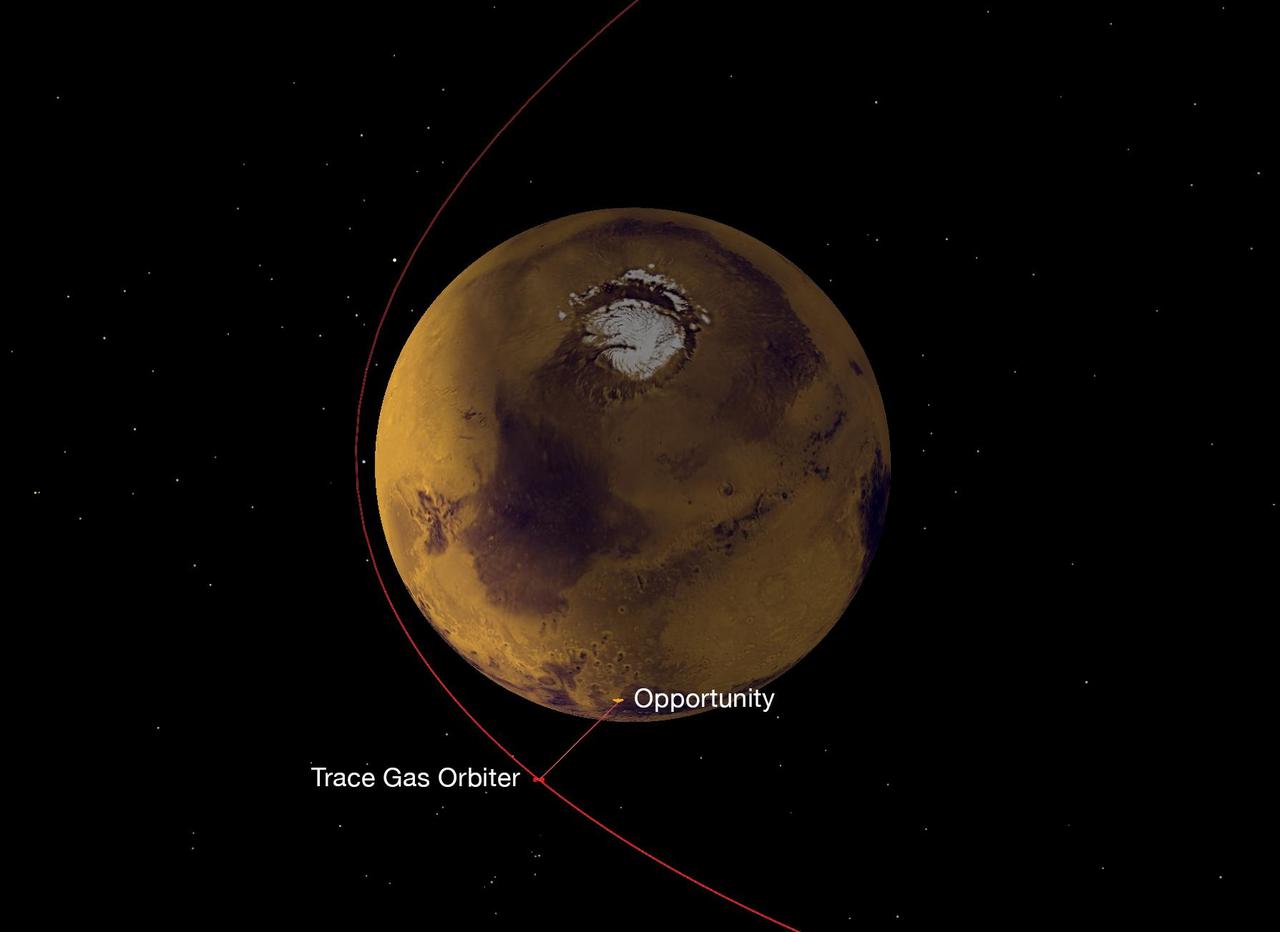
On Nov. 22, 2016, a NASA radio aboard the European Space Agency's (ESA's) Trace Gas Orbiter, which arrived at Mars the previous month, succeeded in its first test of receiving data transmitted from NASA Mars rovers, both Opportunity and Curiosity. This graphic depicts the geometry of Opportunity transmitting data to the orbiter, using the ultra-high frequency (UHF) band of radio wavelengths. The orbiter received that data using one of its twin Electra UHF-band radios. Data that the orbiter's Electra received from the two rovers was subsequently transmitted from the orbiter to Earth, using the orbiter's main X-band radio. The Trace Gas Orbiter is part of ESA's ExoMars program. During the initial months after its Oct. 19, 2016, arrival, it is flying in a highly elliptical orbit. Each loop takes 4.2 days to complete, with distances between the orbiter and the planet's surface ranging from about 60,000 miles (about 100,000 kilometers) to less than 200 miles (less than 310 kilometers). Later, the mission will reshape the orbit to a near-circular path about 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the surface of Mars. Three NASA orbiters and one other ESA orbiter currently at Mars also have relayed data from Mars rovers to Earth. This strategy enables receiving much more data from the surface missions than would be possible with a direct-to-Earth radio link from rovers or stationary landers. Successful demonstration of the capability added by the Trace Gas Orbiter strengthens and extends the telecommunications network at Mars for supporting future missions to the surface of the Red Planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21139

NASA and the European Space Agency are jointly developing the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter mission for launch in 2016.
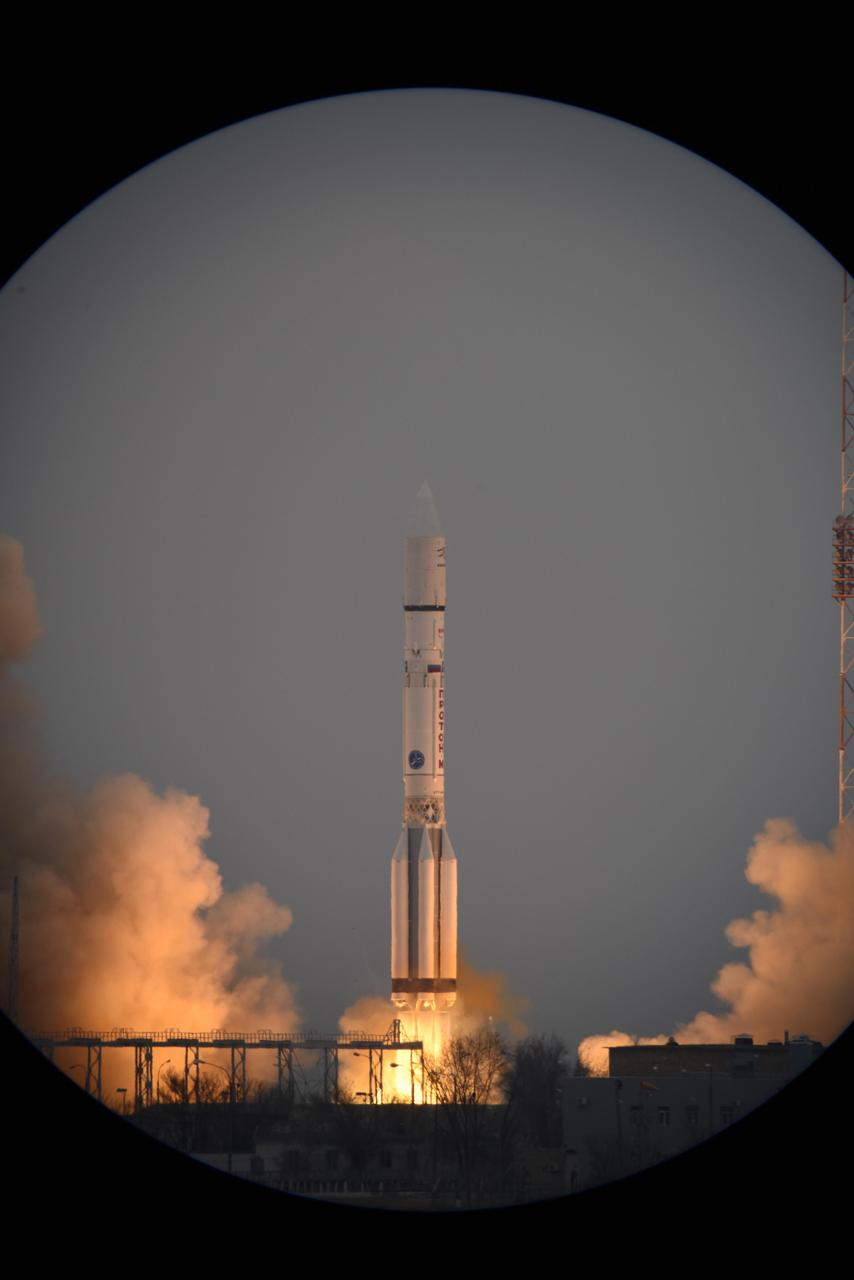

The European Space Agency ExoMars 2016 mission, combining the Trace Gas Orbiter and Schiaparelli landing demonstrator, launches on a Proton launch vehicle from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
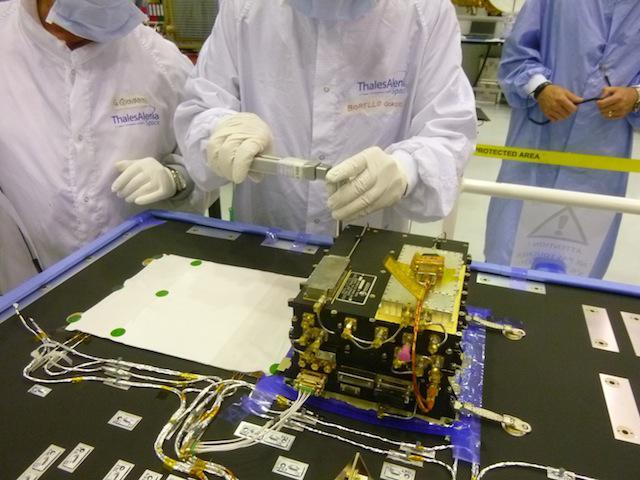

The European Space Agency ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, being assembled in France for a 2016 launch opportunity, will carry two Electra UHF relay radios provided by NASA.
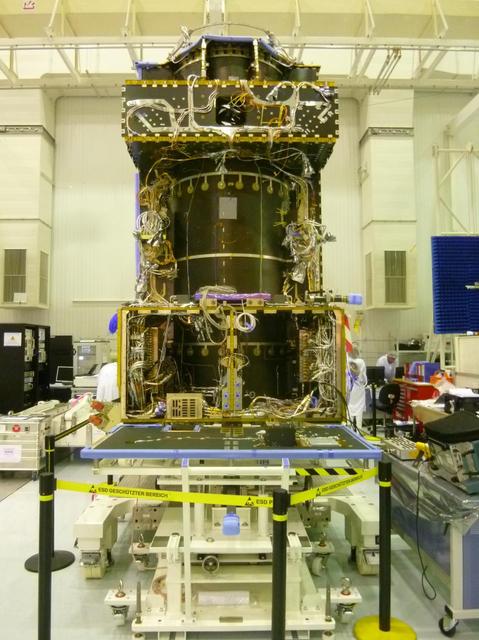

This June 2014 image from the clean room at Thales Alenia Space, in Cannes, France, shows ongoing assembly of the European Space Agency ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, including the first of the orbiter two Electra UHF relay radios provided by NASA.

This image was acquired on May 15, 2018 by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. This observation shows relatively bright mounds scattered throughout darker and diverse surfaces in Chryse Planitia. These mounds are hundreds of meters in size. The largest of the mounds shows a central pit, similar to the collapsed craters found at the summit of some volcanoes on Earth. The origins of these pitted mounds or cratered cones are uncertain. They could be the result of the interaction of lava and water, or perhaps formed from the eruption of hot mud originating from beneath the surface. These features are very interesting to scientists who study Mars, especially to those involved in the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter mission. If these mounds are indeed mud-related, they may be one of the long sought after sources for transient methane on Mars. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22682
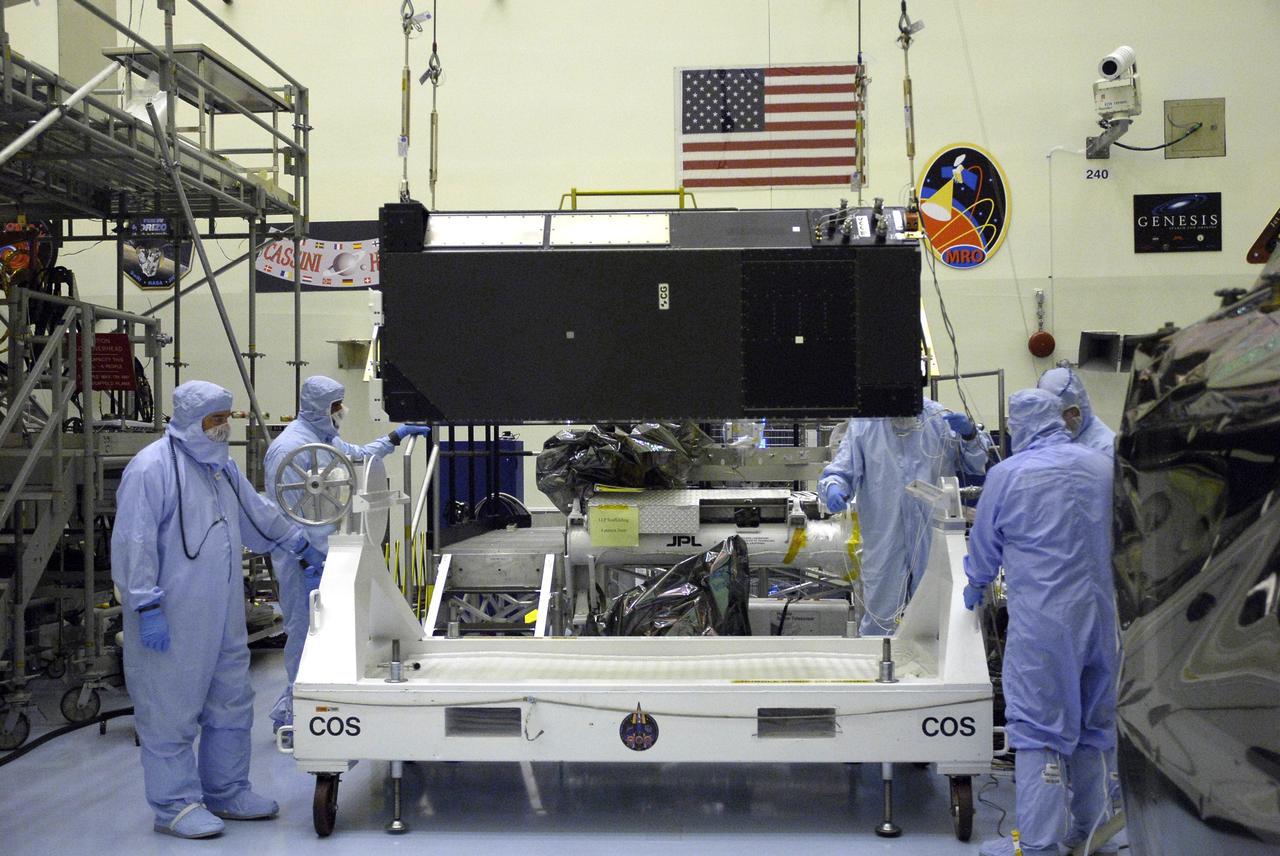

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS is being lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
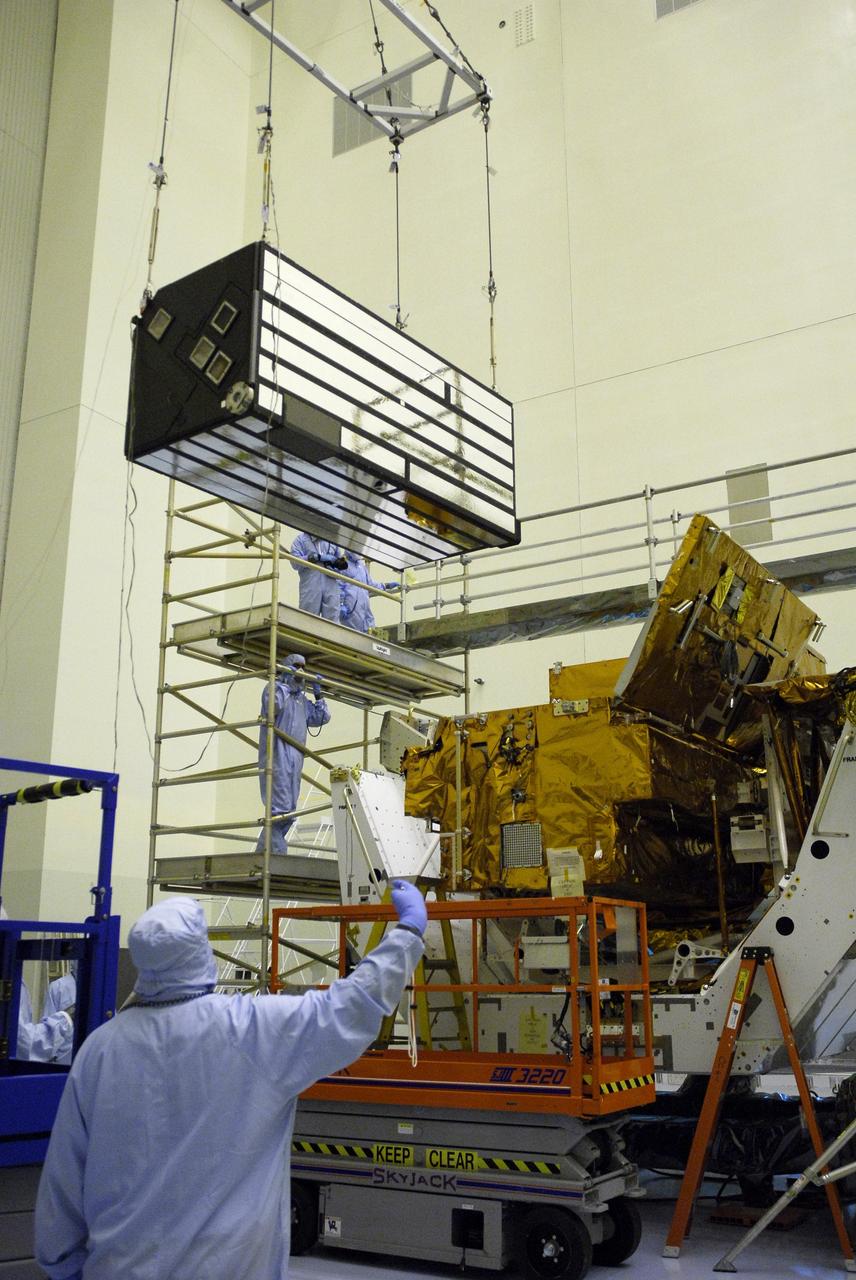

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, toward a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
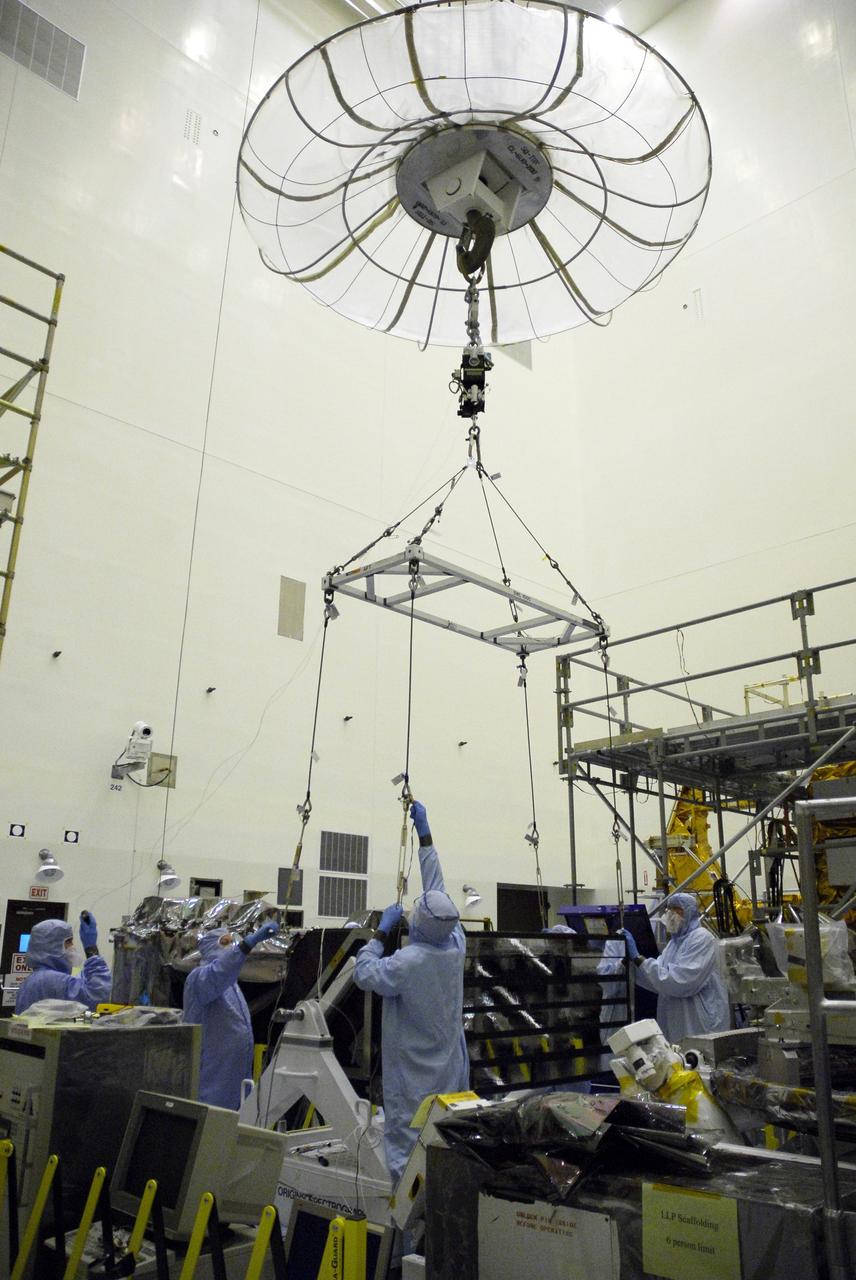

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers prepare to attach an overhead crane to the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS will be lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

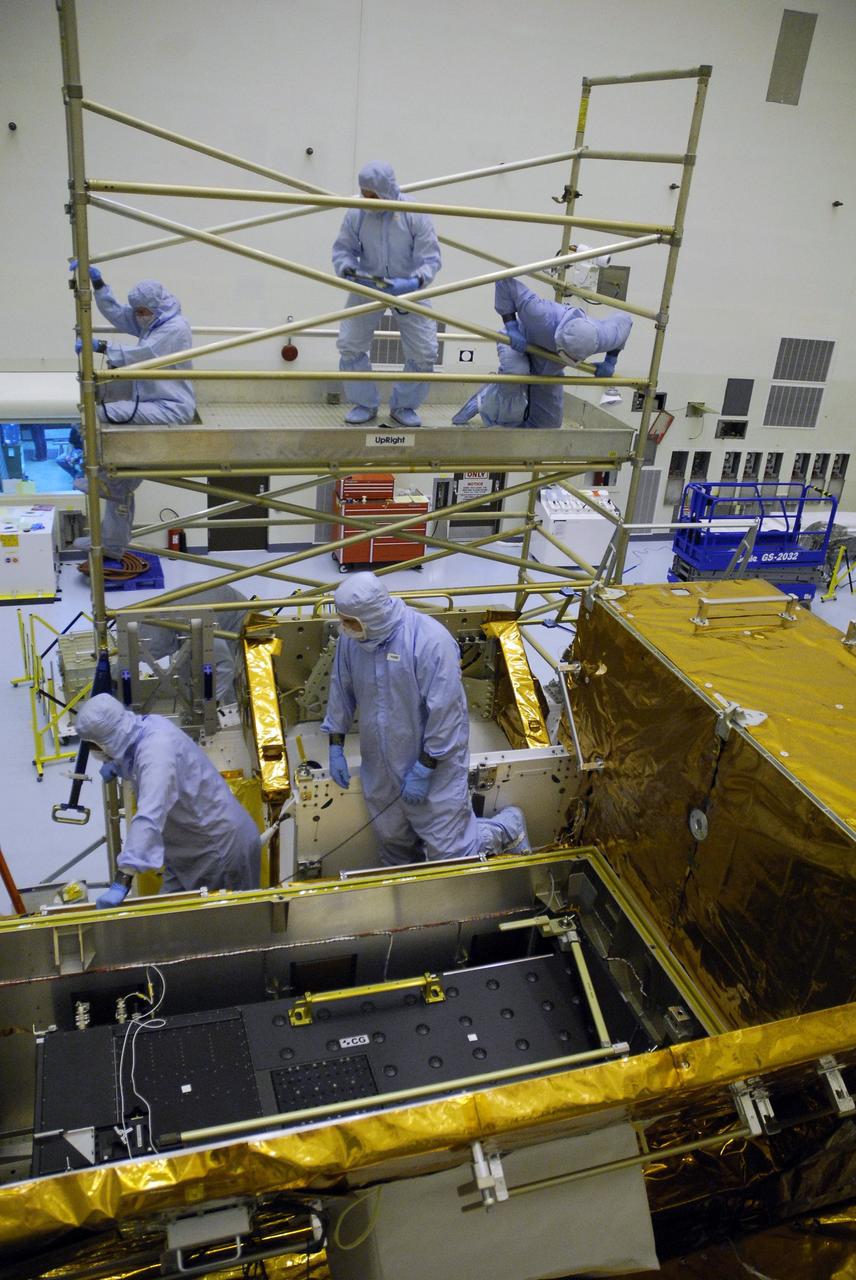
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers attach an overhead crane to the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS is being lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
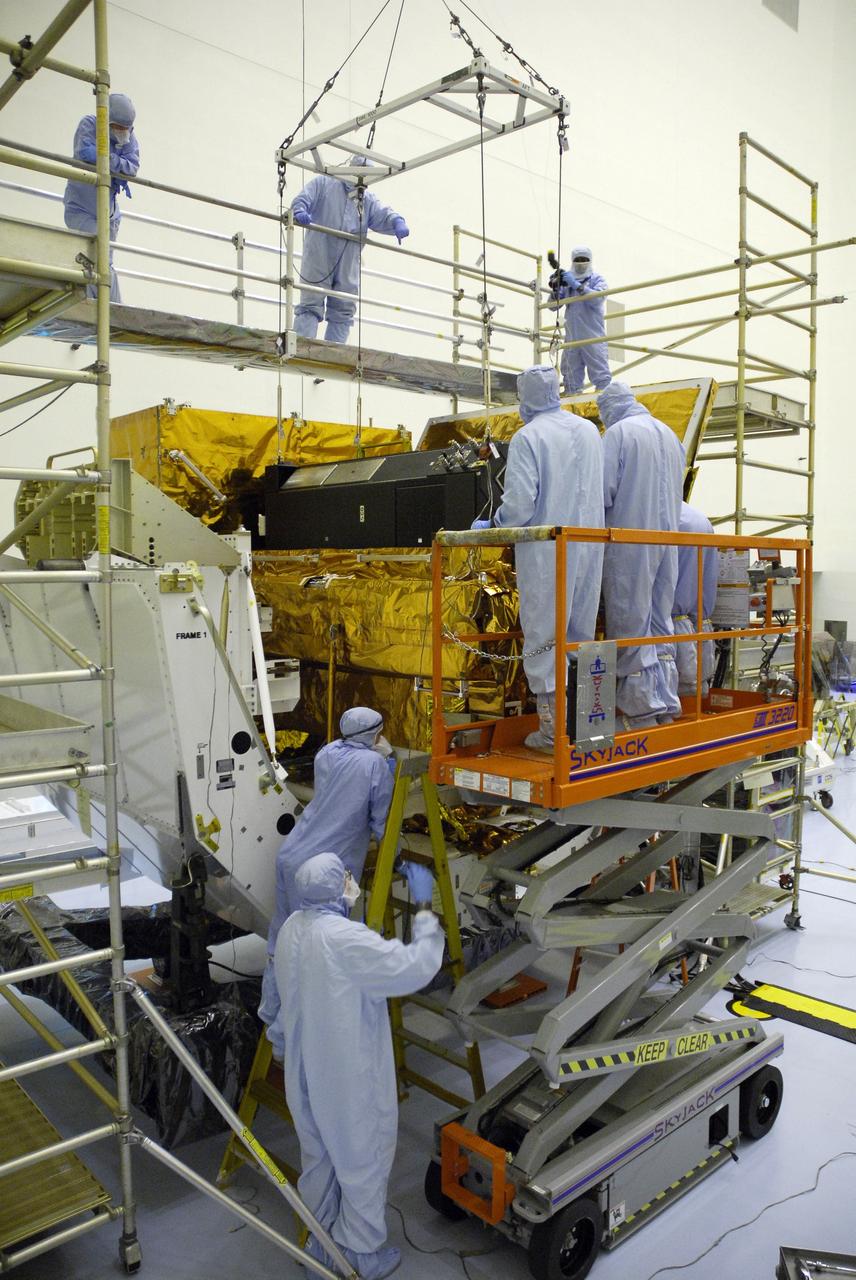

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, into a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, crew members with the STS-125 mission get a close look at some of the equipment associated with their mission to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. Looking at the box containing the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, on the orbital replacement unit carrier are Mission Specialist Michael Good (upper right, on stand) and HST inspectors. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The STS-125 crew is taking part in a crew equipment interface test, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware they will use on their mission. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, toward a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

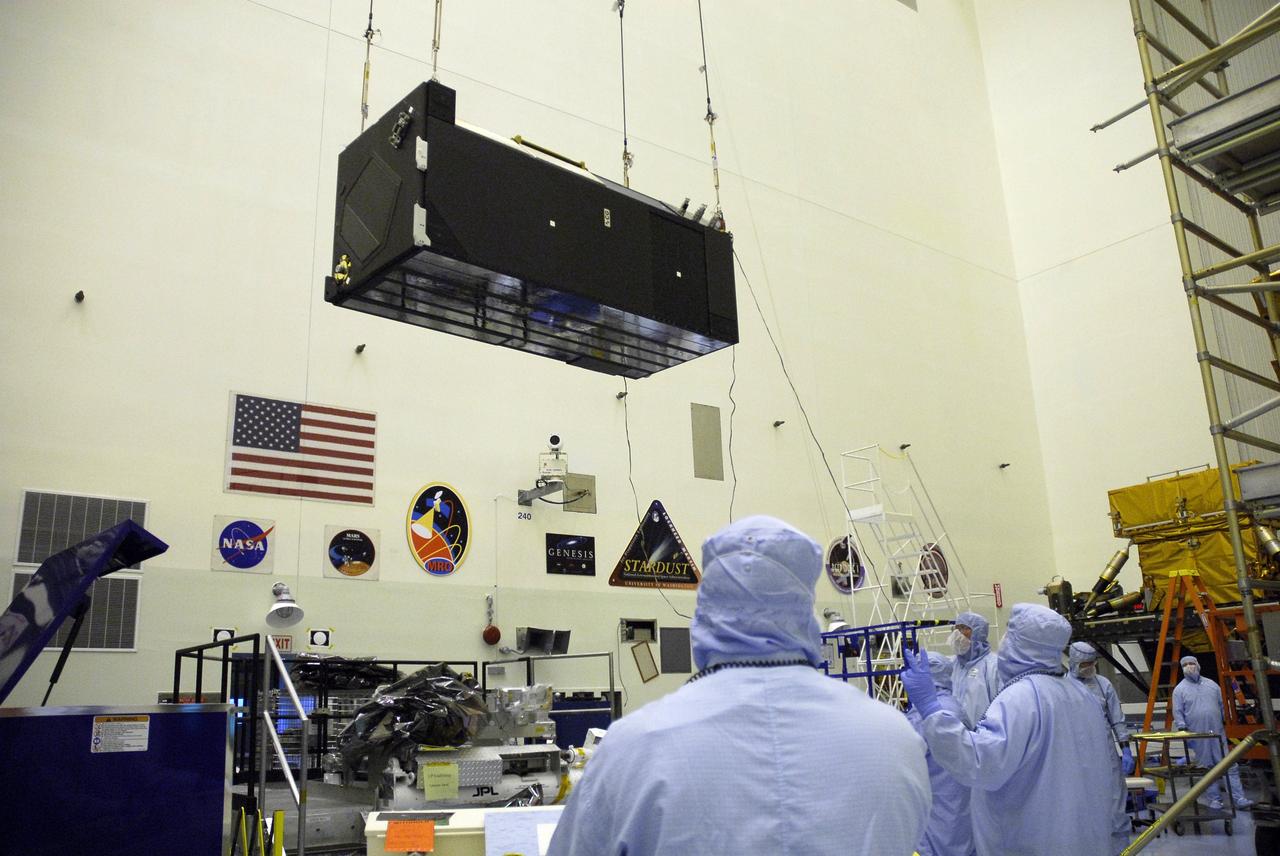
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS is being lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, toward a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

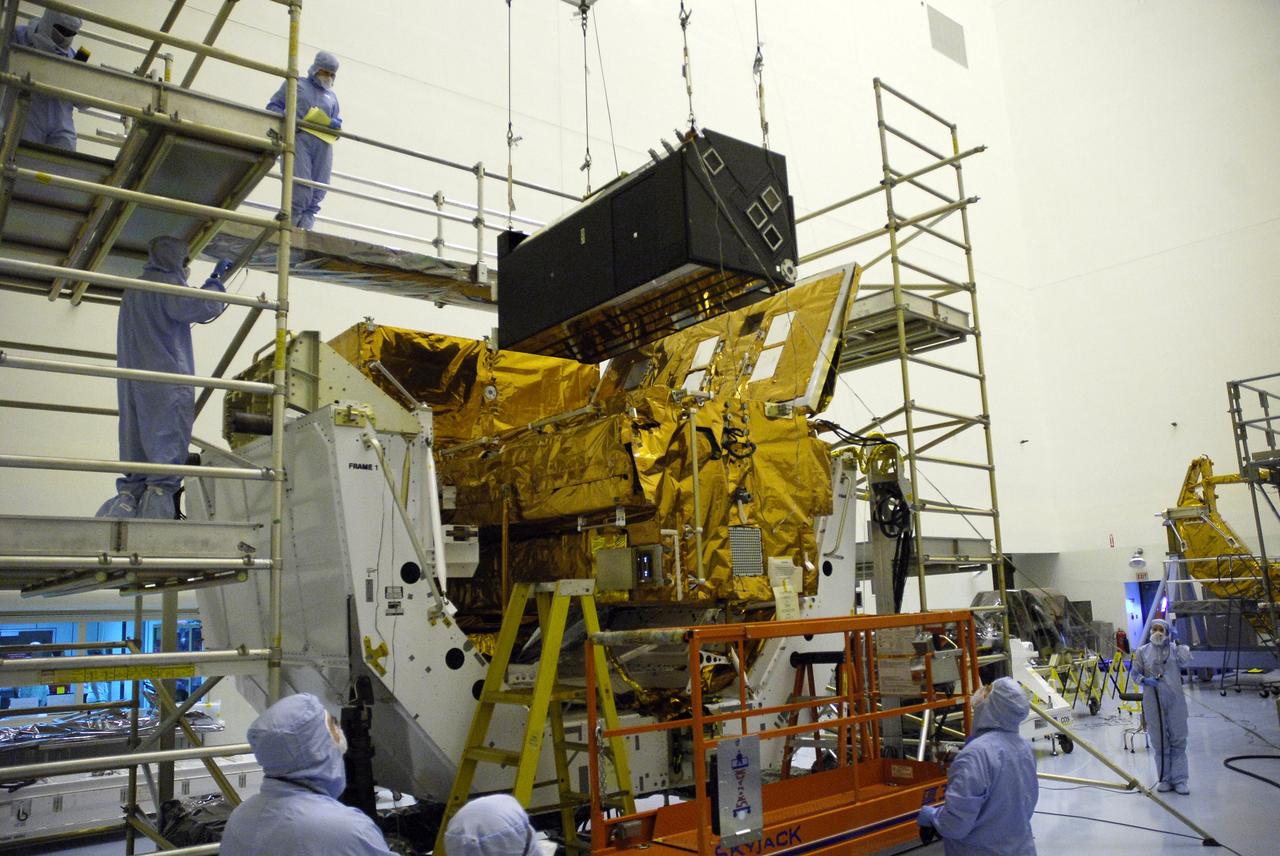
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, toward a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
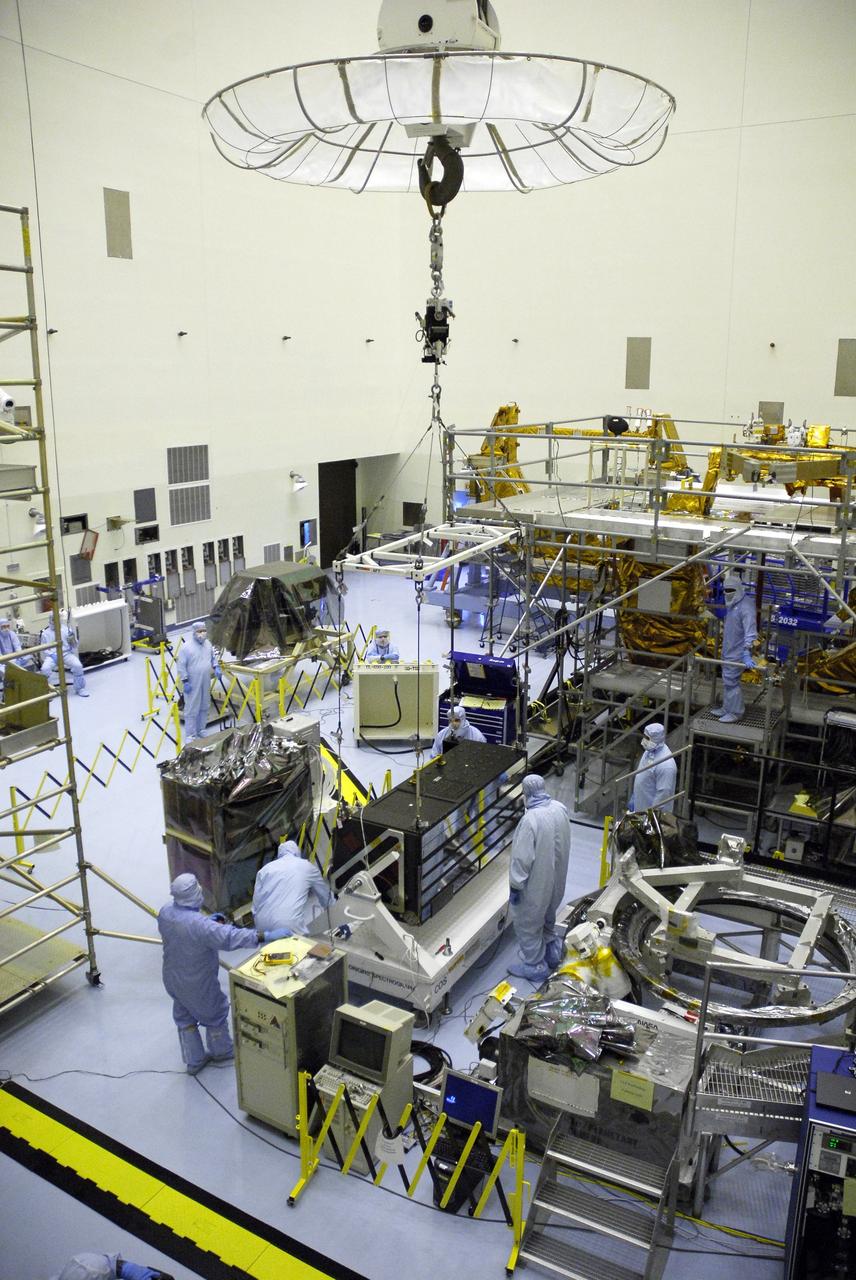

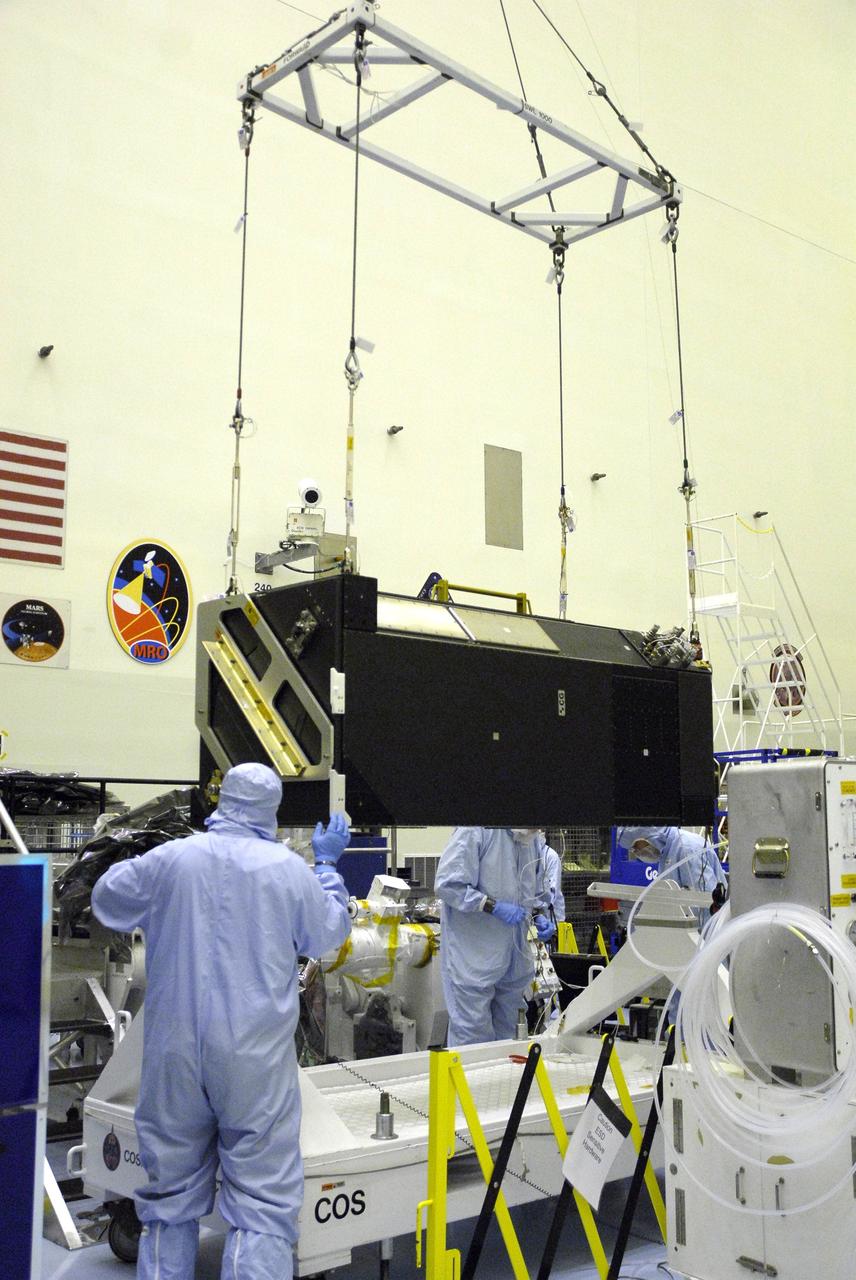
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS is being lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
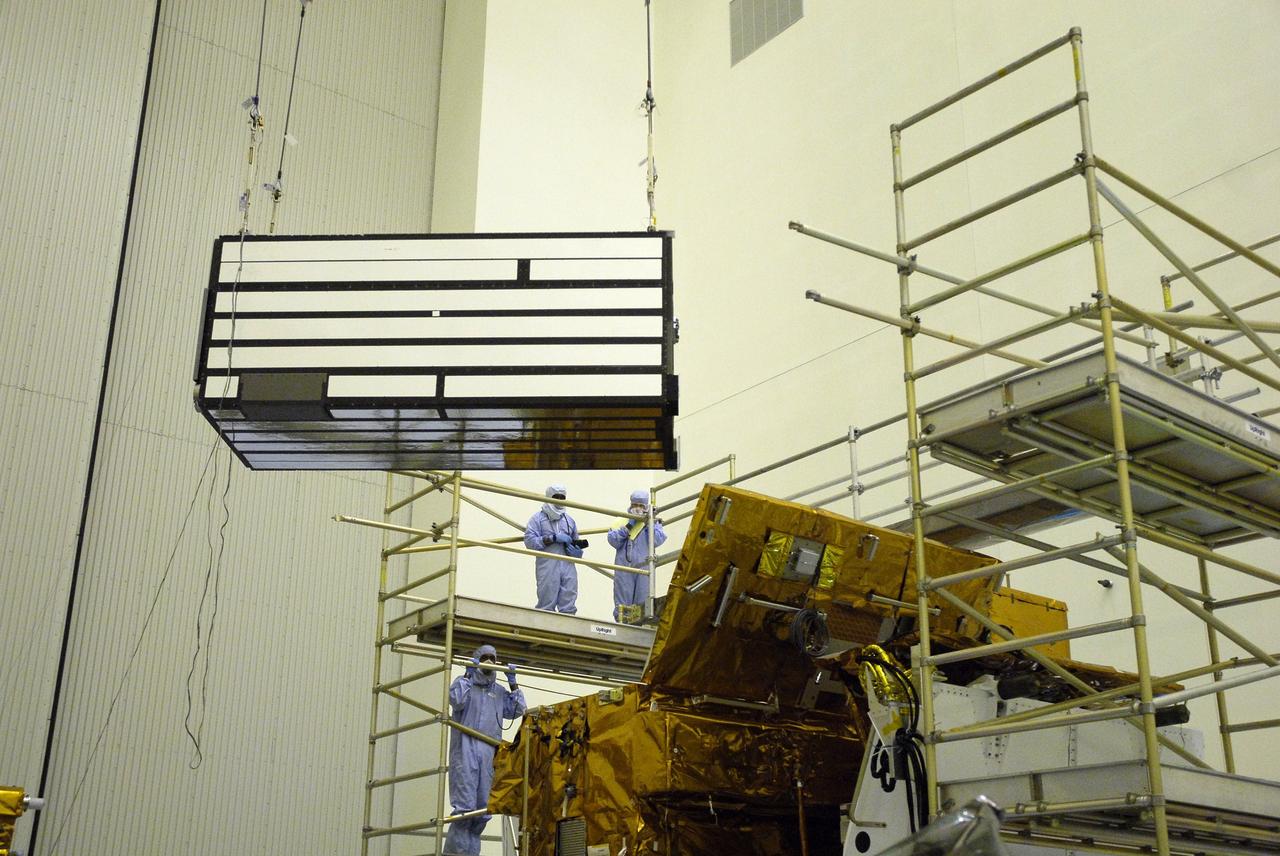

