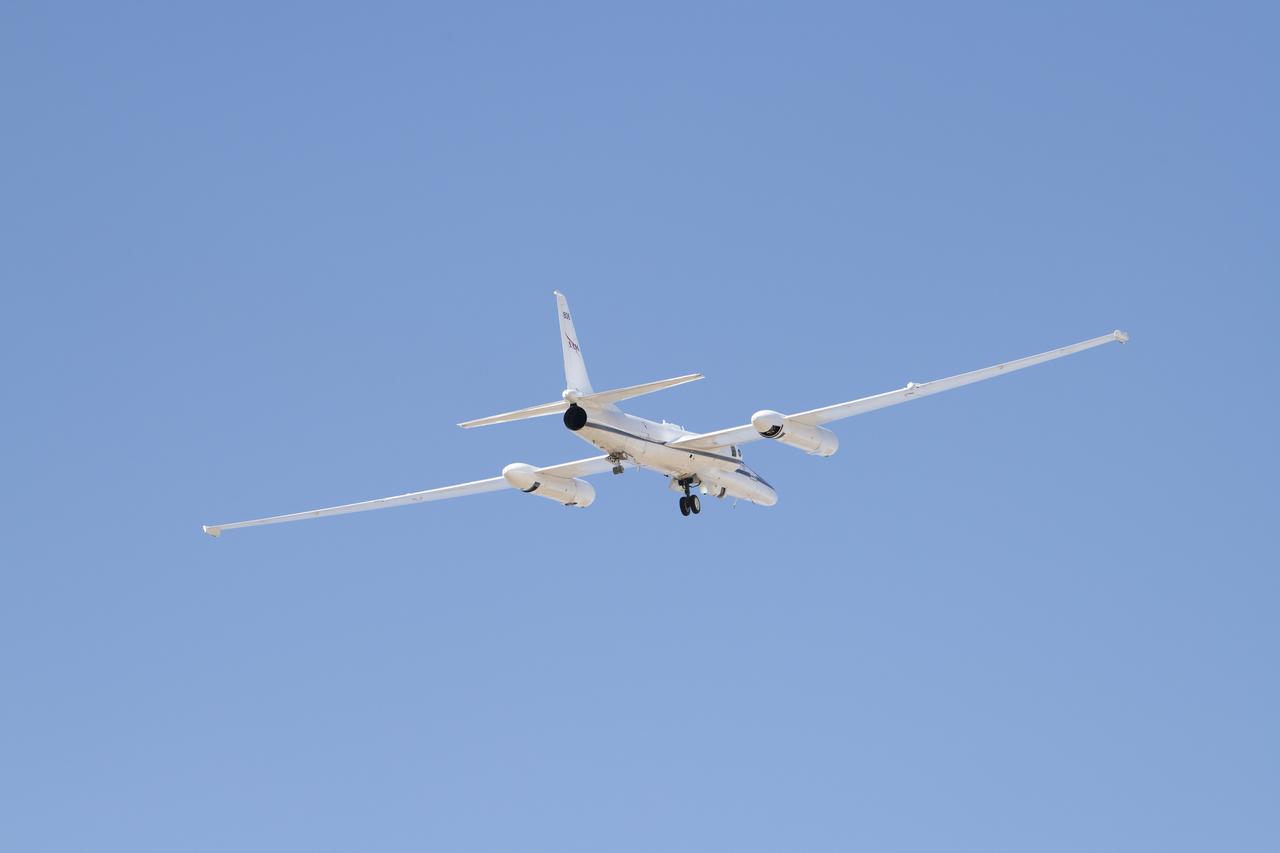

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
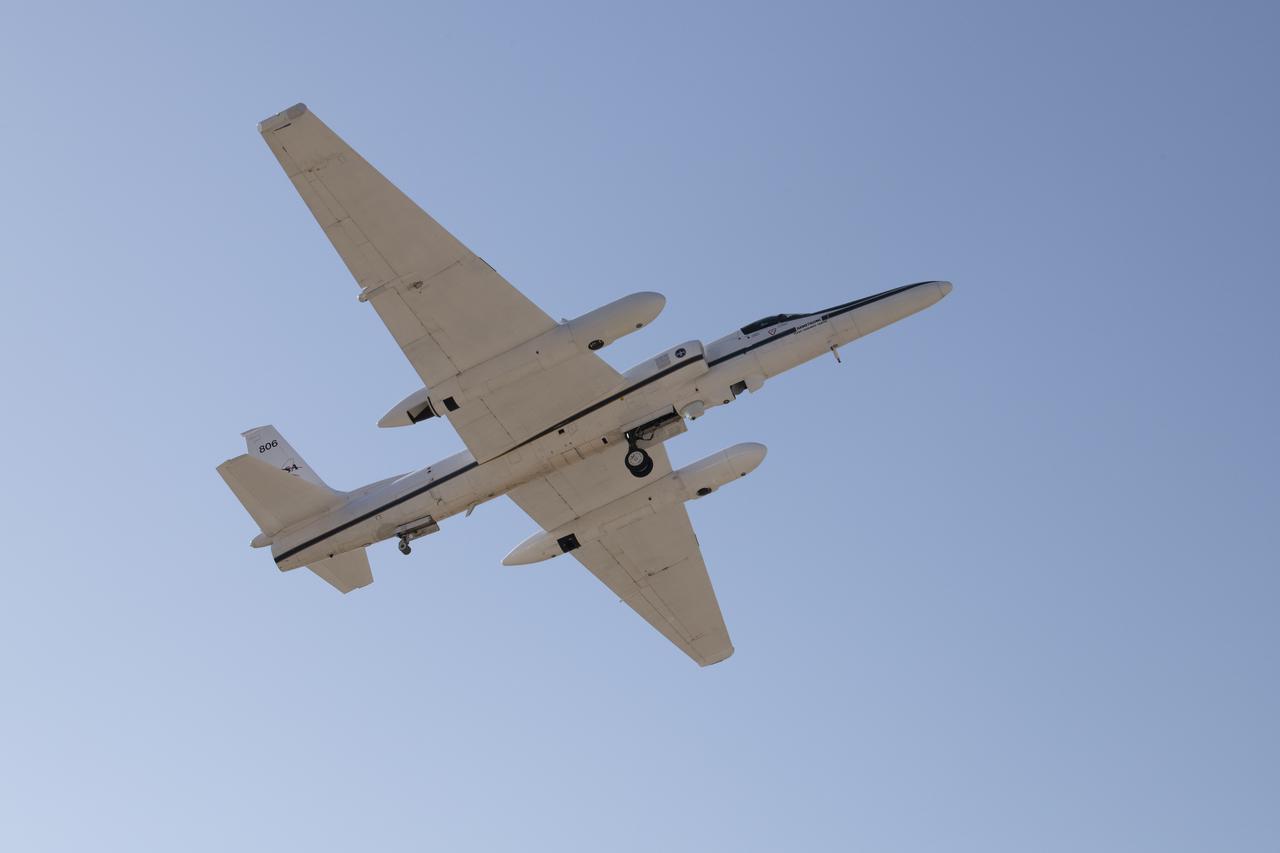

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
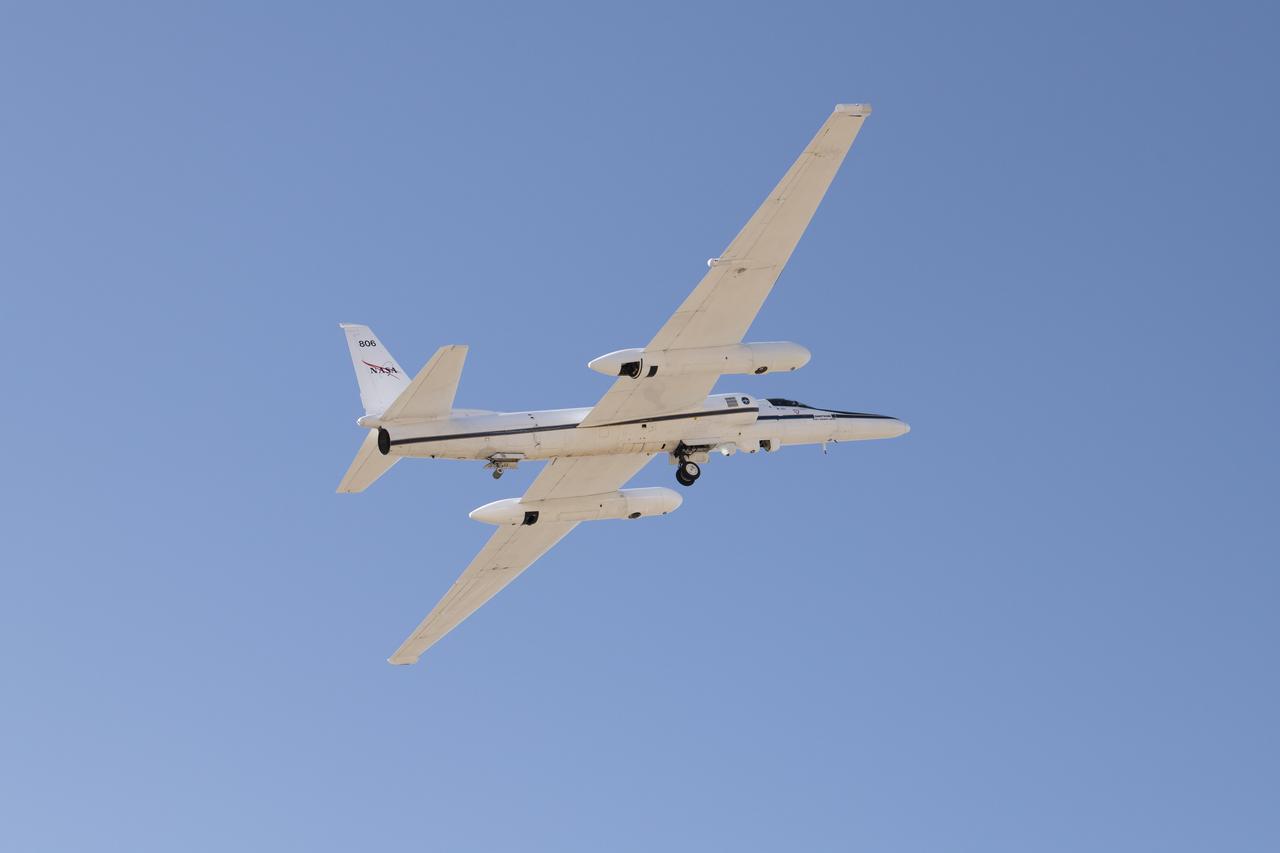

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
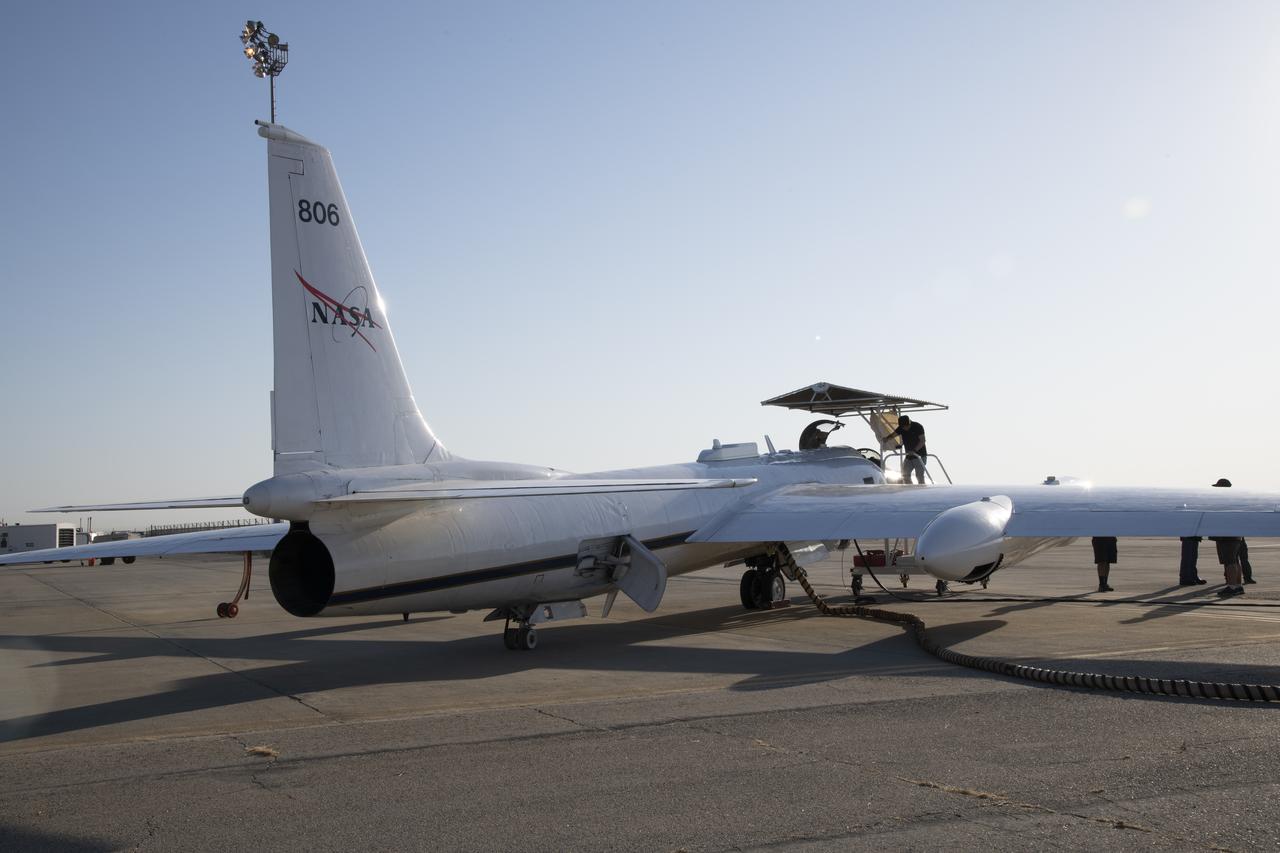

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
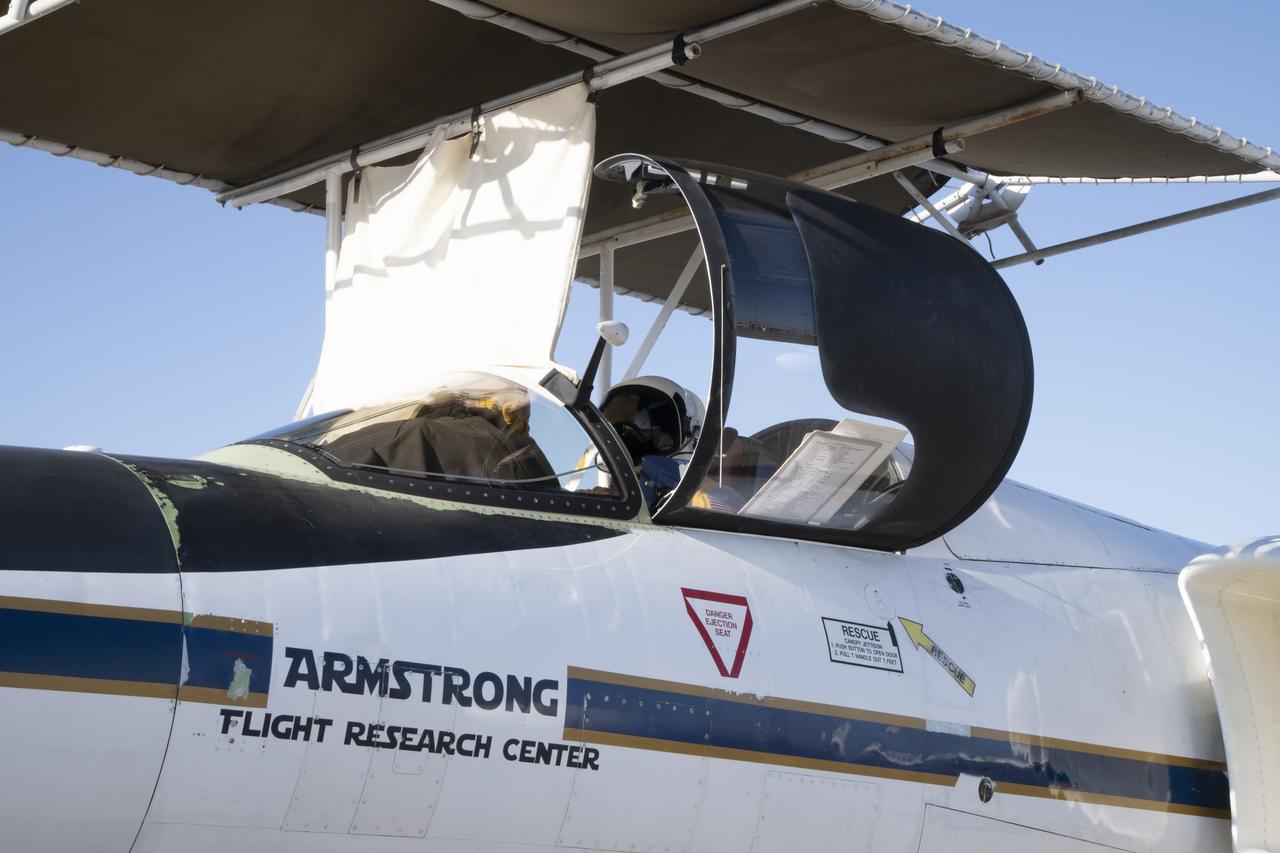

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
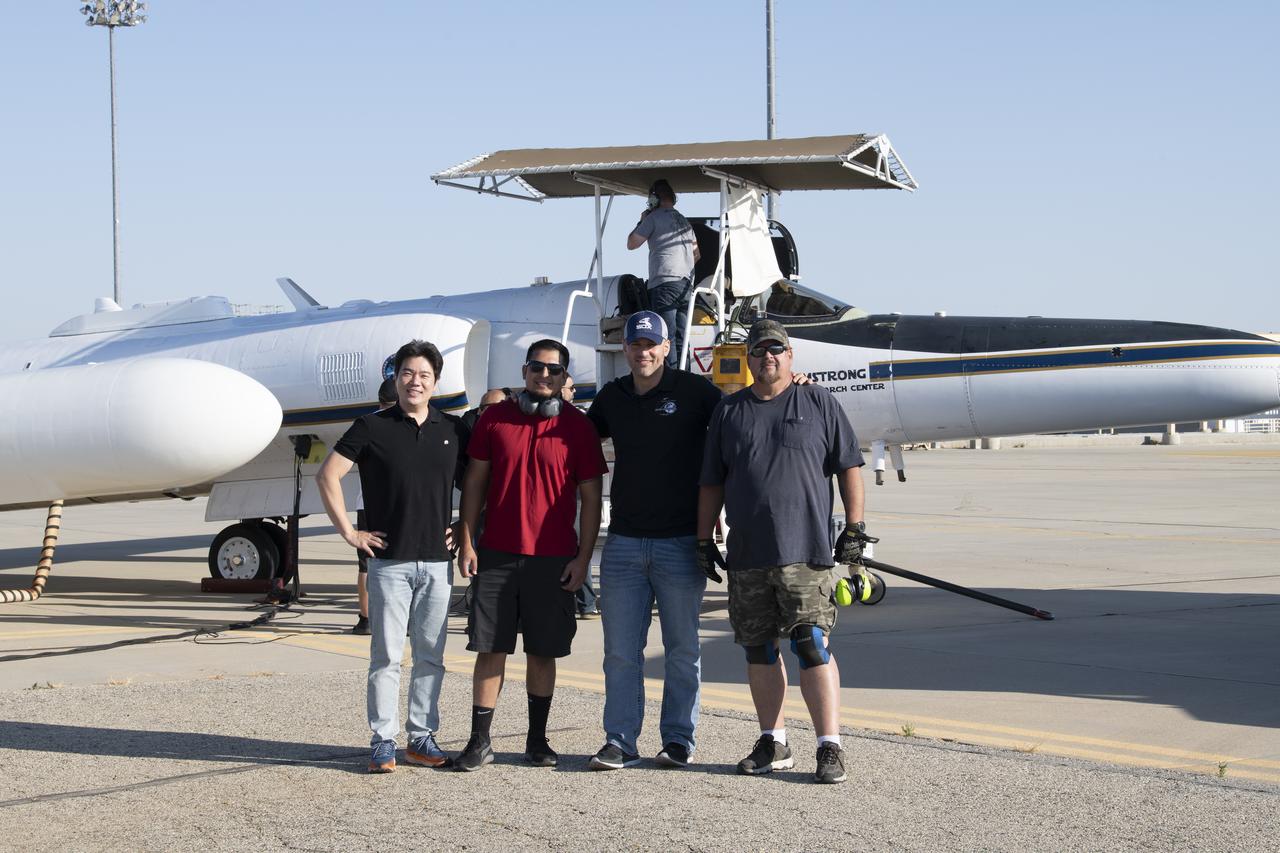

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.
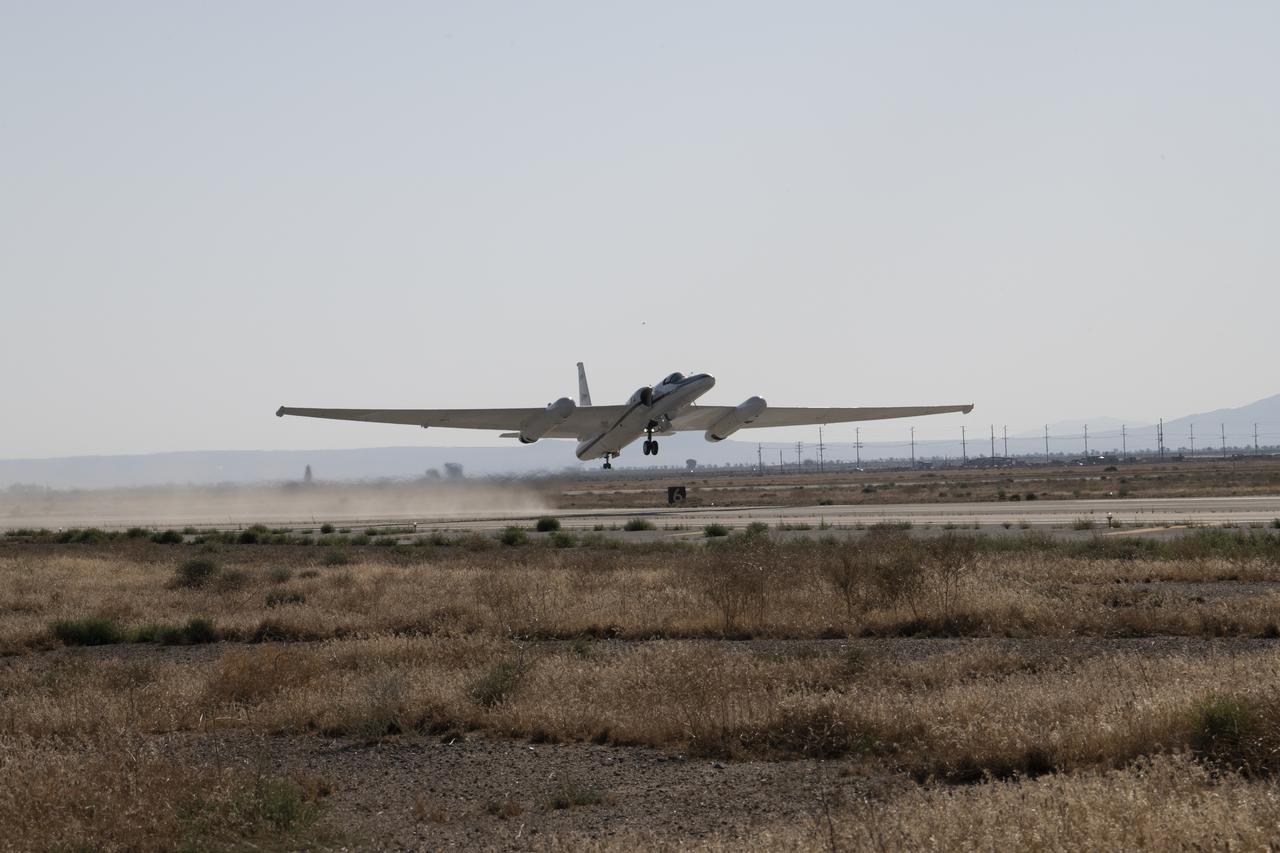

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft deploys for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. A NASA pilot will operate the aircraft while scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret the data from the ground.

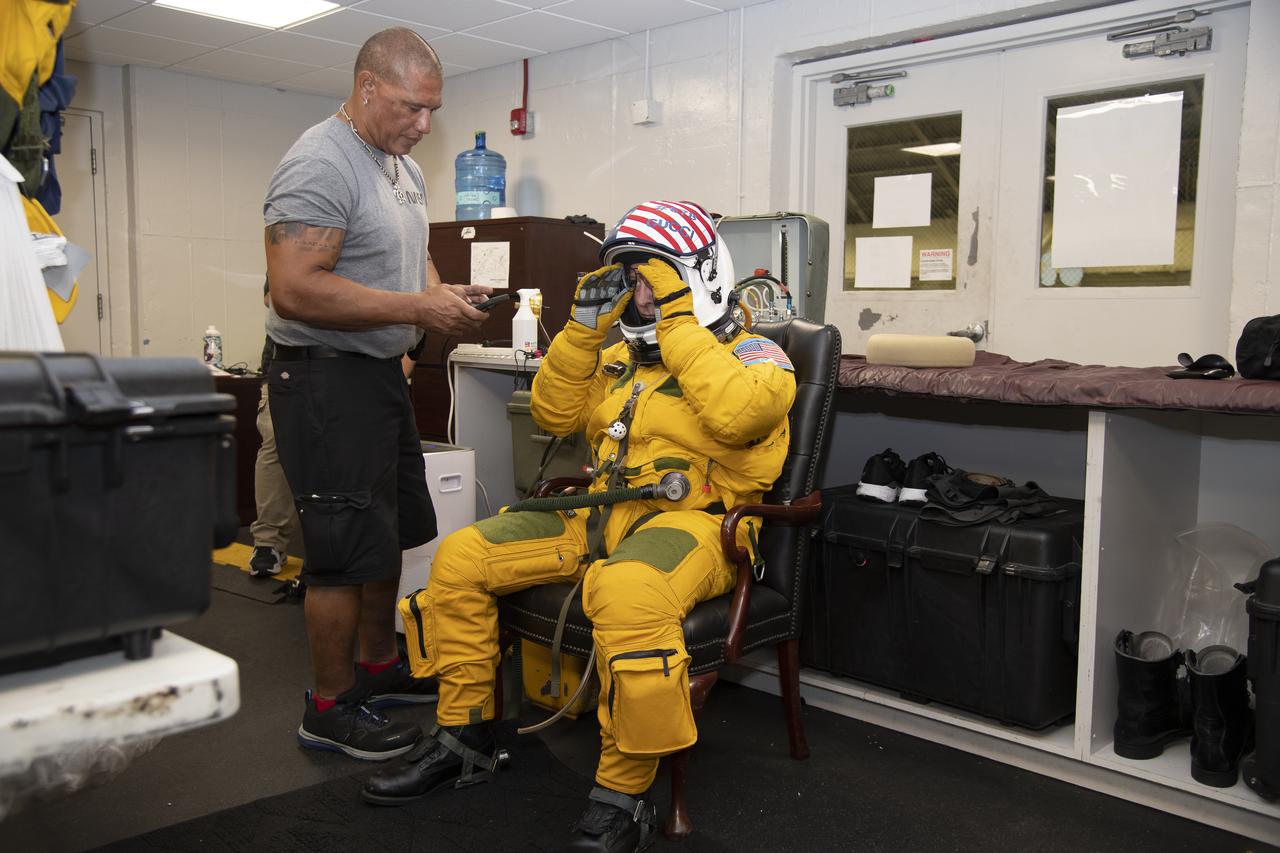
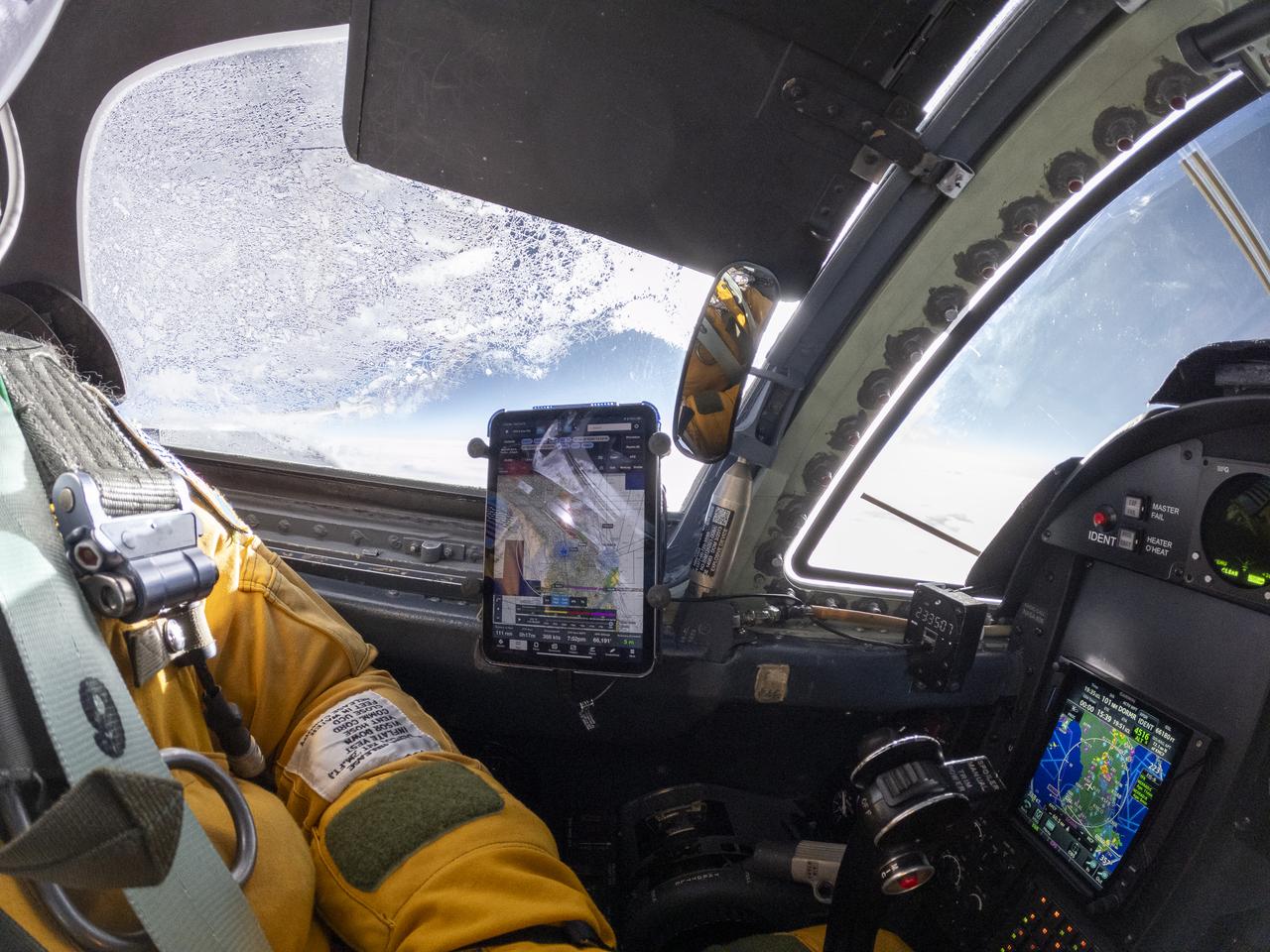
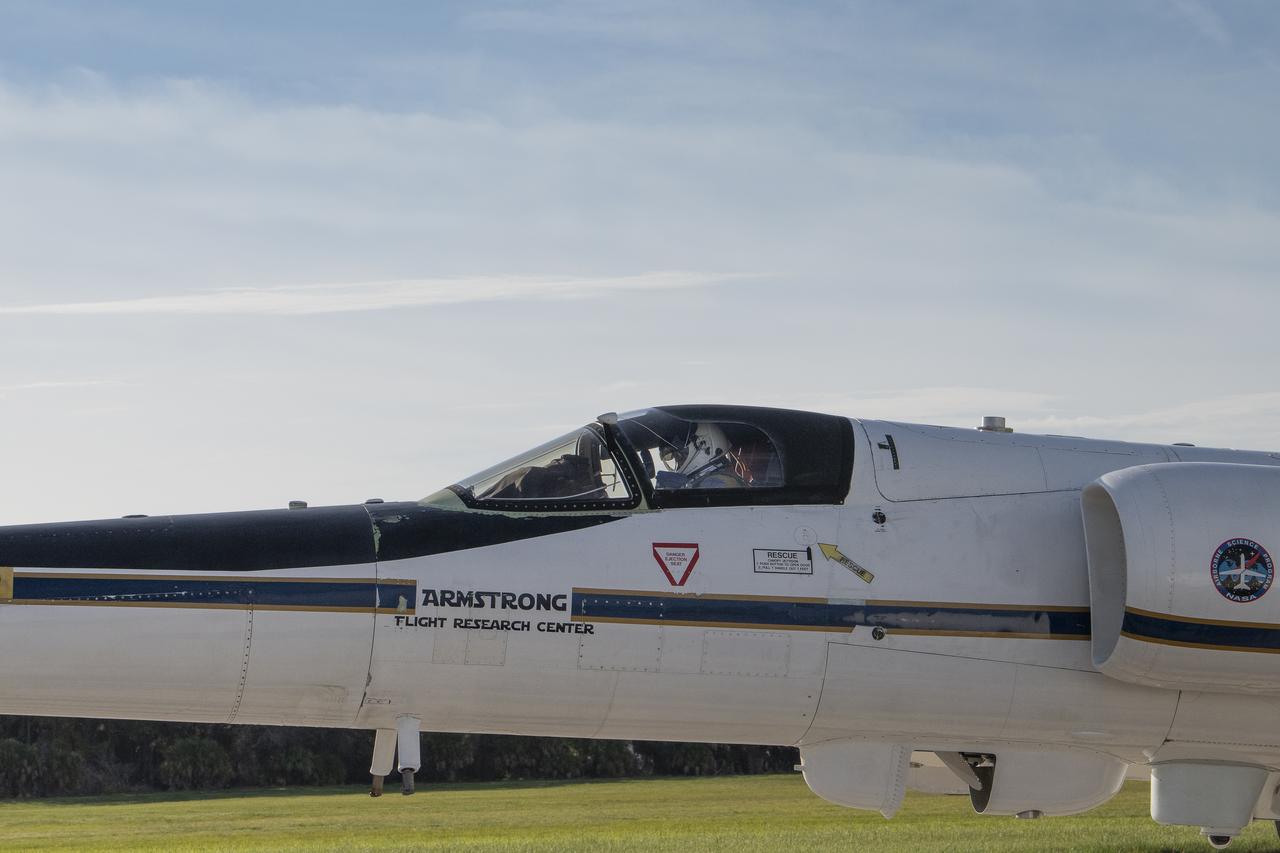
The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
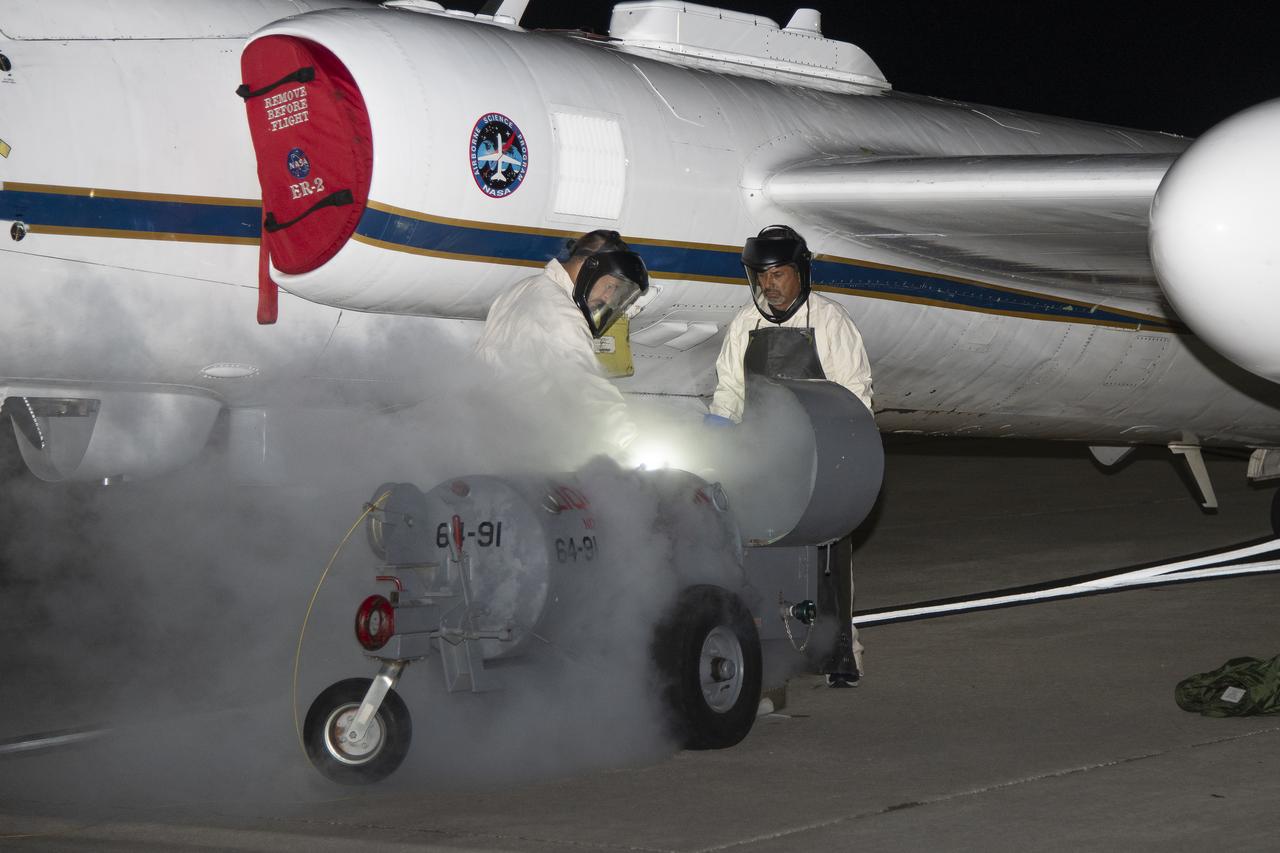

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
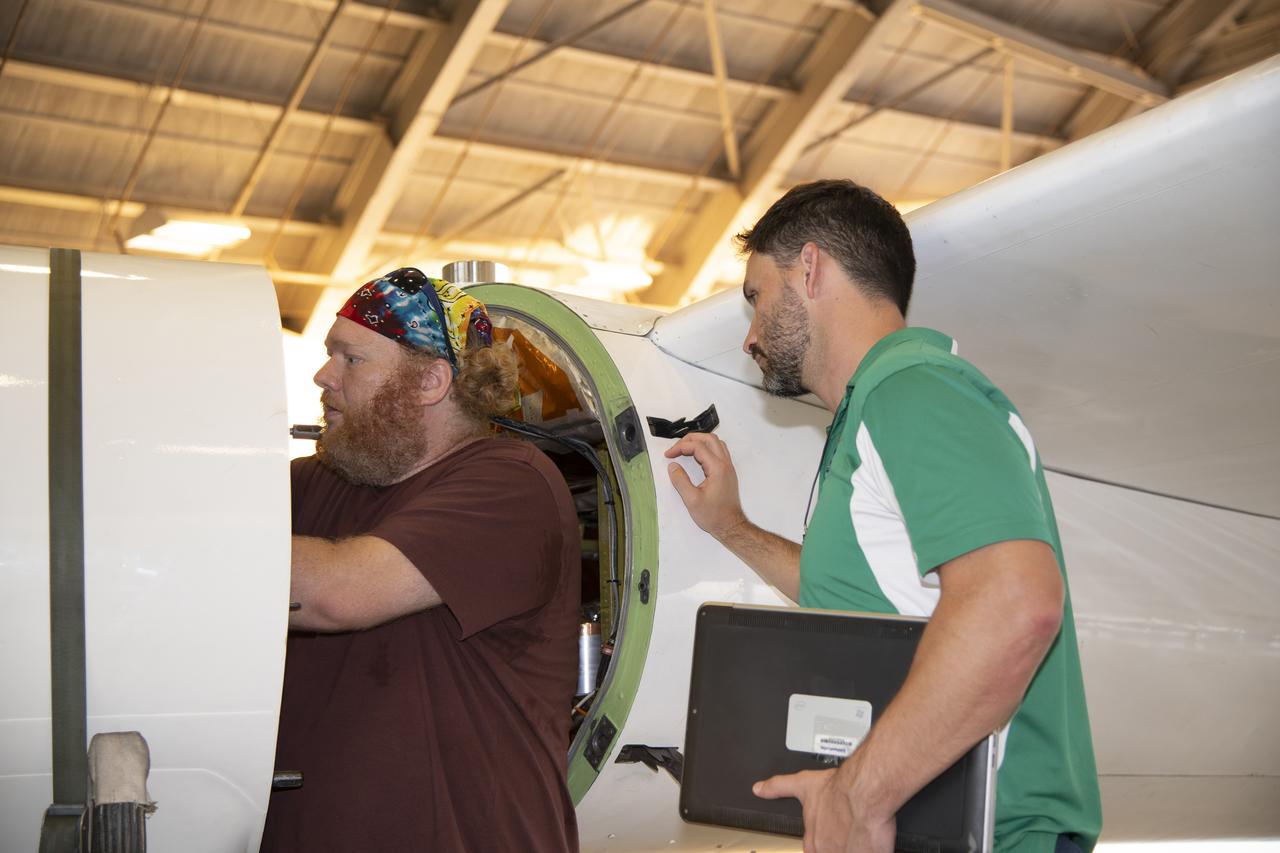

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
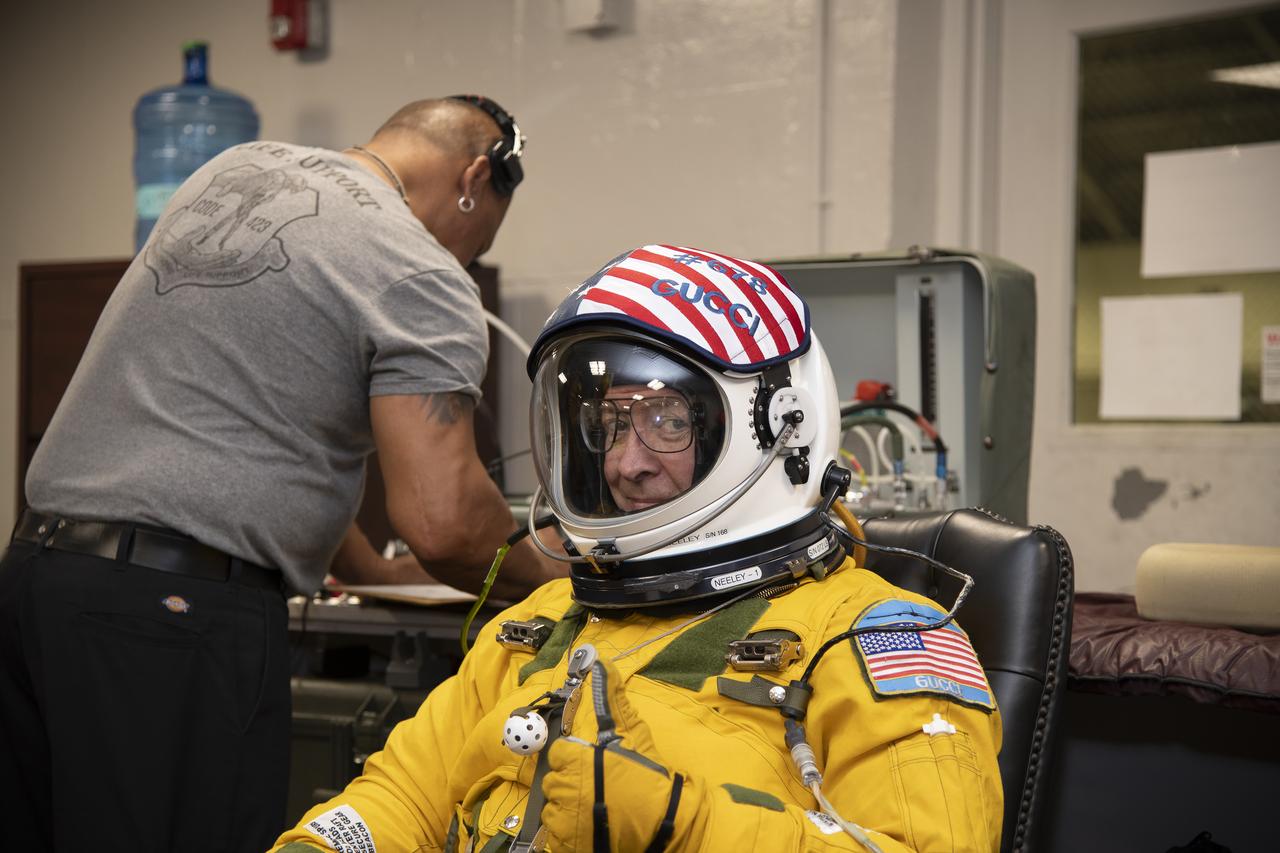

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
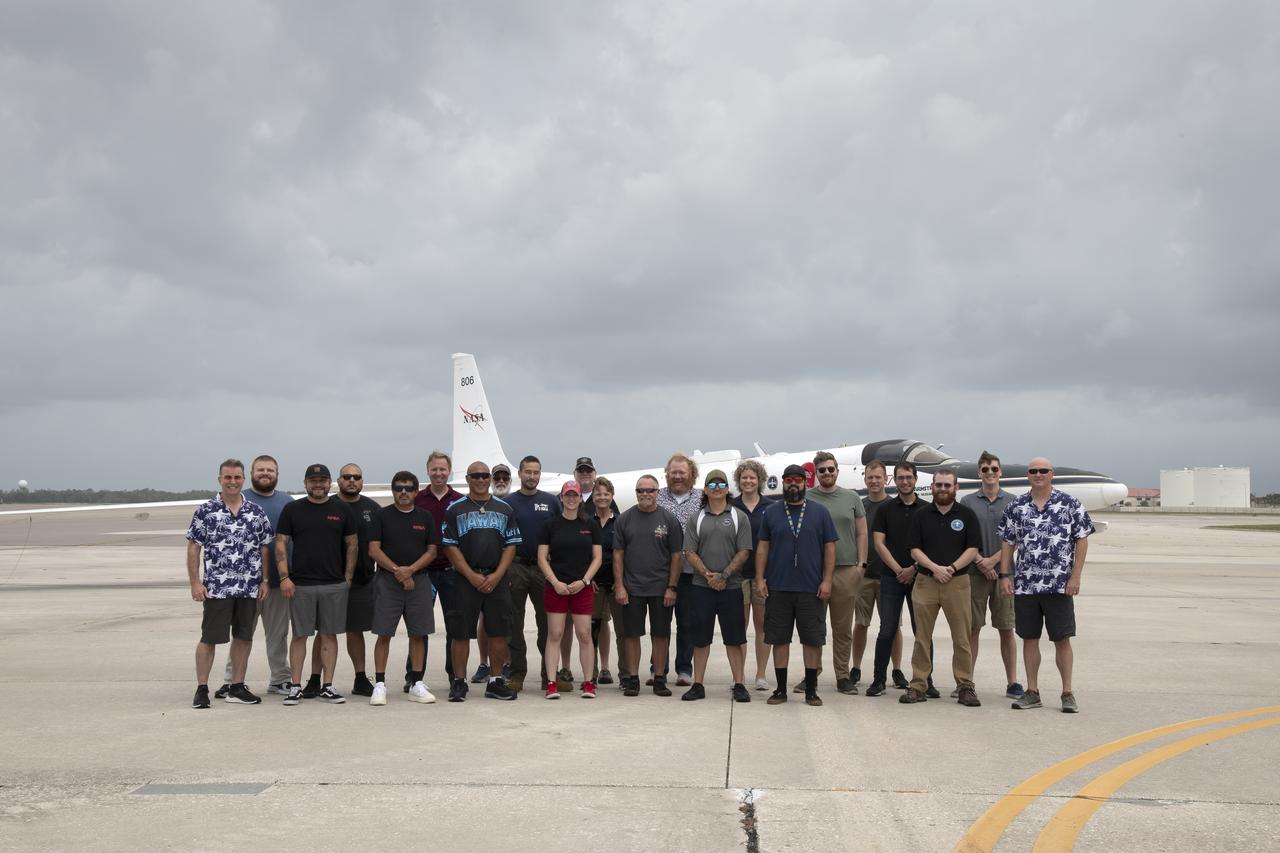

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
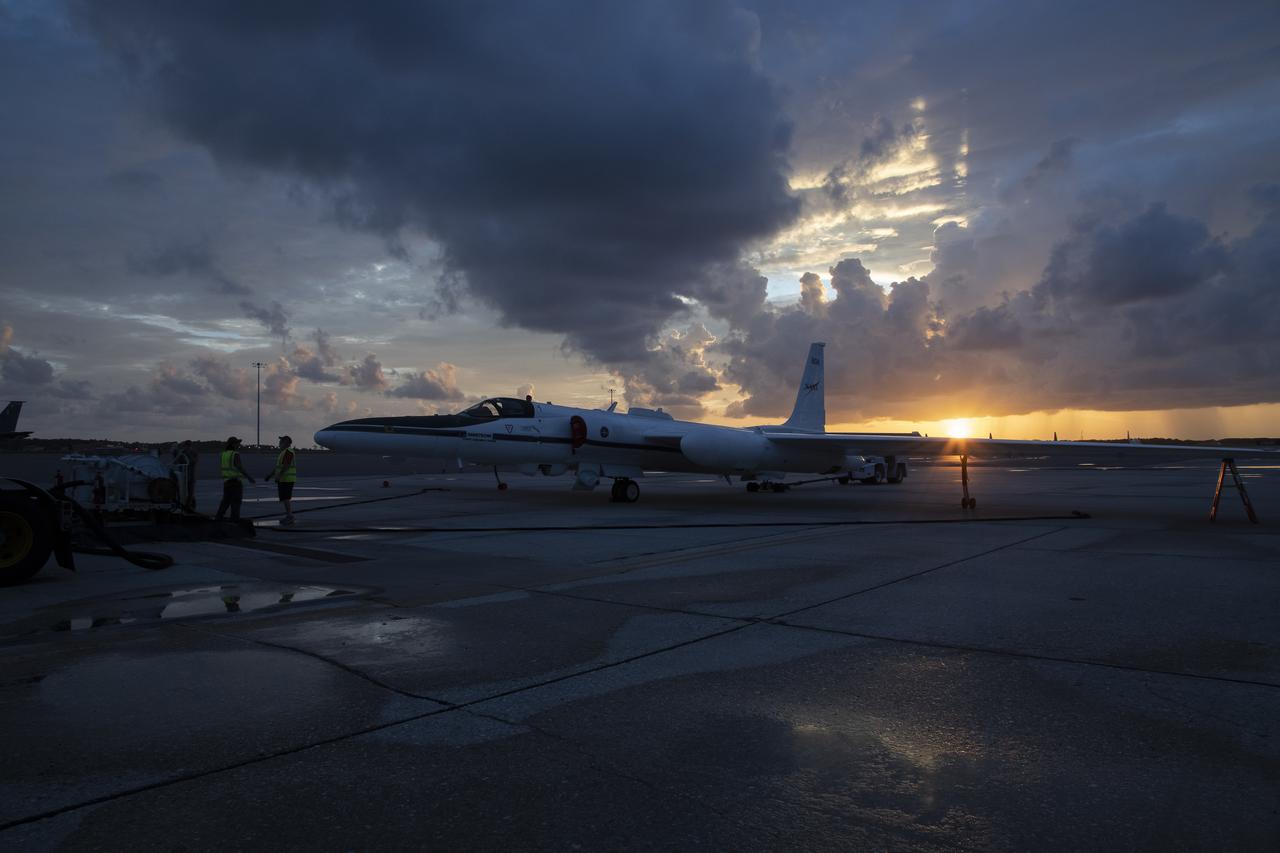

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
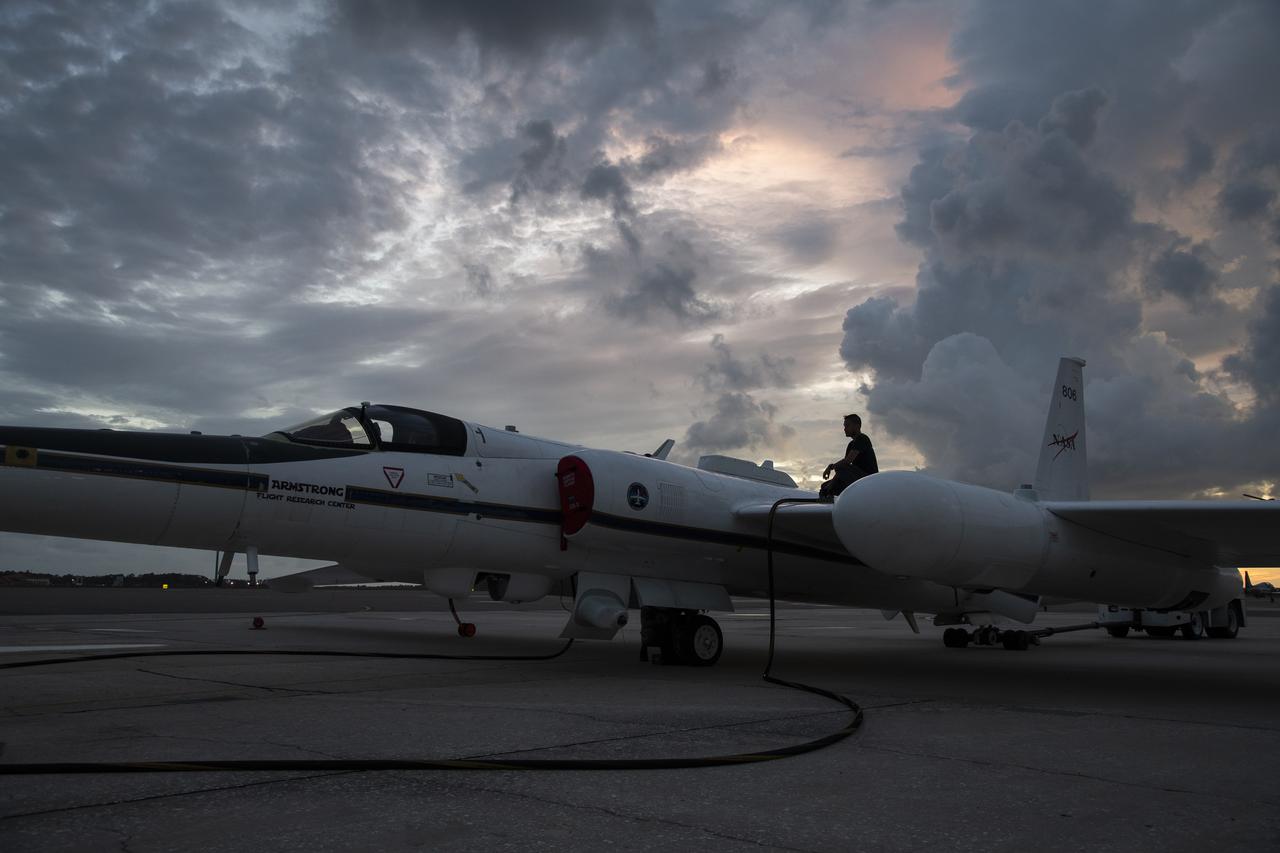

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
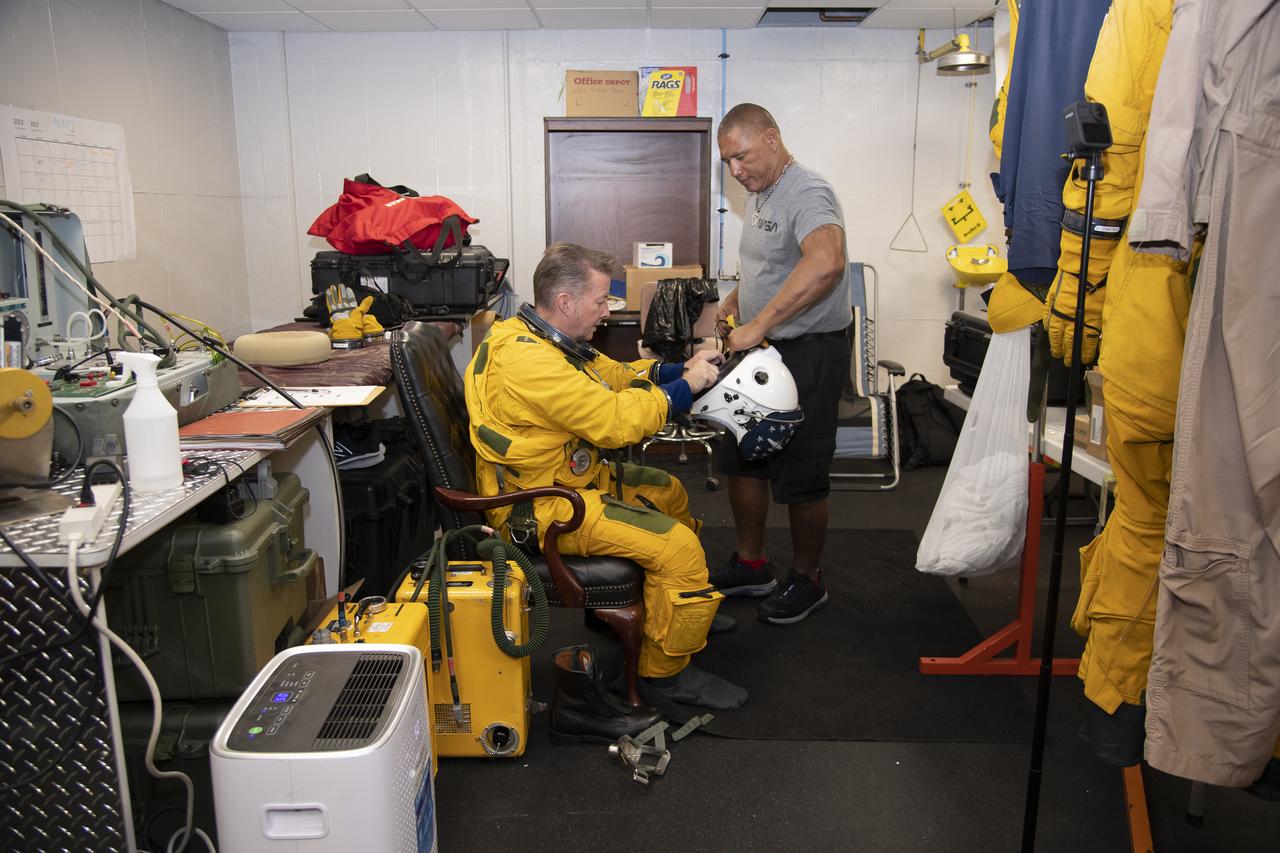

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
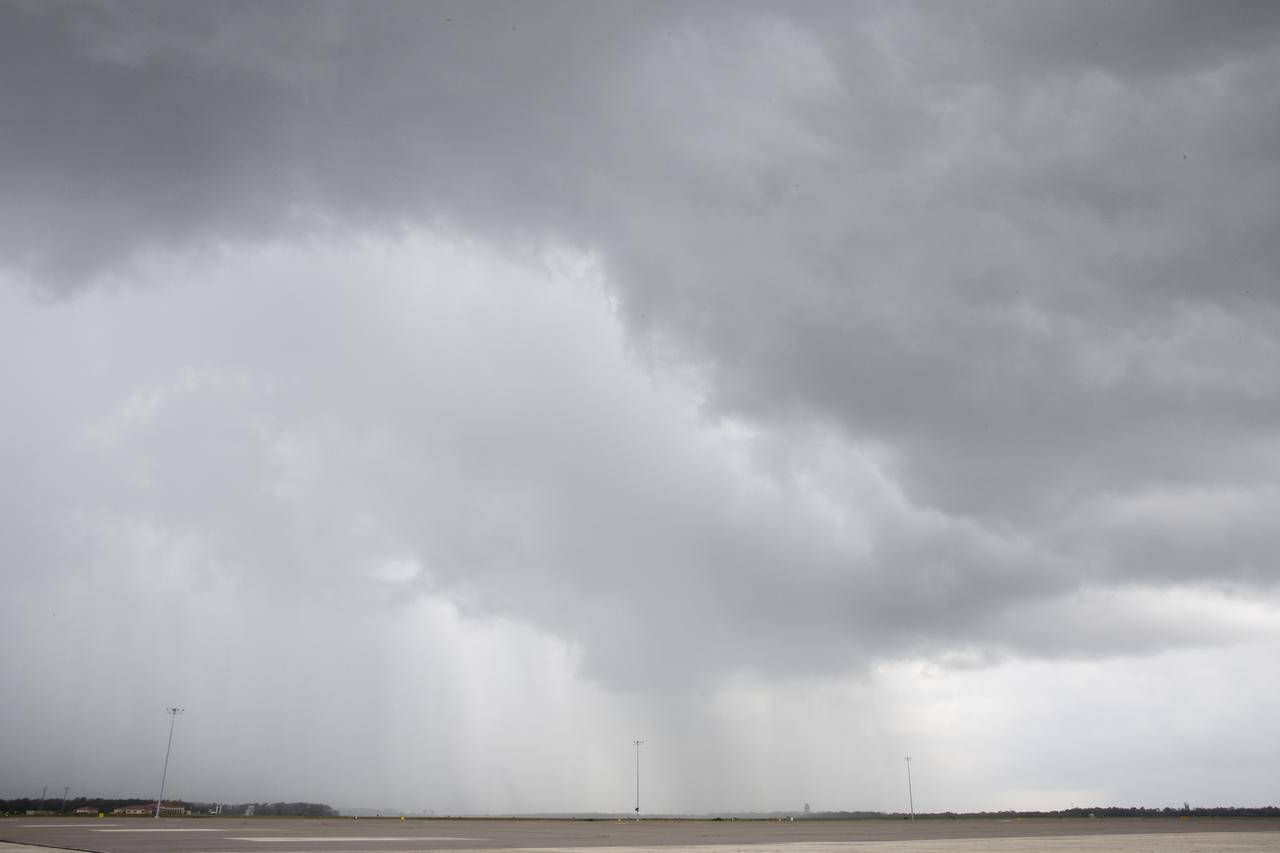

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
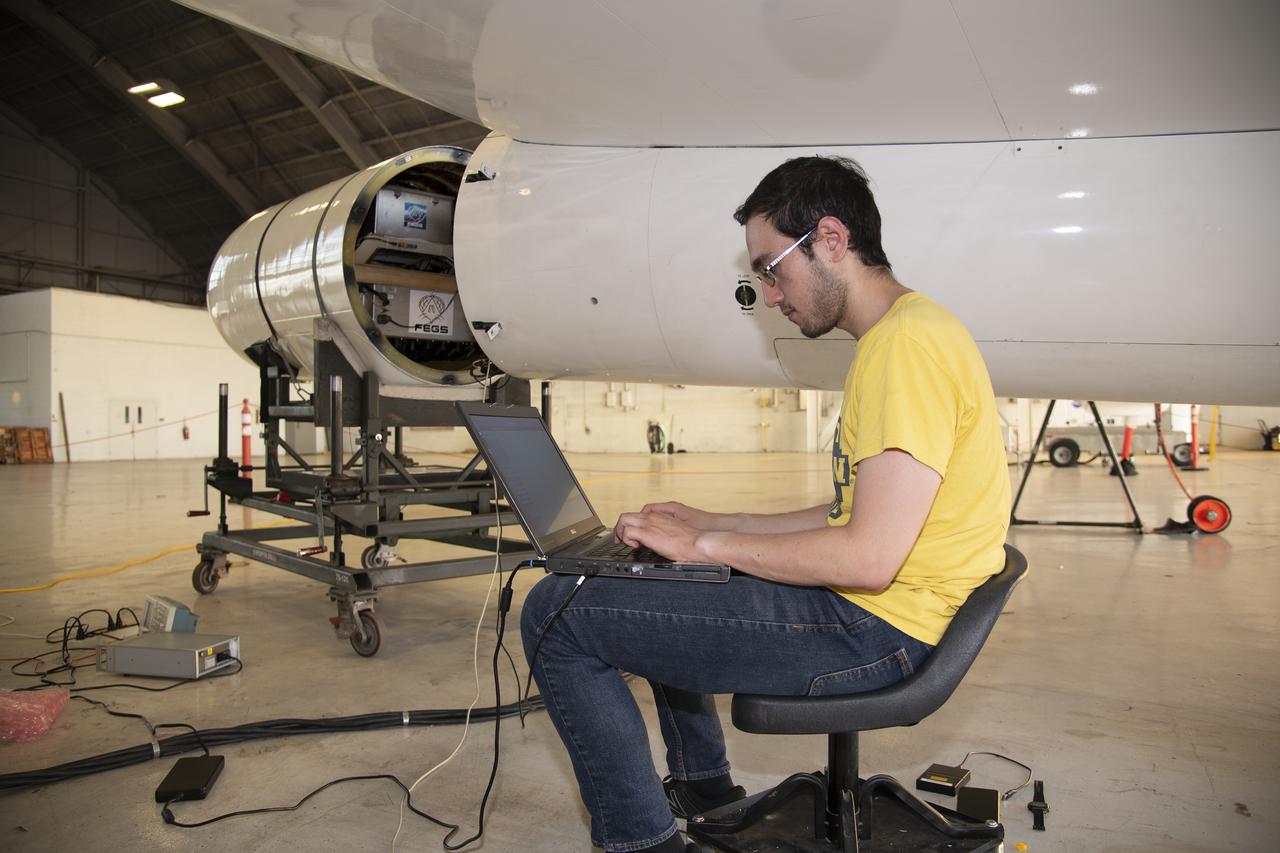

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
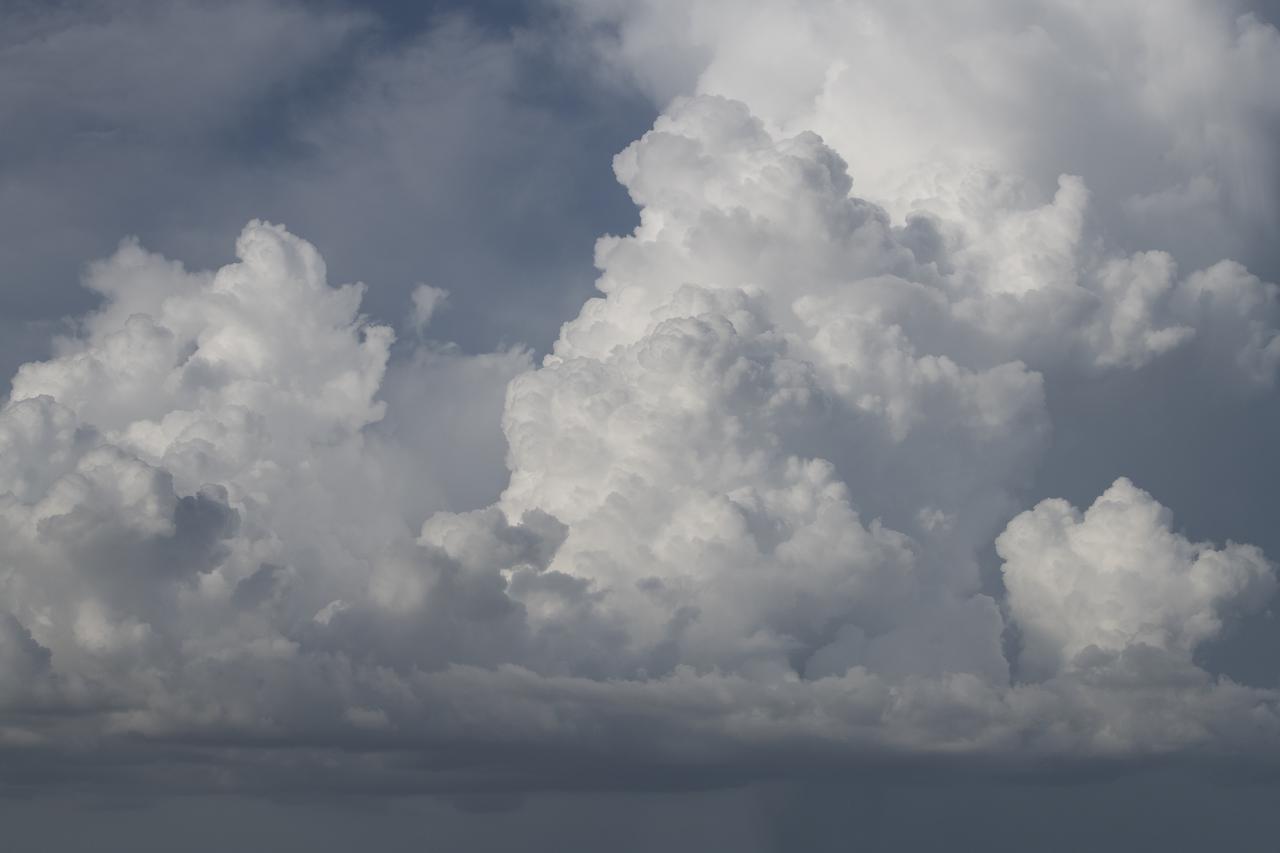

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
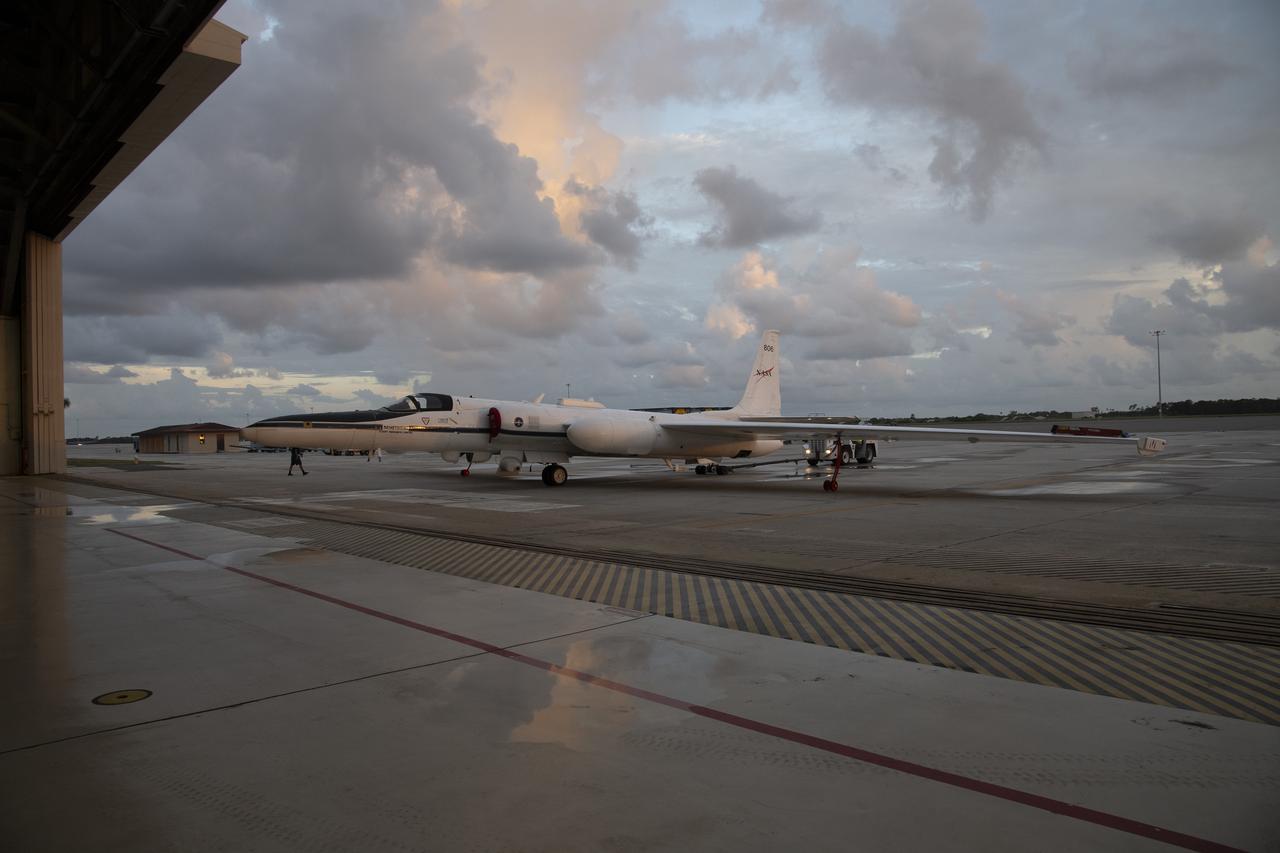

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
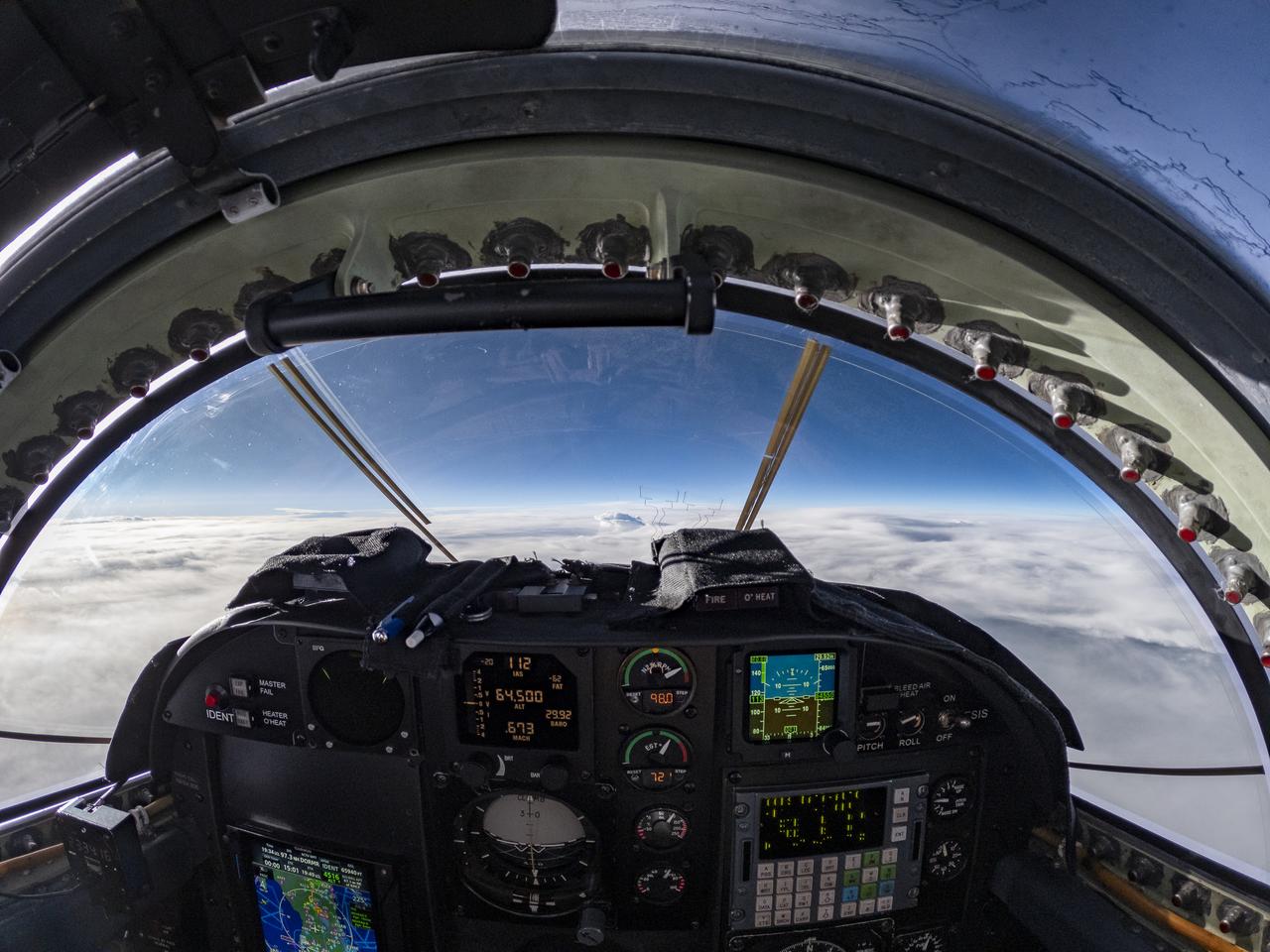

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
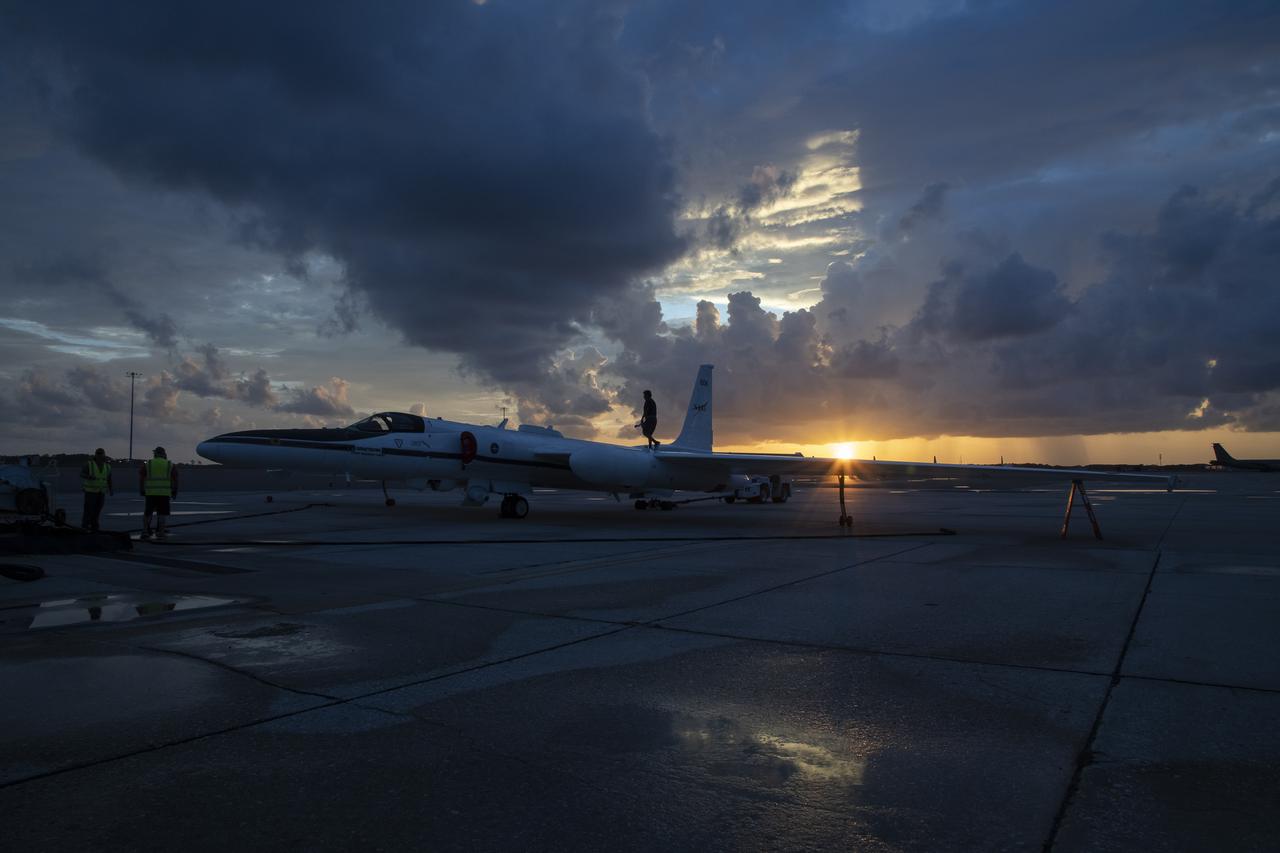

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
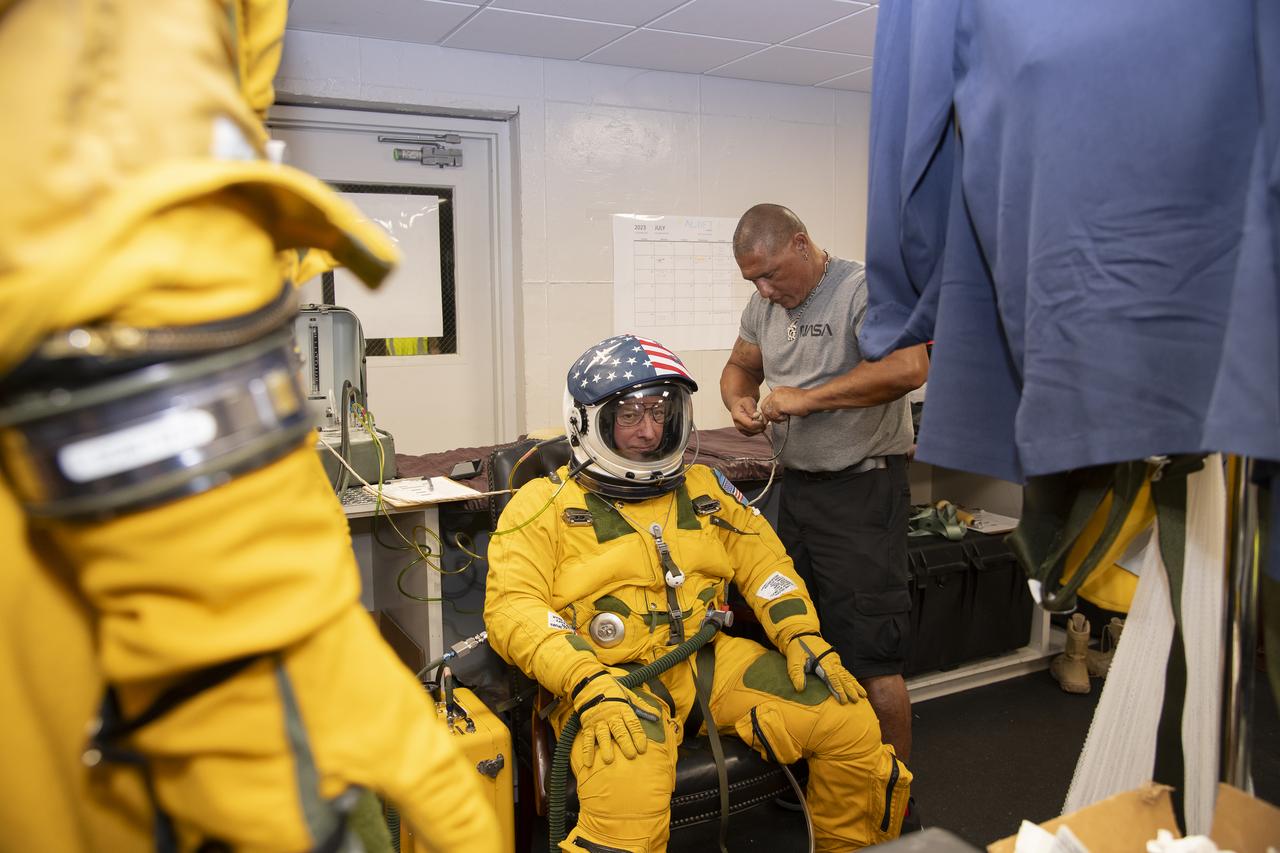

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
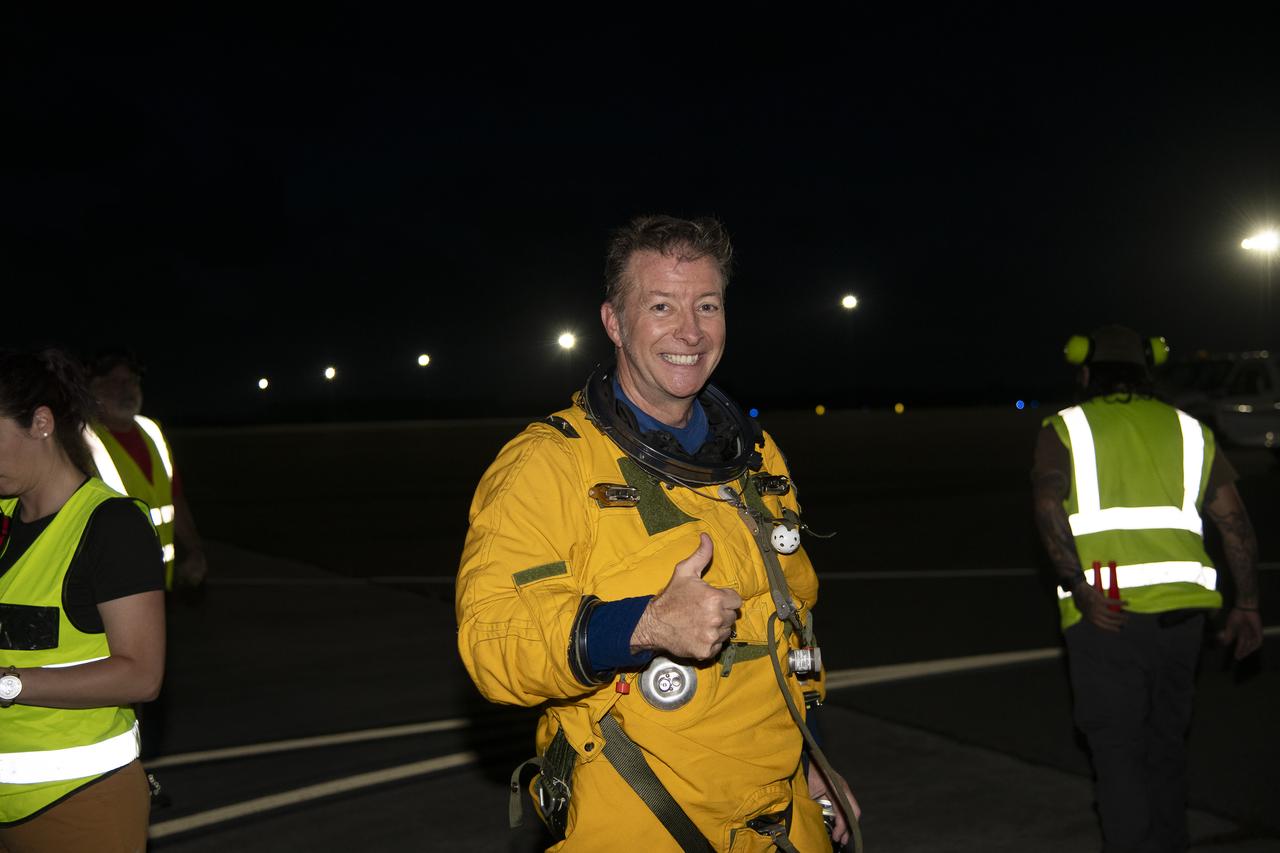

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
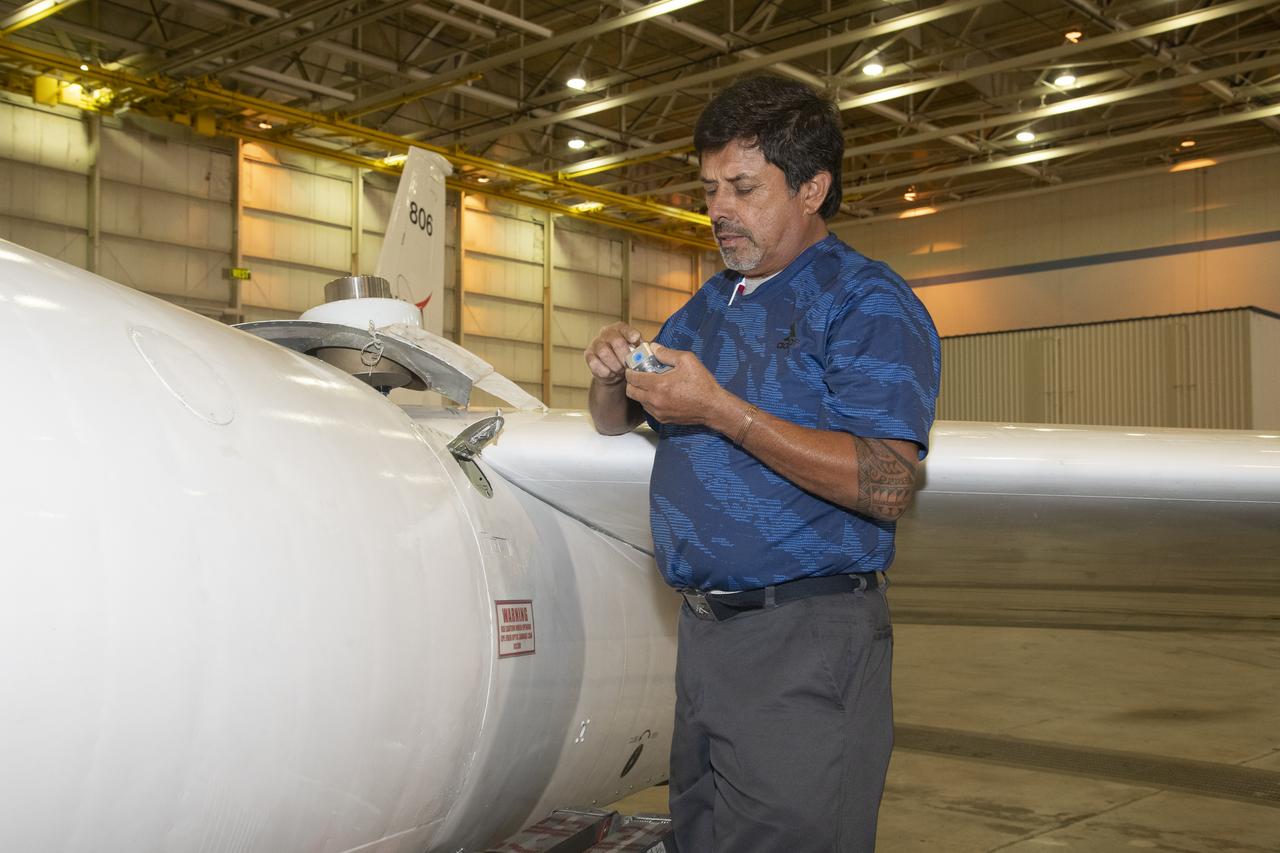

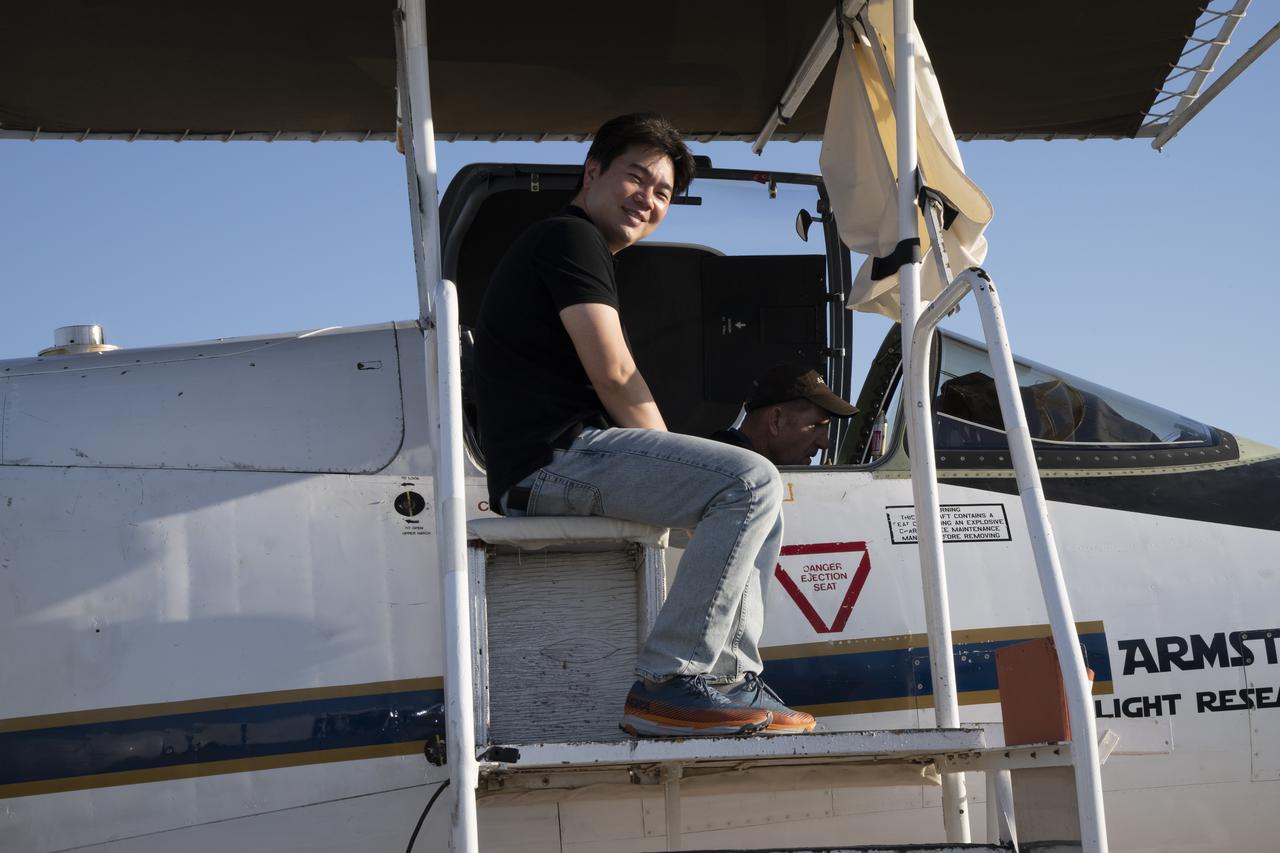
NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
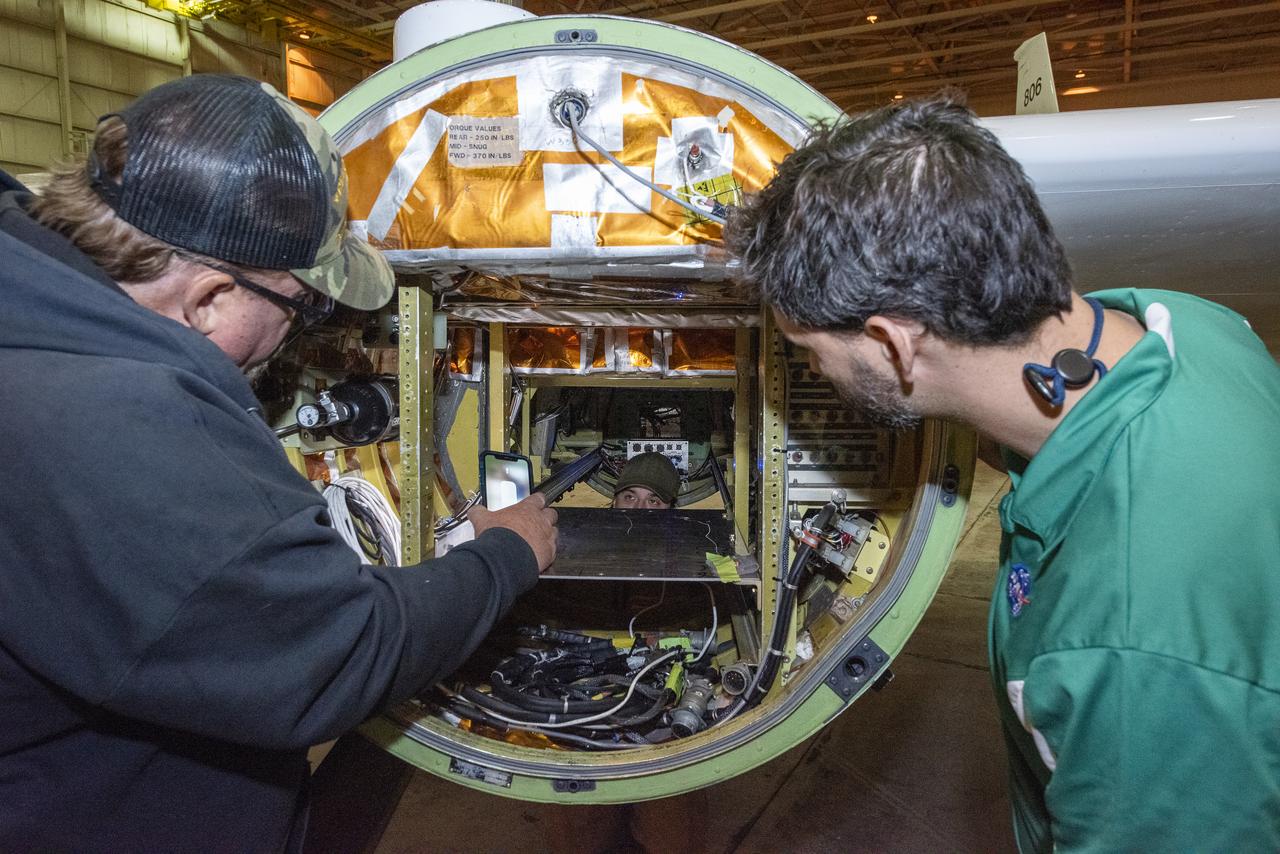

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
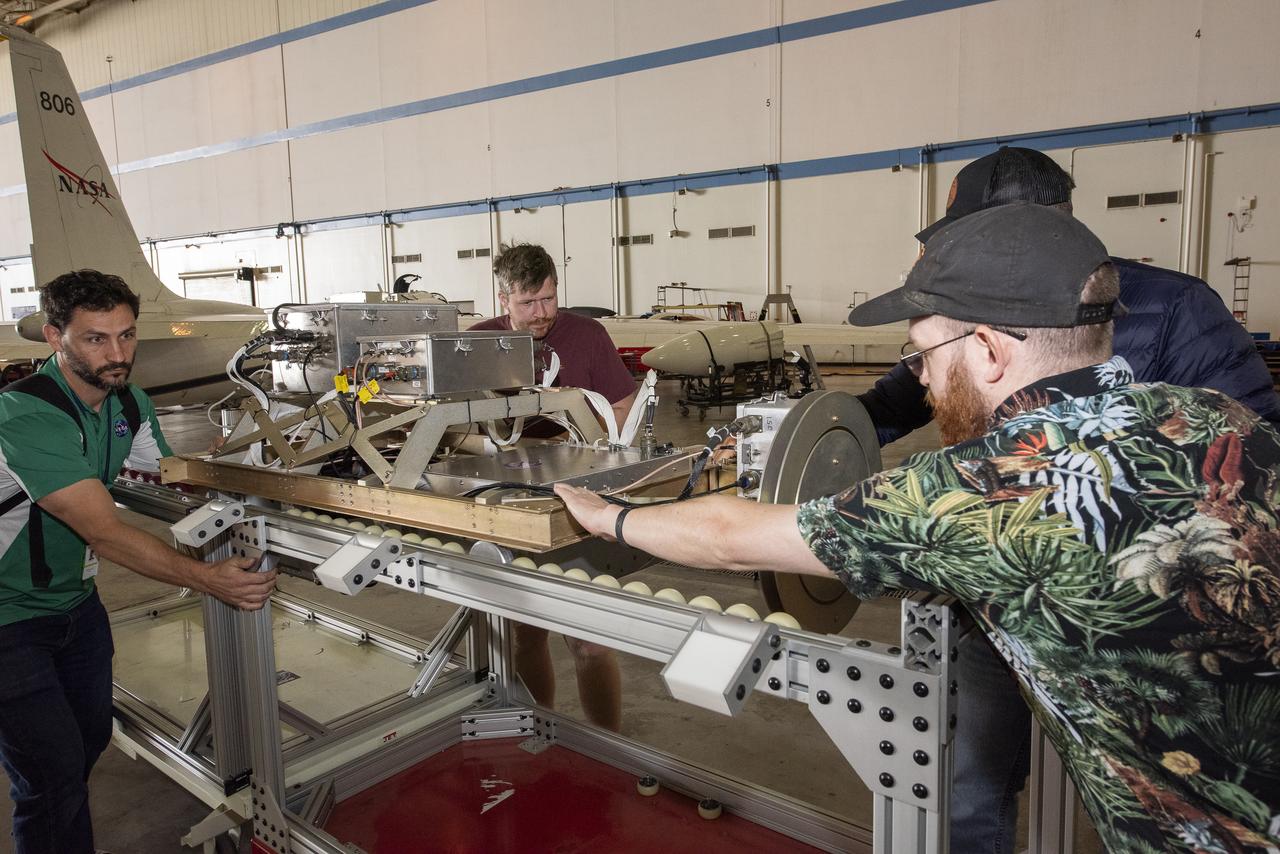

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
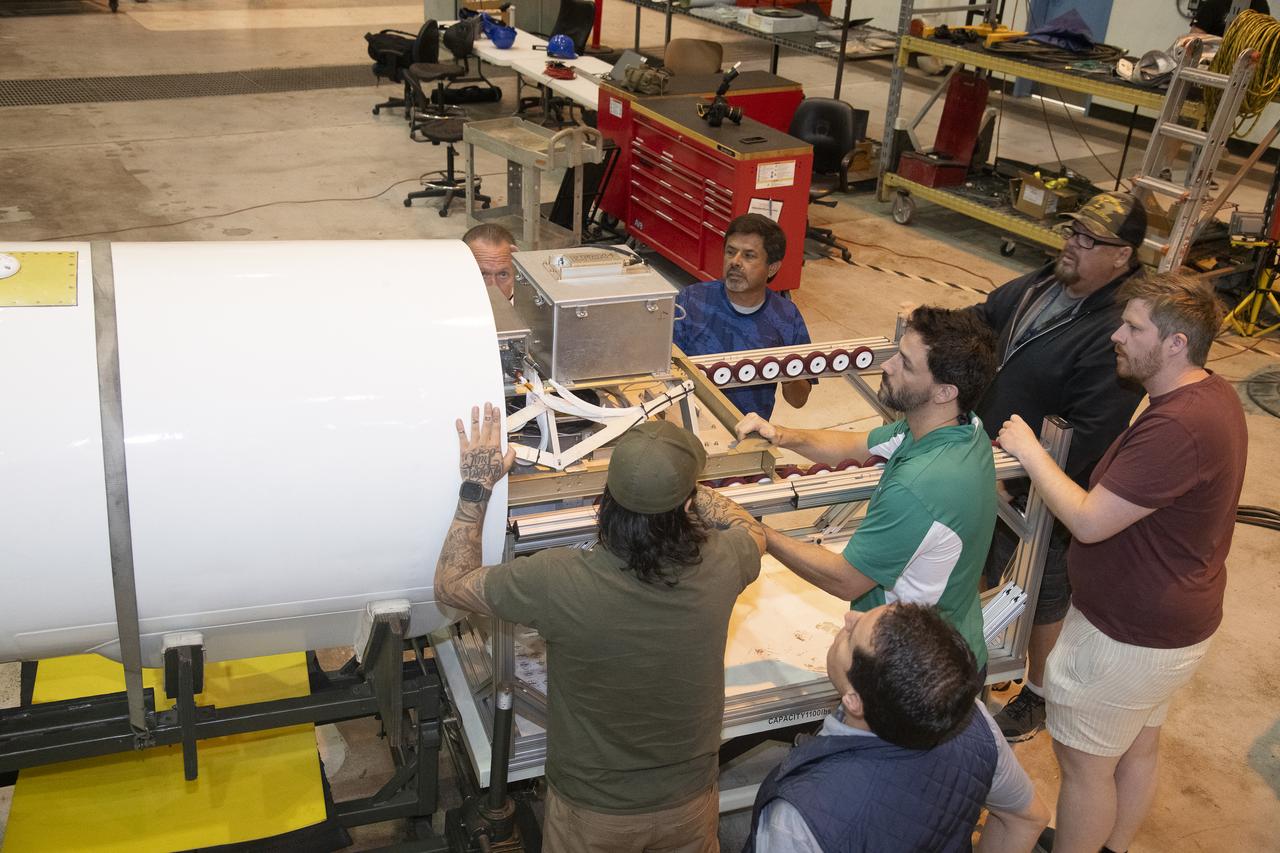

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
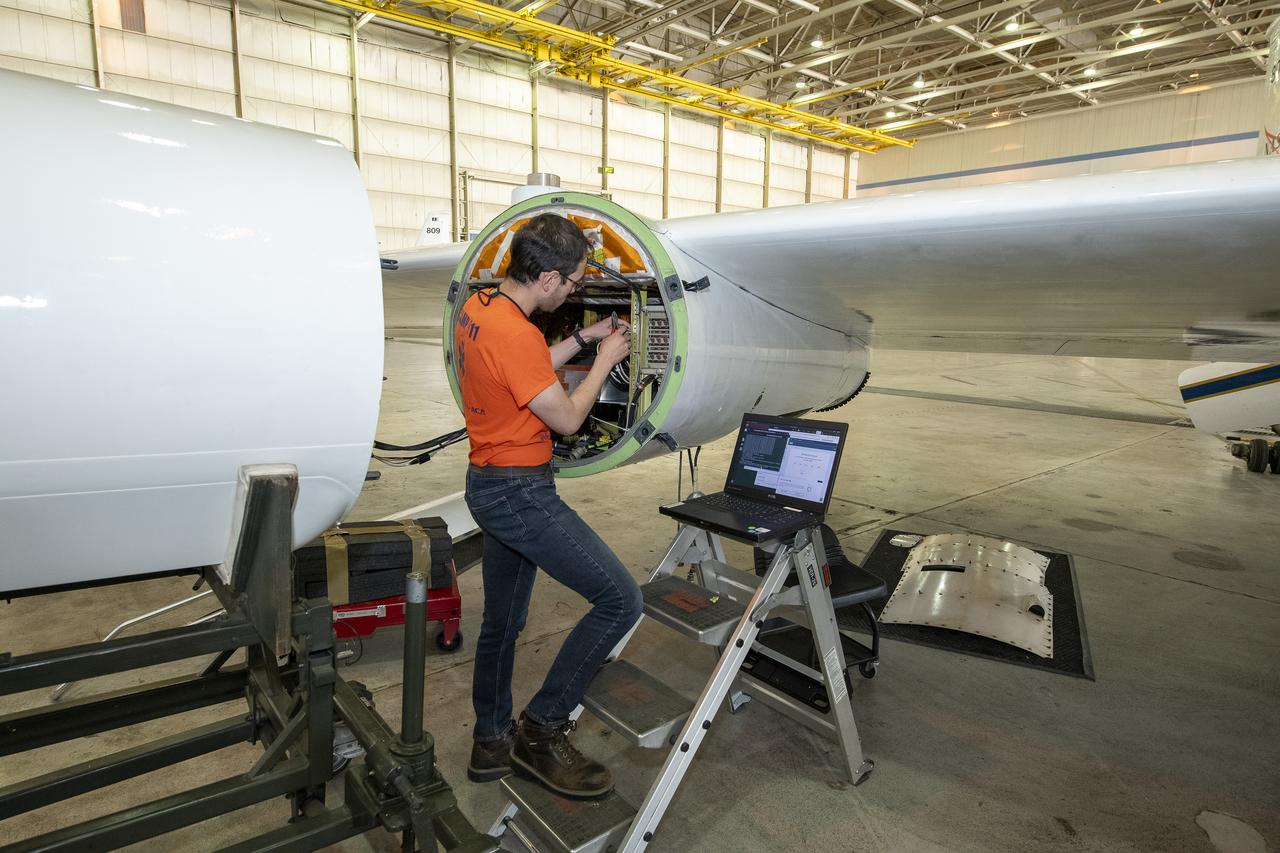

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
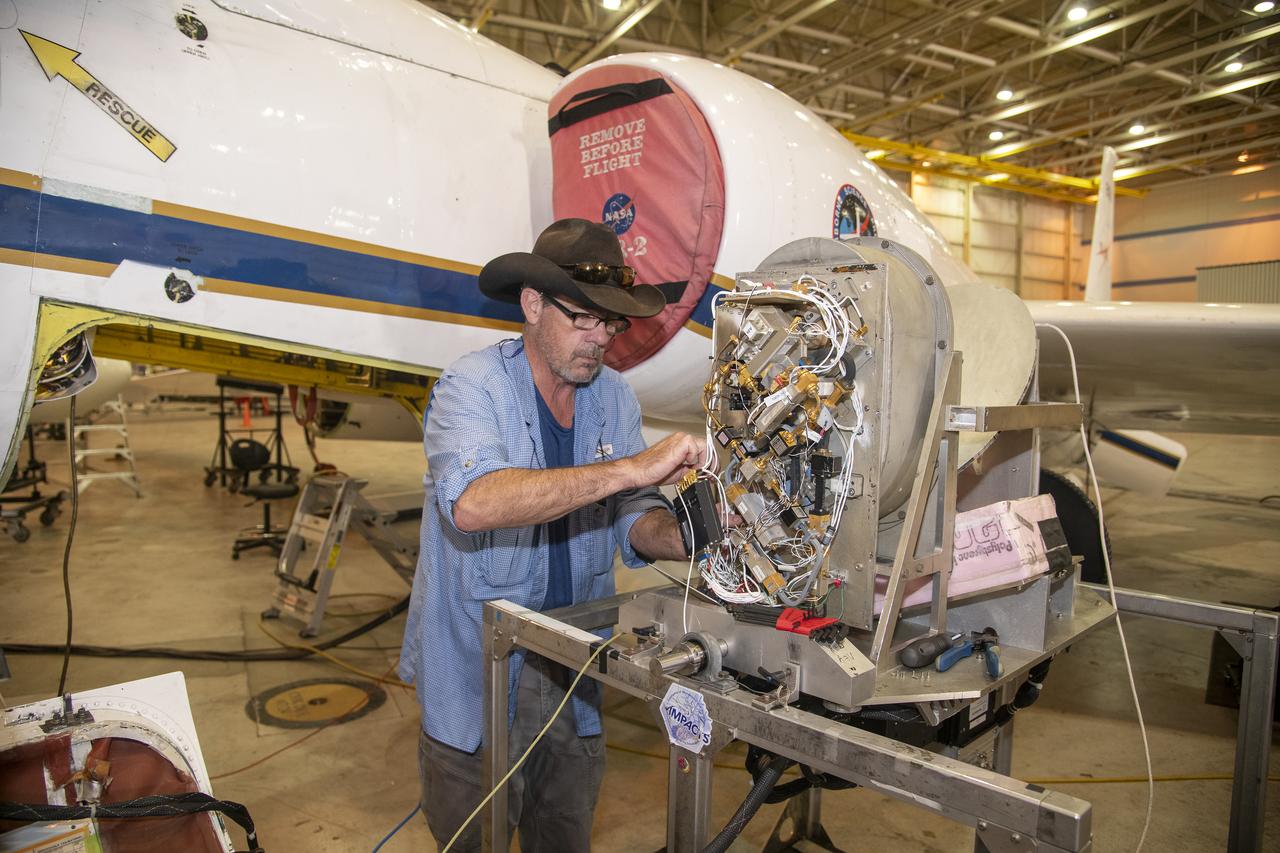

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
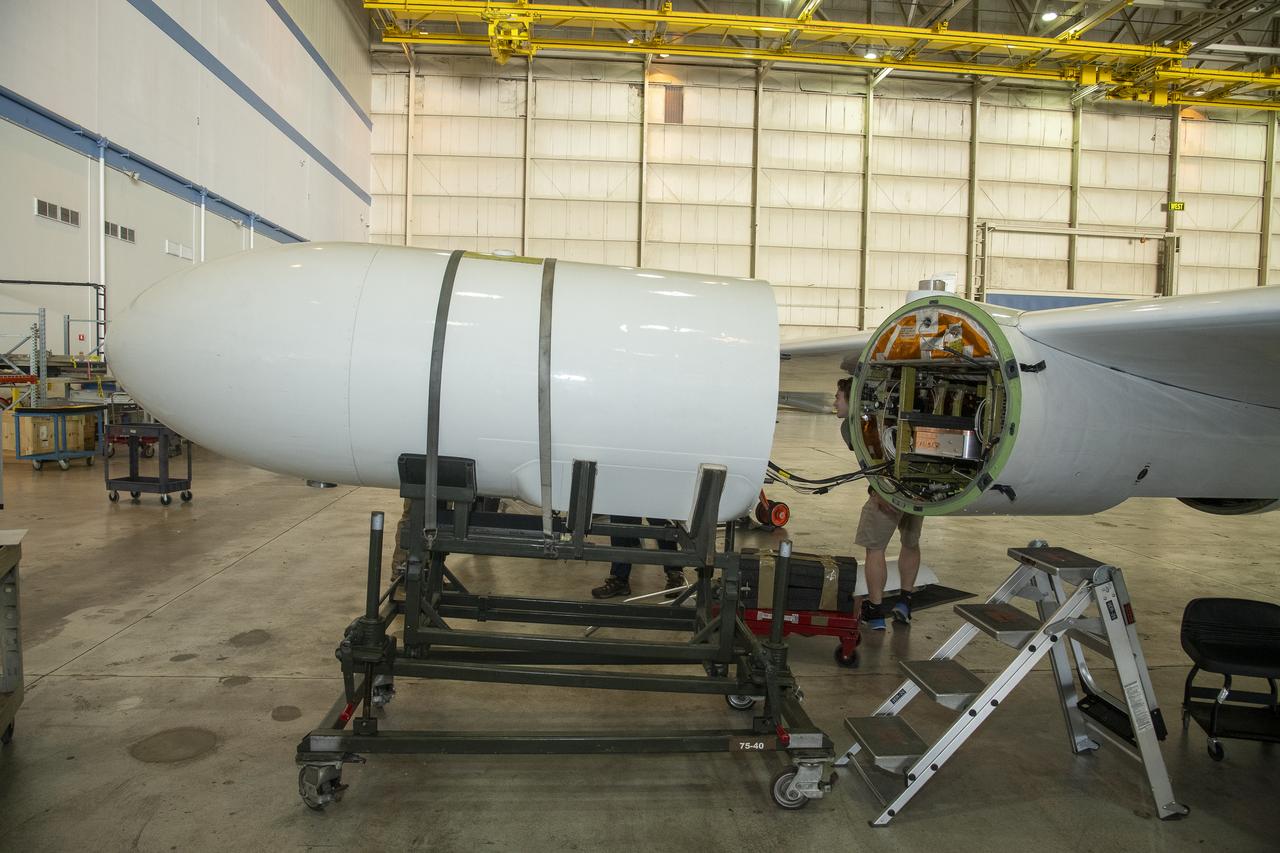

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
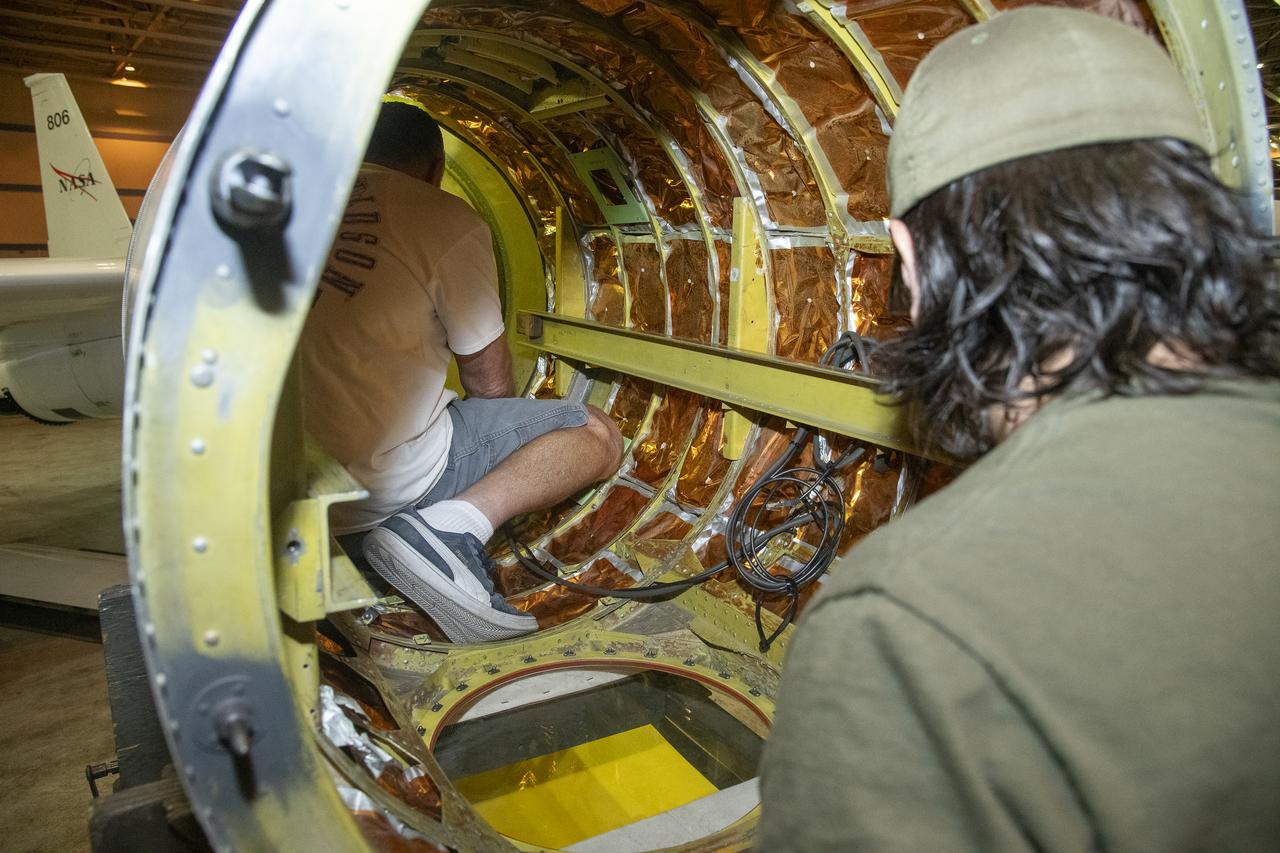

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
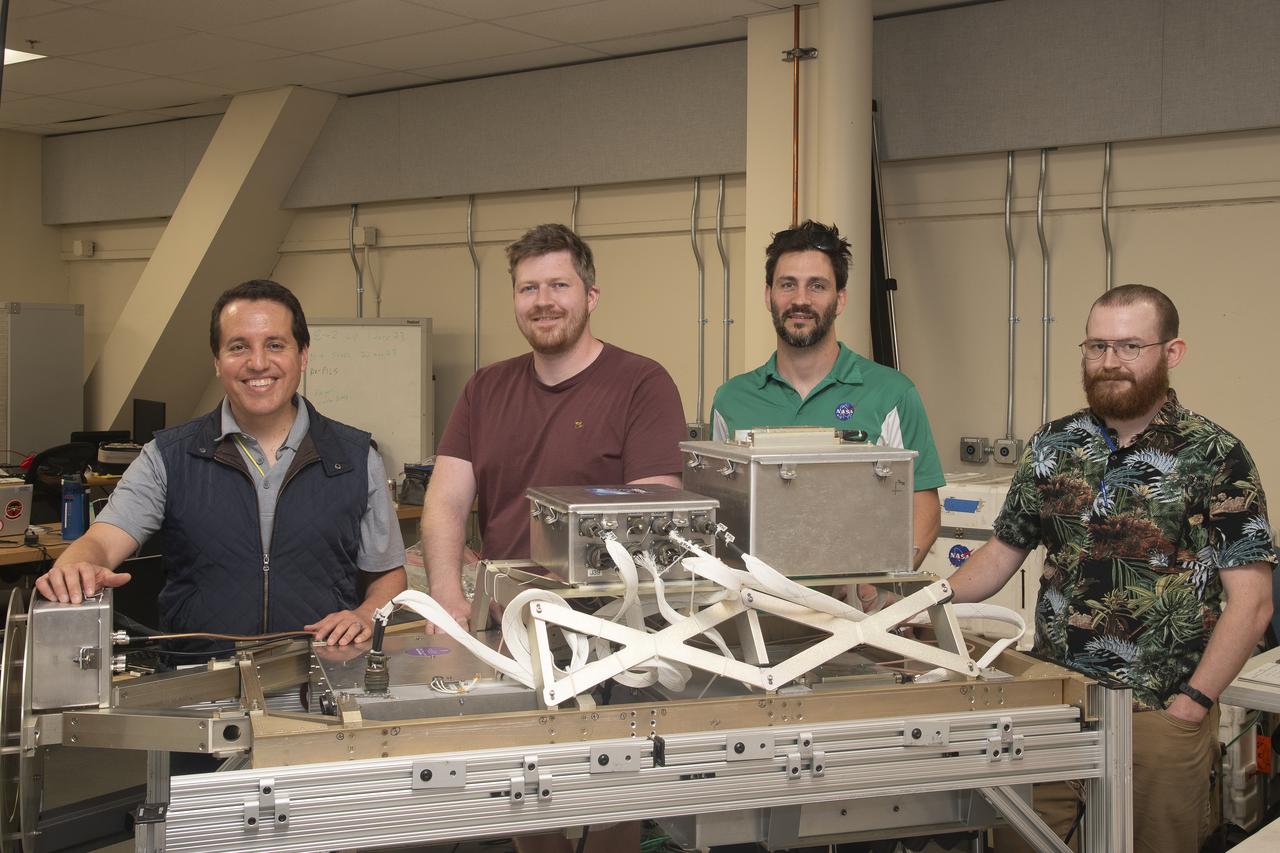
NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
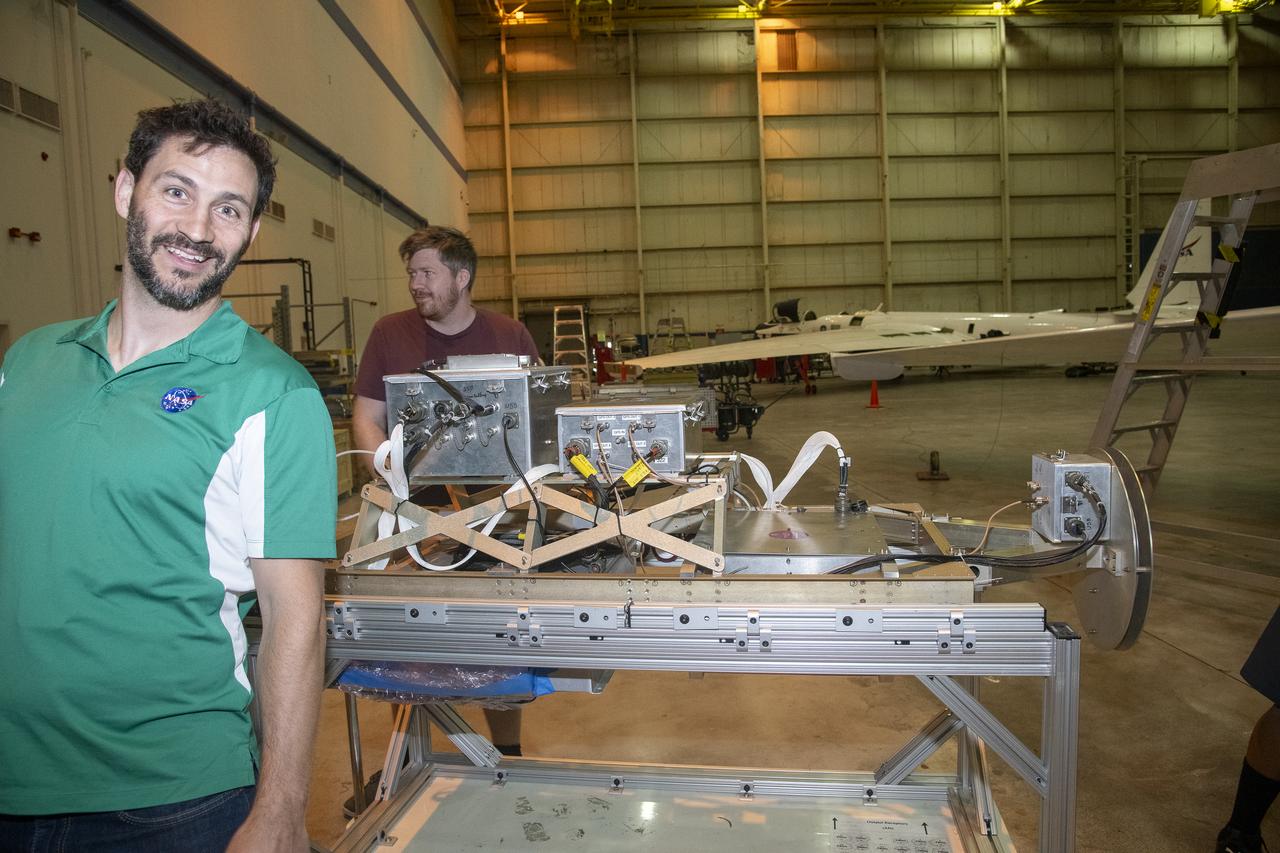

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
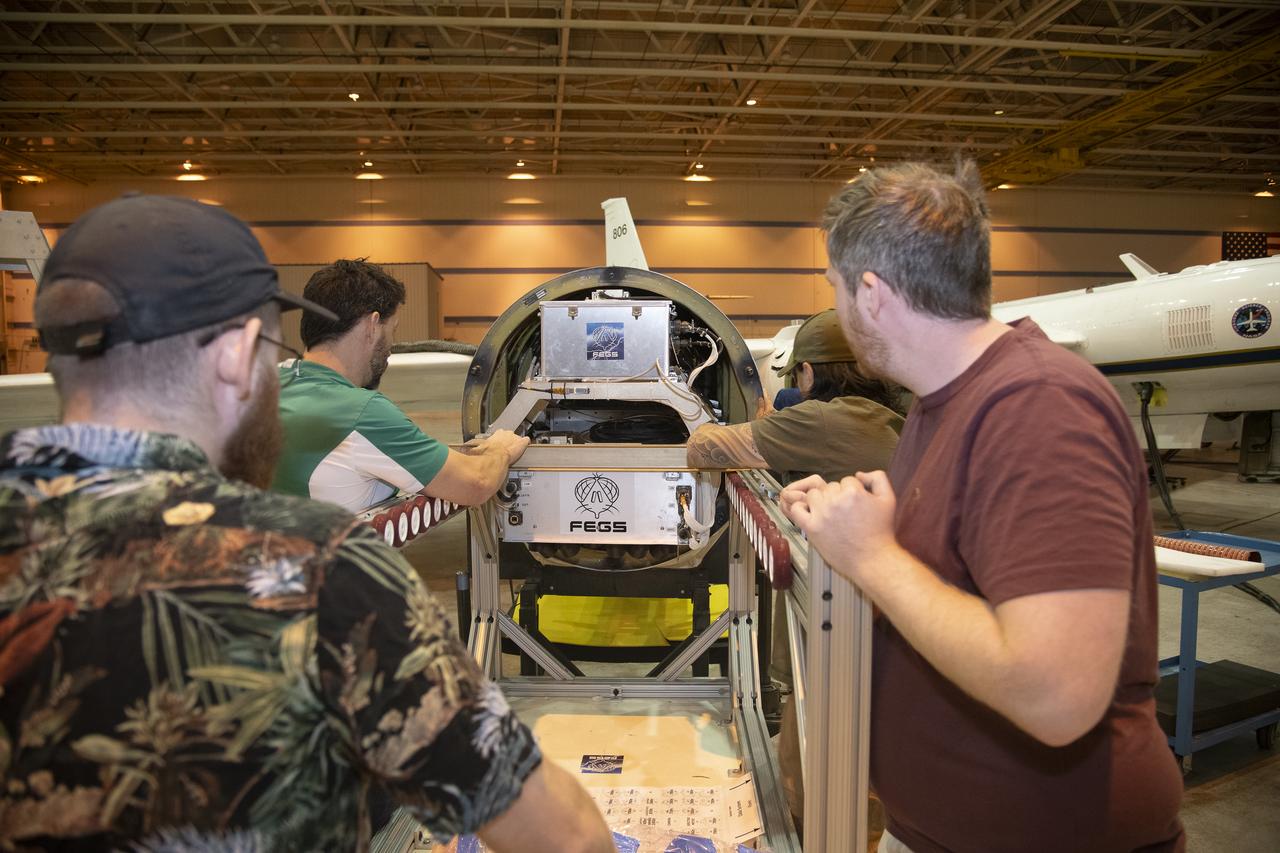

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
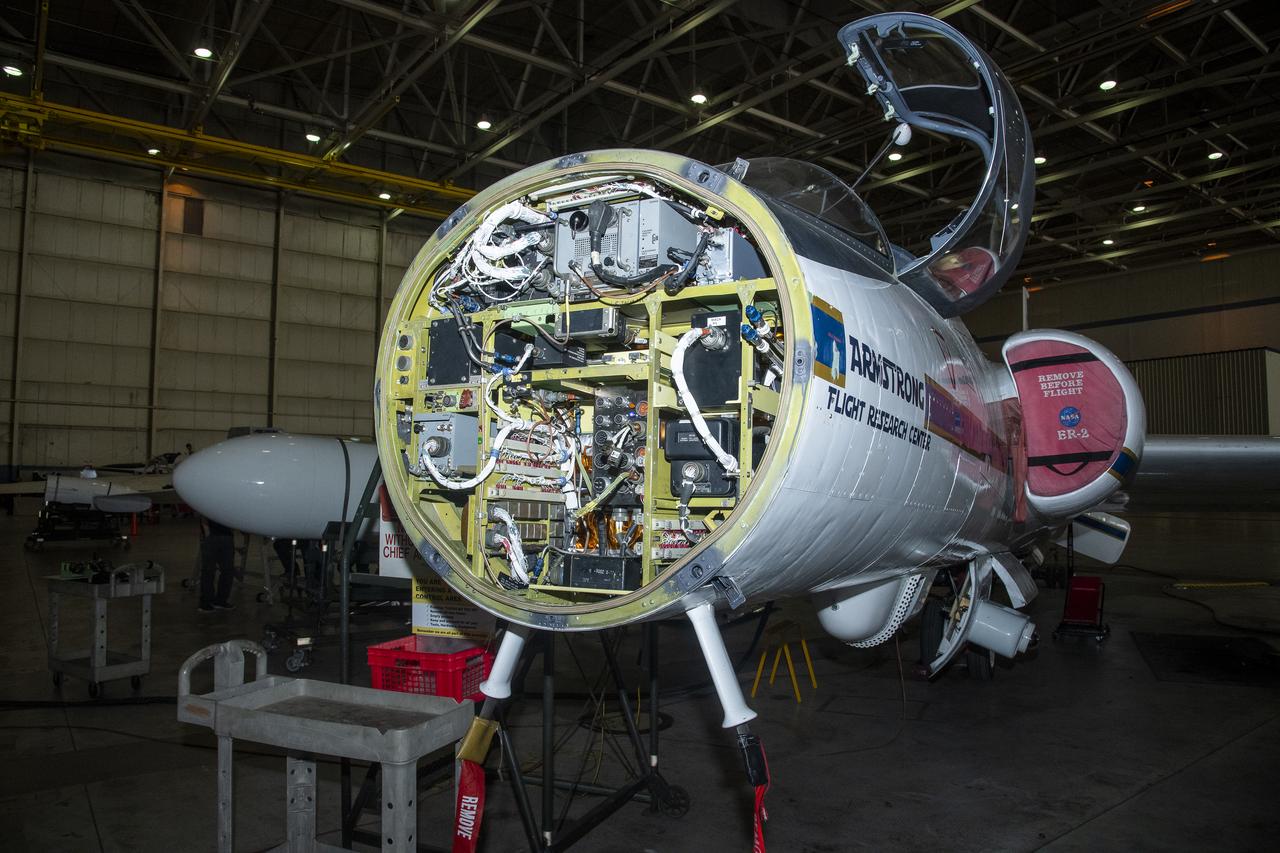

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
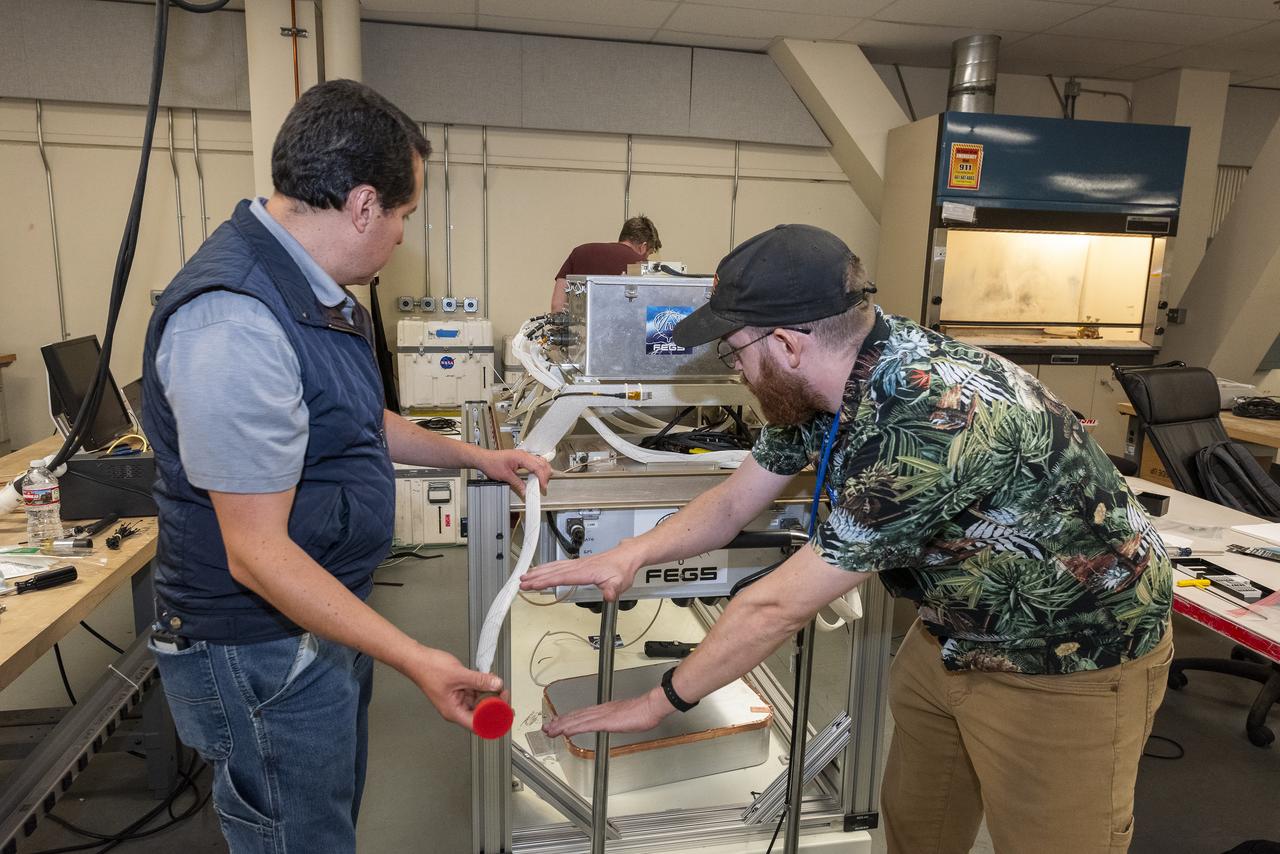

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
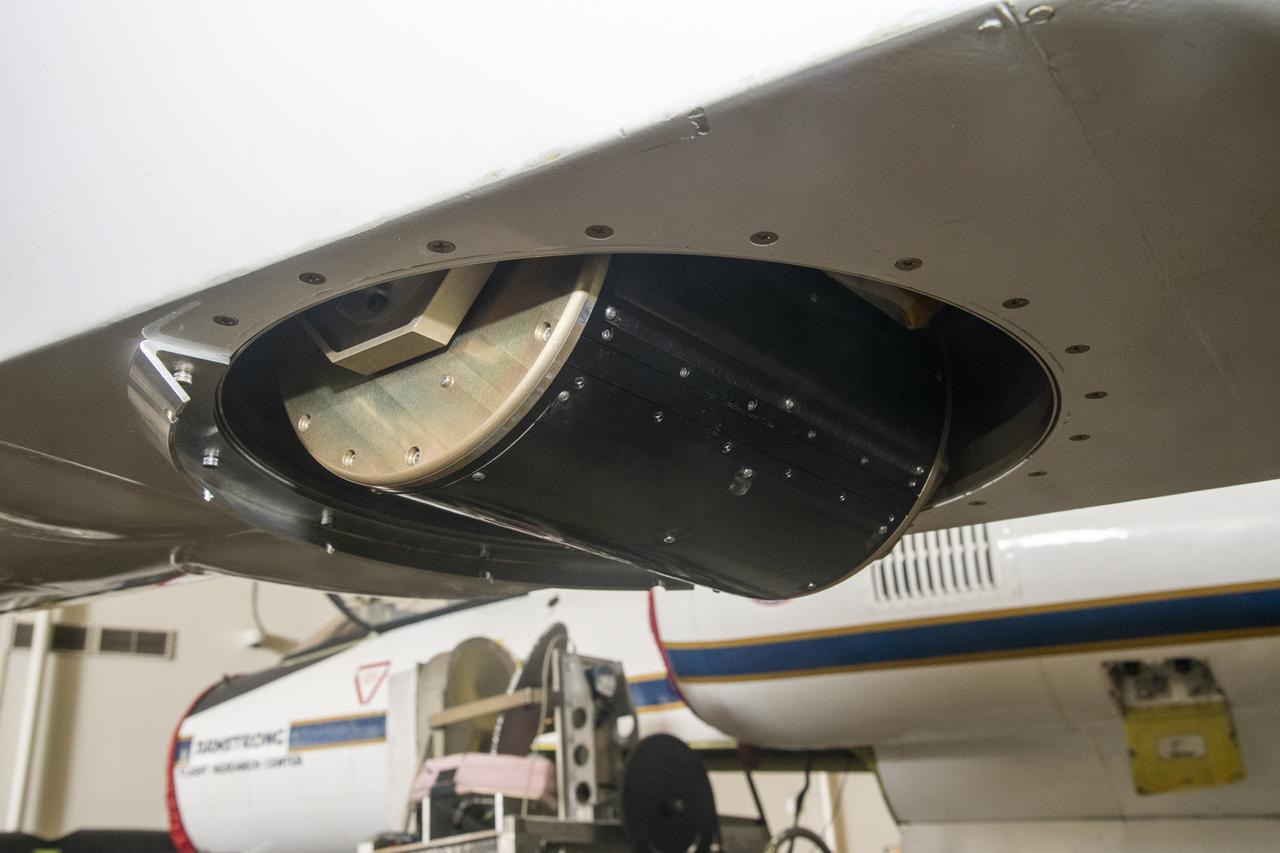

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
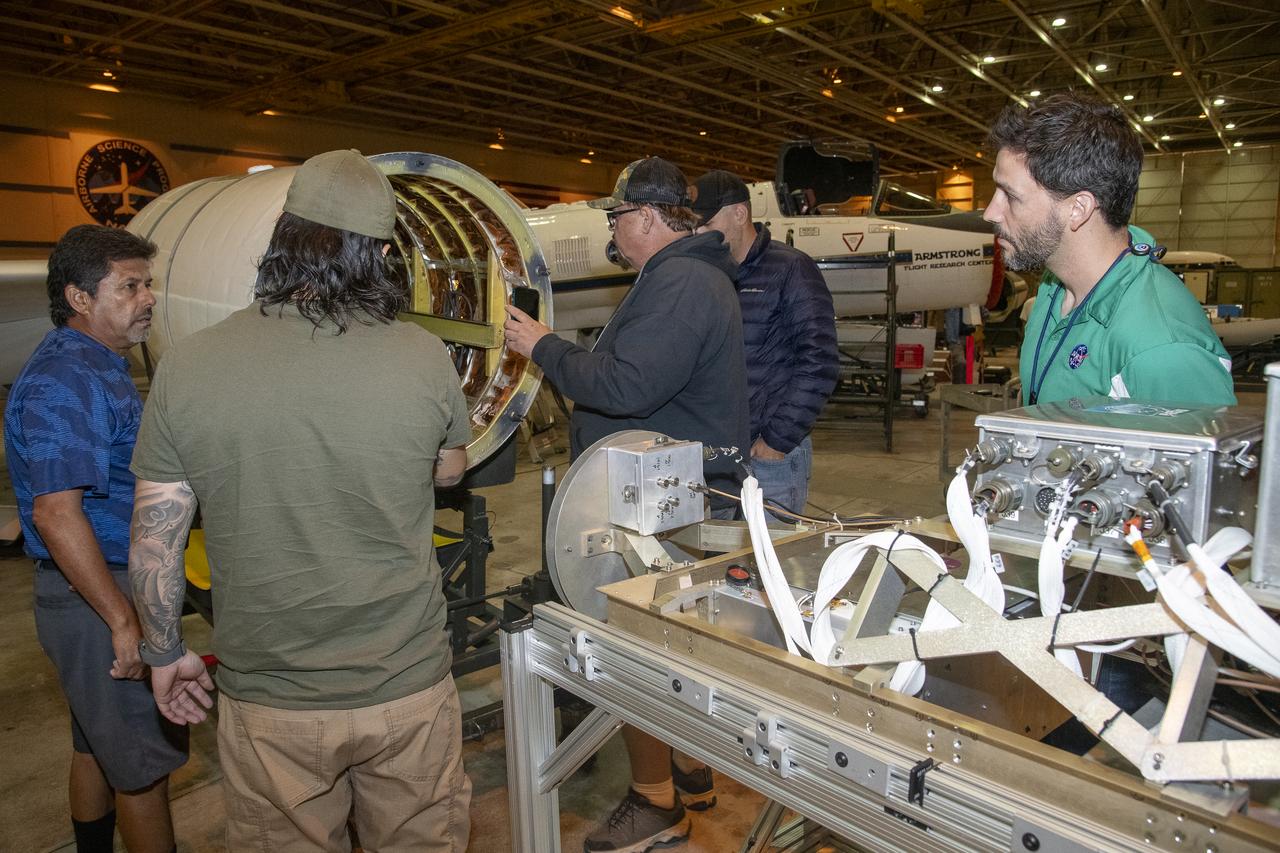

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
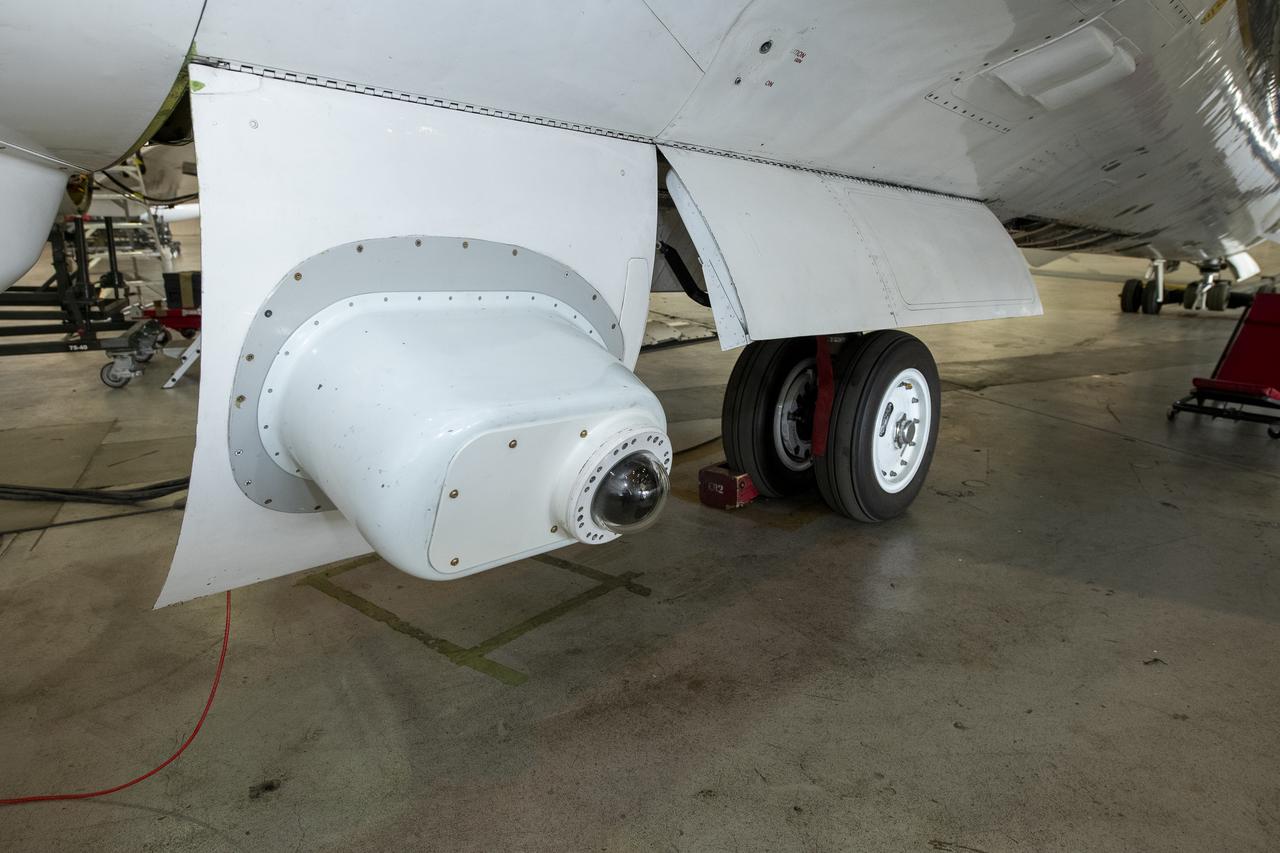

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
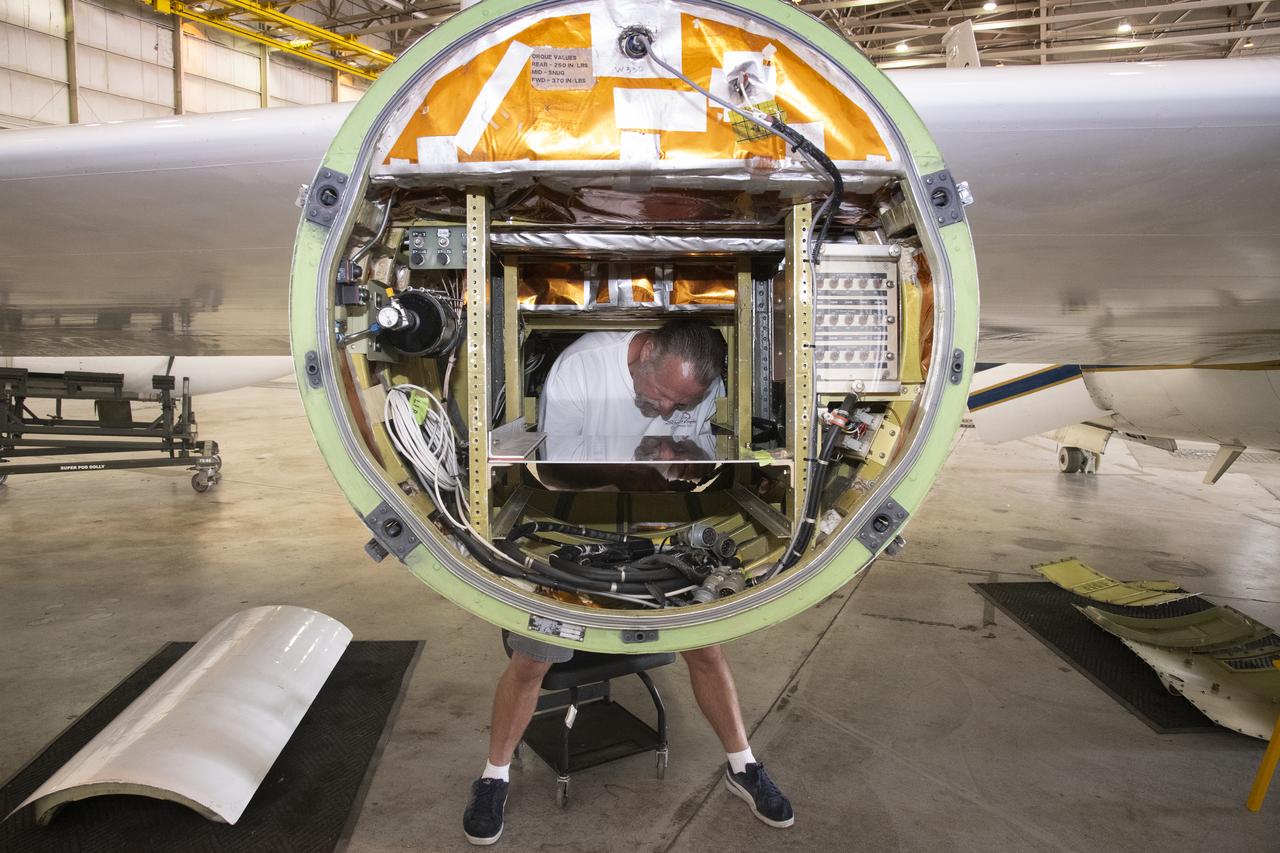

NASA Armstrong’s ER-2 aircraft is uploaded with instruments for its ALOFT mission. The ER-2 will fly at high altitudes above the Floridian coastline to collect data about the energetic characteristics and behavior of lightning and thunderclouds. Scientists from the University of Bergen, Norway will interpret that data from the ground and collaborate with NASA pilots to safely collect the most accurate data for this project about the power of lightning.
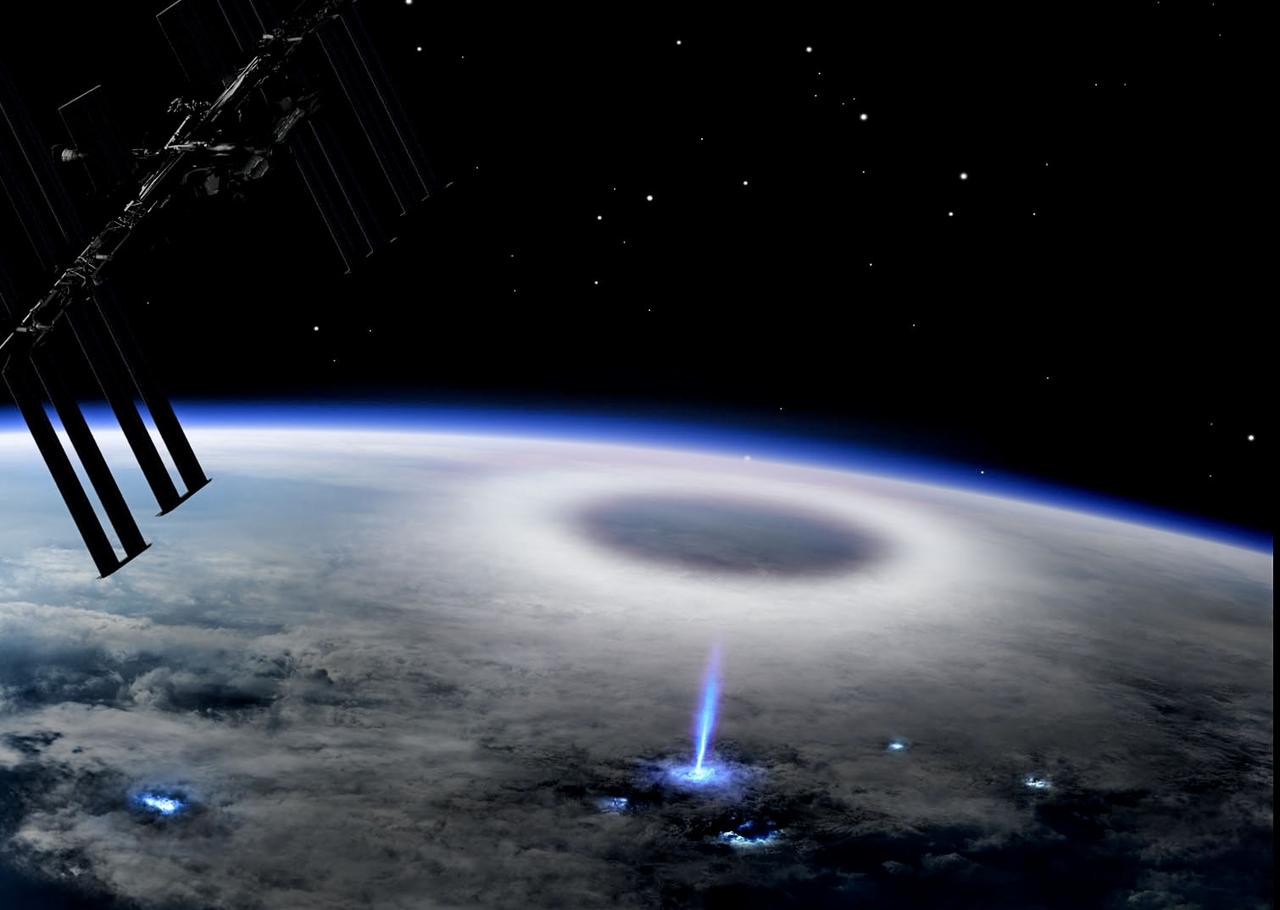

jsc2023e030777 (5/30/2023) --- Artist impression of a blue jet observed from the International Space Station. ESA's Thor-Davis investigation photographs lightning from the vantage point of space. Image courtesy of Mount Visual/University of Bergen/DTU Space.