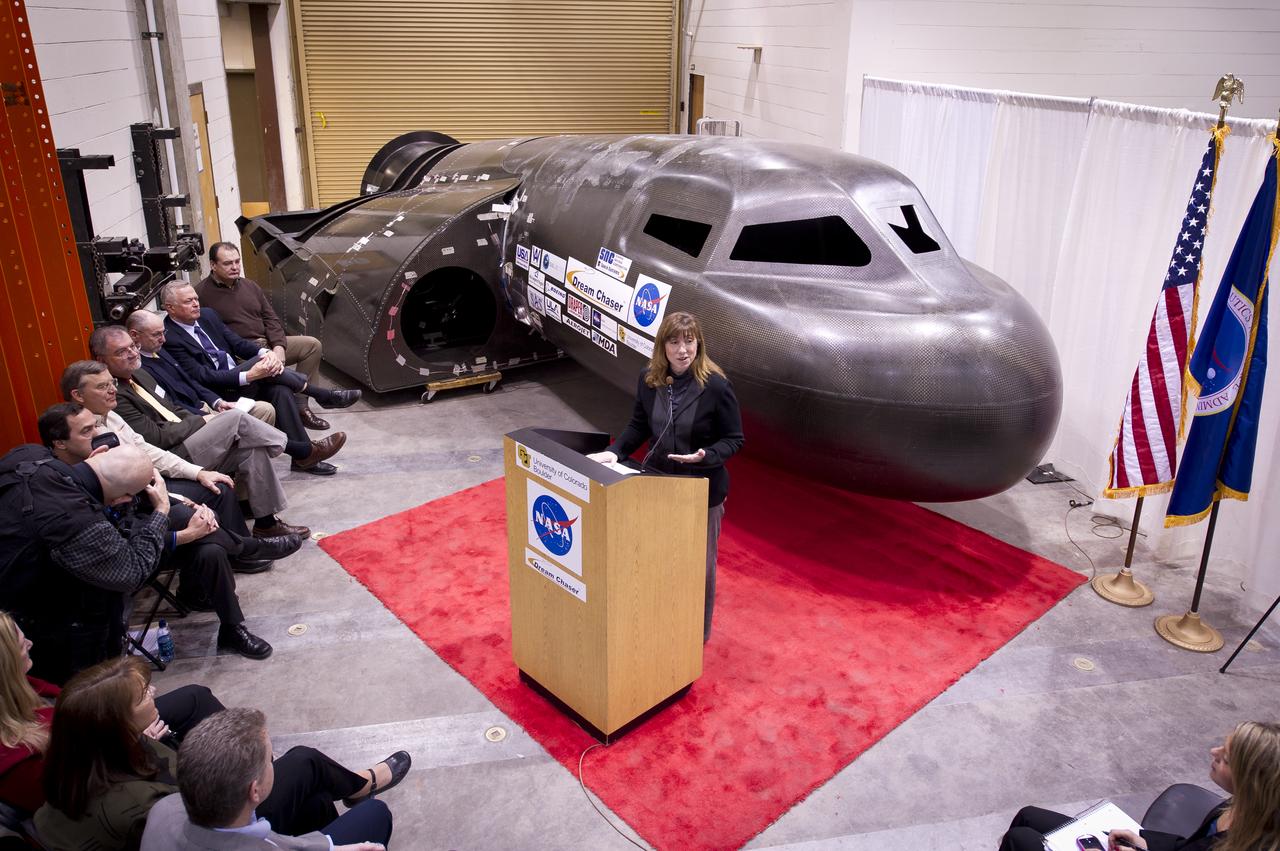

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
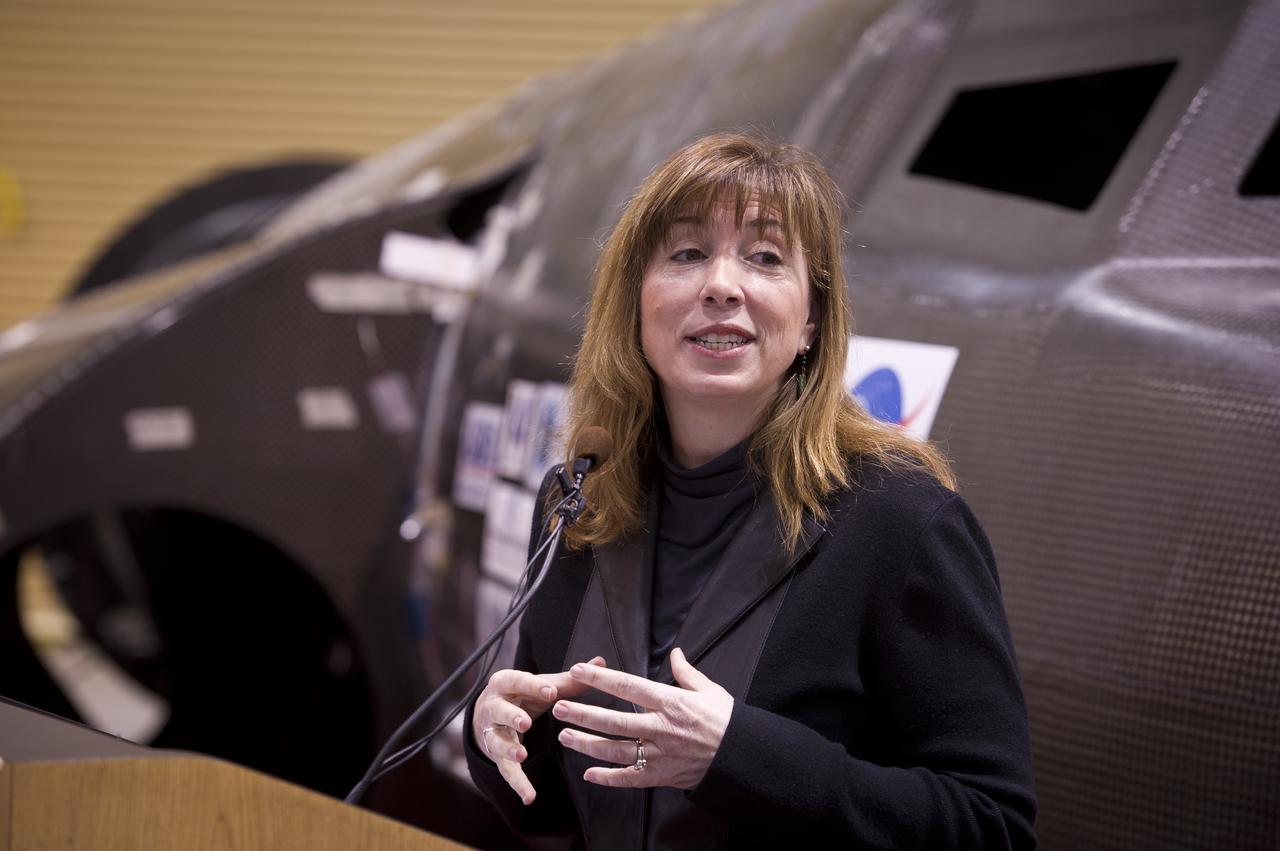

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
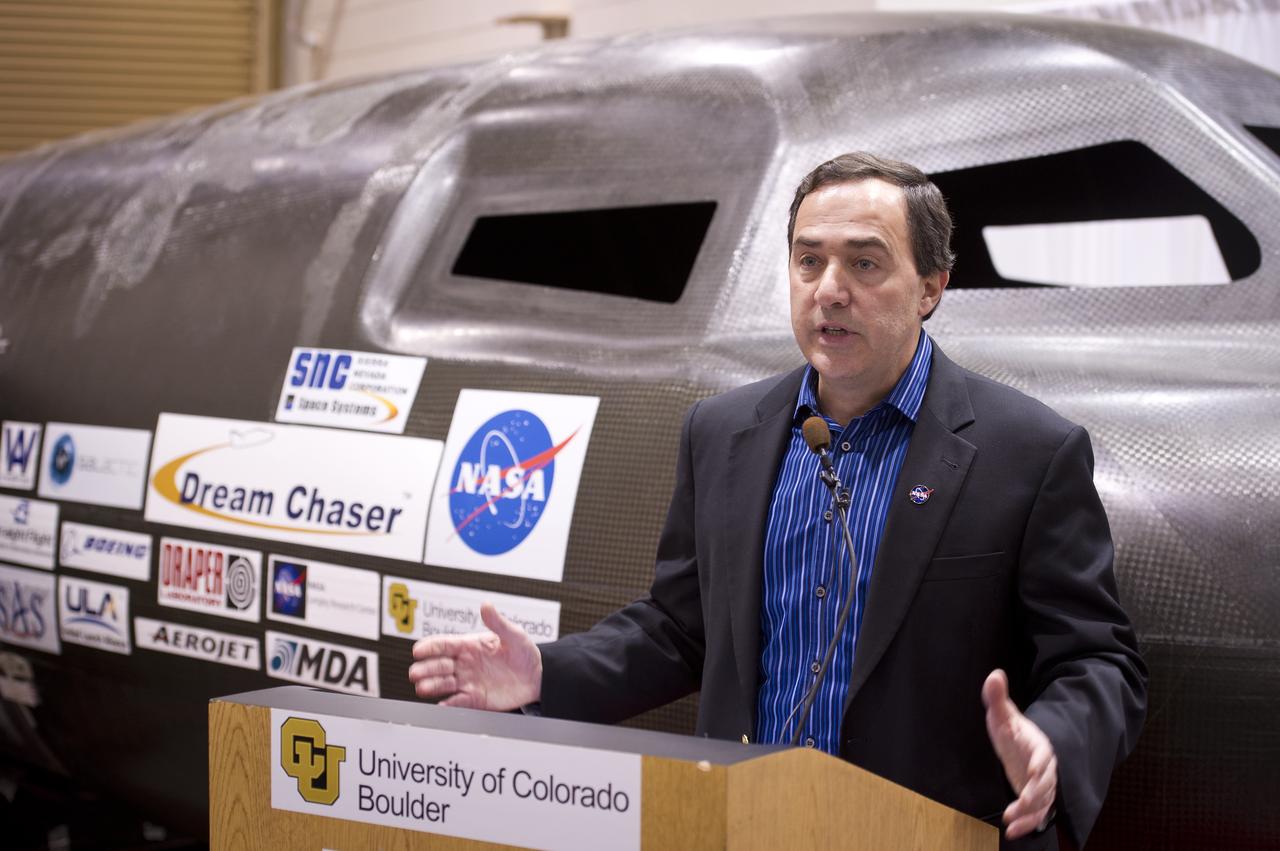

Sierra Nevada Space Systems chairman Mark Sirangello talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
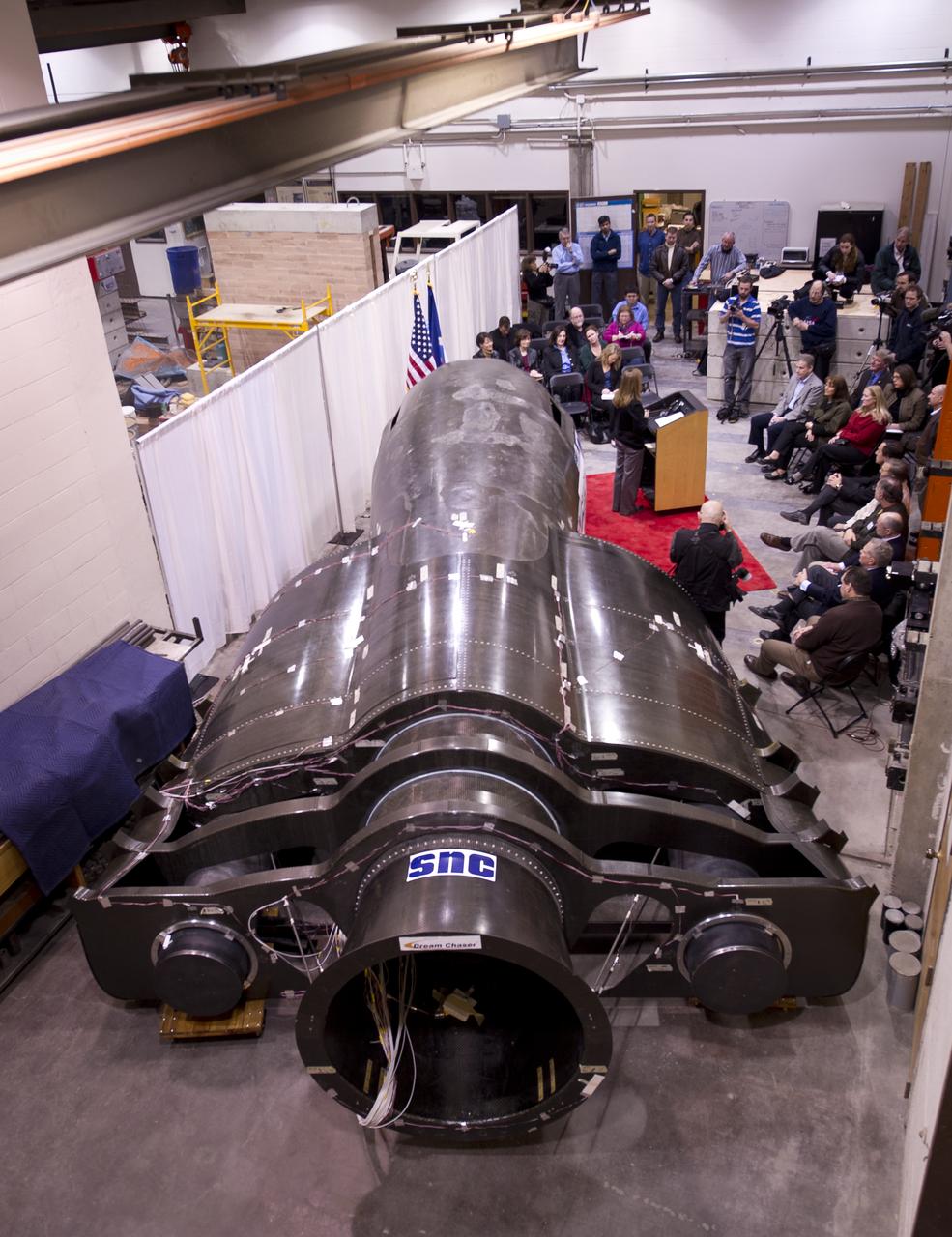

Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is seen as NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
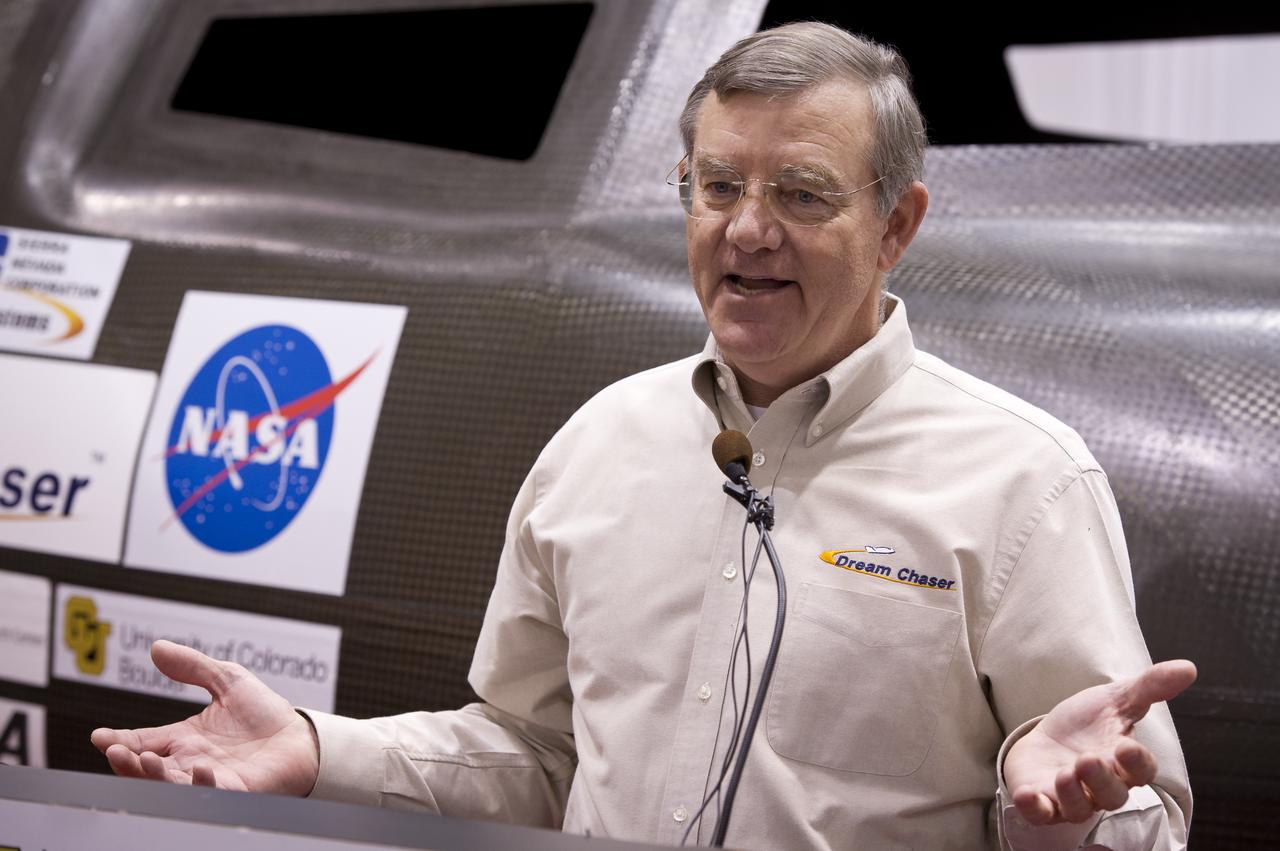

Director of Advanced Programs, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Jim Voss talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
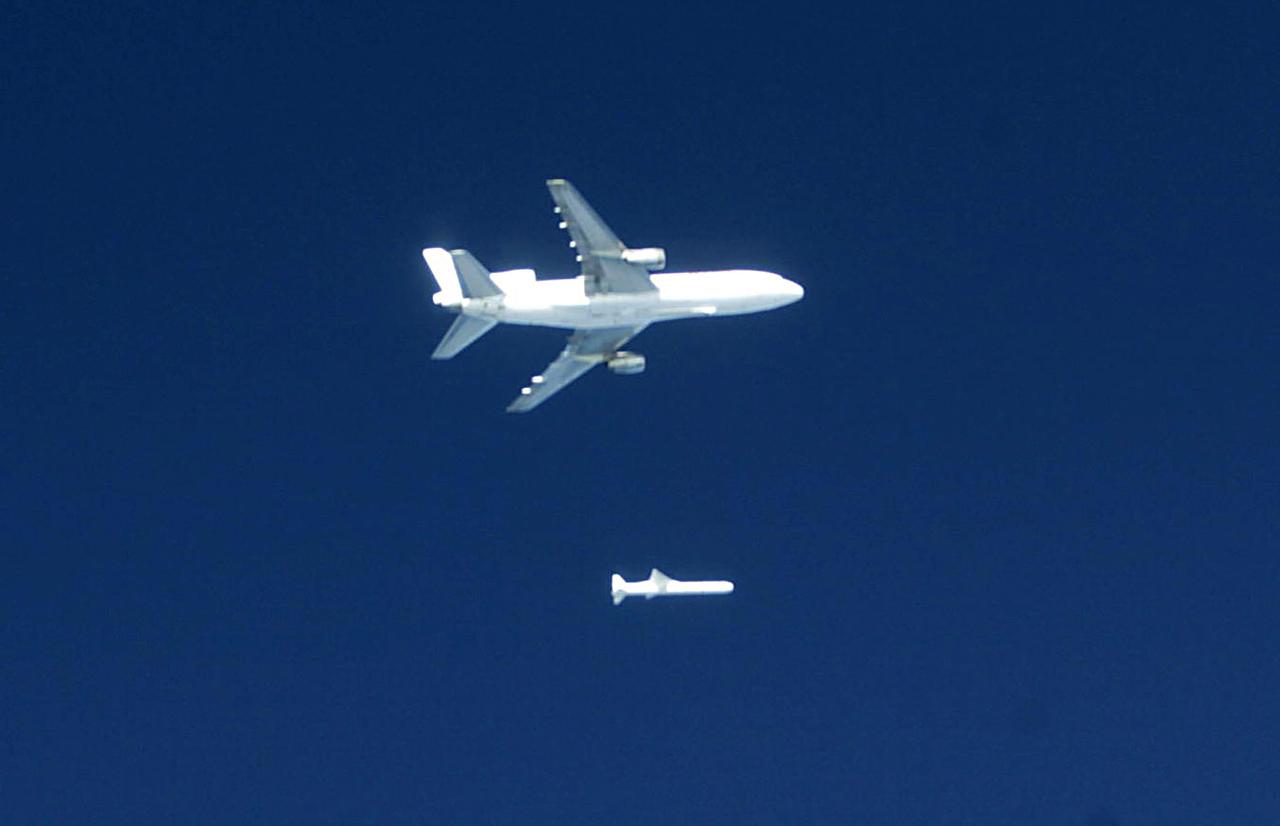

Orbital Sciences Corportation's L1011 releases a Pegasus rocket before ignition, January 25, 2003, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, FL, which will deliver the SORCE satellite, Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, into the low-Earth orbit. The joint project with Orbital, NASA and the University of Colorado satellite is an atmospheric instrument that will measure incoming radiant energy from the sun. Scientists will use this to address long term atmospheric and climate changes. Other uses will be for ozone research and ultraviolet radiation. (Photo by Eric Roback and Rob Rivers, NASA Langley Research Center)
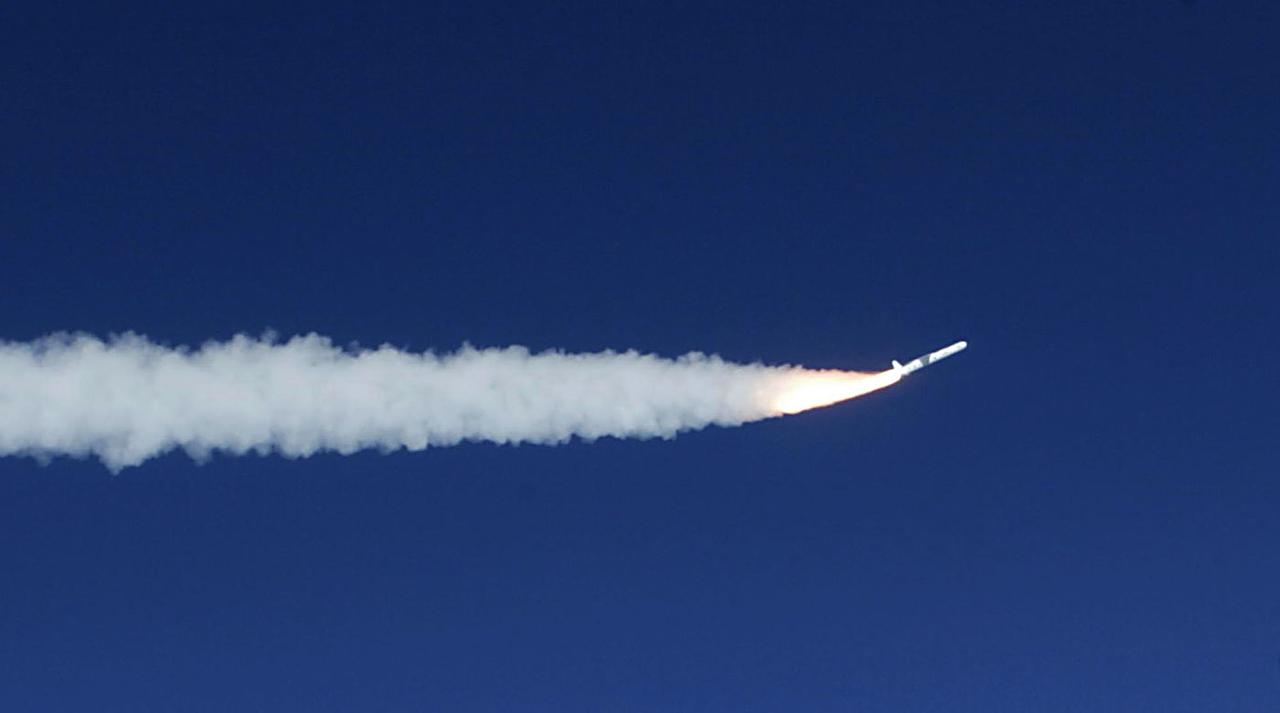

A Pegasus rocket starts it's first stage burn to propel the SORCE Satellite payload into low-Earth orbit, January 25, 2003, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, FL, The SORCE satellite, Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment,is a joint project with Orbital, NASA and the University of Colorado. The satellite is an atmospheric instrument that will measure incoming radiant energy from the sun. Scientists will use this to address long term atmospheric and climate changes. Other uses will be for ozone research and ultraviolet radiation. (Photo by Eric Roback and Rob Rivers, NASA Langley Research Center)
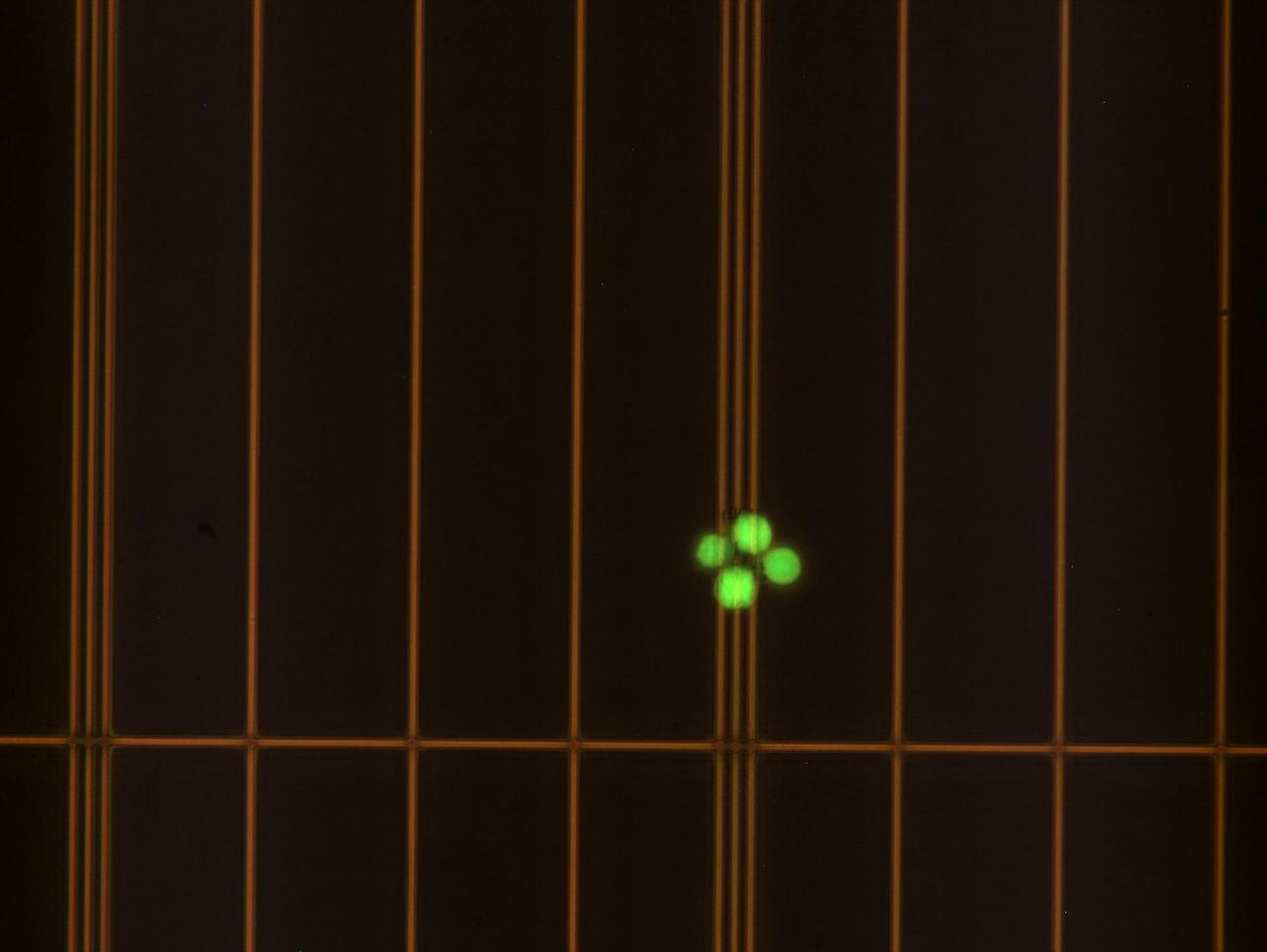
jsc2024e043914 (7/10/2024) --- In-Space Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Clinical Application (InSPA-StemCellEX-H1) continues tests of a technology to produce human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in space. In this image, HSCs were incubated with a fluorescent probe that identifies living cells. Dead cells would fluoresce green. The cells have been loaded into a device called a hemocytometer that provides a grid to make it easy to obtain an accurate count of cells. Astronauts will use a similar technique in space to help determine the rate of HSC expansion over time. Expanding HSC production has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce overall mortality for thousands of people diagnosed and living with blood cancer every year. Image courtesy of University of Colorado Boulder.
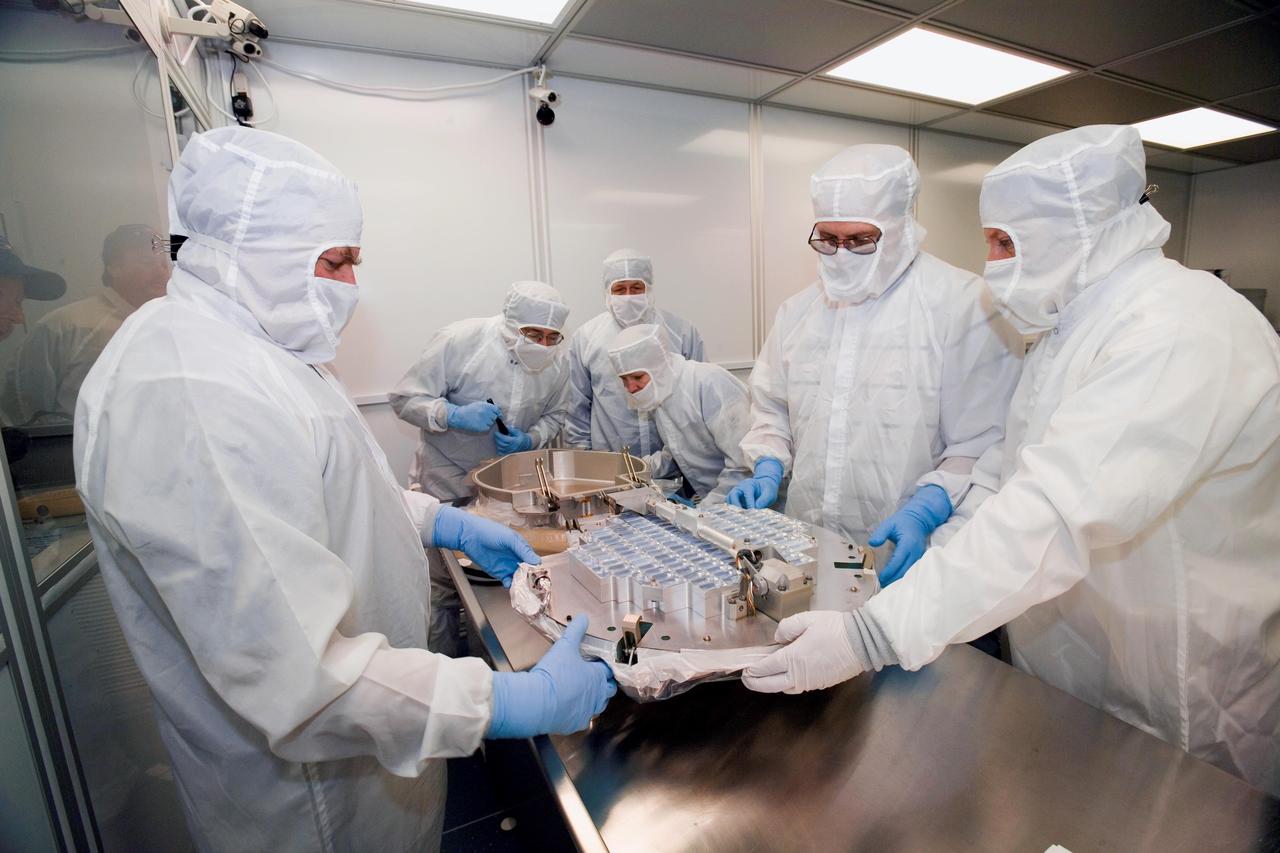

