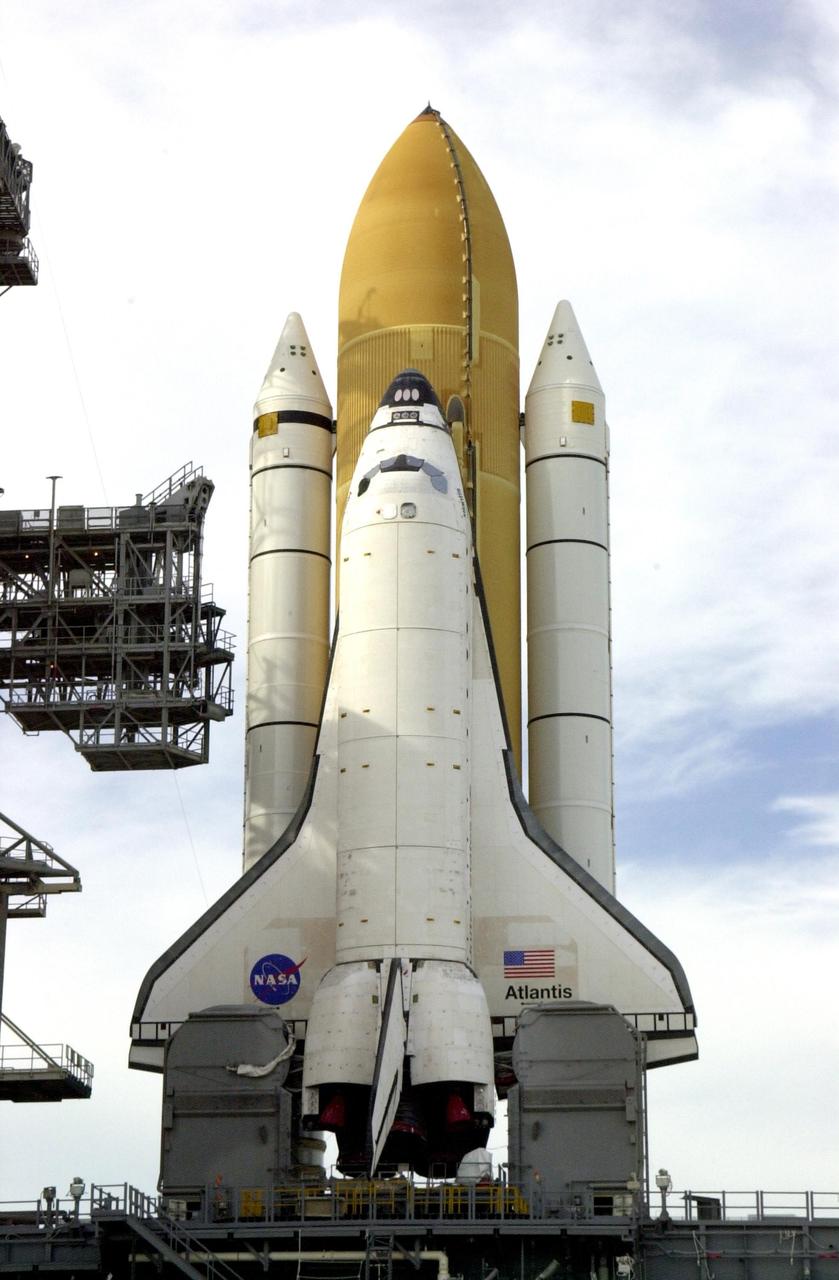
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Resting atop the Mobile Launcher Platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis is viewed from a high level on the Fixed Service Structure. Seen is one of its solid rocket boosters and the external tank. Next to the wing of the orbiter is one of two tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. On the horizon is the Atlantic Ocean. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab has five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
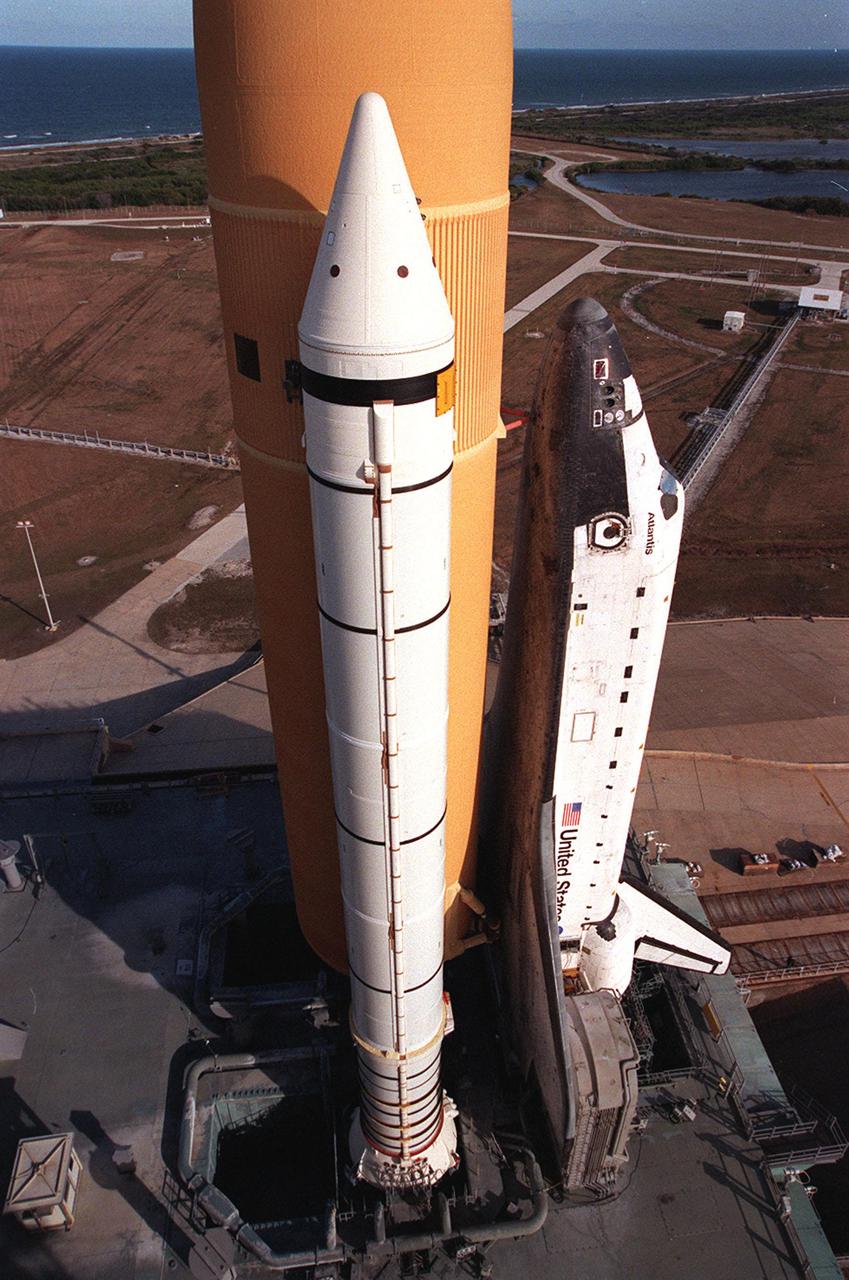

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Resting atop the Mobile Launcher Platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis is viewed from a high level on the Fixed Service Structure. Seen is one of its solid rocket boosters and the external tank. Next to the wing of the orbiter is one of two tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. On the horizon is the Atlantic Ocean. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab has five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on the hardstand of Launch Pad 39B after its nearly 8-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Extending from the fixed service structure on the left is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room on the outer end, adjacent to Atlantis. Below the orbiter, on each side of the main engine nozzles, are the tail service masts that provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Atlantis' launch window begins Aug. 27 for an 11-day mission to the International Space Station. The STS-115 crew of six astronauts will continue construction of the station and install their cargo, the Port 3/4 truss segment with its two large solar arrays. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder & George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure in the early morning hours, Space Shuttle Endeavour sits bathed in light on its Mobile Launcher Platform on Launch Pad 39A. Seen extending to the cockpit area of Endeavour is the orbiter access arm. At the end of the arm is the White Room, an environmental chamber. Below, on either side of Endeavour's tail, are the tail service masts that support fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. STS-111 is the second Utilization Flight to the International Space Station, carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the Mobile Base System (MBS), and a replacement wrist/roll joint for the Canadarm 2. Also onboard Space Shuttle Endeavour is the Expedition 5 crew who will replace Expedition 4 on board the Station. The MBS will be installed on the Mobile Transporter to complete the Canadian Mobile Servicing System, or MSS. The mechanical arm will then have the capability to "inchworm" from the U.S. Lab Destiny to the MSS and travel along the truss to work sites. Expedition 4 crew members will return to Earth with the STS-111 crew on Endeavour. Launch is scheduled for 7:44 p.m. EDT, May 30, 2002
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Floodlights reveal the Space Shuttle Discovery after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure in preparation for launch on mission STS-105. Above the external tank, the “beanie cap” is poised, waiting for loading of the propellants. The cap, or vent hood, is on the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm that allows gaseous oxygen vapors to vent away from the Space Shuttle. Below, on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. On the mission, Discovery will be transporting the Expedition Three crew and several scientific experiments and payloads to the International Space Station, including the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS) tank. The EAS, which will support the thermal control subsystems until a permanent system is activated, will be attached to the Station during two spacewalks. The three-member Expedition Two crew will be returning to Earth aboard Discovery after a five-month stay on the Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:38 p.m. EDT Aug. 9

