
NASA's Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator test vehicle attached to launch tower just prior to take off. LDSD completed its second flight test when the saucer-shaped craft splashed down safely Monday, June 8, 2015, in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of the Hawaiian island of Kauai. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19683
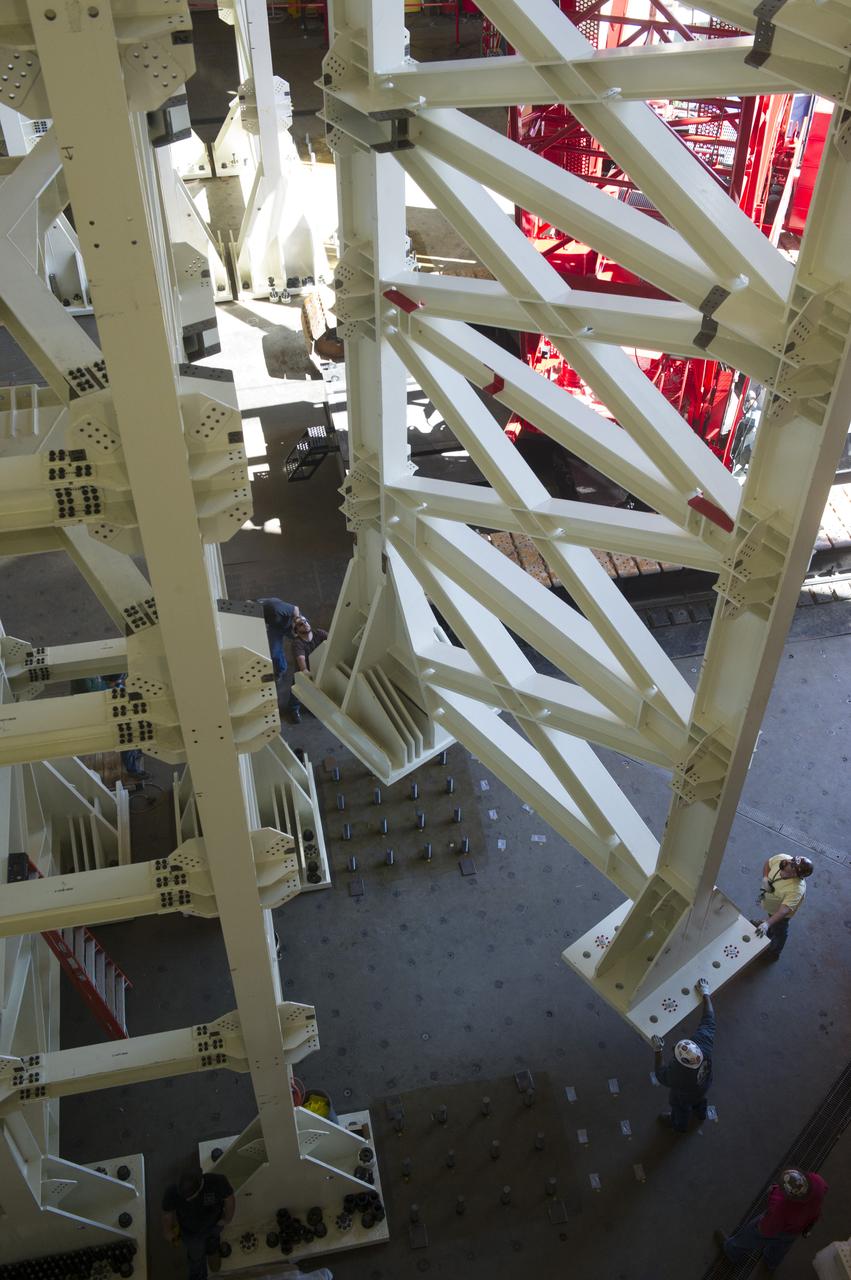
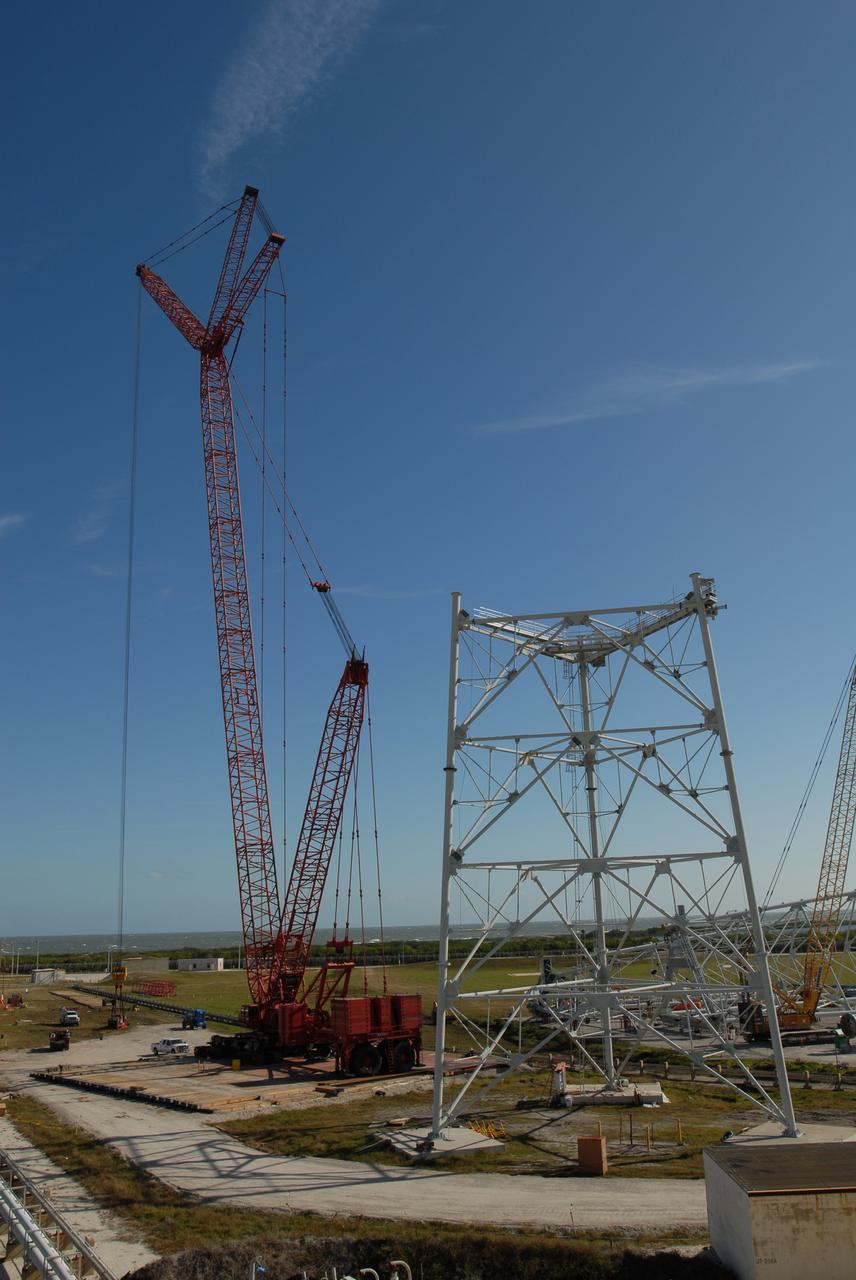
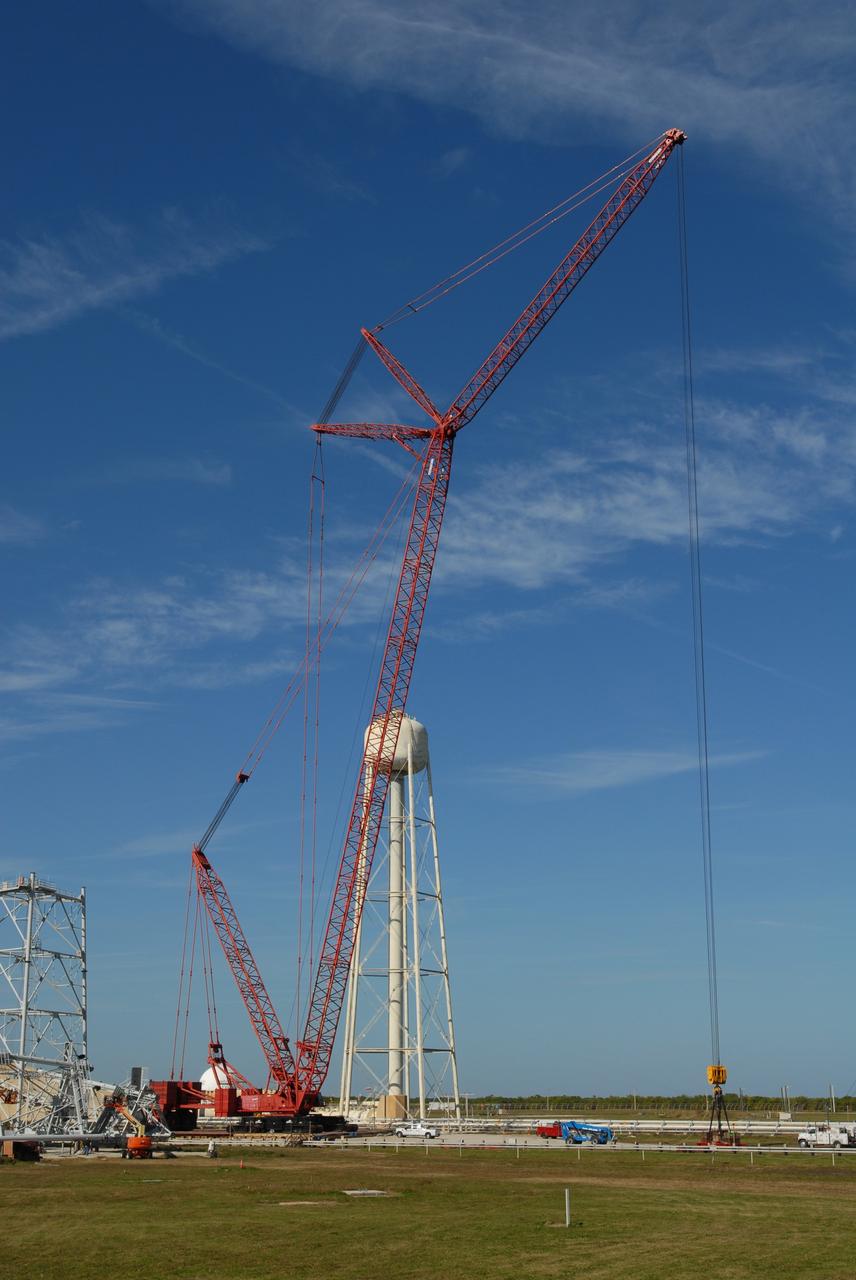
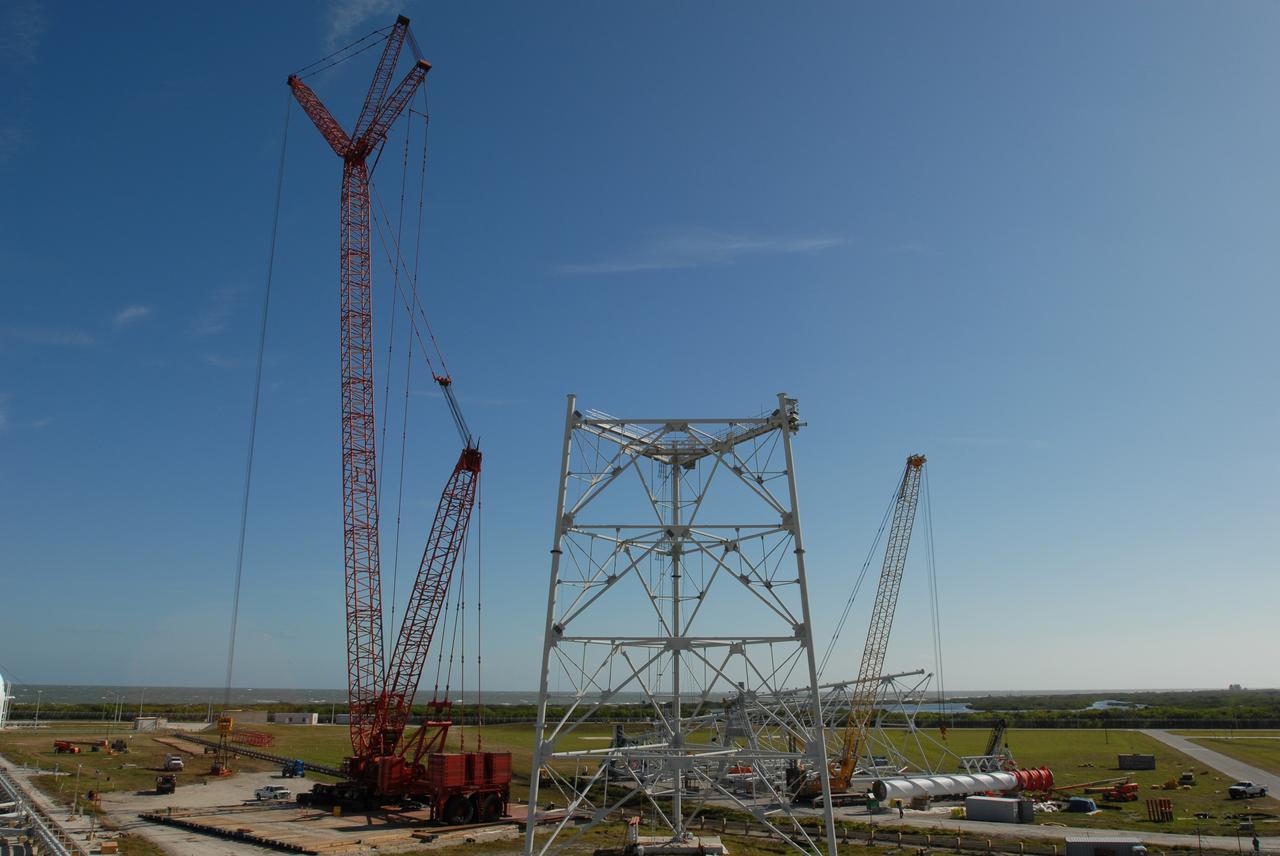
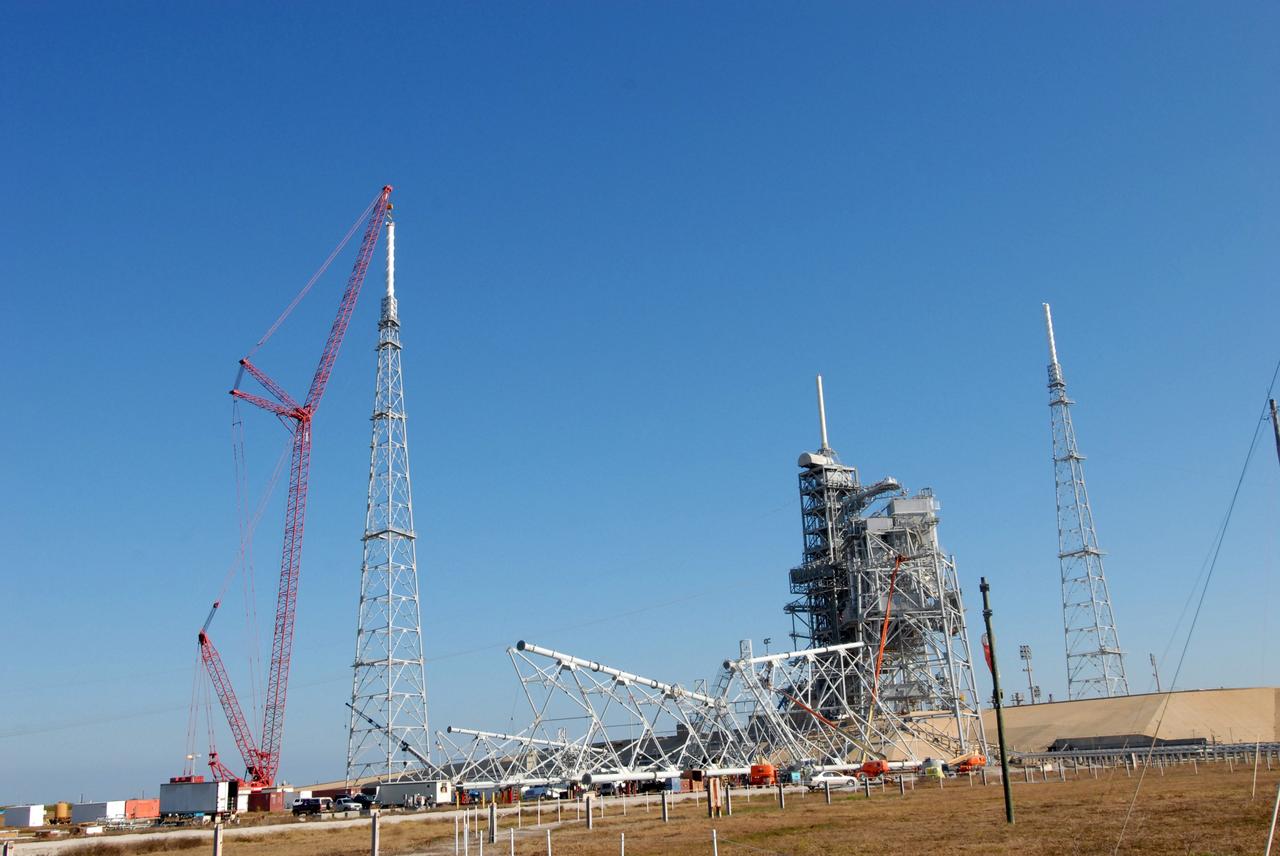
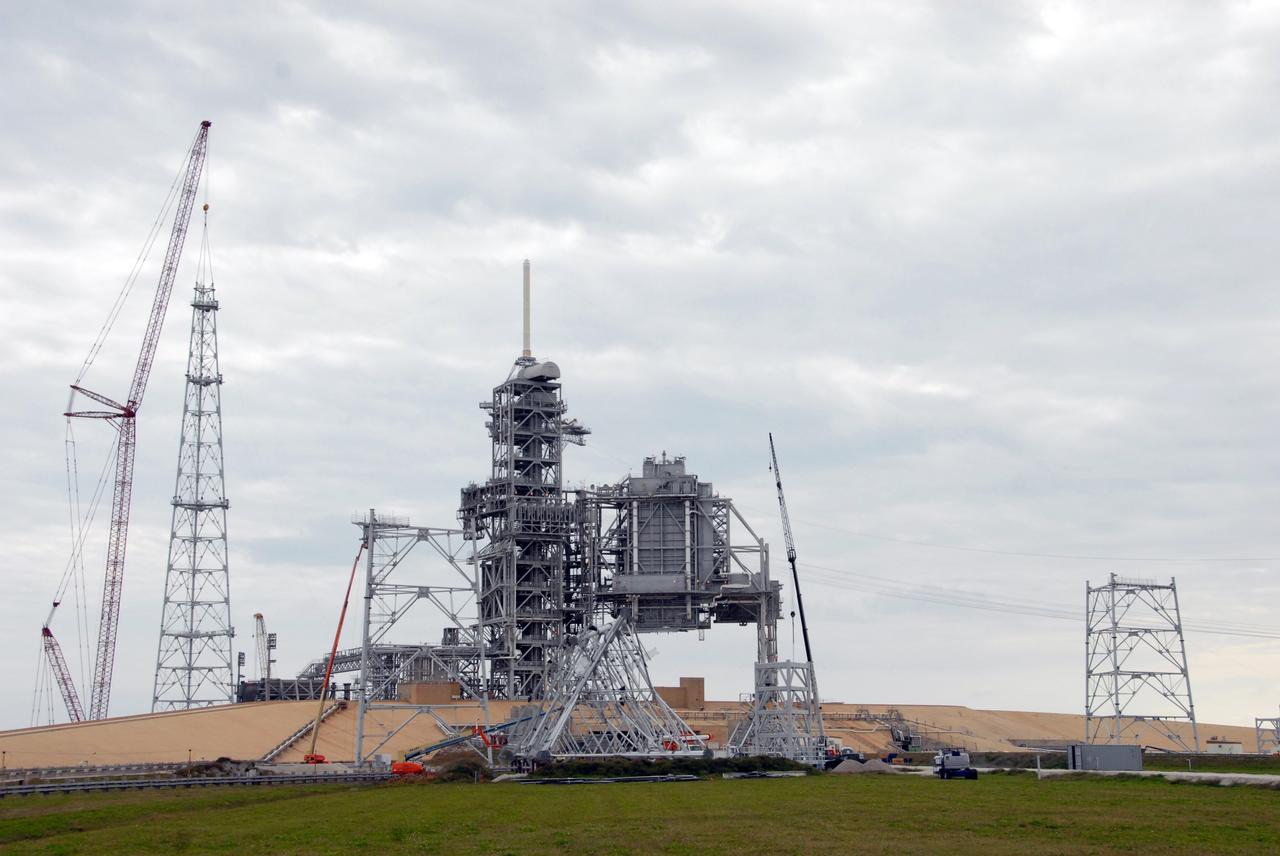
ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
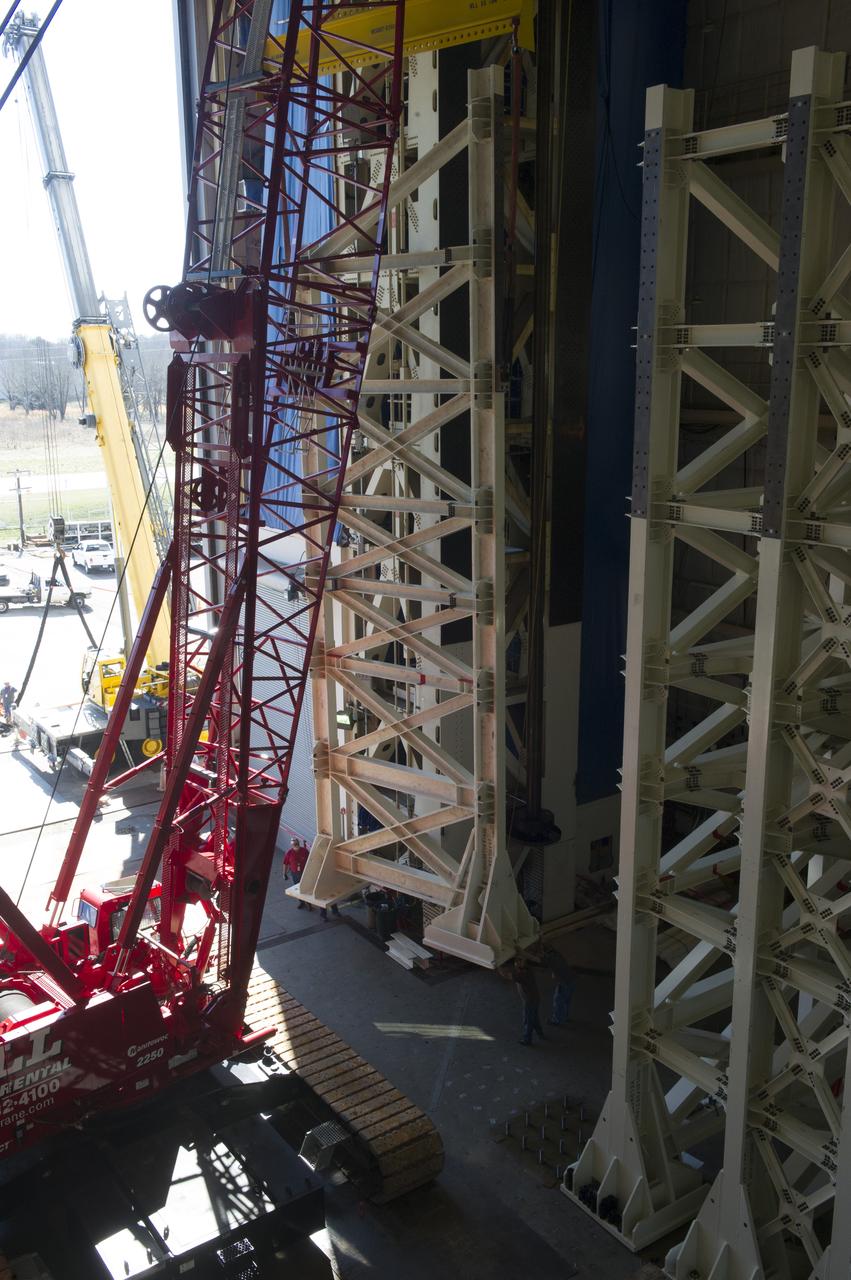

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
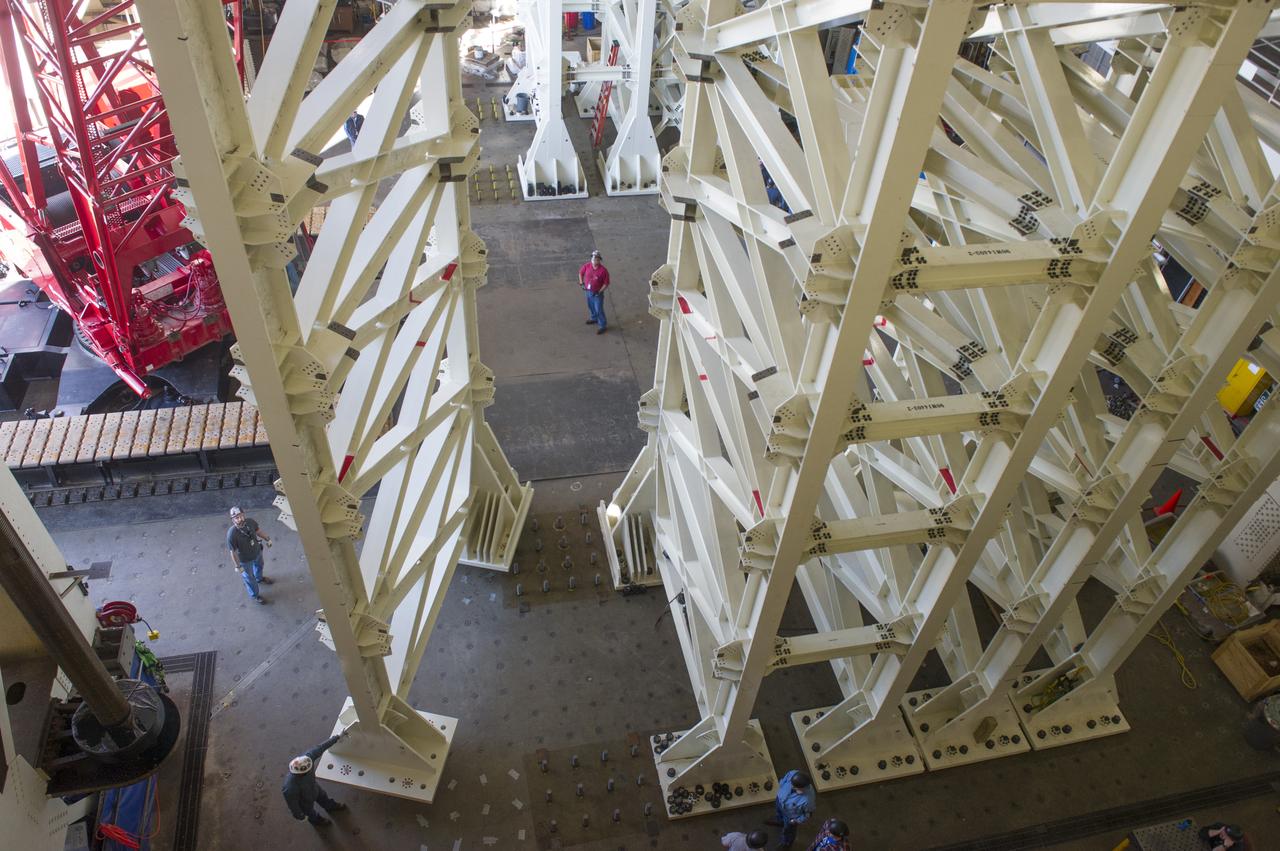

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
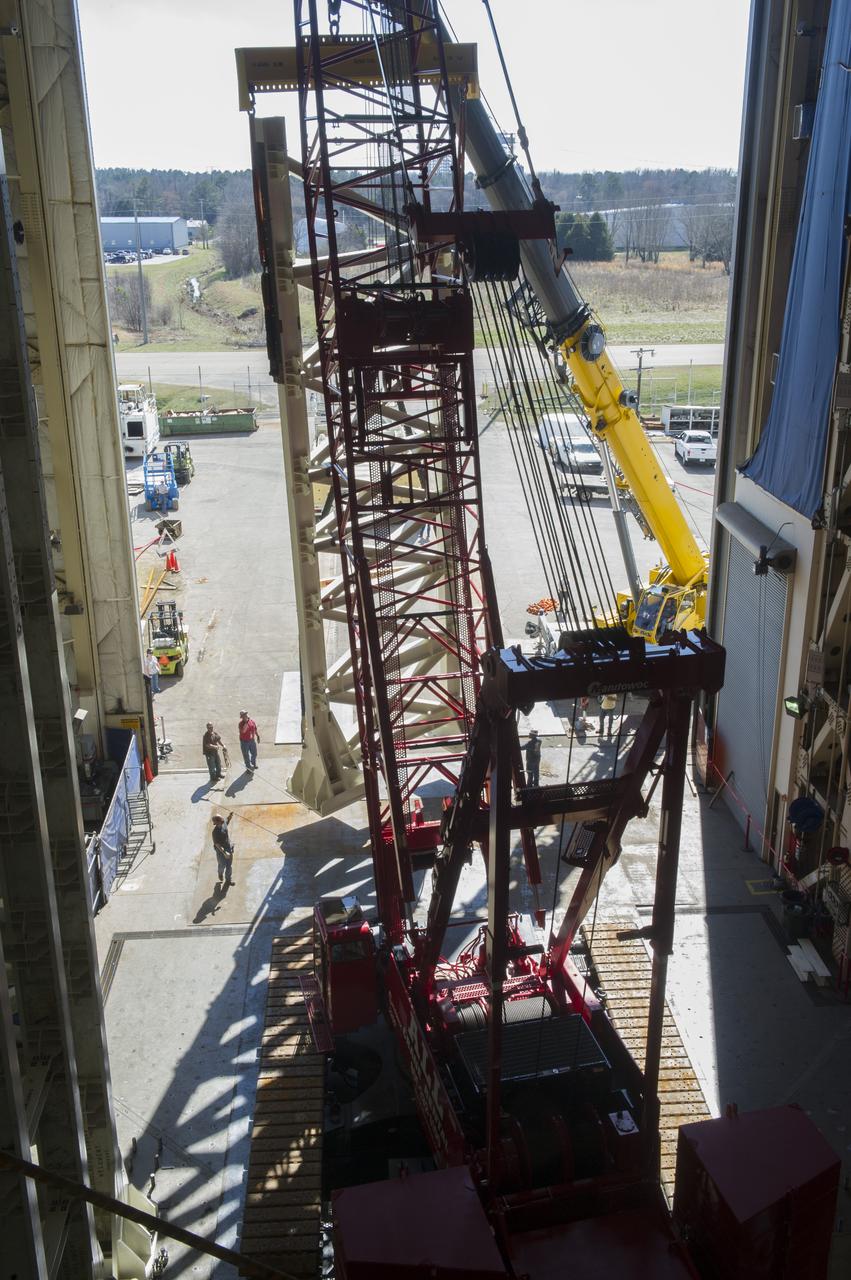

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
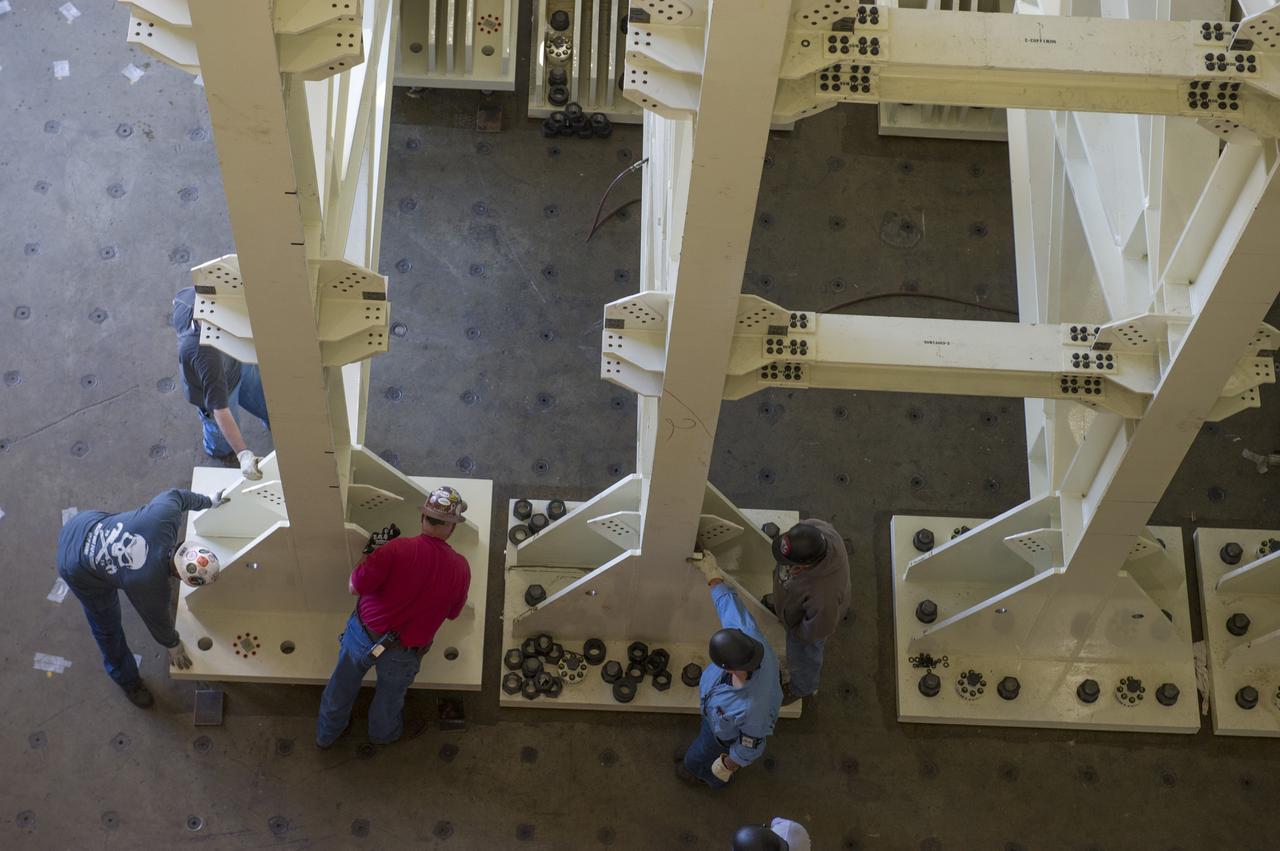

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
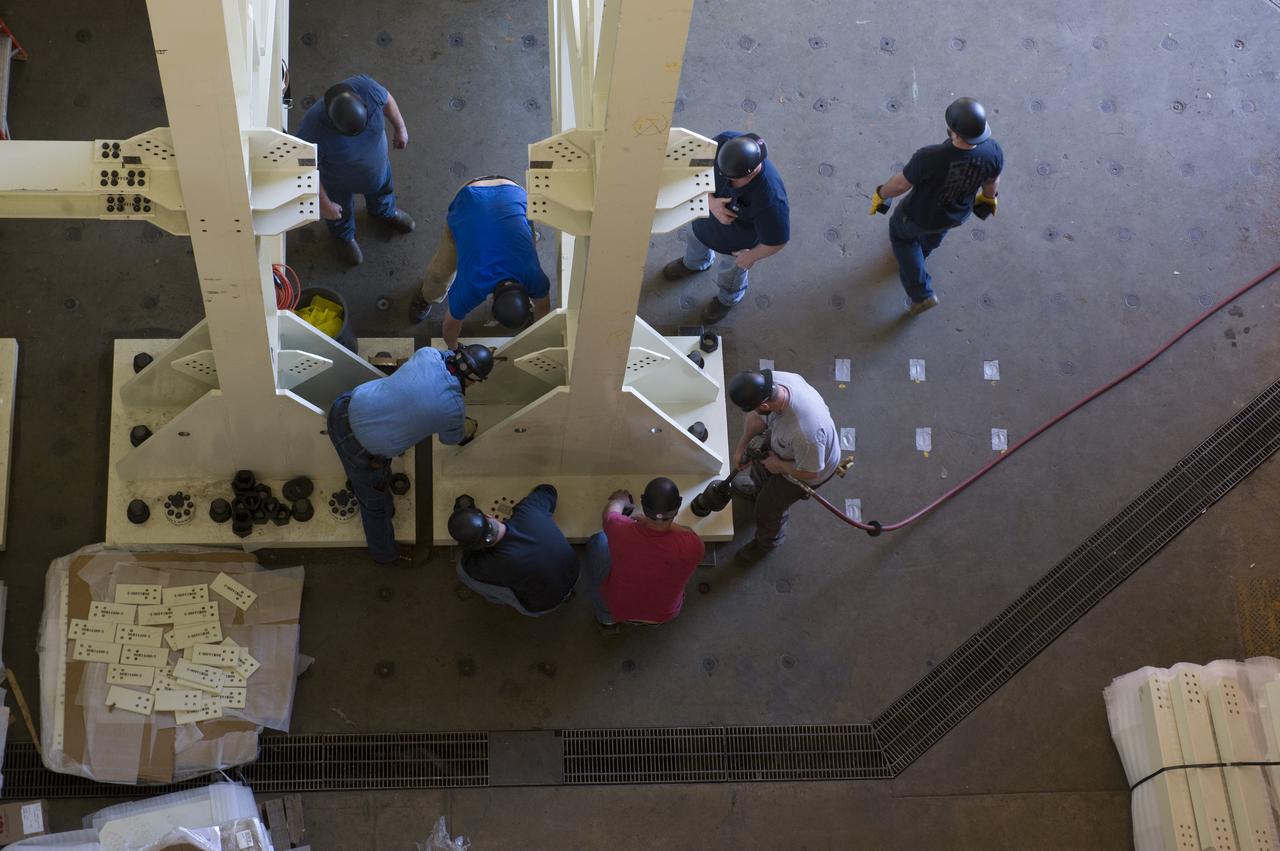

