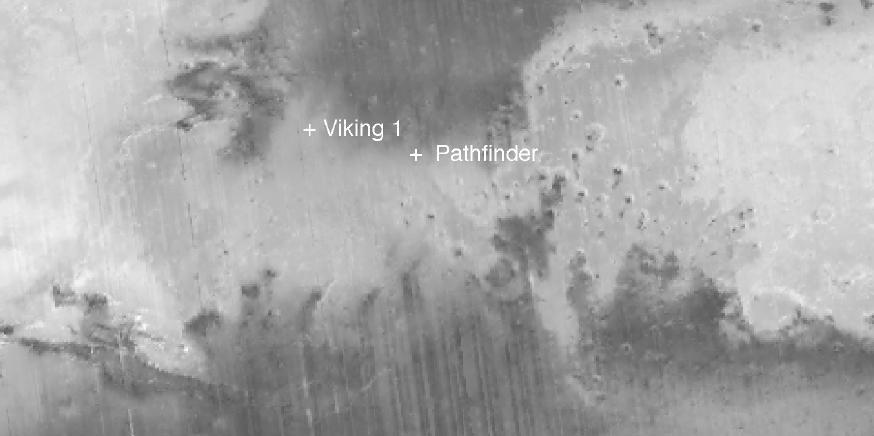

New Views of Mars from the Thermal Emission Spectrometer Instrument
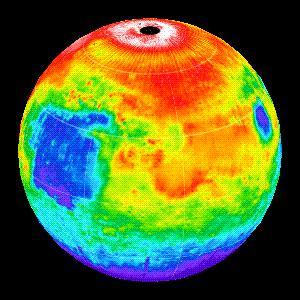
Martian Temperatures Measured by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer TES. Isidis Planitia View
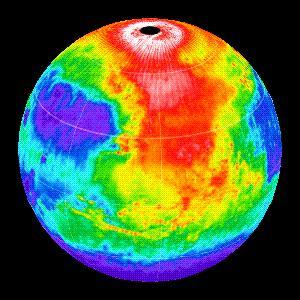
Martian Temperatures Measured by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer TES. Pathfinder Landing Aite View
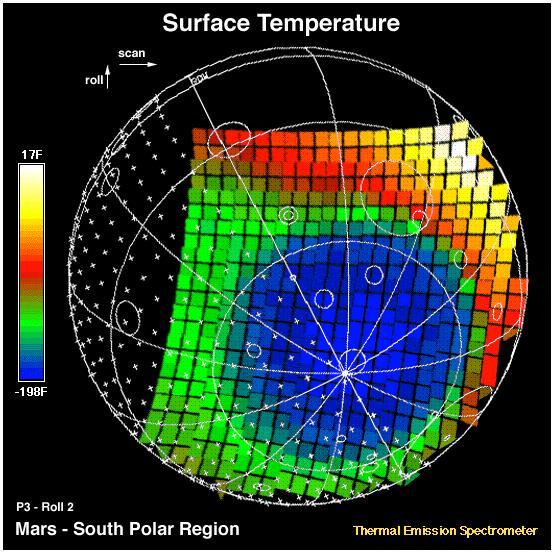
This image shows the temperature of the martian surface measured by the Mars Global Surveyor Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) instrument. On September 15, 3 hours and 48 minutes after the spacecrafts third close approach to the planet, the TES instrument was commanded to point at Mars and measure the temperature of the surface during a four minute scan. At this time MGS was approximately 15,000 miles (~24,000 km) from the planet, with a view looking up from beneath the planet at the south polar region. The circular blue region (- 198 F) is the south polar cap of Mars that is composed of CO2 ice. The night side of the planet, shown with crosses, is generally cool (green). The sunlit side of the planet reaches temperatures near 15 F (yellow). Each square represents an individual observation acquired in 2 seconds with a ground resolution of ~125 miles (~200 km). The TES instrument will remain on and collect similar images every 100 minutes to monitor the temperature of the surface and atmosphere throughout the aerobraking phase of the MGS mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00937
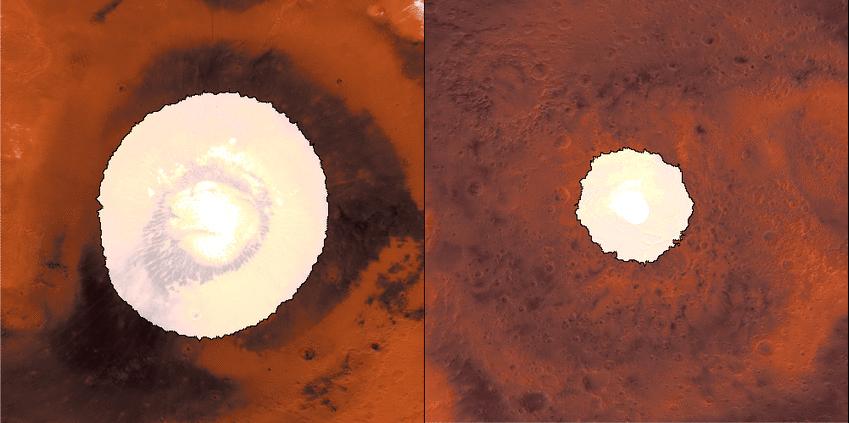

This animation shows a side-by-side comparison of CO2 ice at the north (left) and south (right) Martian poles over the course of a typical year (two Earth years). This simulation isn't based on photos; instead, the data used to create it came from two infrared instruments capable of studying the poles even when they're in complete darkness. As Mars enters fall and winter, reduced sunlight allows CO2 ice to grow, covering each pole. While ice at the north pole is fairly symmetrical, it's somewhat asymmetrical during its retreat from the south pole for reasons scientists still don't understand. Scientists are especially interested in studying how global dust events affect the growth and retreat of this polar ice. Mars' seasons are caused by a tilt in the planet, resulting in winter at one of the planet's poles while it's summer at the other. How do spacecraft observe the Martian surface in the polar night, when the Sun is below the horizon for weeks or even months, or in the spring, when it's hazy? They use infrared instruments measuring surface temperatures, even when the ground is in complete darkness or the atmosphere obscured. CO2 ice (sometimes called dry ice) is the coldest material found on Mars, and it is near -193 degrees Fahrenheit (-125 degrees Celsius), whereas ice free soil is generally warmer. As a result, scientists can track the position of the seasonal caps, even in the dark, using surface temperature measurements. Each panel of the animation is about 3,728 miles (6,000 kilometers) across. This data was collected by the Mars Climate Sounder (MCS) instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and the Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) onboard NASA's now defunct Mars Global Surveyor. The MCS data was collected between mid-2006 and the end of 2013; the TES data was collected between early 1999 to late 2006. Animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22546
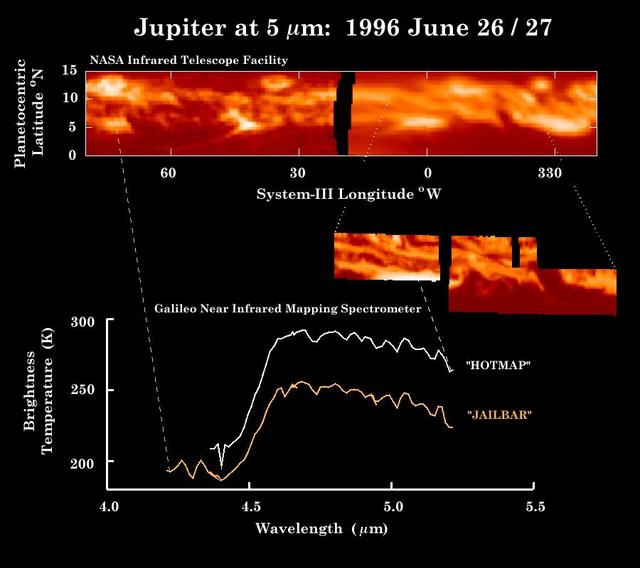
These observations of Jupiter equator in thermal heat emission were made by NASA Infrared Telescope Facility top panel within hours of the Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer NIMS instrument image middle inset and the spectra bottom.

An engineer prepares the Carbon Mapper imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, for testing in a thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in July 2023. This test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers used the chamber to subject the spectrometer to the extreme temperatures it will encounter in the vacuum of space. The instrument was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco on Sept. 12, 2023, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26094
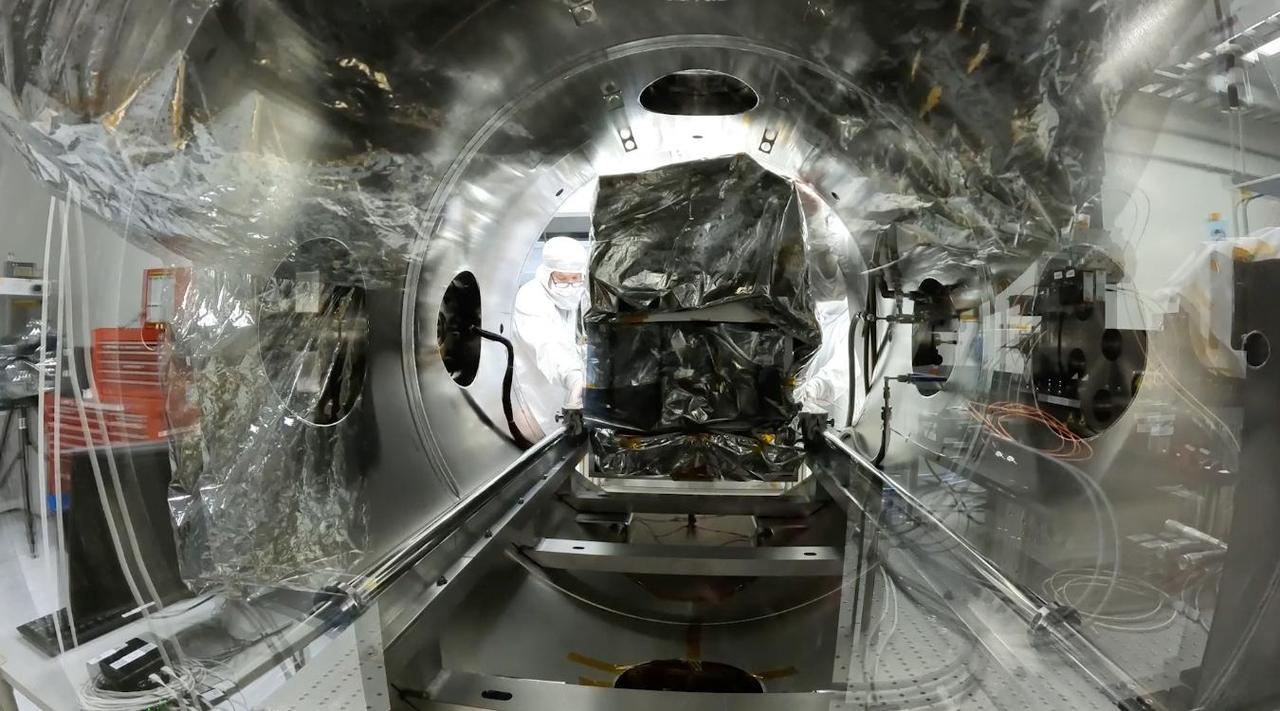

A technician slides an imaging spectrometer instrument, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, into a thermal vacuum test chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in July 2023. The thermal vacuum chamber test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers use the chamber to subject the spectrometer to the extreme temperatures it will encounter in the vacuum of space. The instrument shipped Sept. 12, 2023, from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26098
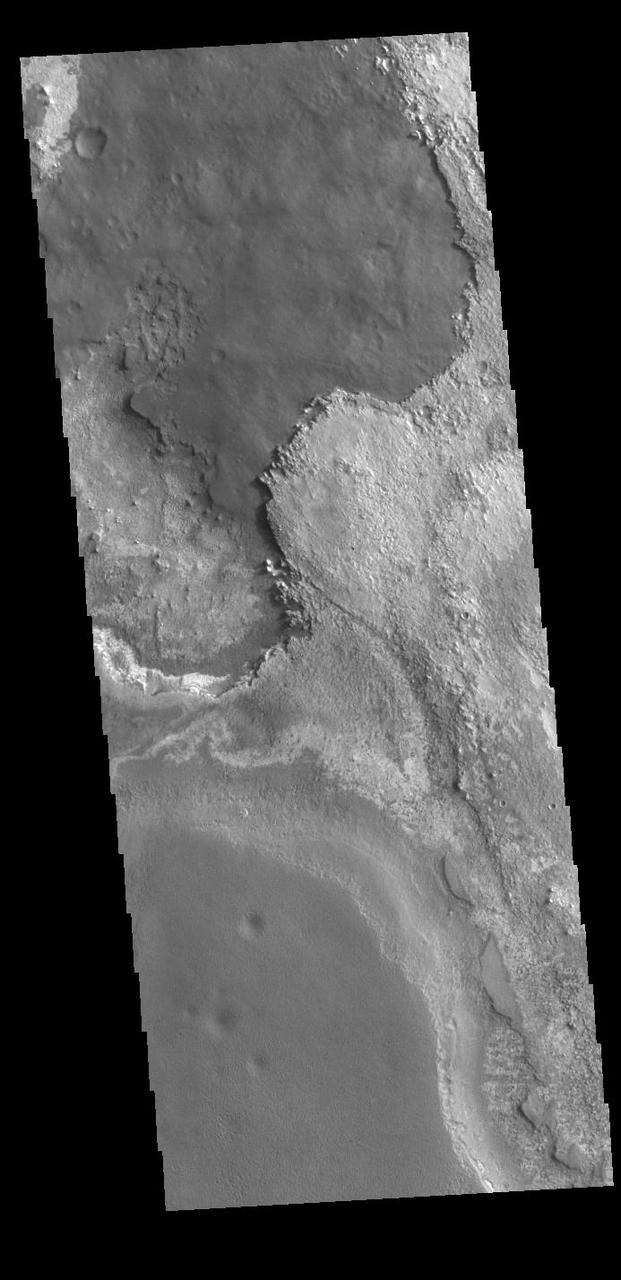

This VIS image shows layering of surface materials in Meridiani Planum. TES (Thermal Emission Spectrometer) initially detected hematite in a surface layer, which was confimed by THEMIS (THermal EMision Imaging System). These findings supported a water rich origin of the hematite and led to the selection of the site for the Opportunity MER (Mars Exploration Rover). Orbit Number: 87337 Latitude: 1.58599 Longitude: 0.436954 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-08-22 15:12 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25221
![Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS)into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0192/KSC01pp0192~medium.jpg)
Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS)into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0193/KSC01pp0193~medium.jpg)
Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![An overhead crane moves The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0191/01pp0191~medium.jpg)
An overhead crane moves The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) is installed by technicians on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0194/01pp0194~medium.jpg)
The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) is installed by technicians on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers attach a crane to the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); to move it into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter.; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0190/01pp0190~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers attach a crane to the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); to move it into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter.; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![An overhead crane moves The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0191/KSC01pp0191~medium.jpg)
An overhead crane moves The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians examine the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is moved to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0189/KSC01pp0189~orig.jpg)
Technicians examine the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is moved to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Two technicians involved with the installation of the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter pose in front of the spacecraft in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0195/01pp0195~medium.jpg)
Two technicians involved with the installation of the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter pose in front of the spacecraft in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) is installed by technicians on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0194/KSC01pp0194~medium.jpg)
The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) is installed by technicians on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians check out the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II) .; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0188/01pp0188~medium.jpg)
Technicians check out the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II) .; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians check out the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II) .; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0188/KSC01pp0188~medium.jpg)
Technicians check out the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II) .; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS)into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0192/01pp0192~medium.jpg)
Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS)into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers attach a crane to the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); to move it into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter.; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0190/KSC01pp0190~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers attach a crane to the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); to move it into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter.; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians examine the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is moved to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0189/01pp0189~medium.jpg)
Technicians examine the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) before it is moved to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility II (SAEF II).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Two technicians involved with the installation of the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter pose in front of the spacecraft in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0195/KSC01pp0195~medium.jpg)
Two technicians involved with the installation of the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter pose in front of the spacecraft in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0193/01pp0193~medium.jpg)
Technicians guide The Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS); into place to be installed on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2).; The orbiter will carry three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
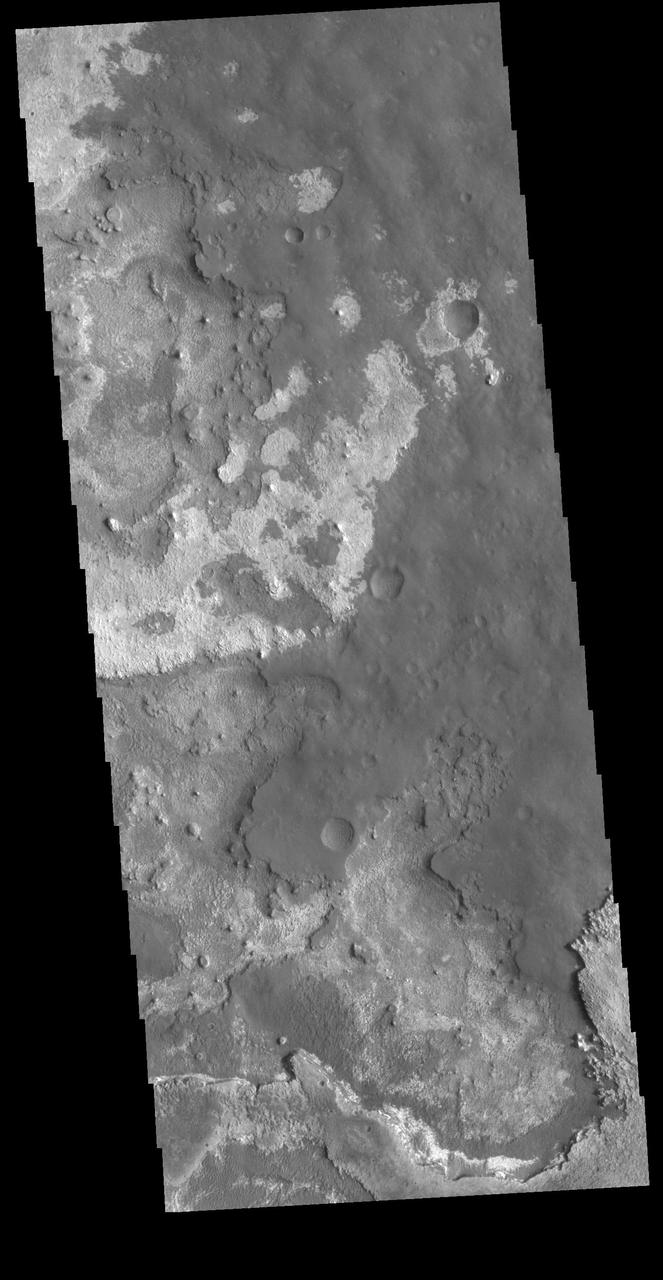

This VIS image shows layering of surface materials in Meridiani Planum. TES (Thermal Emission Spectrometer) initially detected hematite in a surface layer, which was confimed by THEMIS (THrmal EMision Imaging System). These findings supported a water rich origin of the hematite and led to the selection of the site for the Opportunity MER (Mars Exploration Rover). Orbit Number: 80848 Latitude: 1.85739 Longitude: 0.251223 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-03-06 08:13 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23930
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 open the solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, allowing inspection of the panels and giving them access to other components. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0158/KSC01pp0158~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 open the solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, allowing inspection of the panels and giving them access to other components. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
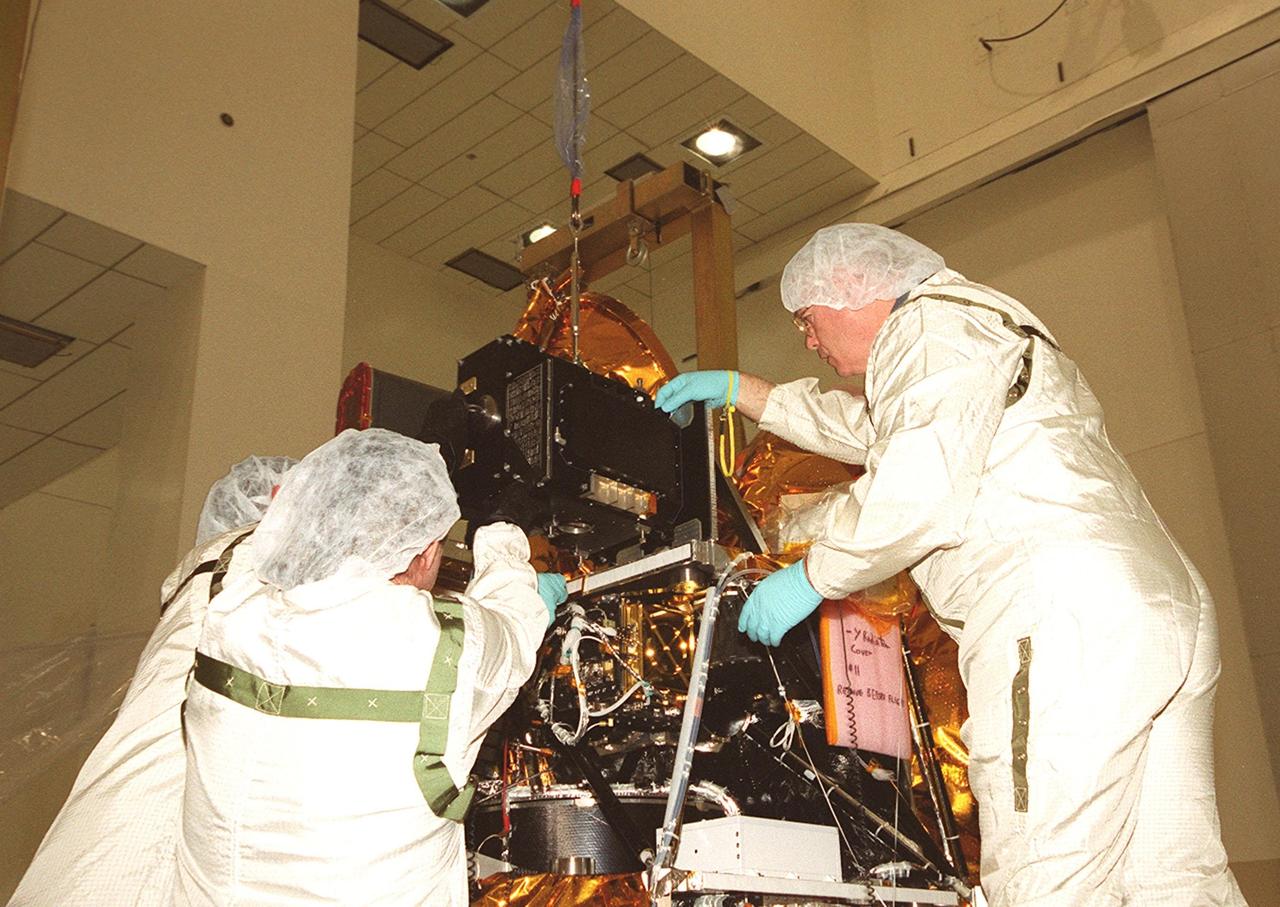

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers help put the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) in its place on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>as it is lowered to a workstand. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0101/KSC01pp0101~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>as it is lowered to a workstand. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers test the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a> to a workstand (left). The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0099/KSC01pp0099~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a> to a workstand (left). The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
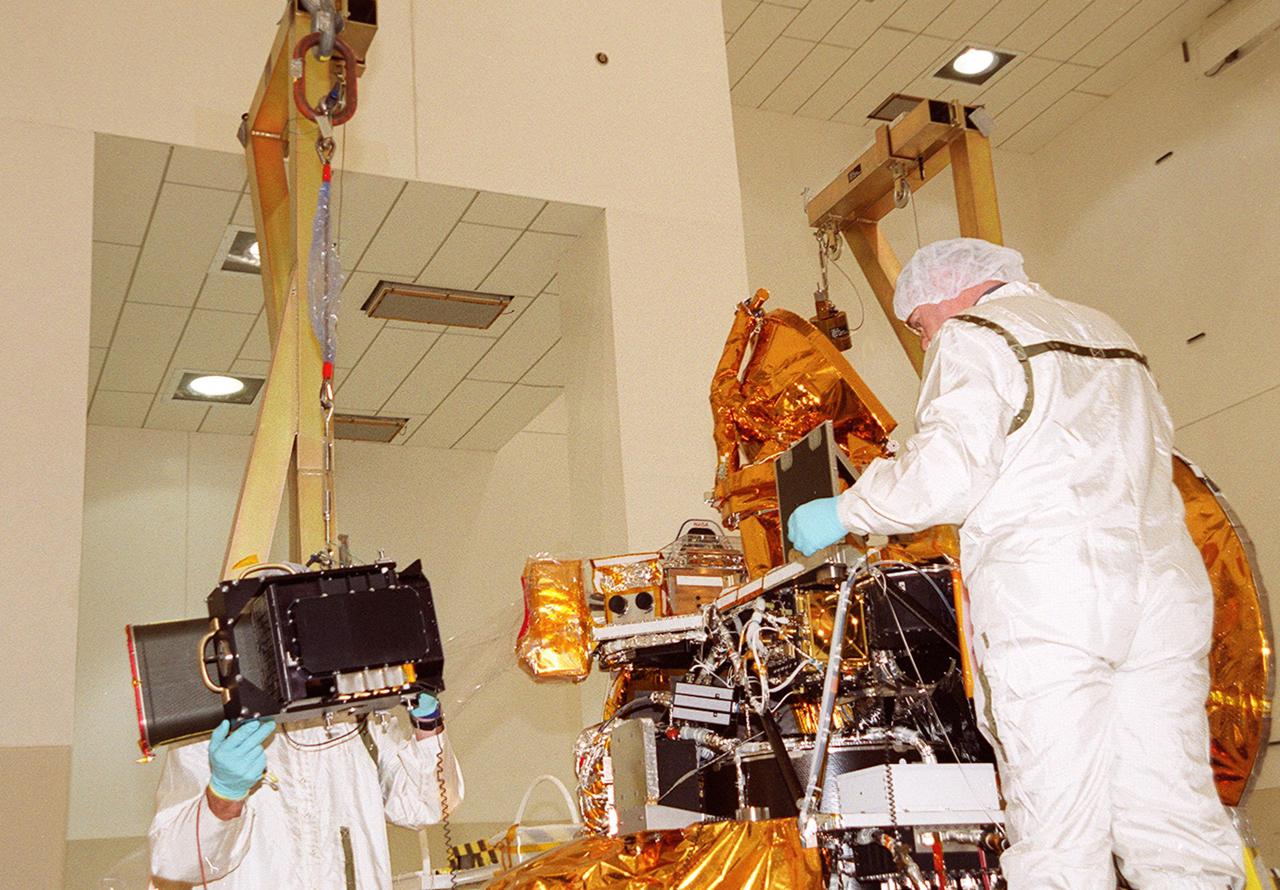

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), left, is moved toward the Mars Odyssey Orbiter, at right. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
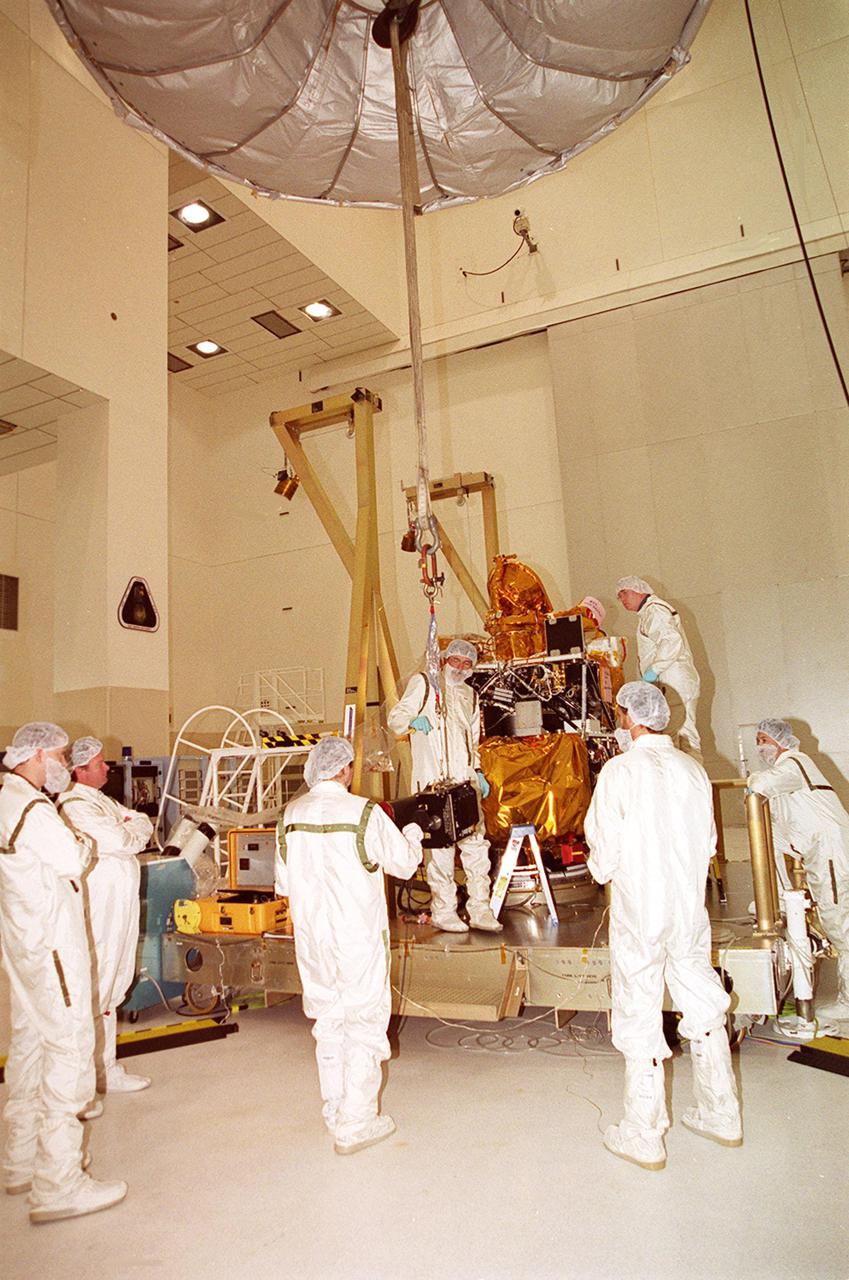

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, an overhead crane lifts and moves the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) toward the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
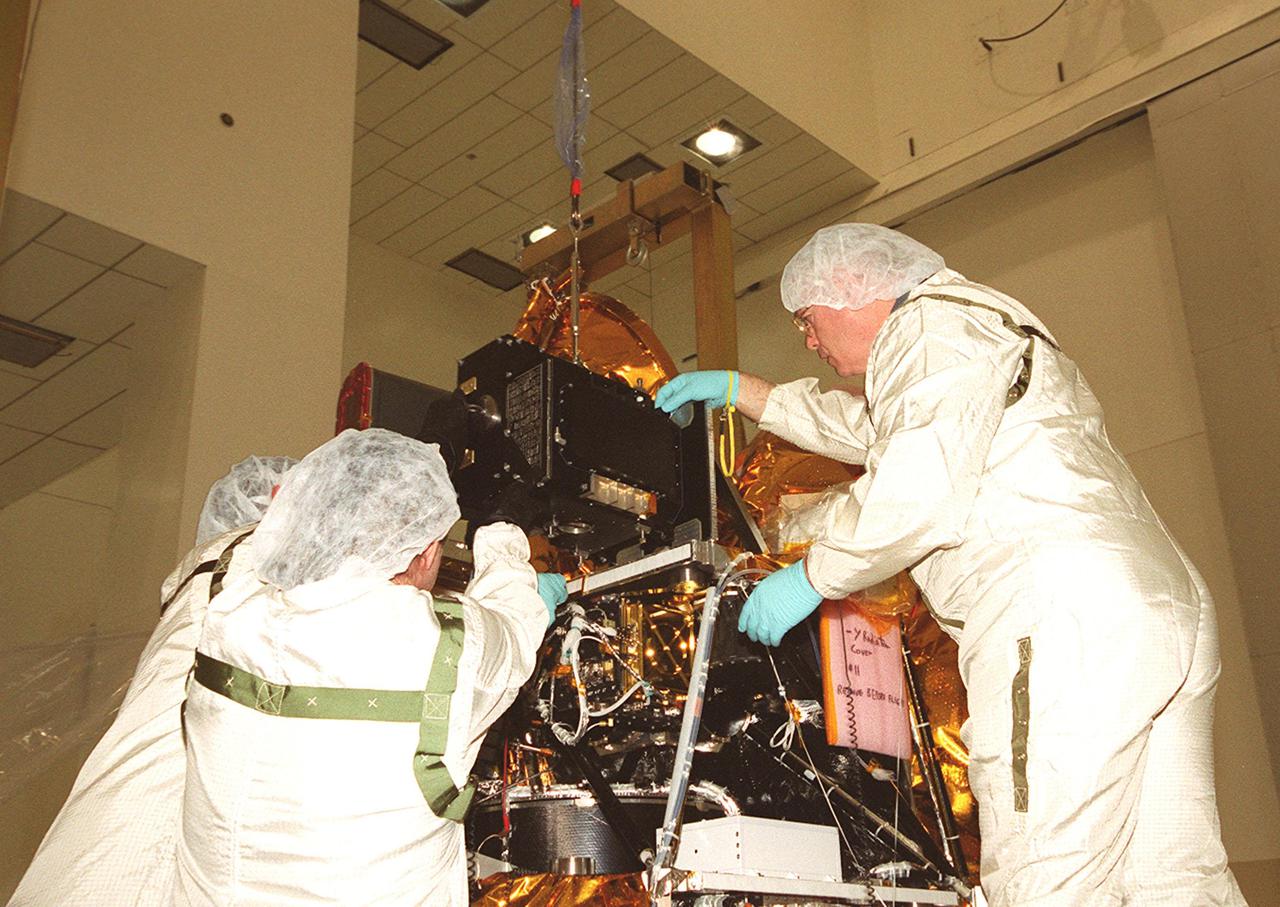

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers help put the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) in its place on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>comes to rest on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2. Workers check the spacecraft’s position. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0102/01pp0102~medium.jpg)
The <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>comes to rest on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2. Workers check the spacecraft’s position. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter is moved toward a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0123/KSC01pp0123~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter is moved toward a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter is moved toward a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0123/01pp0123~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter is moved toward a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a> to a workstand (left). The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0099/01pp0099~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a> to a workstand (left). The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
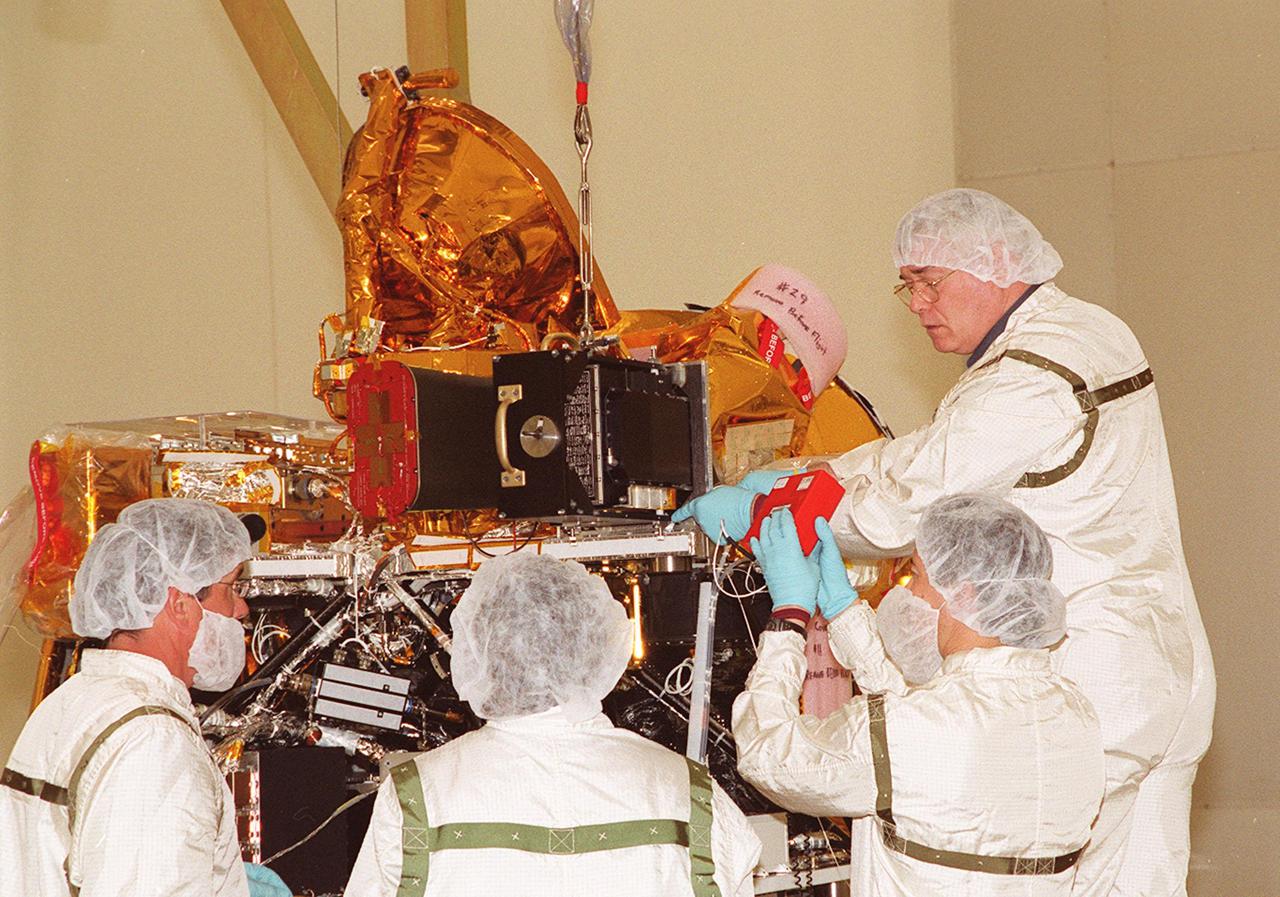