The Tail Service Mast Umbilicals that will connect to NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, containing fluid lines for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellant loading, are photographed on the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B on Nov. 8, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw testing of the pad’s cryogenic systems – the infrastructure that will support the flow of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen from the storage tanks to the rocket – in preparation for the launch of SLS with the Orion spacecraft atop for the uncrewed Artemis I mission. Each of the liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks can hold more than 800,000 gallons of propellant. The liquid oxygen will require the use of pumps to push it from the tank to the rocket, while the lighter liquid hydrogen will make its way up to the pad using gaseous hydrogen to pressurize the sphere.

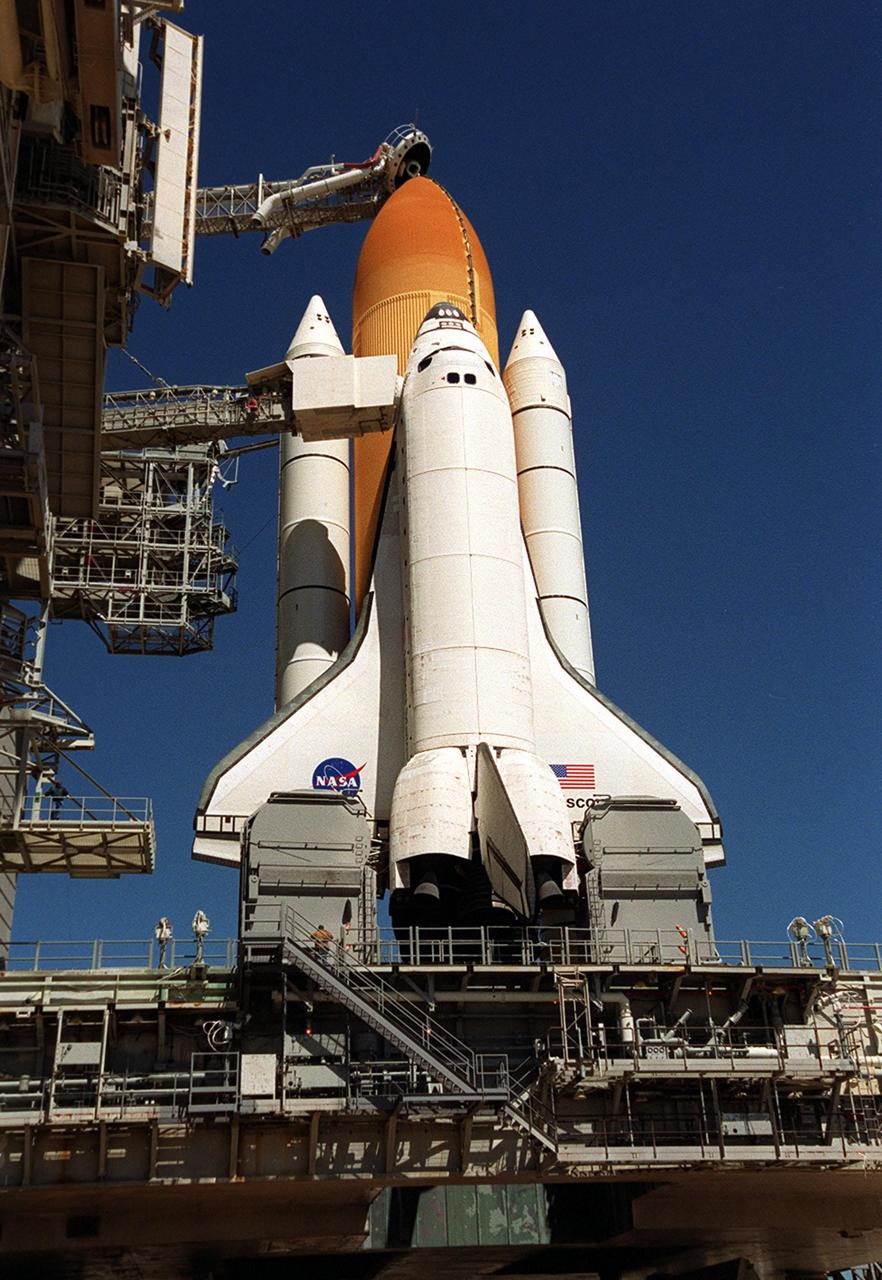
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Bright morning sun shines on Space Shuttle Atlantis as it sits on Launch Pad 39A. In front of the wings, on either side of the orbiter are tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab has five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
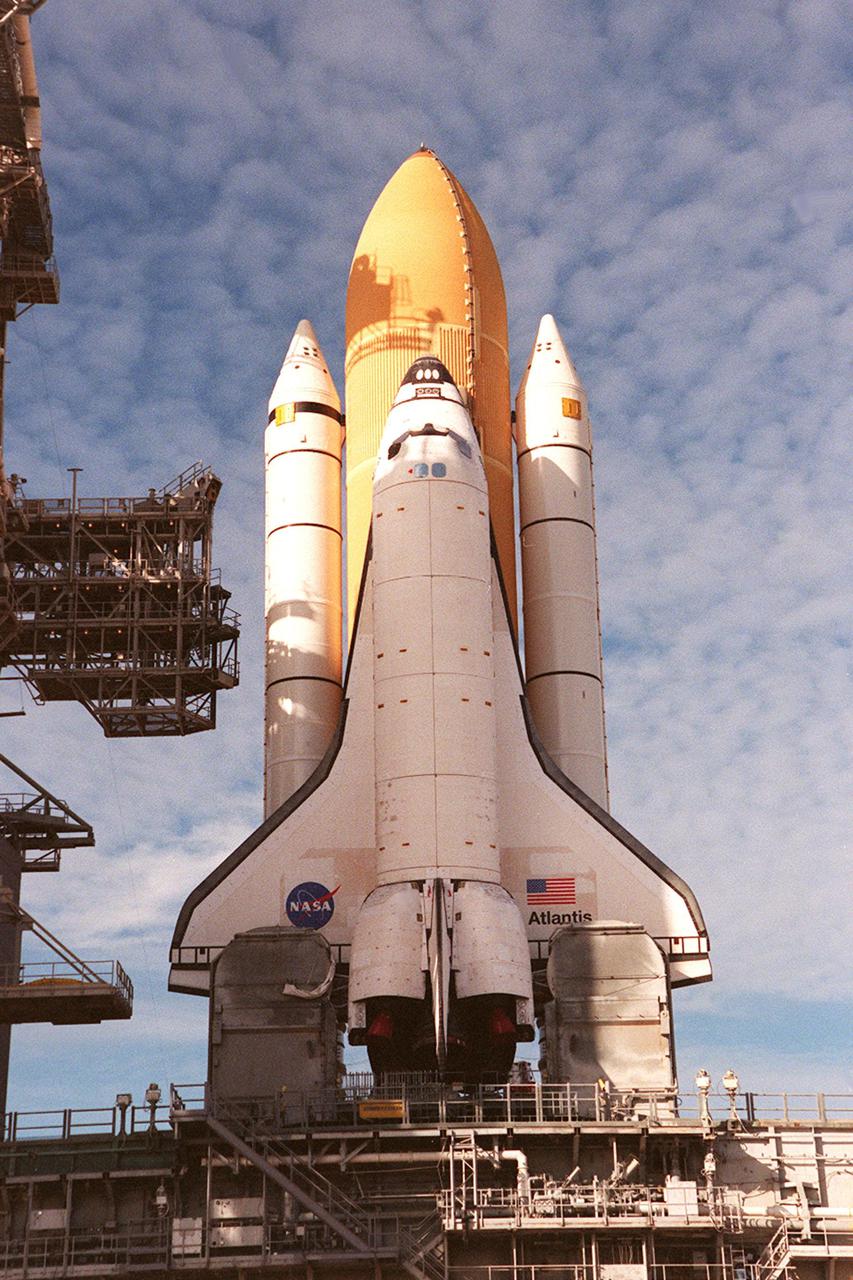

