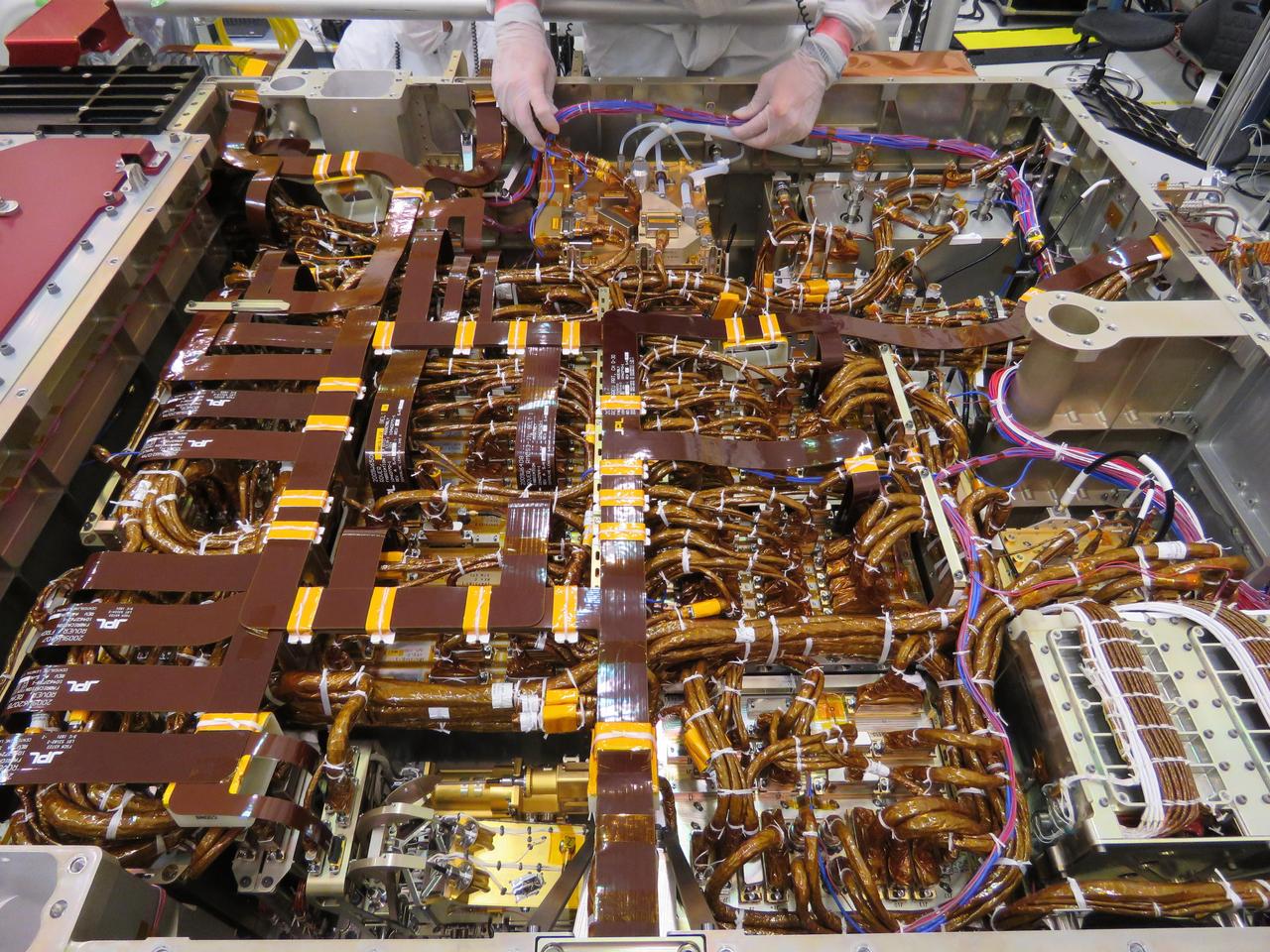
In the image, taken on June 1, 2019, an engineer in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, can be seen working on the exposed belly of the Mars 2020 rover. It has been inverted to allow the 2020 engineers and technicians easier access. The front of the rover is on camera left. The engineer is inspecting wiring directly above the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) instrument. MOXIE will demonstrate a way that future explorers might produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere for propellant and for breathing. In the foreground, just to the left of center and distinctive because of the relative lack of wiring, is the body unit for the SuperCam instrument. The mast unit for SuperCam instrument, which will provide imaging, chemical composition analysis, and mineralogy from its high perch at the top of the rover's remote sensing mast was installed June 25. To the far left, covered by a red-colored shield, is the bay where the Adaptive Caching Assembly (ACA) will document, analyze and process for storage samples of Mars rock and soil for future return to Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23312
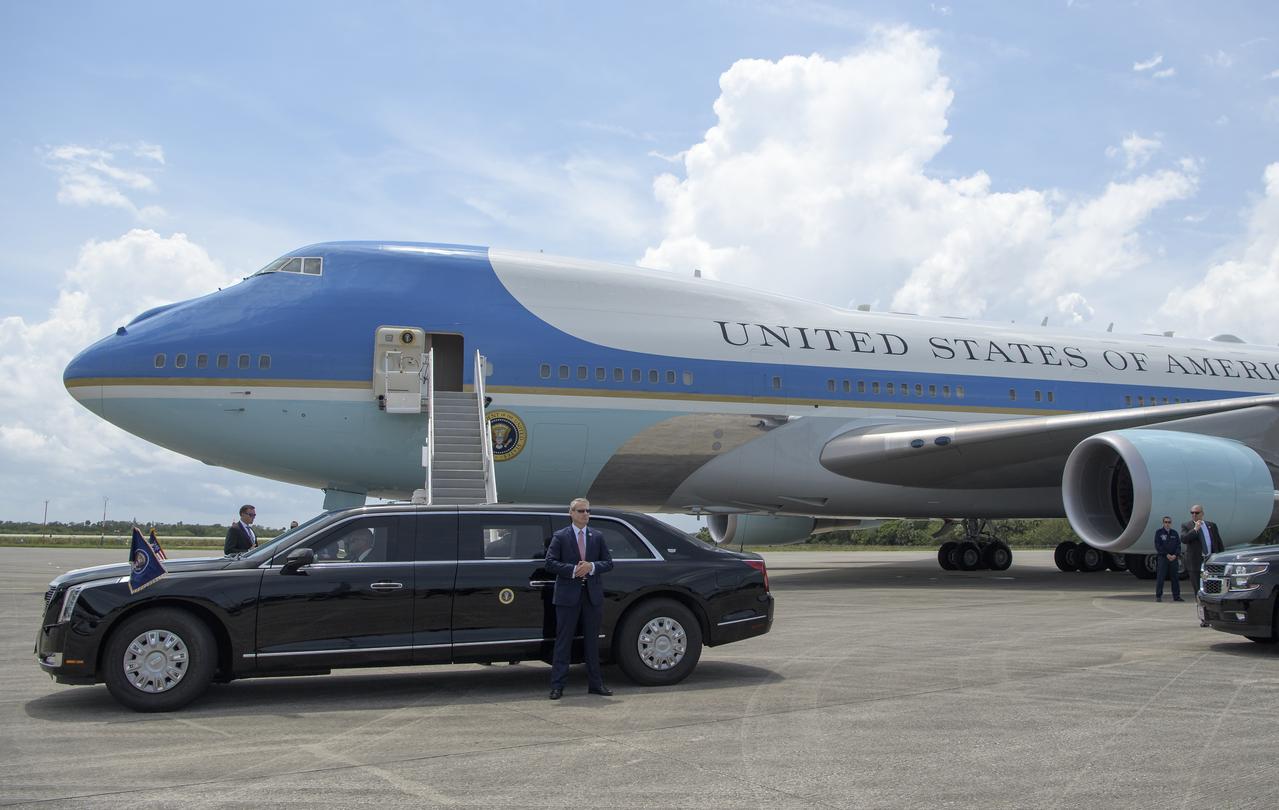

The President’s limousine also know as "the beast," is seen in front of Air Force One after President Donald Trump arrived at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center ahead of SpaceX’s Demo-2 mission, Saturday, May 30, 2020, in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission is the first launch with astronauts of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The test flight serves as an end-to-end demonstration of SpaceX’s crew transportation system. Behnken and Hurley are scheduled to launch at 3:22 p.m. EDT on Saturday, May 30, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. A new era of human spaceflight is set to begin as American astronauts