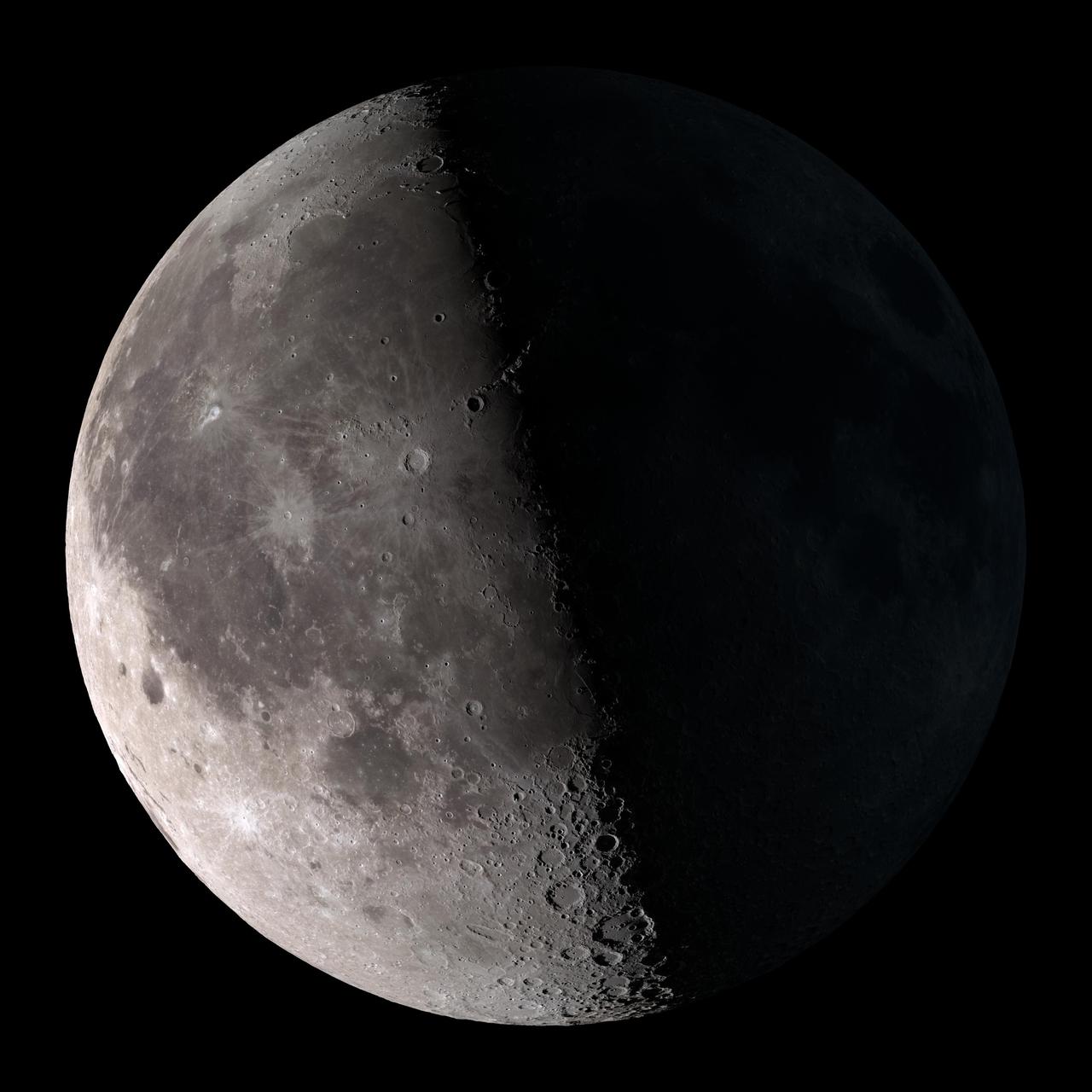

Third quarter. Rises around midnight, visible to the south after sunrise. NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has been in orbit around the Moon since the summer of 2009. Its laser altimeter (LOLA) and camera (LROC) are recording the rugged, airless lunar terrain in exceptional detail, making it possible to visualize the Moon with unprecedented fidelity. This is especially evident in the long shadows cast near the terminator, or day-night line. The pummeled, craggy landscape thrown into high relief at the terminator would be impossible to recreate in the computer without global terrain maps like those from LRO. To download, learn more about this visualization, or to see what the Moon will look like at any hour in 2015, visit <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4236" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4236</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
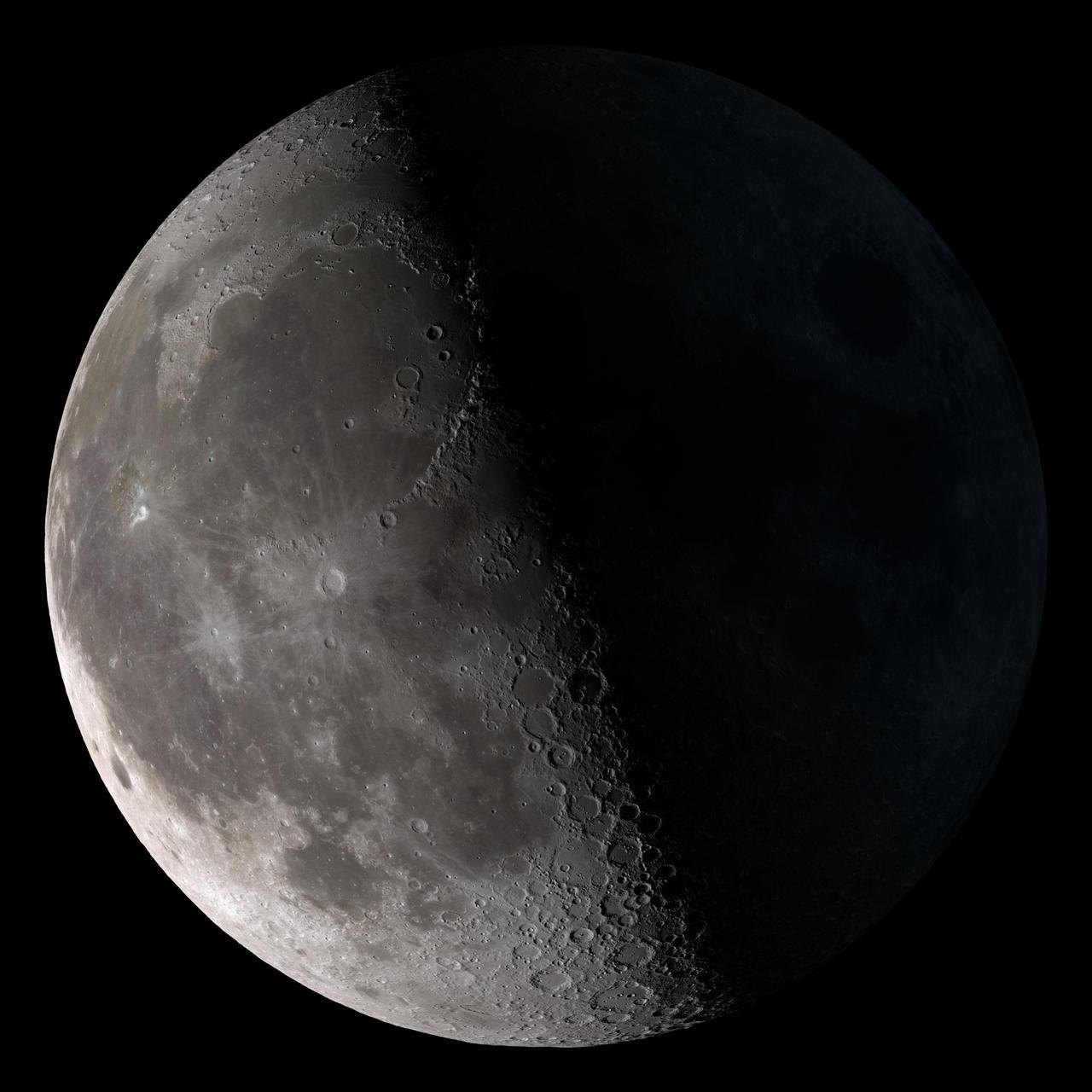

Third quarter. Rises around midnight, visible to the south after sunrise. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

iss071e406275 (July 27, 2024) -- The third quarter moon rises just above Earth's blue horizon as the International Space Station orbited 258 miles above the Red Sea.
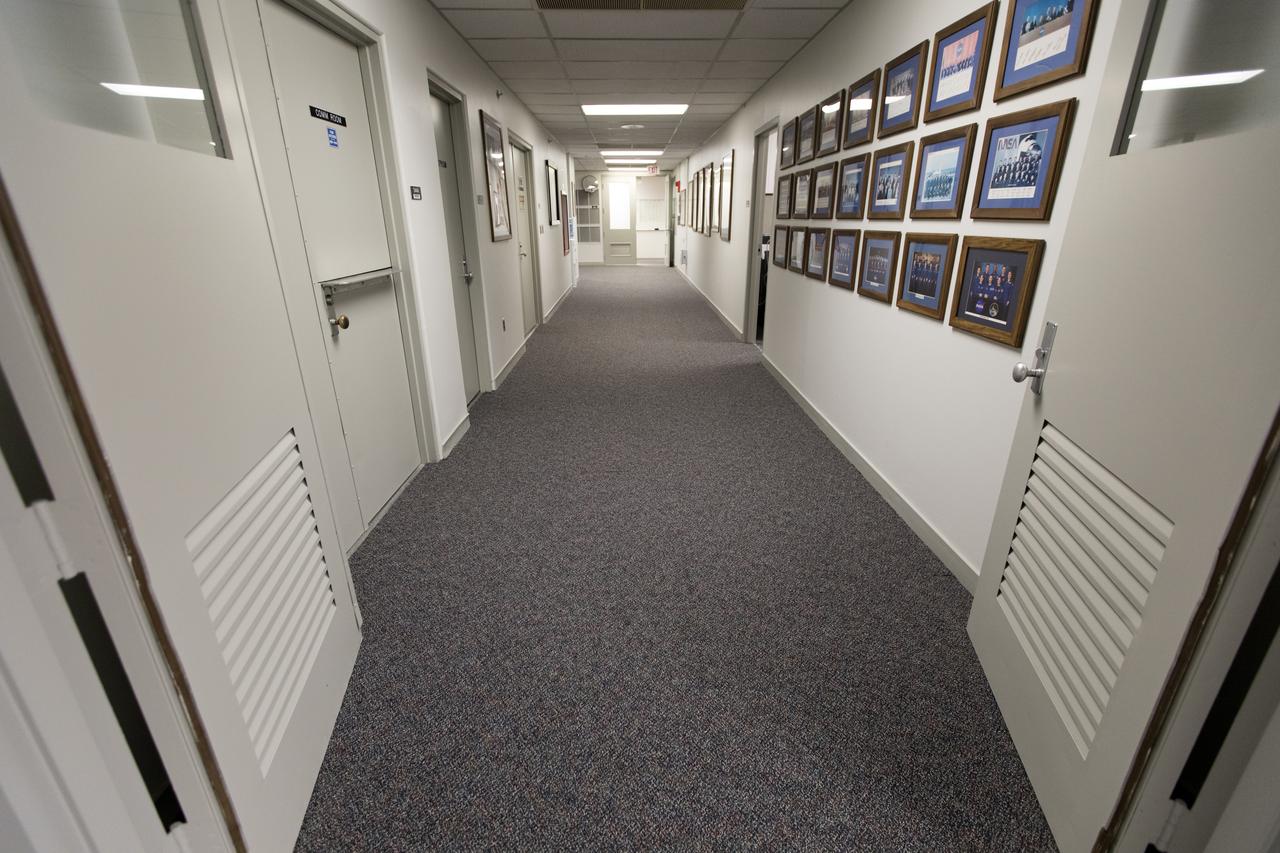

The hallway of the astronaut crew quarters at Kennedy Space Center in Florida reflects new carpeting and a fresh coat of paint. The crew quarters, located on the third floor of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building, has been recently upgraded in preparation for Kennedy’s return to human spaceflight.
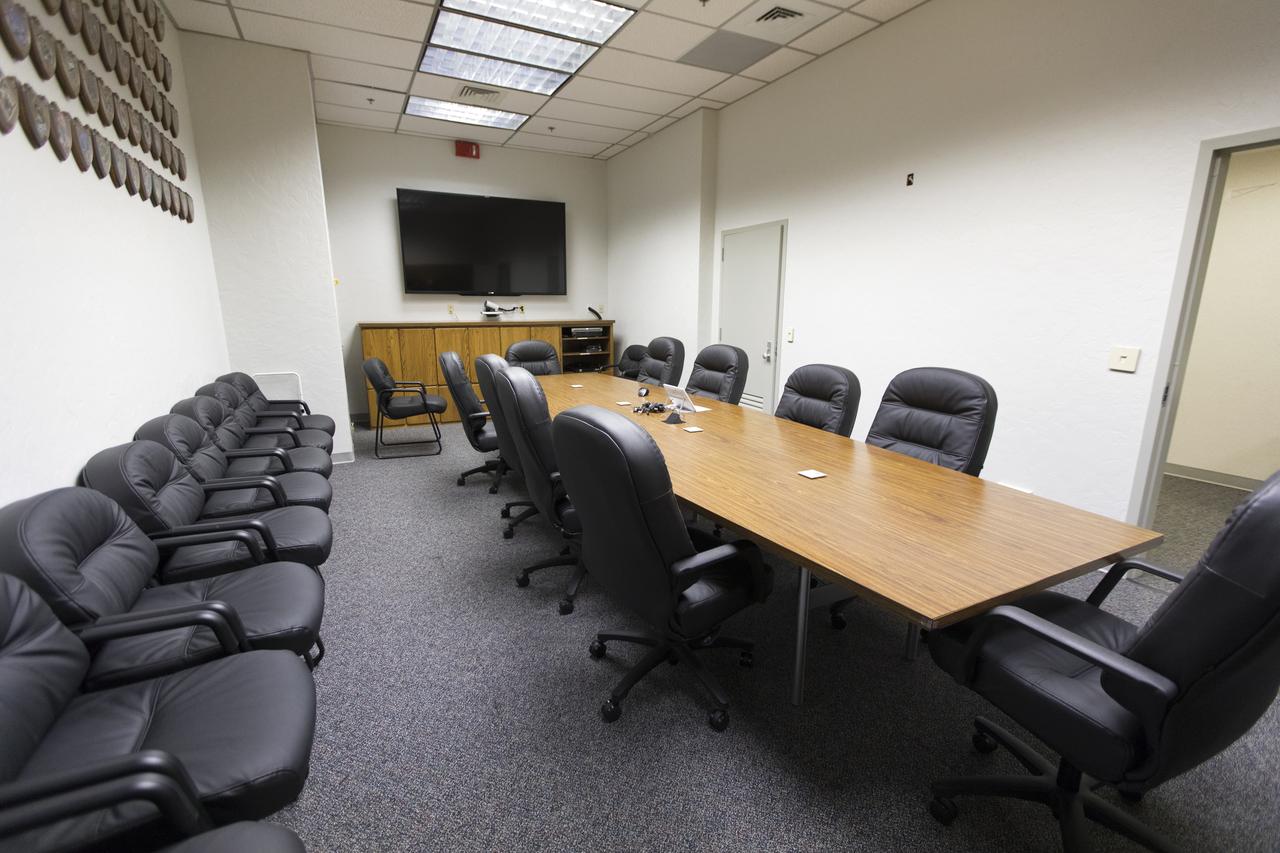

