
The upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will power the agency’s Artemis III mission and send astronauts on to the Moon for a lunar landing arrived at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Poseidon Wharf in Florida on Aug. 9, 2023. Known as the SLS ICPS (interim cryogenic propulsion stage), it will undergo final checkouts by contractors Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance) at ULA’s facilities before it is delivered to NASA’s nearby Kennedy Space Center.

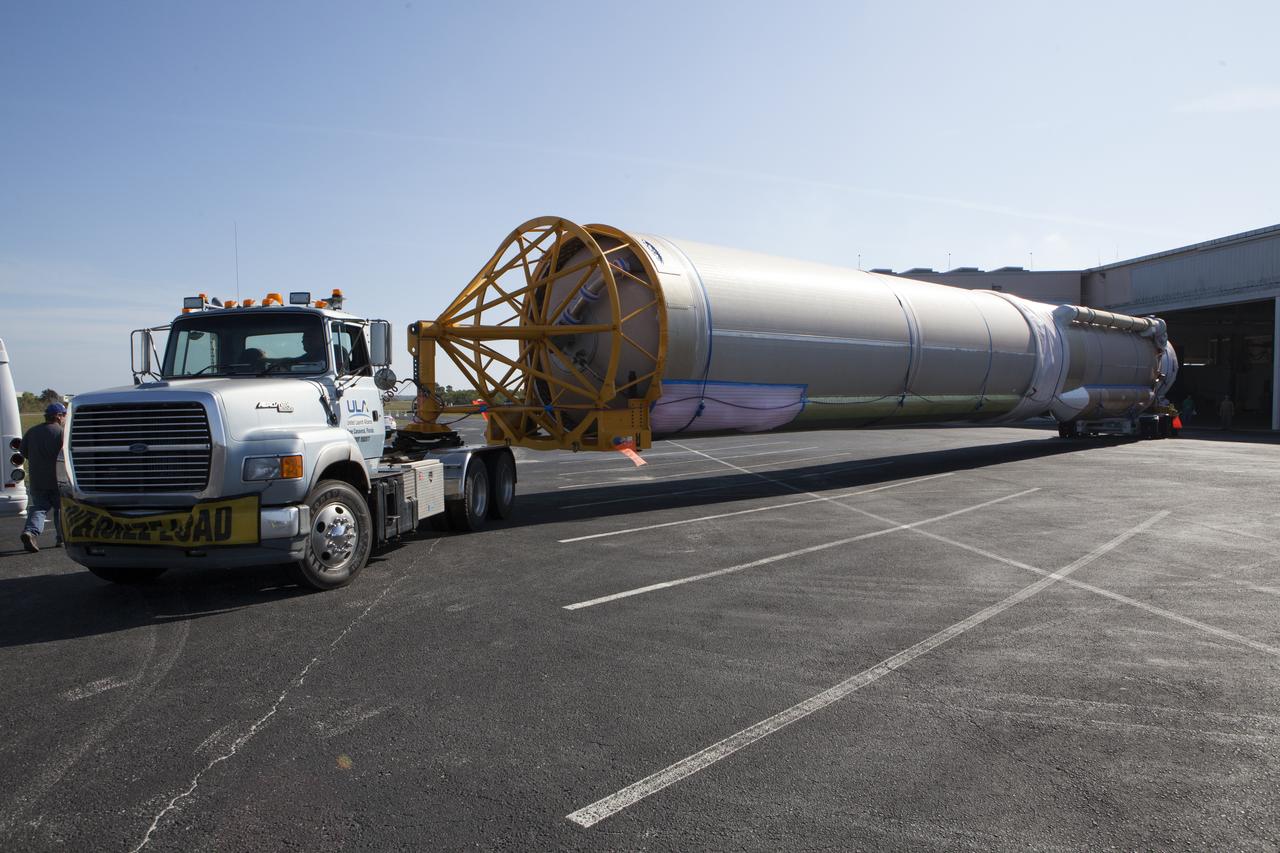
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
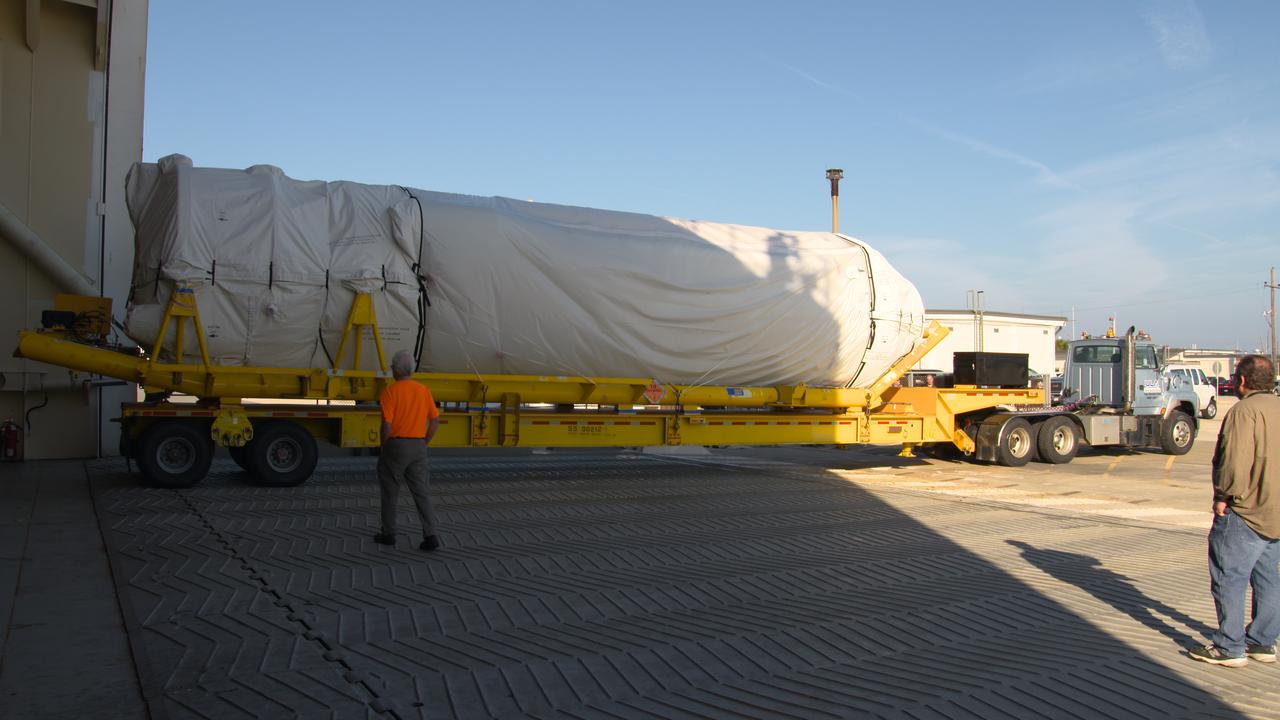

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Centaur upper stage arrived for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Centaur from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
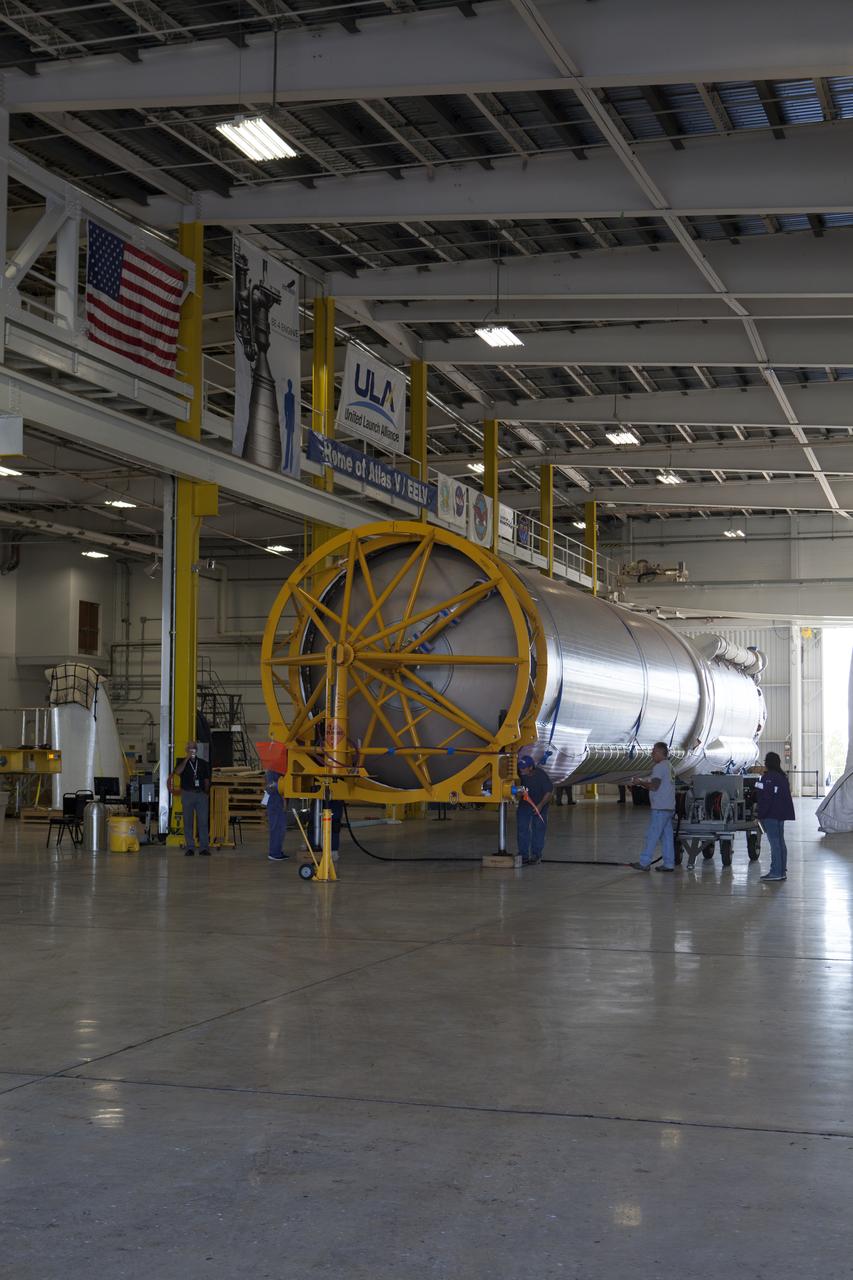

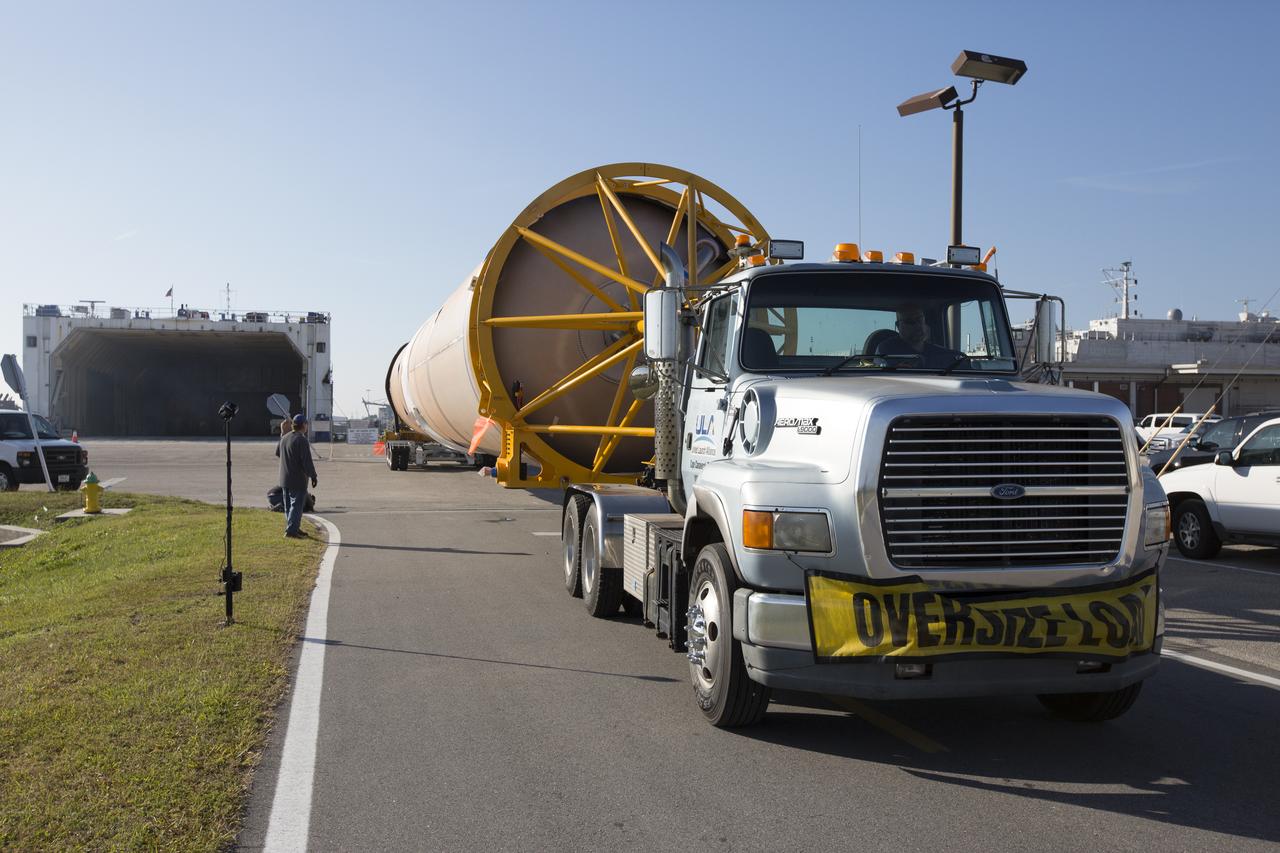
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
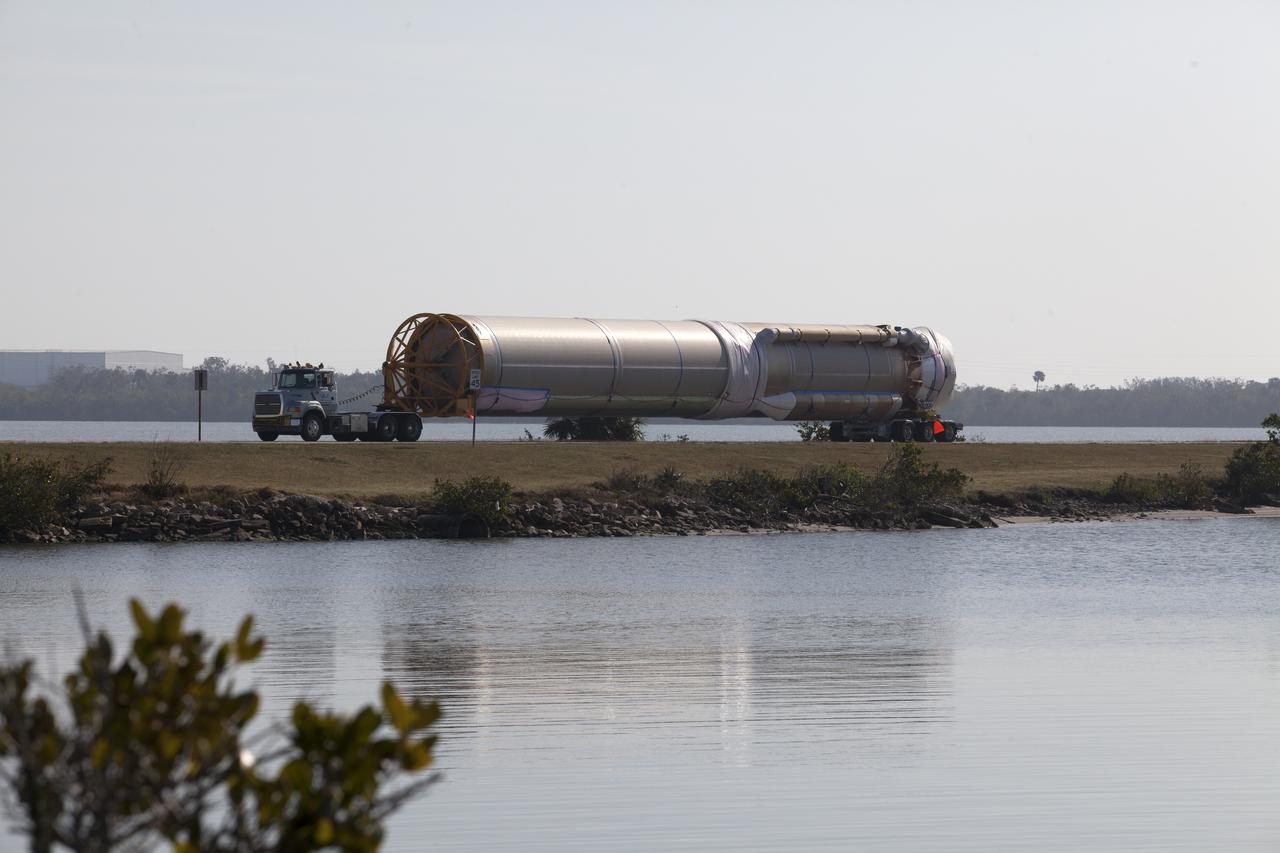

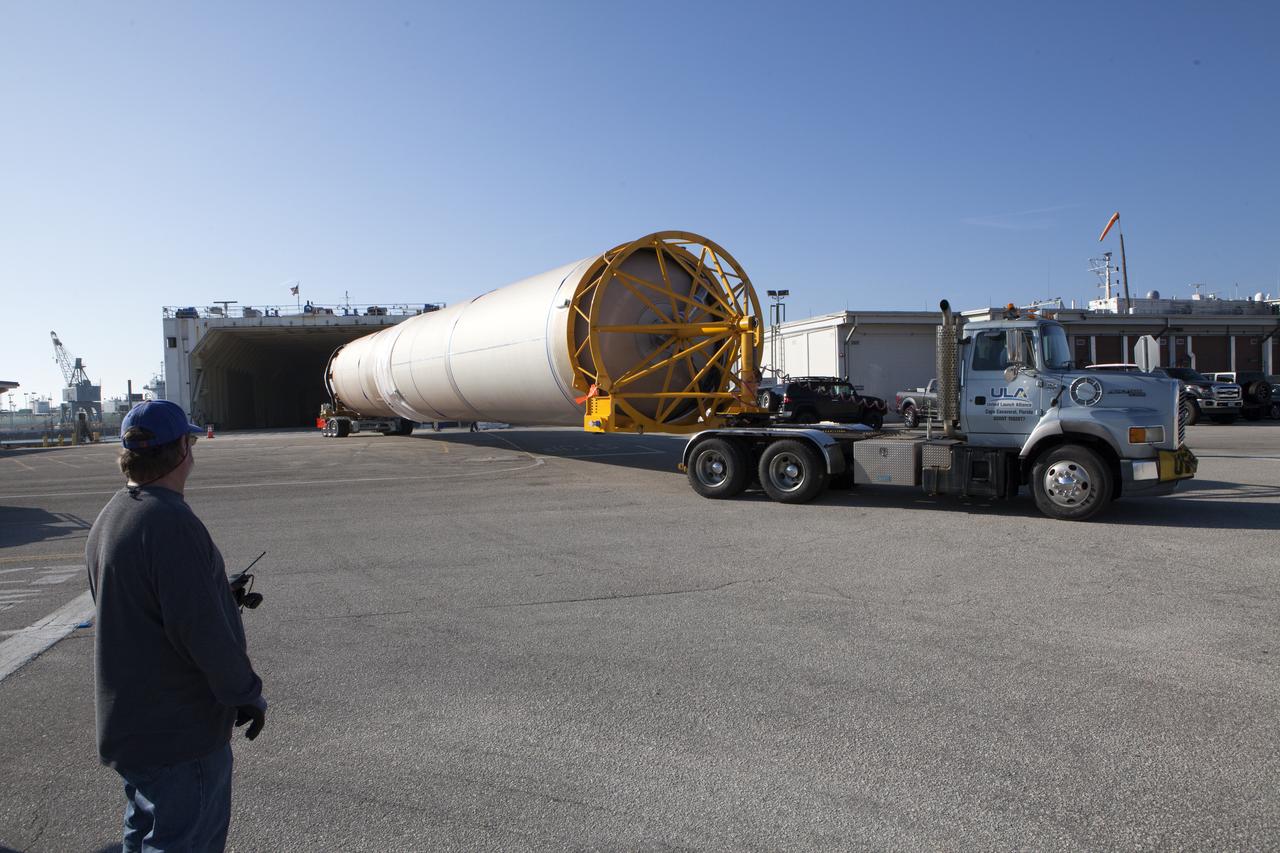
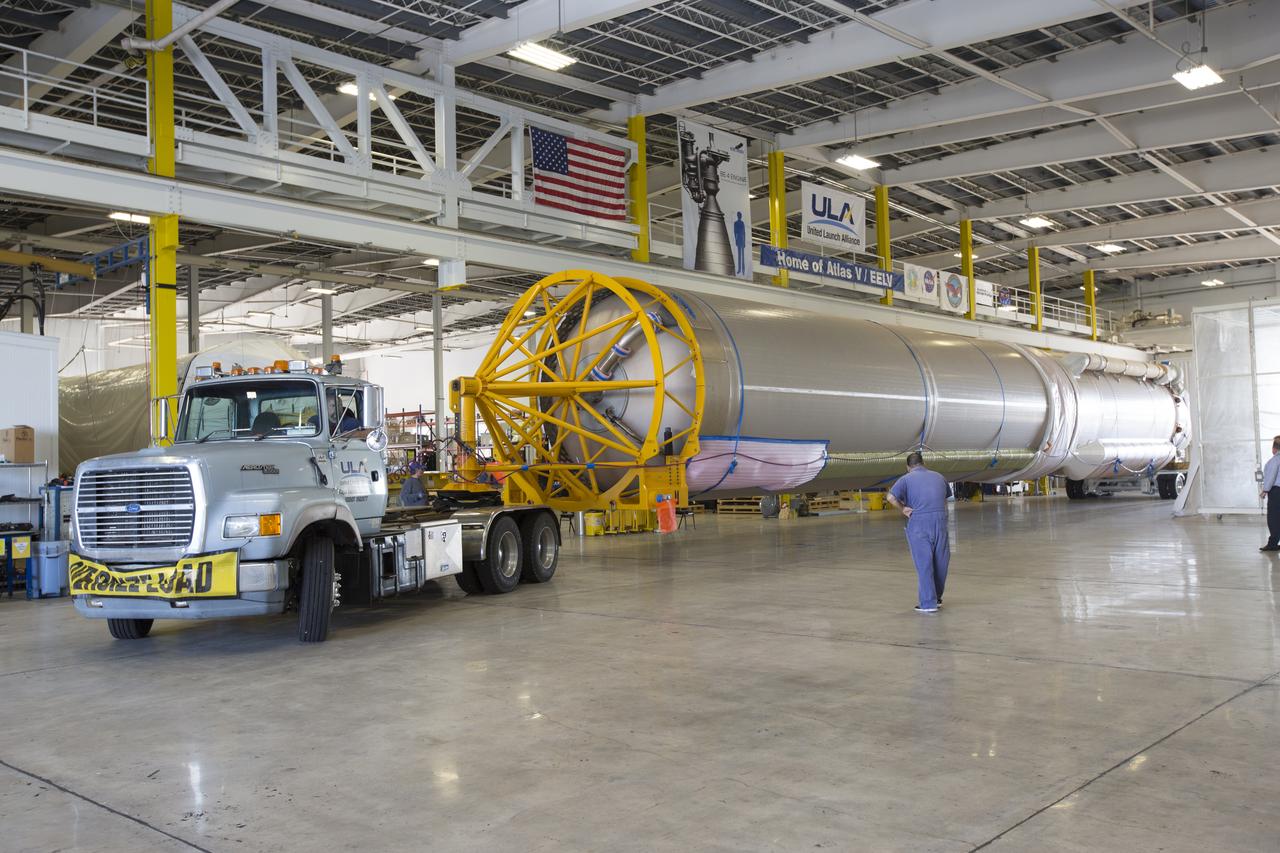
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is on its way to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
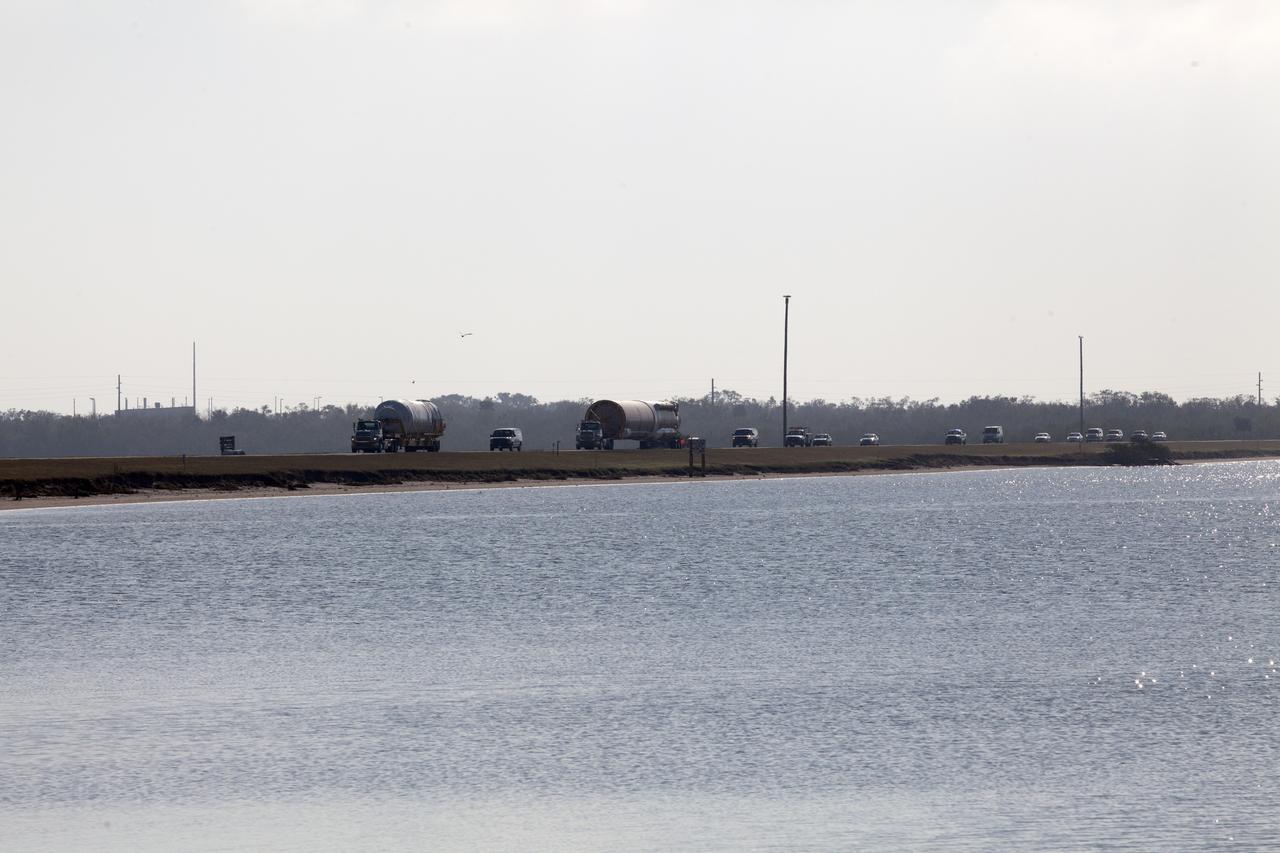

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is on its way to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.

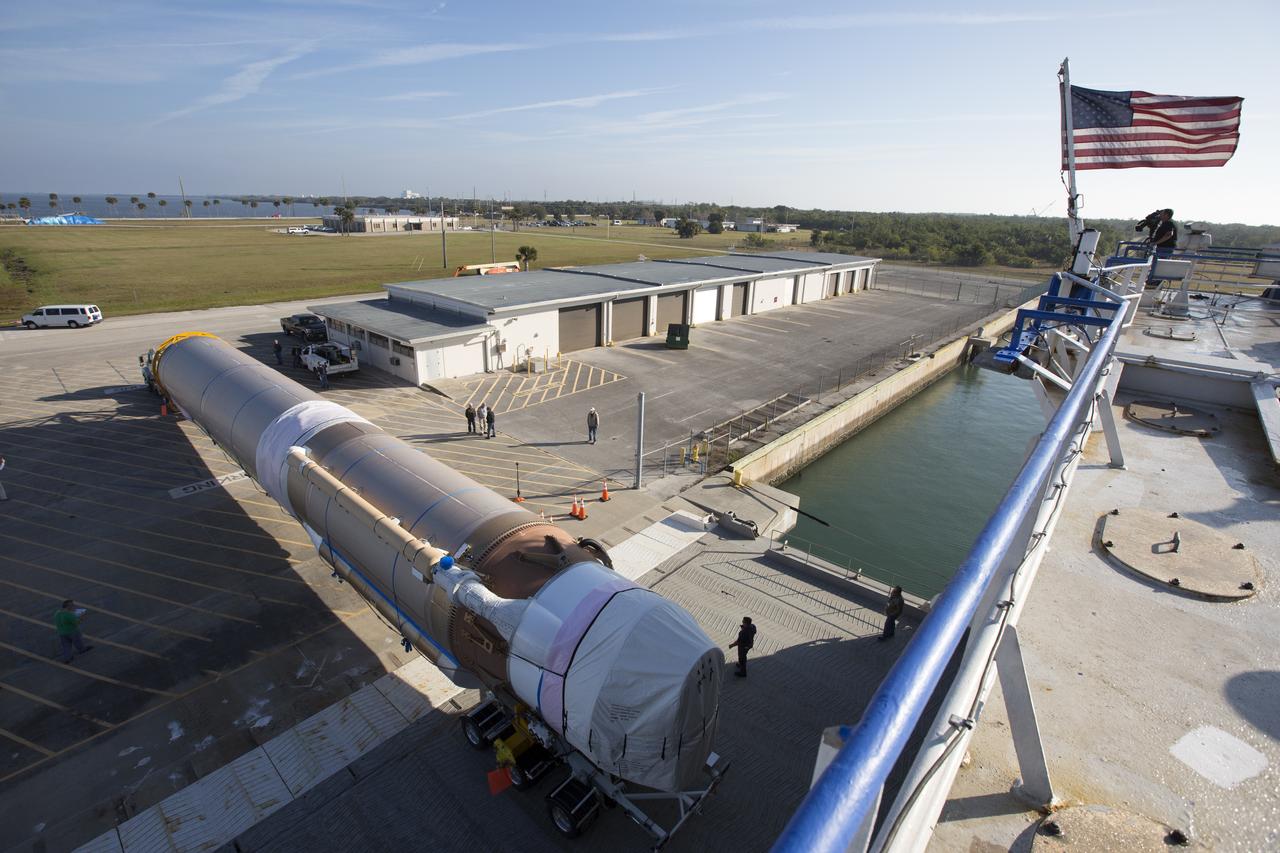
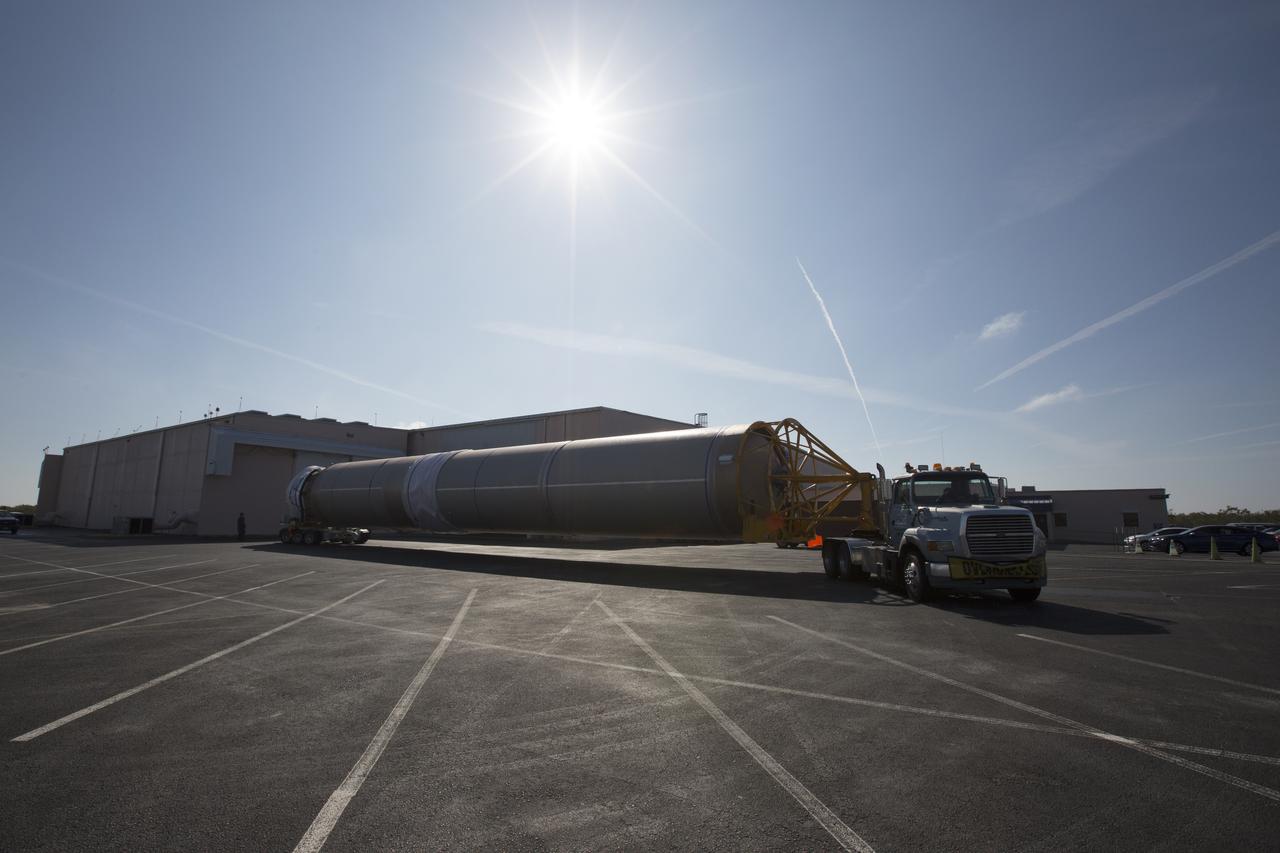
A transport truck is about to take a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster from the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas V is scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. Scheduled to liftoff March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
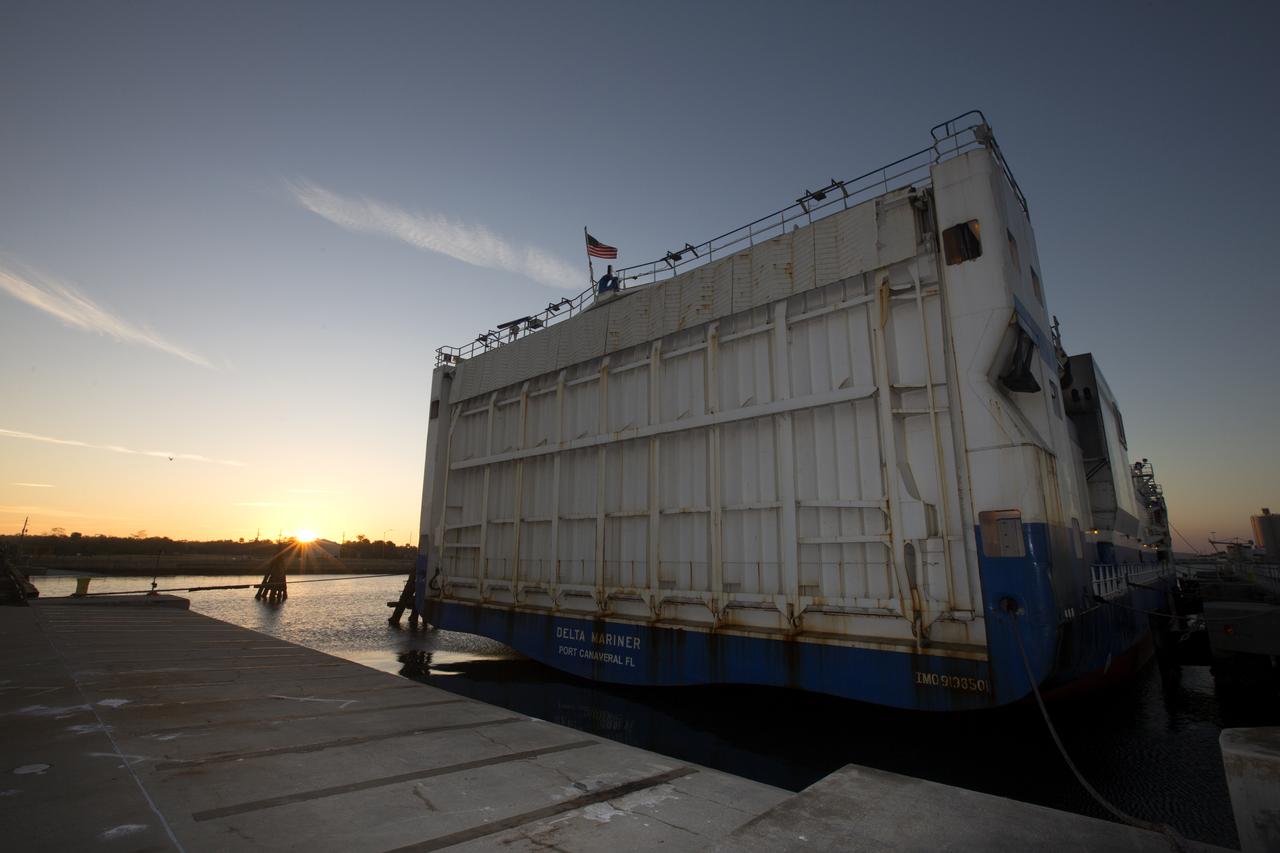

The Mariner cargo ship arrives at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
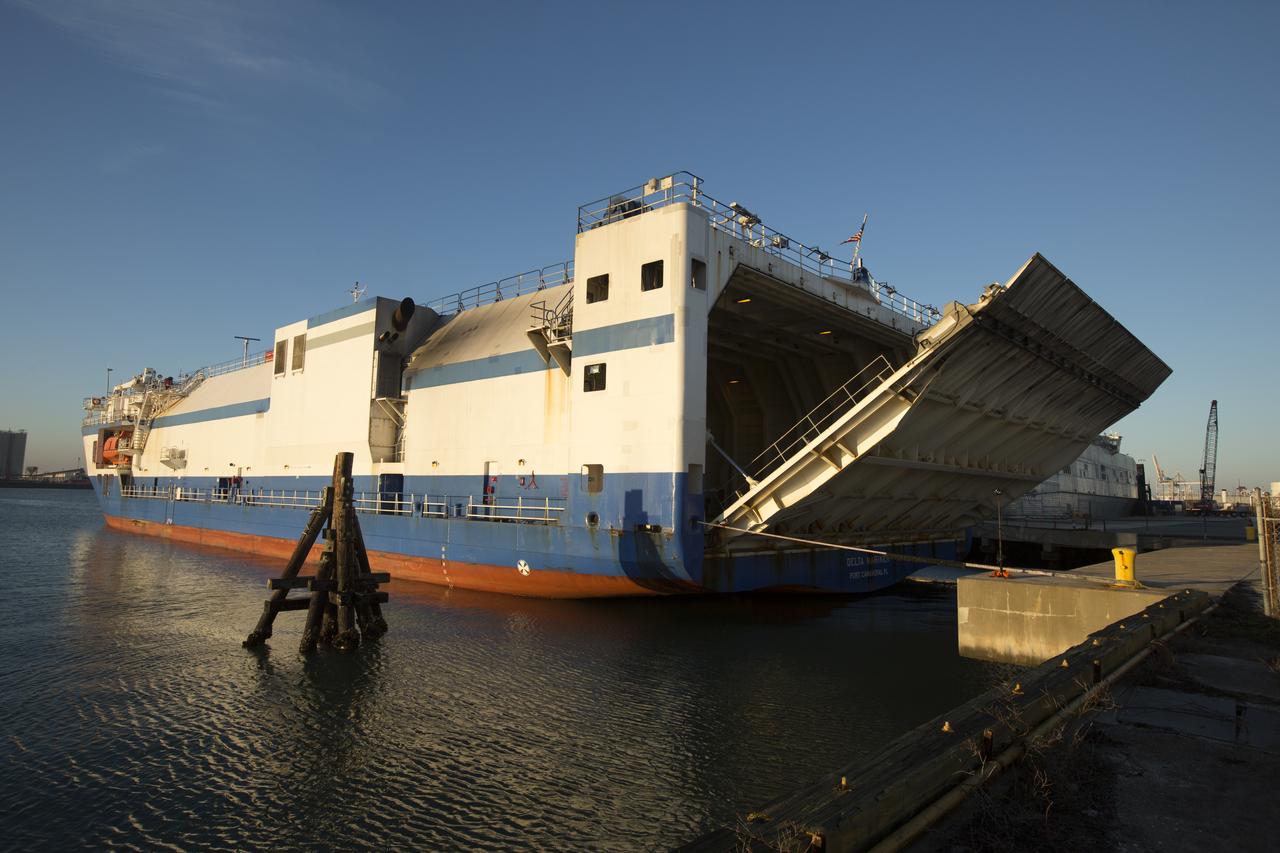

The Mariner cargo ship arrives at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
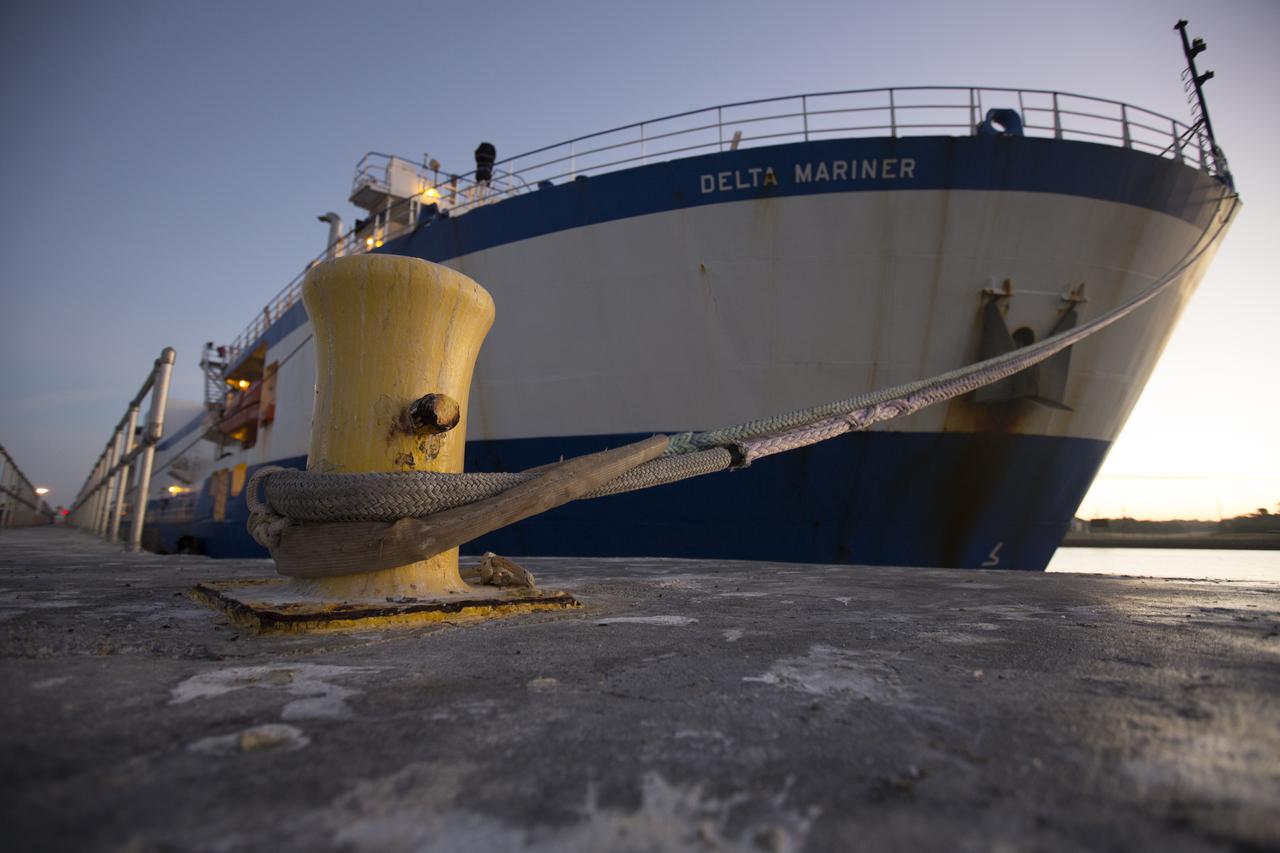

The Mariner cargo ship is docked at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
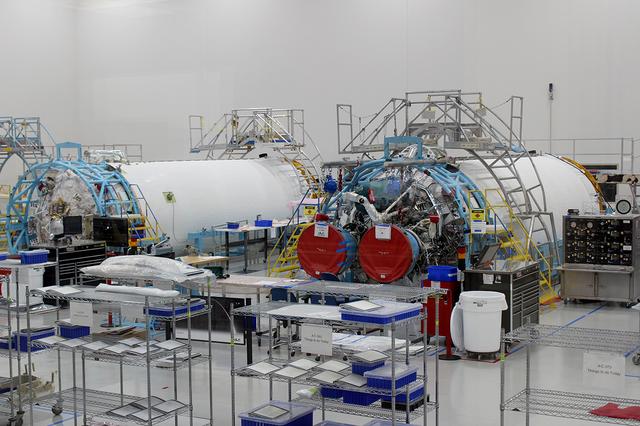

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Crew Flight Test dual engine, at left, and the Orbital Flight test dual engine, at right, for the Centaur stage of the Atlas V rocket are in production on June 11, 2018, at ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
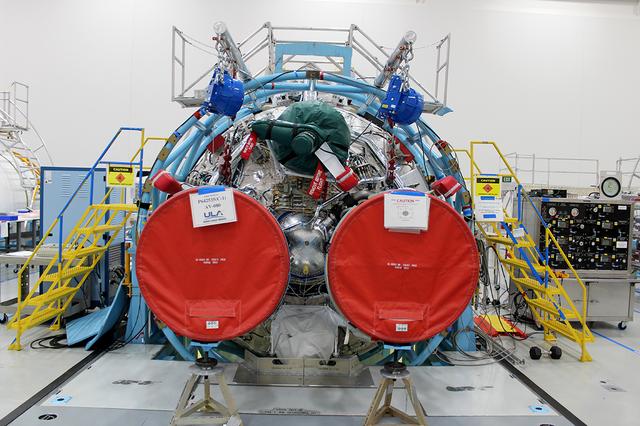

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Orbital Flight Test dual engine Centaur stage of the Atlas V rocket is in the final stage of production and checkout on May 22, 2018, at ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
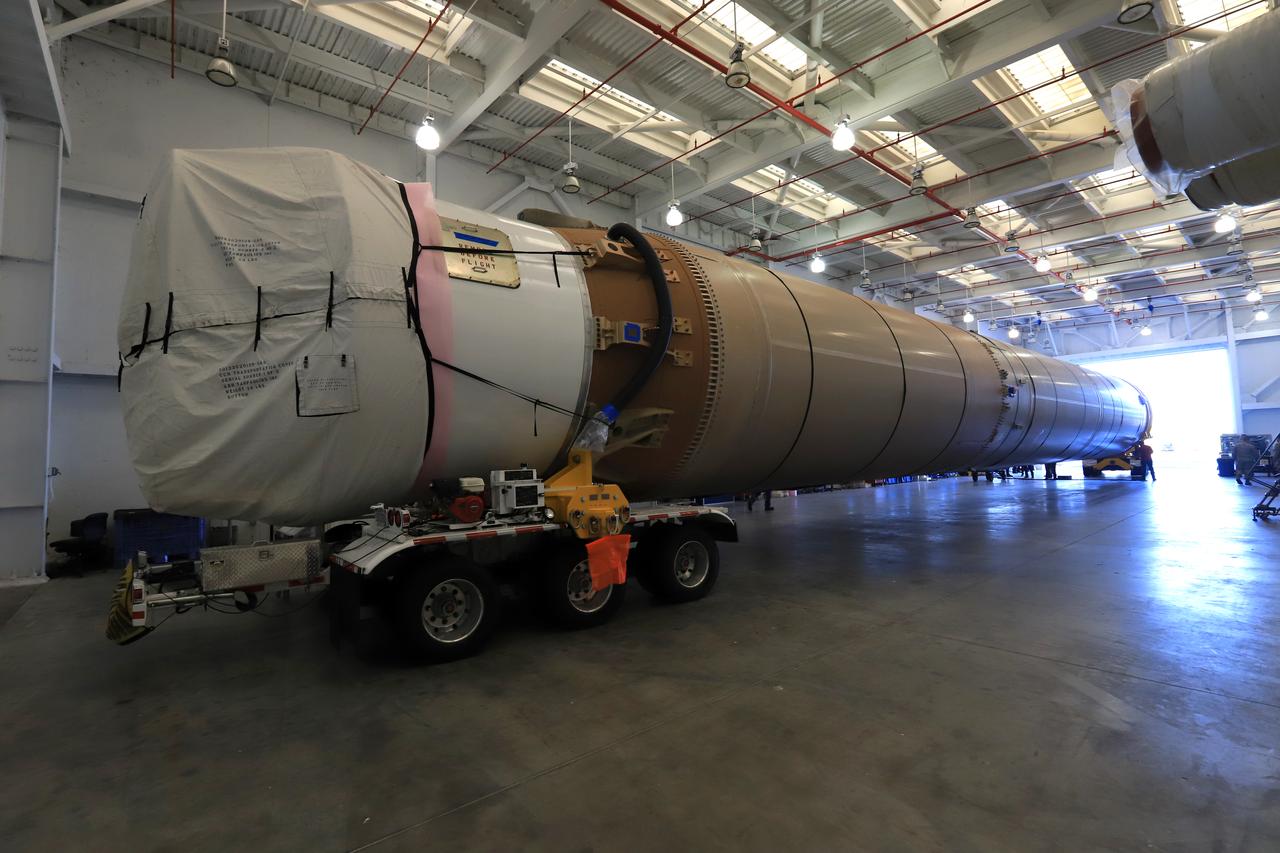

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
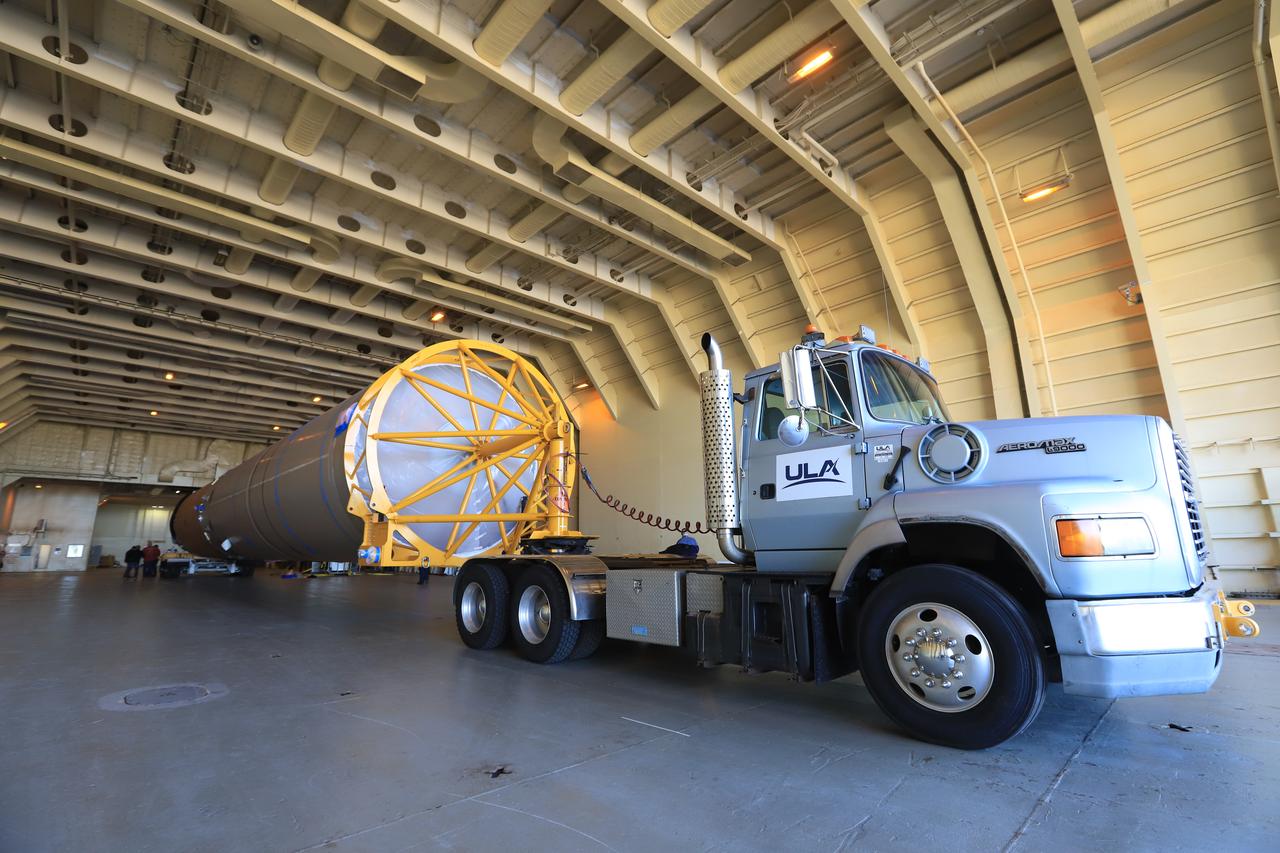

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrived at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
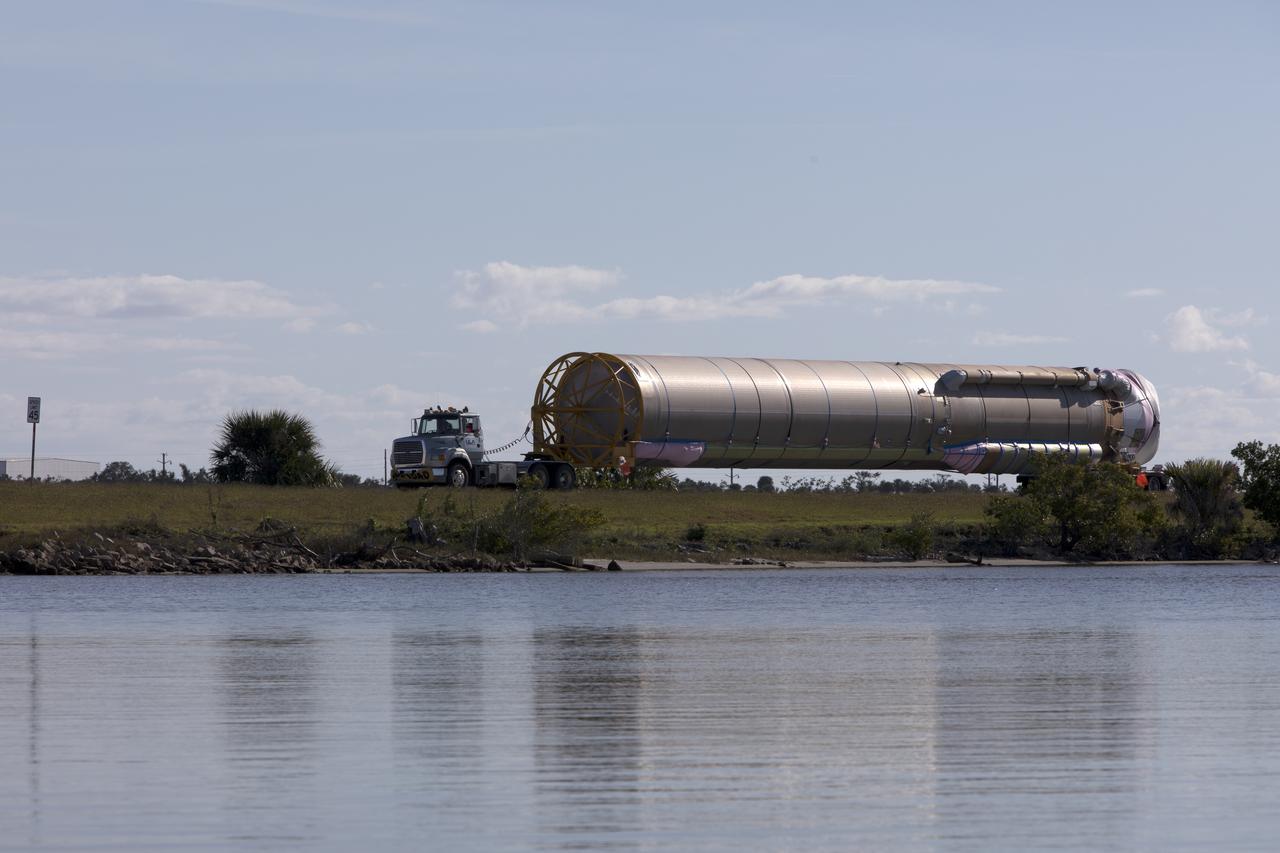

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
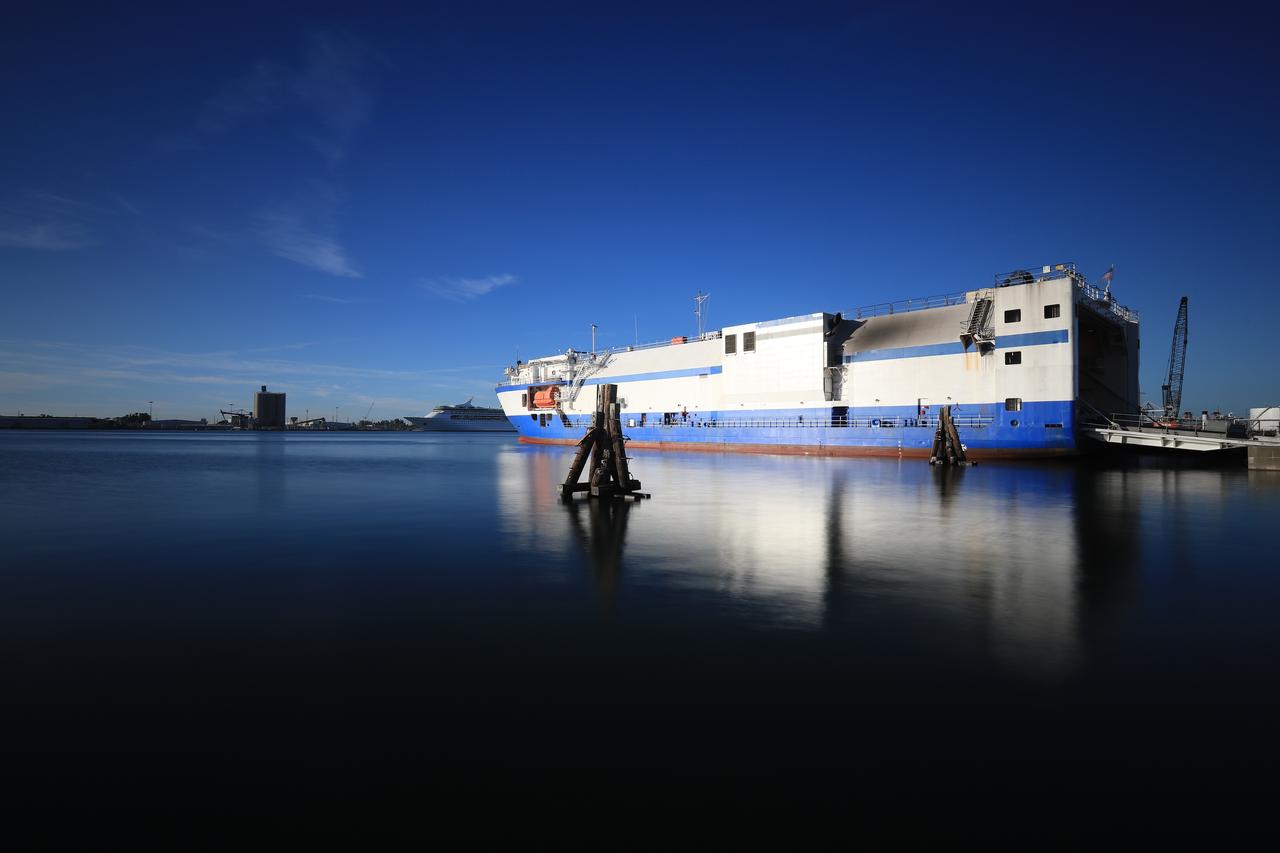

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo vessel arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018, carrying the first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
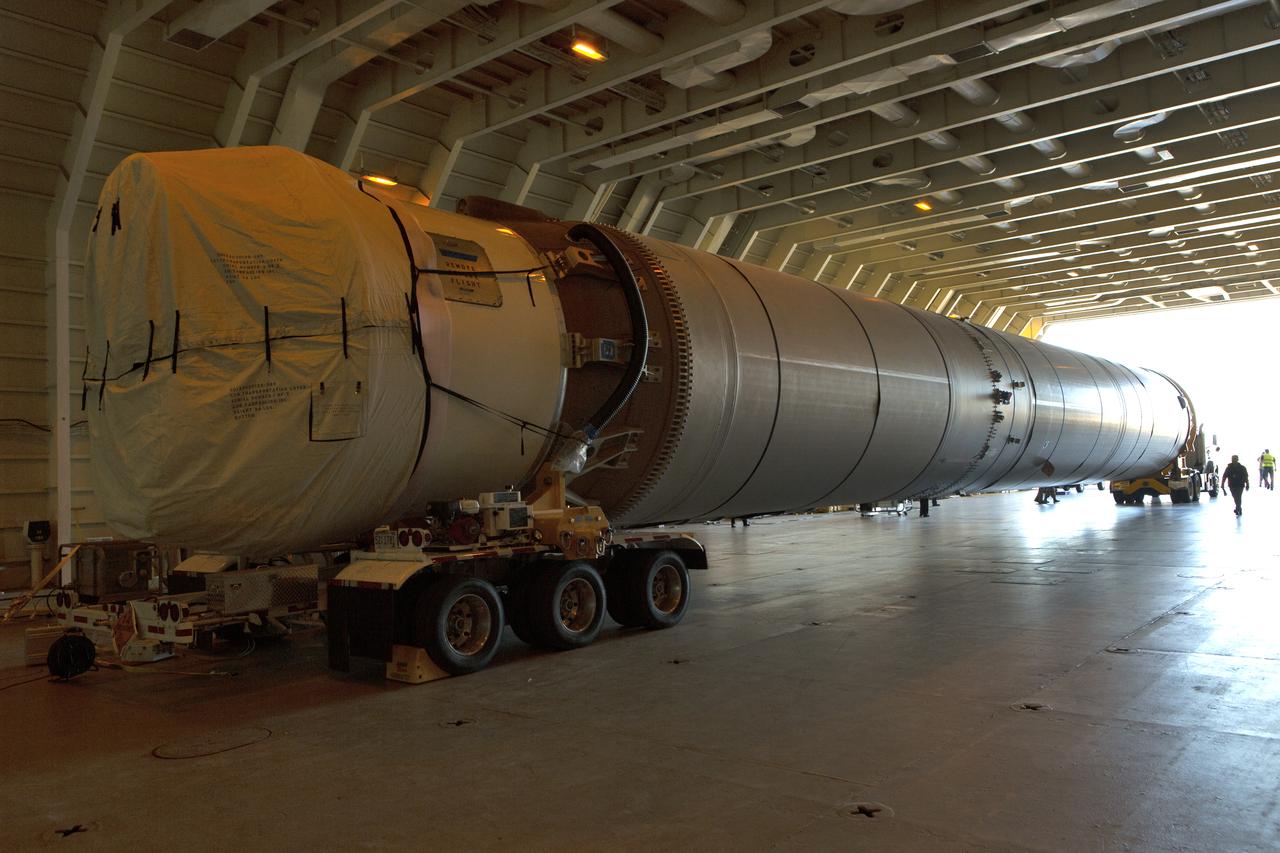

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
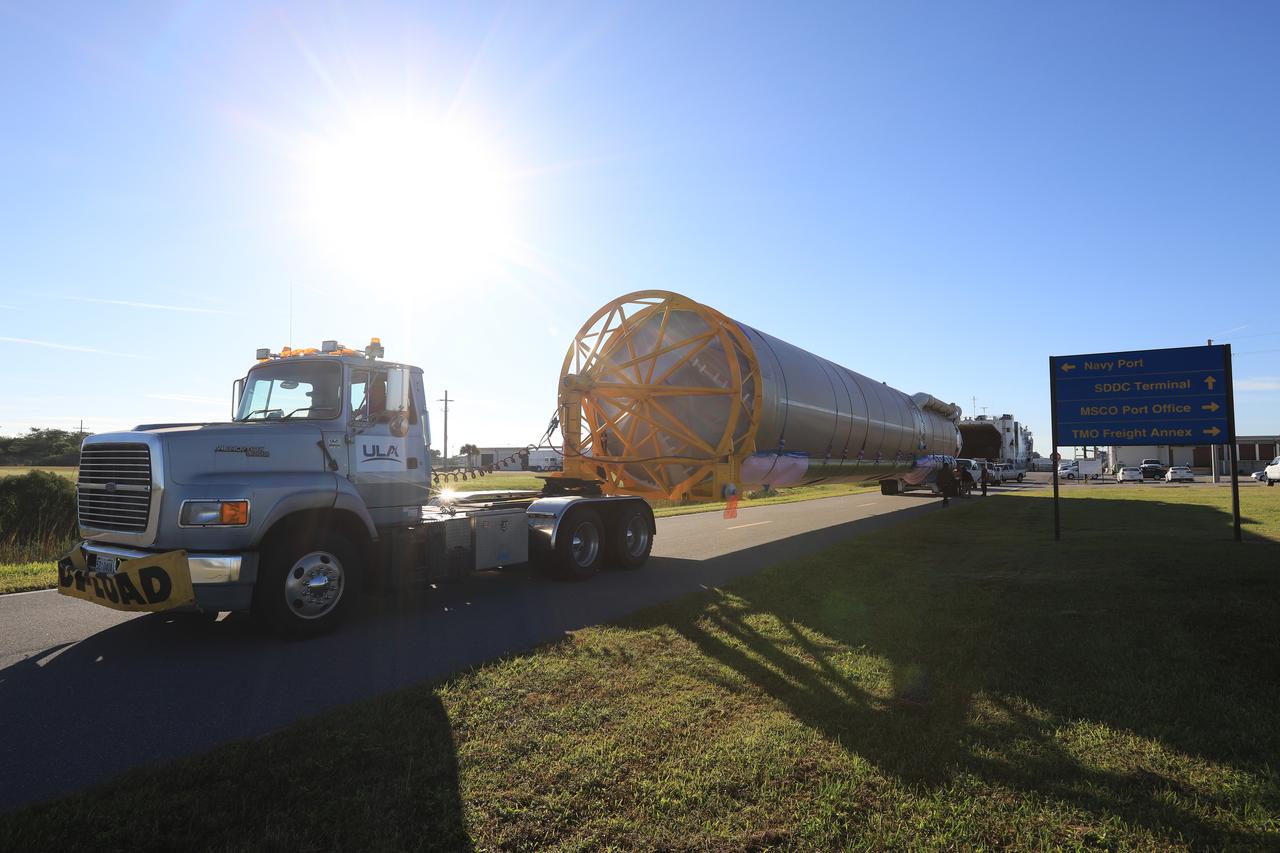

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
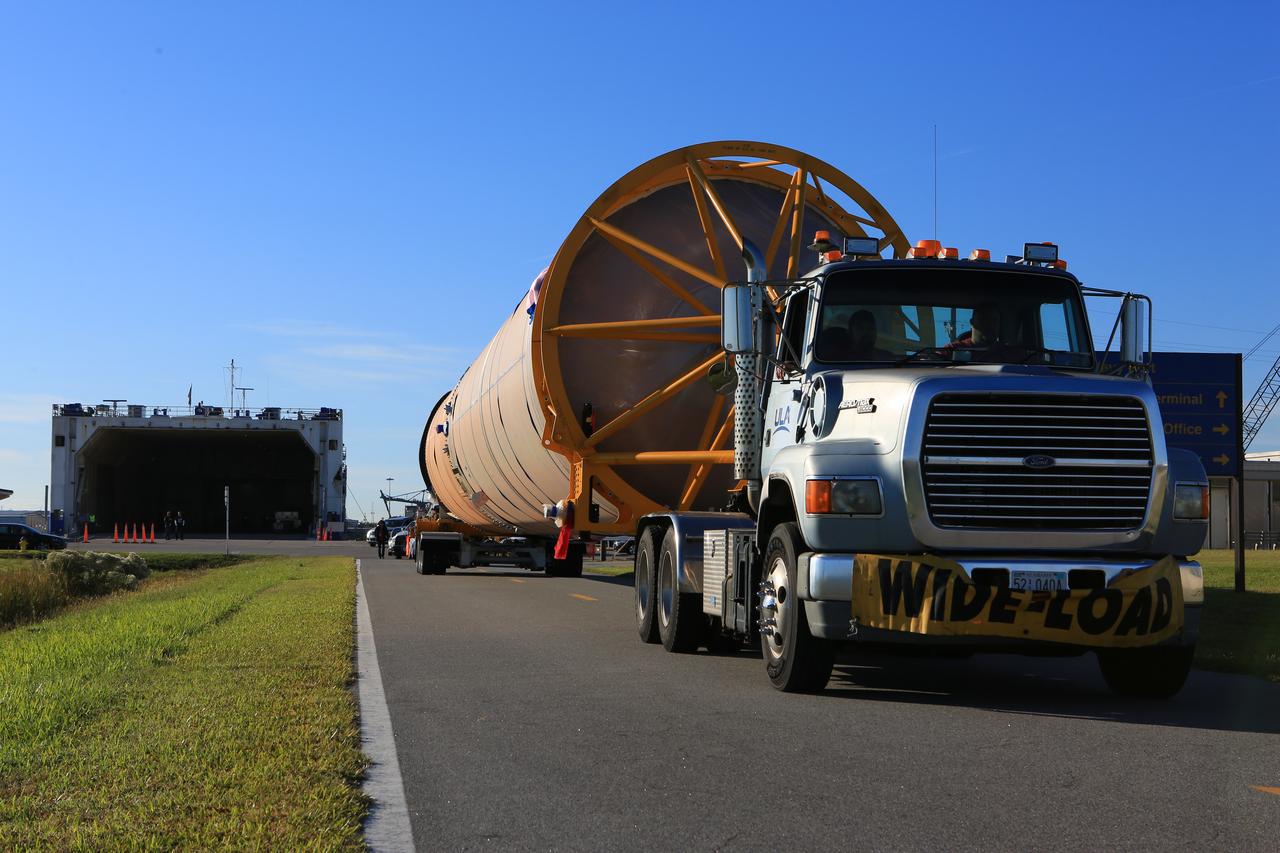

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conducted an emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The emergency egress system will allow for a safe evacuation in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day. The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket, carrying astronauts to the International Space Station.
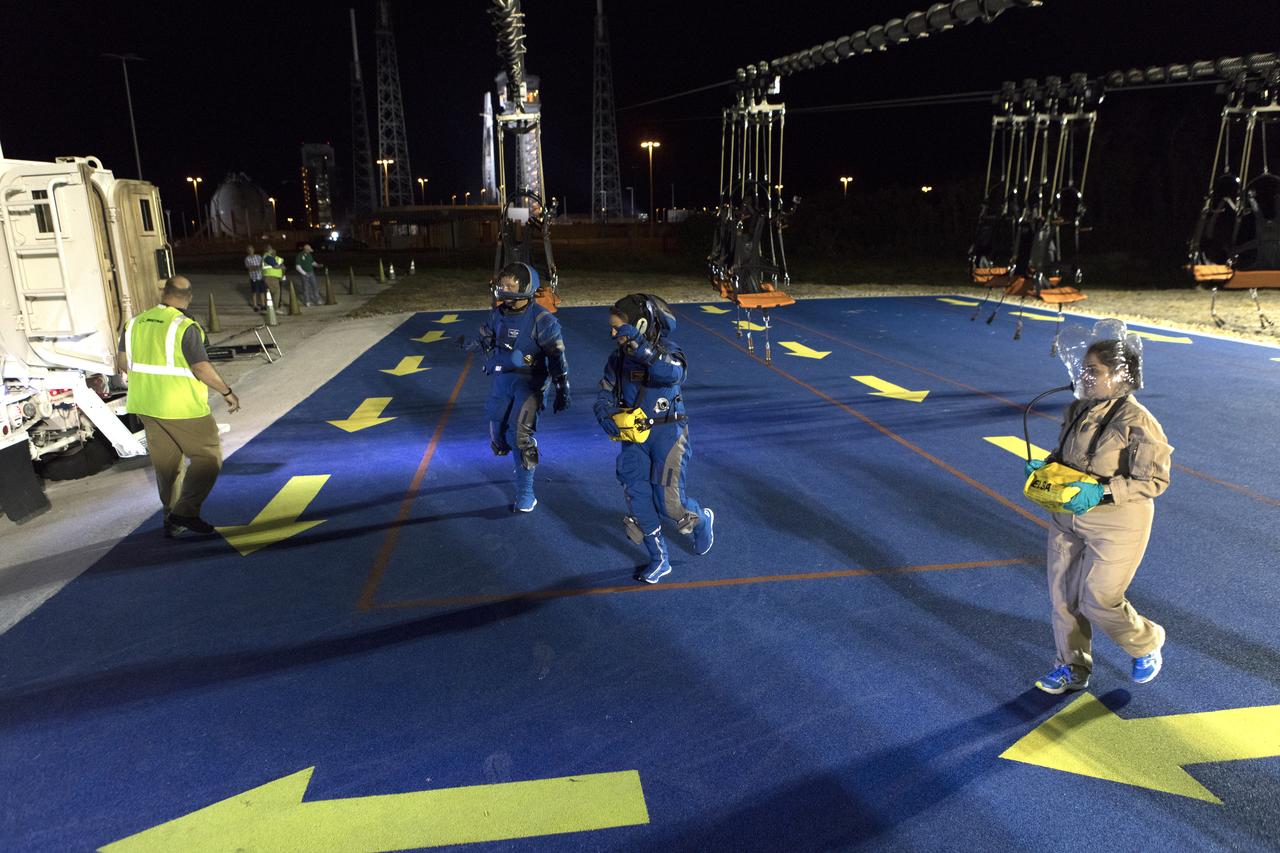

Astronauts participate in a Boeing/United Launch Alliance (ULA) emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The system is designed to safely evacuate astronauts and ground crews in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day. The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket, carrying astronauts to the International Space Station.

Commercial Crew astronauts test out the Boeing/United Launch Alliance (ULA) emergency egress system on June 19, 2018, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida. The emergency egress system provides an escape route in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff on launch day. It will be in place when Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, launched aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket, carries astronauts to the International Space Station.
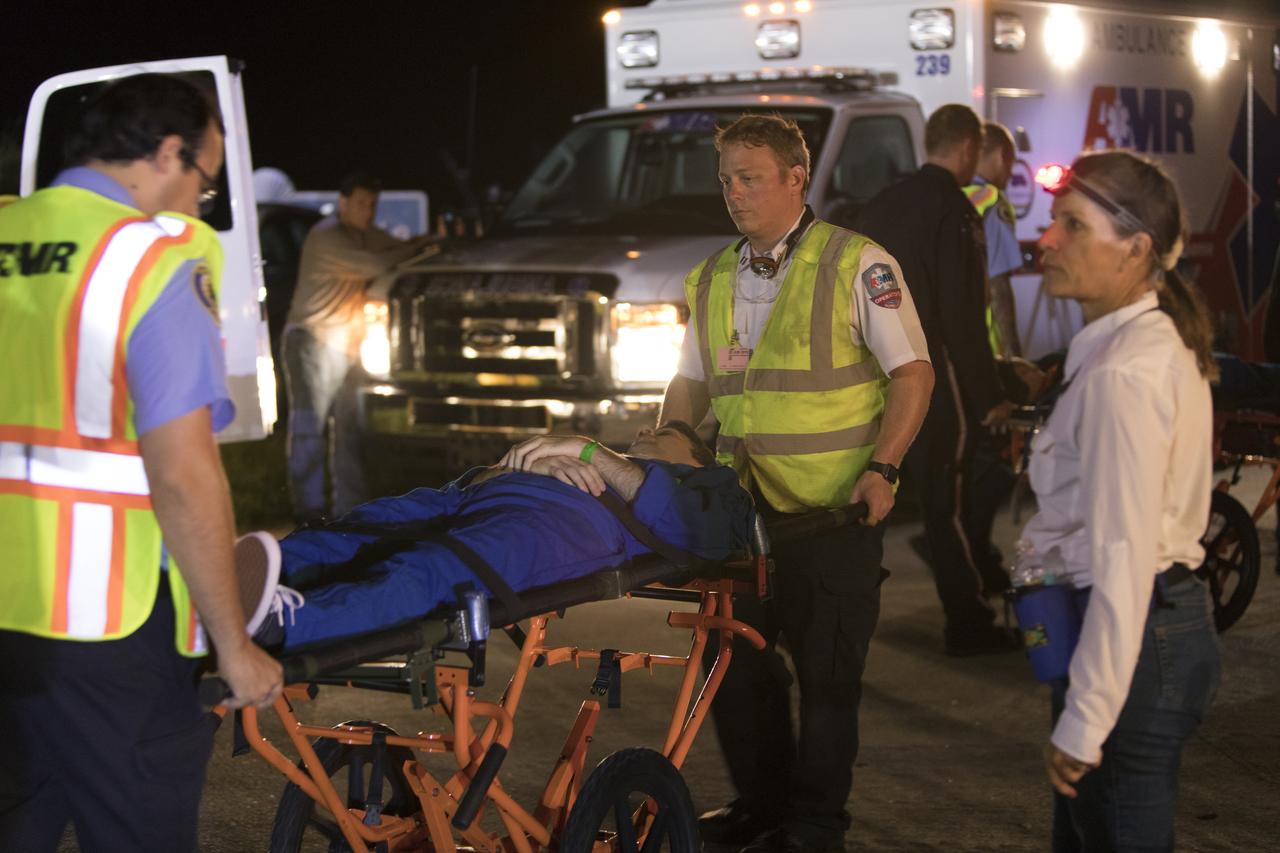

Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conducted an emergency egress system demonstration with Commercial Crew astronauts at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket, carrying astronauts to the International Space Station. The emergency egress system will allow for a safe evacuation in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad.
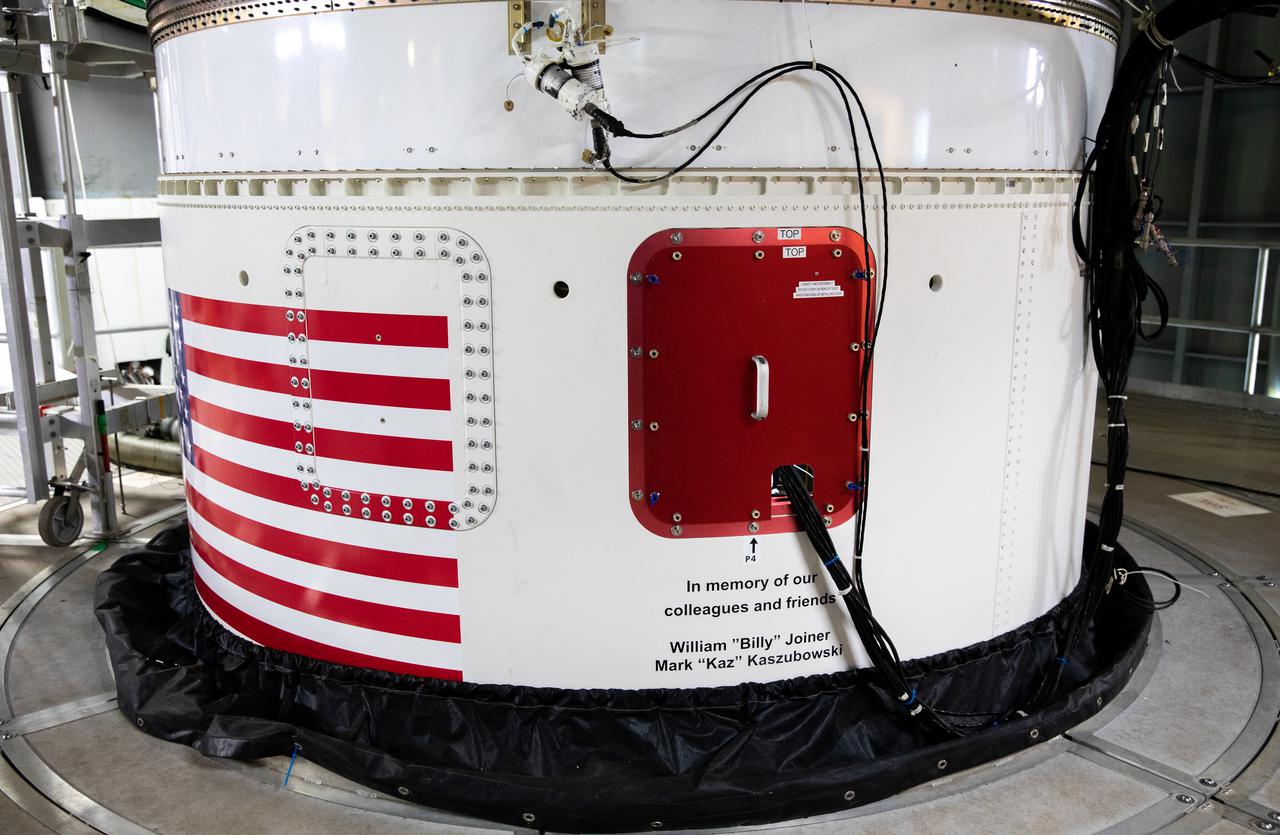
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.
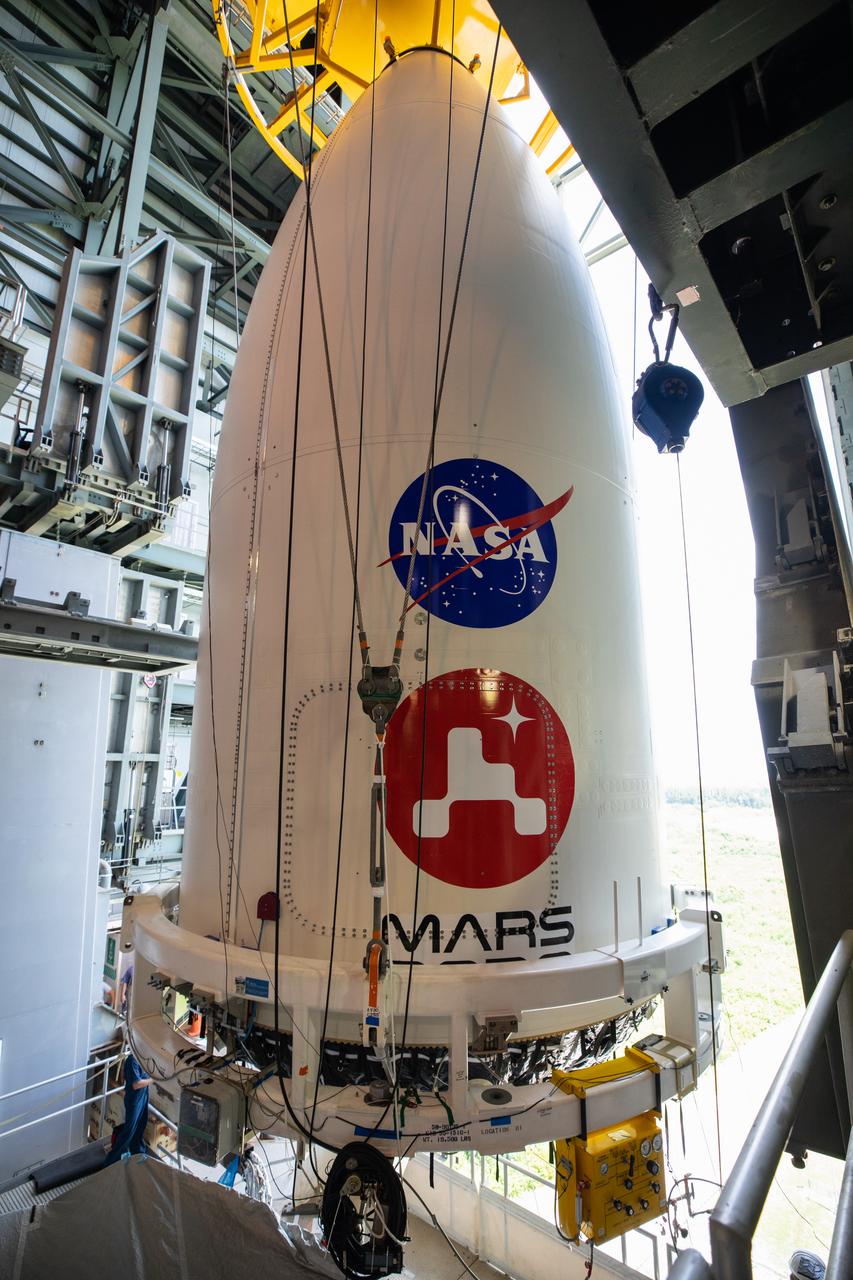

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is positioned on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
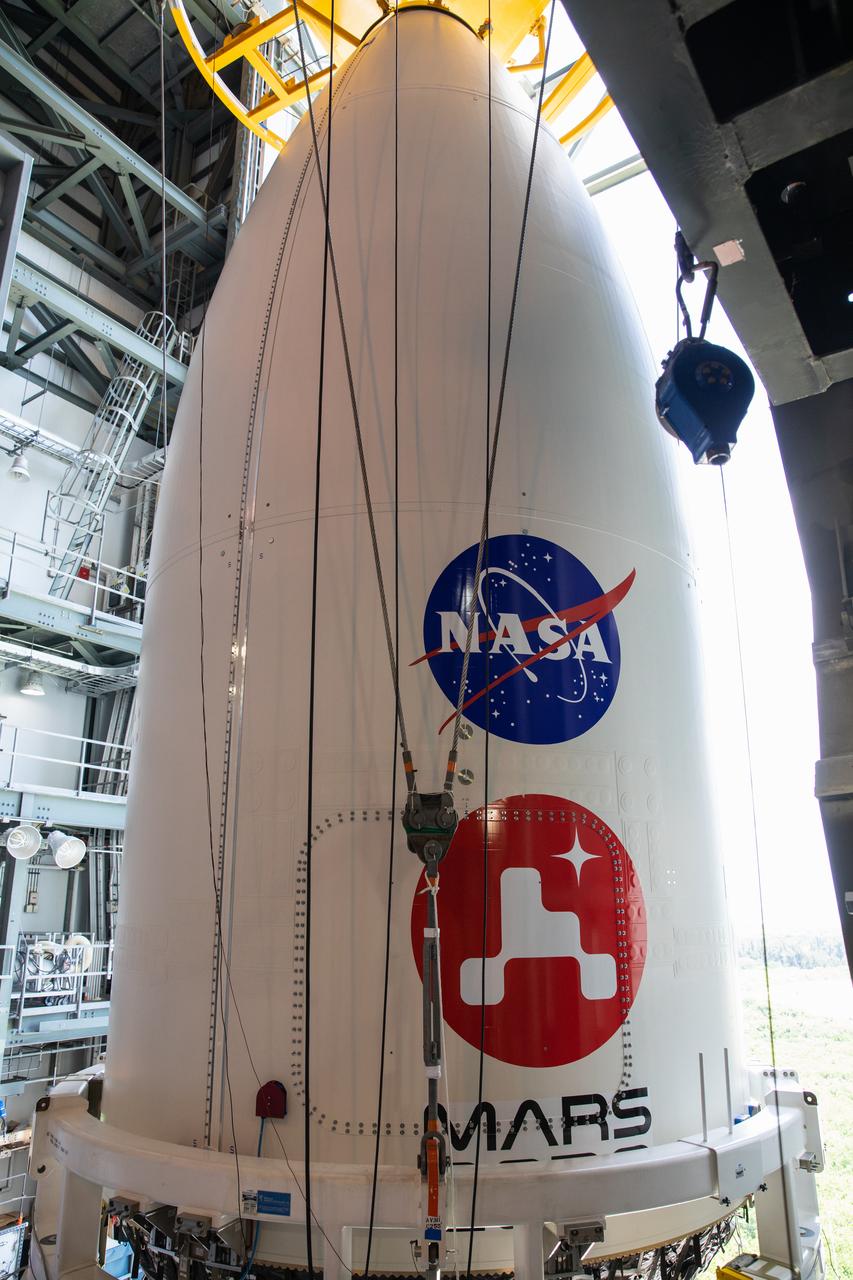
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is positioned on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
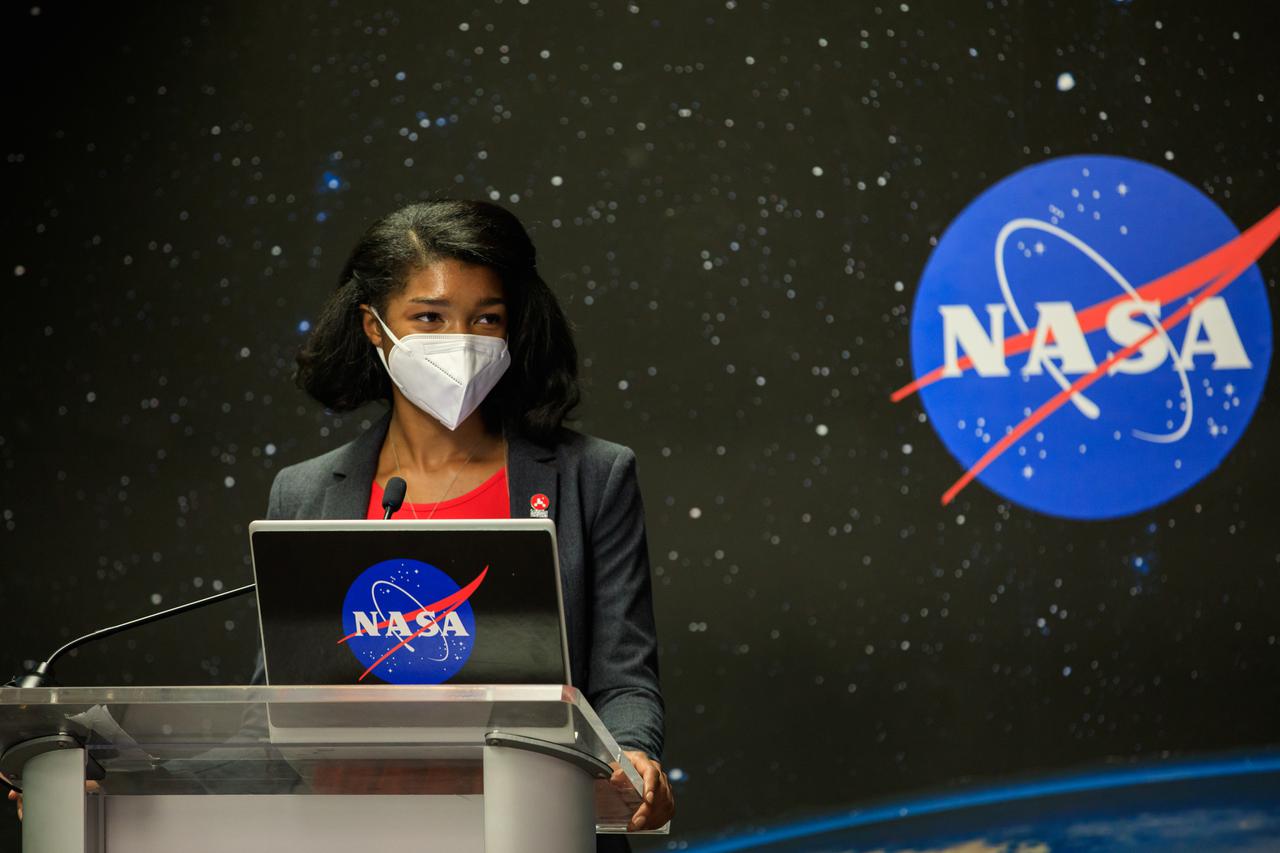

NASA Communications’ Jasmine Hopkins moderates a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. Participants included United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participate in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
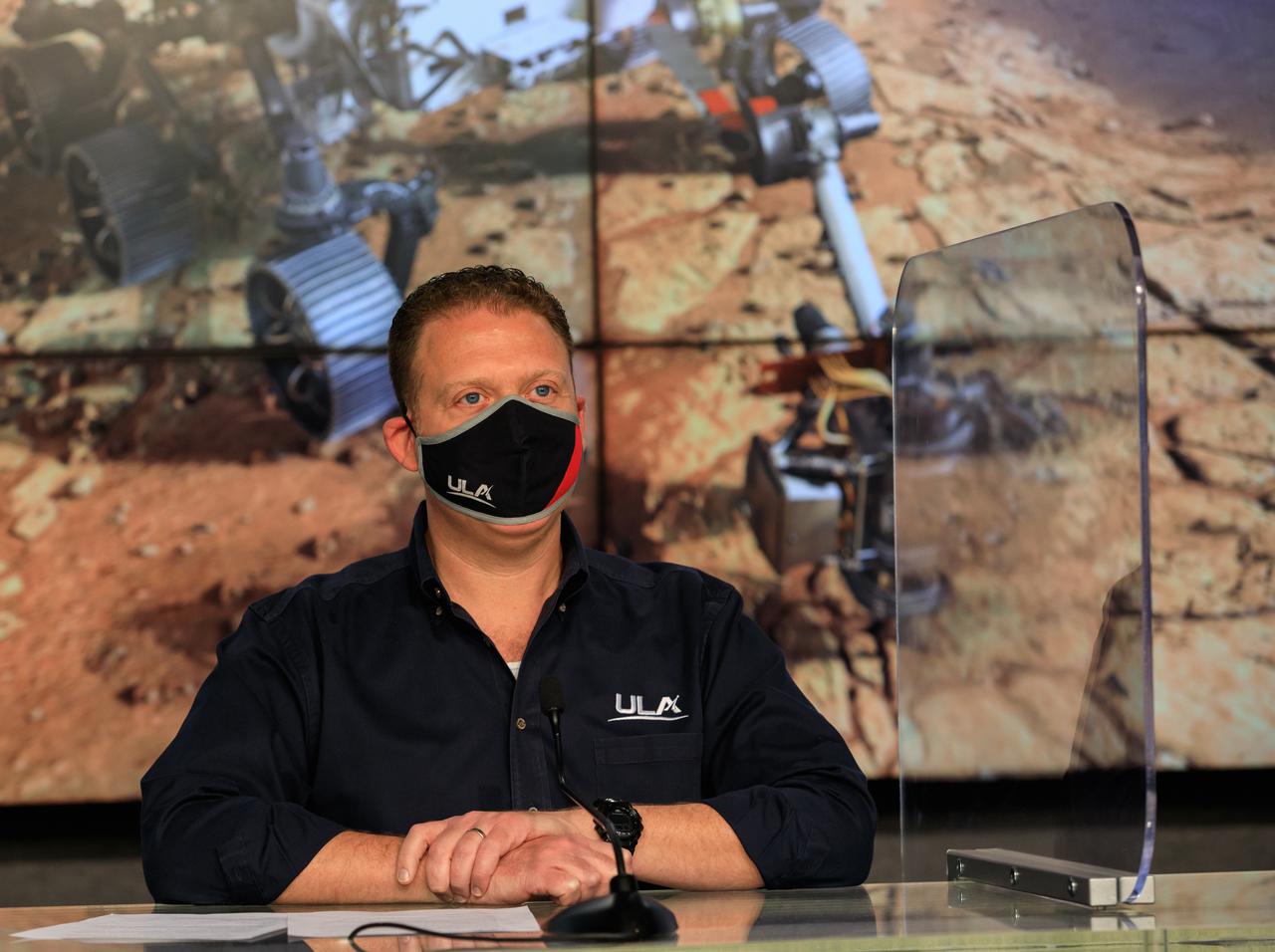

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice participates in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Tim Dunn, launch director for NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
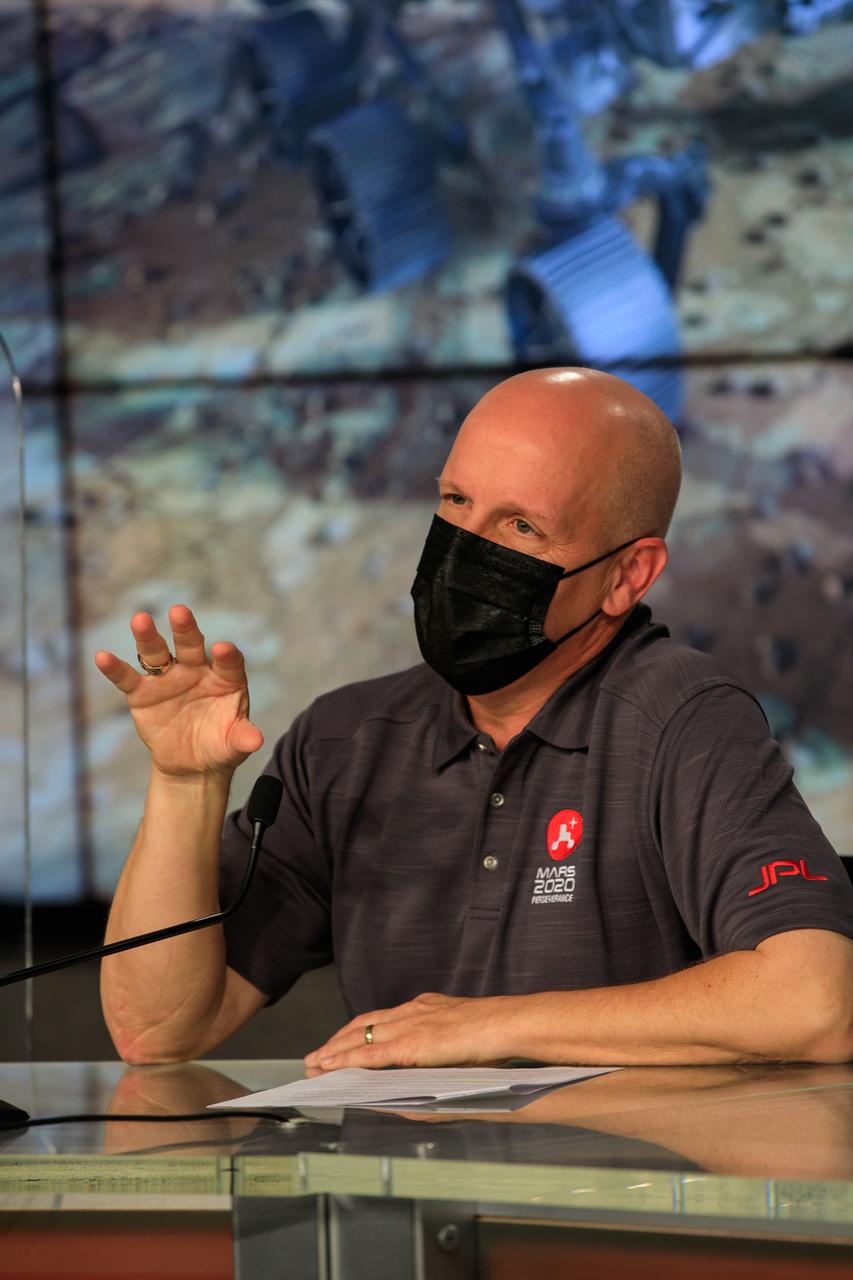

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participates in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Dunn and Dillon Rice, launch conductor for United Launch Alliance (ULA), discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
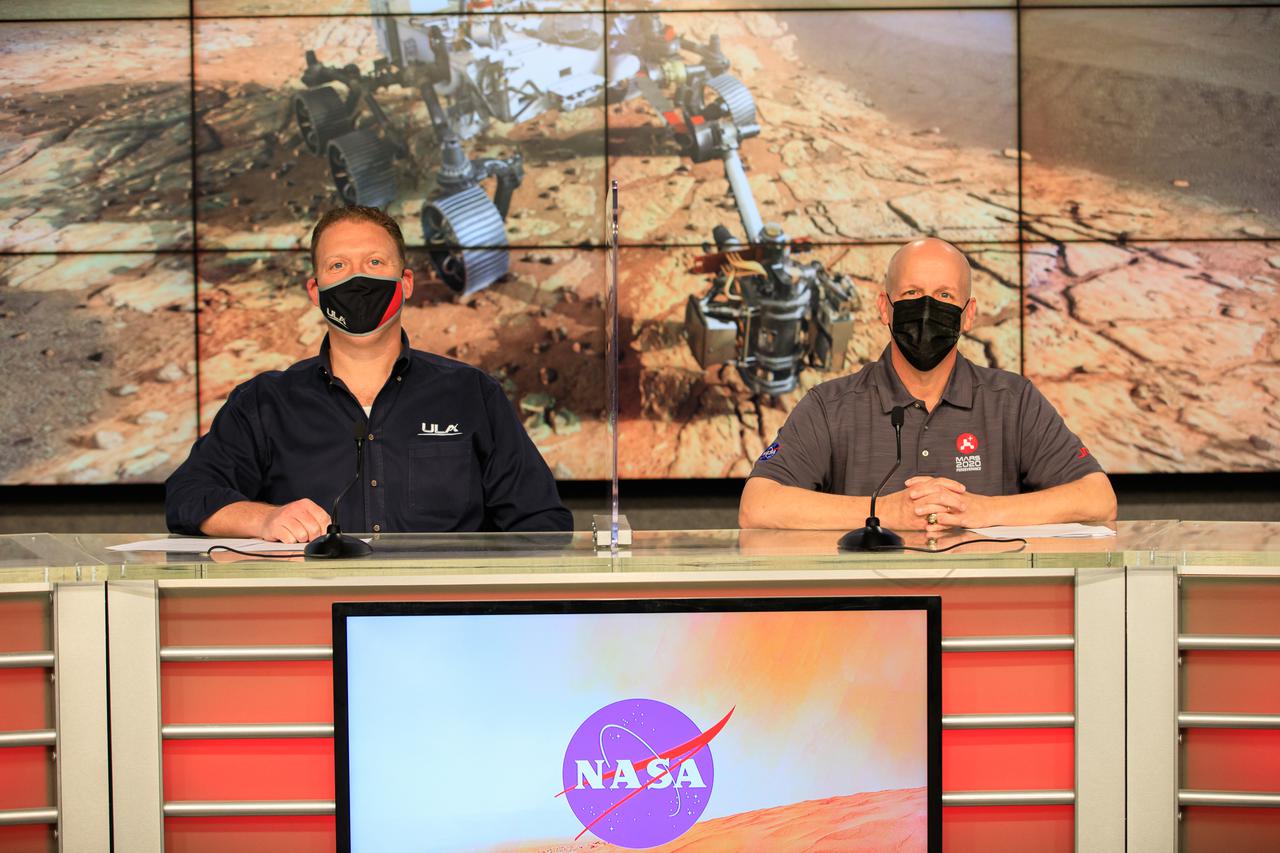

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participate in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
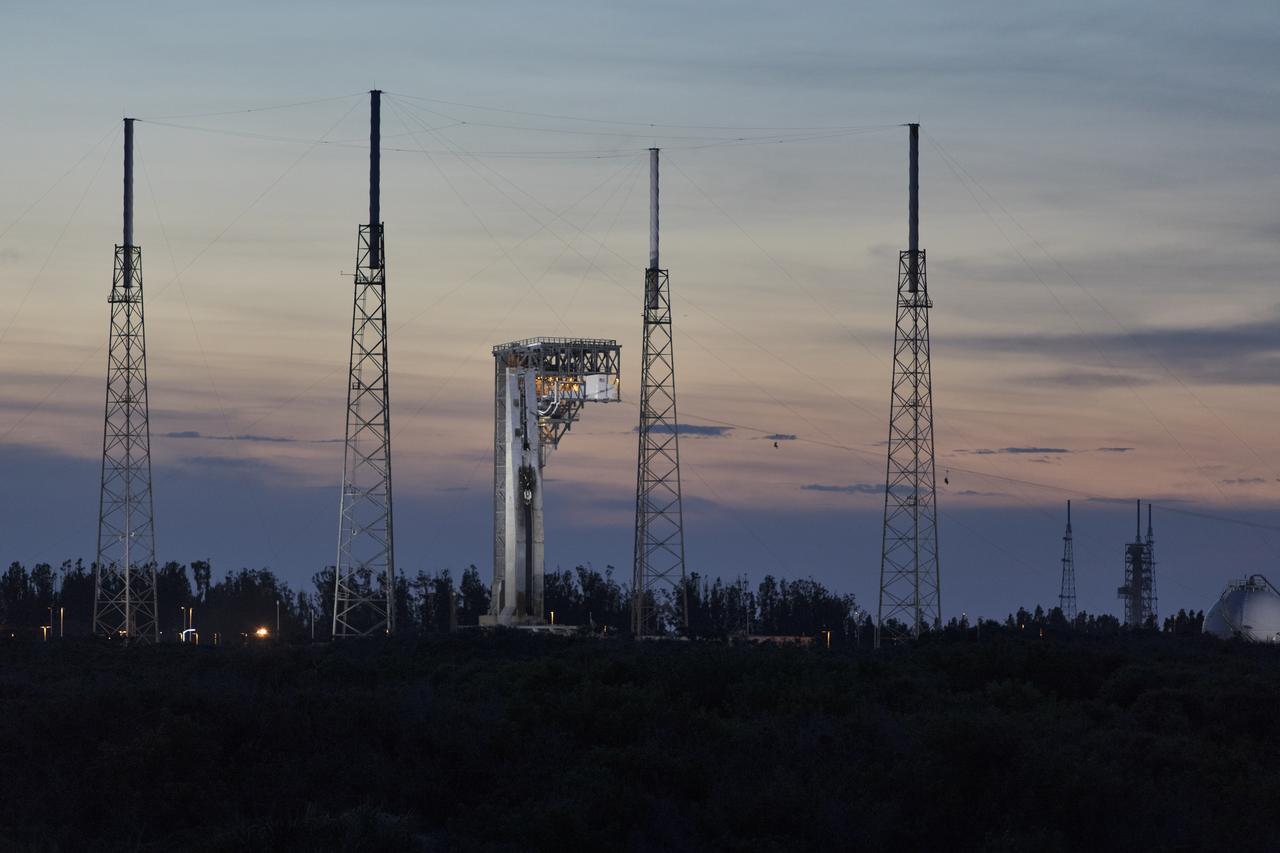

Commercial Crew astronauts participate in a Boeing/United Launch Alliance (ULA) emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The emergency egress system will allow for a safe evacuation in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day. It can carry up to 20 people more than 1,300 feet away from the crew access tower and the launch vehicle. The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket, carrying astronauts to the International Space Station.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Thursday, Sept. 13, 2018, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
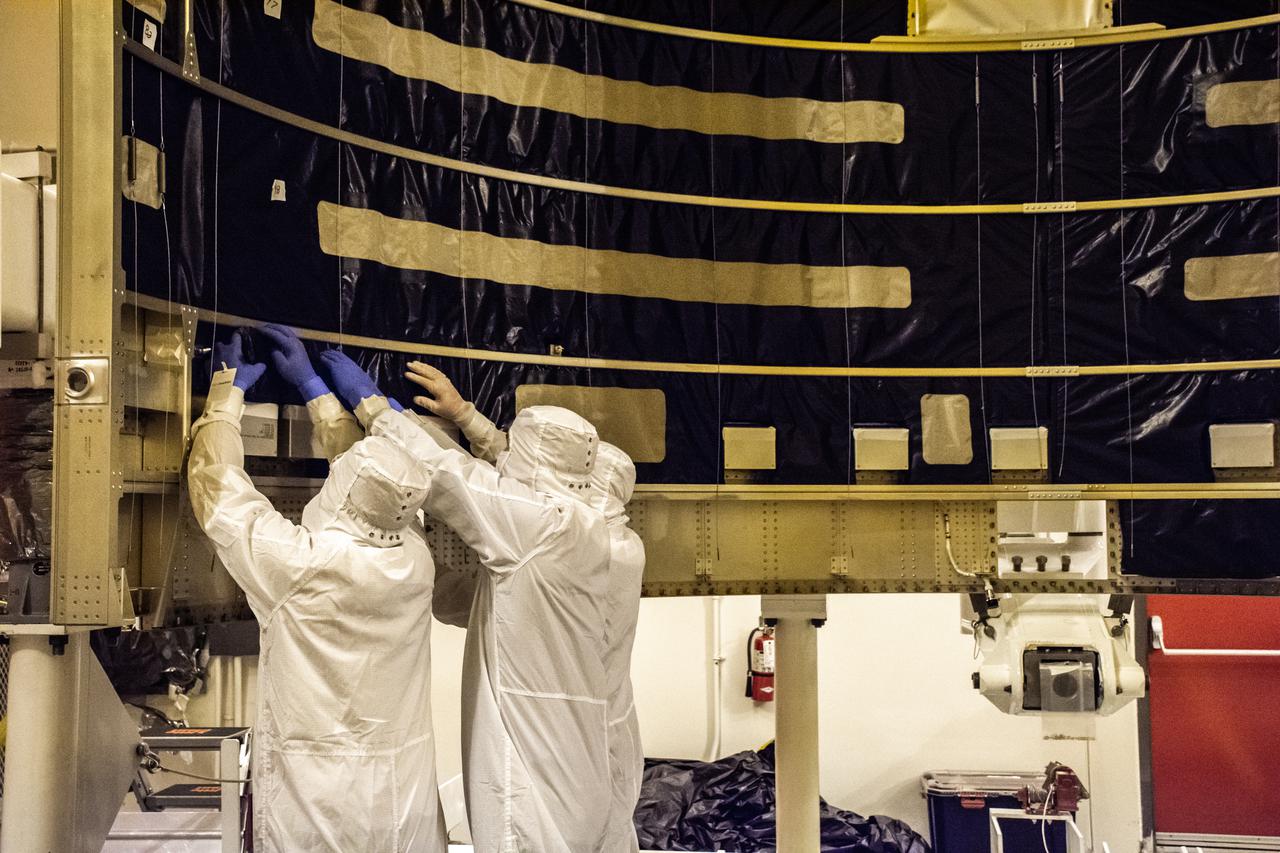

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
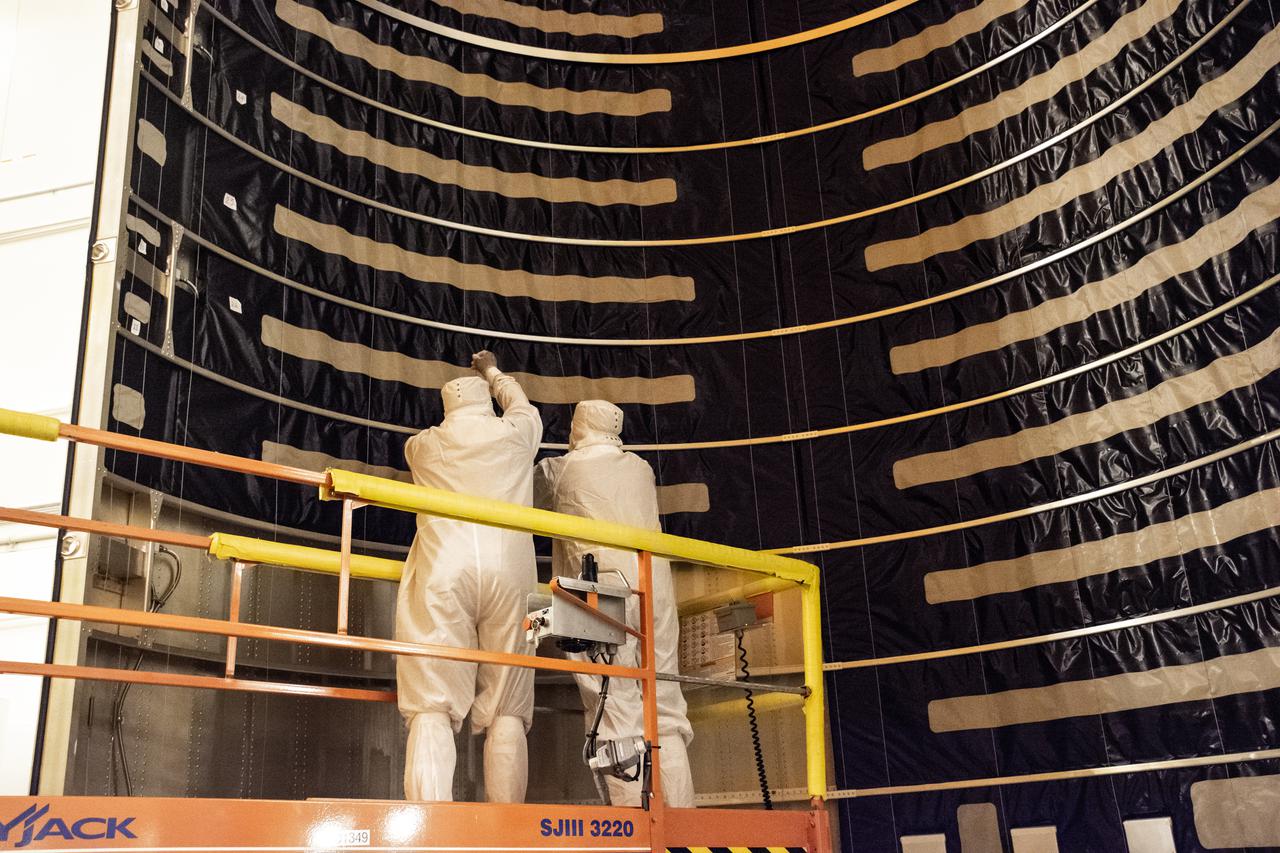

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
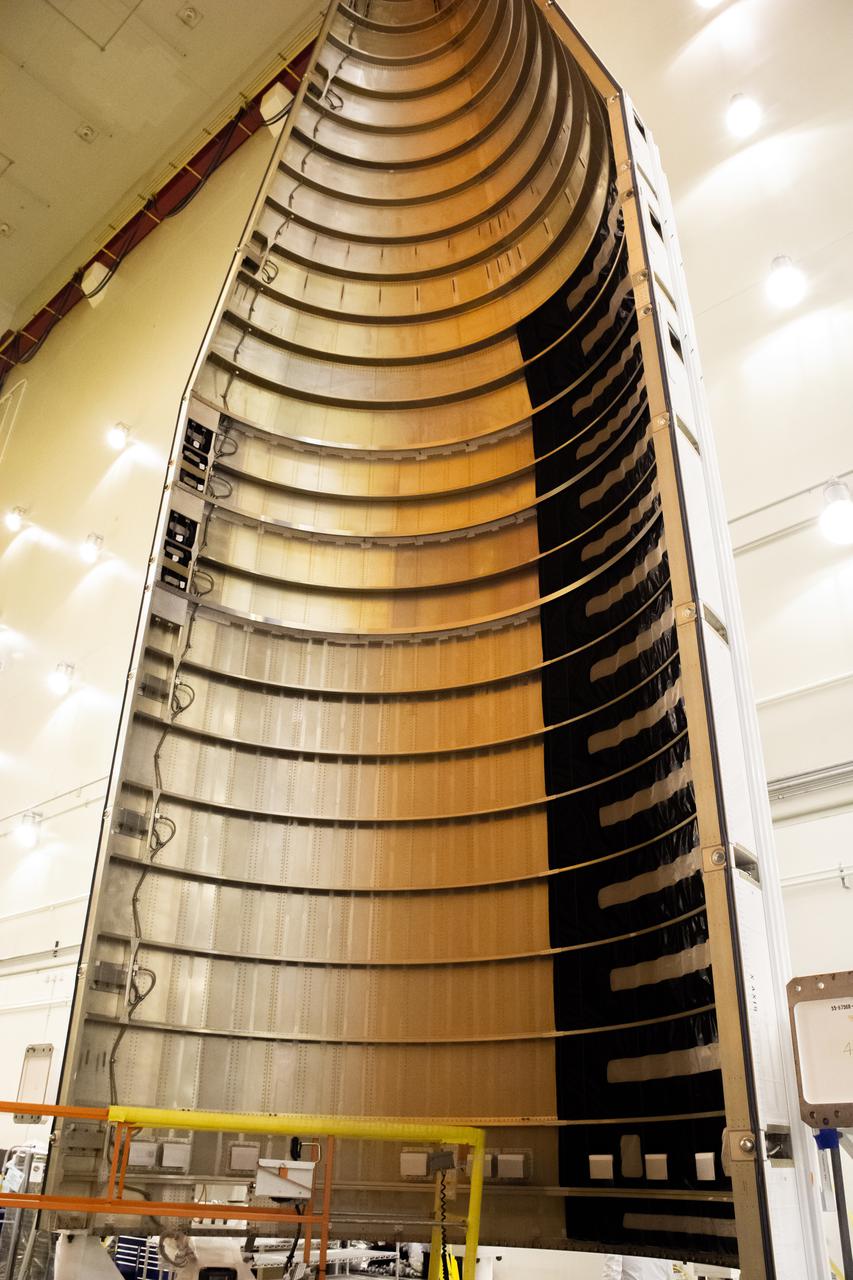

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, protective blanks are removed from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairings for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
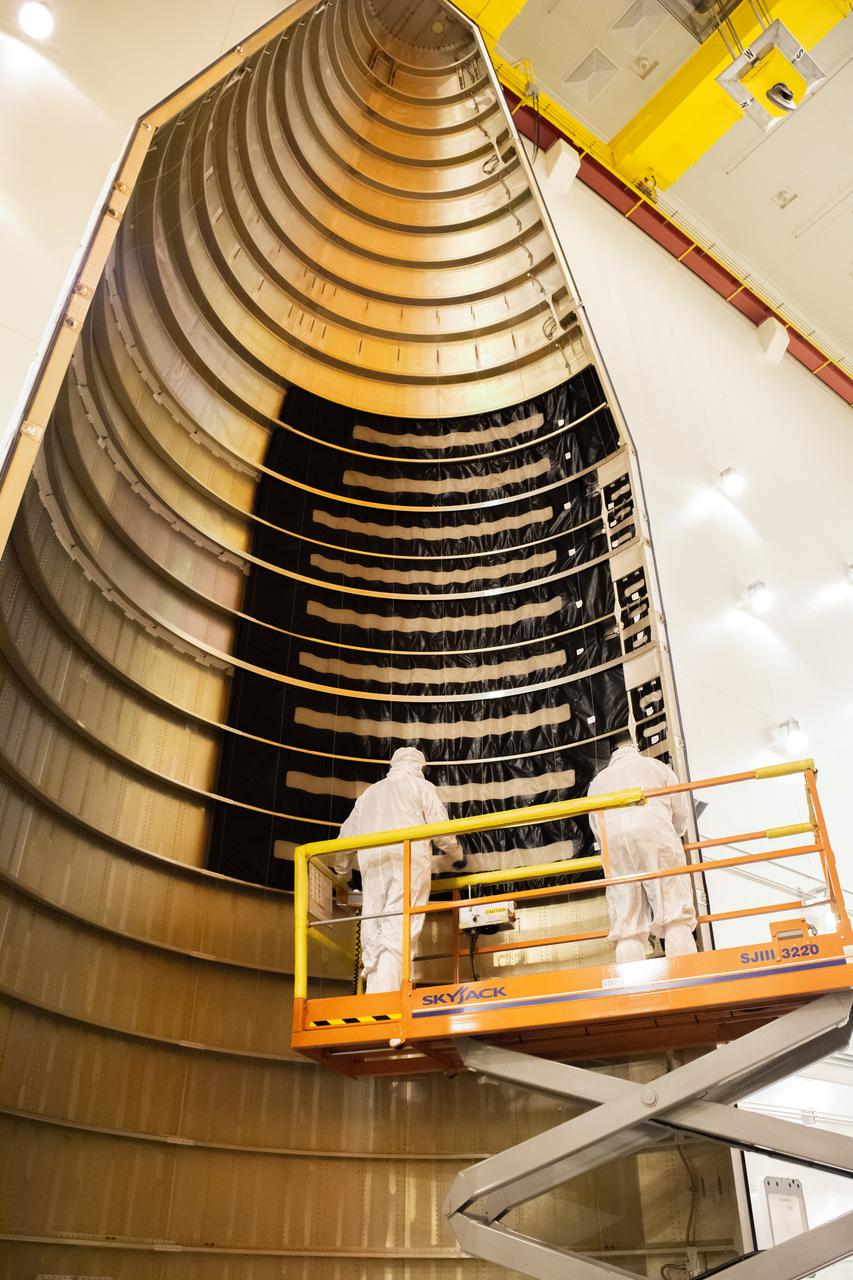

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
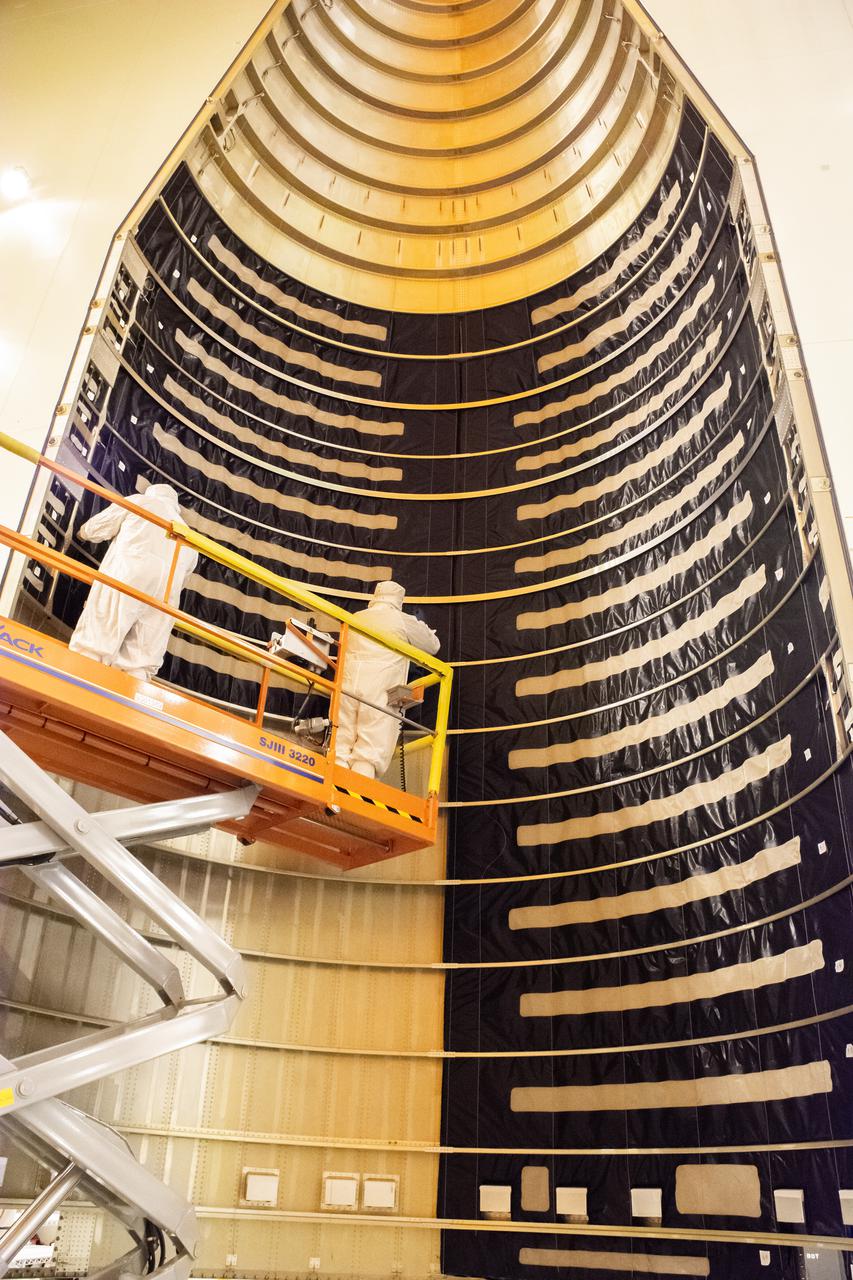

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) remove the protective blankets from one payload fairing half for the Landsat 9 spacecraft on Aug. 2, 2021. The two halves of the ULA payload fairing will be secured around Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
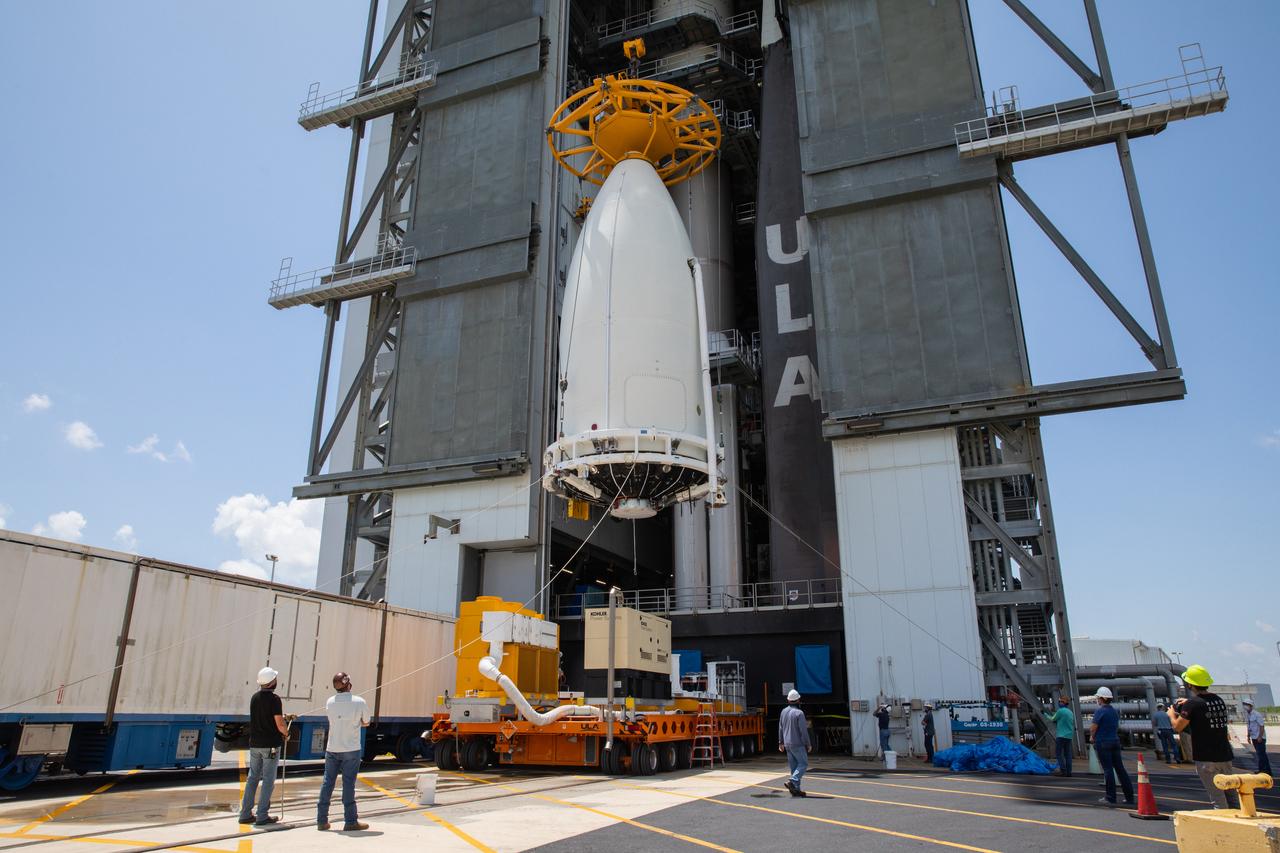

A crane is attached to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
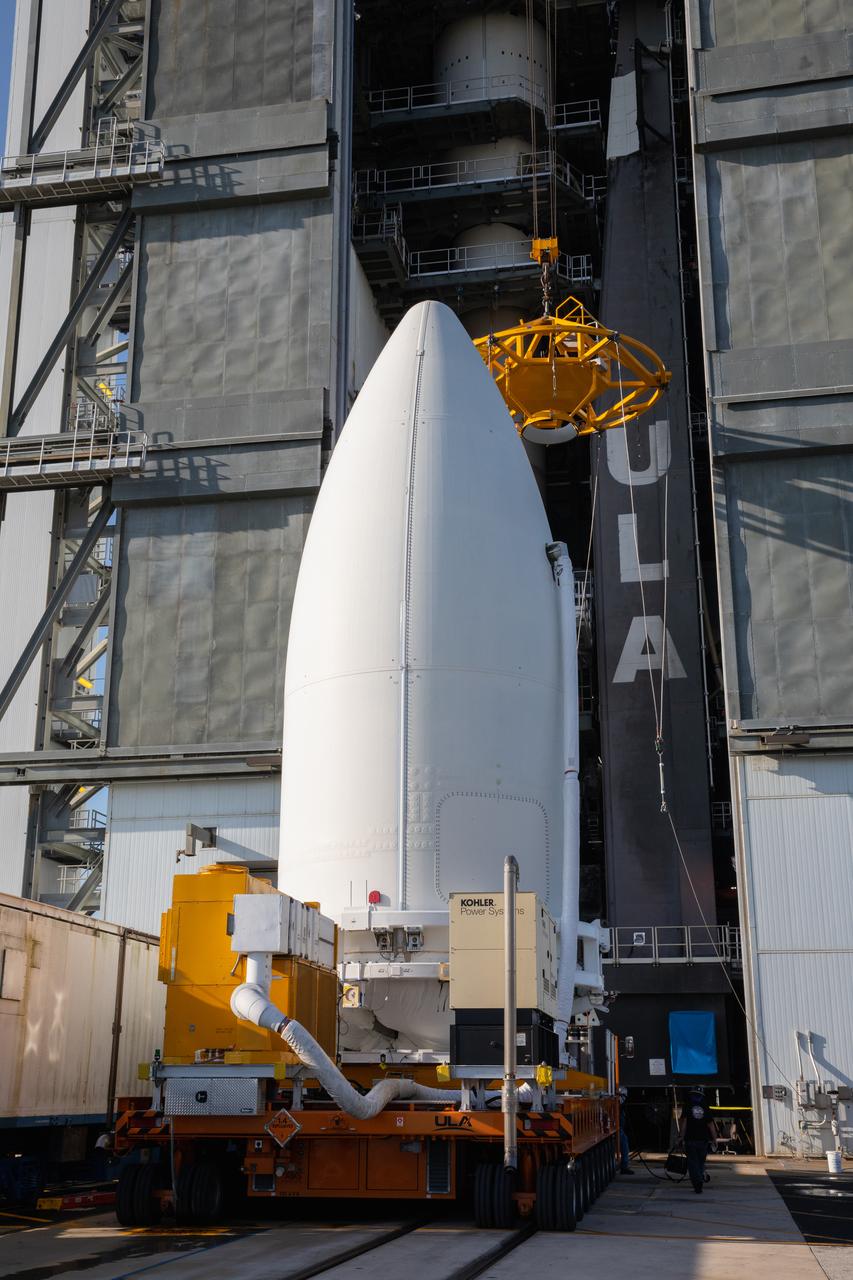

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
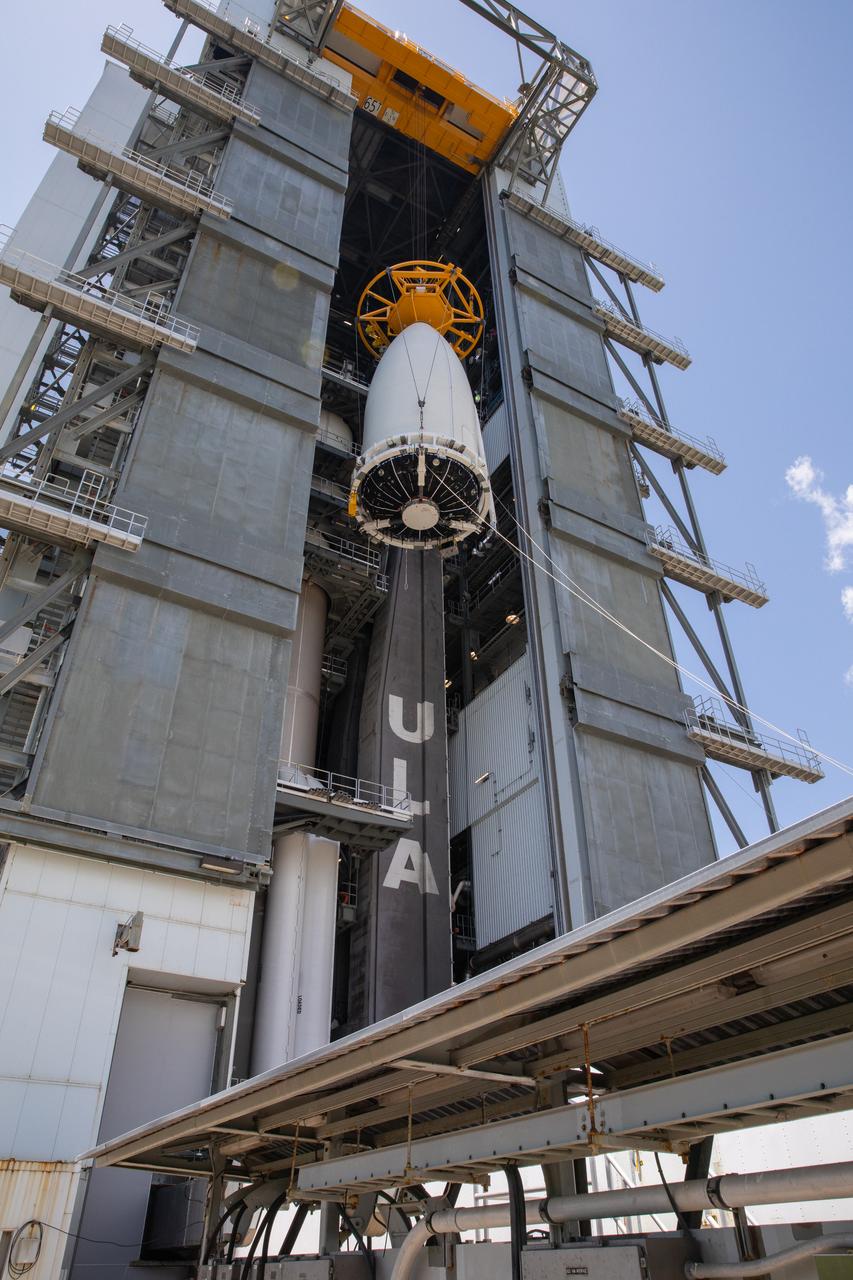

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is lifted high up inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
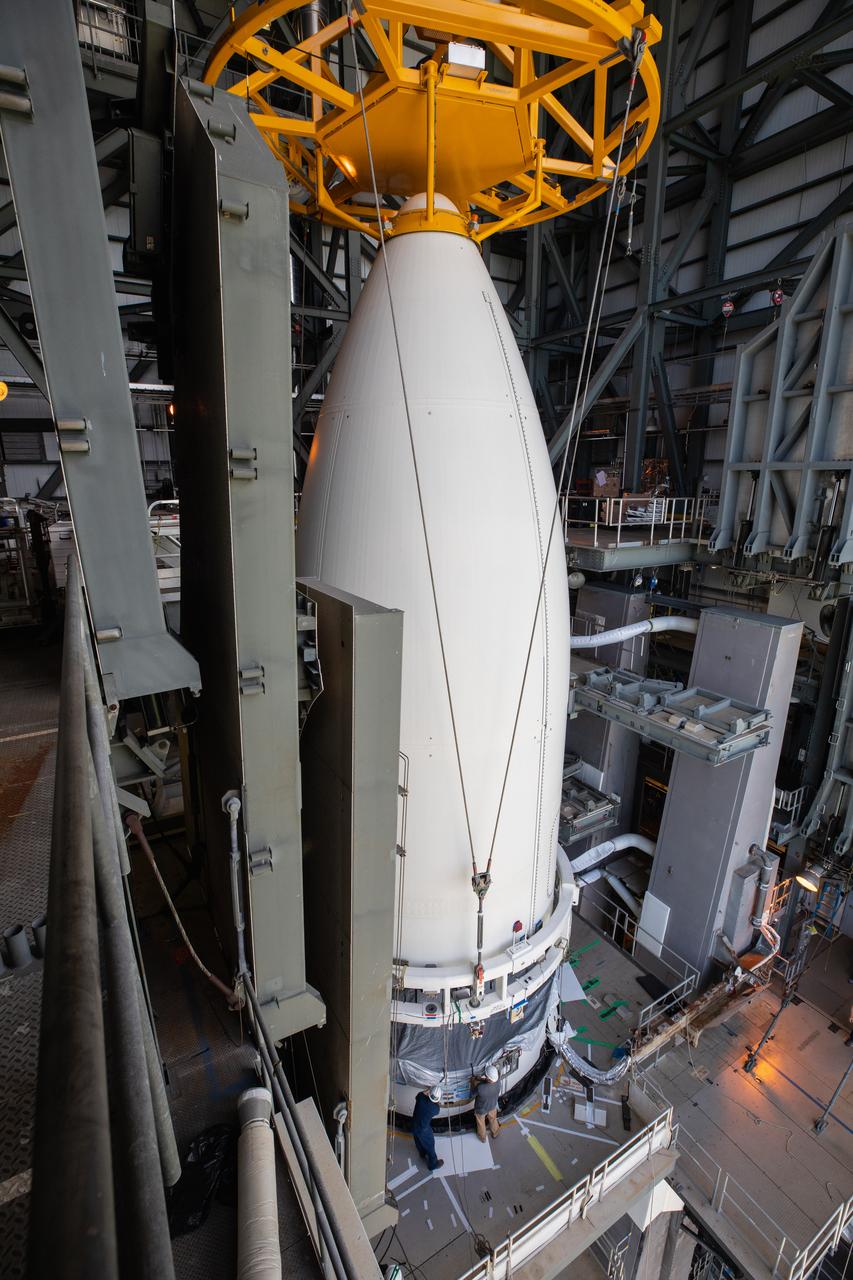

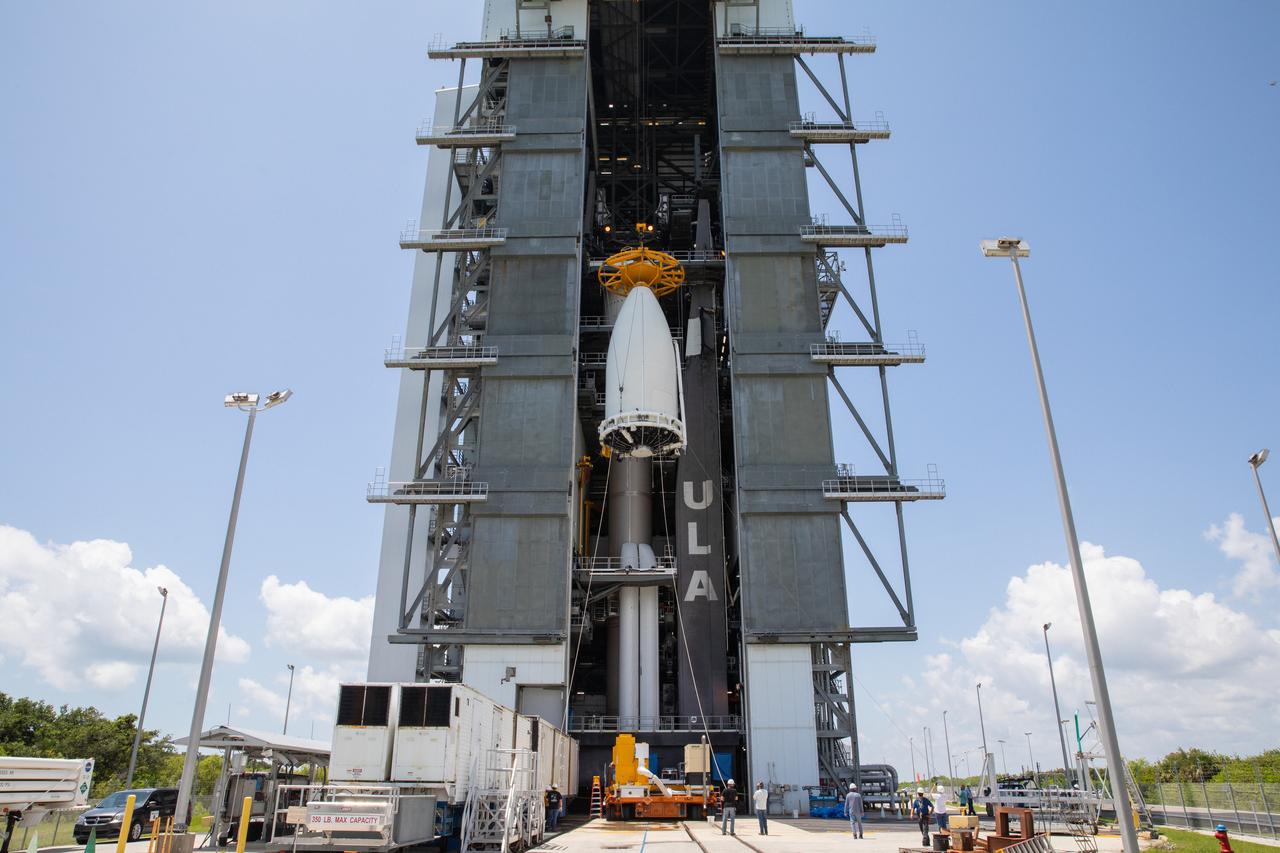
Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside is secured on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket on July 7, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
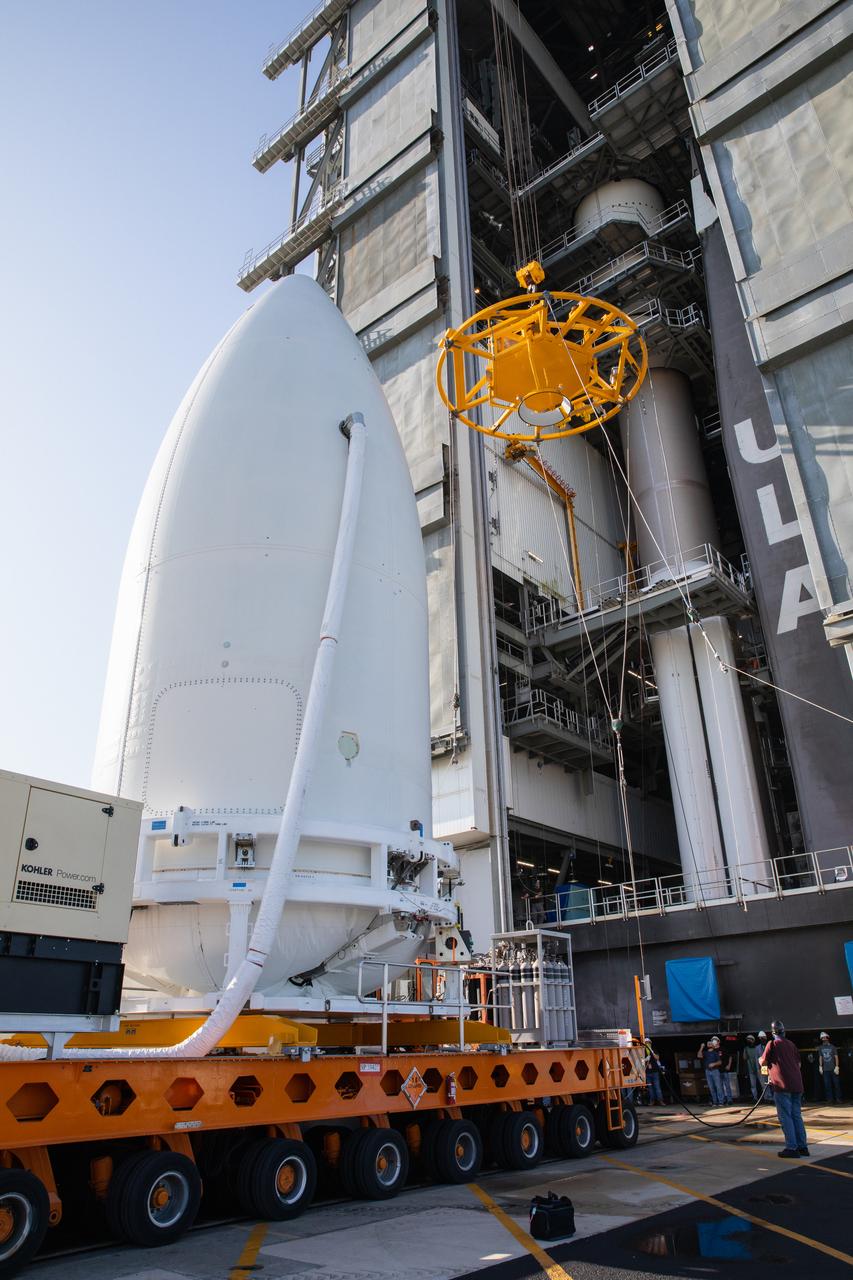

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
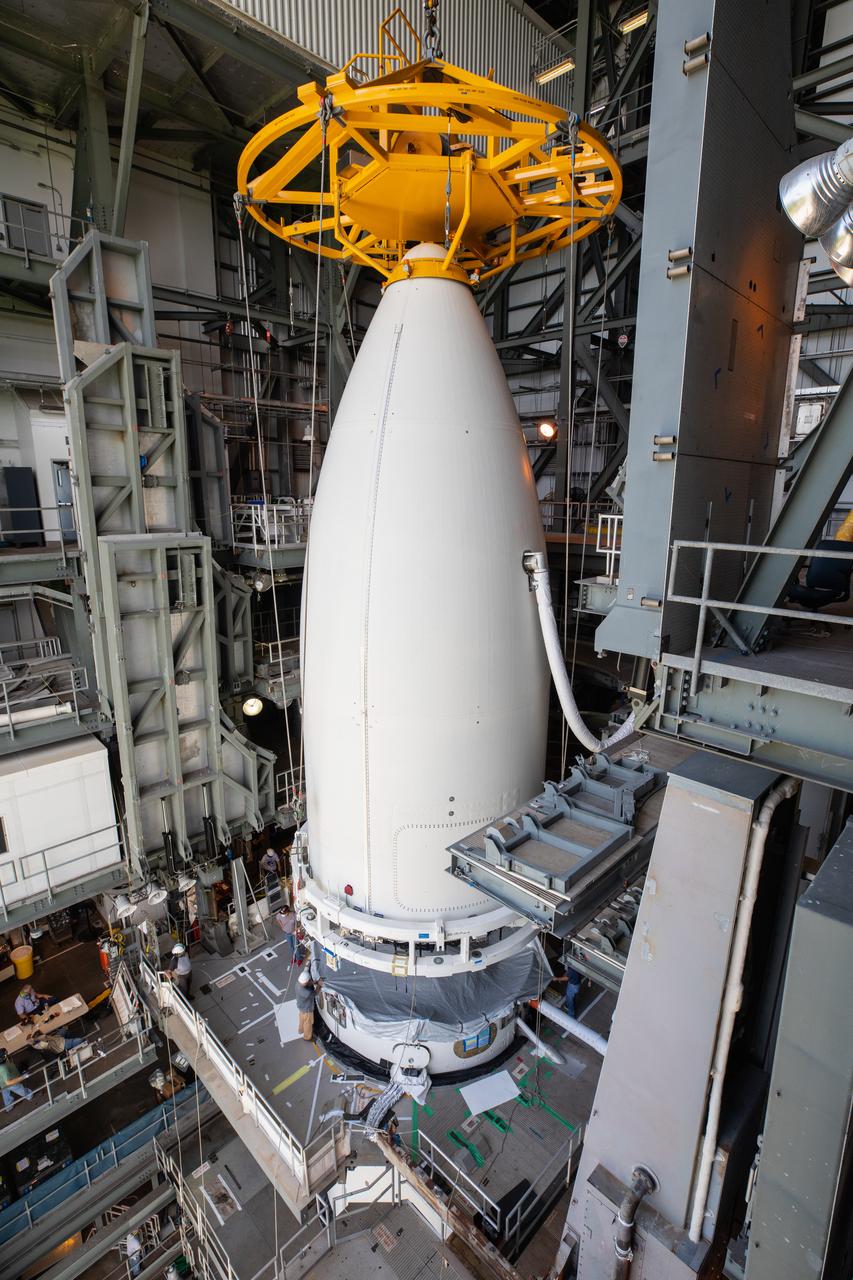

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside is secured on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket on July 7, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

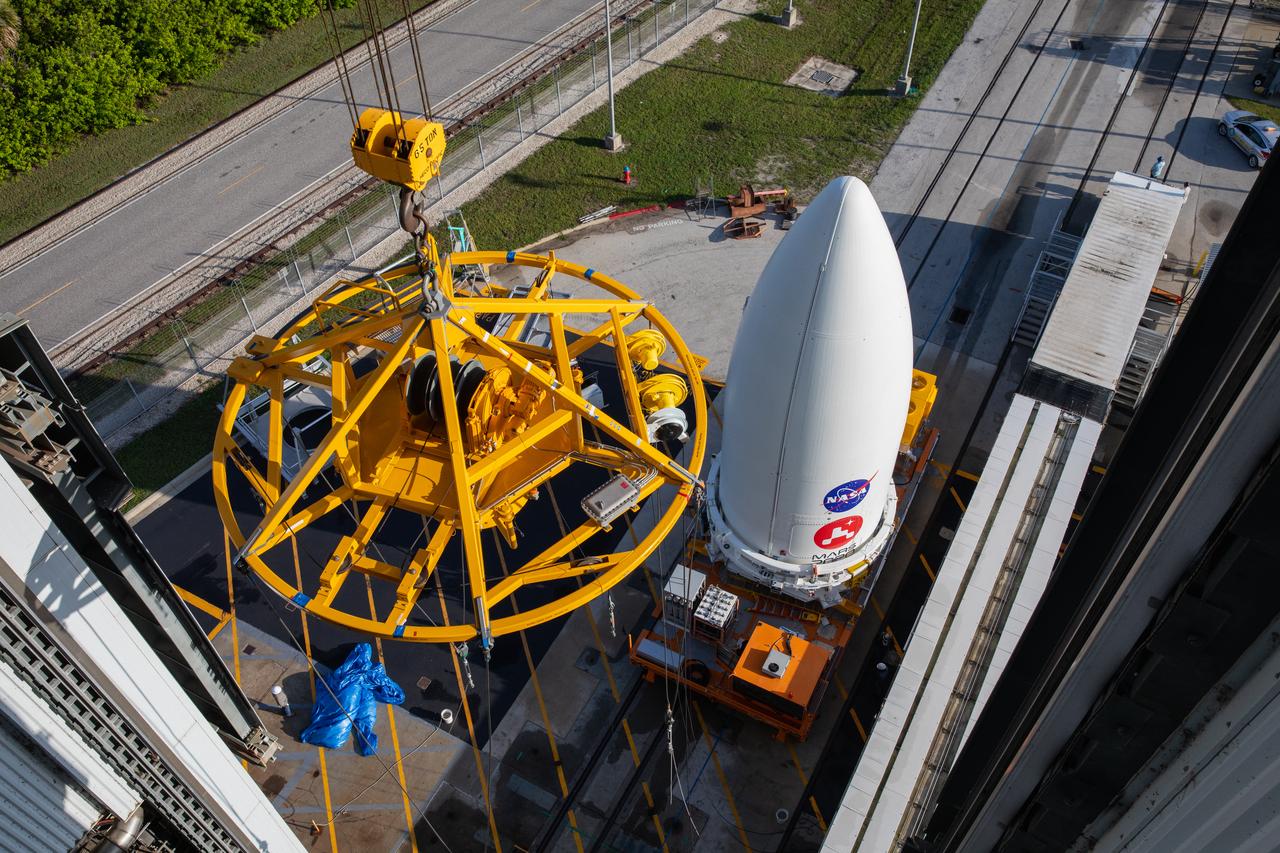
A crane lifts the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
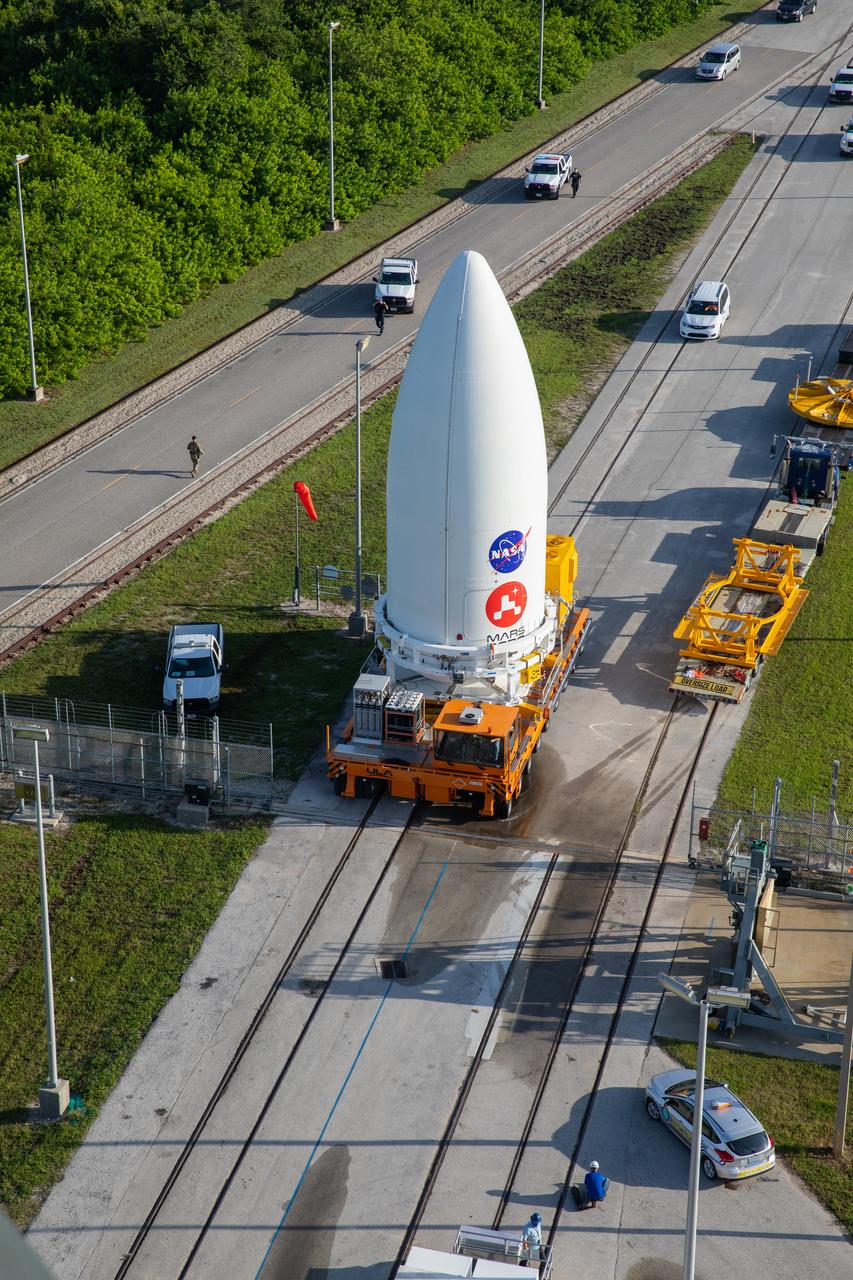

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is transported to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the Vertical Integration Facility where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A crane lifts the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
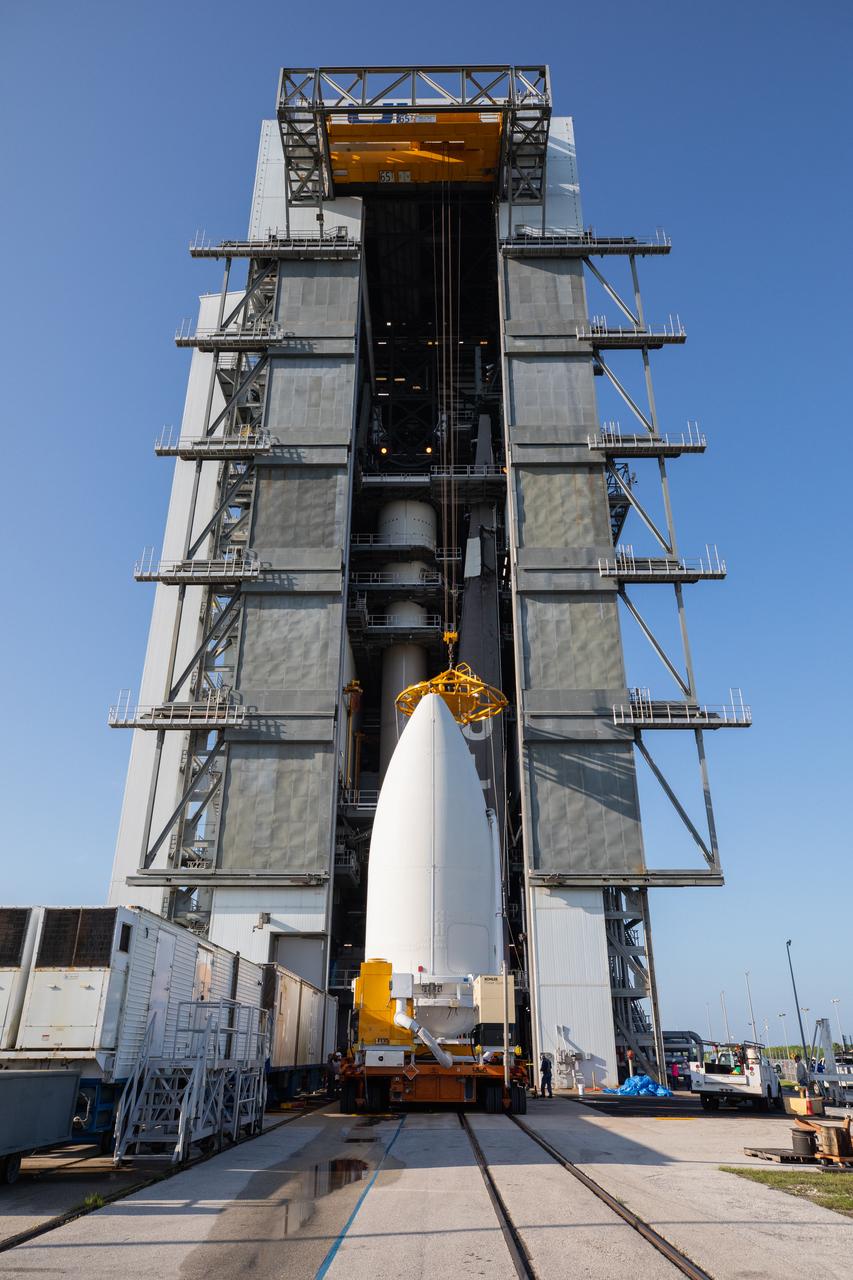

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

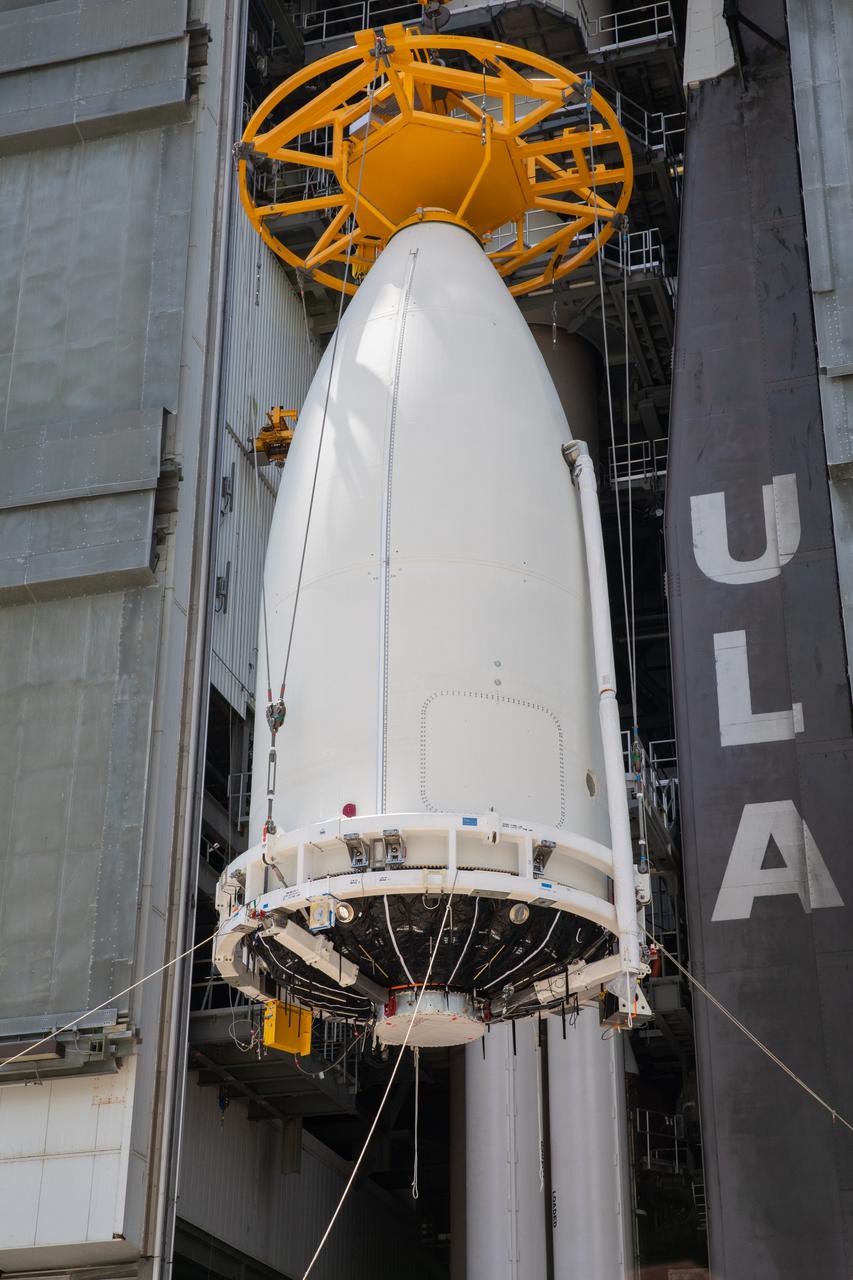
A close-up view of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing is being secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
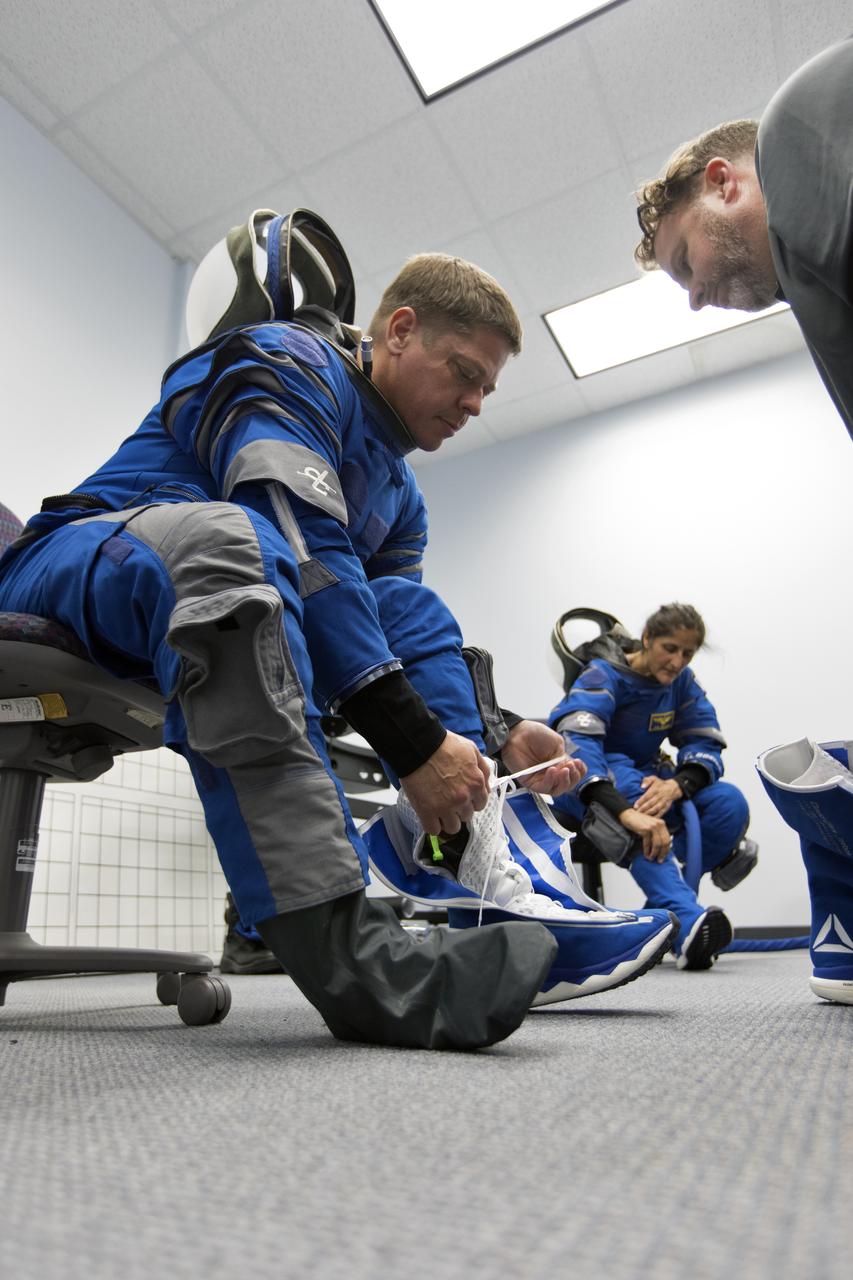

NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Suni Williams get suited up for a Boeing/United Launch Alliance emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. Behnken and other astronauts tested the system, which is designed to evacuate them safely in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day. The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will launch on a ULA Atlas V rocket, carrying astronauts to the International Space Station.
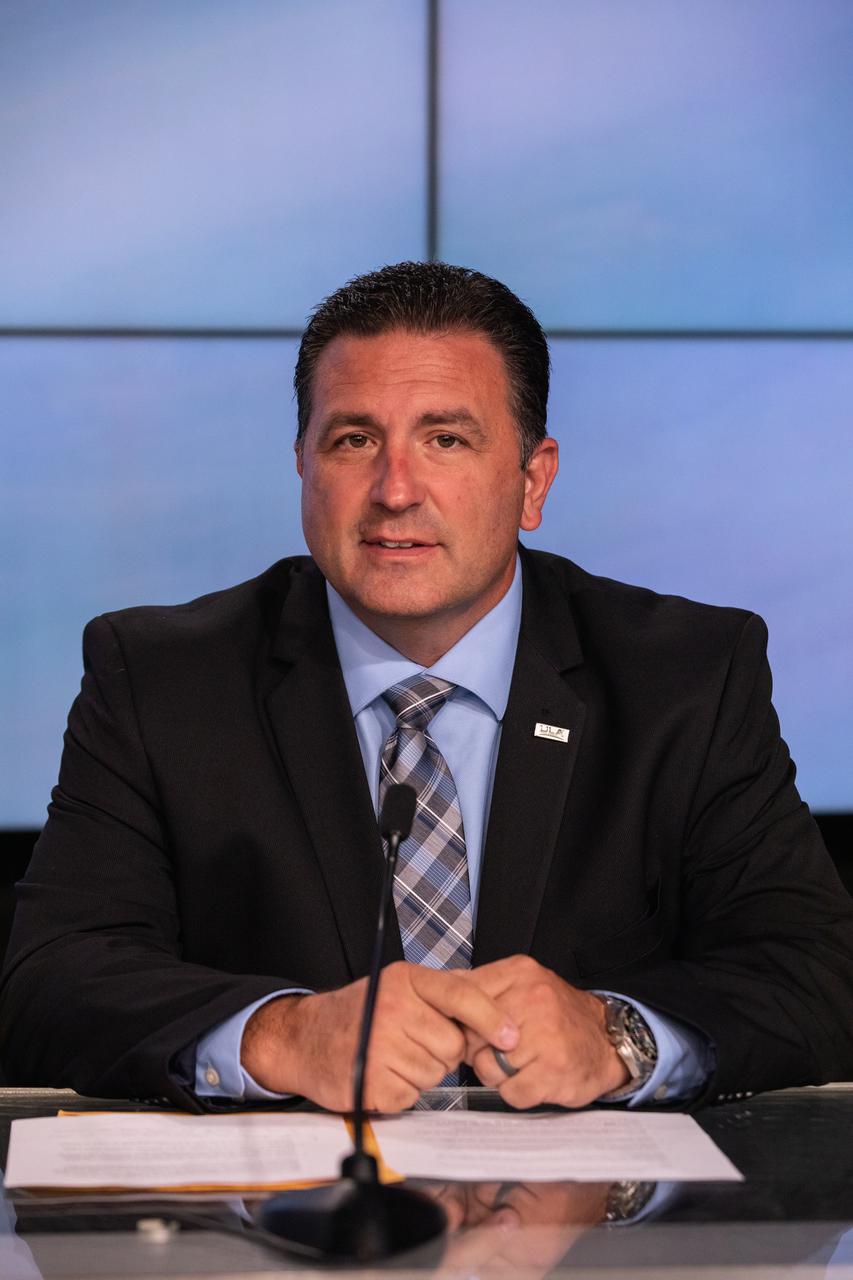

Gary Wentz, vice president, Government and Commercial Programs, United Launch Alliance (ULA), participates in a prelaunch briefing for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, July 27, 2021. Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft will launch atop a ULA Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on a mission to dock with the space station. The uncrewed OFT-2 will be the Starliner’s second flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
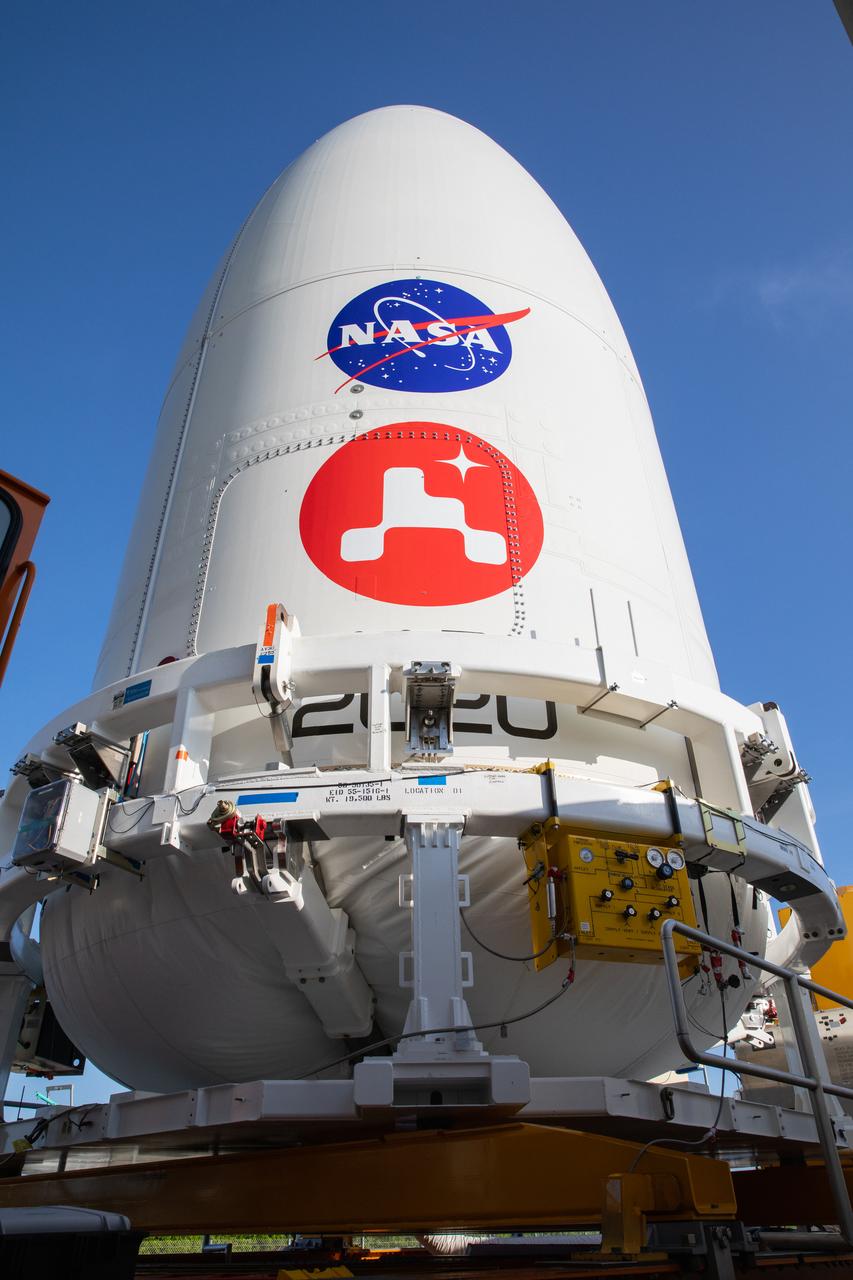

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
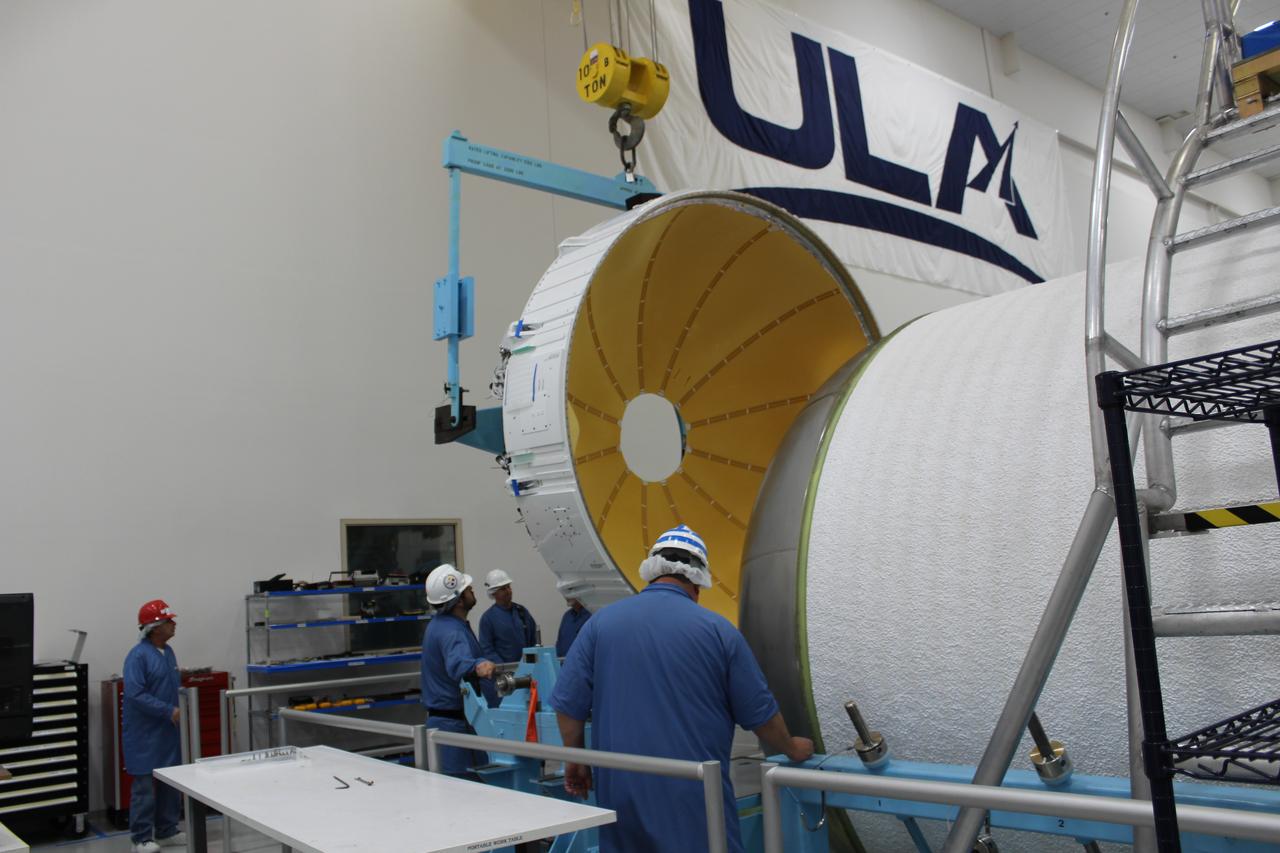

Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.
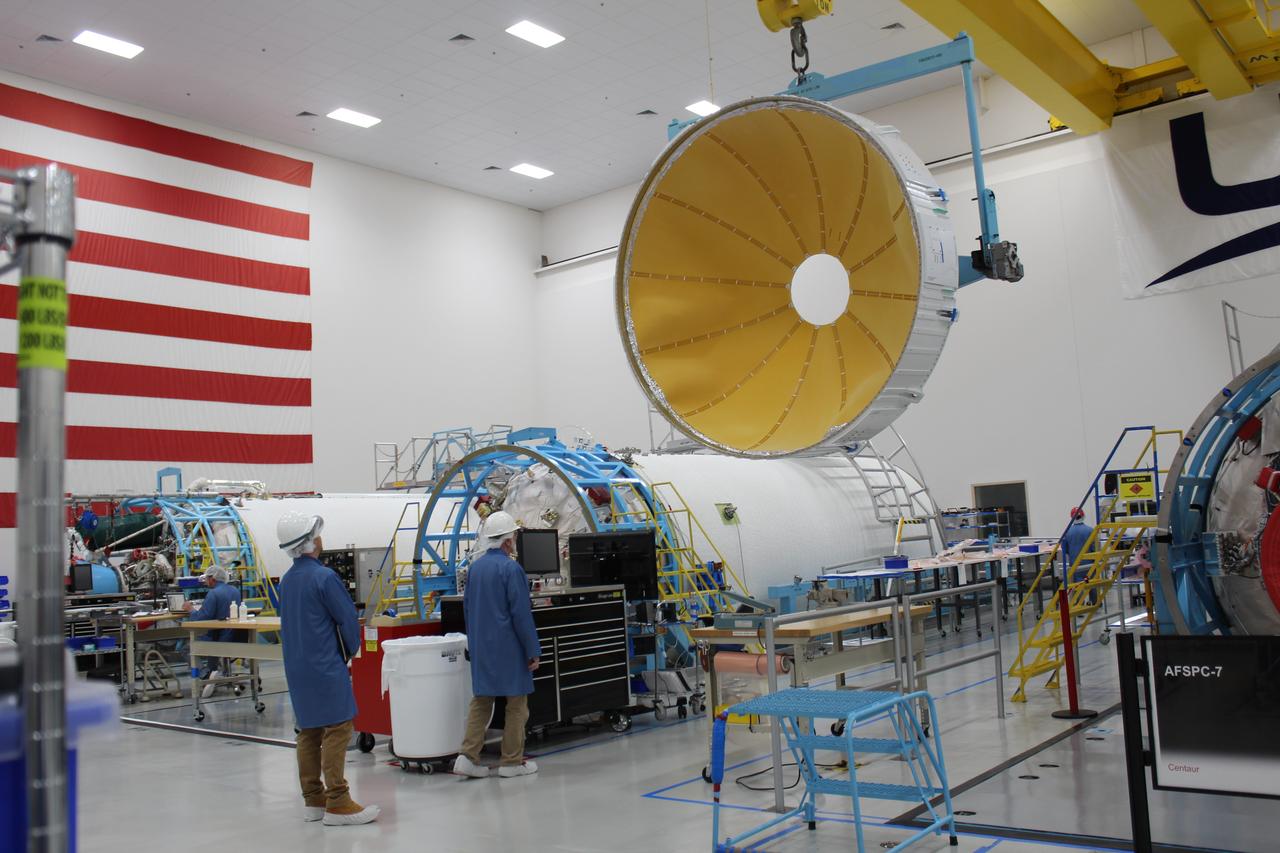

Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.
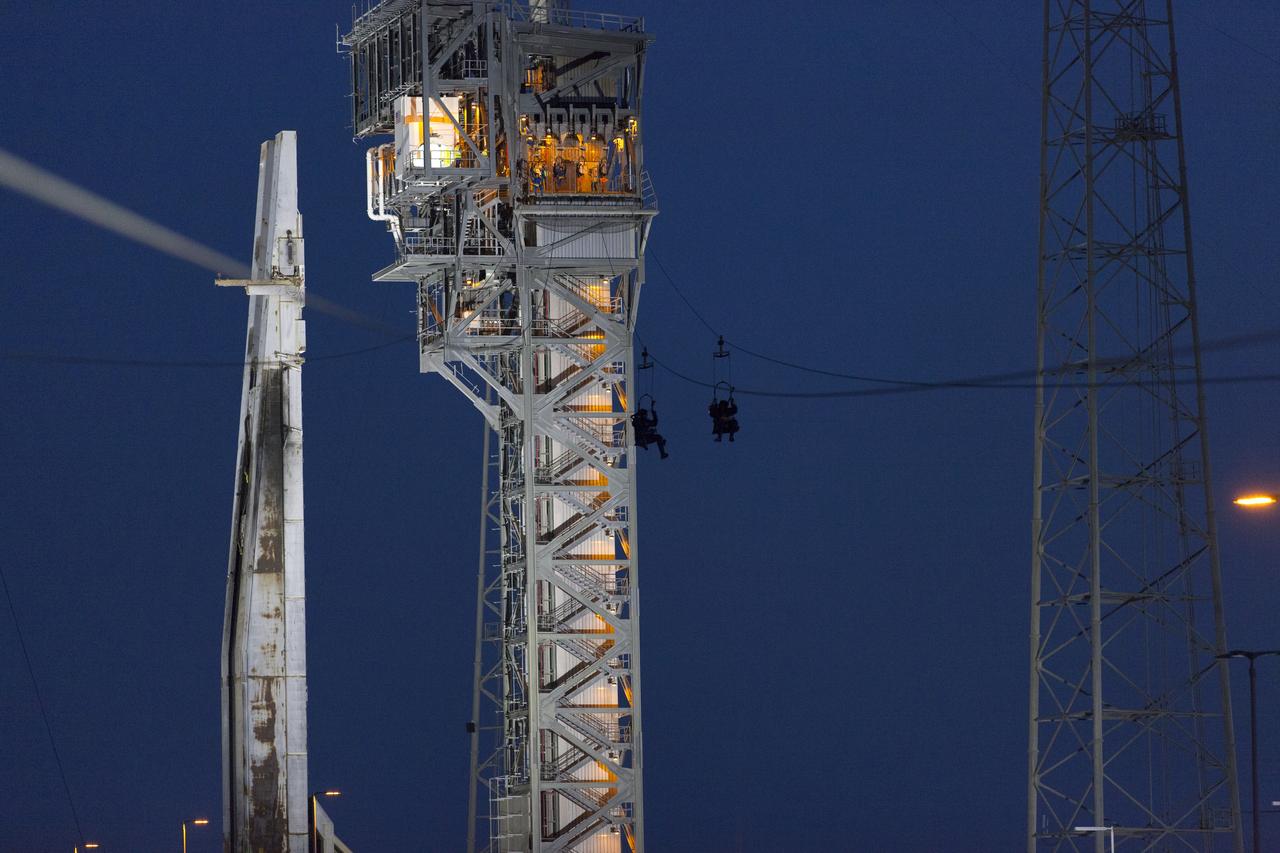

Commercial Crew astronauts participate in a Boeing/United Launch Alliance (ULA) emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The emergency egress system features folding seats attached to slide wires. In the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff on launch day, each person on the Crew Access Tower would get his or her own seat and slide more than 1,300 feet to a safe area.
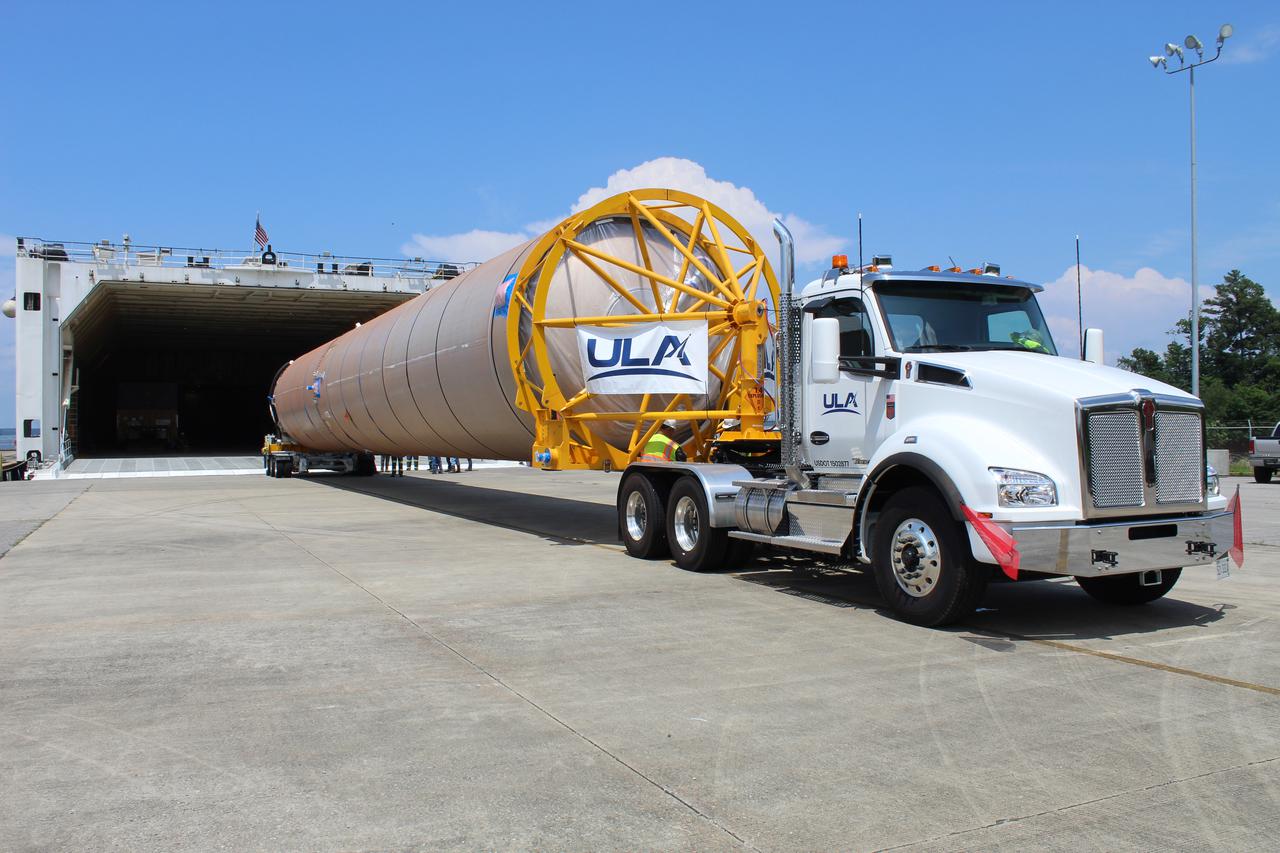

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test (CFT) is loaded onto a rocket-delivery ship at ULA’s manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama, on June 11, 2021, to begin its journey to Cape Canaveral, Florida. Starliner’s first flight with astronauts aboard, CFT will launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The flight test will demonstrate the ability of the Atlas V and Starliner to safely carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
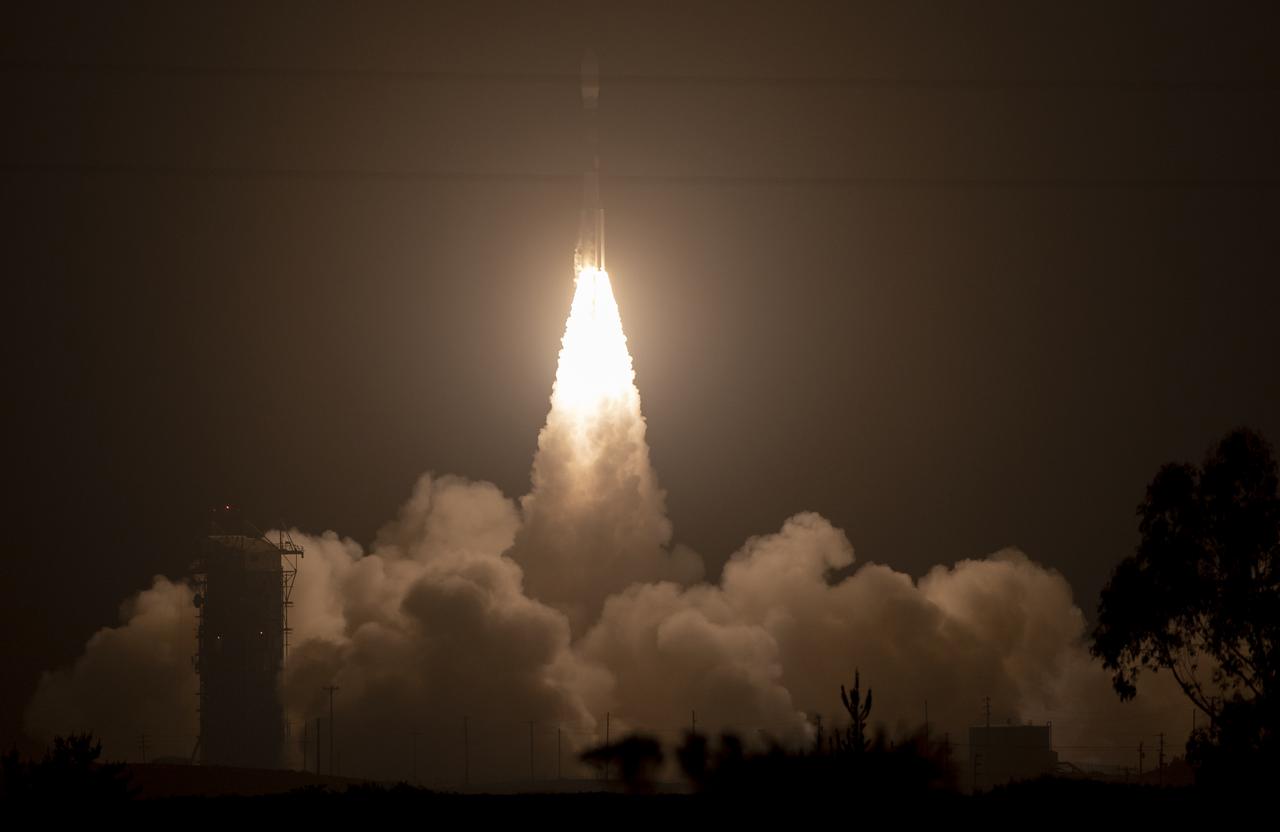

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
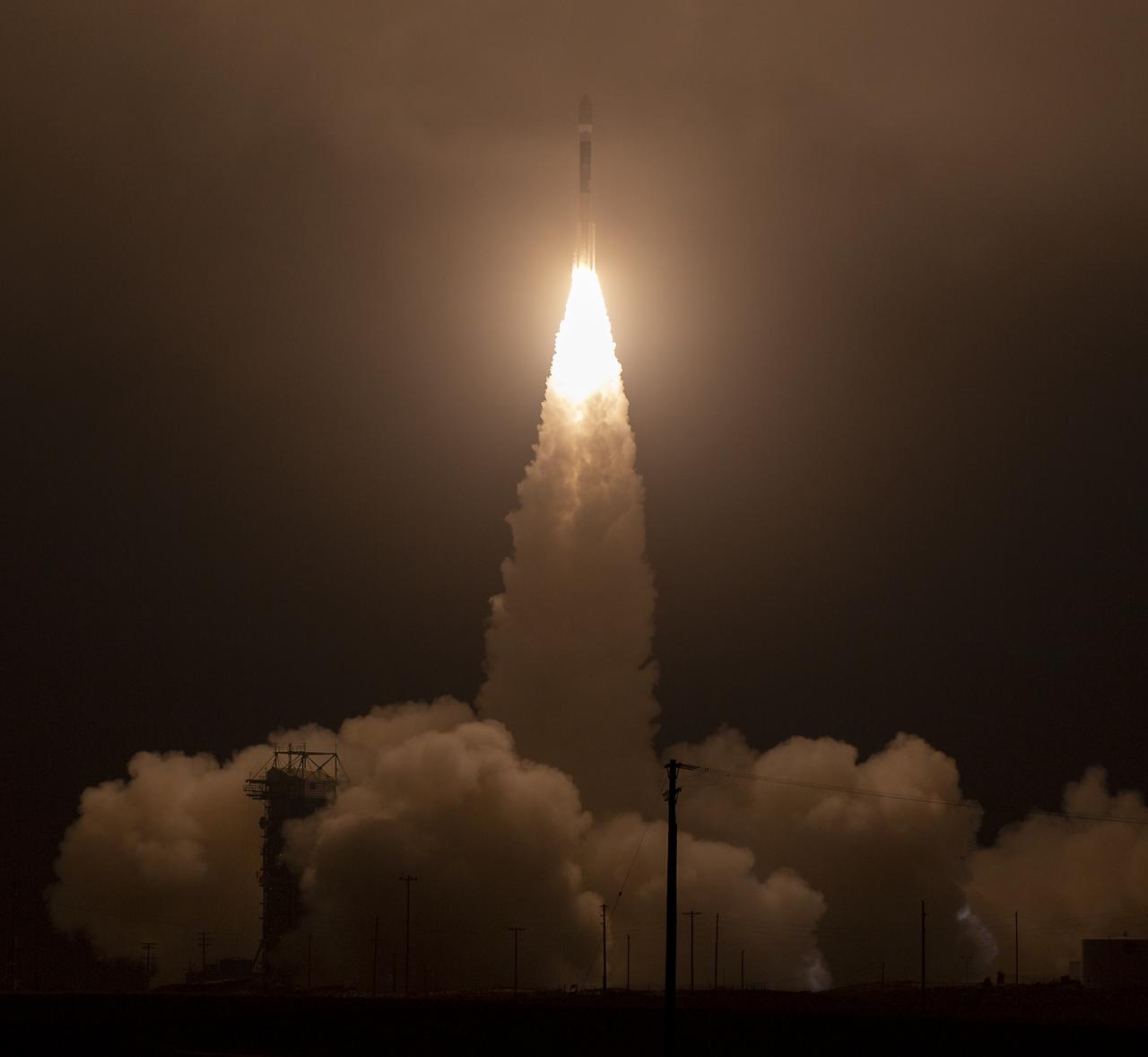

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
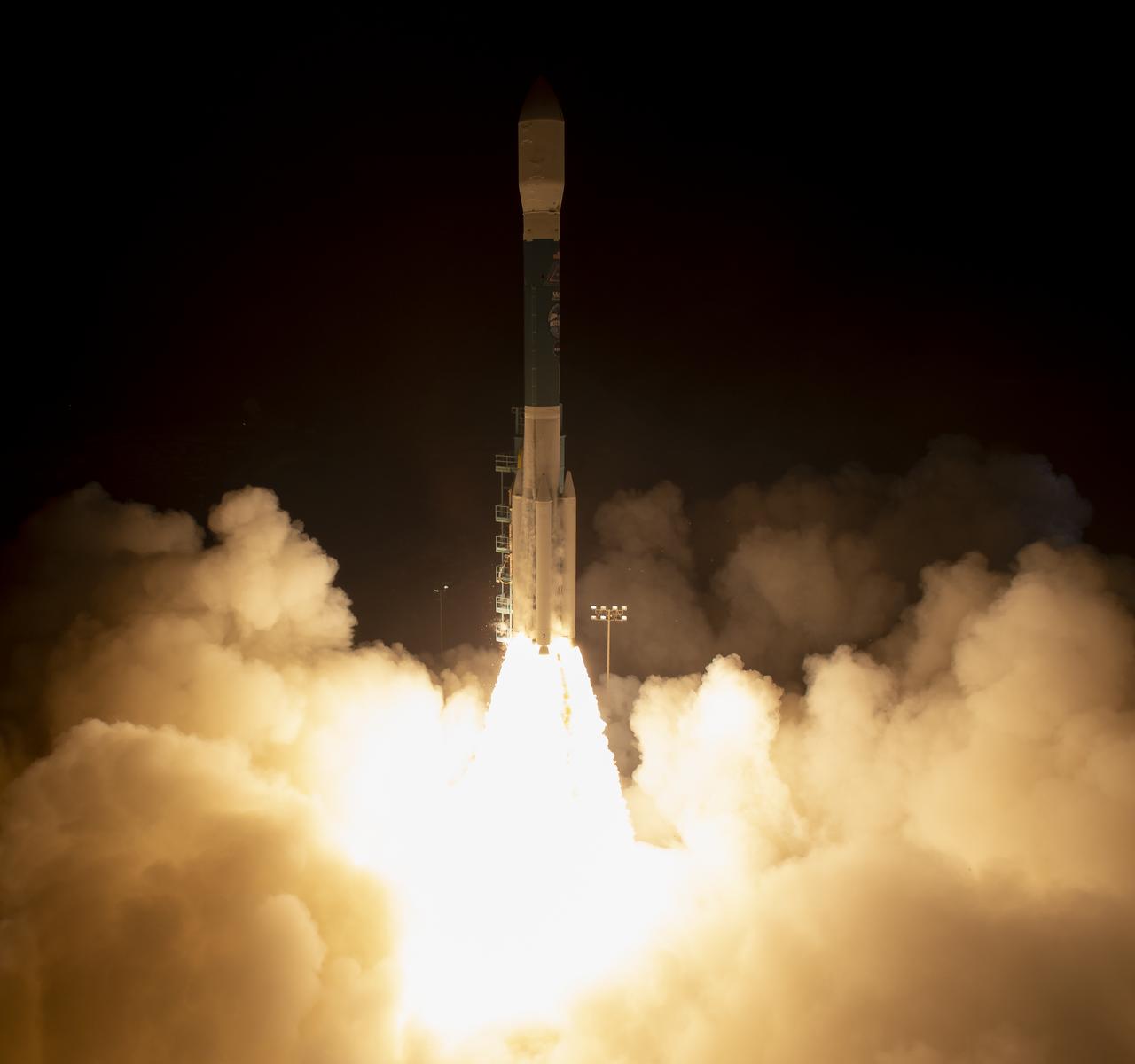

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
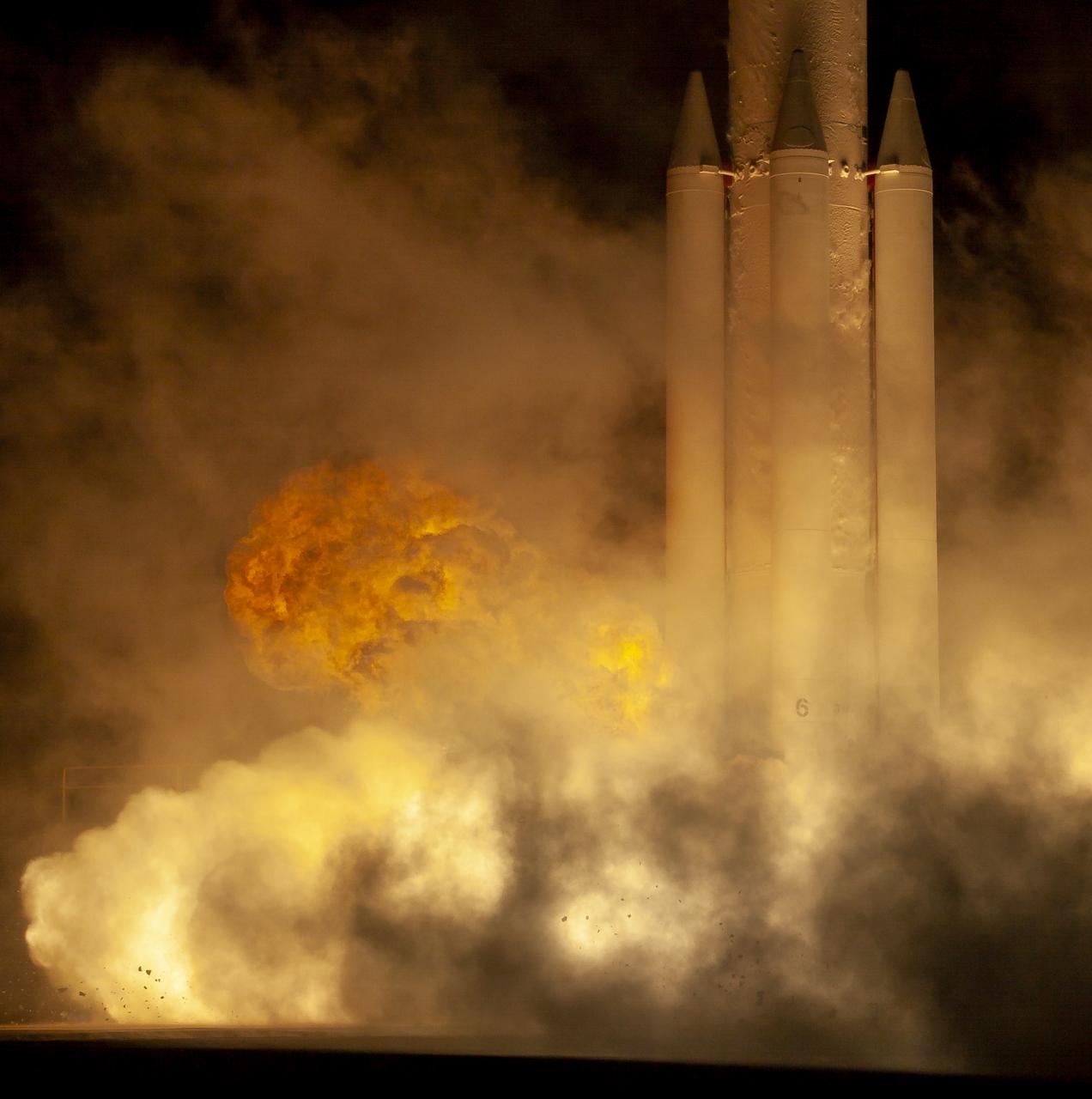

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
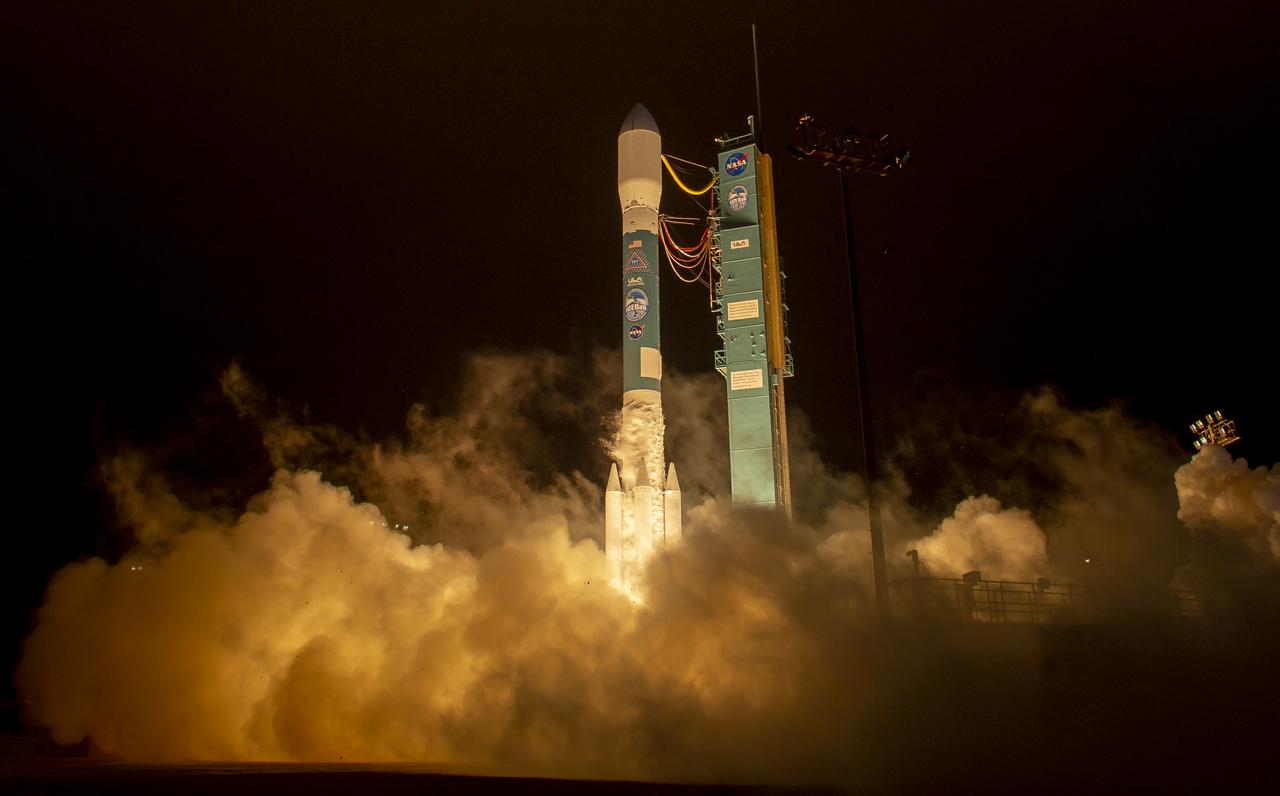

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
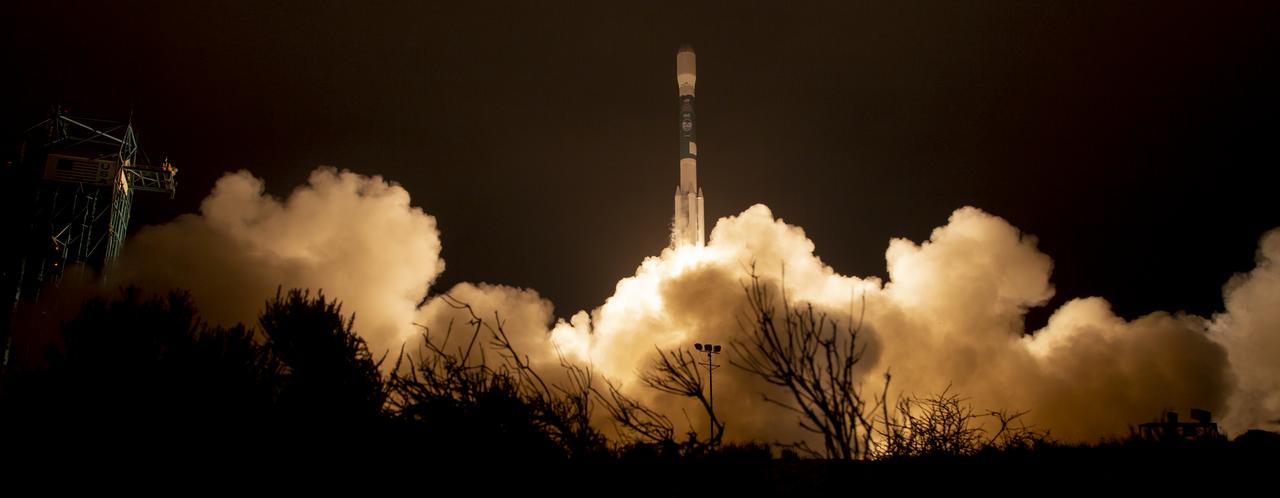

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
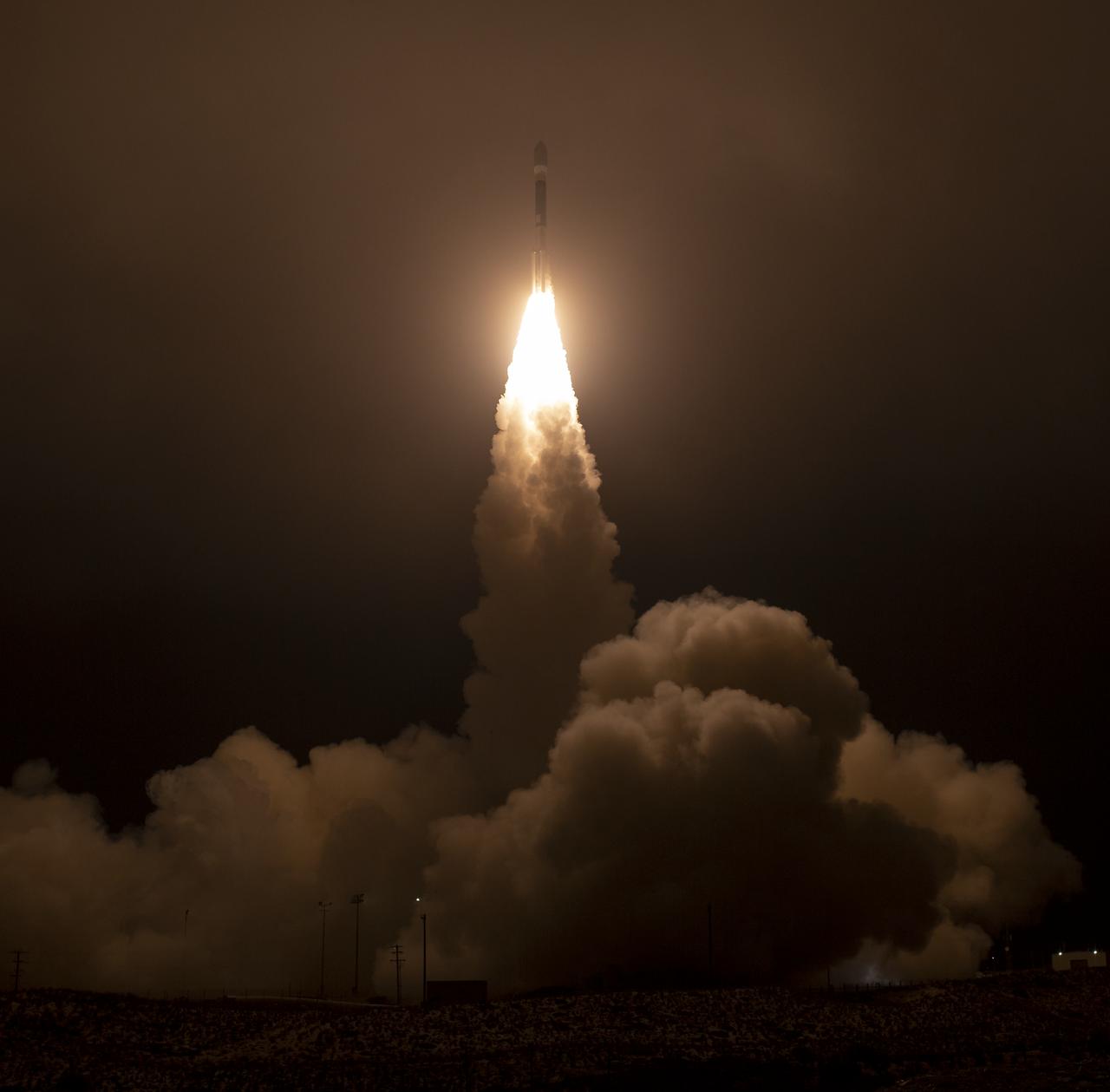

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
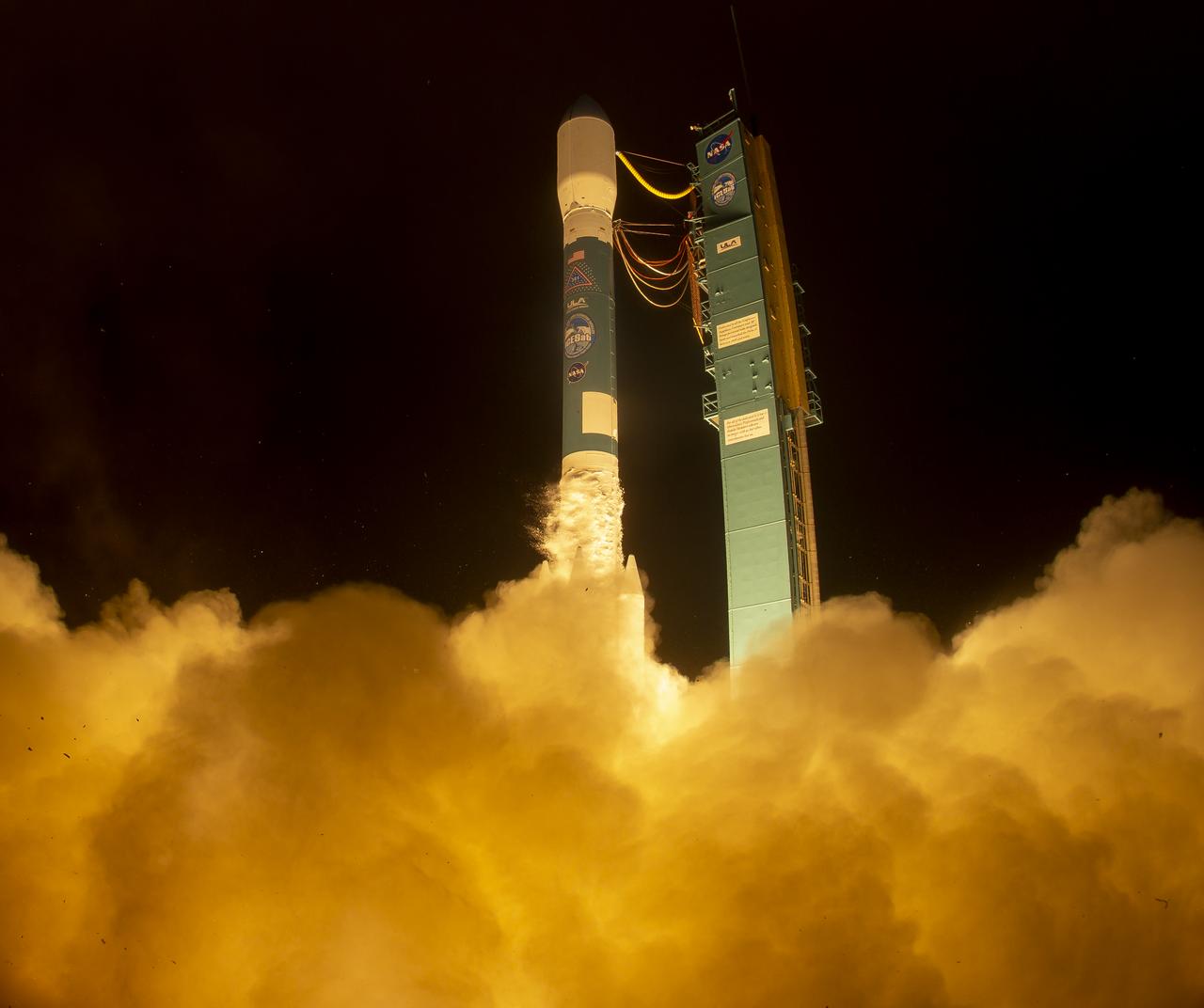

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket launches with the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onboard, Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
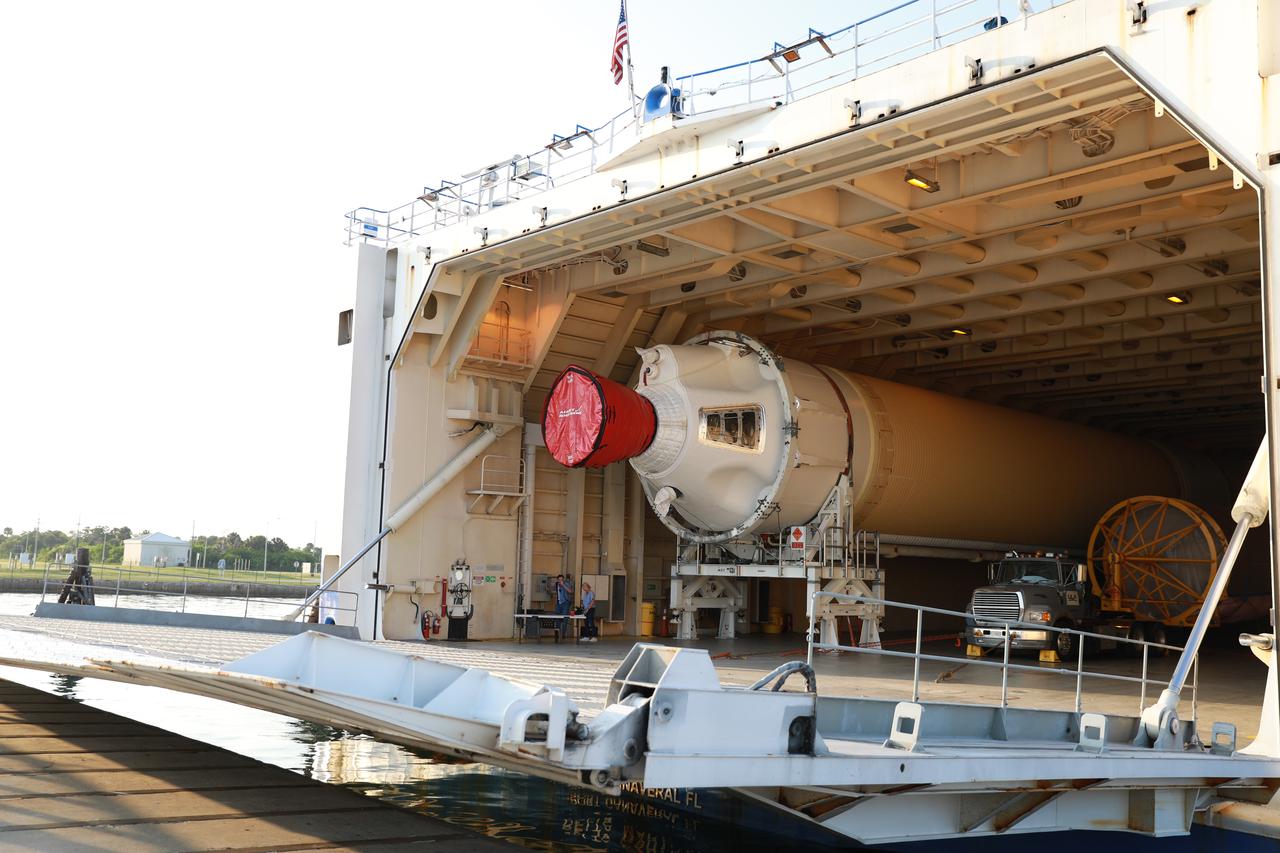

At the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo ship door is lowered on June 5, 2019, for offloading of the ULA Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT). The Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its mission. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

At the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo ship door is lowered on June 5, 2019, for offloading of the ULA Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT). The Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its mission. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
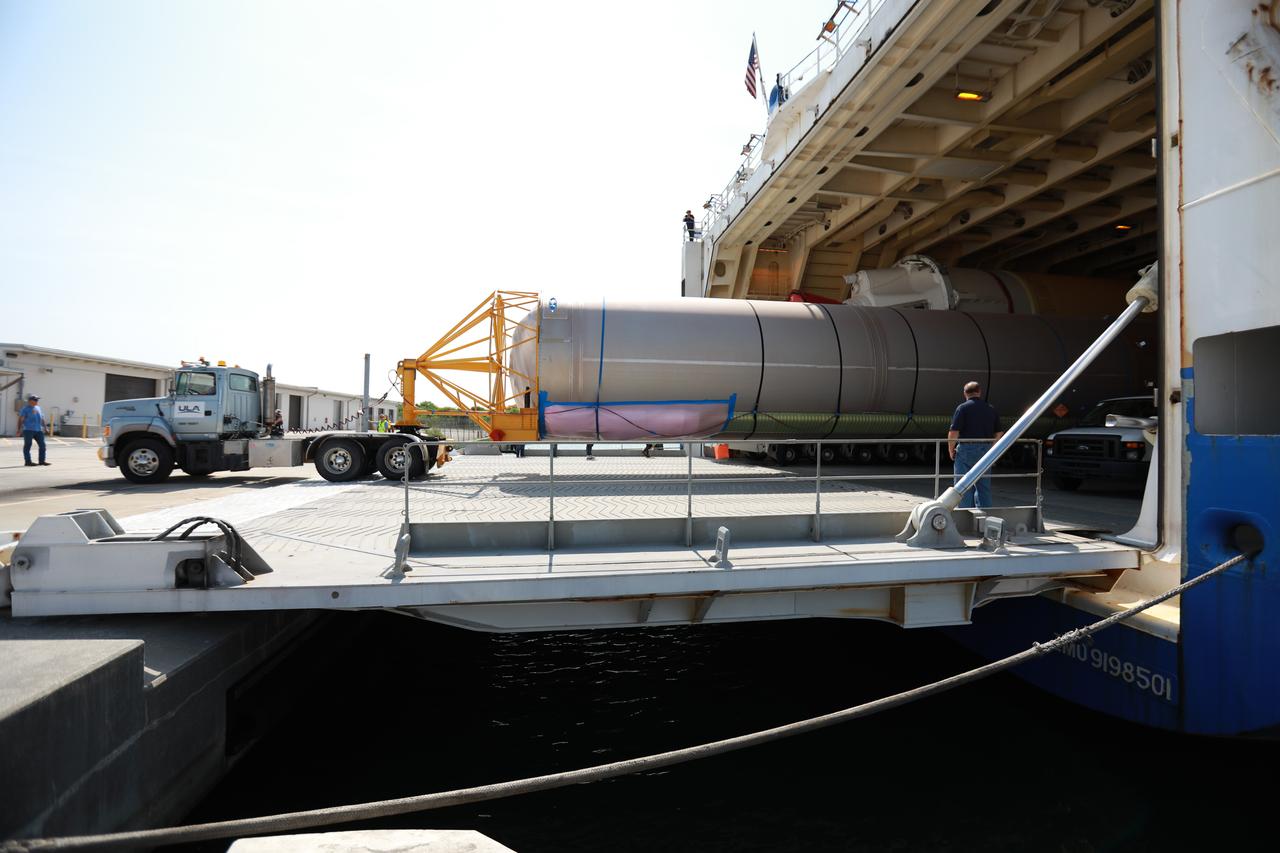

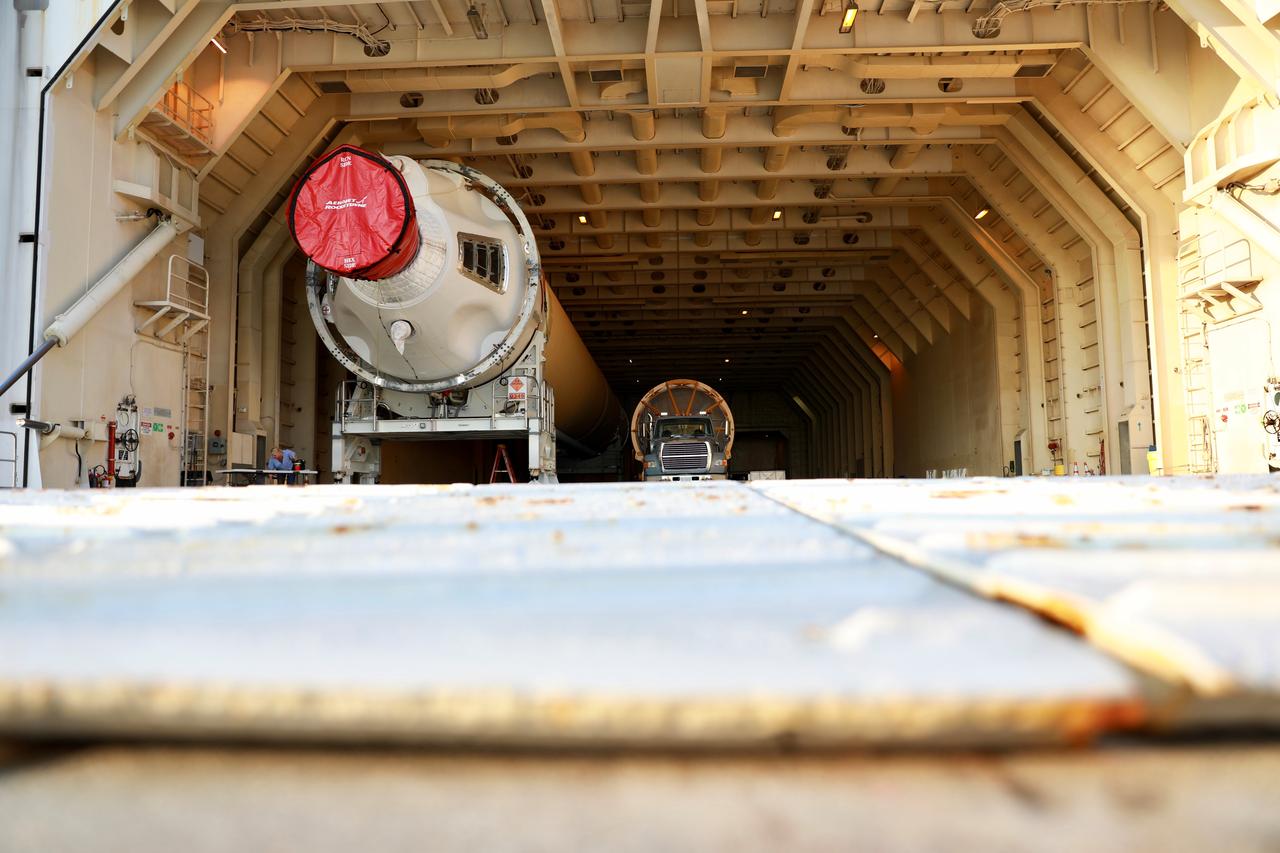
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
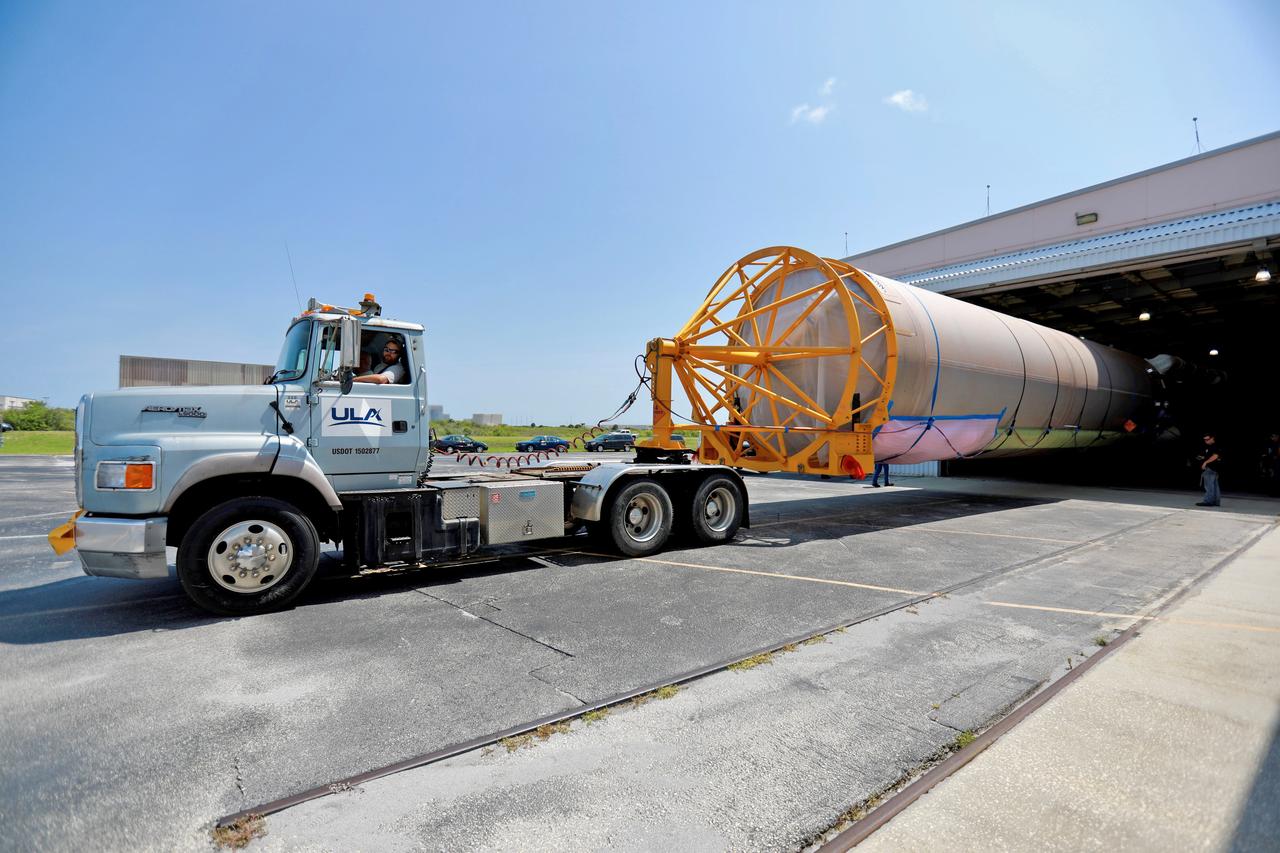

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is backed into the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Inside the ASOC, the booster will await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
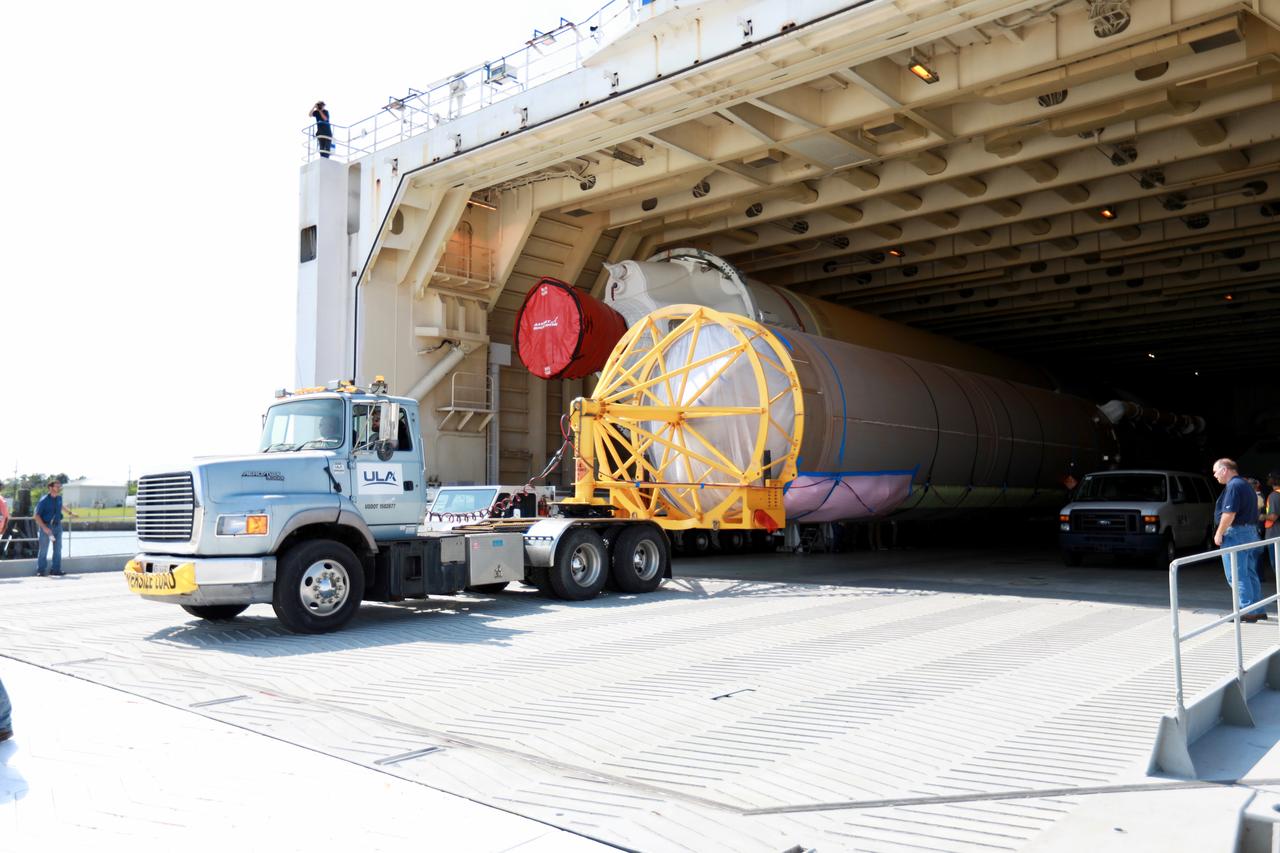

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
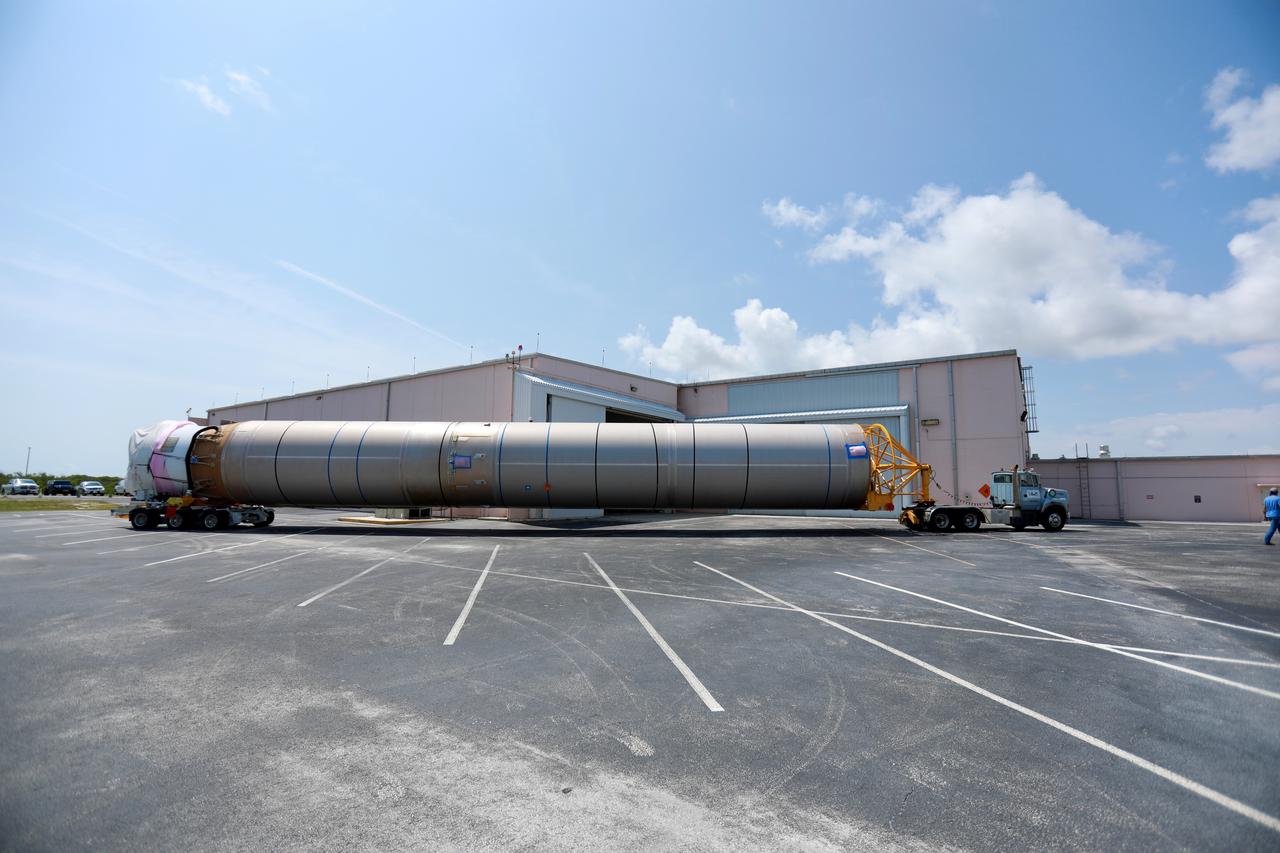

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) nears the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Inside the ASOC, the booster will await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
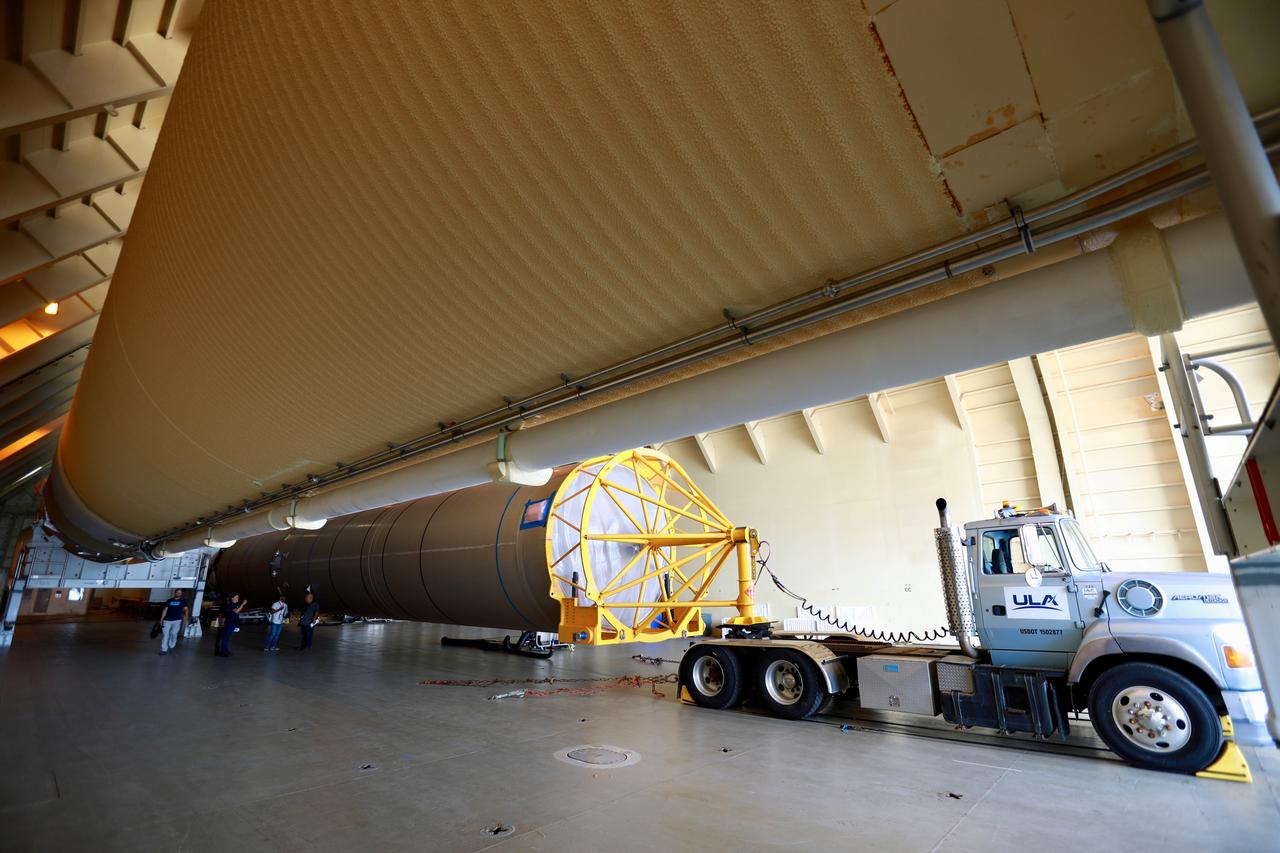

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
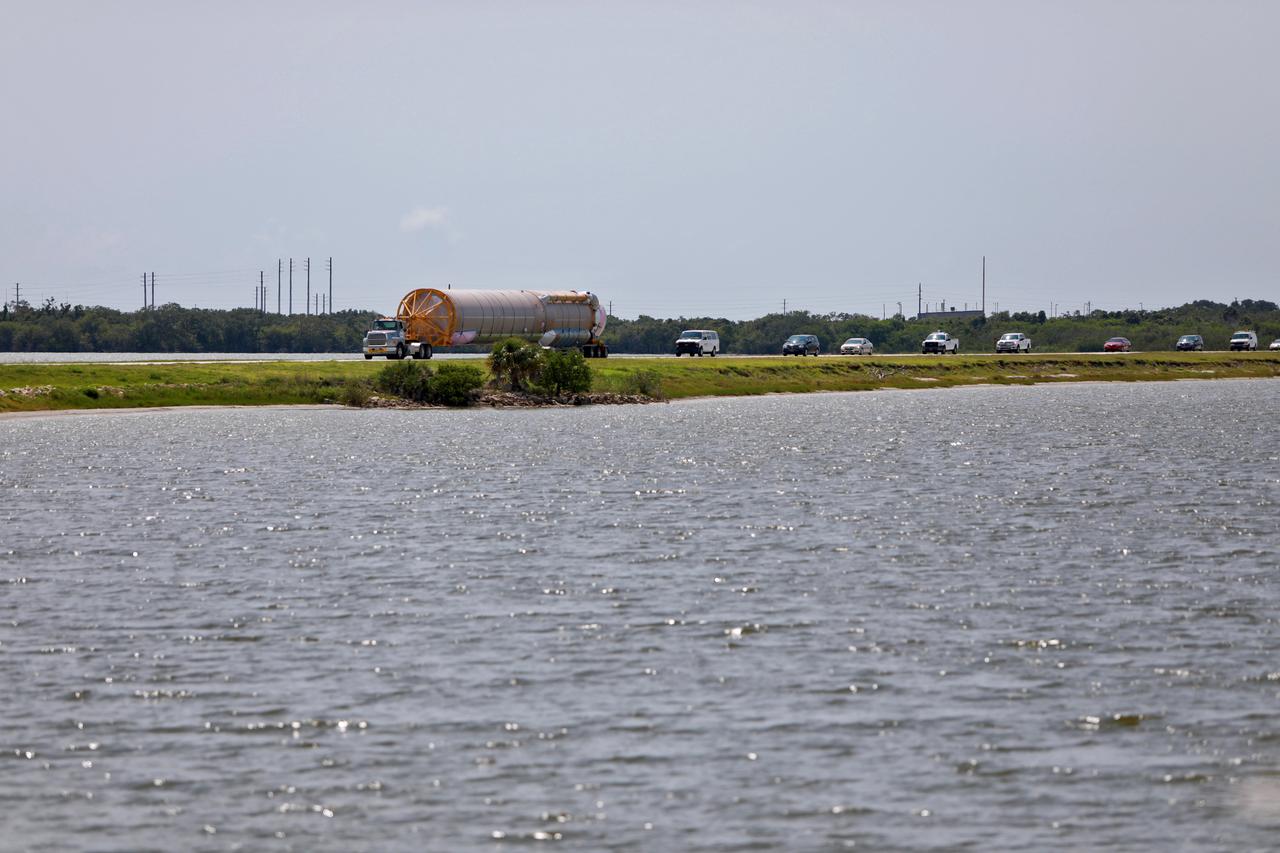

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is being transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Inside the ASOC, the booster will await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
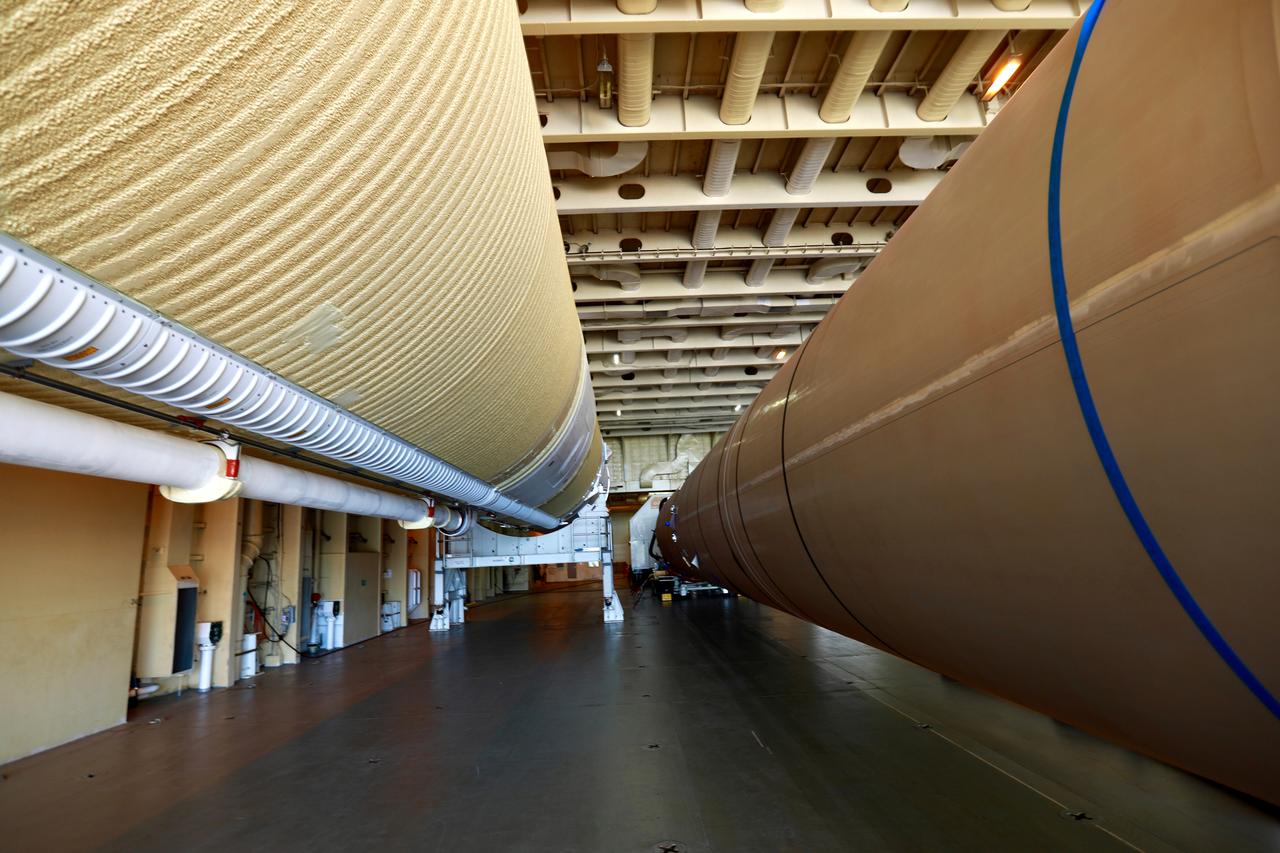

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
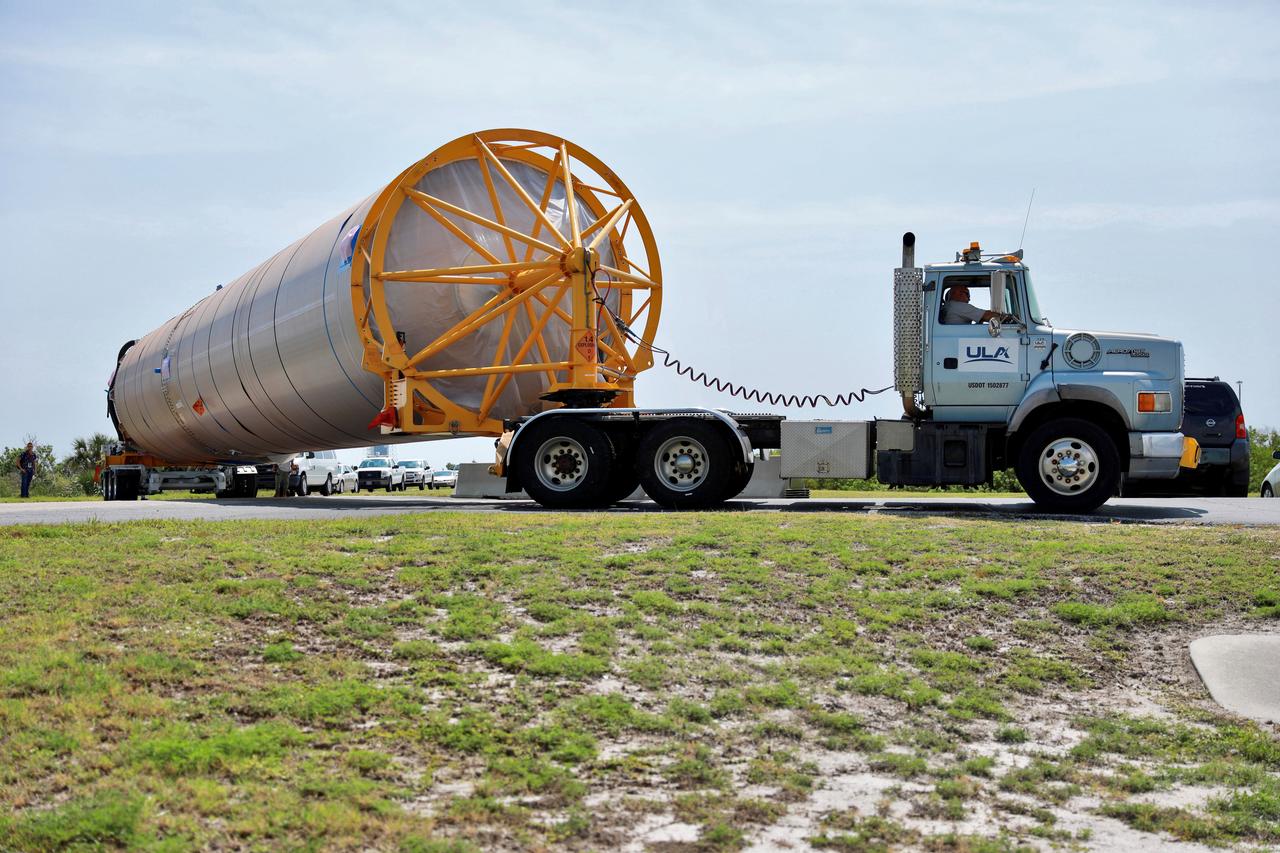

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) nears the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Inside the ASOC, the booster will await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
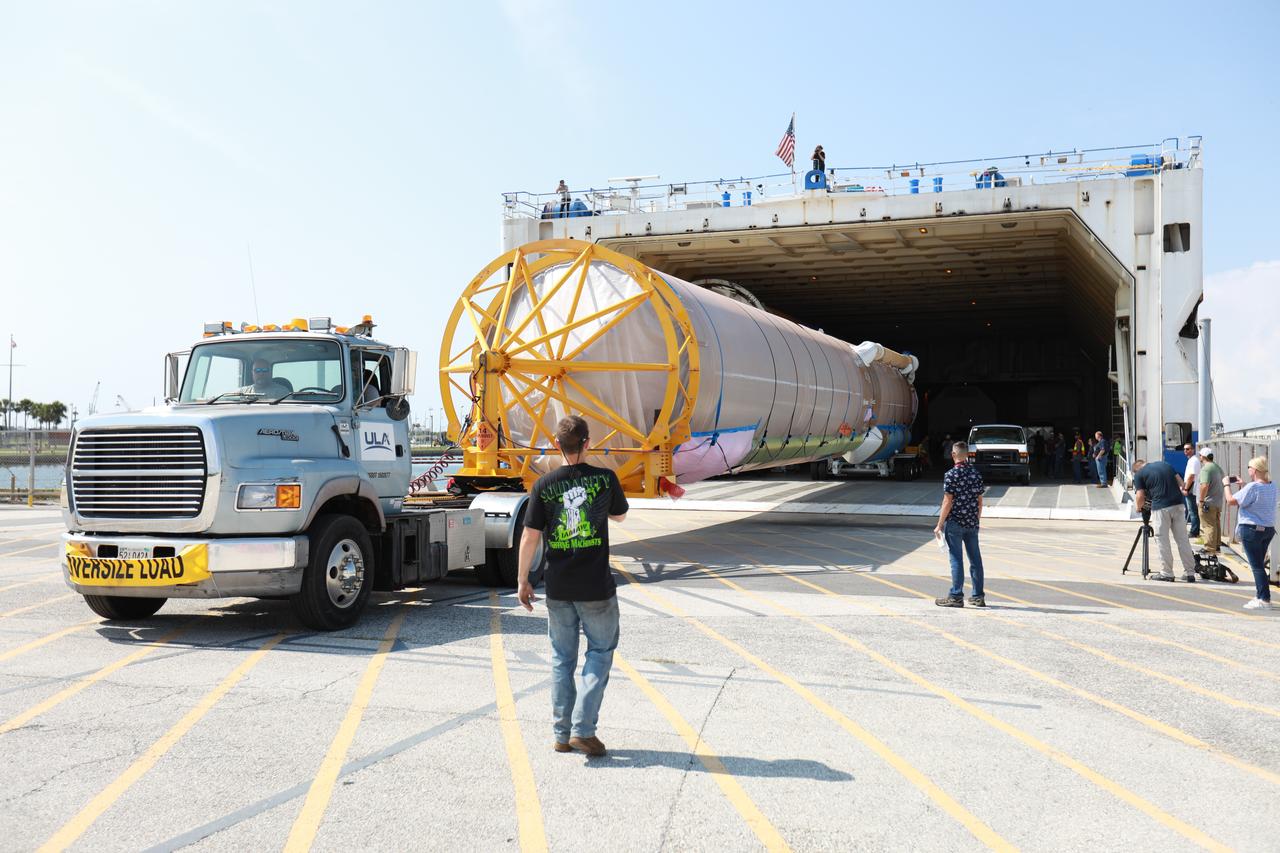

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
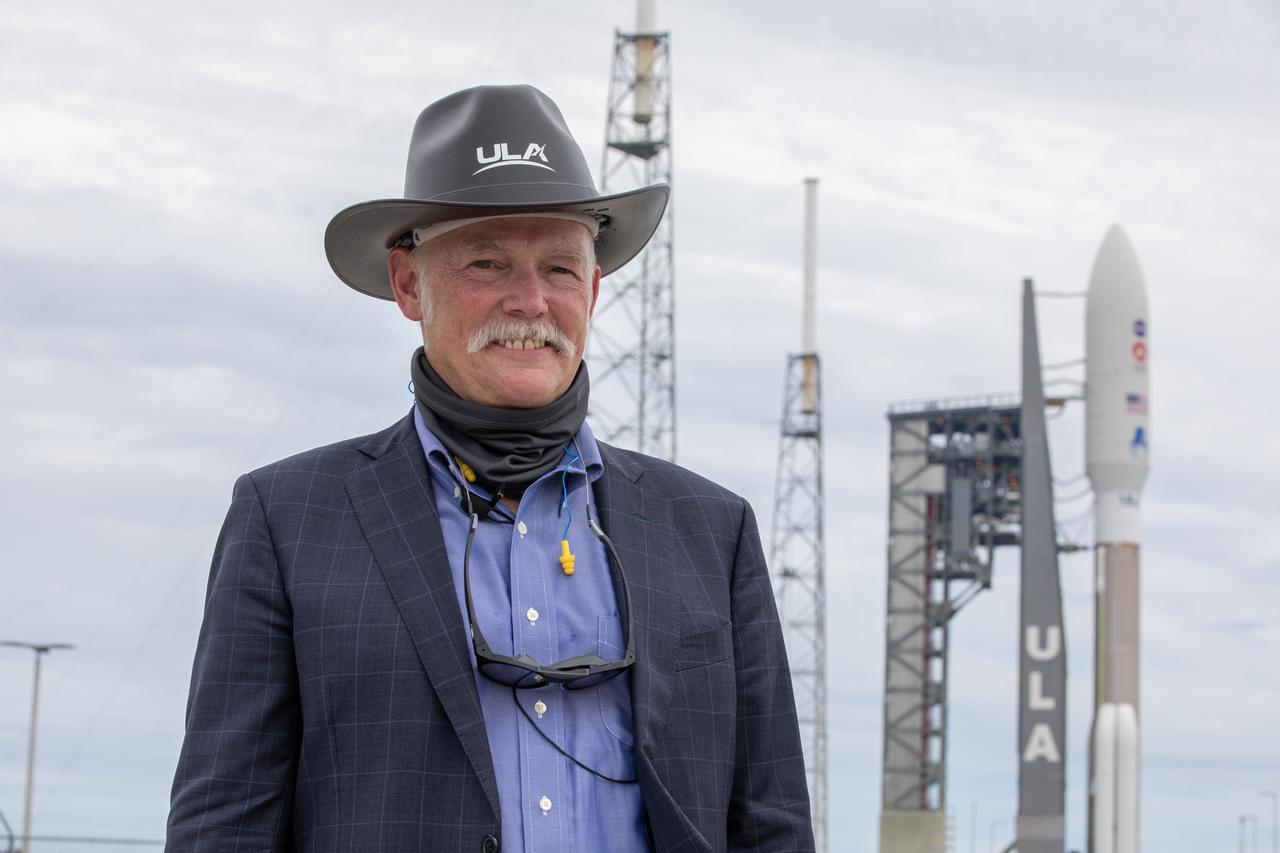

Tory Bruno, CEO of United Launch Alliance (ULA), attends the rollout of the ULA Atlas V 541 rocket, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter, as it rolls along to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on July 28, 2020. First motion was at 10:24 a.m. EDT. Launch of the Mars 2020 mission is scheduled for July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
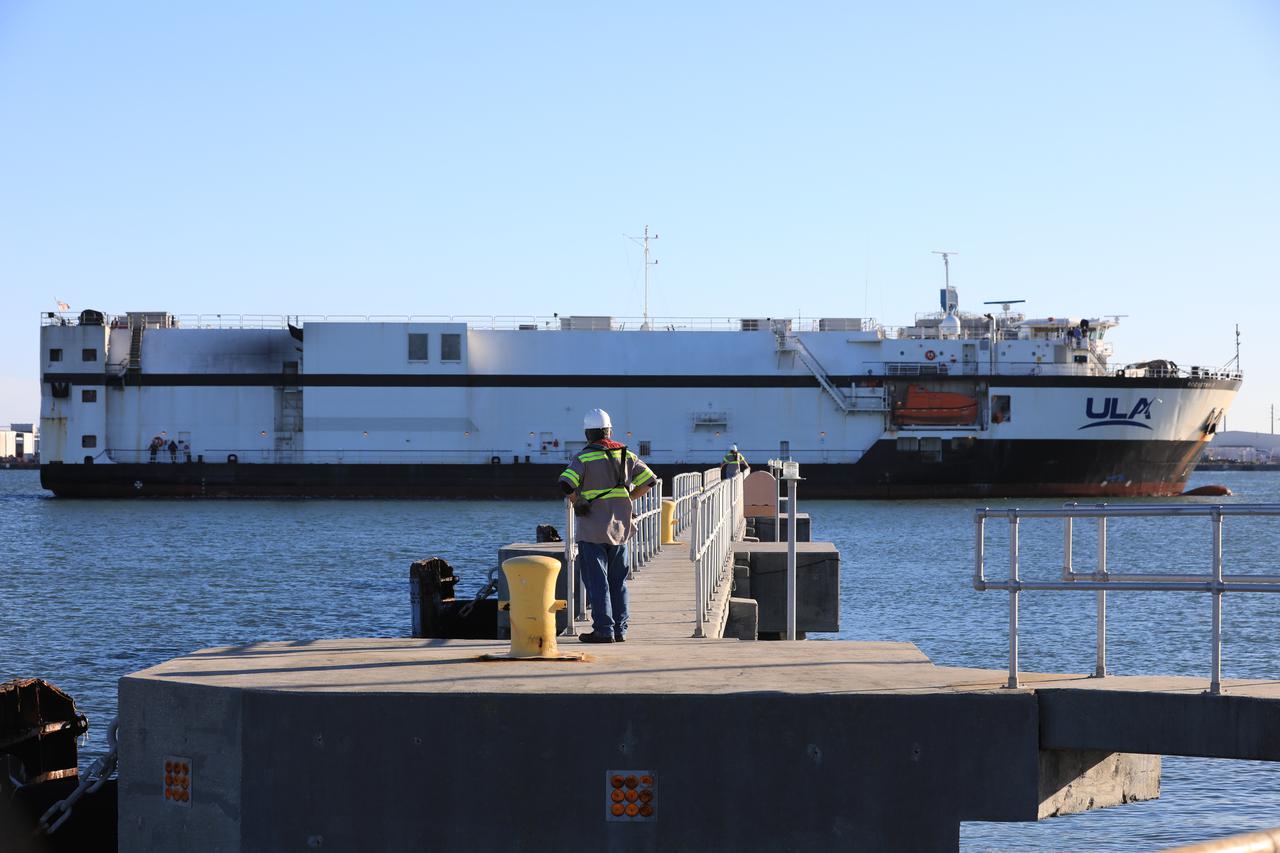

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
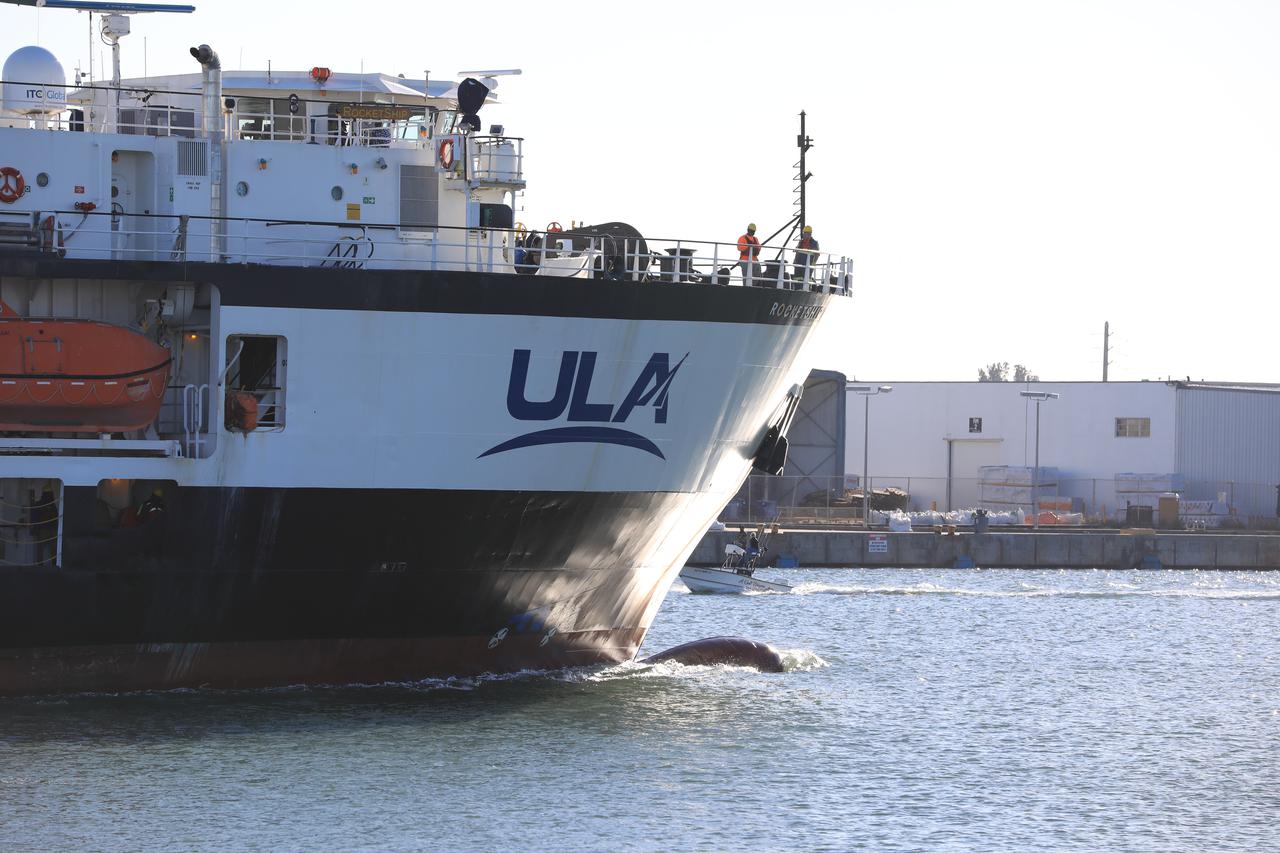

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
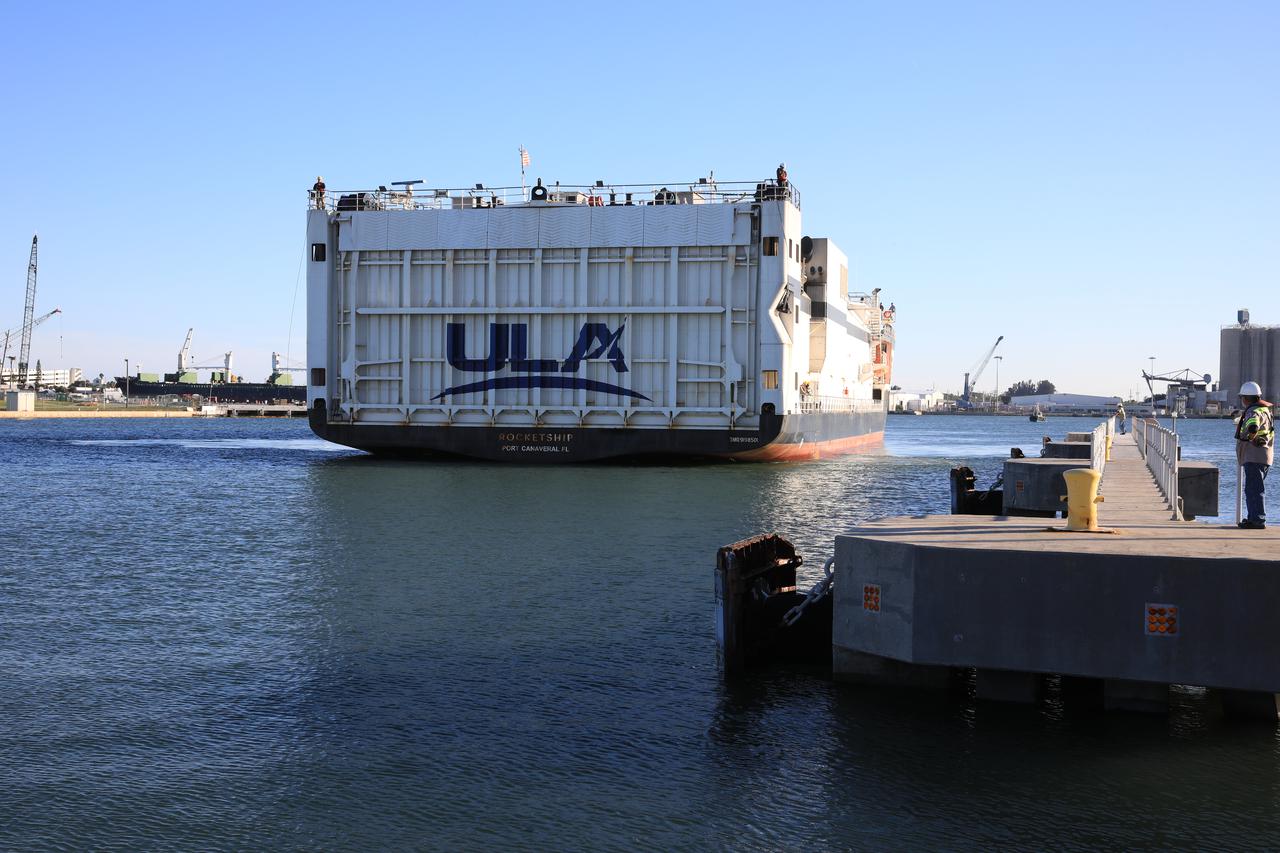

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
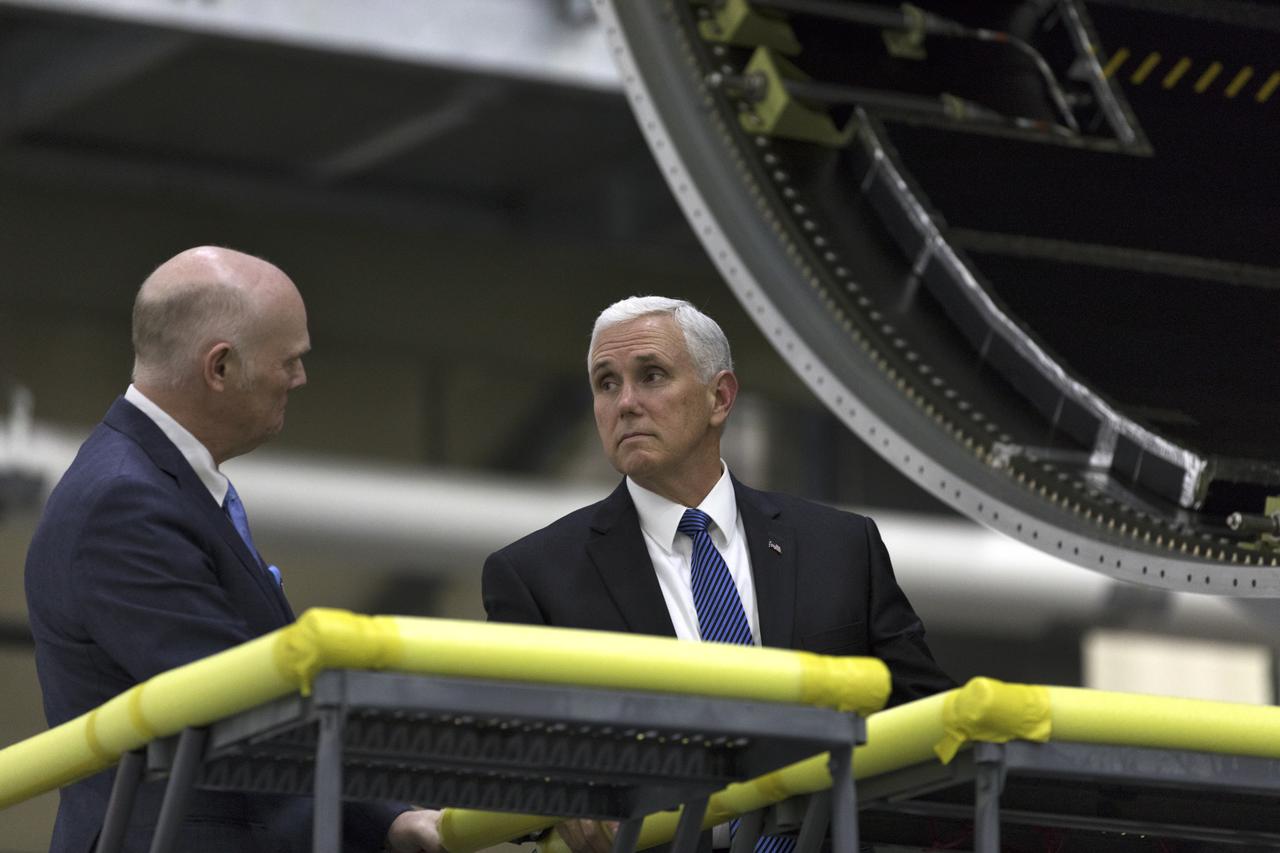

United Launch Alliance (ULA) president and CEO Tory Bruno, left, leads a tour for Vice President Mike Pence on Feb. 20, 2018. They are in the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility (HIF), at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The HIF is where the Delta IV Heavy boosters are being processed for NASA’s upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
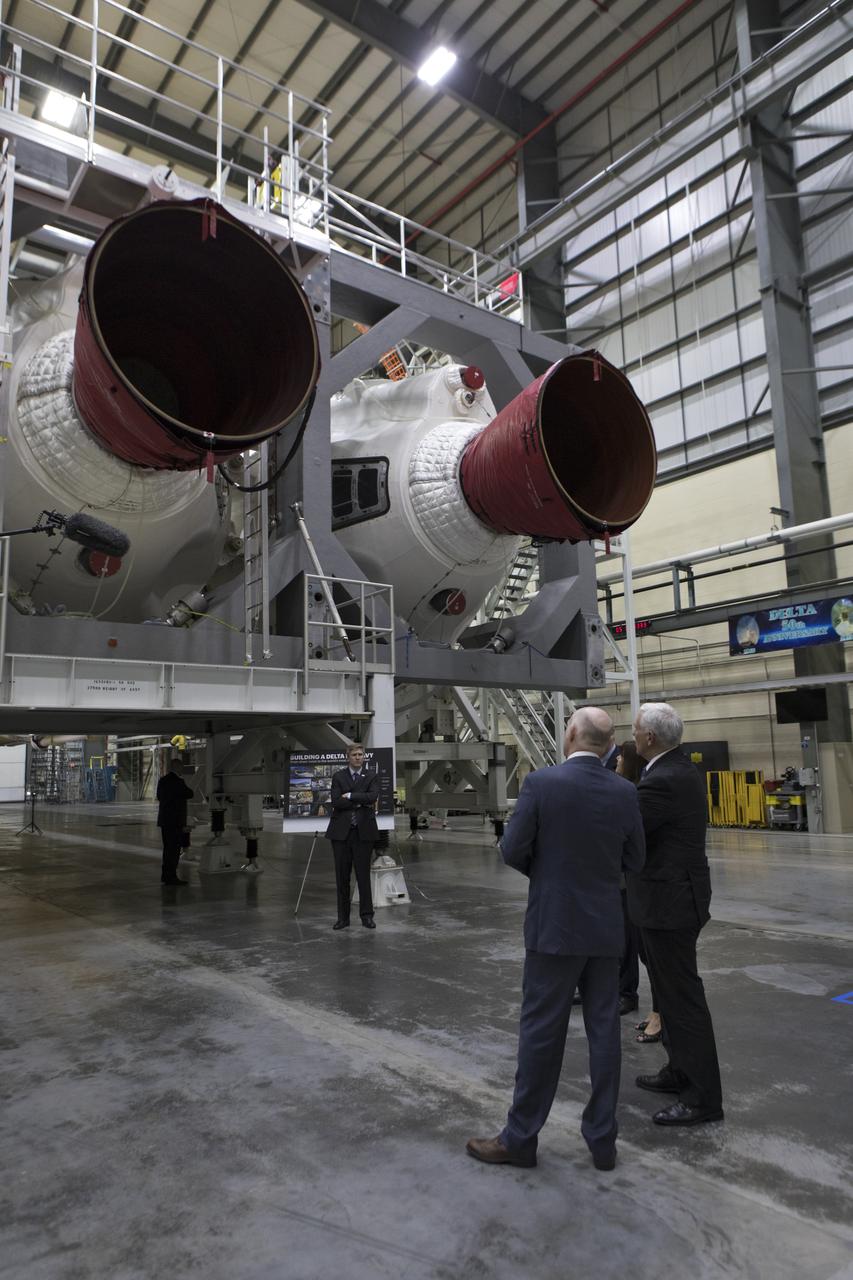

United Launch Alliance (ULA) president and CEO Tory Bruno, left, leads a tour in the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility (HIF), at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for Vice President Mike Pence on Feb. 20, 2018. The HIF is where the Delta IV Heavy boosters are being processed for NASA’s upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
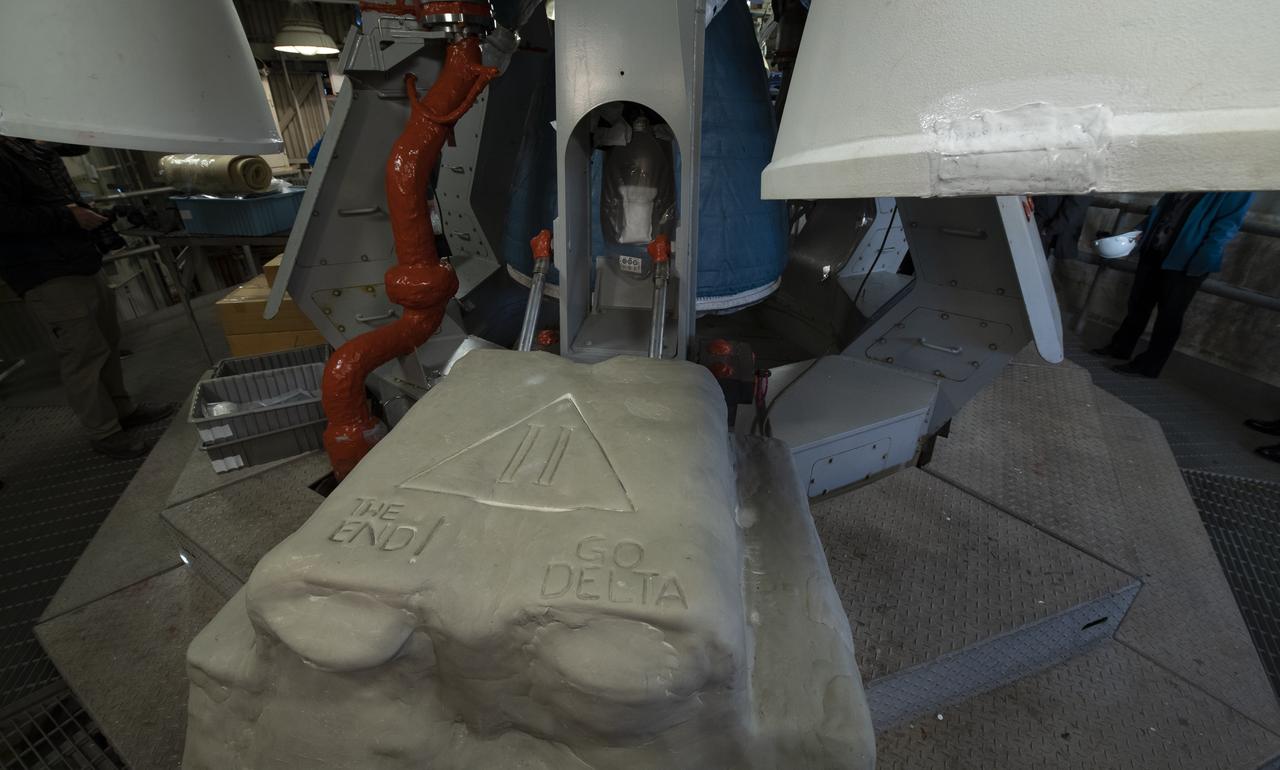

Base of the SLC-2 launch pad is embossed with well wishes for the final launch of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, Thursday, Sept. 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ULA launched NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Saturday, Sept. 15, 2018. The ICESat-2 mission will measure the changing height of Earth's ice. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
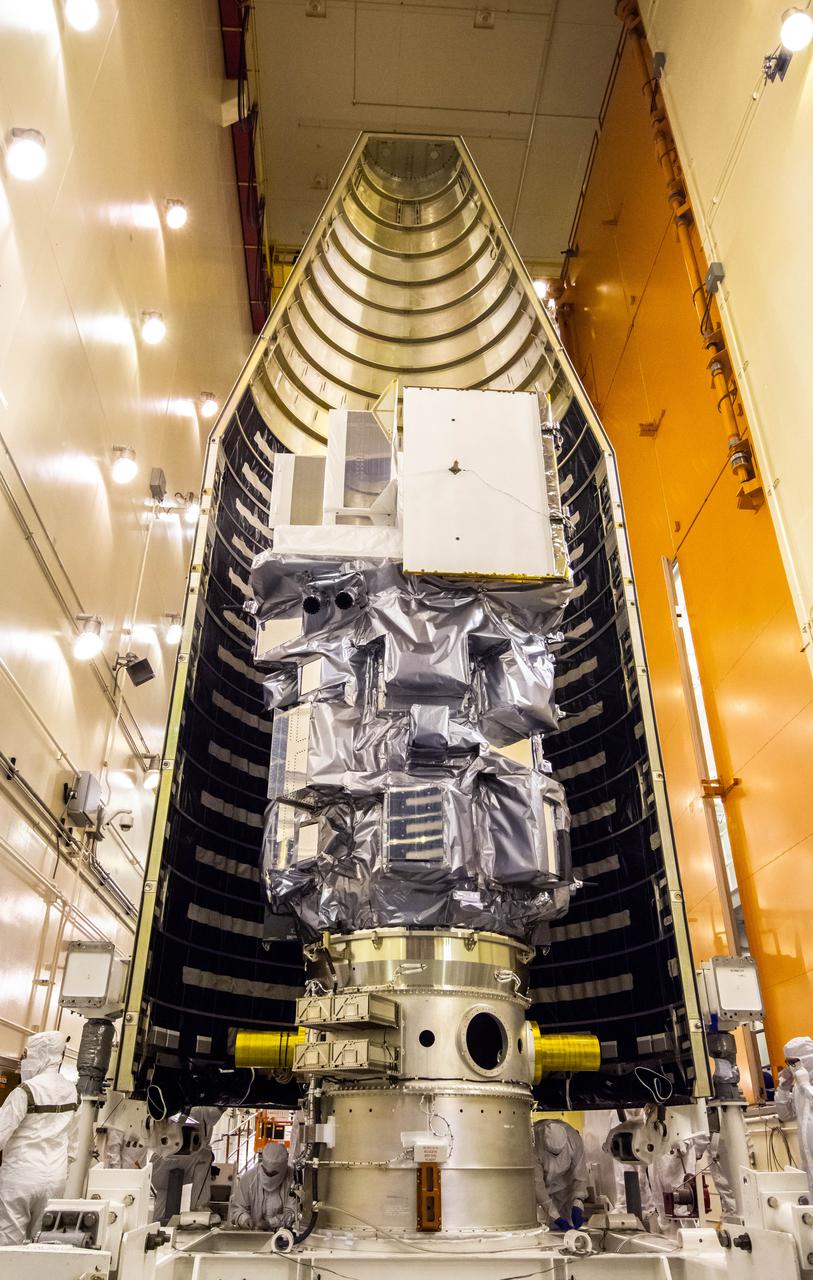

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft is moved into position for encapsulation on Aug. 16, 2021. The two halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing will surround and encase Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the Landsat 9 spacecraft is moved into position for encapsulation on Aug. 16, 2021. The two halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing will surround and encase Landsat 9 to protect it during launch atop the ULA Atlas V rocket. Landsat 9 will launch on the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.