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Bright morning sun shines on Space Shuttle Atlantis as it sits on Launch Pad 39A. In front of the wings, on either side of the orbiter are tail service masts, which support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab has five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
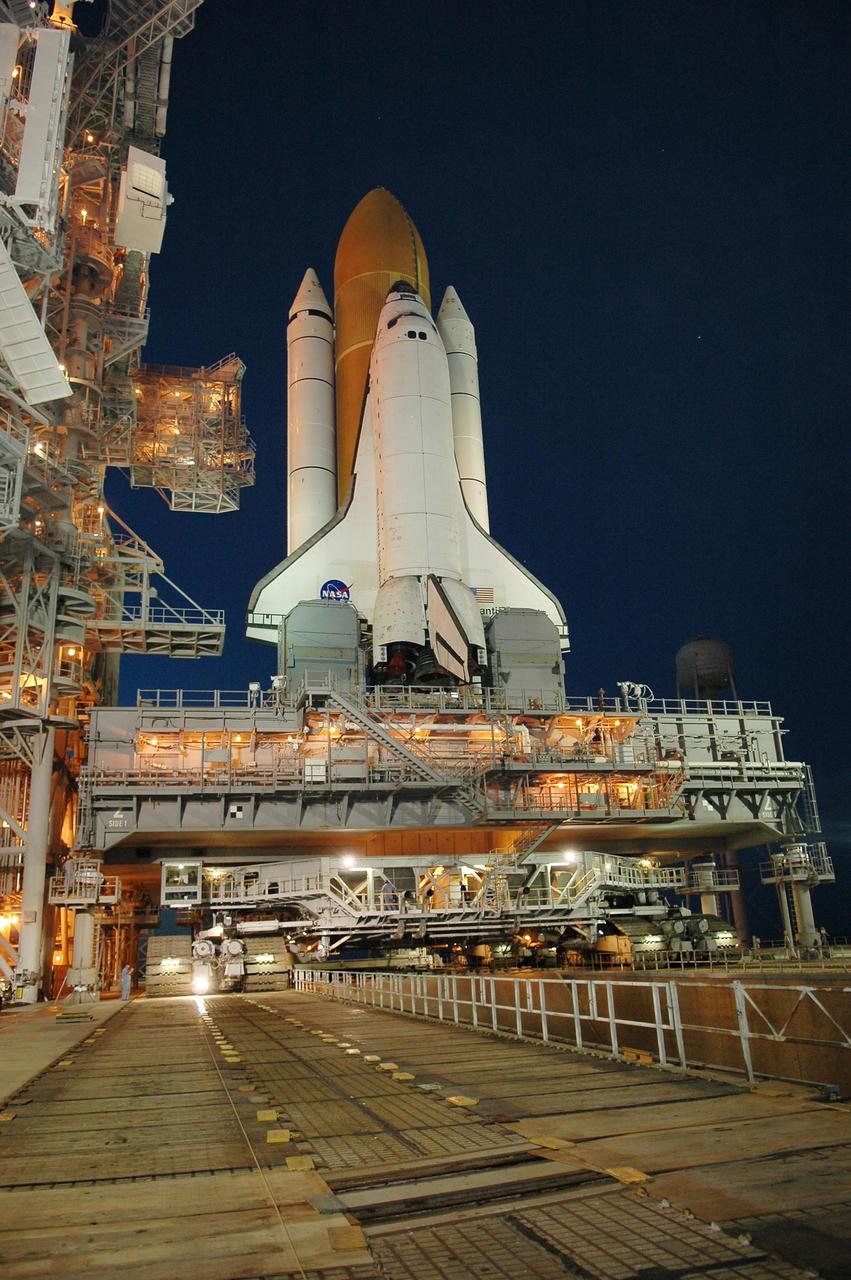

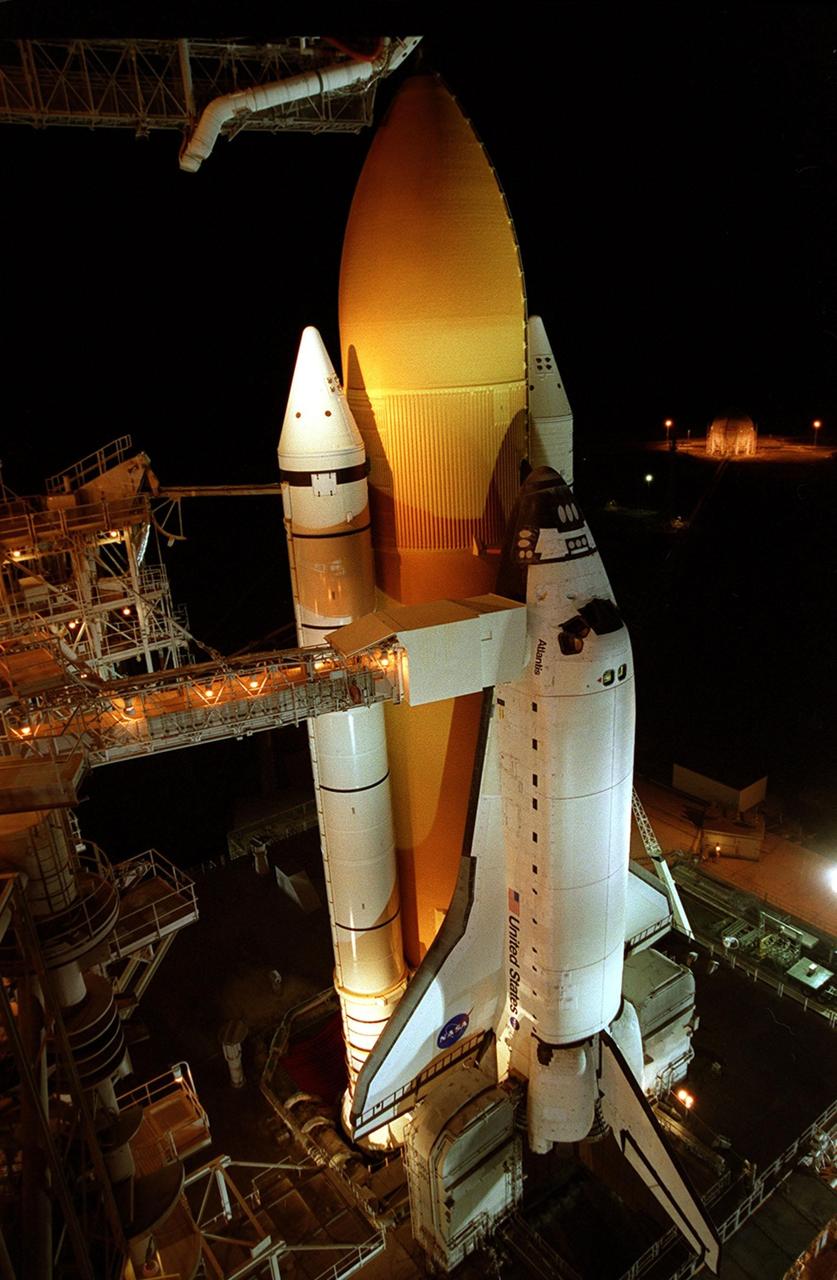
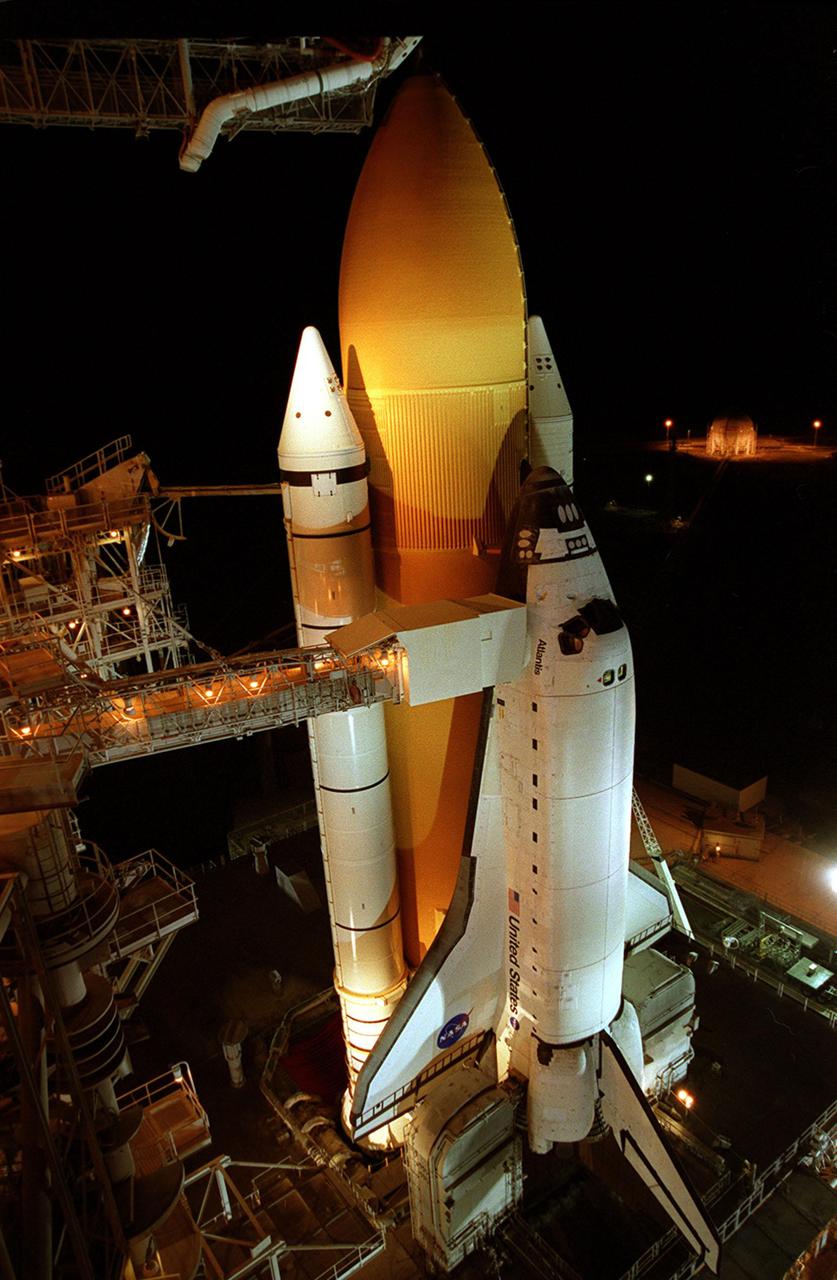
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After sunset, Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light from the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen on either side of Atlantis' engine nozzles are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. The shuttle had been moved off the launch pad due to concerns about the impact of Tropical Storm Ernesto, expected within 24 hours. The forecast of lesser winds expected from Ernesto and its projected direction convinced Launch Integration Manager LeRoy Cain and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach to return the shuttle to the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
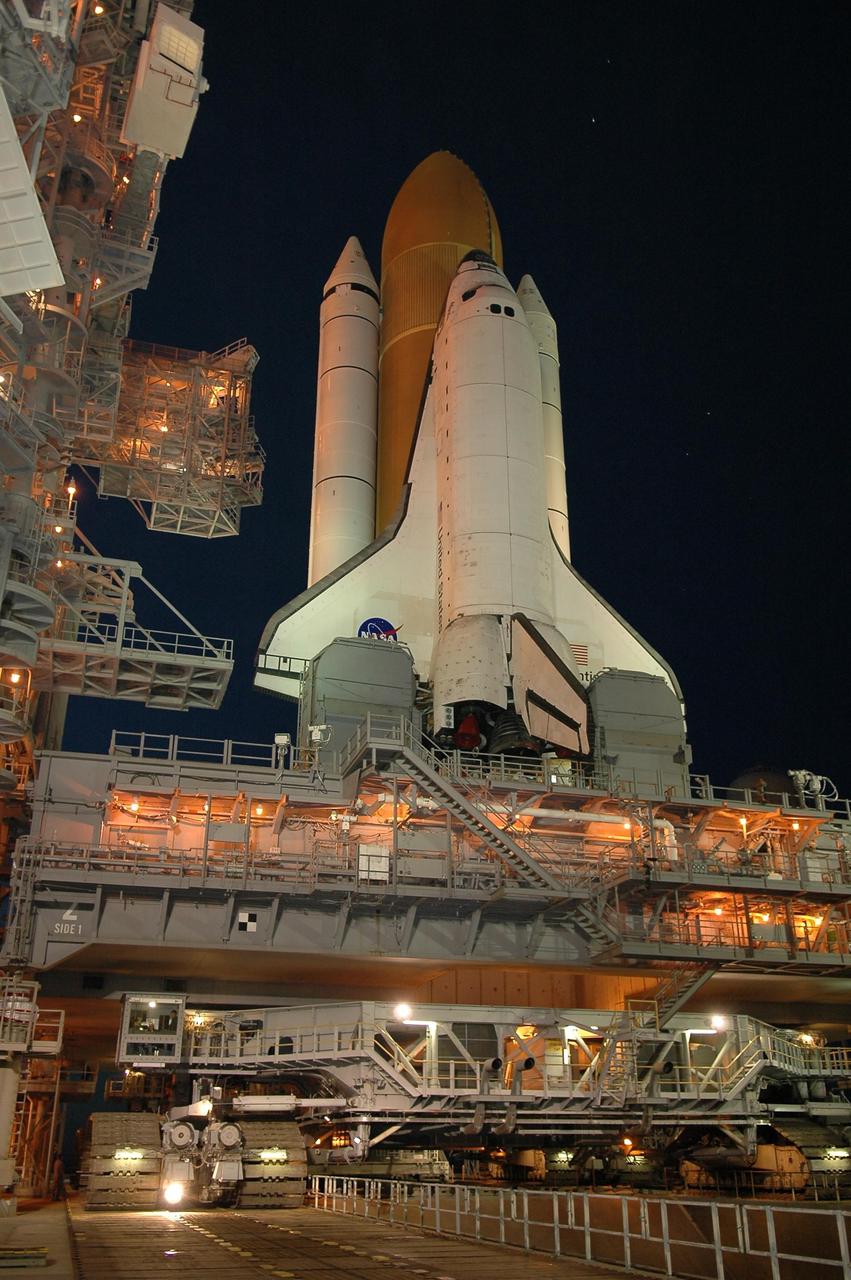

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After sunset, Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light from the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen on either side of Atlantis' engine nozzles are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Below the mobile launcher platform, on which Atlantis rests, is the crawler-transporter beginning to move away from the platform. The shuttle had been moved off the launch pad due to concerns about the impact of Tropical Storm Ernesto, expected within 24 hours. The forecast of lesser winds expected from Ernesto and its projected direction convinced Launch Integration Manager LeRoy Cain and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach to return the shuttle to the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
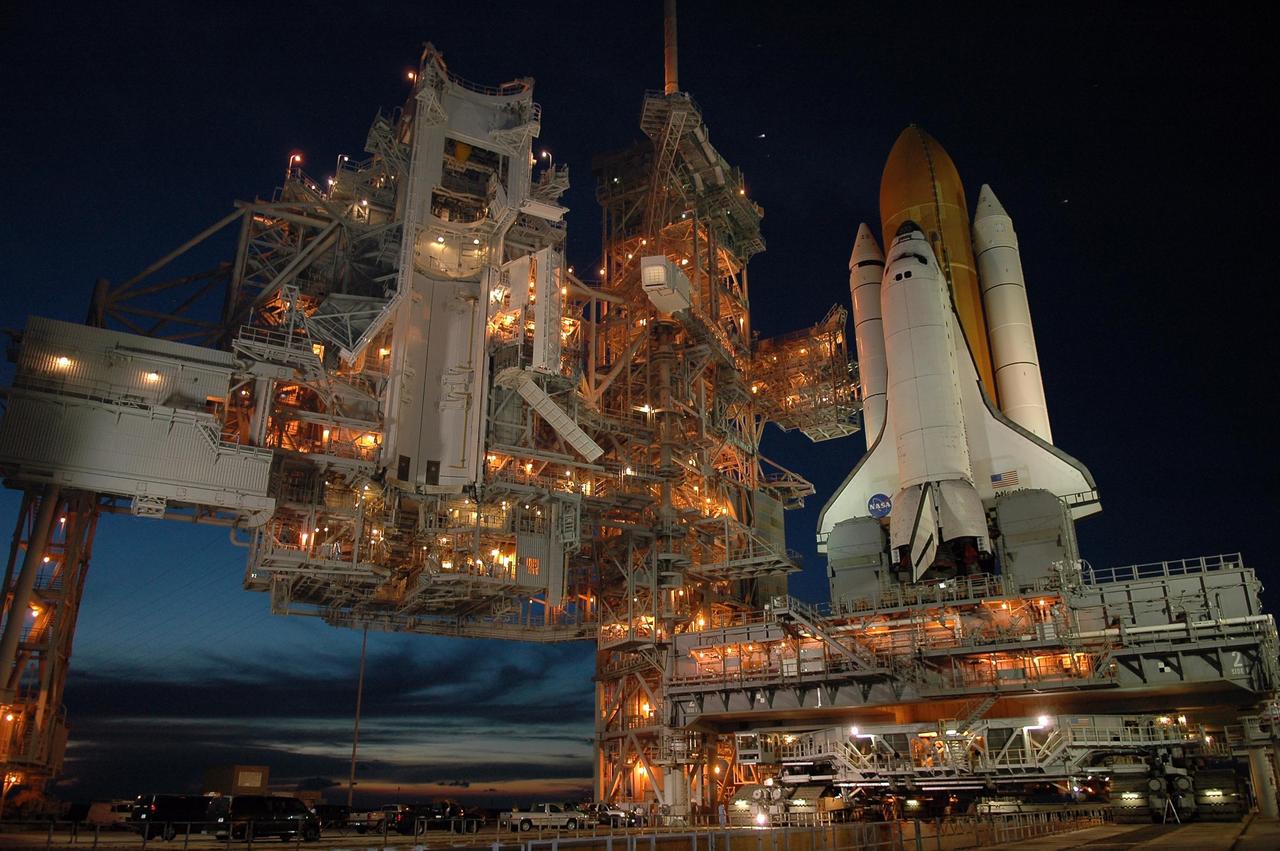