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
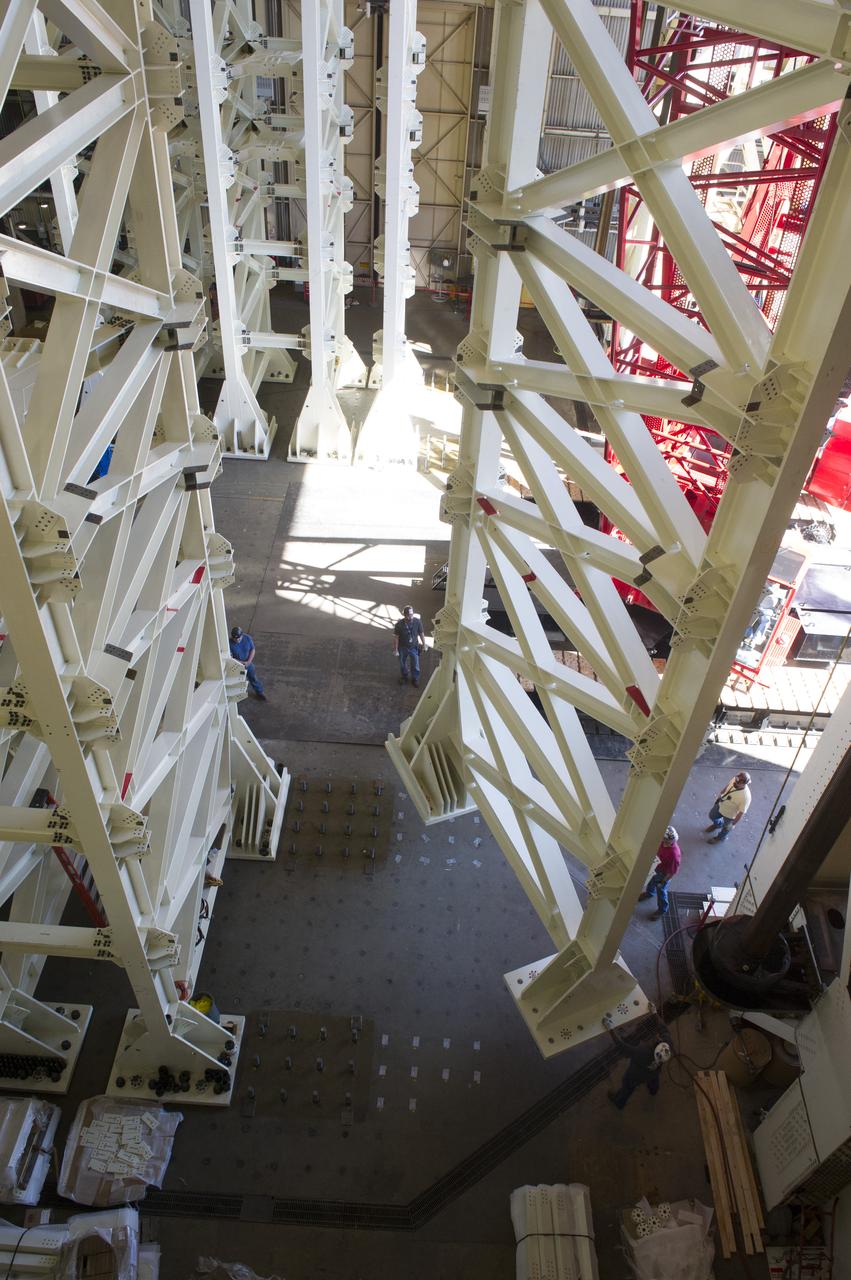

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
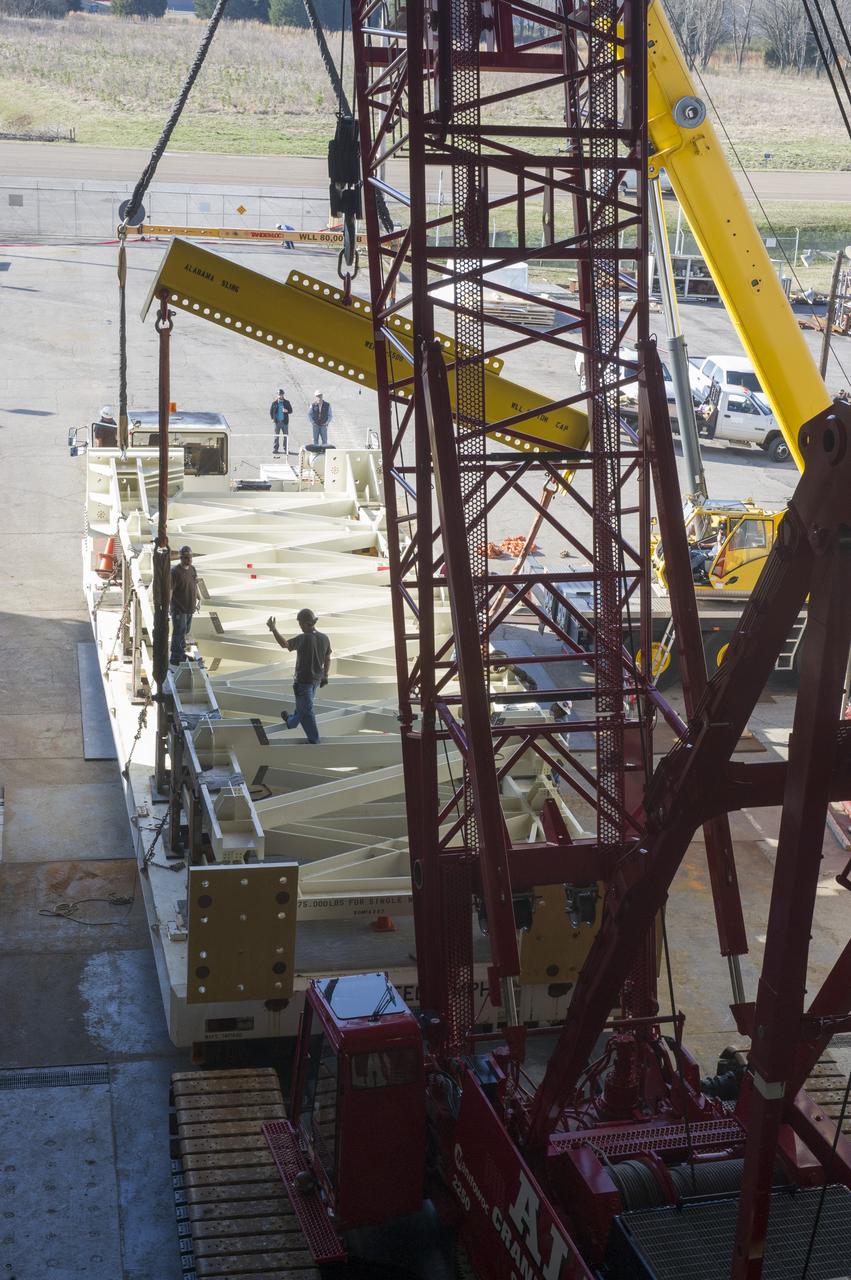

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
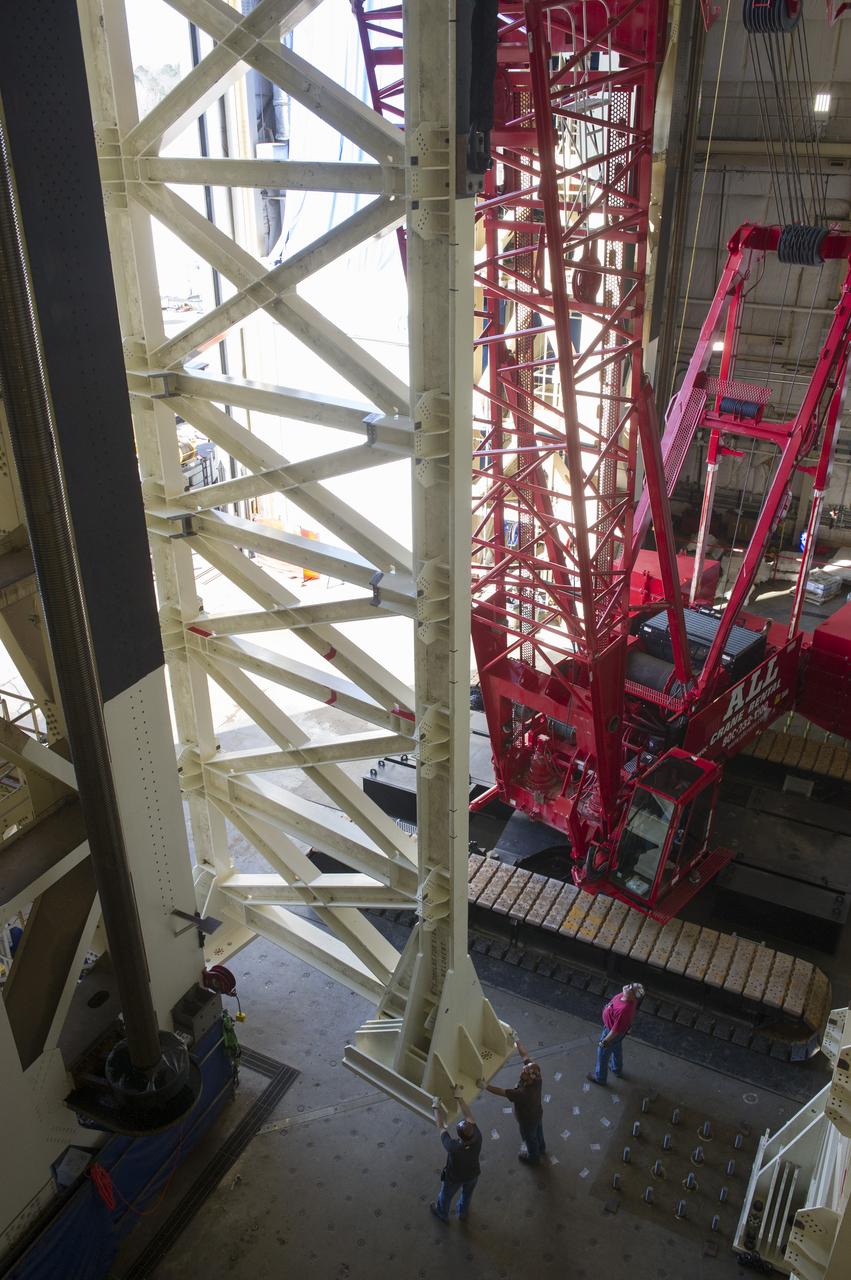

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
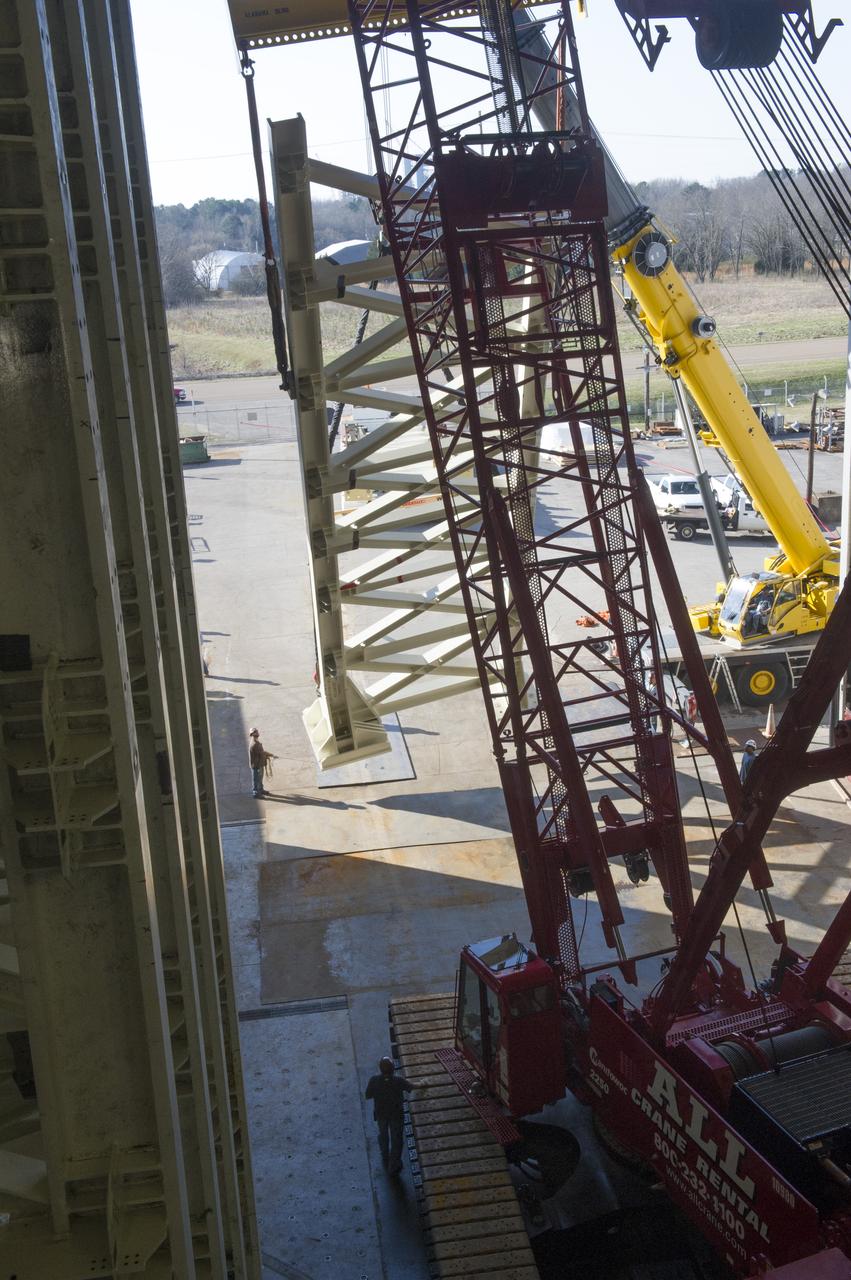

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
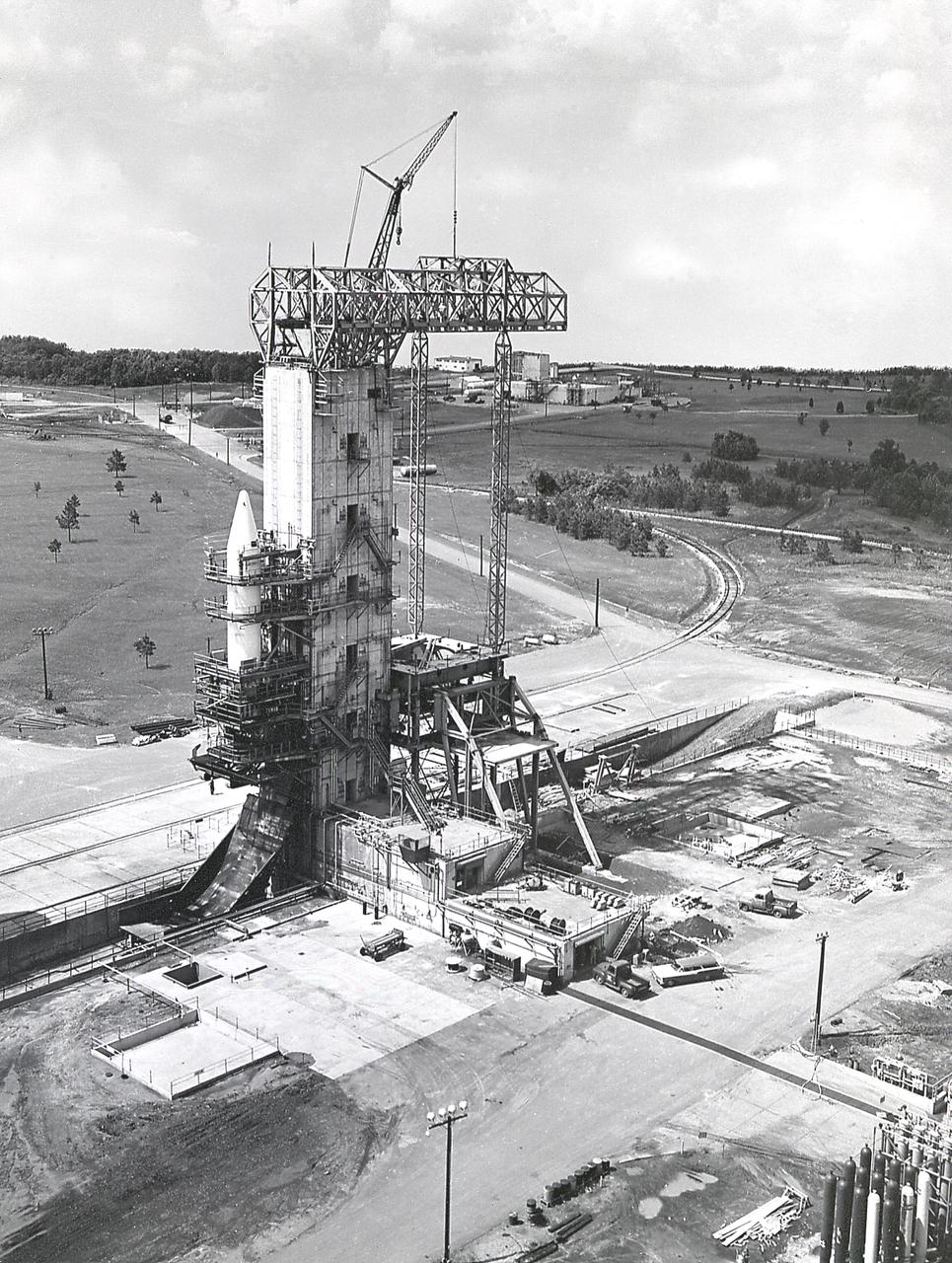
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test tower being modified for testing the Saturn booster.

A Mercury capsule is mounted inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel for a test of its escape tower rockets at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. In October 1959 NASA’s Space Task Group allocated several Project Mercury assignments to Lewis. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was quickly modified so that its 51-foot diameter western leg could be used as a test chamber. The final round of tests in the Altitude Wind Tunnel sought to determine if the smoke plume from the capsule’s escape tower rockets would shroud or compromise the spacecraft. The escape tower, a 10-foot steel rig with three small rockets, was attached to the nose of the Mercury capsule. It could be used to jettison the astronaut and capsule to safety in the event of a launch vehicle malfunction on the pad or at any point prior to separation from the booster. Once actuated, the escape rockets would fire, and the capsule would be ejected away from the booster. After the capsule reached its apex of about 2,500 feet, the tower, heatshield, retropackage, and antenna would be ejected and a drogue parachute would be released. Flight tests of the escape system were performed at Wallops Island as part of the series of Little Joe launches. Although the escape rockets fired prematurely on Little Joe’s first attempt in August 1959, the January 1960 follow-up was successful.
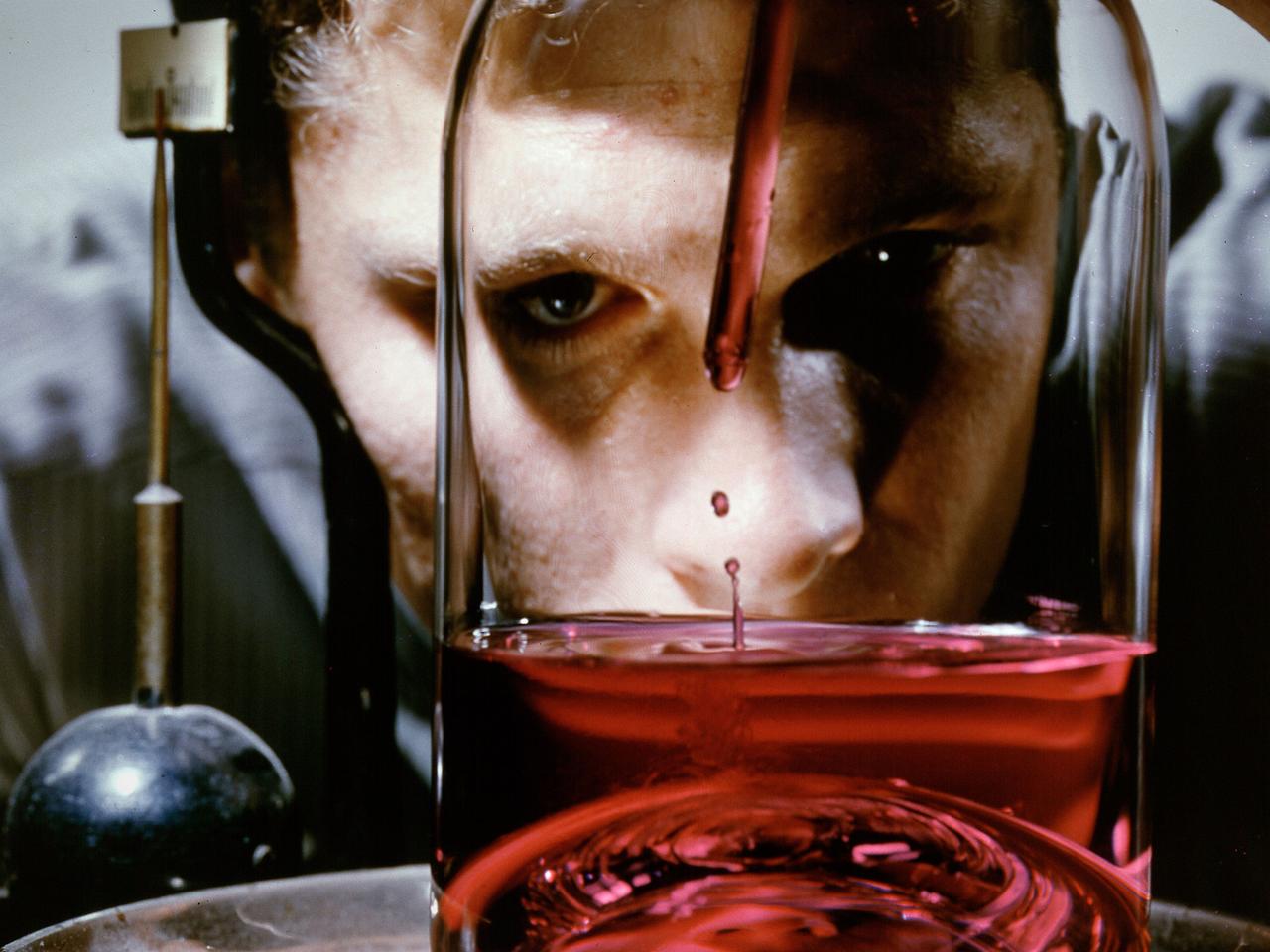

A researcher fills a small container used to represent a liquid hydrogen tank in preparation for a microgravity test in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. For over a decade, NASA Lewis endeavored to make liquid hydrogen a viable propellant. Hydrogen’s light weight and high energy made it very appealing for rocket propulsion. One of the unknowns at the time was the behavior of fluids in the microgravity of space. Rocket designers needed to know where the propellant would be inside the fuel tank in order to pump it to the engine. NASA Lewis utilized sounding rockets, research aircraft, and the 2.2 Second Drop Tower to study liquids in microgravity. The drop tower, originally built as a fuel distillation tower in 1948, descended into a steep ravine. By early 1961 the facility was converted into an eight-floor, 100-foot tower connected to a shop and laboratory space. Small glass tanks, like this one, were installed in experiment carts with cameras to film the liquid’s behavior during freefall. Thousands of drop tower tests in the early 1960s provided an increased understanding of low-gravity processes and phenomena. The tower only afforded a relatively short experiment time but was sufficient enough that the research could be expanded upon using longer duration freefalls on sounding rockets or aircraft. The results of the early experimental fluid studies verified predictions made by Lewis researchers that the total surface energy would be minimized in microgravity.
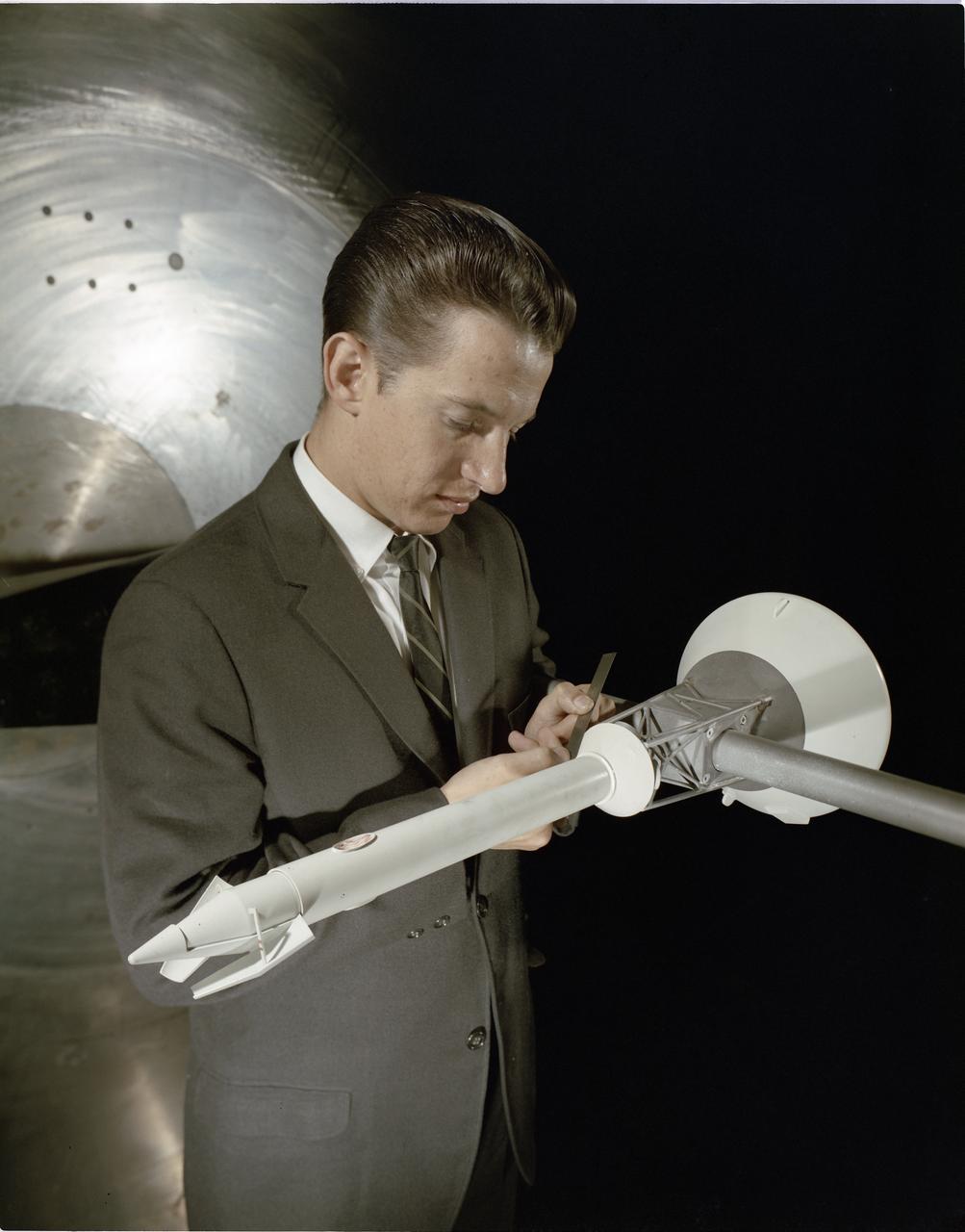

APOLLO STABILITY TEST IN THE 8X6 FOOT WIND TUNNEL - MODEL IS SHOWN WITH MODULE TOWER AND CANARDS
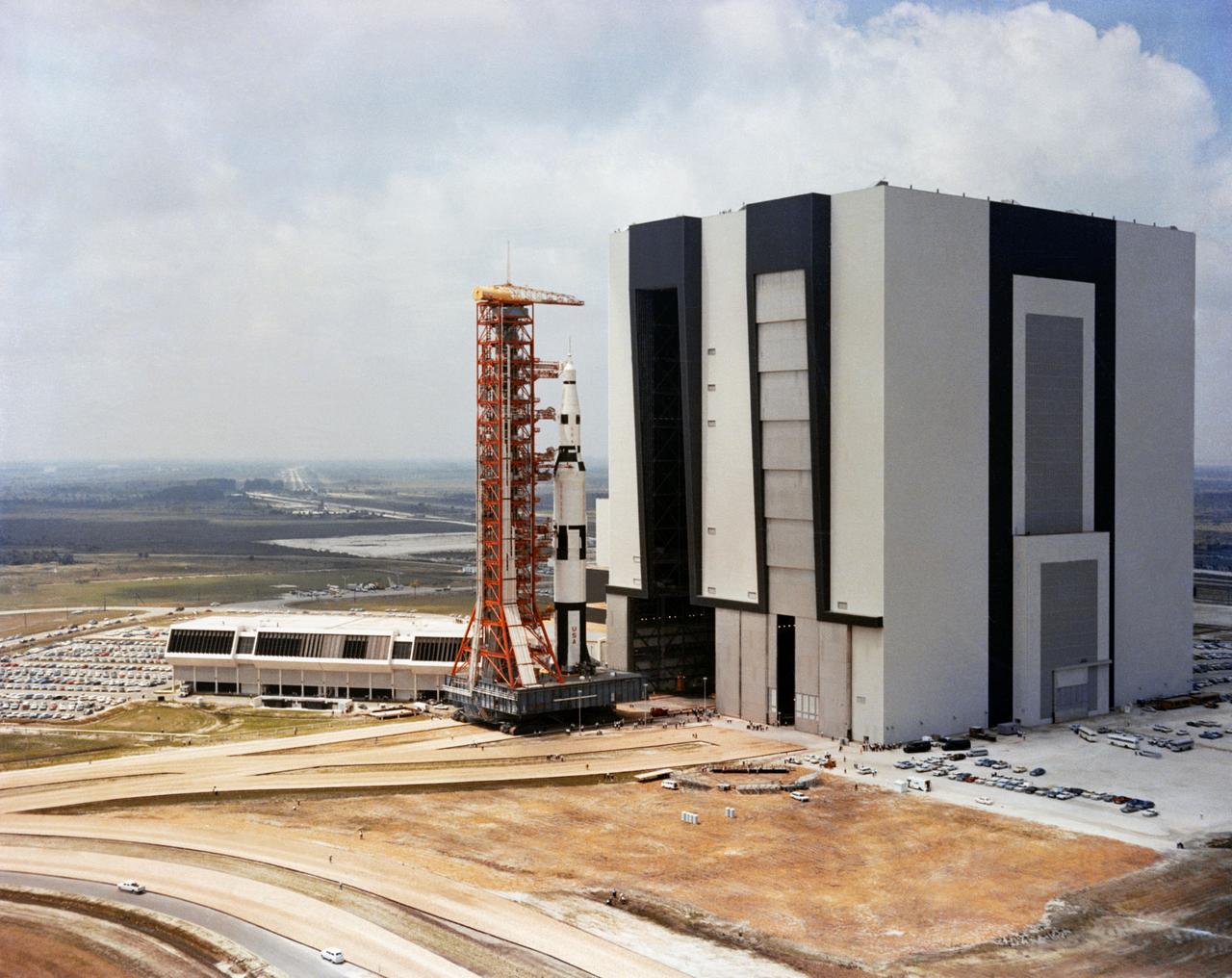

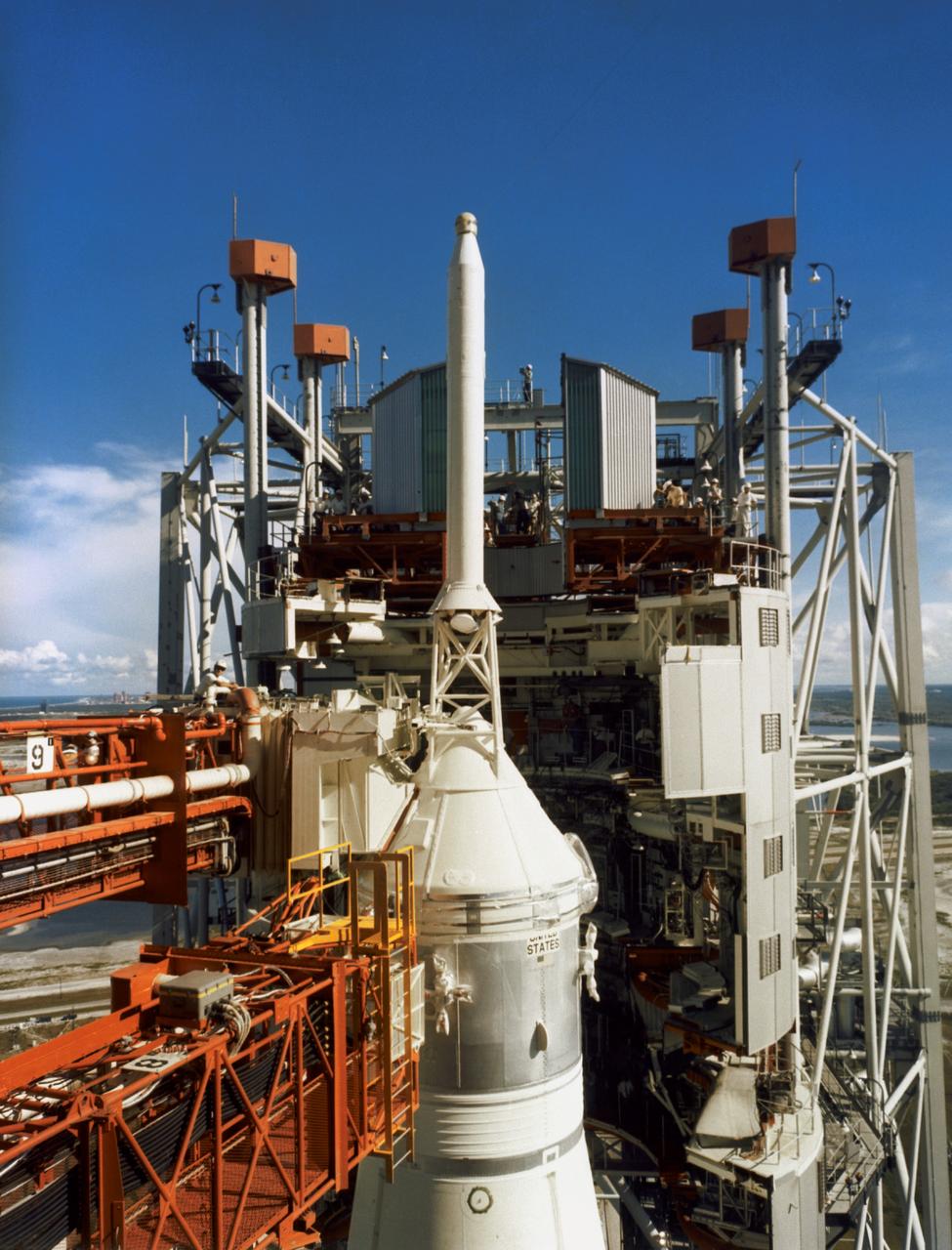
An Apollo/Saturn V facilities Test Vehicle and Launch Umbilical Tower (LUT) atop a crawler-transporter move from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on the way to Pad A. This test vehicle, designated the Apollo/Saturn 500-F, is being used to verify launch facilities, train launch crews, and develop test and checkout procedures.
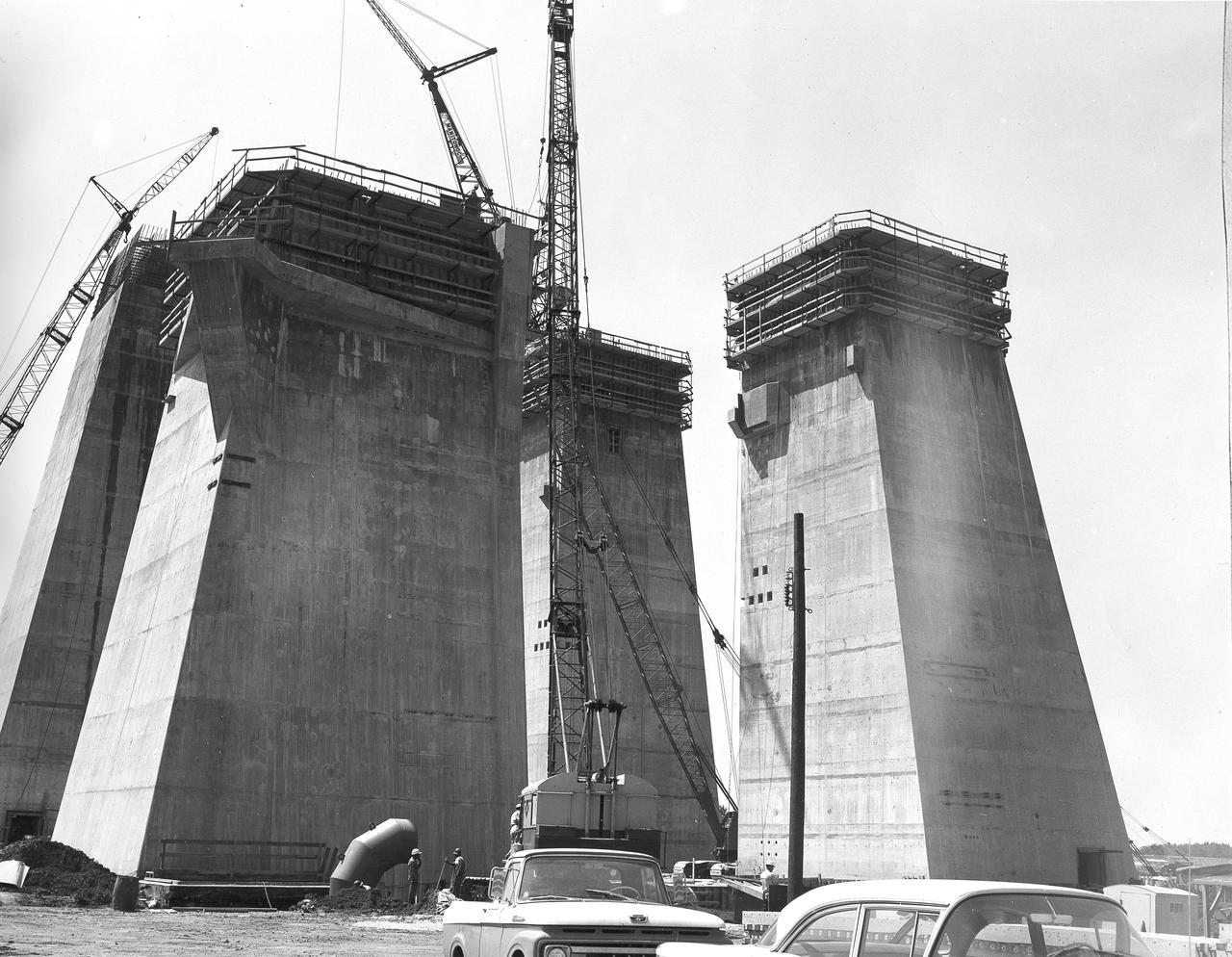