Investigators from University of Washington, Johnson Space Center, and Lockheed Martin Missiles and Space, Denver, Colorado, inspect a canister and sample collector soon after opening a container with Stardust material in a laboratory at the JSC.
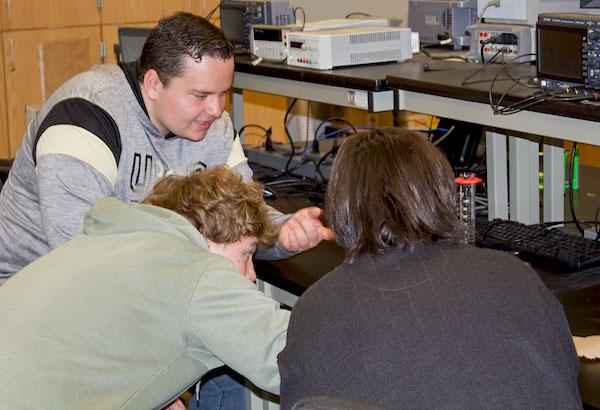

jsc2024e066523 (1/6/2024) --- Colorado Springs students Noah Grebe, Luke Davis, and Blake MacDonald observe crystal growth.Their experiment, Calcium Sulfate Crystal Growth in Microgravity, is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).
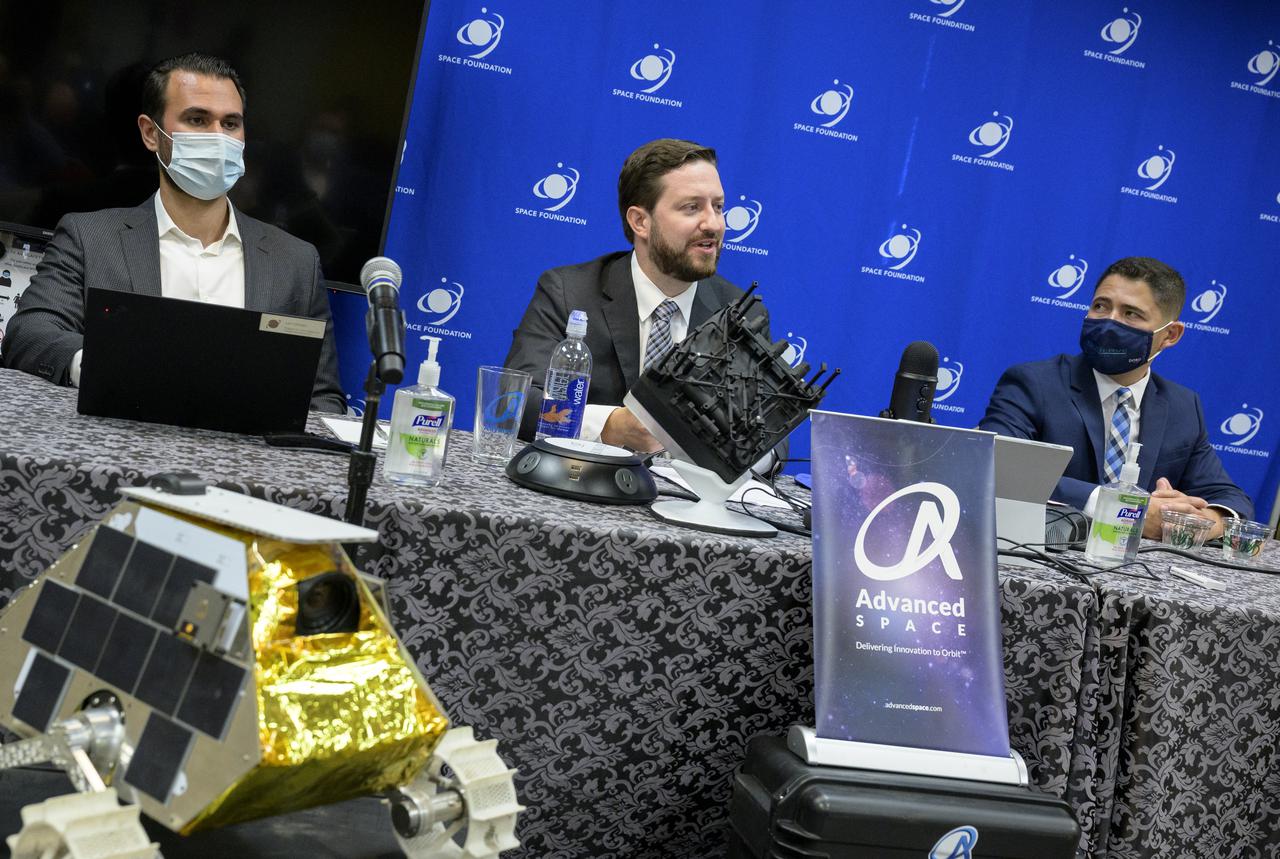

Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado, left, Bradley Cheetham, CEO and president, Advanced Space of Westminster, Colorado, center, and Dr. Luis Zea, implementation project manager, BioServe Space Technologies, Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder, Monday, are seen during a media briefing where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduced the three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
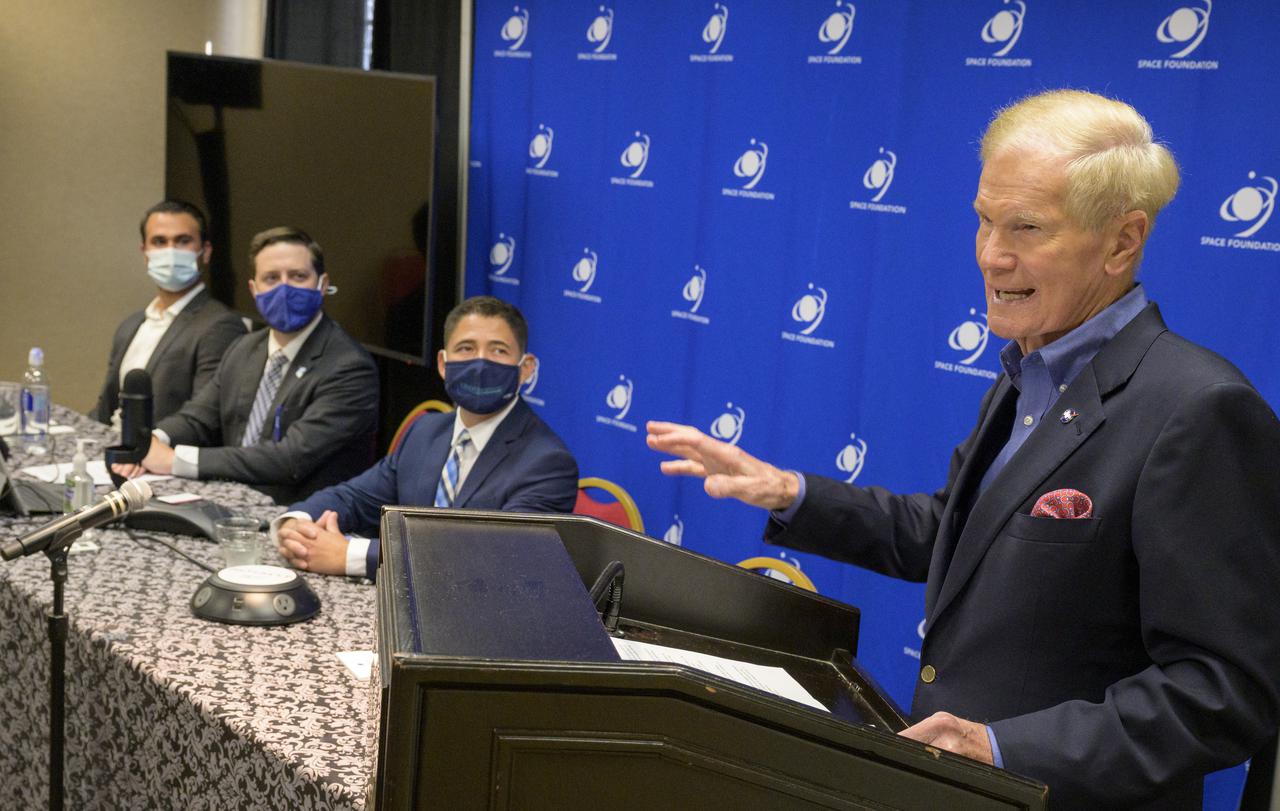

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson hosts an event to introduce media to three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible; Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado, left: Bradley Cheetham, CEO and president, Advanced Space of Westminster, Colorado, center: and Dr. Luis Zea, implementation project manager, BioServe Space Technologies, Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
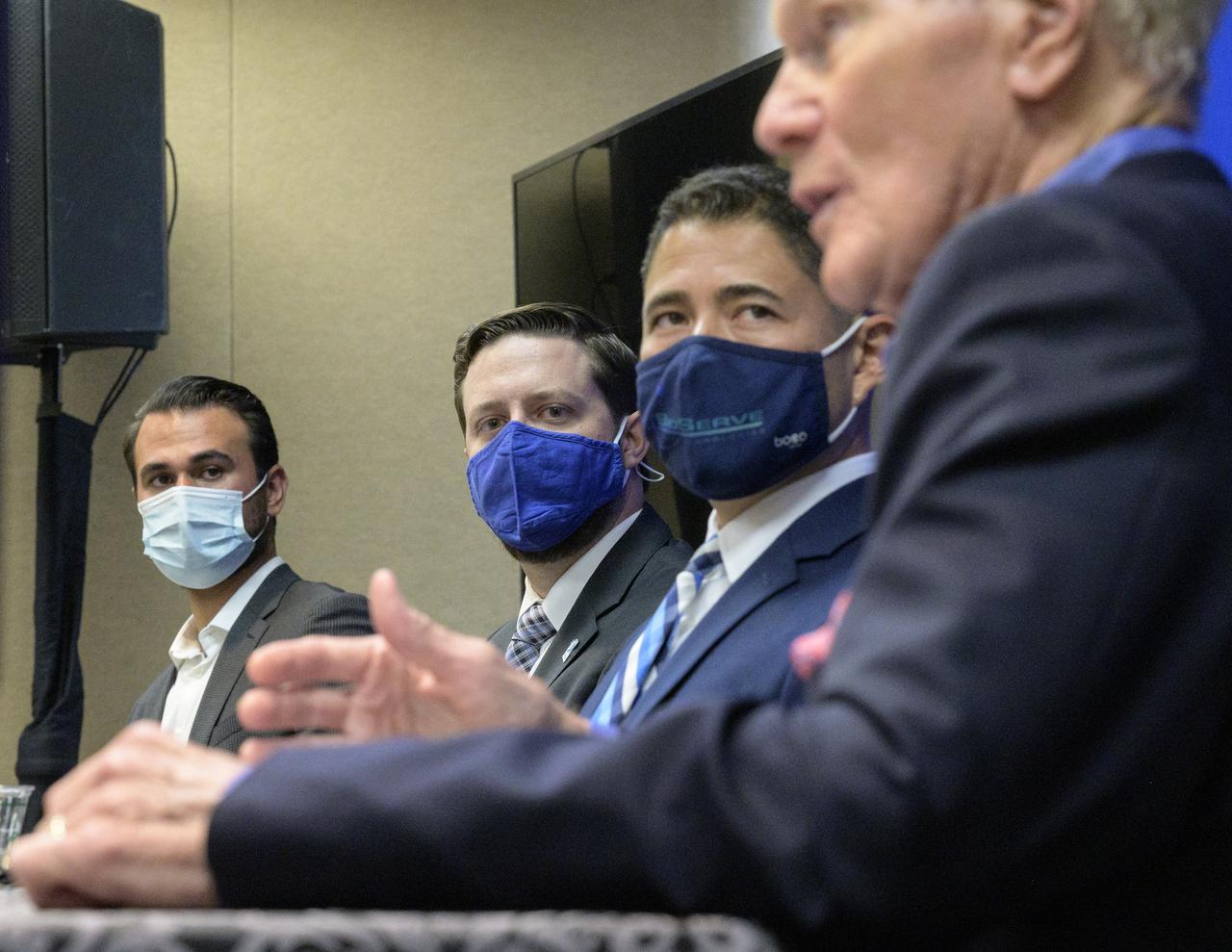

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson hosts an event to introduce media to three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible; Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado, left: Bradley Cheetham, CEO and president, Advanced Space of Westminster, Colorado, center: and Dr. Luis Zea, implementation project manager, BioServe Space Technologies, Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
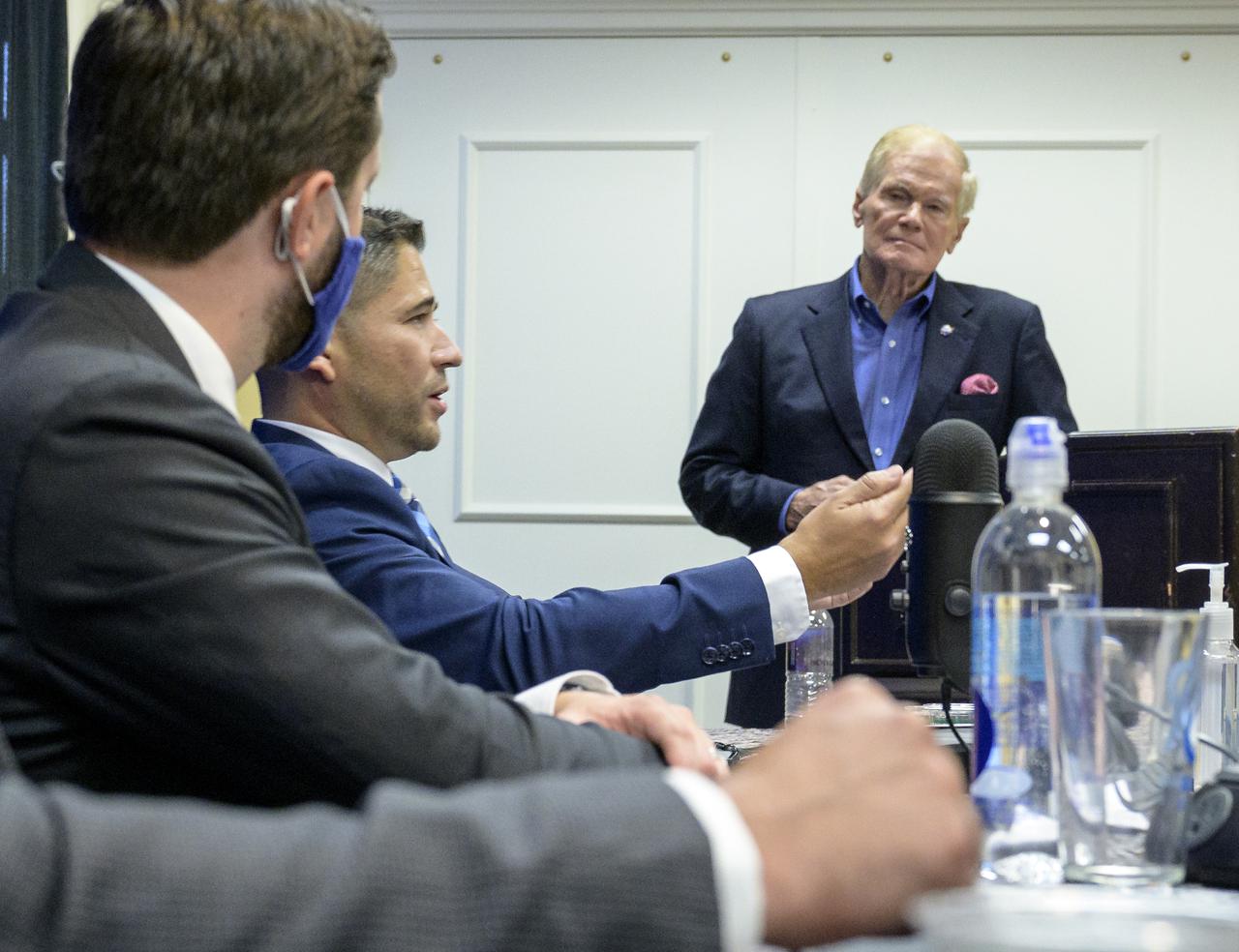

Dr. Luis Zea, implementation project manager, BioServe Space Technologies, Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduce three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Luis Zea, implementation project manager, BioServe Space Technologies, Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduce three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
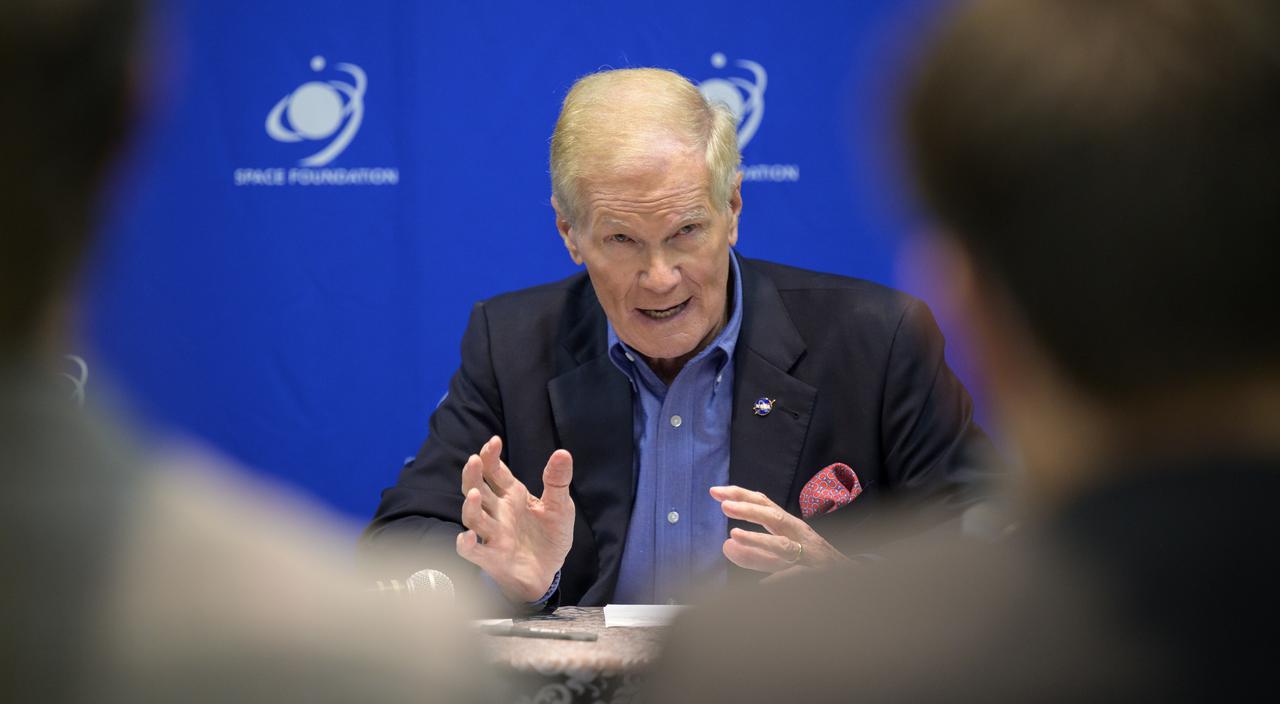

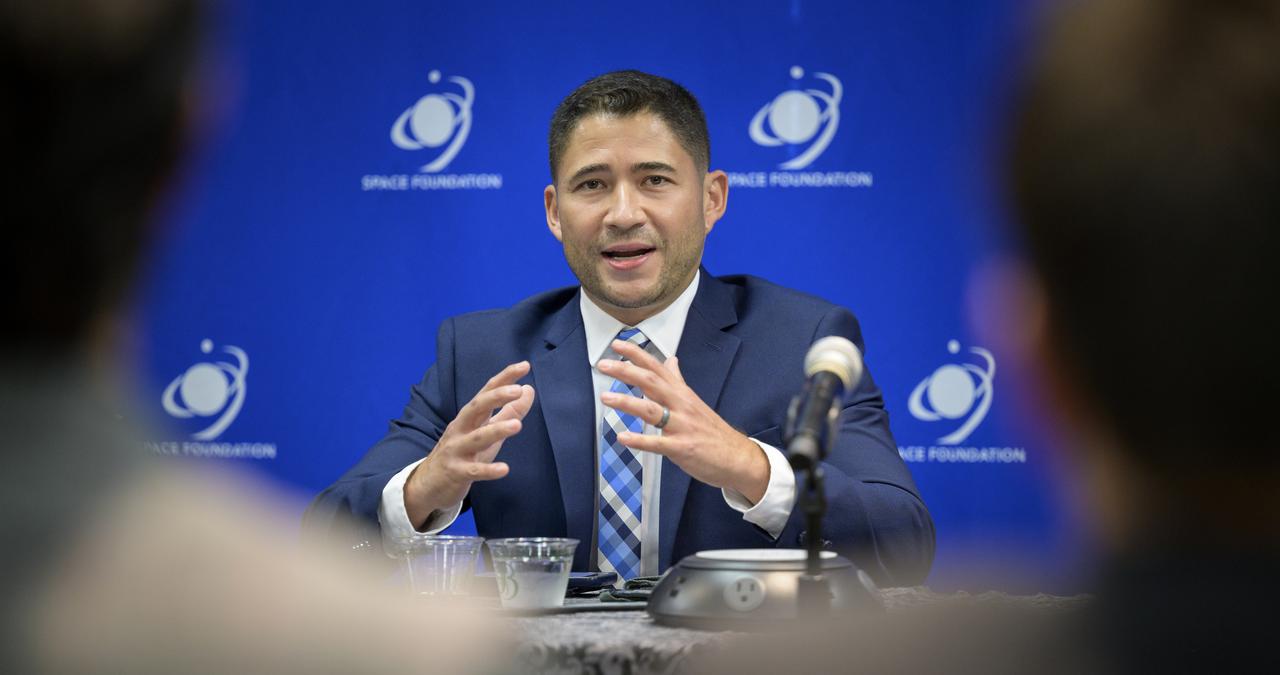
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson hosts an event to introduce media to three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
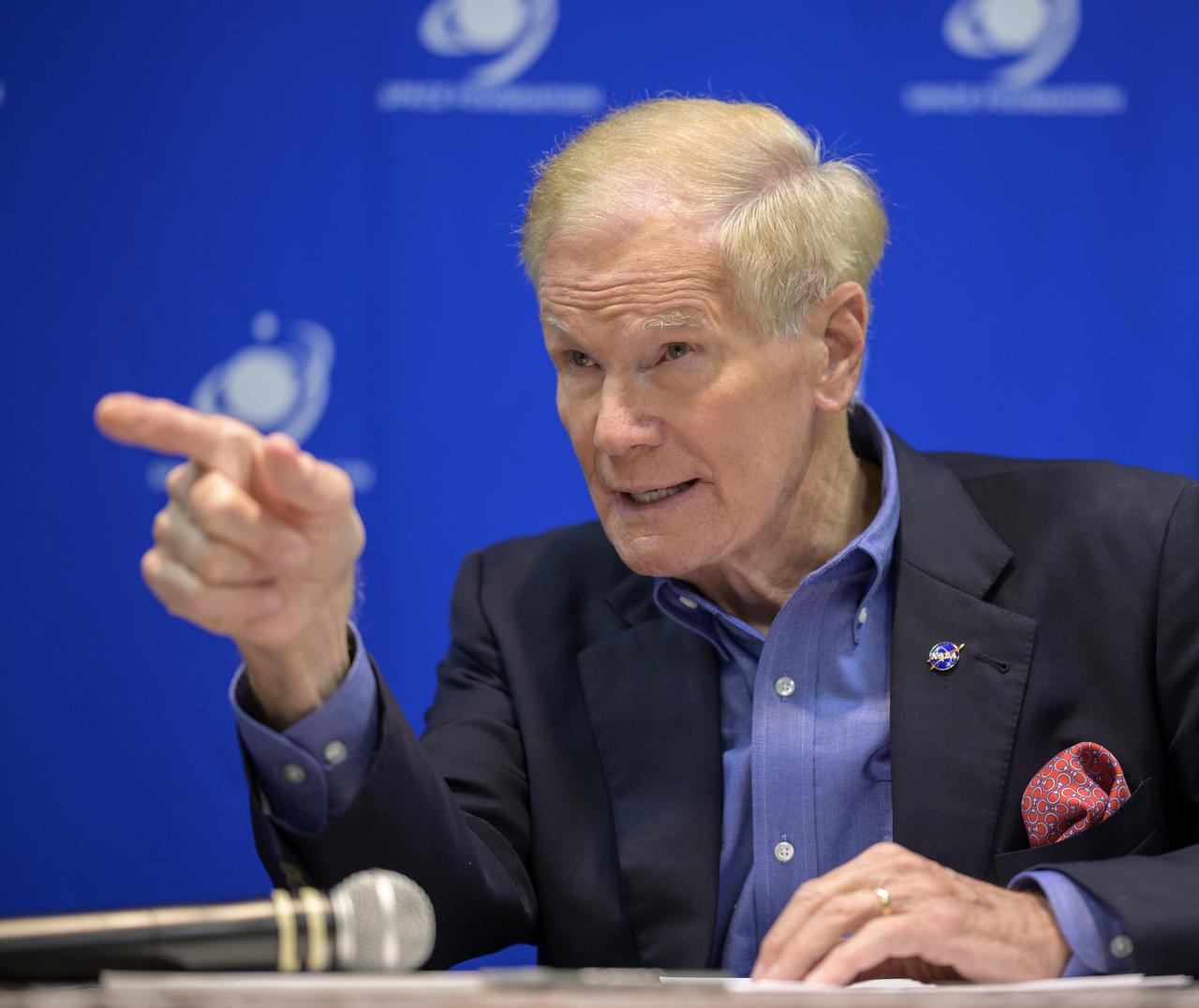

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson hosts an event to introduce media to three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Bradley Cheetham, CEO and president, Advanced Space of Westminster, Colorado listens during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduce three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduced three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduced three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Bradley Cheetham, CEO and president, Advanced Space of Westminster, Colorado gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduce three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado gives comments during a media event where NASA Administrator Bill Nelson introduced three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
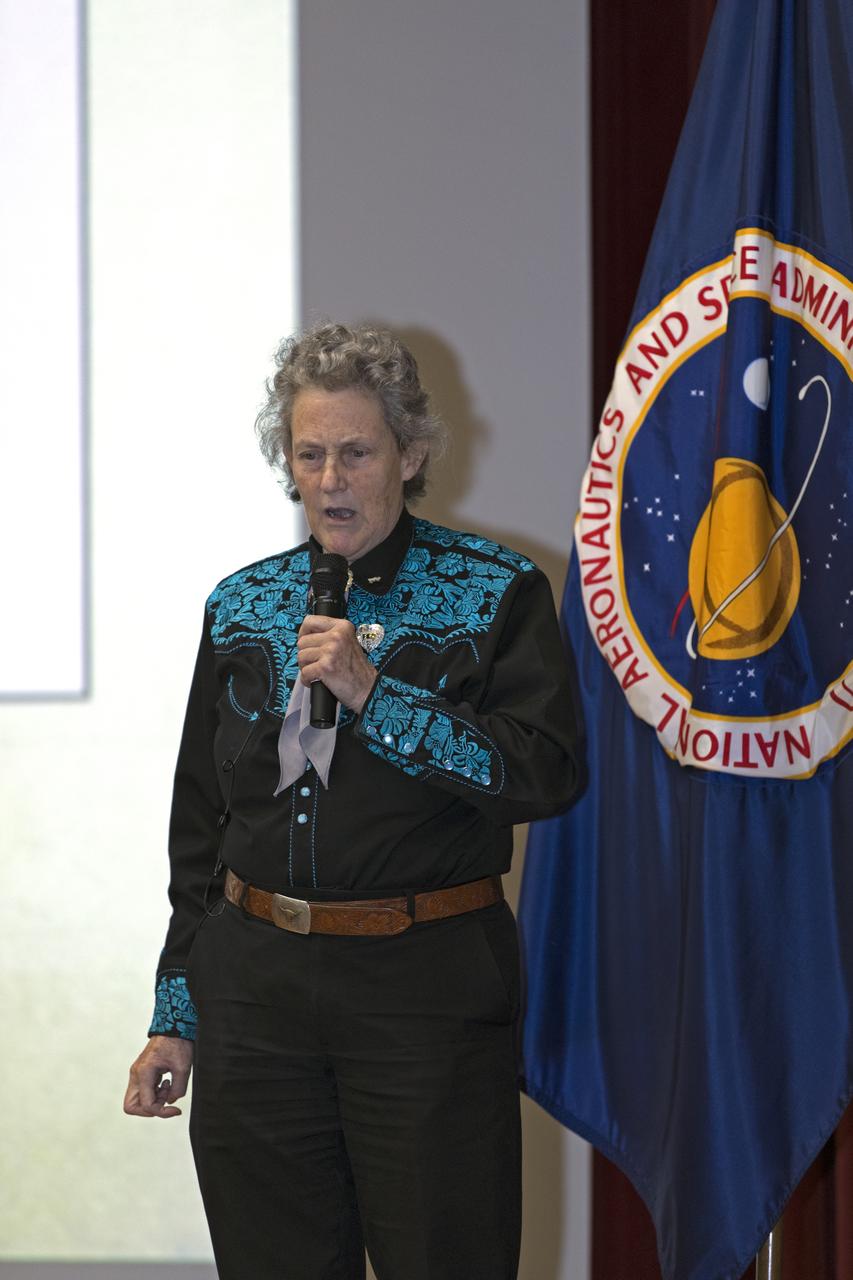

Dr. Temple Grandin addresses employees as the keynote speaker at Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.

Dr. Temple Grandin addresses employees as the keynote speaker at Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.
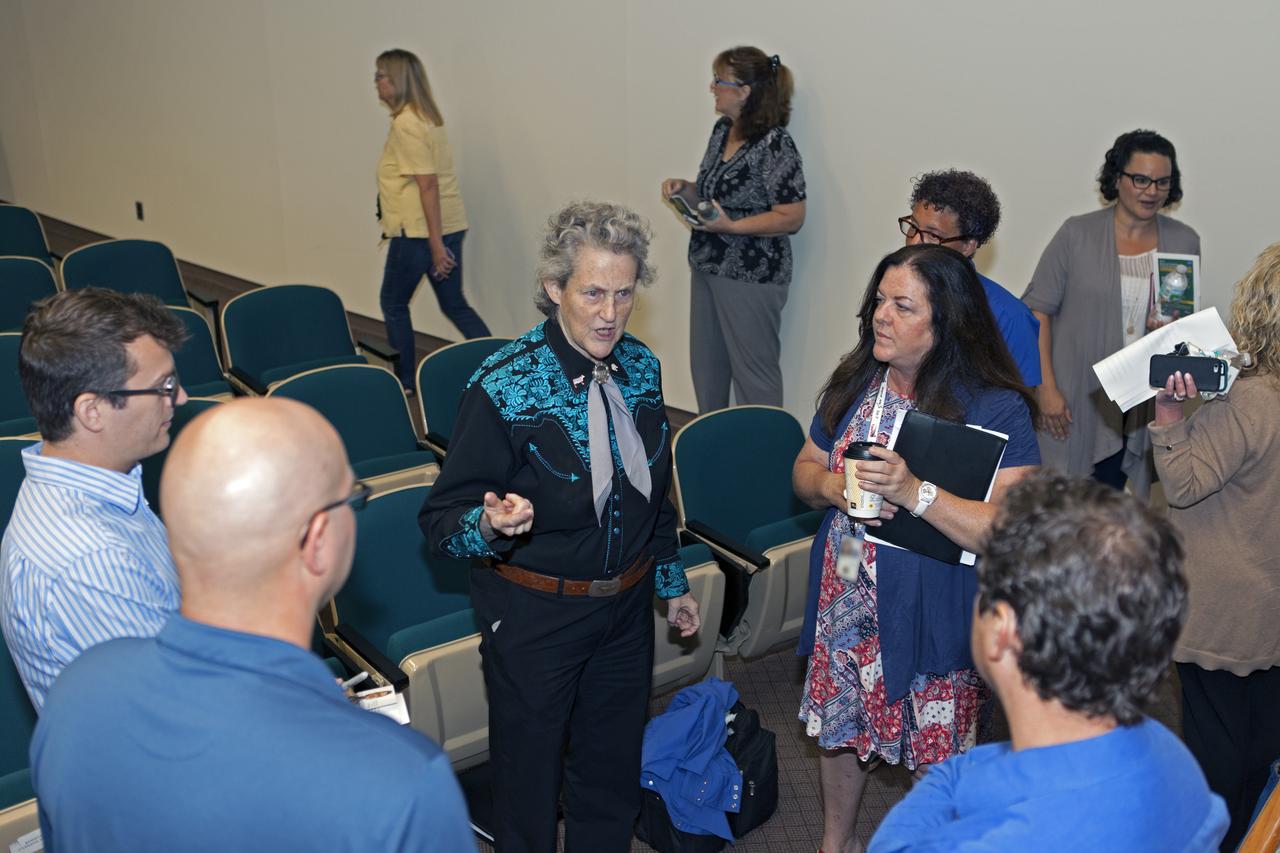

Dr. Temple Grandin speaks with employees following Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. Grandin served as keynote speaker. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.
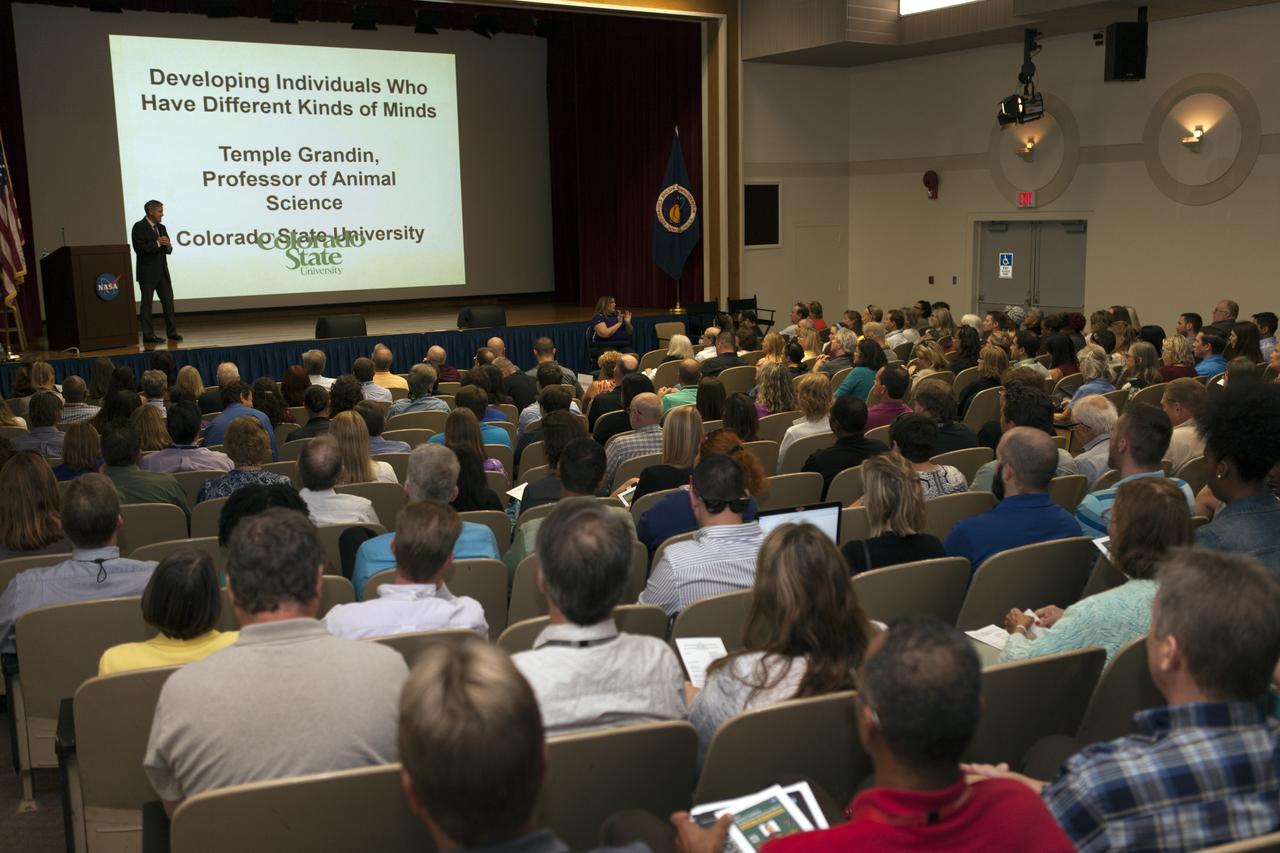

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana addresses employees at the start of the annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event, which featured Dr. Temple Grandin as keynote speaker. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.
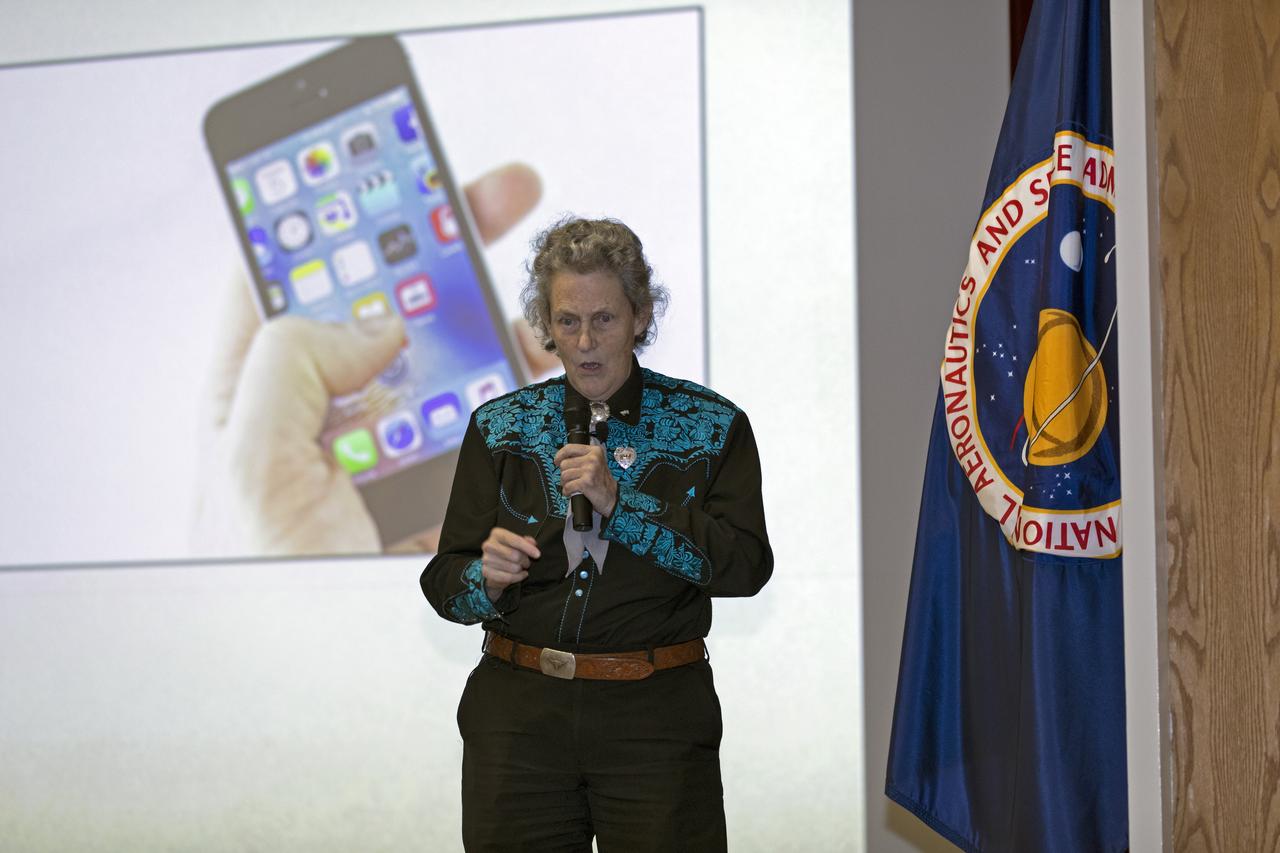

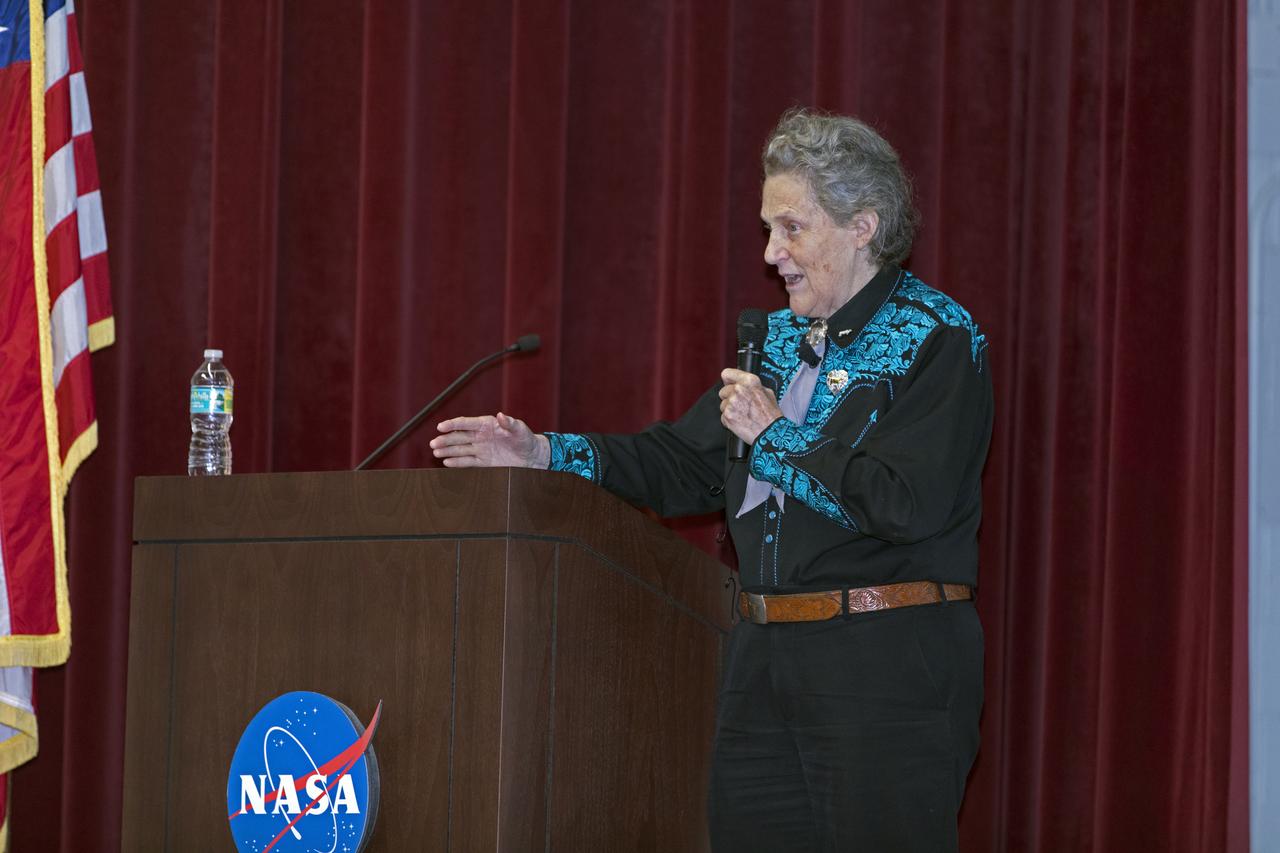
Dr. Temple Grandin addresses employees as the keynote speaker at Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.
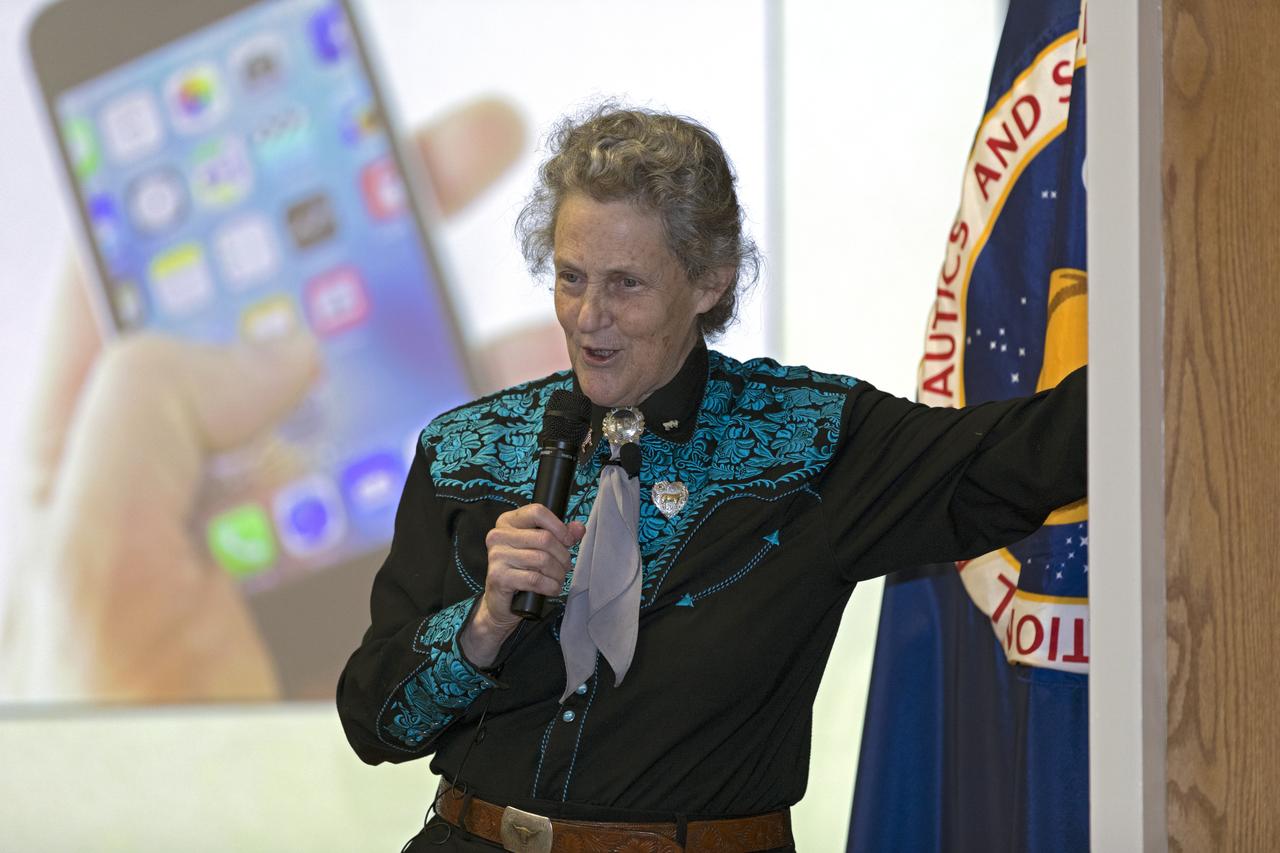

Dr. Temple Grandin addresses employees as the keynote speaker at Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.

Dr. Temple Grandin, right, accepts a NASA photo collage from Kennedy Space Center Chief Financial Officer Susan Kroskey at the center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month event. Grandin served as keynote speaker. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, she is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kroskey is the executive champion of Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group, or DAAWG, which partnered with the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group to sponsor the presentation.

The description on the back of the plaque reads: "This plaque was presented to Administrator James C. Fletcher by the Apollo 11 Crew for award to the future Mars I crew (when the first manned mission to Mars is scheduled), July 20, 1987 at The Case for Mars III Conference at the University of Colorado in Boulder, Colorado." Photographed on Friday, July 11, 2014 in Washington, DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
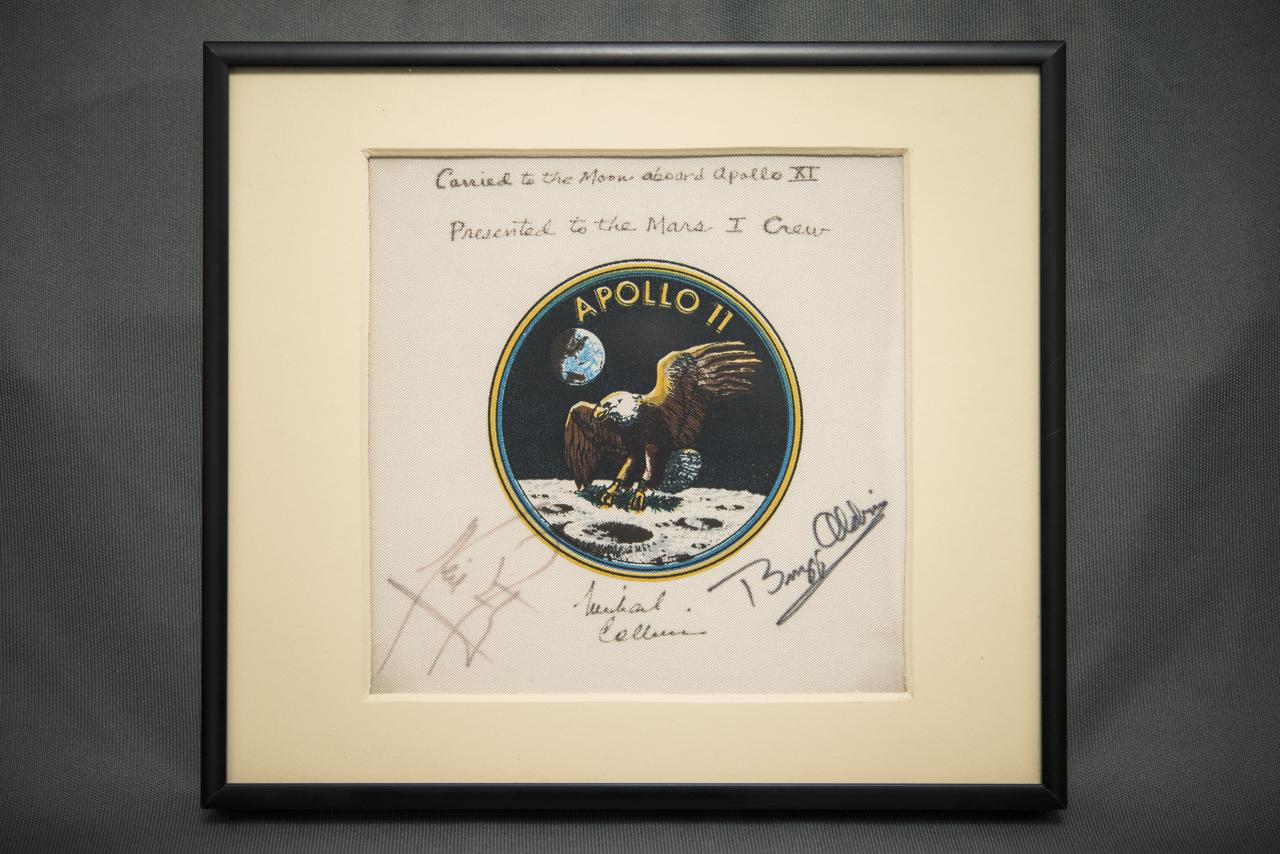

The description on the back of the plaque reads: "This plaque was presented to Administrator James C. Fletcher by the Apollo 11 Crew for award to the future Mars I crew (when the first manned mission to Mars is scheduled), July 20, 1987 at The Case for Mars III Conference at the University of Colorado in Boulder, Colorado." Photographed on Friday, July 11, 2014 in Washington, DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
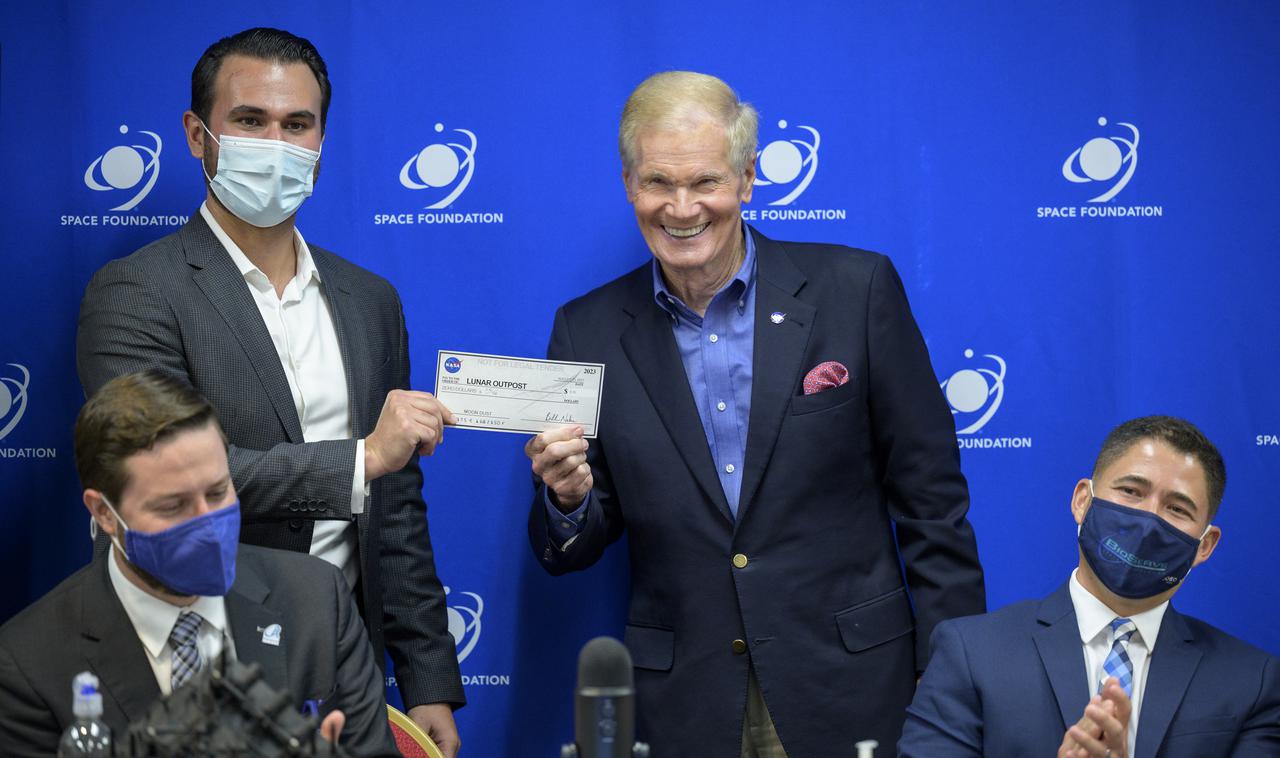

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson presents Justin Cyrus, CEO, Lunar Outpost of Golden, Colorado a check for $0.10 during an event to introduce media to three local Colorado companies and university partners that help make NASA’s missions possible, Monday, Aug. 23, 2021, during the 36th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Lunar Outpost is one of four companies that will collect space resources and transfer ownership to NASA; Lunar Outpost proposed collection for $1 following arrival of a lander to the lunar South Pole in 2023 and is on track to accomplish this a year early as part of the Intuitive Machines 2 Mission in 2022. They recently passed their first milestone and is the first of the four proposals selected to do so, and will receive a payment of $0.10. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Key persornel in the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment at the University of Colorado at Boulder include Tawnya Ferbiak (software engineer), Susan Batiste (research assistant), and Christina Winkler (graduate research assistant). Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. MGM experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. (Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder).
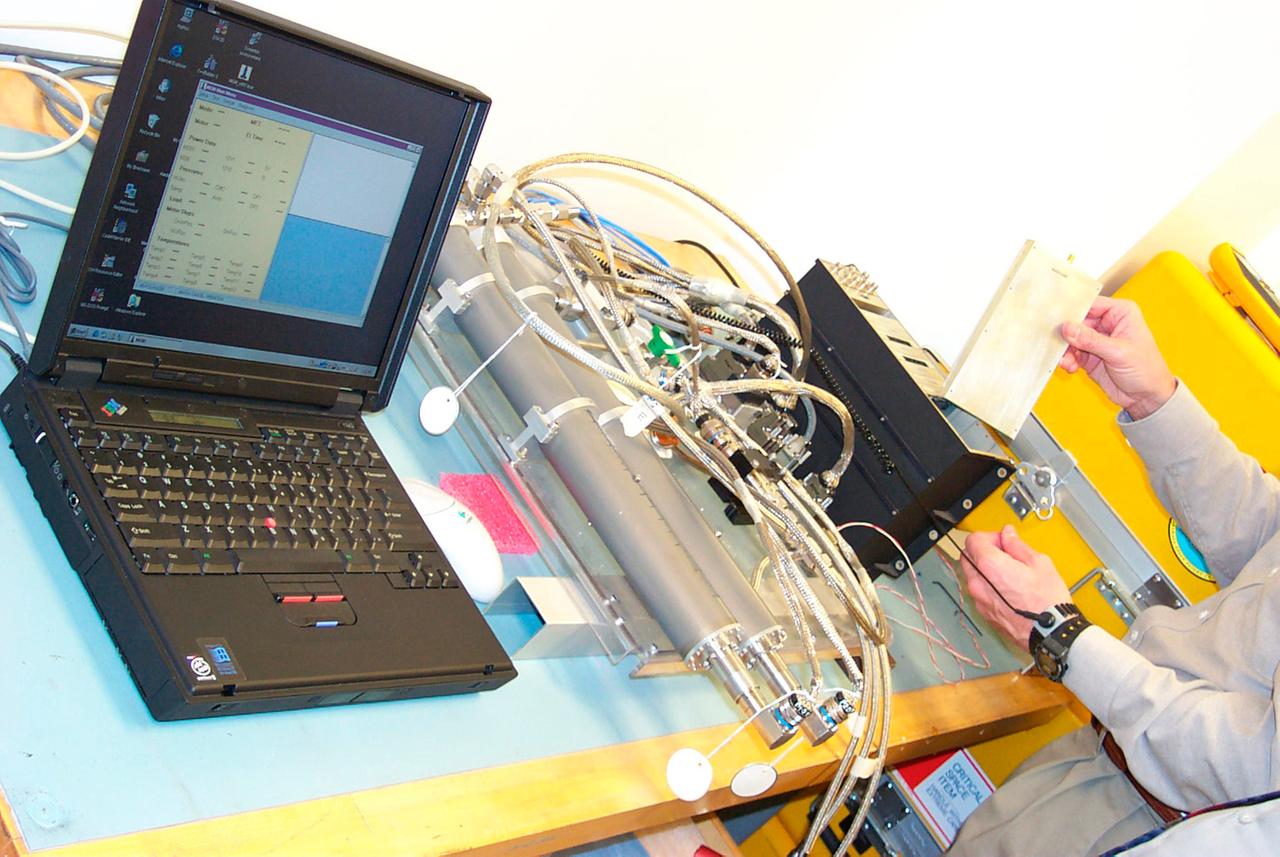

Engineering bench system hardware for the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is tested on a lab bench at the University of Colorado in Boulder. This is done in a horizontal arrangement to reduce pressure differences so the tests more closely resemble behavior in the microgravity of space. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. MGM experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. (Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder).

Key persornel in the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment are Mark Lankton (Program Manager at University Colorado at Boulder), Susan Batiste (research assistance, UCB), and Stein Sture (principal investigator). Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. MGM experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. (Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder).

Harold "Hal" Levison from the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado gives remarks about the Lucy mission during a briefing discussing small bodies missions, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA officials and university investigators outlined science plans for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, mission. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are George Diller of NASA Public Affairs, Michael Meyer, lead Mars Scientist at NASA Headquarters, Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado at Boulder, Janet Luhmann, MAVEN deputy principal investigator from the University of California at Berkeley, Nick Schneider, MAVEN Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph, or IUVS, instrument lead at the University of Colorado, Paul Mahaffy, MAVEN Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer, or NGIMS, instrument lead at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., and David Mitchell, MAVEN Solar Wind Electron Analyzer, or SWEA, instrument lead at the University of California. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch on Nov 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For information on the MAVEN mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
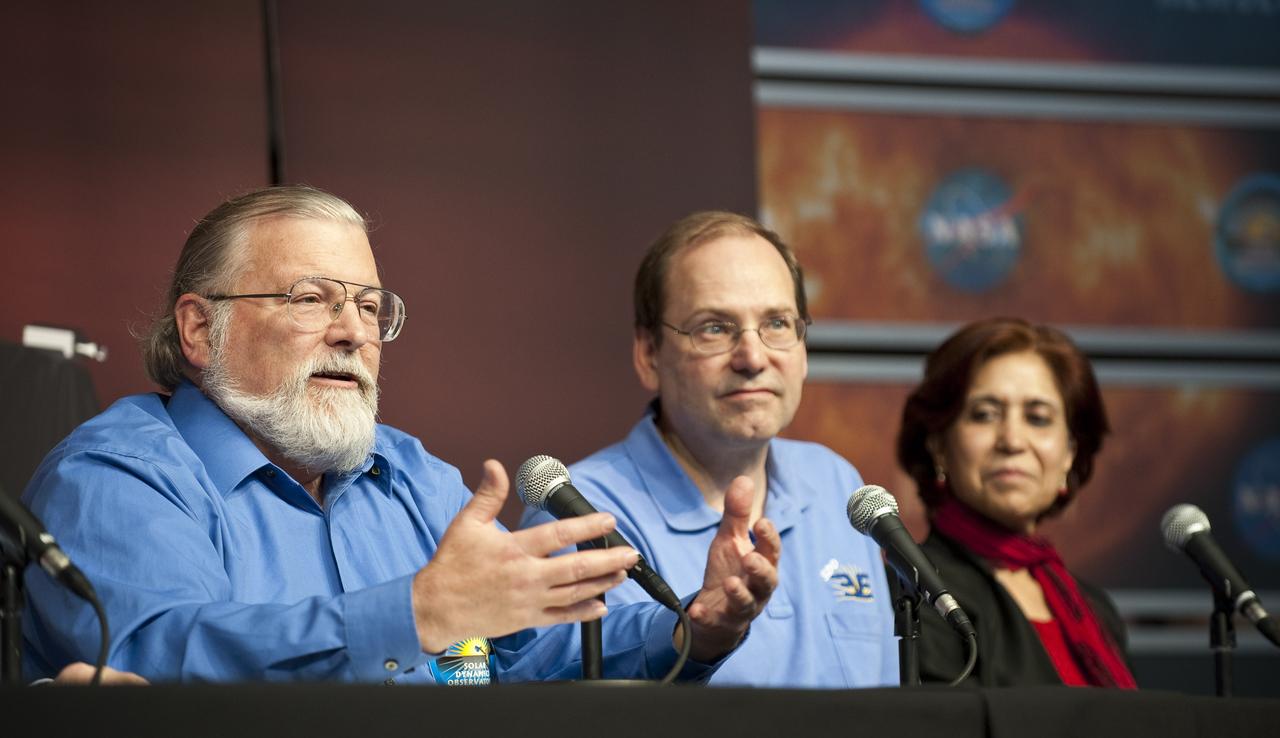

Philip H. Scherrer (left) principal investigator, Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager instrument, Stanford University in Palo Alto, speaks during a briefing to discuss recent images from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, while colleagues Tom Woods, principal investigator, Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment instrument, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado in Boulder and Madhulika Guhathakurta, SDO program scientist, NASA Headquarters (right) look on Wednesday, April 21, 2010, at the Newseum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
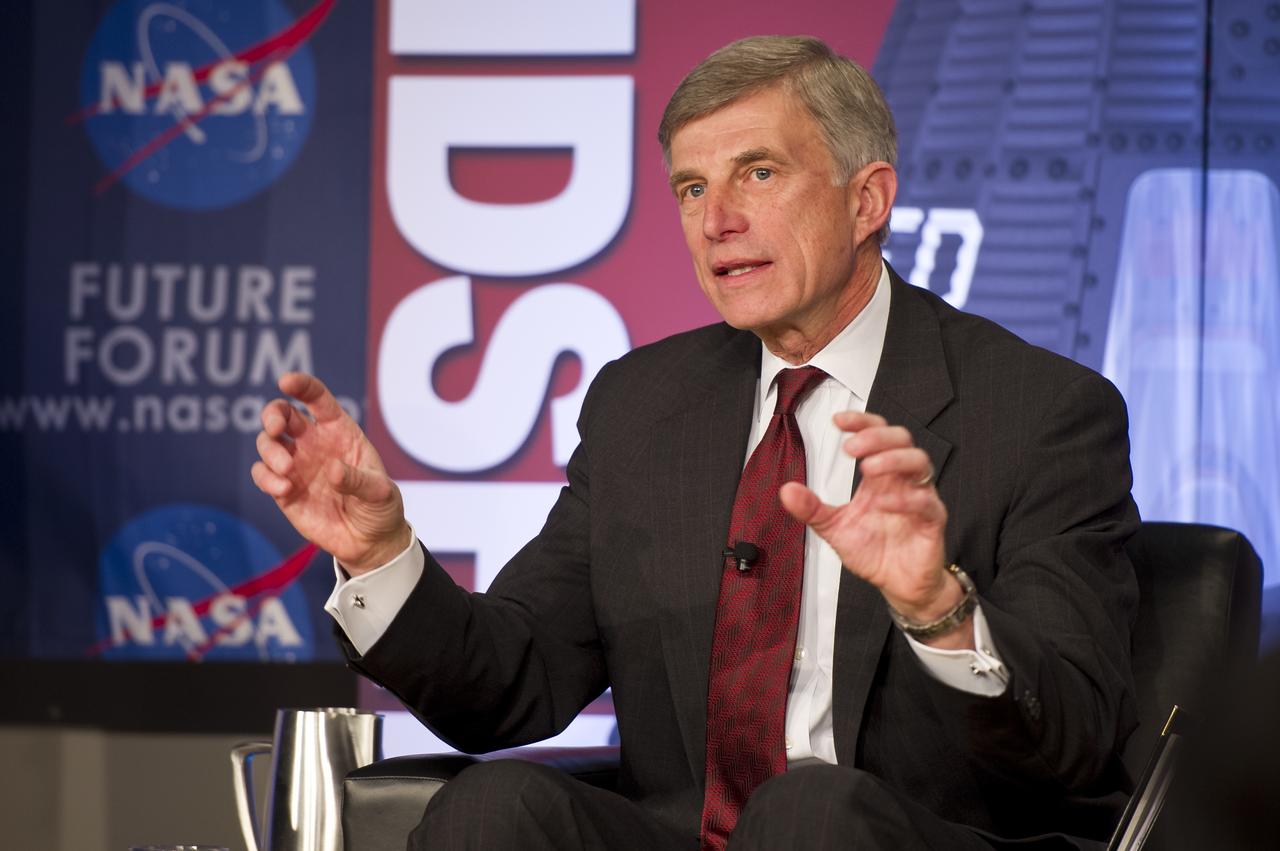

Ron Sega, Vice president and enterprise executive for Energy and the Environment, The Ohio State University and Colorado State University talks during the NASA Future Forum panel titled "Importance of Technology, Science and Innovation for our Economic Future" at The Ohio State University on Tuesday, Feb. 21, 2012 in Columbus, Ohio. The NASA Future Forum features panel discussions on the importance of education to our nation's future in space, the benefit of commercialized space technology to our economy and lives here on Earth, and the shifting roles for the public, commercial and international communities in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
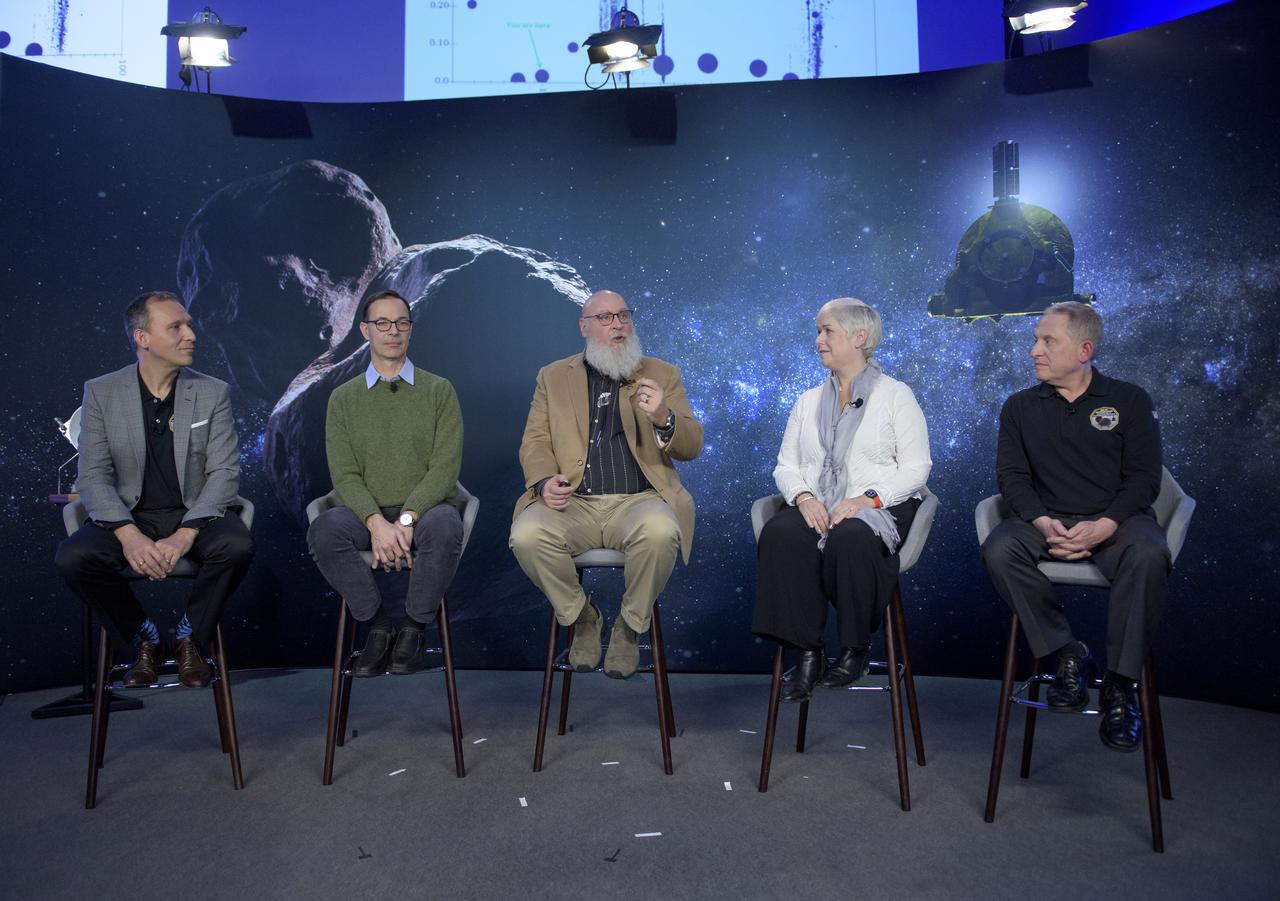

Associate Administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, left, Olivier Barnouin (US Instrument Scientist, Johns Hopkins University/APL), Harold "Hal" Levison from the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado, Lindy Elkins-Tanton Principal Investigator of the Psyche mission from Arizona State University, and New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, right, are seen during a briefing discussing small bodies missions, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
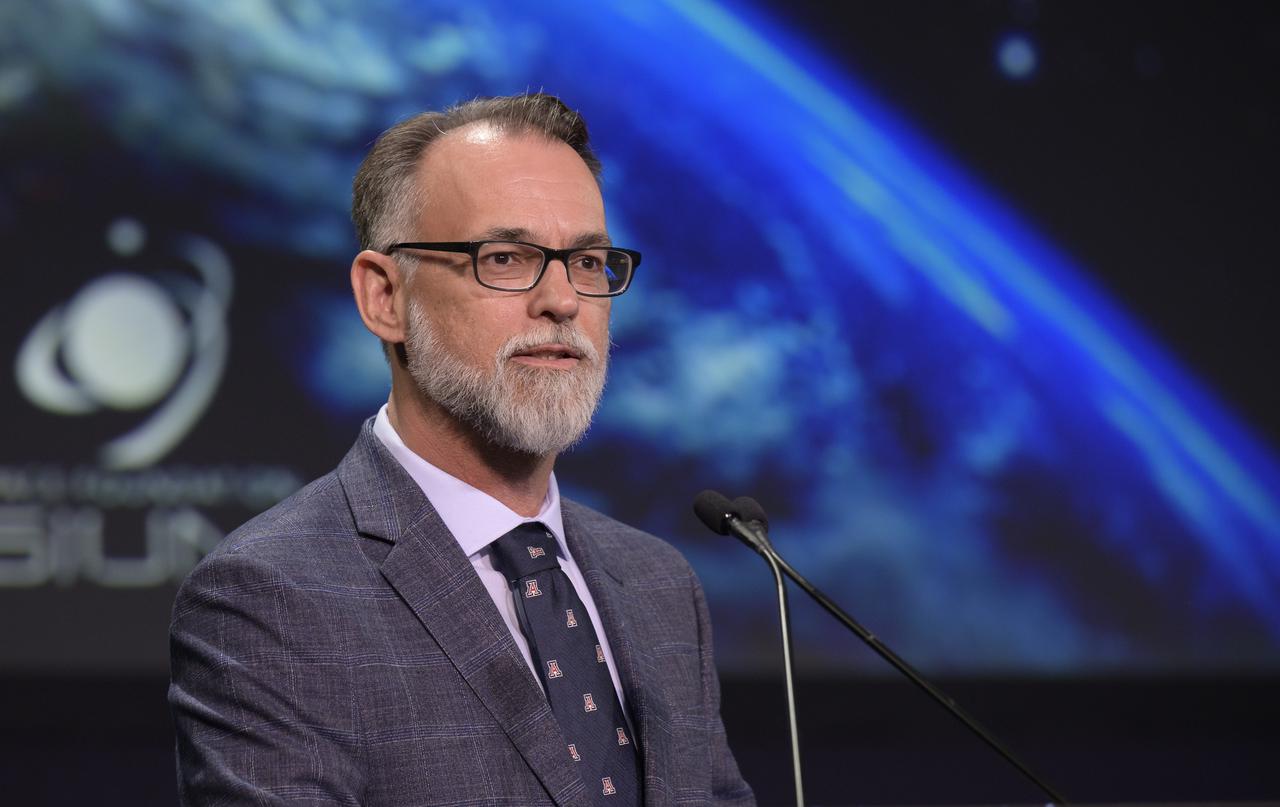

University of Arizona OSIRIS-REx Principal Investigator Dante Lauretta gives remarks after the 2022 John L. “Jack” Swigert, Jr., Award for Space Exploration was presented to the OSIRIS-REx team by the Space Foundation during the 37th Space Symposium, Monday, April 4, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. The John L. “Jack” Swigert, Jr., Award for Space Exploration recognizes extraordinary accomplishments by a company, space agency, or consortium of organizations in the realm of space exploration and discovery. The award honors the memory of astronaut John L. “Jack” Swigert, Jr., one of the inspirations for the creation of Space Foundation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
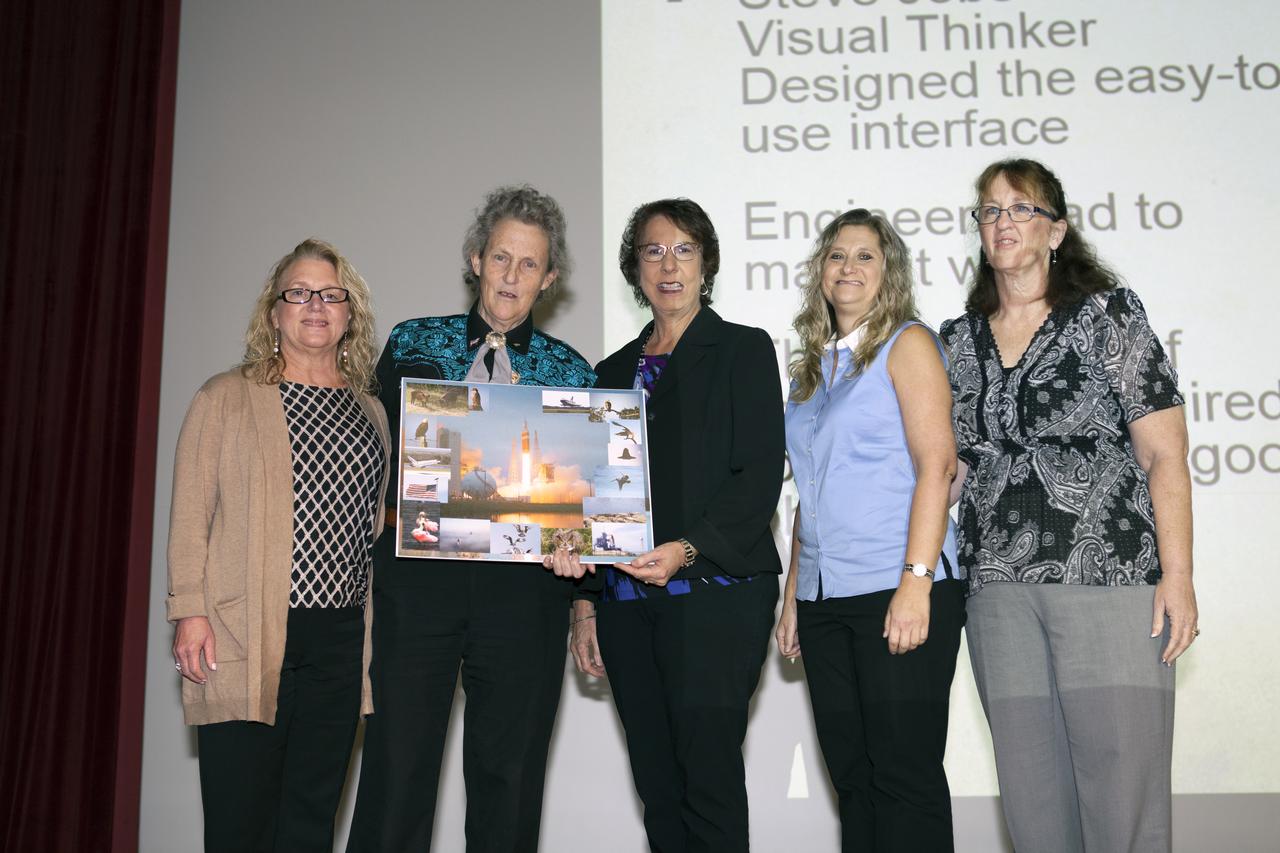

Dr. Temple Grandin, second from left, pauses for a photo after giving the keynote presentation at Kennedy Space Center's annual National Disability Employment Awareness Month (NDEAM) event. From left are Chief Financial Officer Susan Kroskey, executive champion of Kennedy's Disability Awareness and Action Working Group, or DAAWG; Grandin; Joette Feeney, chair of the Kennedy Networking Opportunities for Women group, or KNOW; and DAAWG Co-chairs Nicole Delvesco and Annie Williams. A prominent author and speaker on animal behavior and autism, Grandin is a professor of animal science at Colorado State University in Fort Collins, Colorado. Kennedy's DAAWG and KNOW groups partnered to sponsor the presentation.
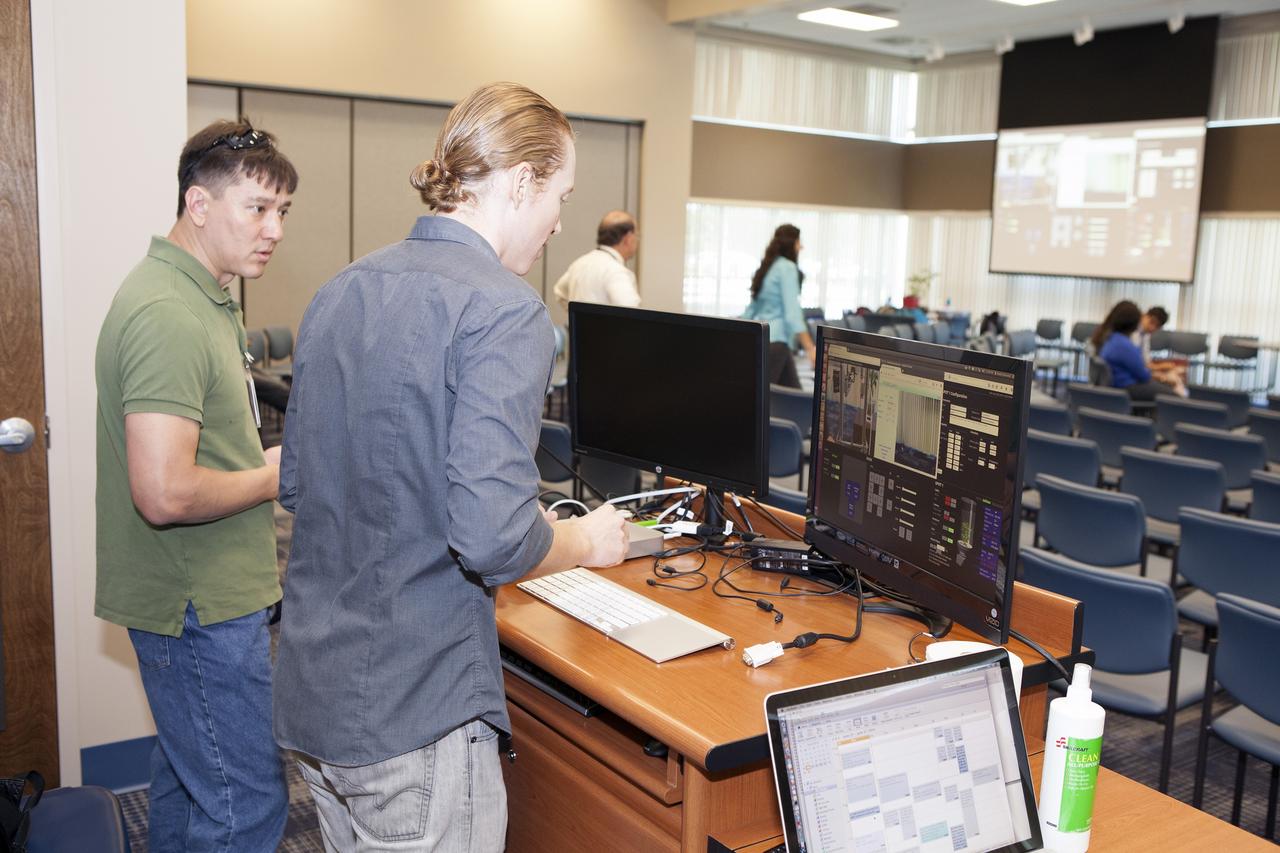

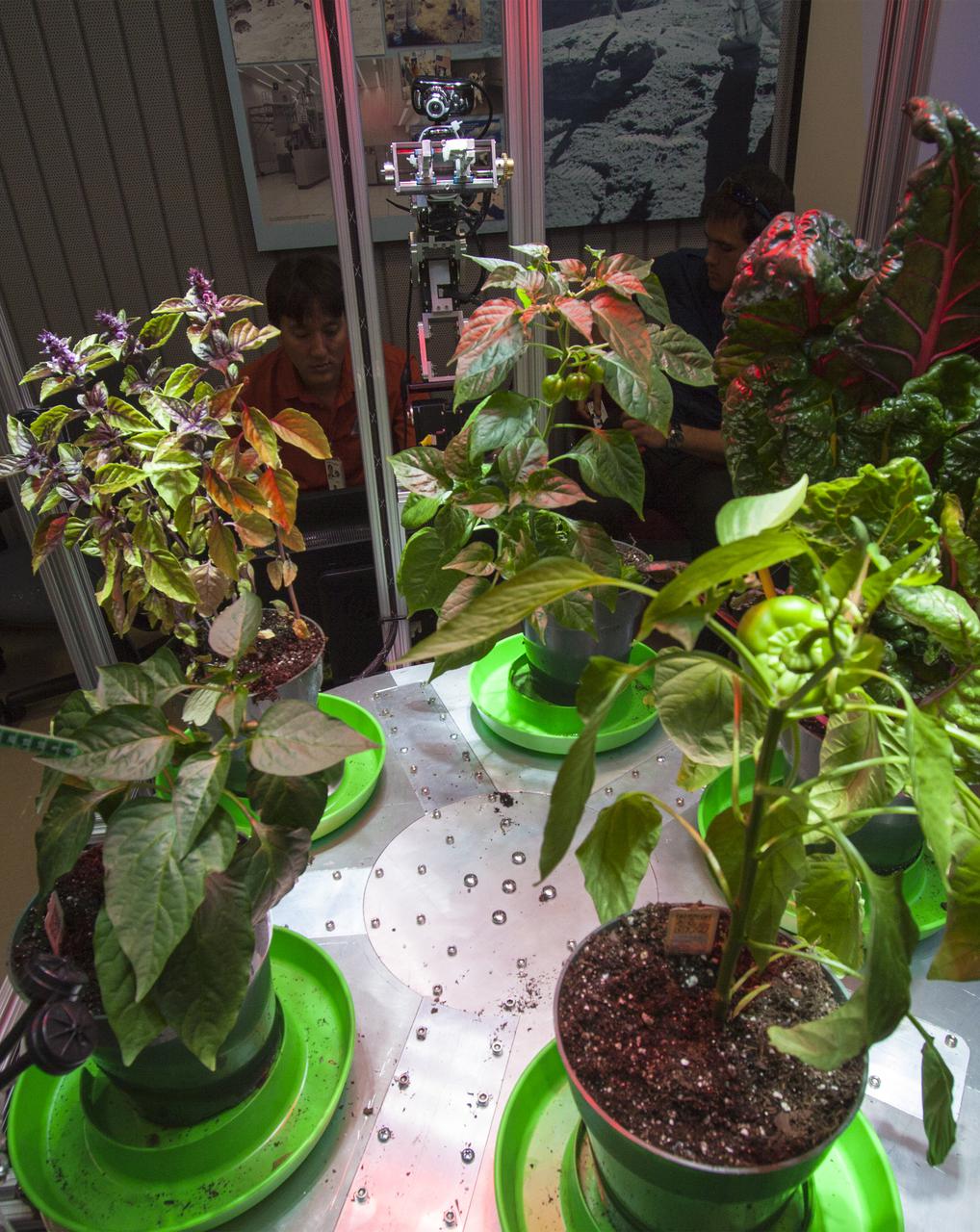
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from the University of Colorado Boulder demonstrated a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants in a deep-space habitat. Daniel Zukowski, a University of Colorado Boulder graduate student, right, and Morgan Simpson of the NASA Ground Processing Directorate, check computer displays during a presentation of the team's entry in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. In their concept called "Plants Anywhere: Plants Growing in Free Habitat Spaces," their approach calls for robotically tended plants to be scattered in any available space in a deep-space habitat instead of an area set aside just for vegetation. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

NASA launched a Terrier-Improved Malemute suborbital sounding rocket carrying the RockSat-X payload with university and community college student experiments at 6:04 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Aug. 12, from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facilityin Virginia. More than 60 students and instructors from across the continental United States, Hawaii and Puerto Rico were on hand to witness the launch of their experiments. The payload flew to an altitude of about 97 miles and descended via parachute into the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Wallops. Payload recovery operations began after lift-off. Developed by students from seven higher education programs, the experiments flew through the RockSat-X program in conjunction with the Colorado Space Grant Consortium. Participating institutions in this flight are the University of Colorado, Boulder; Northwest Nazarene University, Nampa, Idaho; the University of Puerto Rico; the University of Nebraska, Lincoln; Virginia Tech University, Blacksburg; Capitol Technology University, Laurel, Maryland; and University of Hawai'i Community Colleges at the Honolulu, Kapi'olani, Kaua'i, and Windward campuses. The next launch scheduled from Wallops is a NASA Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket carrying several technology development instruments. The launch is scheduled between 7 and 7:41 p.m. Sept. 29. The backup launch days are Sept. 30 through Oct. 12. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, left, and David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland are seen during a media briefing where they and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
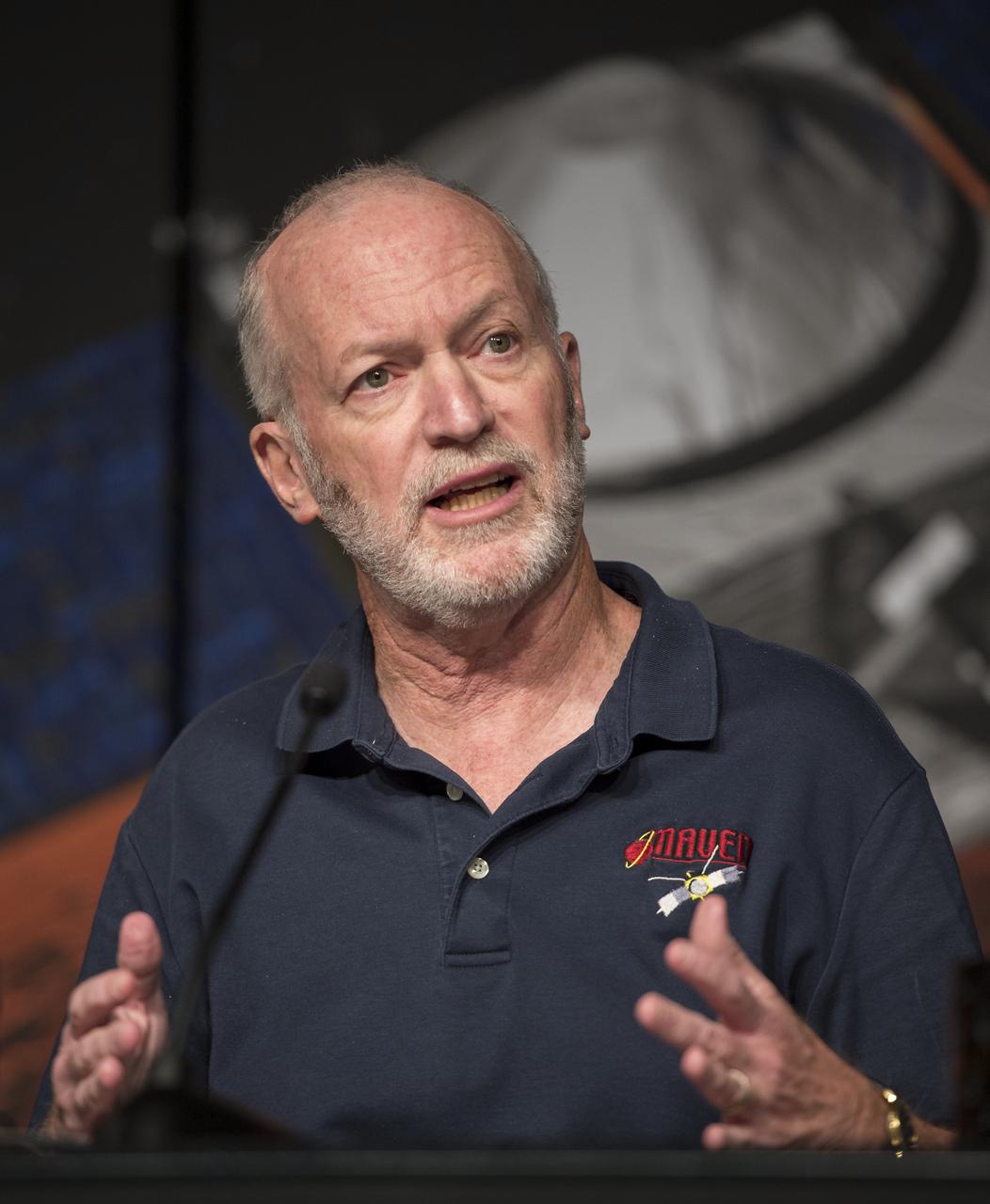

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, is seen during a media briefing where he and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Tom Woods, (second from right), principal investigator, Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment instrument, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado in Boulder speaks during a briefing to discuss recent images from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, Wednesday, April 21, 2010, at the Newseum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Alysha Reinard, as research scientist with National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and the University of Colorado Boulder, speaks during a press briefing, Thursday, Aug. 18, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The briefing was held to discusses new details about the structure of solar storms and the impact they have on Earth. The new information comes from NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, spacecraft and other NASA probes. Photo Credit: (NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth)

Greg Kopp, from the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colo., talks about the launch of the GLORY mission during a news conference at NASA Headquarters, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2011, in Washington. NASA's newest Earth-observing research mission is scheduled for launch form Vandenburg Air Force Base in California on Feb. 23. The mission will improve our understanding of how the sun and tiny atmosppheric particles called aerosols affect Earth's climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Dr. Fran Bagenal, senior scientist at the University of Colorado, far right, speaks during a panel discussion at the "NASA's New Horizons Pluto Mission: Continuing Voyager's Legacy of Exploration" event on Monday, August, 25, 2014, in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The panelists gave their accounts of Voyager's encounter with Neptune and discussed their current assignments on NASA's New Horizons mission to Pluto. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, University of Colorado Boulder Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, discusses the upcoming launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, at a press conference at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Monday, Oct. 28th, 2013. MAVEN is the agency's next mission to Mars and the first devoted to understanding the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet. (Photo credit: NASA/Jay Westcott)

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, left, and David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland are seen during a media briefing where they and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., sits in her launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building before she and the five other crew members of STS-87 depart for Launch Pad 39B. There, the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Born in Karnal, India, Dr. Chawla received her doctorate of philosophy in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado in 1988. This is Chawla’s first mission for NASA
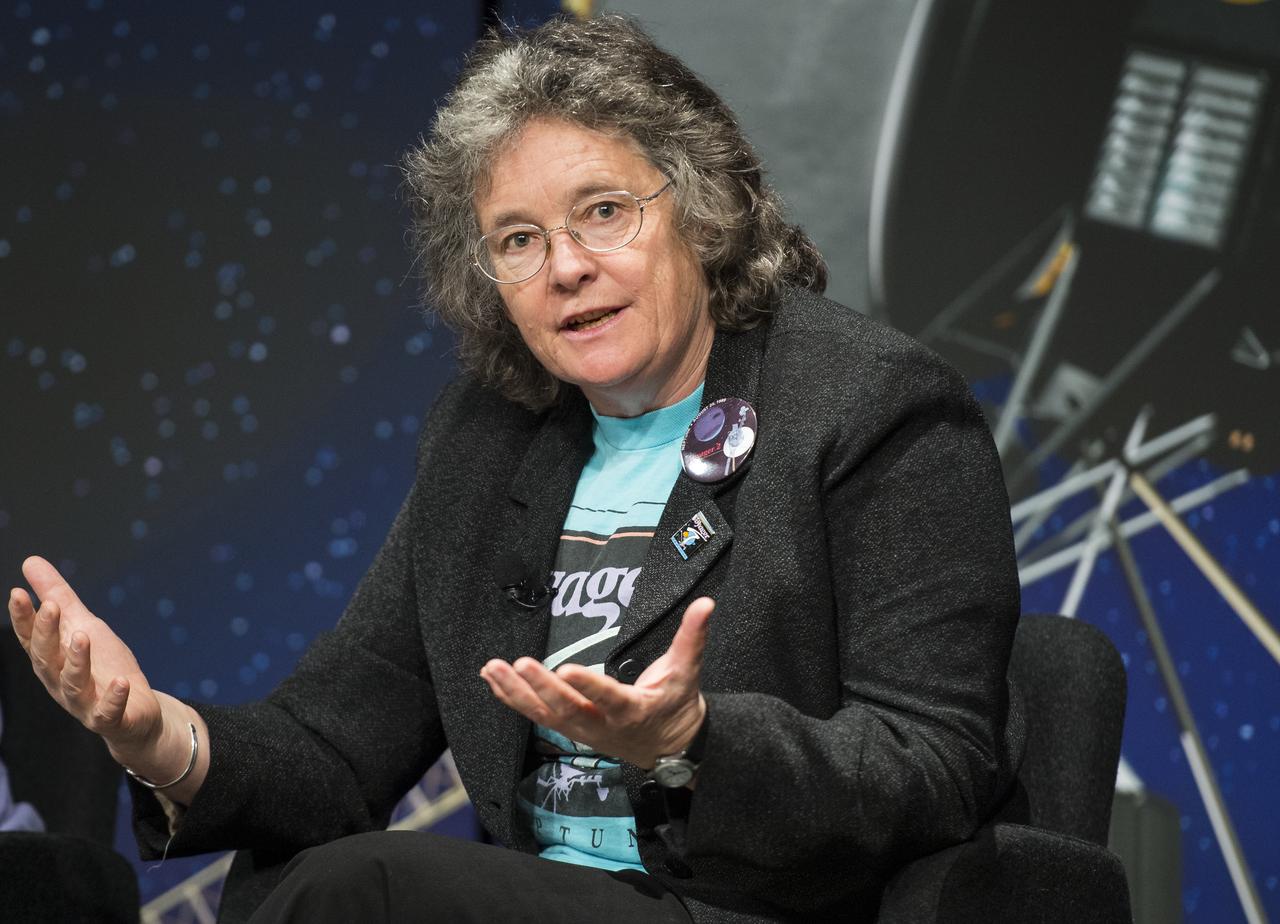

Dr. Fran Bagenal, senior scientist at the University of Colorado, speaks during a panel discussion at the "NASA's New Horizons Pluto Mission: Continuing Voyager's Legacy of Exploration" event on Monday, August, 25, 2014, in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. The panelists gave their accounts of Voyager's encounter with Neptune and discussed their current assignments on NASA's New Horizons mission to Pluto. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. From left are: Dante Lauretta, OSIRIS-REx principal investigator at the University of Arizona, Tucson; Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager at Kennedy; and Scott Messer, program manager for NASA missions at United Launch Alliance in Centennial, Colorado.
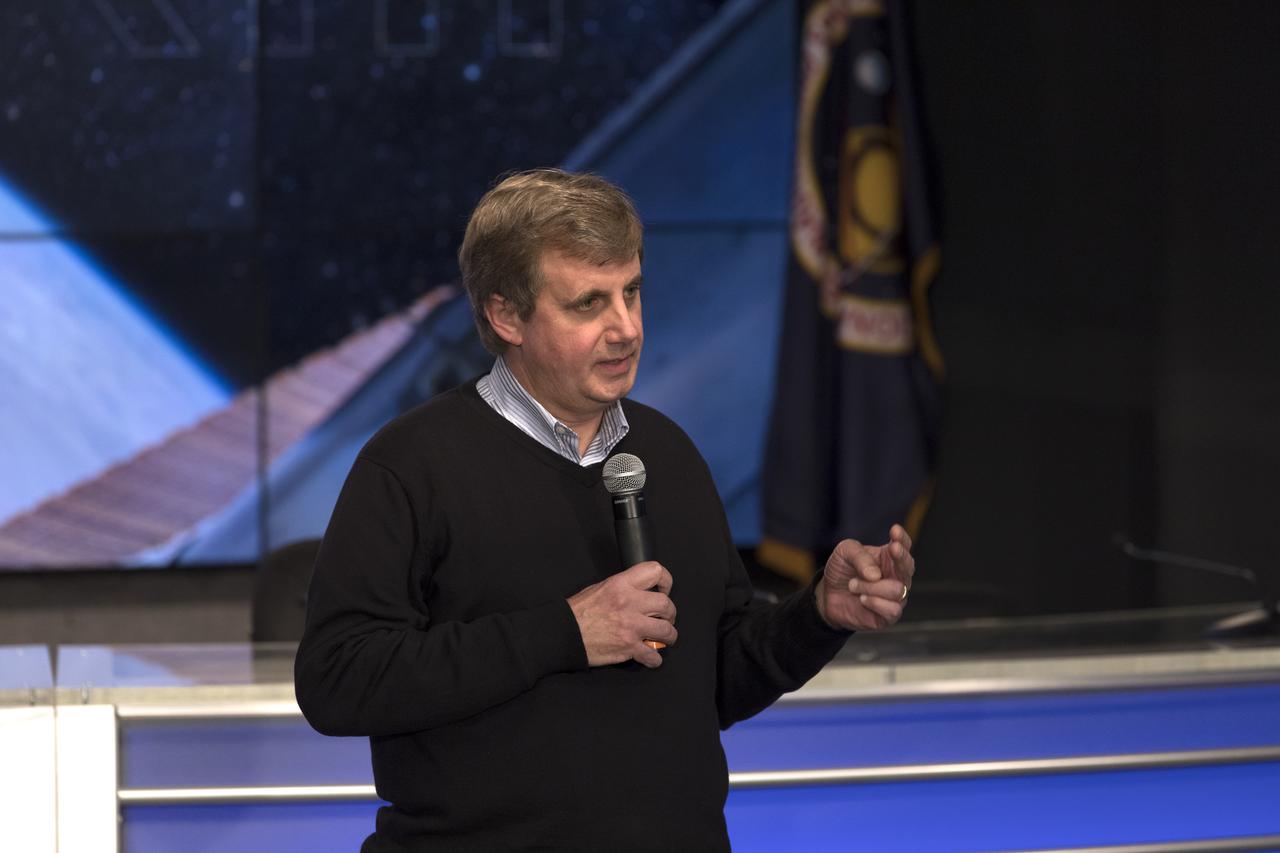

Peter Pilewskie, lead scientist at the University of Colorado-Boulder, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40 at 11:46 a.m. EST, on Dec. 12, 2017. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 13th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
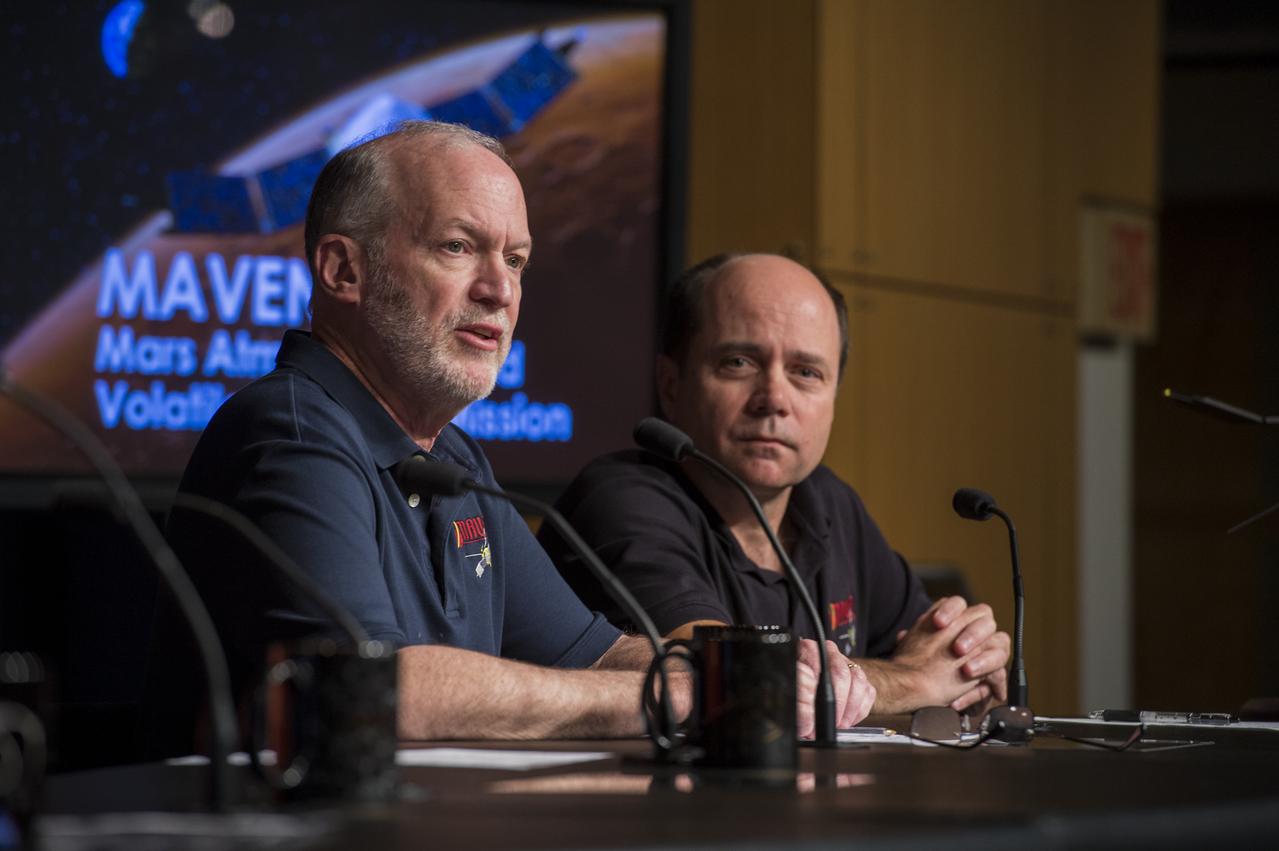

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, University of Colorado Boulder Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, discusses the upcoming launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, at a press conference at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Monday, Oct. 28th, 2013. MAVEN is the agency's next mission to Mars and the first devoted to understanding the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet. (Photo credit: NASA/Jay Westcott)
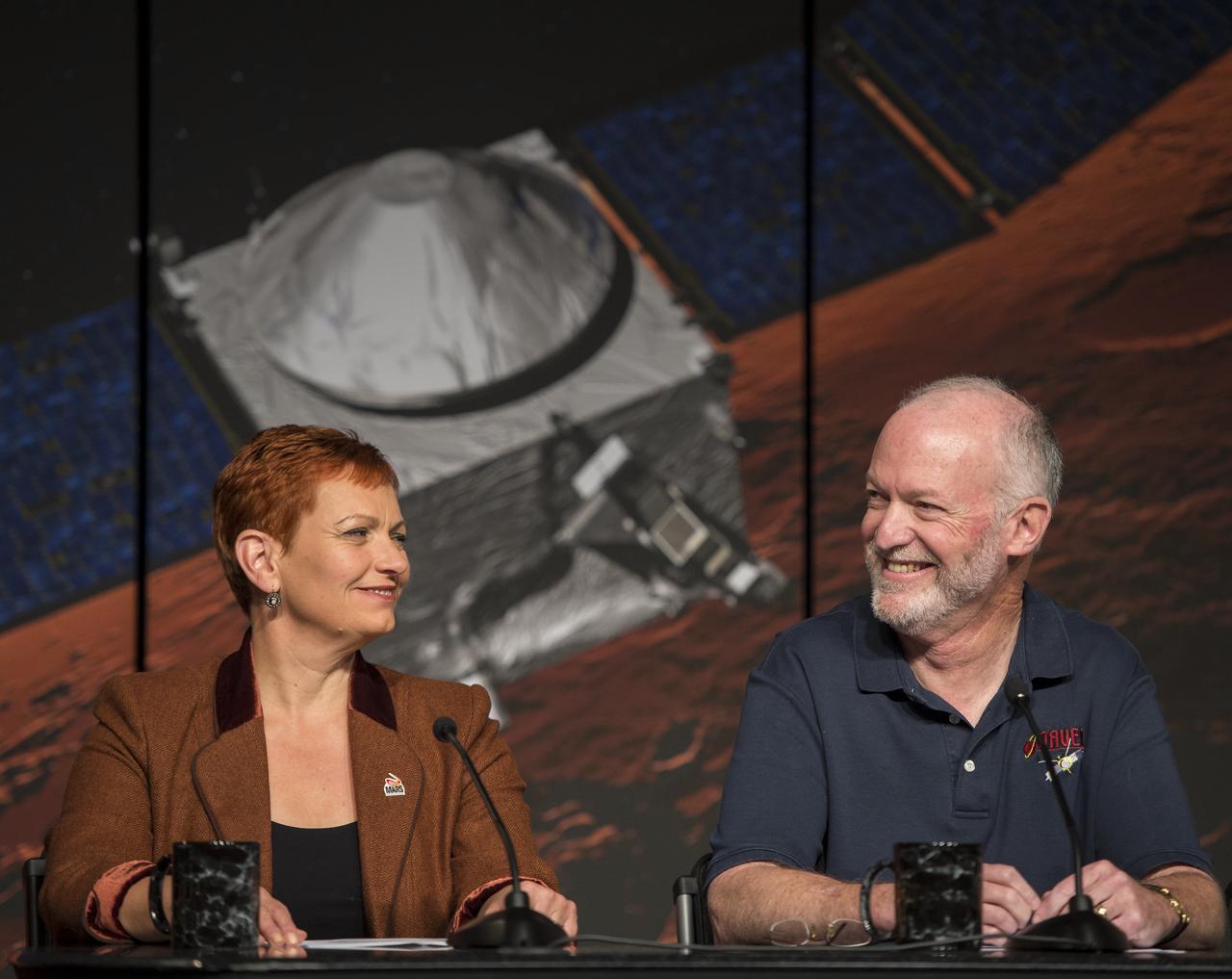

Lisa May, lead program executive, Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters, and Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, are seen during a media briefing where they and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
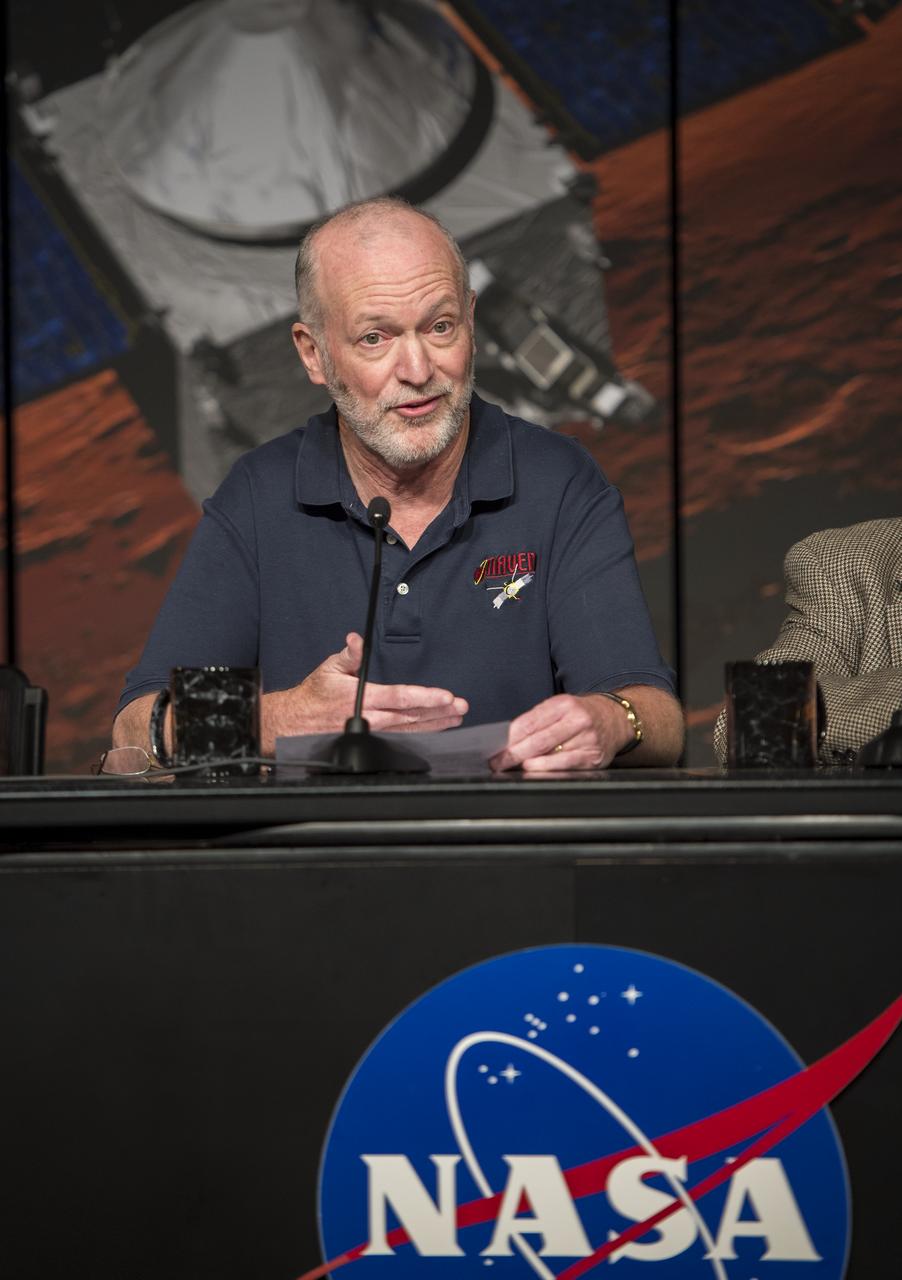

Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, is seen during a media briefing where he and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During this year's NASA MarsPort Engineering Design Student Competition 2002 conference, the University of Colorado at Boulder presents this display. Participants are presenting papers on engineering trade studies to design optimal configurations for a MarsPort Deployable Greenhouse for operation on the surface of Mars. Judges in the competition were from KSC, Dynamac Corporation and Florida Institute of Technology. The winning team's innovative ideas will be used by NASA to evaluate and study other engineering trade concepts.
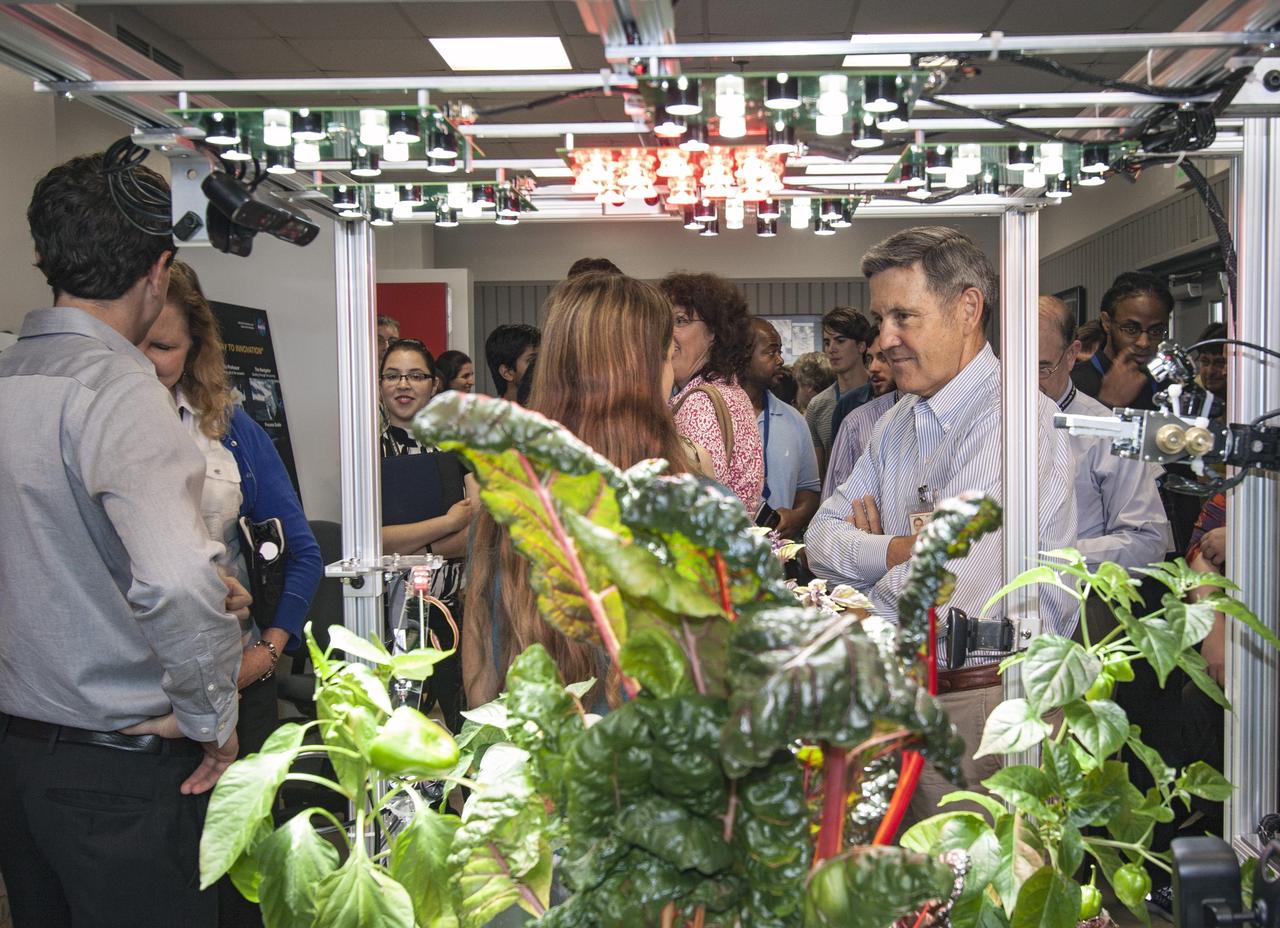

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana listens as a student from University of Colorado describes a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

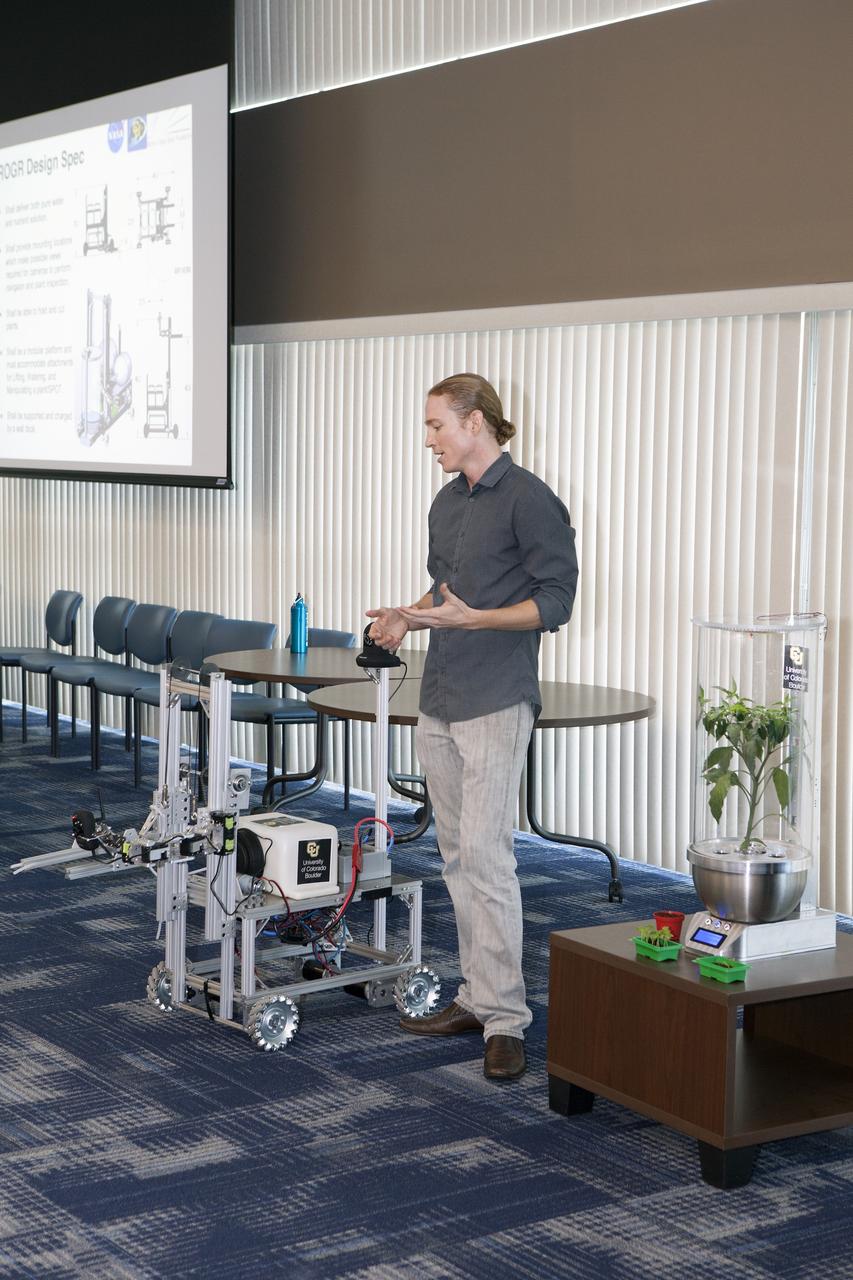
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, makes adjustments on a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend plants on a deep-space habitat. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
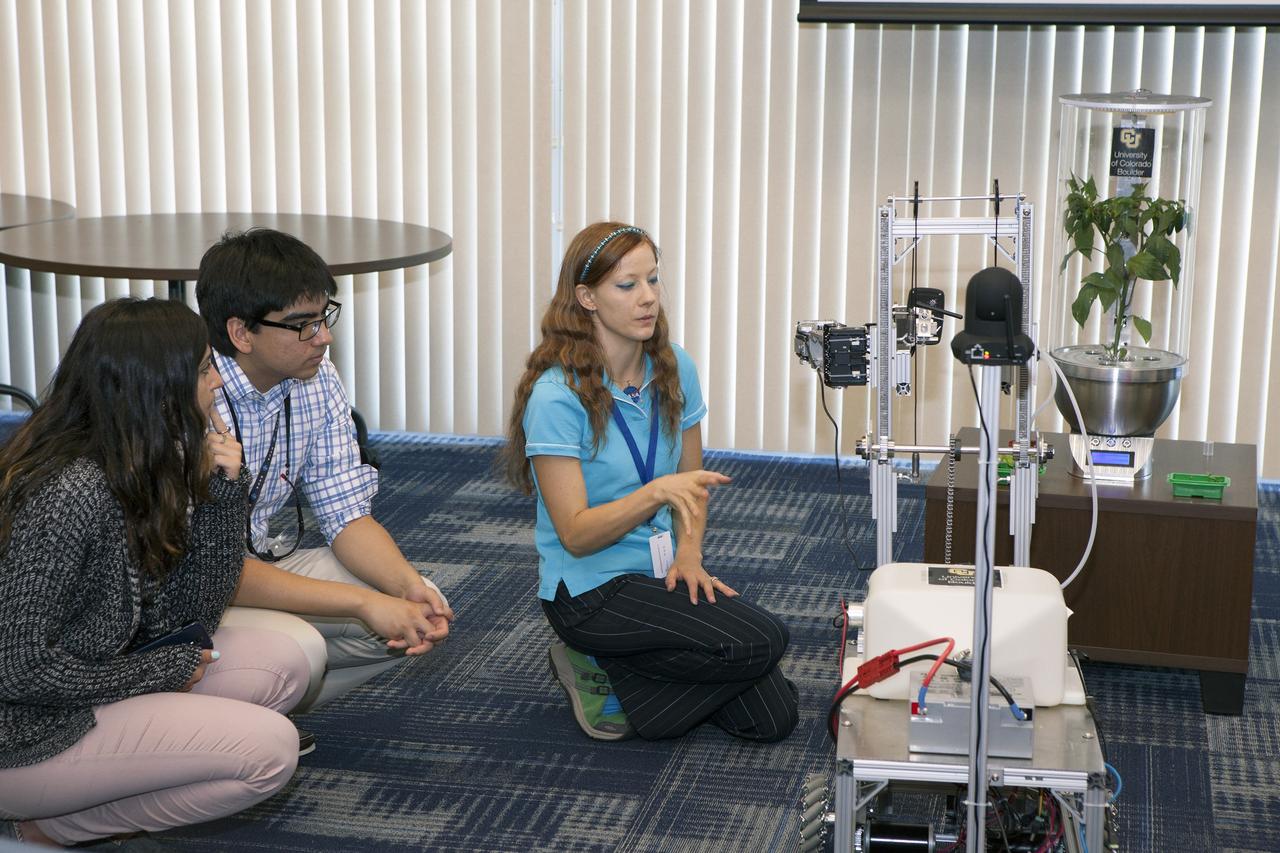
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, describes a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
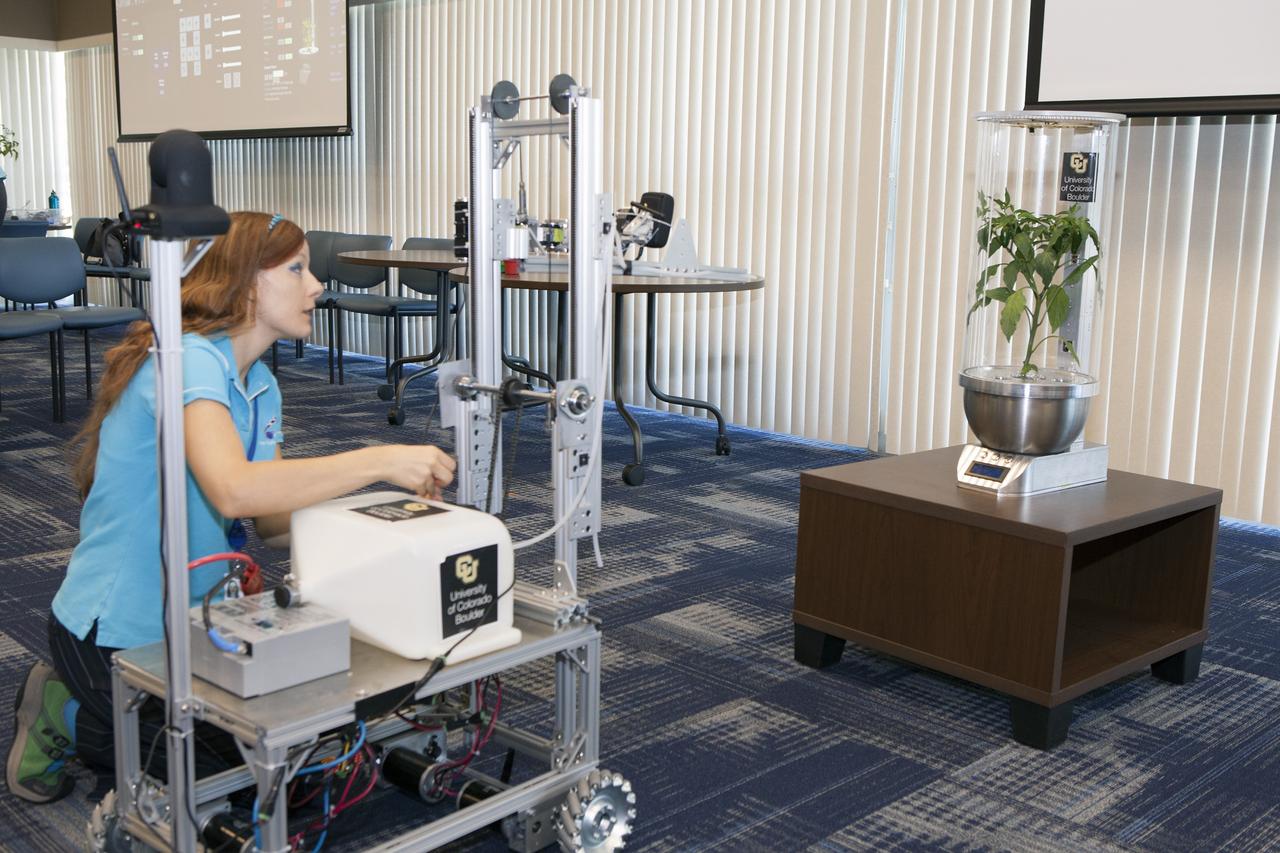

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, makes adjustments on a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
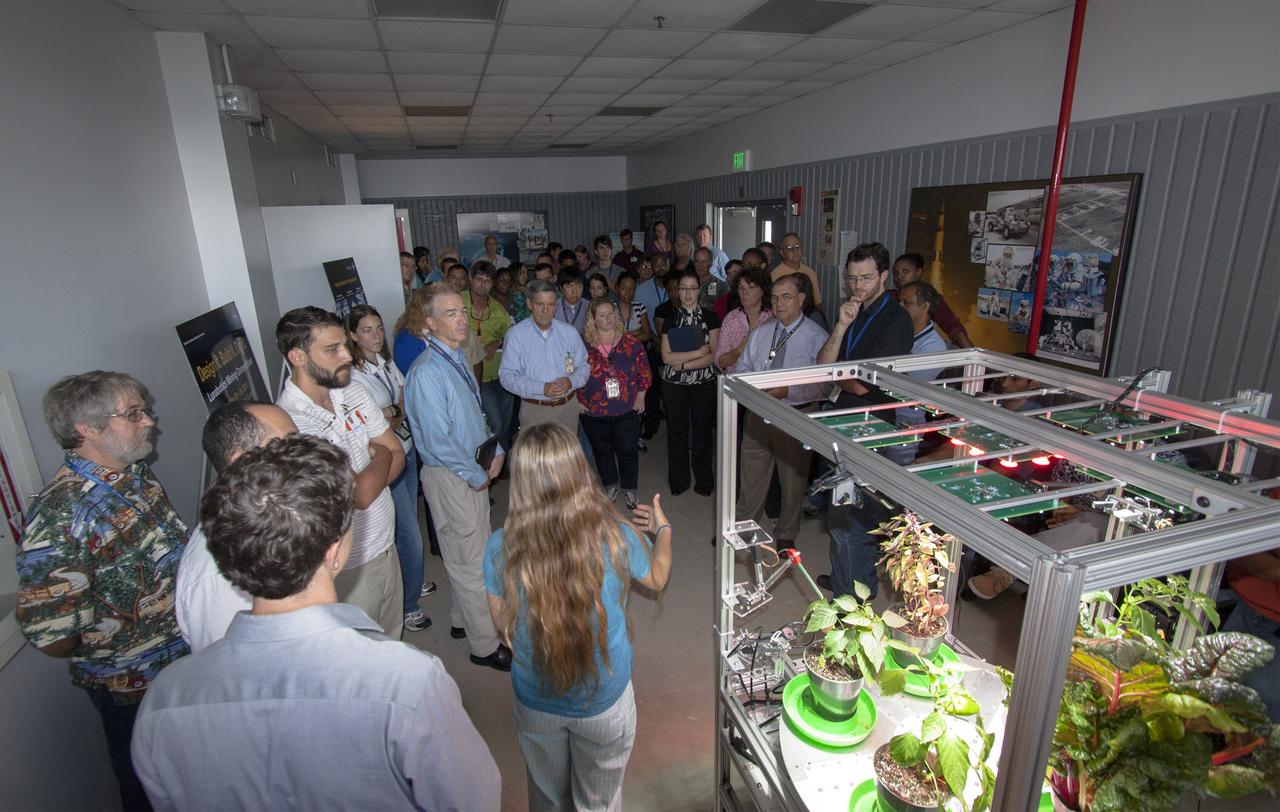

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado describe a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
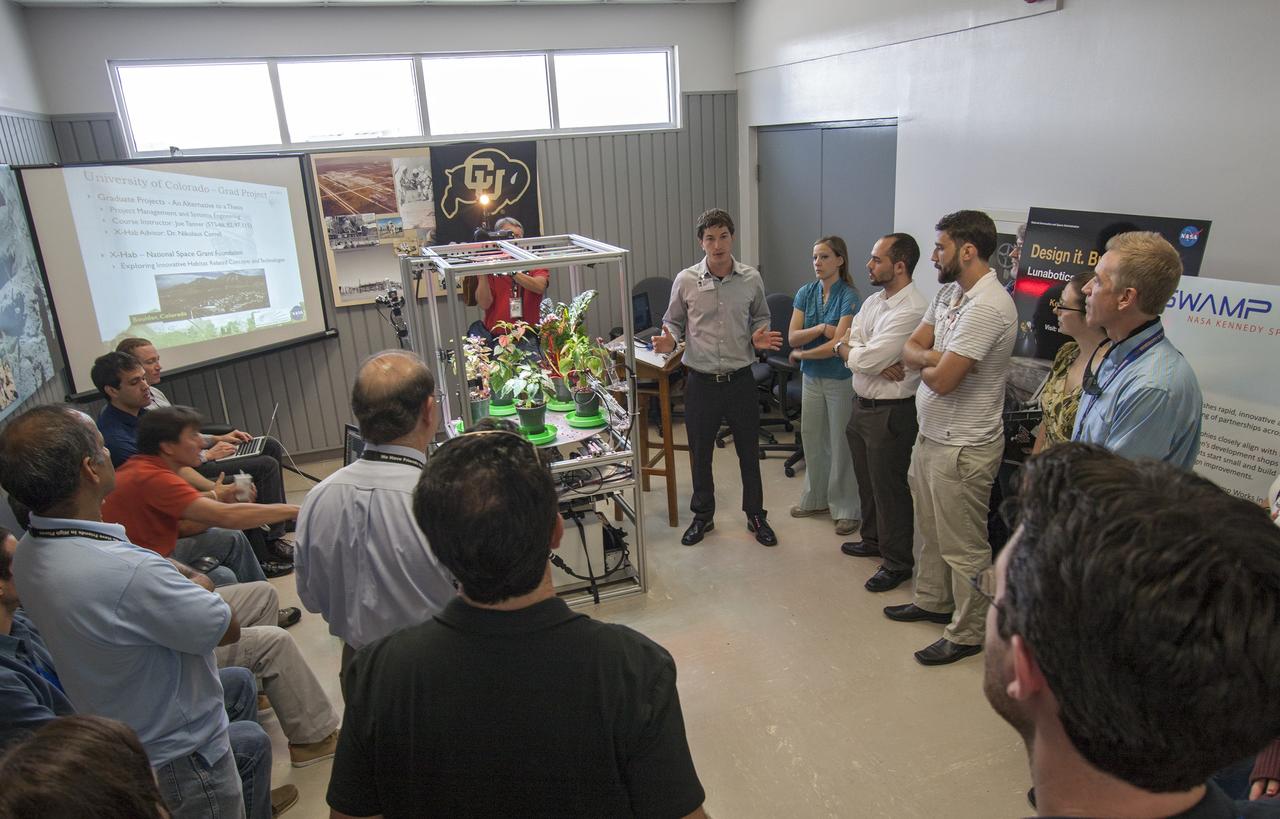

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado describe a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado demonstrated a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http:__www.nasa.gov_exploration_technology_deep_space_habitat_xhab_ Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Daniel Zukowski, a University of Colorado Boulder graduate student, describes a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS, seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitation X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
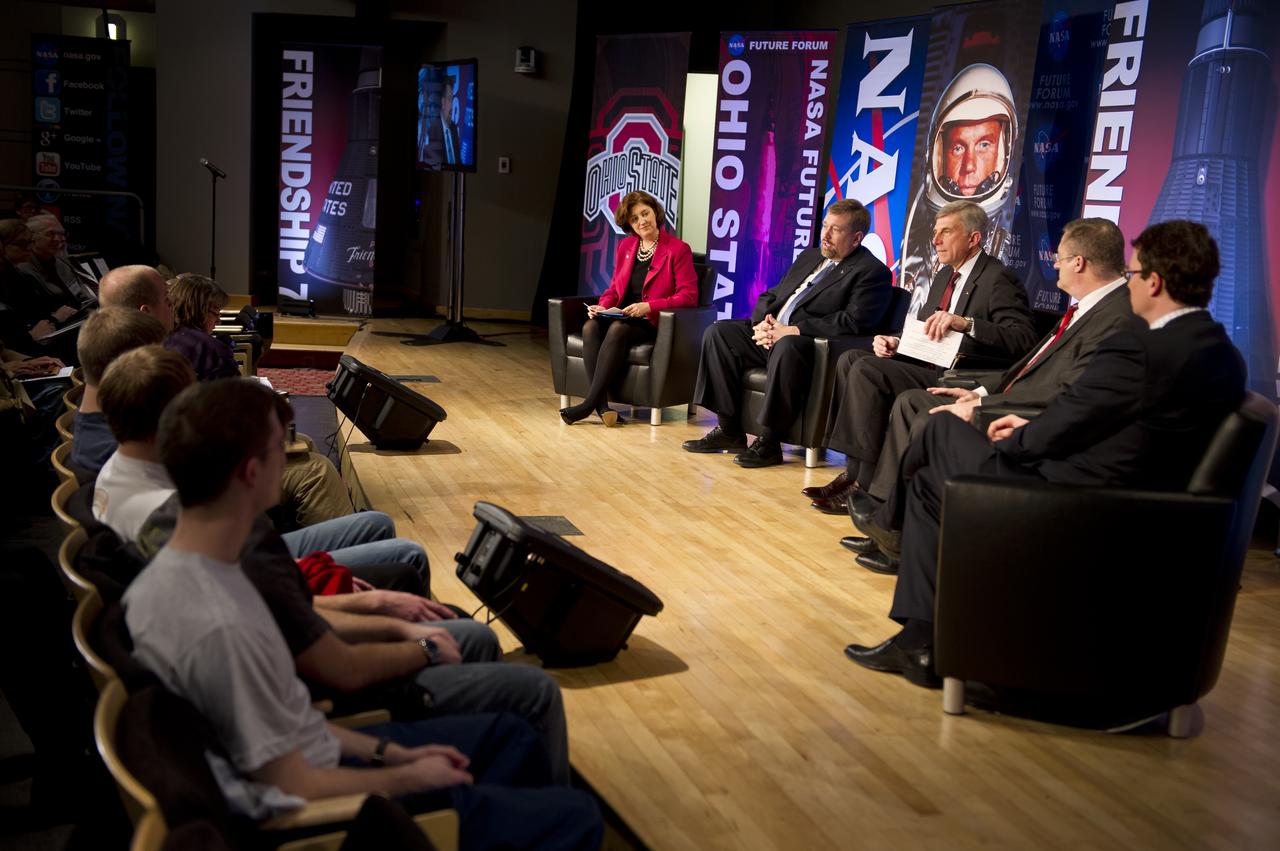

Laurie Leshin, dean of the School of Science, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, left, Mason Peck, NASA Chief Technologist, 2nd from left, Ron Sega, Vice president and enterprise executive for Energy and the Environment, The Ohio State University and Colorado State University, Michael Donovan, technology consultant, New Services Development, Hewlett-Packard Company, and, Jordan Hansell, chairman and CEO, NetJets Inc., right, participate in the NASA Future Forum panel titled "Importance of Technology, Science and Innovation for our Economic Future" at The Ohio State University on Tuesday, Feb. 21, 2012 in Columbus, Ohio. The NASA Future Forum features panel discussions on the importance of education to our nation's future in space, the benefit of commercialized space technology to our economy and lives here on Earth, and the shifting roles for the public, commercial and international communities in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
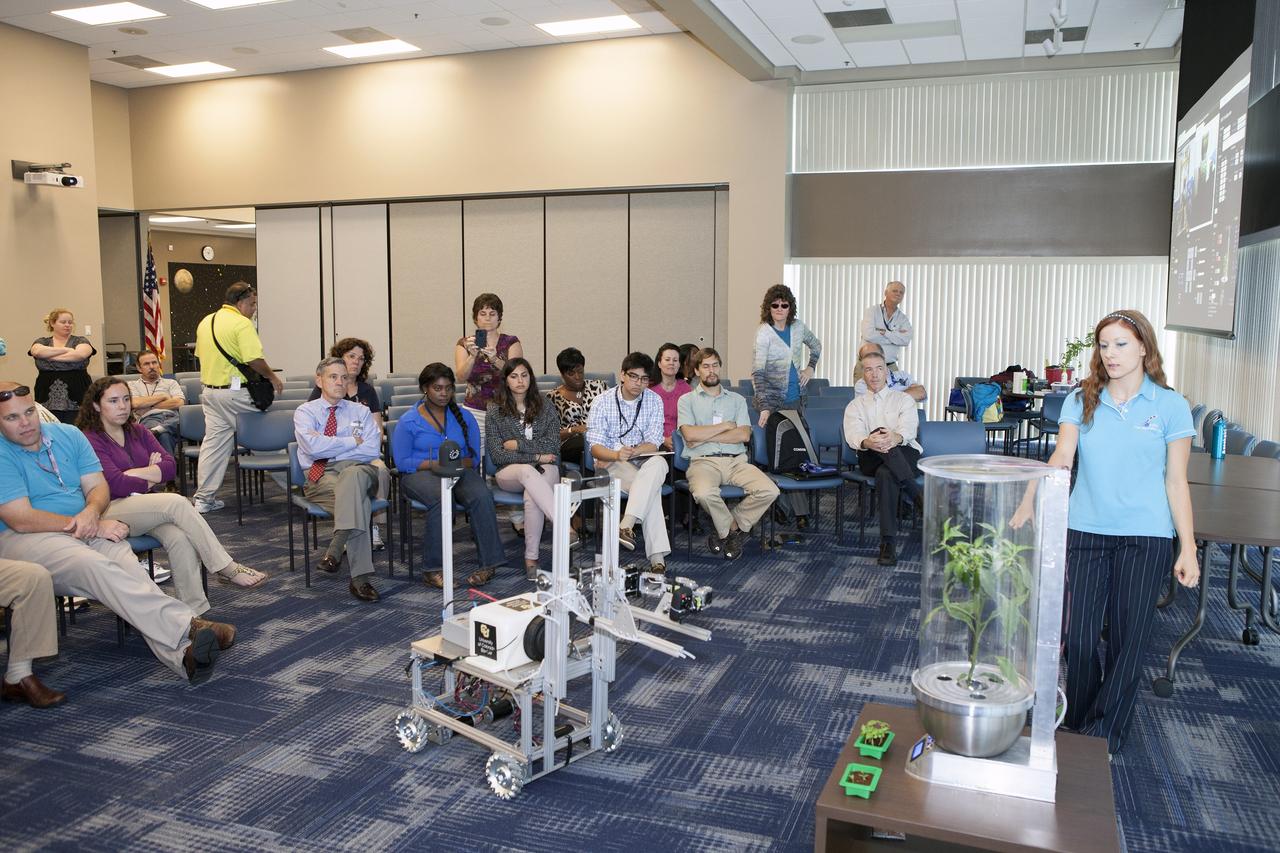

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, right, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, describes a computerized SmartPot, or SPOT, which could be used to grow plants in a deep-space habitat. The SPOTs could be tended by a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, seen on the left. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
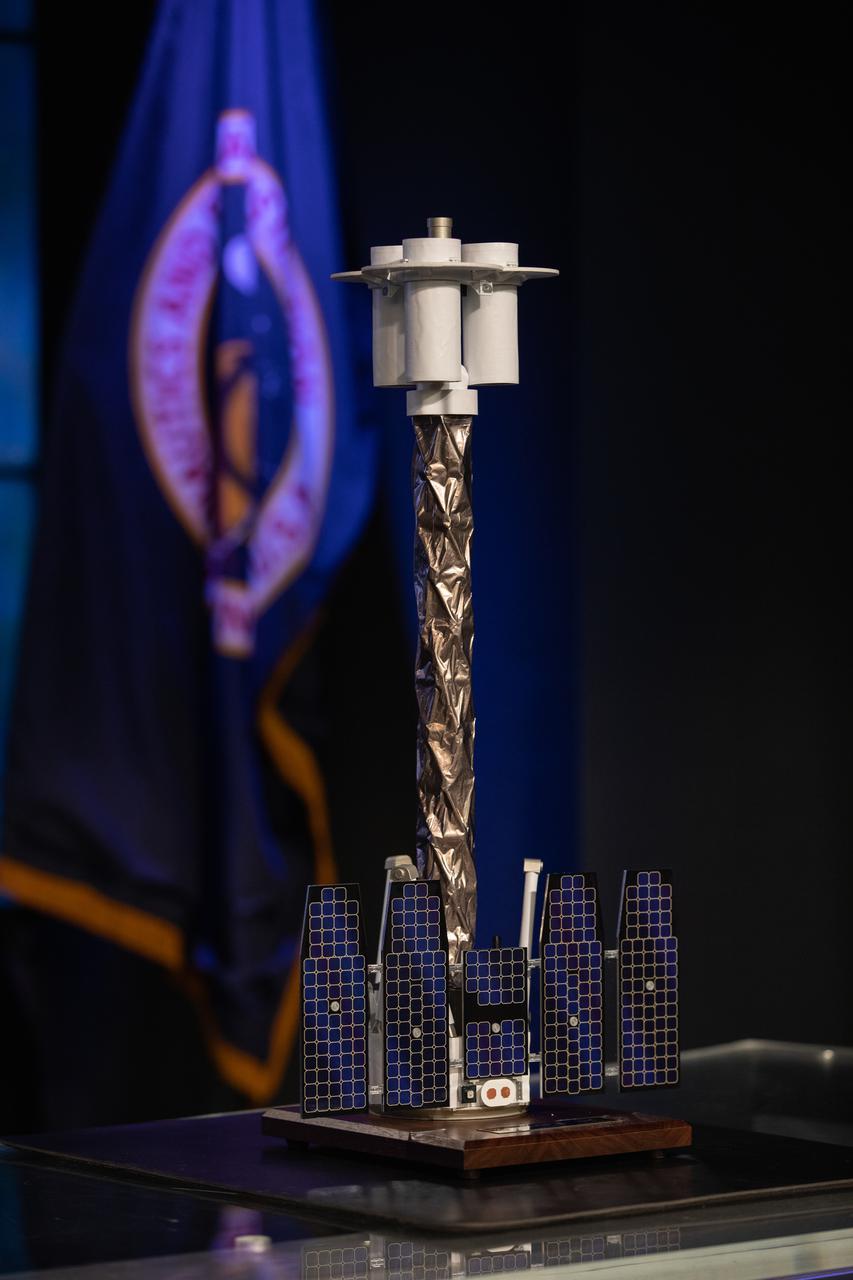

A scale model of NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft is on display during a payload briefing for IXPE on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
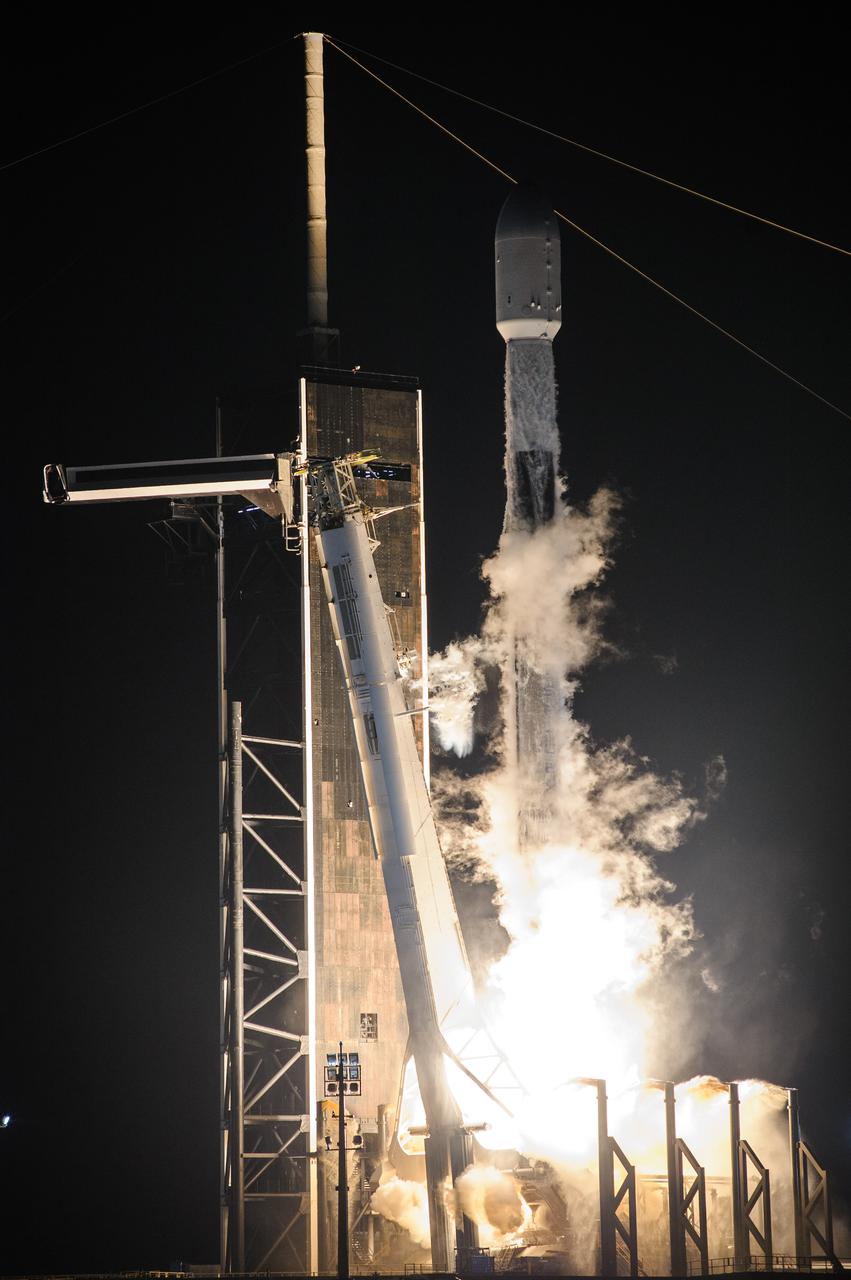

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.

Karen Fox, NASA Communications, moderates a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
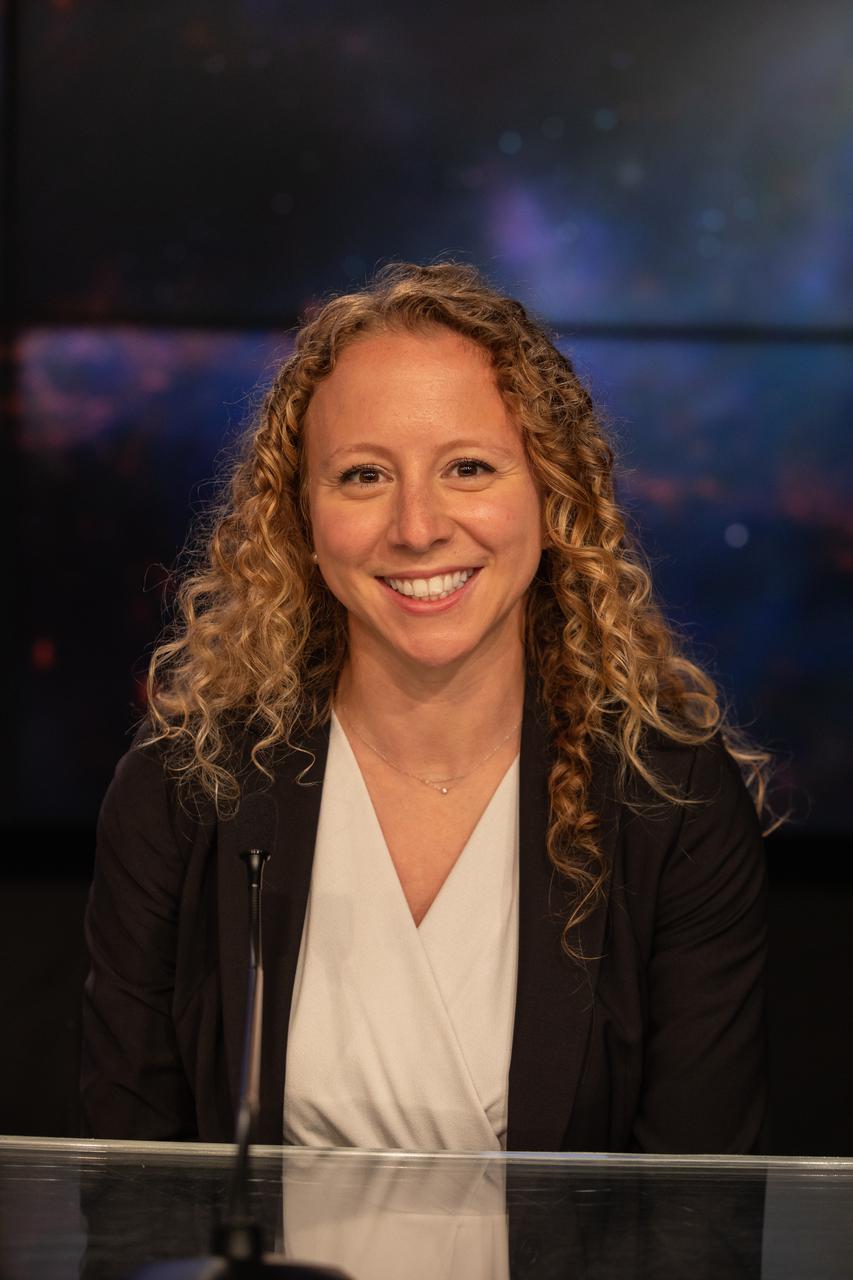

Julianna Scheiman, director, civil satellite missions, SpaceX, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
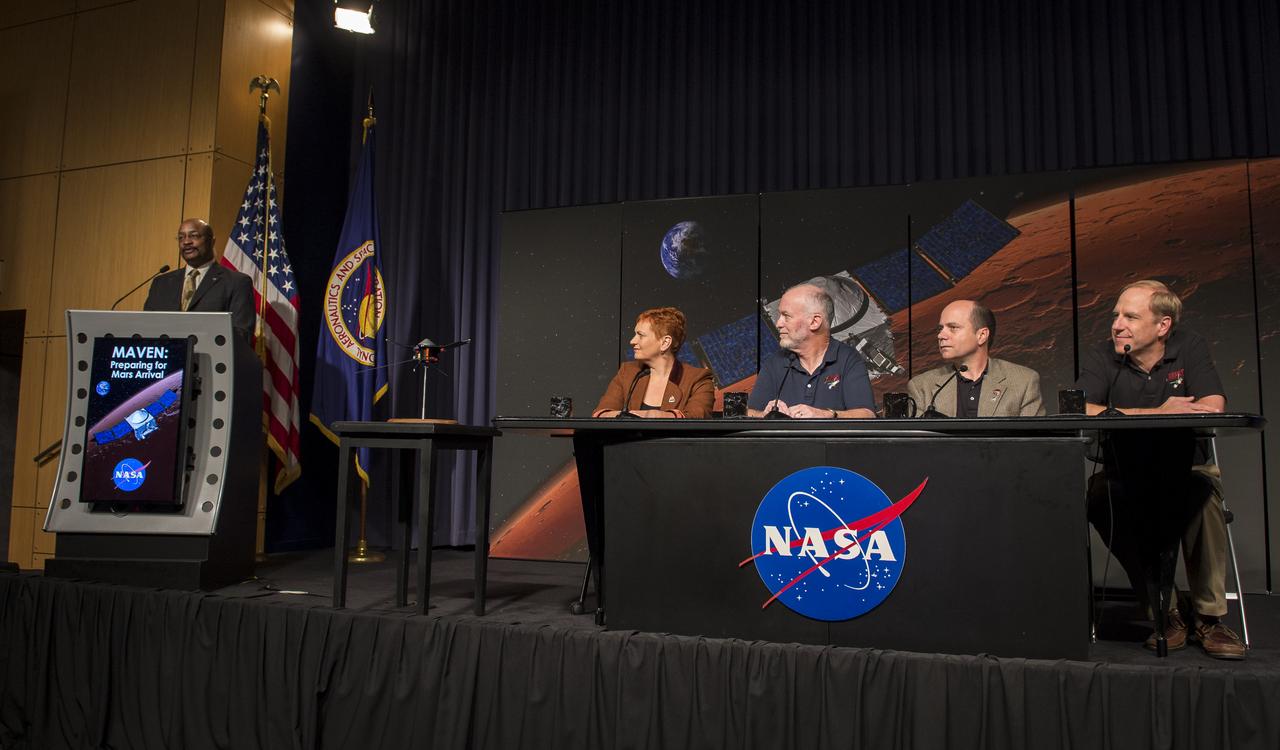

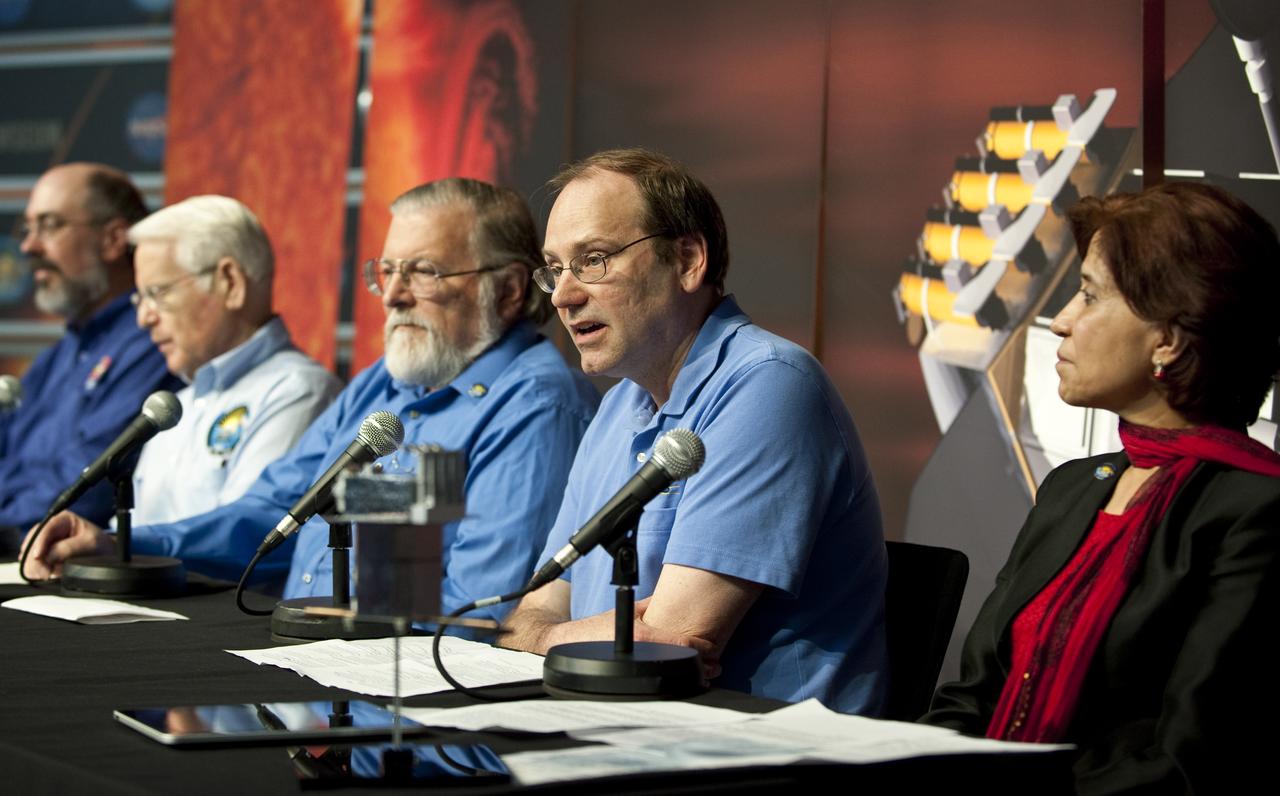
Dwayne Brown, NASA public affairs officer, left, moderates a media briefing where panelist, seated from left, Lisa May, lead program executive, Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters, Washington, Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, and Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado, outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
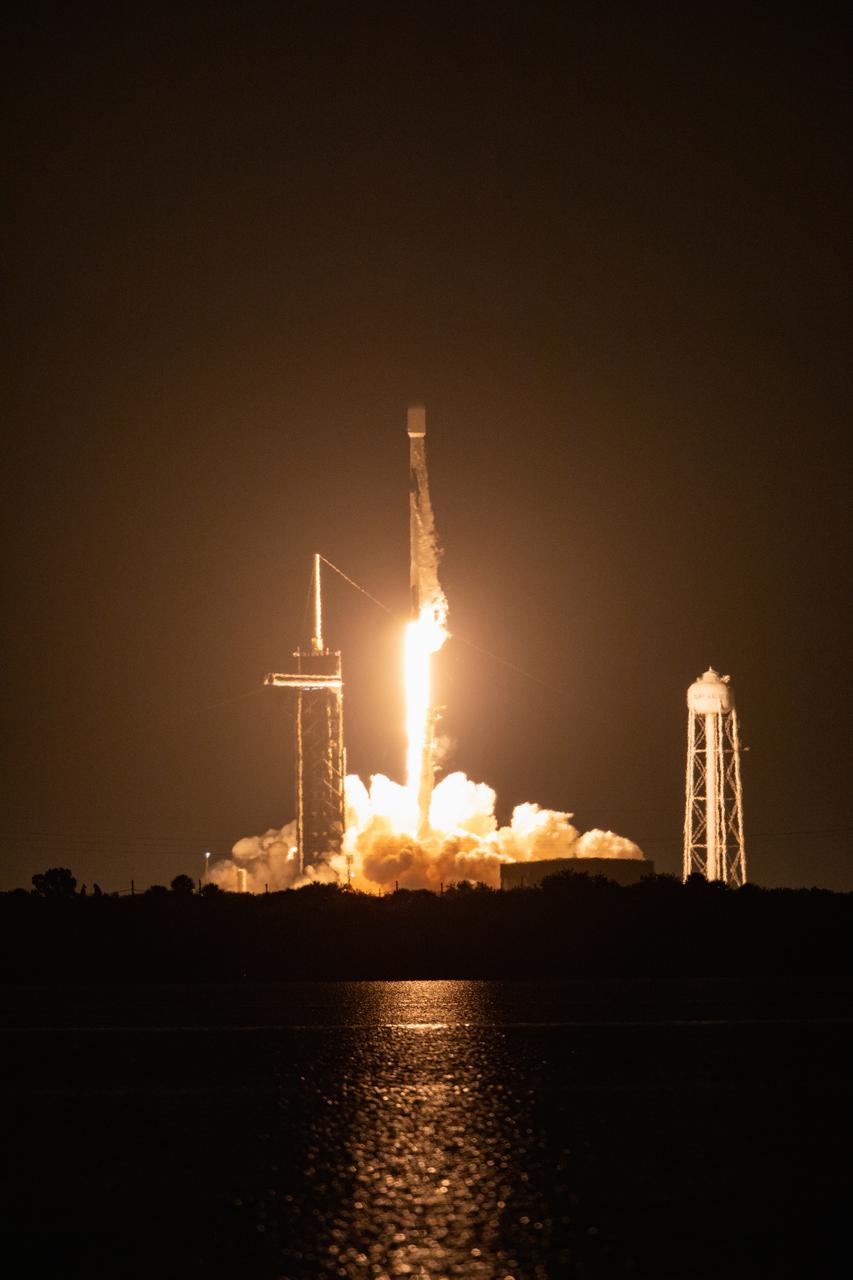

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
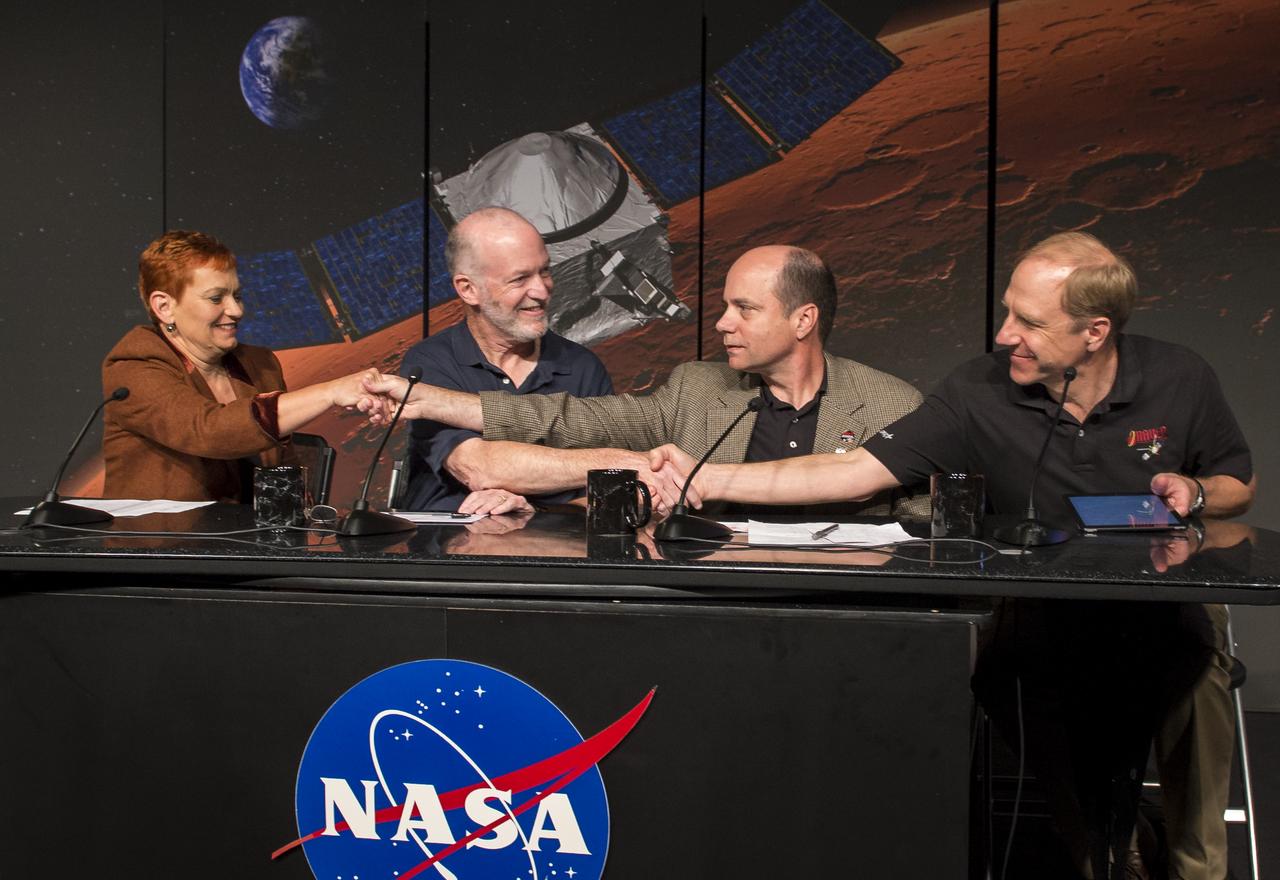

Panelist, from left, Lisa May, lead program executive, Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters, Washington, Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, and Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado, all shake hands at the end of a media briefing where they outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
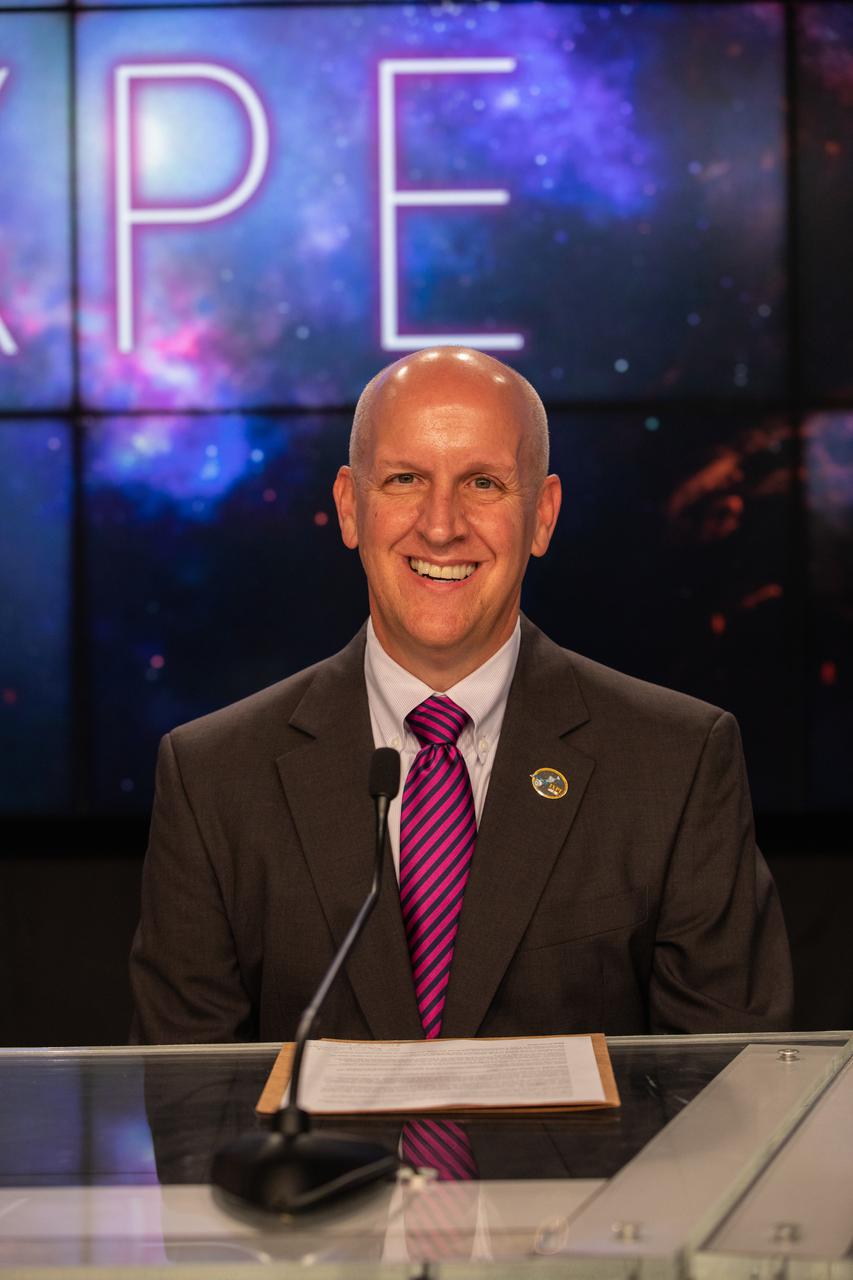

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
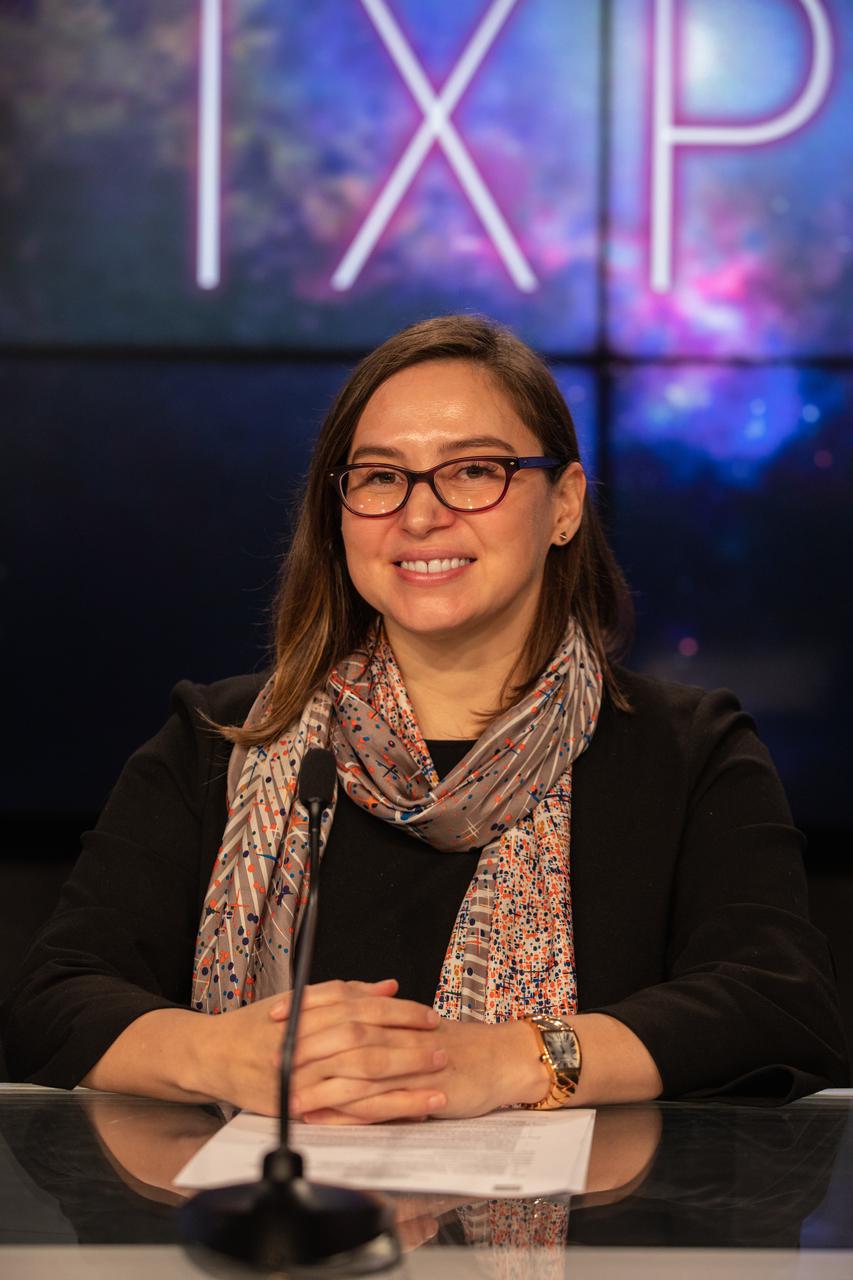

Makenzie Lystrup, vice president and general manager, civil space, Ball Aerospace, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky over the Atlantic Ocean with a Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), attached underneath. The rocket will be dropped from the aircraft at 3:14 p.m. EST. Over the next few days, the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado. [Photo courtesy of Jeff Caplan, Langley Research]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-03pd0177/KSC-03pd0177~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky over the Atlantic Ocean with a Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), attached underneath. The rocket will be dropped from the aircraft at 3:14 p.m. EST. Over the next few days, the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado. [Photo courtesy of Jeff Caplan, Langley Research]
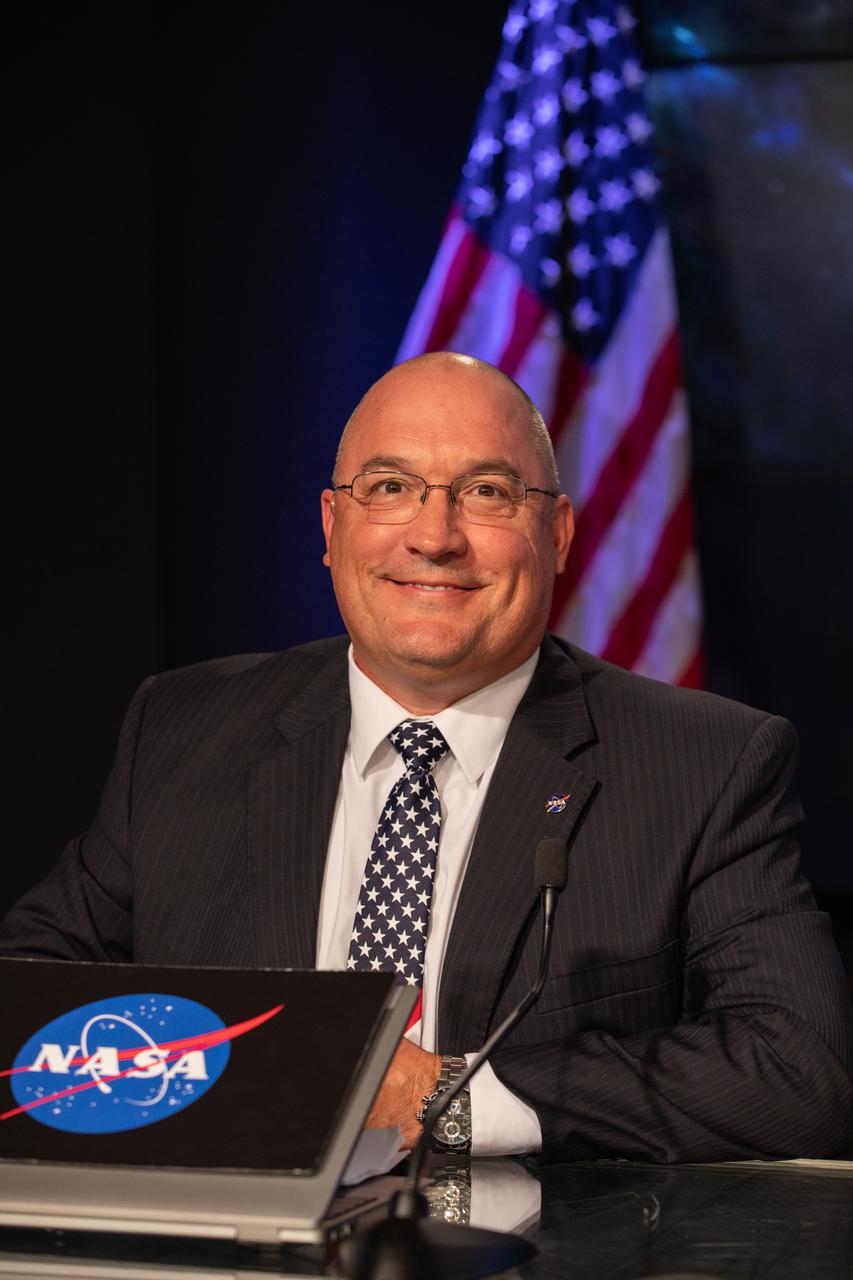

Greg Harland, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
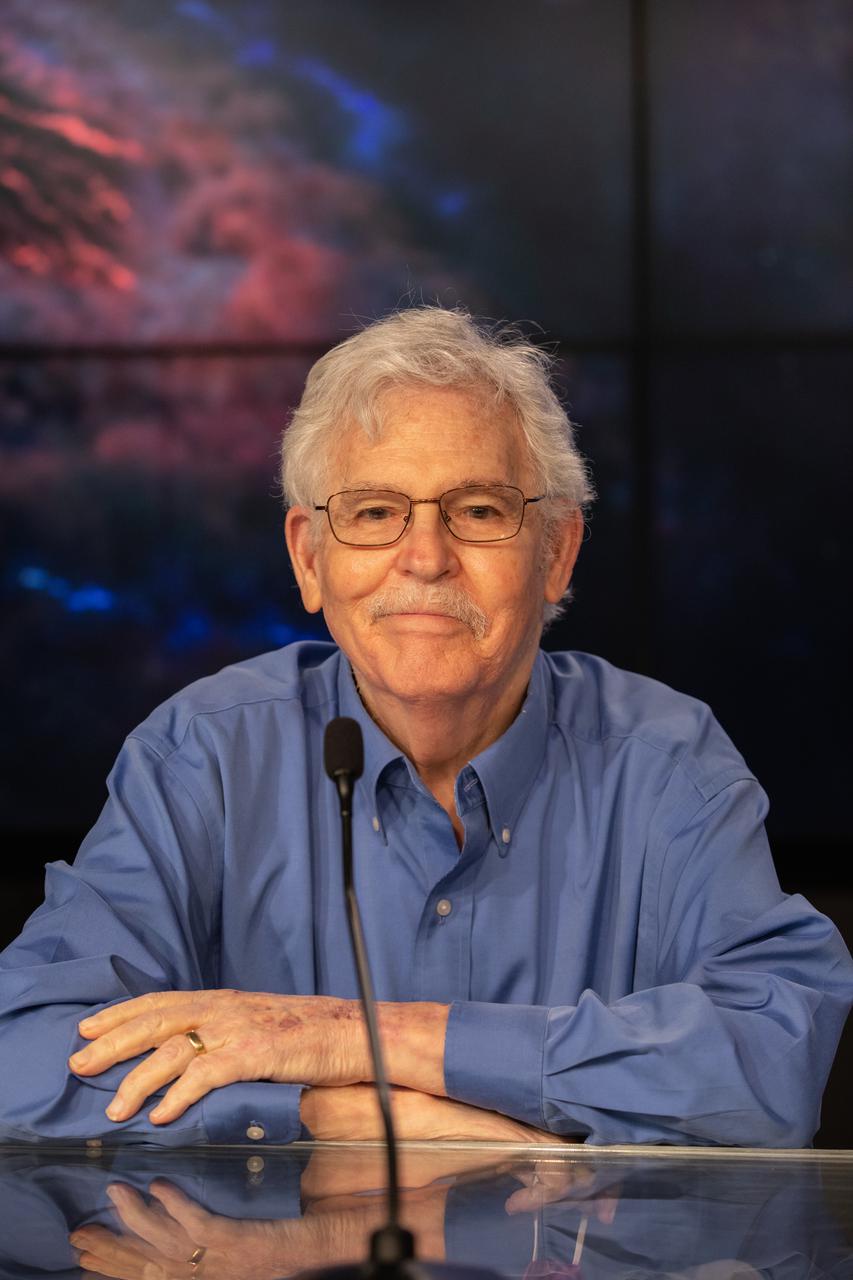

Martin Weisskopf, IXPE principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

The L-1011 aircraft carrying a Pegasus XL rocket with NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) attached takes off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The L-1011 will release the rocket over the Atlantic Ocean at 39,000 feet. After separation from the rocket, initial contact with the satellite will be made and the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado.
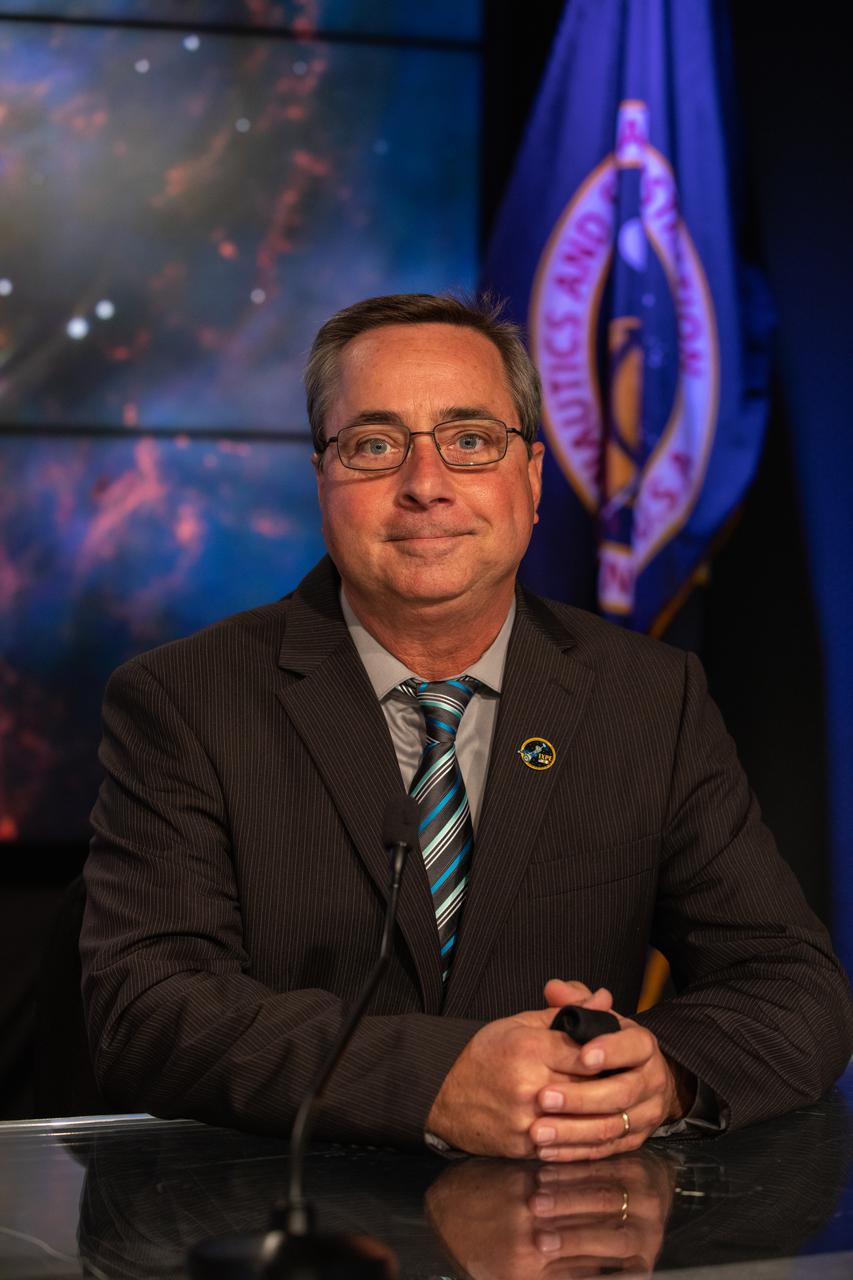

Mike McAleenan, 45th Weather Squadron, Space Launch Delta 45, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky over the Atlantic Ocean with a Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), attached underneath. The rocket will be dropped from the aircraft at 3:14 p.m. EST. Over the next few days, the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado. [Photo courtesy of Jeff Caplan, Langley Research]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-03pd0178/KSC-03pd0178~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky over the Atlantic Ocean with a Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), attached underneath. The rocket will be dropped from the aircraft at 3:14 p.m. EST. Over the next few days, the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado. [Photo courtesy of Jeff Caplan, Langley Research]

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After takeoff off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., the Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE), can be seen attached underneath and between the wheels of the L-1011 aircraft. The L-1011 will release the rocket over the Atlantic Ocean at 39,000 feet. After separation from the rocket, initial contact with the satellite will be made and the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado.
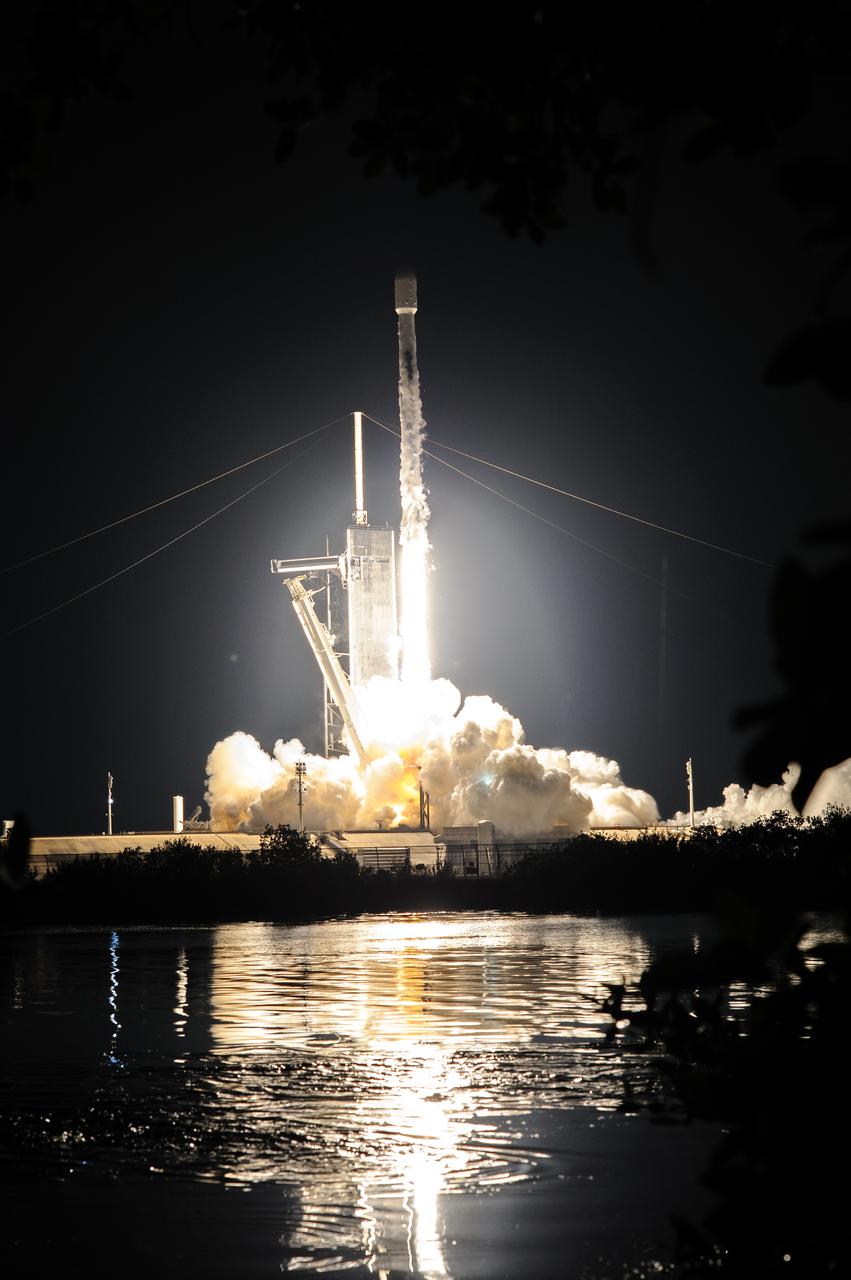

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
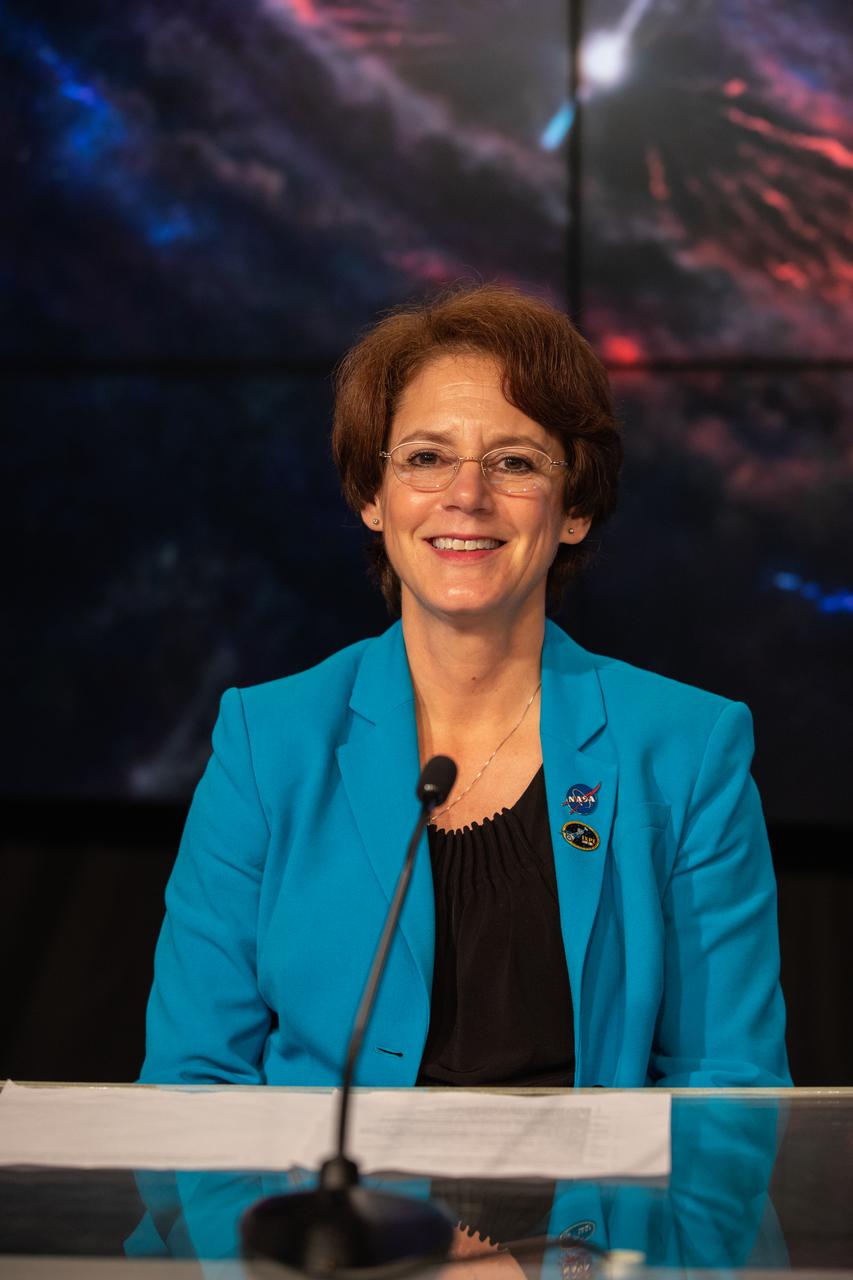

Sandra Connelly, deputy associate administrator for science, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
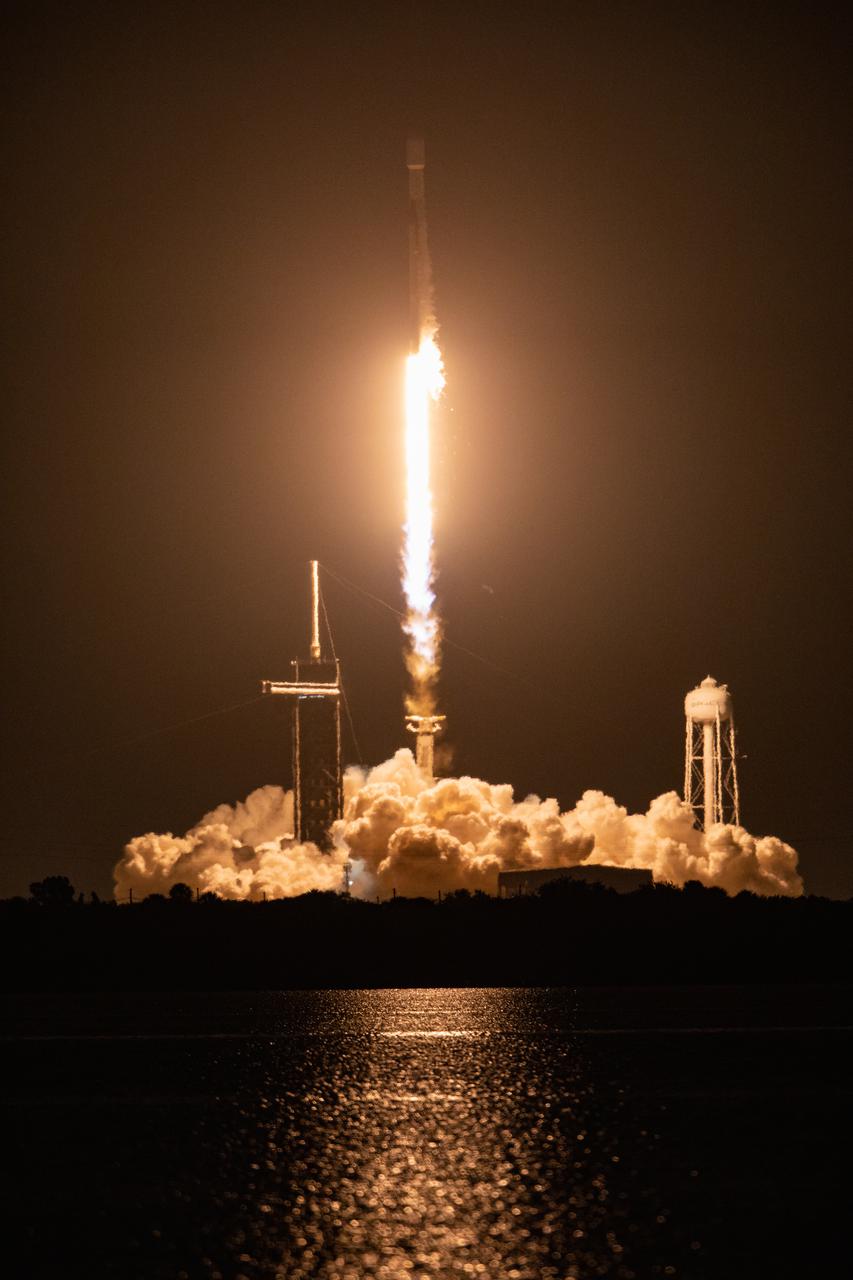

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
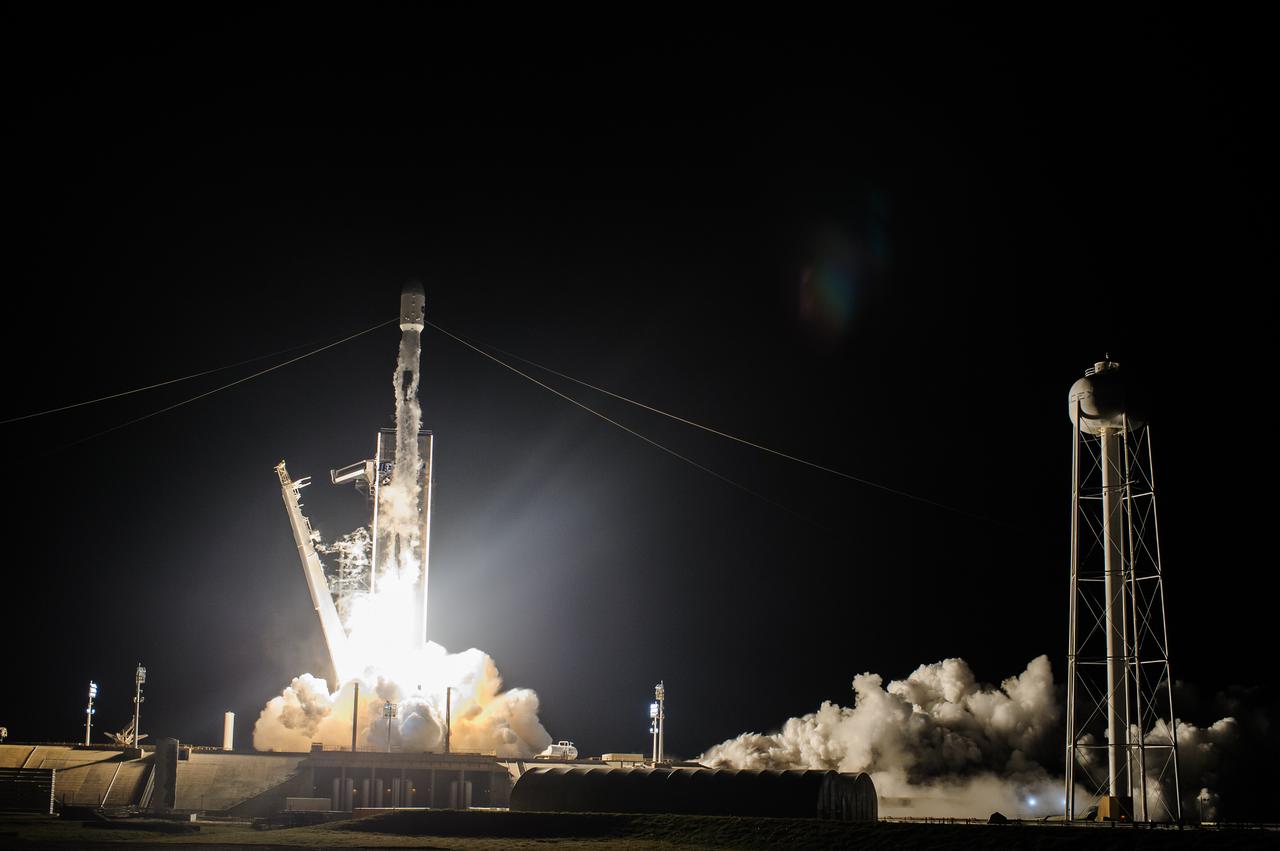

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
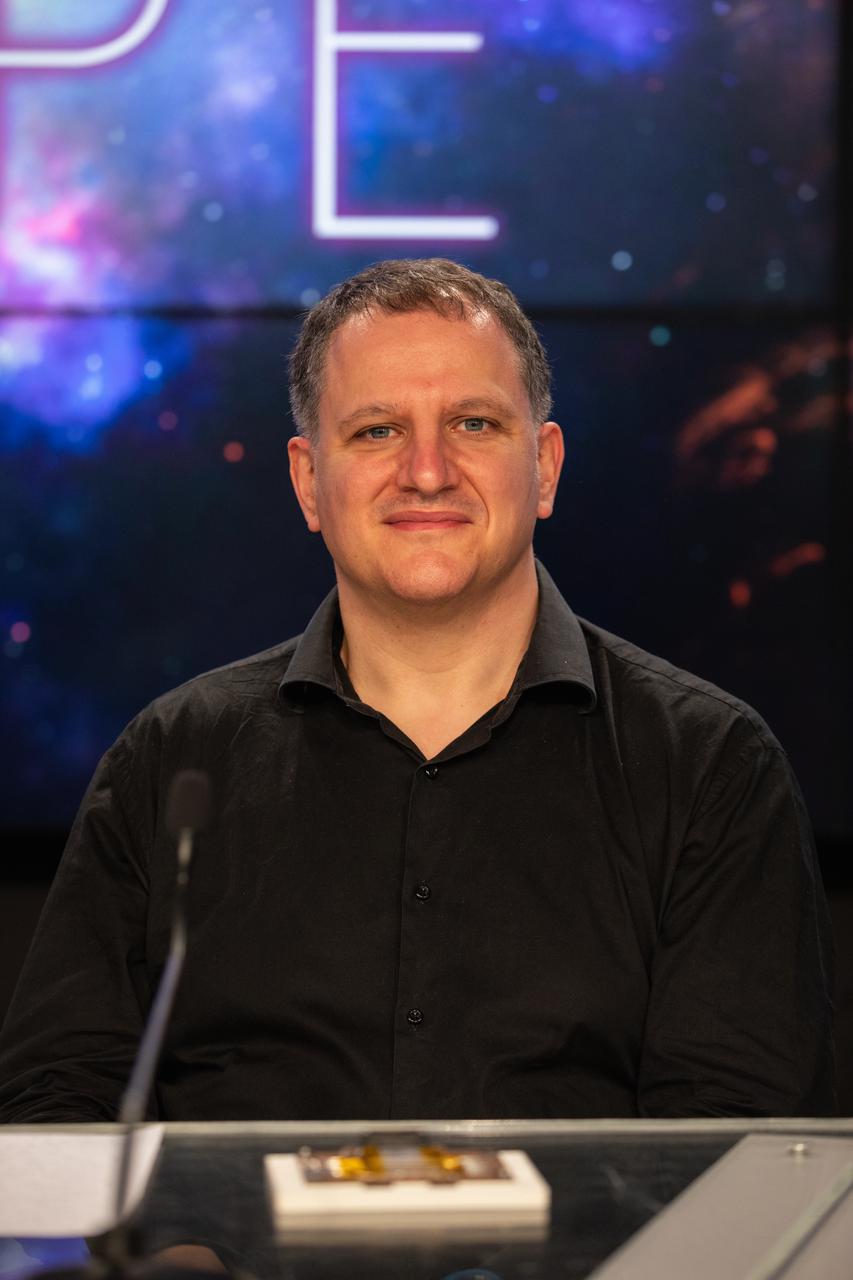

Luca Baldini, Italian co-principal investigator, National Institute for Nuclear Physics, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

The L-1011 aircraft carrying a Pegasus XL rocket with NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) attached takes off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The L-1011 will release the rocket over the Atlantic Ocean at 39,000 feet. After separation from the rocket, initial contact with the satellite will be made and the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- -- The L-1011 aircraft carrying a Pegasus XL rocket with NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) is seen after takeoff off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The L-1011 will release the rocket over the Atlantic Ocean at 39,000 feet. After separation from the rocket, initial contact with the satellite will be made and the mission team will insure that the spacecraft is functioning properly. The SORCE science instruments will then be turned on and their health verified. Approximately 21 days after launch, if all is going well, the instruments will start initial science data collection and calibration will begin. The spacecraft will study the Sun's influence on our Earth and will measure from space how the Sun affects the Earth's ozone layer, atmospheric circulation, clouds, and oceans. This mission is a joint partnership between NASA and the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado.
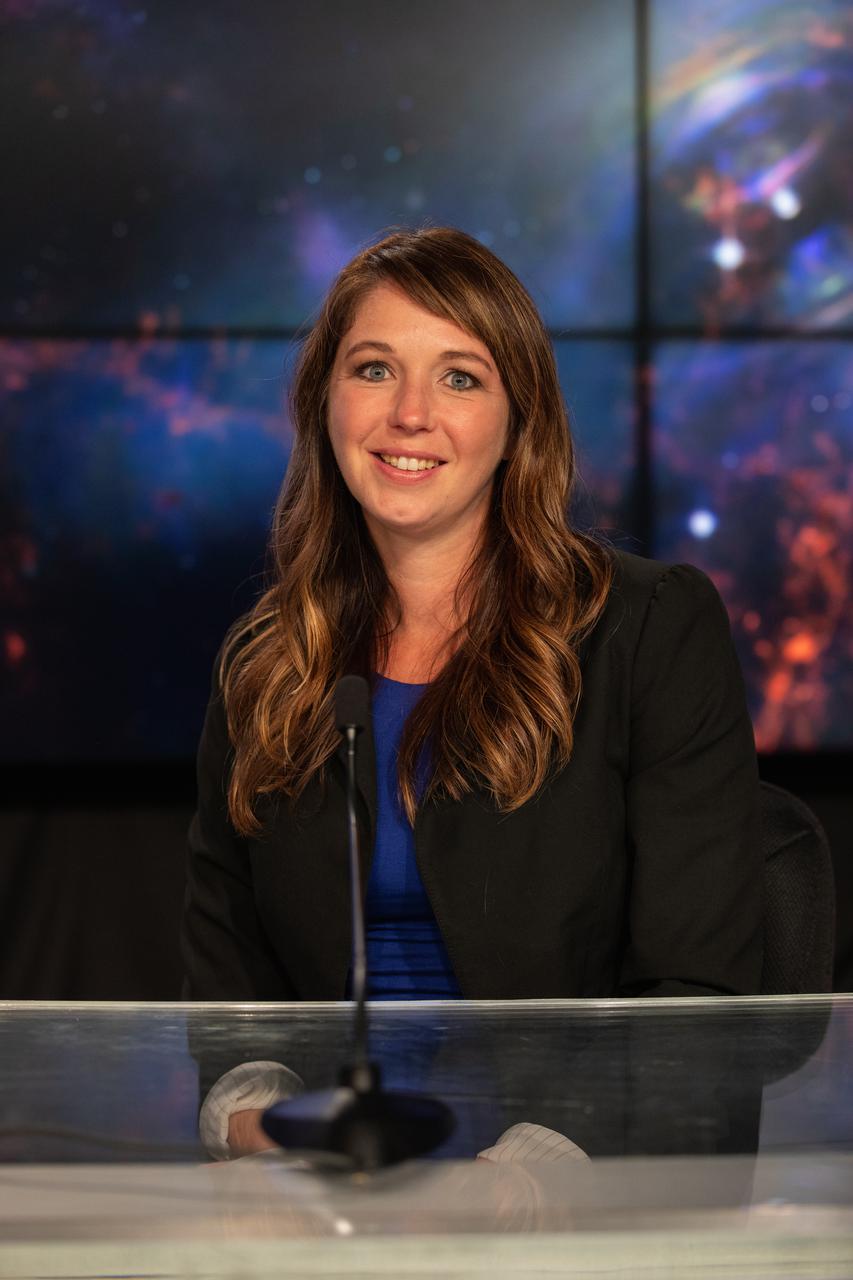

MacKenzie Ferrie, IXPE program manager, Ball Aerospace, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
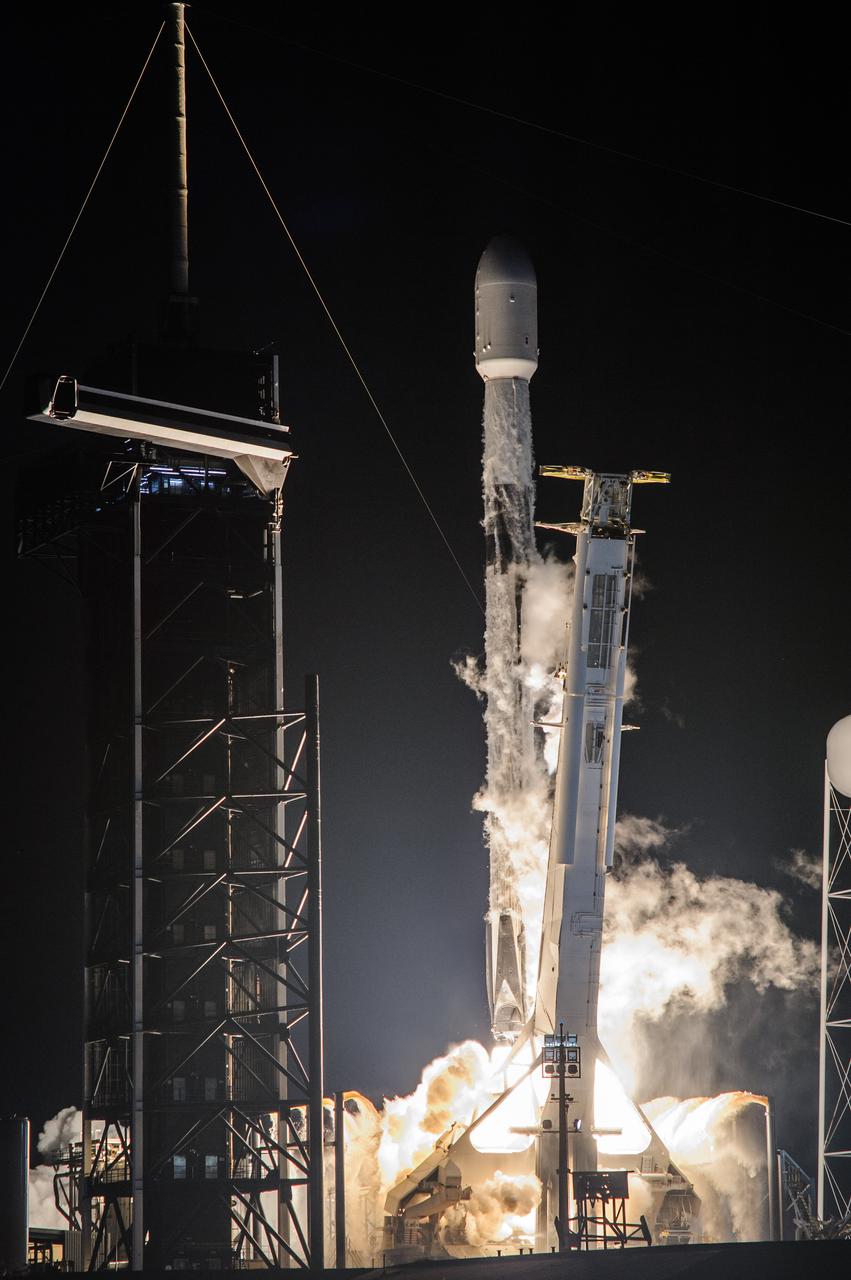

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
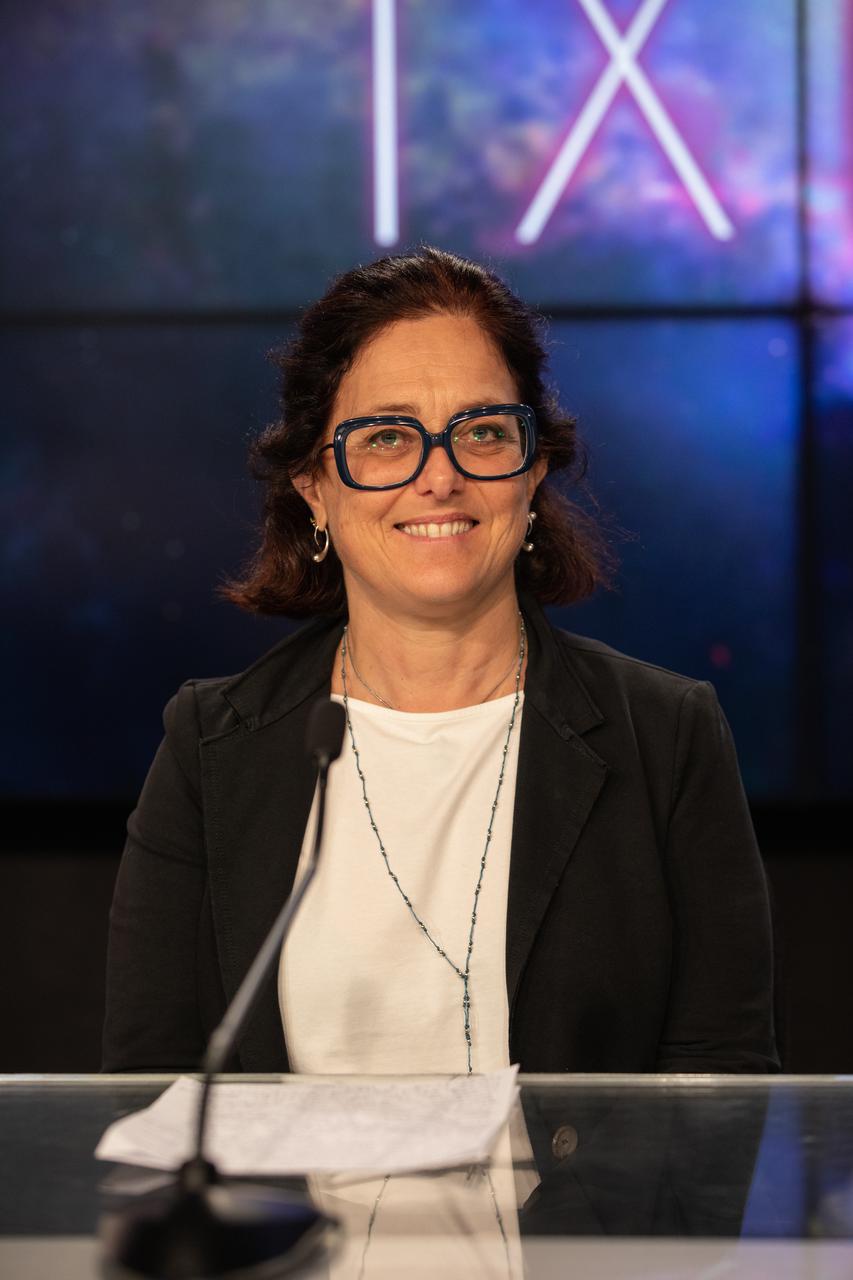

Elisabetta Cavazzuti, ASI IXPE program manager, Italian Space Agency, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
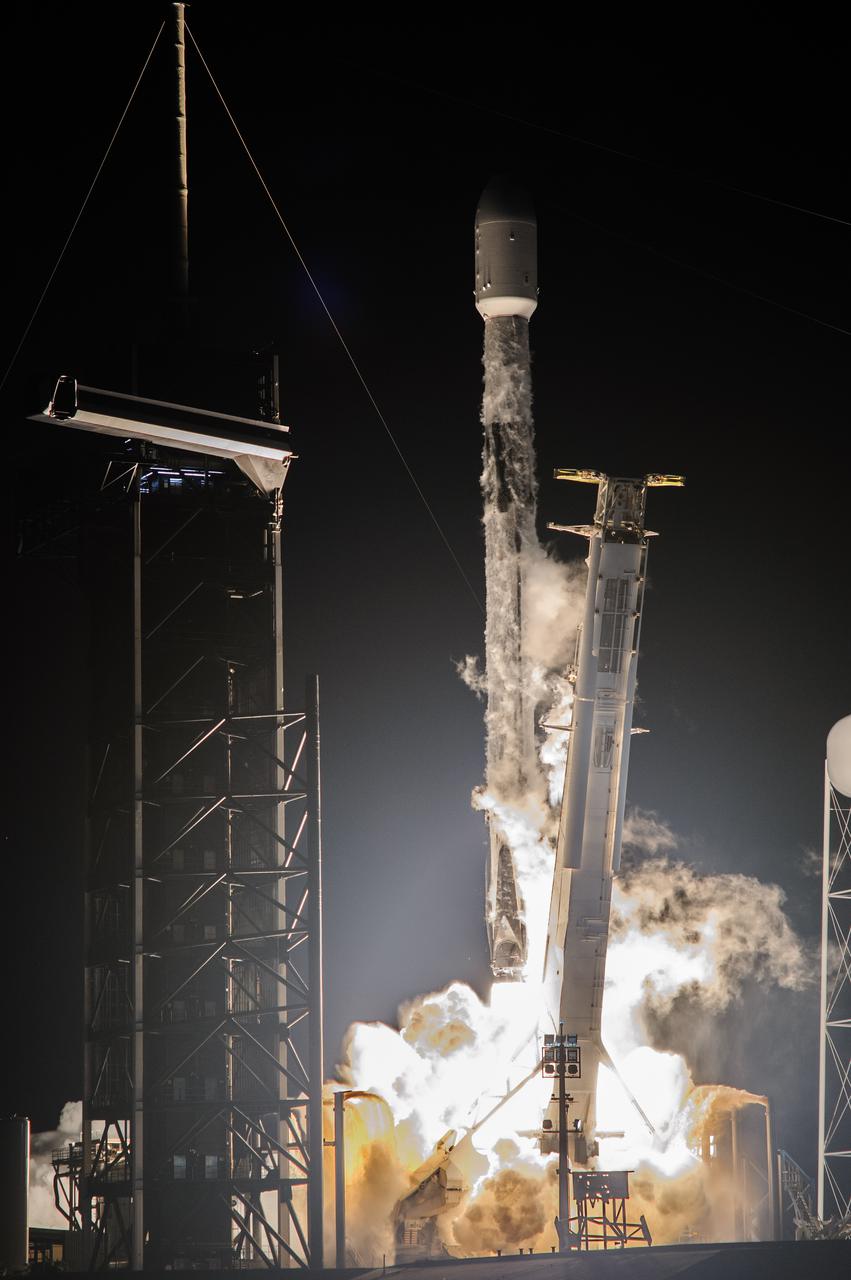

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
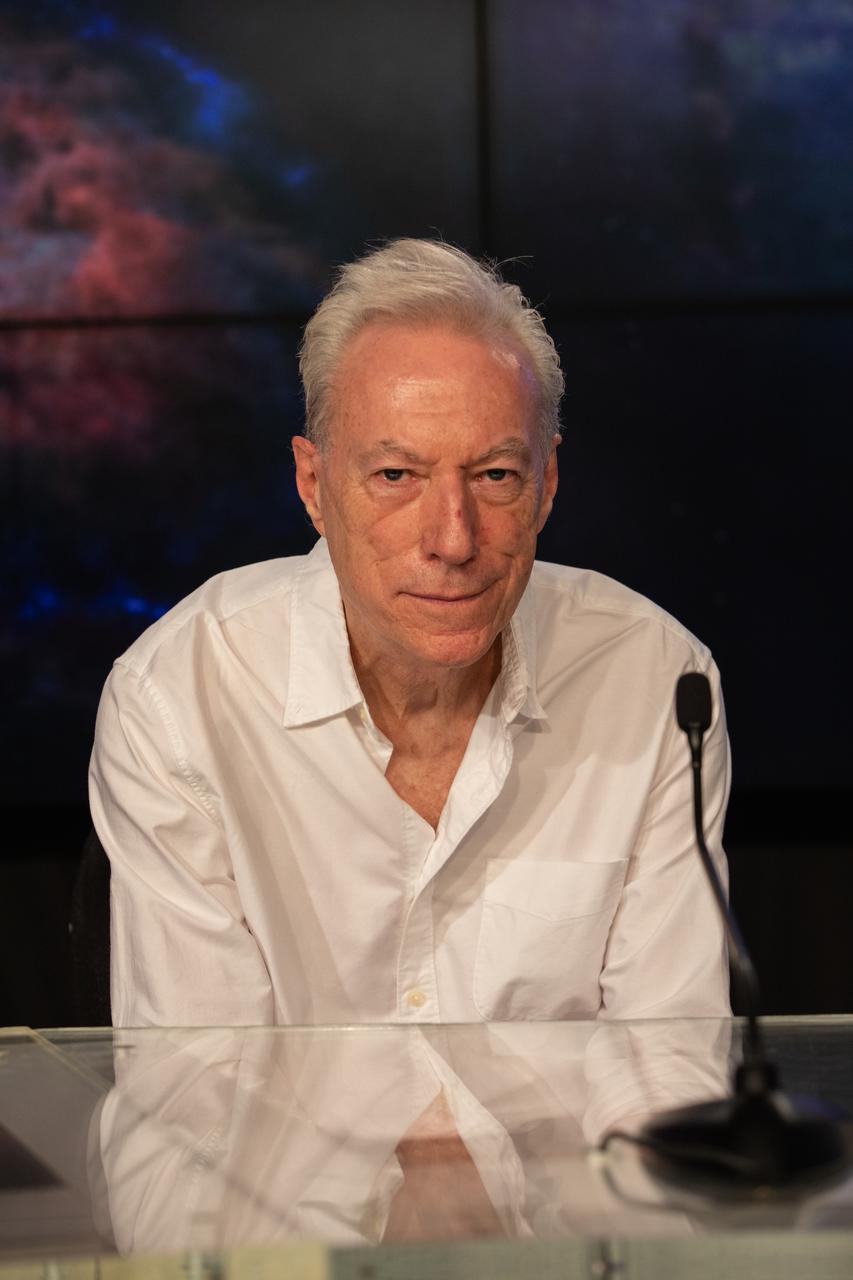

Brian Ramsey, deputy principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
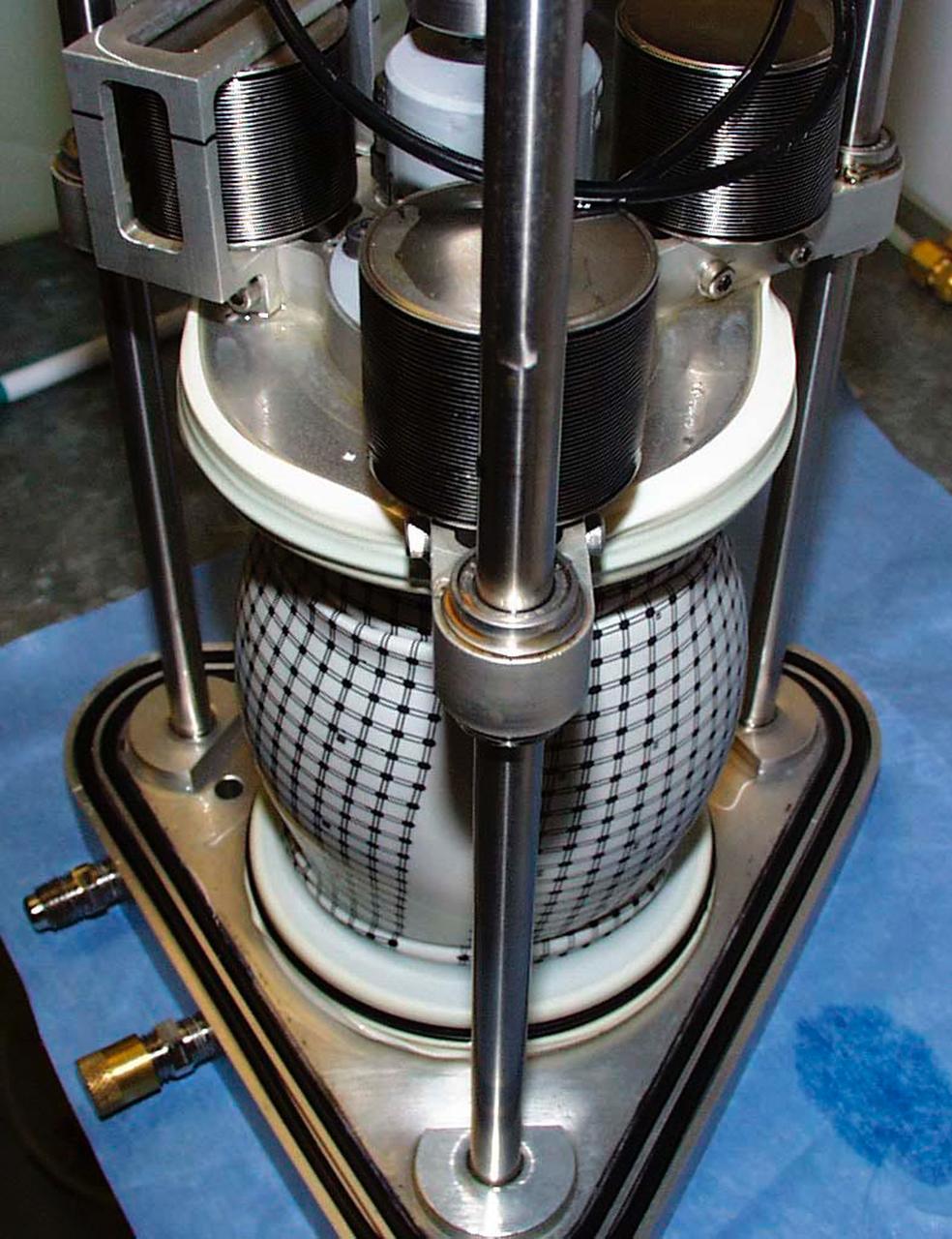

A test cell for Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is tested for long-term storage with water in the system as plarned for STS-107. This view shows the compressed sand column with the protective water jacket removed. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder