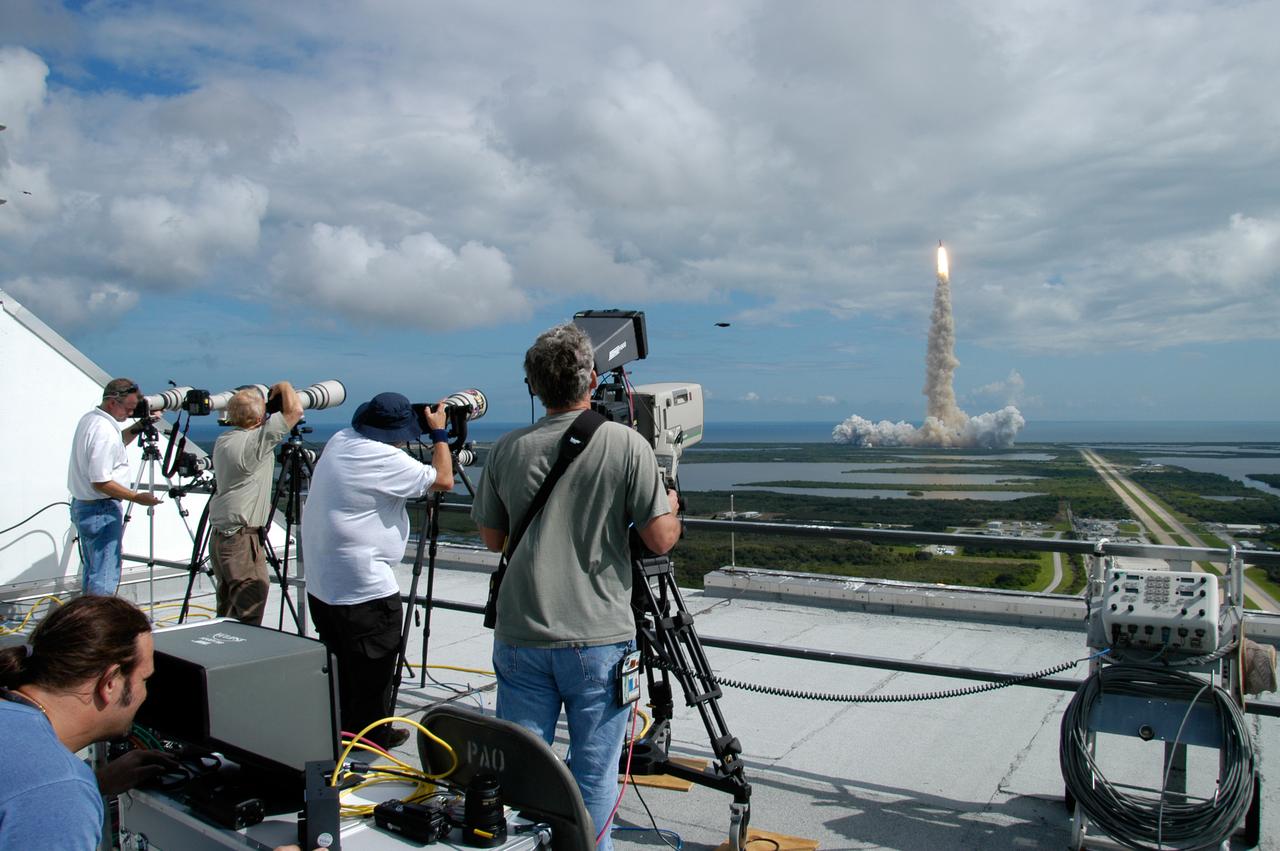

From the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, media photographers capture the launch of space shuttle Discovery as it soars from its seaside launch pad. Liftoff was on time at 11:38:19 a.m. EDT. Discovery carries the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day STS-120 mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them. Discovery is expected to complete its mission and return home at 4:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 6.

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

Transformer Movie Activities Around Press Site, Shot from VAB Roof

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

ML is rolled to Pad 39B, shot from VAB roof

ML is rolled to Pad 39B, shot from VAB roof
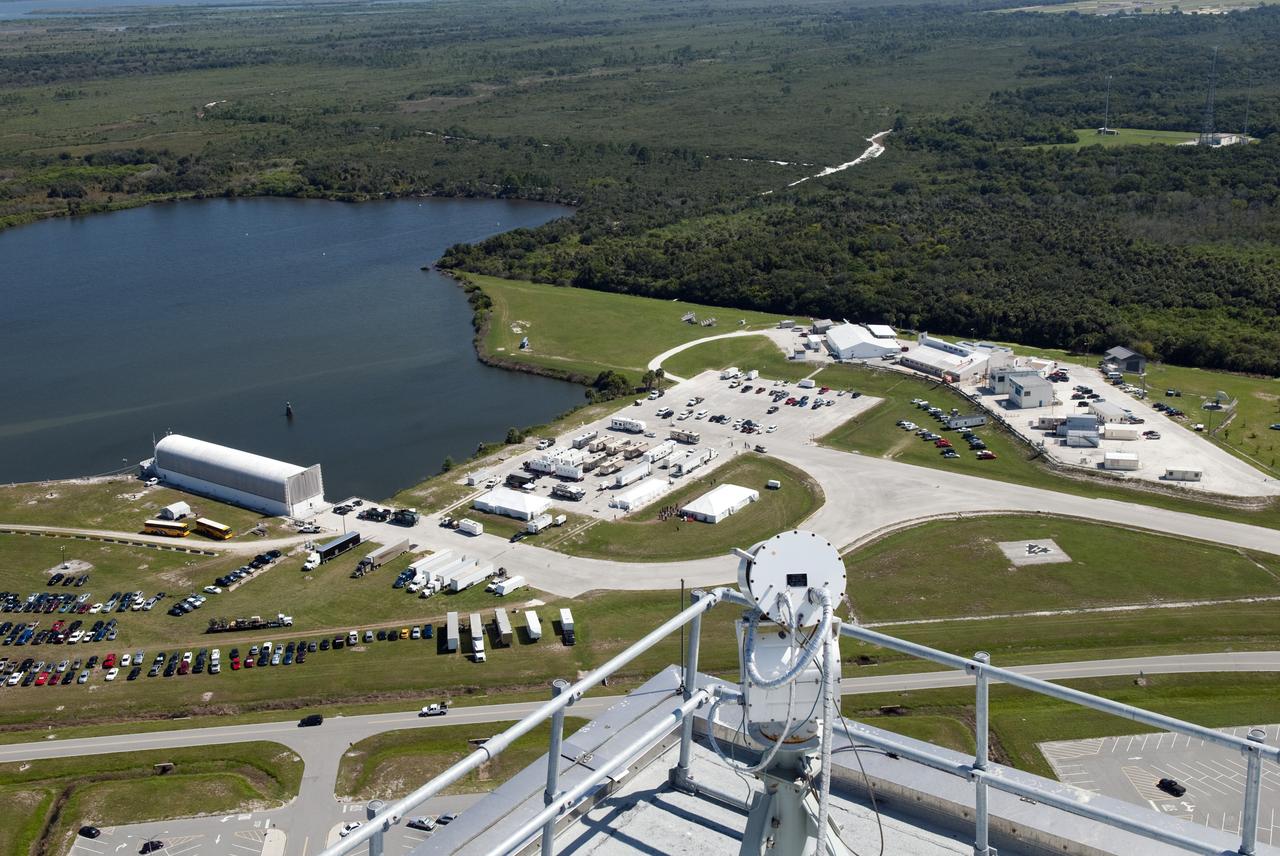

Transformer Movie Activities Around Press Site, Shot from VAB Roof
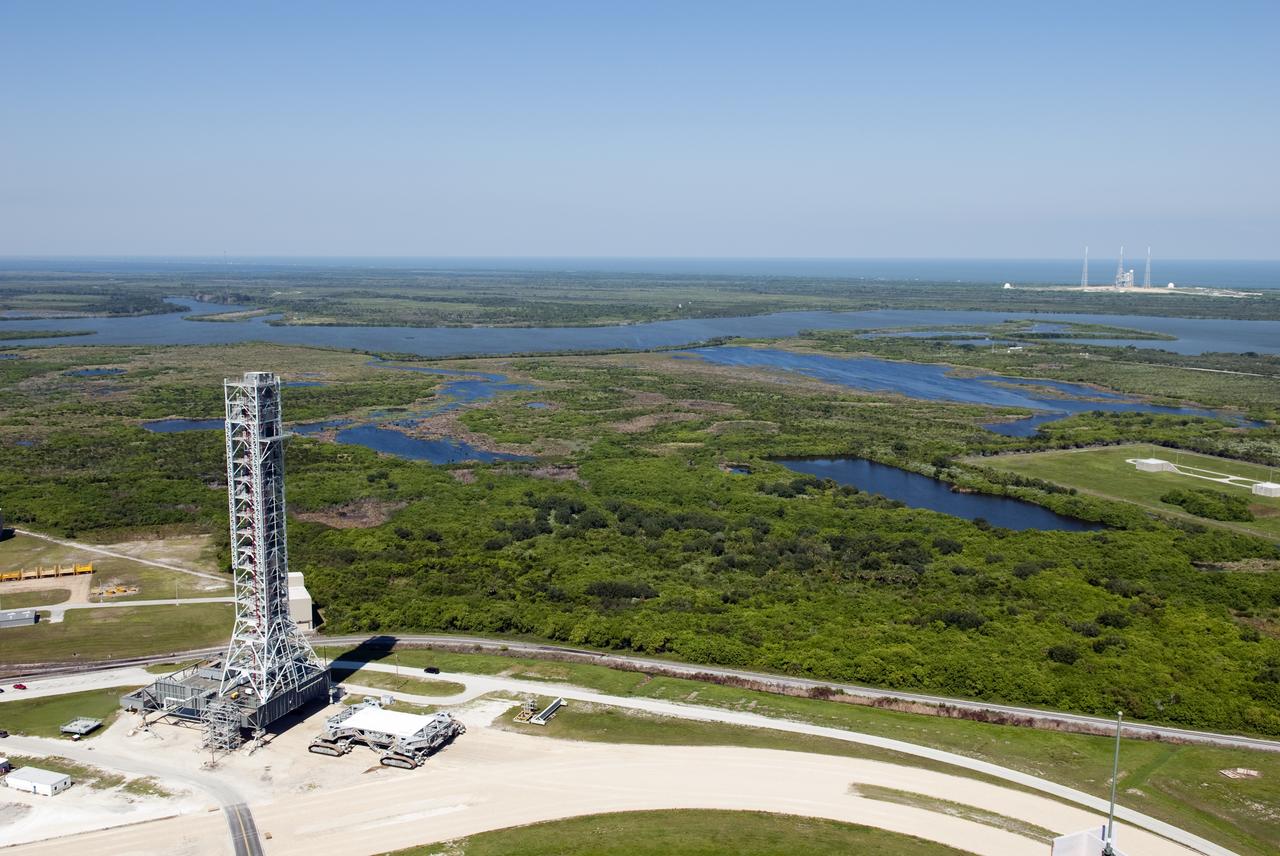

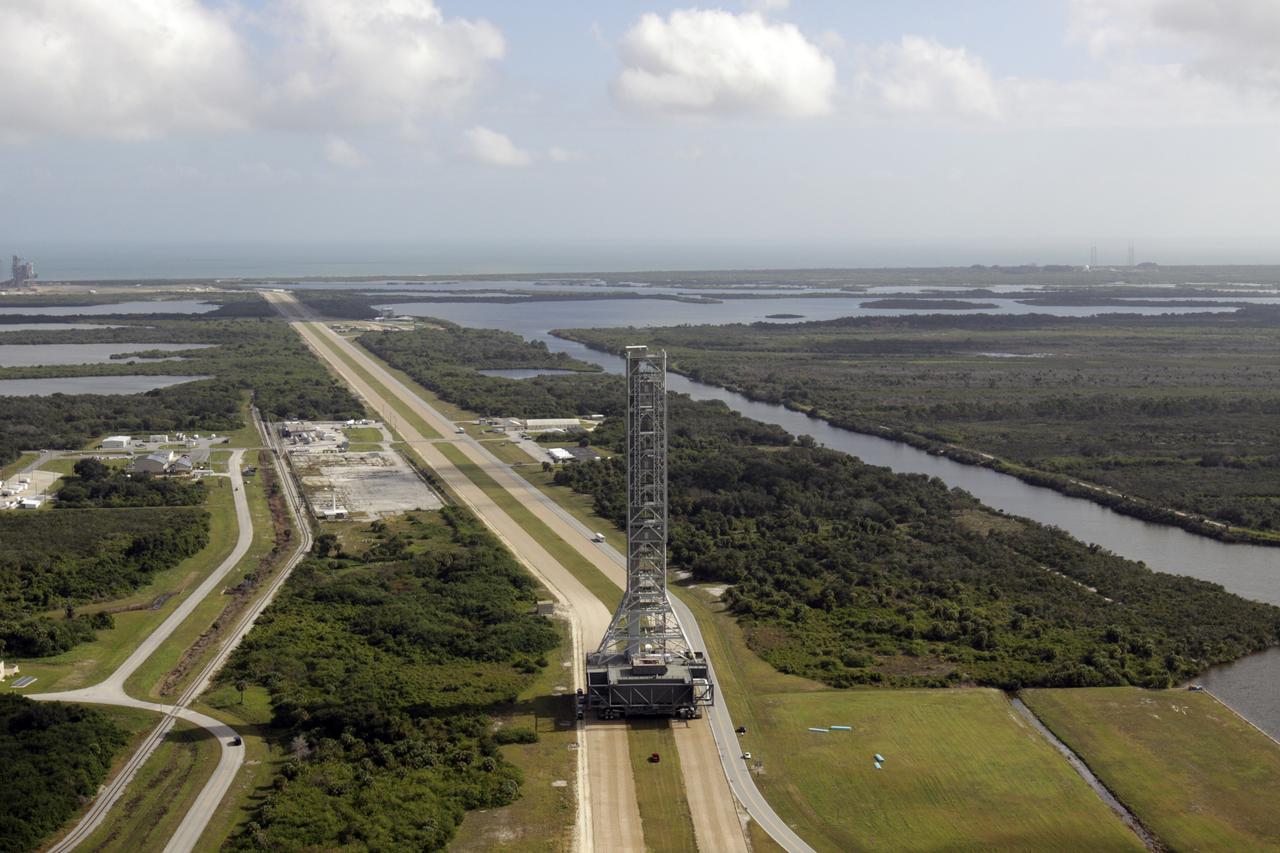
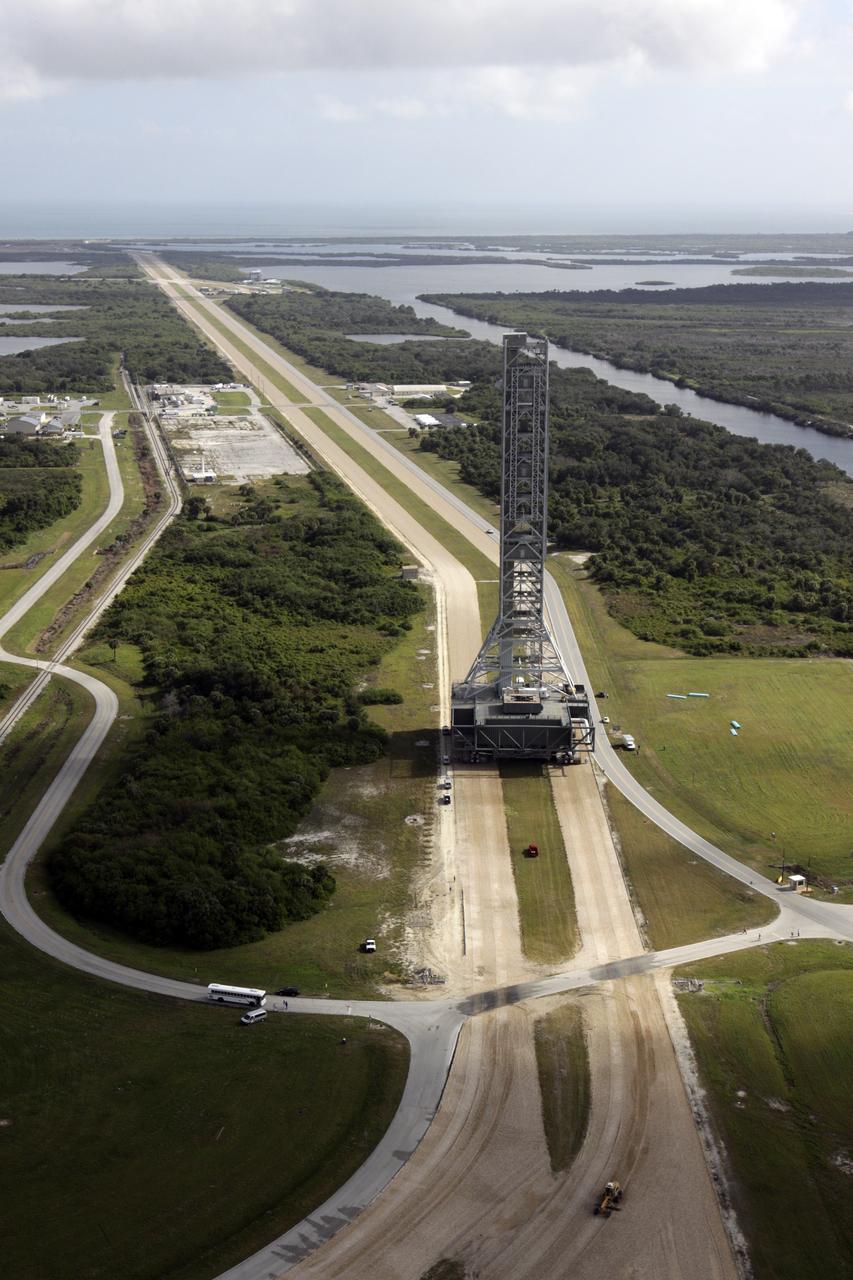
Mobile Launcher in East Park Site, Shot from VAB Roof
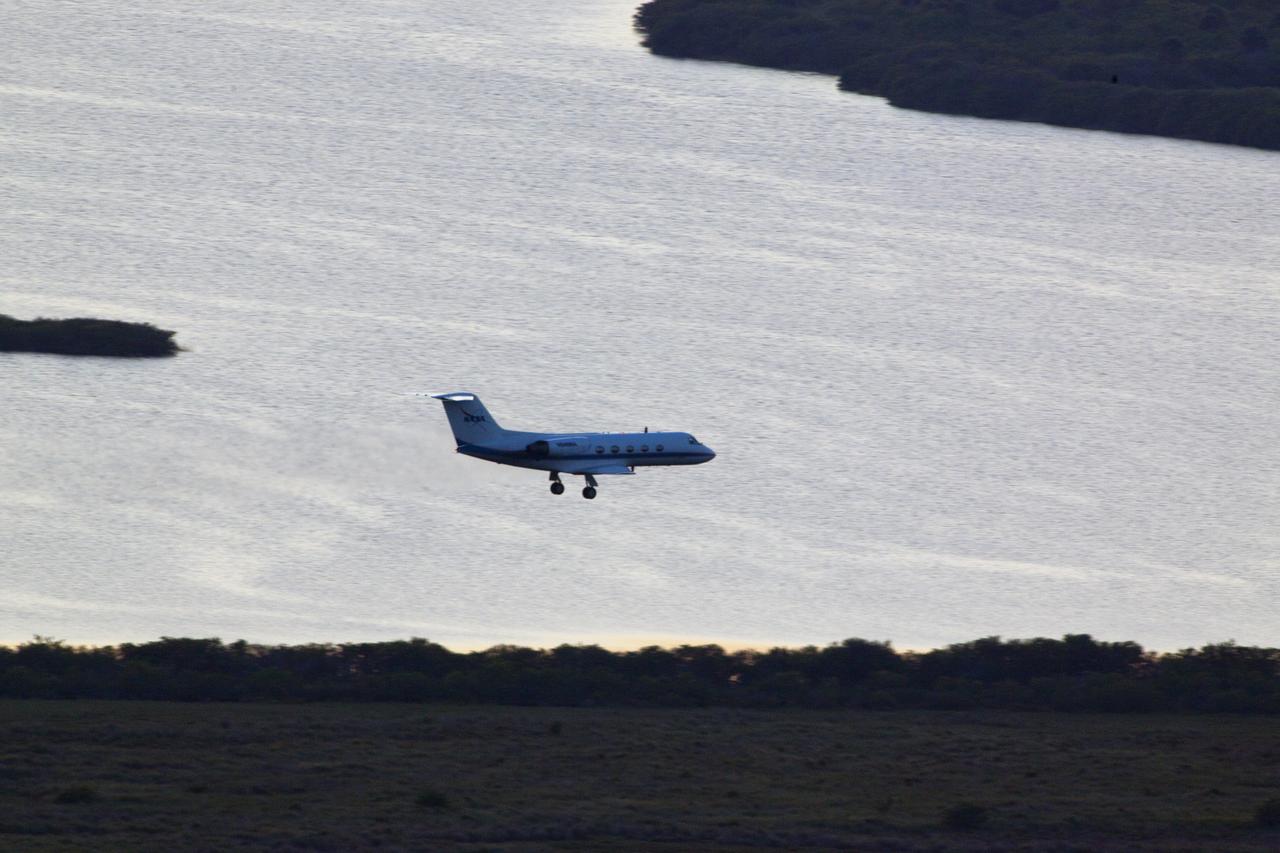

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF

ML is rolled to Pad 39B, shot from VAB roof
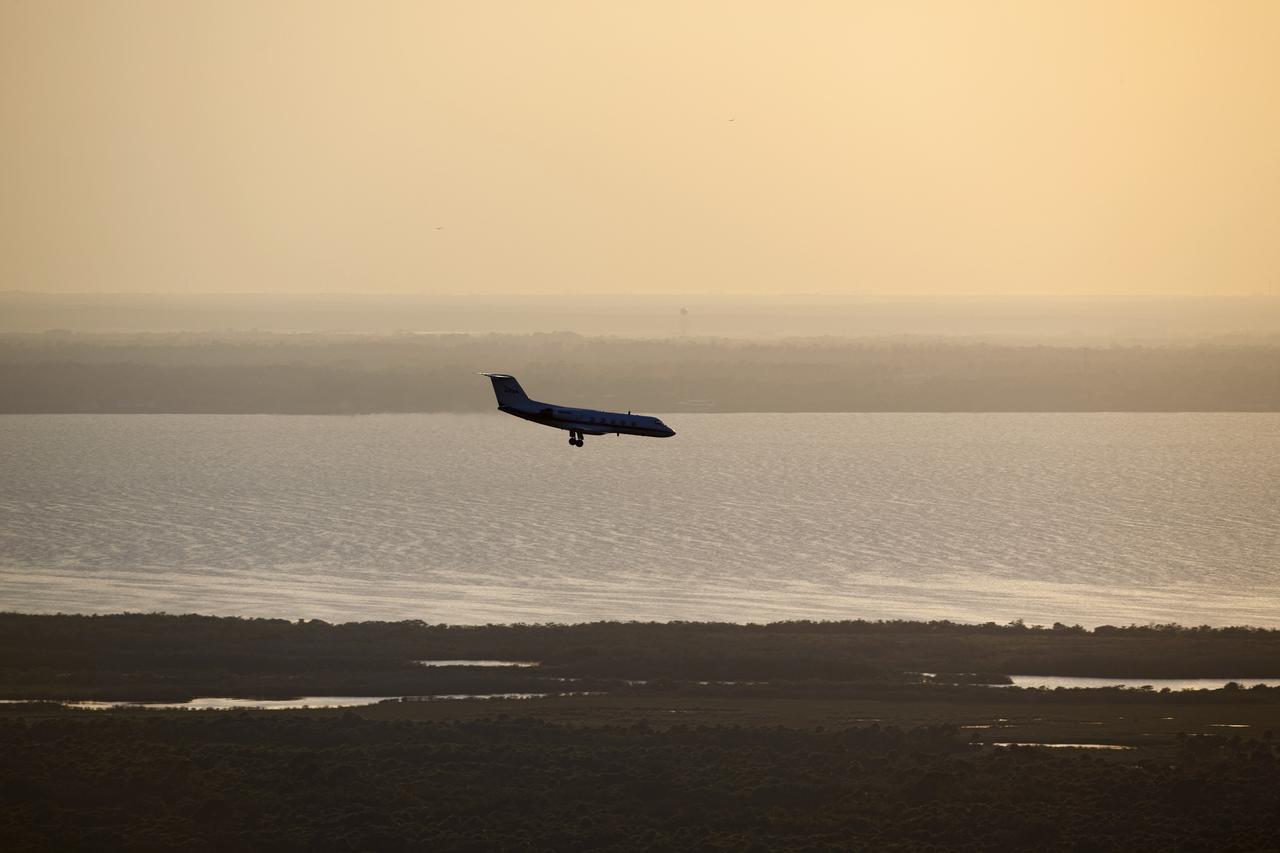

STS-133 TCDT - STA'S WITH MEDIA AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF
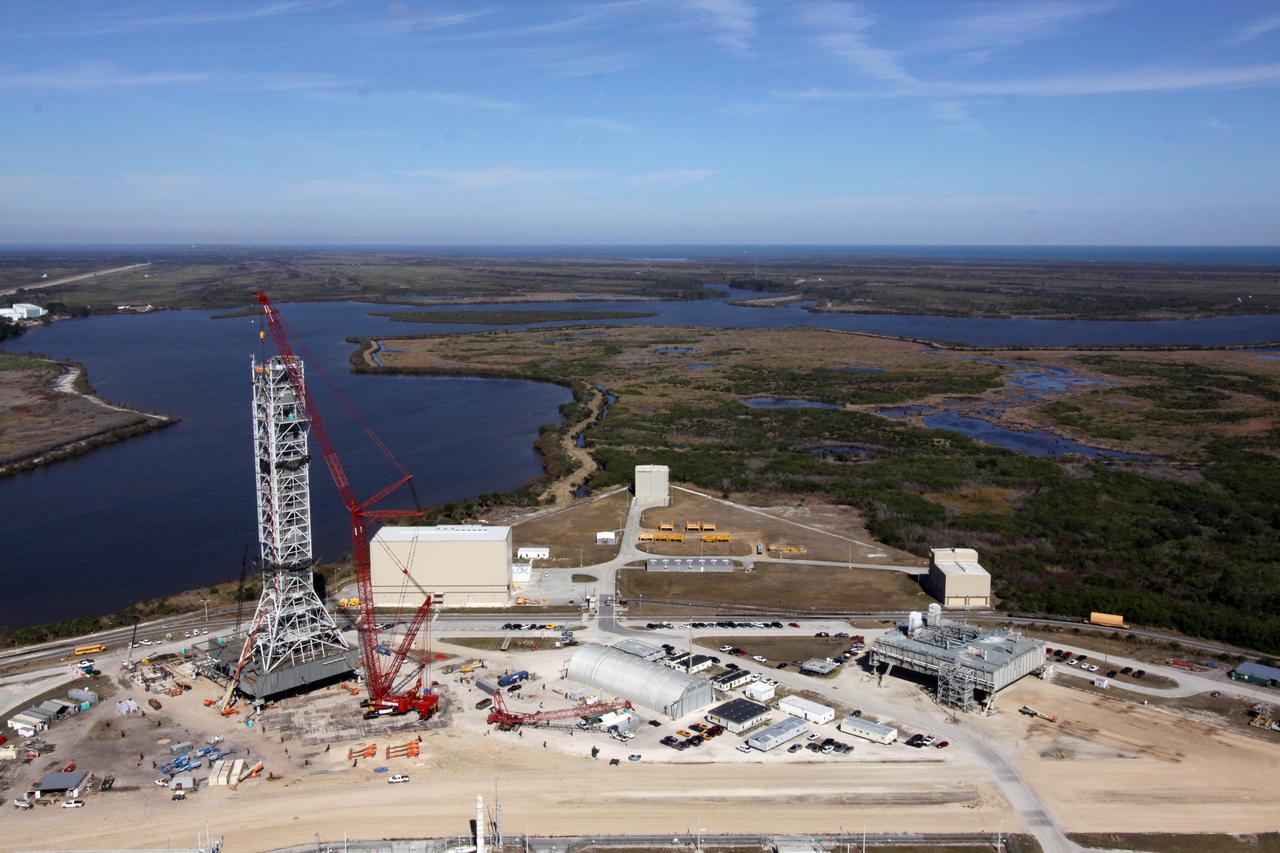

CONSTELLATION - NEW MLP CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS - 10TH SEGMENT TOWER LIFT - AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF
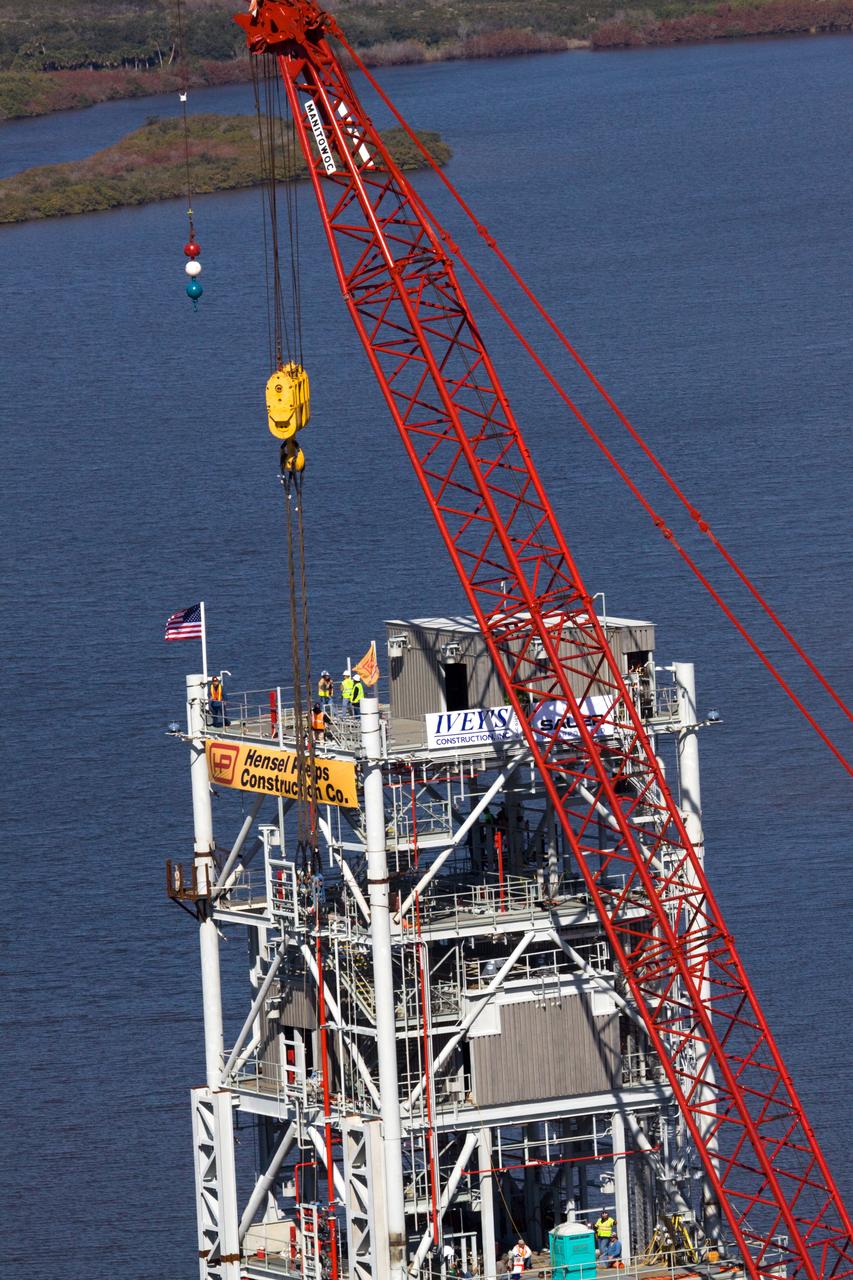

