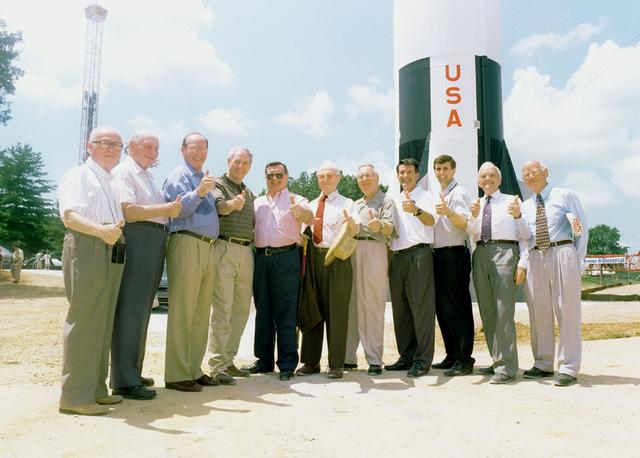

Members of the original Von Braun german rocket team participate in the Saturn V replica didication ceremony at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL. Pictured are (L/R): Walter Jacobi, Konrad Dannenberg, Apollo 14's Edgar Mitchell, NASA Administrator Dan Goldin, Apollo 12's Dick Gordon, Gerhard Reisig, Werner Dahm, MSFC Director Art Stephenson, Director of the U. S. Space and Rocket Center Mike Wing, Walter Haeusserman, and Ernst Stuhlinger.
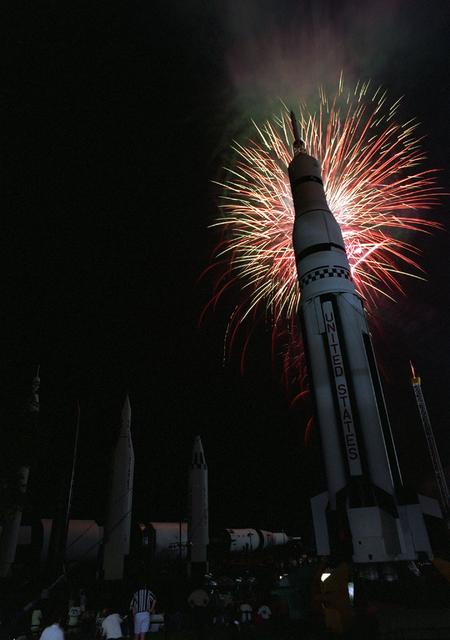

The evening skies over the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL burst into life as members of the Huntsville community gathered to celebrate the 30th arniversary of the Lunar Landing. Commerating this historical achievement for NASA and the US Space Program, a replica of the original Saturn V rocket was built on the grounds of the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL. On the evening of the anniversary thousands of onlookers cheered as fireworks lit up the night sky behind the massive Saturn V rocket.

A replica of the Saturn V rocket that propelled man from the confines of Earth's gravity to the surface of the Moon was built on the grounds of the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL. in time for the 30th arniversary celebration of that historic occasion. Marshall Space Flight Center and its team of German rocket scientists headed by Dr. Wernher von Braun were responsible for the design and development of the Saturn V rocket. Pictured are MSFC's current Center Director Art Stephenson, Alabama Congressman Bud Cramer, NASA Administrator Dan Goldin, and director of the U. S. Space and Rocket Center Mike Wing during the dedication ceremony.

Noted author and previous Marshall Space Flight Center employee Mr. Homer Hickam Jr. poses in front of a placque commemorating his achievement in realizing his dreams of becoming a rocket scientist. The dedication site is located at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL, and is used by amature rocket builders attending the Space Camp to launch their self-made rockets like Mr. Hickam did as a youth growing up in rural West Virginia. Posing with Mr. Hickam is the Madison County Commissioner Mr. Mike Gillispie.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
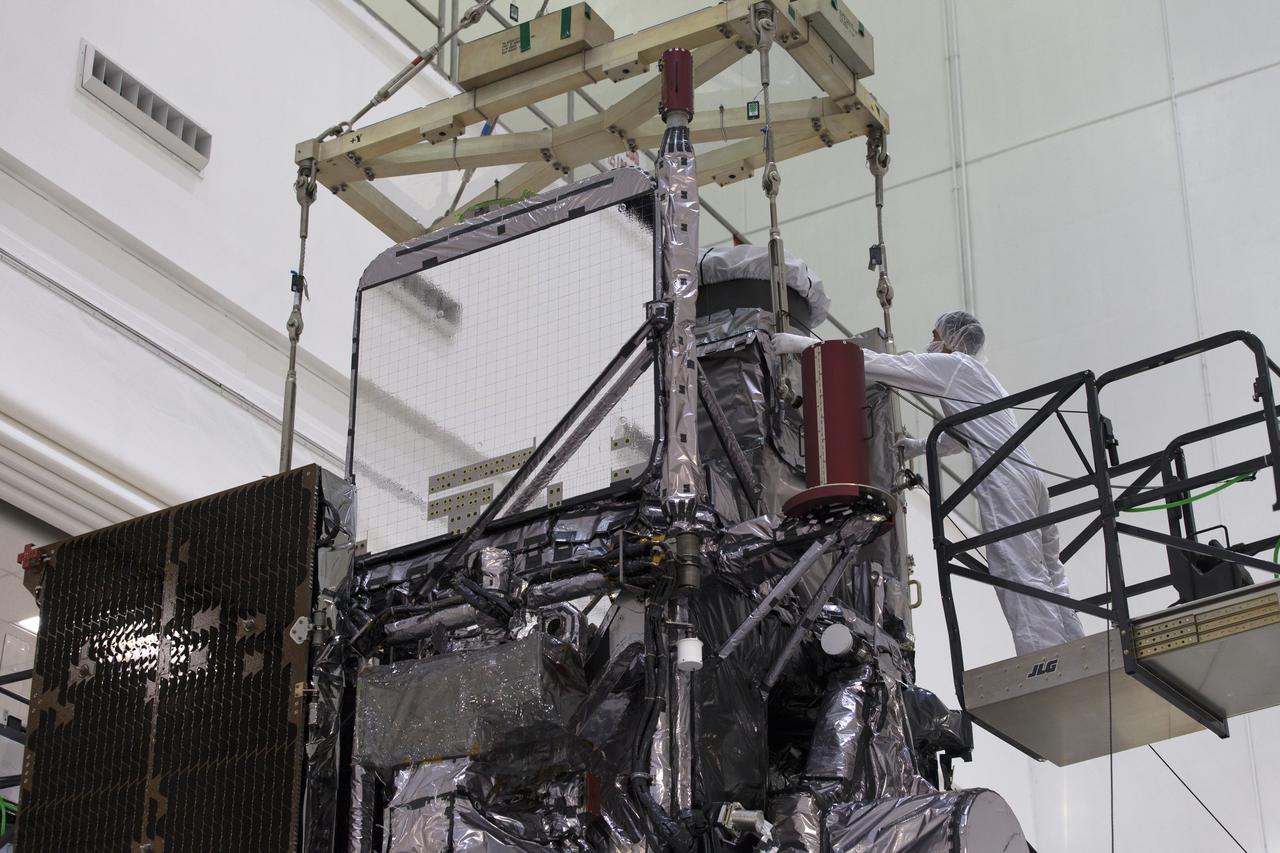

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician inspects NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
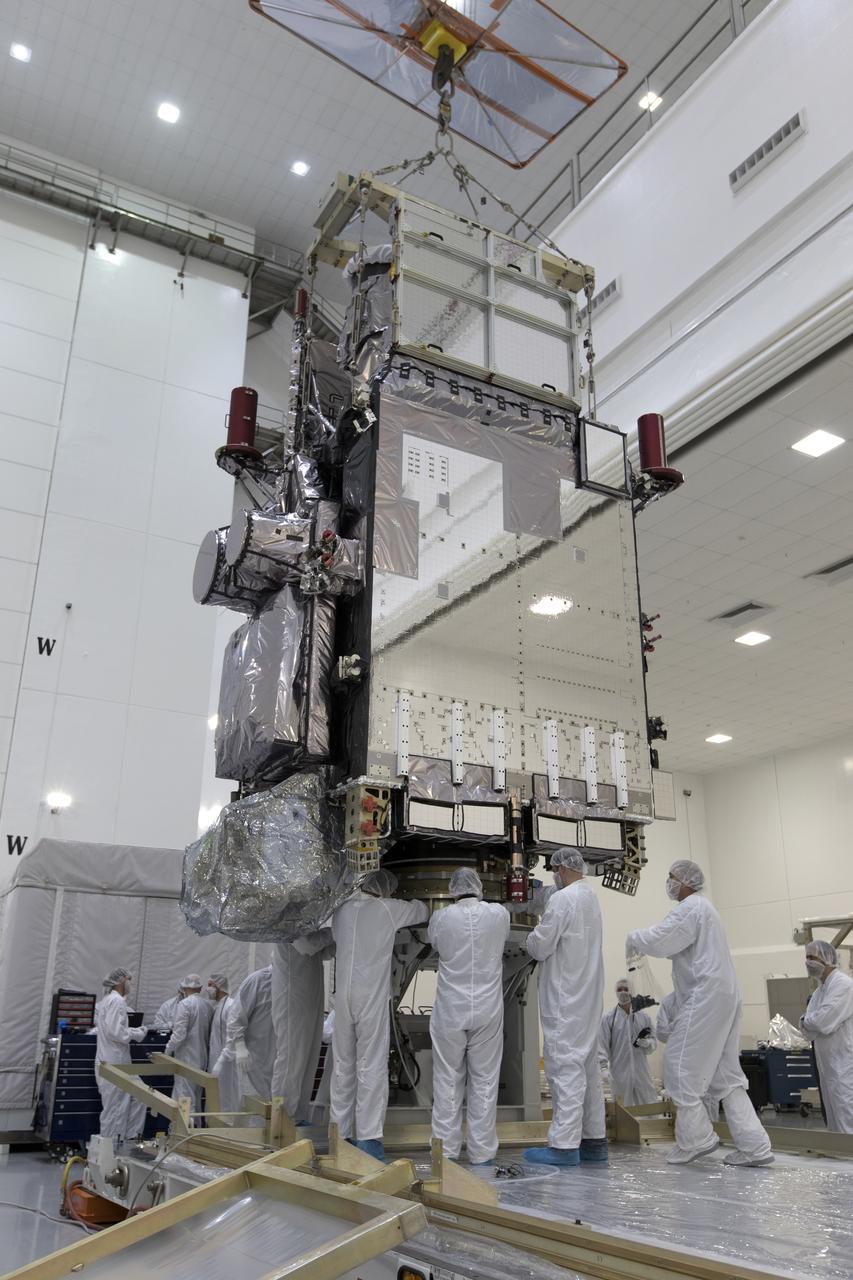

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
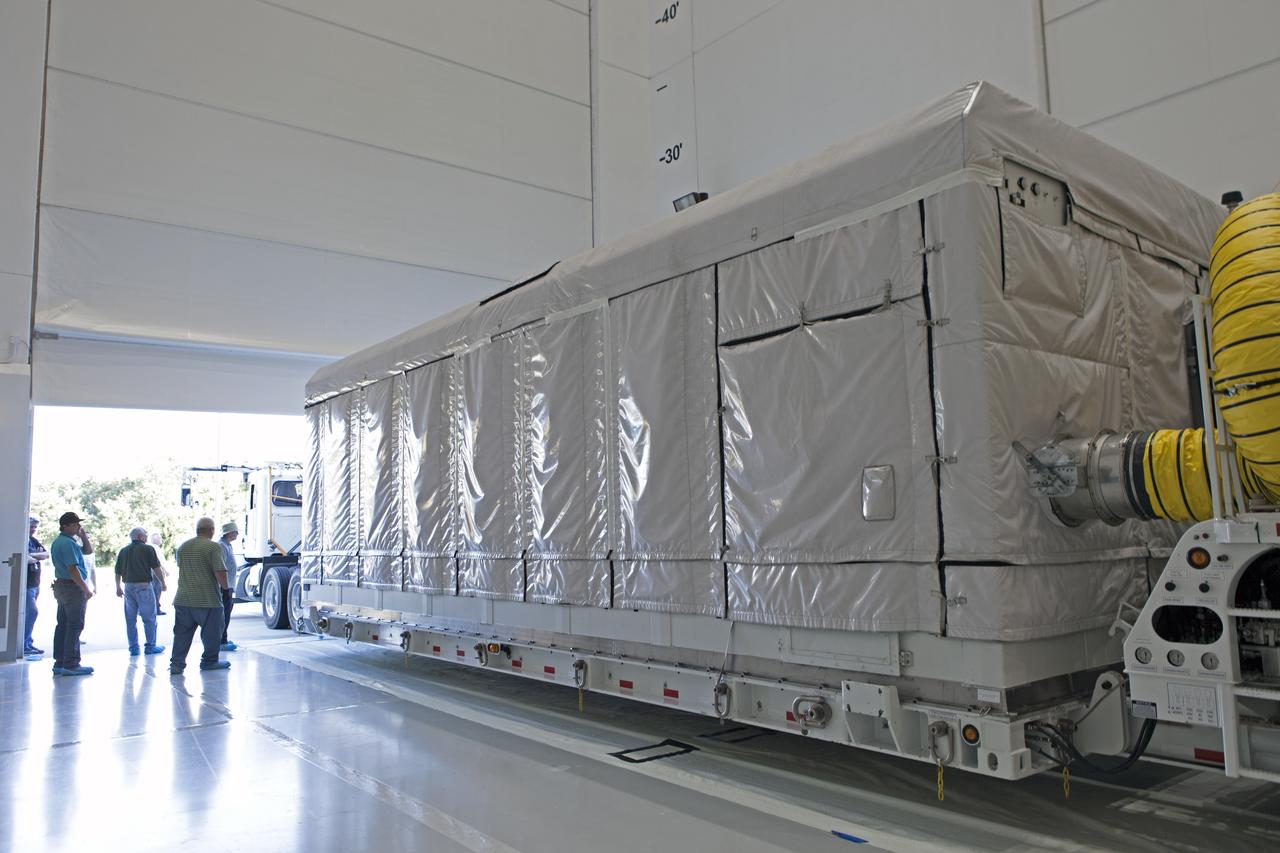

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
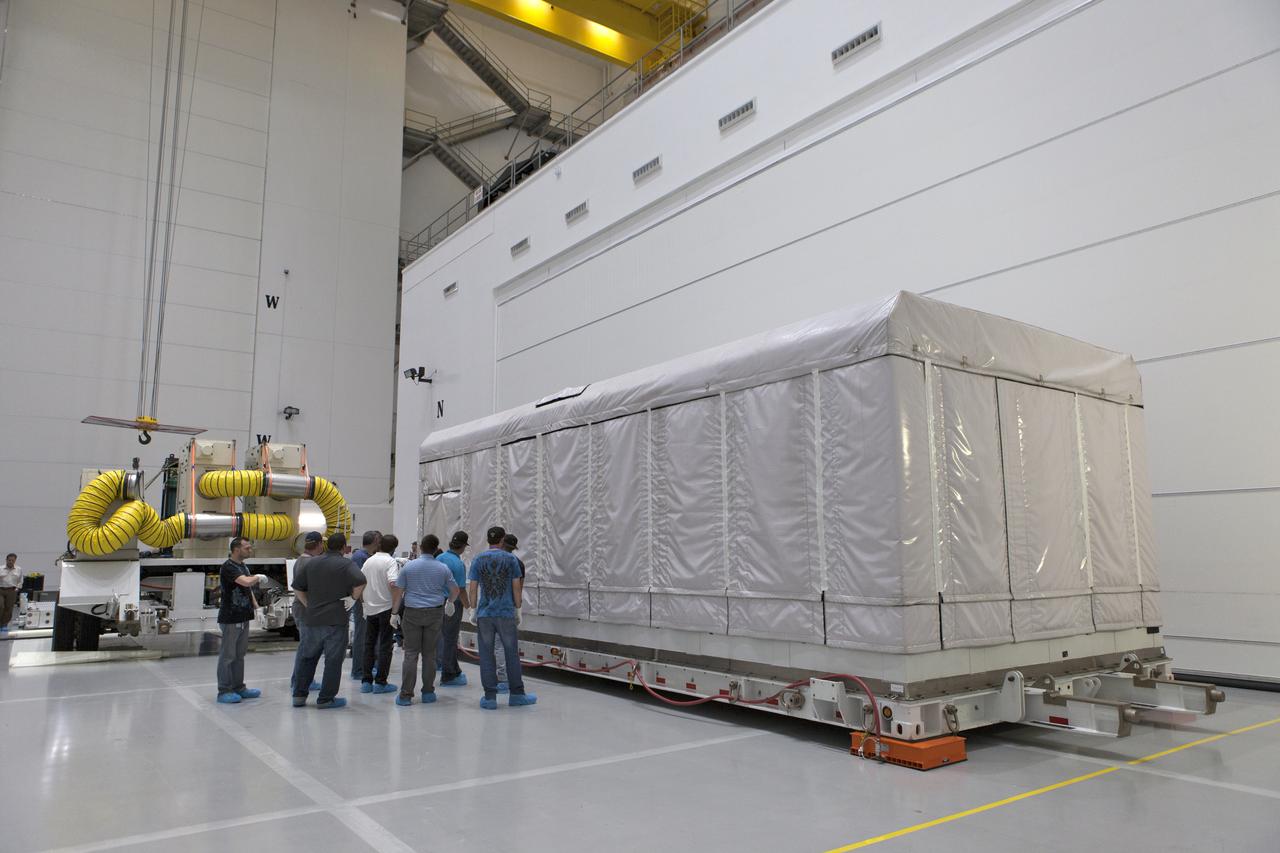

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
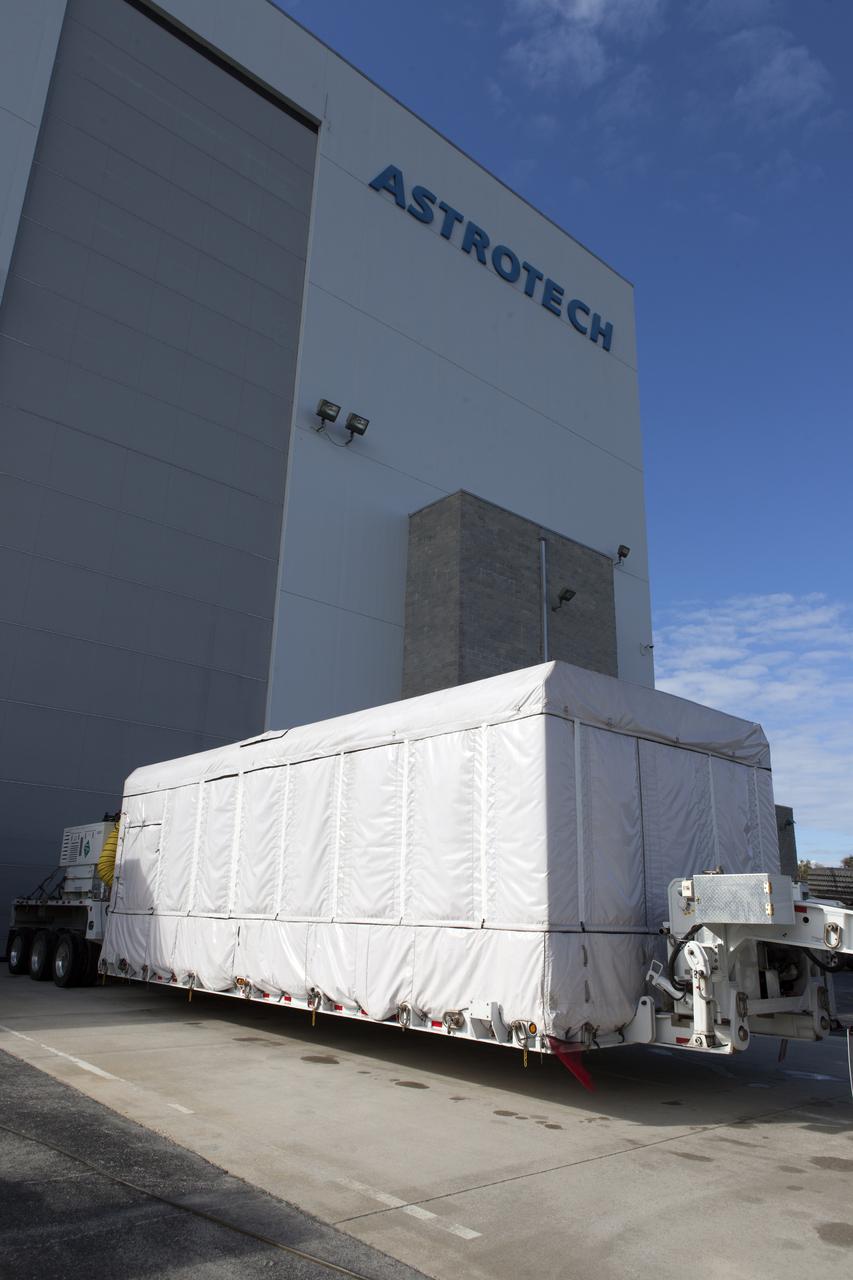

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
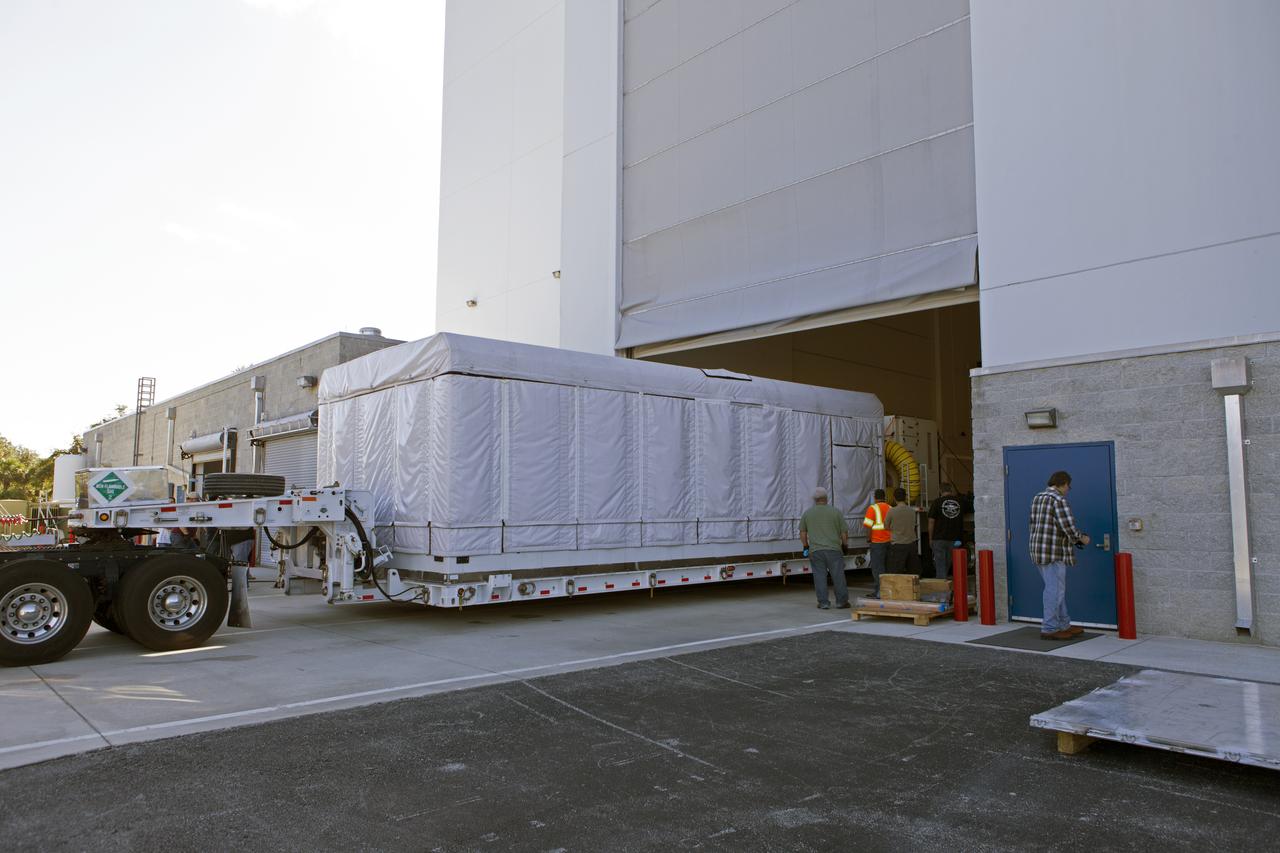

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
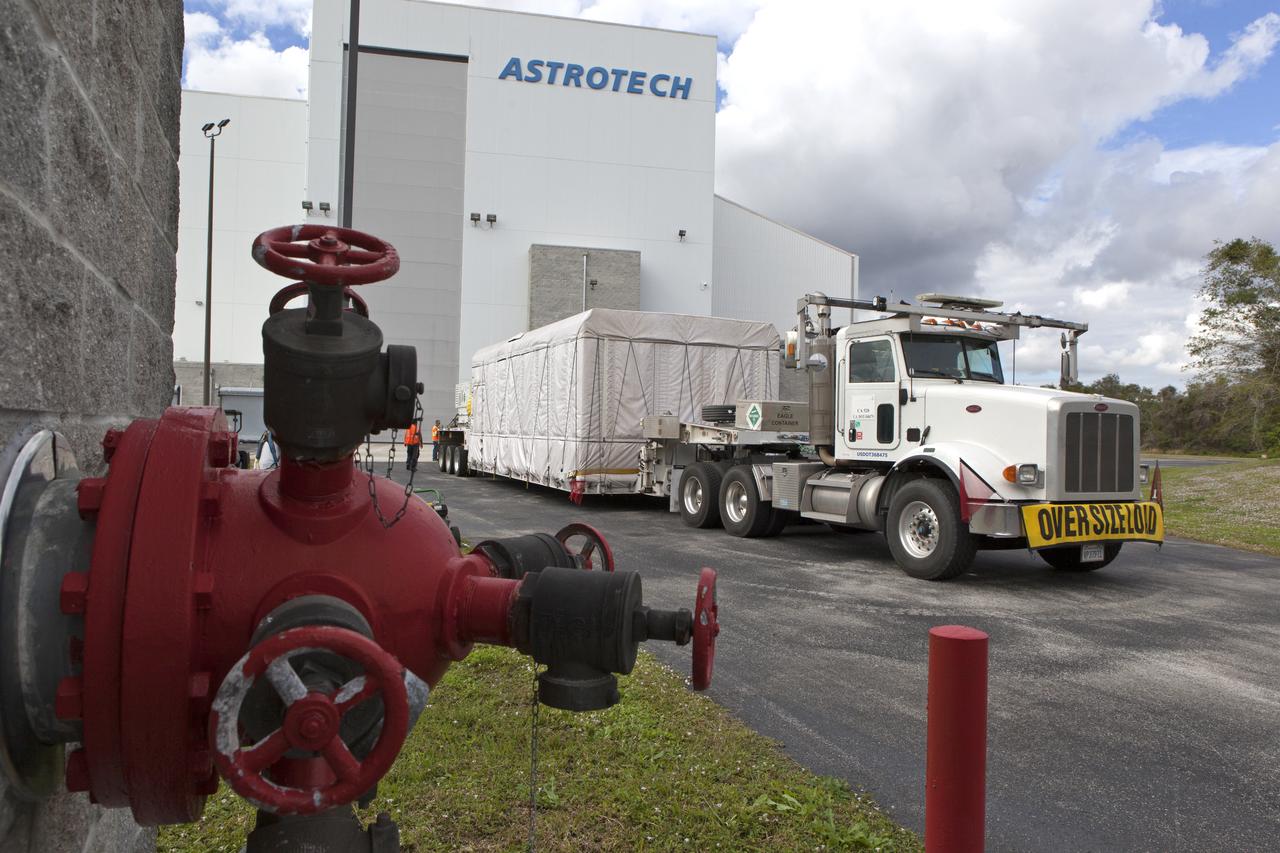

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
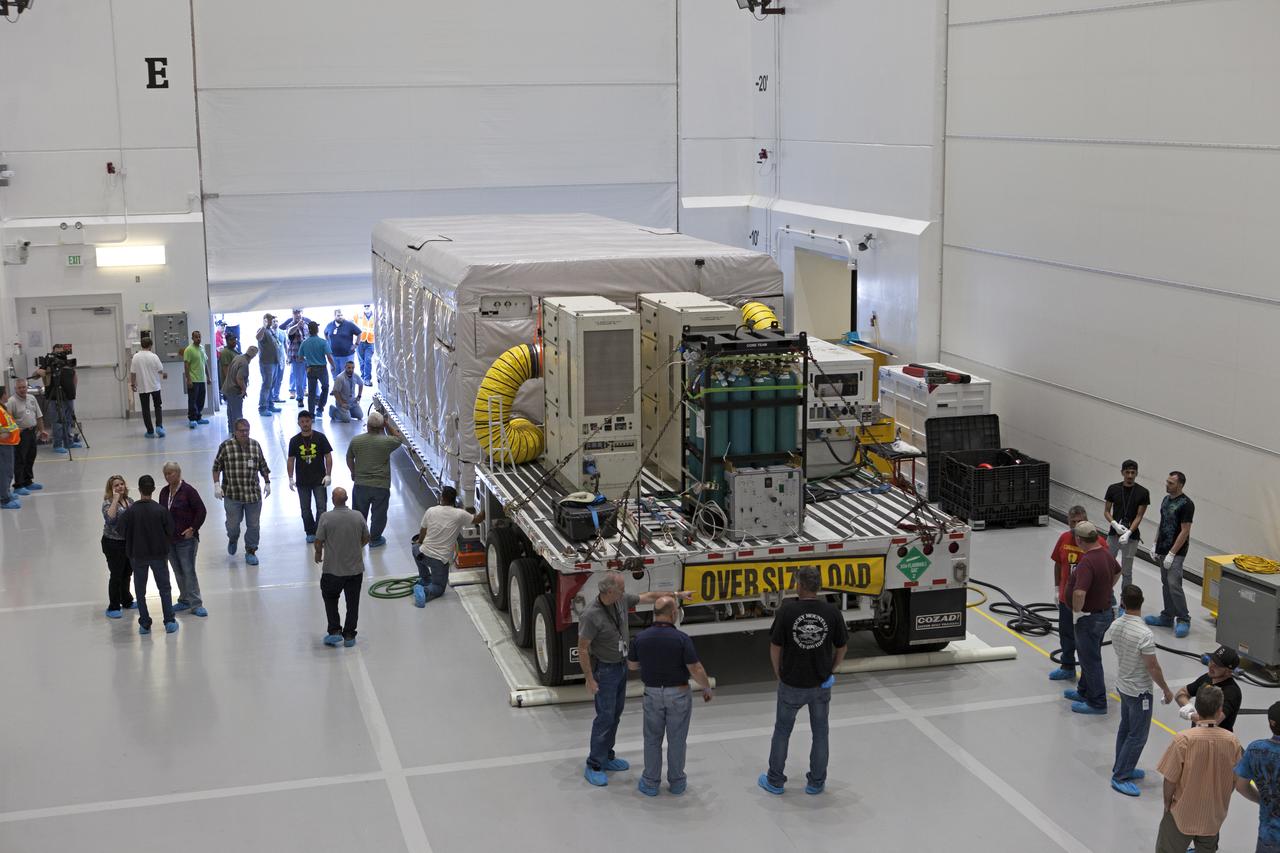

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
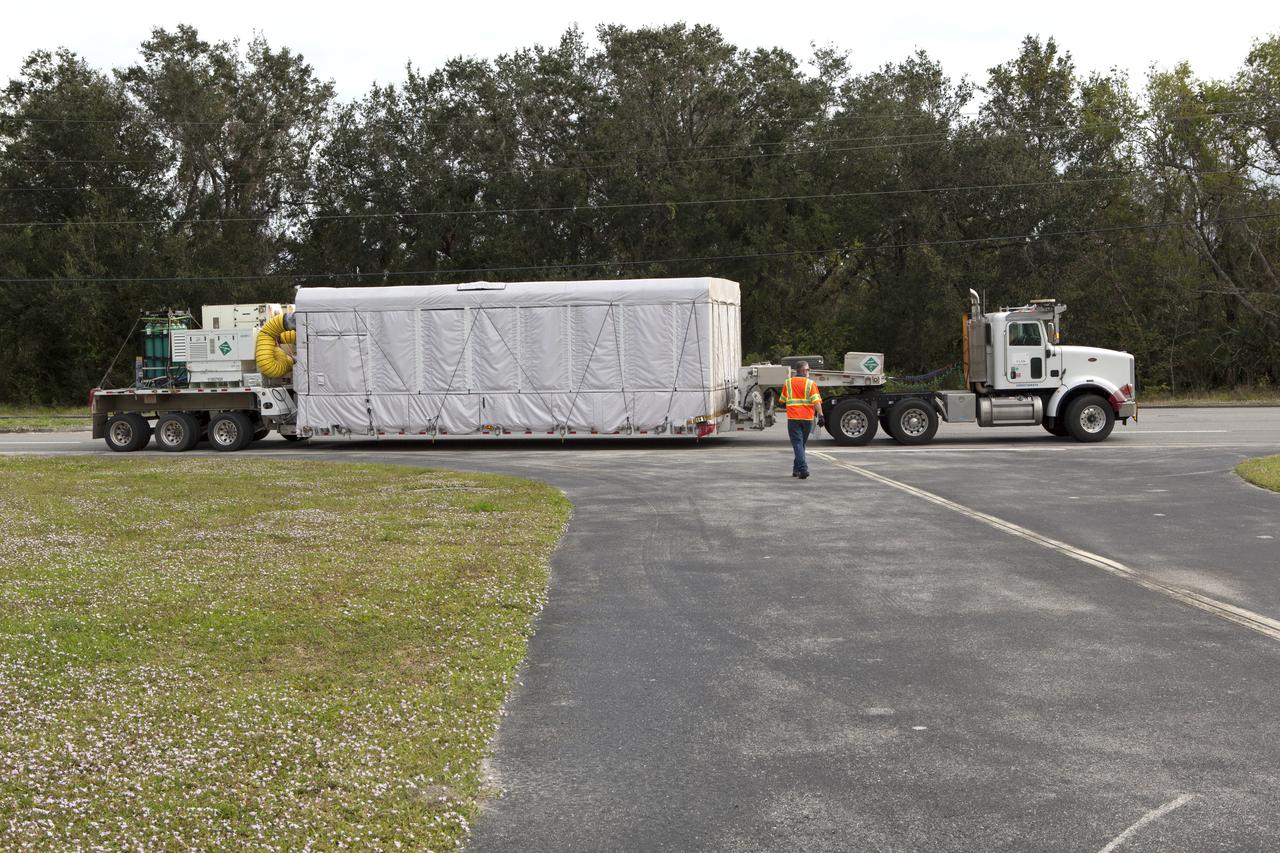

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
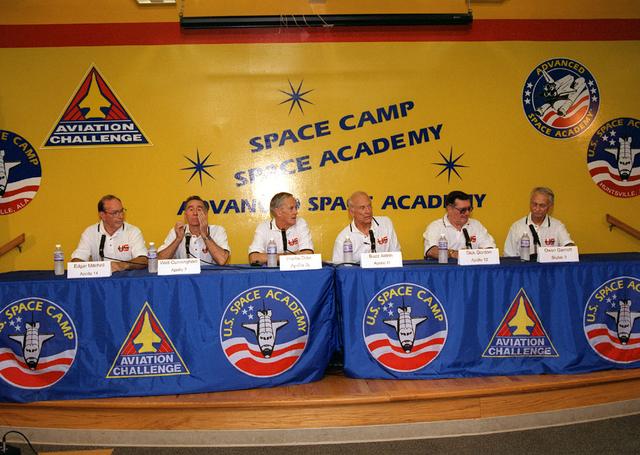

Marking the occasion of the Apollo 11 30th Anniversary, members of the Apollo and Saturn astronaut programs attended festivities at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL. A press conference was held at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center for the visiting astronauts. Pictured are (L/R): Edgar Mitchell, Walt Cunningham, Charlie Duke, Buzz Aldrin, Dick Gordon and Owen Garriott.
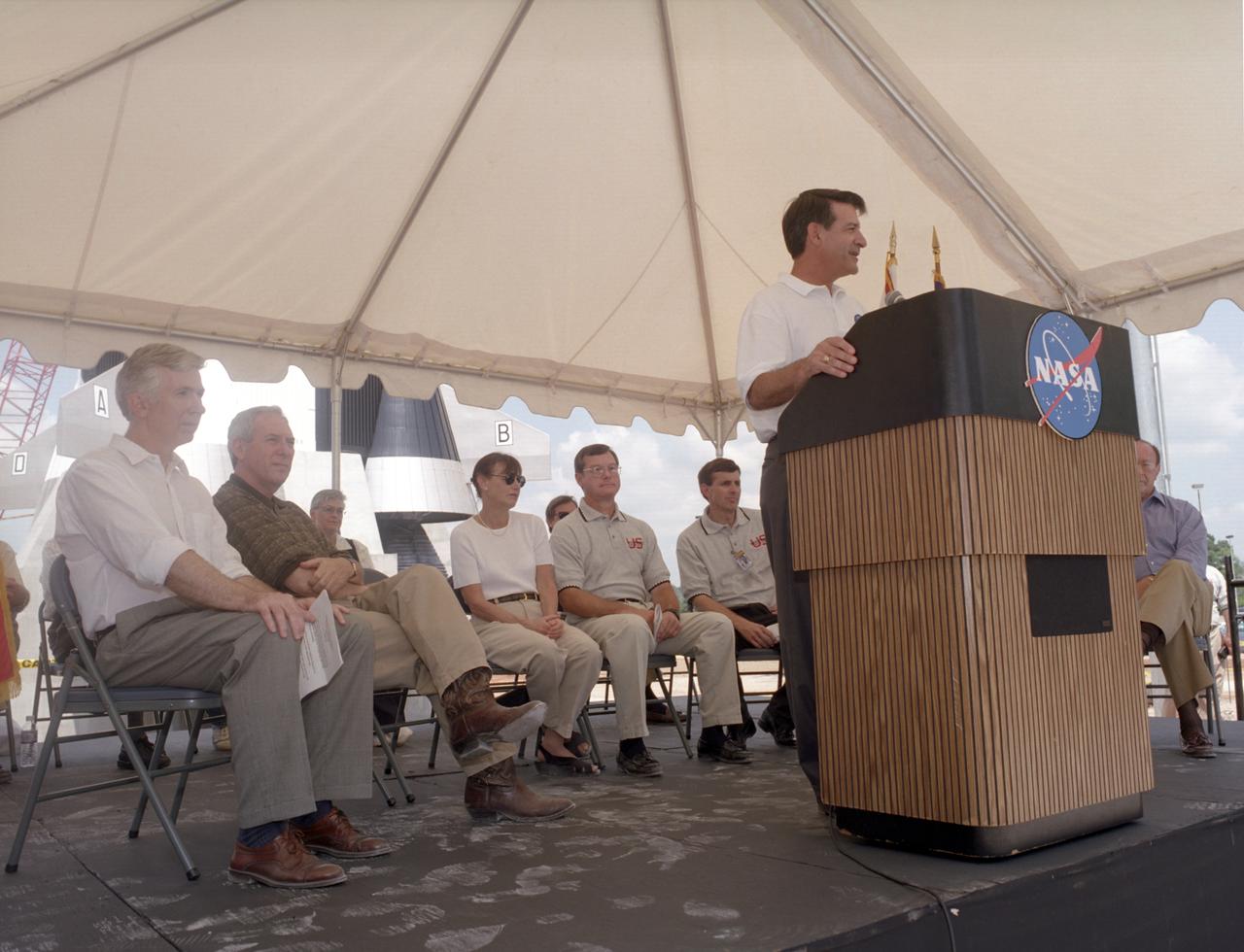

A replica of the Saturn V rocket that propelled man from the confines of Earth's gravity to the surface of the Moon was built on the grounds of the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL. in time for the 30th arniversary celebration of that historic occasion. Marshall Space Flight Center and its team of German rocket scientists headed by Dr. Wernher von Braun were responsible for the design and development of the Saturn V rocket. Pictured are MSFC's current Center Director Art Stephenson, Alabama Congressman Bud Cramer, and NASA Administrator Dan Goldin during the dedication ceremony.

