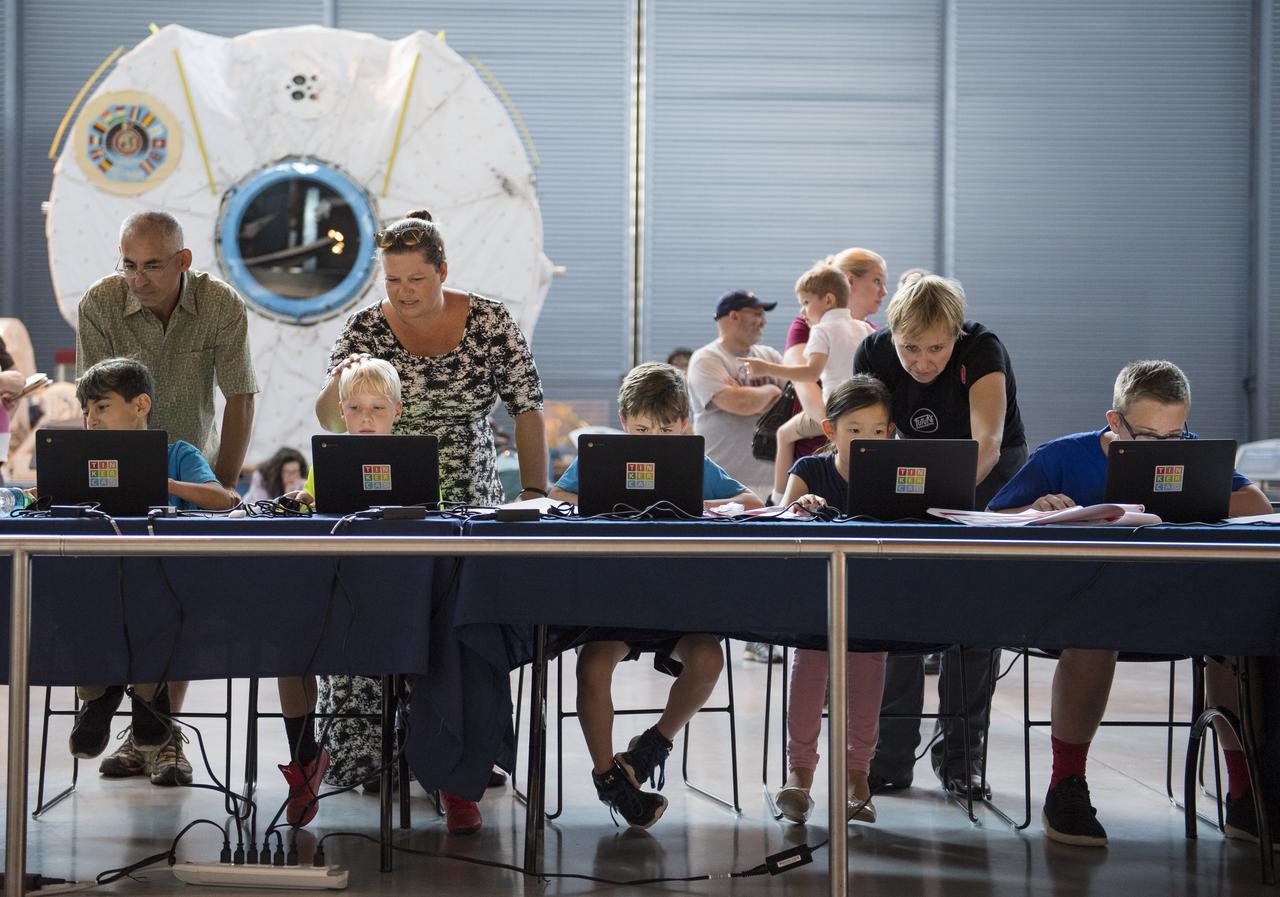

Participants create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. The winner of the Two for the Crew challenge will have their design printed on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
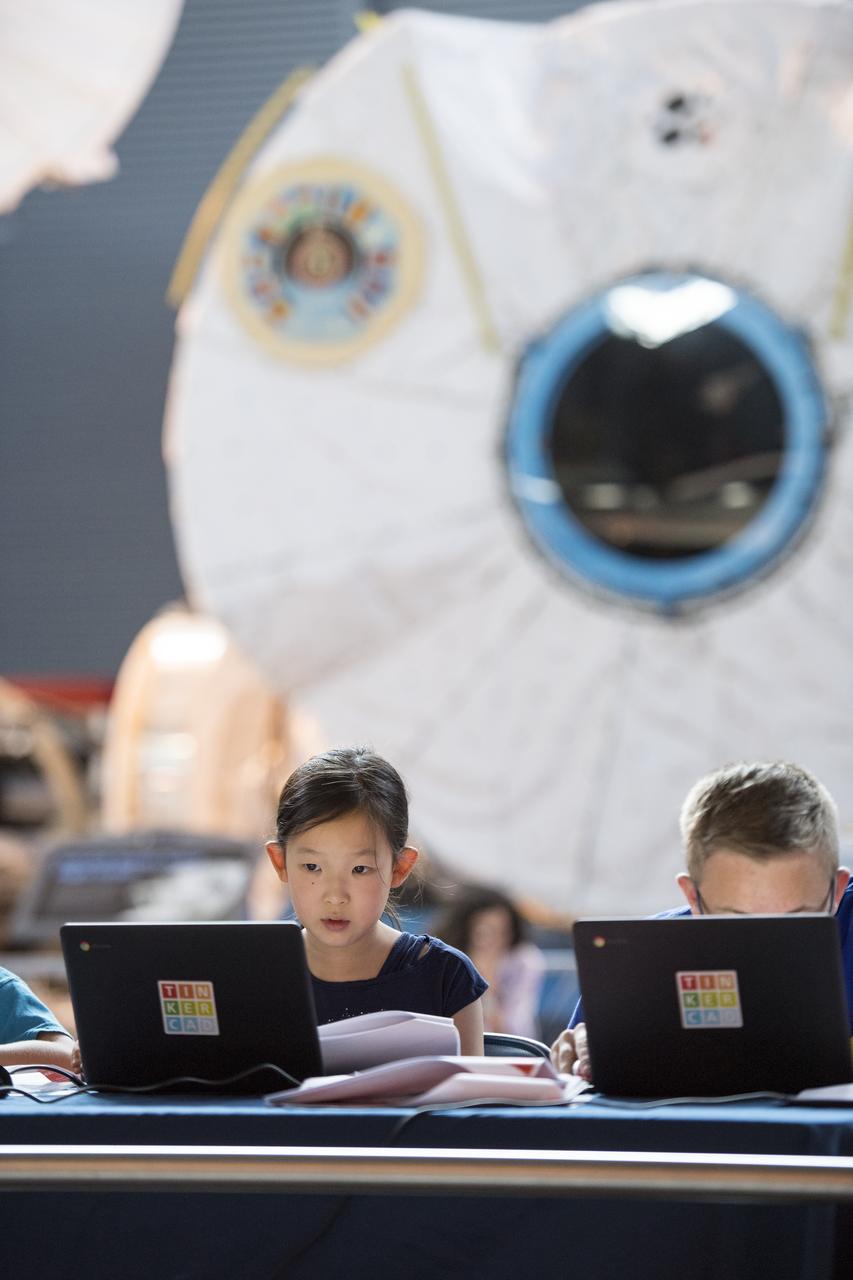

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
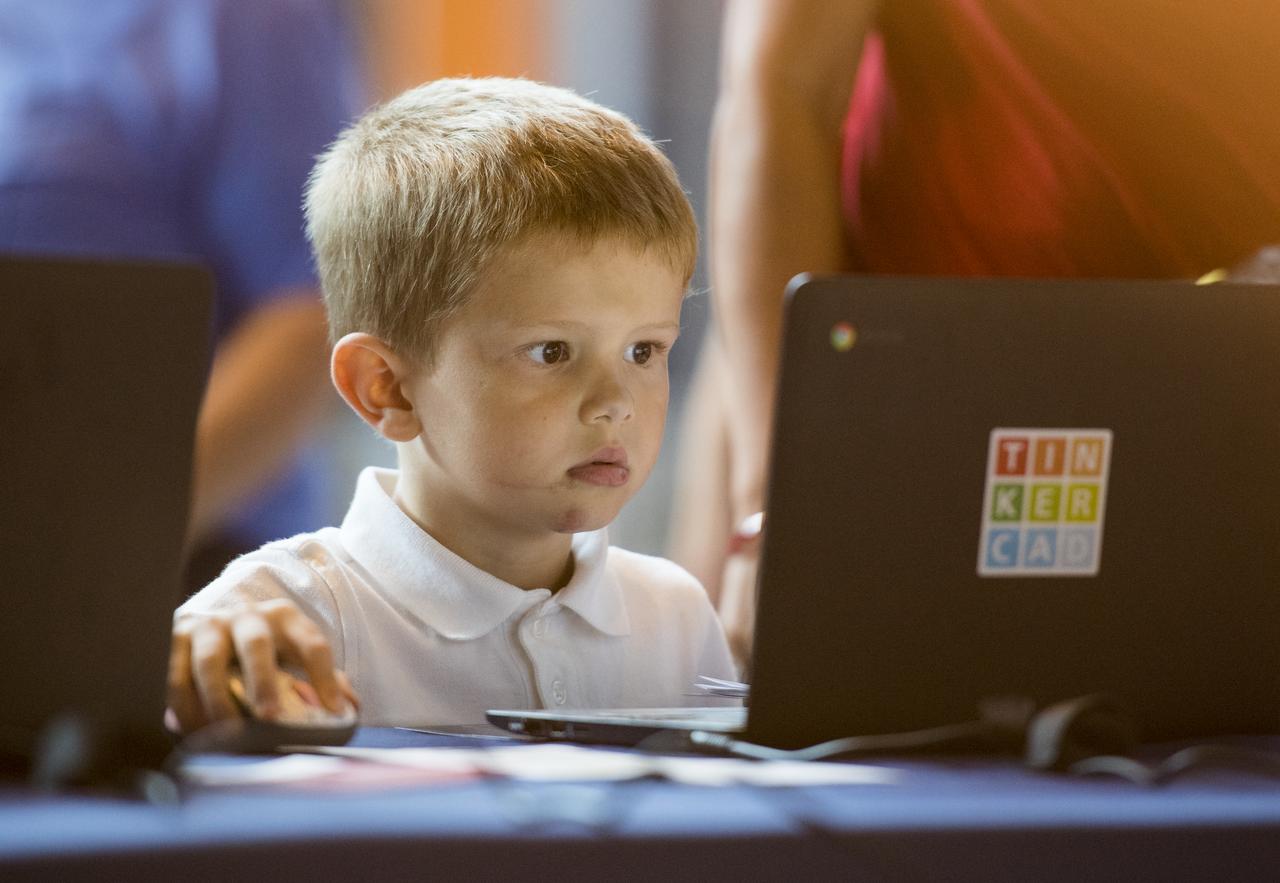

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
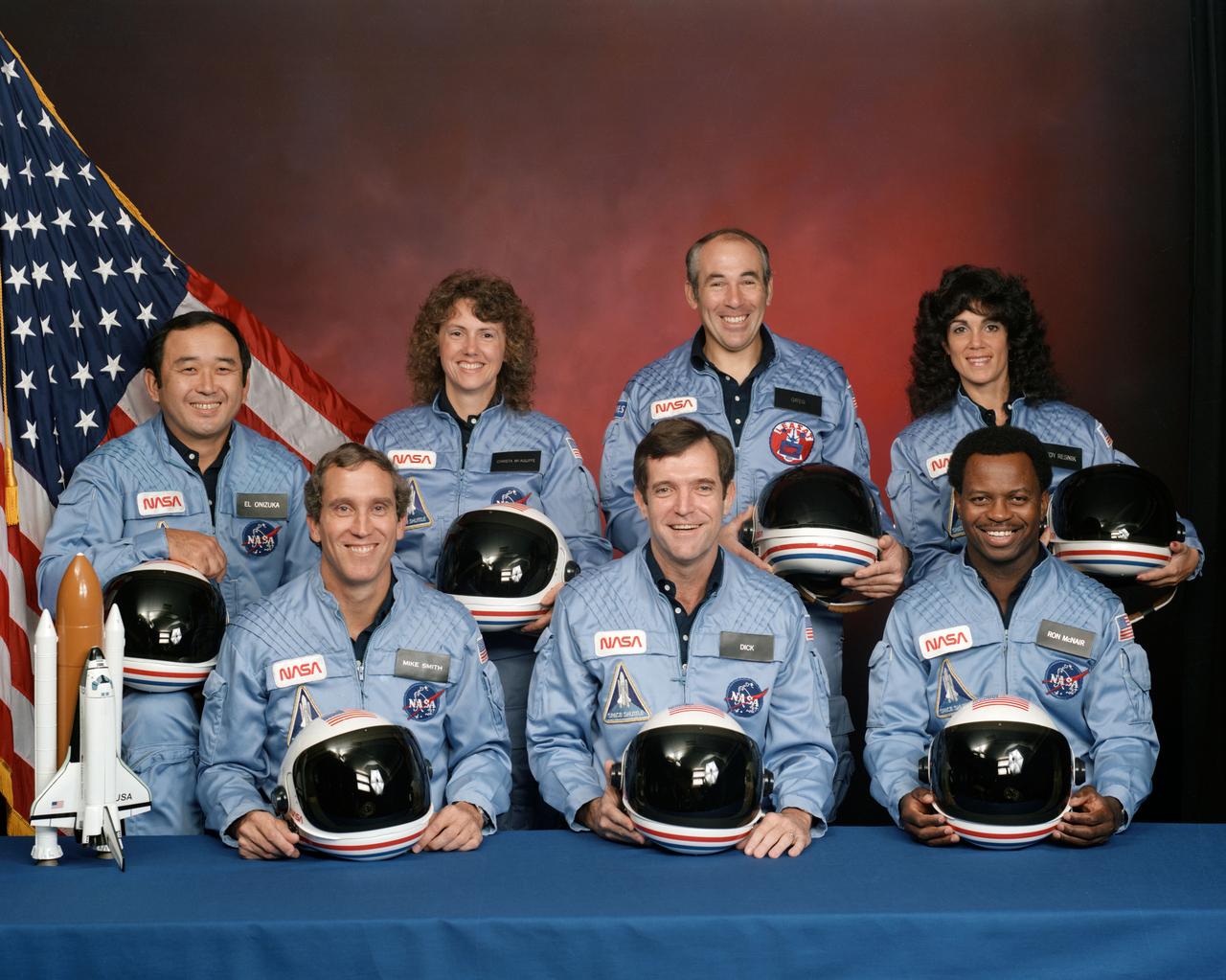

S85-44253 (November 1985) --- Five astronauts and two payload specialists make up the crew, scheduled to fly aboard the space shuttle Challenger in January of 1986. Crew members are (left to right, front row) astronauts Michael J. Smith, Francis R. (Dick) Scobee and Ronald E. McNair; Ellison S. Onizuka, Sharon Christa McAuliffe, Gregory Jarvis and Judith A. Resnik. McAuliffe and Jarvis are payload specialists, representing the Teacher in Space Project and Hughes Company, respectively. Photo credit: NASA (NOTE: On Jan. 28, 1986, the seven Challenger crew members lost their lives following an explosion during the launch phase of the STS-51L mission.)
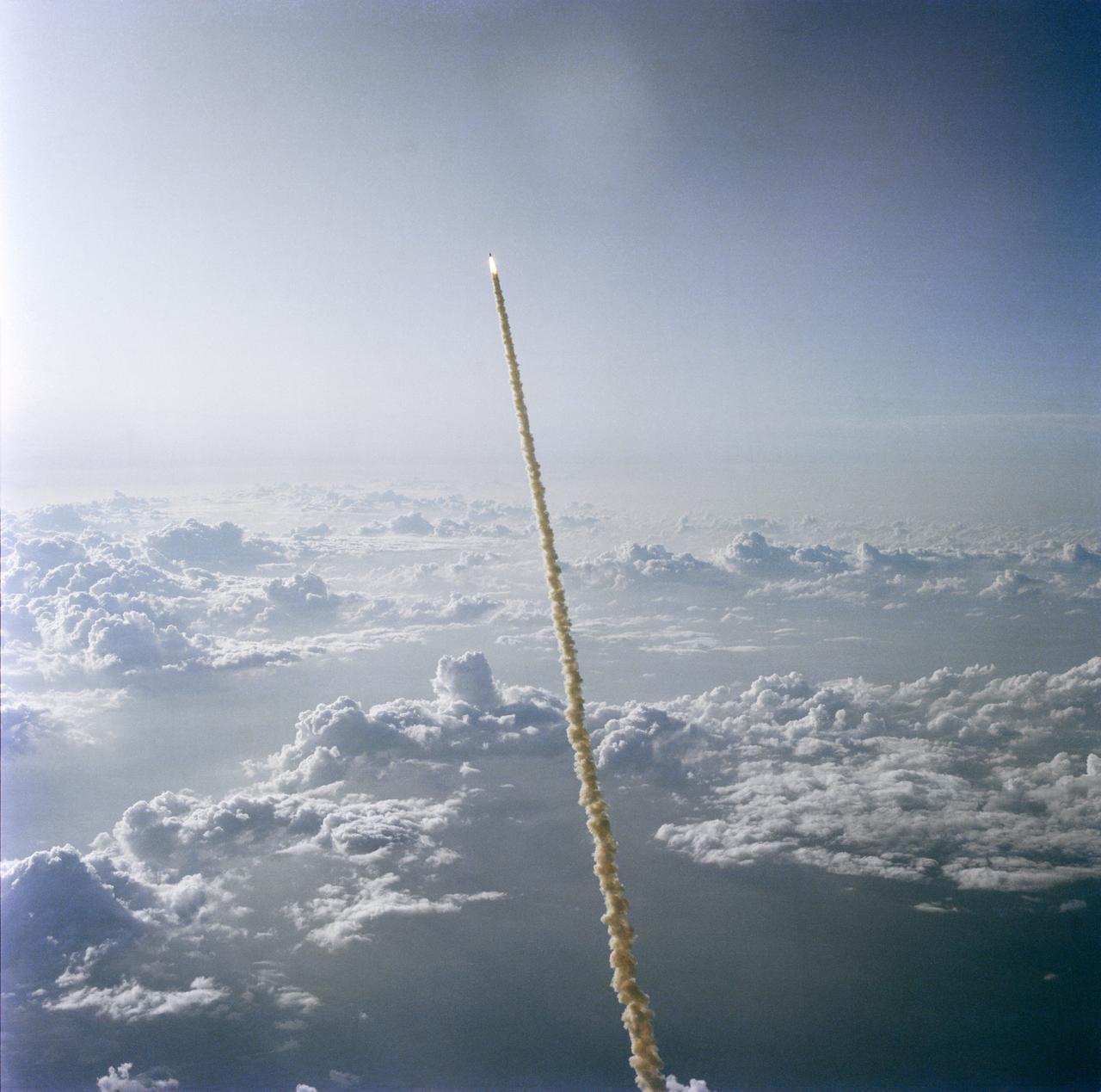

S83-35620 (18 June 1983) --- The space shuttle Challenger, its two solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank carry the five-member STS-7 astronaut crew toward a six-day mission in Earth orbit. This high-angle view of the liftoff, a lengthy stretch of Florida Atlantic coastline and a number of large cumulus clouds was photographed with a handheld 70mm camera by astronaut John W. Young. Young usually pilots the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) for weather monitoring at launch and landing sites for STS missions. The Challenger?s second launch occurred at 7:33 a.m. (EDT) on 18 June 1983. Photo credit: NASA

S84-27219 (3-11 Feb 1984) --- Astronaut Ronald E. McNair, 41-B mission specialist, doubles as "director" for a movie being "produced" aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. McNair’s name tag ("Cecil B. McNair") and beret and slate are all humorous props for application of a serious piece of cargo on this eight day flight - the Cinema 360 camera. Two of the cameras were carried aboard the Challenger to provide a test for motion picture photography in a unique format designed especially for planetarium viewing. This camera was located in the crew cabin area and a second was stowed in a getaway special (GAS) canister in the payload bay. The other camera recorded extravehicular activity (EVA) of the flight’s other two mission specialists, Astronauts Bruce McCandless II and Robert L. Stewart.
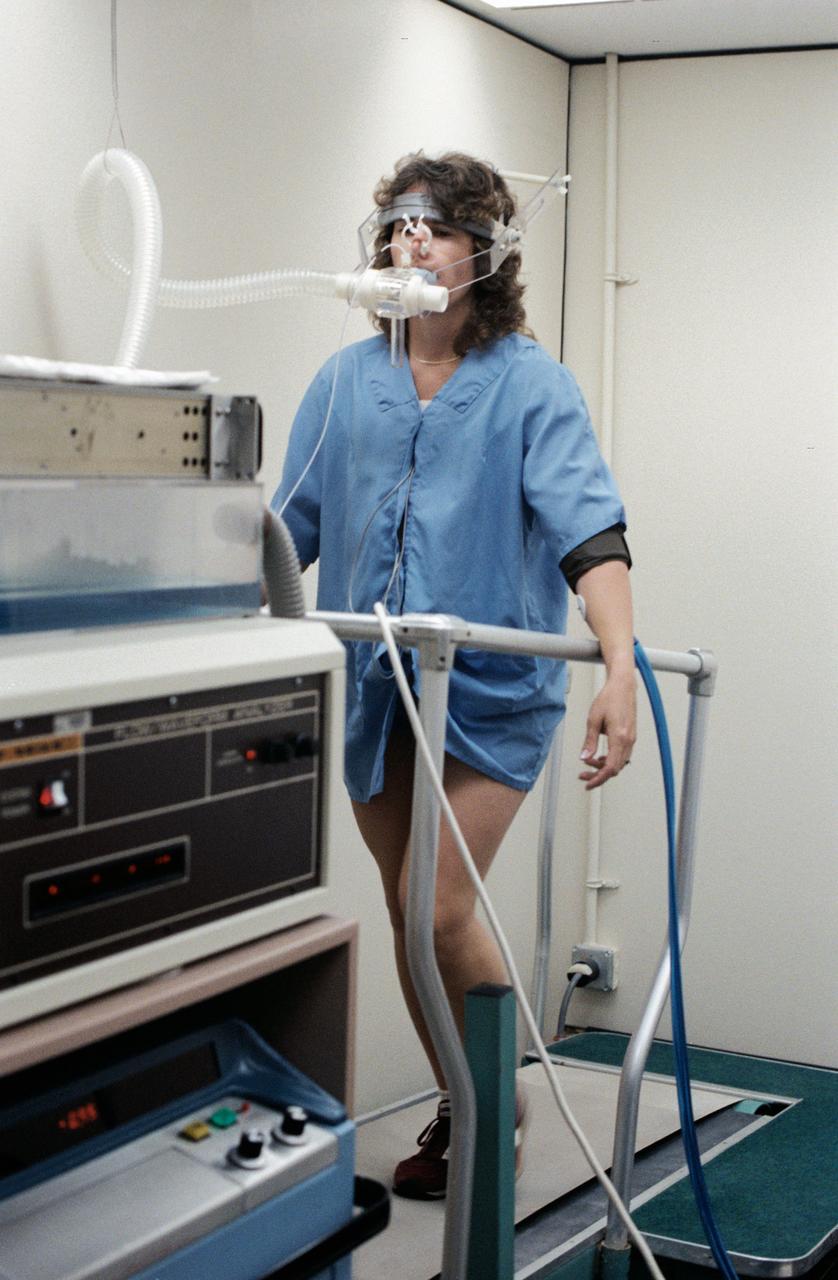
S85-37165 (8-12 July 1985) -- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, runs in place on treadmill to test physiological responses at Johnson Space Center. Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
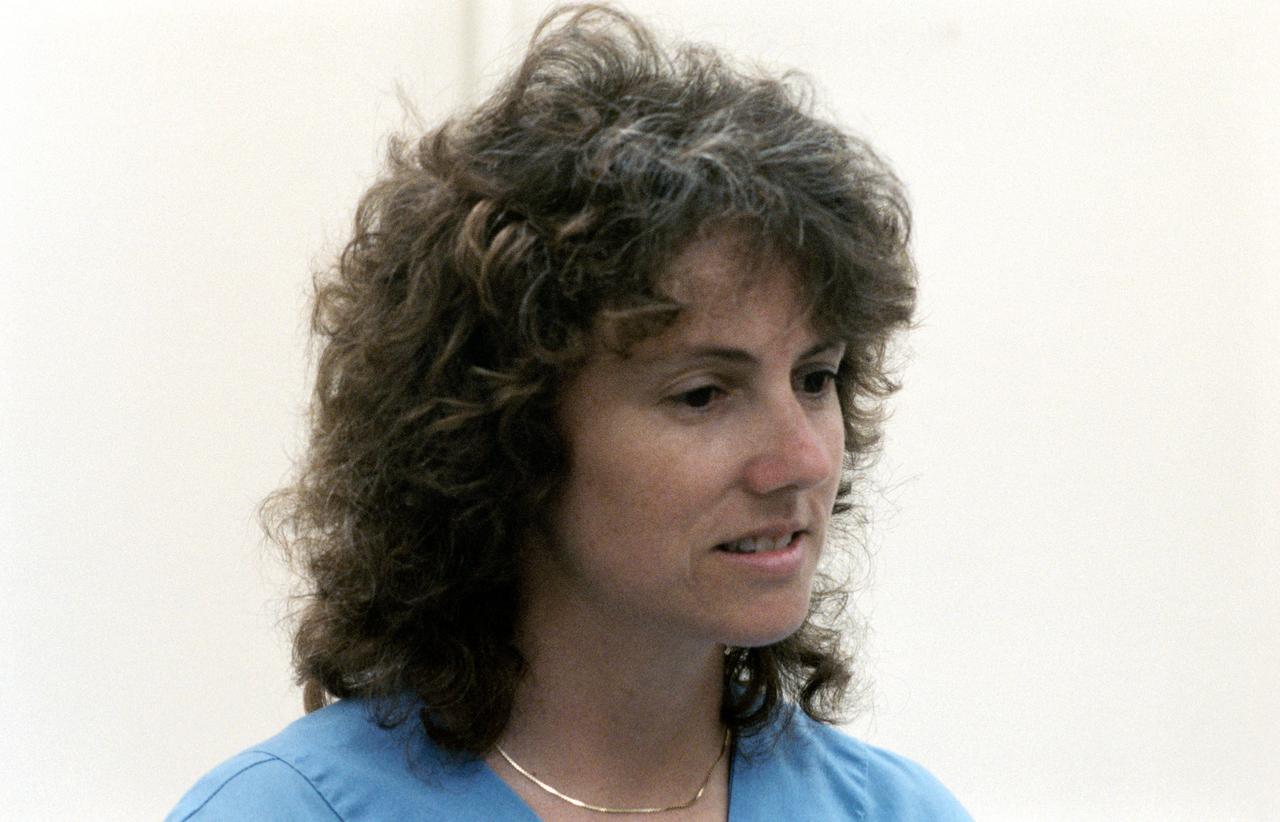

S85-37164 (8-12 July 1985) --- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, talks to the media at Johnson Space Center. Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
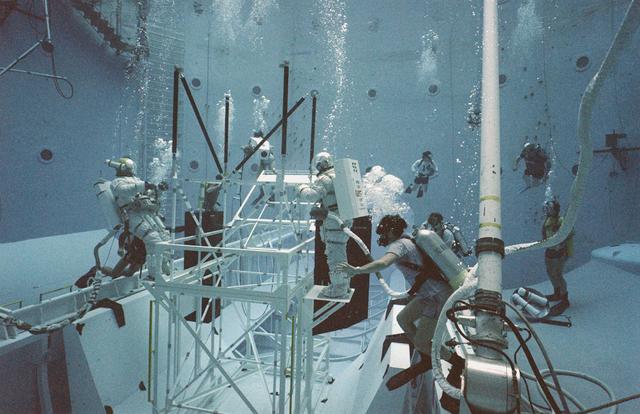

One of the main components of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is the Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) system. This system interfaces with the Support System Module (SSM) for exchange of operational commands and telemetry data. SADE operates and controls the Solar Array Drive Mechanisms (SADM) for the orientation of the Solar Array Drive (SAD). It also monitors the position of the arrays and the temperature of the SADM. During the first HST servicing mission, the astronauts replaced the SADE component because of some malfunctions. This turned out to be a very challenging extravehicular activity (EVA). Two transistors and two diodes had been thermally stressed with the conformal coating discolored and charred. Soldered cornections became molten and reflowed between the two diodes. The failed transistors gave no indication of defective construction. All repairs were made and the HST was redeposited into orbit. Prior to undertaking this challenging mission, the orbiter's crew trained at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) to prepare themselves for working in a low gravity environment. They also practiced replacing HST parts and exercised maneuverability and equipment handling. Pictured are crew members practicing on a space platform.
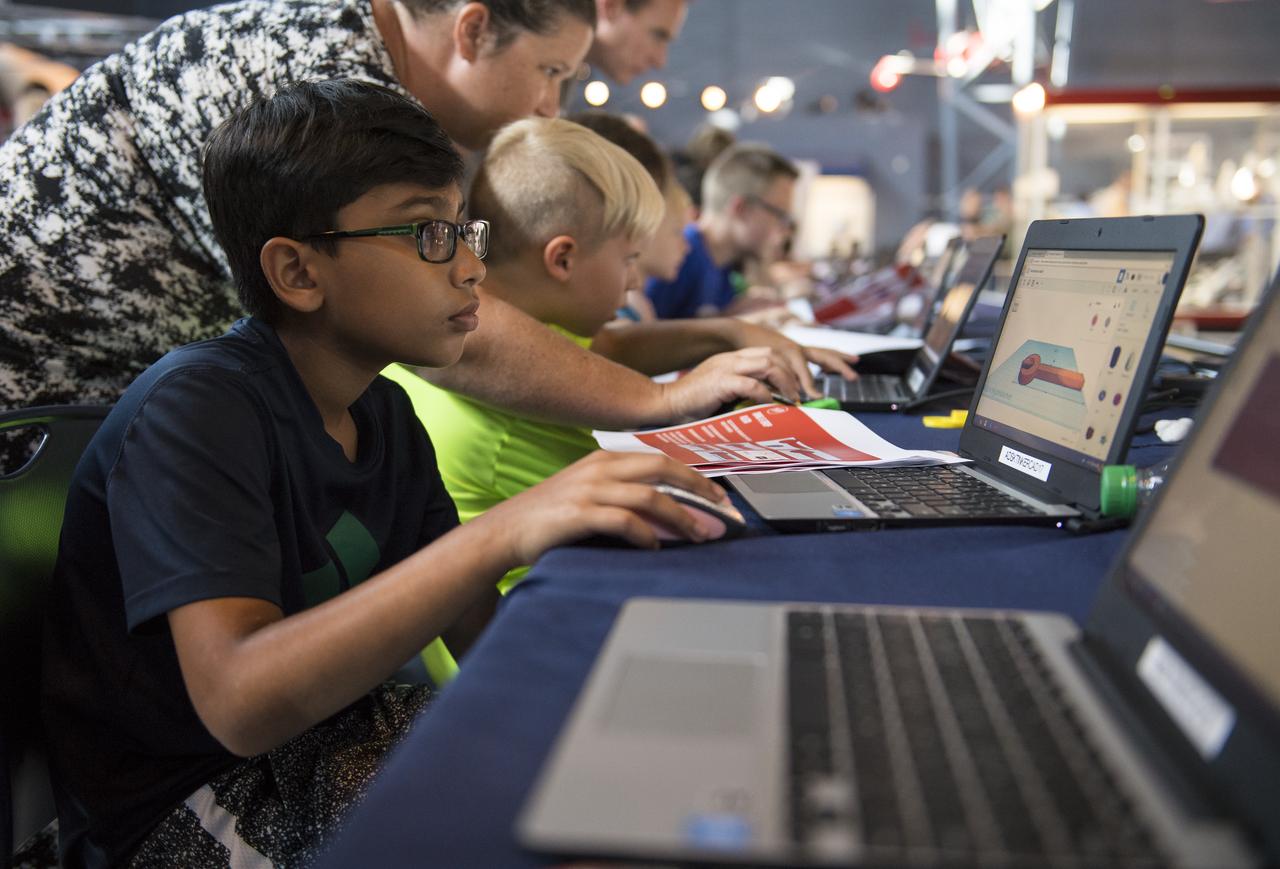

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
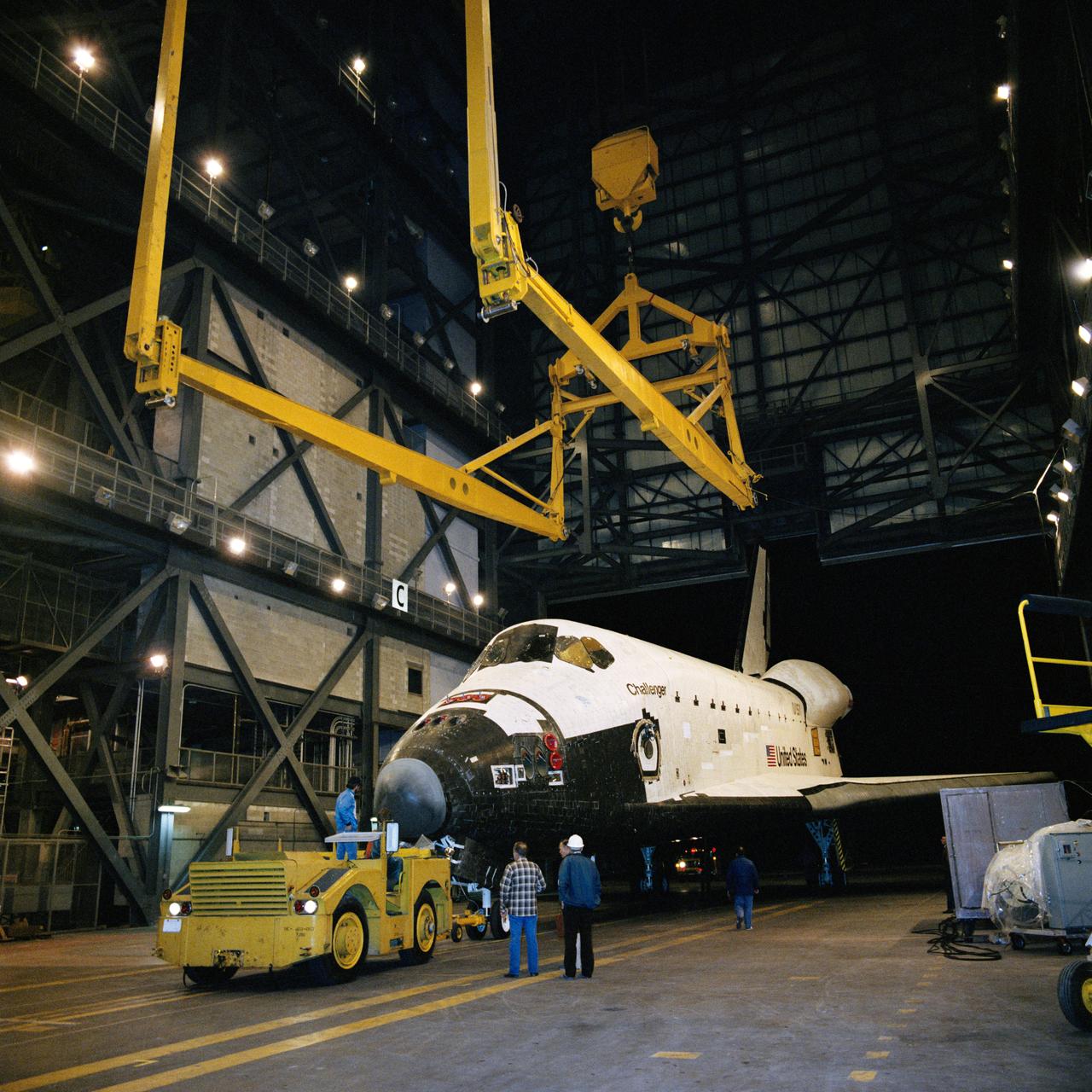

S84-25872 (6 Jan 1984) --- Progress continues at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) as the Space Shuttle Challenger is moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) for mating to its two Solid Rocket Boosters (SRB) and External Fuel Tank (ET). The flight of STS-41B will carry five astronaut crew members into space for the performance of a variety of duties. Launch is scheduled for February 3, 1984.
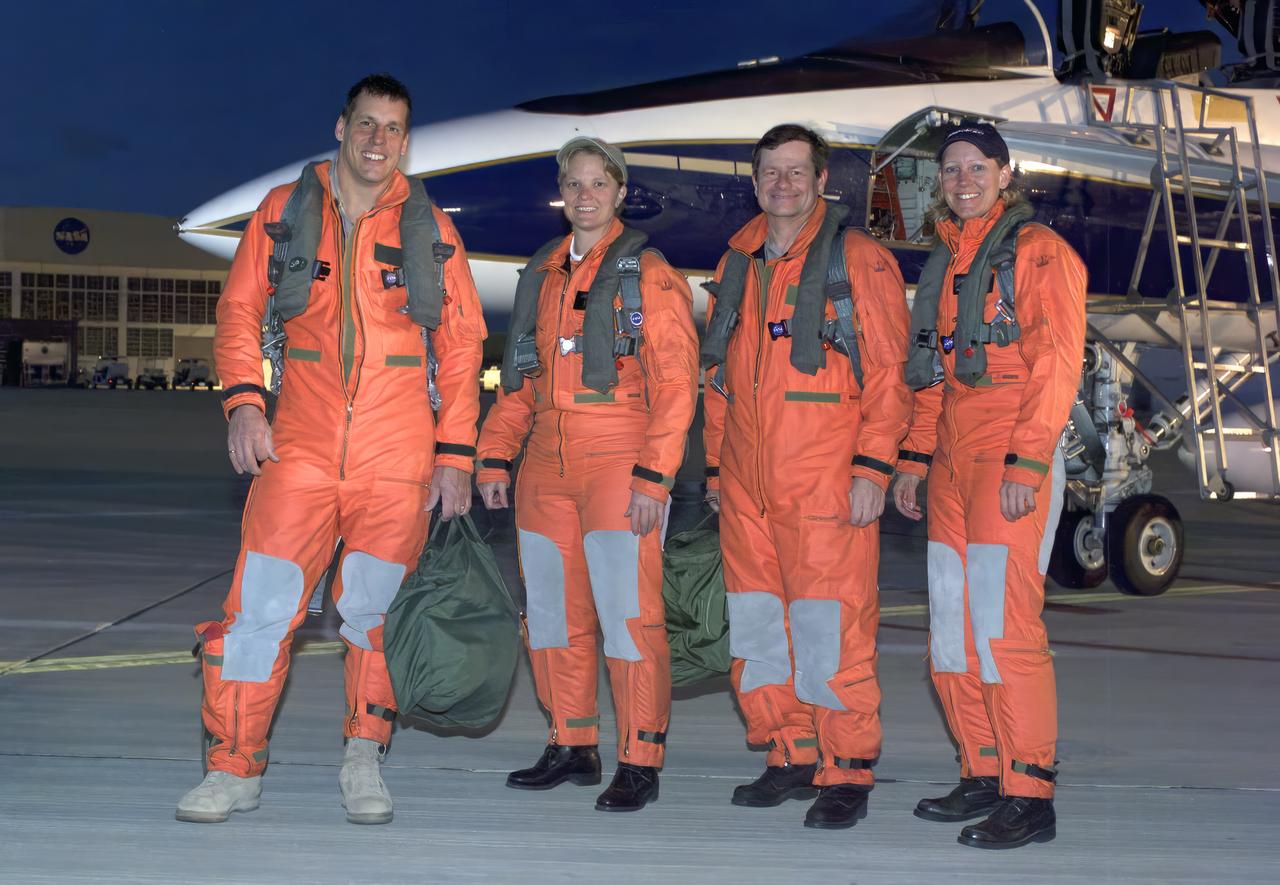

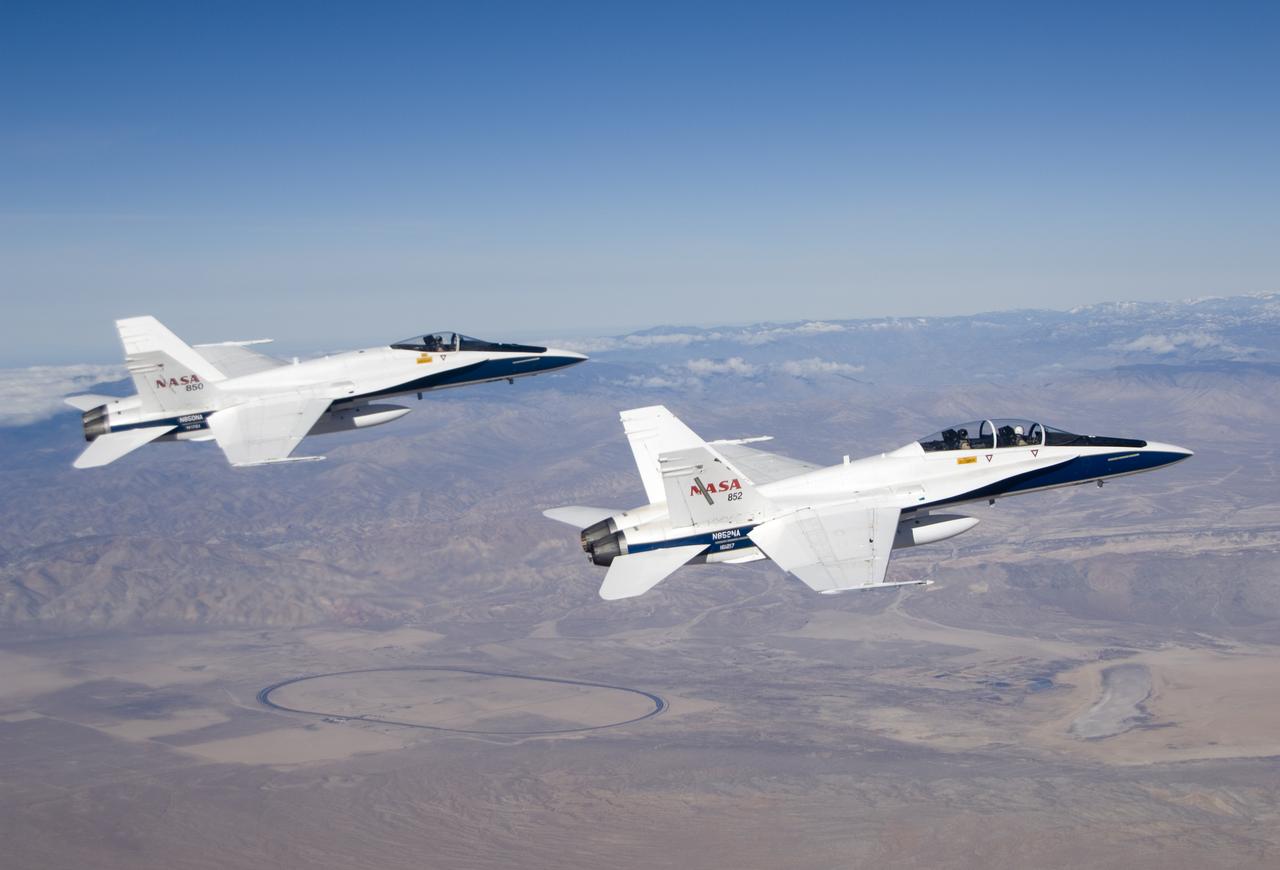
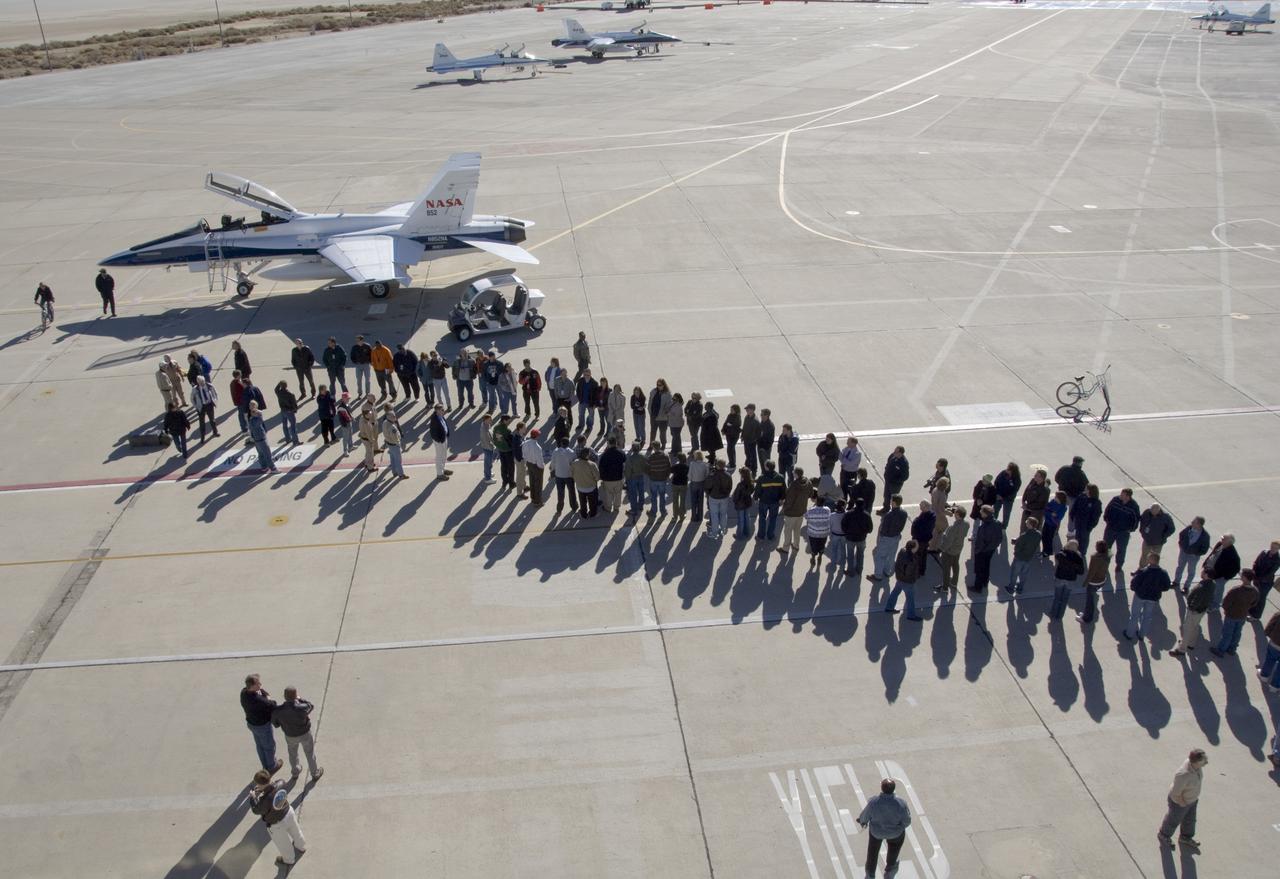
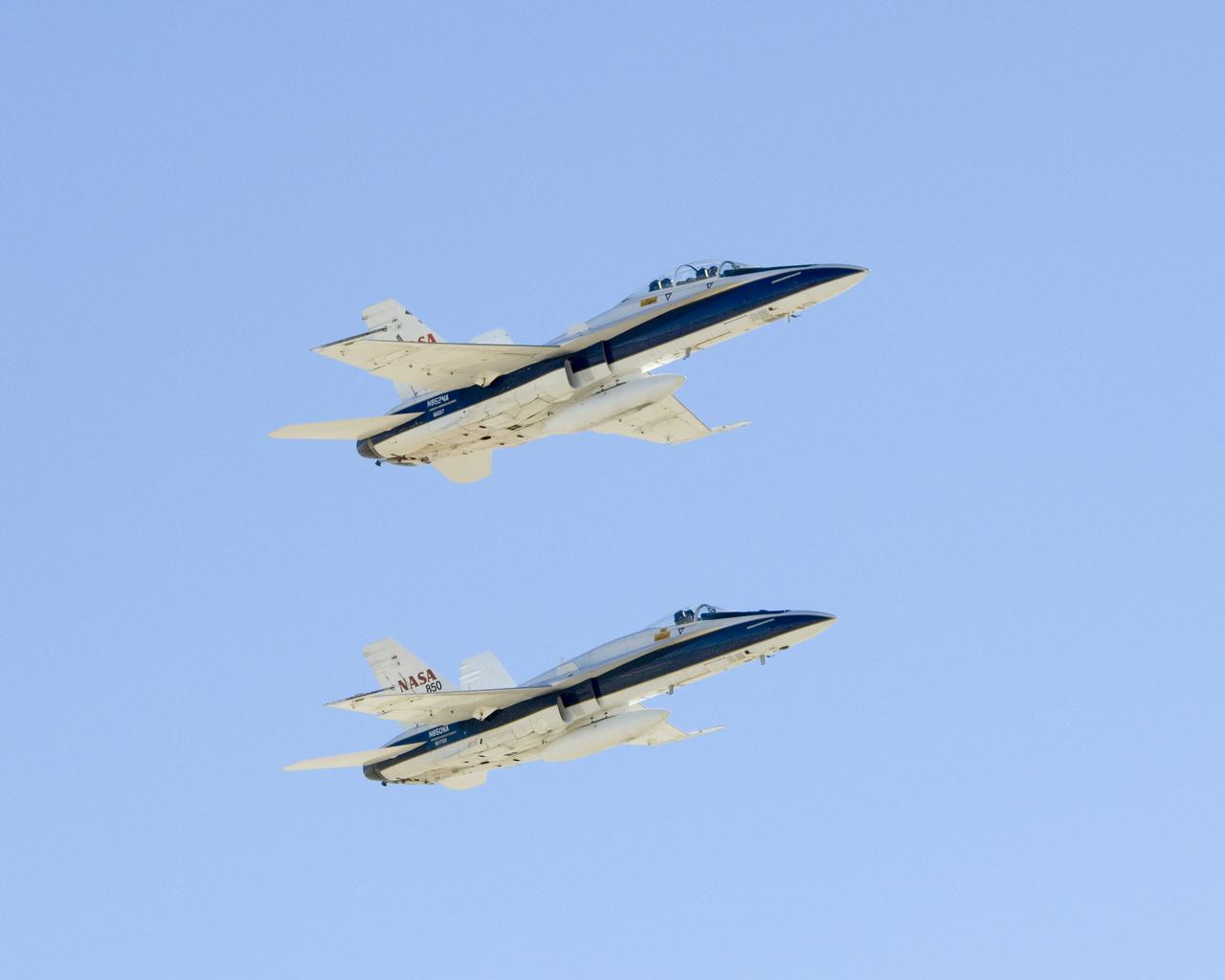
From left, pilot Craig Bomben, photographer Carla Thomas, pilot Frank Batteas, and videographer Lori Losey make up the flight crews for two F-18 high-performance jets to document a flight of NASA’s B-52B carrying a Pegasus booster rocket and the X-43A. A dry run, known as a captive carry mission, was conducted to monitor the research hardware in flight for any challenges. The January 2004 X-43A flight was based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
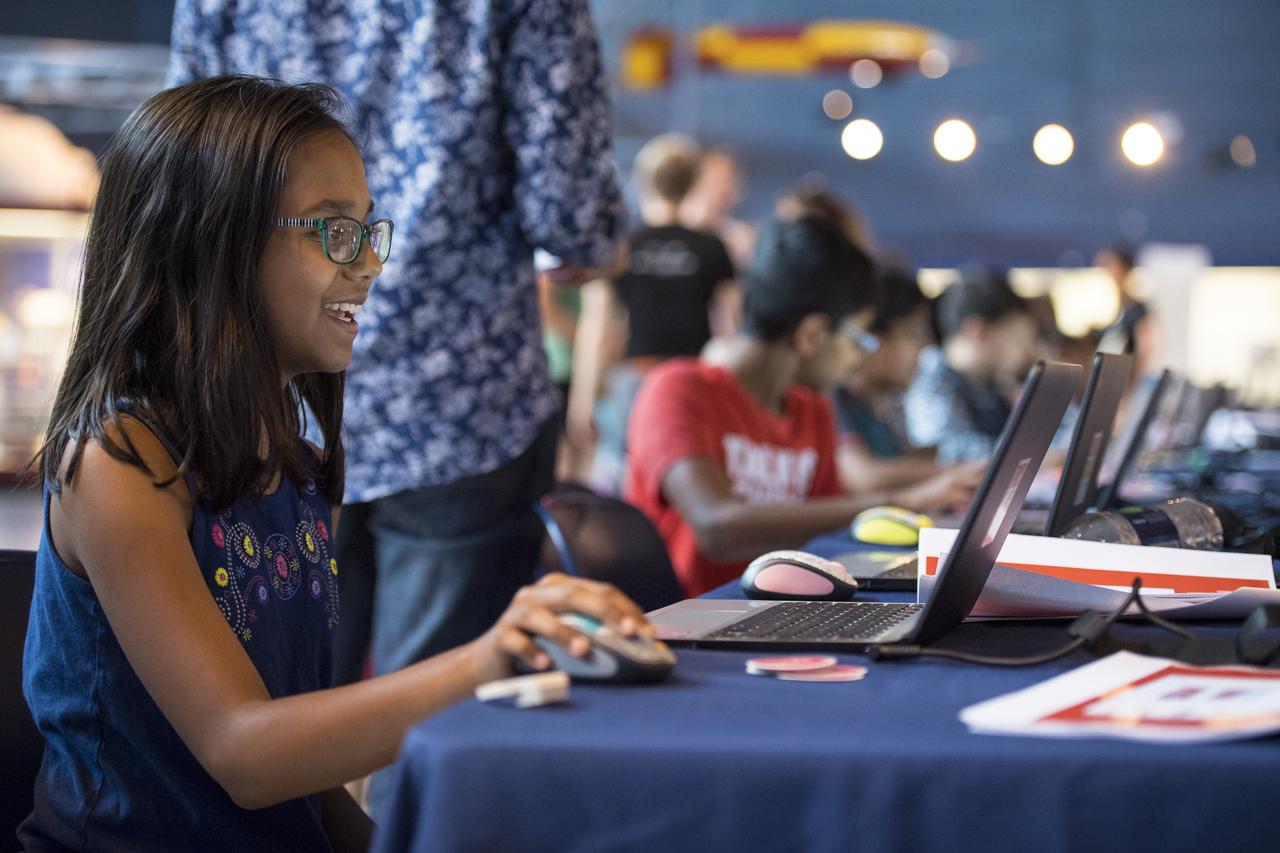

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
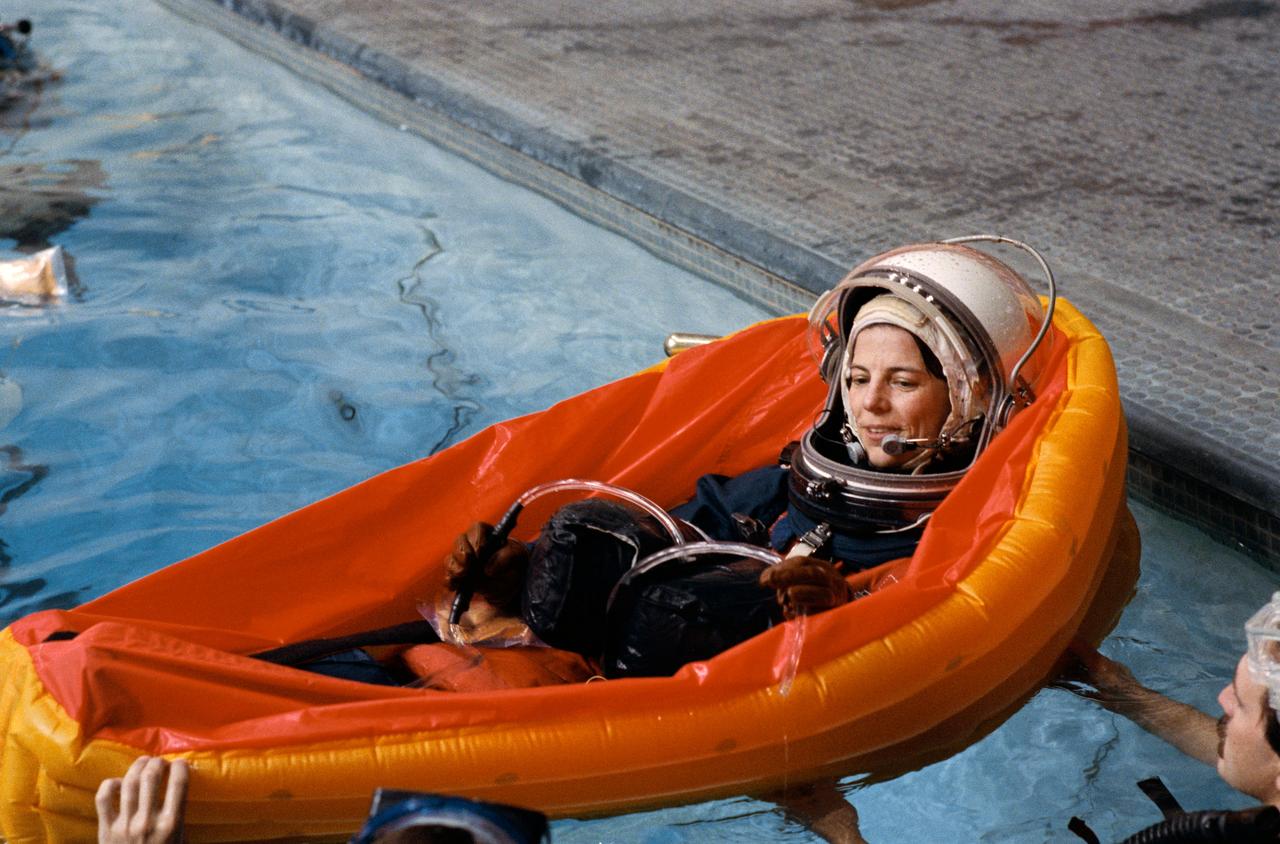

STS-32 Mission Specialist (MS) Bonnie J. Dunbar, wearing a launch and entry suit (LES) and lauch and entry helmet (LEH), in a single-occupant (one man) lift raft enlists the aid of two SCUBA-equipped divers as she floats in 25 ft deep pool located in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. During the exercises the crew practiced the procedures to follow in the event of an emergency aboard the Space Shuttle and familiarized themselves with post-Challenger pole system of emergency egress.
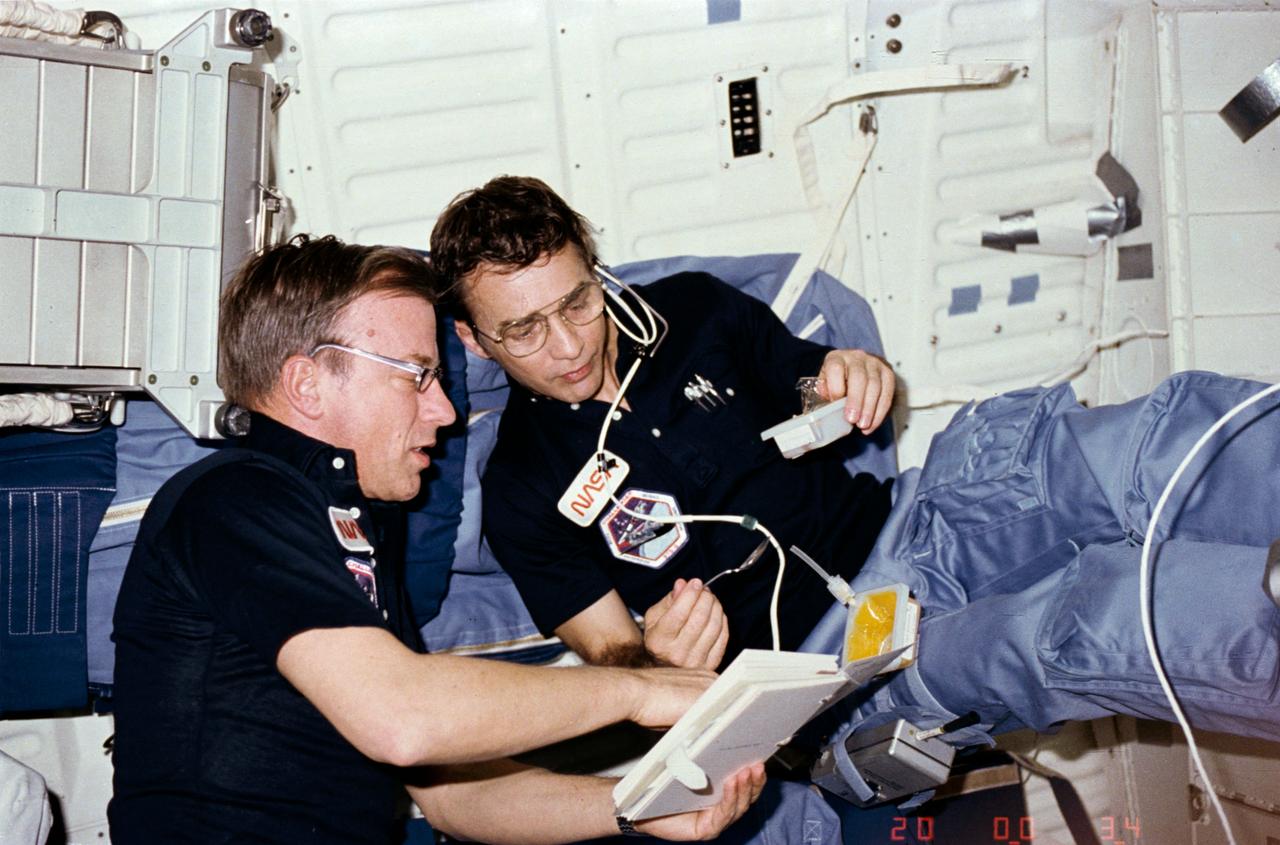

STS006-06-456 (4-9 April 1983) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, STS-6 commander, points out an item in the crew activity plan (CAP) to astronaut Donald H. Peterson as the mission specialist uses a spoon to eat a meal aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. The two are on the middeck. They are wearing the shirt and trouser portions of the blue cotton multi-piece constant wear garments. This frame was photographed with a 35mm camera. Photo credit: NASA
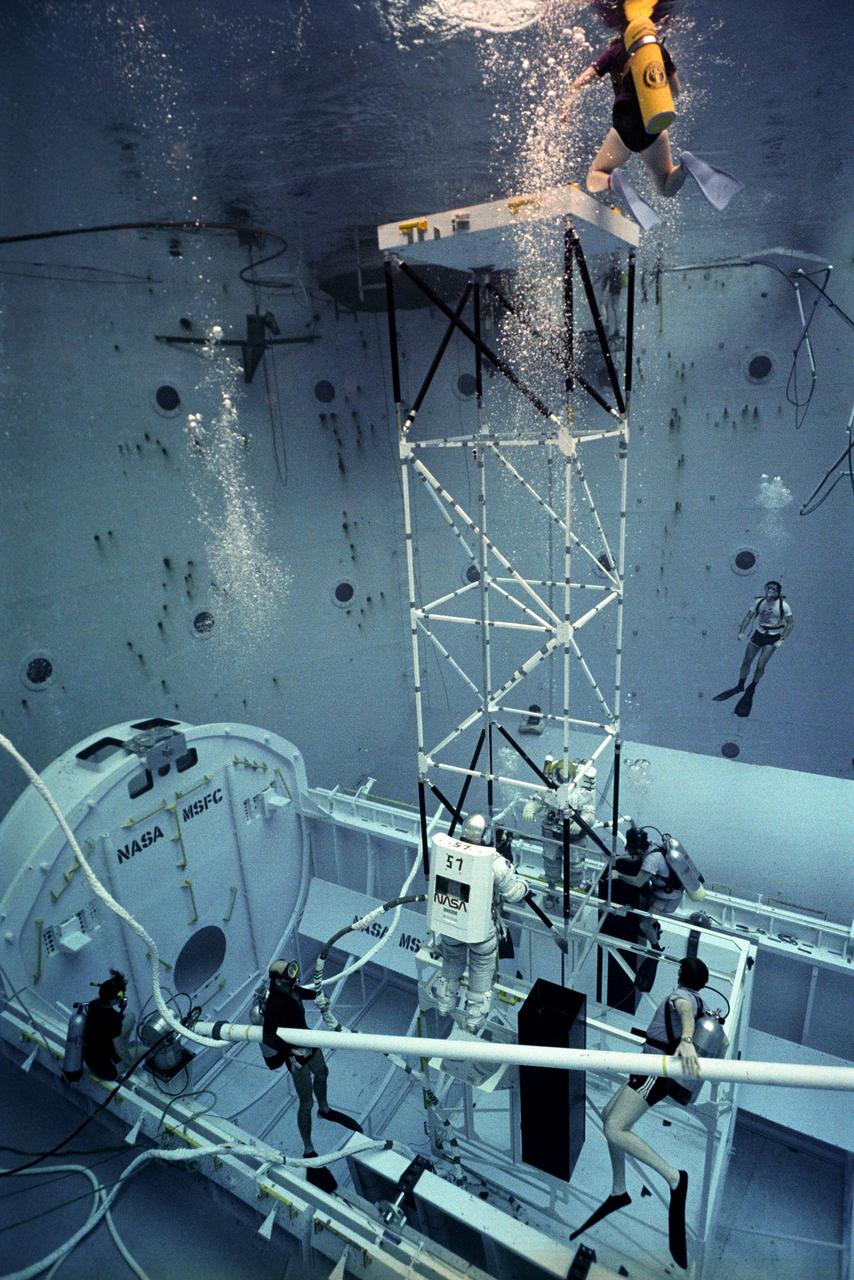

One of the main components of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is the Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) system. This system interfaces with the Support System Module (SSM) for exchange of operational commands and telemetry data. SADE operates and controls the Solar Array Drive Mechanisms (SADM) for the orientation of the Solar Array Drive (SAD). It also monitors the position of the arrays and the temperature of the SADM. During the first HST servicing mission, the astronauts replaced the SADE component because of some malfunctions. This turned out to be a very challenging extravehicular activity (EVA). Two transistors and two diodes had been thermally stressed with the conformal coating discolored and charred. Soldered cornections became molten and reflowed between the two diodes. The failed transistors gave no indication of defective construction. All repairs were made and the HST was redeposited into orbit. Prior to undertaking this challenging mission, the orbiter's crew trained at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) to prepare themselves for working in a low gravity environment. They also practiced replacing HST parts and exercised maneuverability and equipment handling. Pictured is an astronaut practicing climbing a space platform that was necessary in making repairs on the HST.

STS008-16-454 (30 Aug-5 Sept 1983) --- Following a precedent set early two decades ago during the Gemini program, three members of the STS-8 astronaut crew aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger reveal their military backgrounds and loyalties. Astronauts (left to right) Dale A. Gardner, Richard H. Truly and Daniel C. Brandenstein leave no mystery as to their alma mater and gridiron sentimentalities as they display U.S. Navy stickers. The trio was photographed by Astronaut Guion S. Bluford on the flight deck. Truly is crew commander; Brandenstein, pilot; and Gardner and Bluford, along with Dr. William E. Thornton are all mission specialists for this six-day flight.
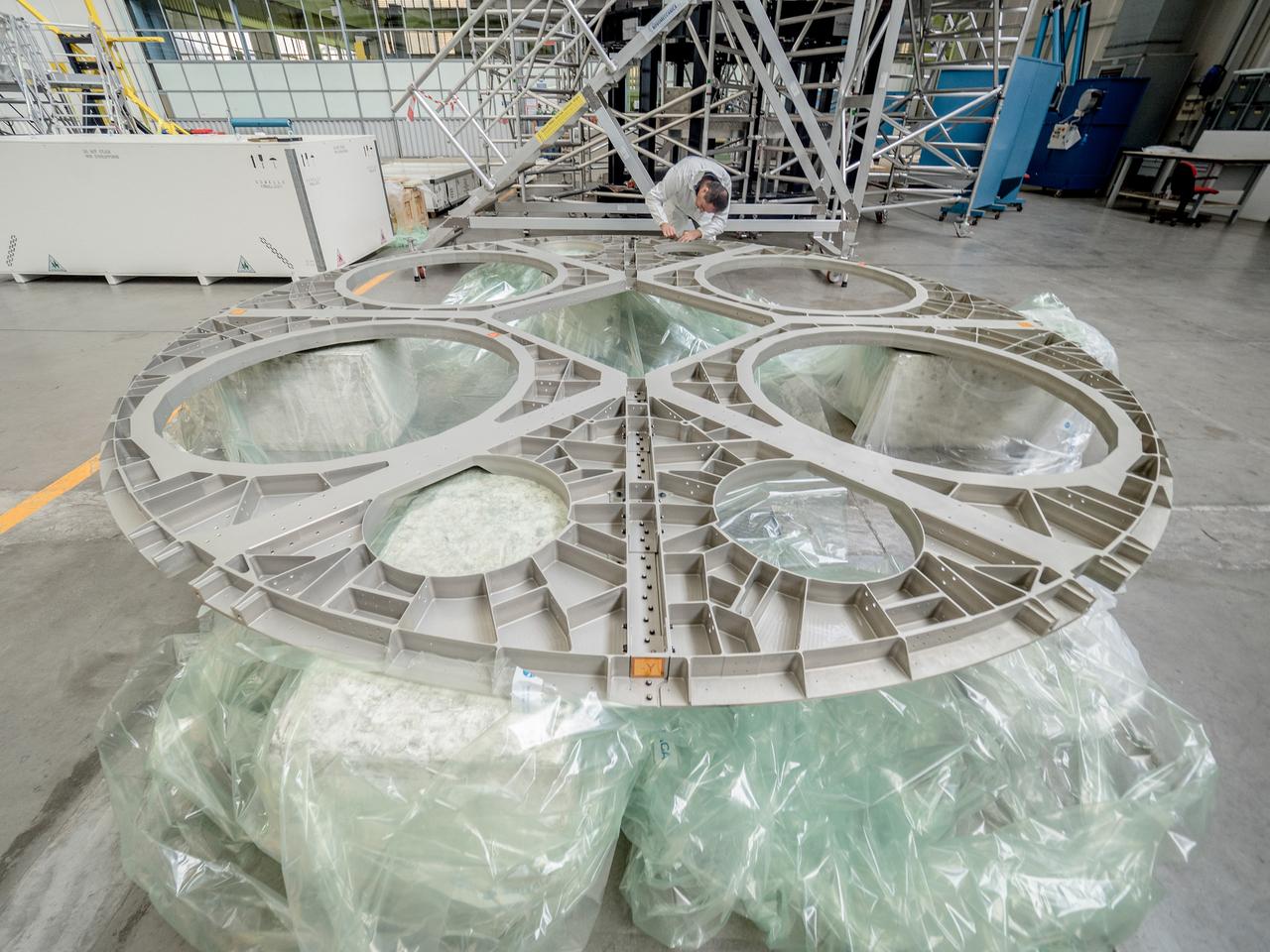

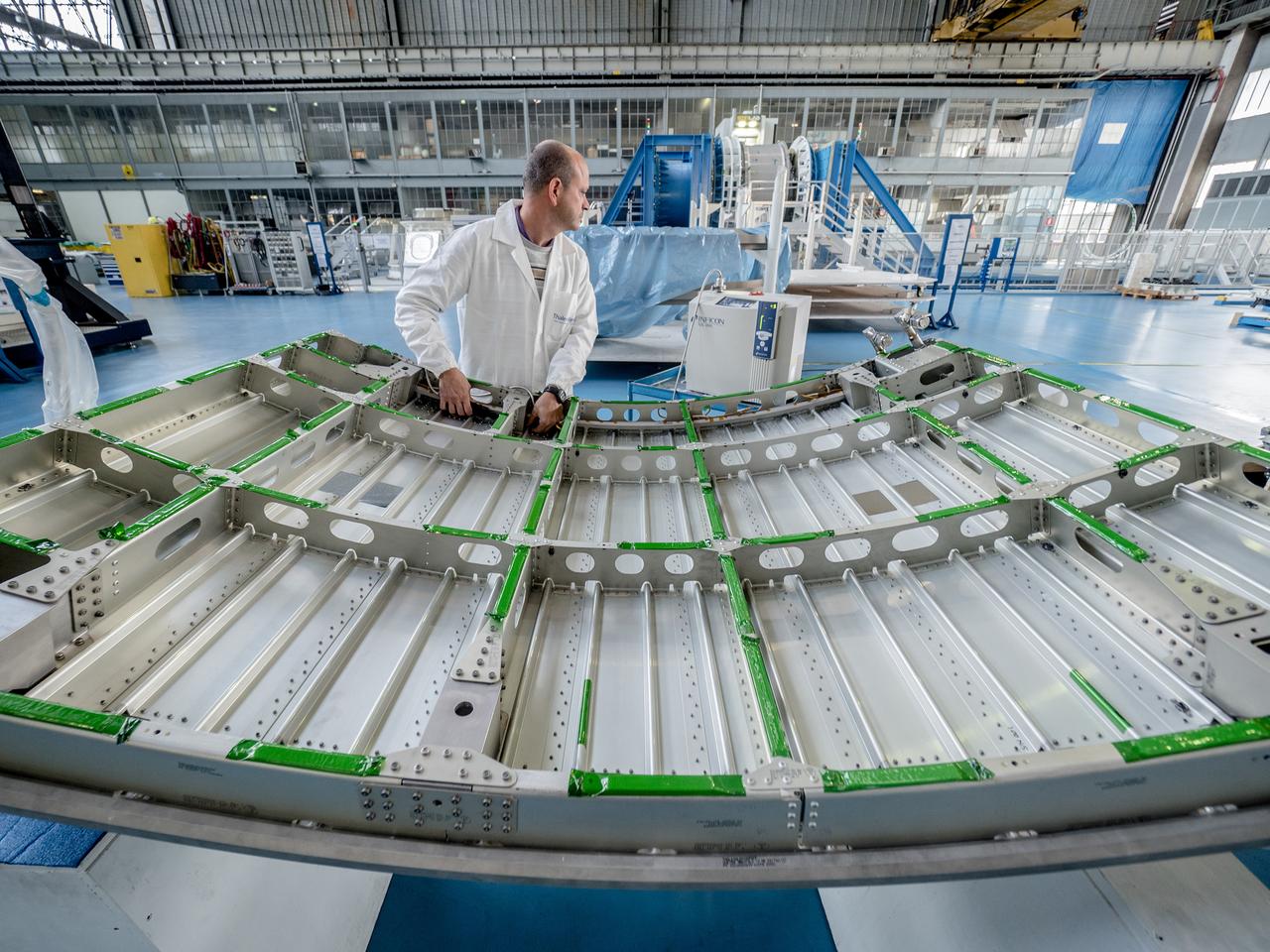
While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
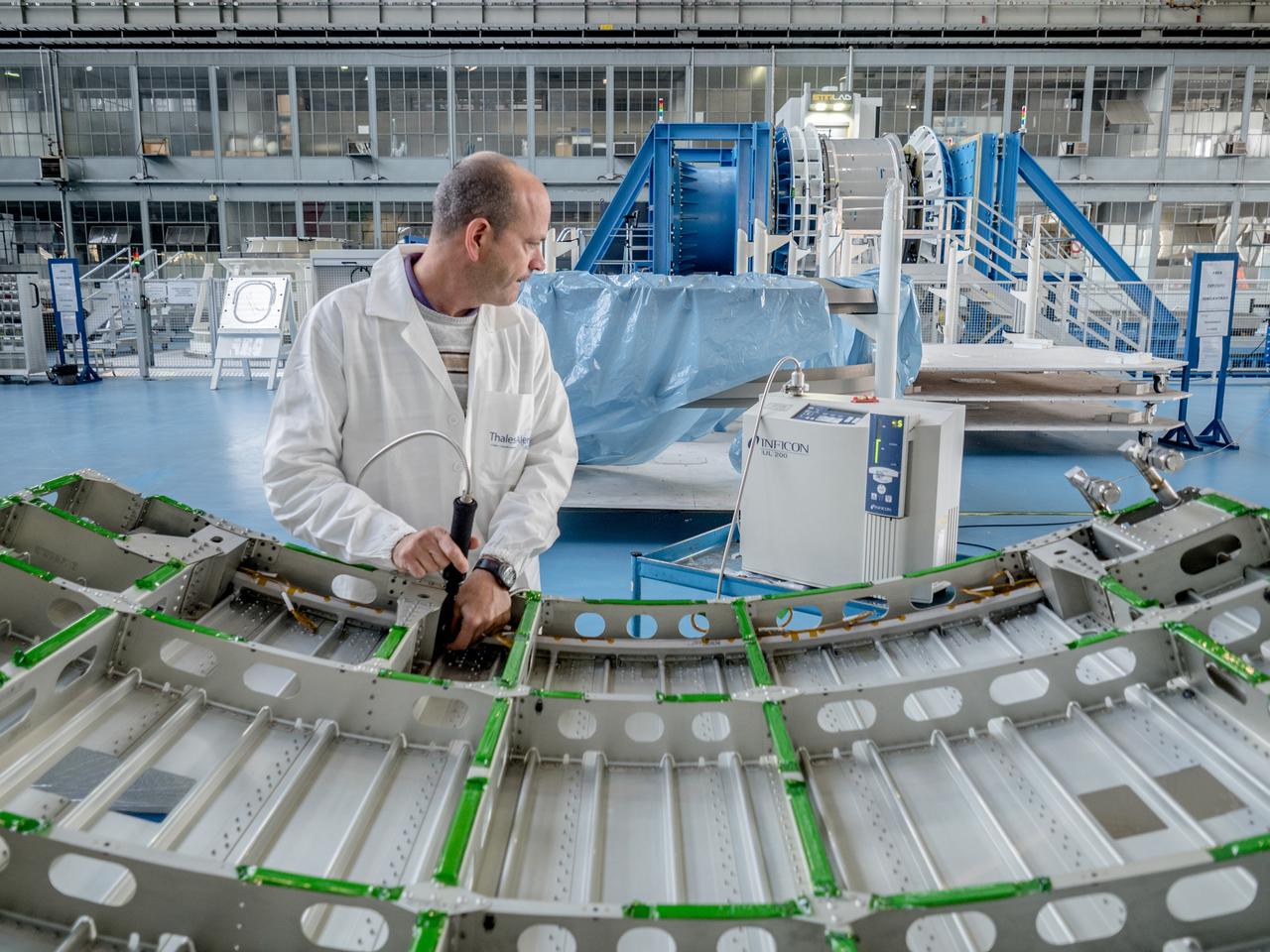

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
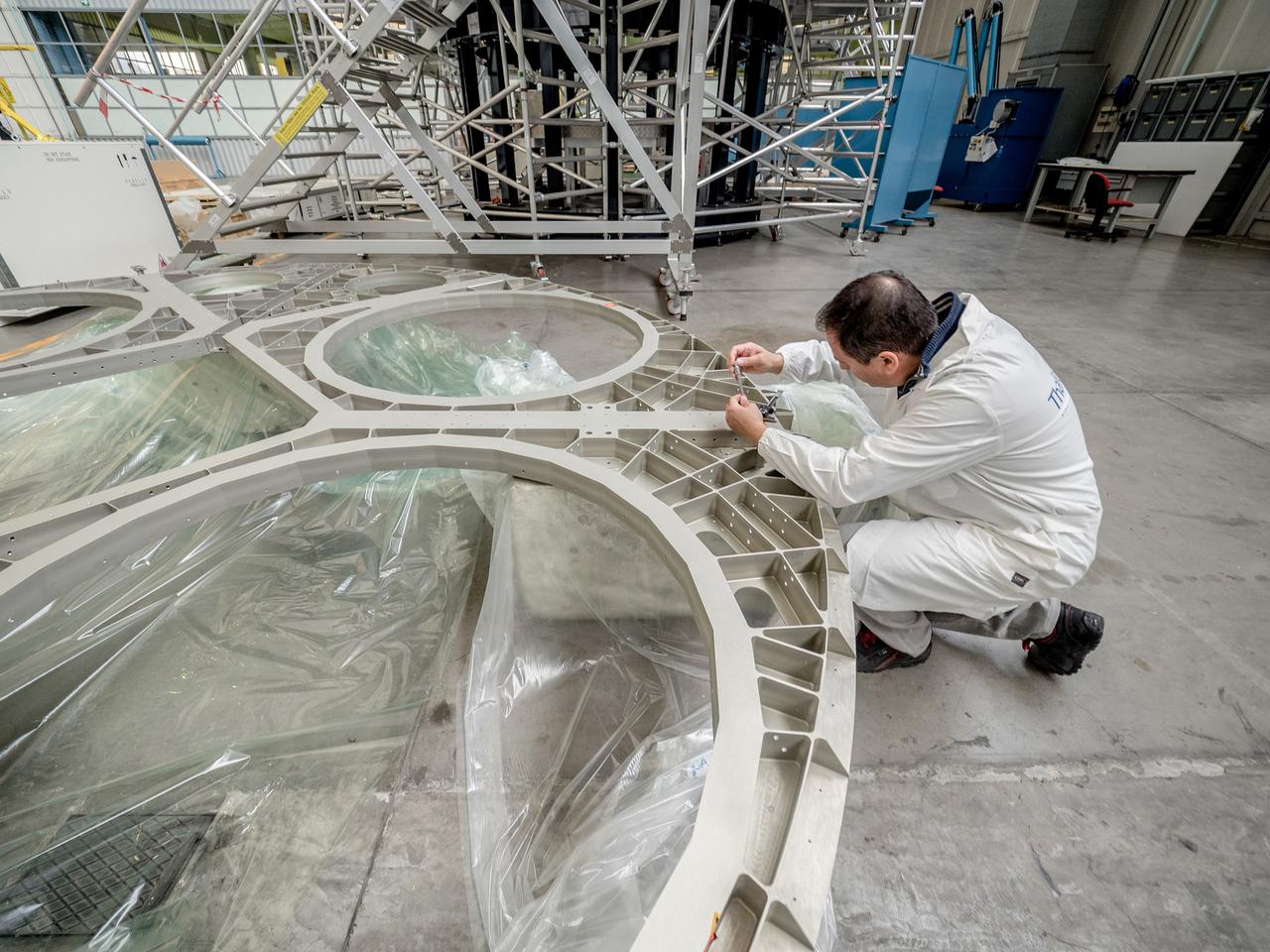

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
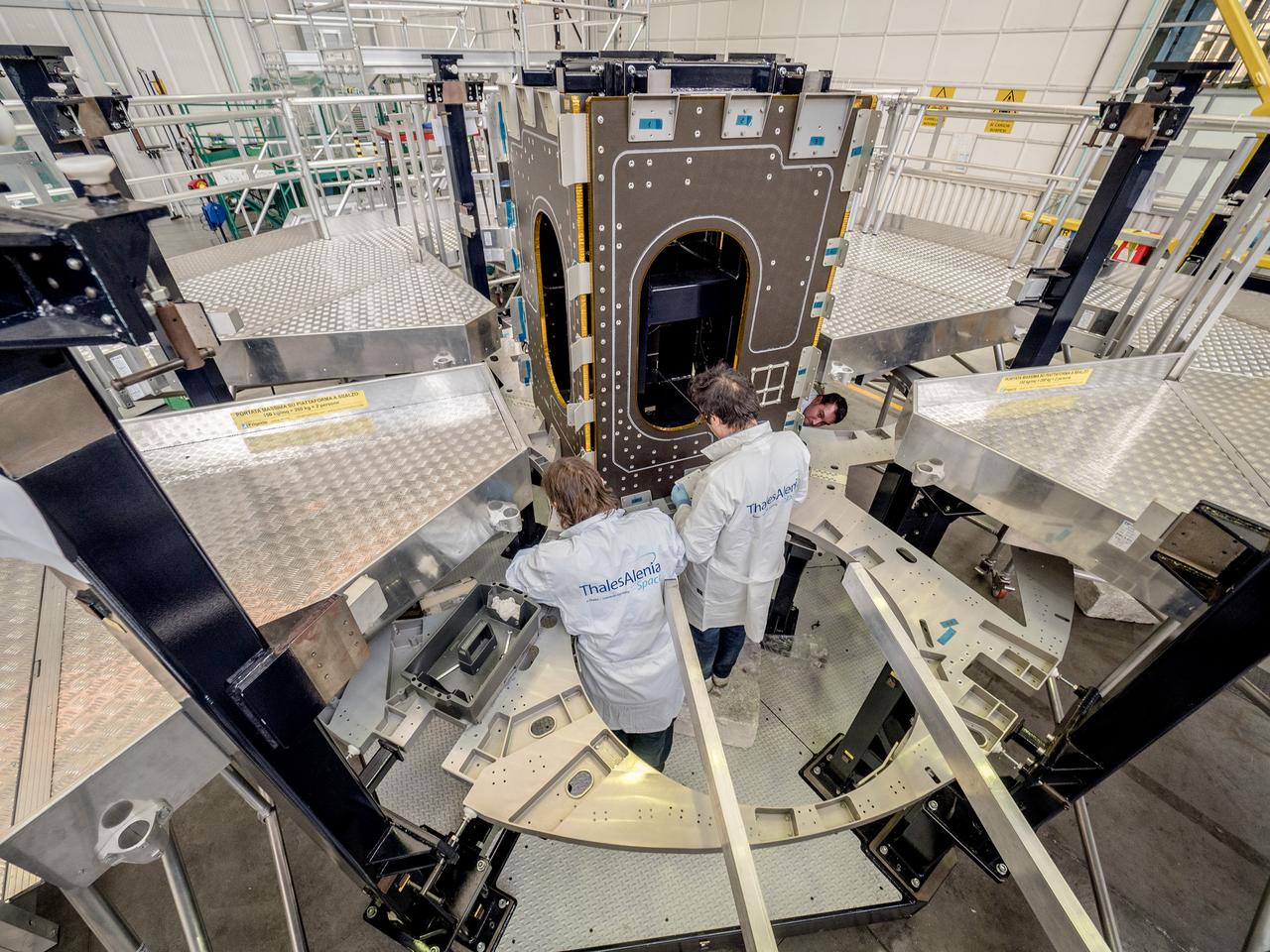

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
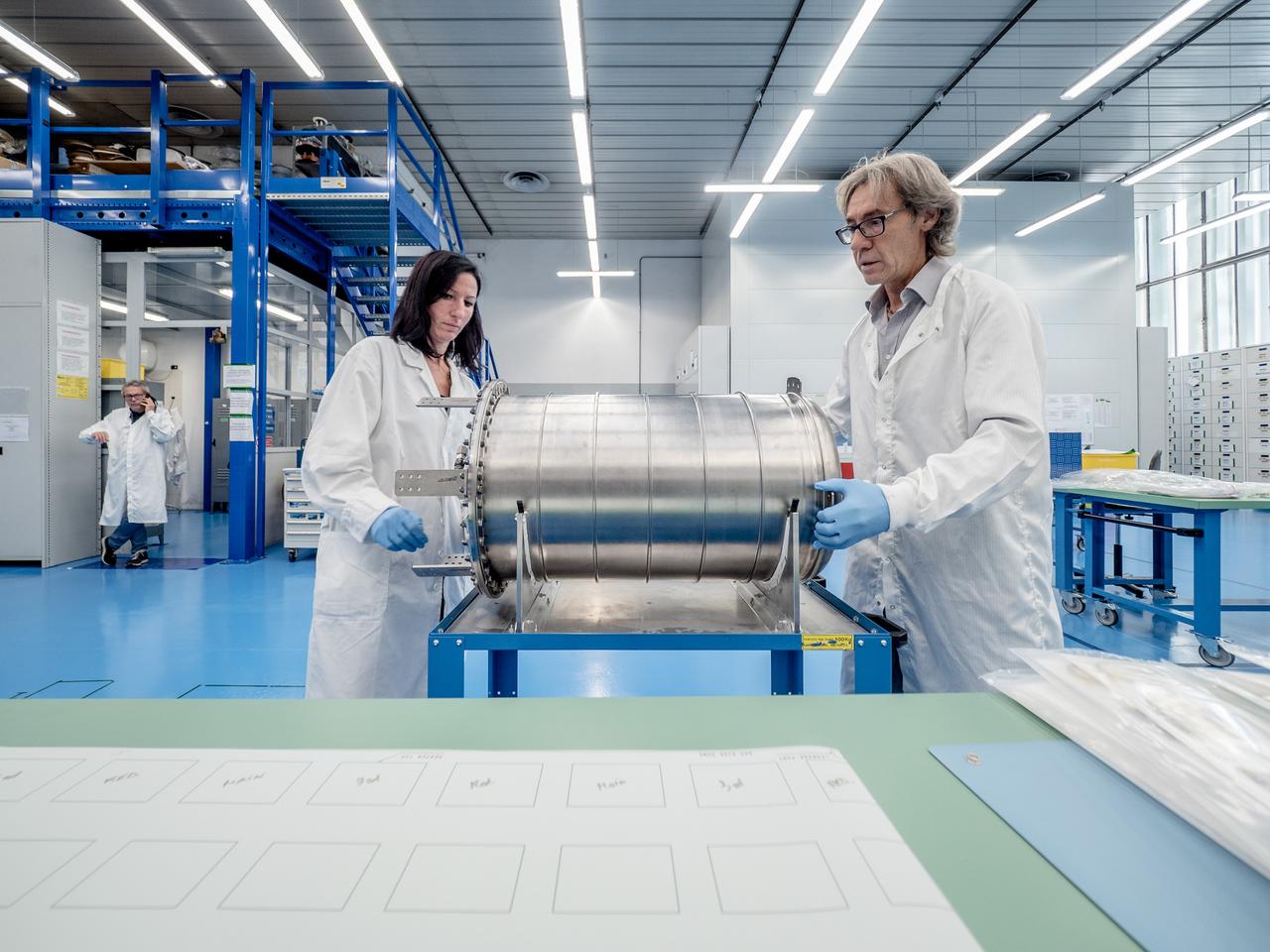

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
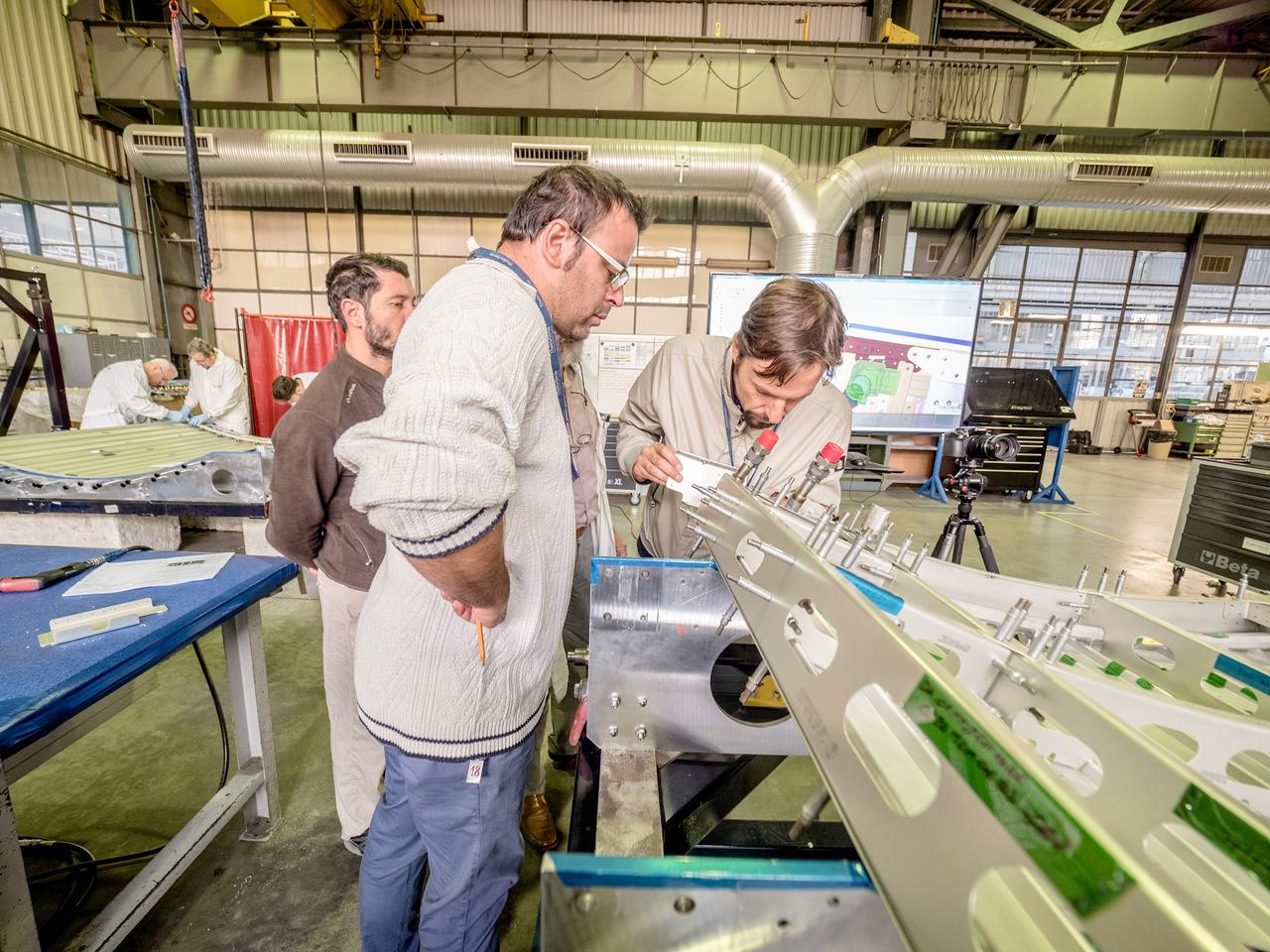

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
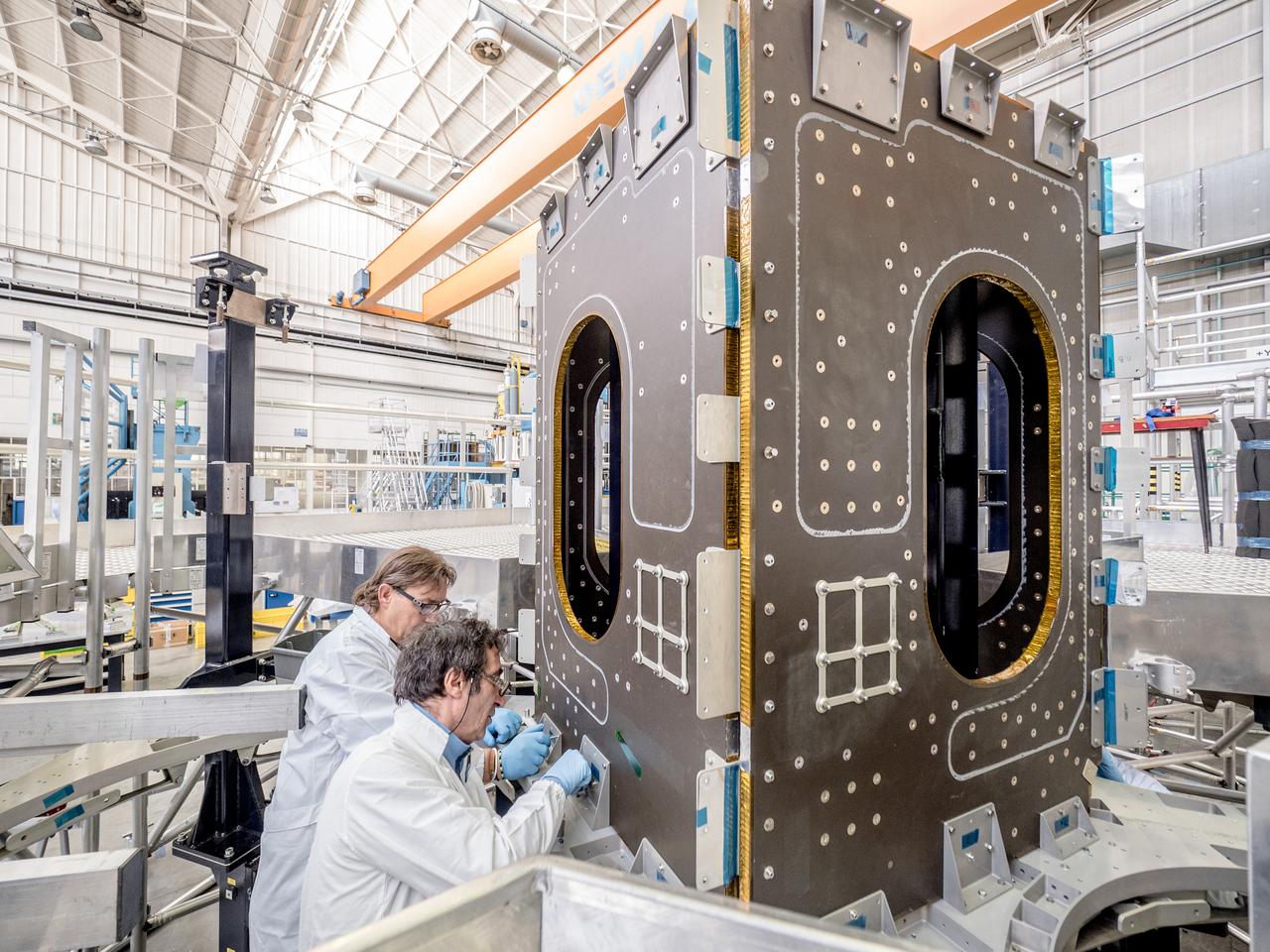

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
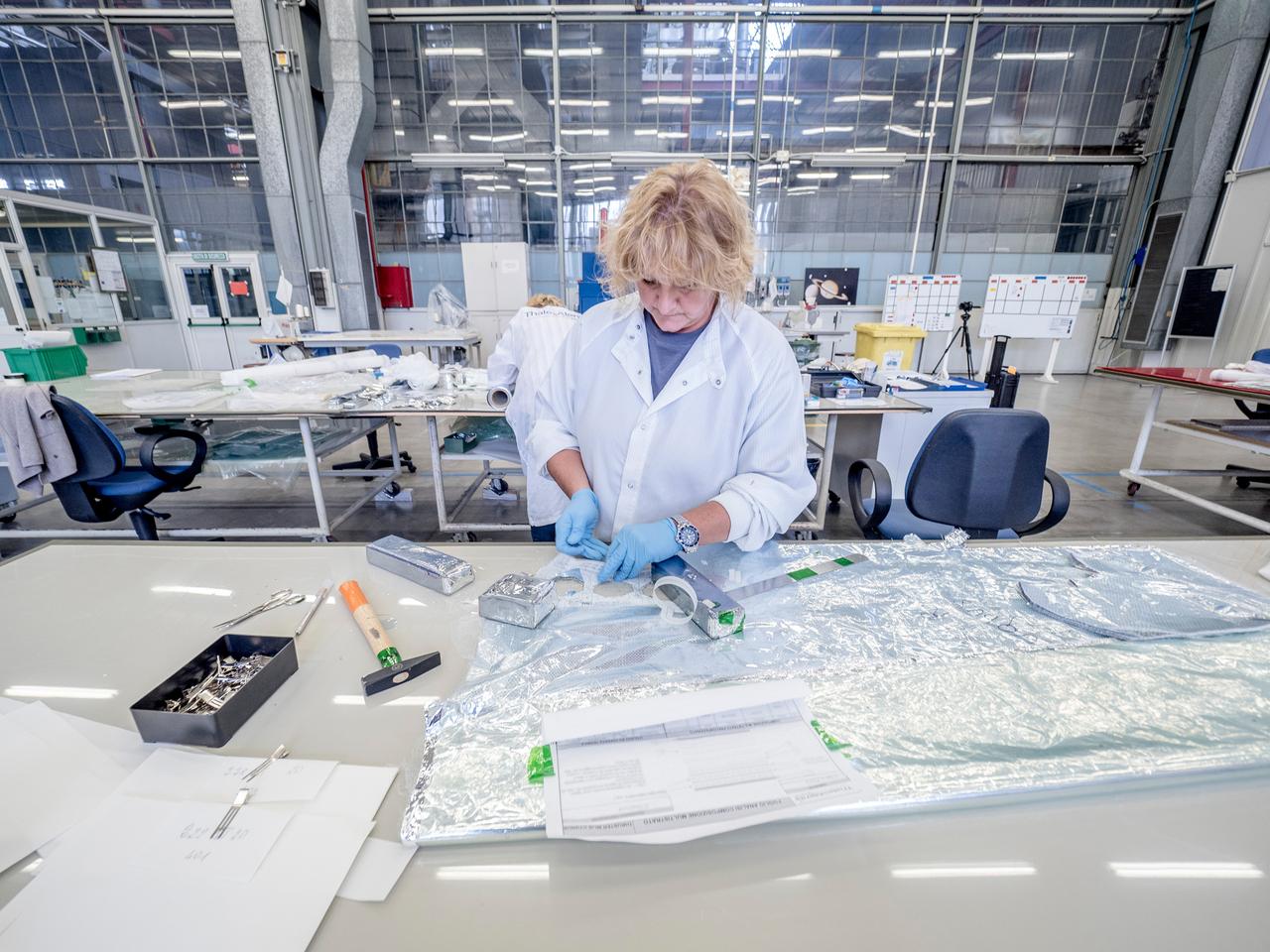

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
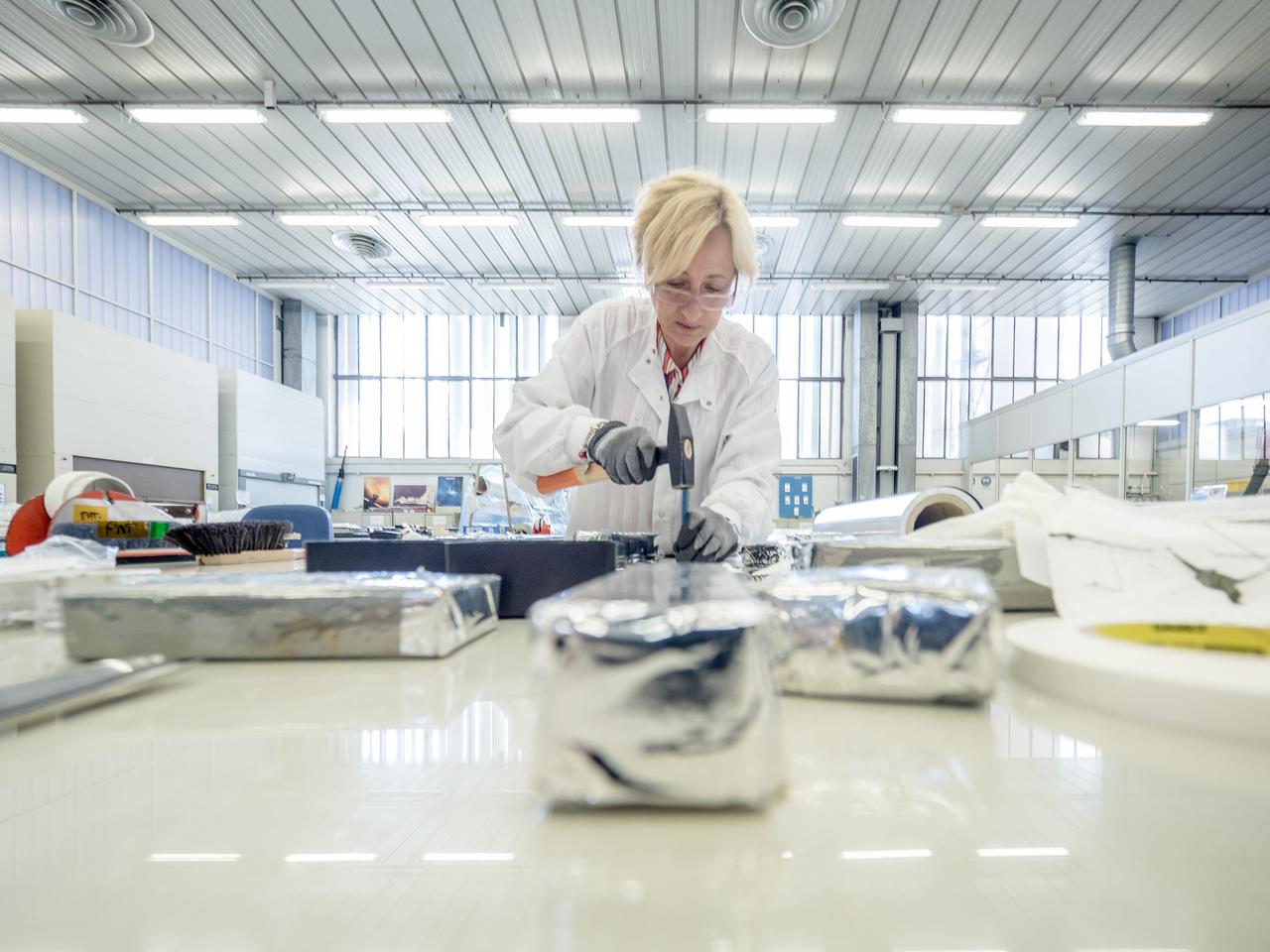

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
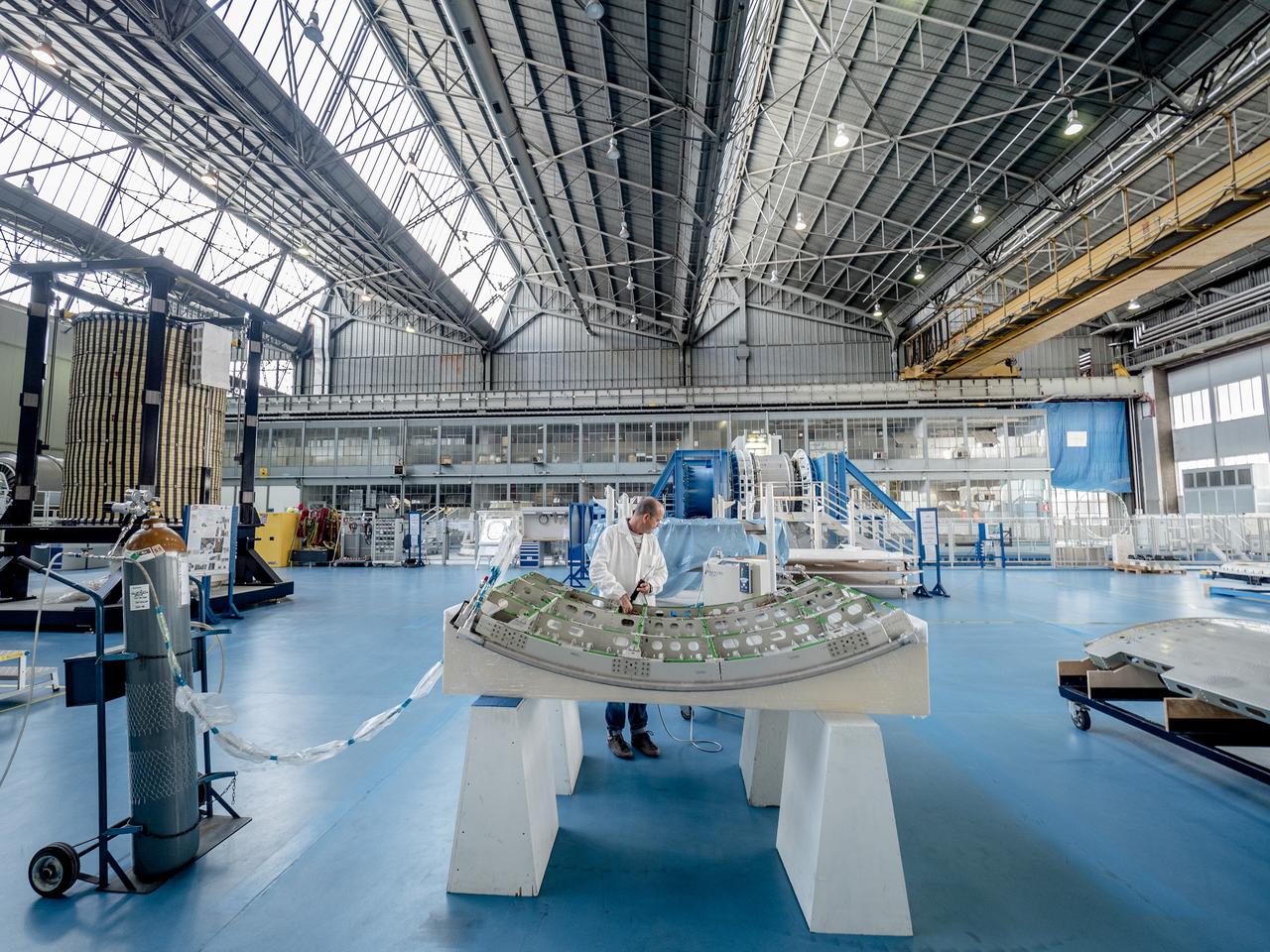

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
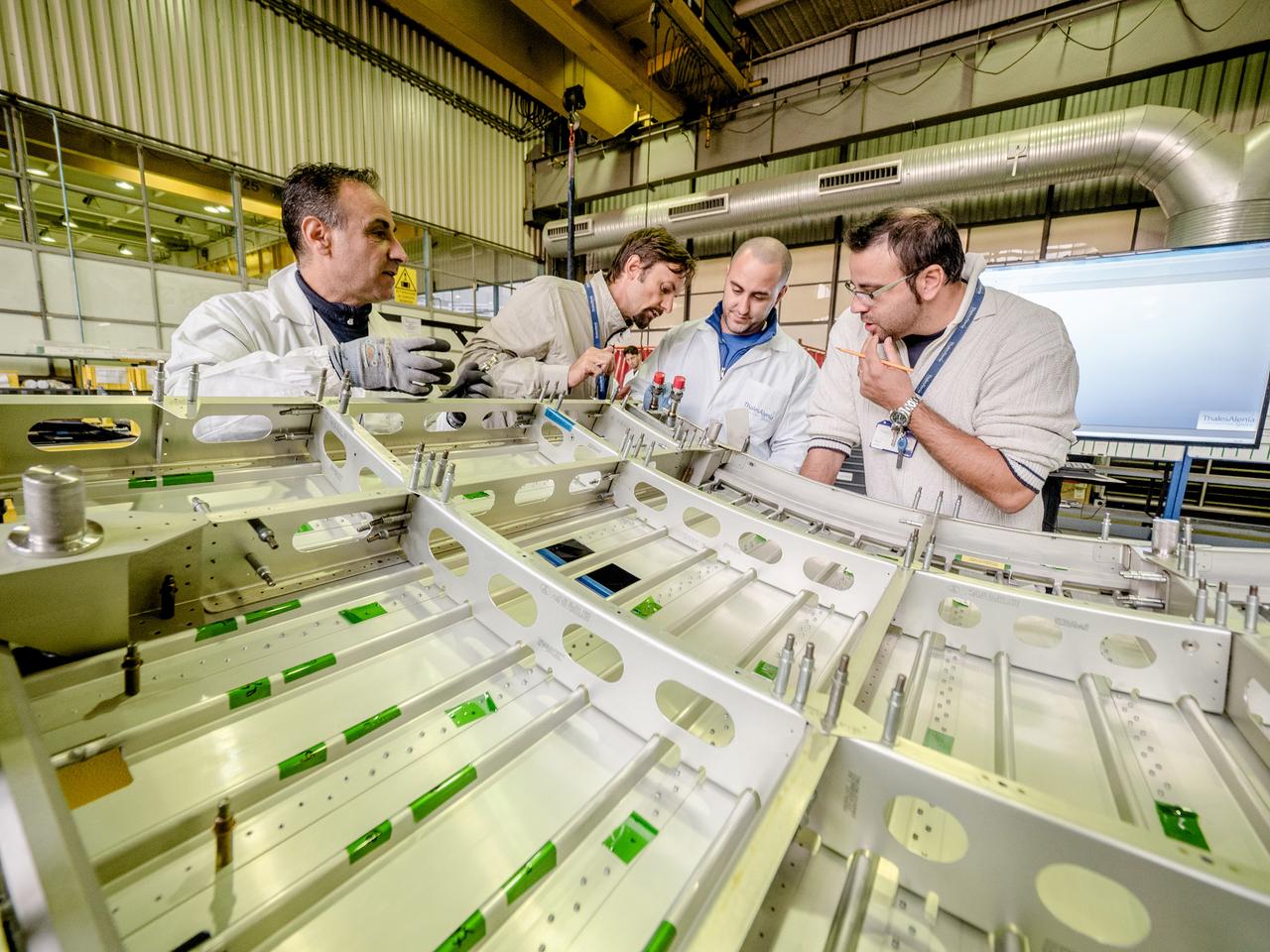

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
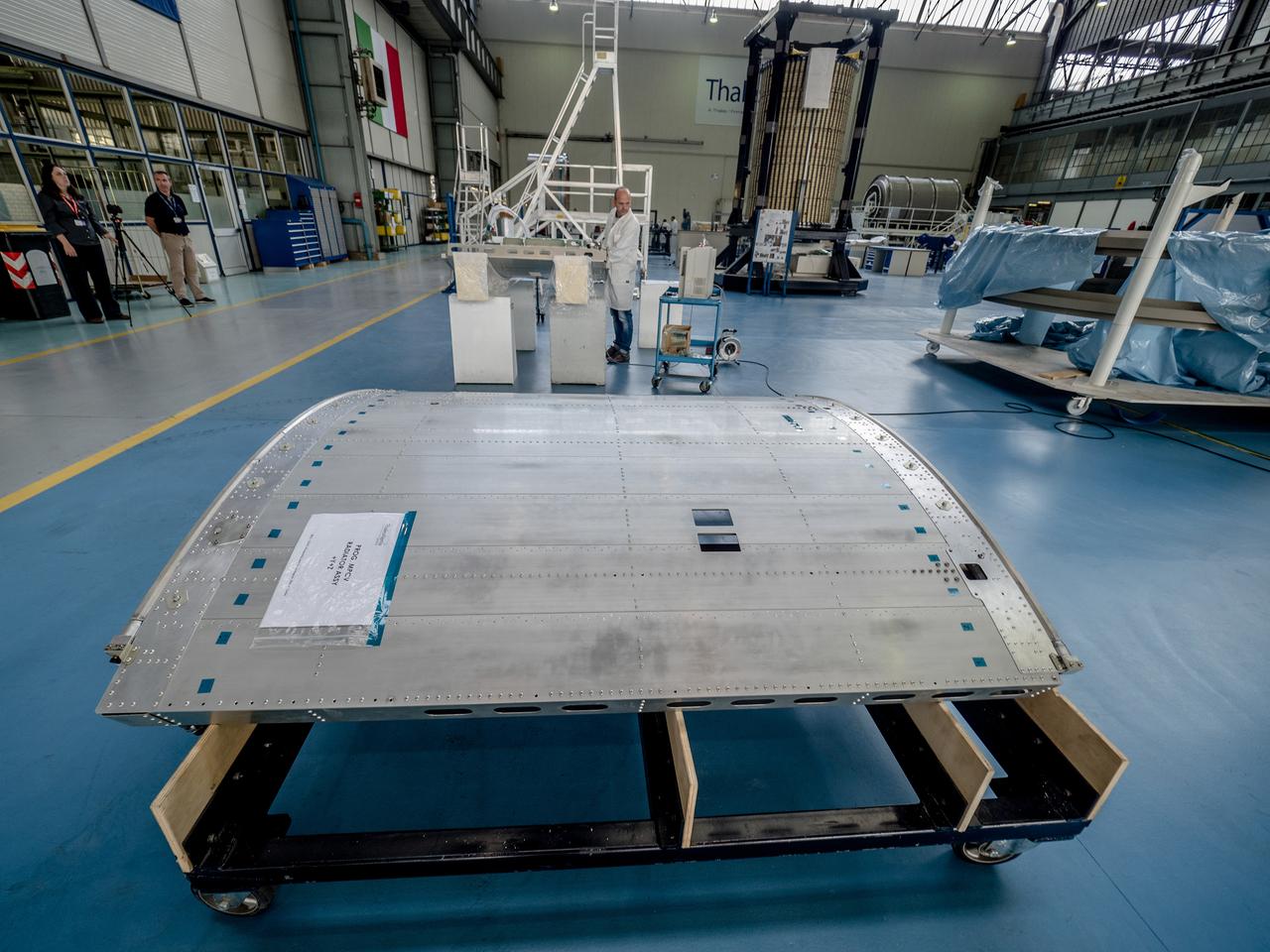

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
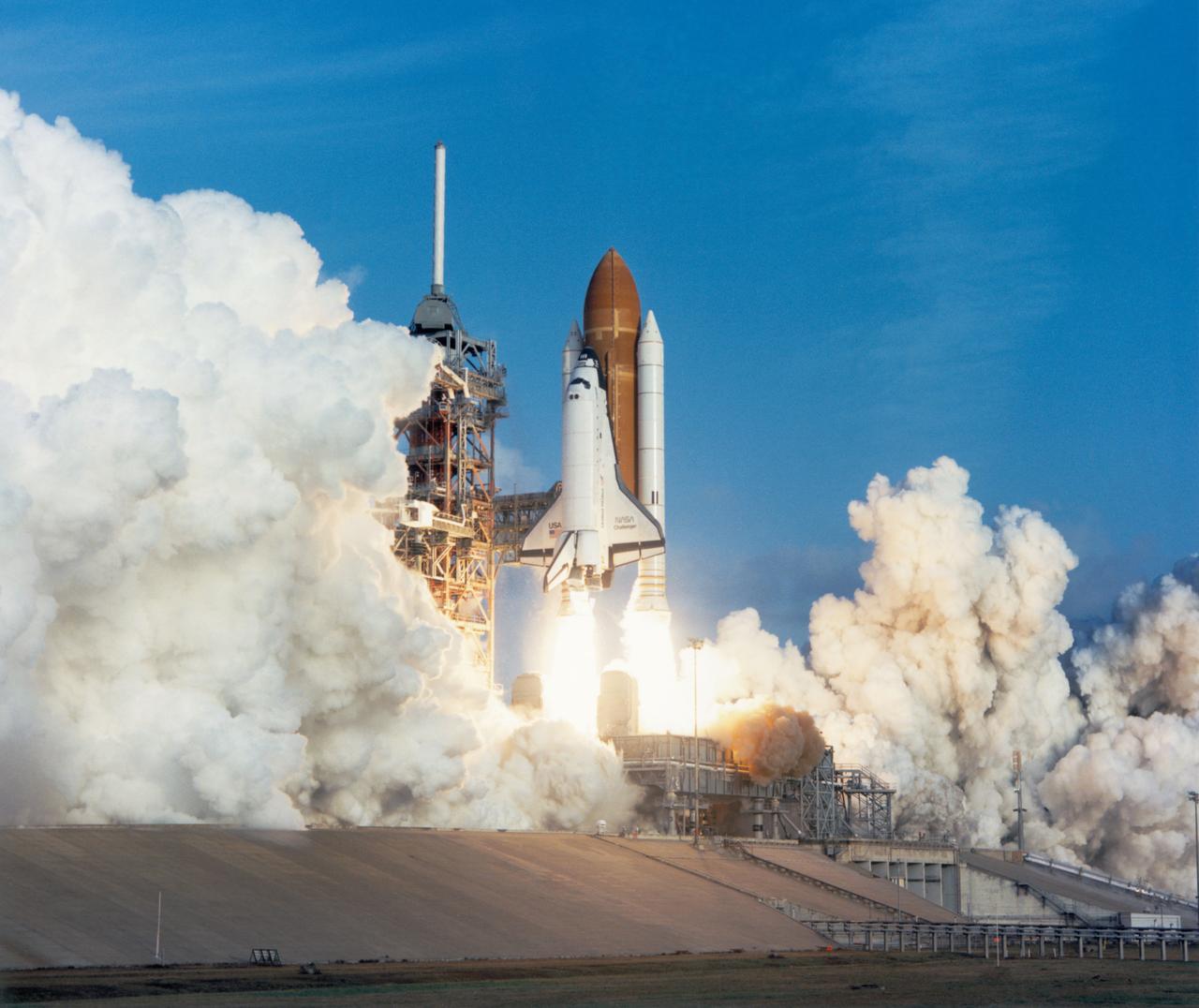

S84-26325 (3 Feb. 1984) --- Beginning a busy year, NASA's space shuttle Challenger, attached to two solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank which it will later jettison, blasts off from Pad A at Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 at 8:00 a.m. (EST), Feb. 3, 1984. Inside the spacecraft are astronauts Vance D. Brand, Robert L. Gibson, Bruce McCandless II, Ronald E. McNair and Robert L. Stewart. Brand is making his first trip in the Challenger but his second STS flight and third spaceflight overall. The rest of the crew members are experiencing space travel for the first time. Marking a space first, this flight will be landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA
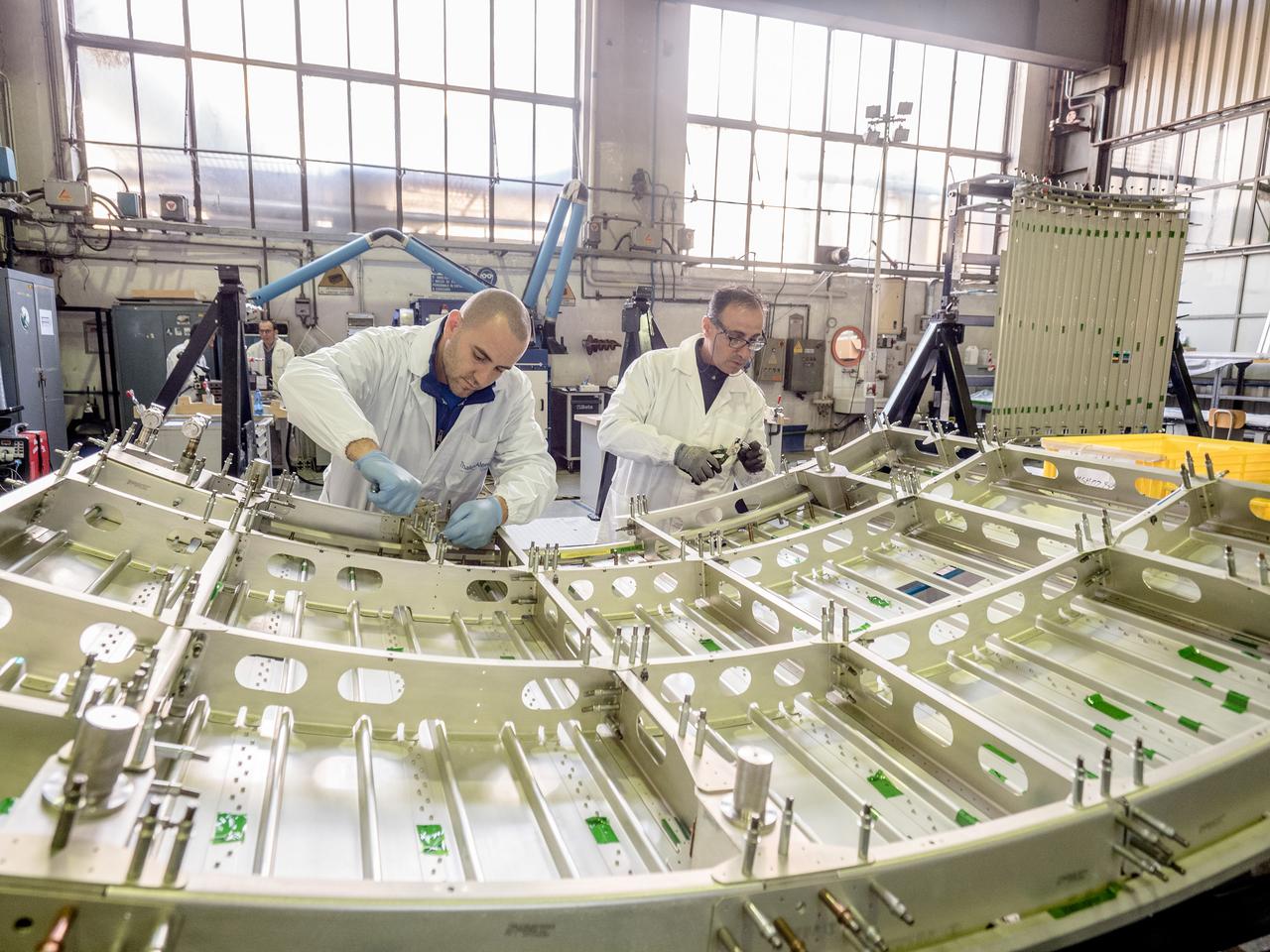

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
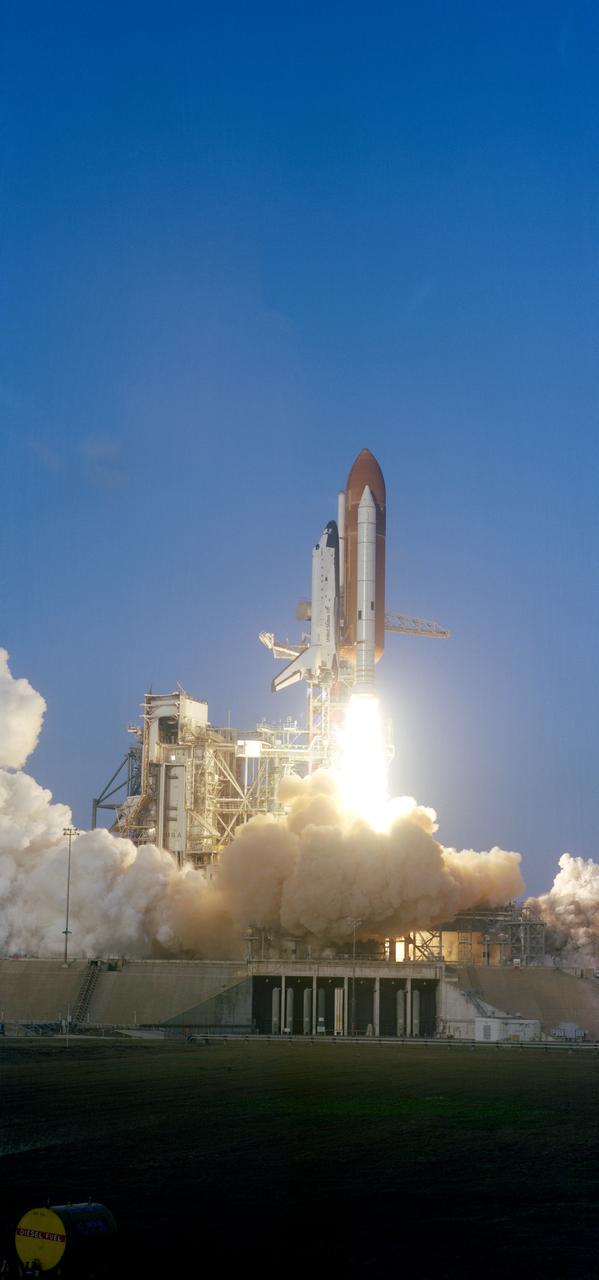

S84-26327 (3 Feb. 1984) --- Beginning a busy year, NASA's space shuttle Challenger, attached to two solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank which it will later jettison, blasts off from Pad A at Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 at 8:00 a.m. (EST), Feb. 3, 1984. Inside the STS 41-B spacecraft are astronauts Vance D. Brand, Robert L. Gibson, Bruce McCandless II, Ronald E. McNair and Robert L. Stewart. Brand is making his first trip in the Challenger but his second STS flight and third spaceflight overall. The rest of the crew members are experiencing space travel for the first time. Marking a space first, this flight will be landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA

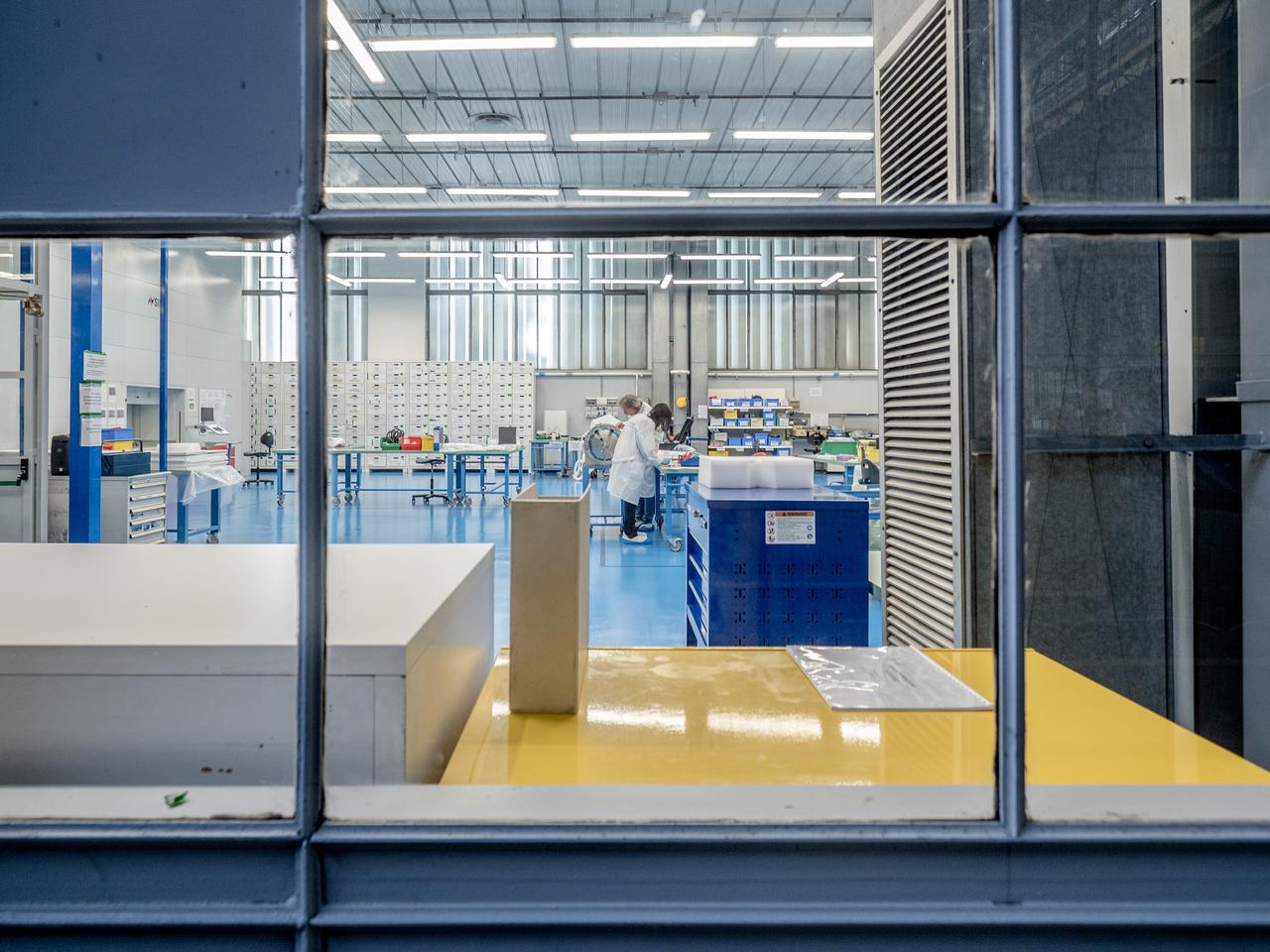
While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
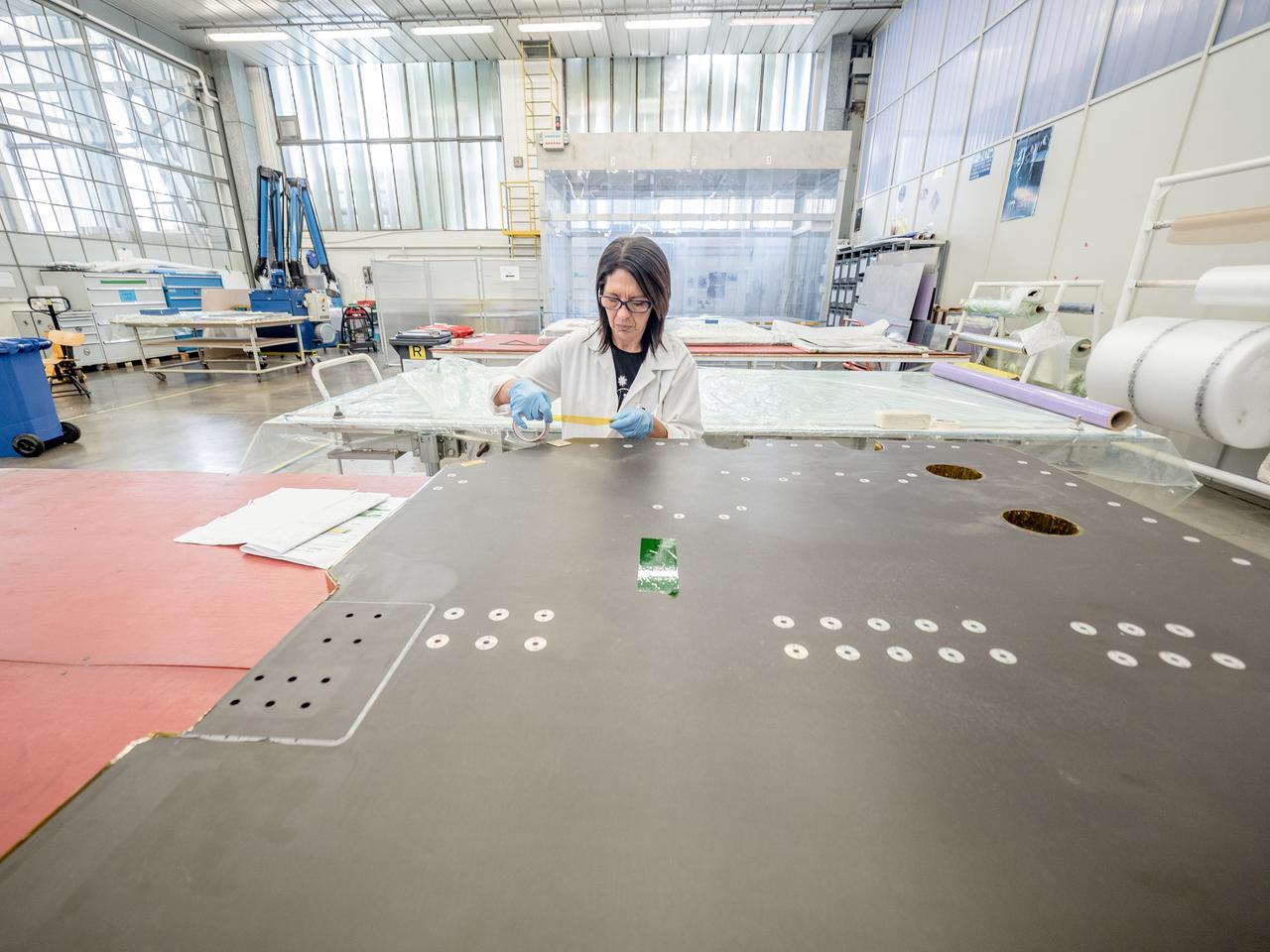

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
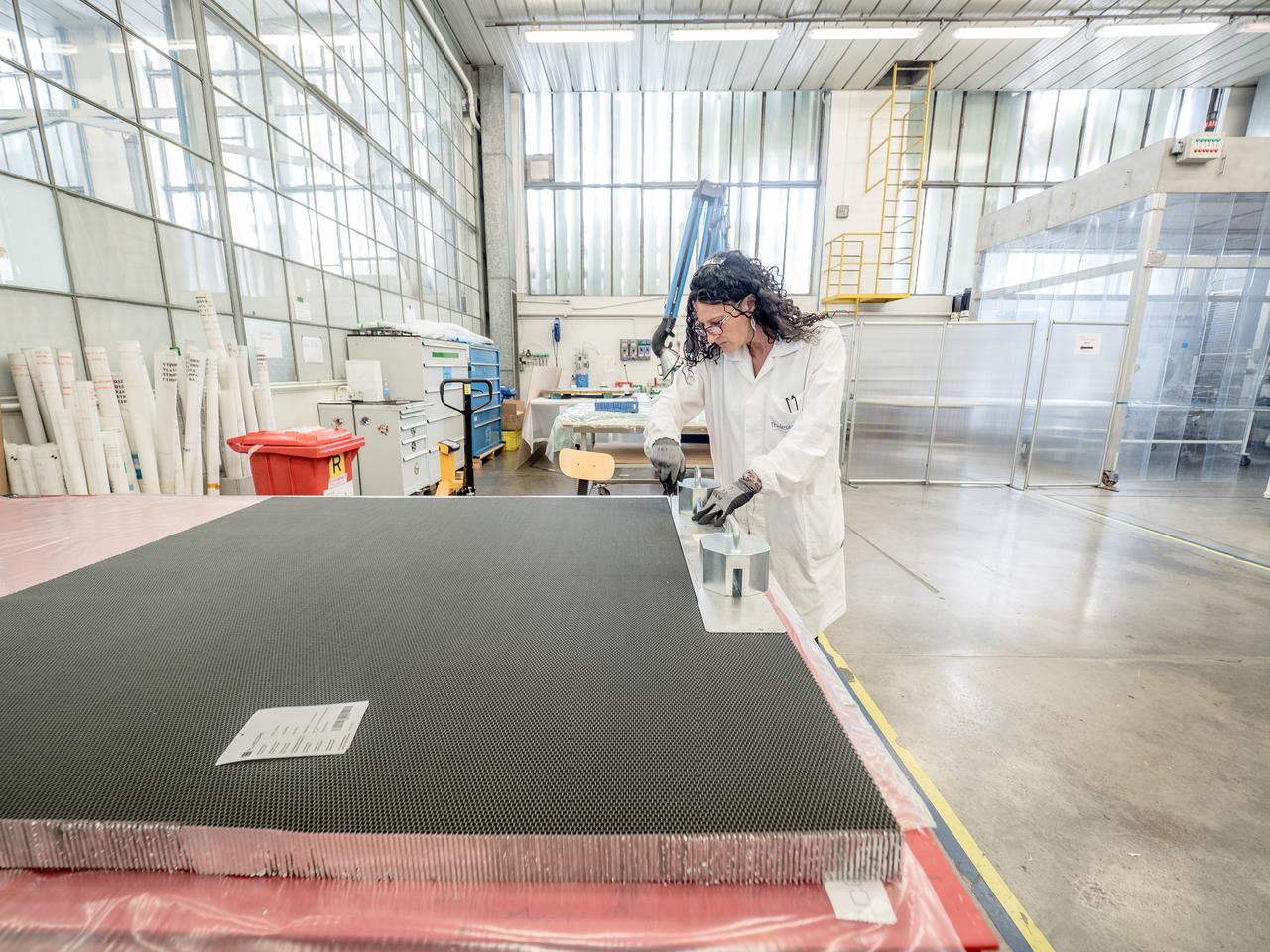

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
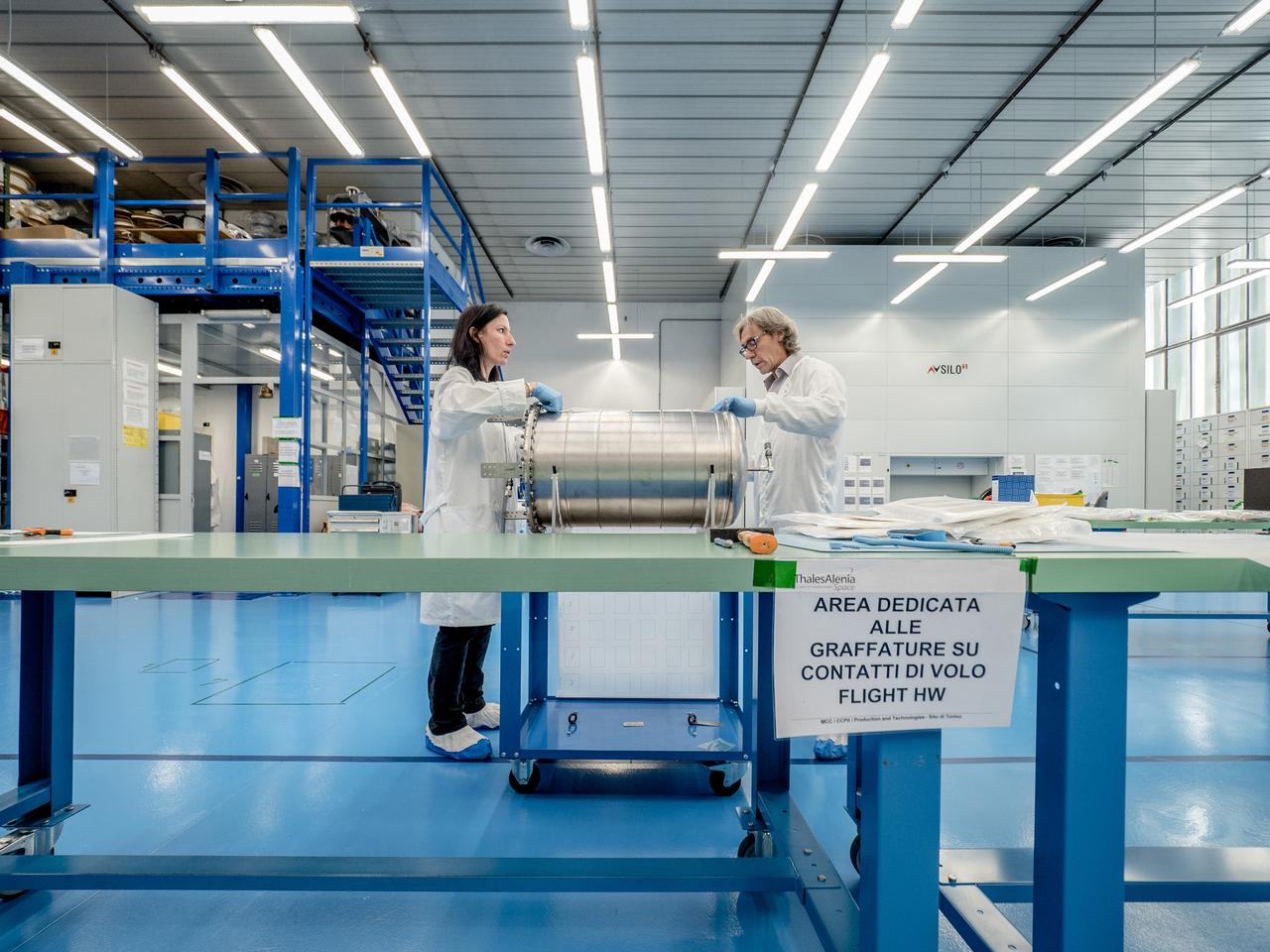

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
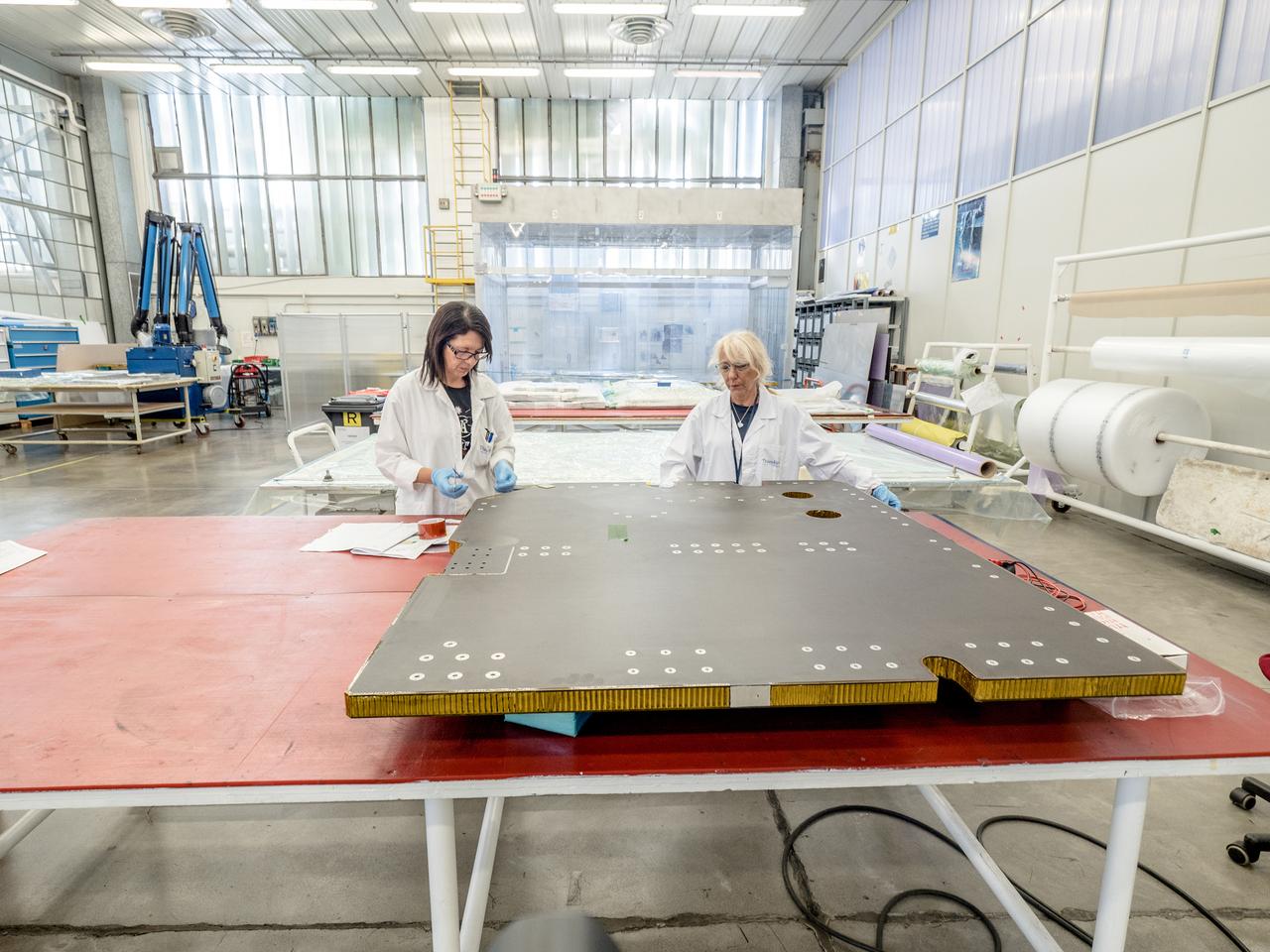

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
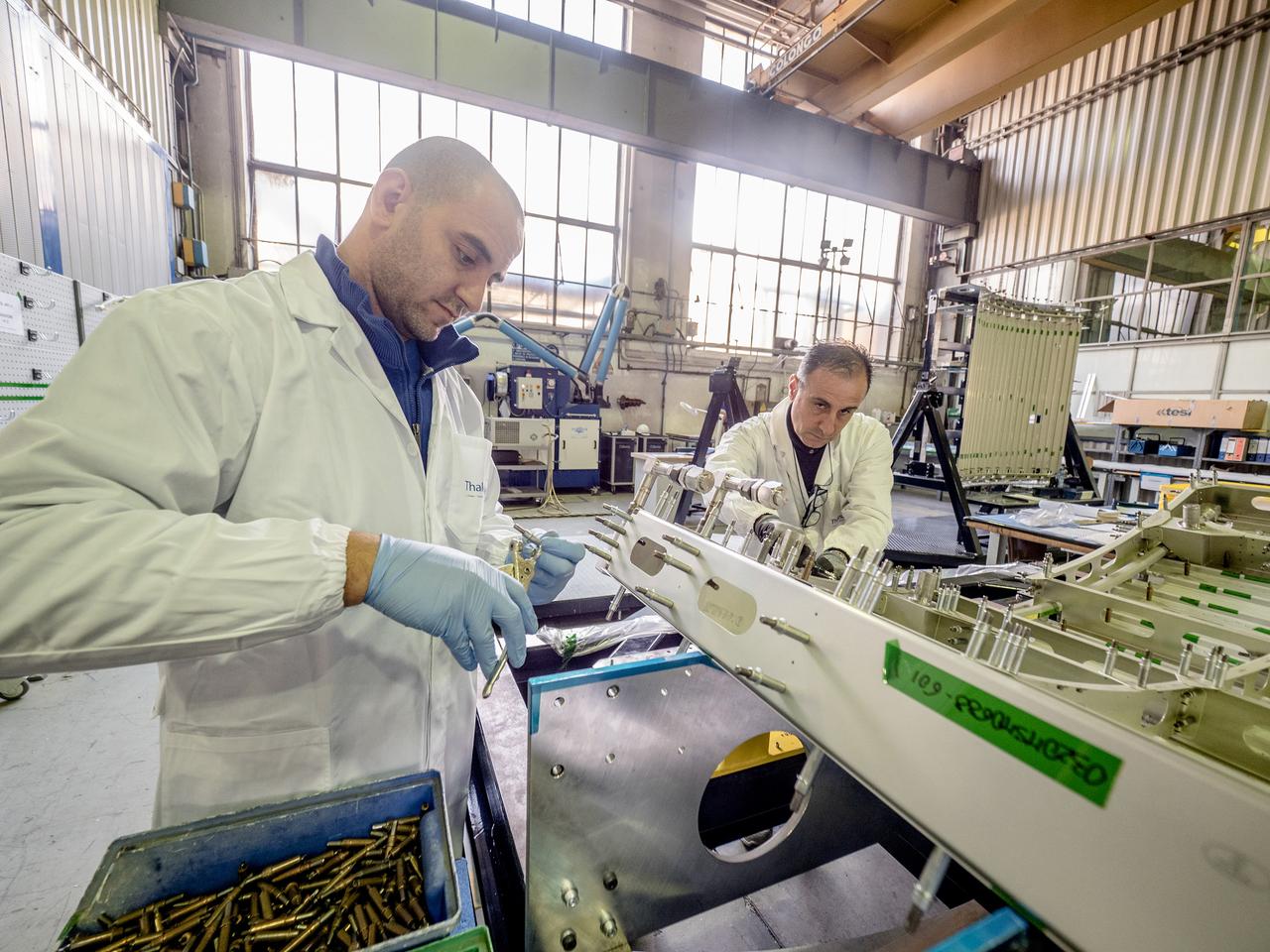

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
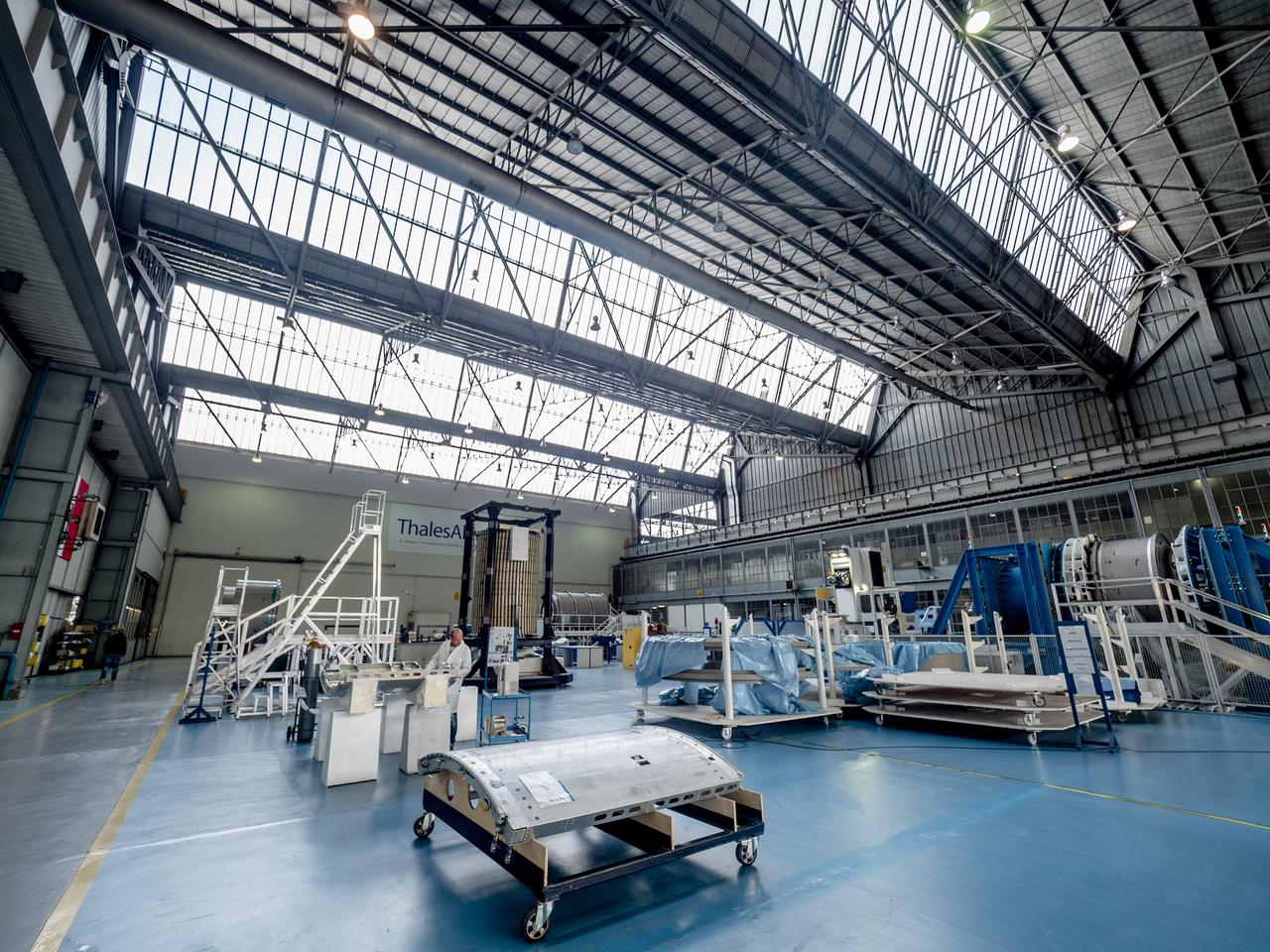

While engineers in Europe continue to outfit the Orion spacecraft’s service module for Artemis I in preparation for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida next year, work is already beginning on the service module that will power, propel, cool and provide air and water for the first crewed mission in the Orion spacecraft in the early 2020s. On Sept. 19, 2017, technicians at Thales Alenia in Turin, Italy, work on the primary structure of the European Service Module that will carry astronauts in Orion beyond the Moon during Artemis II. ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractors are providing Orion’s service module for its first two missions atop the Space Launch System rocket. NASA is leading the next steps in human space exploration and will send astronauts to the vicinity of the Moon to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to deep space destinations including Mars. NASA is working with domestic and international partners to solve the great challenges of deep space exploration.
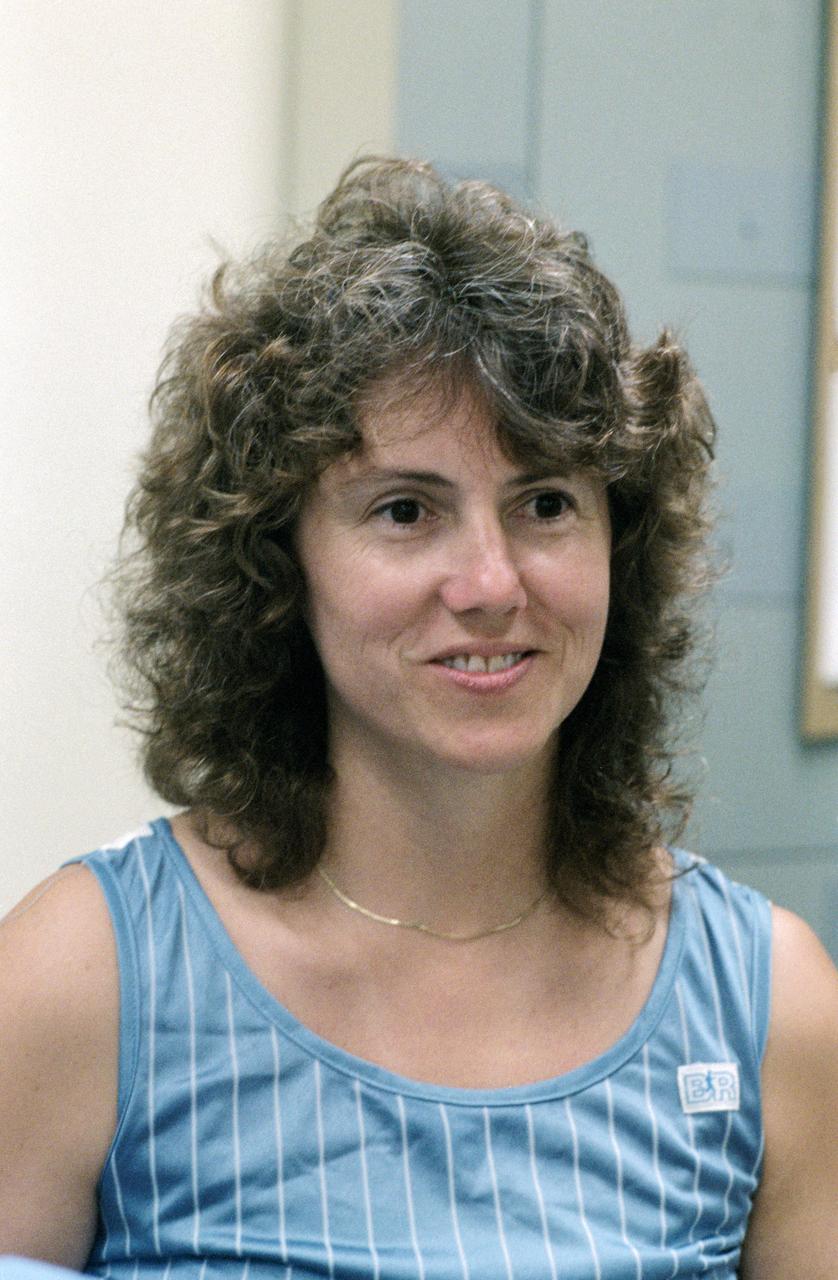
S85-37677 (8-12 July 1985) --- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, talks to nurse during physiological testing on first day at Johnson Space Center (JSC). Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
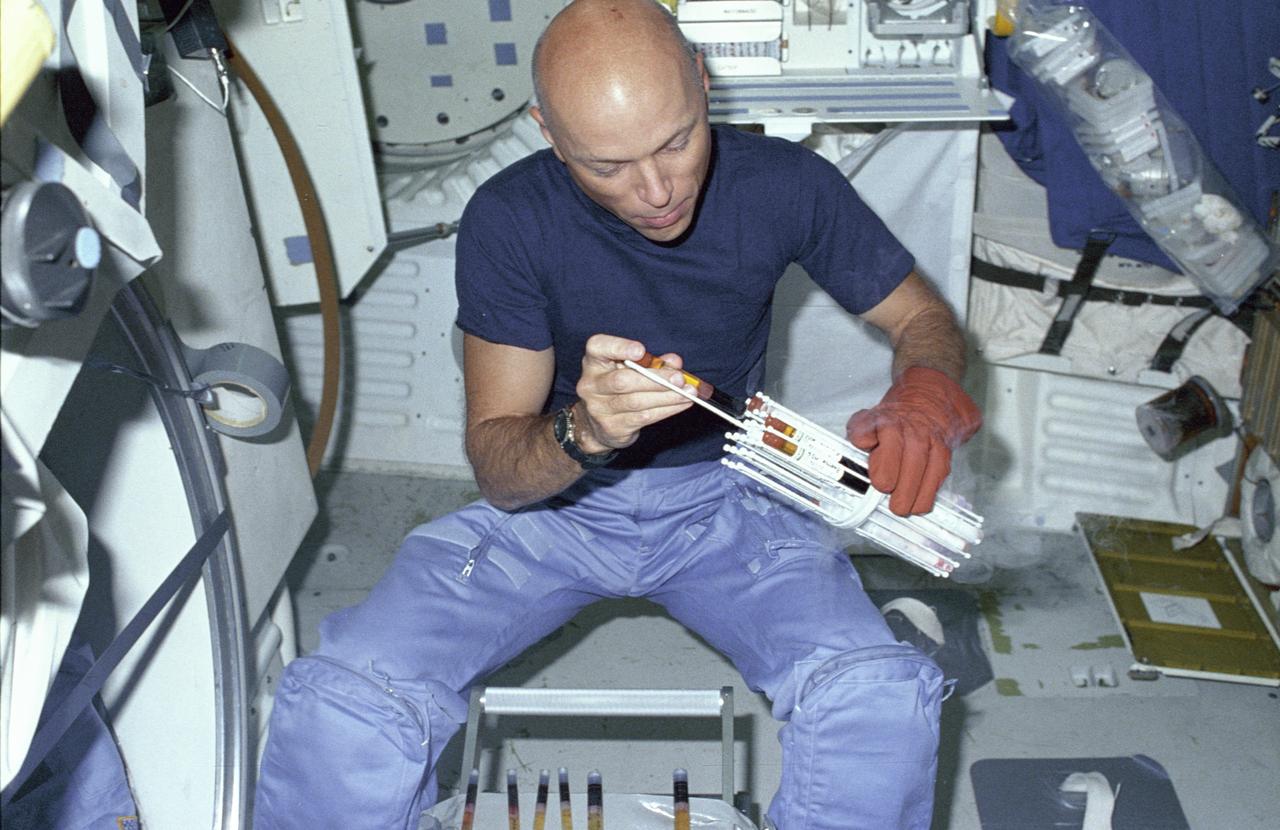

While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin D metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows astronaut Story Musgrave in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger, attending to the blood samples he collected from crew members for the experiment.
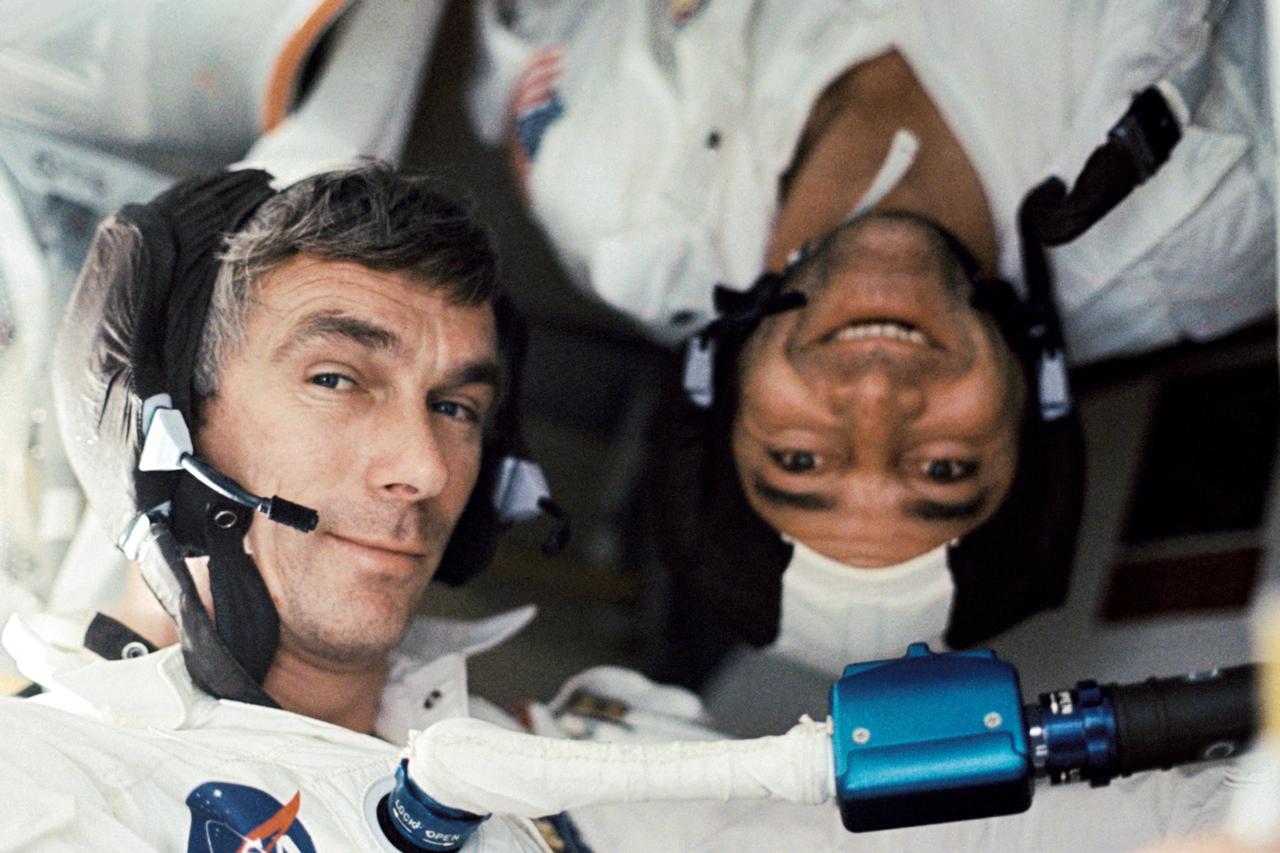

AS17-162-24053 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot, took this photograph of his two fellow crew men under zero-gravity conditions aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. That is astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, who is seemingly "right side up." Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, appears to be "upside down." While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
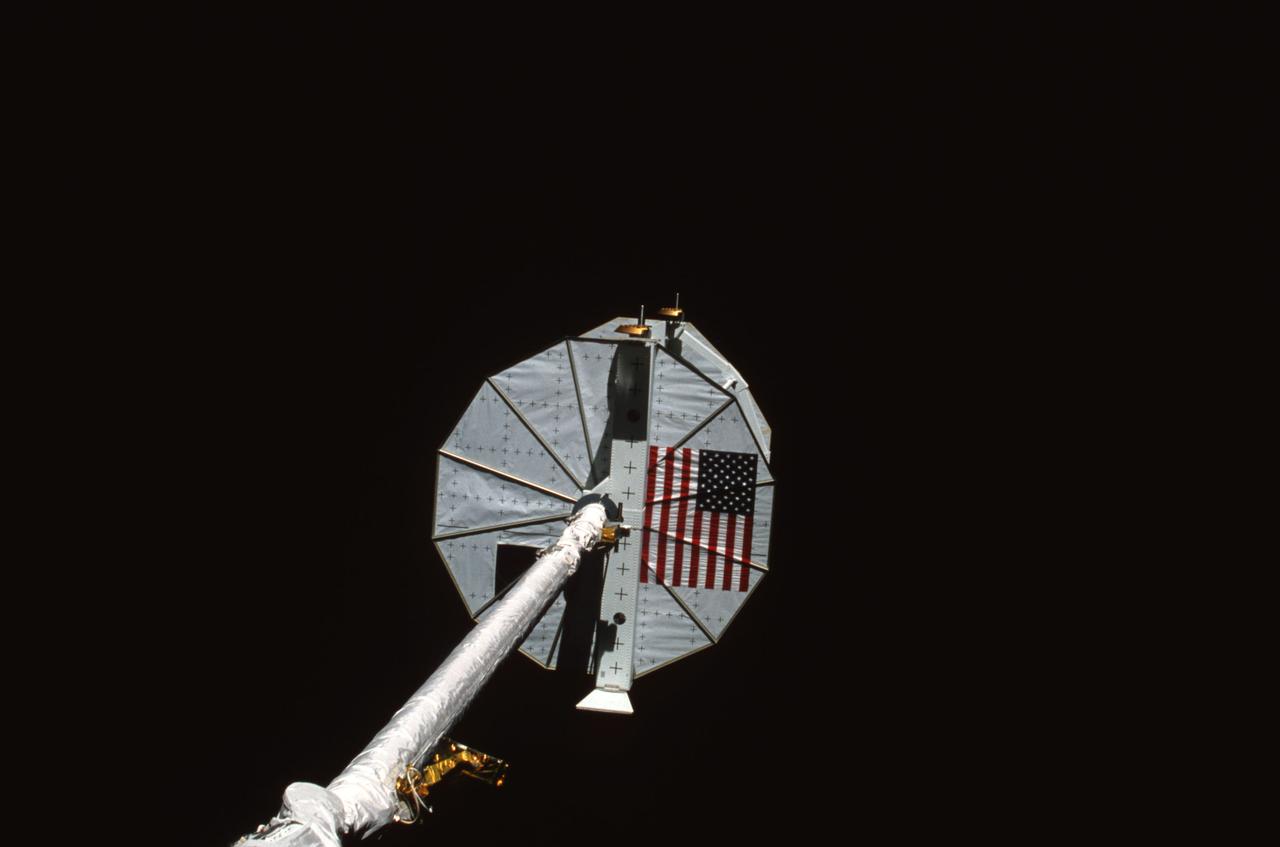
STS008-07-149 (2 Sept 1983) --- Many hours were spent, by its crew members, running tests with the Payload Flight Test Article (PFTA) and the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The bar-bell shaped test device and the arm stand out brilliantly against the darkness of space. The two TV cameras on the "wrist" and "elbow" of the Canadian-built robot arm provided some close-up scenes of the variegated testing with the PFTA. This frame was exposed with a 35mm camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger.
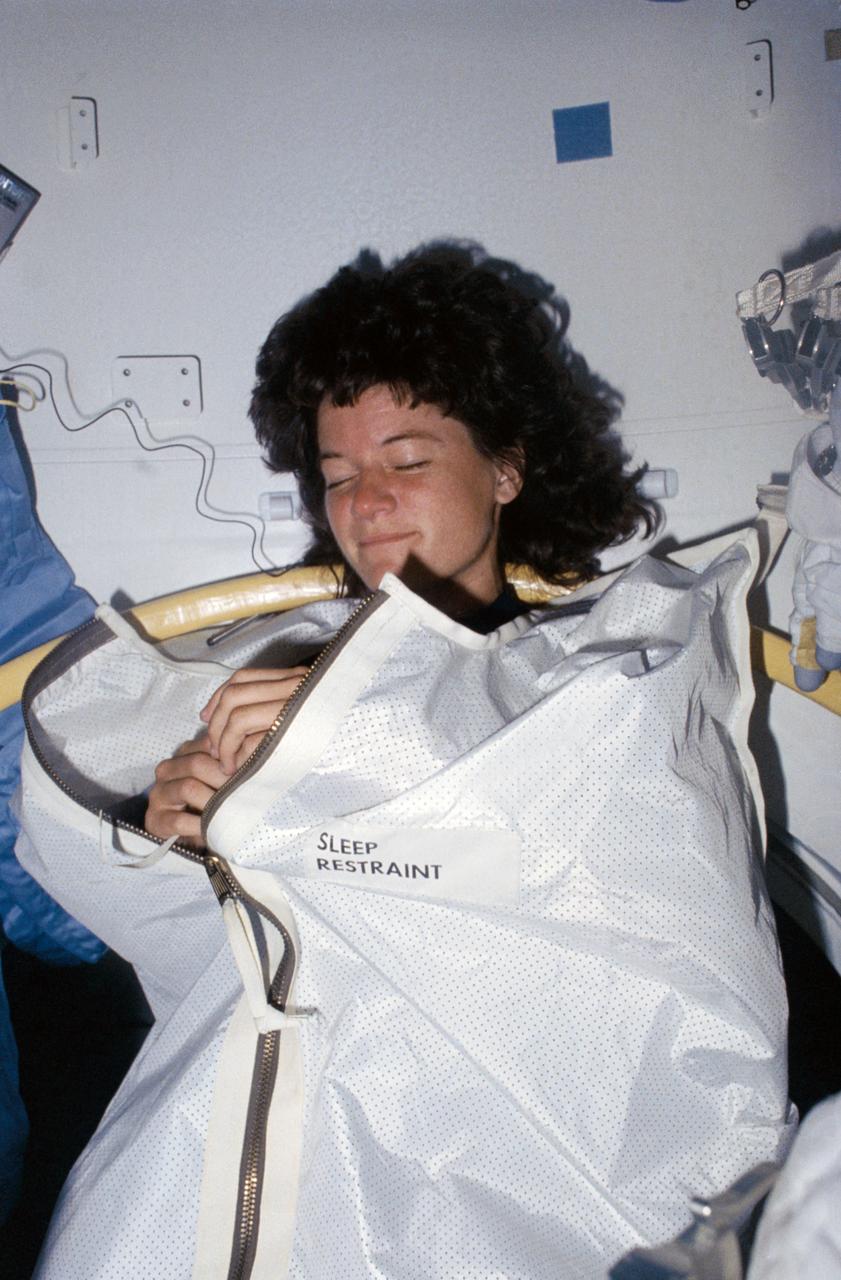

STS007-26-1438 (18-24 June 1983) --- Astronaut Sally K. Ride, mission specialist, was captured at her sleep station in the Space Shuttle Challenger's middeck by a fellow crew member using a 35mm camera. This method of sleep is just one used by the 20 astronauts who have now flown aboard NASA's first two Space Shuttle Orbiters. Some astronauts choose to sleep in various positions with either their feet or upper bodies or both anchored and others elect to use the sleep restraint device demonstrated here by Dr. Ride.

41C-3029 (6 April 1984) --- The space shuttle Challenger and its five-member astronaut crew leave the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center to begin a six-day stay in space. Astronaut John W. Young, a veteran of two shuttle missions and six spaceflights overall, recorded the image with a handheld 70mm camera from the shuttle training aircraft which he was using to monitor environmental conditions around Florida. This is the eighth mission on which Young photographed one of NASA's orbiter vehicles beginning its orbital stay. Photo credit: NASA
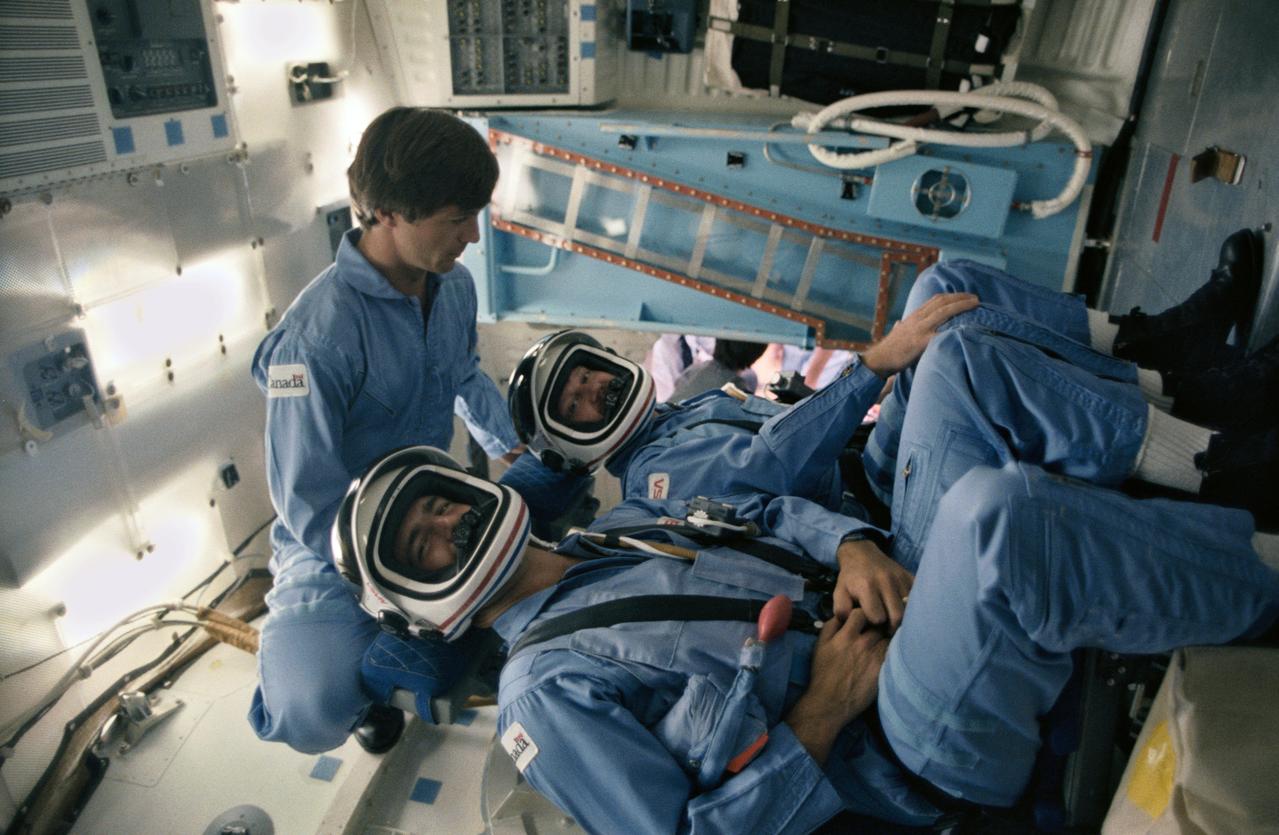

41D-3138 (4 Sept 1984)--- Canada's backup payload specialist assists the two 41-G prime payload specialists during a training session in the Johnson Space Center's Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory. Robert Thirsk (without helmet) represents the National Research Council (NRC) and is backup to Marc Garneau (nearest camera), also of the NRC. Paul D. Scully-Power, seated in the other middeck seat for the launch phase, is a civilian oceanographer with the U.S. Navy. The 41-G flight aboard the Challenger is NASA's first to utilize a crew of more than six persons. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
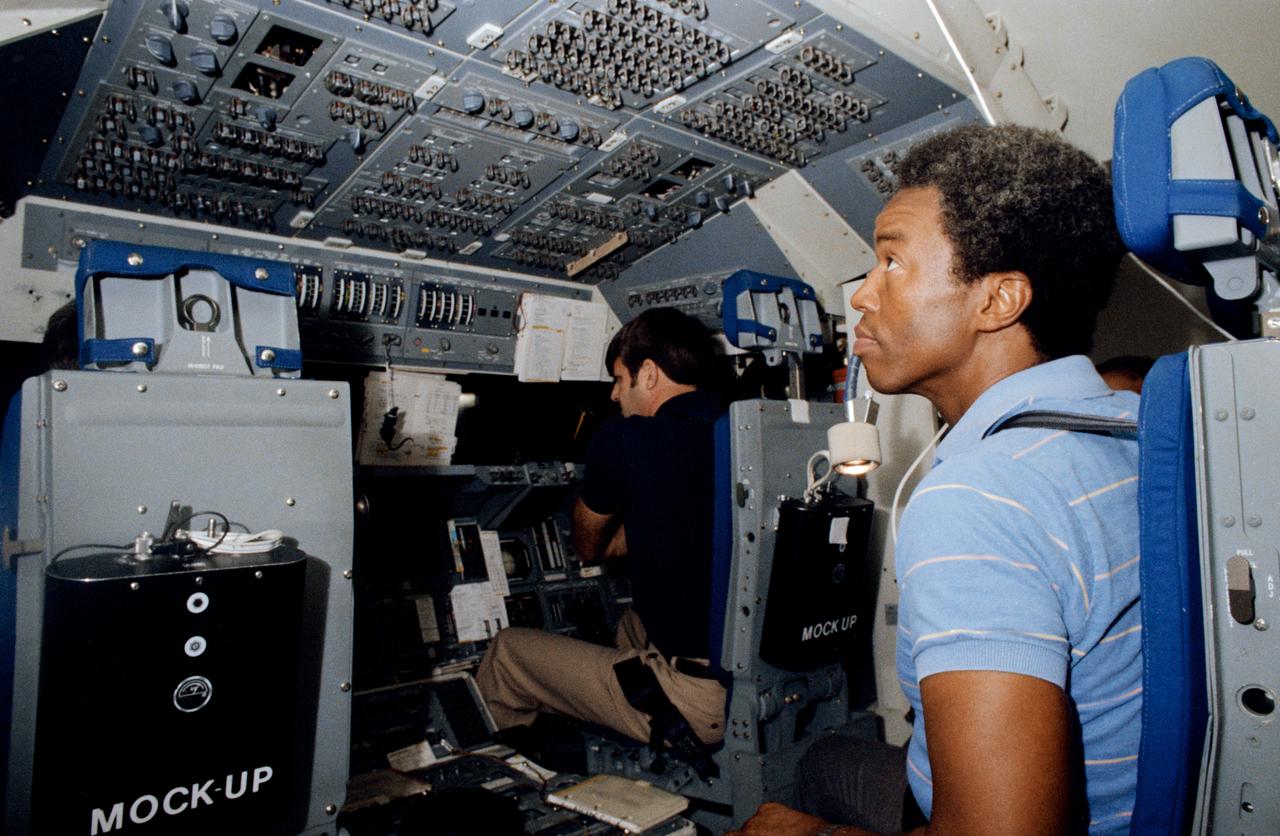

S83-33032 (23 May 1983) --- Astronauts Guion S. Bluford, right, and Daniel C. Brandenstein man their respective Challenger entry and ascent stations in the Shuttle Mission Simulator (SMS) at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) during a training session for the STS-8 mission. Brandenstein is in the pilot's station, while Bluford, a mission specialist, occupies one of the two aft flight deck seats. Both are wearing civilian clothes for this training exercise. This motion based simulator represents the scene of a great deal of training and simulation activity, leading up to crew preparedness for Space Transportation System (STS) mission. Photo credt: NASA/Otis Imboden, National Geographic
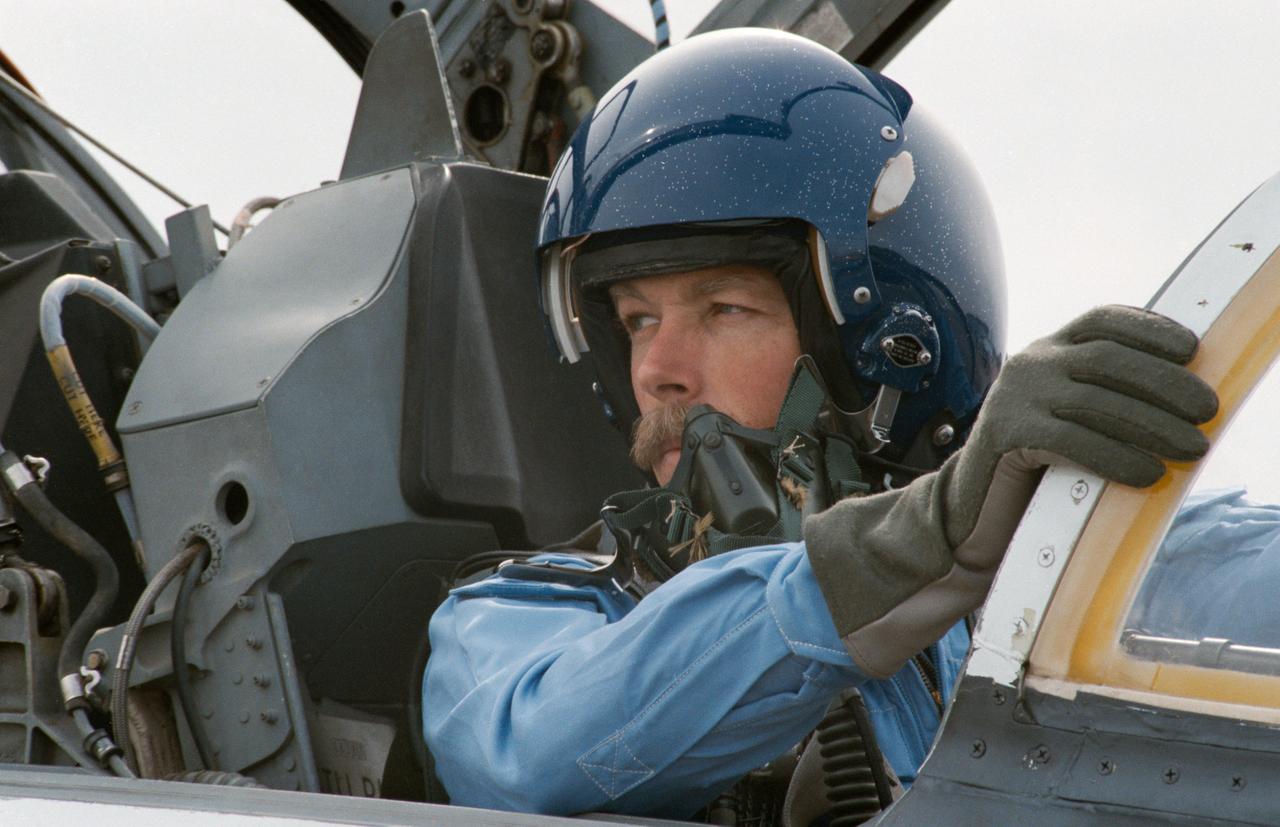

S84-26243 (31 Jan 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Gibson, one of five 41-B crewmembers, prepares to leave Houston?s Ellington Base in a T-38 jet aircraft en route to Florida and the Kennedy Space Center, site of February 3?s launch of the Challenger. Gibson, along with two other members of this crew, began training at JSC in July in 1978. He will be joined by Astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; and Bruce McCandless II, Ronald E. McNair and Robert L. Stewart, all mission specialists. Brand and McCandless came aboard as NASA astronauts in April 1966.
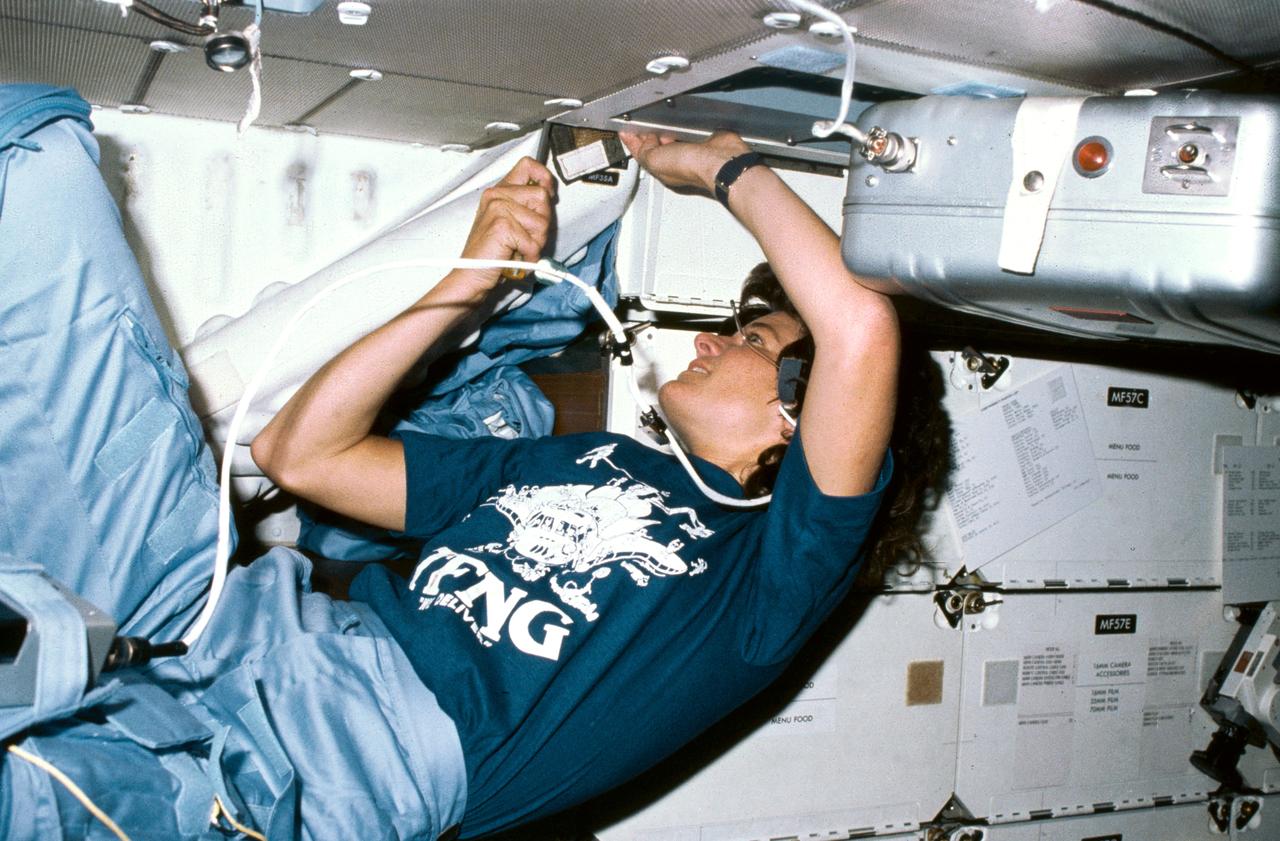

S83-35768 (18-24 June 1983) --- Astronaut Sally K. Ride, mission specialist for STS-7, uses a screw driver in order to clean out an air filtering system in the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. Dr. Ride's constant wear garment bears some extras -- a cartoon of 35 busy astronauts around a Space Shuttle and the acronym TFNG, below which is written, "We deliver!" TFNG stands for thirty-five new guys, referring to the 1978 class of astronaut candidates (ASCAN) from which Dr. Ride and three of her crew members hail. The tiny two-word declarative in white lettering refers to the successful deployment of two communications satellites. This photograph was made with a 35mm camera.
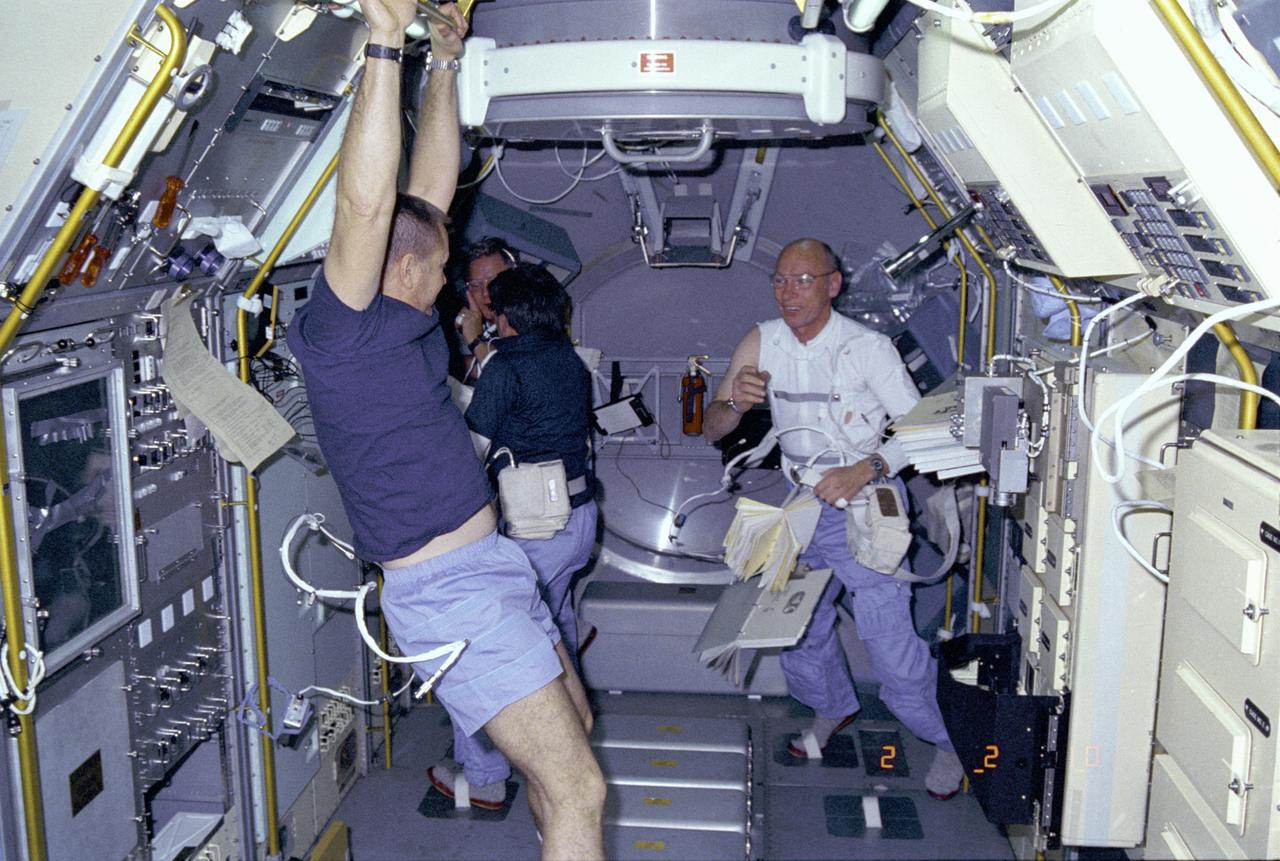