CONSTELLATION - NEW MLP CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS - 10TH SEGMENT TOWER LIFT - AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF
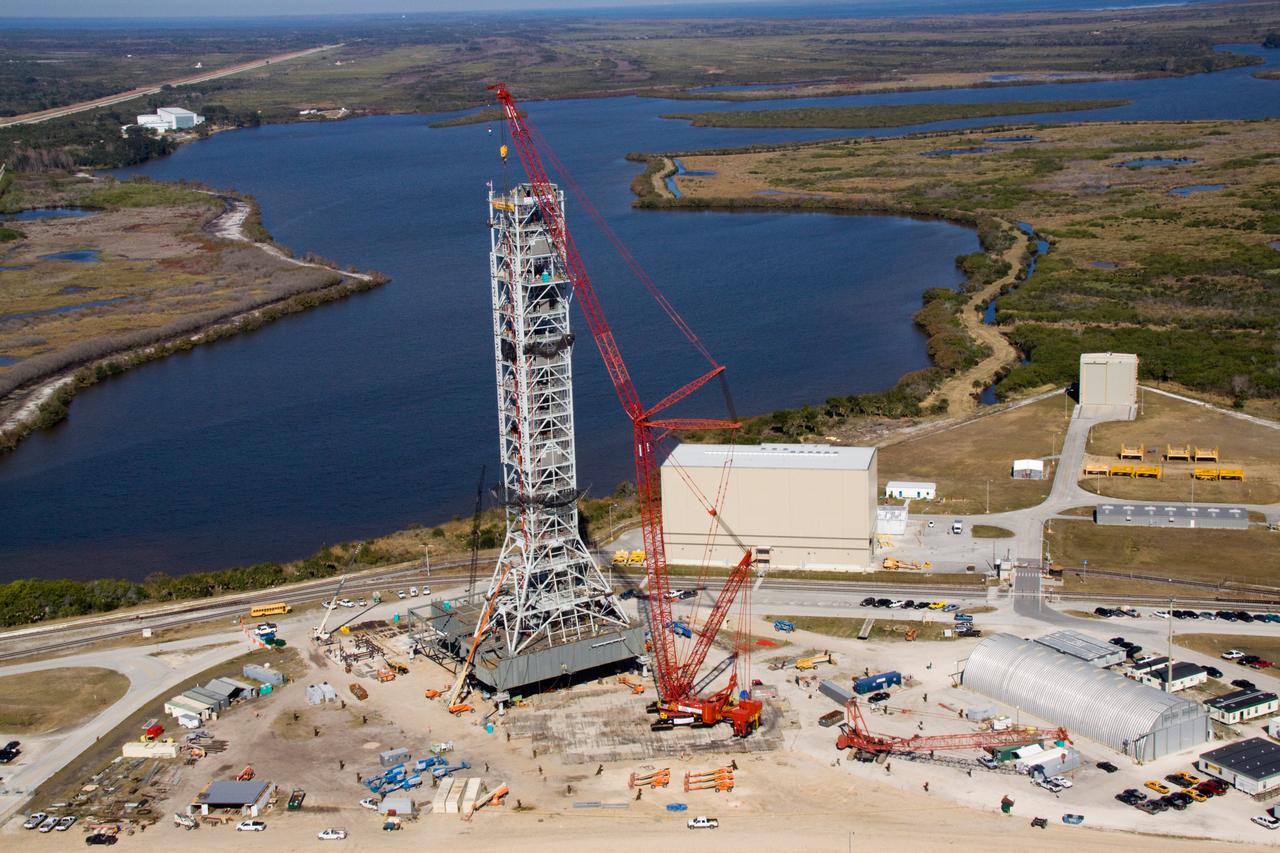

CONSTELLATION - NEW MLP CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS - 10TH SEGMENT TOWER LIFT - AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF
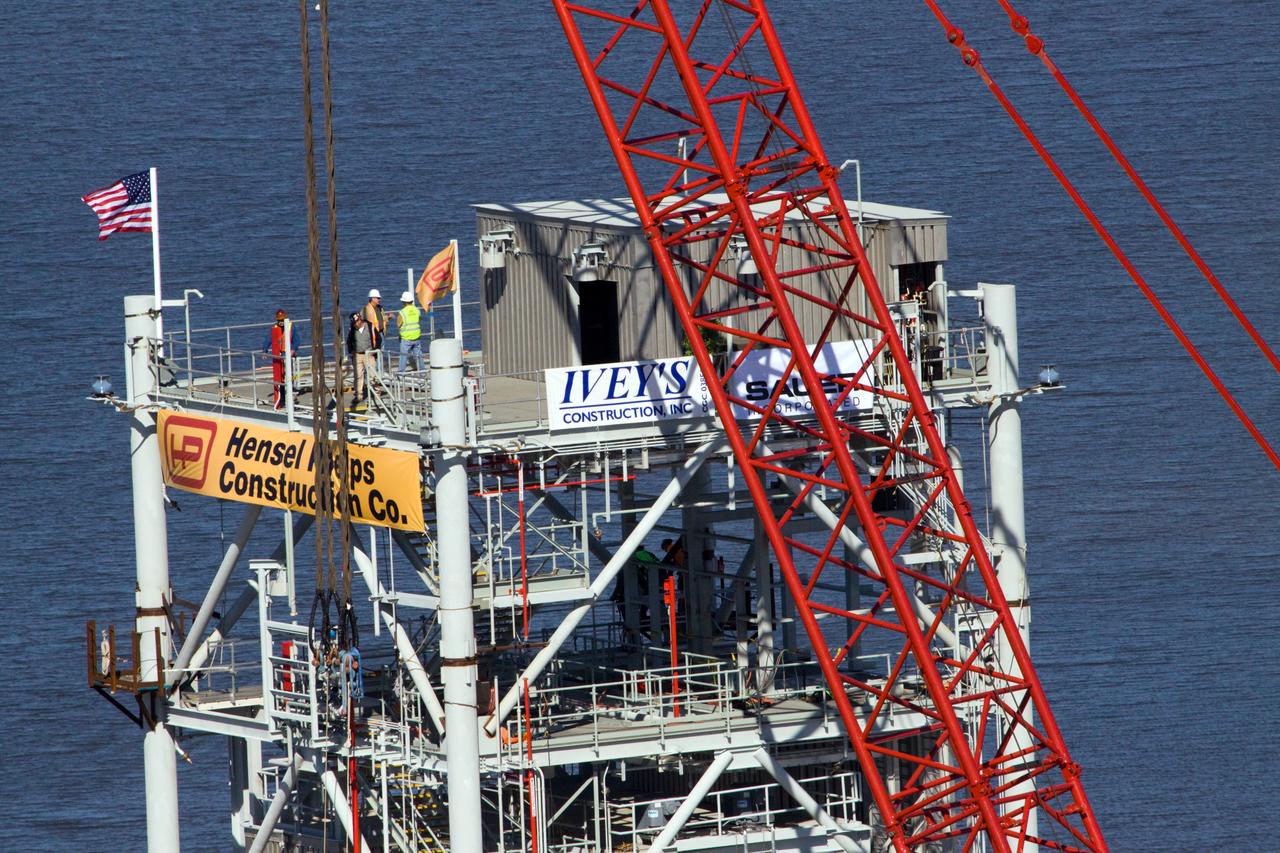

CONSTELLATION - NEW MLP CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS - 10TH SEGMENT TOWER LIFT - AS SEEN FROM VAB ROOF
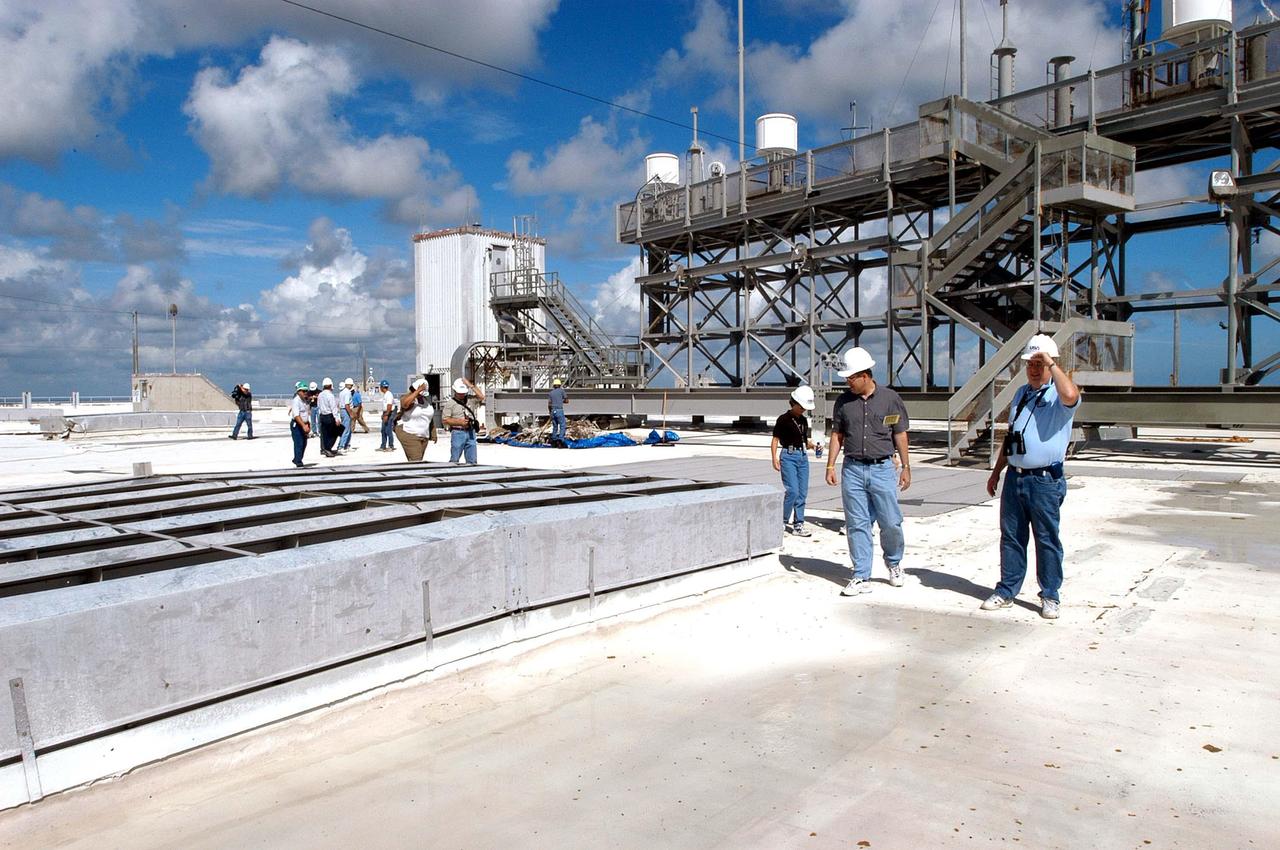

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center tour the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) a week after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. The VAB lost 820, 4- x 16-foot panels from the side walls, or more than 52,000 square feet of its surface.
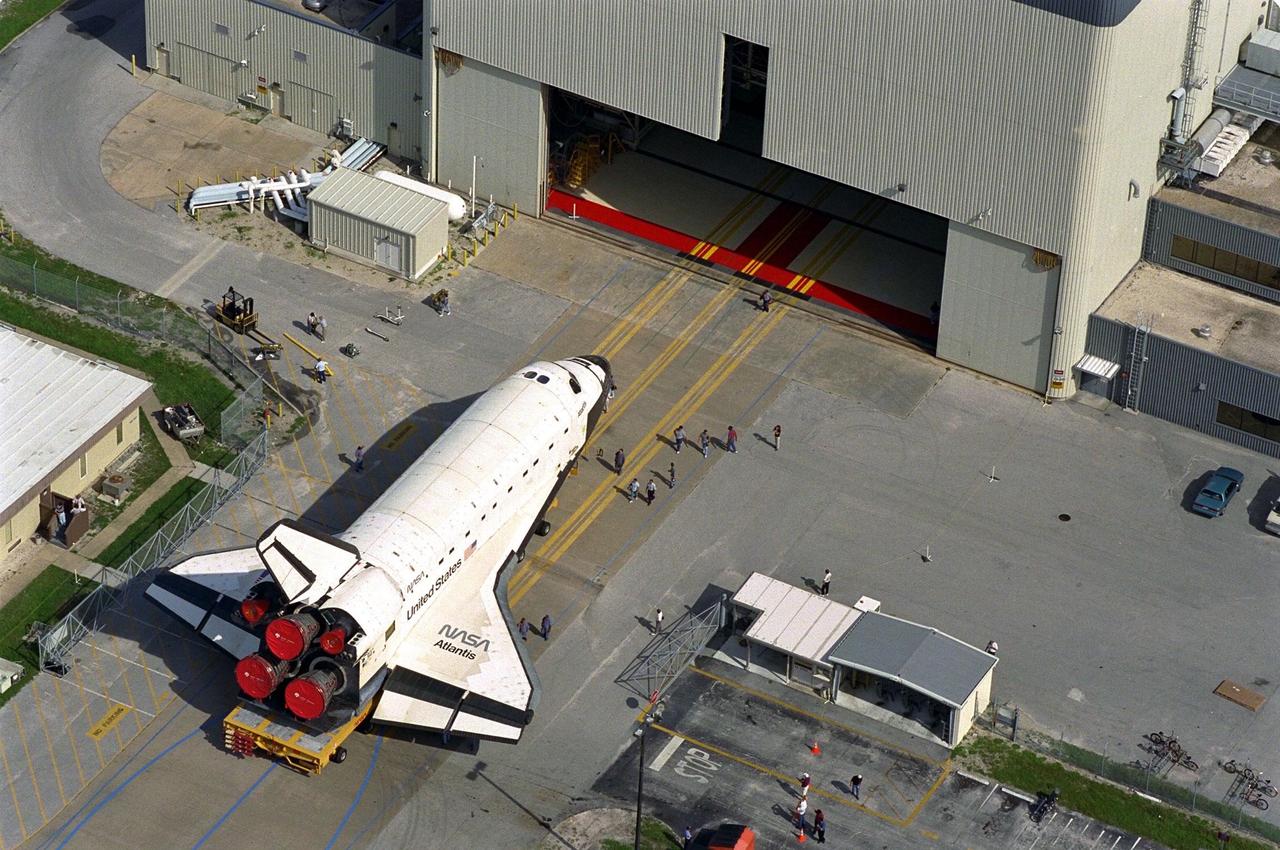

Carried atop an orbiter transporter, the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis rolls out of Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, in background, en route to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). This photo was taken from the roof of the VAB. The "rollover" of the orbiter is one of the prelaunch milestones. Atlantis is being readied for the next mission, STS-86, which is targeted for a September launch. STS-86 will be the seventh of nine planned dockings of the Space Shuttle orbiter with the Russian Space Station Mir
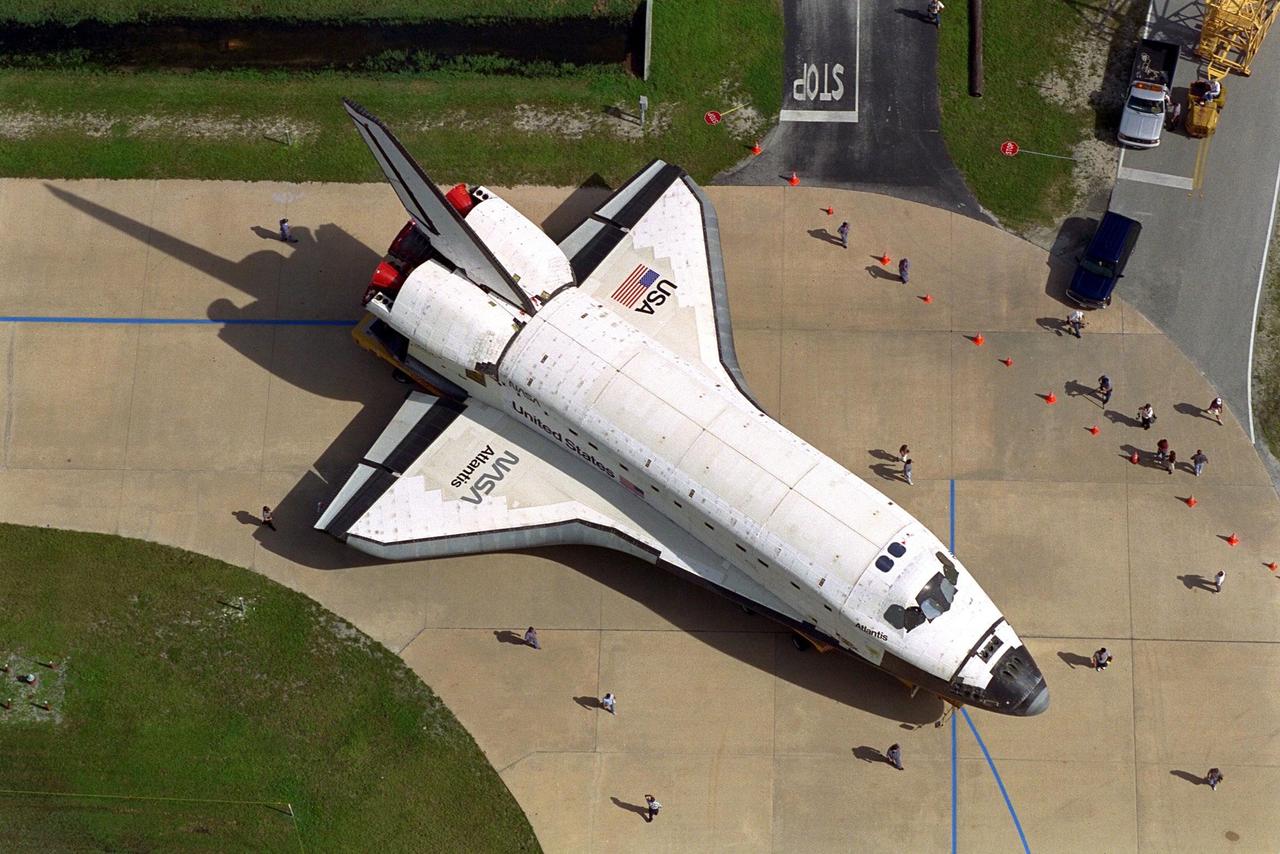

Carried atop an orbiter transporter, the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis makes the short journey from Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). This photo was taken from the roof of the 525-foot-tall VAB. The "rollover" of the orbiter is one of the prelaunch milestones. Atlantis is being readied for the next mission, STS-86, which is targeted for a September launch. STS-86 will be the seventh of nine planned dockings of the Space Shuttle orbiter with the Russian Space Station Mir
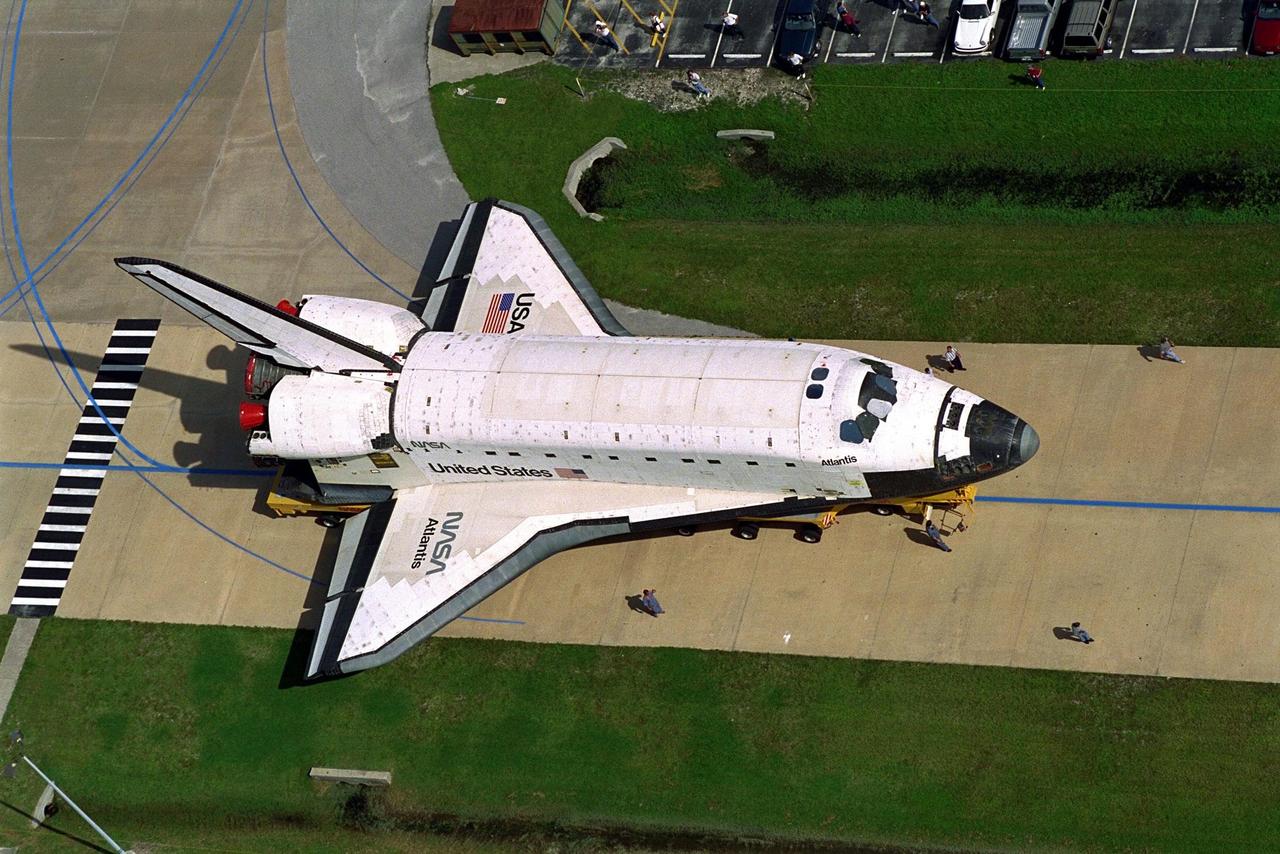

Carried atop an orbiter transporter, the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis makes the short journey from Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). This photo was taken from the roof of the 525-foot-tall VAB. The "rollover" of the orbiter is one of the prelaunch milestones. Atlantis is being readied for the next mission, STS-86, which is targeted for a September launch. STS-86 will be the seventh of nine planned dockings of the Space Shuttle orbiter with the Russian Space Station Mir
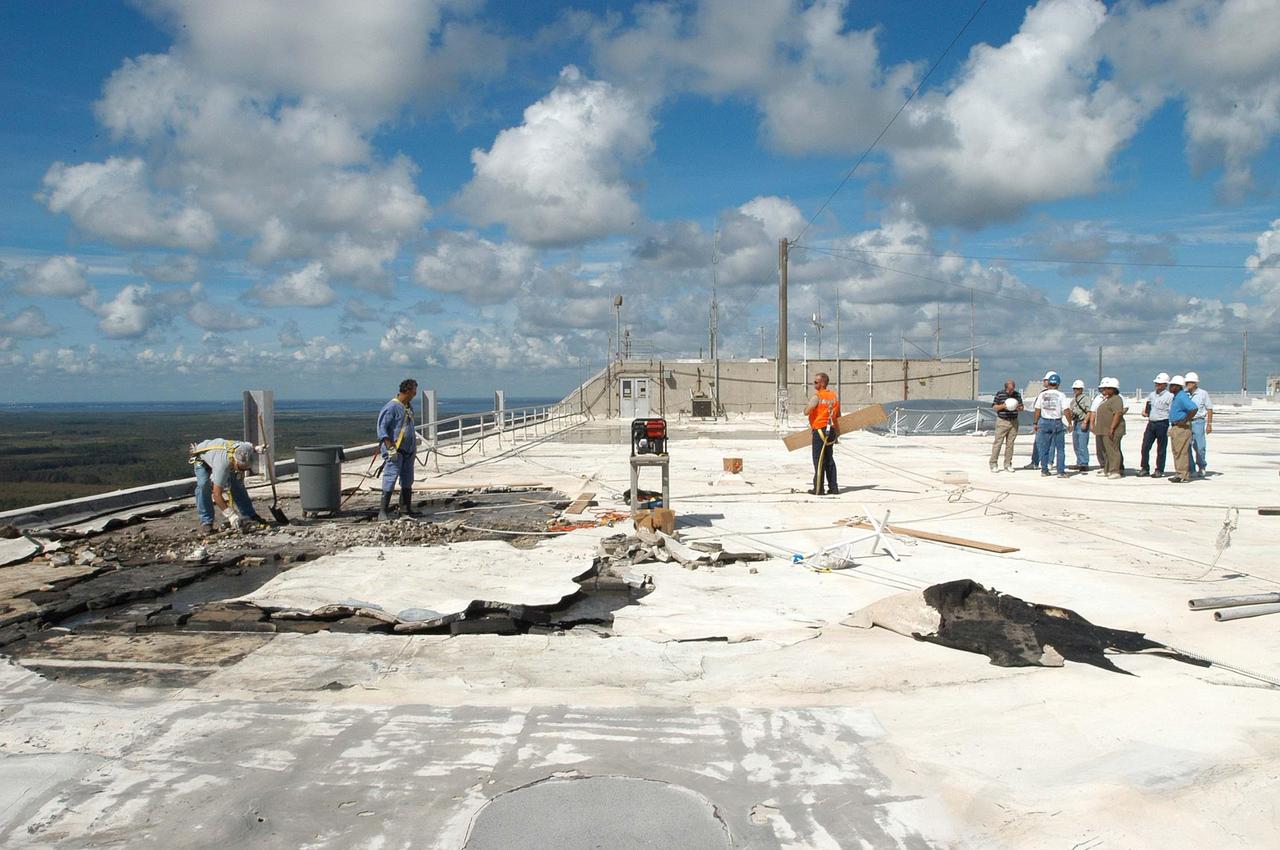

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center look at damage on the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) a week after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. The VAB lost 820, 4- x 16-foot panels from the side walls, or more than 52,000 square feet of its surface.
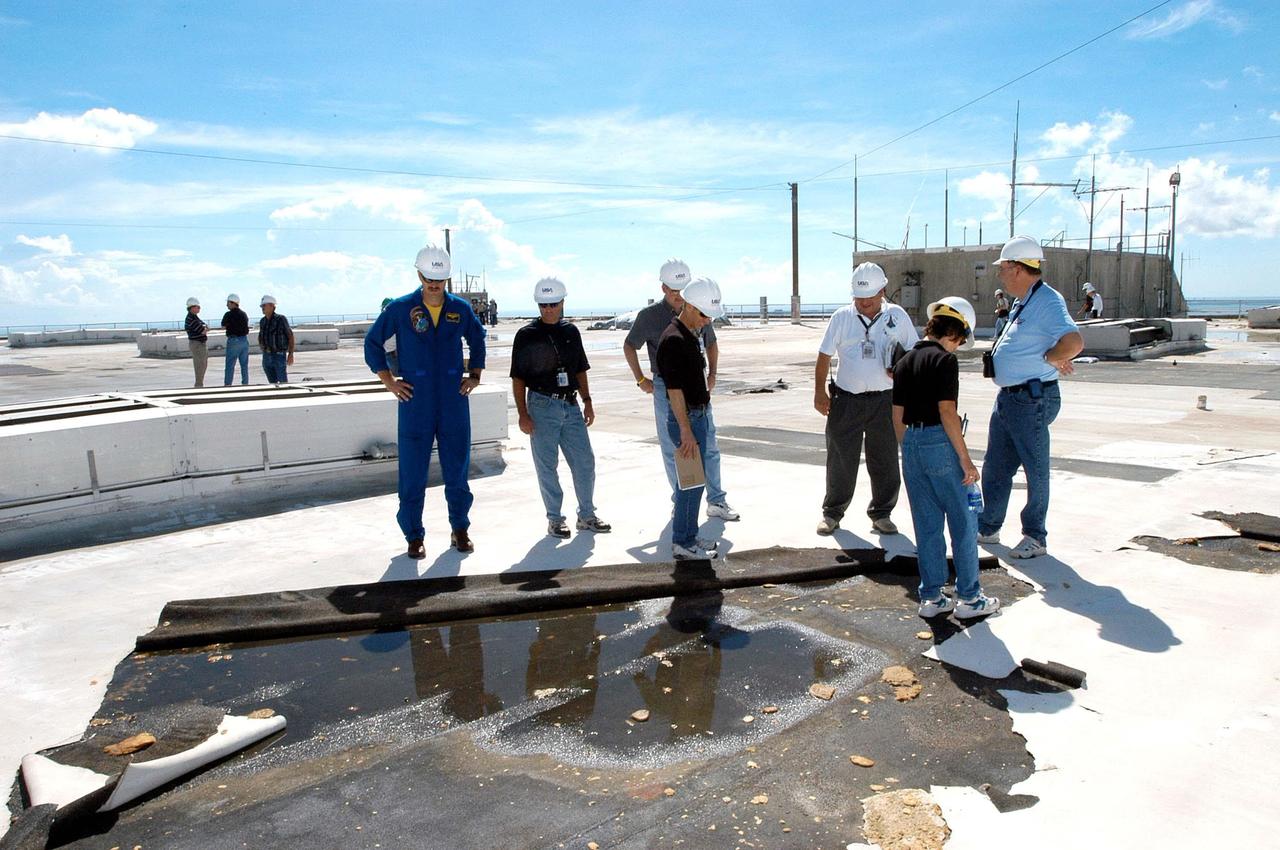

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center look at damage on the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) a week after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. The VAB lost 820, 4- x 16-foot panels from the side walls, or more than 52,000 square feet of its surface. One team member is astronaut Scott Altmann, at far left.
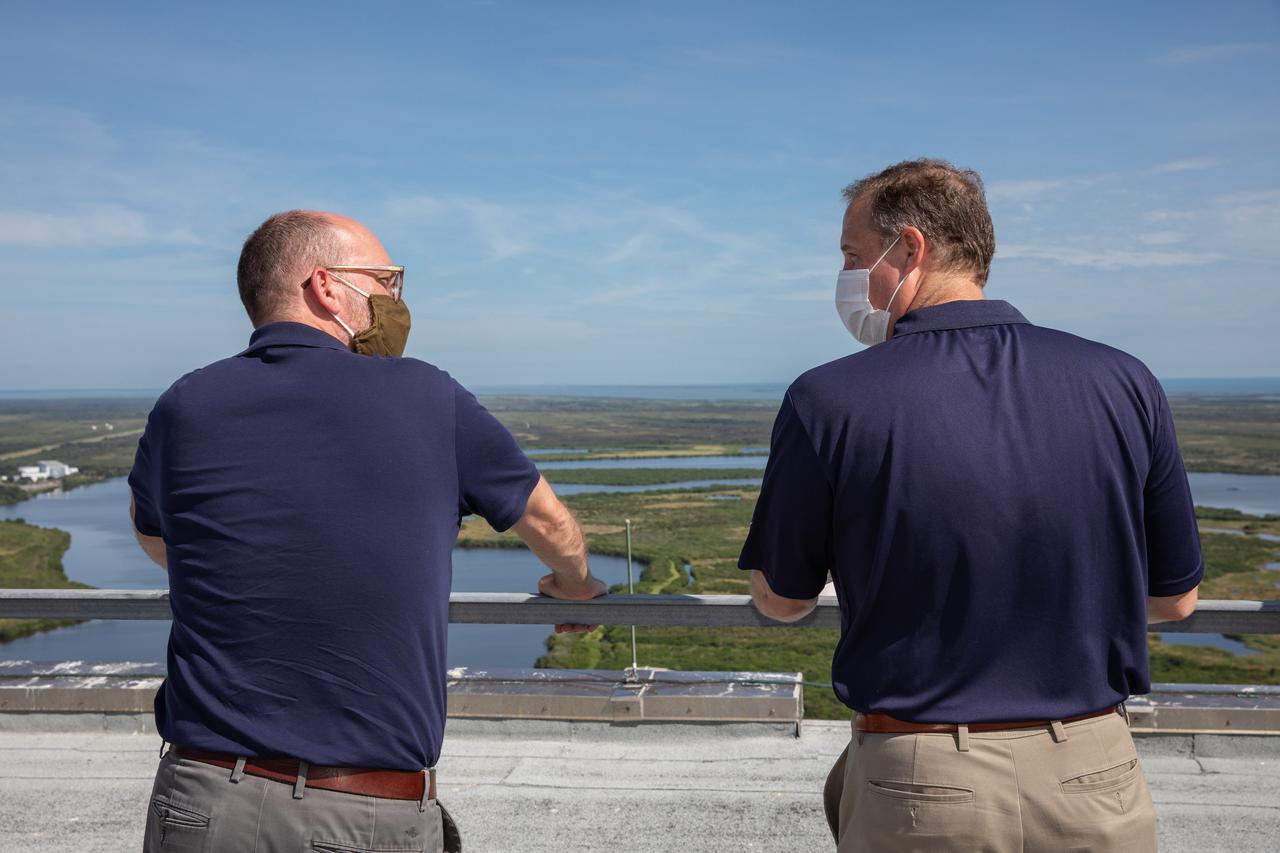

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, at right, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, are on the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) during a tour of the spaceport on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
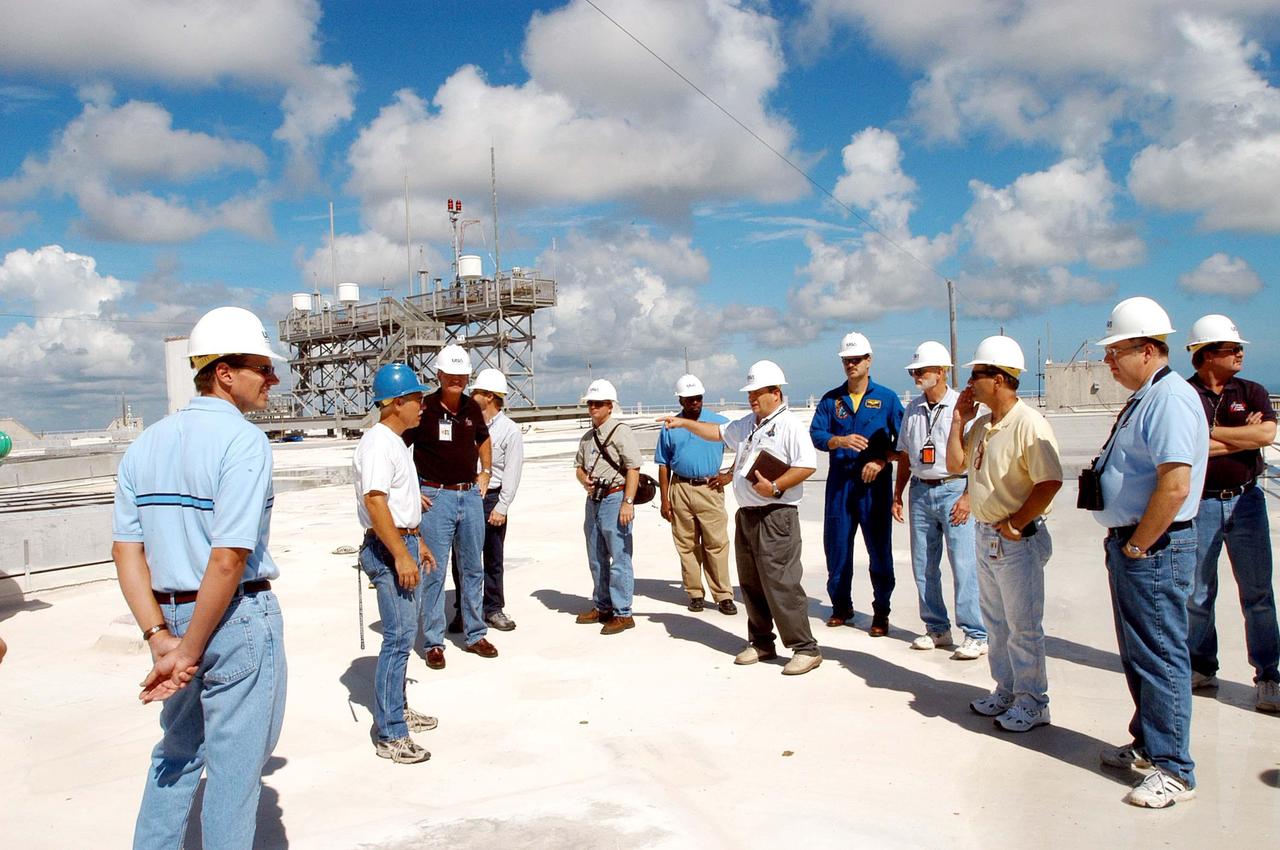

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of a hurricane assessment team from Johnson Space Center and Marshall Space Flight Center tour the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) a week after Hurricane Frances hit the east coast of Central Florida and Kennedy Space Center. The VAB lost 820, 4- x 16-foot panels from the side walls, or more than 52,000 square feet of its surface. One team member is astronaut Scott Altmann, fifth from right.
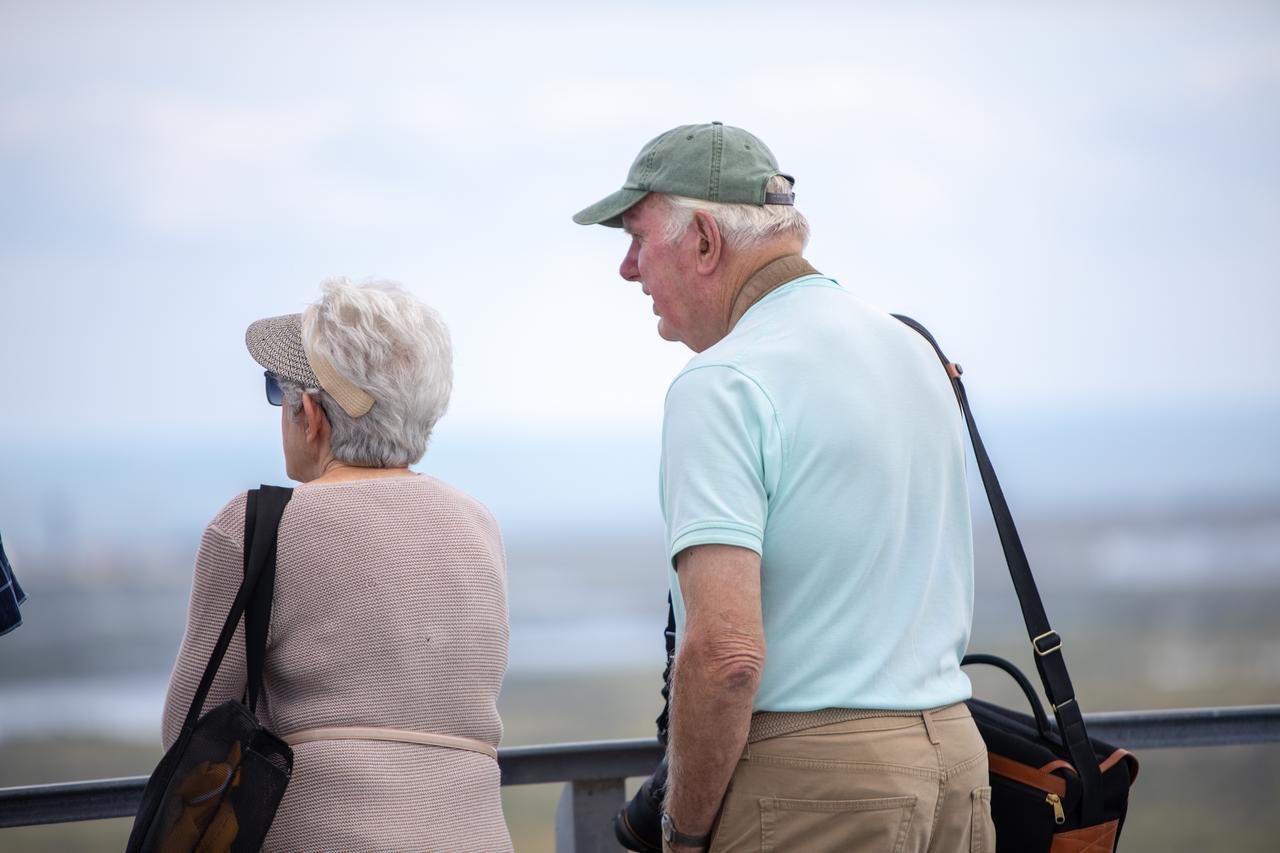

Dick Bergmann, at right, original lead designer for the Vehicle Assembly Building, stands on the roof of the iconic facility during a tour on Nov. 22, 2019 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The VAB was recognized with the National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark award by the Florida Section American Society of Civil Engineers during a ceremony on Jan. 10, 2020. The VAB is the first building at Kennedy Space Center to earn this distinction. At the time of its completion, the 129-million-cubic-foot structure was the largest building in the world. Originally designed and built to accommodate the Saturn V/Apollo used in Project Apollo, the VAB was later modified for its role in the Space Shuttle Program.
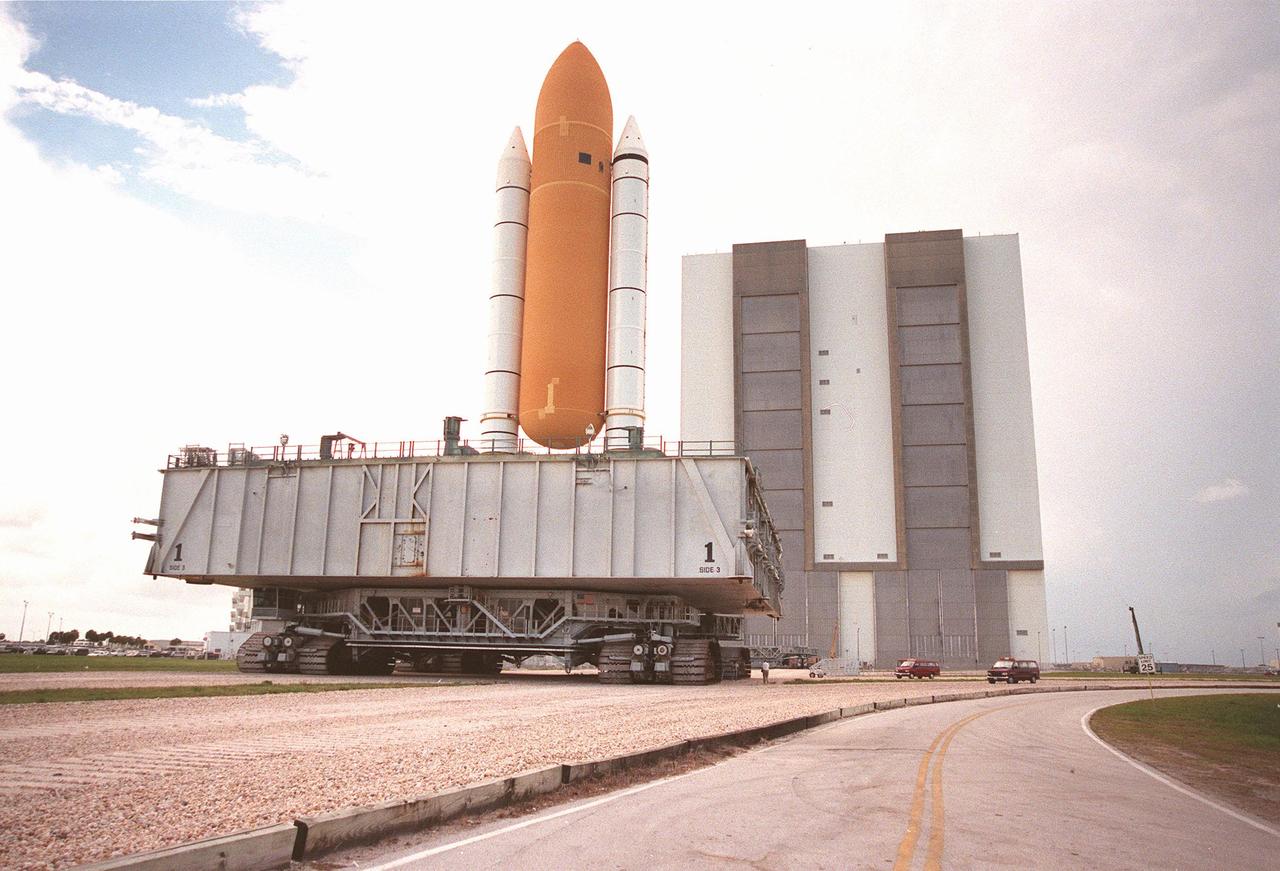

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-93 stack of solid rocket boosters and external tank moves toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) after lightning shield wires were strung from the roof of the VAB for protection. The stack is temporarily being stored outside the VAB while repair work is being done inside on the hail-damaged external tank of Space Shuttle Discovery. Discovery was rolled back from Pad 39B to the VAB for repairs because access to all of the damaged areas was not possible at the pad. The STS-93 stack is expected to be moved back into the VAB after Discovery returns to the pad. The scheduled date for launch of mission STS-96 is no earlier than May 27. STS-93 is targeted for launch on July 22, carrying the Chandra X-ray Observatory
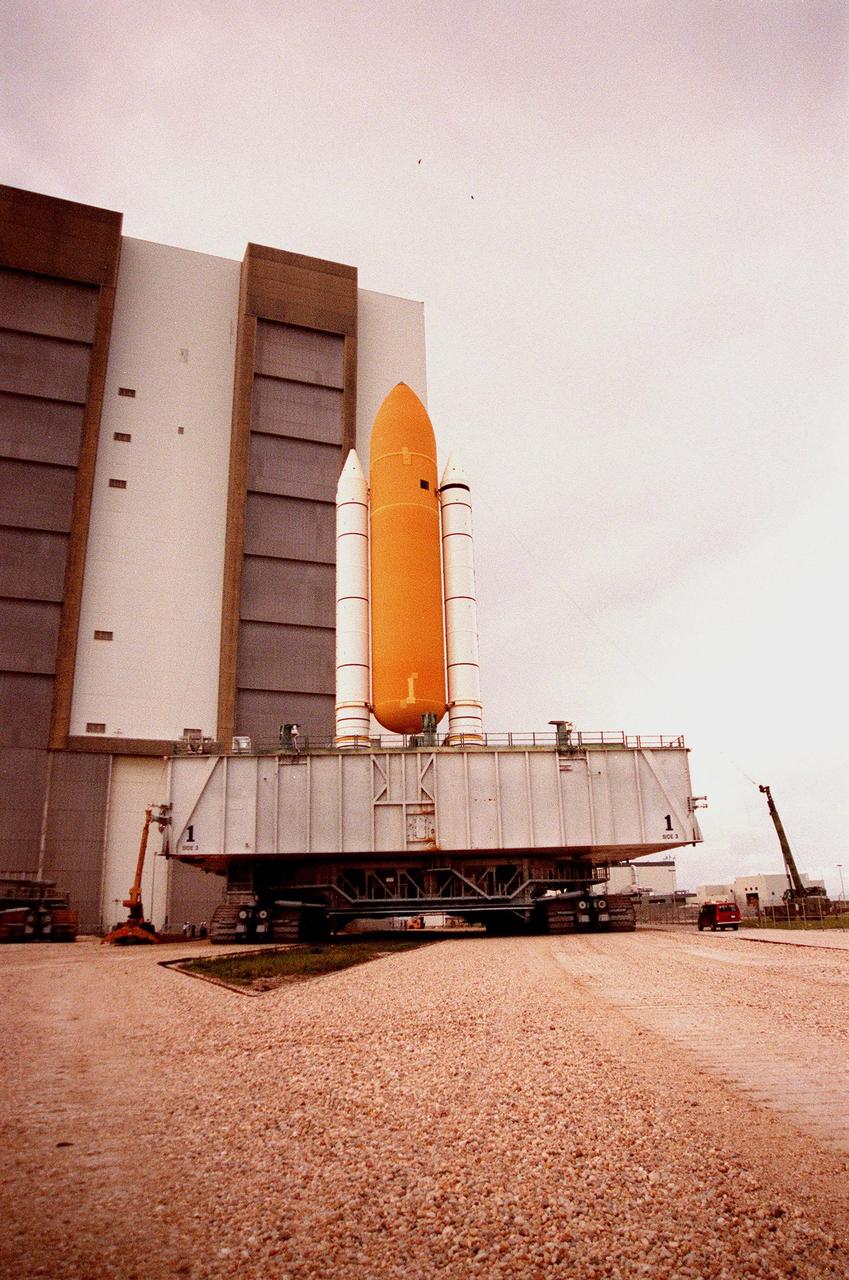

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-93 stack of solid rocket boosters and external tank nears the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) where it will sit underneath the lightning shield wires strung from the roof of the VAB for protection. The stack is temporarily being stored outside while repair work is being done inside on the hail-damaged external tank of Space Shuttle Discovery. Discovery was rolled back from Pad 39B to the VAB for repairs because access to all of the damaged areas was not possible at the pad. The STS-93 stack is expected to be moved back into the VAB after Discovery returns to the pad. The scheduled date for launch of mission STS-96 is no earlier than May 27. STS-93 is targeted for launch on July 22, carrying the Chandra X-ray Observatory
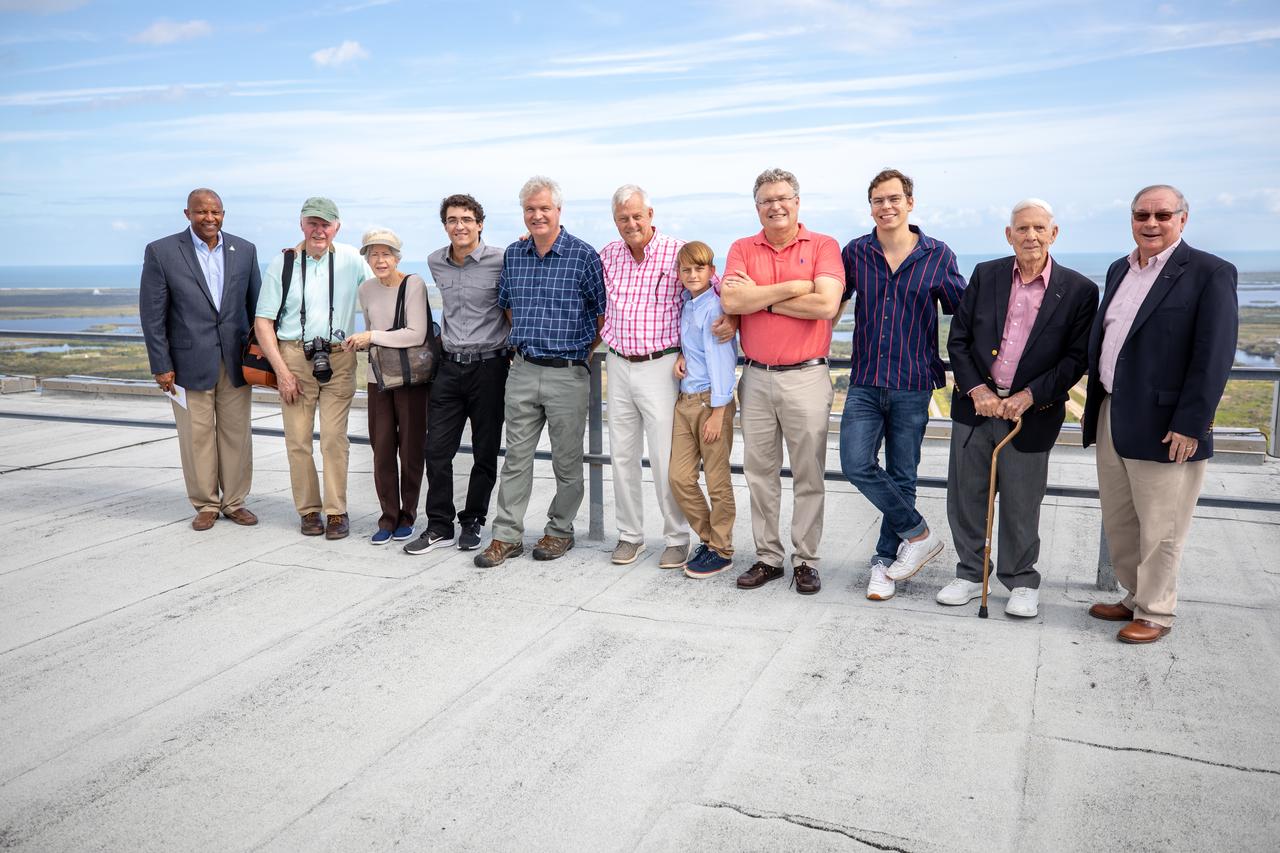

Dick Bergmann, second from left, original lead designer for the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), and Phil Moyer, second from right, original project lead, are on the roof of the VAB during a tour of Kennedy Space Center in Florida with descendants of Max Urbahn, the original architect, on Nov. 22, 2019. At far left is Kelvin Manning, Kennedy associate director, technical. The Florida Section American Society of Civil Engineers bestowed its National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark award to the facility. The VAB is the first building at Kennedy Space Center to earn this distinction. At the time of its completion, the 129-million-cubic-foot structure was the largest building in the world. Originally designed and built to accommodate the Saturn V/Apollo used in Project Apollo, the VAB was later modified for its role in the Space Shuttle Program.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As the STS-93 stack of solid rocket boosters and external tank moves toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), it passes underneath one of the lightning shield wires strung from the roof of the VAB for protection. The stack is temporarily being stored outside while repair work is being done inside on the hail-damaged external tank of Space Shuttle Discovery. Discovery was rolled back from Pad 39B to the VAB for repairs because access to all of the damaged areas was not possible at the pad. The STS-93 stack is expected to be moved back into the VAB after Discovery returns to the pad. The scheduled date for launch of mission STS-96 is no earlier than May 27. STS-93 is targeted for launch on July 22, carrying the Chandra X-ray Observatory

On the Vehicle Assembly Building roof at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, far left, accompanies NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
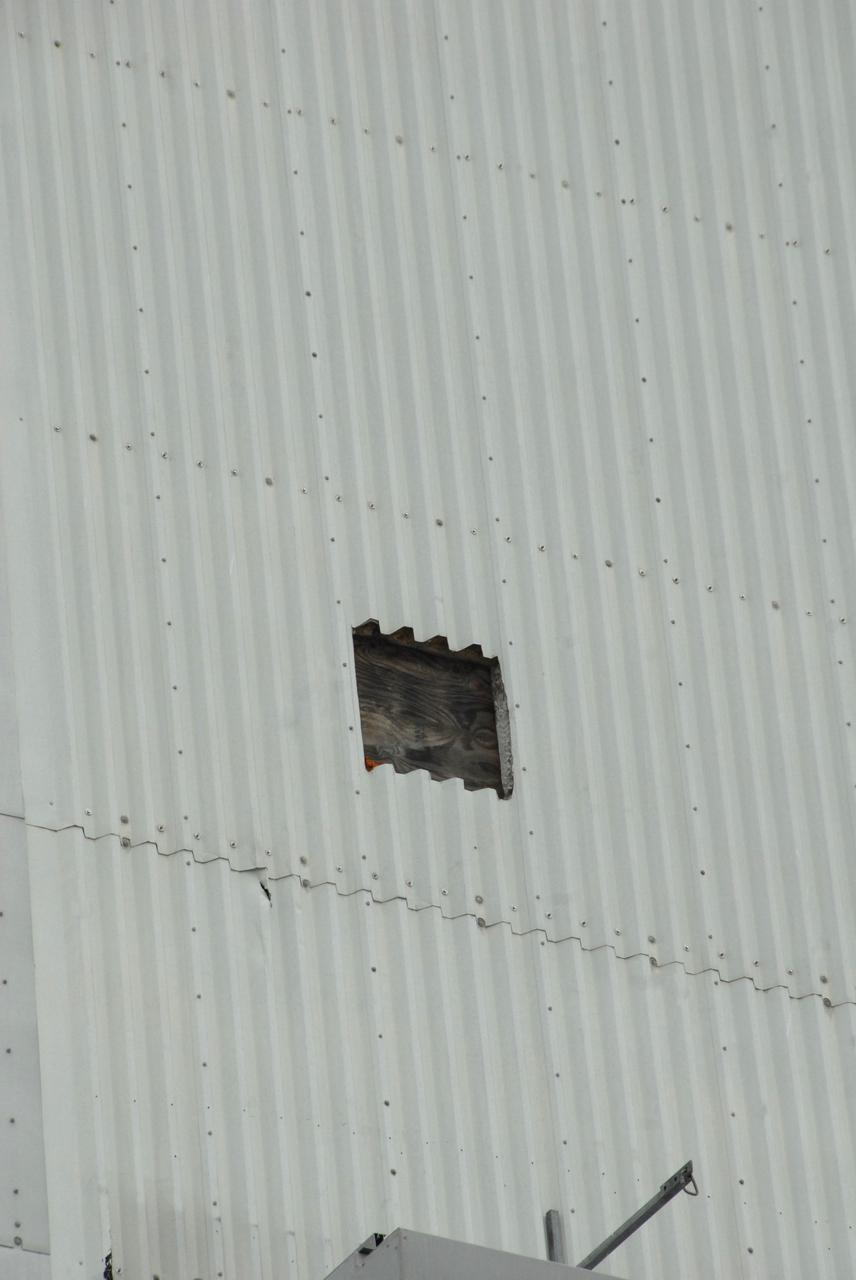

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A minor effect of Tropical Storm Hanna as it passed Florida’s east coast, part of a panel on the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center came off in a burst of high wind, causing minor damage to a UHF antenna on the roof of the Launch Control Center. The panel is on the southeast corner of the VAB. Hanna kept well offshore, bearing only bursts of rain and wind along the coastline as it moved north. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view of the Vehicle Assembly Building at KSC shows more of the patchwork of corrugated steel that covers holes created by recent hurricanes. The VAB lost 820 panels from the south wall during Hurricane Frances, and 25 additional panels pulled off the east wall by Hurricane Jeanne. Employees of Met-Con, a subcontractor in Cocoa, Fla., worked night and day on scaffolds hung from the 525-foot-high roof to close the holes and enable the facility to return to normal operations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view of the Vehicle Assembly Building at KSC shows the patchwork of corrugated steel that covers holes created by recent hurricanes. The VAB lost 820 panels from the south wall during Hurricane Frances, and 25 additional panels pulled off the east wall by Hurricane Jeanne. Employees of Met-Con, a subcontractor in Cocoa, Fla., worked night and day on scaffolds hung from the 525-foot-high roof to close the holes and enable the facility to return to normal operations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Vehicle Assembly Building at KSC sports a patchwork façade after the holes created by recent hurricanes were covered with corrugated steel. The VAB lost 820 panels from the south wall during Hurricane Frances, and 25 additional panels pulled off the east wall by Hurricane Jeanne. Employees of Met-Con, a subcontractor in Cocoa, Fla., worked night and day on scaffolds hung from the 525-foot-high roof to close the holes and enable the facility to return to normal operations.
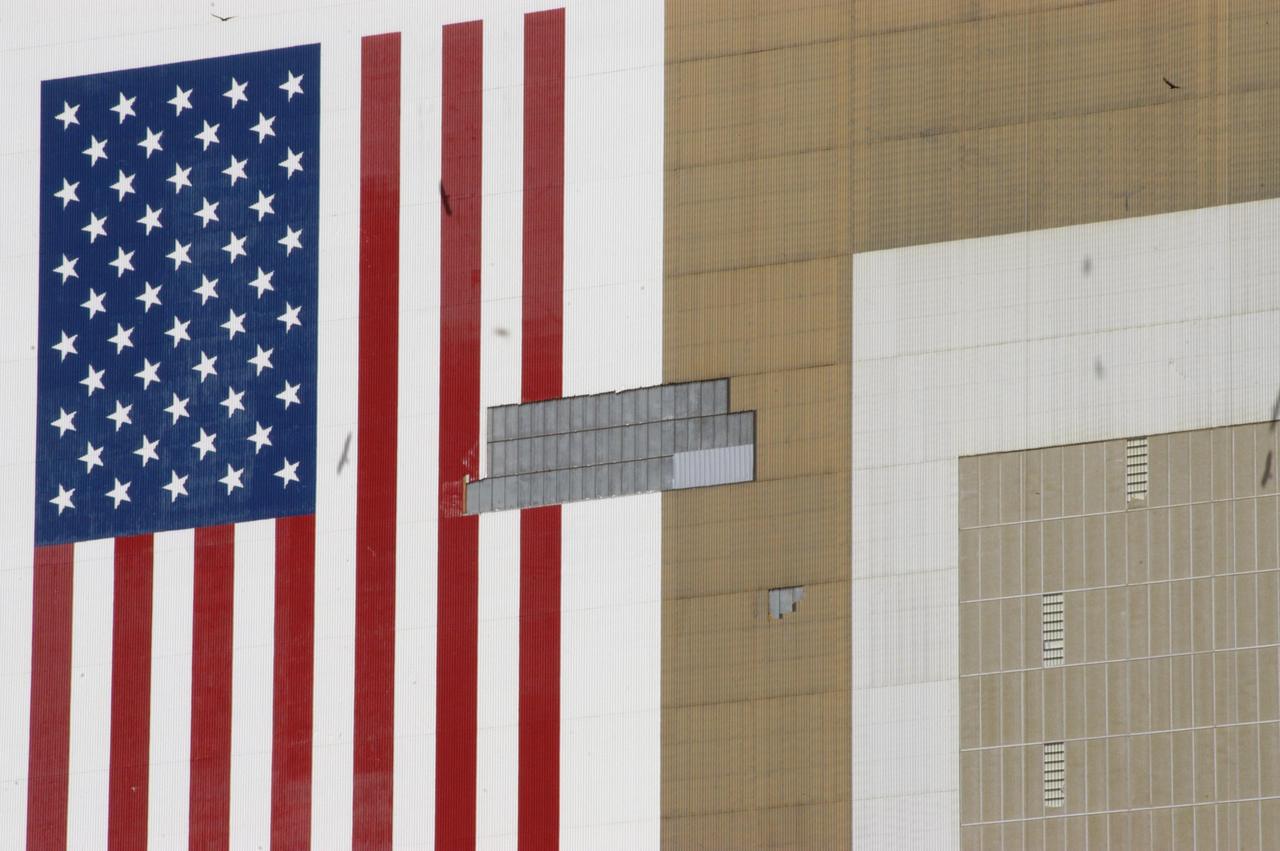
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This closeup of the Vehicle Assembly Building at KSC shows some of the patchwork of corrugated steel that covers holes created by recent hurricanes. The VAB lost 820 panels from the south wall during Hurricane Frances, and 25 additional panels pulled off the east wall by Hurricane Jeanne. Employees of Met-Con, a subcontractor in Cocoa, Fla., worked night and day on scaffolds hung from the 525-foot-high roof to close the holes and enable the facility to return to normal operations.
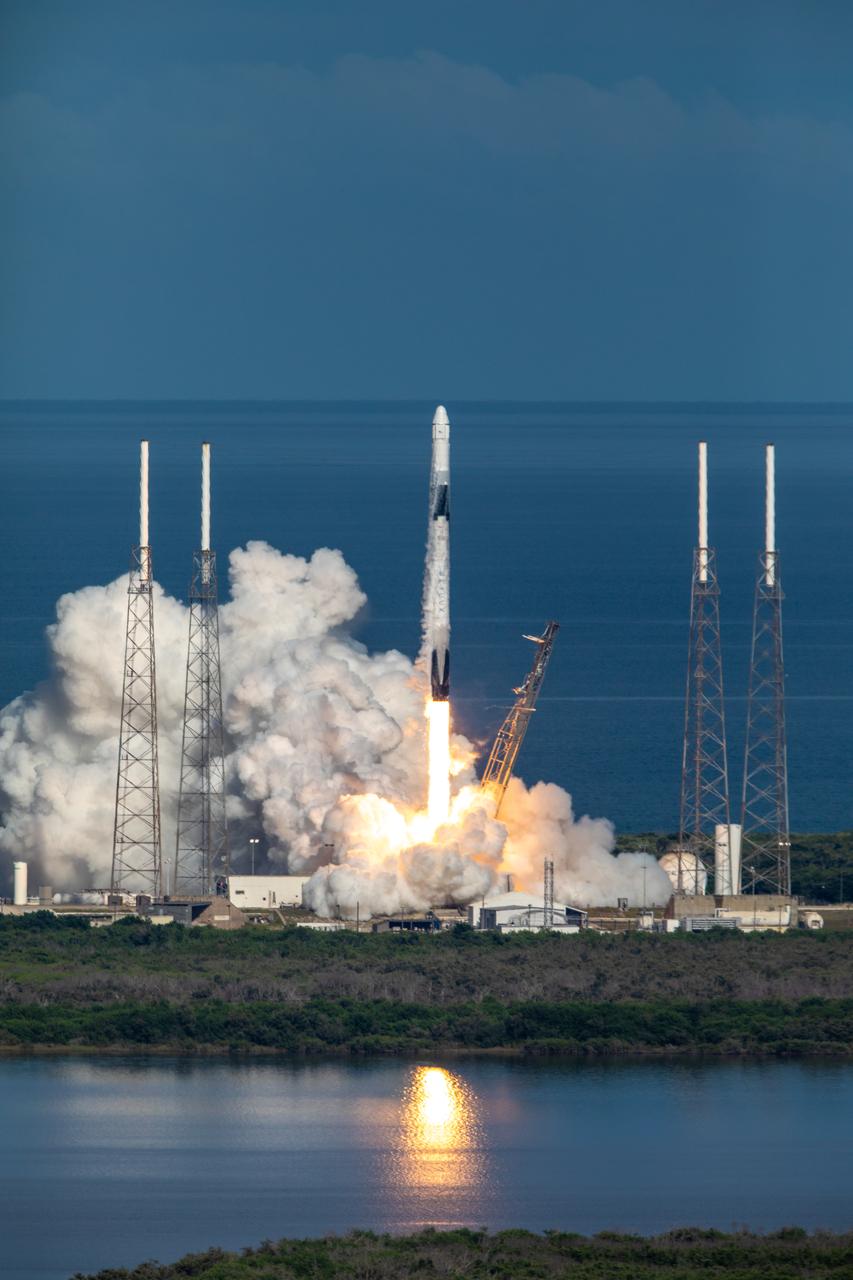

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
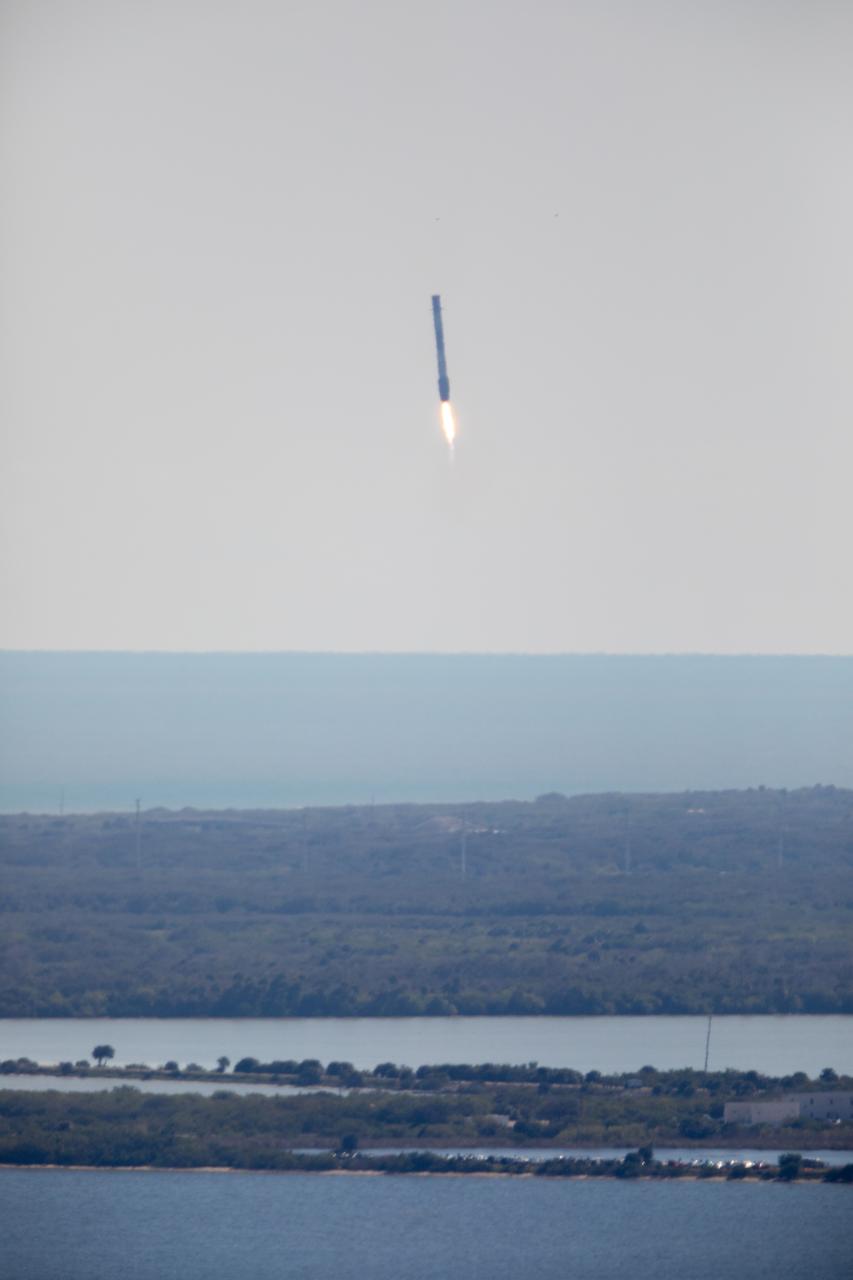

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
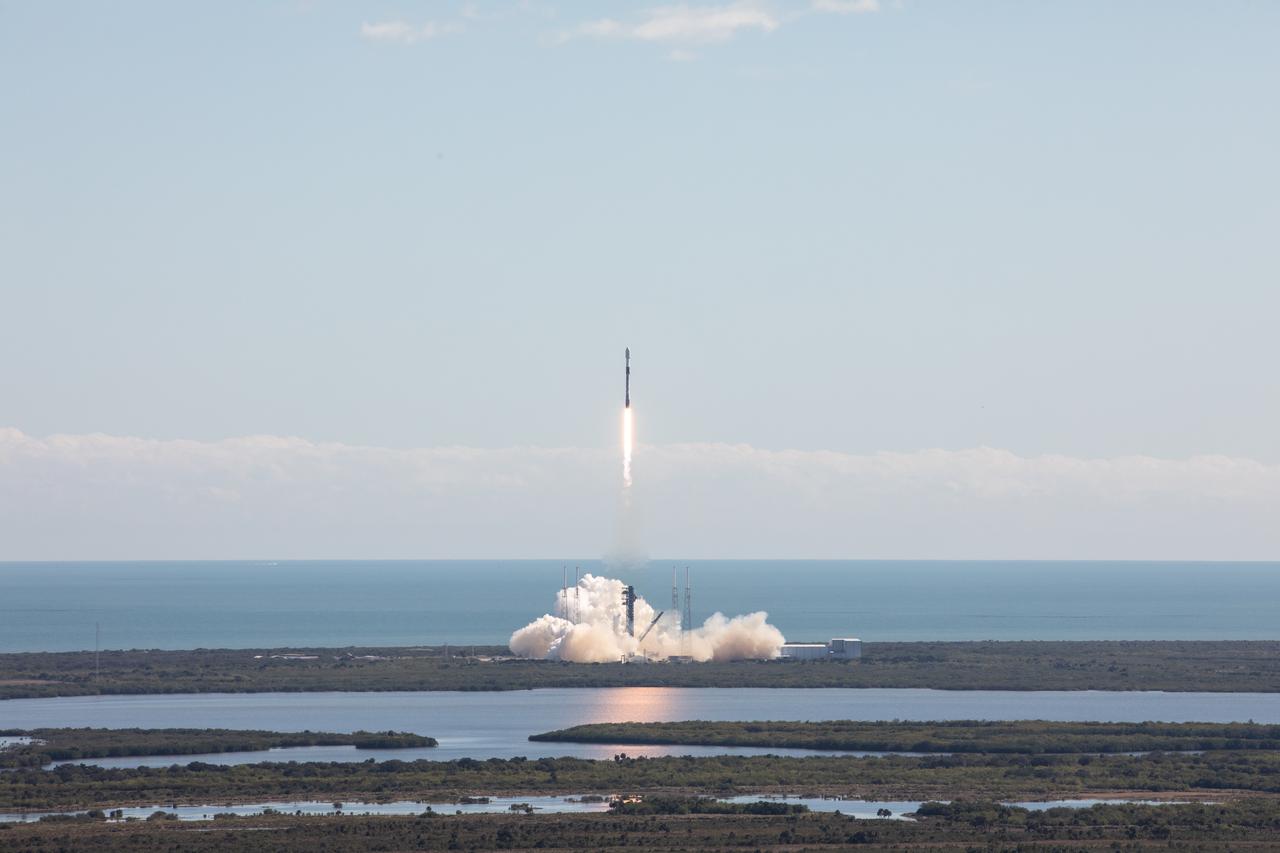

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at 2:30 a.m. EDT on June 25, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Falcon Heavy rocket carries two dozen satellites to space for the U.S. Department of Defense, including four NASA payloads that are part of the Space Test Program (STP-2) mission, managed by the U.S. Air Force Space and Missile Systems Center. The four NASA payloads include two technology demonstrations to improve how spacecraft propel and navigate, as well as two NASA science missions to help us better understand the nature of space and how it impacts technology on spacecraft and the ground.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
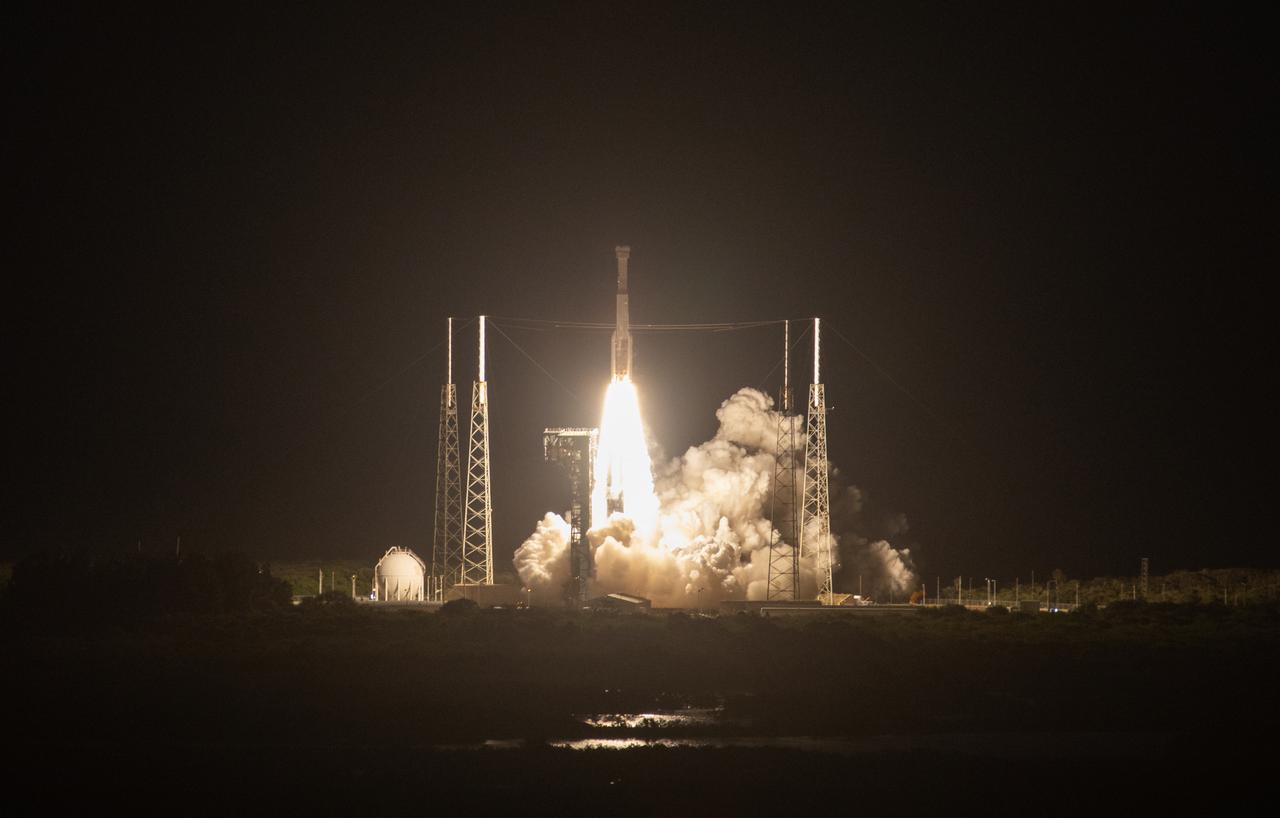

A two-stage United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test, Dec. 20, 2019. Liftoff occurred at 6:36 a.m. EST. The uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is the Starliner’s first flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
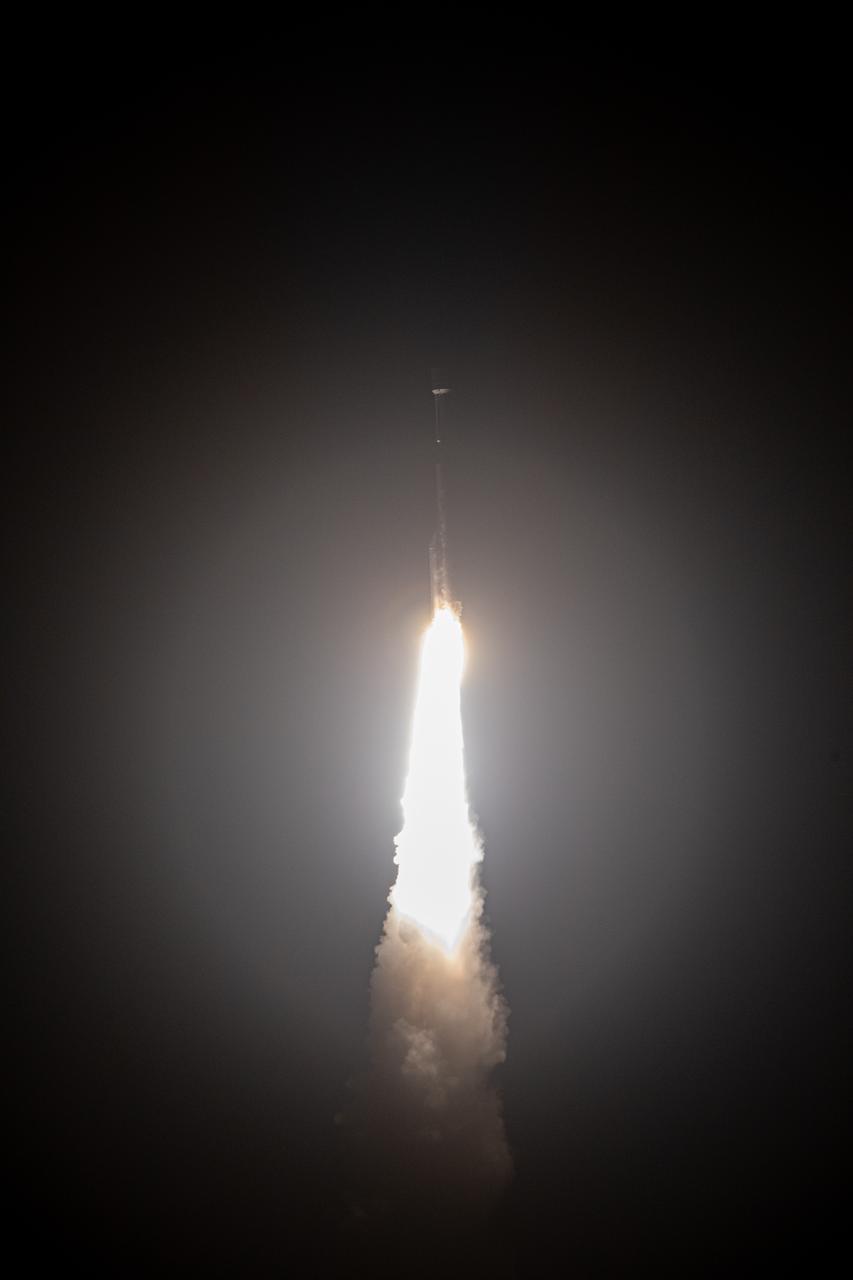

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, carrying the Solar Orbiter, climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in cmsFlorida on Feb. 9, 2020. Liftoff was at 11:03 p.m. EST. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy managed the launch.
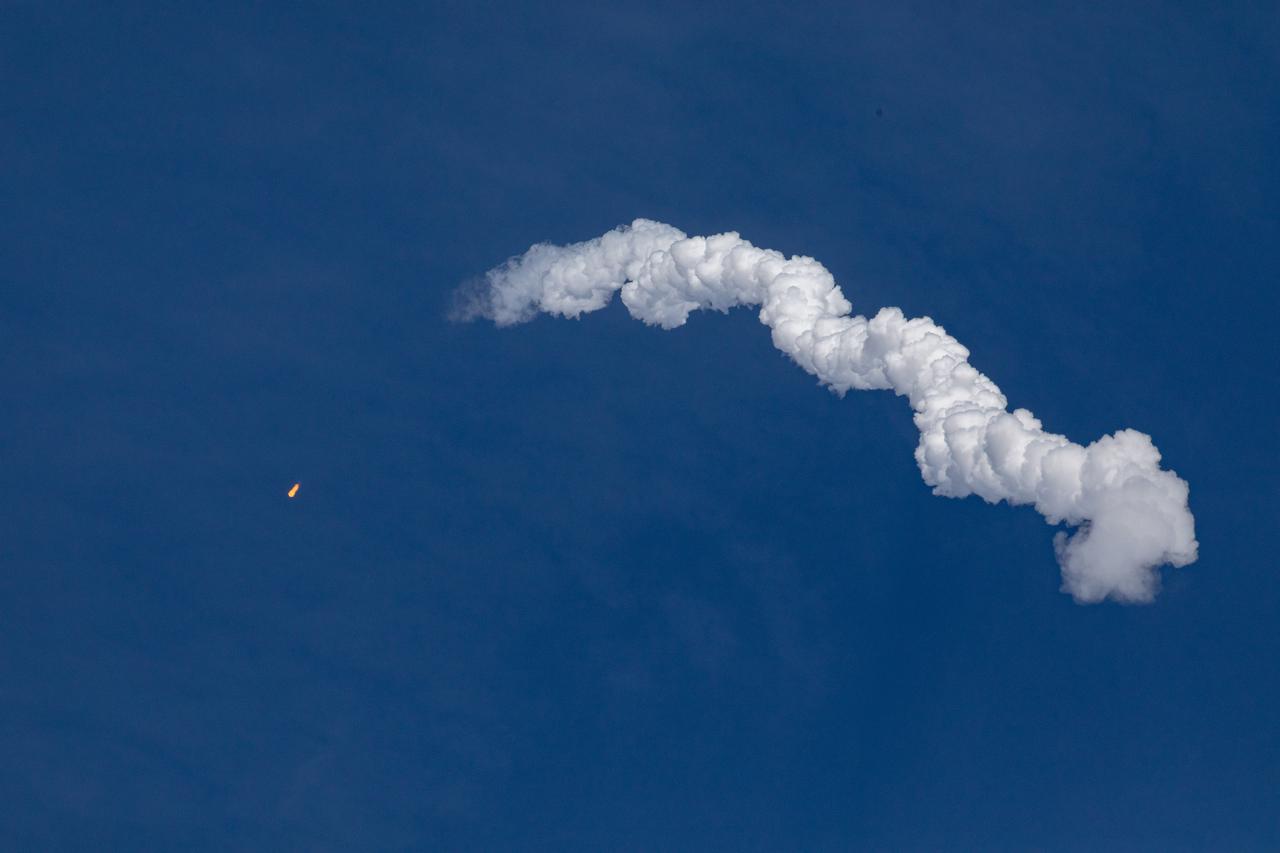

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo spacecraft will deliver about 7,700 pounds of science and research, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
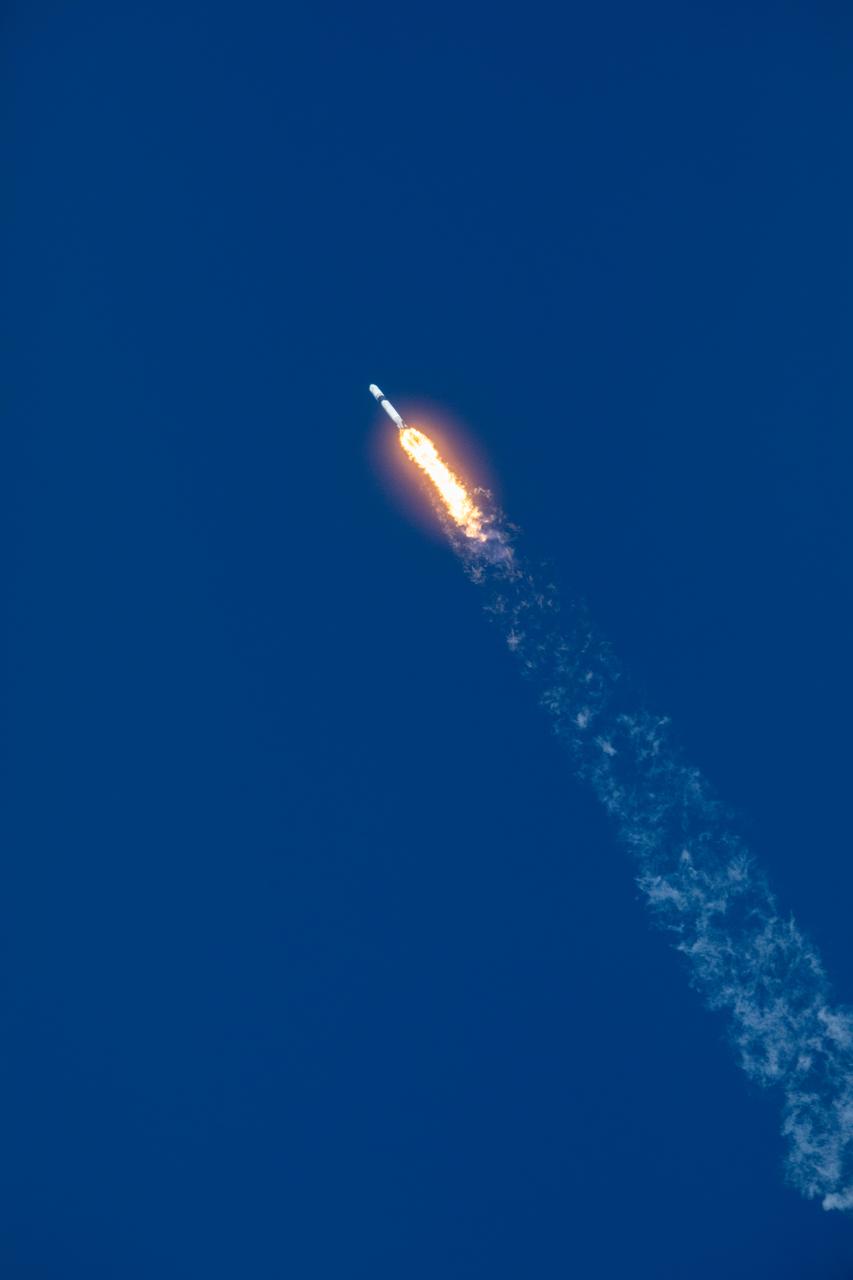

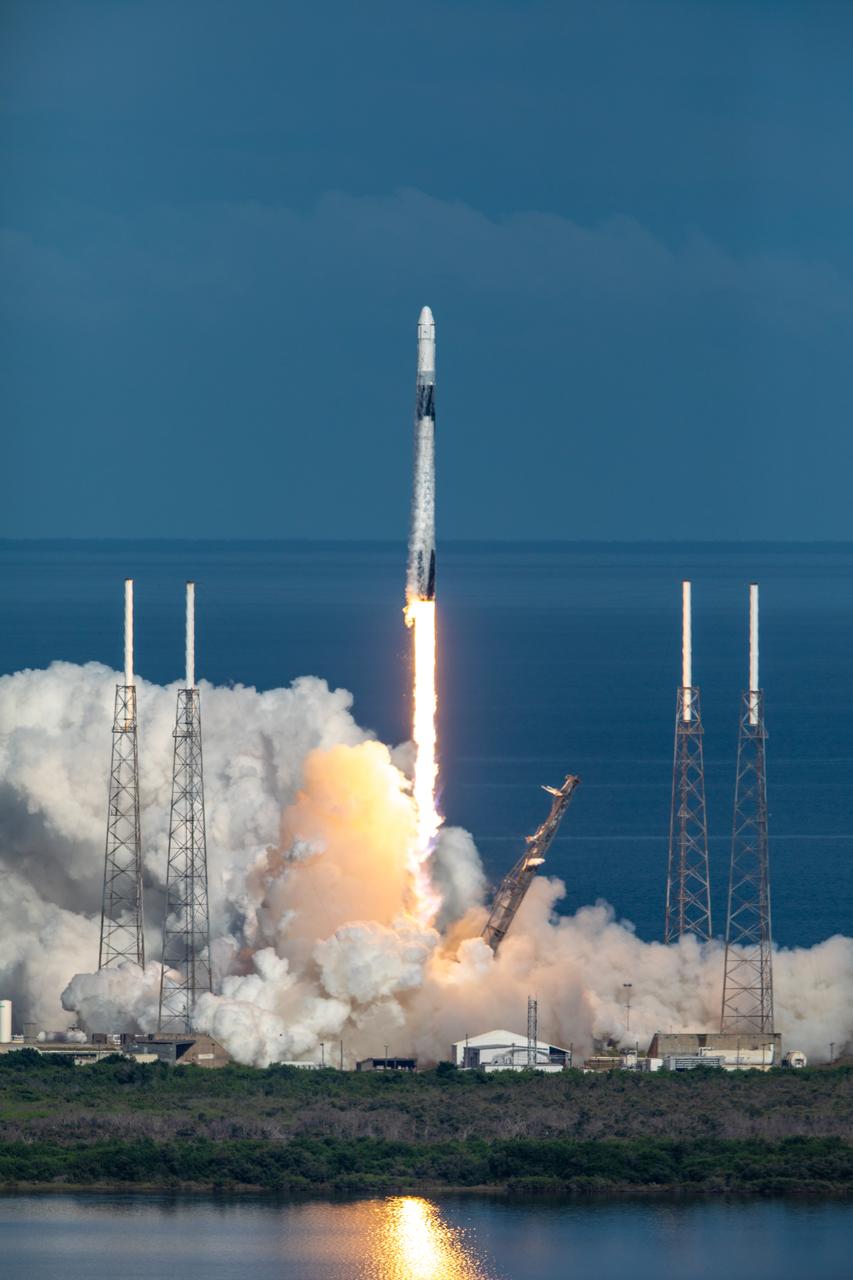
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
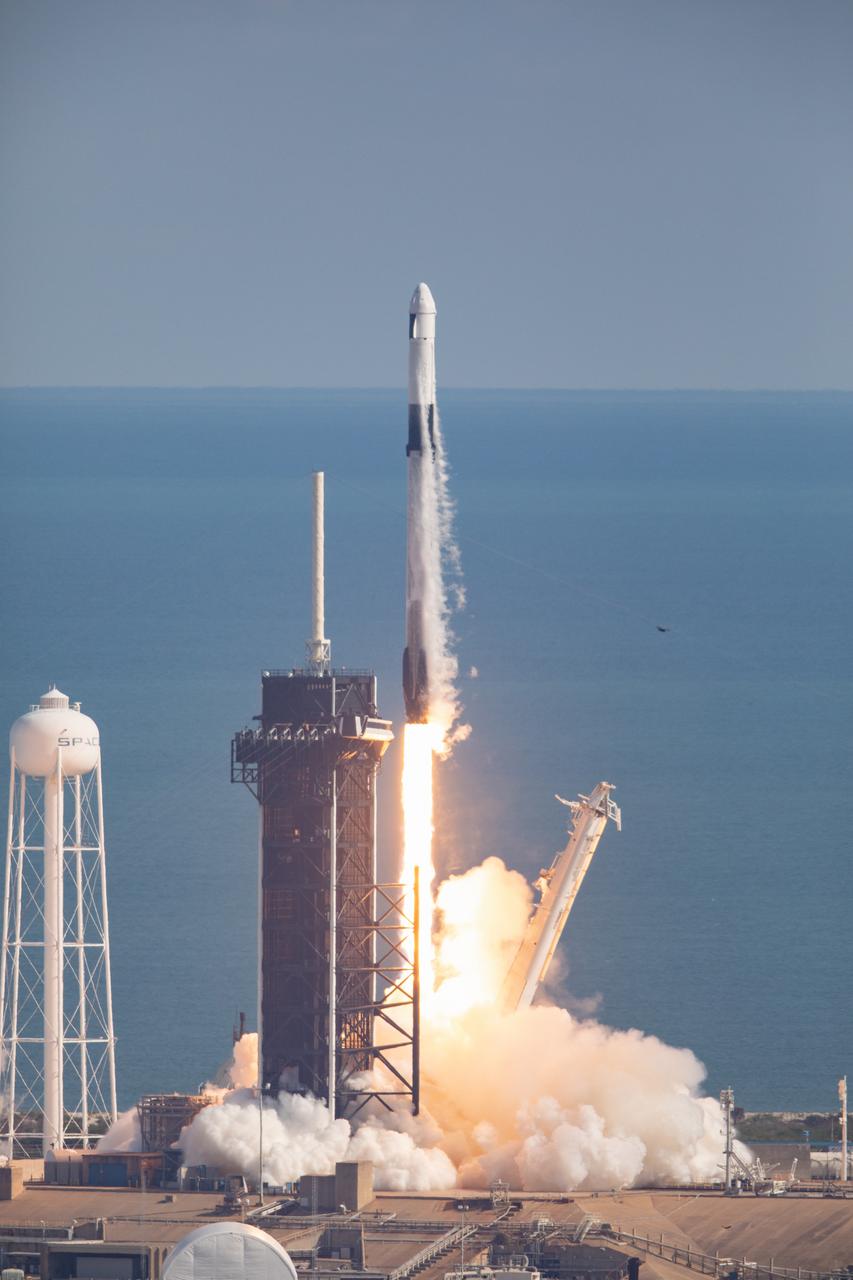

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
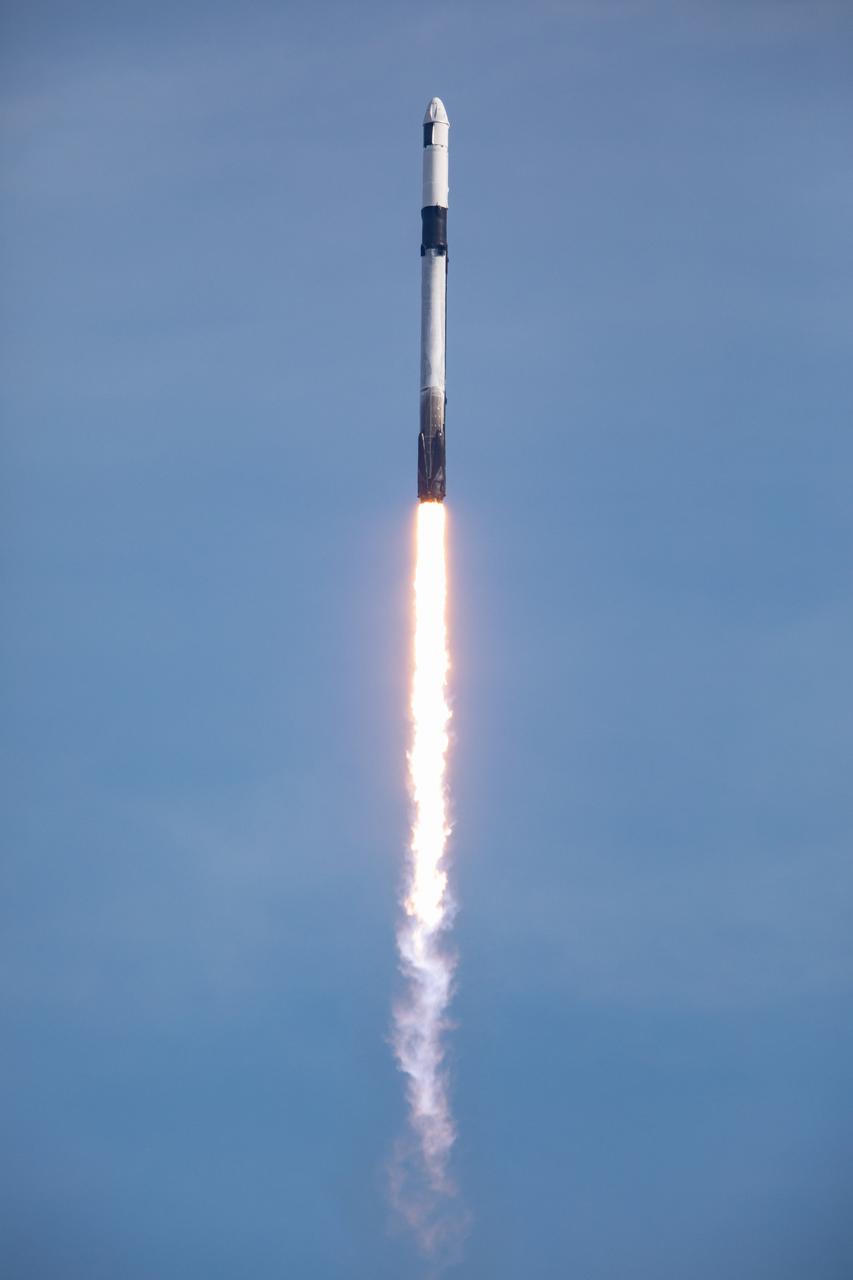

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars into the sky after lifting off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020. The rocket is carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.

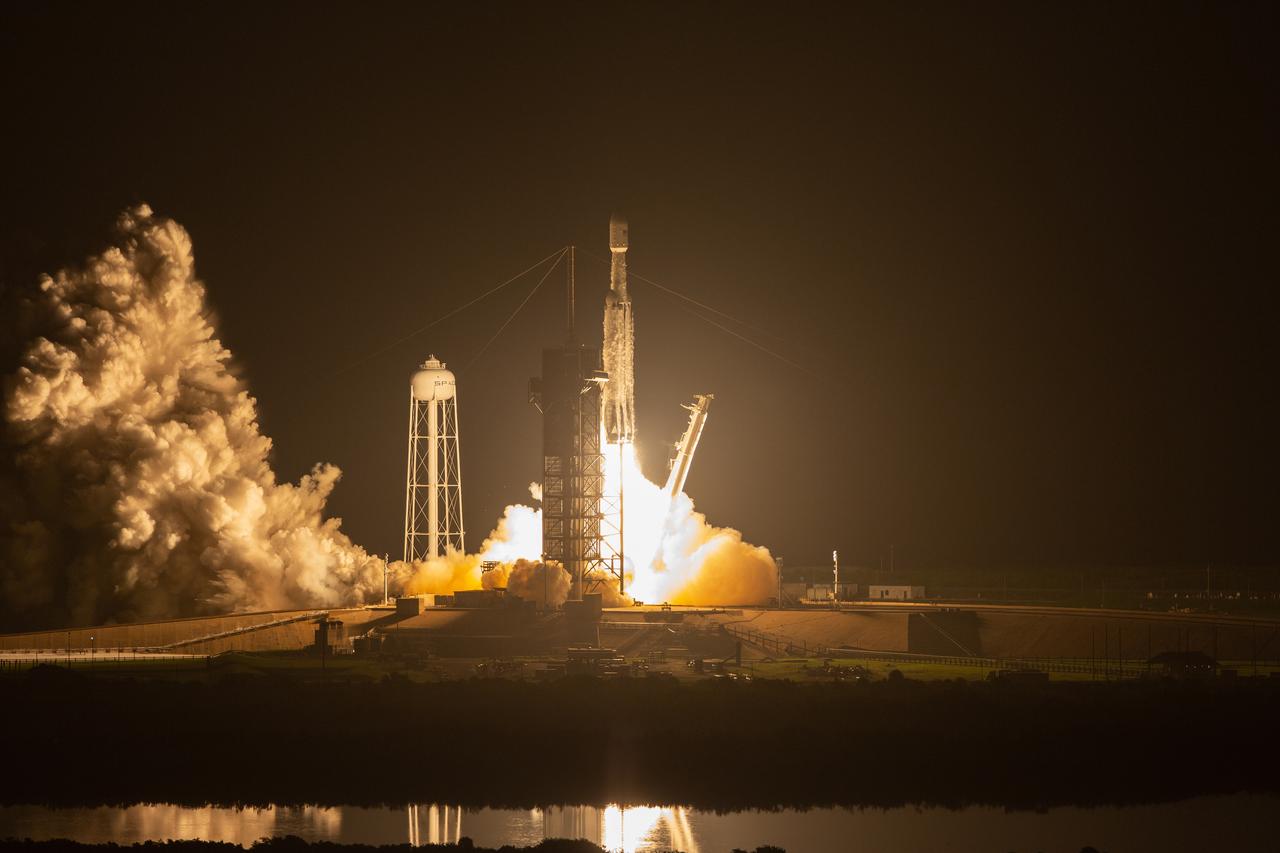
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is seen during sunrise on the launch pad of Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Wednesday, June 5, 2024, ahead of NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test. As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are the first to launch to the International Space Station aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft 10:52 a.m. EDT.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 4:55 p.m. EDT on Thursday, March 21, on the company’s 30th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Dragon will deliver more than 6,200 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA and partner research including a look at plant metabolism in space and a set of new sensors for free-flying Astrobee robots to provide 3D mapping capabilities. Other studies include a fluid physics study that could benefit solar cell technology and a university project from CSA (Canadian Space Agency) that will monitor sea ice and ocean conditions. The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
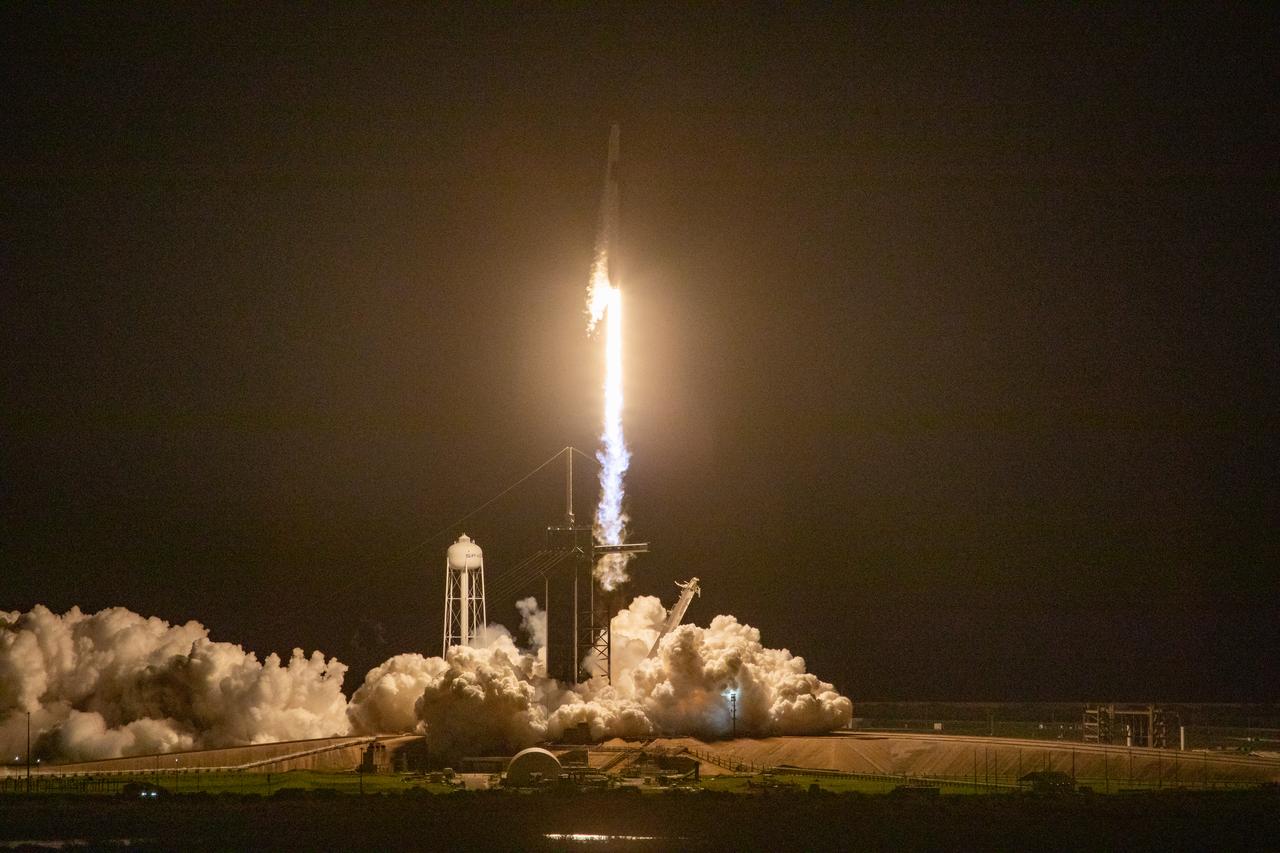

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off at 7:27 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 15, 2020, carrying the company’s Crew Dragon Resilience capsule. Onboard the capsule are NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 NASA astronauts, Michael Hopkins, spacecraft commander; Victor Glover, pilot; Shannon Walker, mission specialist; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Soichi Noguchi, mission specialist. Crew-1 is the first regular crew mission of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew Dragon will dock with the space station and the crew will remain on the orbiting laboratory for a six-month science mission.
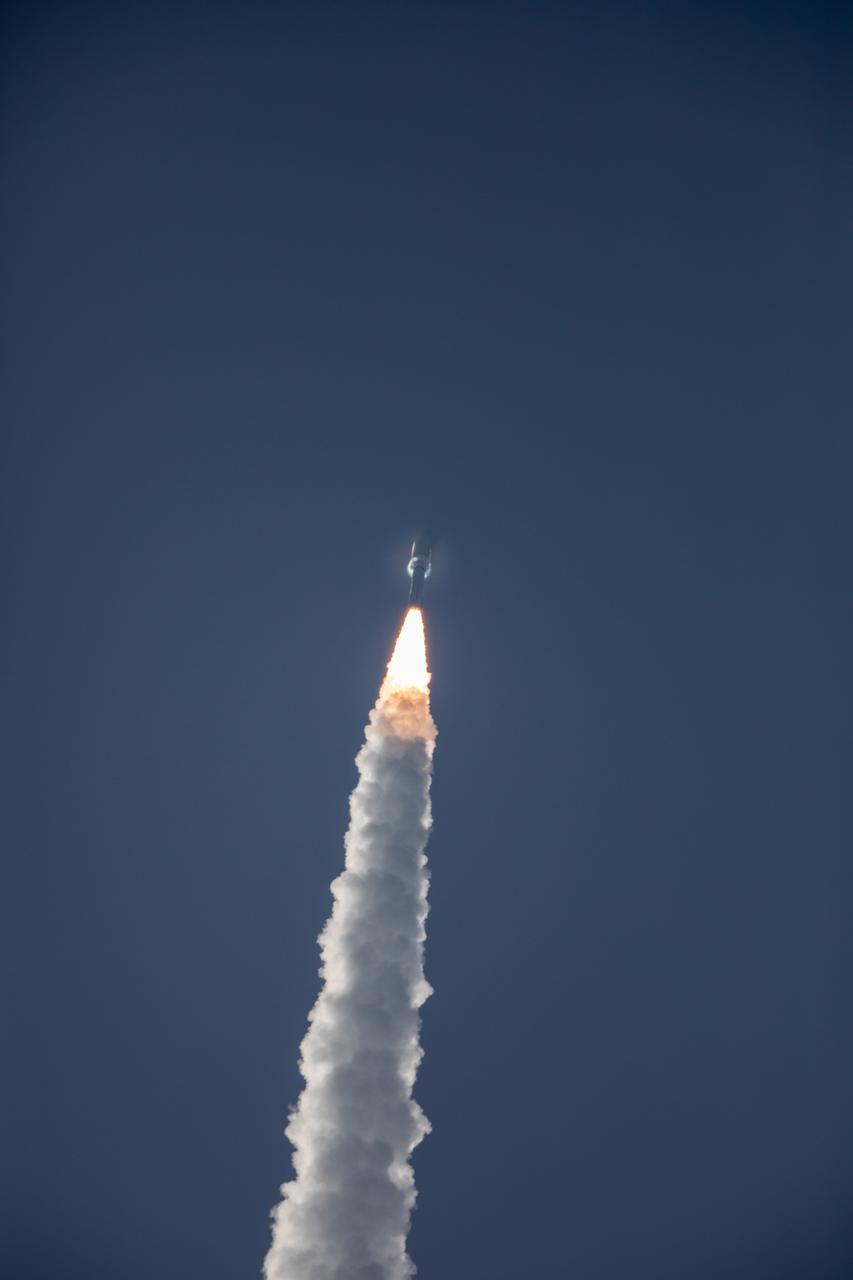

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
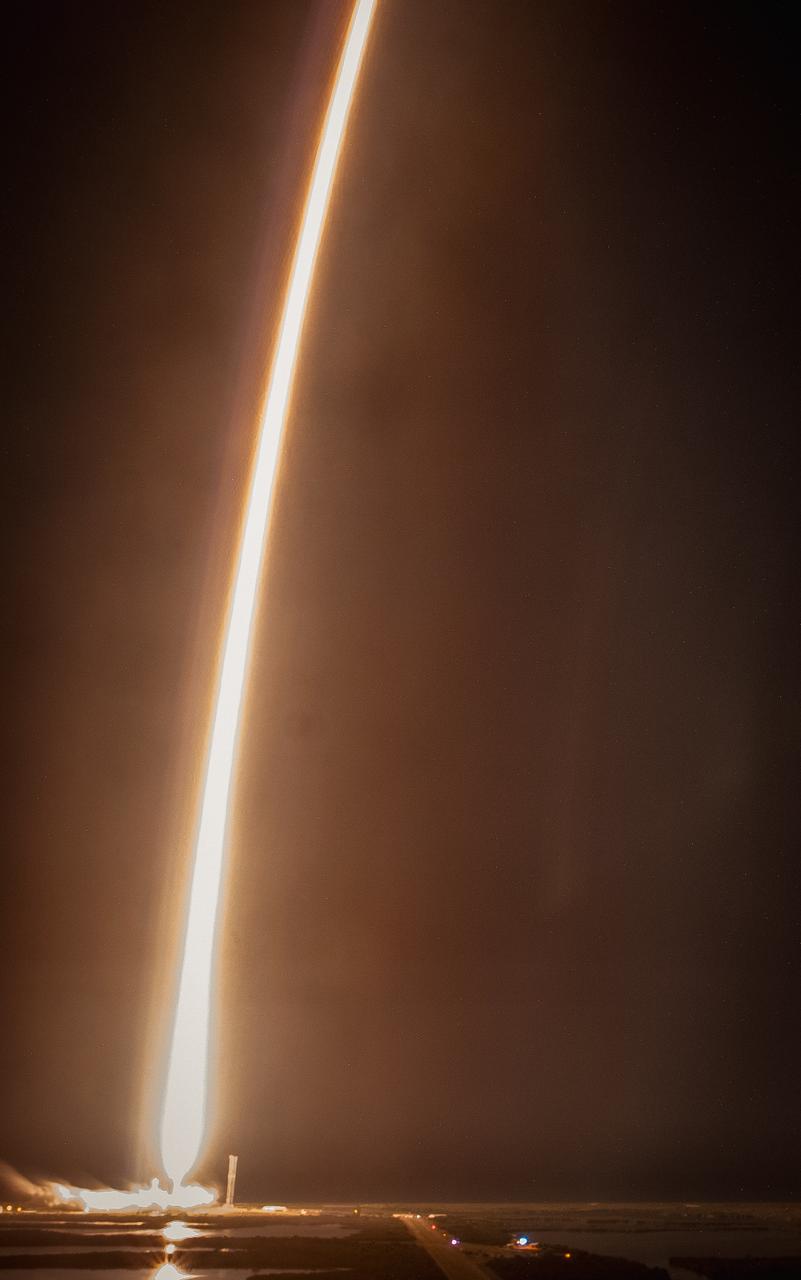

Creating a golden streak in the night sky, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander (IM-2) soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:16 p.m. EST Wednesday, Feb. 26 as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The IM-2 launch is carrying NASA science, technology demonstrations, and other commercial payloads to Mons Mouton, a lunar plateau to advance our understanding of the Moon and planetary processes, while paving the way for future crewed missions.
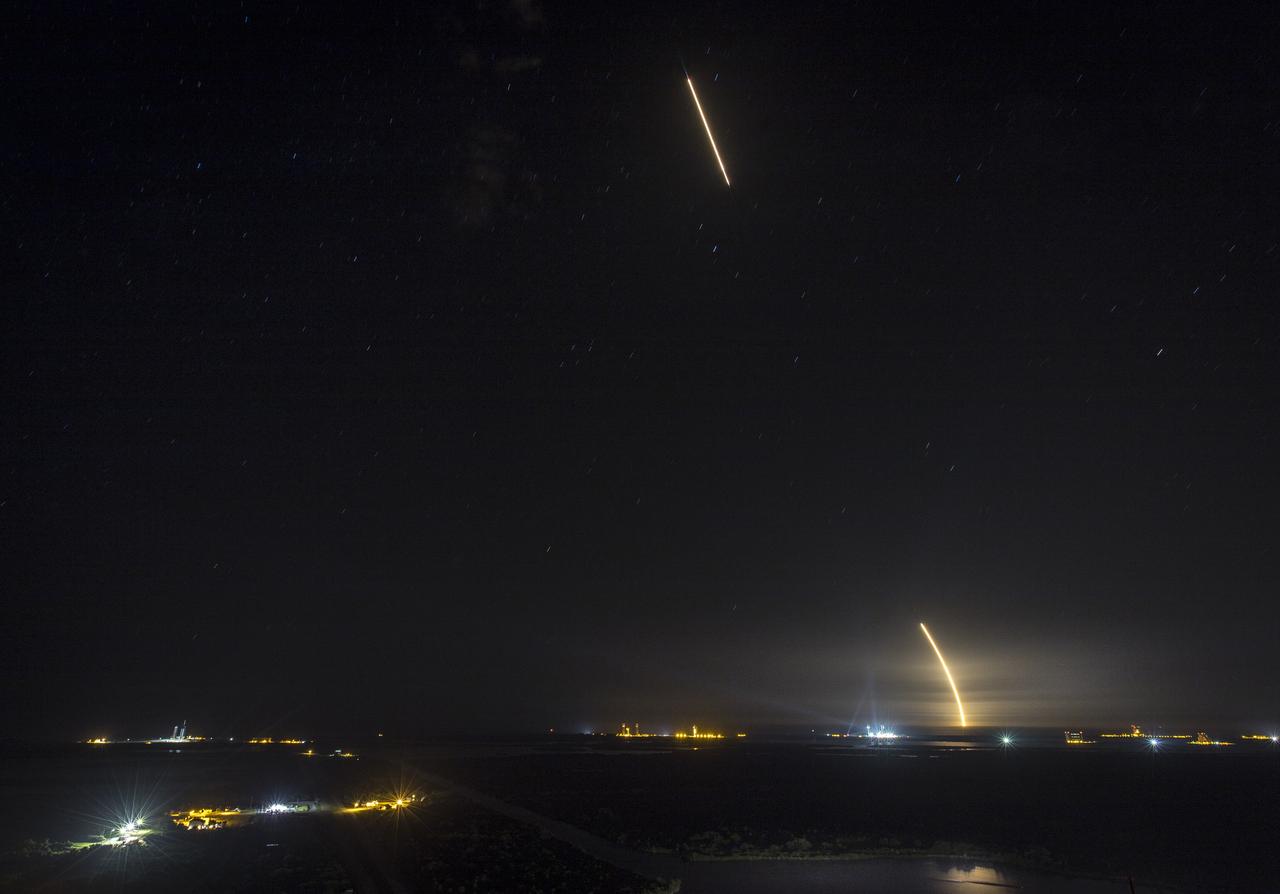

In this long exposure photograph, the first stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands on the company's drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean on May 4, 2019. The Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX's 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
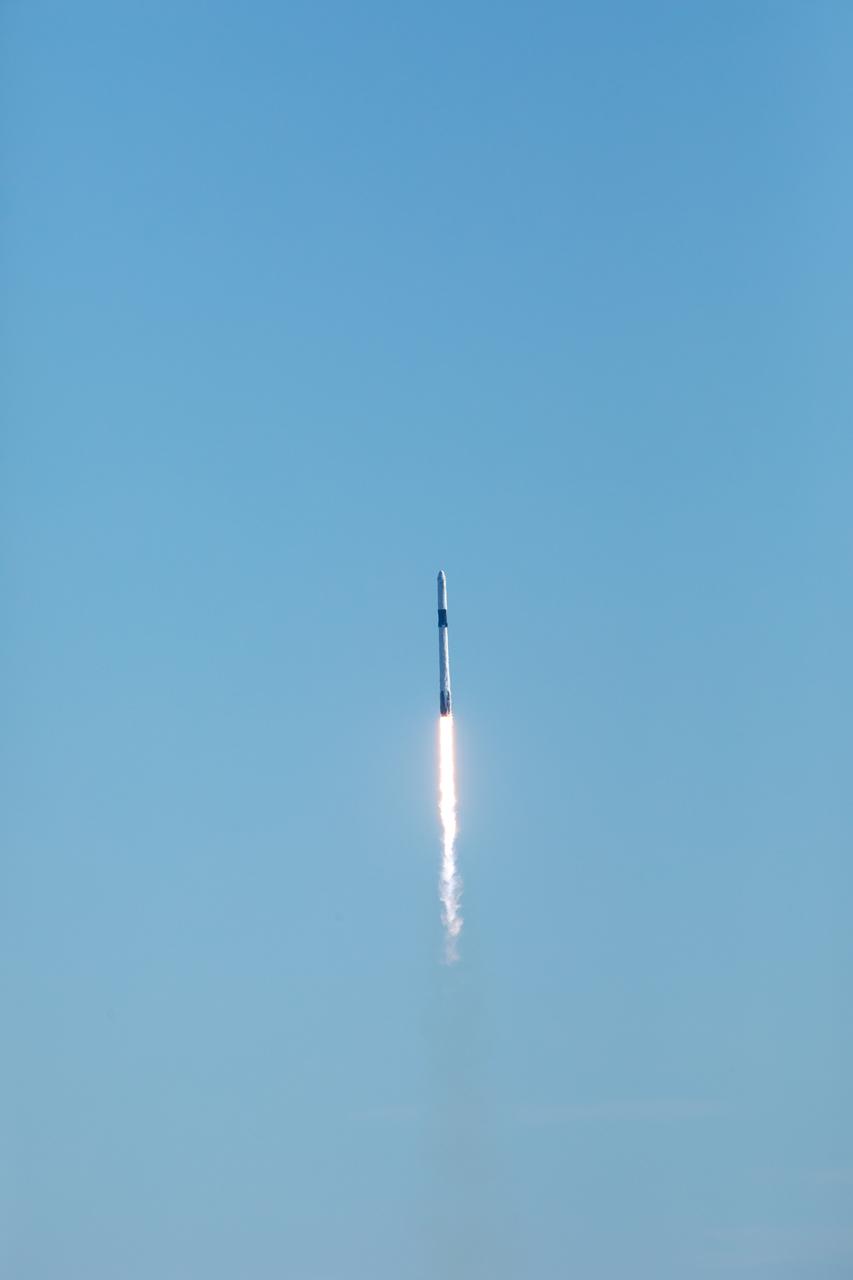

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early afternoon on Dec. 5, 2019. Liftoff was at 12:29 p.m. EST. This is SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-19) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver more than 5,700 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
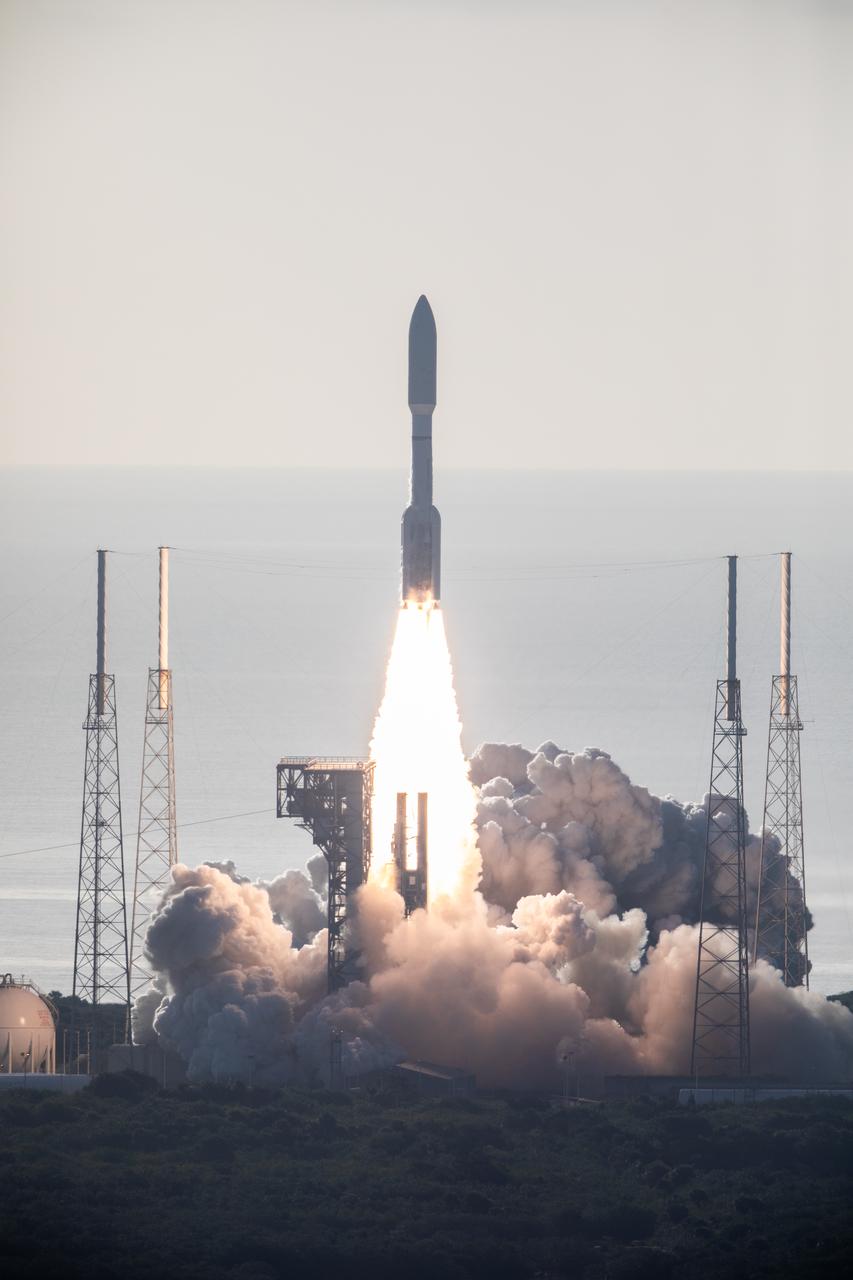

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module creates a streak across the sky as it climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
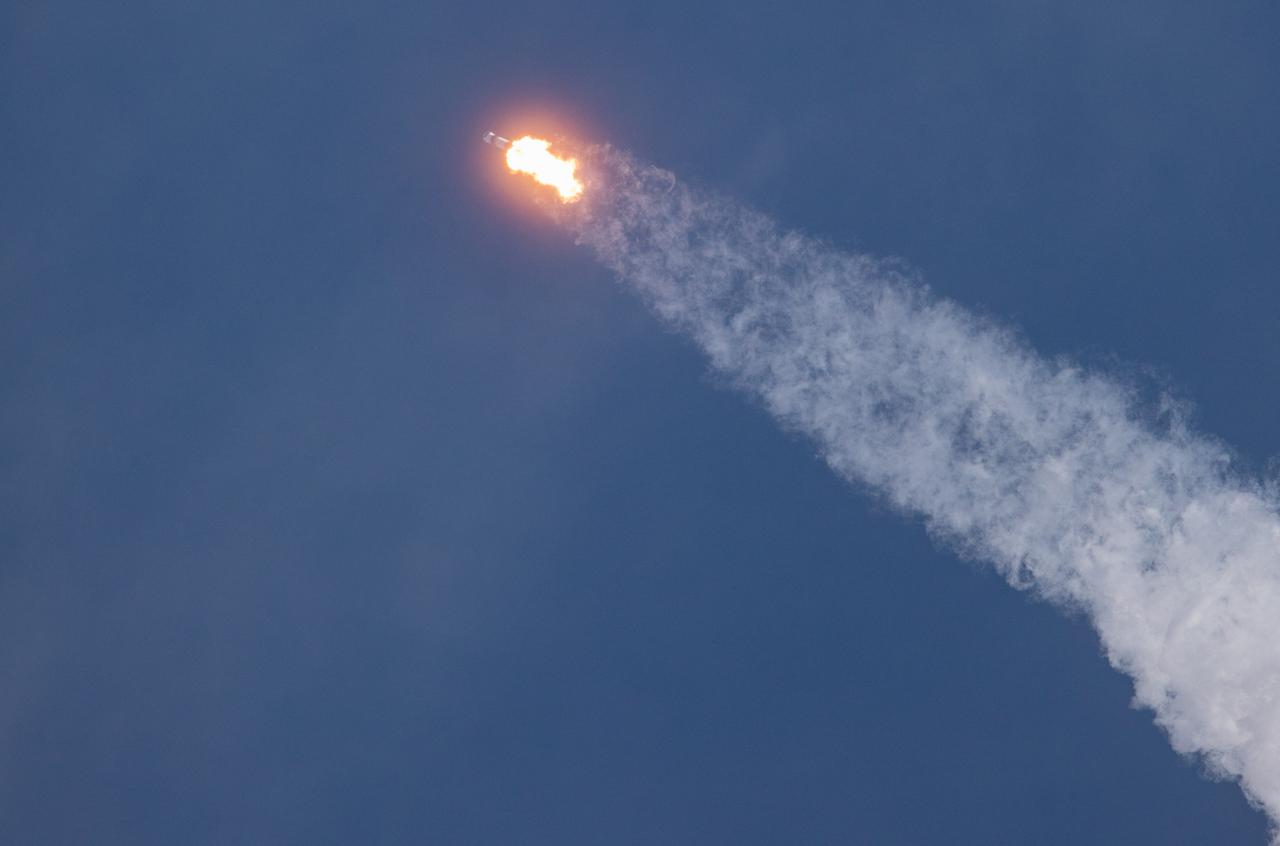

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars into the sky after lifting off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020. The rocket is carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.
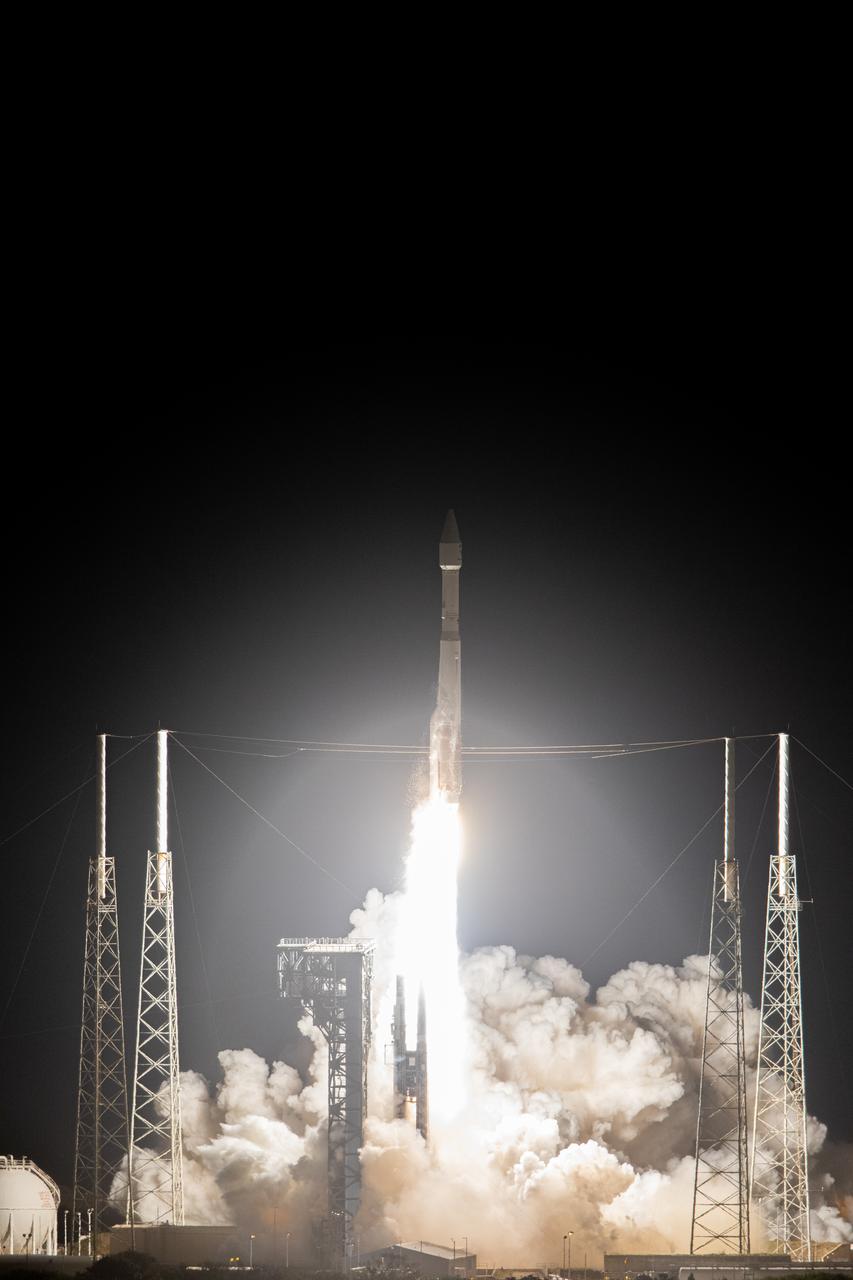

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, carrying the Solar Orbiter, climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in cmsFlorida on Feb. 9, 2020. Liftoff was at 11:03 p.m. EST. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy managed the launch.
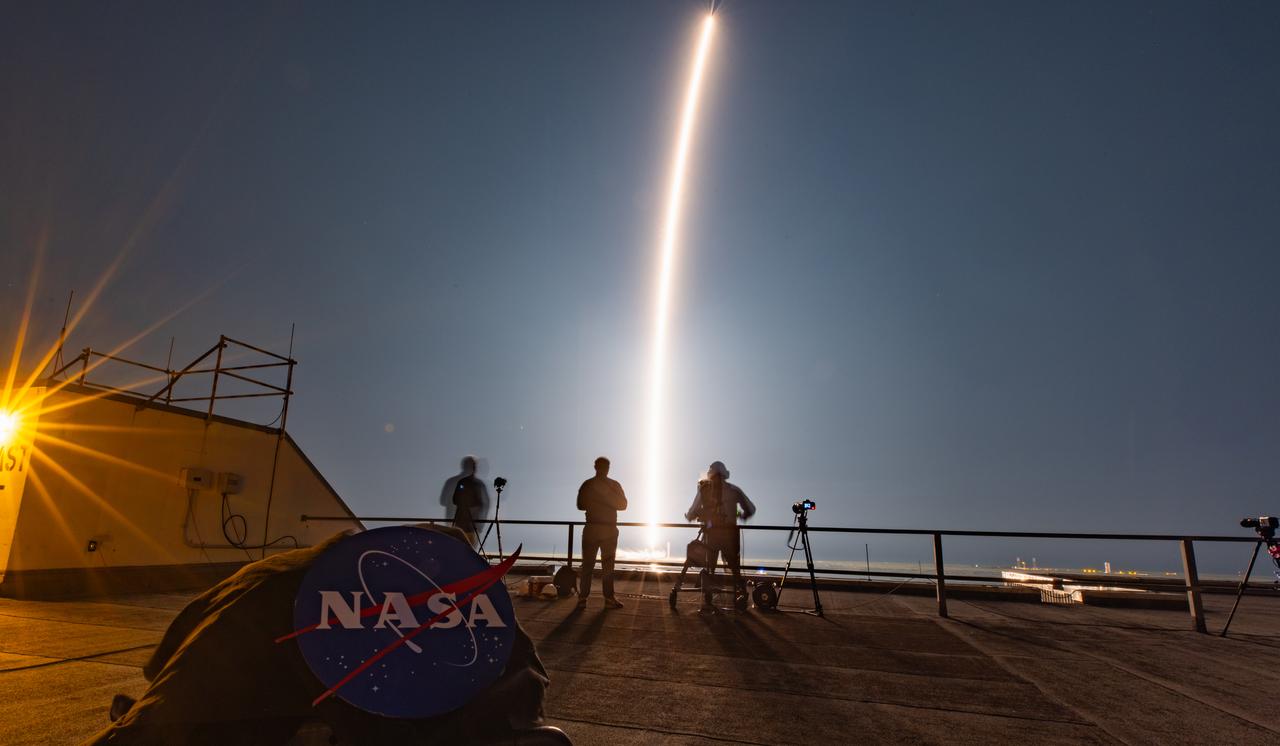

Creating a golden streak in the night sky, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander (IM-2) soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:16 p.m. EST Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2025, as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The IM-2 launch is carrying NASA science, technology demonstrations, and other commercial payloads to Mons Mouton, a lunar plateau to advance our understanding of the Moon and planetary processes, while paving the way for future crewed missions.
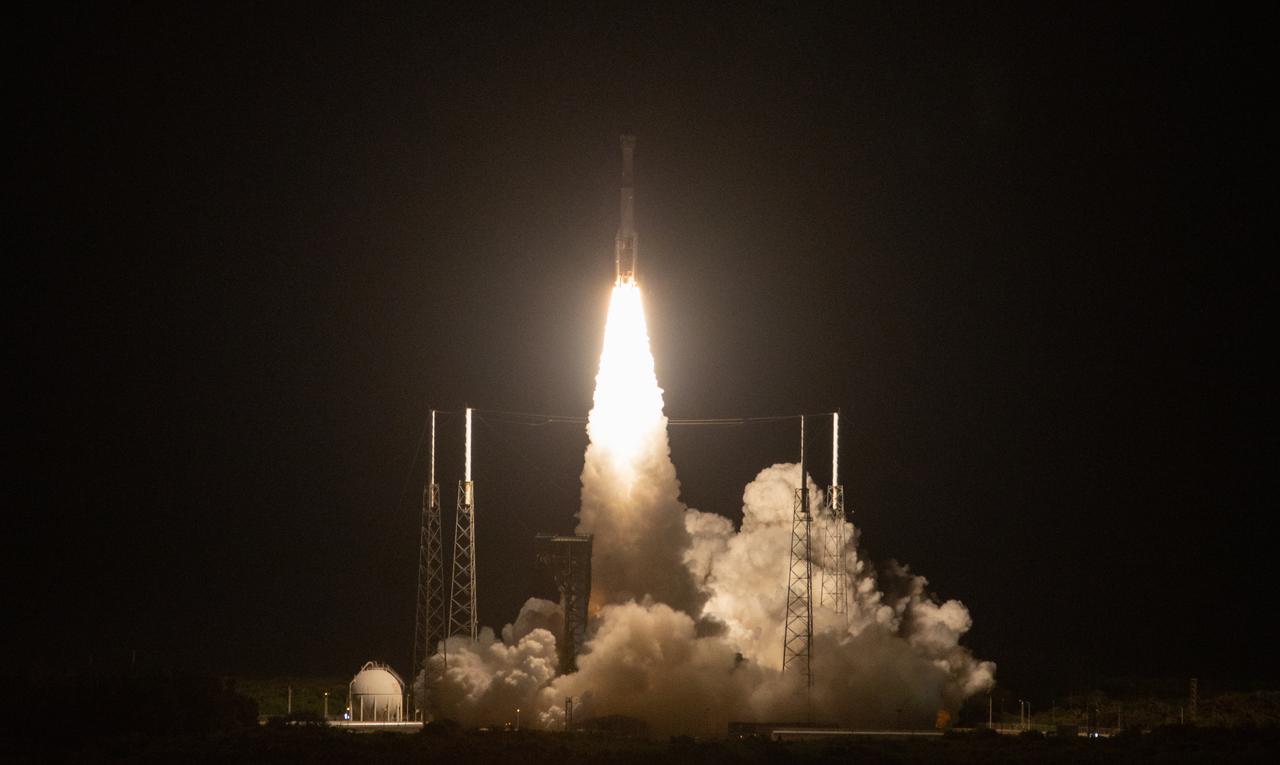

A two-stage United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test, Dec. 20, 2019. Liftoff occurred at 6:36 a.m. EST. The uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is the Starliner’s first flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

As seen in a long exposure image, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Dragon spacecraft lifts off on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission to the International Space Station with NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov aboard Saturday, Sept. 28, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Crew-9 is the ninth crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Hague and Gorbunov launched at 1:17 p.m. EDT to begin a mission aboard the orbital outpost lasting about five months.

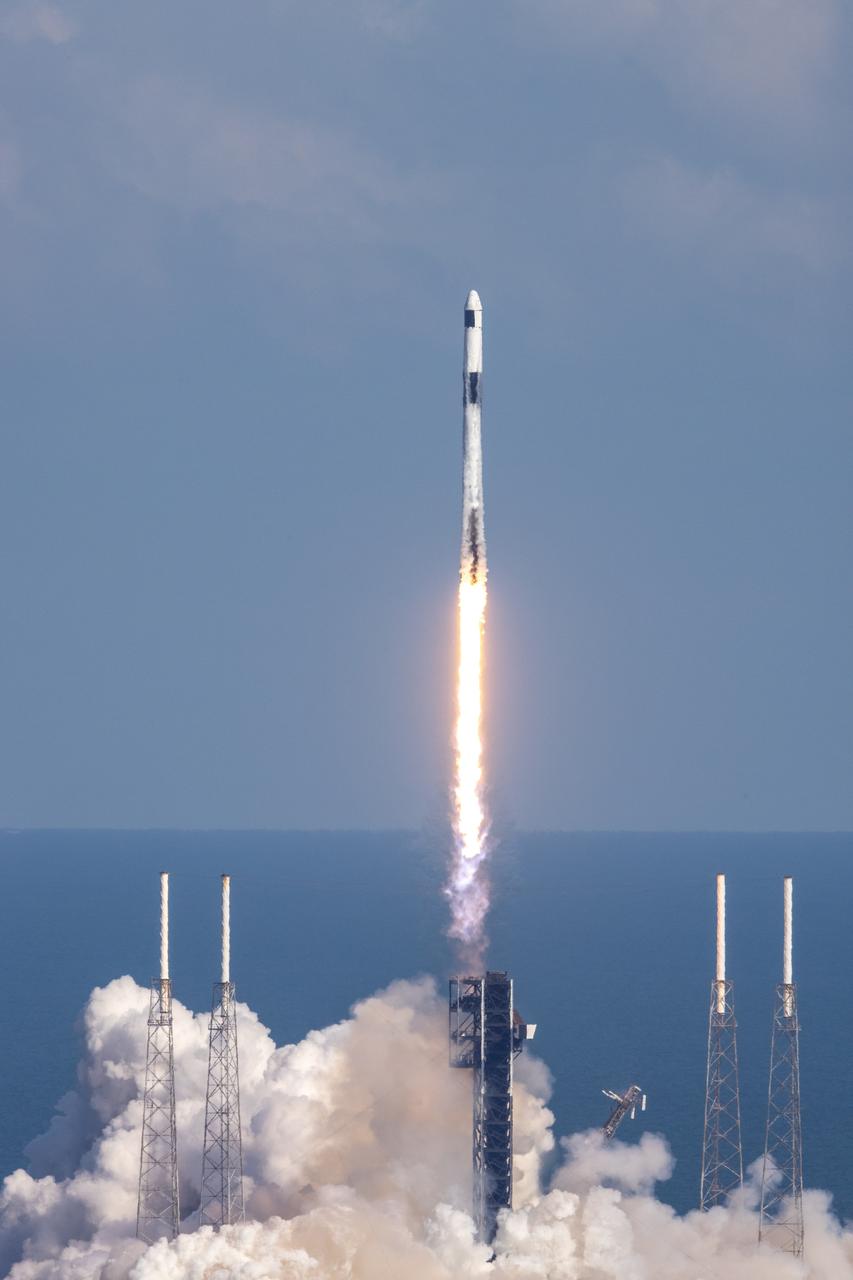
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at 2:30 a.m. EDT on June 25, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Falcon Heavy rocket carries two dozen satellites to space for the U.S. Department of Defense, including four NASA payloads that are part of the Space Test Program (STP-2) mission, managed by the U.S. Air Force Space and Missile Systems Center. The four NASA payloads include two technology demonstrations to improve how spacecraft propel and navigate, as well as two NASA science missions to help us better understand the nature of space and how it impacts technology on spacecraft and the ground.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 4:55 p.m. EDT on Thursday, March 21, on the company’s 30th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Dragon will deliver more than 6,200 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA and partner research including a look at plant metabolism in space and a set of new sensors for free-flying Astrobee robots to provide 3D mapping capabilities. Other studies include a fluid physics study that could benefit solar cell technology and a university project from CSA (Canadian Space Agency) that will monitor sea ice and ocean conditions. The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
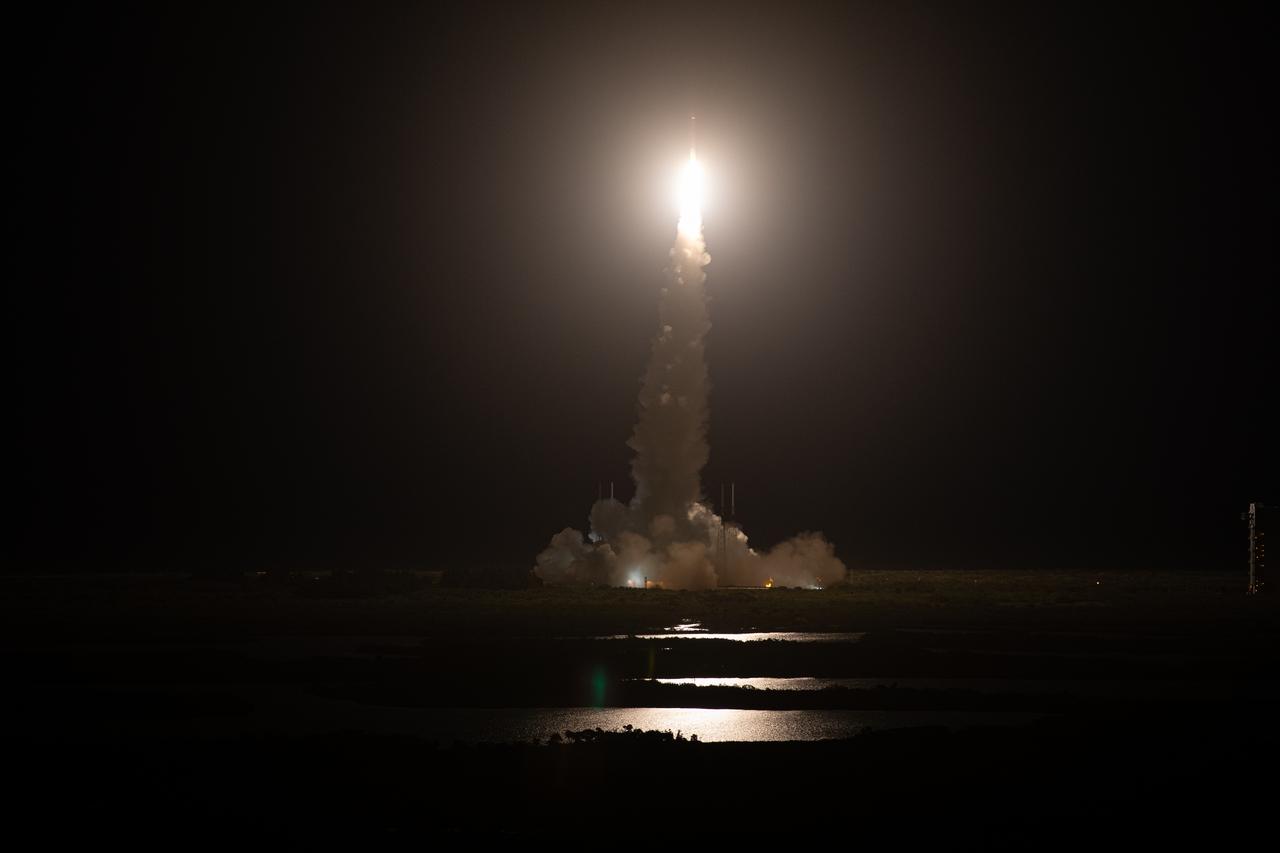

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, carrying the Solar Orbiter, climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 9, 2020. Liftoff was at 11:03 p.m. EST. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy managed the launch.
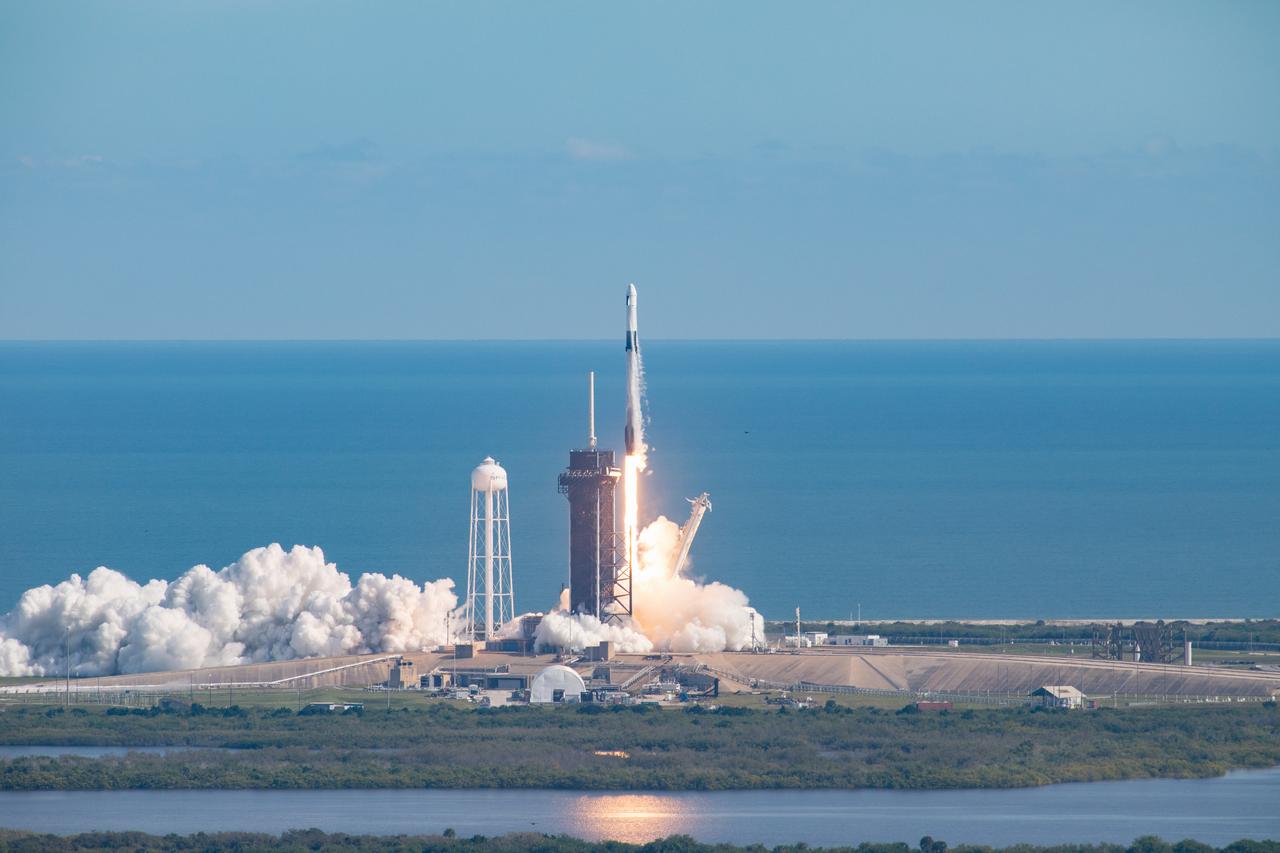

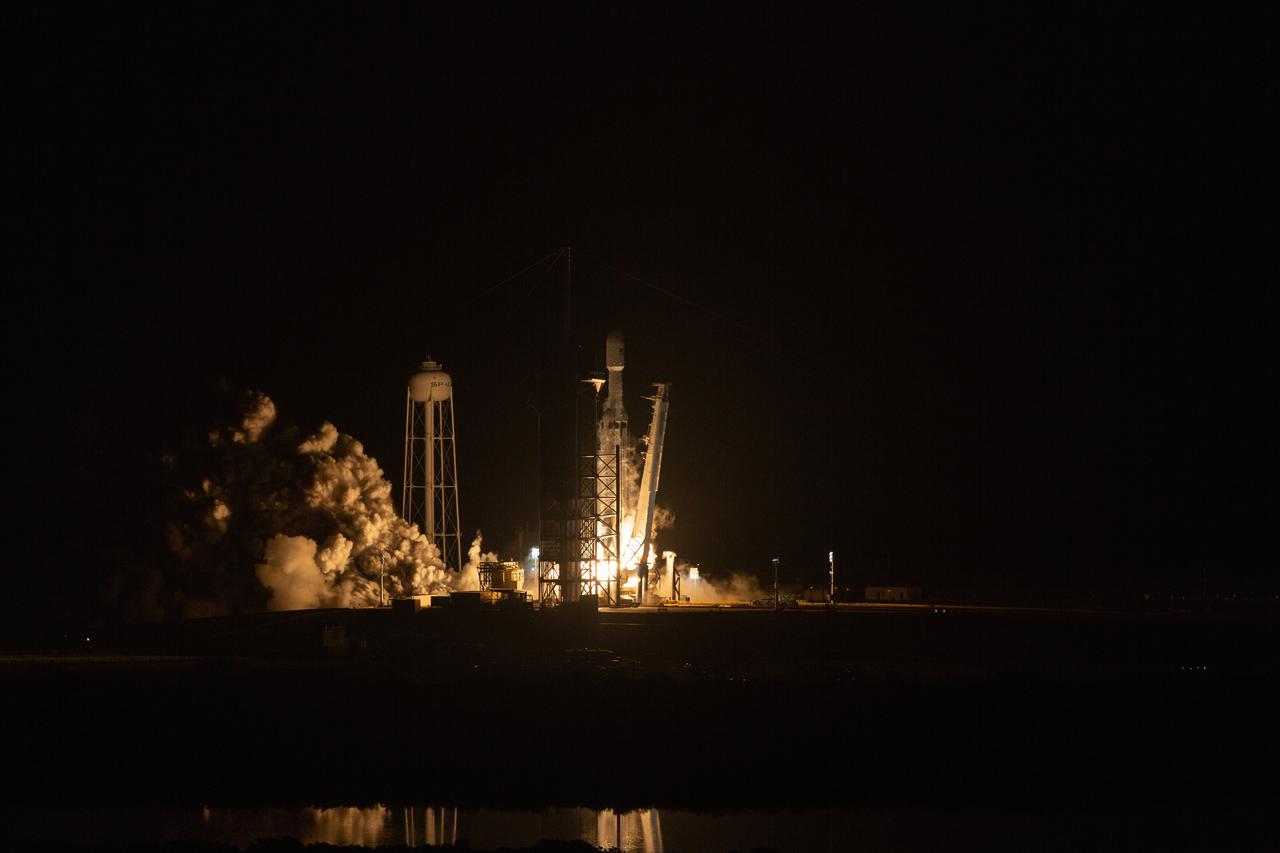
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.
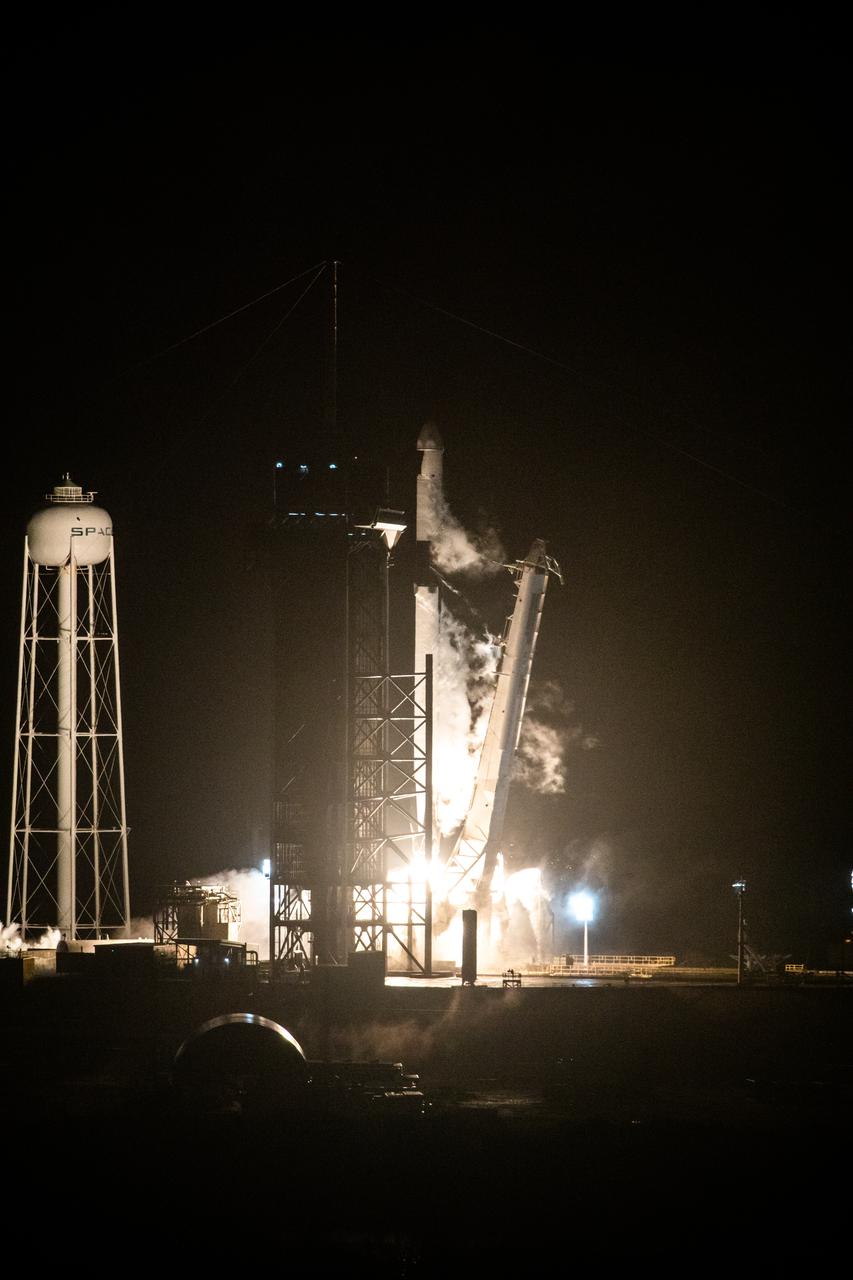

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 5:07 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Dec. 21, 2021, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station. SpaceX’s 24th commercial resupply services mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew on board the space station. Arrival to the orbiting laboratory is planned for Wednesday, Dec. 22.
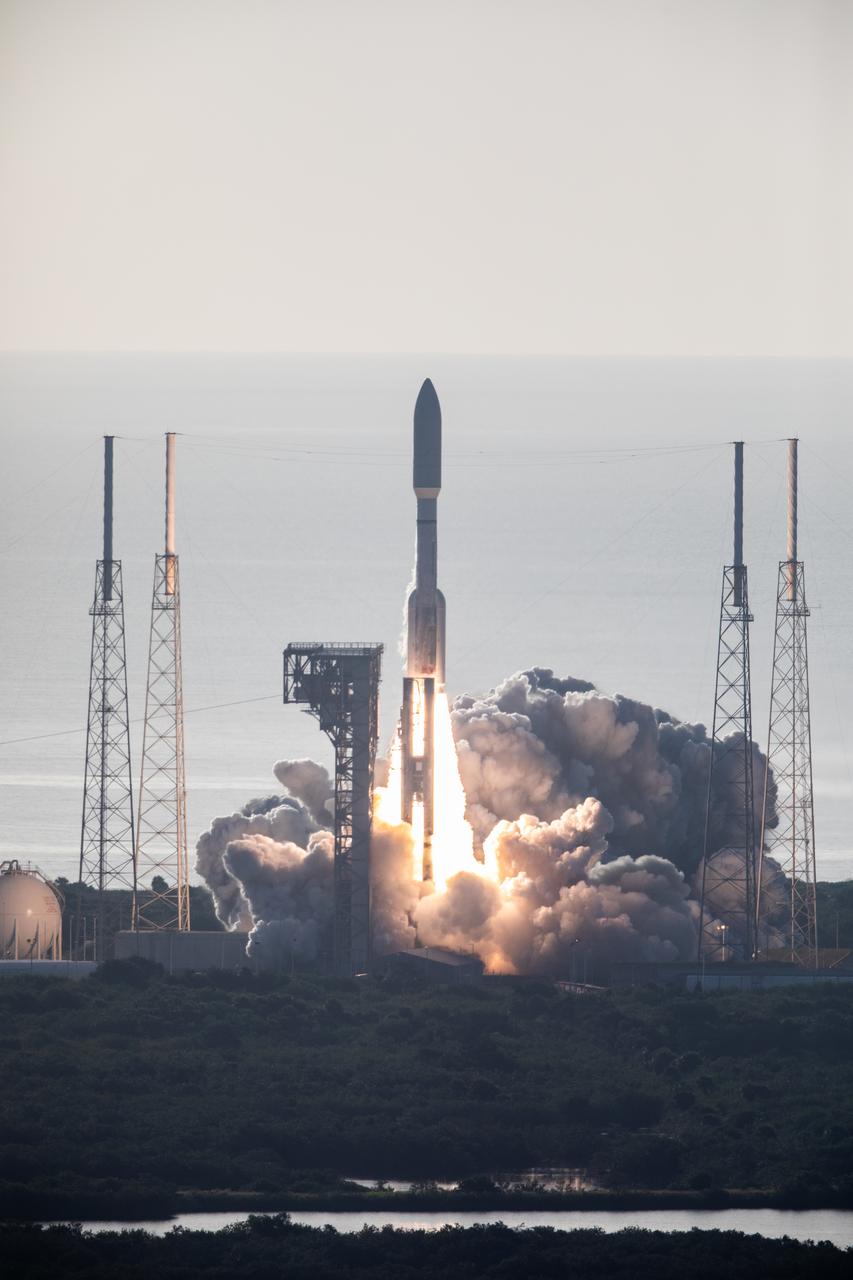

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
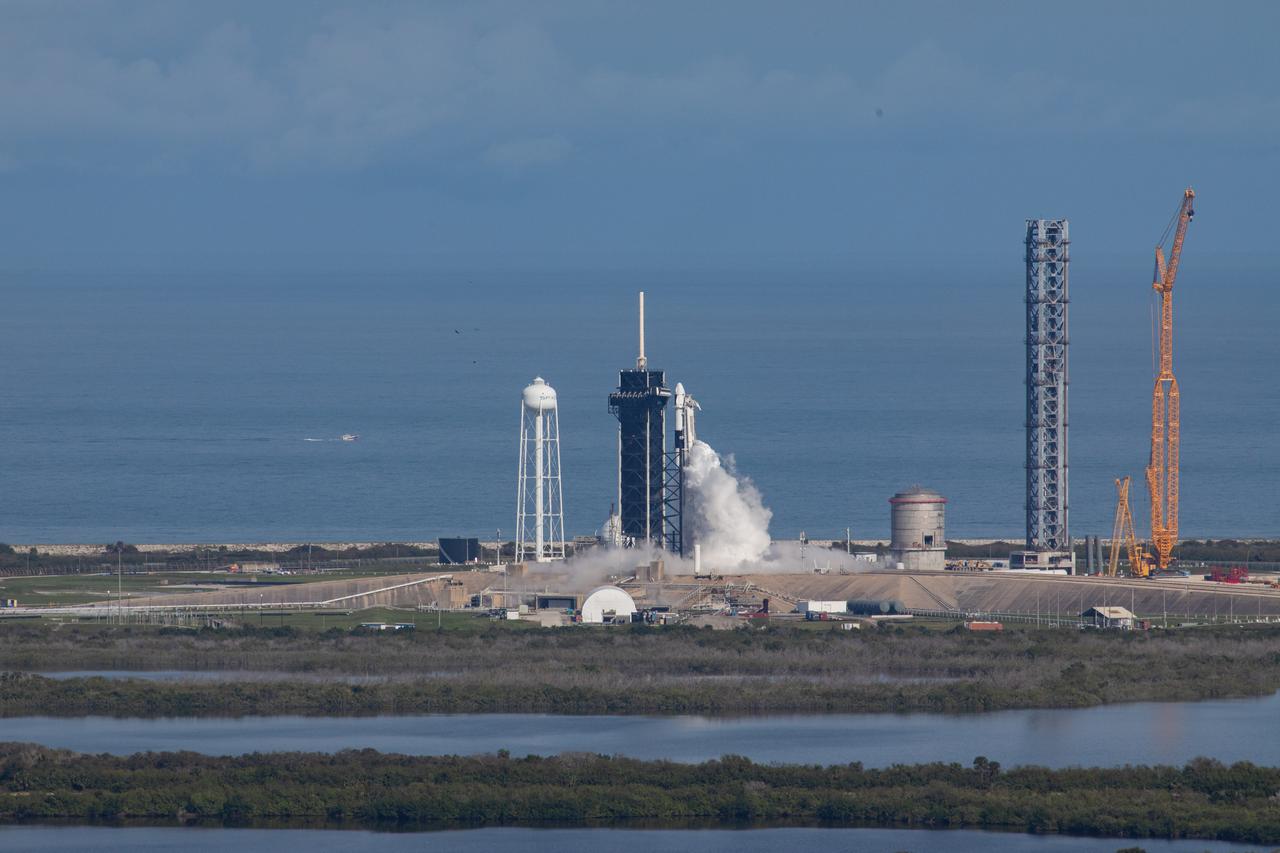

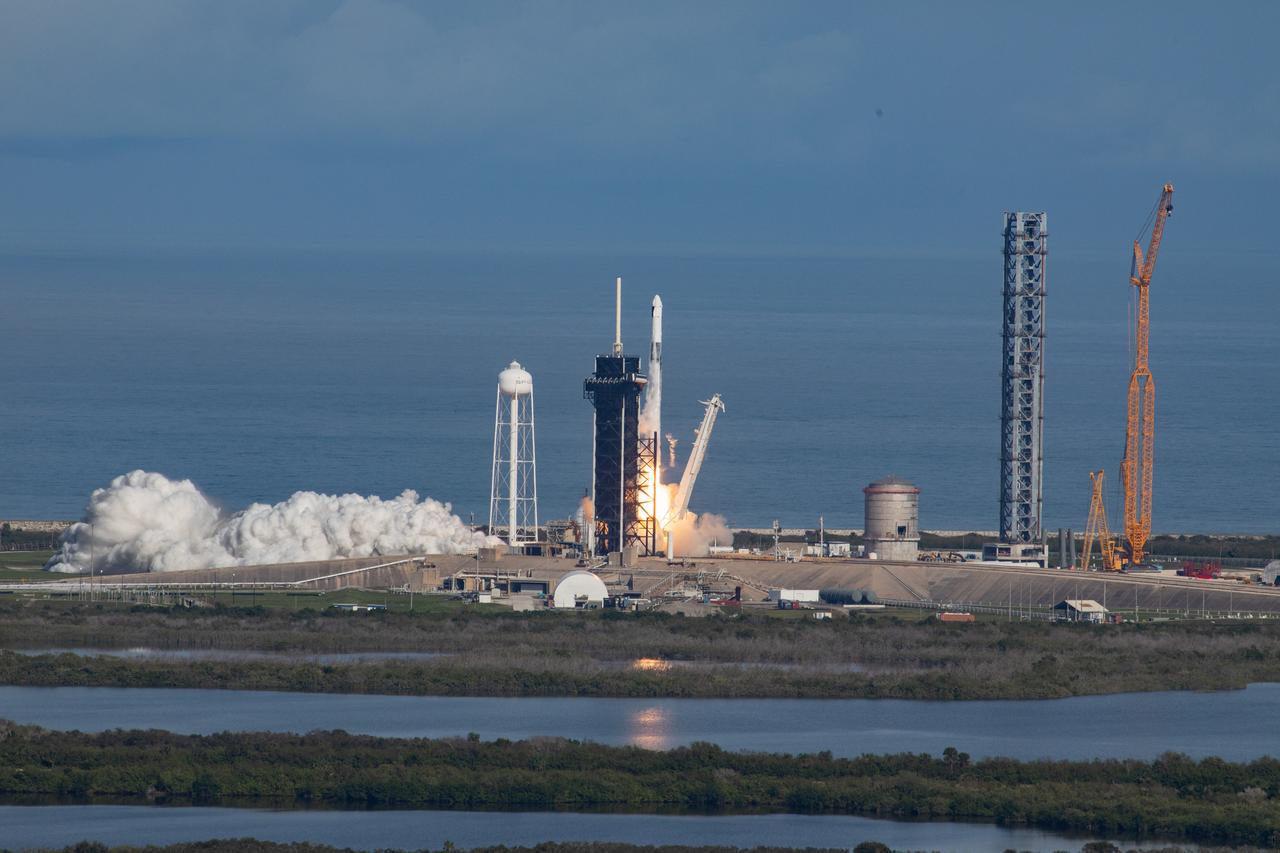
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
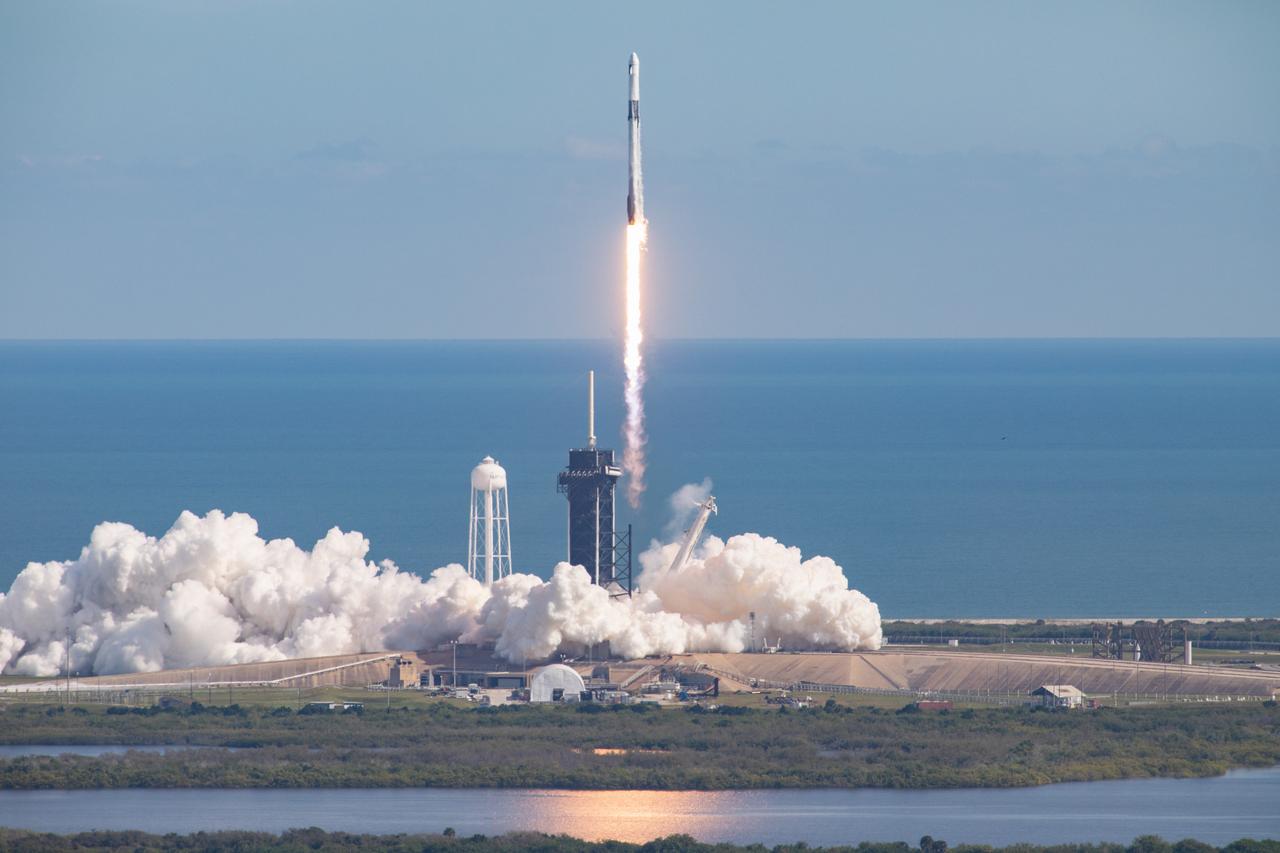

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars into the sky after lifting off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020. The rocket is carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.
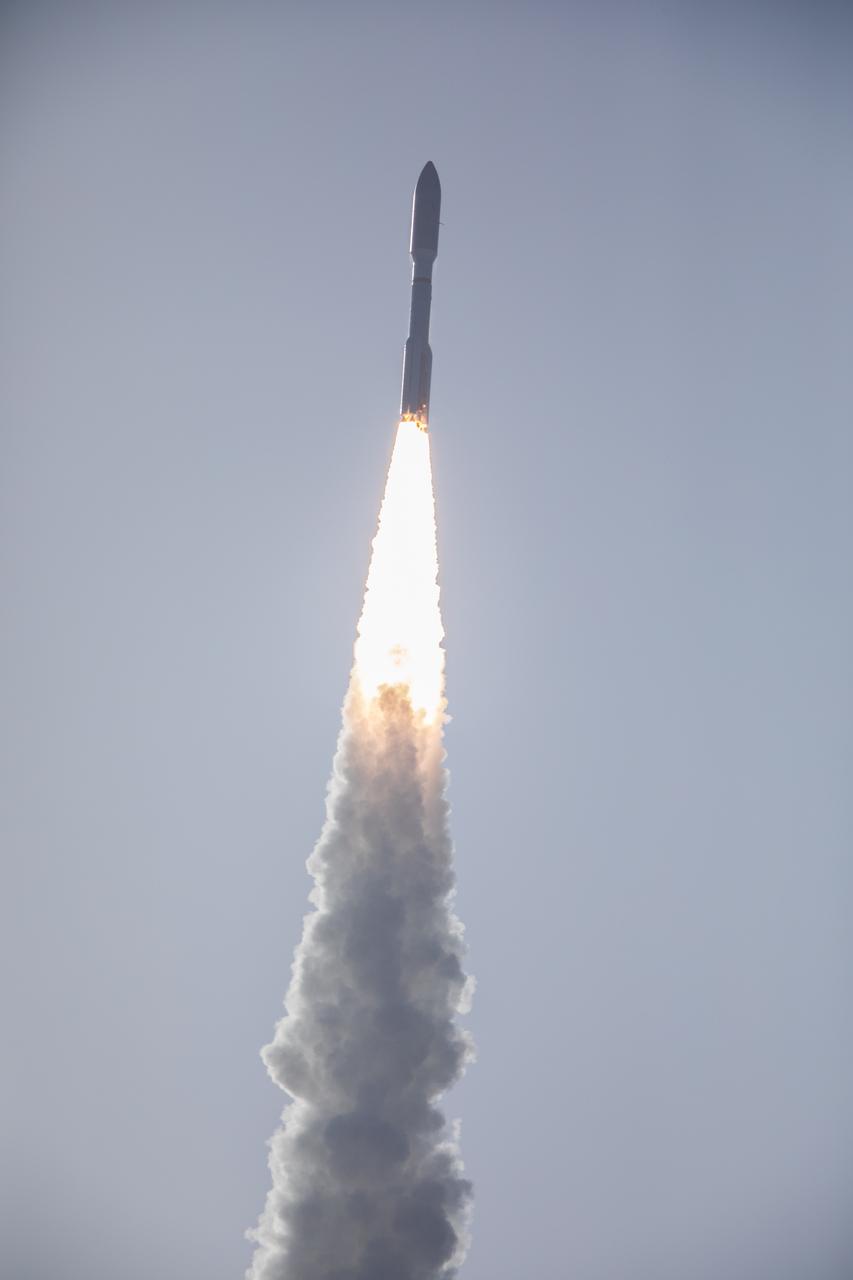

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
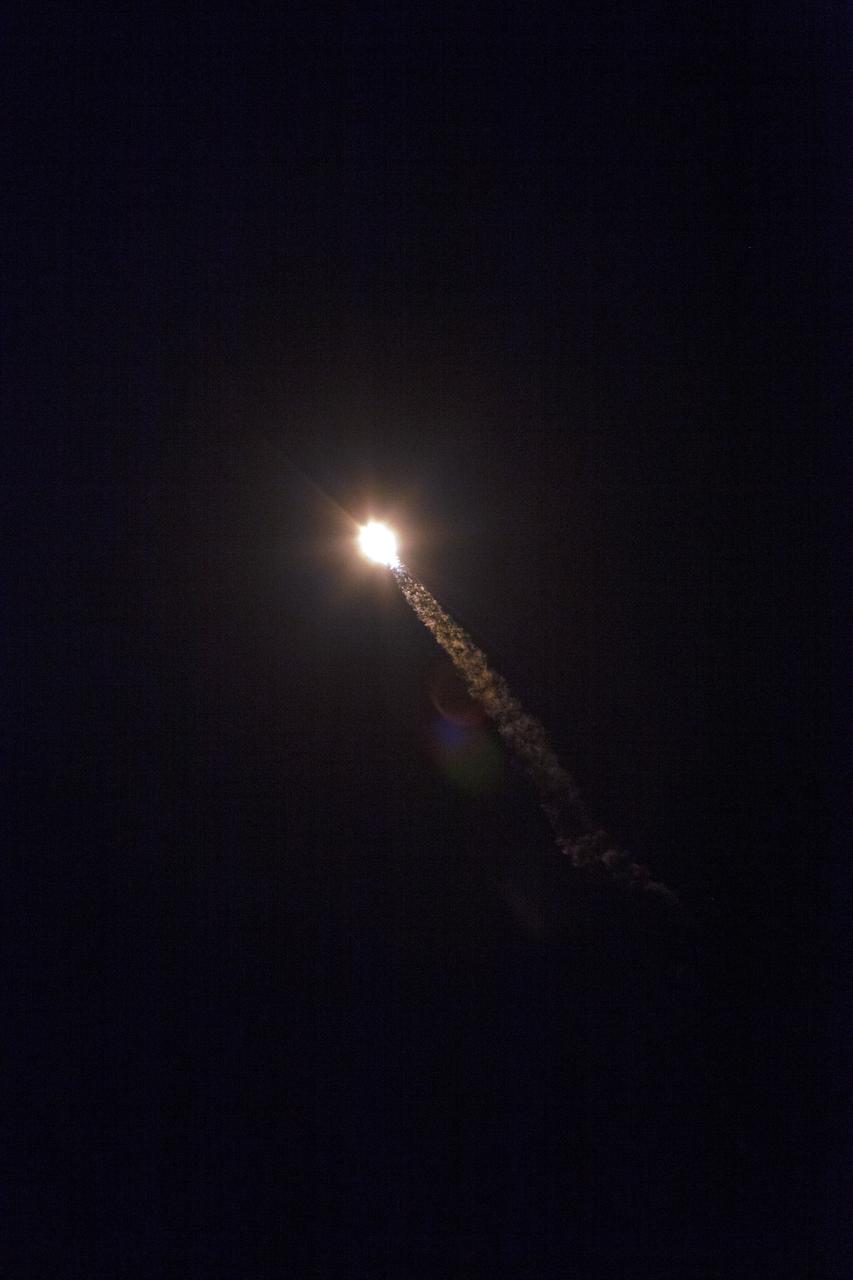

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
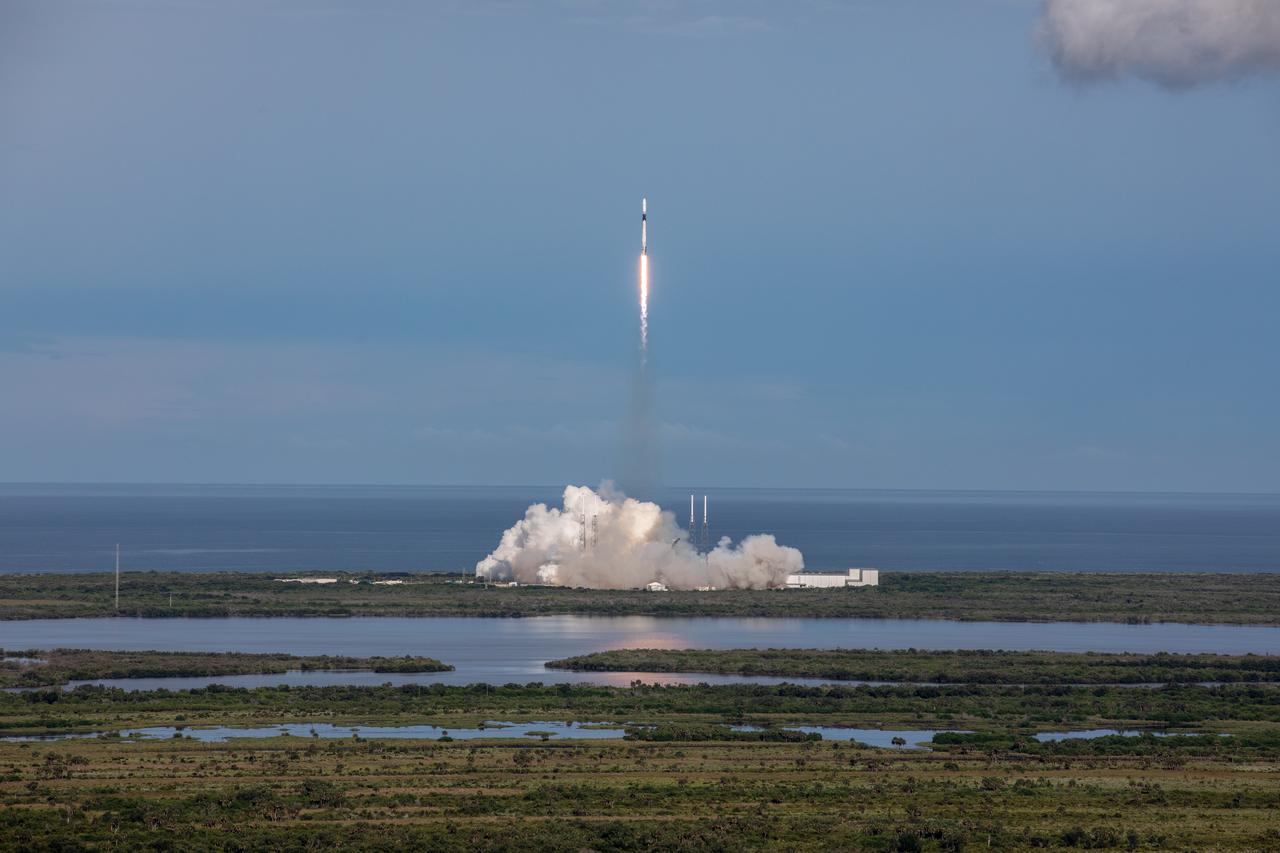

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
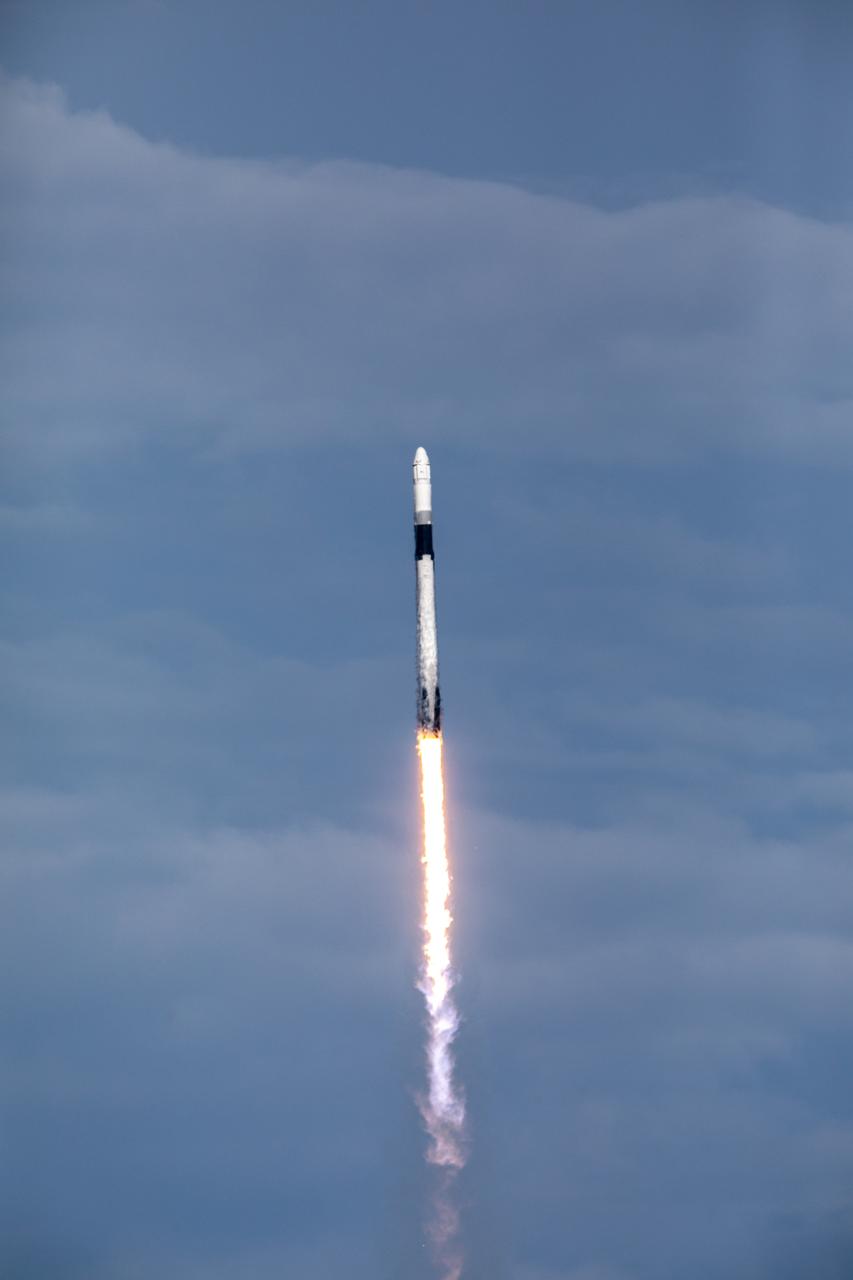

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.
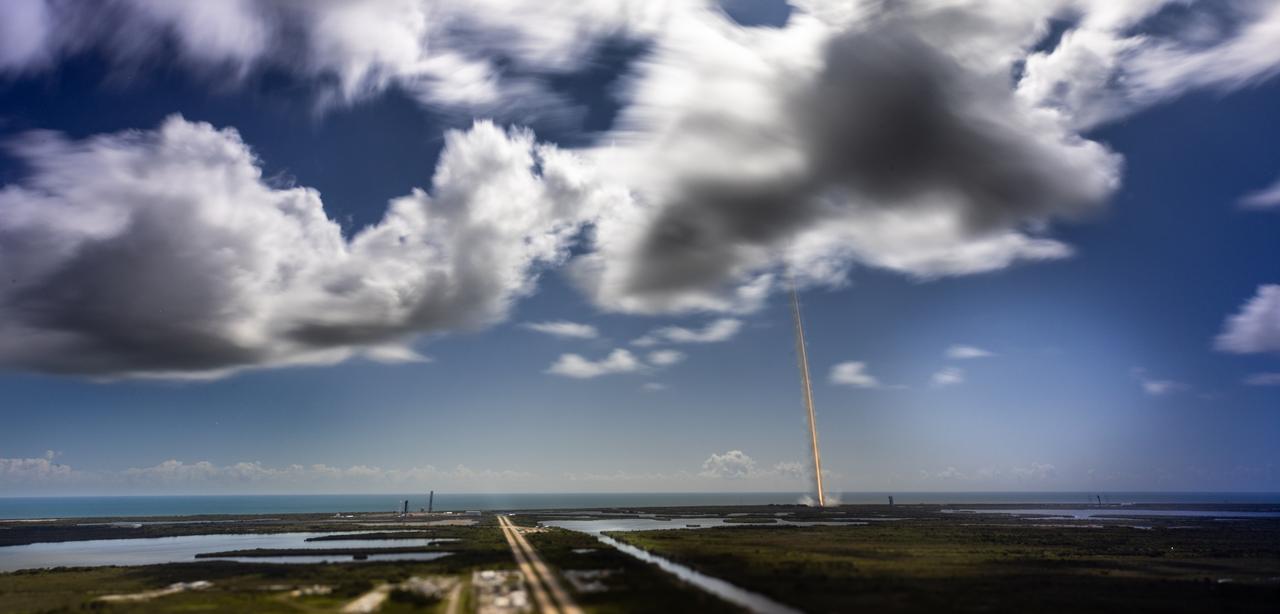

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying a Boeing Starliner spacecraft launches NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test with NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams aboard at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday, June 5, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Wilmore and Williams are the first to launch aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
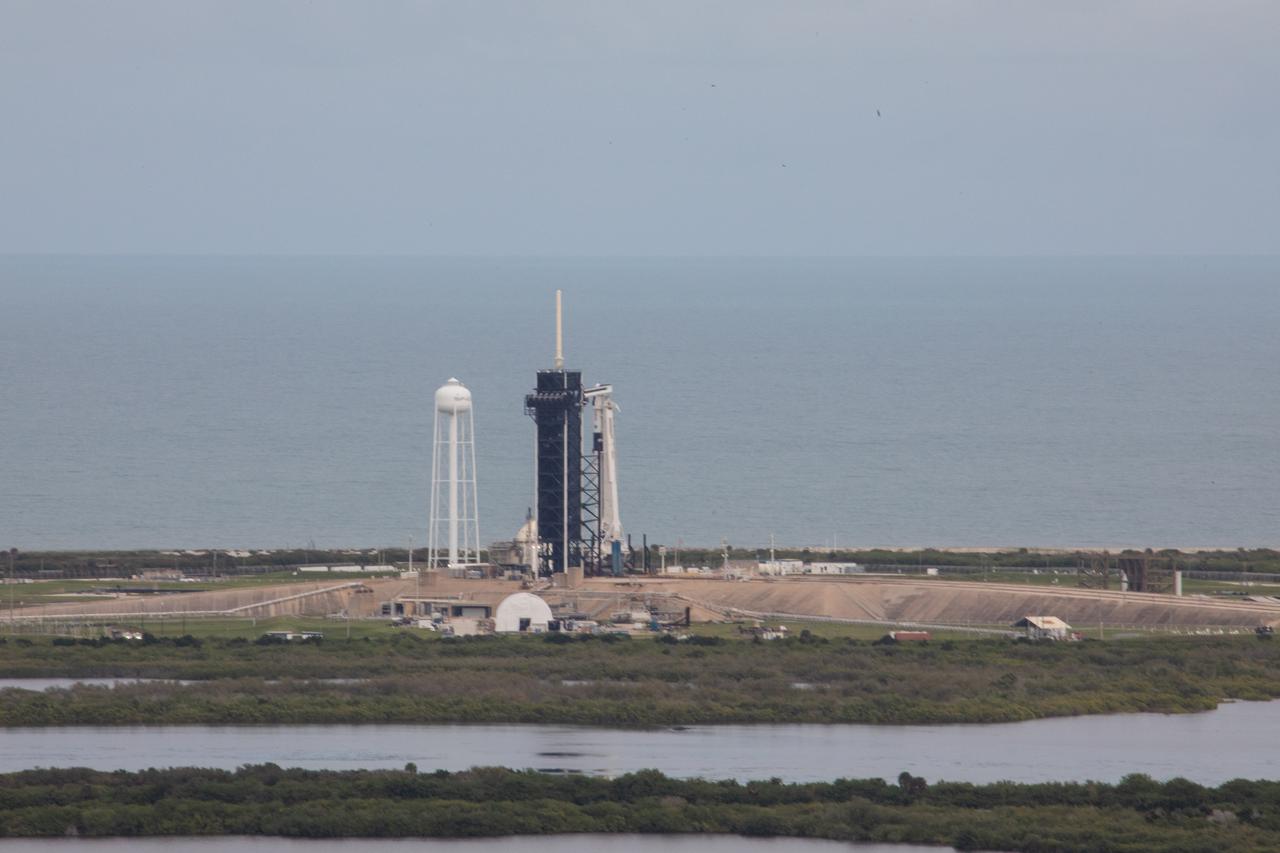

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket sits on Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 15, 2020, ready for launch. The Crew Dragon Resilience capsule sits atop with NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 NASA astronauts, Michael Hopkins, spacecraft commander; Victor Glover, pilot; Shannon Walker, mission specialist; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Soichi Noguchi, mission specialist. Crew-1 is the first regular crew mission of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew Dragon will dock with the space station and the crew will remain on the orbiting laboratory for a six-month science mission.
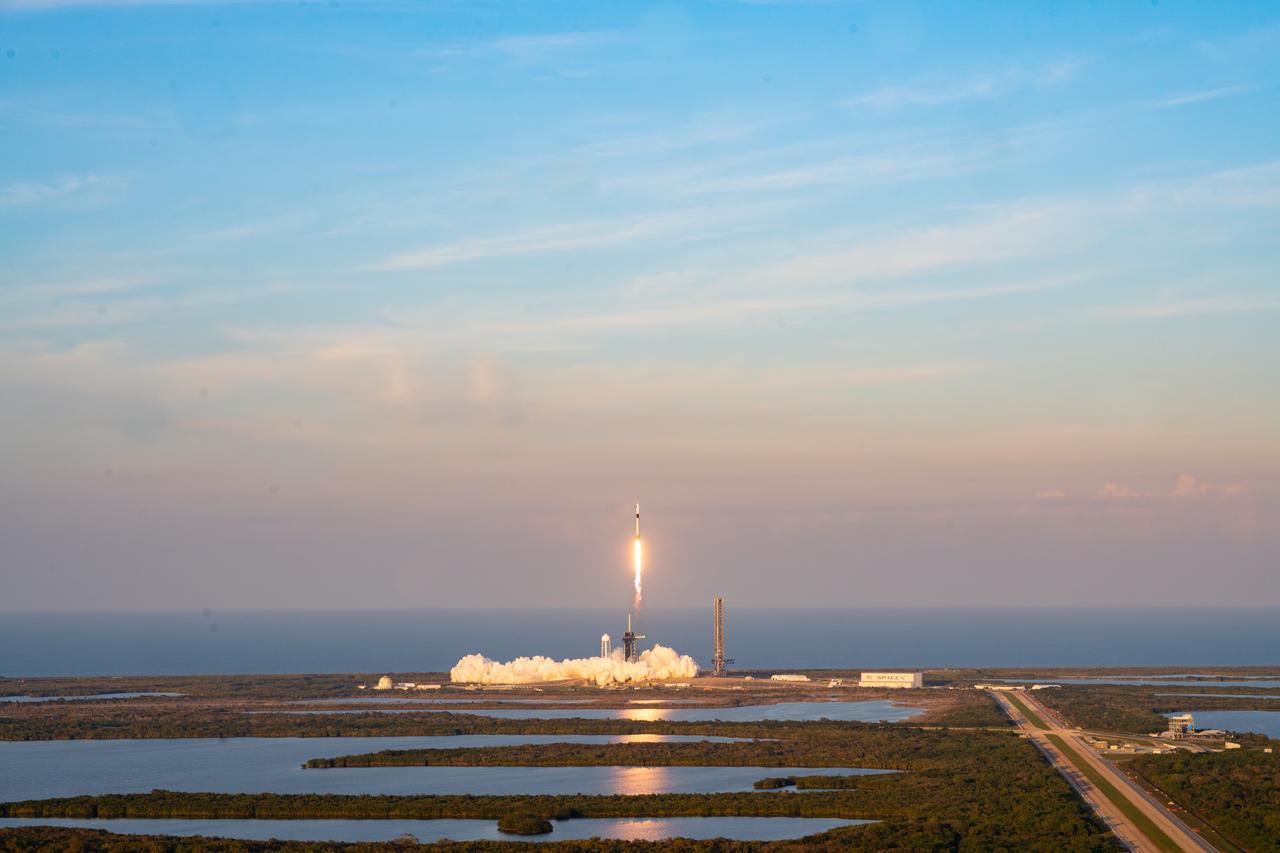

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the company's Dragon spacecraft lifts off on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station with NASA astronauts Anne McClain and Nichole Ayers, along with JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Takuya Onishi and Roscosmos cosmonaut Kirill Peskov aboard at 7:03 p.m. EDT Friday, March 14, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Crew-10 is the 10th crew rotation mission of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
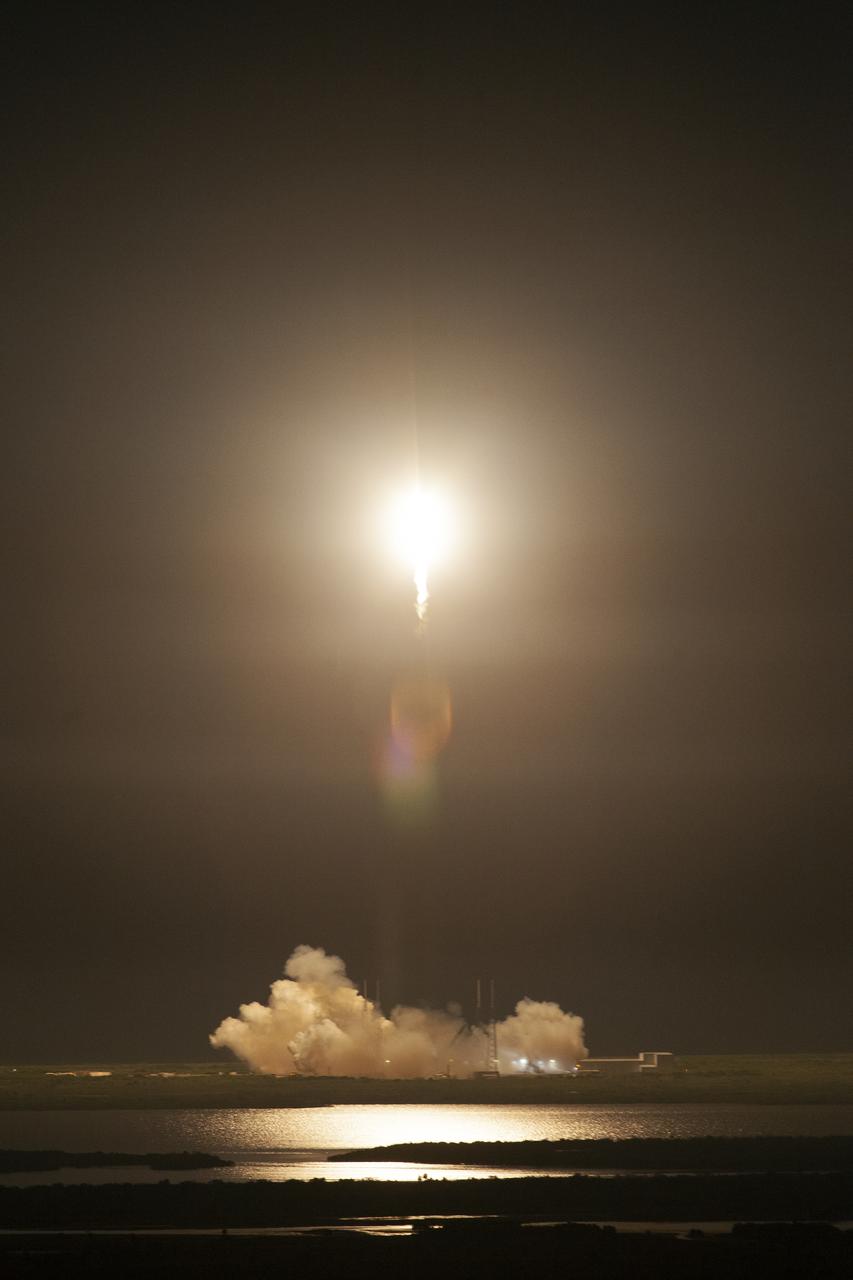

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket climbs upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
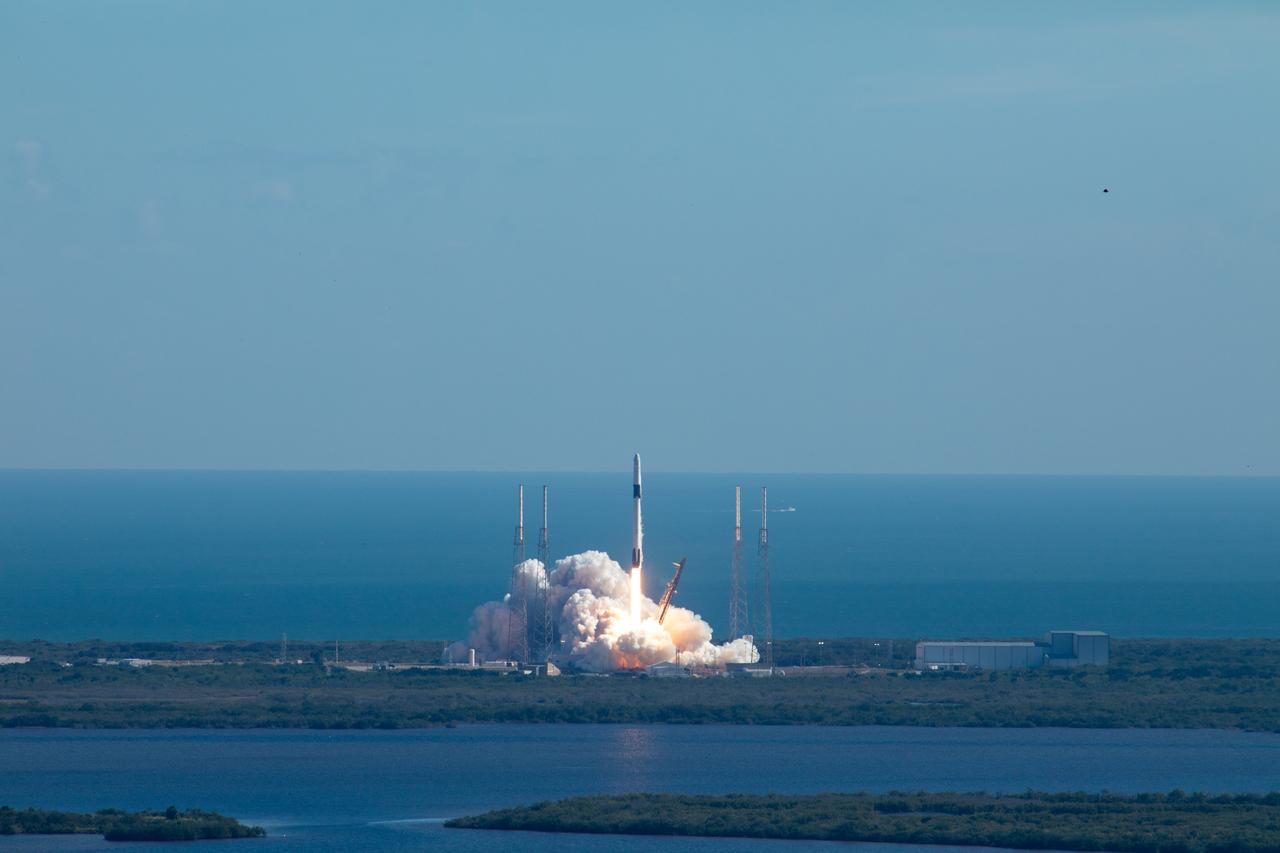

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early afternoon on Dec. 5, 2019. Liftoff was at 12:29 p.m. EST. This is SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-19) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver more than 5,700 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket soars upward after lifting off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 30, 2020, at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
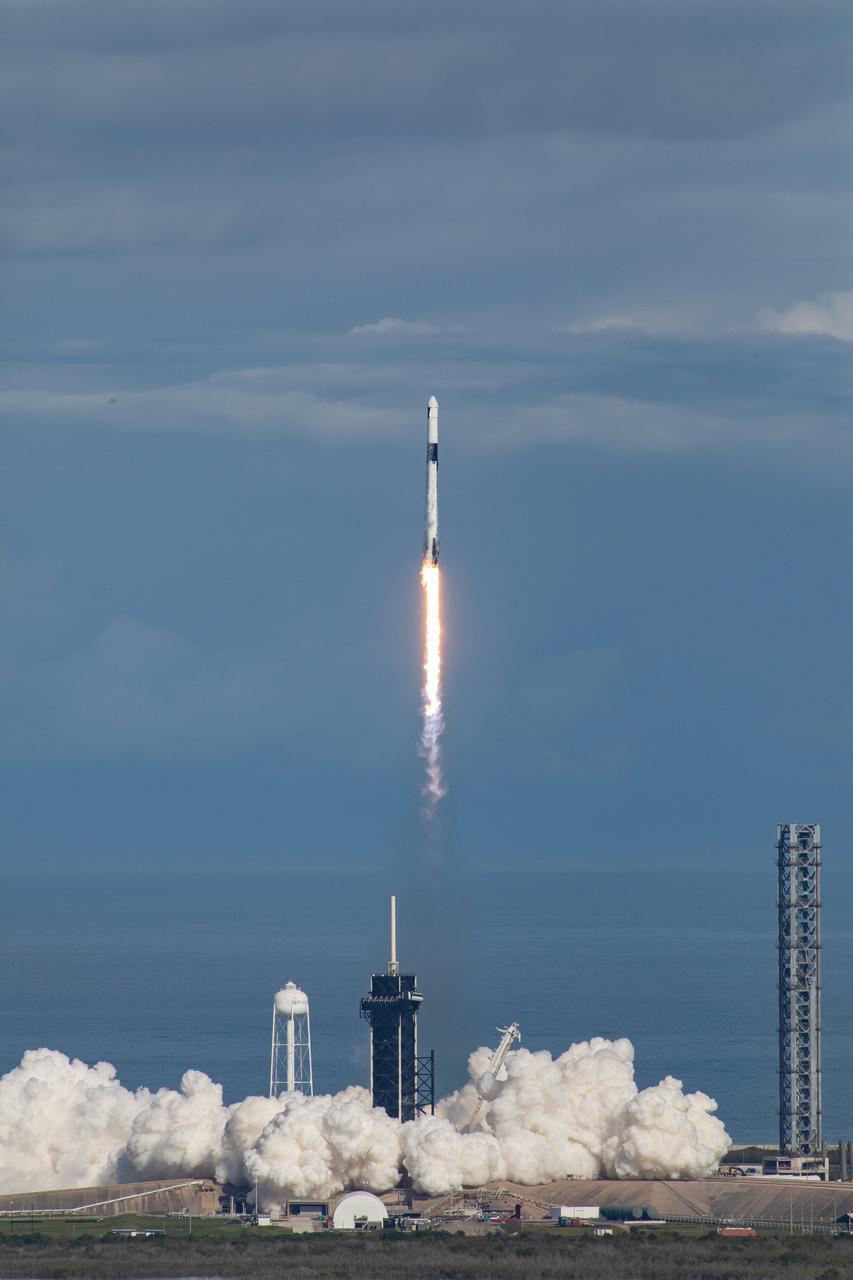

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
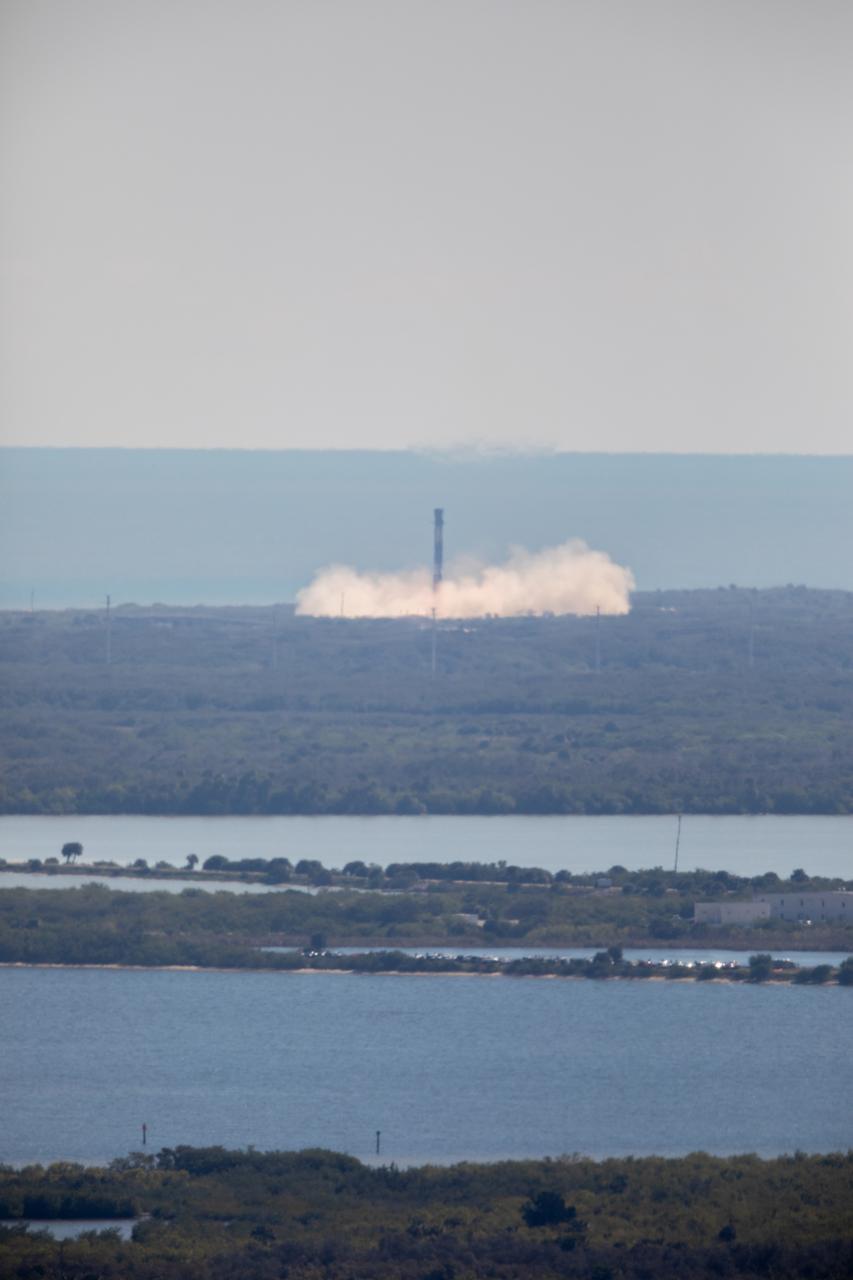

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
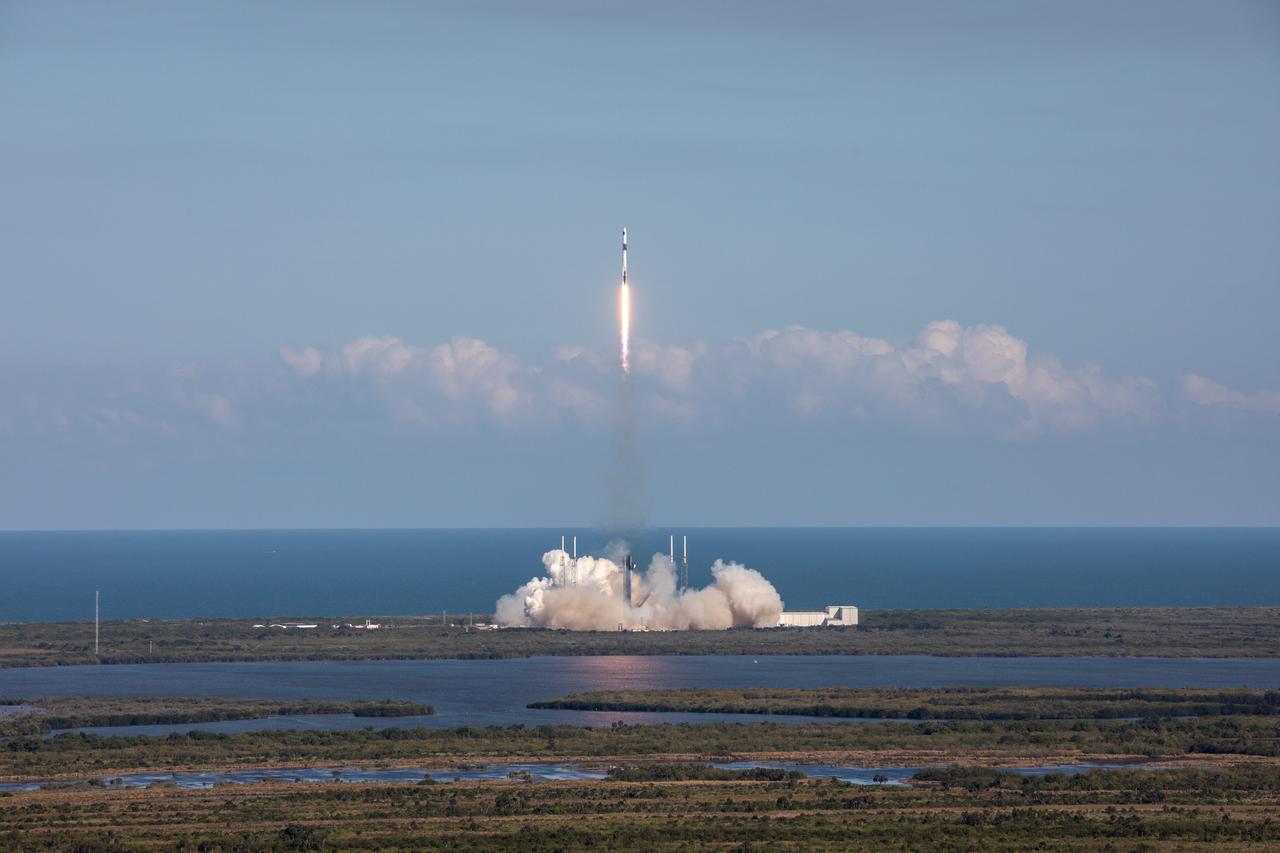

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 4:55 p.m. EDT on Thursday, March 21, on the company’s 30th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Dragon will deliver more than 6,200 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA and partner research including a look at plant metabolism in space and a set of new sensors for free-flying Astrobee robots to provide 3D mapping capabilities. Other studies include a fluid physics study that could benefit solar cell technology and a university project from CSA (Canadian Space Agency) that will monitor sea ice and ocean conditions. The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
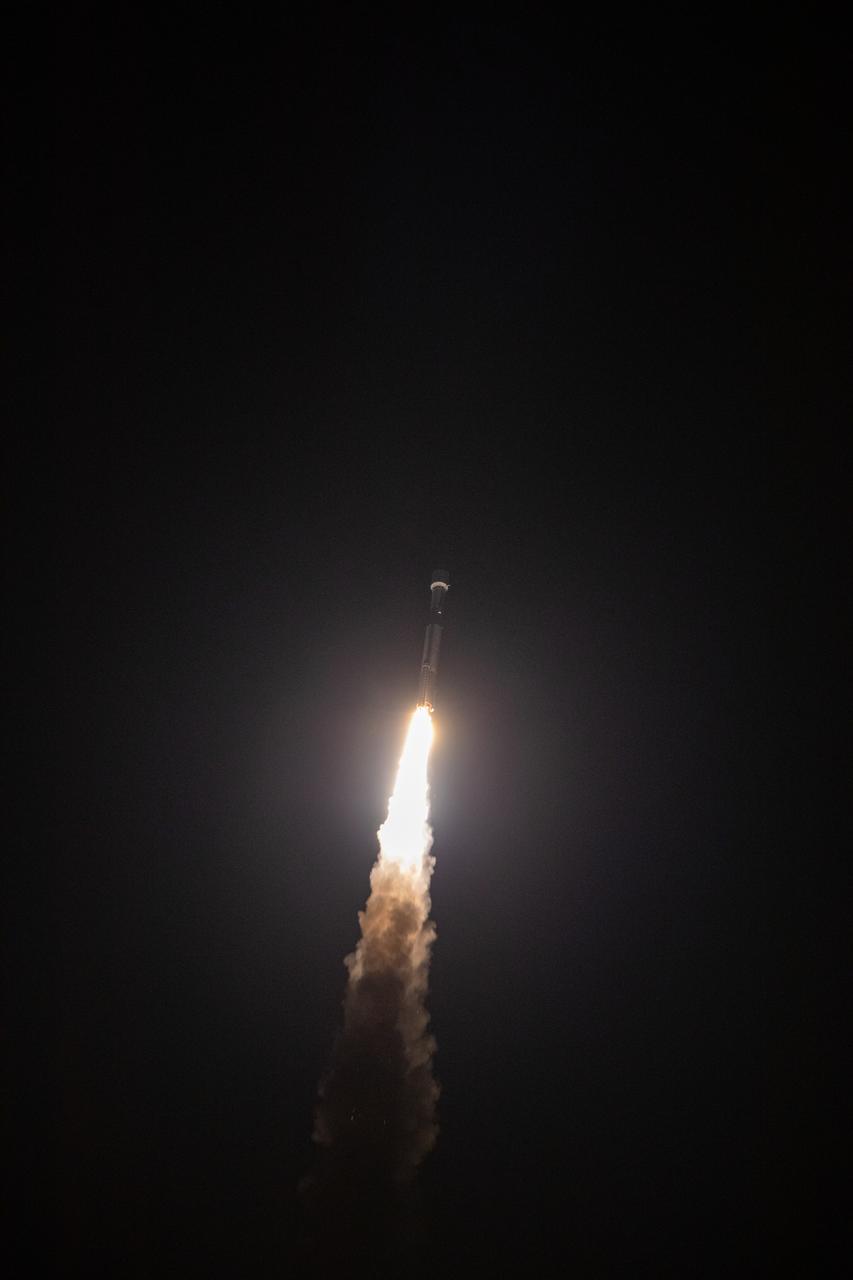

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, carrying the Solar Orbiter, climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in cmsFlorida on Feb. 9, 2020. Liftoff was at 11:03 p.m. EST. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy managed the launch.
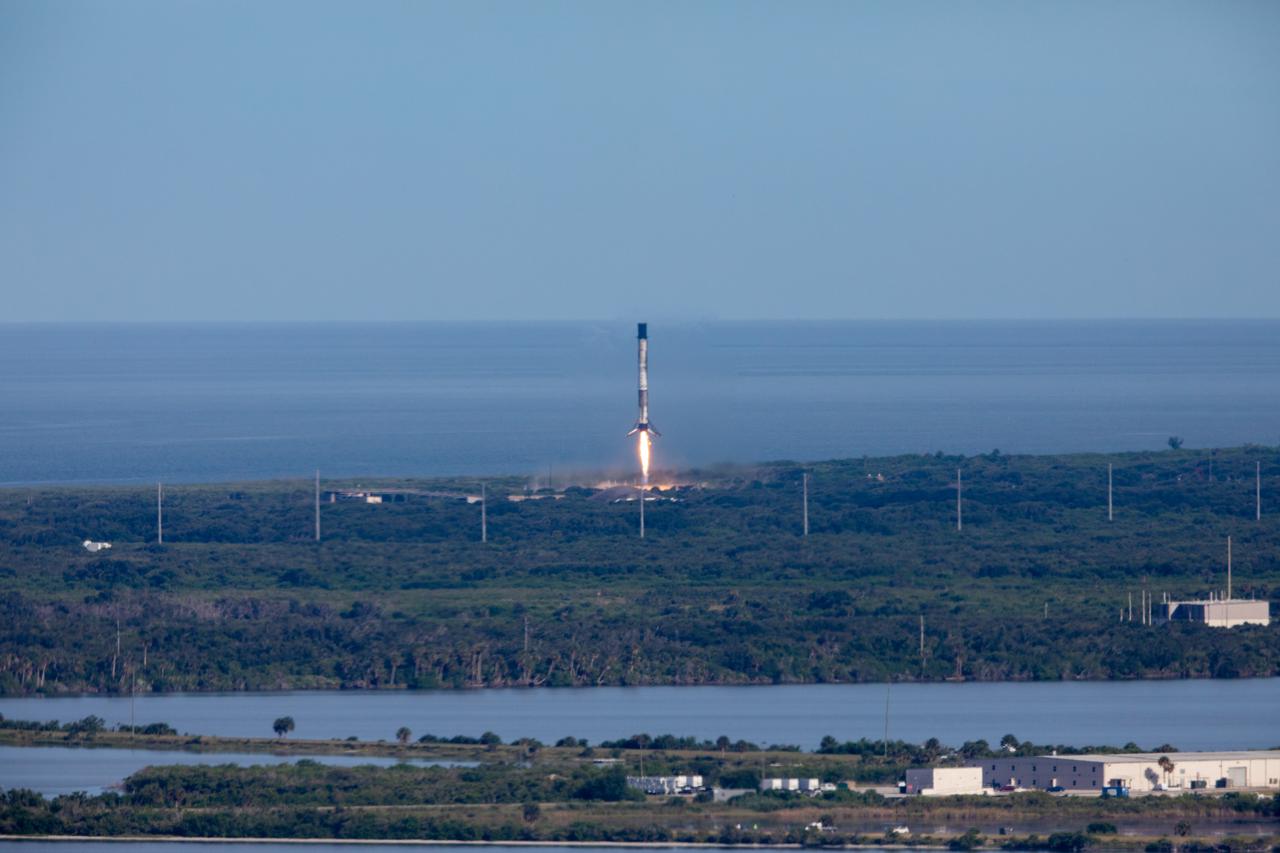

After boosting a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft on its way to the International Space Station for the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services mission, the first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 25, 2019. The rocket lifted off minutes earlier, at 6:01 p.m. EDT, from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
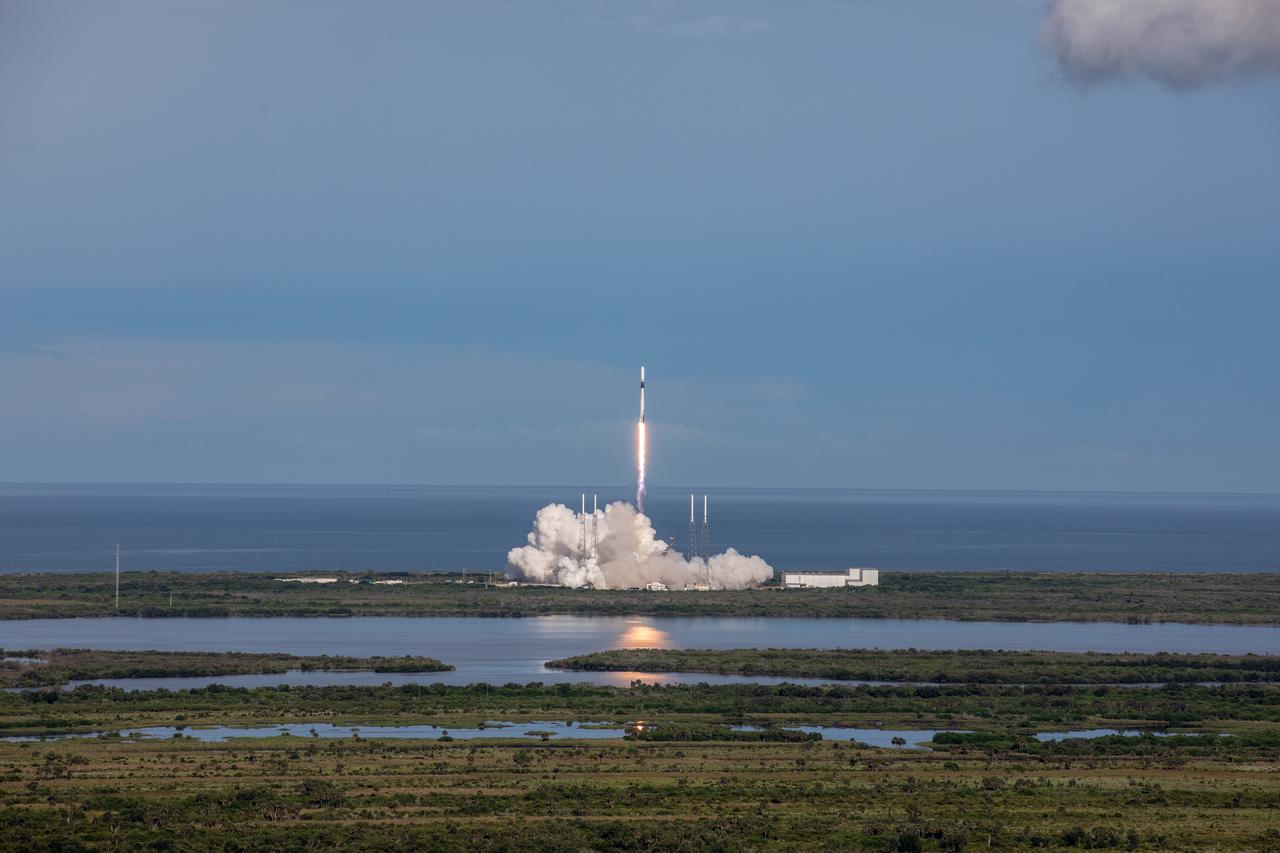

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
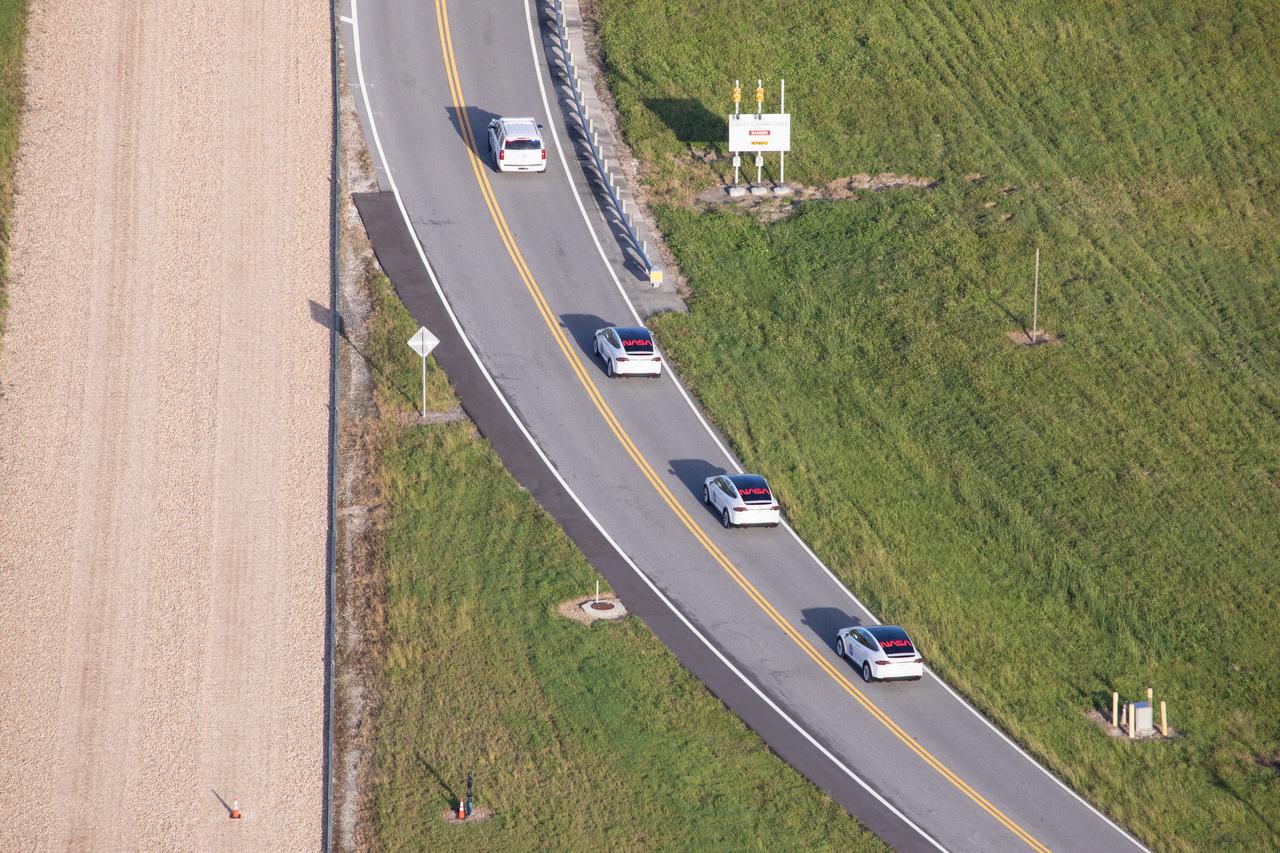

Two Tesla vehicles carrying the NASA SpaceX Crew-1 astronauts are on their way to Launch Complex 39A on Nov. 15, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the vehicles are NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, spacecraft commander; NASA astronaut Victor Glover, pilot; NASA astronaut Shannon Walker, mission specialist; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Soichi Noguchi, mission specialist. Crew-1 is the first regular crew mission of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience capsule will launch atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Pad 39A to the space station for a six-month science mission.