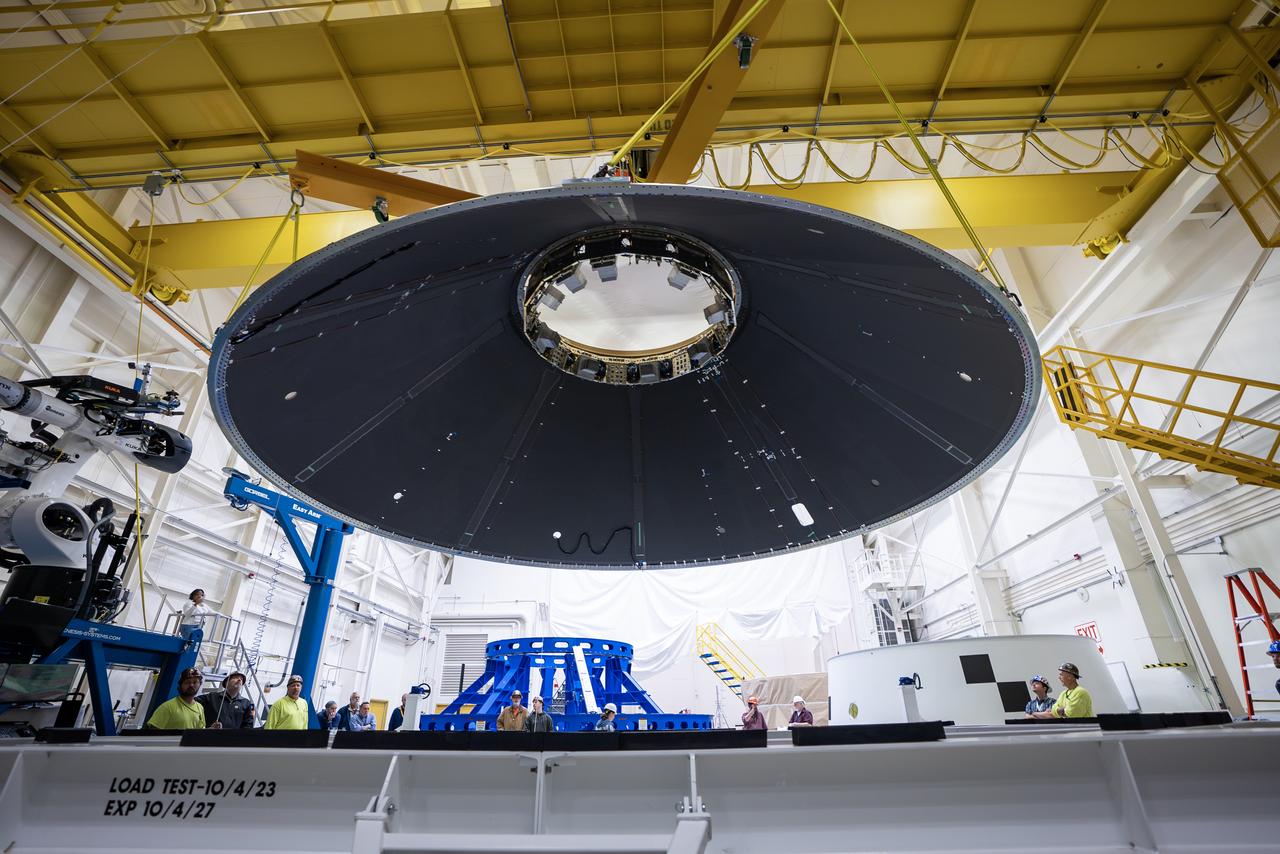

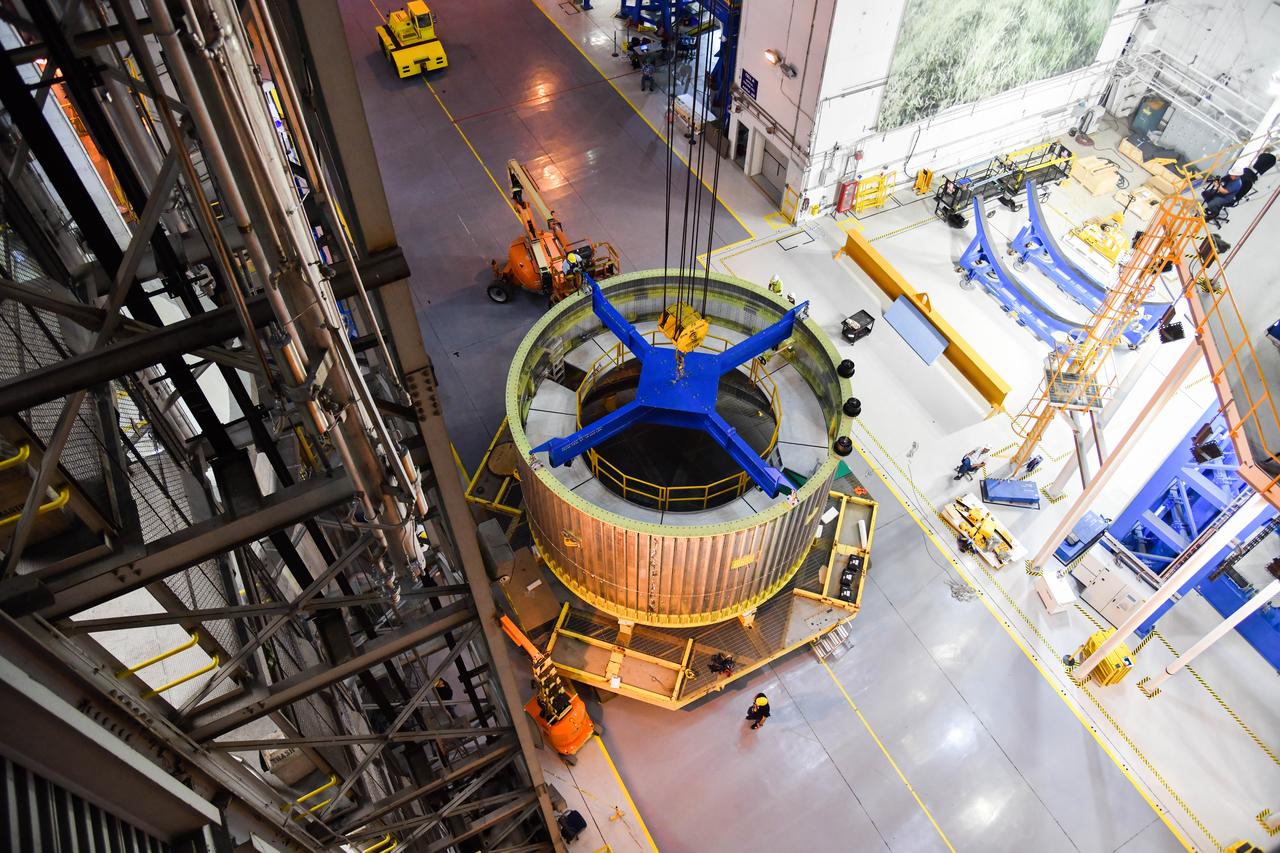
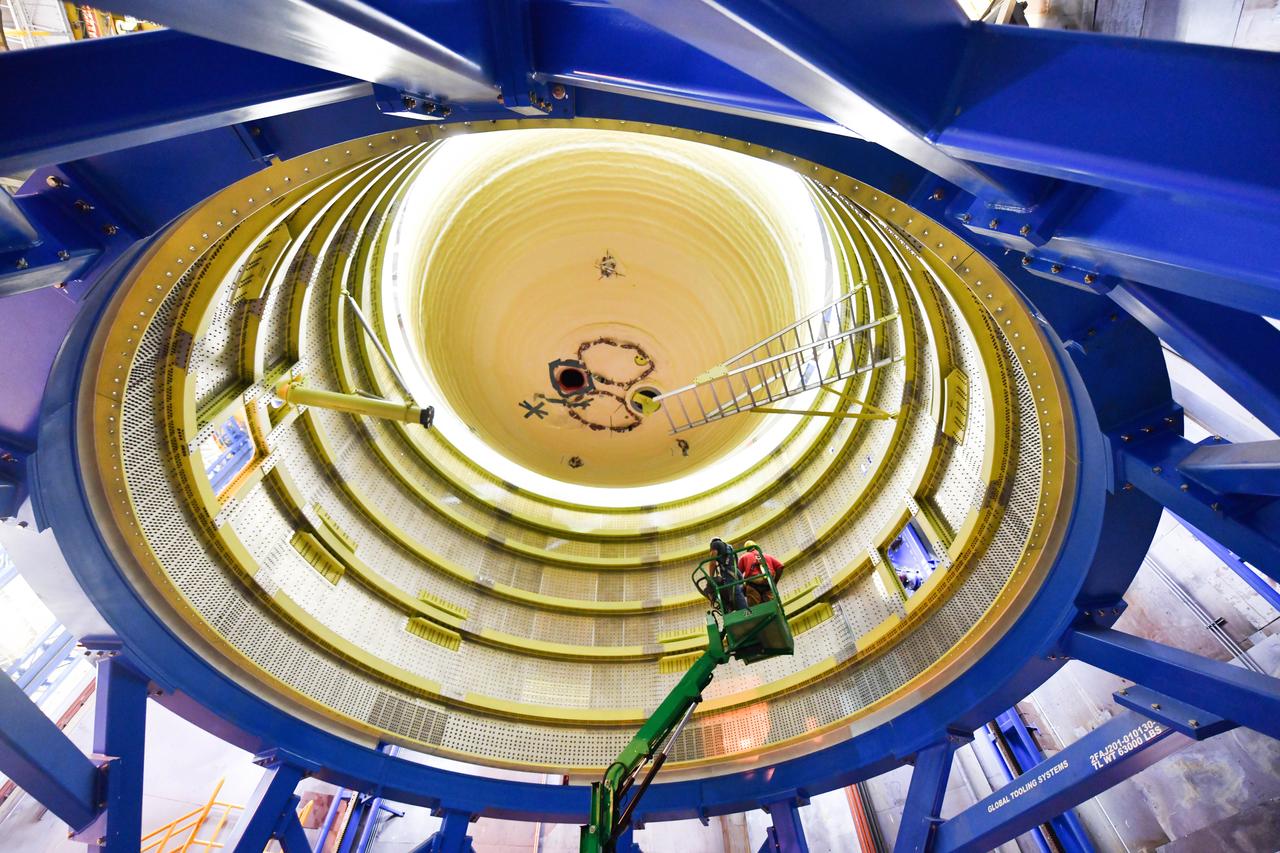
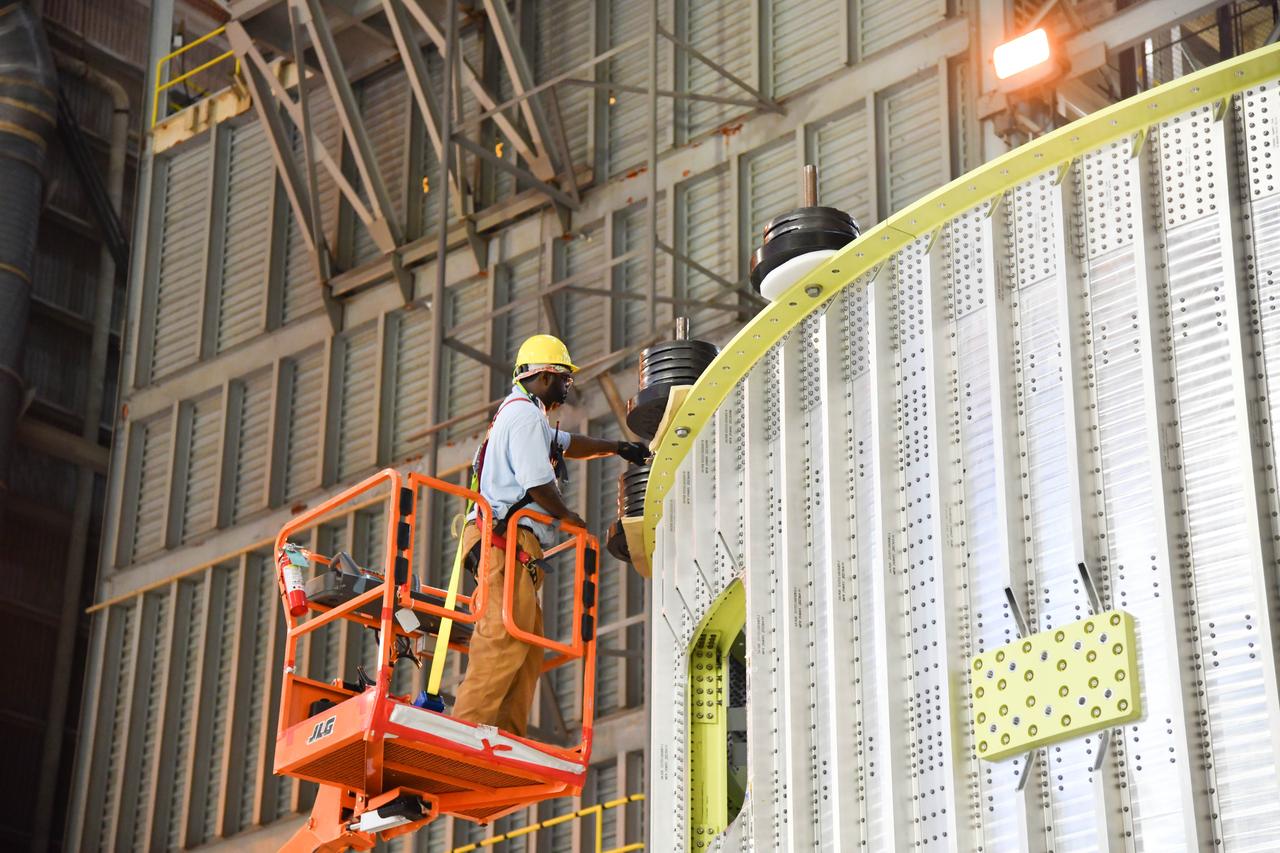
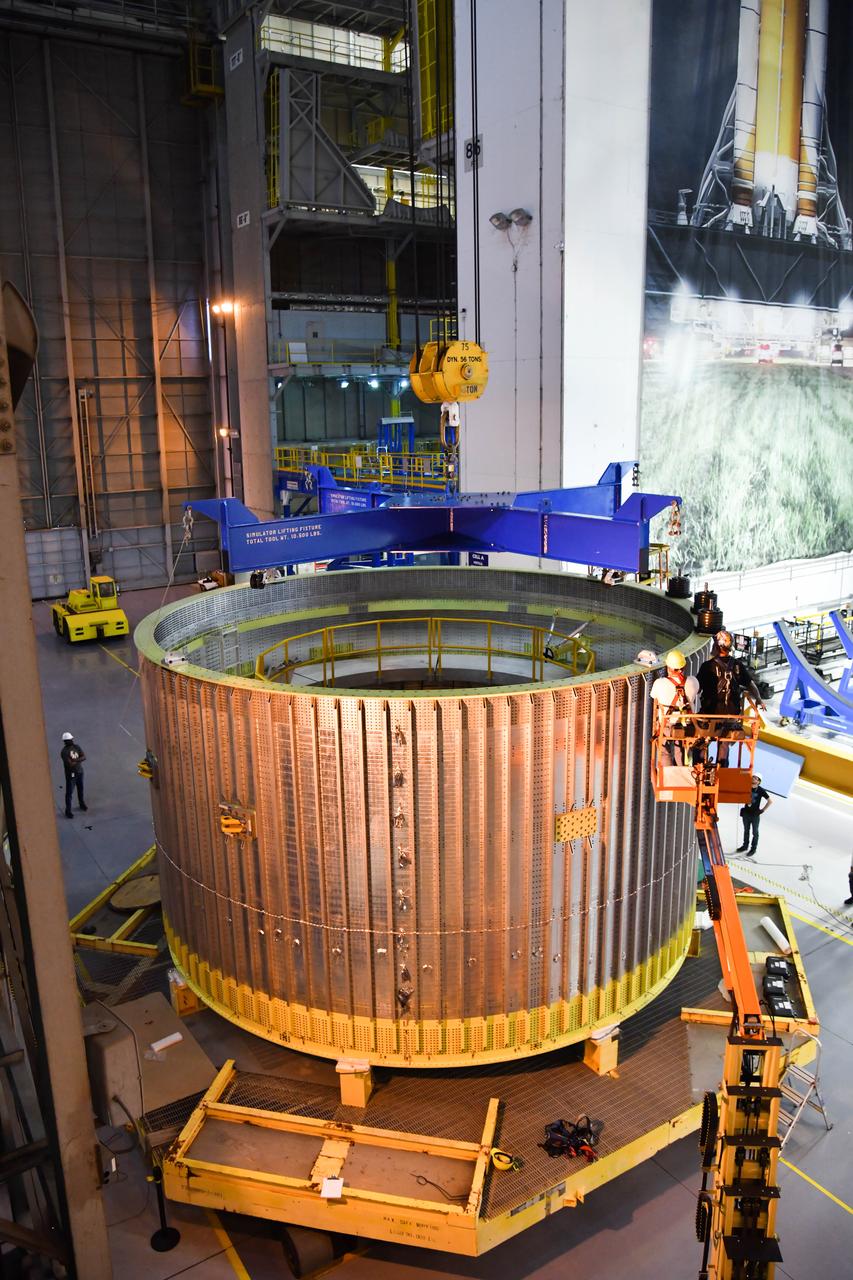
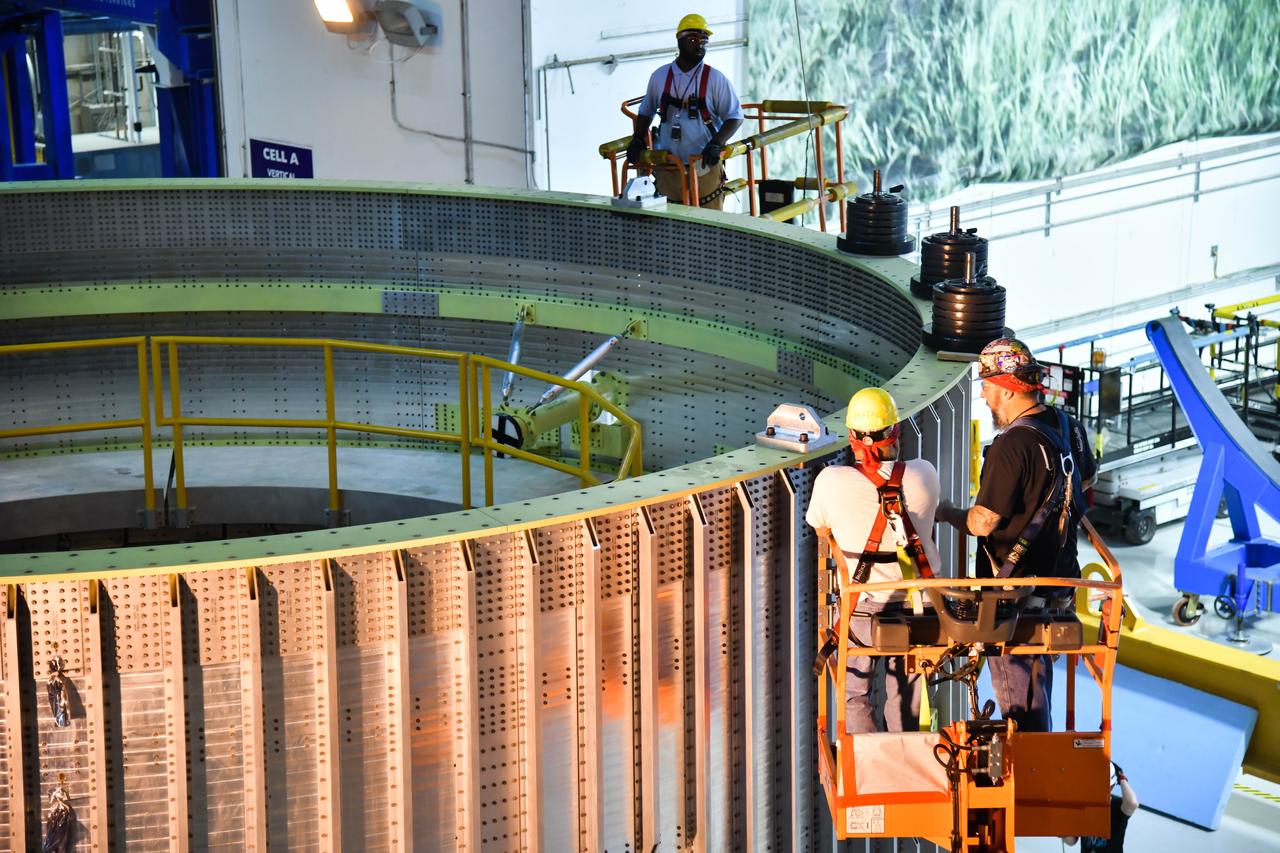
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
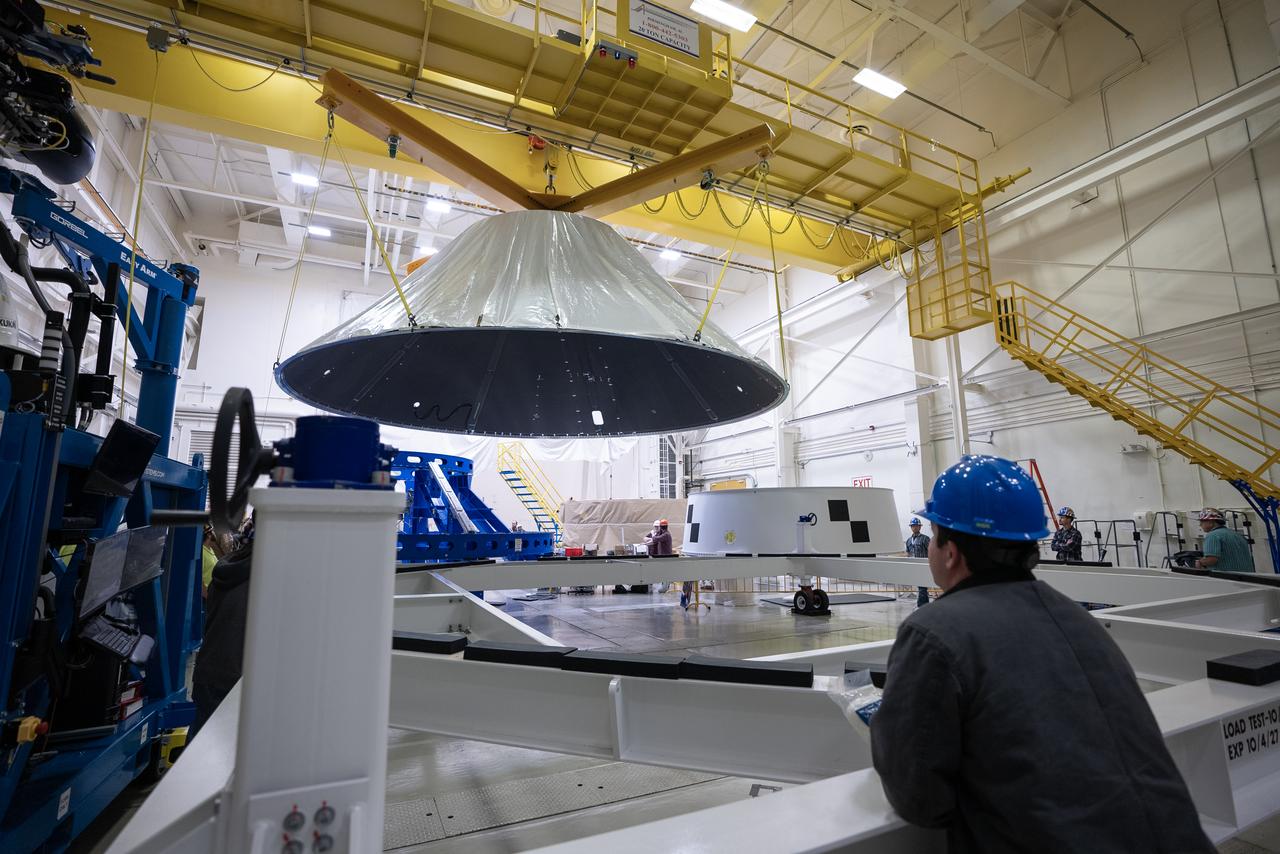

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
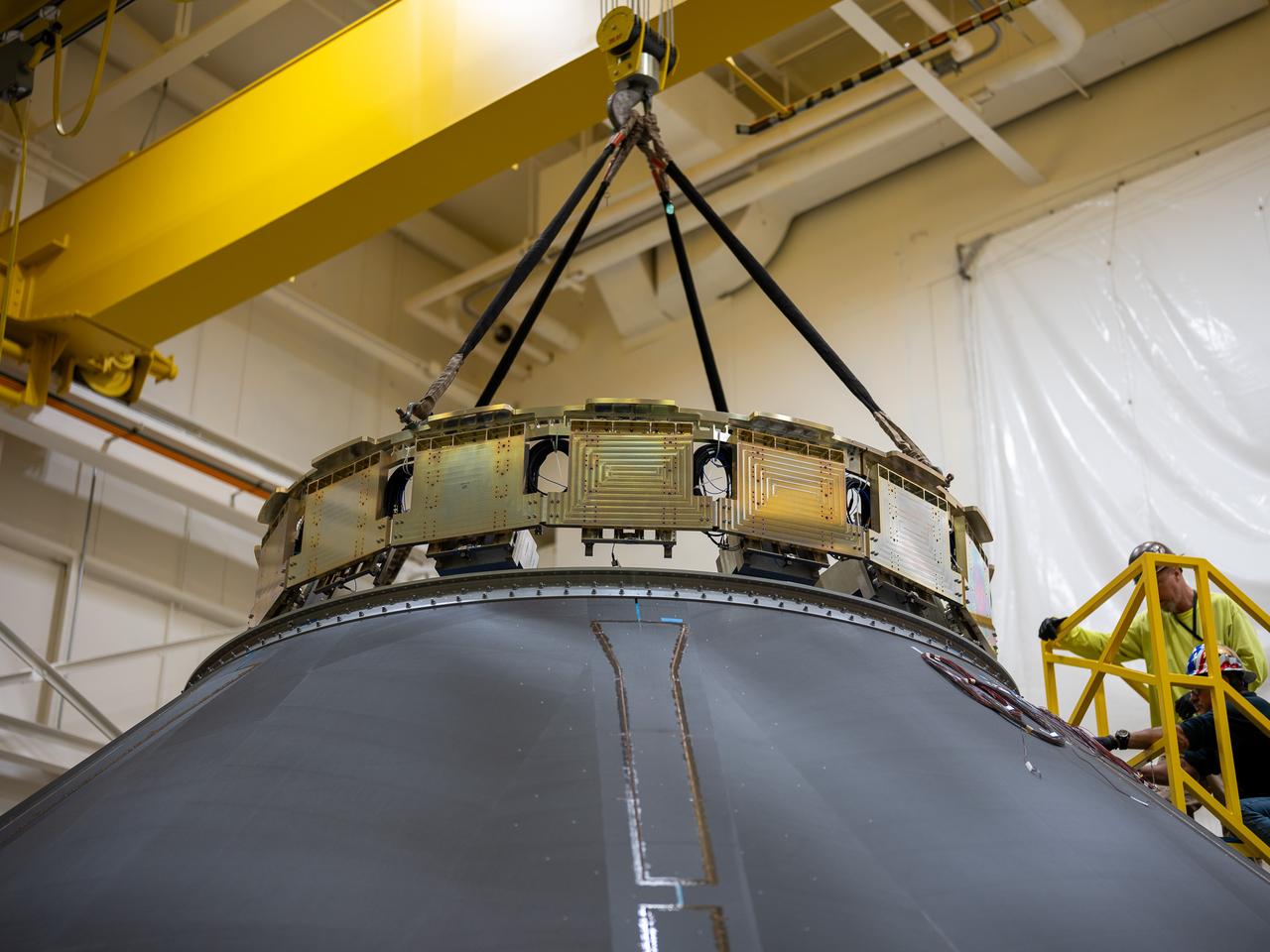

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
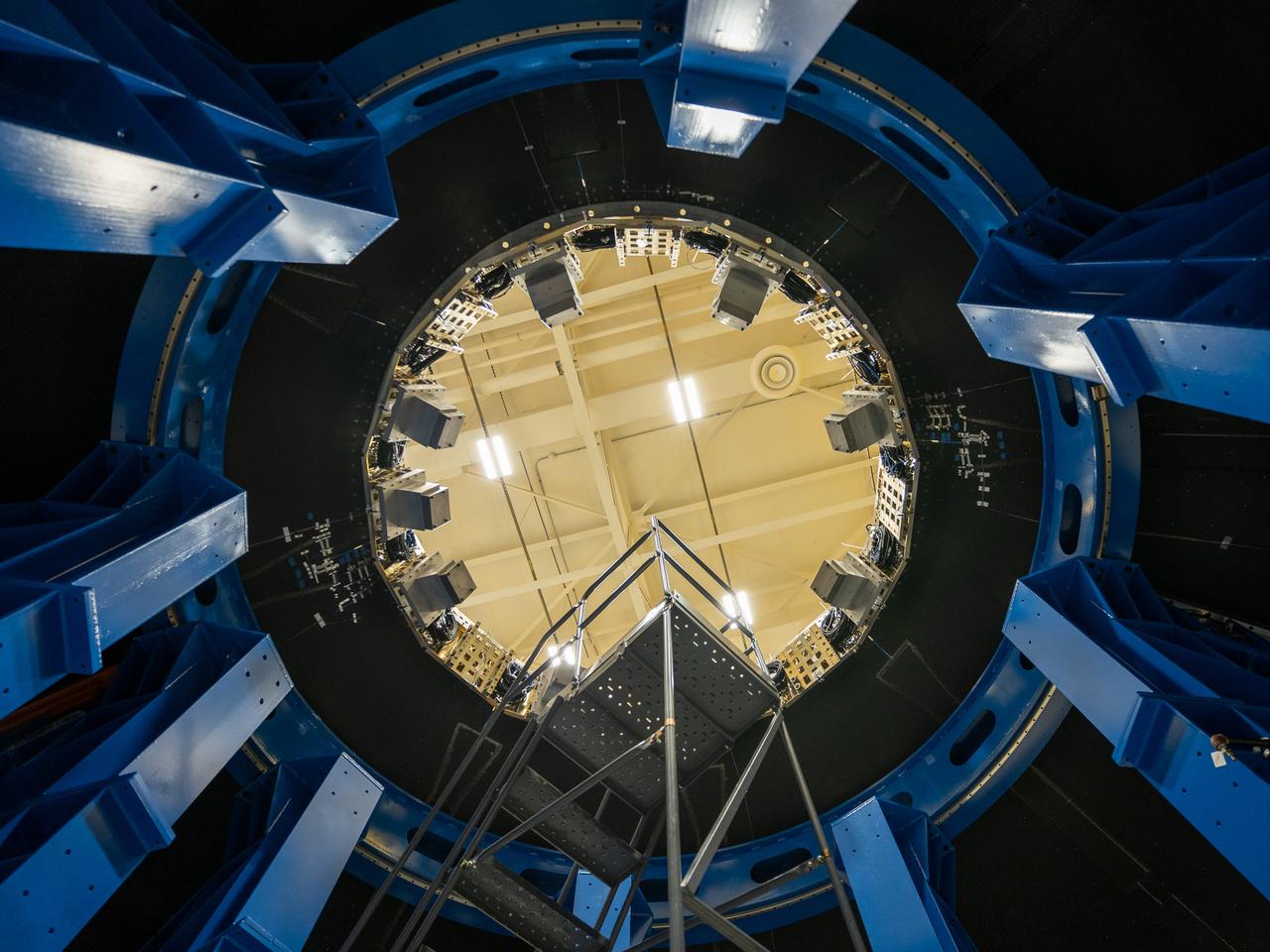

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
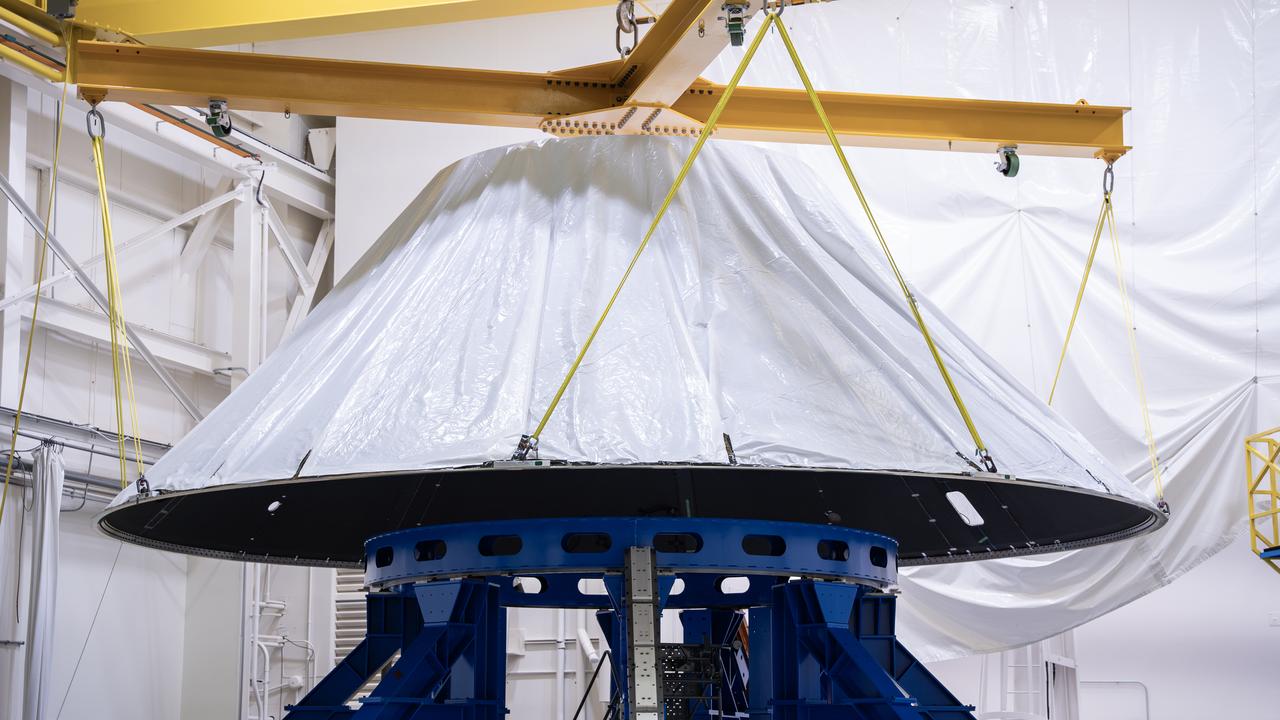

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
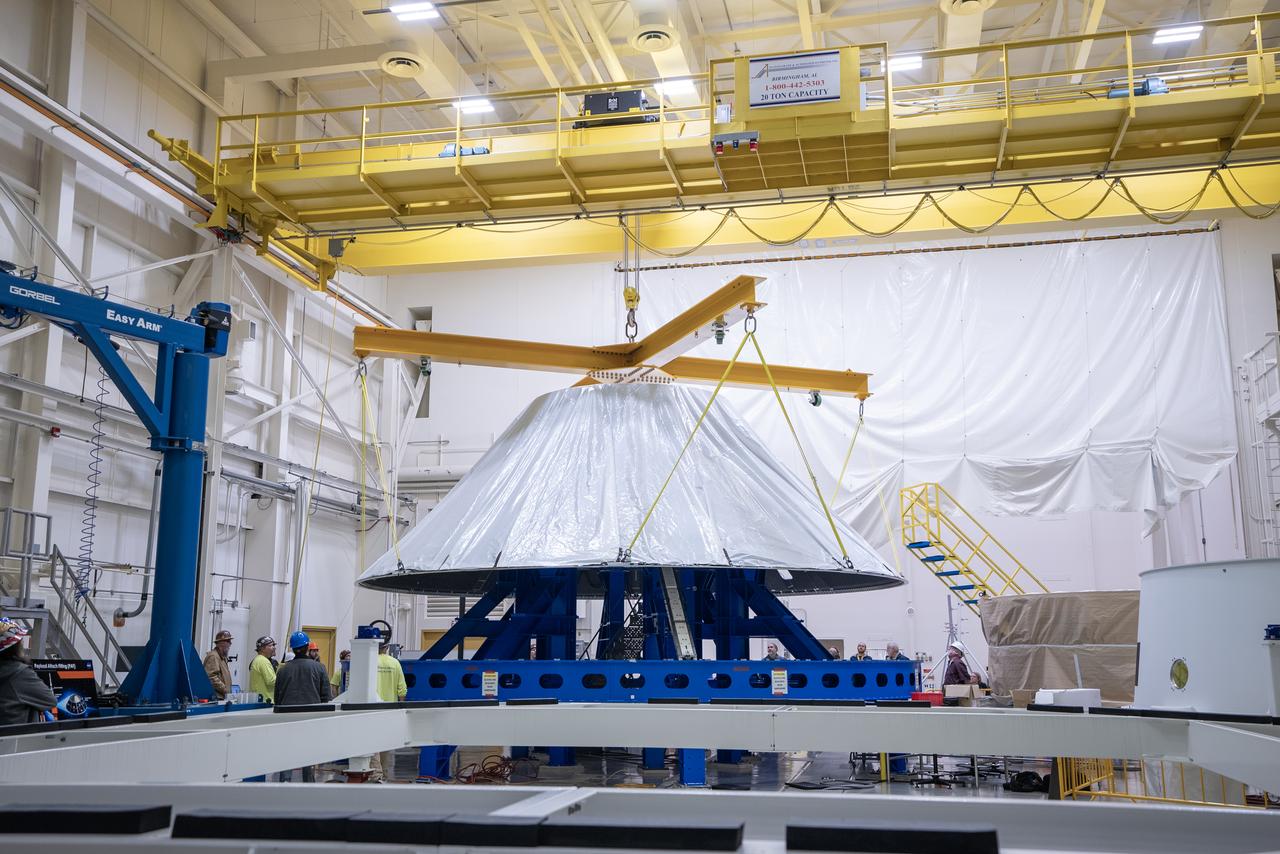