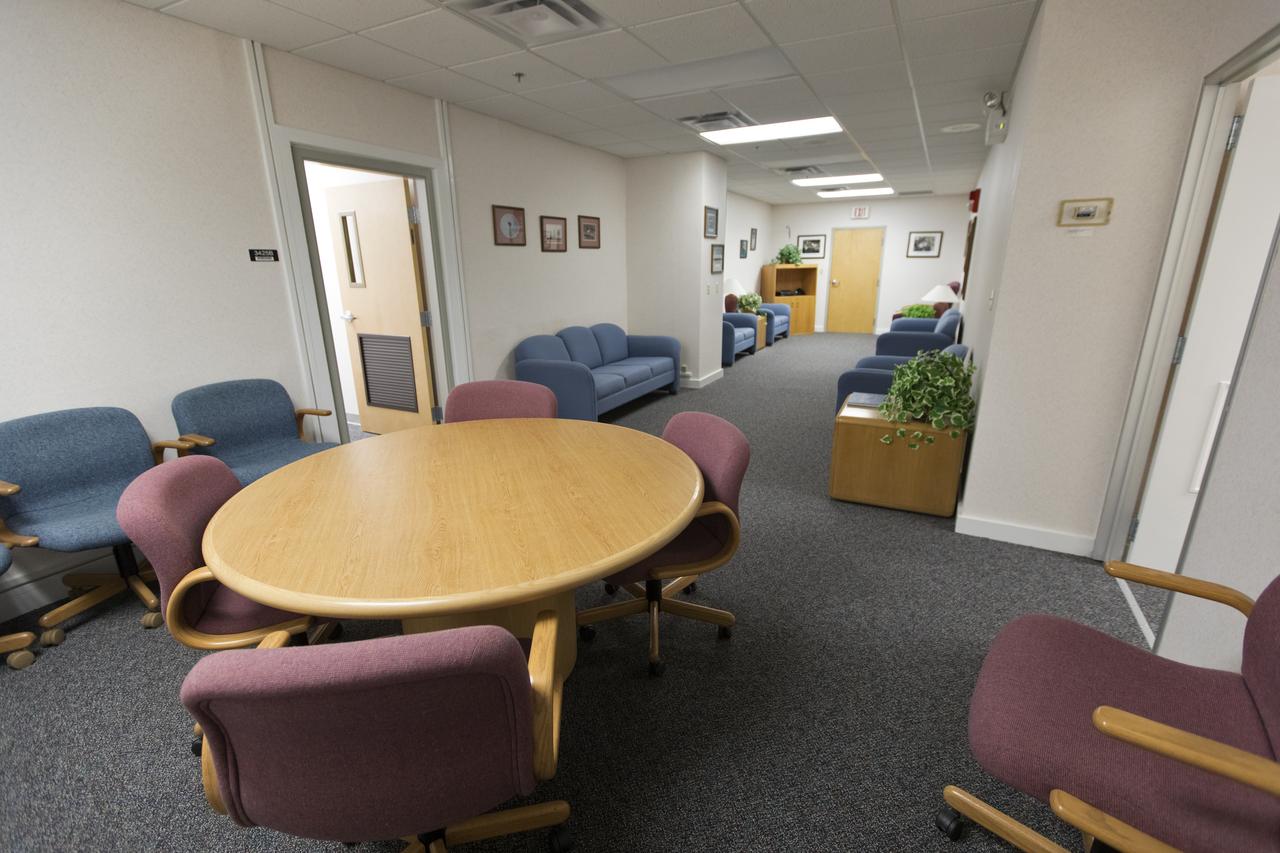
Several upgrades have been completed in the crew quarters at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This includes new carpeting, paint, furniture and ceiling tiles. Located on the third floor of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building, the crew quarters serves as the astronauts’ home as they prepare for missions. This will once again be the case as Kennedy moves closer to a return to human spaceflight. Pictured is a meeting room in the crew quarters.
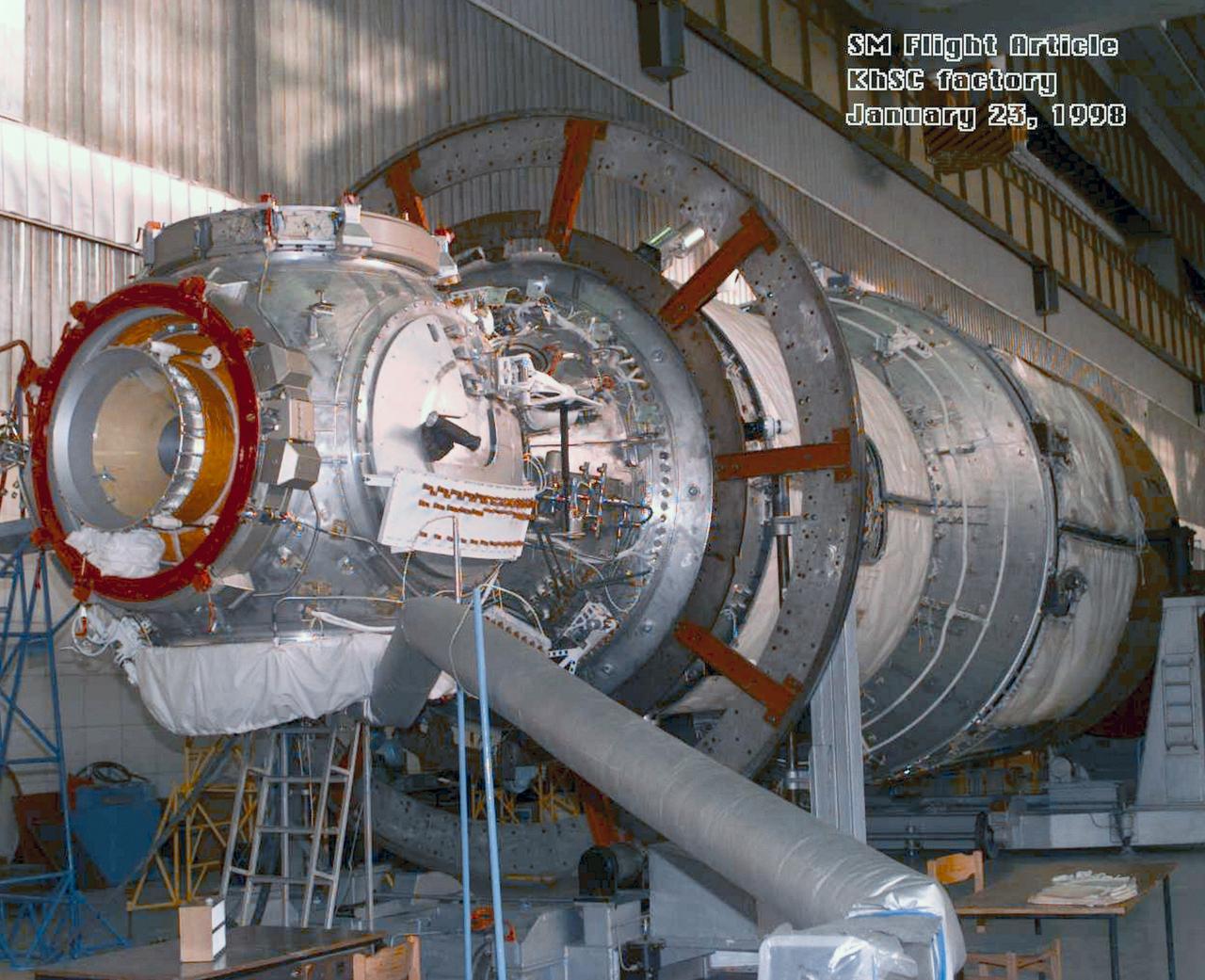
S98-04906 (23 Jan. 1998) --- A three-quarter frontal view of the flight article of the Service Module (SM) for the International Space Station (ISS). The first fully Russian contribution to ISS, the SM will provide early power, propulsion, life support, communications and living quarters for the station. It will be the third station element to be launched and join the United States-funded, Russian-built Functional Cargo Block (FGB) and the United States connecting module Node 1 in orbit.

The lounge area inside the astronaut crew quarters is where astronauts’ family members waited for their return upon landing during the Space Shuttle Program. The crew quarters, located on the third floor of Kennedy Space Center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building, recently received a number of upgrades, including new paint, ceiling tiles, carpeting, appliances and furniture.
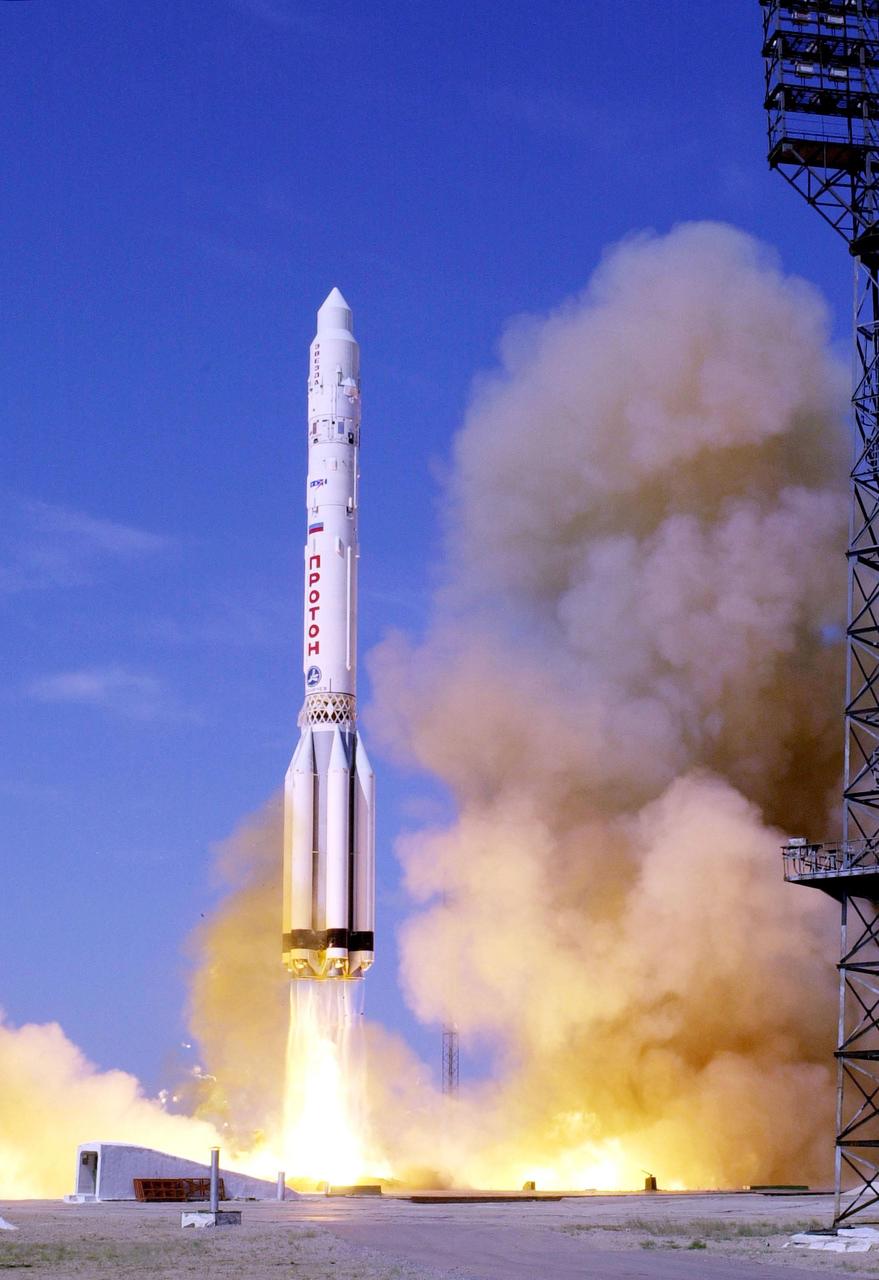

A Russian 3-stage Proton rocket blasts into the sky at 12:56 a.m. EDT with the Russian-built Zvezda module in a successful launch from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. Zvezda is the primary Russian contribution to the International Space Station, serving as the early Station living quarters. It will also provide early propulsive attitude control and reboost capabilities and be the main docking port for Russian Progress cargo resupply vehicles. The third Station component, Zvezda will dock by remote control with the already orbiting Zarya and Unity modules at an altitude of about 245 by 230 statute miles. <i>(Image taken with Nikon D1 digital camera.)</i

At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 50-51 crewmember Thomas Pesquet of the European Space Agency (second from left) plants a tree bearing his name in traditional ceremonies Nov. 10 as his crewmates, Oleg Novitskiy of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, far left) and Peggy Whitson of NASA (third from left) look on. Joining them on the right are backup crewmembers Paolo Nespoli of the European Space Agency, Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos and Jack Fischer of NASA. Novitskiy, Whitson and Pesquet will launch Nov. 18, Baikonur time, on the Soyuz MS-03 spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Alexander Vysotsky
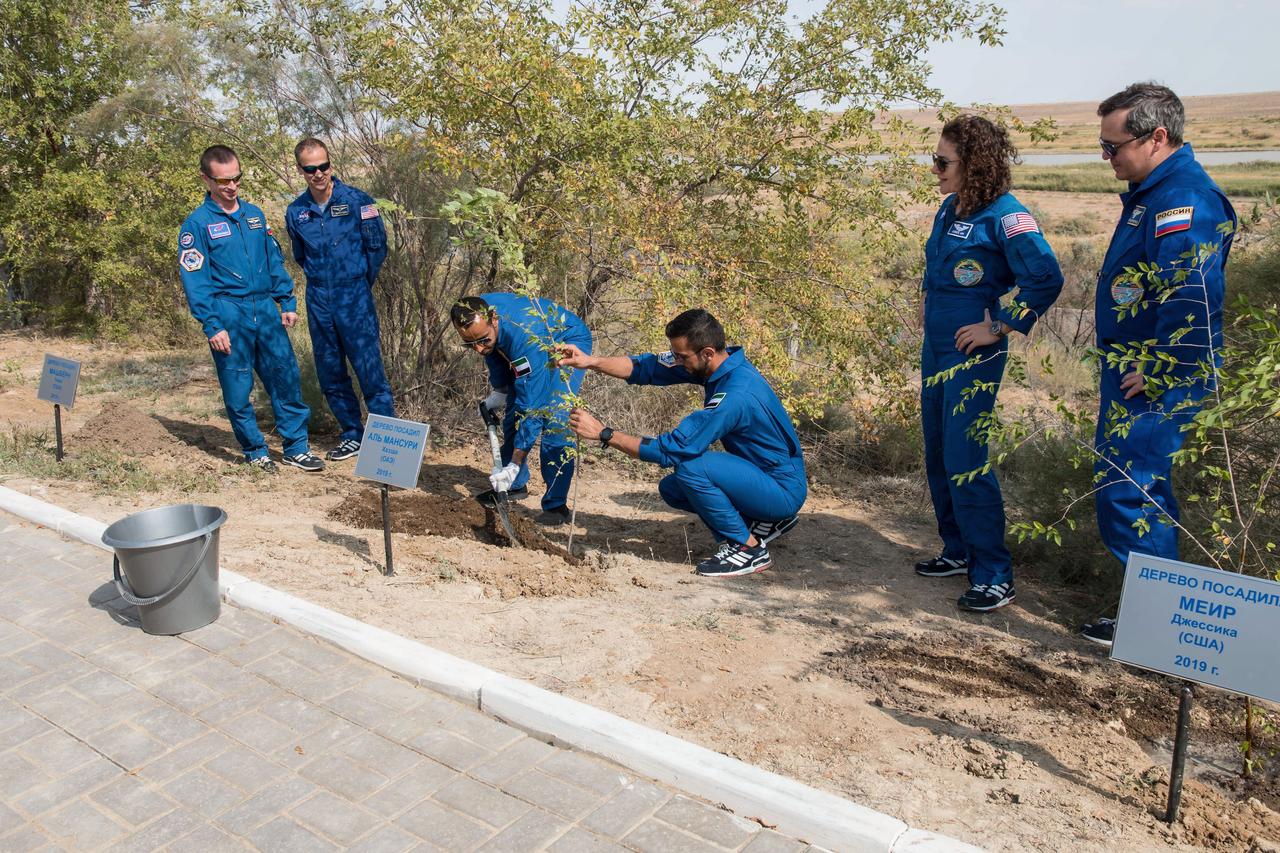

jsc2019e053725 - At the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, spaceflight participant Hazzaa Ali Almansoori of the United Arab Emirates (third from left) plants a tree in his name Sept. 18 as part of traditional pre-launch activities. Assisting him is backup spaceflight participant Sultan Al-Neyadi of the United Arab Emirates. Looking on from left to right are backup Expedition 61 crewmembers Sergey Ryzhikov of Roscosmos and Tom Marshburn of NASA and the prime crewmembers, Jessica Meir of NASA and Oleg Skripochka of Roscosmos, who along with Almansoori, will launch Sept. 25 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the Soyuz MS-15 spacecraft for a mission on the International Space Station...NASA/Victor Zelentsov
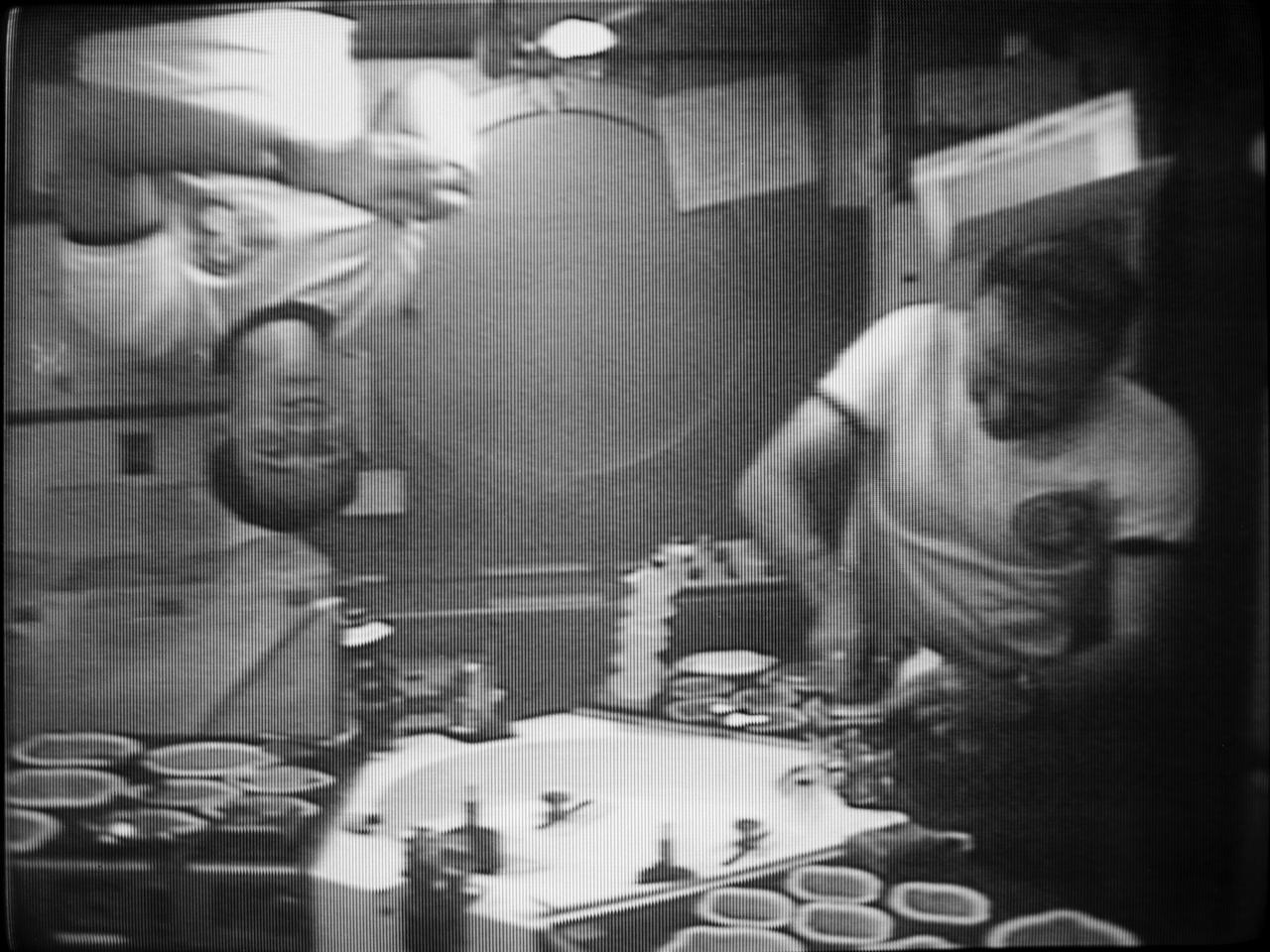

S73-37650 (28 Nov. 1973) --- Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, right, Skylab 4 commander, enjoys a meal aboard the orbiting Skylab space station in this photographic reproduction from a television of Nov. 28, 1973. Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot for the third manned Skylab flight, demonstrates the zero-gravity environment by turning upside. The two crewmen were joined by astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, for the evening meal. The food station is in the wardroom of the Crew Quarters in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA
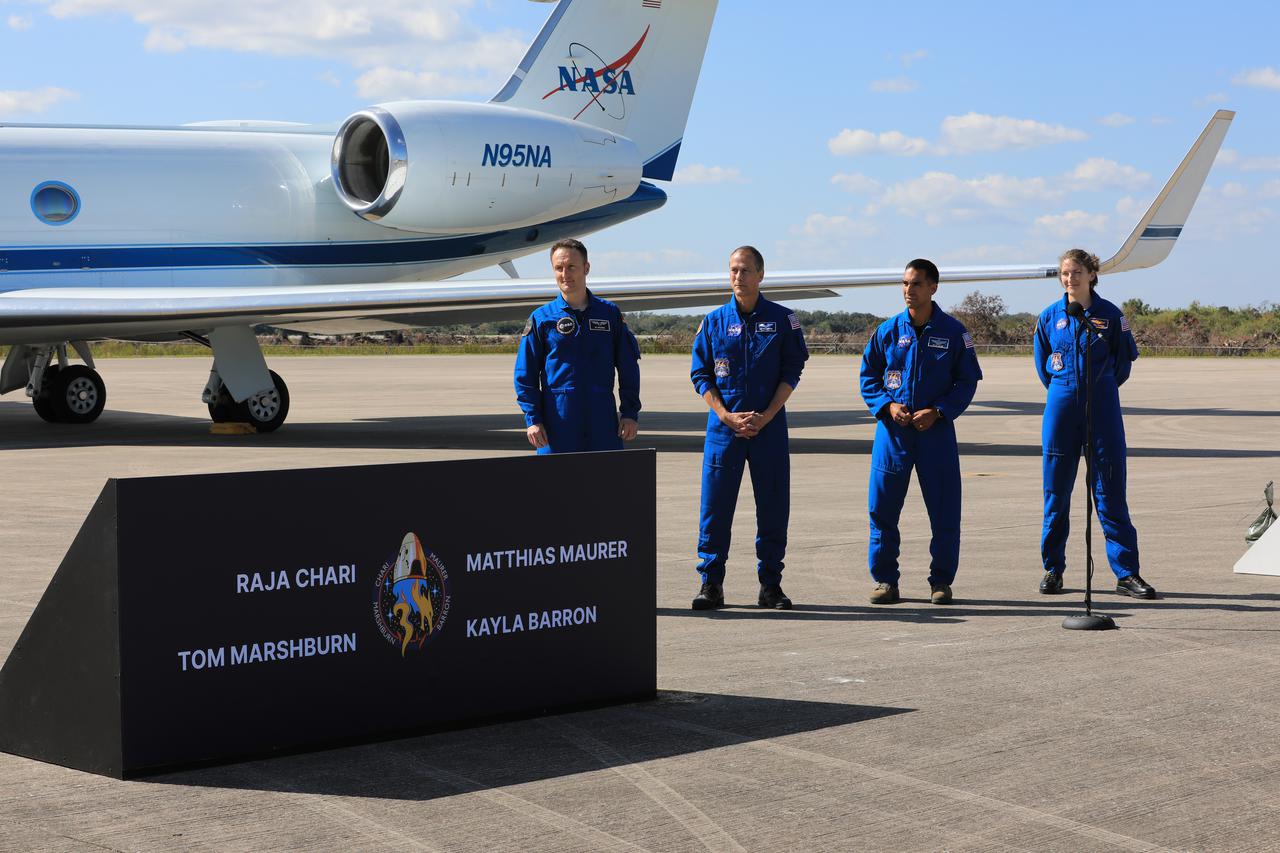

Crew members for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 mission to the International Space Station arrive at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Oct. 26, 2021. From left, European Space Agency astronaut Matthias Maurer, and NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Raja Chari, and Kayla Barron speak to members of the news media. The crew will enter quarantine at the center’s Crew Quarters as they await launch aboard the Crew Dragon on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Launch is targeted for 2:21 a.m. EDT on Oct. 31 from Launch Complex 39A. Crew-3 is the third crew rotation flight for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, and the first flight of a new Crew Dragon spacecraft.
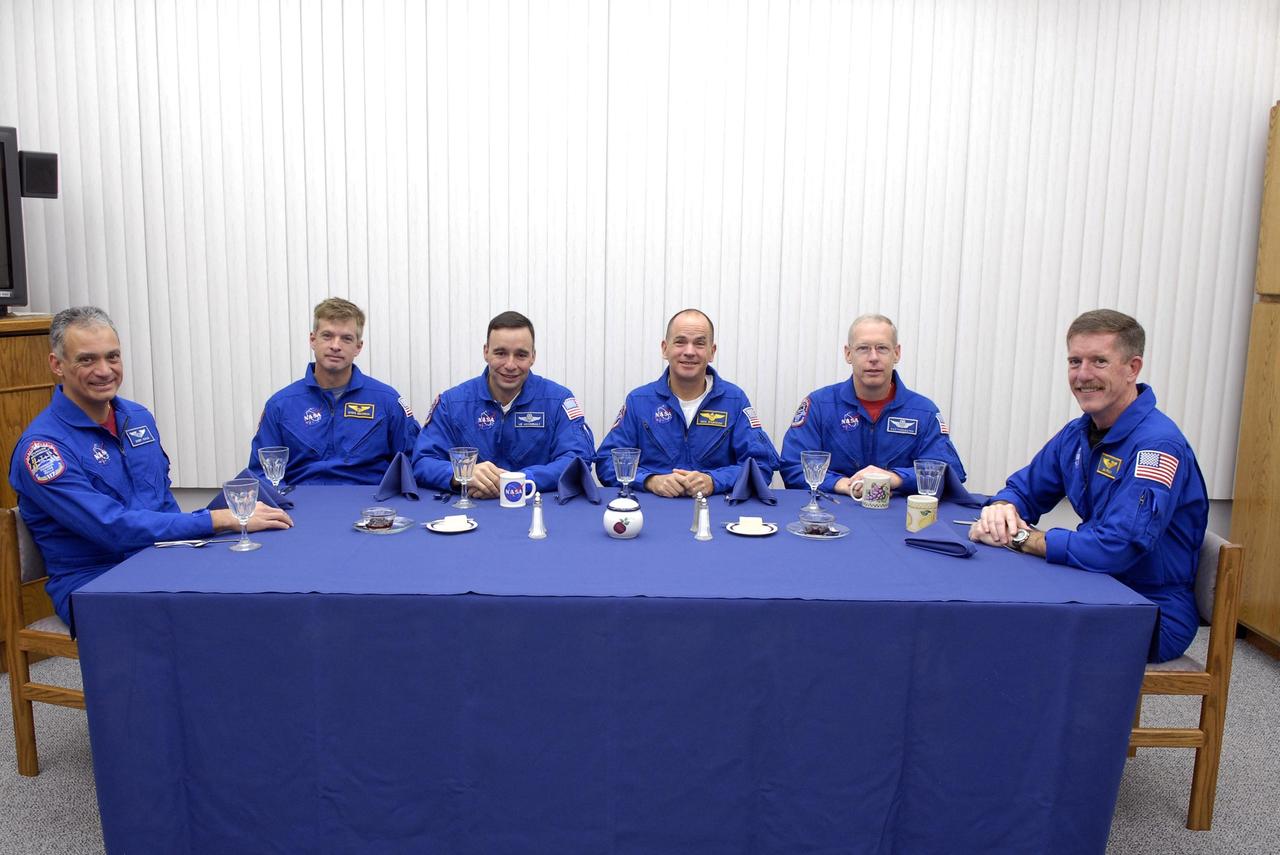

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the crew quarters at the Operations and Checkout Building, the Mission STS-117 crew members enjoy breakfast before resuming Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From left are Mission Specialists Danny Olivas and Steven Swanson, Pilot Lee Archambault, Commander Rick Sturckow and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
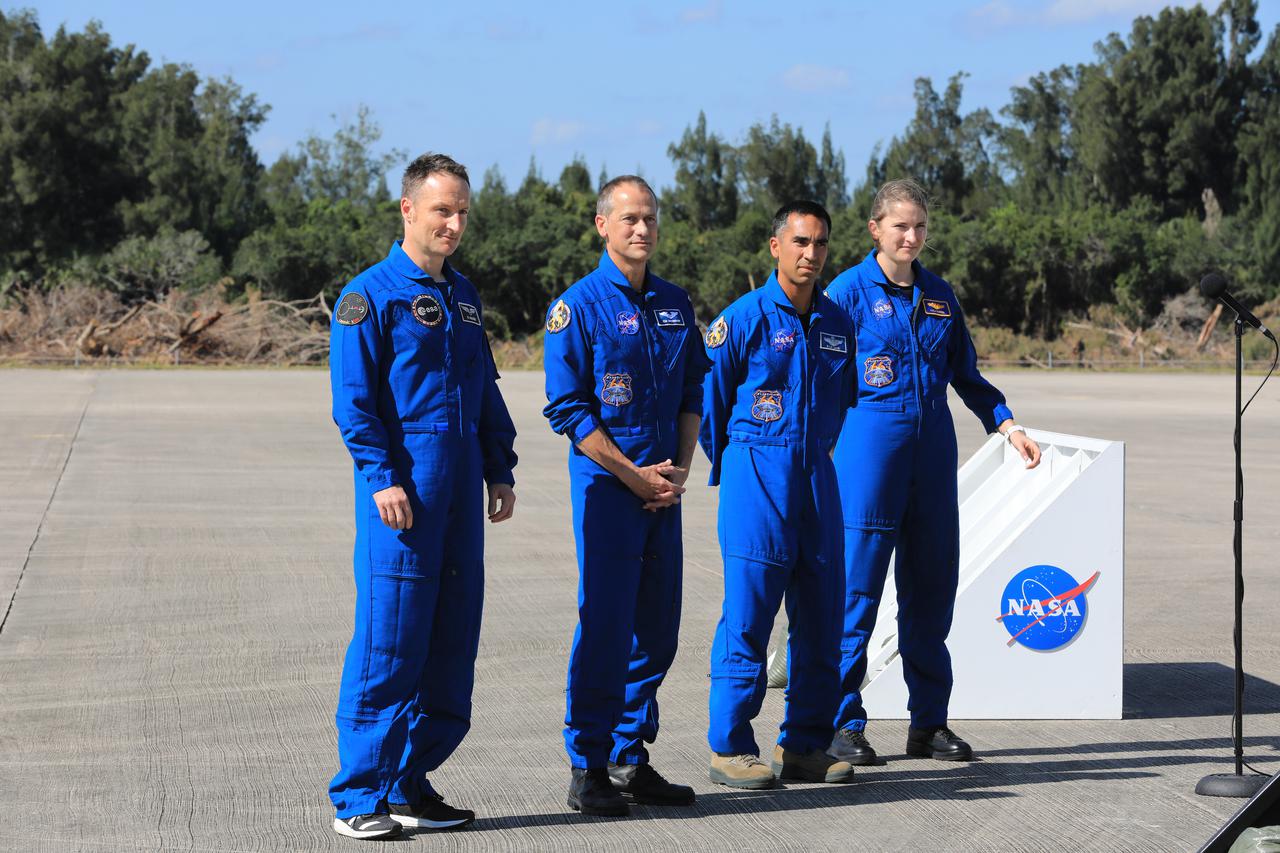

Crew members for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 mission to the International Space Station arrive at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on Oct. 26, 2021. From left, European Space Agency astronaut Matthias Maurer, and NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Raja Chari, and Kayla Barron speak to members of the news media. The crew will enter quarantine at the center’s Crew Quarters as they await launch aboard the Crew Dragon on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Launch is targeted for 2:21 a.m. EDT on Oct. 31 from Launch Complex 39A. Crew-3 is the third crew rotation flight for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, and the first flight of a new Crew Dragon spacecraft.
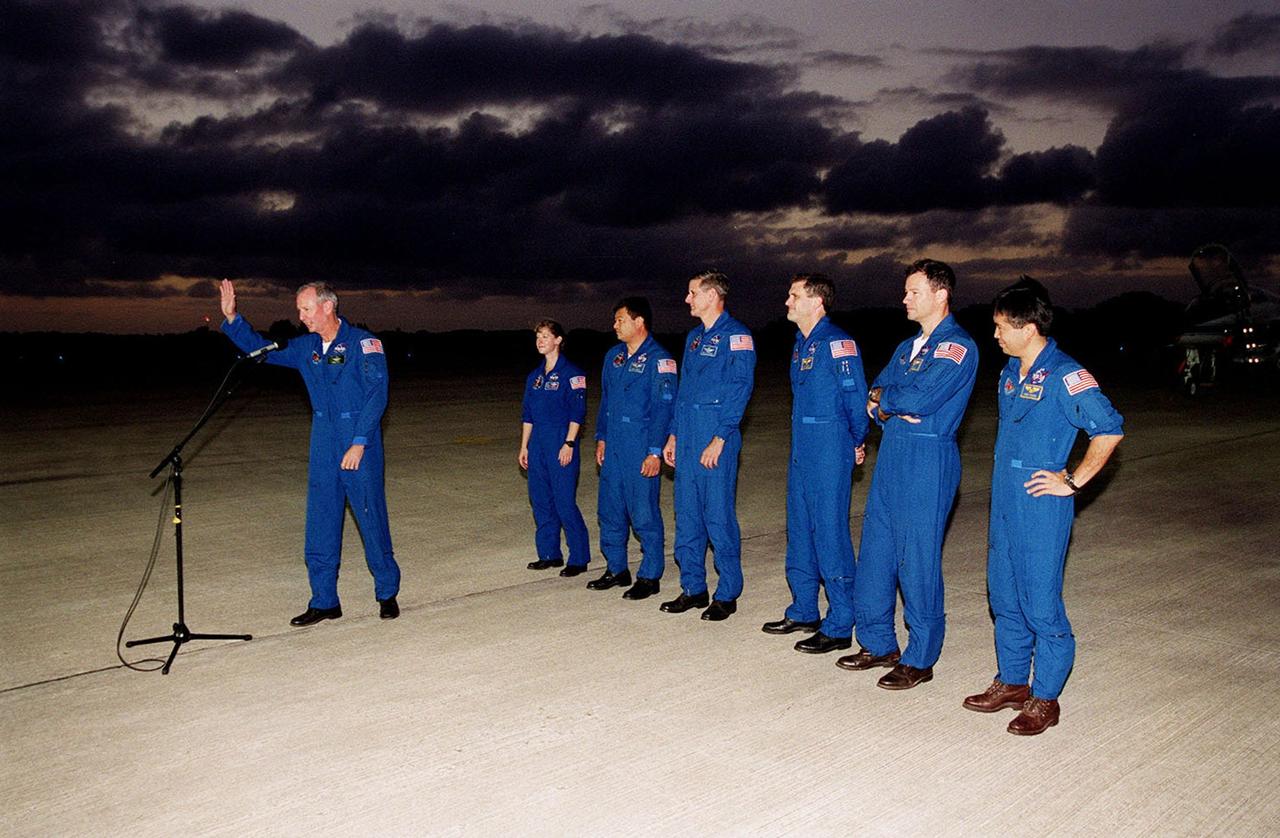

Gathered on the parking apron at the Shuttle Landing Facility after their arrival is the STS-92 crew. Commander Brian Duffy waves to the media (out of view) before heading to the bus for the short trip to crew quarters at the Operations and Checkout Building. Standing behind Duffy are (left to right) Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
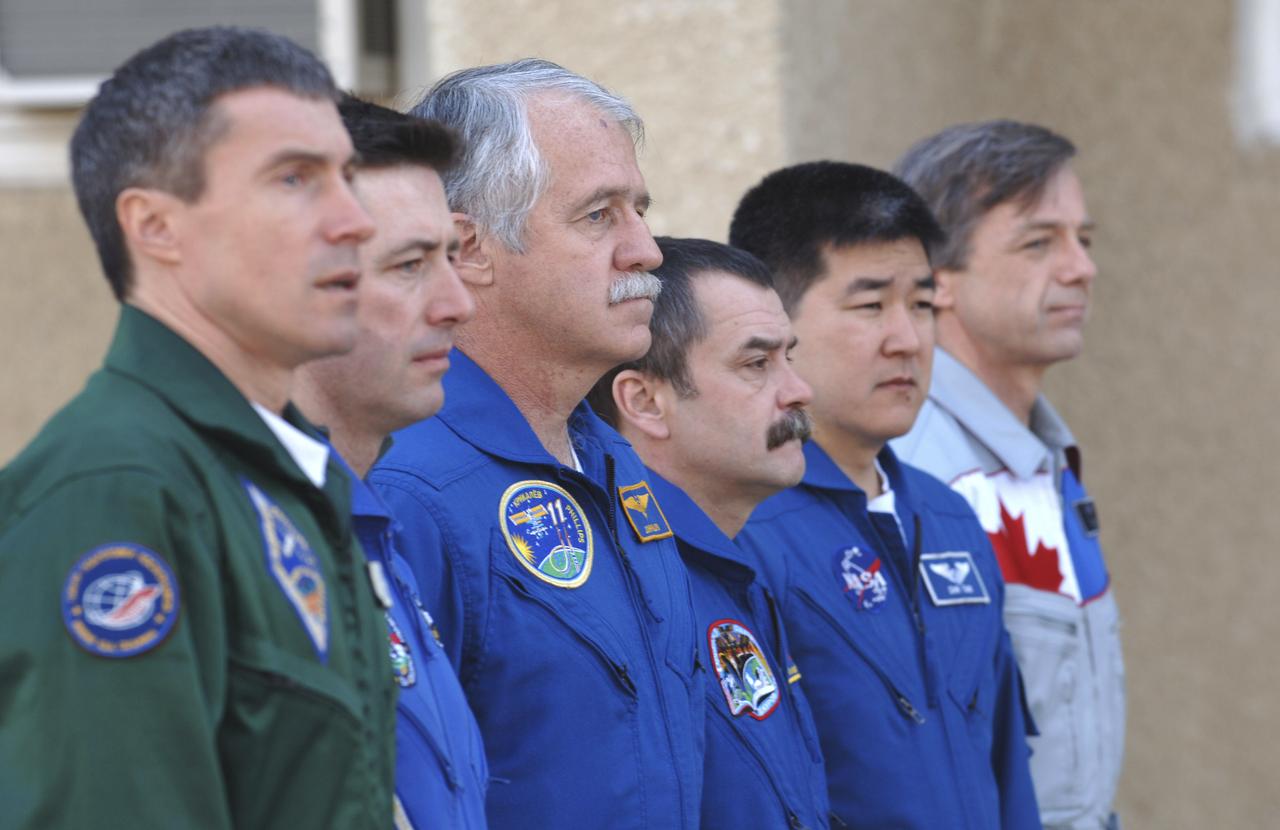

Expedition 11 Commander Sergei Krikalev, left, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, of Italy, Flight Engineer John Phillips, third from left, along with their backups, Russian Commander Mikhail Tyurin, American Dan Tani and Robert Thirsk, of Canada, far right, participate in the traditional raising of their countries’ flags outside their crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan on Monday, April 11, 2005, during preparations for the April 15 launch on a Soyuz TMA-6 spacecraft to the International Space Station. Krikalev and Phillips will spend six months in space and greet the first Shuttle crew to fly in more than two years when it arrives at the station, while Vittori spends eight days on the station under a commercial contract between ESA and the Russian Federal Space Agency. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
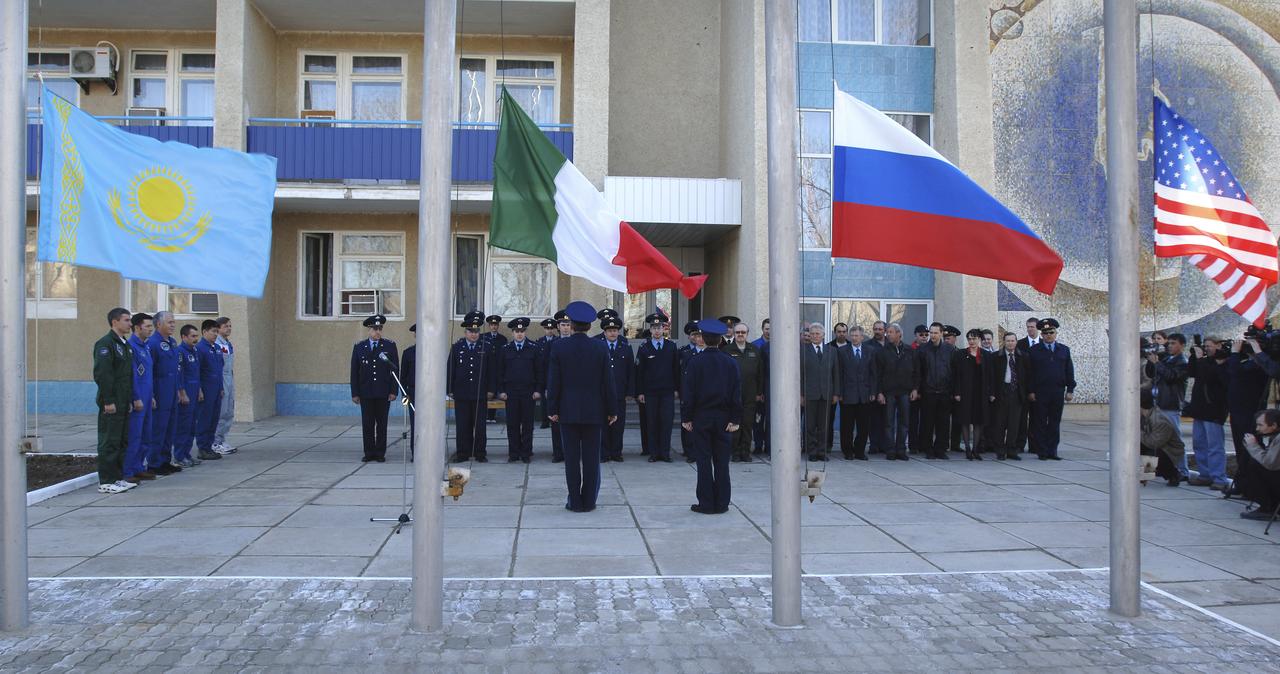

Expedition 11 Commander Sergei Krikalev, left, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, of Italy, Flight Engineer John Phillips, third from left, along with their backups, Russian Commander Mikhail Tyurin, American Dan Tani and Robert Thirsk, of Canada, far right, participate in the traditional raising of their countries’ flags outside their crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan on Monday, April 11, 2005, during preparations for the April 15 launch on a Soyuz TMA-6 spacecraft to the International Space Station. Krikalev and Phillips will spend six months in space and greet the first Shuttle crew to fly in more than two years when it arrives at the station, while Vittori spends eight days on the station under a commercial contract between ESA and the Russian Federal Space Agency. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
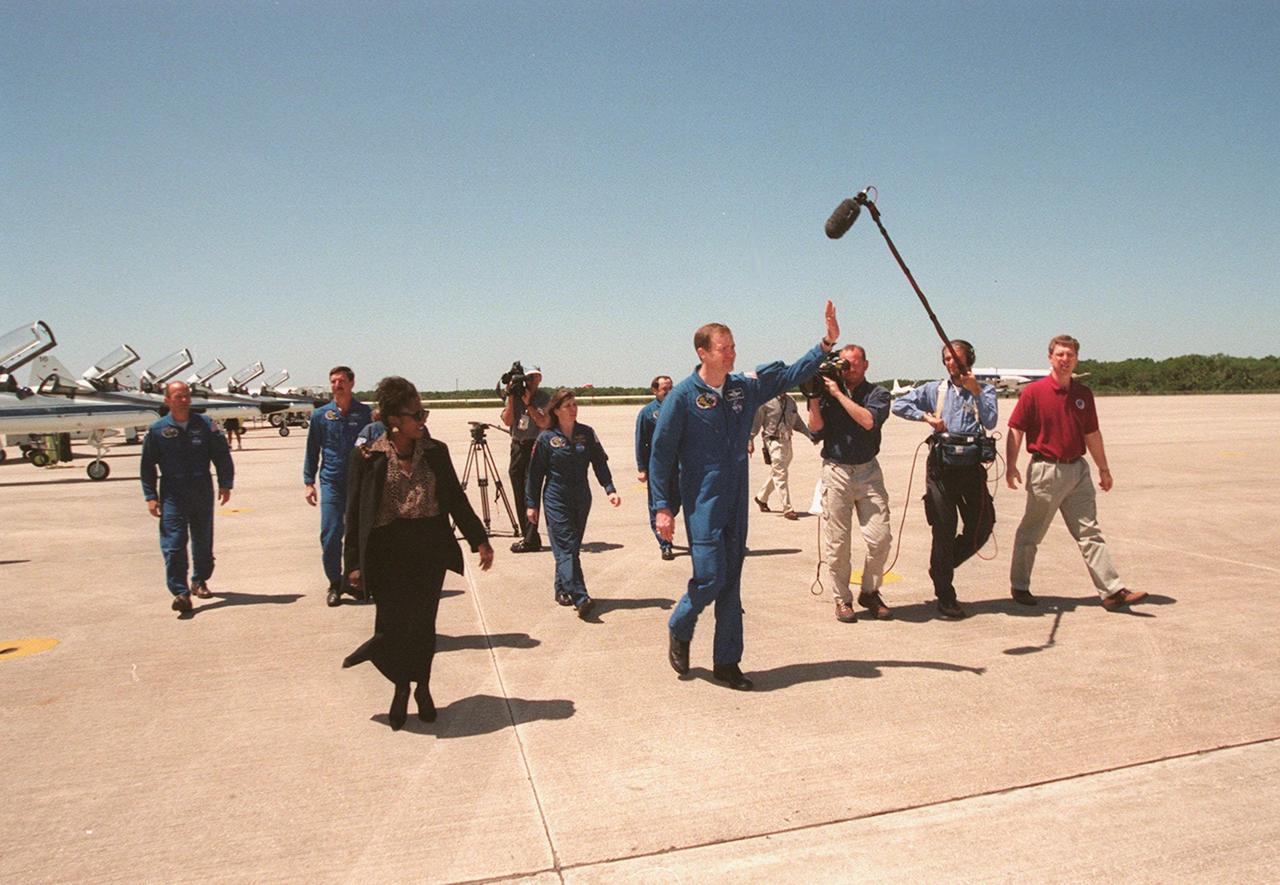

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-101 Commander James Halsell waves to the media as he and other crew members cross the tarmac to a waiting bus. At right is a film crew; in the foreground at left is Delores Green, flight crew support specialist lead for the astronaut crew quarters. Other crew members in the background are Mission Specialist Jeffrey Williams, Pilot Scott Horowitz, and Mission Specialists Mary Ellen Weber and Yury Usachev. Not visible in the photo is Mission Specialist Susan Helms. During their mission to the International Space Station, the STS-101 crew will be delivering logistics and supplies, plus preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station. This will be the third assembly flight for the Space Station. STS-101 is scheduled to launch April 24 at 4:15 p.m. from Launch Pad 39A

Behind the Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 36/37 Flight Engineer Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency plants a tree in his name in a traditional ceremony May 22 as backup crewmates Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (left) and Mikhail Tyurin (hidden) look on, along with prime Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchkhin (third from right), backup crewmember Rick Mastracchio of NASA (second from right) and prime Flight Engineer Karen Nyberg of NASA (far right). Nyberg, Yurchikhin and Parmitano are preparing for their launch May 29, Kazakh time, in the Soyuz TMA-09M spacecraft to begin a 5 ½ month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov
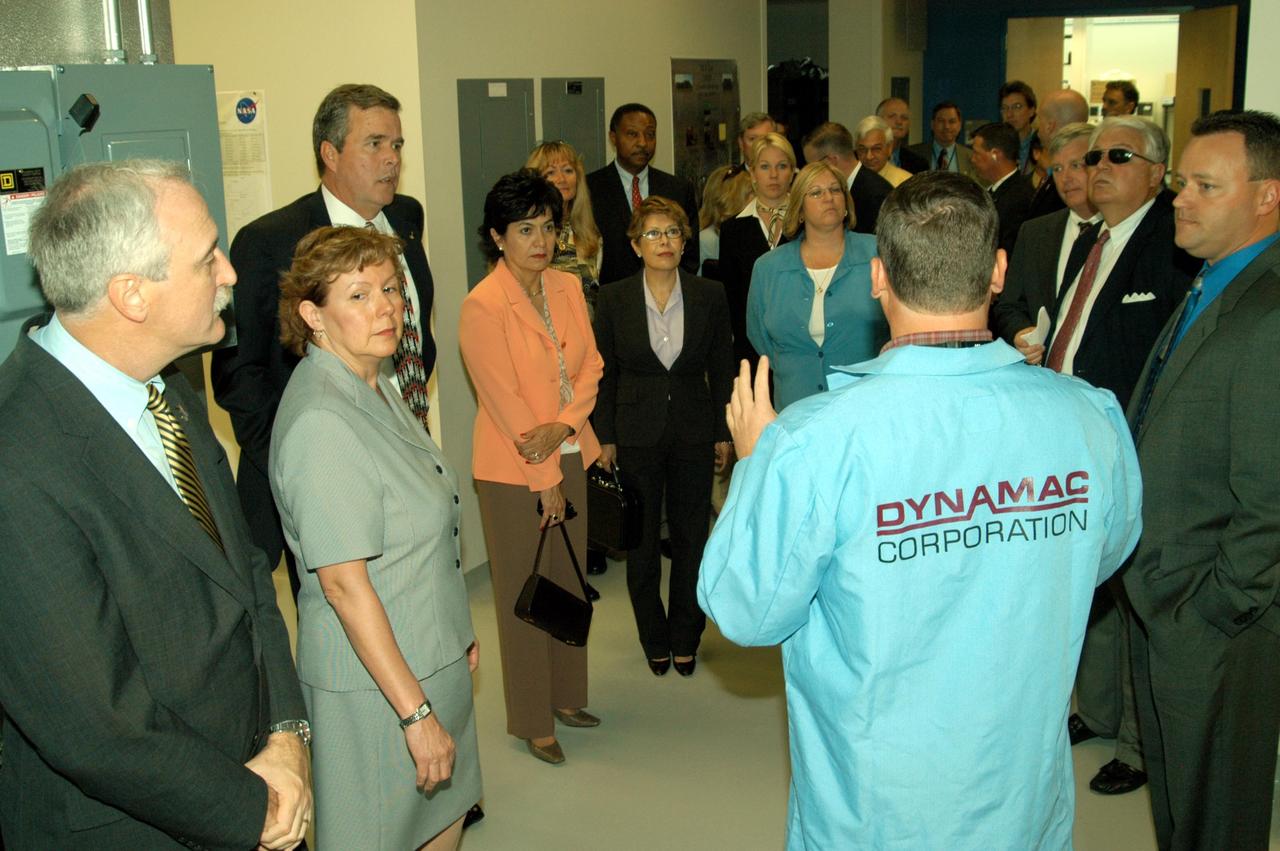

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Neil Yorio, a Dynamac scientist (right), explains the function of the KSC Space Life Sciences (SLS) Lab to a prestigious tour group. From left are NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe and his wife, Laura; Florida Gov. Jeb Bush; Bernadette Kennedy, wife of the Center Director (CD); Columba Bush, wife of the governor; behind Mrs. Bush, former astronaut Winston Scott; and third from right, CD Jim Kennedy. The new lab is a state-of-the-art facility built for ISS biotechnology research. It was developed as a partnership between NASA-KSC and the State of Florida. The tour followed the launching ceremony at the KSC Visitor Complex for the new Florida quarter issued by the U.S. Mint. The ceremony was emceed by Kennedy and included remarks by O’Keefe, Bush, U.S. Mint Director Henrietta Holsman Fore and Deputy Secretary of the Treasury Samuel W. Bodman.
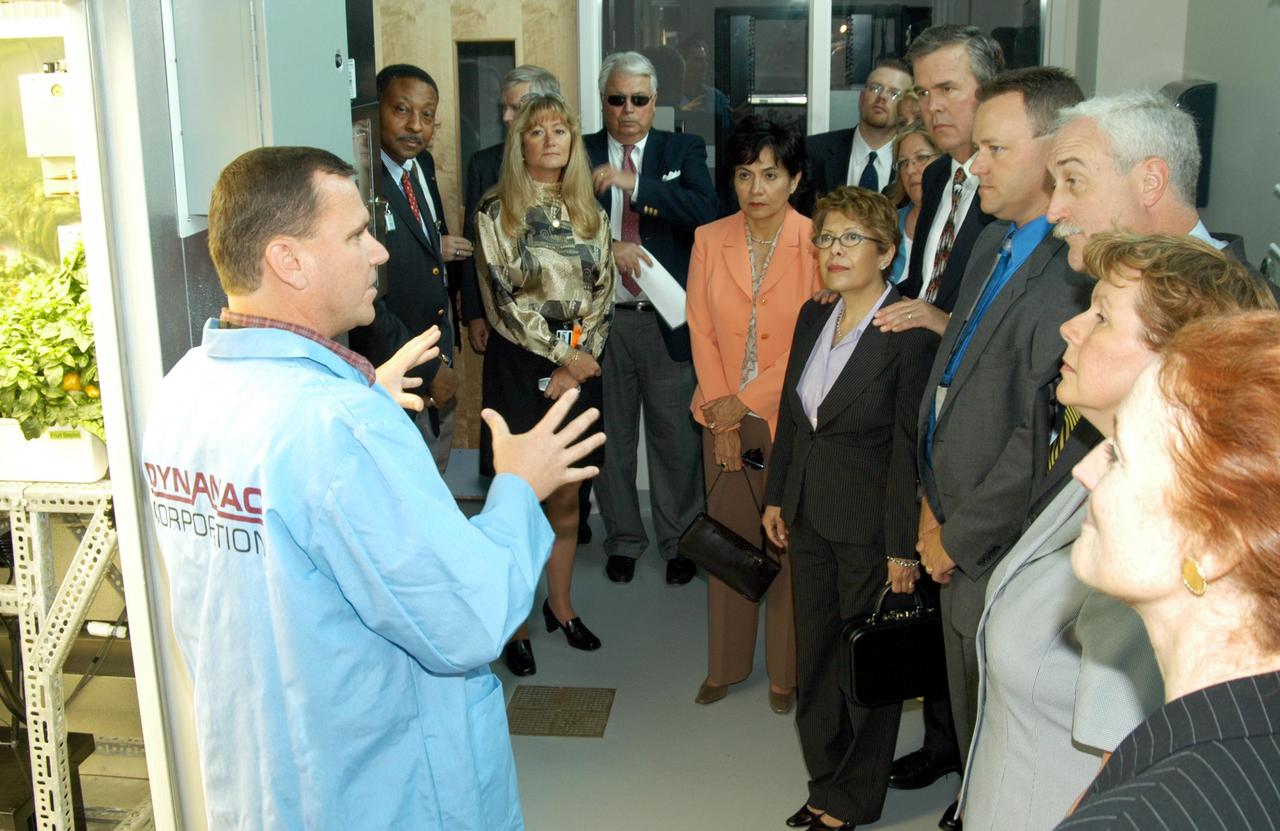

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Neil Yorio, a Dynamac scientist(left), explains the function of the KSC Space Life Sciences (SLS) Lab to a prestigious tour group. In the background at left is former astronaut Winston Scott; at center is Bernadette Kennedy, wife of the Center Director (CD); next to her are Columba and Florida Gov. Jeb Bush; third from right is NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe, next to his wife, Laura; and on the far right is U.S. Mint Director Henrietta Holsman Fore. The new lab is a state-of-the-art facility built for ISS biotechnology research. It was developed as a partnership between NASA-KSC and the State of Florida. The tour followed the launching ceremony at the KSC Visitor Complex for the new Florida quarter issued by the U.S. Mint. The ceremony was emceed by CD Jim Kennedy and included remarks by O’Keefe, Bush, Fore and Deputy Secretary of the Treasury Samuel W. Bodman.
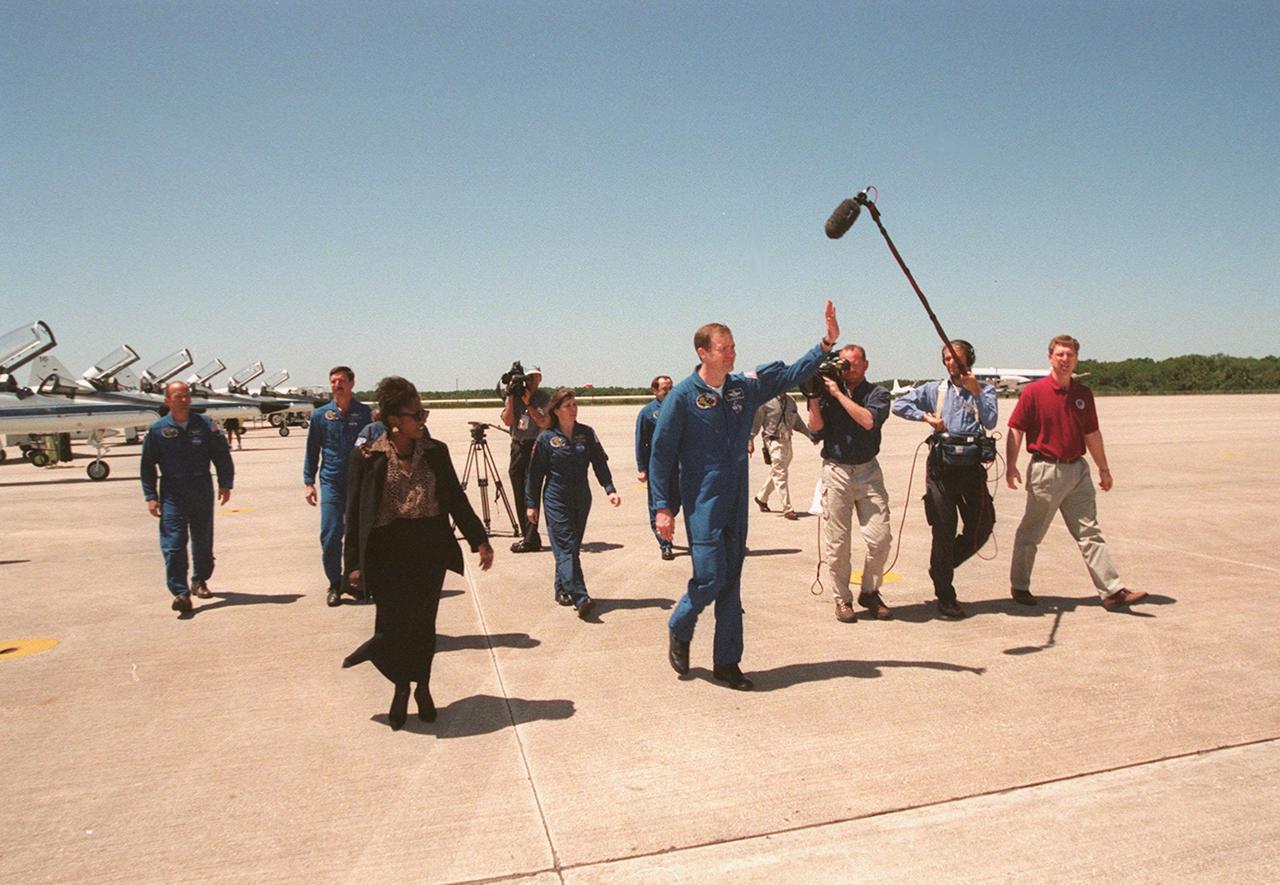

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-101 Commander James Halsell waves to the media as he and other crew members cross the tarmac to a waiting bus. At right is a film crew; in the foreground at left is Delores Green, flight crew support specialist lead for the astronaut crew quarters. Other crew members in the background are Mission Specialist Jeffrey Williams, Pilot Scott Horowitz, and Mission Specialists Mary Ellen Weber and Yury Usachev. Not visible in the photo is Mission Specialist Susan Helms. During their mission to the International Space Station, the STS-101 crew will be delivering logistics and supplies, plus preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. Also, the crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station. This will be the third assembly flight for the Space Station. STS-101 is scheduled to launch April 24 at 4:15 p.m. from Launch Pad 39A
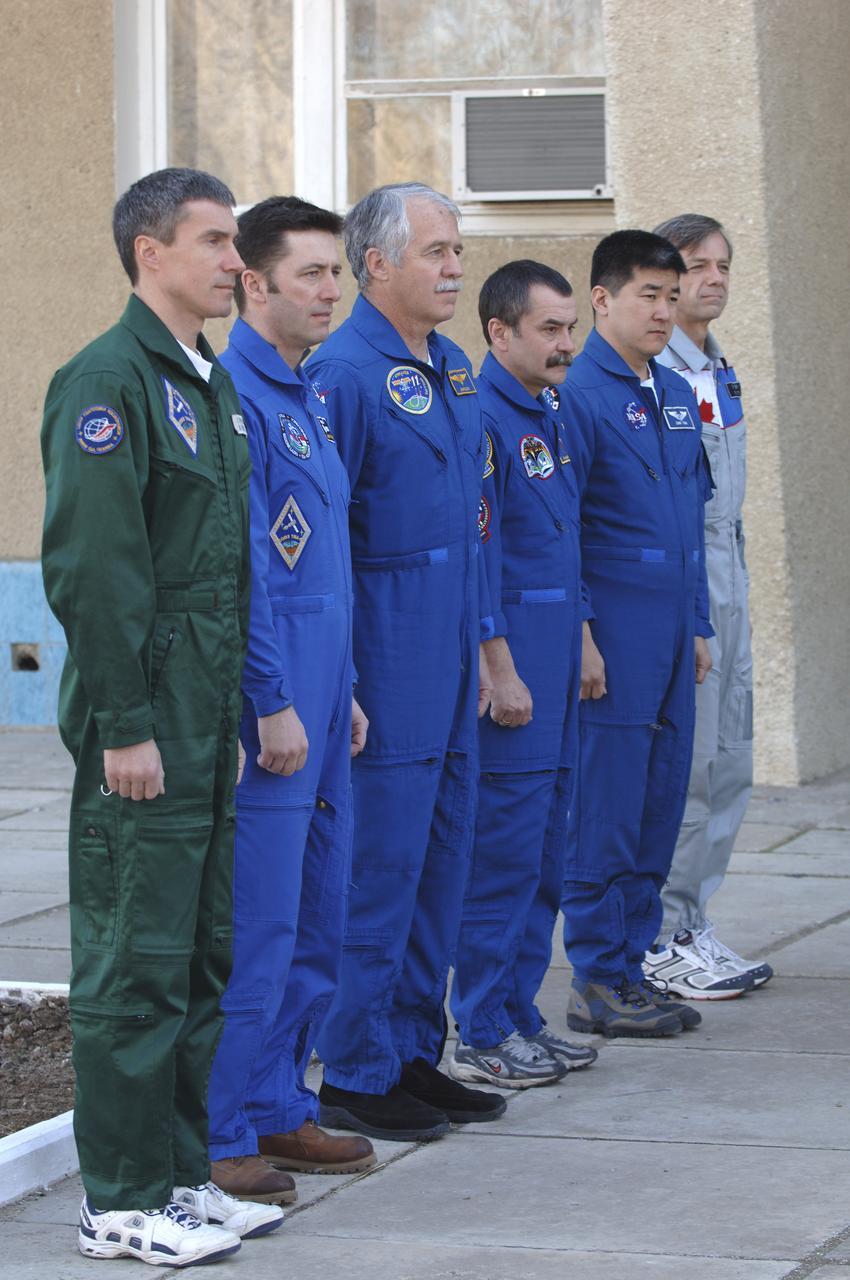

Expedition 11 Commander Sergei Krikalev, left, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, of Italy, Flight Engineer John Phillips, third from left, along with their backups, Russian Commander Mikhail Tyurin, American Dan Tani and Robert Thirsk, of Canada, far right, participate in the traditional raising of their countries’ flags outside their crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan on Monday, April 11, 2005, during preparations for the April 15 launch on a Soyuz TMA-6 spacecraft to the International Space Station. Krikalev and Phillips will spend six months in space and greet the first Shuttle crew to fly in more than two years when it arrives at the station, while Vittori spends eight days on the station under a commercial contract between ESA and the Russian Federal Space Agency. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
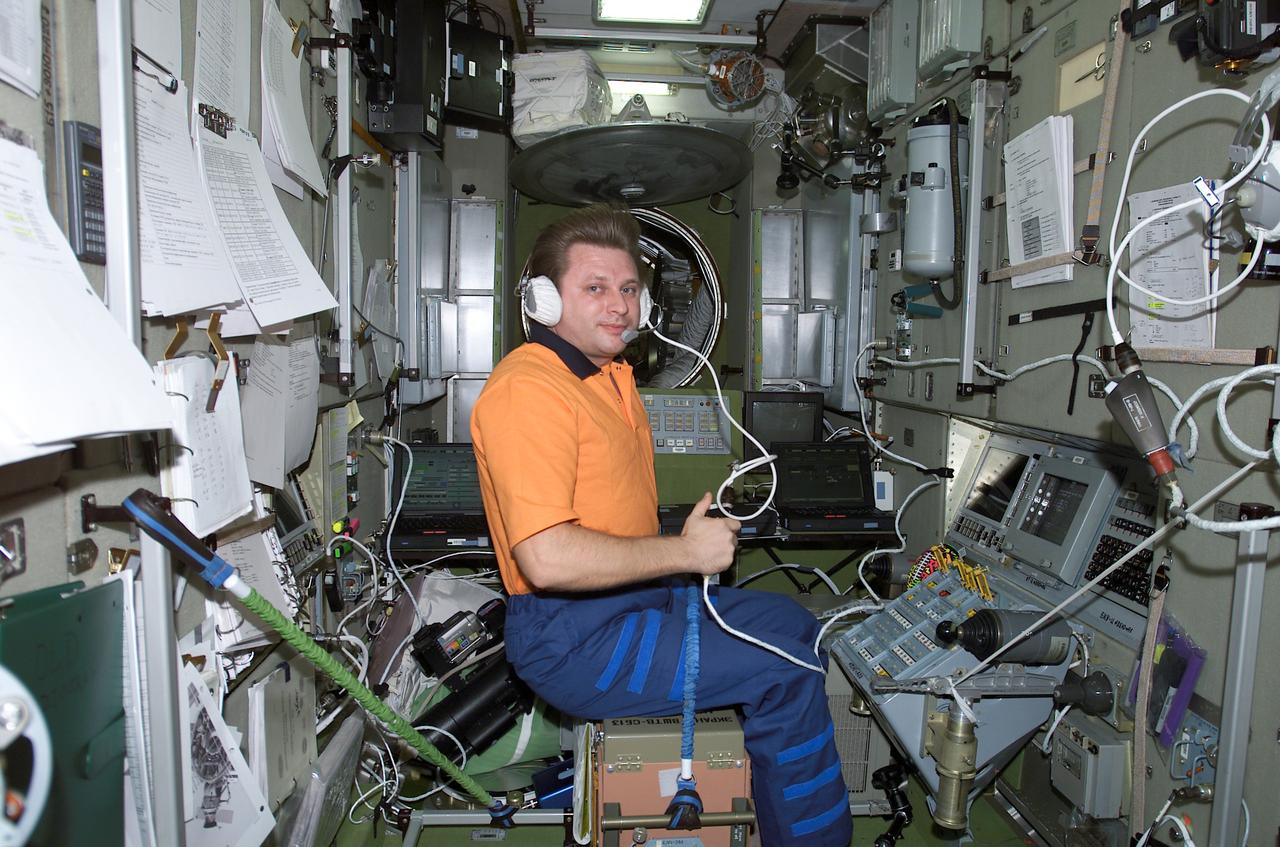

Cosmonaut Yury I. Onufrienko, Expedition Four mission commander, uses a communication system in the Russian Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). The Zvezda is linked to the Russian-built Functional Cargo Block (FGB) or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity. The third component of the ISS, Zvezda (Russian word for star), the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
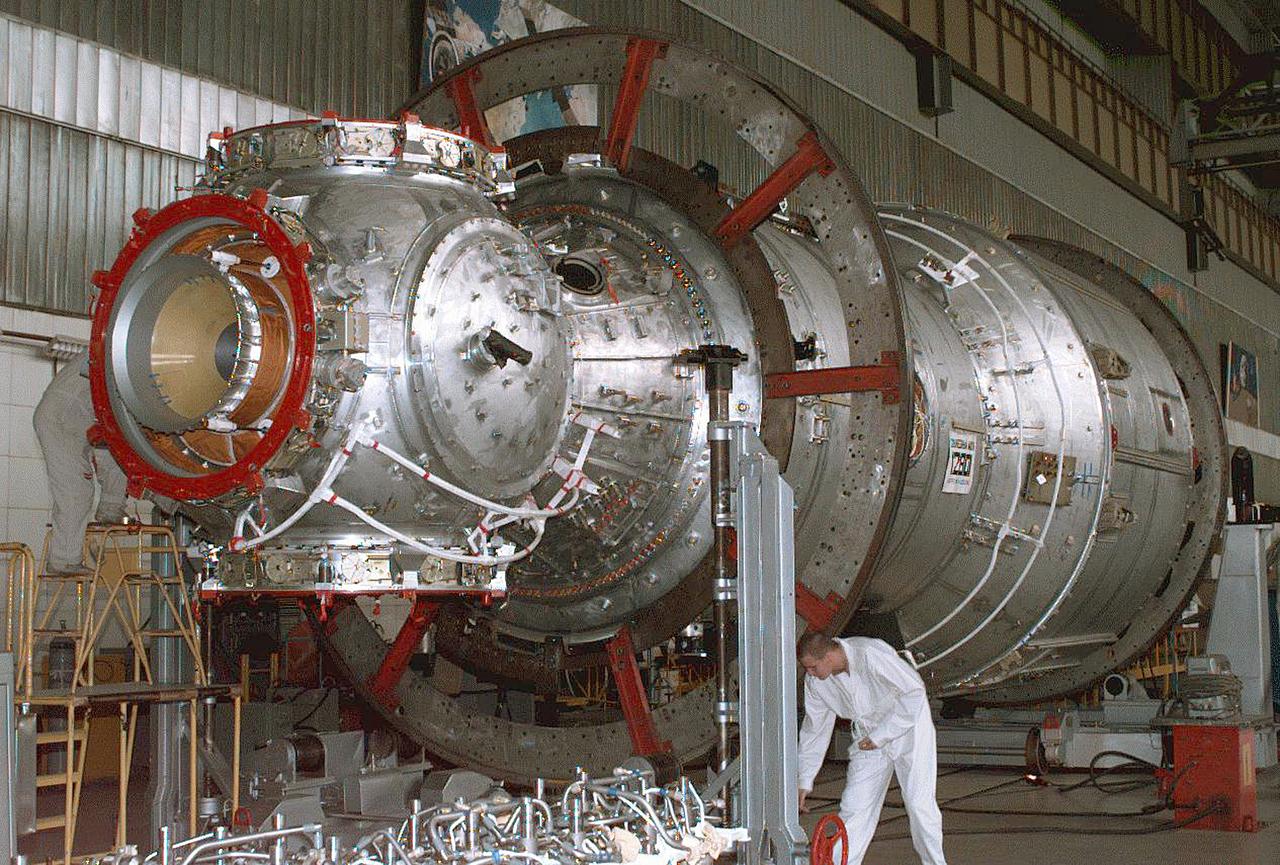
The Zvezda Service Module, the first Russian contribution and third element to the International Space Station (ISS), is shown under construction in the Krunichev State Research and Production Facility (KhSC) in Moscow. Russian technicians work on the module shortly after it completed a pressurization test. In the foreground is the forward portion of the module, including the spherical transfer compartment and its three docking ports. The forward port docked with the cornected Functional Cargo Block, followed by Node 1. Launched via a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000, the Zvezda Service Module serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, life support system, electrical power distribution, data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
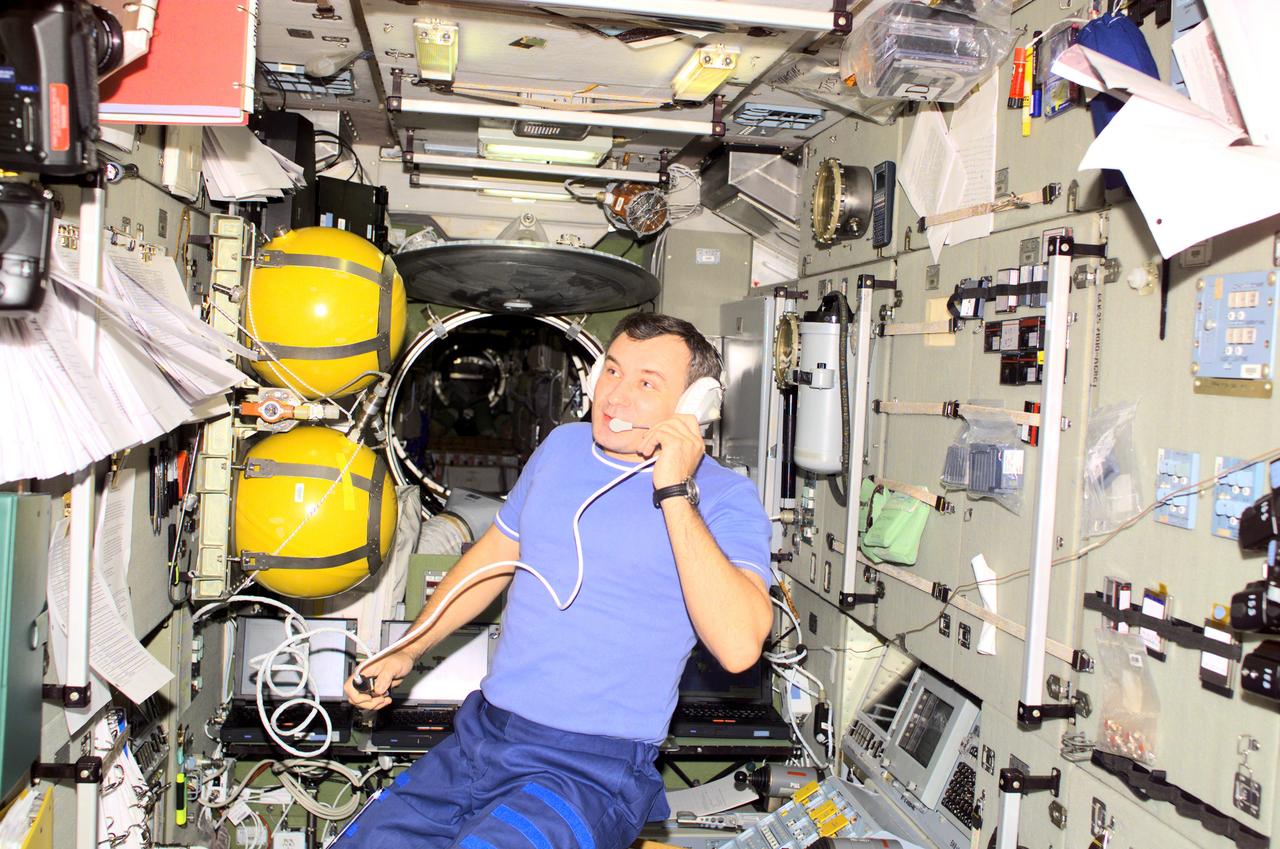

Aboard the International Space Station (ISS), Cosmonaut and Expedition Three flight engineer Vladimir N. Dezhurov, representing Rosaviakosmos, talks with flight controllers from the Zvezda Service Module. Russian-built Zvezda is linked to the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity. The third component of the ISS, Zvezda (Russian word for star), the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
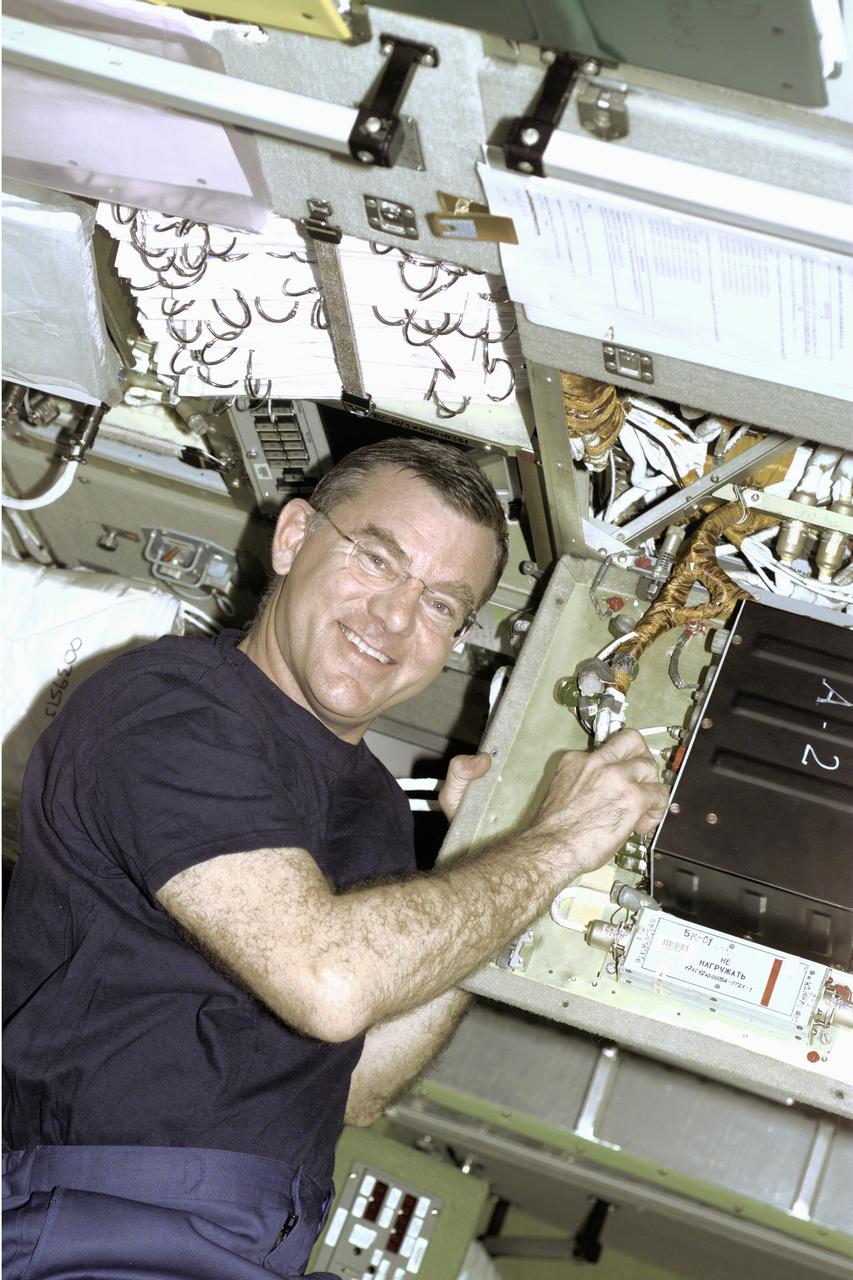

Astronaut James S. Voss, Expedition Two flight engineer, performs an electronics task in the Russian Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Zvezda is linked to the Russian-built Functional Cargo Block (FGB), or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity, the first U.S.-built component to the ISS. Zvezda (Russian word for star), the third component of the ISS and the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, a flight control system, and a propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
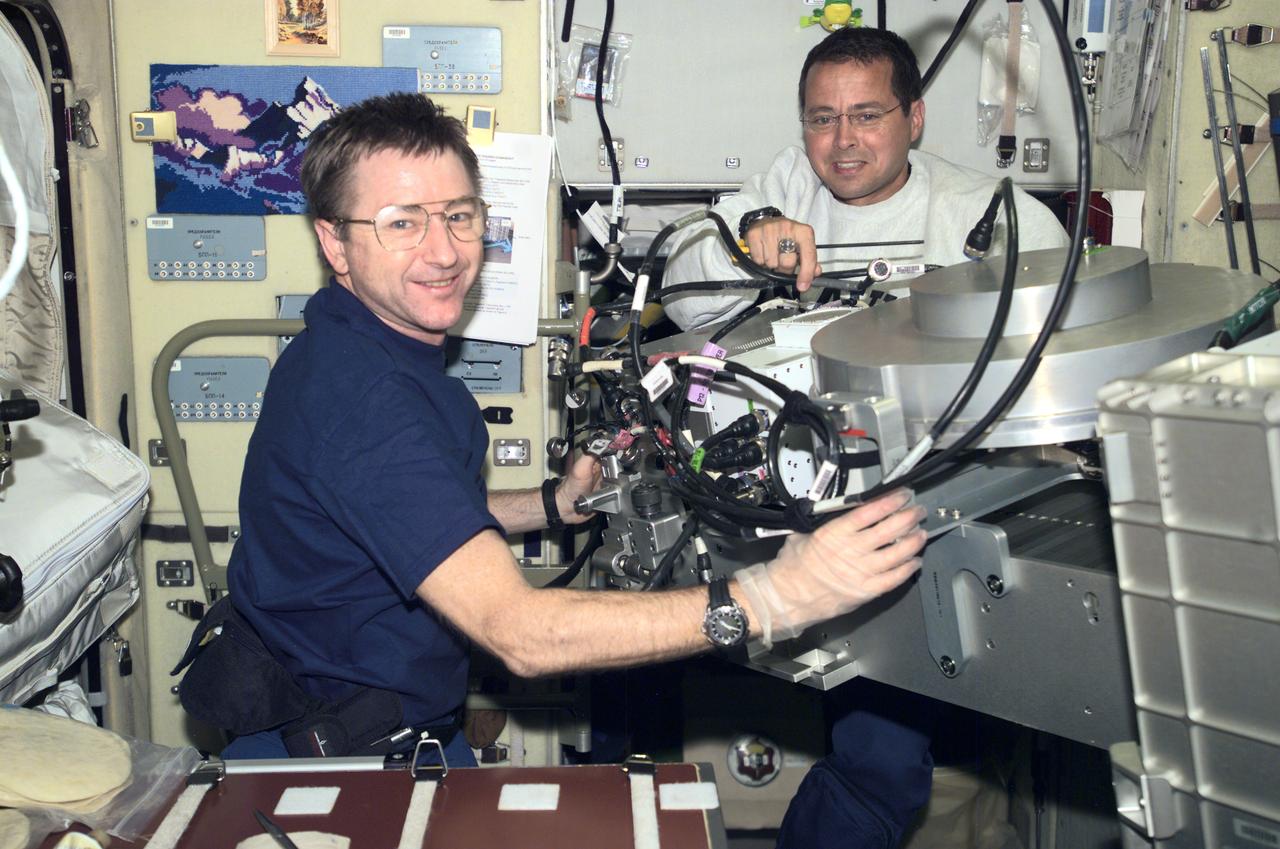

Astronauts Frank L. Culbertson, Jr. (left), Expedition Three mission commander, and Daniel W. Bursch, Expedition Four flight engineer, work in the Russian Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Zvezda is linked to the Russian built Functional Cargo Block (FGB), or Zarya, the first component of the ISS. Zarya was launched on a Russian Proton rocket prior to the launch of Unity. The third component of the ISS, Zvezda (Russian word for star), the primary Russian contribution to the ISS, was launched by a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000. Zvezda serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, a life support system, electrical power distribution, a data processing system, a flight control system, and a propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000 pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
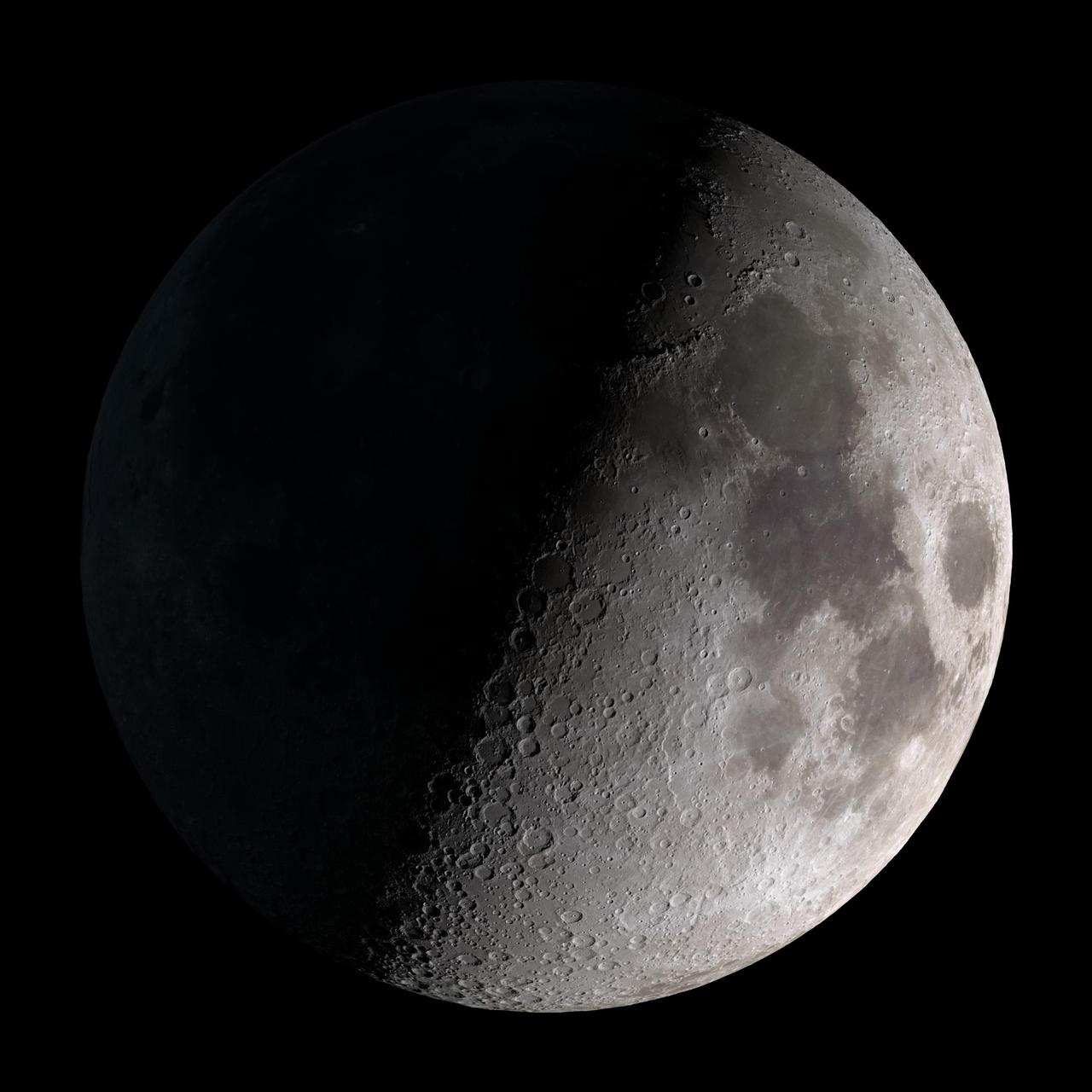

First quarter. Visible high in the southern sky in early evening. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
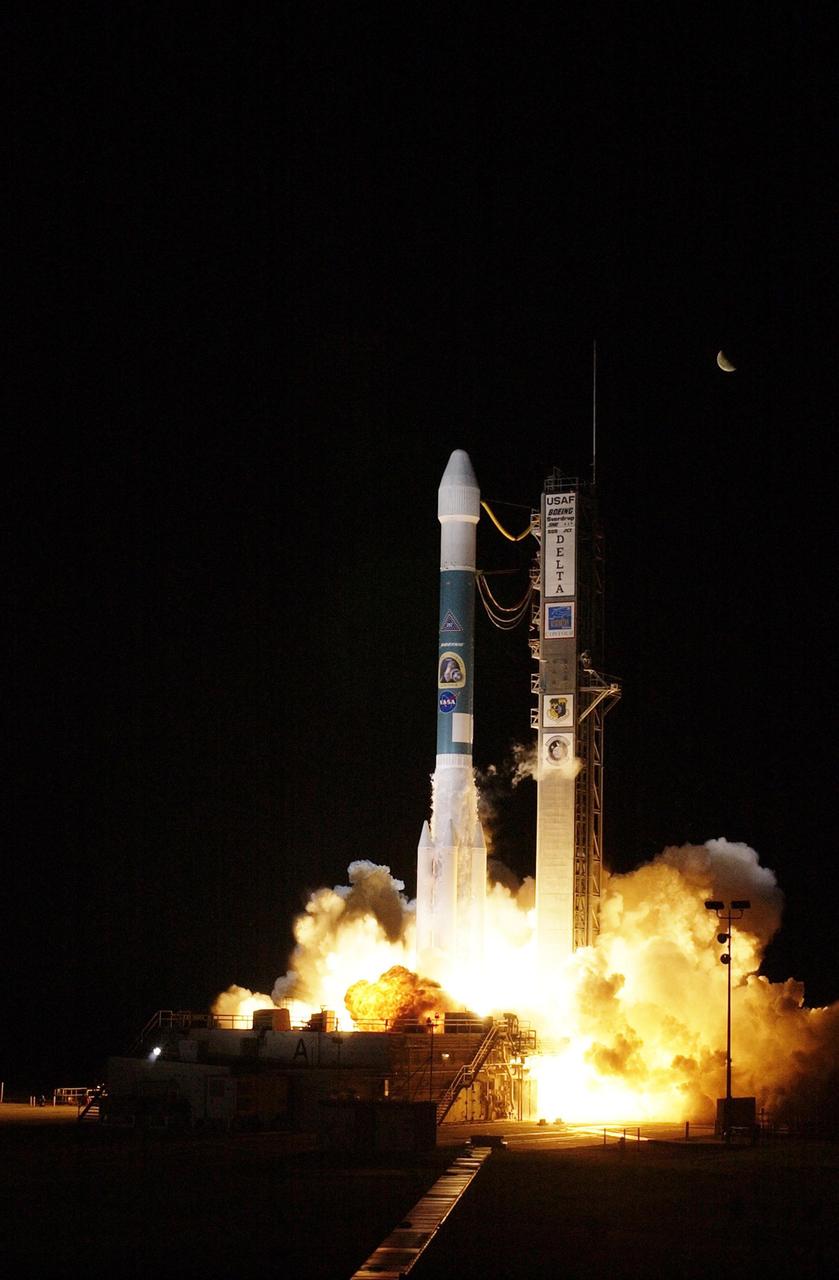

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A third-quarter moon is the only visible element in the sky as NASA's Comet Nucleus Tour (CONTOUR) spacecraft successfully launches at 2:47 a.m. EDT aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Designed and built by The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Md., the 2,138-pound (970-kilogram) spacecraft was placed into an elliptical Earth orbit 63 minutes after launch. About 19 minutes later the mission operations team at APL acquired a signal from the spacecraft through the Deep Space Network antenna station in Goldstone, Calif., and by 5:45 a.m. EDT Mission Director Dr. Robert W. Farquhar of the Applied Physics Lab confirmed the craft was operating normally and ready to carry out its early orbit maneuvers. CONTOUR will orbit Earth until Aug. 15, when it is scheduled to fire its main engine and enter a comet-chasing orbit around the sun. The mission's flexible four-year plan includes encounters with comets Encke (Nov. 12, 2003) and Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 (June 19, 2006), though it can add an encounter with a "new" and scientifically valuable comet from the outer solar system, should one be discovered in time for CONTOUR to fly past it. CONTOUR's four scientific instruments will take detailed pictures and measure the chemical makeup of each comet's nucleus -- a chunk of ice and rock -- while analyzing the surrounding gas and dust.
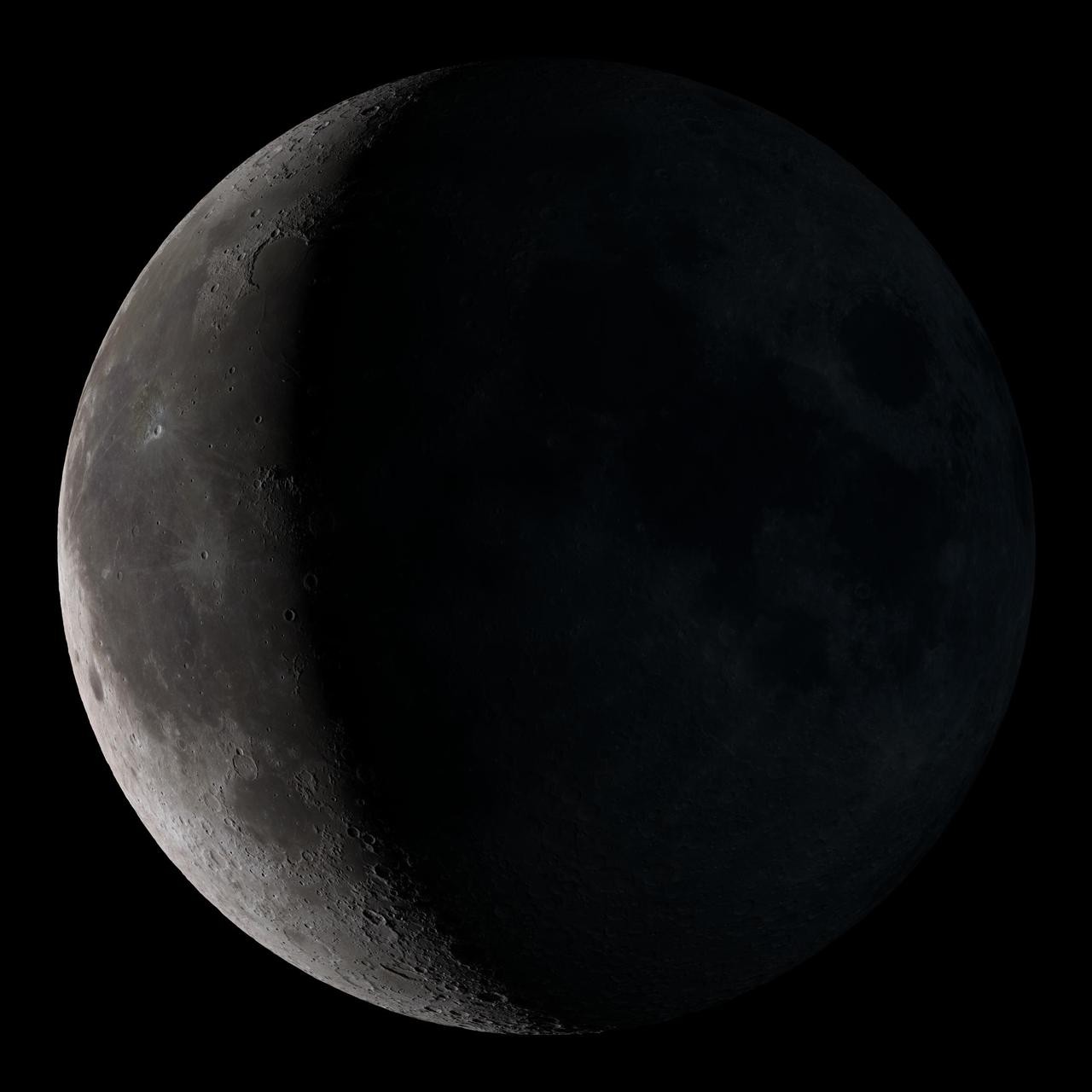

Waning crescent. Low to the east before sunrise. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Waxing gibbous. Visible to the southeast in early evening, up for most of the night. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
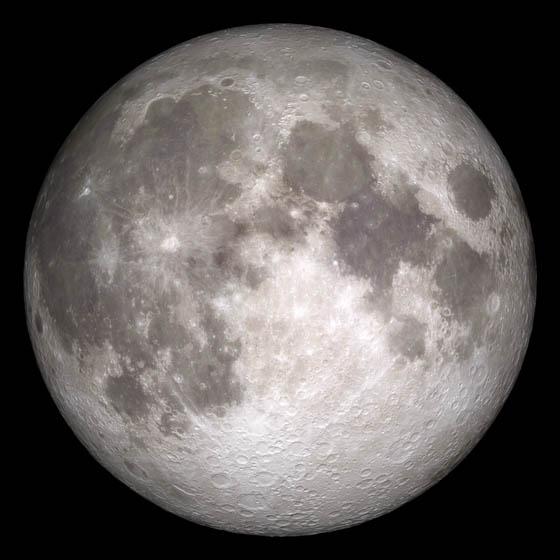

Current moon as viewed on Wednesday, June 15, 2011, 19:00 UT (Phase 100%) This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Full Moon. Rises at sunset, high in the sky around midnight. Visible all night. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
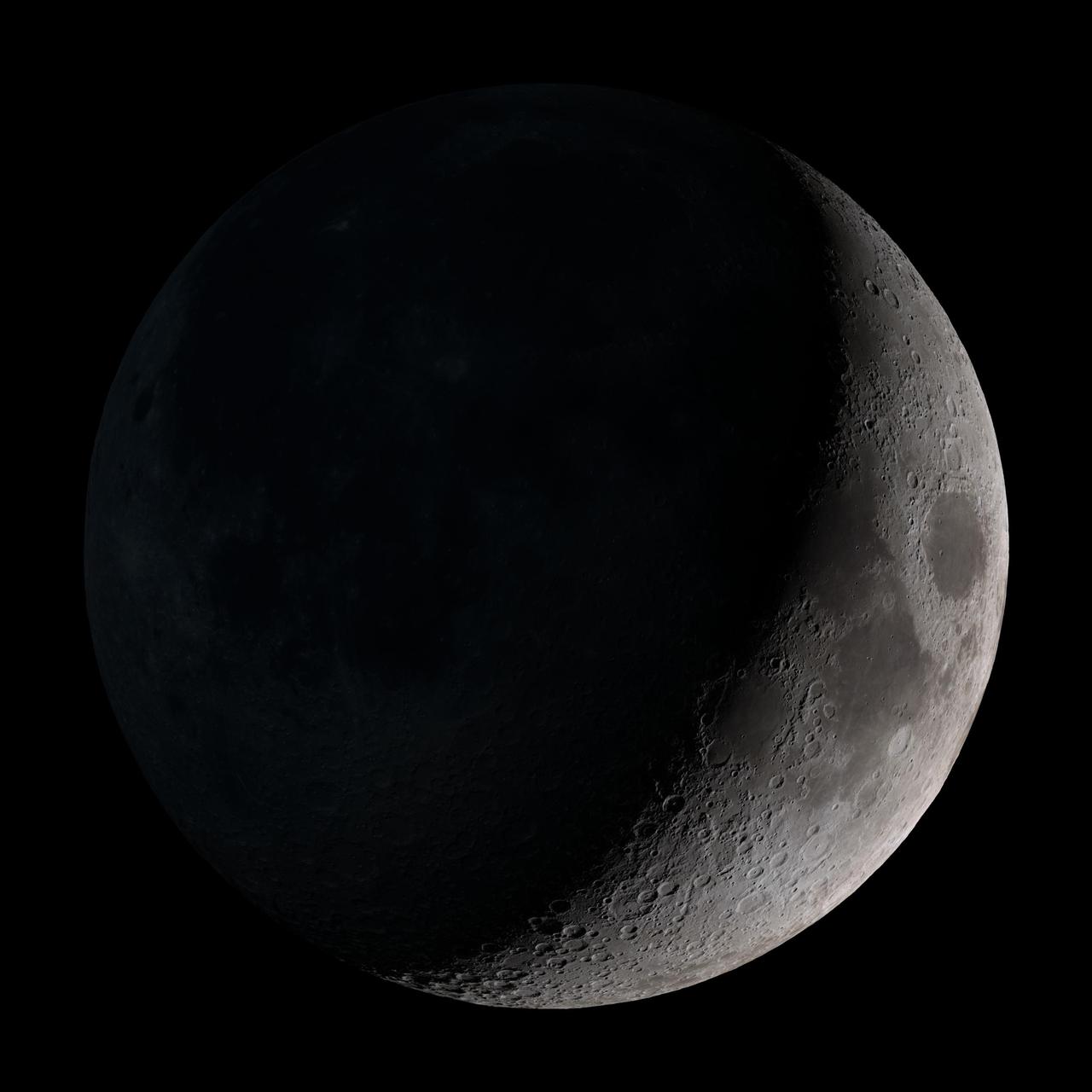

Waxing crescent. Visible toward the southwest in early evening. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
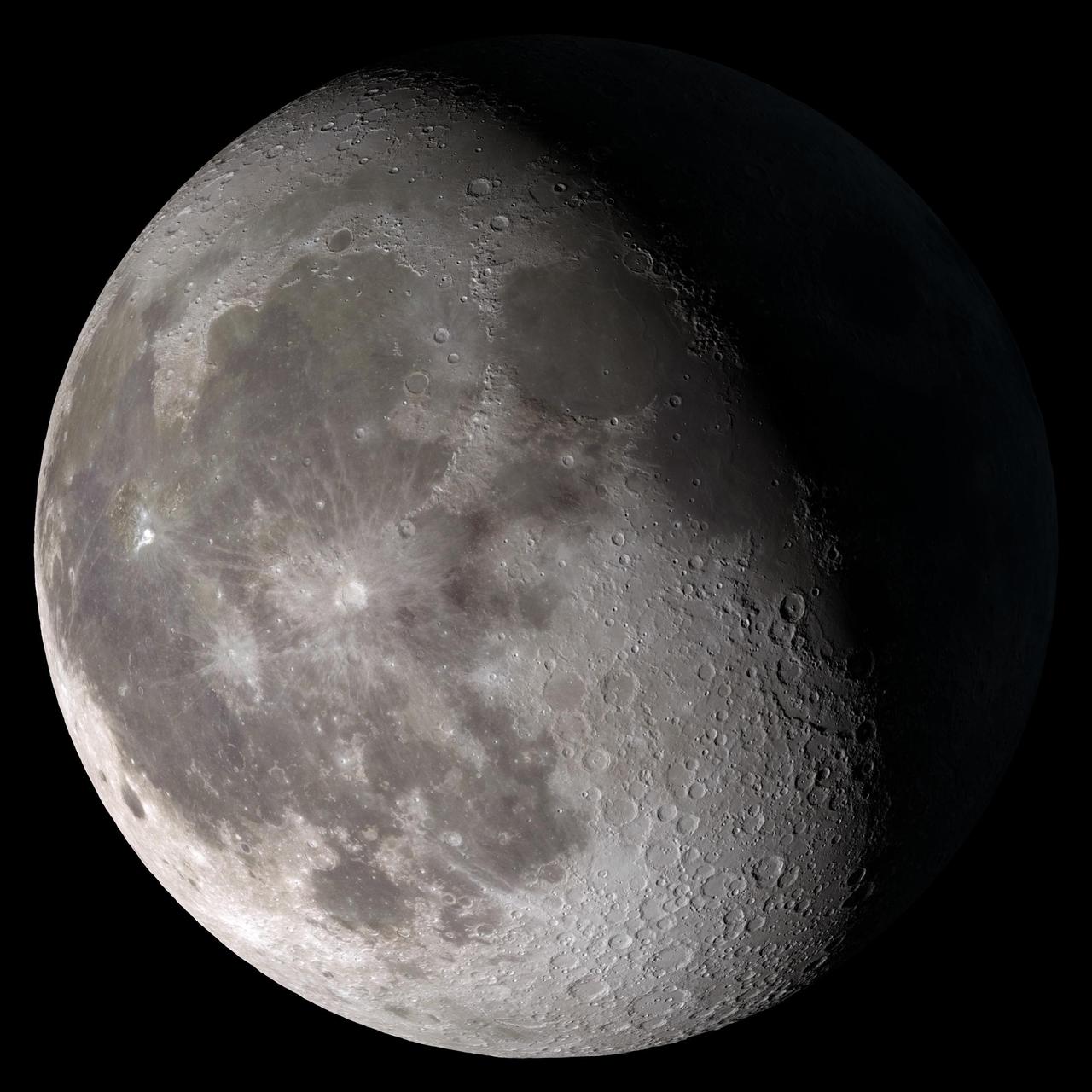

Waning gibbous. Rises after sunset, high in the sky after midnight, visible to the southwest after sunrise. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
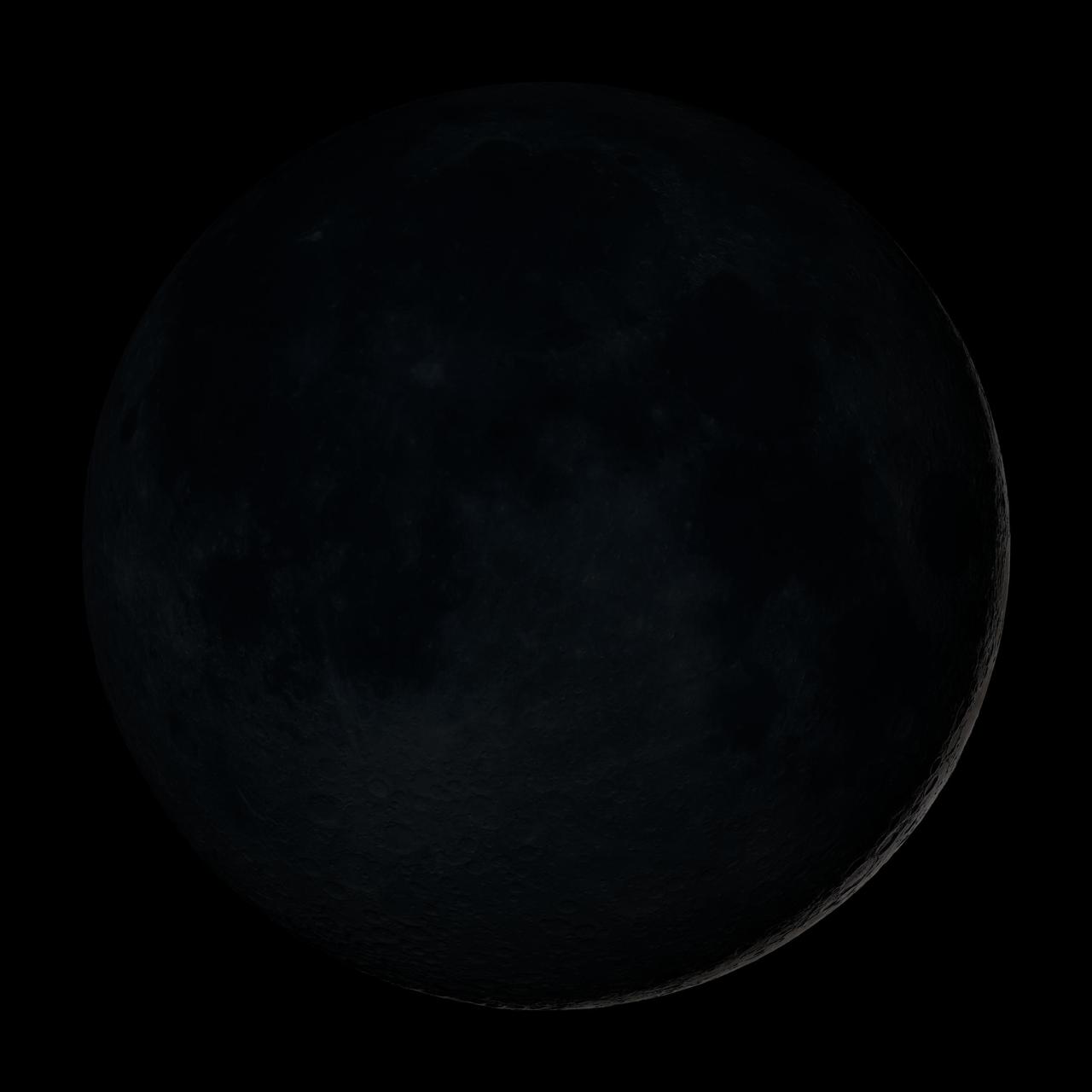

New Moon. By the modern definition, New Moon occurs when the Moon and Sun are at the same geocentric ecliptic longitude. The part of the Moon facing us is completely in shadow then. Pictured here is the traditional New Moon, the earliest visible waxing crescent, which signals the start of a new month in many lunar and lunisolar calendars. This marks the first time that accurate shadows at this level of detail are possible in such a computer simulation. The shadows are based on the global elevation map being developed from measurements by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). LOLA has already taken more than 10 times as many elevation measurements as all previous missions combined. The Moon always keeps the same face to us, but not exactly the same face. Because of the tilt and shape of its orbit, we see the Moon from slightly different angles over the course of a month. When a month is compressed into 12 seconds, as it is in this animation, our changing view of the Moon makes it look like it's wobbling. This wobble is called libration. The word comes from the Latin for "balance scale" (as does the name of the zodiac constellation Libra) and refers to the way such a scale tips up and down on alternating sides. The sub-Earth point gives the amount of libration in longitude and latitude. The sub-Earth point is also the apparent center of the Moon's disk and the location on the Moon where the Earth is directly overhead. The Moon is subject to other motions as well. It appears to roll back and forth around the sub-Earth point. The roll angle is given by the position angle of the axis, which is the angle of the Moon's north pole relative to celestial north. The Moon also approaches and recedes from us, appearing to grow and shrink. The two extremes, called perigee (near) and apogee (far), differ by more than 10%. The most noticed monthly variation in the Moon's appearance is the cycle of phases, caused by the changing angle of the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth. The cycle begins with the waxing (growing) crescent Moon visible in the west just after sunset. By first quarter, the Moon is high in the sky at sunset and sets around midnight. The full Moon rises at sunset and is high in the sky at midnight. The third quarter Moon is often surprisingly conspicuous in the daylit western sky long after sunrise. Celestial north is up in these images, corresponding to the view from the northern hemisphere. The descriptions of the print resolution stills also assume a northern hemisphere orientation. To adjust for southern hemisphere views, rotate the images 180 degrees, and substitute "north" for "south" in the descriptions. Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
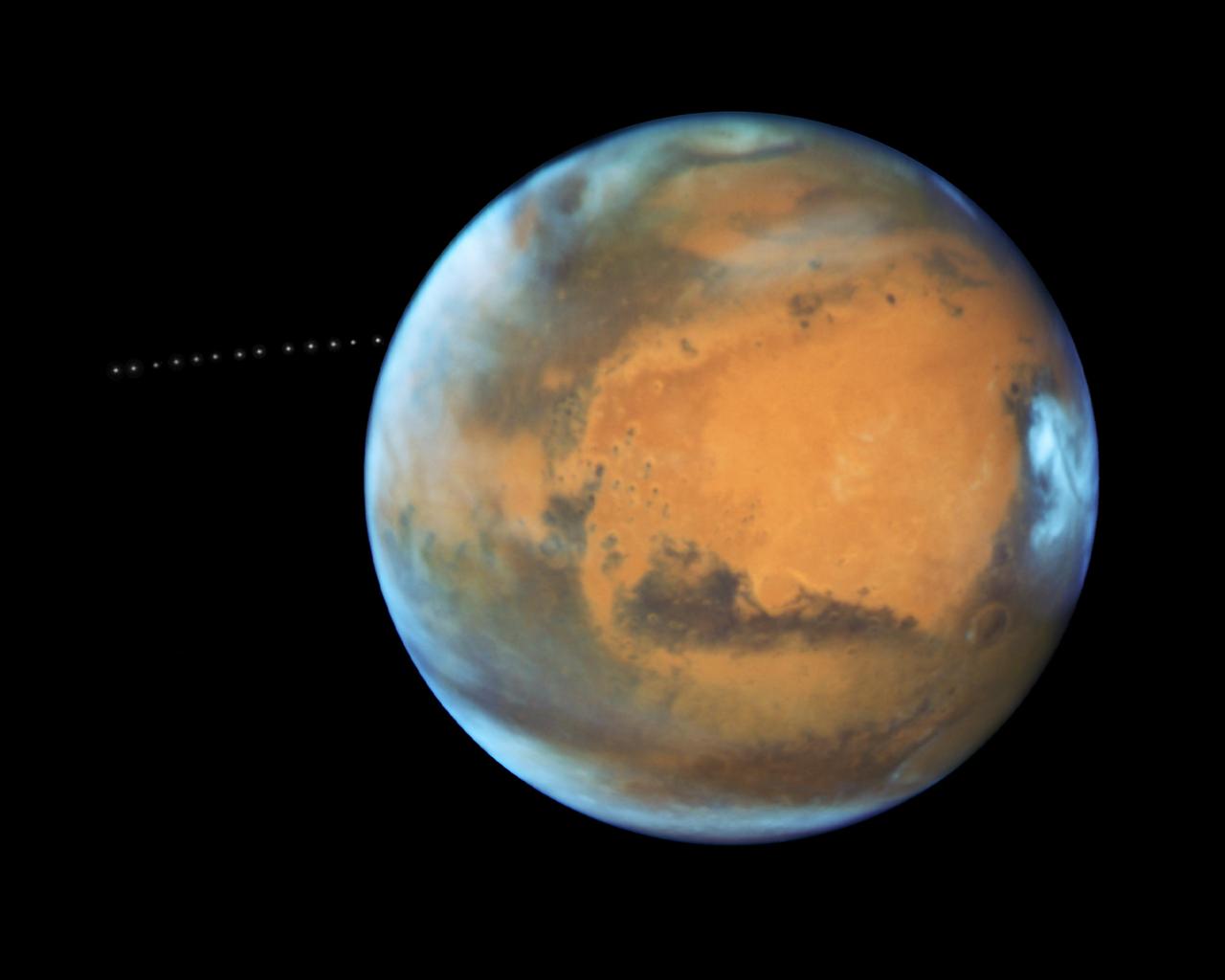
The sharp eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured the tiny moon Phobos during its orbital trek around Mars. Because the moon is so small, it appears star-like in the Hubble pictures. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble took 13 separate exposures, allowing astronomers to create a time-lapse video showing the diminutive moon's orbital path. The Hubble observations were intended to photograph Mars, and the moon's cameo appearance was a bonus. A football-shaped object just 16.5 miles by 13.5 miles by 11 miles, Phobos is one of the smallest moons in the solar system. It is so tiny that it would fit comfortably inside the Washington, D.C. Beltway. The little moon completes an orbit in just 7 hours and 39 minutes, which is faster than Mars rotates. Rising in the Martian west, it runs three laps around the Red Planet in the course of one Martian day, which is about 24 hours and 40 minutes. It is the only natural satellite in the solar system that circles its planet in a time shorter than the parent planet's day. About two weeks after the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing on July 20, 1969, NASA's Mariner 7 flew by the Red Planet and took the first crude close-up snapshot of Phobos. On July 20, 1976 NASA's Viking 1 lander touched down on the Martian surface. A year later, its parent craft, the Viking 1 orbiter, took the first detailed photograph of Phobos, revealing a gaping crater from an impact that nearly shattered the moon. Phobos was discovered by Asaph Hall on August 17, 1877 at the U.S. Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., six days after he found the smaller, outer moon, named Deimos. Hall was deliberately searching for Martian moons. Both moons are named after the sons of Ares, the Greek god of war, who was known as Mars in Roman mythology. Phobos (panic or fear) and Deimos (terror or dread) accompanied their father into battle. Close-up photos from Mars-orbiting spacecraft reveal that Phobos is apparently being torn apart by the gravitational pull of Mars. The moon is marred by long, shallow grooves that are probably caused by tidal interactions with its parent planet. Phobos draws nearer to Mars by about 6.5 feet every hundred years. Scientists predict that within 30 to 50 million years, it either will crash into the Red Planet or be torn to pieces and scattered as a ring around Mars. Orbiting 3,700 miles above the Martian surface, Phobos is closer to its parent planet than any other moon in the solar system. Despite its proximity, observers on Mars would see Phobos at just one-third the width of the full moon as seen from Earth. Conversely, someone standing on Phobos would see Mars dominating the horizon, enveloping a quarter of the sky. From the surface of Mars, Phobos can be seen eclipsing the sun. However, it is so tiny that it doesn't completely cover our host star. Transits of Phobos across the sun have been photographed by several Mars-faring spacecraft. The origin of Phobos and Deimos is still being debated. Scientists concluded that the two moons were made of the same material as asteroids. This composition and their irregular shapes led some astrophysicists to theorize that the Martian moons came from the asteroid belt. However, because of their stable, nearly circular orbits, other scientists doubt that the moons were born as asteroids. Such orbits are rare for captured objects, which tend to move erratically. An atmosphere could have slowed down Phobos and Deimos and settled them into their current orbits, but the Martian atmosphere is too thin to have circularized the orbits. Also, the moons are not as dense as members of the asteroid belt. Phobos may be a pile of rubble that is held together by a thin crust. It may have formed as dust and rocks encircling Mars were drawn together by gravity. Or, it may have experienced a more violent birth, where a large body smashing into Mars flung pieces skyward, and those pieces were brought together by gravity. Perhaps an existing moon was destroyed, reduced to the rubble that would become Phobos. Hubble took the images of Phobos orbiting the Red Planet on May 12, 2016, when Mars was 50 million miles from Earth. This was just a few days before the planet passed closer to Earth in its orbit than it had in the past 11 years. A time-lapse video captures a portion of the path that tiny Phobos takes around Mars. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble snapped 13 separate exposures of the little Martian moon. The video can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21837