
On Jan. 18, 1986, NASA Voyager 2 discoverd three Uranus satellites. All three lie outside the orbits of Uranus nine known rings, the outermost of which, the epsilon ring, is seen at upper right. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00368
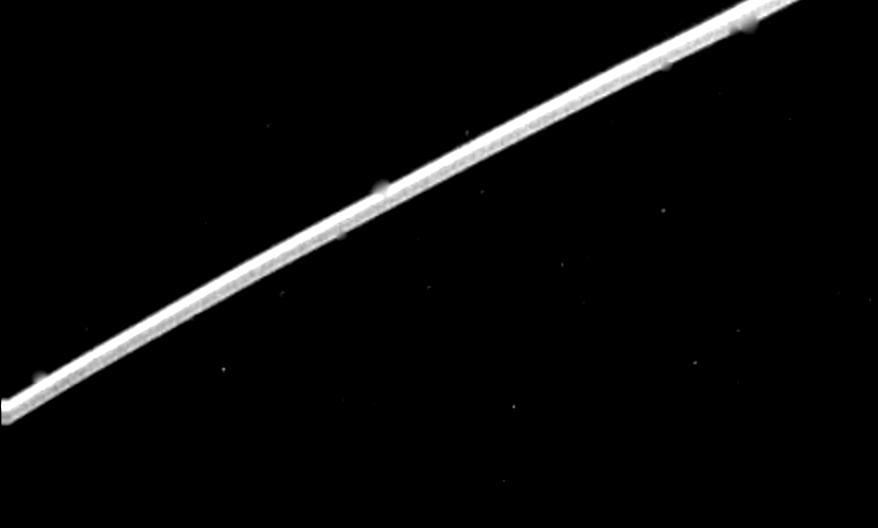

NASA Voyager 2 acquired this high-resolution image of the epsilon ring of Uranus on Jan. 23, 1986. This clear-filter image from Voyager narrow-angle camera has a resolution of about 10 km 6 mi.
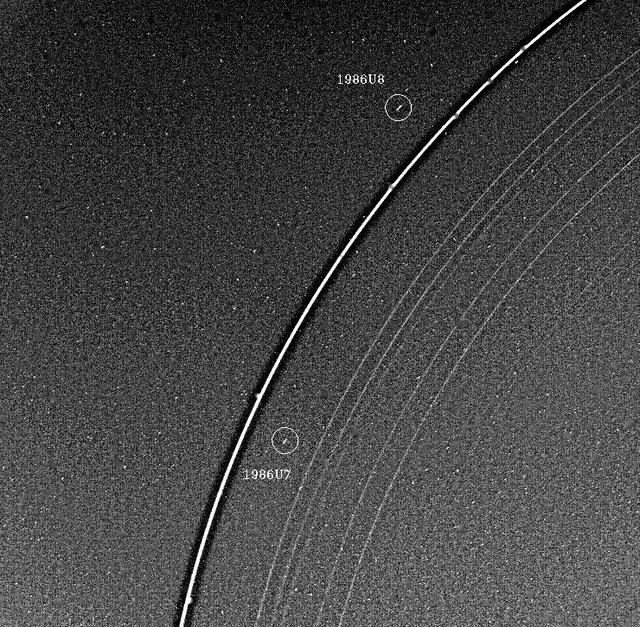

Voyager 2 has discovered two hepherd satellites associated with the rings of Uranus. The two moons, designated 1986U7 and 1986U8, are seen here on either side of the bright epsilon ring; all nine of the known Uranian rings are visible.
NASA Voyager 2 took this wide-angle image of Uranus rings as the spacecraft neared the plane of the rings less than an hour before closest approach to the planet.
This false-color view of the rings of Uranus was made from images taken by NASA Voyager 2 on Jan. 21, 1986. All nine known rings are visible here; the somewhat fainter, pastel lines seen between them are contributed by the computer enhancement. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00033

This silhouetted image of the rings of Uranus was taken by NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft on Jan. 24, 1986, just 27 minutes before its closest approach to the planet.
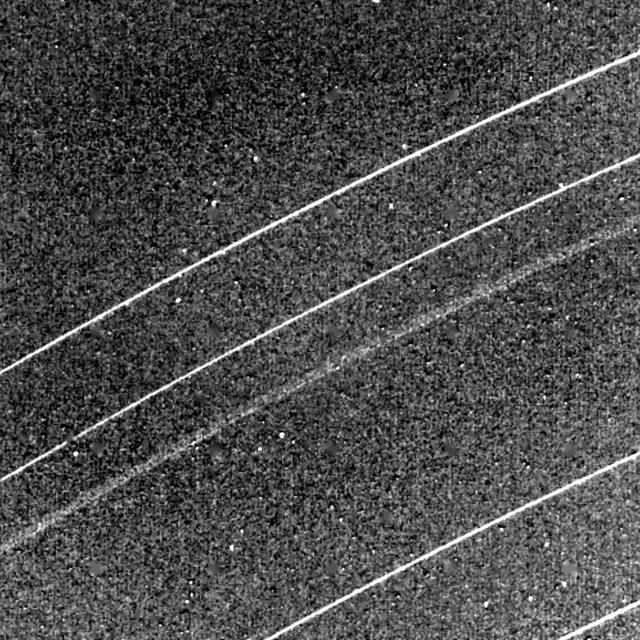

This NASA Voyager 2 image of the Uranian rings delta, gamma, eta, beta and alpha from top was taken Jan. 23, 1986.
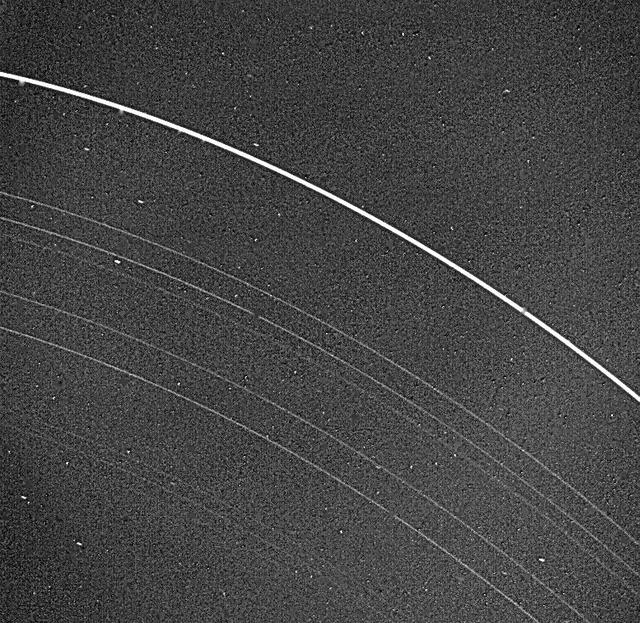

NASA Voyager 2 returned this picture of the Uranus rings on Jan. 22, 1986, from a distance of 2.52 million kilometers 1.56 million miles. All nine known rings are visible in this image.
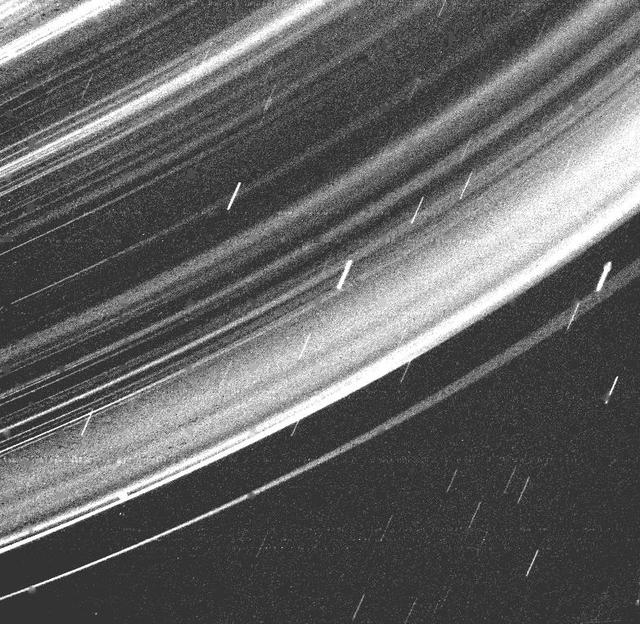

This image captured by NASA's Voyager 2 in 1986 revealed a continuous distribution of small particles throughout the Uranus ring system. This unique geometry, the highest phase angle at which Voyager imaged the rings, allowed us to see lanes of fine dust. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00142
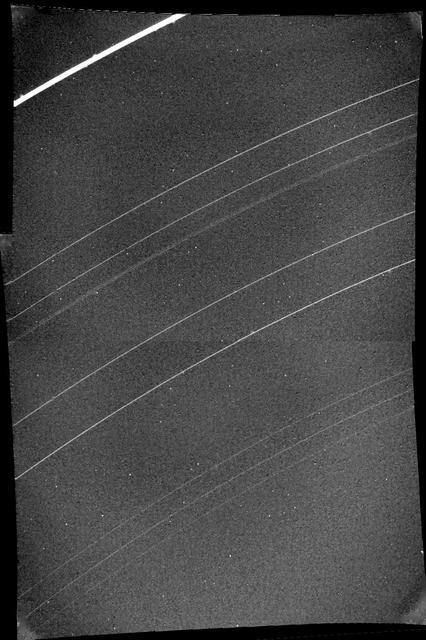

On Jan. 23, 1986, NASA Voyager 2 discovered a tenth ring orbiting Uranus. The tenth ring is about midway between the bright, outermost epsilon ring and the next ring down, called delta. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00035
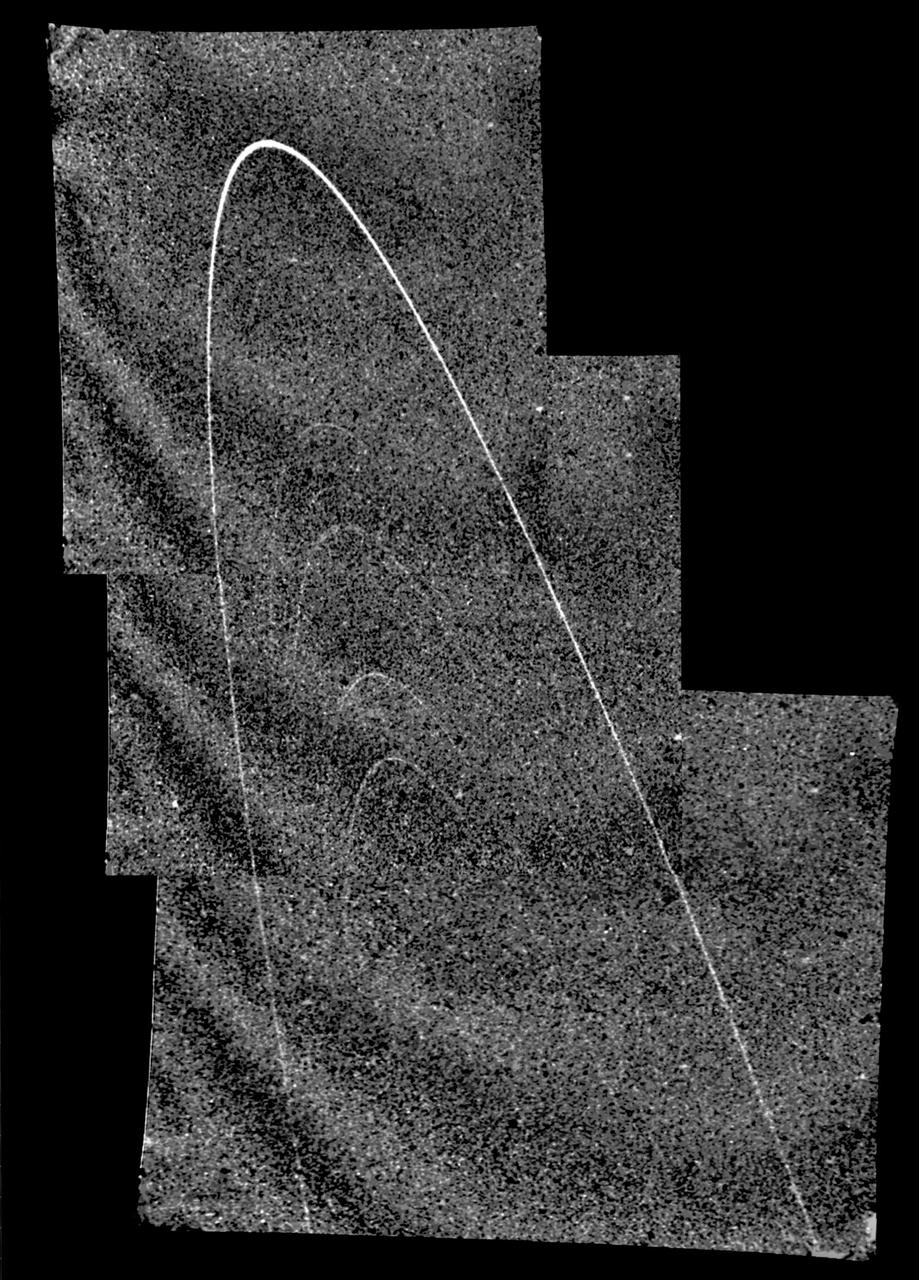

Uranus rings, photographed by NASA Voyager 2 in 1986 as it approached the plane of the Uranian ring system.

The outer rings of Uranus are visible in this image, obtained by NASA Voyager 2 on Jan. 23, 1986. The outermost and brightest ring, called epsilon, is visible along with the fainter and narrower delta and gamma rings from left.

The STS-78 patch links past with present to tell the story of its mission and science through a design imbued with the strength and vitality of the 2-dimensional art of North America's northwest coast Indians. Central to the design is the space Shuttle whose bold lines and curves evoke the Indian image for the eagle, a native American symbol of power and prestige as well as the national symbol of the United States. The wings of the Shuttle suggest the wings of the eagle whose feathers, indicative of peace and friendship in Indian tradition, are captured by the U forms, a characteristic feature of Northwest coast Indian art. The nose of the Shuttle is the strong downward curve of the eagle's beak, and the Shuttle's forward windows, the eagle's eyes, represented through the tapered S forms again typical of this Indian art form. The basic black and red atoms orbiting the mission number recall the original NASA emblem while beneath, utilizing Indian ovoid forms, the major mission scientific experiment package LMS (Life and Materials Sciences) housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay is depicted in a manner reminiscent of totem-pole art. This image of a bird poised for flight, so common to Indian art, is counterpointed by an equally familiar Tsimshian Indian symbol, a pulsating sun with long hyperbolic rays, the symbol of life. Within each of these rays are now encased crystals, the products of this mission's 3 major, high-temperature materials processing furnaces. And as the sky in Indian lore is a lovely open country, home of the Sun Chief and accessible to travelers through a hole in the western horizon, so too, space is a vast and beckoning landscape for explorers launched beyond the horizon. Beneath the Tsimshian sun, the colors of the earth limb are appropriately enclosed by a red border representing life to the Northwest coast Indians. The Indian colors of red, navy blue, white, and black pervade the STS-78 path. To the right of the Shuttle-eagle, the constellation Delphinus recalls the dolphin, friend of ancient sailors and, now perhaps too, of the 9 space voyagers suggested by this constellation's blaze of 9 stars. The patch simultaneously celebrates international unity fostered by the Olympic spirit of sports competition at the 1996 Olympic Games in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Deliberately poised over the city of Atlanta, the Space Shuttle glows at its base with the 5 official Olympic rings in the 5 Olympic colors which can also be found throughout the patch, rings and colors which signify the 5 continents of the earth. This is an international mission and for the first time in NASA patch history, astronauts have dispensed with identifying country flags beneath their names to celebrate the spirit of international unity so characteristic of this flight.