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
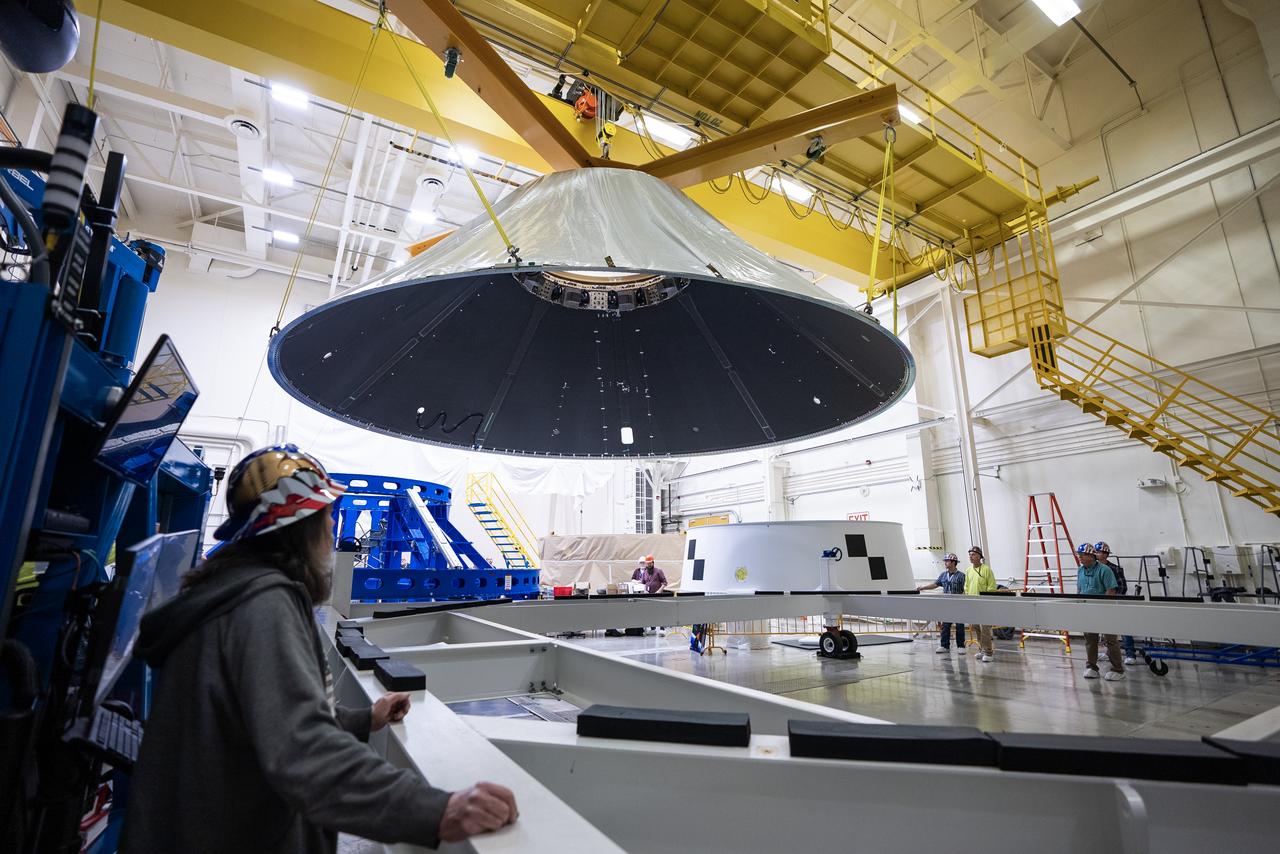

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
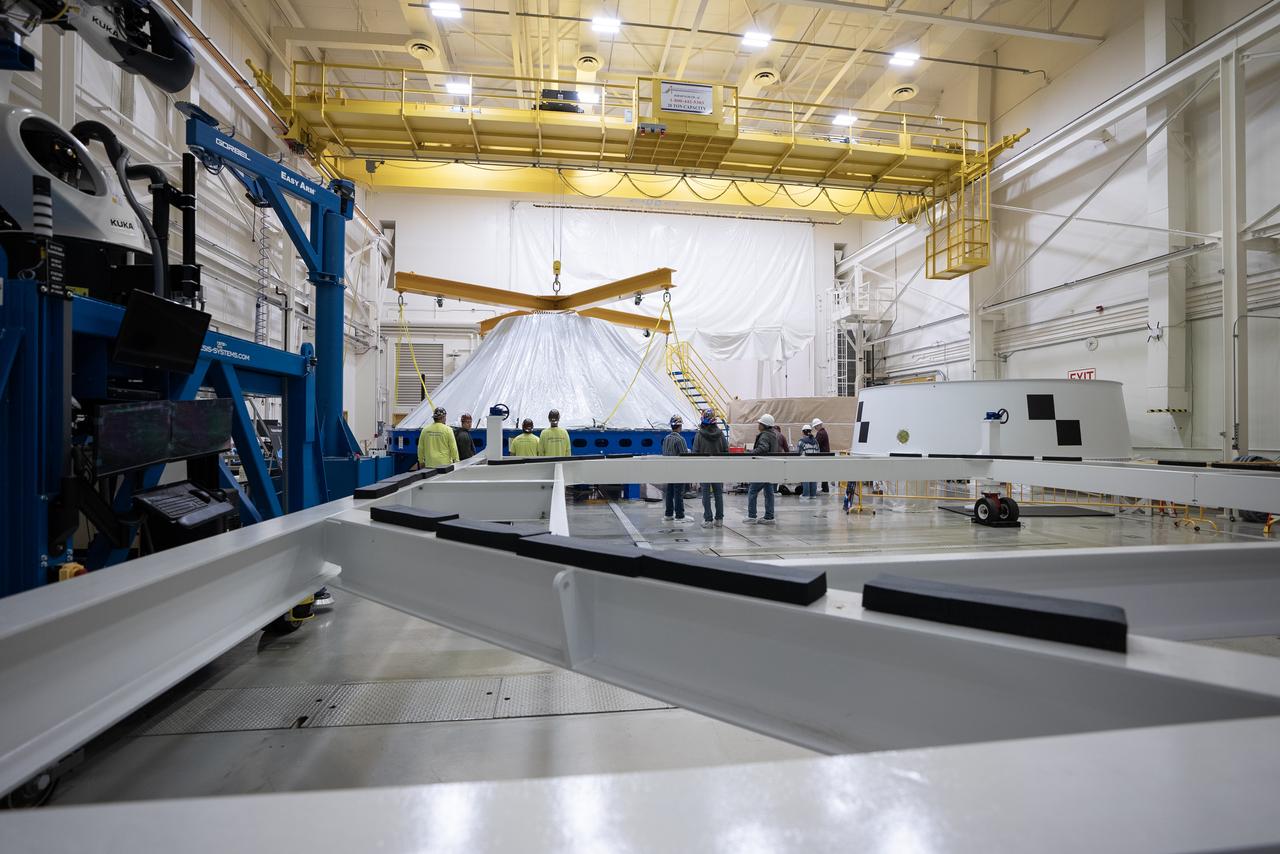

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
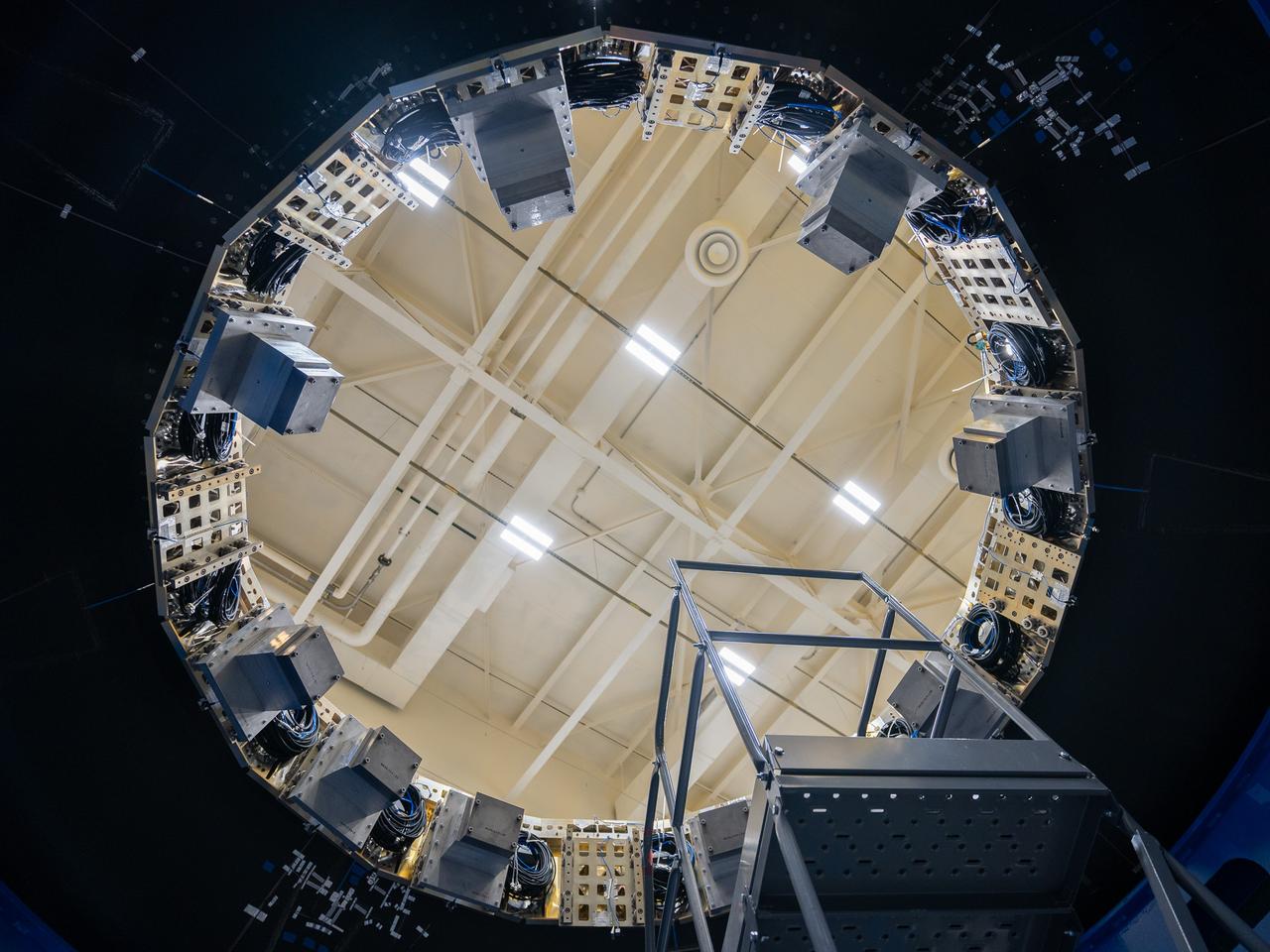

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
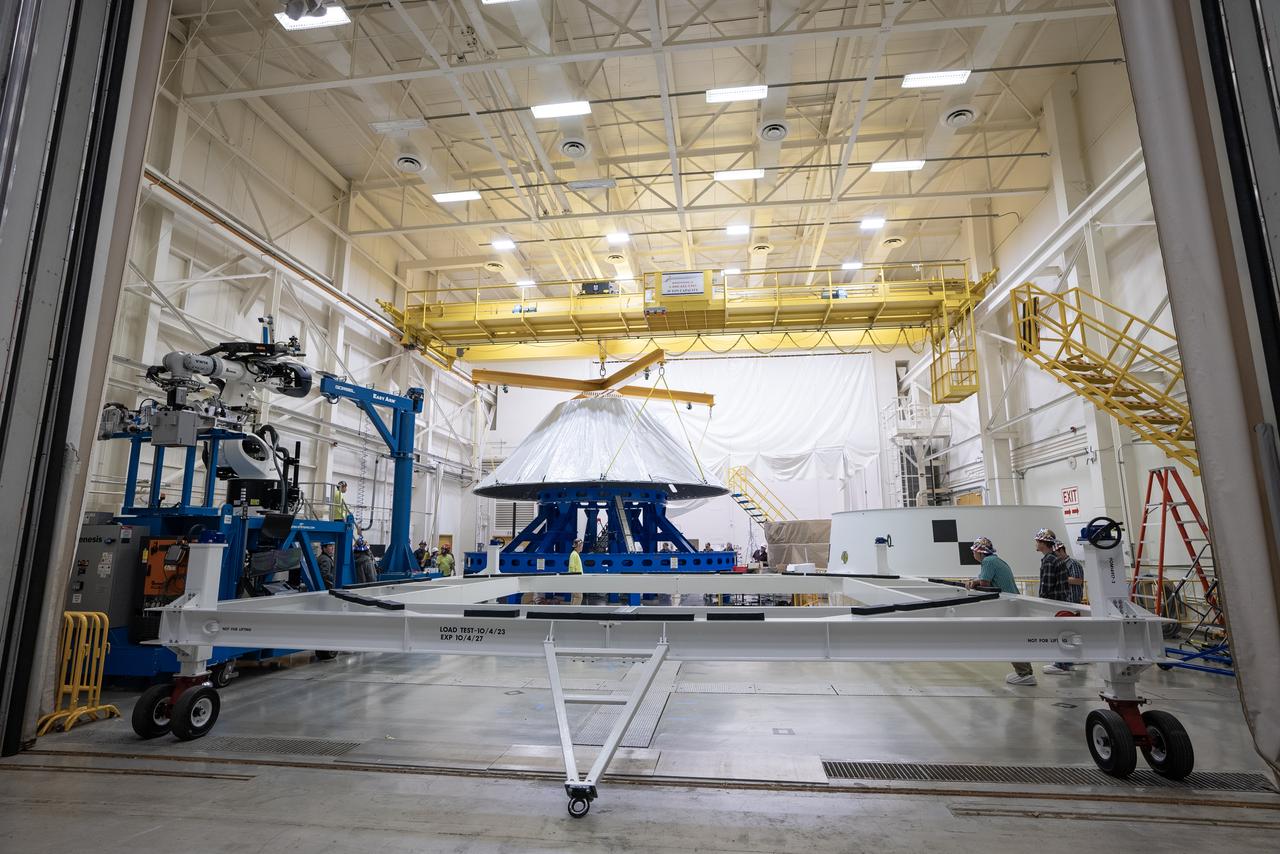

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
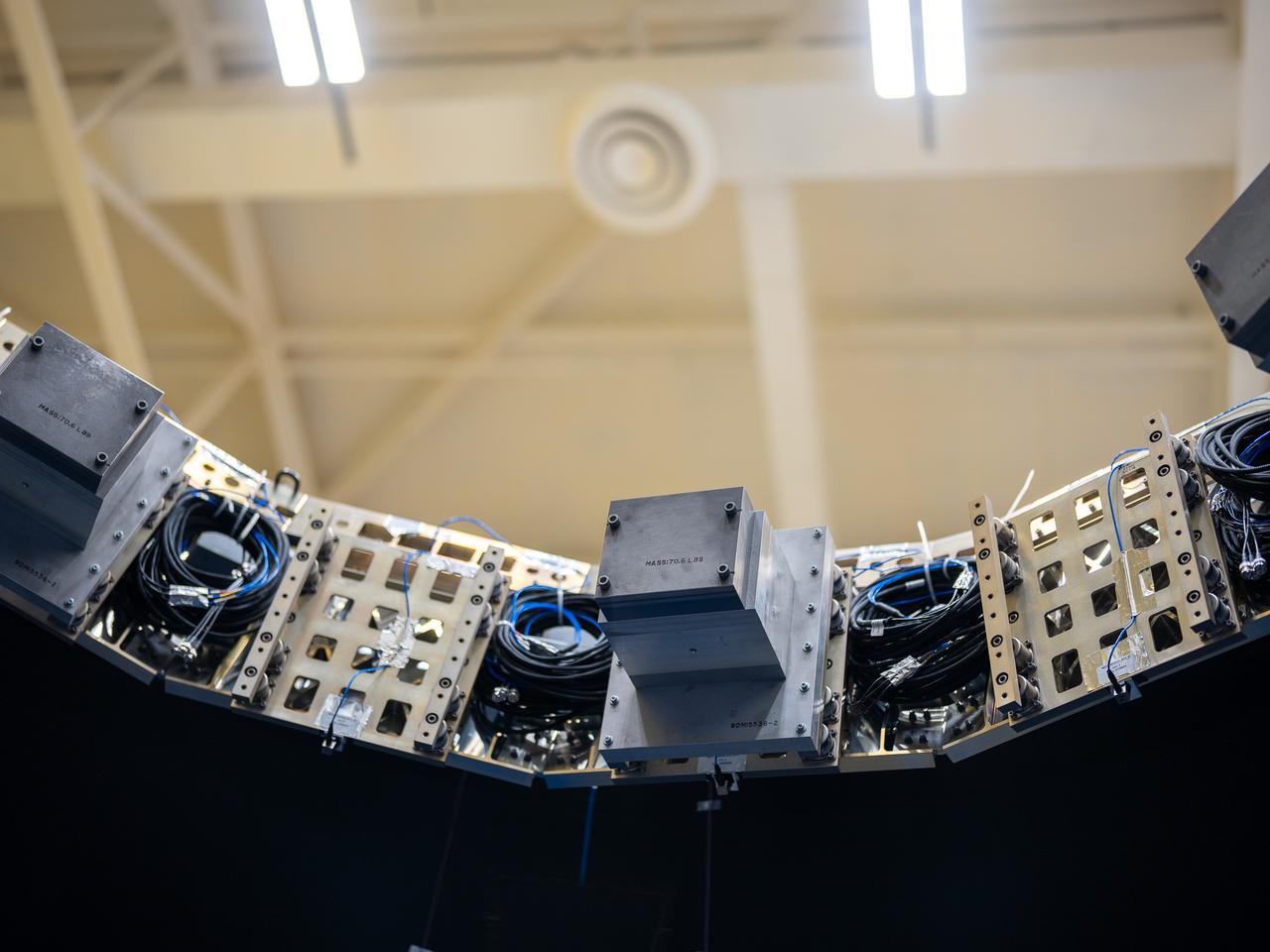
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
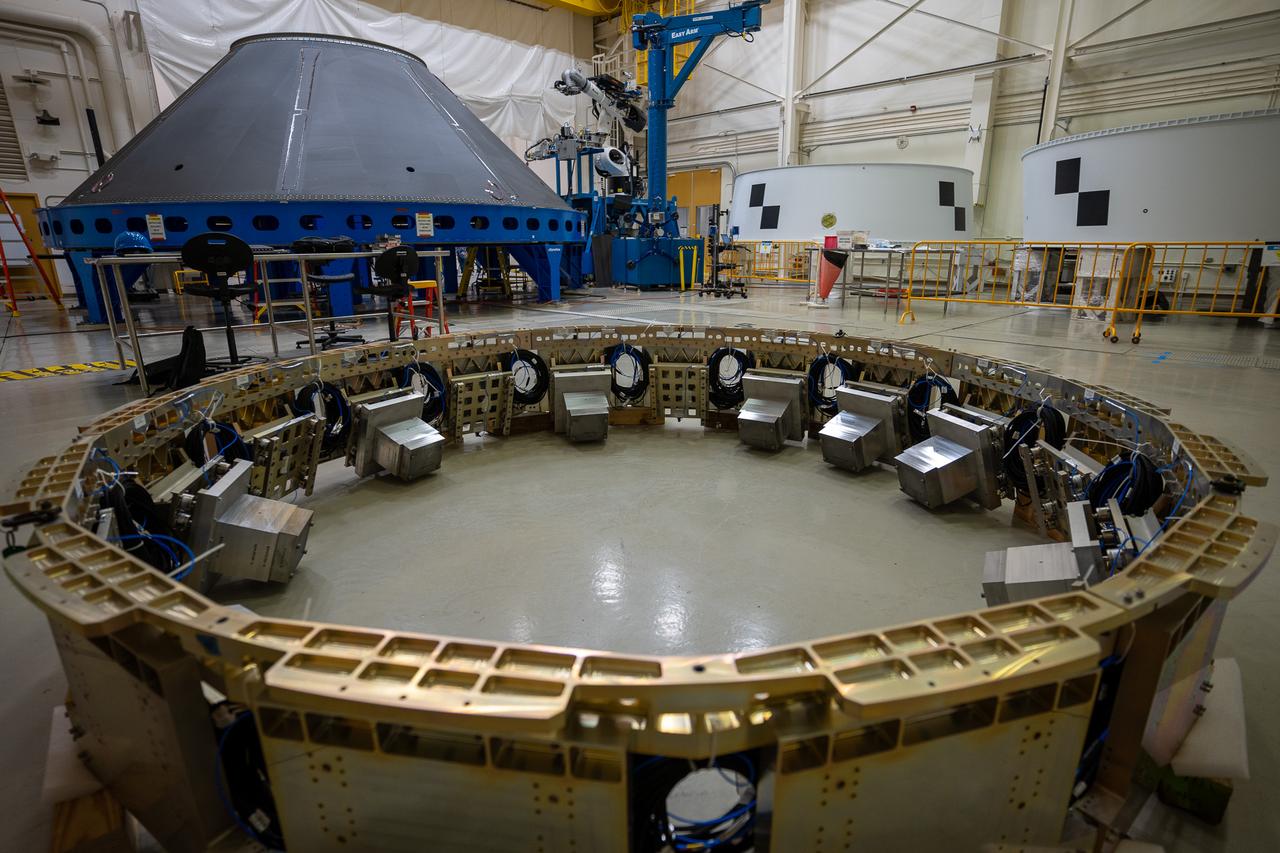

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
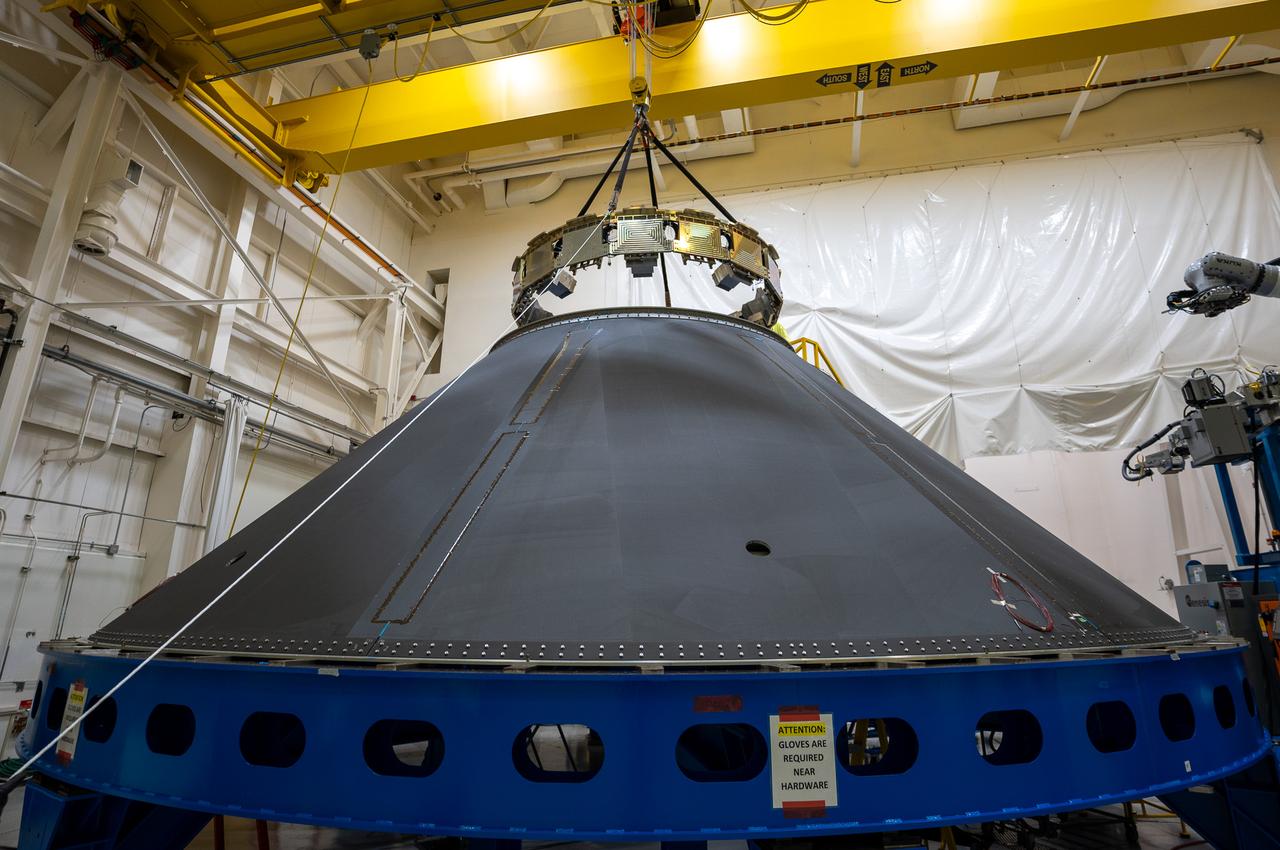

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
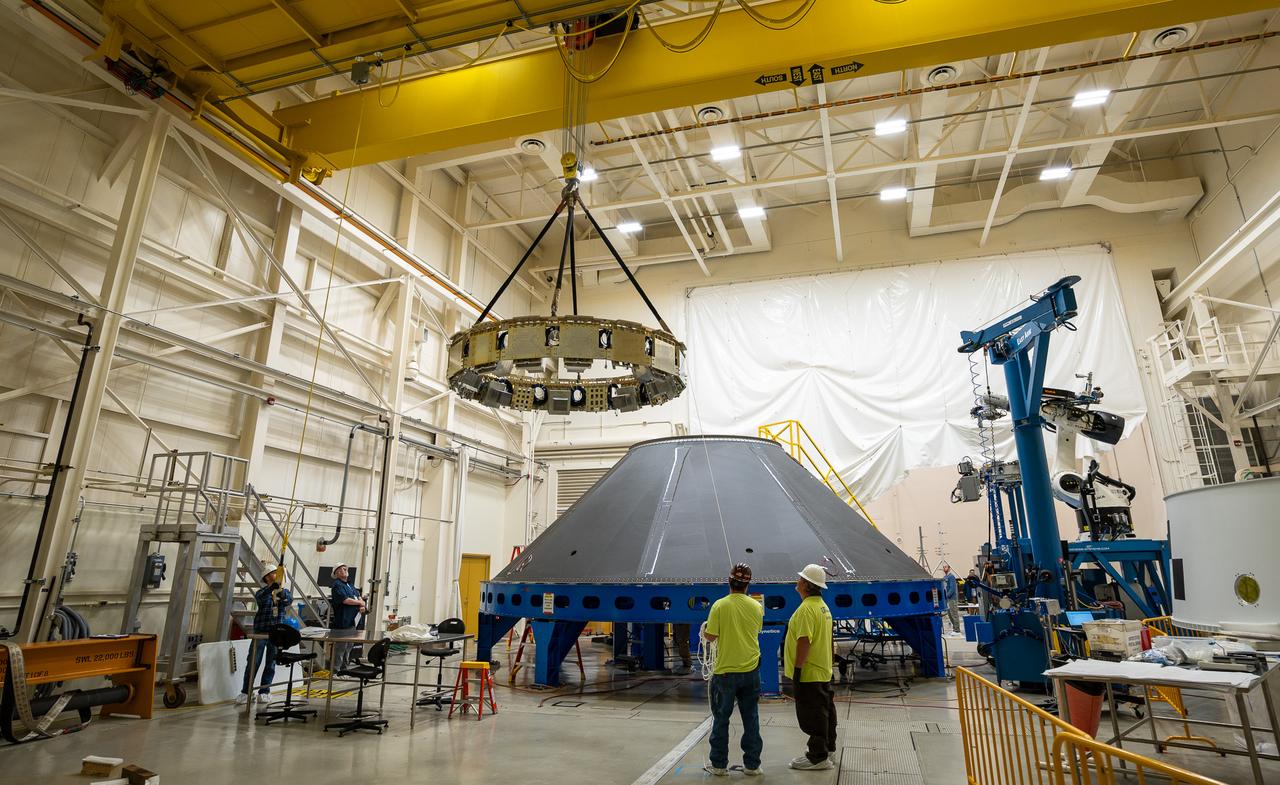

