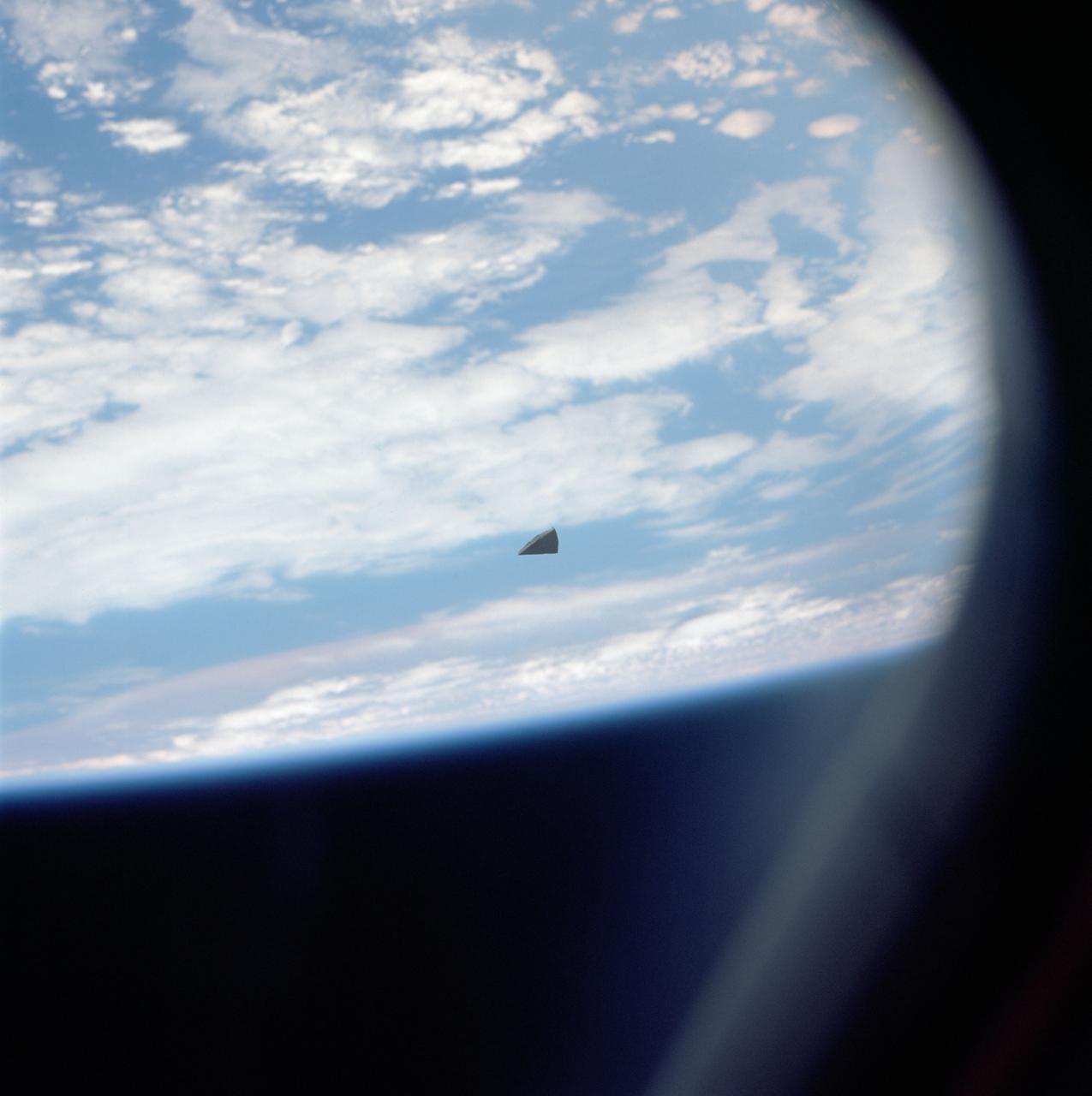

A small piece of thermal insulation tile floats in space near the Shuttle Columbia. The cloudy surface of the earth is used as a background.
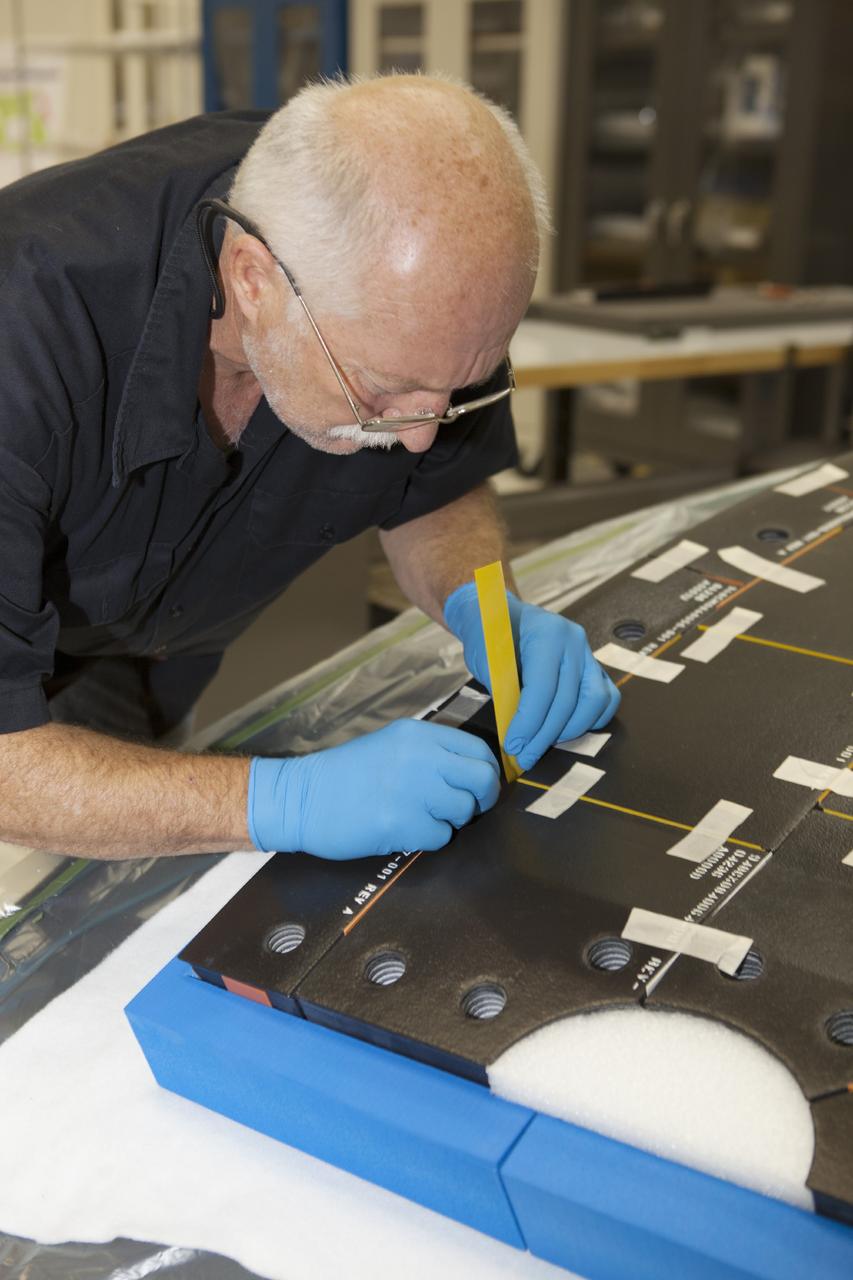

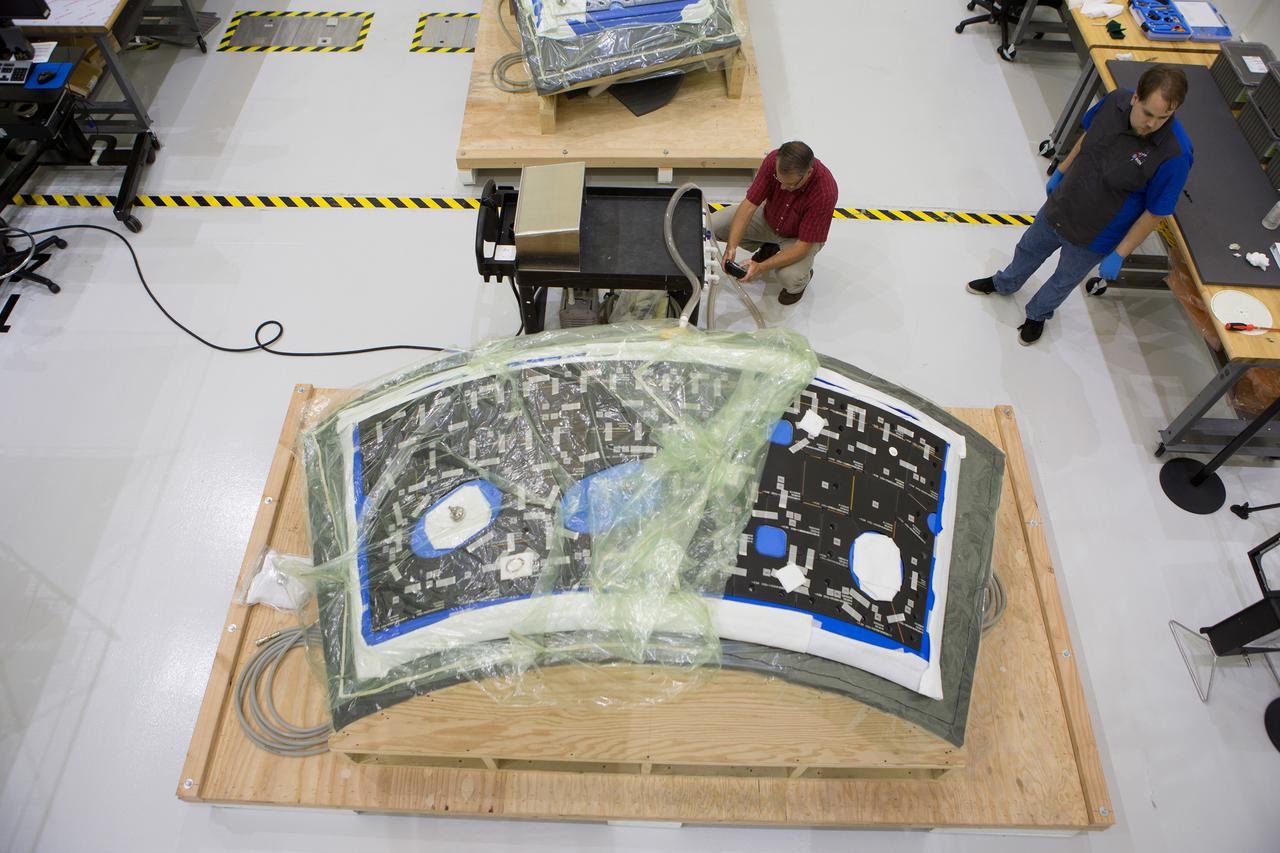
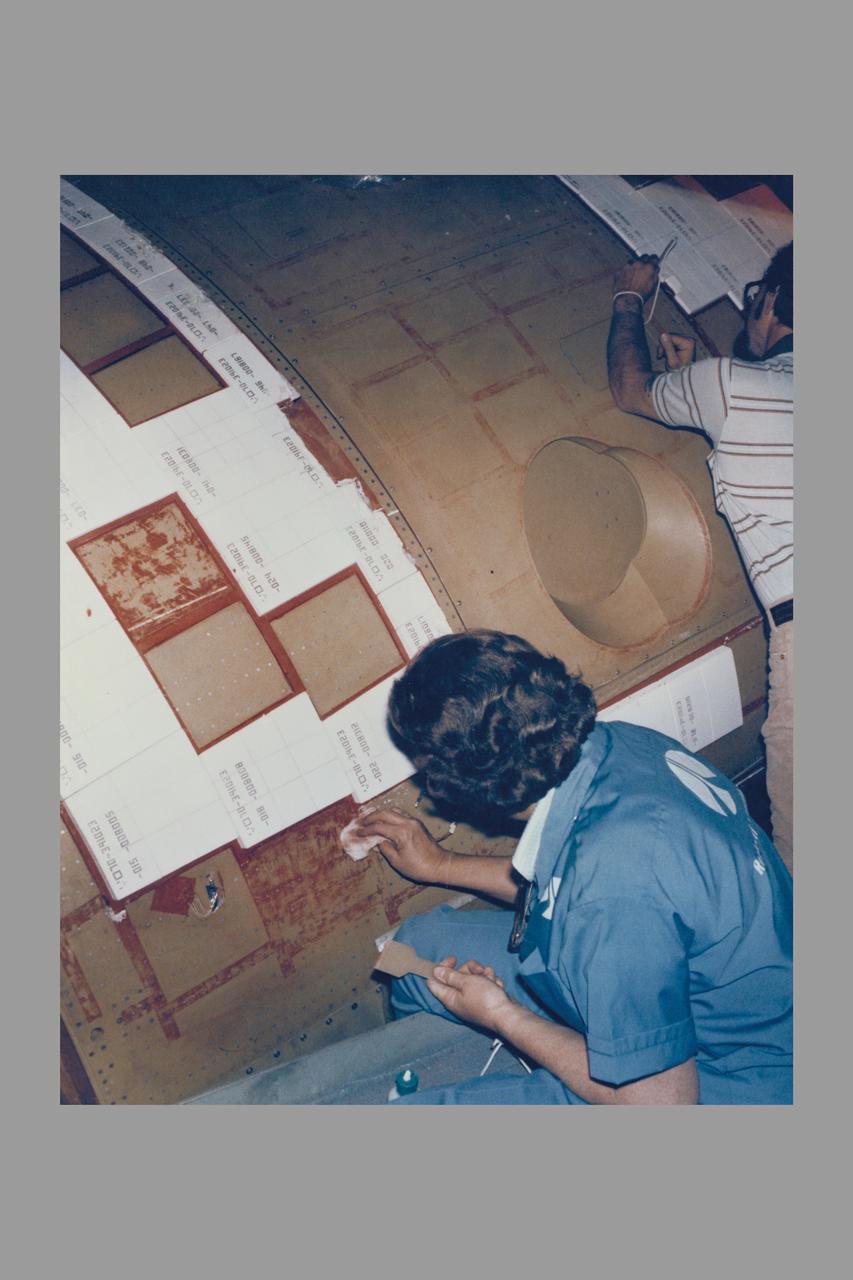
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a tile technician places spacers between the thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
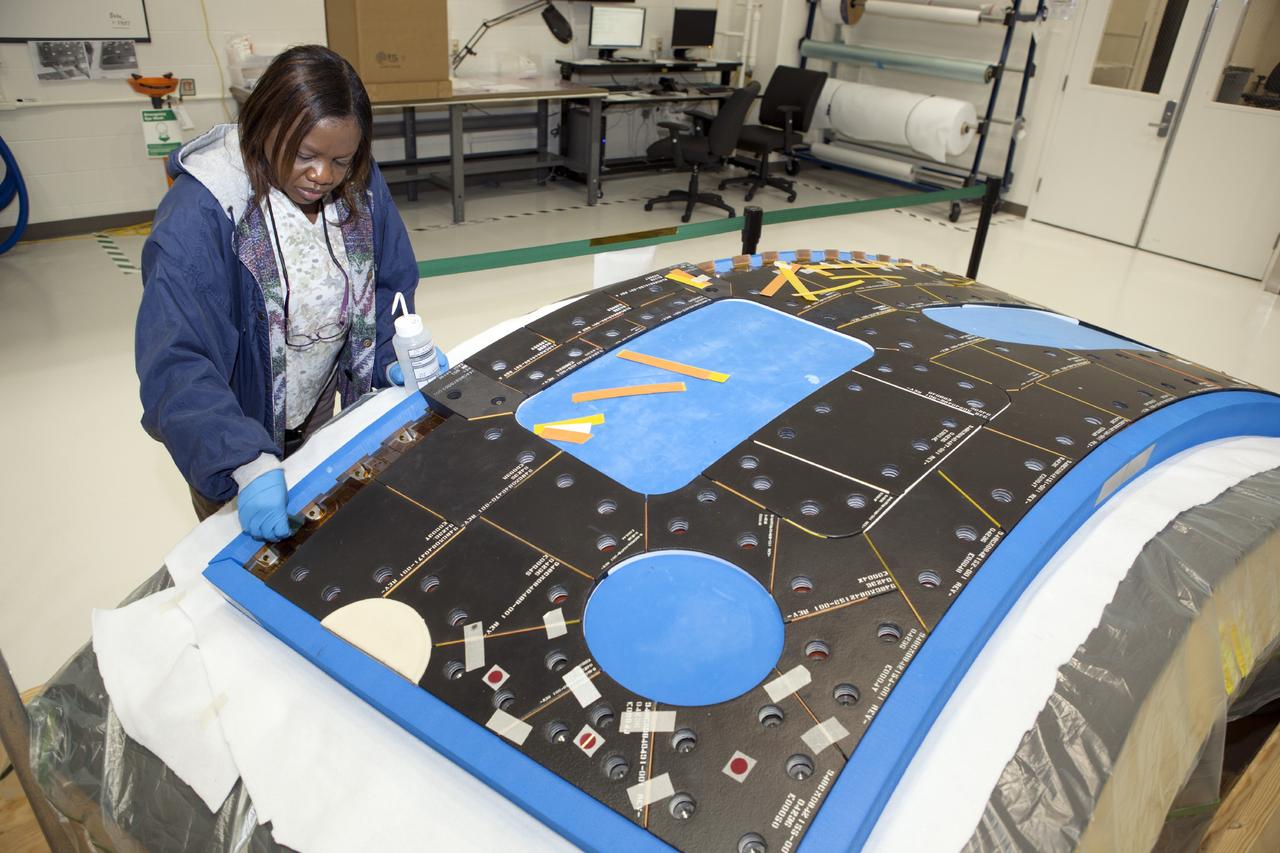

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a tile technician works on a section of thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
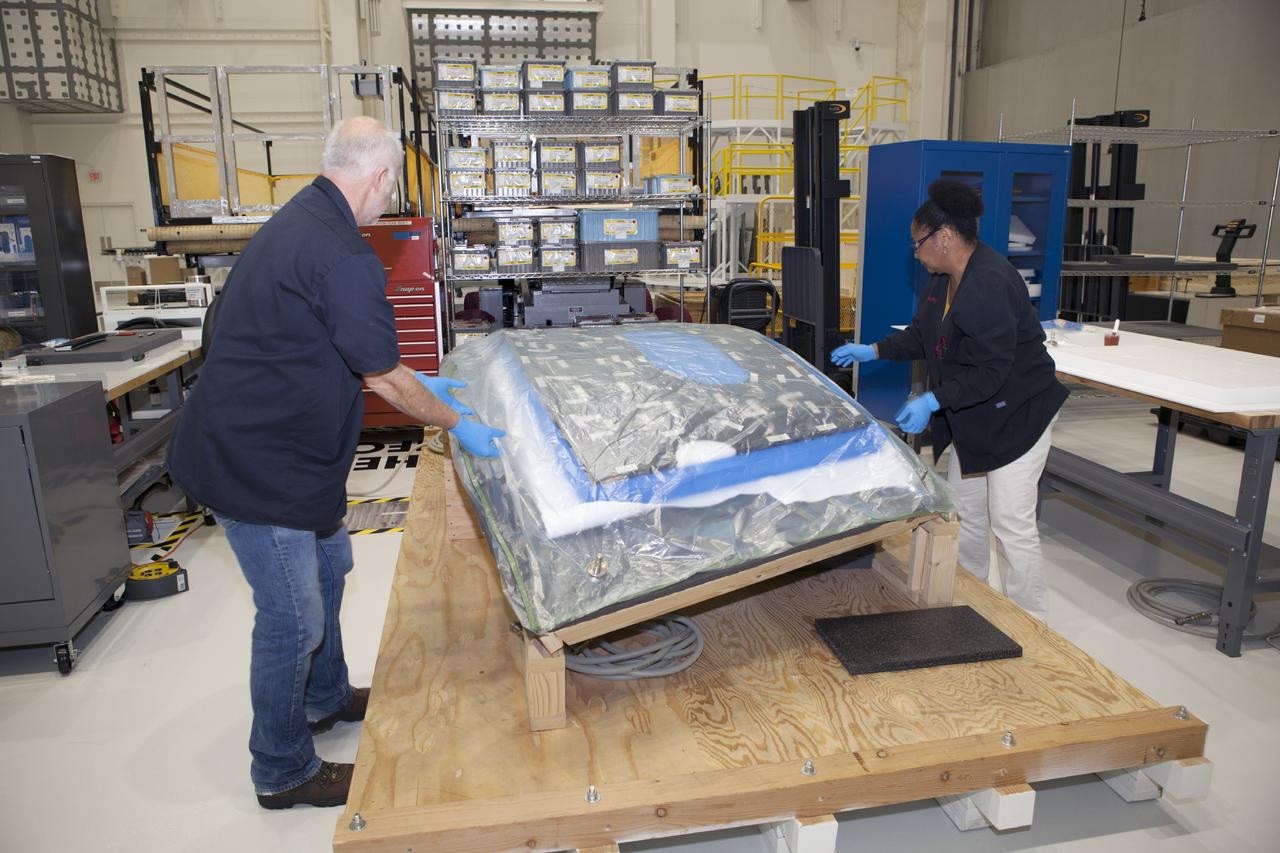

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, two tile technicians wrap a section of the thermal protection system tiles that will be installed on the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
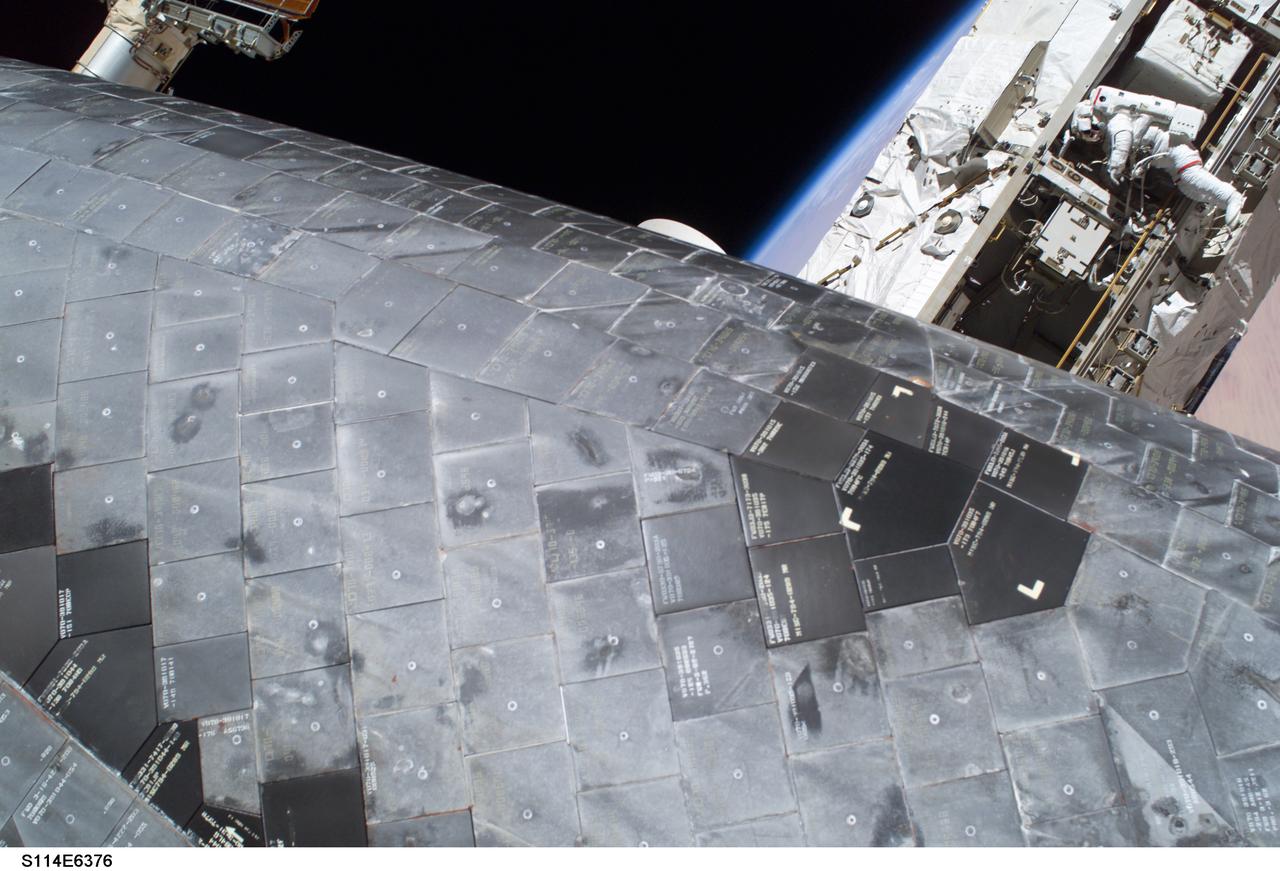

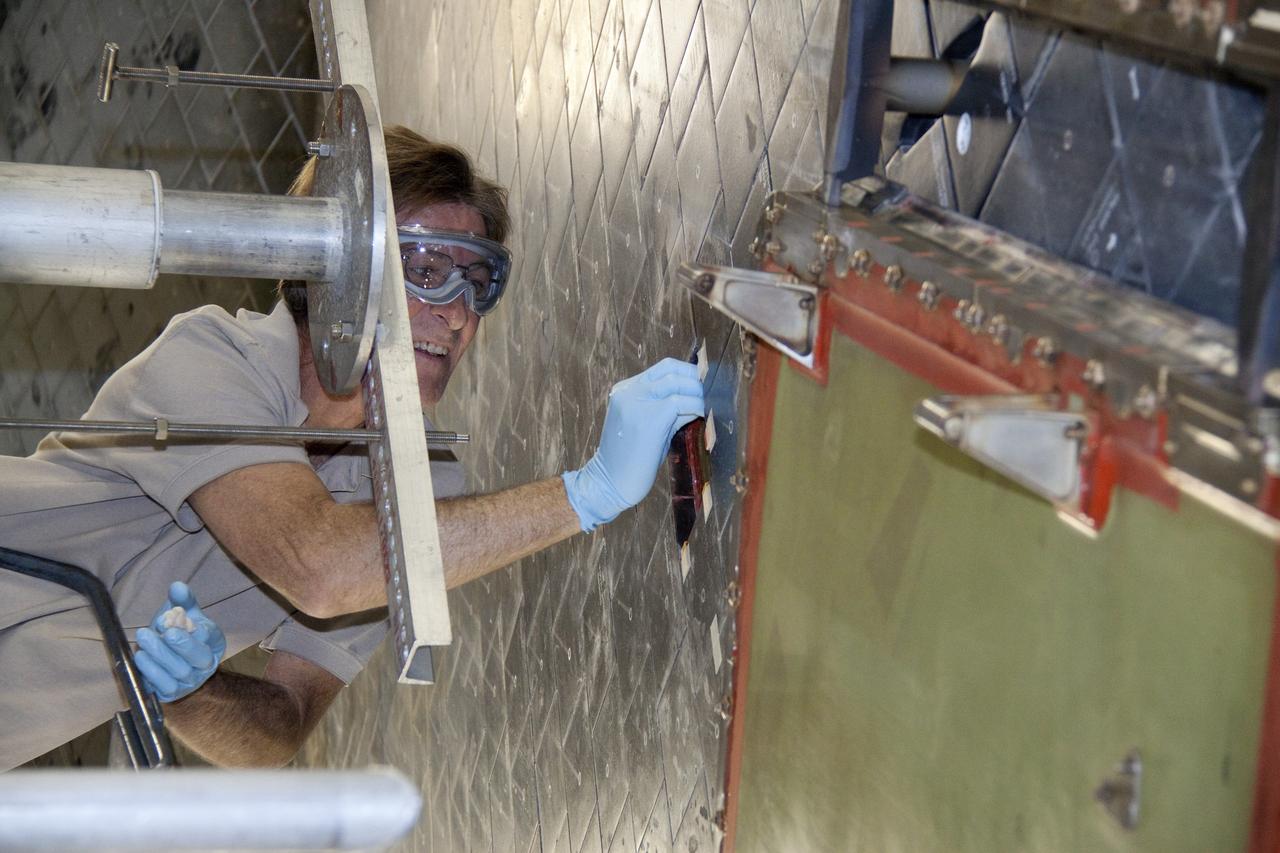
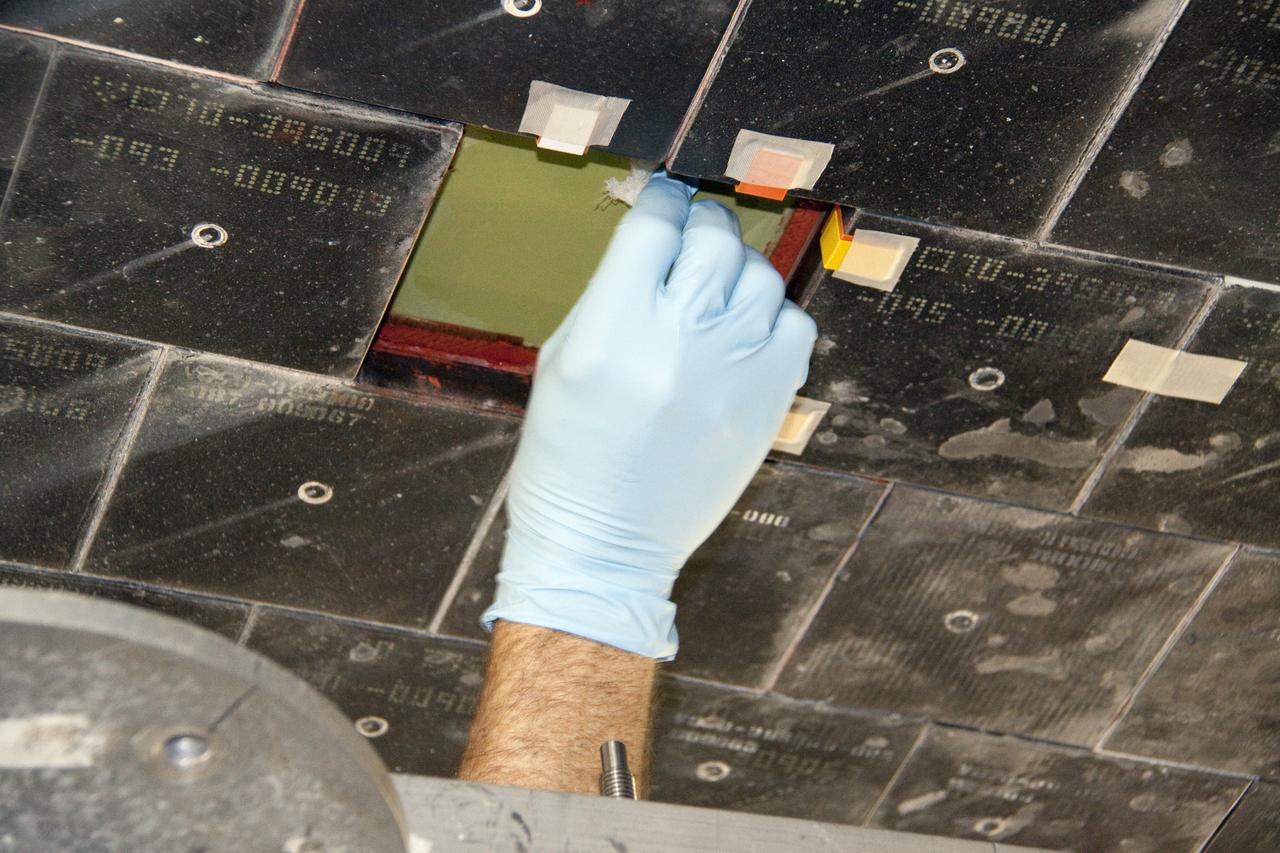
Launched on July 26 2005, from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This close up of the thermal tiles was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist (out of frame). Astronaut Soichi Noguchi, STS-114 mission specialist representing the Japan Aerospace Exploration (JAXA), can be seen in the background perched on a Space Station truss.
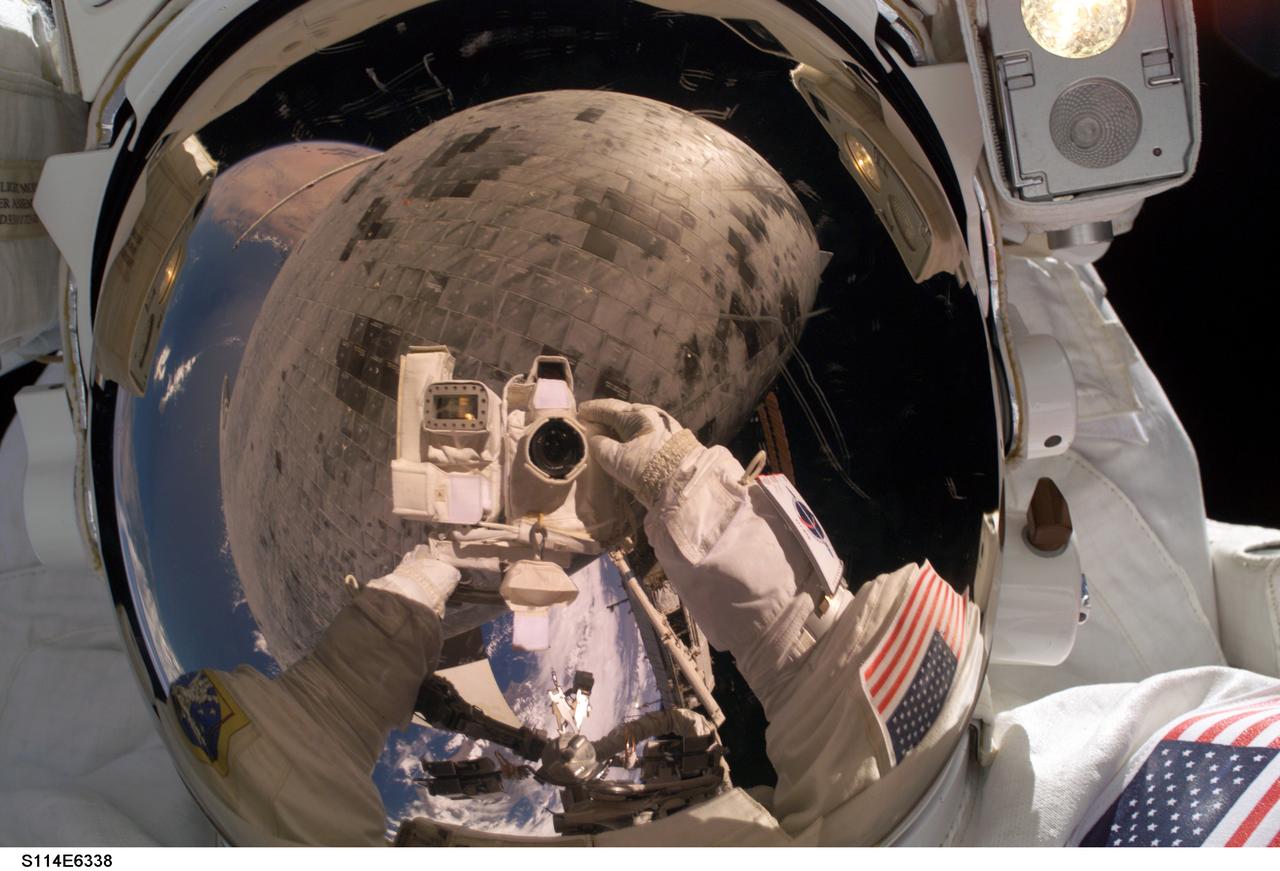

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. Astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, used the pictured still digital camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the EVA. Also visible in the reflection are thermal protection tiles on Discovery’s underside.
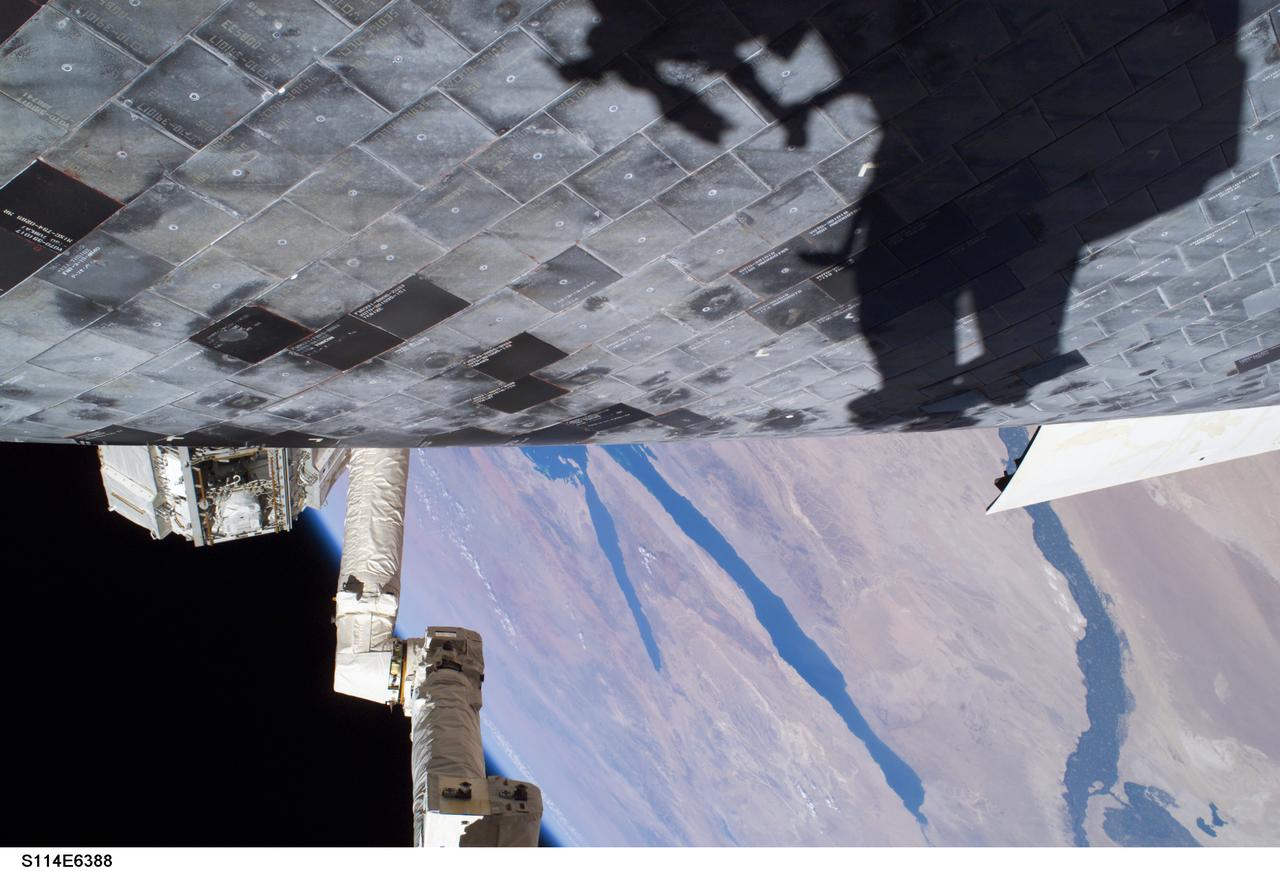