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After sunset, Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light from the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen on either side of Atlantis' engine nozzles are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Below the mobile launcher platform, on which Atlantis rests, is the crawler-transporter beginning to move away from the platform. The shuttle had been moved off the launch pad due to concerns about the impact of Tropical Storm Ernesto, expected within 24 hours. The forecast of lesser winds expected from Ernesto and its projected direction convinced Launch Integration Manager LeRoy Cain and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach to return the shuttle to the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
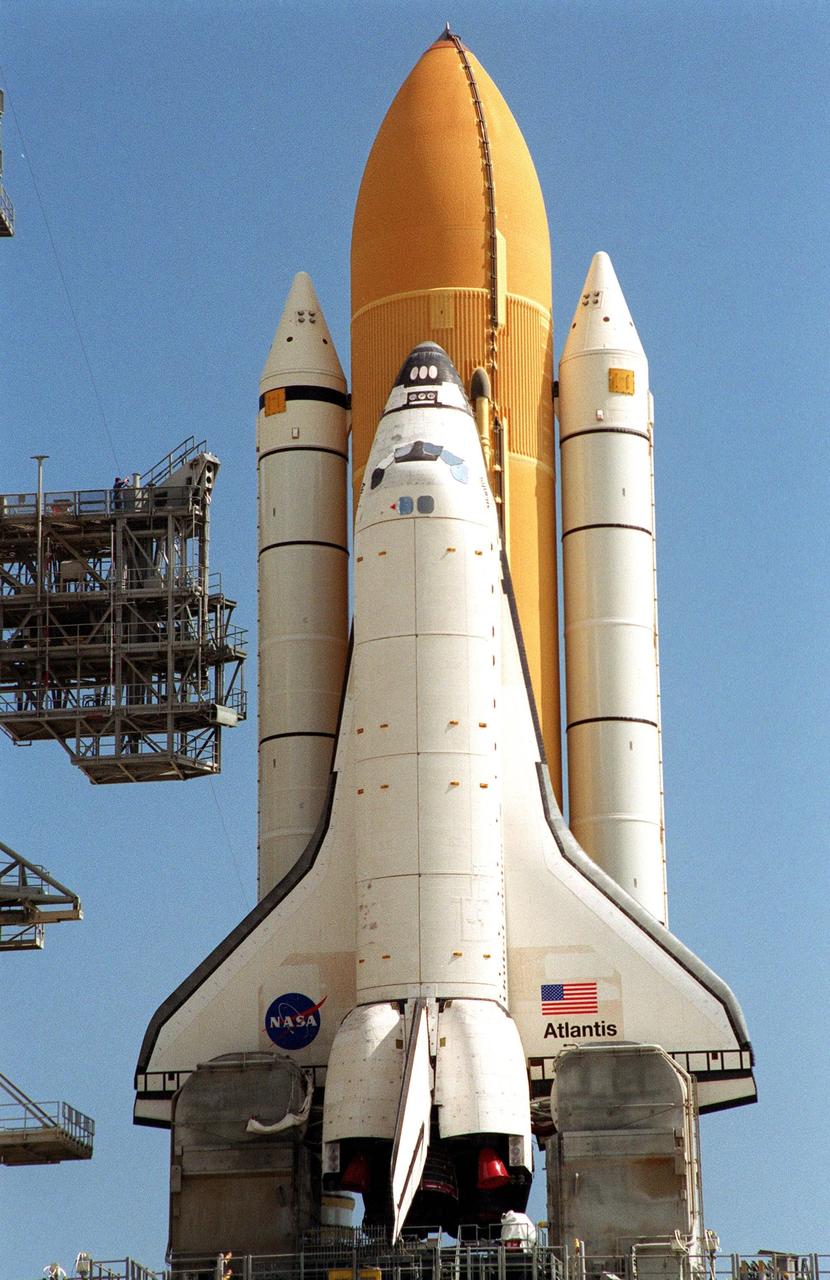

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis, with its orange external tank and white solid rocket boosters, sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
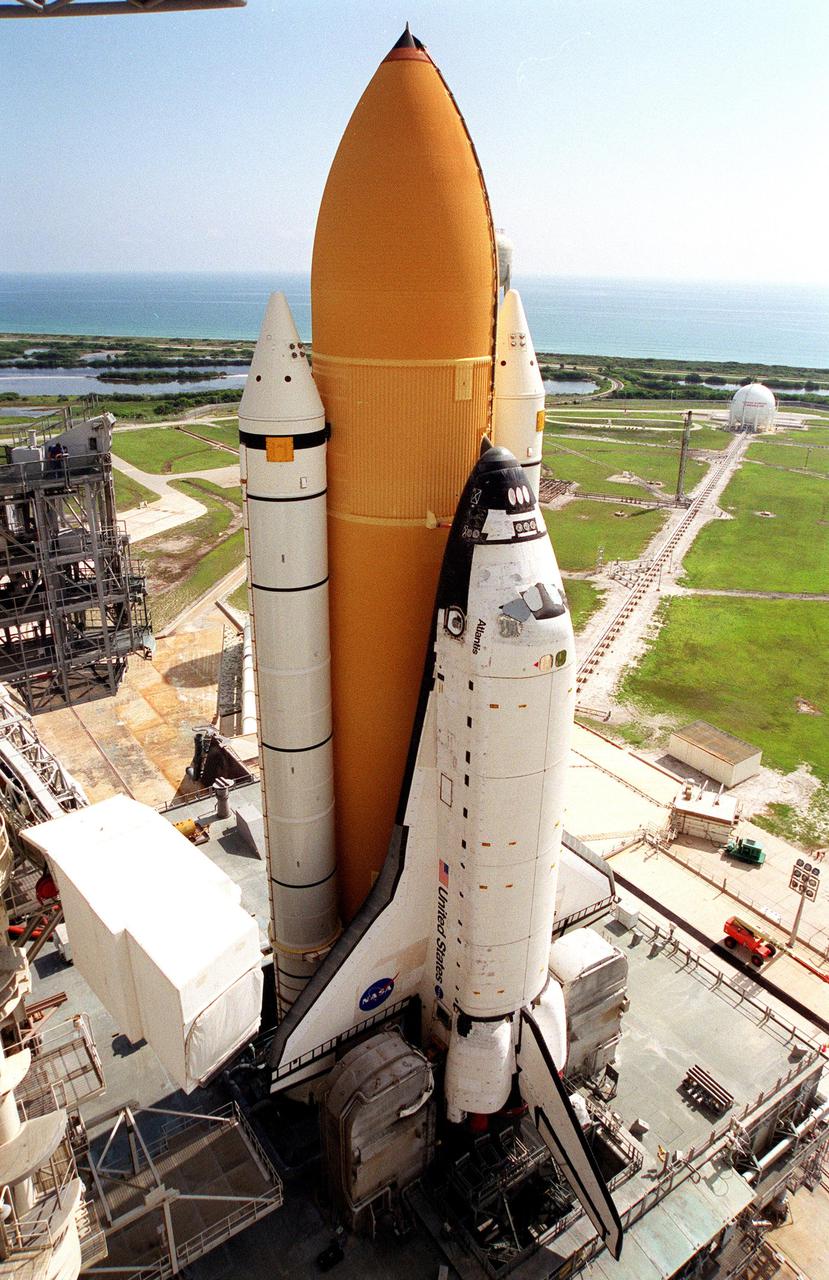