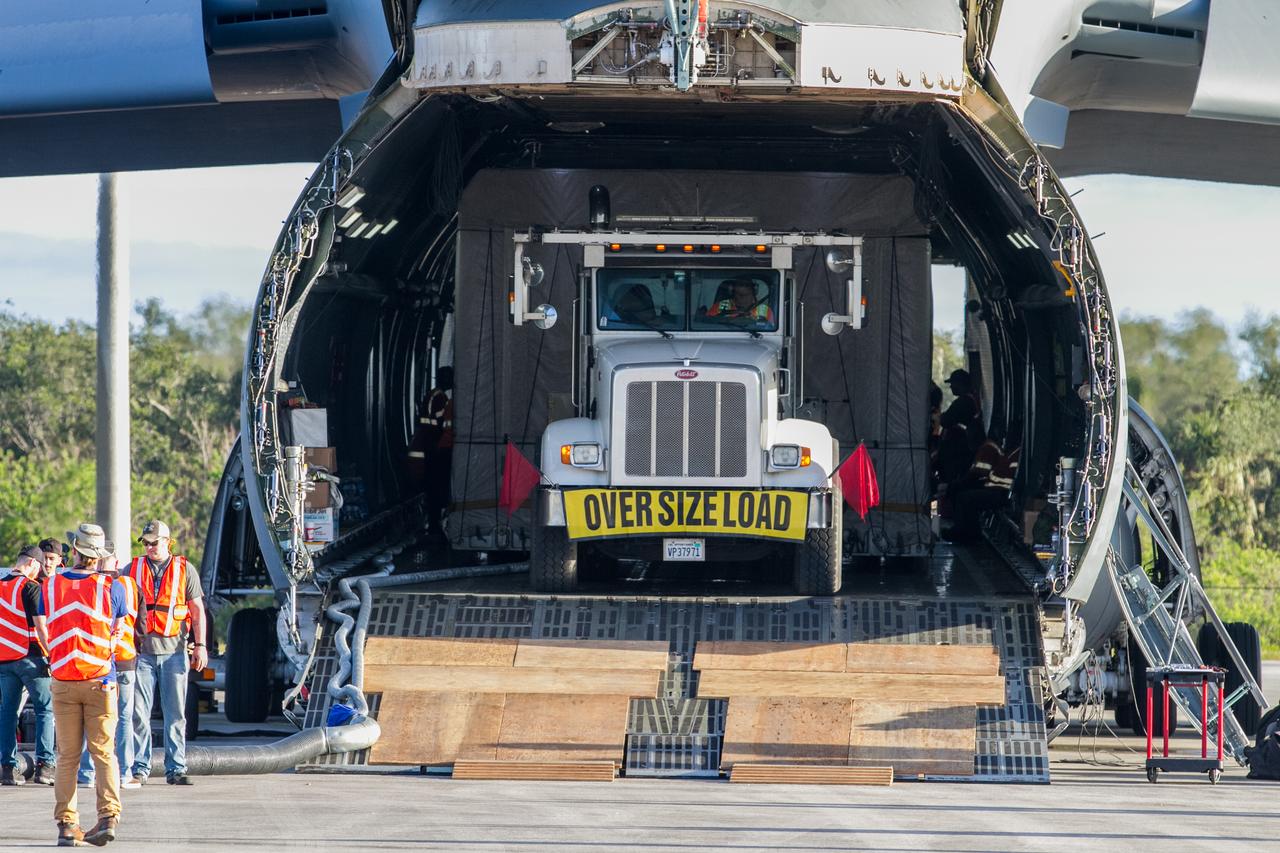
At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being loaded into the cargo hold of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being loaded into the cargo hold of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
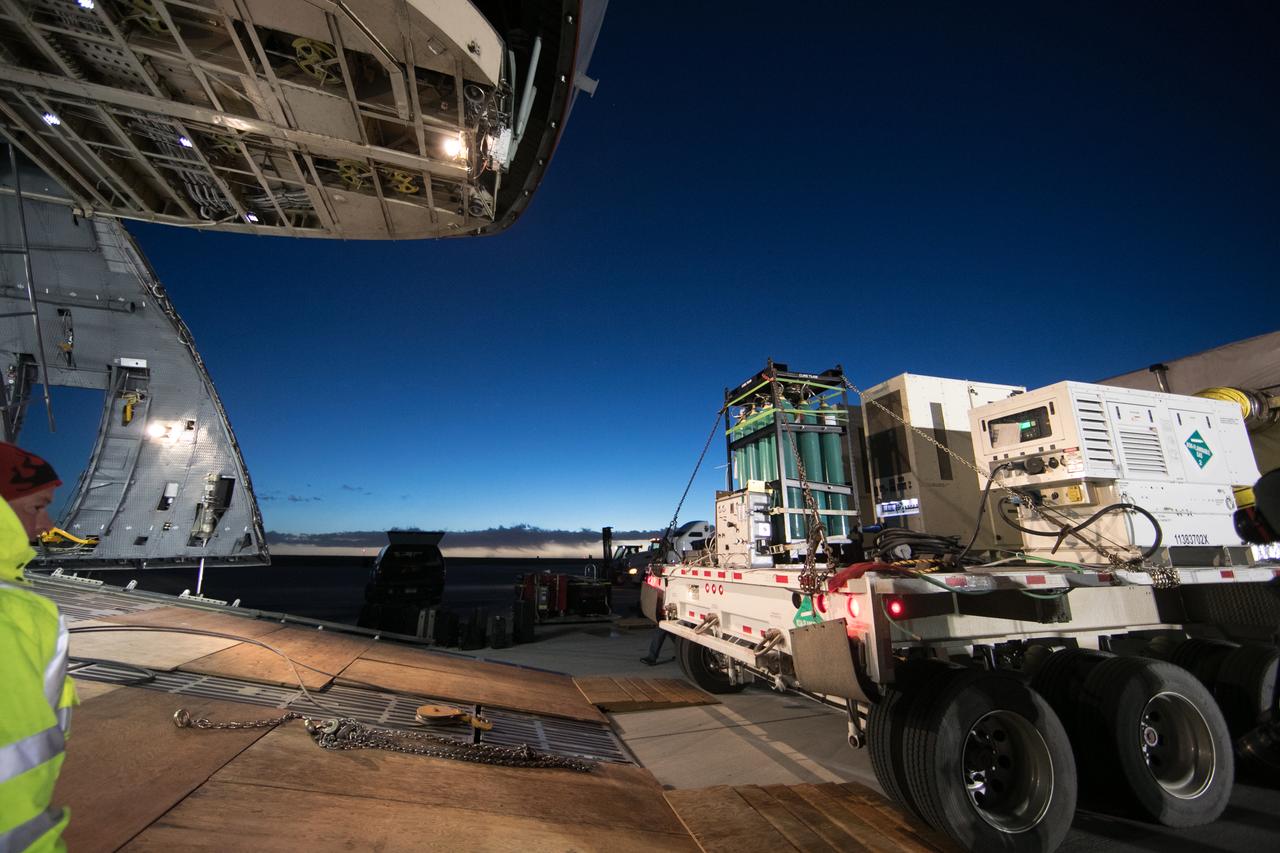

At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being loaded into the cargo hold of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
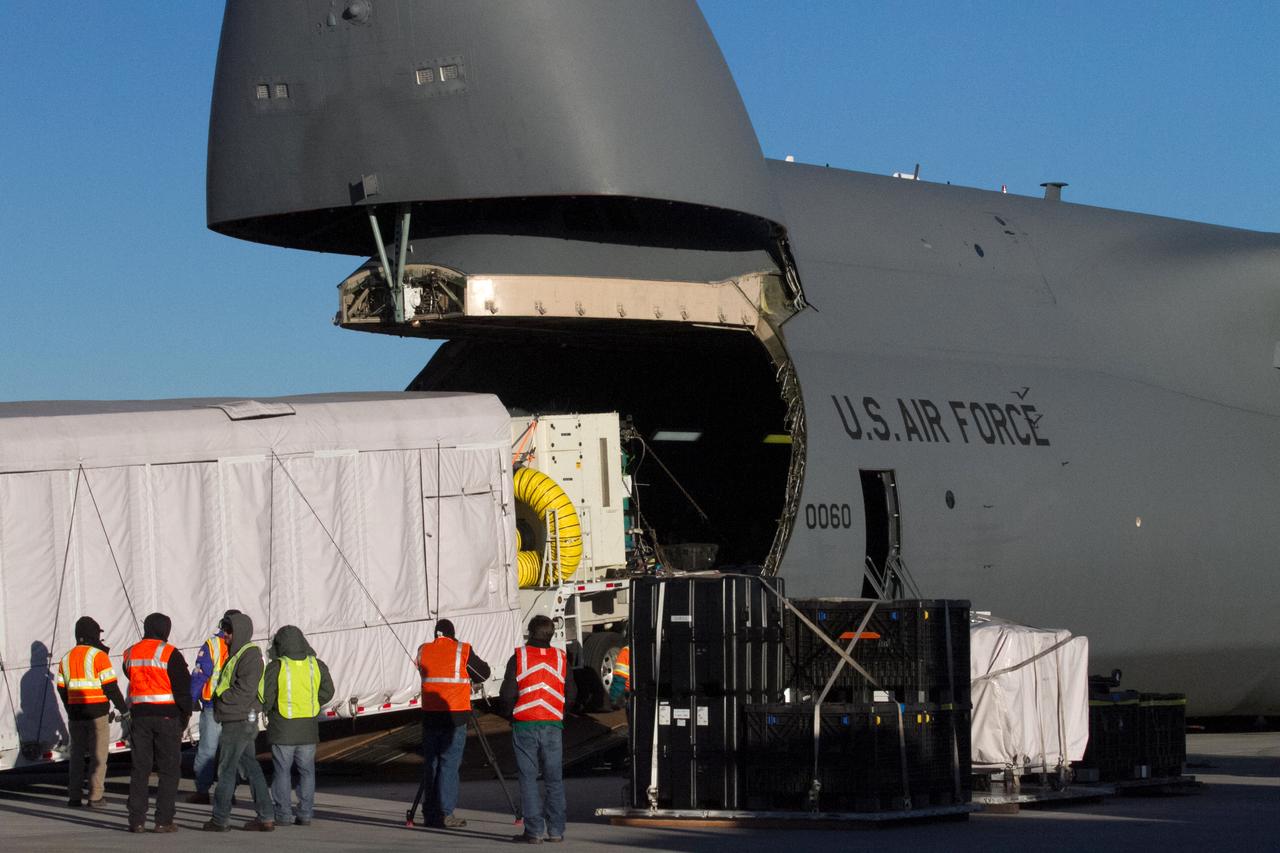

At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being loaded into the cargo hold of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
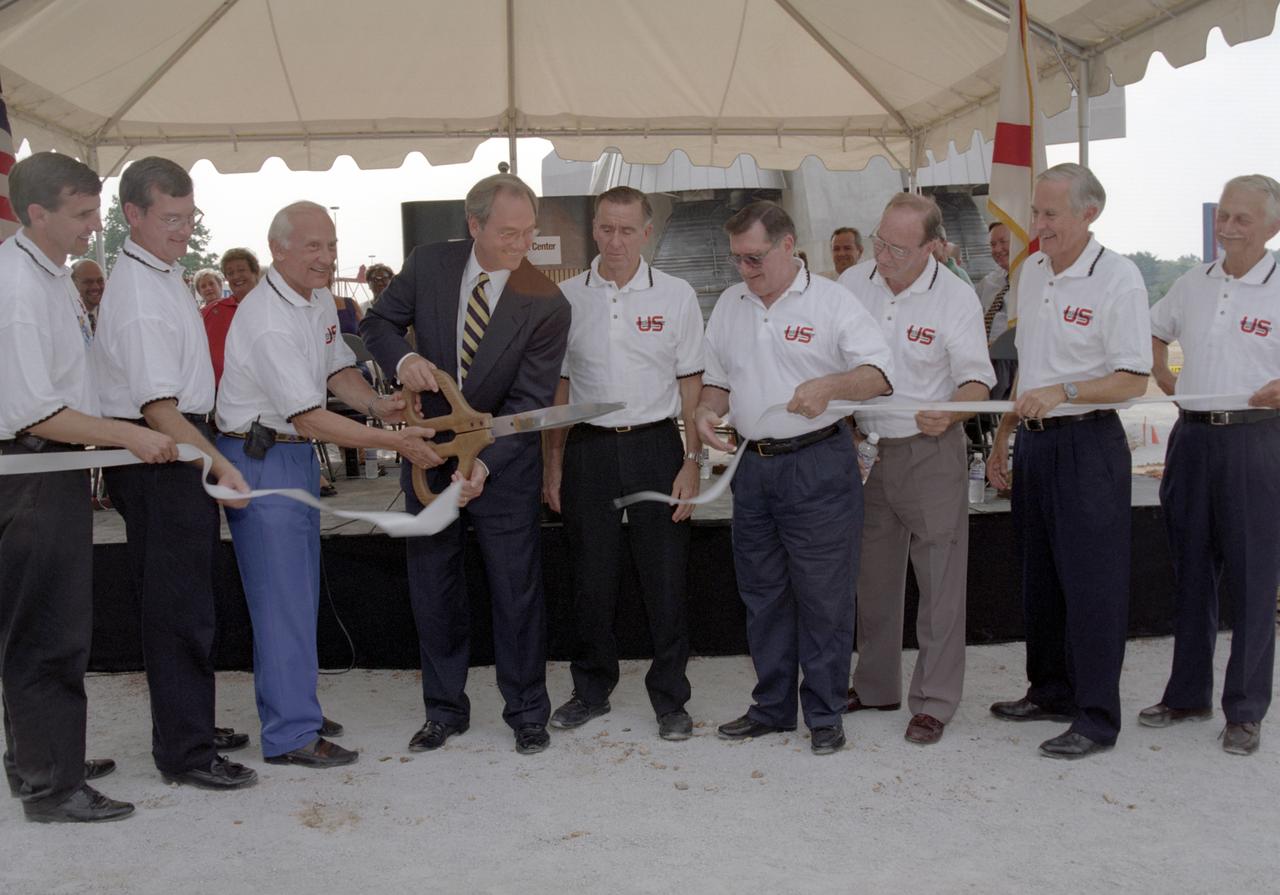

Alabama Governor Don Seigleman cuts the ribbon marking the dedication of the Saturn V rocket replica that was constructed at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in honor of the 30th arniversary of the lunar landing. Accompanying the Governor are (L/R): Mike Wing, CEO US Space Rocket Center; Mike Gillespie, Madison County Commissioner, Dist. Seven; Buzz Aldrin, Apollo 11 Astronaut; Governor Seigleman; Walt Cunningham, Apollo 7 Astronaut; Dick Gordon, Apollo 12 Astronaut; Ed Mitchell, Apollo 14 Astronaut; Charlie Duke, Apollo 16 Astronaut; and Owen Garriott, Skylab 3 Astronaut.
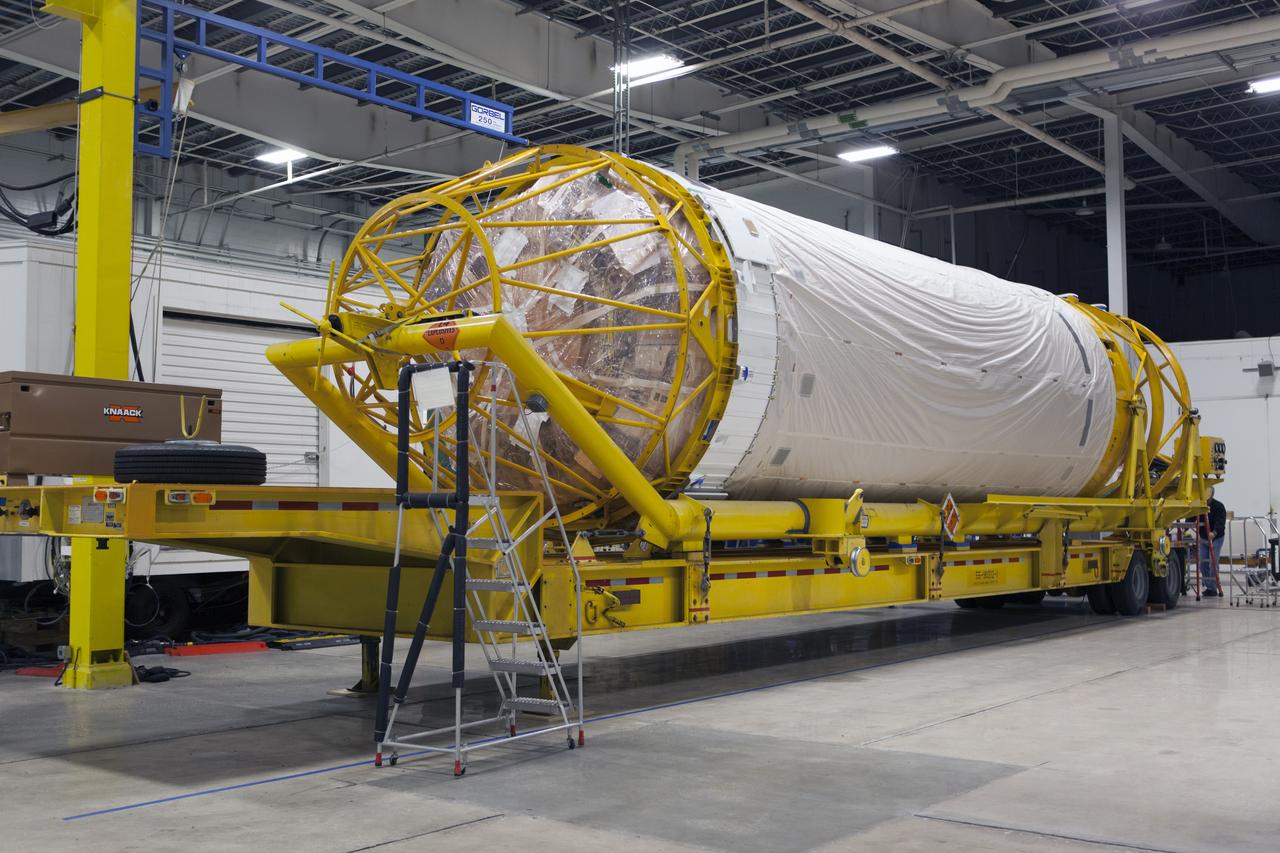

Inside the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Centaur upper stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being prepared for transport to the Delta Operations Center for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
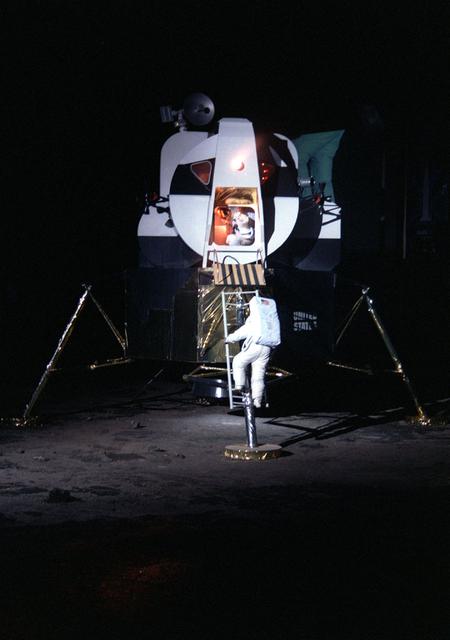

The re-enactment of astronaut Neil Armstrong's first steps off the lunar lander provided quite the occasion for many of the on-lookers at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, AL, during the celebration of the 30th arniversary of the Apollo 11 lunar landing. The celebration in Huntsville lasted over the weekend with visitors including Buzz Aldrin and other Apollo astronauts.
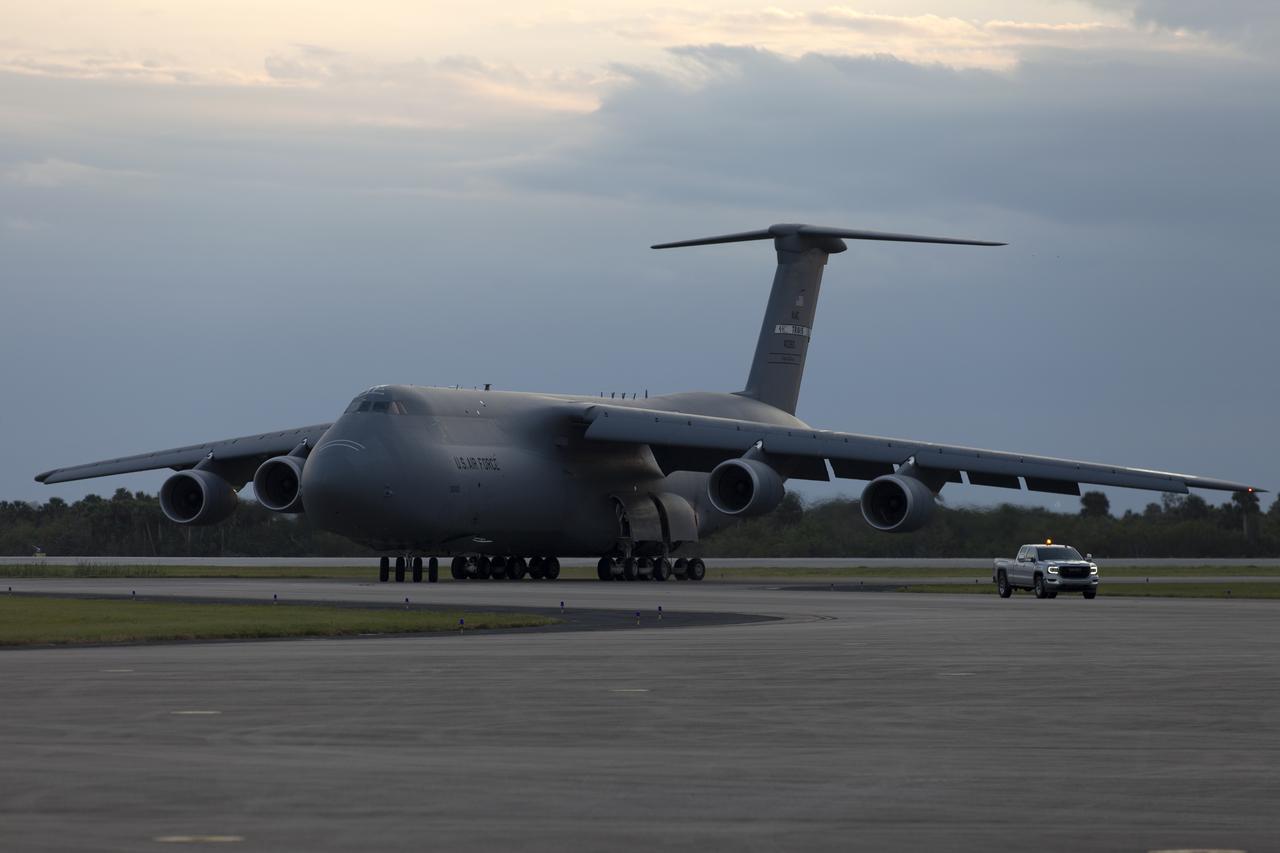

A C-5 transport aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The satellite will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
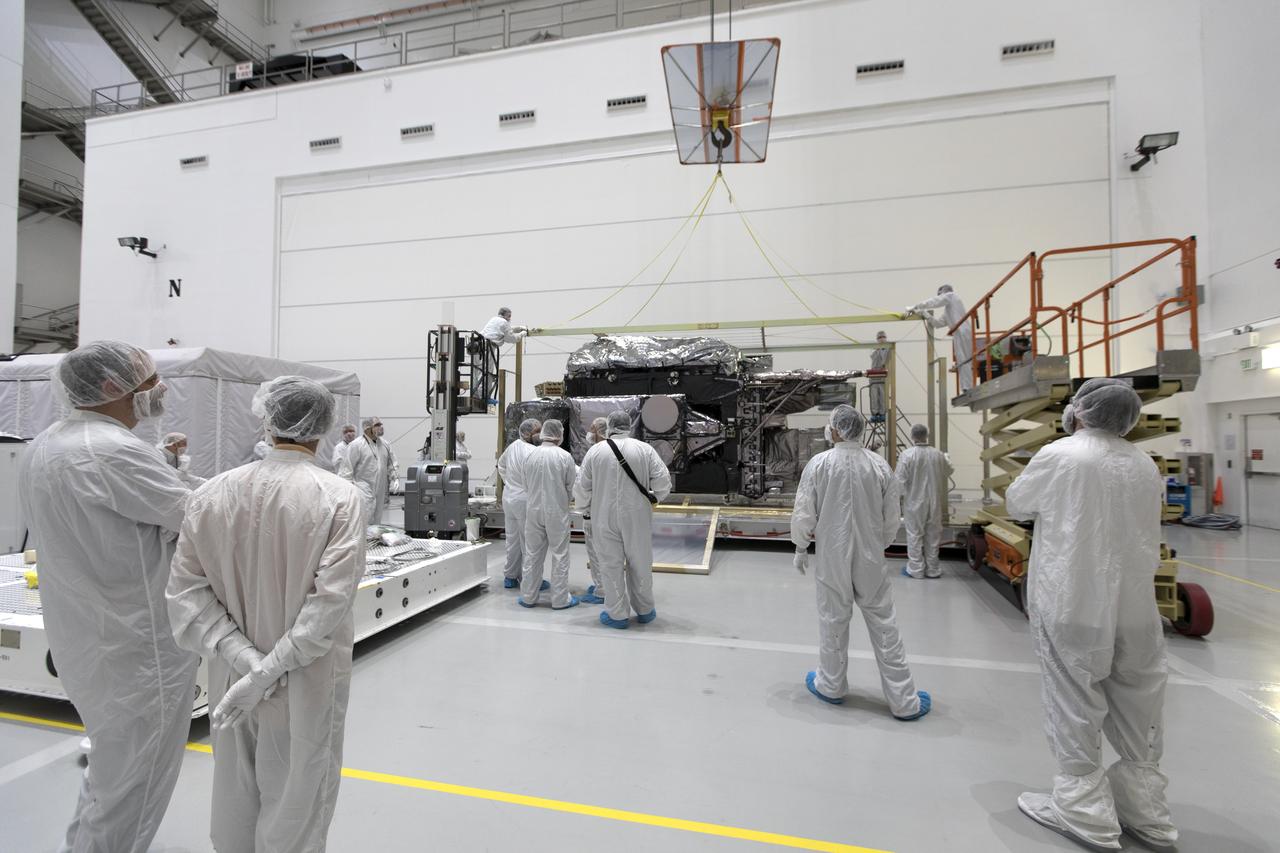

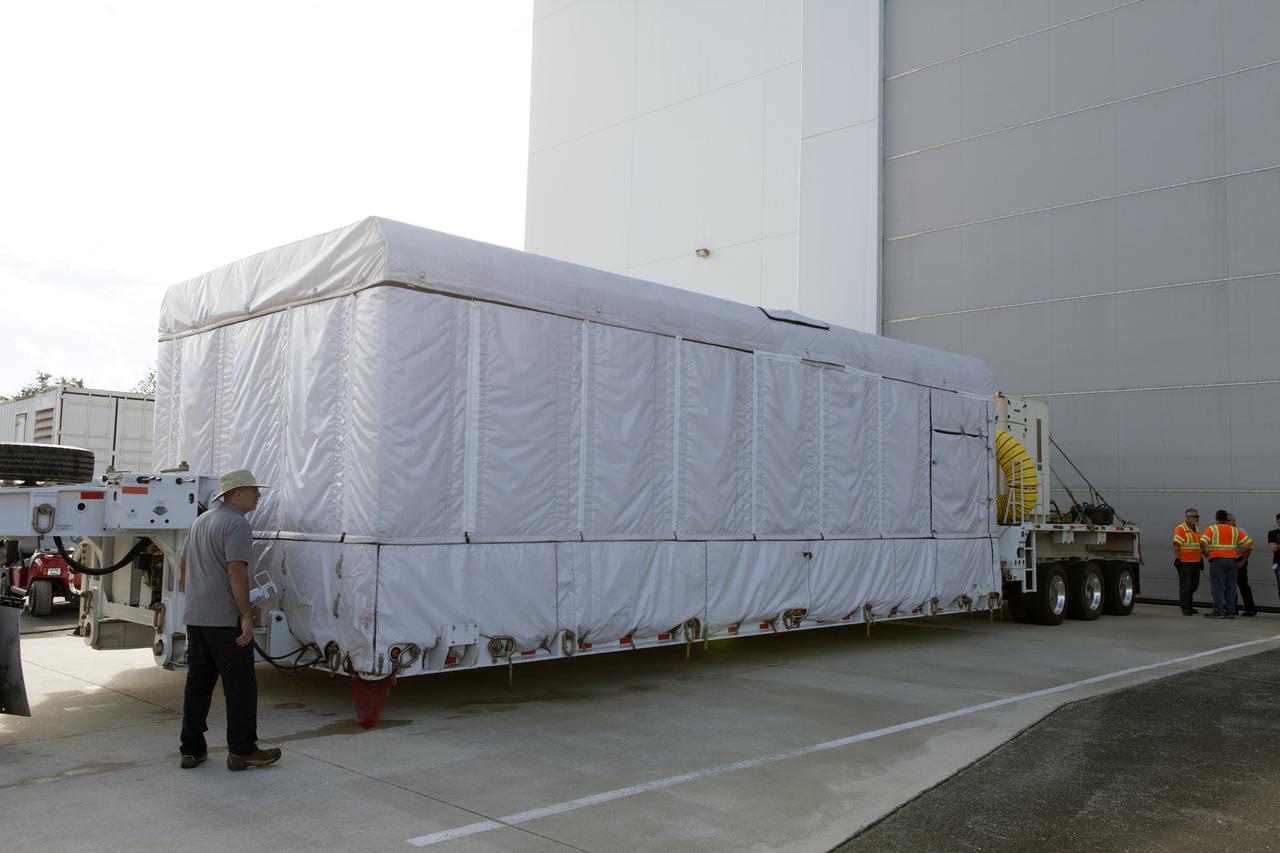
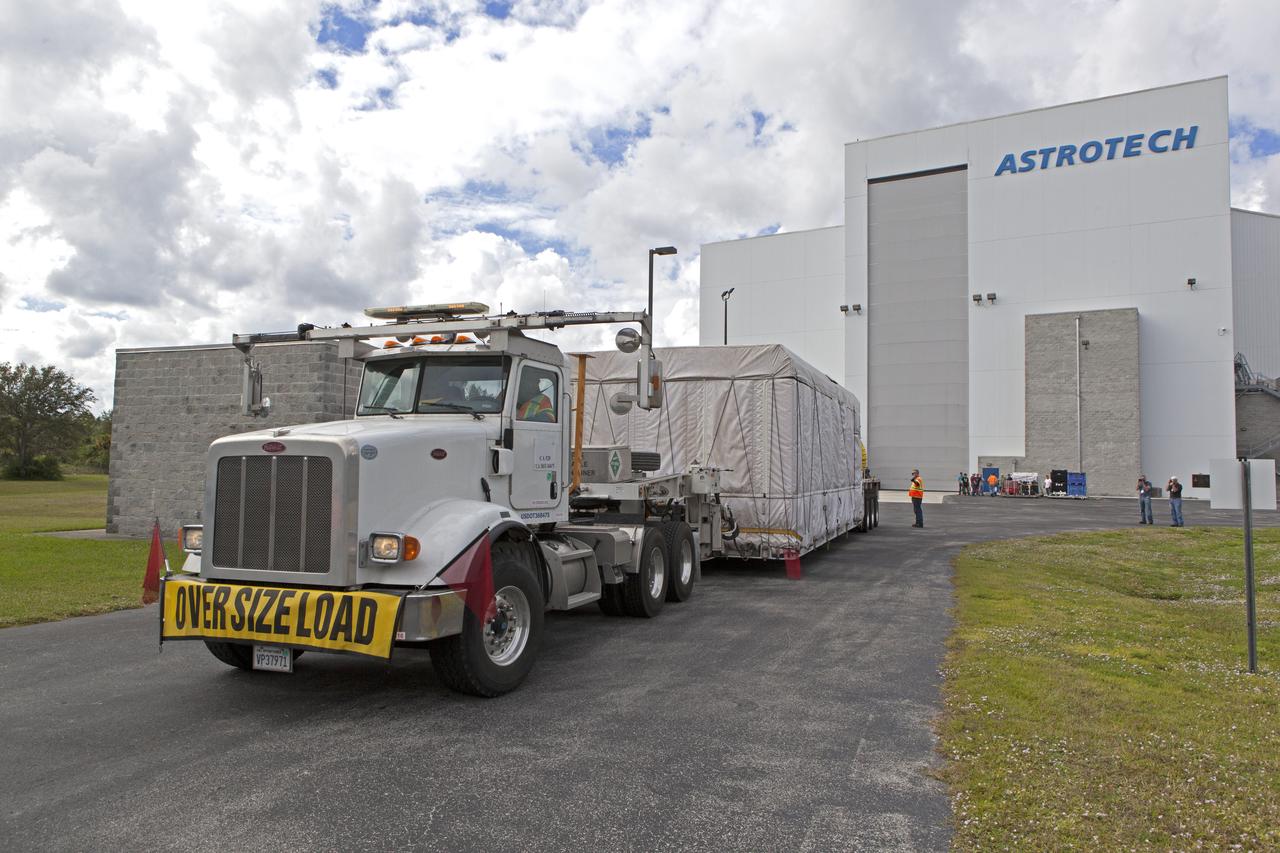
At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
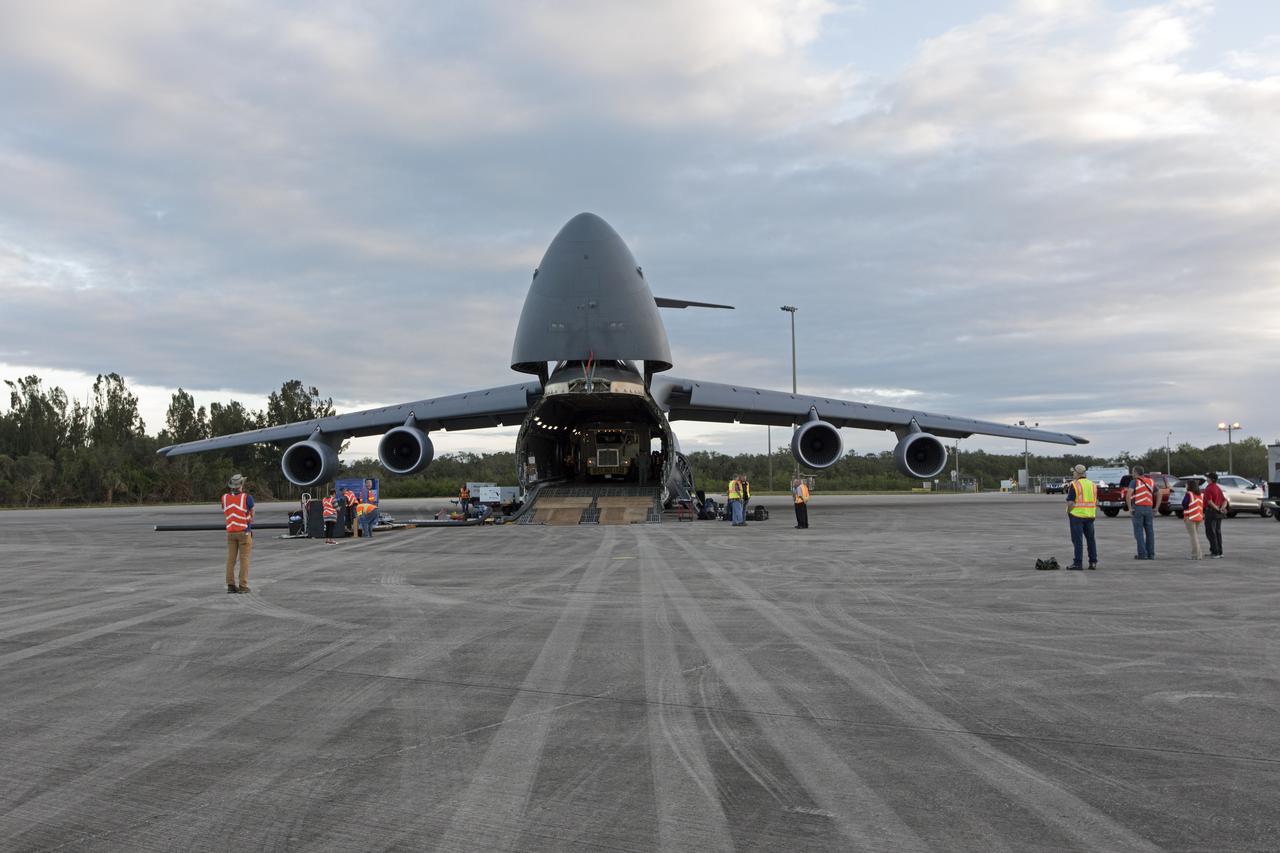

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
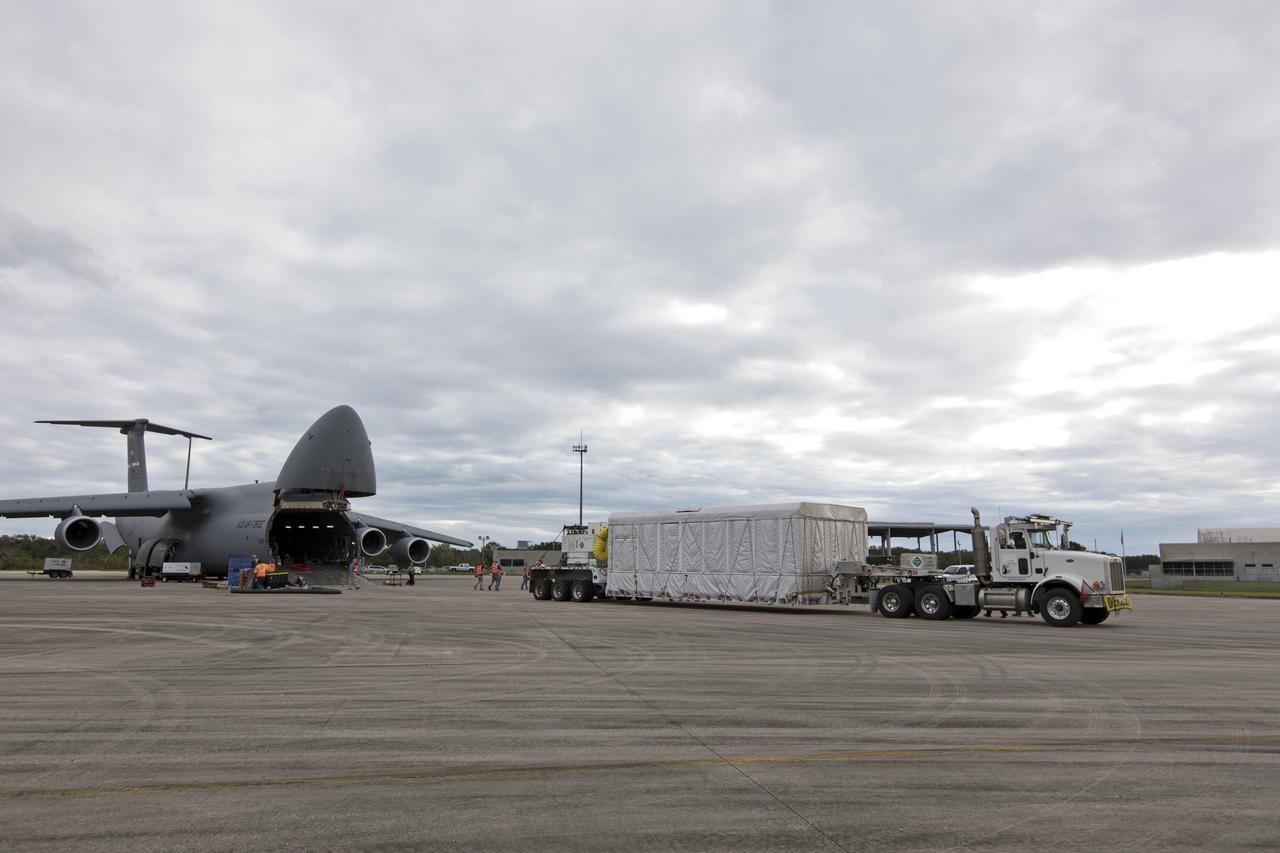

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft and secured onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
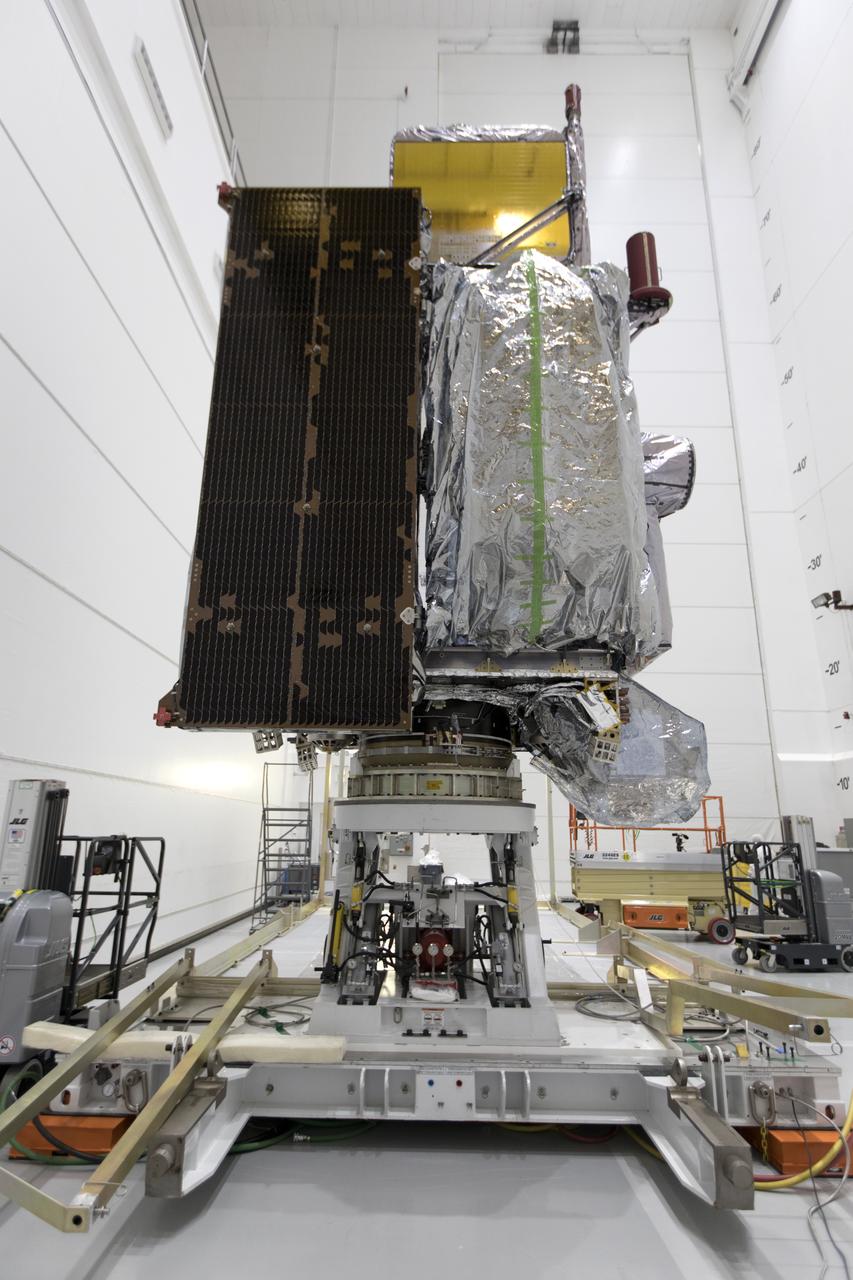

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
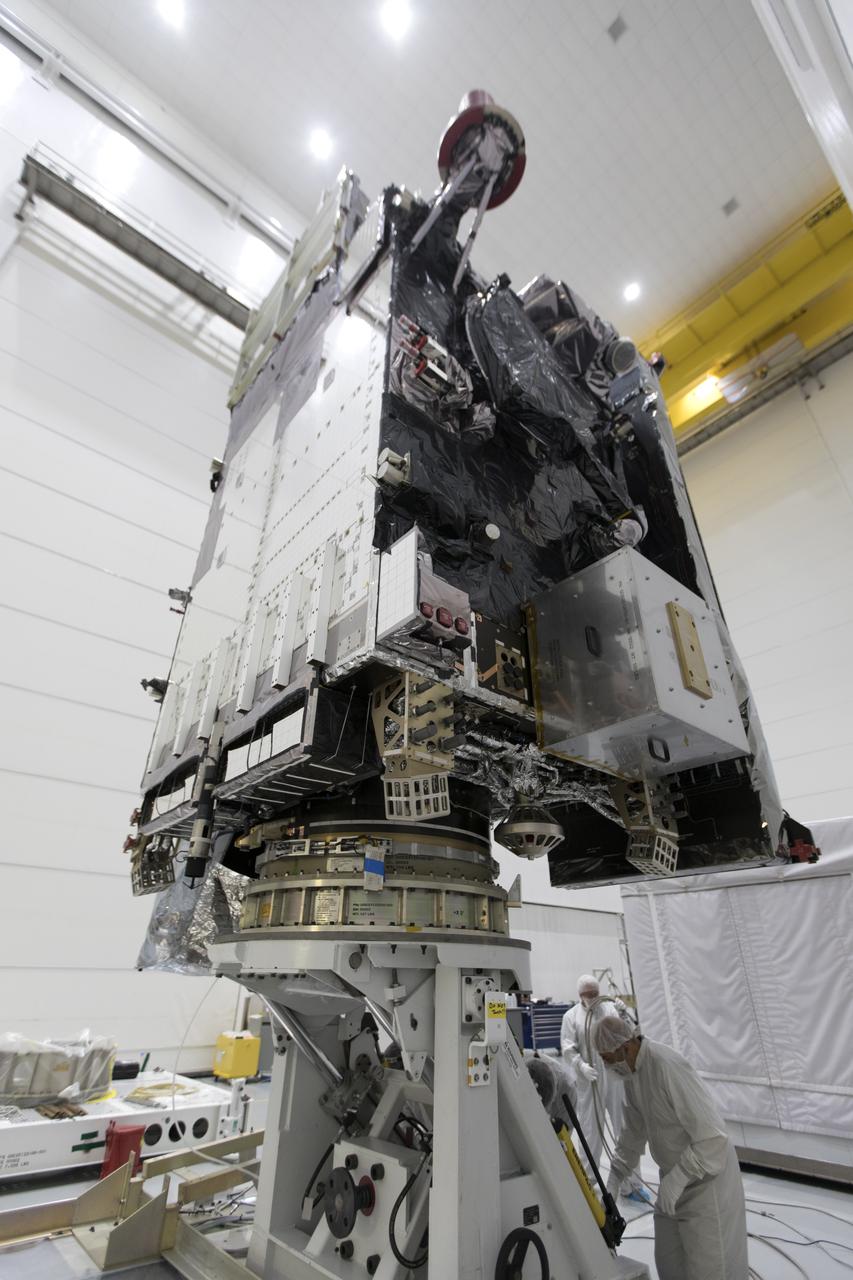

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
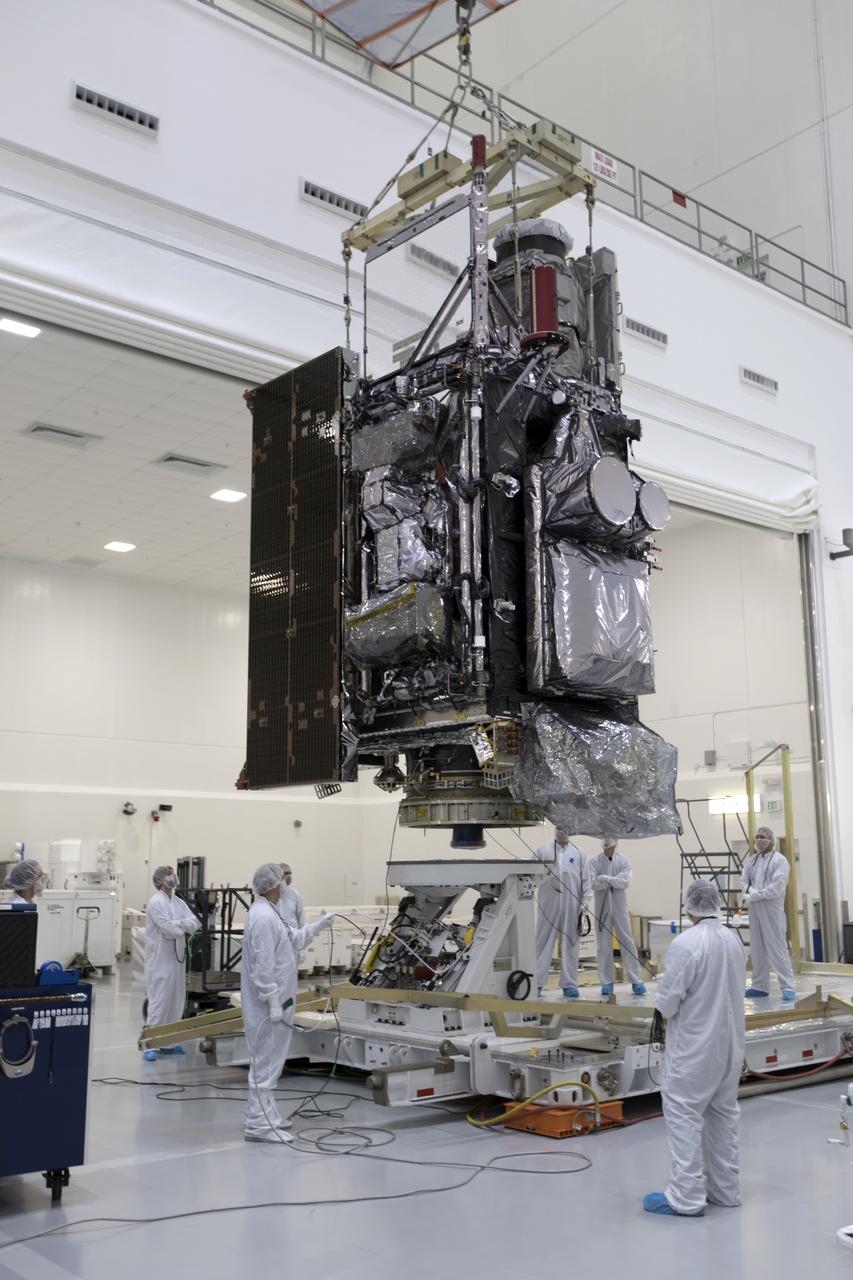

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
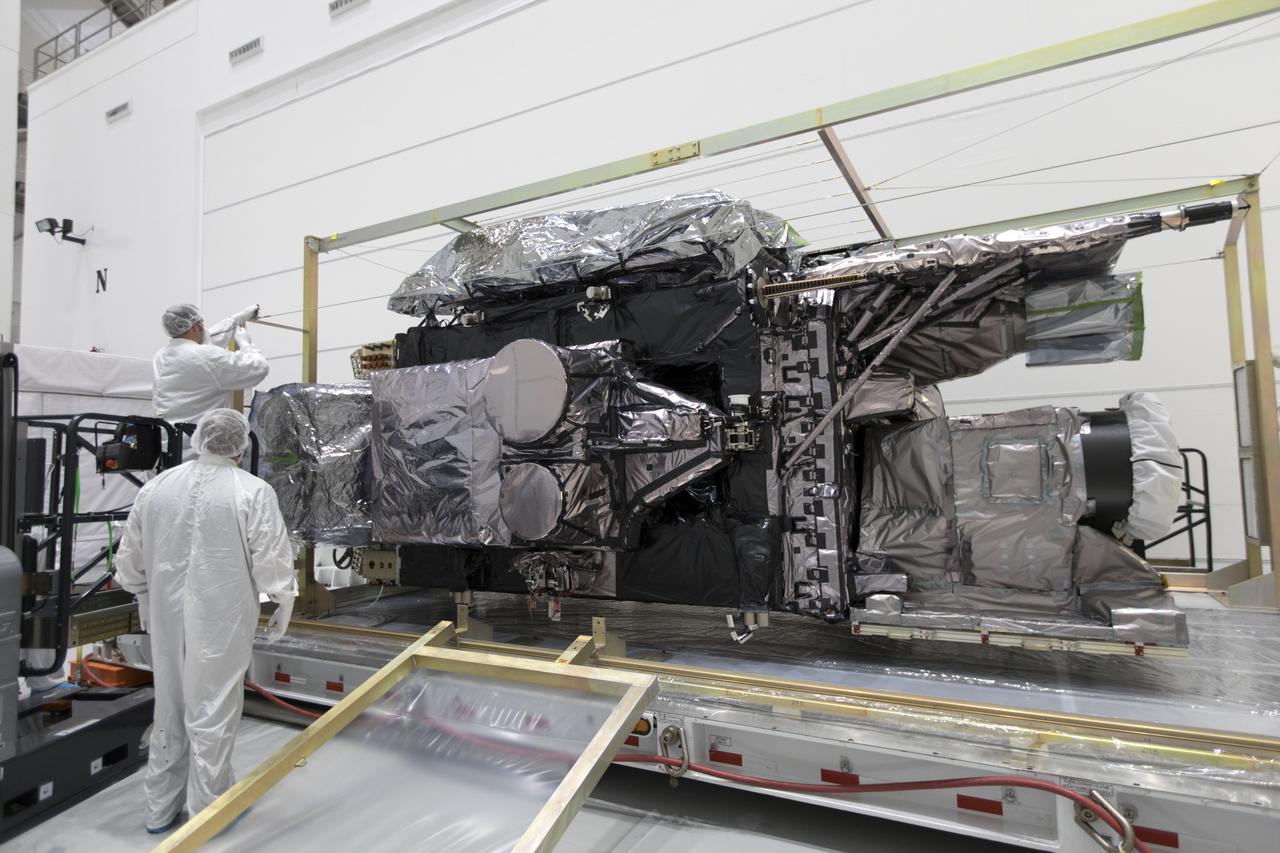

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician inspects NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
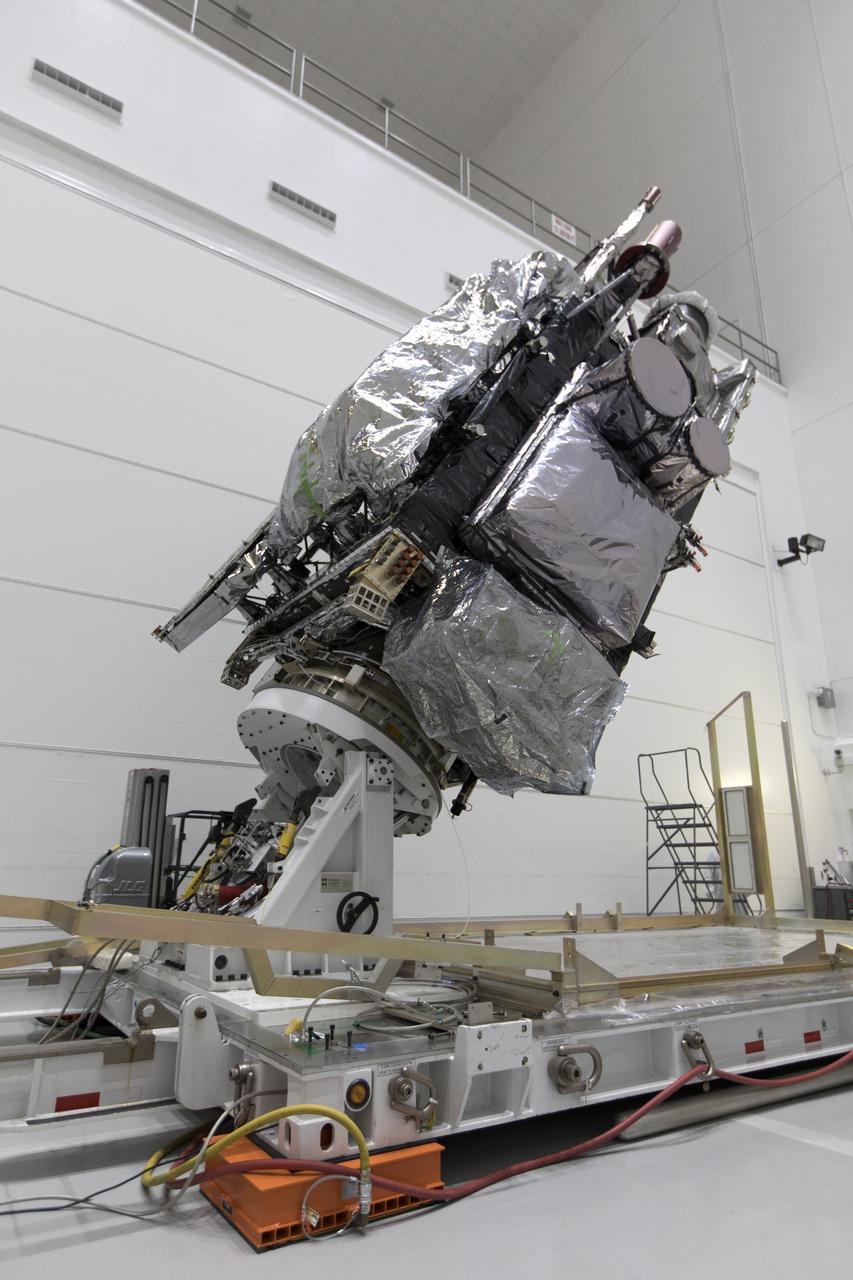

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
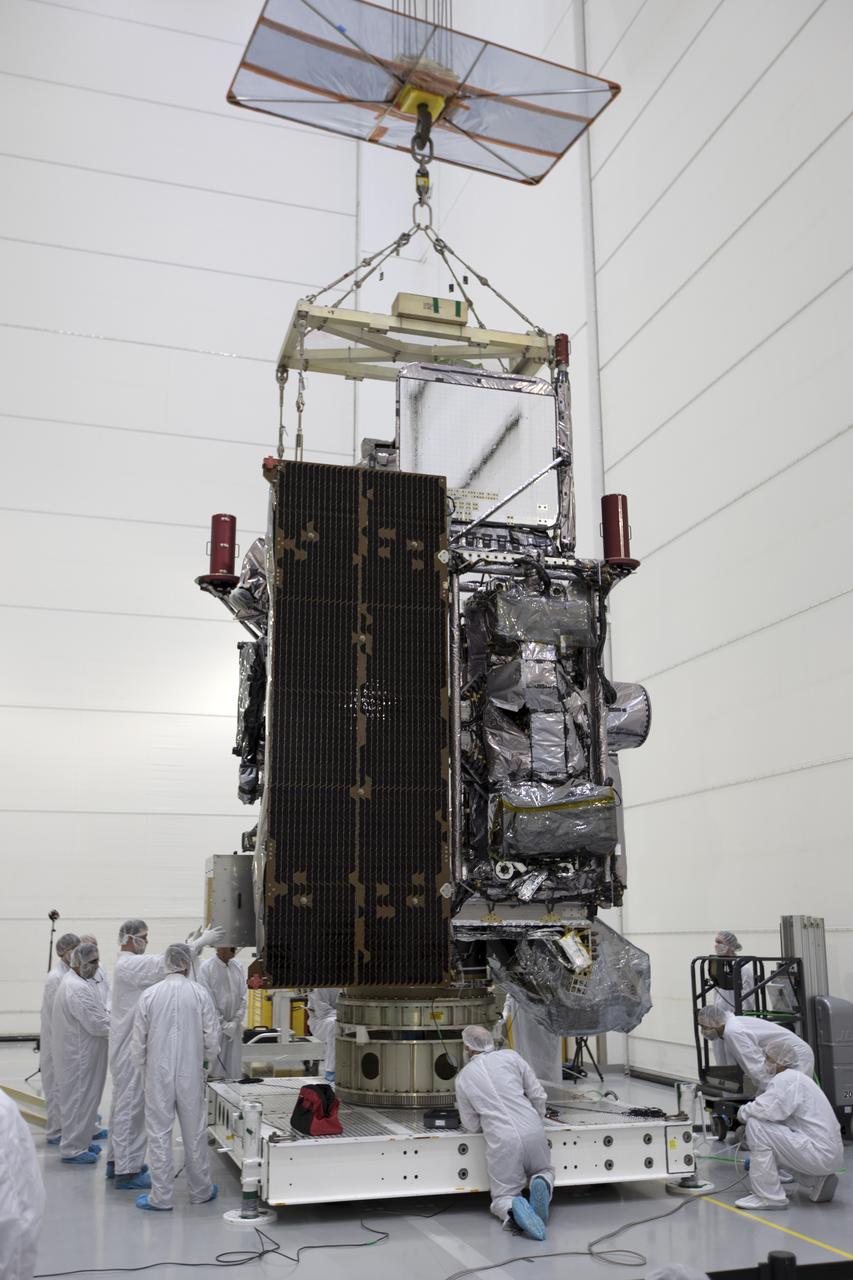

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
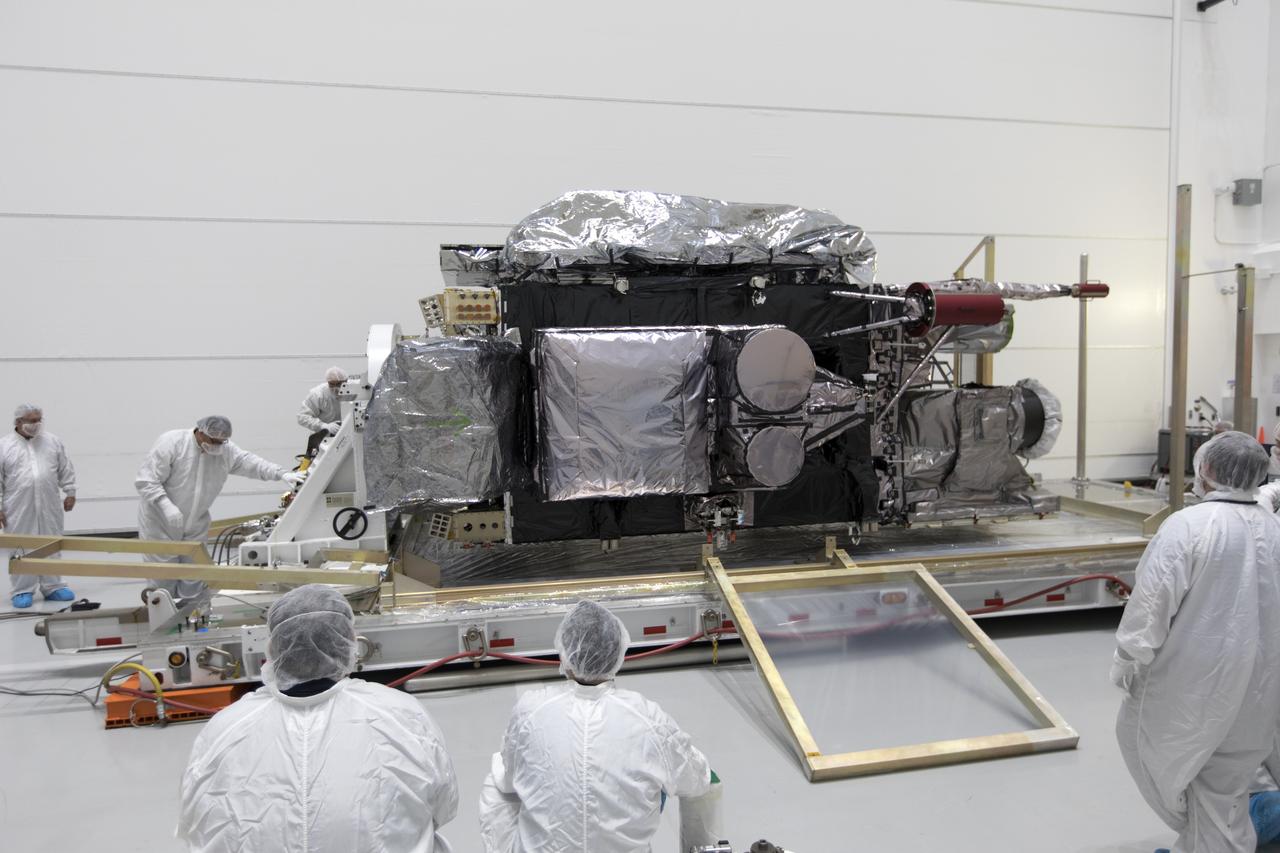

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
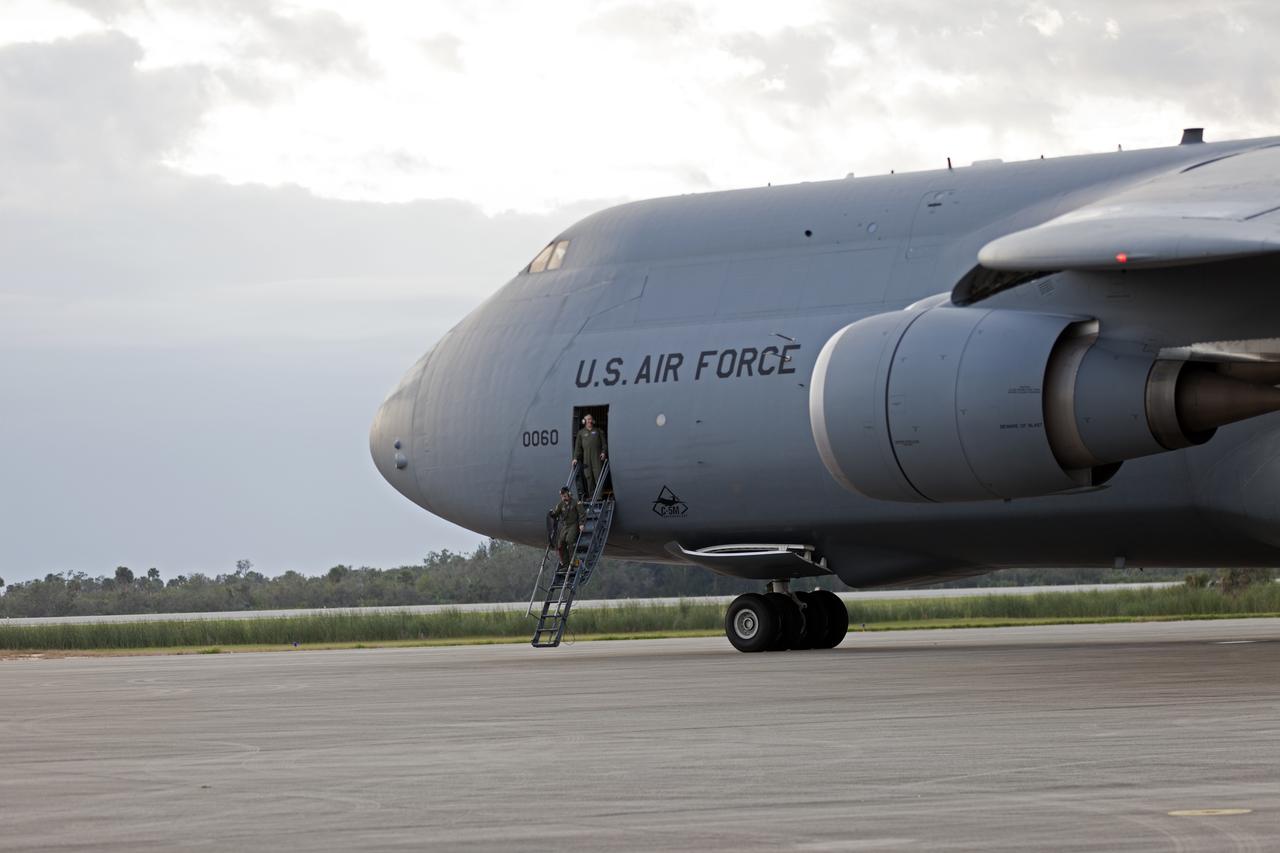

A C-5 transport aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The satellite will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
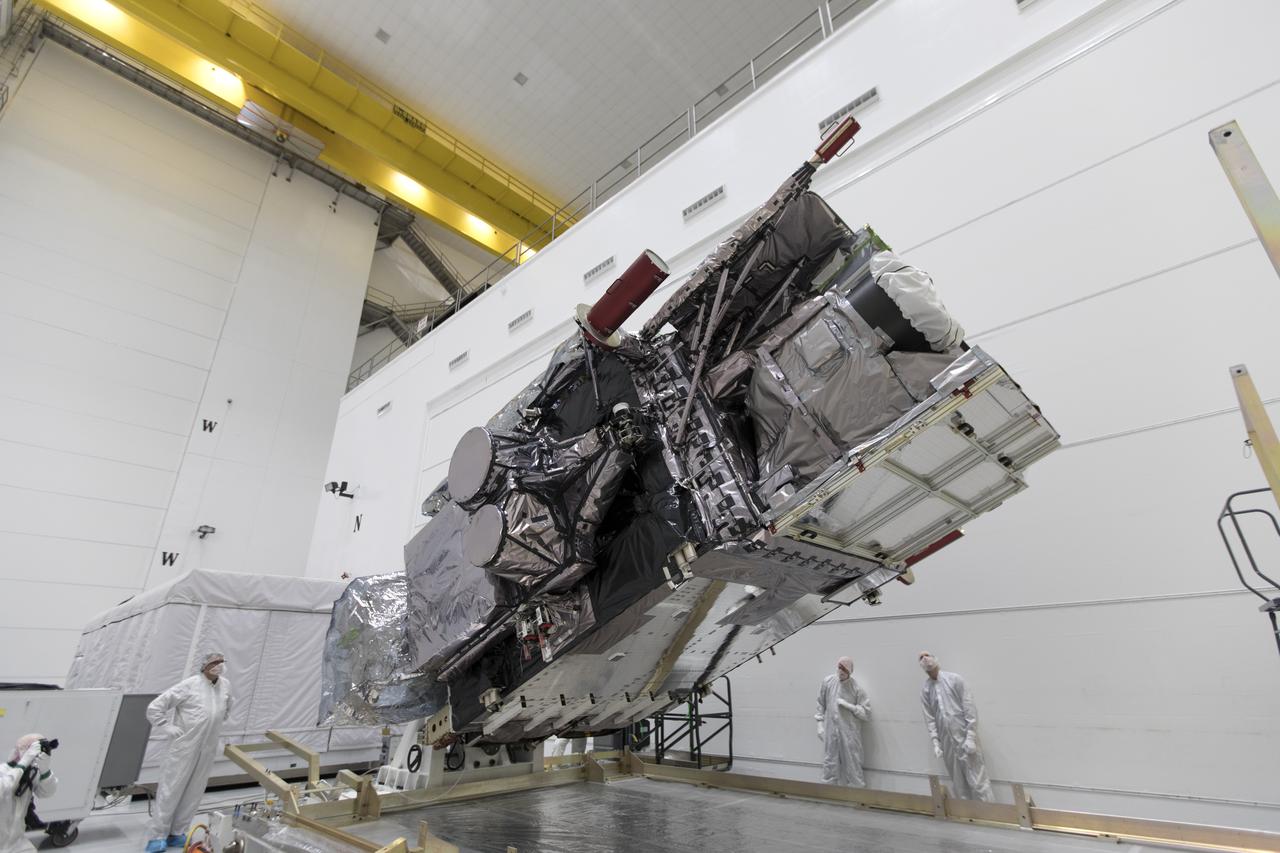

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
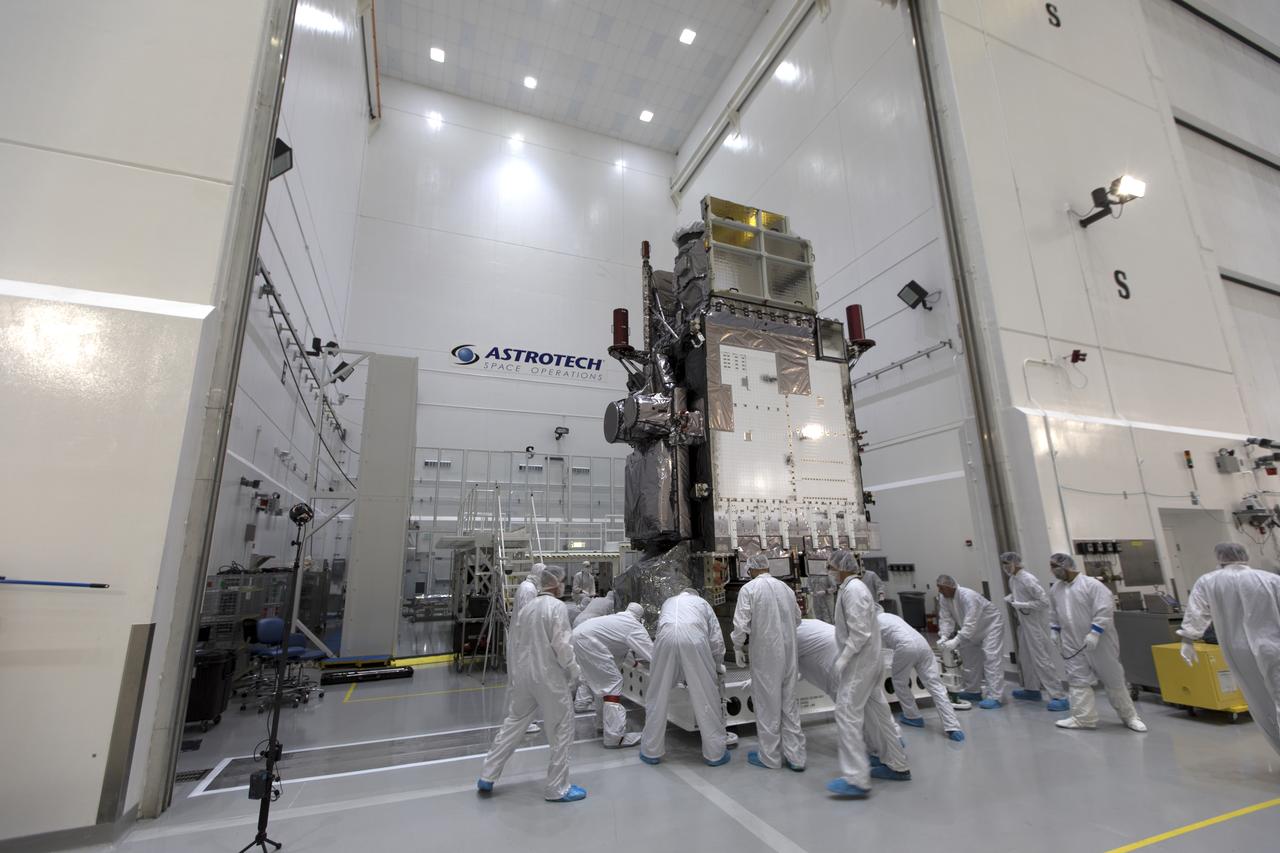

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers move NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) into a clean room for further processing. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
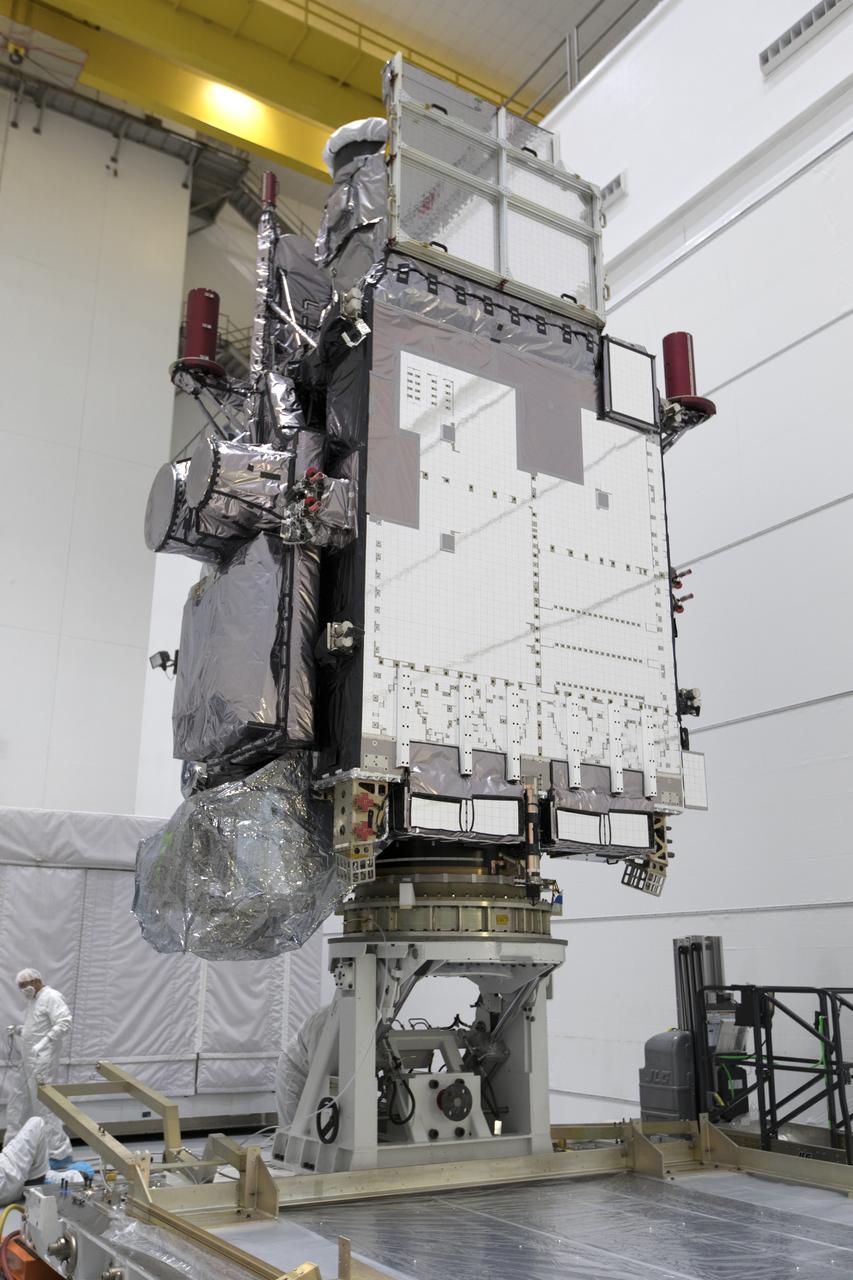

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
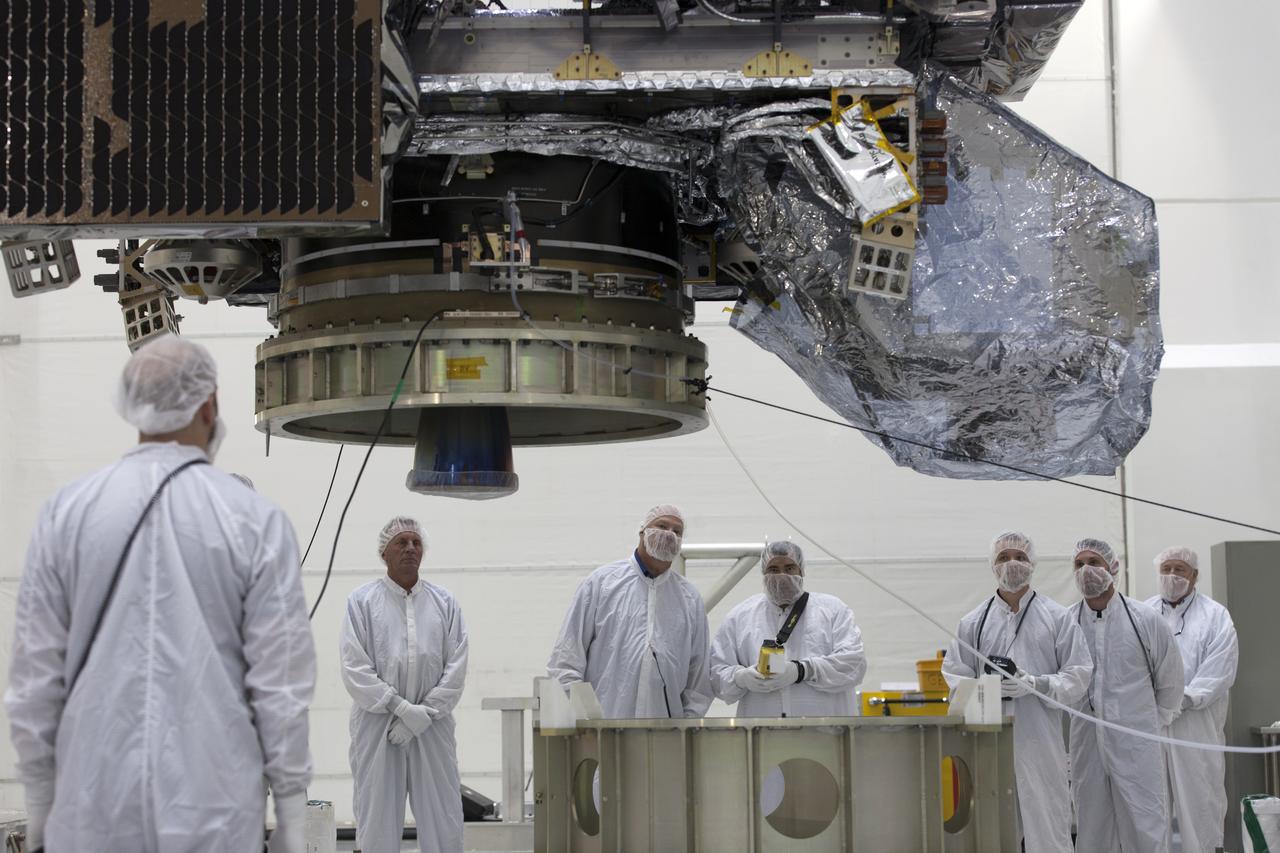

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
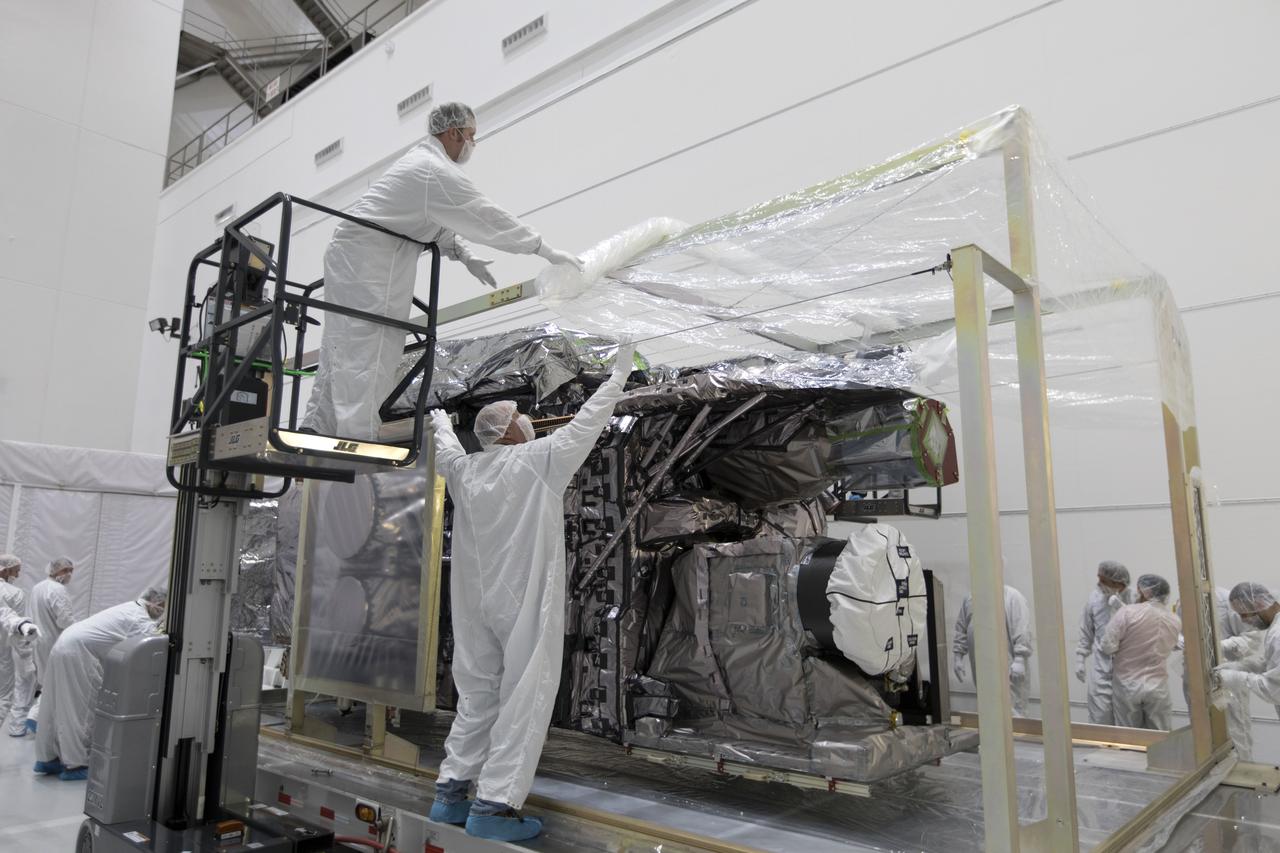

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
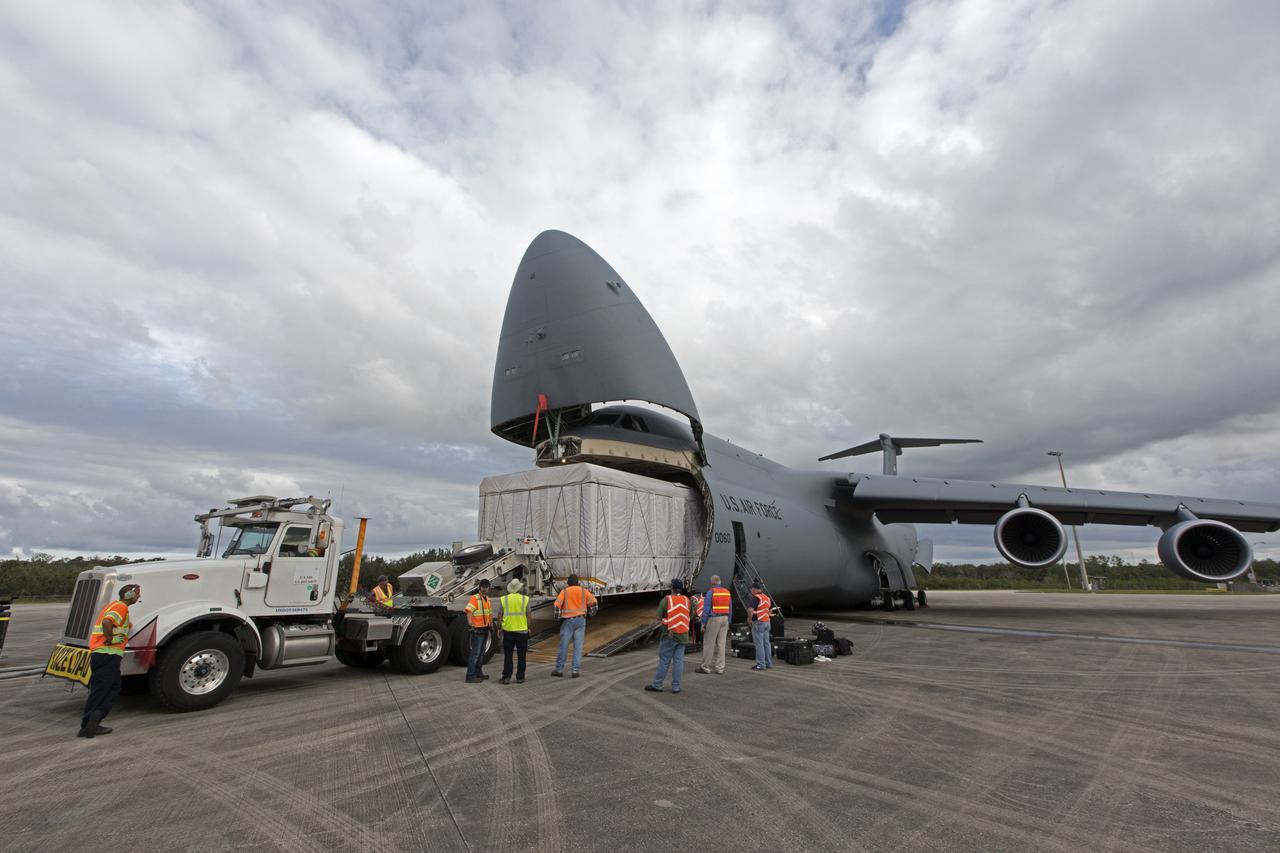

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
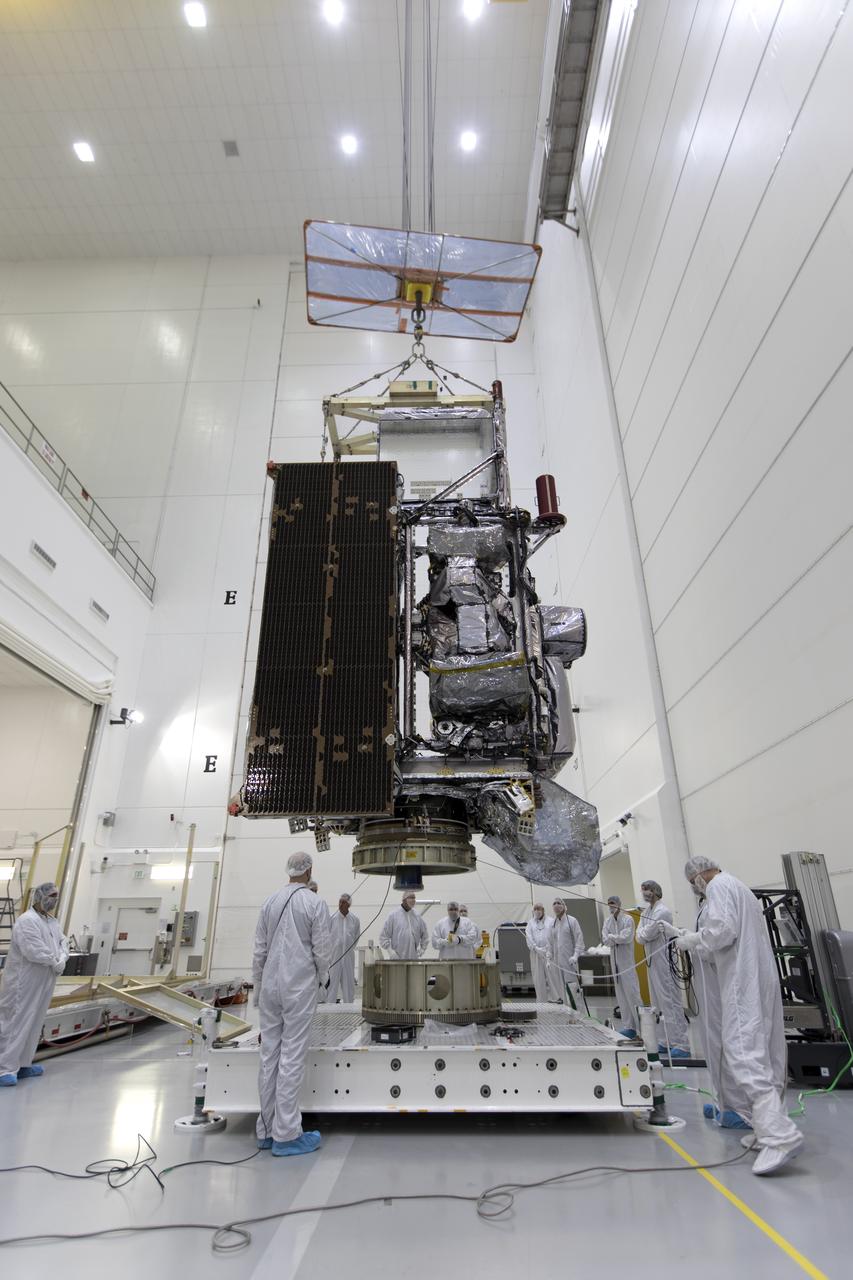

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
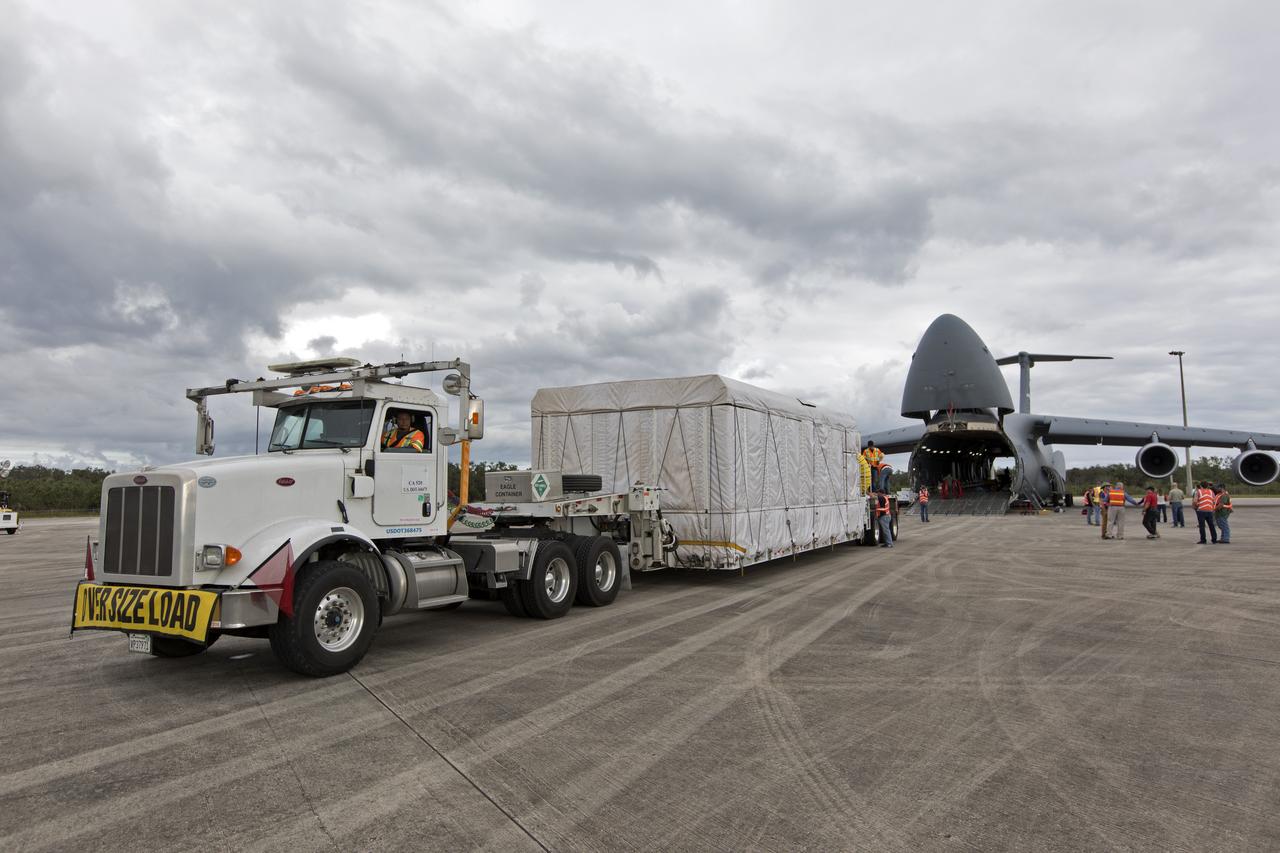

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft and secured onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
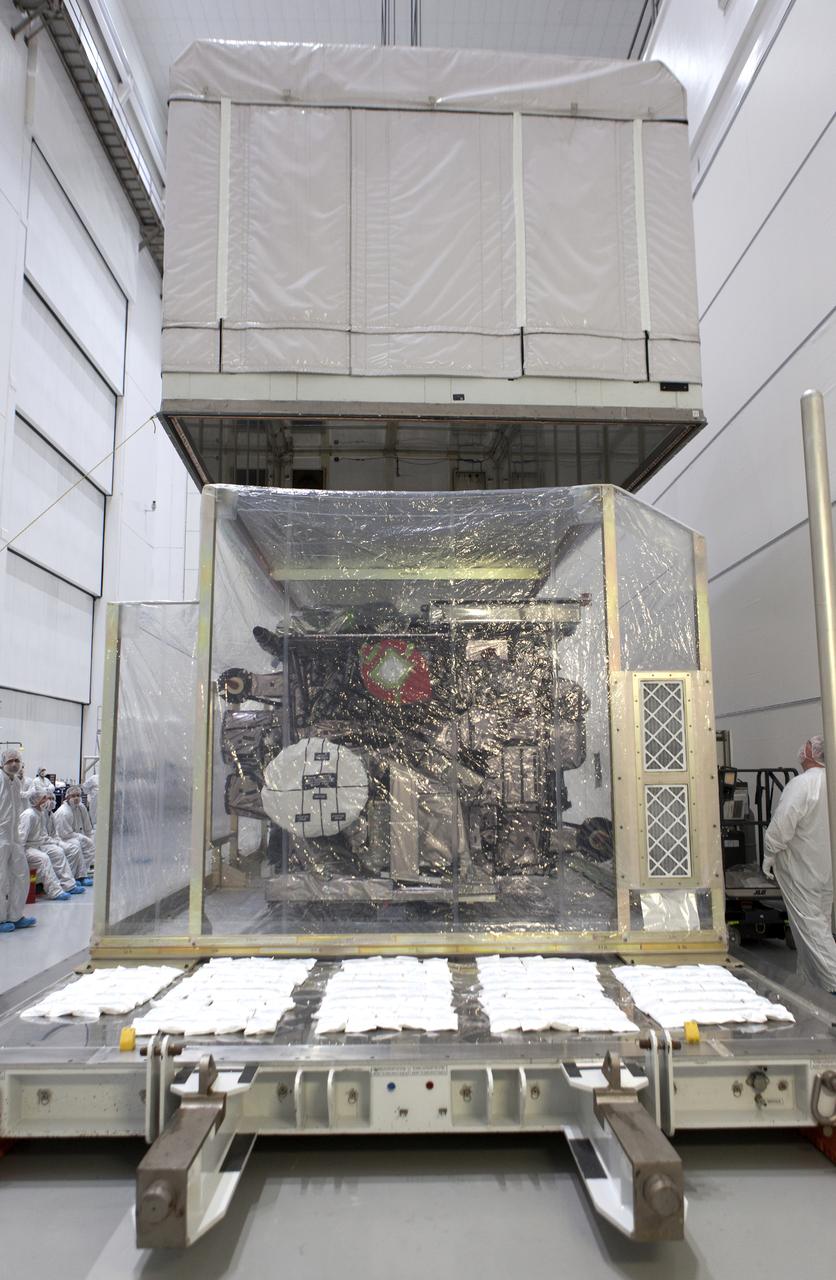

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
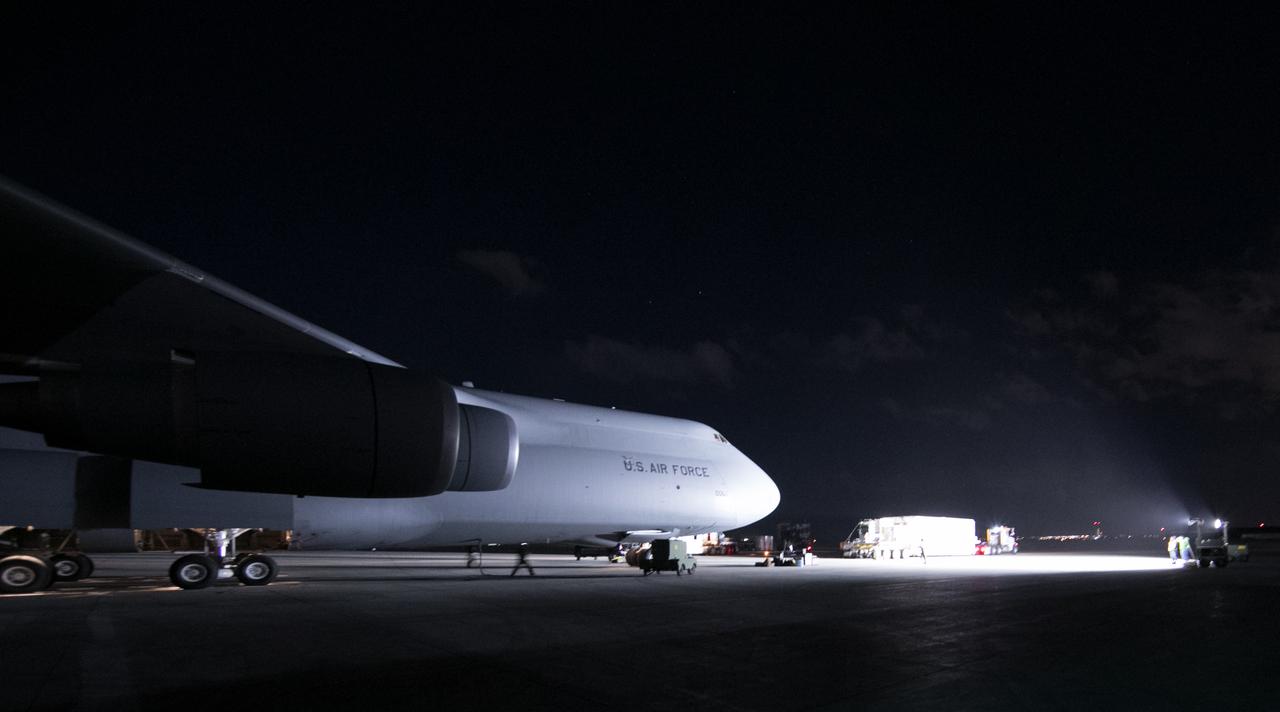

NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) will be loaded into a U.S. Air Force C-5M Super Galaxy cargo aircraft and flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
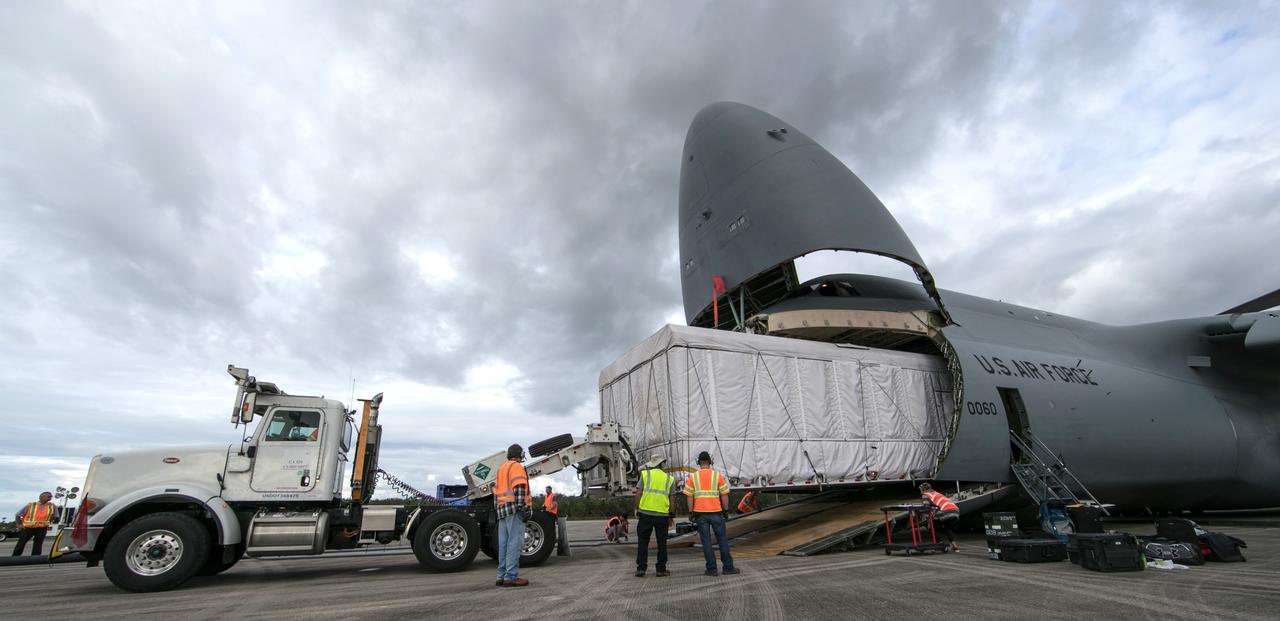

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
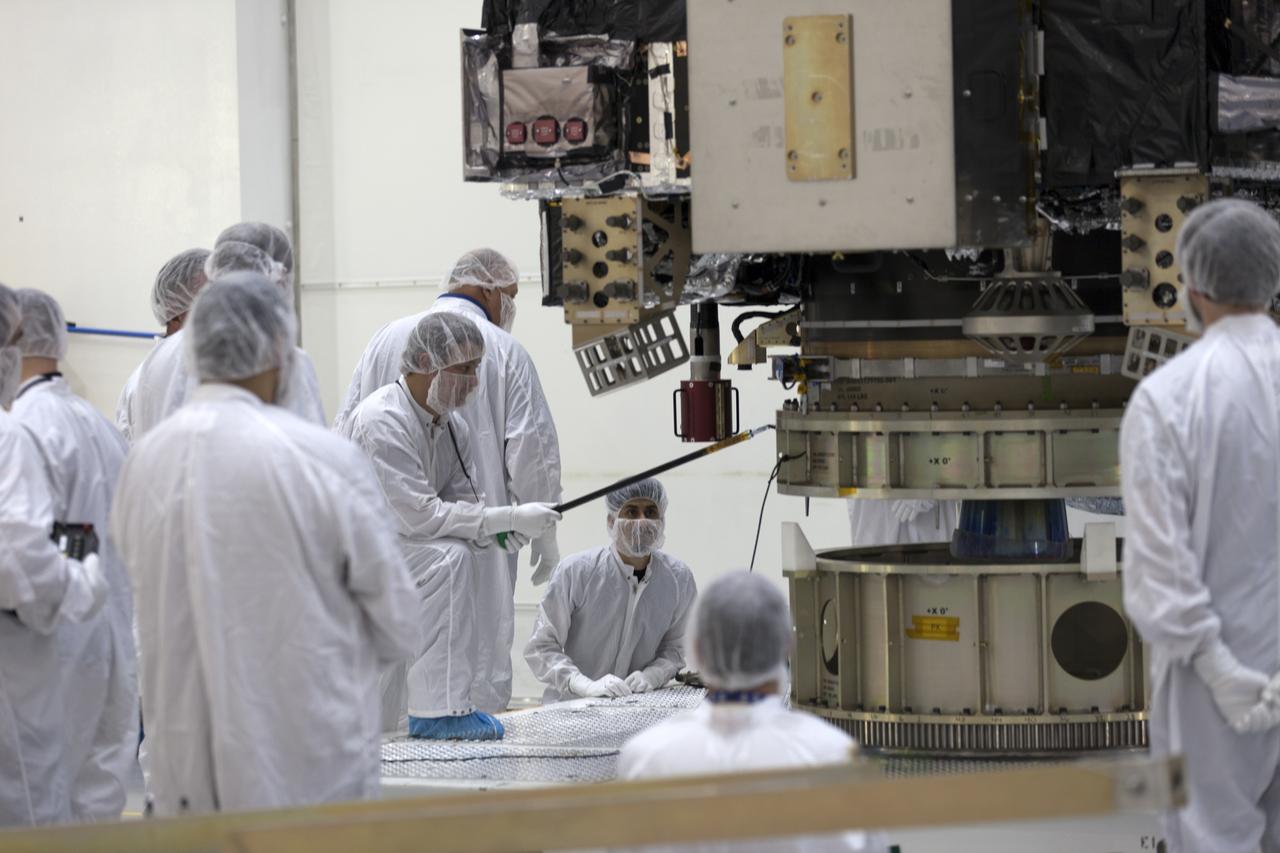

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
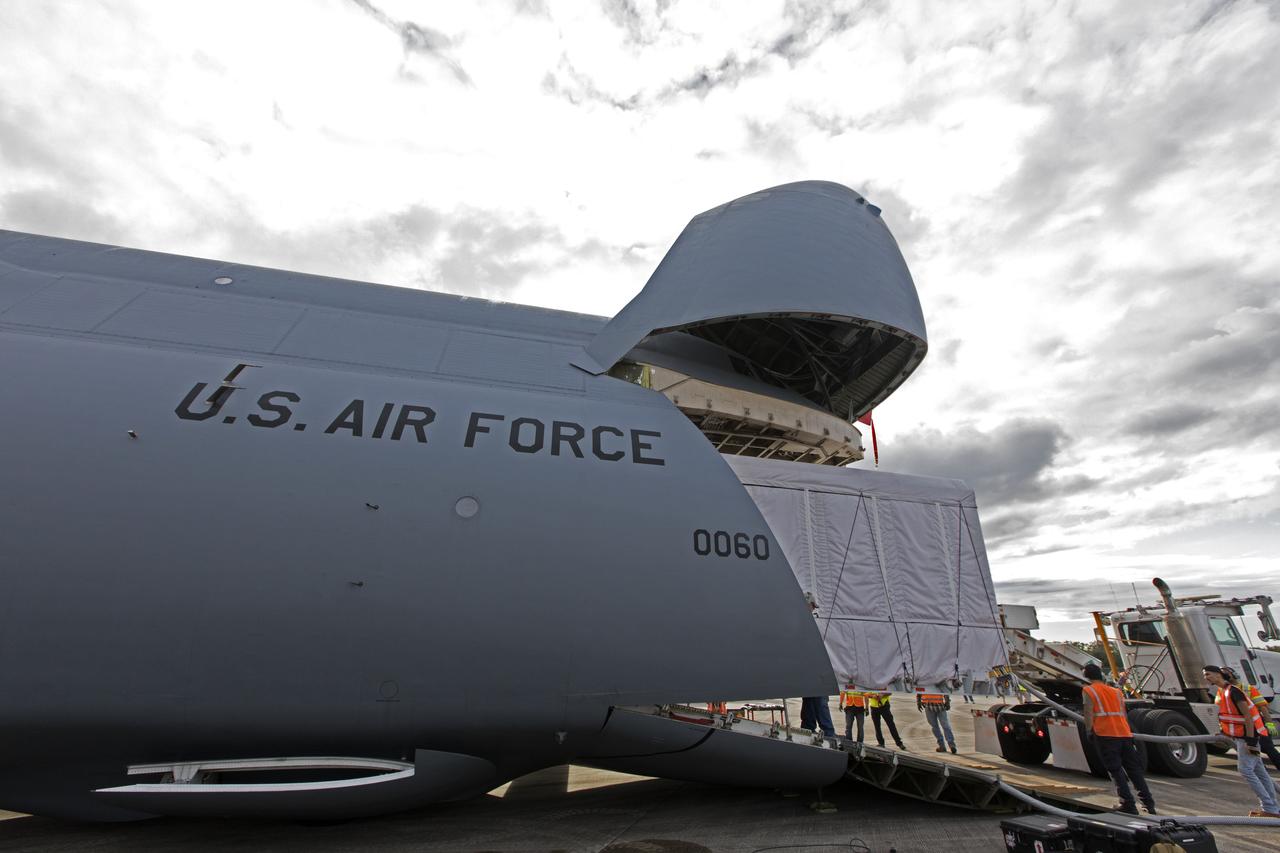

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
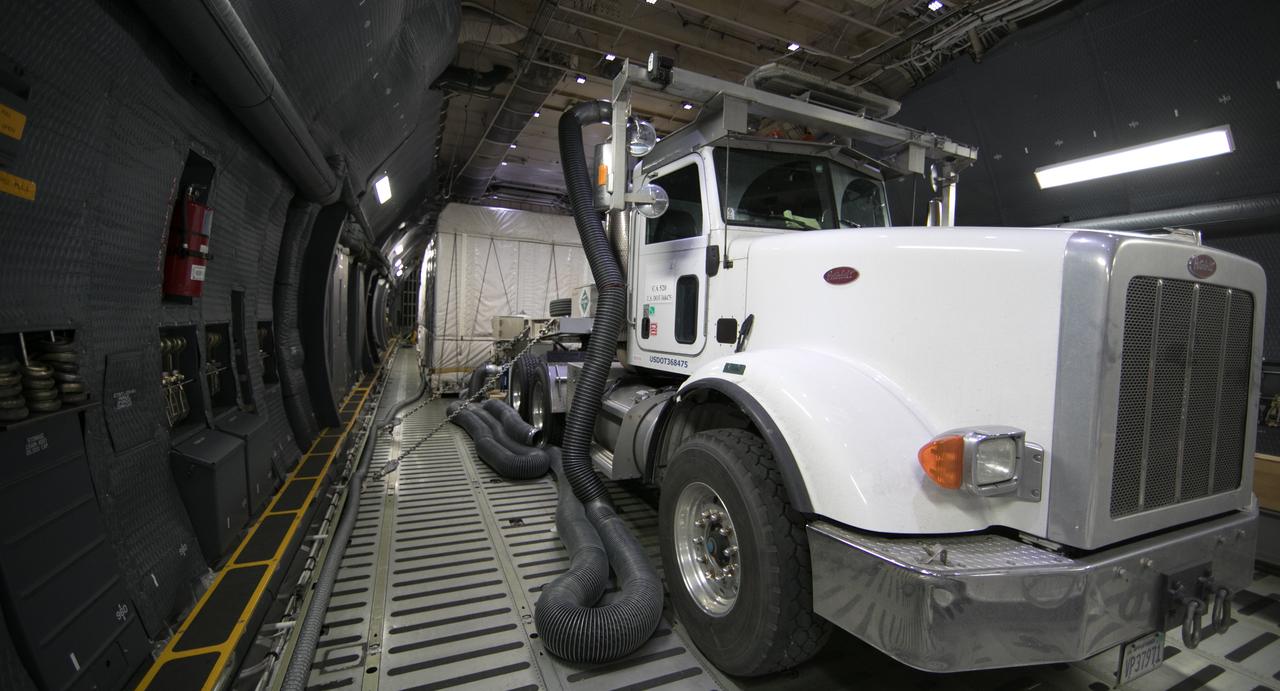

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
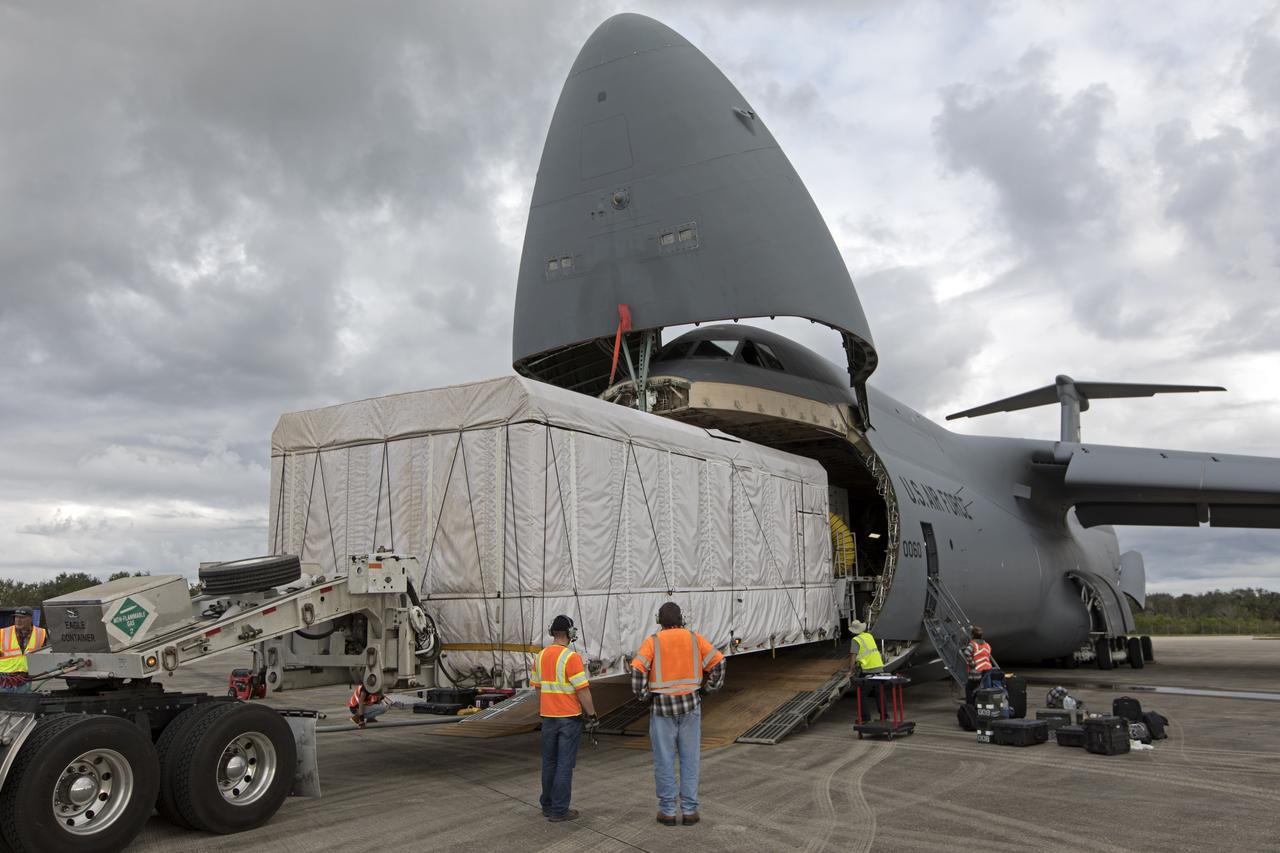

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
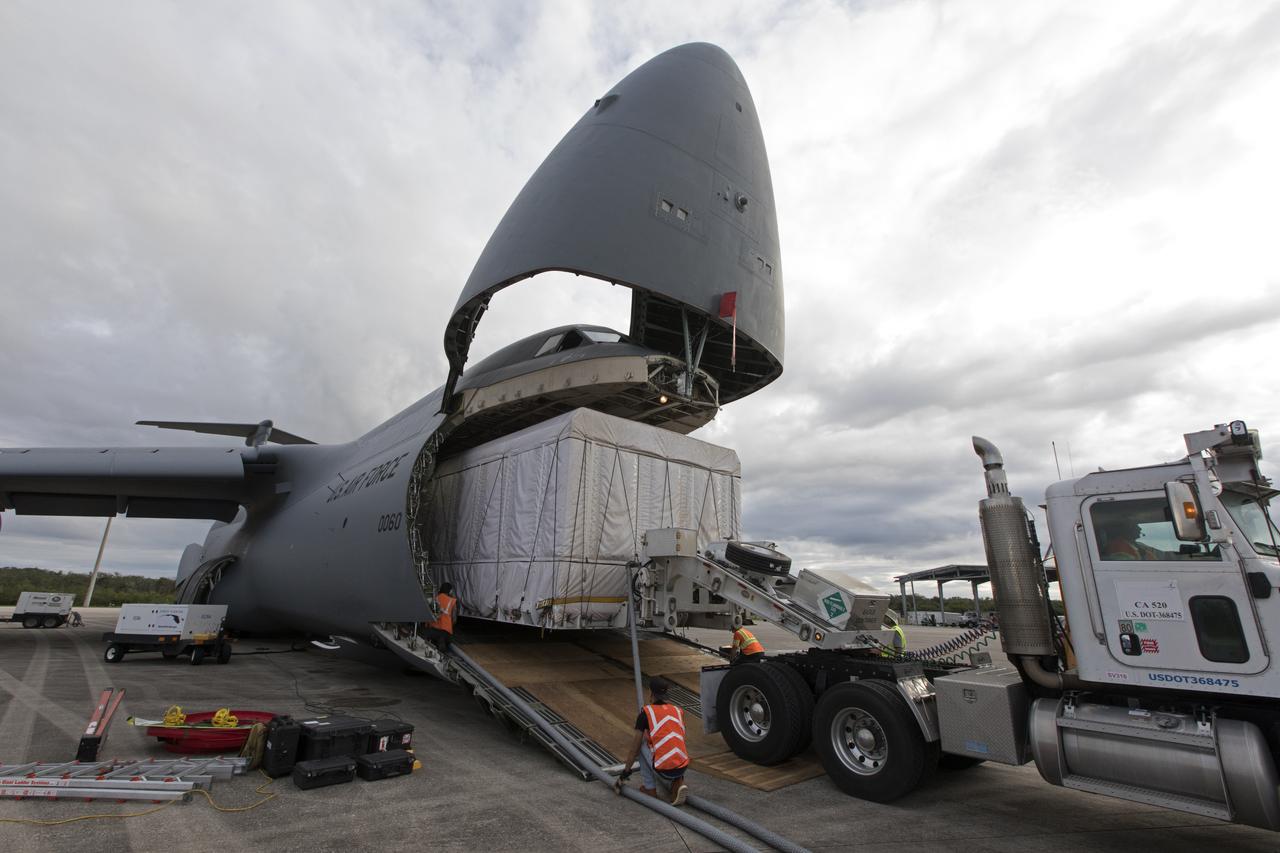

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
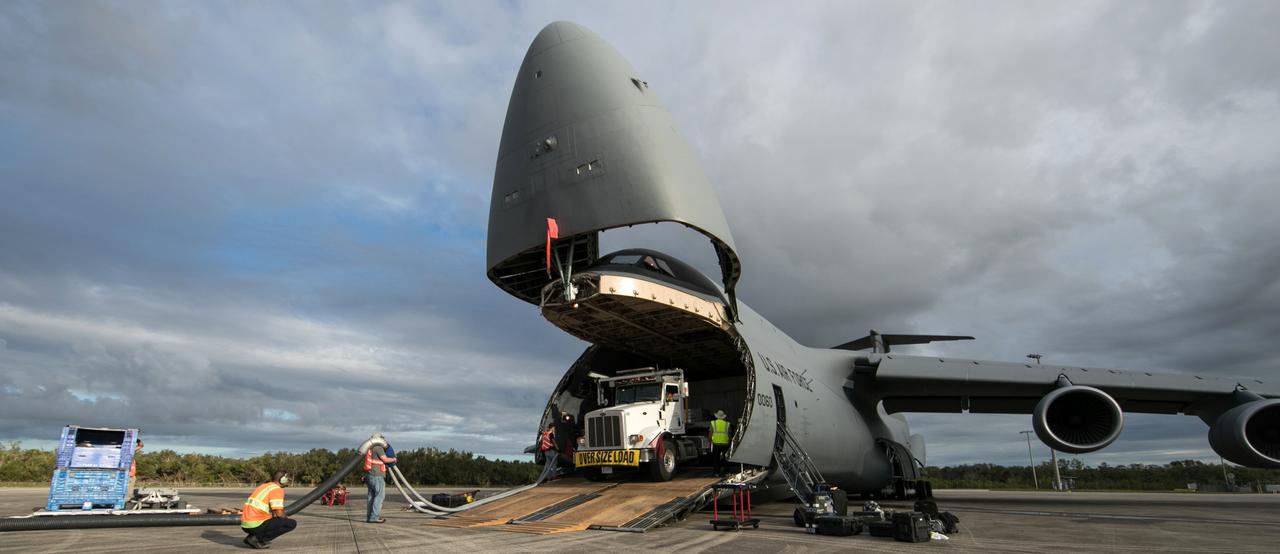

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
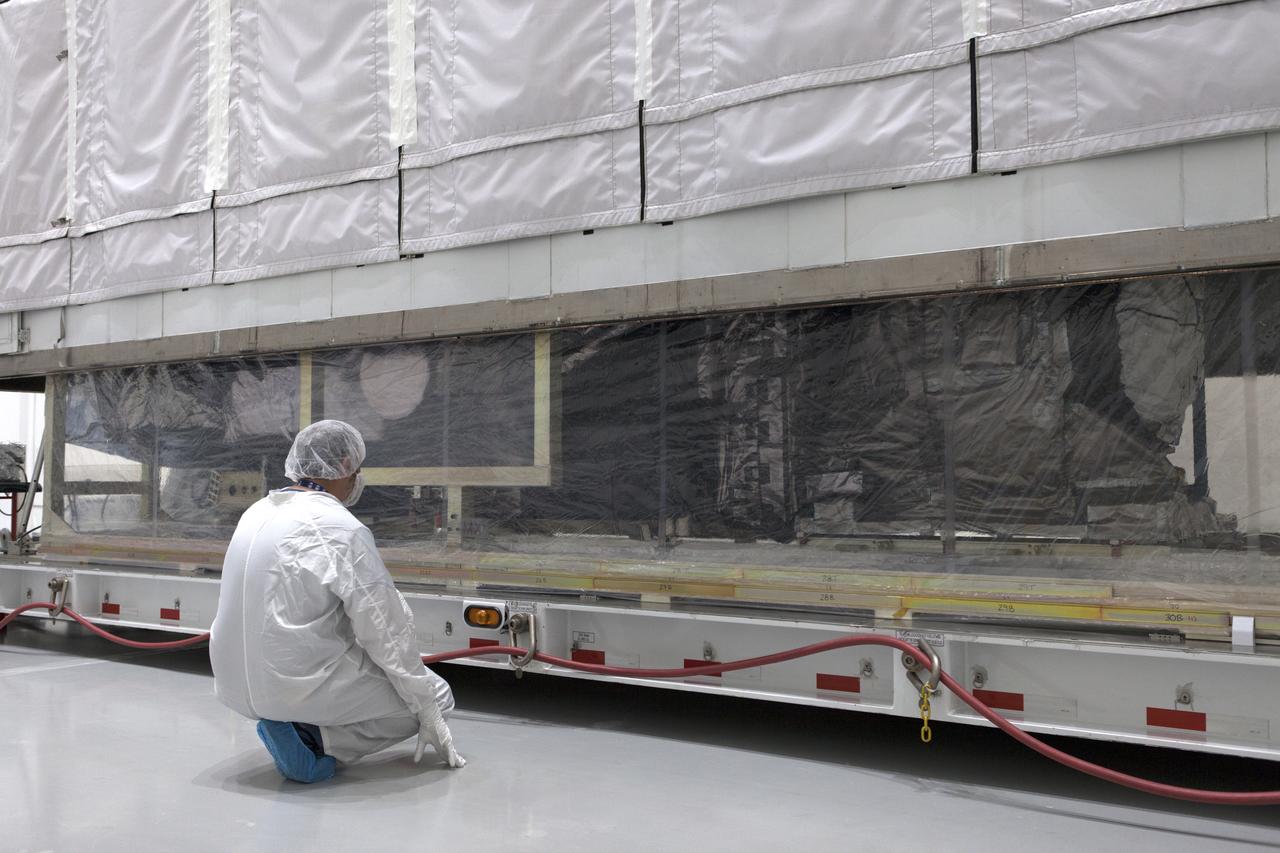

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
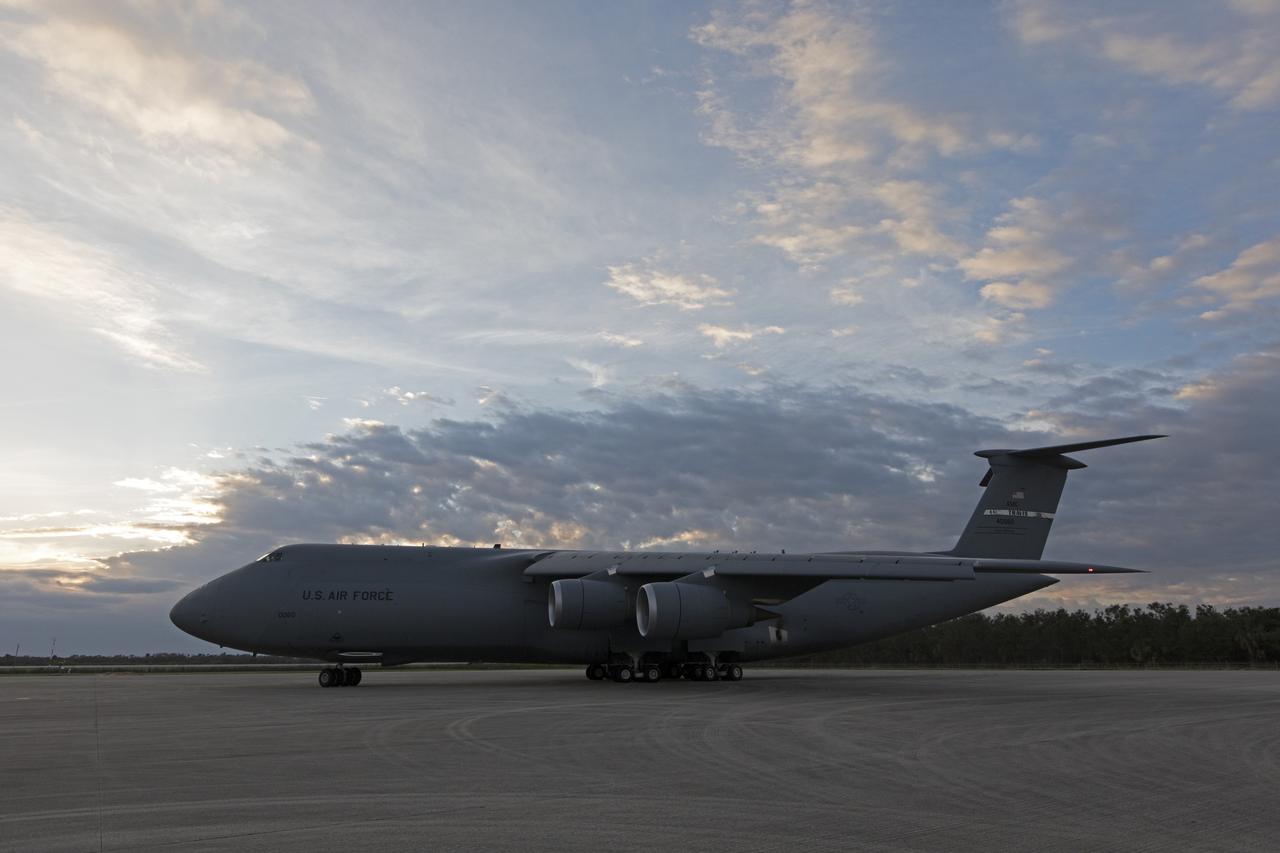

A C-5 transport aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The satellite will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
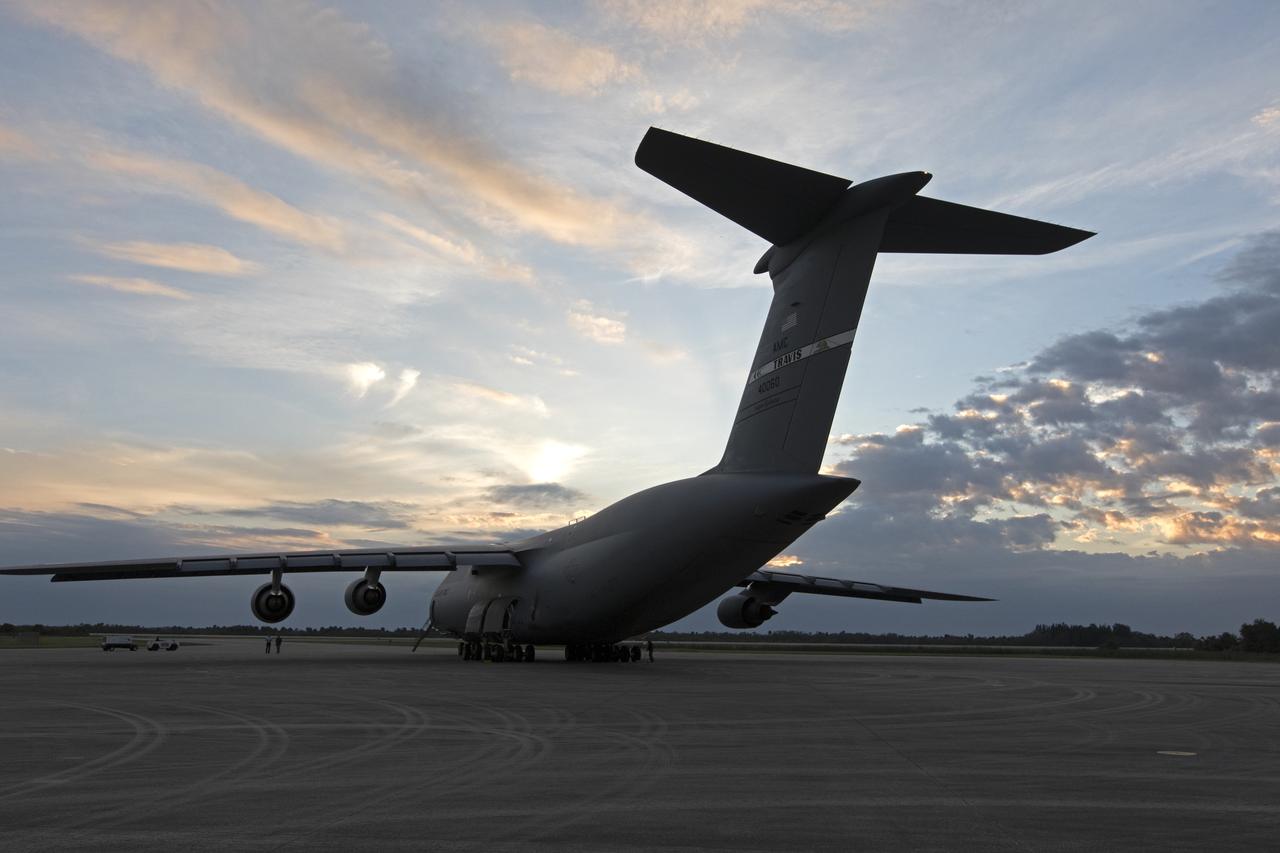

A C-5 transport aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying the Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The satellite will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
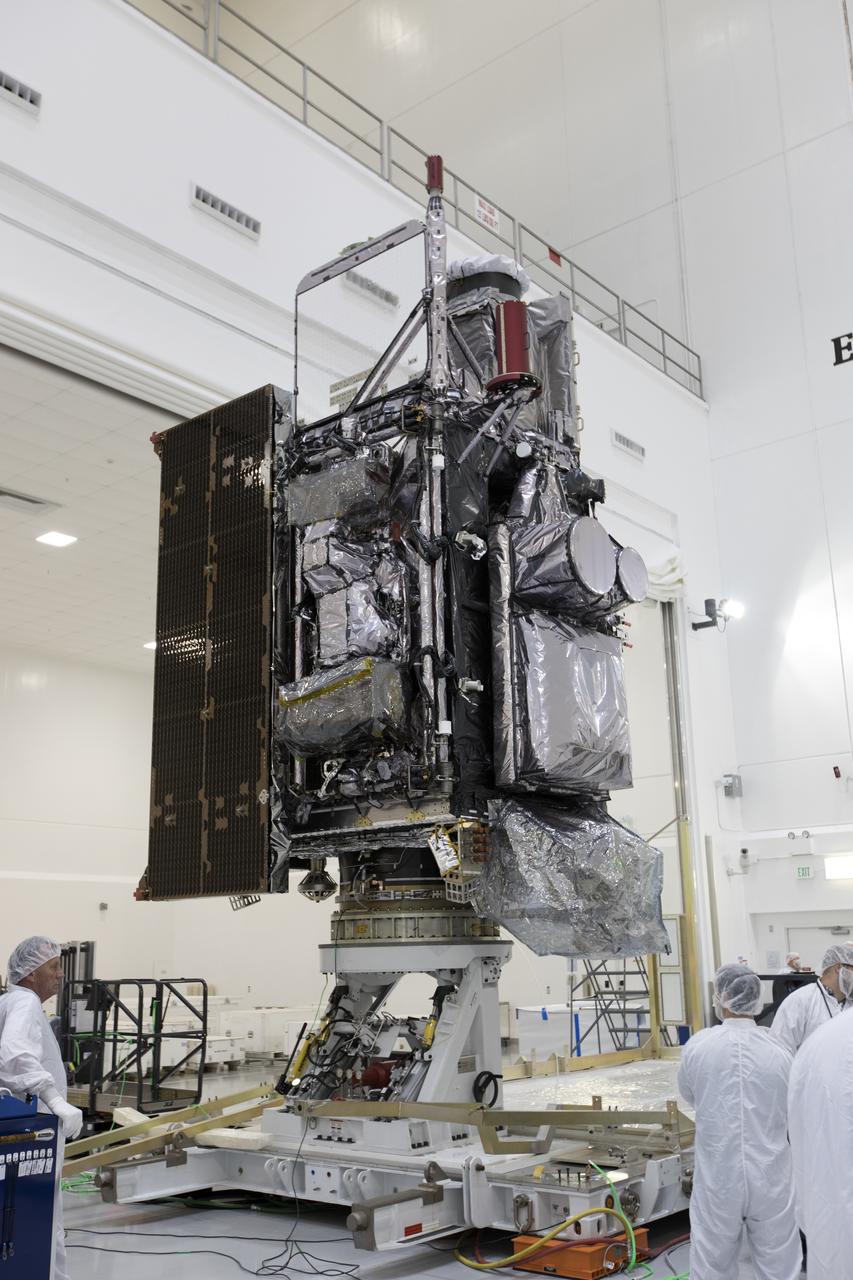

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
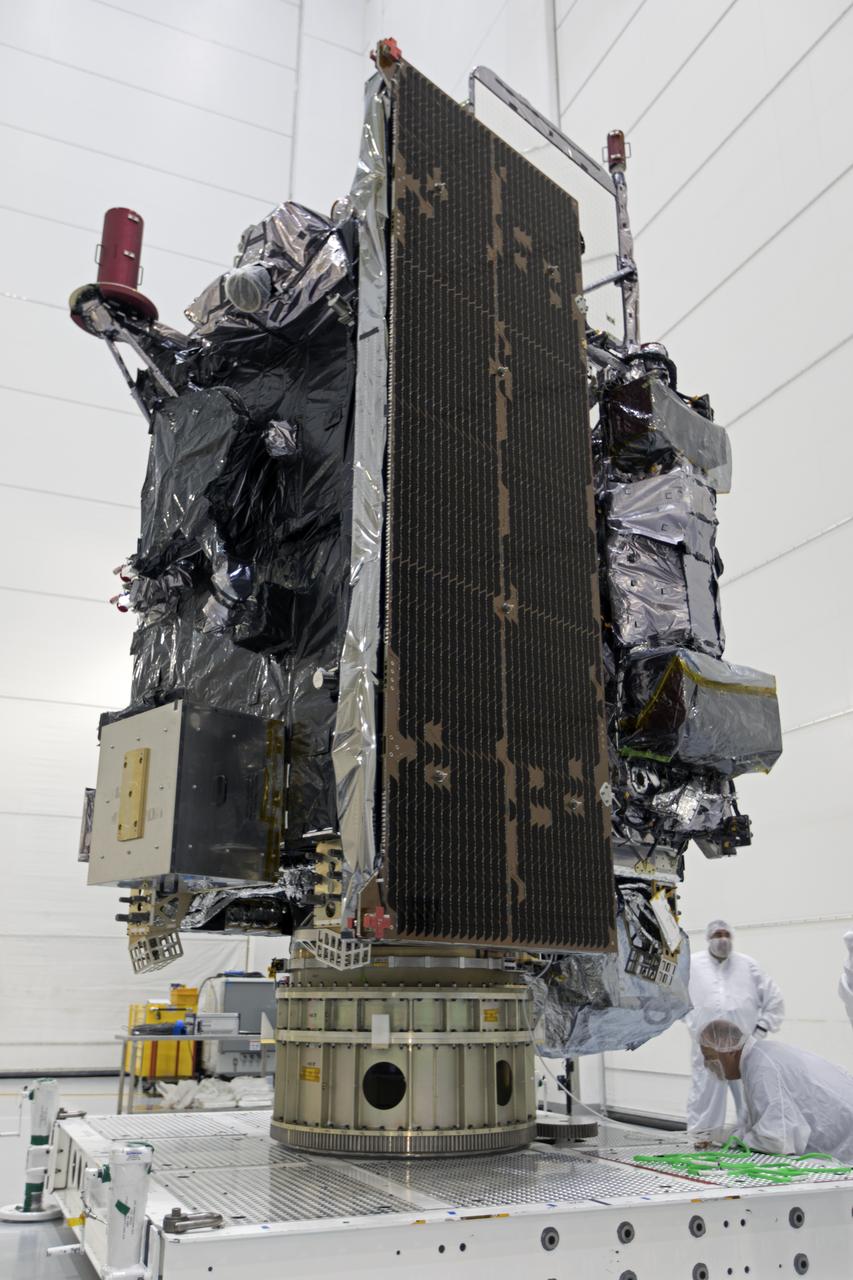

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was positioned on a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
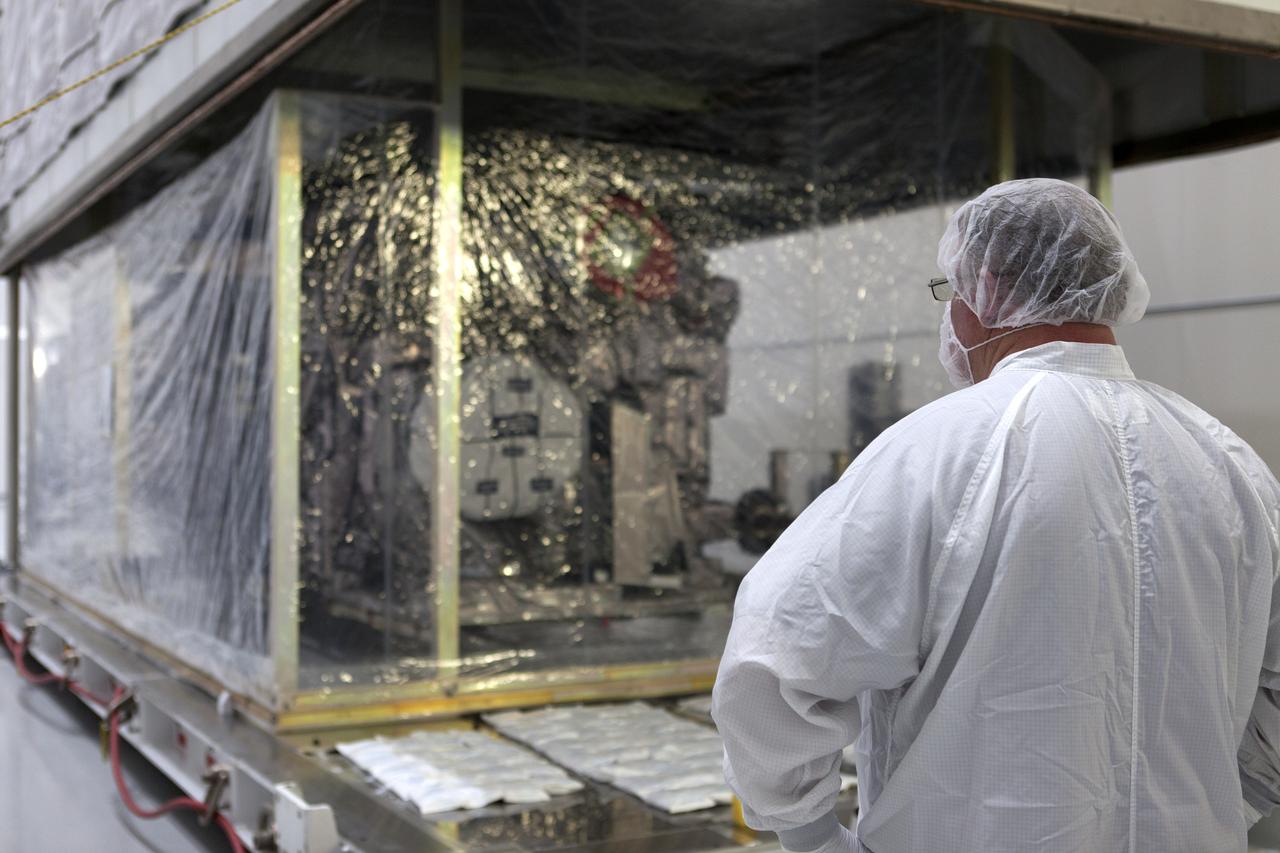

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, a technician watches as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
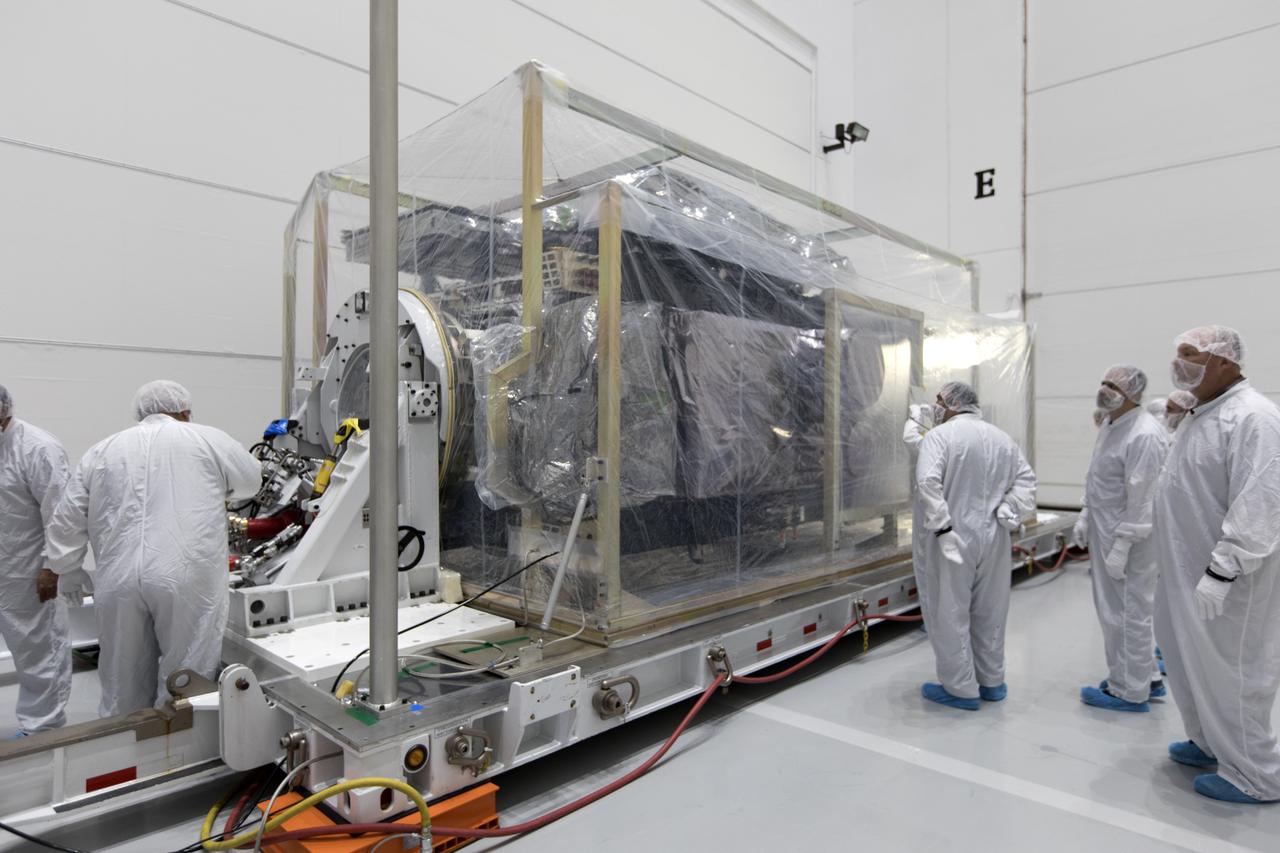

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technician and engineers inspect NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
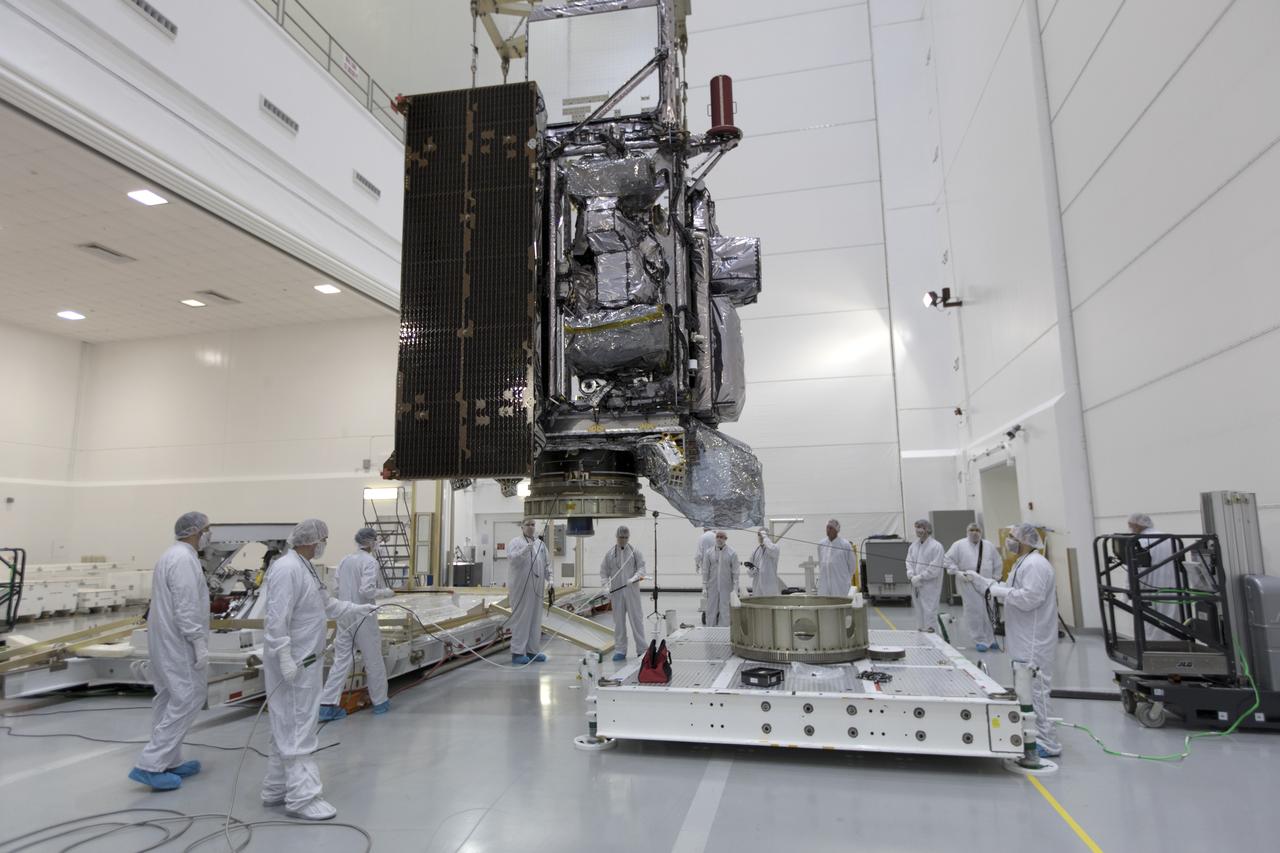

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers keep a watchful eye on NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) as it is moved to a work stand. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
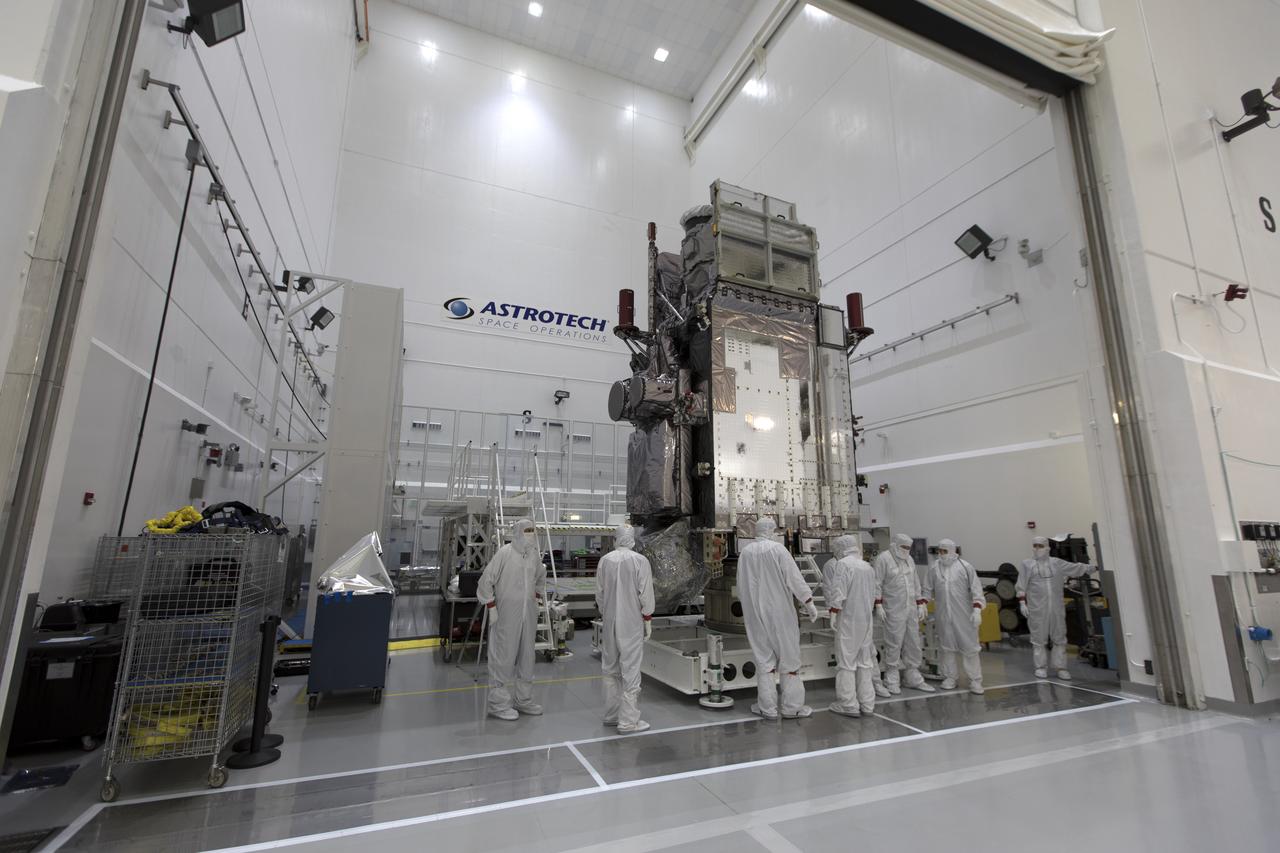

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers move NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) into a clean room for further processing. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
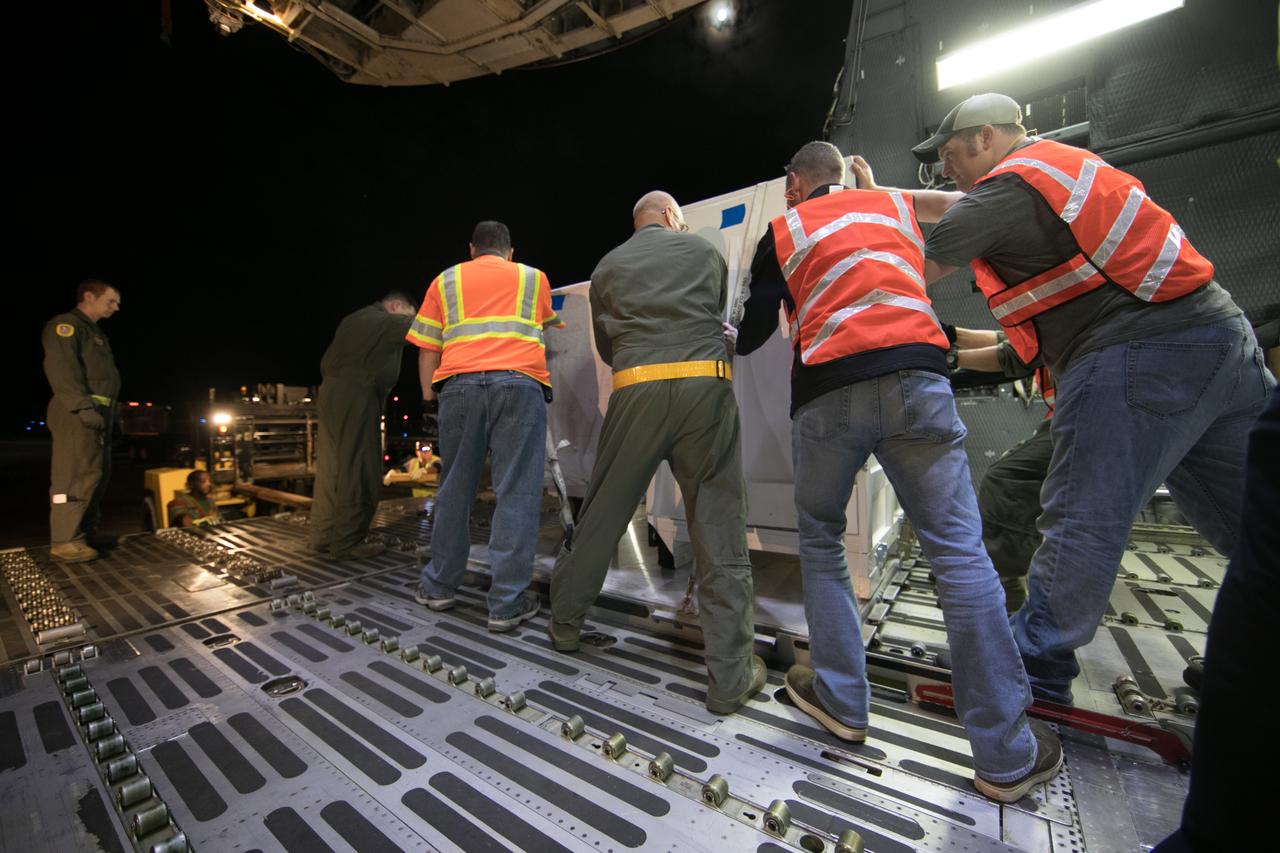

NOAA's Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is being offloaded from a C-5 transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite will be transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
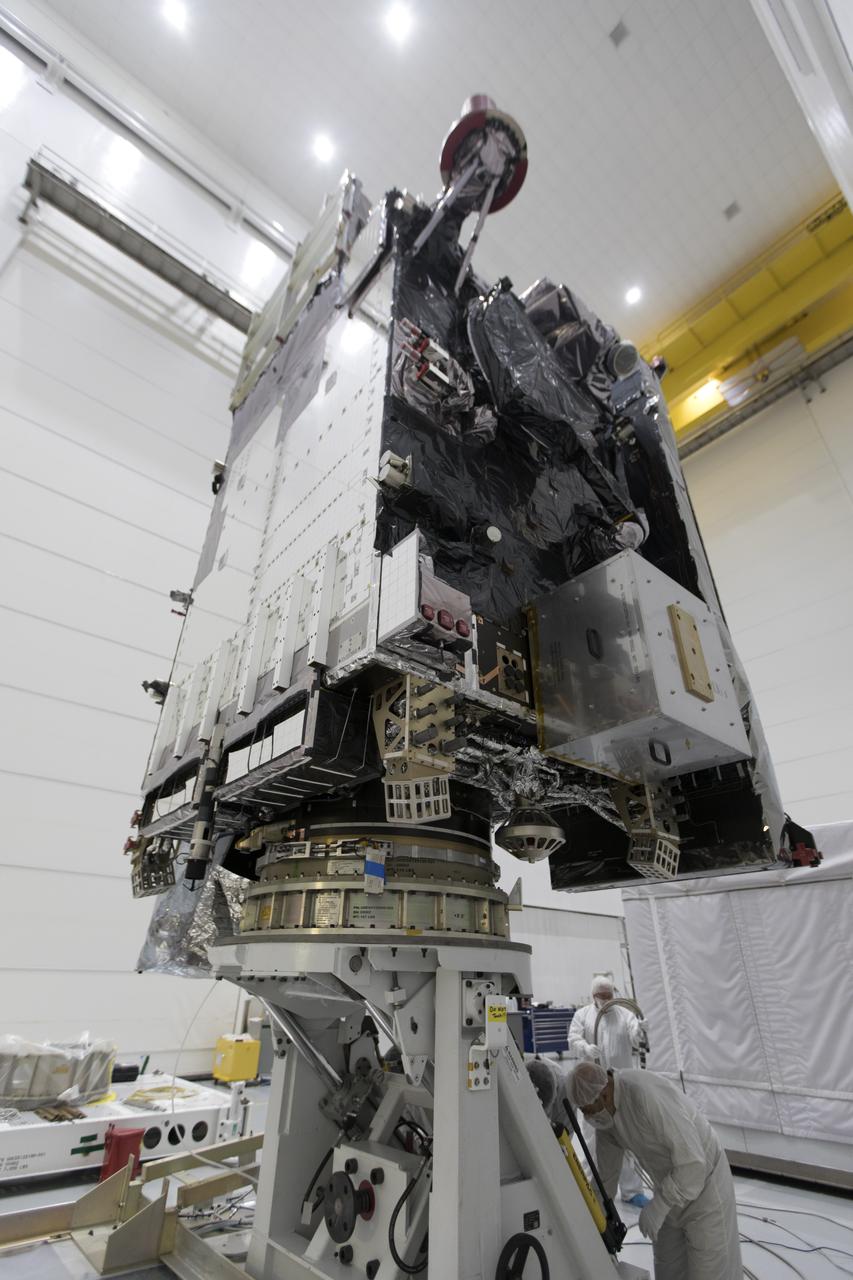

At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) has been rotated to a vertical position after it was uncrated from its shipping container. The facility is located near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The crew insignia for STS Flight 51-C includes the names of its five crewmembers. The STS 51-C mission marked the third trip of the Space Shuttle Discovery into space. It was the first Space Shuttle mission totally dedicated to the Department of Defense. The U. S. Air Force Inertial Upper Stage Booster Rocket was successfully deployed. Due to the nature of the mission, few additional details of the flight were made available. Landing was made at the Kennedy Space Center, FL on January 27 at 4:23 PM EST. Mission duration was three days, one hour and 33 minutes.
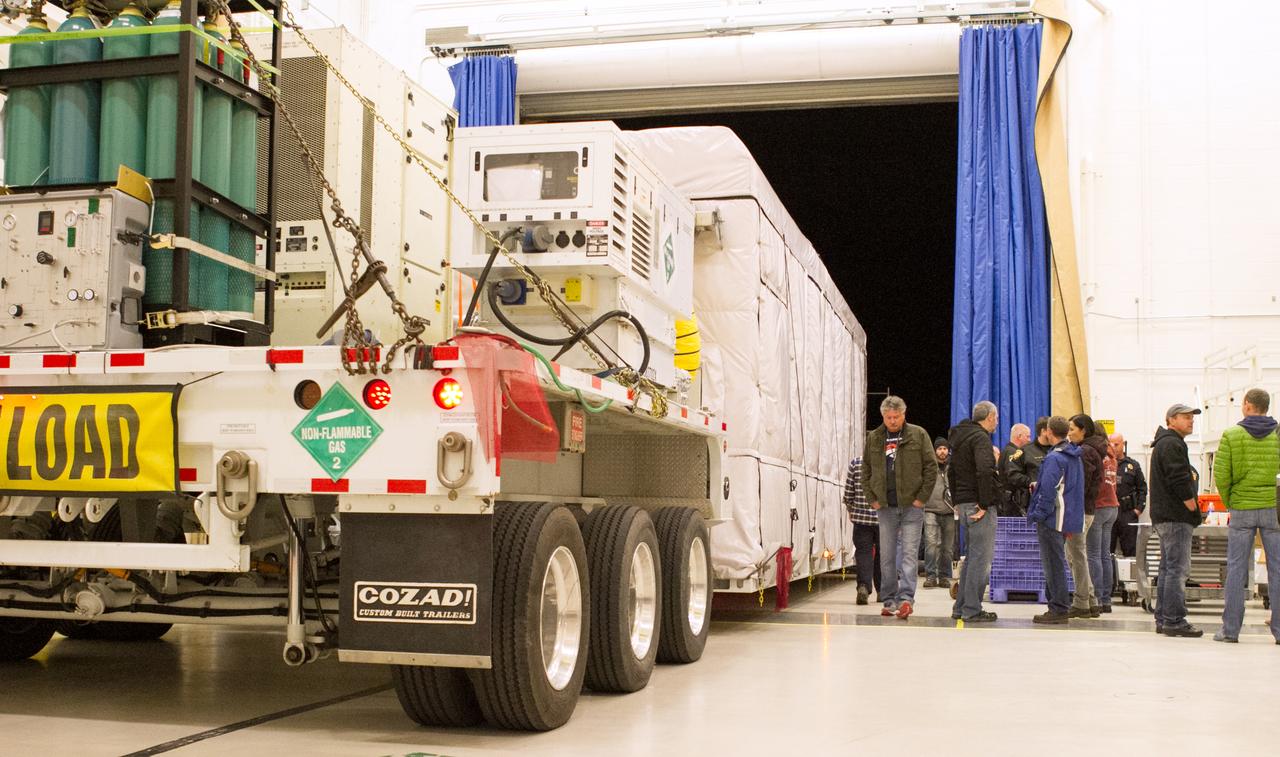

NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) is prepared for transport at the Lockheed Martin facility in Littleton, Colorado, where it was built and assembled. GOES-S will be loaded into a U.S. Air Force C-5M Super Galaxy cargo aircraft at Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, and flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
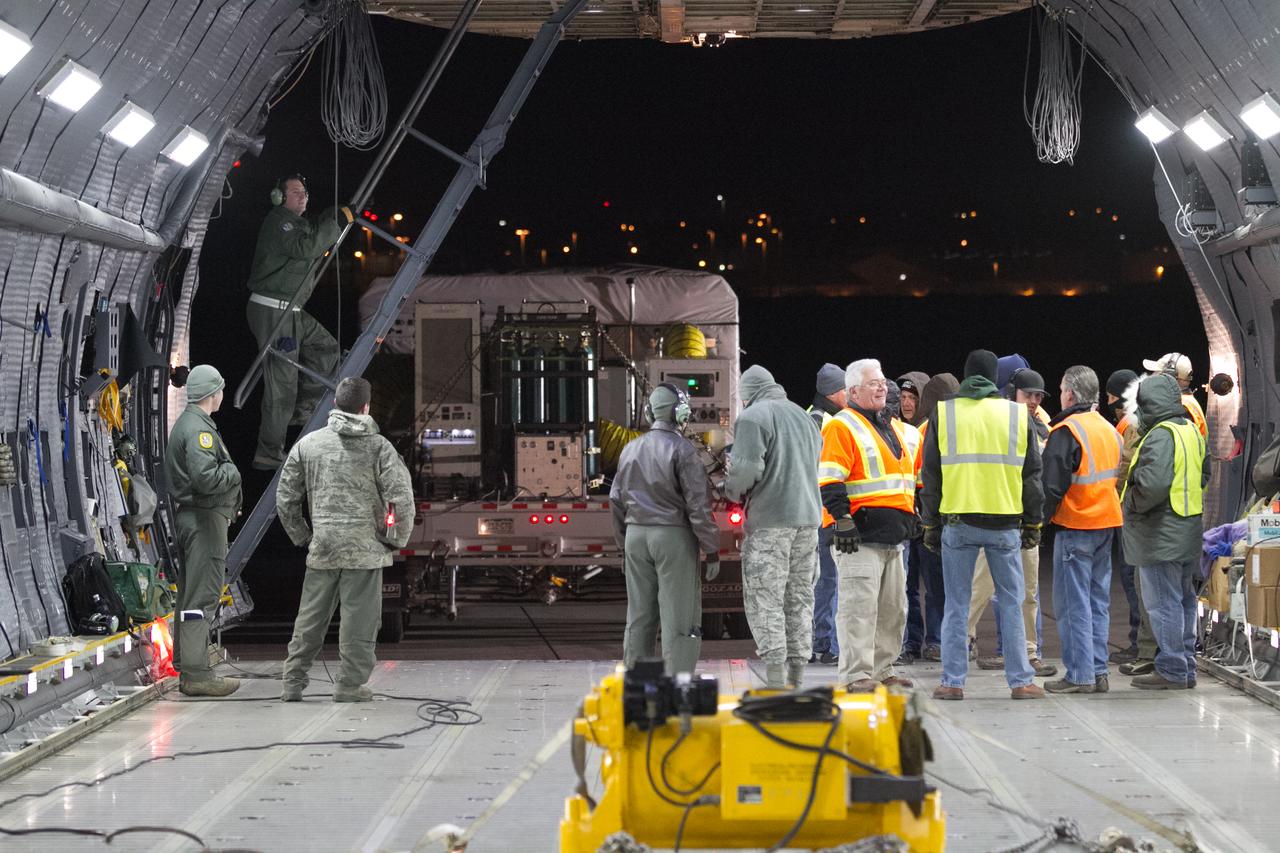

At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, the front of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft has been raised to allow NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) to be loaded into the cargo hold. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
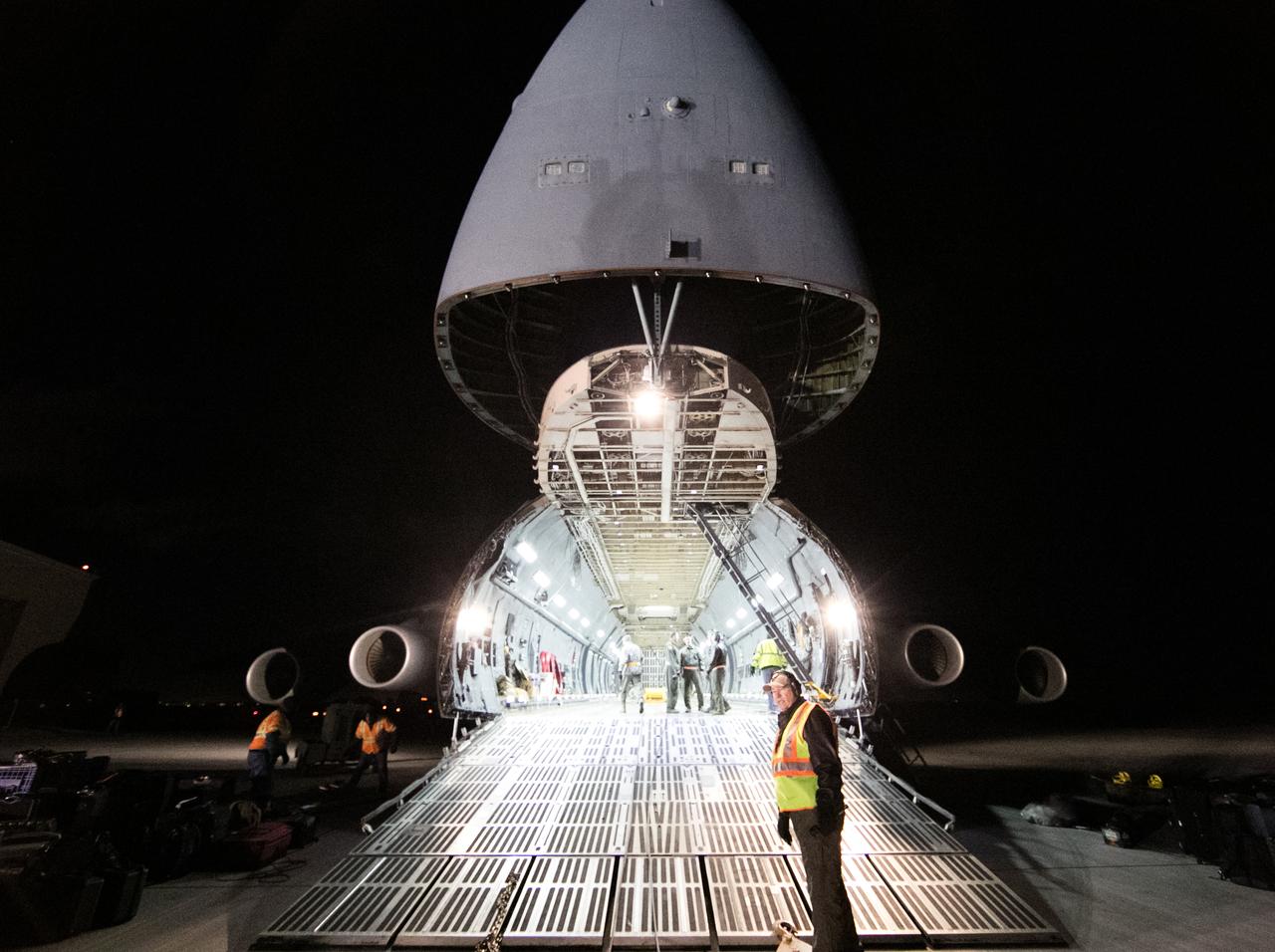

At Buckley Air Force Base in Aurora, Colorado, the front of a U.S. Air Force C-5M super Galaxy cargo aircraft has been raised to allow NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) to be loaded into the cargo hold. GOES-S will be flown to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After it arrives at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility, it will be offloaded and transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to prepare it for launch. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
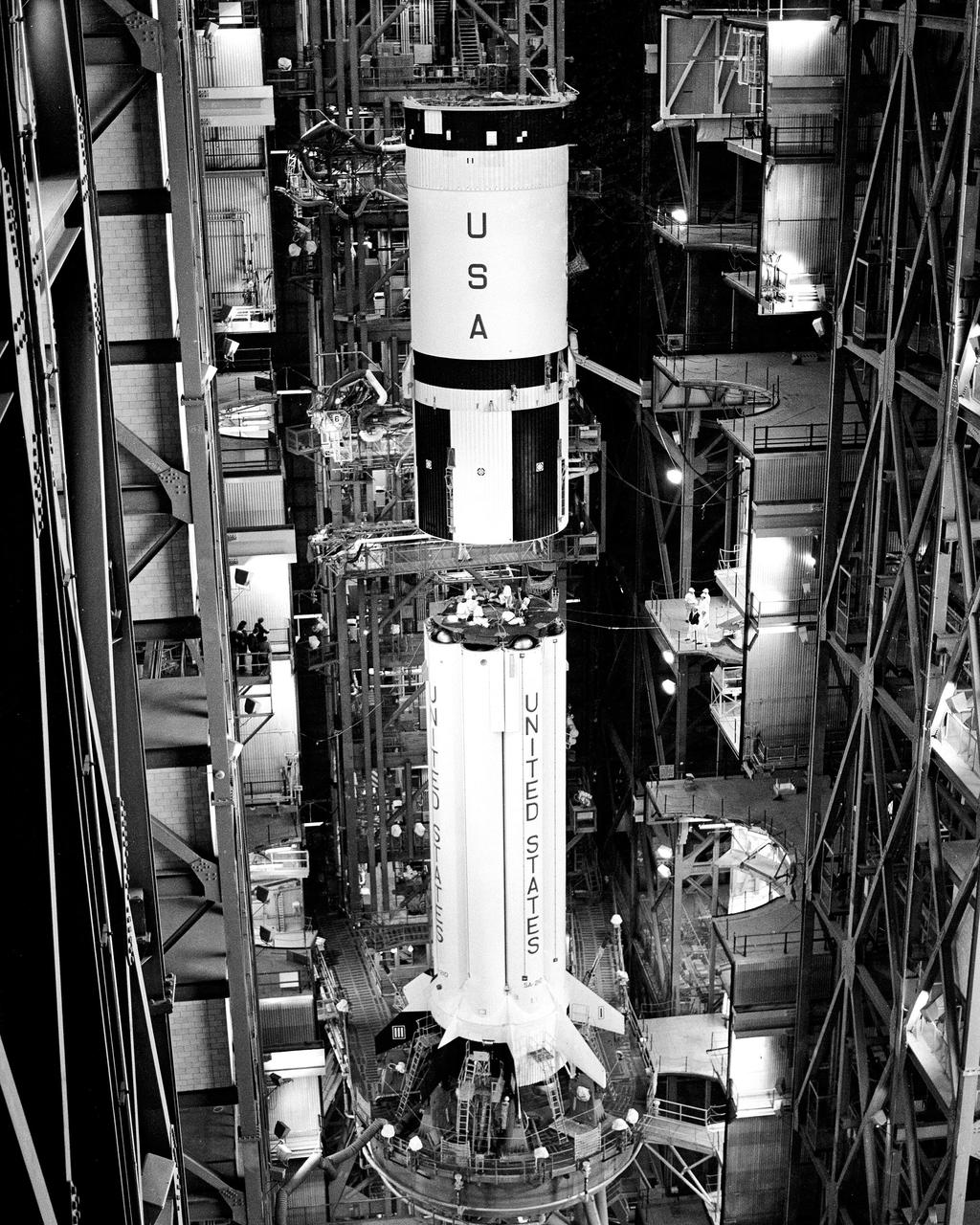

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The second stage of the Saturn 1B booster for the United States mission on the Apollo Soyuz Test Project was mated with the Saturn 1B first stage in the Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building today. Mating was completed at 9:50 a.m. The U. S. ASTP launch with mission commander Thomas Stafford, command module pilot Vance Brand and docking module pilot Donald Slayton is scheduled at 3:50 p.m. EDT July 15. The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Photo credit: NASA
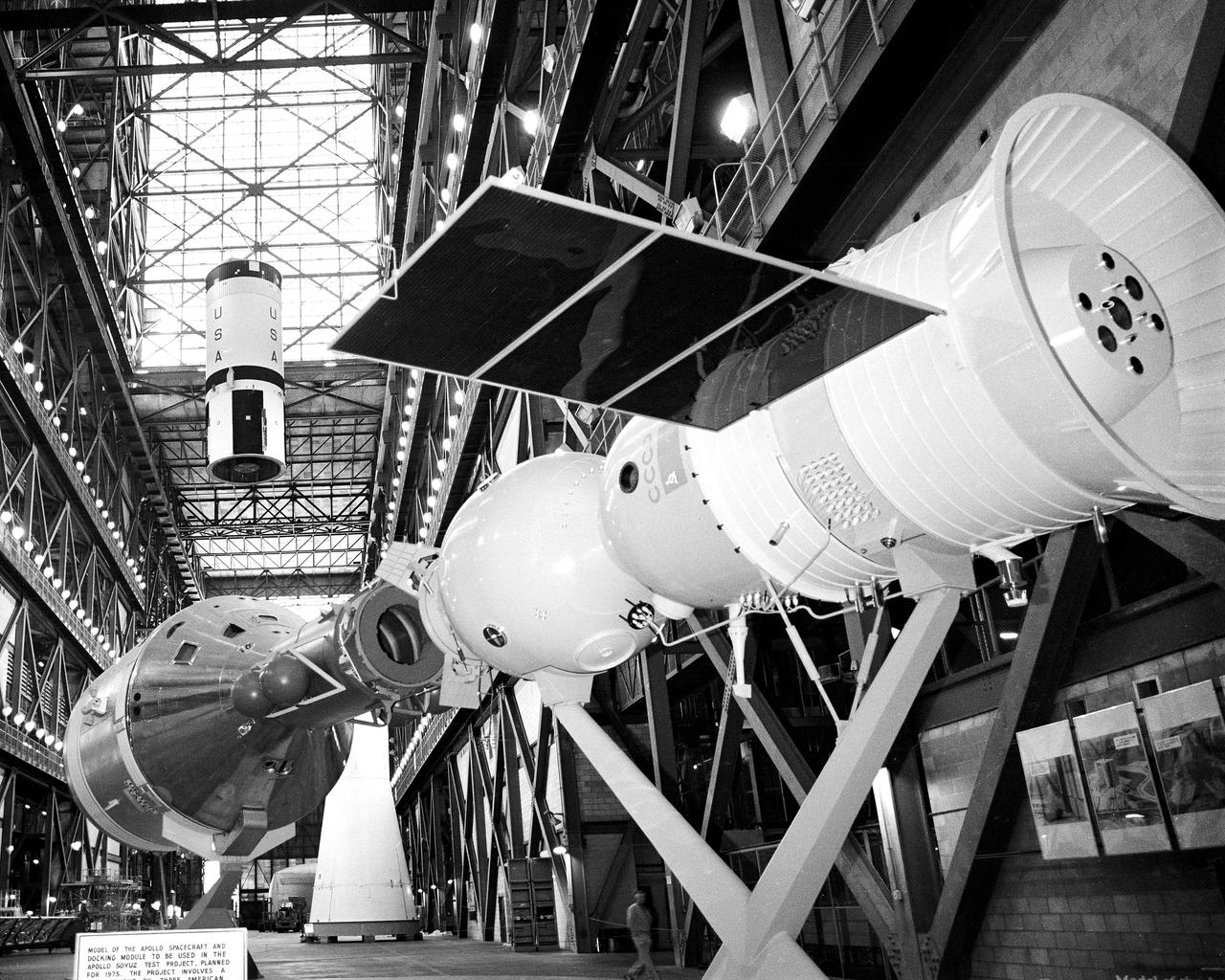

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Model of docked Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft in the foreground and skylight in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay frame the second stage of the Saturn 1B booster that will launch the United States ASTP mission as a crane raises it prior to its mating with the Saturn 1B first stage. Mating of the Saturn 1B first and second stages was completed this morning. The U. S. ASTP launch with mission commander Thomas Stafford, command module pilot Vance Brand and docking module pilot Donald Slayton is scheduled at 3:50 p.m. EDT July 15. The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Photo credit: NASA
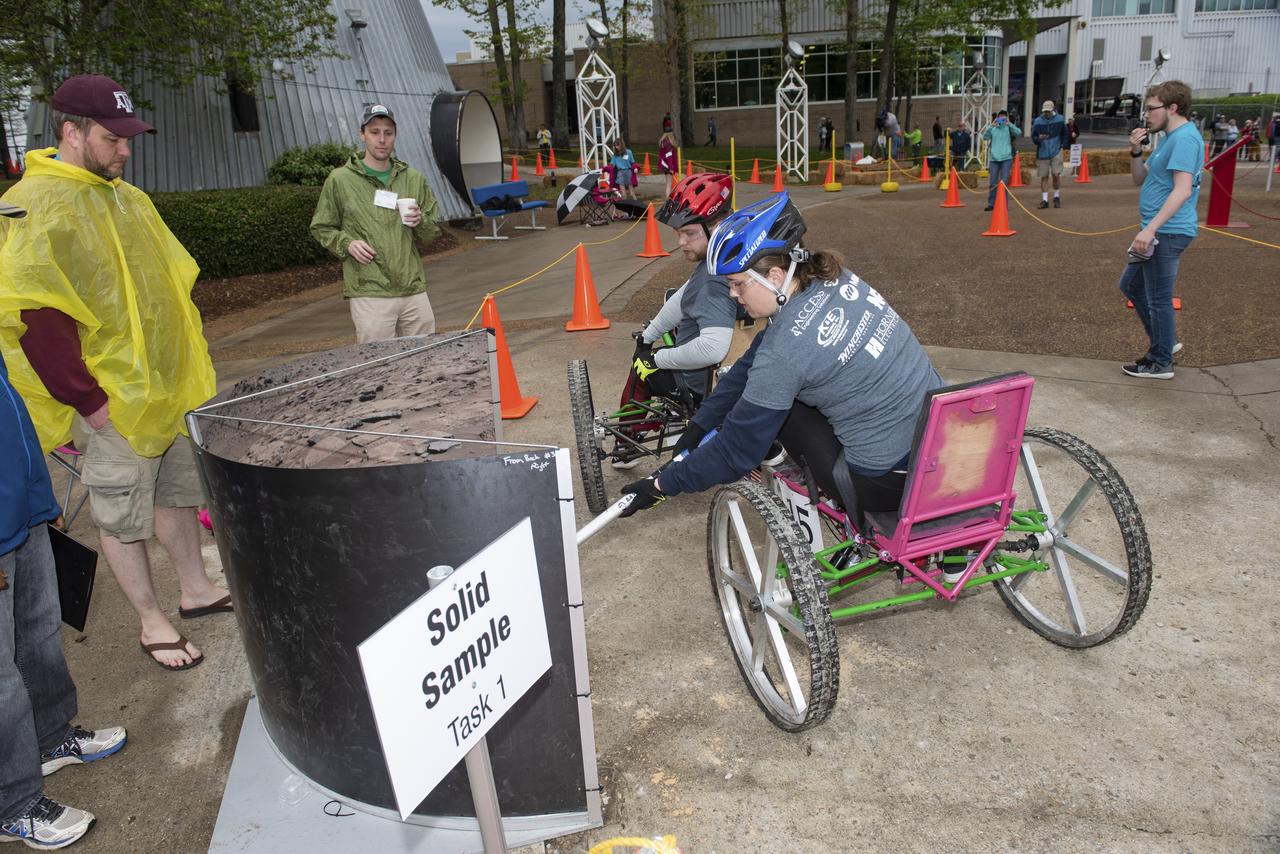

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
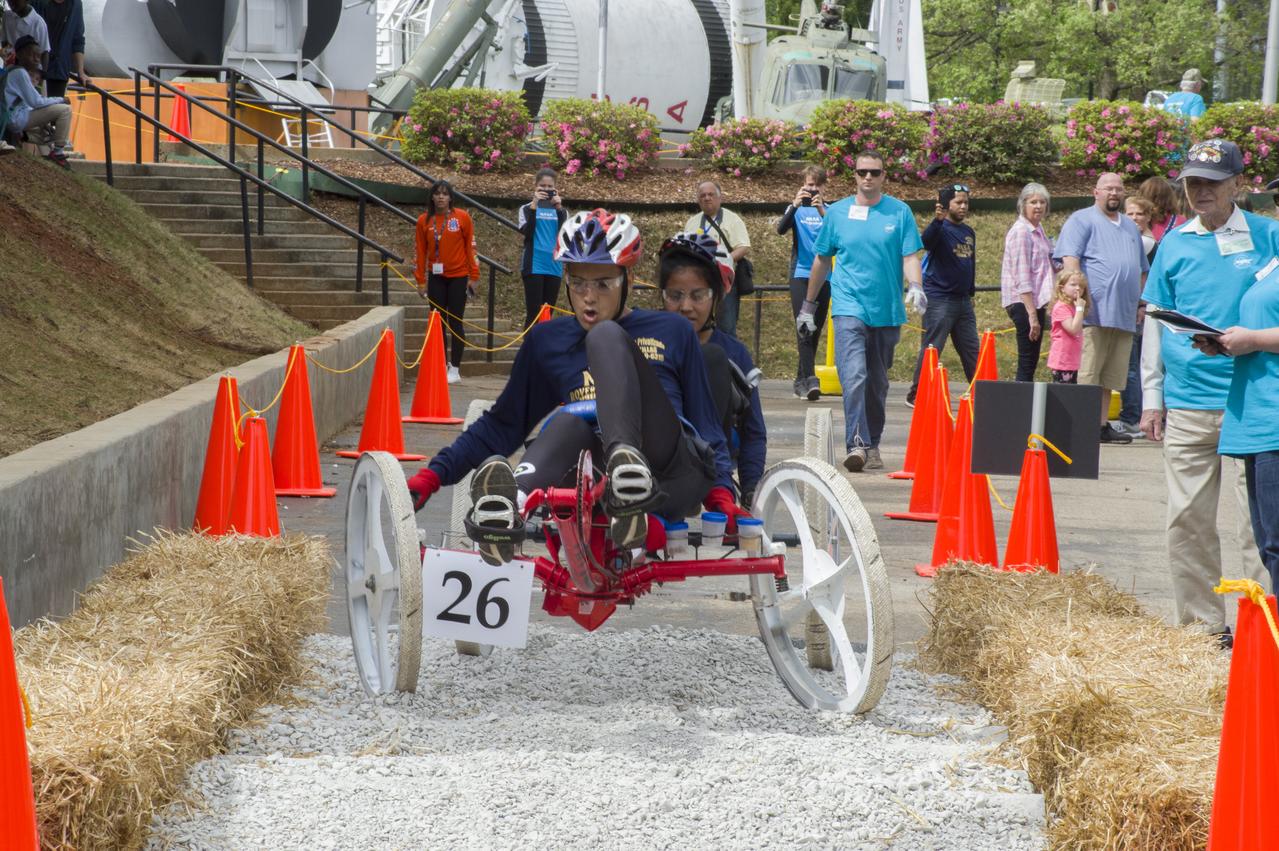

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
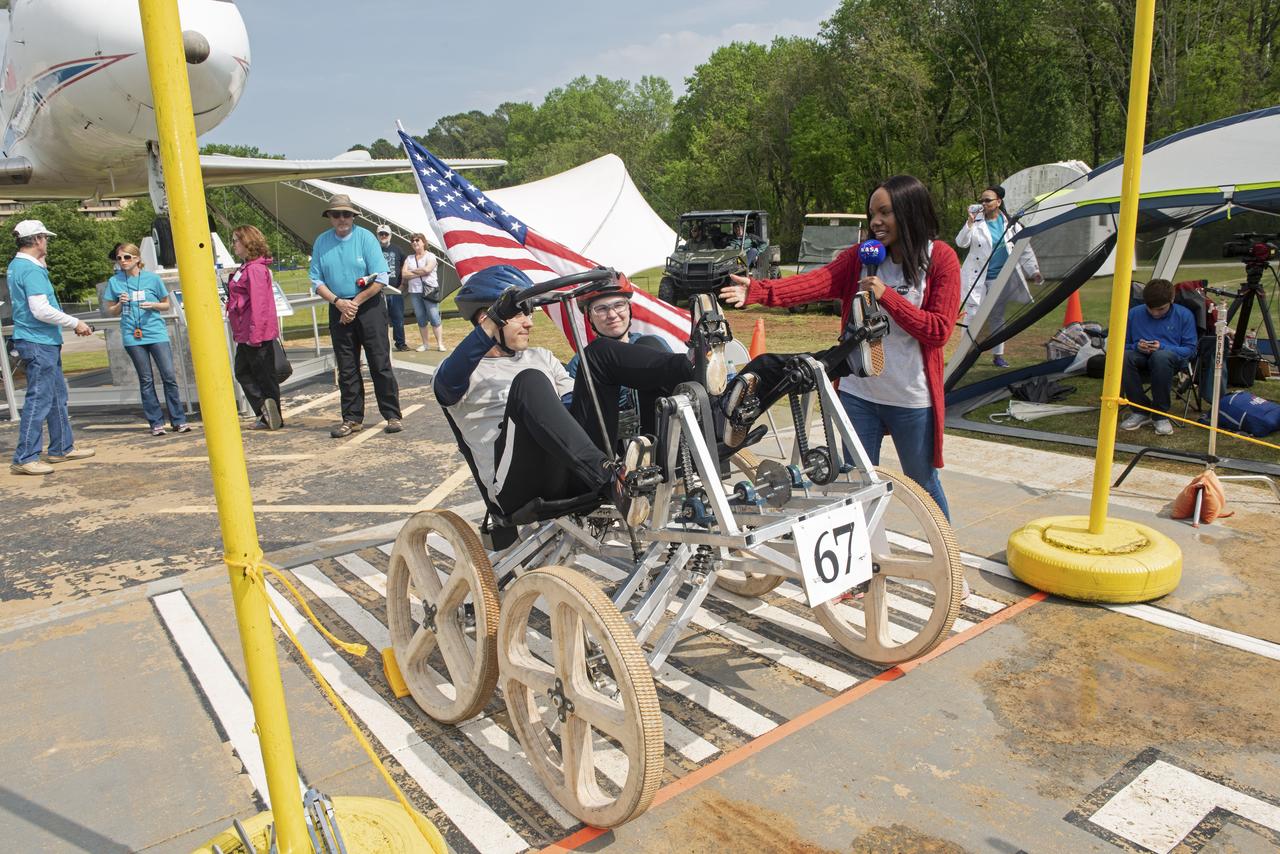

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
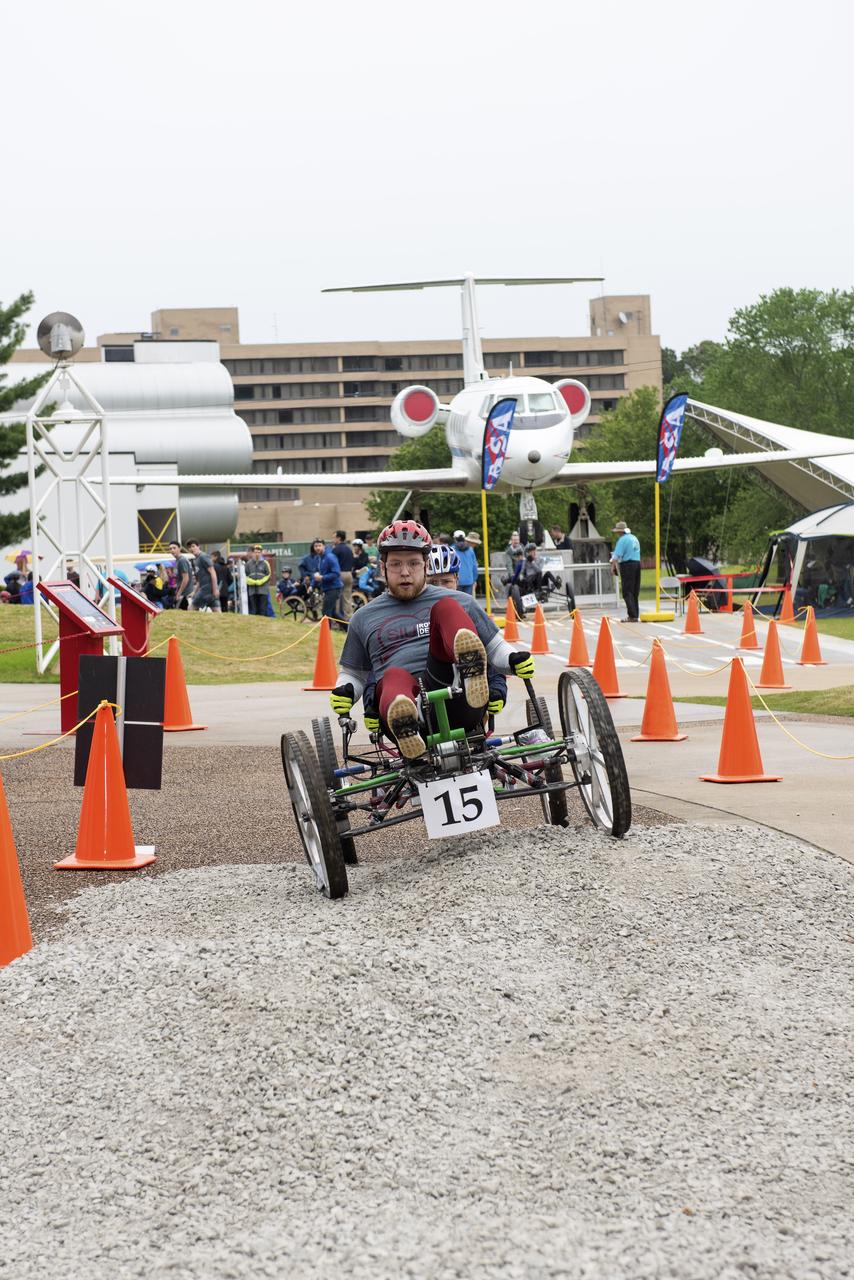

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
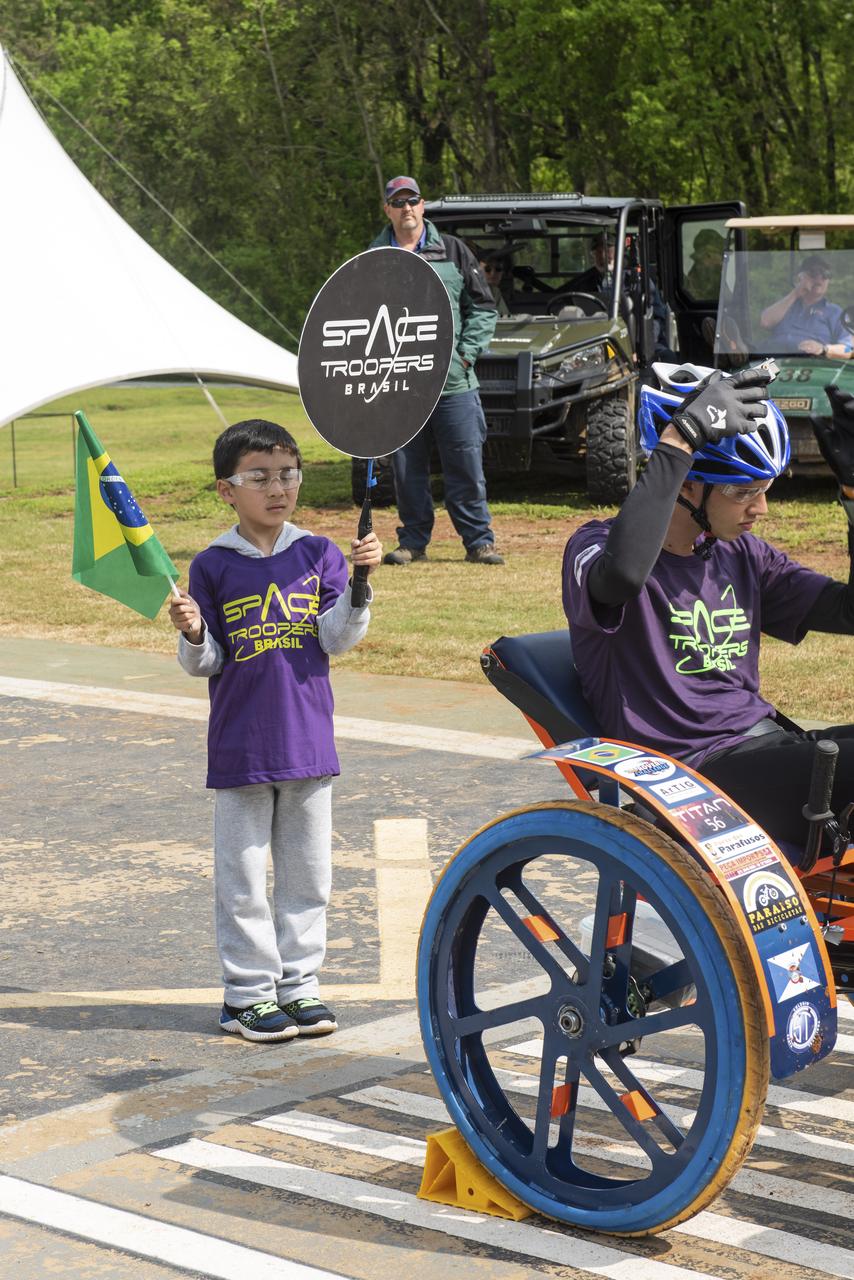

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
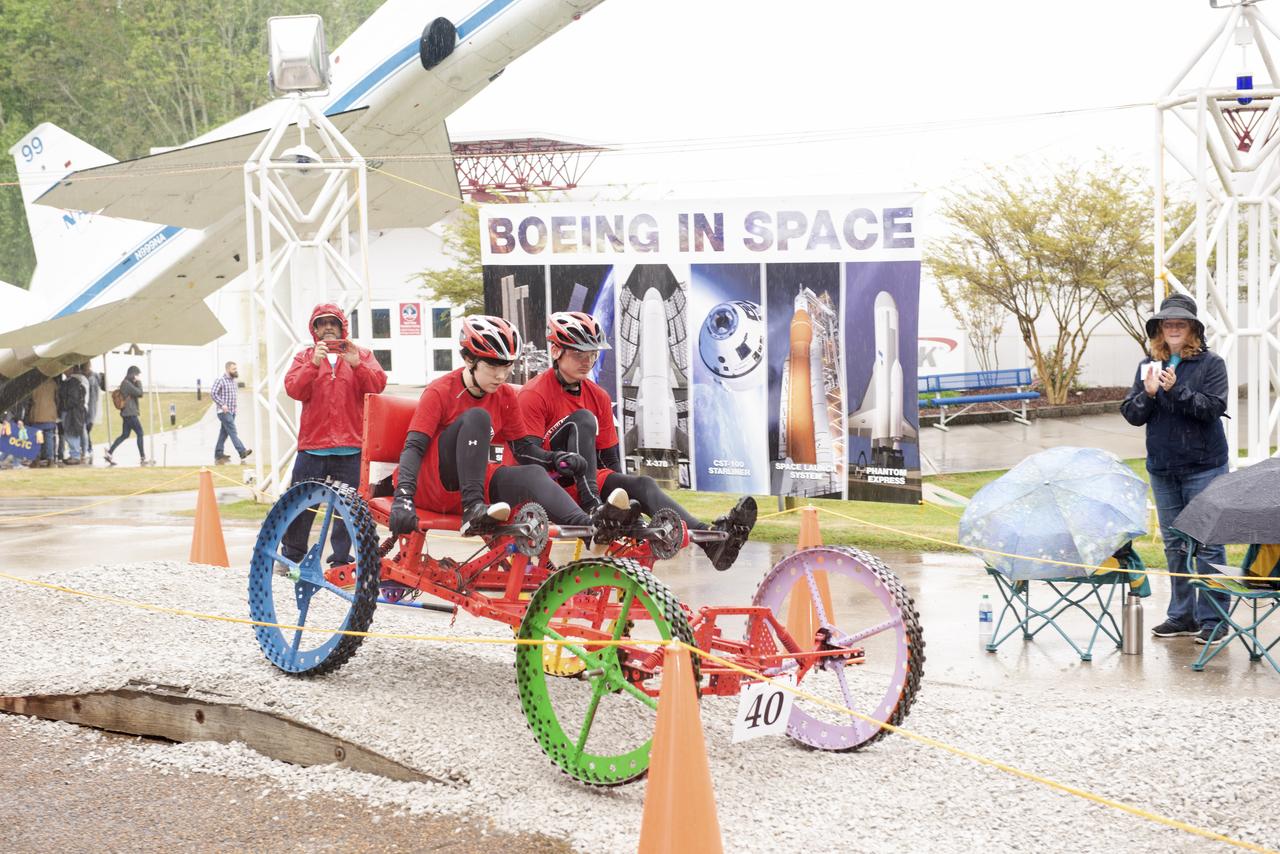

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
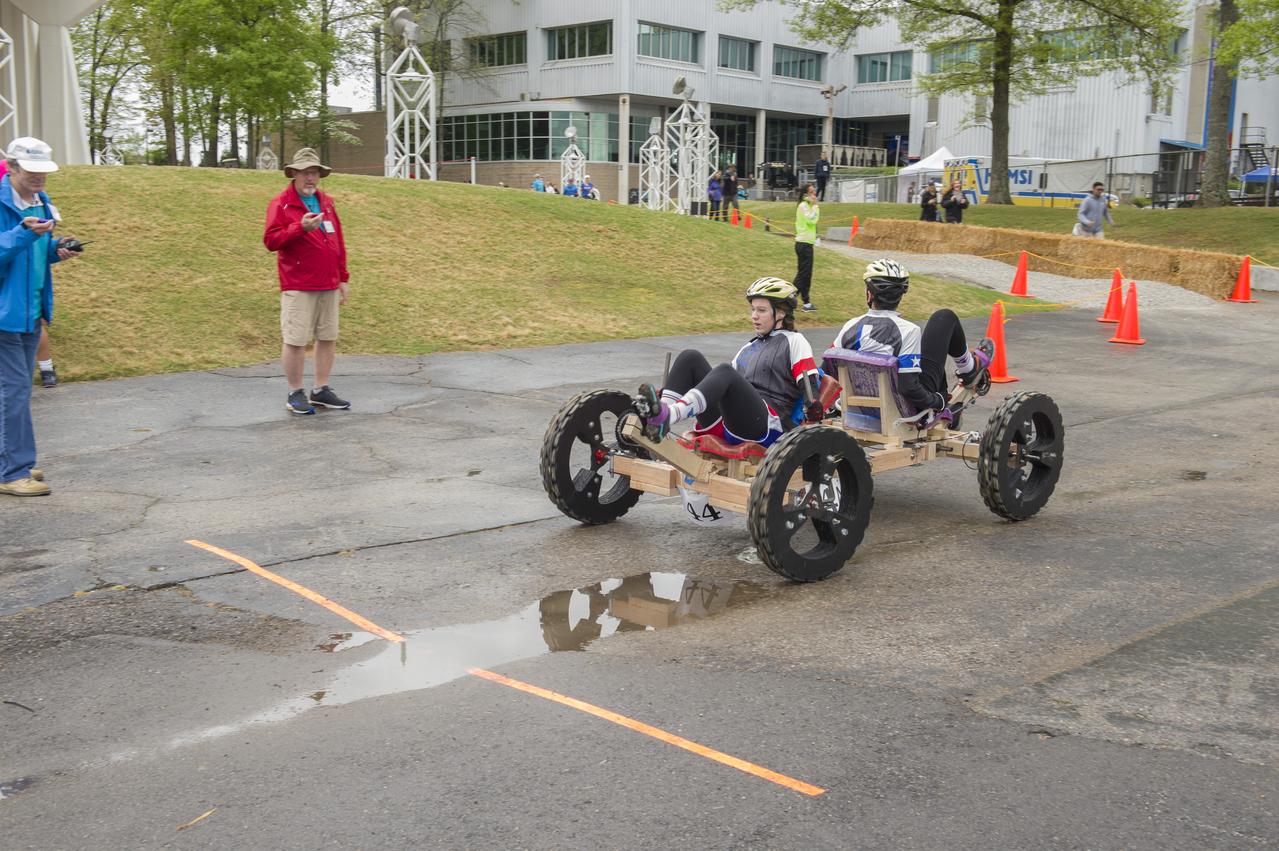

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
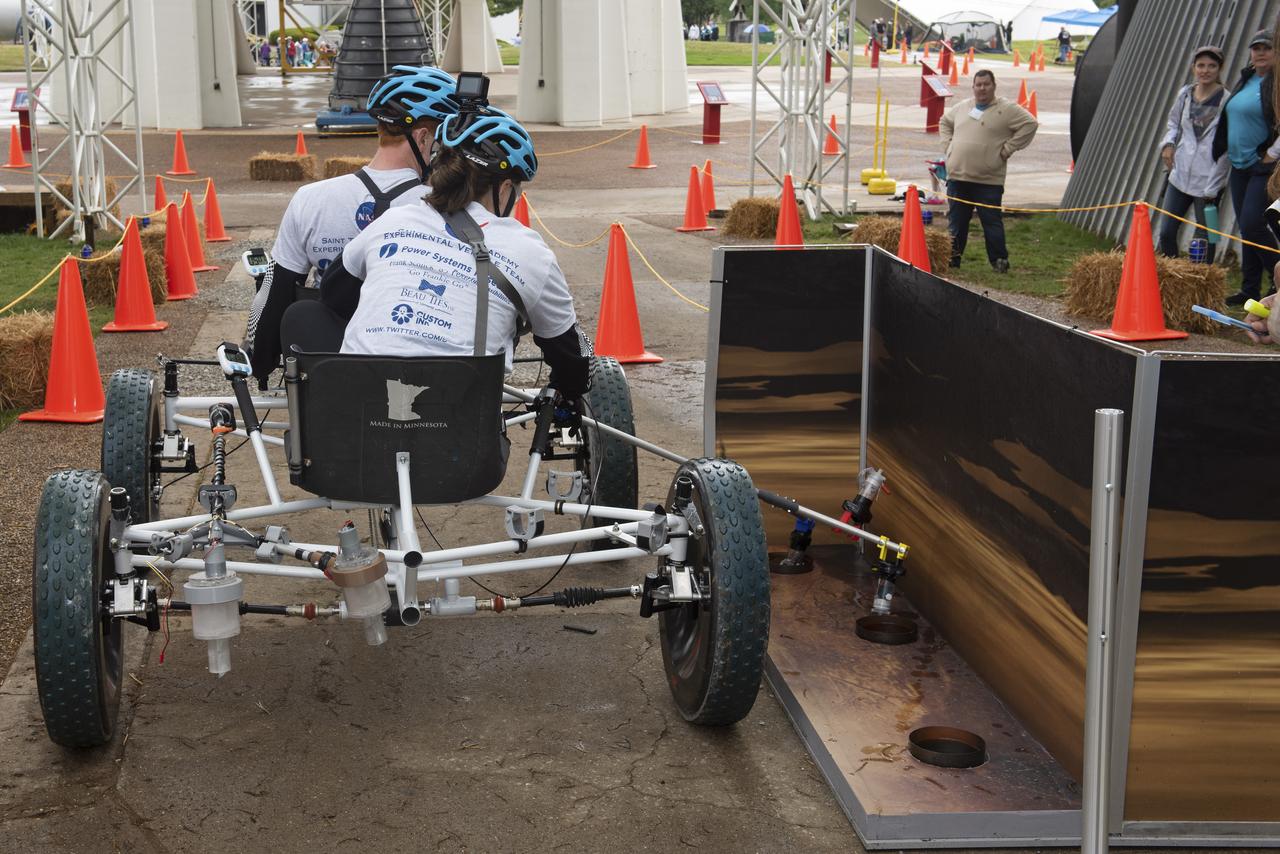

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
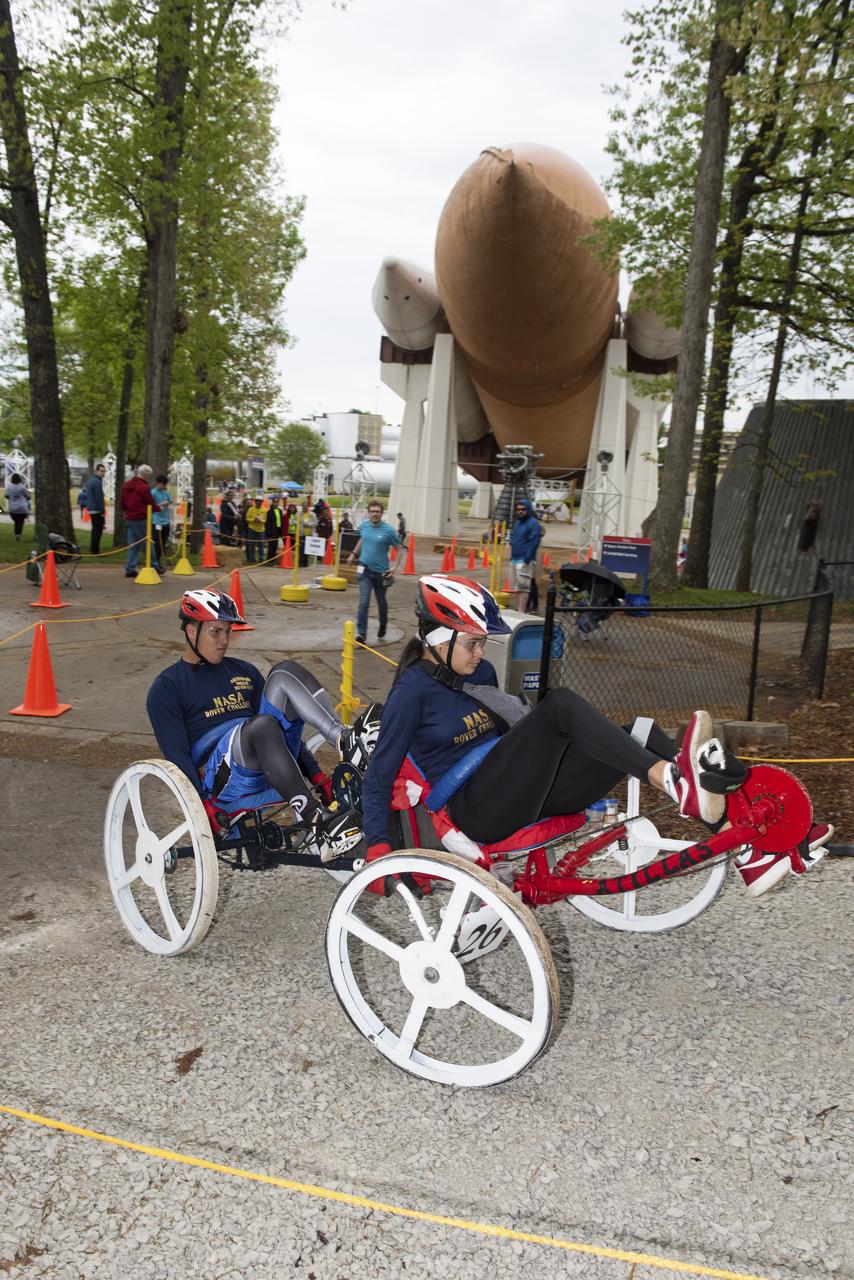

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
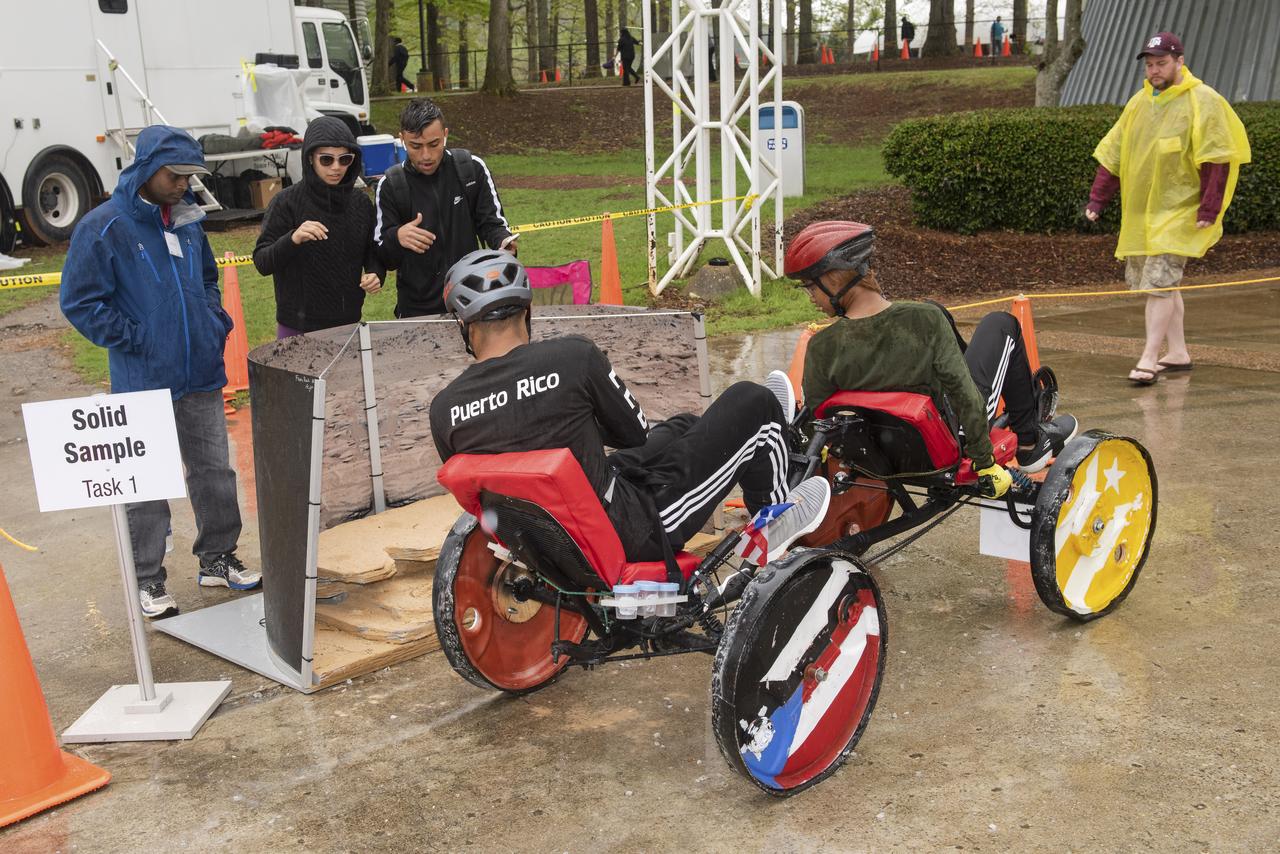

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
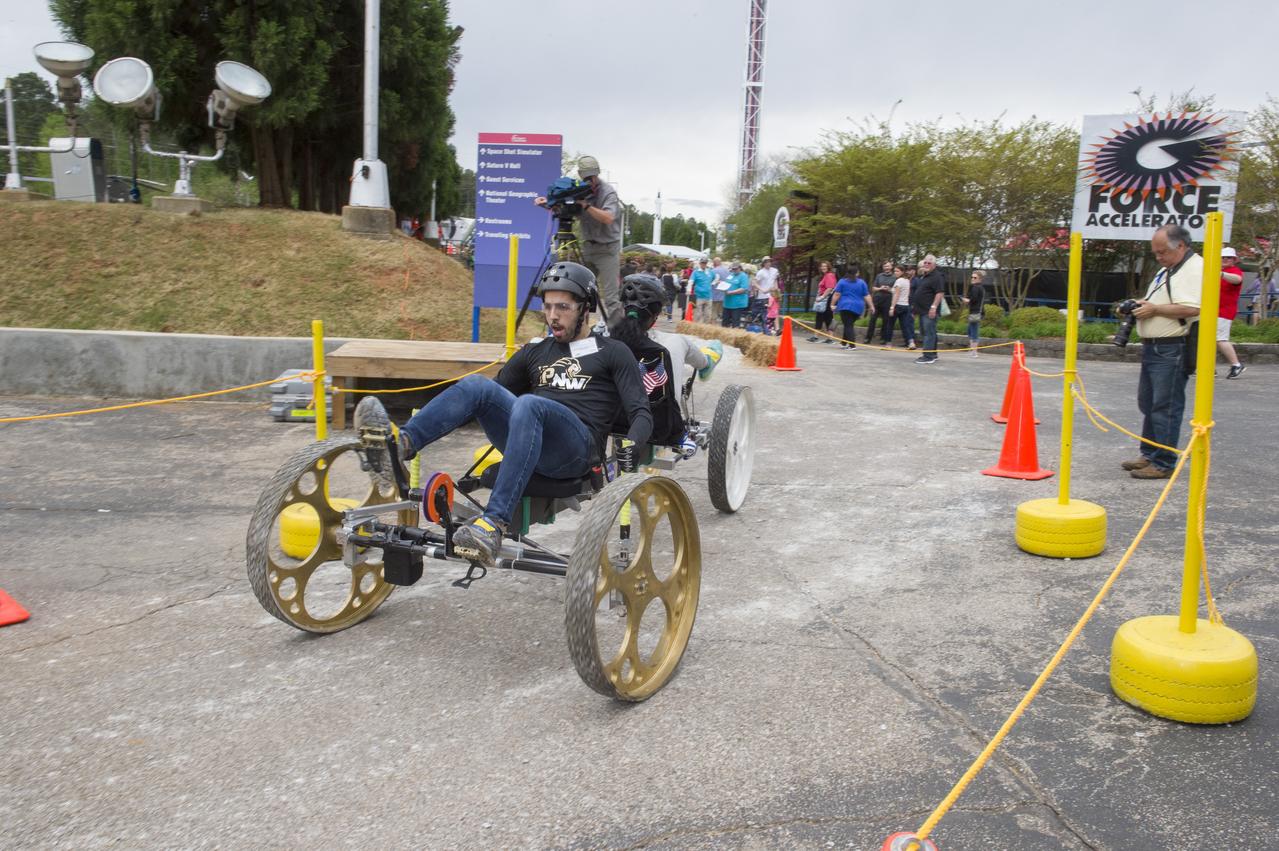

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
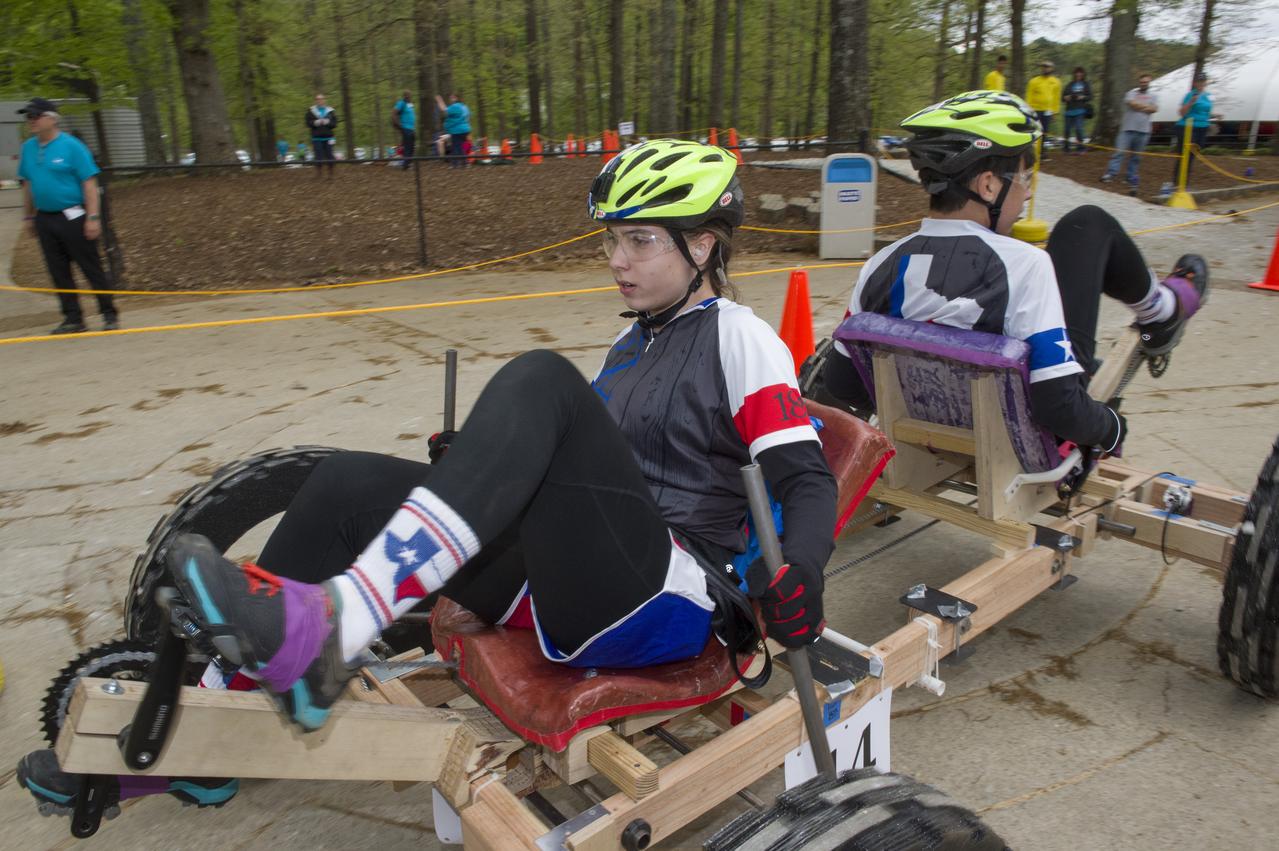

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
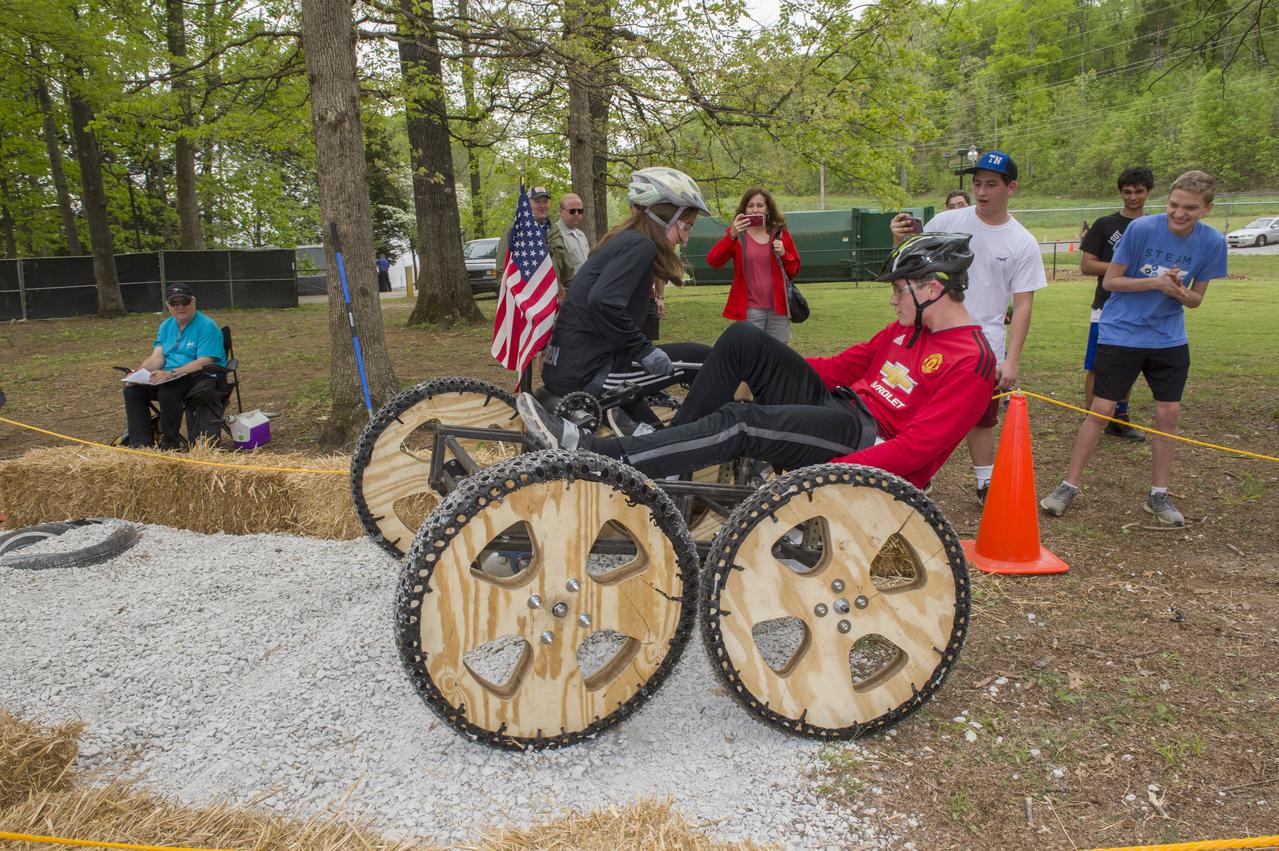

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
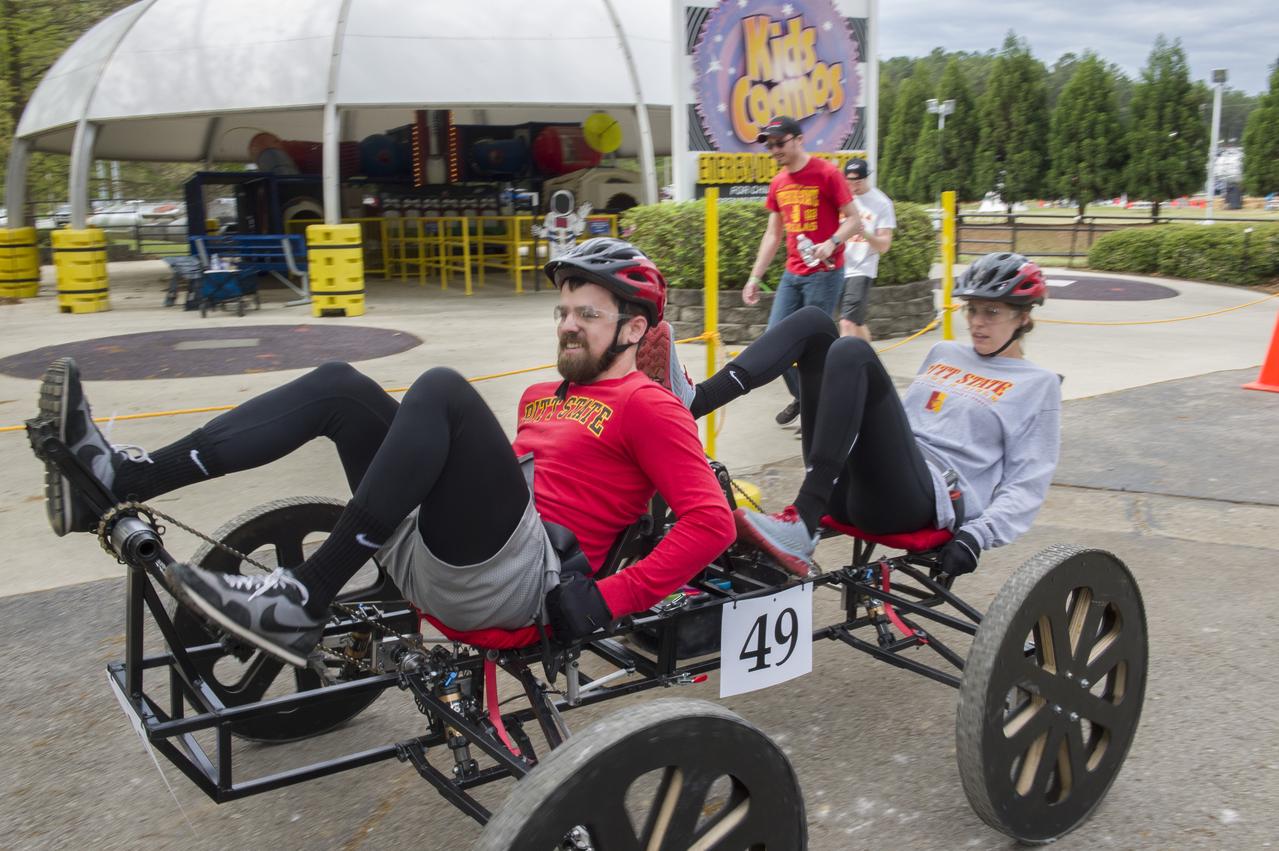

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
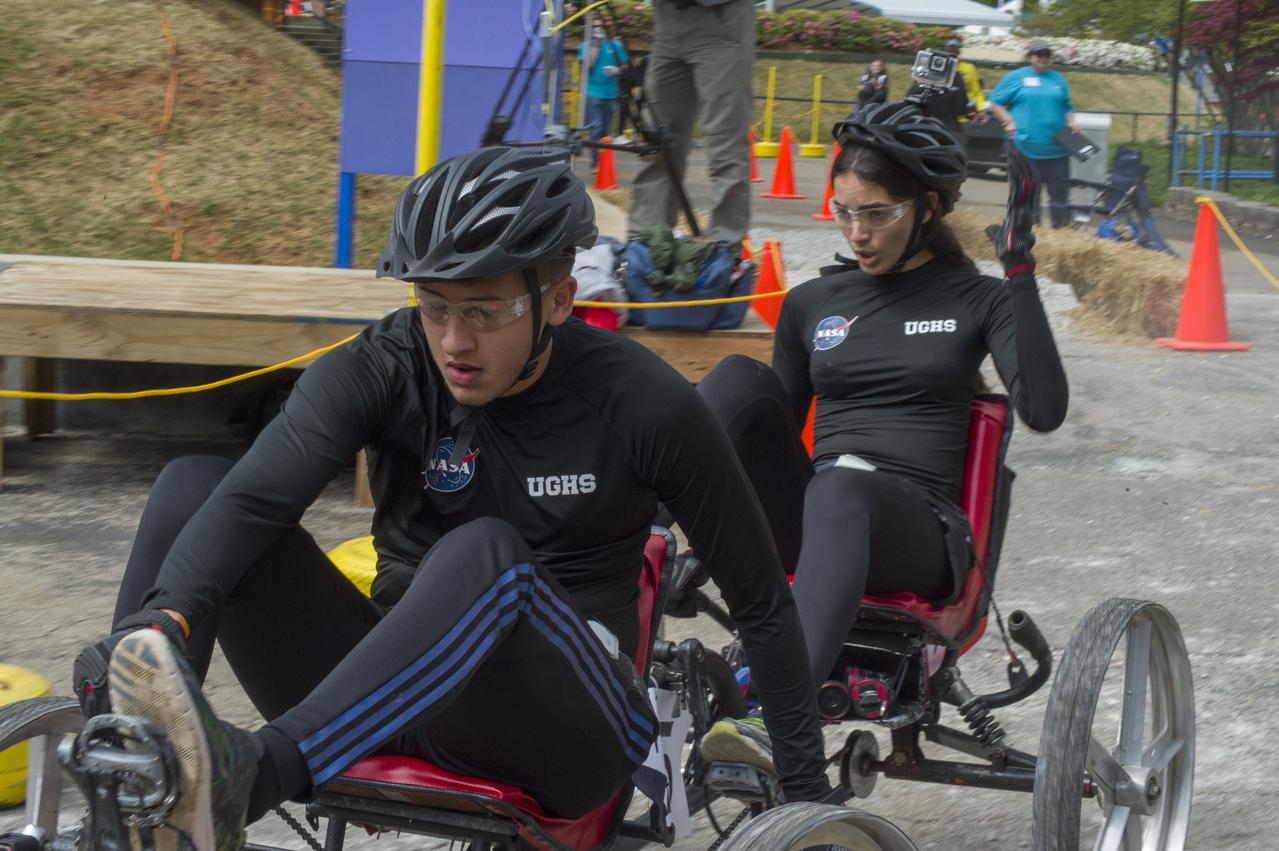

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
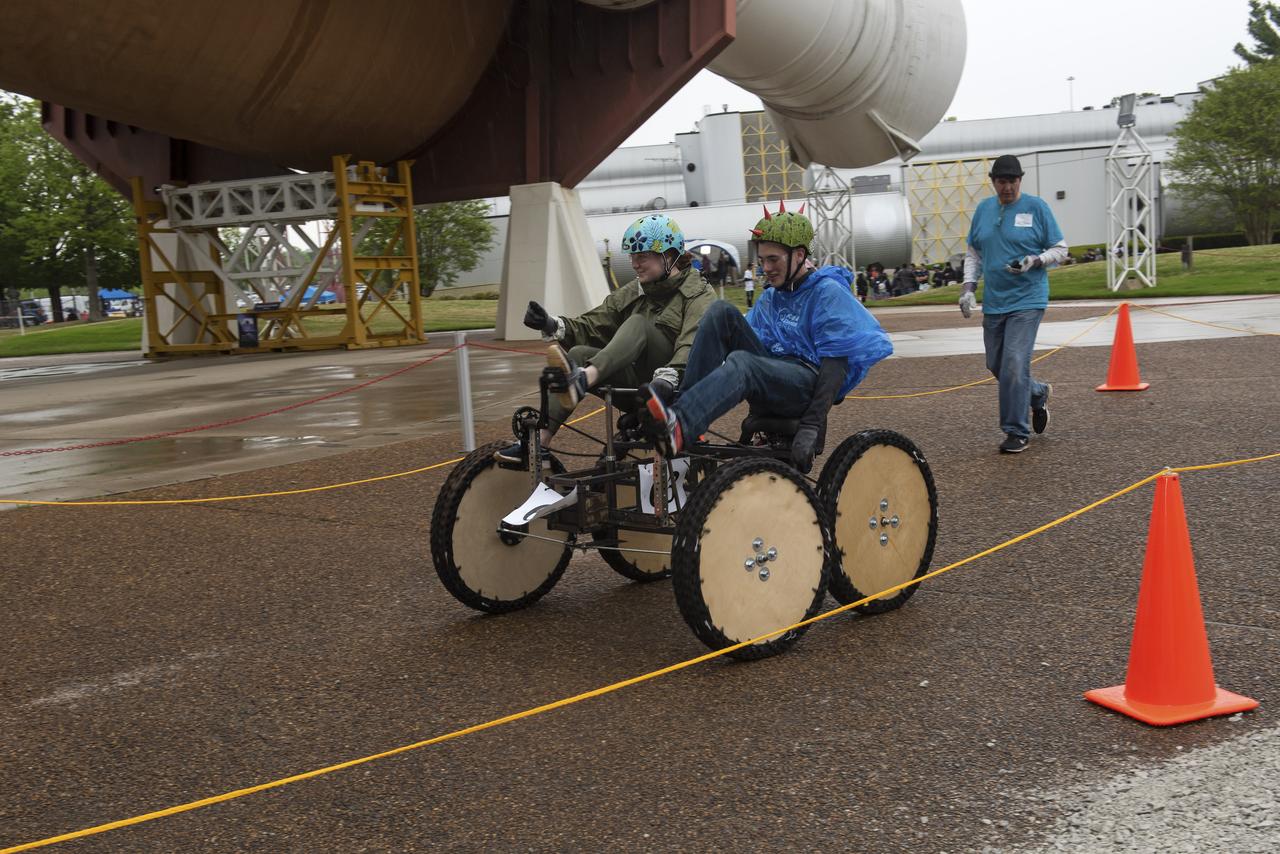

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
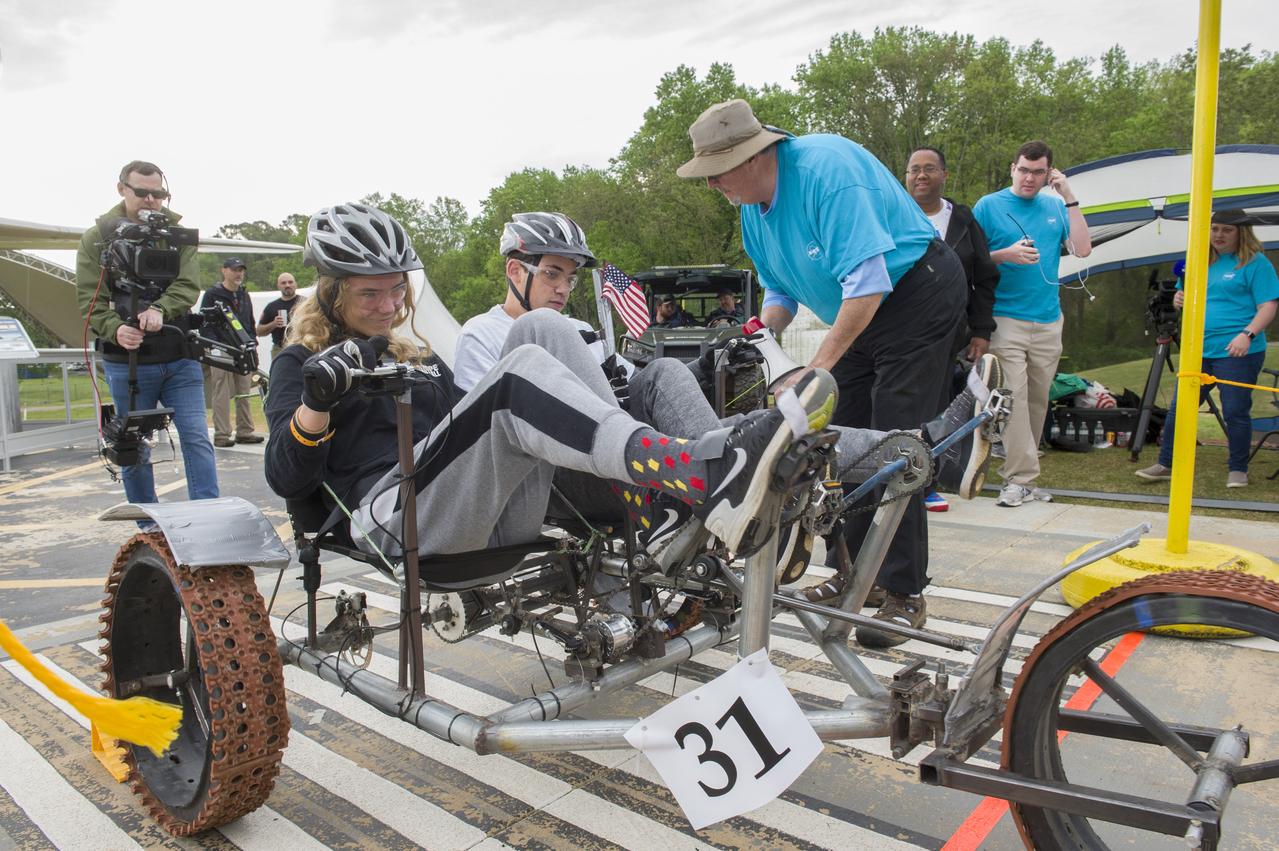
The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
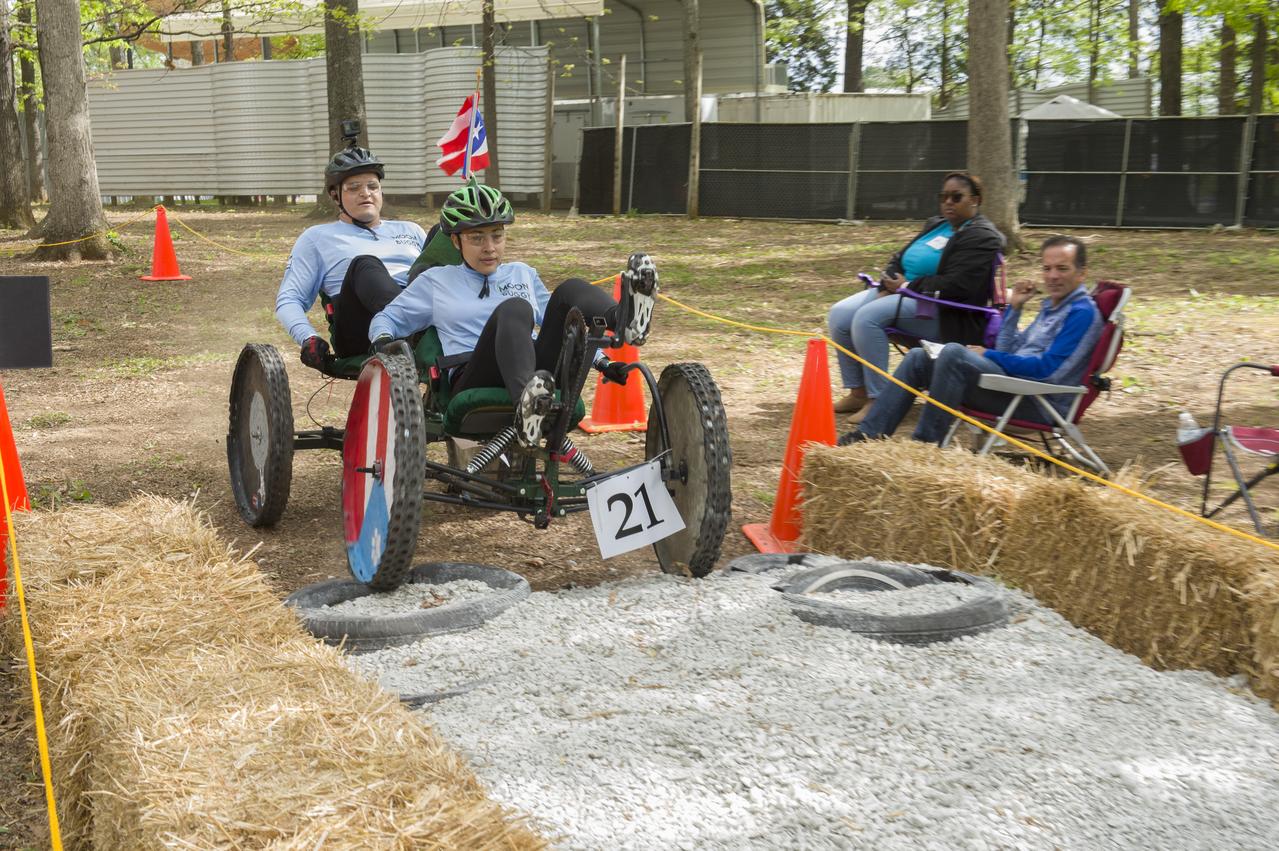

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
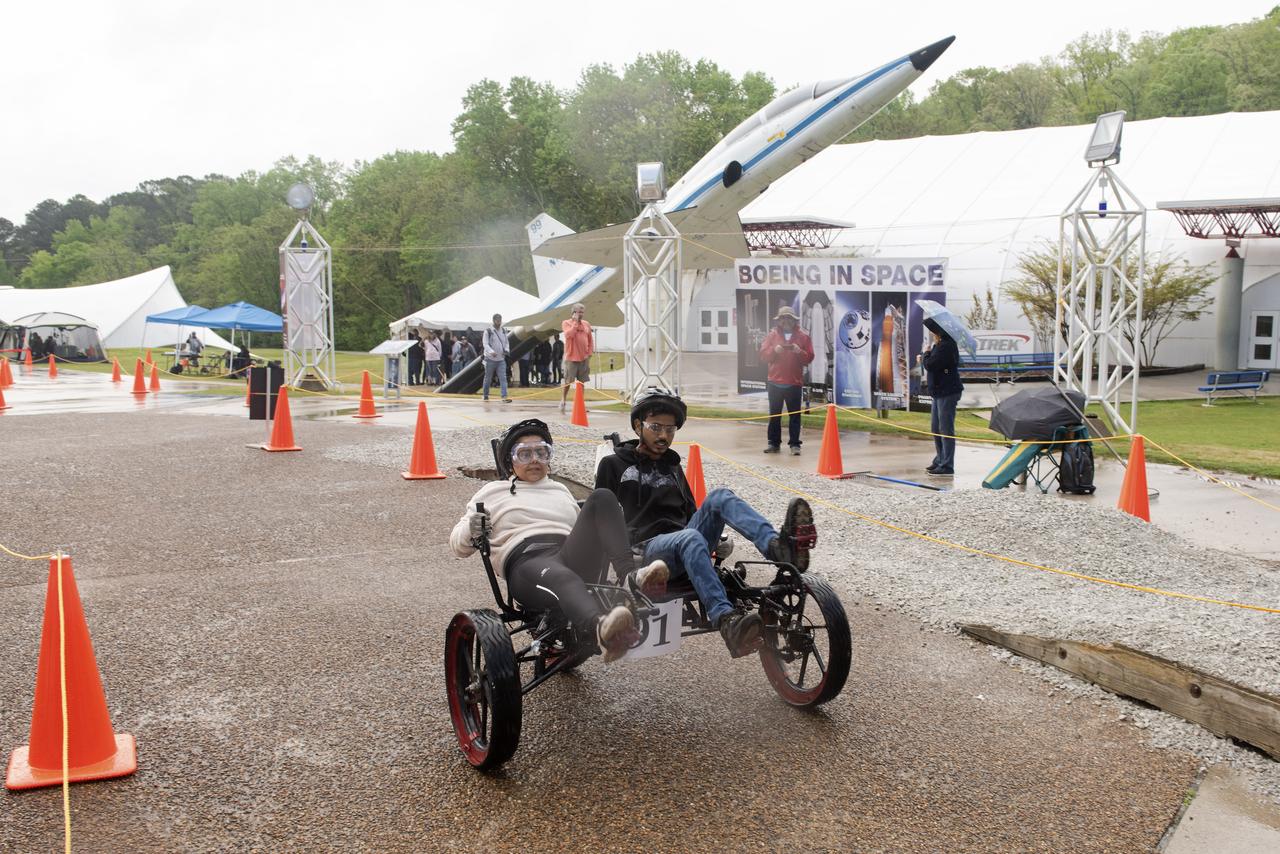

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
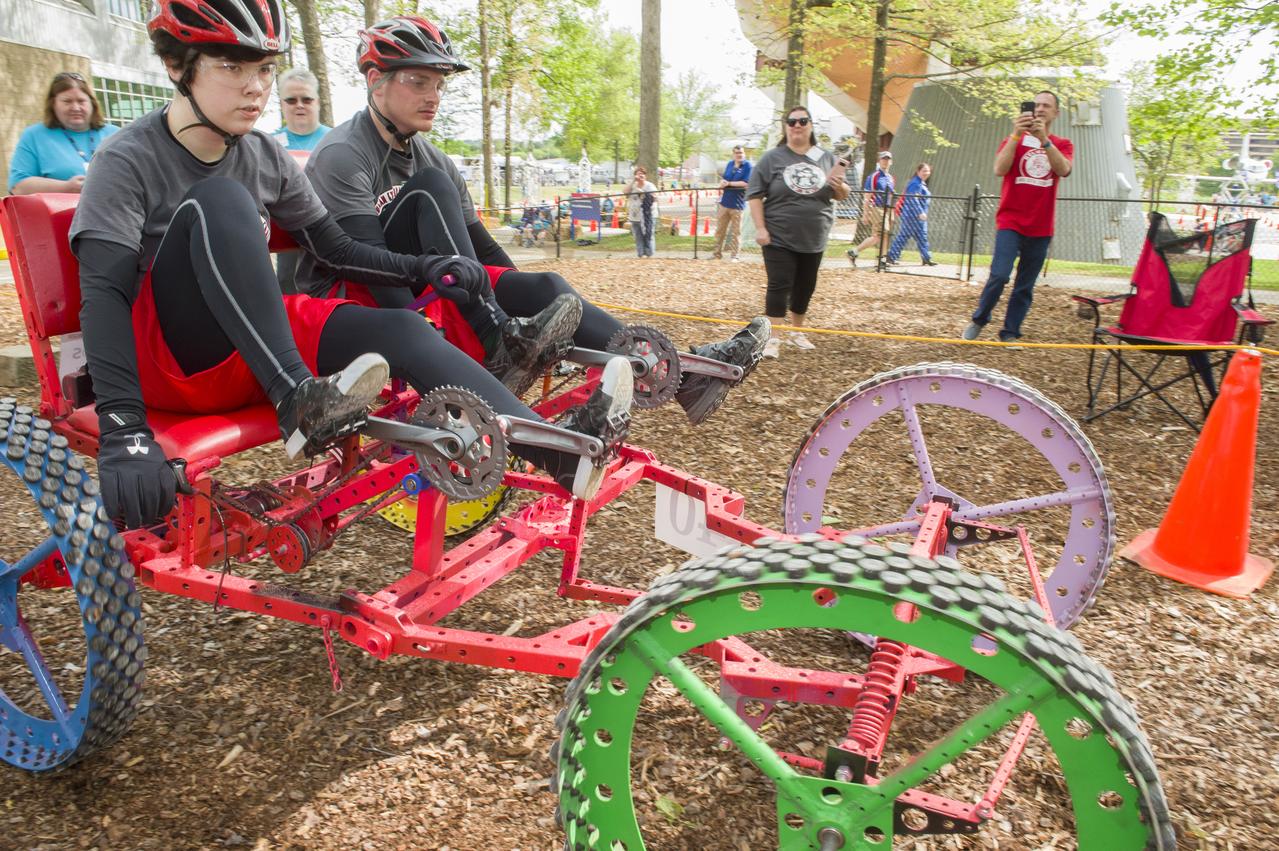

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
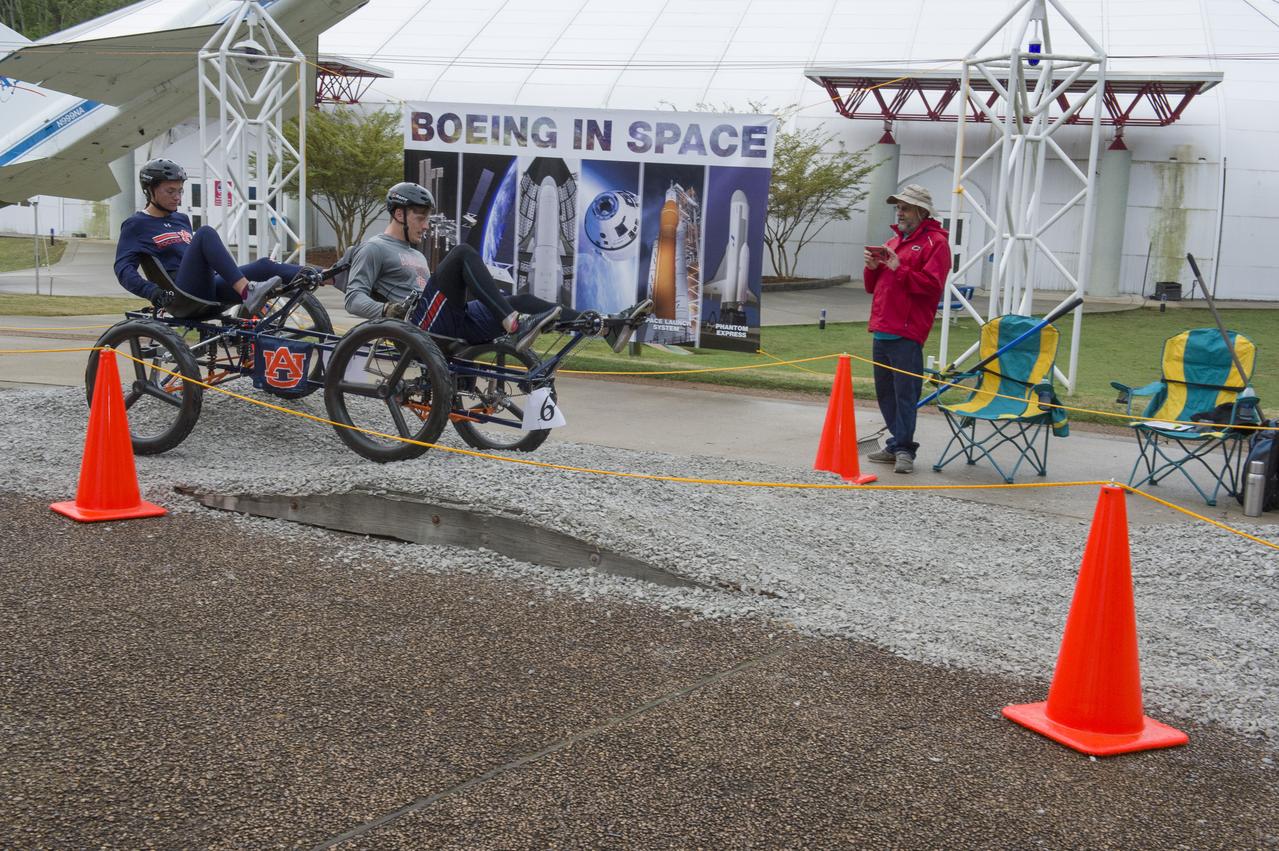

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.
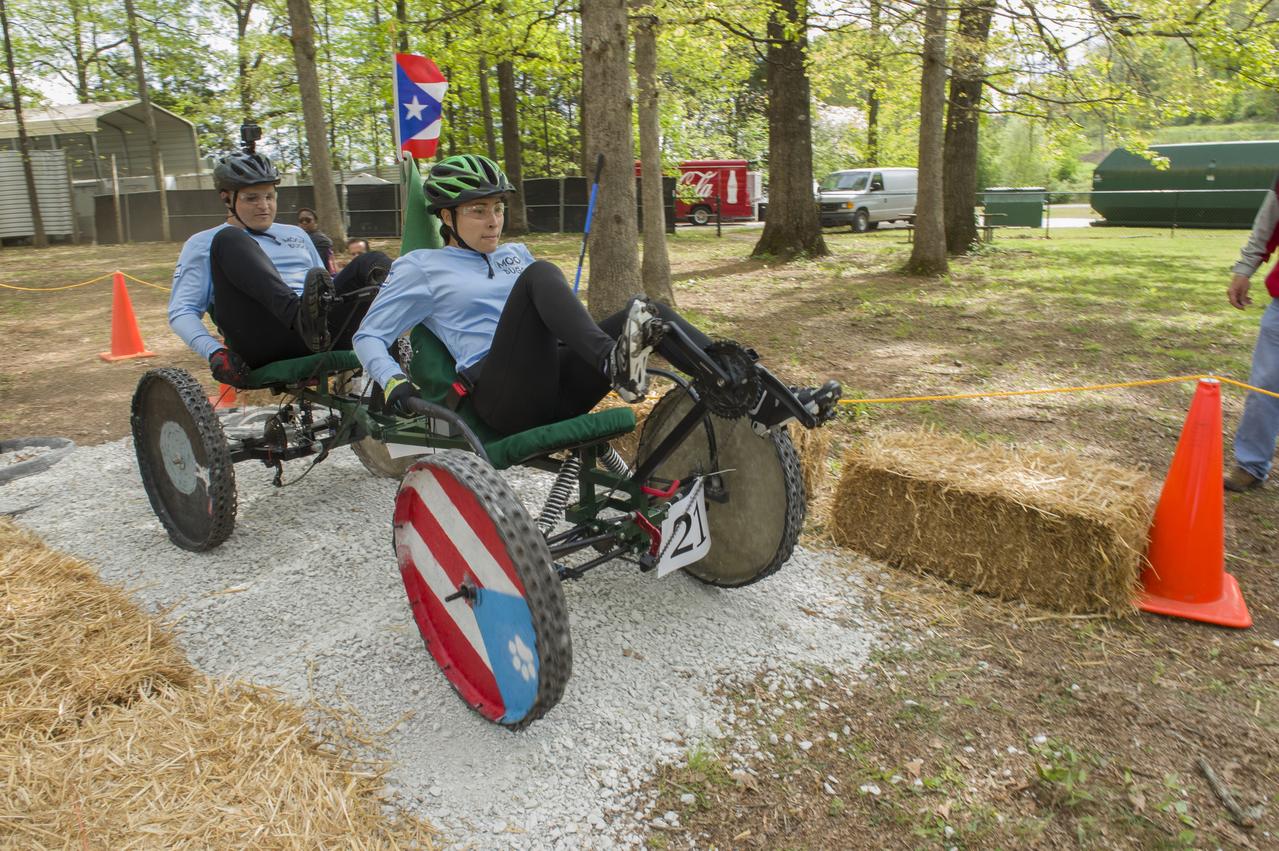

The 2019 Lunar Rover Challenge Competition was hosted by the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This annual event celebrated the 25th anniversary of what began as the Great Moonbuggy Race in 1994. High school and College teams from the United States and foreign countries competed. The awards ceremony was held at the adjacent Marriott on Saturday evening.