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This particular photo was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, whose shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles, and a portion of the Canadian built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) robotic arm and the Nile River is visible at the bottom.
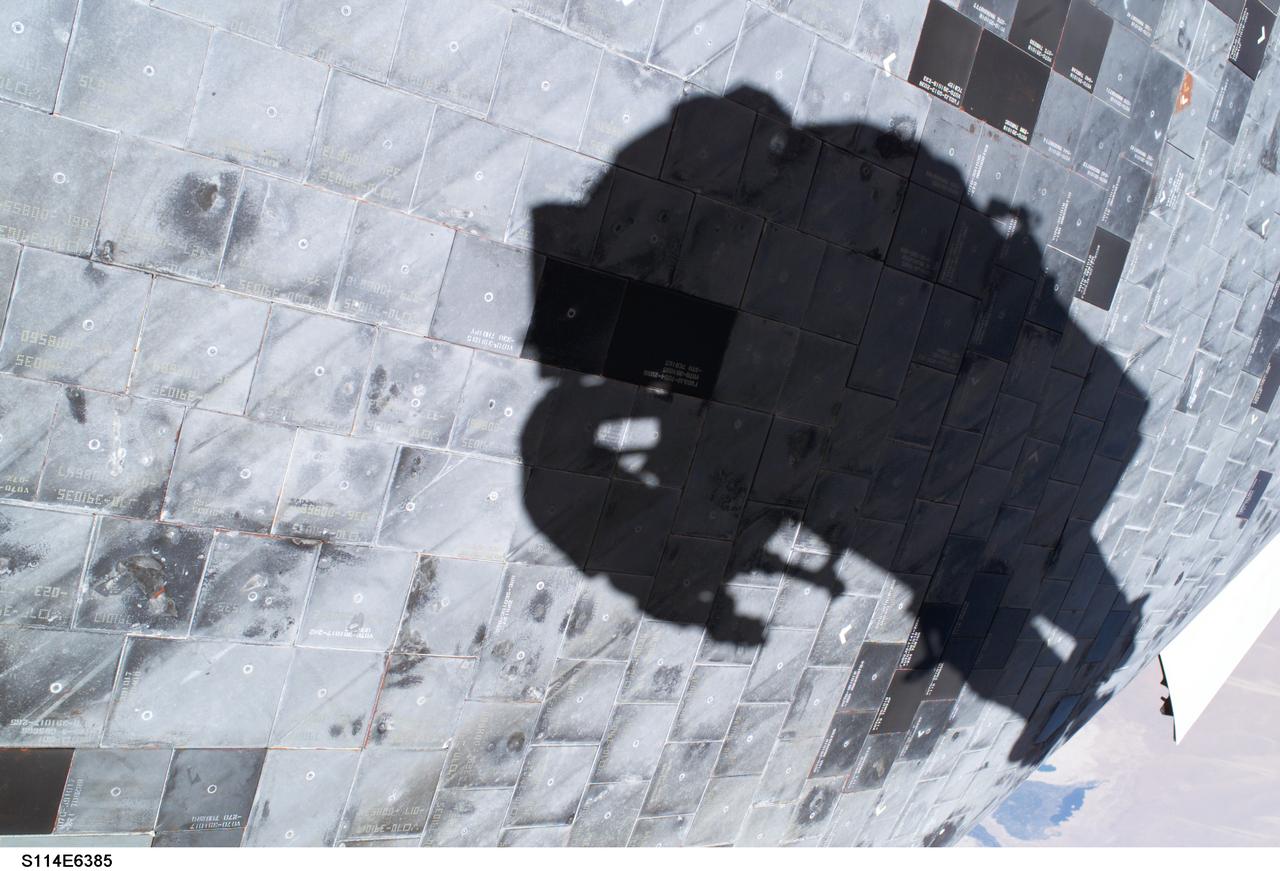

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. This particular photo was taken by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, whose shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles.
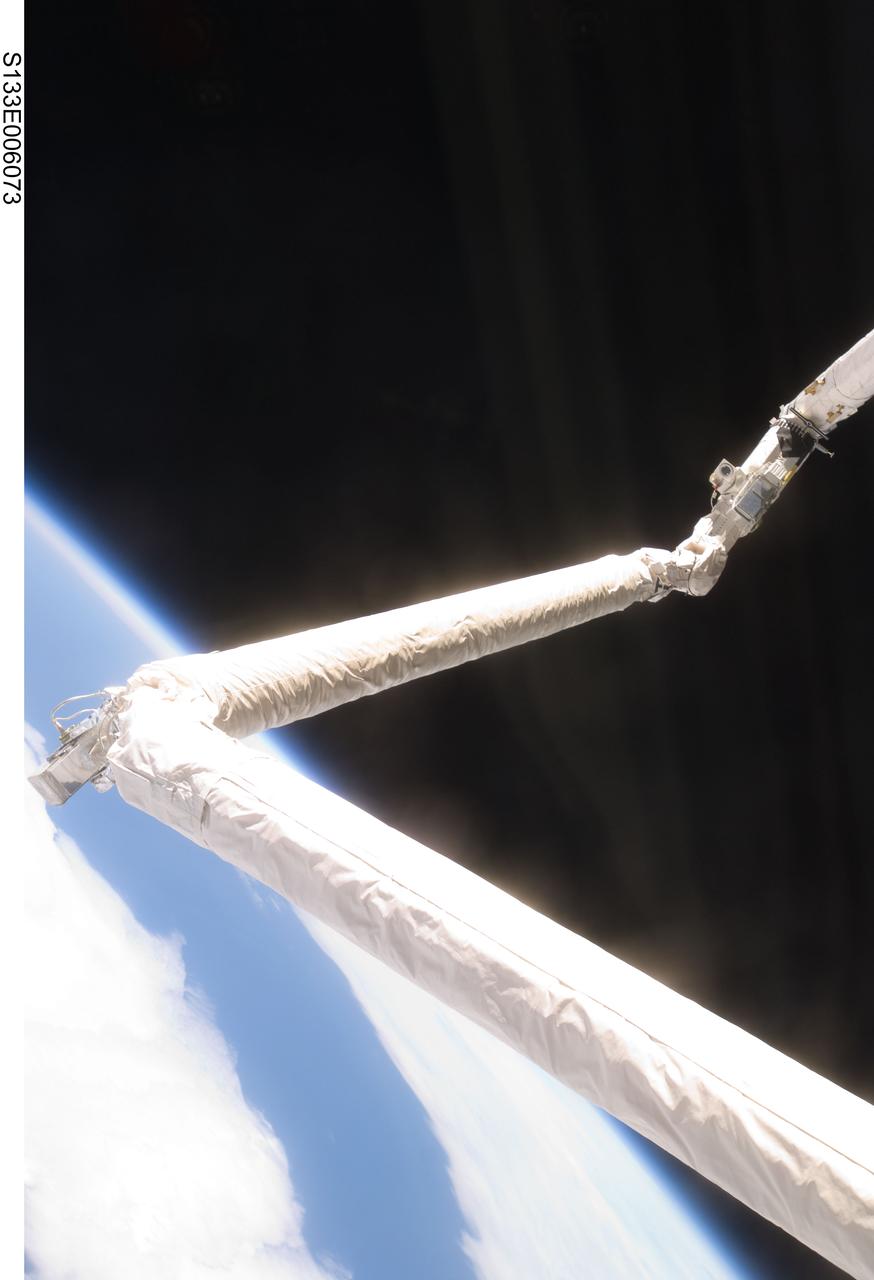

S133-E-006073 (25 Feb. 2011) --- Controlled by the STS-133 astronauts inside Discovery's cabin, the Remote Manipulator System/Orbiter Boom Sensor System (RMS/OBSS) equipped with special cameras, begins to conduct thorough inspections of the shuttle’s thermal tile system on flight day 2. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
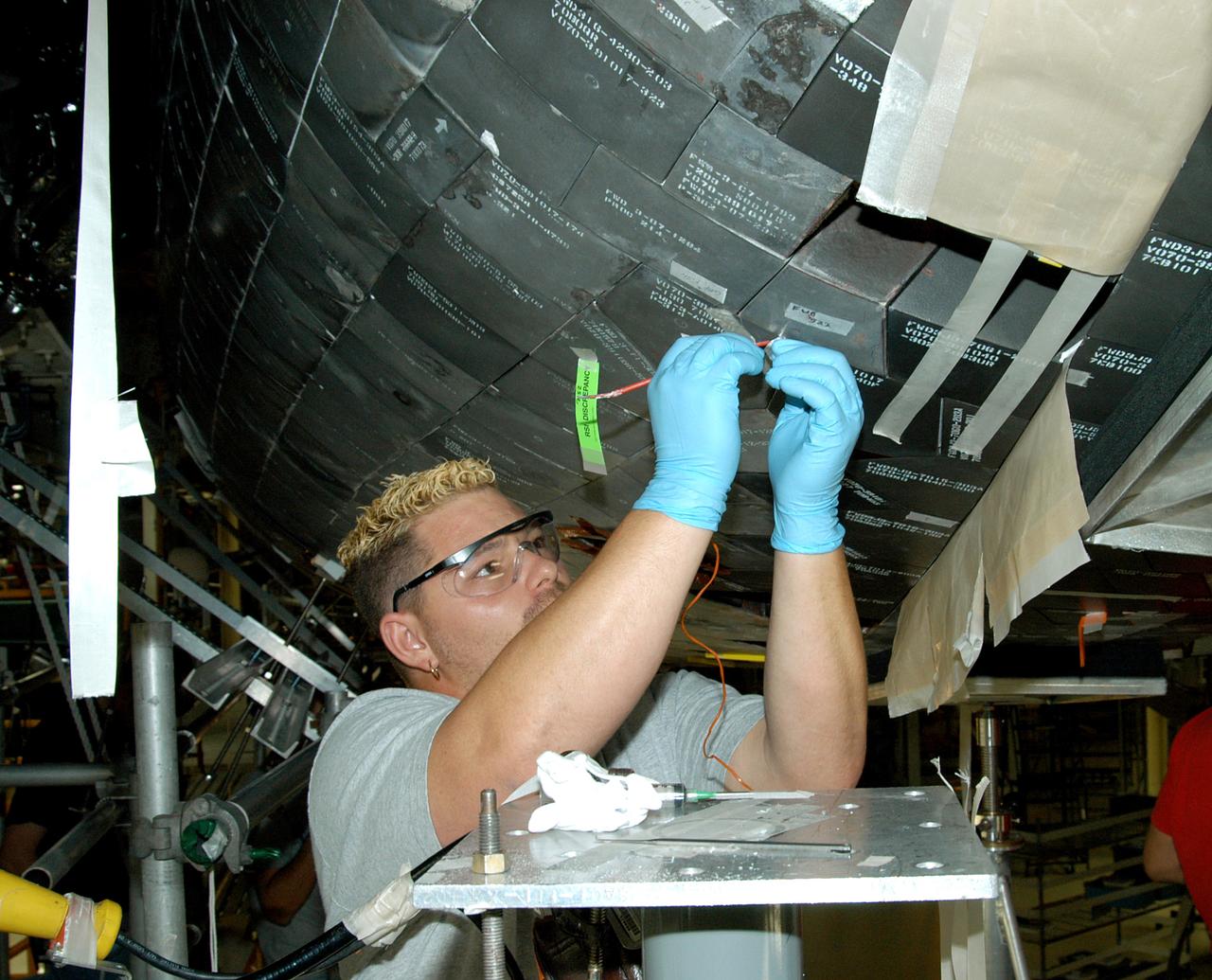

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, KSC employee Chris Moore repairs tile on the forward area of the orbiter Discovery. The vehicle has undergone Orbiter Major Modifications in the past year, which includes tile check and repair. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000° Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Discovery is scheduled to fly on mission STS-121 to the International Space Station.
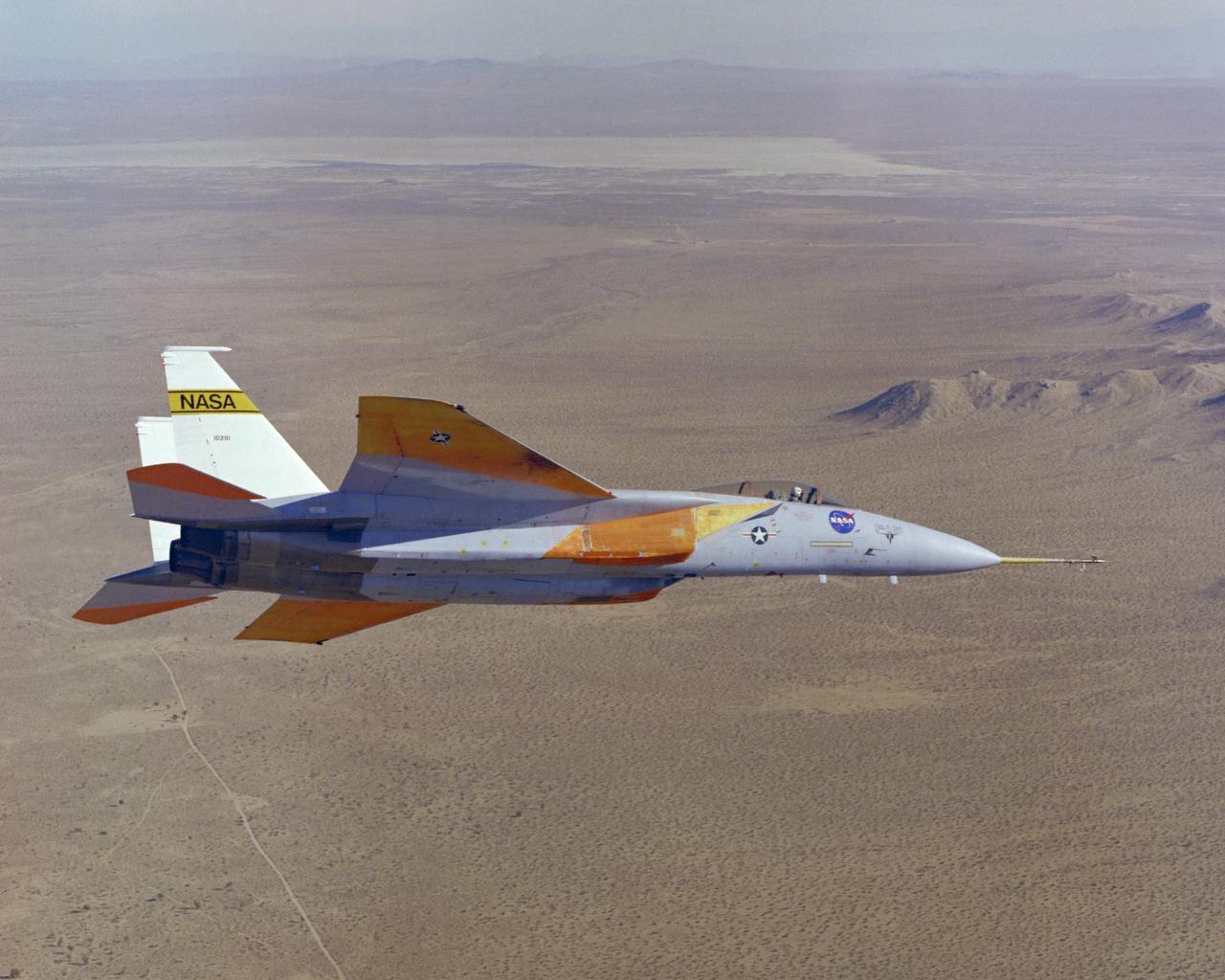

The number two F-15A (Serial #71-0281) was obtained by NASA from the U.S. Air Force in 1976 and was used for more than 25 advanced research projects involving aerodynamics, performance, propulsion control, control integration, instrumentation development, human factors, and flight test techniques. Included in these projects was its role as a testbed to evaluate aerodynamic pressures on Space Shuttle thermal protection tiles at specific altitudes and speeds.
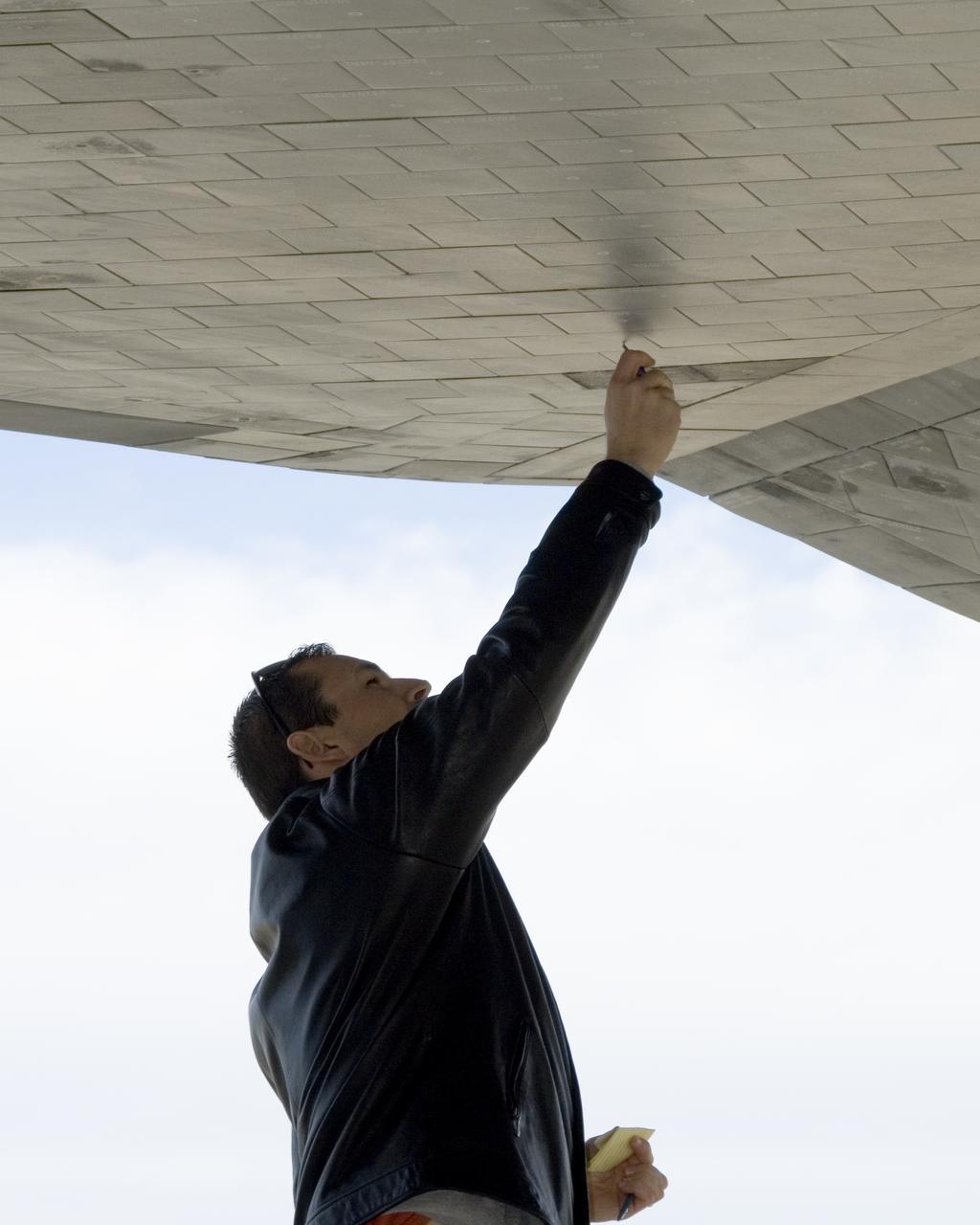

A United Space Alliance technician carefully checks the thermal tiles on the underside of Space Shuttle Endeavour for nicks and dings following its landing at Edwards Air Force Base to conclude mission STS-126.
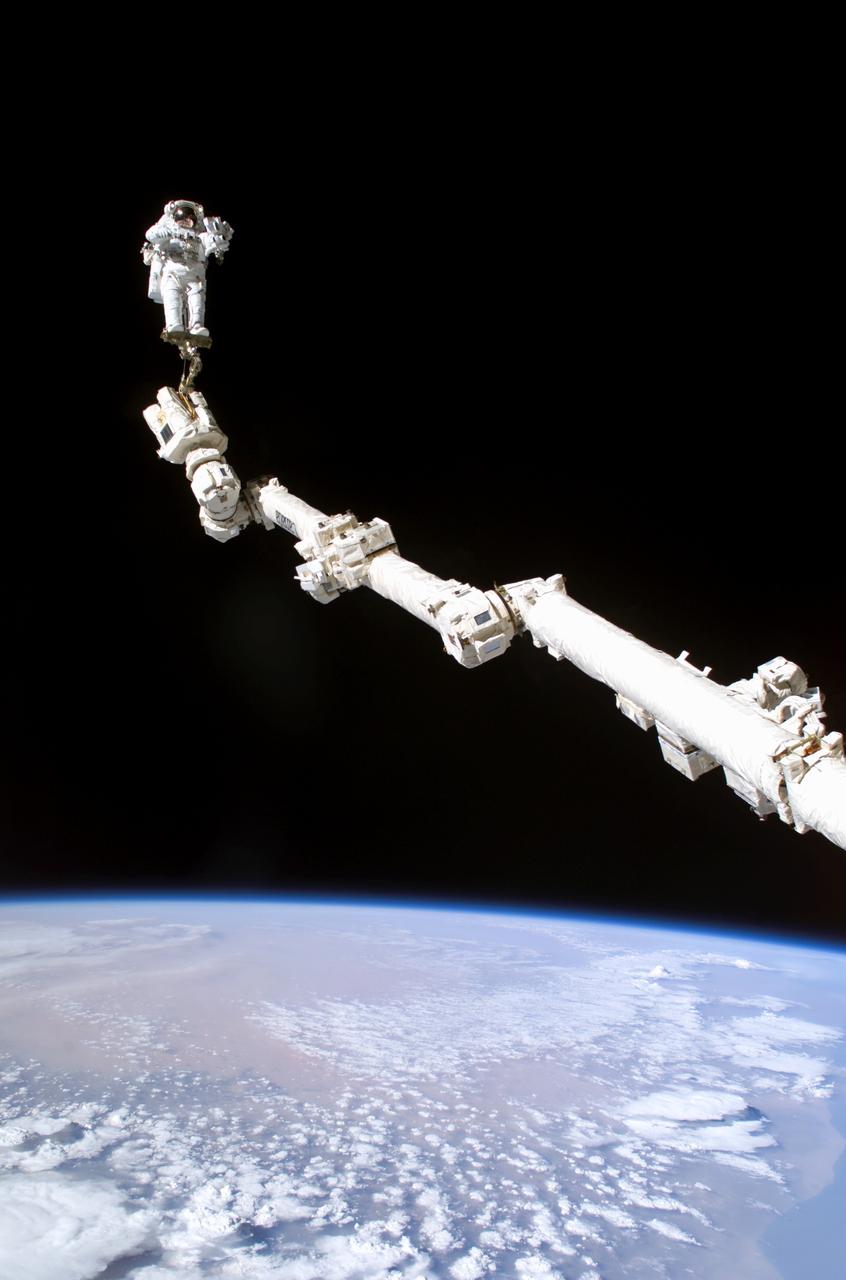

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. The mission’s third and final Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) included taking a close-up look and the repair of the damaged heat shield. Gap fillers were removed from between the orbiter’s heat-shielding tiles located on the craft’s underbelly. Never before had any repairs been done to an orbiter while still in space. Back dropped by the blackness of space and Earth’s horizon, astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, is anchored to a foot restraint on the extended ISS’s Canadarm-2.
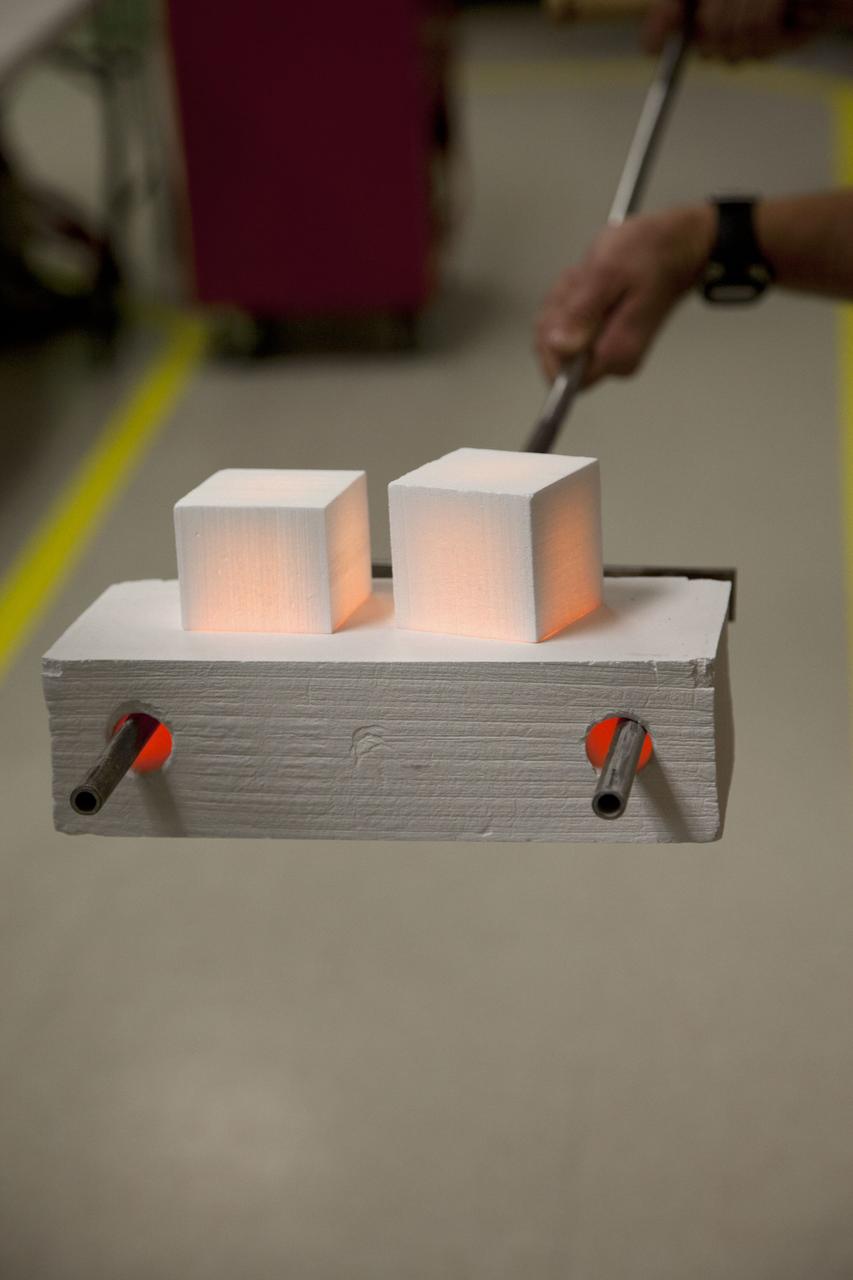
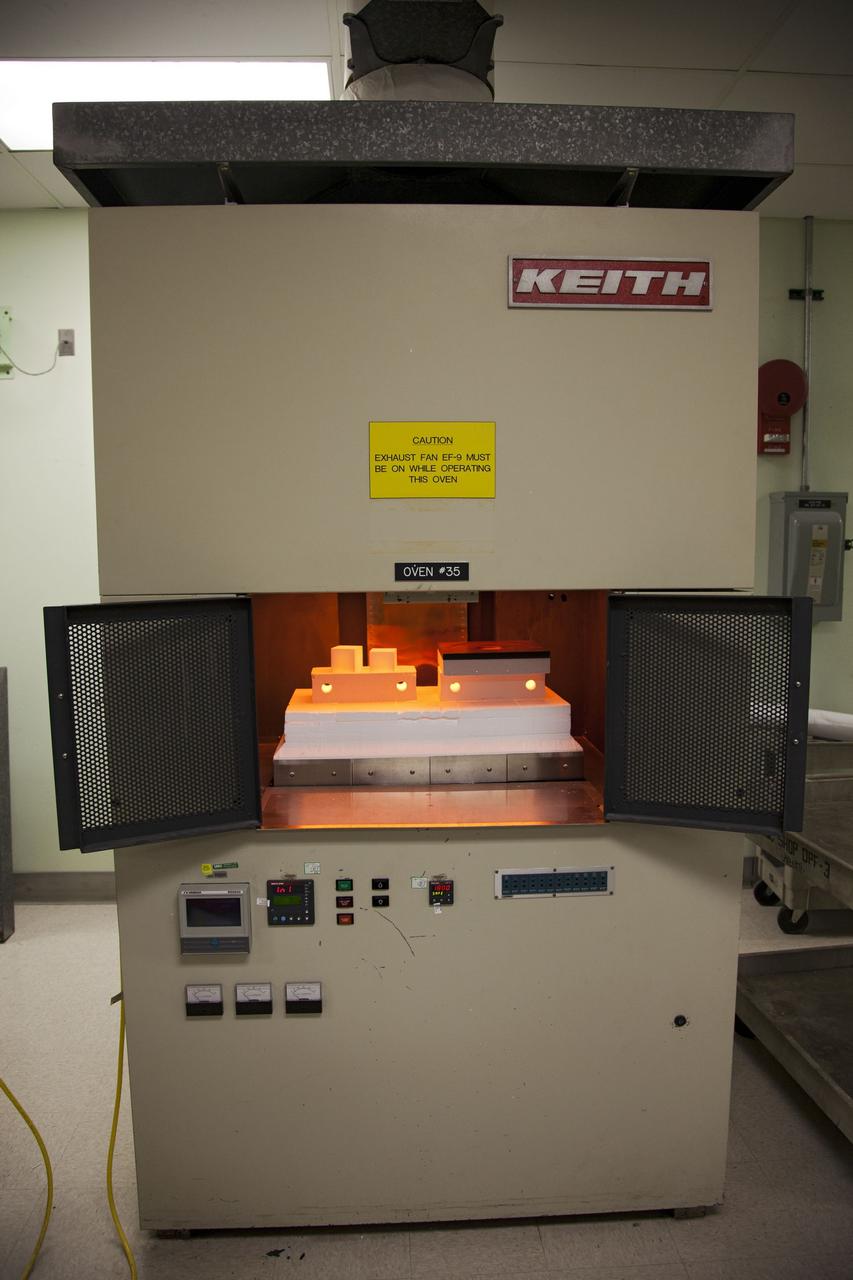
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule are removed from a Keith thermal automation oven. Inside, the tiles were baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

Space Shuttle Tile Thermal Protection System testing in Ames Arc Jet facilities

Space Shuttle Tile Thermal Protection System testing in Ames Arc Jet facilities
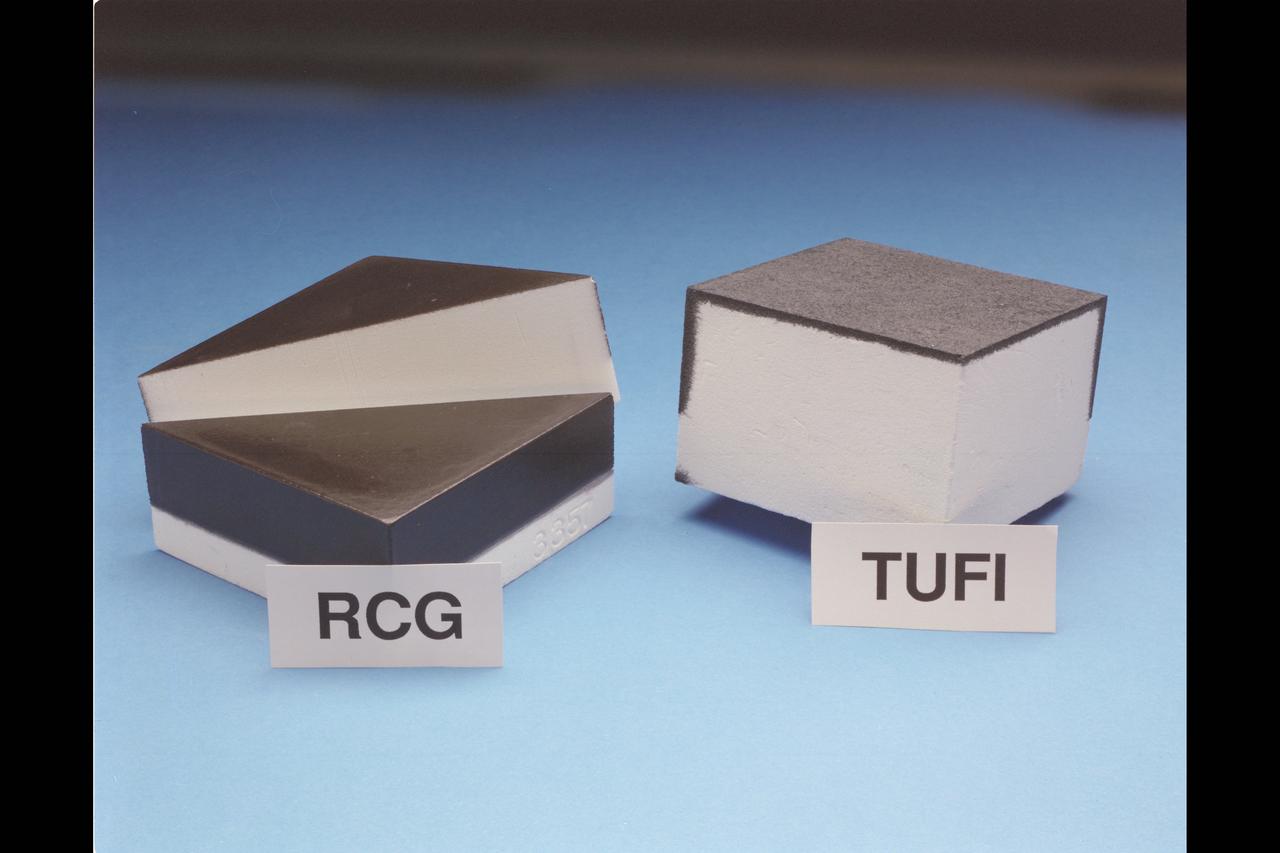
Studio portrait of Ames Developed Thermal Protection System (TPS) tiles - the RCG and TUFI
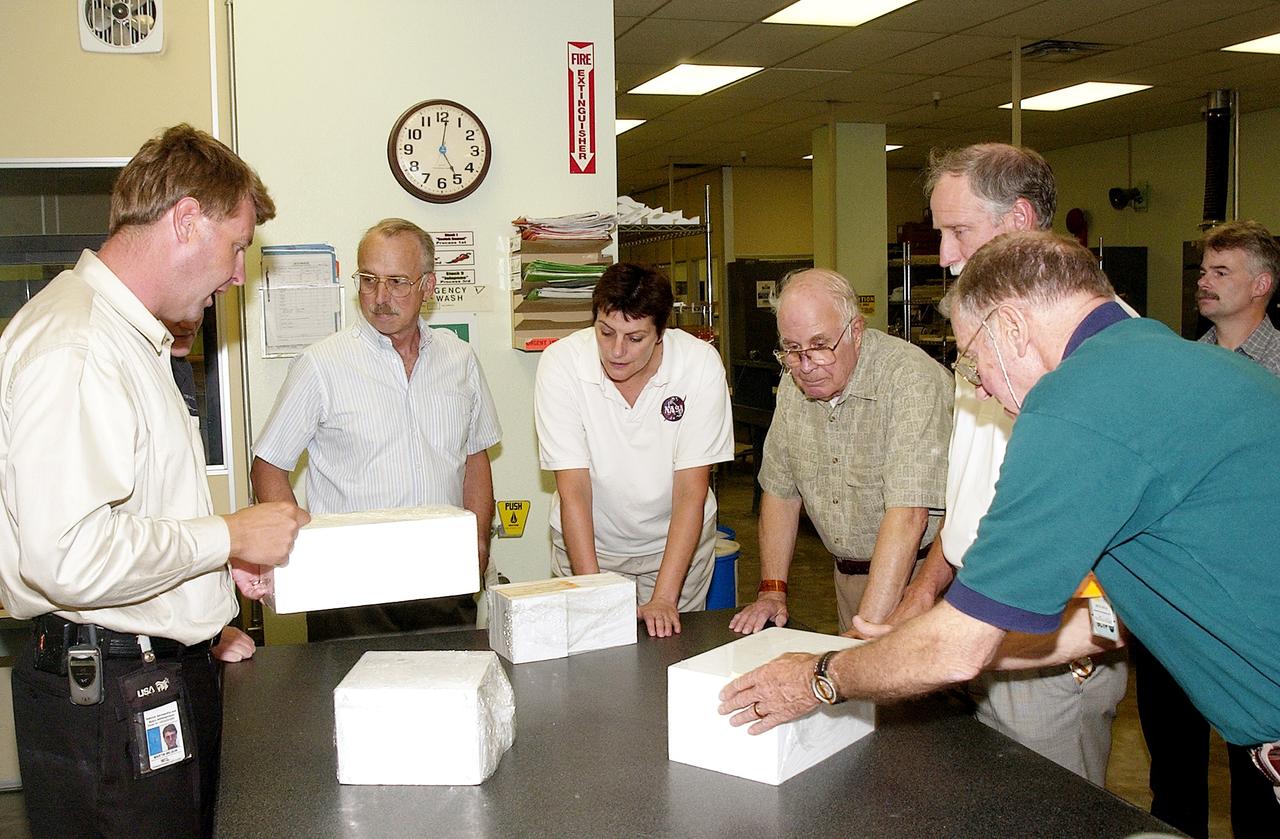

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a tour of the Tile Shop, members of the Stafford-Covey Return to Flight Task Group (SCTG) learn about PU-tiles, part of an orbiter’s Thermal Protection System. At left is Martin Wilson, with United Space Alliance. Others (left to right) around the table are James Adamson, Dr. Kathryn Clark, William Wegner, Richard Covey and Joe Engle. Covey, former Space Shuttle commander, is co-chair of the SCTG, along with Thomas P. Stafford, Apollo commander. Chartered by NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe, the task group will perform an independent assessment of NASA’s implementation of the final recommendations by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.