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. This photograph, taken May 7, 1963, gives a close look at the four concrete tower legs of the S-IC test stand at their completed height.
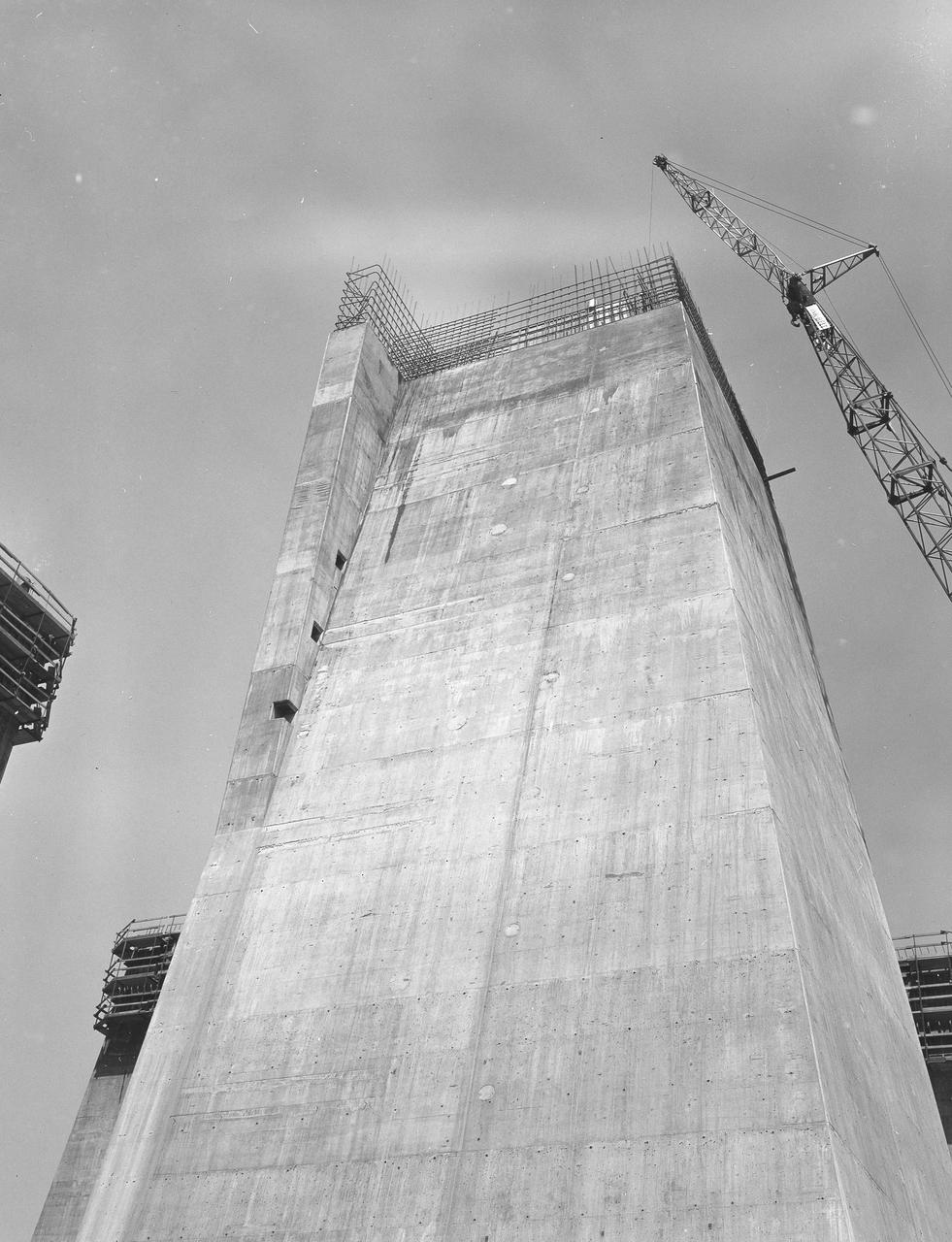

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. This photograph, taken from ground level on May 7, 1963, gives a close look at one of the four towers legs of the S-IC test stand nearing its completed height.
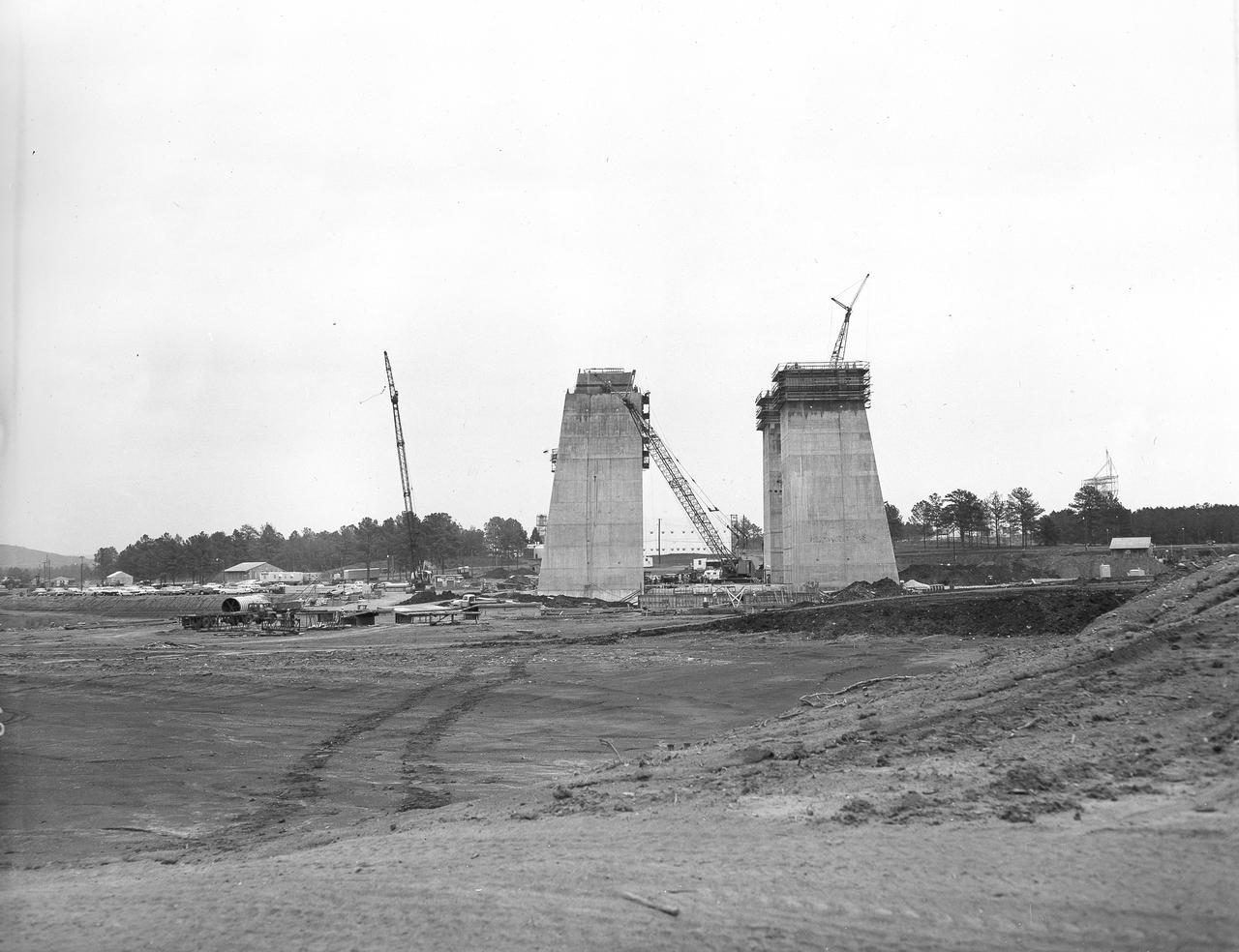

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. This photograph taken April 17, 1963, gives a look at the four tower legs of the S-IC test stand at their completed height.
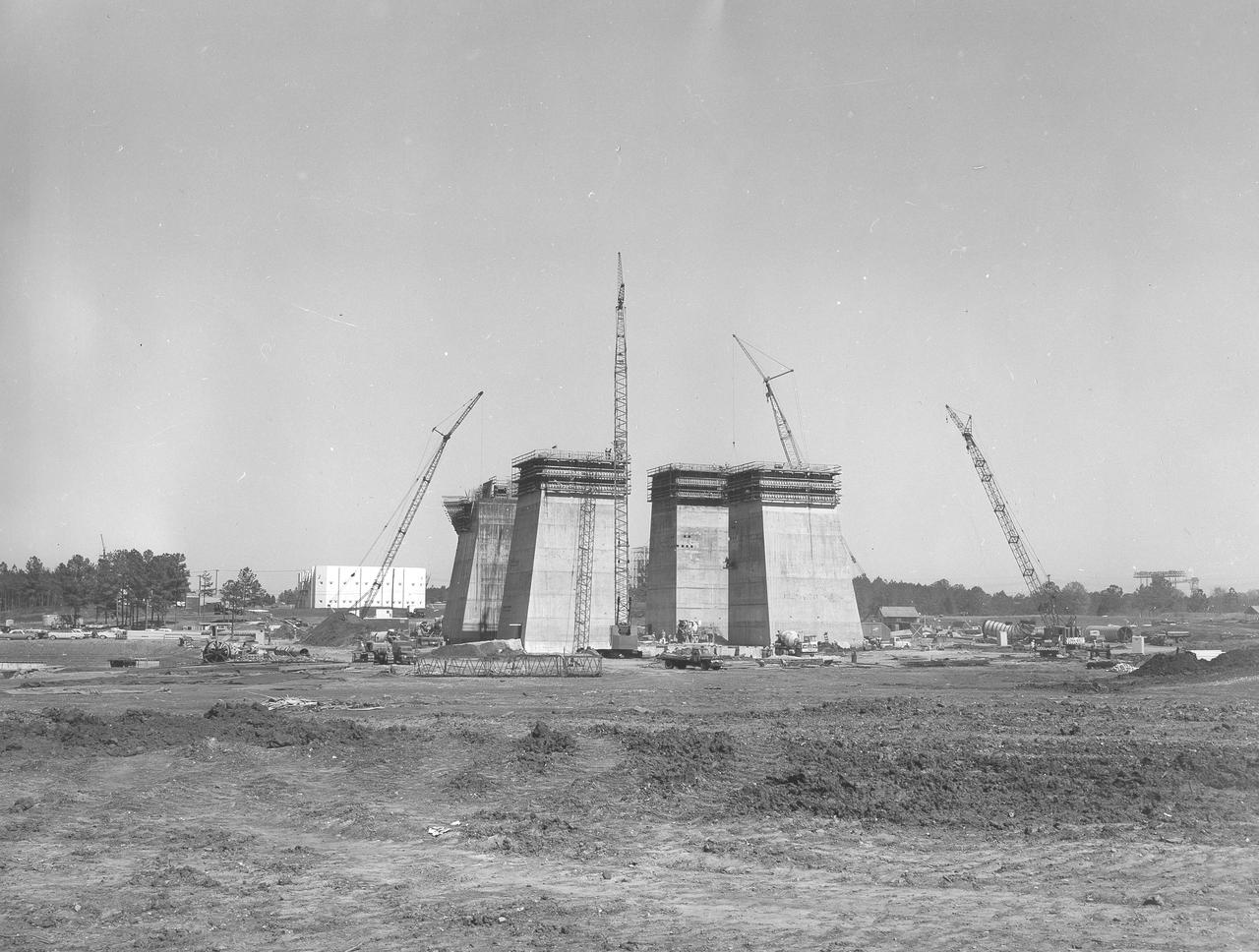

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. This photograph, taken April 4, 1963, gives a close up look at the ever-growing four towers of the S-IC Test Stand.
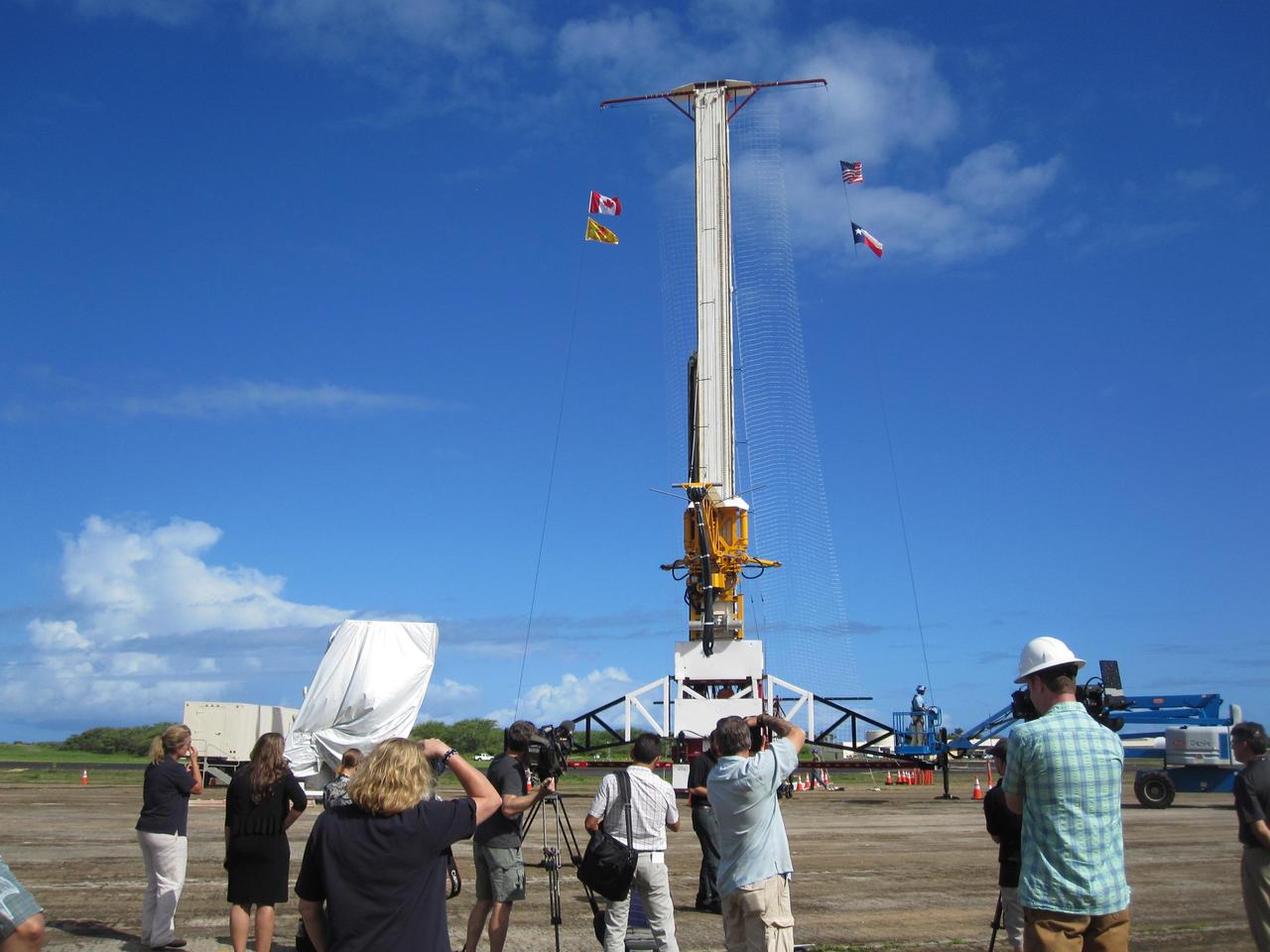

This image shows the tower from which the test vehicle for NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator LDSD will hang before a balloon lifts it to high altitudes.
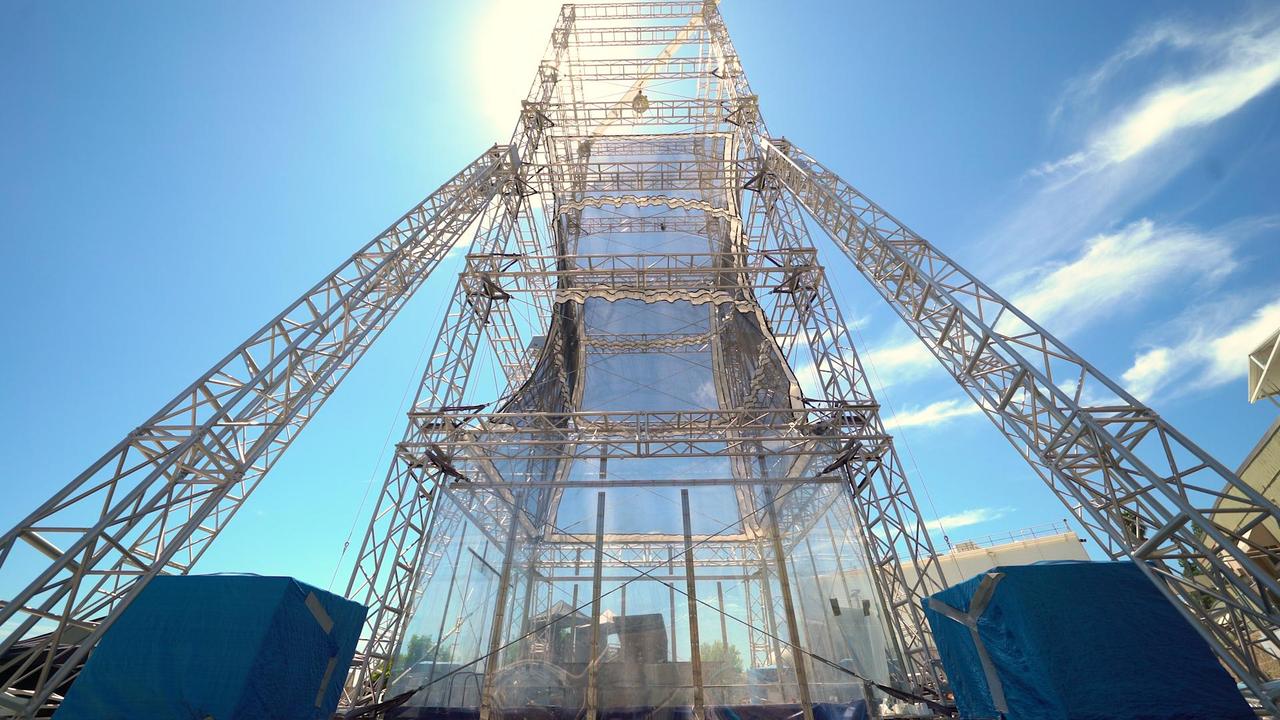

This drop tower at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California includes a bow launch system, which can hurl test articles 110 mph into the ground, re-creating the forces they would experience during a Mars landing. The drop tower was used for testing the collapsible-base of a prototype Mars lander design called SHIELD (Simplified High Impact Energy Landing Device) on Aug. 12, 2022. The SHIELD concept could one day allow lower-cost missions to reach the Martian surface. In this image, the SHIELD base prototype can be seen being lifted up to the top of the tower. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25581

NASA's Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) hangs from a launch tower at U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii. The saucer-shaped vehicle will test two devices for landing heavy payloads on Mars: an inflatable donut-shaped device and a supersonic parachute. The launch tower helps link the vehicle to a balloon; once the balloon floats up, the vehicle is released from the tower and the balloon carries it to high altitudes. The vehicle's rocket takes it to even higher altitudes, to the top of the stratosphere, where the supersonic test begins. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19342
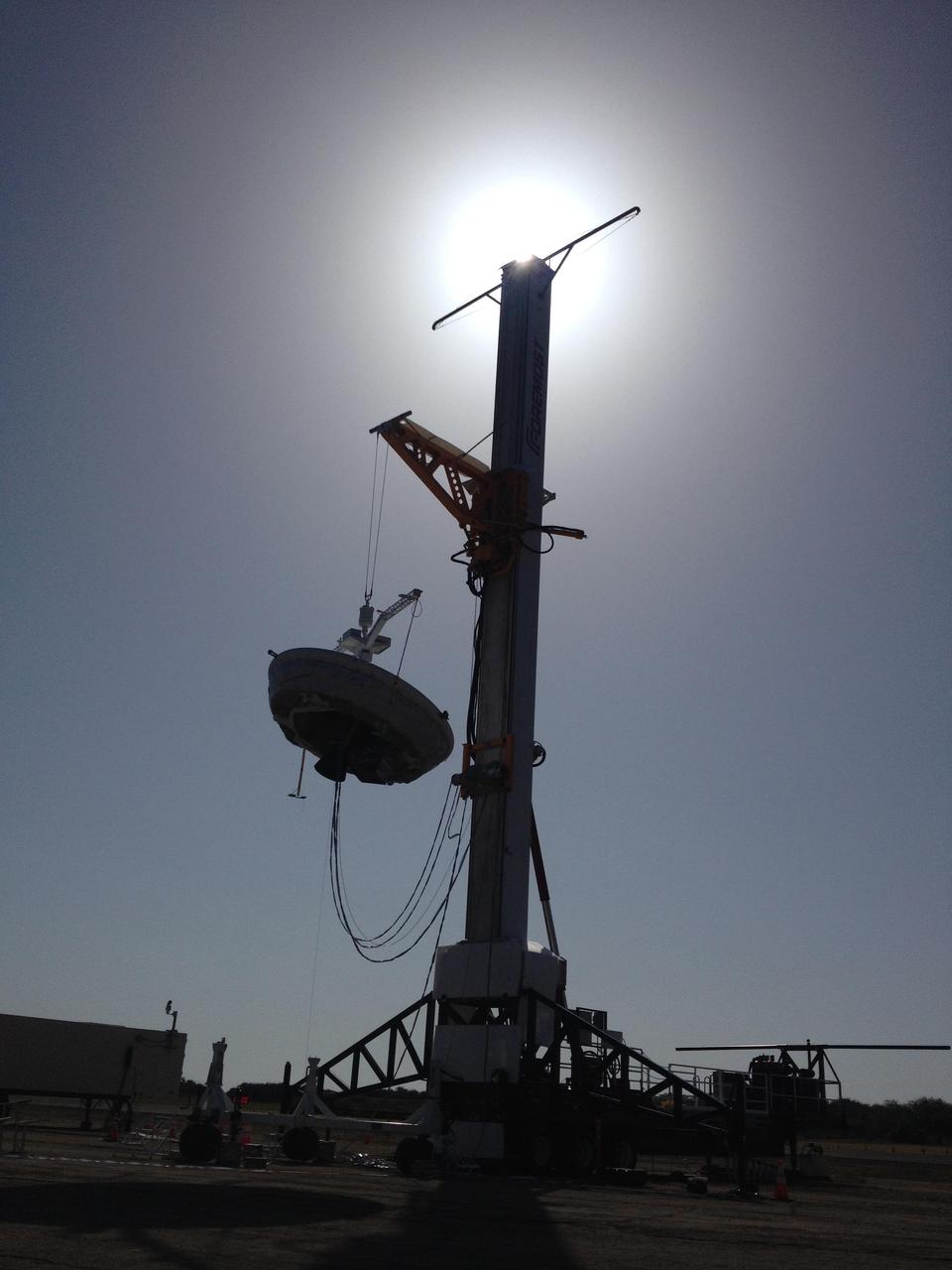

A saucer-shaped vehicle part of NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator LDSD project designed to test interplanetary landing devices hangs on a tower in preparation for launch at the Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii.

InSight Atlas V tower roll testing at Launch Complex 3, located at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
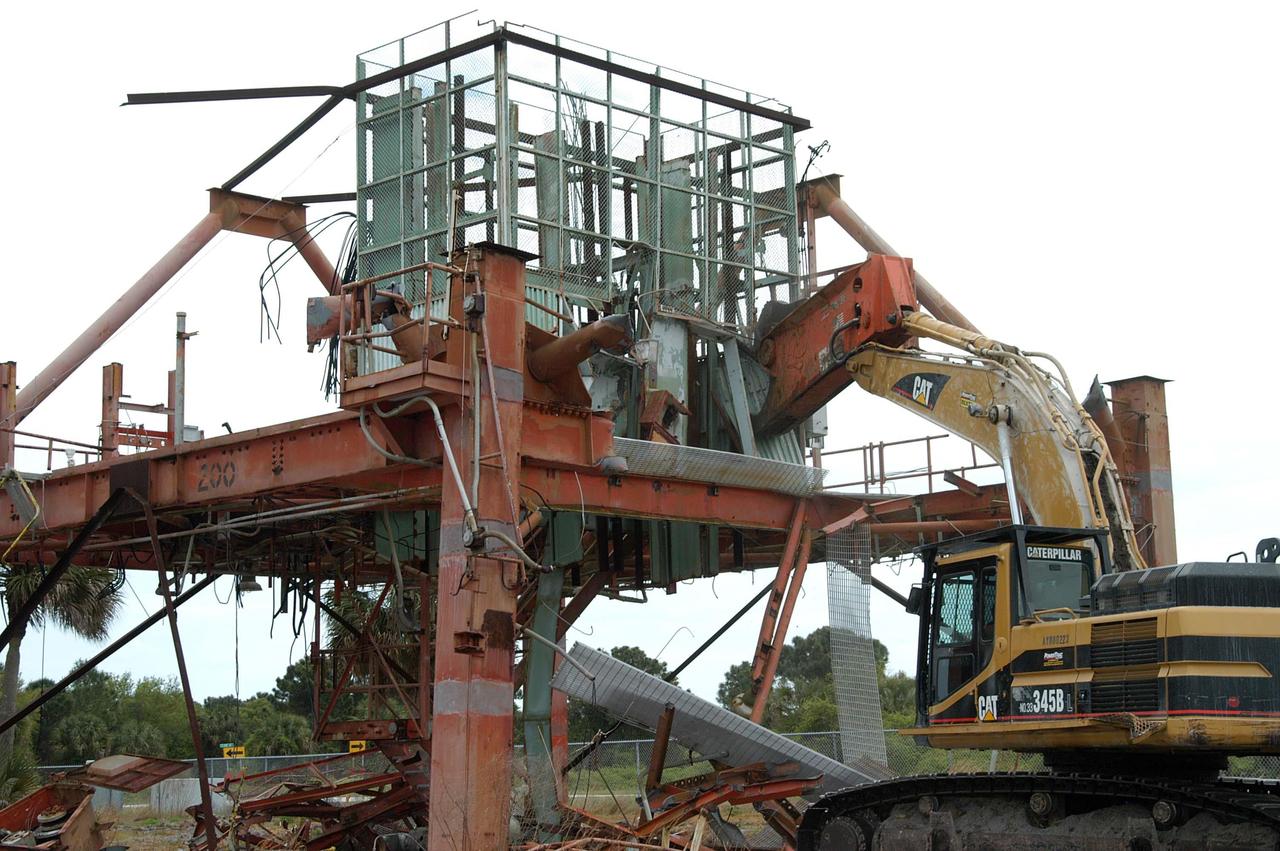

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC is being demolished with the Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment. Seen is the base of tower; the upright tower extended more than 398 feet above the launch pad. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
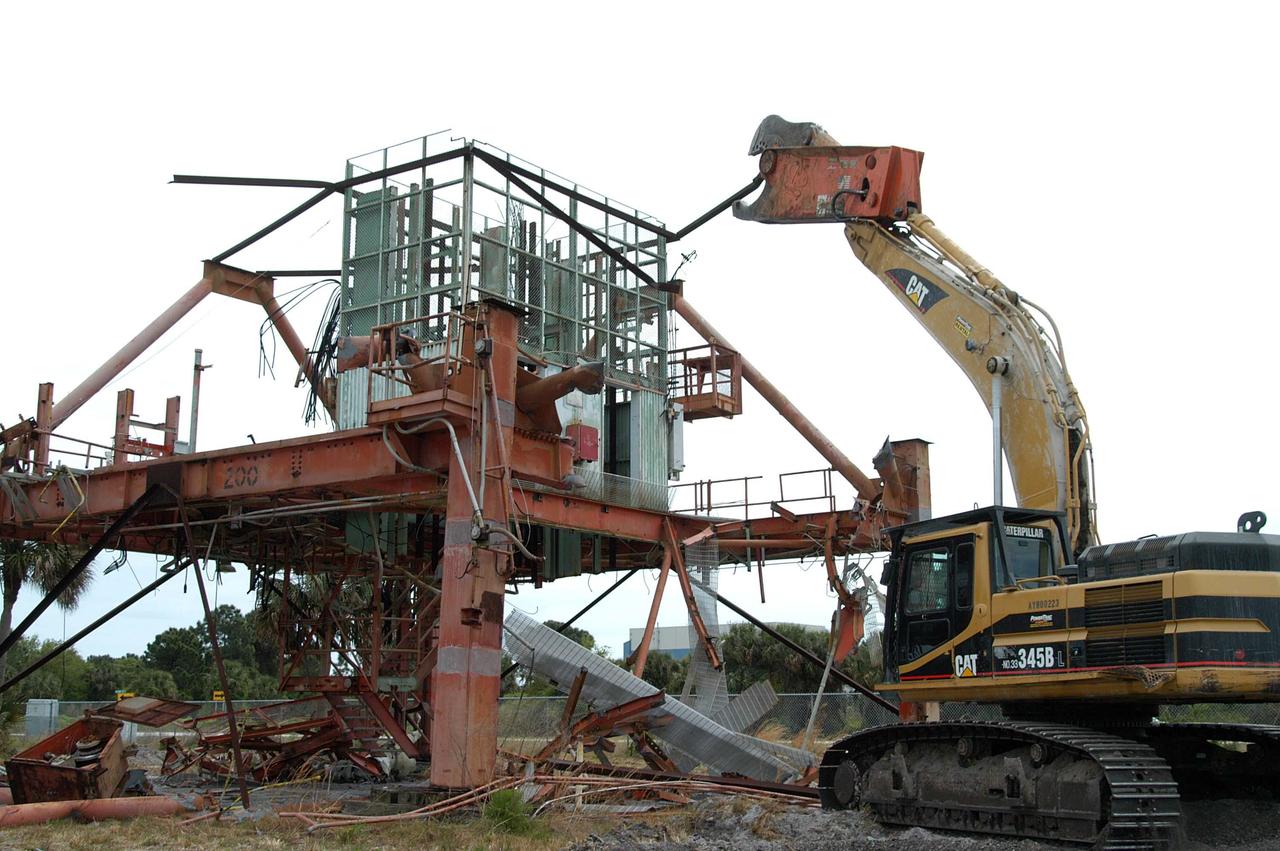

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC is being demolished with a Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment. Seen is the base of tower; the upright tower extended more than 398 feet above the launch pad. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
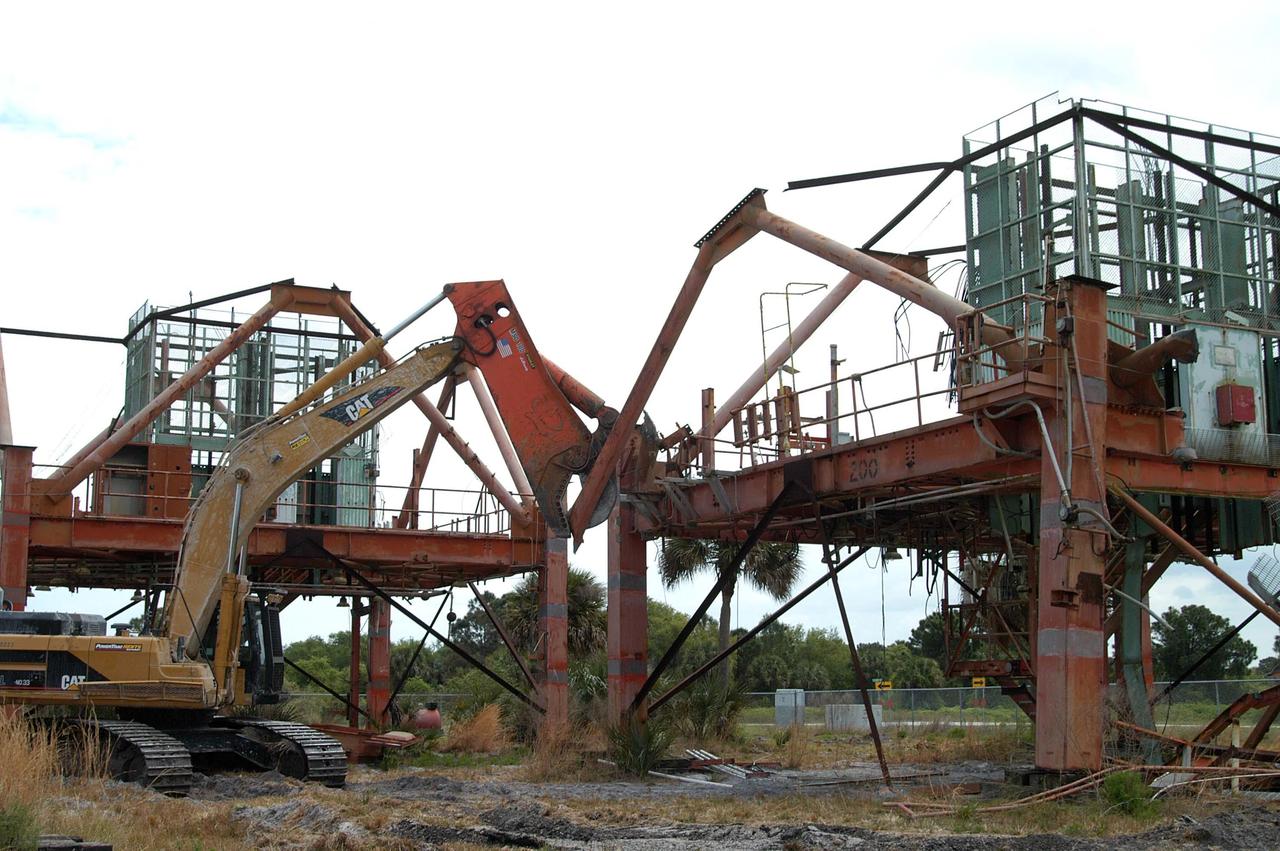

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- - Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC is being demolished with a Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment. Seen is the base of tower; the upright tower extended more than 398 feet above the launch pad. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC is being demolished with a Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment. Seen is the base of tower; the upright tower extended more than 398 feet above the launch pad. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
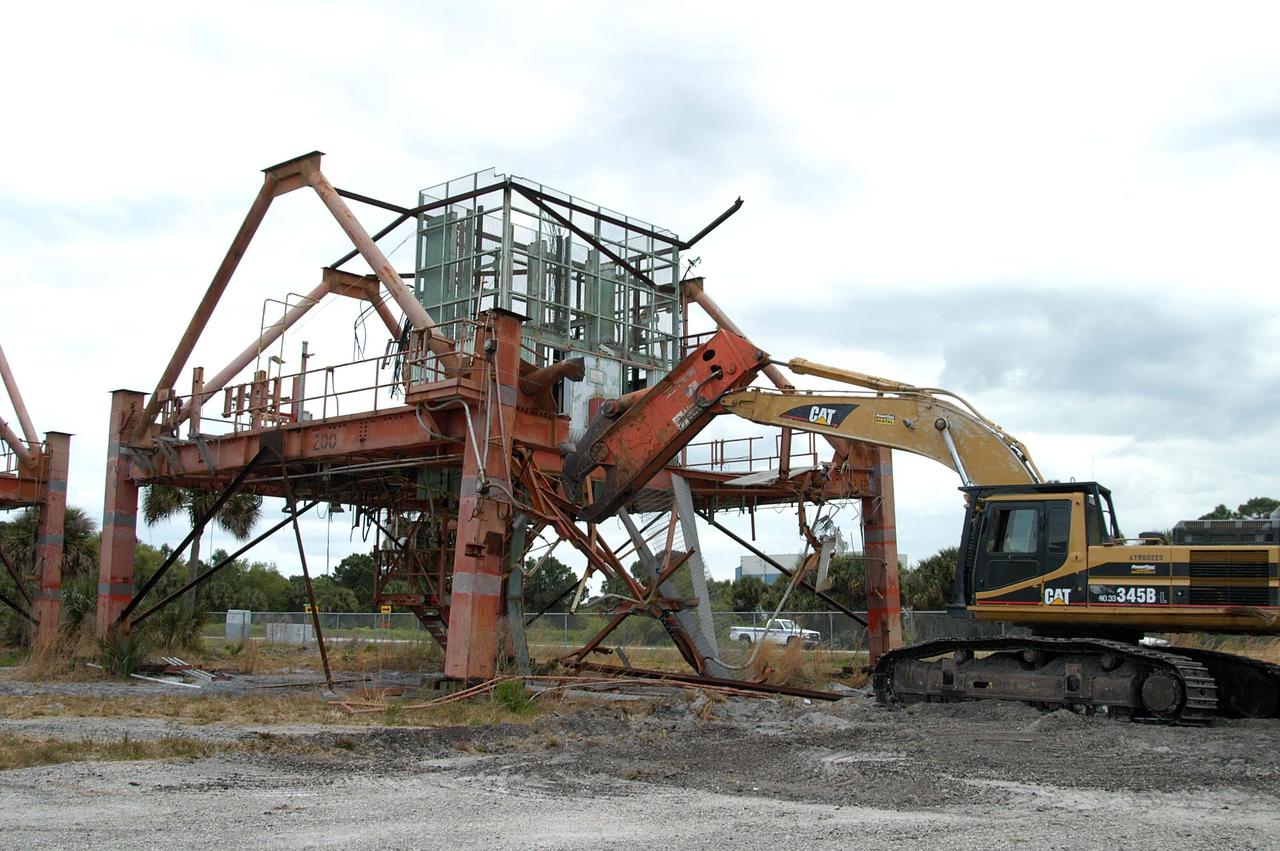

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1), stored in the Industrial Area of KSC, is being demolished using a Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment. Seen is the base of tower; the upright tower extended more than 398 feet above the launch pad. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear being used for demolition is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a load test is conducted on a giant crane. The crane will aid in construction of lightning towers that will hold catenary wires as part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. One of the towers under construction is at right. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a load test is conducted on a giant crane. The crane will aid in construction of lightning towers that will hold catenary wires as part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. One of the towers under construction is at far left. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a load test is conducted on a giant crane. The crane will aid in construction of lightning towers that will hold catenary wires as part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. One of the towers under construction is in the foreground. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane places a 100-foot fiberglass lightning mast on top of the 500-foot tower. The tower is one of three being constructed for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Another tower is seen at right. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane places a 100-foot fiberglass lightning mast on top of the 500-foot tower. The tower is one of three being constructed for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Another tower is seen at right. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane (at left) completes construction of one of the towers in the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. At right, another tower is being constructed. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

Personnel atop the 402-ft. Mobile Service Structure look back at the Apollo 11 spacecraft as the tower is moved away during a Countdown Demonstration Test. Photo filed 11 July 1969.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team gathered with a special banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. One of the test team members signs a banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team signed a special banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
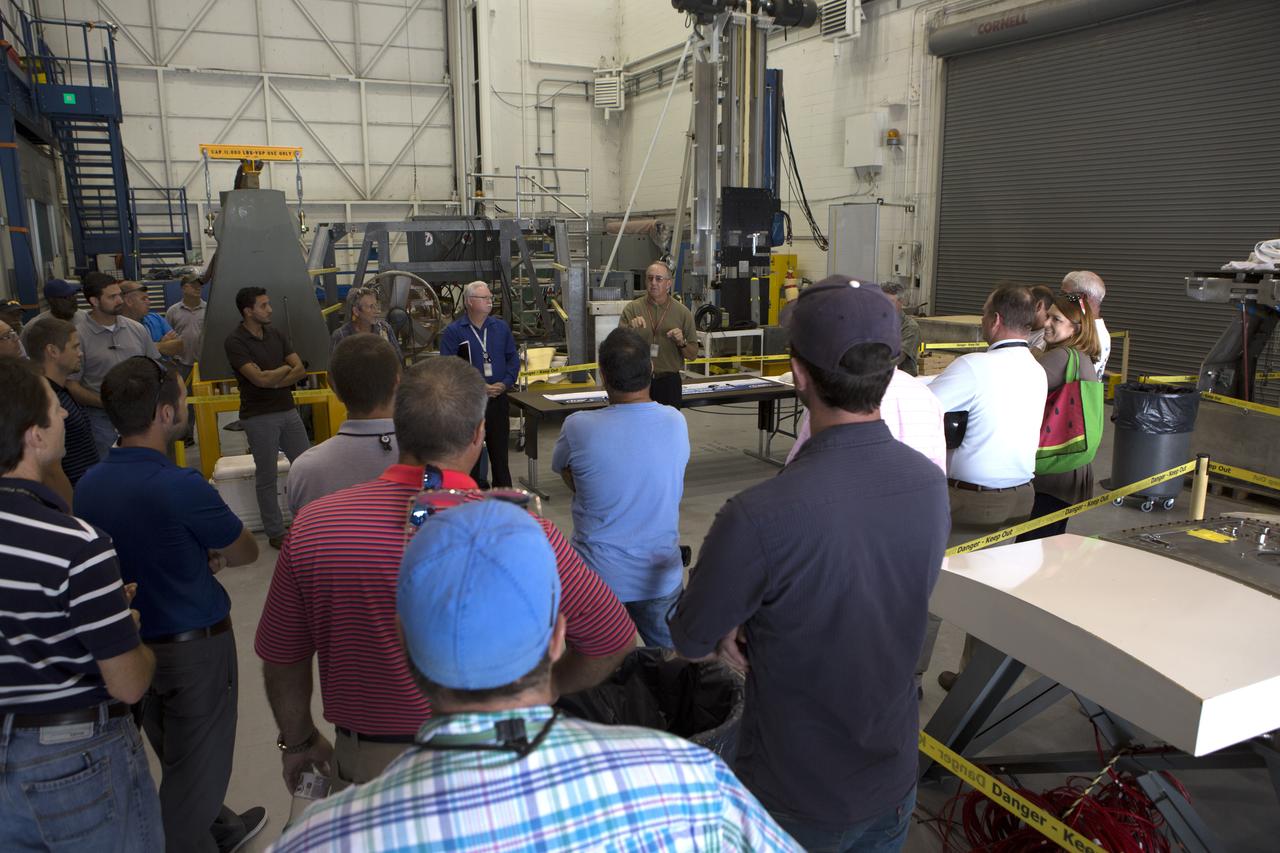

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. Patrick Simpkins, director of Engineering, speaks to the test team during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
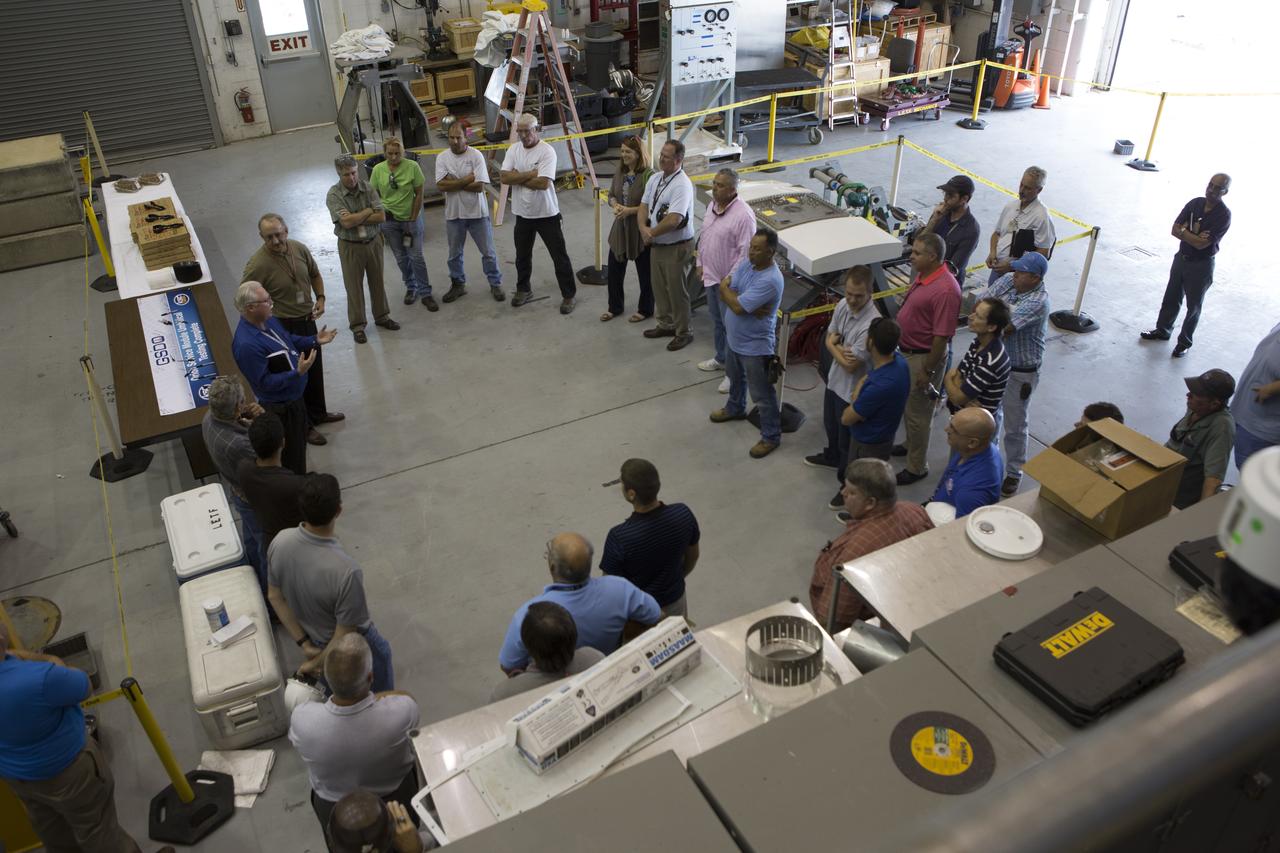

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team gathered for an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
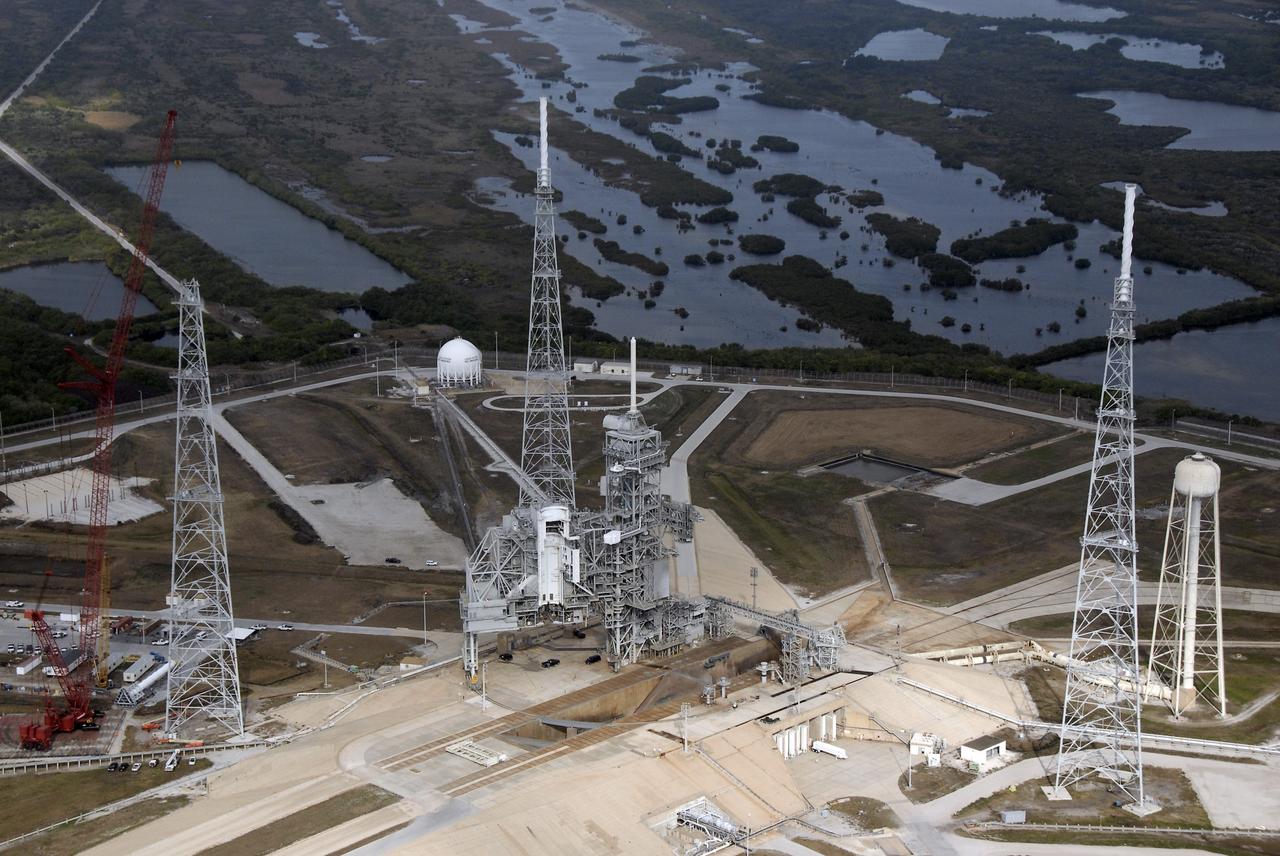

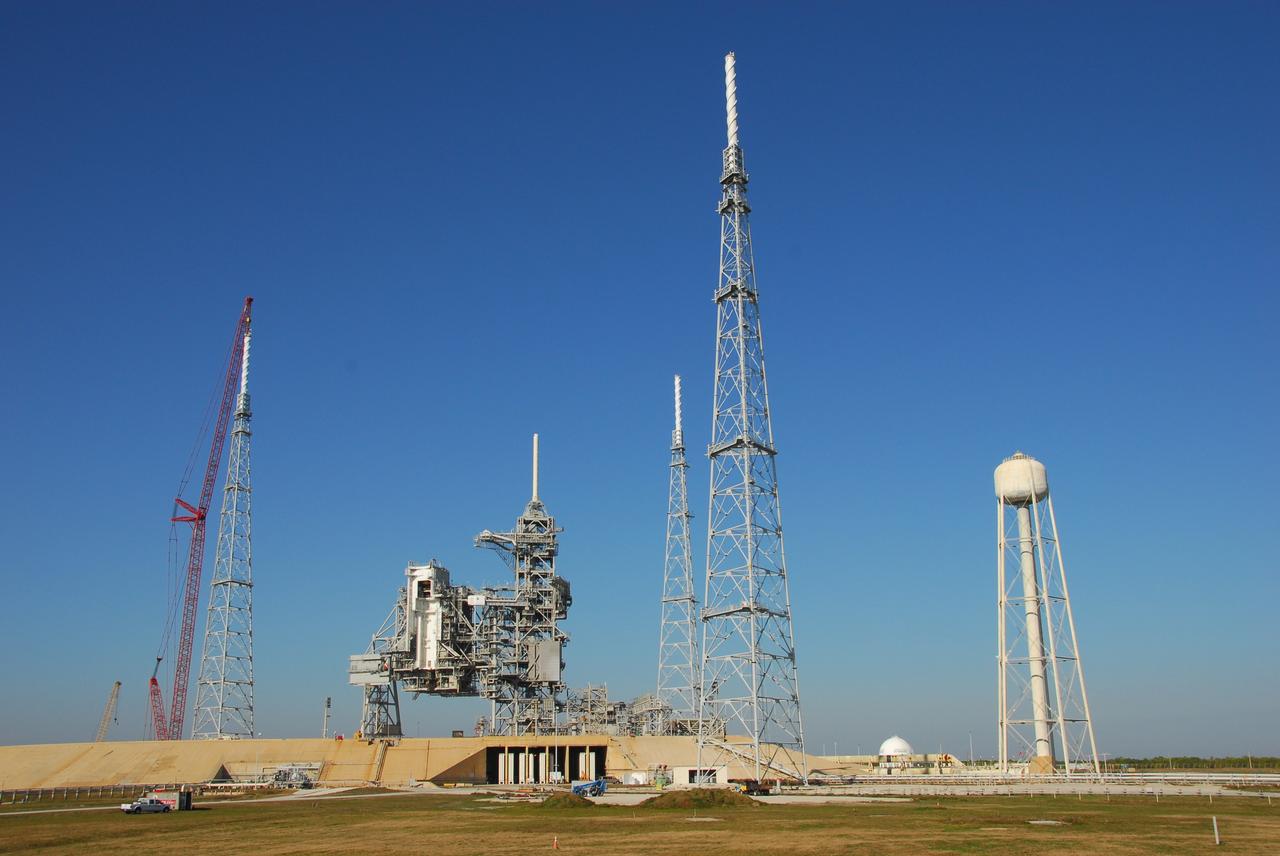
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The two towers at center and right contain the lightning mast on top; the one at left does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. In the foreground is the tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used for sound suppression during a shuttle liftoff. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares rocket launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
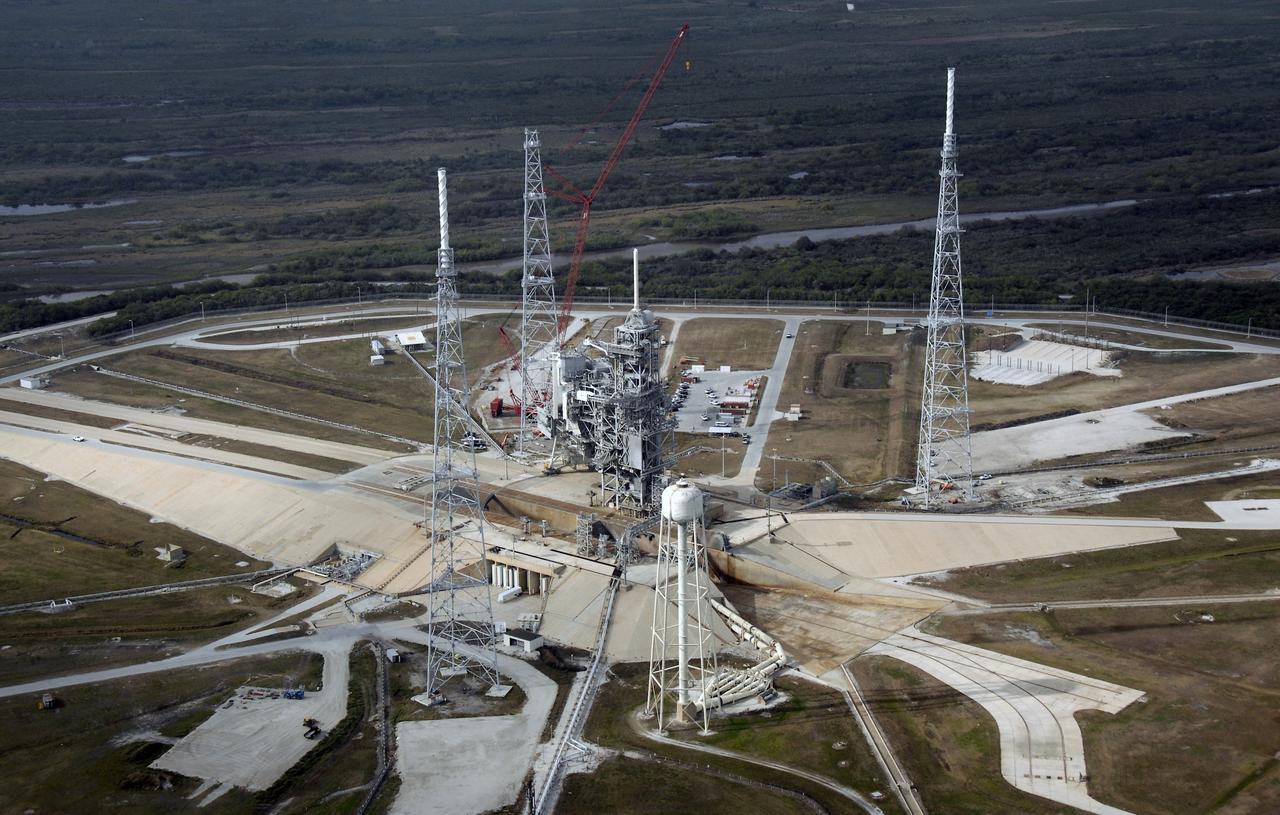

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The two towers at left and right contain the lightning mast on top; the one at center does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. In the foreground is the tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used for sound suppression during a shuttle liftoff. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares rocket launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a giant crane (far left) places the 100-foot lightning mast on top of the newly erected lightning tower. Three new towers surround the pad. In the middle are the fixed and rotating service structures that serve the Space Shuttle Program. At far right is the tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used for sound suppression during a shuttle launch. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
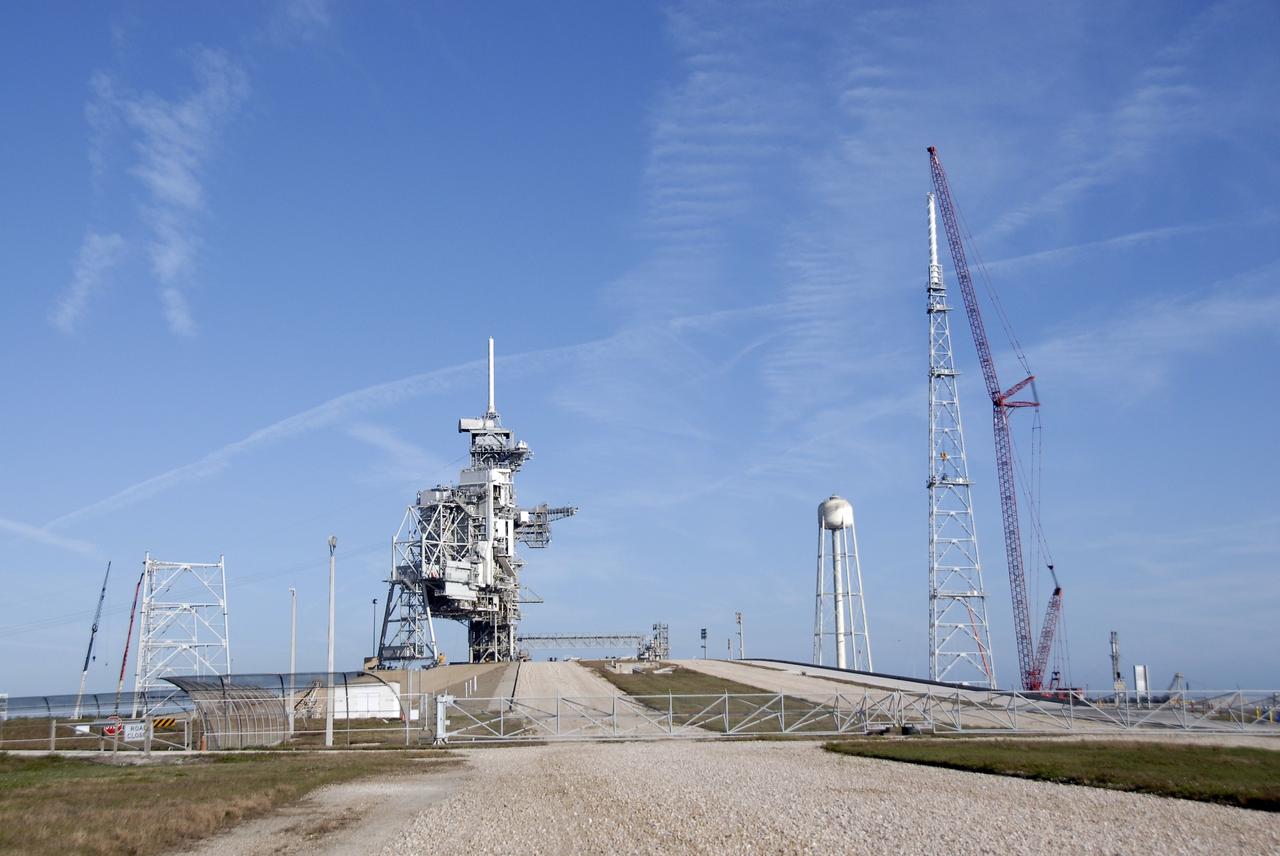

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane places the 100-foot fiberglass mast atop the new lightning tower constructed on the pad. The towers are part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. At left of the service structures is another tower under construction. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with the additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
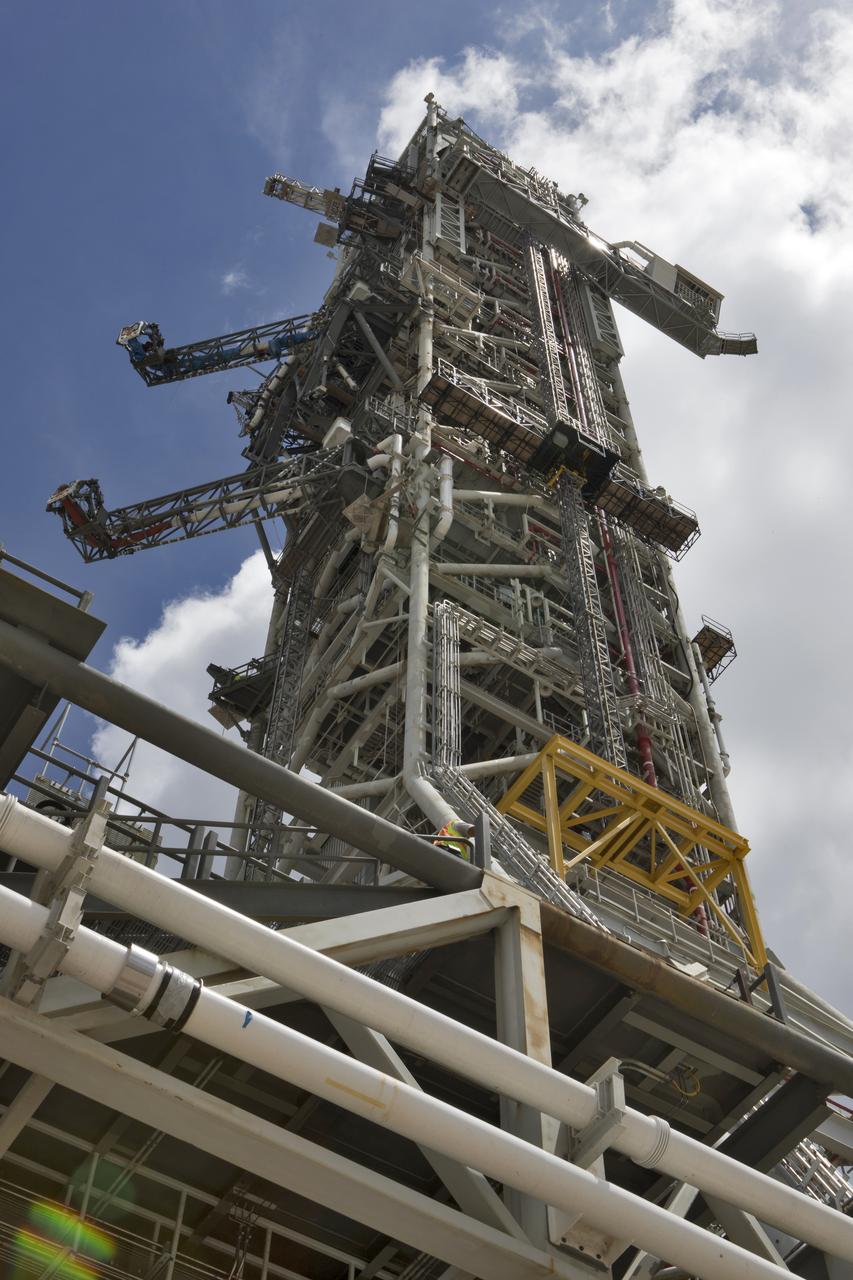

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, top right, is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
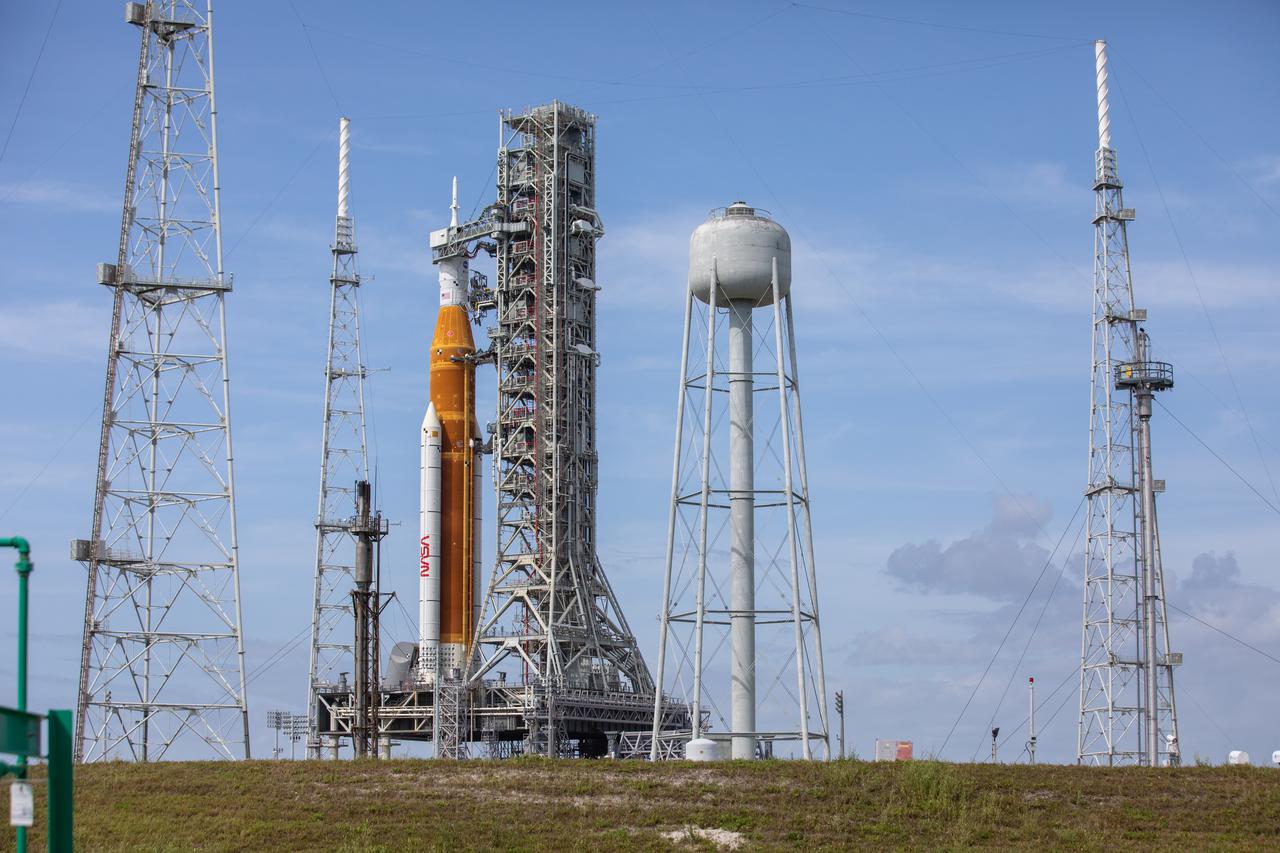

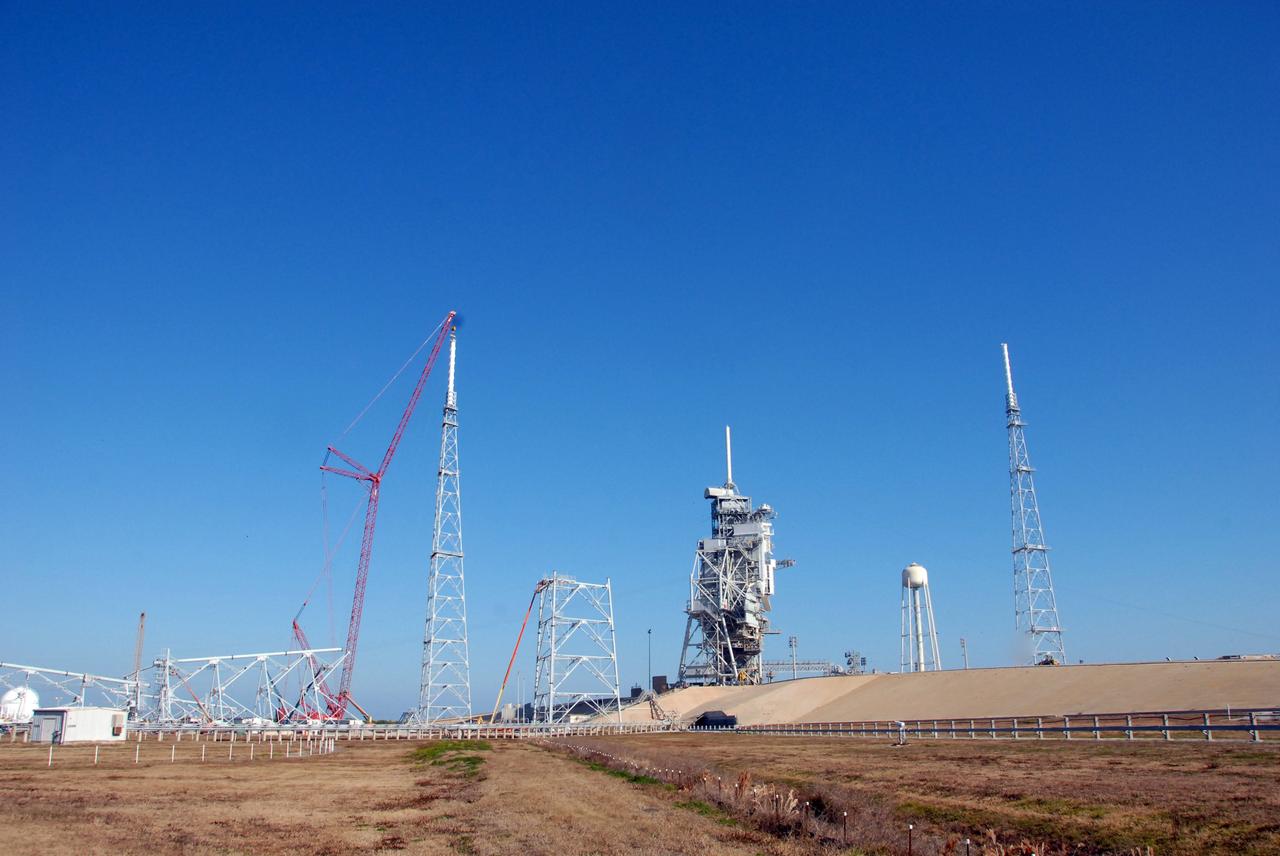
A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are the three lightning protection towers and water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
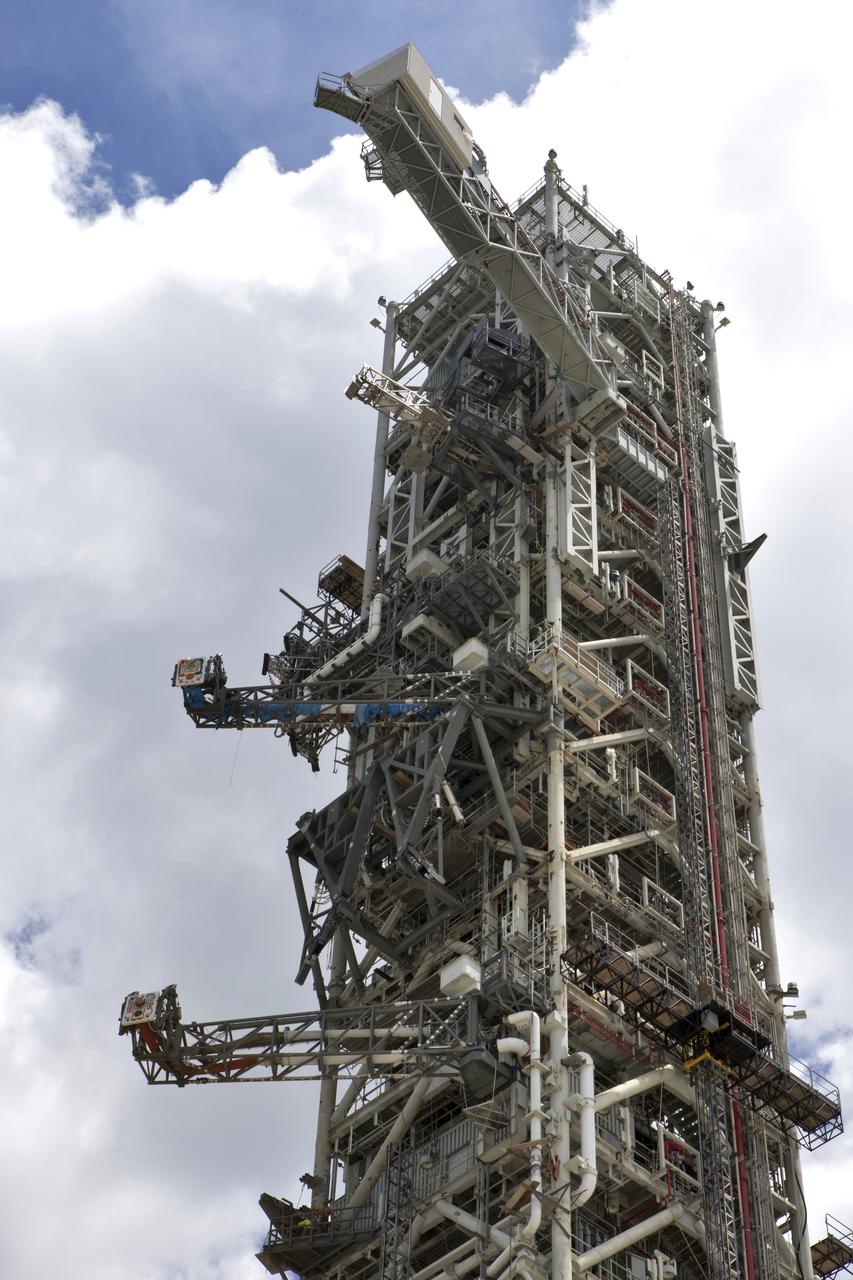

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, topmost umbilical, is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
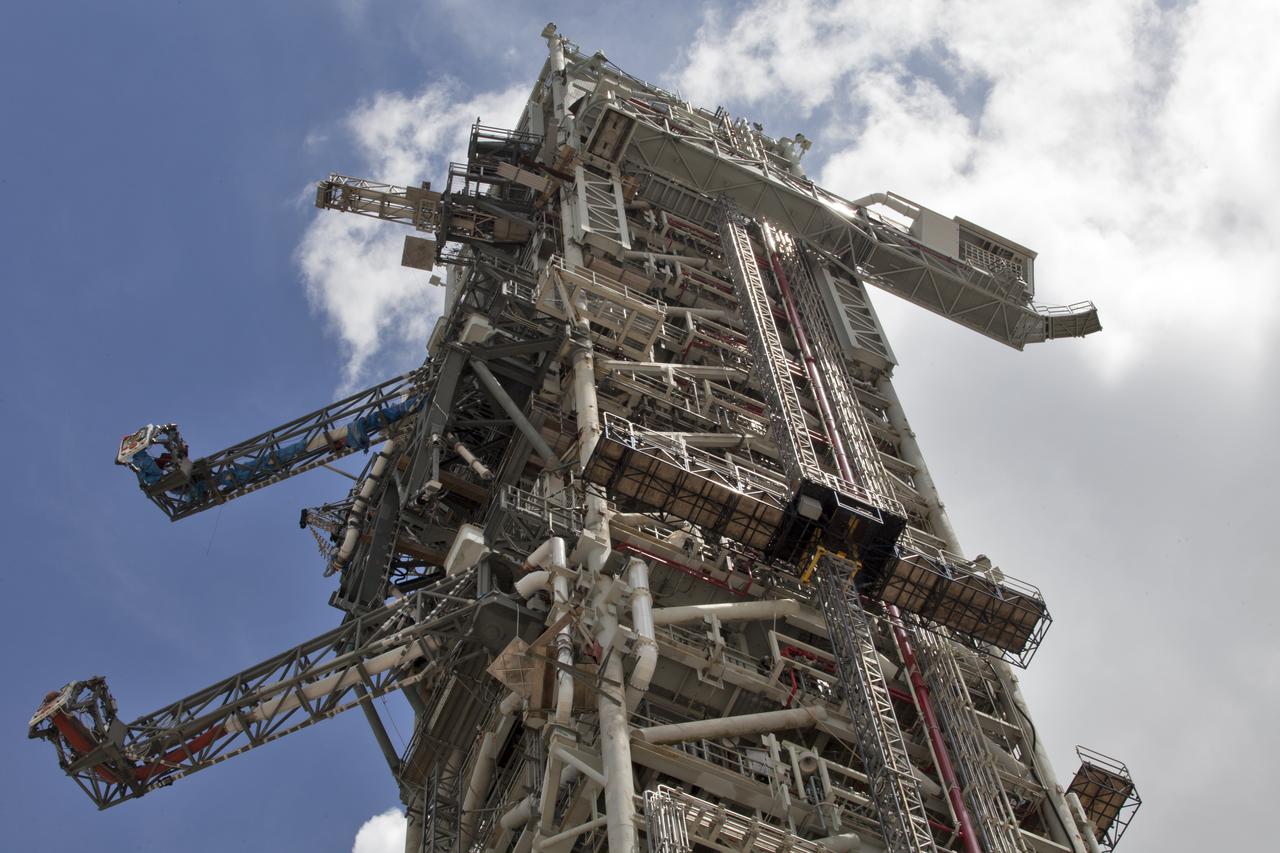

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, top right, begins on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
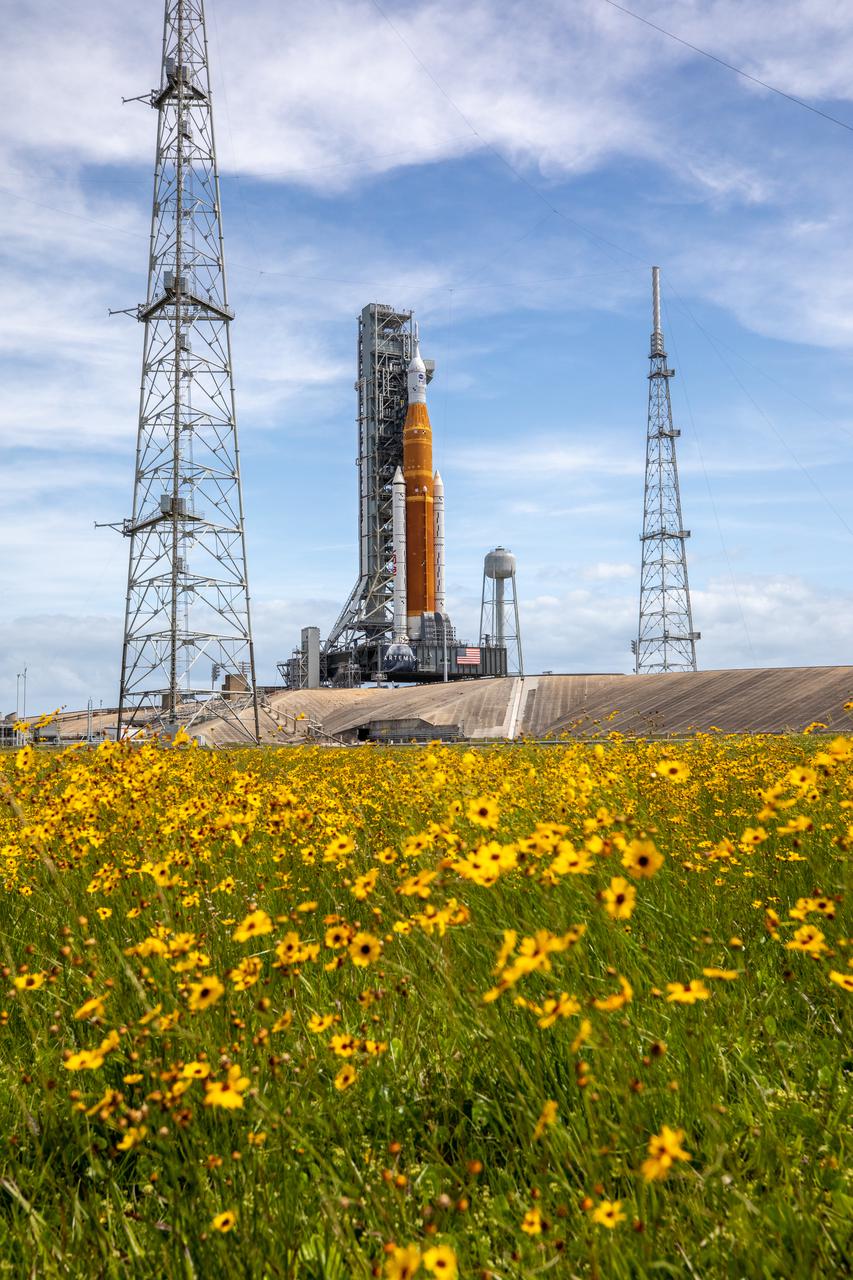

Wildflowers frame a view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are two of the three lightning protection towers and the water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
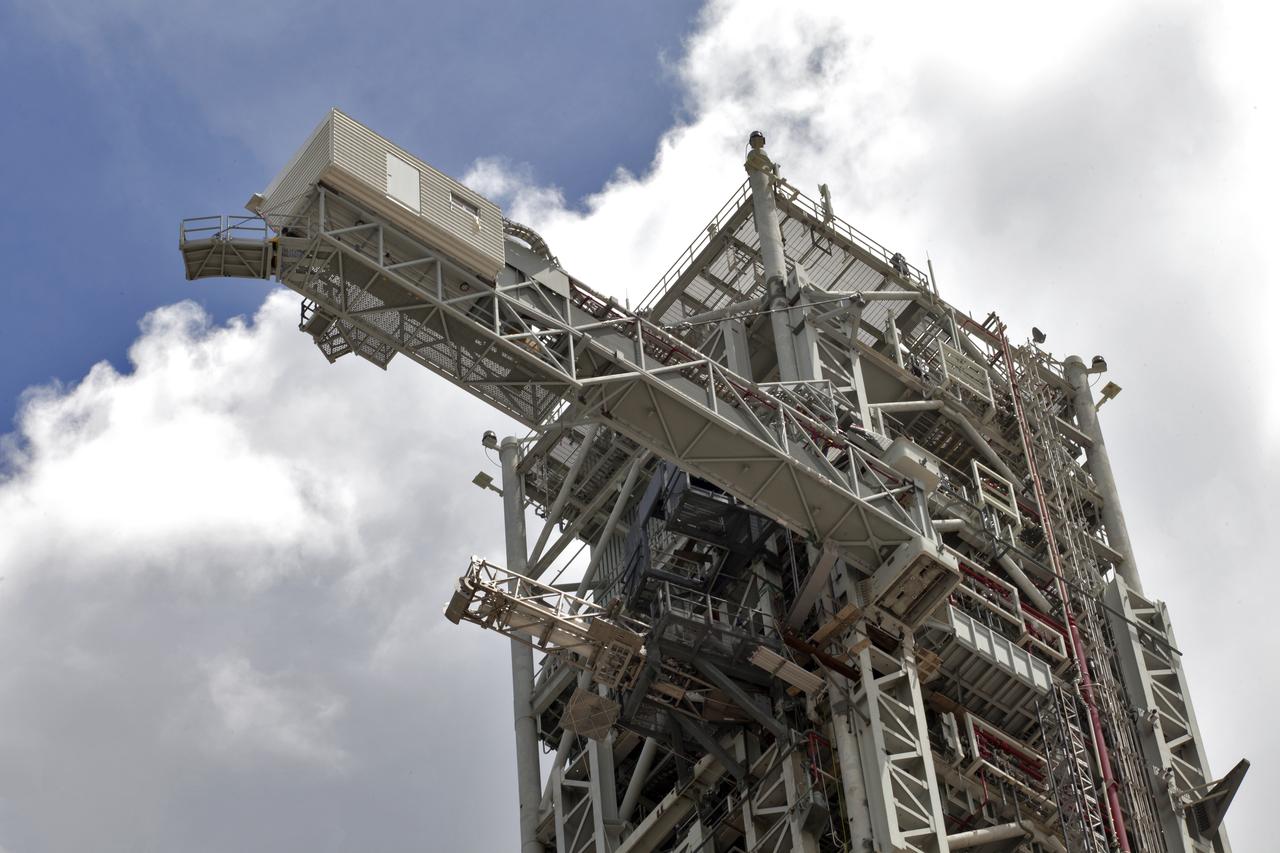

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, topmost umbilical, is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
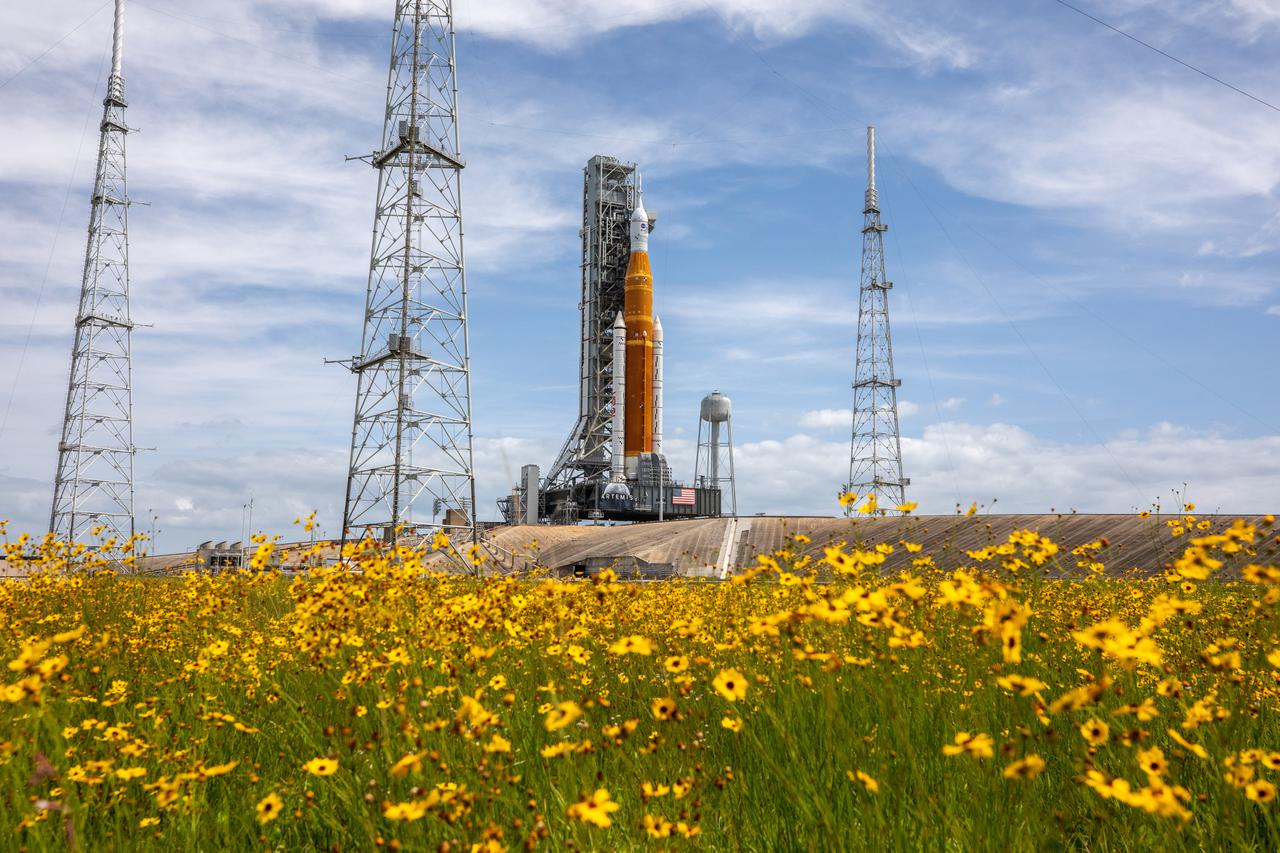

Wildflowers frame a view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are the three lightning protection towers and the water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
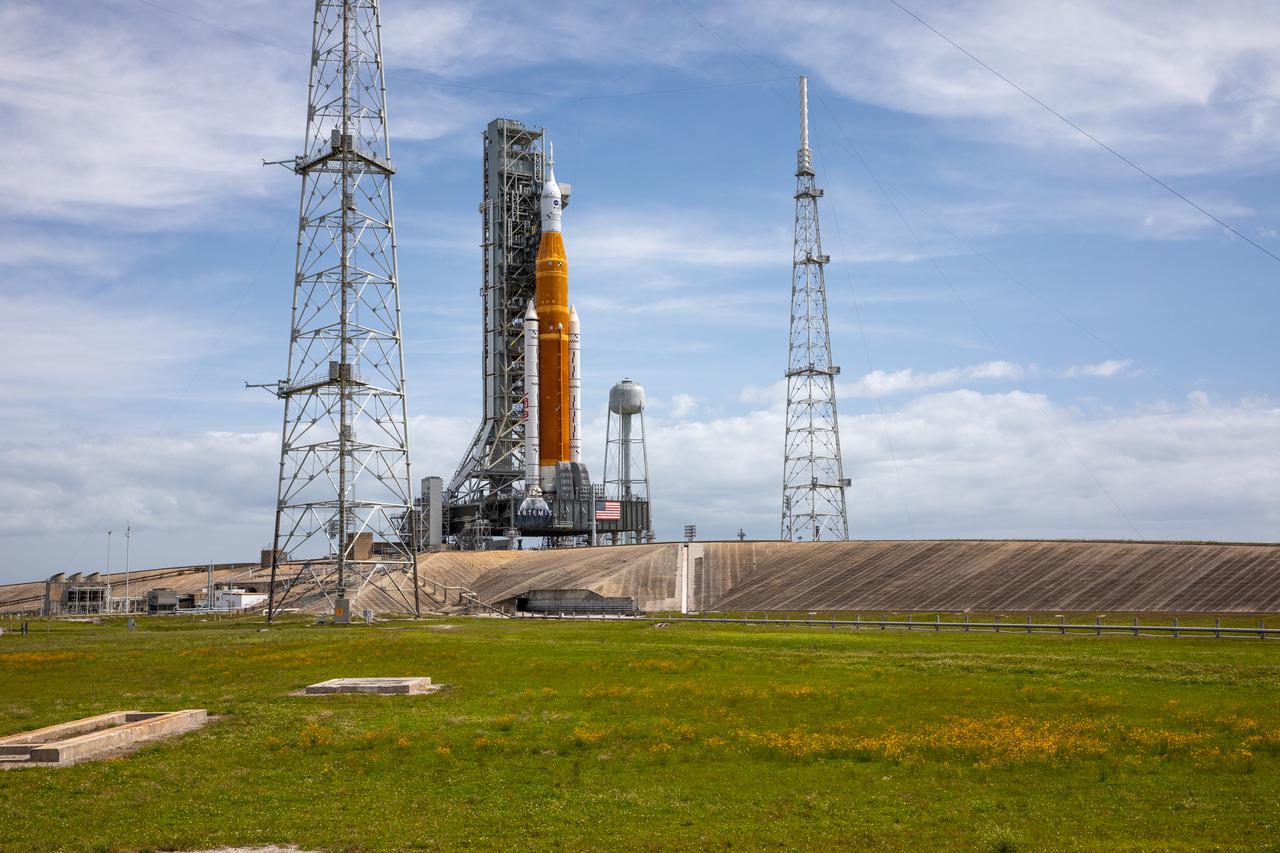

A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are two of the three lightning protection towers and the water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
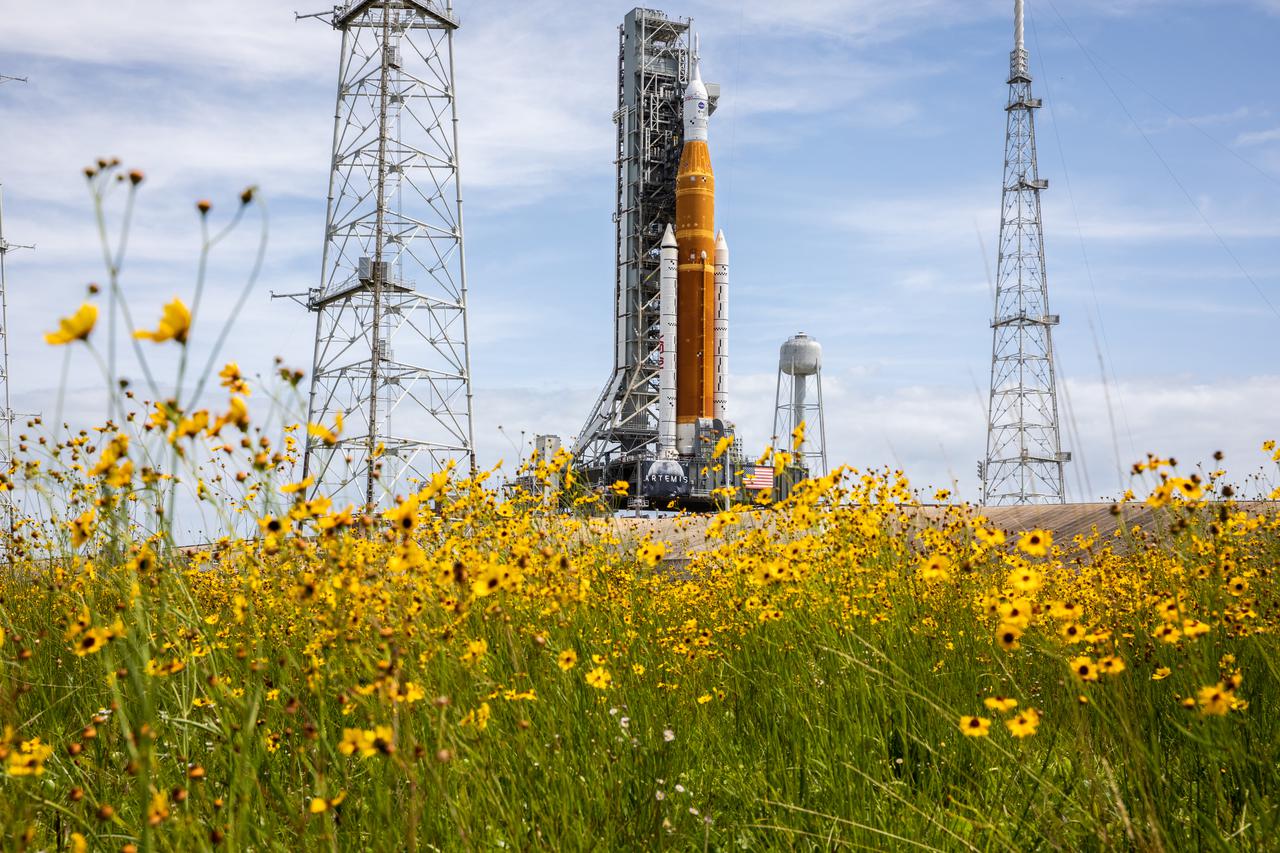

Wildflowers frame a view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are two of the three lightning protection towers and the water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
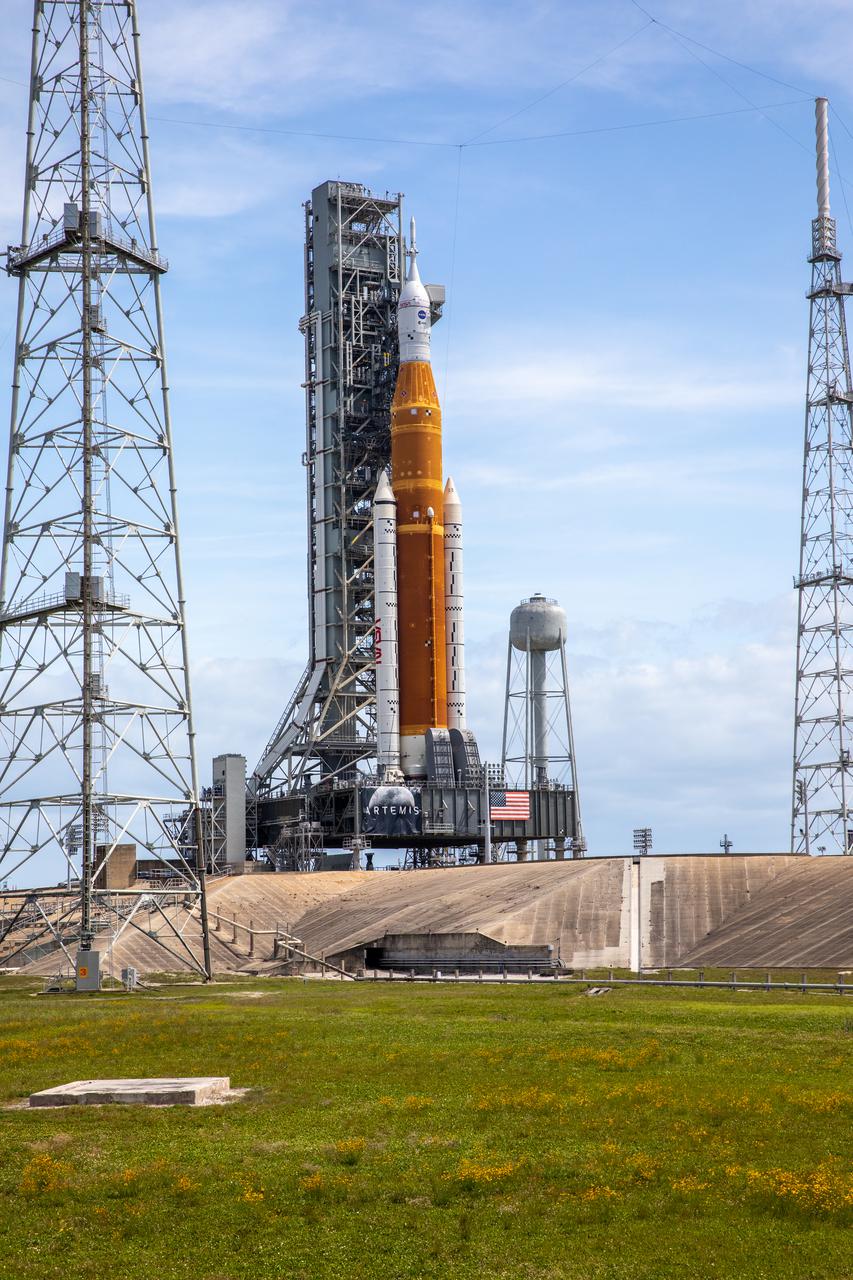

A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are two of the three lightning protection towers and the water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
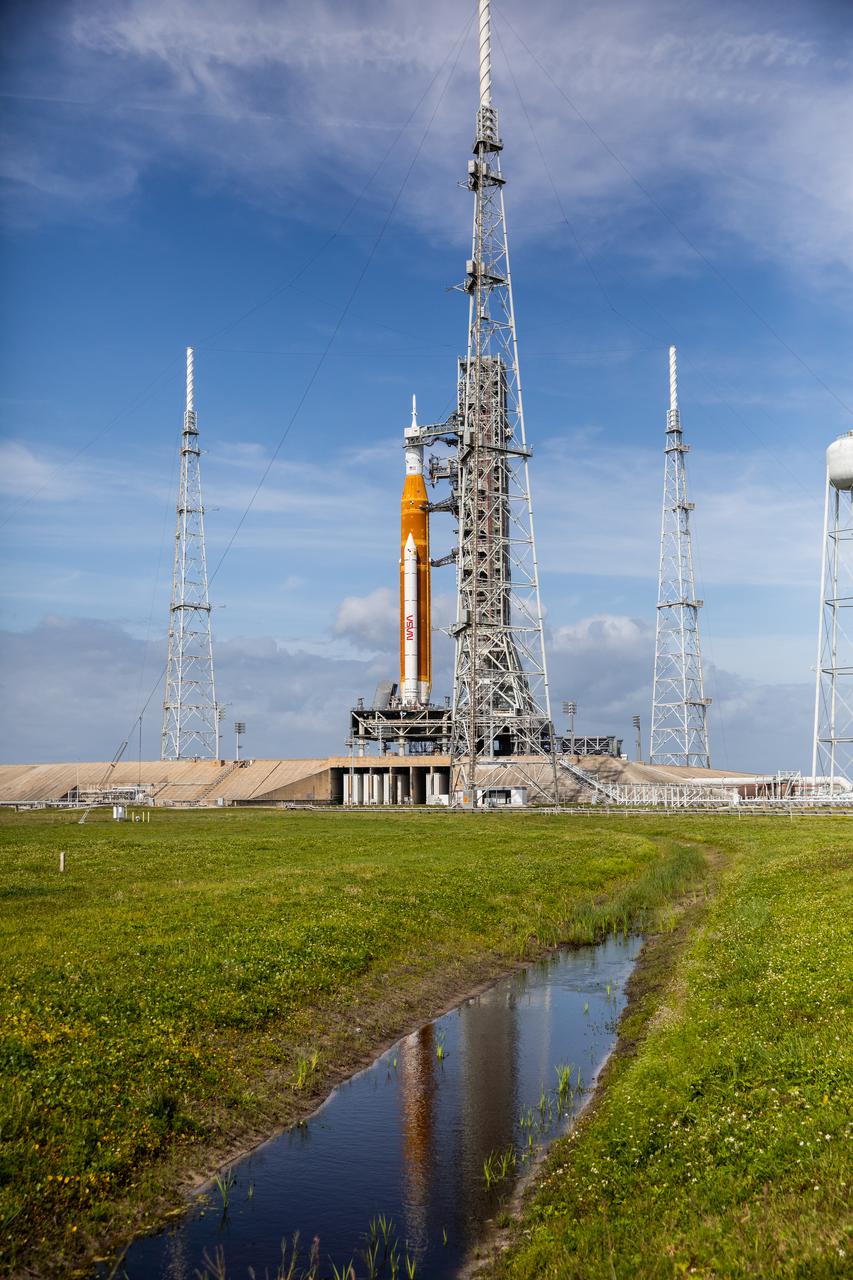

A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2022. Also in view are the three lightning protection towers and water tower. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
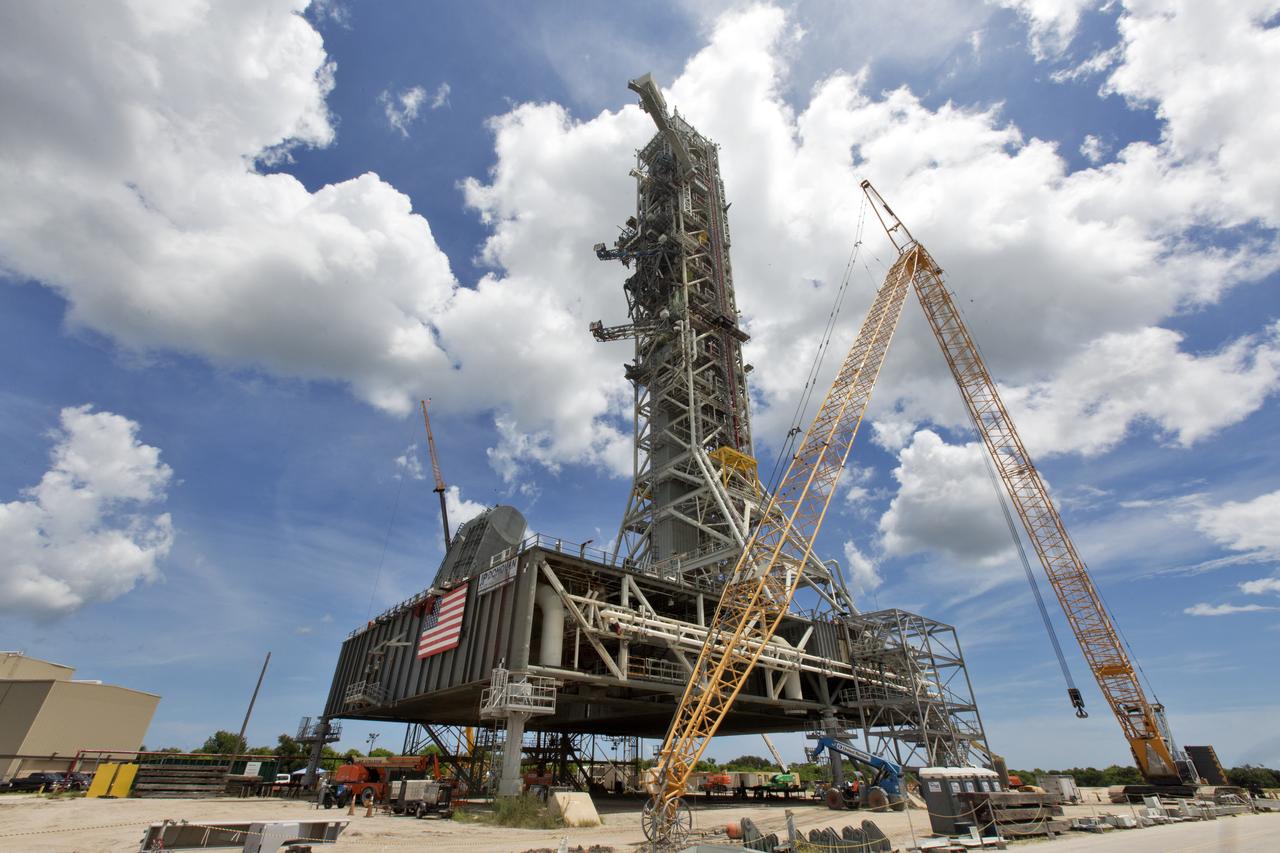

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, topmost umbilical, is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
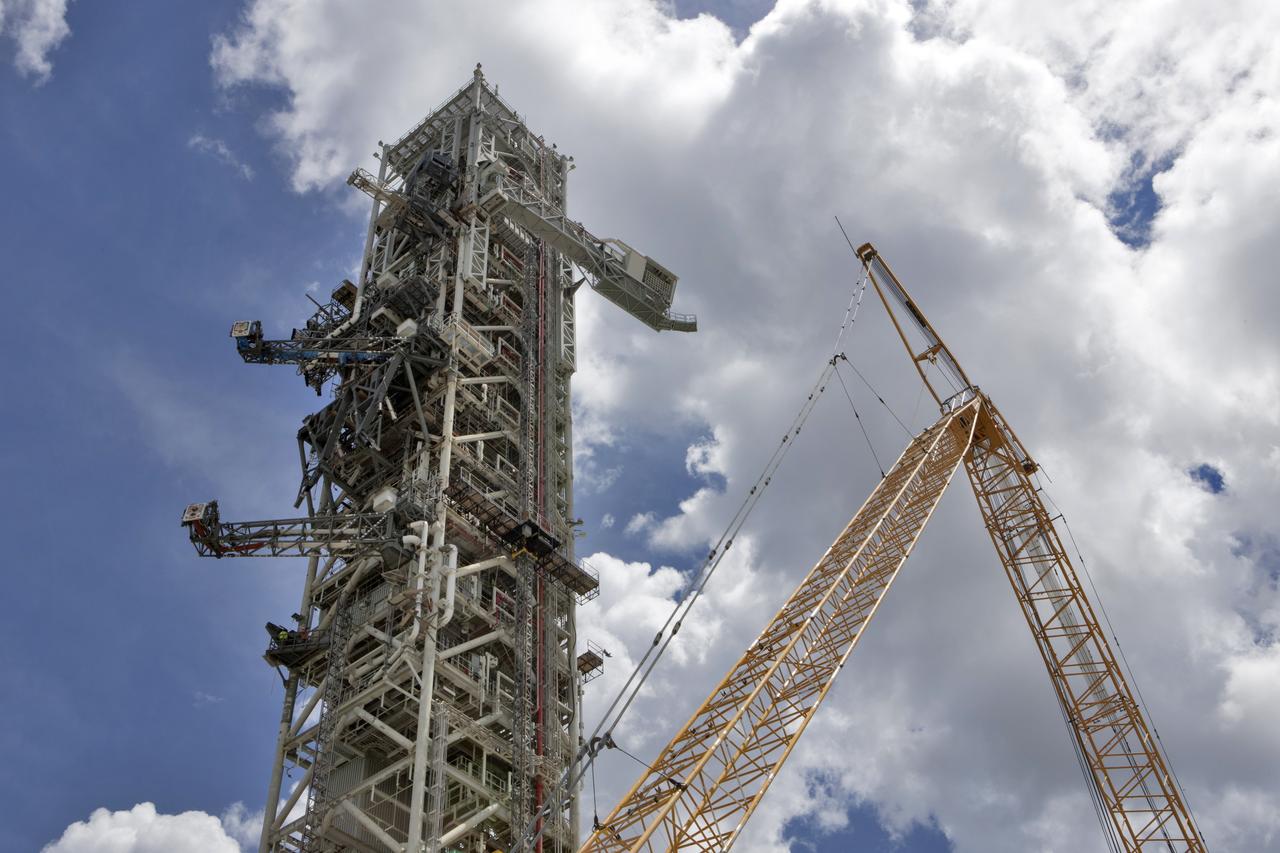

A swing test of the Orion crew access arm, top right, is in progress on the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 21, 2018. The crew access arm is located at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. Exploration Ground Systems extended all of the launch umbilicals on the ML tower to test their functionality before the mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, is moved to Launch Pad 39B and the Vehicle Assembly Building.
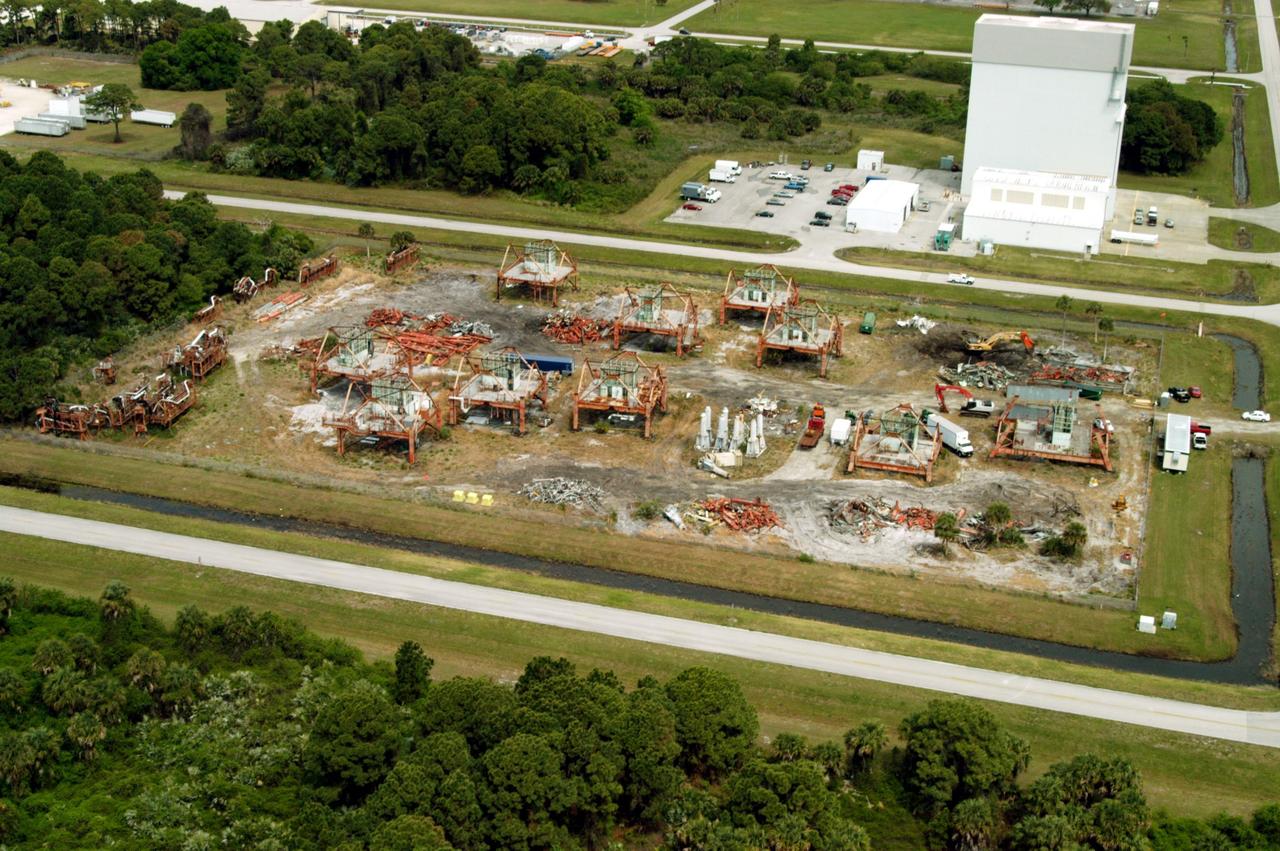