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 check the placement of the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
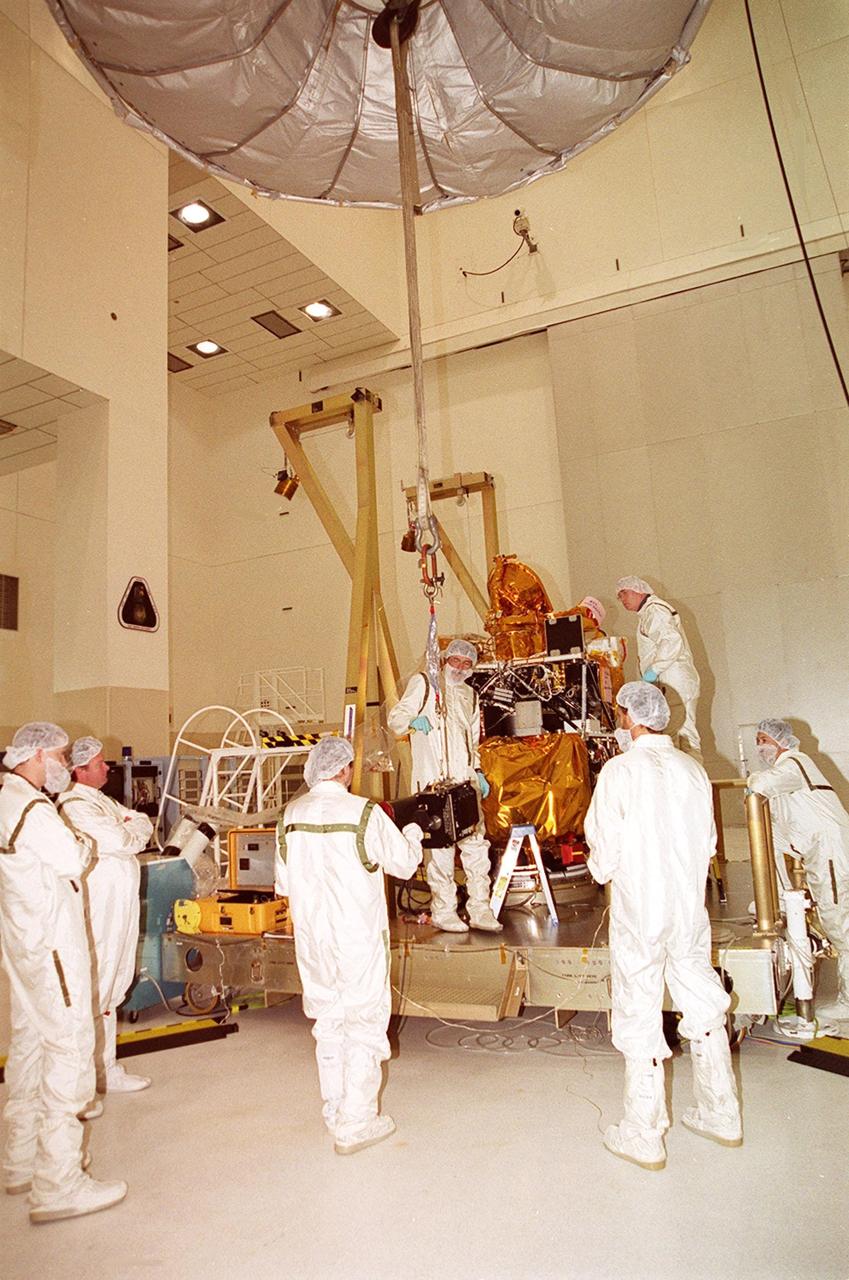

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, an overhead crane lifts and moves the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) toward the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>comes to rest on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2. Workers check the spacecraft’s position. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0102/KSC01pp0102~medium.jpg)
The <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>comes to rest on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2. Workers check the spacecraft’s position. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
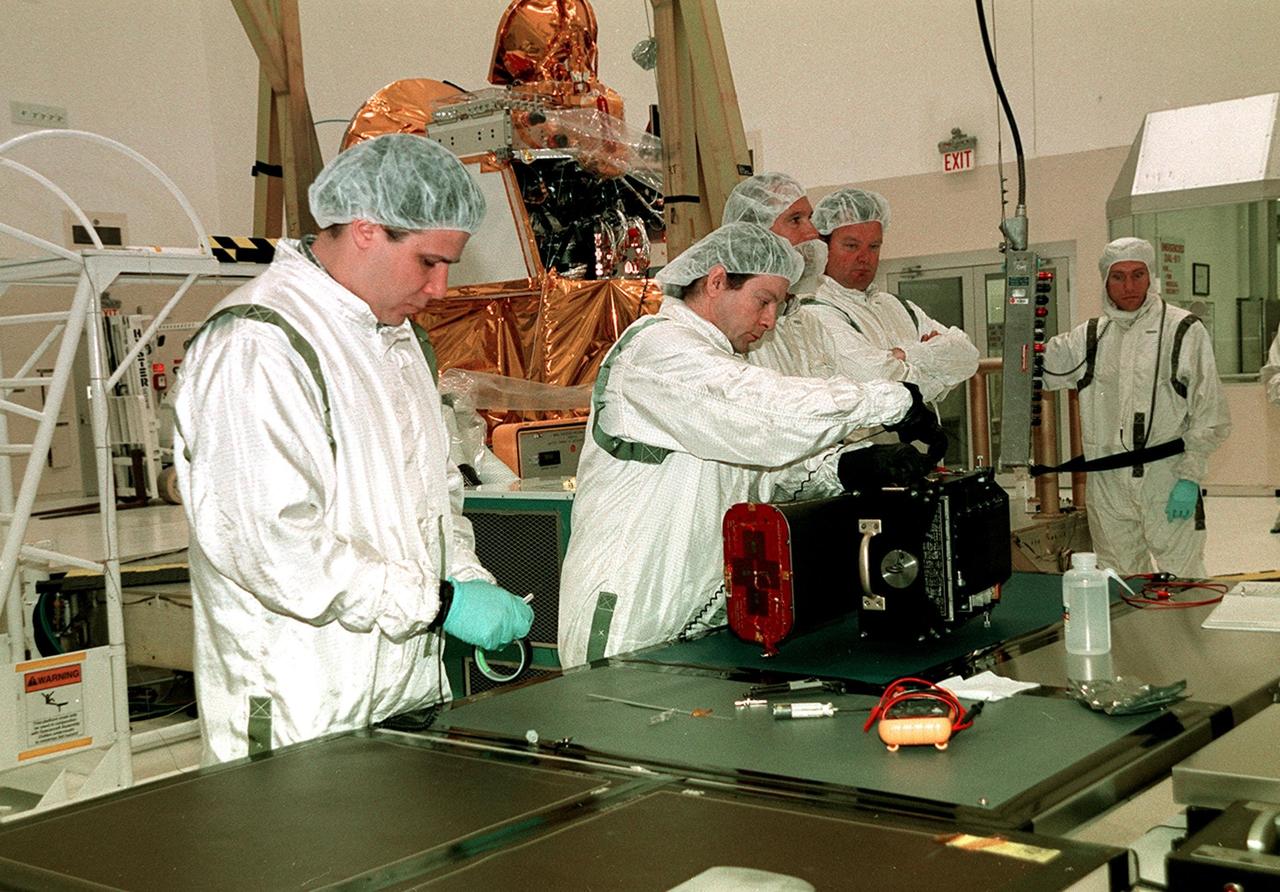
At a work bench in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers test the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers check the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter (background). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter</a> is safely placed on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0103/KSC01pp0103~medium.jpg)
The <a href=http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter</a> is safely placed on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
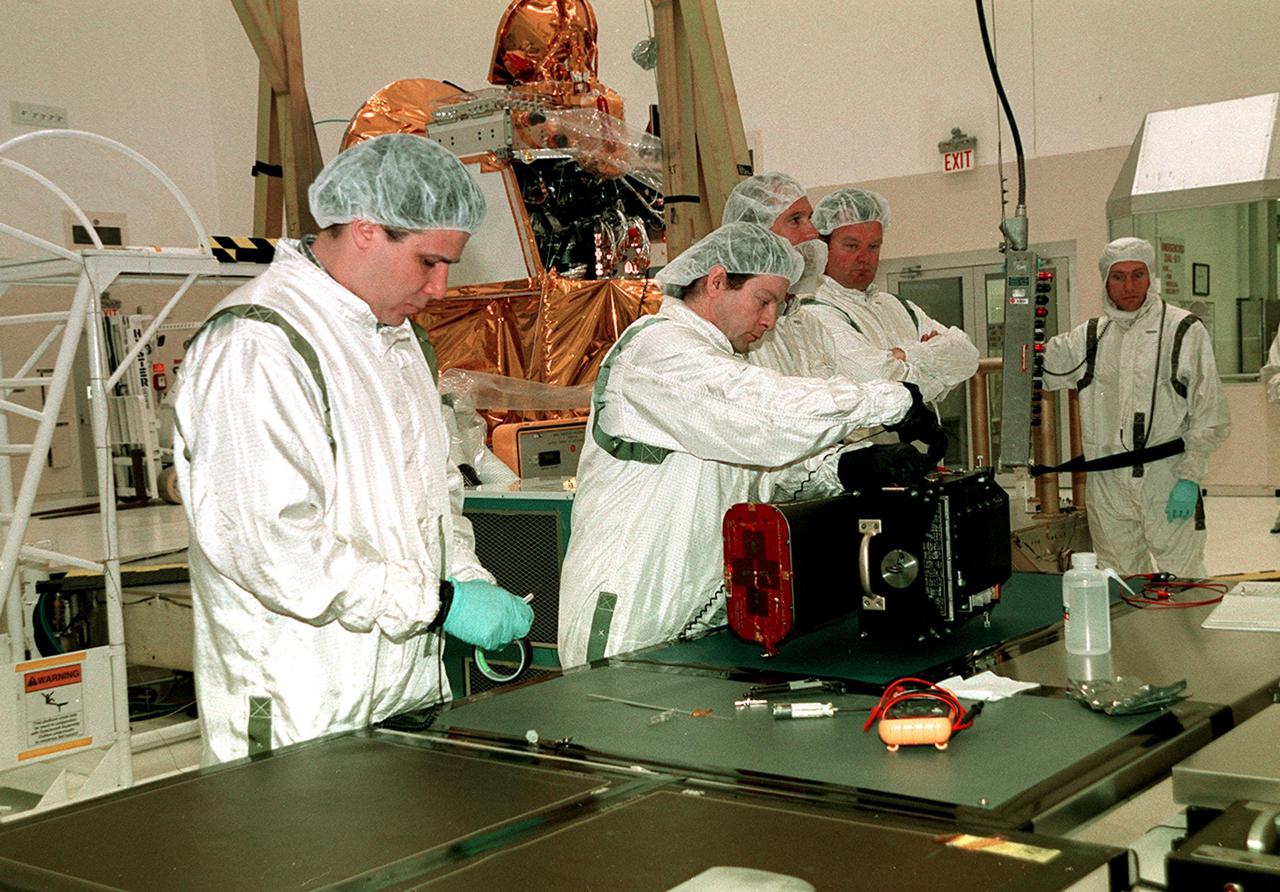
At a work bench in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers test the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter onto a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0124/01pp0124~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter onto a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
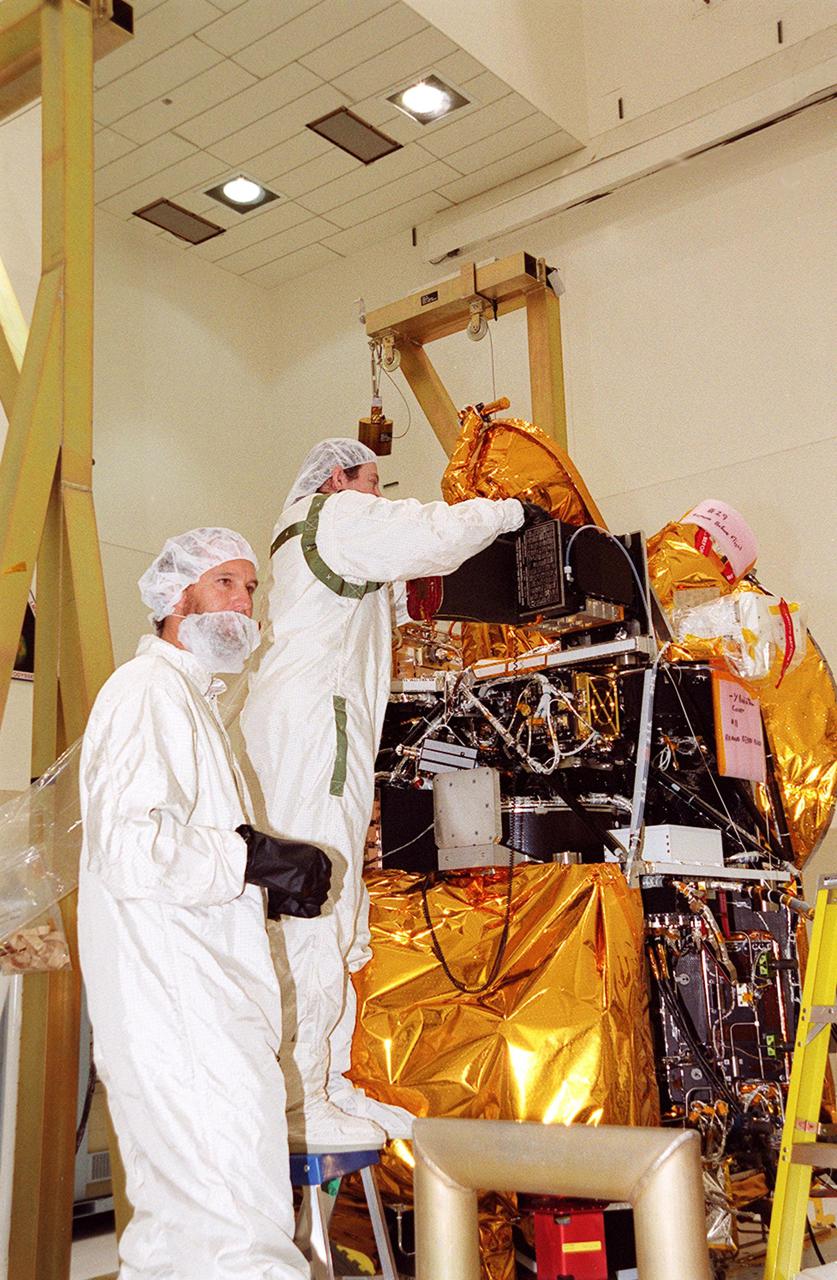

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 adjust the placement of the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 take a close look at the back side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0160/01pp0160~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 take a close look at the back side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers oversee removal of the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0121/KSC01pp0121~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers oversee removal of the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>as it is lowered to a workstand. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0101/01pp0101~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>as it is lowered to a workstand. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
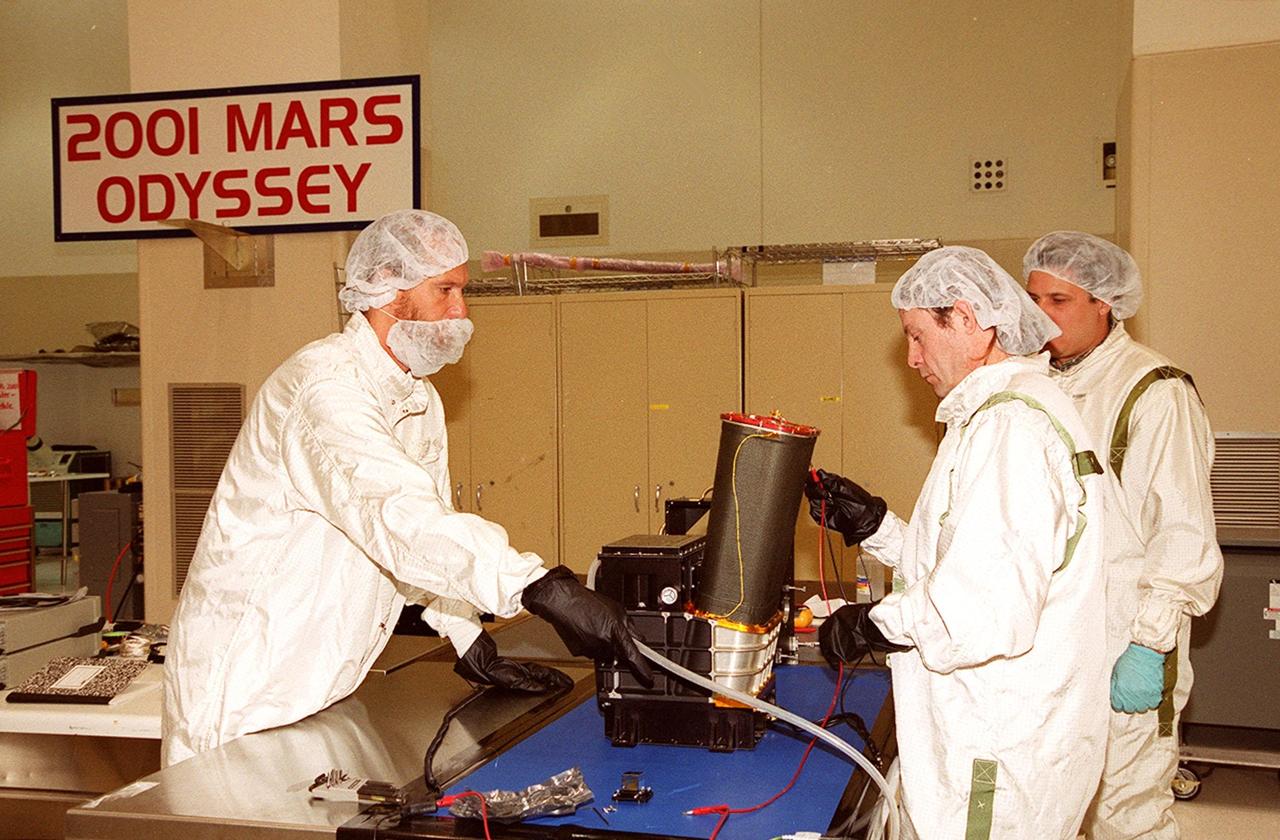

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers test the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 take a close look at the back side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0160/KSC01pp0160~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 take a close look at the back side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 open the solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, allowing inspection of the panels and giving them access to other components. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0158/01pp0158~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 open the solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter, allowing inspection of the panels and giving them access to other components. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers oversee removal of the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0121/01pp0121~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers oversee removal of the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 make a visual check of the front side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0159/01pp0159~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 make a visual check of the front side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter onto a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0124/KSC01pp0124~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers help guide the solar array from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter onto a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
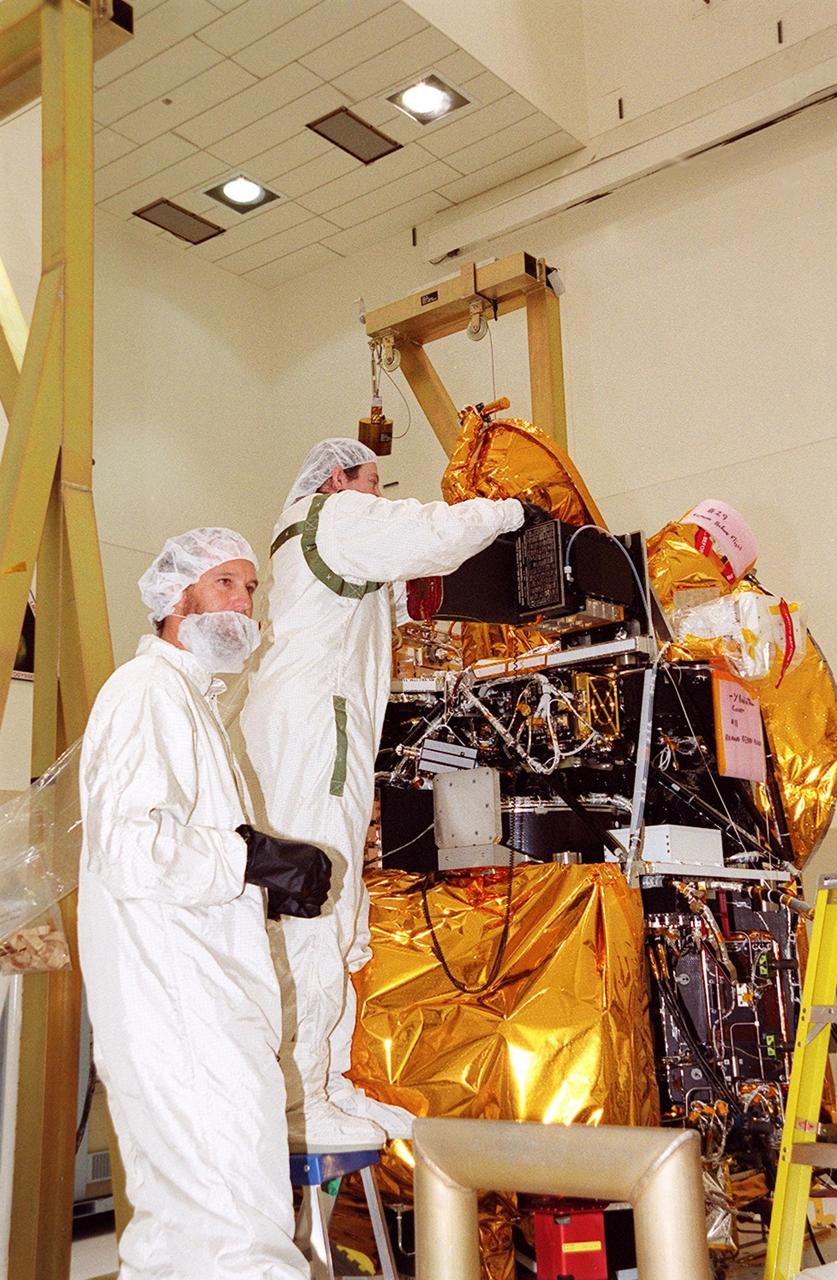