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. To the left of the orbiter is the white environmental chamber (white room) that mates with the orbiter and holds six persons. It provides access to the orbiter crew compartment. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
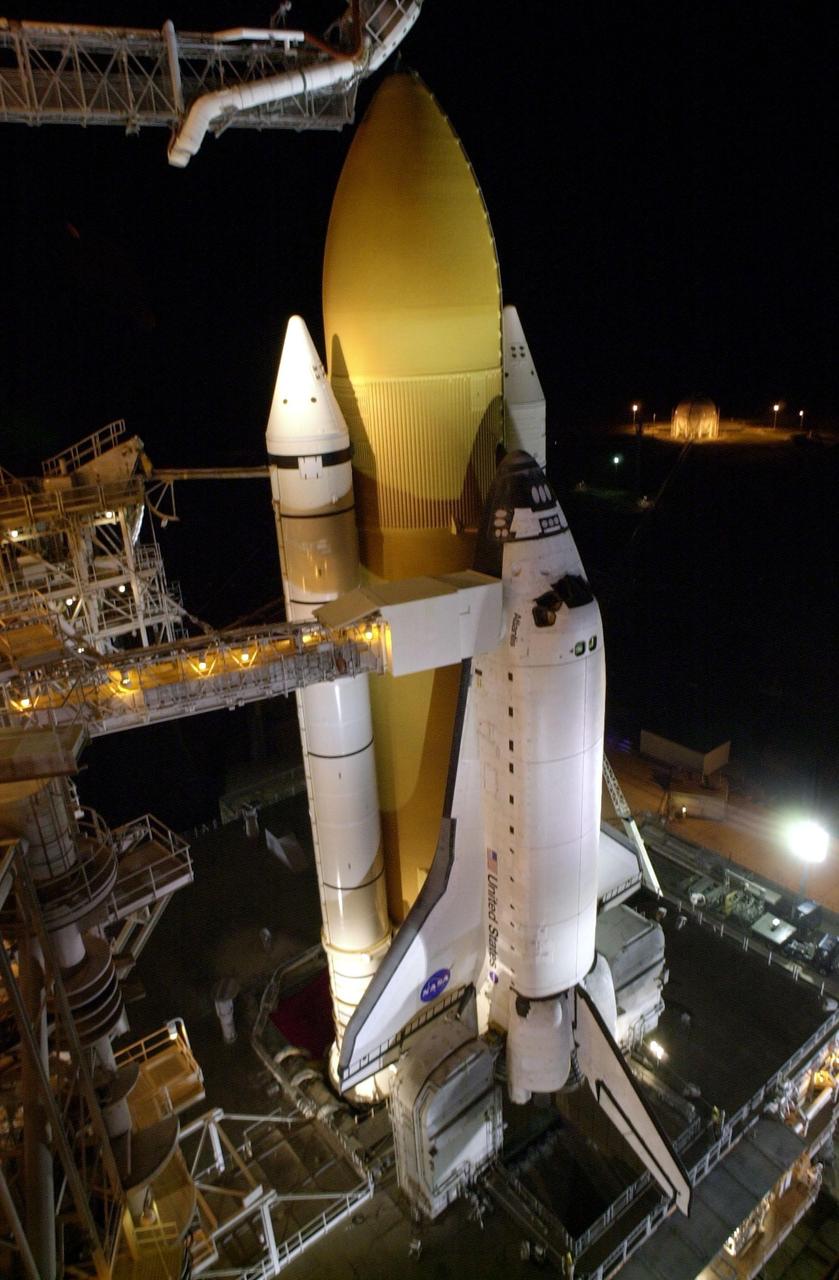

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This closeup reveals Space Shuttle Atlantis after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Below Atlantis, on either side of the tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
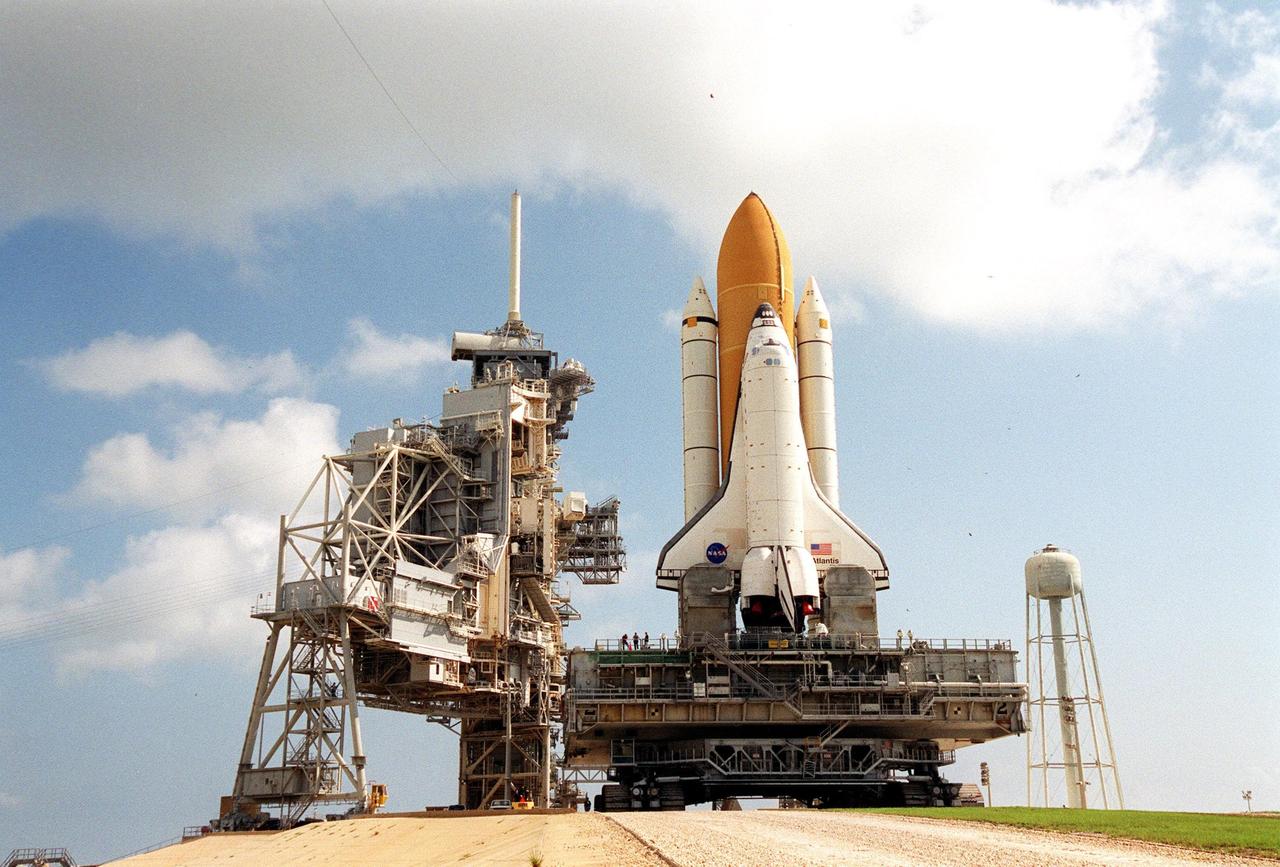

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis arrives on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
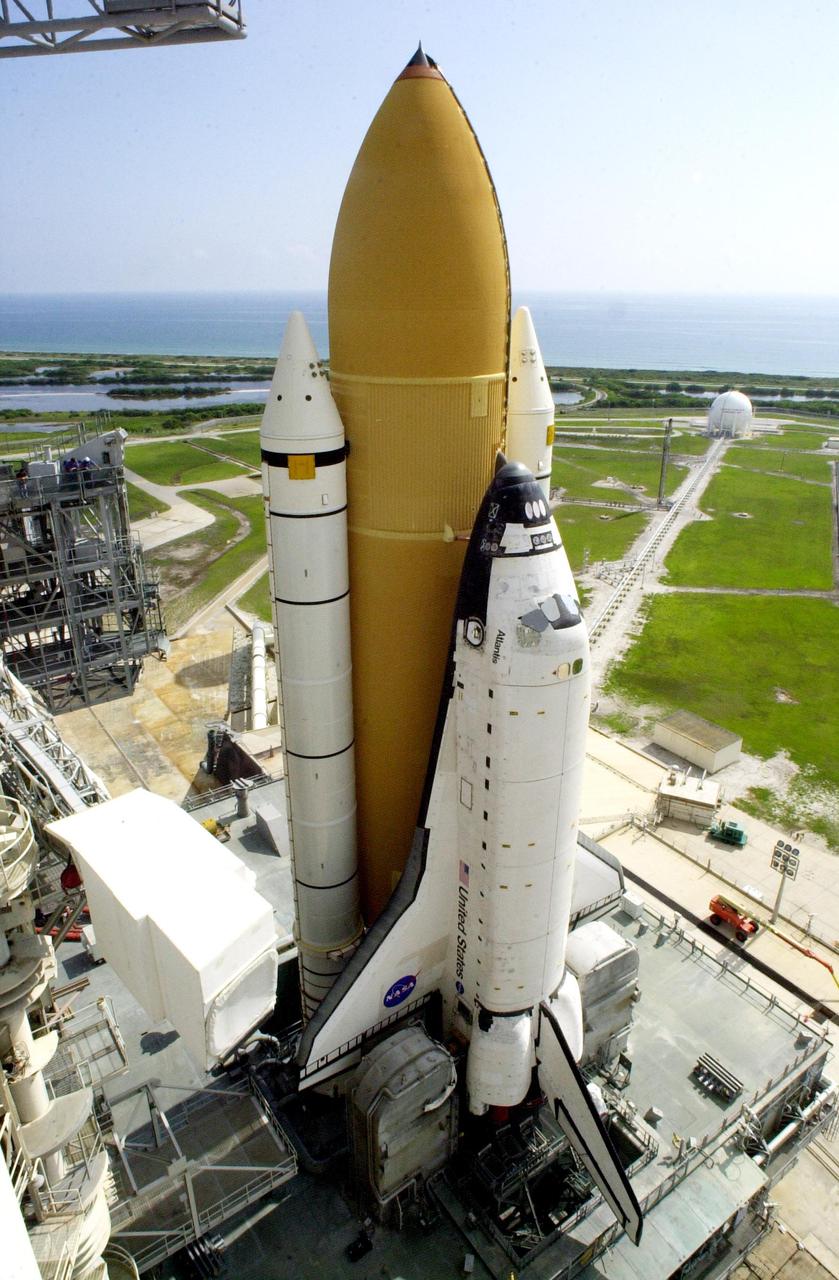

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. To the left of the orbiter is the white environmental chamber (white room) that mates with the orbiter and holds six persons. It provides access to the orbiter crew compartment. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
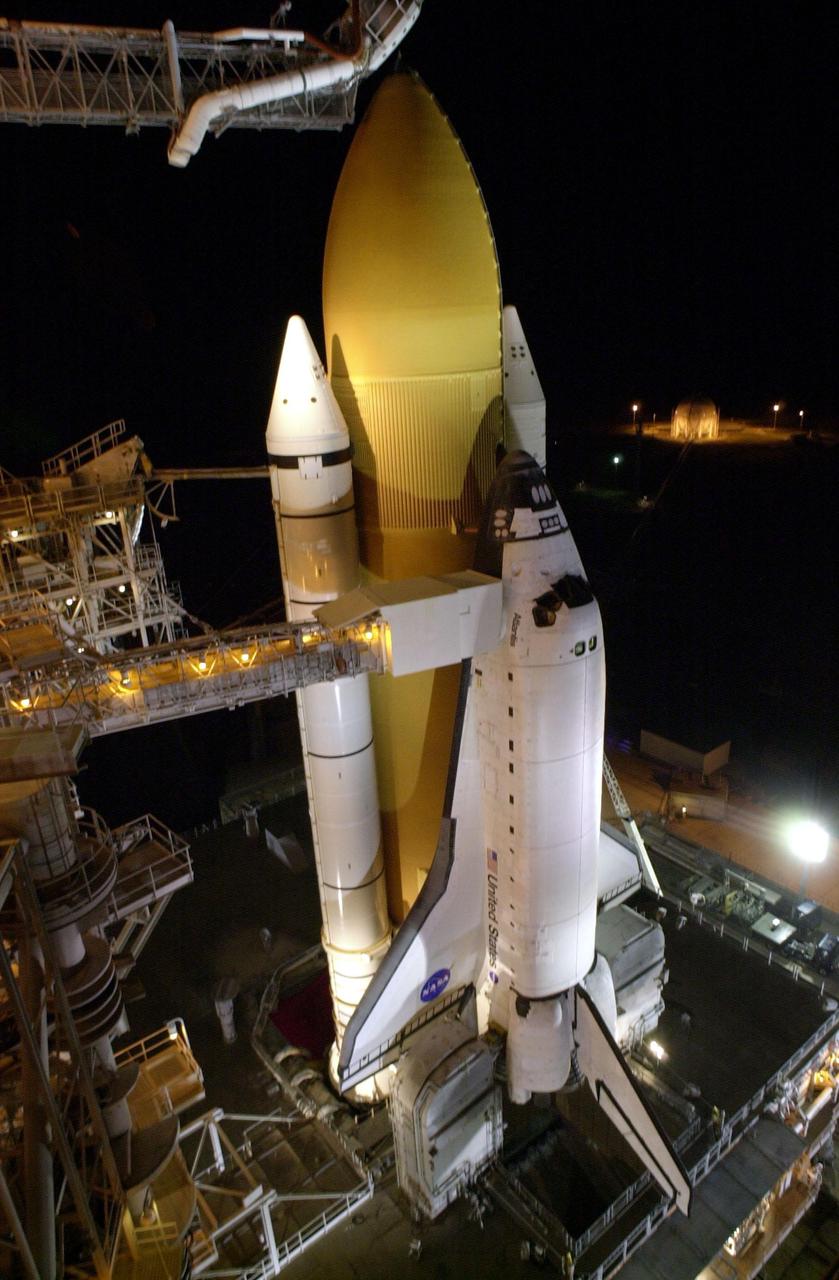

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- This closeup reveals Space Shuttle Atlantis after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Below Atlantis, on either side of the tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
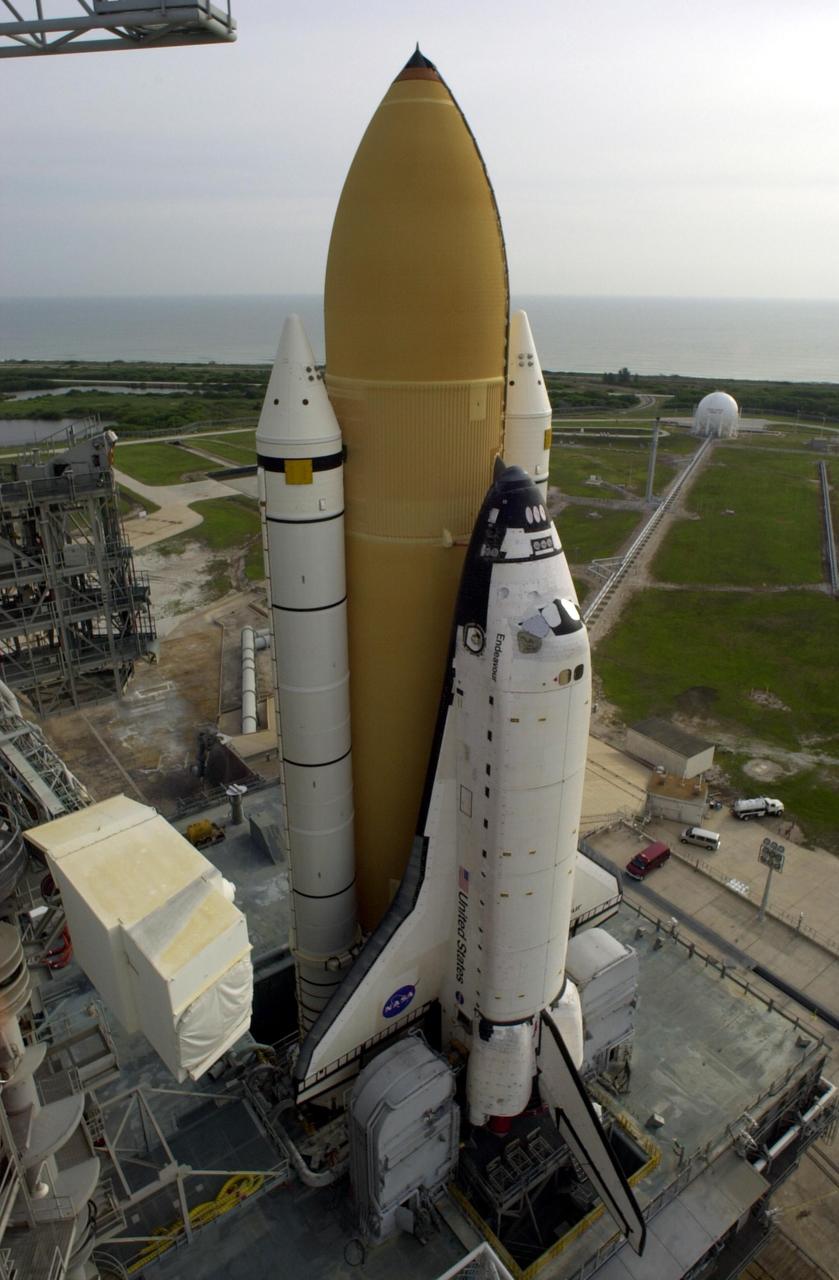

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Endeavour rests on Launch Pad 39A after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle comprises the orbiter, in front, and the taller orange external tank behind it flanked by twin solid rocket boosters. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform that straddles the flame trench below. On either side of Endeavour's tail and main engines are the tail service masts that support the fluid,, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxyen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. In the foreground, left, is the White Room, located at the end of the orbiter access arm. This environmentally controlled area provides access to the cockpit of the orbiter. Mission STS-111 is designated UF-2, the 14th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Endeavour's payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and Mobile Base System. The mission also will swap resident crews on the Station, carrying the Expedition 5 crew and returning to Earth Expedition 4. Liftoff of Endeavour is scheduled between 4 and 8 p.m. May 30, 2002
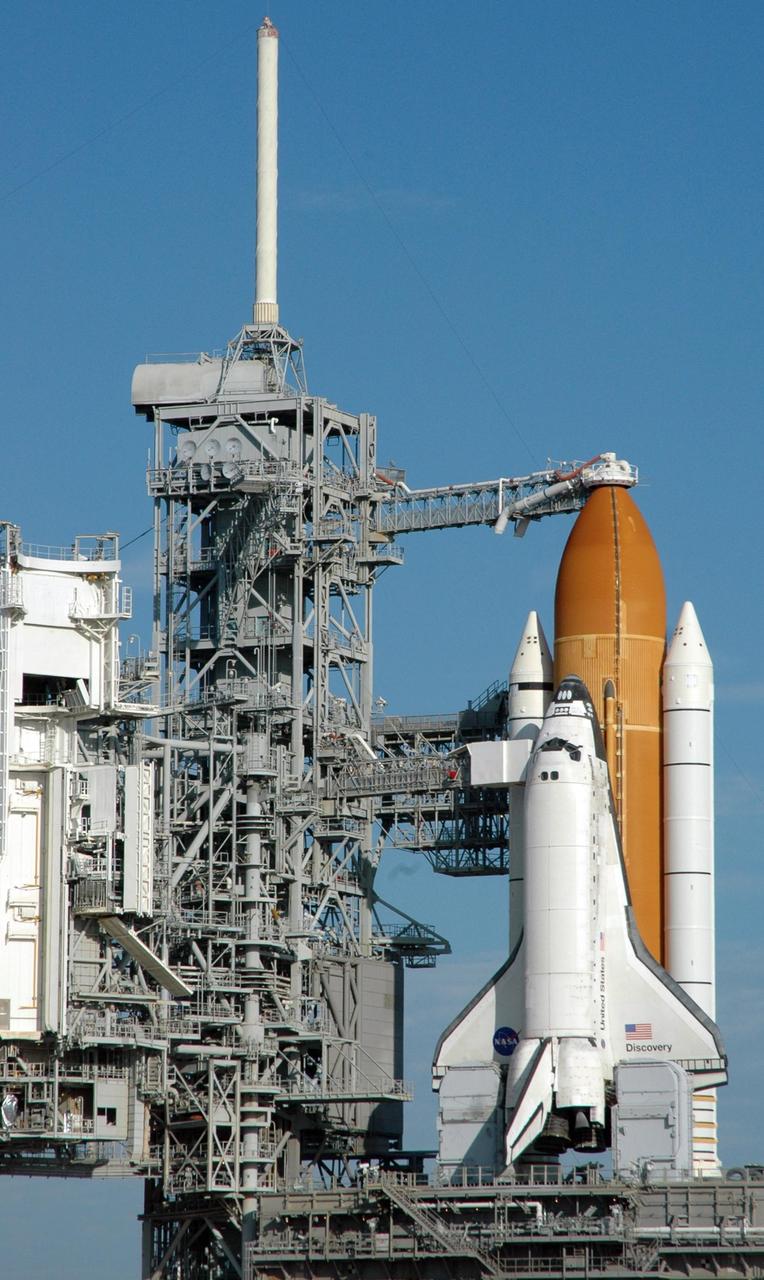

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Under a clear blue sky, Space Shuttle Discovery is ready for launch of mission STS-116 from Launch Pad 39B. Atop the fixed service structure at left looms the 80-foot-high lightning mast, part of the lightning protection system on the pad. Beneath Discovery's wings are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Seen above the golden external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the FSS. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below it, also extending toward Discovery from the FSS, is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. Discovery is scheduled to launch on mission STS-116 at 9:35 p.m. today. On the mission, the crew will deliver truss segment, P5, to the International Space Station and begin the intricate process of reconfiguring and redistributing the power generated by two pairs of U.S. solar arrays. The P5 will be mated to the P4 truss that was delivered and attached during the STS-115 mission in September. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
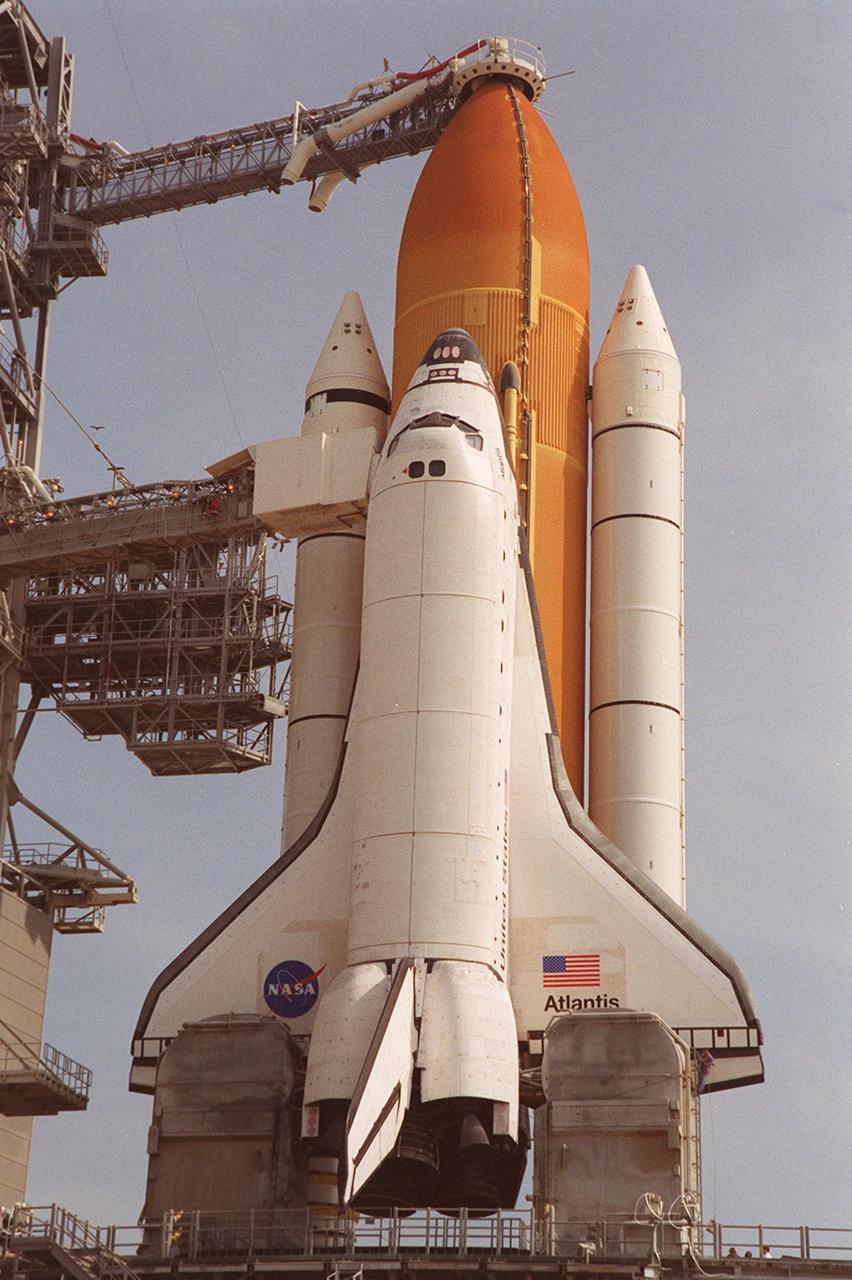
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After RSS rollback, Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready for final launch preparations. The orbiter access arm, with the environmentally controlled White Room at the end, is extended to the orbiter to allow entry into Atlantis. Above it is the gaseous oxygen vent arm with its characteristic “beanie cap” or hood placed over the external tank. The retractable arm and vent hood assembly allows gaseous oxygen vapors to vent away from the Space Shuttle vehicle. The vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boils off. At the lower end of Atlantis are the tail service masts, in front of either wing. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload