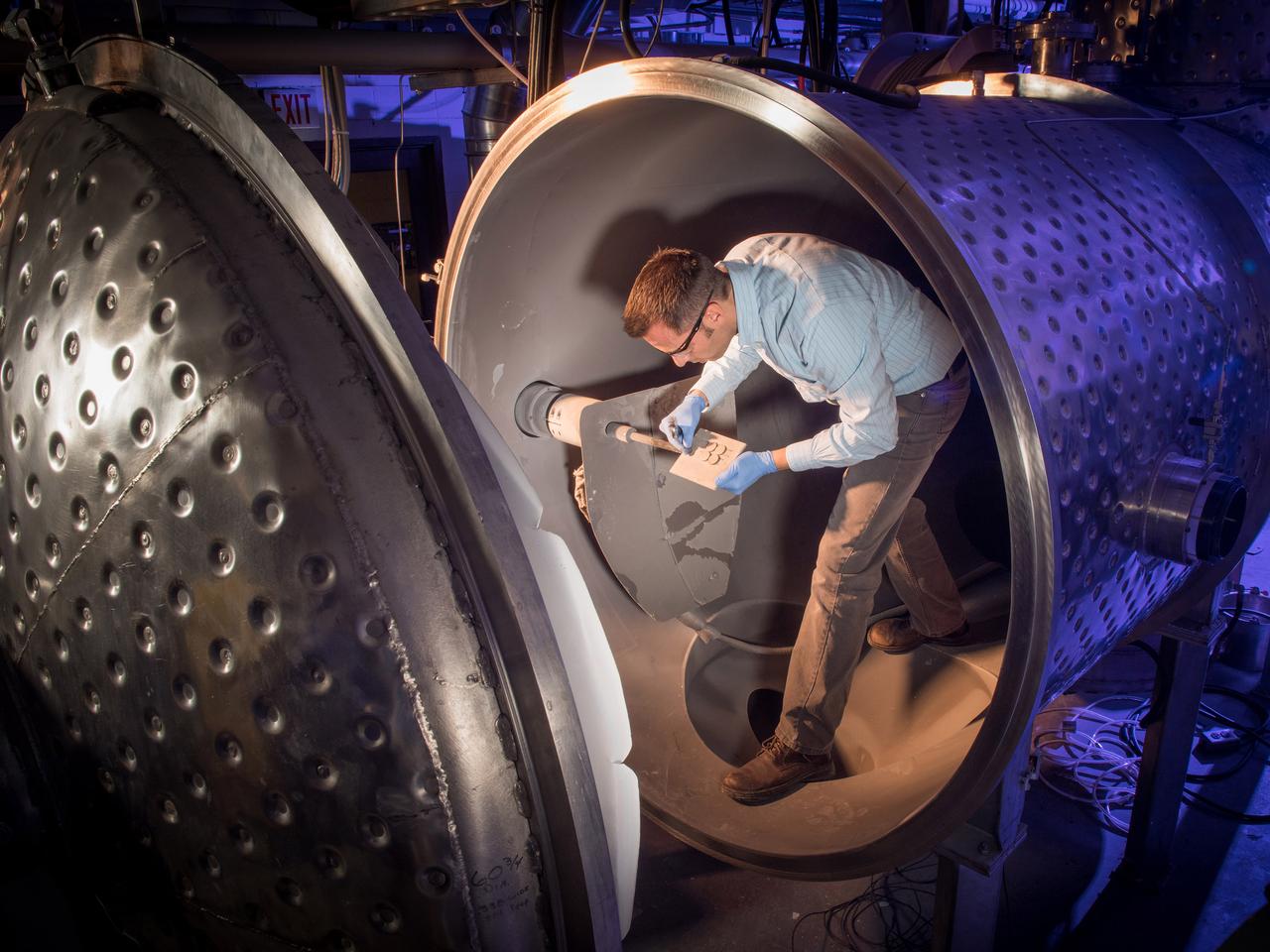

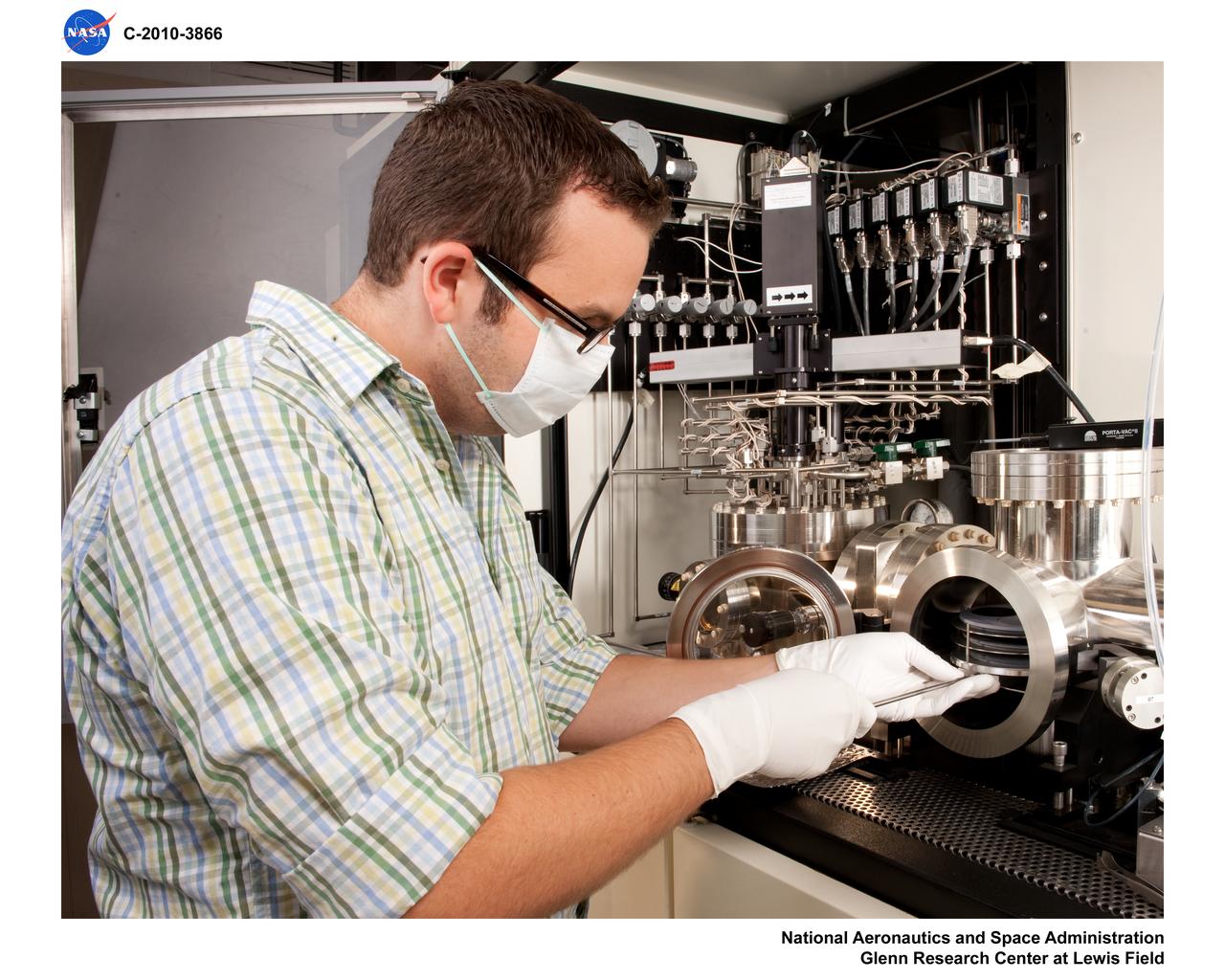
The Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition (PS-PVD) Rig at NASA Glenn Research Center. The rig helps develop coatings for next-generation aircraft turbine components and create more efficient engines.

Eyeing the Sky Water Vapor
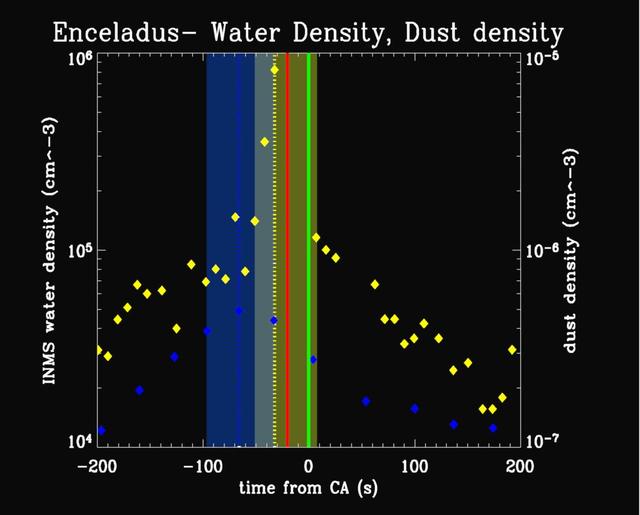
Water Vapor & Particles Over Enceladus
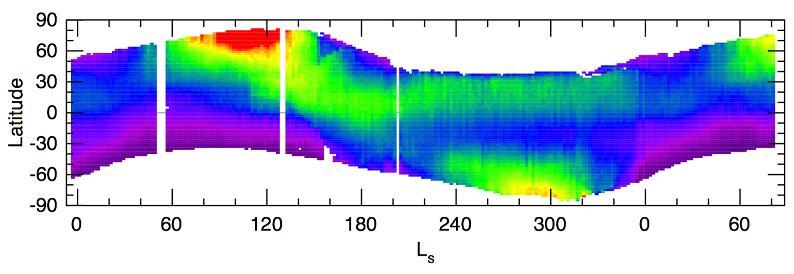
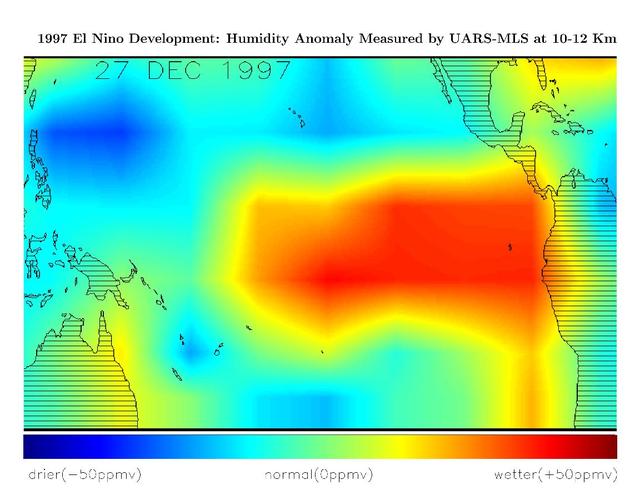
Seasonal Trend in Water Vapor Seen from Orbit
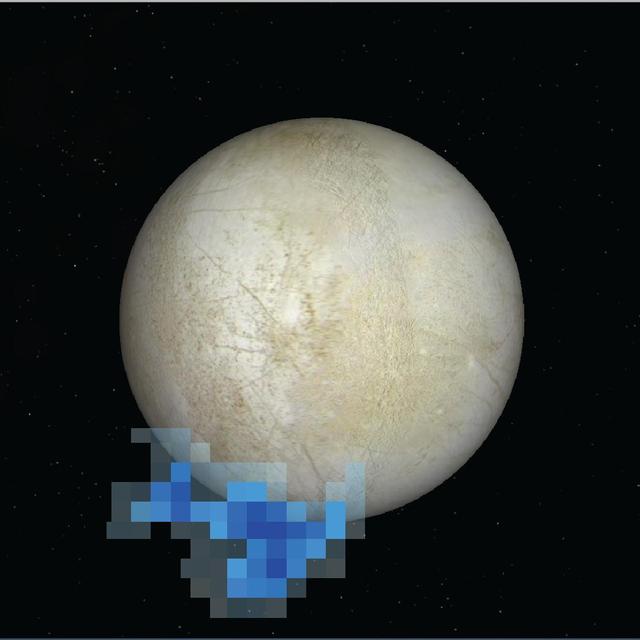

This graphic shows the location of water vapor detected over Europa south pole in observations taken by NASA Hubble Space Telescope in December 2012. This is the first strong evidence of water plumes erupting off Europa surface.
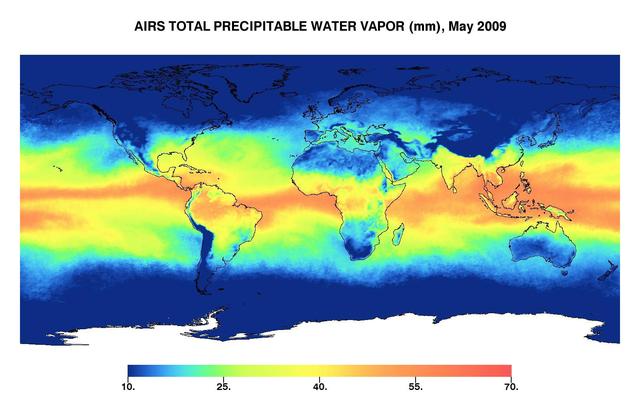
This image represents the total precipitable water vapor for May 2009 as observed by JPL Atmospheric Infrared Sounder on NASA Aqua satellite.
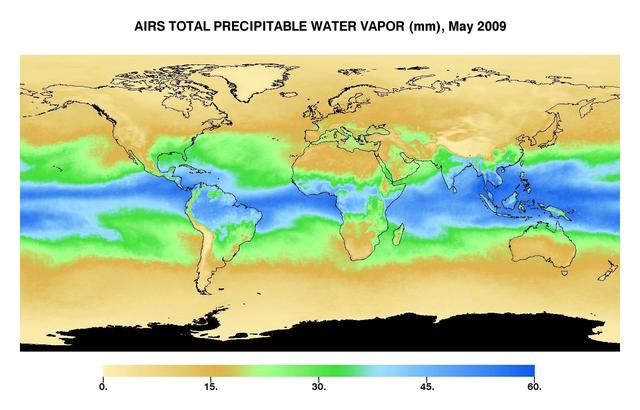
This image represents the total precipitable water vapor for May, 2009 as observed by JPL Atmospheric Infrared Sounder on NASA Aqua satellite.
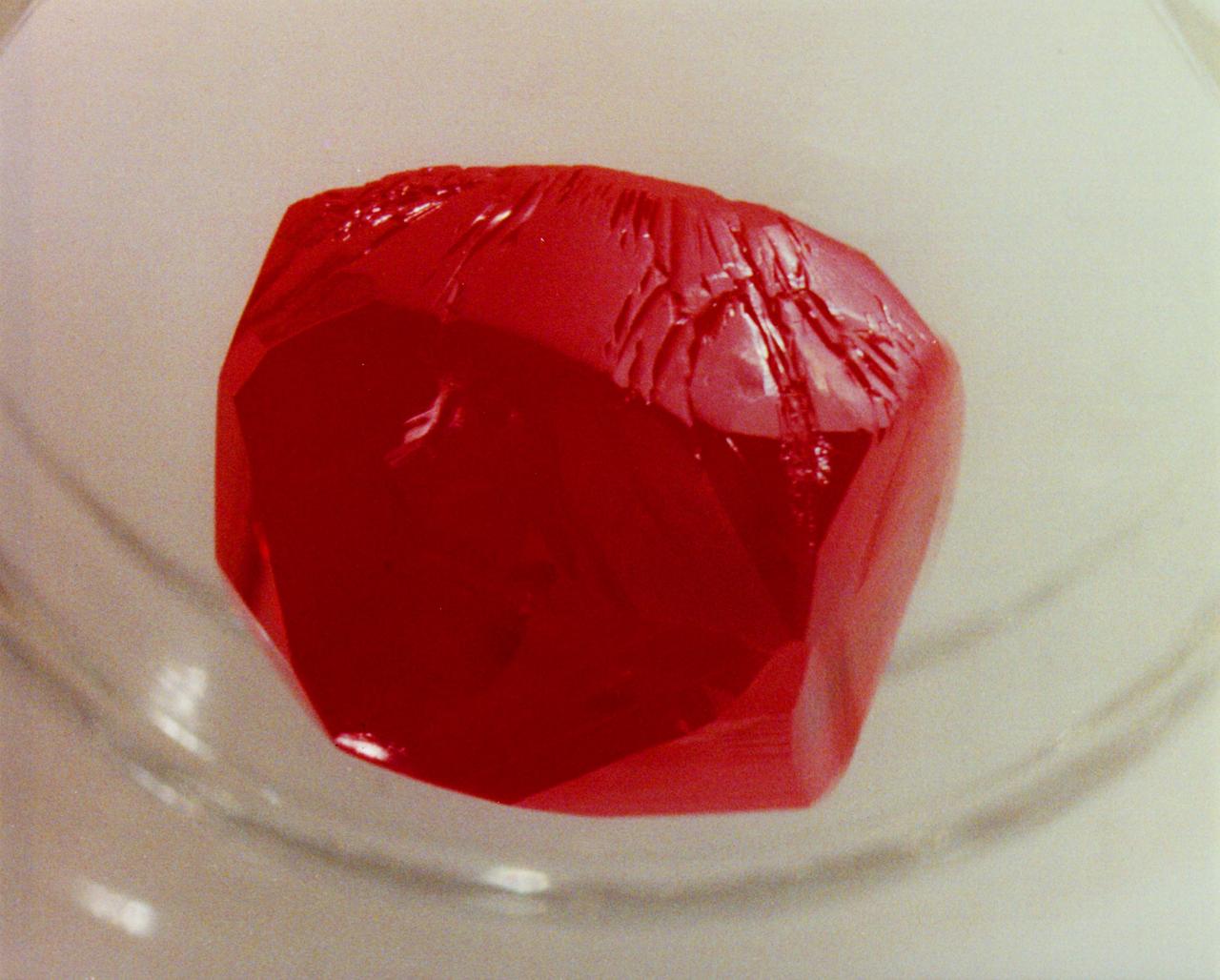

Vapor Crystal Growth System developed in IML-1, Mercuric Iodide Crystal grown in microgravity FES/VCGS (Fluids Experiment System/Vapor Crystal Growth Facility). During the mission, mercury iodide source material was heated, vaporized, and transported to a seed crystal where the vapor condensed. Mercury iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive X-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their excellent optical properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature, which makes them useful for portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications, and astronomical observing.
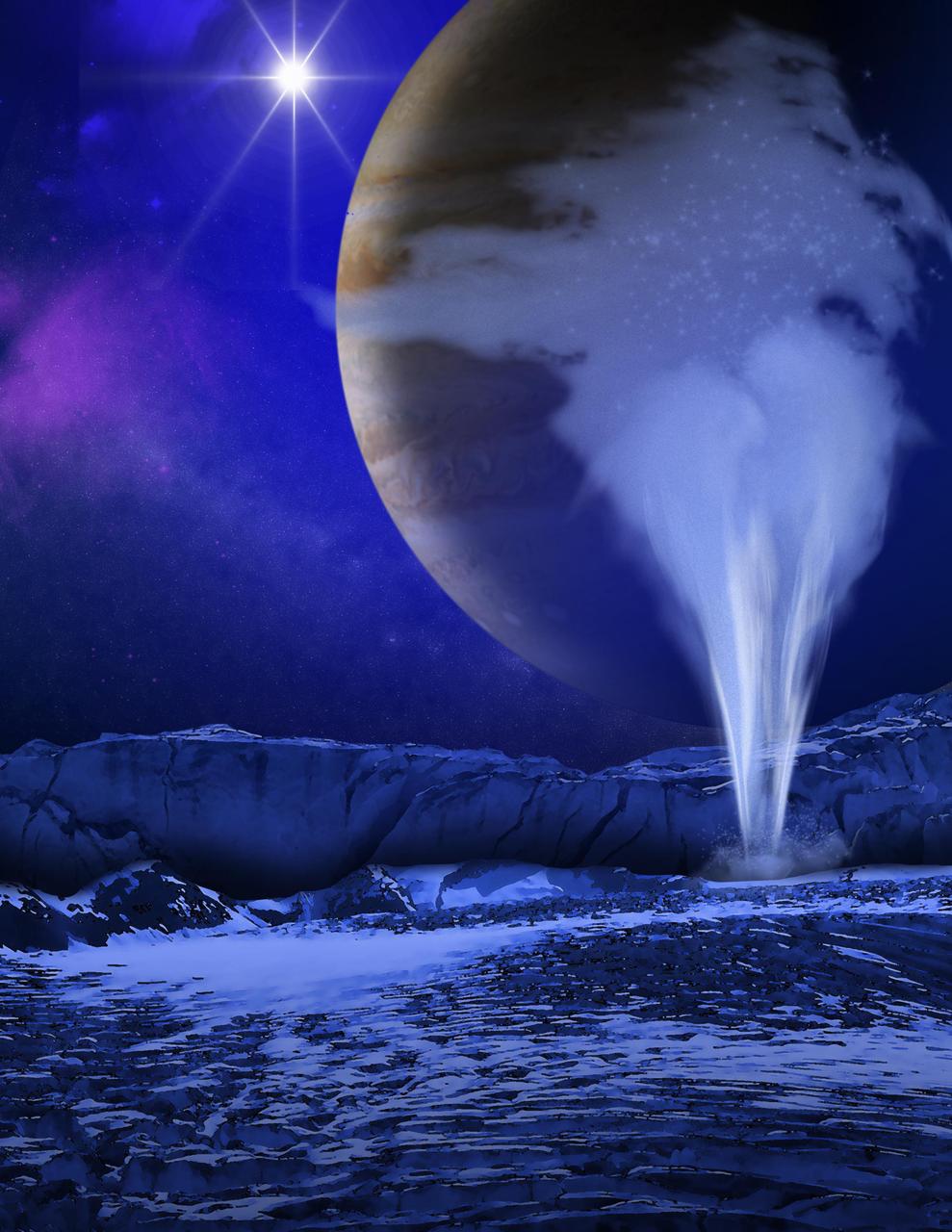

This is an artist concept of a plume of water vapor thought to be ejected off the frigid, icy surface of the Jovian moon Europa, located about 500 million miles 800 million kilometers from the sun.
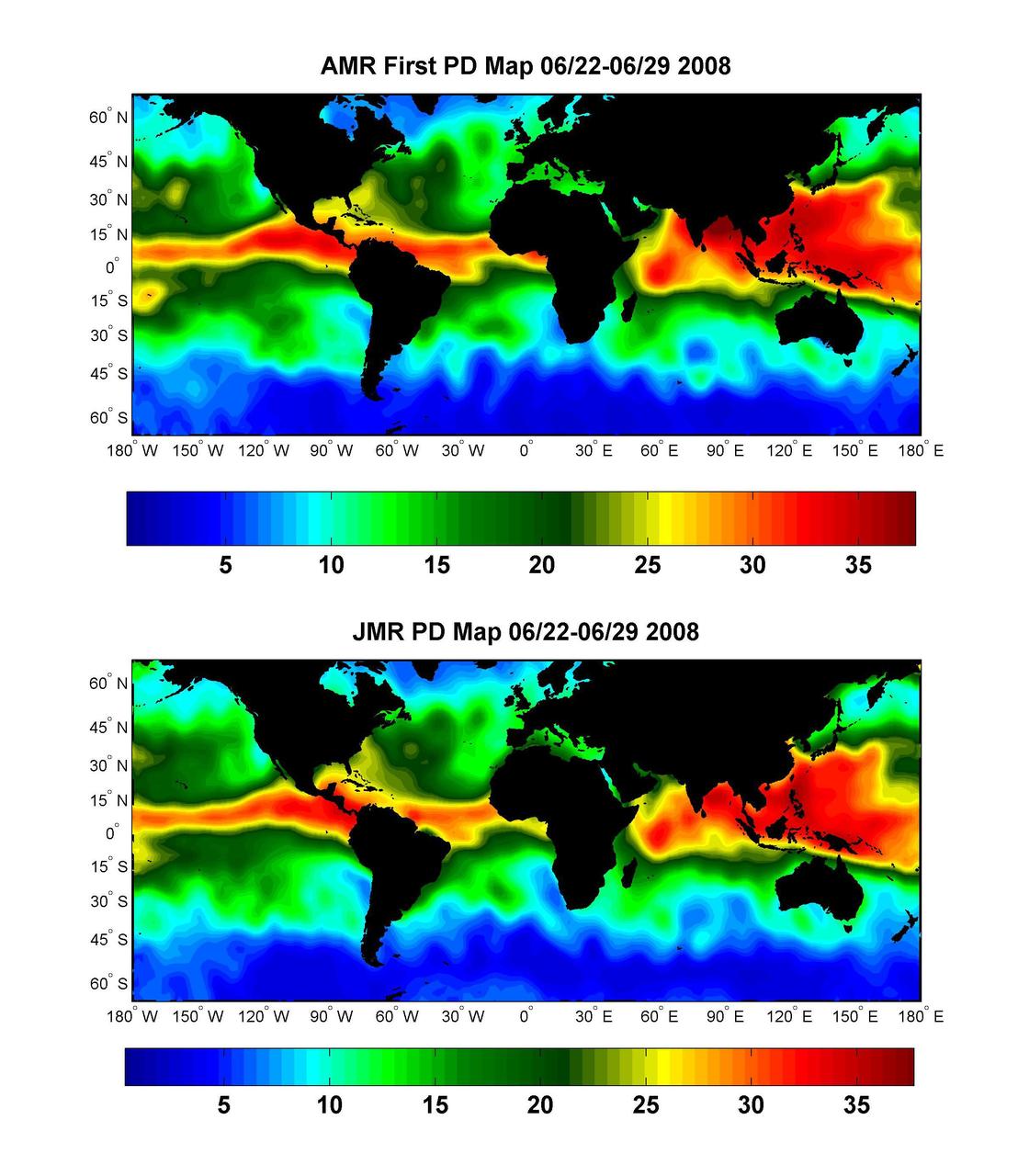
Global Views of Atmospheric Water Vapor:<br />First Data from OSTM/Jason-2 Advanced Microwave Radiometer

Artist concept illustrates a quasar, or feeding black hole, similar to APM 08279+5255, where astronomers discovered huge amounts of water vapor. Gas and dust likely form a torus around the central black hole, with clouds of charged gas above and below.
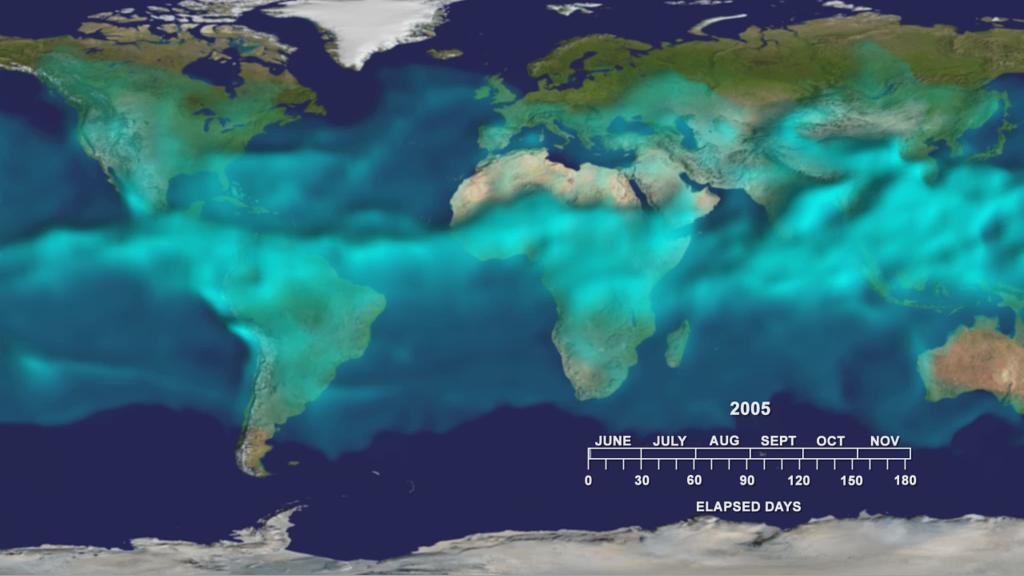
This visualization from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite shows variations in the three dimensional distribution of water vapor in the atmosphere during the summer and fall of 2005.
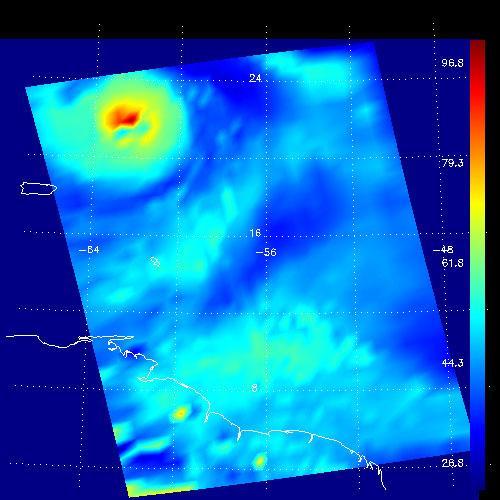
This false-color image shows the amount of atmospheric water vapor observed by AIRS two weeks prior to the passage of Hurricane Isabel, and then when it was a Category 5 storm. The region shown includes parts of South America and the West Indies. Puerto Rico is the large island below the upper left corner. Total water vapor represents the depth of a layer if all the water vapor in the atmosphere were to condense and fall to the surface. The color bar on the right sides of the plots give the thickness of this layer in millimeters (mm). The first image, from August 28, shows typical tropical water vapor amounts over the ocean: between roughly 25 and 50 mm, or 1 to 2 inches. The highest values of roughly 80 mm, seen as a red blob over South America, corresponds to intense thunderstorms. Thunderstorms pull in water vapor from surrounding regions and concentrate it, with much of it then falling as rain. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00430
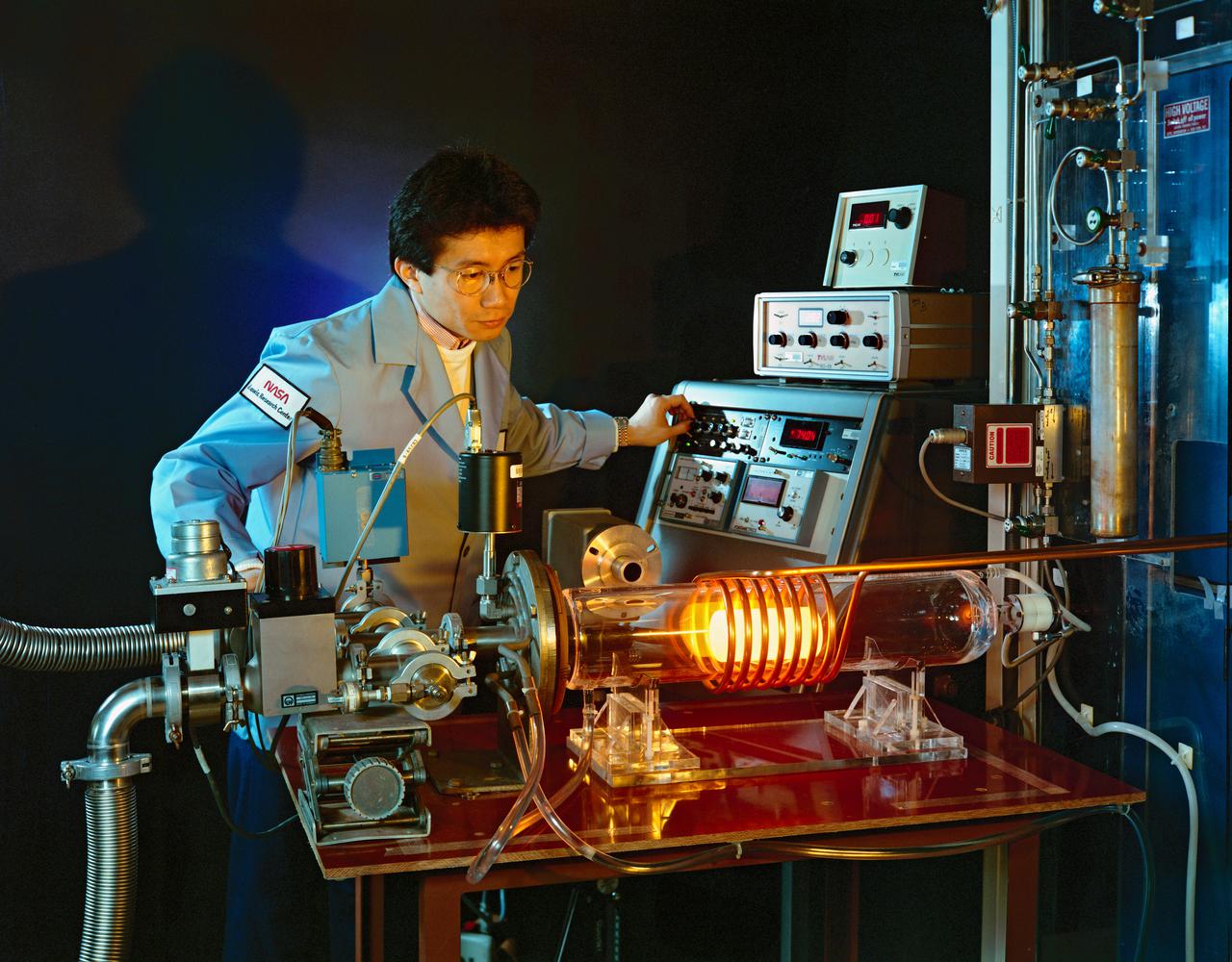
Shigehiro Nishino -- Visiting faculty fellow Dr. Shigehiro Nishino introduced the Lewis team to a unique chemical vapor deposition (CVD) strategy to grow silicon carbide crystals on silicon wafers.
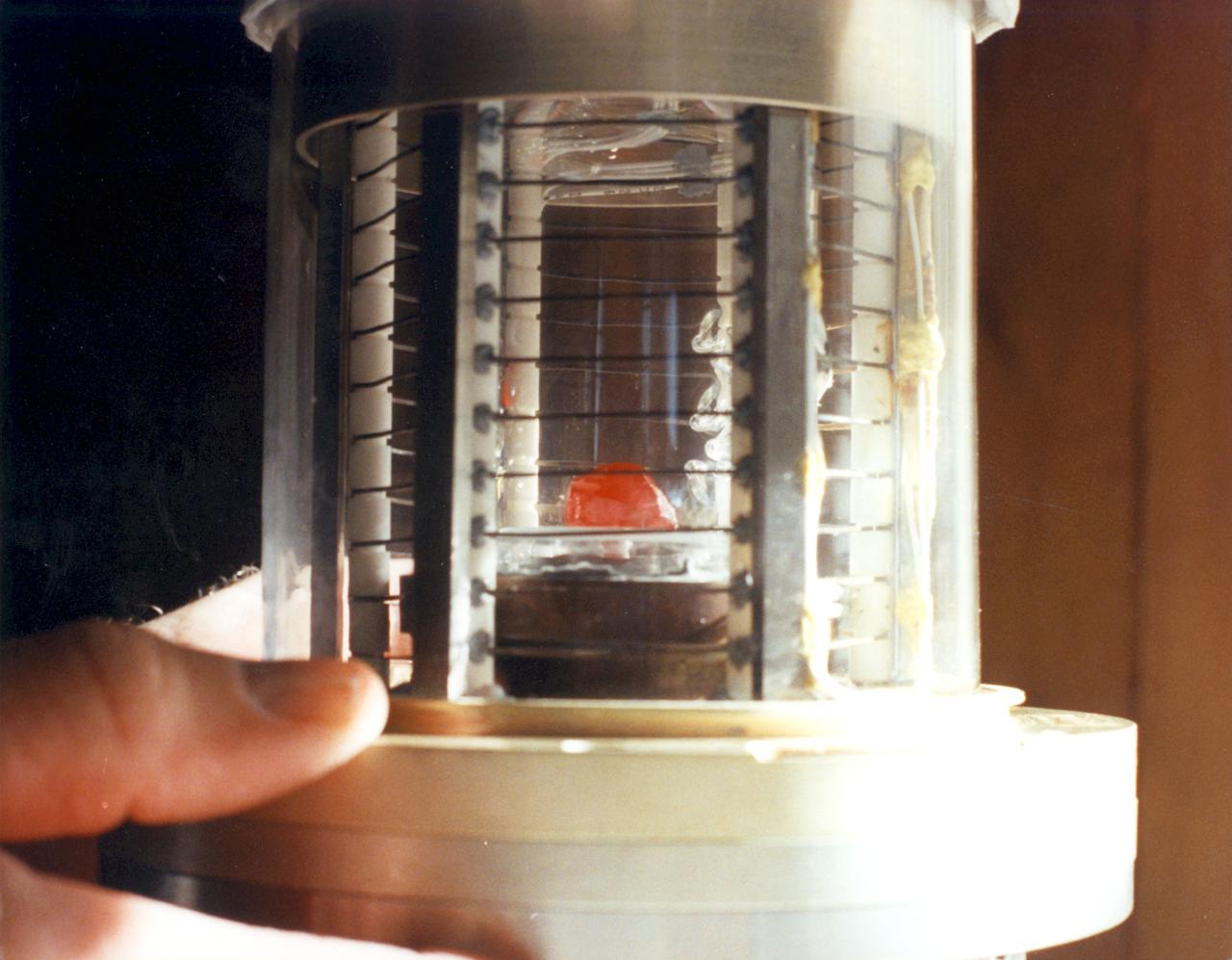
Ampoule view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Prinicipal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
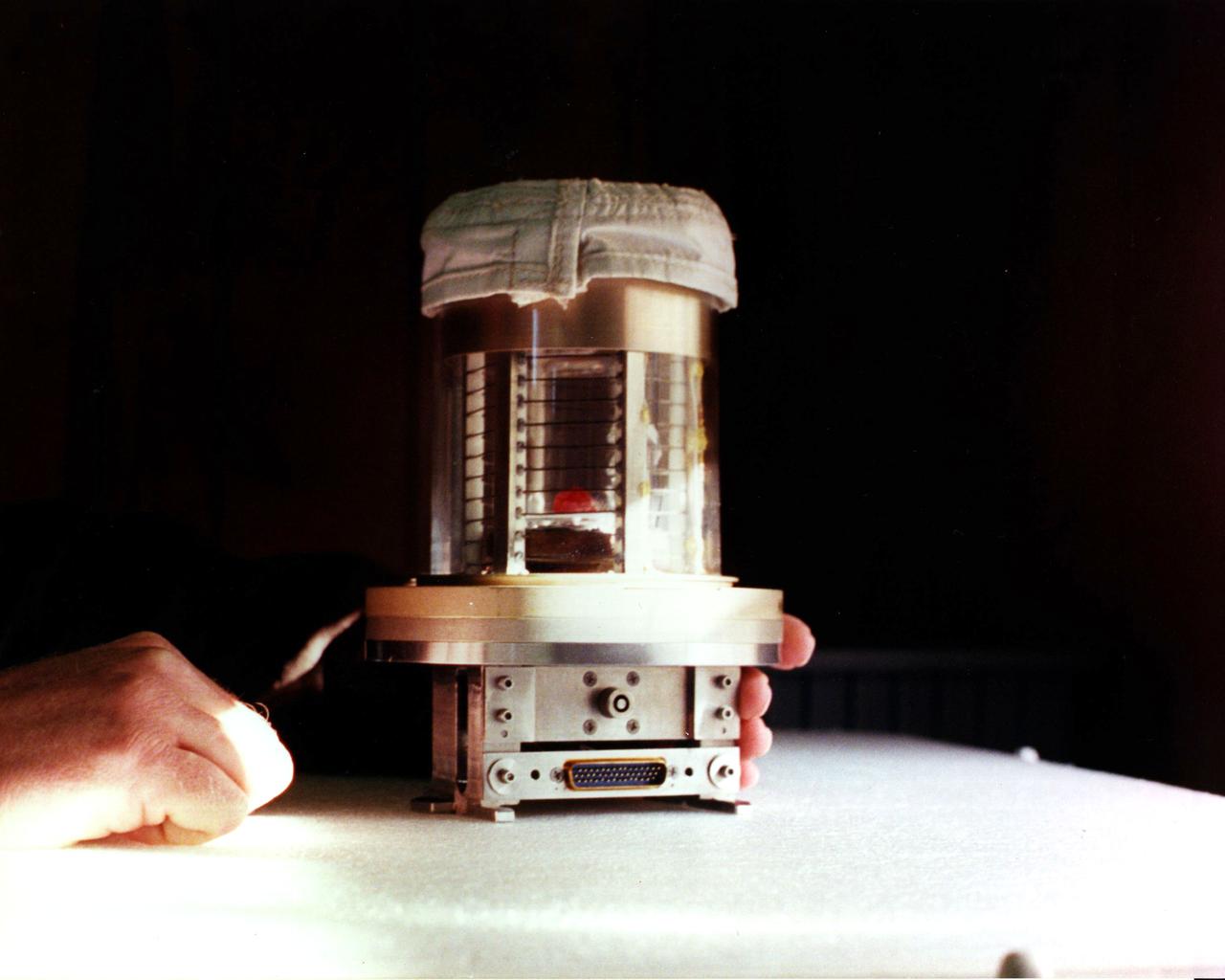
Overall view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Principal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
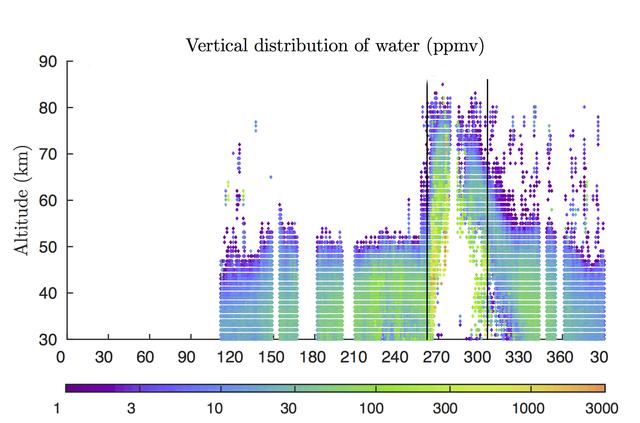
Rising air during a 2007 global dust storm on Mars lofted water vapor into the planet's middle atmosphere, researchers learned from data graphed here, derived from observations by the Mars Climate Sounder instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The two vertical black lines in the right half of the graph (at about 260 and 310 on the horizontal scale) mark the beginning and end of the most recent global dust storm on Mars, which burst from regional scale to globe-encircling scale in July 2007. The presence of more colored dots, particularly green ones, in the upper portion of the graph between those lines, compared to the upper portion of the graph outside those lines, documents the uplift of water vapor in connection with the global dust storm. The vertical scale is altitude, labeled at left in kilometers above the surface of Mars (50 kilometers is about 30 miles; 80 kilometers is about 50 miles). The color bar below the graph gives the key to how much water vapor each dot represents, in parts per million, by volume, in Mars' atmosphere. Note that green to yellow represents about 100 times as much water as purple does. The horizontal axis of the graph is time, from January 2006 to February 2008. It is labeled with numbers representing the 360 degrees of Mars' orbit around the Sun, from zero to 360 degrees and then further on to include the first 30 degrees of the following Martian year. (The zero point is autumnal equinox -- end of summer -- in Mars' northern hemisphere.) This graph, based on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observations, was used in a January 2018 paper in Nature Astronomy by Nicholas Heavens of Hampton University in Hampton, Virginia, and co-authors. The paper presents Martian dust storms' uplifting effect on water vapor as a factor in seasonal patterns that other spacecraft have detected in the rate of hydrogen escaping from the top of Mars' atmosphere. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22080
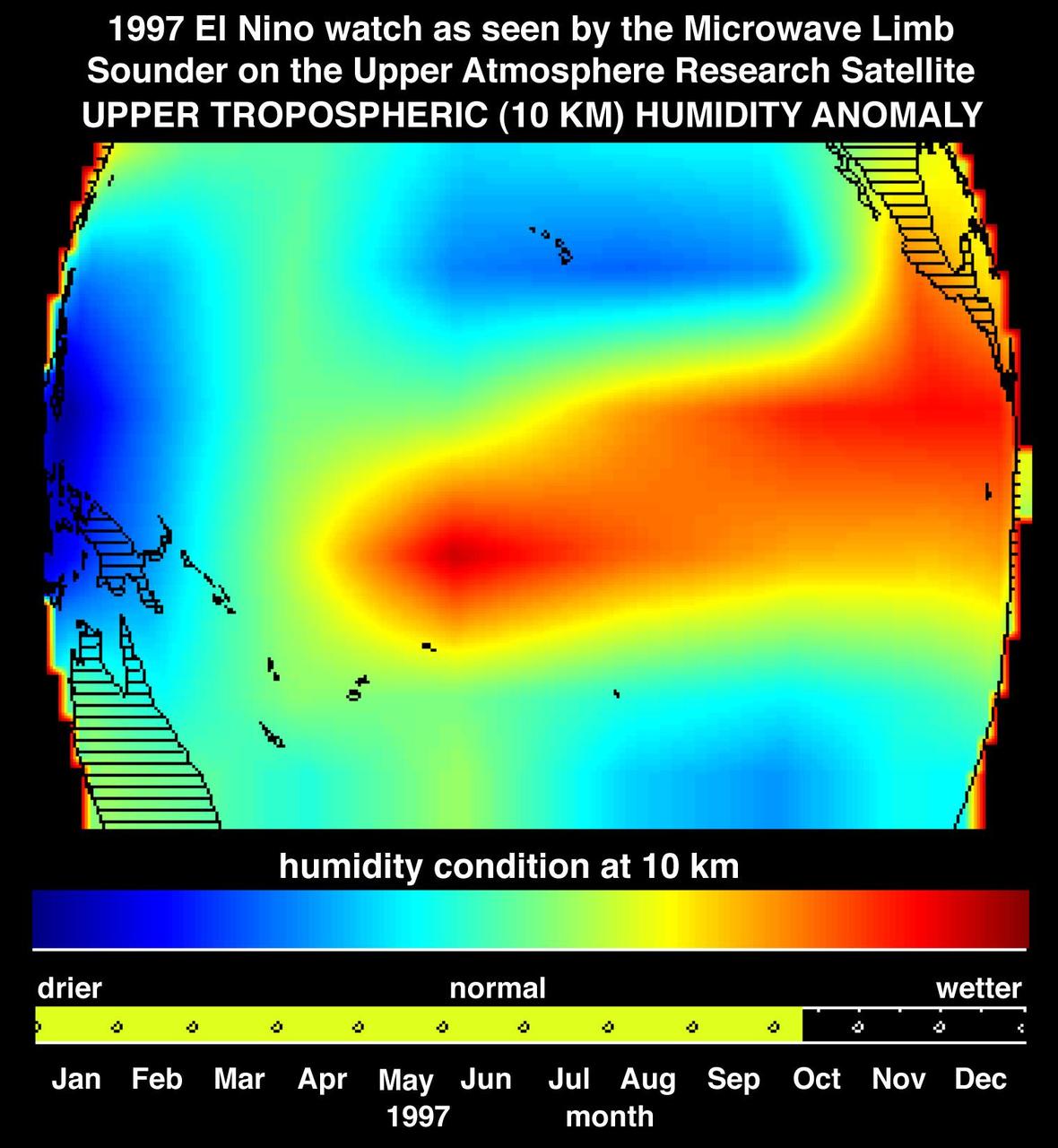
This image shows atmospheric water vapor in Earth upper troposphere, about 10 kilometers 6 miles above the surface, as measured by NASA Microwave Limb Sounder MLS instrument flying aboard the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite.
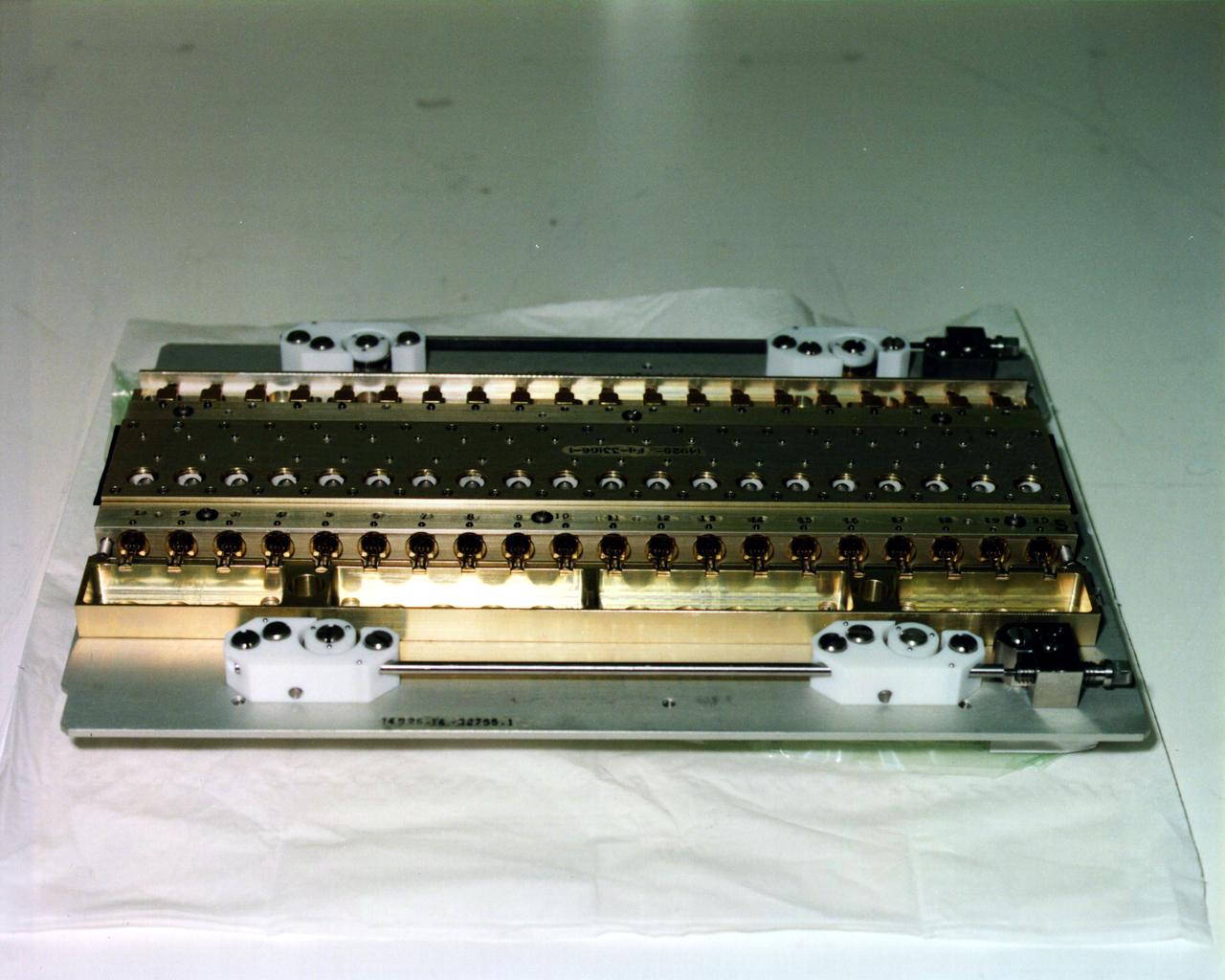
These Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA) trays were first flown in the Thermal Enclosure System (TES) during the USMP-2 (STS-62) mission. Each tray can hold 20 protein crystal growth chambers. Each chamber contains a double-barrel syringe; one barrel holds protein crystal solution and the other holds precipitant agent solution. During the microgravity mission, a torque device is used to simultaneously retract the plugs in all 20 syringes. The two solutions in each chamber are then mixed. After mixing, droplets of the combined solutions are moved onto the syringe tips so vapor diffusion can begin. During the length of the mission, protein crystals are grown in the droplets. Shortly before the Shuttle's return to Earth, the experiment is deactivated by retracting the droplets containing protein crystals, back into the syringes.
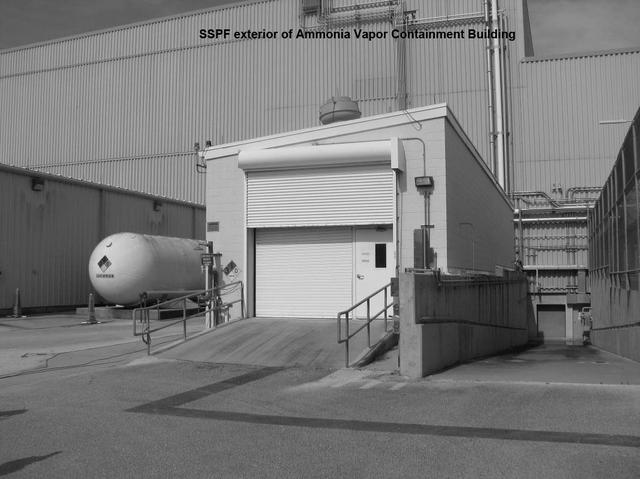

Exterior view of the Ammonia Vapor Containment Building
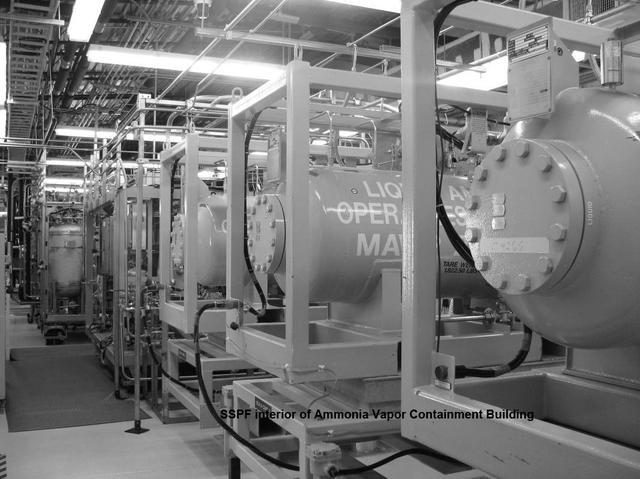

Interior view of the Ammonia Vapor Containment Building
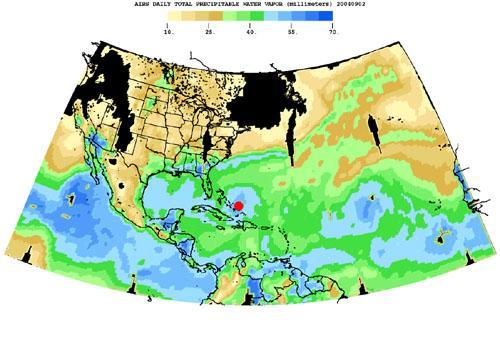
Born in the Atlantic, Hurricane Frances became a category 4 hurricane on August 31, 2004, as seen by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounding System AIRS on NASA Aqua. Expectations are the hurricane will hit the Space Coast of Florida in Brevard County early Sunday morning. This frame from a movie is a time-series of maps that show AIRS observations of the total amount of water vapor present in the atmospheric column above each point of the Earth's surface. If all the water vapor in the column were forced to fall as rain, the depth of the resulting puddle on the surface at that point is equal to the value shown on the map. Fifty millimeters (mm) is about 2 inches. The large band of maximum water vapor in the neighborhood of the equator is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a region of strong convection and powerful thunderstorms. The movie (see PIA00433) shows the total precipitable water vapor from August 23 through September 2, 2004. You can see Hurricane Frances as it moves through the Caribbean toward Florida, and the changes in intensity are visible. The eye has been marked with a red spot. The water vapor encompassed by the hurricane is also the result of the very strong convection which is an integral part of the formation and intensification of tropical storms. If you look at the last frame of the movie in the lower right corner, you can see the emergence of a new tropical storm. Ivan makes its debut in the Atlantic. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00433
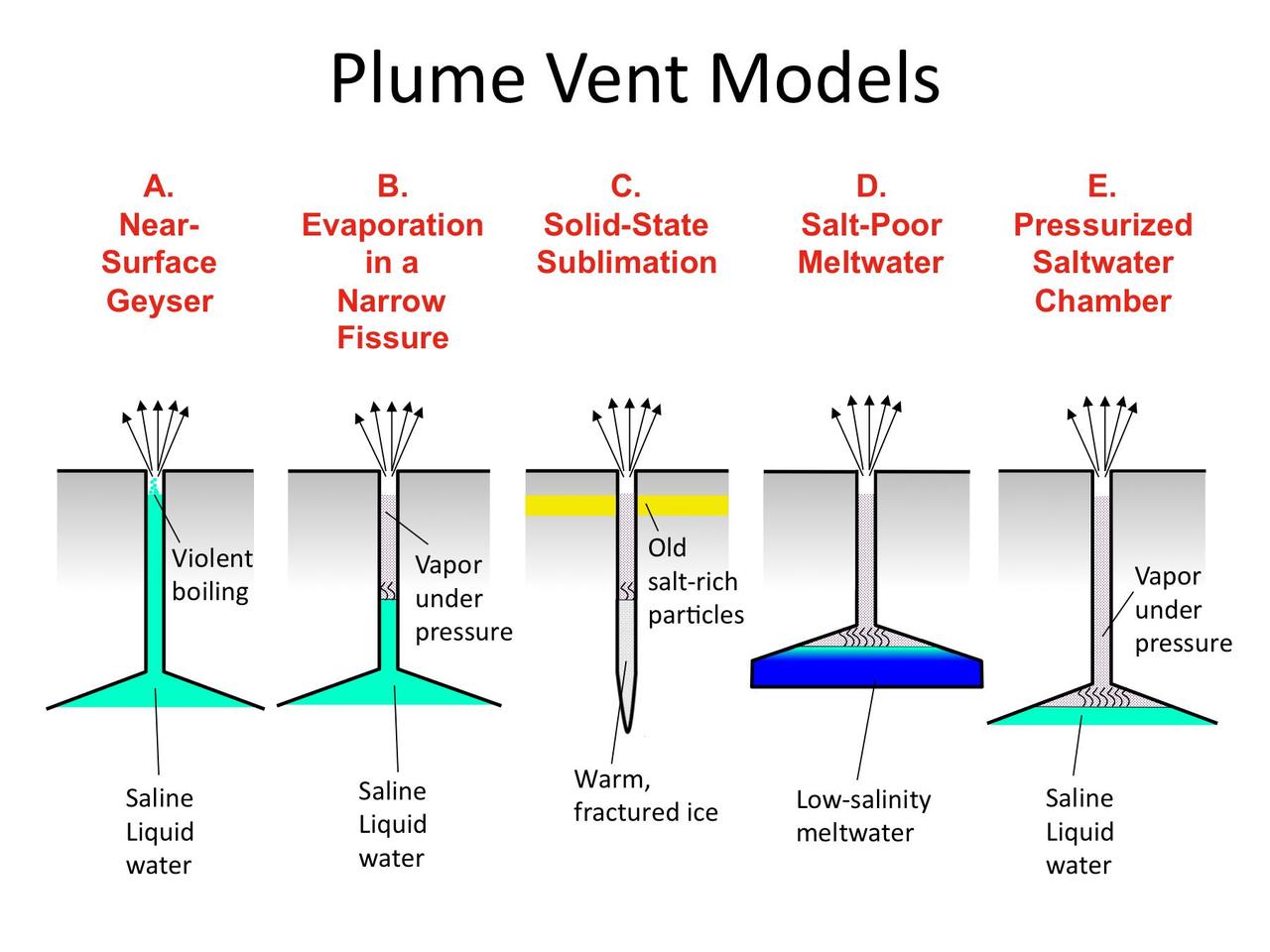
These illustrations indicate possible ways in which the water vapor and ice particles in the plume of Enceladus may be formed.
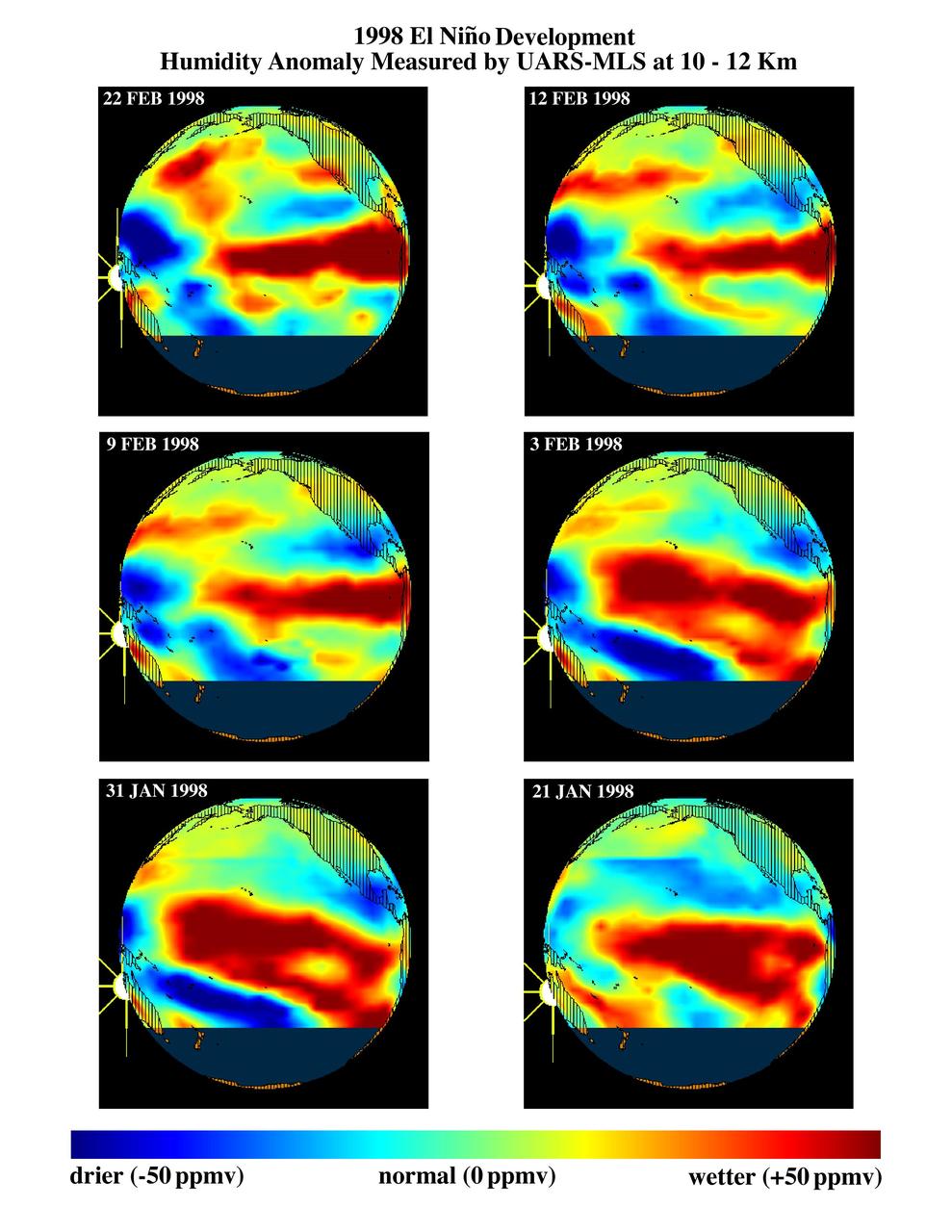
This series of six images shows the evolution of atmospheric water vapor over the Pacific Ocean during the 1998 El Niño condition.
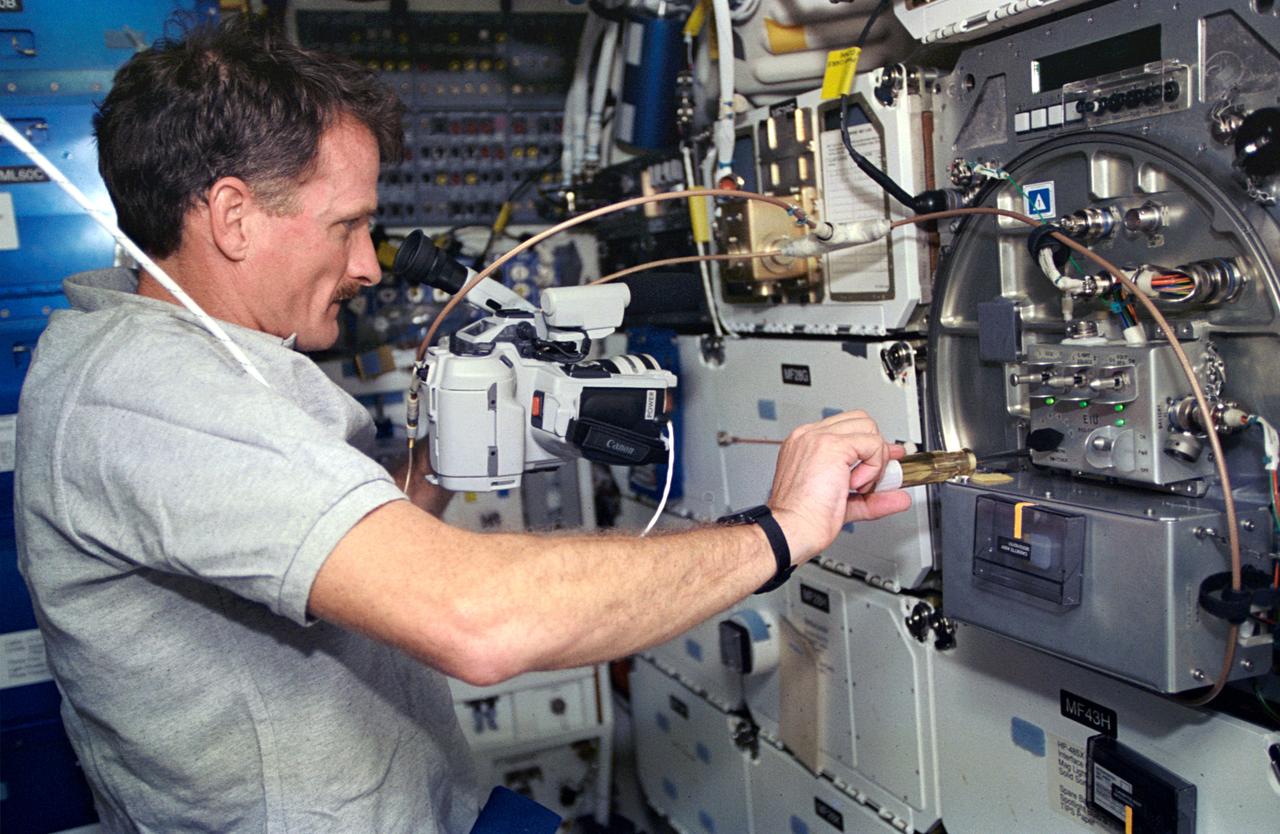

On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, works at area amidst several lockers onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES) which is out of frame, the Cos/TES represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
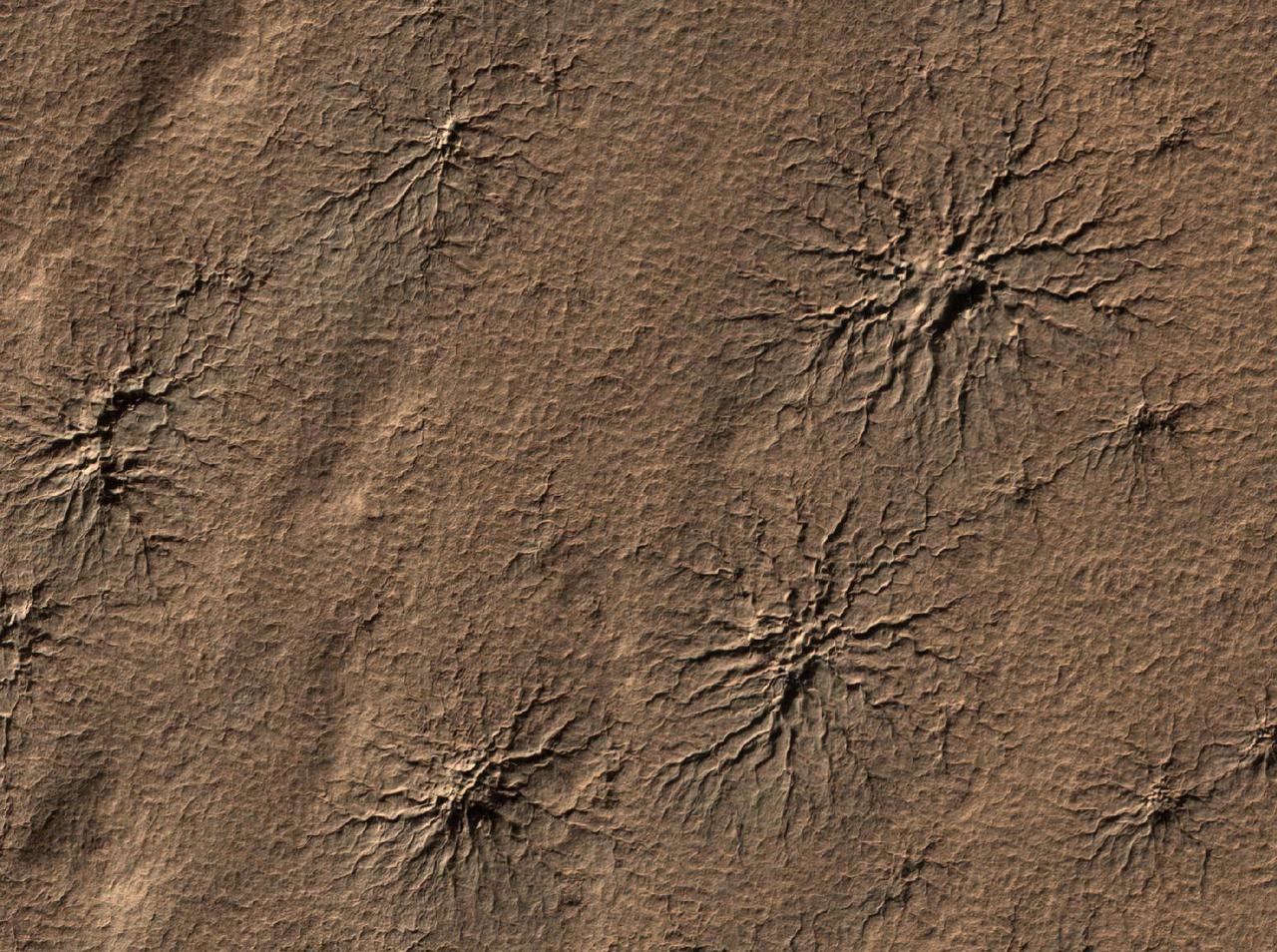

The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of spider-shaped features on Mars, carved by vaporizing dry ice.
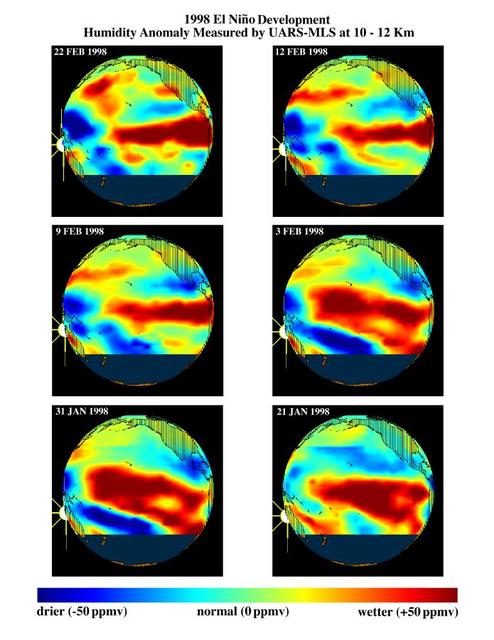
This series of six images shows the evolution of atmospheric water vapor over the Pacific Ocean during the 1998 El Ni?o condition.

This image shows differences in atmospheric water vapor relative to a normal average year in the Earth upper troposphere about 10 kilometers 6 miles above the surface.
This image shows differences in atmospheric water vapor relative to a normal average year in the Earth upper troposphere about 10 kilometers 6 miles above the surface.
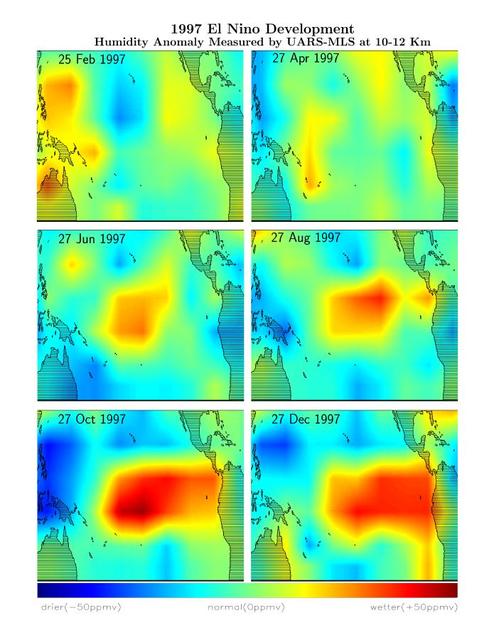
This series of six images shows the movement of atmospheric water vapor over the Pacific Ocean during the formation of the 1997 El Niño condition.
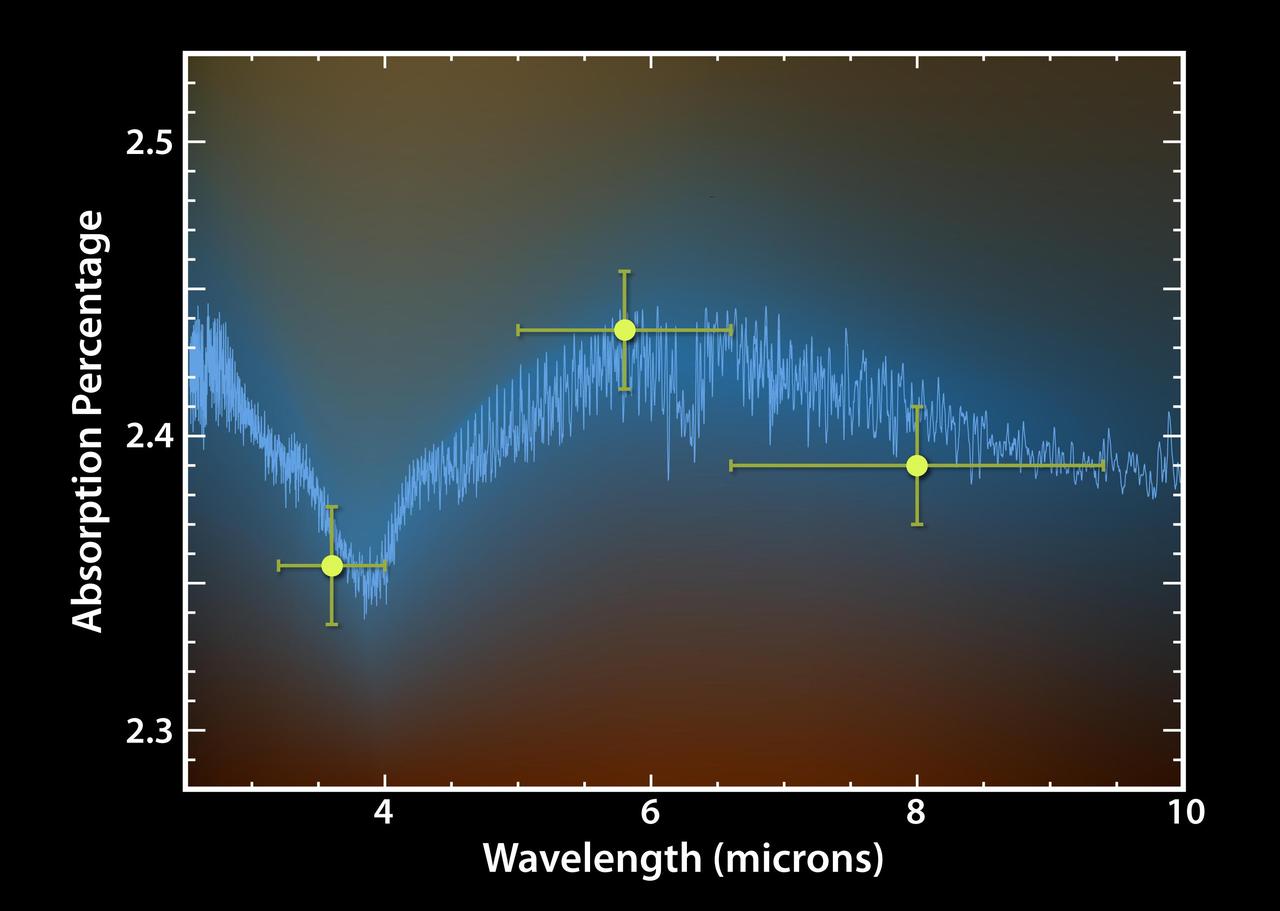
This plot of data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope tells astronomers that a toasty gas exoplanet, or a planet beyond our solar system, contains water vapor.
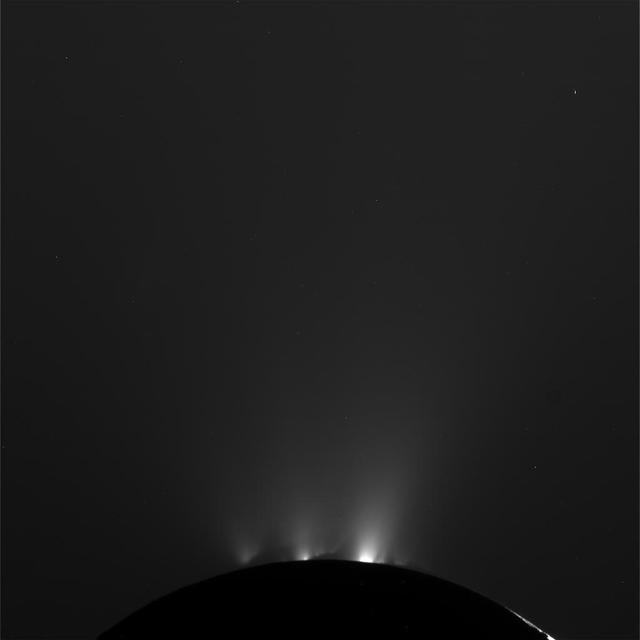

NASA Cassini spacecraft successfully completed its Oct. 1, 2011 flyby of Saturn moon Enceladus and its jets of water vapor and ice.
CONSTRAINED VAPOR BUBBLE
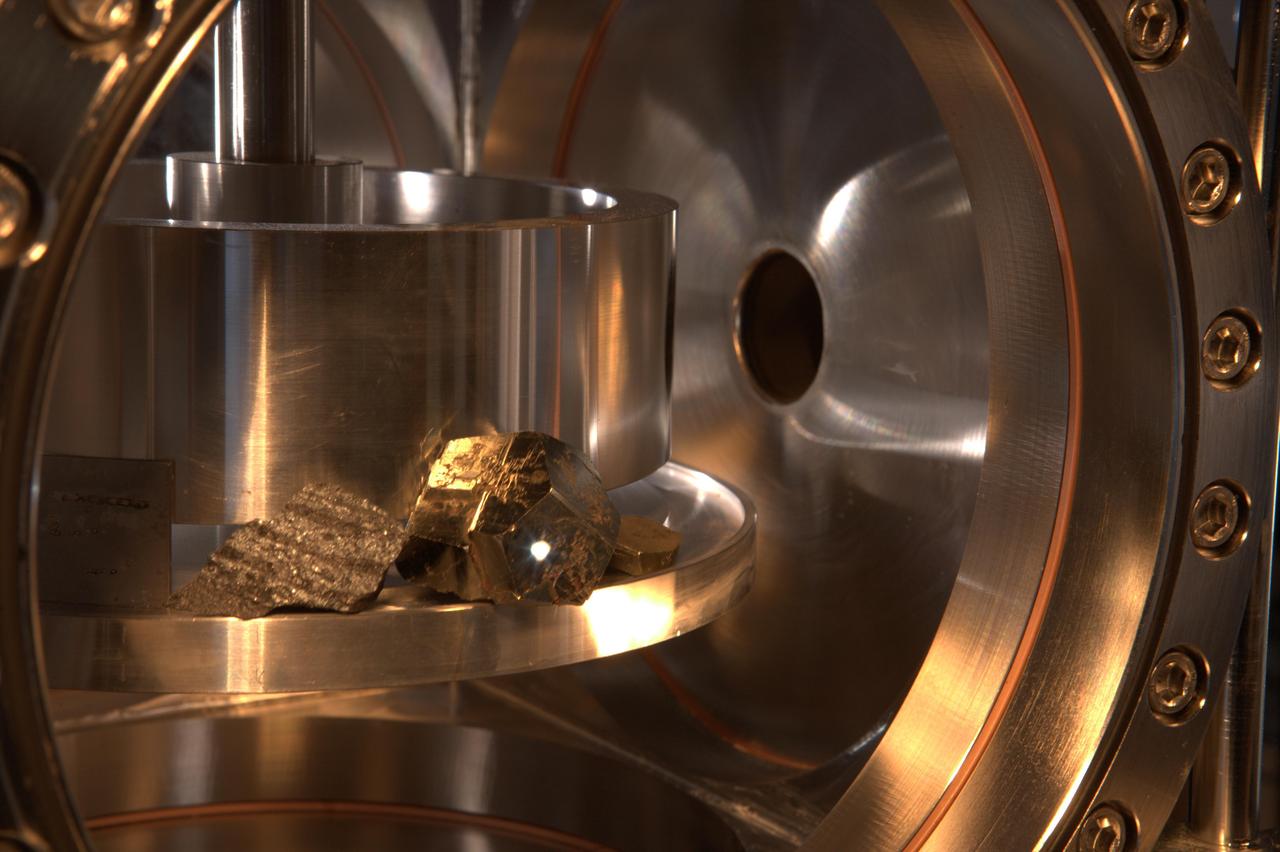

The ChemCam instrument for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission uses a pulsed laser beam to vaporize a pinhead-size target, producing a flash of light from the ionized material plasma that can be analyzed to identify chemical elements in the target.
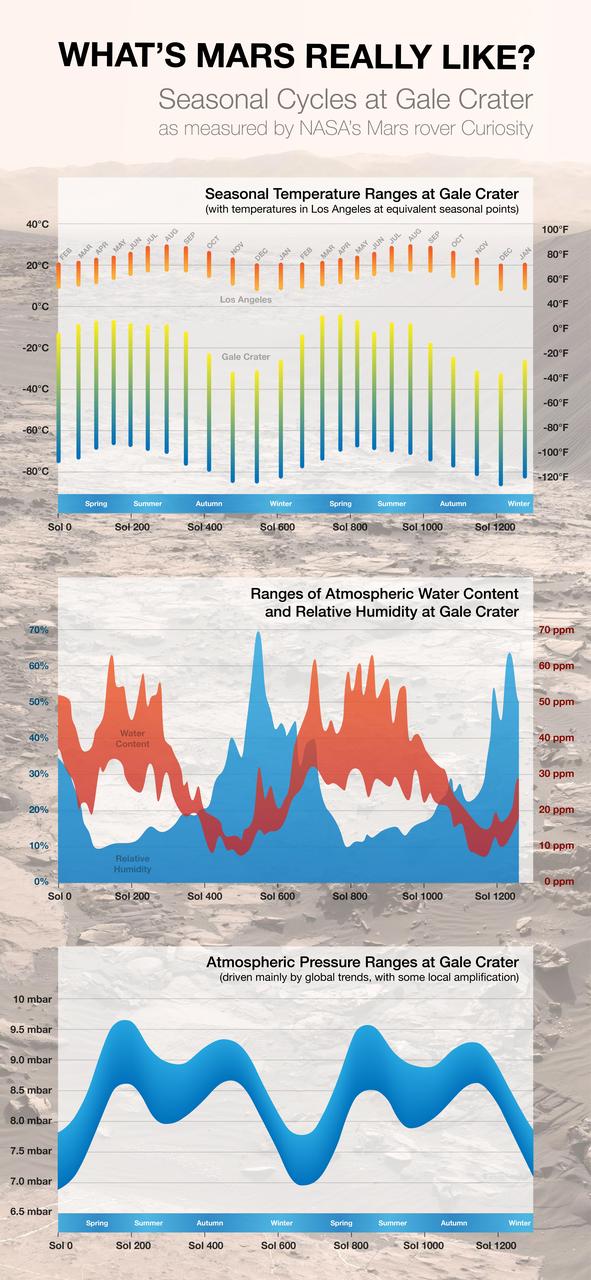
By monitoring weather throughout two Martian years since landing in Gale Crater in 2012, NASA Curiosity Mars rover has documented seasonal patterns such as shown in these graphs of temperature, water-vapor content and air pressure.
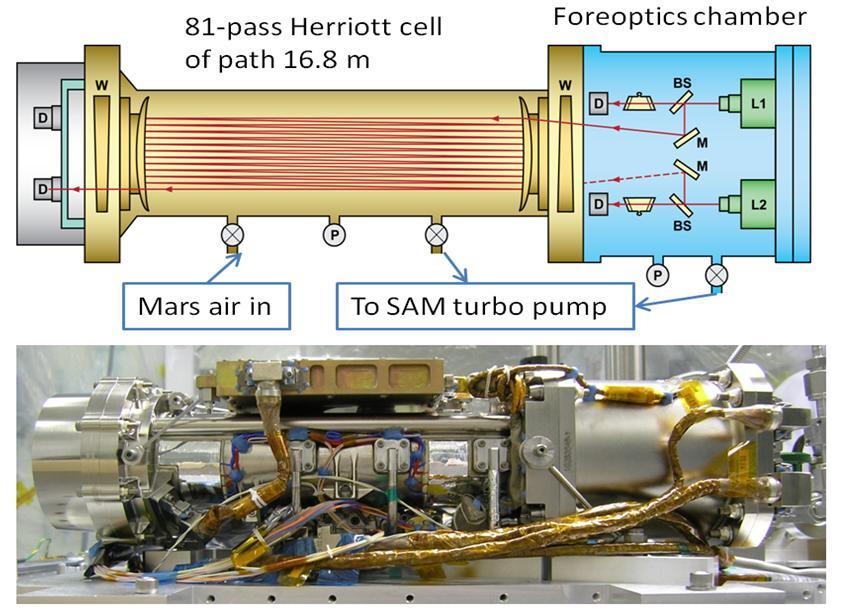
By measuring absorption of light at specific wavelengths, Tunable Laser Spectrometer TLS onboard NASA Curiosity measures concentrations of methane, carbon dioxide and water vapor in Mars atmosphere.
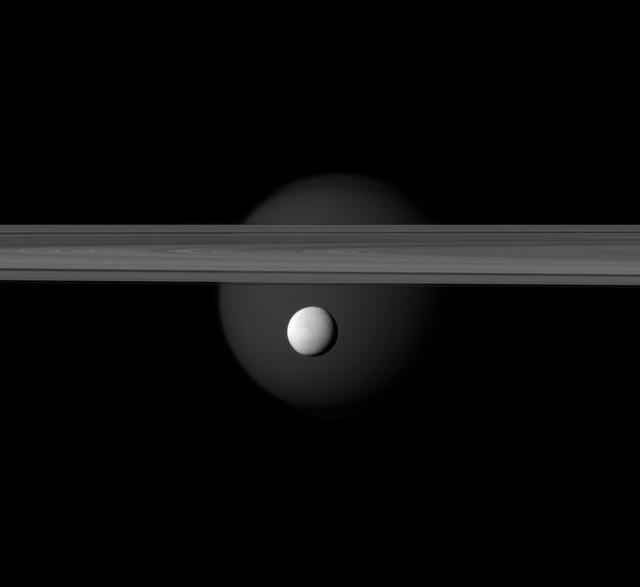

The brightly reflective moon Enceladus appears before Saturn rings while the larger moon Titan looms in the distance. Jets of water ice and vapor emanating from the south pole of Enceladus hinting at subsurface sea rich in organics.
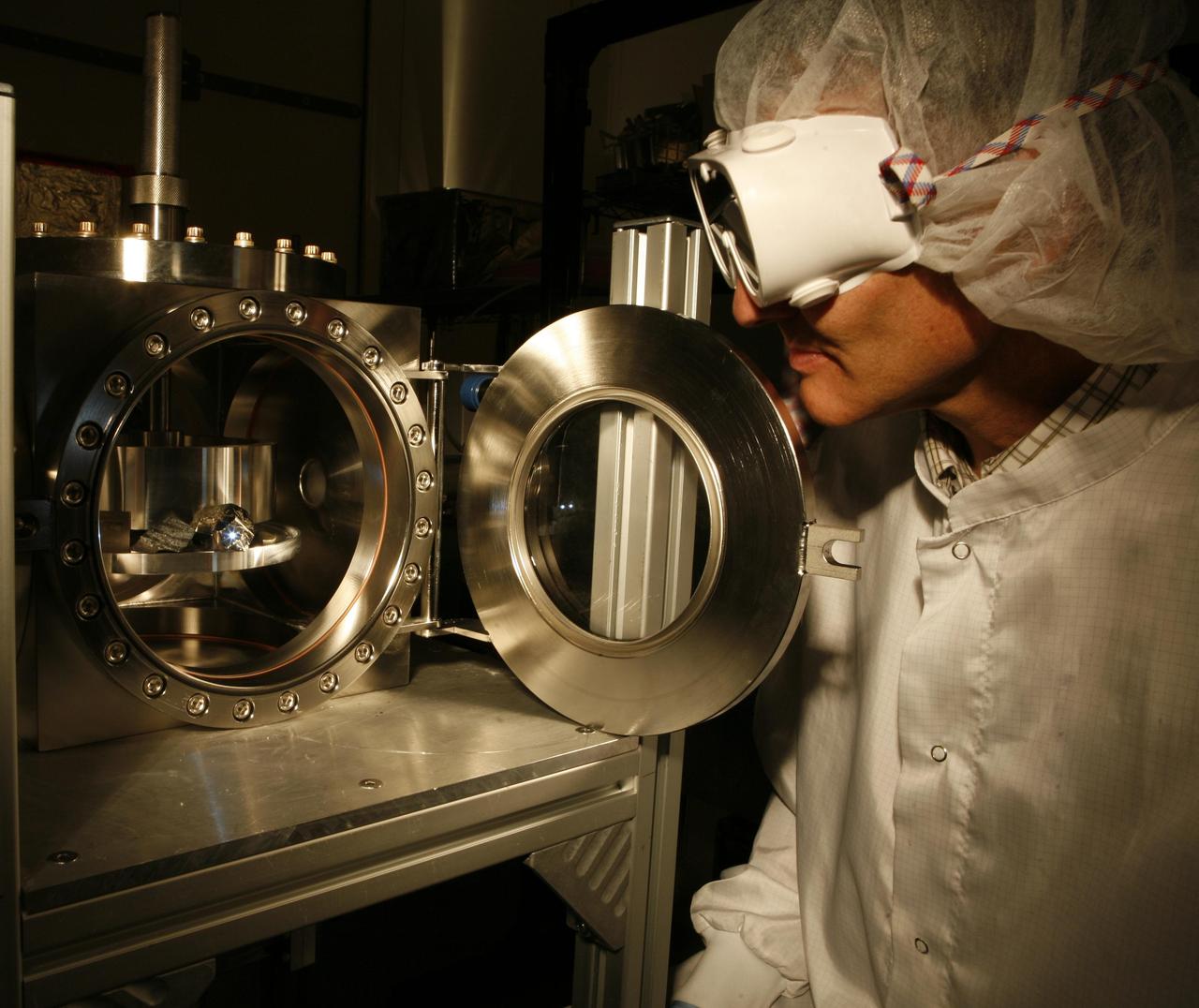

The ChemCam instrument for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission uses a pulsed laser beam to vaporize a pinhead-size target, producing a flash of light from the ionized material plasma that can be analyzed to identify chemical elements in the target.
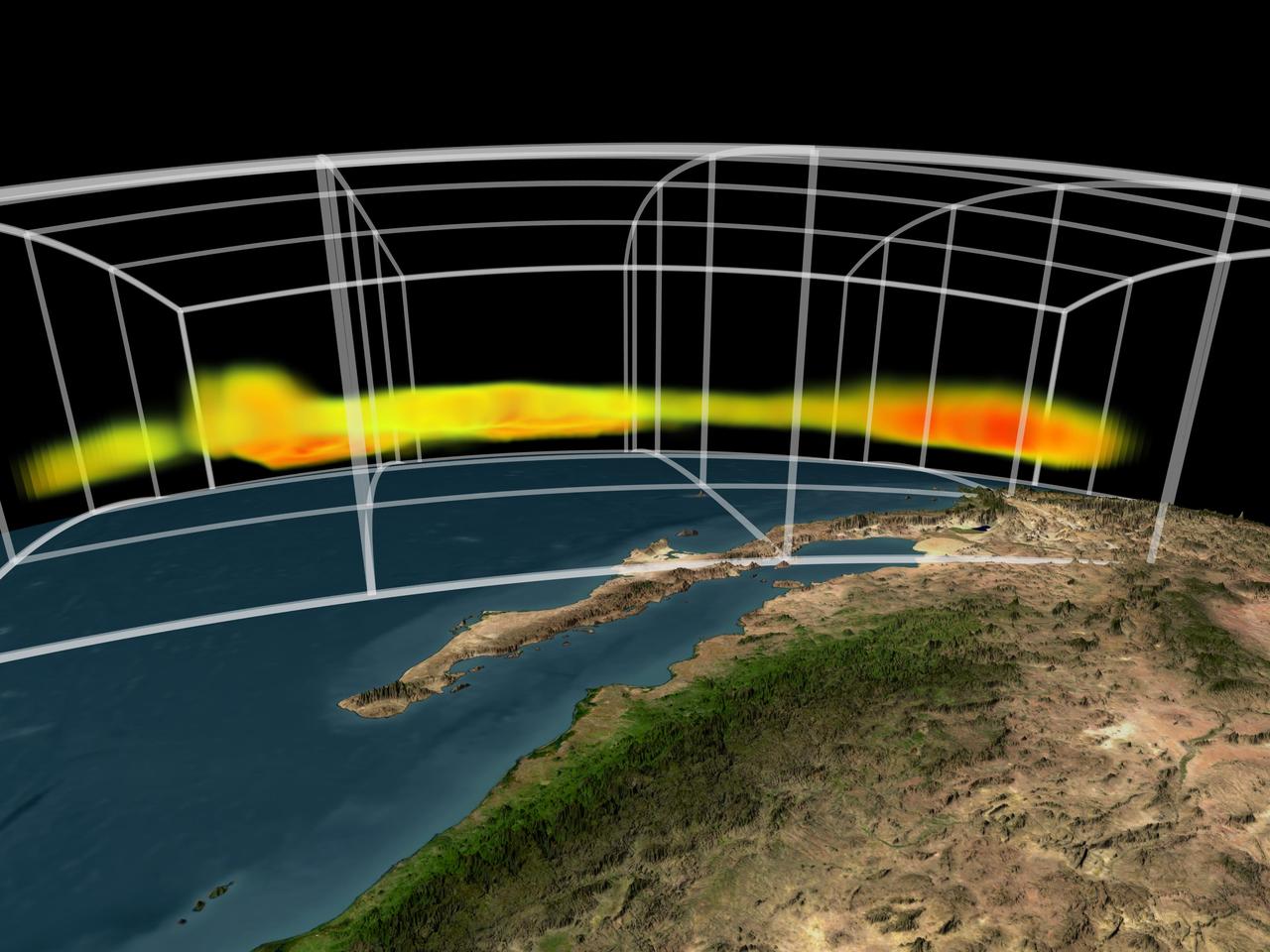
NASA Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument is able to peel back cloud cover to reveal 3-D structure of a storm water vapor content, information that can be used to improve weather forecast models.

The Mars Climate Sounder instrument on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter maps the vertical distribution of temperatures, dust, water vapor and ice clouds in the Martian atmosphere as the orbiter flies a near-polar orbit.

The bizarre patterns on the floor of this crater in Nilosyrtis Mensae imaged by NASA Mars Odyssey defy an easy explanation. It is possible that some form of periglacial process combined with the vaporization of ground ice to form these patterns.

This vertical profile view from the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer TES instrument on NASA Aura satellite depicts the distribution of water vapor molecules over Earth tropics across one transect of the satellite orbit on January 6, 2006.
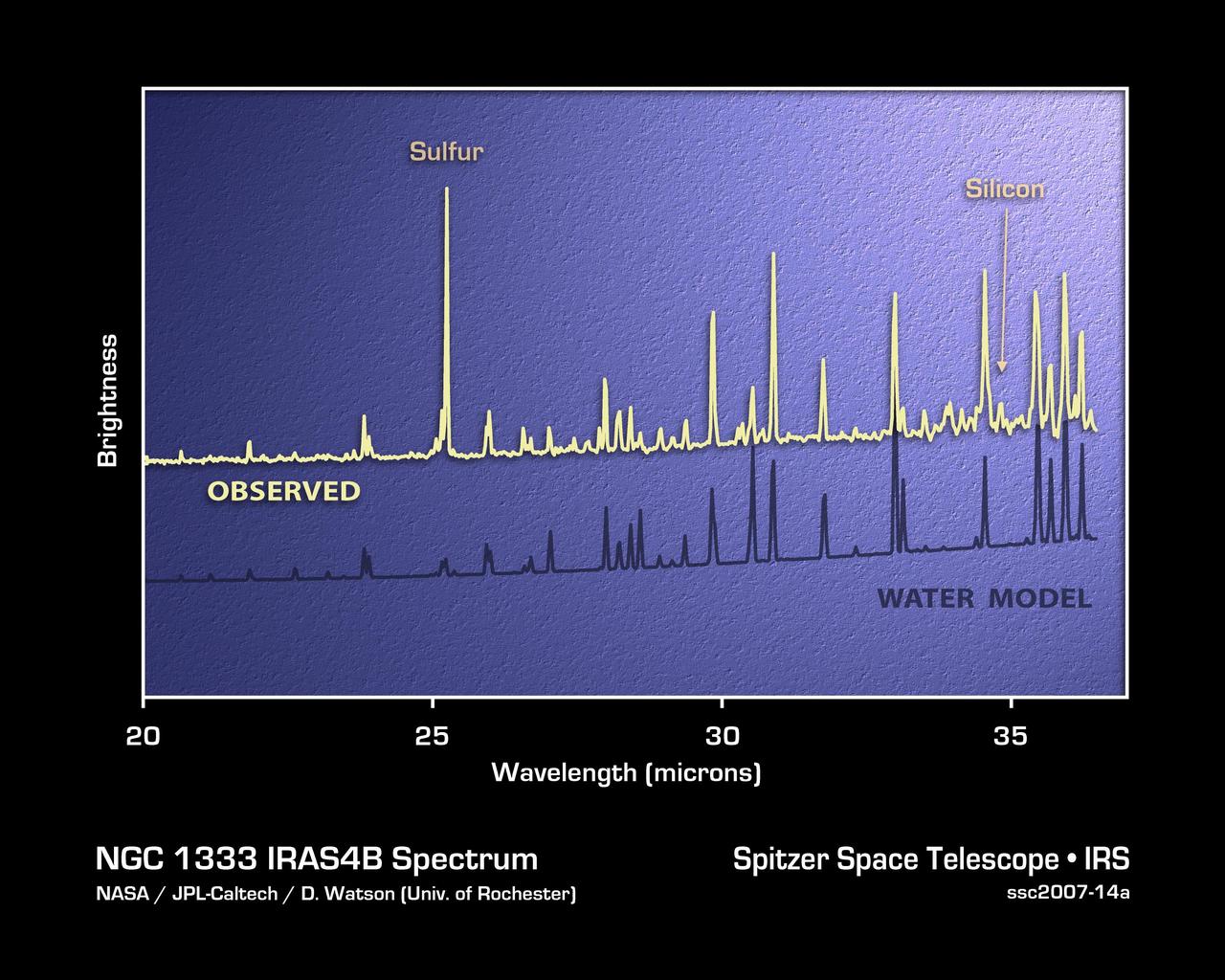
This plot of infrared data, called a spectrum, shows the strong signature of water vapor deep within the core of an embryonic star system, called NGC 1333-IRAS 4B. The data were captured by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
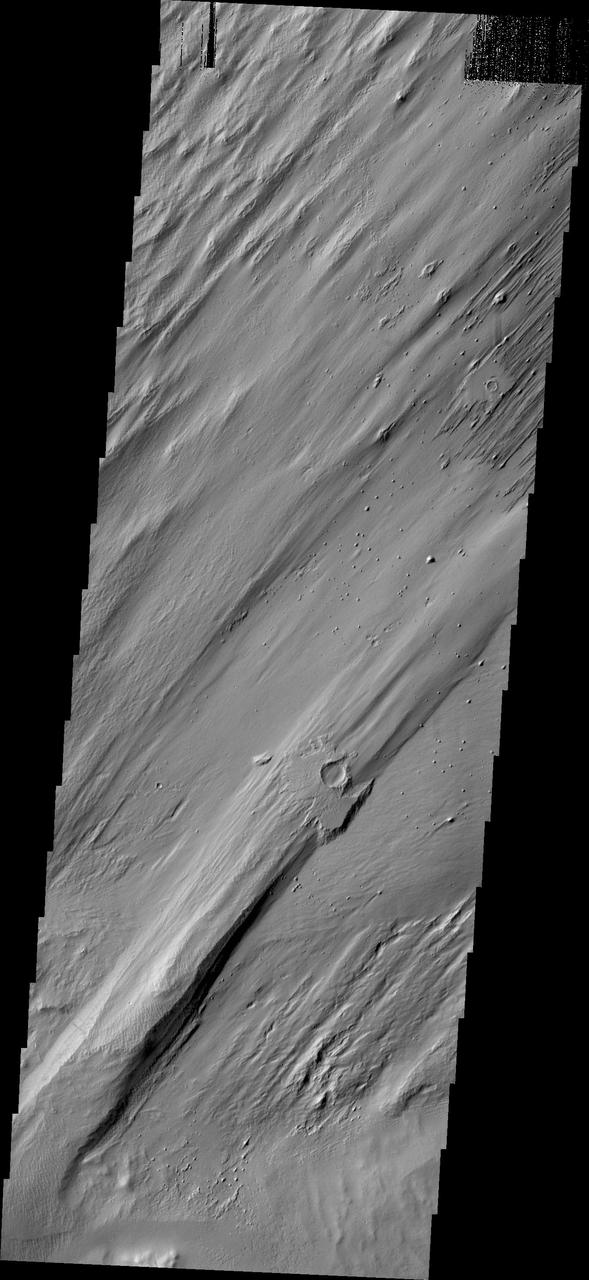

When a large impact occurs it vaporizes the surface and deposits hot debris around the newly formed crater as shown in this image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
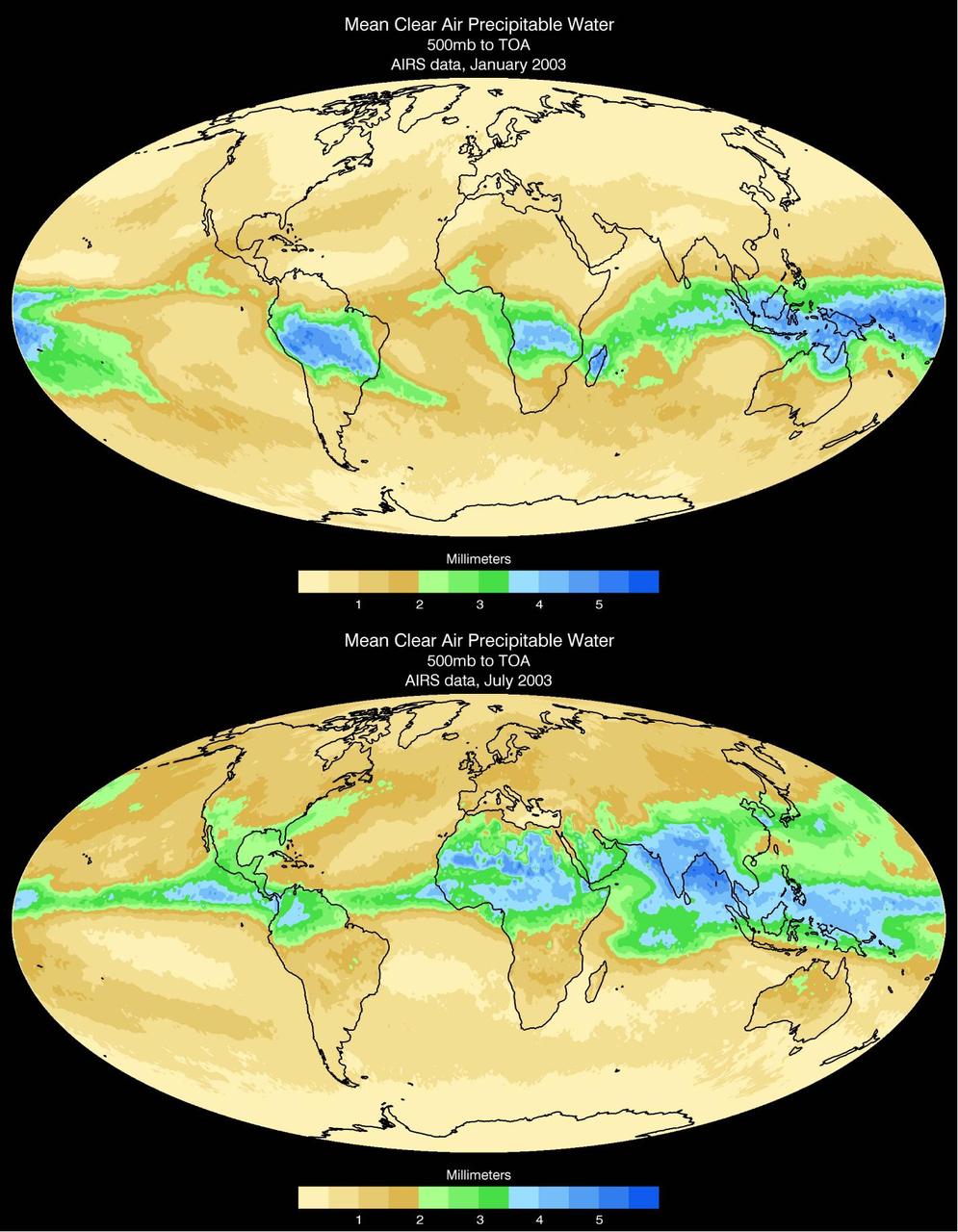
Water vapor is the dominant greenhouse gas in our atmosphere. Mean clear air precipitable water, 500mb to top of atmosphere from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite.
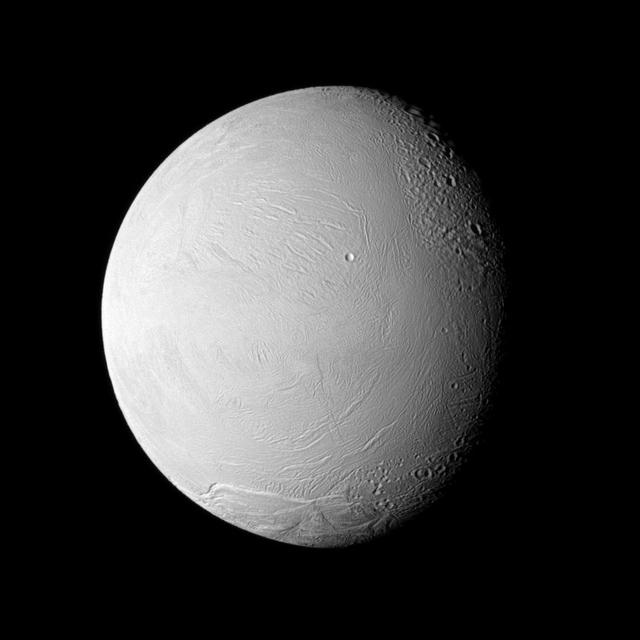

NASA Cassini spacecraft examines old and new terrain on Saturn fascinating Enceladus, a moon where jets of water ice particles and vapor spew from the south pole. Newly created terrain is at the bottom, in the center and on the left of this view.
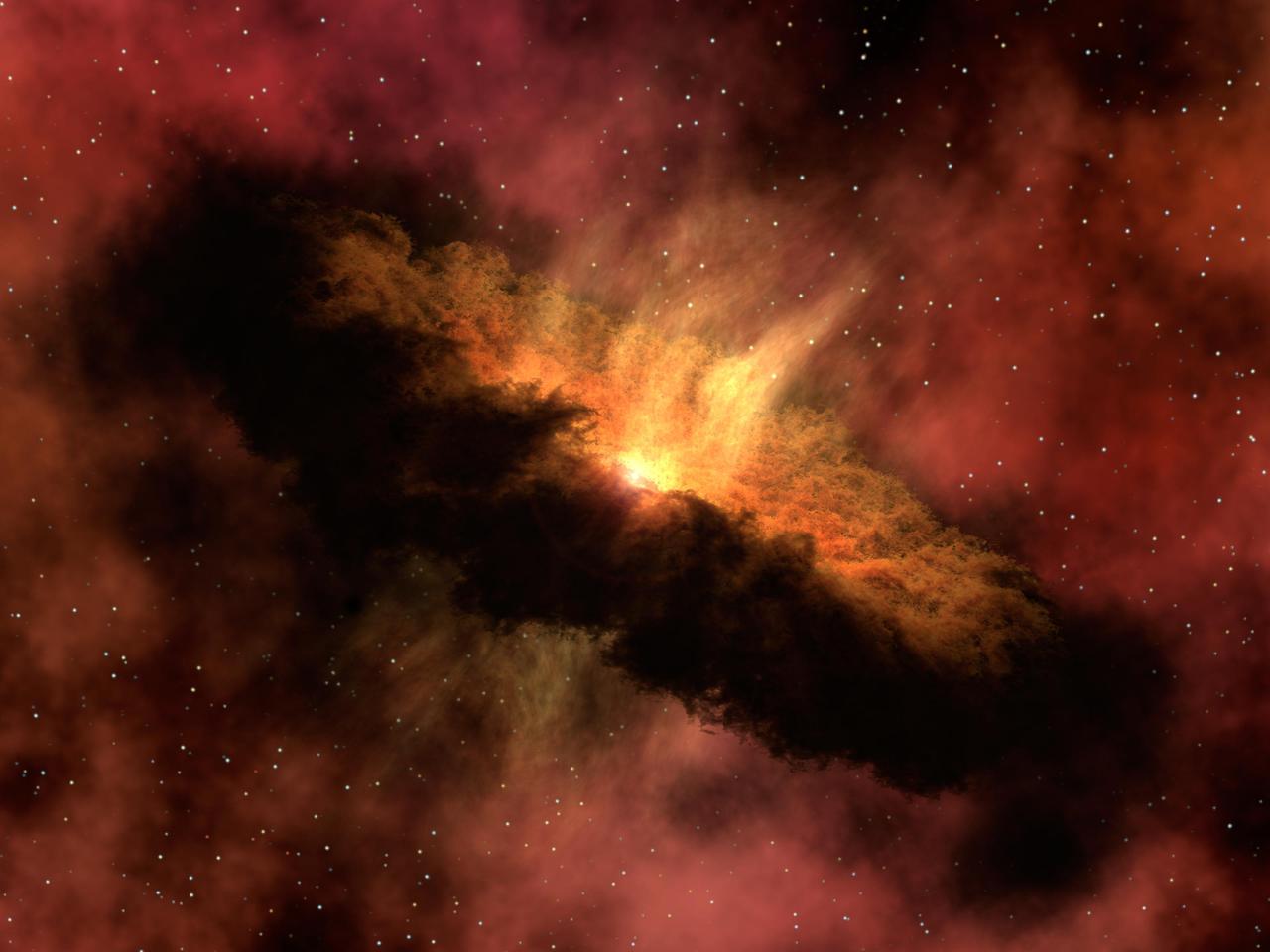

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope observed a fledgling solar system like the one depicted in this artist concept, and discovered deep within it enough water vapor to fill the oceans on Earth five times.

STS066-13-029 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, mission specialist, works at one of two areas onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (STES). Together with the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES) the VDA represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses. In addition to using the microgravity of space to grow high-quality protein crystals for structural analyses, the experiments are expected to help develop technologies and methods to improve the protein crystallization process on Earth as well as in space.

Organomatelic Vapor Phase Epitaxy (OMVPE)
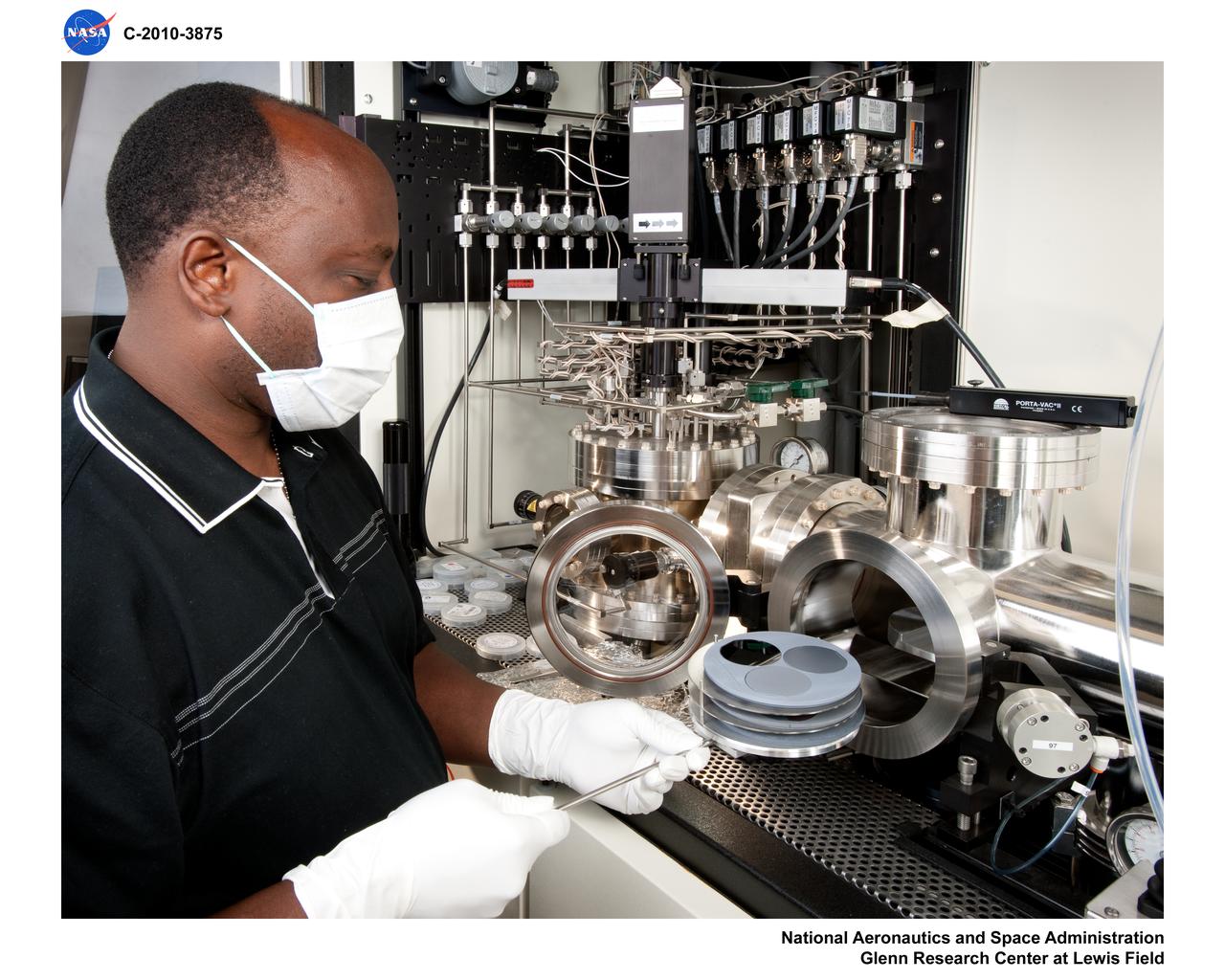

Organomatelic Vapor Phase Epitaxy (OMVPE)
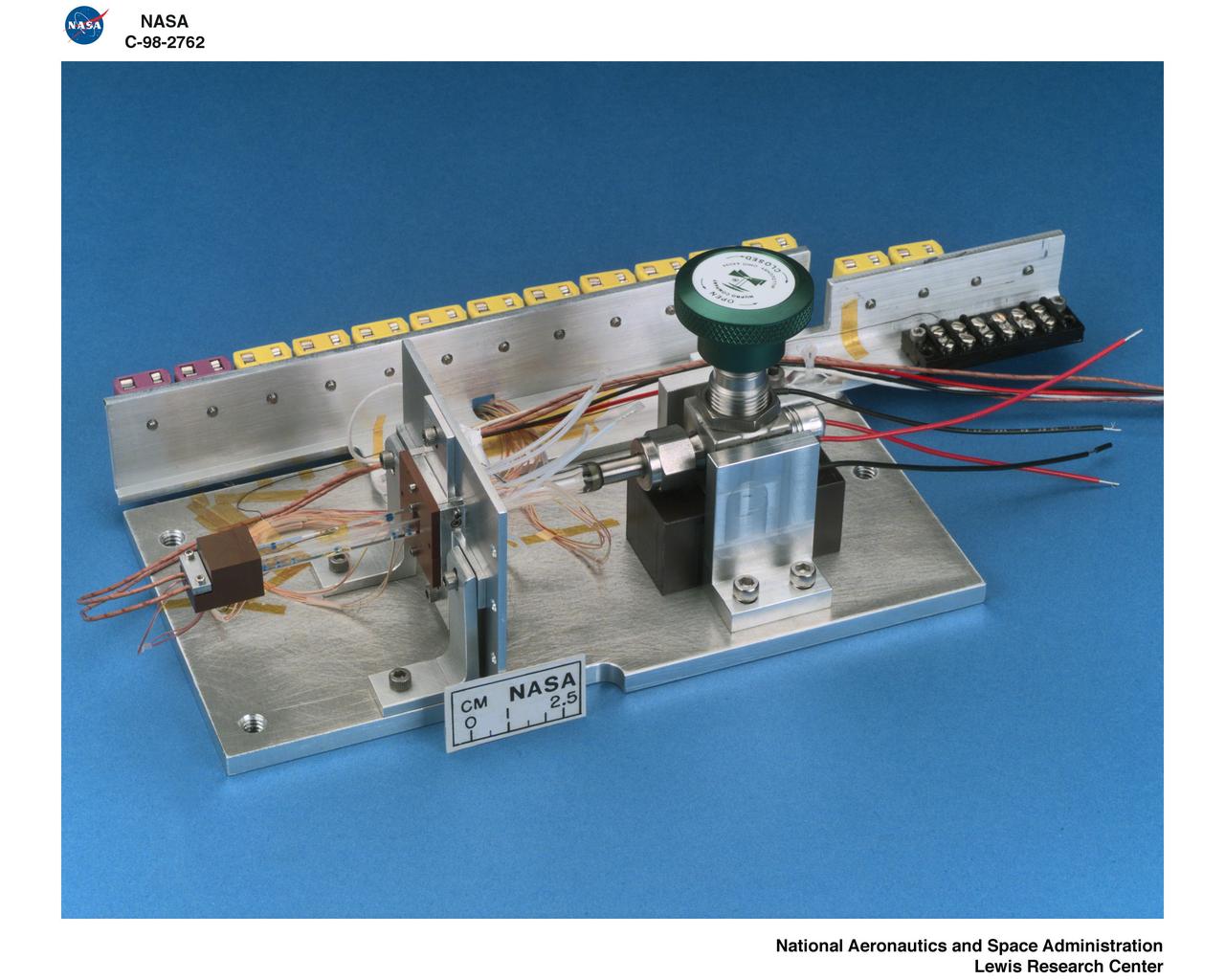
CONSTRAINED VAPOR BUBBLE CVB SAMPLE

A vapor cloud is seen after launch of a Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket, launched at 7:07 p.m., Wednesday October 7, 2015. (NASA Photo/J. Adkins) A Black Brant IX suborbital rocket was launched from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The launch occurred at 7:07 p.m. The primary purpose of the flight was to test the performance of the second-stage Black Brant motor. Preliminary indications are that the motor performed as planned. Preliminary data analysis of the technology experiments (vapor tracer deployments) on the payload is in progress. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
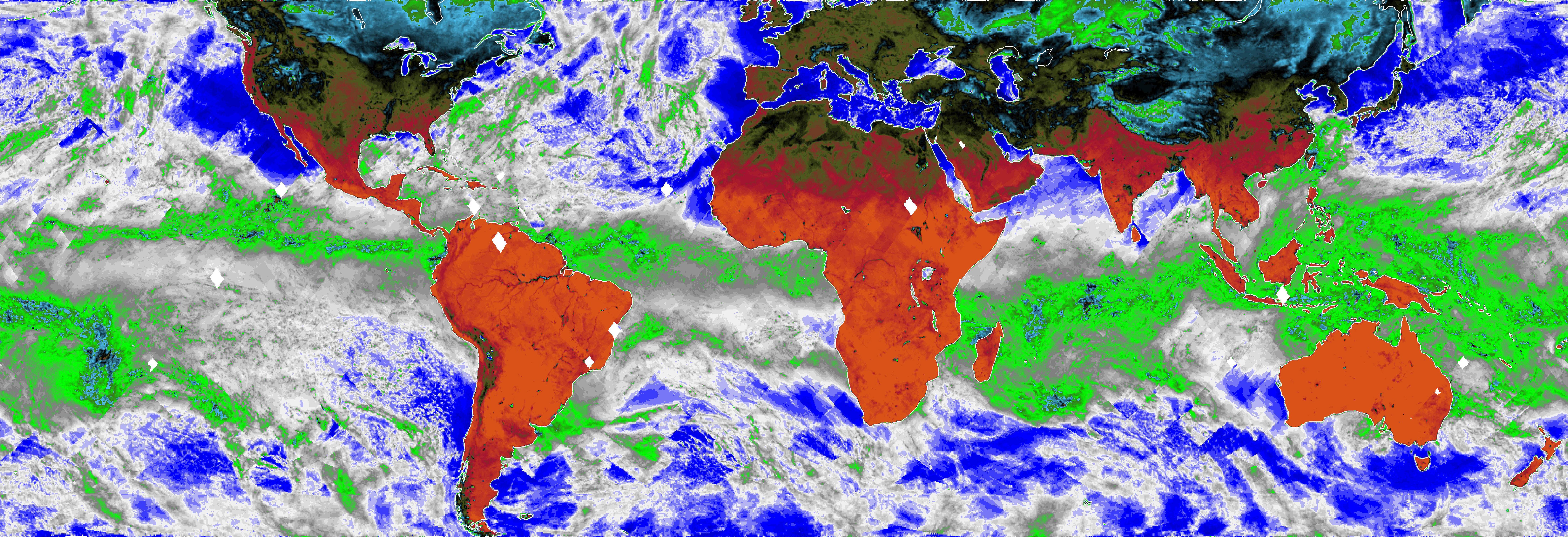
This map, made using the Compact Ocean Wind Vector Radiometer (COWVR) instrument's observations from Jan. 16 to 23, 2022, shows Earth's microwave emissions at a frequency of 34 gigahertz. This frequency provides information on the strength of winds at the ocean surface, the amount of water in clouds, and the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere. Green and white indicate higher water vapor and clouds, while dark blue over the ocean indicates drier air and clear sky. Typical weather patterns for January, such as tropical moisture and rain (the green band stretching across the center of the map), are visible. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24985

jsc2023e046631 (7/25/2023) --- Plexiglass is shown burning in Spacecraft Fire Experiment-IV (Saffire-IV). The flame appears orange because of the soot that is produced as it burns. As the plexiglass burns, the solid is melted, vaporized, and then the vapor burns. The bright flame balls in the flame is vapor burning as it is expelled from the surface. Saffire-VI burns plexiglass at higher oxygen concentrations. The Saffire experiments aim to inform the development of fire safety equipment and strategies for future spacecraft.

Astronaut Candidate Individual Portrait, Nichole Ayers - ASCAN Class of 2021. Photo Date: December 3, 2021. Location: Building 8, Room 183 - Photo Studio. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
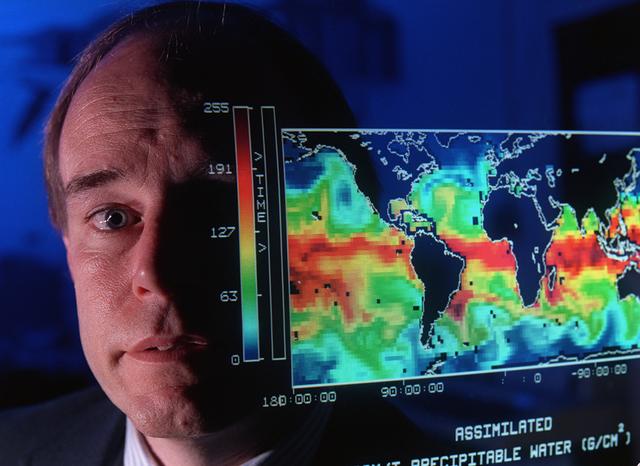
This map shows the presence of water vapor over global oceans. The imagery was produced by combining Special Sensor Microwave Imager measurements and computer models. This data will help scientists better understand how weather systems move water vapor from the tropics toward the poles producing precipitation.
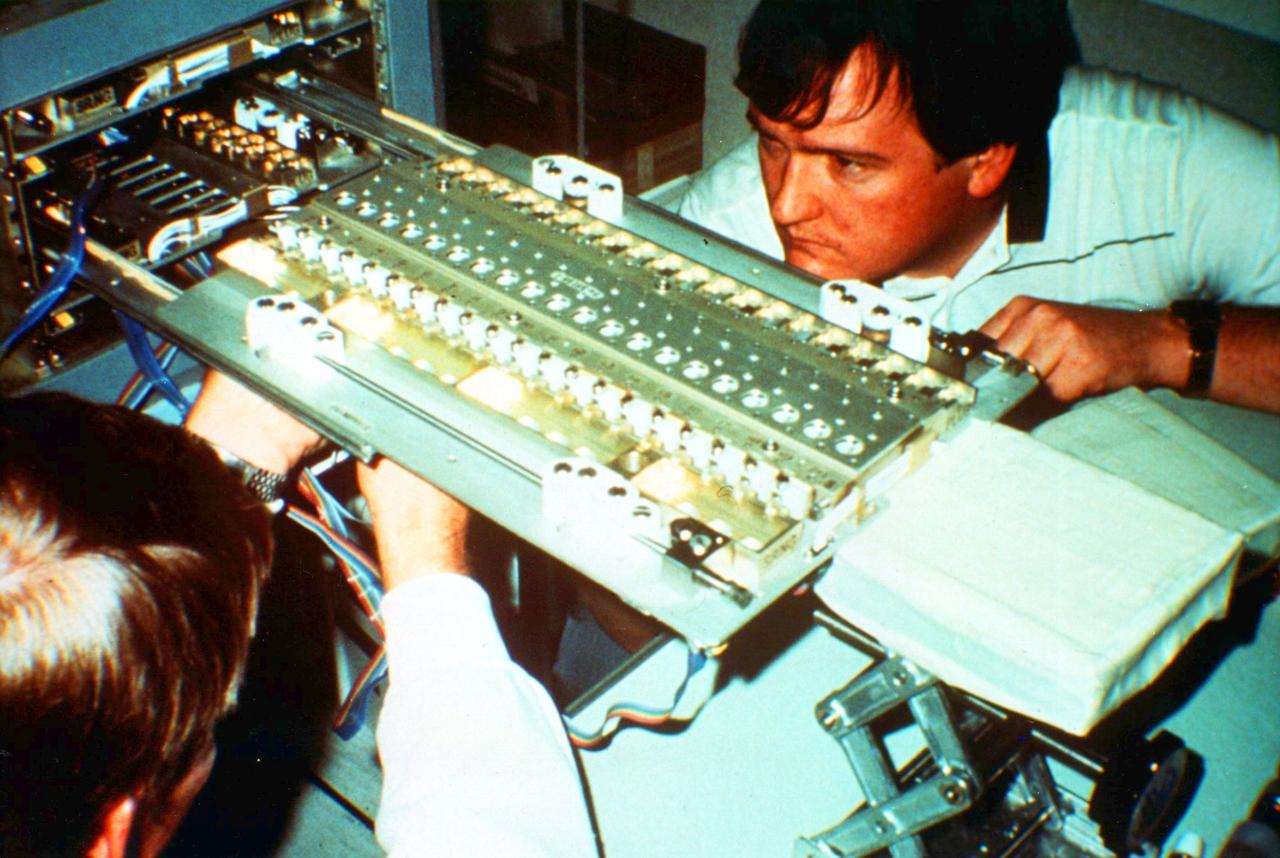
Final (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray adjustments before loading into shuttle.
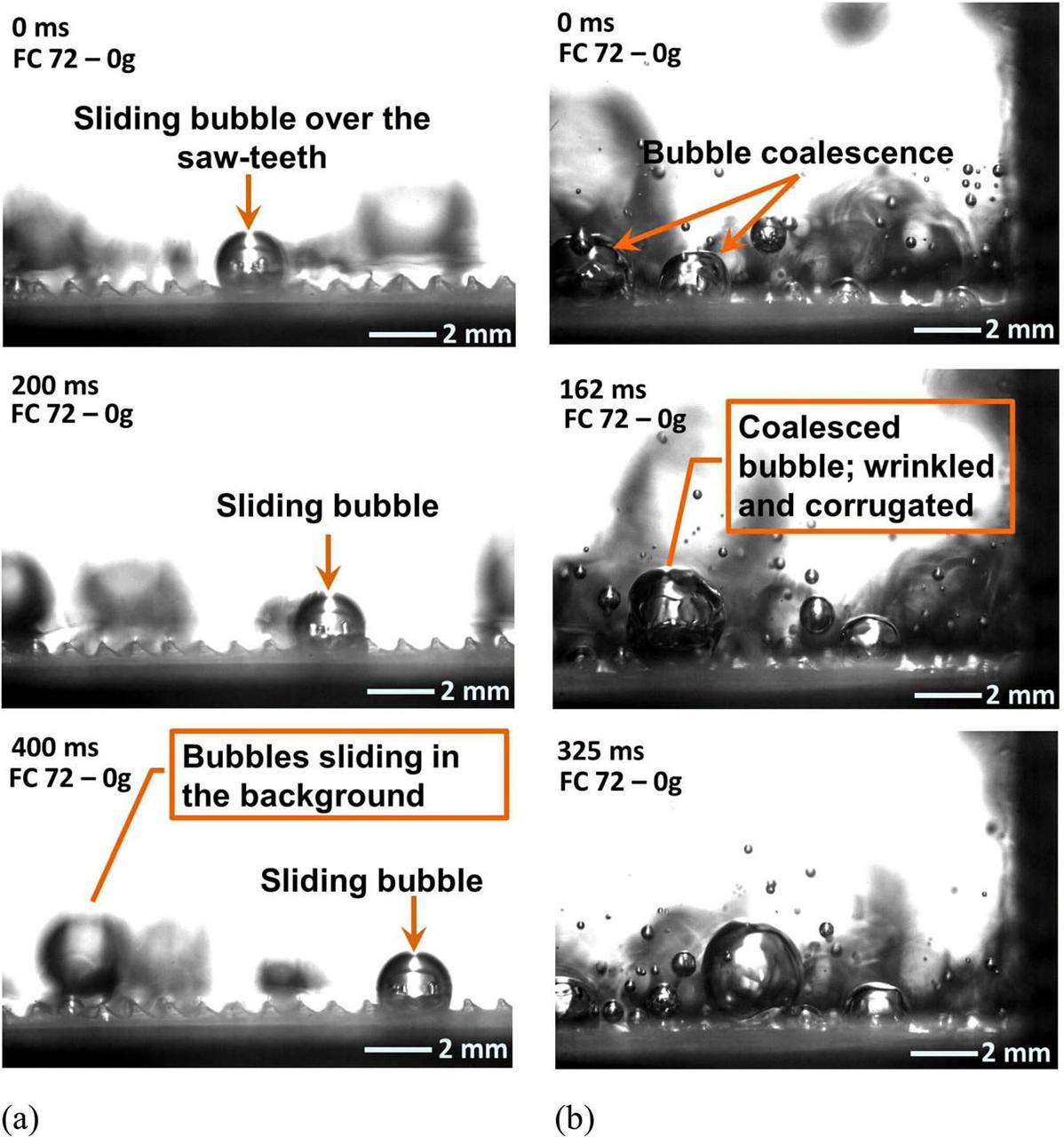
jsc2020e030483 (4/20/2020) --- A preflight image sequence from parabolic flight experiments indicating motion of vapor bubble on heated ratchet surface. Asymmetric Sawtooth and Cavity-Enhanced Nucleation-Driven Transport (PFMI-ASCENT) demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a microstructured surface. When fluids boil over flat heated surfaces in microgravity, vapor bubbles grow larger in size, causing poor heat transfer that can lead to damage of devices. Adding microscopic rachets on the surface may passively enable mobility of vapor bubbles and prevent this damage. (Image courtesy of: Techshot, Inc.)

A Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket is launched at 7:07 p.m., Wednesday October 7, 2015. (NASA Photo/A. Stancil) A Black Brant IX suborbital rocket was launched from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The launch occurred at 7:07 p.m. The primary purpose of the flight was to test the performance of the second-stage Black Brant motor. Preliminary indications are that the motor performed as planned. Preliminary data analysis of the technology experiments (vapor tracer deployments) on the payload is in progress. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
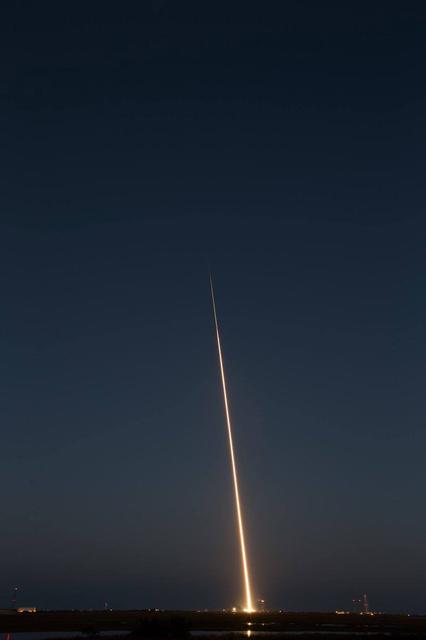

A Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket is launched at 7:07 p.m., Wednesday October 7, 2015. (NASA Photo/T. Zaperach) A Black Brant IX suborbital rocket was launched from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The launch occurred at 7:07 p.m. The primary purpose of the flight was to test the performance of the second-stage Black Brant motor. Preliminary indications are that the motor performed as planned. Preliminary data analysis of the technology experiments (vapor tracer deployments) on the payload is in progress. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
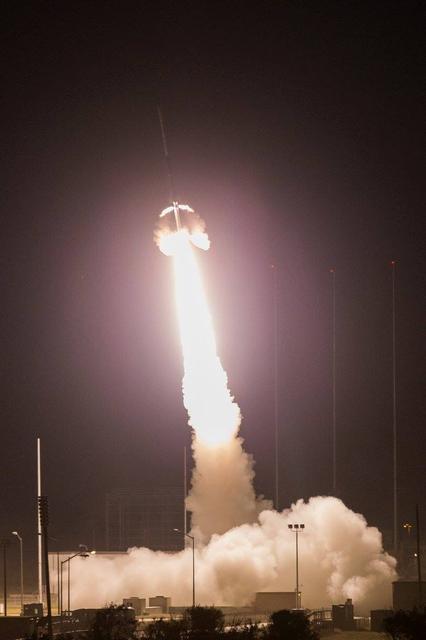

A Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket is launched at 7:07 p.m., Wednesday October 7, 2015. (NASA Photo/A. Stancil) A Black Brant IX suborbital rocket was launched from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The launch occurred at 7:07 p.m. The primary purpose of the flight was to test the performance of the second-stage Black Brant motor. Preliminary indications are that the motor performed as planned. Preliminary data analysis of the technology experiments (vapor tracer deployments) on the payload is in progress. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
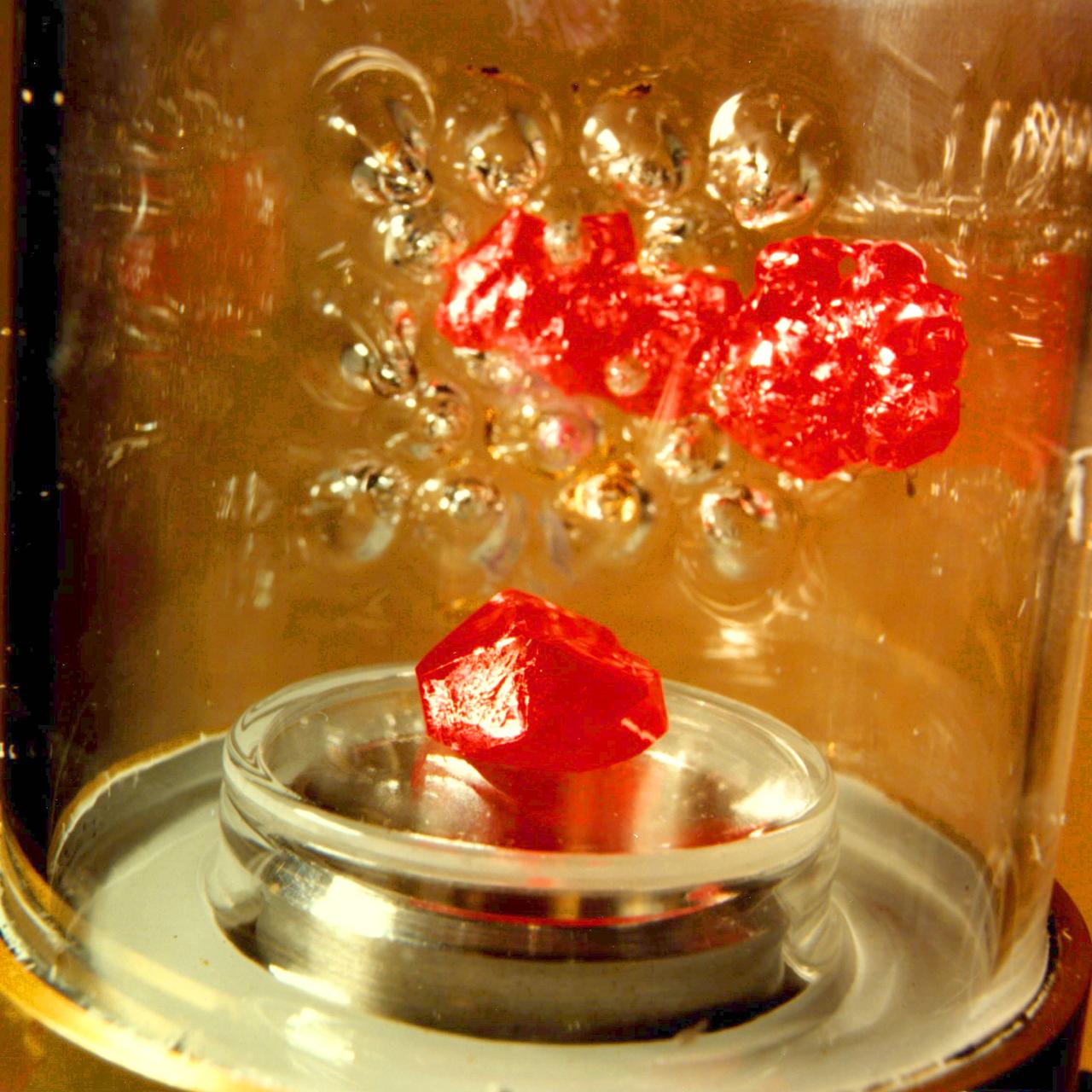

Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS), Flown on IML-1, Spacelab 3, Principal Investigator: Lodewijk van den Berg

The Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition, PS-PVD, Rig, Coatings for Next-Generation Turbine Components, Creating Efficient Engines
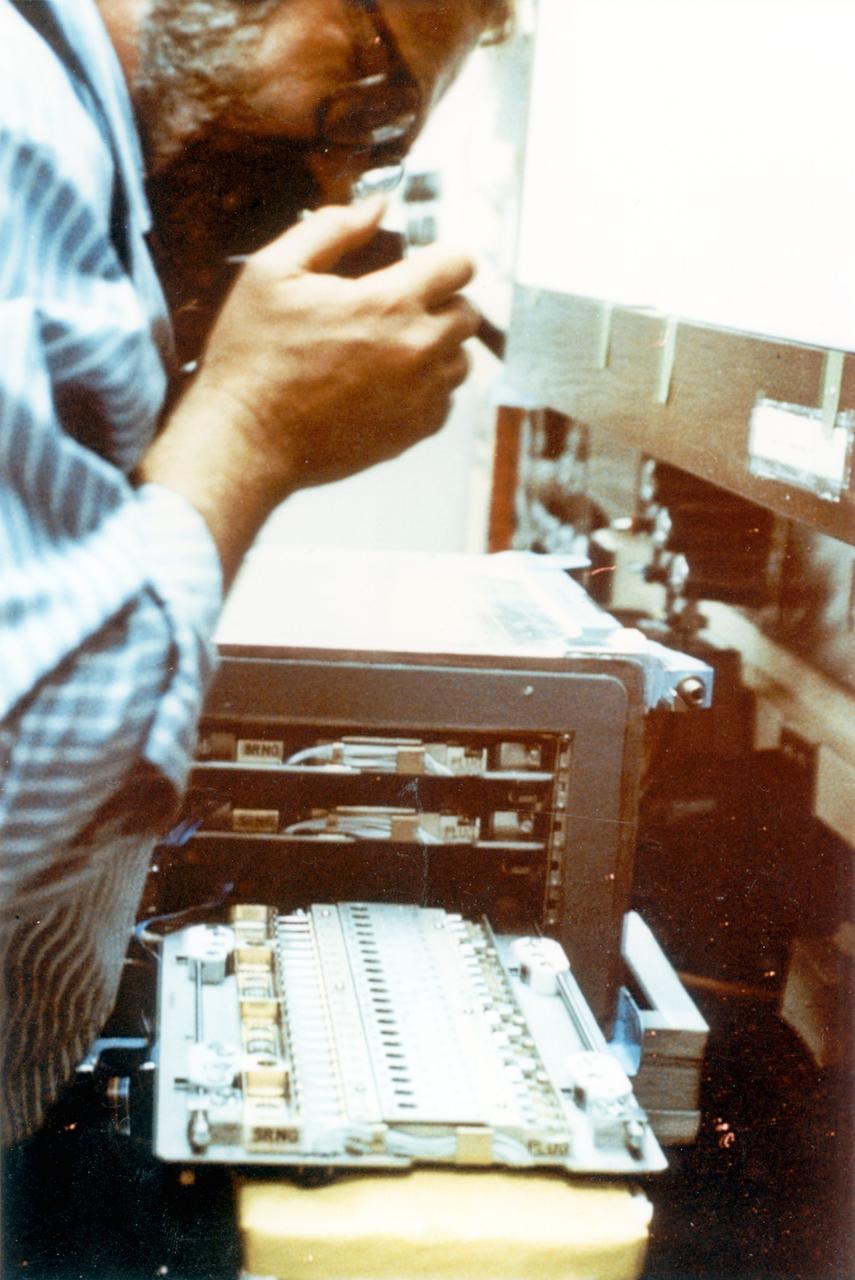

Scientist photographs STS- 26 Post-flight (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray with (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Samples.
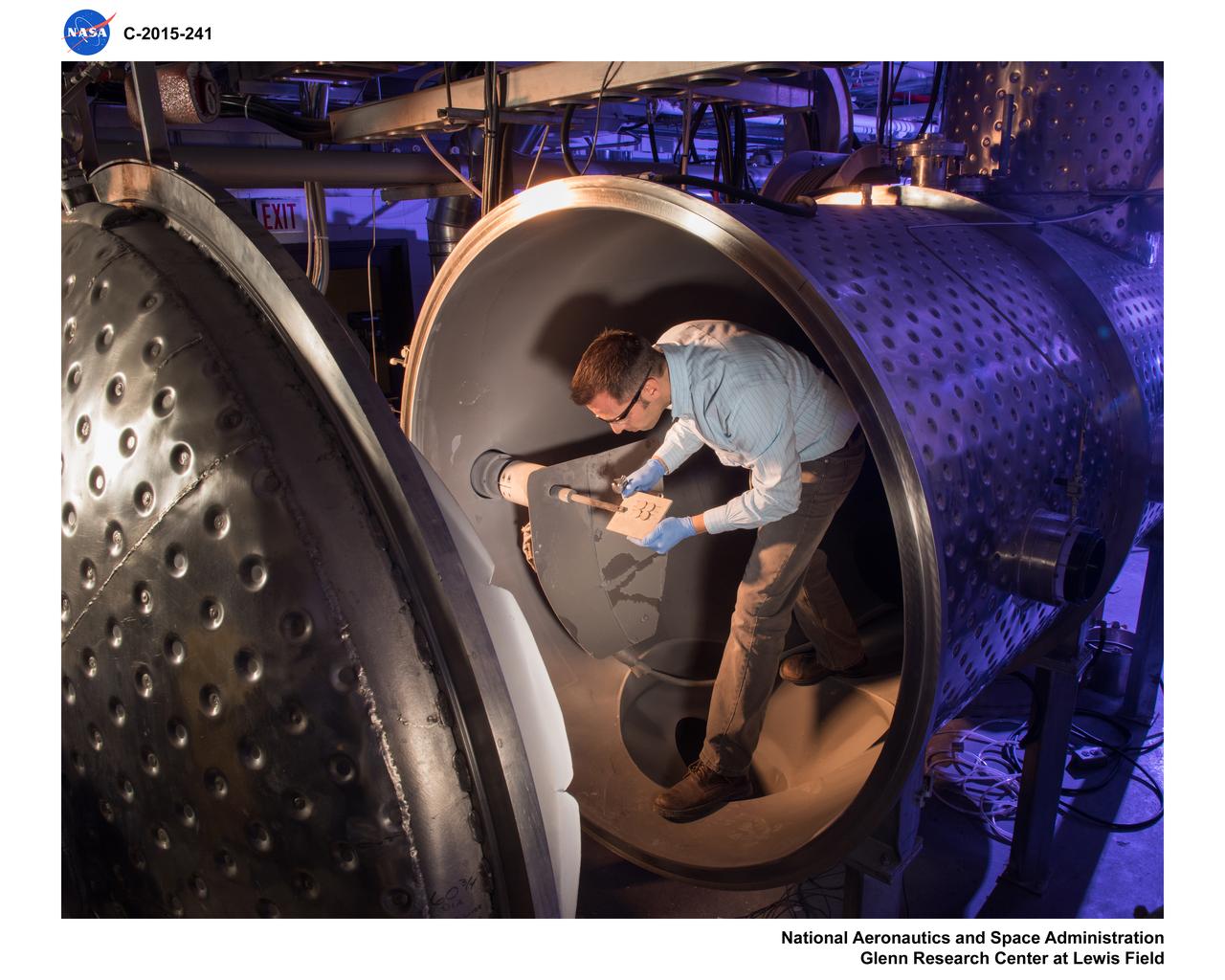

The Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition, PS-PVD, Rig, Coatings for Next-Generation Turbine Components, Creating Efficient Engines
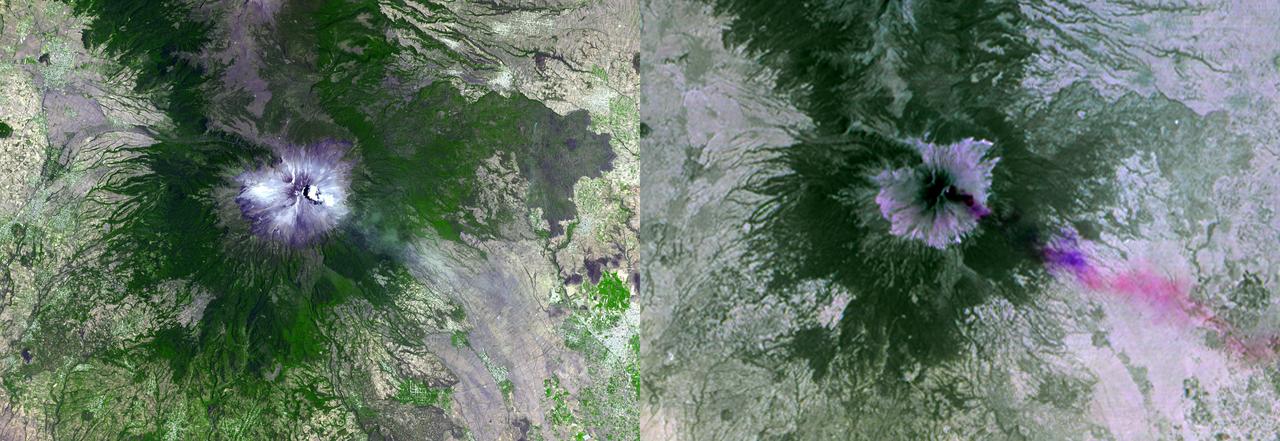

NASA Terra spacecraft shows Mexico active Popocatepetl volcano, located about 40 miles southeast of Mexico City, spewing water vapor, gas, ashes and glowing rocks since its most recent eruption period began in April 2012.
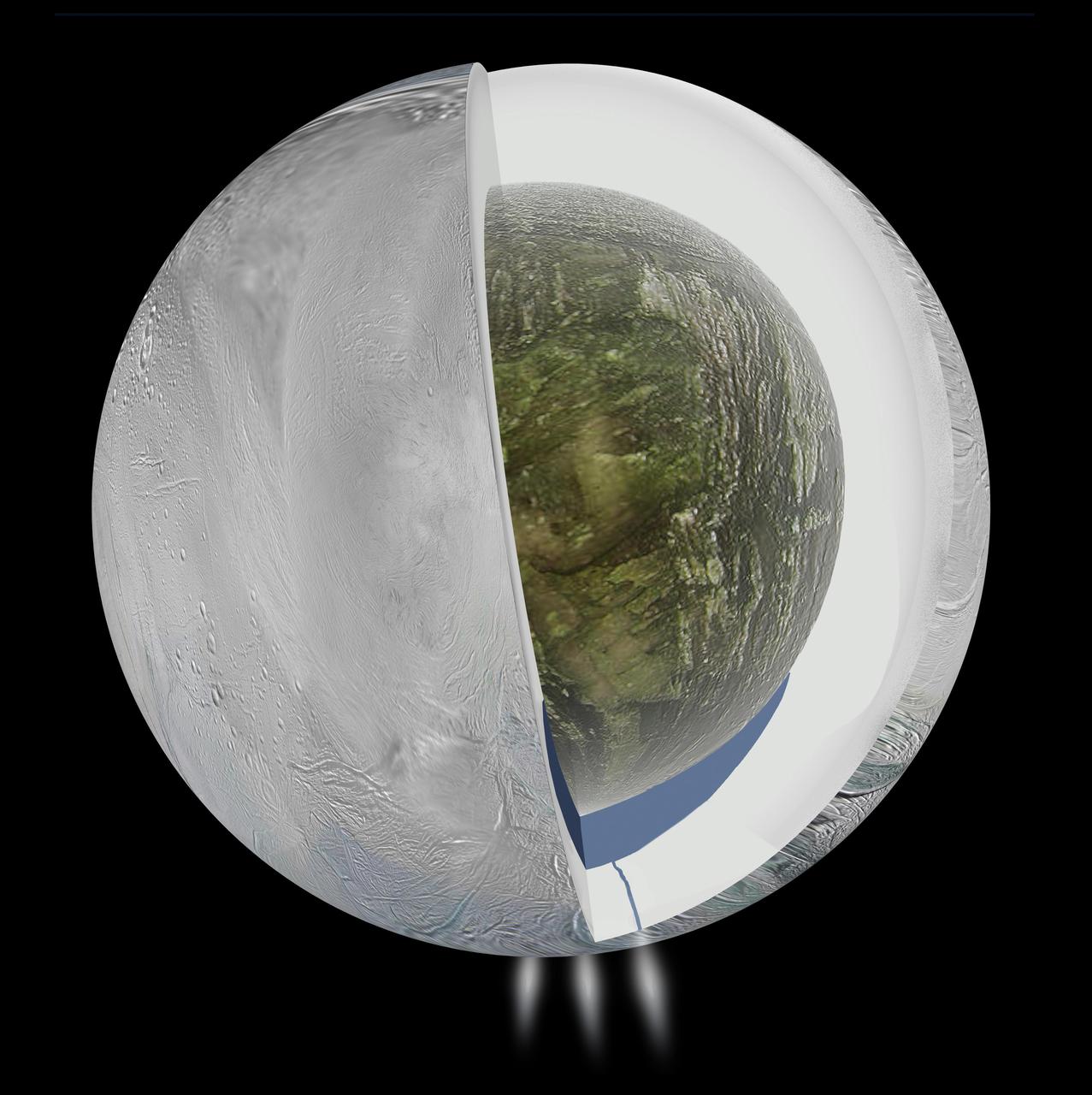
Gravity measurements by NASA Cassini spacecraft and Deep Space Network suggest that Saturn moon Enceladus, which has jets of water vapor and ice gushing from its south pole, also harbors a large interior ocean beneath an ice shell.