once again launch on an American rocket from American soil to low-Earth orbit for the first time since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A massive cluster of galaxies, called SpARCS1049+56, can be seen in this multi-wavelength view from NASA Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes. At the middle of the picture is the largest, central member of the family of galaxies (upper right red dot of central pair). Unlike other central galaxies in clusters, this one is bursting with the birth of new stars. Scientists say this star birth was triggered by a collision between a smaller galaxy and the giant, central galaxy. The smaller galaxy's wispy, shredded parts, called a tidal tail, can be seen coming out below the larger galaxy. Throughout this region are features called "beads on a string," which are areas where gas has clumped to form new stars. This type of "feeding" mechanism for galaxy clusters -- where gas from the merging of galaxies is converted to new stars -- is rare. The Hubble data in this image show infrared light with a wavelength of 1 micron in blue, and 1.6 microns in green. The Spitzer data show infrared light of 3.6 microns in red. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19837

ISS028-E-018562 (22 July 2011) --- Island of Crete, Greece is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 28 crew member on the International Space Station. In classical Greek mythology the island of Crete was home to King Minos and the terrible Minotaur, a beast that was half man and half bull. The known historical record of Crete is no less impressive. The island was the center of the Bronze Age Minoan civilization that flourished from approximately 2700 – 1420 BC. There is archeological, geological, and cultural evidence to suggest that a cataclysmic volcanic eruption in approximately 1620 BC of Santorini volcano was a major cause of the decline – if not complete destruction – of the Minoan civilization. Today, Crete is the largest and most heavily populated island of Greece (or the Hellenic Republic). The island extends for approximately 260 kilometers and is approximately 60 kilometers across at its widest point. The terrain of Crete is rugged and includes mountains, plateaus, and several deep gorges. The largest city on the island, Heraklion, is located along the northern coastline (center). Several smaller islands ring Crete; two of the largest of these, Dia and Gavdos are sparsely populated year-round, although Gavdos hosts numerous summer visitors. The western and central parts of Crete appear surrounded by quicksilver in this photograph. This phenomenon is known as sunglint, caused by light reflecting off of the sea surface directly toward the observer. The point of maximum reflectance is visible as a bright white region to the northwest of the island (lower right). Surface currents causing variations in the degree of reflectance are visible near the southwestern shoreline of Crete and the smaller island of Gavdos (upper right).
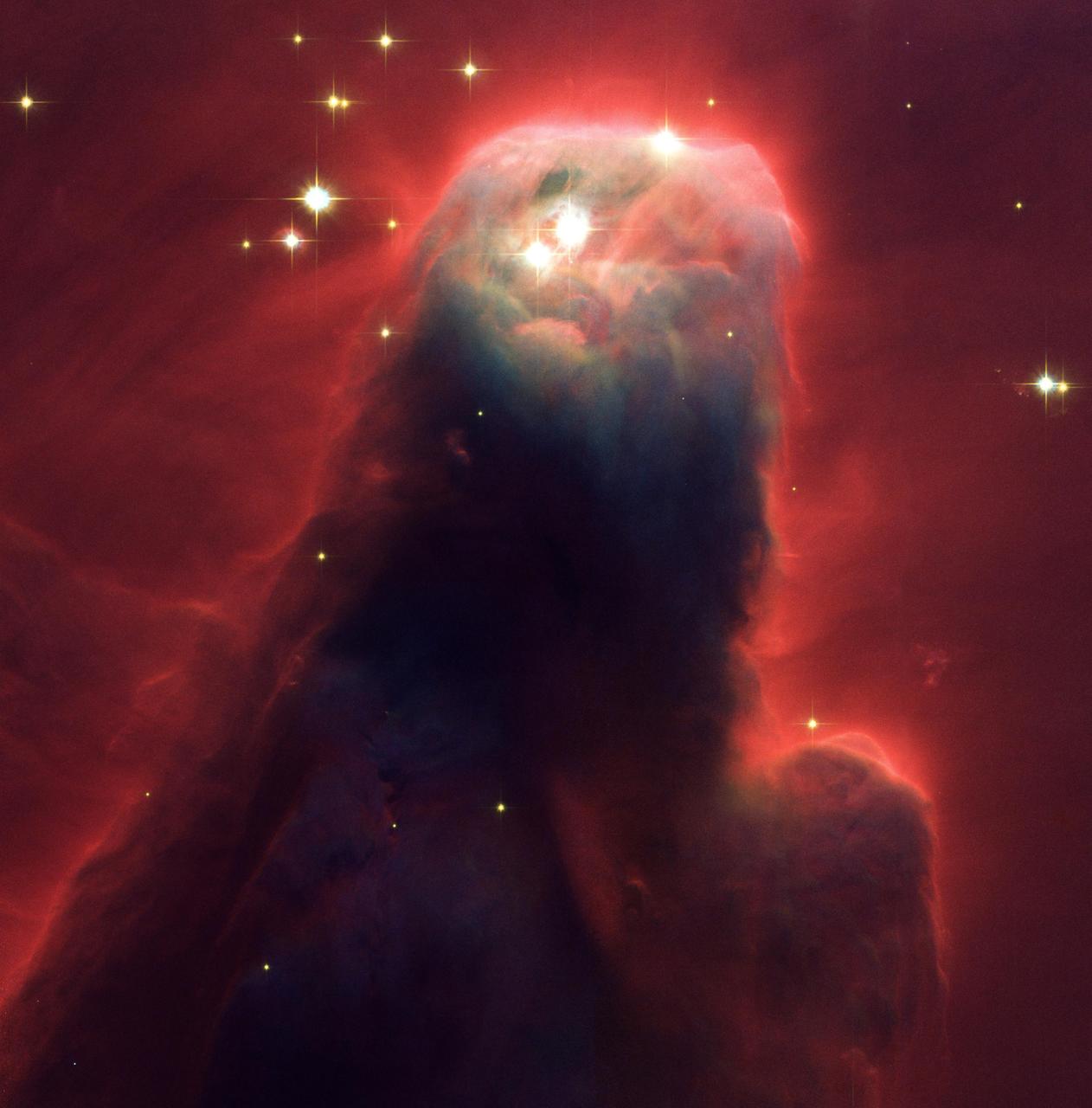

Resembling a nightmarish beast rearing its head from a crimson sea, this monstrous object is actually an irnocuous pillar of gas and dust. Called the Cone Nebula (NGC 2264), this giant pillar resides in a turbulent star-forming region. This picture, taken by the newly installed Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) aboard Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during Space Shuttle STS-109 mission in March 2002, shows the upper 2.5 light-years of the nebula, a height that equals 23 million roundtrips to the Moon. The entire nebula is 7 light-years long. The Cone Nebula resides 2,500 light-years away in the constellation Monoceros. Radiation from hot, young stars (located beyond the top of the image) has slowly eroded the nebula over millions of years. Ultraviolet light heats the edges of the dark cloud, releasing gas into the relatively empty region of surrounding space. There, additional ultraviolet radiation causes the hydrogen gas to glow, which produces the red halo of light seen around the pillar. A similar process occurs on a much smaller scale to gas surrounding a single star, forming the bow-shaped arc seen near the upper left side of the Cone. This arc, seen previously with the HST, is 65 times larger than the diameter of our solar system. The blue-white light from surrounding stars is reflected by dust. Background stars can be seen peeking through the evaporating tendrils of gas, while the turbulent base is pockmarked with stars reddened by dust. Credit: NASA, H. Ford (JHU), G. Illingworth (USCS/LO), M. Clampin (STScI), G. Hartig (STScI), the ACS Science Team, and ESA.
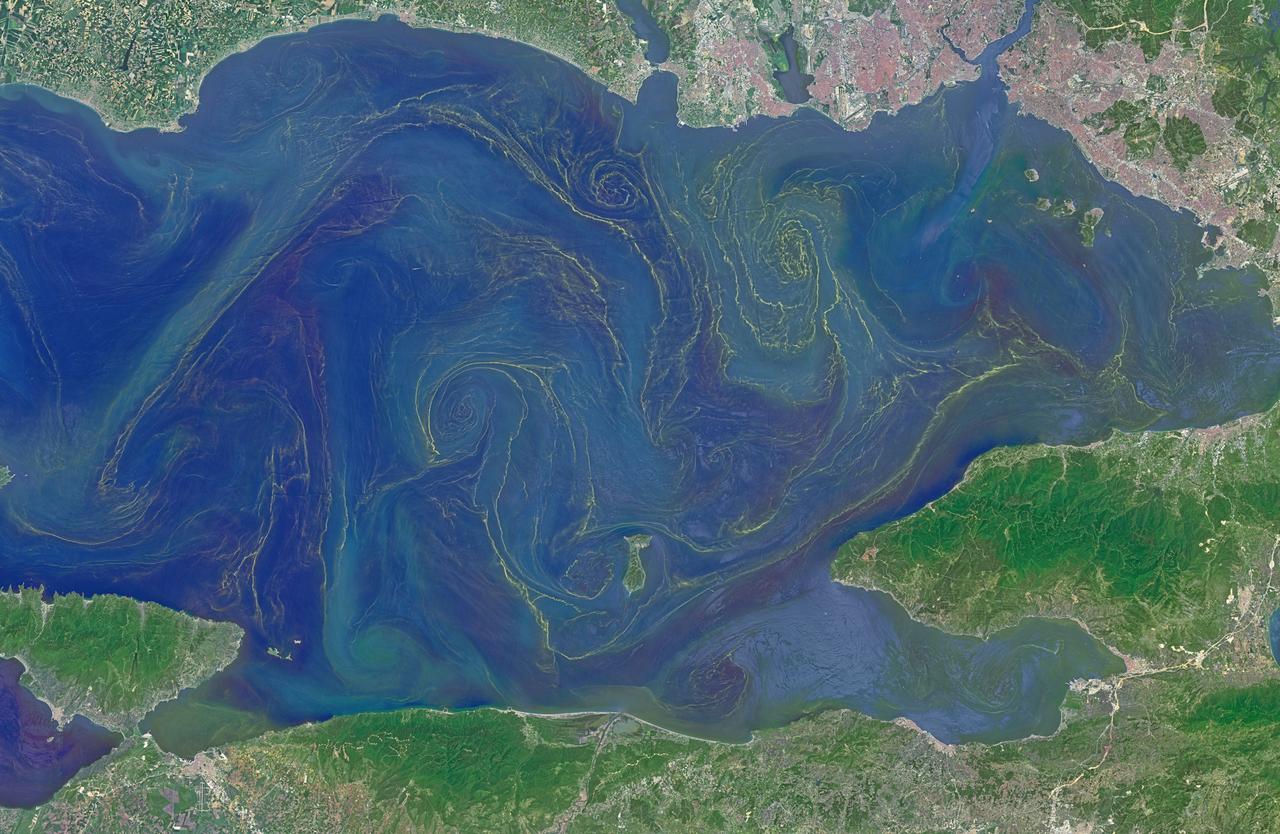

Situated between the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara is full of a rich soup of nutrients and life and surrounded by a rich history of civilization. Like the Black Sea to its northeast, the Marmara has an unusual layered structure with fresher water near the surface and much saltier water near the bottom. That fresh surface is fed by exchanges with the Black Sea and by flows from the Susurluk, Biga, and Gonen Rivers. The fresh water (just two thirds the salinity of the ocean) makes it easier for floating, plant-like organisms—phytoplankton—to grow, as does the abundance of nutrients pouring into the seas from European and Turkish rivers. The Operational Land Imager on the Landsat 8 satellite captured this image of a phytoplankton bloom in the Sea of Marmara on May 17, 2015. The sea is surrounded on all sides by the nation of Turkey. The swirling shapes on the water are phytoplankton, with the yellow-green and red-purple filaments likely (but not necessarily) representing different species. Those wavy colored lines not only show where the densest concentrations of plankton are floating, but also reveal the eddies and currents within the small sea. Waters rushing in through the narrow Bosphorous Strait (at Istanbul) and Dardanelles Strait (off the left side of the image), as well as a jagged coastline and tectonically fractured seafloor on this edge of the Asian and European continents, all conspire to create intricate mixing patterns. If you download the large image and open it in full resolution, you also can see ship tracks crossing the bloom lines. “I often see features in imagery and wonder: what could be causing that?” said Norman Kuring, an ocean color specialist at NASA Goddard. “Remote sensing is great for the big picture, but it still needs data from the surface for validation and interpretation.” According to scientists Baris Salihoglu of Turkey’s Institute of Marine Sciences and Ahsen Yuksek of Istanbul University, the blooms in the satellite image are mostly Prorocentrum micans and Noctiluca scintillans. They recently sampled the waters of the Marmara and found that Prorocentrum bloomed first, though Noctiluca eventually dominated. According to Ajit Subramaniam of the Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, both species are dinoflagellates, known to discolor the water (red tides). Neither is directly toxic to humans, but they can kill marine life by becoming caught in fish gills, depleting the sea of oxygen, or excreting ammonia into the water. “Noctiluca is phagotrophic—a really interesting beast since it eats other phytoplankton that can then change its color,” Subramaniam noted. “It switches from being photosynthetic to becoming heterotrophic.” The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured wider views of bloom events in the Sea of Marmara on on May 23 and May 25. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=85947" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=85947</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>