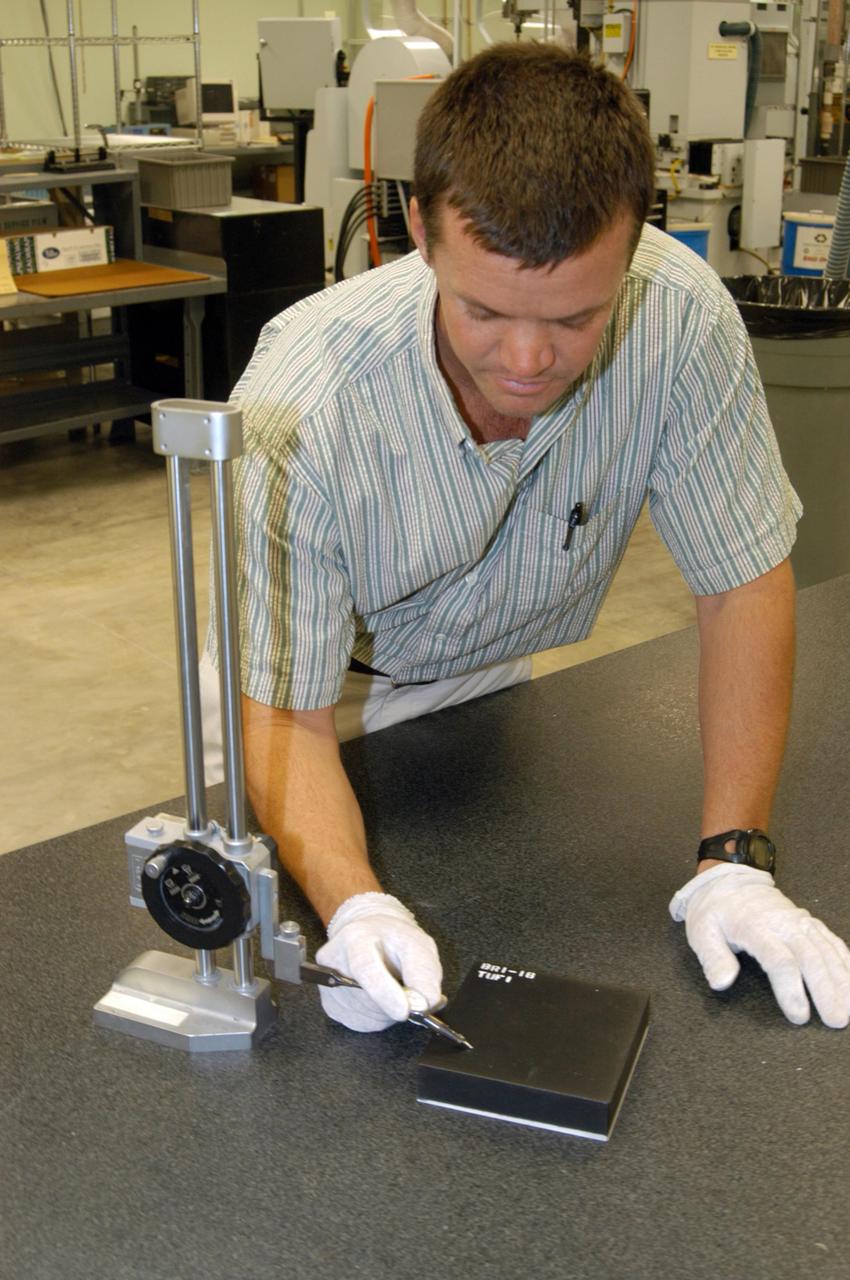
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, shelves are stacked with Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, shelves are stacked with Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
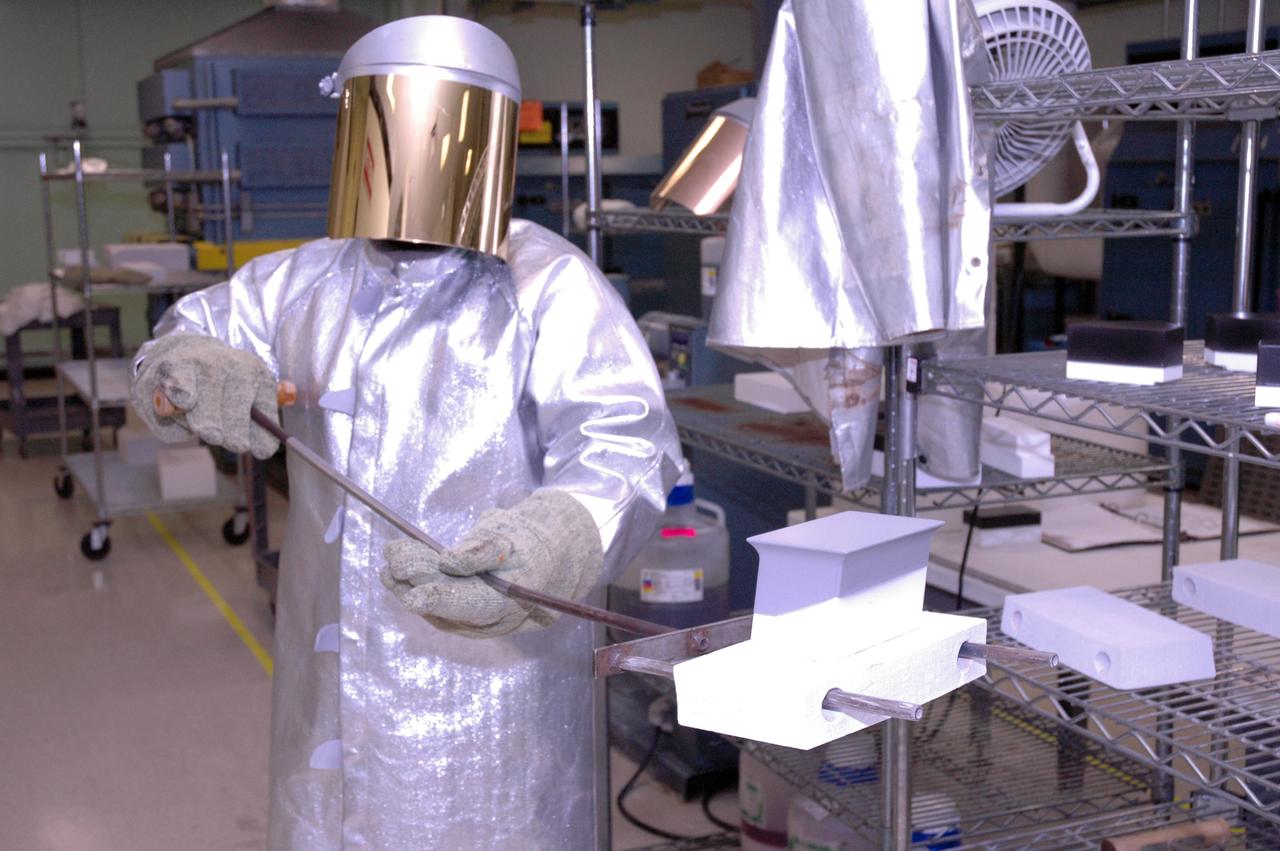

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker is ready to place a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile in the oven. The tile will be baked at 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit to cure the ceramic coating, part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
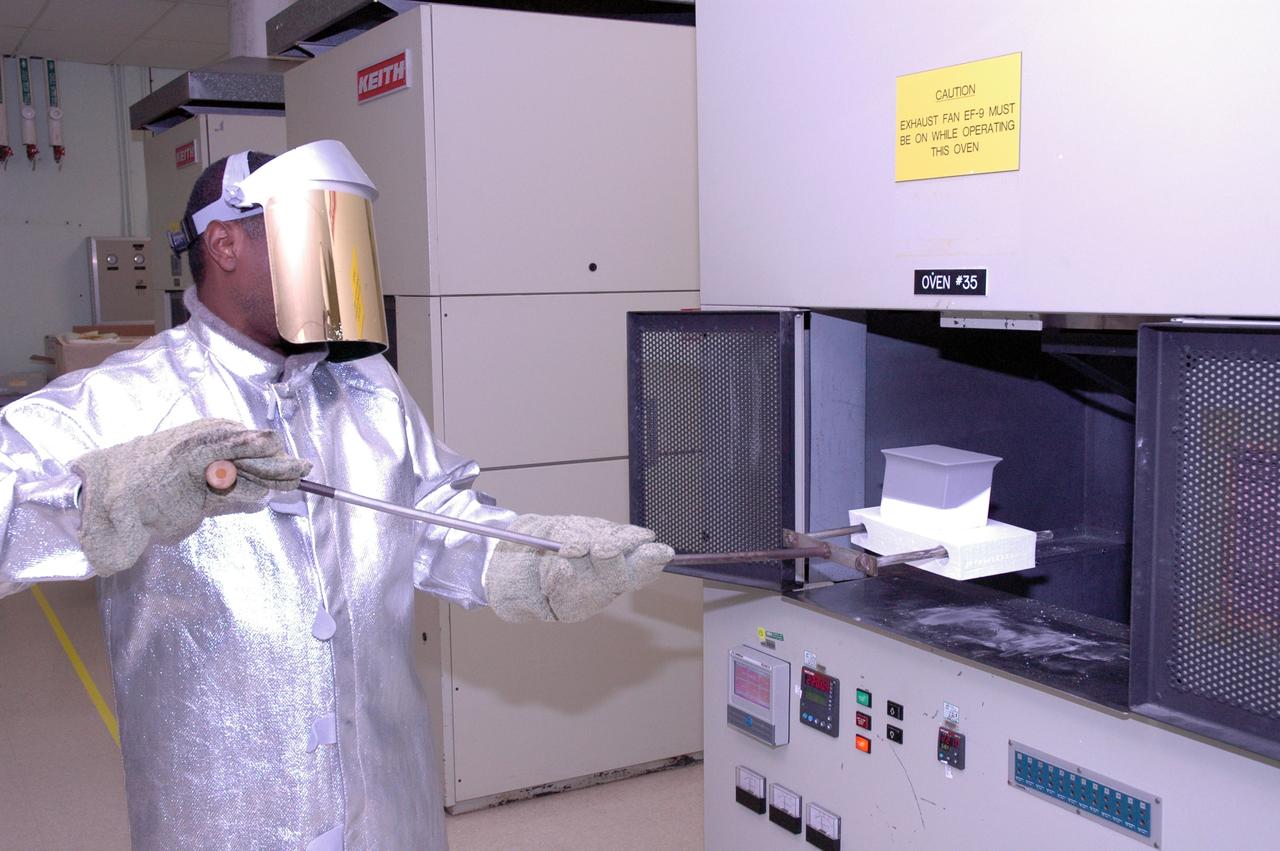

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker places a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile in the oven. The tile will be baked at 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit to cure the ceramic coating, part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
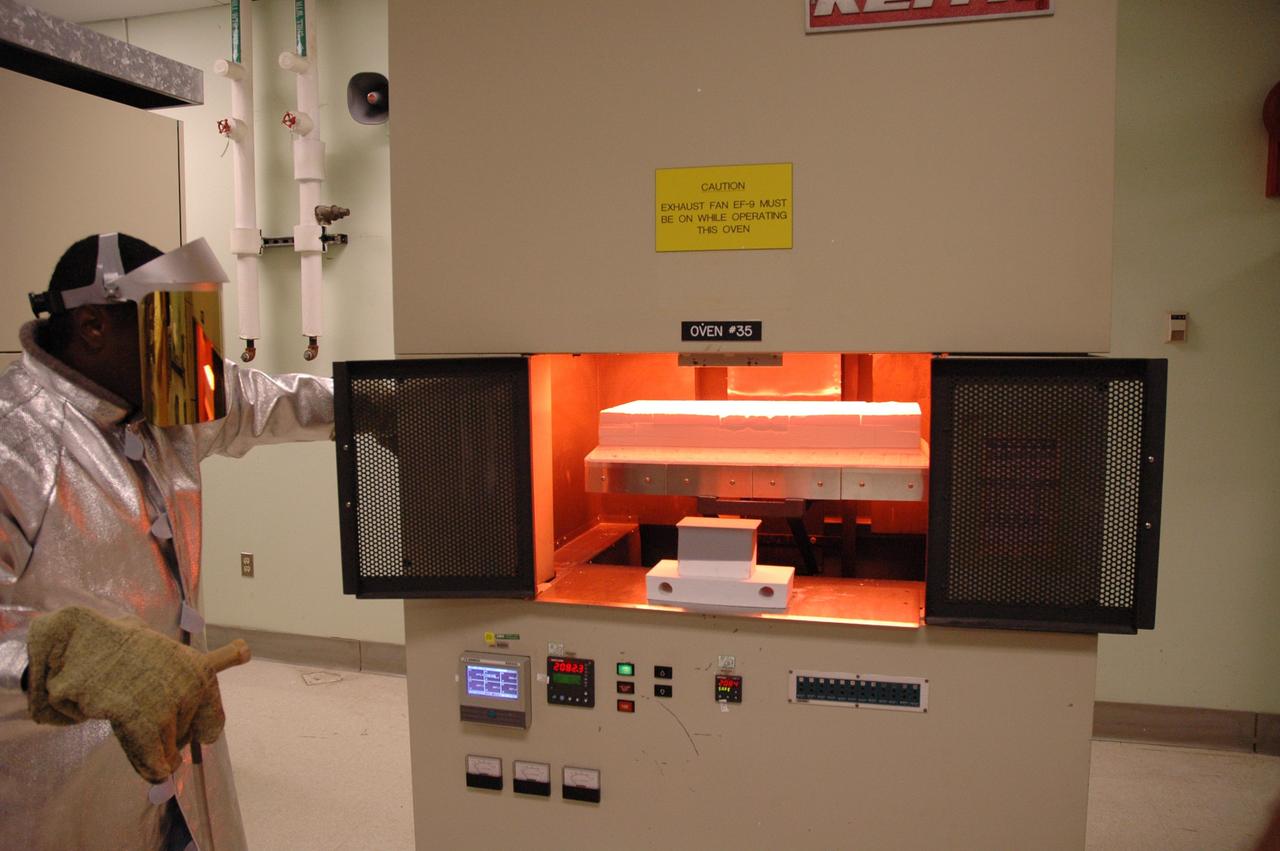

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker reaches for the door to close the oven with the Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile inside. The tile will be baked at 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit to cure the ceramic coating, part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
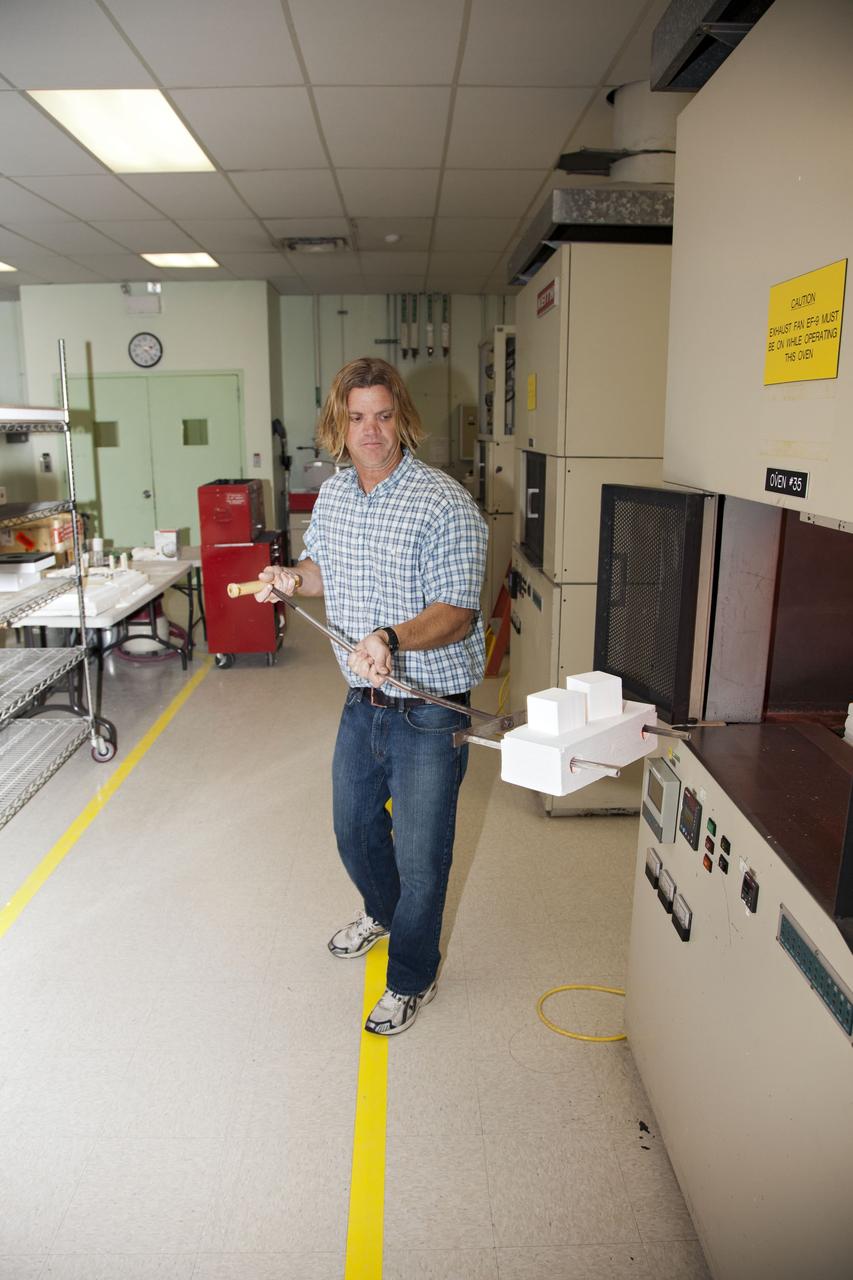

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, removes the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule from a Keith thermal automation oven. Inside, the tiles were baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
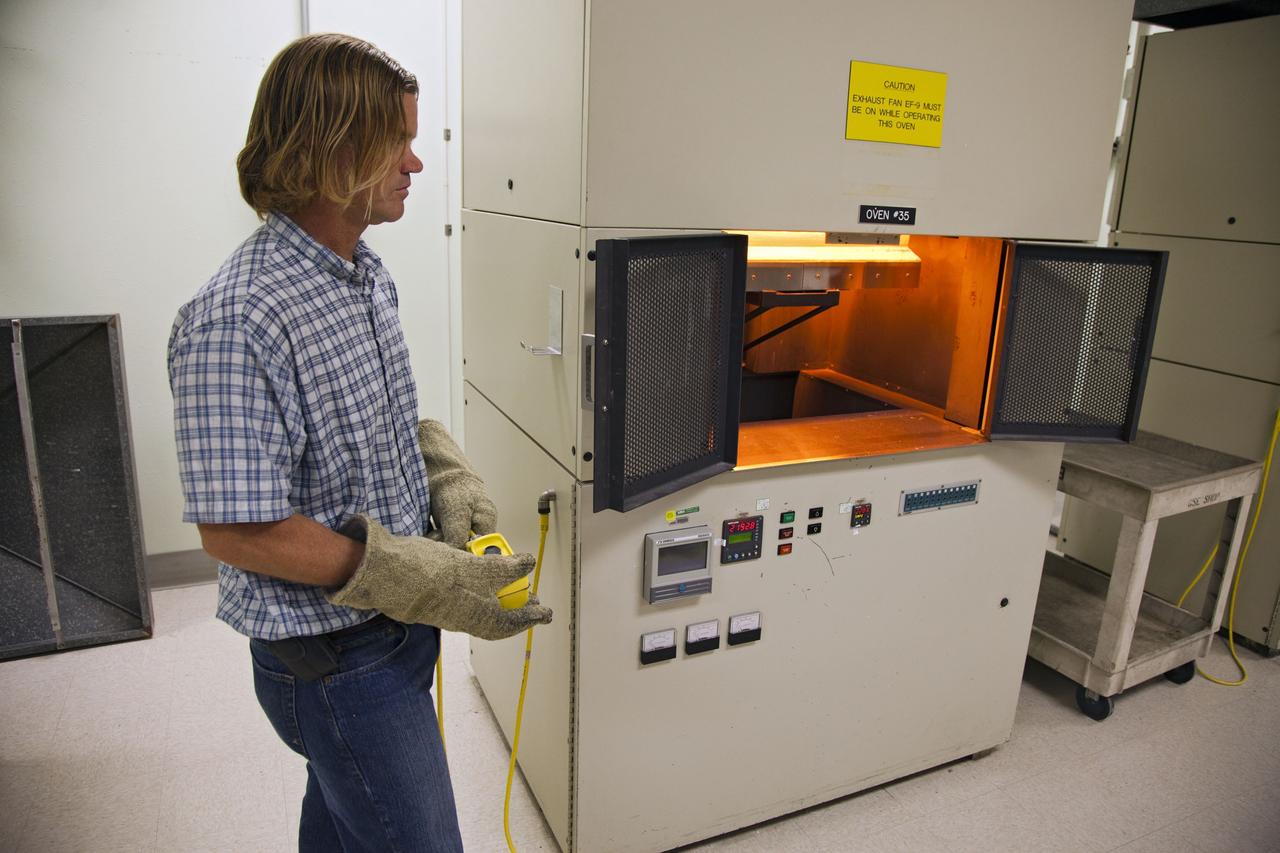

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, put the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule in a Keith thermal automation oven. The tiles will be baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
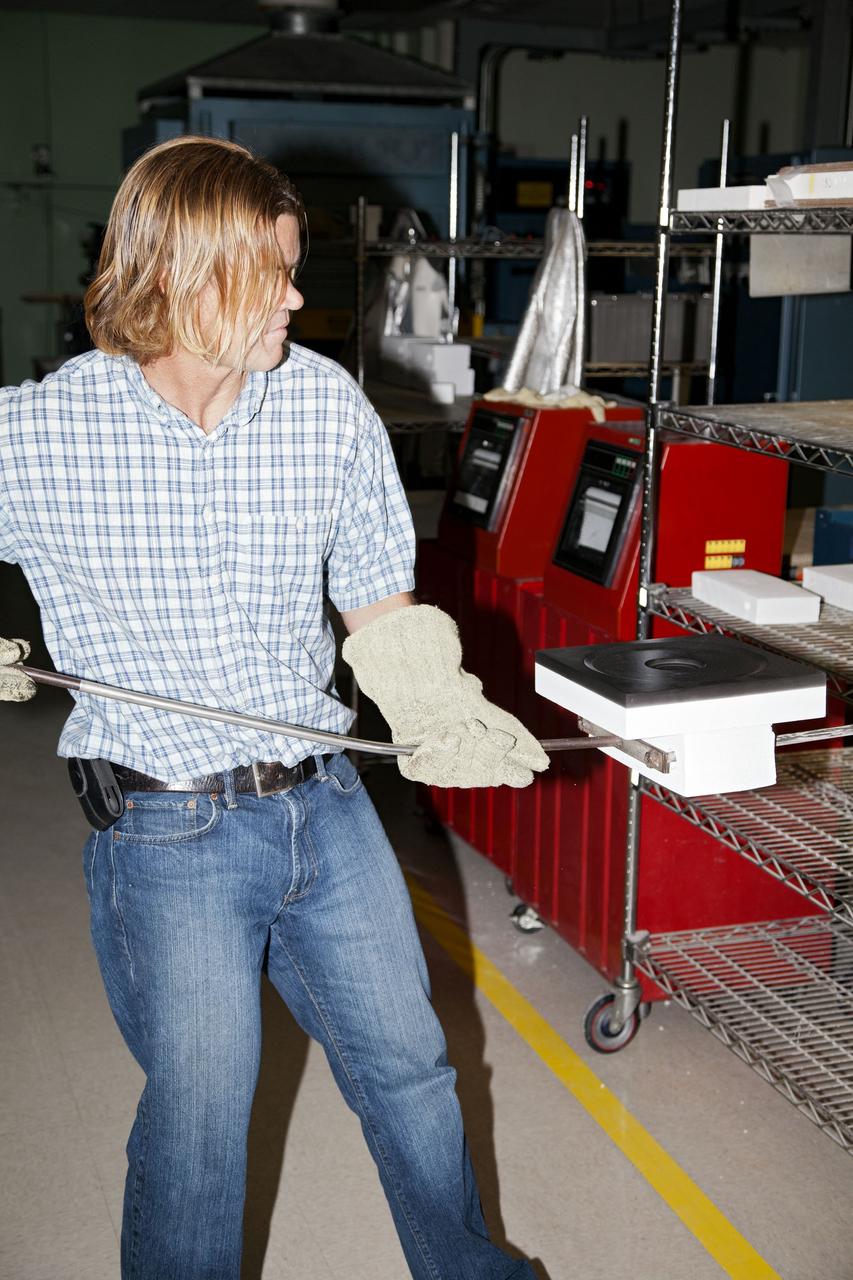

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, removes the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule from a Keith thermal automation oven. Inside, the tiles were baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
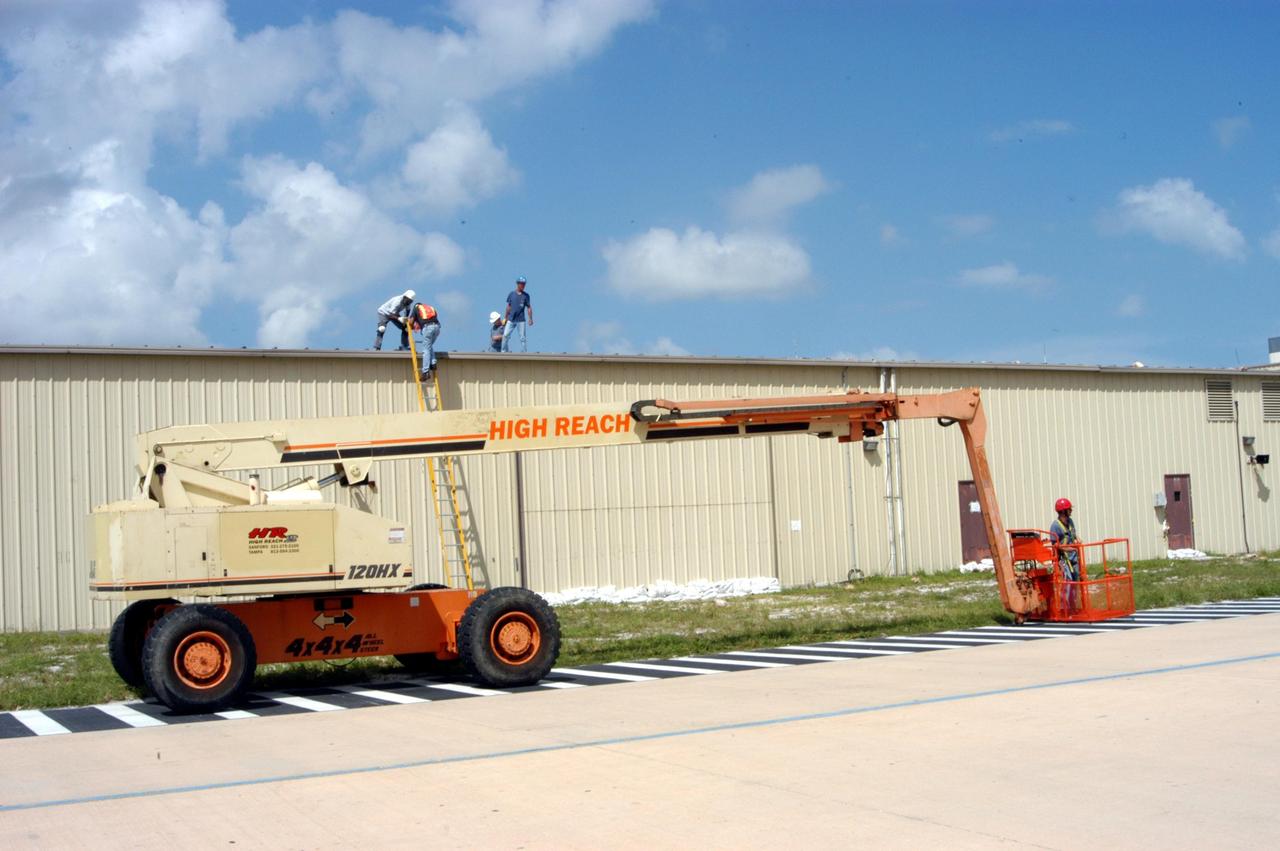

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers attempt to secure the roof of the Tile Shop in the Thermal Protection System Facility (TPSF) in preparation for Hurricane Jeanne, which is expected to impact Central Florida Sunday. The TPSF, which creates the TPS tiles, blankets and all the internal thermal control systems for the Space Shuttles, lost approximately 35 percent of its roof during Hurricane Frances, which blew across Central Florida Sept. 4. Jeanne is the fourth hurricane in 45 days to make landfall somewhere in the state.
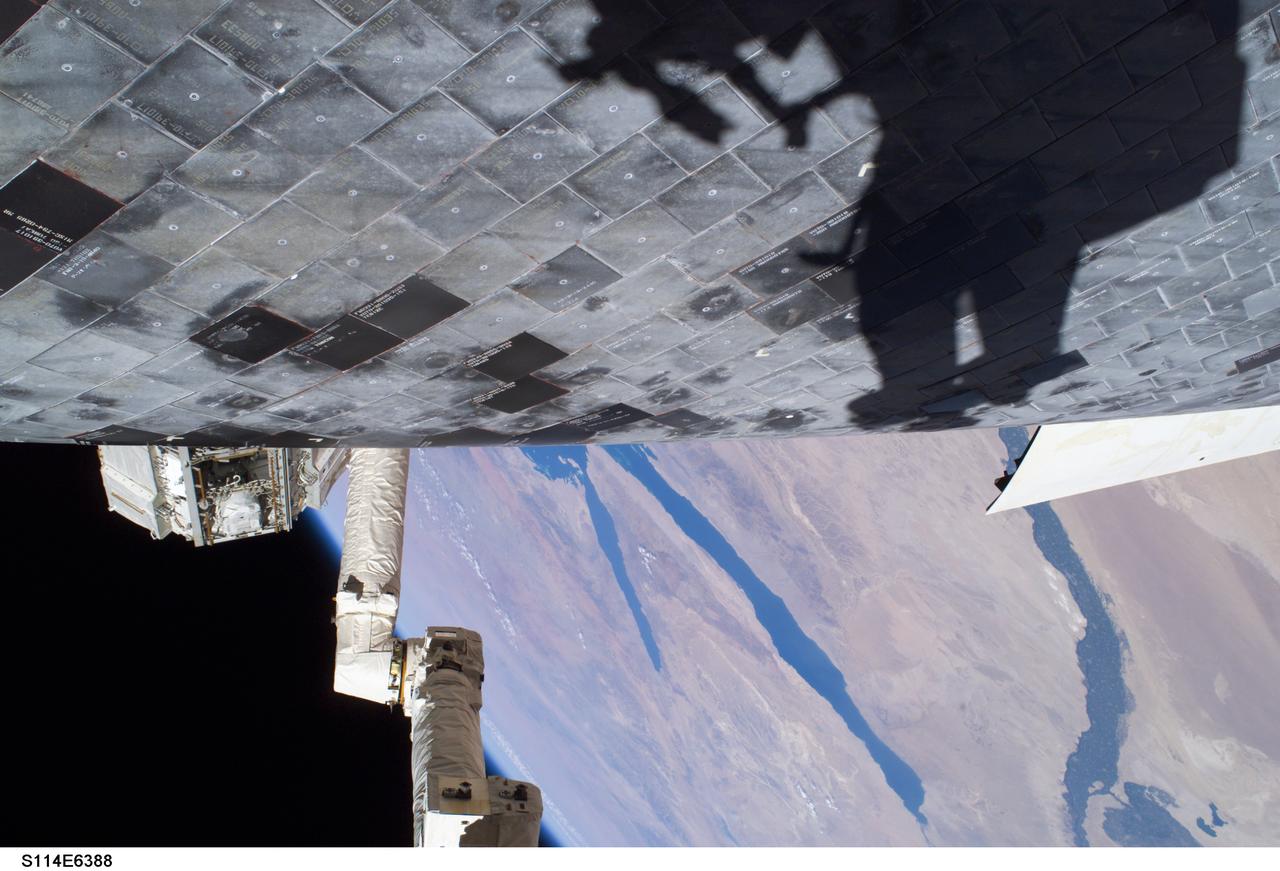

S114-E-6388 (3 August 2005) --- A close-up view of a portion of the thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA). Robinson’s shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles and a portion of the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) robotic arm and the Nile River is visible at bottom.
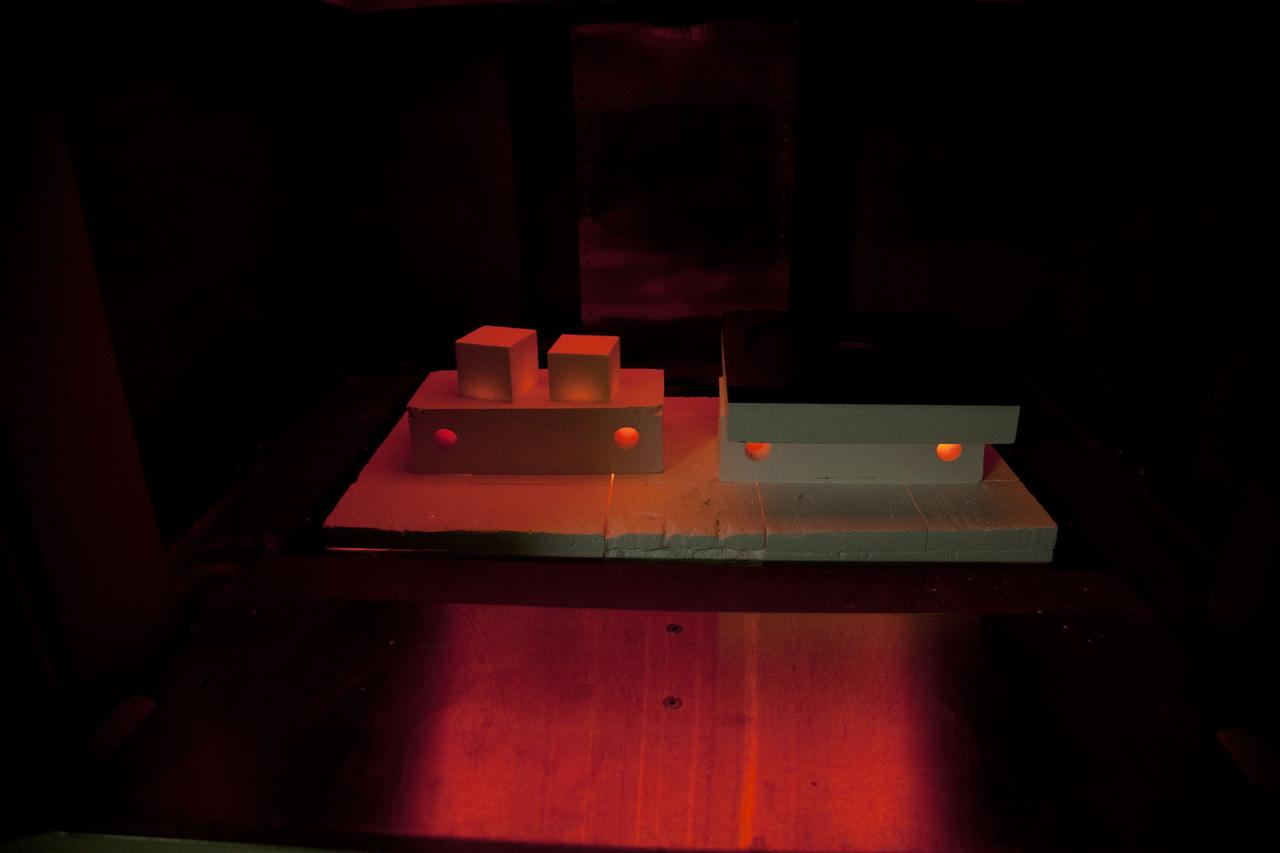
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule are in a Keith thermal automation oven in the Thermal Protection System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the oven, the tiles will be baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule are in a Keith thermal automation oven in the Thermal Protection System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the oven, the tiles will be baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

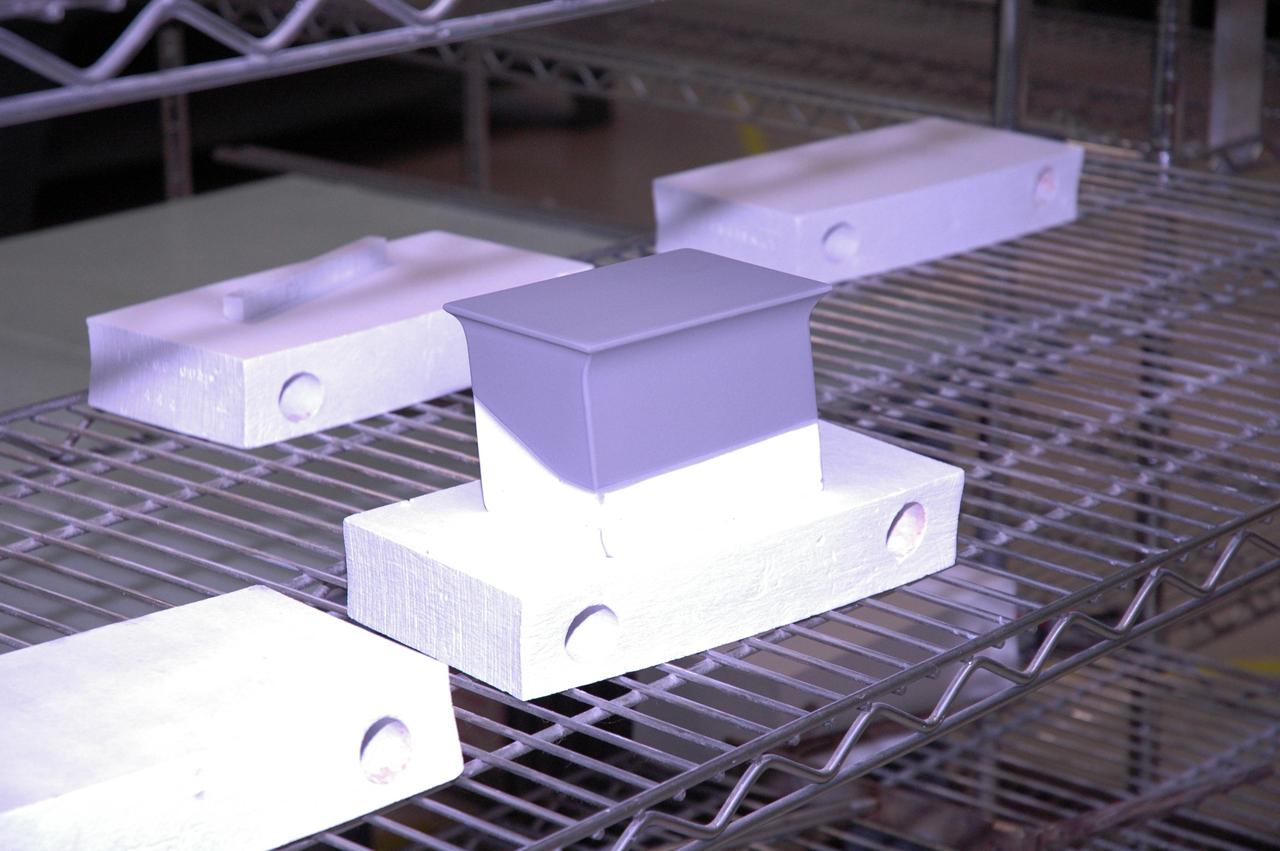
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Thermal Protection System Facility, Tim Wright, engineering manager with United Space Alliance, tests a new tile, called "Boeing replacement insulation" or "BRI-18." The new tiles will gradually replace older tiles around main landing gear doors, external tank doors and nose landing gear doors. Currently, 10 tiles have been processed inside the facility. Discovery will receive the first BRI-18 tiles. Technicians inside the Orbiter Processing Facility are performing fit checks and will begin bonding the tiles to the vehicle this month. The raw material is manufactured by The Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif. Replacing older tile with the BRI-18 tile in strategic areas is one of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board's recommendations to strengthen the orbiters. The tiles are more impact resistant than previous designs, enhancing the crew’s safety.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Thermal Protection System Facility, Tim Wright, engineering manager with United Space Alliance, tests a new tile, called "Boeing replacement insulation" or "BRI-18." The new tiles will gradually replace older tiles around main landing gear doors, external tank doors and nose landing gear doors. Currently, 10 tiles have been processed inside the facility. Discovery will receive the first BRI-18 tiles. Technicians inside the Orbiter Processing Facility are performing fit checks and will begin bonding the tiles to the vehicle this month. The raw material is manufactured by The Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif. Replacing older tile with the BRI-18 tile in strategic areas is one of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board's recommendations to strengthen the orbiters. The tiles are more impact resistant than previous designs, enhancing the crew’s safety.
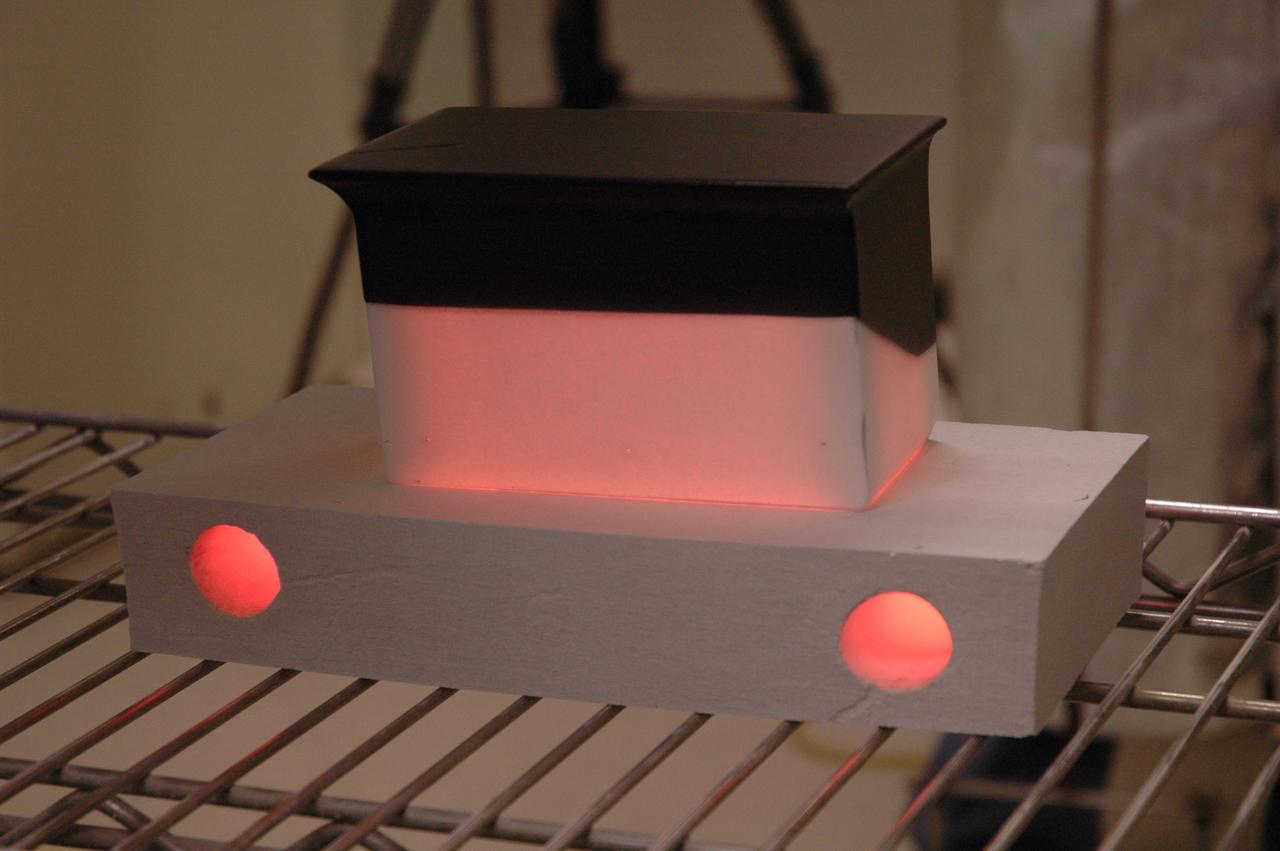
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile still glows after being baked in a 2,200-degree oven. The baking is part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
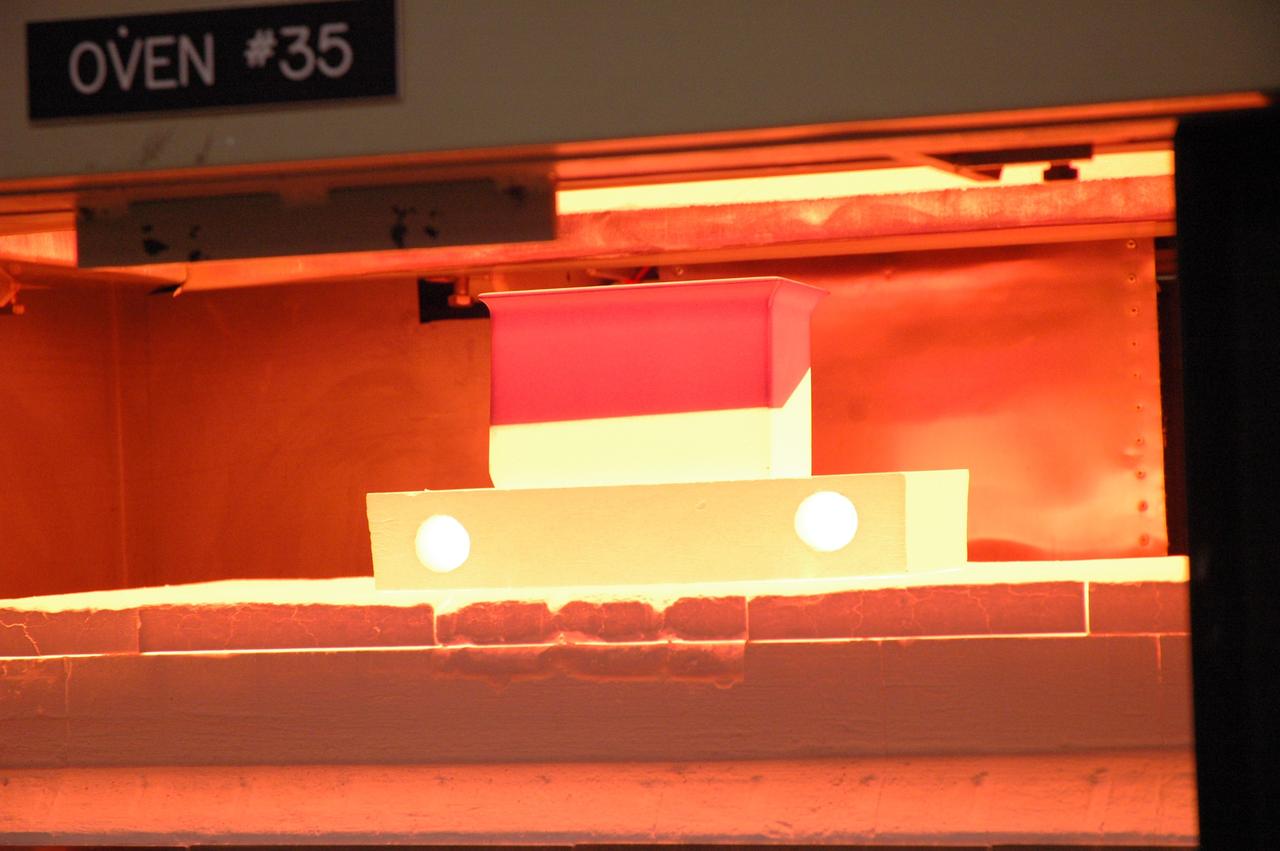
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile bakes in a 2,200-degree oven to cure the ceramic coating. The baking is part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile is ready to be baked at 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit to cure the ceramic coating, part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
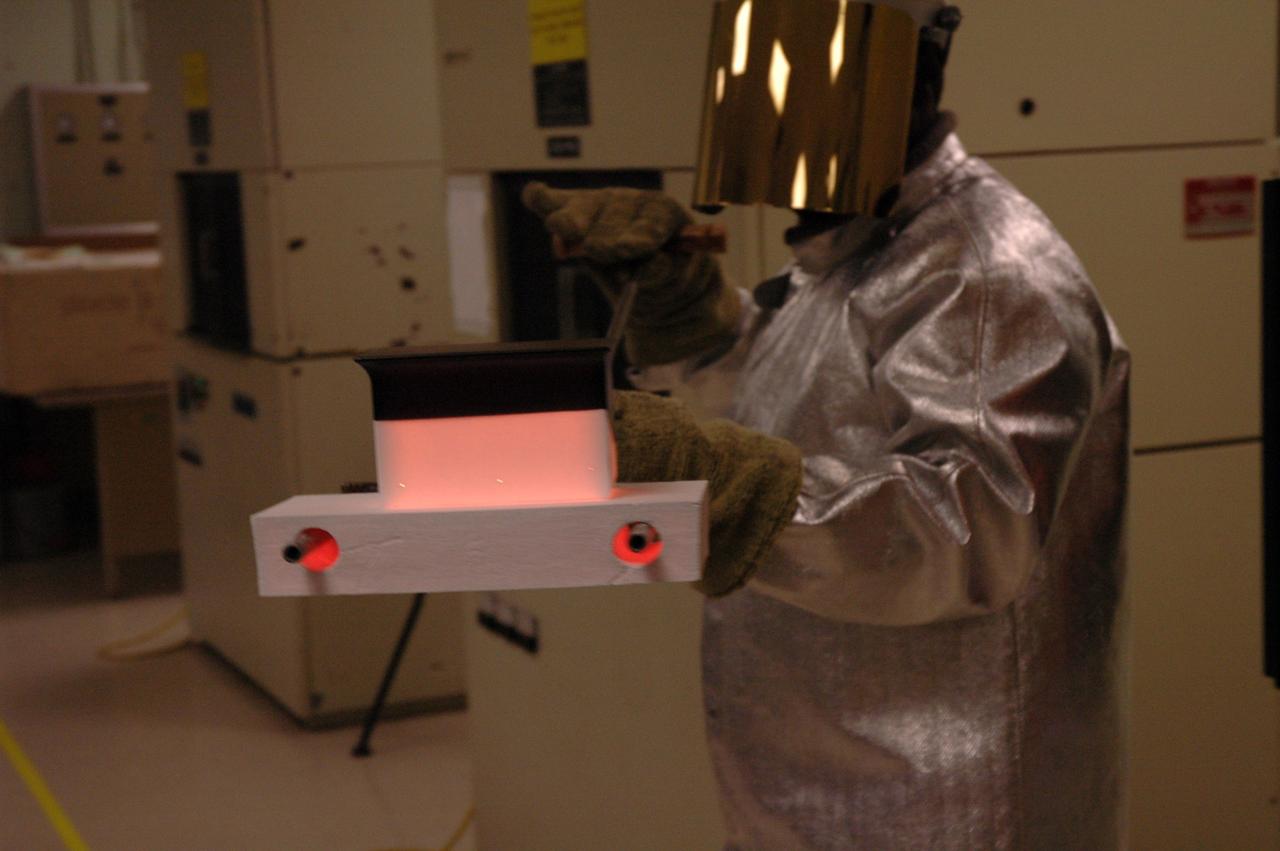
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker removes a Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tile from a 2,200-degree oven. The baking is part of the process to prepare the tiles for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
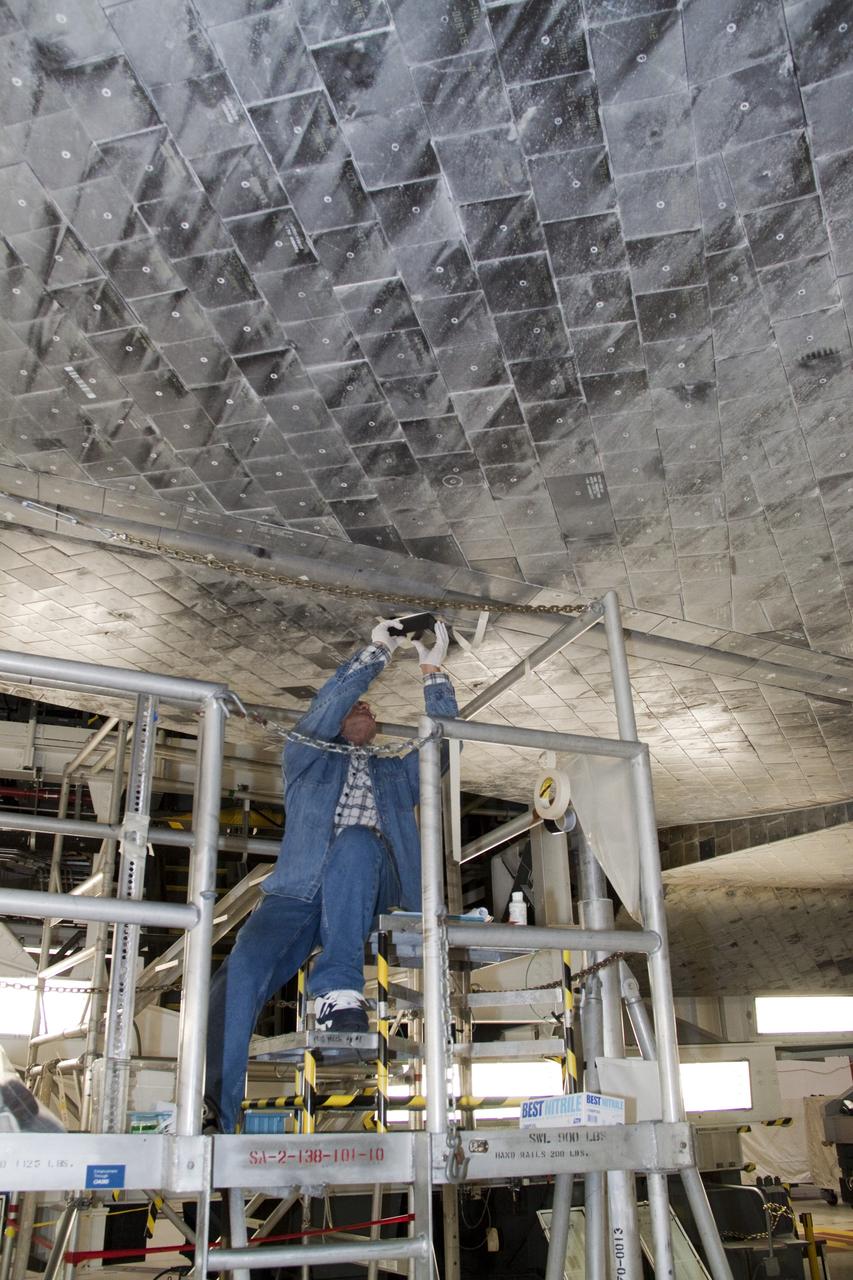

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is replacing a heat shield tile under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
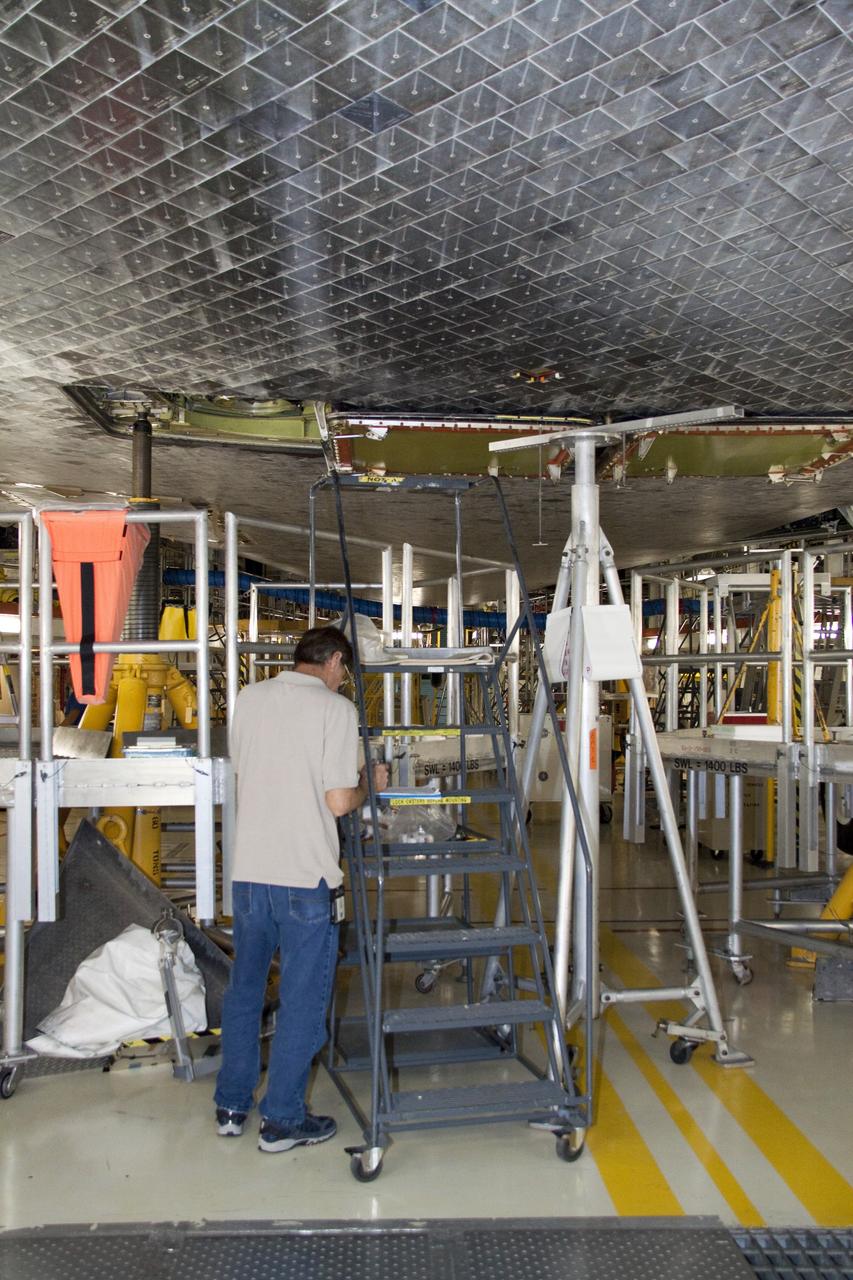

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is ready to work on replacing some of space shuttle Atlantis' heat shield tiles. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
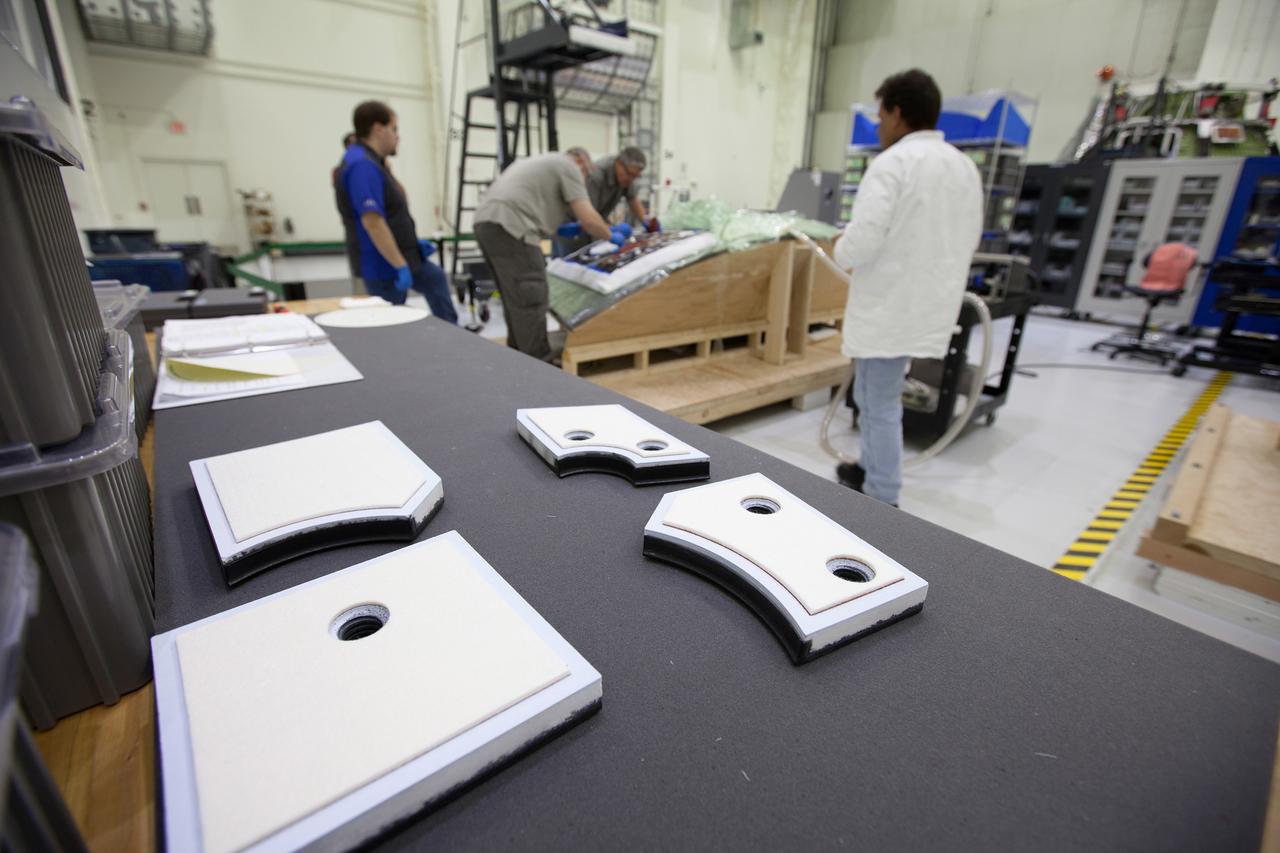

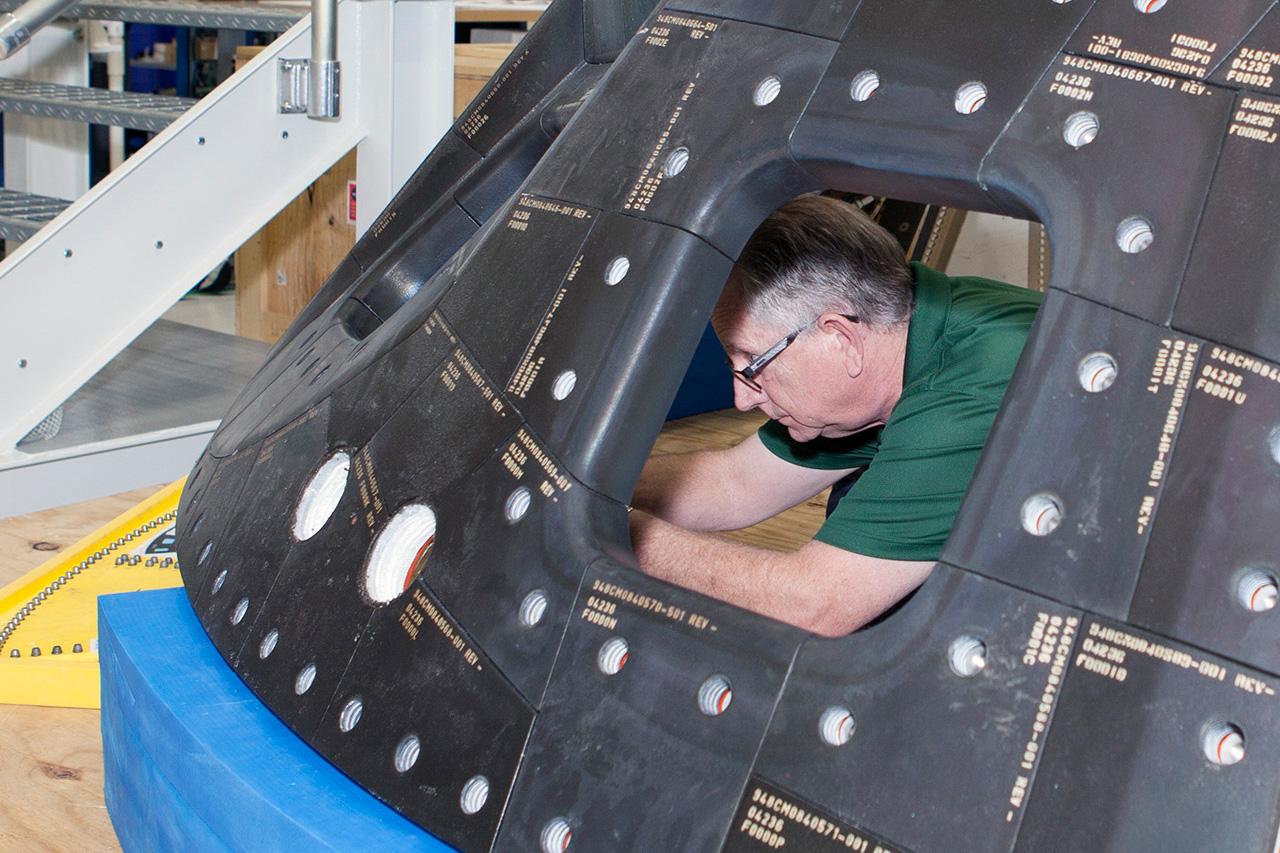
At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians bond thermal protection system tiles to Orion's backshell panels on July 8, 2016...While similar to those used on the space shuttle, Orion only requires about 1,300 tiles compared to more than 24,000 on the shuttle. The tiles, along with the spacecraft’s heat shield, will protect Orion from the 5,000 degree Fahrenheit heat of re-entry.
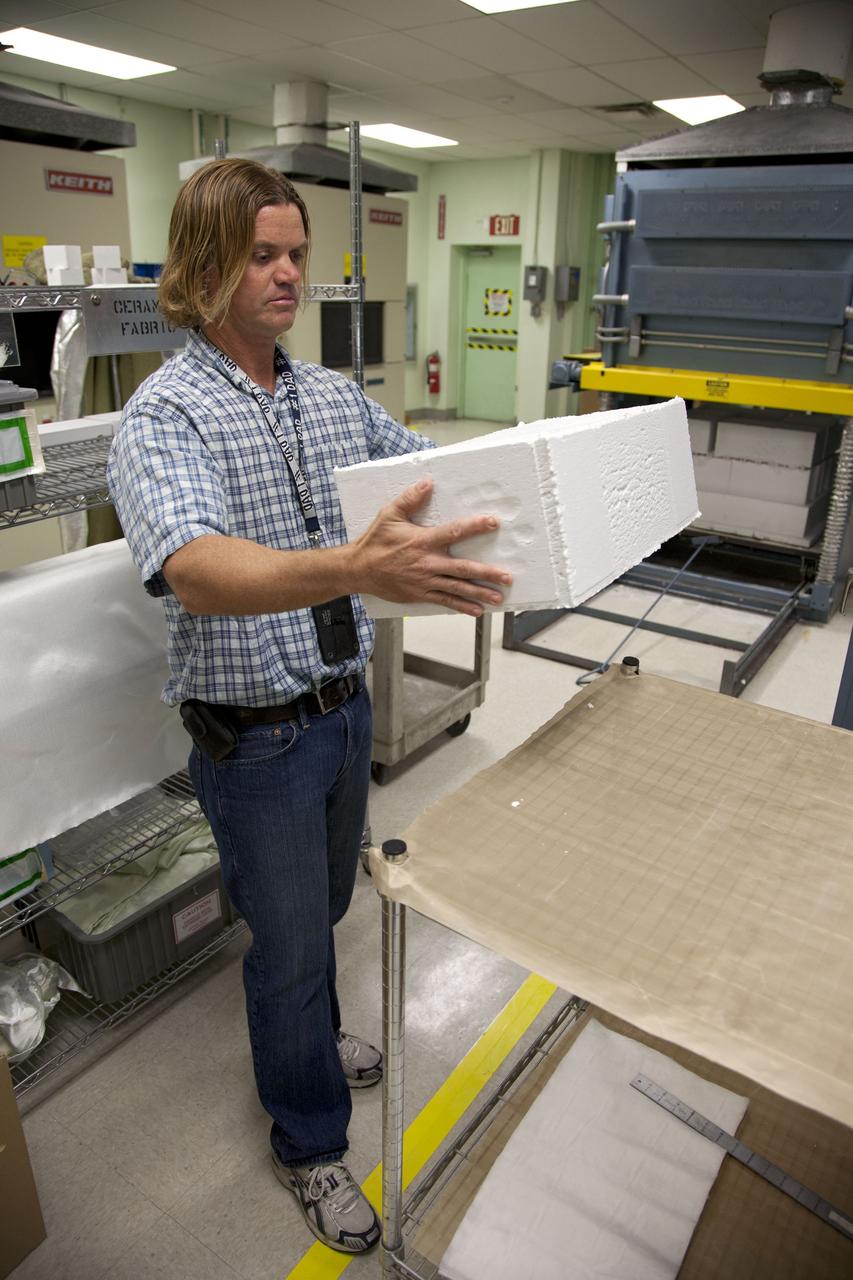

Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, unpacks the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The tiles are being manufactured and inspected in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. The tiles will be baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

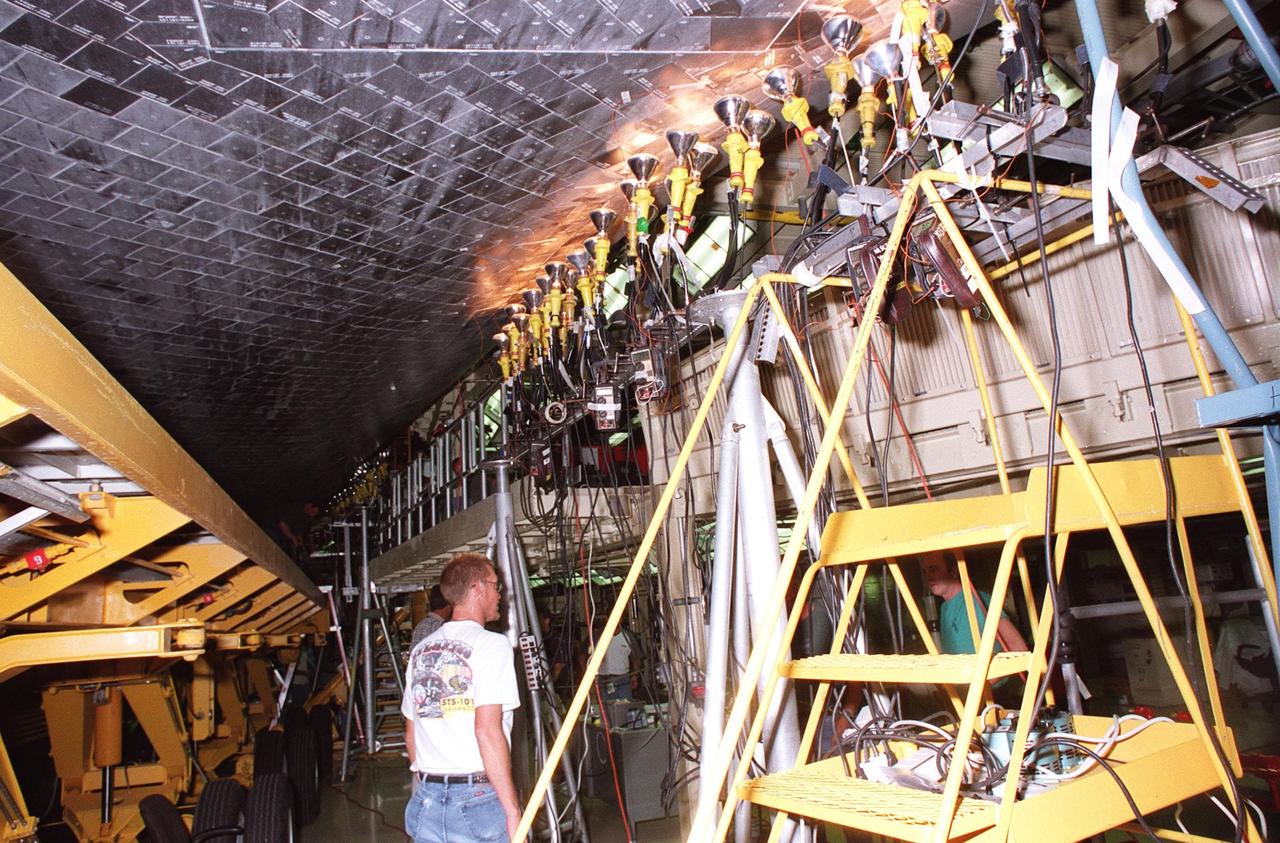
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker points to some of the tiles on orbiter Atlantis that are being dried by clusters of 200-300 watt heat lamps. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused a moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing. Engineers are evaluating the current procedures to assure the tiles are in a safe and flight-ready condition

At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians bond thermal protection system tiles to Orion's backshell panels on July 8, 2016...While similar to those used on the space shuttle, Orion only requires about 1,300 tiles compared to more than 24,000 on the shuttle. The tiles, along with the spacecraft’s heat shield, will protect Orion from the 5,000 degree Fahrenheit heat of re-entry.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker points to some of the tiles on orbiter Atlantis that are being dried by clusters of 200-300 watt heat lamps. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused a moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing. Engineers are evaluating the current procedures to assure the tiles are in a safe and flight-ready condition

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance technician Damon Petty appies a TUFI coating to Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
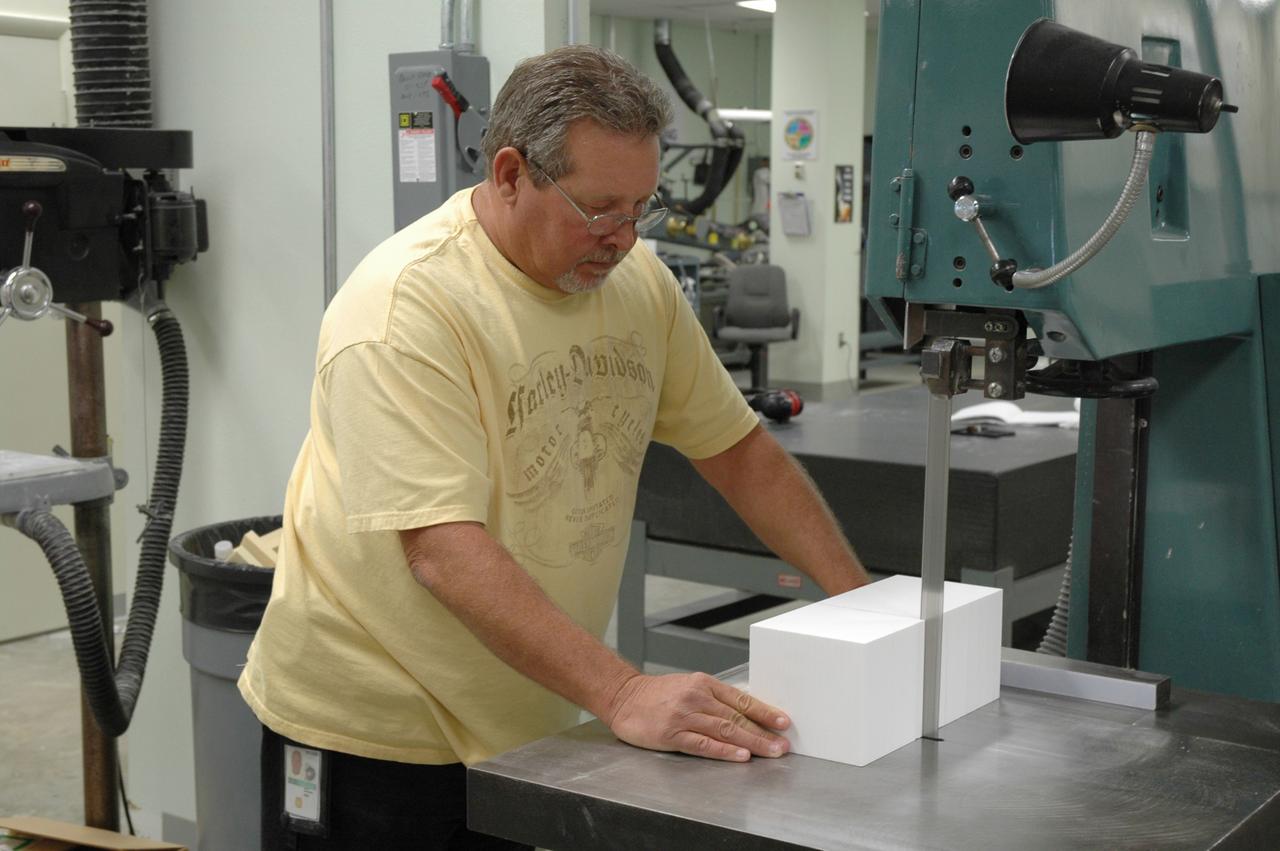

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician cuts a block of Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
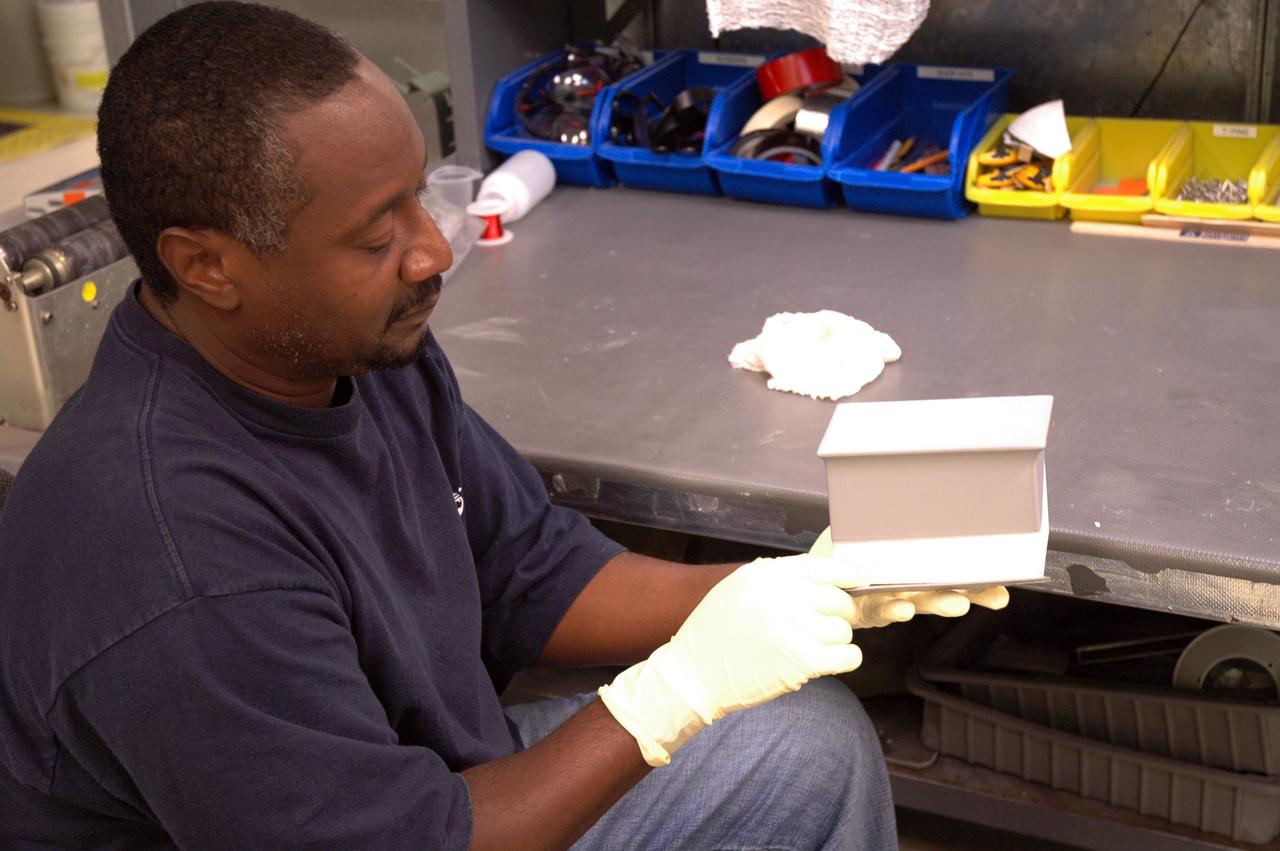

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the tile shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker holds one of the Boeing Replacement Insulation 18, or BRI-18, tiles being prepared for installation on space shuttles. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing other tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high, such as the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
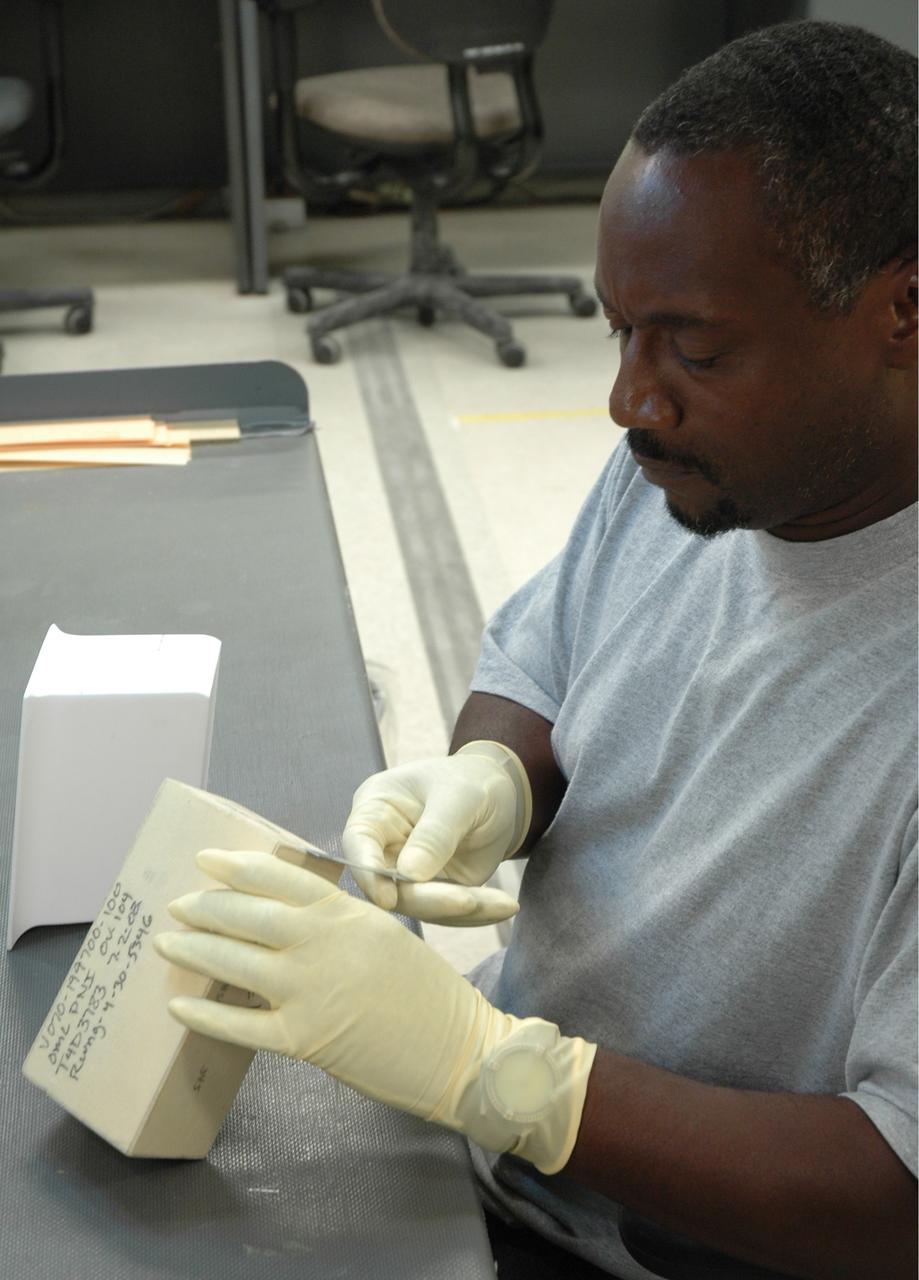

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks a Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
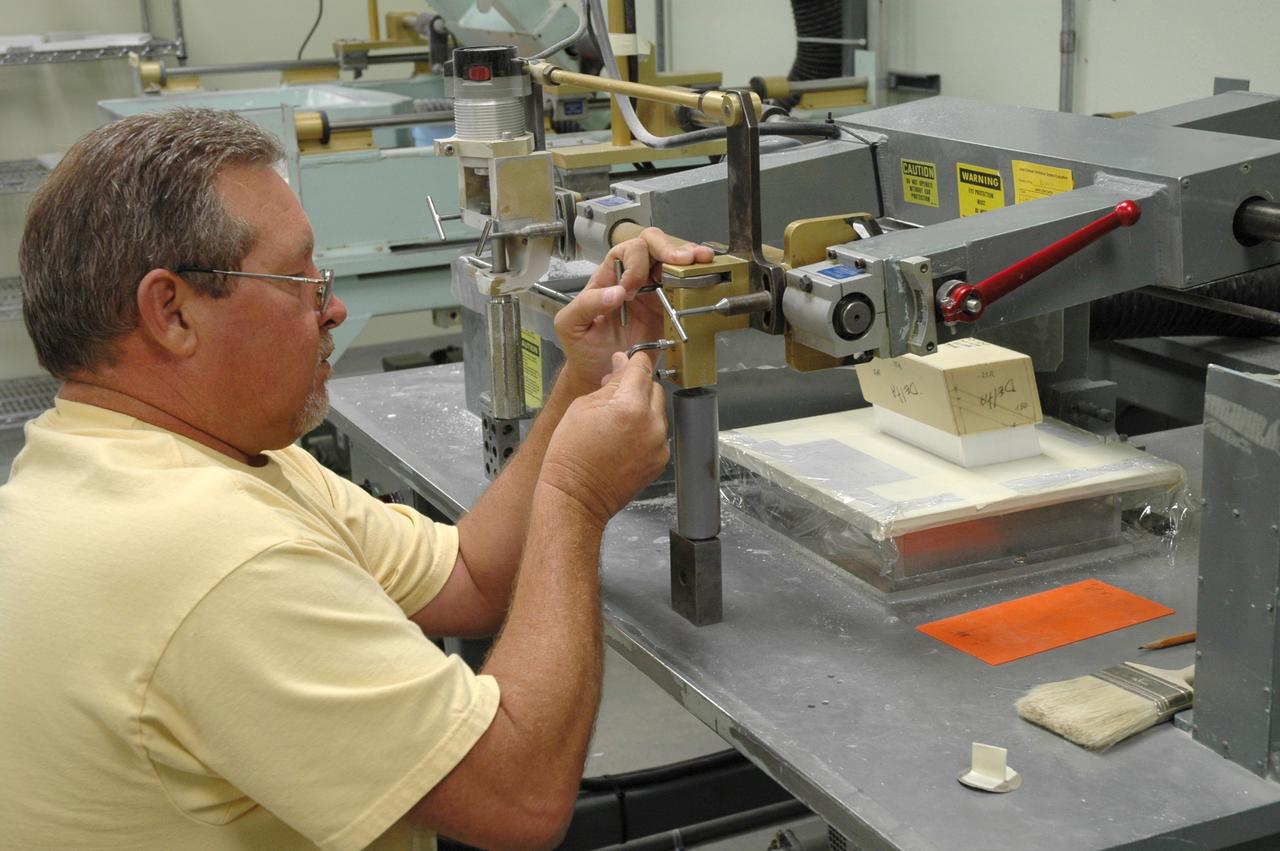

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance machinist, Tony Rollins, is setting up the tracer mill to machine the Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
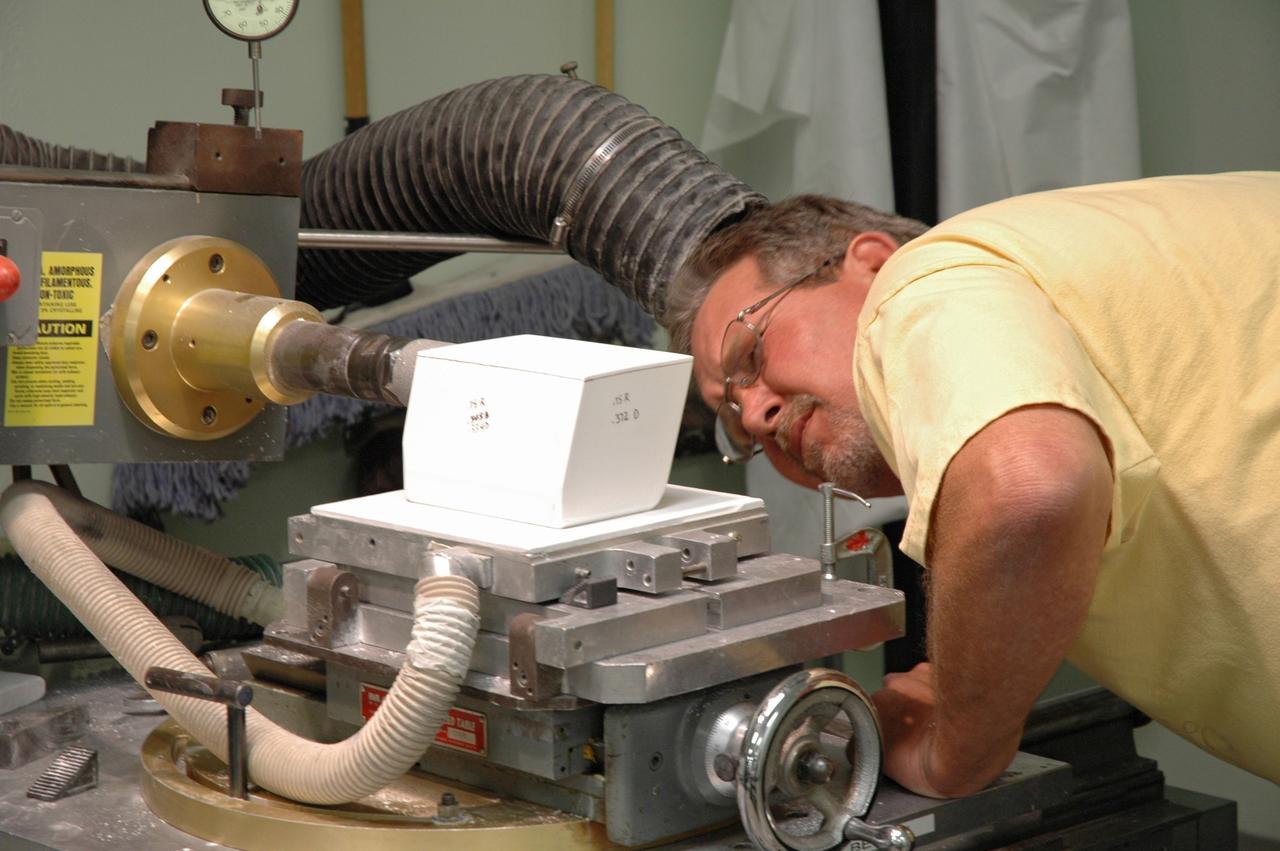

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks the shape of Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile he cut. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
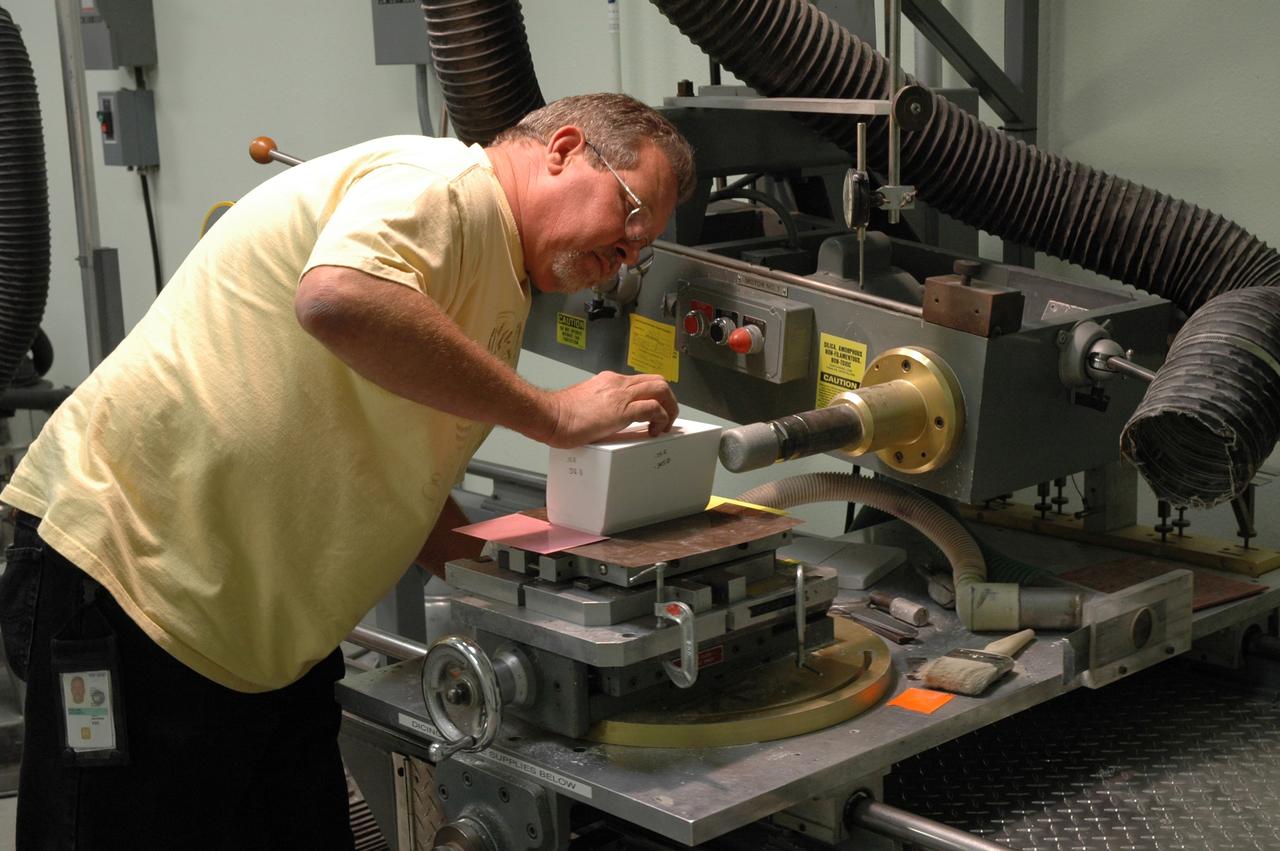

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a United Space Alliance technician checks the Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tile he cut. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
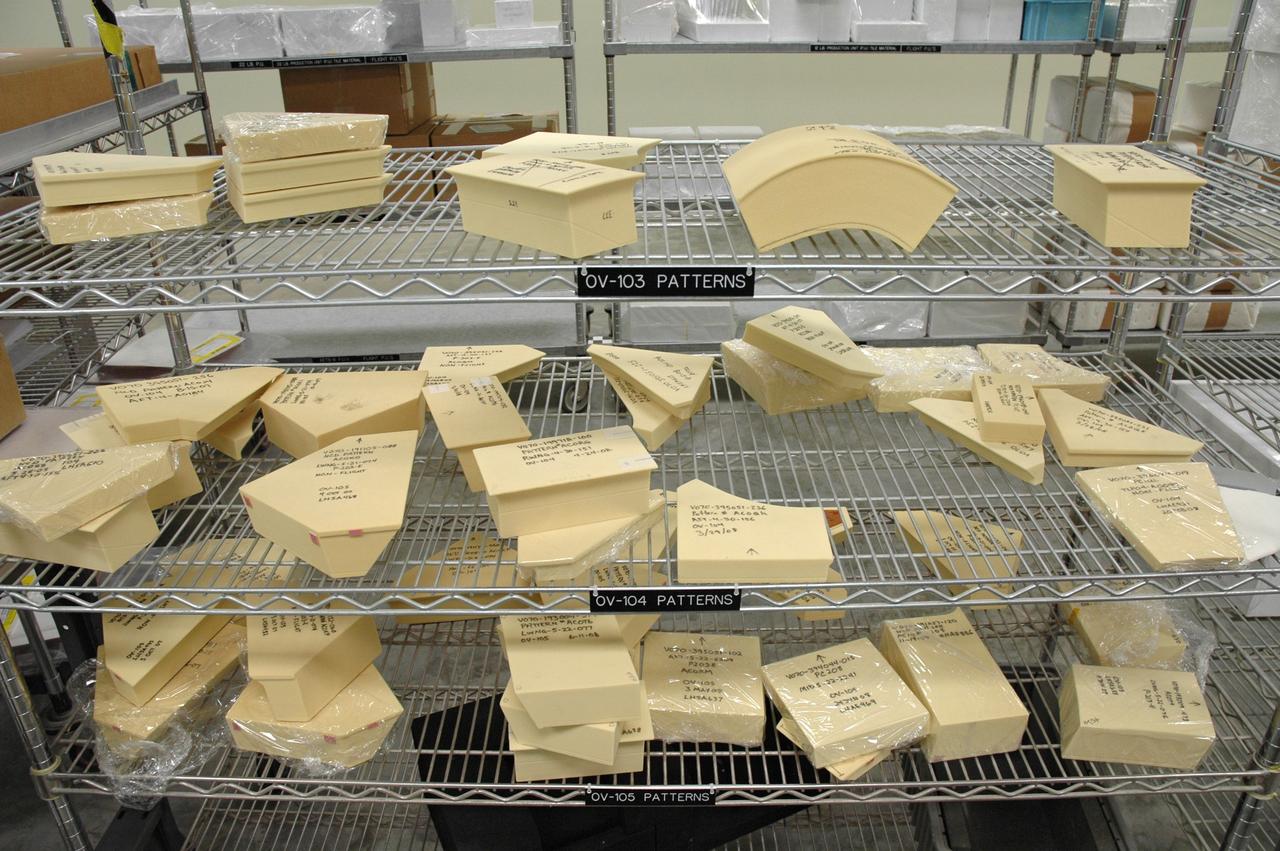

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Tile Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Boeing Rigid Insulation-18, or BRI-18, tiles of different shapes await use on the three orbiters: Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour. BRI-18 is the strongest material used for thermal insulation on the orbiters and, when coated to produce toughened unipiece fibrous insulation, provides a tile with extremely high-impact resistance. It is replacing tiles on areas of the vehicle where impact risk is high. These areas include the landing gear doors, the wing leading edge and the external tank doors. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
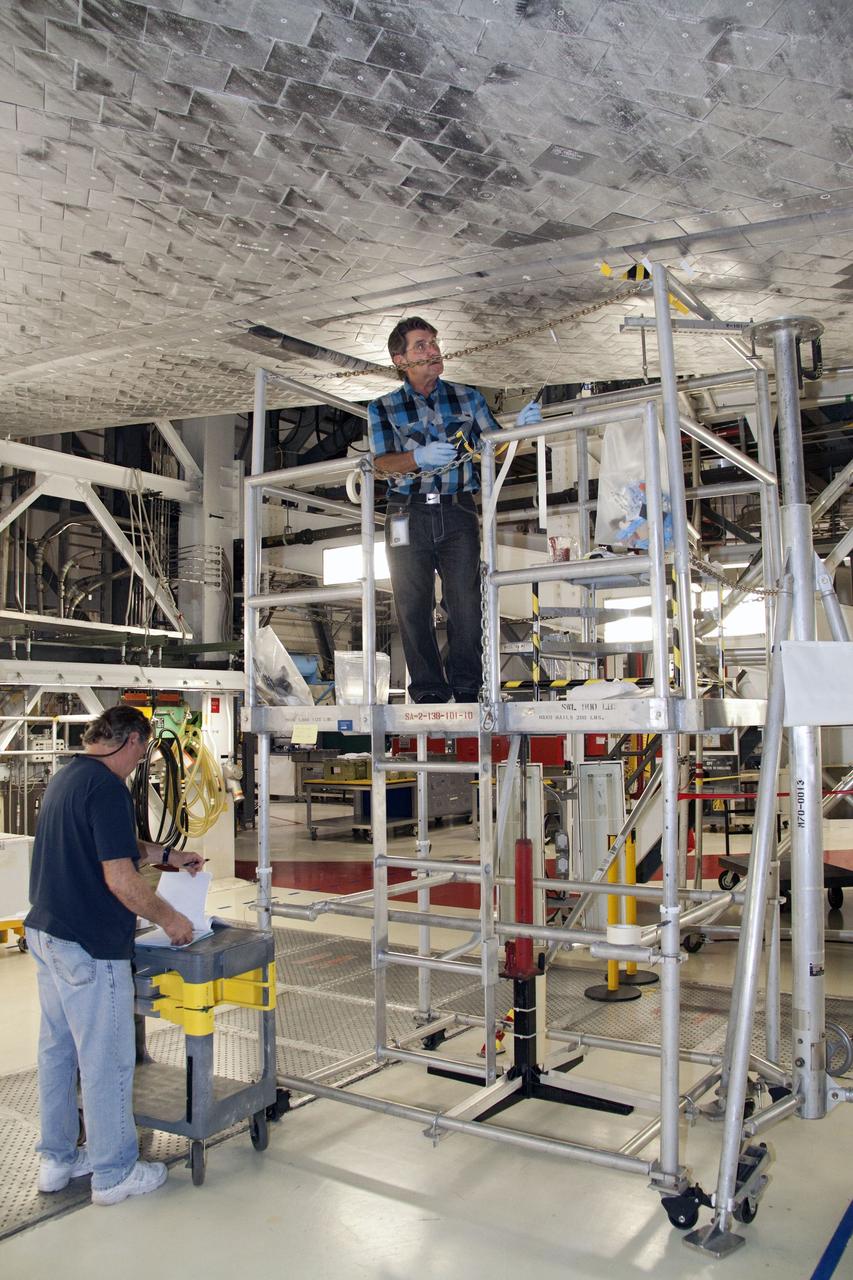

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician is preparing to work on replacing some of space shuttle Atlantis' heat shield tiles. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
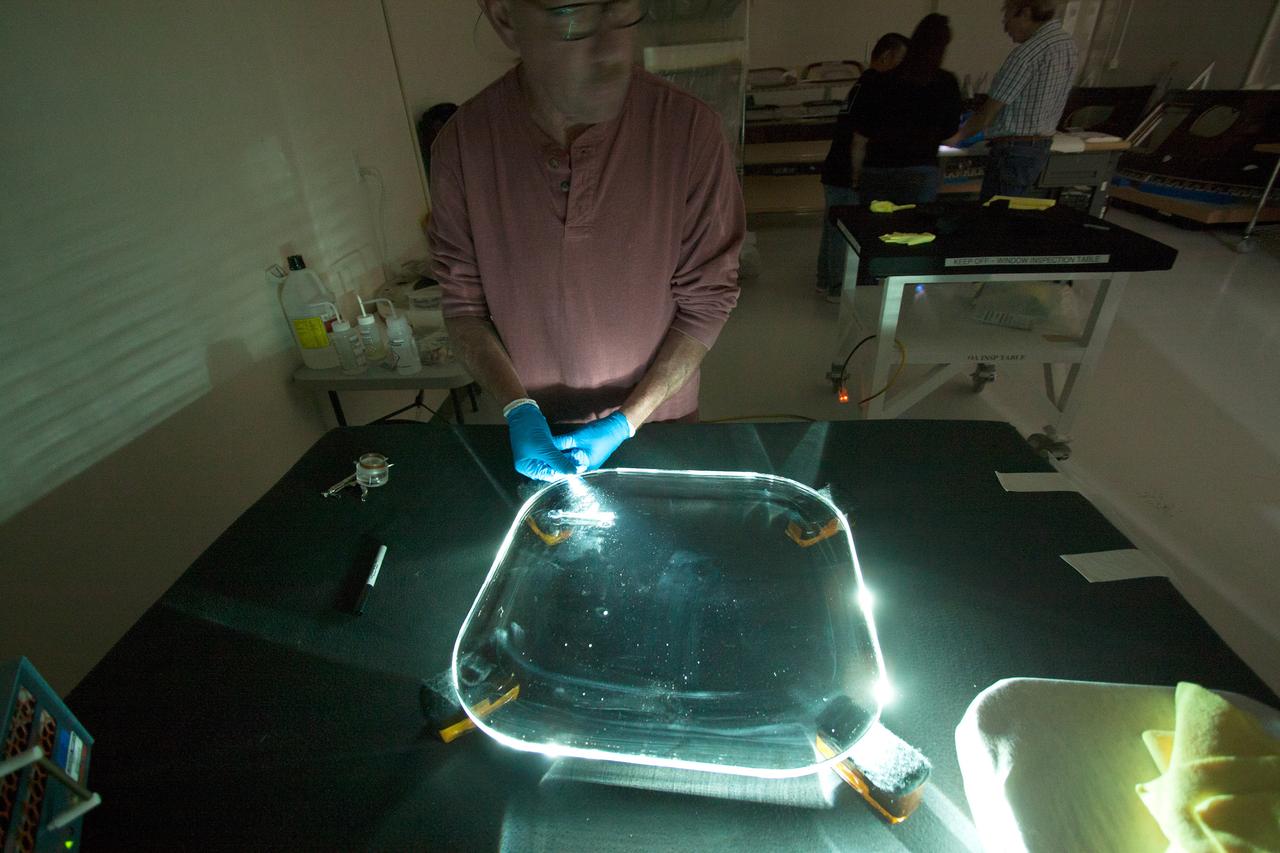

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
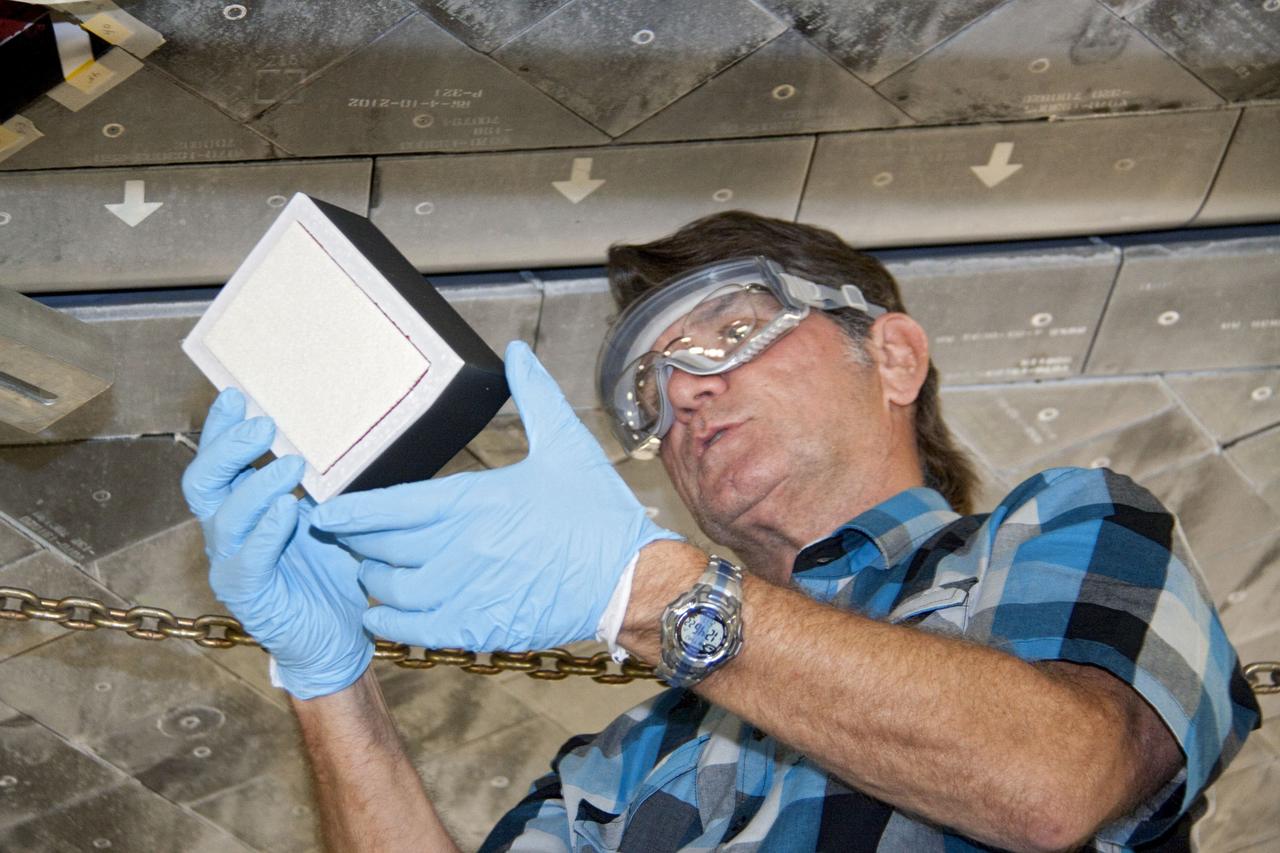

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician closely inspects a heat shield tile for space shuttle Atlantis before securing it into position. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
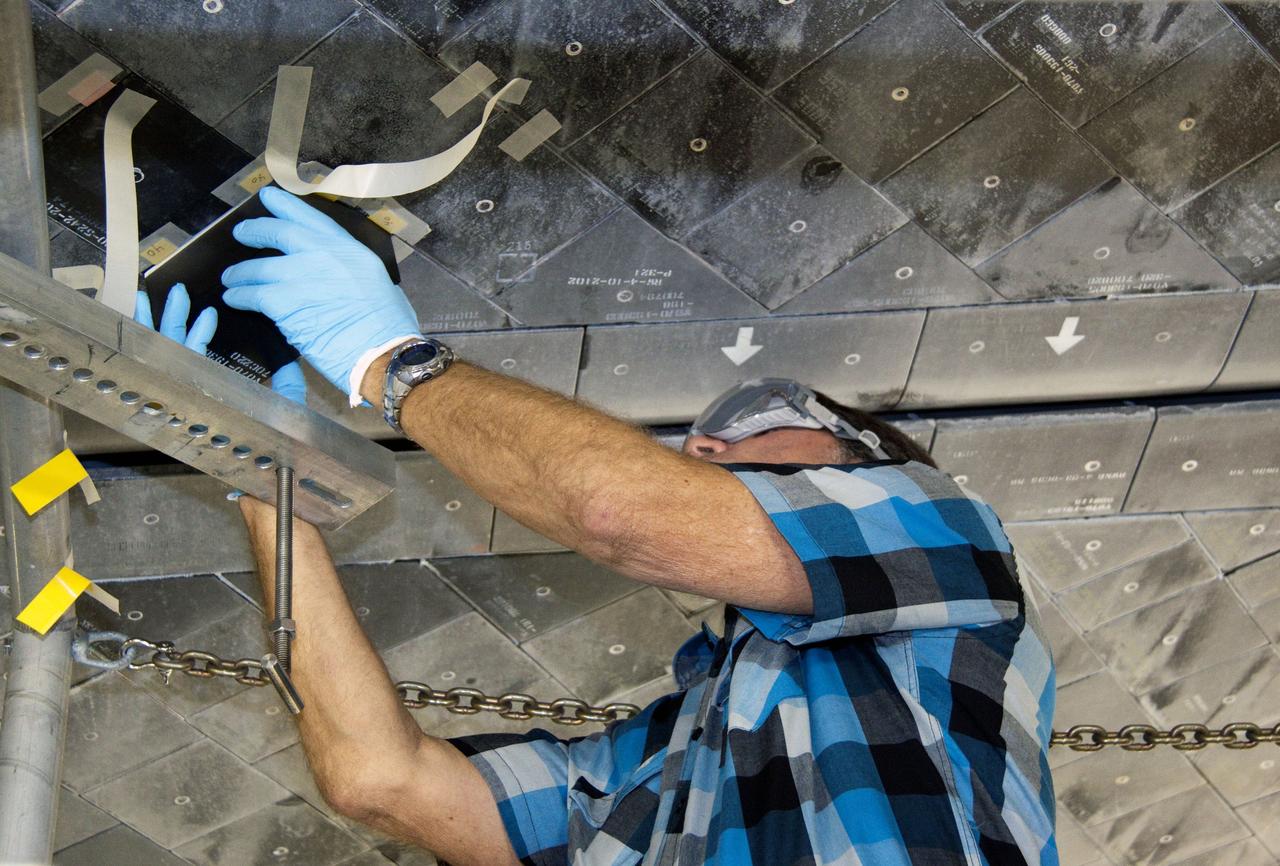

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician places a heat shield tile into position under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
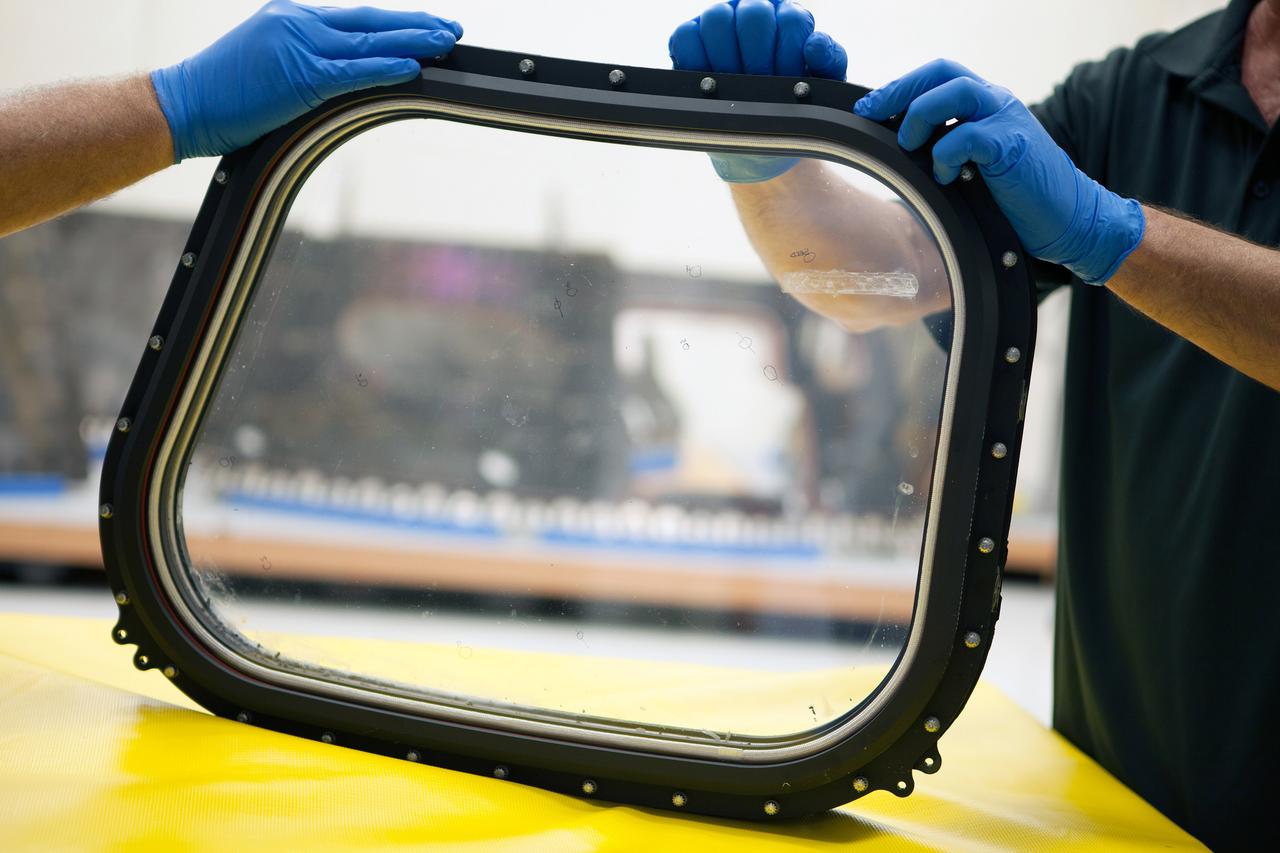

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
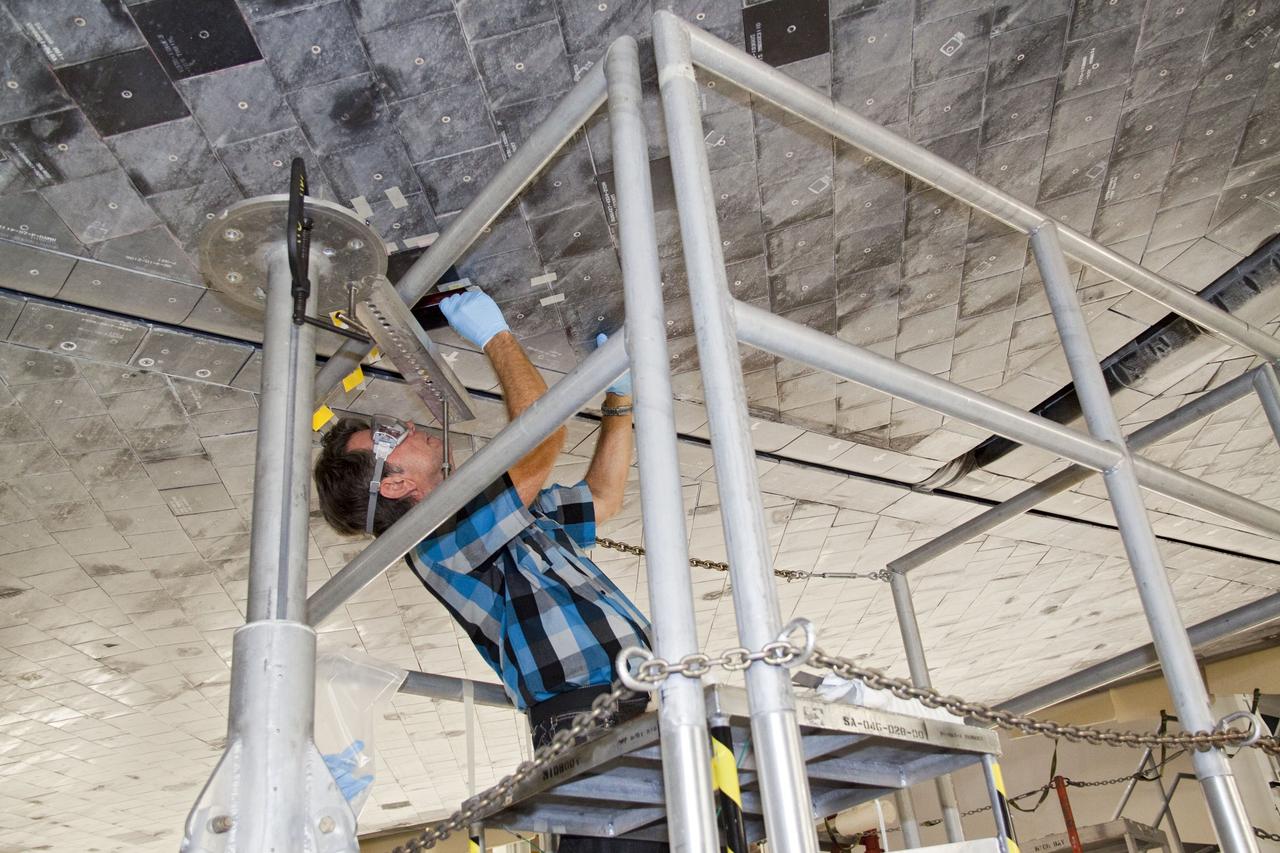

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician inspects the area on space shuttle Atlantis' underside before a heat shield tile is installed. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System that protects the shuttle against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will carry the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
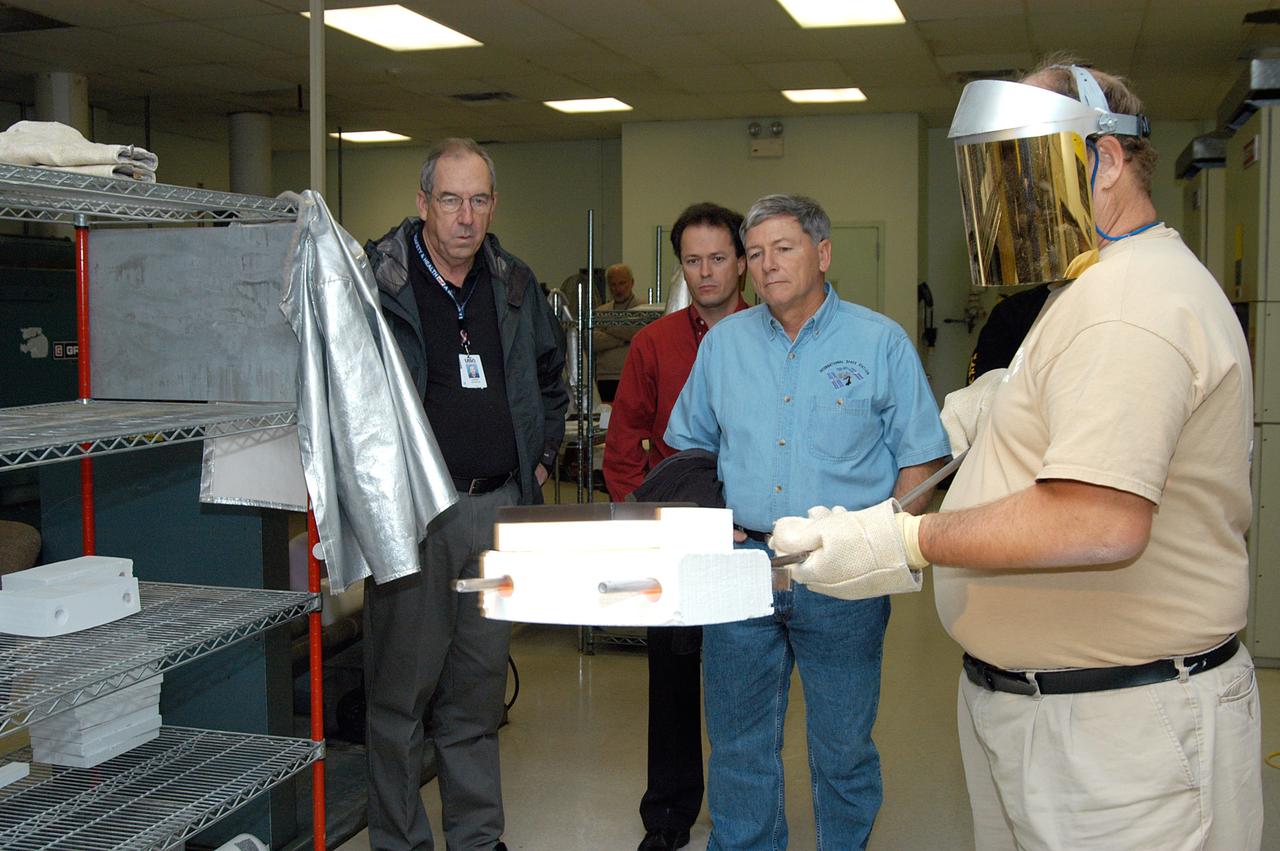

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance (USA) Vice President and Space Shuttle Program Manager Howard DeCastro (left) and NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Station and Shuttle Programs Michael Kostelnik (third from left) watch as a USA technician (right) creates a tile for use in the Shuttle's Thermal Protection System (TPS). NASA and USA Space Shuttle program management are participating in a leadership workday. The day is intended to provide management with an in-depth, hands-on look at Shuttle processing activities at KSC.
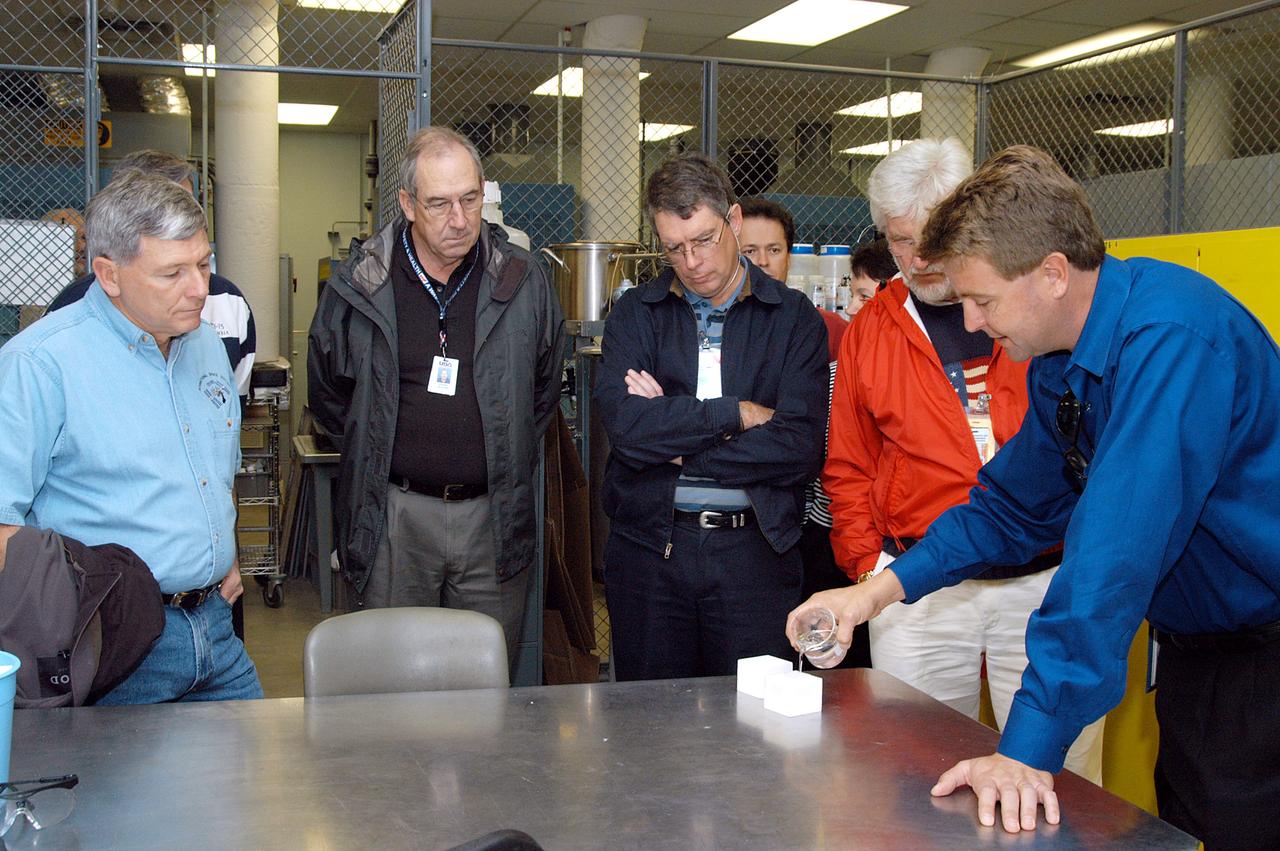

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- From left, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Station and Shuttle Programs Michael Kostelnik and United Space Alliance (USA) Vice President and Space Shuttle Program Manager Howard DeCastro are briefed on the properties of the tile used in the Shuttle's Thermal Protection System (TPS) by USA Manager of the TPS Facility Martin Wilson (right). NASA and USA Space Shuttle program management are participating in a leadership workday. The day is intended to provide management with an in-depth, hands-on look at Shuttle processing activities at KSC.
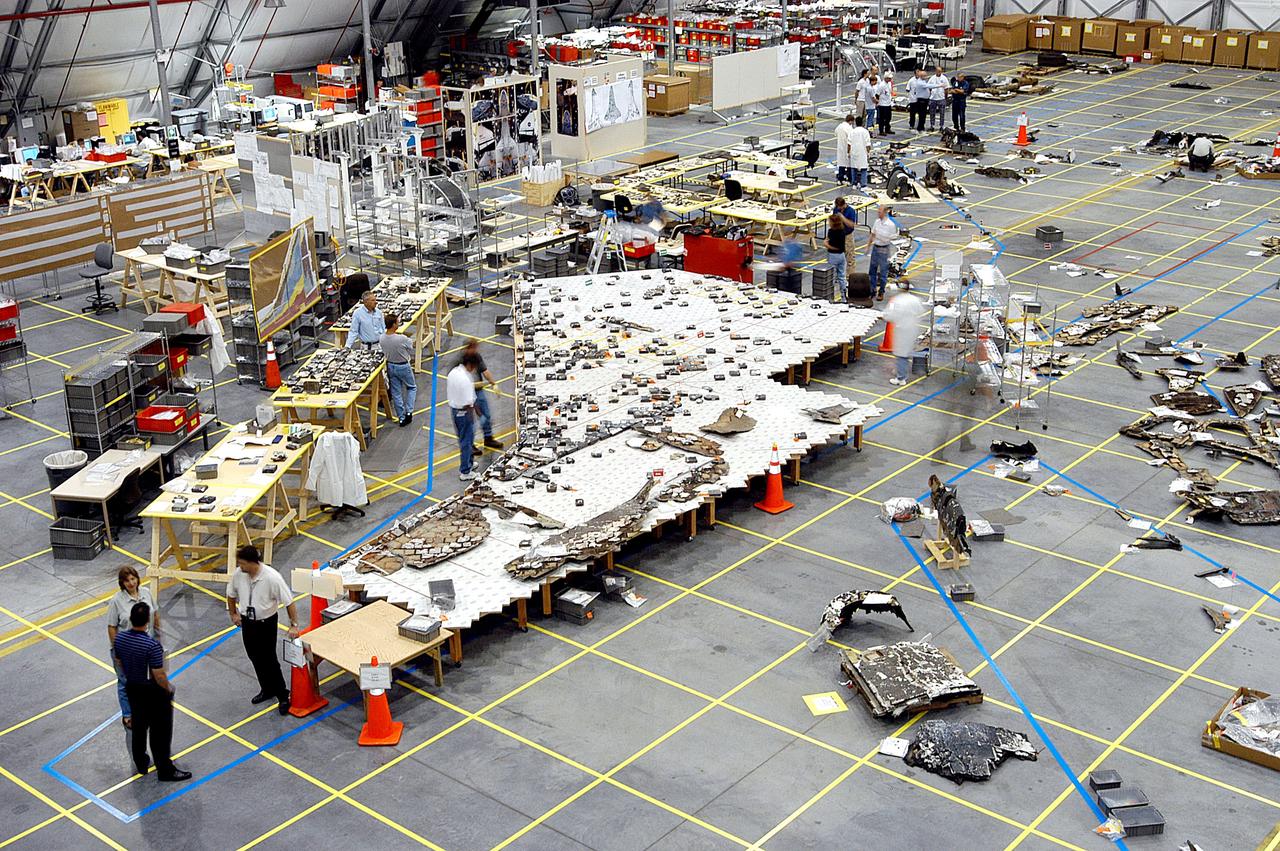

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV hangar, members of the Columbia Reconstruction Team work to identify pieces of Thermal Protection System tile from the left wing of Columbia recovered during the search and recovery efforts in East Texas. The items shipped to KSC number more than 82,000 and weigh 84,800 pounds or 38 percent of the total dry weight of Columbia. Of those items, 78,760 have been identified, with 753 placed on the left wing grid in the Hangar.
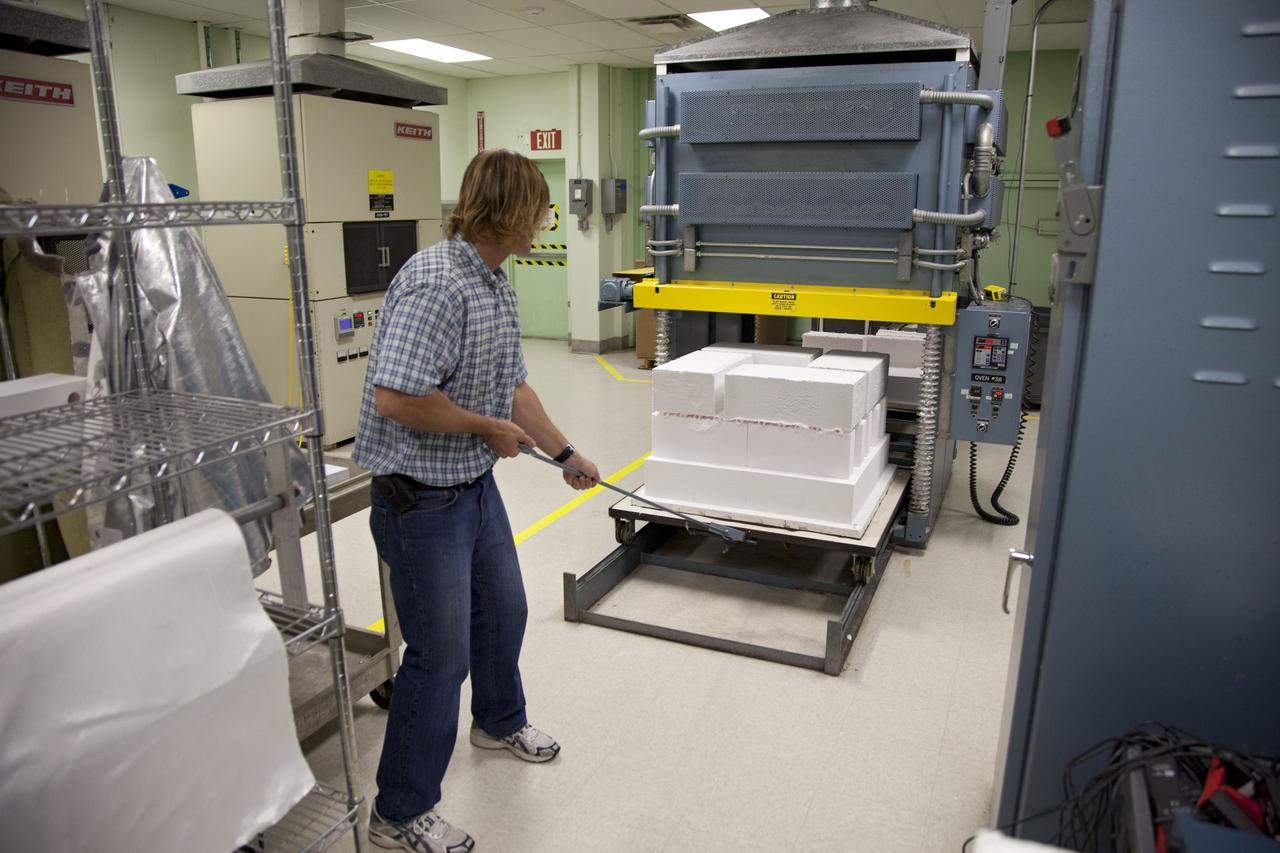

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, unloads the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The tiles are being manufactured and inspected in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. The tiles will be baked at 2,200 degrees F to cure their ceramic coating. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician prepares the surface under space shuttle Atlantis before installing a heat shield tile. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician has secured a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician prepares the surface under space shuttle Atlantis before installing a heat shield tile. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
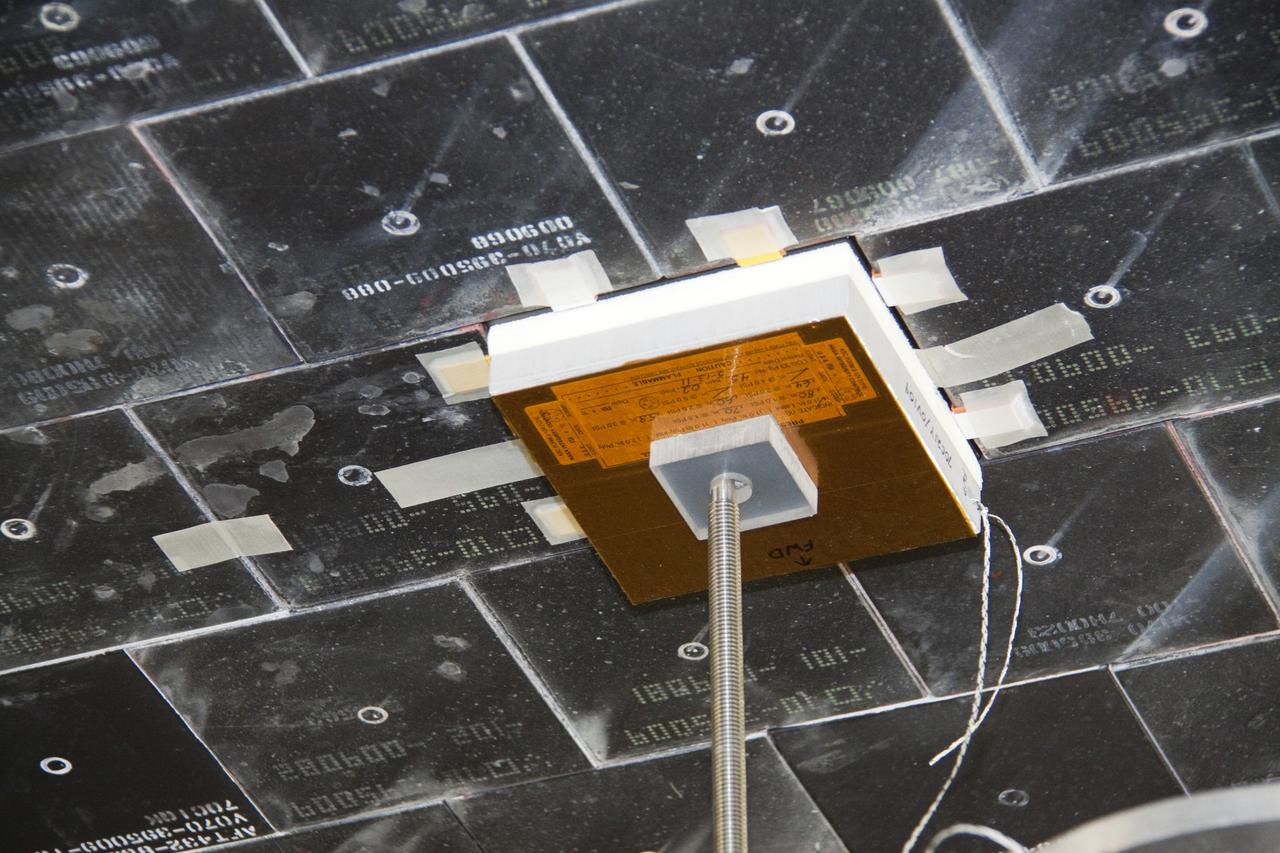
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician has secured a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis with a pressure fitting to ensure a tight bond. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a thermal protection system technician secures a newly installed heat shield tile in place under space shuttle Atlantis. The tiles are part of the Orbiter Thermal Protection System, thermal shields to protect against temperatures as high as 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit, which are produced during descent for landing. Atlantis is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. STS-135 is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last spaceflight for the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
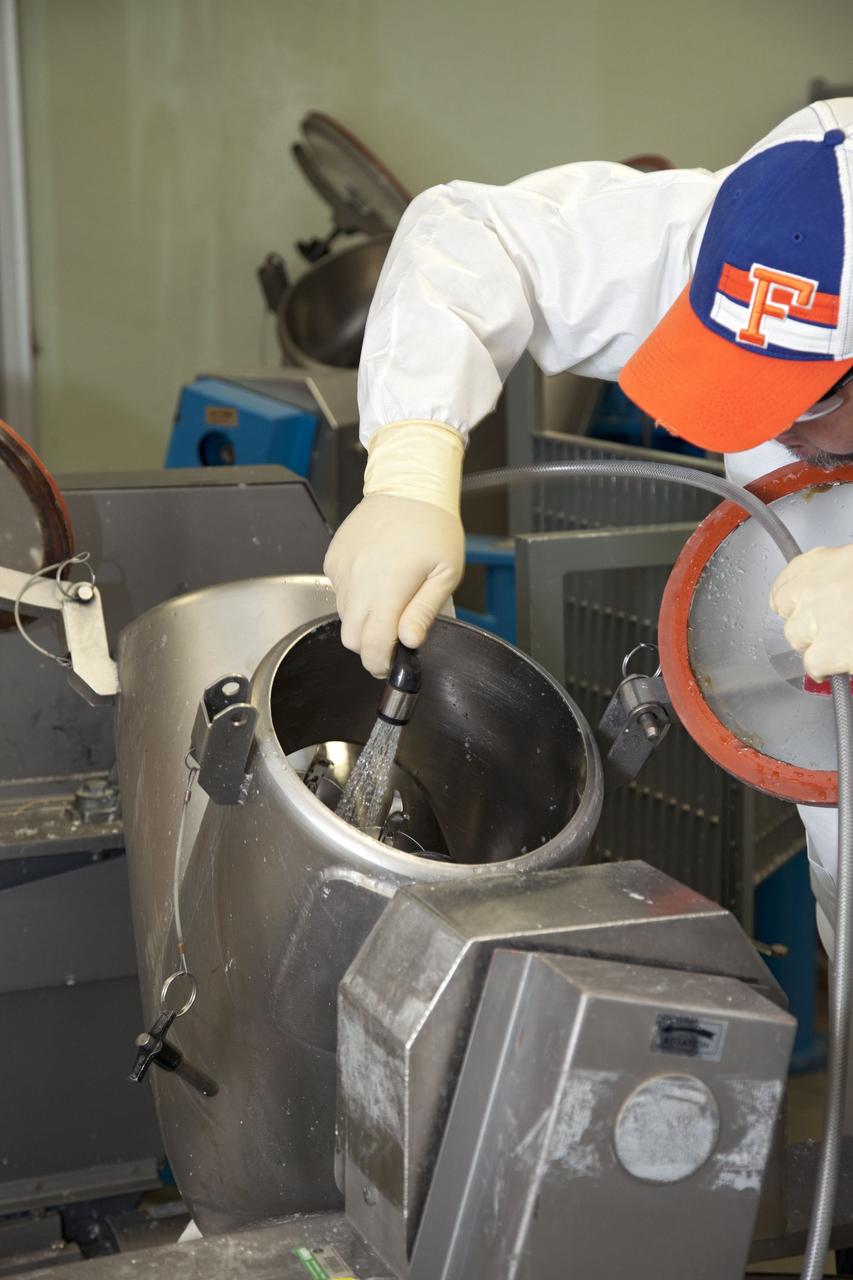

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
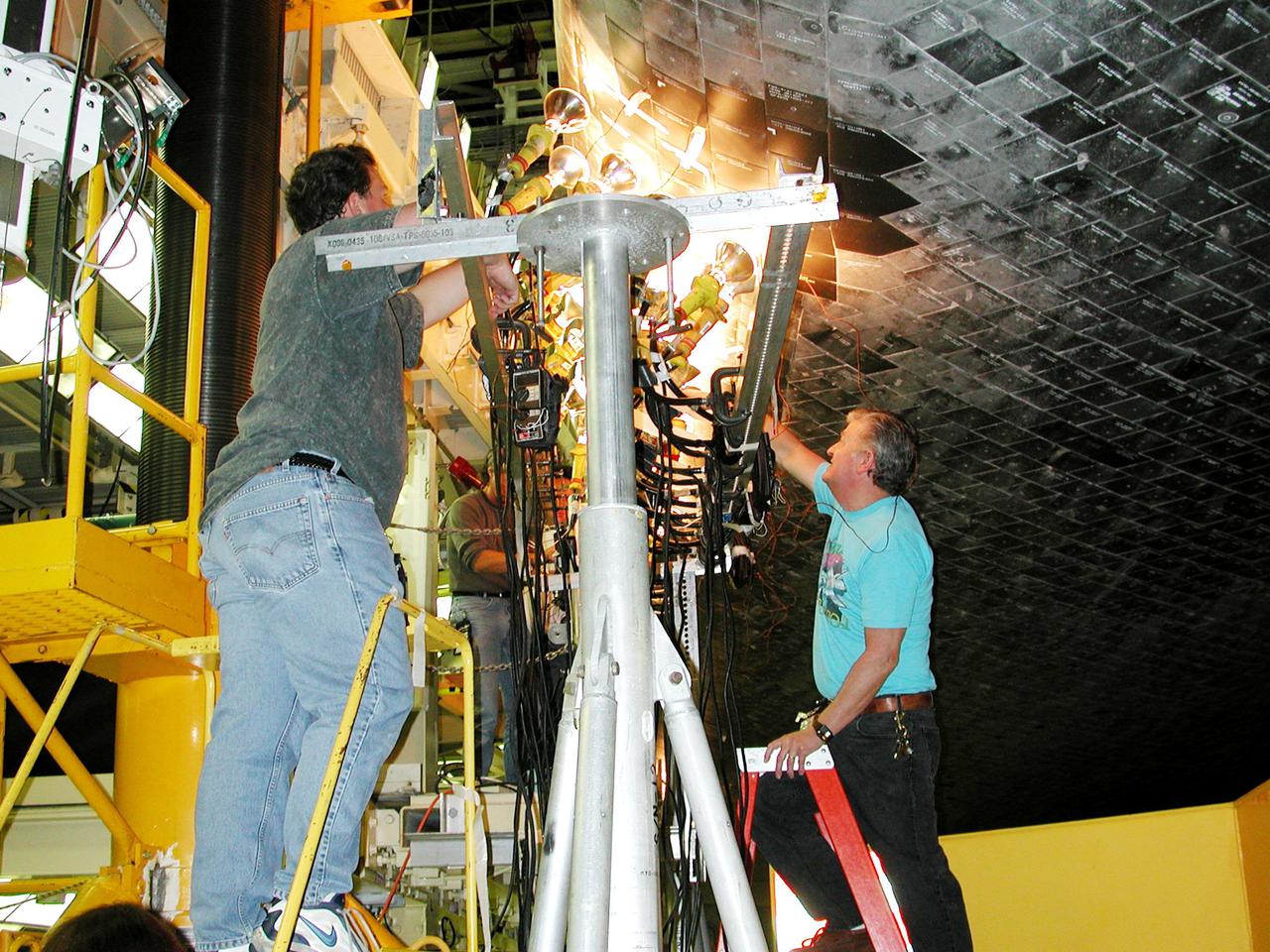

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
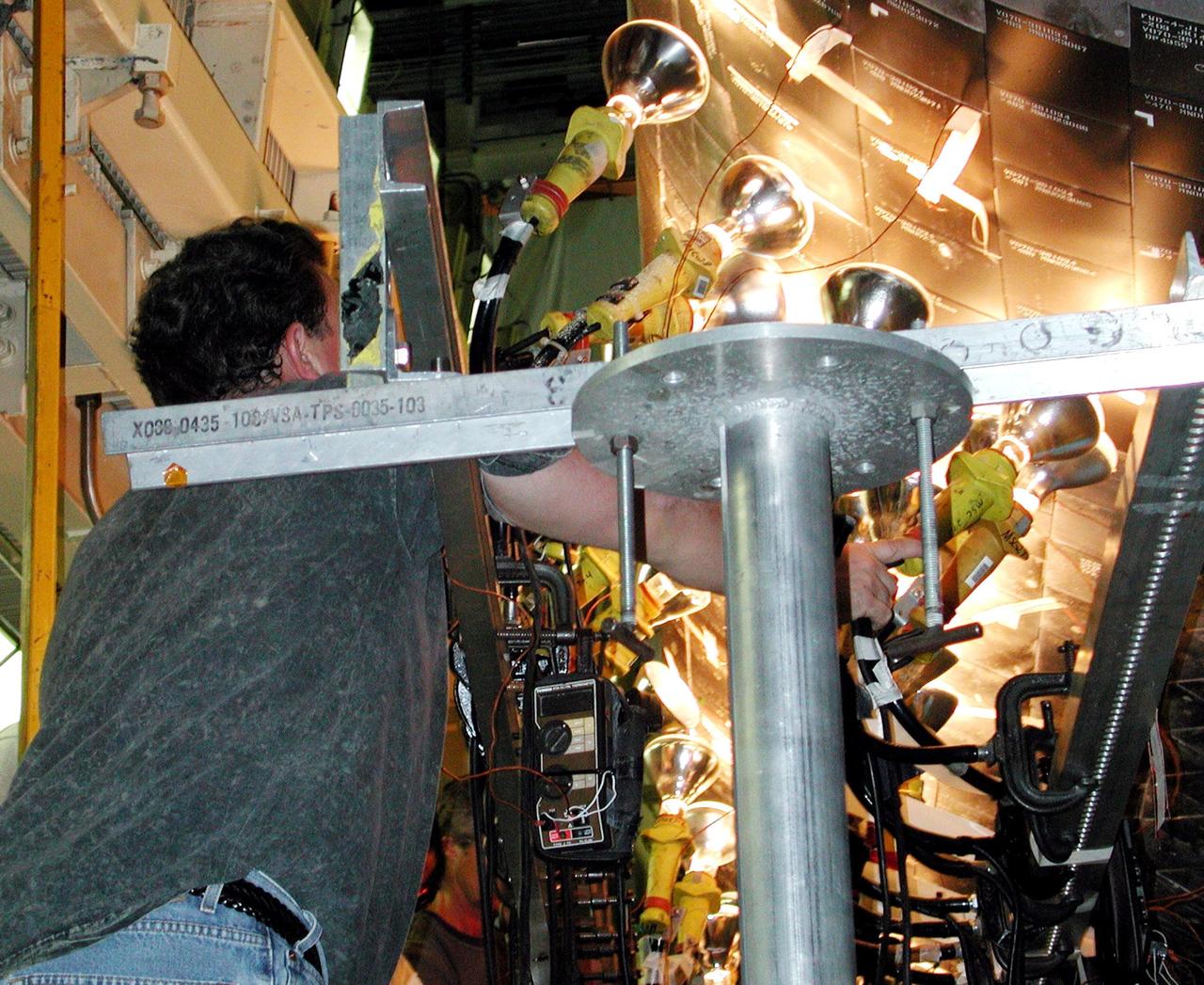

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing
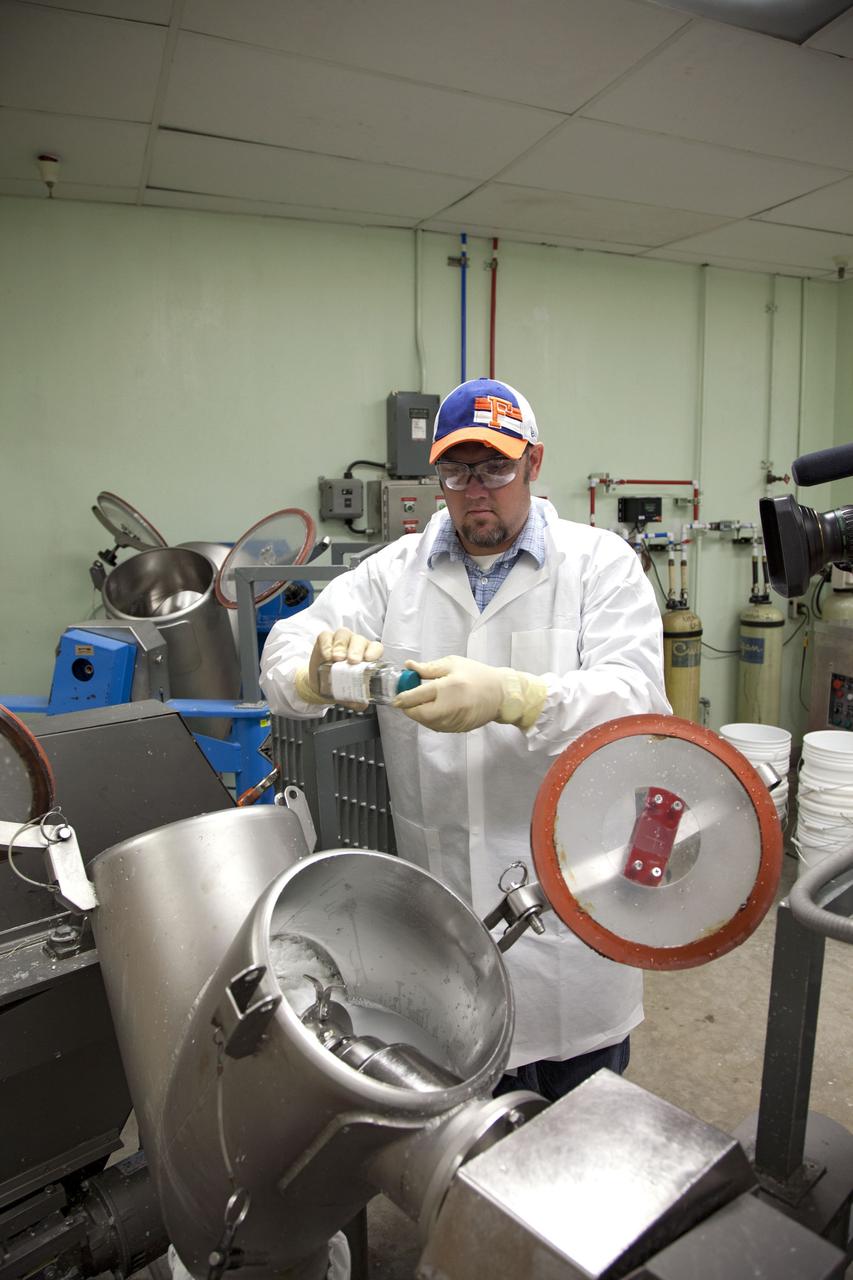

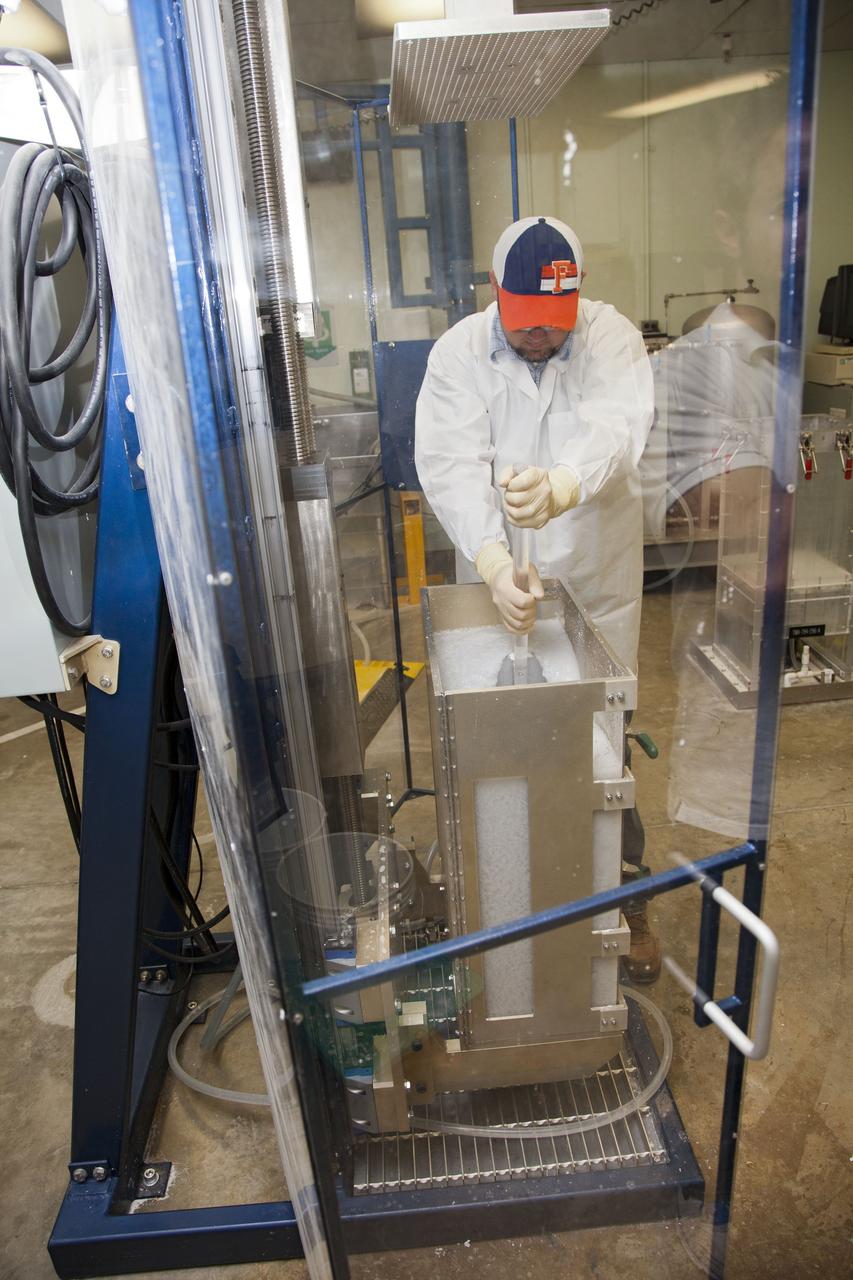
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
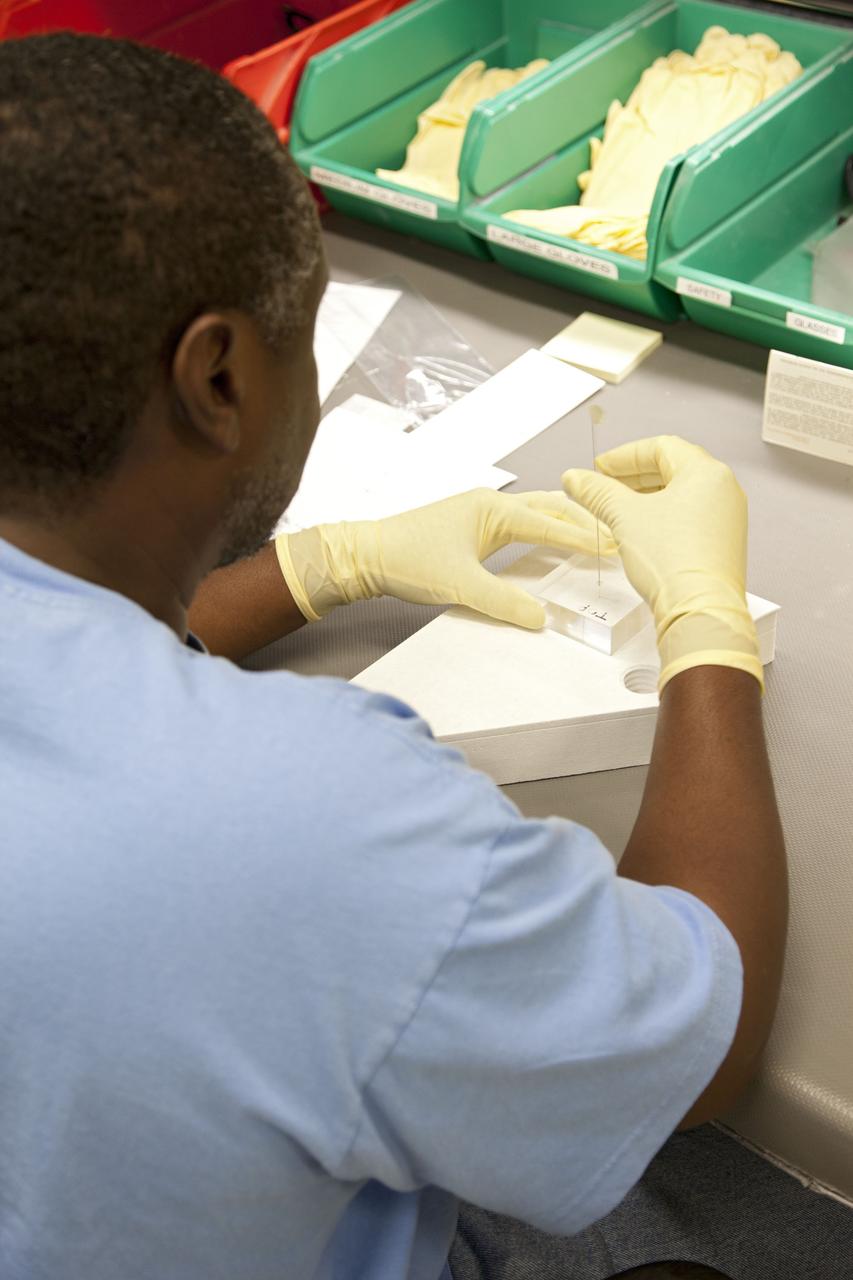
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Damon Petty, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects a heat shield tile that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing
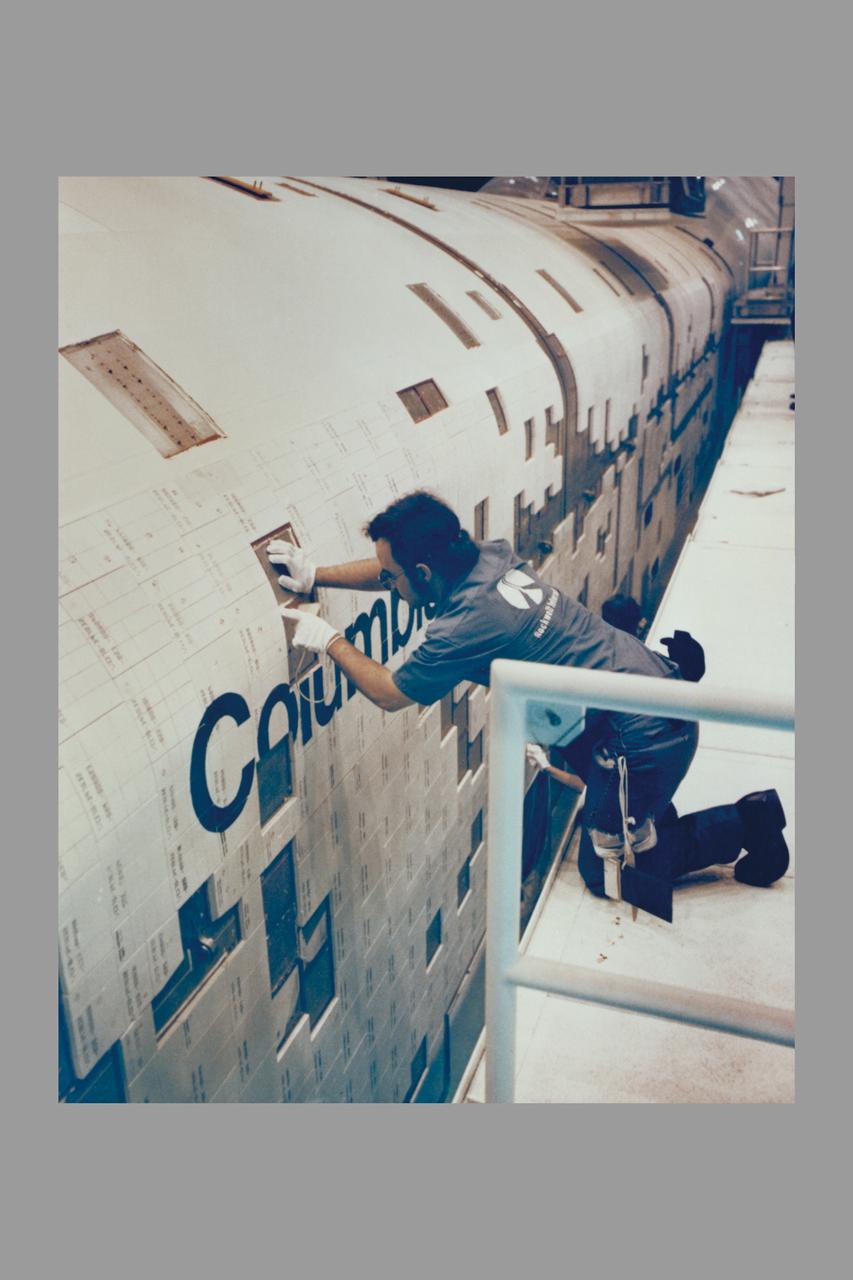

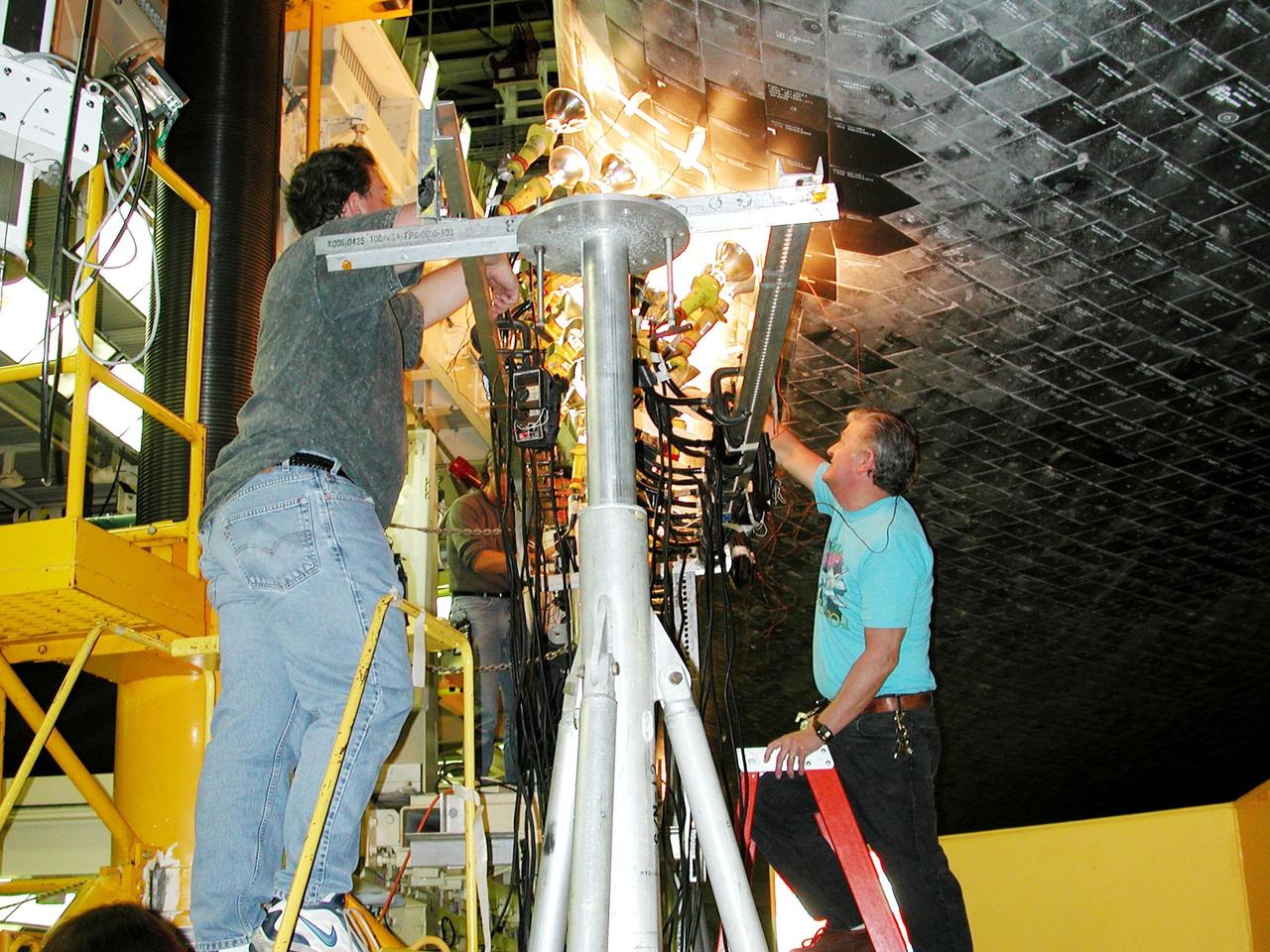
ROCKWELL INTERNATIONAL TECHNICIANS MOUNT SOME OF THE NEARLY 8,000 CERAMIC-COATED TILES THAT REMAIN TO BE INSTALLED ON THE EXTERNAL SURFACES OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA TO COMPLETE THE THERMAL PROTECTION SYSTEM THAT WILL ABSORB THE INTENSE HEAT OF REENTERING THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE AFTER A MISSION IN SPACE. TILE INSTALLATION IS DONE ON AN AROUND-THE-CLOCK BASIS IN THE ORBITER PROCESSING FACILITY WHERE COLUMBIA, THE FIRST IN A NEW BREED OF MANNED, REUSABLE SPACECRAFT, IS BEING READIED FOR THE FIRST LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE LATER THIS YEAR.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- John Livingston, a United Space Alliance engineer at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, describes the properties of the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The tiles are being manufactured and inspected in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
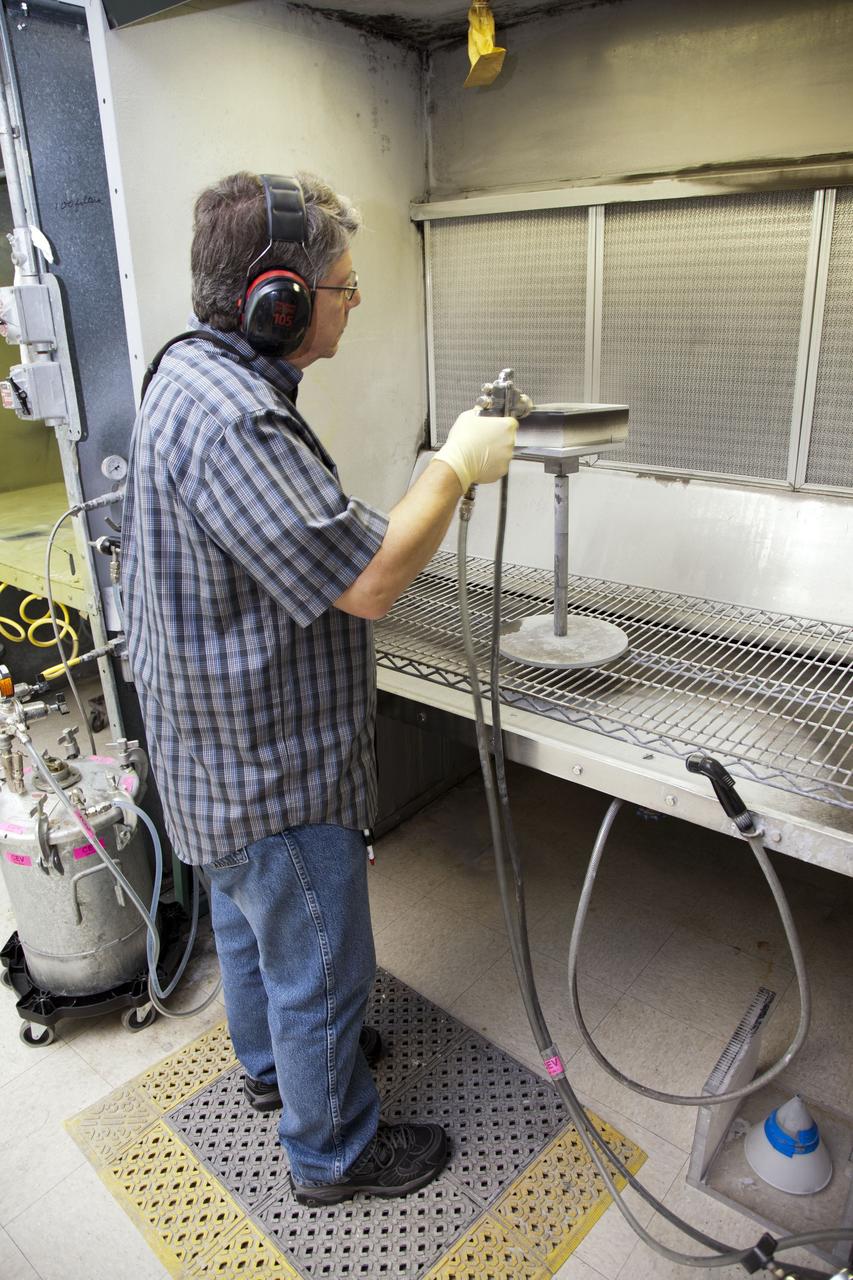

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Frank Pelkey, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects a heat shield tile that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
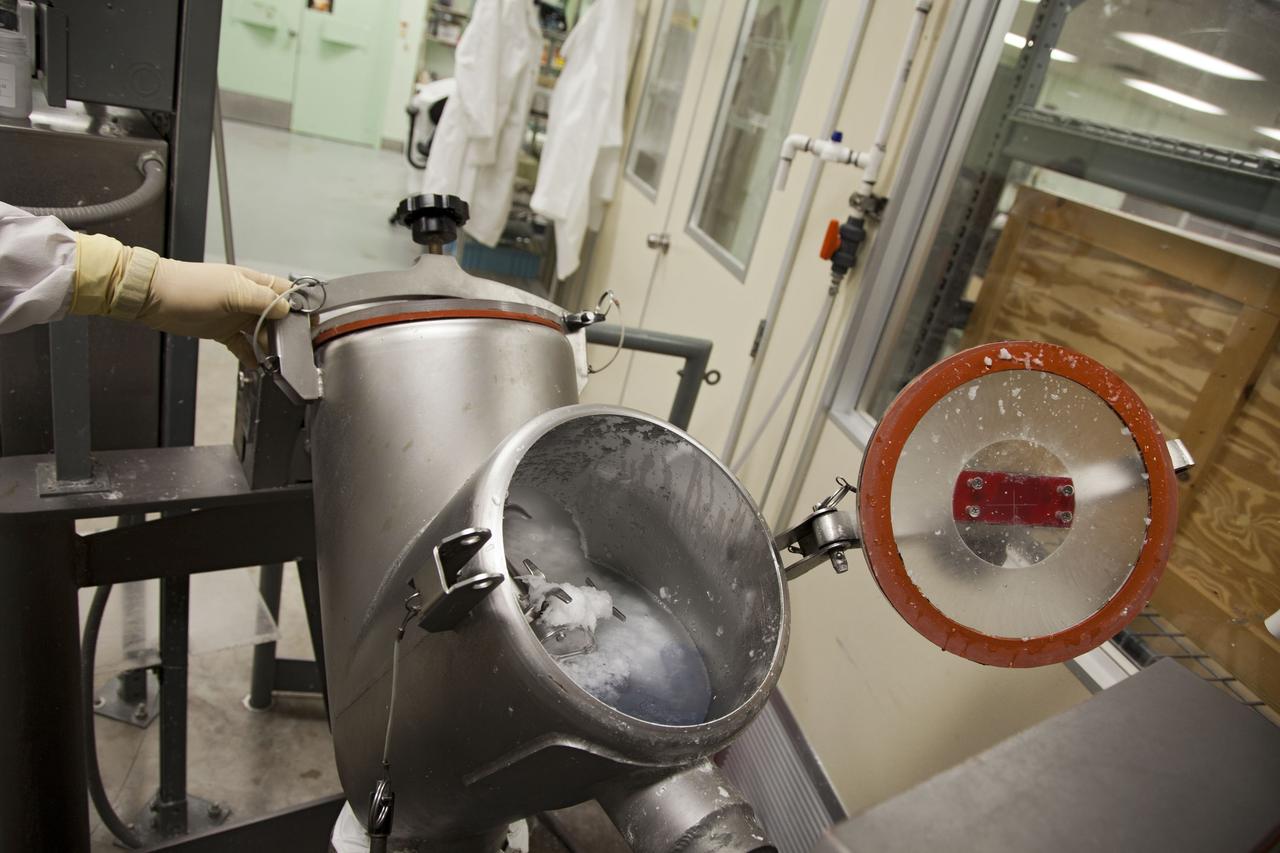

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
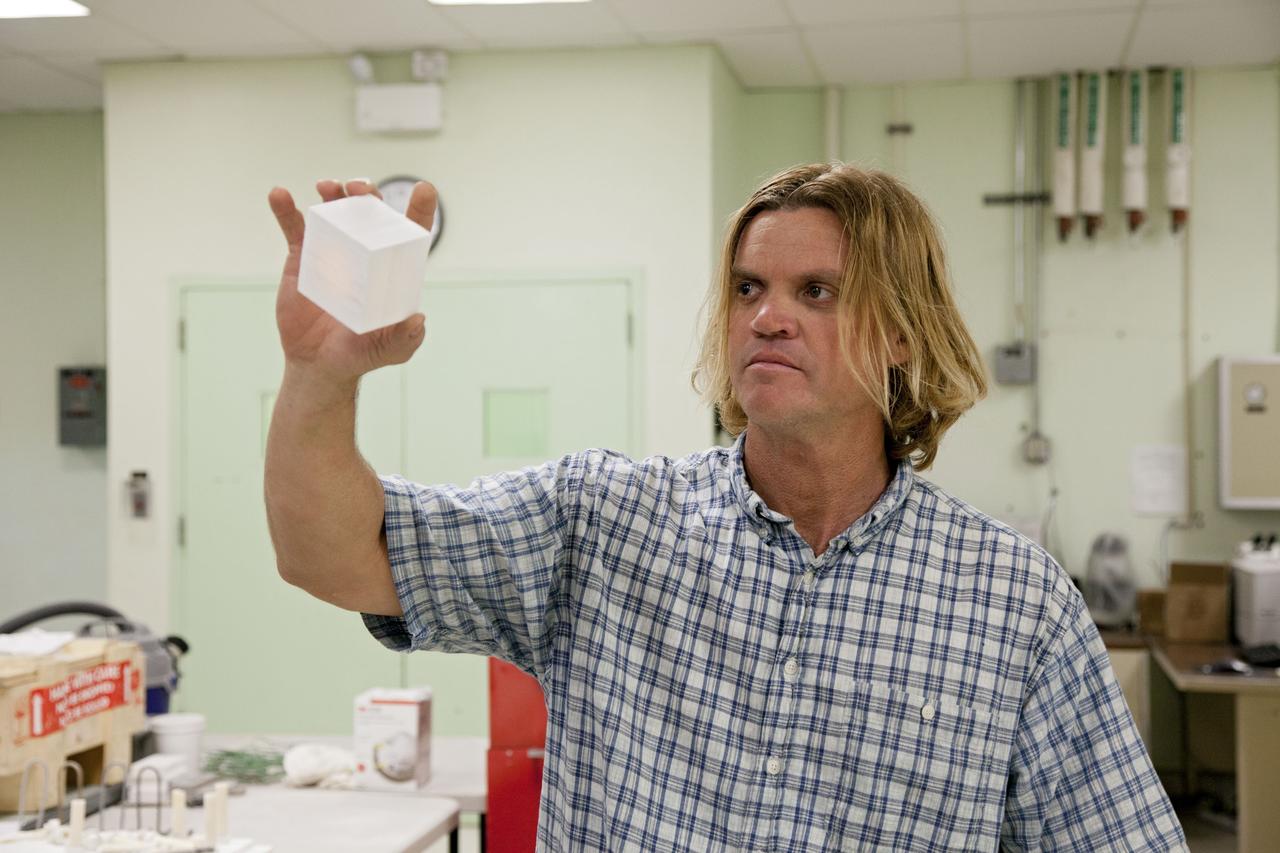

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tim Wright, a United Space Alliance engineering manager at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, explains the properties of the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin

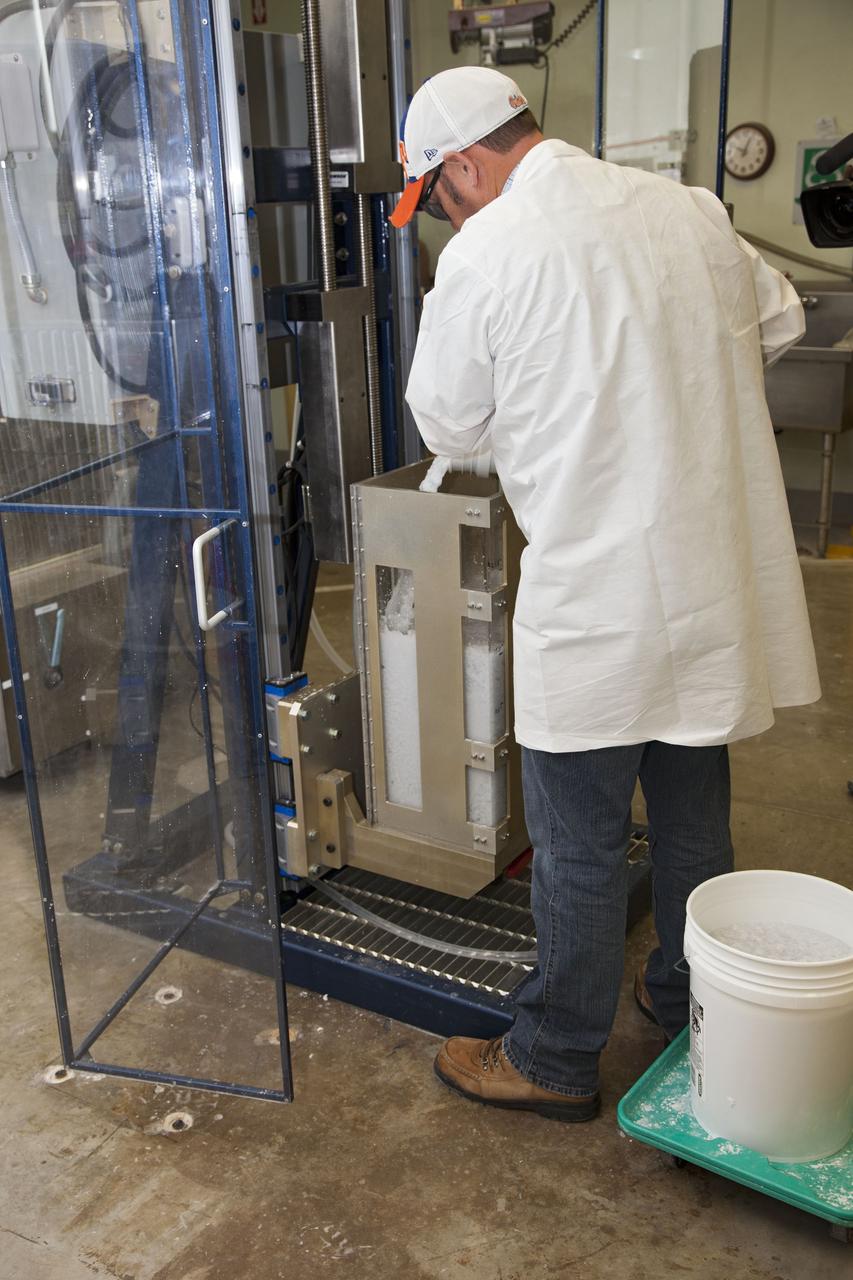
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Frank Pelkey, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects a heat shield tile that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
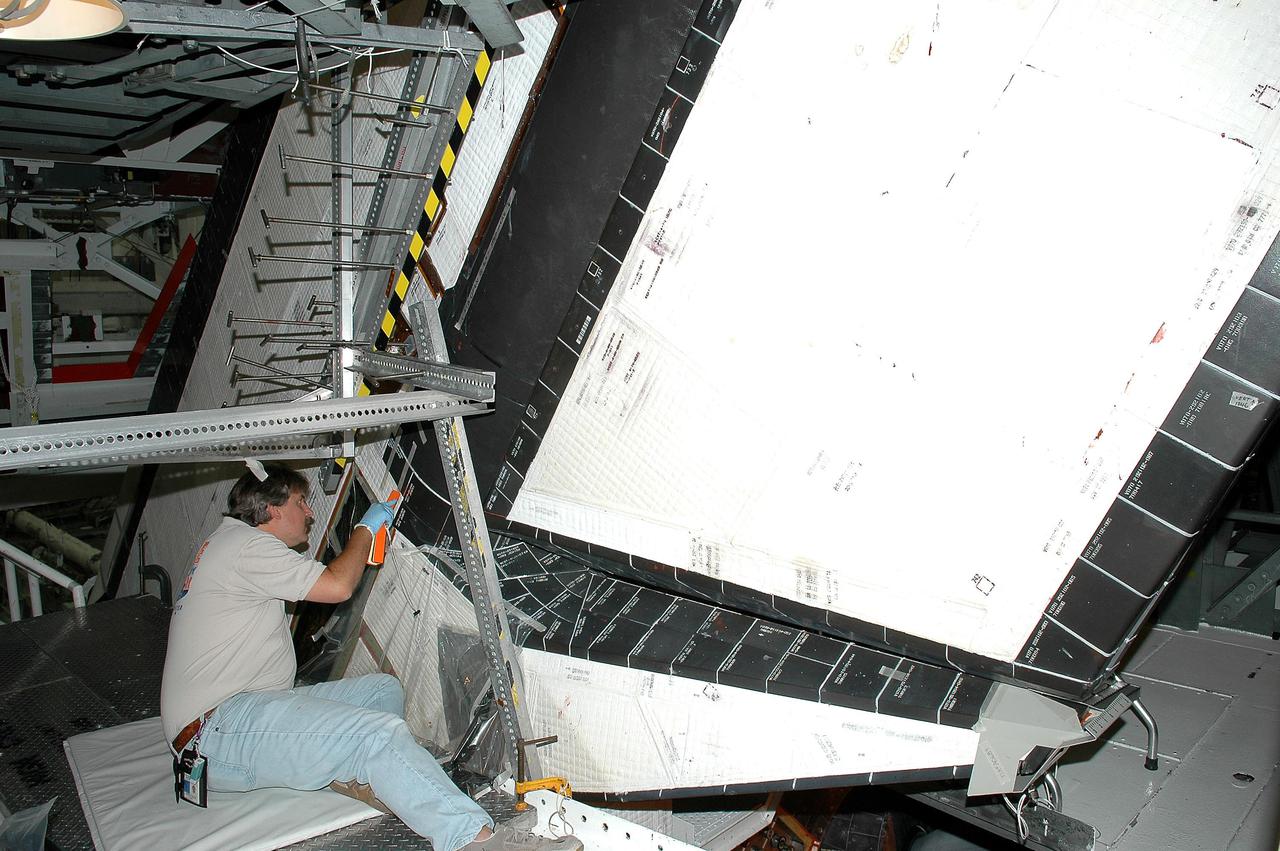

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance tile technician Tim Marks places Thermal Protection System tiles on Atlantis’ rudder speed brake. Atlantis is being processed for launch on the second Return to Flight mission, STS-121, which is scheduled to fly in July.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Chris Keeling, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, manufactures the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
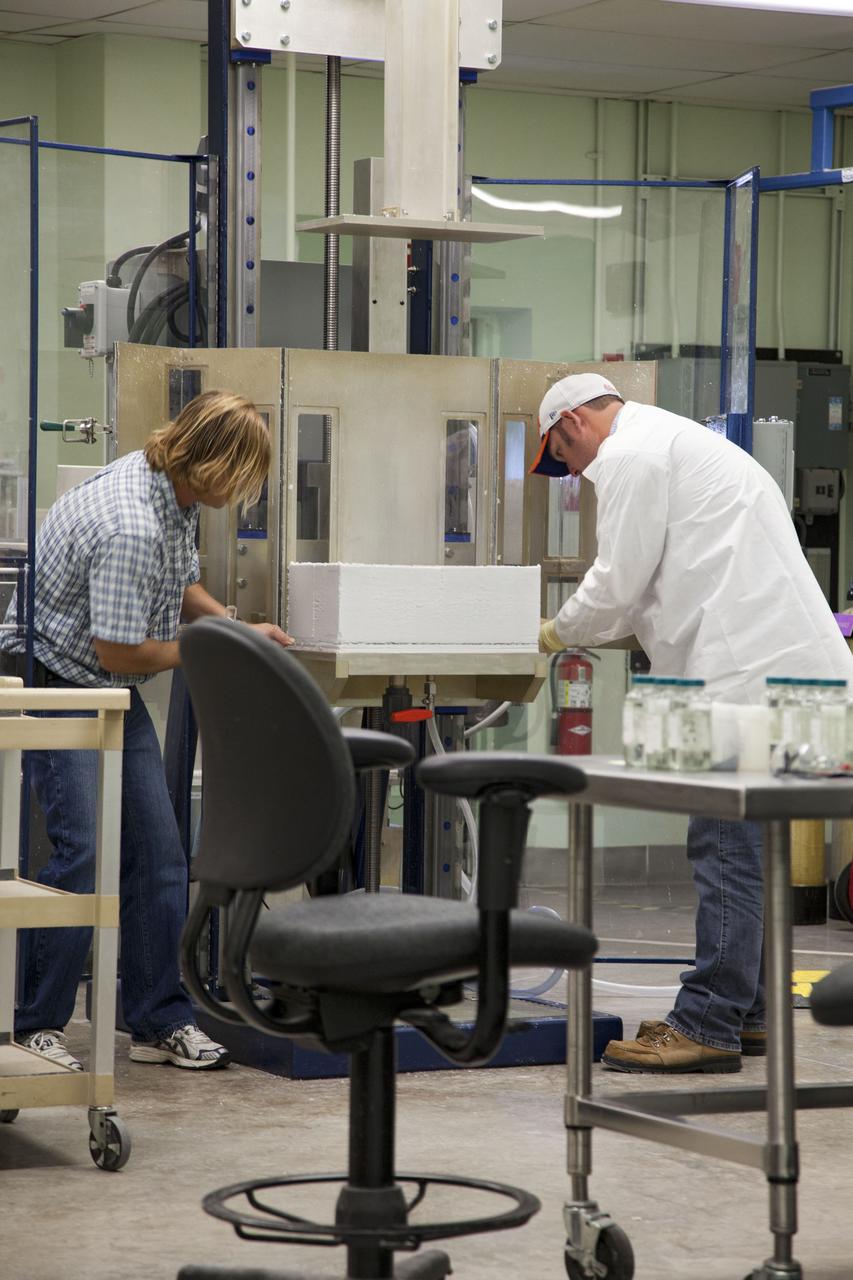

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- United Space Alliance workers, Tim Wright, left, and Chris Keeling, manufacture the heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in the Thermal Protection System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
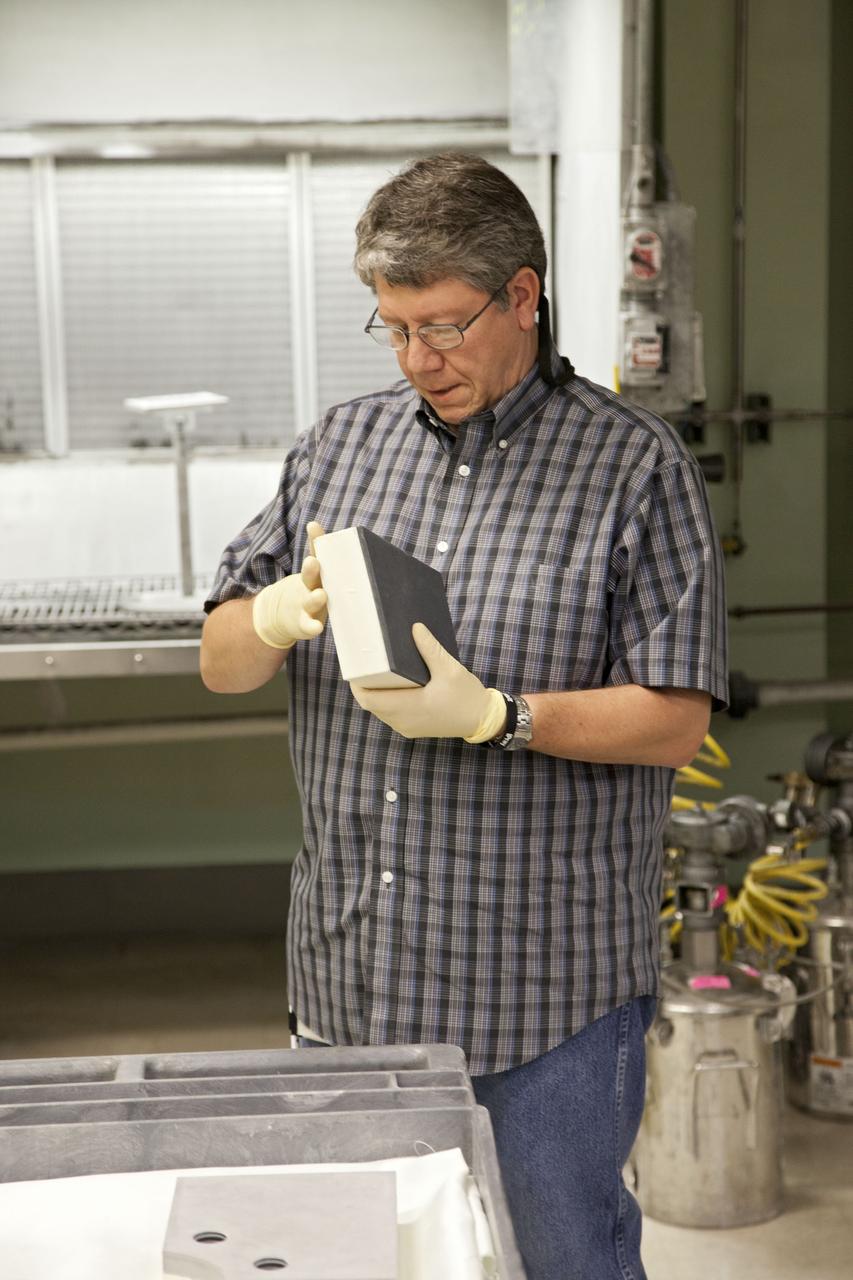

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Frank Pelkey, a United Space Alliance technician at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects a heat shield tile that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
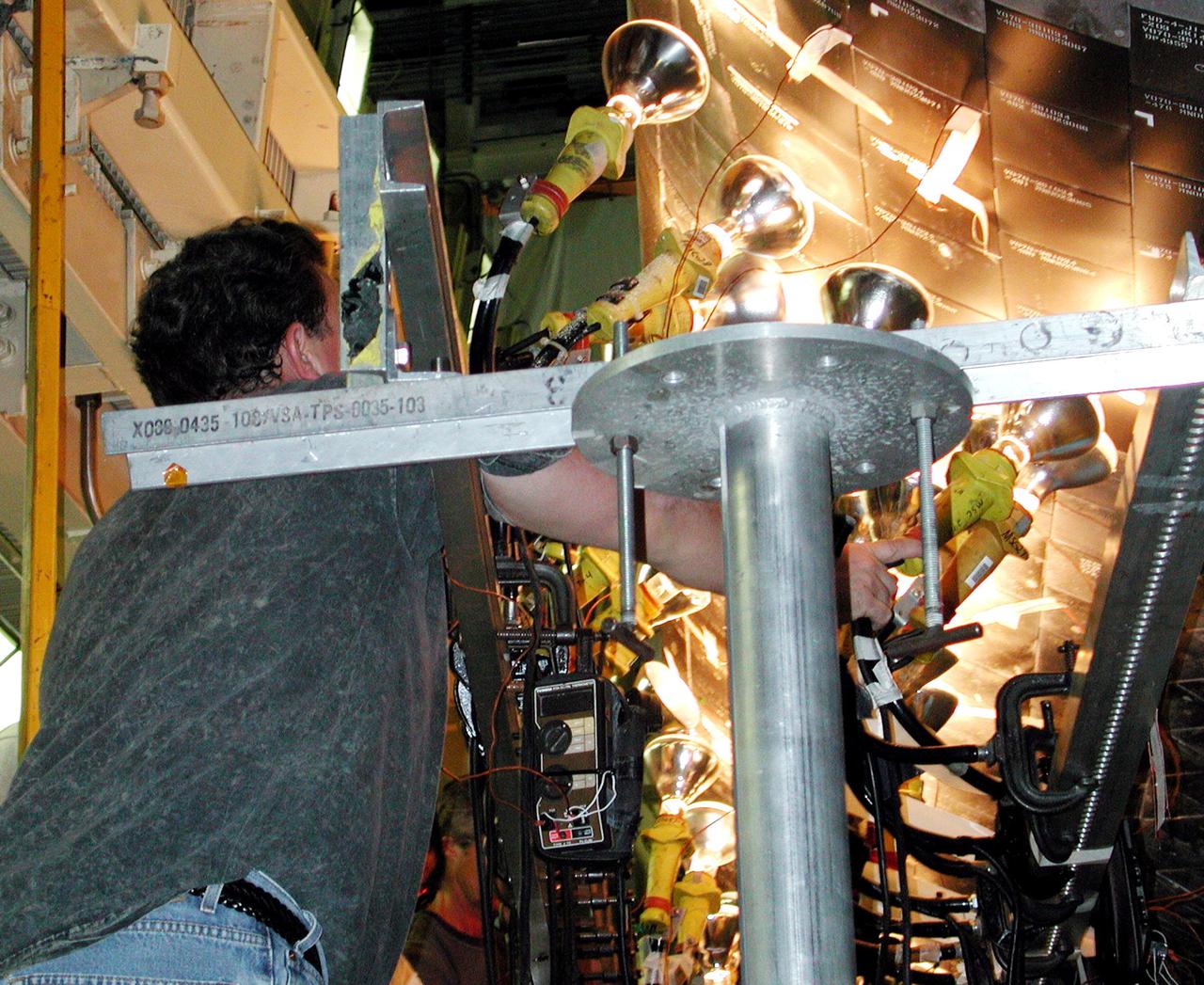

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Banks of lights dry tiles on orbiter Atlantis in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Significant rainstorms during the orbiter’s turnaround for a ferry flight home from Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., caused the moisture problem. The tiles are part of the Thermal Protection System used on orbiters for extreme temperatures encountered during landing

ROCKWELL INTERNATIONAL TECHNICIANS MOUNT SOME OF THE NEARLY 8,000 CERAMIC-COATED TILES THAT REMAIN TO BE INSTALLED ON THE EXTERNAL SURFACES OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA TO COMPLETE THE THERMAL PROTECTION SYSTEM THAT WILL ABSORB THE INTENSE HEAT OF REENTERING THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE AFTER A MISSION IN SPACE. TILE INSTALLATION IS DONE ON AN AROUND-THE-CLOCK BASIS IN THE ORBITER PROCESSING FACILITY WHERE COLUMBIA, THE FIRST IN A NEW BREED OF MANNED, REUSABLE SPACECRAFT, IS BEING READIED FOR THE FIRST LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE LATER THIS YEAR.

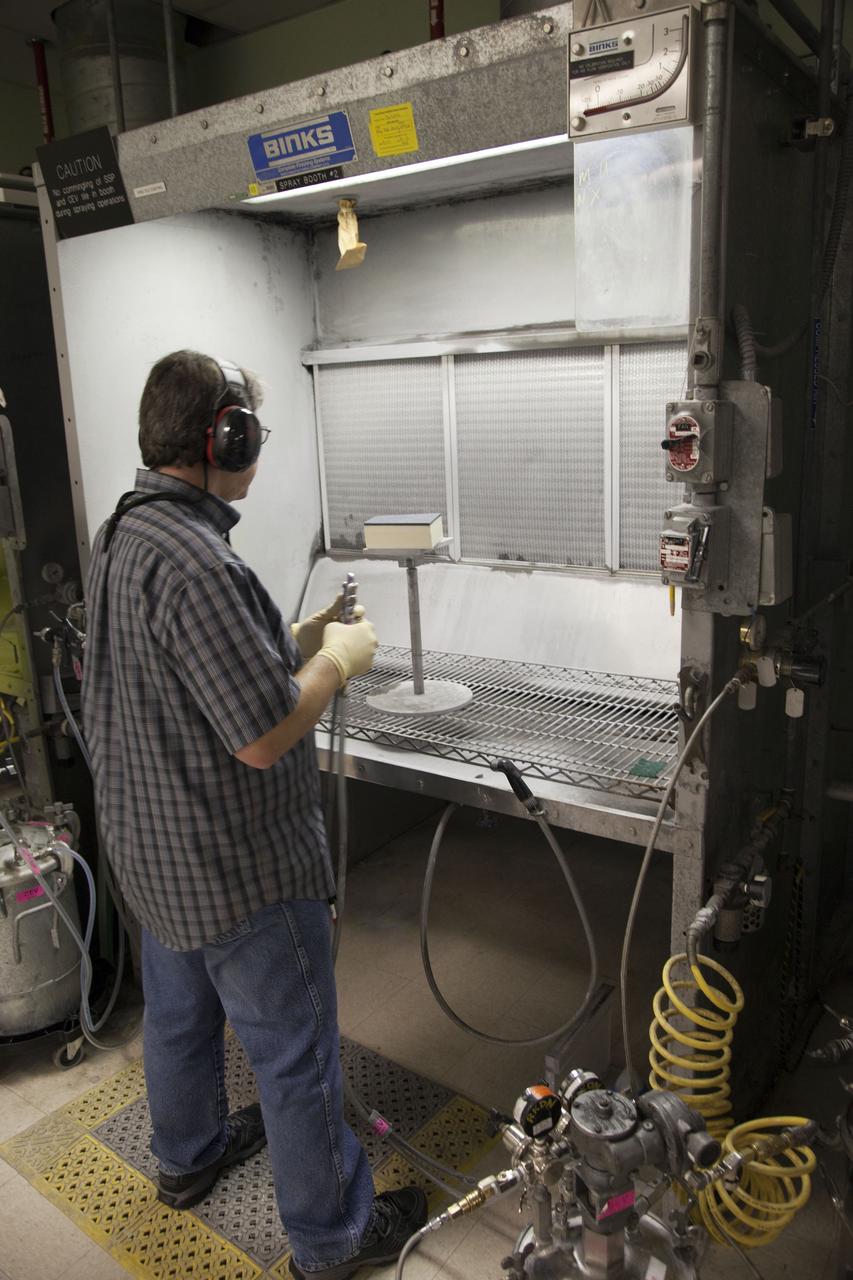
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Jimmy Savastio, a United Space Alliance machinist at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, monitors the properties of a heat shield tile that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule. The work to manufacture and inspect the tiles is taking place in Kennedy's Thermal Protection System Facility. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin
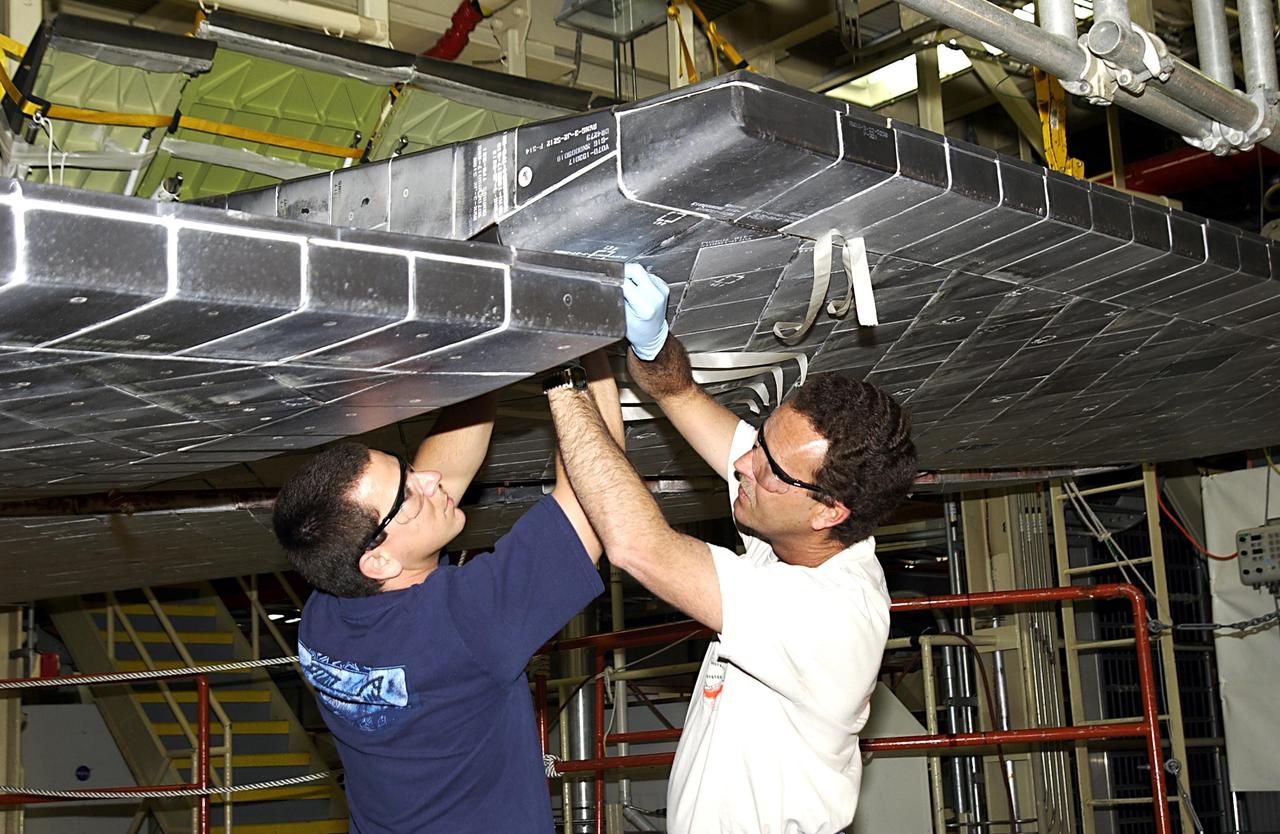

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance (USA) technicians install thermal protection system tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery. Discovery is undergoing its Orbiter Major Modification Period, a regularly scheduled structural inspection and modification downtime, which began in September 2002. .
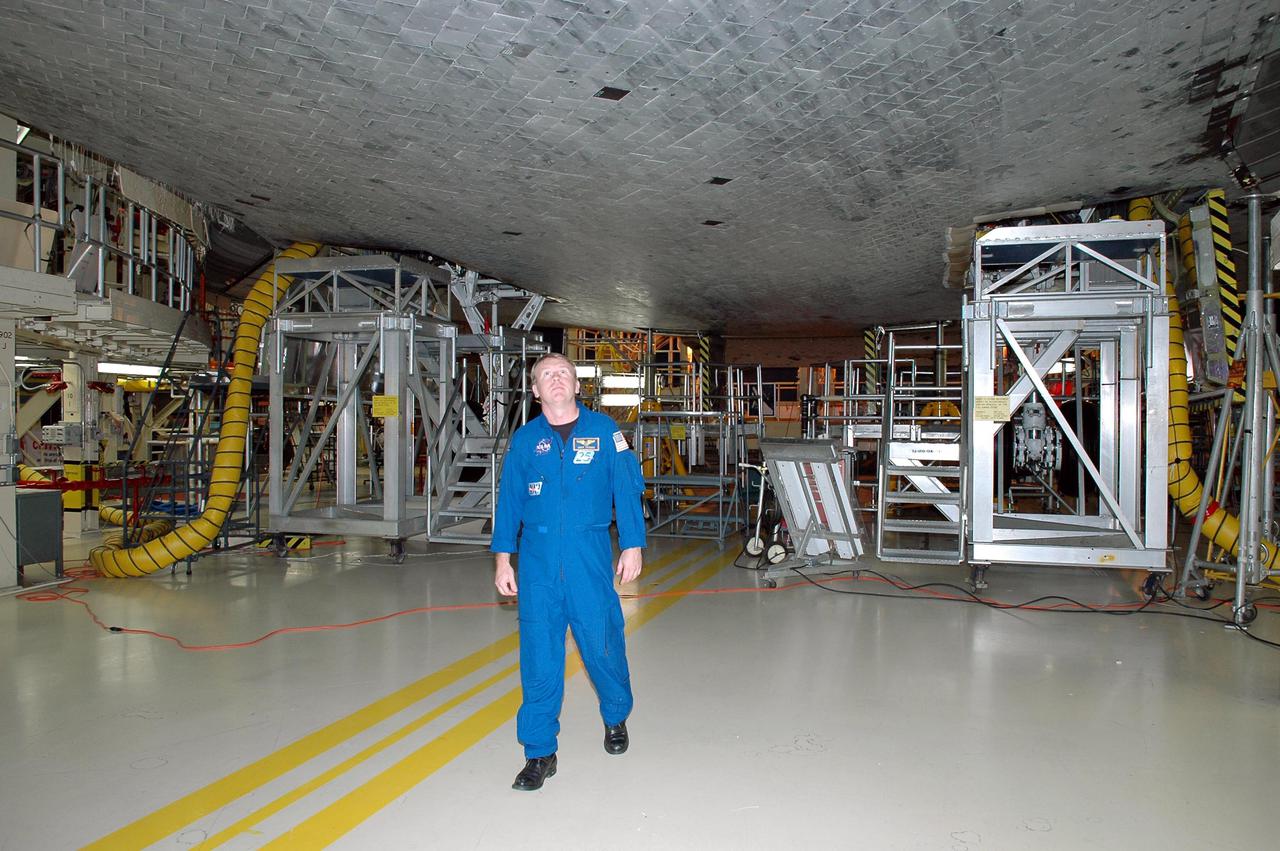

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a visit to Kennedy, STS-114 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas looks at the tiles, part of the Thermal Protection System, on the belly of the orbiter Discovery. The designated vehicle for the mission, Discovery is in the Orbiter Processing Facility for launch processing. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.
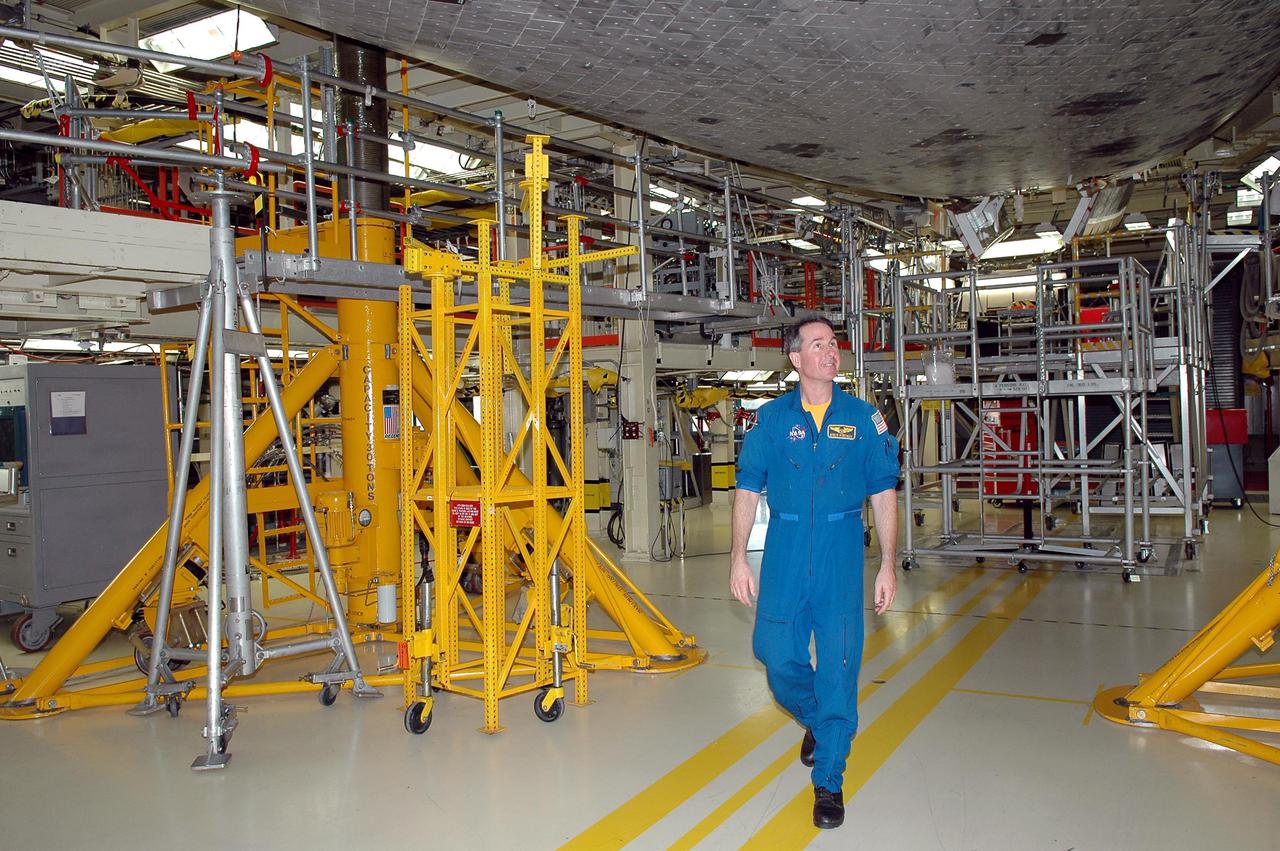

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a visit to Kennedy, STS-114 Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson looks at the tiles, part of the Thermal Protection System, on the belly of the orbiter Discovery. The designated vehicle for the mission, Discovery is in the Orbiter Processing Facility for launch processing. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.

S114-E-6412 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside thermal protection tiles are featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA).
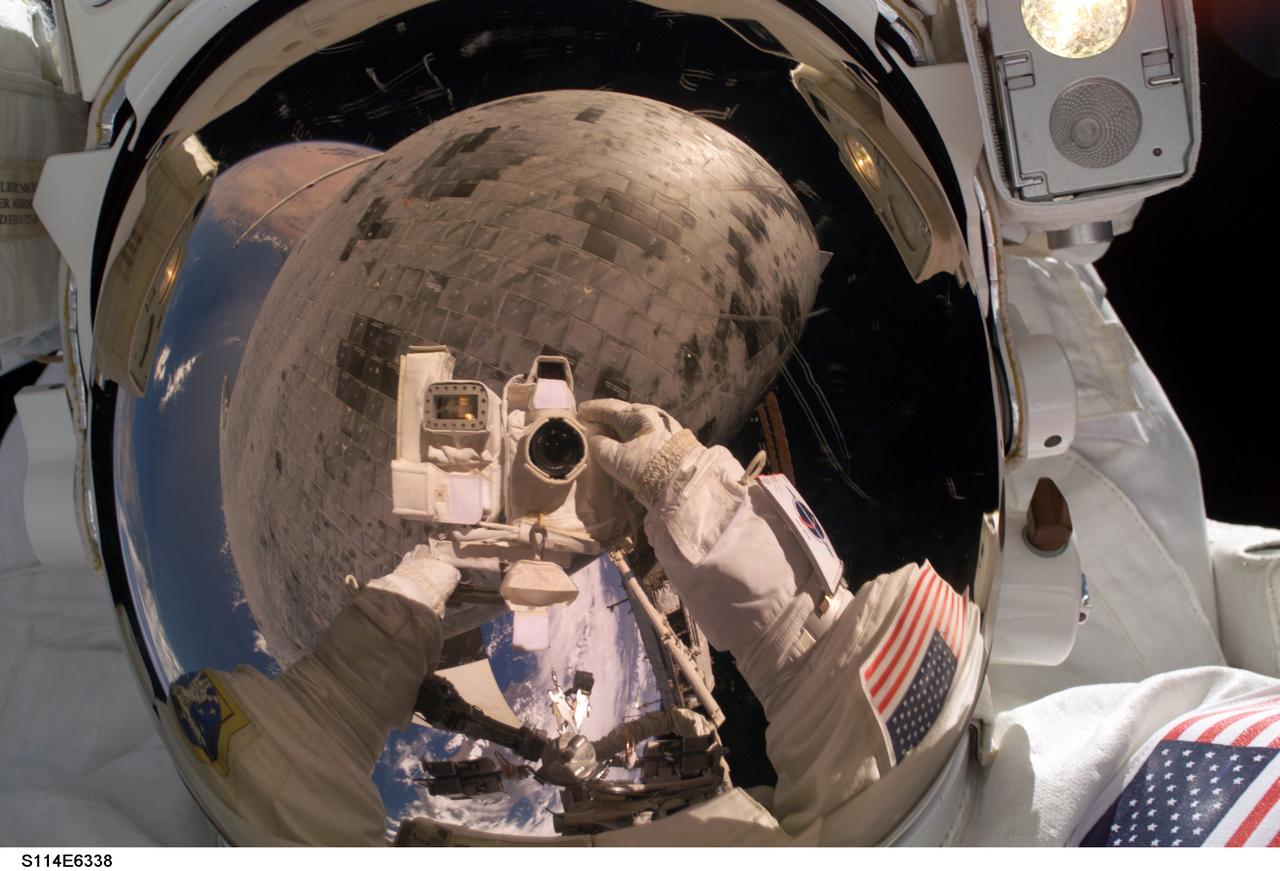

S114-E-6338 (3 August 2005) --- Astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, used the pictured digital camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during today;s extravehicular activities (EVA). Also visible in the reflection are thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery;s underside.
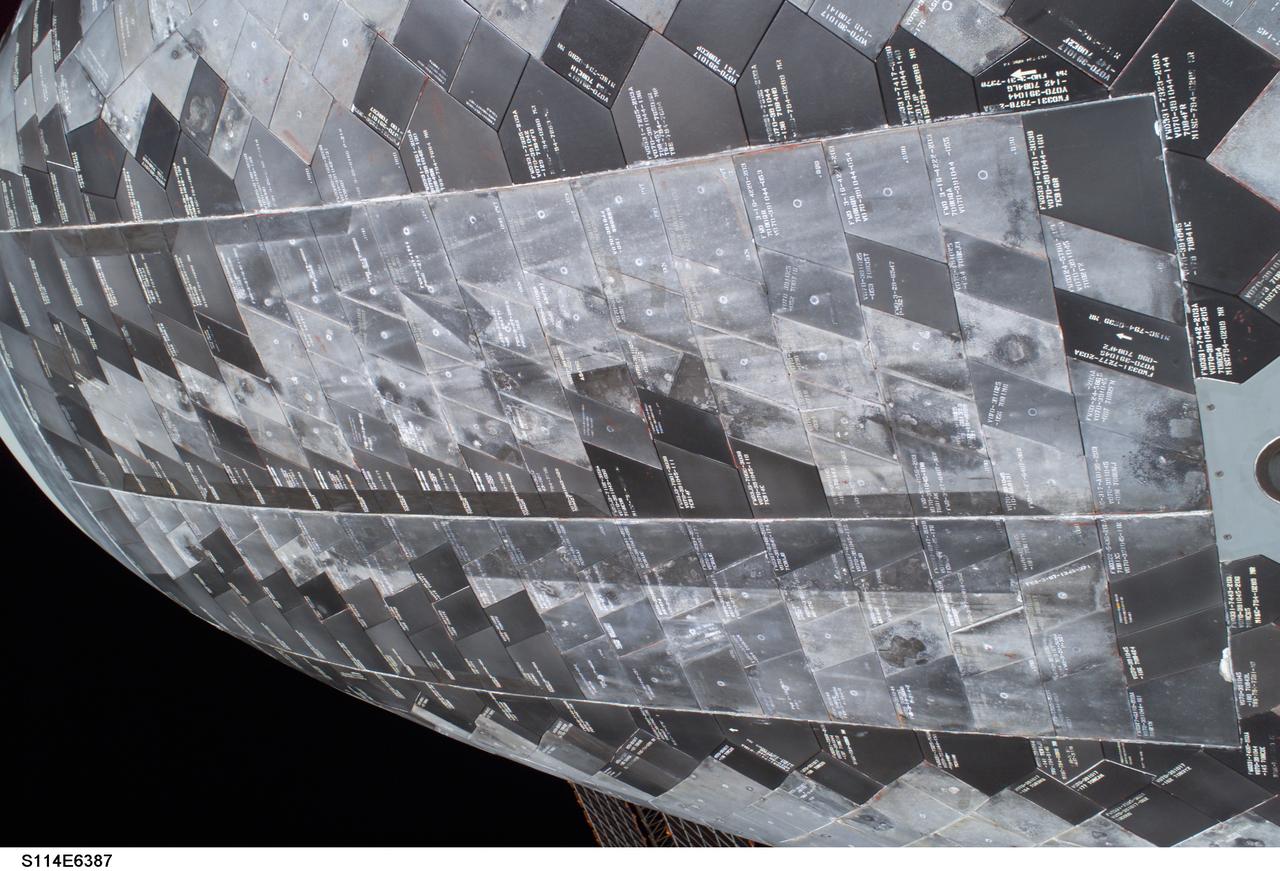

S114-E-6387 (3 August 2005) --- A close-up view of a portion of the thermal protection tiles on Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activities (EVA).
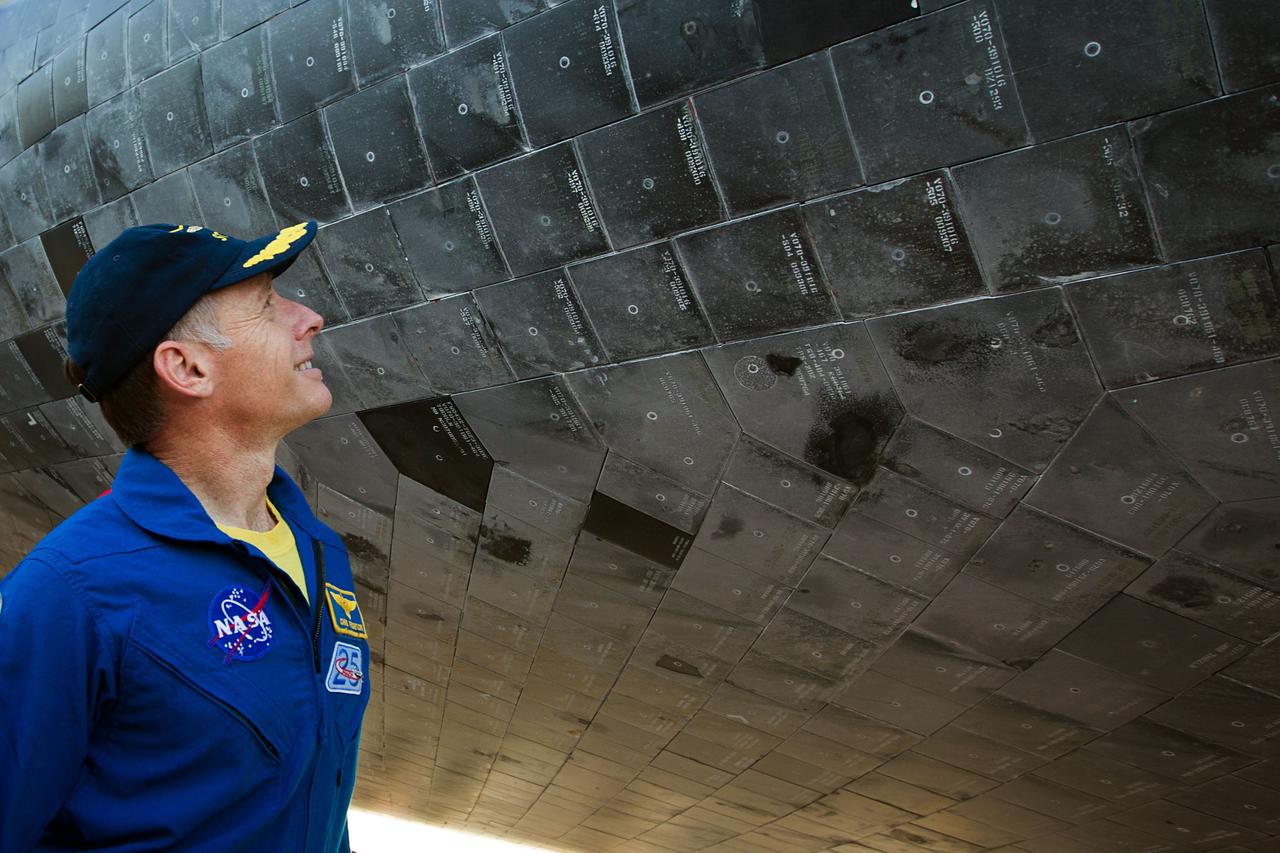

NASA astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-135 commander, examines the thermal tiles of the orbiter after the space shuttle Atlantis landed at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida completing STS-135, the final mission of the NASA shuttle program, on Thursday, July 21, 2011. ( NASA Photo / Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool )
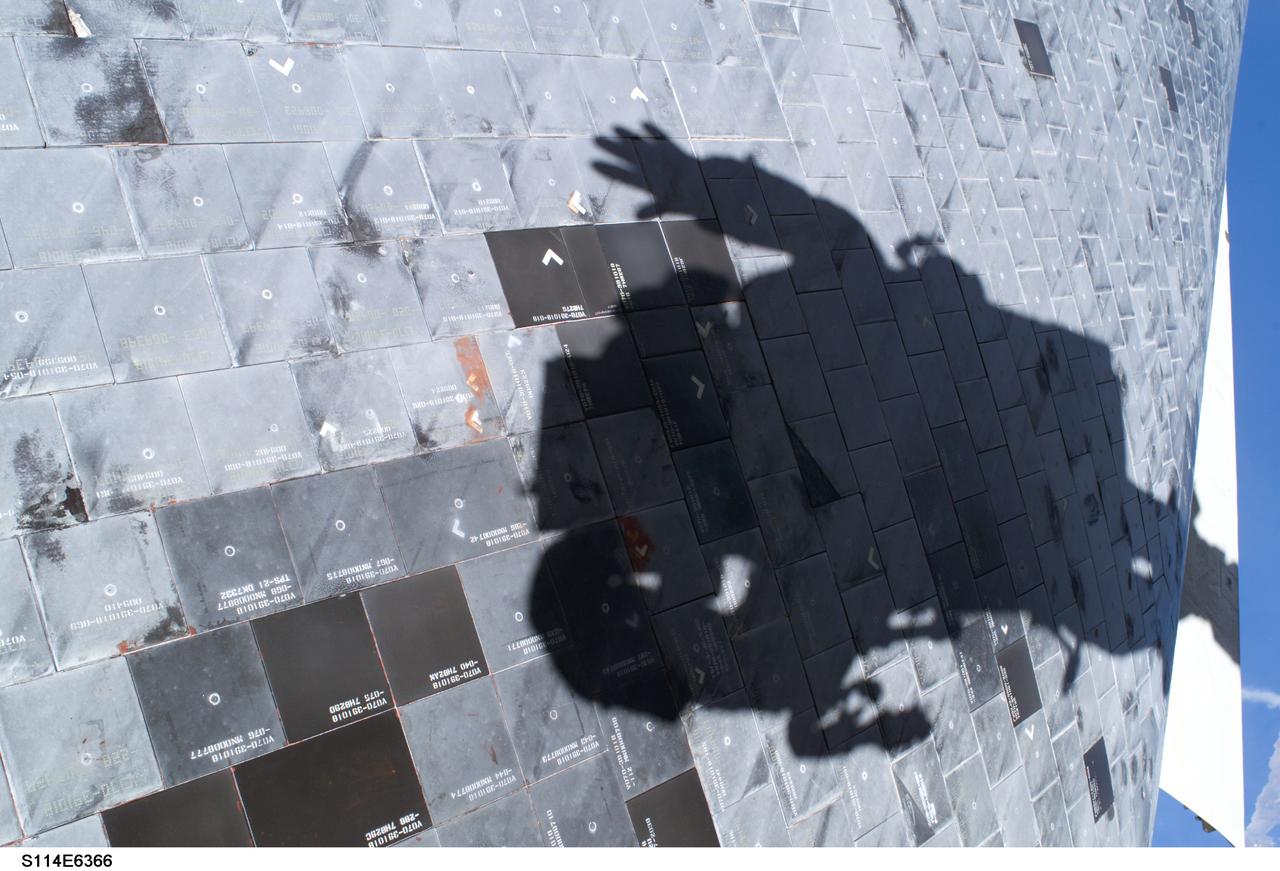

S114-E-6366 (3 August 2005) --- Space Shuttle Discovery’s underside is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Stephen K. Robinson, STS-114 mission specialist, during today’s extravehicular activities (EVA). Robinson’s shadow is visible on the thermal protection tiles.
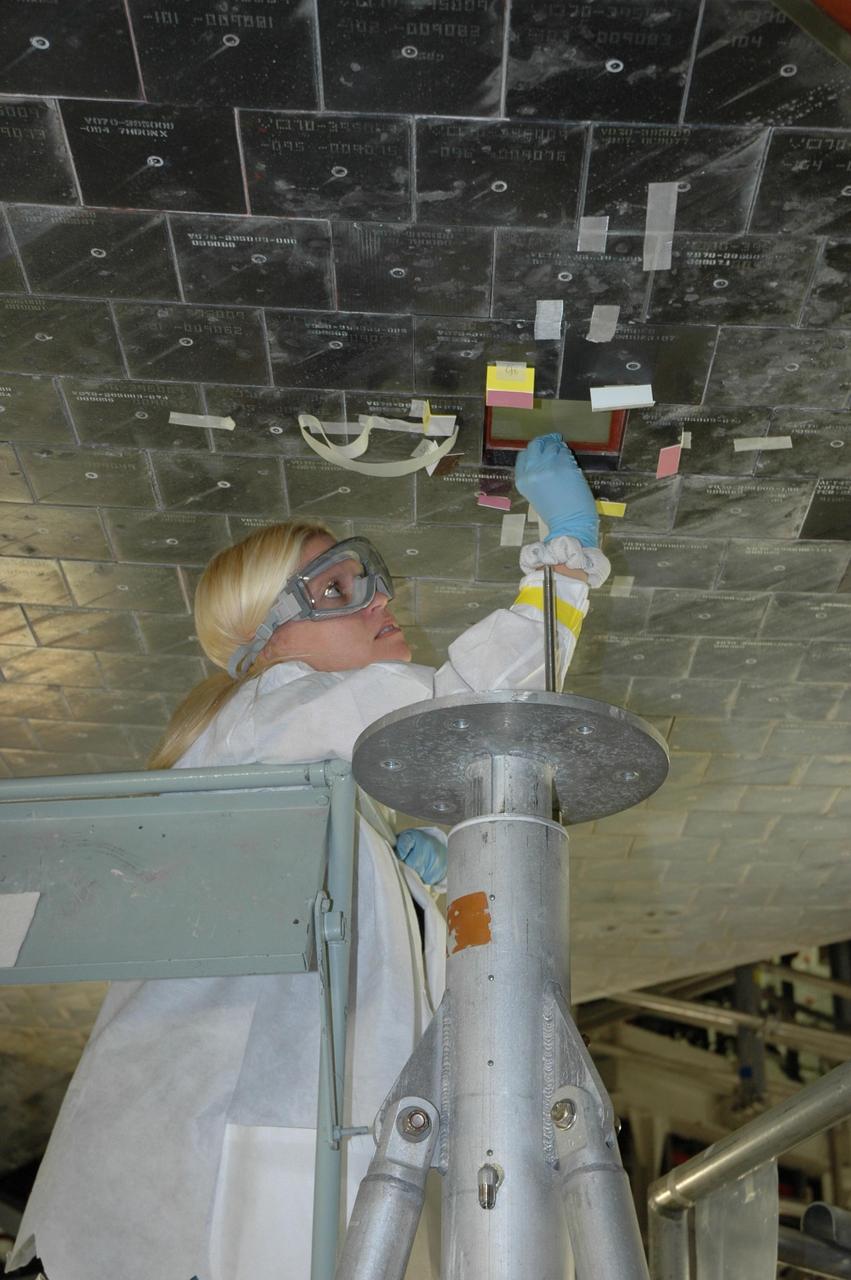

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a United Space Alliance technician prepares the surface of Atlantis for installation of a thermal protection system tile. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted for launch on mission STS-122 on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
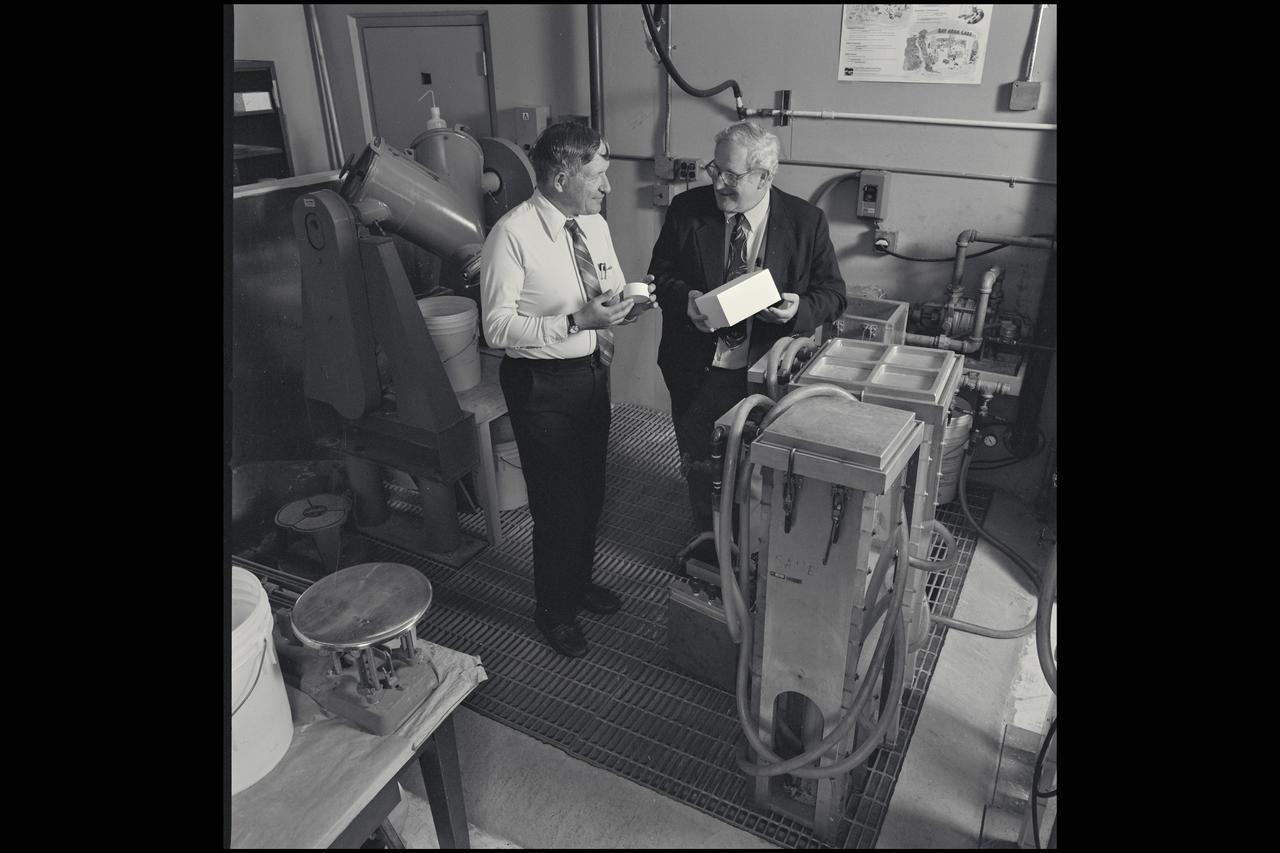

Harold Goldstein (R) and Dan Leiser (L) discuss bone implant development in the the Shuttle Tile Laboratory N-242. A spin-off of Ames research on both bone density in microgravity and on thermal protection foams is the bone-growth implant shown in 1993.
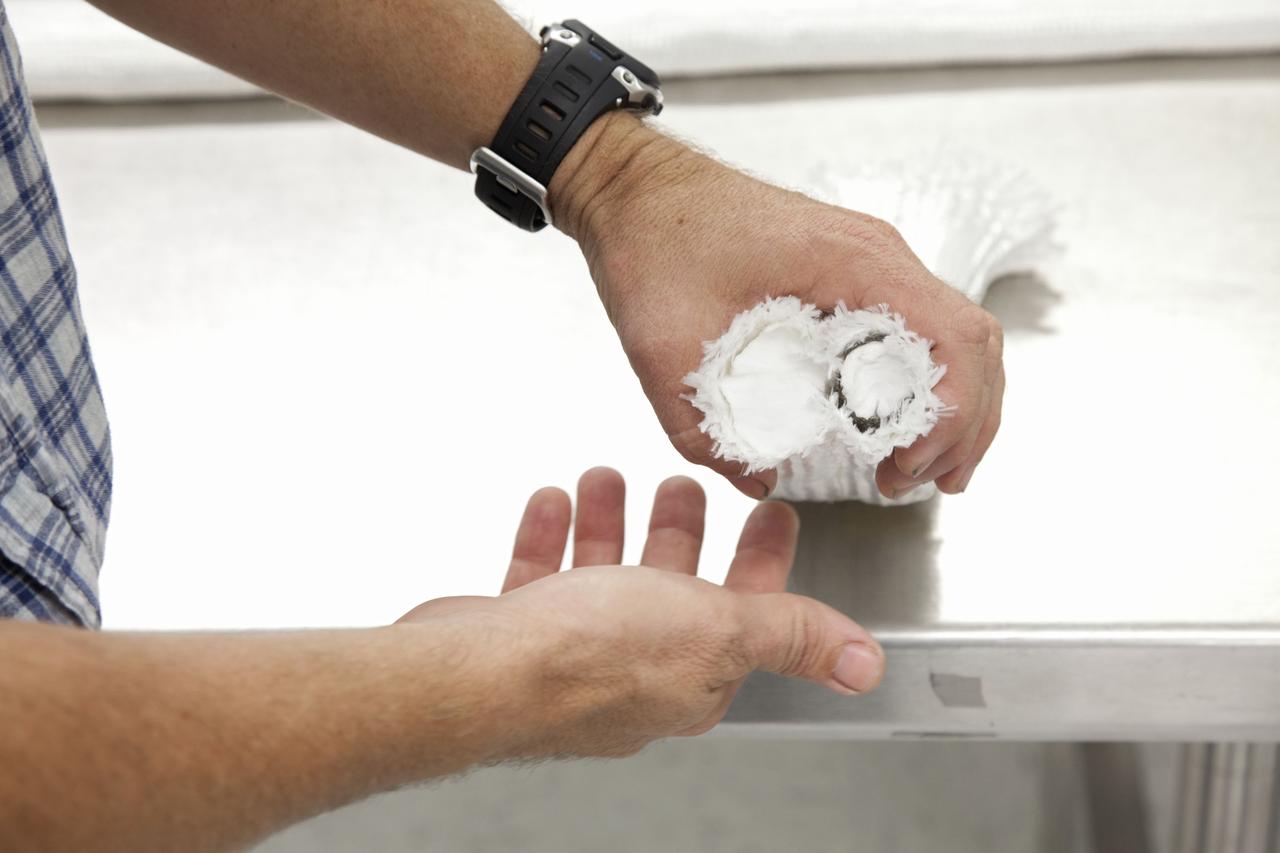

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The heat shield tiles that will be installed to the backshell of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle's Exploration Flight Test EFT-1 capsule are manufactured inside the Thermal Protection System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The insulation includes thermal barriers that are used around hatches, thrusters and other open areas of the backshell to protect the joints from heat. EFT-1 will be used during Orion's first test flight in space. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Frankie Martin