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

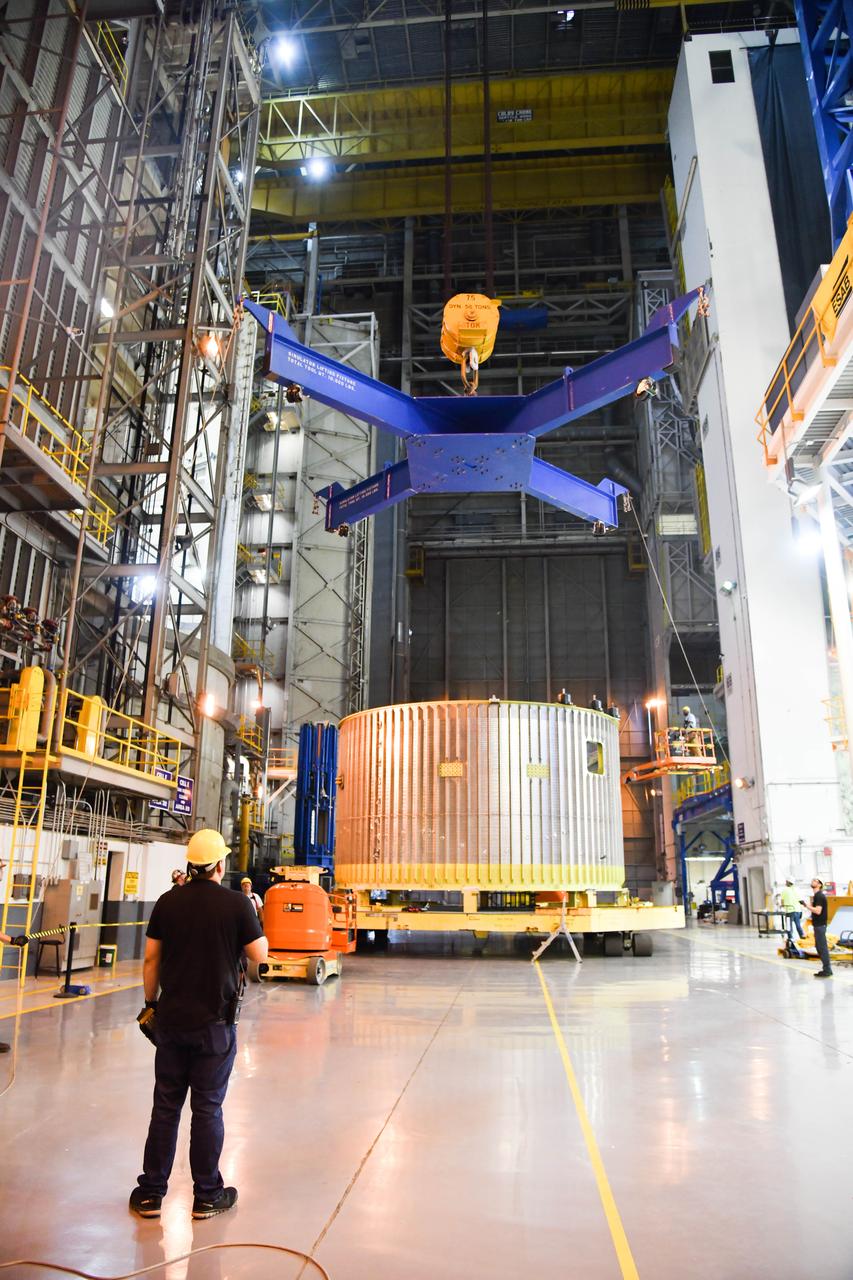
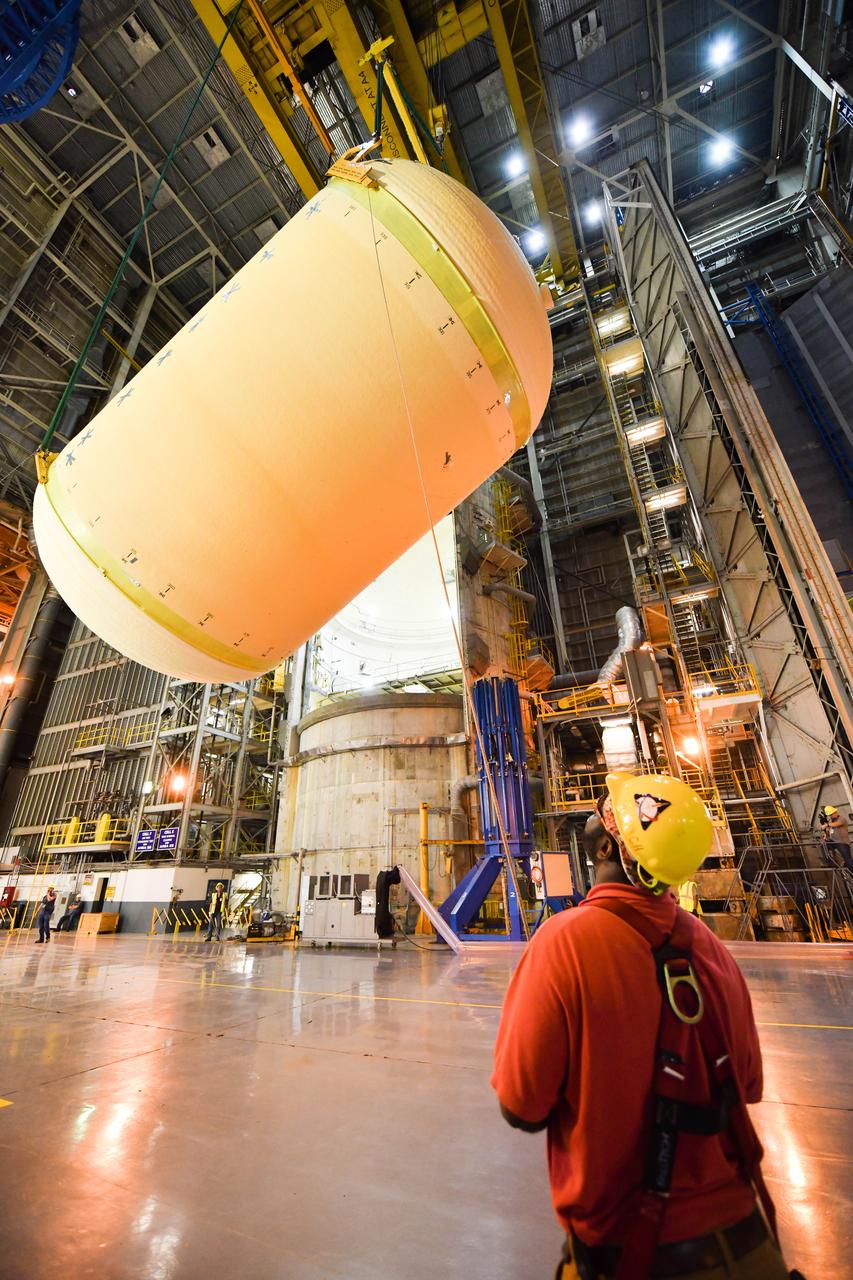
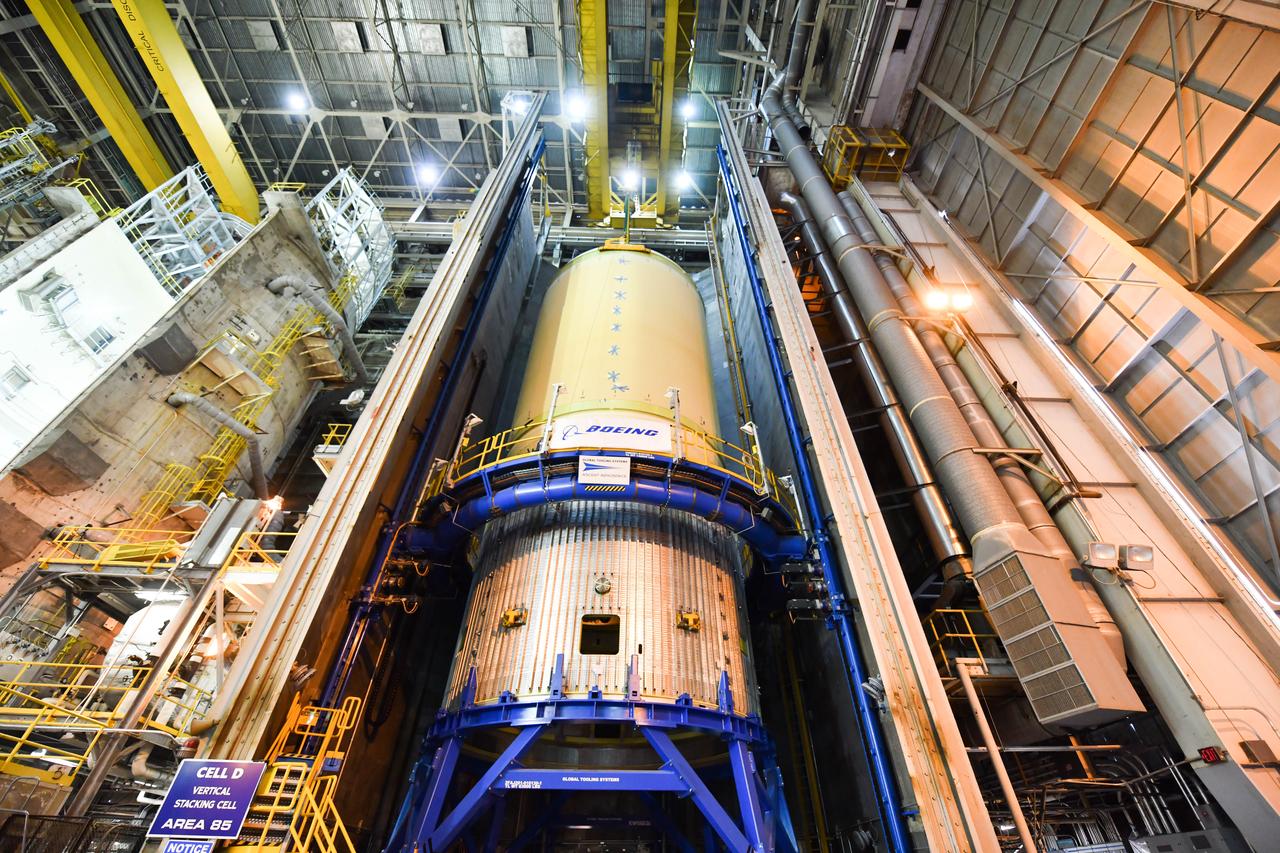
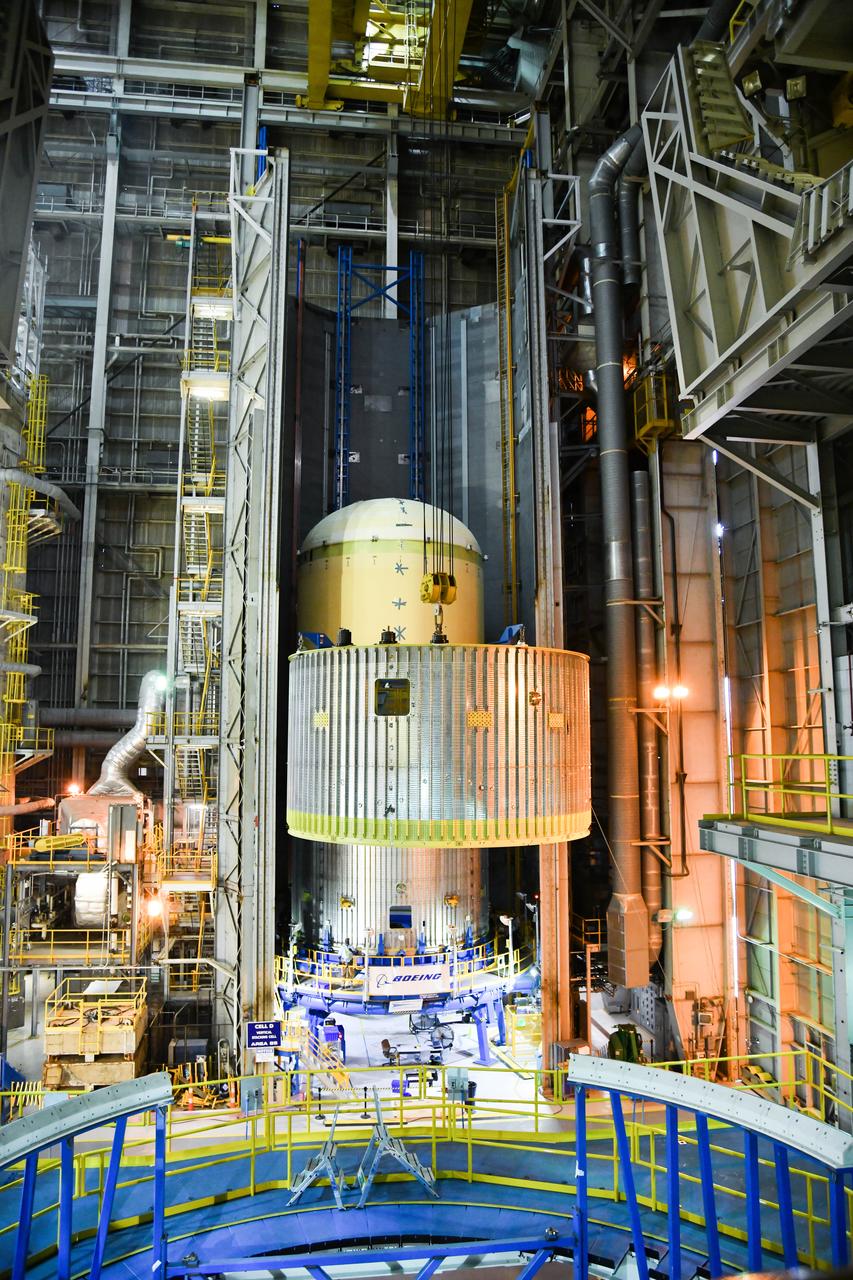
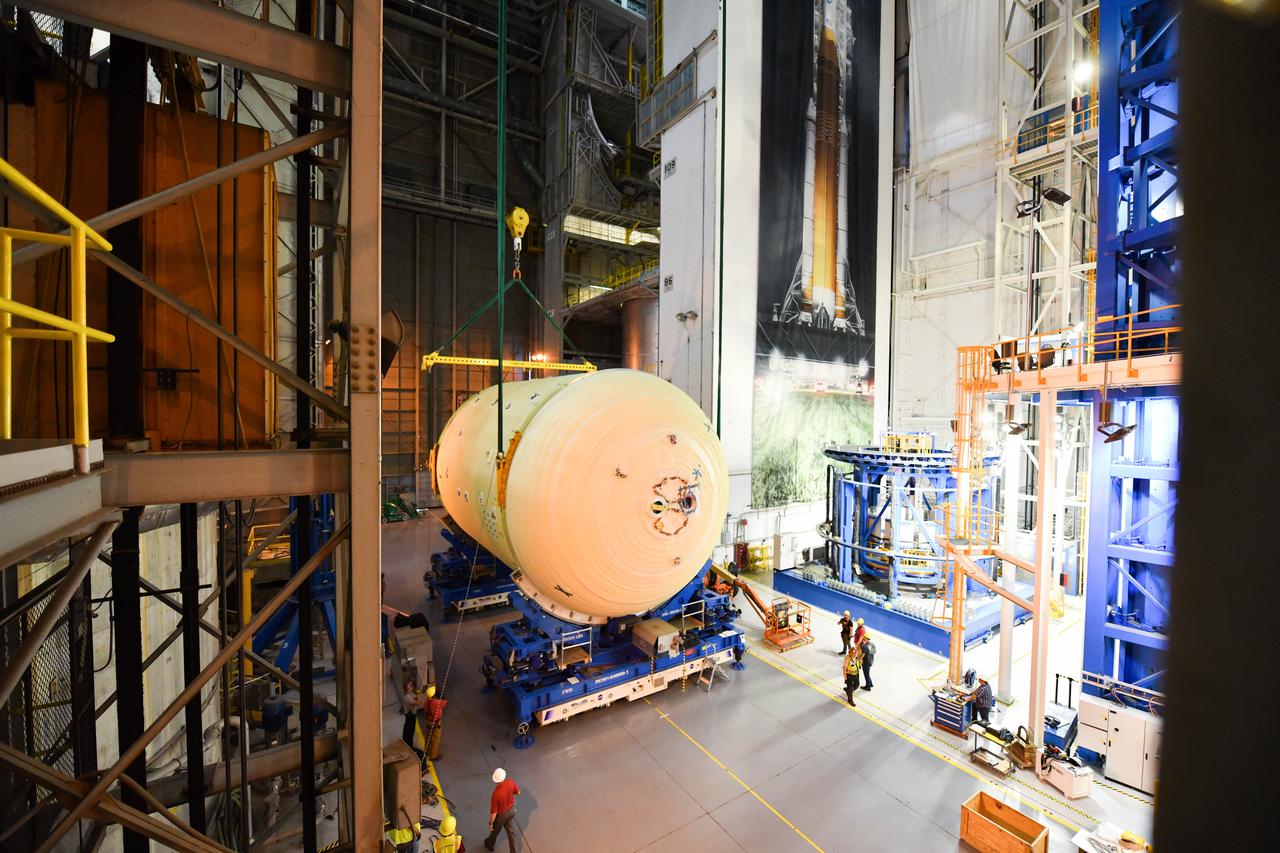
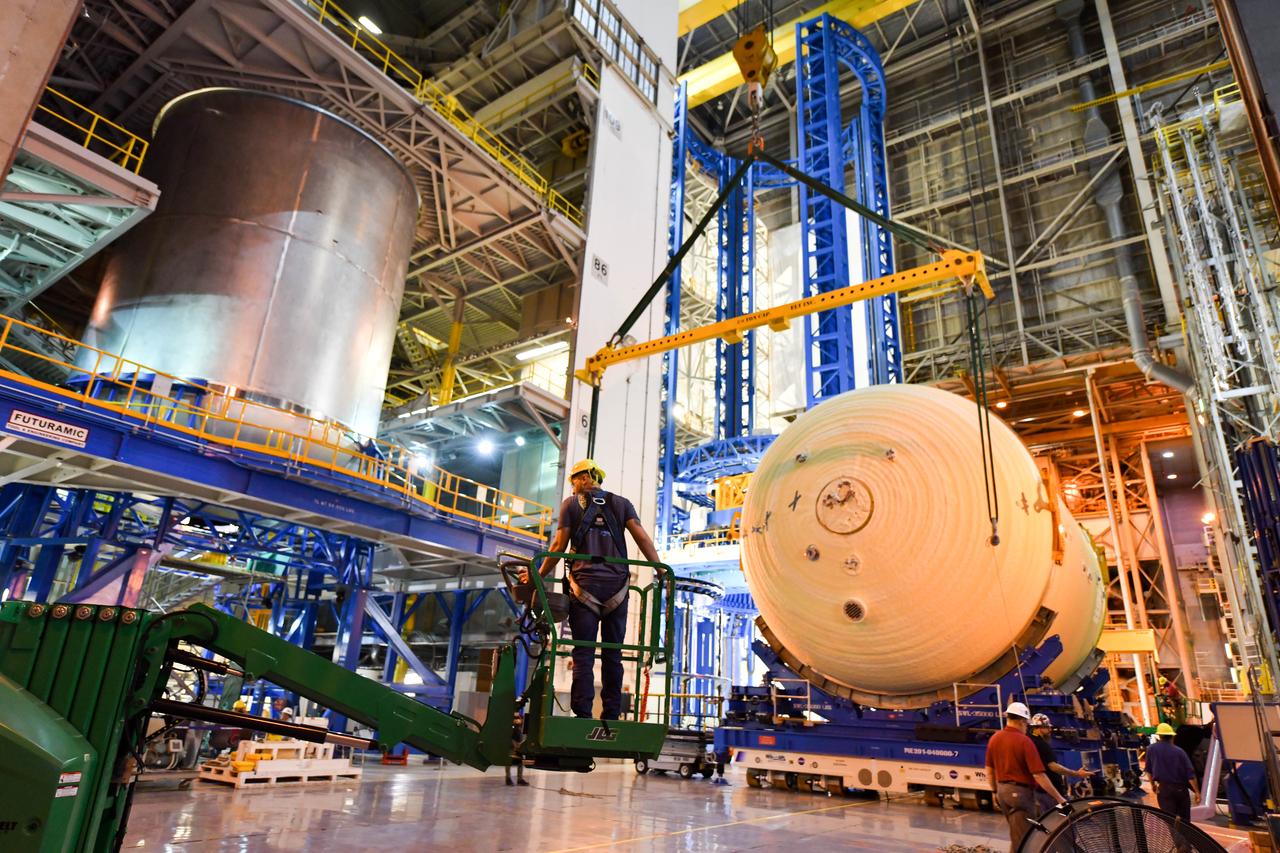
The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
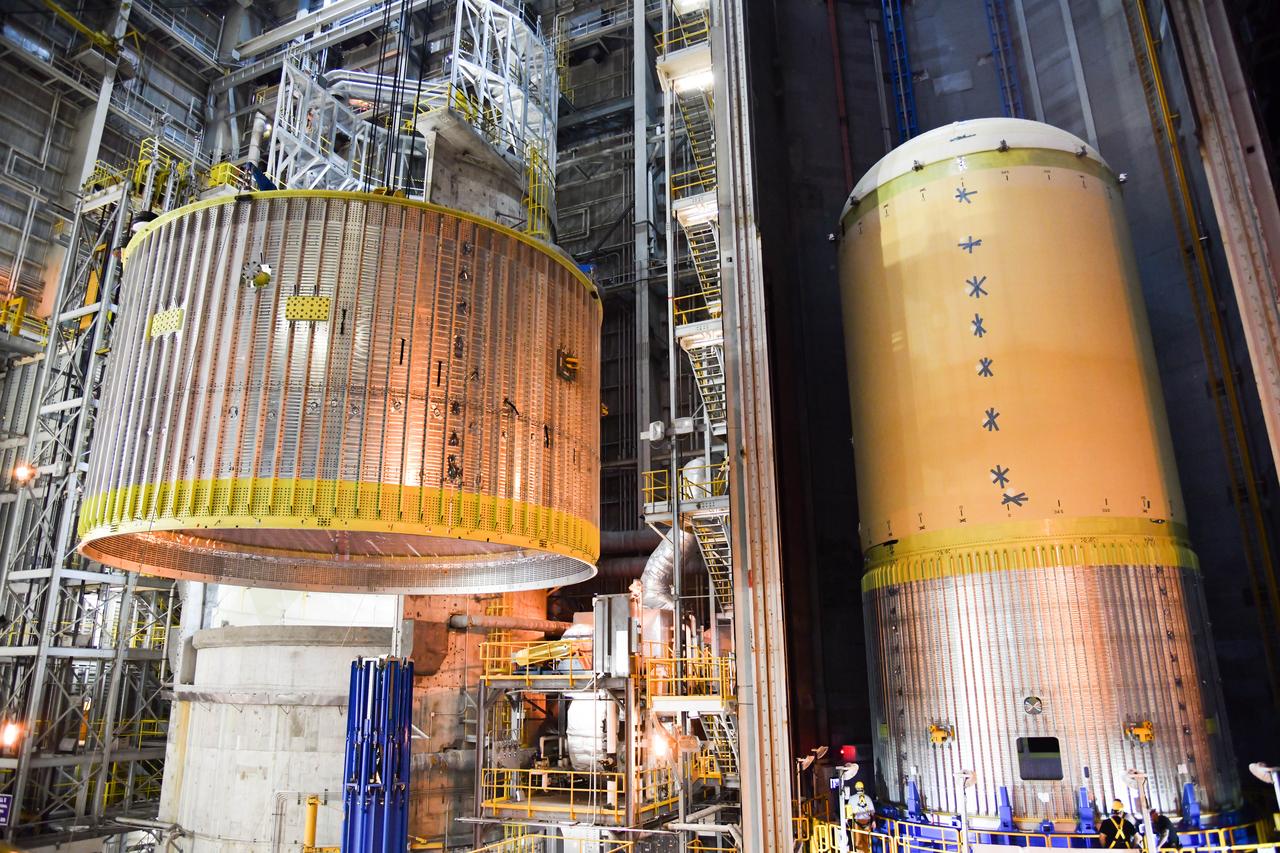

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
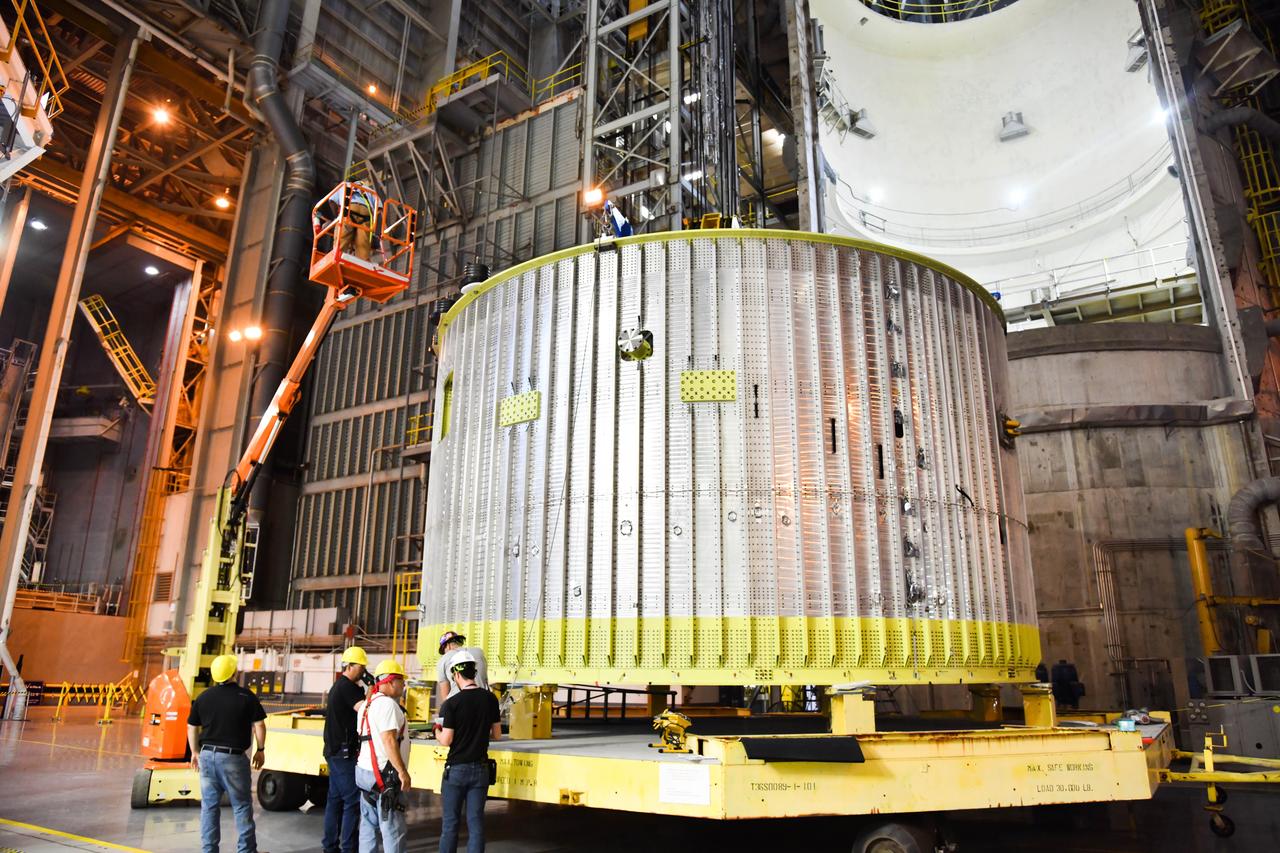

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
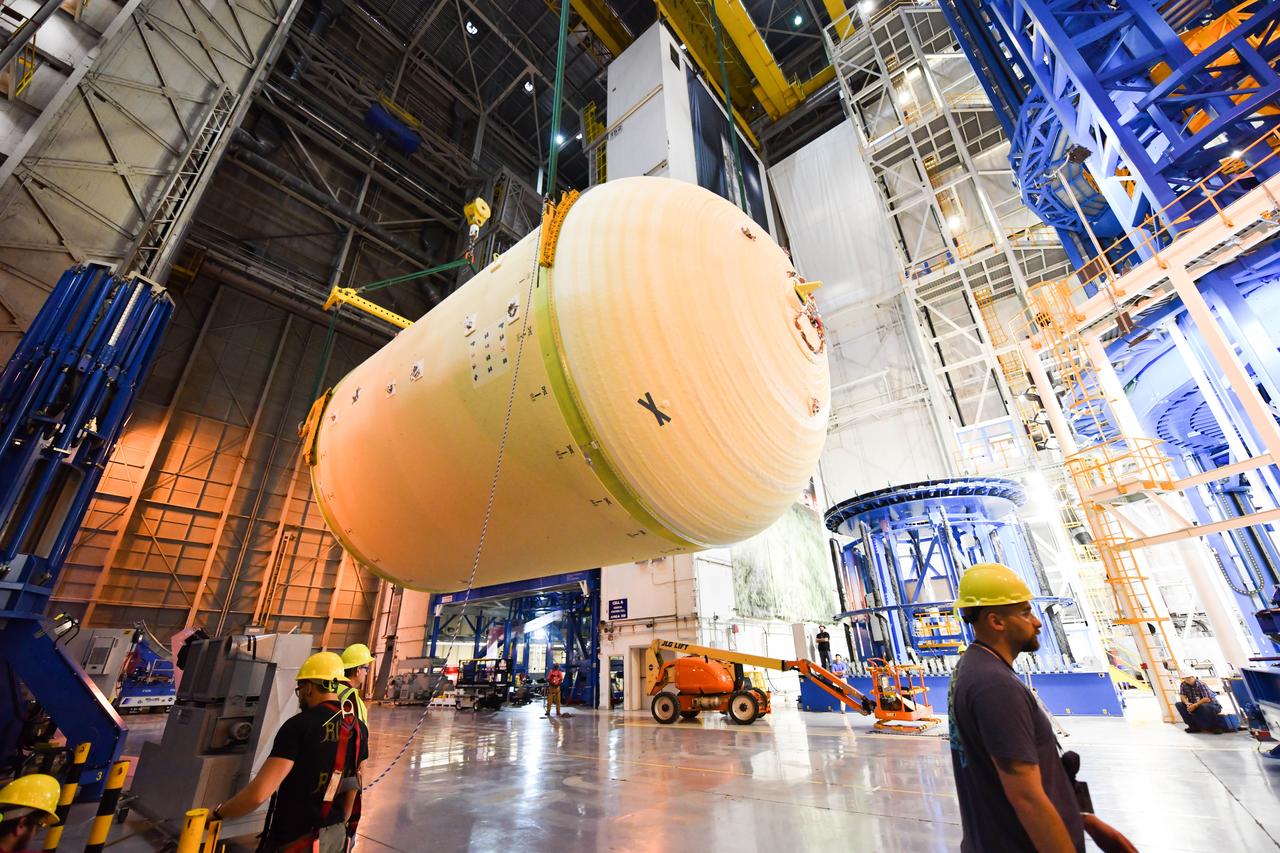

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
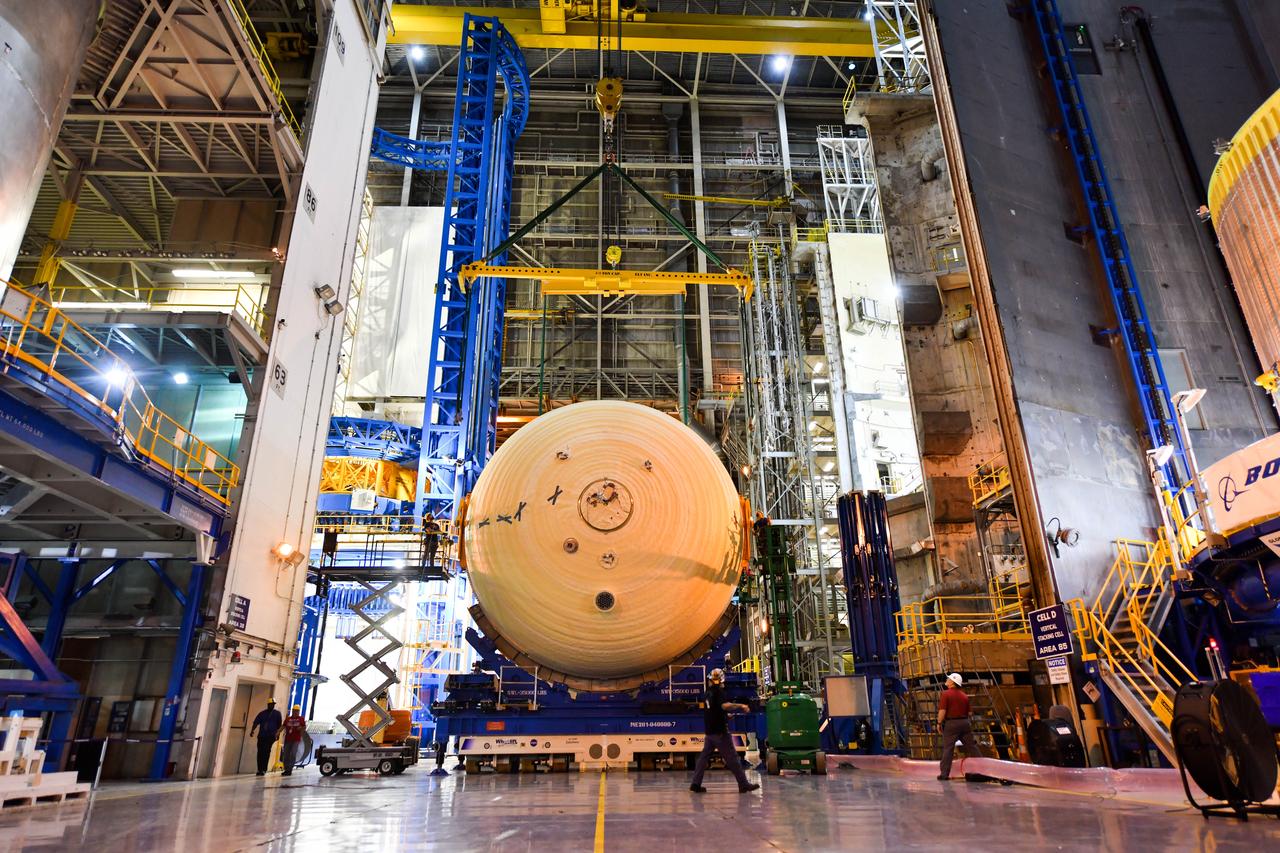

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
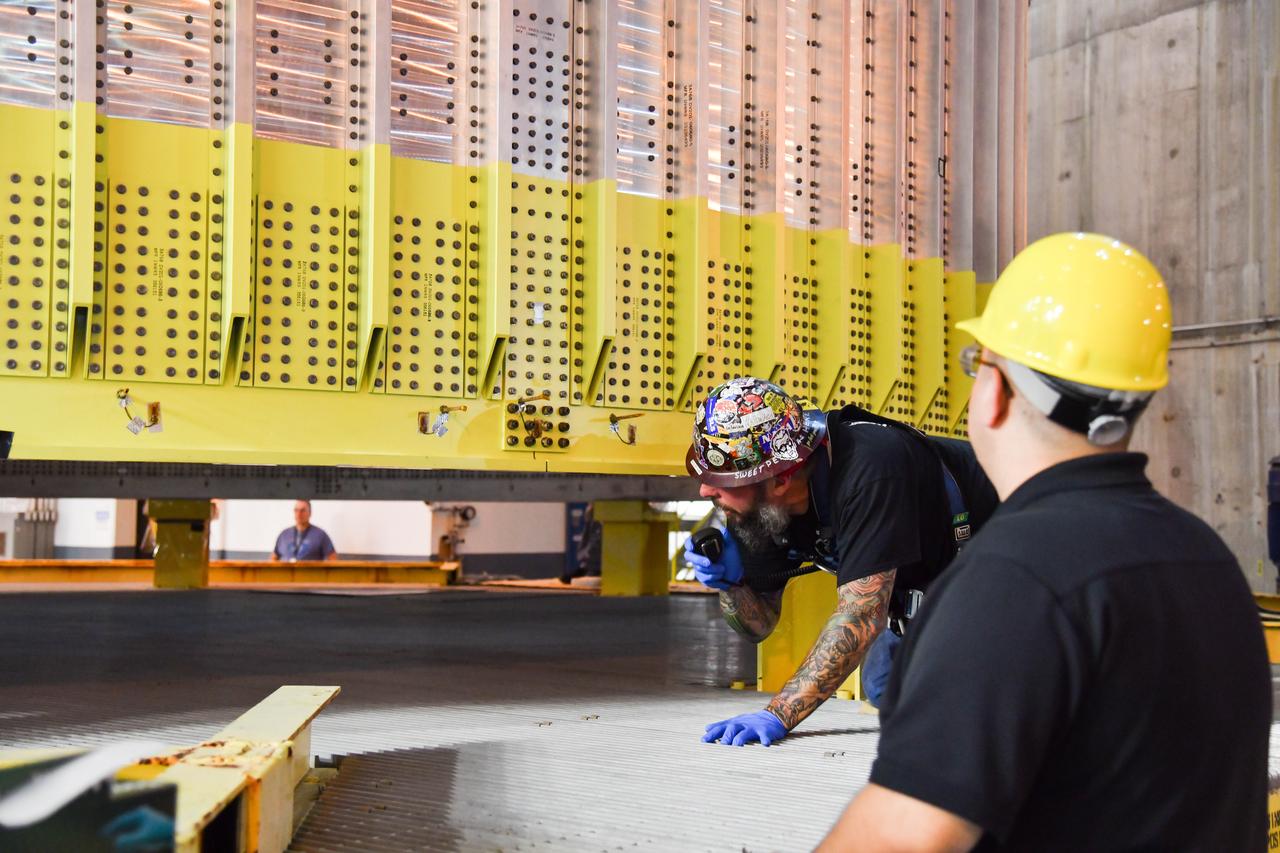

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
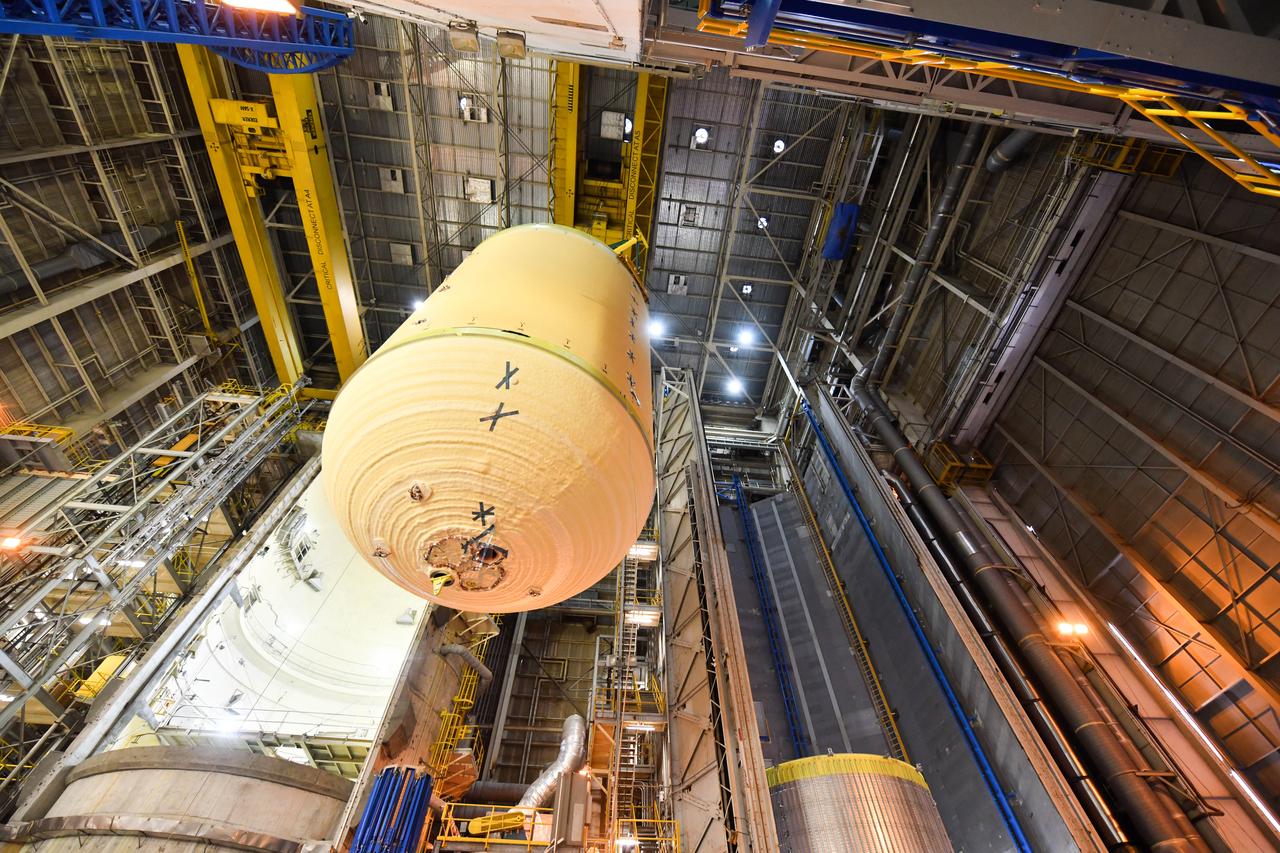

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
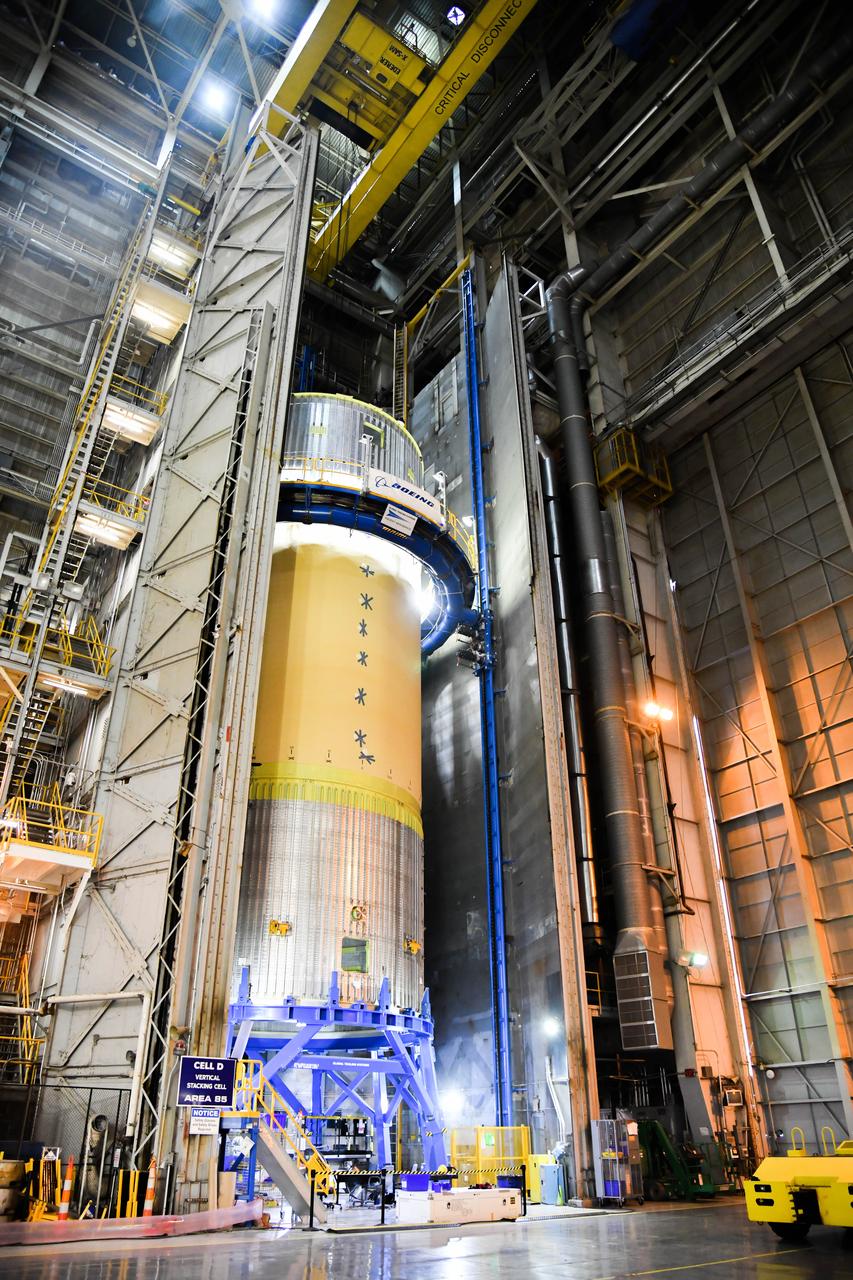

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
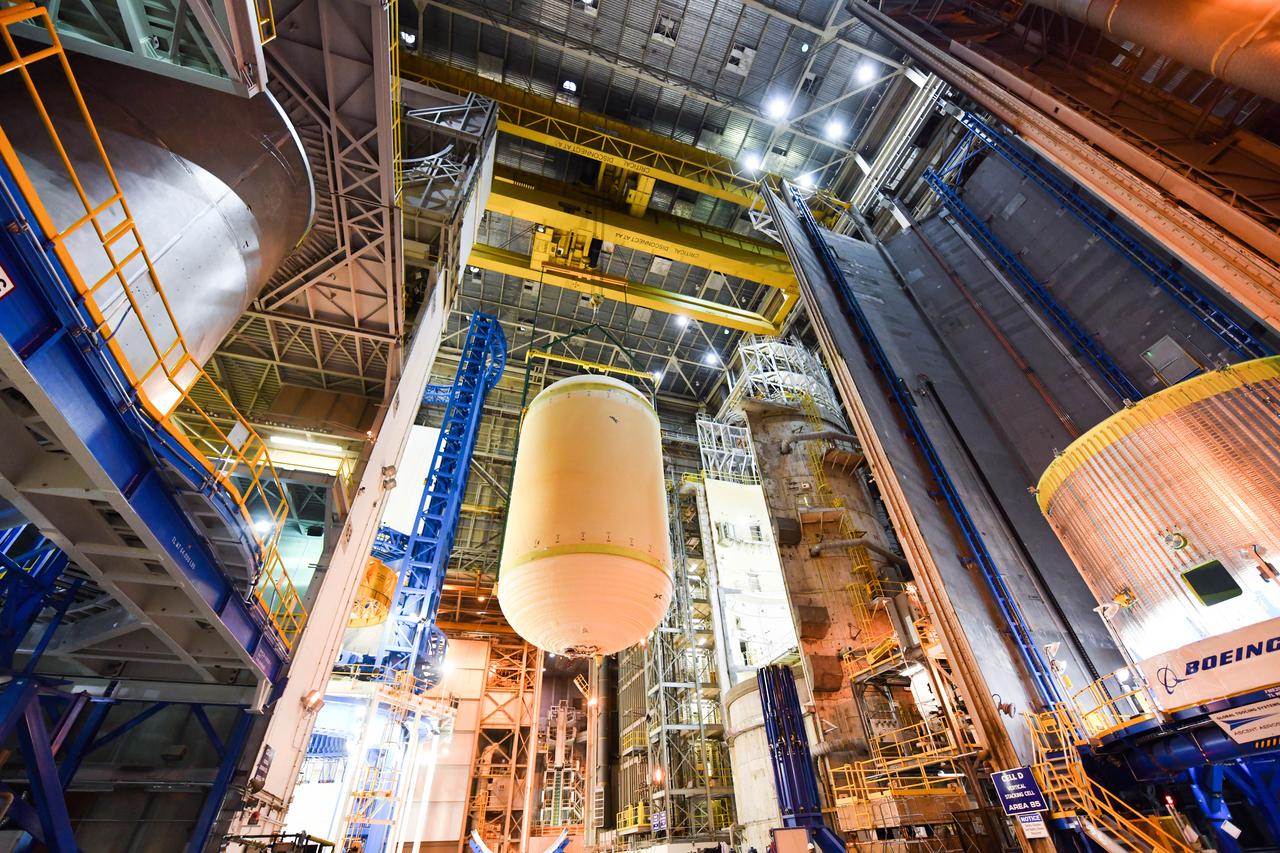

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
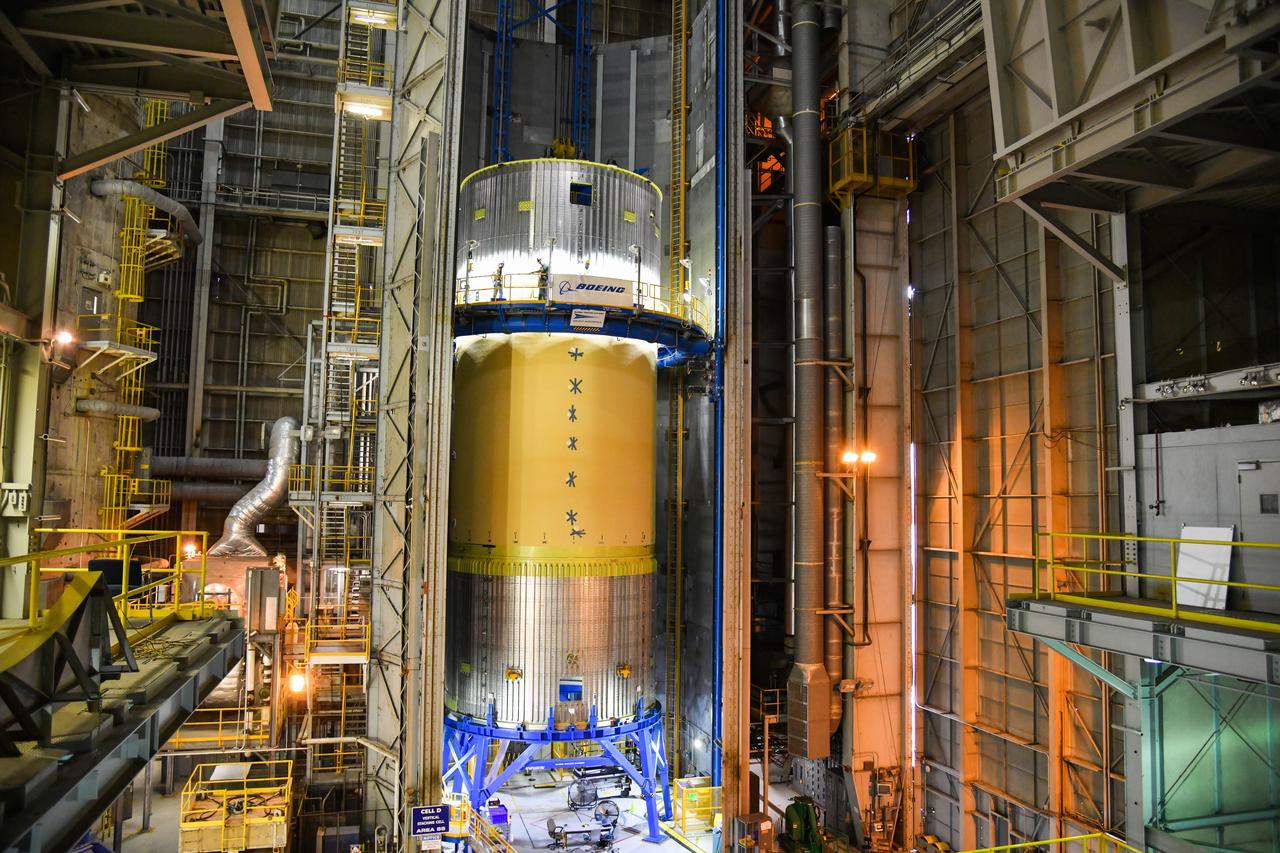

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
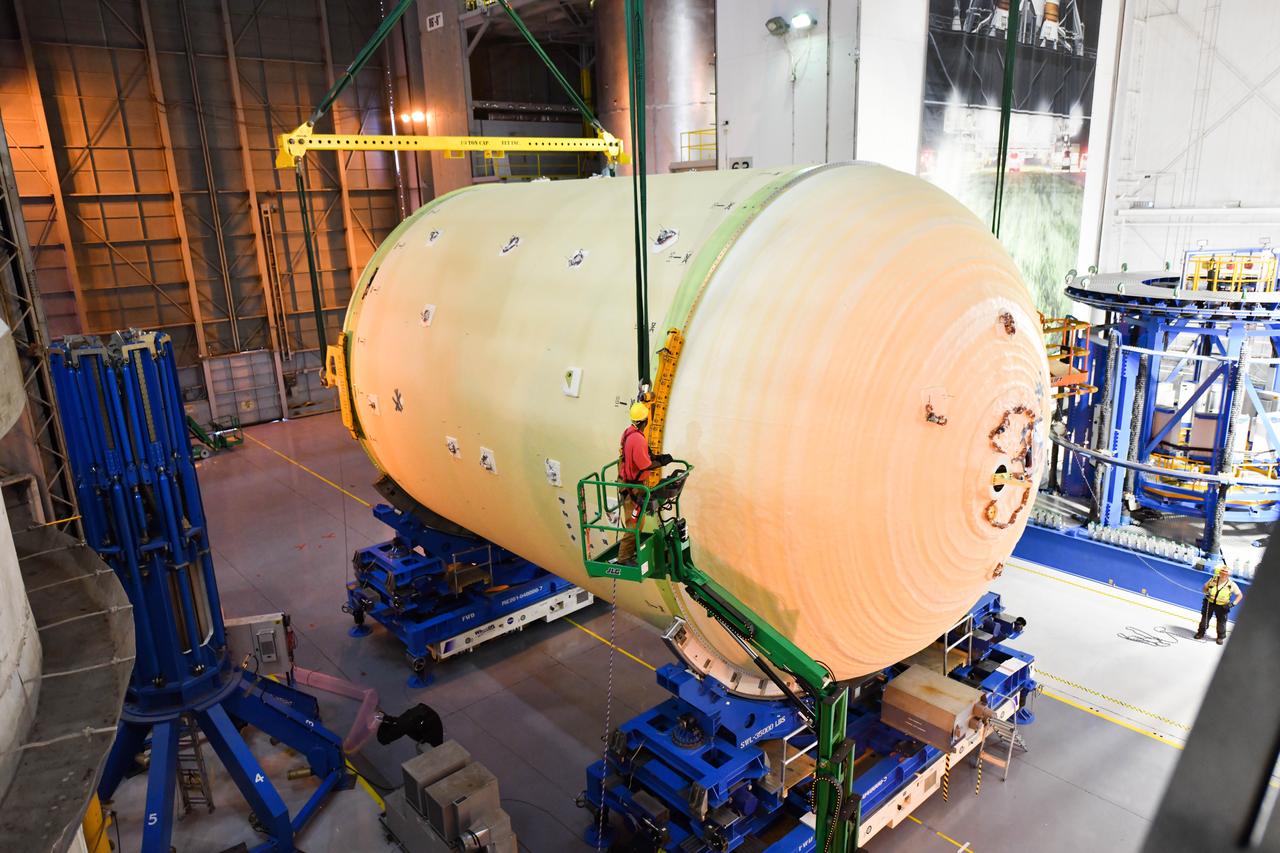

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
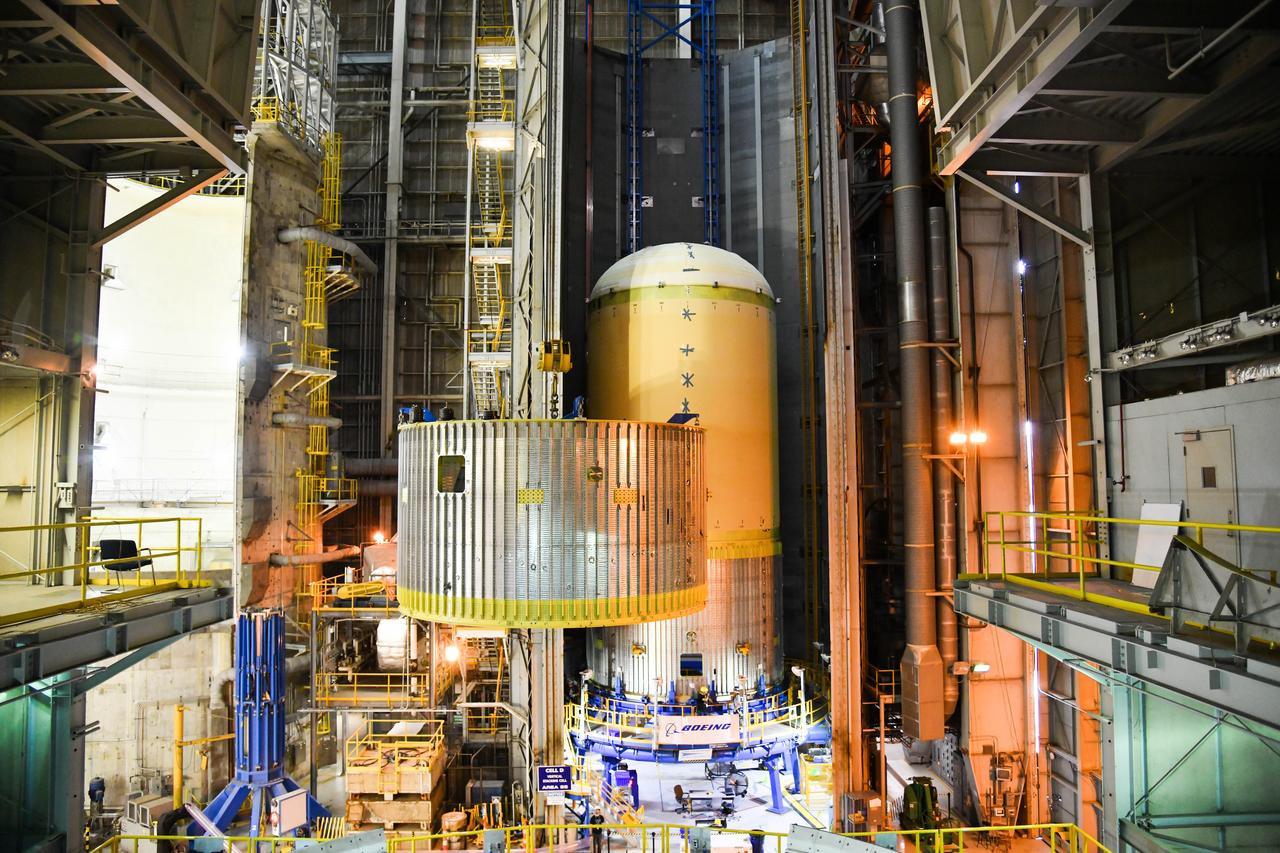

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
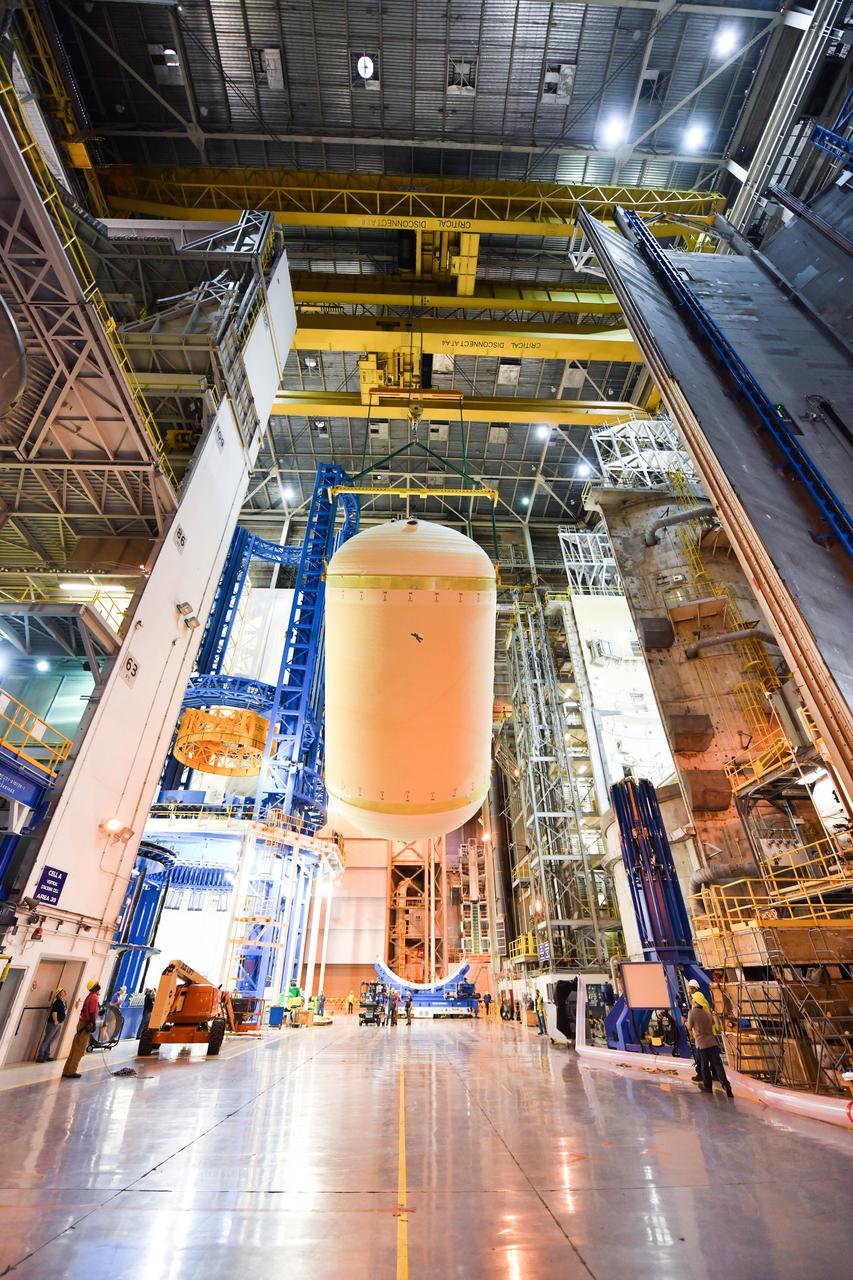

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
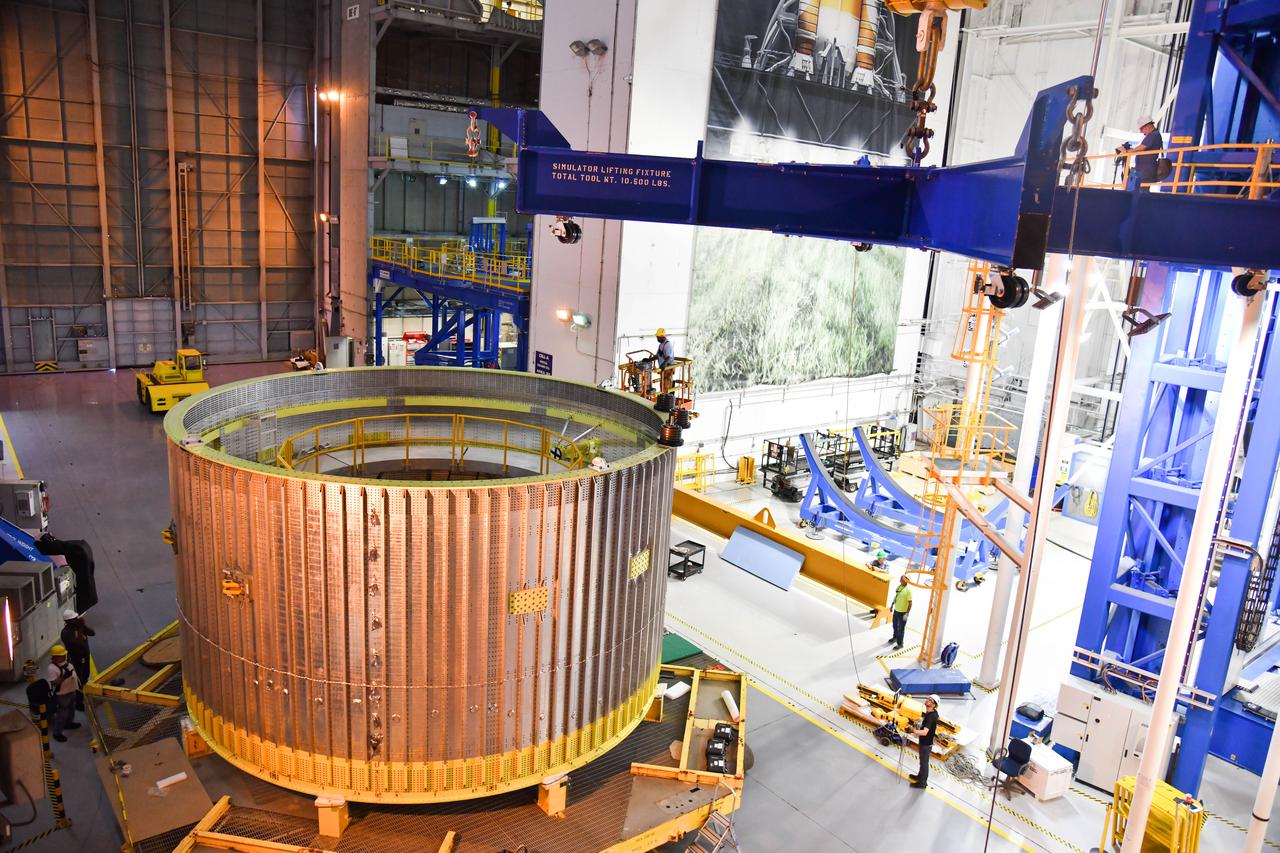

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
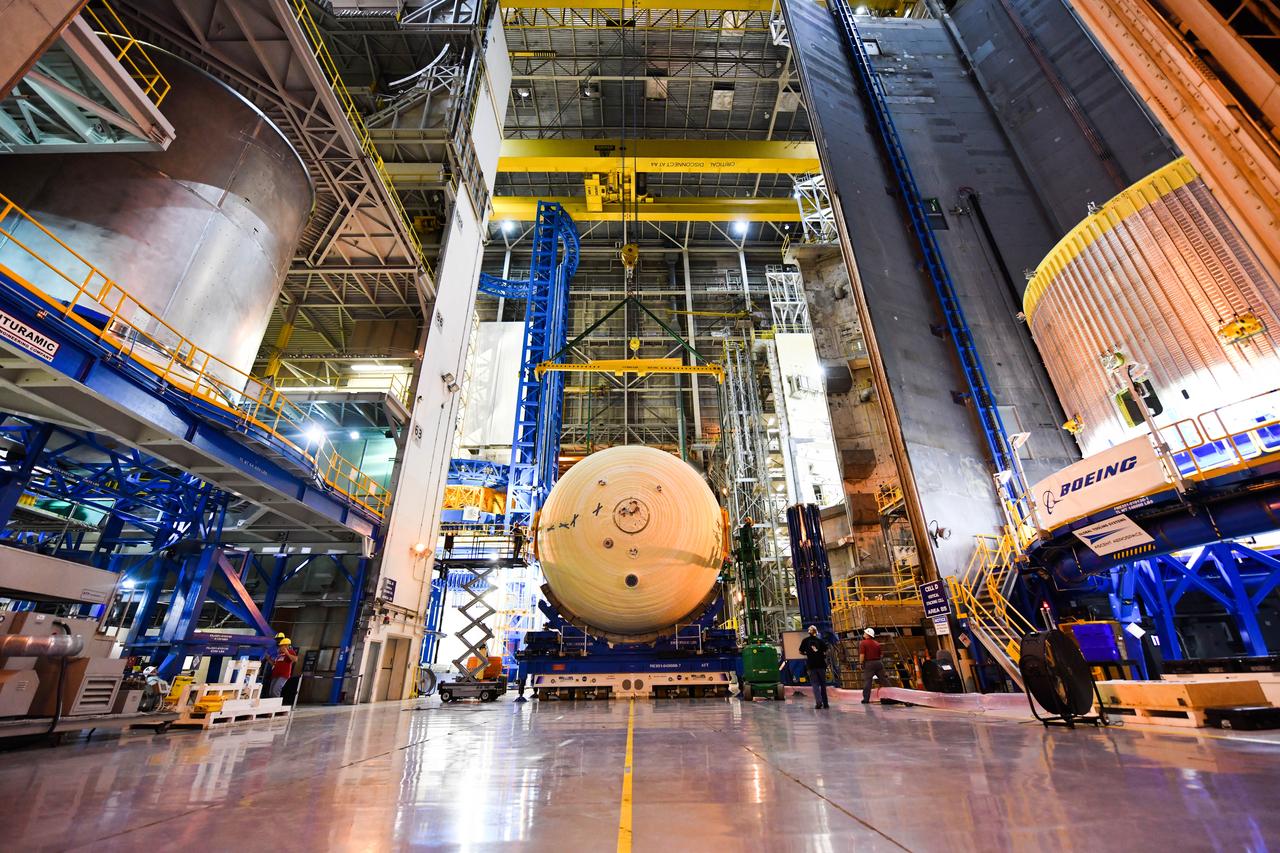

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
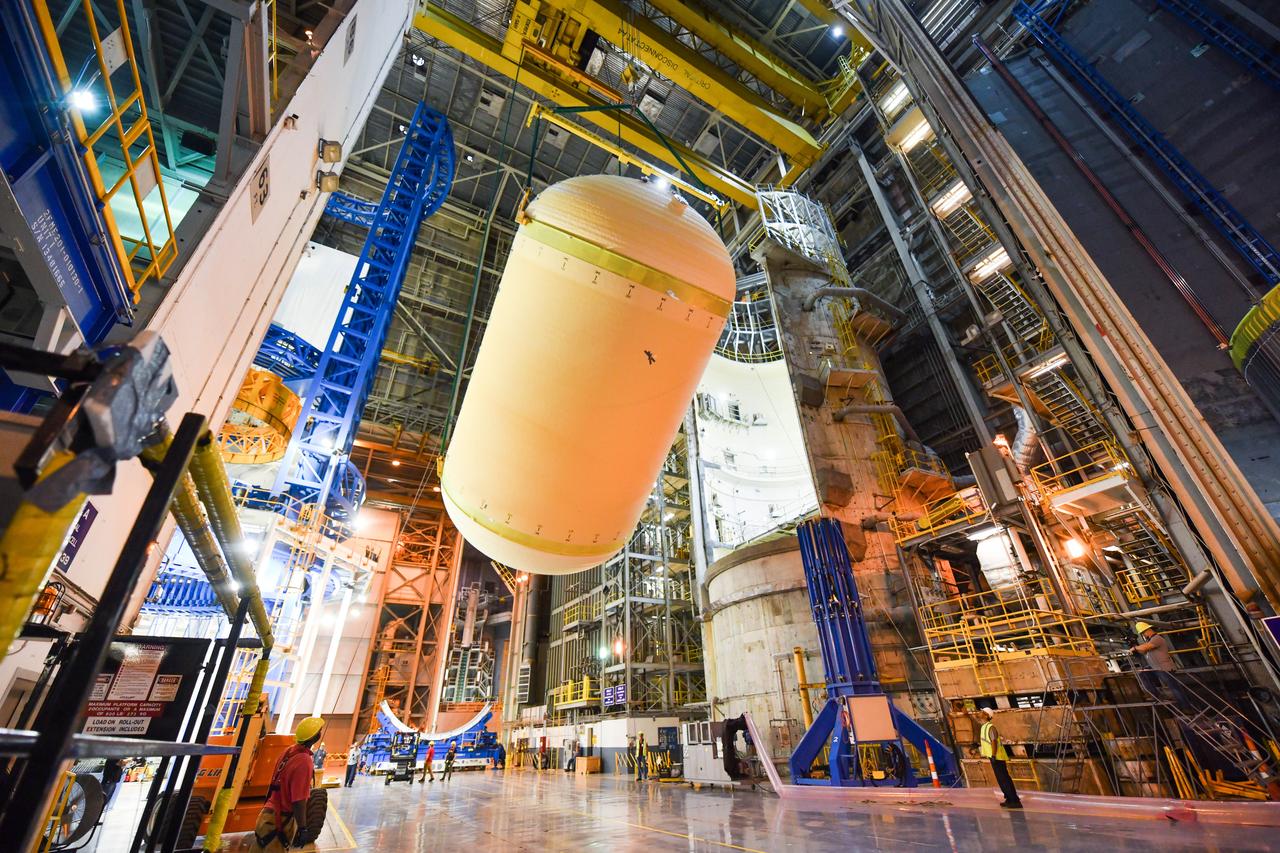

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
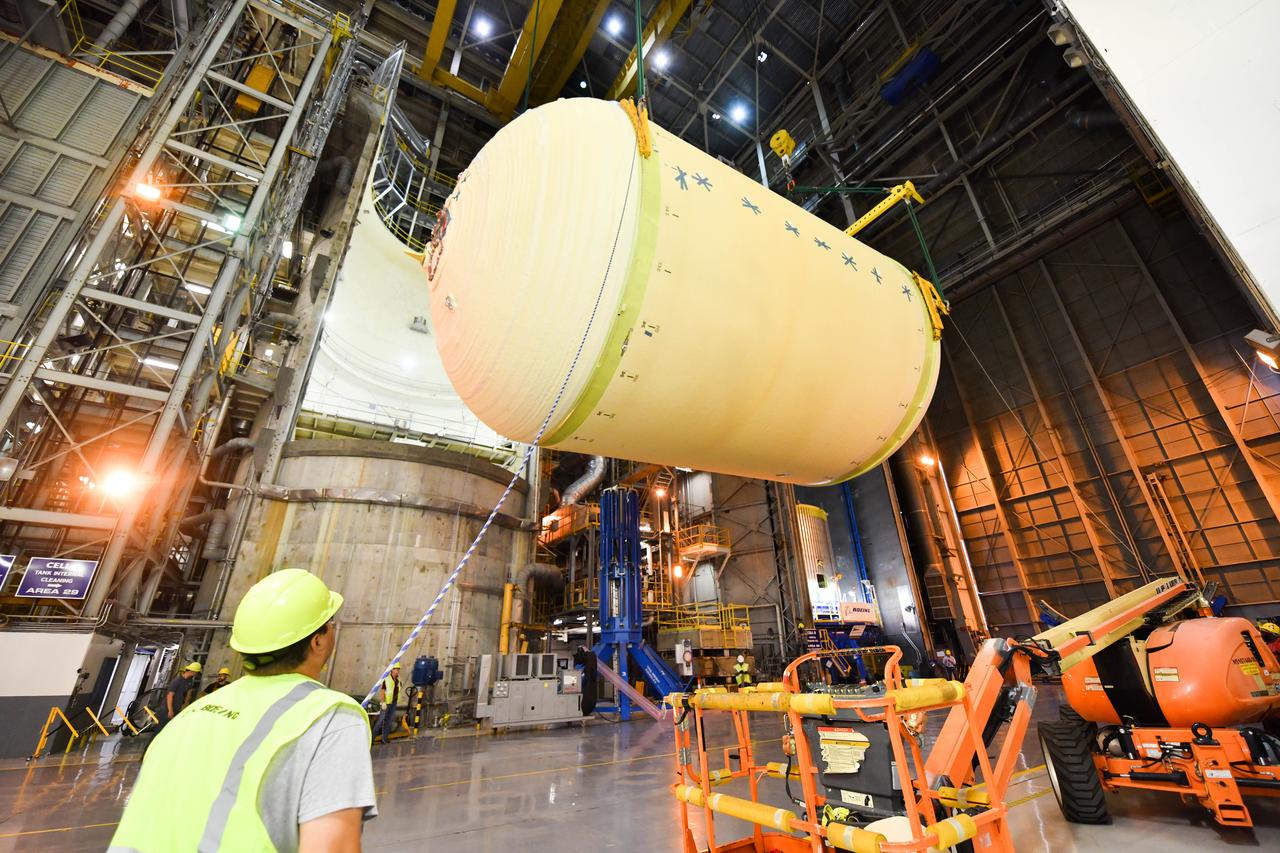

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
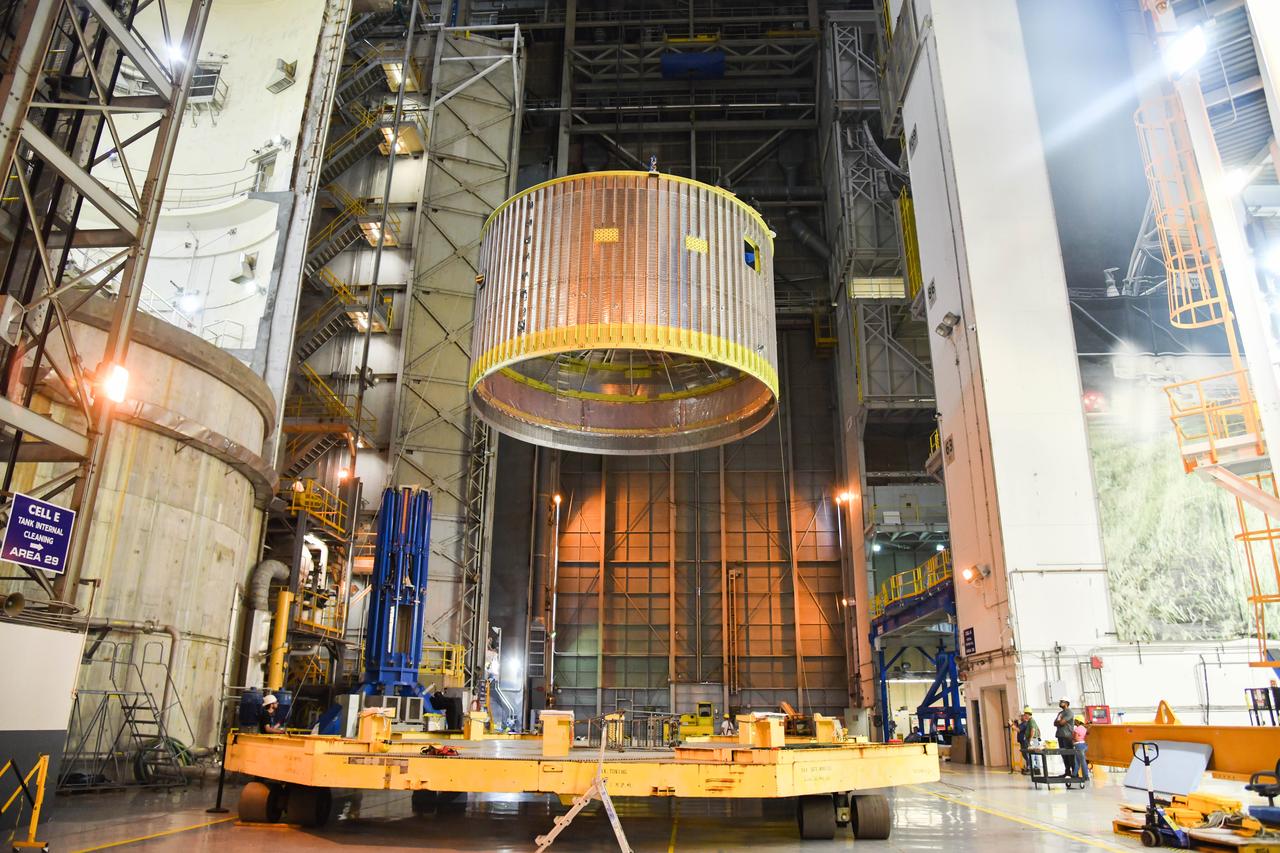

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
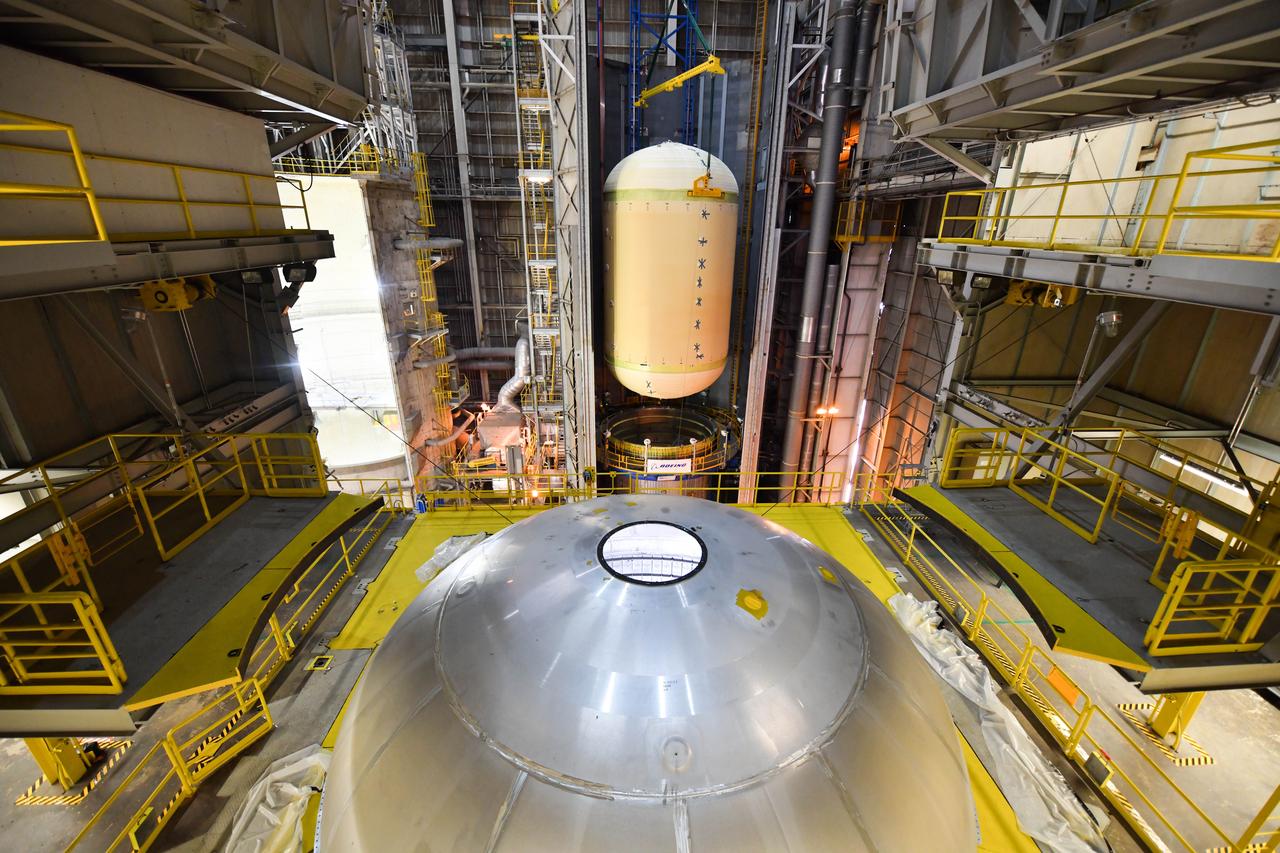

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
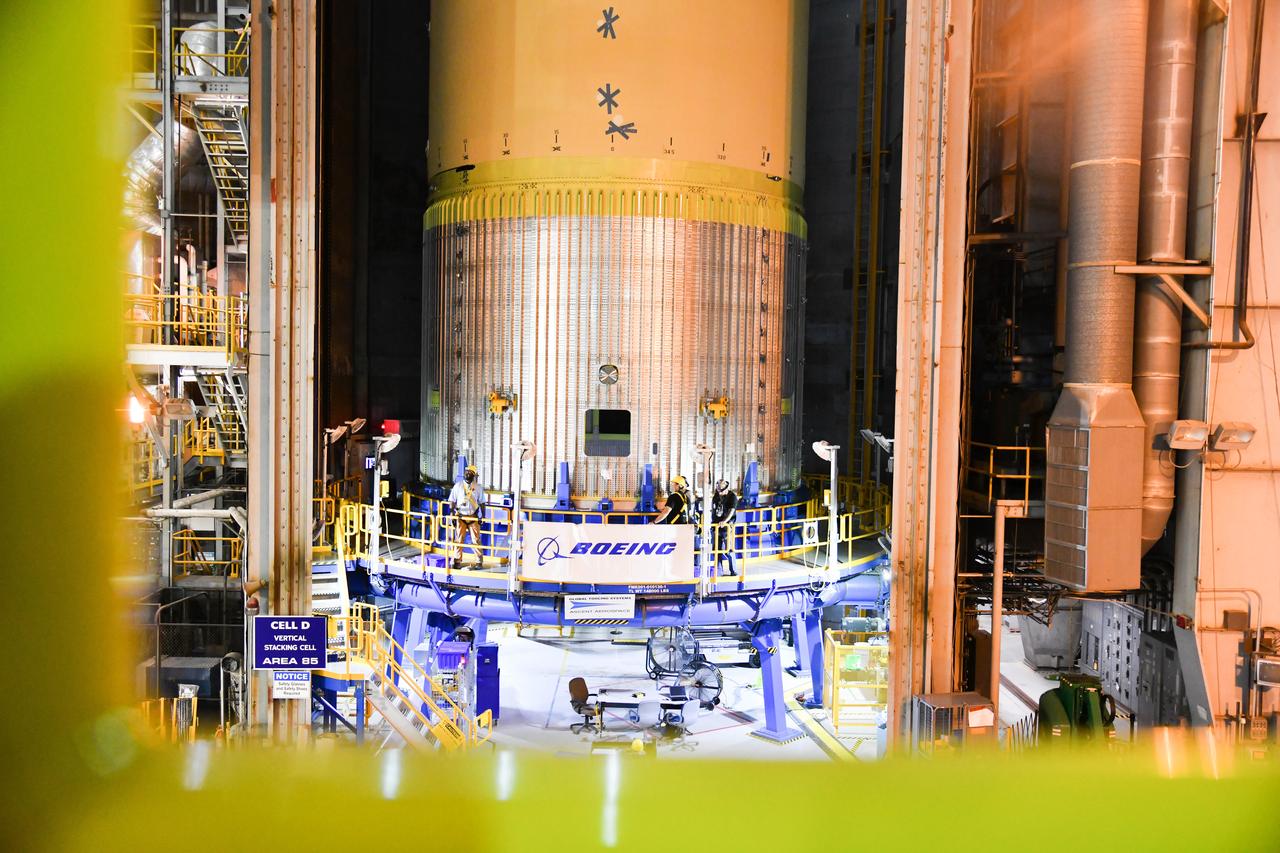

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
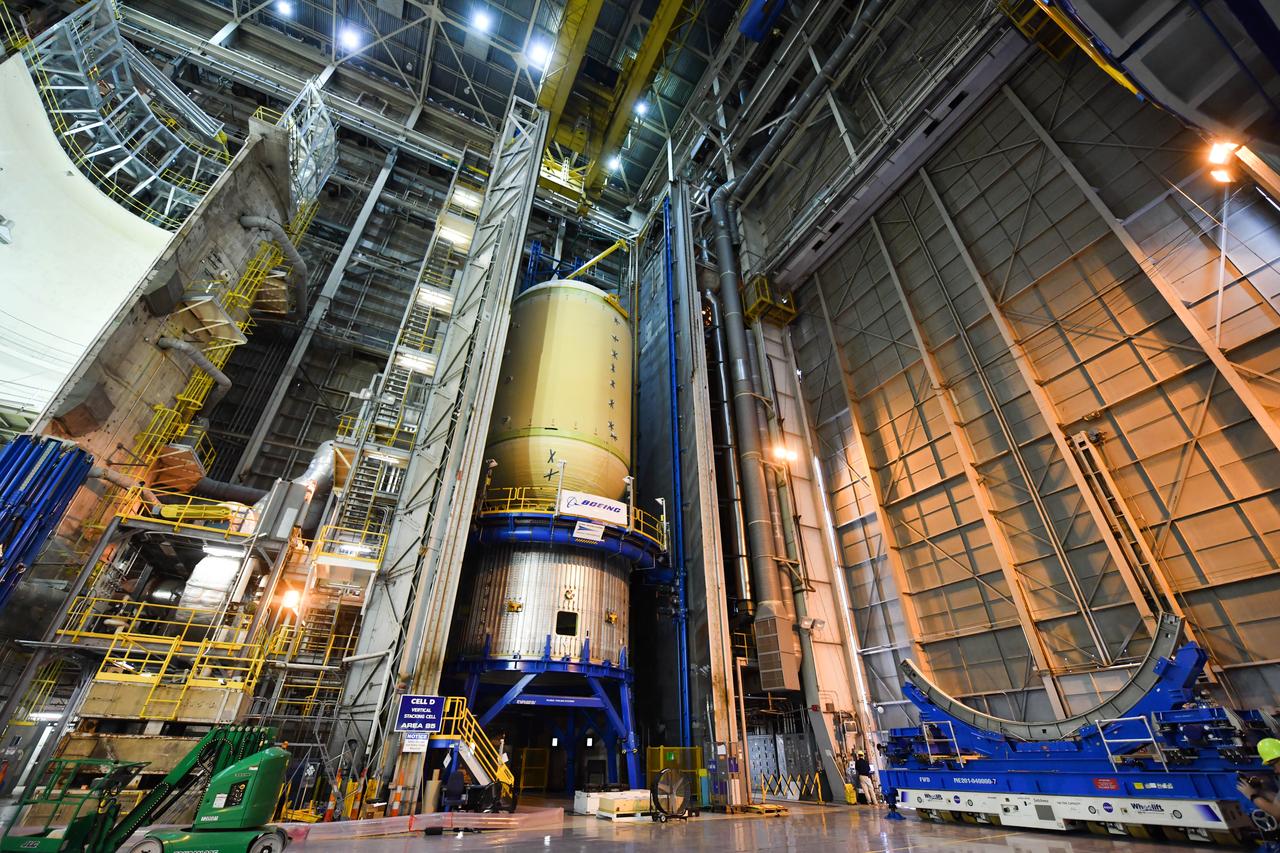

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
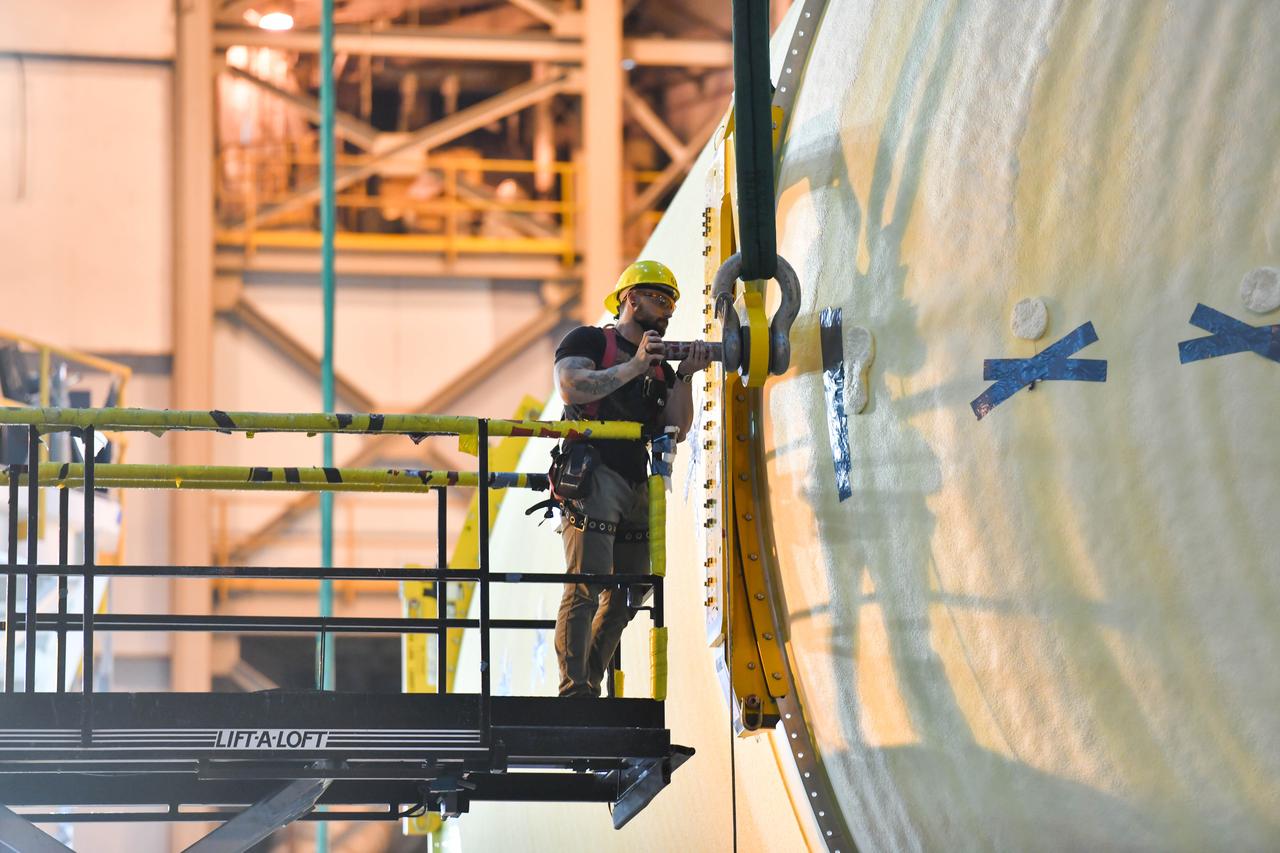

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
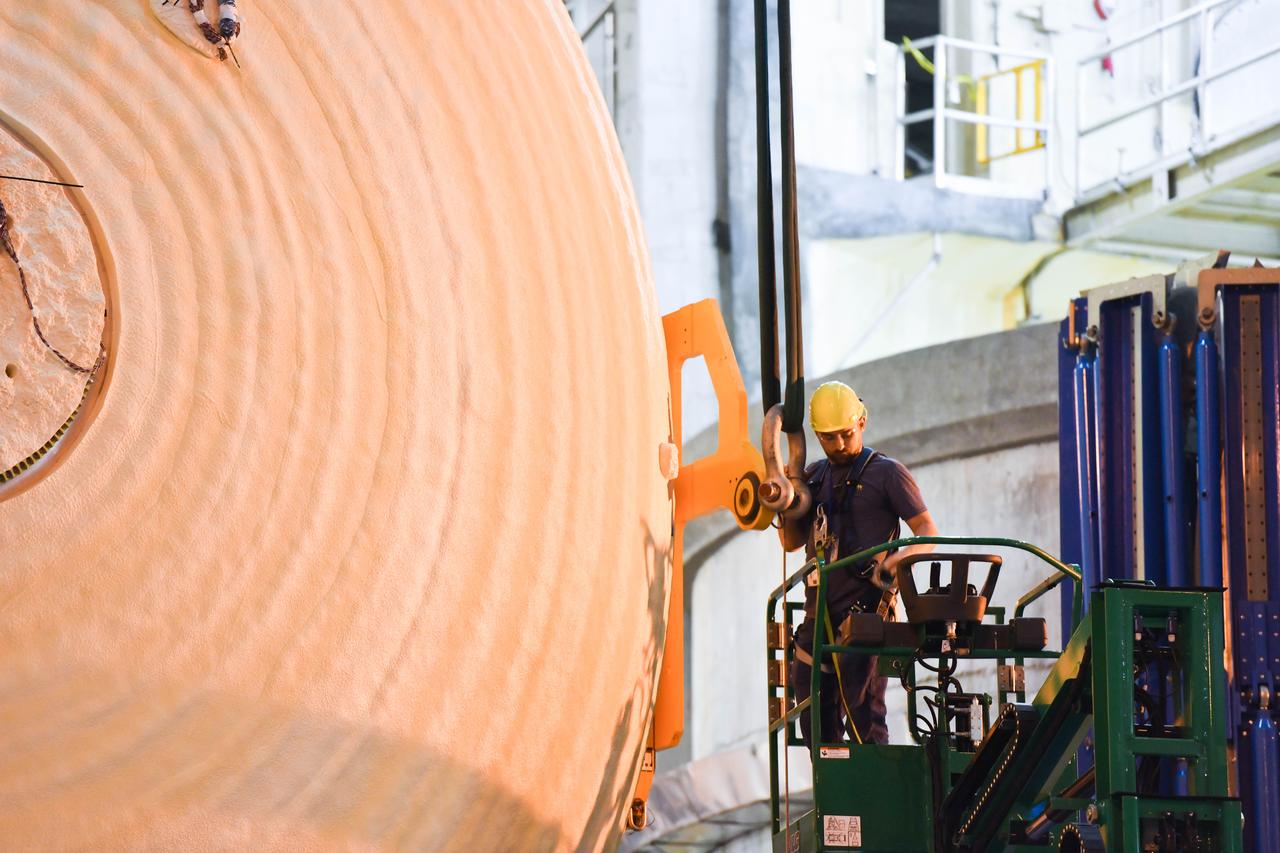

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
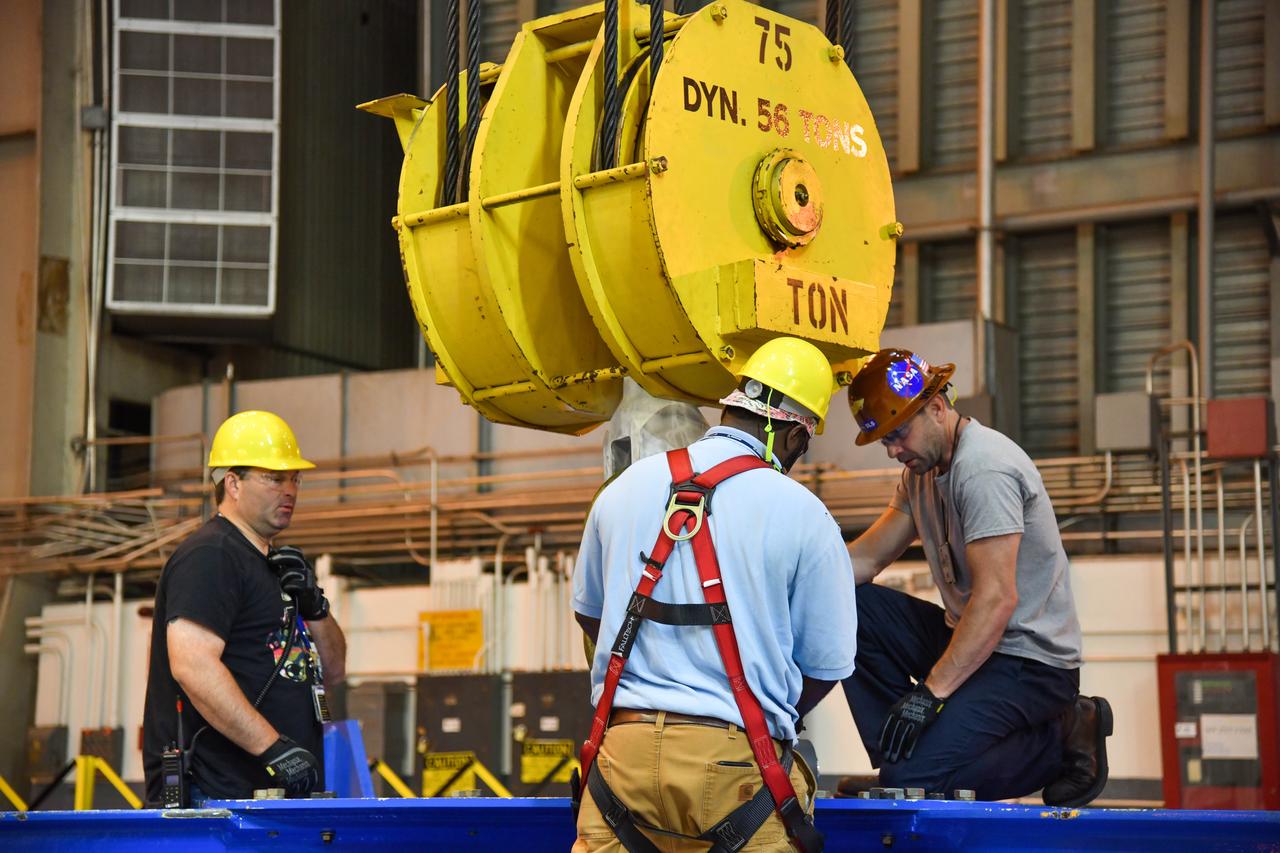

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
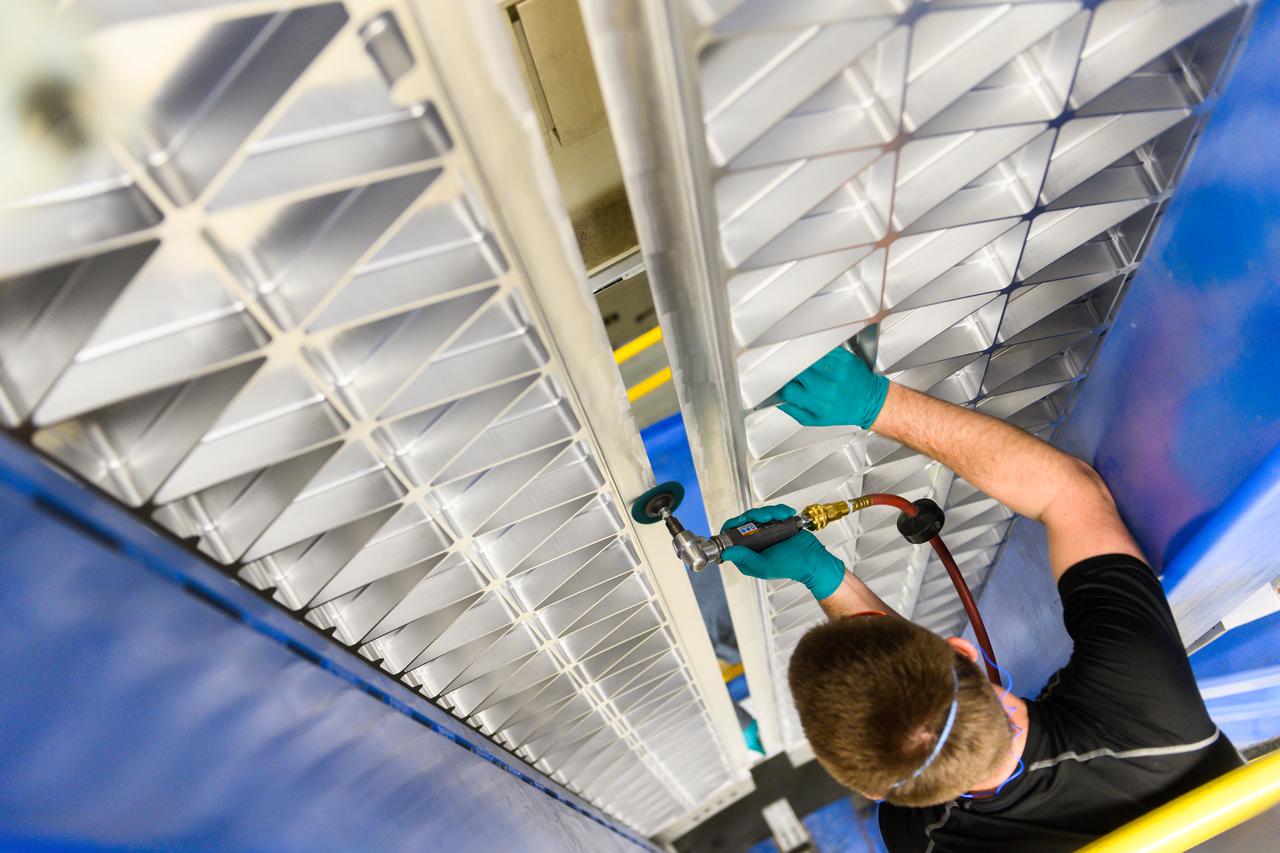

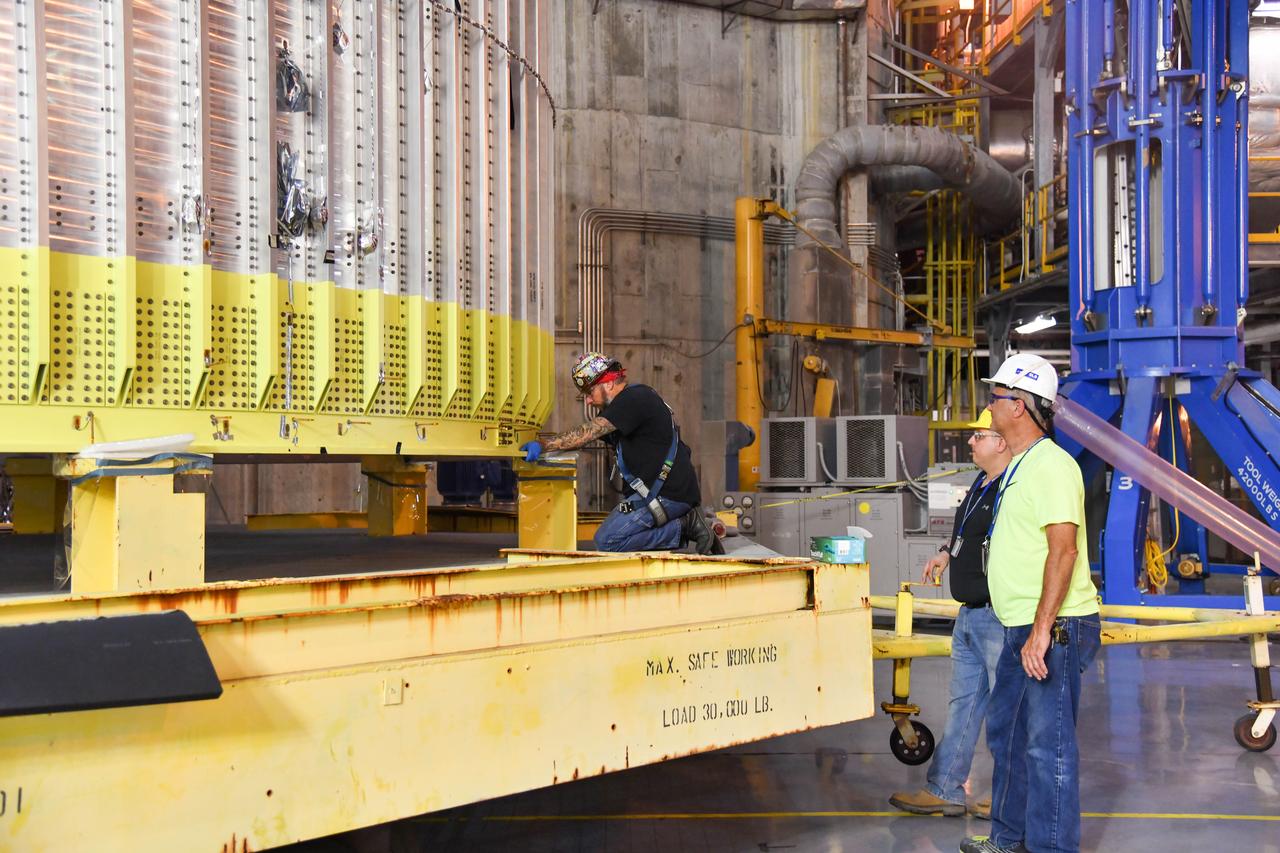
Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
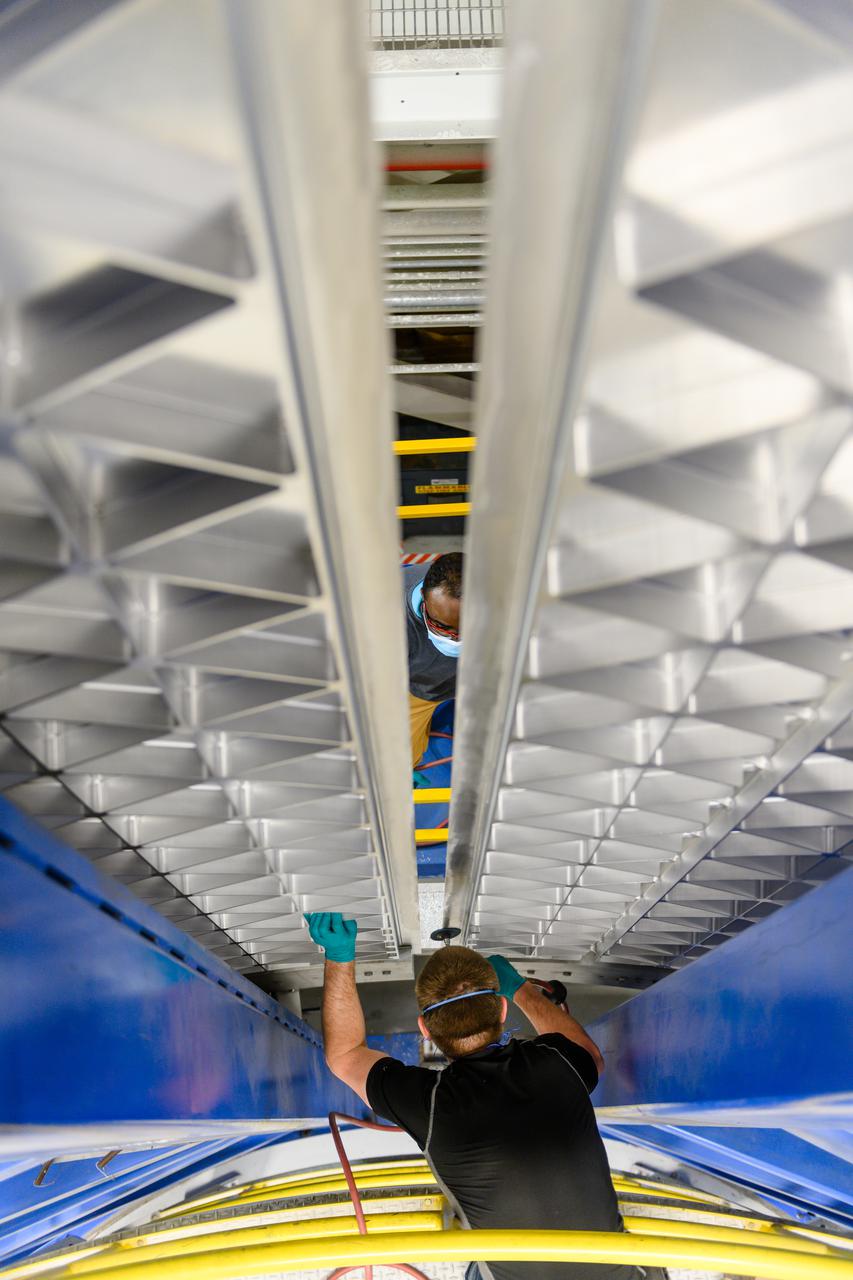

Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
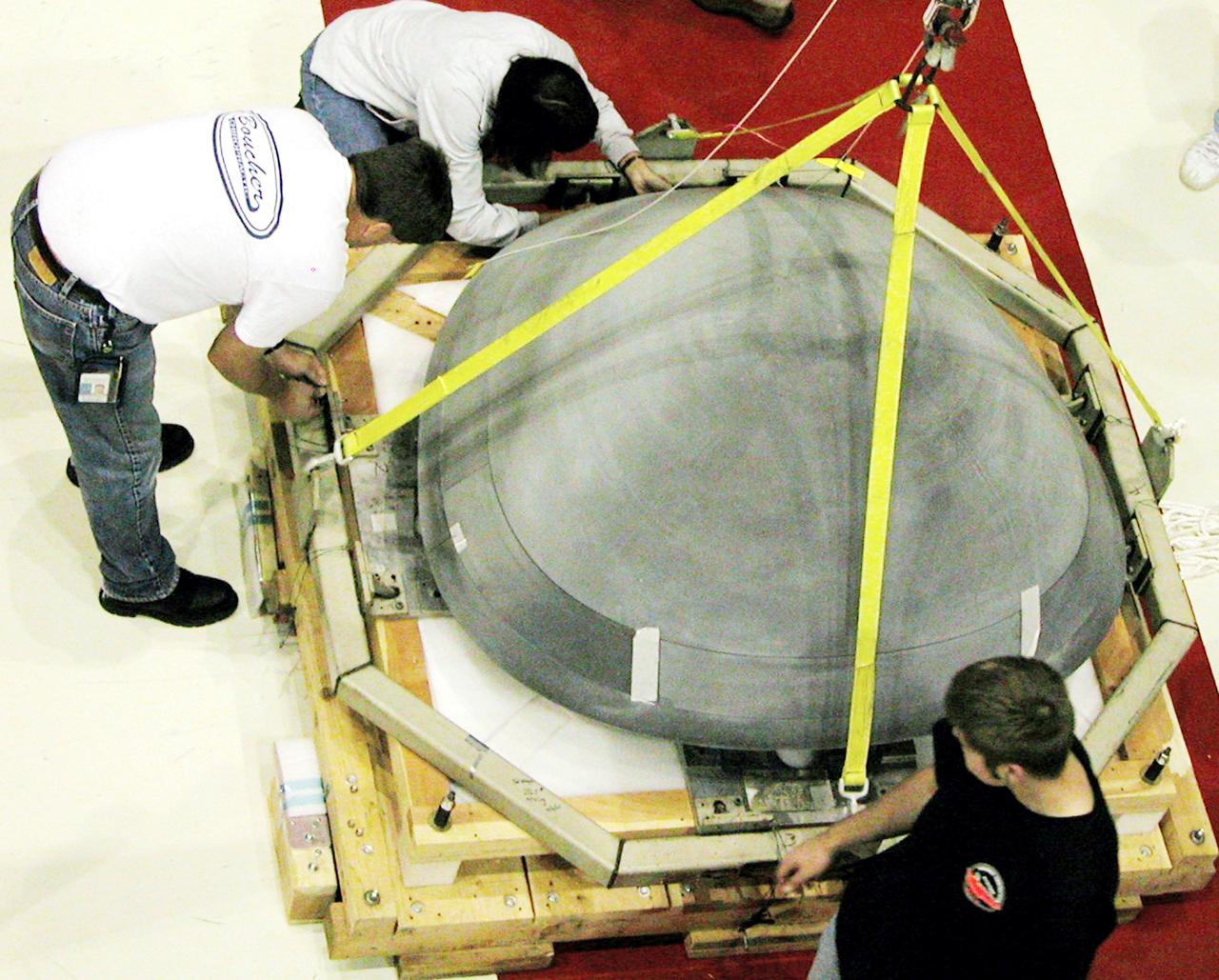

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is secured on a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is lowered toward a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

SOURCE DIAGNOSTIC TEST BLADE MANUFACTURE
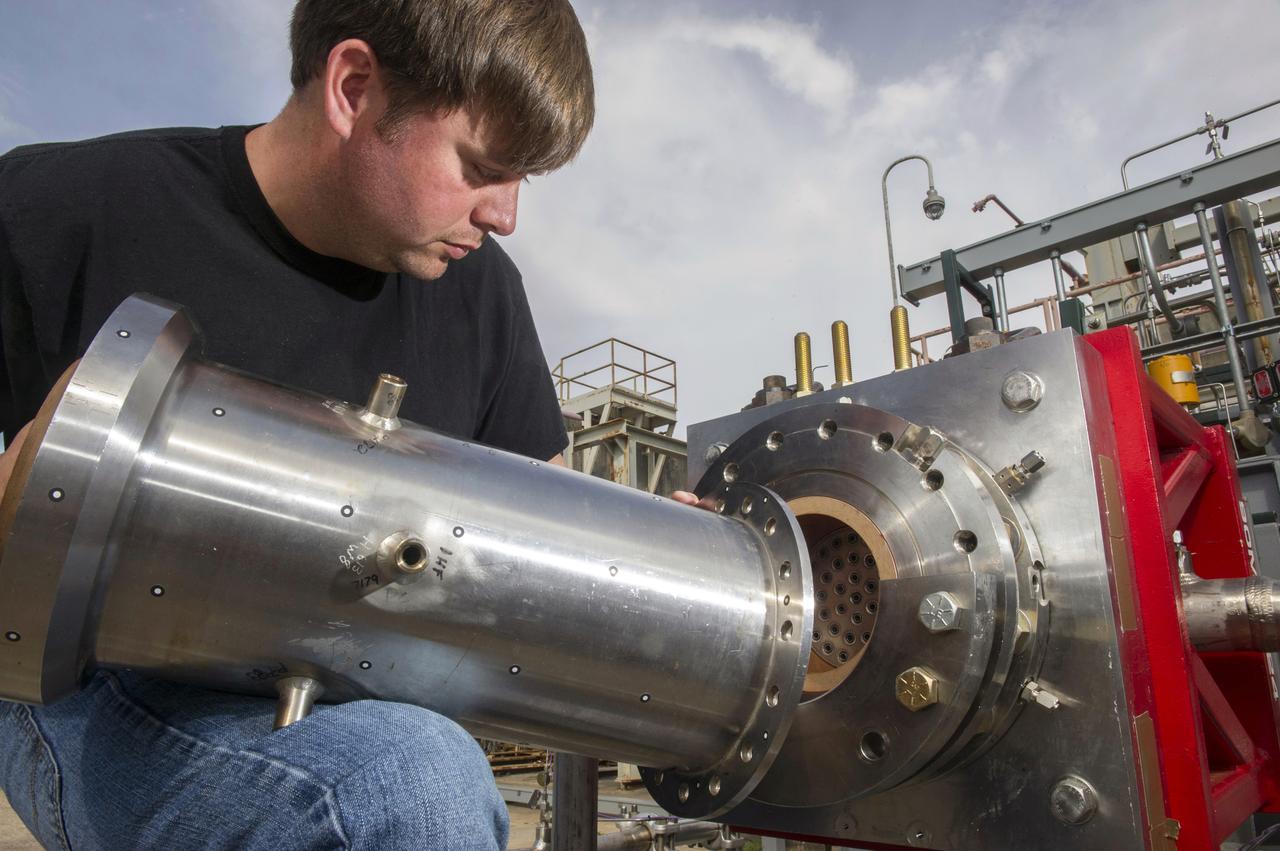

1. ENGINEERS AND TECHNICIANS PREPARE FOR AN UPCOMING HOT-FIRE TEST OF A ROCKET INJECTOR MANUFACTURED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING…RANDALL MCALLISTER, INFOPRO TECHNICIAN, FITS NOZZLE TO ROCKET INJECTOR
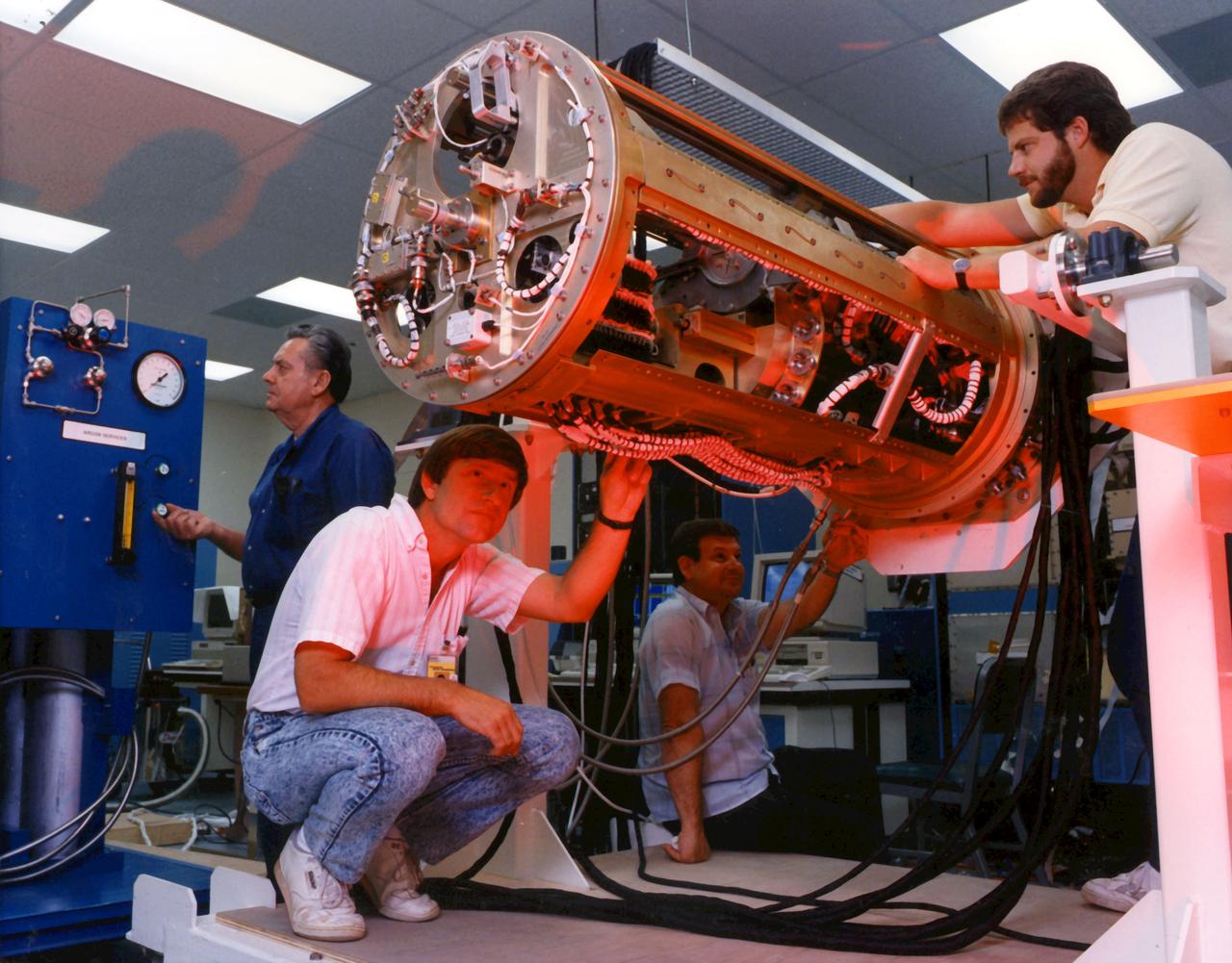
Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Being Tested at Manufacturing Facilty
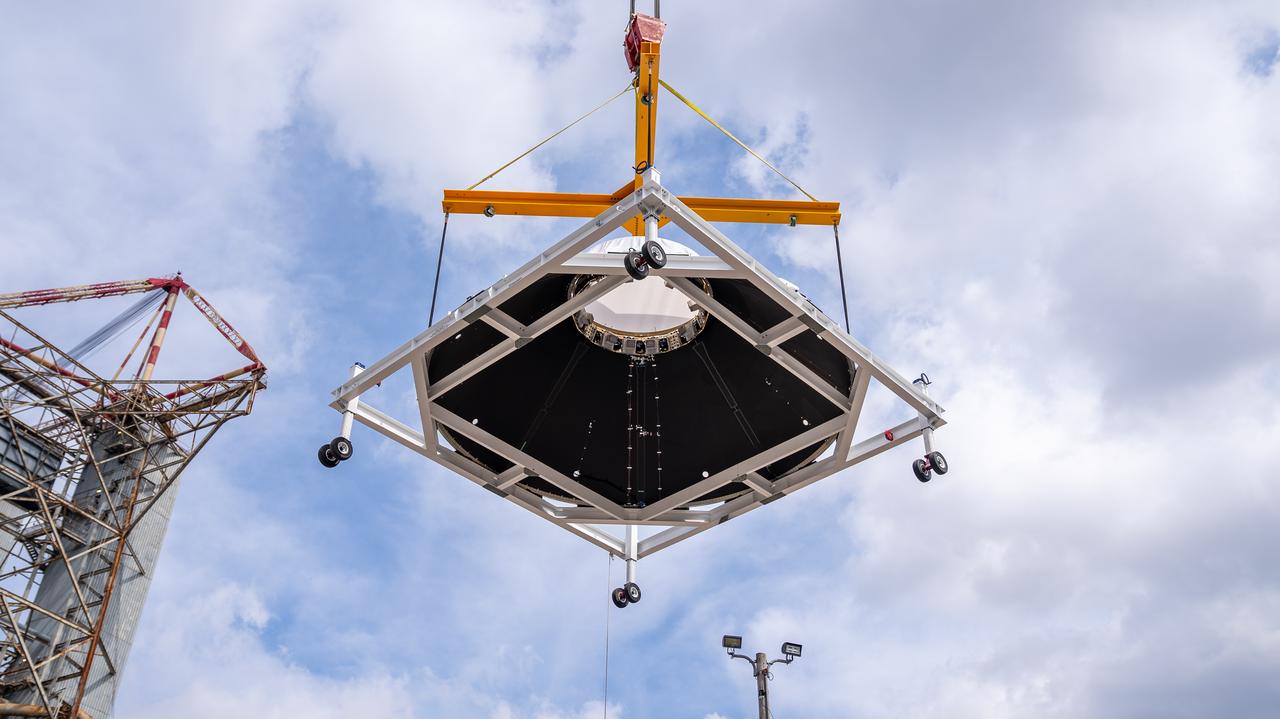

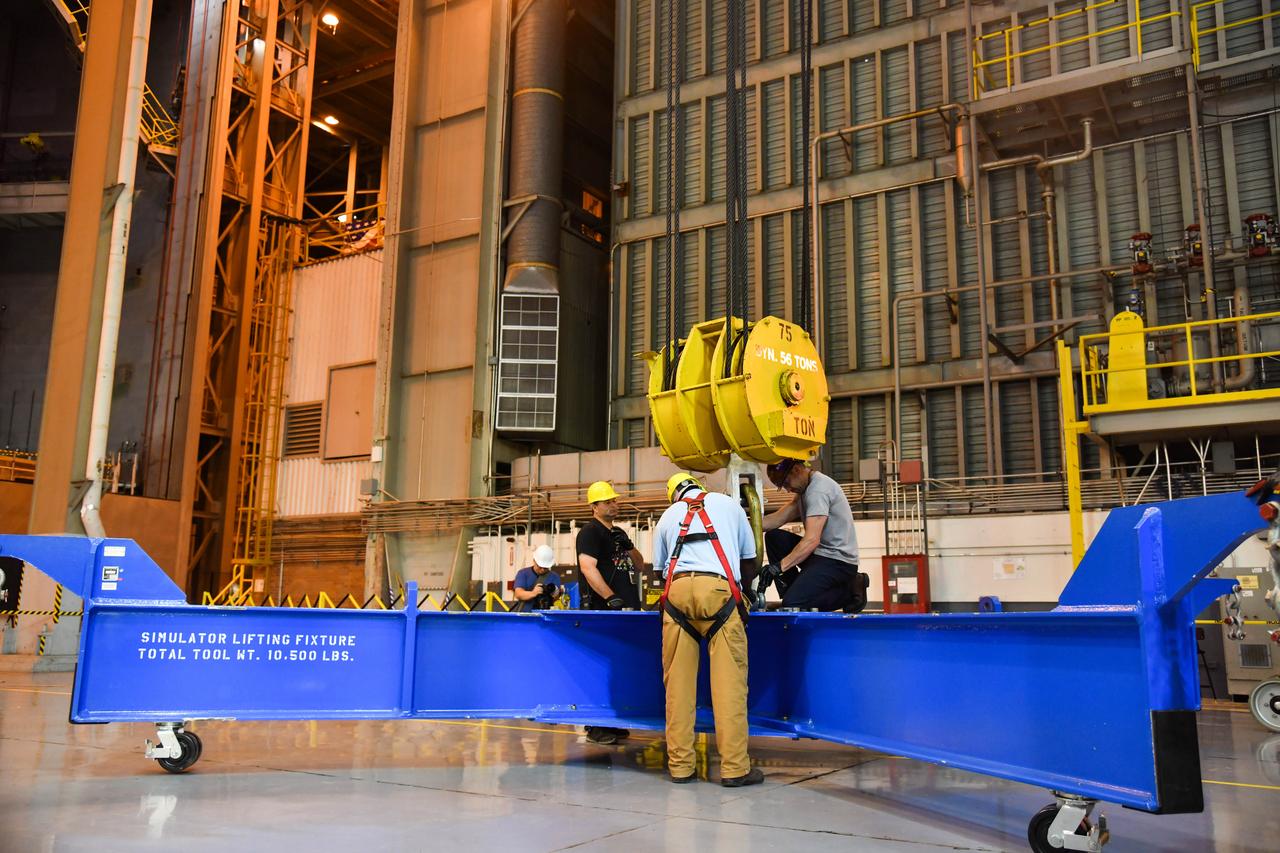
Crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13.
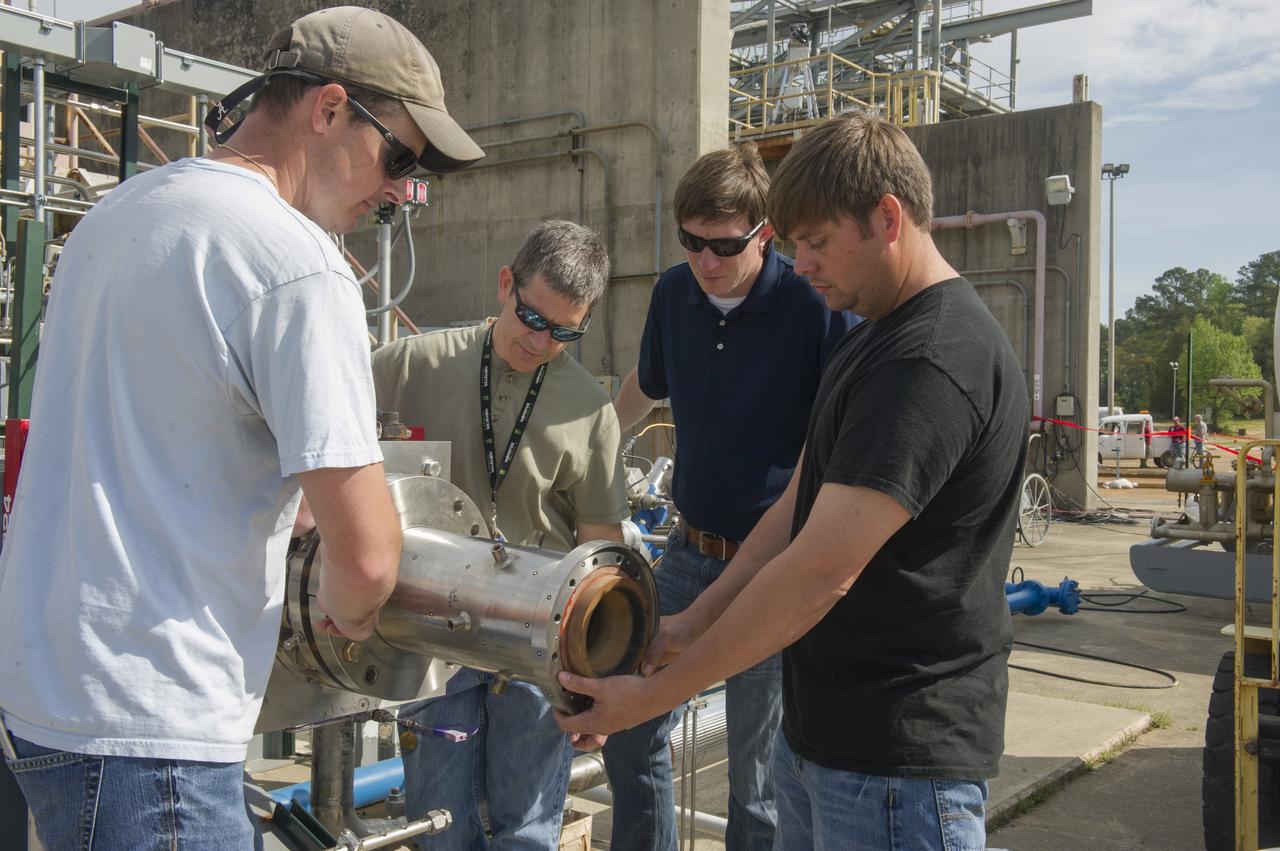