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, toward a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
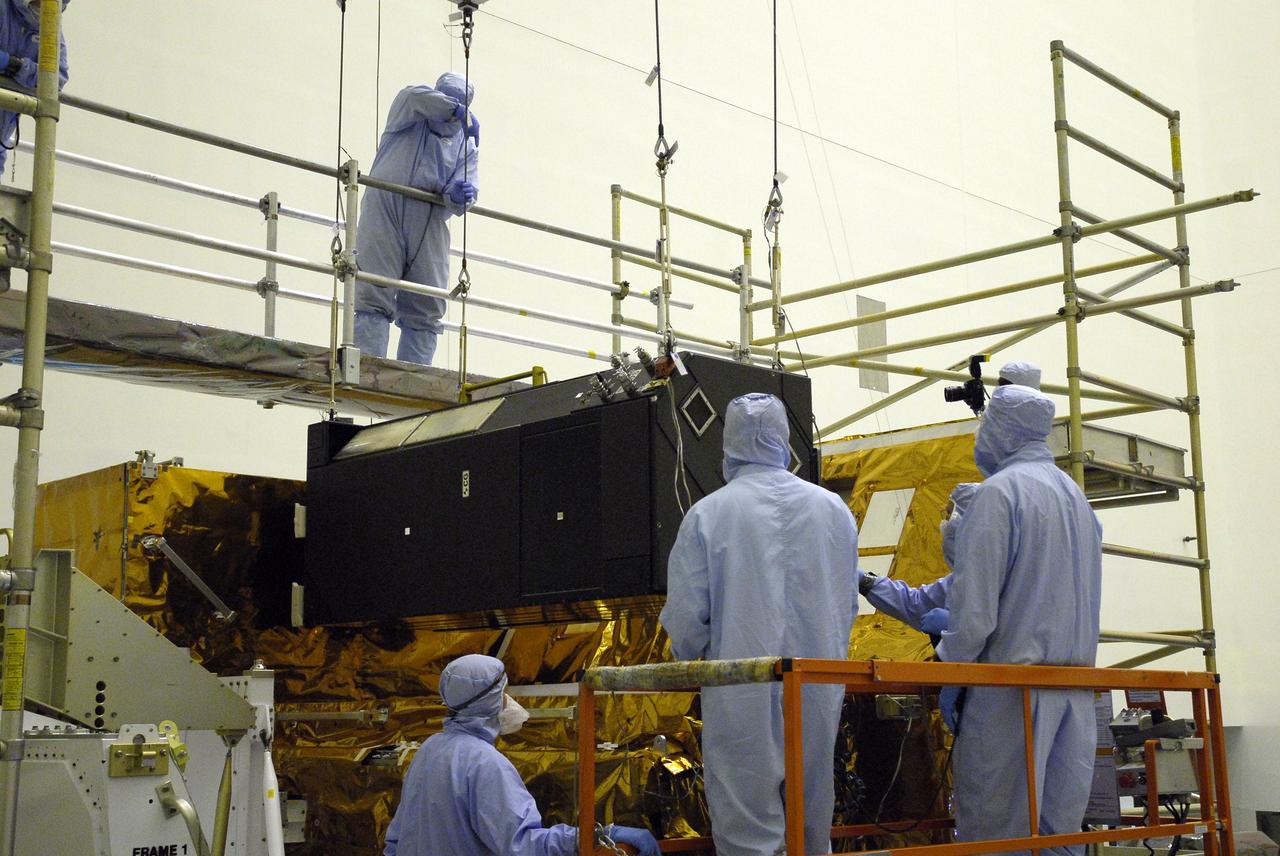

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, into a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS. The COS is being lifted and moved to a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
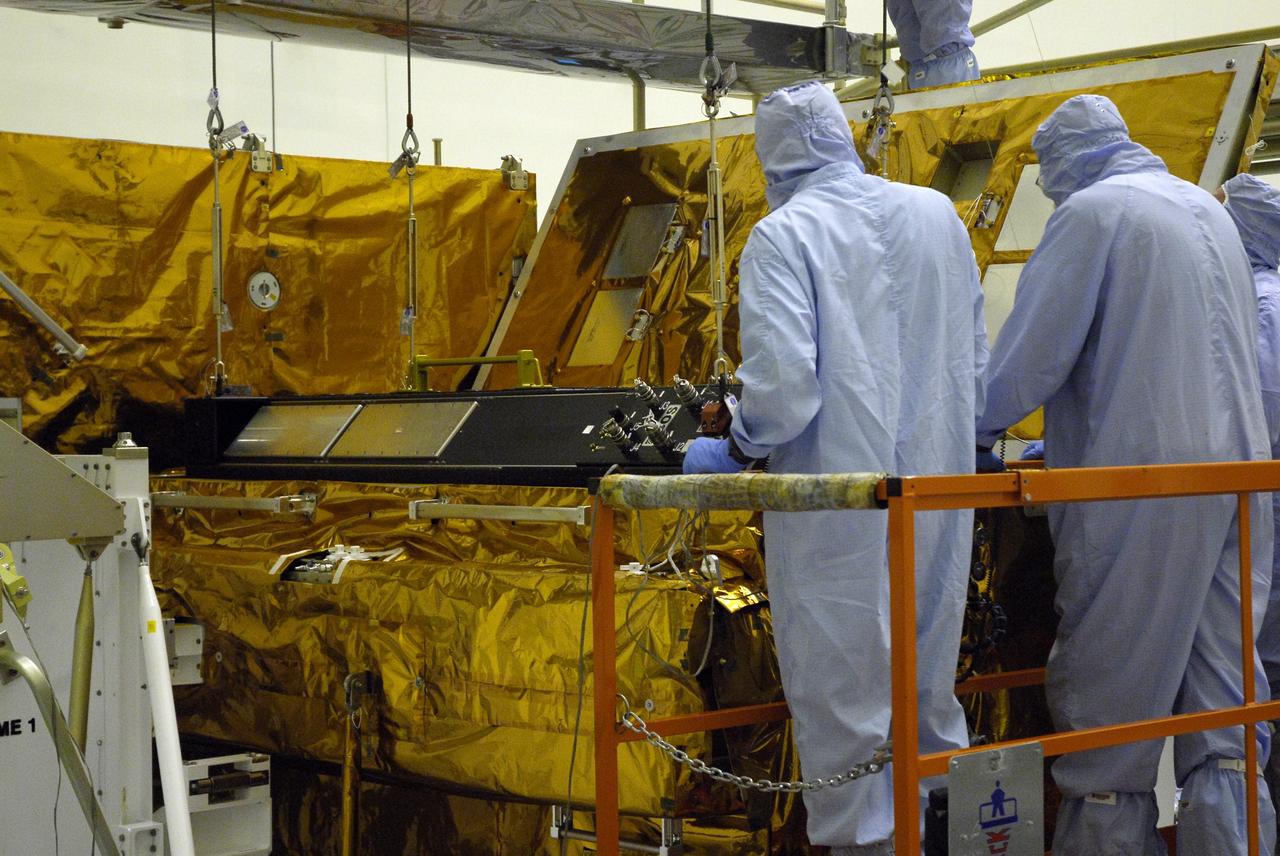

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane settles the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, in a protective enclosure on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the payload for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Other payloads include the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The COS far-ultraviolet channel has a sensitivity 30 times greater than that of previous spectroscopic instruments for the detection of extremely low light levels. Launch of Atlantis on the STS-125 mission is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
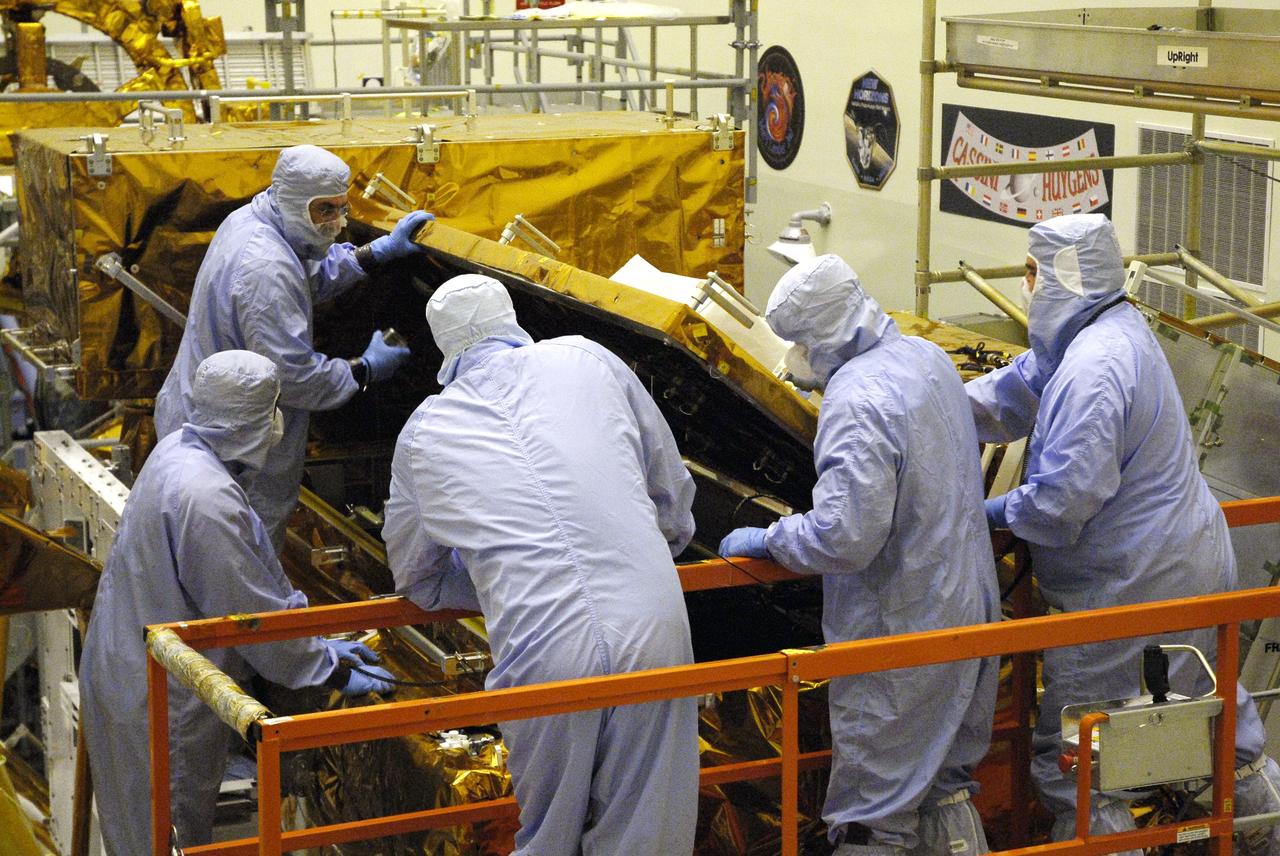

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, crew members with the STS-125 mission get a close look at some of the equipment associated with their mission to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. In the foreground, center, are Mission Specialists Mike Massimino and Michael Good, looking at the box containing the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, or COS, on the orbital replacement unit carrier. COS will be the most sensitive ultraviolet spectrograph ever flown on Hubble and will probe the "cosmic web" - the large-scale structure of the universe whose form is determined by the gravity of dark matter and is traced by galaxies and intergalactic gas. The STS-125 crew is taking part in a crew equipment interface test, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware they will use on their mission. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft is of a landing site that the flattest, safest place on Mars: part of Meridiani Planum, close to where the Opportunity rover landed. In March 2016, the European Space Agency in partnership with Roscosmos will launch the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter. This orbiter will also carry an Entry, Descent, and Landing Demonstration Module (EDM): a lander designed primarily to demonstrate the capability to land on Mars. The EDM will survive for only a few days, running on battery power, but will make a few environmental measurements. The landing site is the flattest, safest place on Mars: part of Meridiani Planum, close to where the Opportunity rover landed. This image shows what this terrain is like: very flat and featureless. A full-resolution sample reveals the major surface features: small craters and wind ripples. HiRISE has been imaging the landing site region in advance of the landing, and will re-image the site after landing to identify the major pieces of hardware: heat shield, backshell with parachute, and the lander itself. The distribution of these pieces will provide information about the entry, descent and landing. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20159
![This is one of three views of locations where hardware from the European Space Agency's Schiaparelli test lander reached the surface of Mars on Oct. 19, 2016, combine two orbital views from different angles as a stereo pair. The view was created to appear three-dimensional when seen through red-blue glasses with the red lens on the left, though the scene is too flat to show much relief. The stereo preparation uses images taken on Oct. 25, 2016, [PIA21131] and Nov. 1, 2016, [PIA21132] by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The left-eye (red-tinted) component of the stereo is from the earlier observation, which was taken from farther west than the second observation. These views shows three sites where parts of the Schiaparelli spacecraft hit the ground: the lander module itself in the upper portion, the parachute and back shell at lower left, and the heat shield at lower right. The parachute's shape on the ground changed between the two observation dates, cancelling the three-dimensional effect of having views from different angles. The scale bar of 20 meters (65.6 feet) applies to all three portions. Schiaparelli was one component of the European Space Agency's ExoMars 2016 project, which placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into orbit around Mars on the same arrival date. The ExoMars project received data from Schiaparelli during its descent through the atmosphere. ESA has reported that the heat shield separated as planned, the parachute deployed as planned but was released (with back shell) prematurely, and the lander hit the ground at a velocity of more than 180 miles per hour (more than 300 kilometers per hour). More views are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21135](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21135/PIA21135~thumb.jpg)
This is one of three views of locations where hardware from the European Space Agency's Schiaparelli test lander reached the surface of Mars on Oct. 19, 2016, combine two orbital views from different angles as a stereo pair. The view was created to appear three-dimensional when seen through red-blue glasses with the red lens on the left, though the scene is too flat to show much relief. The stereo preparation uses images taken on Oct. 25, 2016, [PIA21131] and Nov. 1, 2016, [PIA21132] by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The left-eye (red-tinted) component of the stereo is from the earlier observation, which was taken from farther west than the second observation. These views shows three sites where parts of the Schiaparelli spacecraft hit the ground: the lander module itself in the upper portion, the parachute and back shell at lower left, and the heat shield at lower right. The parachute's shape on the ground changed between the two observation dates, cancelling the three-dimensional effect of having views from different angles. The scale bar of 20 meters (65.6 feet) applies to all three portions. Schiaparelli was one component of the European Space Agency's ExoMars 2016 project, which placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into orbit around Mars on the same arrival date. The ExoMars project received data from Schiaparelli during its descent through the atmosphere. ESA has reported that the heat shield separated as planned, the parachute deployed as planned but was released (with back shell) prematurely, and the lander hit the ground at a velocity of more than 180 miles per hour (more than 300 kilometers per hour). More views are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21135
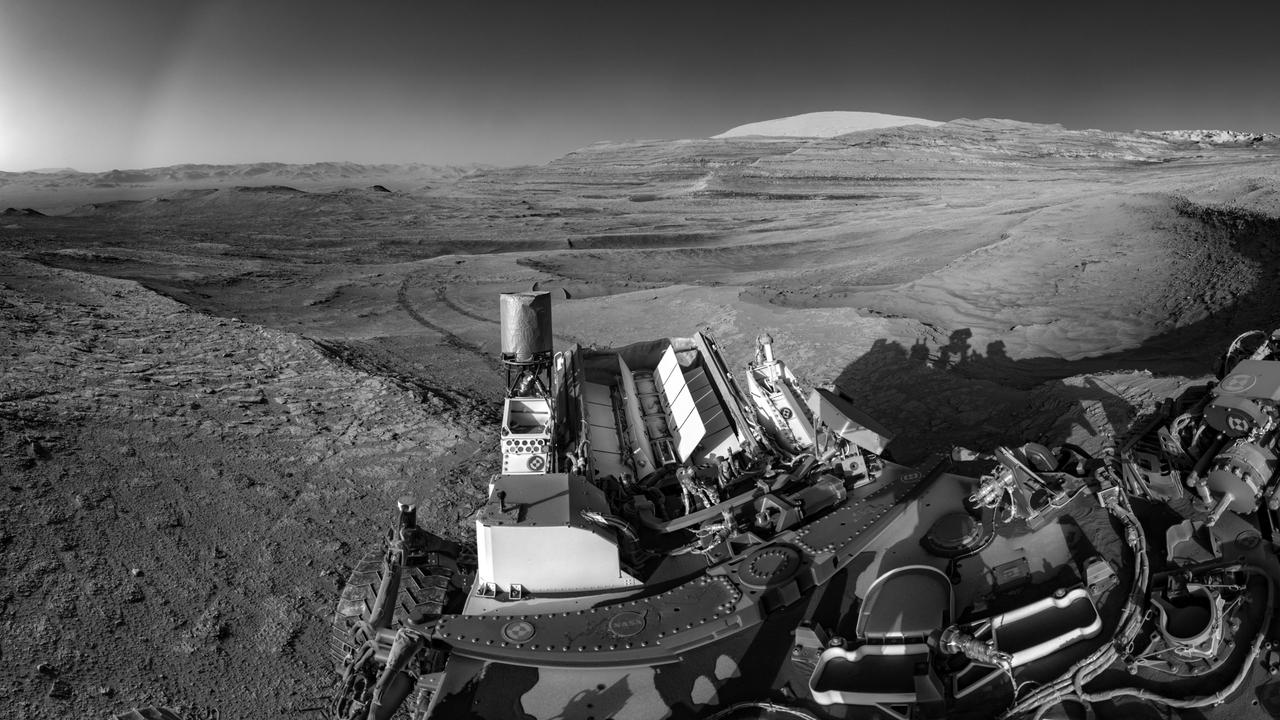

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover demonstrated a new multitasking capability when capturing this view: It snapped the 15 images that make up the mosaic while simultaneously communicating with an orbiter. The images were taken by the right navigation camera on Curiosity's mast July 26, 2025, the 4,611th sol, or day, of the mission. The rover's tracks cross through a region filled with boxwork formations – hardened ridges created by mineral deposits from subsurface water billions of years ago. This boxwork region is in the lower foothills of Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) mountain in the center of Gale Crater. Being able to combine tasks shortens the rover's daily plan, requiring less power from Curiosity's nuclear power source, called a multi-mission radioisotope thermonuclear generator (MMRTG), which is lined with rows of white fins at the back of the rover. NASA's Perseverance rover is also equipped with an MMRTG; the generator uses the heat from decaying plutonium pellets to charge batteries on the rovers. The can-like cylinder to the left of the MMRTG is Curiosity's ultrahigh frequency (UHF) antenna, which communicates with spacecraft in orbit around Mars. To capture a mosaic like this, the rover would normally require nine minutes of awake time devoted solely to imaging. However, while snapping the images for this mosaic, Curiosity was also sending data to ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Trace Gas Orbiter, essentially saving several minutes of battery time. After being sent to Earth, the images were stitched together and the seams between them smoothed out before the mosaic was processed to enhance details. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26632
![On Nov. 1, 2016, the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observed the impact site of Europe's Schiaparelli test lander, gaining the first color view of the site since the lander's Oct. 19, 2016, arrival. These cutouts from the observation cover three locations where parts of the spacecraft reached the ground: the lander module itself in the upper portion, the parachute and back shell at lower left, and the heat shield at lower right. The heat shield location was outside of the area covered in color. The scale bar of 10 meters (32.8 feet) applies to all three cutouts. Schiaparelli was one component of the European Space Agency's ExoMars 2016 project, which placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into orbit around Mars on the same arrival date. The ExoMars project received data from Schiaparelli during its descent through the atmosphere. ESA reports that the heat shield separated as planned, the parachute deployed as planned but was released (with back shell) prematurely, and the lander hit the ground at a velocity of more than 180 miles per hour (more than 300 kilometers per hour). Information gained from the Nov. 1 observation supplements what was learned from an Oct. 25 HiRISE observation, at PIA21131, which also shows the locations of these three cutouts relative to each other. Where the lander module struck the ground, dark radial patterns that extend from a dark spot are interpreted as "ejecta," or material thrown outward from the impact, which may have excavated a shallow crater. From the earlier image, it was not clear whether the relatively bright pixels and clusters of pixels scattered around the lander module's impact site are fragments of the module or image noise. Now it is clear that at least the four brightest spots near the impact are not noise. These bright spots are in the same location in the two images and have a white color, unusual for this region of Mars. The module may have broken up at impact, and some fragments might have been thrown outward like impact ejecta. The parachute has a different shape in the Nov. 1 image than in the Oct. 25 one, apparently from shifting in the wind. Similar shifting was observed in the parachute of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission during the first six months after the Mars arrival of that mission's Curiosity rover in 2012 [PIA16813]. At lower right are several bright features surrounded by dark radial impact patterns, located where the heat shield was expected to impact. The bright spots appear identical in the Nov. 1 and Oct. 25 images, which were taken from different angles, so these spots are now interpreted as bright material, such as insulation layers, not glinting reflections. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21132](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21132/PIA21132~thumb.jpg)
On Nov. 1, 2016, the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observed the impact site of Europe's Schiaparelli test lander, gaining the first color view of the site since the lander's Oct. 19, 2016, arrival. These cutouts from the observation cover three locations where parts of the spacecraft reached the ground: the lander module itself in the upper portion, the parachute and back shell at lower left, and the heat shield at lower right. The heat shield location was outside of the area covered in color. The scale bar of 10 meters (32.8 feet) applies to all three cutouts. Schiaparelli was one component of the European Space Agency's ExoMars 2016 project, which placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into orbit around Mars on the same arrival date. The ExoMars project received data from Schiaparelli during its descent through the atmosphere. ESA reports that the heat shield separated as planned, the parachute deployed as planned but was released (with back shell) prematurely, and the lander hit the ground at a velocity of more than 180 miles per hour (more than 300 kilometers per hour). Information gained from the Nov. 1 observation supplements what was learned from an Oct. 25 HiRISE observation, at PIA21131, which also shows the locations of these three cutouts relative to each other. Where the lander module struck the ground, dark radial patterns that extend from a dark spot are interpreted as "ejecta," or material thrown outward from the impact, which may have excavated a shallow crater. From the earlier image, it was not clear whether the relatively bright pixels and clusters of pixels scattered around the lander module's impact site are fragments of the module or image noise. Now it is clear that at least the four brightest spots near the impact are not noise. These bright spots are in the same location in the two images and have a white color, unusual for this region of Mars. The module may have broken up at impact, and some fragments might have been thrown outward like impact ejecta. The parachute has a different shape in the Nov. 1 image than in the Oct. 25 one, apparently from shifting in the wind. Similar shifting was observed in the parachute of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission during the first six months after the Mars arrival of that mission's Curiosity rover in 2012 [PIA16813]. At lower right are several bright features surrounded by dark radial impact patterns, located where the heat shield was expected to impact. The bright spots appear identical in the Nov. 1 and Oct. 25 images, which were taken from different angles, so these spots are now interpreted as bright material, such as insulation layers, not glinting reflections. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21132

This Oct. 25, 2016, image shows the area where the European Space Agency's Schiaparelli test lander reached the surface of Mars, with magnified insets of three sites where components of the spacecraft hit the ground. It is the first view of the site from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter taken after the Oct. 19, 2016, landing event. The Schiaparelli test lander was one component of ESA's ExoMars 2016 project, which placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into orbit around Mars on the same arrival date. This HiRISE observation adds information to what was learned from observation of the same area on Oct. 20 by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's Context Camera (CTX). Of these two cameras, CTX covers more area and HiRISE shows more detail. A portion of the HiRISE field of view also provides color information. The impact scene was not within that portion for the Oct. 25 observation, but an observation with different pointing to add color and stereo information is planned. This Oct. 25 observation shows three locations where hardware reached the ground, all within about 0.9 mile (1.5 kilometer) of each other, as expected. The annotated version includes insets with six-fold enlargement of each of those three areas. Brightness is adjusted separately for each inset to best show the details of that part of the scene. North is about 7 degrees counterclockwise from straight up. The scale bars are in meters. At lower left is the parachute, adjacent to the back shell, which was its attachment point on the spacecraft. The parachute is much brighter than the Martian surface in this region. The smaller circular feature just south of the bright parachute is about the same size and shape as the back shell, (diameter of 7.9 feet or 2.4 meters). At upper right are several bright features surrounded by dark radial impact patterns, located about where the heat shield was expected to impact. The bright spots may be part of the heat shield, such as insulation material, or gleaming reflections of the afternoon sunlight. According to the ExoMars project, which received data from the spacecraft during its descent through the atmosphere, the heat shield separated as planned, the parachute deployed as planned but was released (with back shell) prematurely, and the lander hit the ground at a velocity of more than 180 miles per hour (more than 300 kilometers per hour). At mid-upper left are markings left by the lander's impact. The dark, approximately circular feature is about 7.9 feet (2.4 meters) in diameter, about the size of a shallow crater expected from impact into dry soil of an object with the lander's mass -- about 660 pounds (300 kilograms) -- and calculated velocity. The resulting crater is estimated to be about a foot and a half (half a meter) deep. This first HiRISE observation does not show topography indicating the presence of a crater. Stereo information from combining this observation with a future one may provide a way to check. Surrounding the dark spot are dark radial patterns expected from an impact event. The dark curving line to the northeast of the dark spot is unusual for a typical impact event and not yet explained. Surrounding the dark spot are several relatively bright pixels or clusters of pixels. They could be image noise or real features, perhaps fragments of the lander. A later image is expected to confirm whether these spots are image noise or actual surface features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21131

This image depicts a vast canyon of dust and gas in the Orion Nebula from a 3-D computer model based on observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and created by science visualization specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. A 3-D visualization of this model takes viewers on an amazing four-minute voyage through the 15-light-year-wide canyon. Credit: NASA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (STScI/AURA) Go here to learn more about Hubble 3D: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premiere.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premier...</a> or <a href="http://www.imax.com/hubble/" rel="nofollow">www.imax.com/hubble/</a> Take an exhilarating ride through the Orion Nebula, a vast star-making factory 1,500 light-years away. Swoop through Orion's giant canyon of gas and dust. Fly past behemoth stars whose brilliant light illuminates and energizes the entire cloudy region. Zoom by dusty tadpole-shaped objects that are fledgling solar systems. This virtual space journey isn't the latest video game but one of several groundbreaking astronomy visualizations created by specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The cinematic space odysseys are part of the new Imax film "Hubble 3D," which opens today at select Imax theaters worldwide. The 43-minute movie chronicles the 20-year life of Hubble and includes highlights from the May 2009 servicing mission to the Earth-orbiting observatory, with footage taken by the astronauts. The giant-screen film showcases some of Hubble's breathtaking iconic pictures, such as the Eagle Nebula's "Pillars of Creation," as well as stunning views taken by the newly installed Wide Field Camera 3. While Hubble pictures of celestial objects are awe-inspiring, they are flat 2-D photographs. For this film, those 2-D images have been converted into 3-D environments, giving the audience the impression they are space travelers taking a tour of Hubble's most popular targets. "A large-format movie is a truly immersive experience," says Frank Summers, an STScI astronomer and science visualization specialist who led the team that developed the movie visualizations. The team labored for nine months, working on four visualization sequences that comprise about 12 minutes of the movie. "Seeing these Hubble images in 3-D, you feel like you are flying through space and not just looking at picture postcards," Summers continued. "The spacescapes are all based on Hubble images and data, though some artistic license is necessary to produce the full depth of field needed for 3-D." The most ambitious sequence is a four-minute voyage through the Orion Nebula's gas-and-dust canyon, about 15 light-years across. During the ride, viewers will see bright and dark, gaseous clouds; thousands of stars, including a grouping of bright, hefty stars called the Trapezium; and embryonic planetary systems. The tour ends with a detailed look at a young circumstellar disk, which is much like the structure from which our solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago. Based on a Hubble image of Orion released in 2006, the visualization was a collaborative effort between science visualization specialists at STScI, including Greg Bacon, who sculpted the Orion Nebula digital model, with input from STScI astronomer Massimo Roberto; the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; and the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. For some of the sequences, STScI imaging specialists developed new techniques for transforming the 2-D Hubble images into 3-D. STScI image processing specialists Lisa Frattare and Zolt Levay, for example, created methods of splitting a giant gaseous pillar in the Carina Nebula into multiple layers to produce a 3-D effect, giving the structure depth. The Carina Nebula is a nursery for baby stars. Frattare painstakingly removed the thousands of stars in the image so that Levay could separate the gaseous layers on the isolated Carina pillar. Frattare then replaced the stars into both foreground and background layers to complete the 3-D model. For added effect, the same separation was done for both visible and infrared Hubble images, allowing the film to cross-fade between wavelength views in 3-D. In another sequence viewers fly into a field of 170,000 stars in the giant star cluster Omega Centauri. STScI astronomer Jay Anderson used his stellar database to create a synthetic star field in 3-D that matches recent razor-sharp Hubble photos. The film's final four-minute sequence takes viewers on a voyage from our Milky Way Galaxy past many of Hubble's best galaxy shots and deep into space. Some 15,000 galaxies from Hubble's deepest surveys stretch billions of light-years across the universe in a 3-D sequence created by STScI astronomers and visualizers. The view dissolves into a cobweb that traces the universe's large-scale structure, the backbone from which galaxies were born. In addition to creating visualizations, STScI's education group also provided guidance on the "Hubble 3D" Educator Guide, which includes standards-based lesson plans and activities about Hubble and its mission. Students will use the guide before or after seeing the movie. "The guide will enhance the movie experience for students and extend the movie into classrooms," says Bonnie Eisenhamer, STScI's Hubble Formal Education manager. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) and is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. The institute is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, D.C.