Activities inside the laboratory module during the Spacelab-3 mission are shown in this photograph. Left to right are astronauts Robert Overmyer, Commander of the mission; Don Lind, Mission Specialist; Lodewijk van den Berg, Payload Specialist; and William Thornton, Mission Specialist. The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew did research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger on April 29, 1985. The Marshall Space Flight Center had managing responsibilities of the mission.
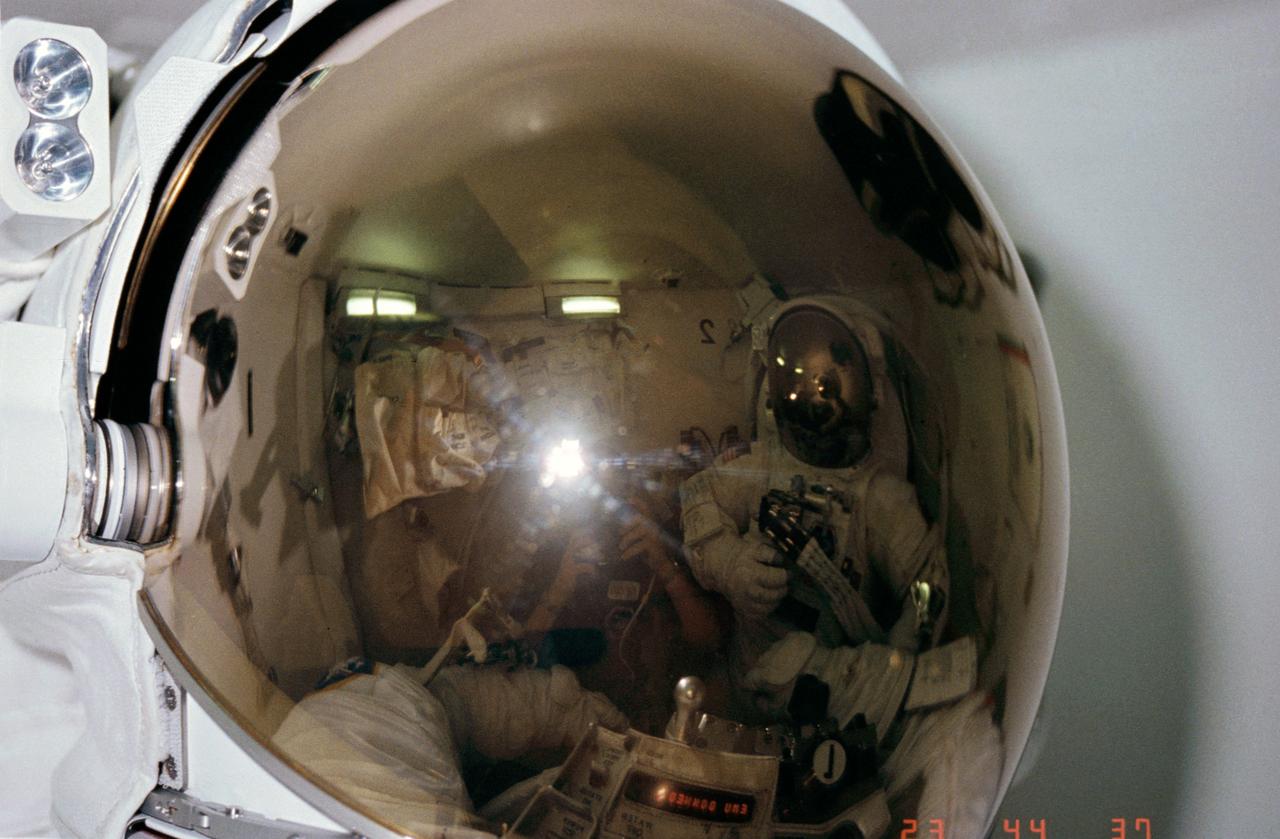

STS006-06-465 (7 April 1983) --- Three-fourths of the STS-6 astronaut crew appears in this unusual 35mm frame exposed in the airlock of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. Astronaut F. Story Musgrave’s helmet visor encompasses all the action in the frame. Dr. Musgrave and astronaut Donald H. Peterson (reflected on right side of the visor) were fully suited in their Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits and were participating in EVA preparation exercises. Astronaut Karol J. Bobko, STS-6 pilot, wearing conventional onboard shuttle clothing, photographed the two during their procedures and appears at center of frame. The reversed number (1 and 2 in the mirrored image represent the EVA designations for the two mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
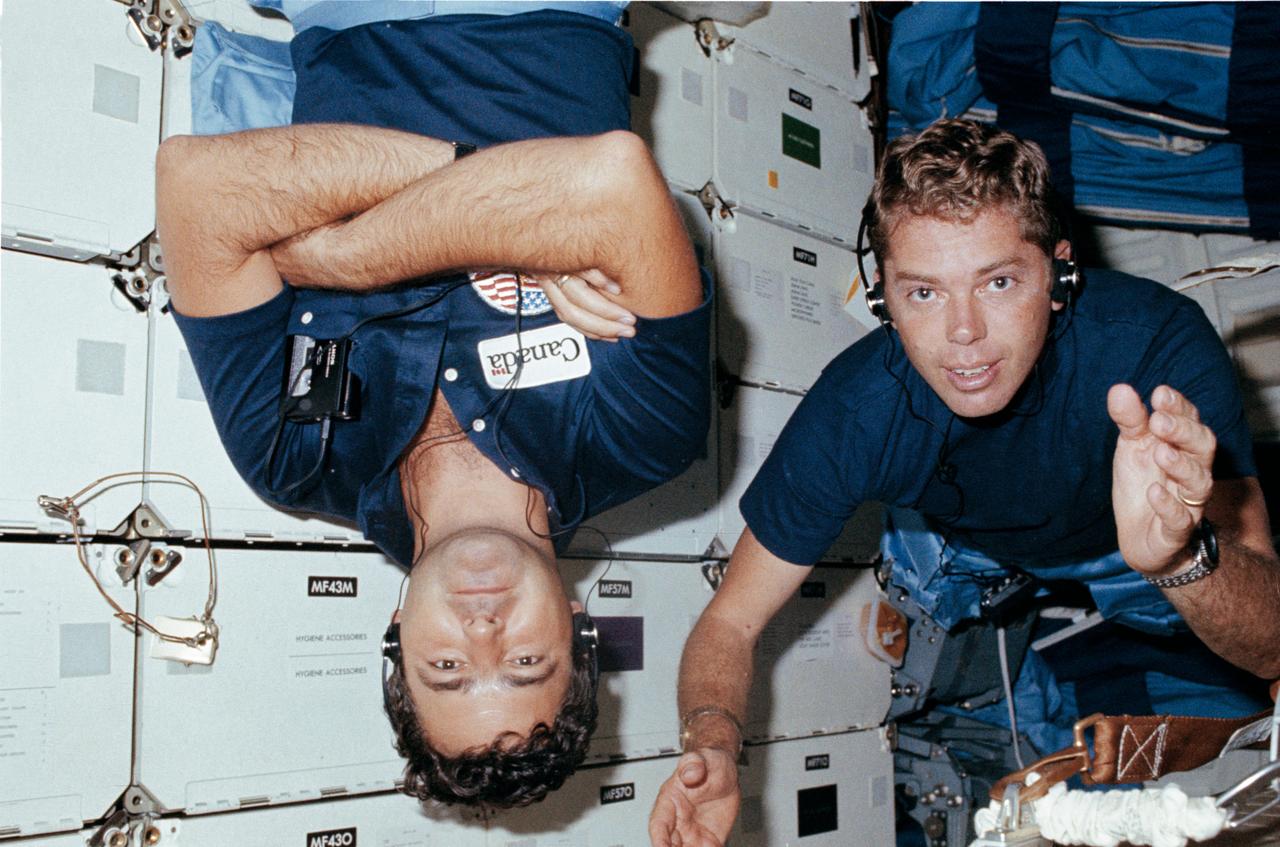

41G-101-039 (5-13 Oct 1984) --- Two members of a record seven-person crew are pictured during Intravehicular Activity (IVA) aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. Hold picture with open hand at right center edge. Astronaut David C. Leestma, mission specialist, is at right observing a test by payload specialist Marc Garneau, representing the National Research Council (NRC) of Canada. Garneau spent much of his on-duty time conducting a series of experiments for the NRC. The crew consisted of astronauts Robert L. Crippen, commander; Jon A. McBride, pilot; mission specialist's Kathryn D. Sullivan, Sally K. Ride, and David D. Leestma; Canadian astronaut Marc Garneau, and Paul D. Scully-Power, payload specialist's. EDITOR'S NOTE: The STS-41G mission had the first American female EVA (Sullivan); first seven-person crew; first orbital fuel transfer; and the first Canadian (Garneau).
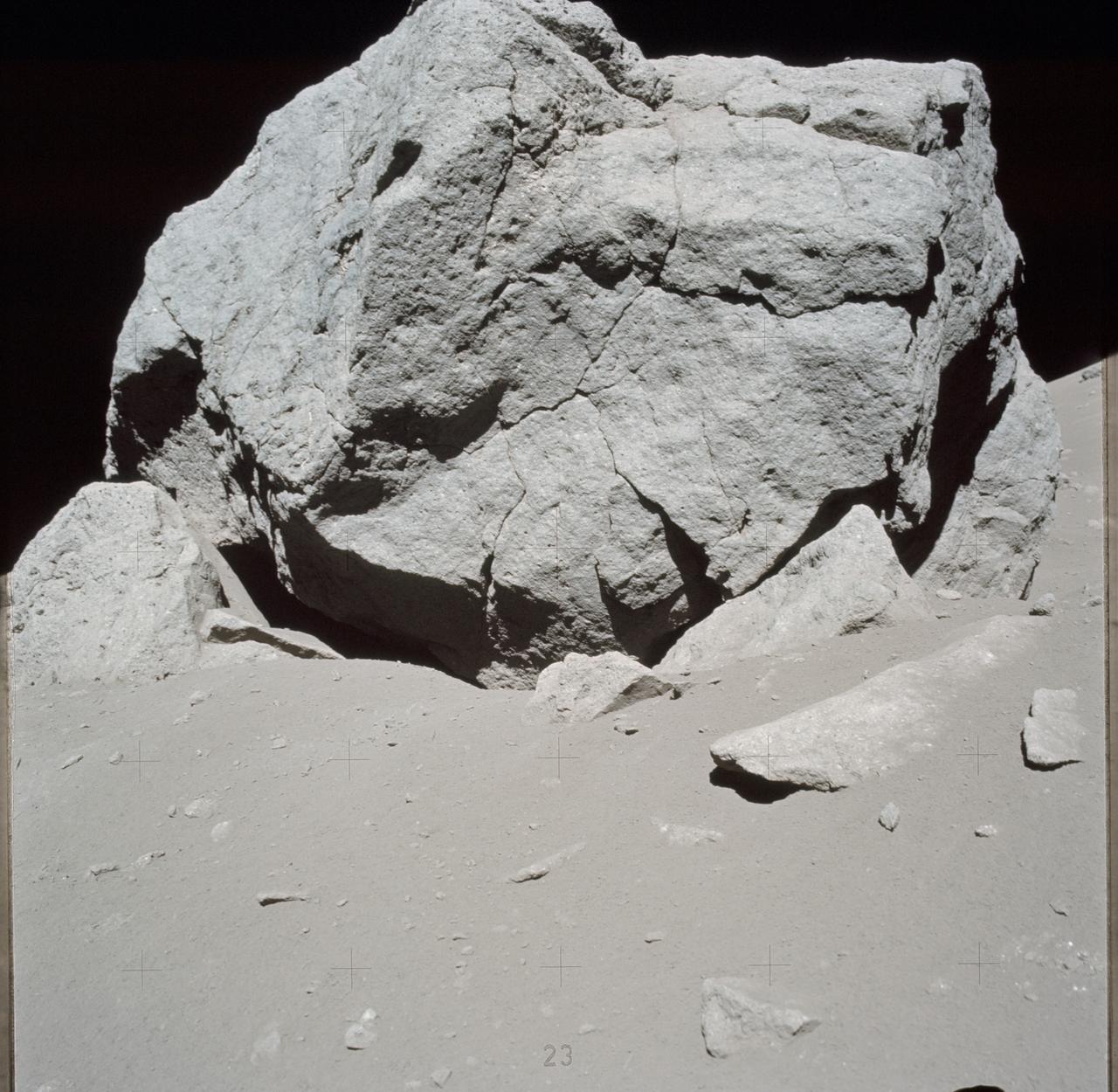

AS17-140-21438 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This 70mm frame features a close-up view of a large multi-cracked boulder discovered by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. (Jack) Schmitt, lunar module pilot, during their visit to extravehicular activity (EVA) Station 6. This boulder, referred to as number two, provided several samples for the crew members' record-setting volume of rock collections. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Cernan and Schmitt were the last crew members to explore the moon in the Apollo Program.

The STS-90 crew patch reflects the dedication of the mission to neuroscience in celebration of the decade of the brain. Earth is revealed through a neuron-shaped window, which symbolizes new perspectives in the understanding of nervous system development, structure and function, both here on Earth and in the microgravity environment of space. The Space Shuttle Columbia is depicted with its open payload bay doors revealing the Spacelab within. An integral component of the mission, the laboratory/science module provided by the European Space Agency (ESA), signifies the strong international involvement in the mission. The seven crew members and two alternate payload specialists, Chiaki Naito-Mukai and Alexander W. Dunlap, are represented by the nine major stars of the constellation Cetus (the whale) in recognition of the International Year of the Ocean. The distant stars illustrate the far reaching implications of the mission science to the many sponsoring agencies, helping prepare for long-duration space flight aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The moon and Mars are depicted to reflect the crew's recognition that those two celestial bodies will be the next great challenges in human exploration of space and represent the key role that life science research will play in supporting such missions.
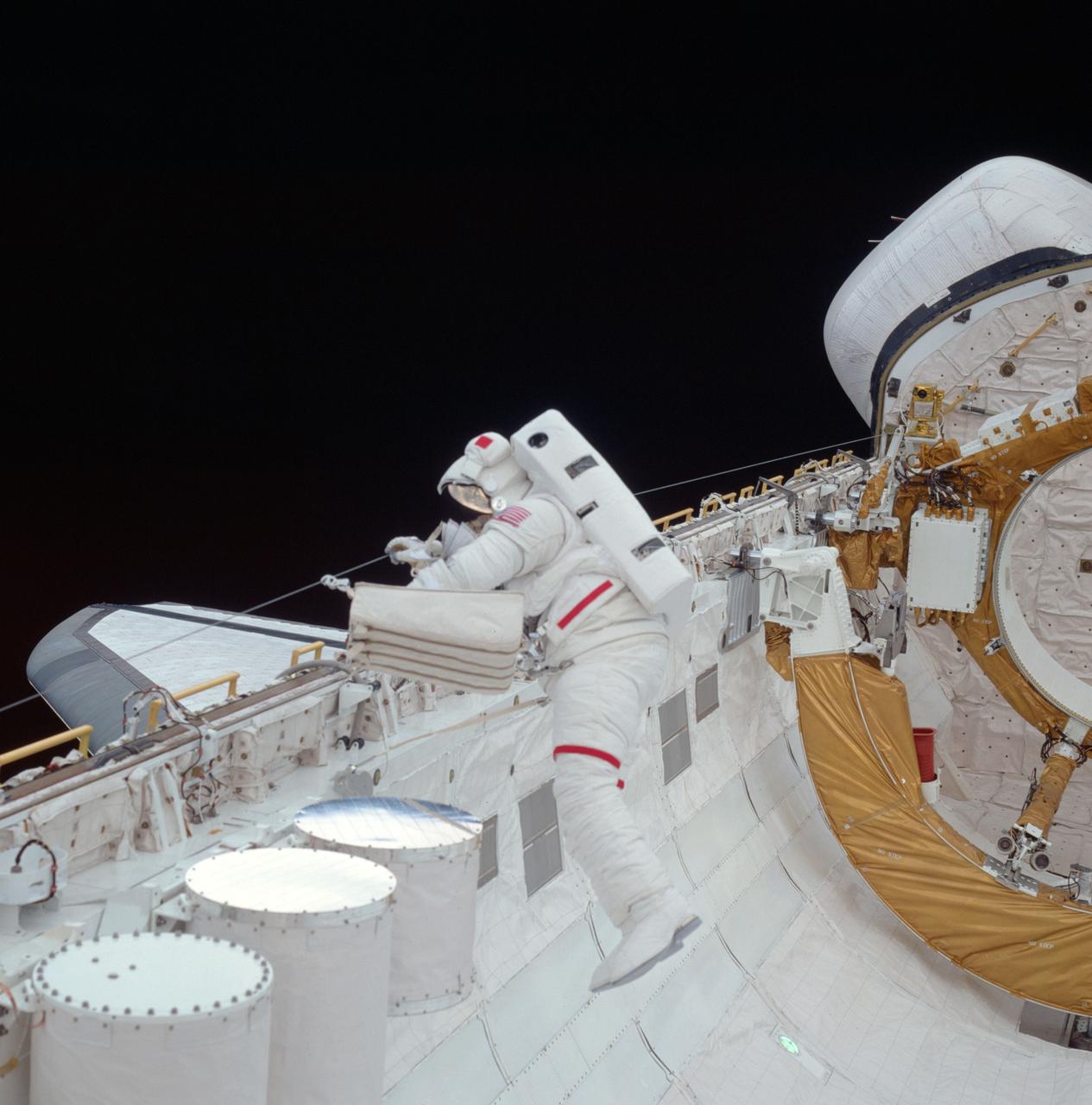

STS006-45-124 (7 April 1983) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, STS-6 mission specialist, translates down the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger’s payload bay door hinge line with a bag of latch tools. This photograph is among the first five still frames that recorded the April 7 extravehicular activity (EVA) of Dr. Musgrave and Donald H. Peterson, the flight’s other mission specialist. It was photographed with a handheld 70mm camera from inside the cabin by one of two crew members who remained on the flight deck during the EVA. Dr. Musgrave’s task here was to evaluate the techniques required to move along the payload bay’s edge with tools. In the lower left foreground are three canisters containing three getaway special (GAS) experiments. Part of the starboard wind and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod are seen back dropped against the blackness of space. The gold-foil protected object partially out of frame on the right is the airborne support equipment for the now vacated inertial upper stage (IUS) which aided the deployment of the tracking and data relay satellite on the flight’s first day. Astronauts Paul J. Weitz, command and Karol J. Bobko, pilot, remained inside the Challenger during the EVA. Photo credit: NASA
The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew did research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new mini-labs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. The instruments requiring direct exposure to space were mounted outside in the open payload bay of the Shuttle. Spacelab represented the merger of science and marned spaceflight. It opened remarkable opportunities to push the frontiers of knowledge beyond the limits of research on Earth. Scientists in space performed experiments in close collaboration with their colleagues on the ground. On the Spacelab-3 mission, managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, this versatile laboratory entered routine operation service for the next two decades. Spacelab-3 (STS-51B mission) was launched aboard Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
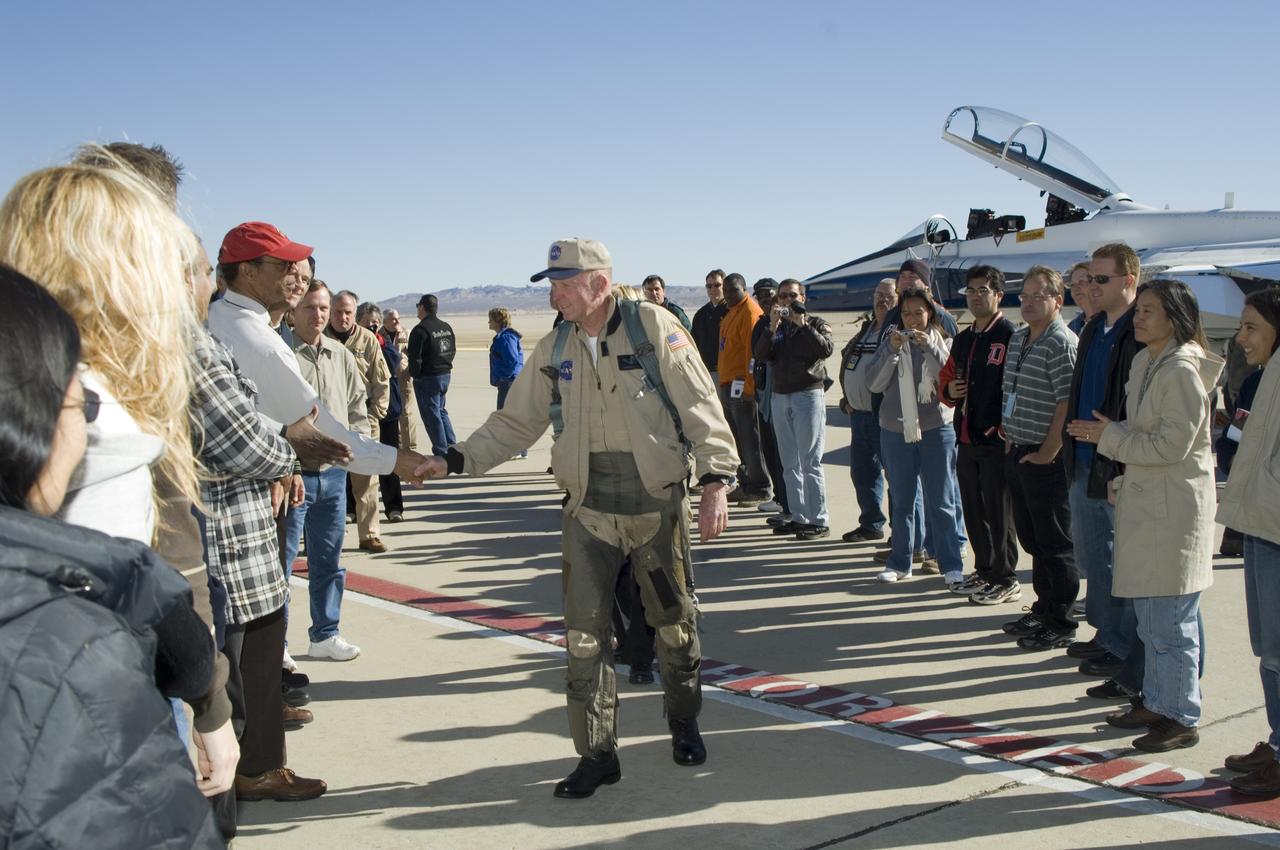

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
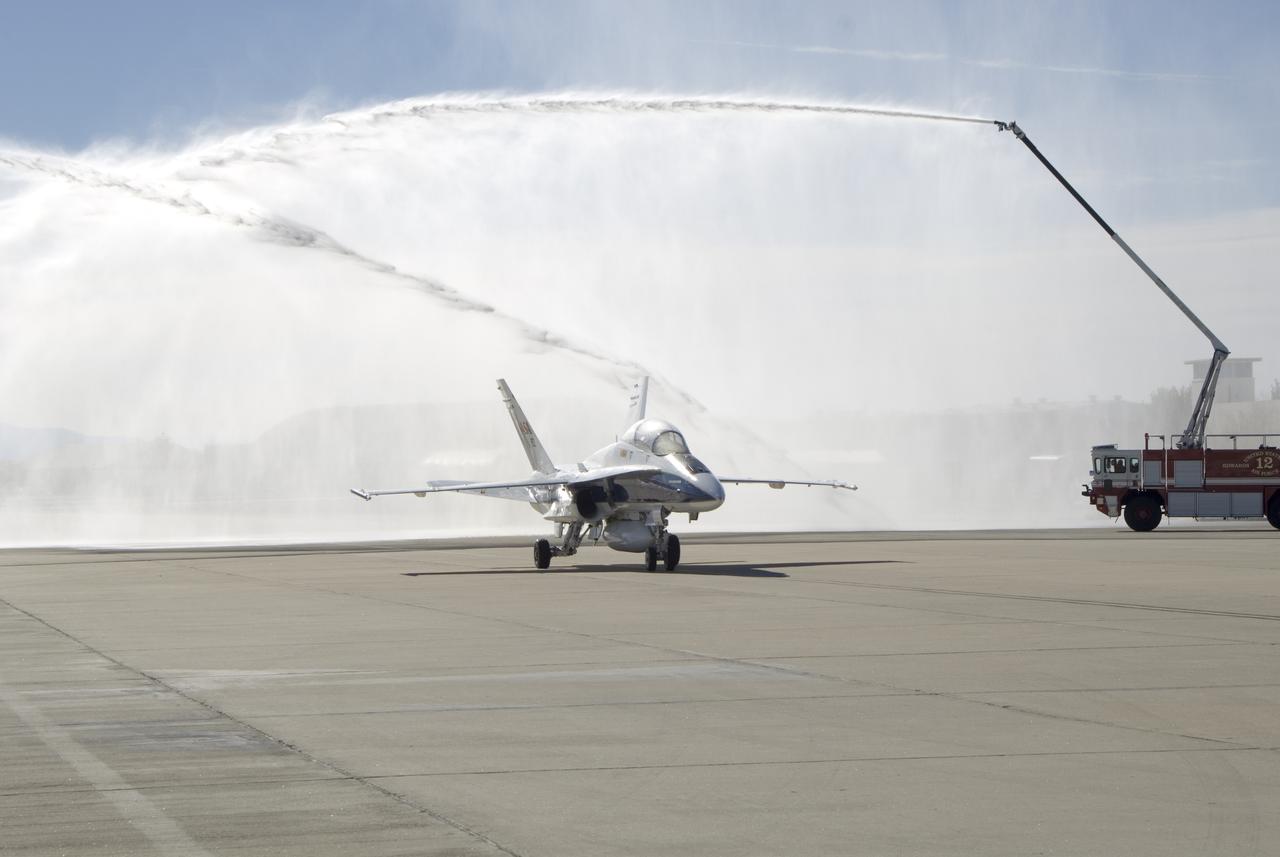

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
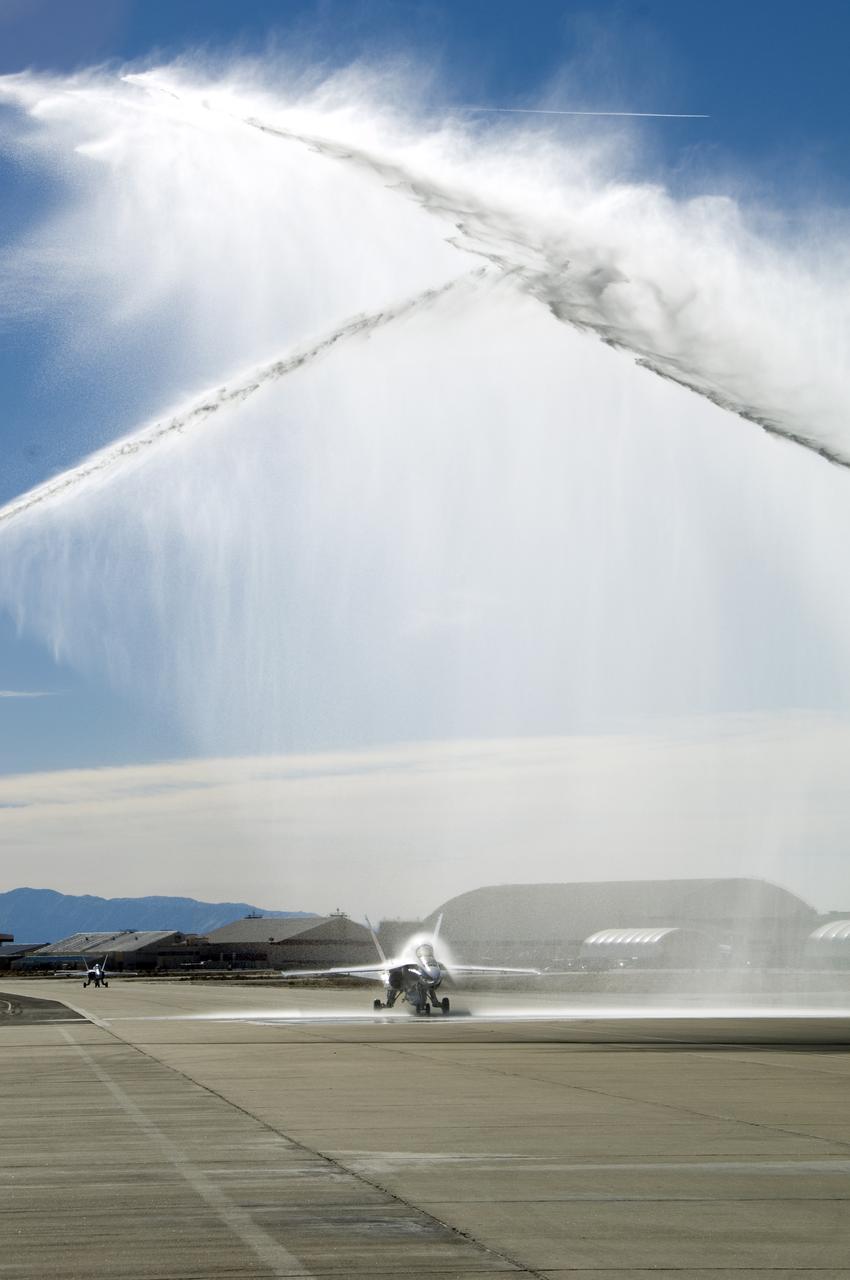

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
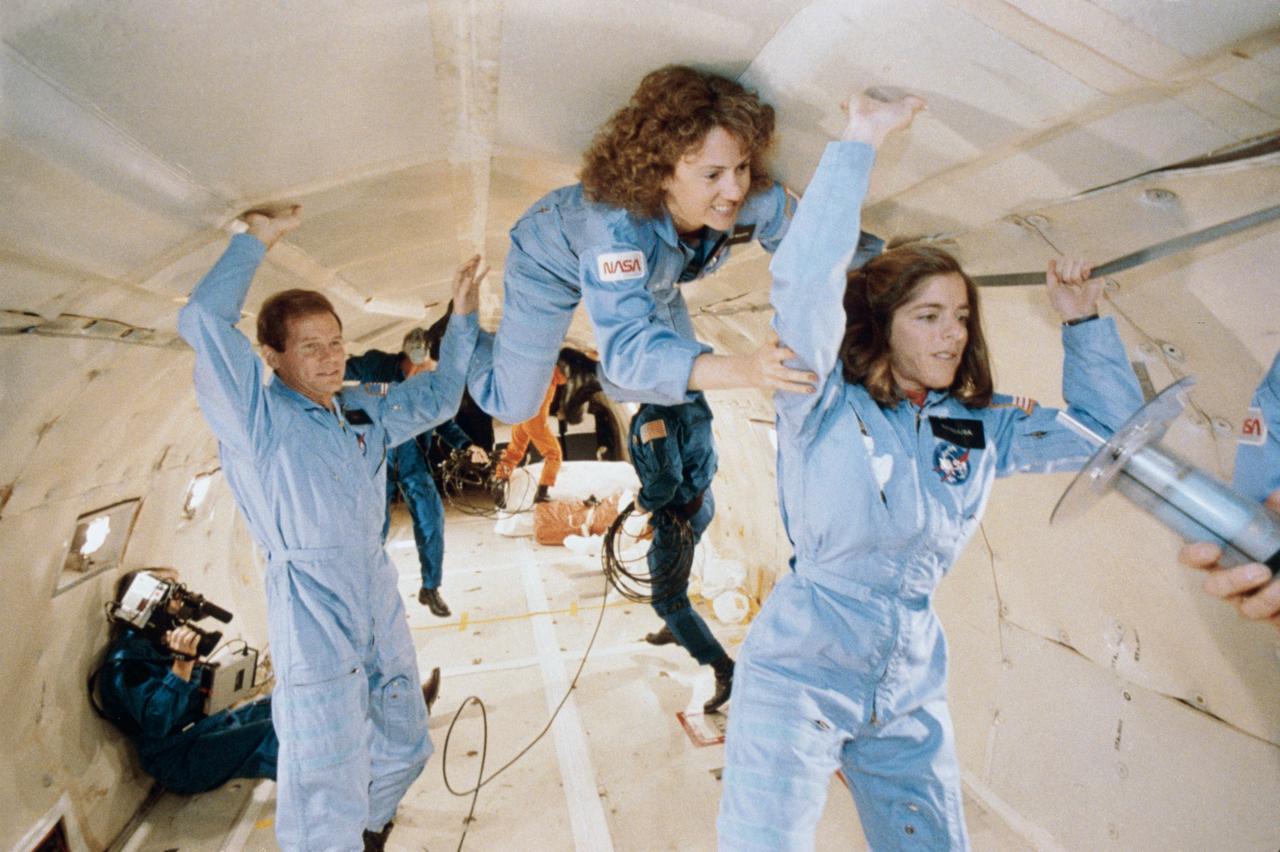

S86-25192 (January 1986) --- Two payload specialists in training for the STS-51L mission, and a payload specialist from STS-61C share a ?zero-gravity? flight aboard a KC-135 aircraft over the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right are United States Representative Bill Nelson (Democrat, Florida), Sharon Christa McAuliffe, and Barbara R. Morgan. The congressman is a payload specialist for the STS-61C mission. McAuliffe is the prime payload specialist for the Teacher-in-Space Project aboard the STS-51L mission; and Morgan is her backup. The photo was taken by Keith meyers of the New York Times. EDITOR?S NOTE: The STS-51L crew members lost their lives in the space shuttle Challenger accident moments after launch on Jan. 28, 1986 from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Photo credit: NASA
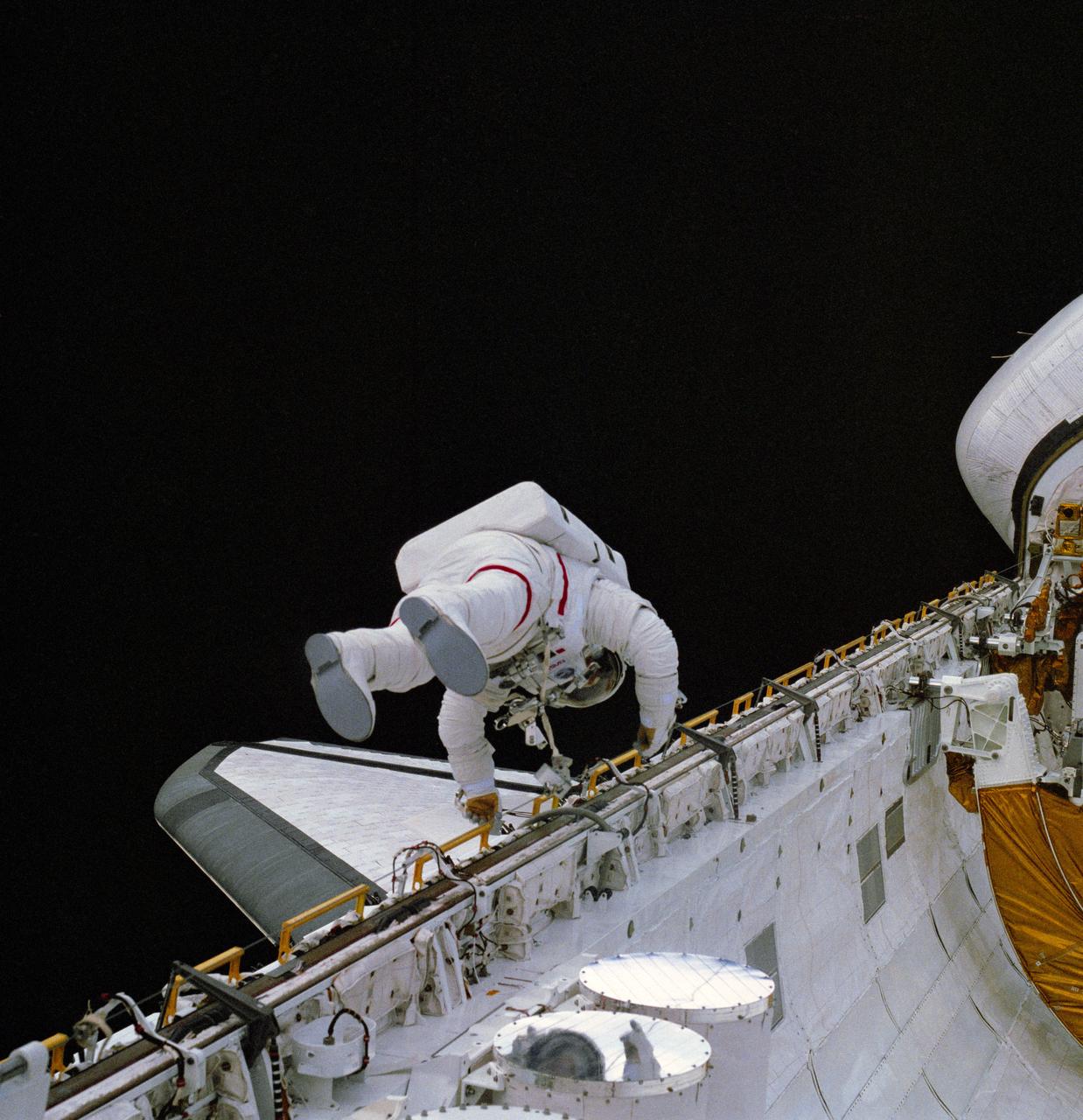

S83-30215 (7 April 1983) --- This photograph of astronaut Story Musgrave, STS-6 mission specialist, translating along the longerons on the port side of the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger was taken with a hand-held 70mm camera from some 18 meters (60 feet) away by one of two crew members who remained inside the cabin. Astronauts Musgrave and Donald H. Peterson (out of frame) were in the midst of NASA?s first ever shuttle extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Karol J. Bobko, pilot, took a number of photographs through the aft flight deck?s windows, and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, mission commander, also exposed some images but remained in control of the orbiter during the EVA. Photo credit: NASA
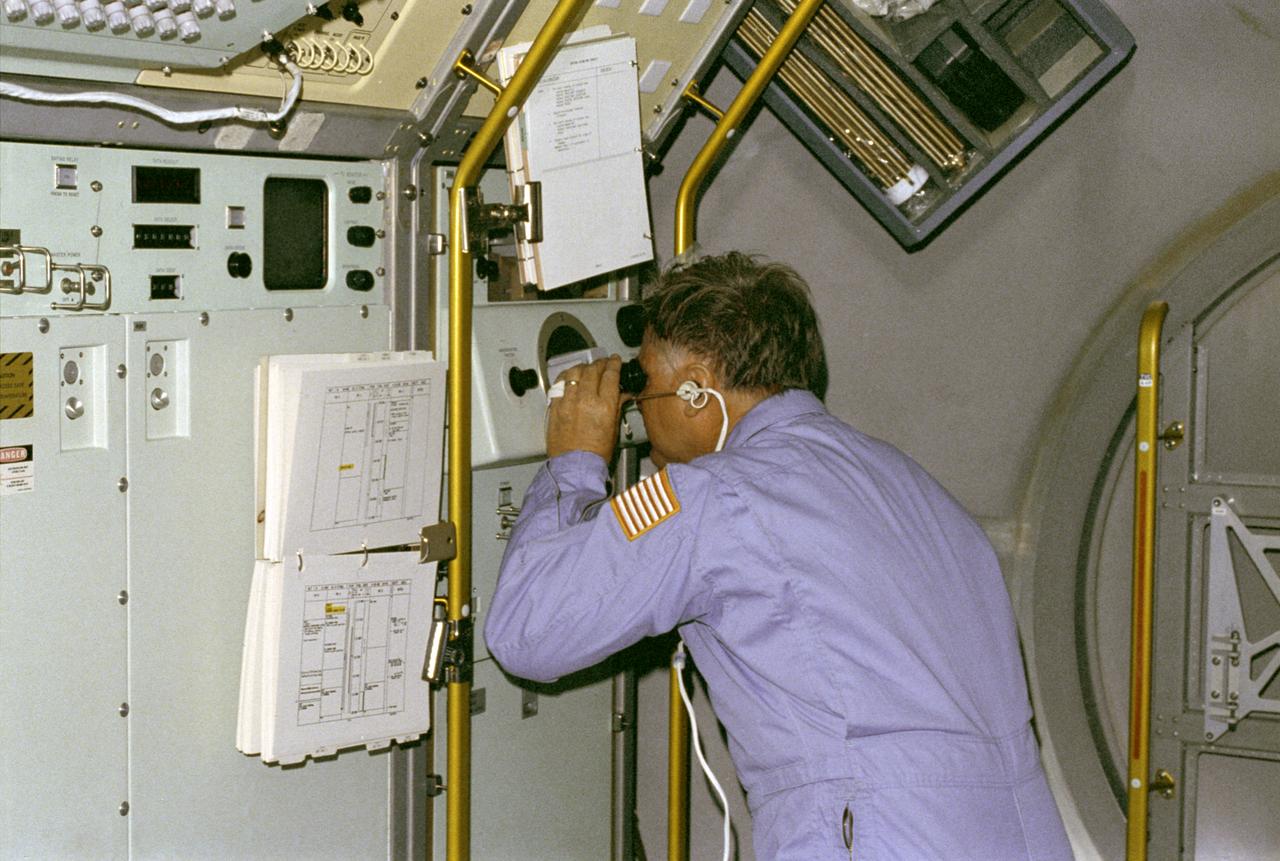

The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew performed research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. In this photograph, astronaut Don Lind observes the mercuric iodide growth experiment through a microscope at the vapor crystal growth furnace. The goals of this investigation were to grow near-perfect single crystals of mercuric iodide and to gain improved understanding of crystal growth by a vapor process. Mercuric iodide crystals have practical use as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors, and in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and in astronomical instruments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.

S85-46260 (20 Dec. 1985) --- Members of the STS-51L crew designed this patch which will represent their participation on NASA's late January 1986 mission aboard the space shuttle Challenger, depicted launching from Florida and soaring into space to carry out a variety of goals. Among the prescribed duties of the five astronauts and two payload specialists will be observation and photography of Halley's Comet, backdropped against the United States flag in the insignia. Surnames of the crew members encircle the scene, with the payload specialists being recognized below. Surname of the first teacher in space, Sharon Christa McAuliffe, is followed by a symbolic apple. Gregory Jarvis, representing Hughes, is the industrial payload specialist for the flight. NASA's crew members are astronauts Francis R. (Dick) Scobee, commander; Michael J. Smith, pilot; and Ronald E. McNair, Ellison S. Onizuka and Judith A. Resnik - all mission specialists. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
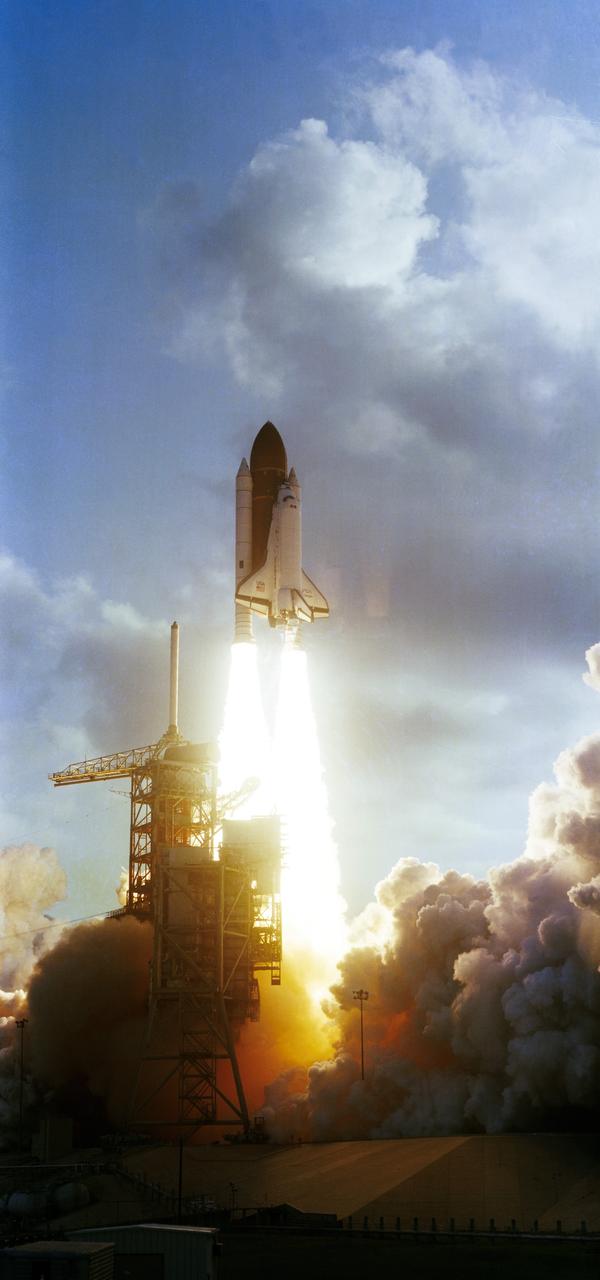

S83-35702 (18 June 1983) --- The seventh launch of the NASA Space Transportation System and the second lift-off of the space shuttle Challenger occurred at 7:33 a.m. (EDT) today from the Pad 39A launch site, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The six-day mission will be highlighted by the first direct landing from space by an orbiter to the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). The crew consists of astronauts Robert Crippen, commander, the first two-time space shuttle astronaut; Frederick H. Hauck, pilot; and three mission specialists -- Sally K. Ride, John M. Fabian and Norman E. Thagard. During the mission the crew will deploy the Indonesian PALAPA-B and the Canadian ANIK-C communications satellites. They will also use the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm to deploy and retrieve a platform for space experiments called the Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS), and serve as a spaceborne laboratory for OSTA-2, a scientific payload. Getaway Special canisters and materials processing experiments will fill out the complement of payloads on the mission. Photo credit: NASA
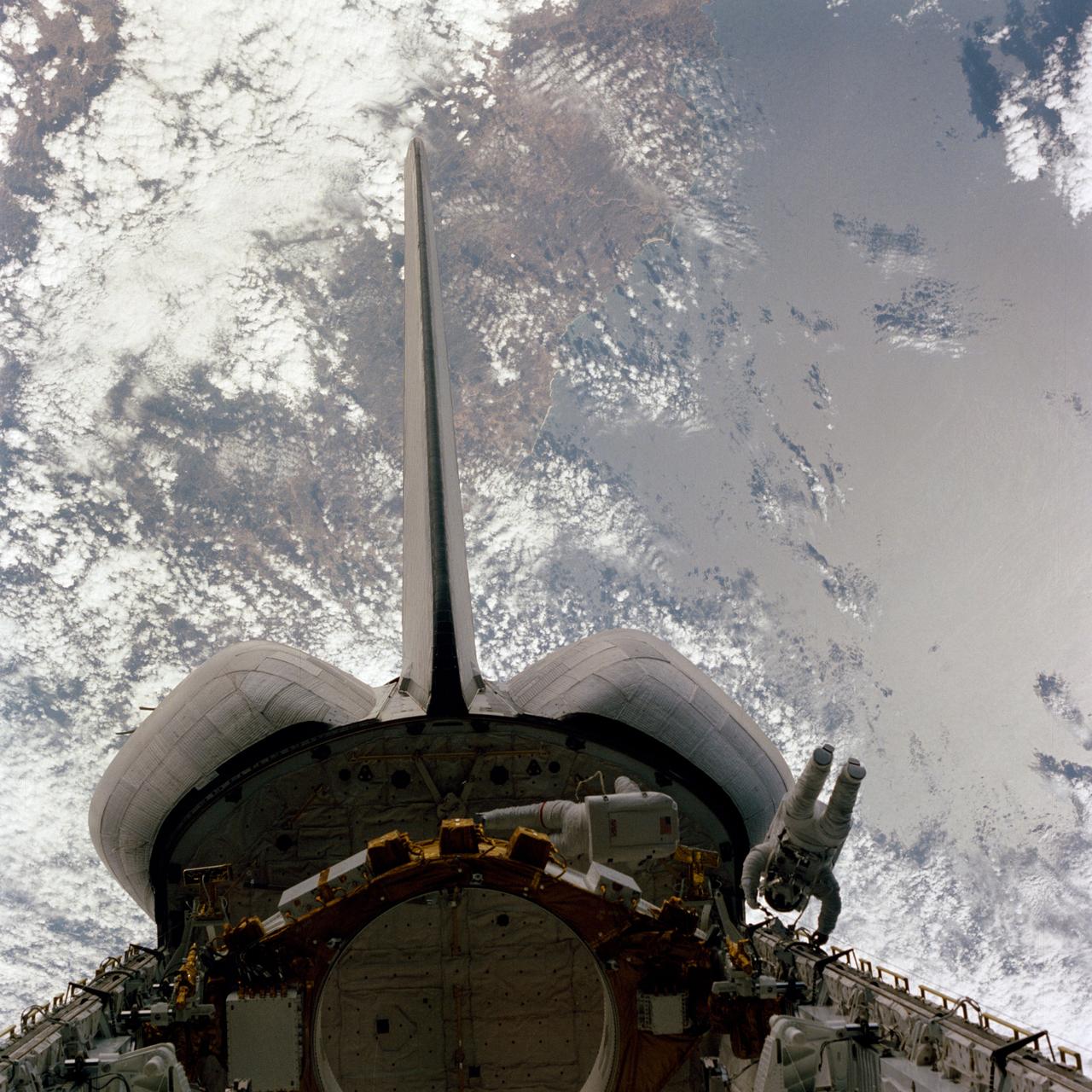

STS006-45-111 (7 April 1983) --- Astronaut Donald H. Peterson (port side) and F. Story Musgrave, STS-6 mission specialists, evaluate the handrail system on the starboard longeron and aft bulkhead, respectively, during a long extravehicular activity (EVA) aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. The vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods frame a portion of Mexico?s state of Jalisco below. Punta Farallon and Sahta da Tencatita, about 120 kilometers (75 miles) south of Puerto Vallarta, are visible. Pacific waters form about half of the backdrop for this scene, photographed by one of two crew members who remained inside the spacecraft during the EVA. Astronaut Karol J. Bobko, pilot, took a number of pictures of his fellow crew members during their outside tasks and astronaut Paul J. Weitz, commander, took some photographs while remaining in command of the reusable vehicle. Photo credit: NASA
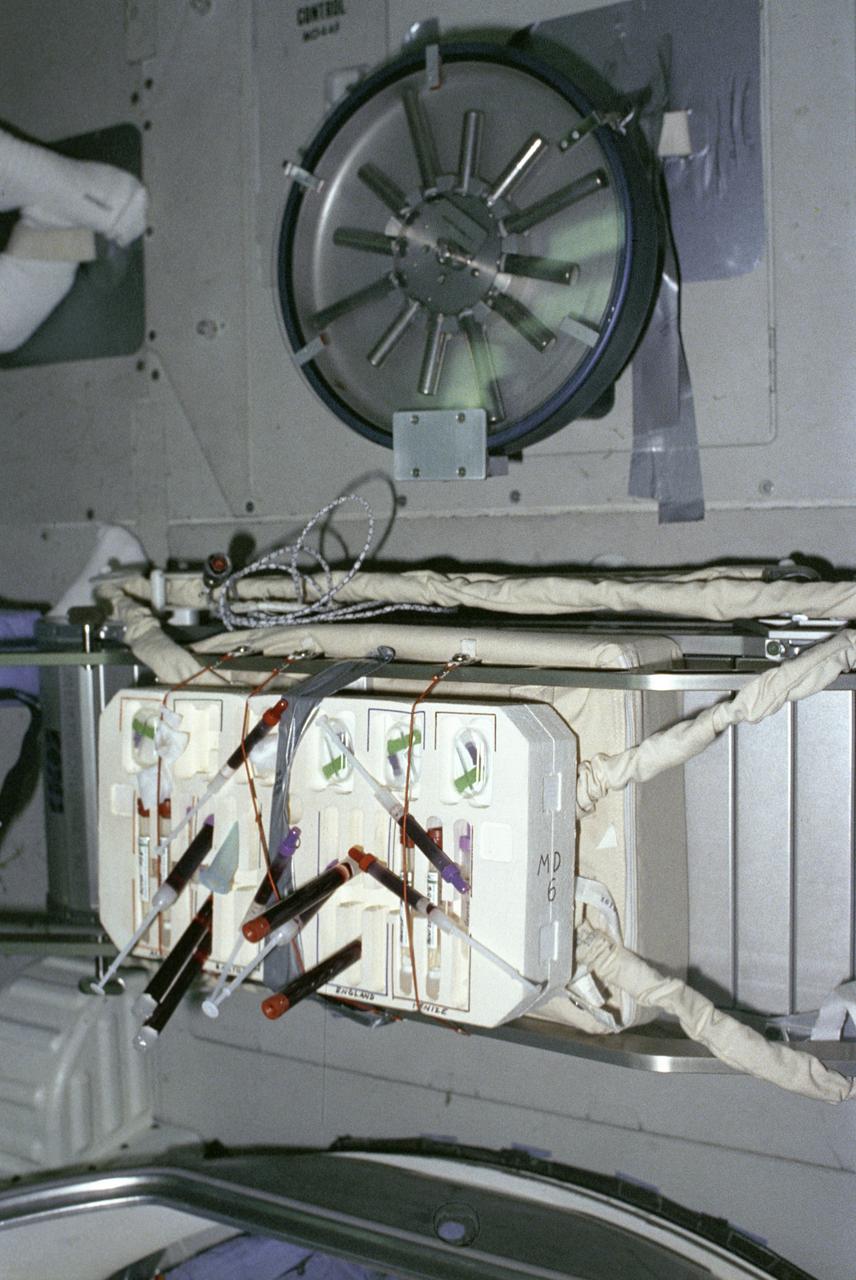
While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin d metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows a blood draw test kit and centrifuge used for the experiment aboard the Spacelab-2. Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities of all Spacelab missions.
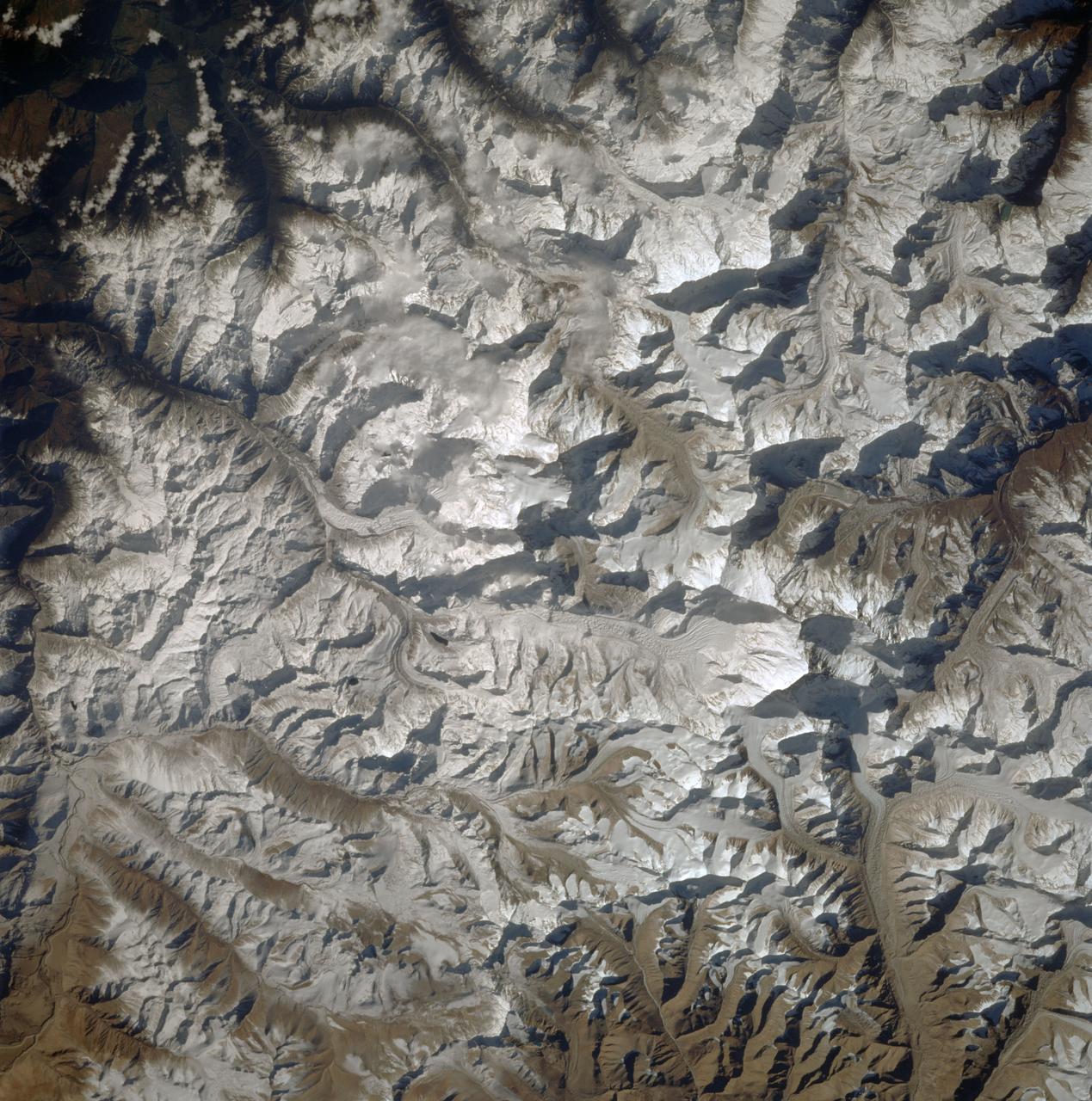

STS087-716-080 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- Featured in this view is Mount Everest. It is called “Sagarmatha” in Nepal and “Qomolangma Feng” Qomolangma in China (both names meaning “Goddess Mother of the World”), but is known to the western world as Mount Everest. At an altitude of 29,028 feet (8,848 meters) the summit of tallest mountain on Earth (above sea level) reaches two-thirds of the way through the atmosphere. Situated on the border between Nepal and China (27°59’N, 86°56’E), Mount Everest with its low oxygen levels, powerful winds, and extremely cold temperatures has captured the imagination of adventuresome men and women. Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay were the first persons to surmount Mount Everest in 1953. While climbing Everest can be challenging, it can also be tragic. On May 10, 1996, after reaching the summit and descending to camp, several climbers were trapped by a severe and sudden storm. A total of eight people died, making this day the deadliest single tragedy in the history of Mount Everest. This picture is one of the 70mm Earth observations visuals used by the crew at its post flight presentation events.
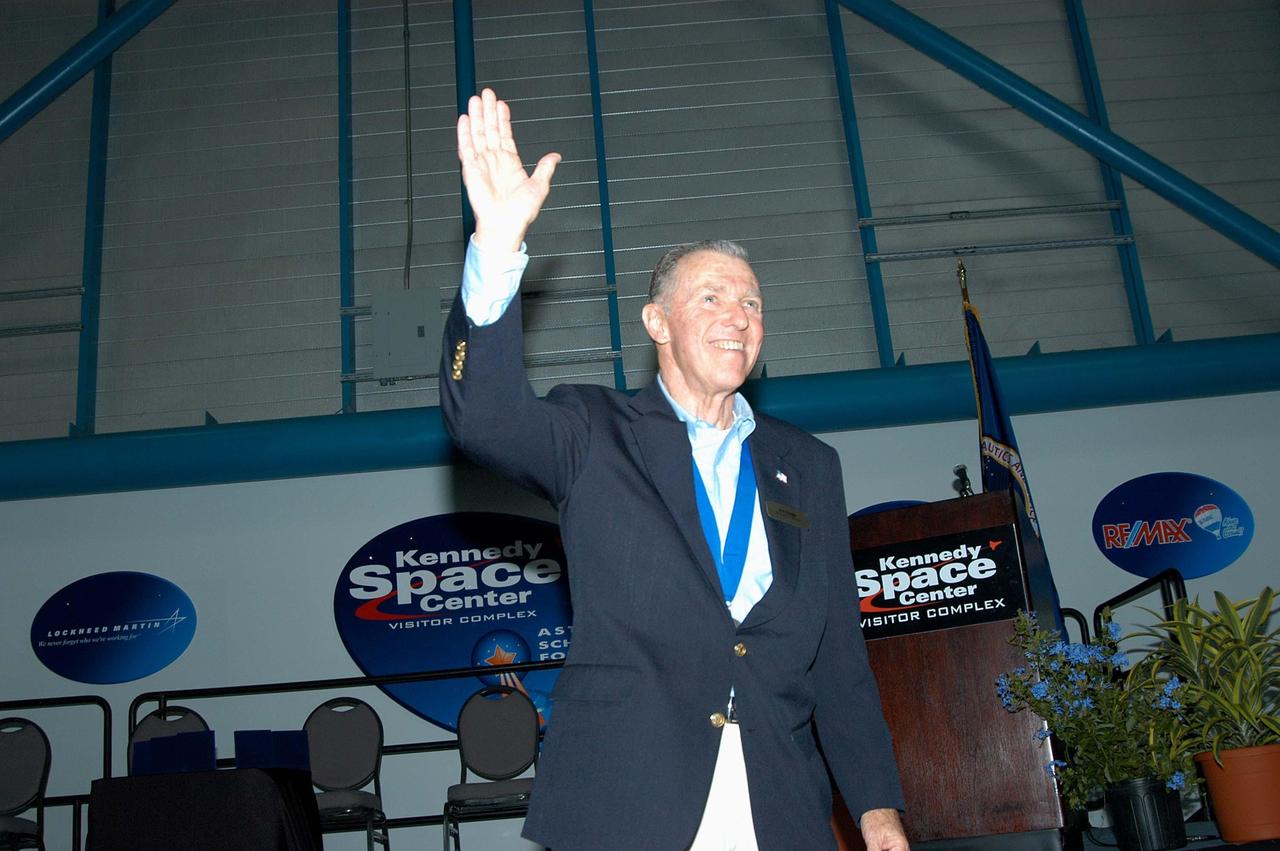

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former astronaut Joe Engle acknowledges the applause as he is introduced as a previous inductee into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame. He and other Hall of Fame members were present for the induction of five new space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame: Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. Engle made 16 flights in the X-15 rocket plane before he became a NASA astronaut and flew two Space Shuttle missions. In 1981, he commanded the second flight of Columbia, the first manned spacecraft to be reflown in space, and in 1985 he commanded a five-man crew on the 20th shuttle flight, a satellite-deploy and repair mission. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
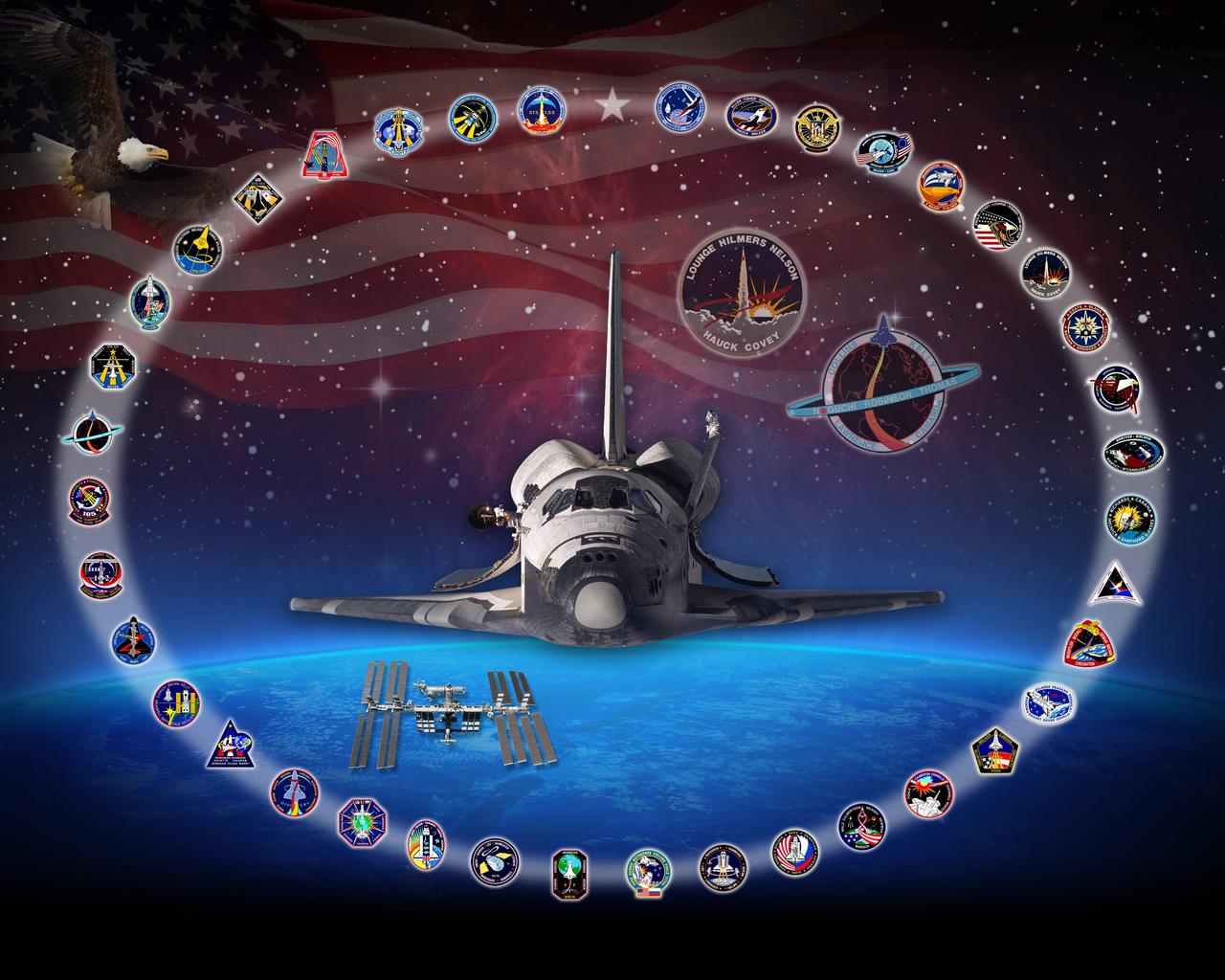

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This orbiter tribute of space shuttle Discovery, or OV-103, hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC