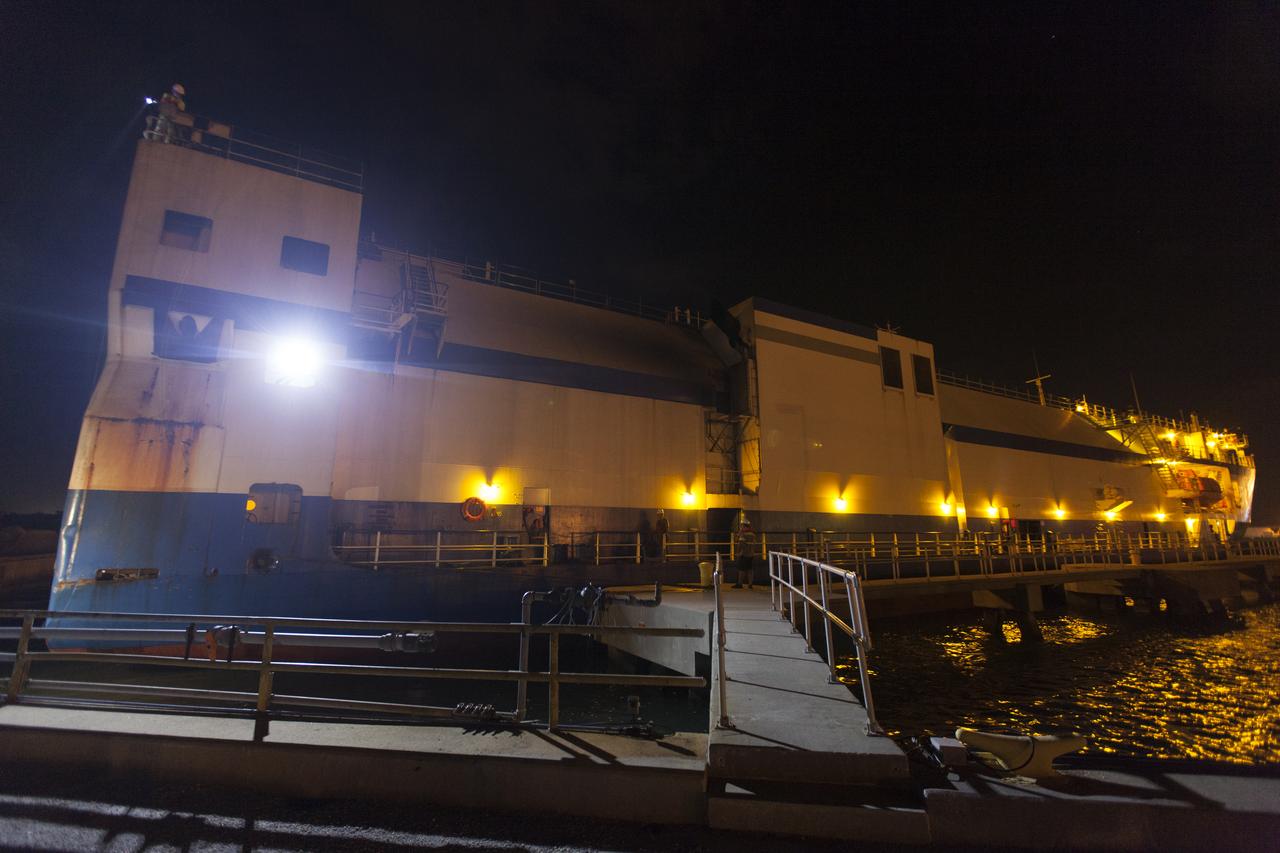

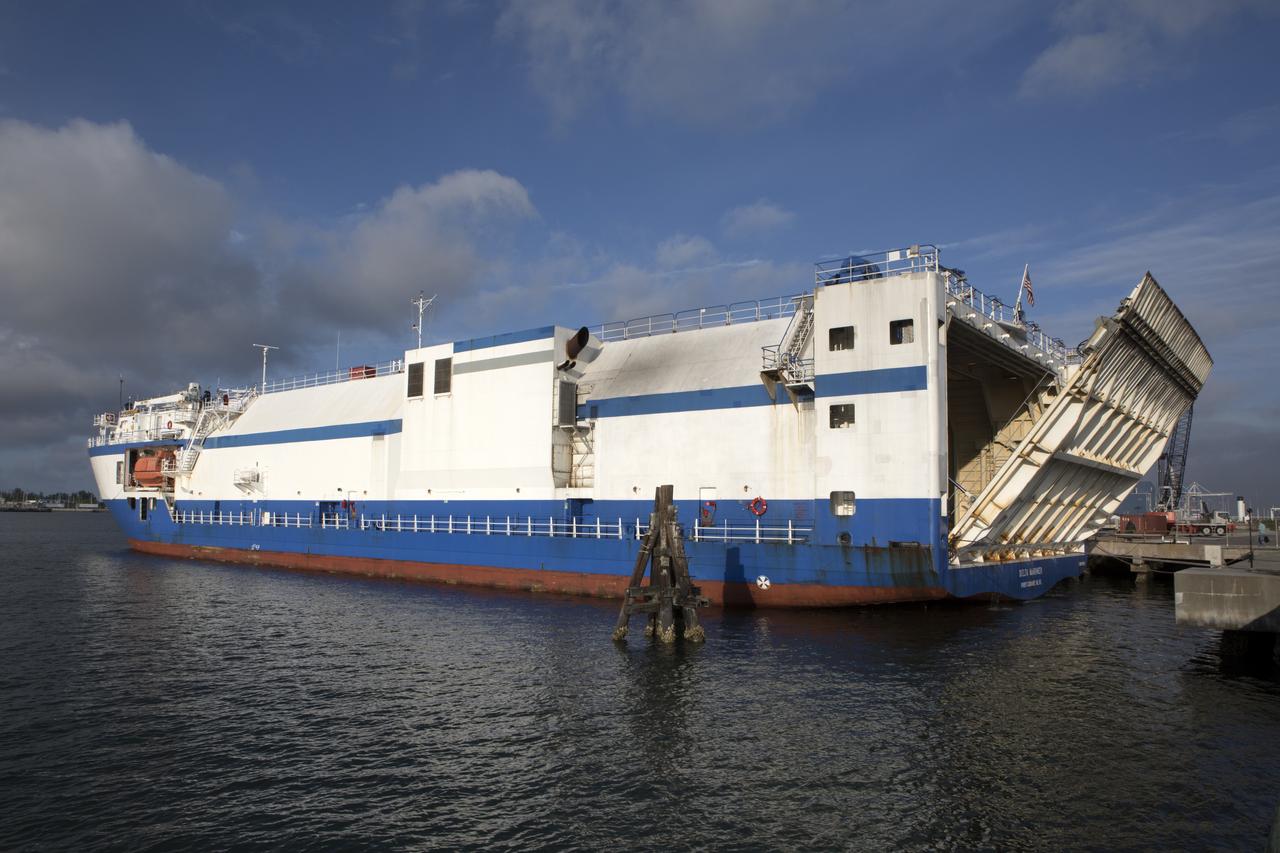
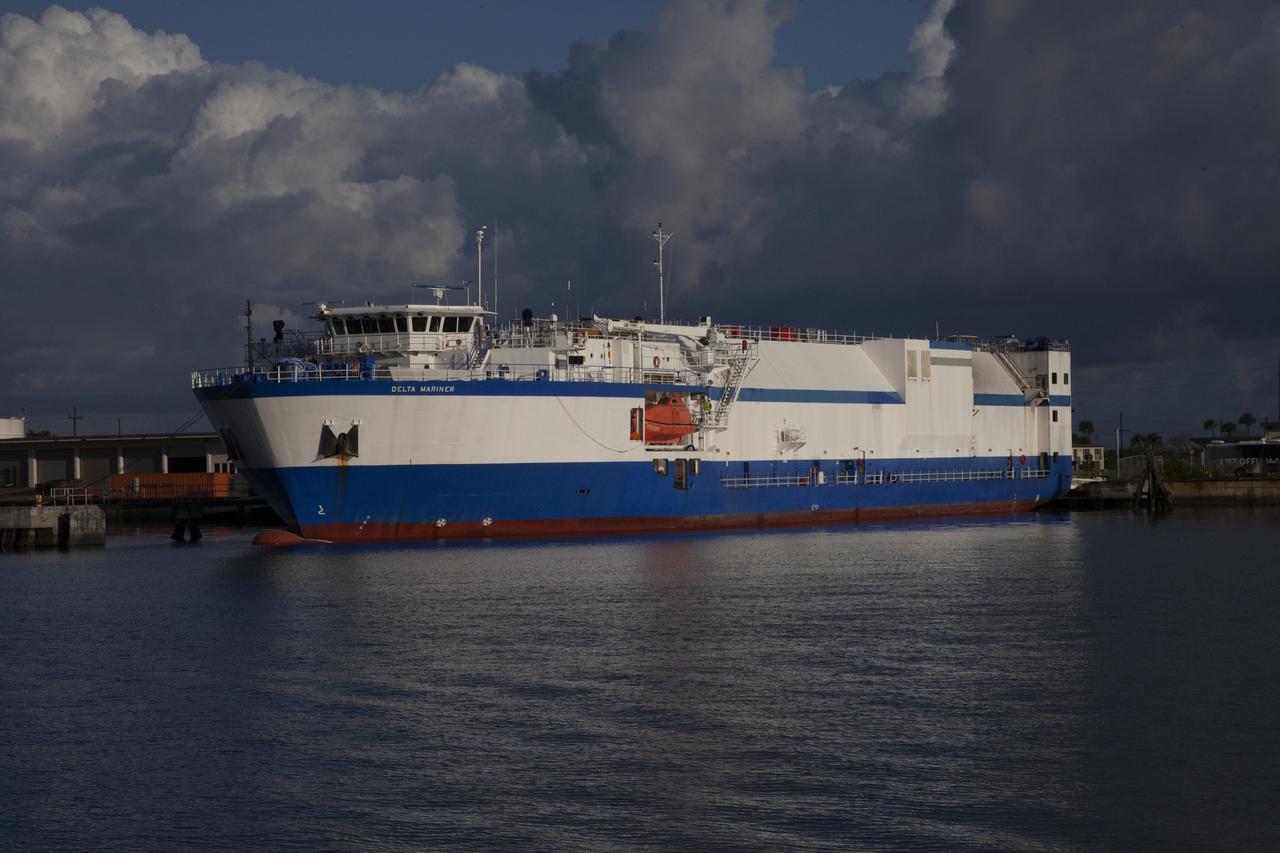
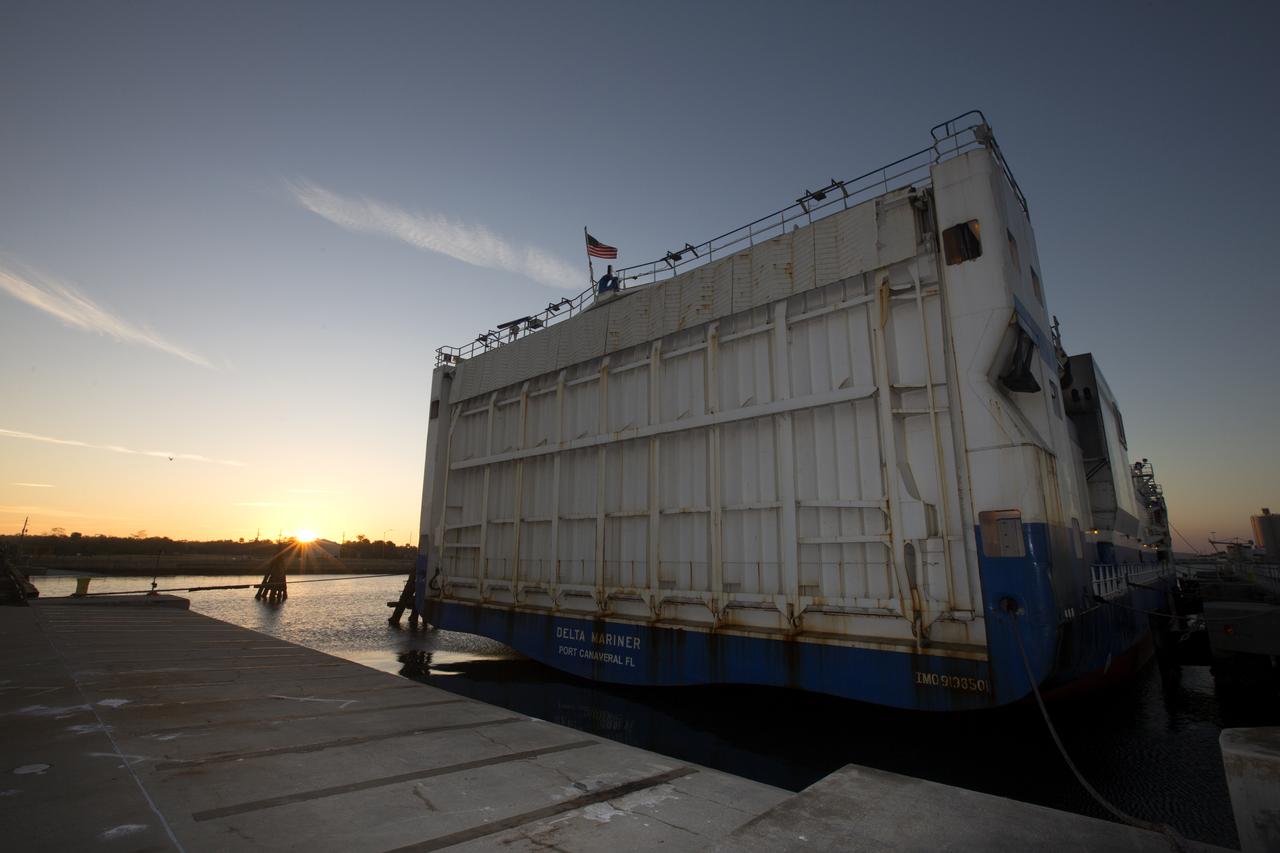
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner docks at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying two of the three Delta IV Heavy Common Booster Cores for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
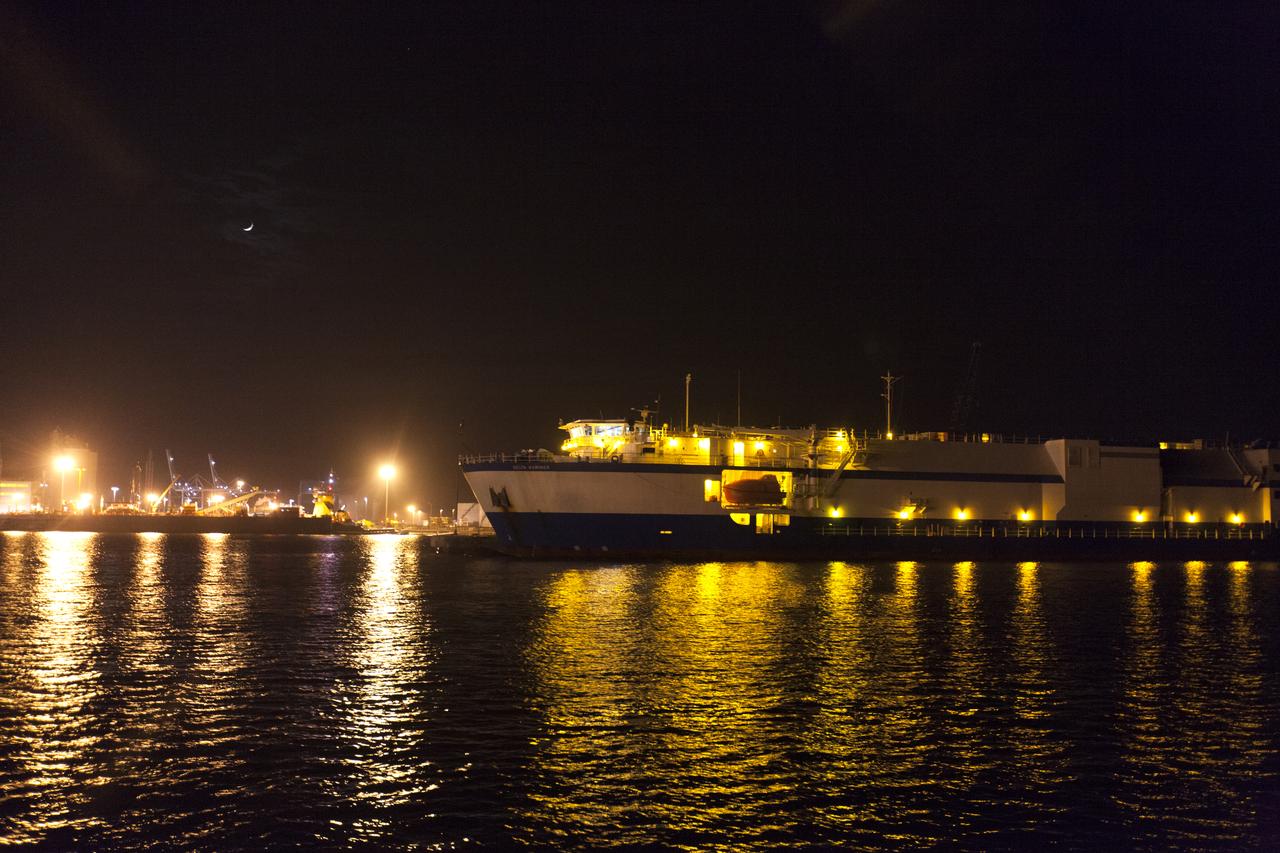

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner docks at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying two of the three Delta IV Heavy Common Booster Cores for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
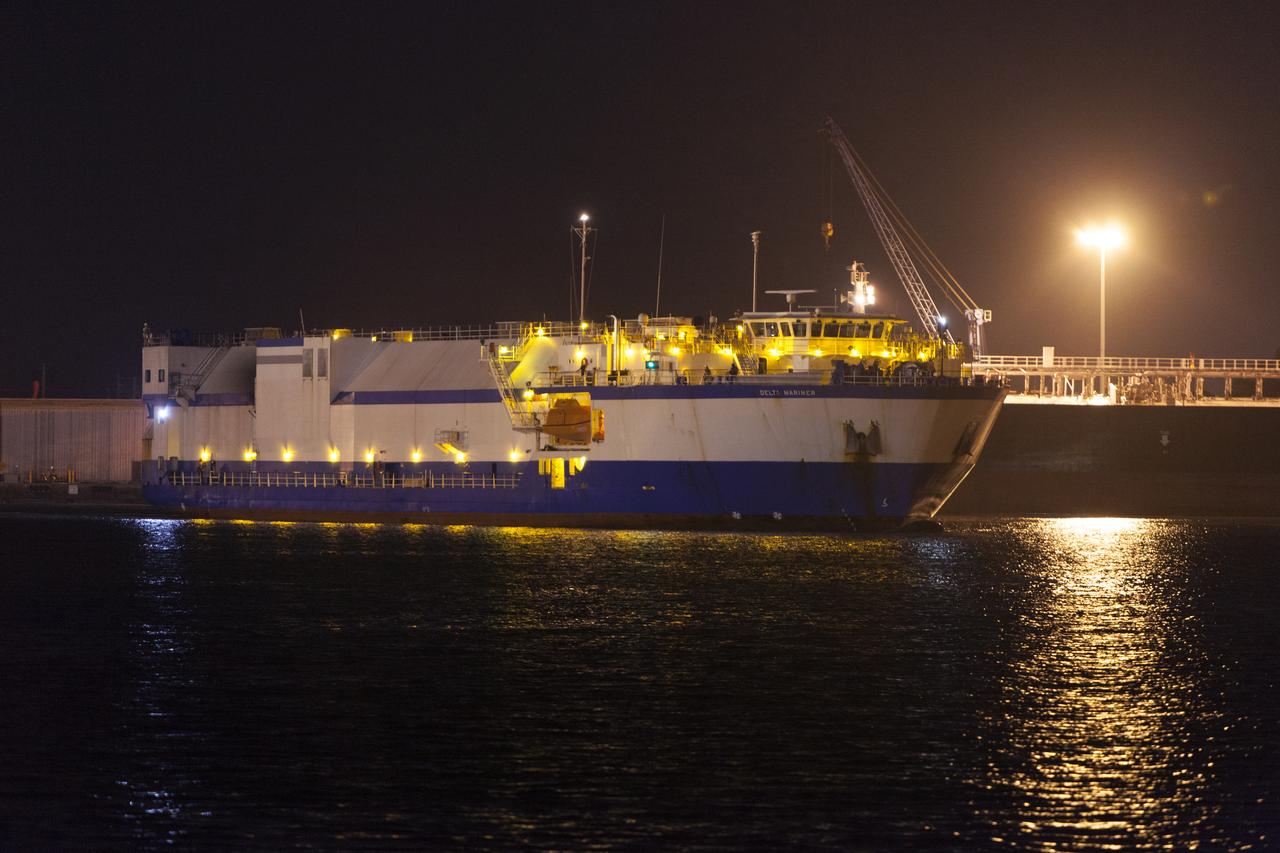

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying two of the three Delta IV Heavy Common Booster Cores for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.

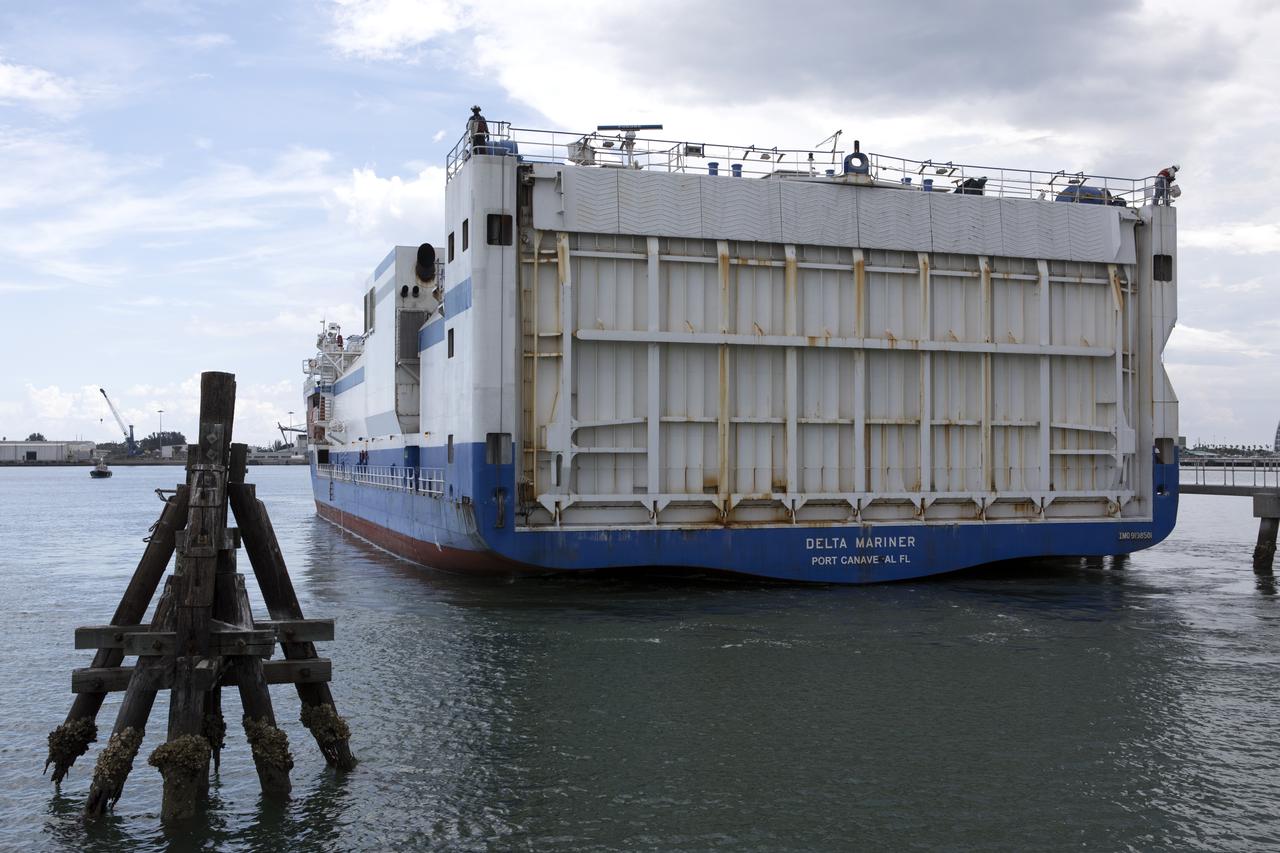
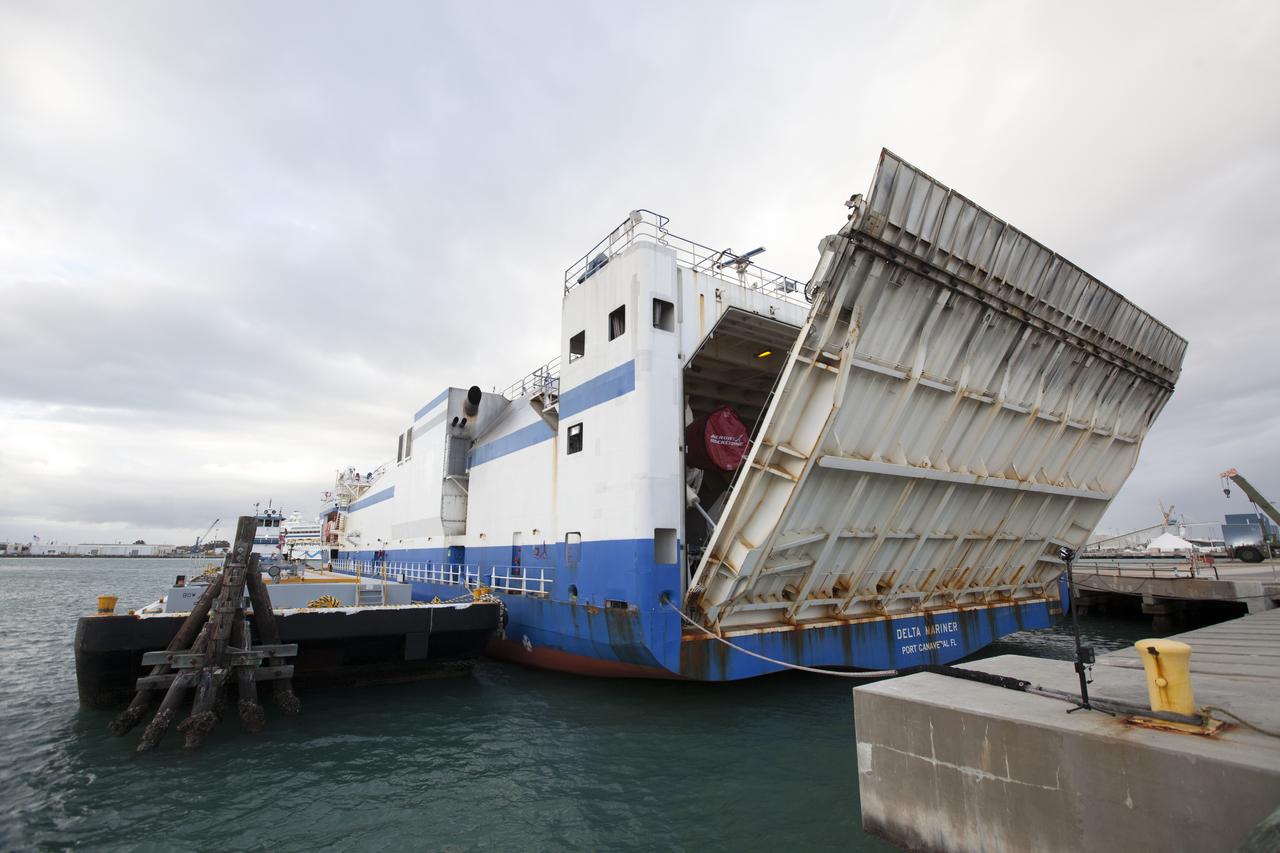
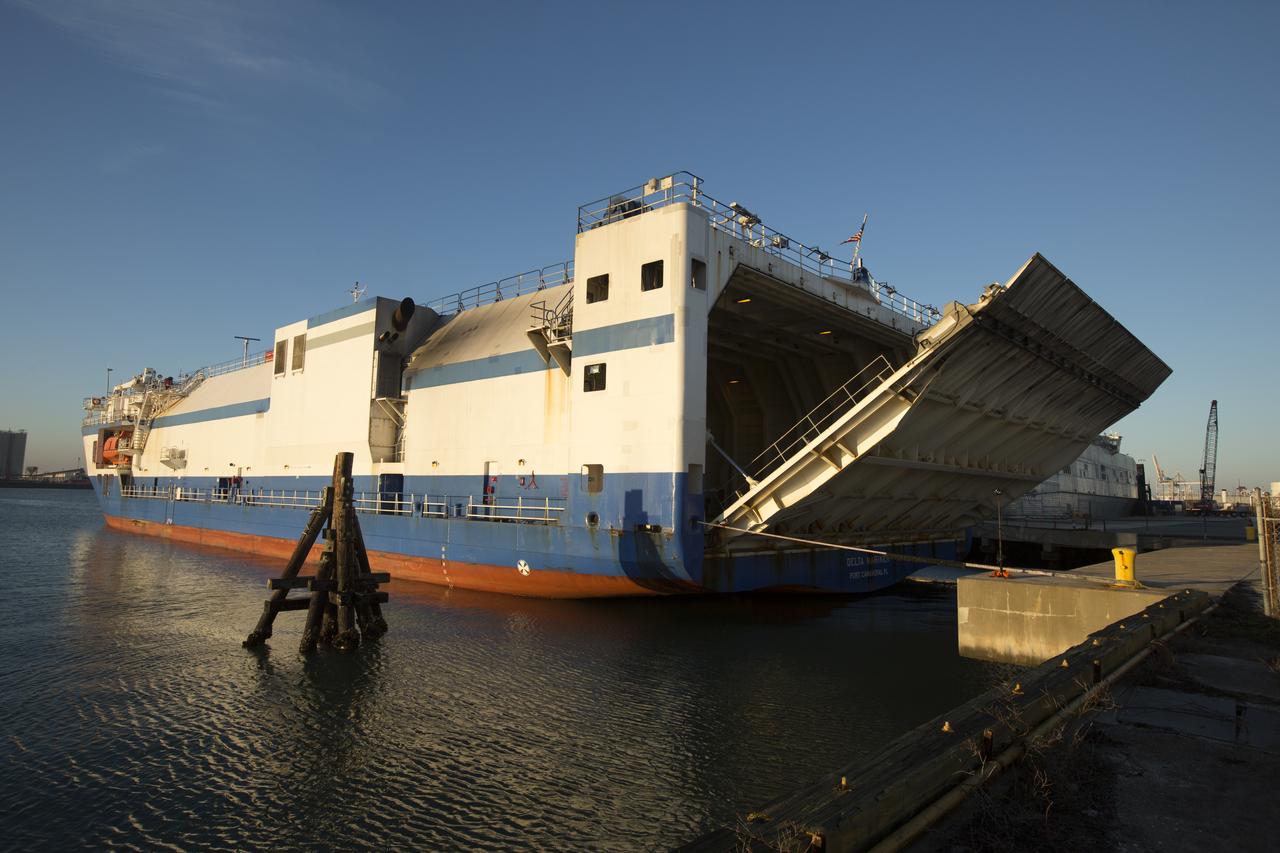
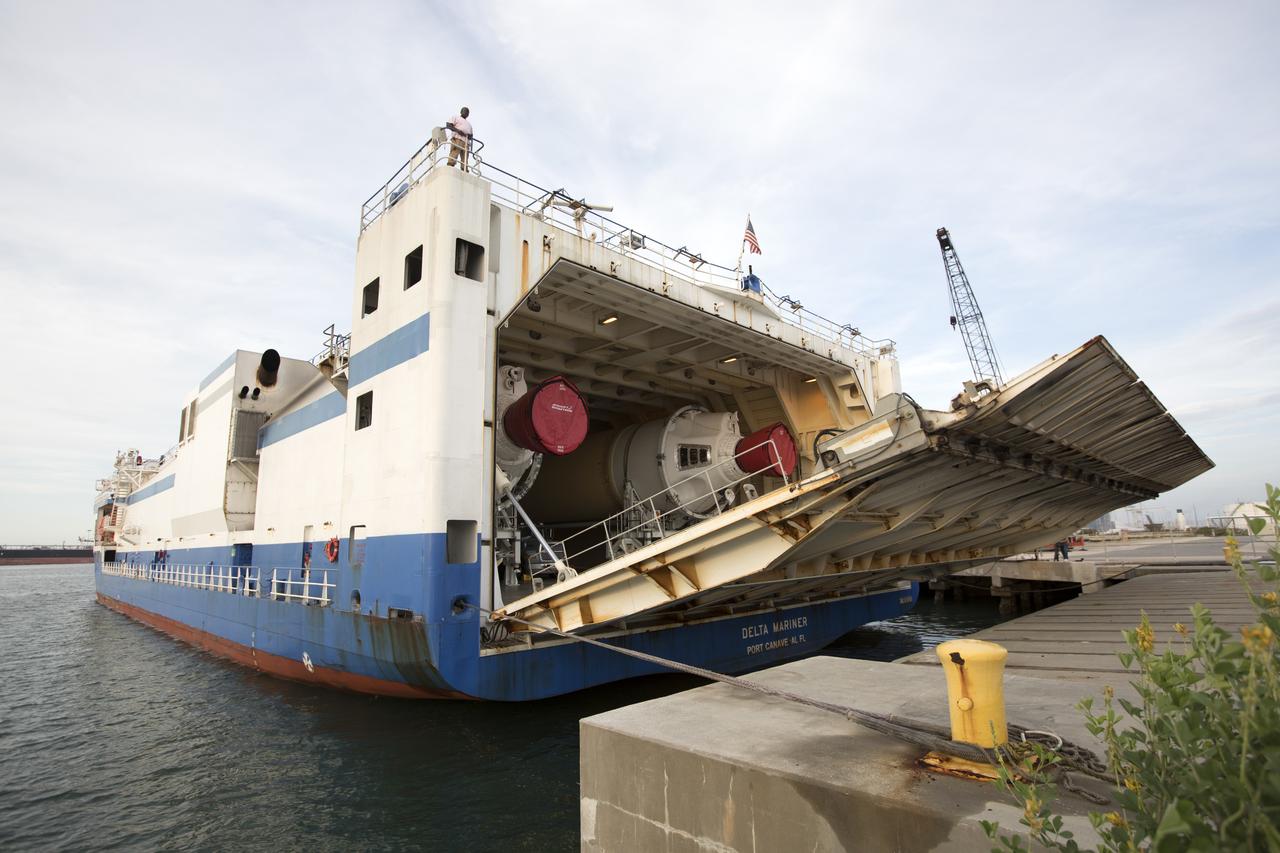
At the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo ship door is lowered on June 5, 2019, for offloading of the ULA Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT). The Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its mission. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

At the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo ship door is lowered on June 5, 2019, for offloading of the ULA Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT). The Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its mission. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test (CFT) is moved out of the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 5, 2019. The ULA Atlas V rocket will launch the CST-100 Starliner and its crew, NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center to await the start of operations for its missions. The CFT will demonstrate Starliner and Atlas V’s ability to safely carry crew to and from the orbiting laboratory.
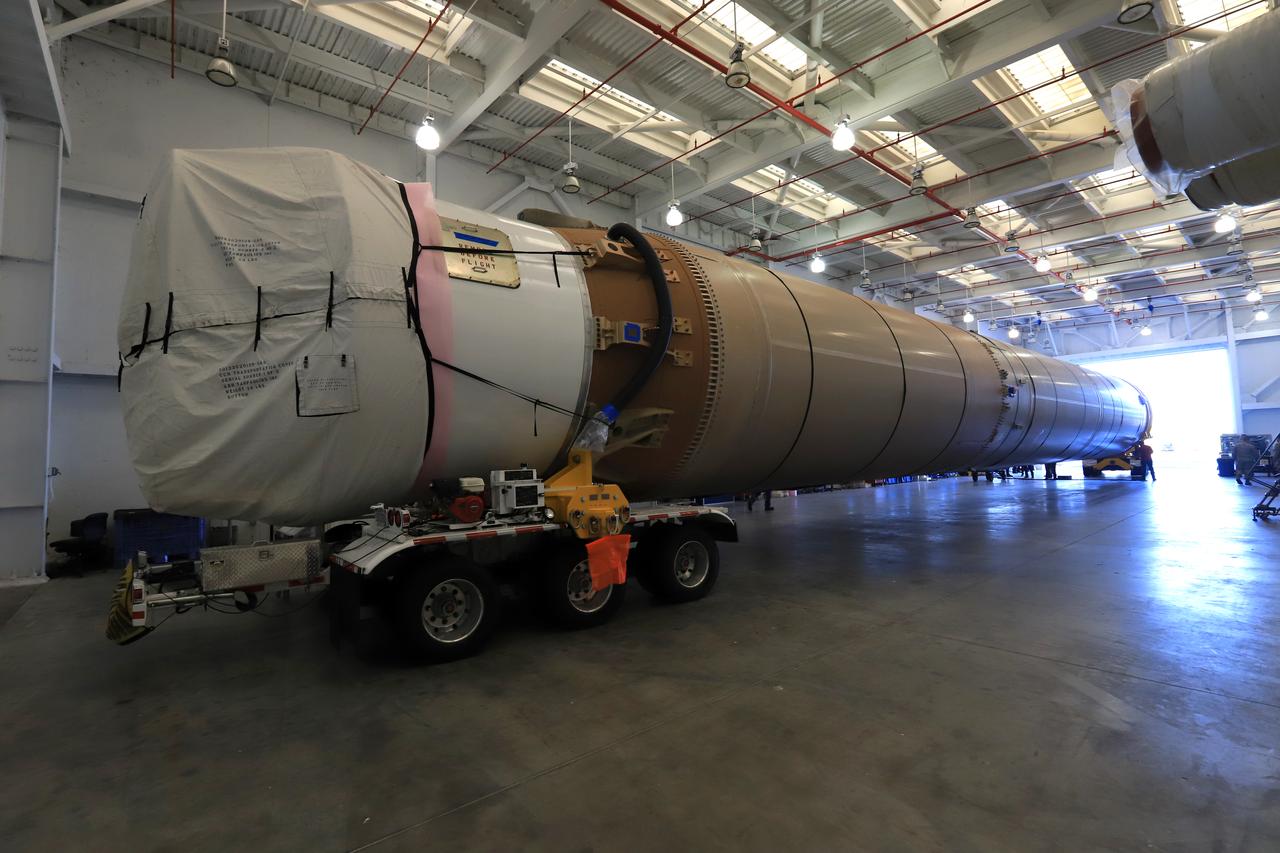

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrived at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo vessel arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018, carrying the first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

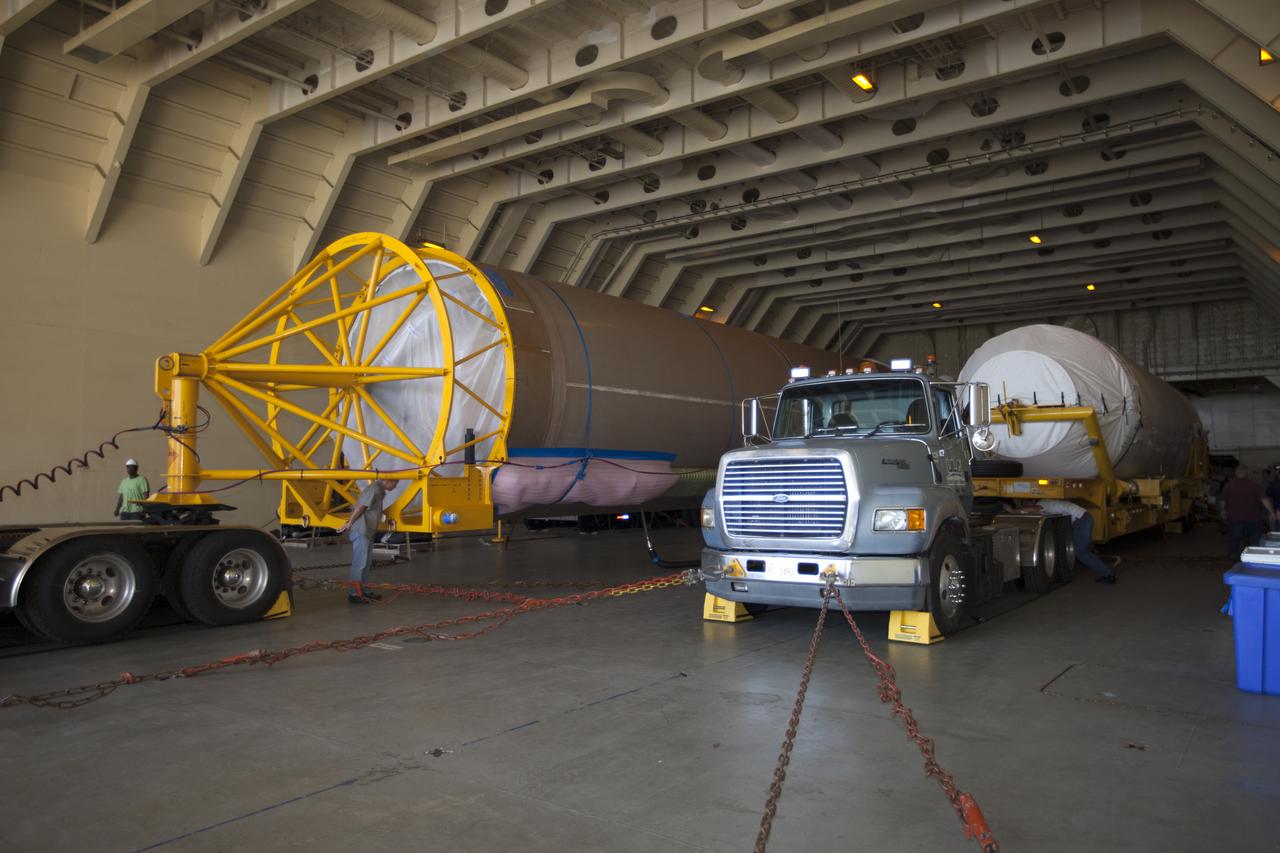
The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) was offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, and is being transported to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

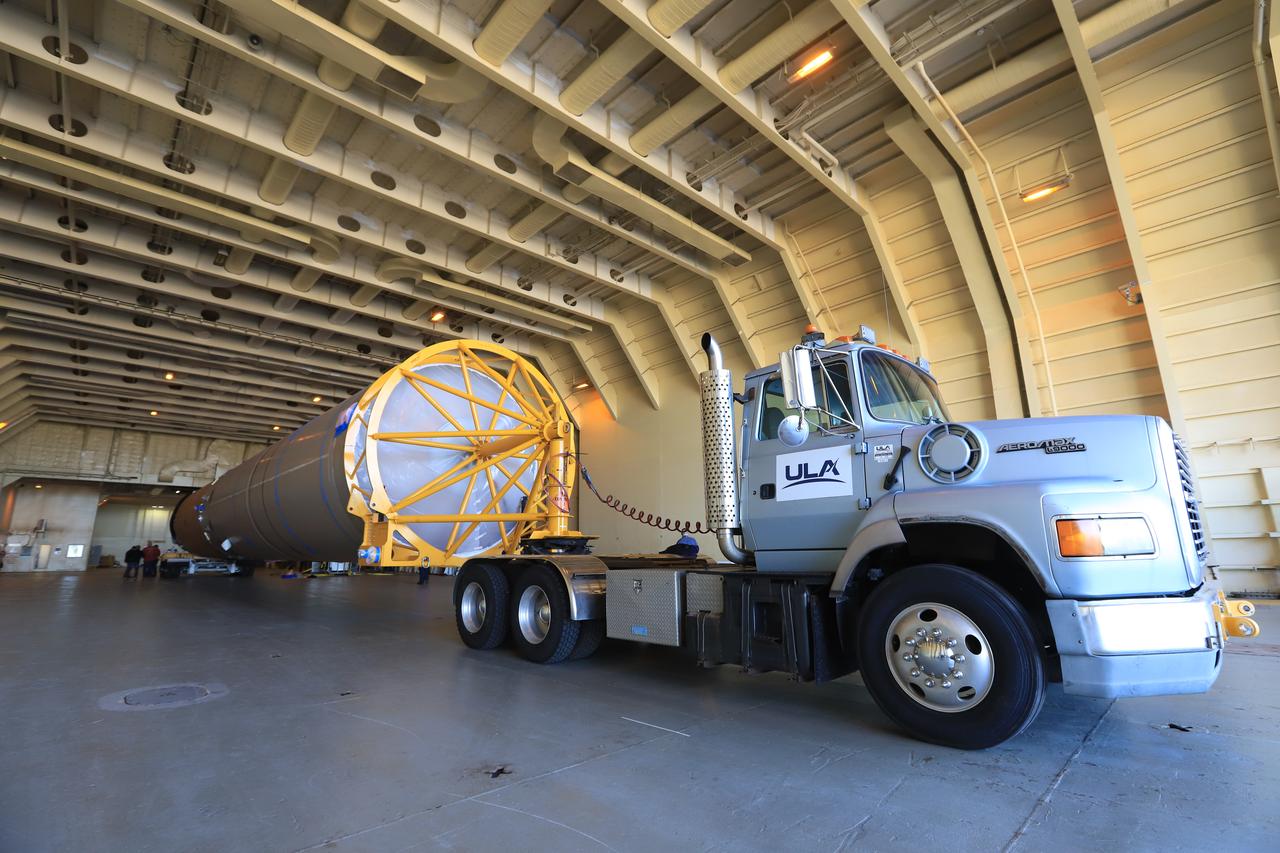
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage is in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test. Soon the upper stage will be assembled with the first stage booster and shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the International Space Station from U.S. soil.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) has arrived aboard the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. Preparations are underway to offload the ICPS and transport it to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) was offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, and transported to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

The Mariner barge arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) is offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Atlas V from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.

A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Centaur upper stage arrived for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. A transport truck is taking the Centaur from the Mariner cargo ship in the background, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will lift off atop the ULA Atlas V rocket to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The Mariner barge arrives at a dock at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The Mariner barge is docked at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, with the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) inside, at right. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
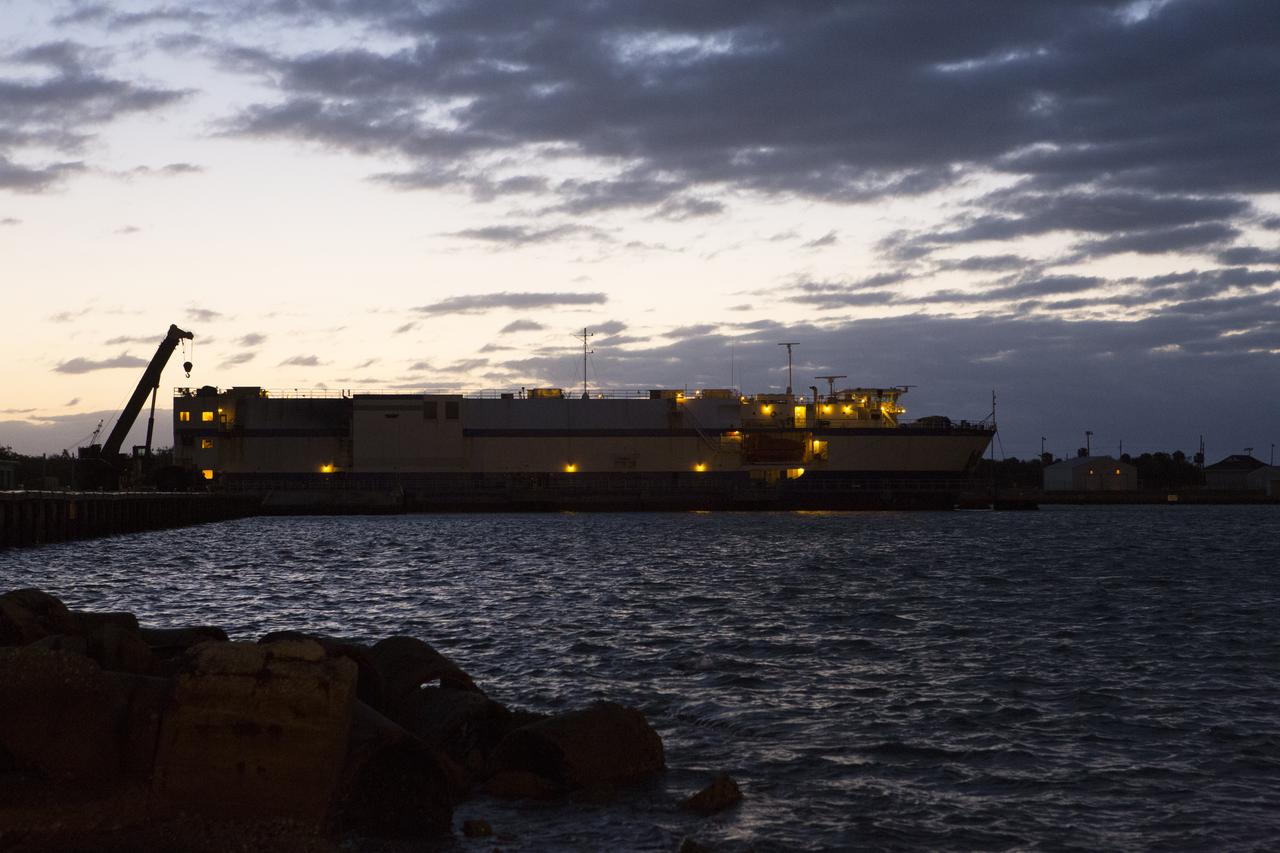

The Mariner barge arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
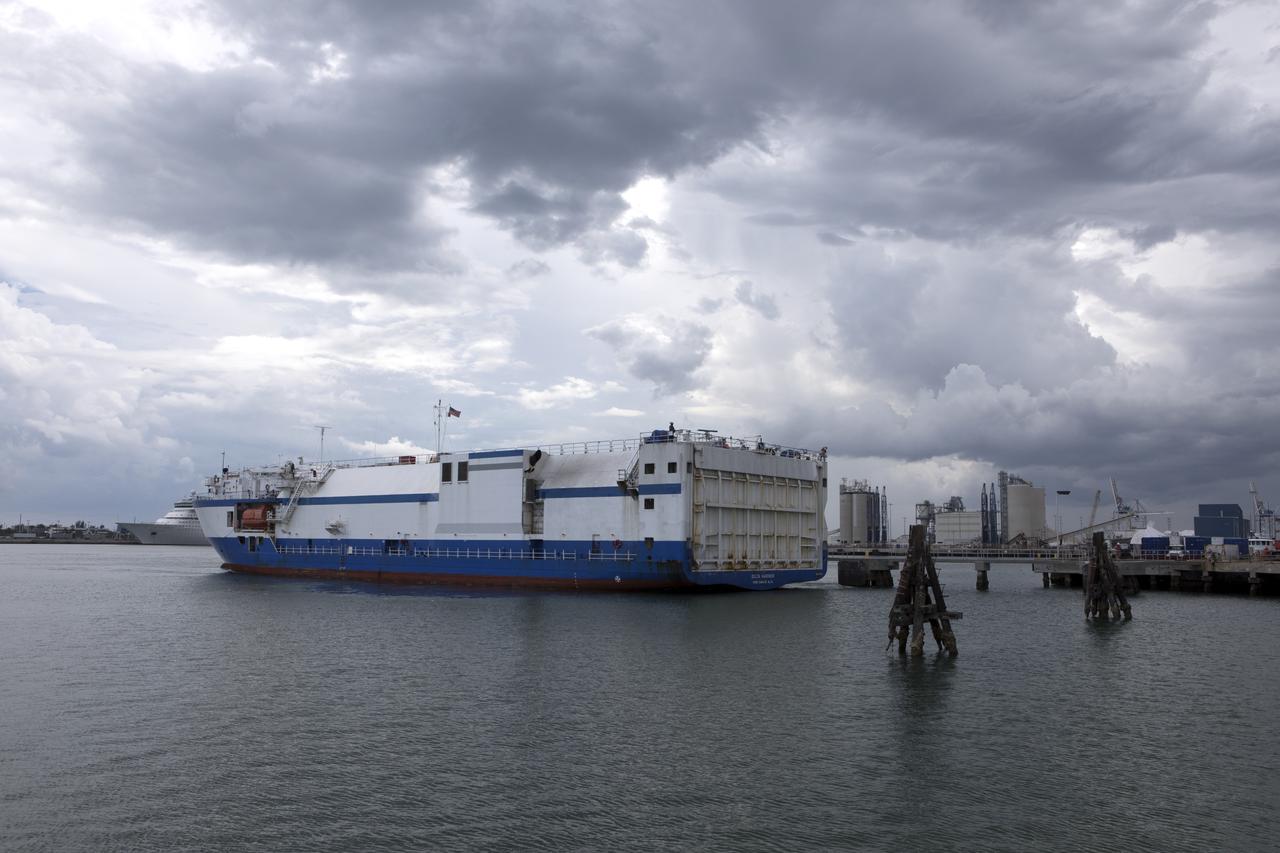

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying an Atlas V rocket booster bound for nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped aboard the Mariner barge from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
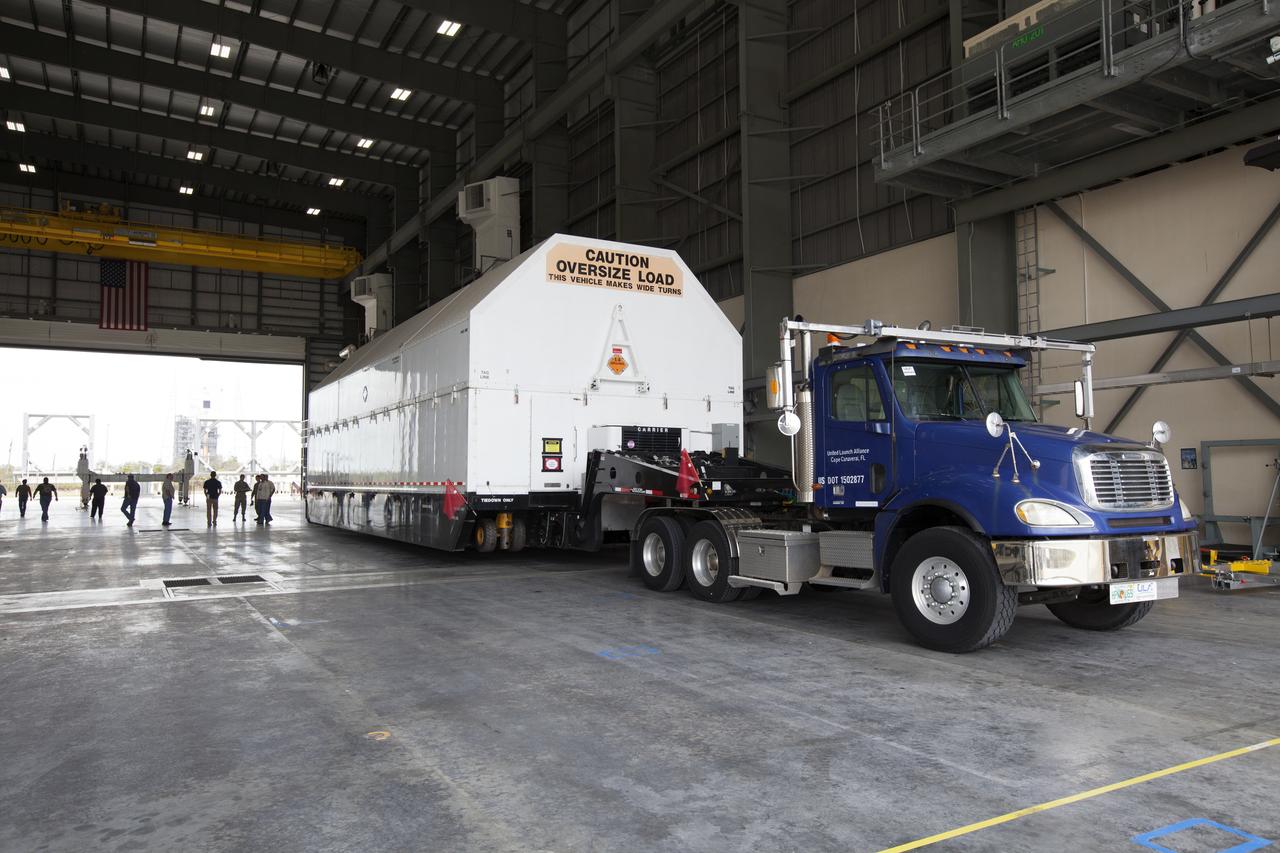

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS arrived aboard the Mariner barge from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
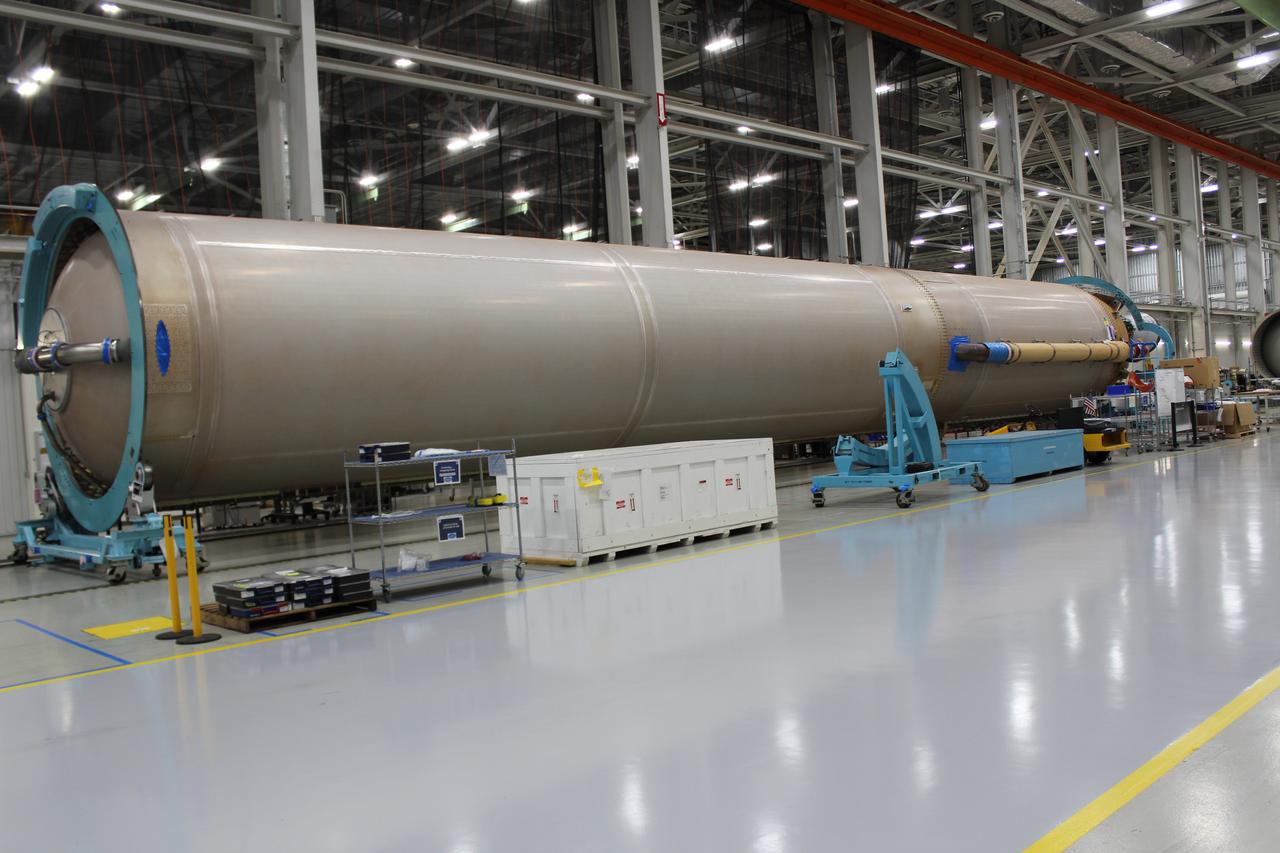

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster for the Crew Flight Test of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner is in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. Soon the booster will be assembled with the dual engine Centaur upper stage. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner ship arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying a two-engine Centaur upper stage for the upcoming uncrewed Orbital Flight Test of a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft. As part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP), the Starliner is part of the next generation of American spacecraft that will launch astronauts to the International Space Station. Starliner will launch early next year atop a ULA Atlas V rocket with the Centaur upper stage from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Statin. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
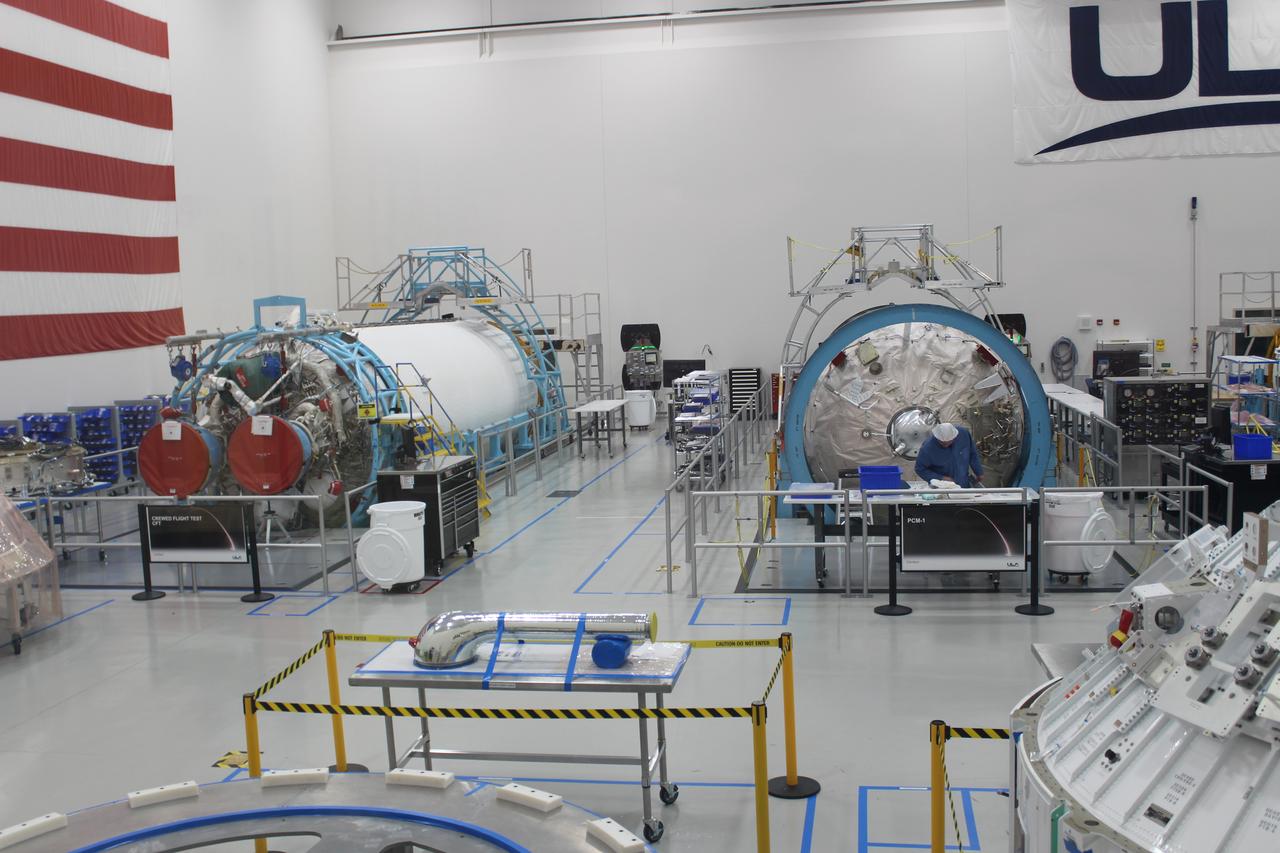

Two United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stages are in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. One is for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test on the CST-100 Starliner, and the other will be used for the first crew rotation mission on the Starliner. One of the Centaur upper stages will be assembled to the first stage booster. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.
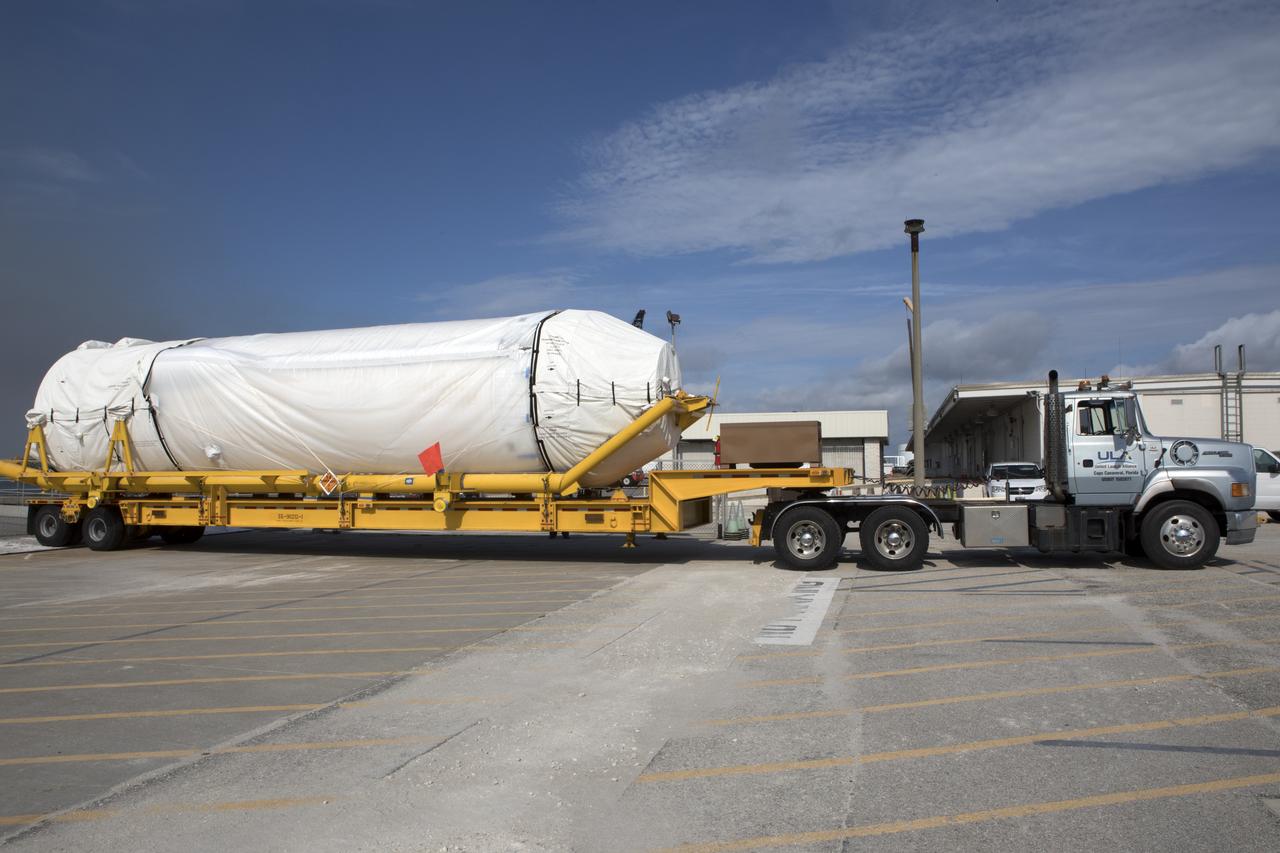

At Port Canaveral in Florida, a United Launch Alliance Centaur uppoer stage is transported from the company's Mariner ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

A transport truck is about to take a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster from the Mariner cargo ship at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas V is scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. Scheduled to liftoff March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

At Port Canaveral in Florida, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket booster is transported from the company's Mariner ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.
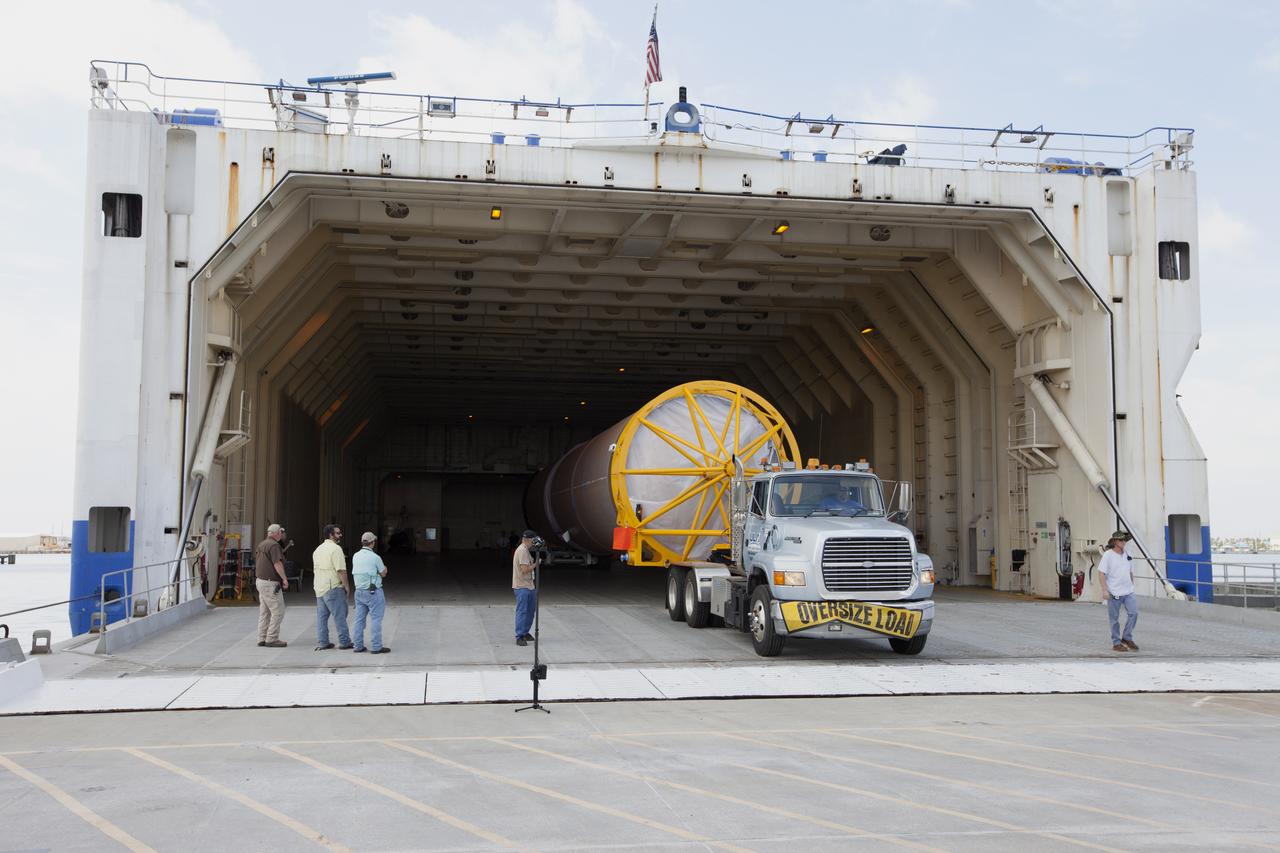

At Port Canaveral in Florida, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket booster is transported from the company's Mariner ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.

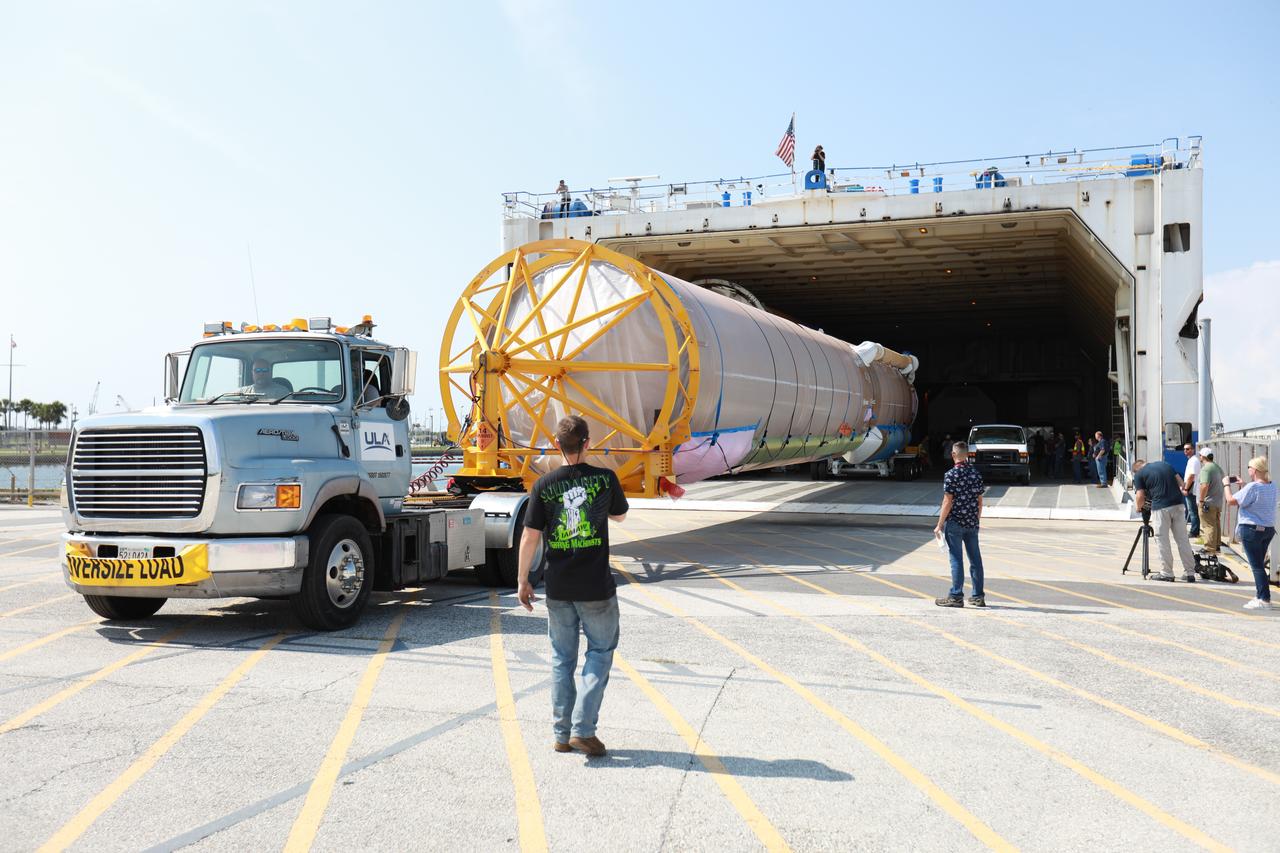
The Mariner cargo ship arrives at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The Mariner cargo ship arrives at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), located south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The Mariner cargo ship is docked at the Army Outpost wharf at Port Canaveral, Florida, near the Kennedy Space Center. Aboard is the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for the Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station. After the rocket is offloaded, a transport truck will take the Atlas V to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC), south of Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Scheduled to launch a Cygnus spacecraft on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

At Port Canaveral in Florida, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket booster and Centaur upper stage are about to be transported from the company's Mariner ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.
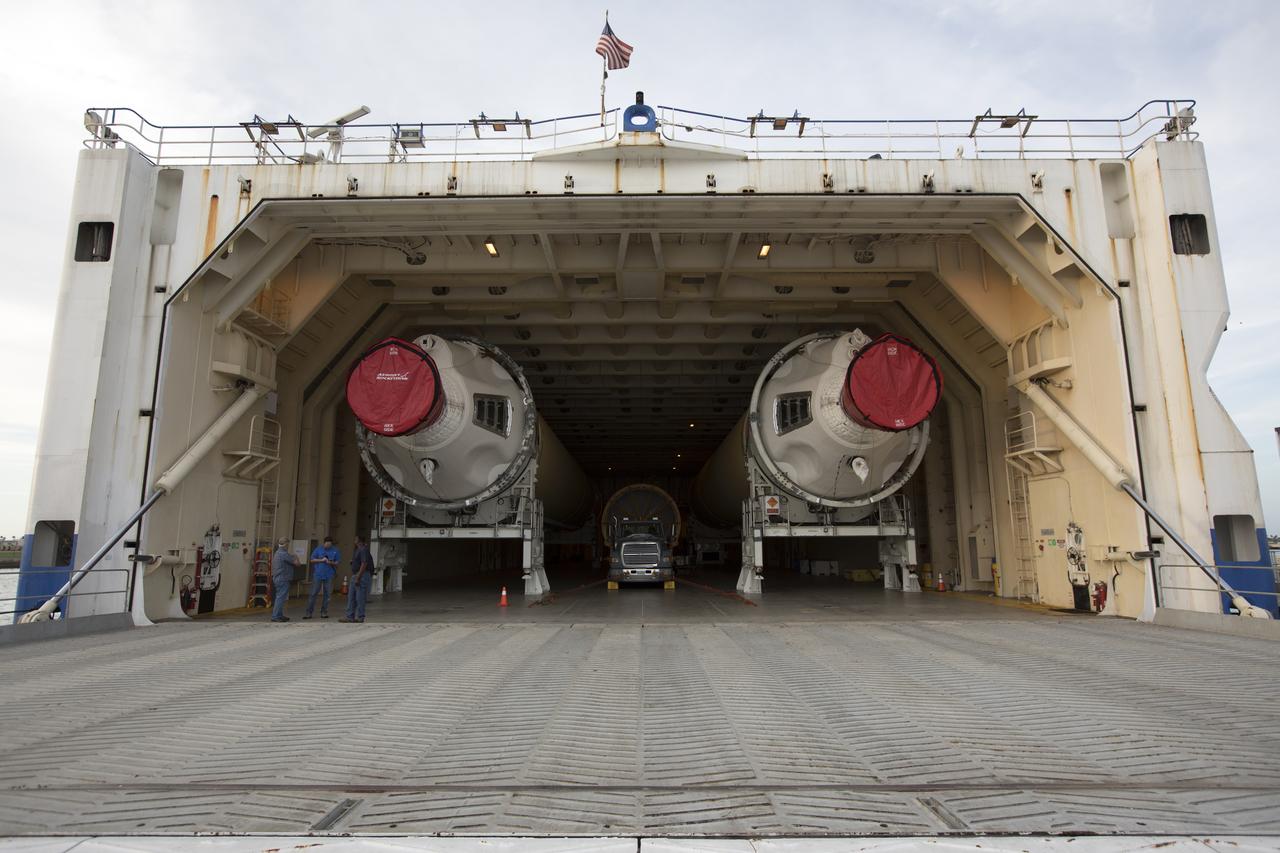

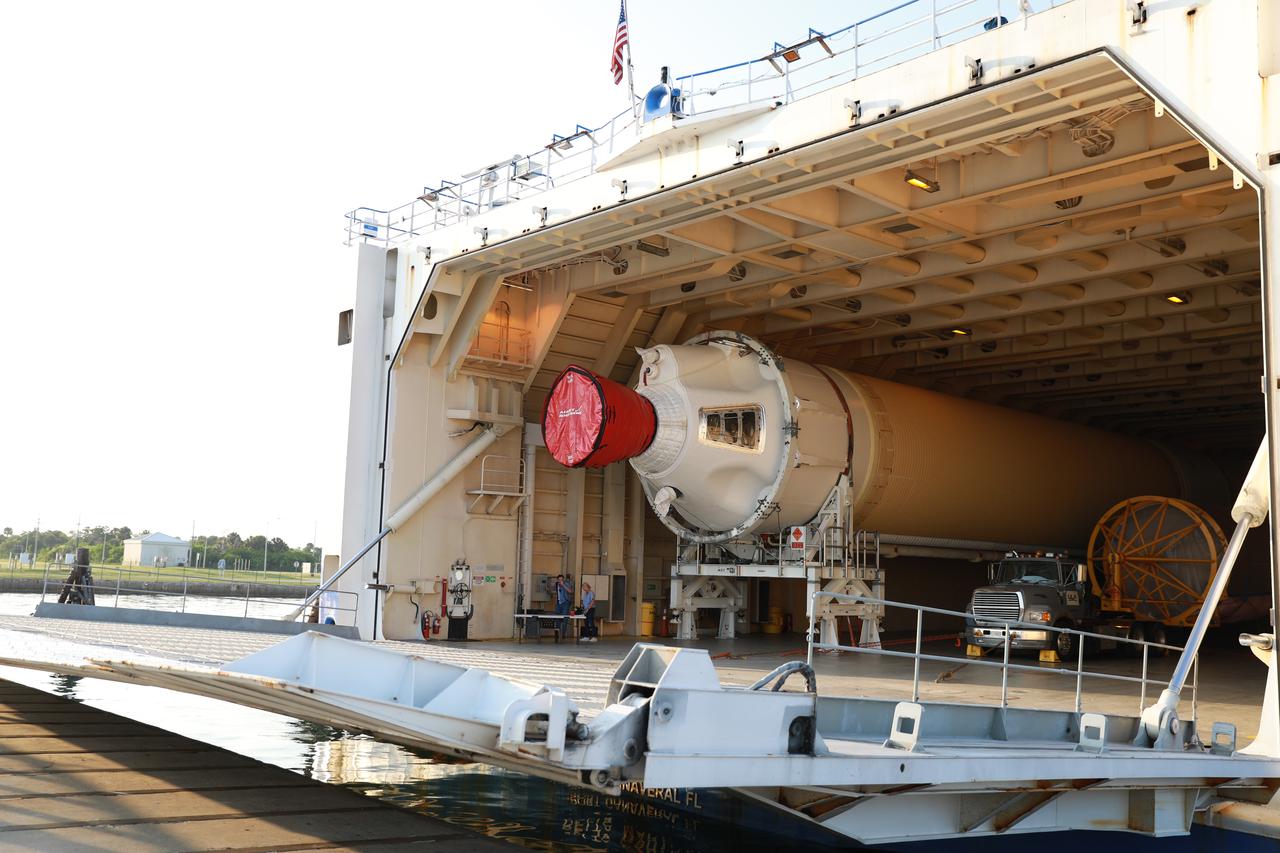
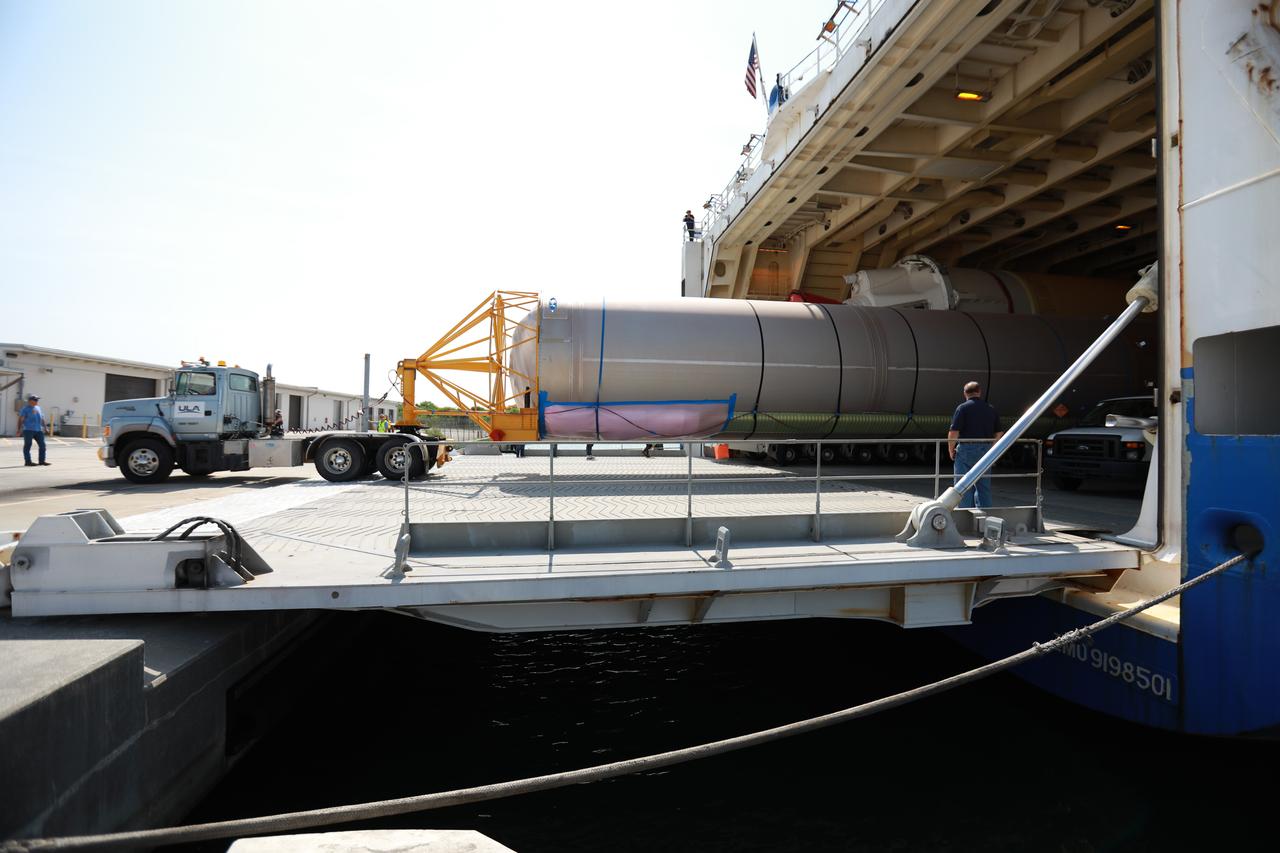
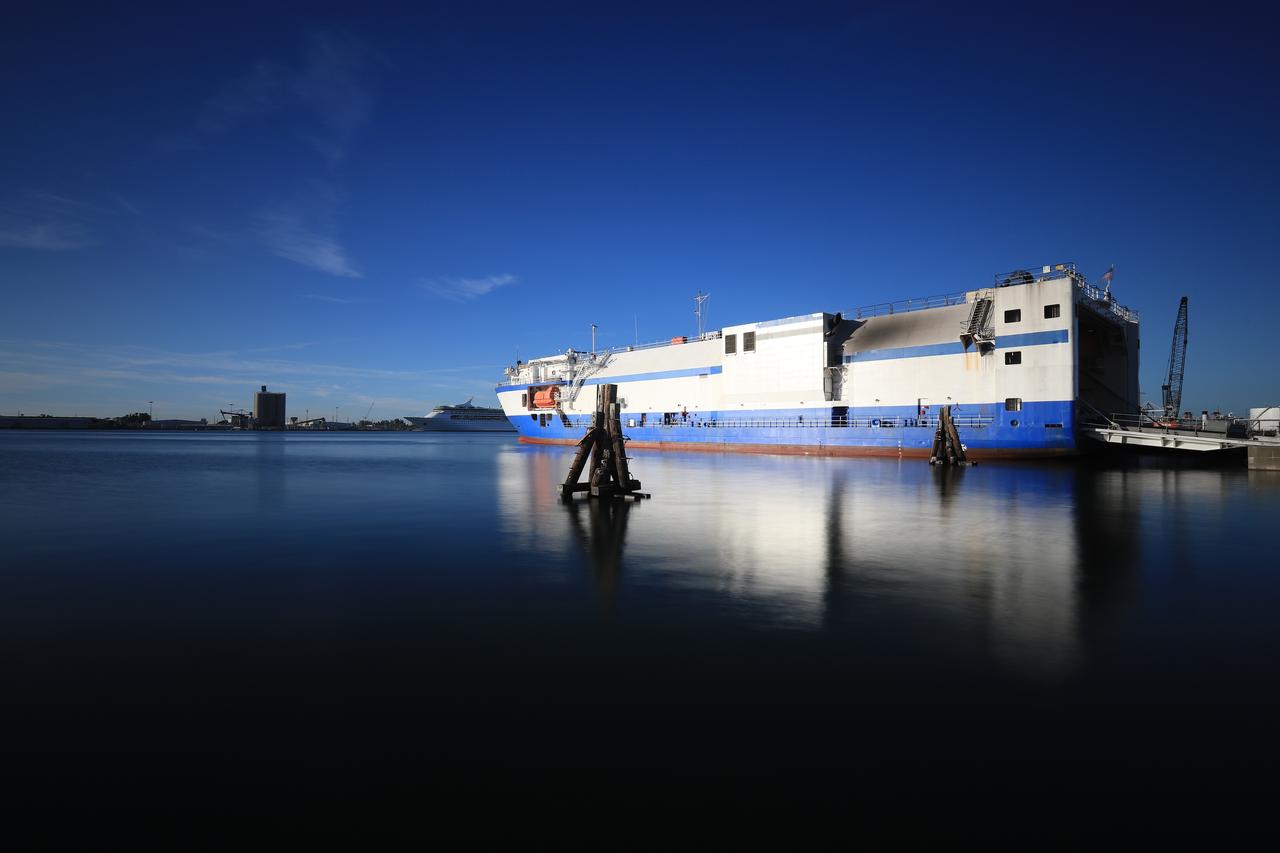
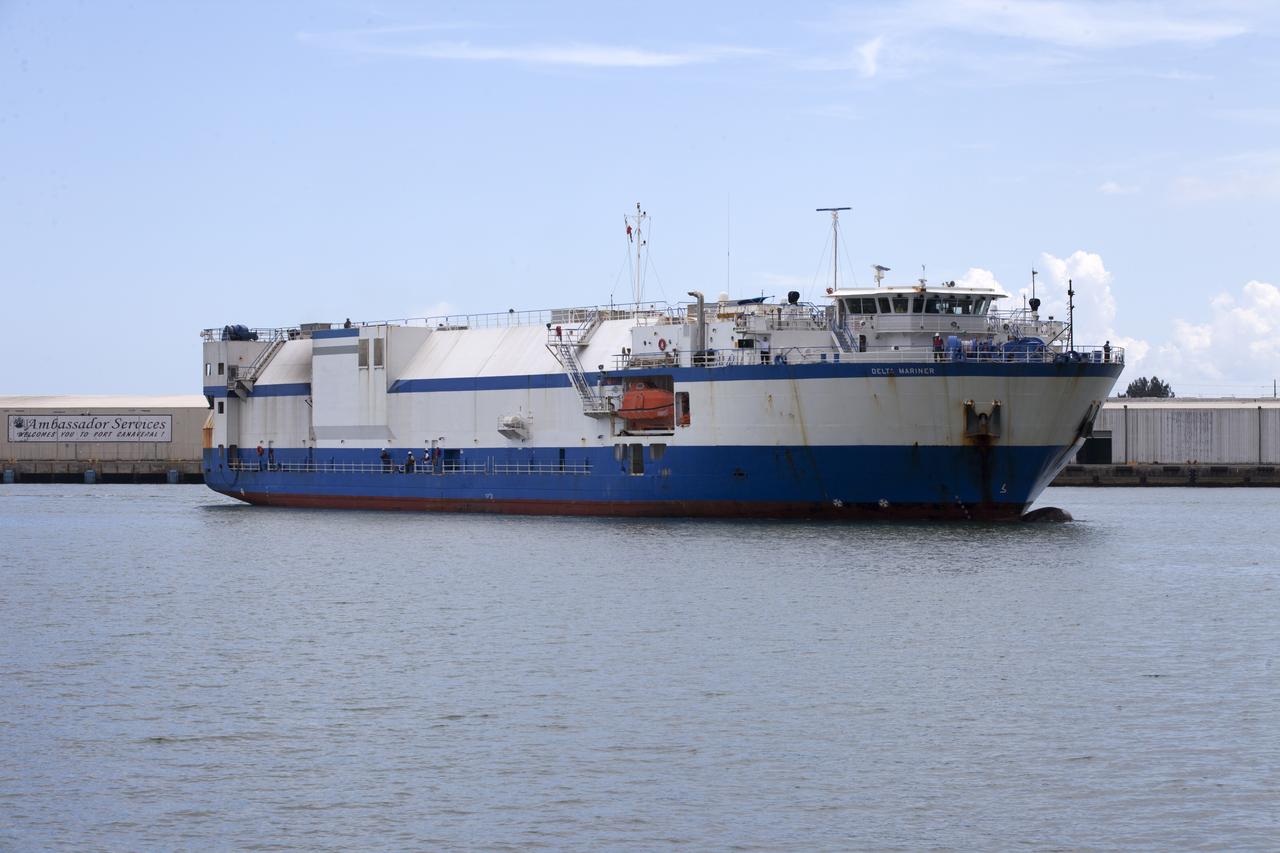
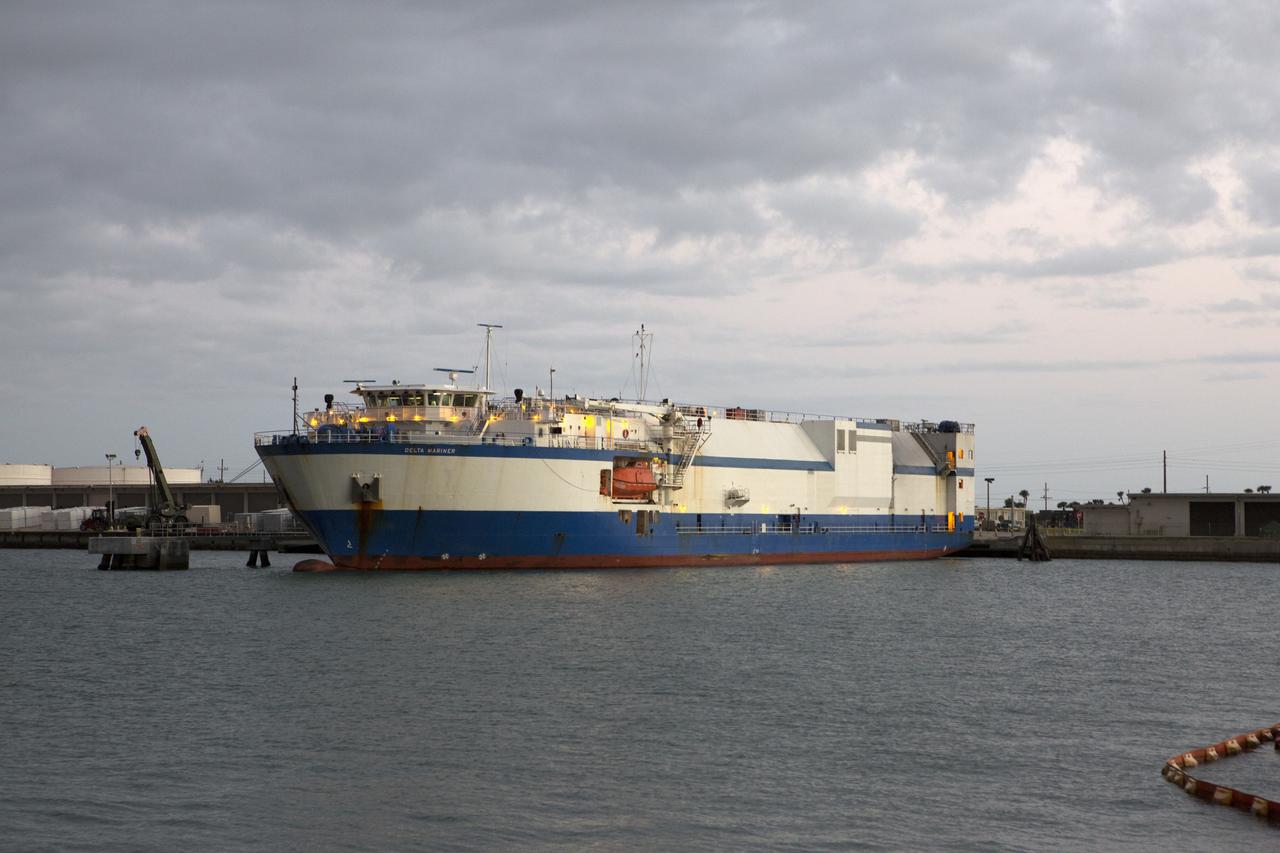
The United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives aboard the company's Mariner ship and prepared for offload at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.

Preparations are underway to offload the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.

Preparations are underway to offload the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.

The United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives aboard the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
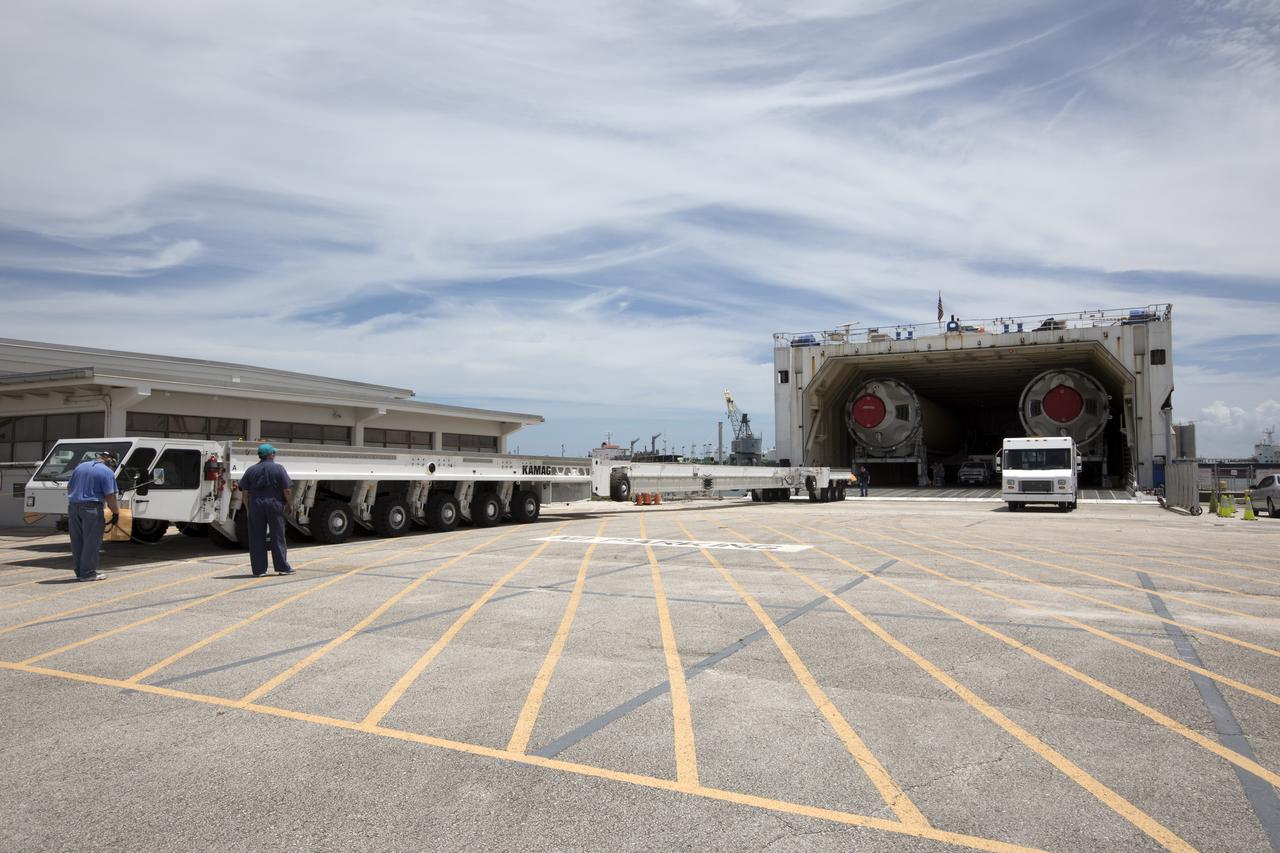

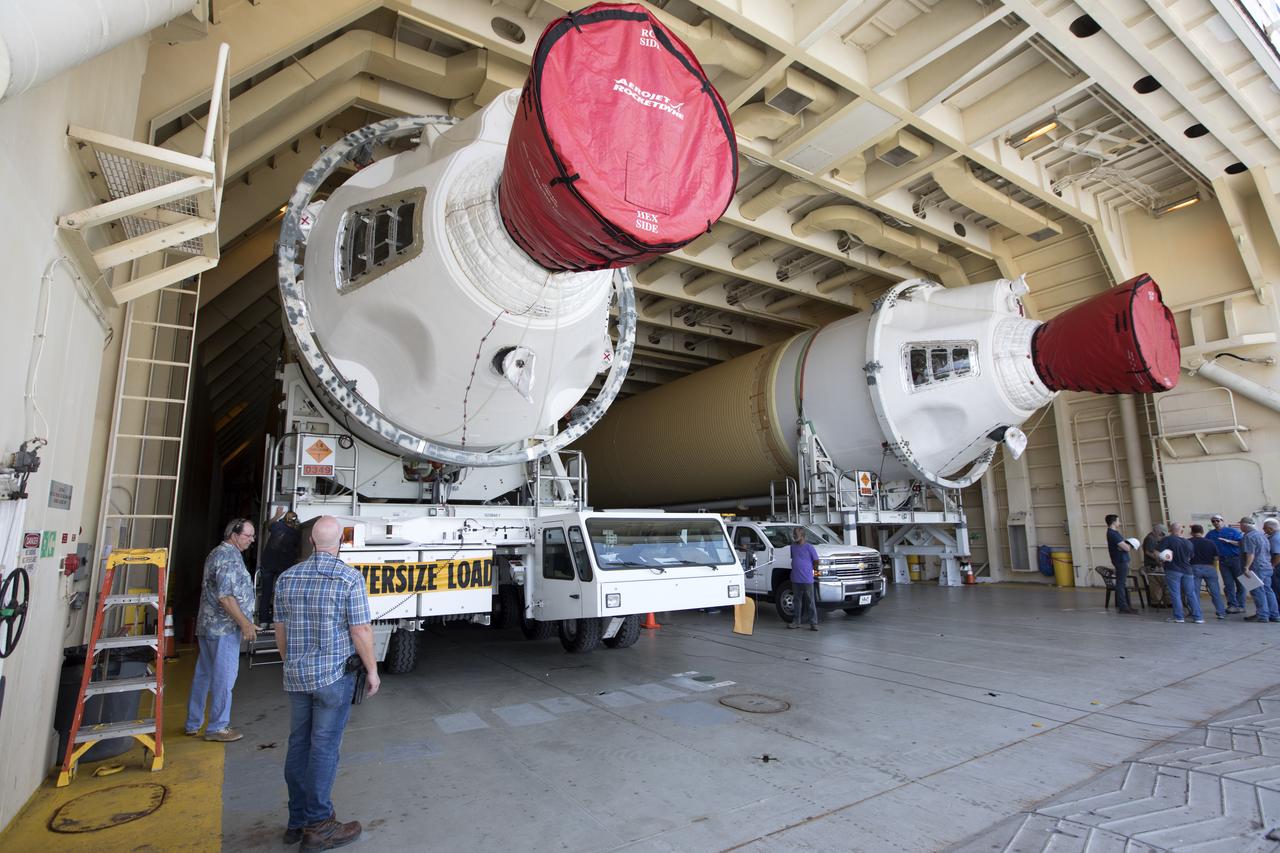
The United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives aboard the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. Preparations are underway to offload the booster onto a transporter. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
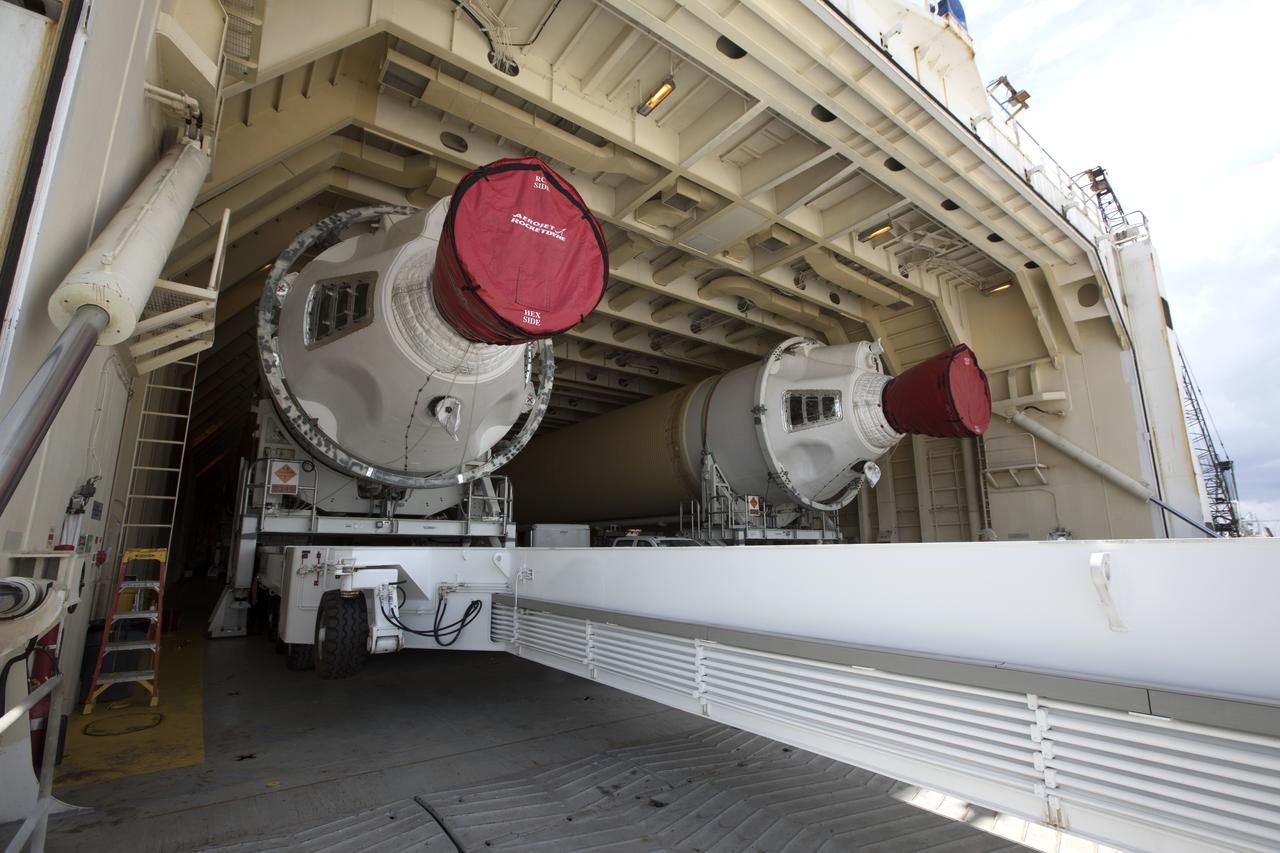

The United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is being offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.

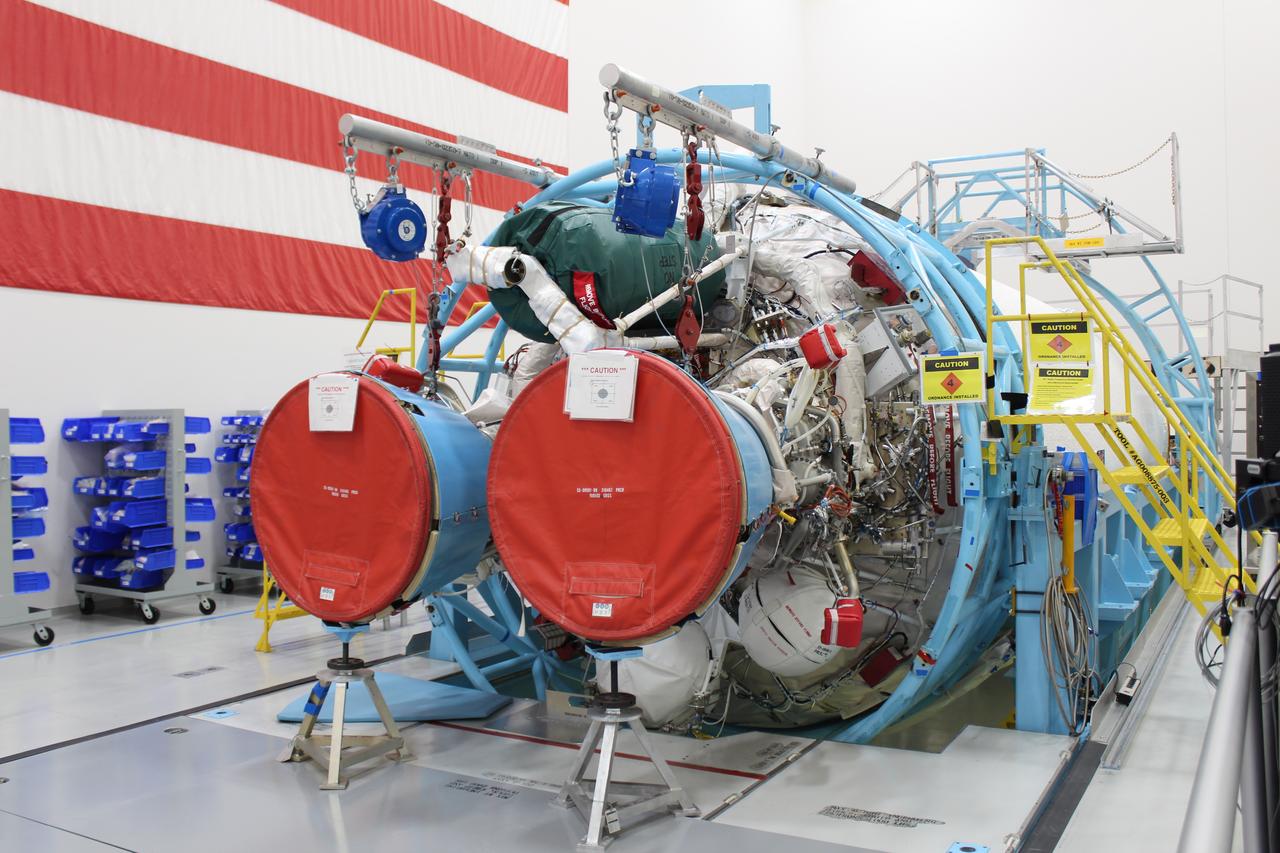
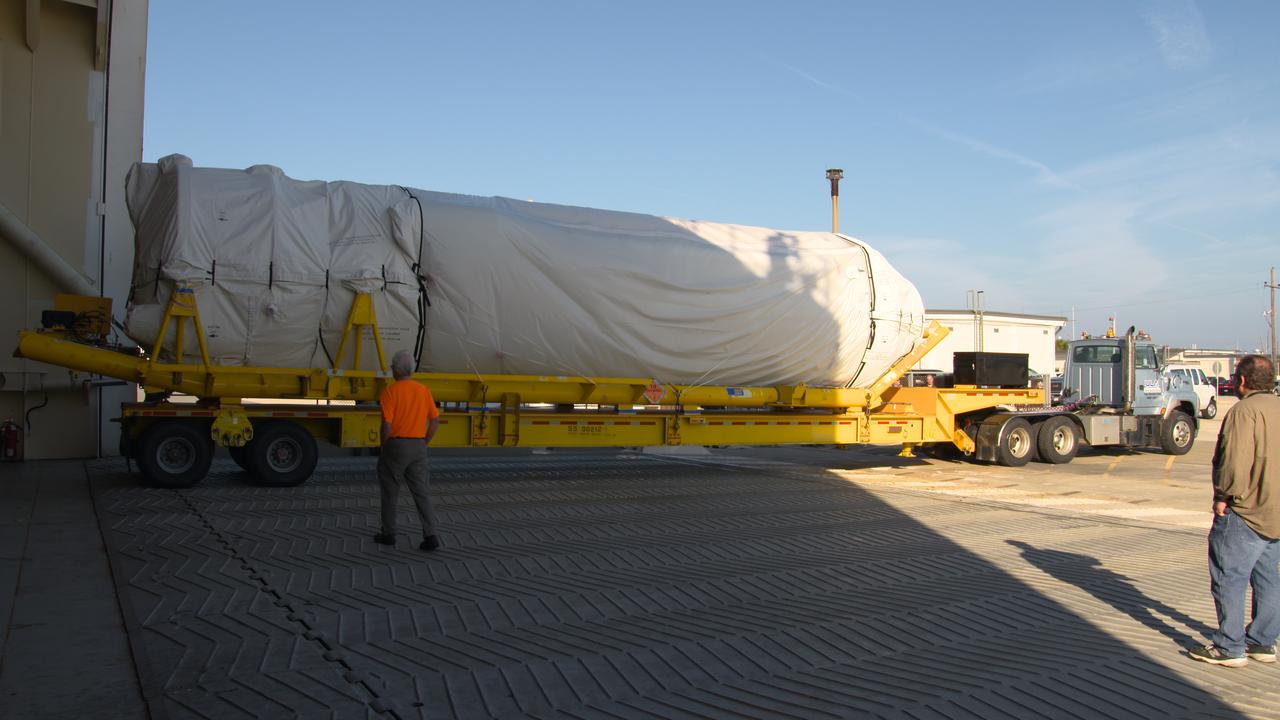
The Launch Vehicle Adapter (LVA) that will attach Boeing’s first Starliner spacecraft to the Atlas V launch vehicle is unloaded from the Mariner cargo vessel at Cape Canaveral in Florida on November 12, 2018, following transport from United Launch Alliance's manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama. Technicians transported the LVA to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to begin integrated operations with the Centaur upper stage.The LVA is the specially-designed structure that will be fitted to the top of Centaur. It will soon be attached to the Centaur during pre-launch stacking operations and eventually support the Starliner spacecraft during launch of the Orbital Flight Test next year. Also part of the LVA is the aeroskirt, which ULA designed in collaboration with Boeing and NASA for added aerodynamic stability during the flight. This metallic orthogrid structure will smooth the air flow over the Starliner-Atlas V vehicle, and will be nominally jettisoned after the first stage of flight. The aeroskirt also has provisions for venting in the event the Starliner abort engines are fired.
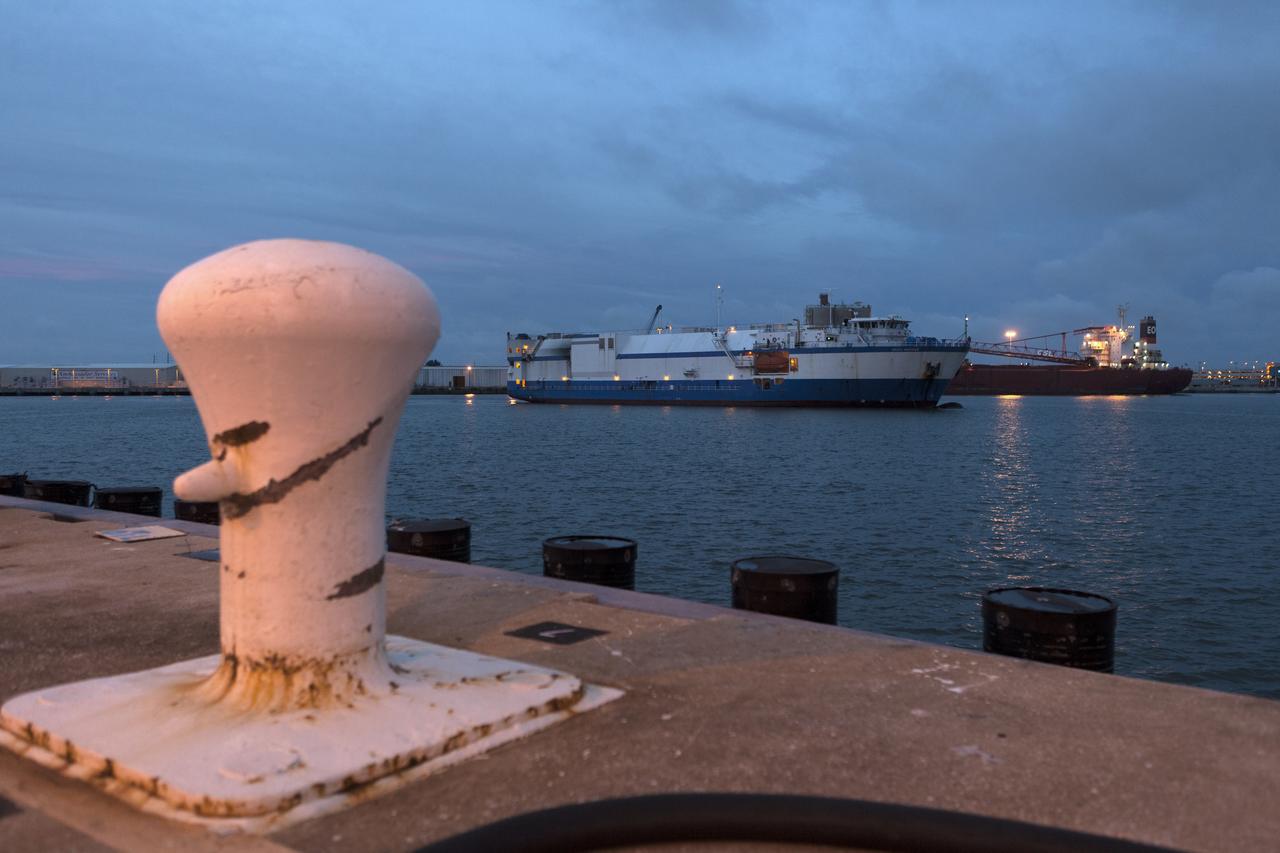

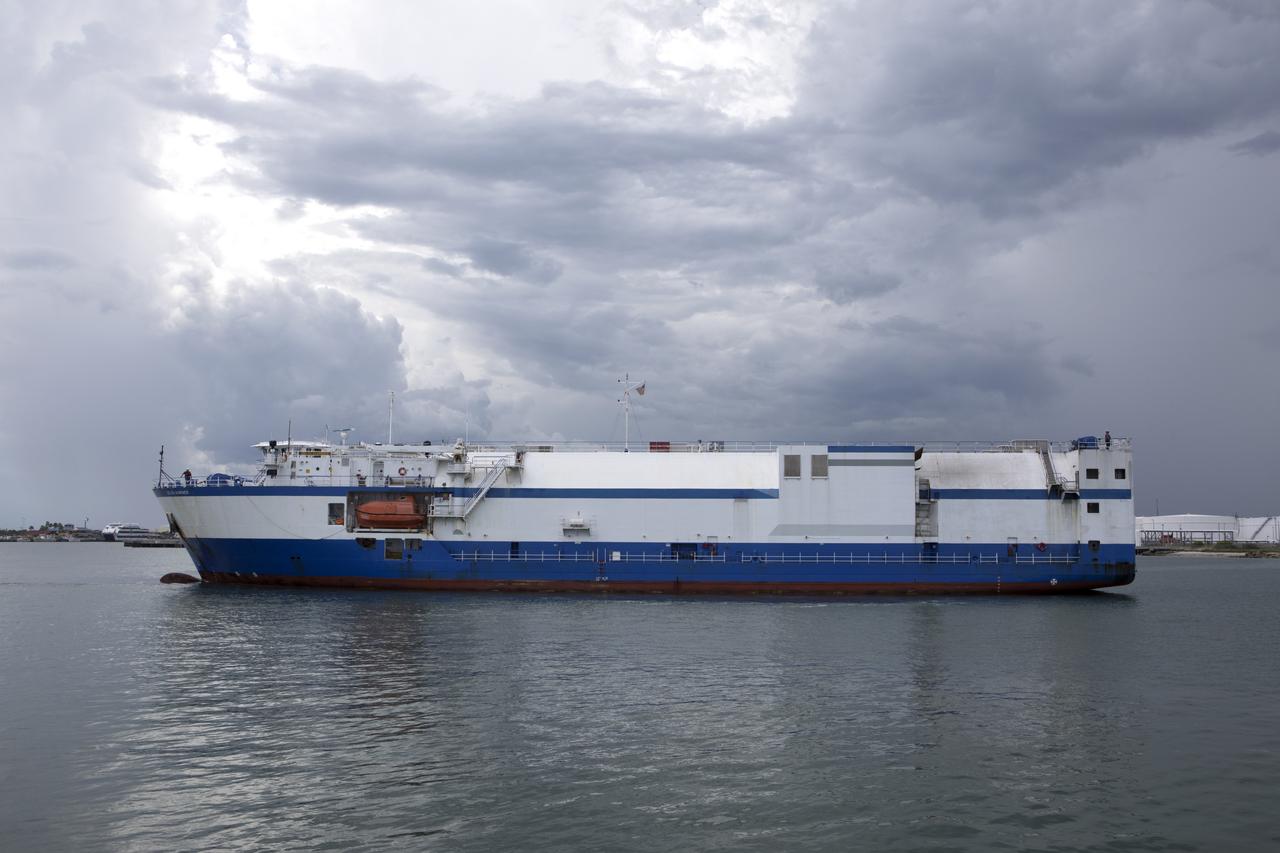
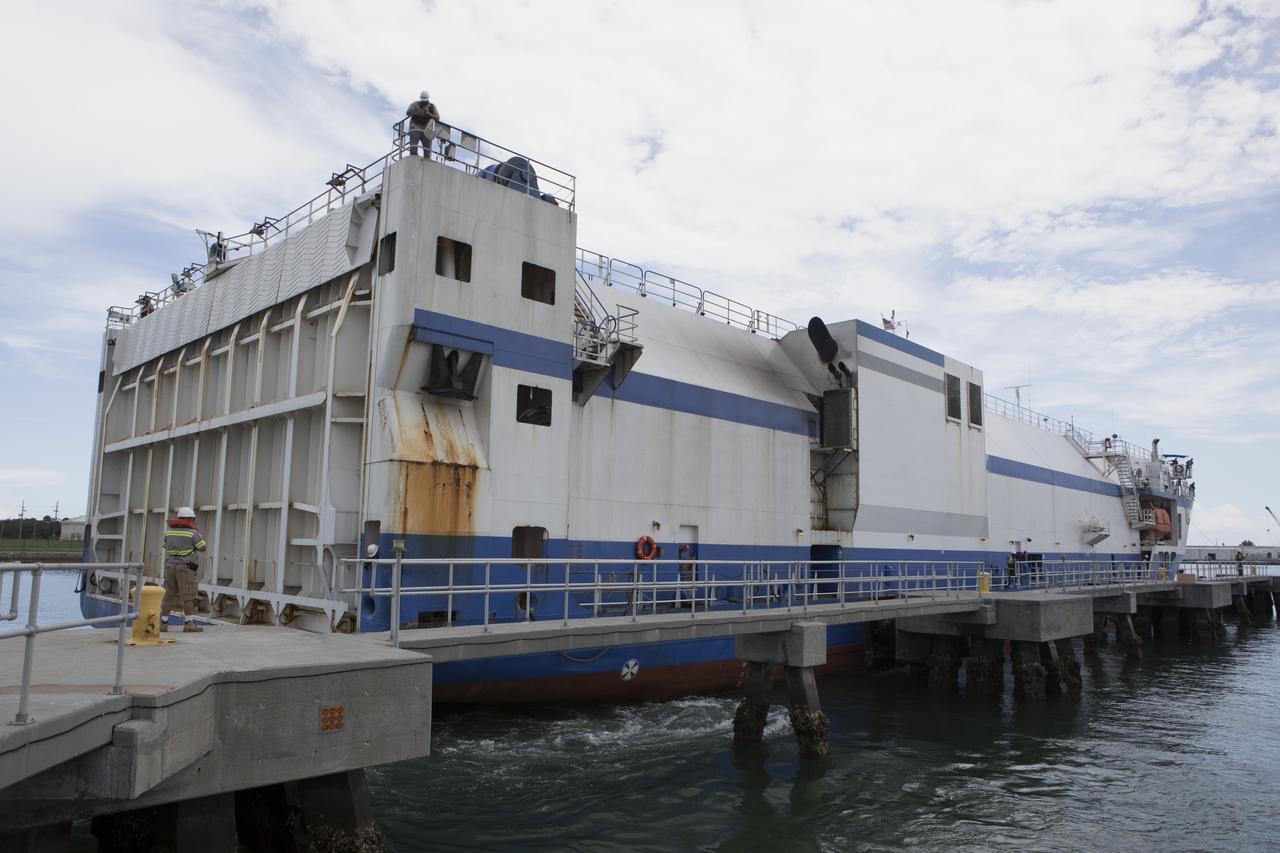
The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
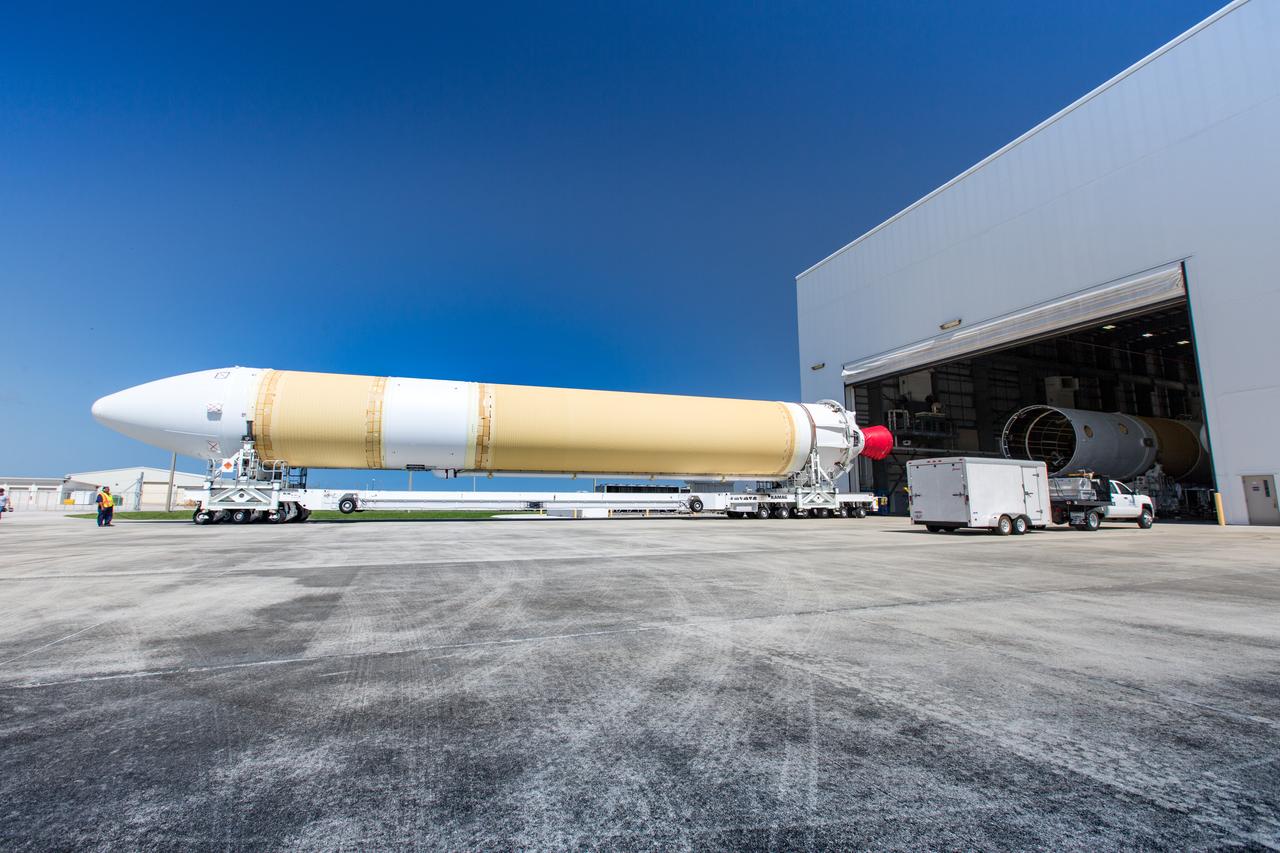

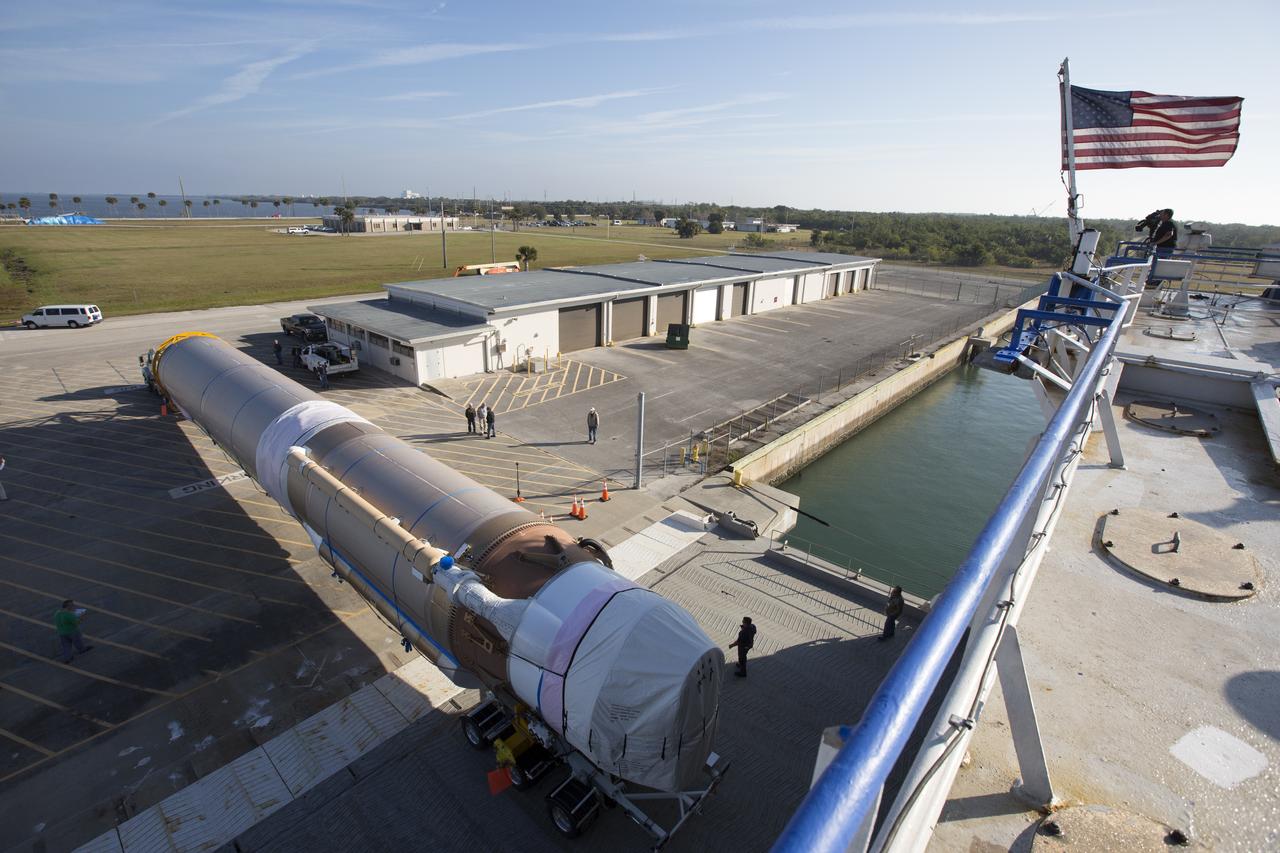
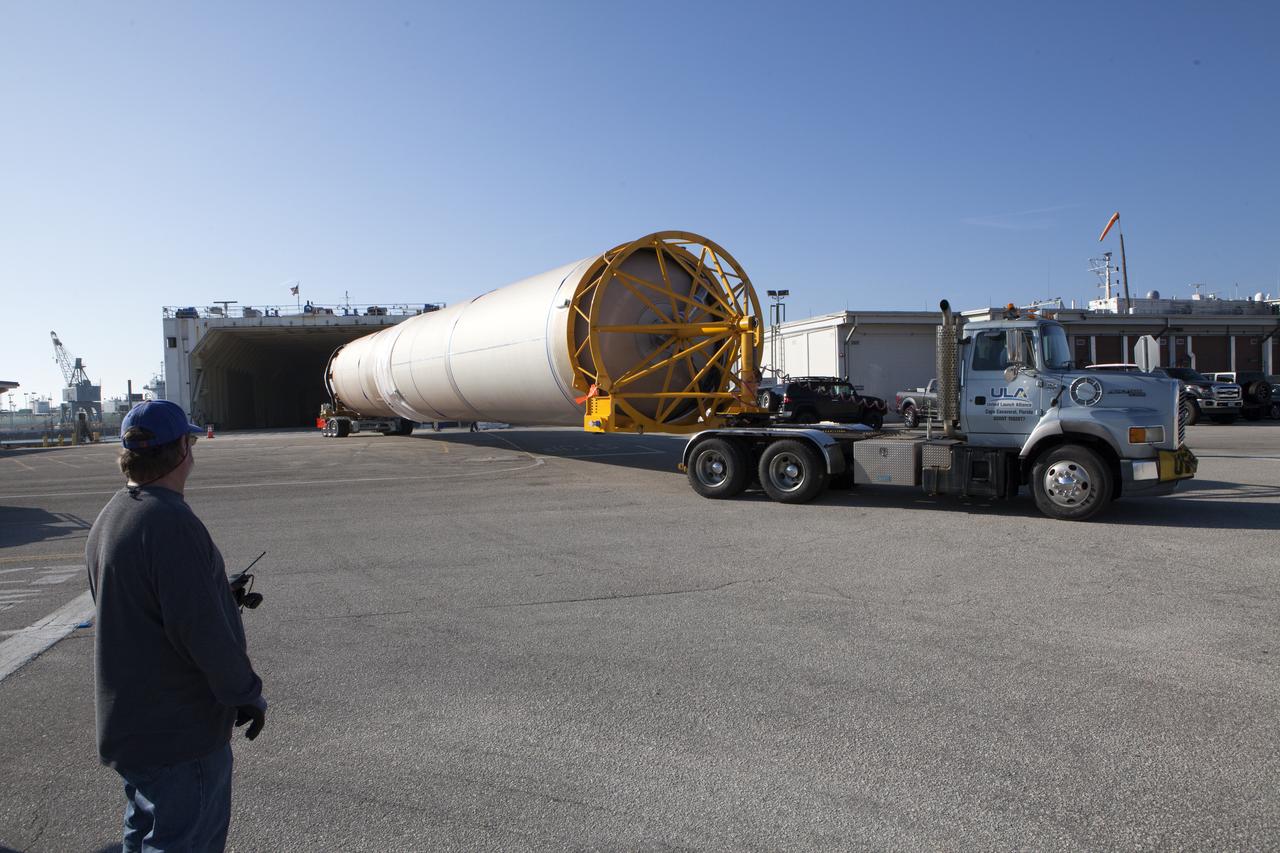
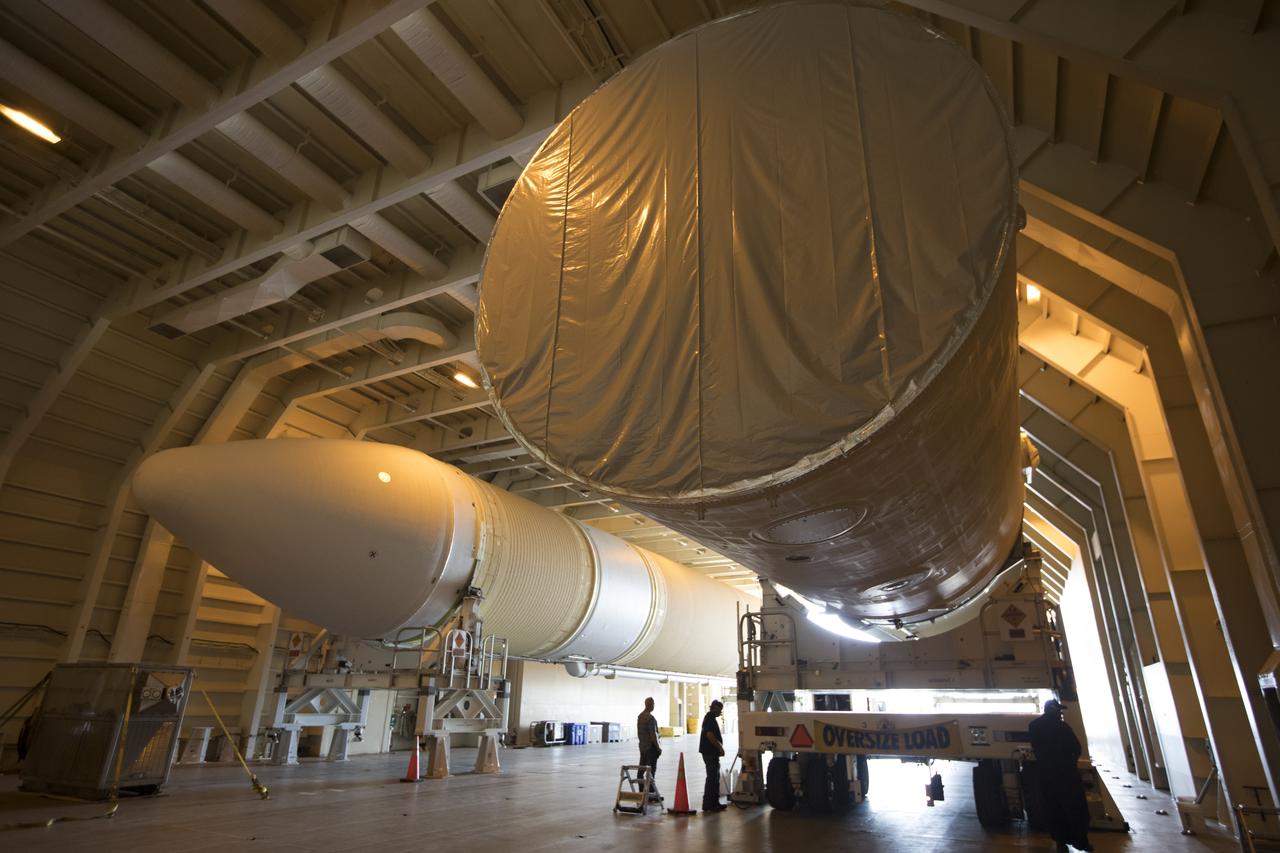
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
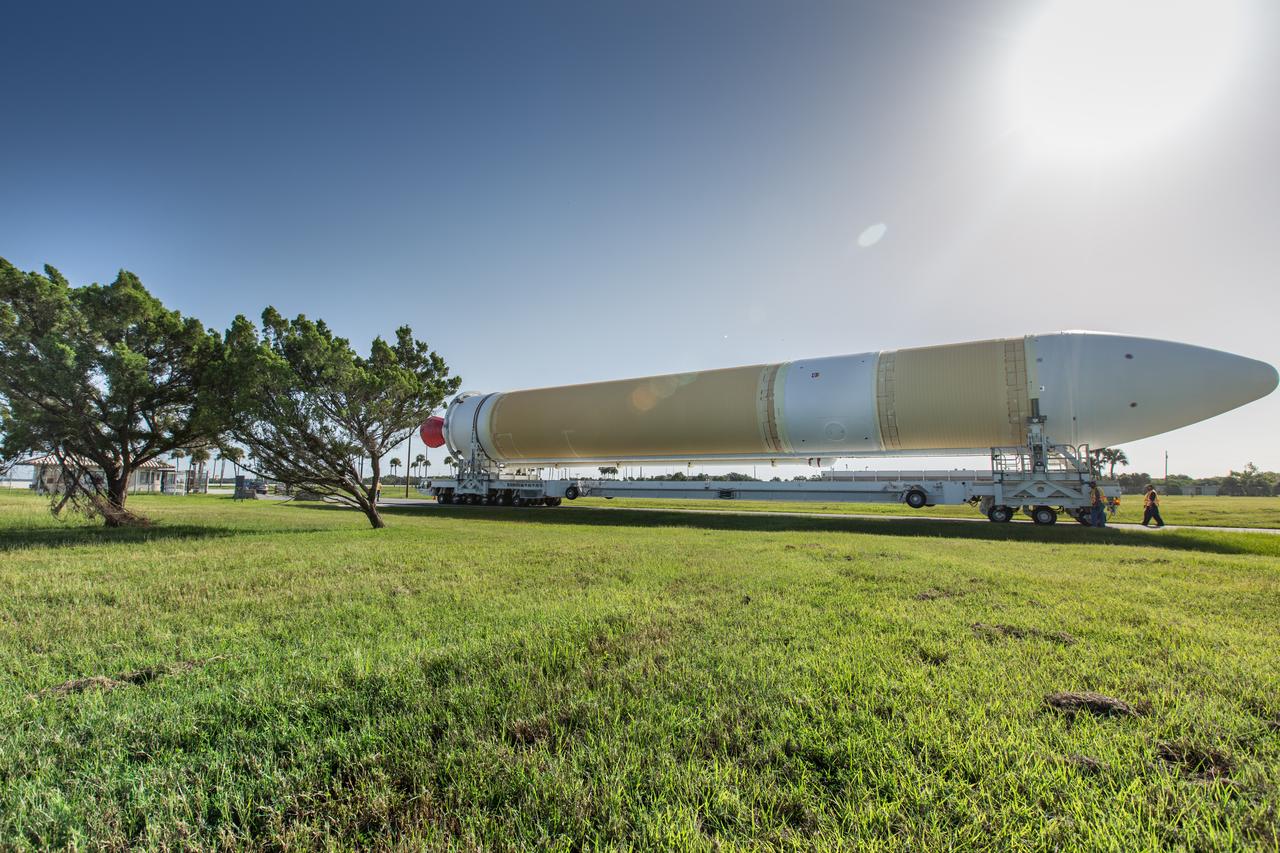

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported to the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
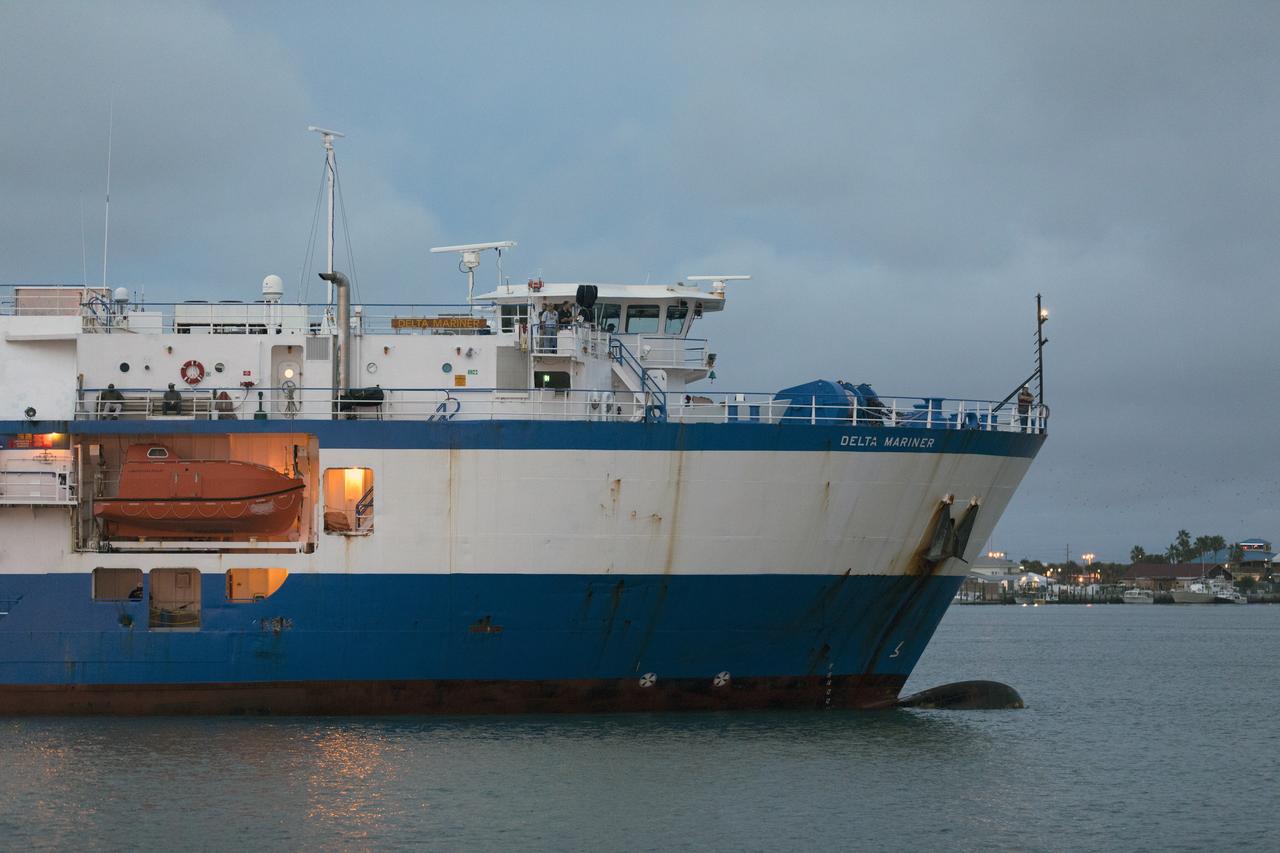

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
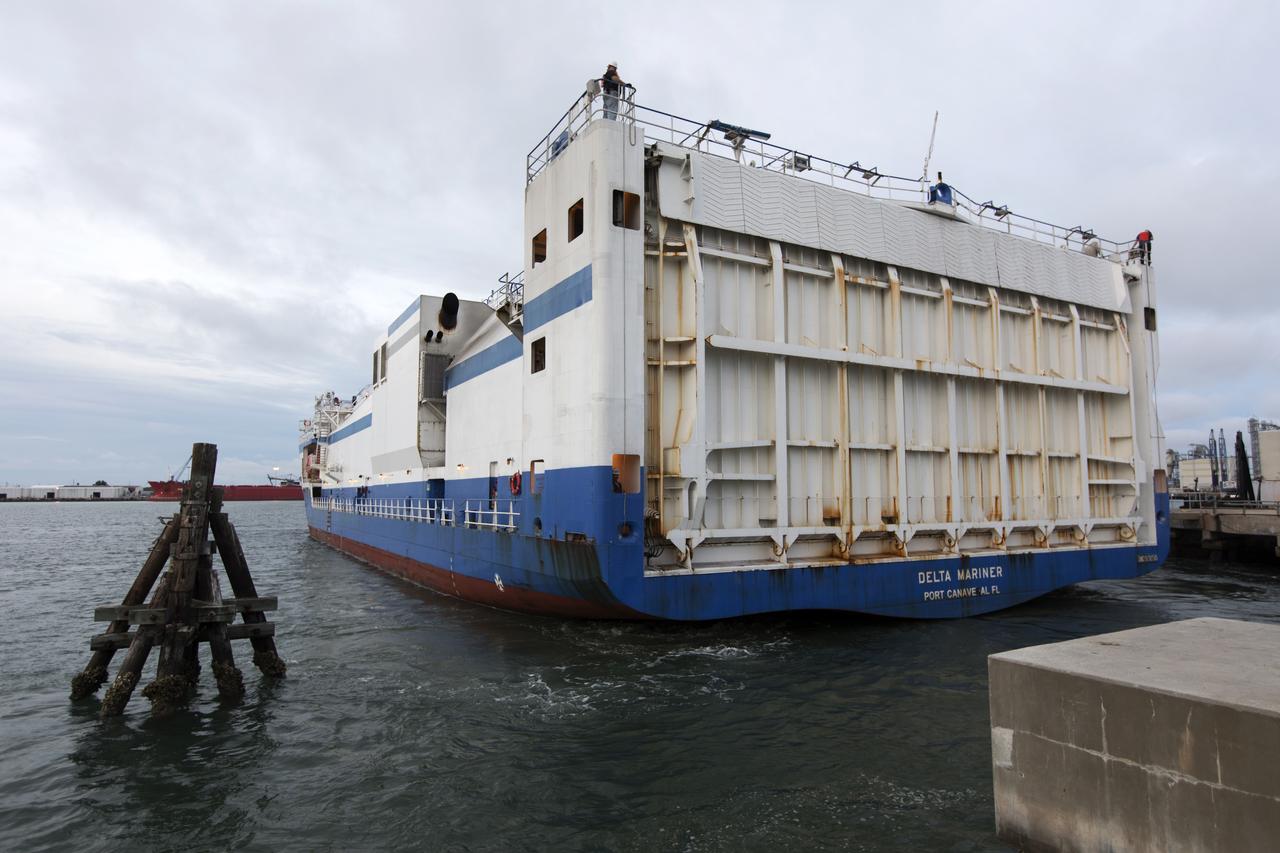

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
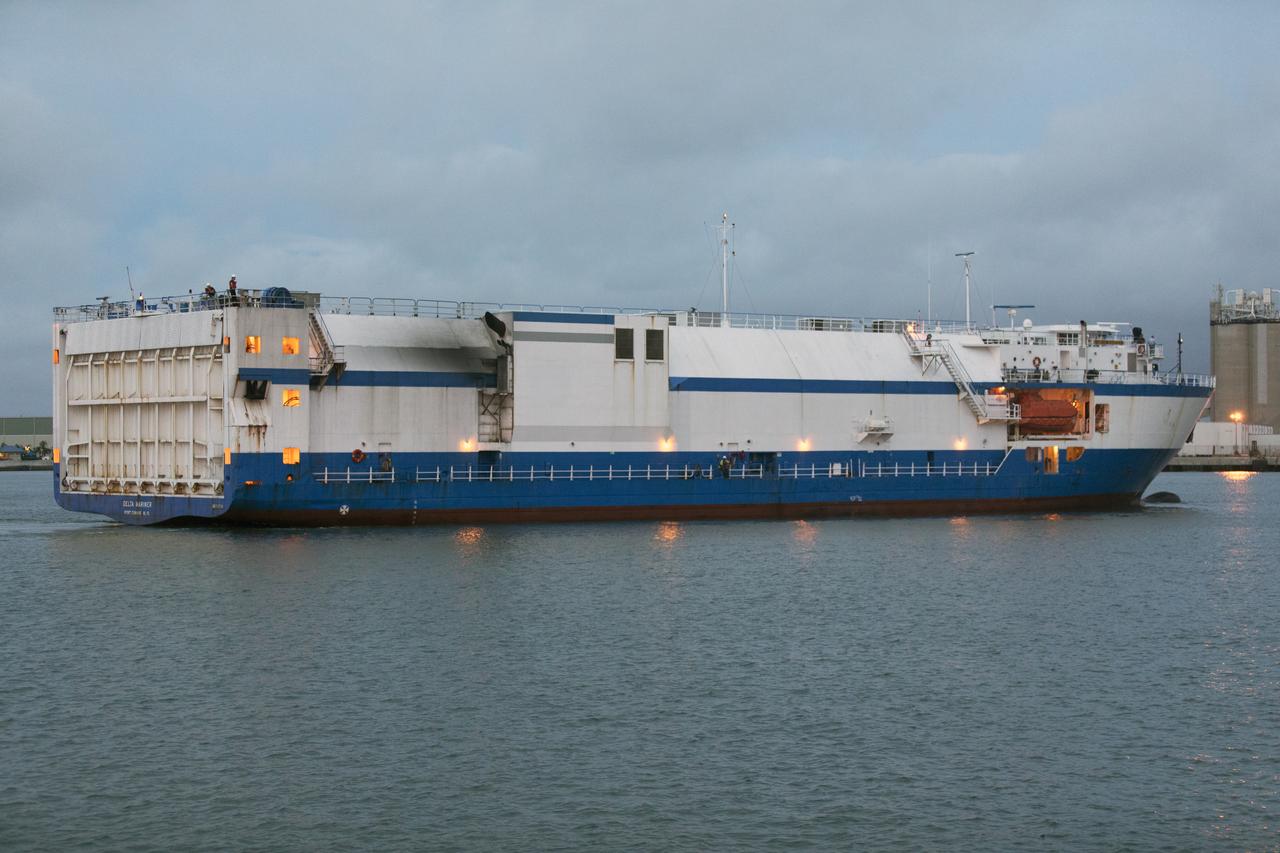

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
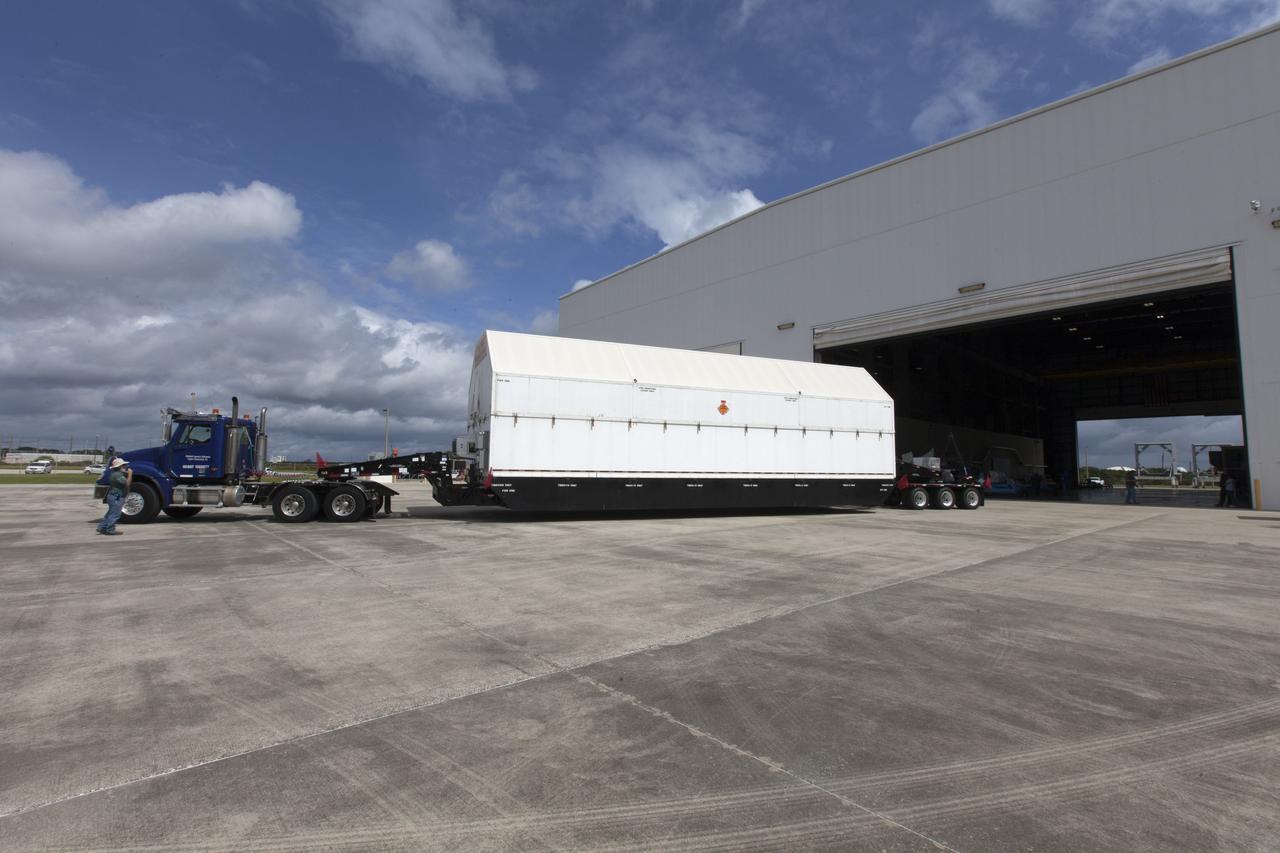

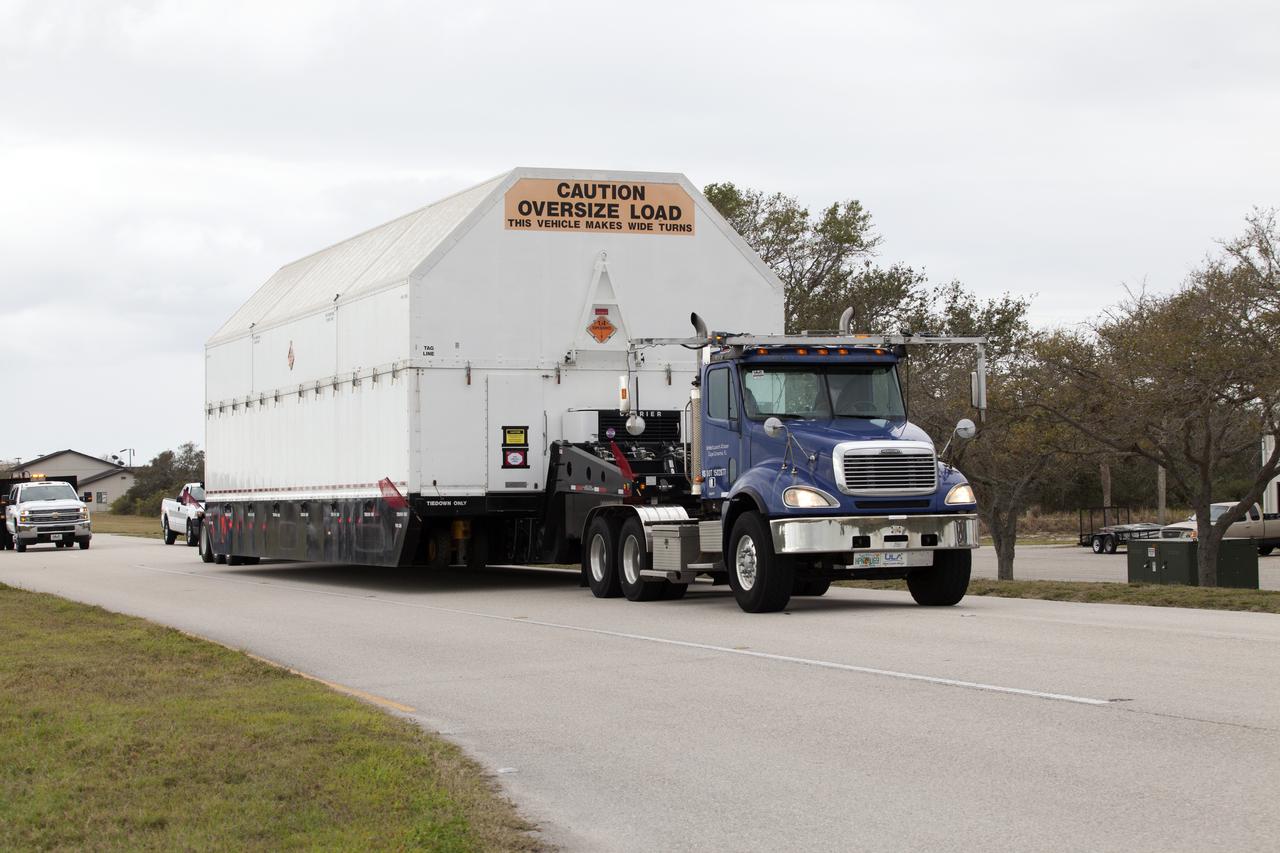
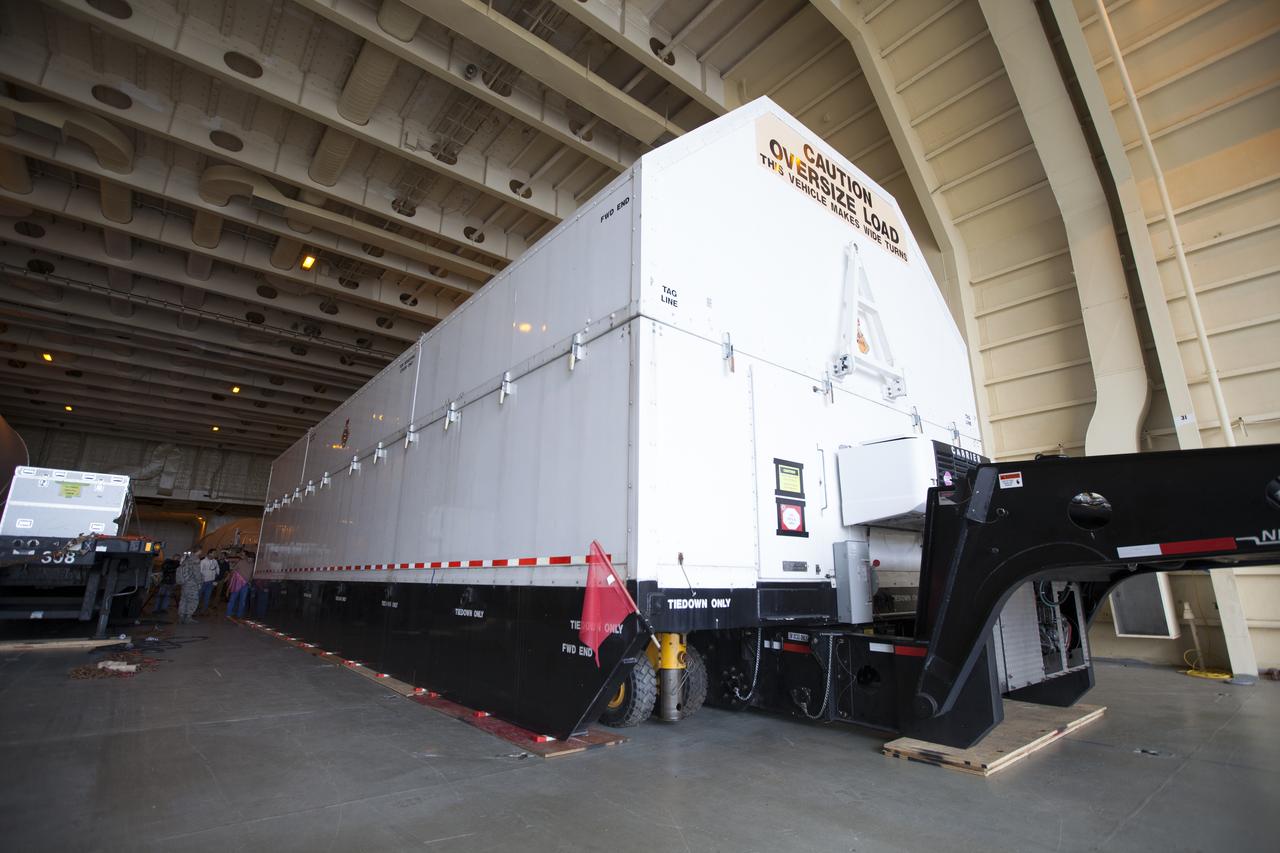
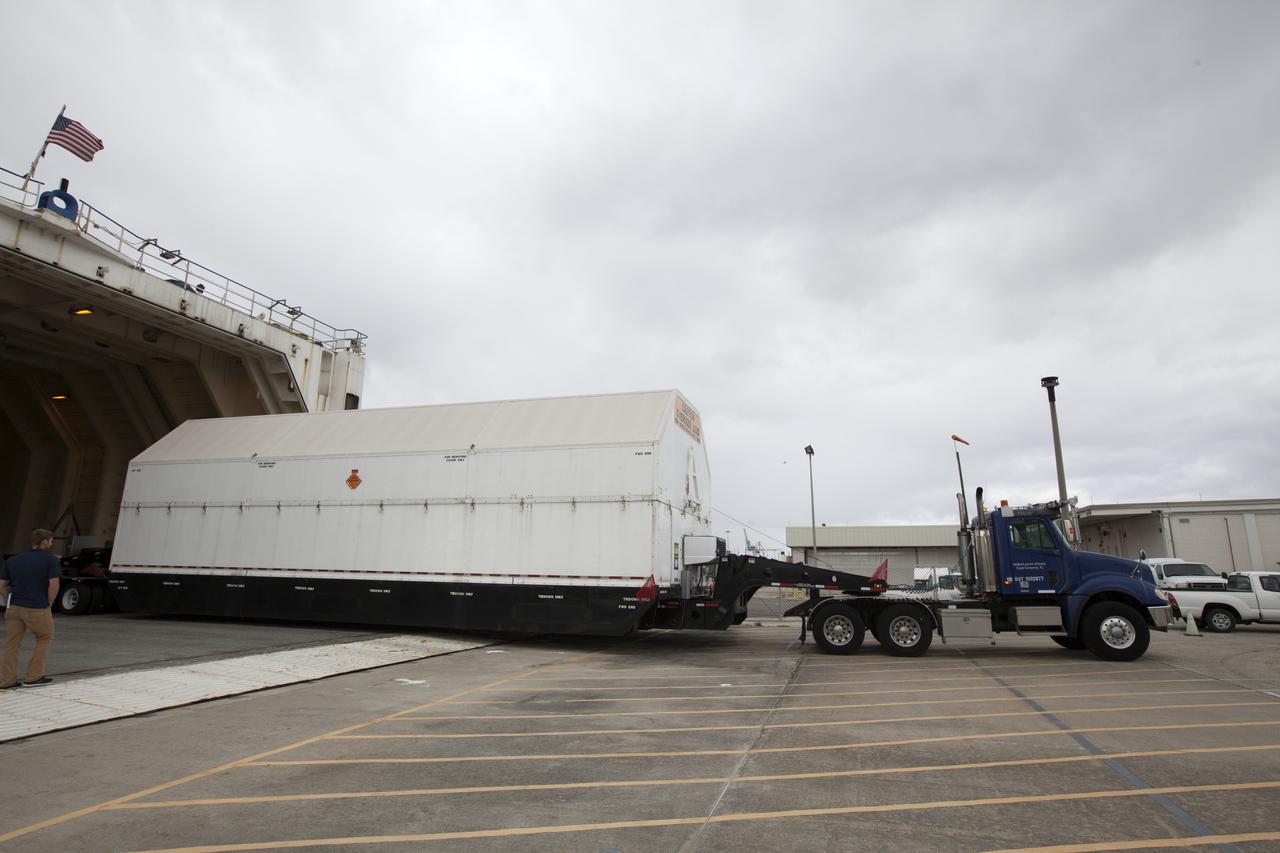
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy second stage, packaged in its shipping container, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
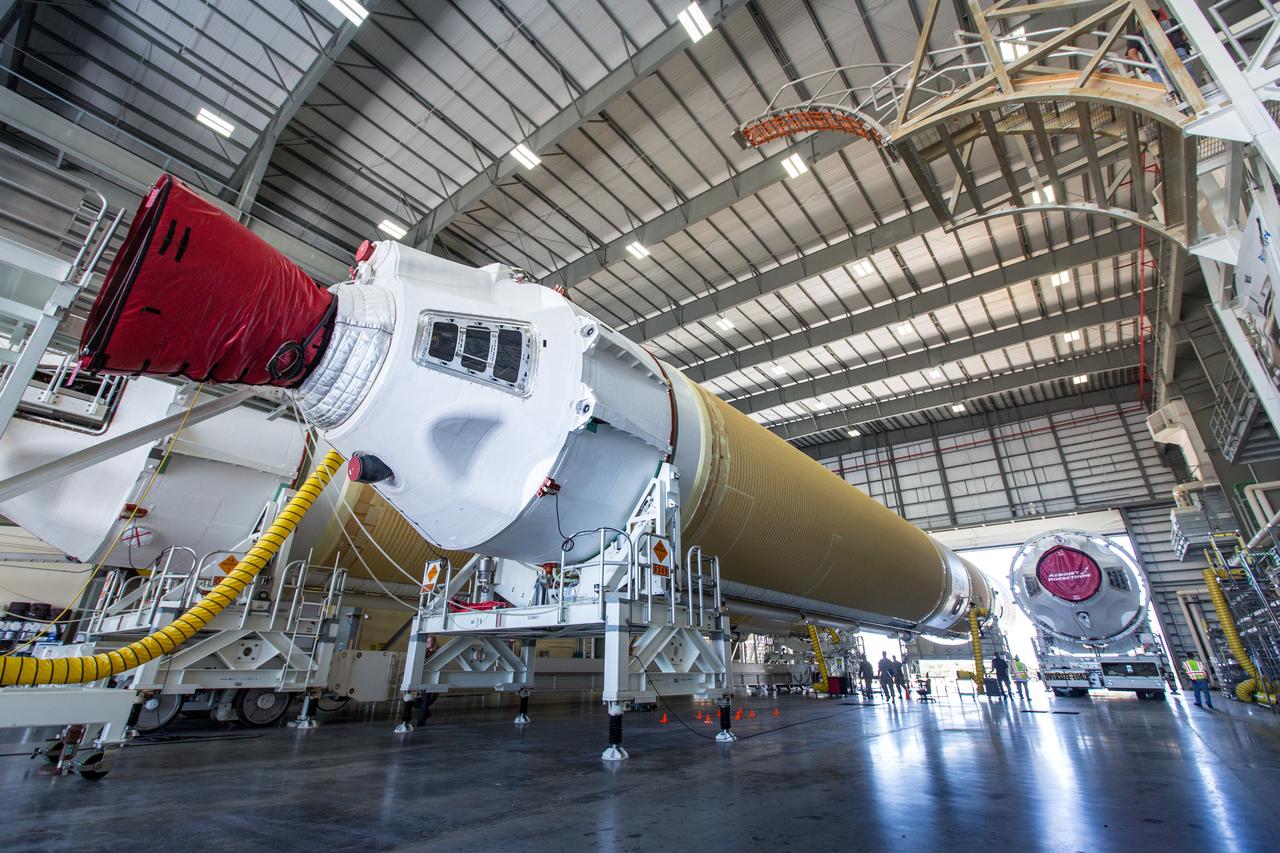

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
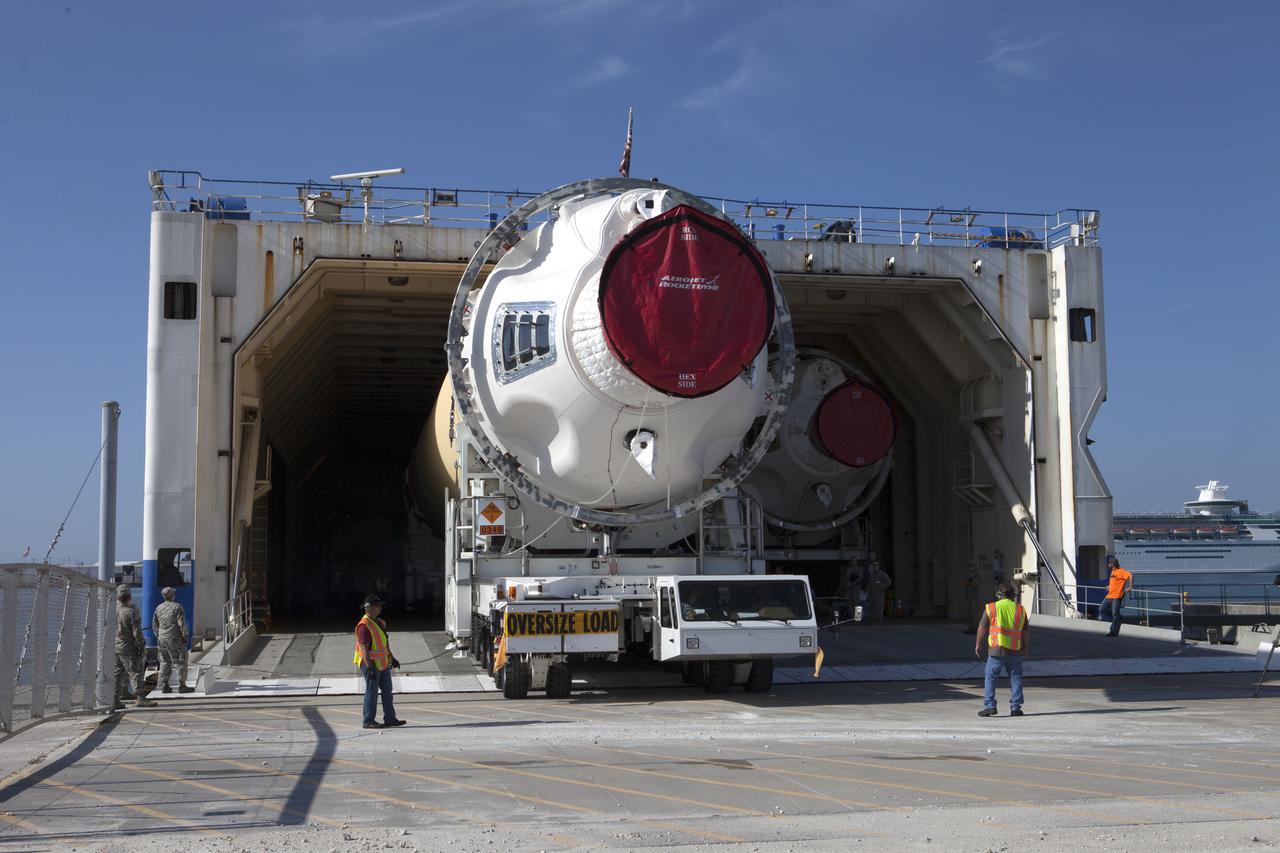

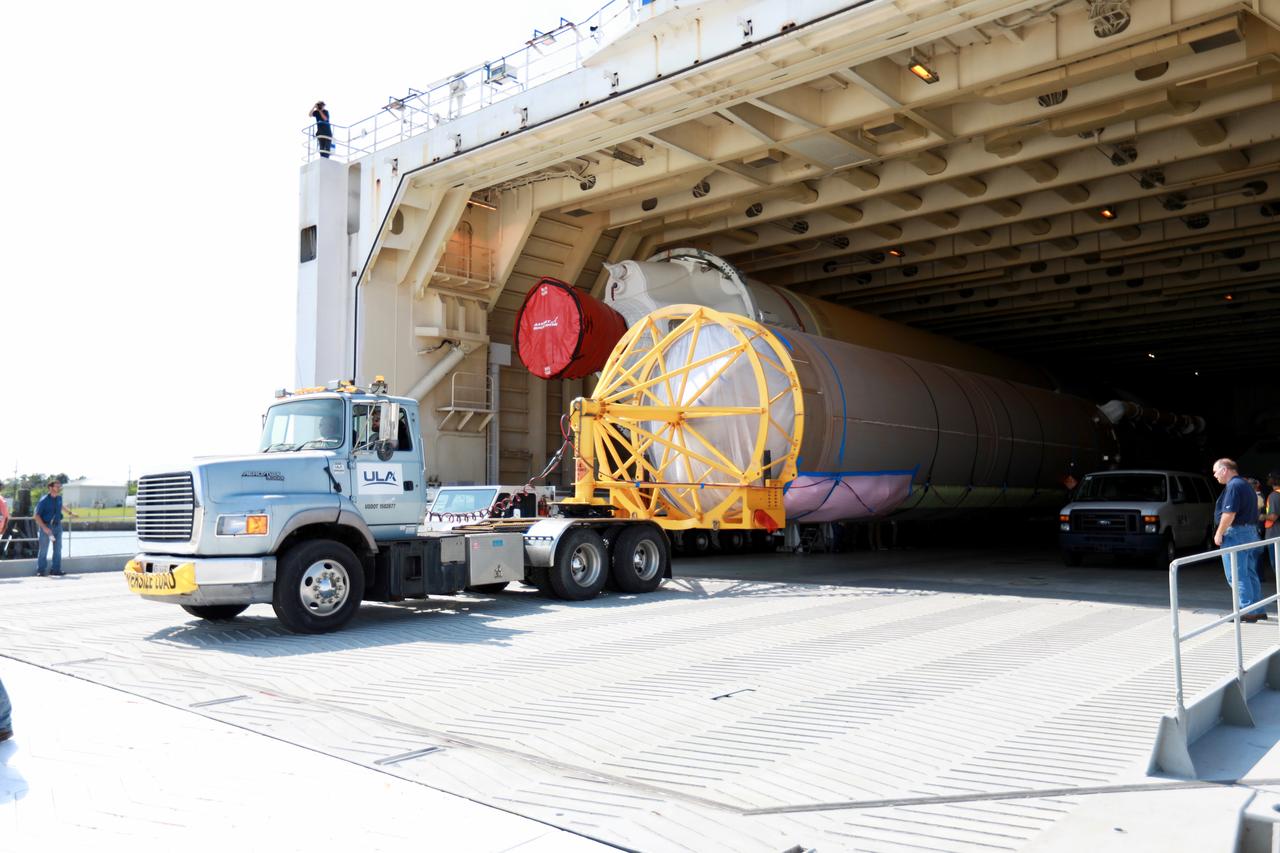
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
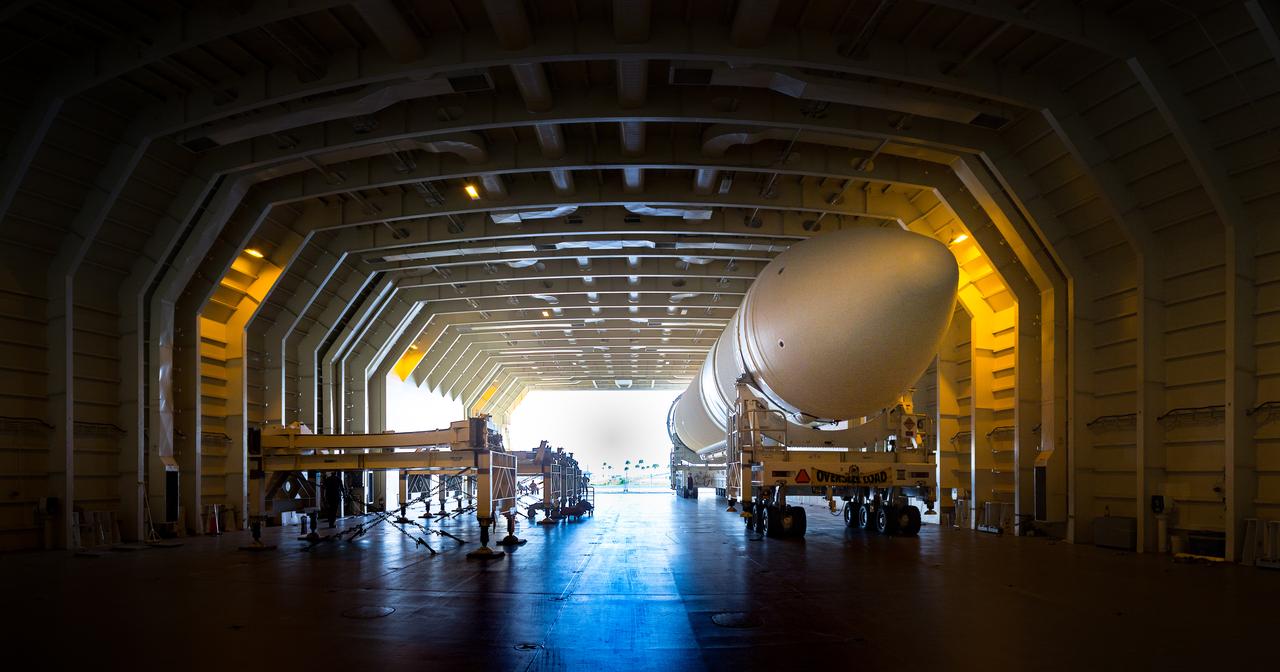

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is about to be offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
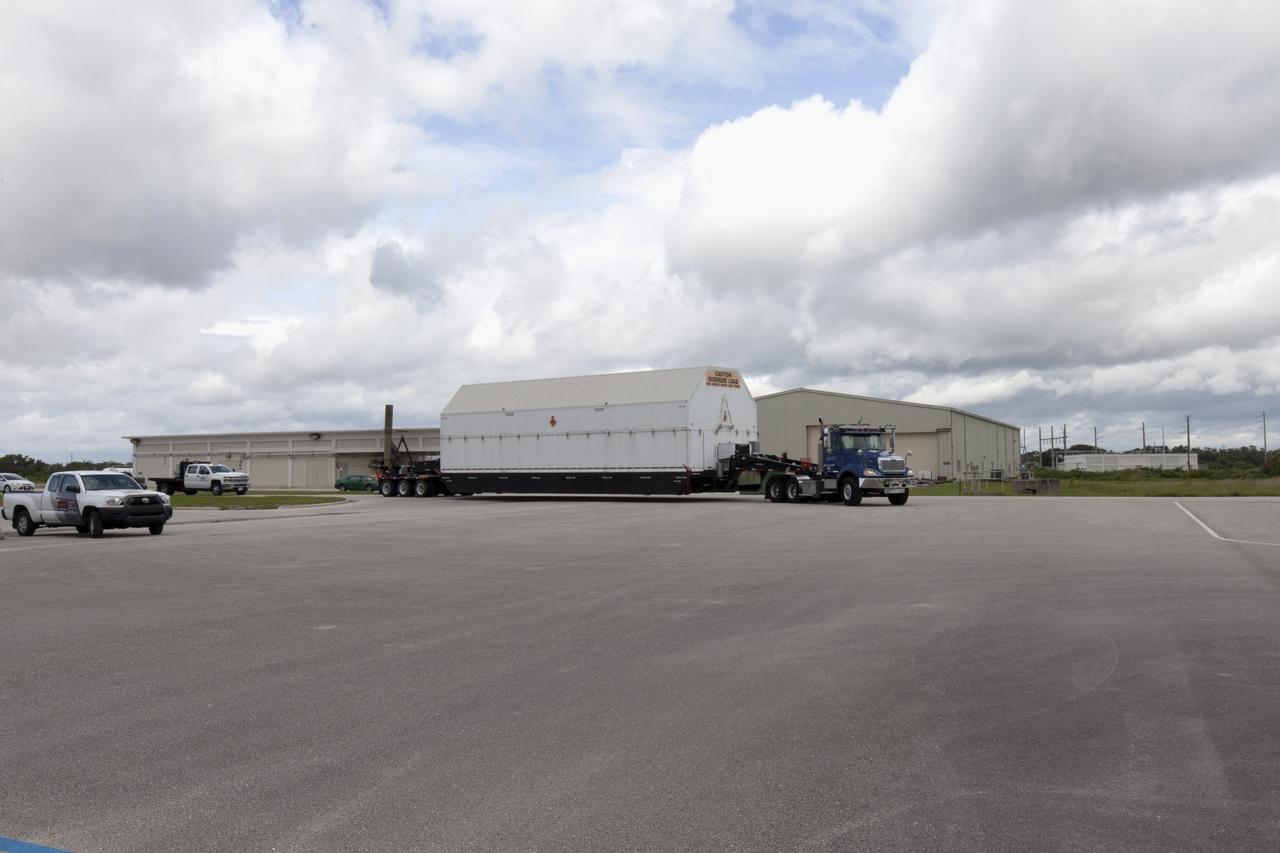

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy second stage, packaged in its shipping container, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
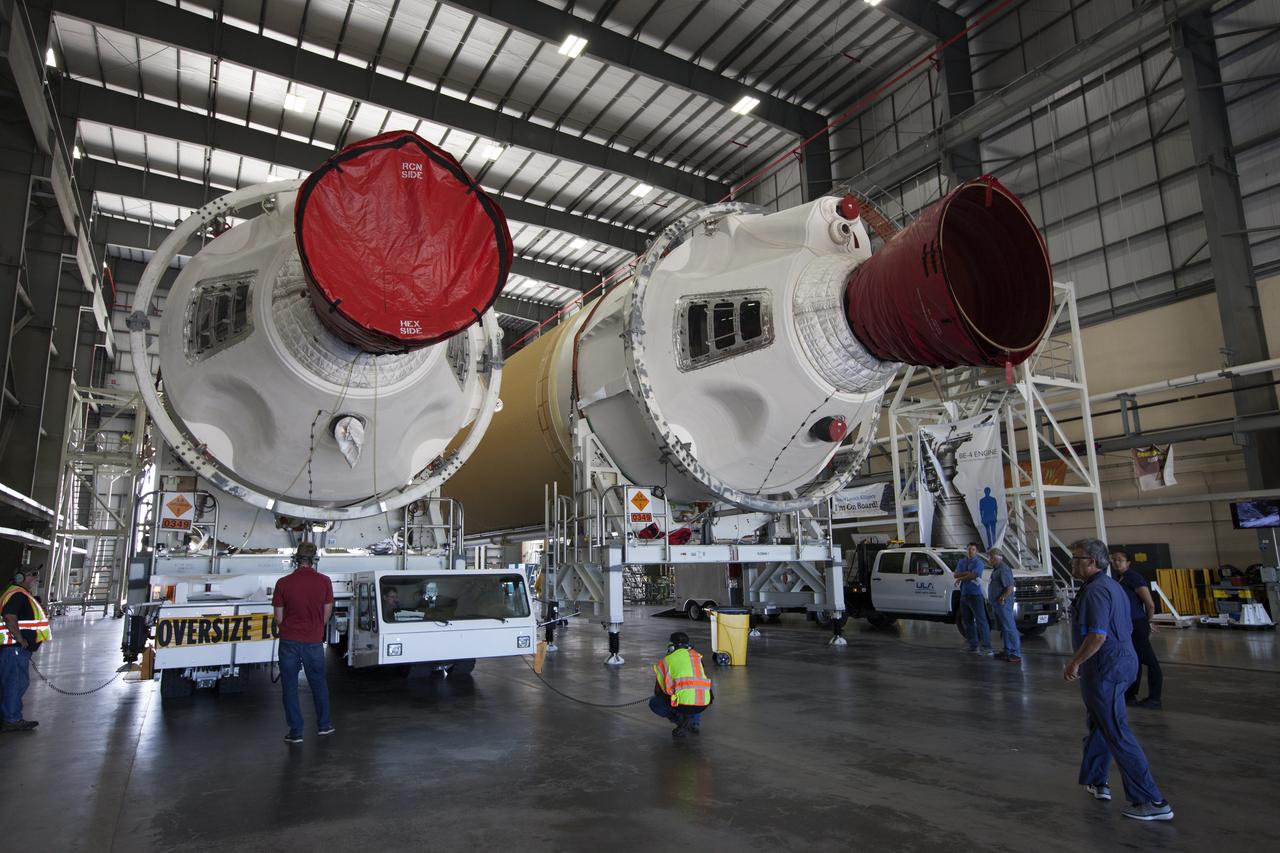

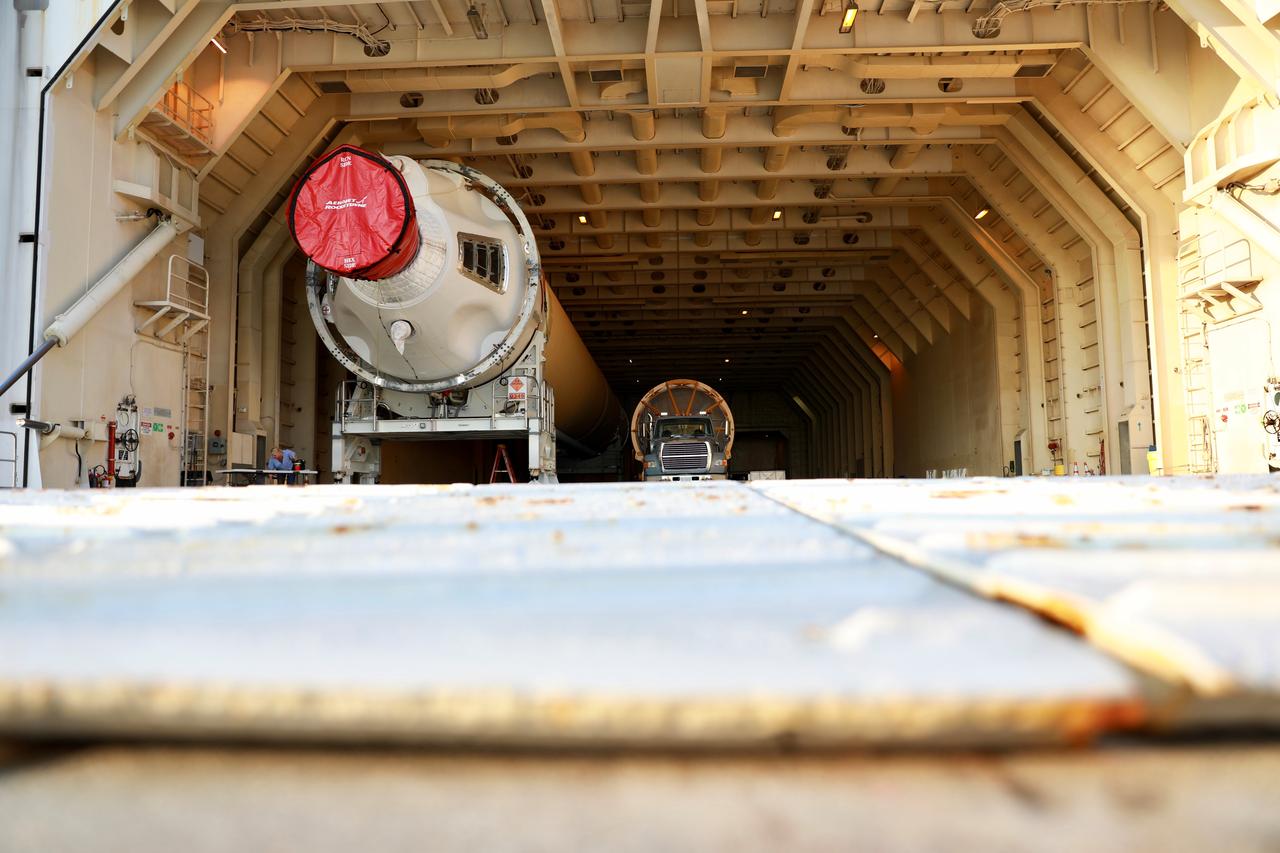
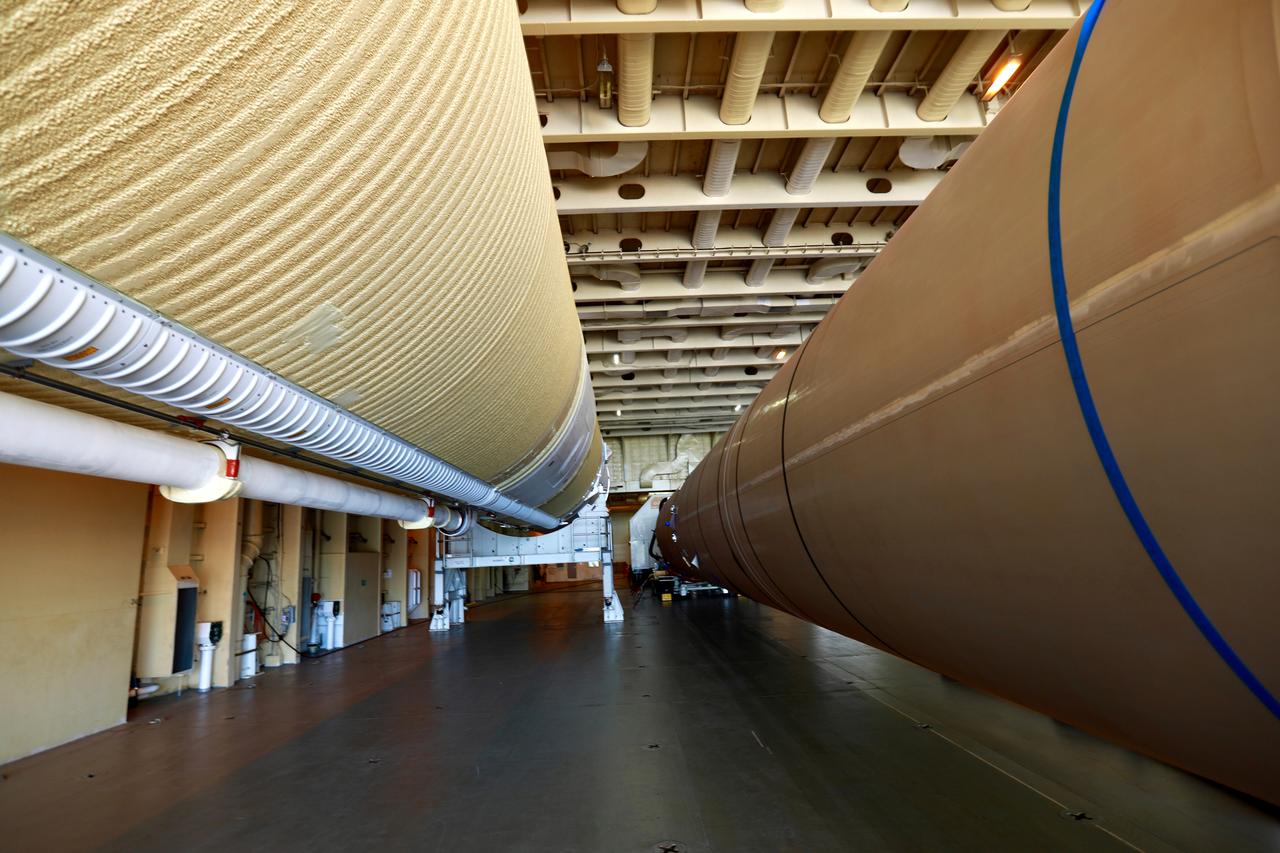
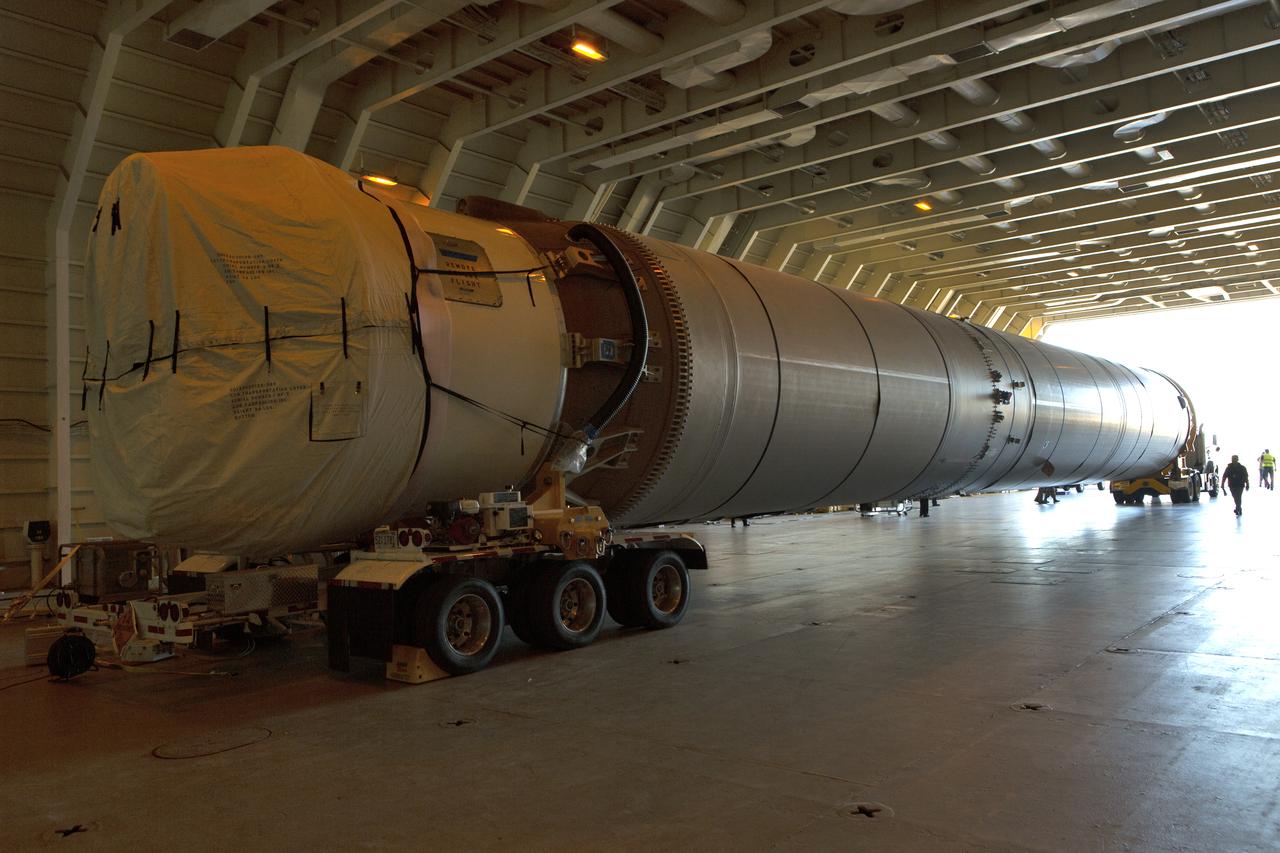
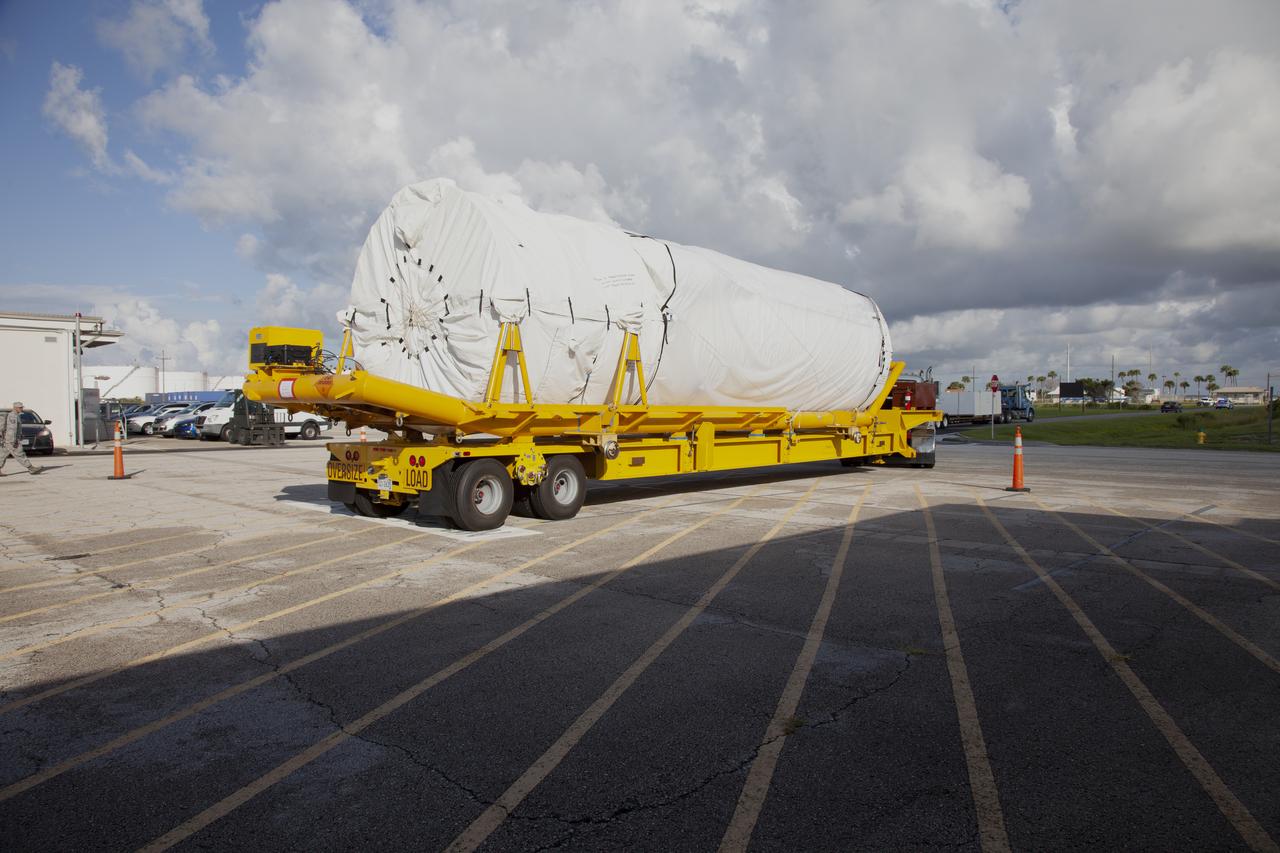
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is placed beside an additional core inside Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
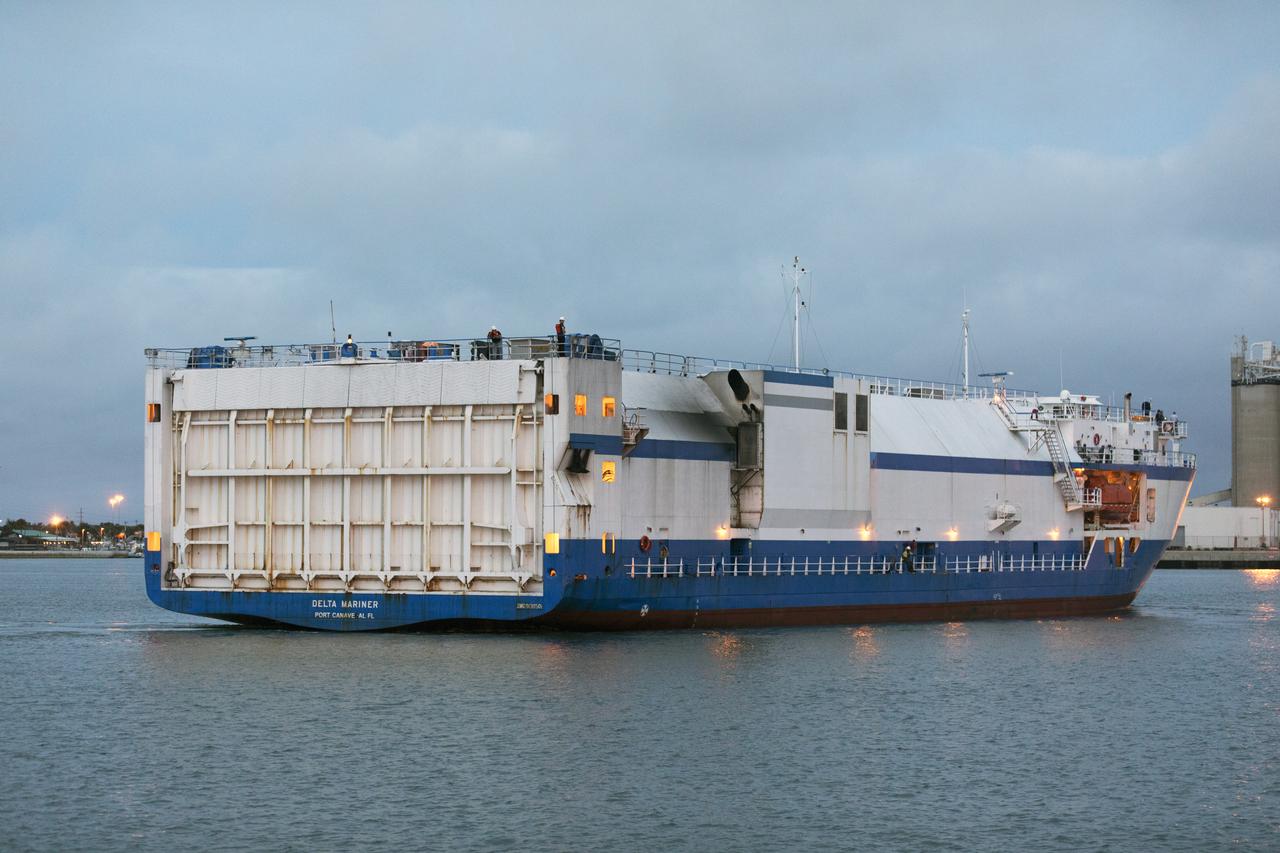

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
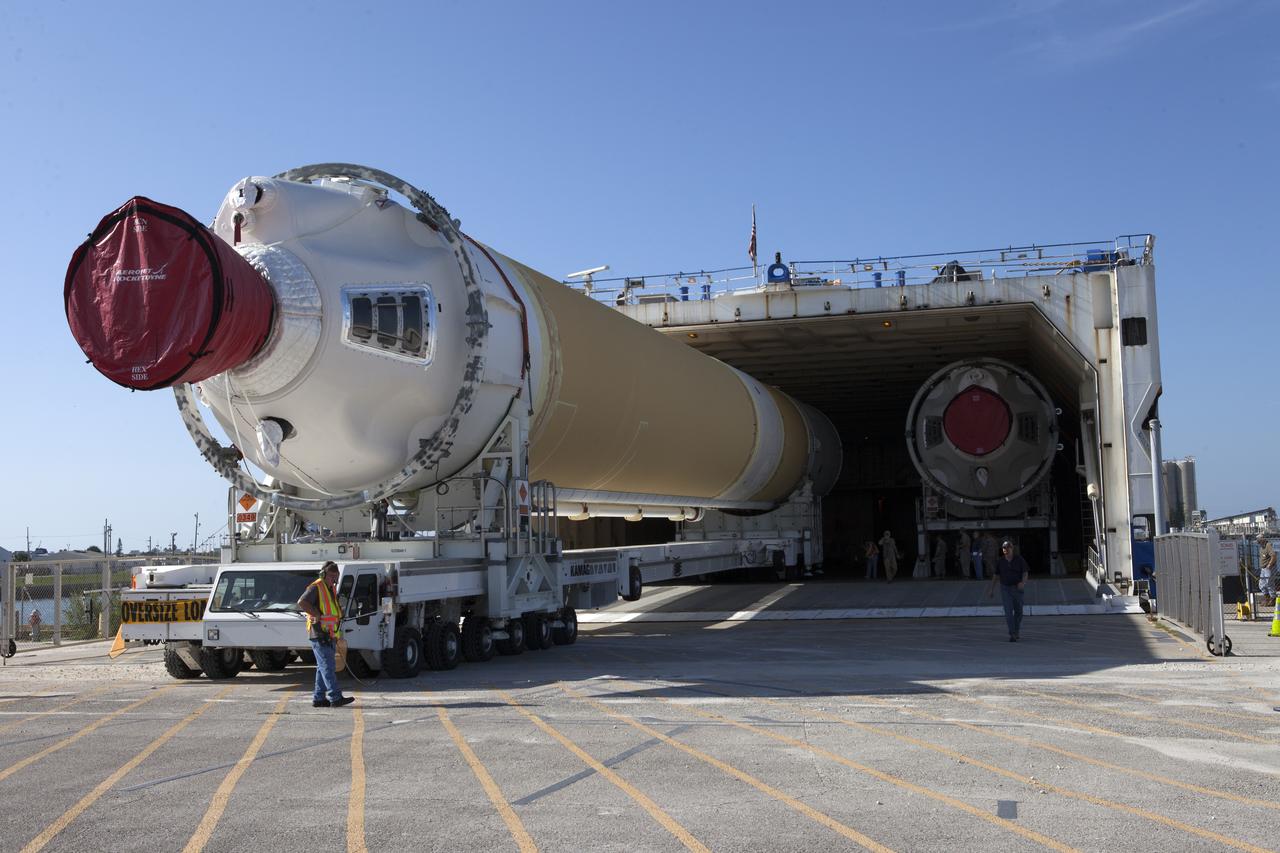

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
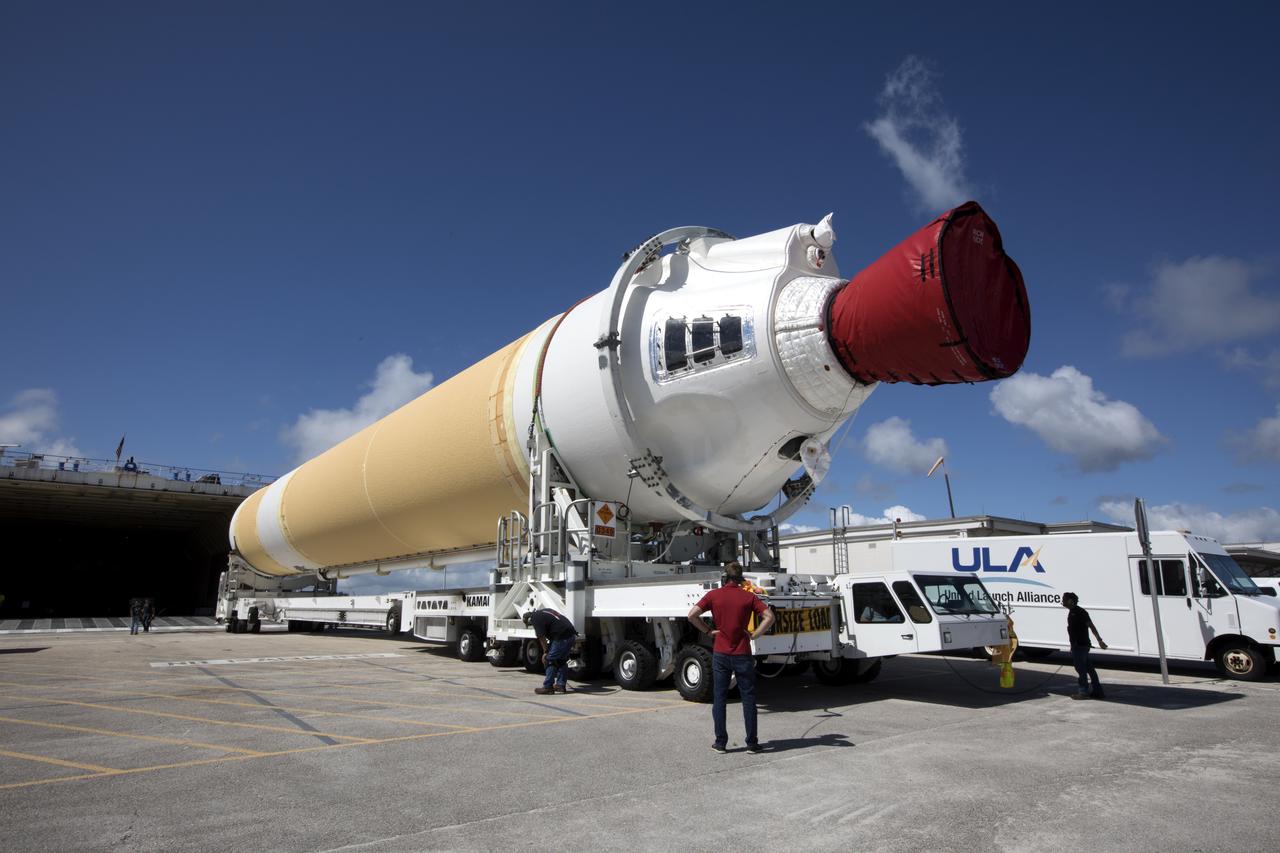

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
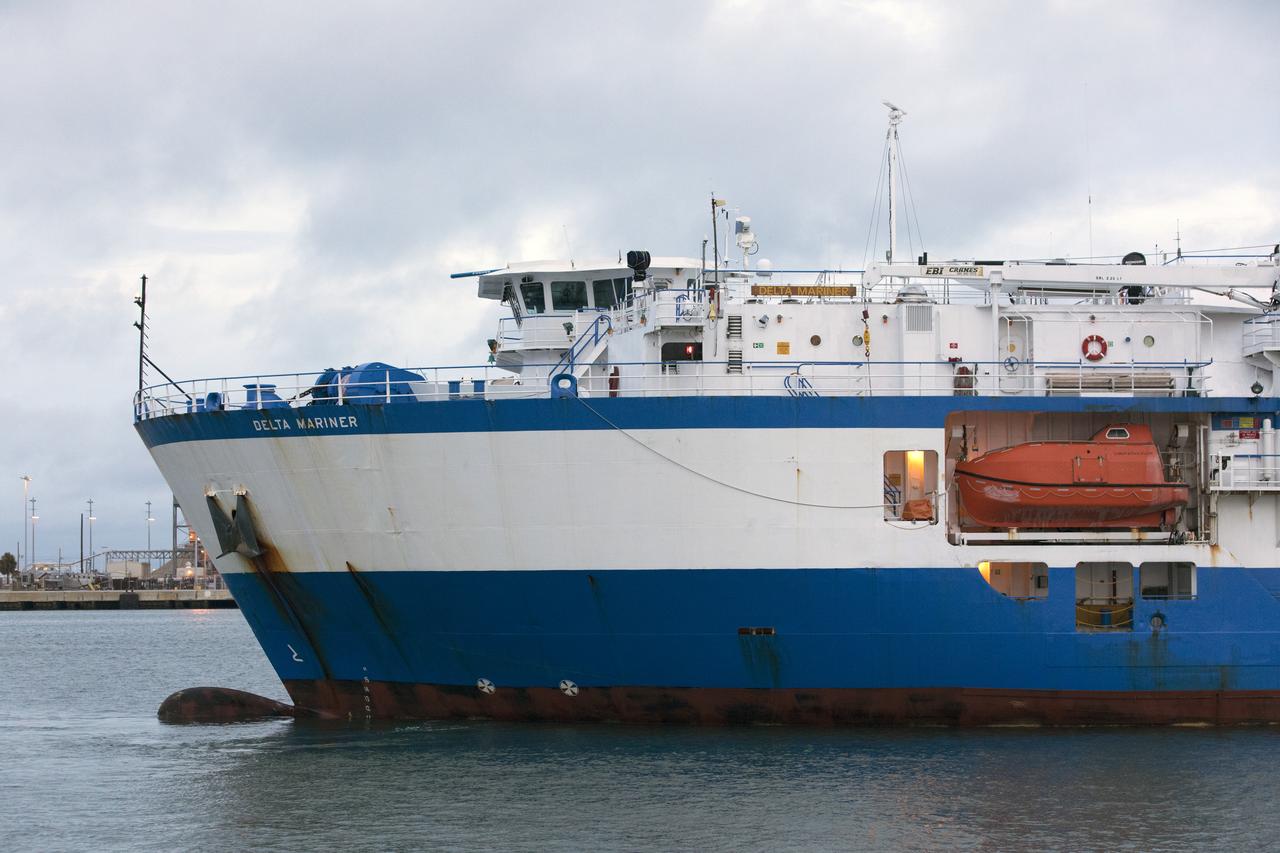

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
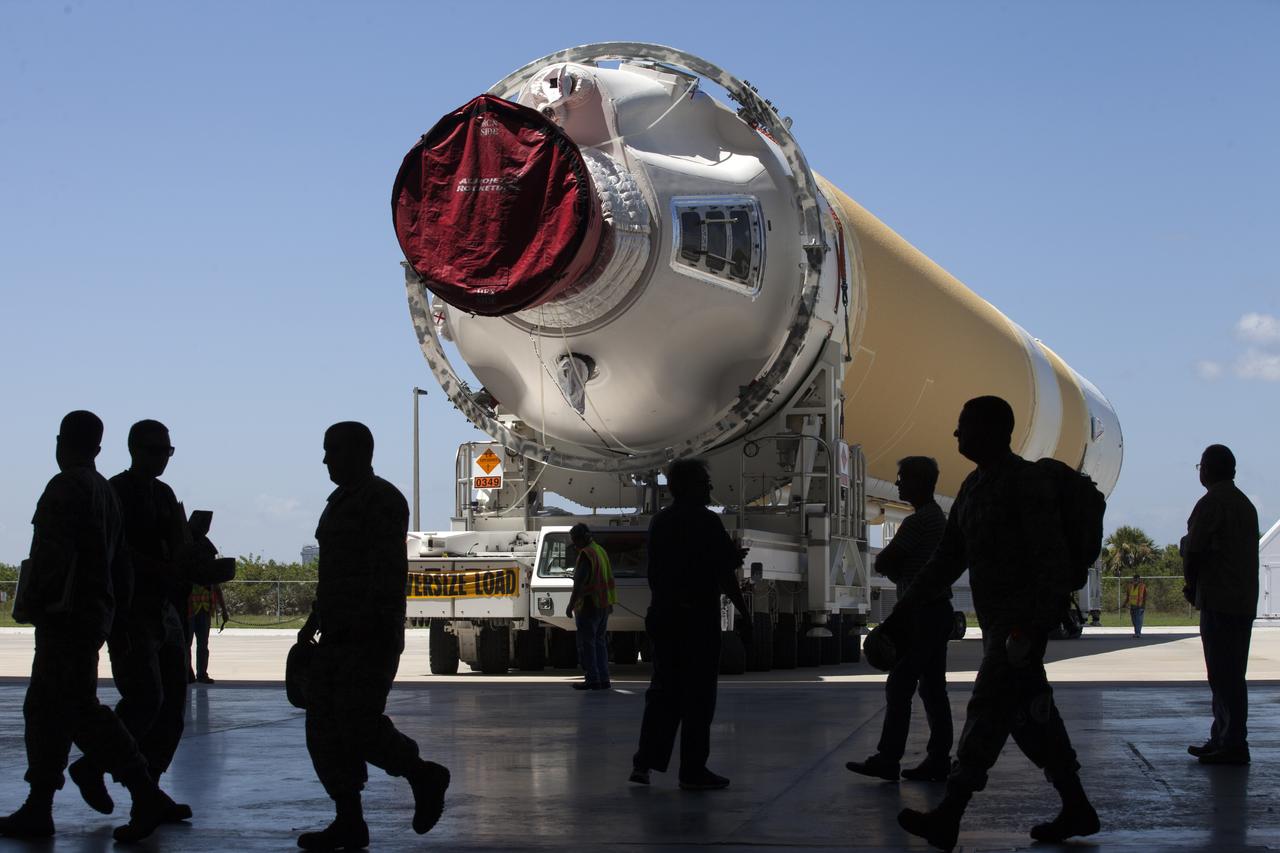

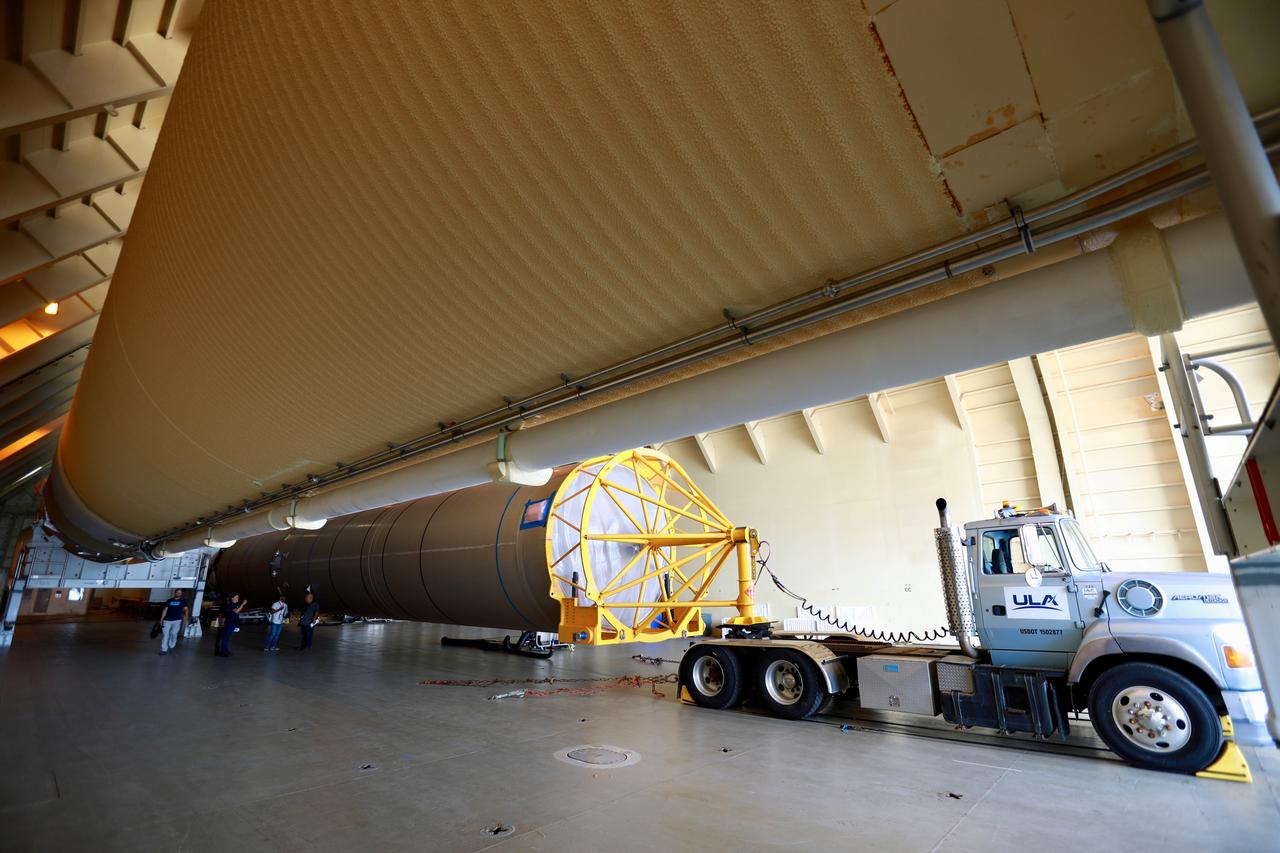
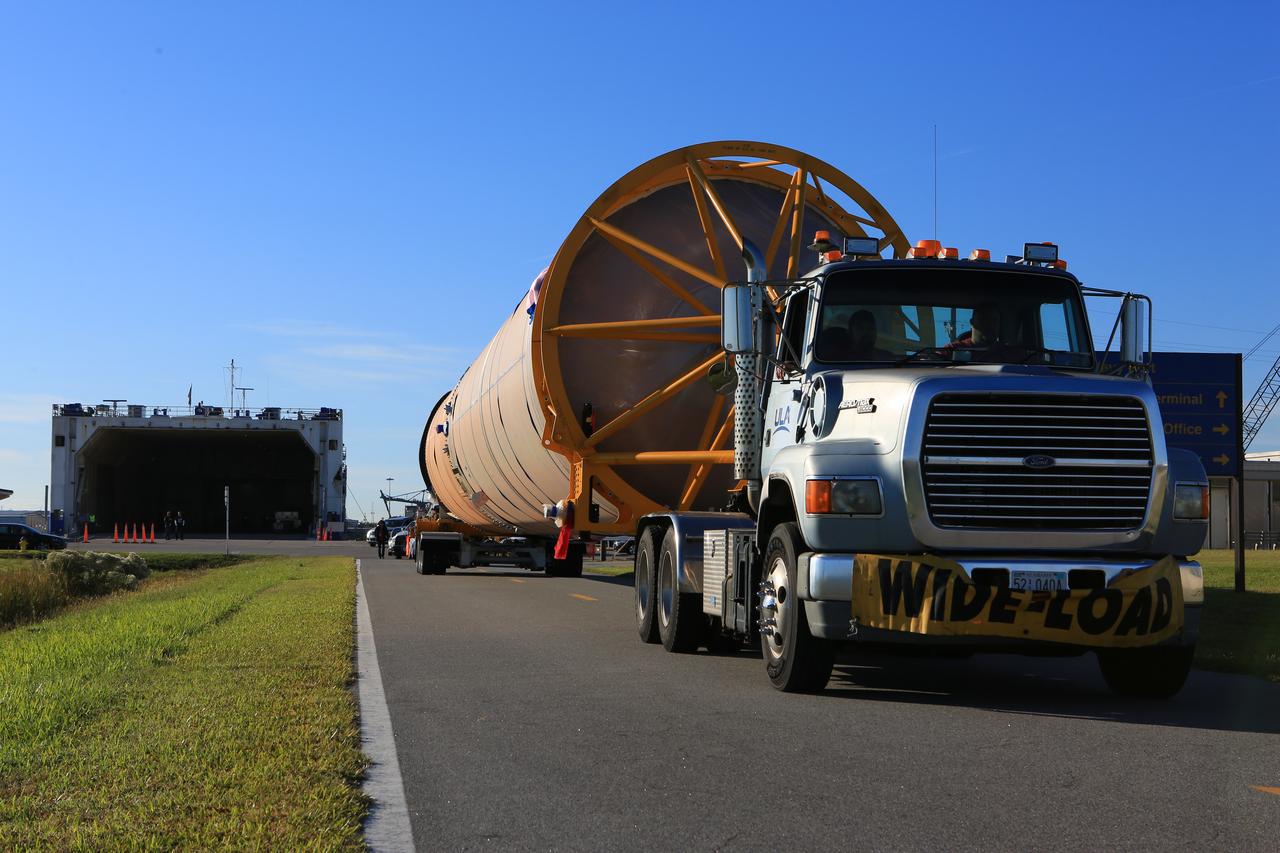
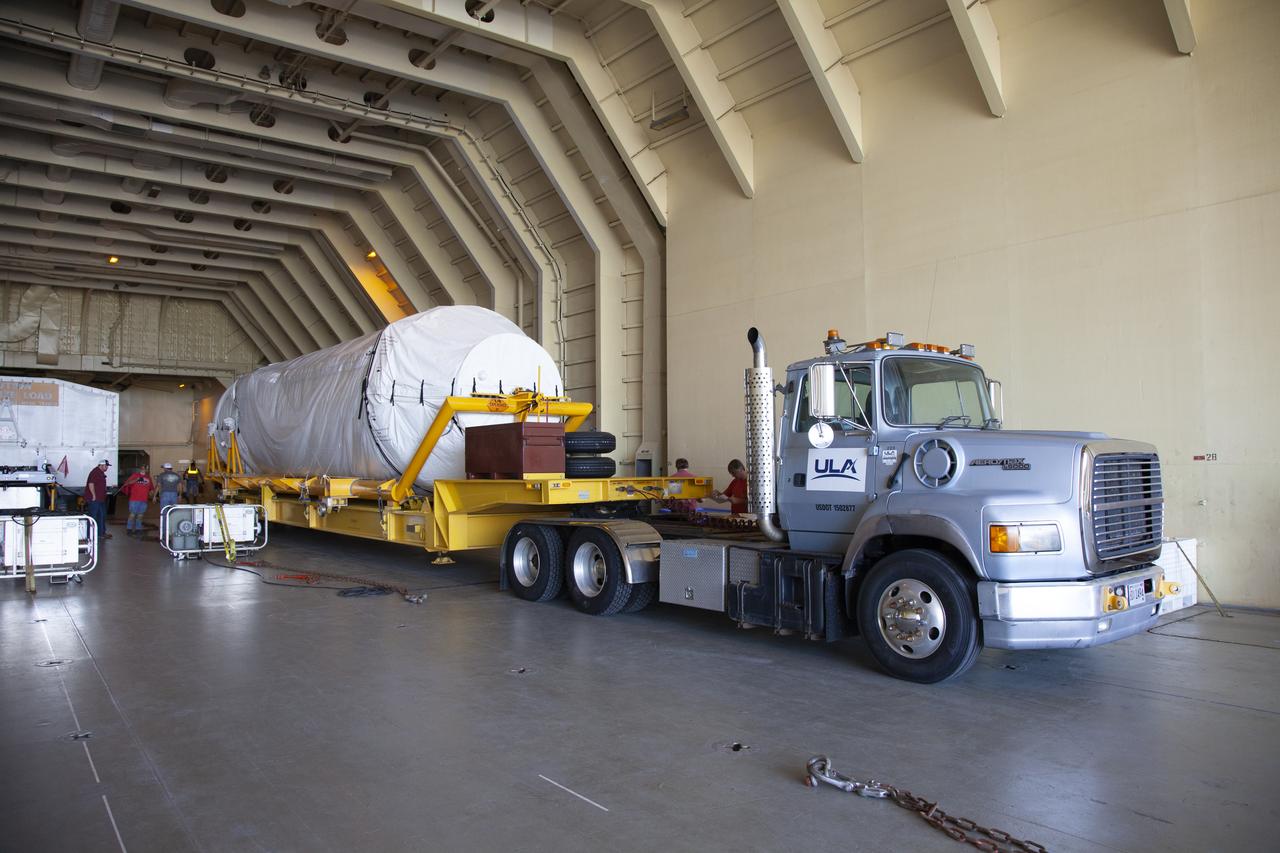
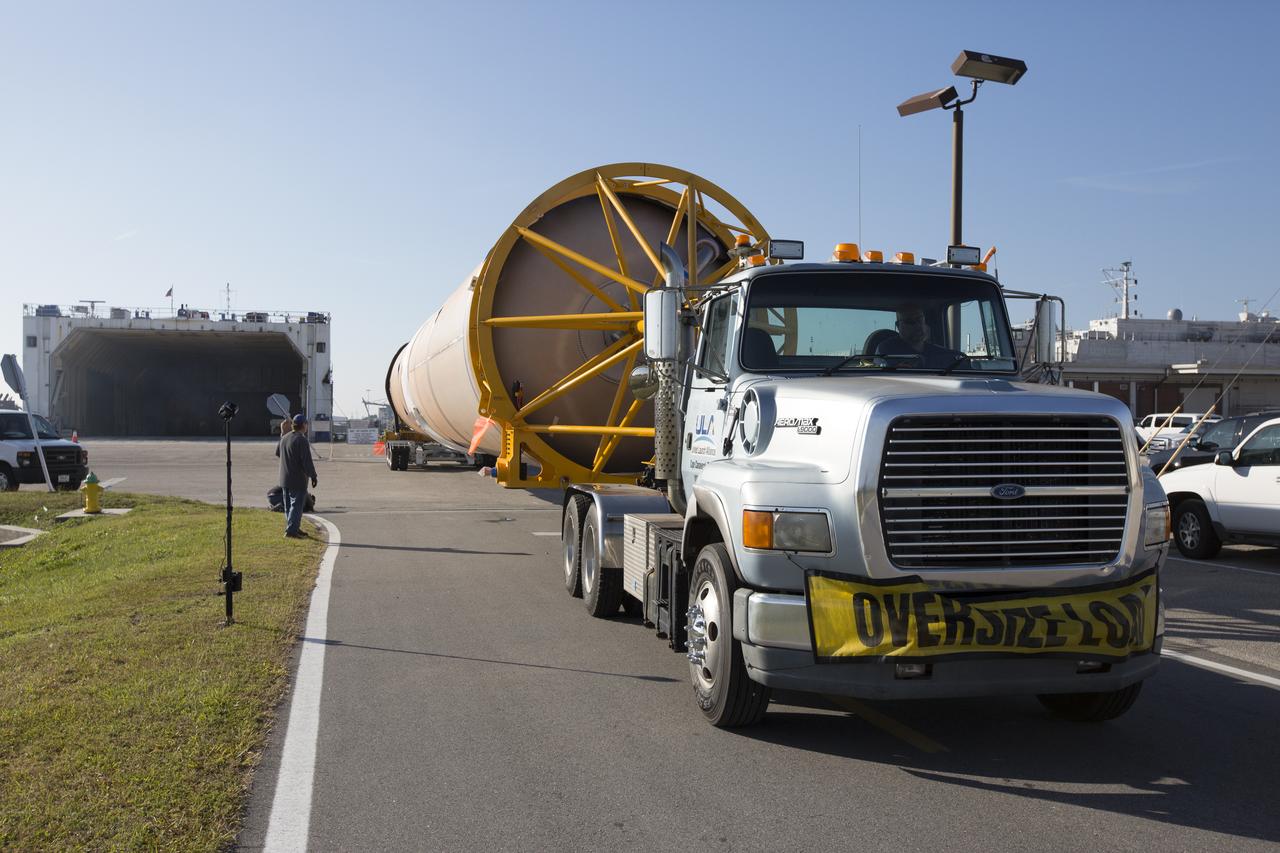
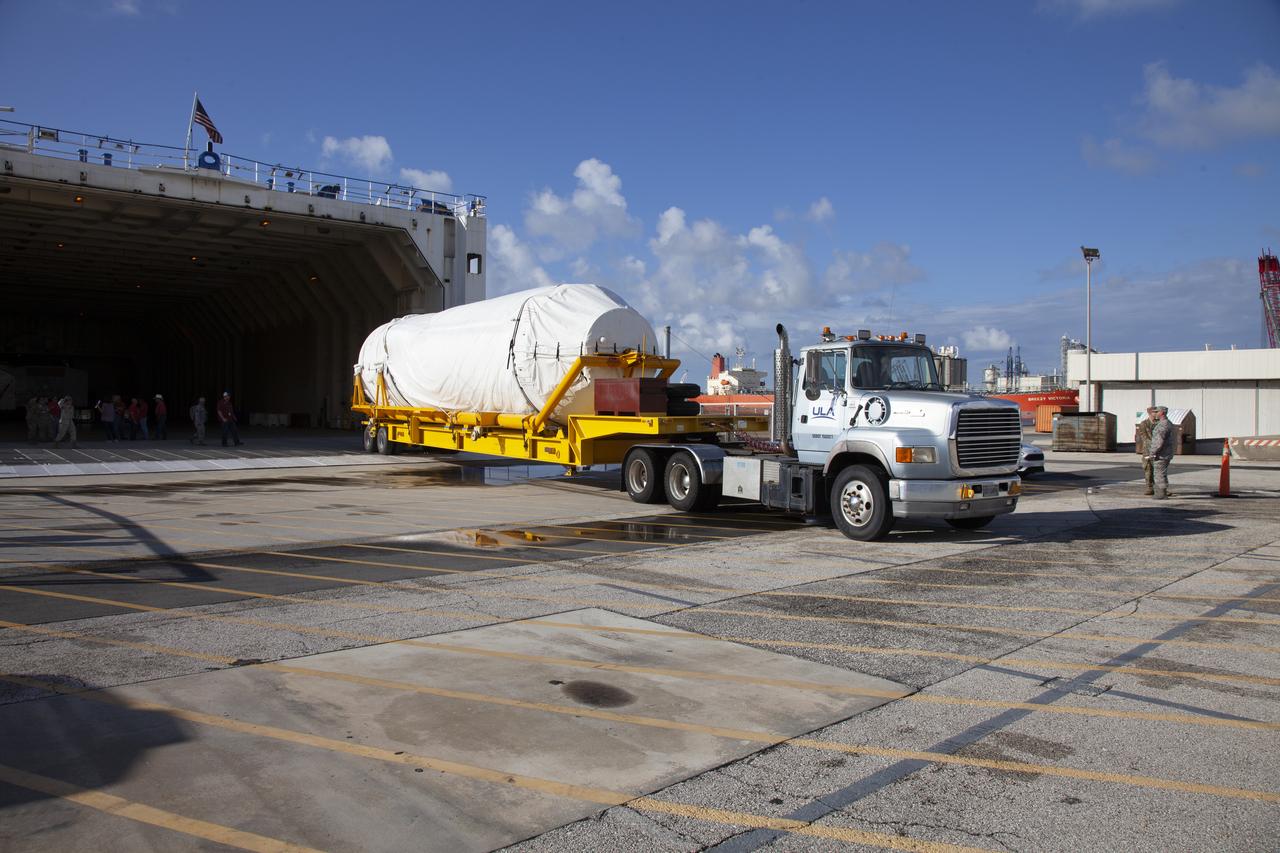
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives by truck at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
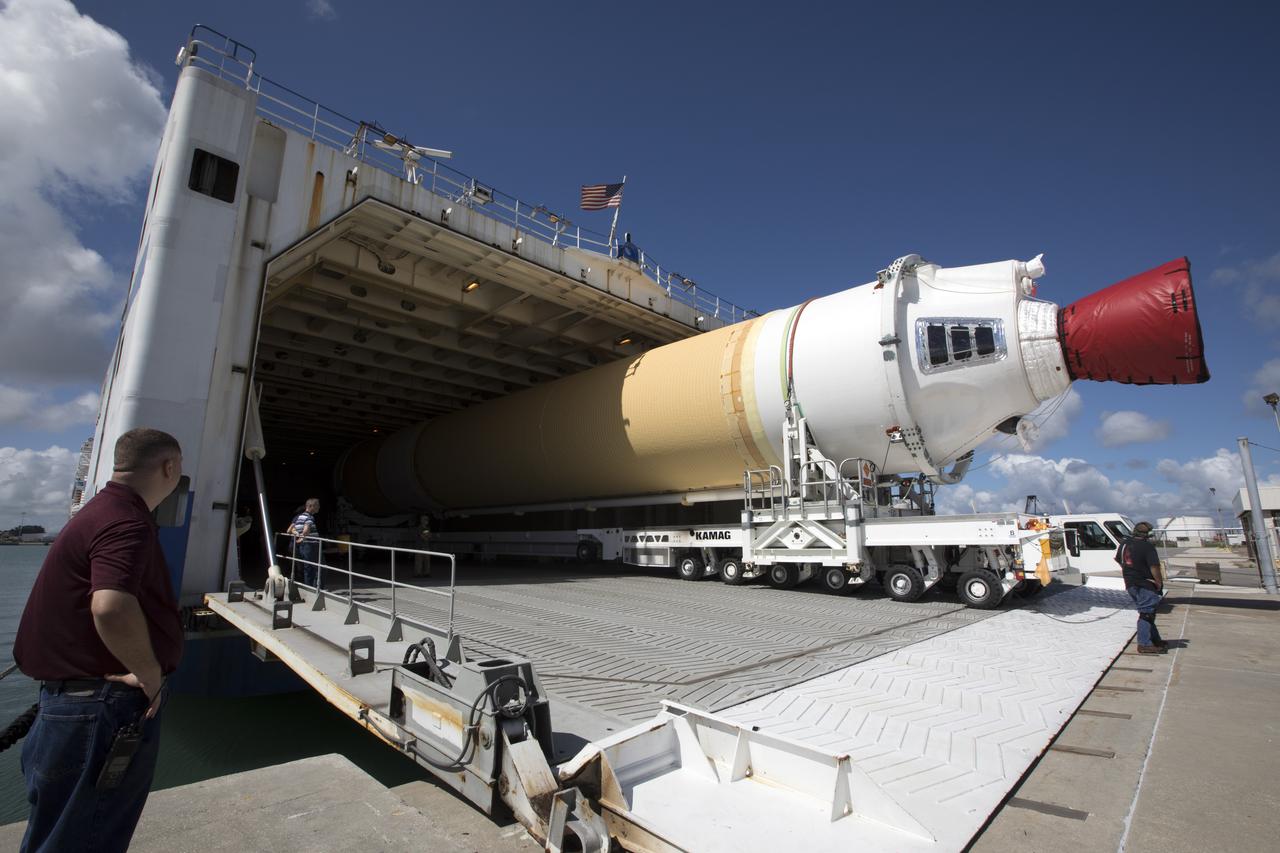

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
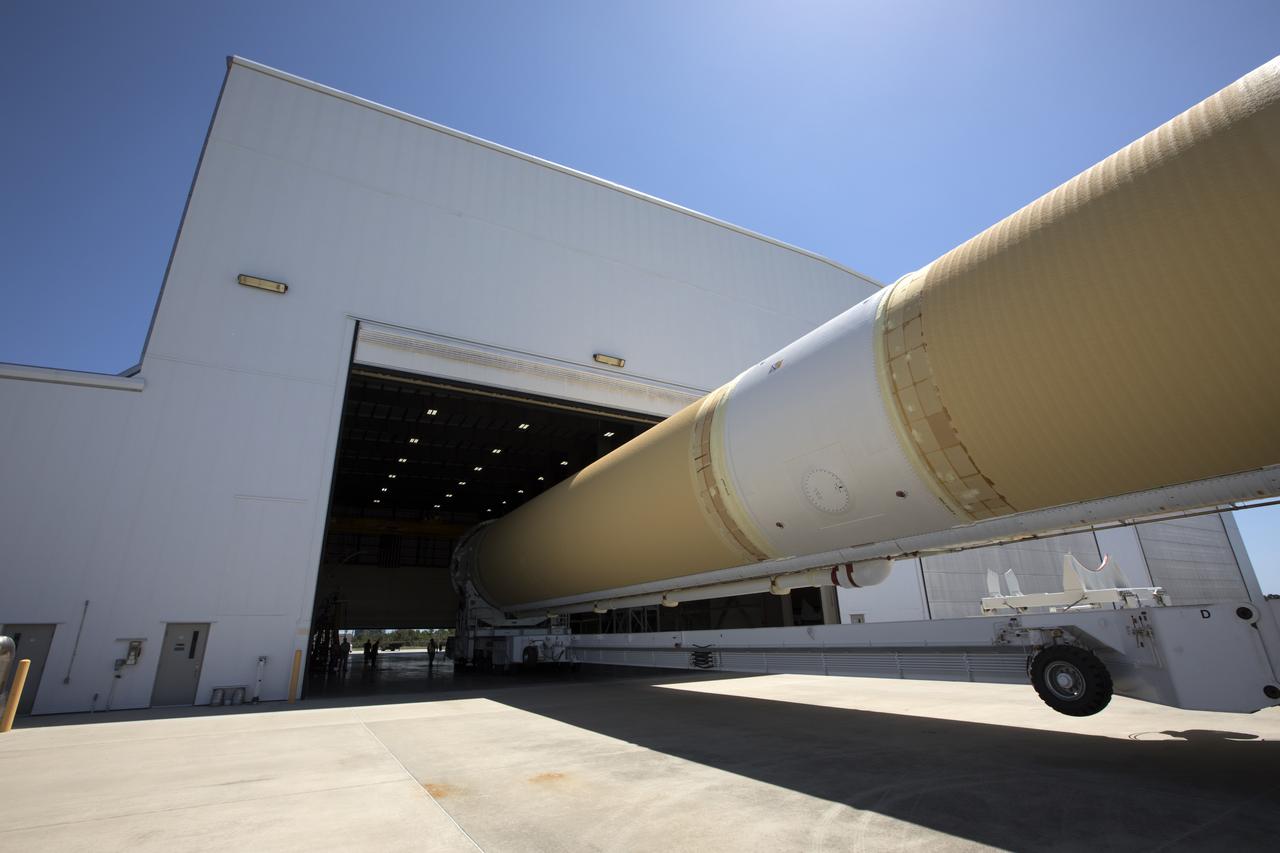

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck inside Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
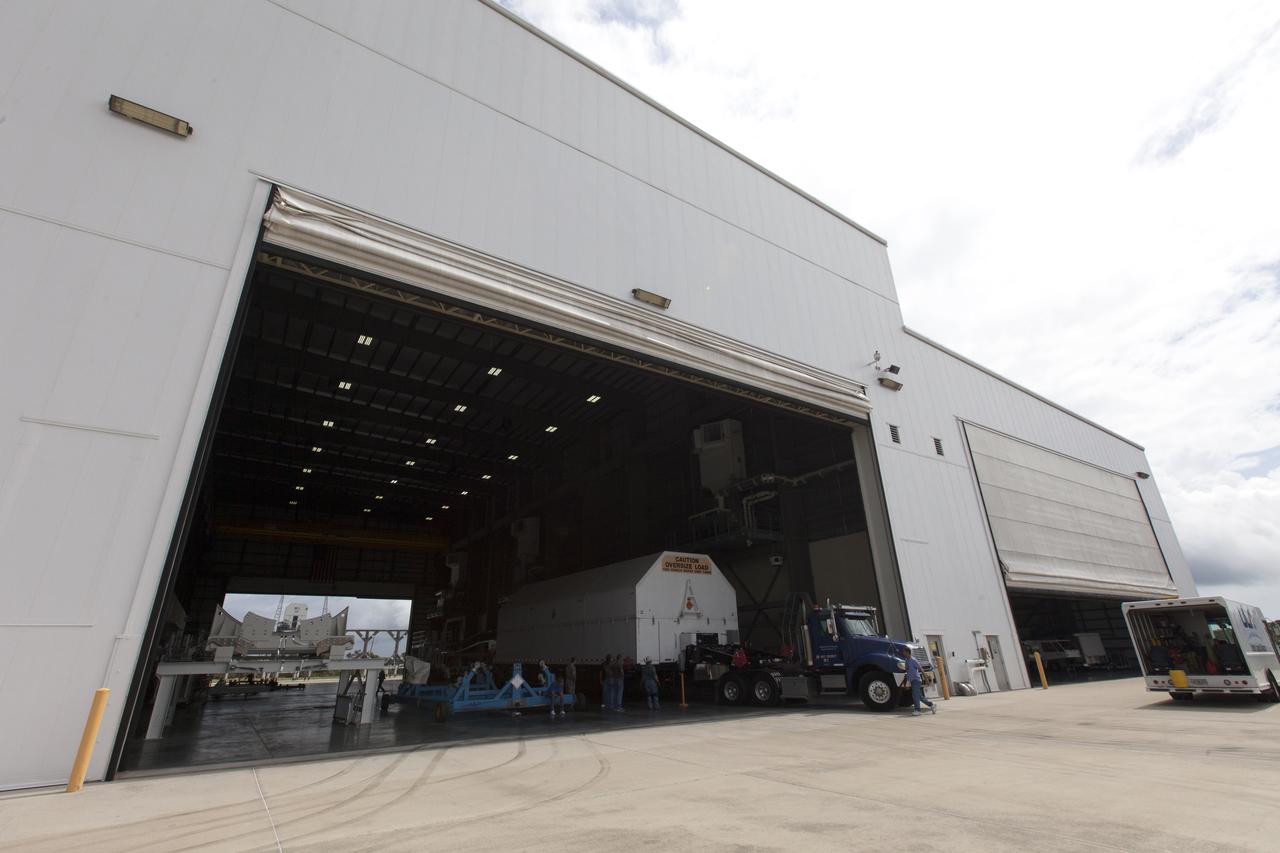

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy second stage, packaged in its shipping container, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
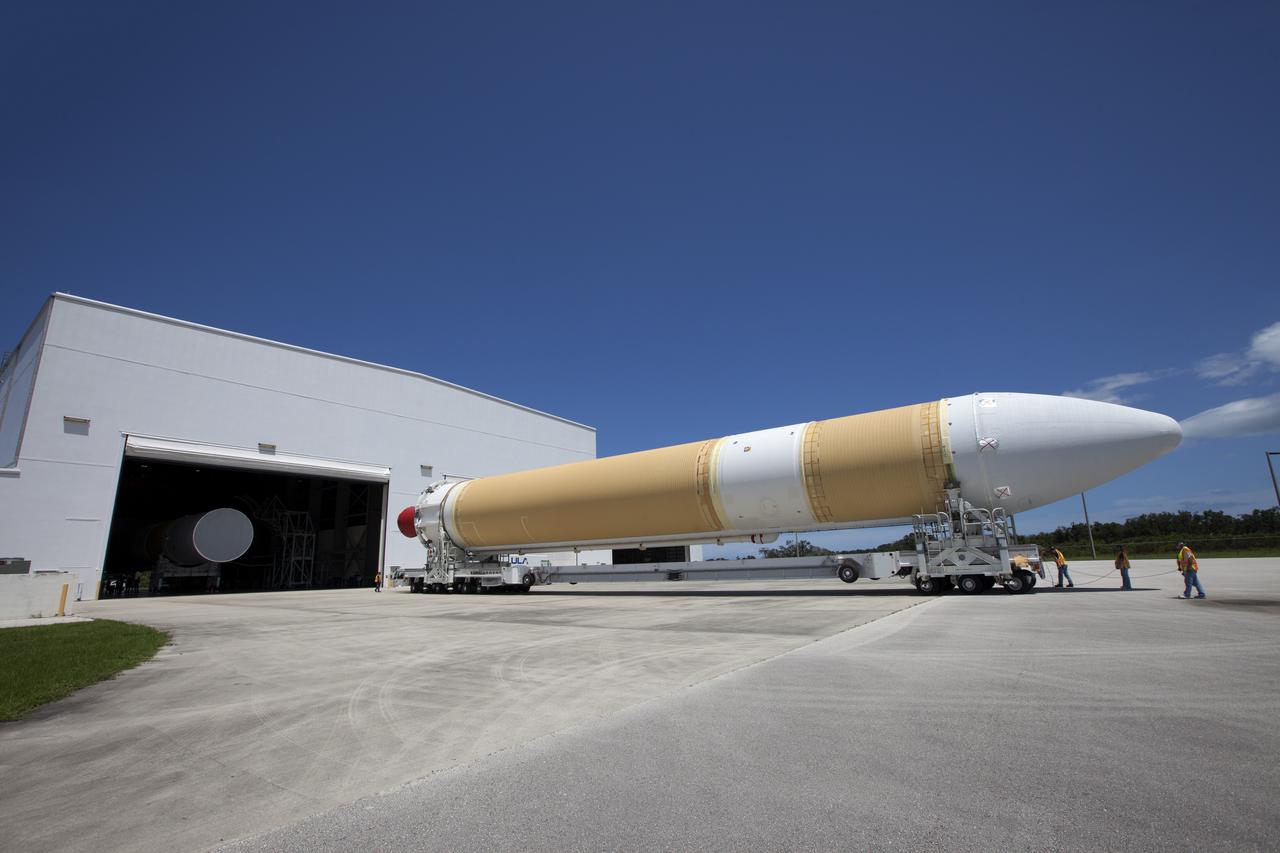

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core arrives by truck at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
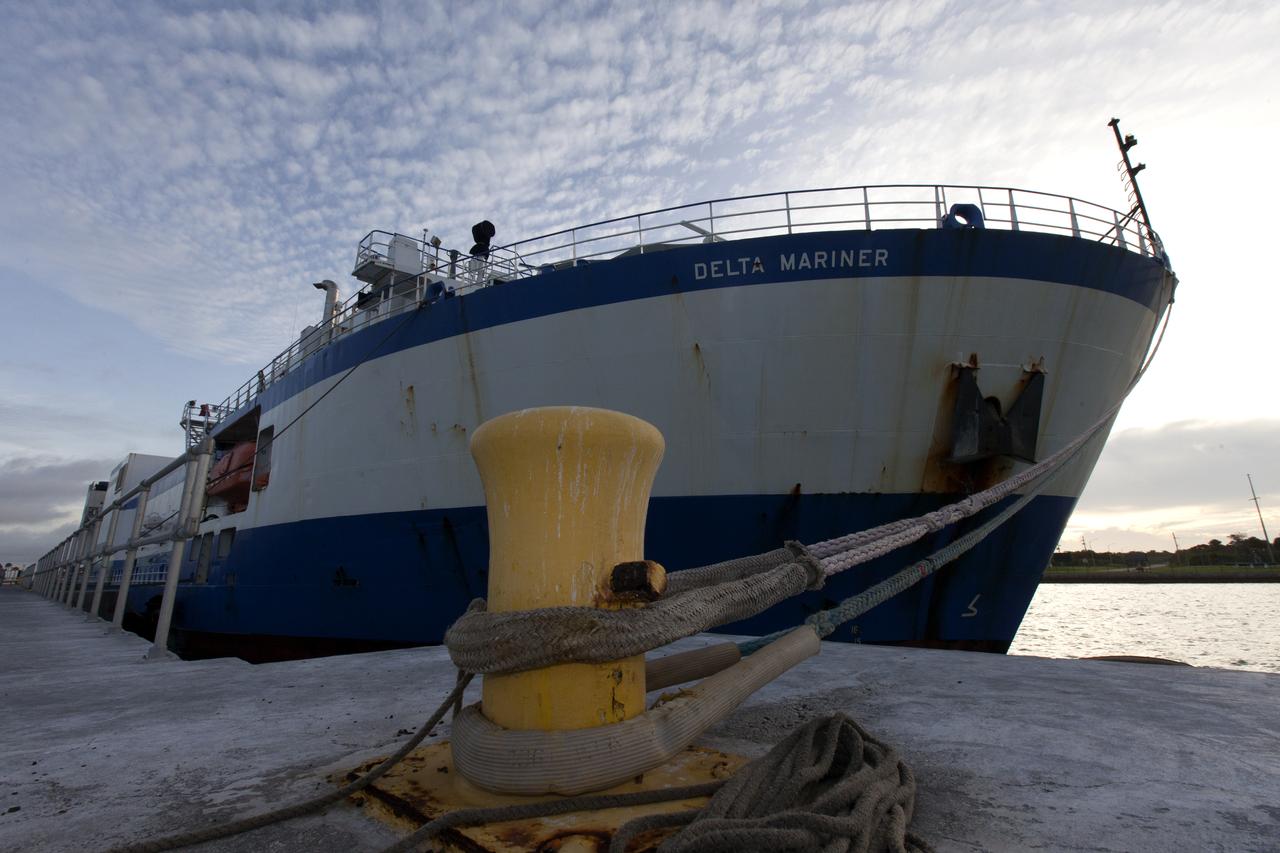

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
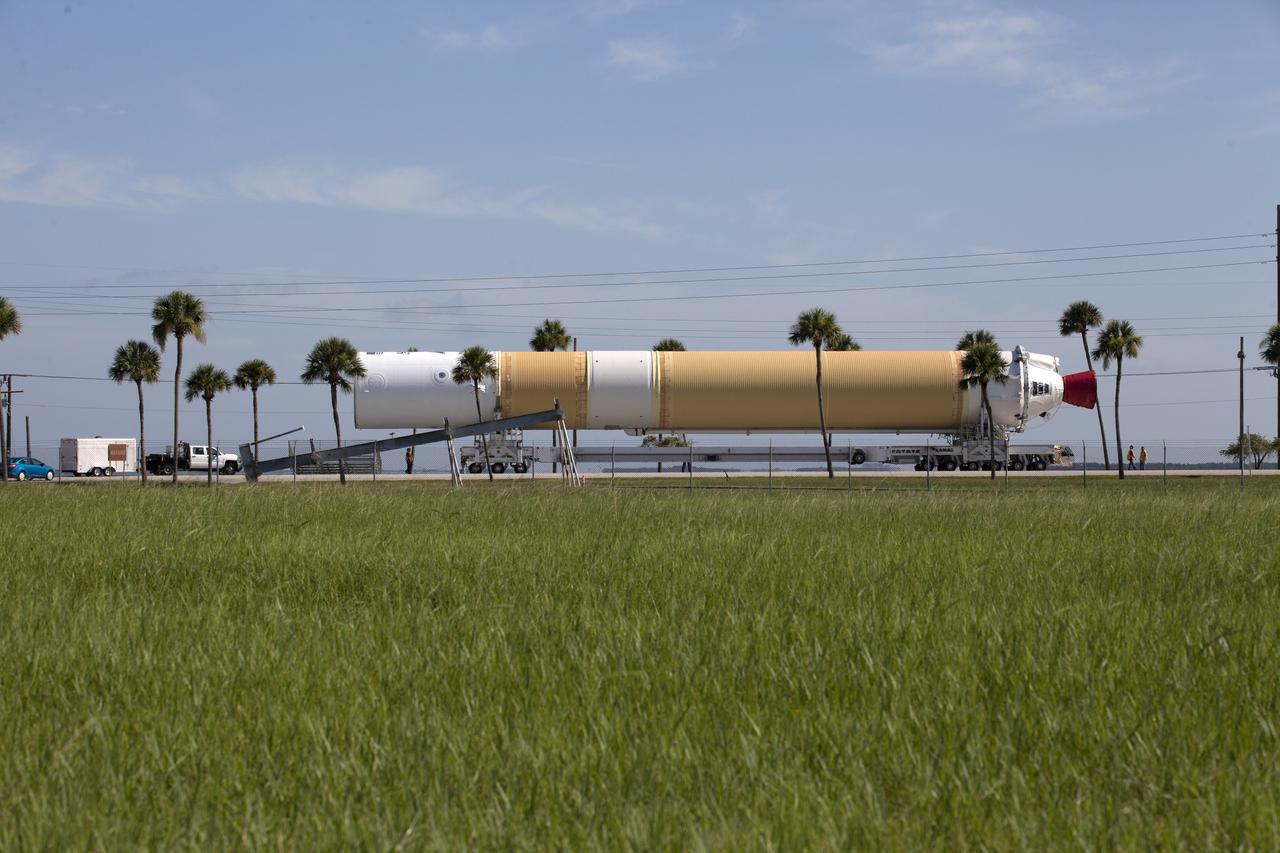

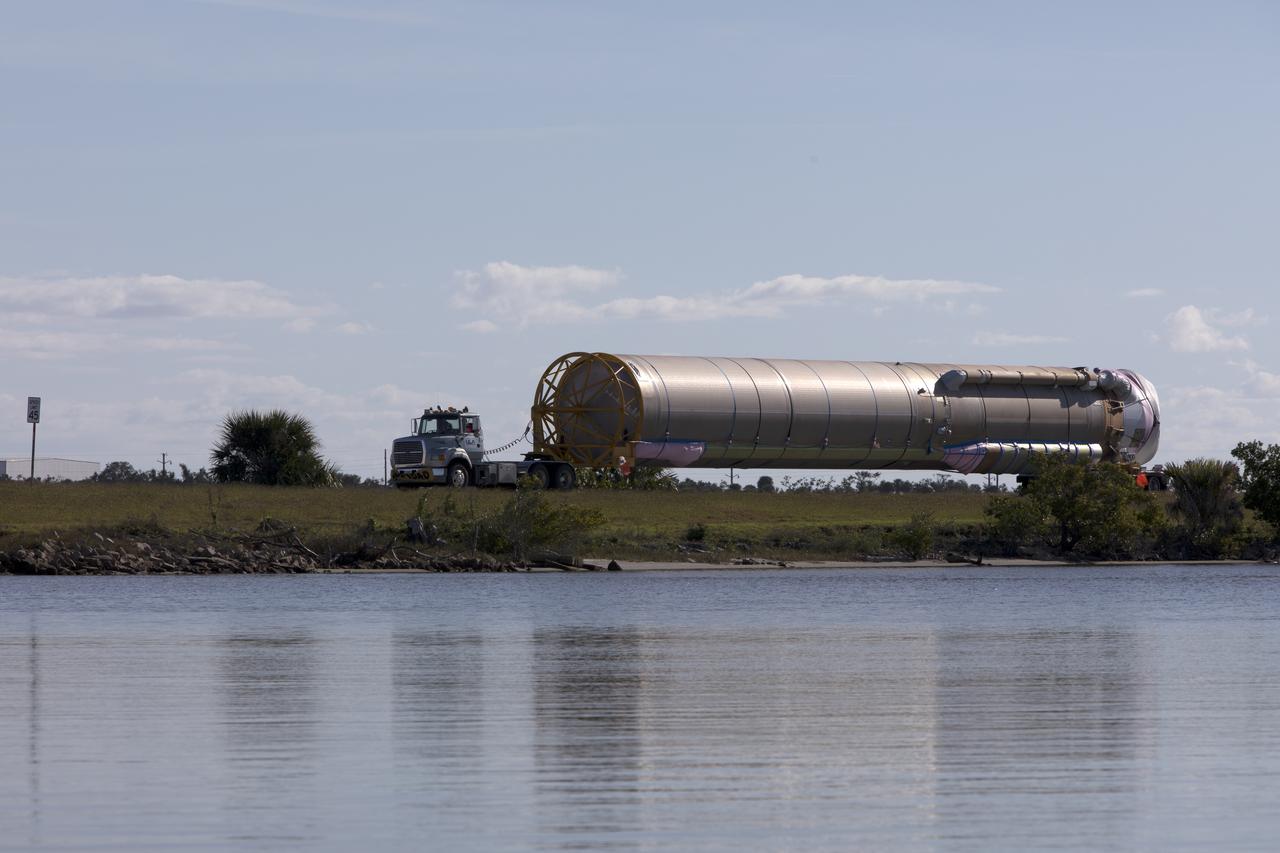
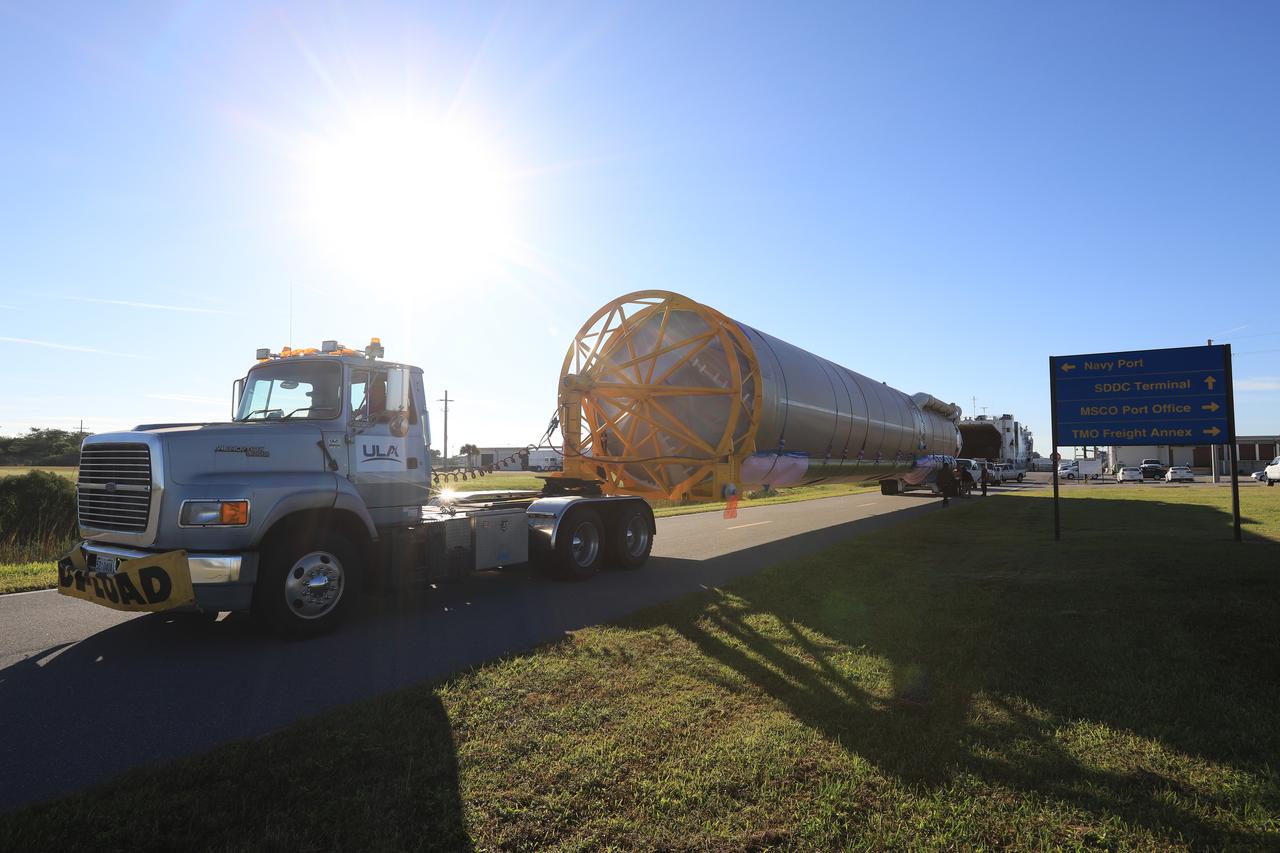
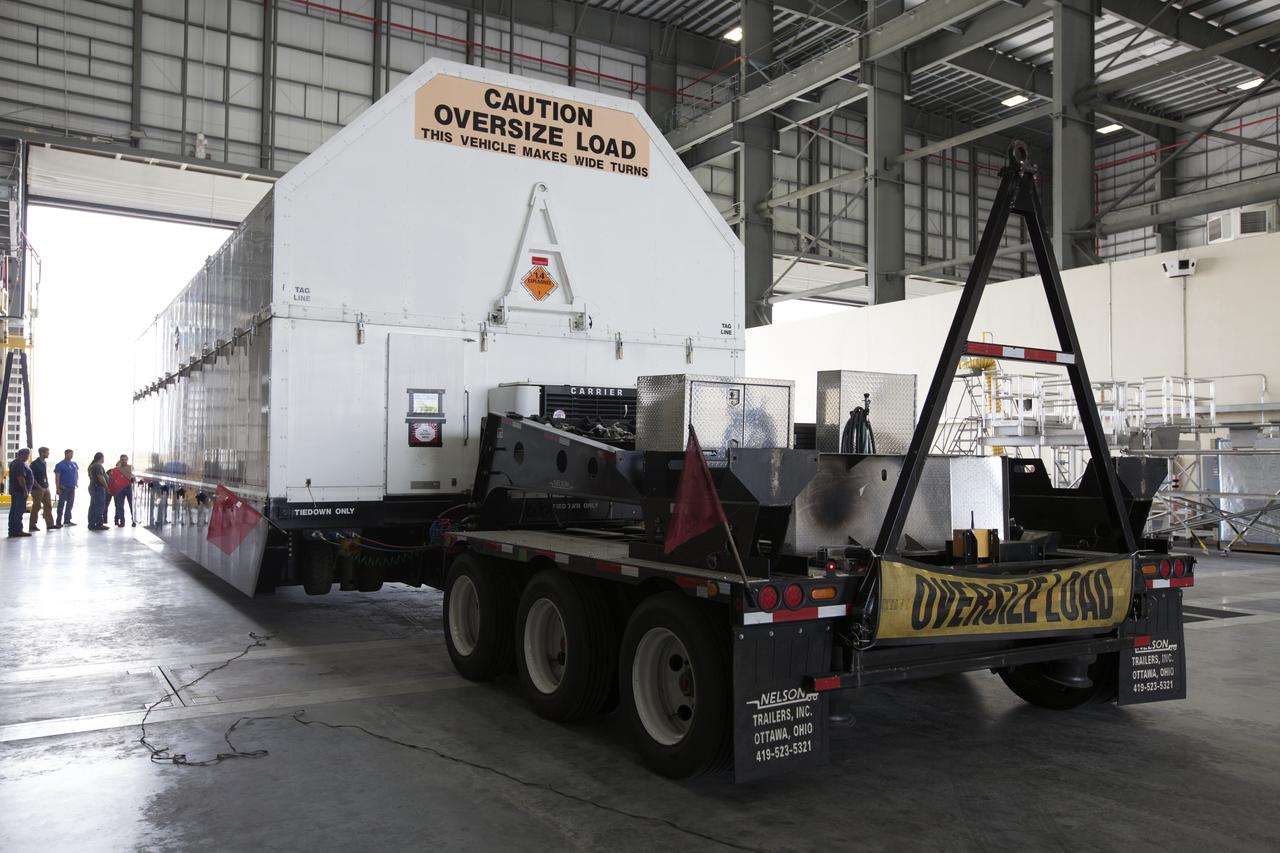
Framed by a series of cabbage palms, a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility after arriving at Port Canaveral. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
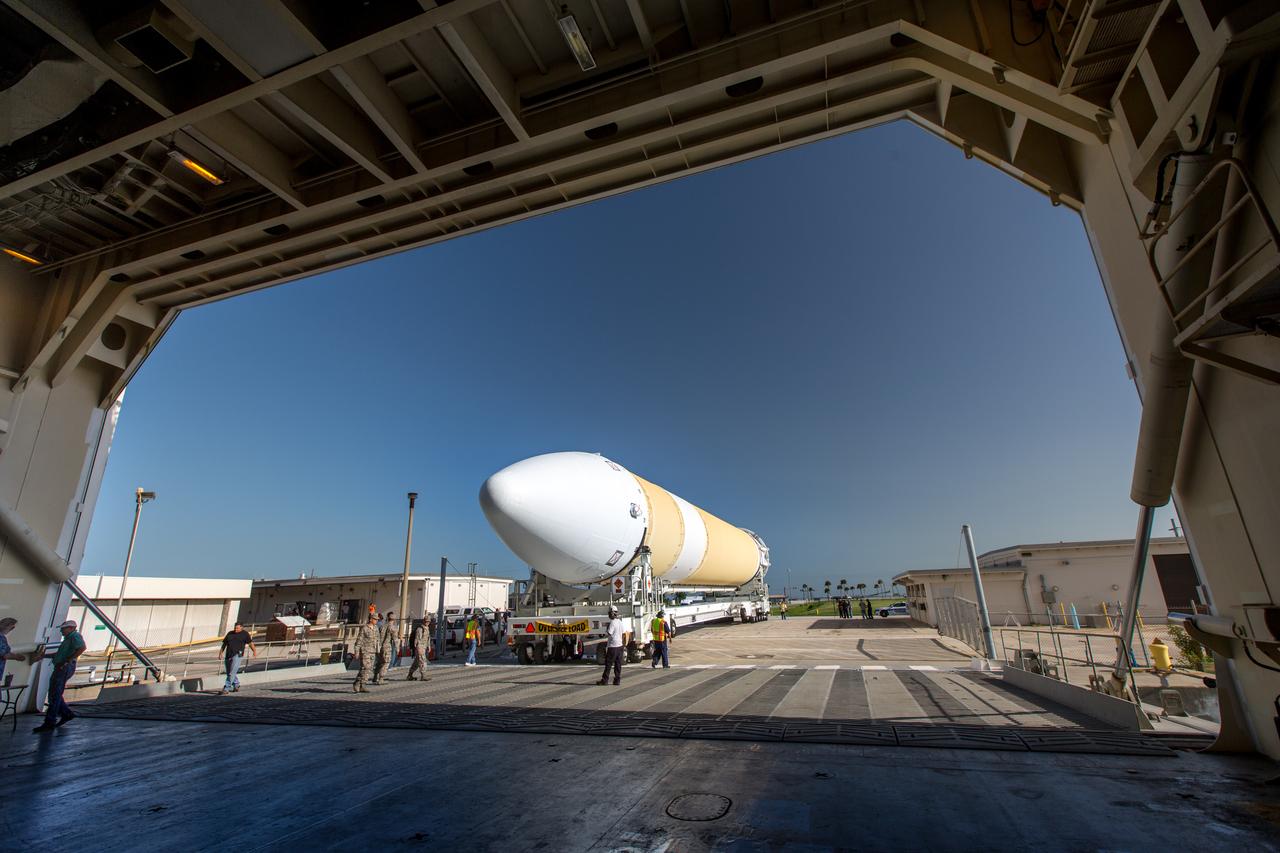

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
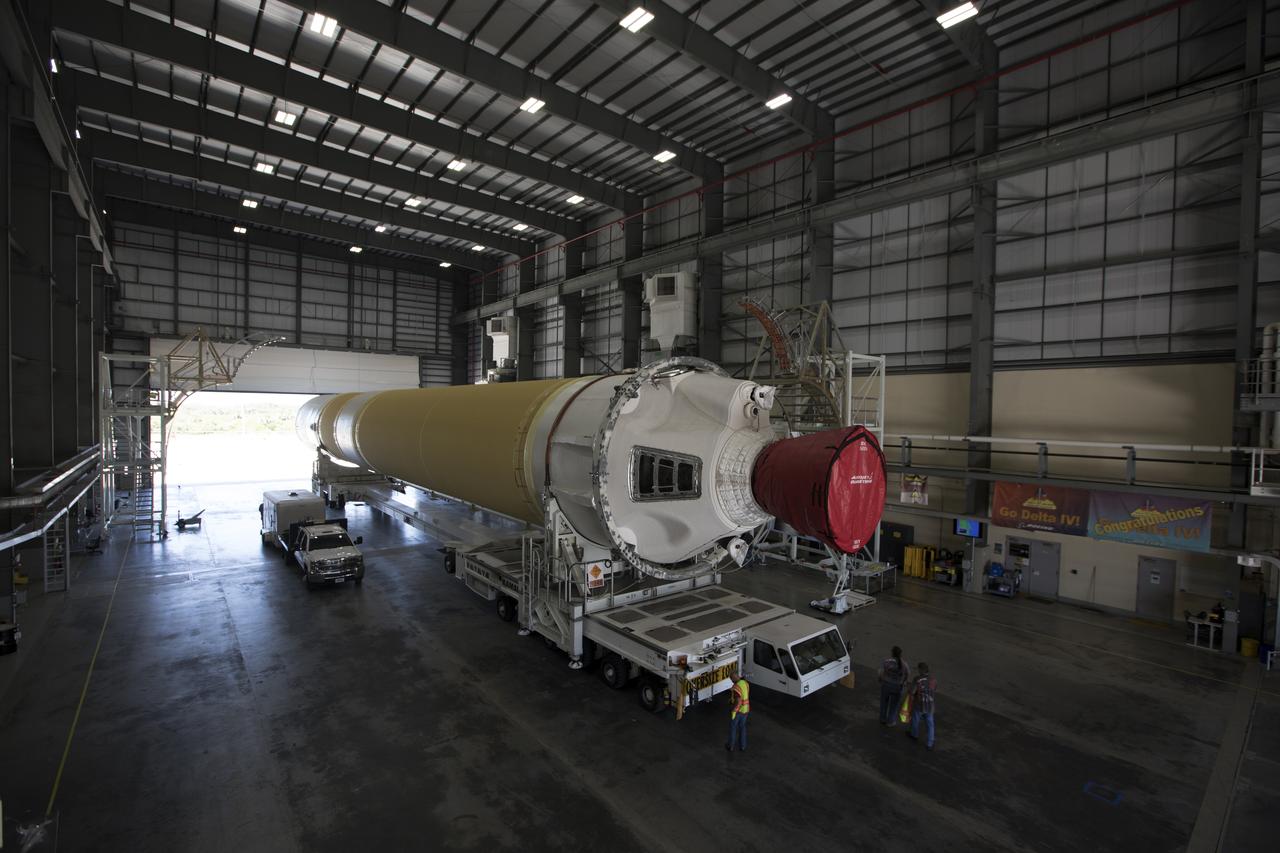

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck inside Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
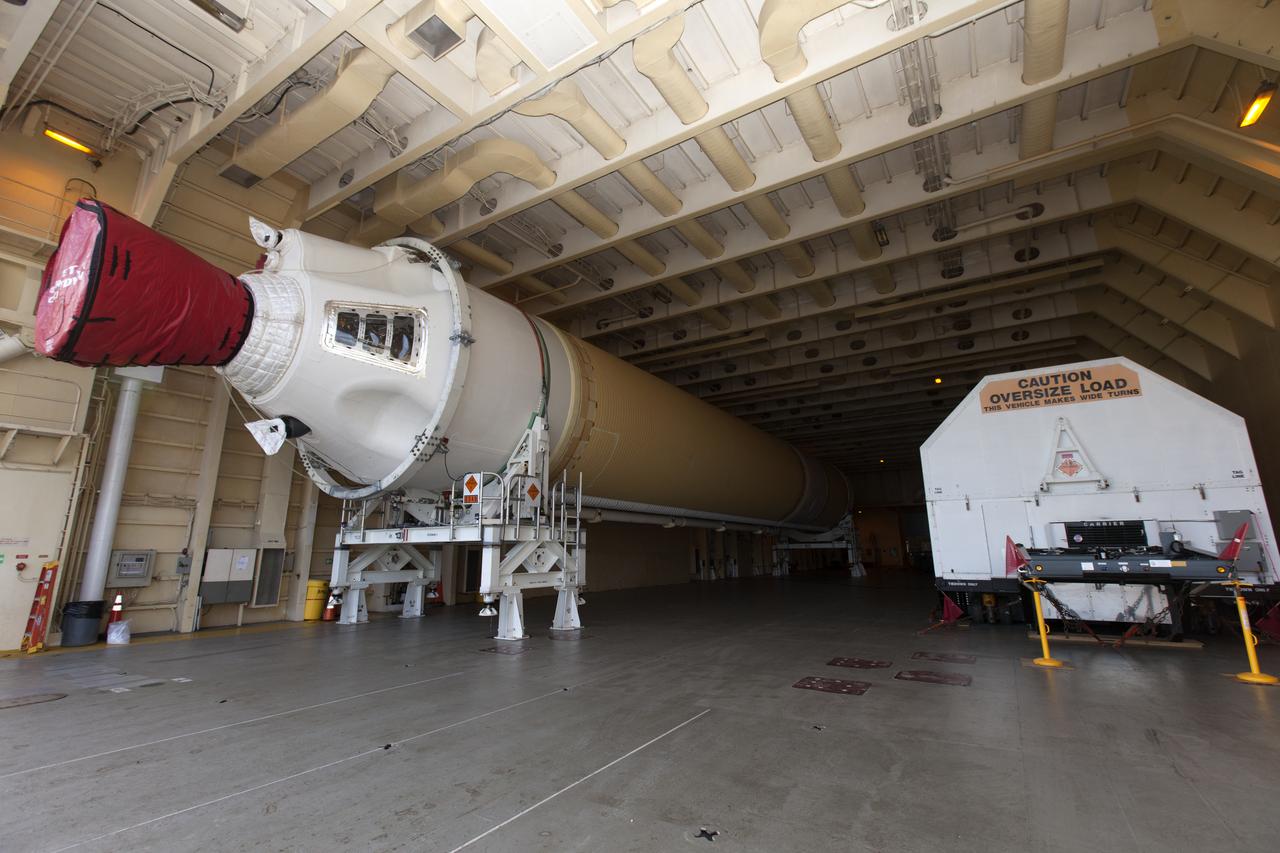

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
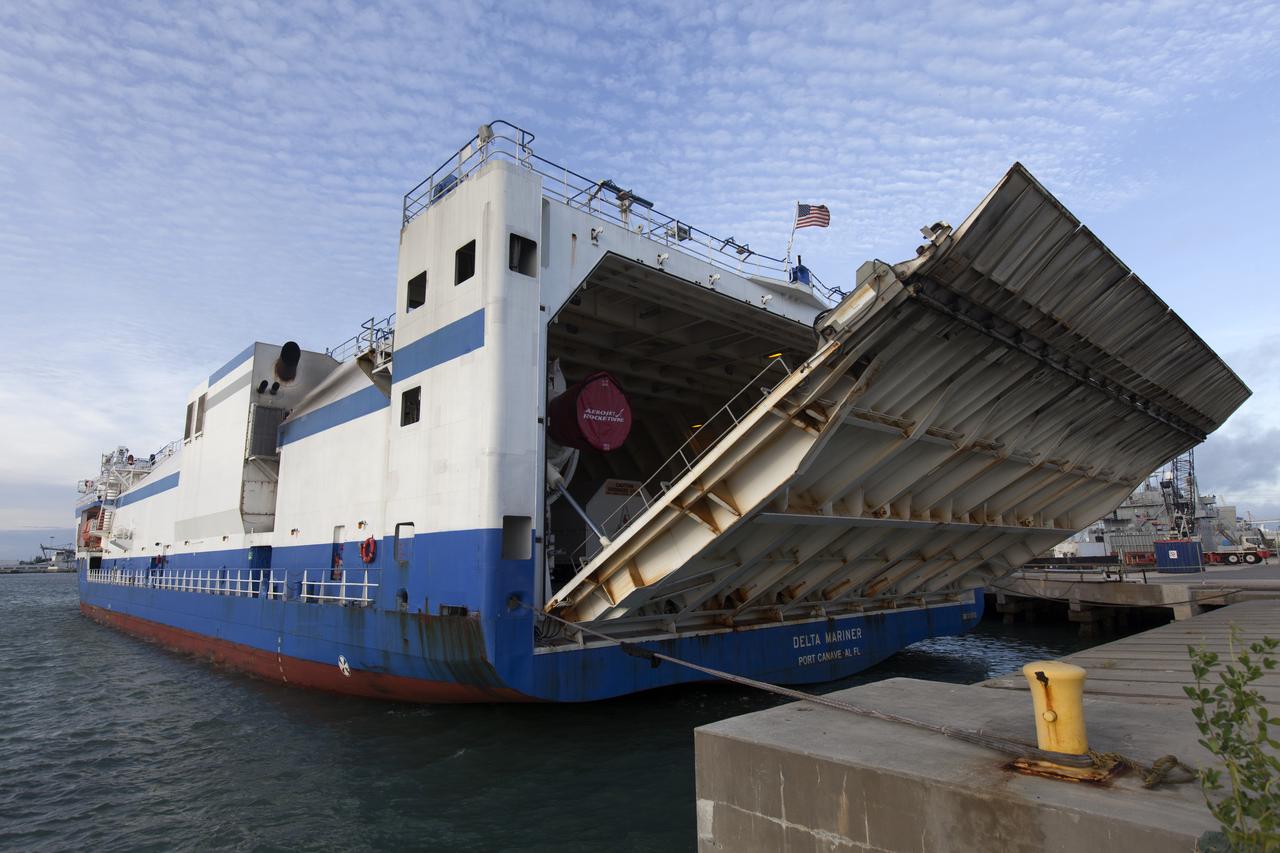

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
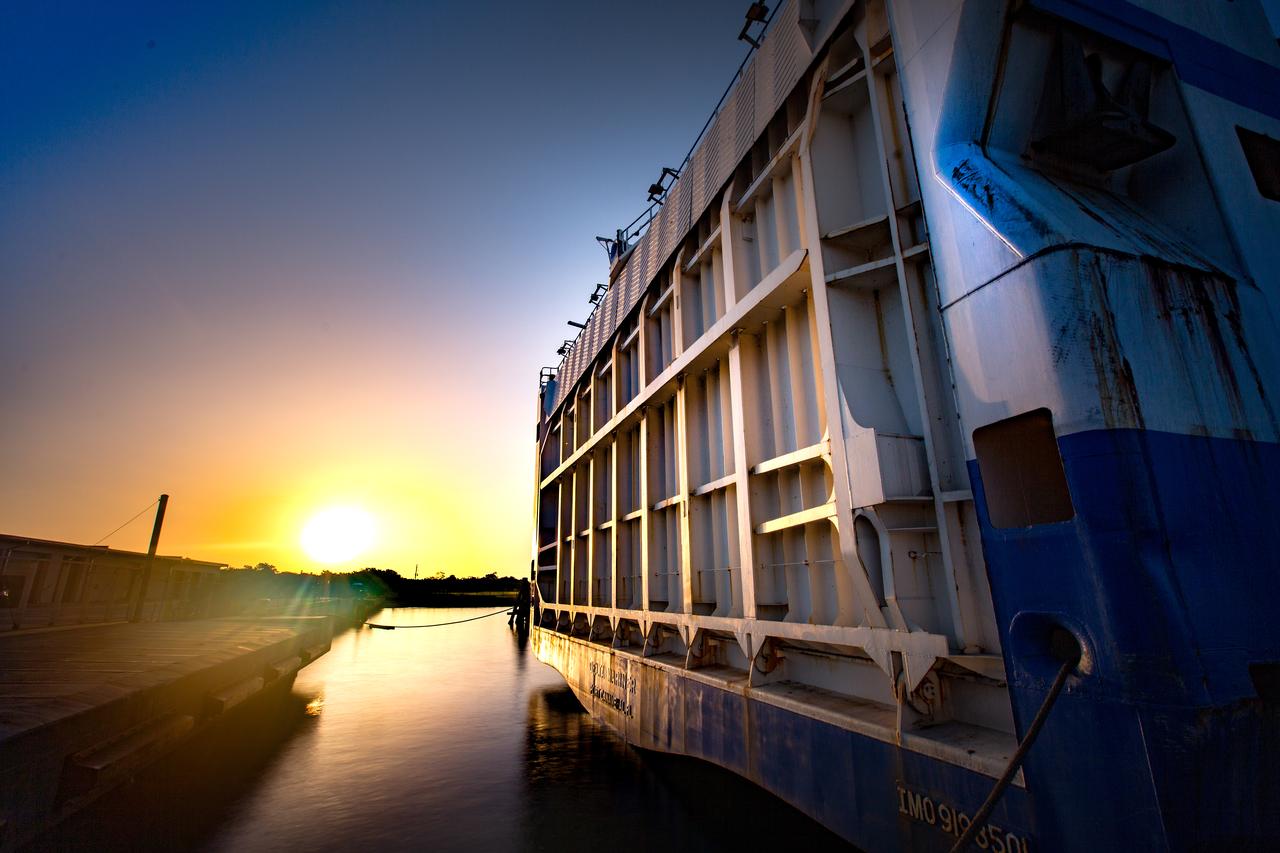

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
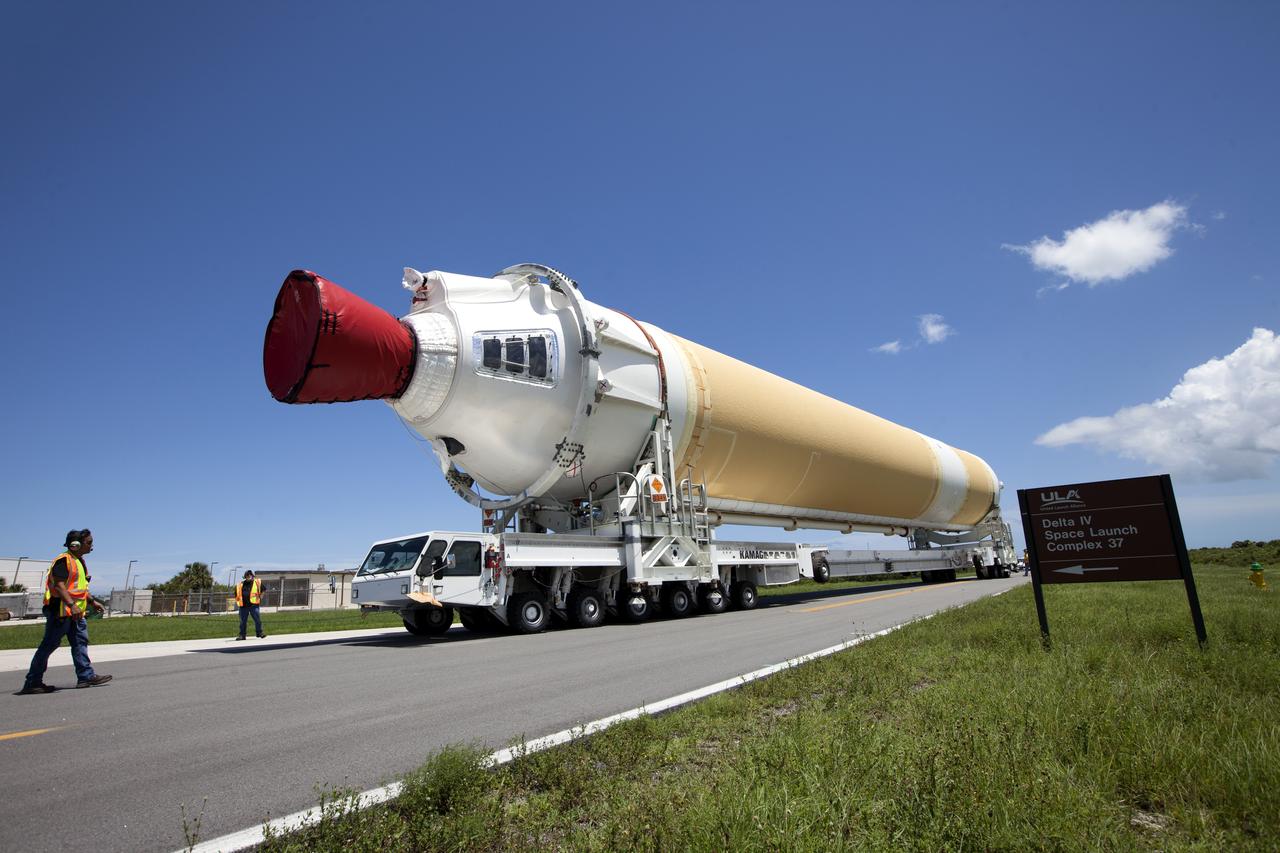

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility after arriving at Port Canaveral. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
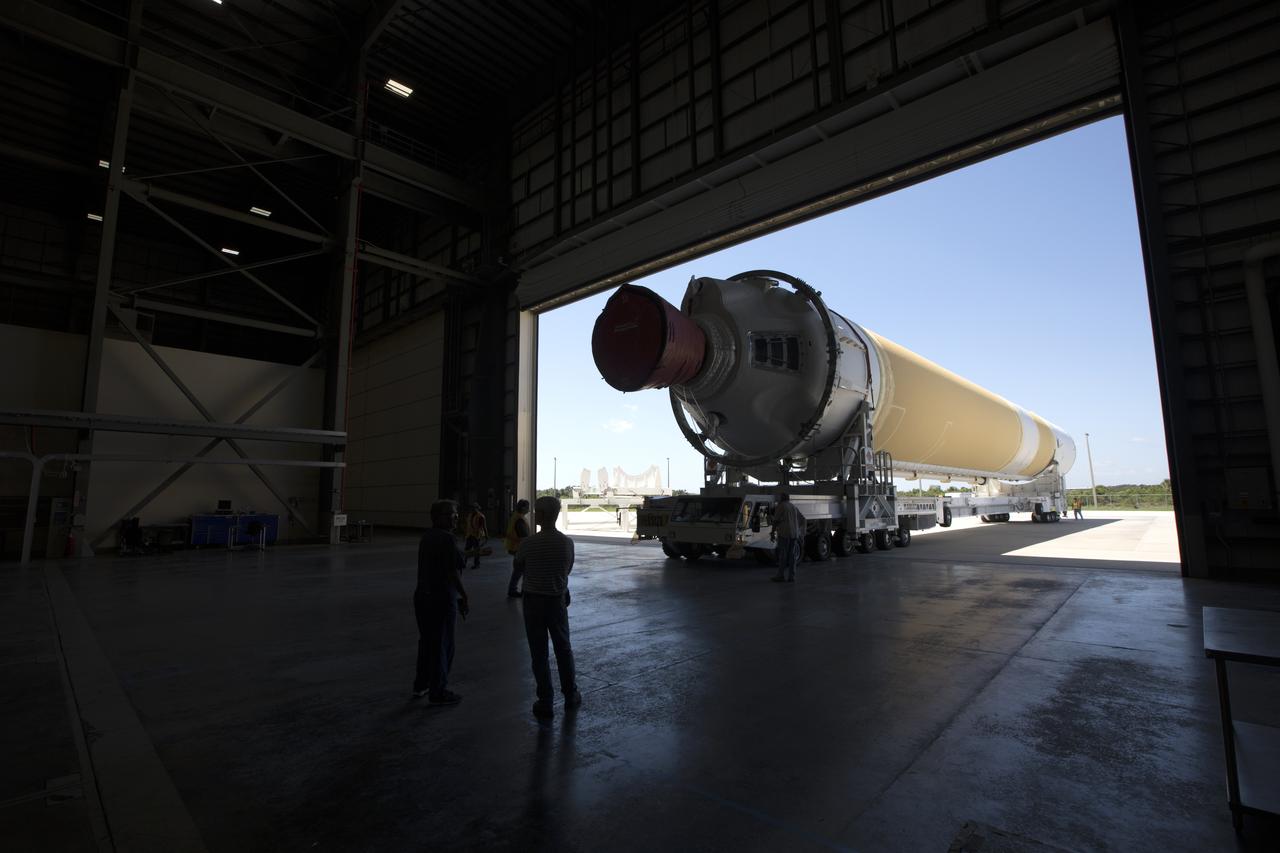

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck inside Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
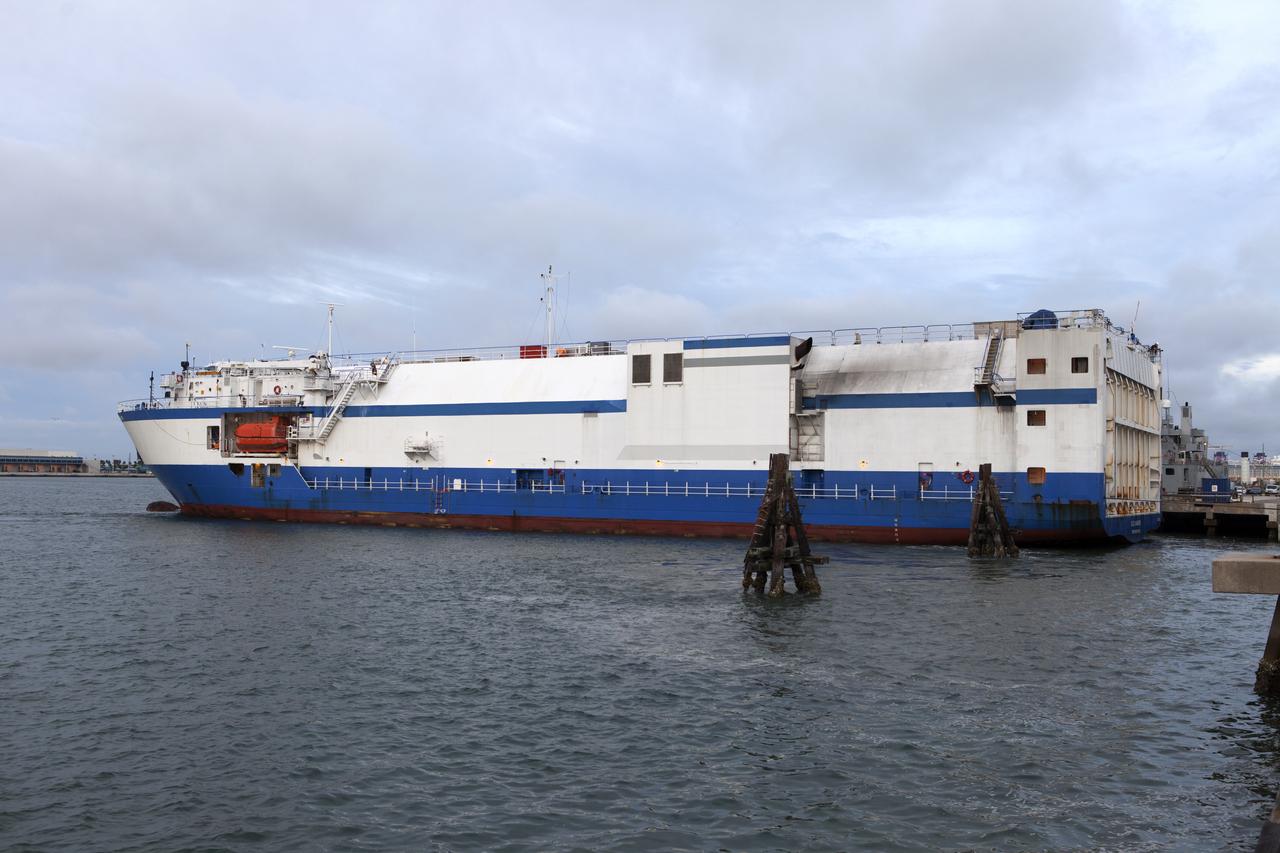

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
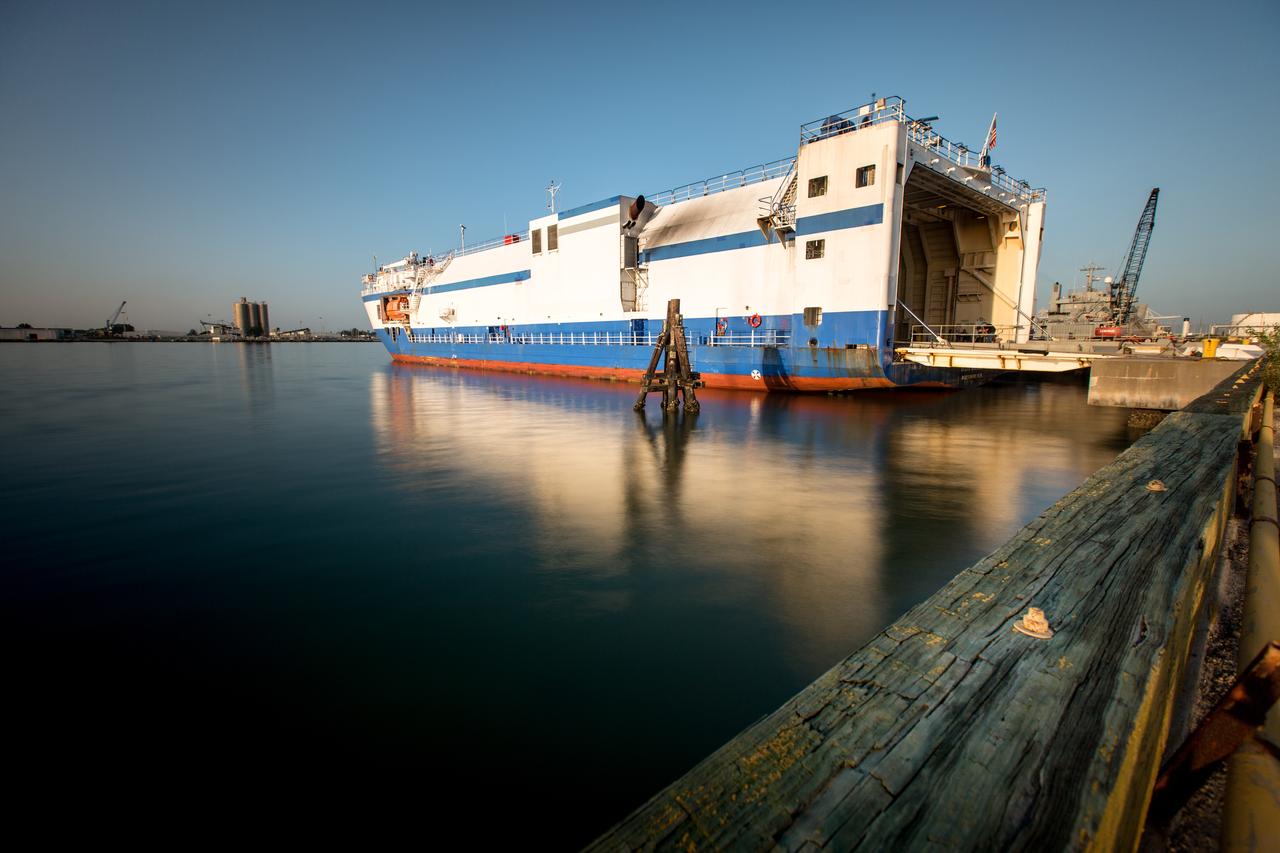

The United Launch Alliance Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral's Army Warf carrying the third Delta IV Heavy common booster core and second stage for NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe spacecraft. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
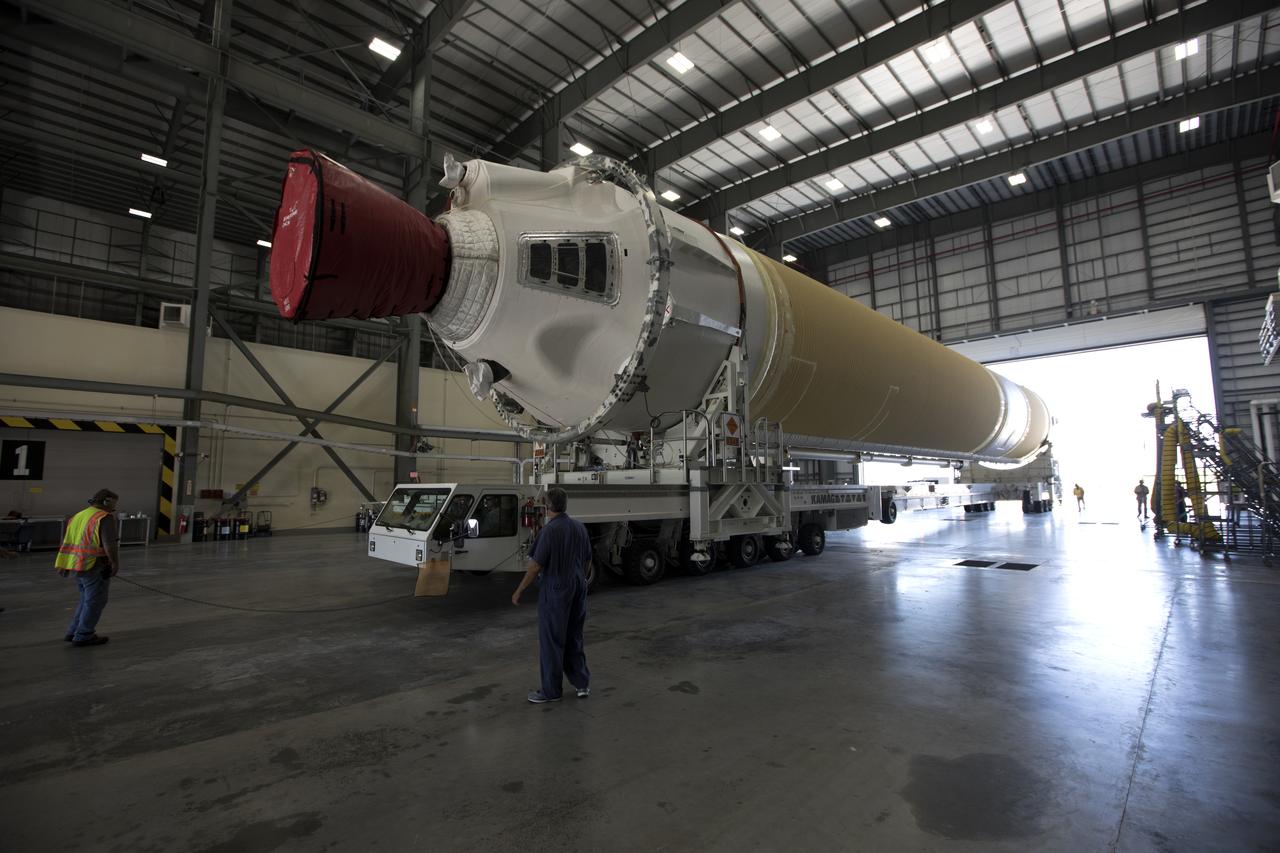

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck inside Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
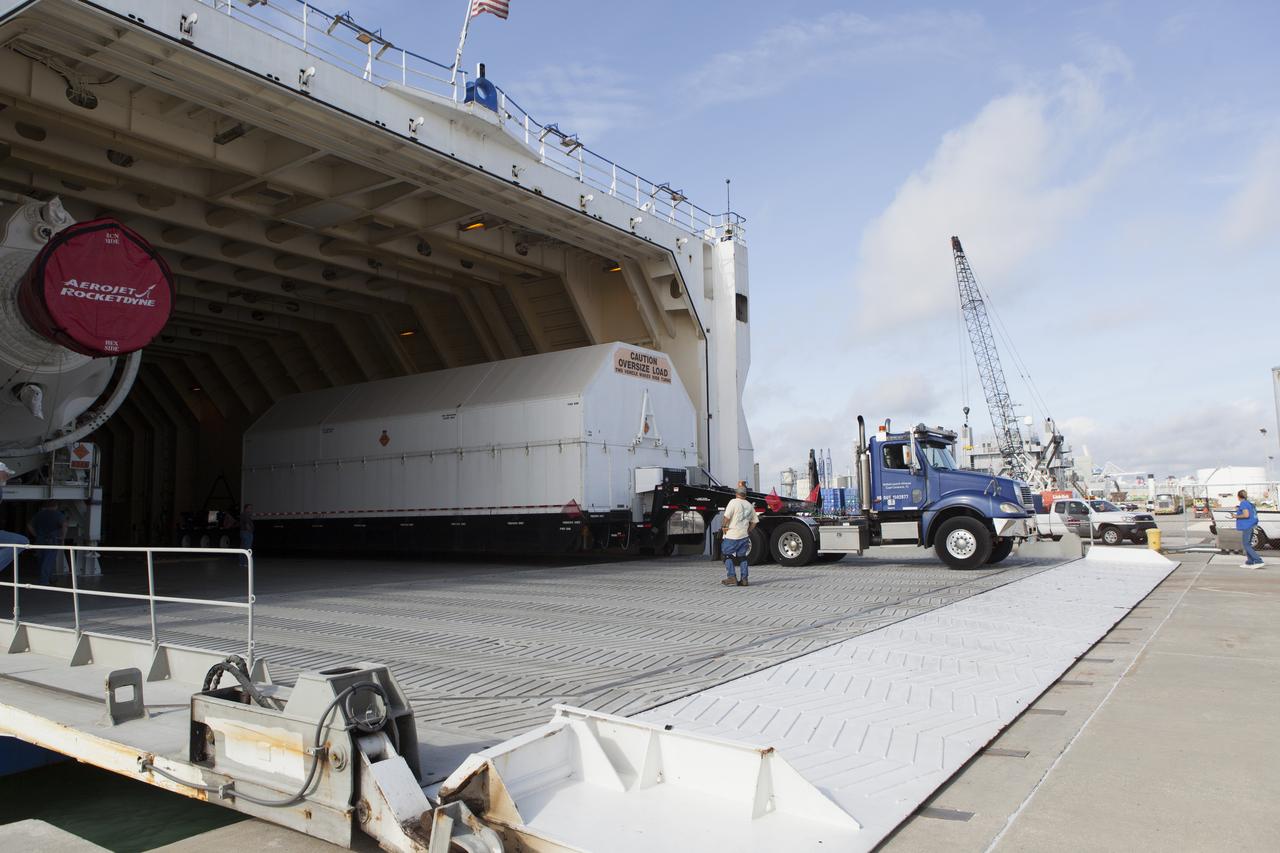

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy second stage, packaged in its shipping container, is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
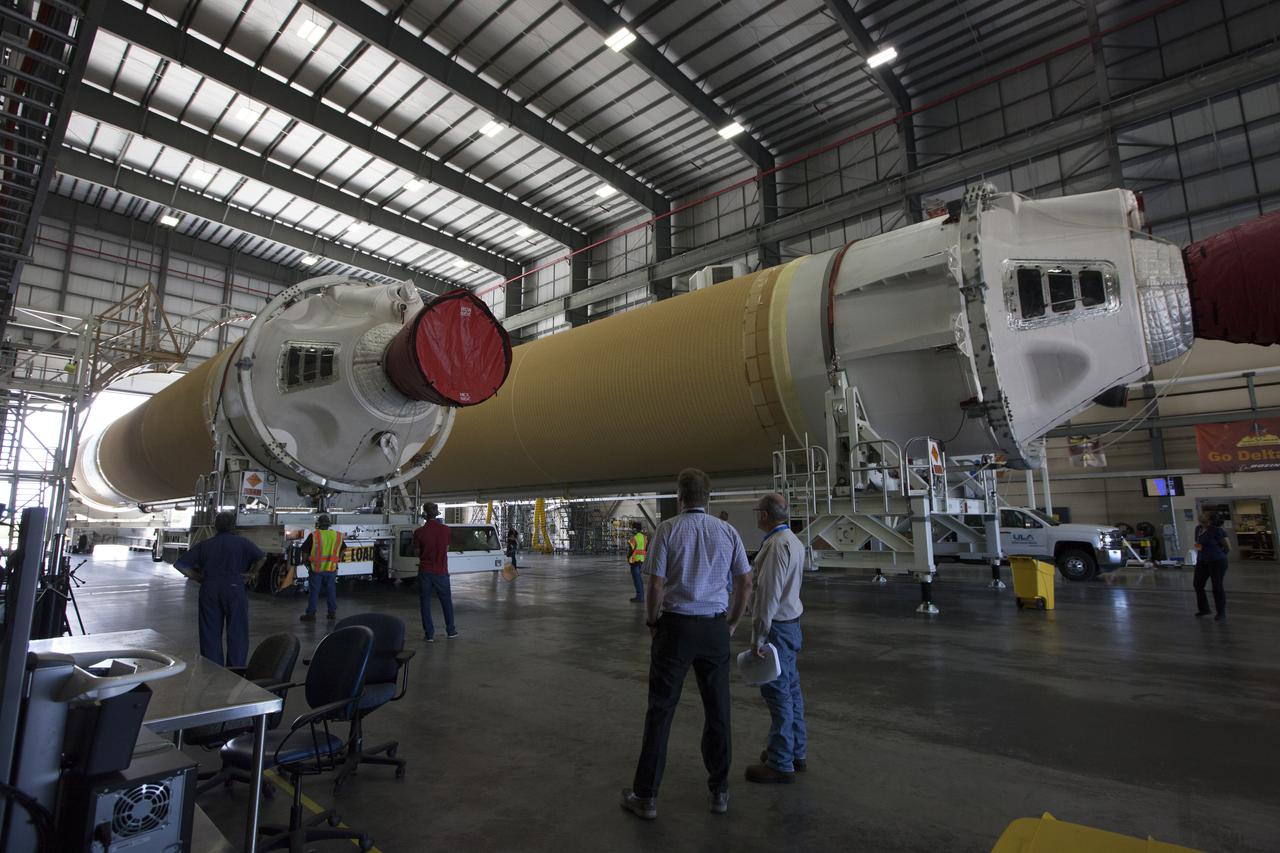

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck into Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
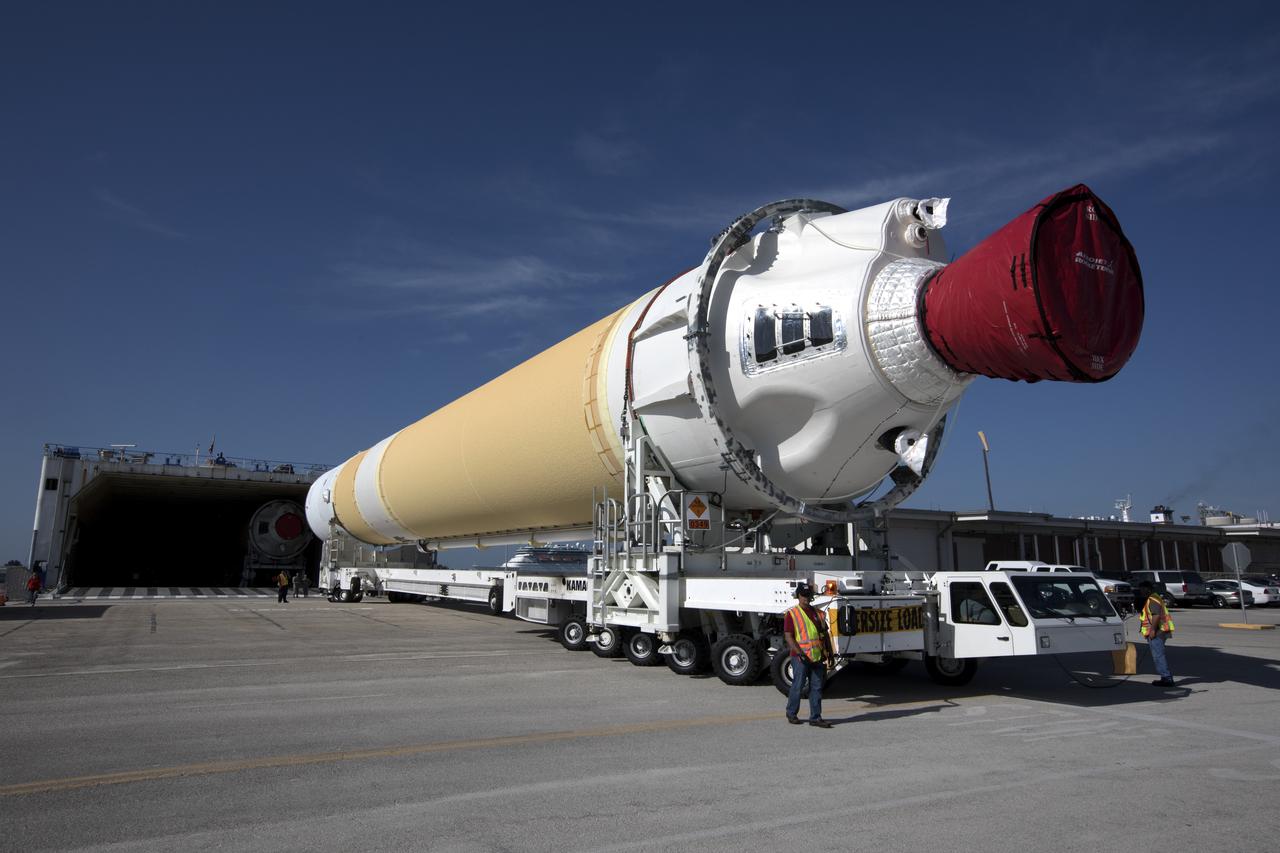

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
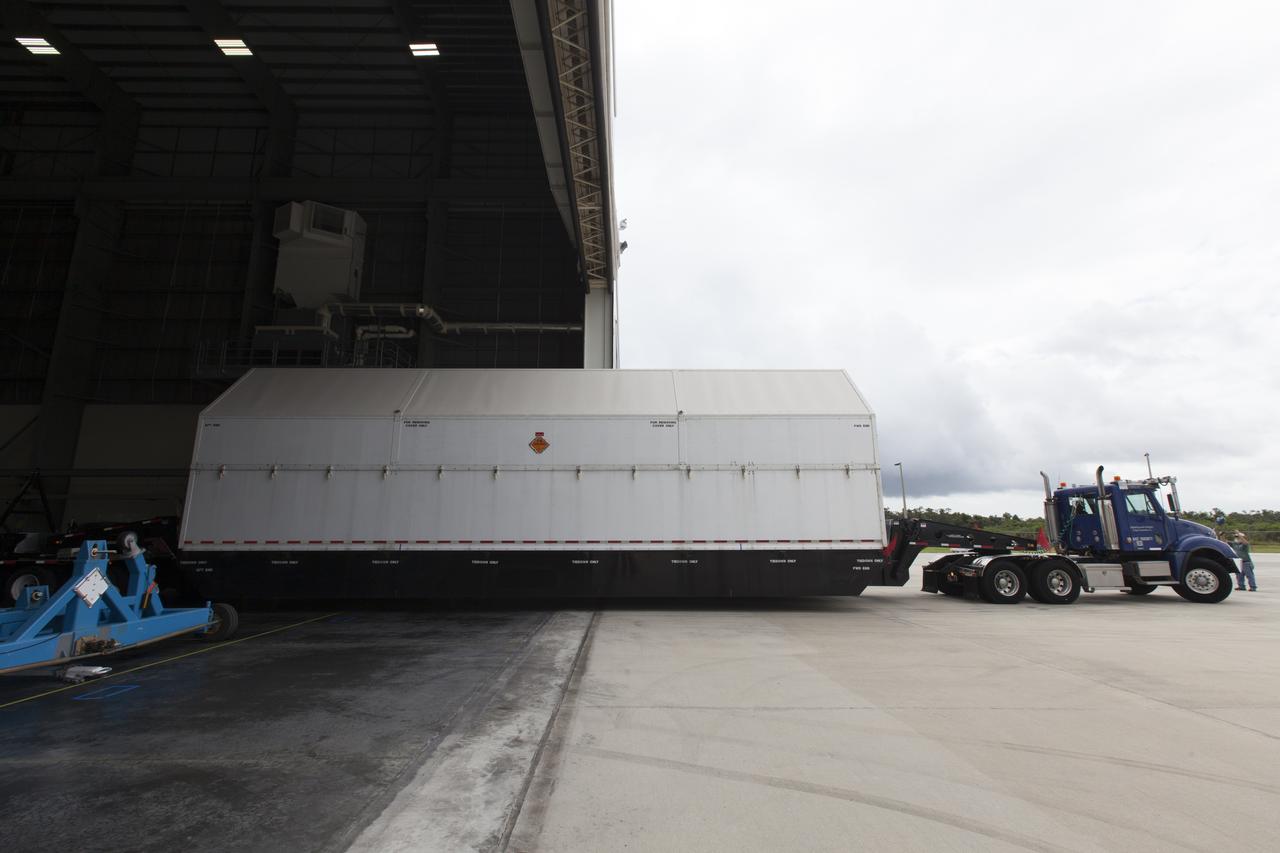

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy second stage, packaged in its shipping container, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preflight processing. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
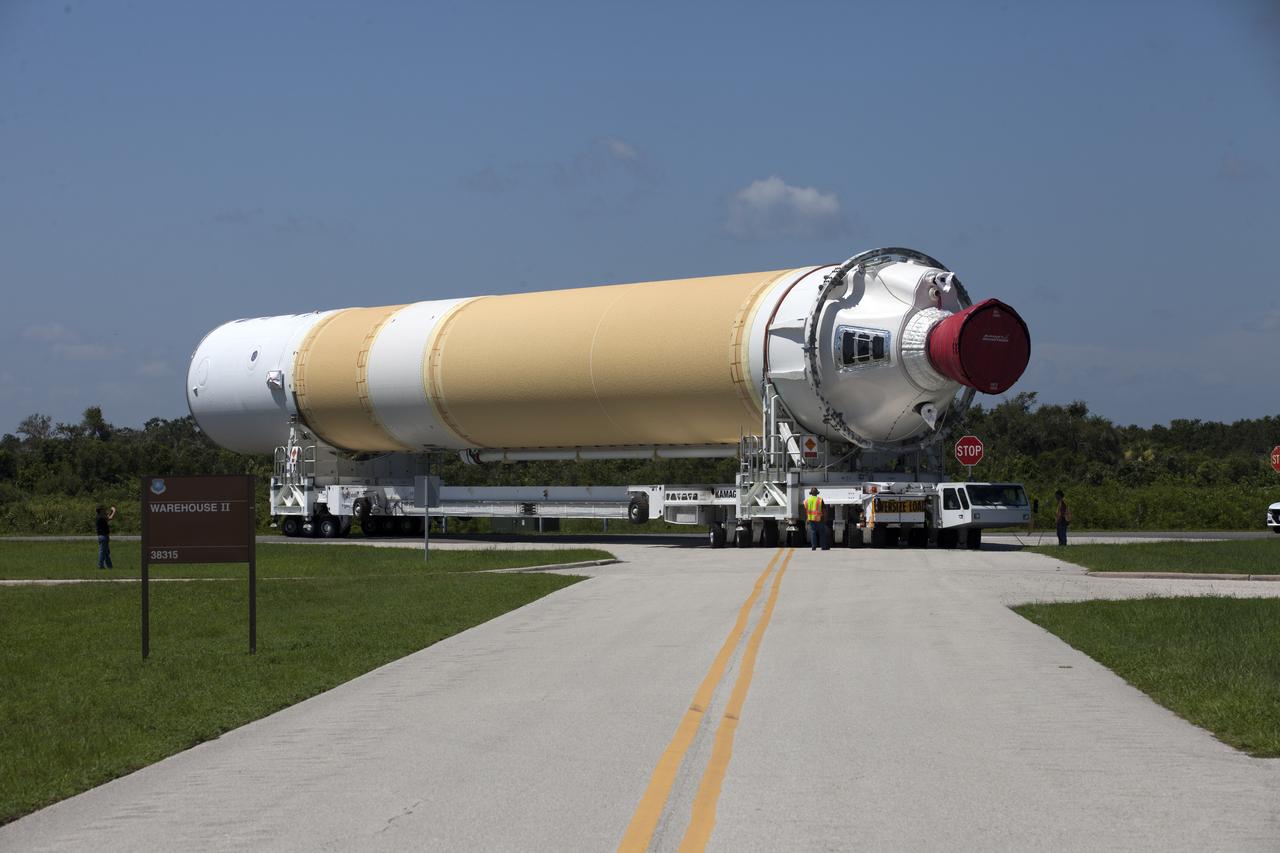

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is transported by truck to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 37 Horizontal Processing Facility after arriving at Port Canaveral. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
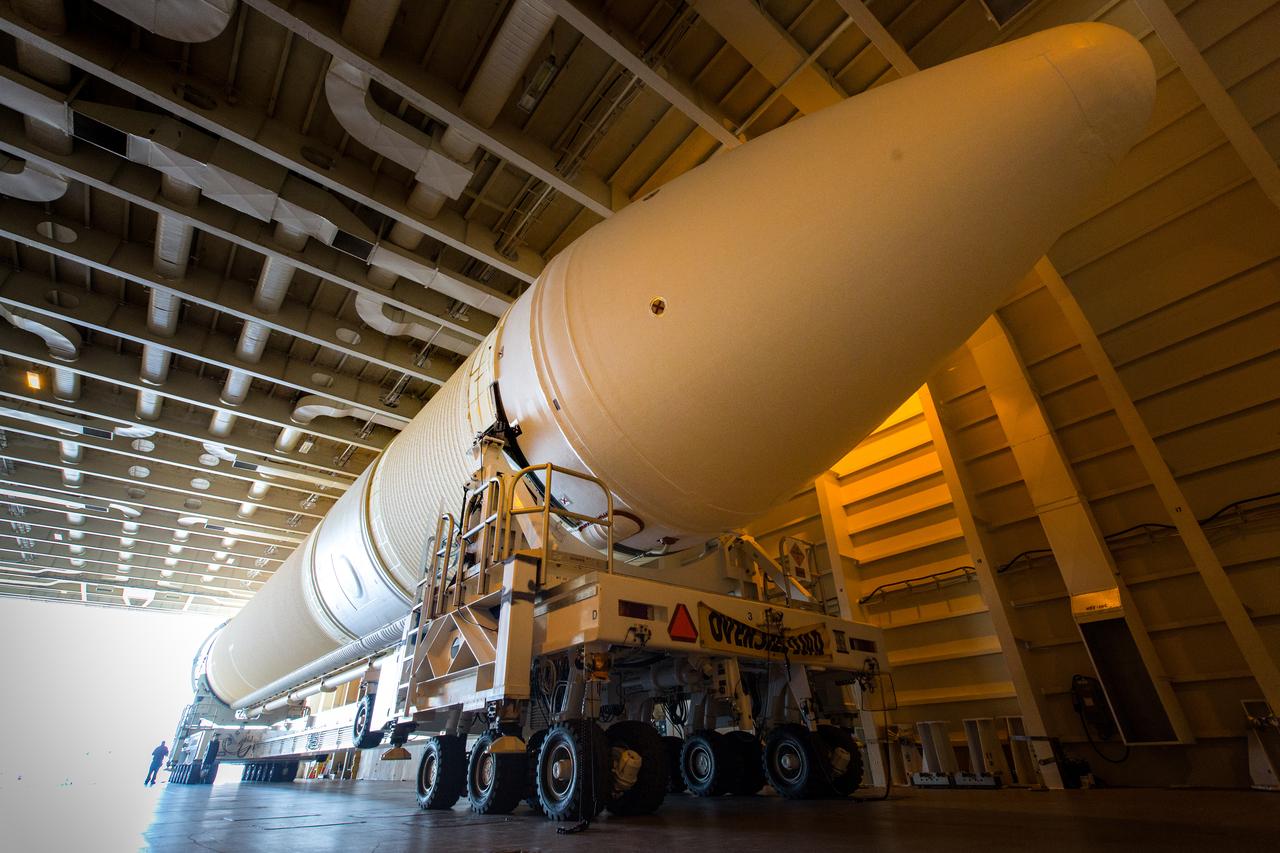

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is about to be offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.
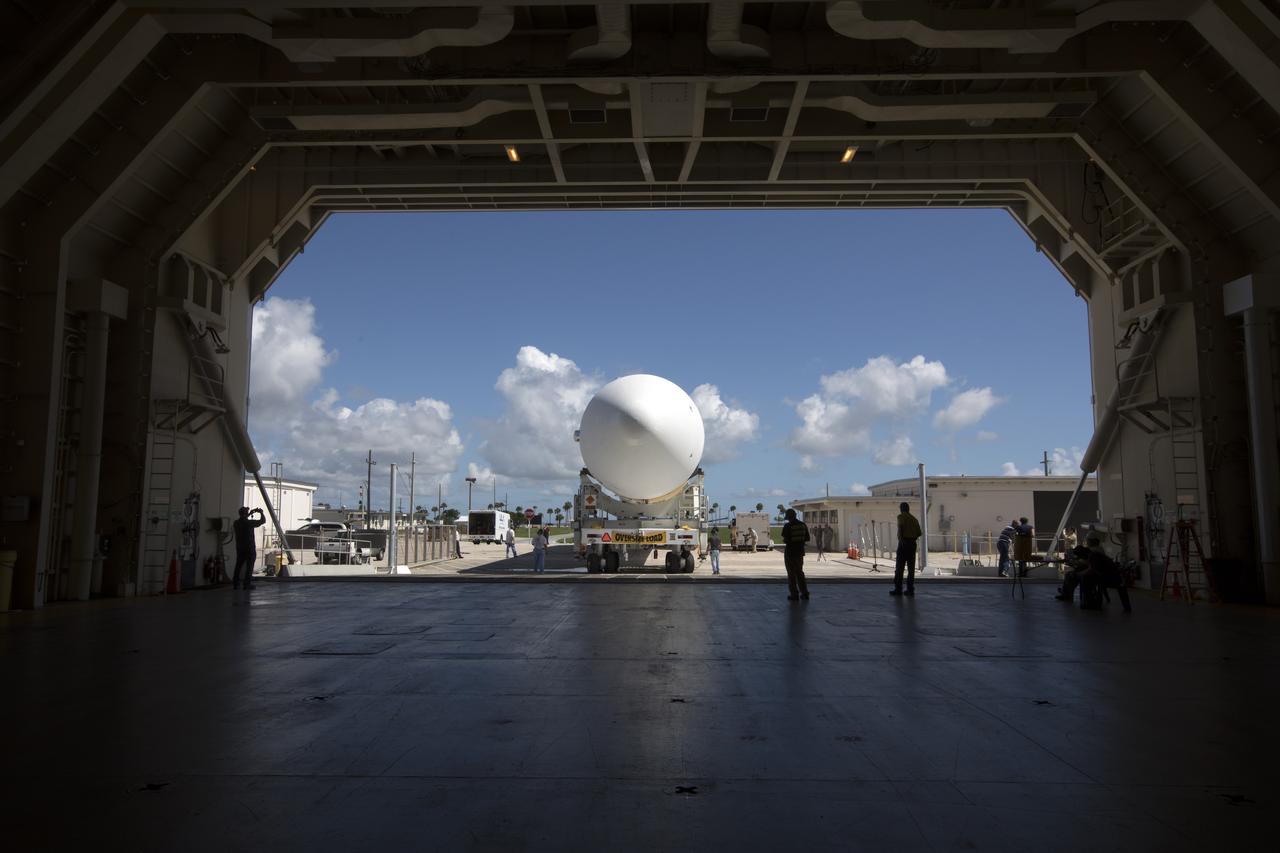

A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy common booster core is offloaded from the company's Mariner ship at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Delta IV Heavy will launch NASA's upcoming Parker Solar Probe mission. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection. Liftoff atop the Delta IV Heavy rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 37 in summer 2018.