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 adjust the placement of the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
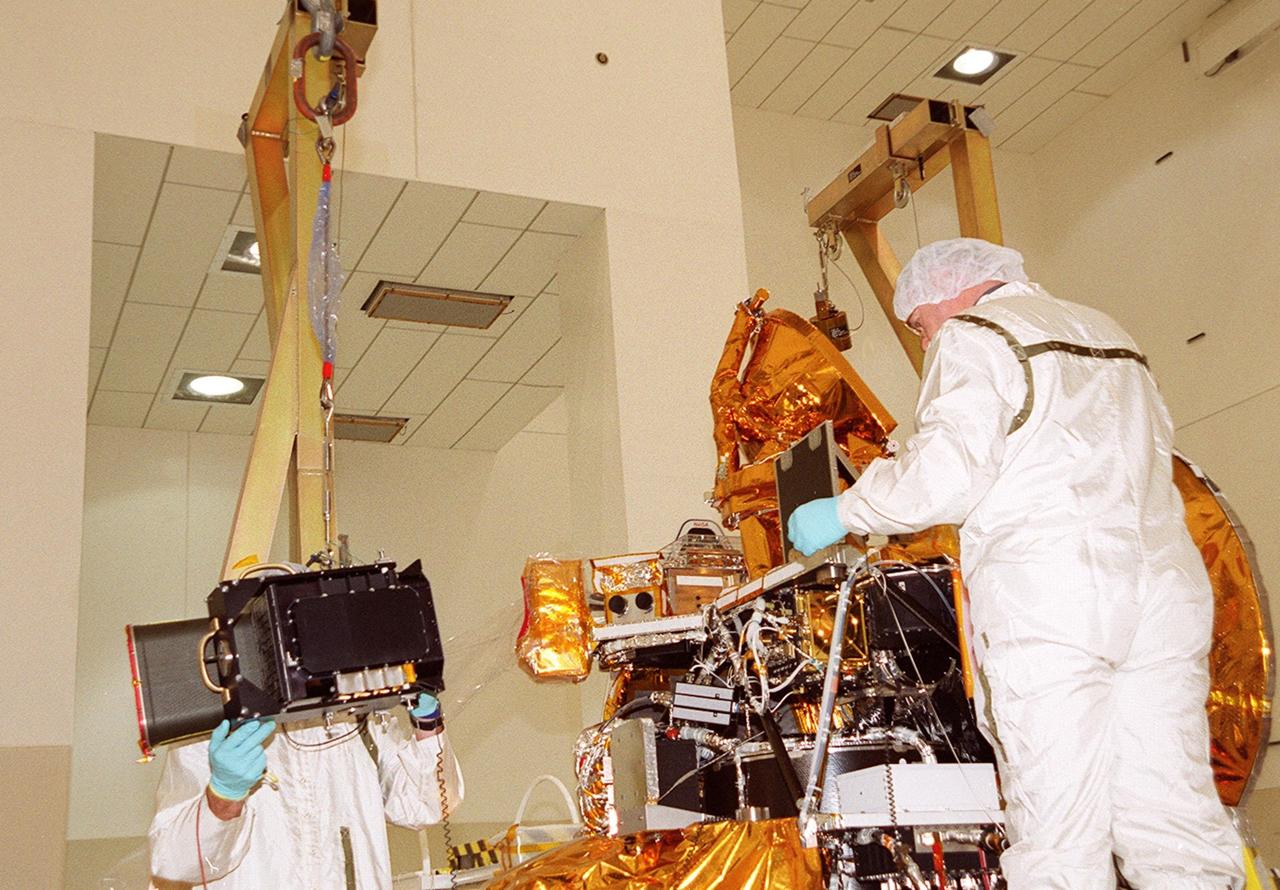

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), left, is moved toward the Mars Odyssey Orbiter, at right. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 make a visual check of the front side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0159/KSC01pp0159~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 make a visual check of the front side of the opened solar array panels from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![The <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter<_a> is safely placed on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0103/01pp0103~medium.jpg)
The <a href=http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter<_a> is safely placed on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
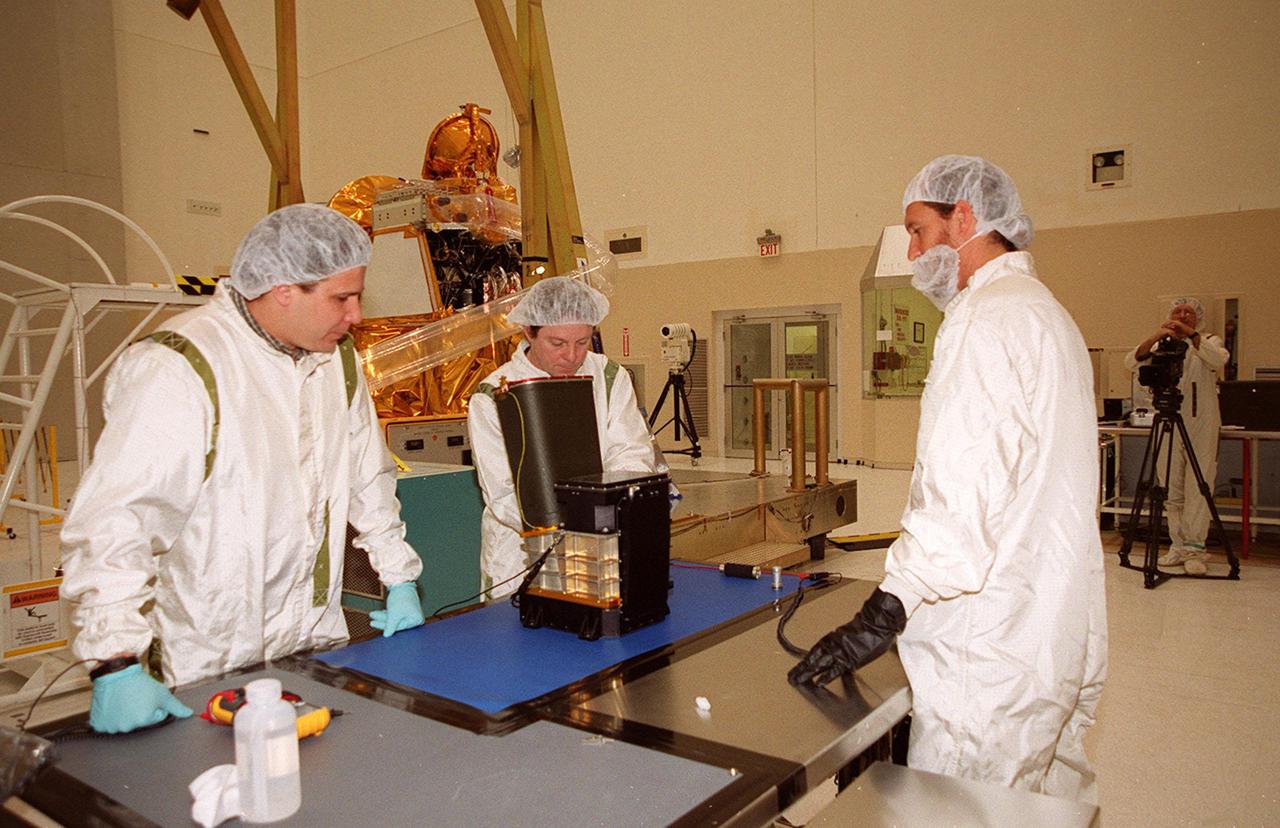

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF 2), workers check the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) before attaching to the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter (background). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
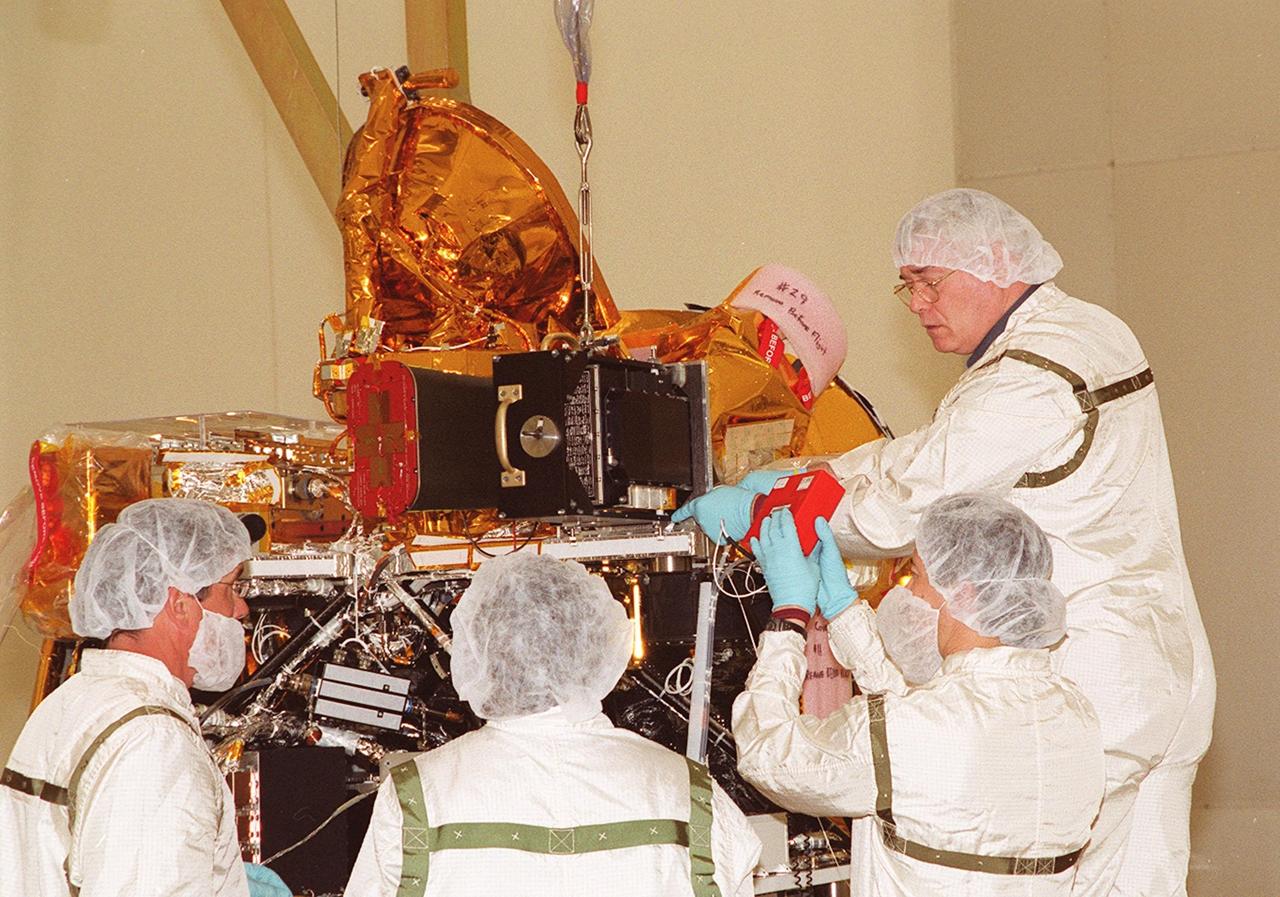

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 check the placement of the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on the Mars Odyssey Orbiter. THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The orbiter will carry three science instruments: THEMIS, the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment with regards to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

The Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS) on Galileo obtained this image of half of Io's disk in darkness on September 19, 1997. This image, at 5 microns, shows several hot spots on Io, which are volcanic regions of enhanced thermal emission. The area shown is part of the leading hemisphere of Io. Two new hot spots are shown and indicated in the image (New, and Shamshu). Neither of these hot spots were seen by NIMS or the Solid State Imaging Experiment, (SSI) prior to this observation, becoming only recently active. Several other previously known hot spots are labelled in the image. Galileo was at a distance of 342,000 km from Io when this observation was made. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01226
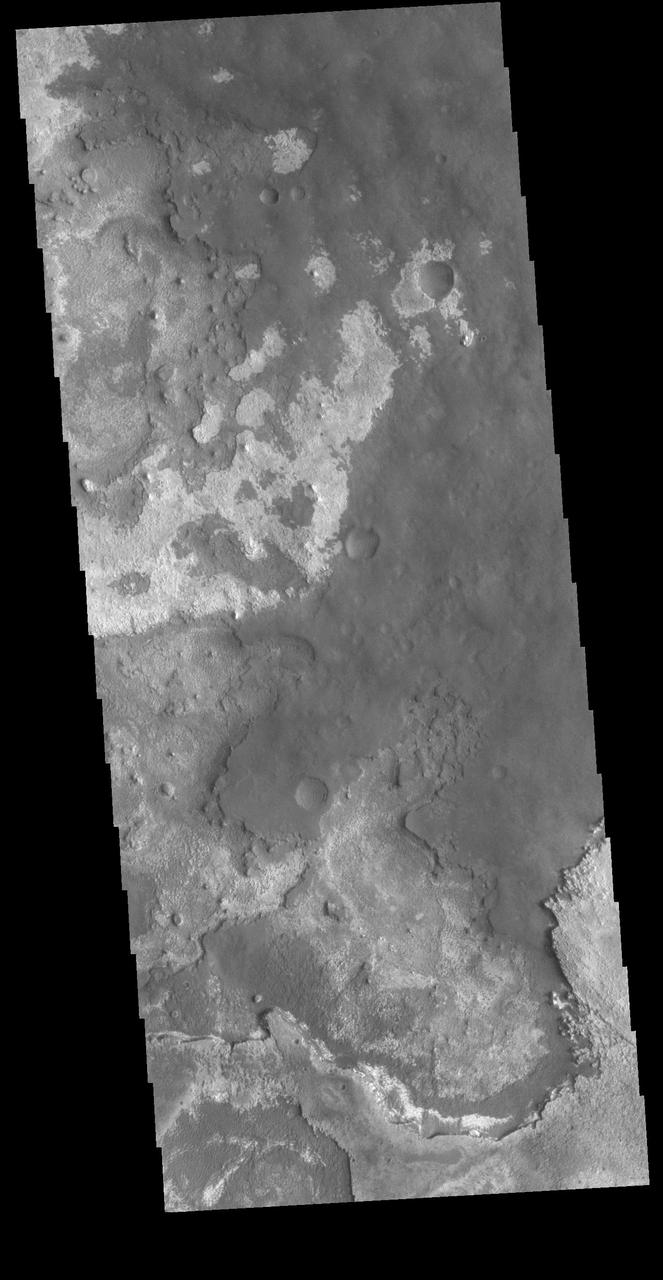

This VIS image shows layering of surface materials in Meridiani Planum. TES (Thermal Emission Spectrometer) initially detected hematite in a surface layer, which was confirmed by THEMIS (THrmal EMision Imaging System). These findings supported a water rich origin of the hematite and led to the selection of the site for the Opportunity MER (Mars Exploration Rover). The TES instrument was located on the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. THEMIS is onboard the Mars 2001 Odyssey spacecraft. Orbit Number: 89658 Latitude: 1.83323 Longitude: 0.267191 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-03-01 17:54 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25457

The Delta II rocket that will launch the Mars Odyssey spacecraft towards the Red Planet exhibits the mission logo (seen from the right). The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004
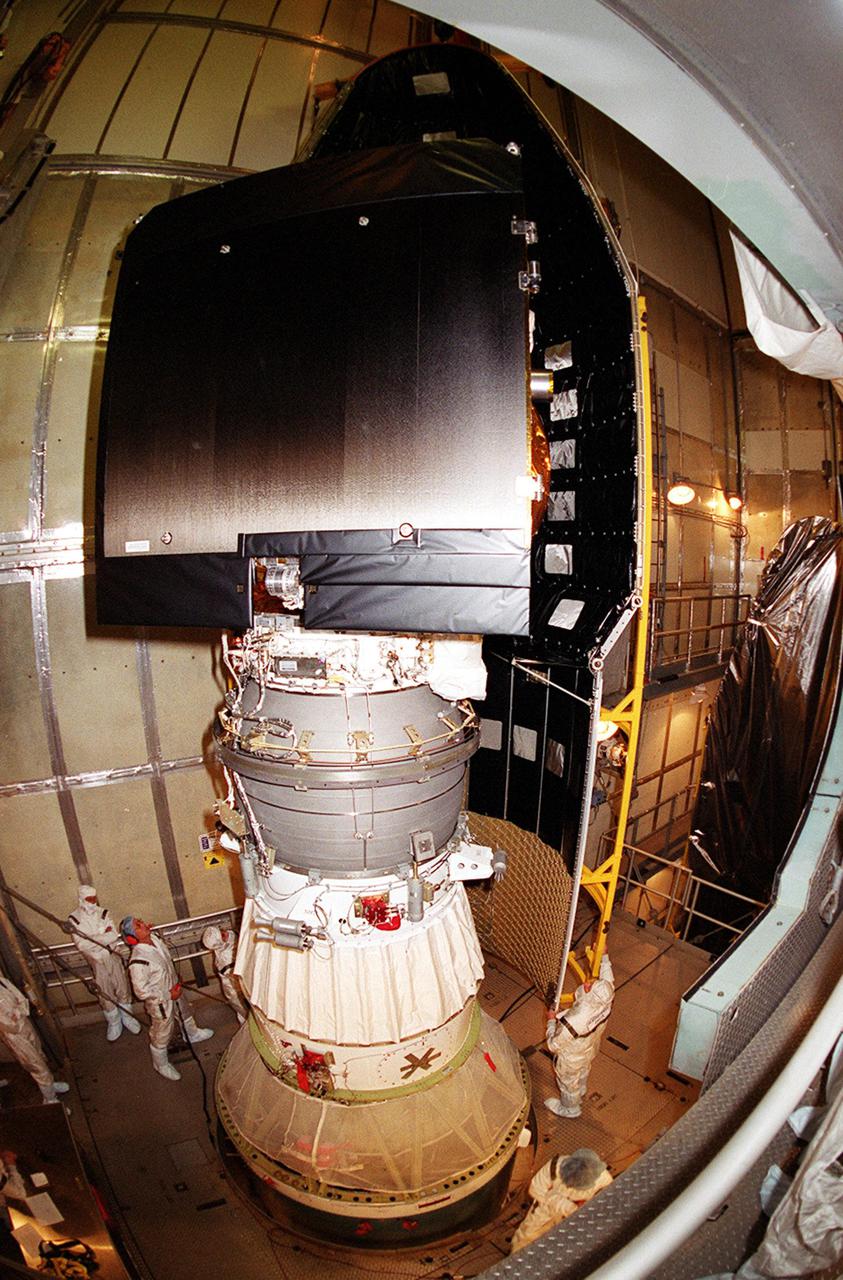
At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a piece of the Delta rocket fairing moves closer to the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, watch as a piece of the Delta rocket fairing is moved into place around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers move another piece of the Delta rocket fairing that will enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
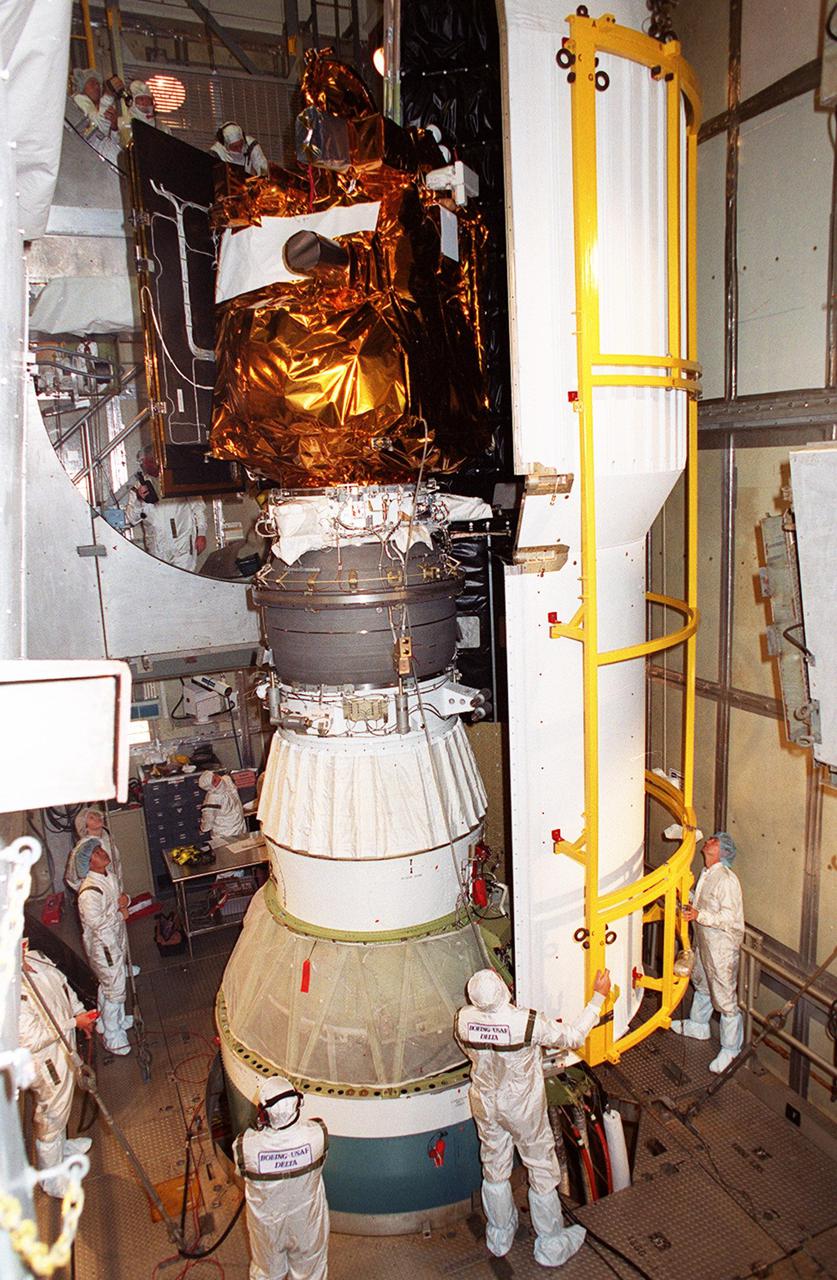

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carefully maneuver the Delta rocket fairing as it closes in on the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
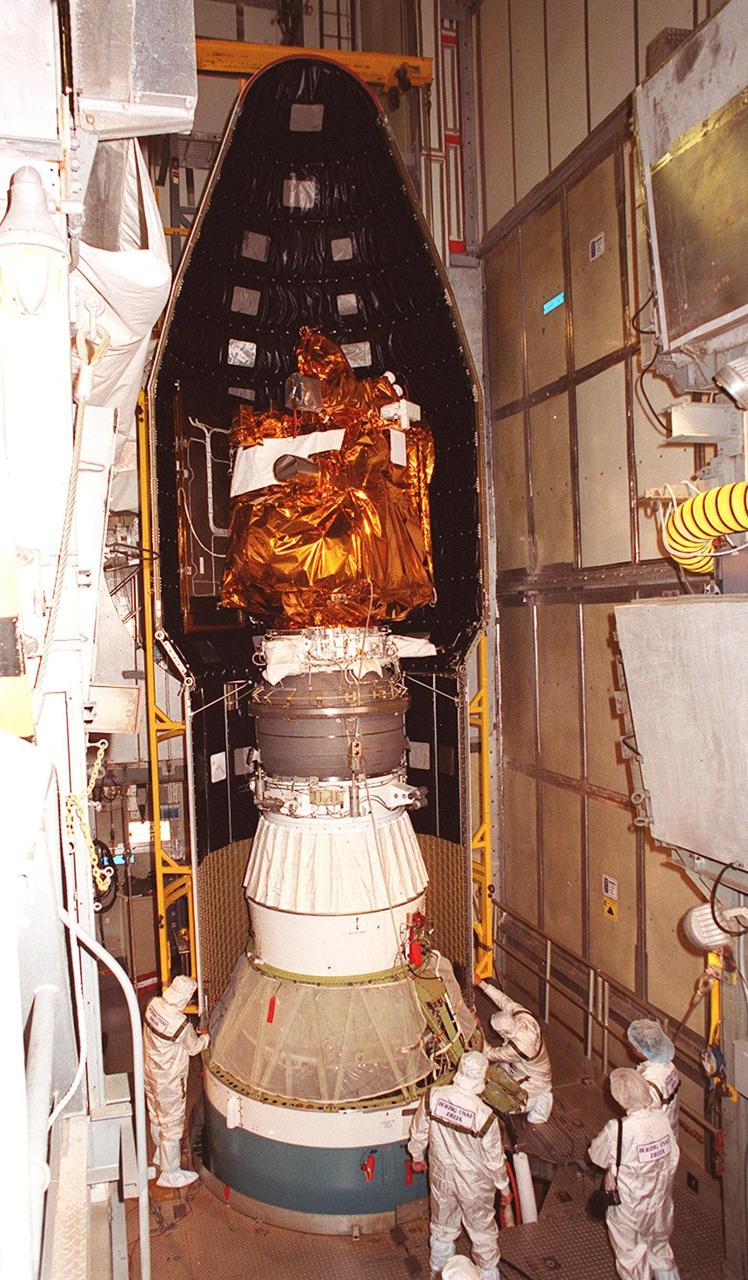

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers begin placing the Delta rocket fairing around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
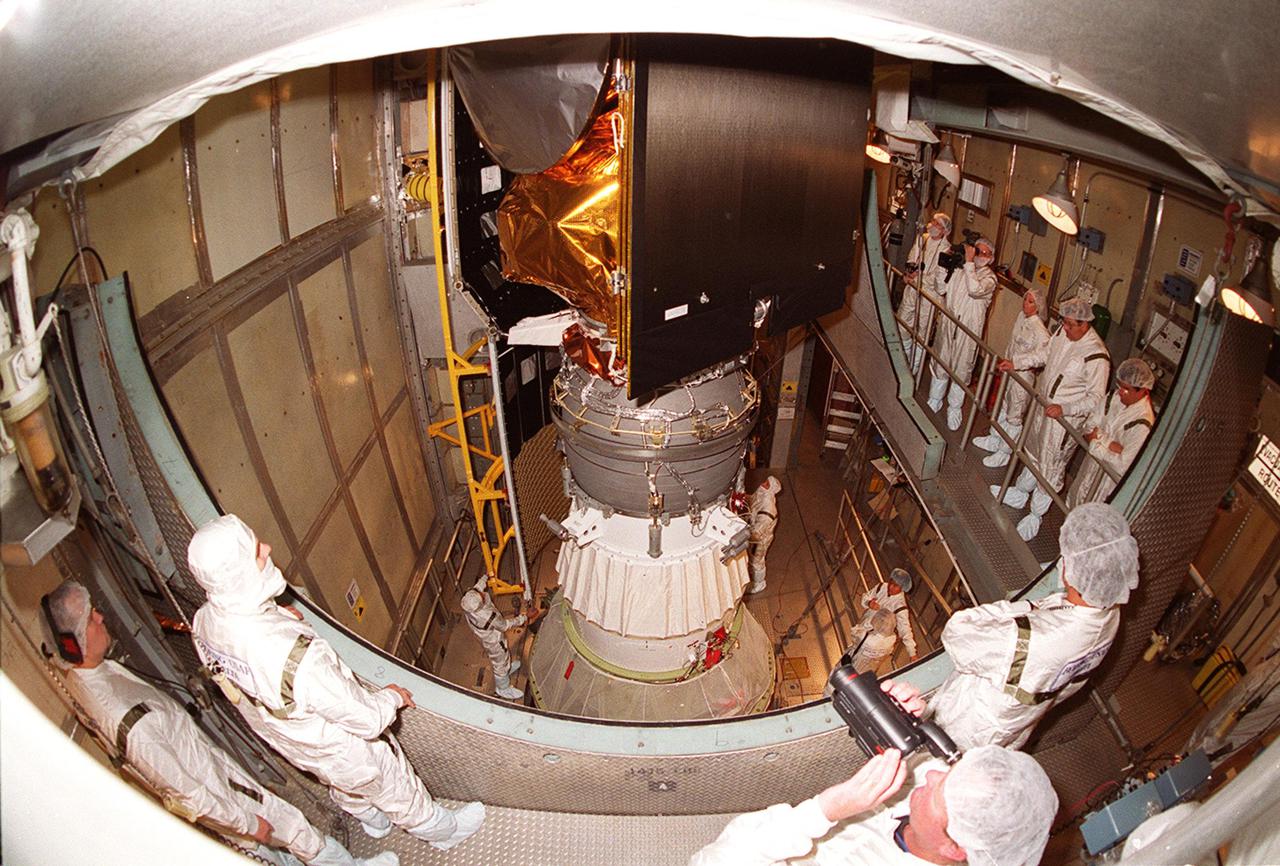

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, watch as a piece of the Delta rocket fairing is moved into place around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
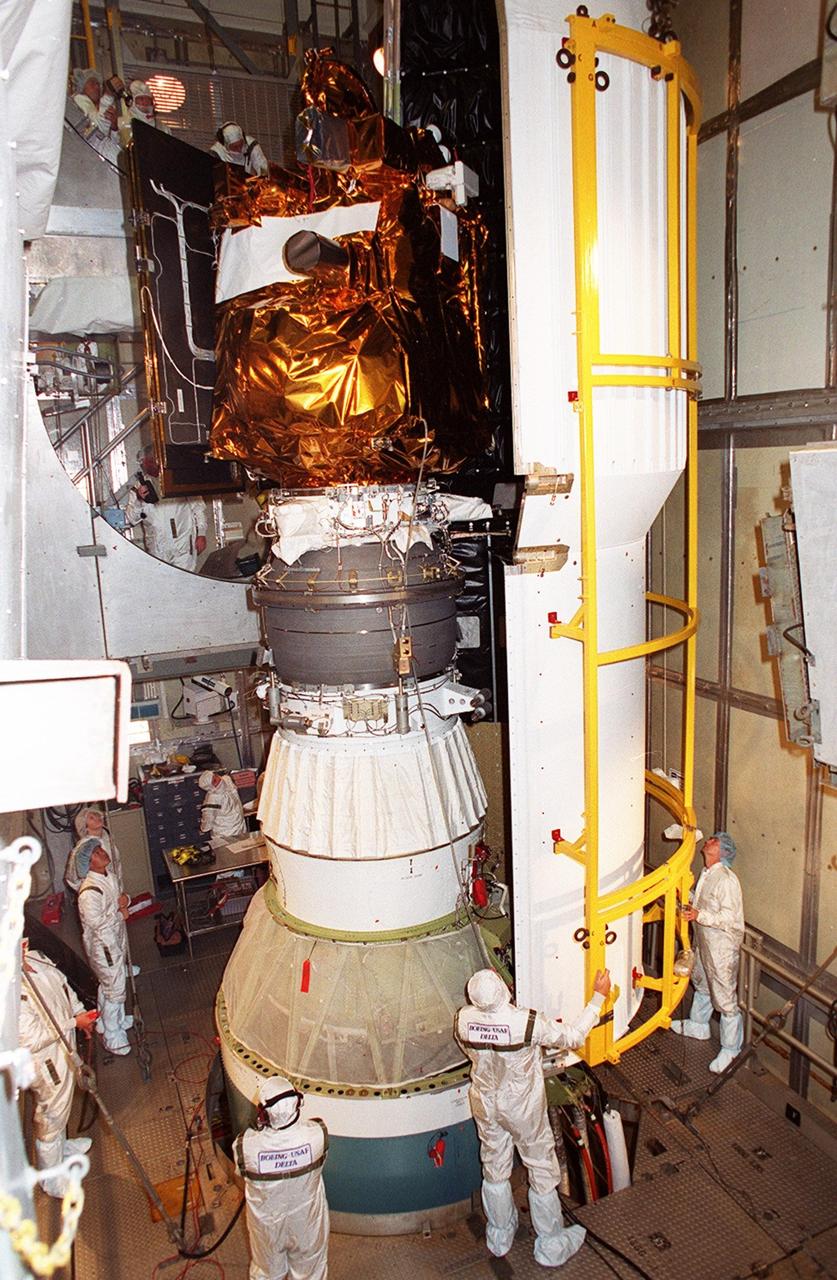

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carefully maneuver the Delta rocket fairing as it closes in on the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
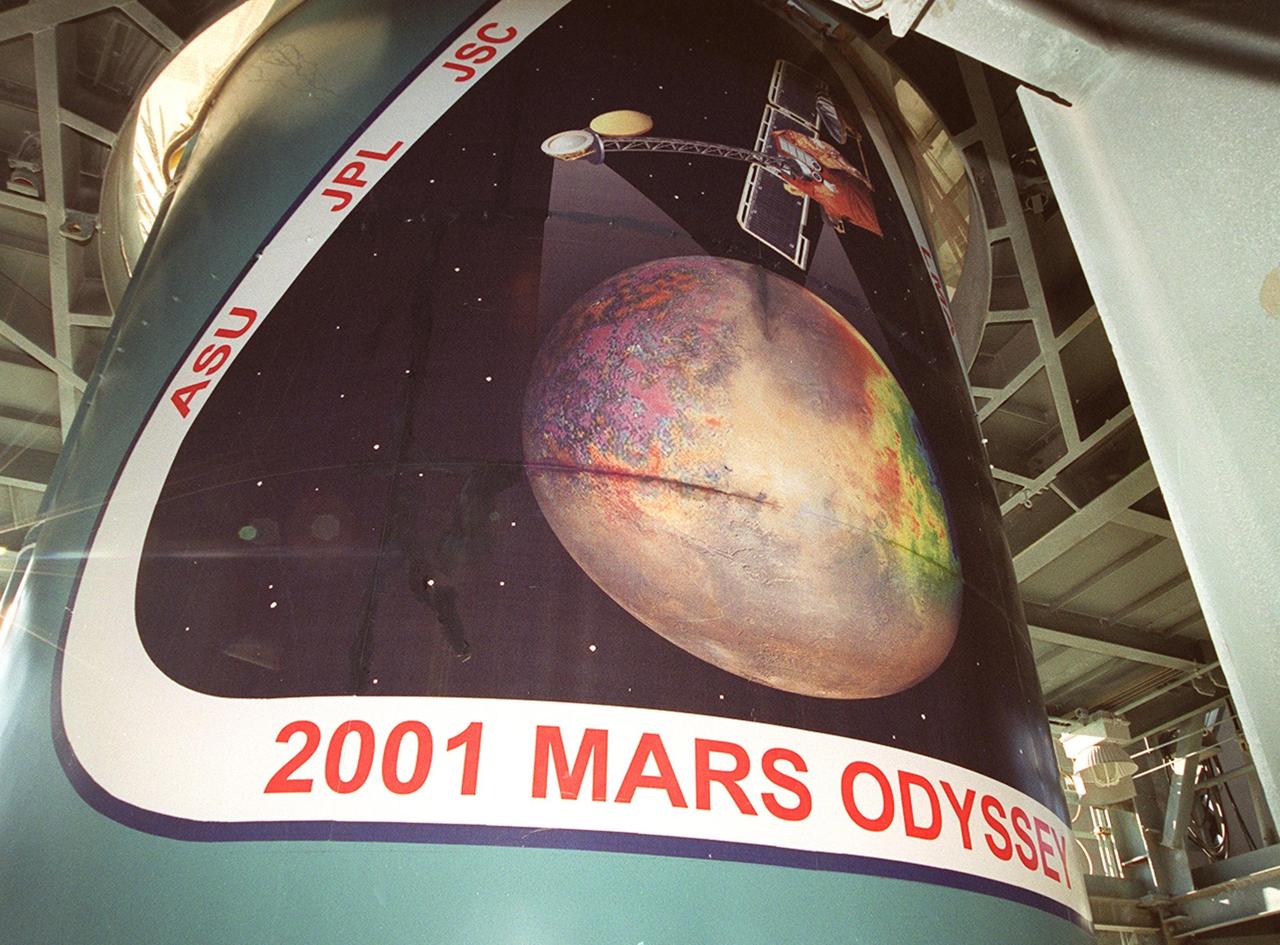

