
NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the final in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

The mission insignia of NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) mission is pictured in front of the satellite in a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

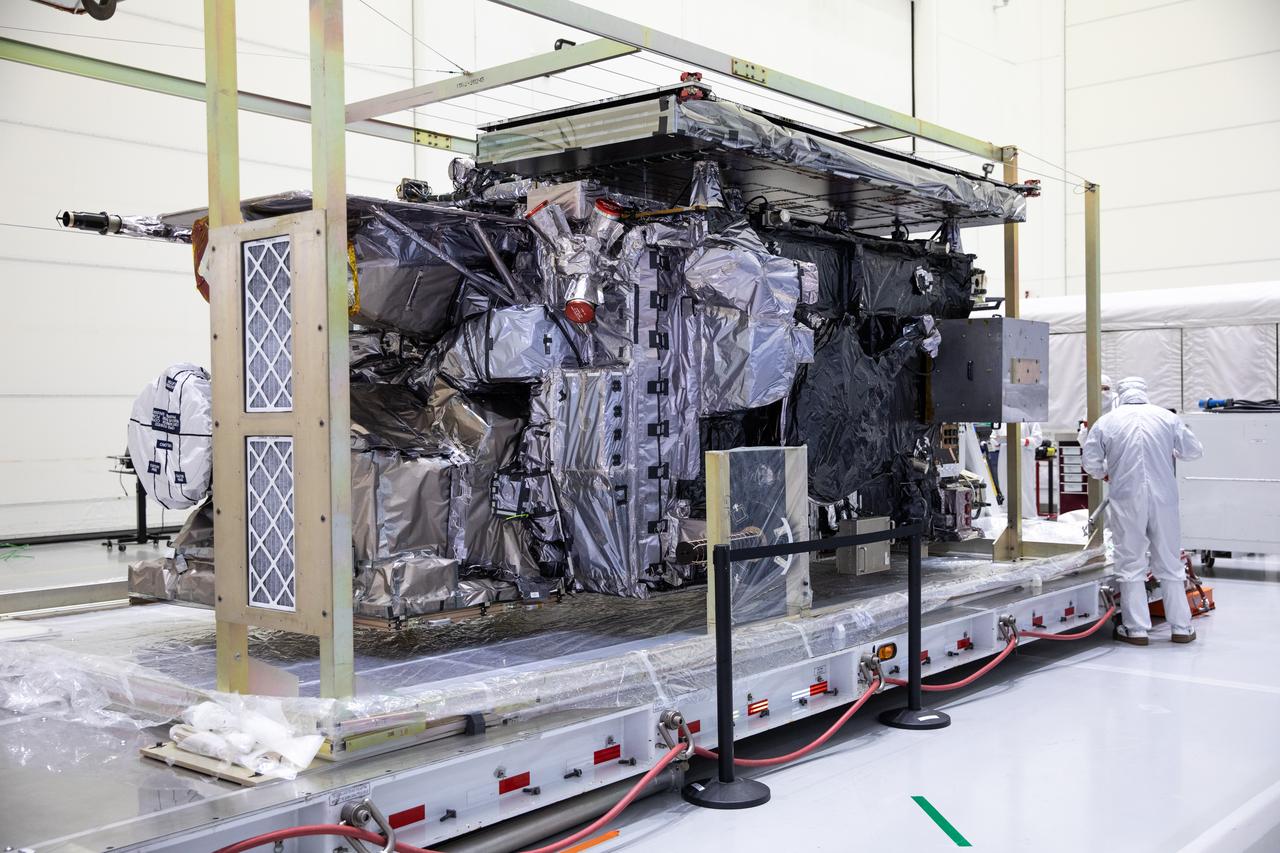
Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
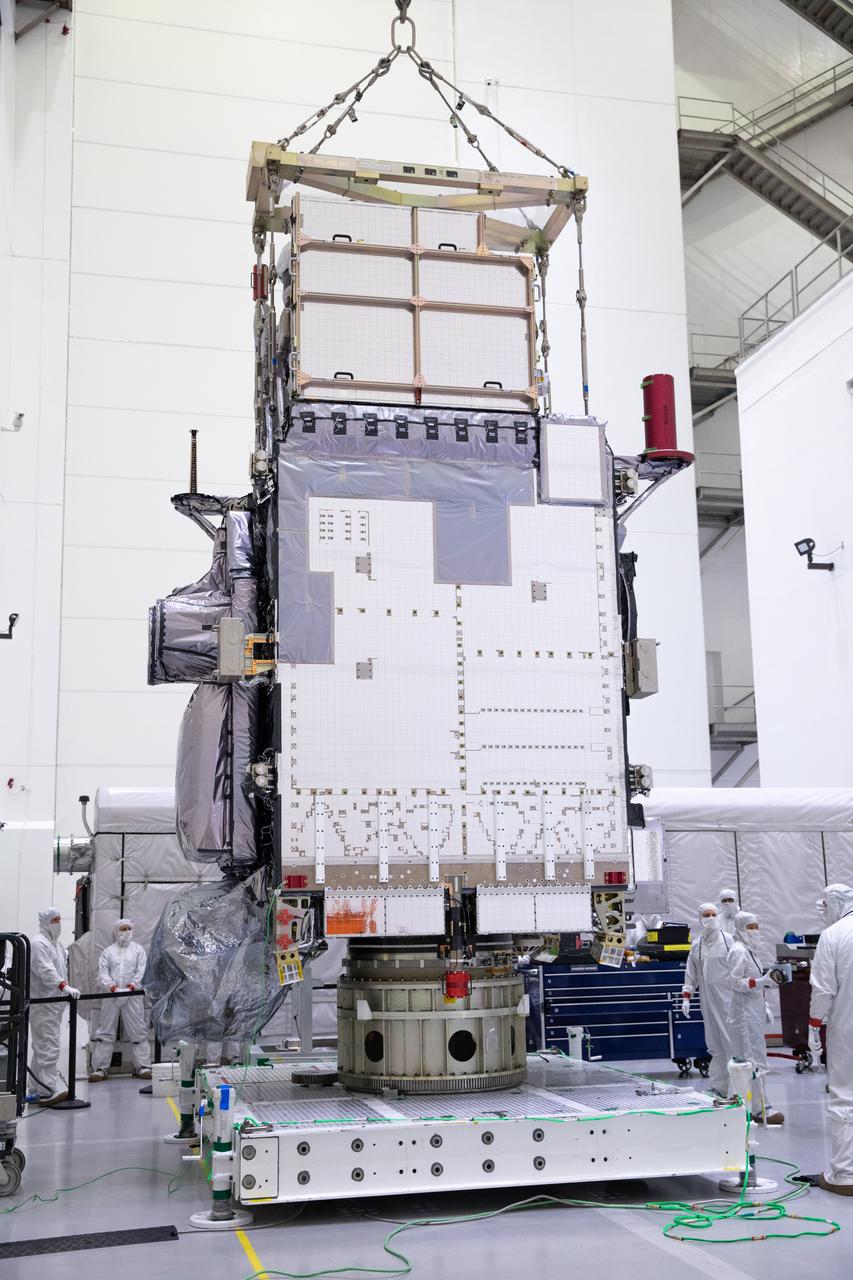
Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
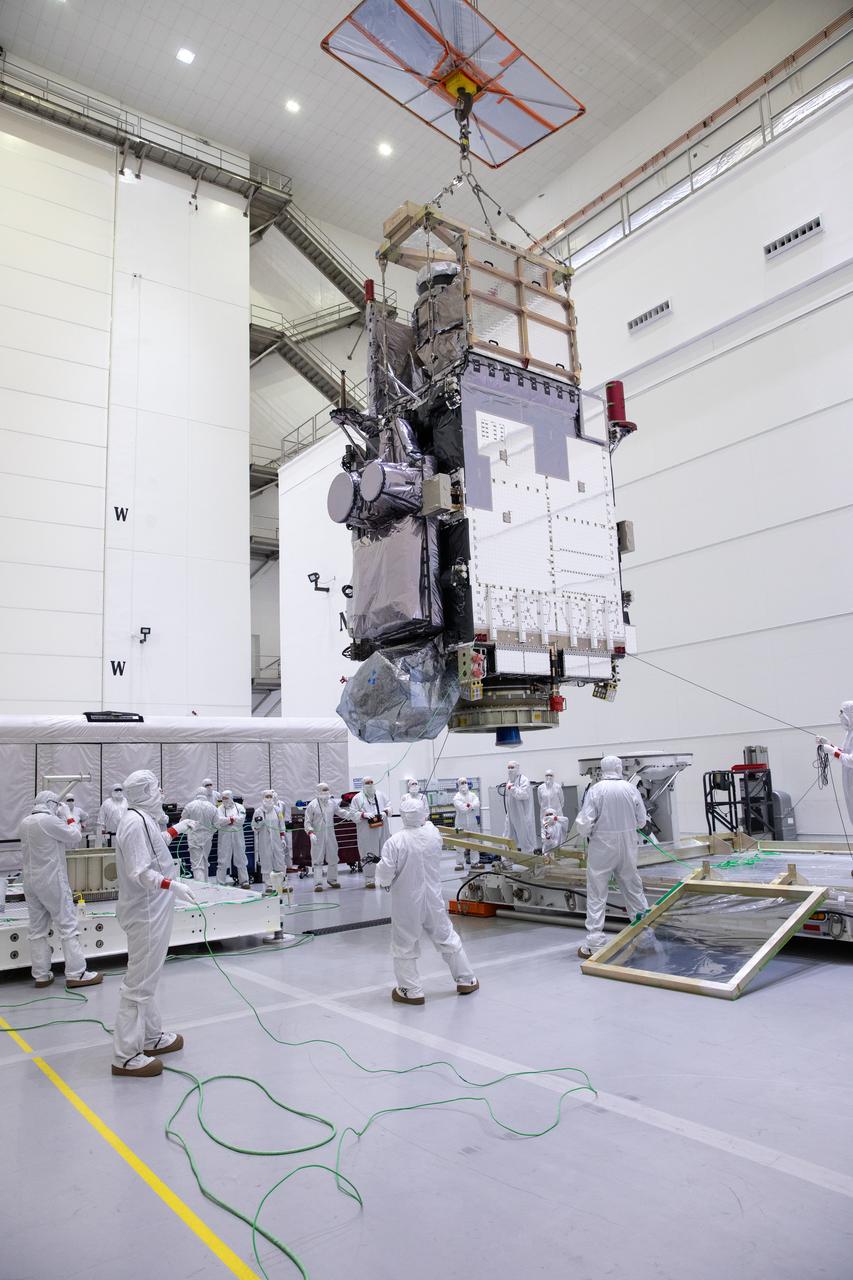

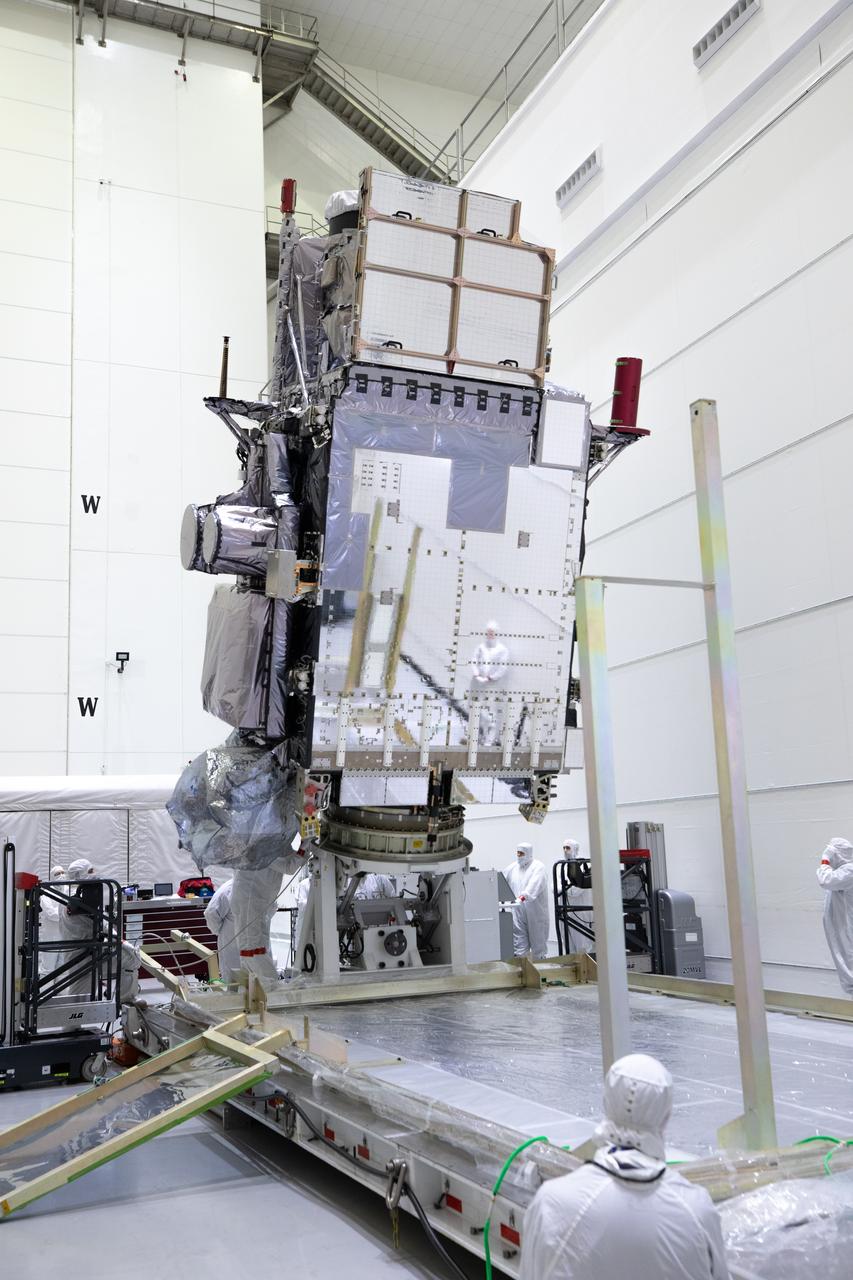
Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
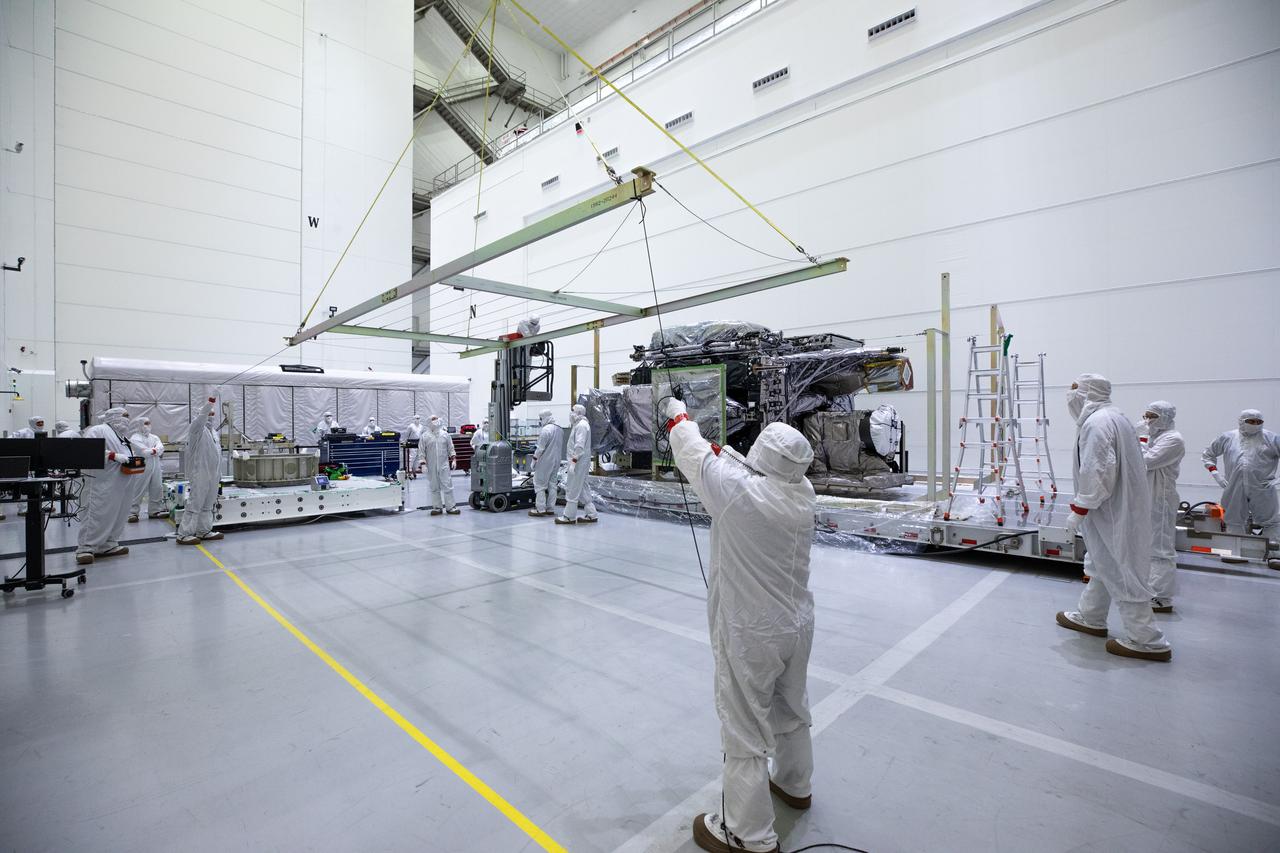

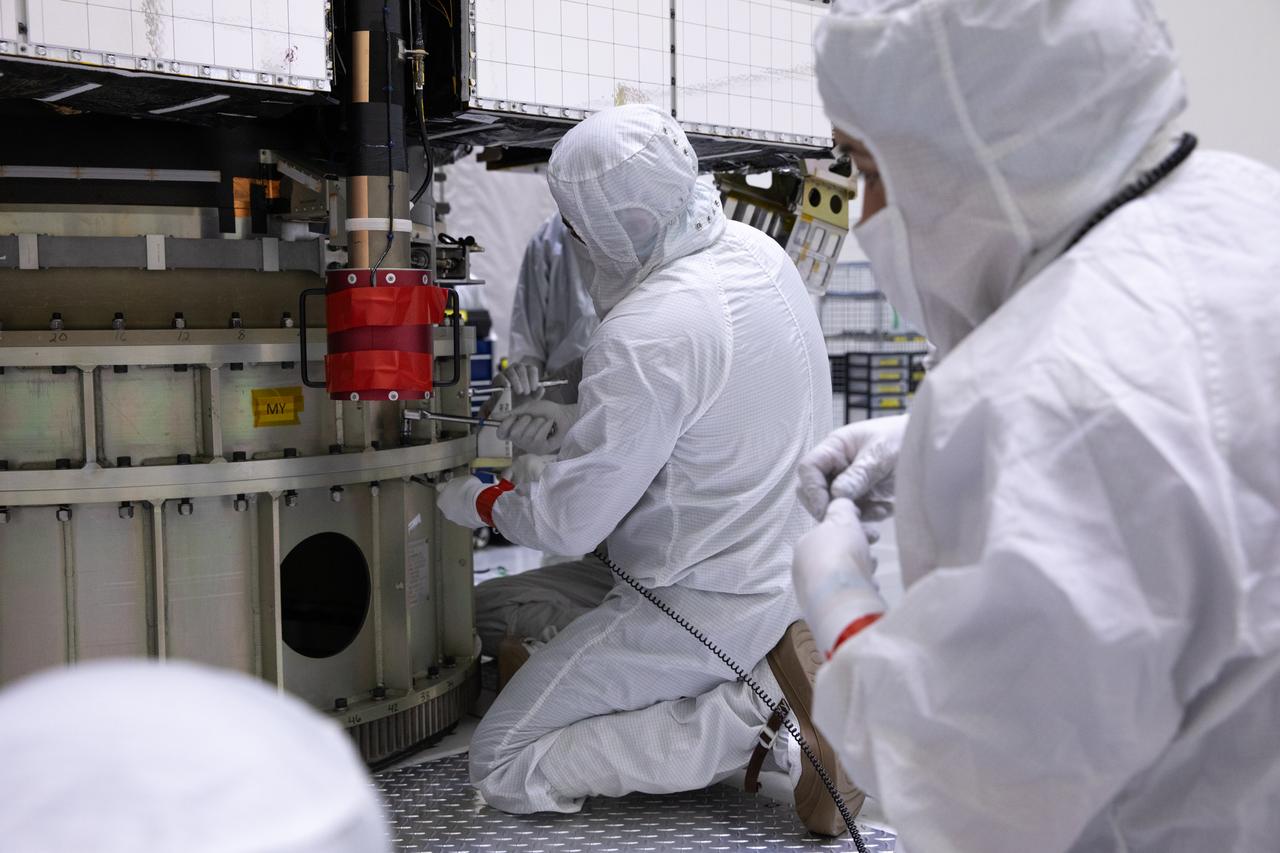
Technicians remove part of a protective enclosure as they prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
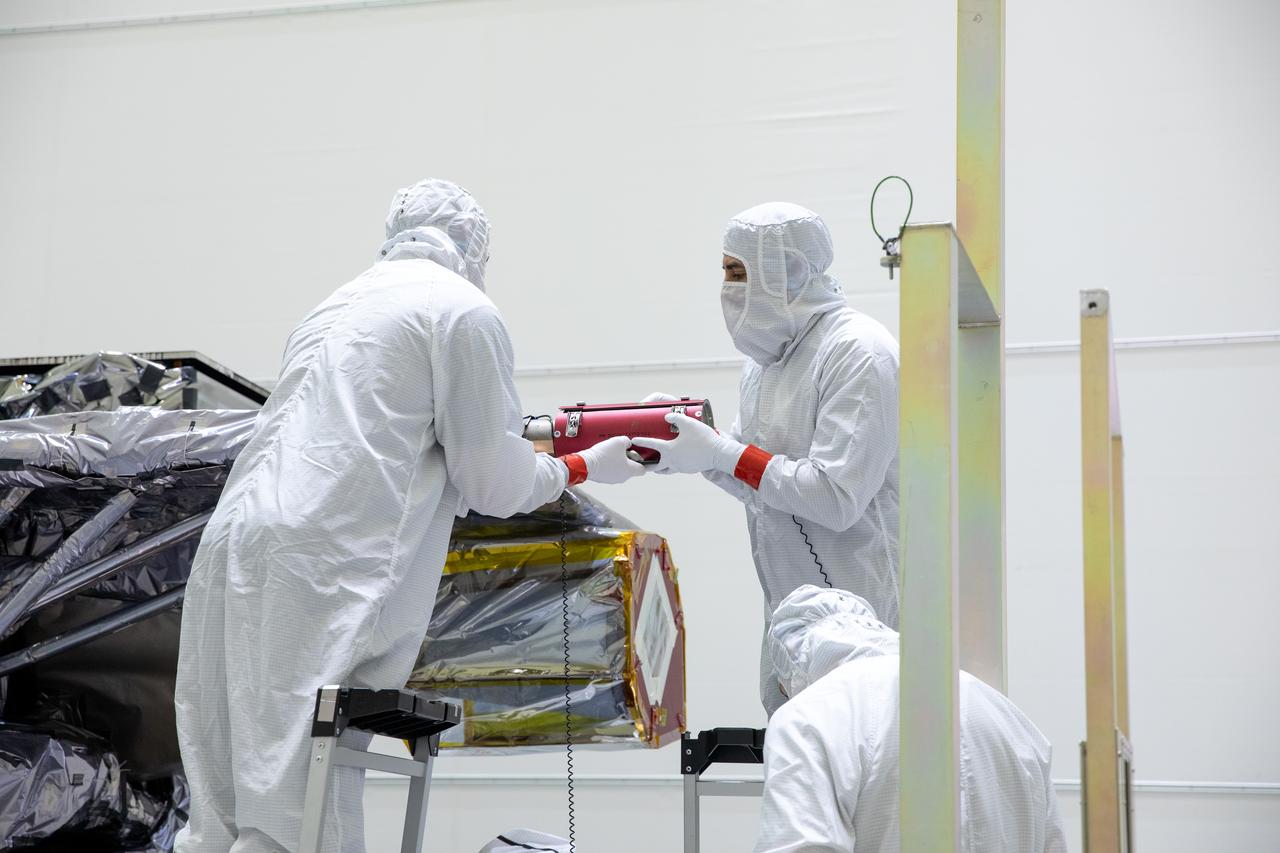

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
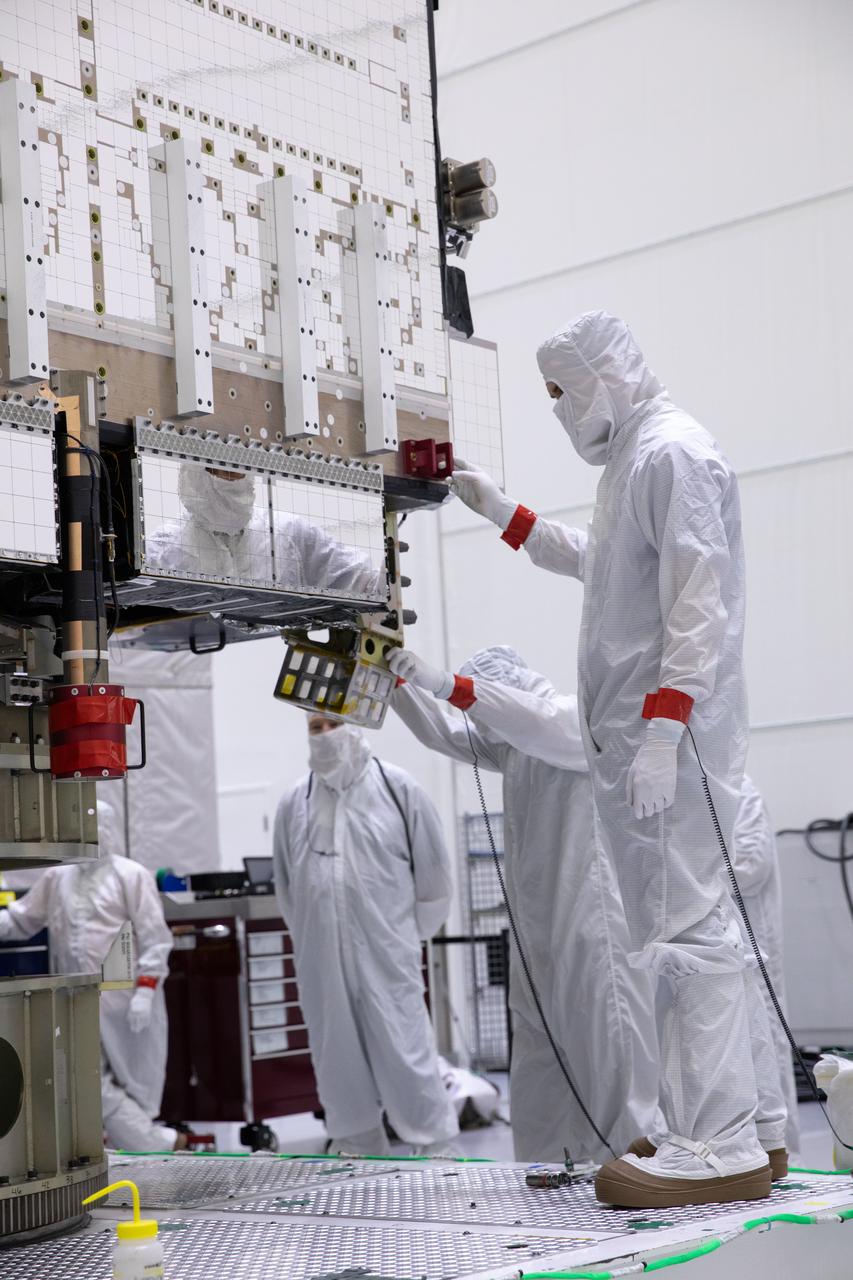

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
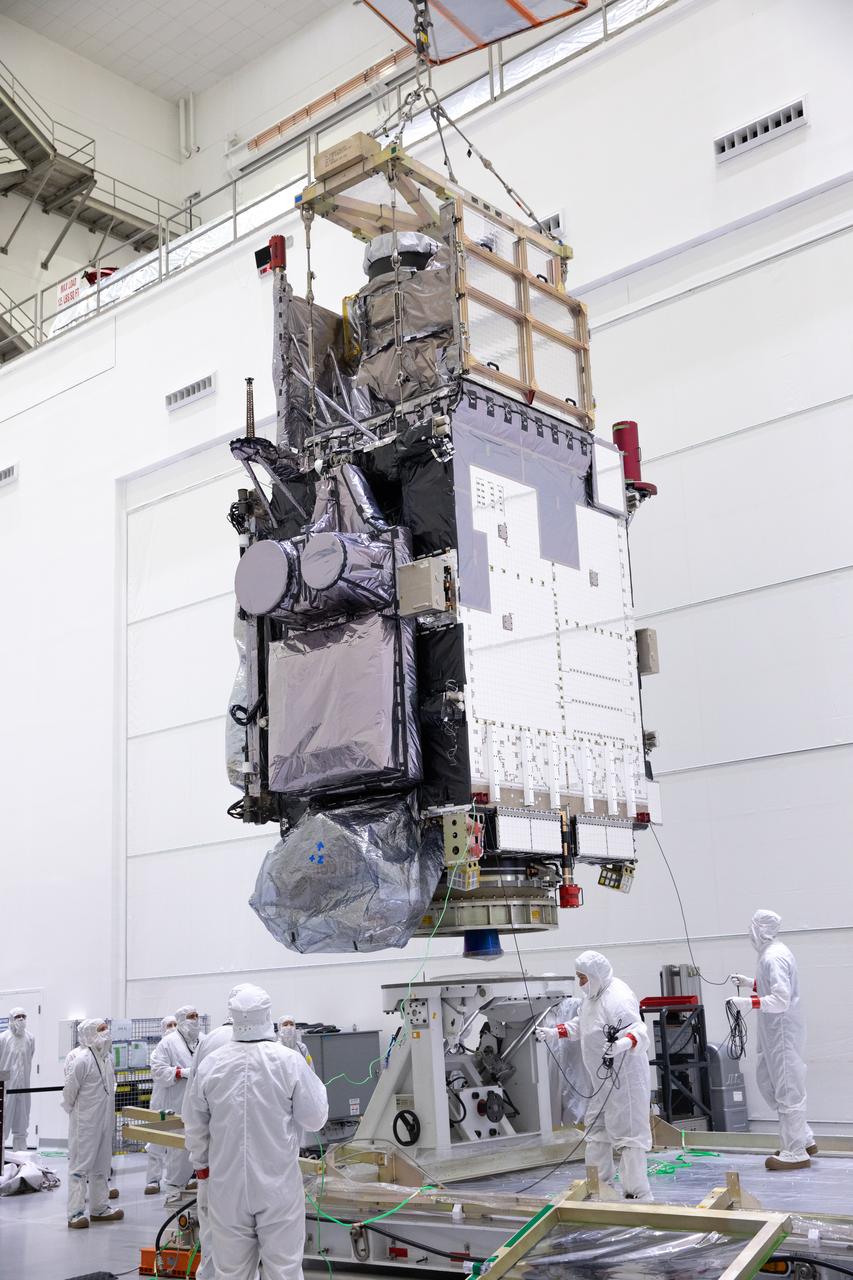

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
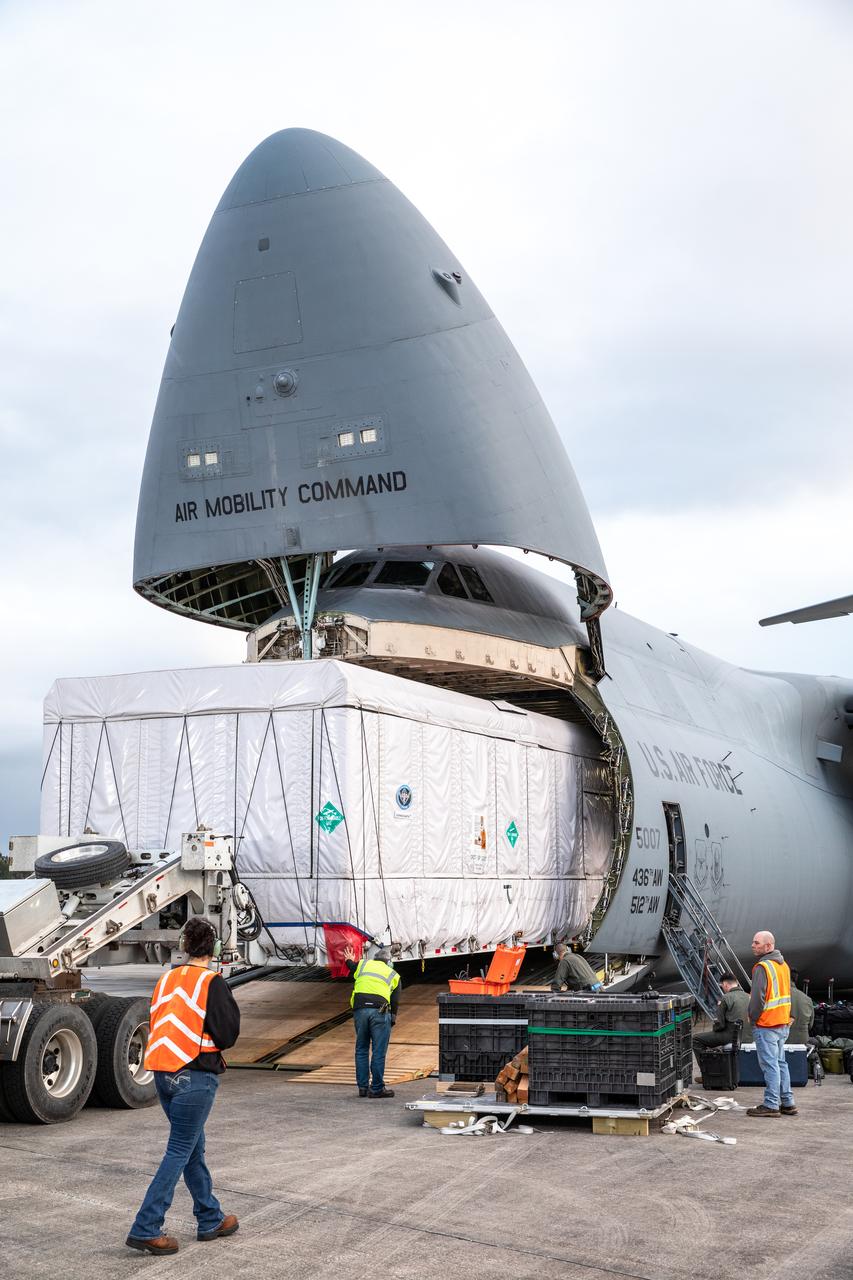

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
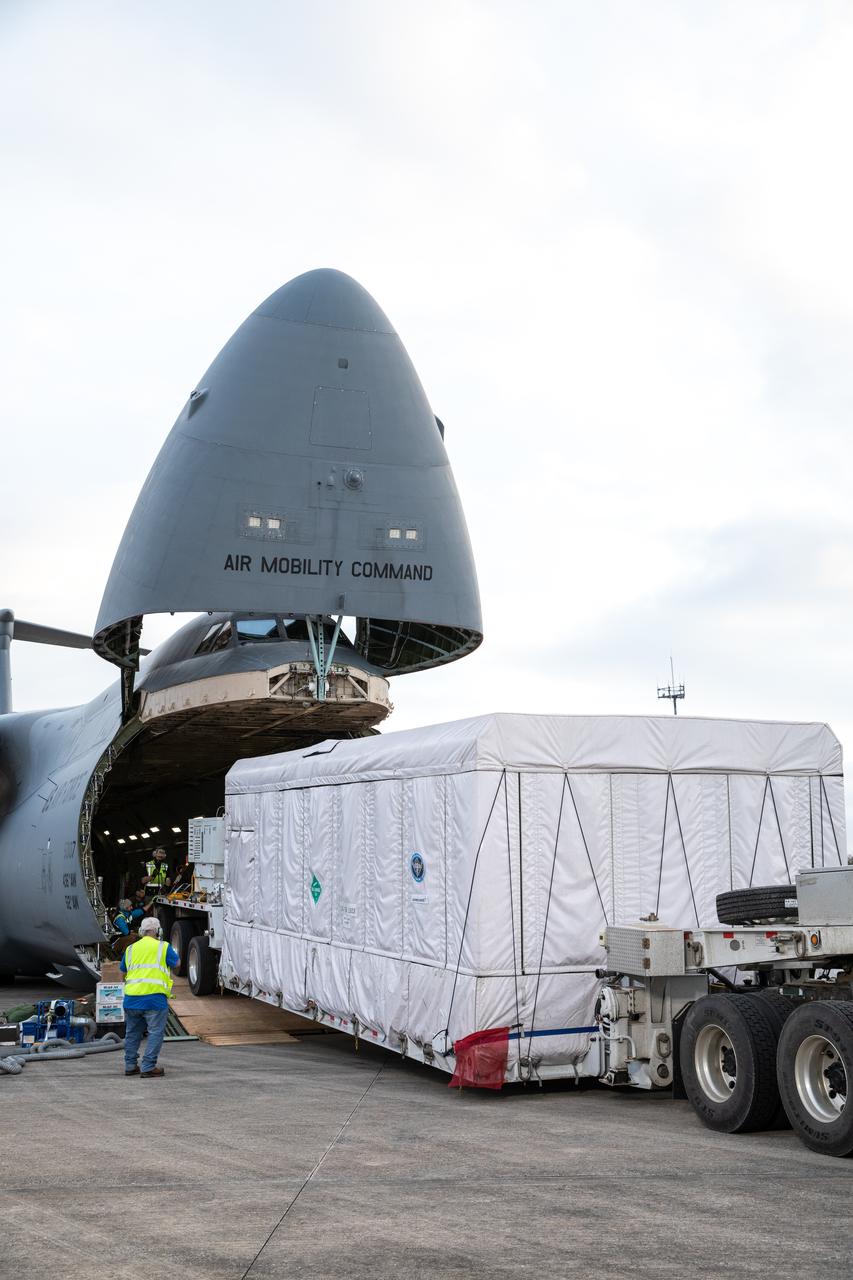

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
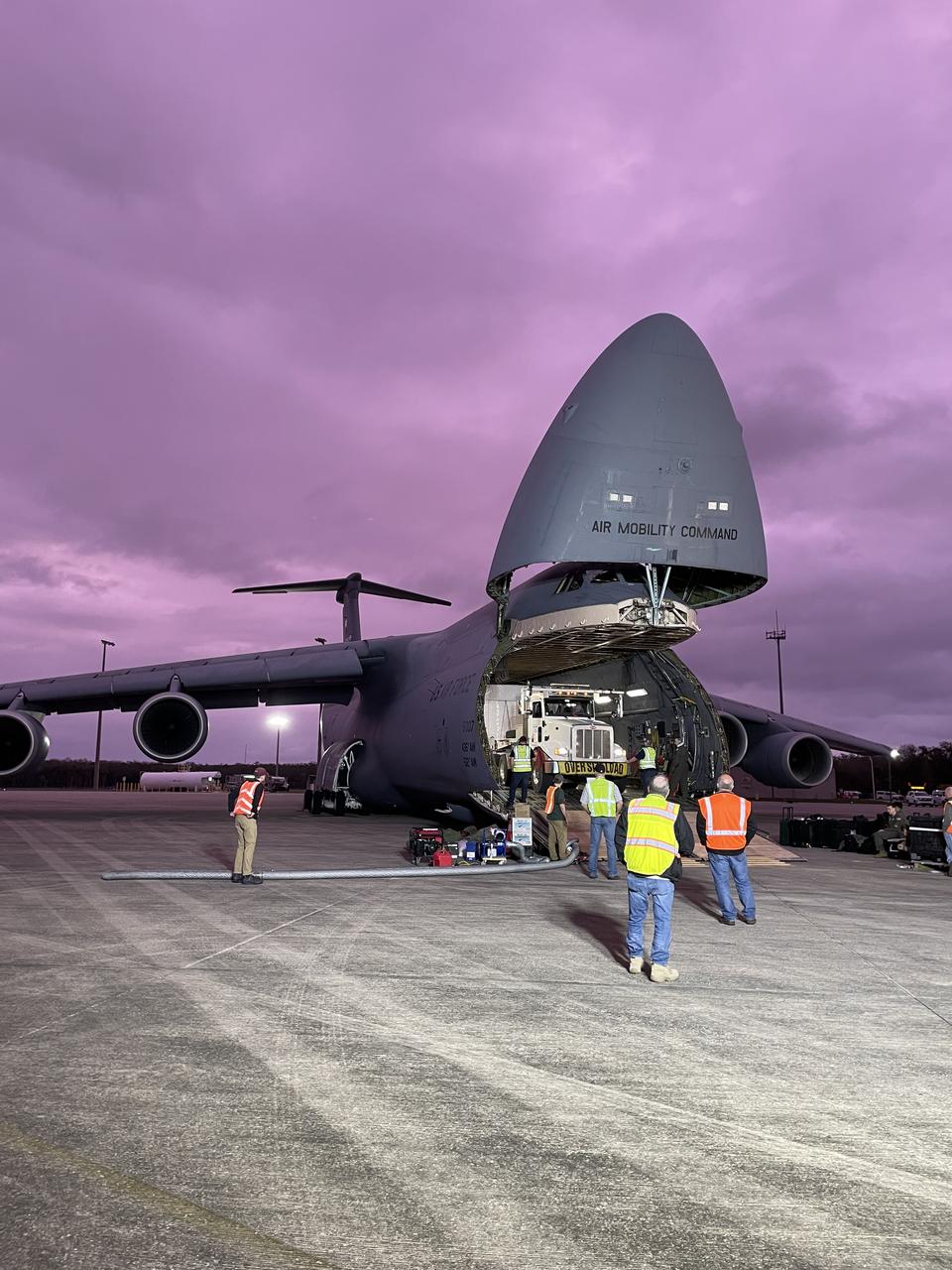

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
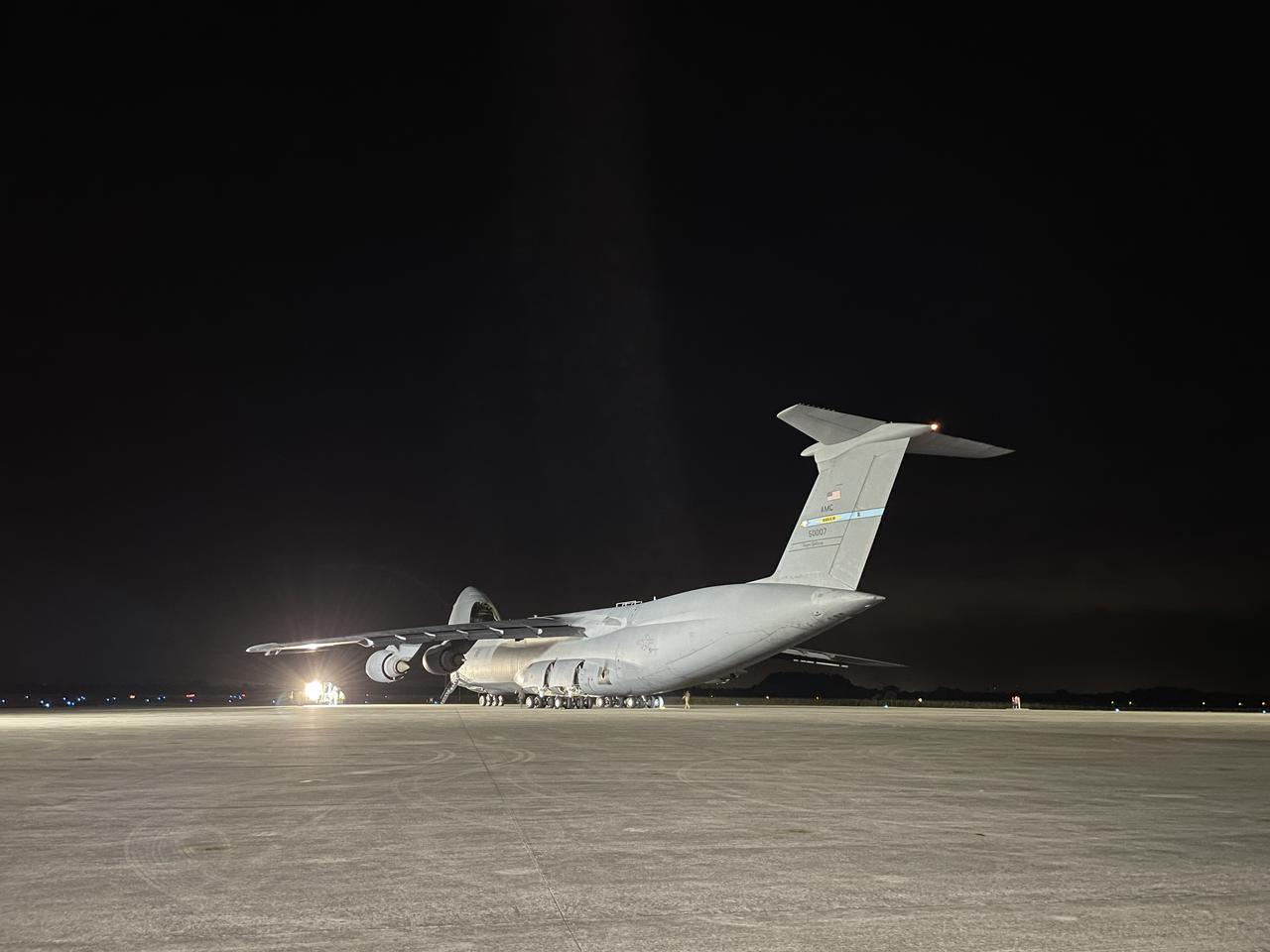

A C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft carrying NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) arrives at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews offloaded and transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
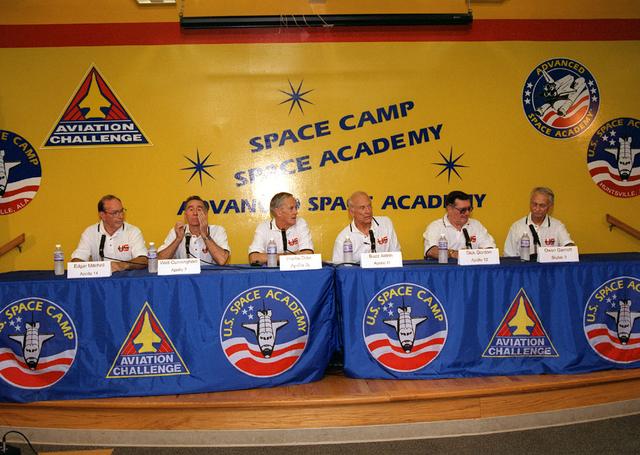

Marking the occasion of the Apollo 11 30th Anniversary, members of the Apollo and Saturn astronaut programs attended festivities at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL. A press conference was held at the U. S. Space and Rocket Center for the visiting astronauts. Pictured are (L/R): Edgar Mitchell, Walt Cunningham, Charlie Duke, Buzz Aldrin, Dick Gordon and Owen Garriott.

Officials from NASA, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), and the Embassy of India hold a send-off ceremony for the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload on Feb. 3, 2023, outside a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The payload is scheduled to be shipped to India in March. Pictured left to right: Karen St. Germain, director, Earth Science Division, NASA; Mitra Dutta, NISAR program executive, NASA; Sripriya Ranganathan, ambassador and deputy chief of mission, Indian Embassy; Larry James, deputy director, JPL; Bhavya Lal, associate administrator for technology, policy, and strategy, NASA; Jim Graf, director, Earth Science and Technology Directorate, JPL; S. Somanath, chairman, ISRO; Laurie Leshin, director, JPL; Krunal Joshi, counselor, space and ISRO technical liaison officer, Indian Embassy; M. Sankaran, director, U R Rao Satellite Centre, ISRO; Shantanu Bhatawdekar, scientific secretary, ISRO; Paul Rosen, NISAR project scientist, JPL; CV Shrikant, NISAR project director, ISRO; Phil Barela, NISAR project manager, JPL; and Gerald Bawden, NISAR program scientist, NASA. NISAR – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25600