2. ENGINEERS AND TECHNICIANS PREPARE FOR AN UPCOMING HOT-FIRE TEST OF A ROCKET INJECTOR MANUFACTURED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING…(L TO R) WILLIE PARKER, INFOPRO TECHNICIAN, BRAD BULLARD, NASA, NICK CASE, NASA, AND RANDALL MCALLISTER, INFOPRO TECHNICIAN
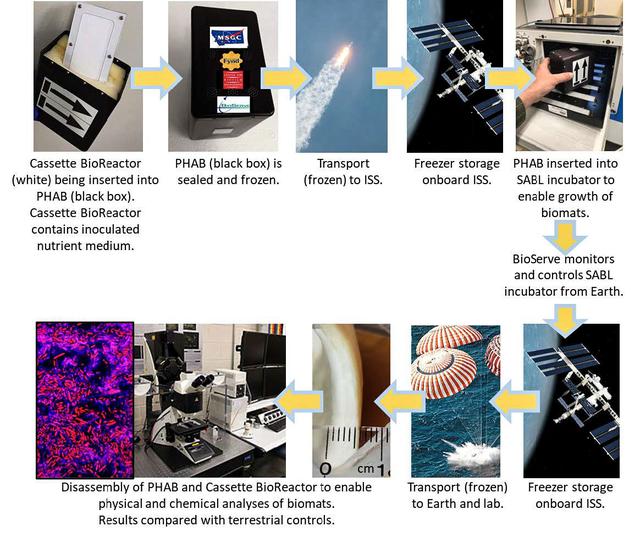
jsc2022e031226 (4/26/2022) --- A mission overview of the Protein Manufacturing investigation shows hardware, operations, and scientific details. The Protein Manufacturing project demonstrates and tests the operation of a novel bioreactor technology to support robust fungal growth for the production of high-protein food in a low-Earth orbit, space environment. Image courtesy of BioServe.
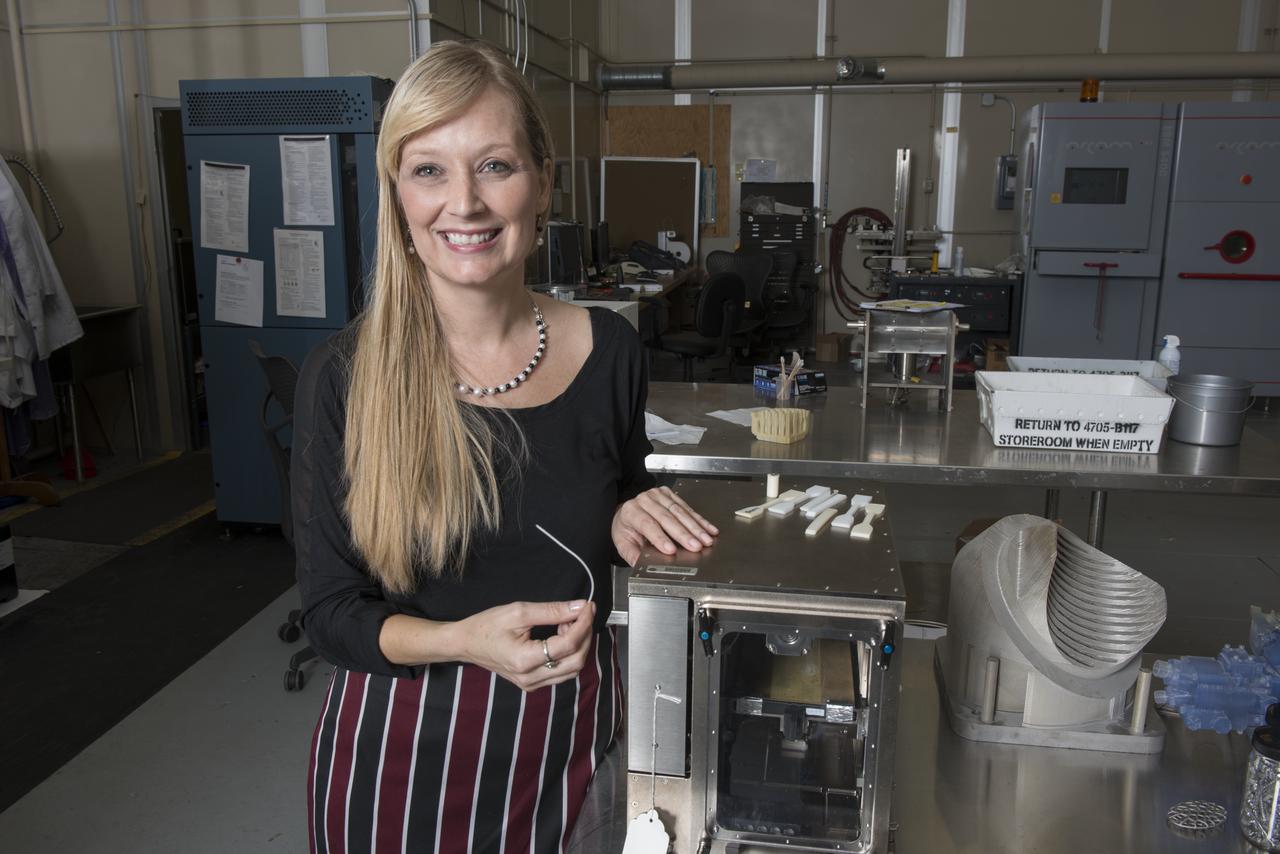

NIKKI WERKHEISER EXAMINES THE RAW MATERIAL USED IN THE FIRST 3-D PRINTER TO BE SENT TO THE ISS WHICH IS DESIGNED TO BE A TEST BED FOR MANUFACTURING SMALL AS ARTICLES AS NEEDED.
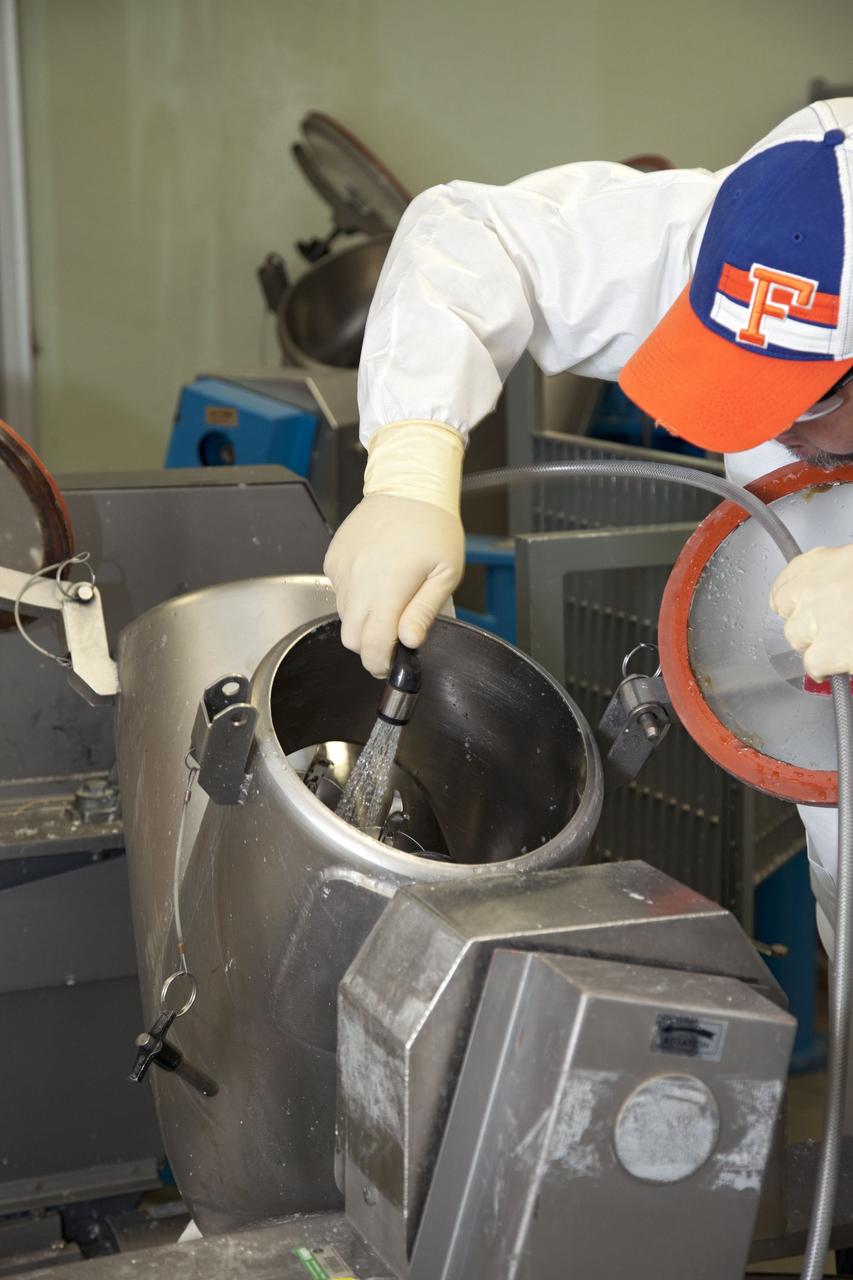

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
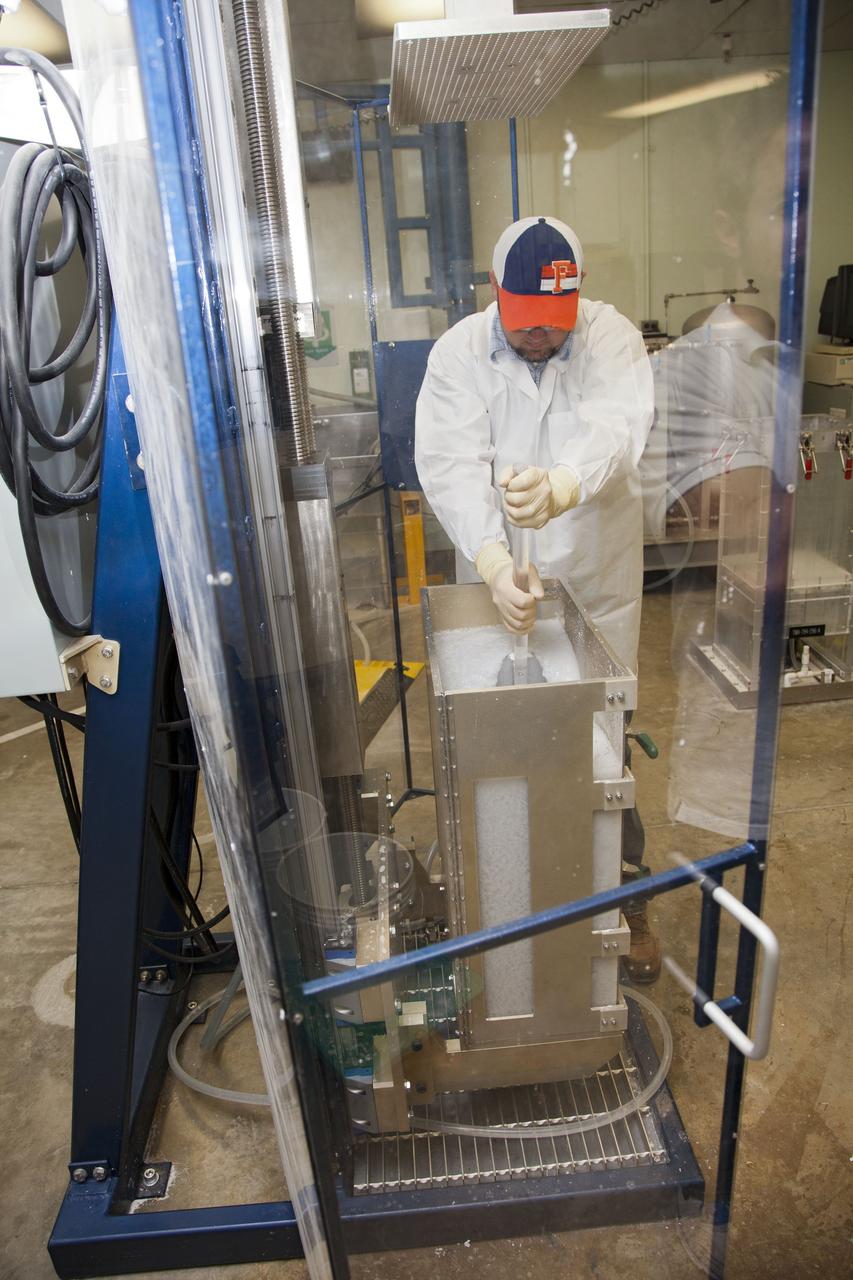

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
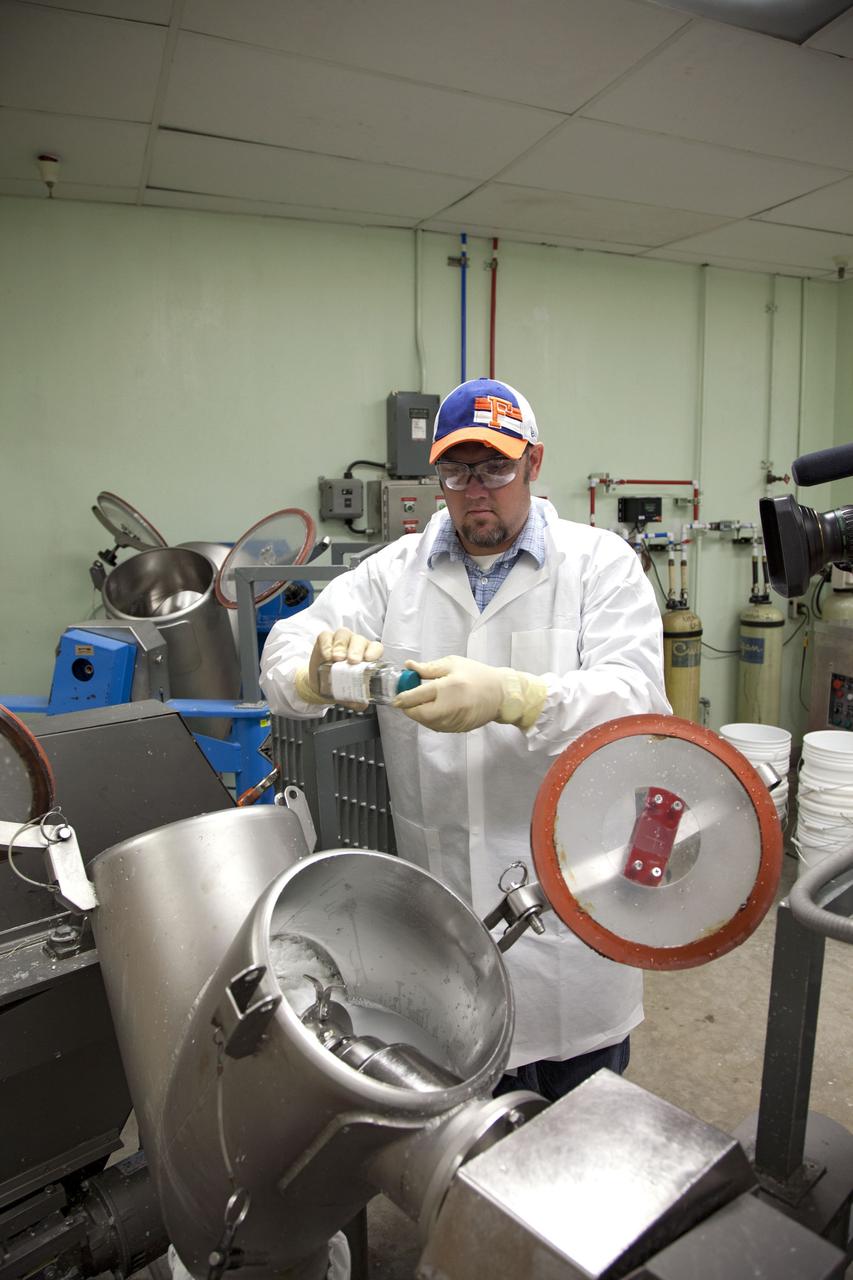

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
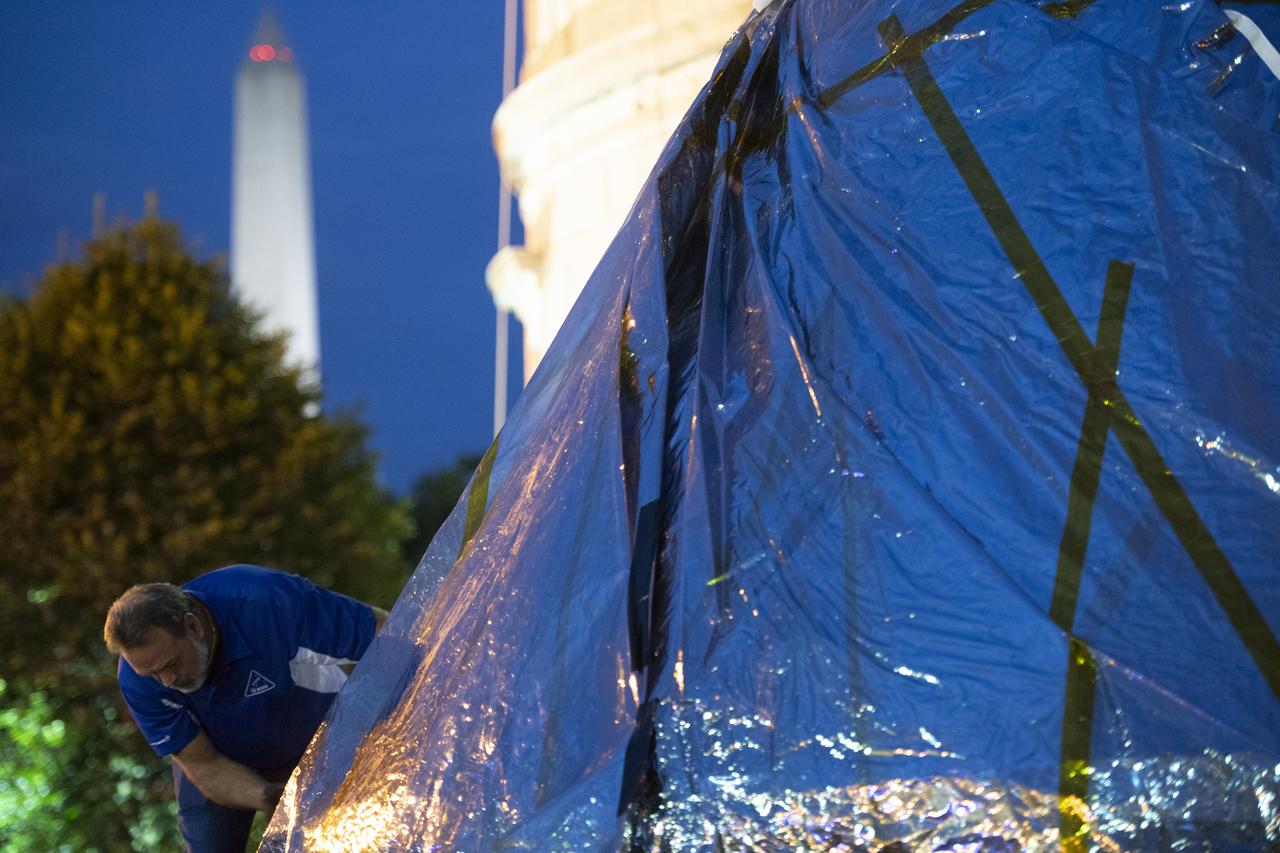

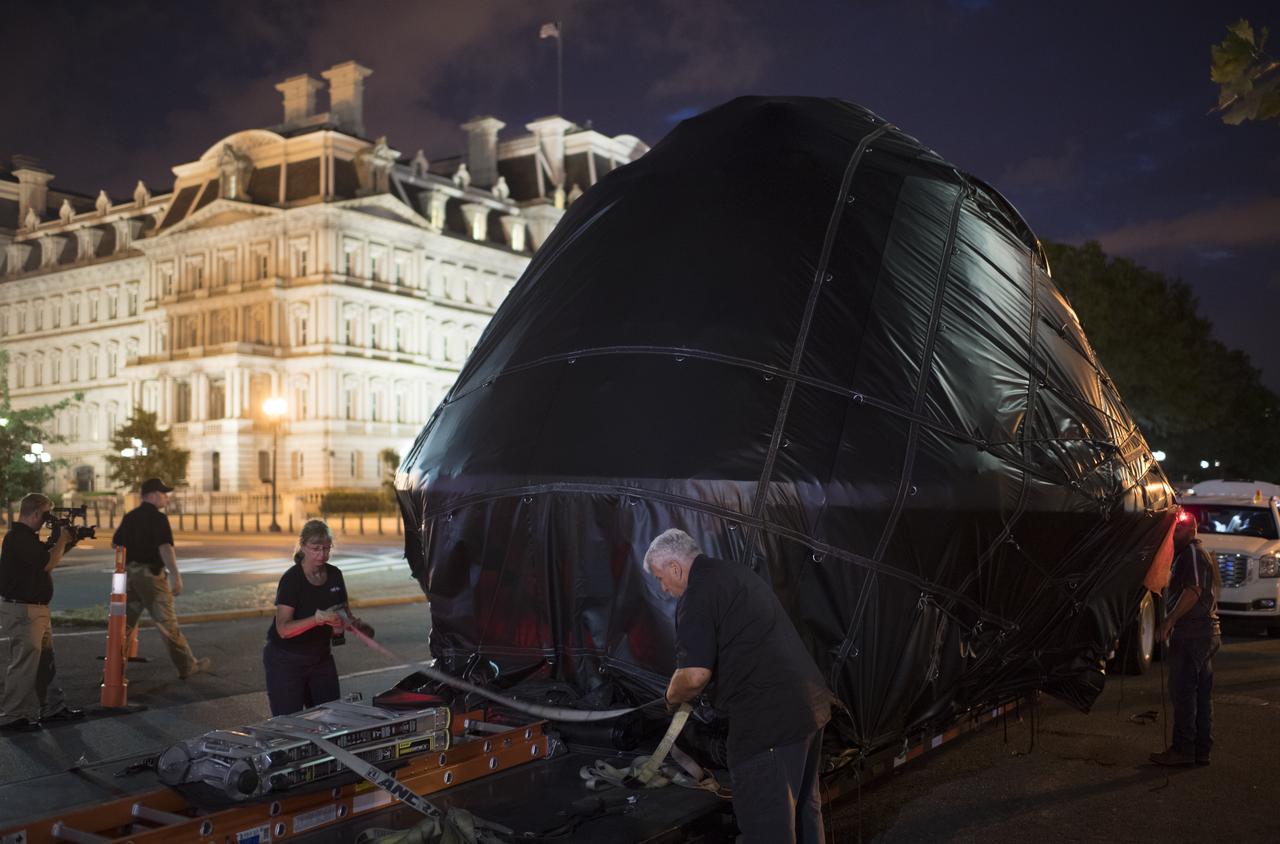
NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
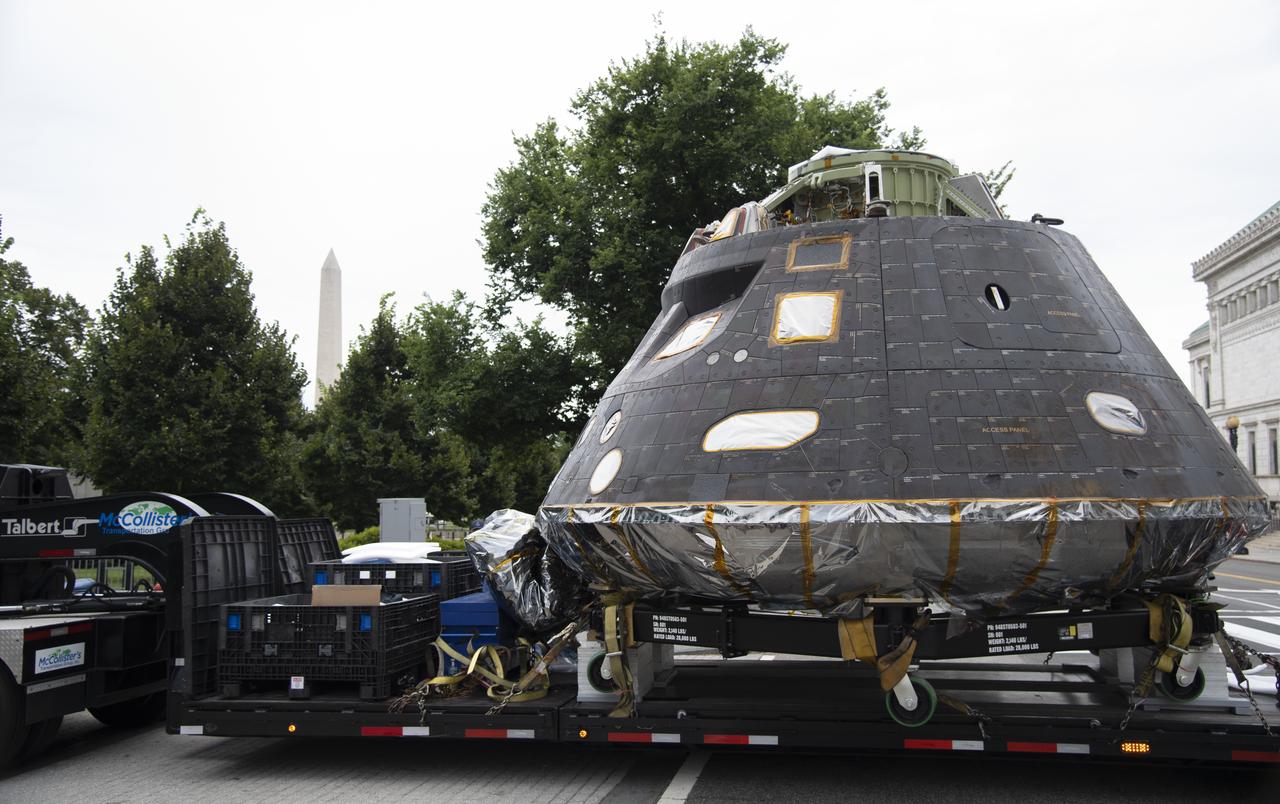

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
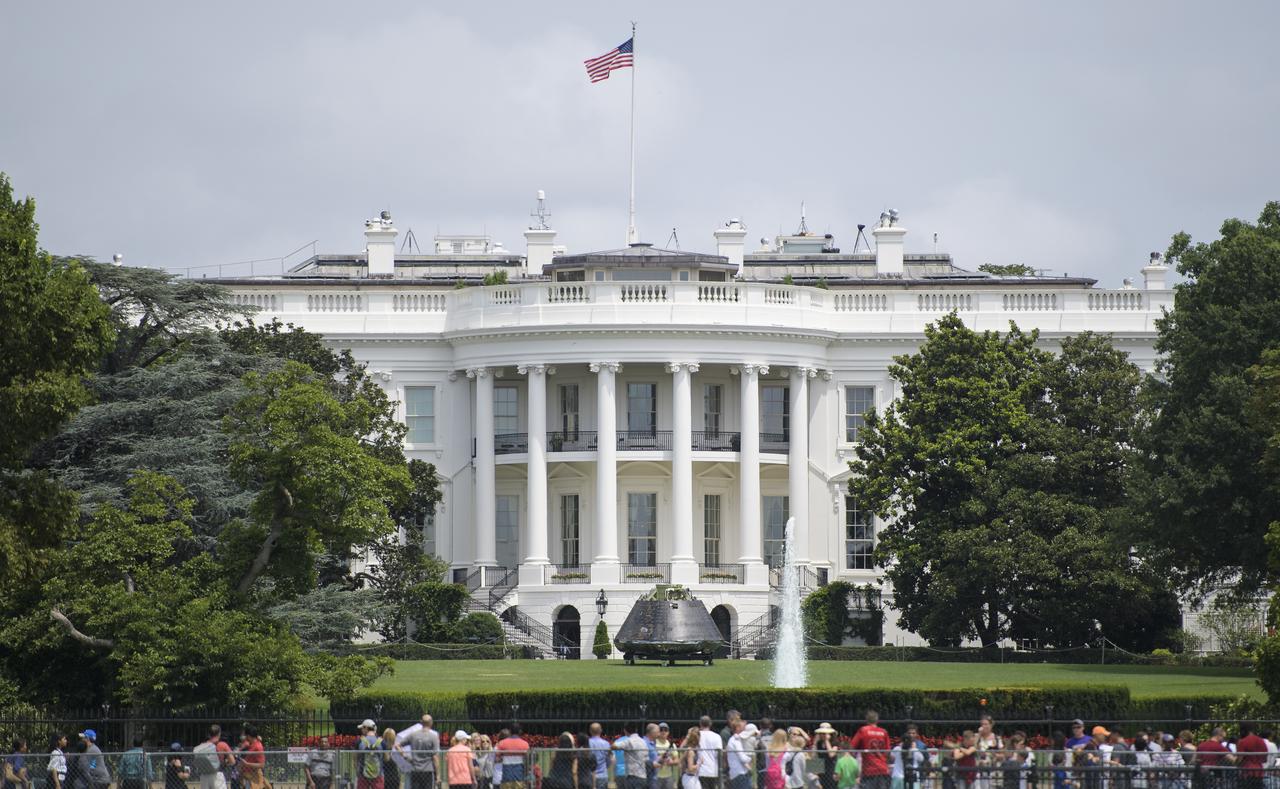

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen on the South Lawn of the White House, Sunday, July 22, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
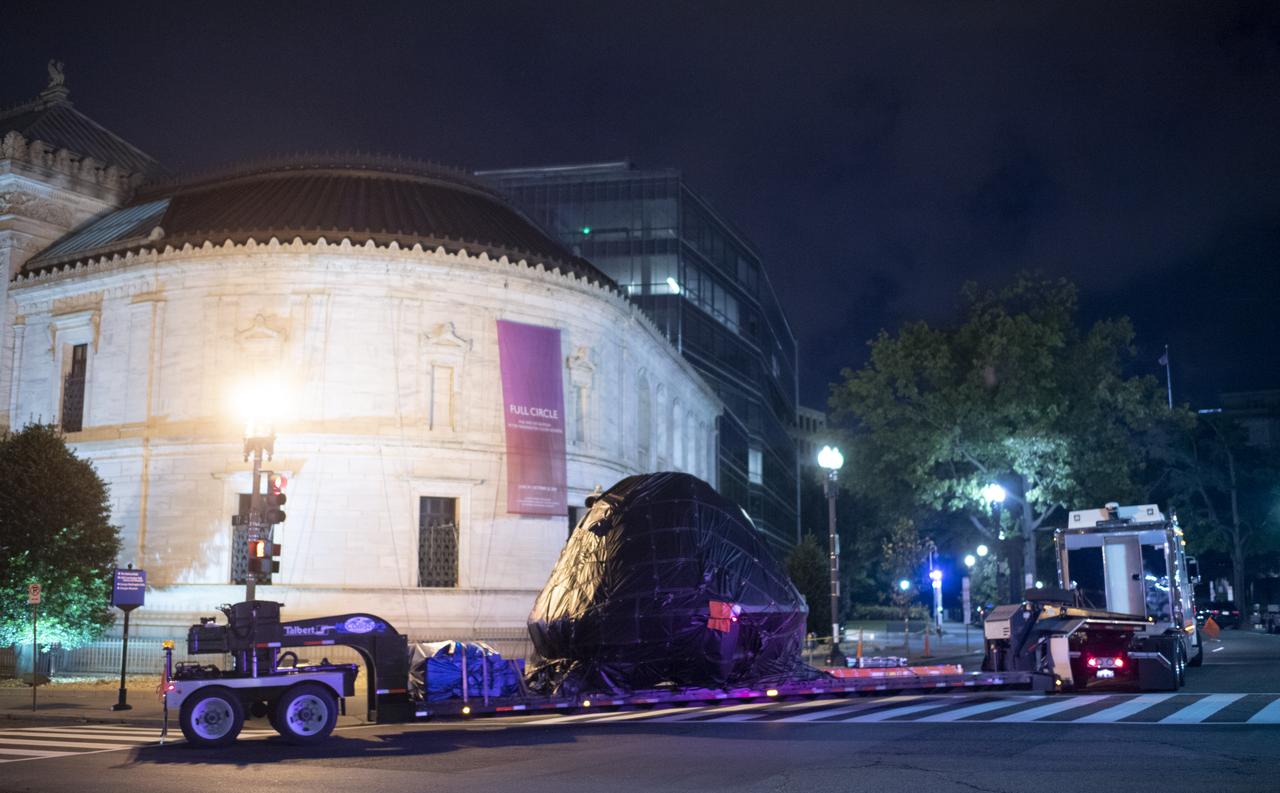

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
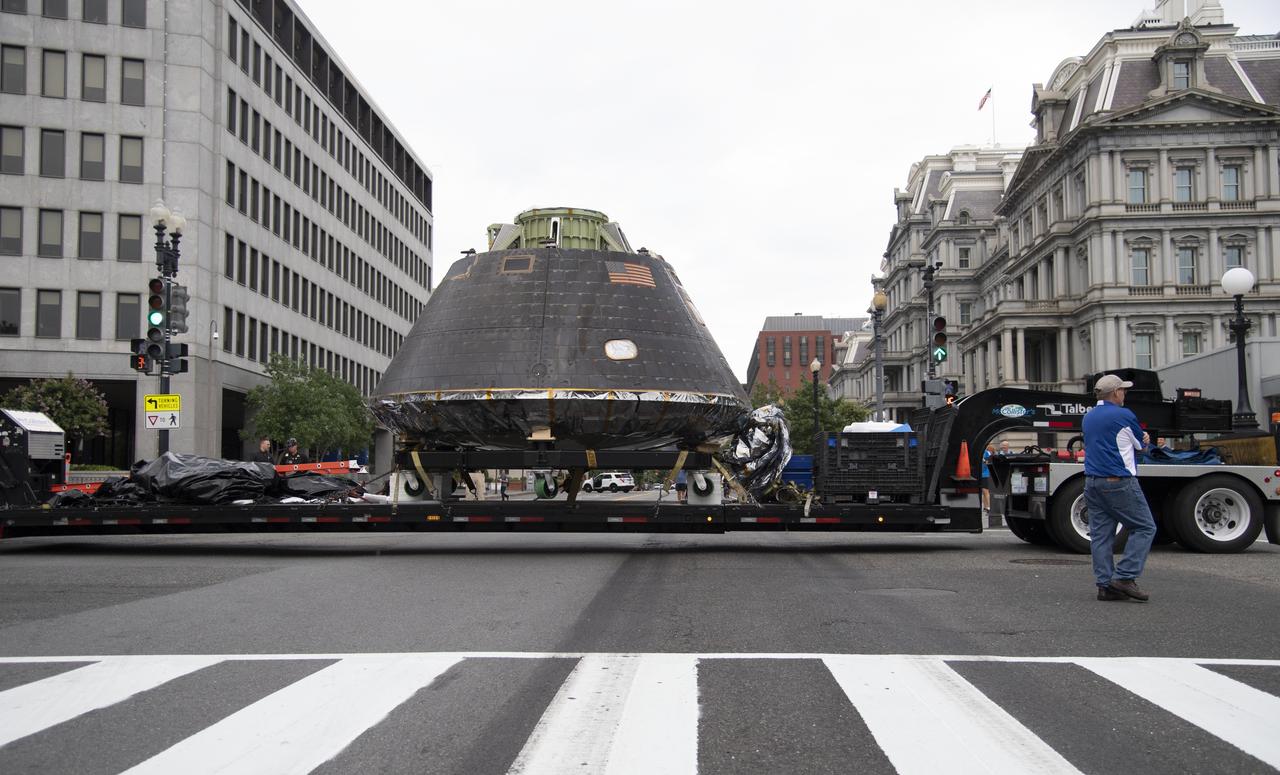

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
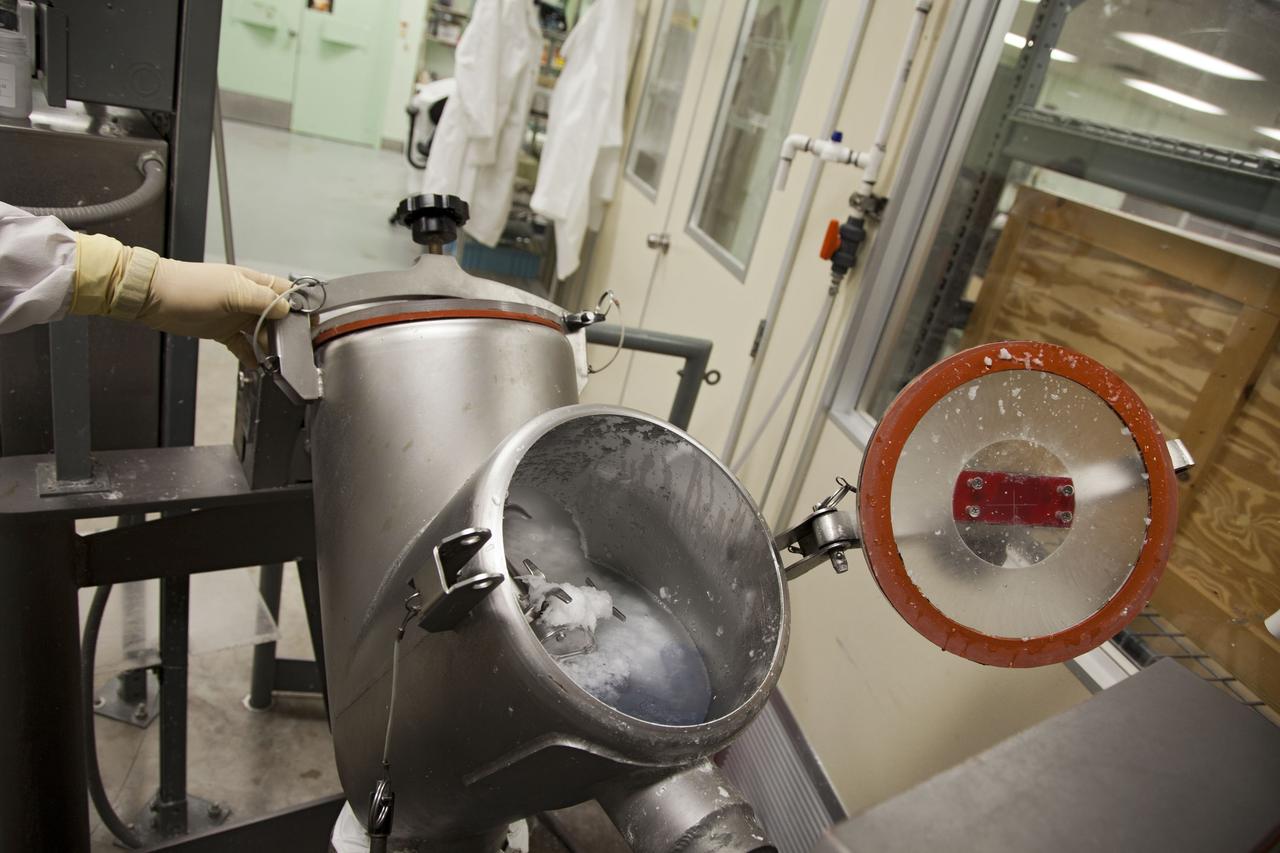

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

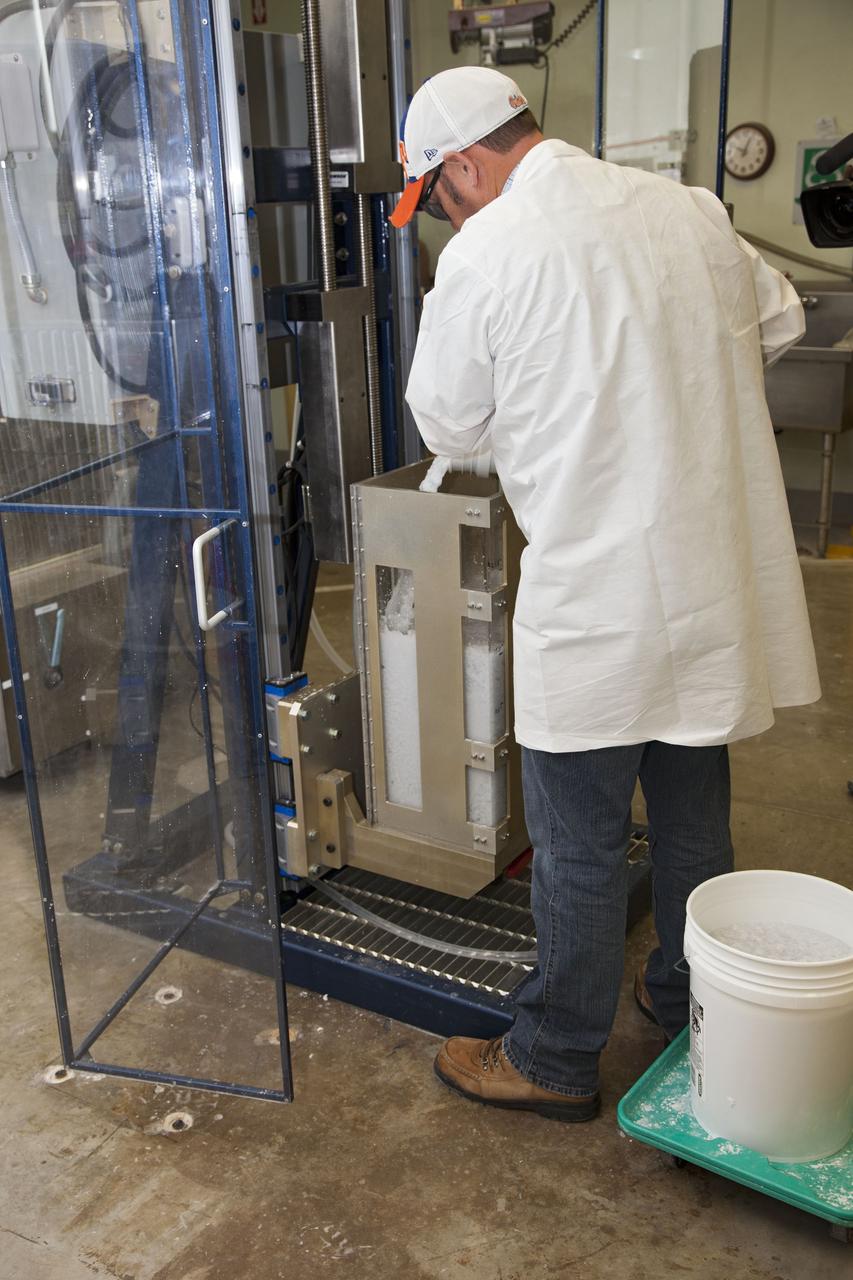
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
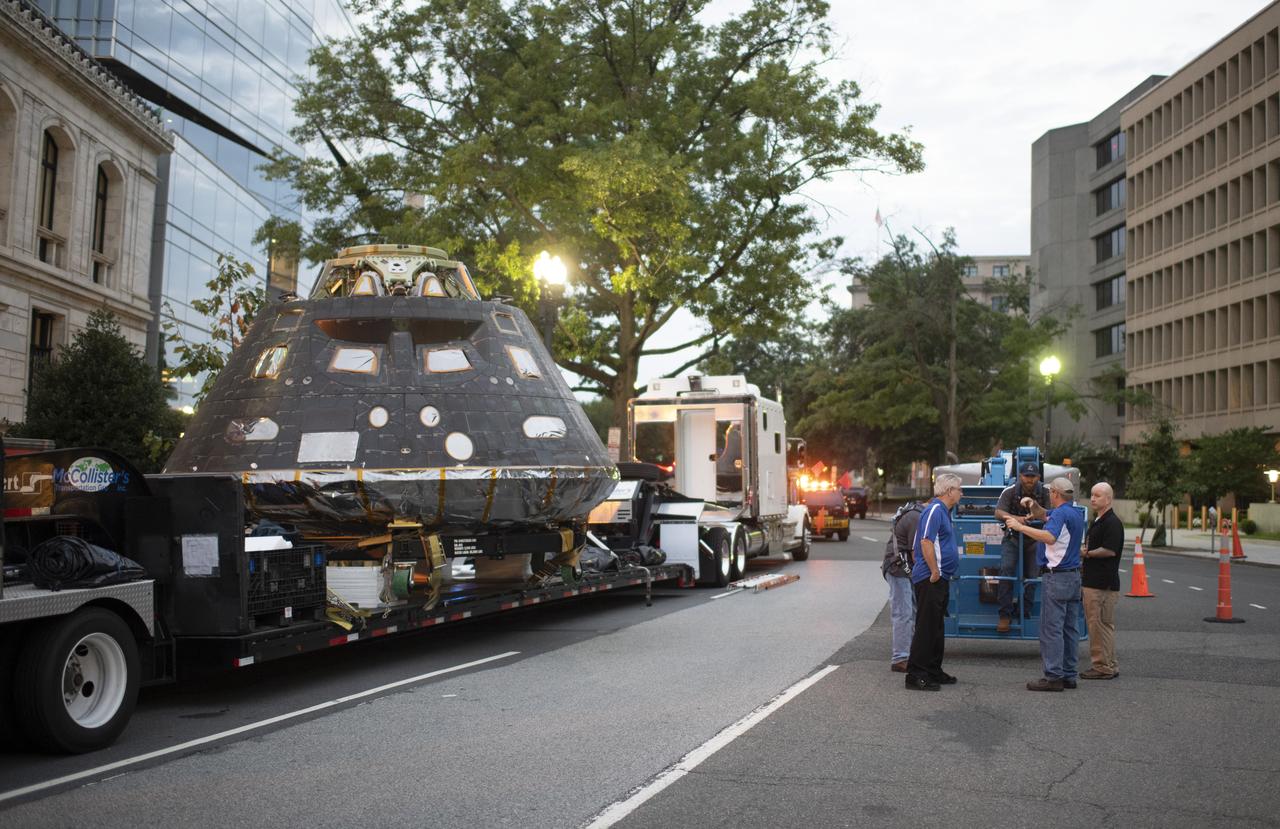

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
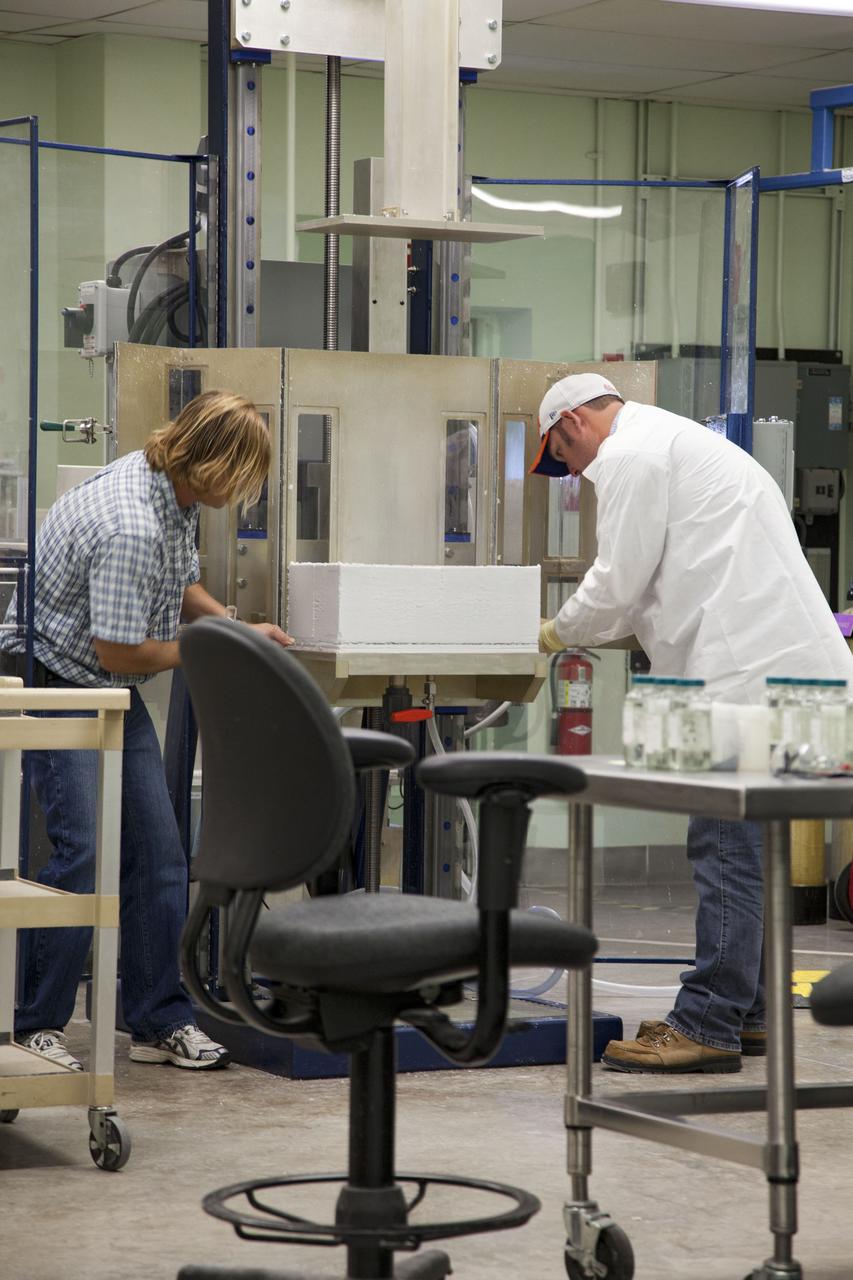

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- United Space Alliance workers, Tim Wright, left, and Chris Keeling, manufacture the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in the Thermal Protection System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
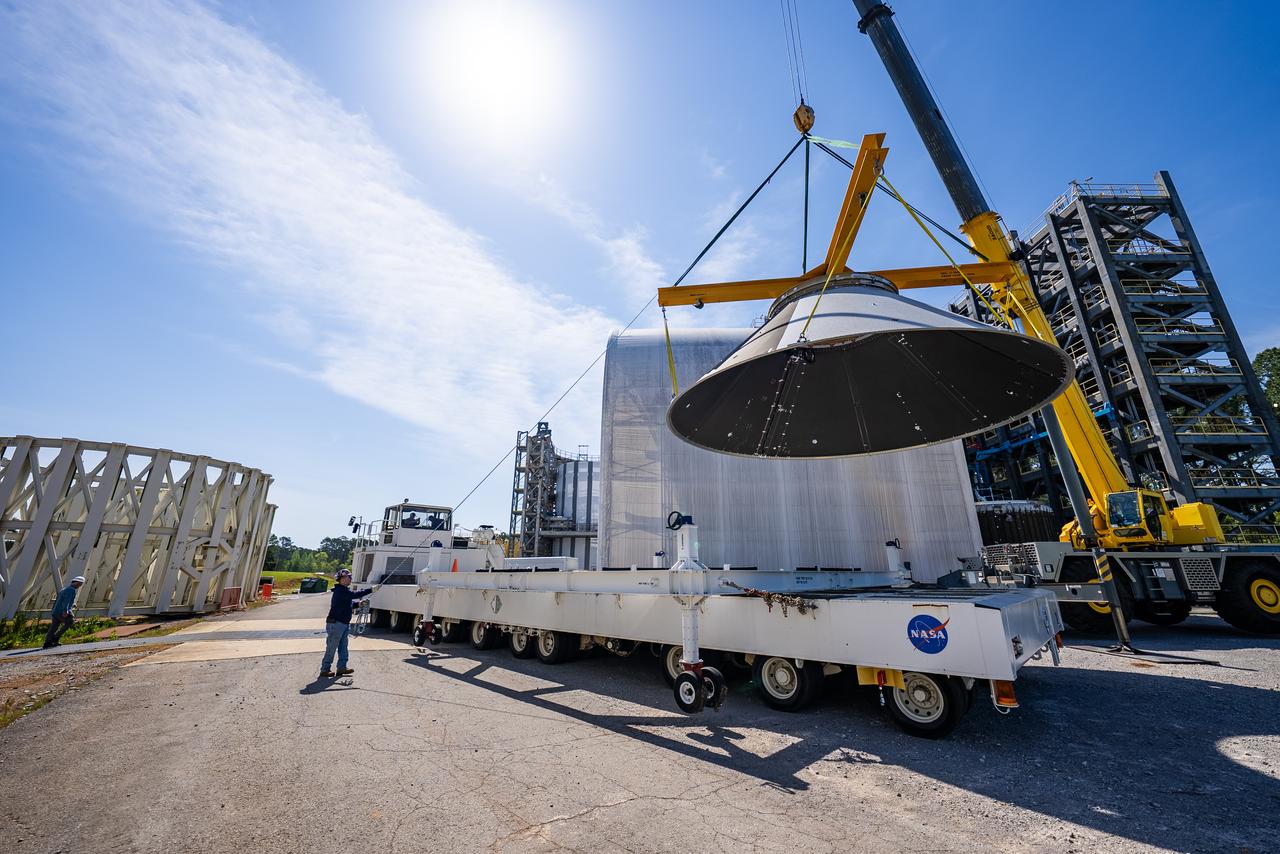

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
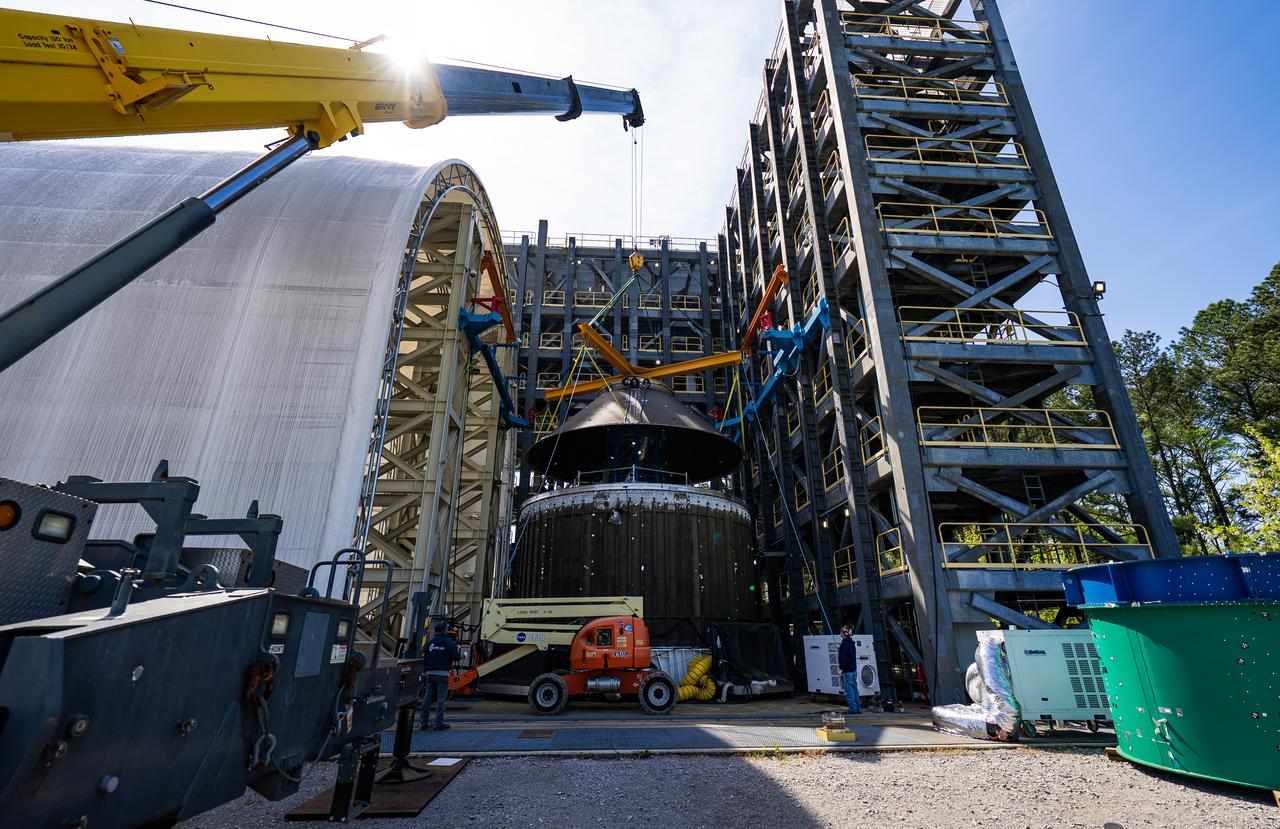

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
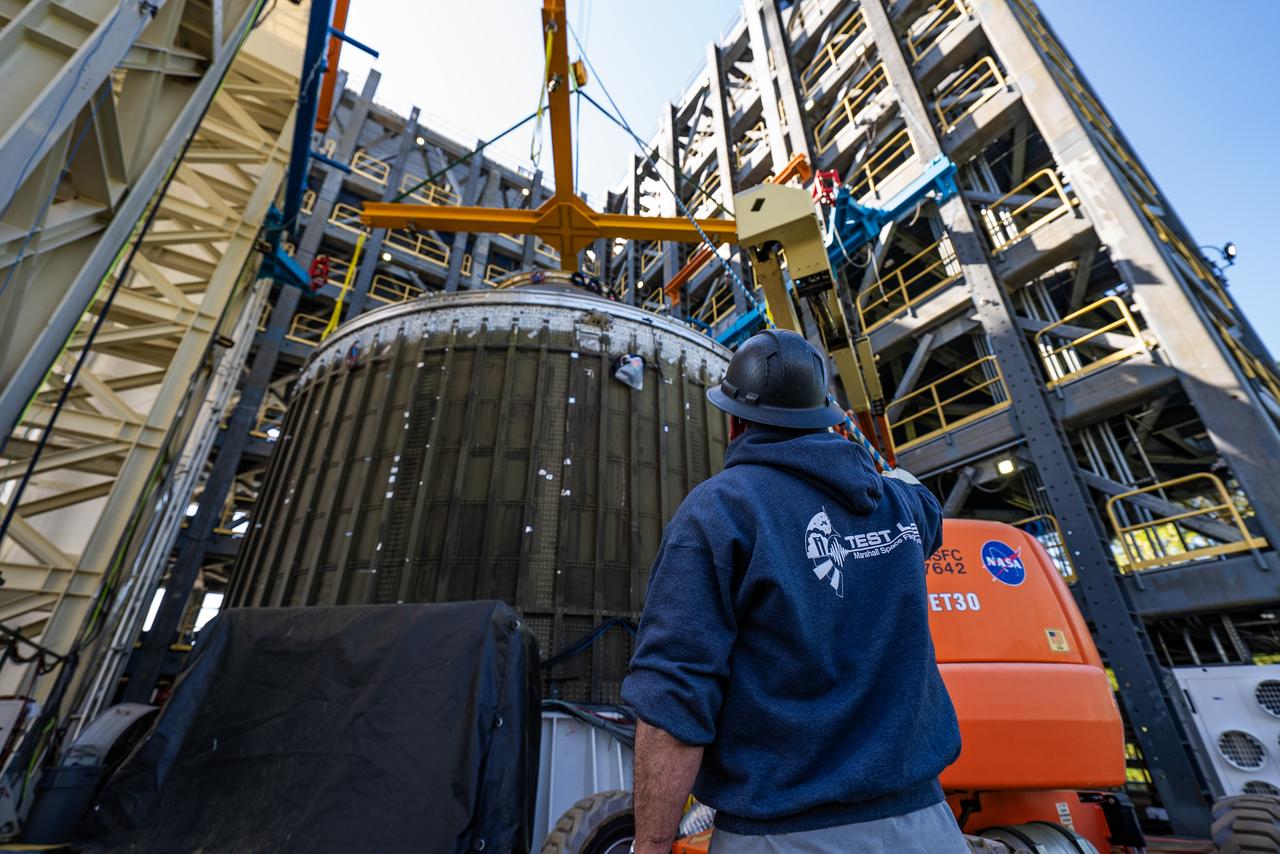

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
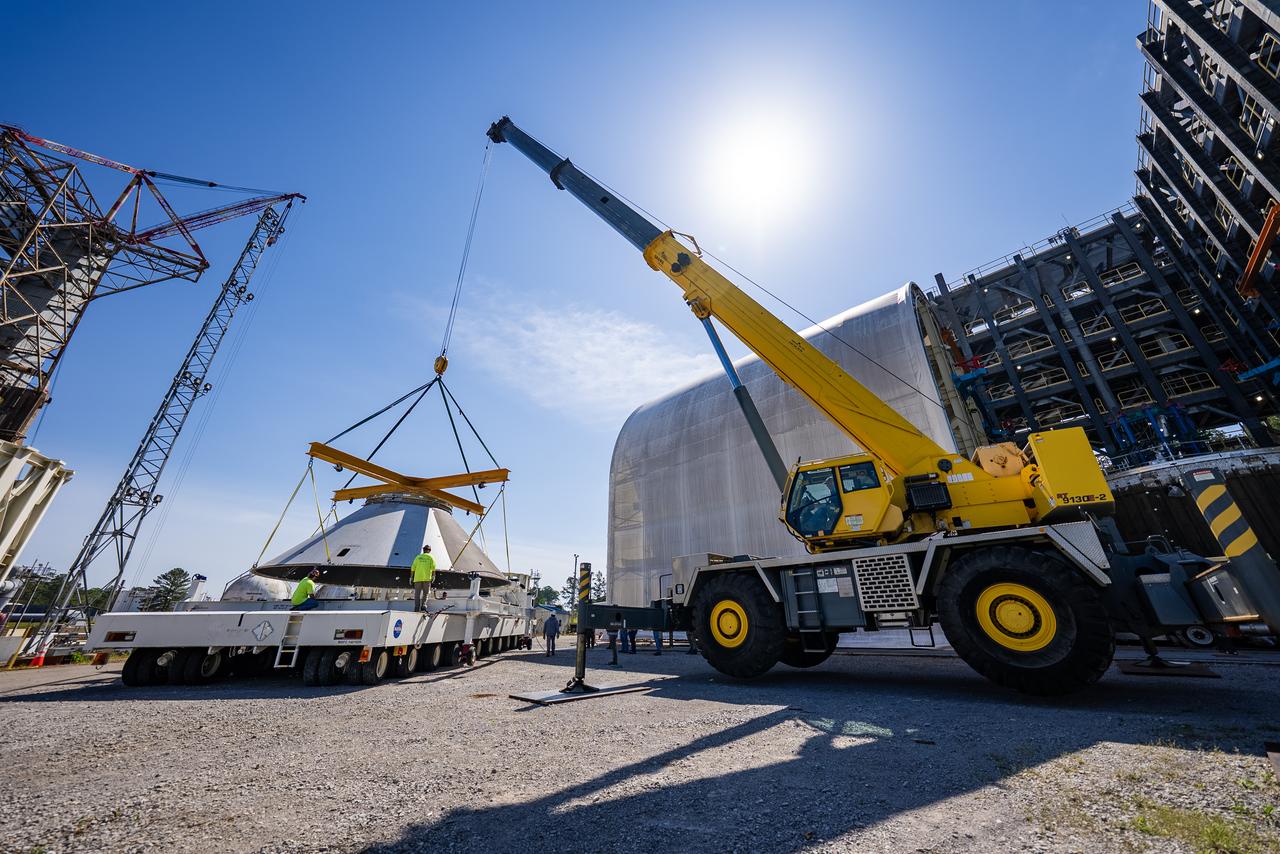

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
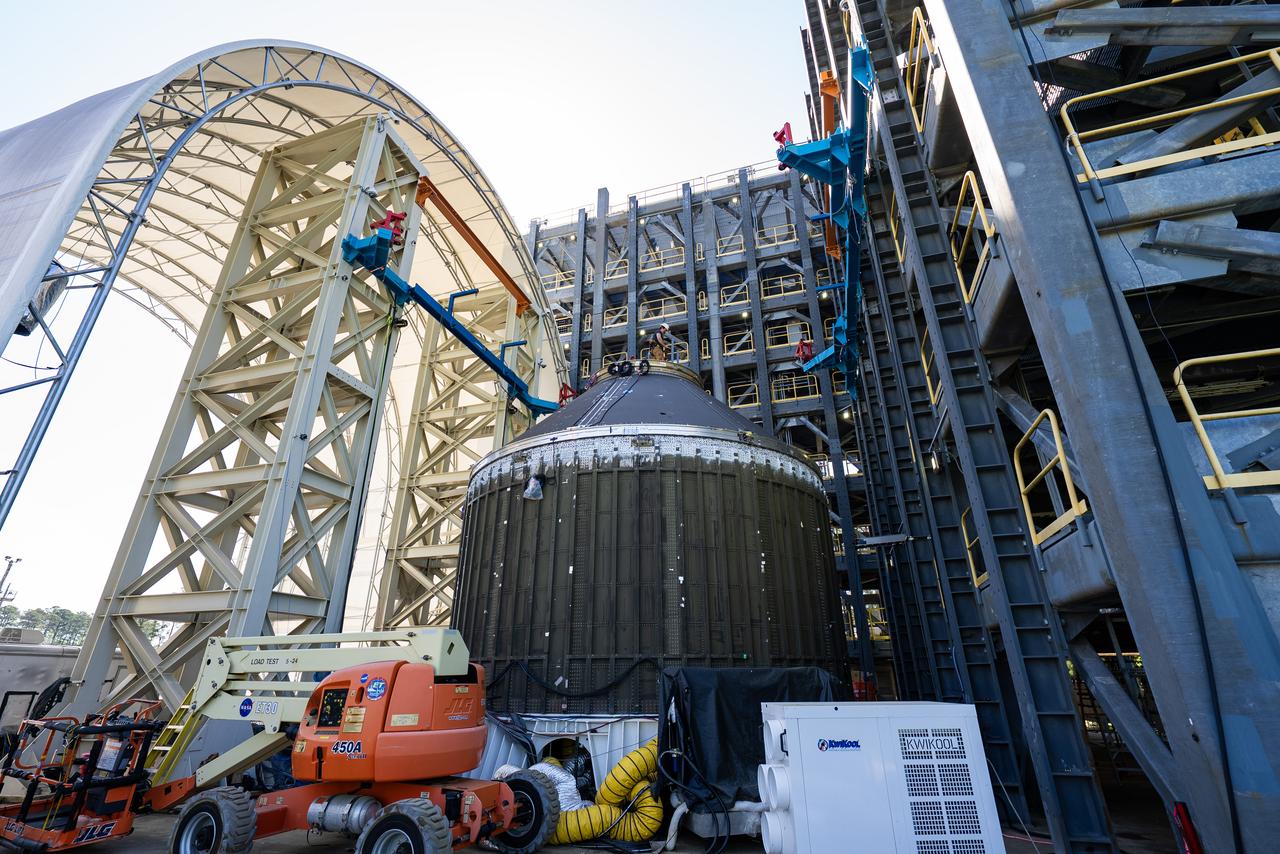

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
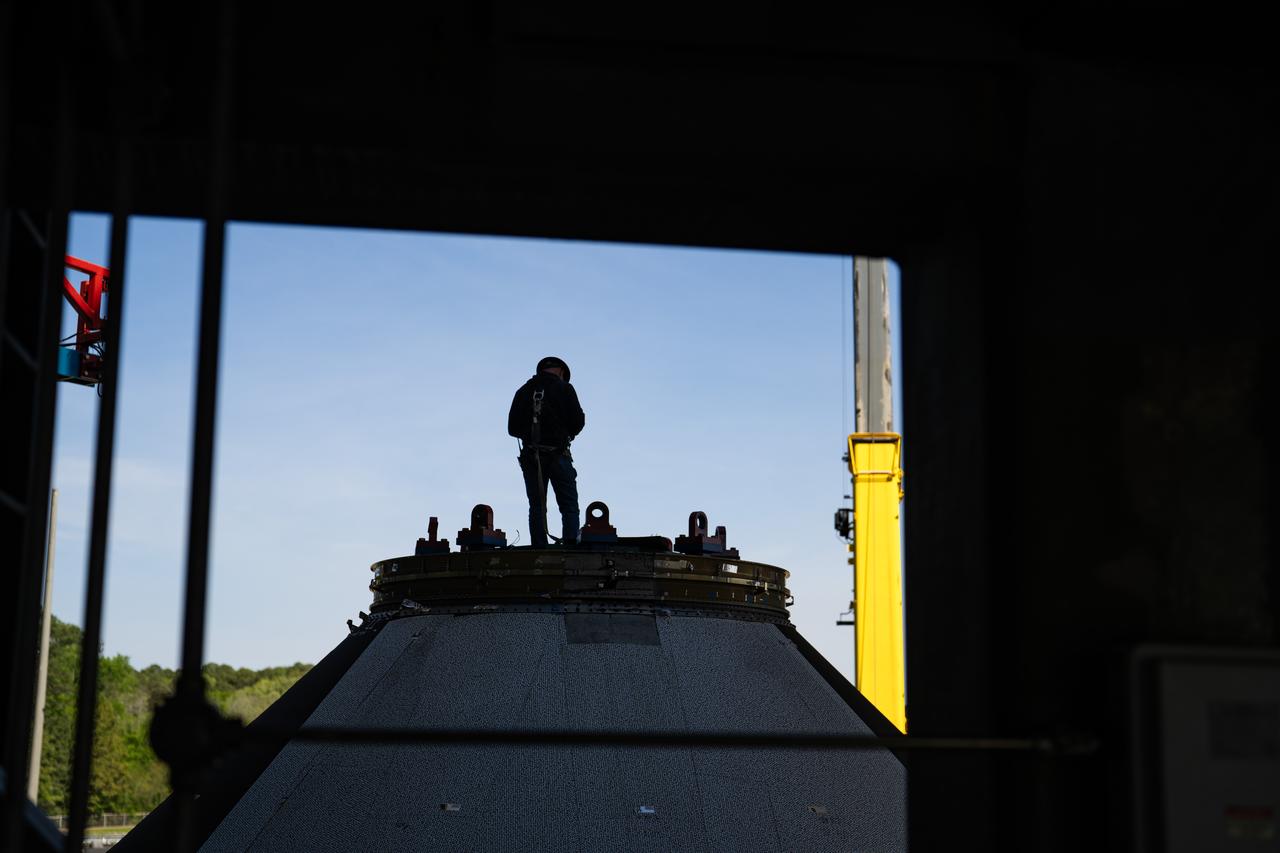

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
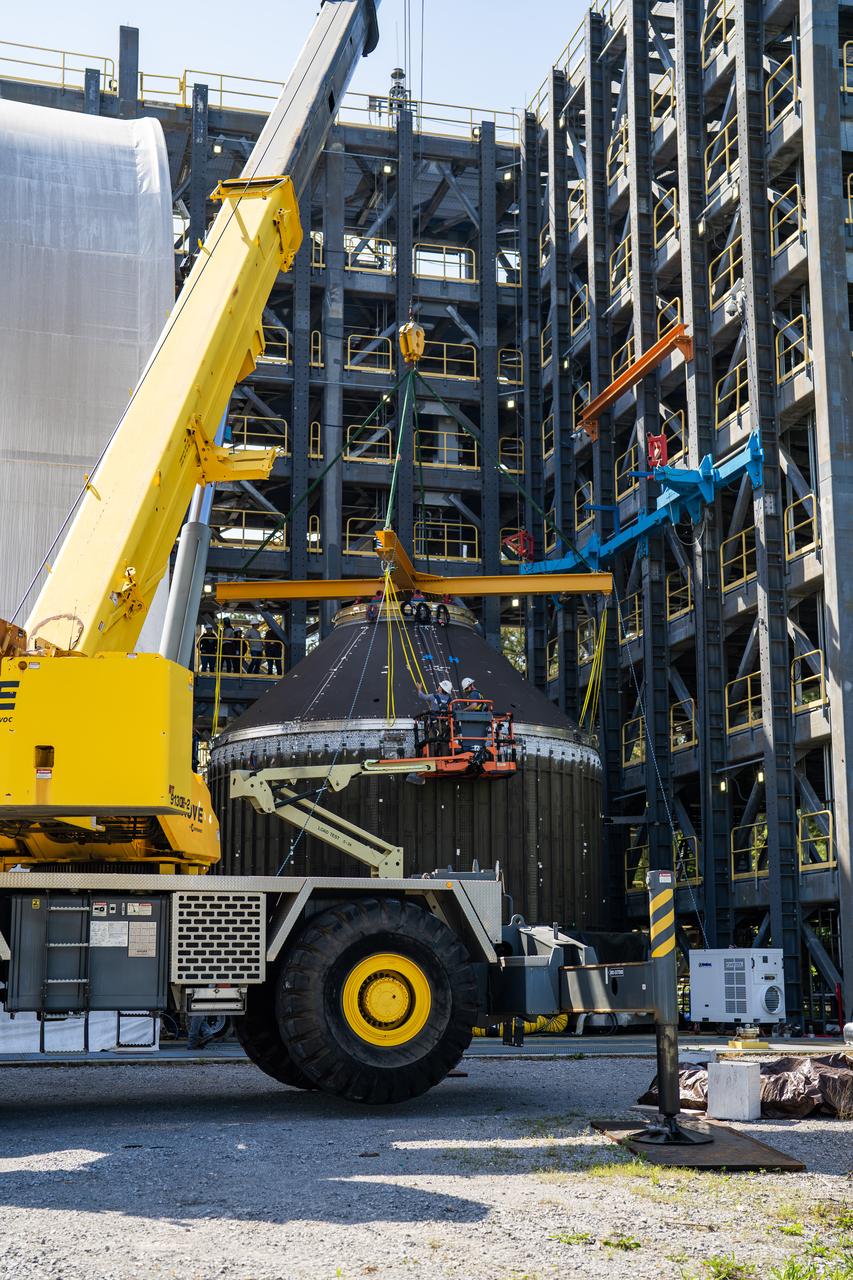

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
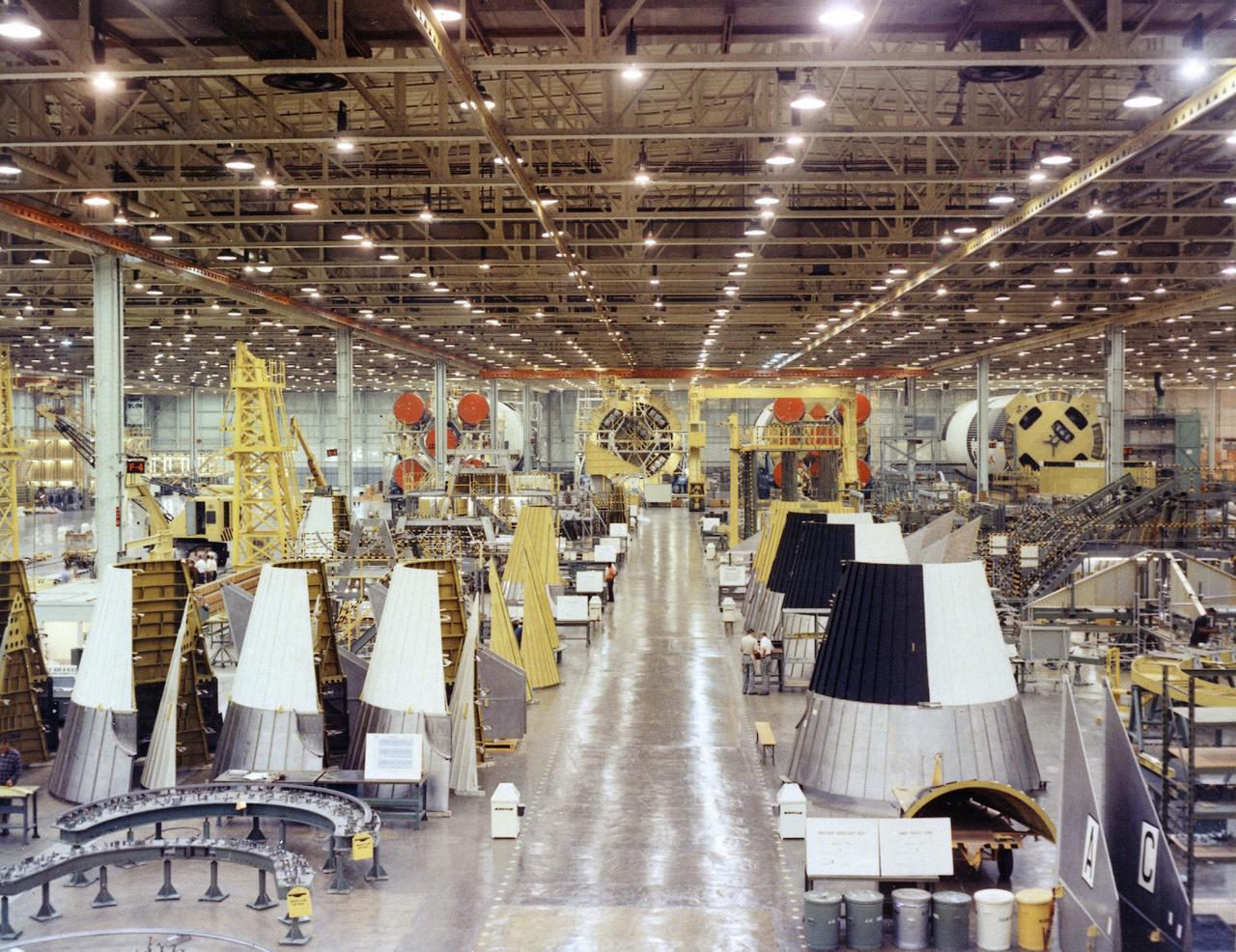

The Saturn IB and Saturn V flight vehicles first stages were manufactured at the Michoud Assembly Facility located 24 kilometers (approximately 15 miles) east of downtown New Orleans, Louisiana. The basic manufacturing building boasted 43 acres under one roof. By 1964, NASA added a separate engineering and office building, vertical assembly building, and test stage building. By 1966, other changes to the site included enlarged barge facilities and other miscellaneous support buildings. The image is a view of various vehicle components in the manufacturing plant.
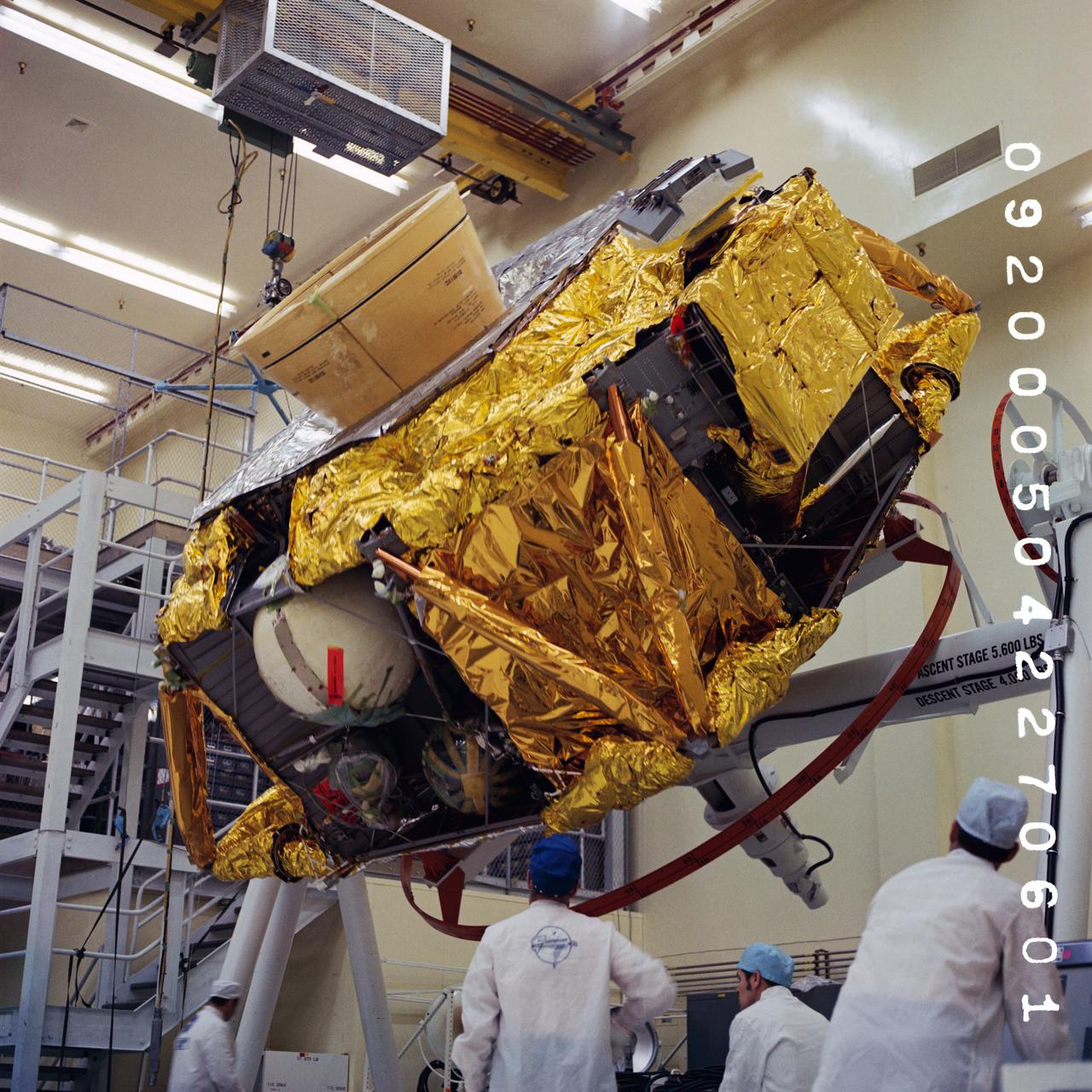

S70-39998 (2 June 1970) --- Manufacturing and testing view of Lunar Module (LM)-9 Descent Stage to Rotate & Clean Fixture at the Grumman, Bethpage, NY, Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Grumman

The abort motor for Orion’s launch abort system fired for five seconds in a test at the Promontory, Utah facility of manufacturer Orbital ATK on June 15, 2017. Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
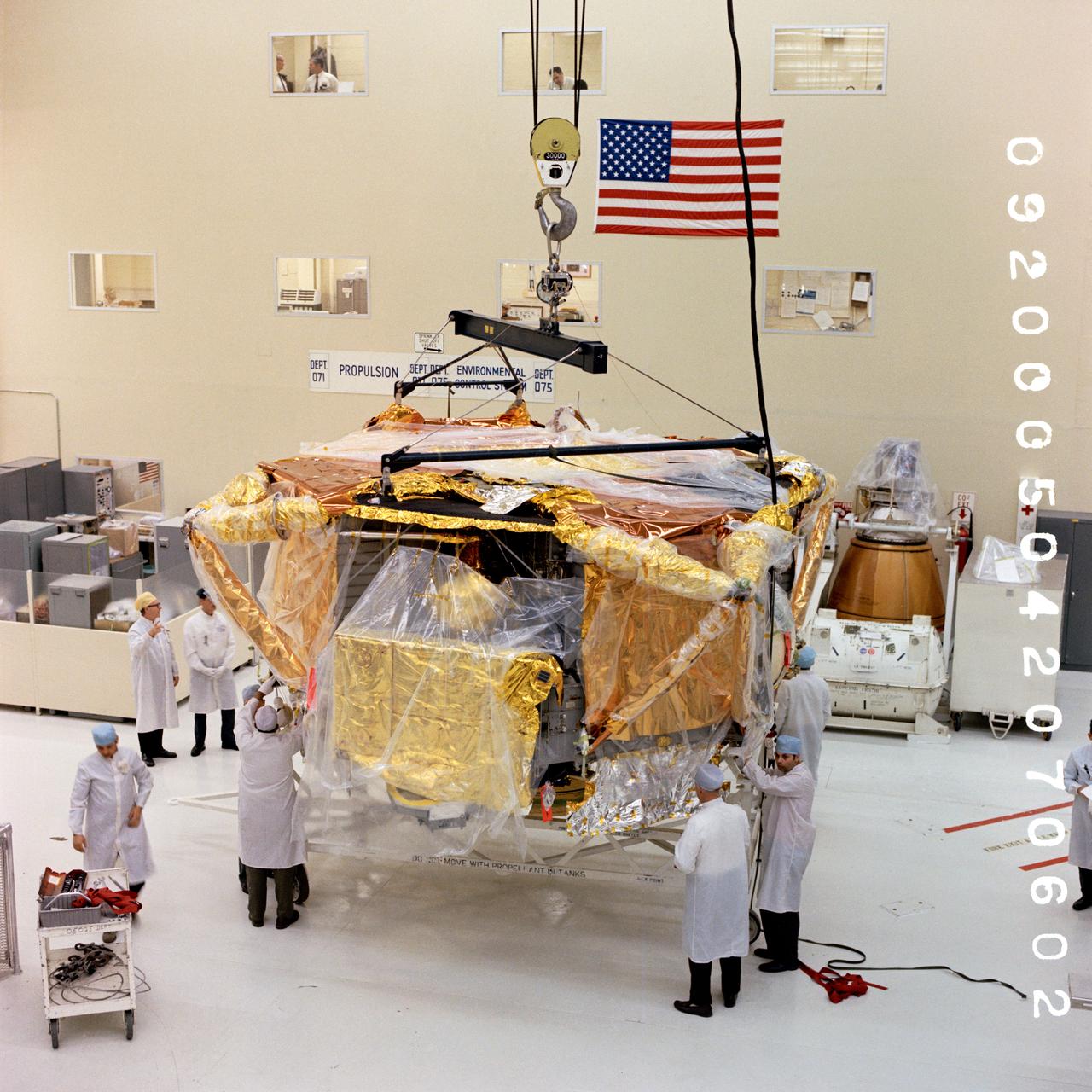

S70-39997 (2 June 1970) --- Manufacturing and testing view of Lunar Module (LM)-9 Descent Stage to Rotate & Clean Fixture at the Grumman, Bethpage, NY, Facility. Photo credit: NASA/Grumman
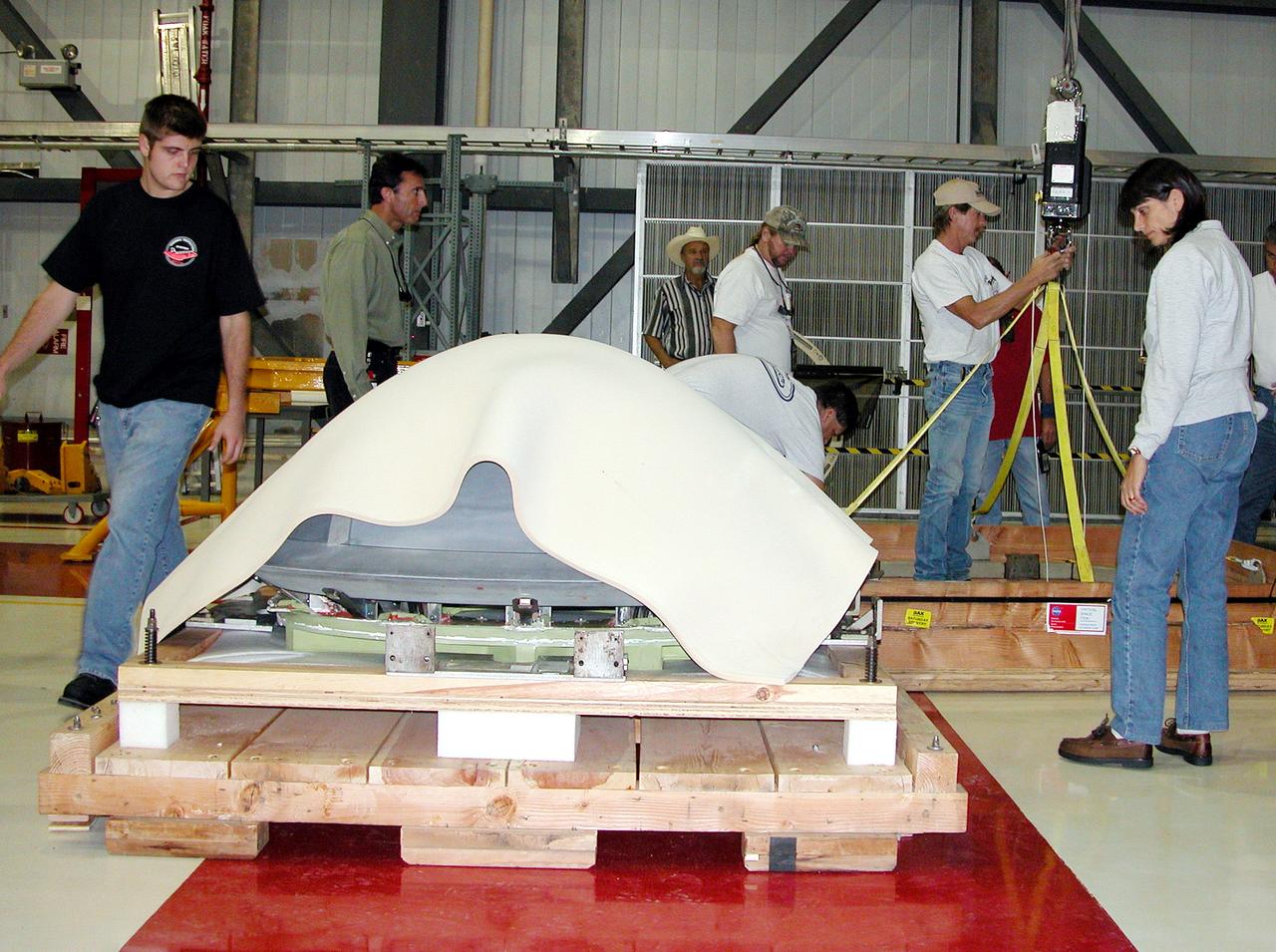

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, packing material is placed over the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
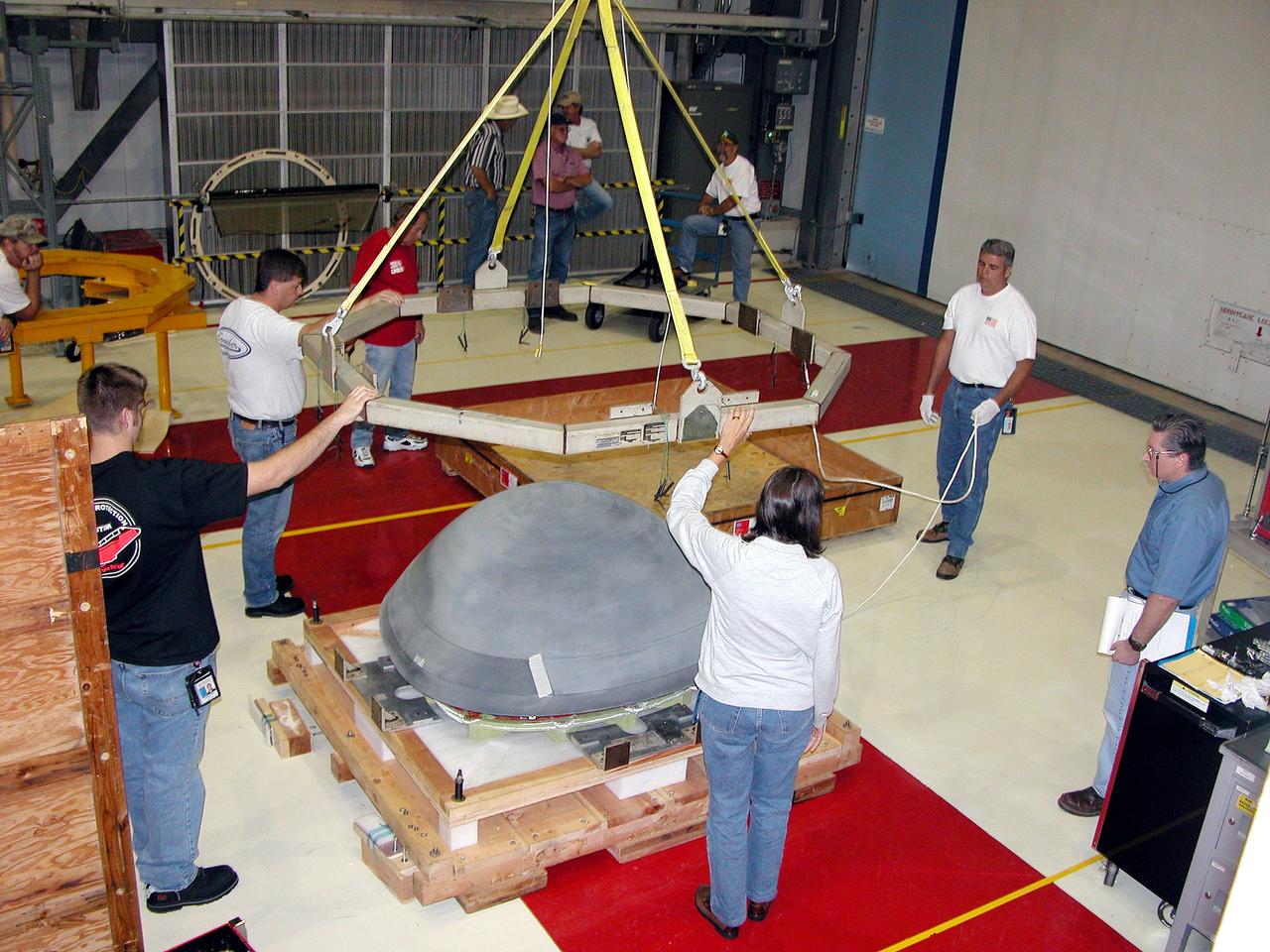

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers remove the overhead crane from the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

iss063e107043 (10/11/2020) --- A view of the Tango Lab CubeLab from the University of Adelaide. The Evaluation of Long-Term Stability of Pharmaceutical Ingredients in an Excipient Matrix for Use in Potential Future On-Orbit Manufacturing (Pharmaceutical Excipient Ingredient Stability in Microgravity) is an investigation by the University of Adelaide that tests long-duration stability providing data for potential future on-orbit manufacturing of medicines in space. The stability of medicines, encapsulated flavors, and vitamins will be studied as a function of their formulation environment, i.e., the pharmaceutical excipients which form a tablet.

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen after being uncovered in preparation for being moved onto the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
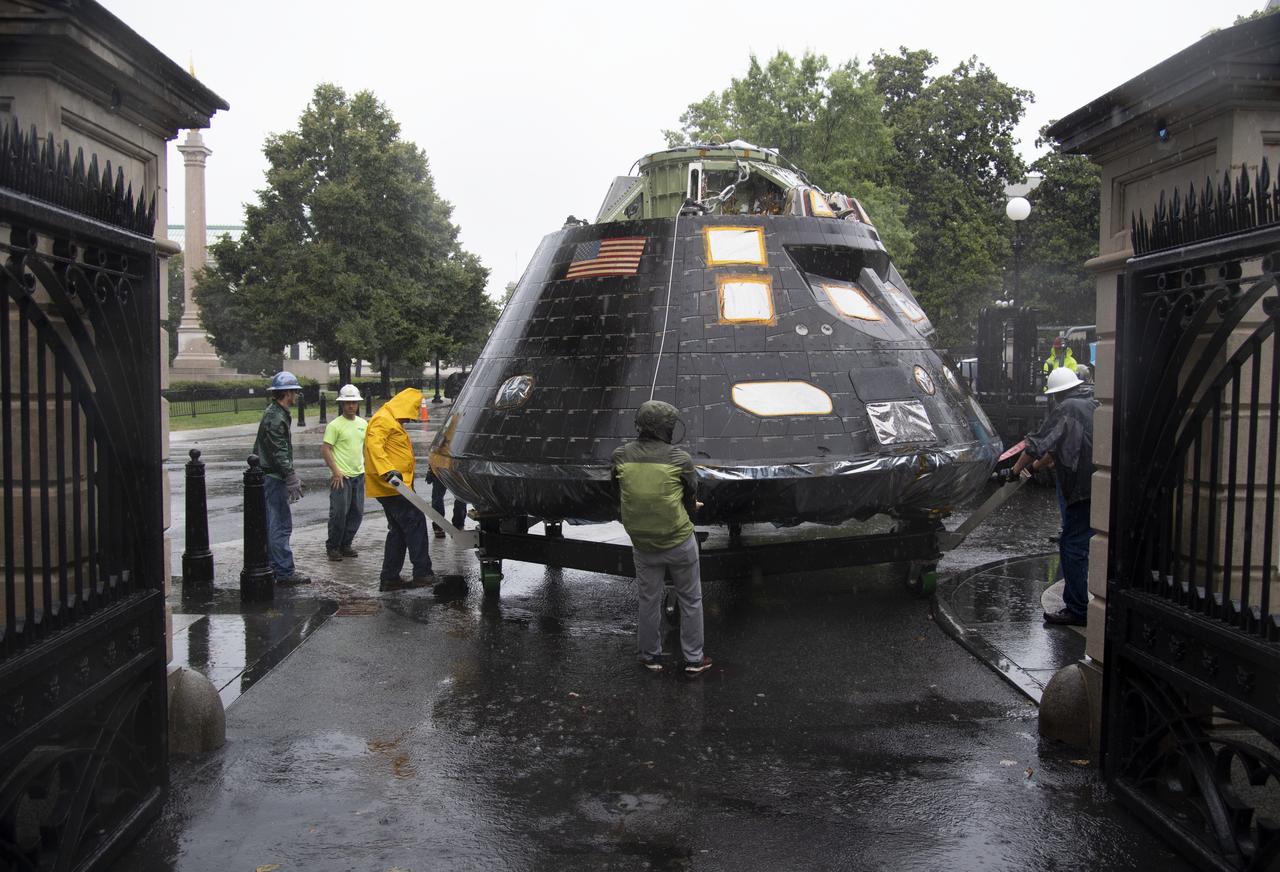

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen while being moved into position to be lifted over a gate and onto the South Lawn of the White House, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
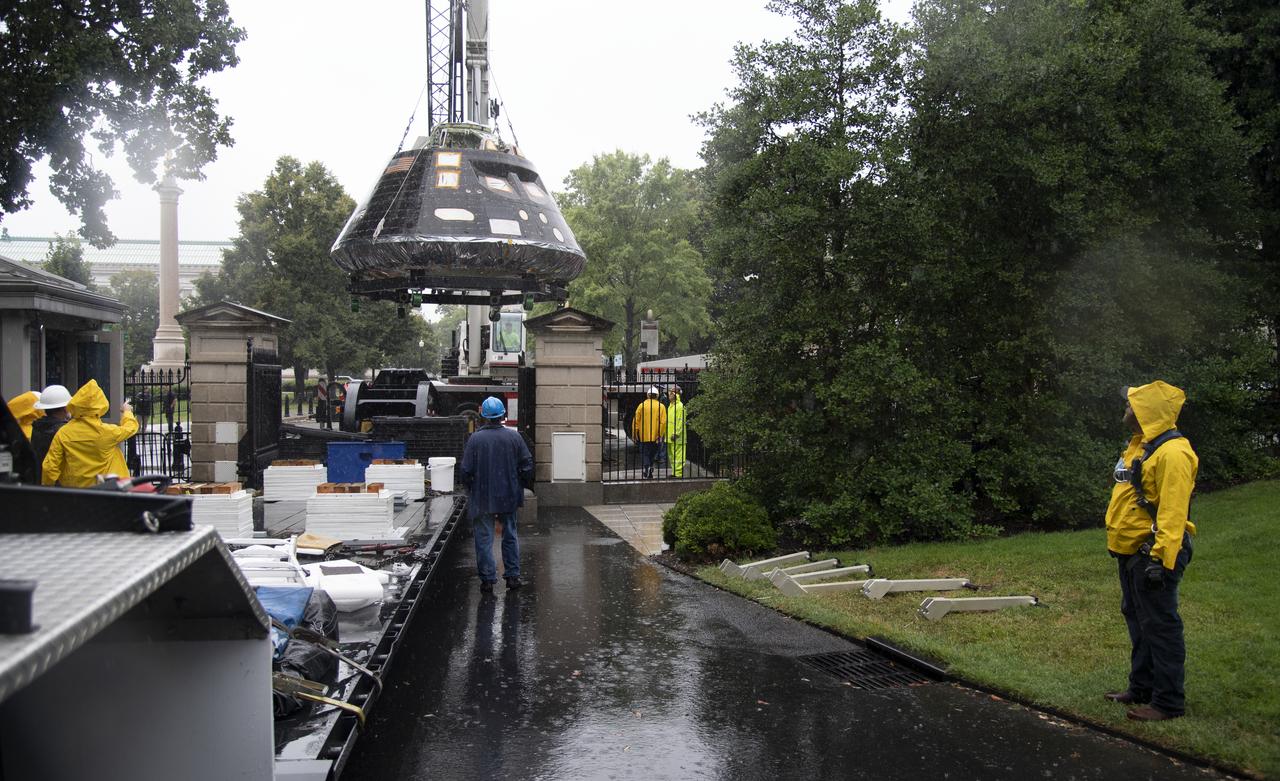

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen while being lifted over a gate and onto the South Lawn of the White House, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
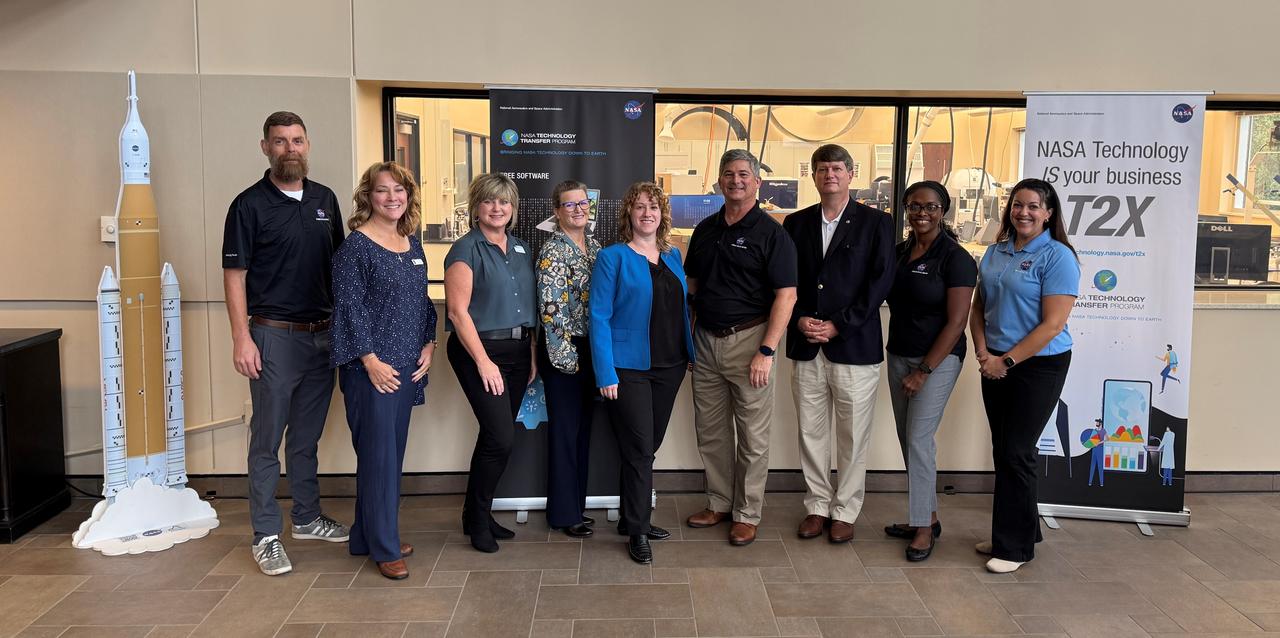

Participants in A Day with NASA at The Accelerator in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, included: (left to right) Marc Shoemaker with the NASA Stennis Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer Office; Kay Doane with the NASA Stennis Office of Small Business Programs; Sandy Crist with the Mississippi Manufacturers Association Manufacturing Extension Program; Dr. Monica Tisack with the Mississippi Polymer Institute; Caitlyne Shirley with the Mississippi Polymer Institute; Top Lipski with the NASA Stennis Technology Transfer Expansion Team; Thom Jacks with the NASA Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Dawn Davis with the NASA Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Kelly McCarthy with the NASA Stennis Office of STEM Engagement; and Janet Parker with Innovate Mississippi.
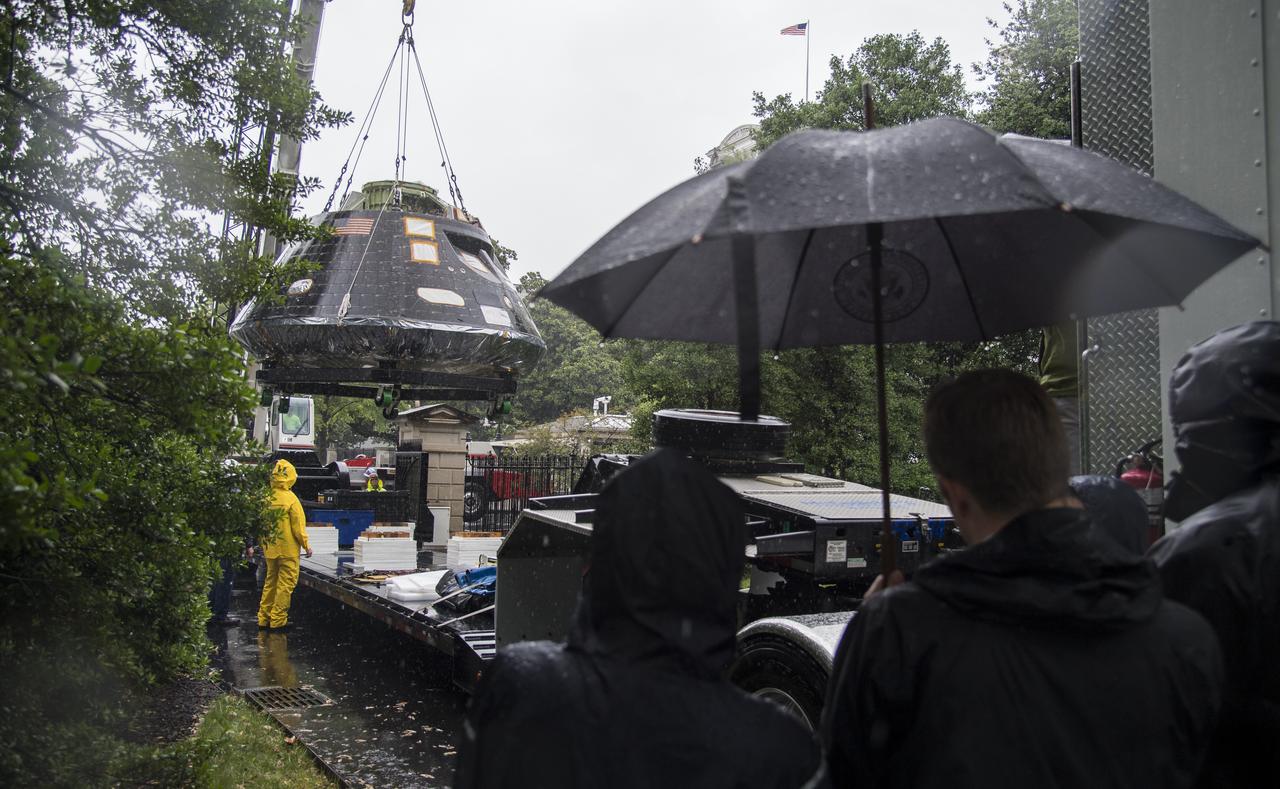

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen while being lifted over a gate and onto the South Lawn of the White House, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
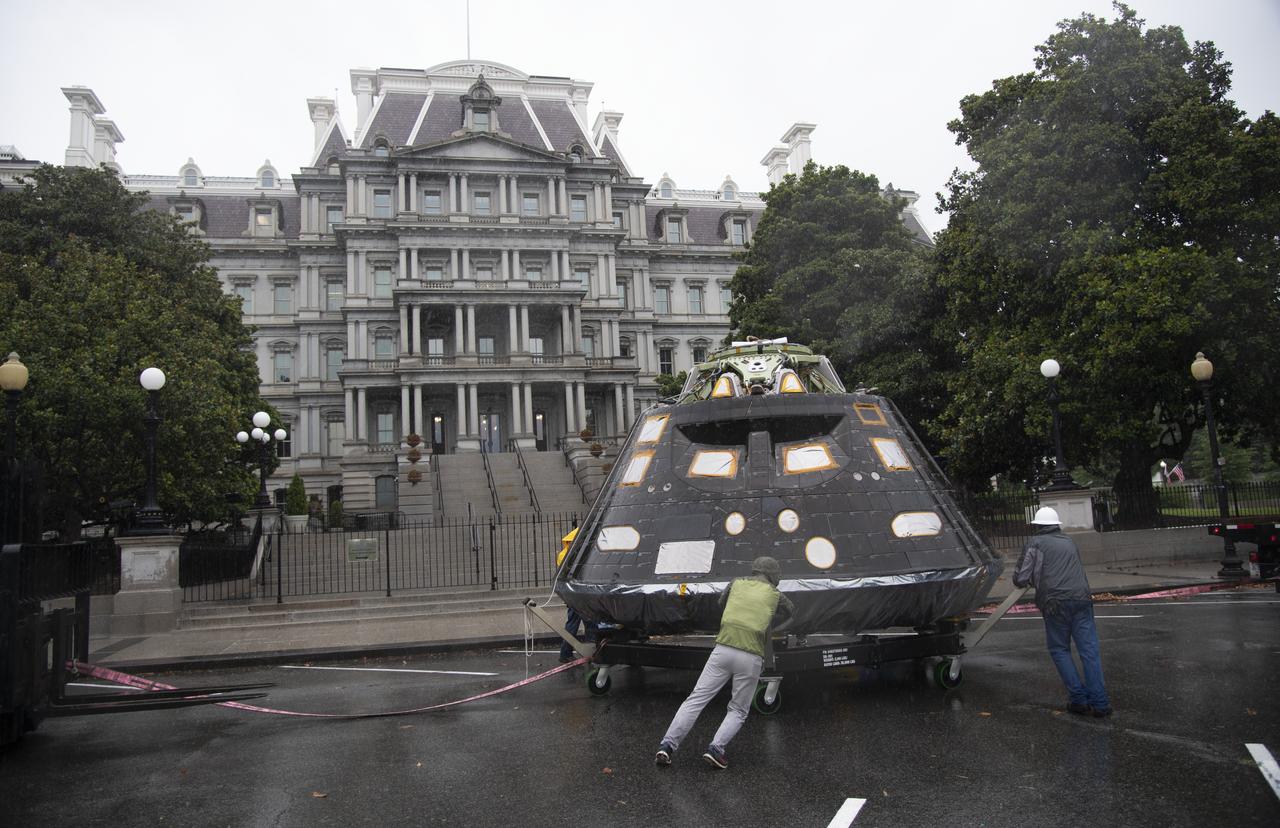

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen in front of the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
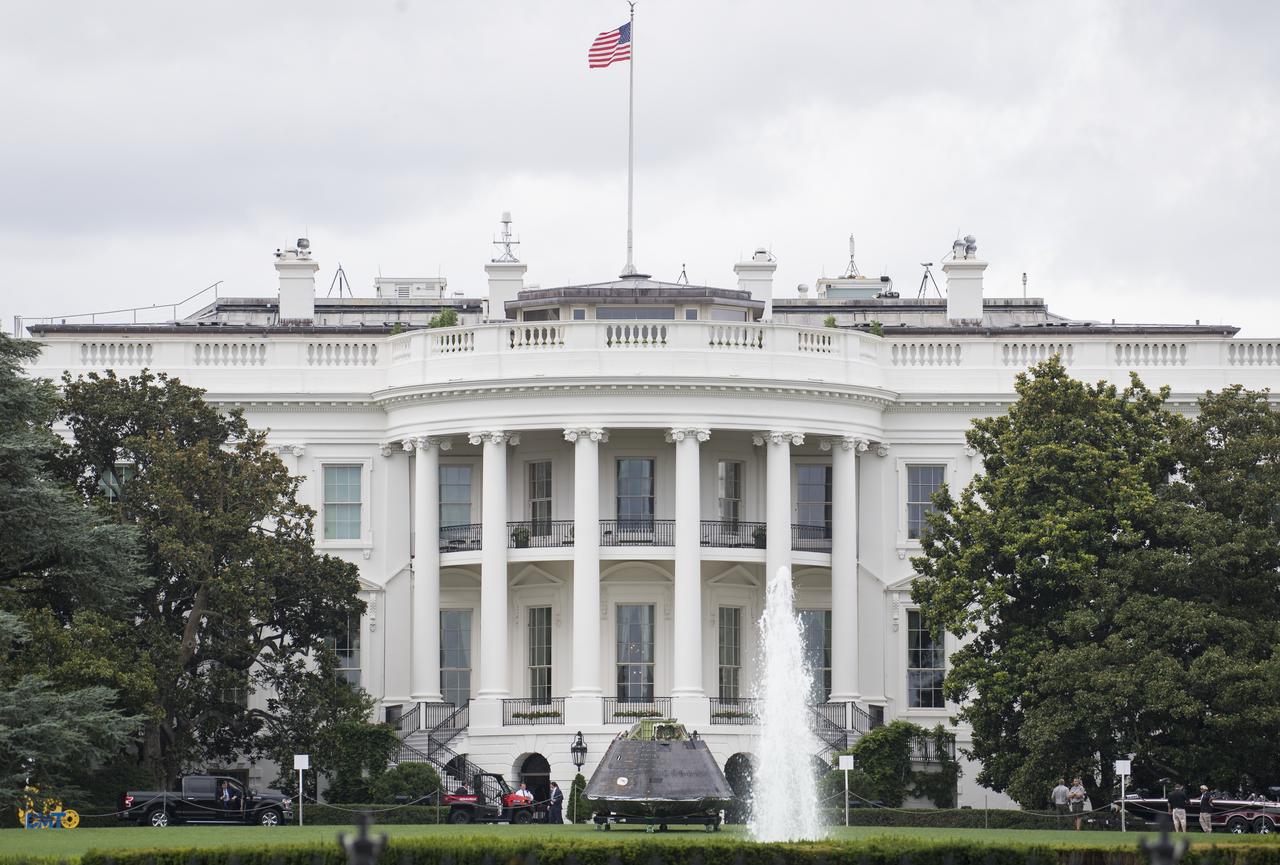

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew on Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014, is seen on the south lawn of the White House during a Made in America Product Showcase, Monday, July 23, 2018 in Washington. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)