The Delta II rocket that will launch the Mars Odyssey spacecraft towards the Red Planet exhibits the mission logo (seen from the left). The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004
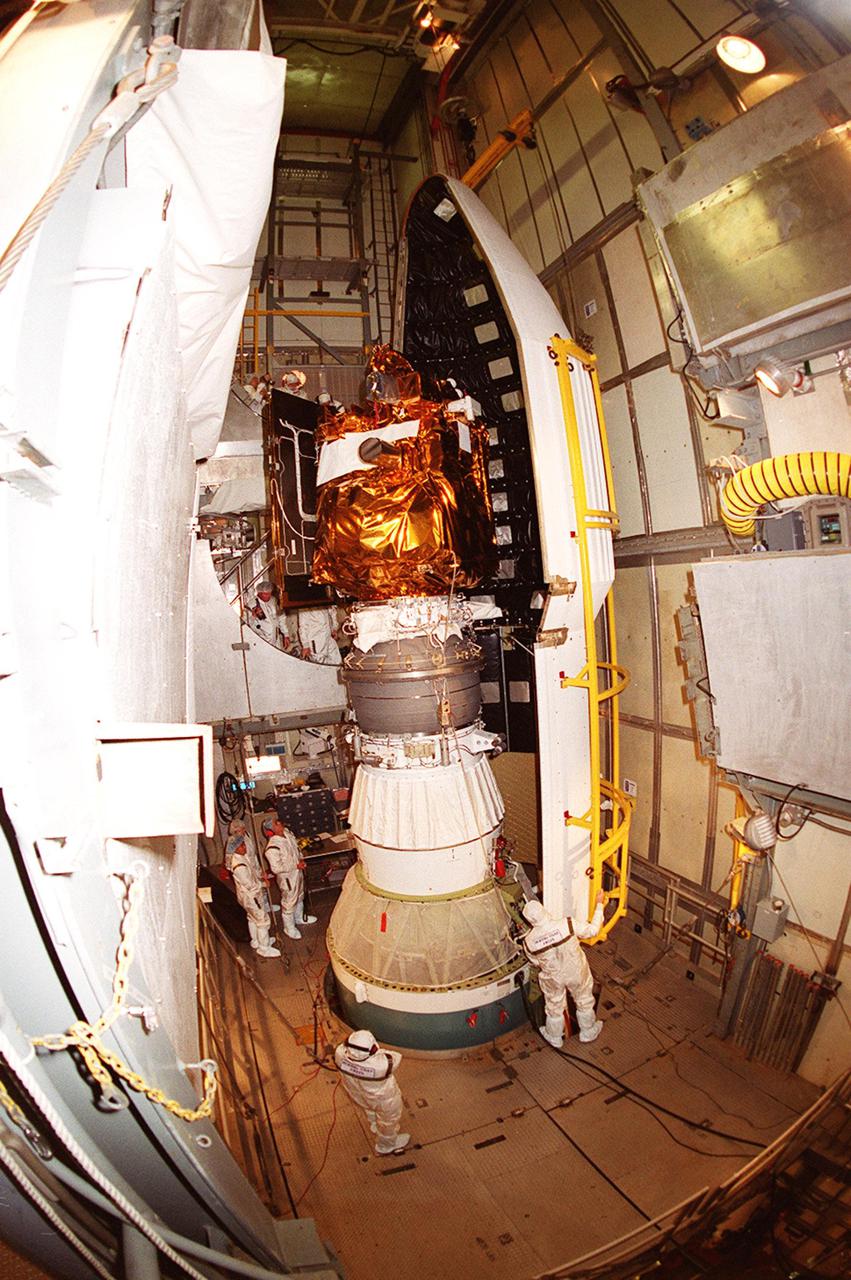
Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carefully maneuver the Delta rocket fairing as it closes in on the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
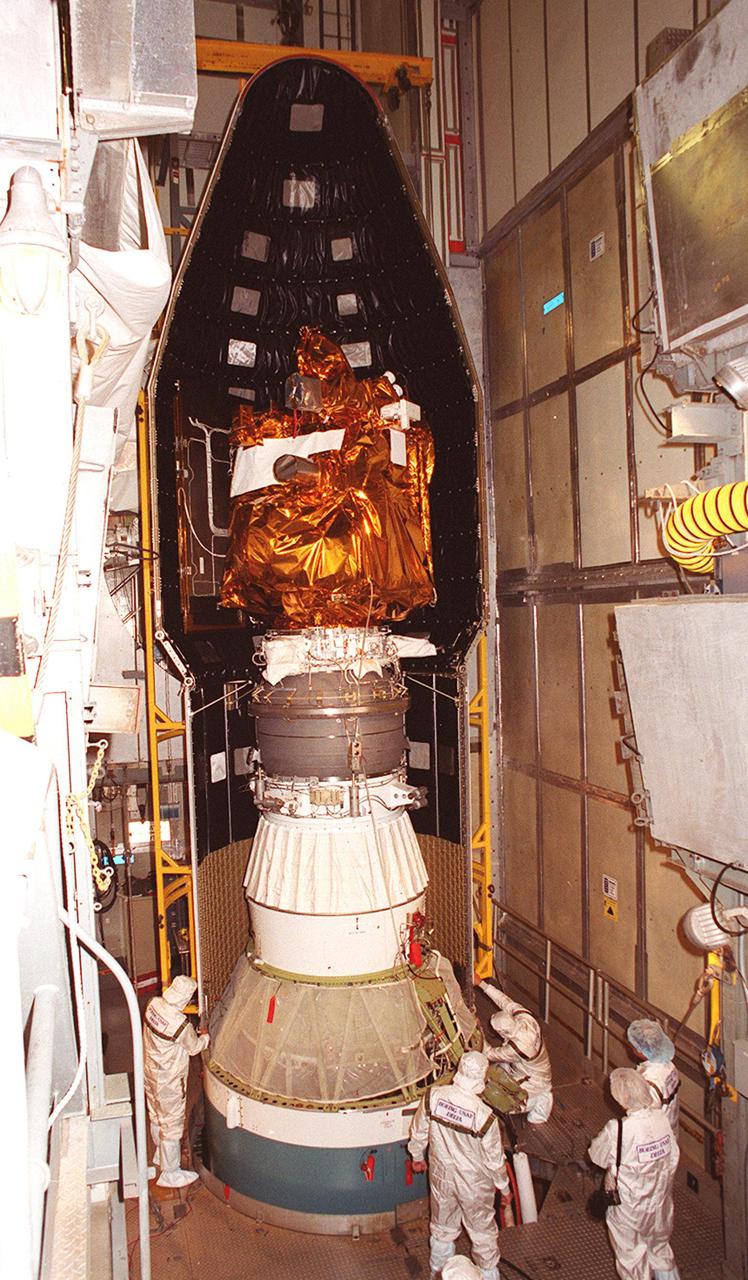

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers begin placing the Delta rocket fairing around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
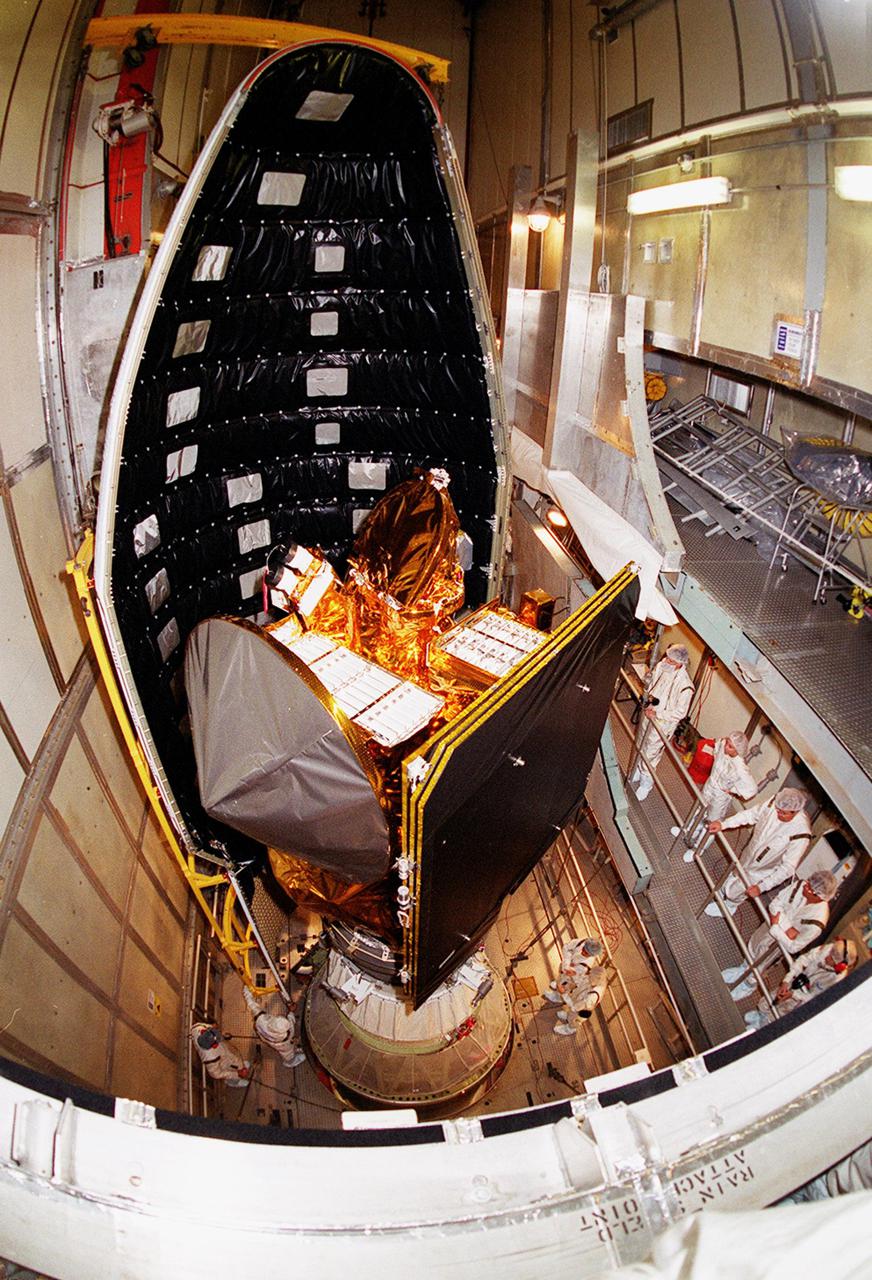

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers stand by as a piece of the Delta rocket fairing is moved into place around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
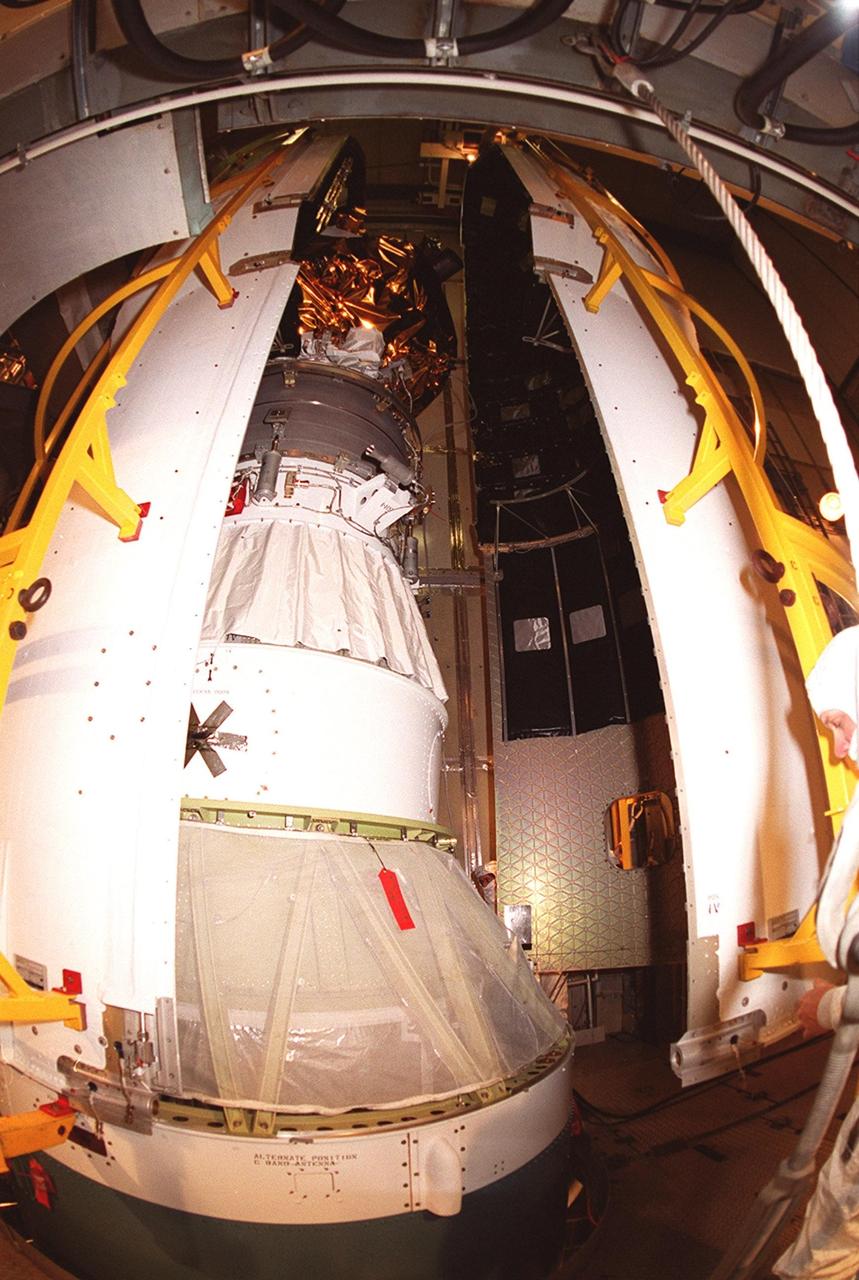

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the two parts of the Delta rocket fairing enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
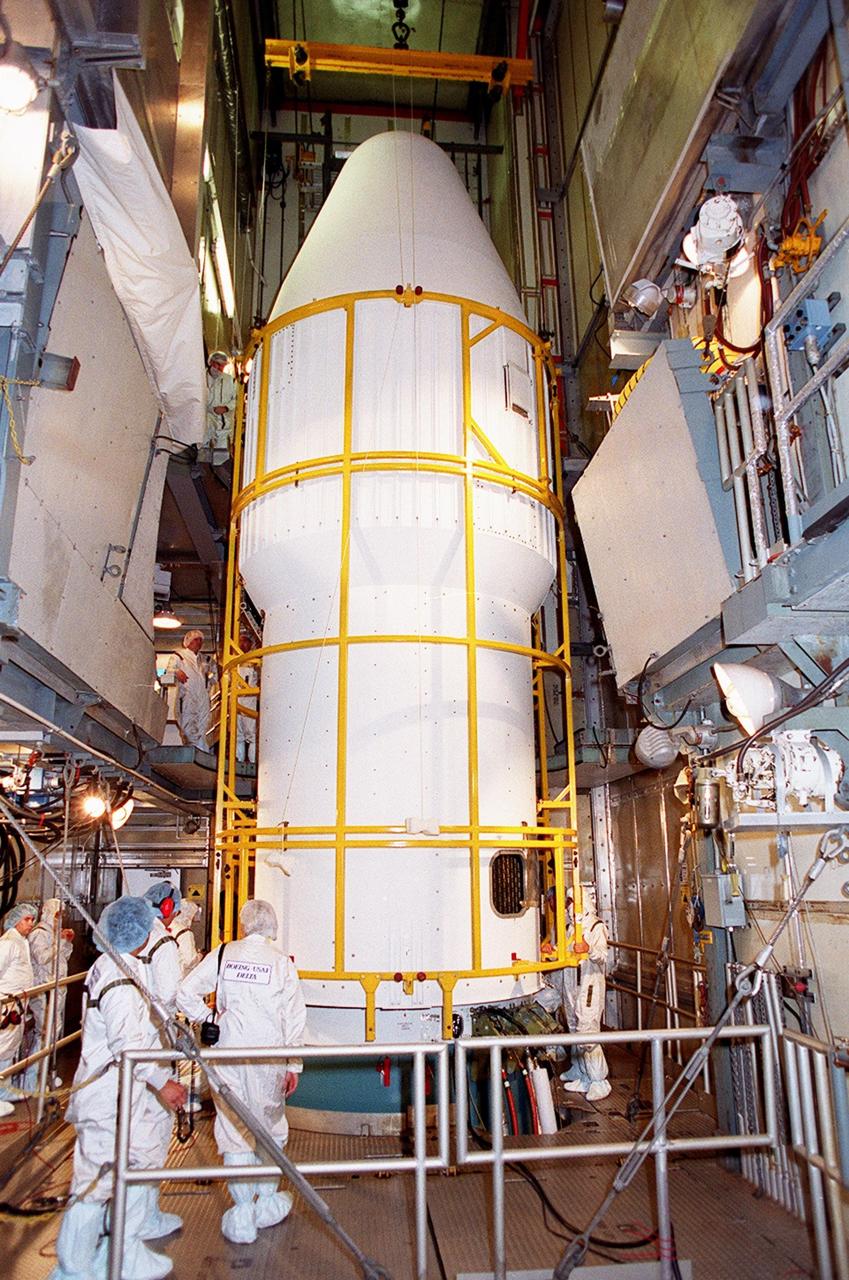

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check the fairing now enclosing the Mars Odyssey spacecraft inside. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004
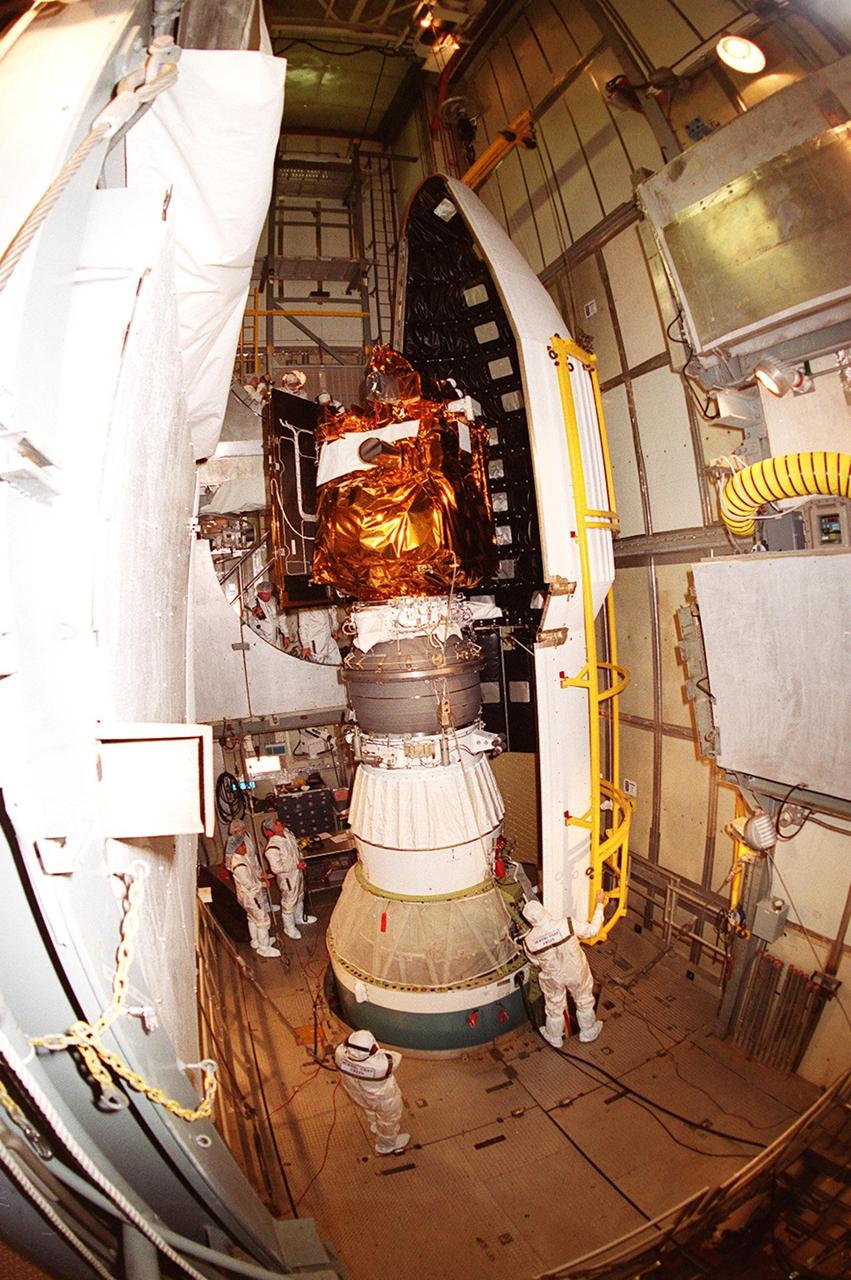

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carefully maneuver the Delta rocket fairing as it closes in on the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
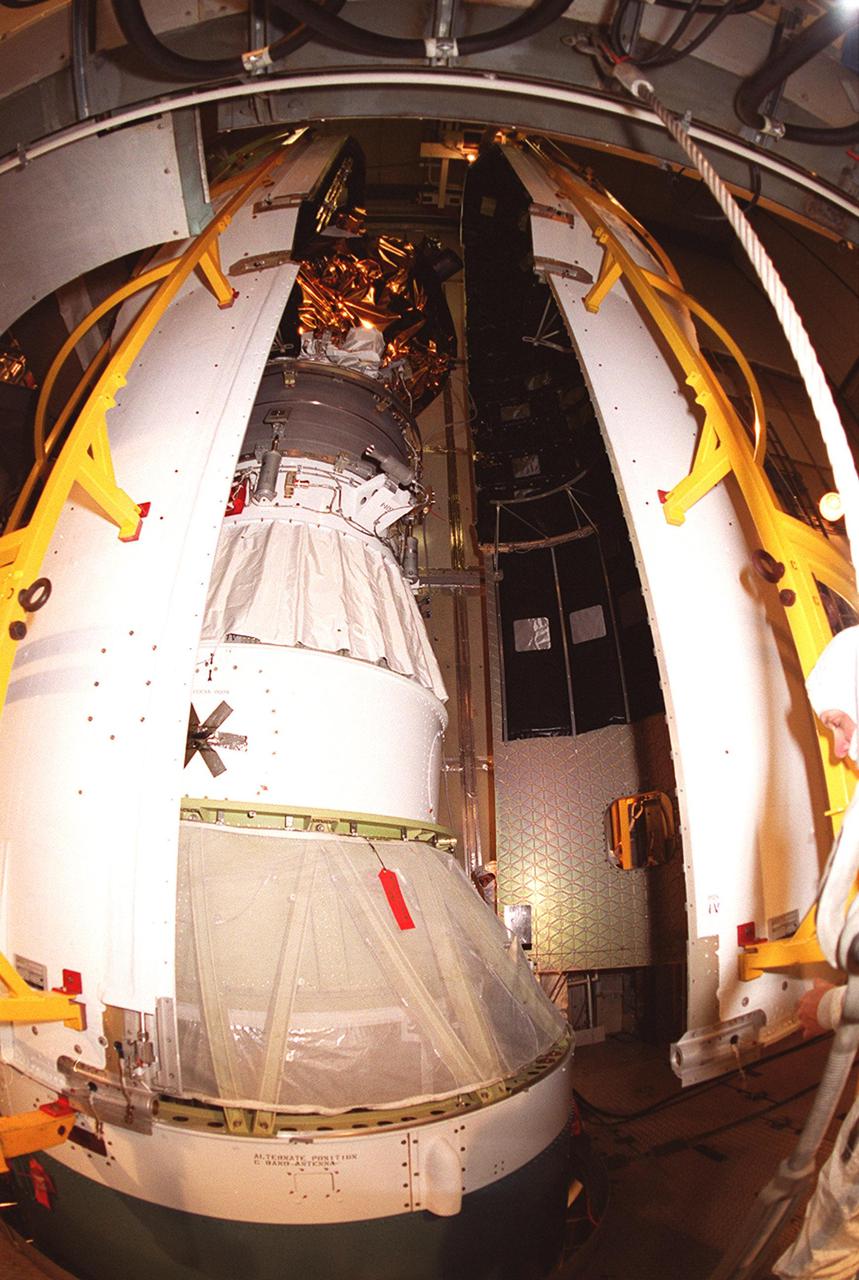

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the two parts of the Delta rocket fairing enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
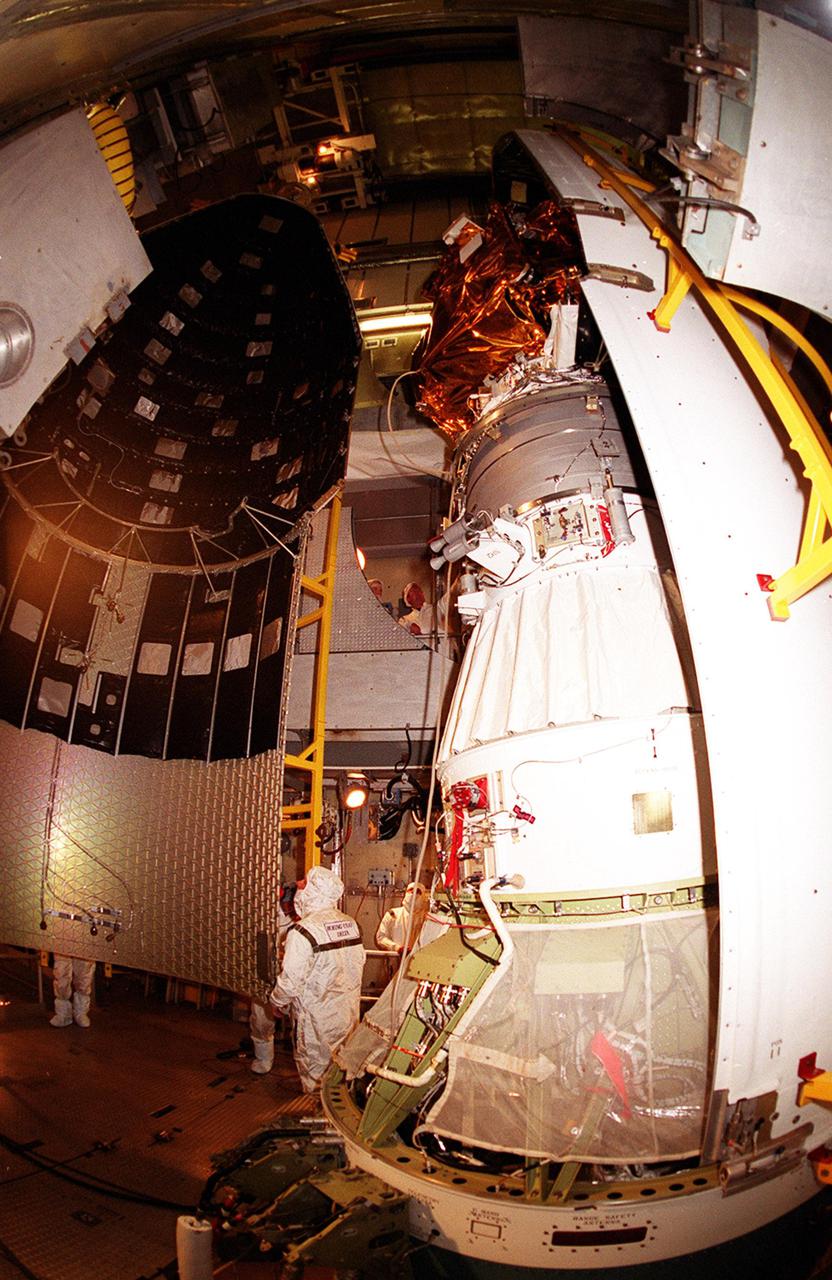

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers move another piece of the Delta rocket fairing that will enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
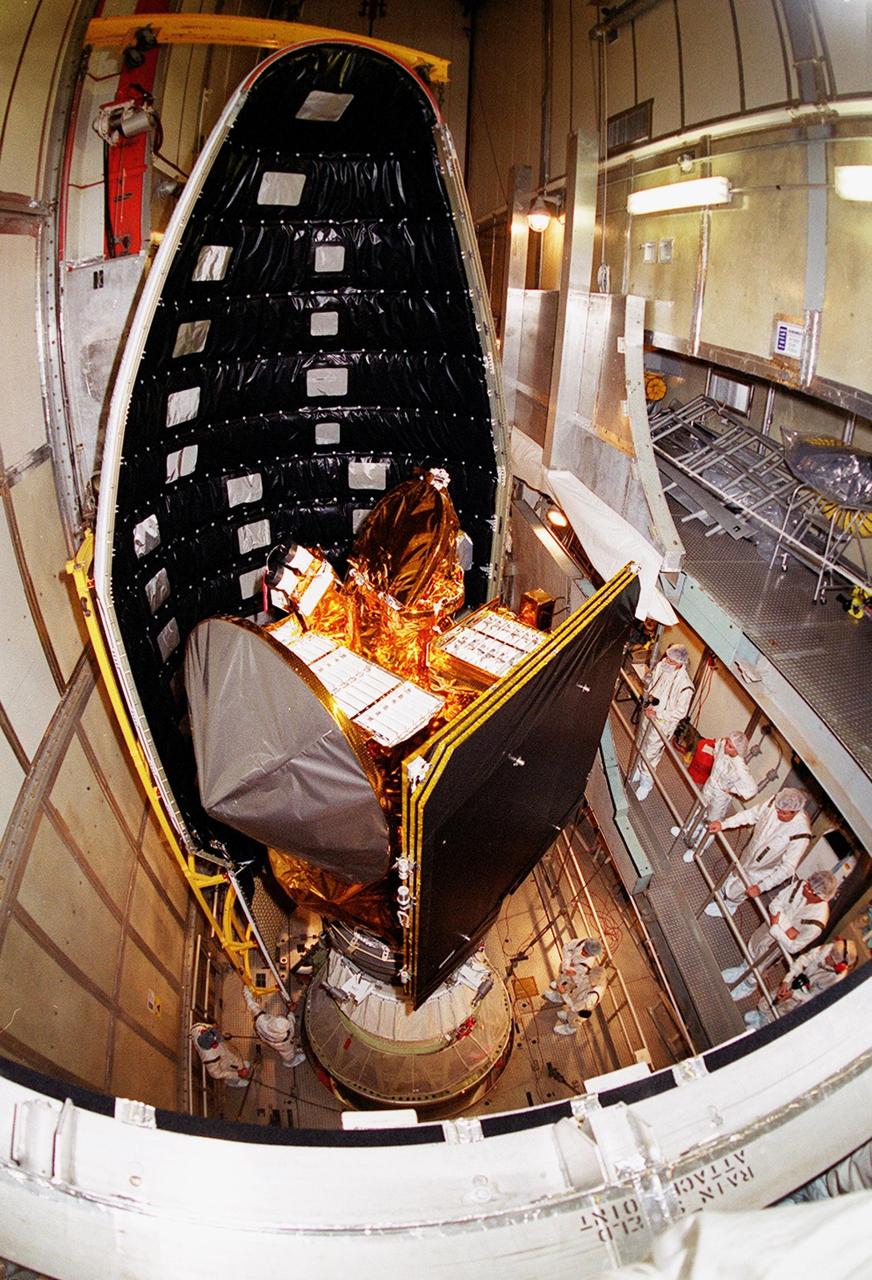

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers stand by as a piece of the Delta rocket fairing is moved into place around the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
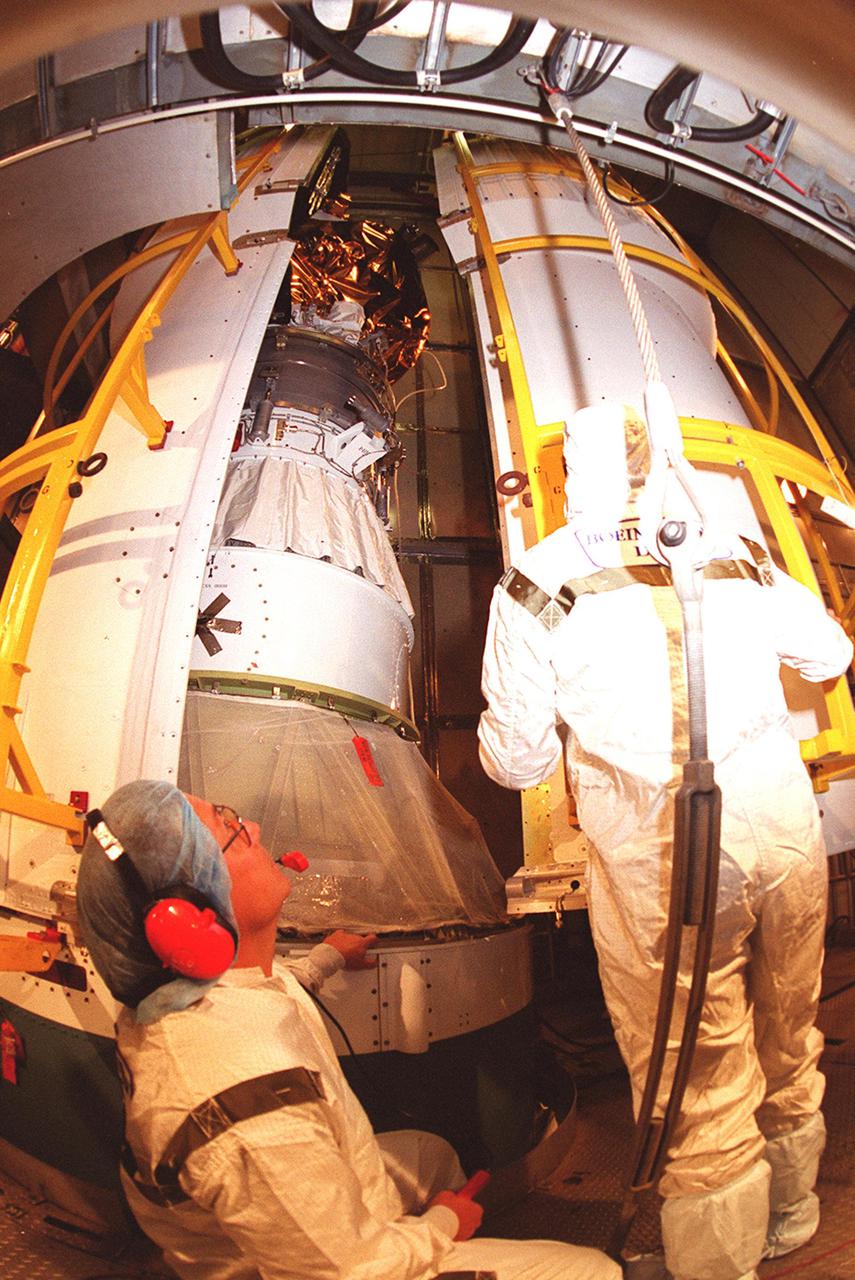

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, watch as the two parts of the Delta rocket fairing enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
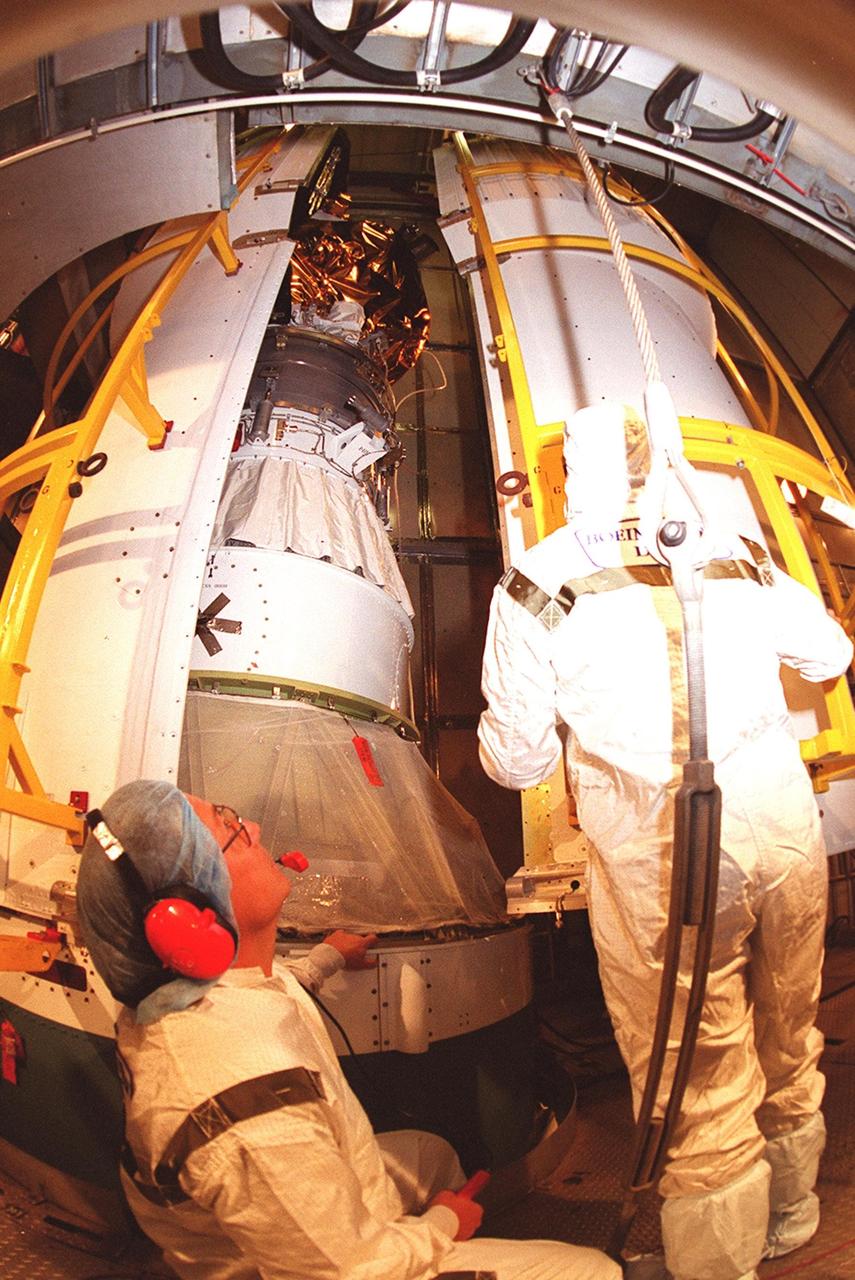

Workers at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, watch as the two parts of the Delta rocket fairing enclose the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST
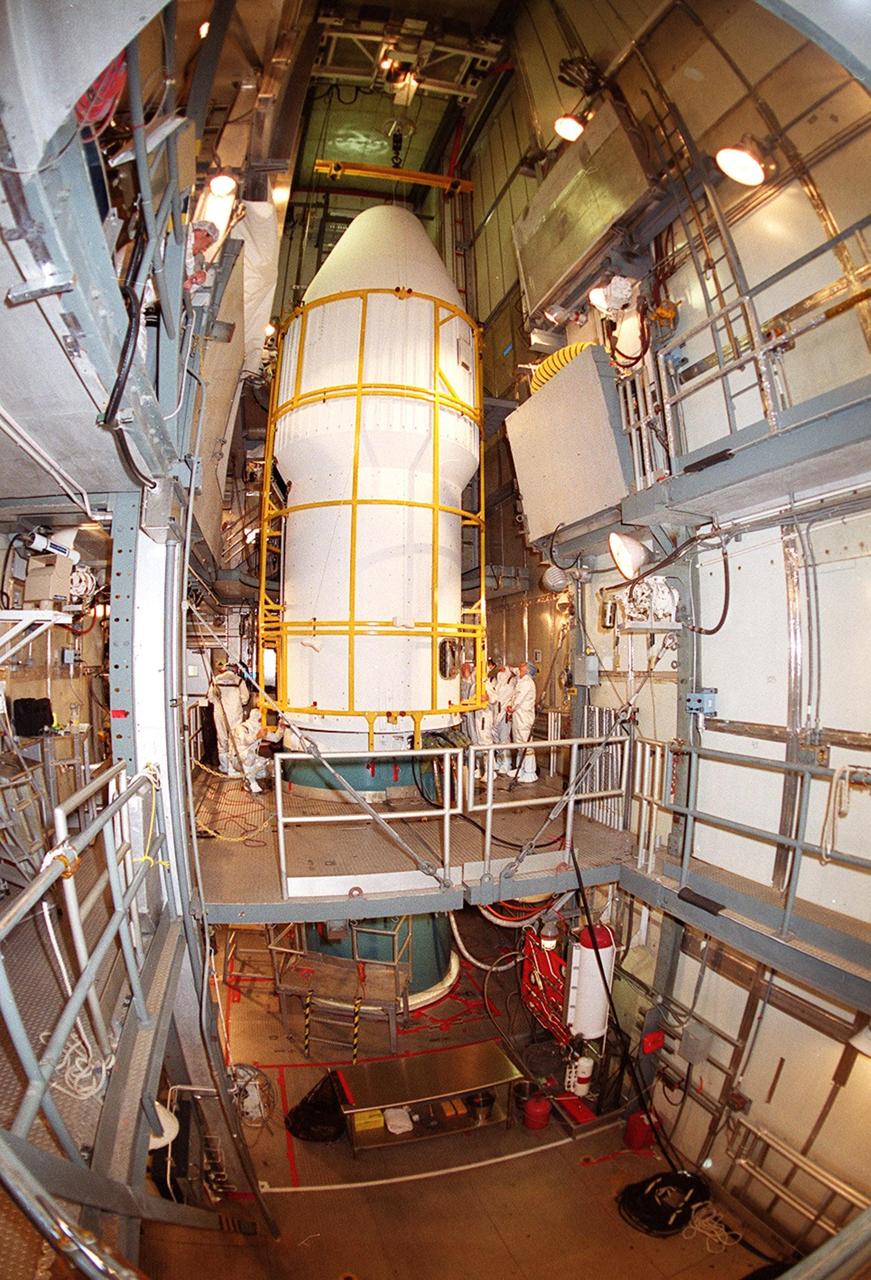

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the pristine white fairing comes together, enclosing the Mars Odyssey spacecraft inside. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003/2004
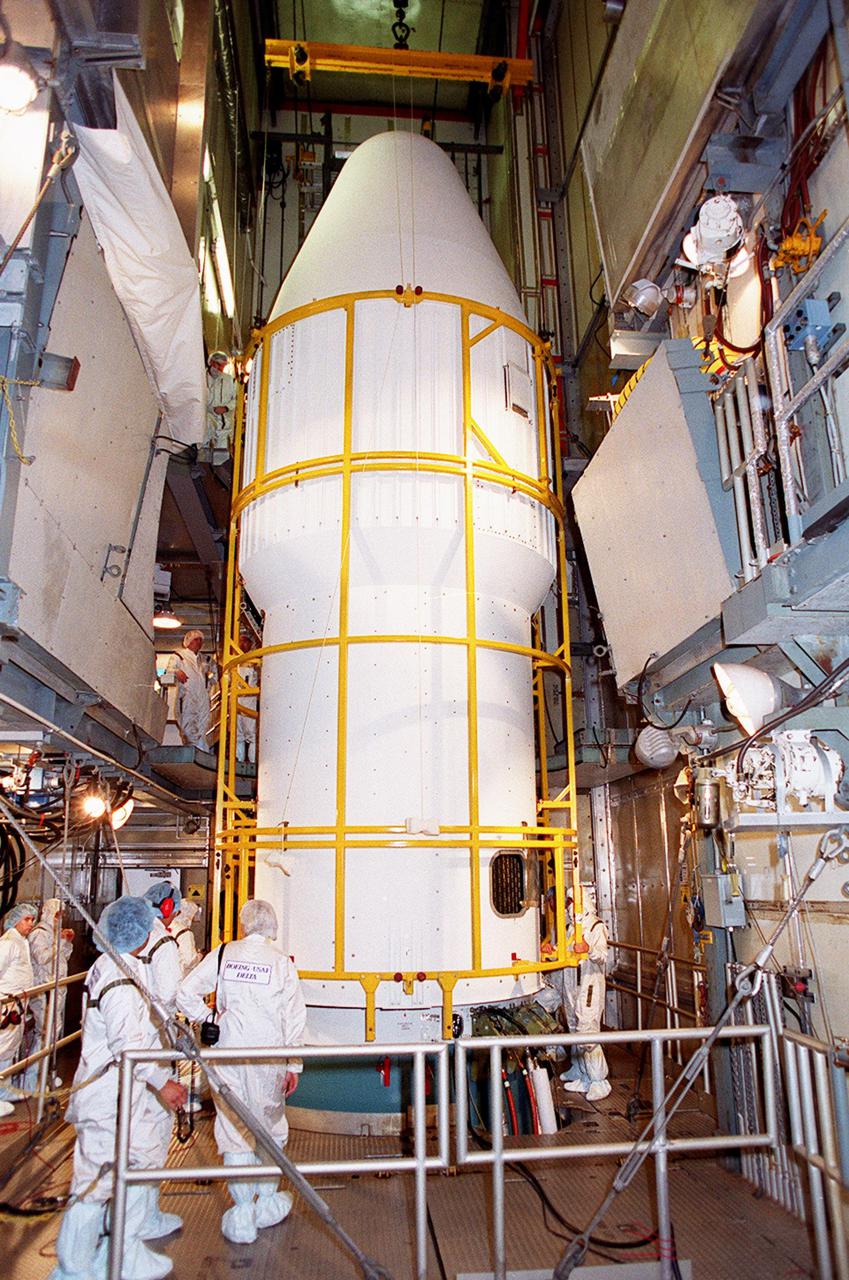

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check the fairing now enclosing the Mars Odyssey spacecraft inside. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004
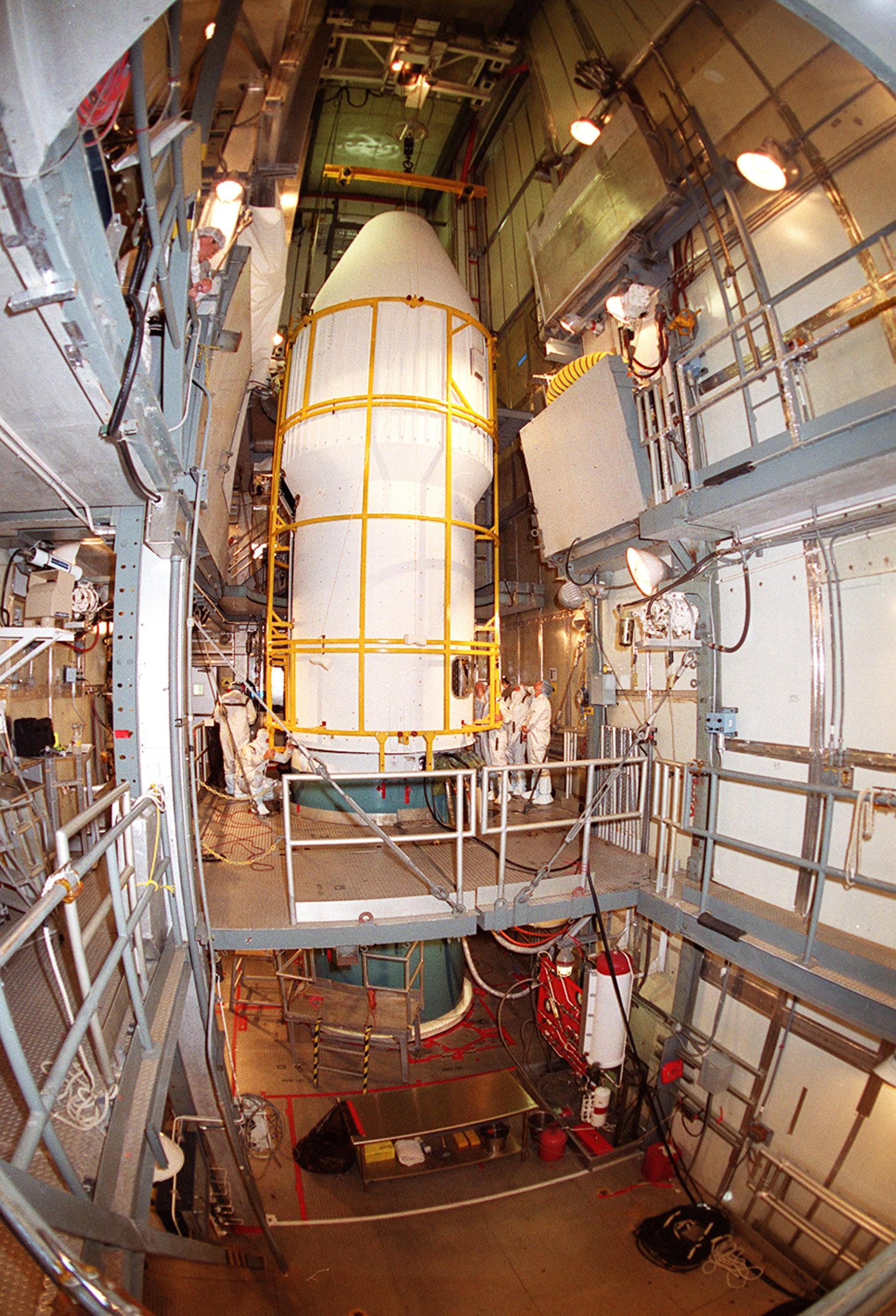

At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the pristine white fairing comes together, enclosing the Mars Odyssey spacecraft inside. The Mars Odyssey is scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket April 7, 2001, at 11:02 a.m. EST. NASA’s latest explorer carries three scientific instruments to map the chemical and mineralogical makeup of Mars: a thermal-emission imaging system, a gamma ray spectrometer and a Martian radiation environment experiment. The imaging system will map the planet with high-resolution thermal images and give scientists an increased level of detail to help them understand how the mineralogy of the planet relates to the land forms. In addition, Odyssey will serve as a communications relay for U.S. and international landers arriving at Mars in 2003_2004
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, the 2001 <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>is lifted from a platform by an overhead crane while workers help guide it. The Odyssey is being moved to a workstand in the SAEF-2. The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0098/KSC01pp0098~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, the 2001 <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a>is lifted from a platform by an overhead crane while workers help guide it. The Odyssey is being moved to a workstand in the SAEF-2. The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers check the movement of the <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a> as it is carried to the workstand at right. The circular object facing forward on the spacecraft is a high-gain antenna. On the right side is the rectangular solar array assembly. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0100/01pp0100~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers check the movement of the <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a> as it is carried to the workstand at right. The circular object facing forward on the spacecraft is a high-gain antenna. On the right side is the rectangular solar array assembly. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 help guide the solar array just removed from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter toward a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0122/KSC01pp0122~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2 help guide the solar array just removed from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter toward a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, the 2001 <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>is lifted from a platform by an overhead crane while workers help guide it. The Odyssey is being moved to a workstand in the SAEF-2. The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0098/01pp0098~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, the 2001 <a href='http:__mars.jpl.nasa.gov_2001_'>Mars Odyssey Orbiter <_a>is lifted from a platform by an overhead crane while workers help guide it. The Odyssey is being moved to a workstand in the SAEF-2. The spacecraft carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers attach an overhead crane to the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to move the component to a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0120/KSC01pp0120~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers attach an overhead crane to the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to move the component to a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 help guide the solar array just removed from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter toward a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0122/01pp0122~medium.jpg)
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2 help guide the solar array just removed from the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter toward a nearby workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers attach an overhead crane to the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to move the component to a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0120/01pp0120~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2, workers attach an overhead crane to the solar array on the 2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter to move the component to a workstand. This will give workers access to other components of the spacecraft and allow inspection of the array. The Mars Odyssey carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
![In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers check the movement of the <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a> as it is carried to the workstand at right. The circular object facing forward on the spacecraft is a high-gain antenna. On the right side is the rectangular solar array assembly. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01pp0100/KSC01pp0100~medium.jpg)
In the Spacecraft Assembly & Encapsulation Facility -2, workers check the movement of the <a href="http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/2001/">2001 Mars Odyssey Orbiter </a> as it is carried to the workstand at right. The circular object facing forward on the spacecraft is a high-gain antenna. On the right side is the rectangular solar array assembly. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter carries three science instruments: the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS), and the Mars Radiation Environment Experiment (MARIE). THEMIS will map the mineralogy and morphology of the Martian surface using a high-resolution camera and a thermal infrared imaging spectrometer. The GRS will achieve global mapping of the elemental composition of the surface and determine the abundance of hydrogen in the shallow subsurface. [The GRS is a rebuild of the instrument lost with the Mars Observer mission.] The MARIE will characterize aspects of the near-space radiation environment as related to the radiation-related risk to human explorers. The Mars Odyssey Orbiter is scheduled for launch on April 7, 2001, aboard a Delta 7925 rocket from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
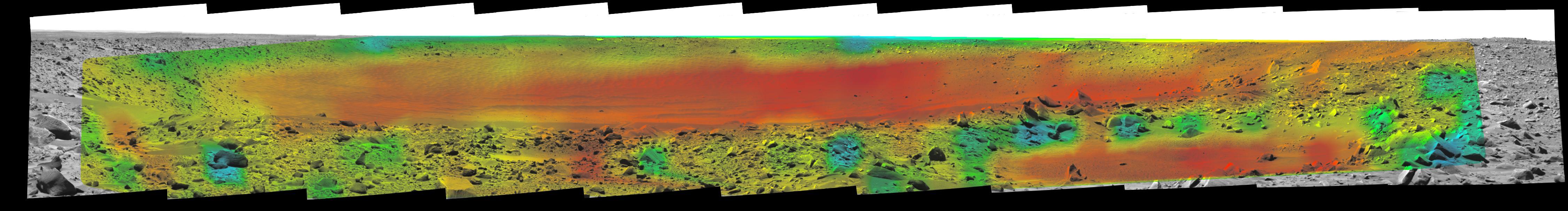
Rates of change in surface temperatures during a martian day indicate differences in particle size in and near "Bonneville Crater." This image is the third in a series of five with color-coded temperature information from different times of day. This one is from 1:35 p.m. local solar time at the site where NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit is exploring Mars. Temperature information from Spirit's miniature thermal emission spectrometer is overlaid onto a view of the site from Spirit's panoramic camera. In this color-coded map, quicker reddening during the day suggests sand or dust. (Red is about 270 Kelvin or 27 degrees Fahrenheit.) An example of this is in the shallow depression in the right foreground. Areas that stay blue longer into the day have larger rocks. (Blue indicates about 230 Kelvin or minus 45 Degrees F.) An example is the rock in the left foreground. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05930
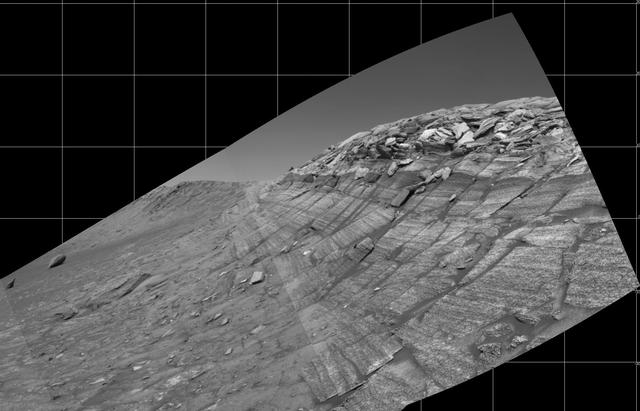

NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity captured this view from the base of "Burns Cliff" during the rover's 280th martian day (Nov. 6, 2004). This cliff in the inner wall of "Endurance Crater" displays multiple layers of bedrock for the rover to examine with its panoramic camera and miniature thermal emission spectrometer. The rover team has decided that the farthest Opportunity can safely advance along the base of the cliff is close to the squarish white rock near the center of this image. After examining the site for a few days from that position, the the rover will turn around and head out of the crater. The view is a mosaic of frames taken by Opportunity's navigation camera. The rover was on ground with a slope of about 30 degrees when the pictures were taken, and the view is presented here in a way that corrects for that tilt of the camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07039
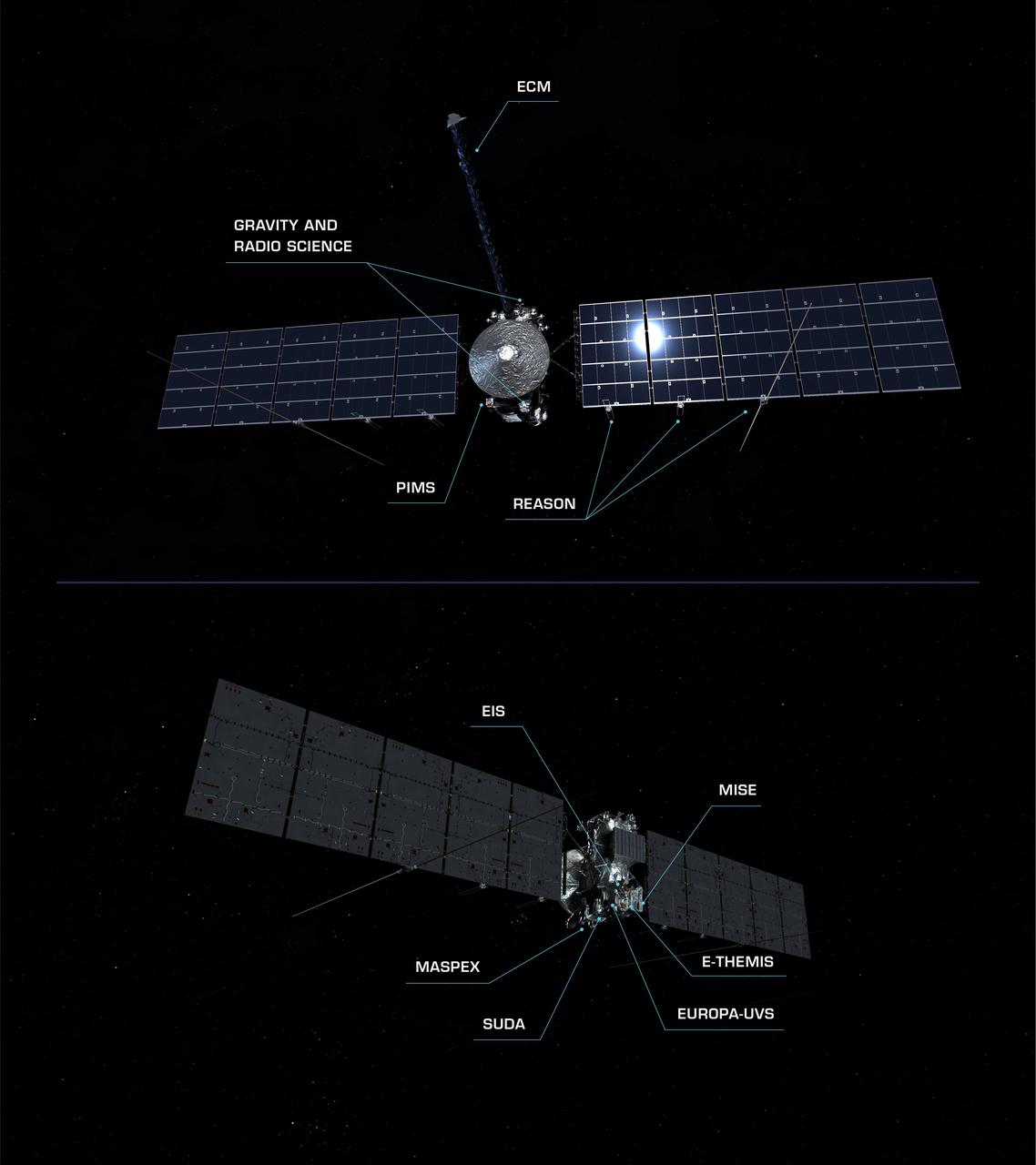
To conduct its detailed investigations of Jupiter's icy moon Europa, NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft carries a suite of nine science instruments and a gravity experiment that uses its telecommunications system. These components are depicted in this pair of artist's concepts showing each side of the spacecraft, and include: Europa Imaging System (EIS) Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS) Europa Ultraviolet Spectrograph (Europa-UVS) Mapping Imaging Spectrometer for Europa (MISE) Europa Clipper Magnetometer (ECM) Plasma Instrument for Magnetic Sounding (PIMS) Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface (REASON) MAss Spectrometer for Planetary EXploration/Europa (MASPEX) Surface Dust Analyzer (SUDA) Gravity and Radio Science Experiment (G/RS) Europa Clipper's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26439

Heron Island is located in Queensland, Australia, approximately 45 miles (72 kilometers) off the Australian mainland, to the northeast of Gladstone. Part of Australia's Great Barrier Reef, the island is an evergreen coral cay surrounded by Wistari coral reef. Although just 42 acres in size, the island is home to a large resort and the University of Queensland's Heron Island Research Station. The island is famous for diving and snorkeling and is a World Heritage-Listed Marine National Park. It is one of two locations on the Great Barrier Reef that are serving as bases for in-water validation activities for NASA's Coral Reef Airborne Laboratory (CORAL) mission, which is studying the condition and function of the Great Barrier Reef and selected reef systems worldwide using NASA's airborne Portable Remote Imaging Spectrometer (PRISM) instrument from an altitude of 28,000 feet (8,500 meters). The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft acquired this image of Heron Island and its surroundings on December 22, 2001. The island appears at the left of the reef (Heron Reef) in the center of the image. Vegetation is red on the image. The image covers an area of 10.3 by 18.6 miles (16.5 by 30.0 kilometers), and is located at 23.5 degrees south, 151.9 degrees east. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20900

This image shows one of two shoebox-size satellites that make up NASA's Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment (PREFIRE) mission. PREFIRE will measure the amount of heat Earth emits into space from two of the coldest, most remote regions on the planet. Data from the cube satellites, or CubeSats, will improve computer models researchers use to predict how Earth's ice, seas, and weather will change in a warming world. Earth absorbs a lot of the Sun's energy at the tropics, and weather and ocean currents transport that heat to the poles. Ice, snow, clouds, and other parts of the polar environment emit the heat into space, much of it in the form of far-infrared radiation. The difference between this incoming and outgoing heat helps to determines the planet's temperature and drives a dynamic system of climate and weather. But far-infrared emissions at the poles have never been systematically measured. This is where PREFIRE comes in. The crucial instrument on each spacecraft is a thermal infrared spectrometer, which will measure wavelengths of light in the far-infrared range. The mission will help researchers gain a clearer understanding of when and where Earth's poles emit far-infrared radiation, as well as how atmospheric water vapor and clouds influence the amount that escapes to space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26186