NASA Terra spacecraft shows Popocatepetl, the nearly 18.000-foot-high volcano about 40 miles southeast of Mexico City, continuing to spew water vapor, gas, ashes and glowing rocks from its latest eruption, which started in mid-April 2012.
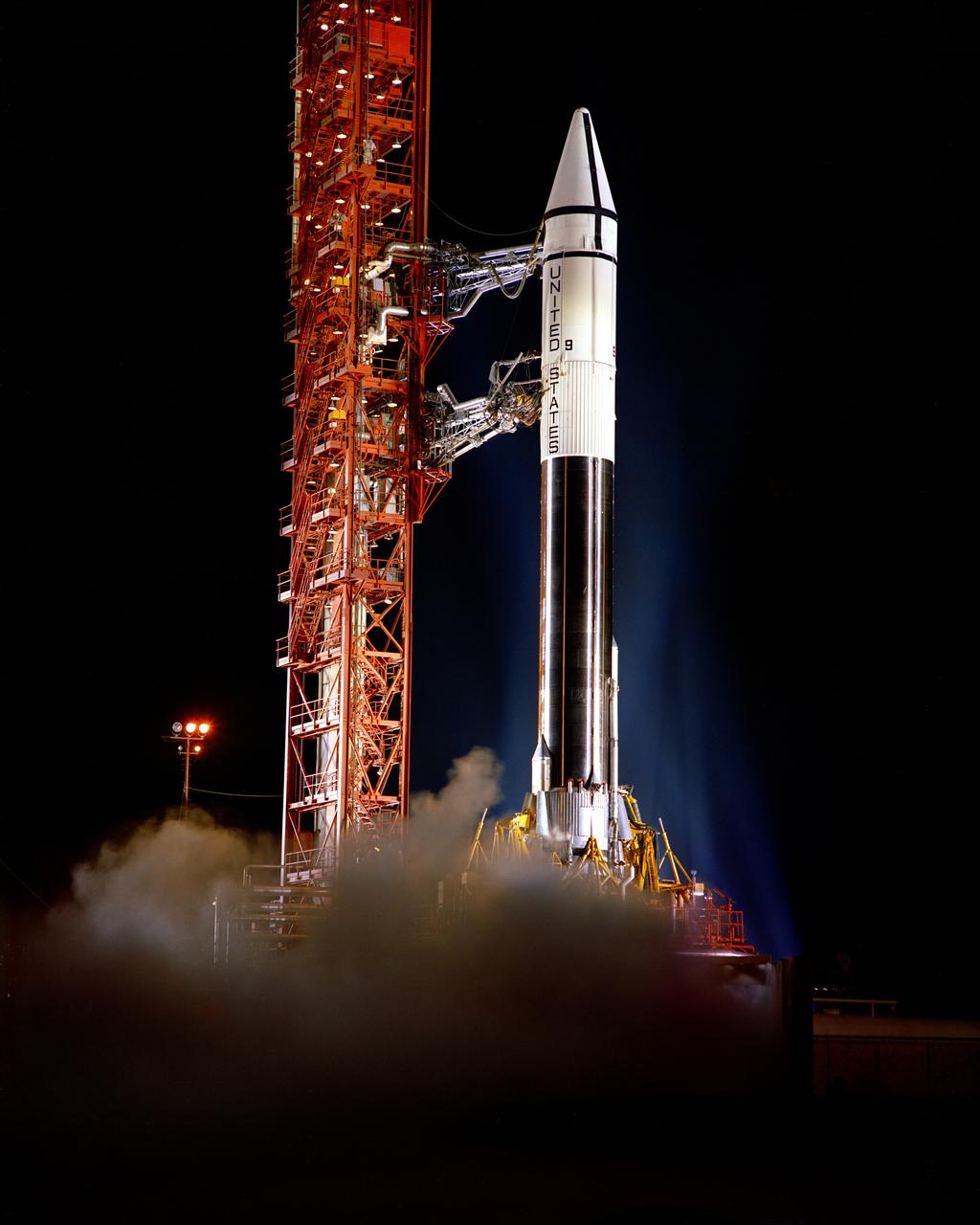

Pre-launch alert, Complex 36B. Gantry pull back with LOX vapor around launcher, Centaur 9. Surveyor Mass Model Spacecraft.
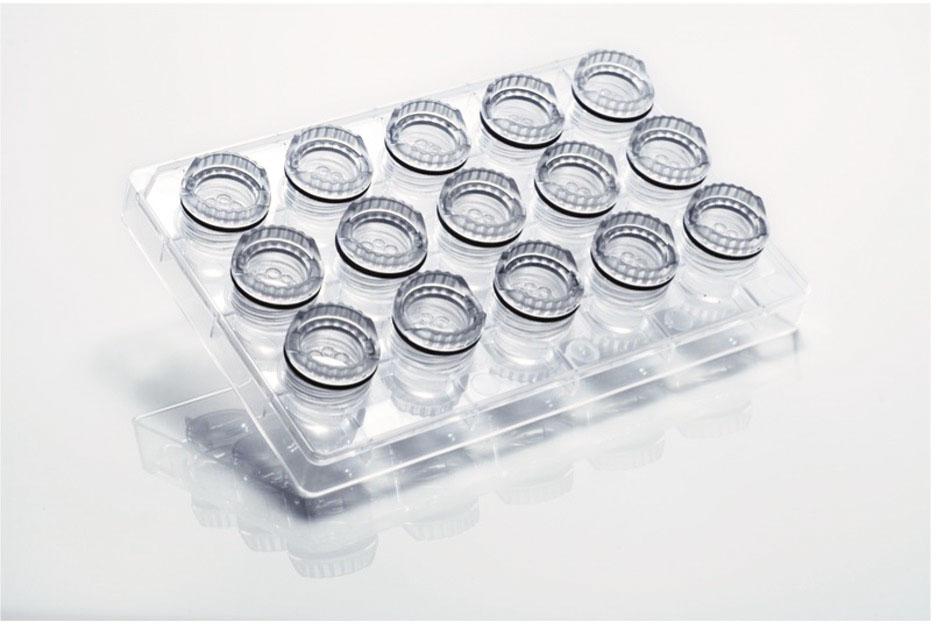

jsc2021e010281 (3/10/2021) --- A preflight view of the EasyXtal hanging-drop vapor diffusion crystal plates. Photo courtesy of Timothy Mueser.
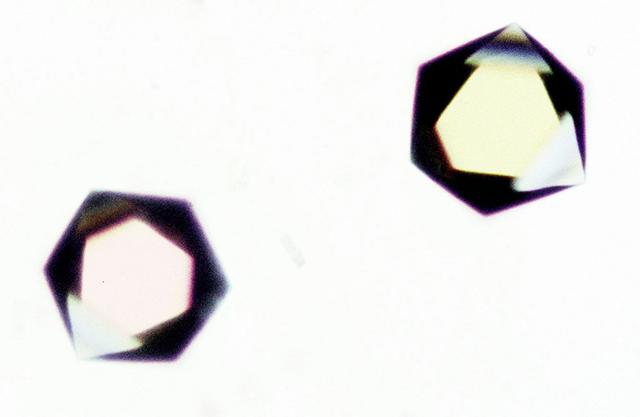
Crystals of Proteinase K complex grown in the VDA-2 (Vapor Diffusion Apparatus) hardware aboard MSL-1. Principal Investigator: Larry DeLucas
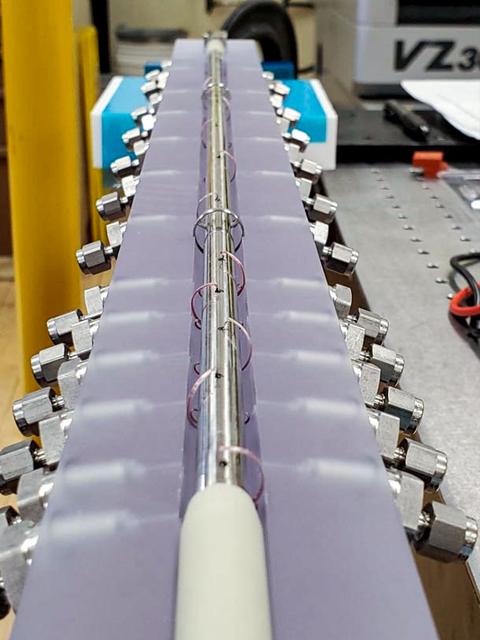

jsc2023e038724 (6/28/2023) --- An interior view of the FBCE-CM-HT test section. Test fluid is vaporized and pumped through the steel tube embedded in an insulating material while space station cooling water is flown around the outer annulus of the steel tube causing the internal vapor to condense. Both cooling water and test fluid temperatures are measured using a system of.thermocouples to calculate heat transfer. Image courtesy of NASA Glenn Research Center..
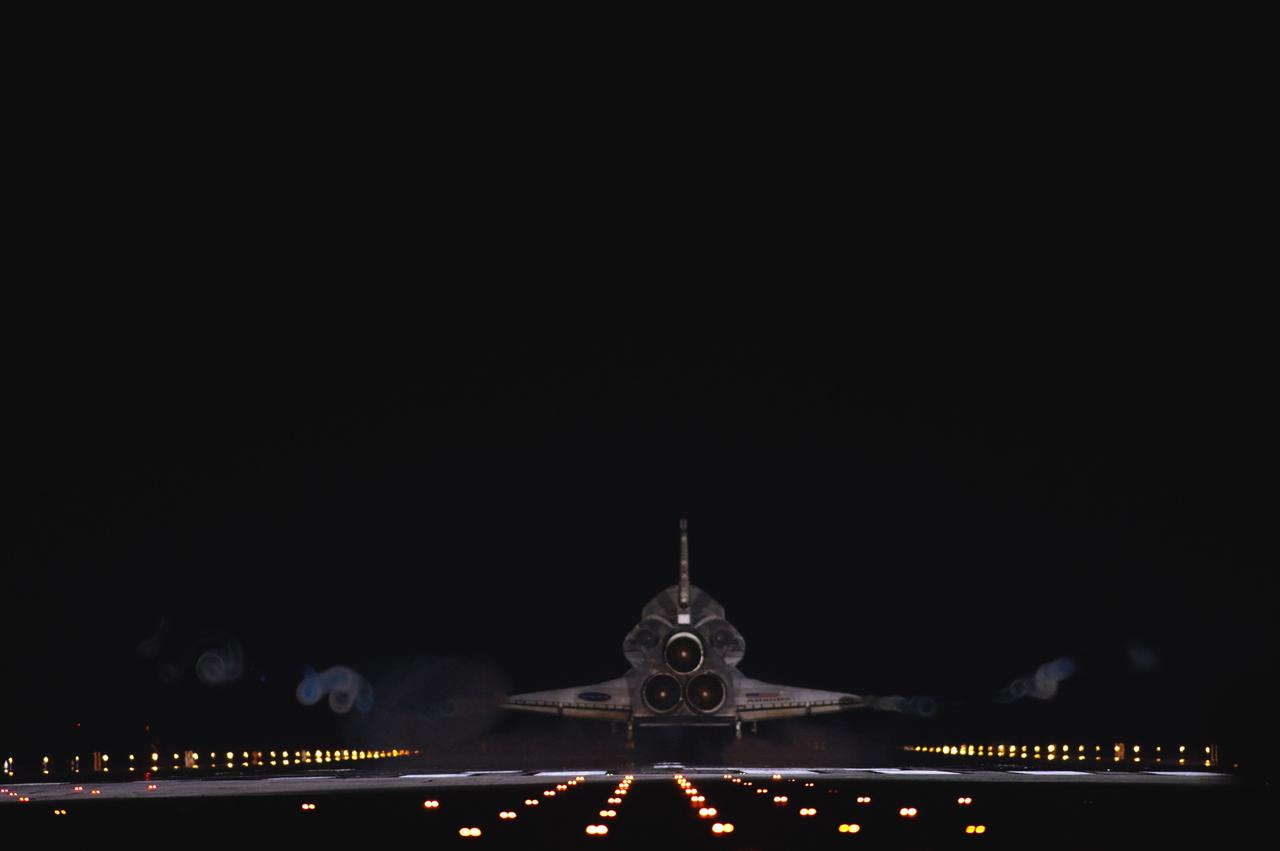

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it touches down on Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
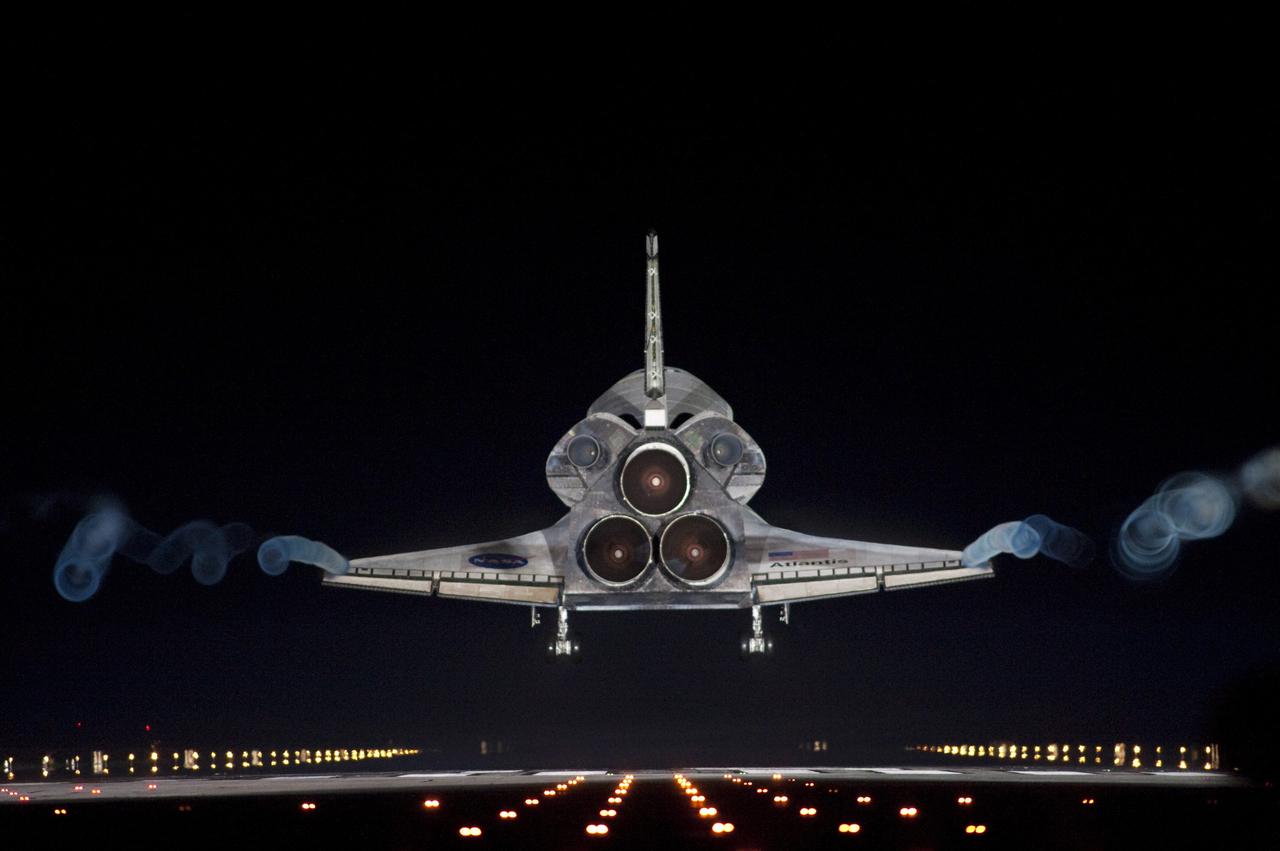

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
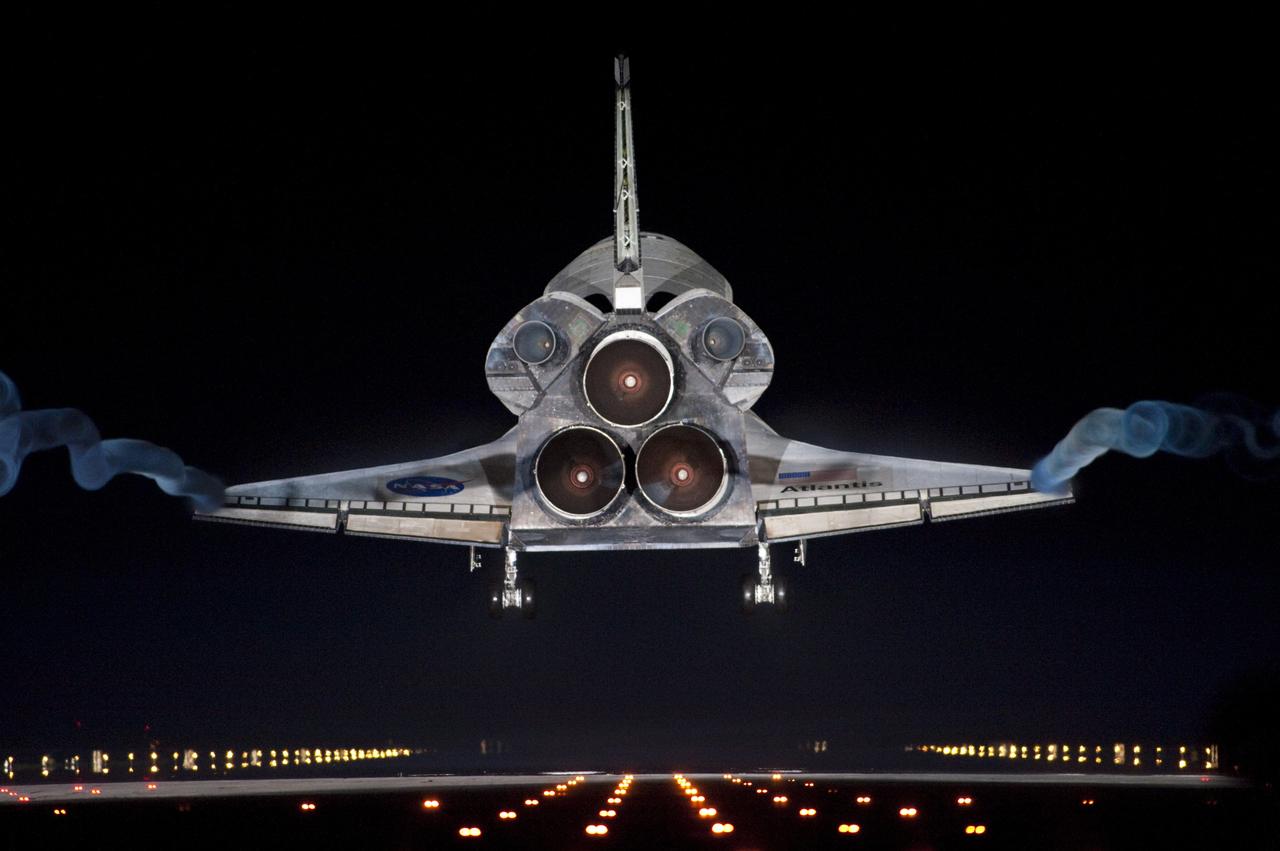

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
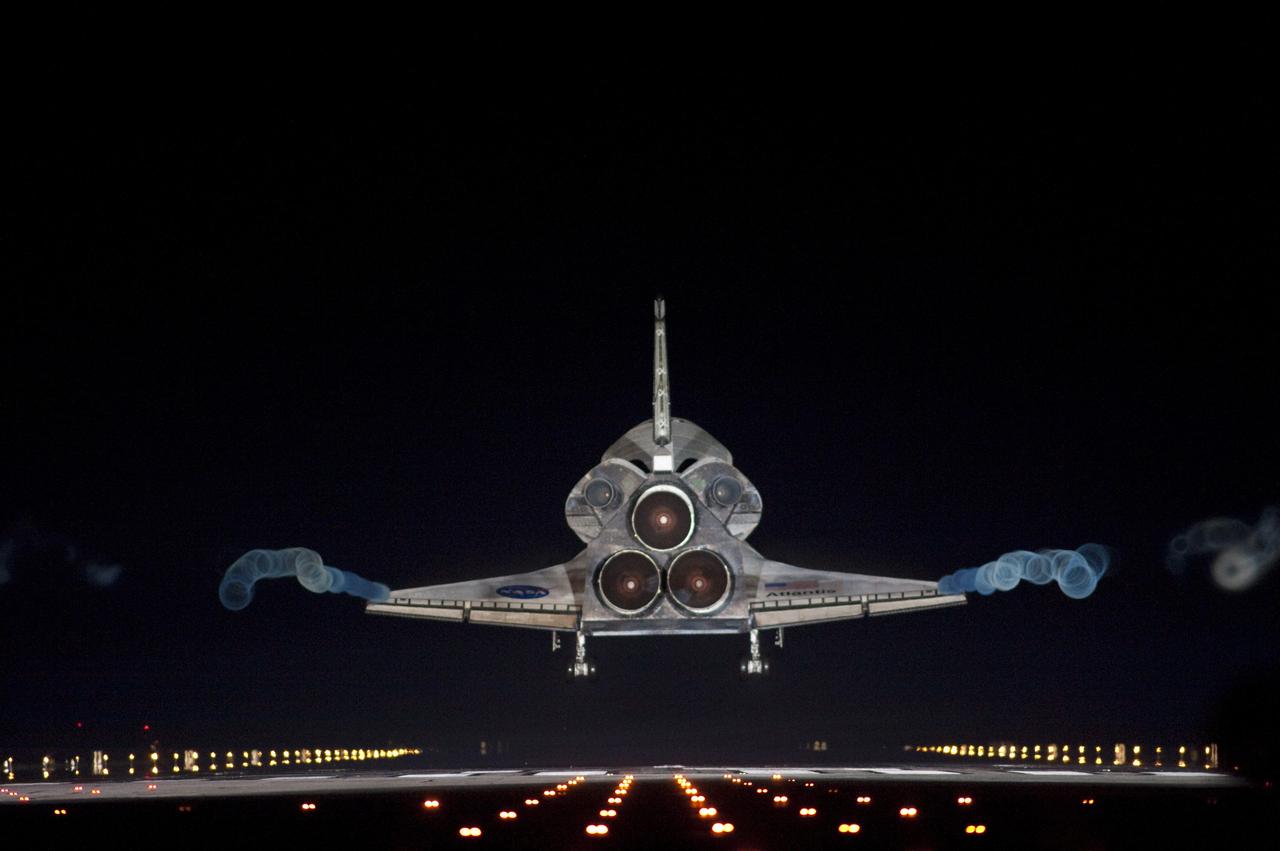

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
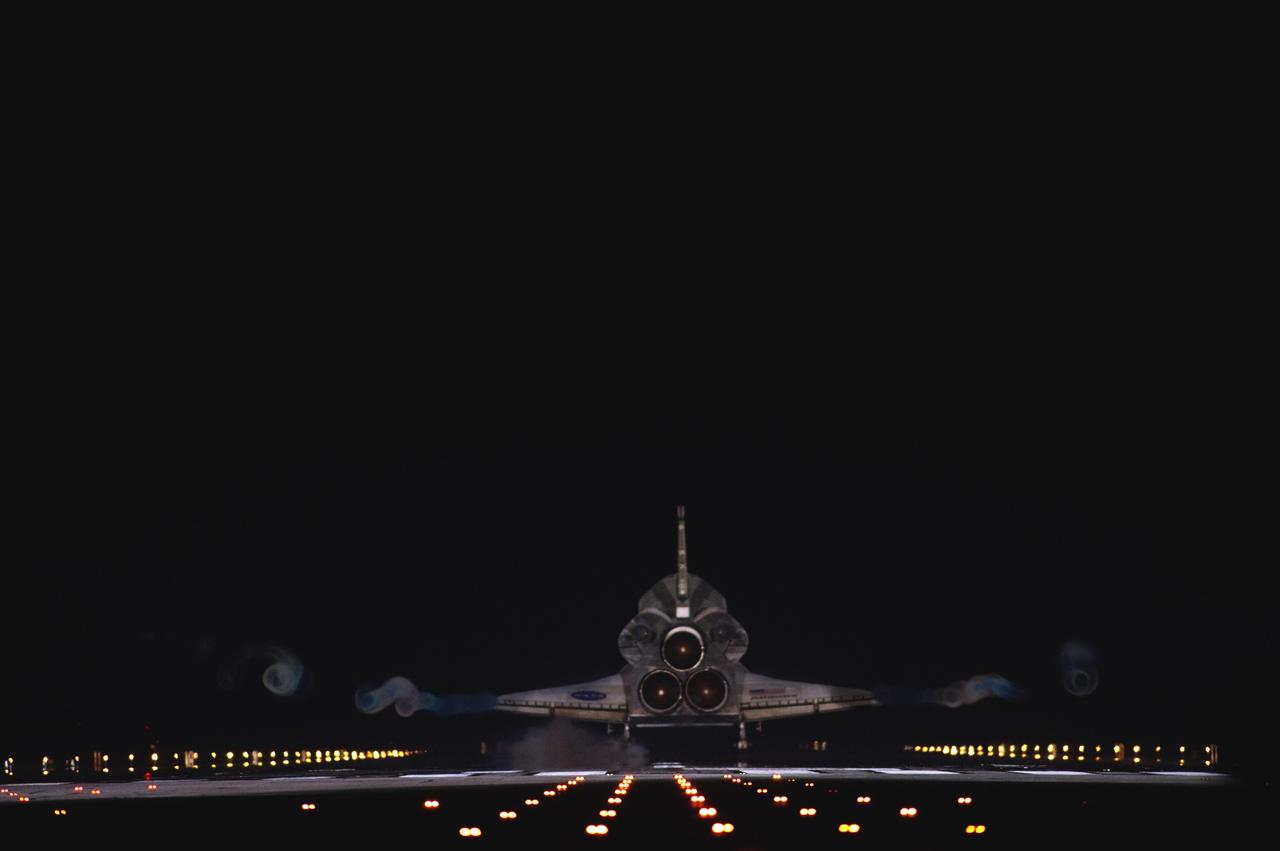

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it touches down on Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Atlantis as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. It also was the final mission for the shuttle program. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information on the space shuttle era, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/flyout. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
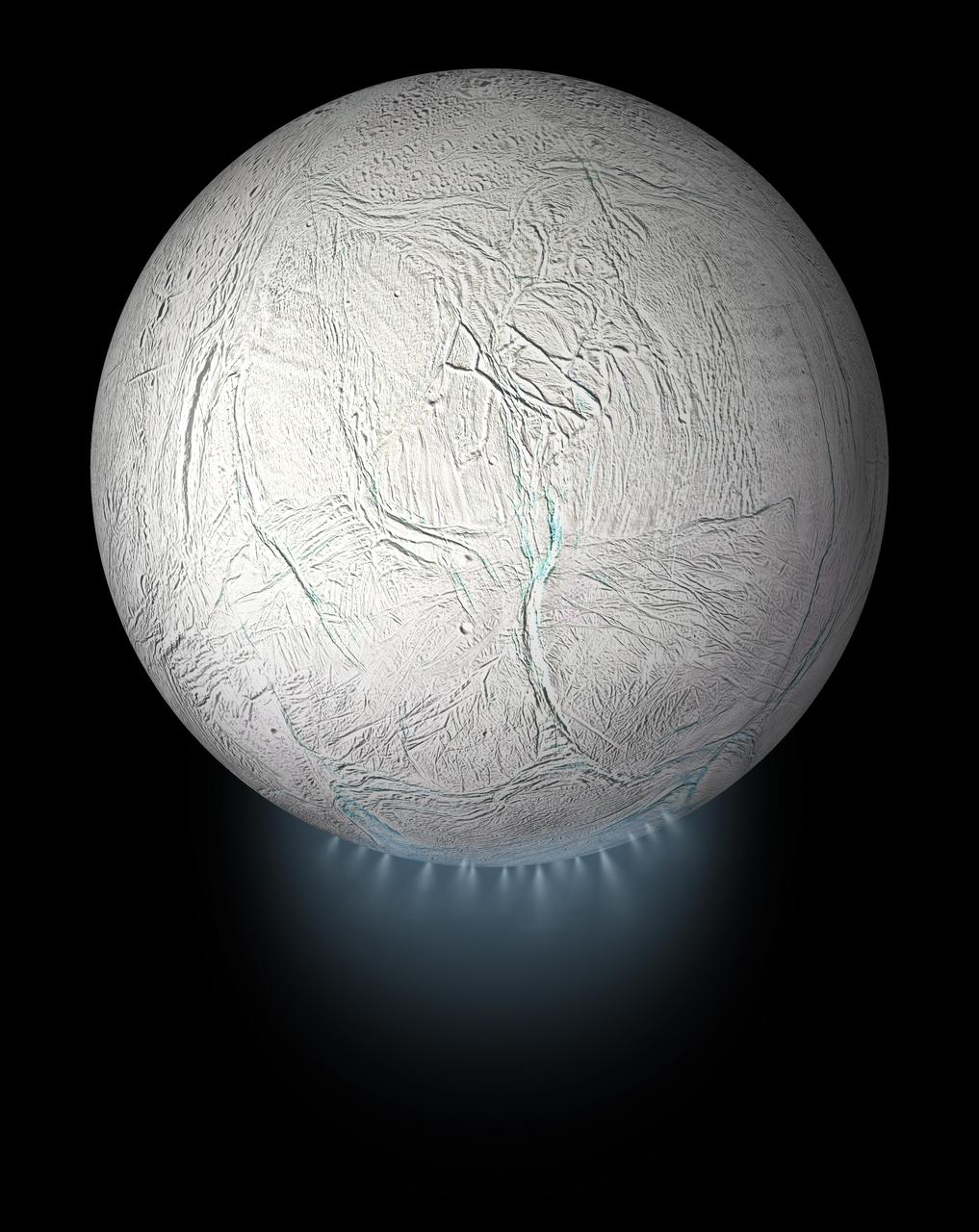

This illustration shows Saturn's icy moon Enceladus with the plume of ice particles, water vapor and organic molecules that sprays from fractures in the moon's south polar region. A cutaway version of this graphic is also available, showing the moon's interior ocean and hydrothermal activity — both of which were discovered by NASA's Cassini mission (see PIA20013). This global view was created using a Cassini-derived map of Enceladus (see PIA18435). More information about Enceladus is available at https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/moons/saturn-moons/enceladus/in-depth/. For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/cassini/overview/. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23175
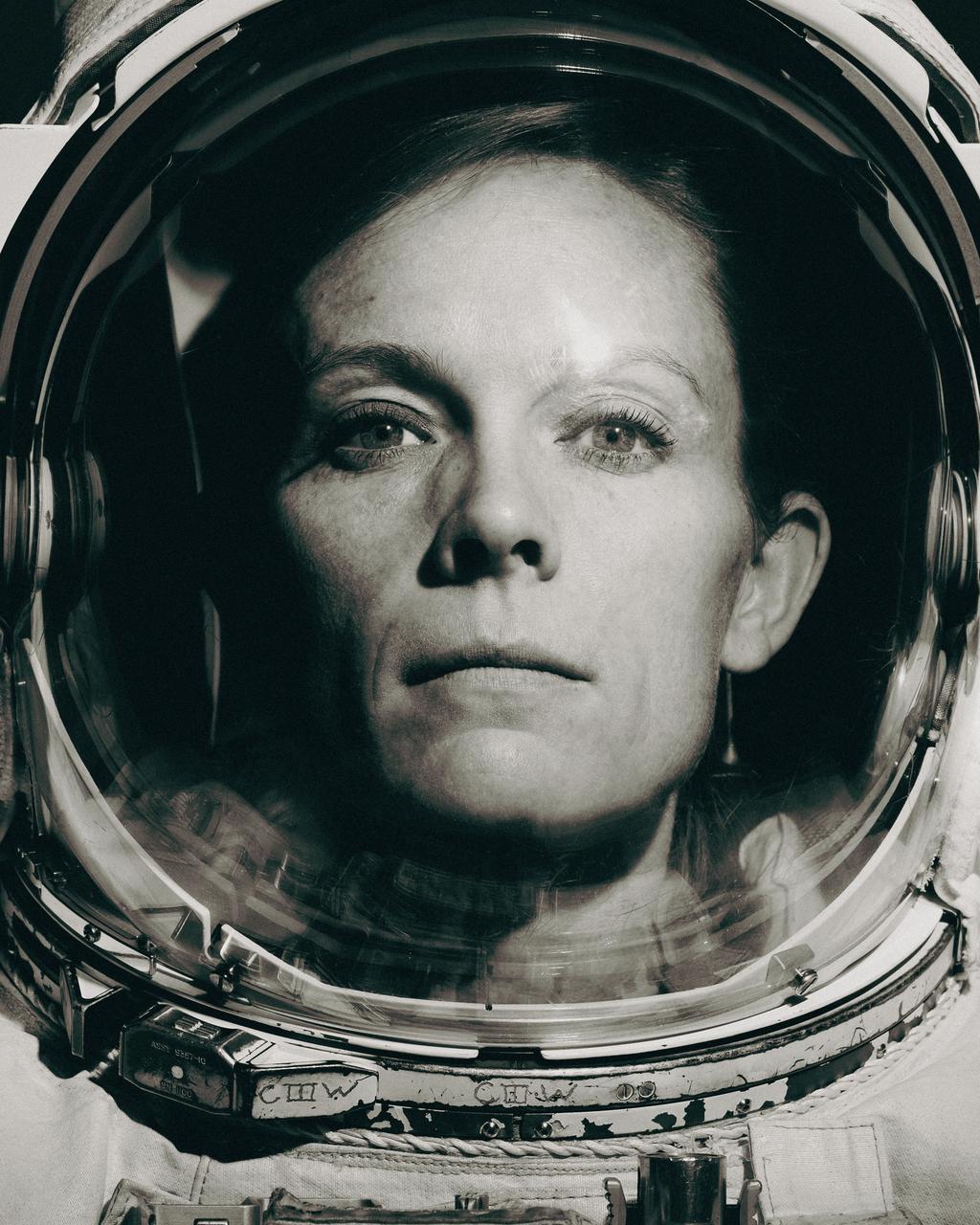

jsc2024e069023_alt NASA astronaut Nichole “Vapor” Ayers at the NASA Johnson Space Center photo studio on October 24, 2024. Photographer: Josh Valcarcel – Johnson Space Center
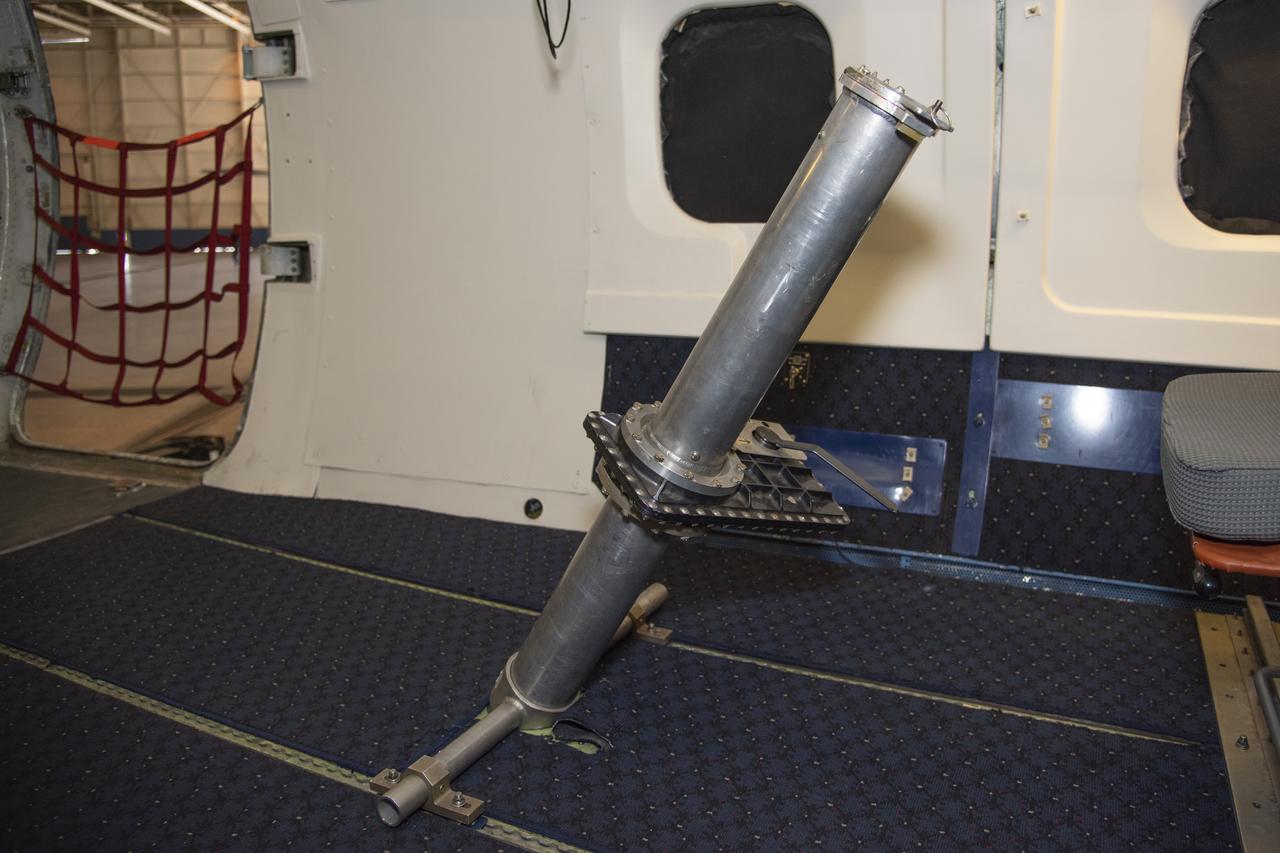

To verify the lidar data they're collecting on the DC-8 airborne science laboratory, Aeolus mission scientists will use dropsondes, which are devices they'll drop from this tube in the aircraft to collect wind and water vapor data.
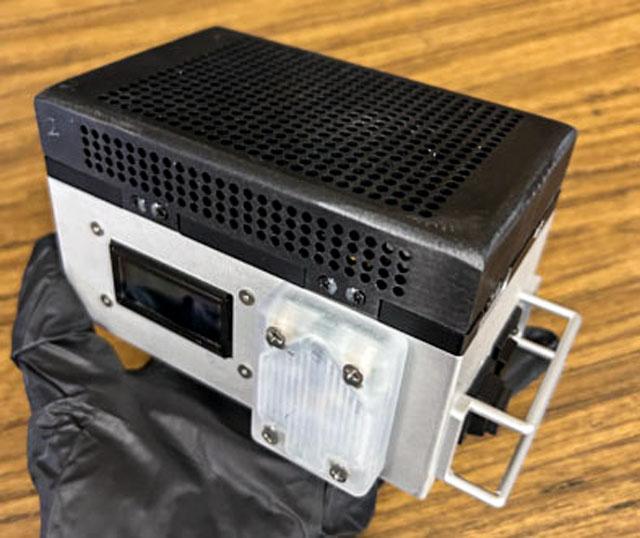

jsc2025e059518 (617/2025) --- A preflight view of the Portable Tunable Laser Spectrometer (PTLS) sensor package. PTLS uses a sensor network to measure the distribution of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and oxygen over time. Image courtesy of JPL.
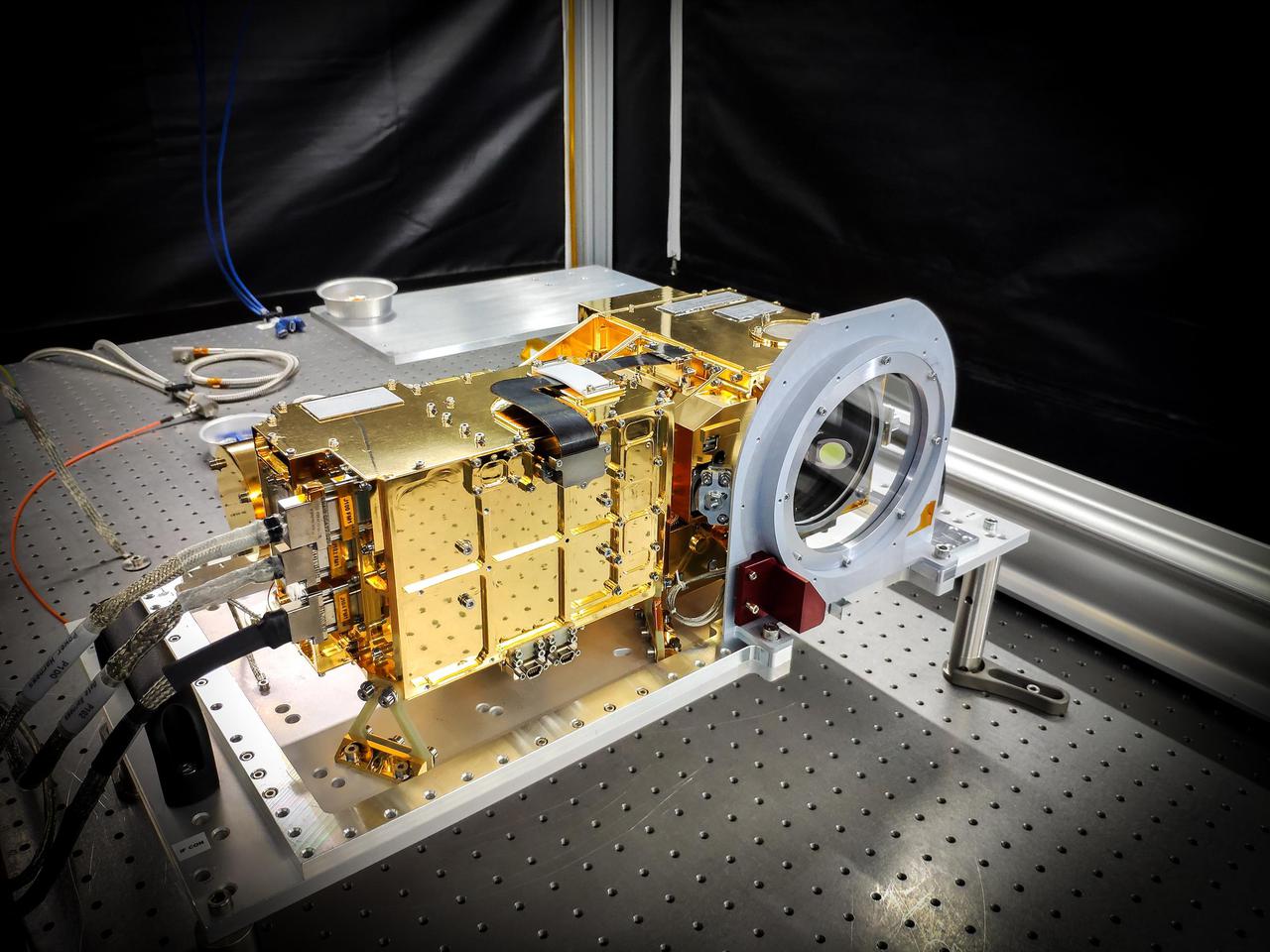
SuperCam's mast unit before being installed atop the Perseverance rover's remote sensing mast. SuperCam fires a laser at rock or soil targets up to 20 feet (7 meters) away, and then analyzes the vaporized rock to reveal the composition. SuperCam's telescope peers out through a window seen on the right side of the unit, above a microphone (hidden by a red protective cover in this image), which will pick up the sounds of rocks being vaporized by the laser. The electronics are inside the gold-plated box on the left. The end of the laser peeks out from behind the left side of the electronics. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24208
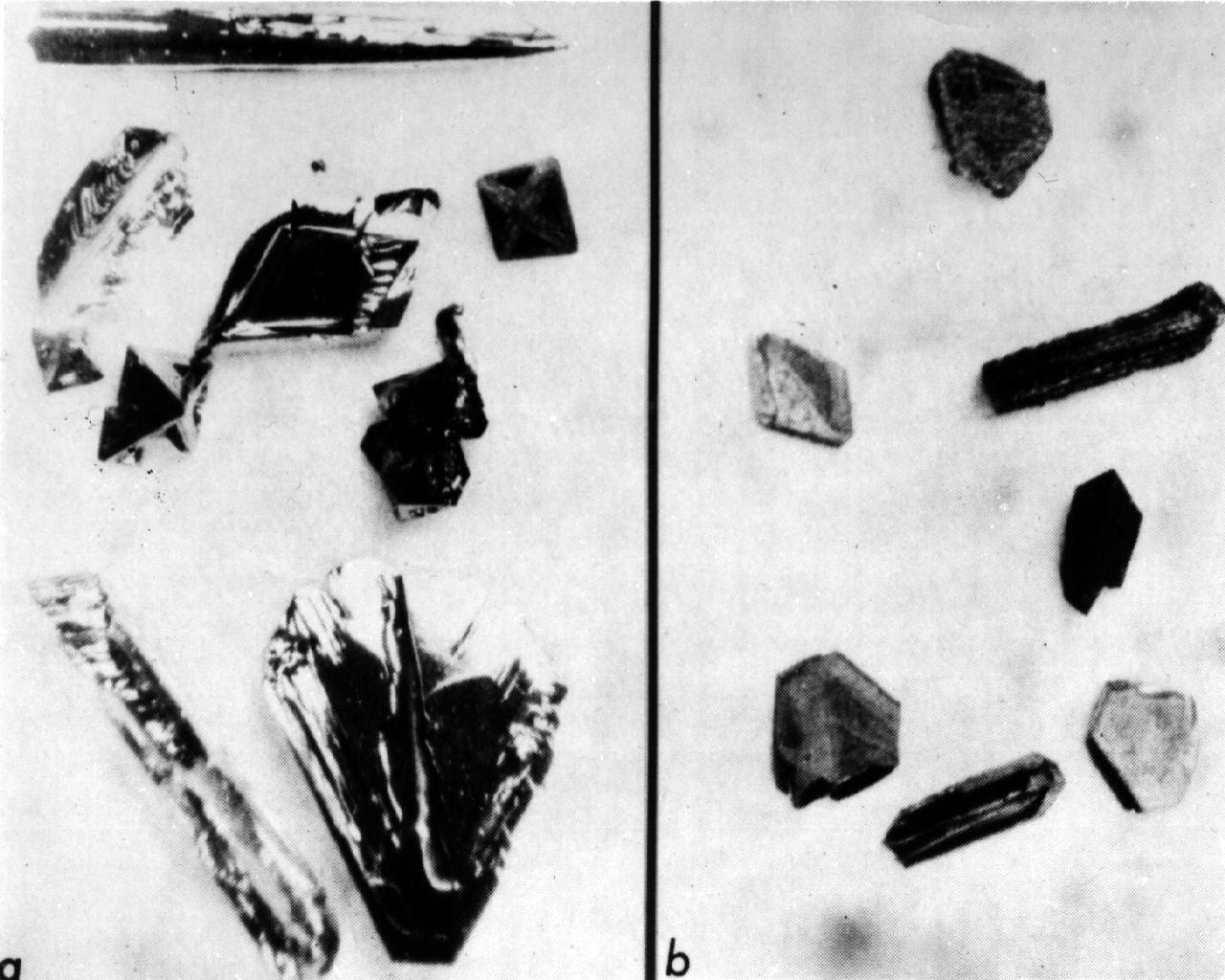
Comparison of Germanium Telluride (GeTe) Crystals grown on Earth (left) and in space (right) during the Skylab SL-3 mission. These crystals were grown using a vapor transport crystal growth method in the Multipurpose Electric Furnace System (MEFS). Crystals grown on earth are needles and platelettes with distorted surfaces and hollow growth habits. The length of the ground-based needle is approximately 2 mm and the average lenth of the platelets is 1 mm. The dull appearance of the Skylab crystals resulted from condensation of the transport agent during the long cooling period dictated by the Skylab furnace. In a dedicated process, this would be prevented by removing the ampoule from the furnace and quenching the vapor source.
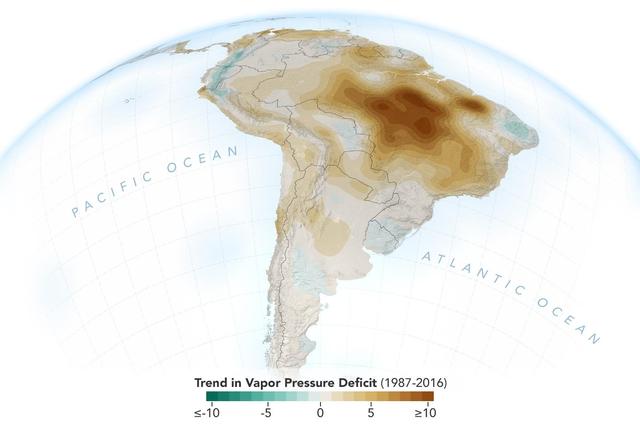
The image shows the trend of vapor pressure deficit over the Amazon rainforest during the dry season months — August through October — from 1987 to 2016. The measurements are shown in millibars — a standard unit of measure for atmospheric pressure. Vapor pressure deficit is the ratio of how much moisture is present in the atmosphere compared to how much moisture the atmosphere can hold. The trend shows the decline of moisture in the air, particularly across the south and southeastern Amazon, which is caused by a combination of human activities, including changes in land use, forest burning and its byproduct, black carbon, along with activities that have increased carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide levels in the region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23425
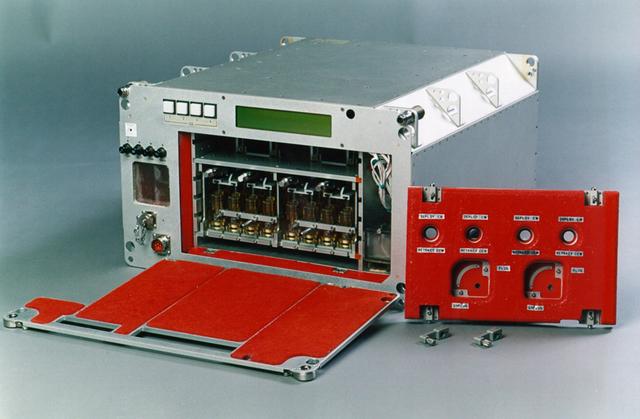
The Commercial Vapor Diffusion Apparatus will be used to perform 128 individual crystal growth investigations for commercial and science research. These experiments will grow crystals of several different proteins, including HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor, Glycogen Phosphorylase A, and NAD Synthetase. The Commercial Vapor Diffusion Apparatus supports multiple commercial investigations within a controlled environment. The goal of the Commercial Protein Crystal Growth payload on STS-95 is to grow large, high-quality crystals of several different proteins of interest to industry, and to continue to refine the technology and procedures used in microgravity for this important commercial research.
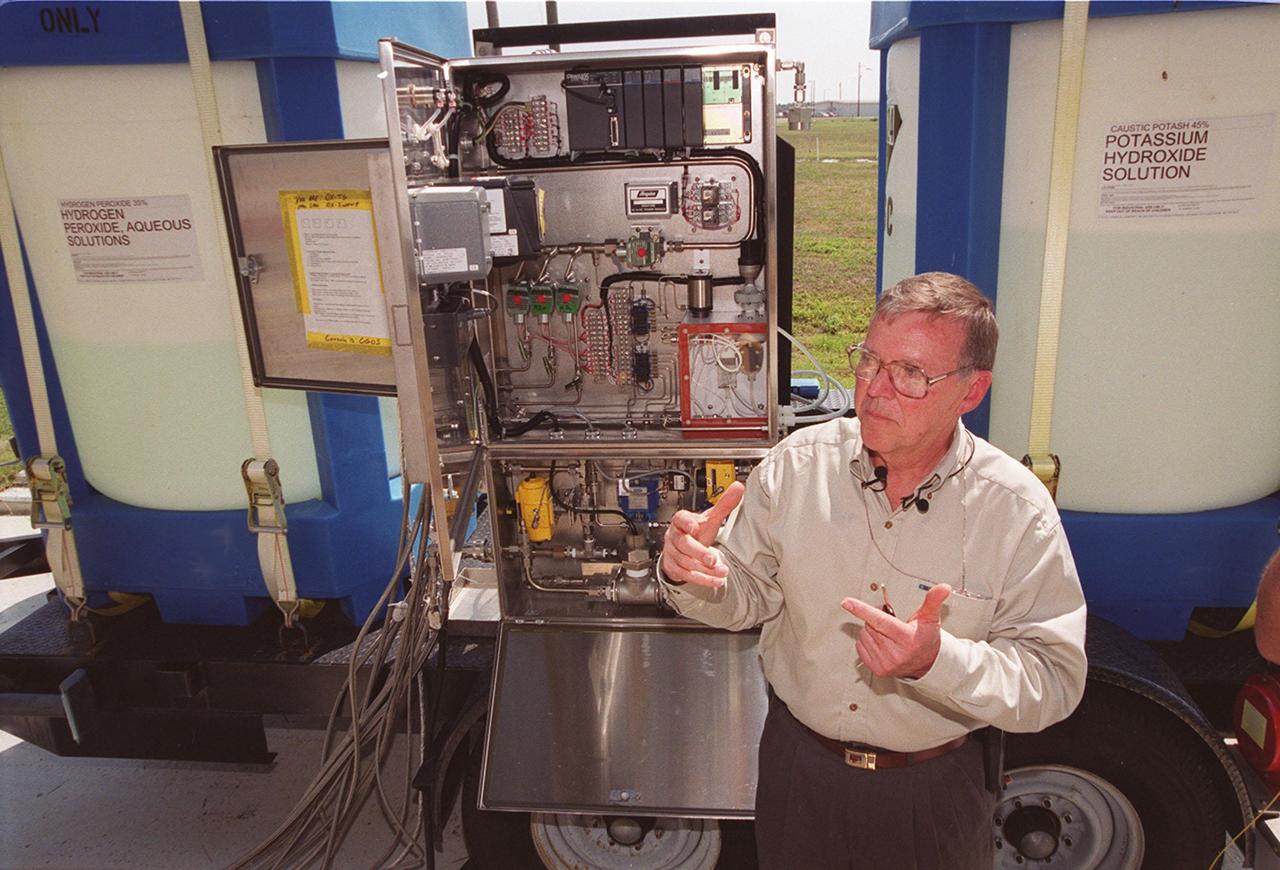

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Clyde Parrish, a NASA/KSC engineer, explains how the fertilizer scrubber control panel (center) works to turn nitrogen tetroxide vapor into fertilizer, potassium hydroxide. Parrish developed the system, which uses a "scrubber," to capture nitrogen tetroxide vapor that develops as a by-product when it is transferred from ground storage tanks into the Shuttle storage tanks. Nitrogen tetroxide is used as the oxidizer for the hypergolic propellant in the Shuttle's on-orbit reaction control system. The scrubber then uses hydrogen peroxide to produce nitric acid, which, after adding potassium hydroxide, converts to potassium nitrate. The resulting fertilizer will be used on the orange groves that KSC leases to outside companies
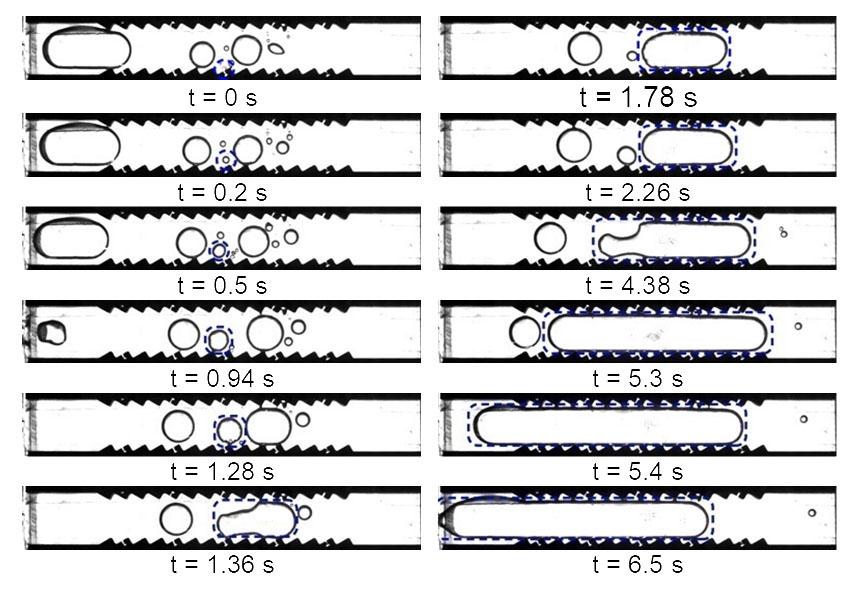
jsc2020e030484 (4/20/2020) --- A preflight image sequence from terrestrial experiments with two vertically oriented ratchet surfaces; subcooling: 9.5 ℃; heat flux: 1.31 W/cm2. Asymmetric Sawtooth and Cavity-Enhanced Nucleation-Driven Transport (PFMI-ASCENT) demonstrates a passive cooling system for electronic devices in microgravity using a microstructured surface. When fluids boil over flat heated surfaces in microgravity, vapor bubbles grow larger in size, causing poor heat transfer that can lead to damage of devices. Adding microscopic rachets on the surface may passively enable mobility of vapor bubbles and prevent this damage. (Image courtesy of: Techshot, Inc.)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Clyde Parrish, a NASA/KSC engineer, explains how the fertilizer scrubber control panel (center) works to turn nitrogen tetroxide vapor into fertilizer, potassium hydroxide. Parrish developed the system, which uses a "scrubber," to capture nitrogen tetroxide vapor that develops as a by-product when it is transferred from ground storage tanks into the Shuttle storage tanks. Nitrogen tetroxide is used as the oxidizer for the hypergolic propellant in the Shuttle's on-orbit reaction control system. The scrubber then uses hydrogen peroxide to produce nitric acid, which, after adding potassium hydroxide, converts to potassium nitrate. The resulting fertilizer will be used on the orange groves that KSC leases to outside companies
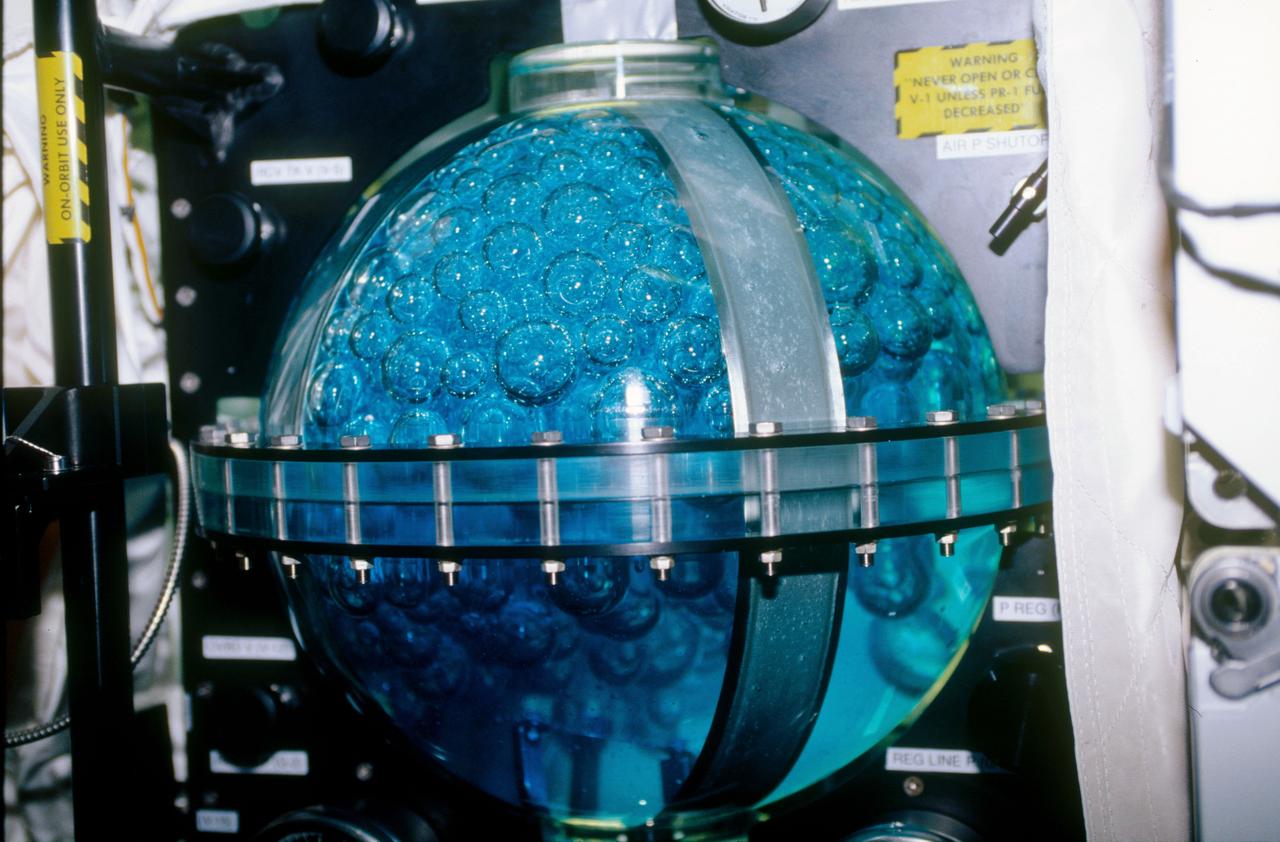

STS053-09-019 (2 - 9 Dec 1992) --- A medium close-up view of part of the Fluid Acquisition and Resupply Equipment (FARE) onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. Featured in the mid-deck FARE setup is fluid activity in one of two 12.5-inch spherical tanks made of transparent acrylic. Pictured is the receiver tank. The other tank, out of frame below, is for supplying fluids. The purpose of FARE is to investigate the dynamics of fluid transfer in microgravity and develop methods for transferring vapor-free propellants and other liquids that must be replenished in long-term space systems like satellites, Extended-Duration Orbiters (EDO), and Space Station Freedom. Eight times over an eight-hour test period, the mission specialists conducted the FARE experiment. A sequence of manual valve operations caused pressurized air from the bottles to force fluids from the supply tank to the receiver tank and back again to the supply tank. Baffles in the receiver tank controlled fluid motion during transfer, a fine-mesh screen filtered vapor from the fluid, and the overboard vent removed vapor from the receiver tank as the liquid rose. FARE is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama. The basic equipment was developed by Martin Marietta for the Storable Fluid Management Demonstration. Susan L. Driscoll is the principal investigator.
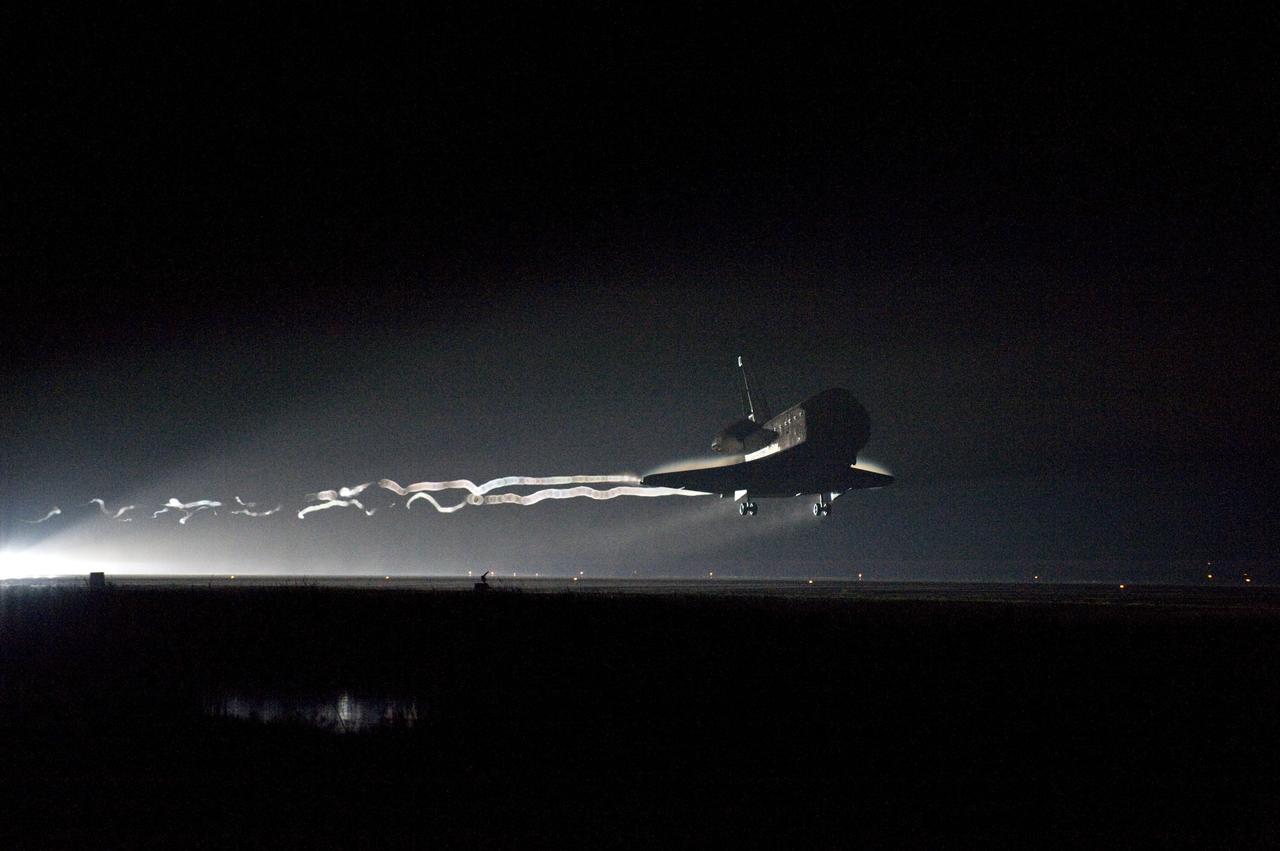

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Endeavour as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. On board are STS-134 Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Mike Fincke, Drew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and the European Space Agency's Roberto Vittori. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell
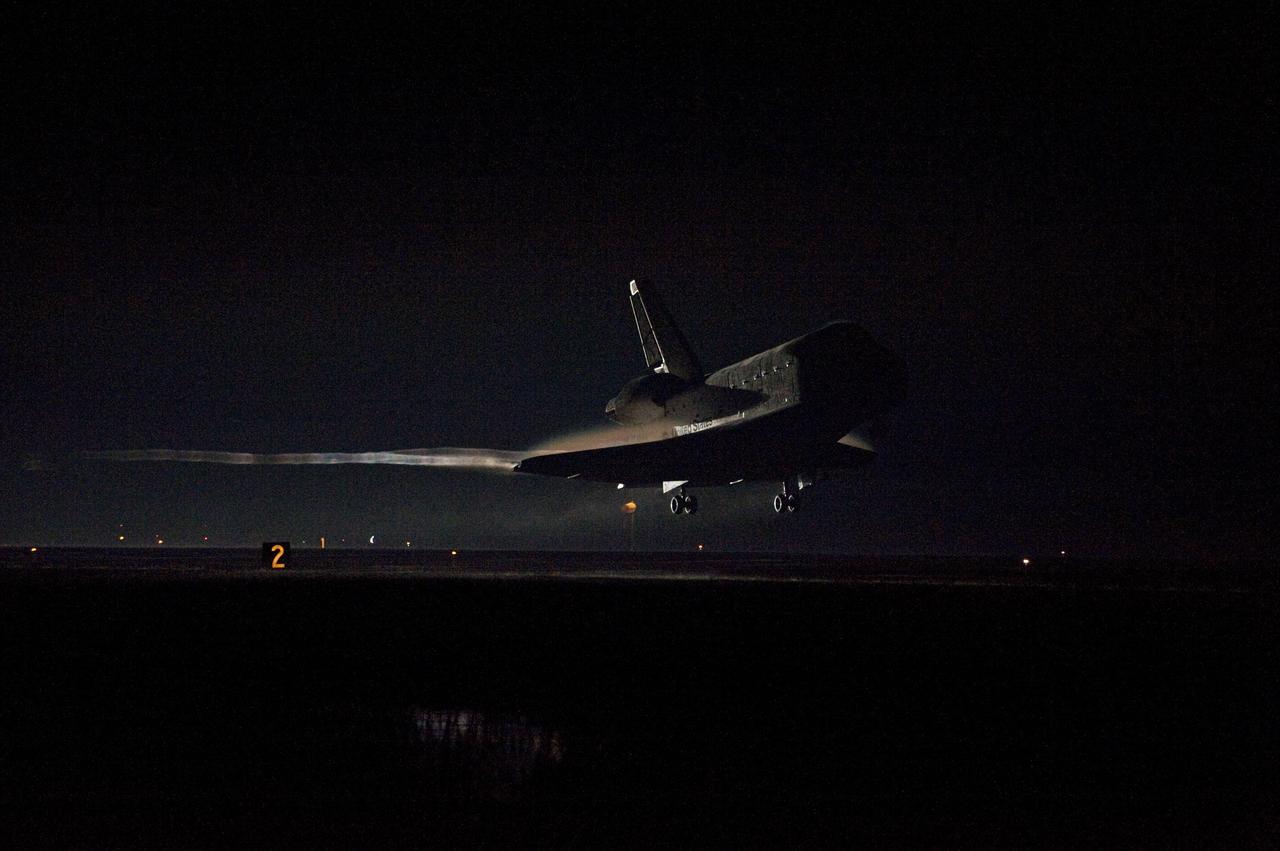

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vapor trails follow space shuttle Endeavour as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. On board are STS-134 Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Mike Fincke, Drew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and the European Space Agency's Roberto Vittori. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A vapor trail follows space shuttle Endeavour as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. On board are STS-134 Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Mike Fincke, Drew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and the European Space Agency's Roberto Vittori. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Chuck Tintera

STS053-04-018 (2-9 Dec 1992) --- Astronauts Guion S. Bluford (left) and Michael R. U. (Rich) Clifford monitor the Fluid Acquisition and Resupply Equipment (FARE) onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. Clearly visible in the mid-deck FARE setup is one of two 12.5-inch spherical tanks made of transparent acrylic, one to supply and one to receive fluids. The purpose of FARE is to investigate the dynamics of fluid transfer in microgravity and develop methods for transferring vapor-free propellants and other liquids that must be replenished in long-term space systems like satellites, Extended-Duration Orbiters (EDO), and Space Station Freedom. Eight times over an eight-hour test period, the mission specialists conducted the FARE experiment. A sequence of manual valve operations caused pressurized air from the bottles to force fluids from the supply tank to the receiver tank and back again to the supply tank. Baffles in the receiver tank controlled fluid motion during transfer, a fine-mesh screen filtered vapor from the fluid, and the overboard vent removed vapor from the receiver tank as the liquid rose. FARE is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama. The basic equipment was developed by Martin Marietta for the Storable Fluid Management Demonstration. Susan L. Driscoll is the principal investigator.
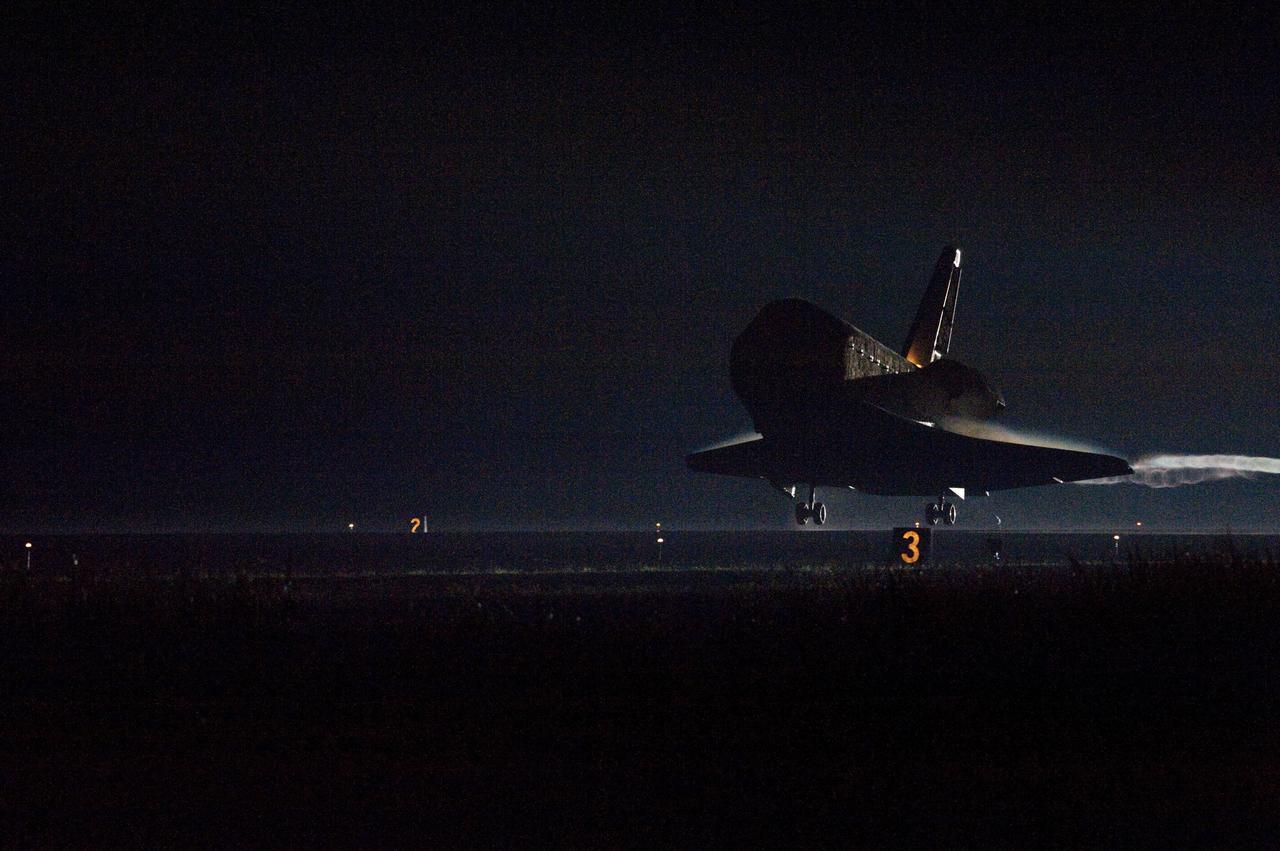

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A vapor trail follows space shuttle Endeavour as it approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. A vapor trail, known as a contrail, is a cloud of water vapor that condenses and freezes around the small particles in aircraft exhaust. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. On board are STS-134 Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Greg H. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Mike Fincke, Drew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and the European Space Agency's Roberto Vittori. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Joseph
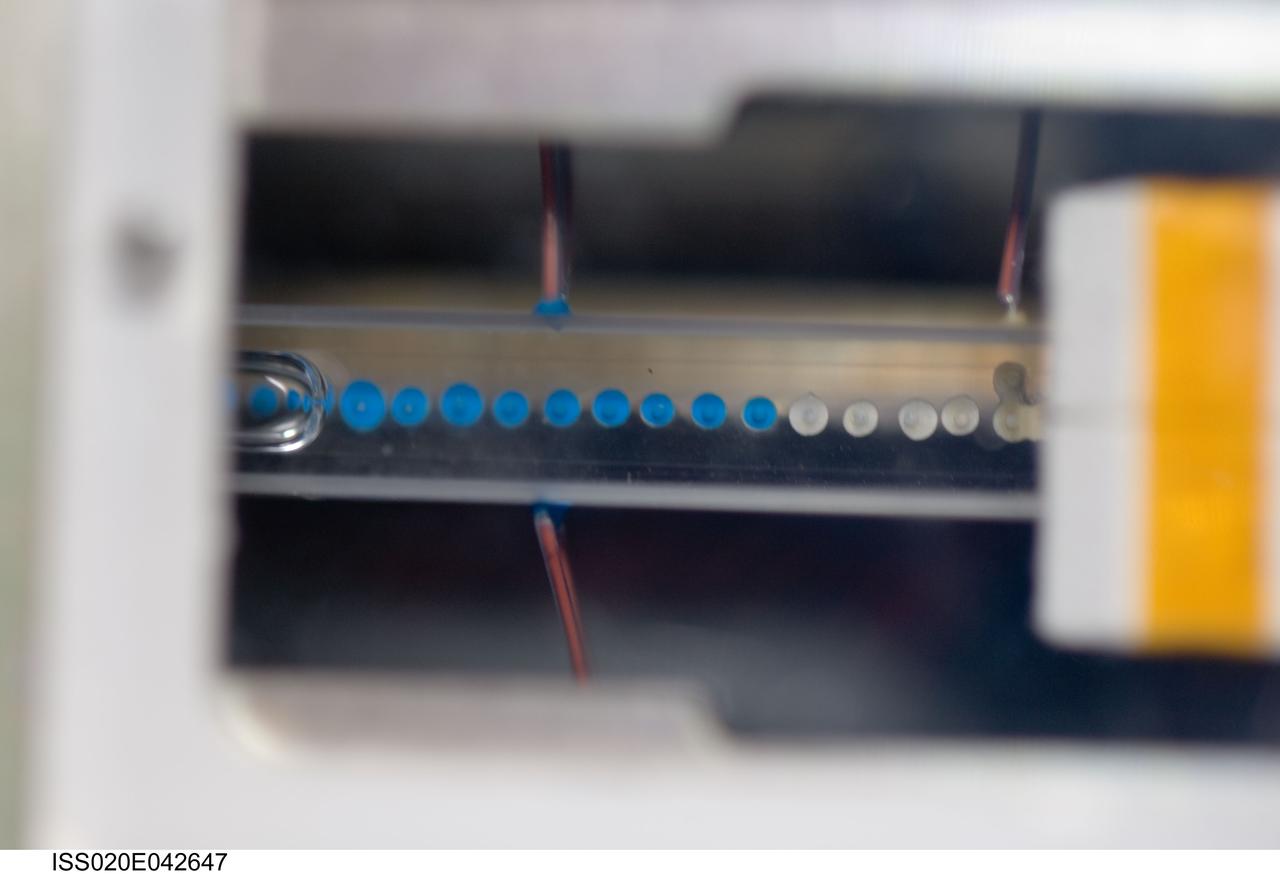

iss020e042647 (Sep. 26, 2009) --- Constrained Vapor Bubble (CVB) module with the science sample on the Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR). CVB aims to better understand the physics of evaporation and condensation to help create an efficient and highly reliable cooling equipment for space, where replacement parts are difficult or impossible.
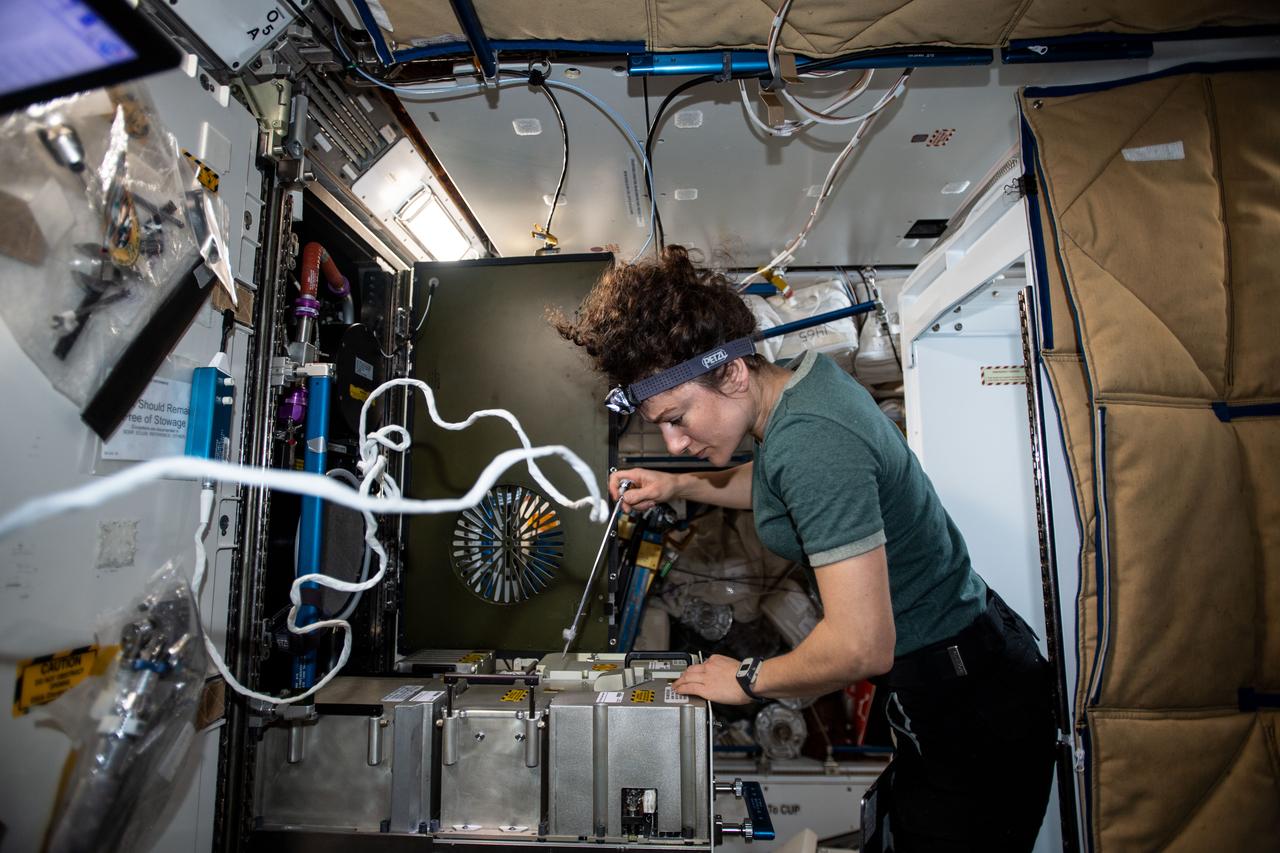

iss062e103552 (March 20, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 62 Flight Engineer Jessica Meir works on the Major Constituent Analyzer, a device that measures the orbiting lab’s atmosphere. The life support gear monitors a variety of major constituents, such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor to ensure a safe breathing environment for the crew.
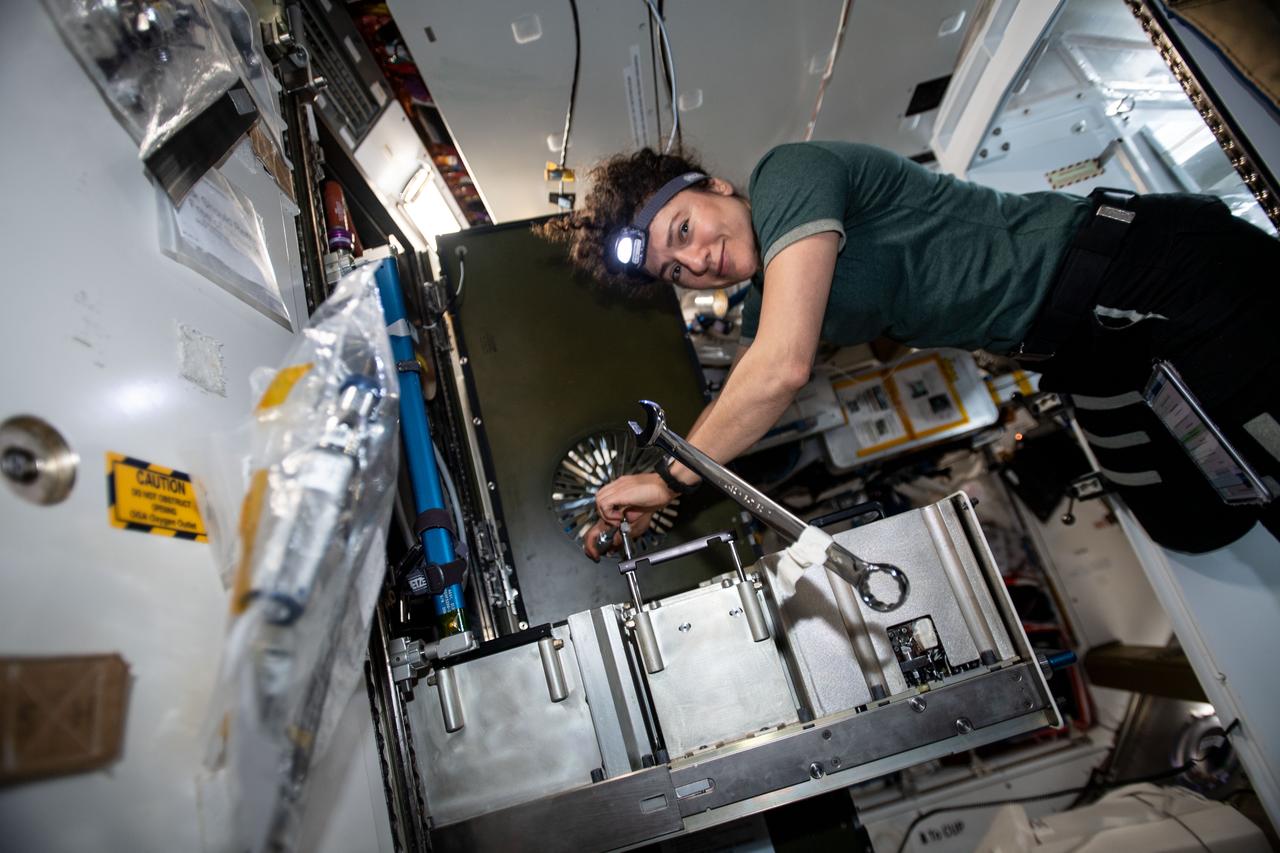

iss062e103558 (March 20, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 62 Flight Engineer Jessica Meir works on the Major Constituent Analyzer, a device that measures the orbiting lab’s atmosphere. The life support gear monitors a variety of major constituents, such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor to ensure a safe breathing environment for the crew.
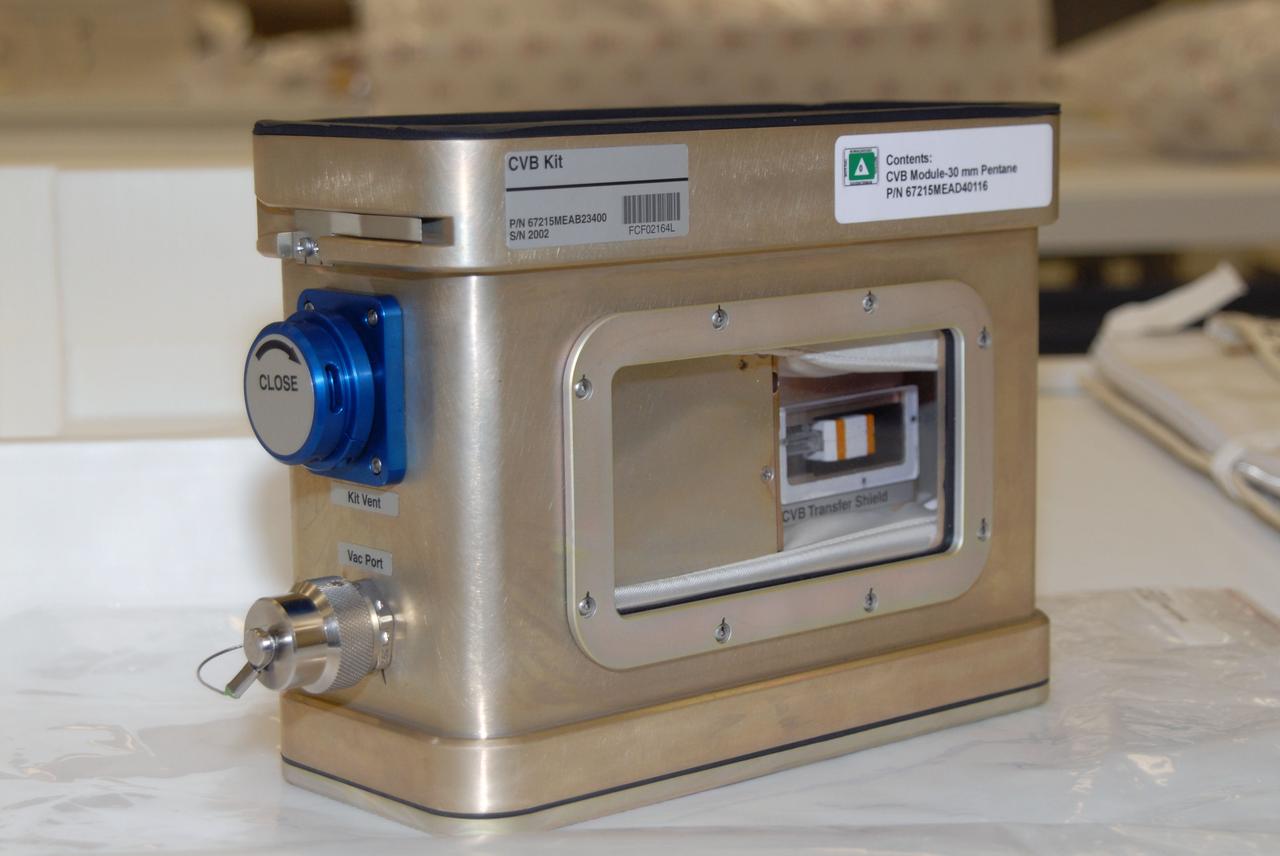

jsc2009e141390 (Apr. 23, 2009) --- Constrained Vapor Bubble (CVB) Experiment at NASA's Johnson Space Center. CVB aims to better understand the physics of evaporation and condensation to help create an efficient and highly reliable cooling equipment for space, where replacement parts are difficult or impossible.