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial photo shows the storage area containing Launch Umbilical Towers that were used during the early years of the Space Program. In the upper right corner of the storage field is a Caterpillar excavator with a 48-inch shear demolishing LUT-1, used to launch Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
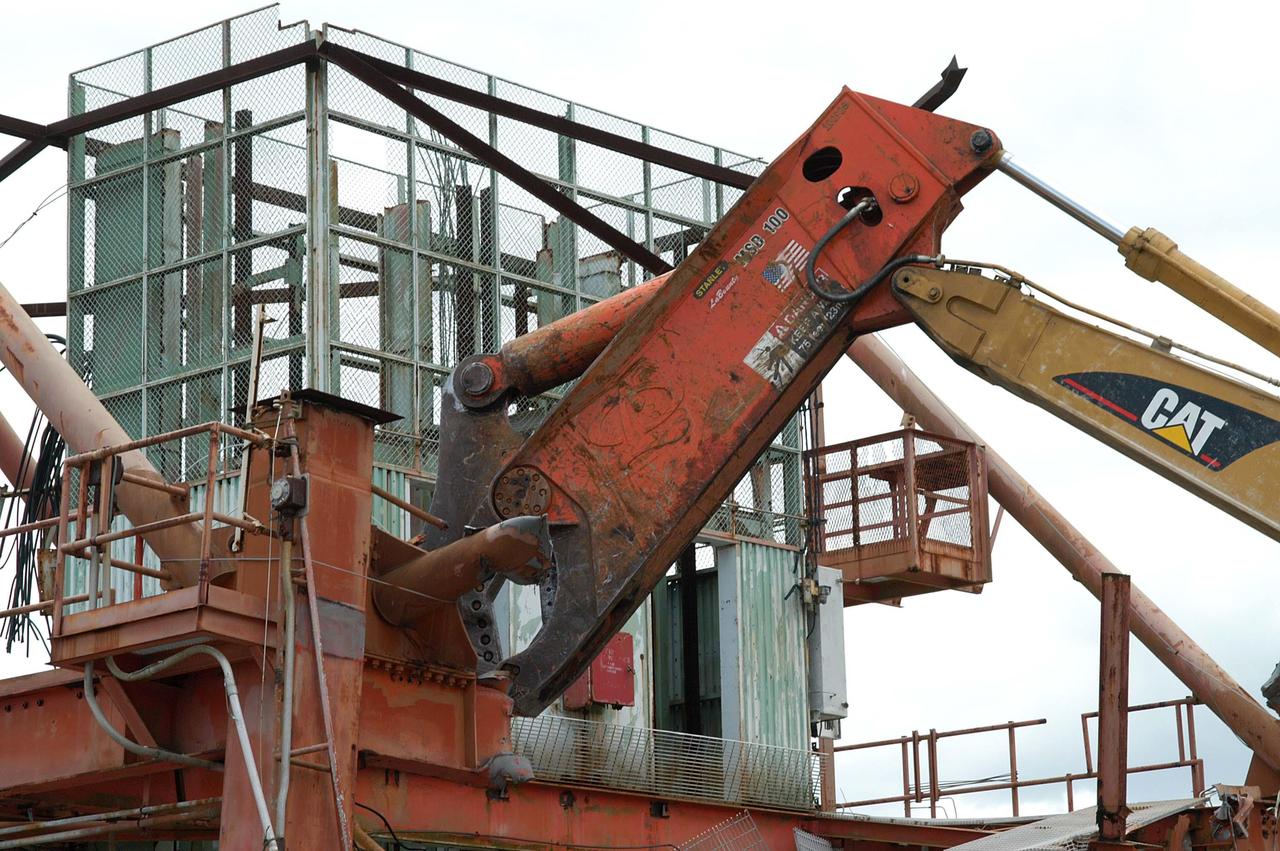

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking like a prehistoric monster crunching on its prey, the Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment tear down Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
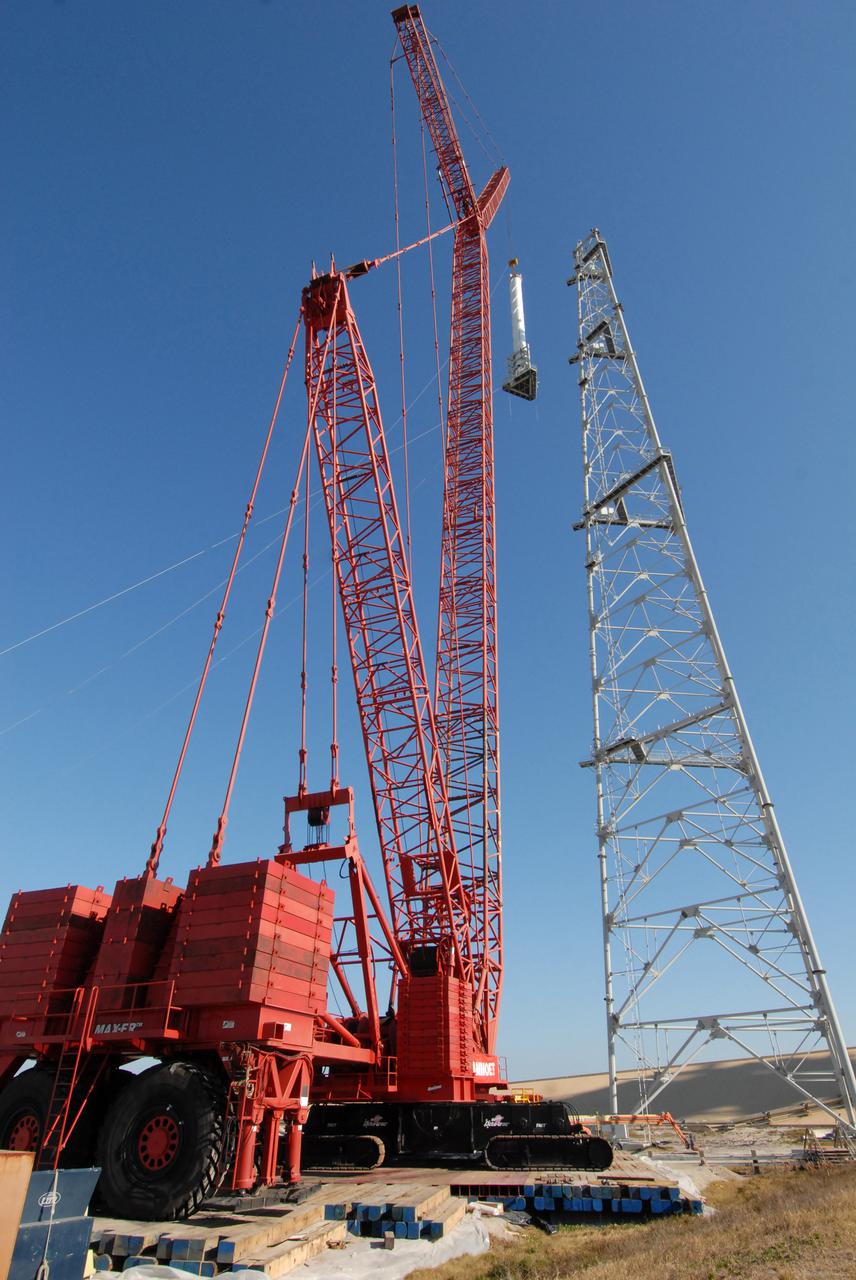

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts a 100-foot fiberglass lightning mast alongside the 500-foot tower where it will be installed. The tower is one of three being constructed for the Constellation Program and Ares_Orion launches. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009.
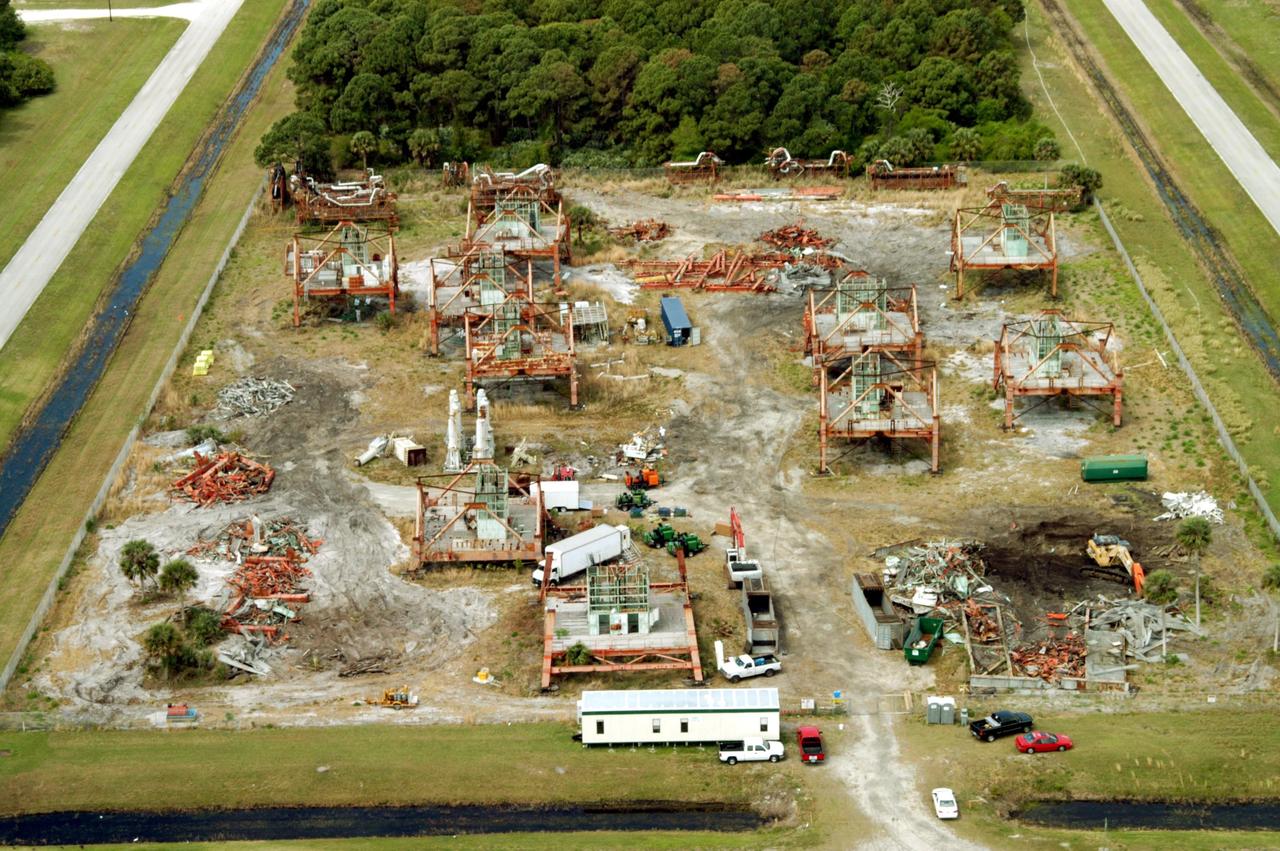

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial photo shows the storage area containing Launch Umbilical Towers that were used during the early years of the Space Program. In the lower right corner of the storage field is a Caterpillar excavator with a 48-inch shear demolishing LUT-1, used to launch Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
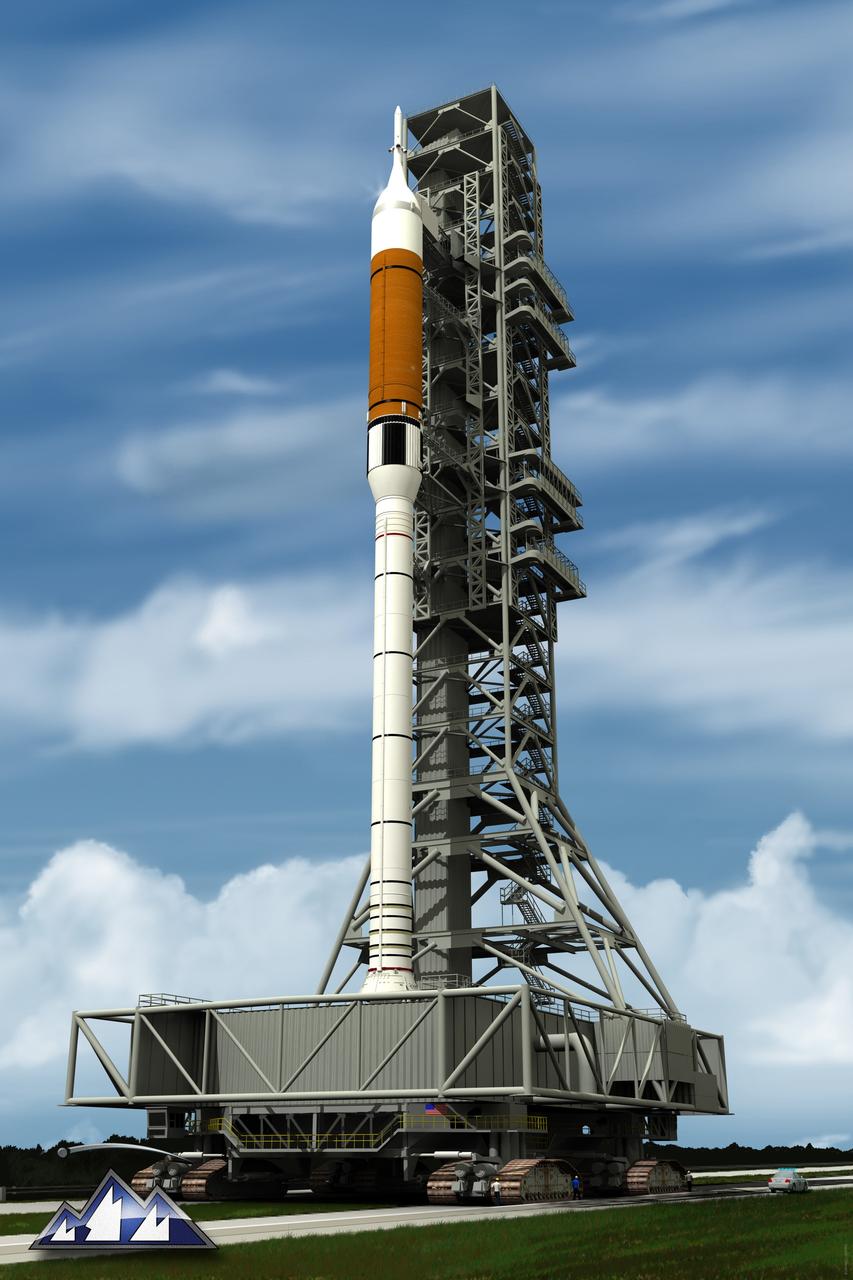

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Artist's rendering of the Constellation Program's mobile launcher platform with an Ares I rocket attached. The tower of the mobile launcher will have multiple platforms for personnel access and will be approximately 390 feet tall. The tower will be used in the assembly, testing and servicing of the Ares rockets at Kennedy and will also transport the Ares rockets to the launch pad and provide ground support for launches.
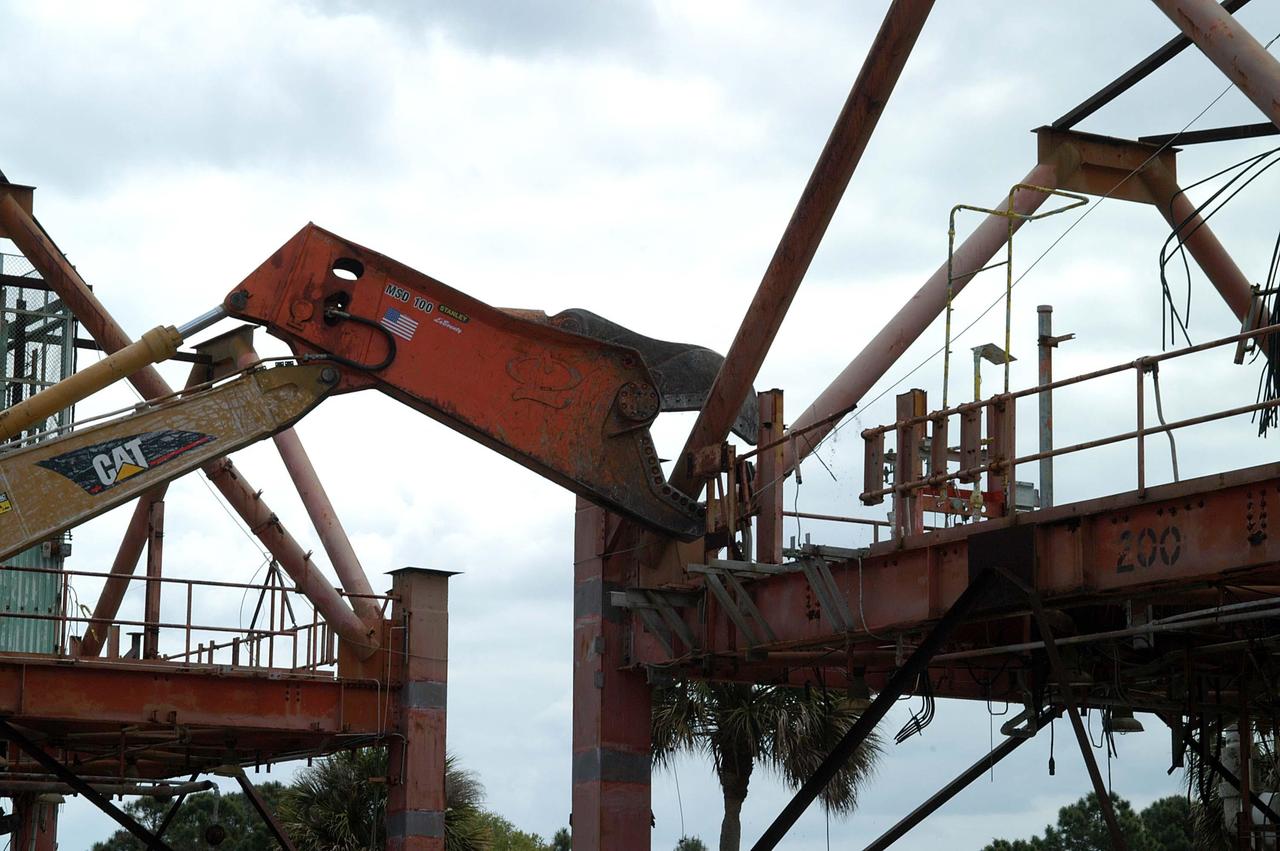

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking like a prehistoric monster crunching on its prey, the Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment tear down Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Artist's rendering of the empty Constellation Program's mobile launcher platform planned for the Ares I rocket. The tower of the mobile launcher will have multiple platforms for personnel access and will be approximately 390 feet tall. The tower will be used in the assembly, testing and servicing of the Ares rockets at Kennedy and will also transport the Ares rockets to the launch pad and provide ground support for launches.
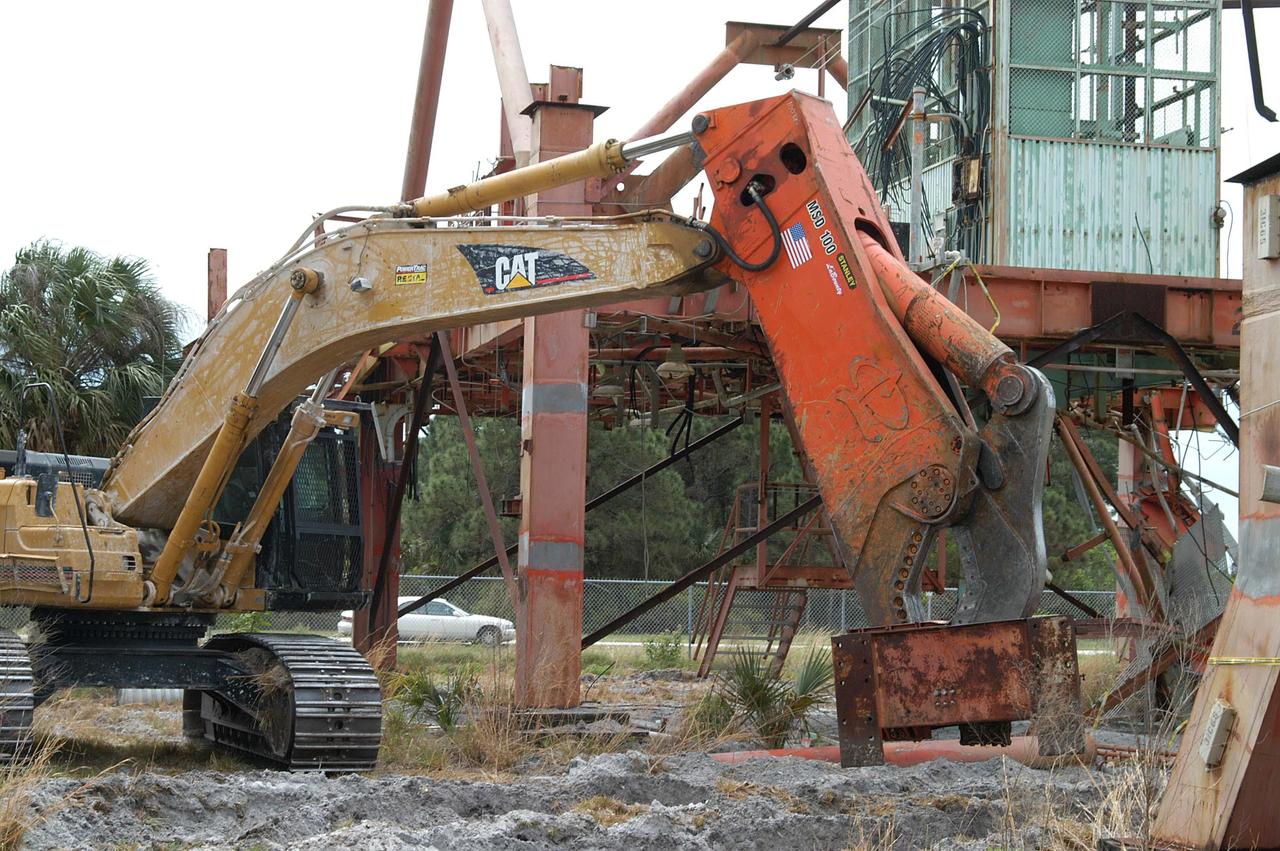

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking like a prehistoric monster crunching on its prey, the Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment tear down Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
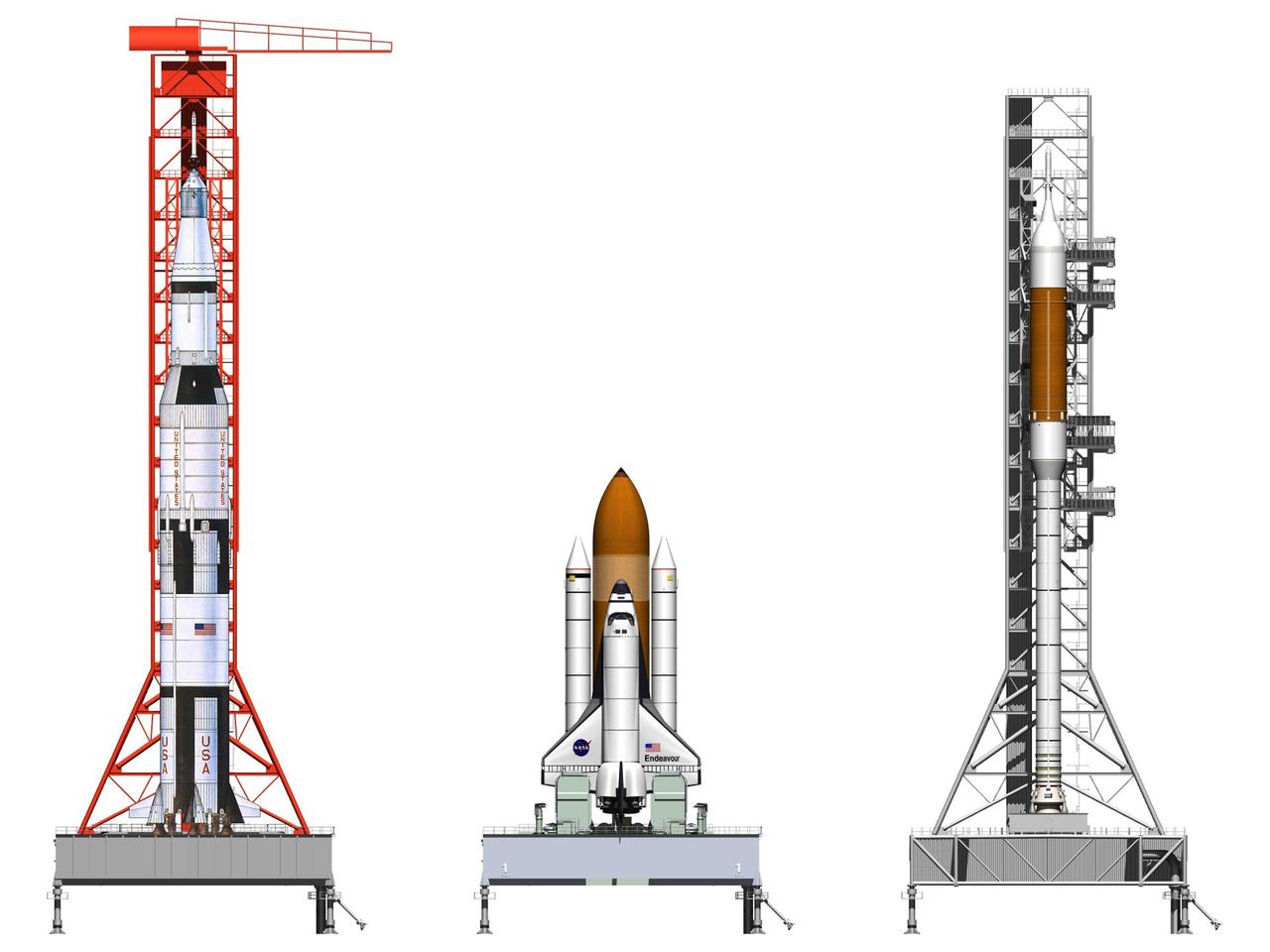
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Artist's rendering of the Constellation Program's Ares V rocket on the mobile launcher platform (left) and the Ares I rocket on the platform (right) with the space shuttle in between for comparison. The tower of the mobile launcher will have multiple platforms for personnel access and will be approximately 390 feet tall. The tower will be used in the assembly, testing and servicing of the Ares rockets at Kennedy and will also transport the Ares rockets to the launch pad and provide ground support for launches.
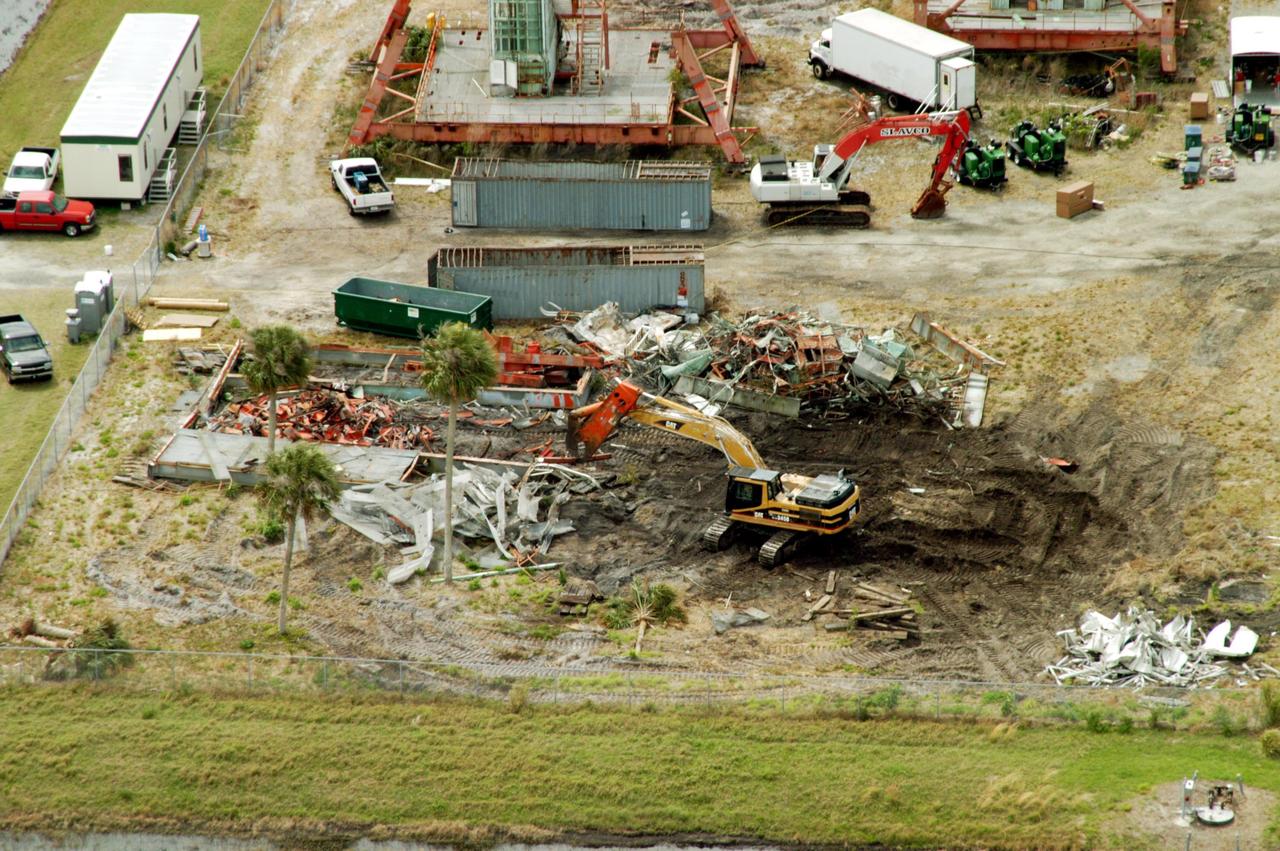

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial photo shows the storage area containing Launch Umbilical Towers that were used during the early years of the Space Program. The central focus is a Caterpillar excavator with a 48-inch shear demolishing LUT-1, used to launch Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
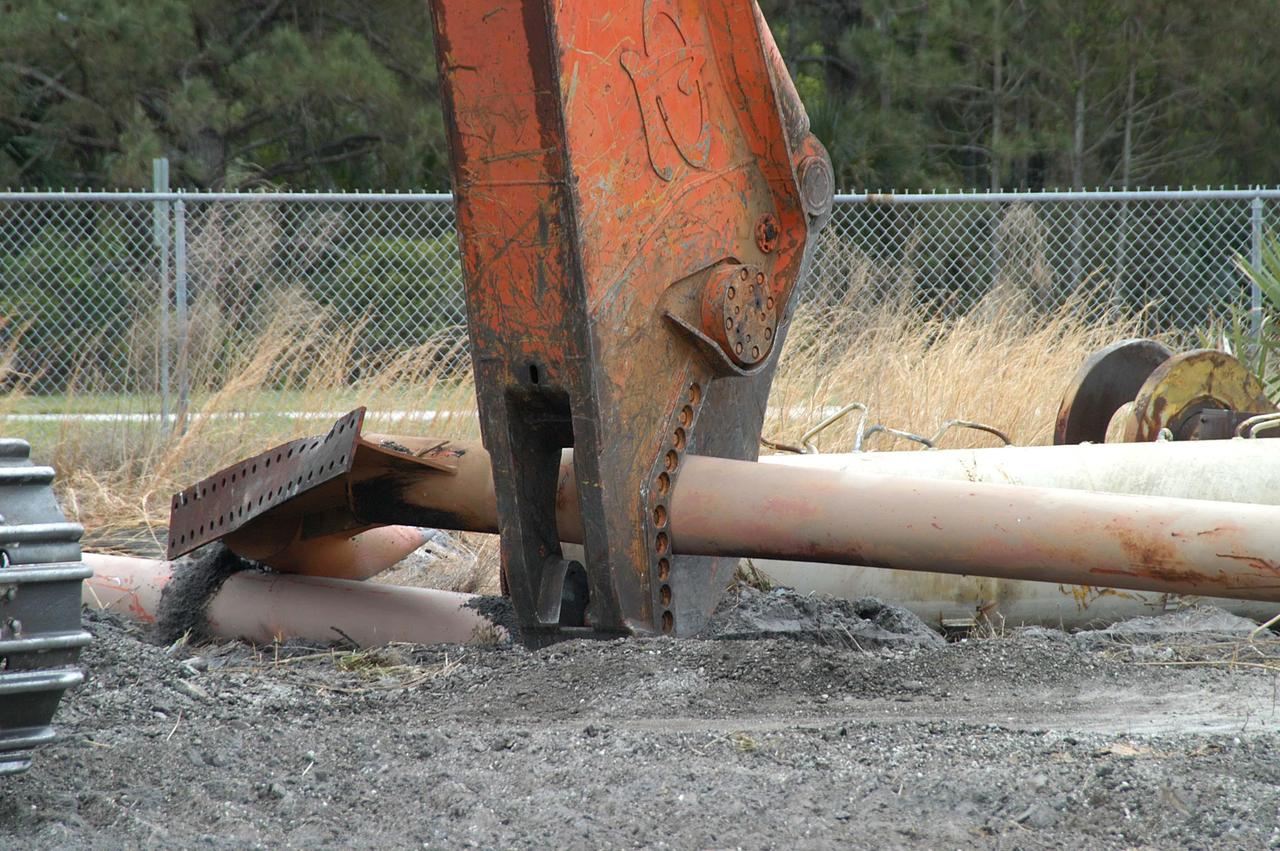

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Like a dinosaur crunching on its prey, the Caterpillar excavator and 48-inch shear attachment tear down Launch Umbilical Tower No. 1 (LUT-1) stored in the Industrial Area of KSC. The LUT-1 was part of the launch system used for Apollo-Saturn V, launching Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
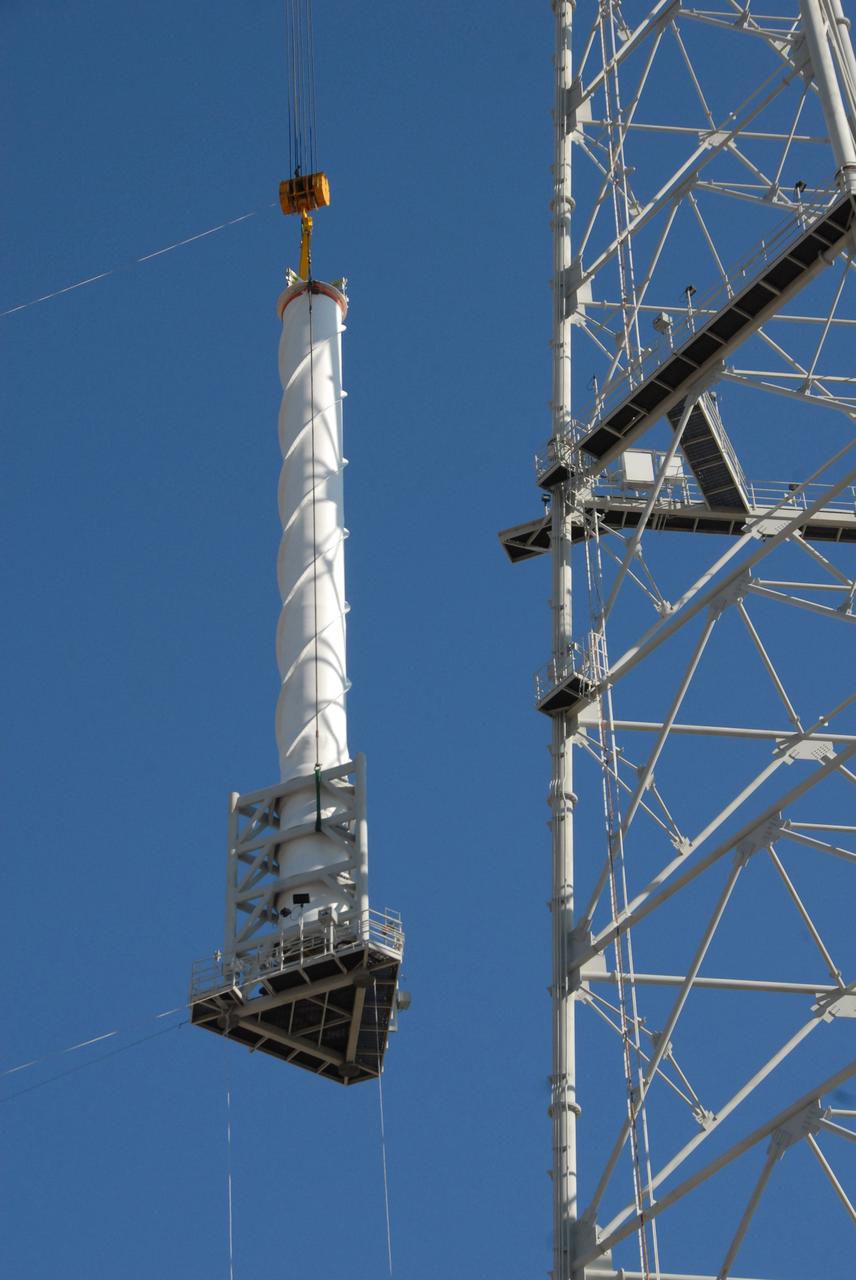

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts a 100-foot fiberglass lightning mast alongside the 500-foot tower where it will be installed. The tower is one of three being constructed for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009.
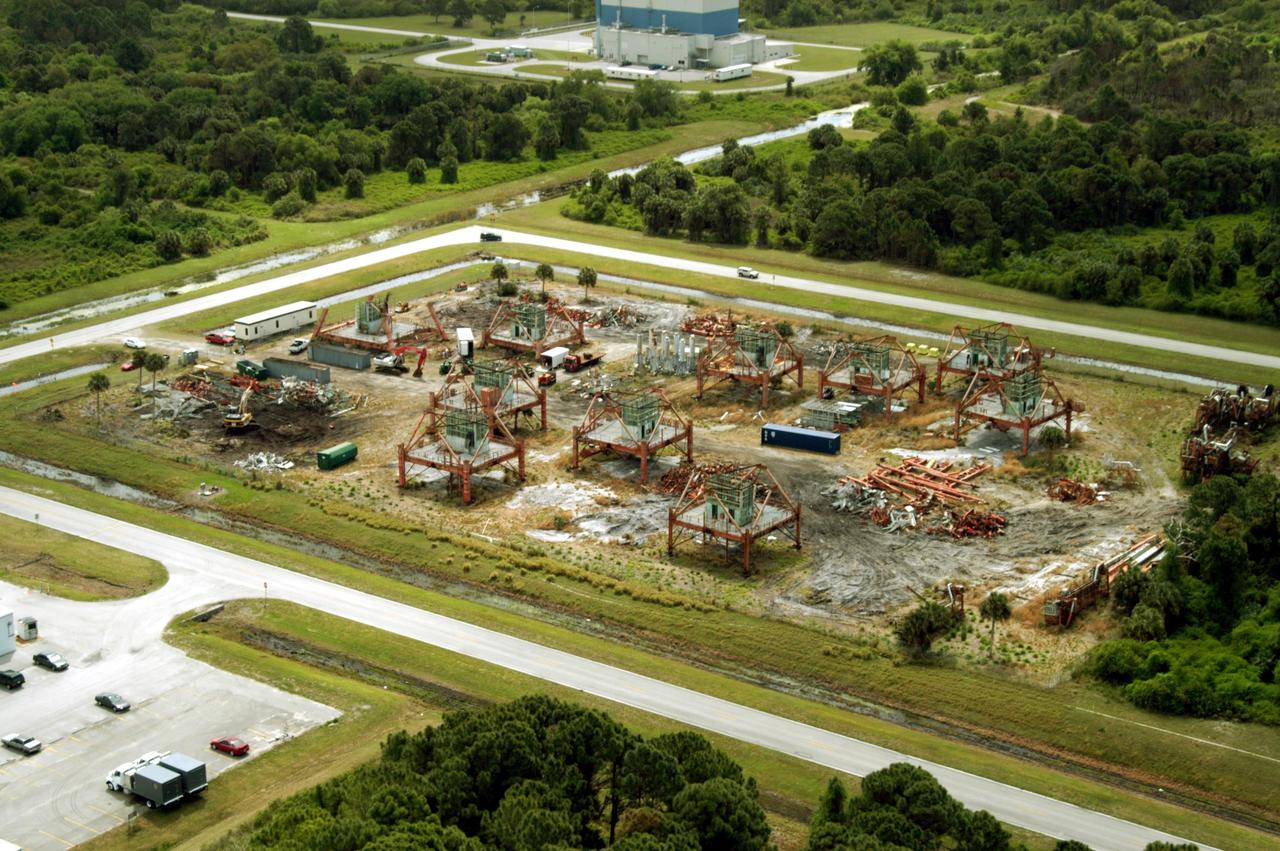

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This aerial photo shows the storage area containing Launch Umbilical Towers that were used during the early years of the Space Program. In the lower left corner of the storage field is a Caterpillar excavator with a 48-inch shear demolishing LUT-1, used to launch Apollo 8, Apollo 11, Skylab manned missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The shear is one used in the deconstruction of the Twin Towers in New York City after 9/11.
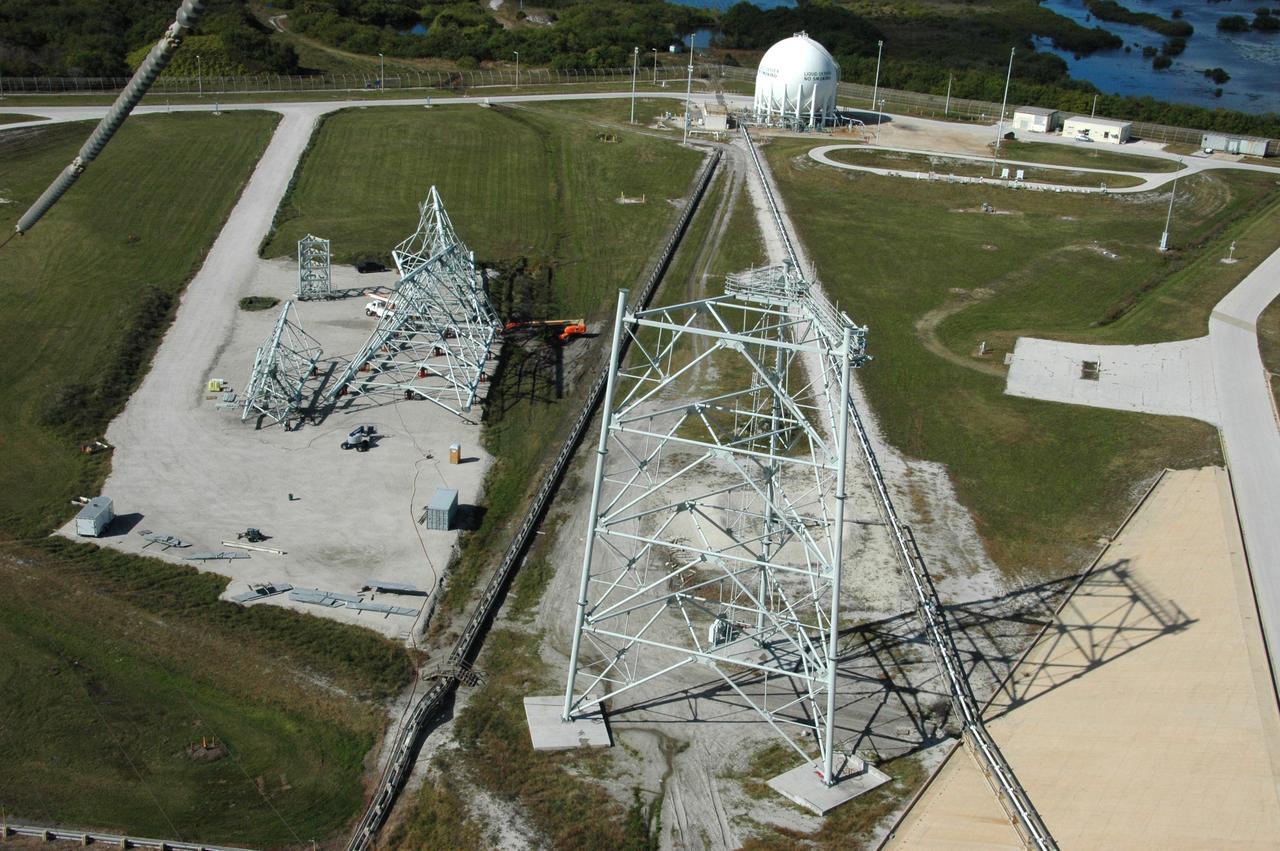

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the new lightning towers is under construction. The towers will hold catenary wires as part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
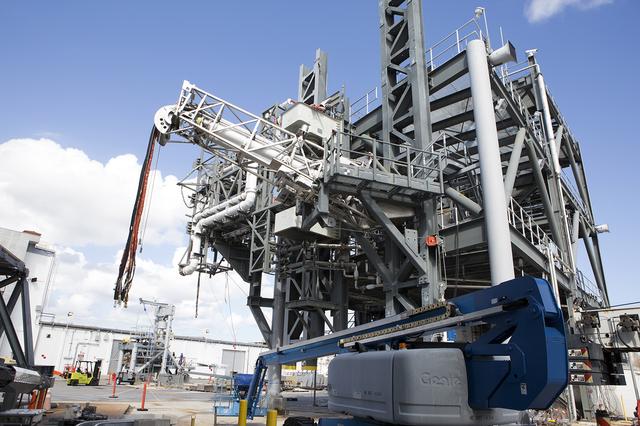

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
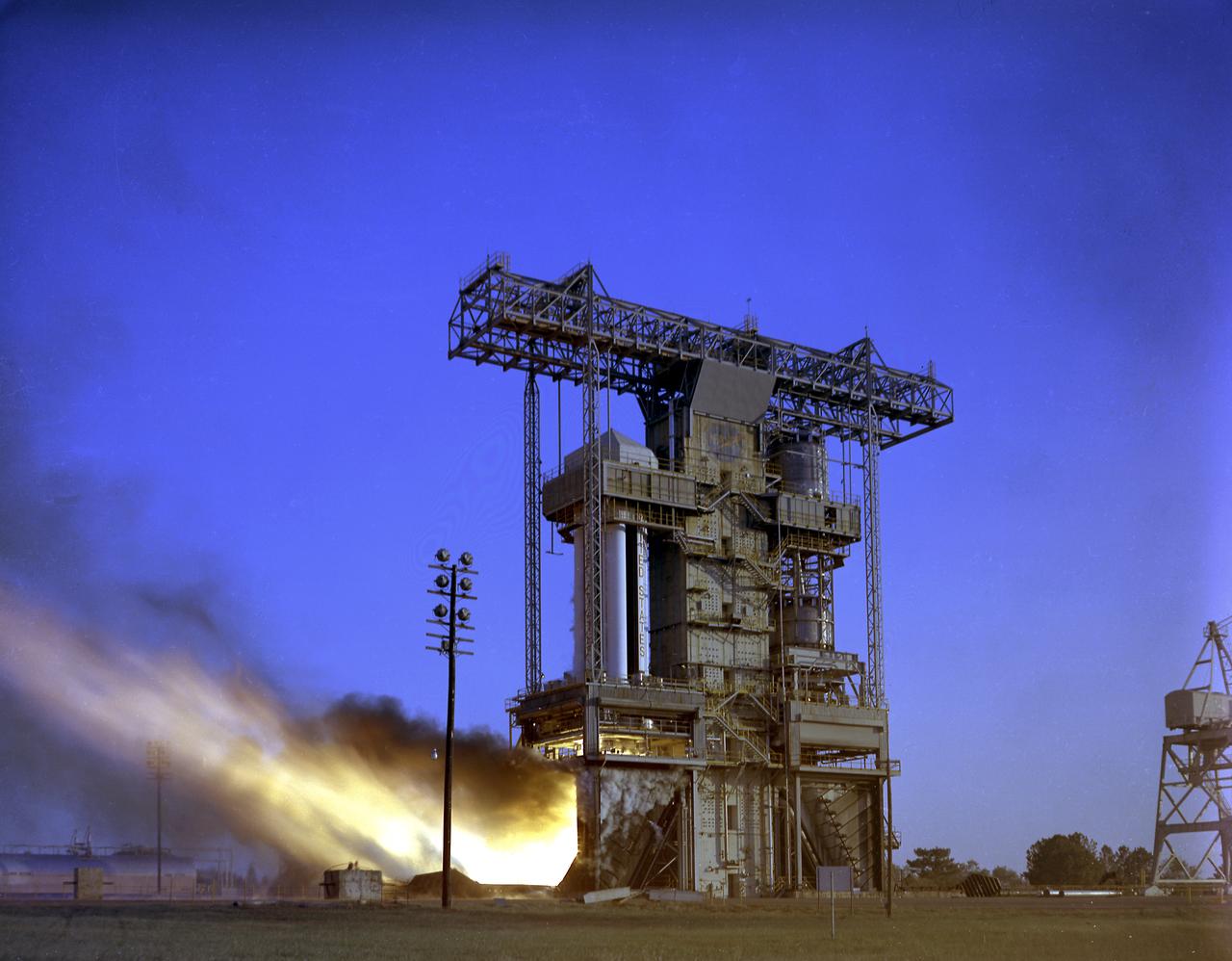

Test firing of the Saturn I S-I Stage (S-1-10) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. This test stand was originally constructed in 1951 and sometimes called the Redstone or T tower. In l961, the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stages, which produced a total thrust of 1,600,000 pounds. The name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket rides aboard a crawler-transporter as it exits the massive Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket is bolted to its mobile launcher platform for the move to the launch pad. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket moves away from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket's slow, 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

The CPS controls operations used by Glenn Research Center's wind tunnels, propulsion systems lab, engine components research lab, and compressor, turbine and combustor test cells. Used widely throughout the lab, it operates equipment such as exhausters, chillers, cooling towers, compressors, dehydrators, and other such equipment.
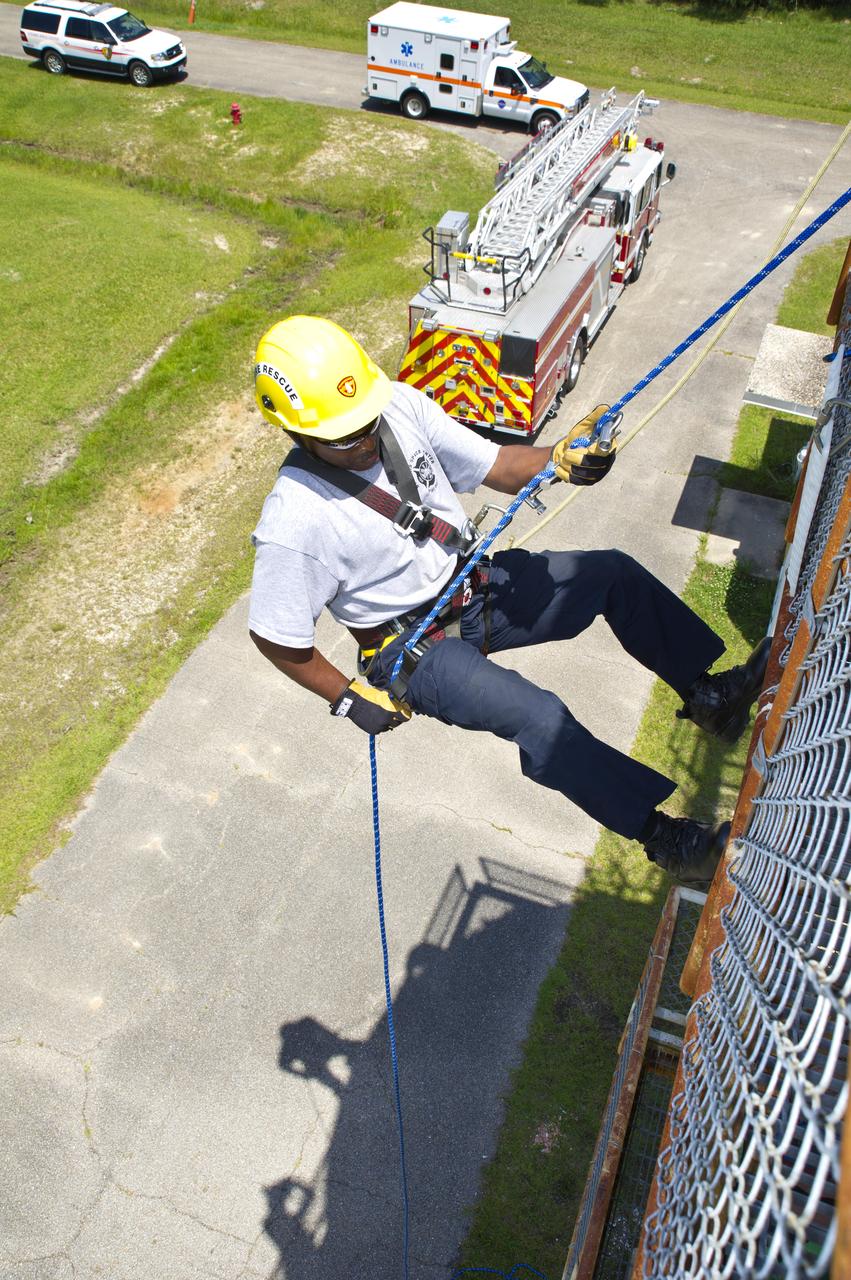

Stennis Space Center firefighter Rodney Boone rappels a tower structure during an onsite training exercise May 11, 2012. The training focused on high-angle rope rescues, which could be needed on the new 300-foot-tall A-3 Test Stand at Stennis.
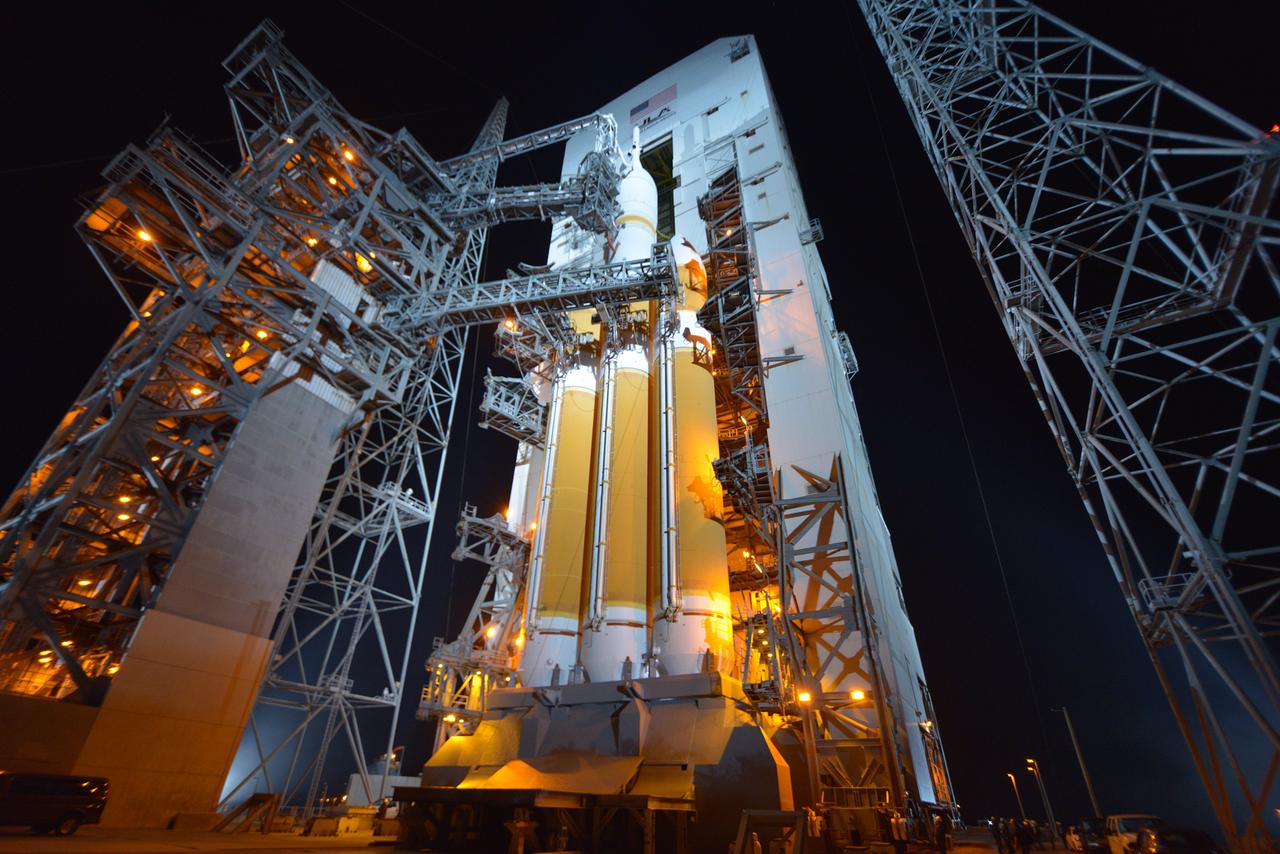
The full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
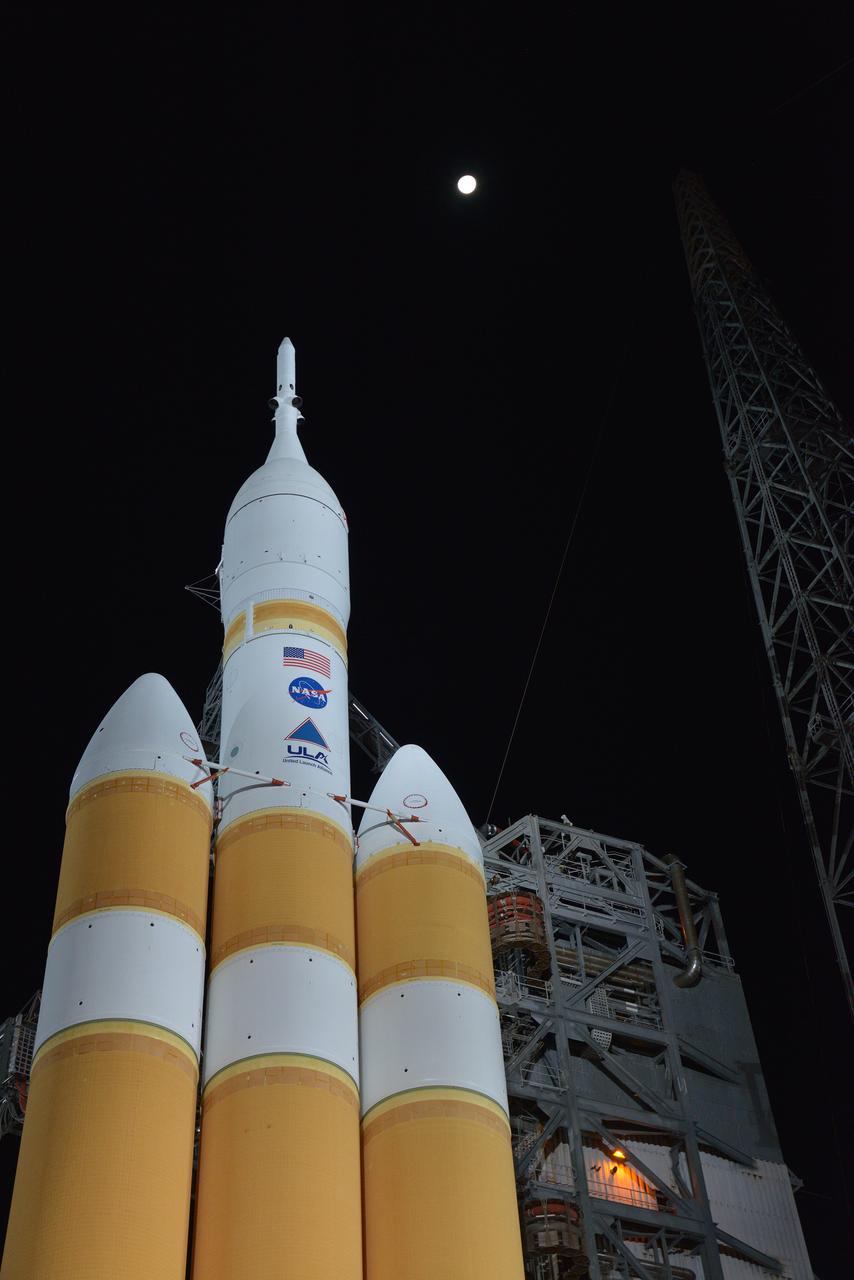

TThe full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
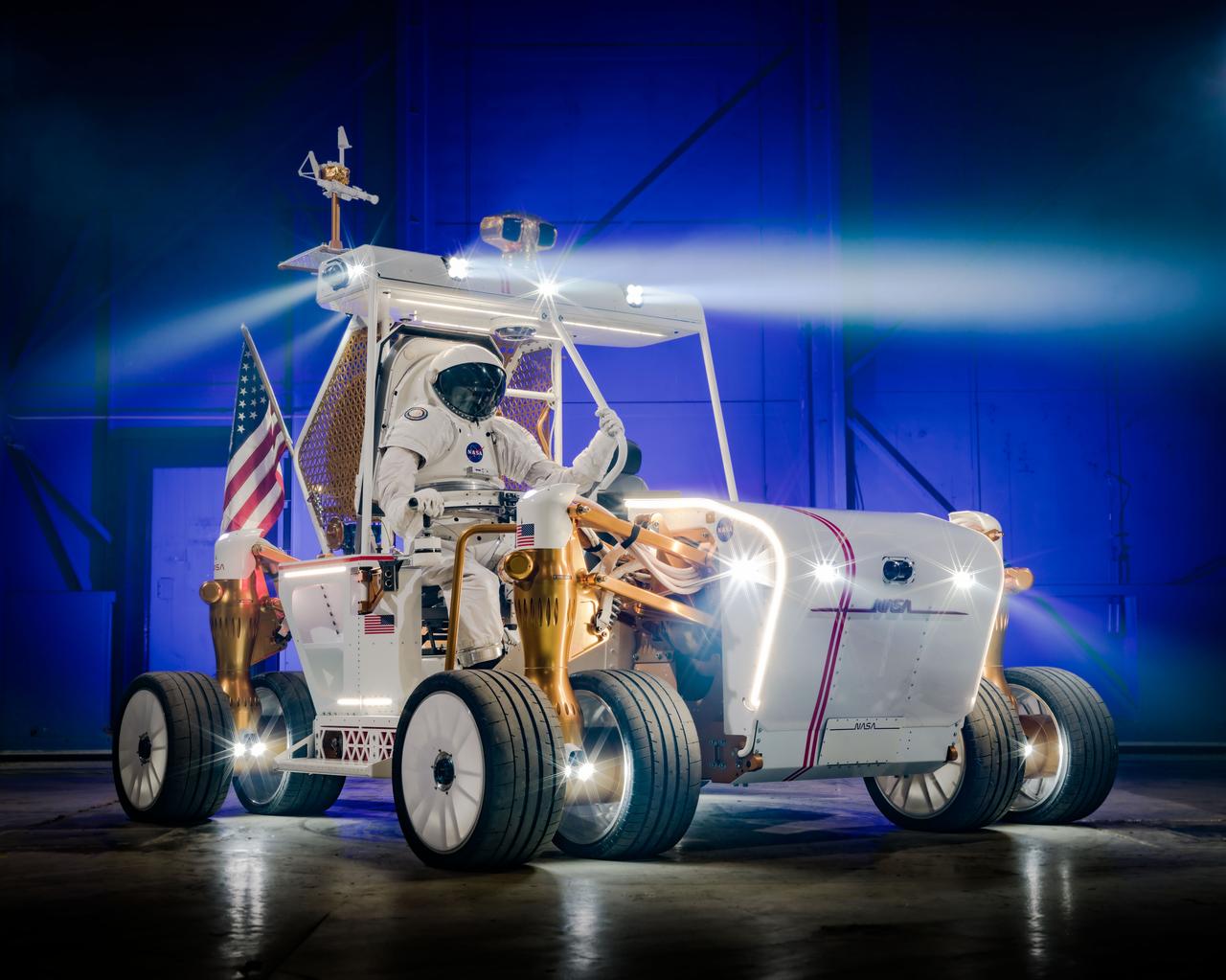
PHOTO DATE: 11-22-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 49 - West High Bay Tower SUBJECT: Production Photography of Lunar Terrain Vehicle Ground Test Unit PHOTO CREDIT: NASA / BILL STAFFORD AND HELEN ARASE VARGAS
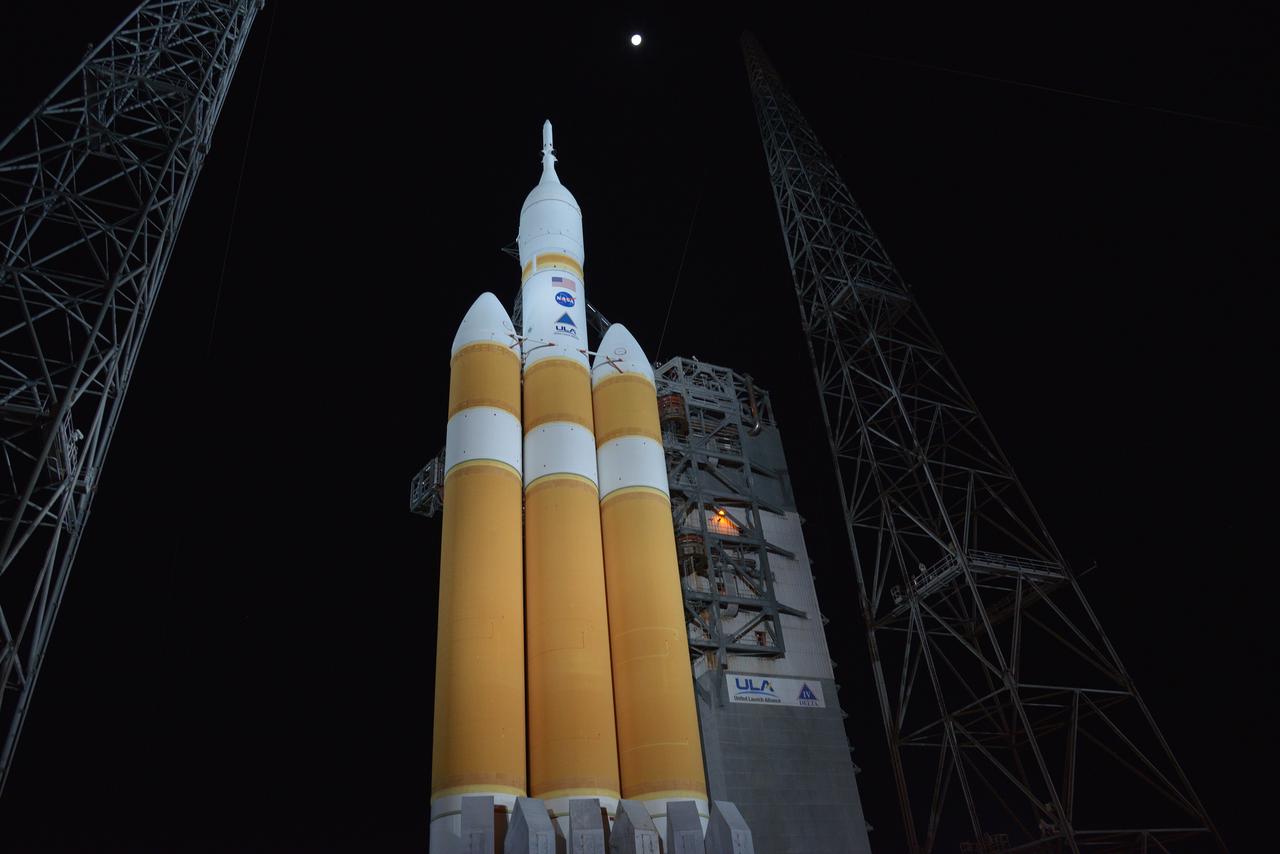

The full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The test subject of Airspace Technology Demonstration 2 is “Integrated Arrivals Departures Scheduling,” a software tool that coordinates schedules between the ramp, tower, terminal and center control facilities, allowing air traffic controllers to better predict where and when to send aircraft in order to reduce congestion.
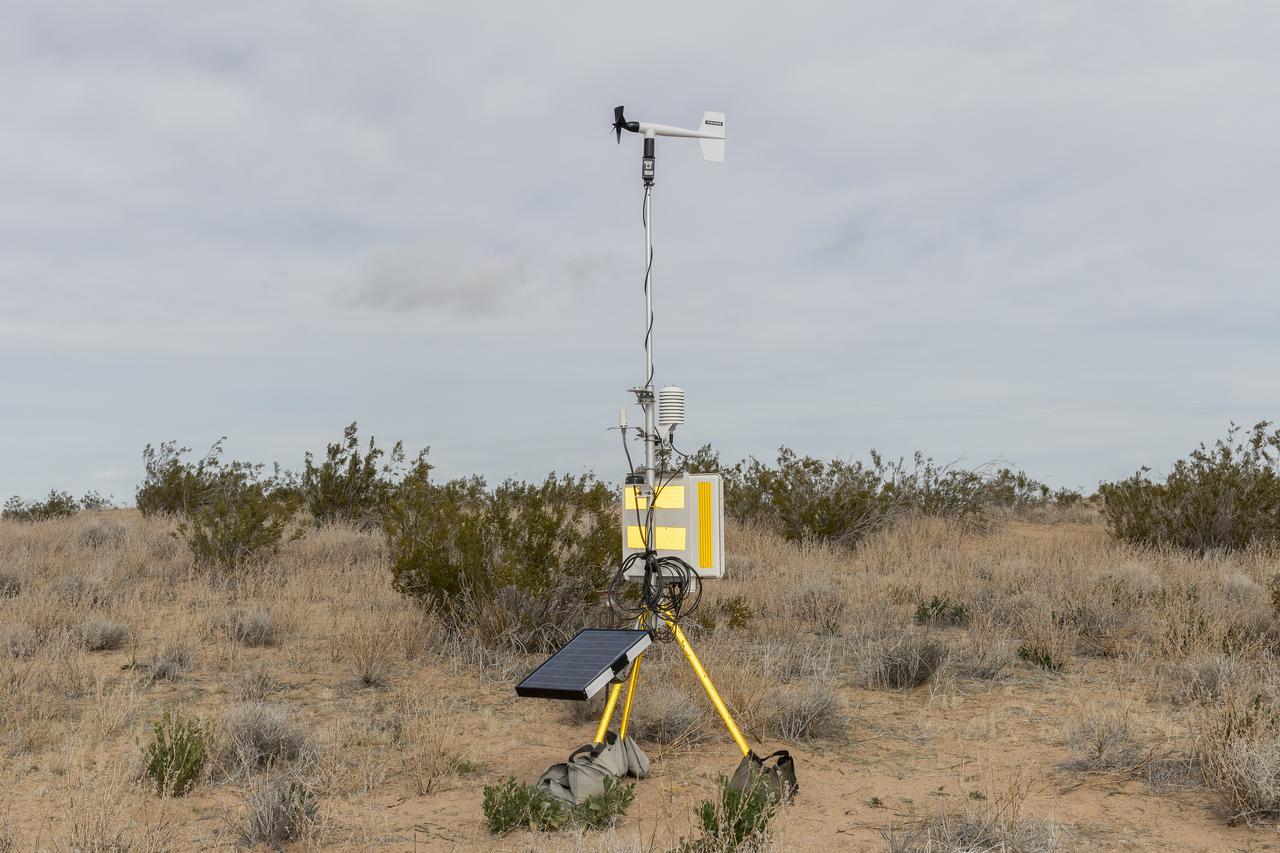

The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. Researchers used three weather towers and a sonic anemometer to collect weather and atmospheric data while recording sonic booms generated by an F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center.
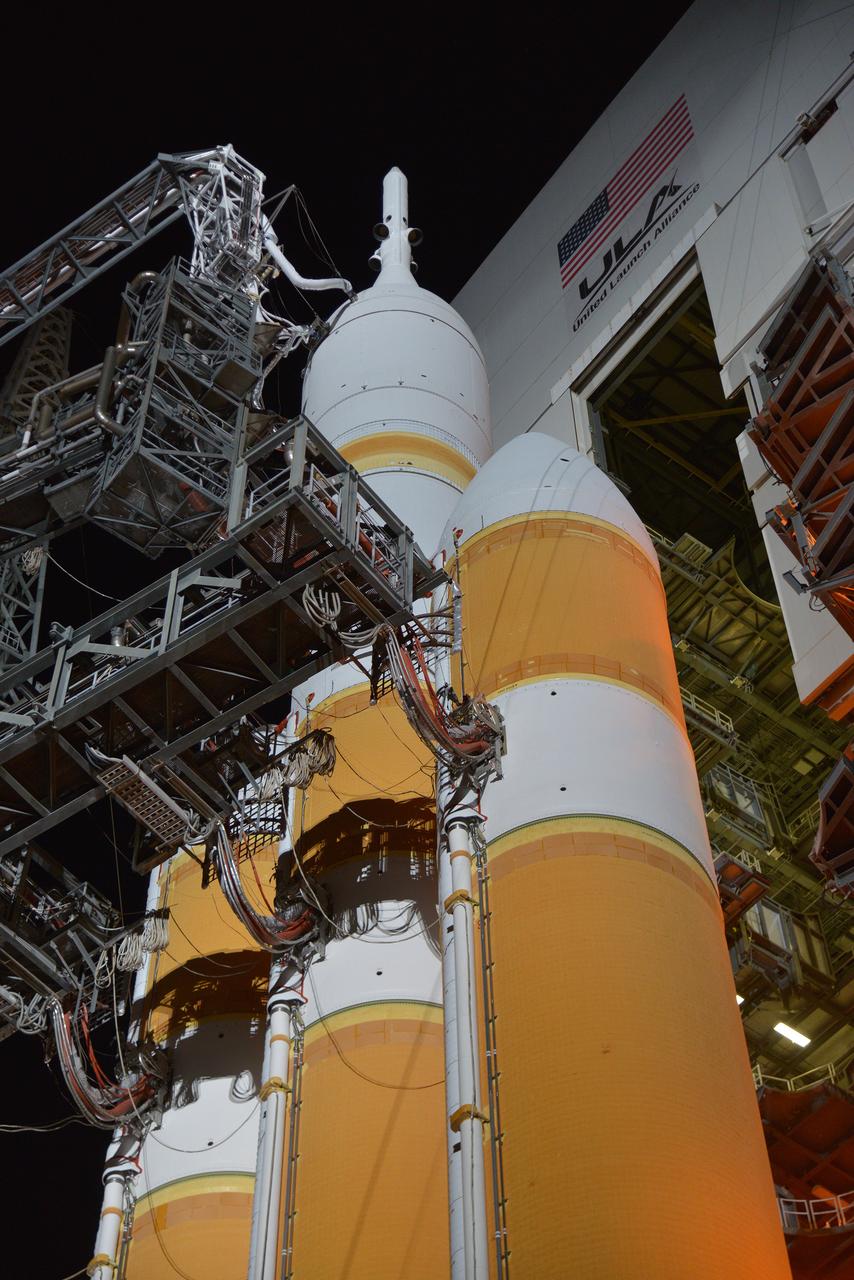

The full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
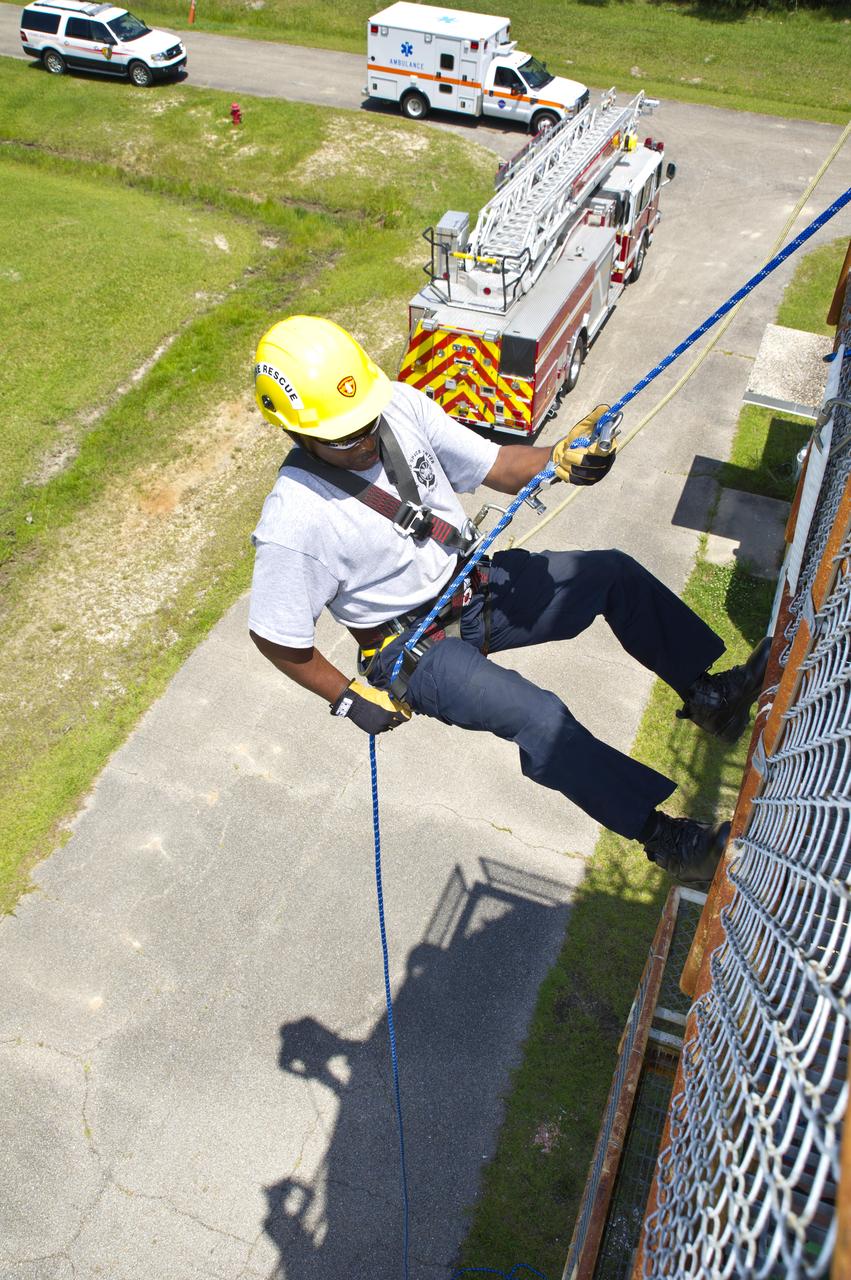

Stennis Space Center firefighter Rodney Boone rappels a tower structure during an onsite training exercise May 11, 2012. The training focused on high-angle rope rescues, which could be needed on the new 300-foot-tall A-3 Test Stand at Stennis.
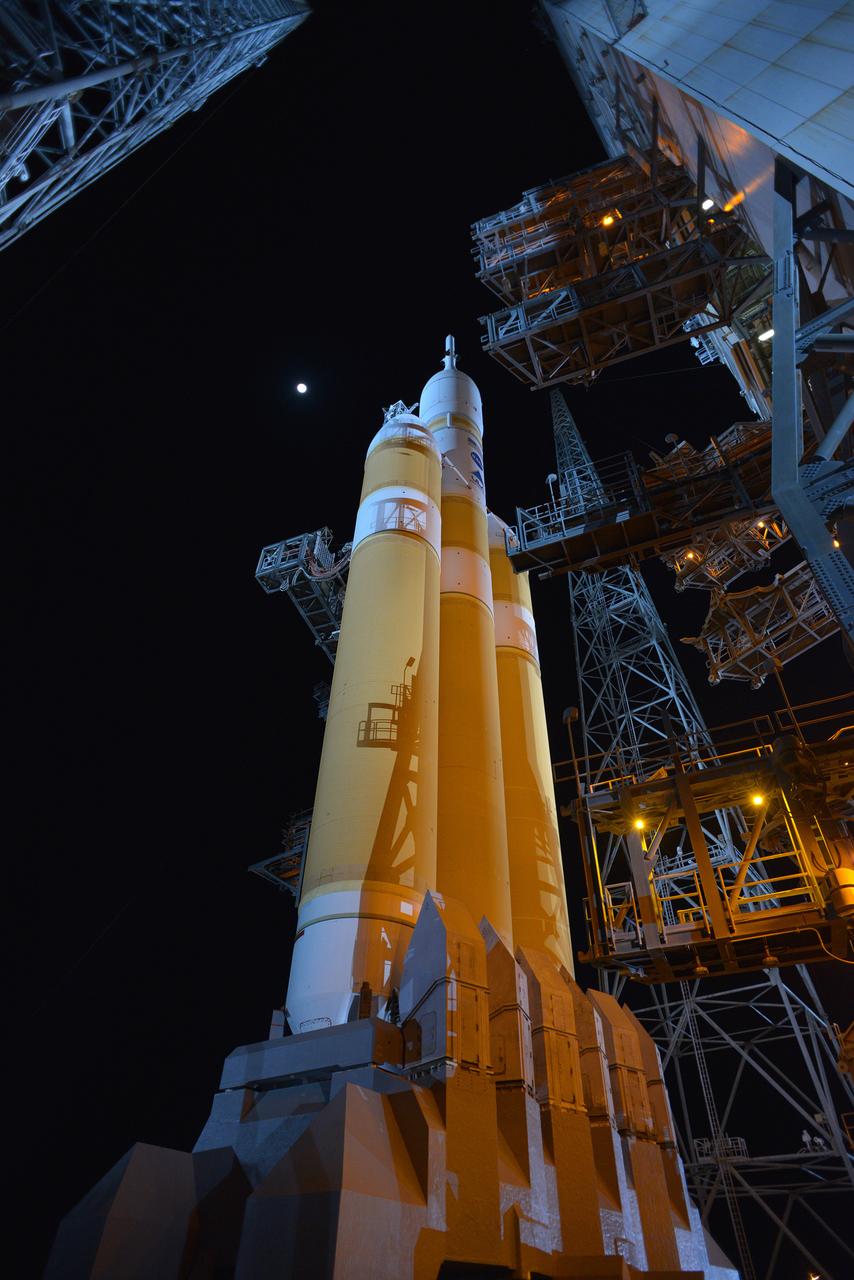

The full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The full United Delta IV Heavy with Orion on top is revealed on Dec. 3, 2014 as the mobile service tower is rolled back in preparation for the 7:05 am Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
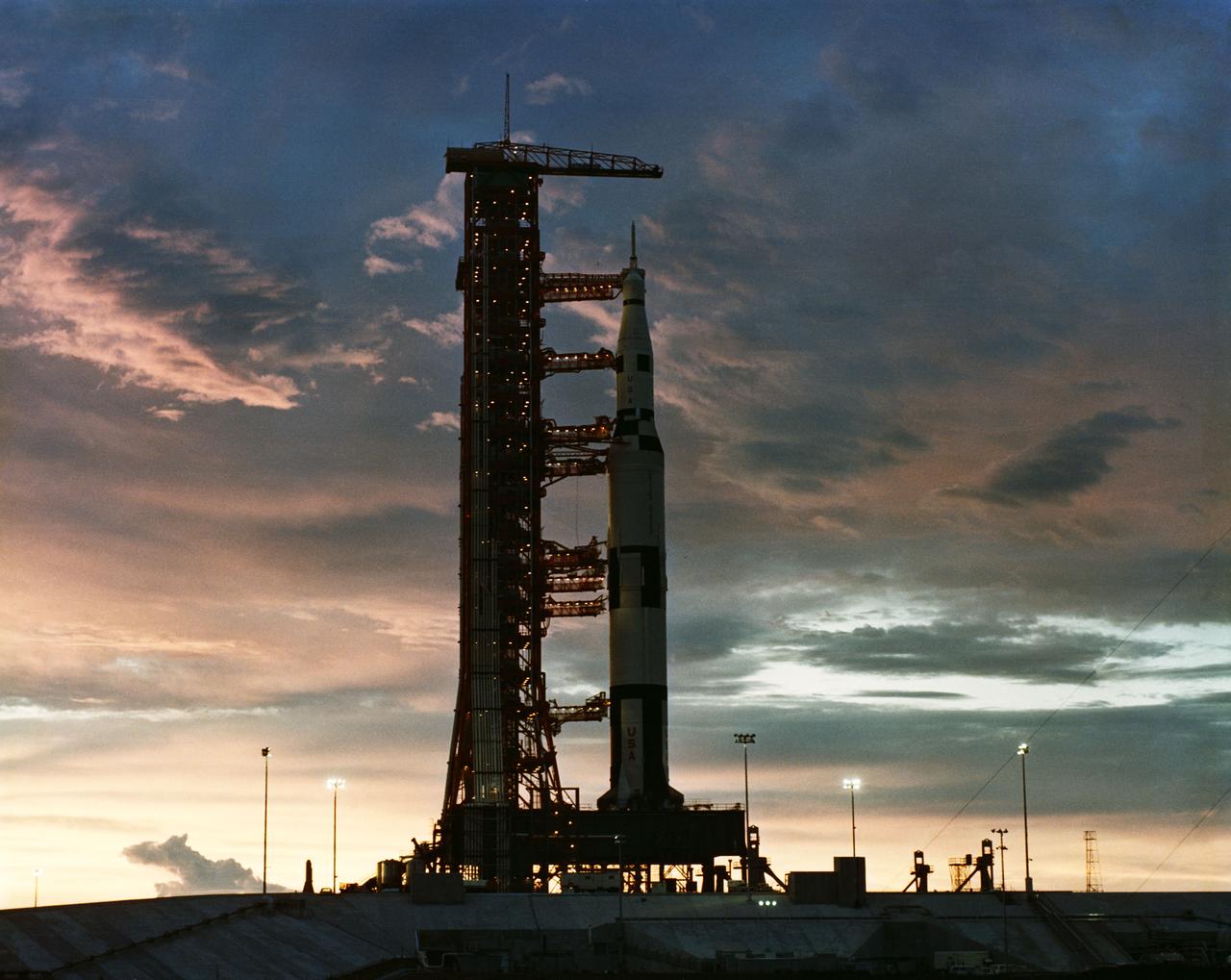

S66-41179 (25 May 1966) --- Sunrise at Pad 39A during a checkout of facilities. An Apollo/Saturn Facilities Test Vehicle and Launch Umbilical Tower (LUT) stand atop the pad's bandstand. This test vehicle, designated Apollo/Saturn 500-F, is being used to verify launch facilities, train launch crews, and develop test and checkout procedures.
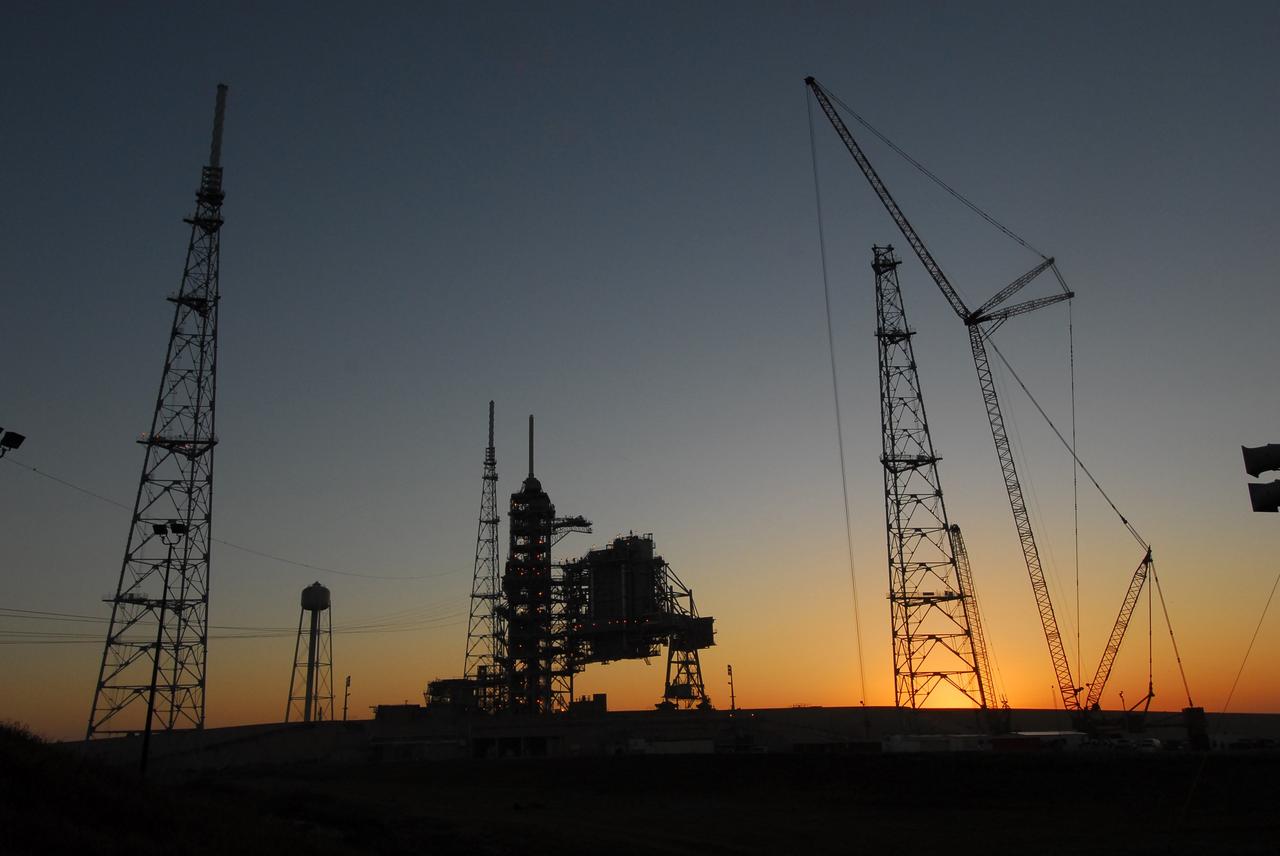

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The rosy dawn sky over NASA's Kennedy Space Center reveals the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B. The two towers at left contain the lightning mast on top; the one at right does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

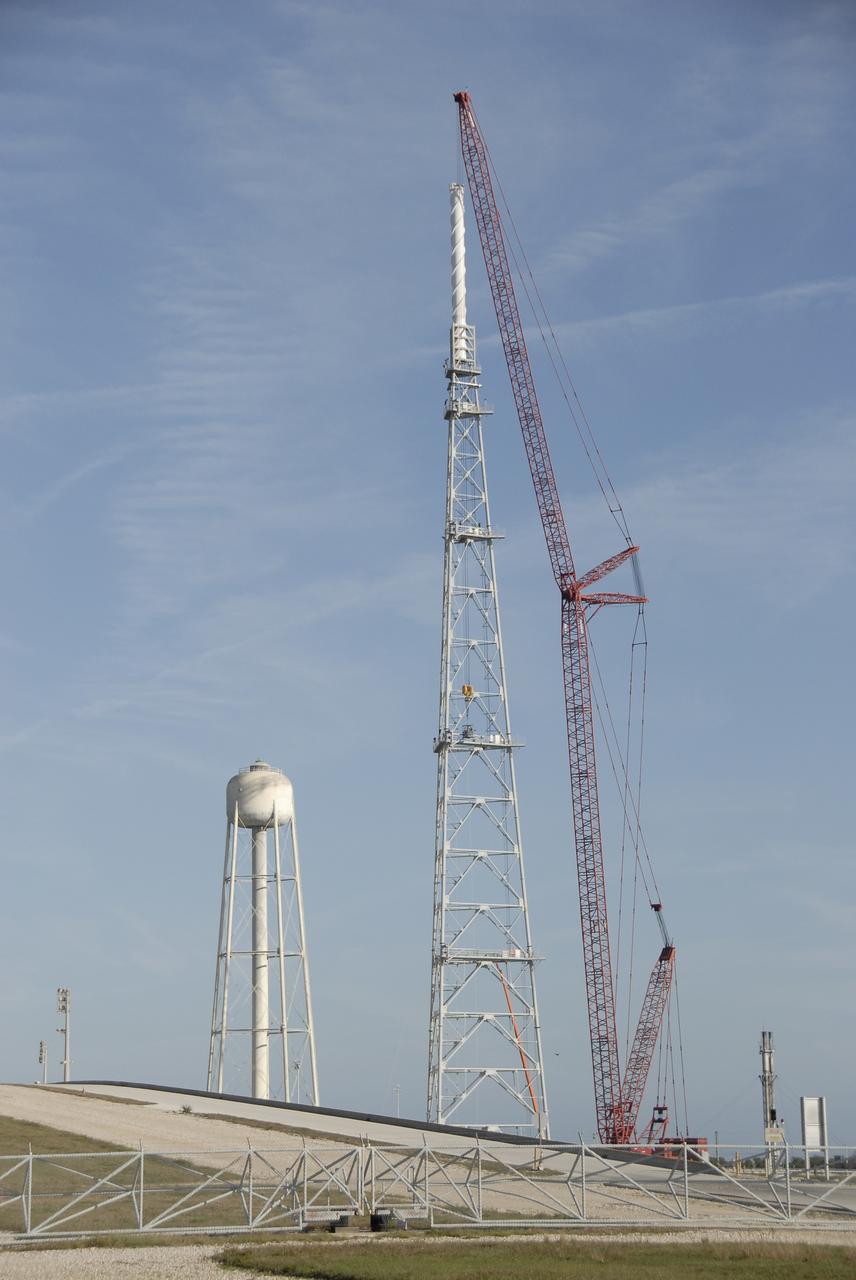
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A lightning mast remains to be lifted atop the third and final lightning tower erected on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Three towers surround the pad. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane places the 100-foot fiberglass mast atop the new lightning tower constructed on the pad. The towers are part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with the additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
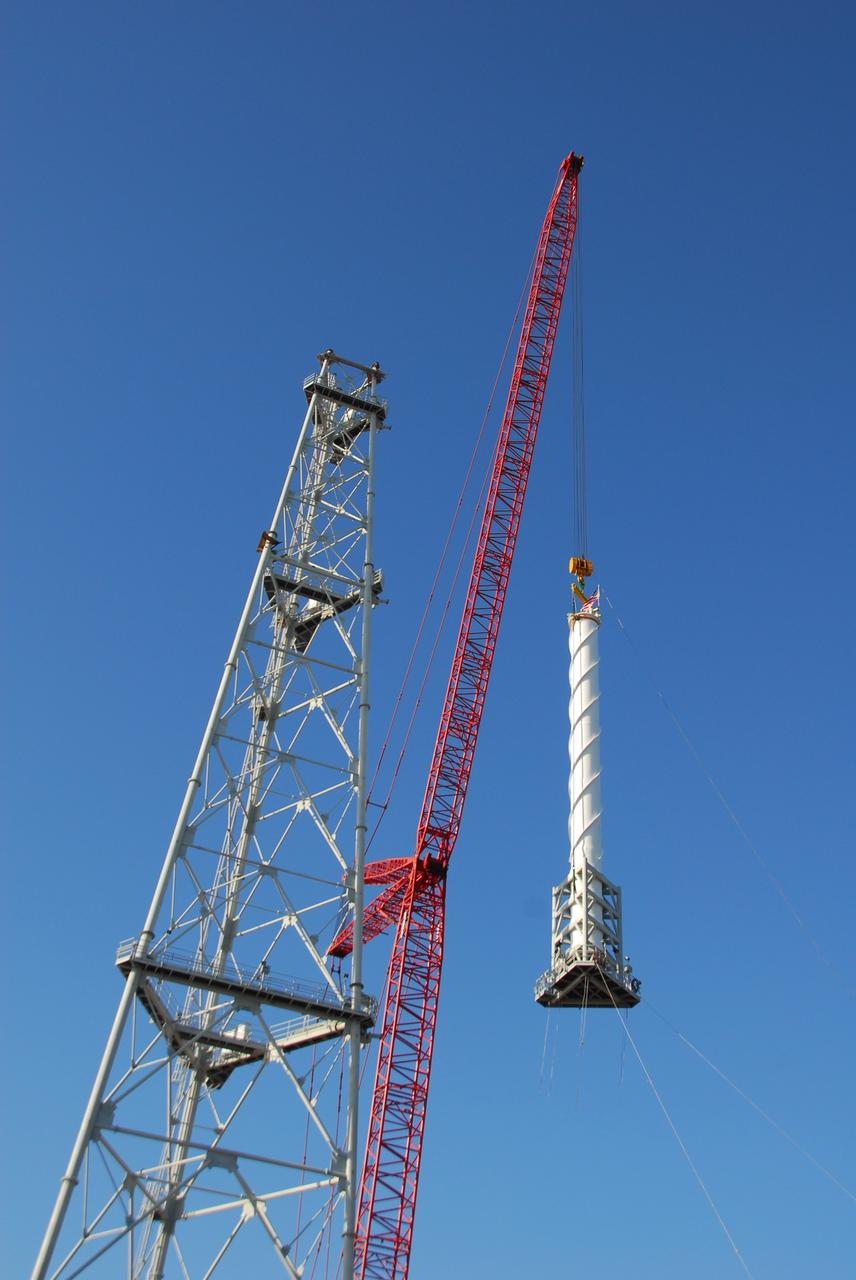

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a giant crane lifts the 100-foot lightning mast alongside the newly erected lightning tower, one of three around the pad. The mast will be installed on top of the tower. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
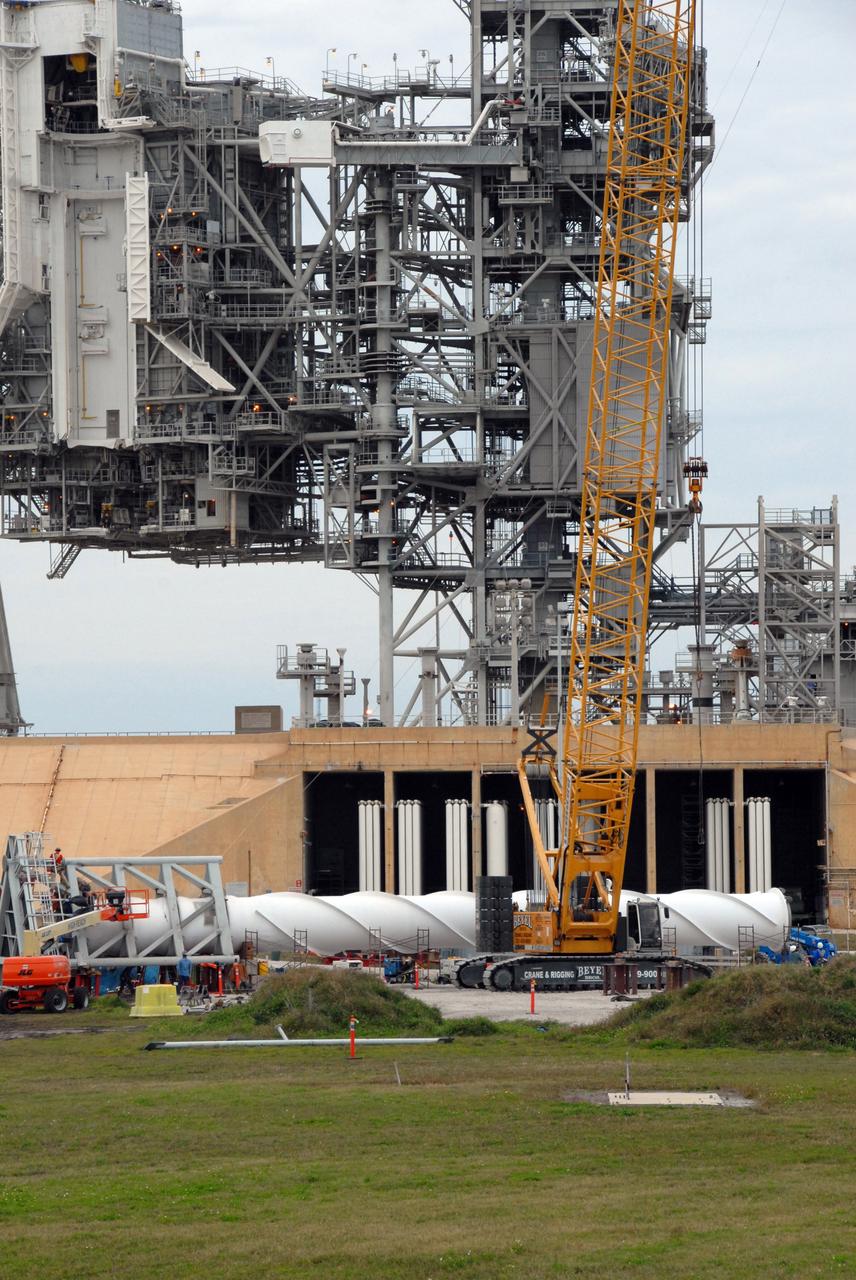

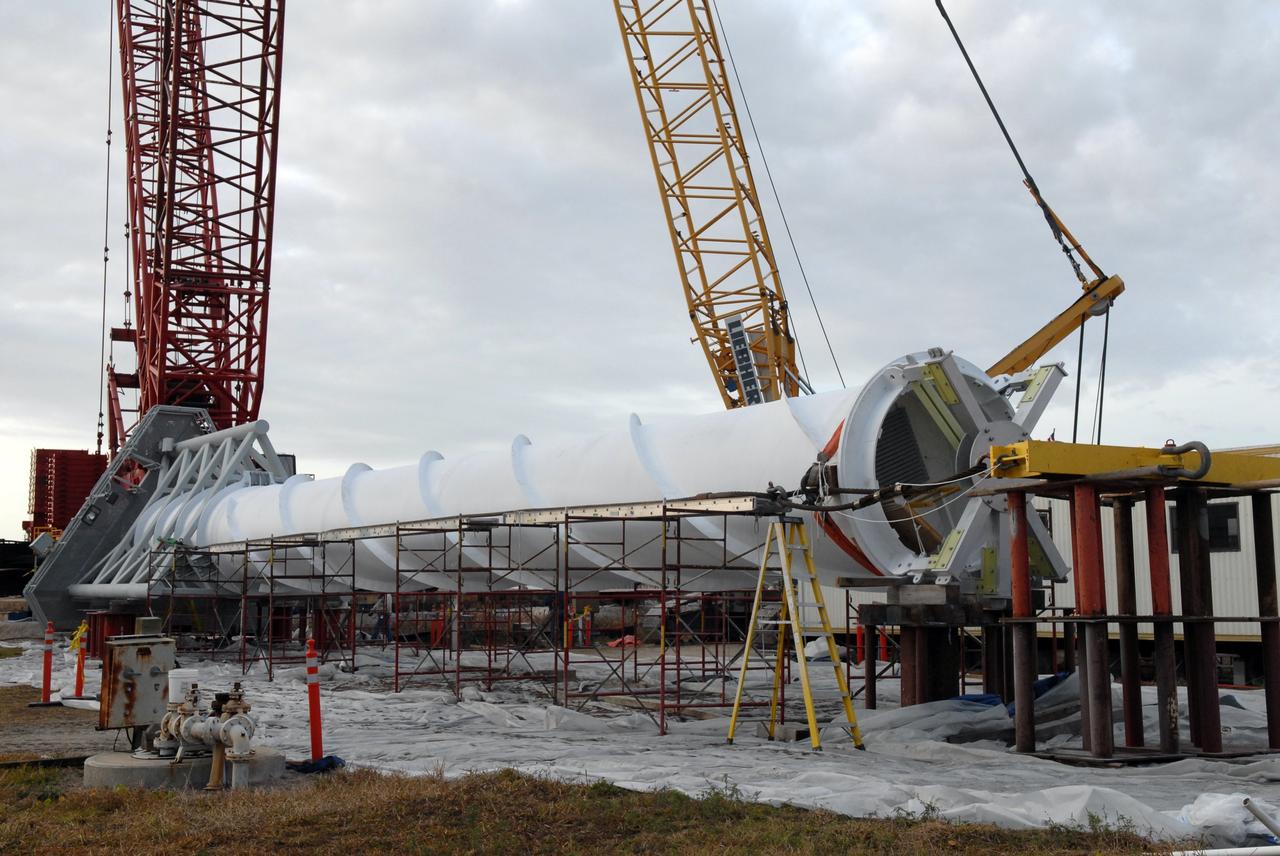
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, equipment surrounds the service structures for the construction of towers in the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. In the foreground is part of the giant crane used to place segments on the towers. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast (seen on the ground) atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
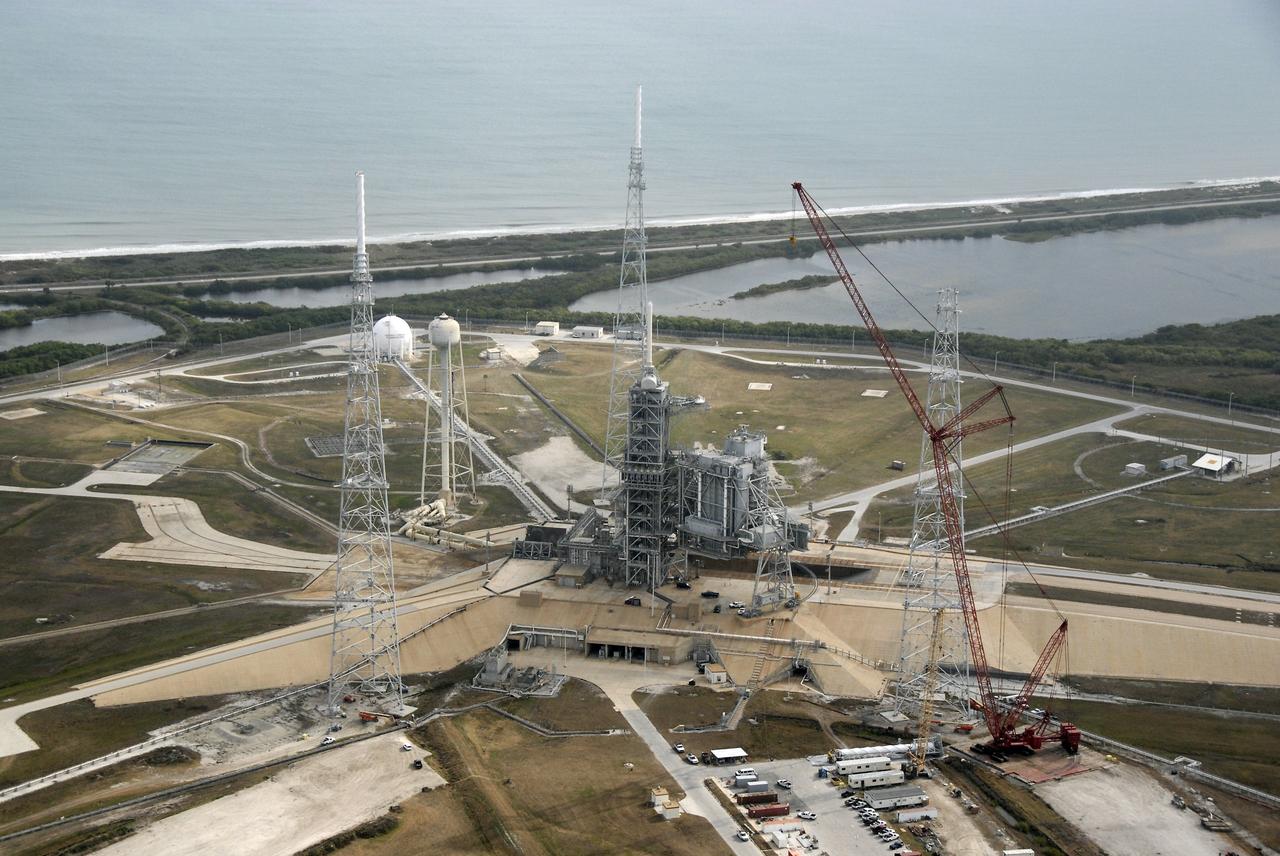

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The two towers at left and center contain the lightning mast on top; the one at right does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. Beyond the pad is the Atlantic Ocean. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
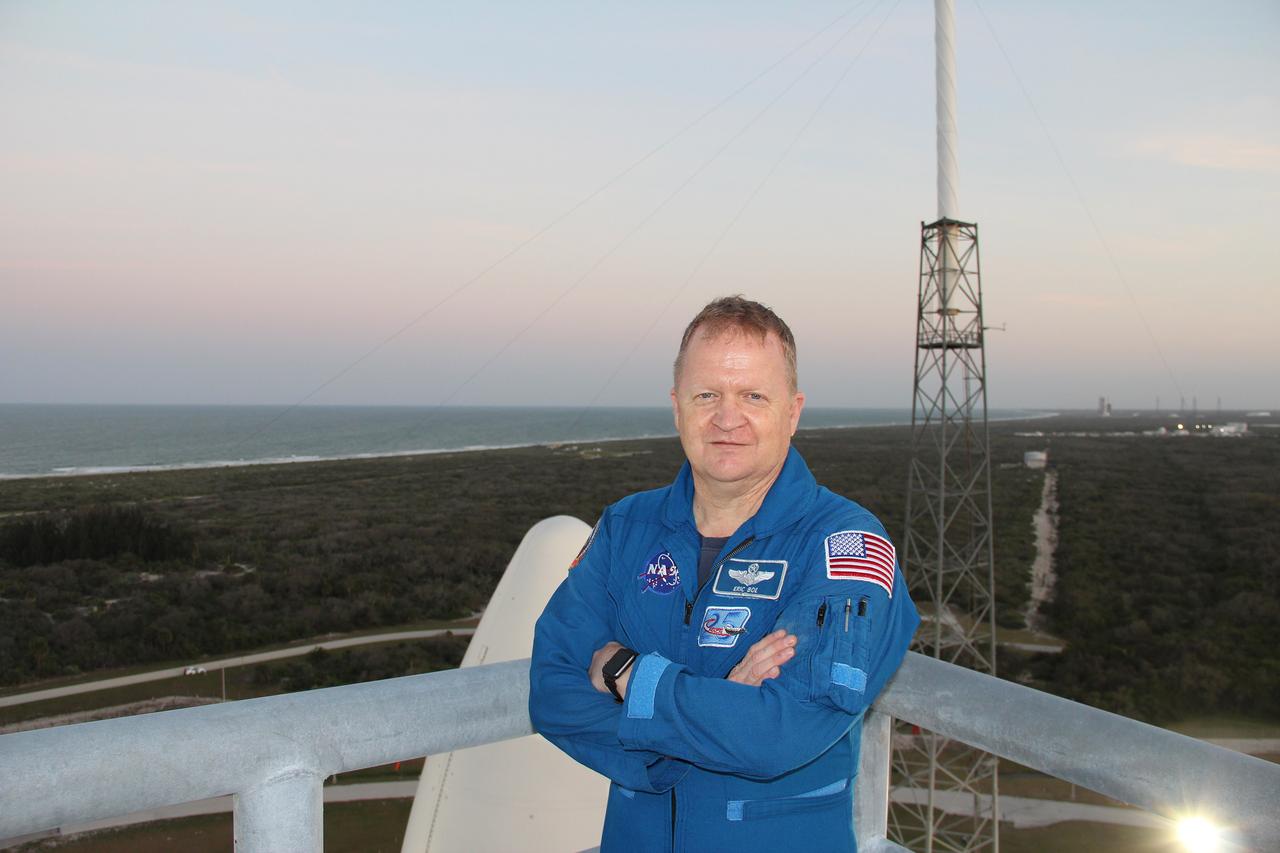

NASA astronaut Eric Boe, one of four astronauts working with the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, checked out the Crew Access Tower at Space Launch Complex 41. Boe is standing on the tower's uppermost level. Visible behind his right arm is the aerodynamic enclosure designed to protect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S during launch – which successfully occurred March 1. To Boe’s left, one of four protective lightning masts is in view. Accompanied by NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance engineers, Boe inspected the launch tower to establish whether spotlight and lighting conditions will be acceptable after dark. The survey was required to ensure crew members will have suitable visibility as they prepare to board Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft and launch on missions such as the Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station, targeted for later this year.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane places the 100-foot fiberglass mast atop the new lightning tower constructed on the pad. The towers are part of the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with the additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
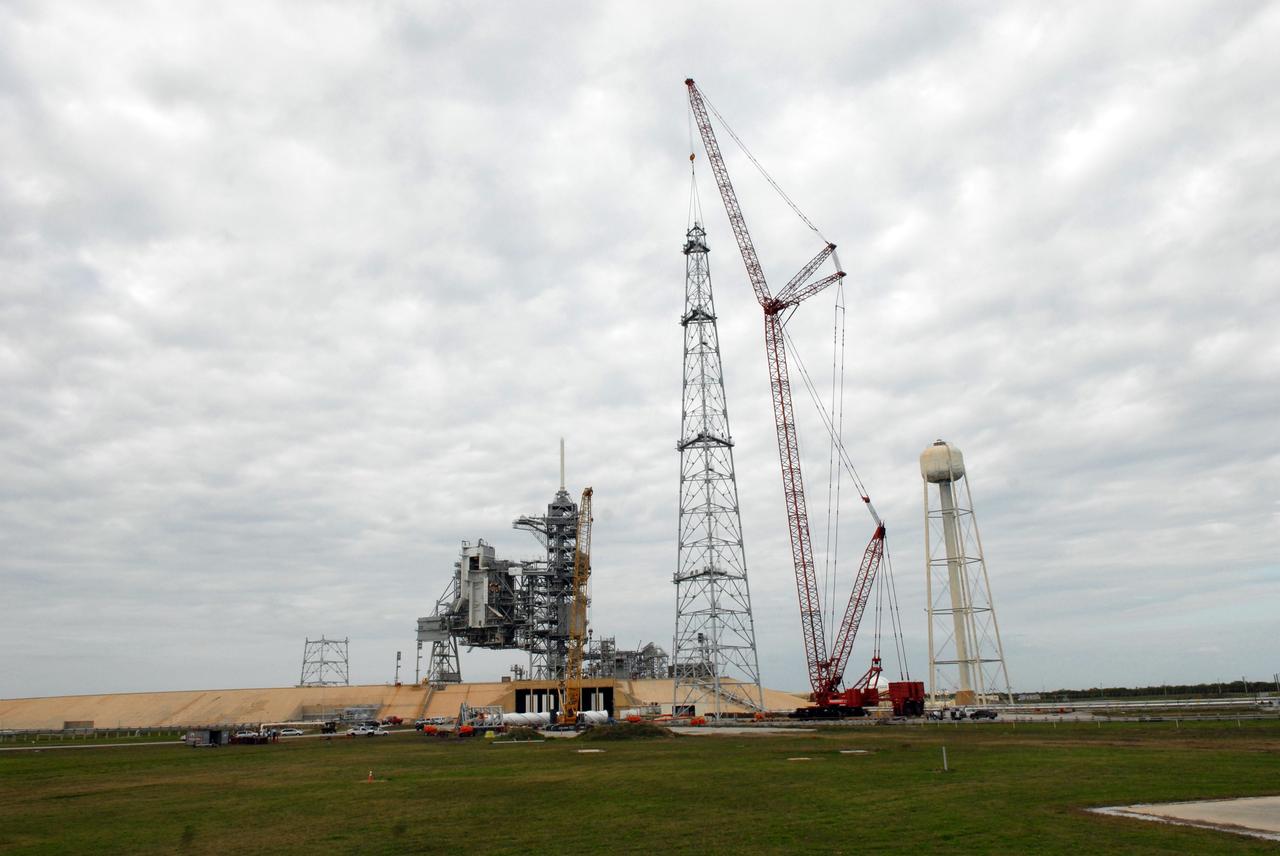

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane completes construction of one of the towers in the new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Other towers are being constructed at left and behind the service structures on the pad. Each of the three new lightning towers will be 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder