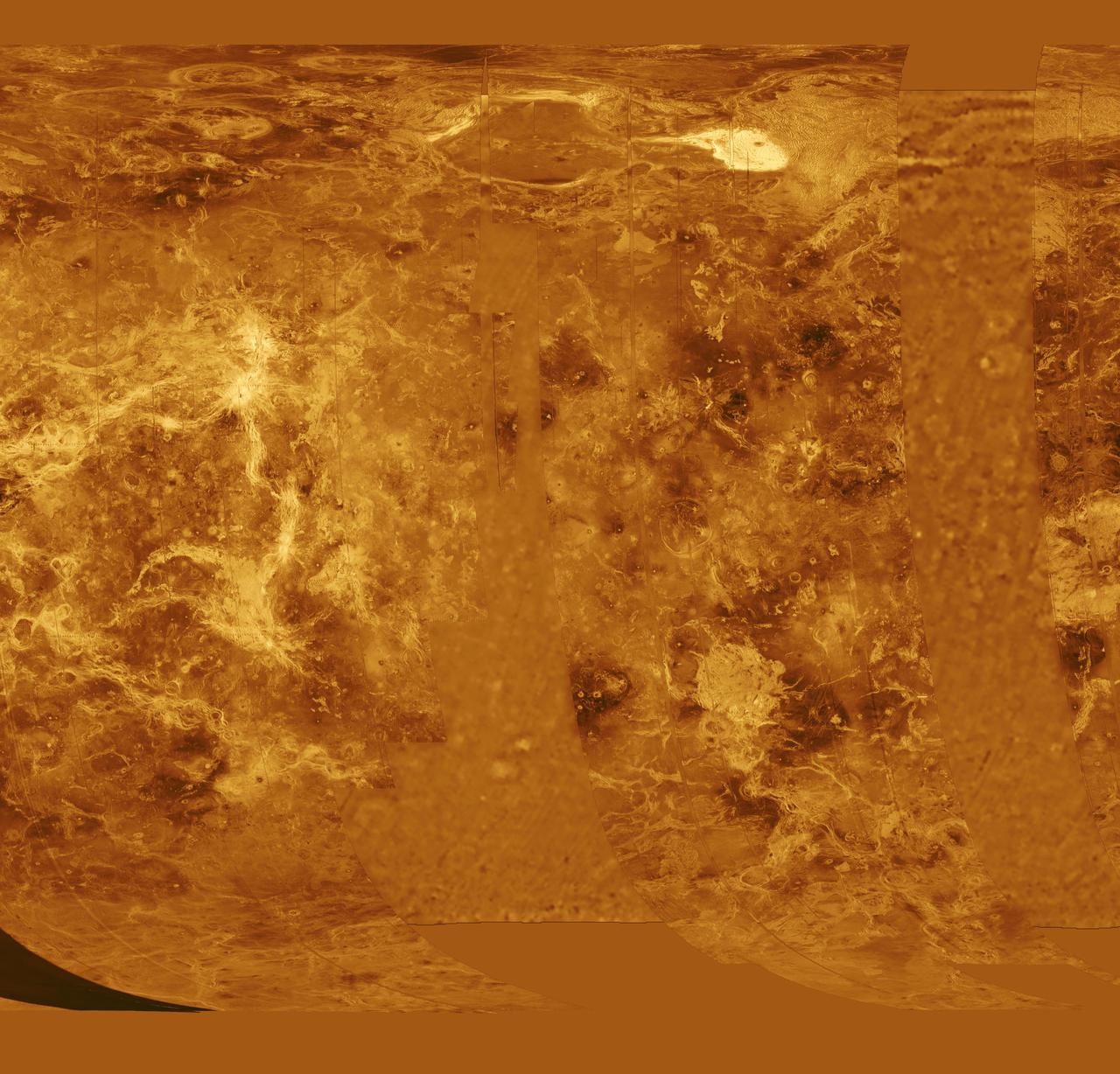
The western half of the planet is displayed in this simple cylindrical map of the surface of Venus obtained by NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00255
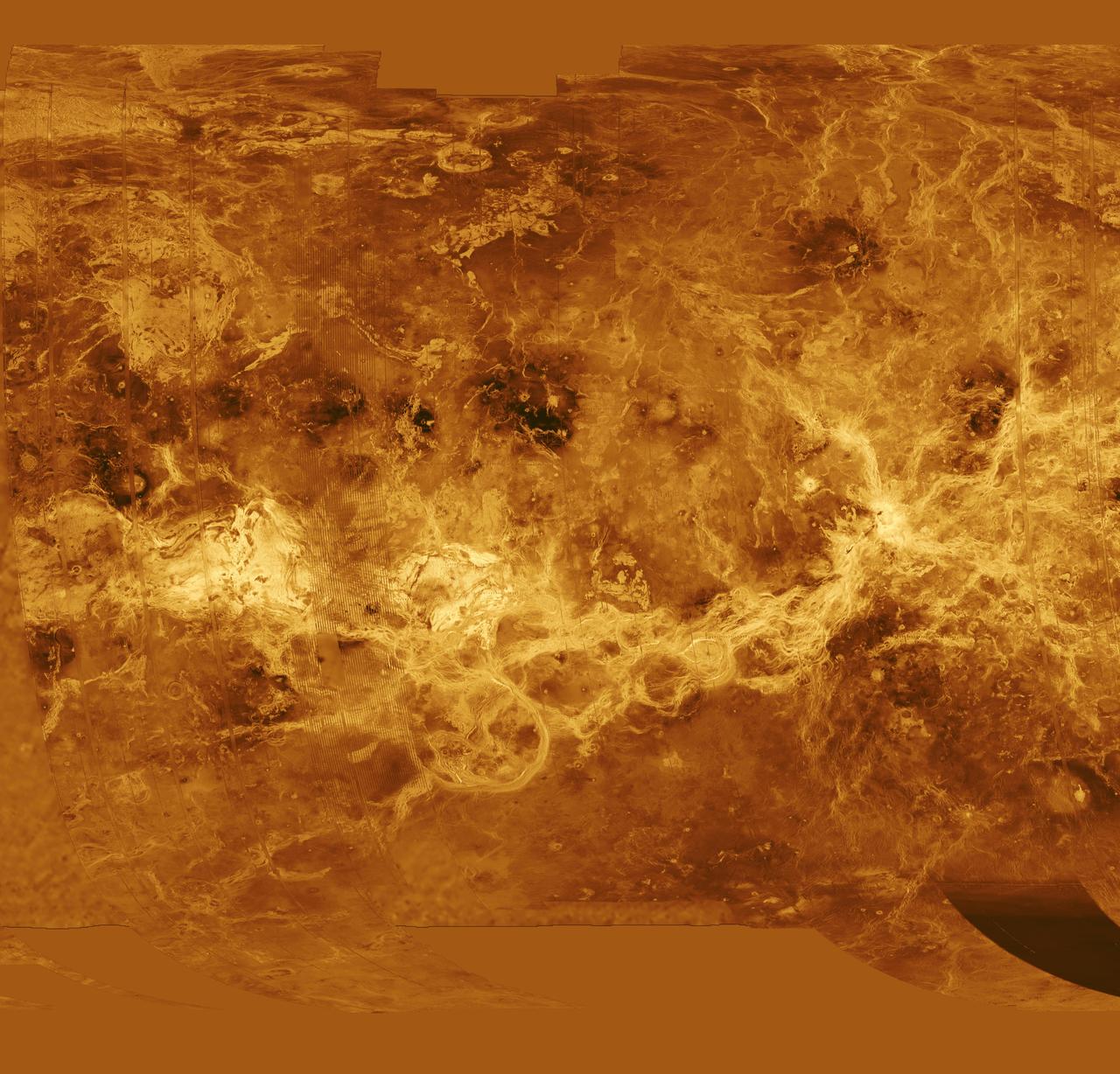
The eastern half of the planet is displayed in this simple cylindrical map of the surface of Venus obtained by NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00256
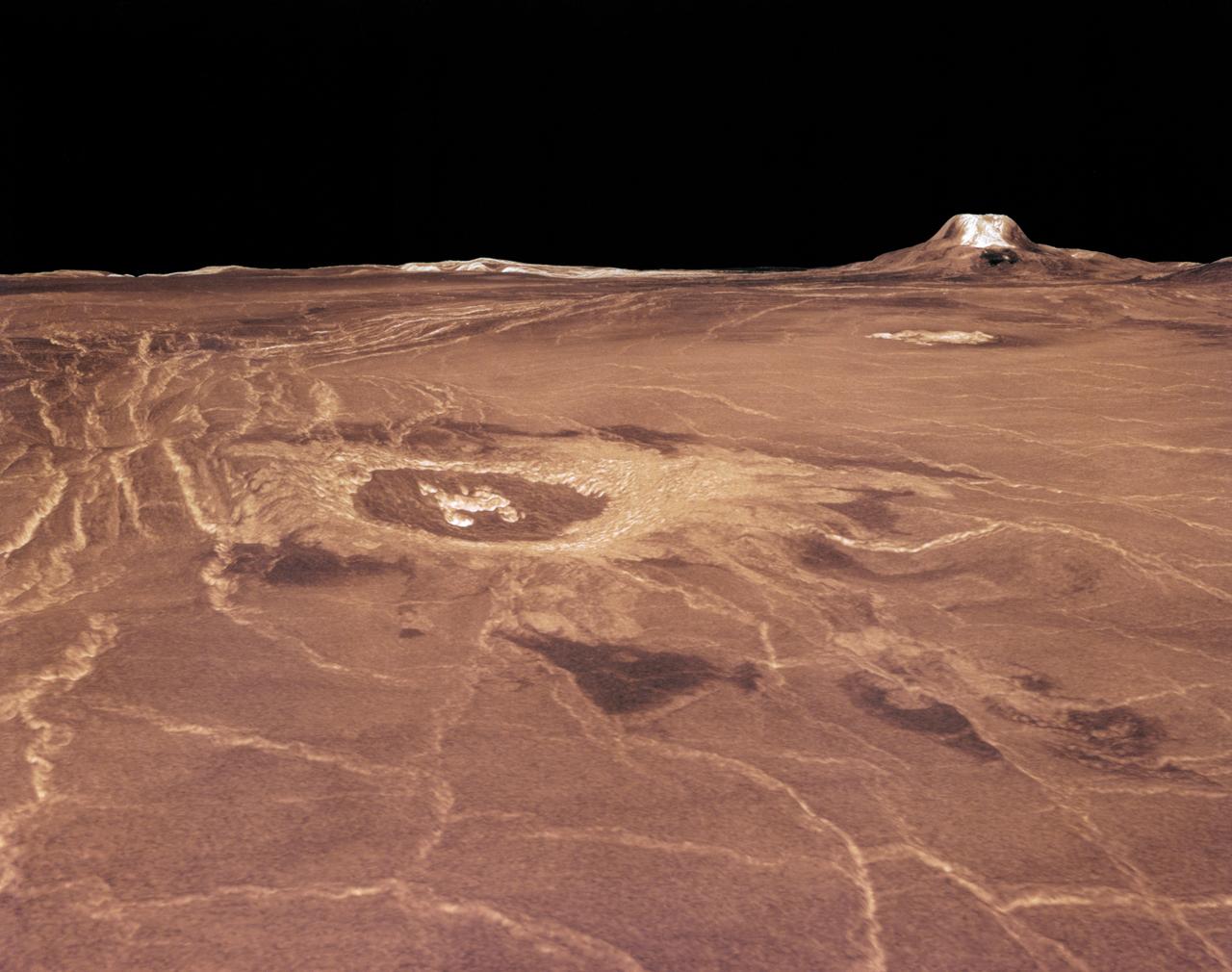
Magellan synthetic aperture radar data was used to create this three- dimensional (3D) perspective view of Venus' western Eistla Regio. This viewpoint is located at 1,310 kilometers (812 miles) southwest of Gula Mons at an elevation of 0.178 kilometers (0.48 miles). The view is of the northeast with Gula Mons appearing on the horizon. Gula Mons, a 3 kilometer (1.86 mile) high volcano, is located at approximately 22 degrees north latitude, 359 degrees east longitude. The impact crater Cunitz, named for the astronomer and mathematician Maria Cunitz, is visible in the center of the image. The crater is 48.5 kilometers (30 miles) in diameter and is 215 kilometers (133 miles) from the viewer's position. Magellan synthetic aperture radar data is combined with radar altimetry to develop a 3D map of the surface. Rays cast in a computer intersect the surface to create a 3D view. Simulated color and a digital elevation map developed by the United States (U.S.) Geological Survey is used to enhance small-scale structure. The simulated hues are based on color images recorded by the Soviet Venera 13 and 14 spacecraft. The image was produced at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Multimission Image Processing Laboratory and is a single frame from a video released at the JPL news conference 03-05-91. View was provided by JPL with alternate number P-38720 MGN76.

A portion of Alpha Regio is displayed in this three-dimensional perspective view of the surface of Venus from NASA Magellan spacecraft. In 1963, Alpha Regio was the first feature on Venus to be identified from Earth-based radar.
Sif Mons is displayed in this computer-simulated view obtained by NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00108
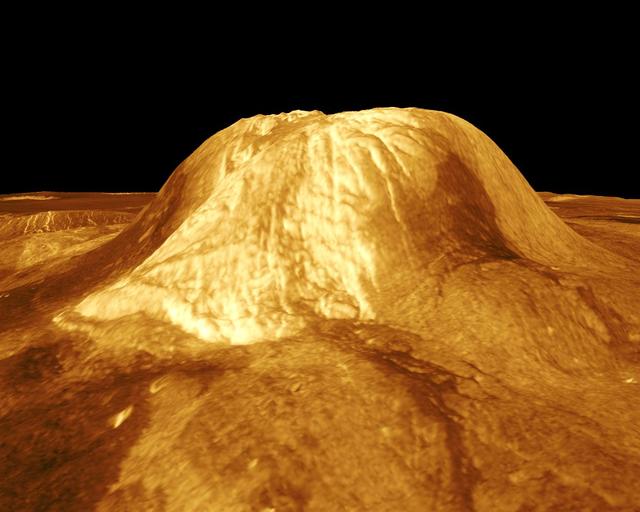
Gula Mons is displayed in this computer-simulated view from NASA Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00234
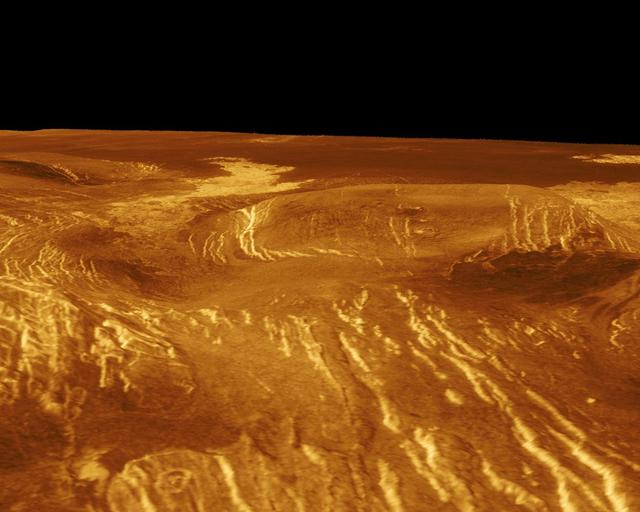
A corona is displayed in this computer-simulated view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00109

The northern hemisphere is displayed in this global view of the surface of Venus as seen by NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00271

The northern hemisphere is displayed in this global view of the surface of Venus as seen by NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00270
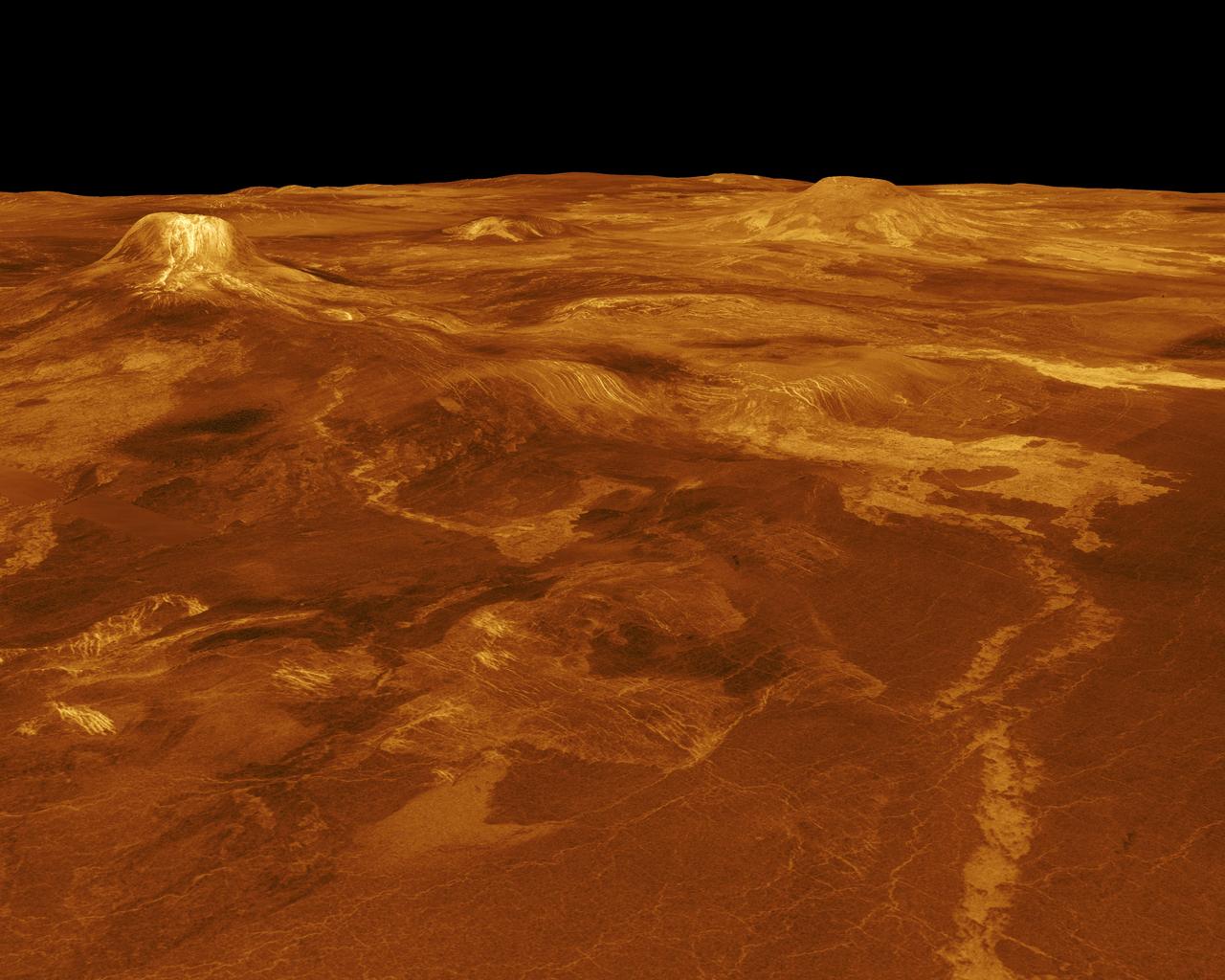
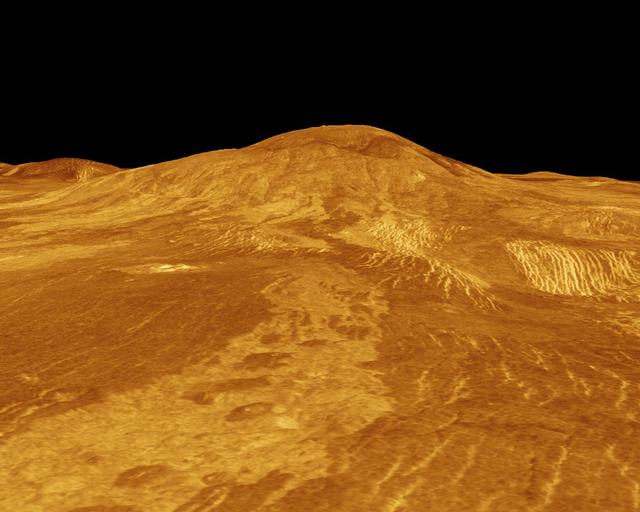
A portion of western Eistla Regio is displayed in this three-dimensional perspective view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00102
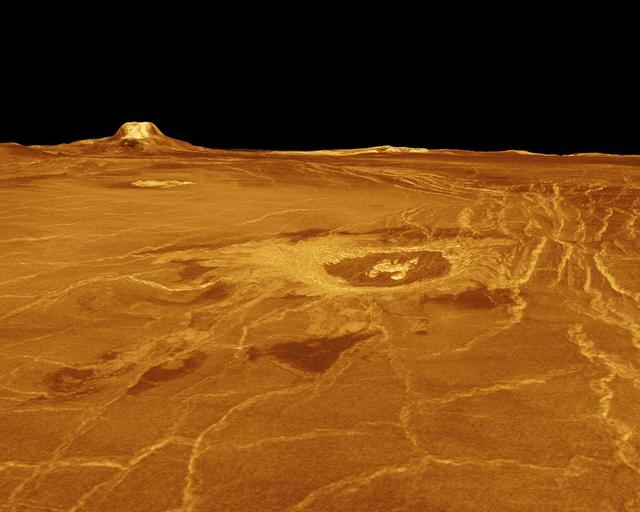

A portion of western Eistla Regio is displayed in this three-dimensional perspective view of the surface of Venus as seen by NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00233

This global view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft is of the surface of Venus is centered at 180 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00104

Sapas Mons is displayed in the center of this computer-generated three-dimensional perspective view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00107
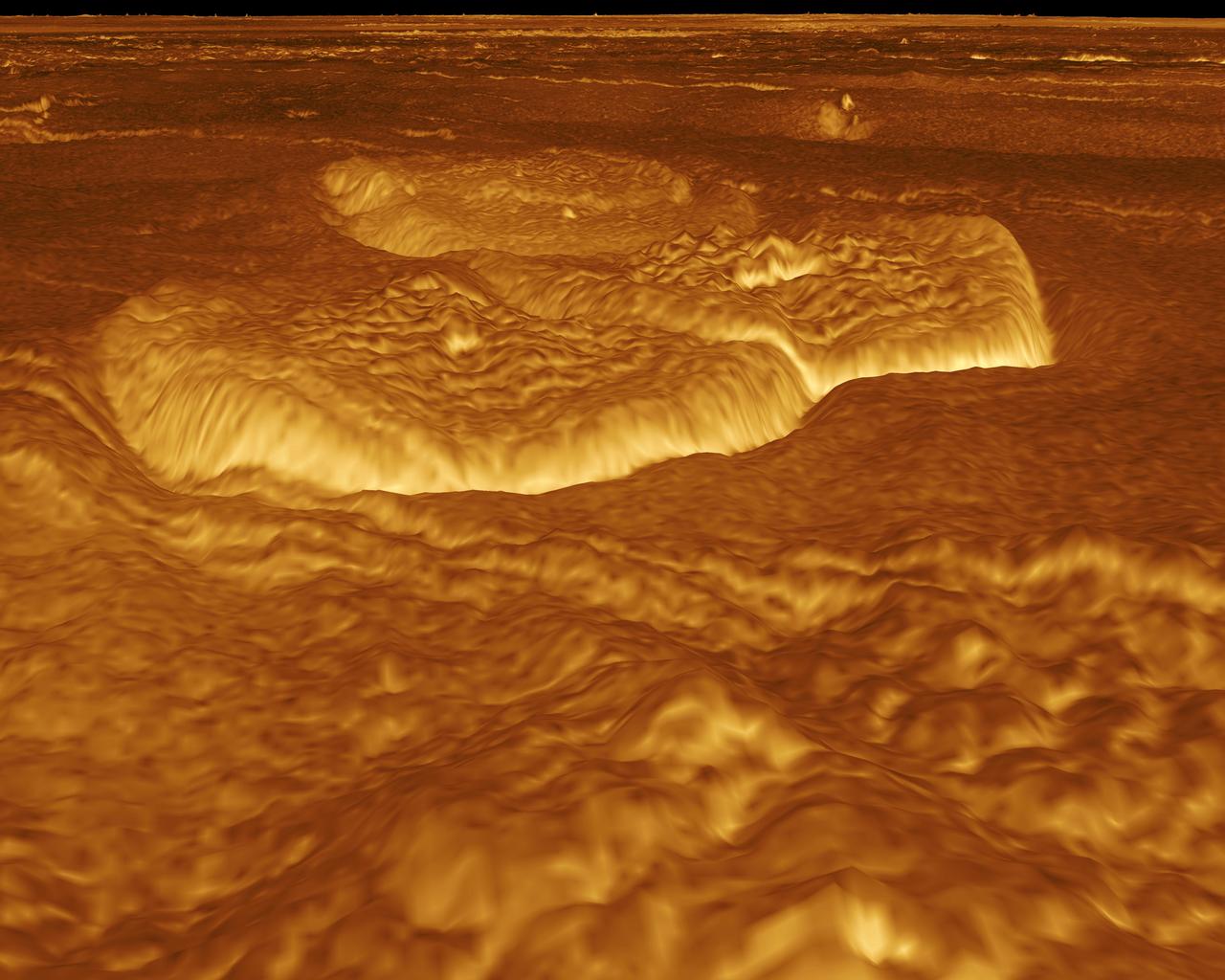
A portion of the eastern edge of Alpha Regio is displayed in this three-dimensional perspective view of the surface of Venus from NASA Magellan spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00246
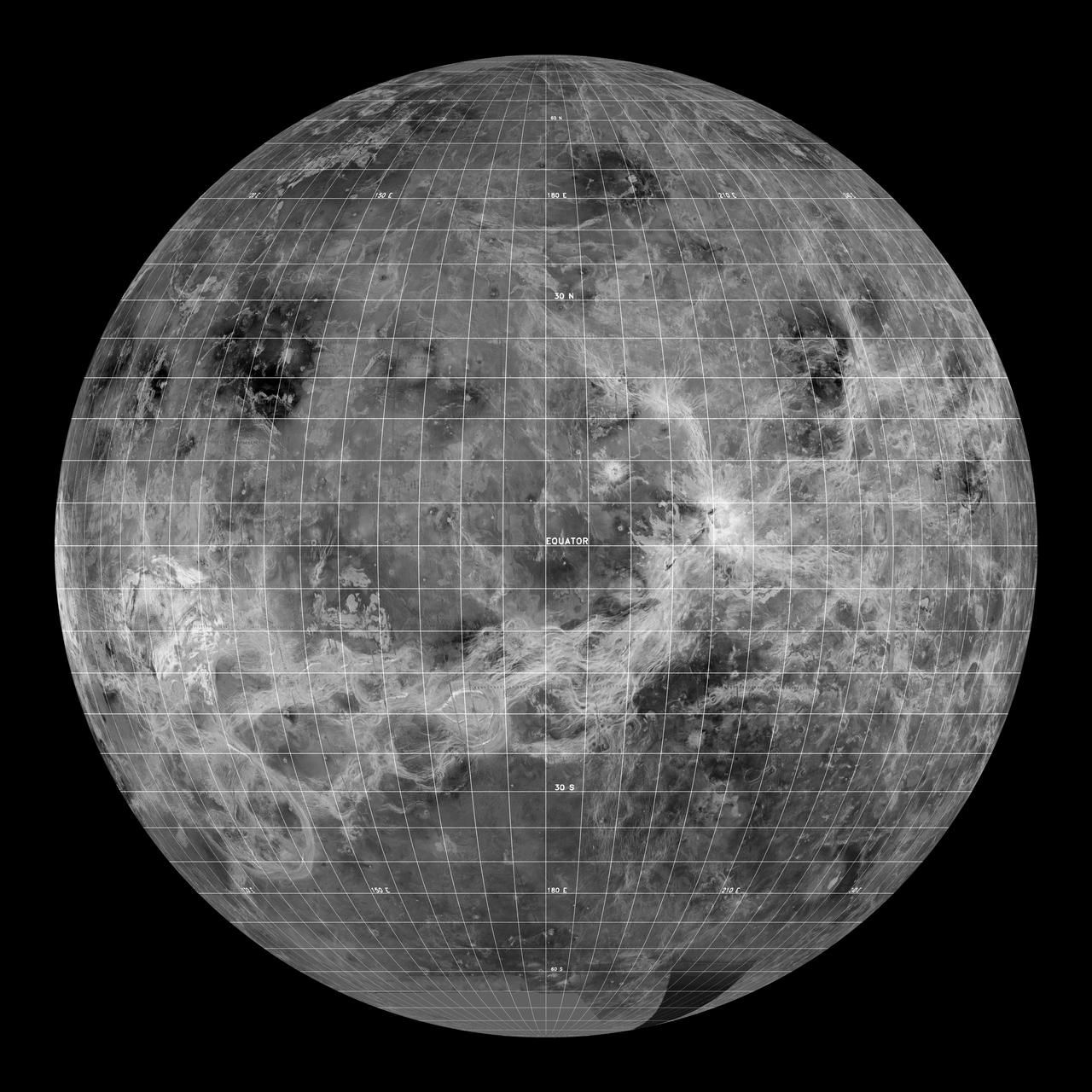
This global view of the surface of Venus is centered at 180 degrees east longitude. Magellan synthetic aperture radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magellan mapping, and a 5 degree latitude-longitude grid, are mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create this image. Data gaps are filled with Pioneer-Venus Orbiter data, or a constant mid-range value. The image was produced by the Solar System Visualization project and the Magellan Science team at the JPL Multimission Image Processing Laboratory. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00478
Photograph by Pioneer Venus Recent computer enchanced surface relief images of Venus.
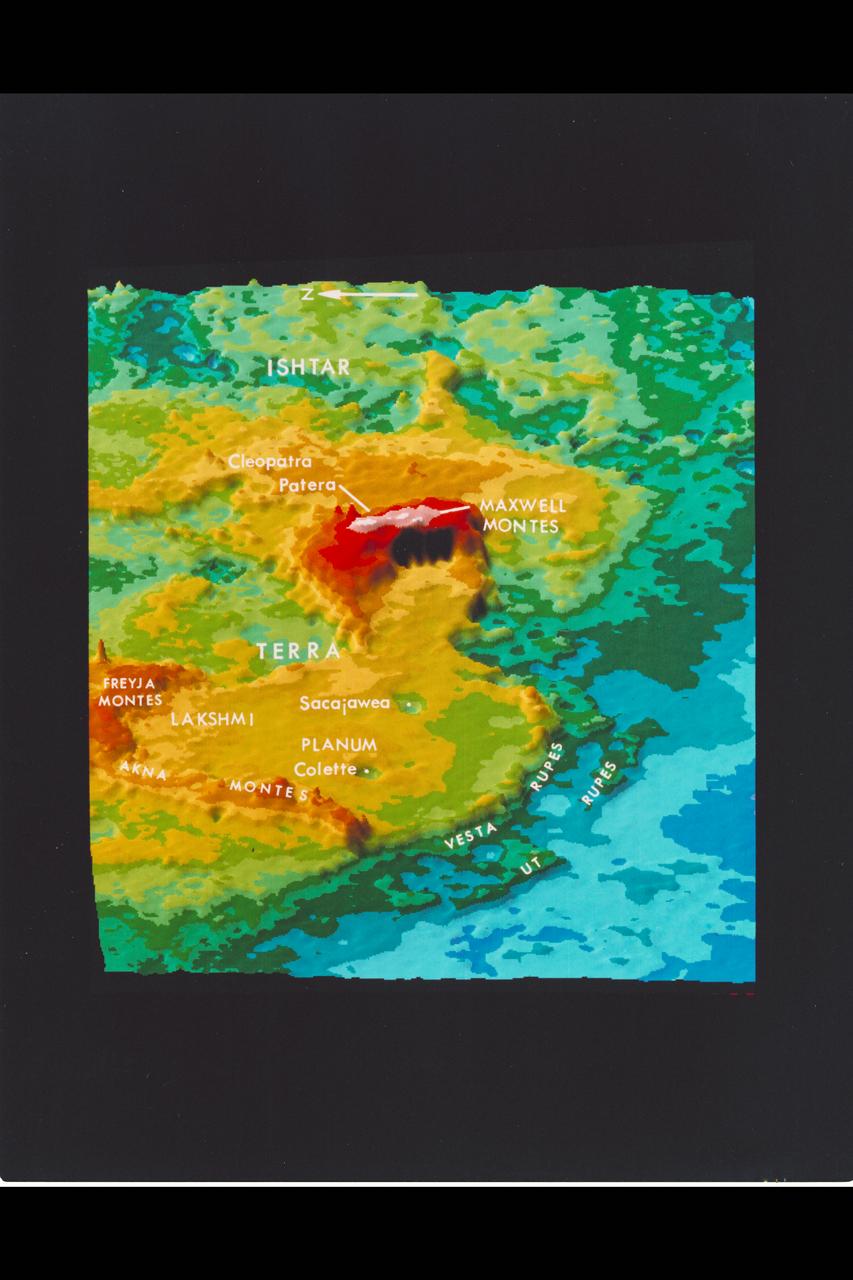
Photograph by Pioneer Venus Recent computer enchanced surface relief images of Venus.
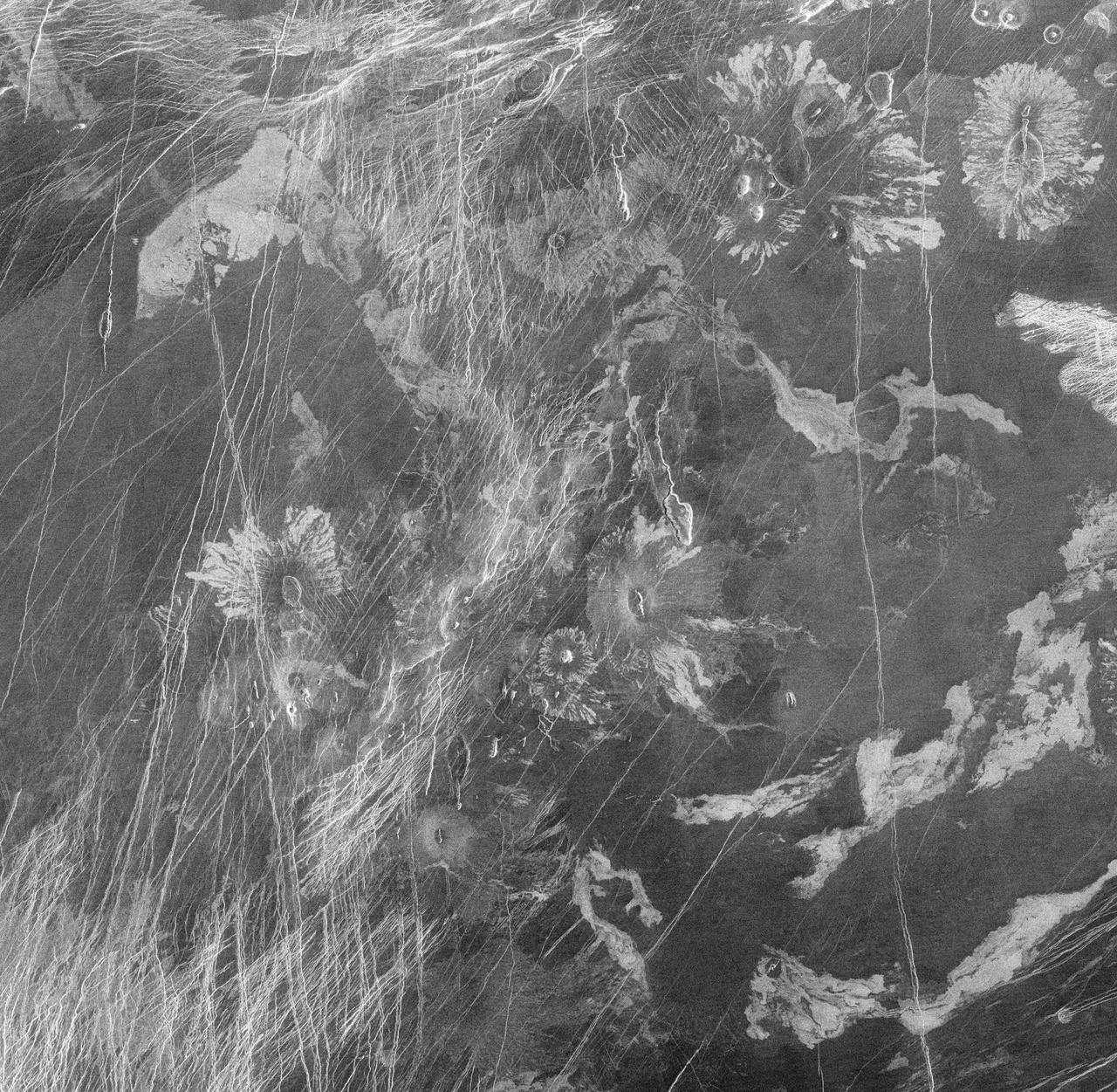

This image from the Atla region of Venus obtained by NASA Magellan spacecraft shows several types of volcanic features and superimposed surface fractures. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00201
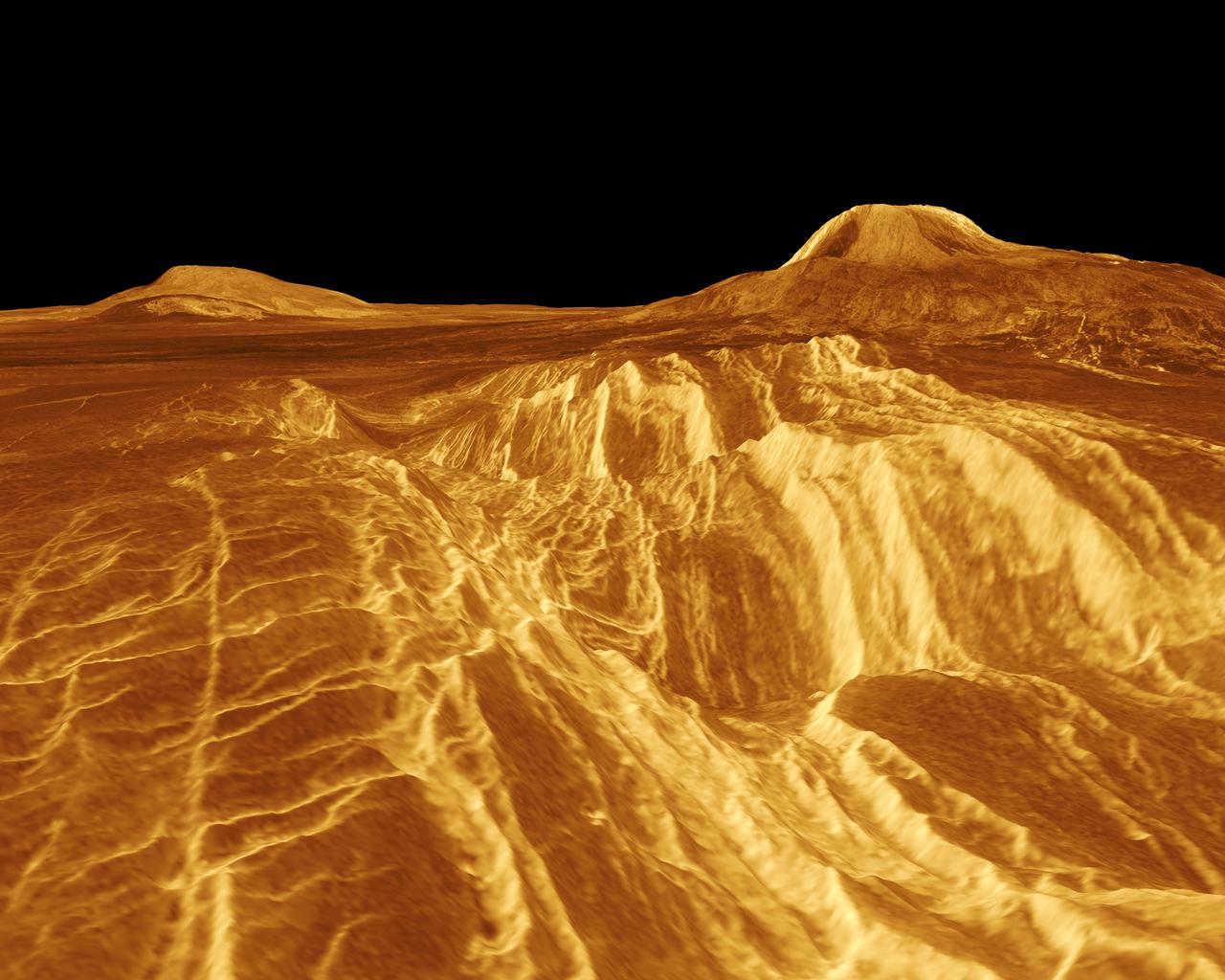
A portion of western Eistla Regio is shown in this three dimensional, computer-generated view of the surface of Venus. This NASA Magellan image was released on April 22, 1992. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00200
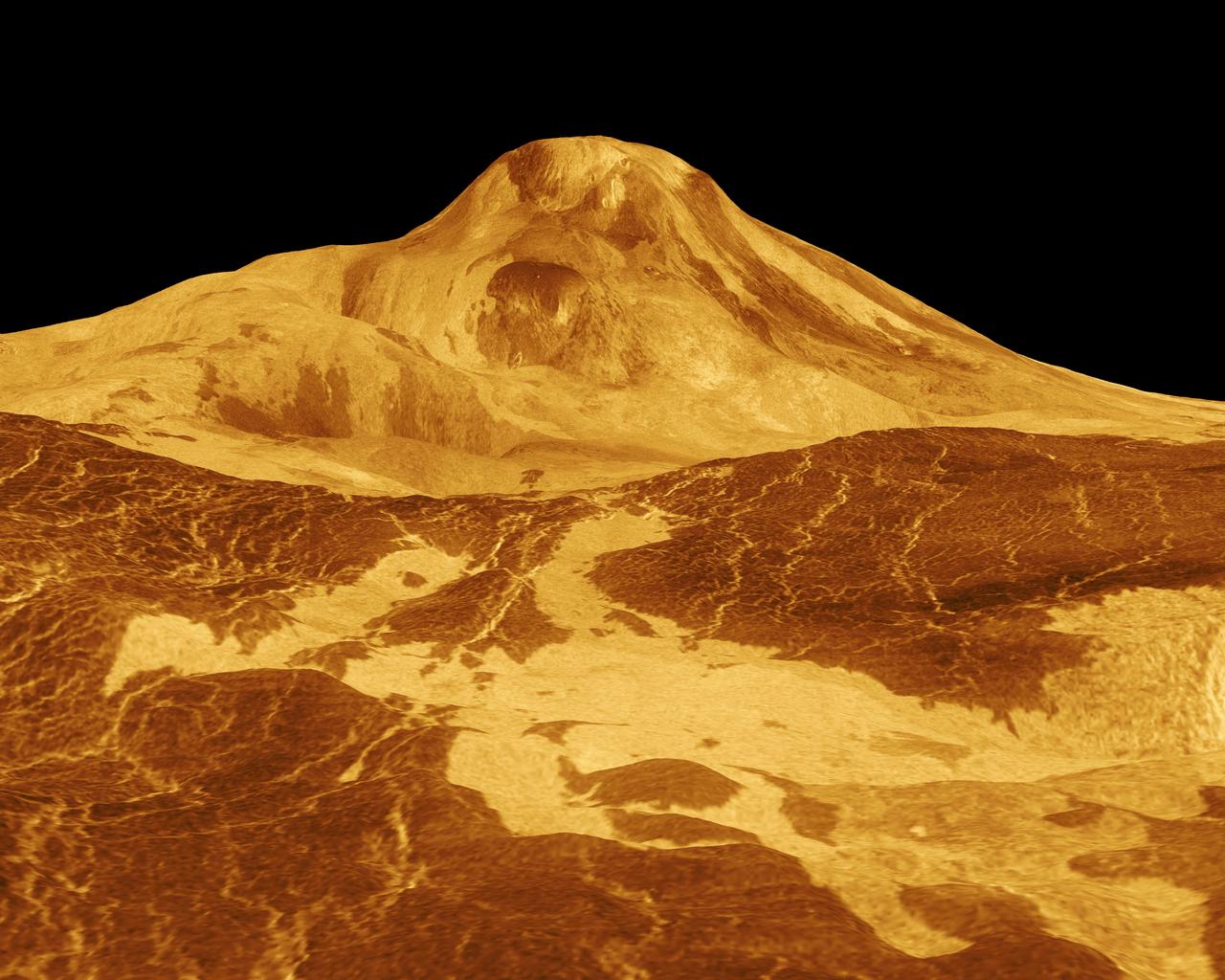
Maat Mons is displayed in this 3-dimensional perspective view of the surface of Venus taken by NASA Magellan. The viewpoint is located north of Maat Mons. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00254
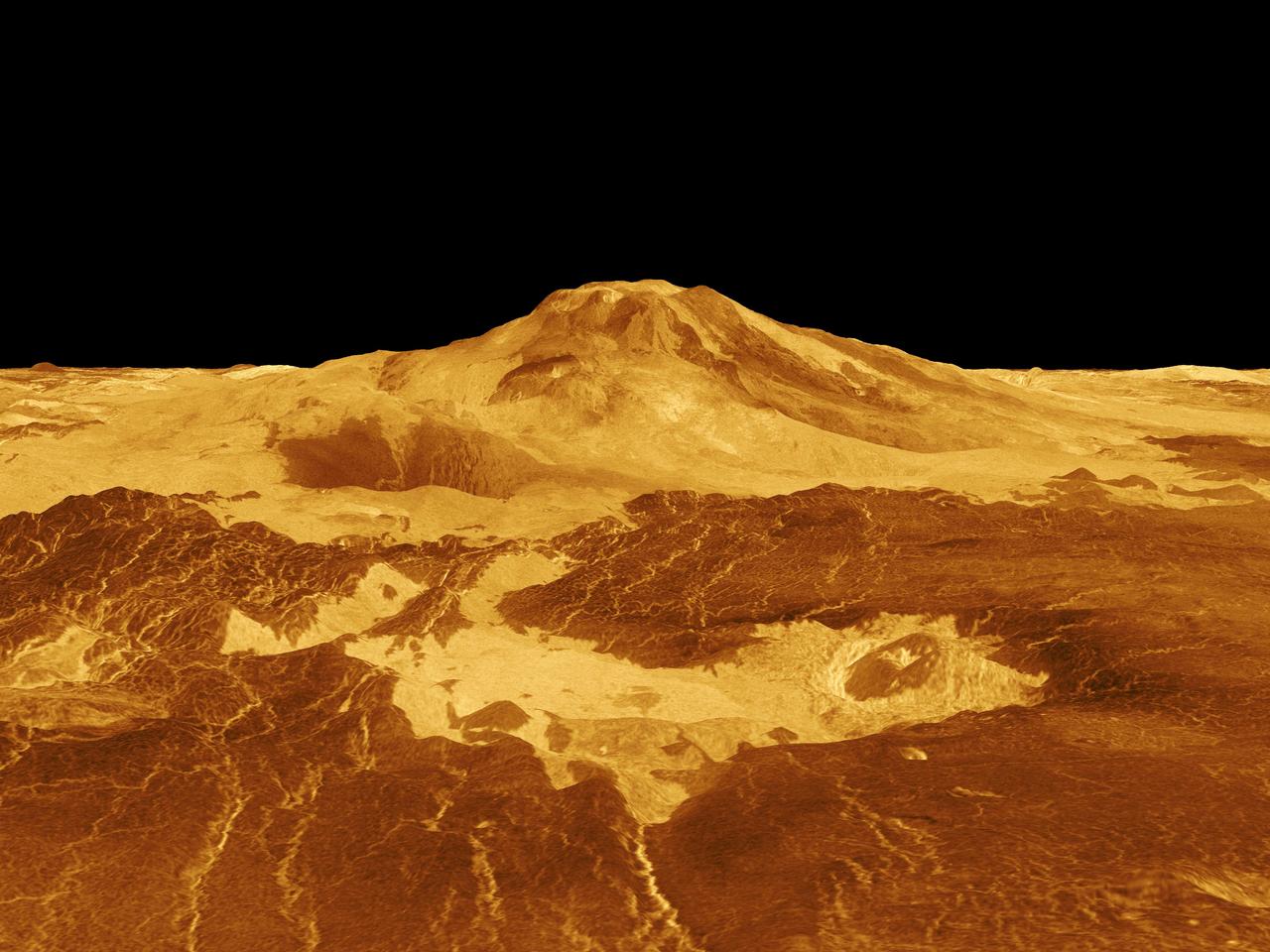
Maat Mons is displayed in this computer generated three-dimensional perspective of the surface of Venus. This NASA's Magellan image was released on April 22, 1992. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00106
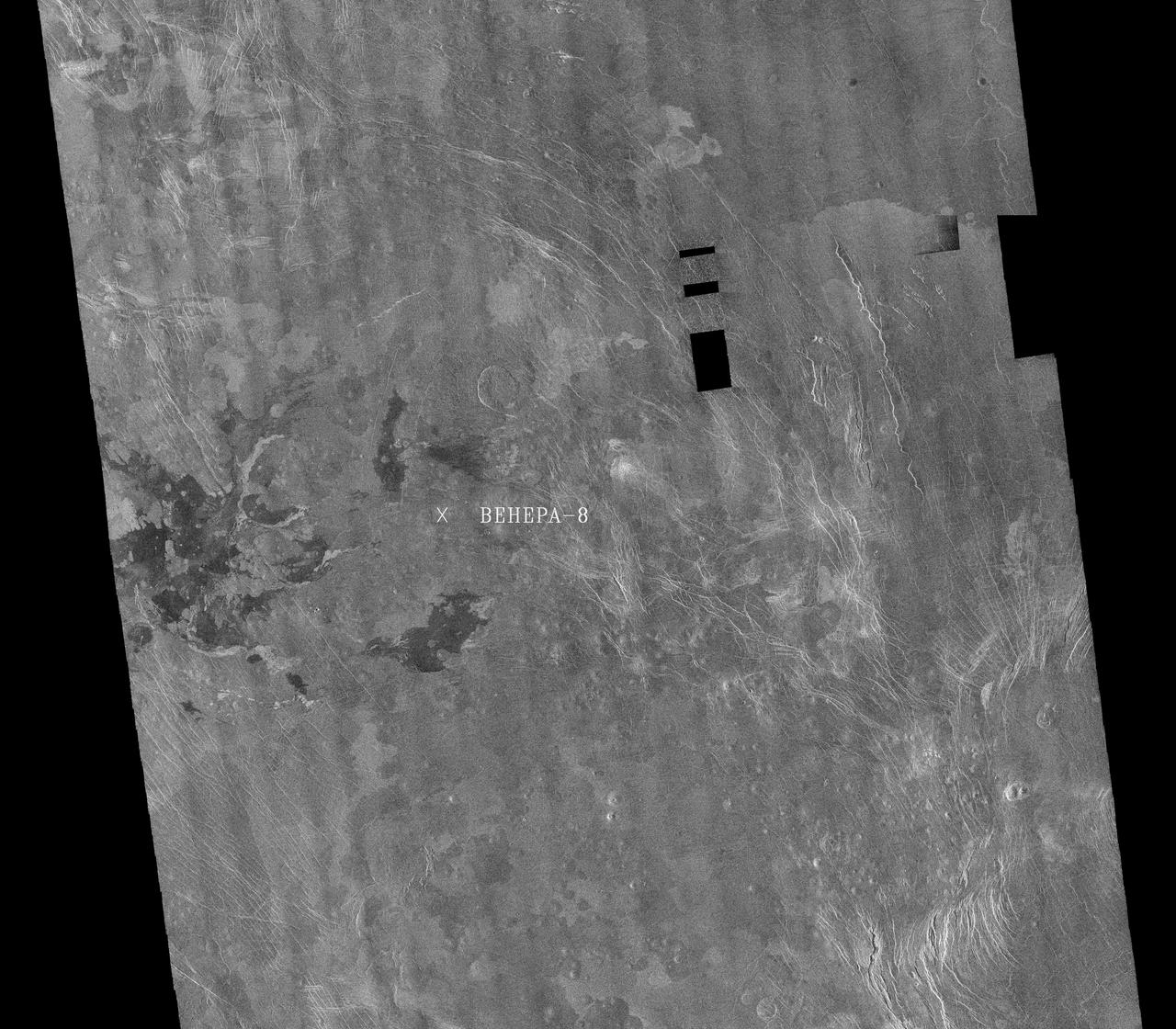
This image is a mosaic of 24 orbits of the Navka region of Venus. The image is centered at about 10 degrees south latitude and 335 degrees east longitude. The image is about 400 km (240 miles) across. 'Behepa 8' marks the approximate landing site of the Soviet Venera 8 lander, which took measurements at the surface of Venus in 1972. The Venera 8 lander measured granitic or continental-like materials at the landing site. Magellan data reveals the landing site to lie in a region of plains cut by tectonic ridges and troughs. Volcanic domes and flows are seen throughout the region. Studying the regional setting of the Venera landing sites is important in linking information about surface composition to surface morphology seen in radar images. Resolution of the Magellan data is about 120 meters (400 feet). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00460
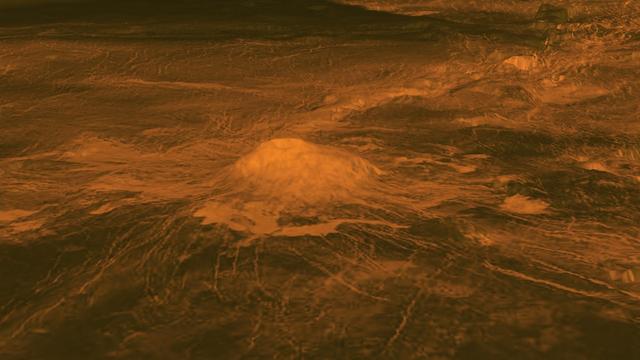
This figure shows the volcanic peak Idunn Mons in the Imdr Regio area of Venus. The topographic backbone brown color was derived from data obtained by NASA Magellan spacecraft and the overlay was derived from data from ESA Venus Express Spacecraft.
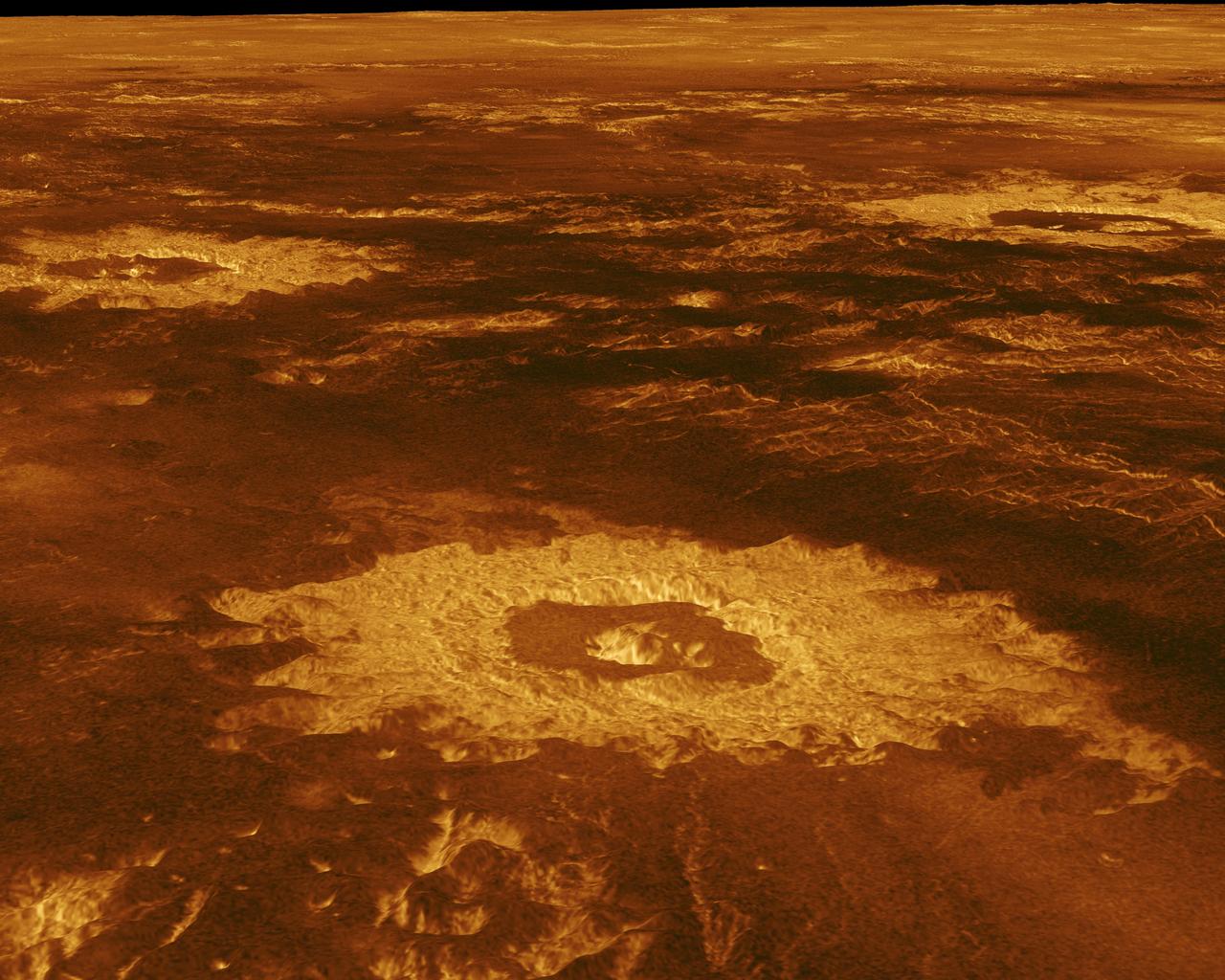

Three impact craters are displayed in this three-dimensional perspective view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. The center of the image is located in the northwestern portion of Lavinia Planitia. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00103
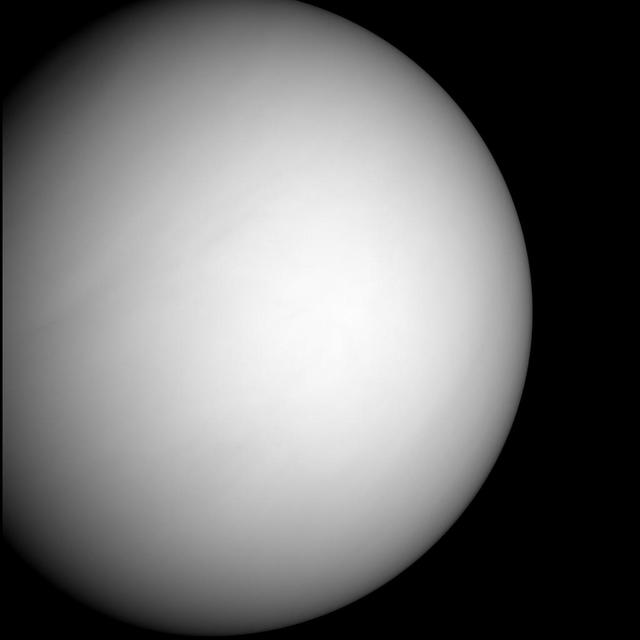

NASA MESSENGER spacecraft snapped a series of images as it approached Venus on June 5. The planet is enshrouded by a global layer of clouds that obscures its surface to the MESSENGER Dual Imaging System MDIS cameras.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.

Artist: Rick Guidice Artist conception of surface of Venus.
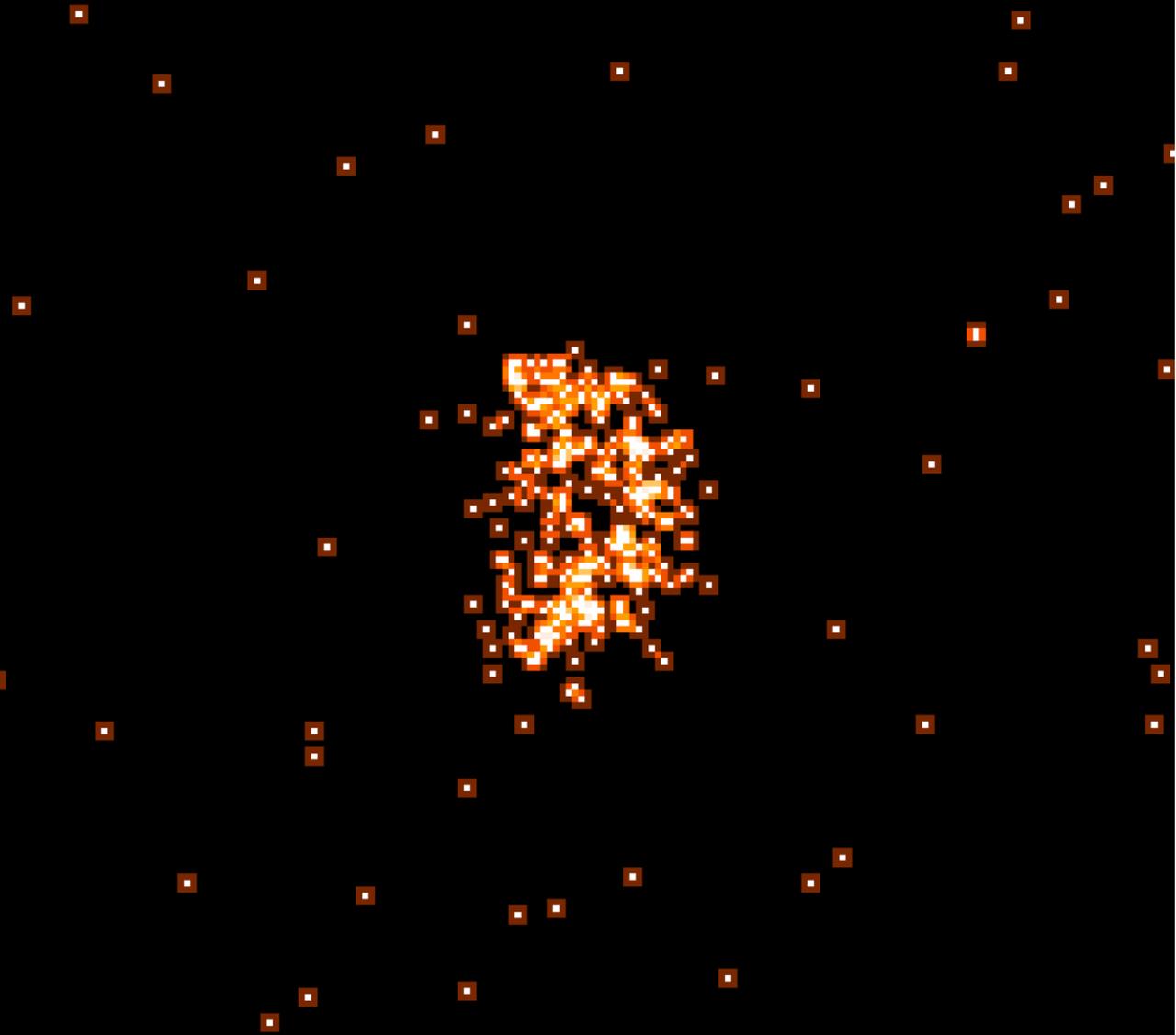
This Chandra image, the first x-ray image ever made of Venus, shows a half crescent due to the relative orientation of the Sun, Earth, and Venus. The x-rays are produced by fluorescent radiation from oxygen and other atoms in the atmosphere between 120 and 140 kilometers above the surface of the planet. In contrast, the optical light from Venus is caused by the reflection from clouds 50 to 70 kilometers above the surface.
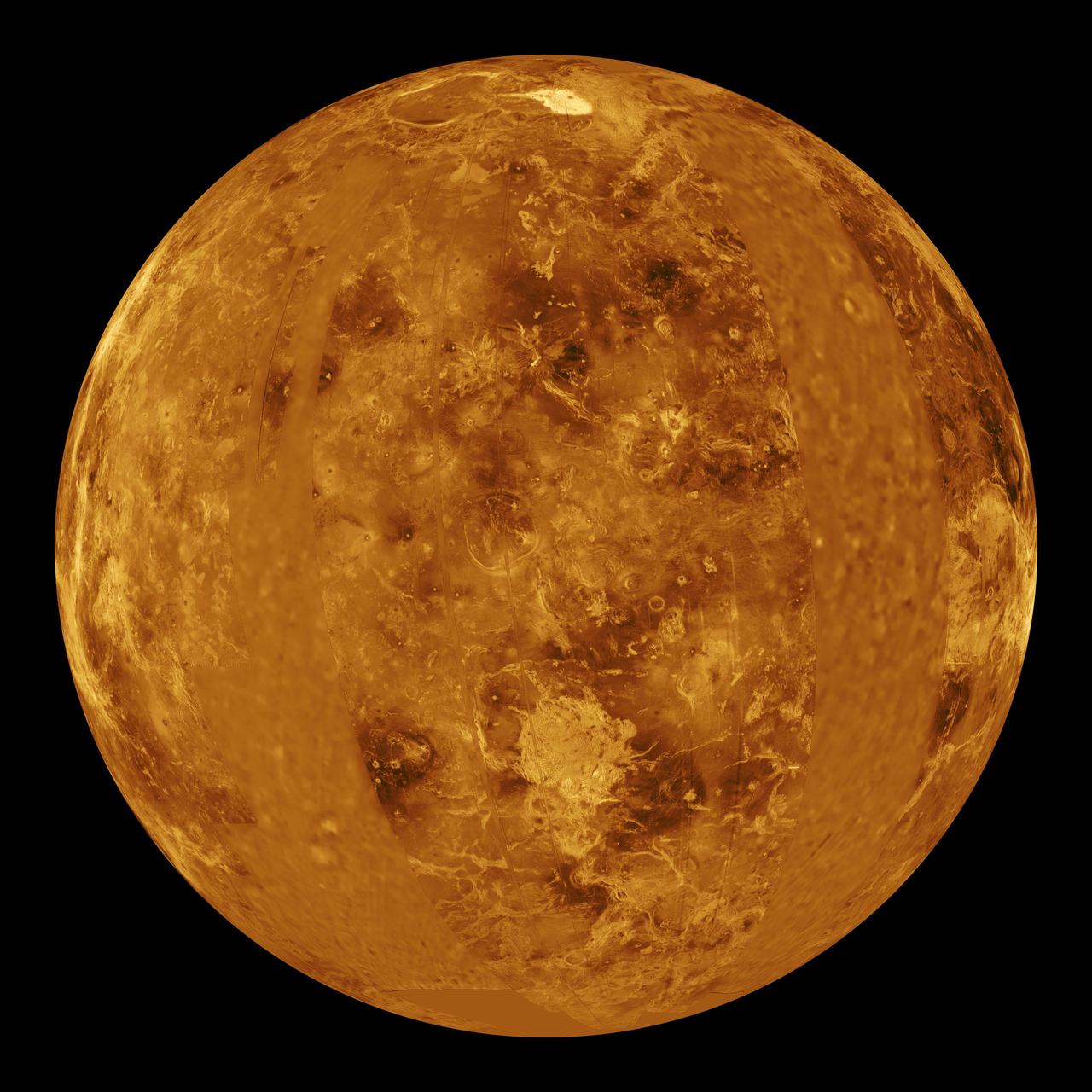

This global view of the surface of Venus is centered at 0 degrees east longitude. NASA Magellan synthetic aperture radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magellan mapping were mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create this image. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00257
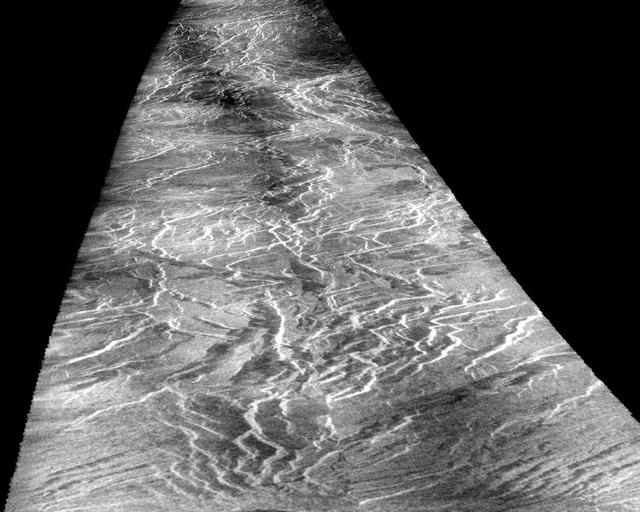
This view of the surface of Venus acquired by NASA Magellan spacecraft shows a geographically young region of lowland plains. The location is near the equator between two highland areas known as Asteria Regio and Phoebe Regio. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00237
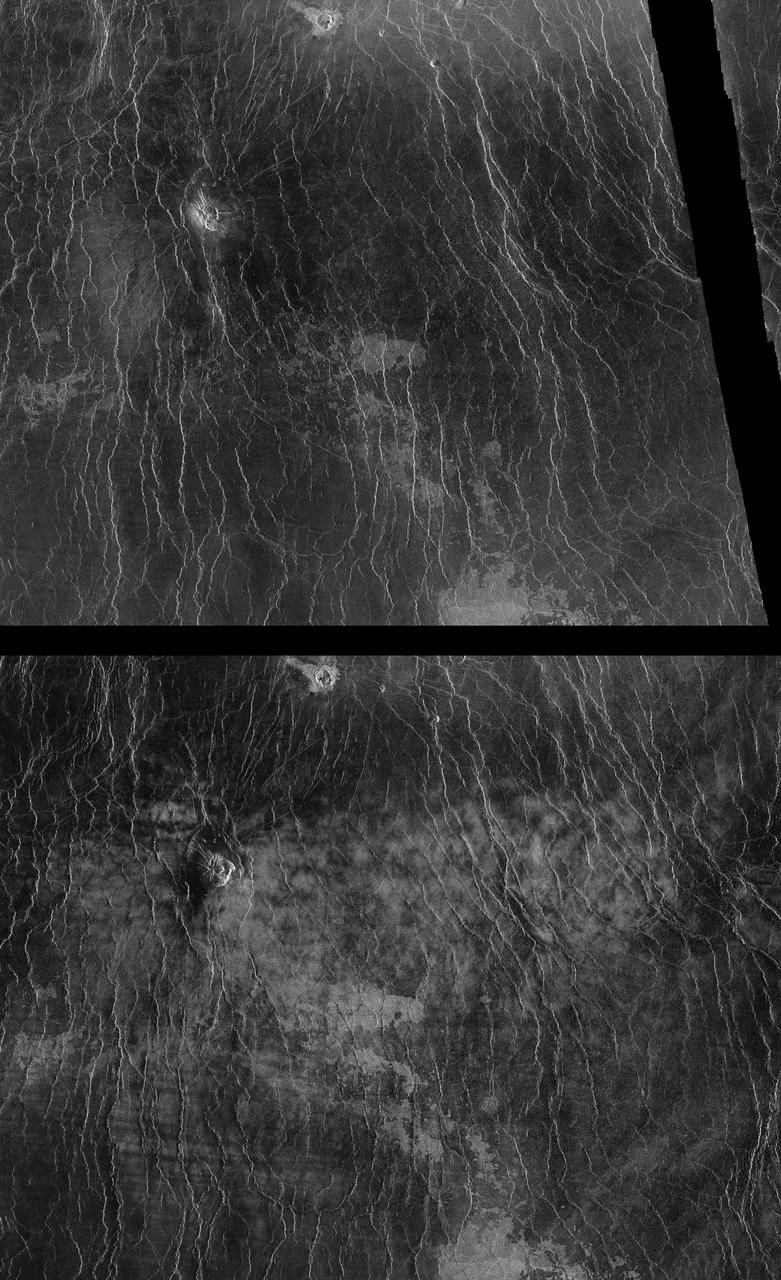
As NASA Magellan mission progressed, areas of Venus became accessible for a second look. During Magellan second 243-day global mapping cycle, the spacecraft was rotated 180 degrees to view the surface from the opposite direction. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00260
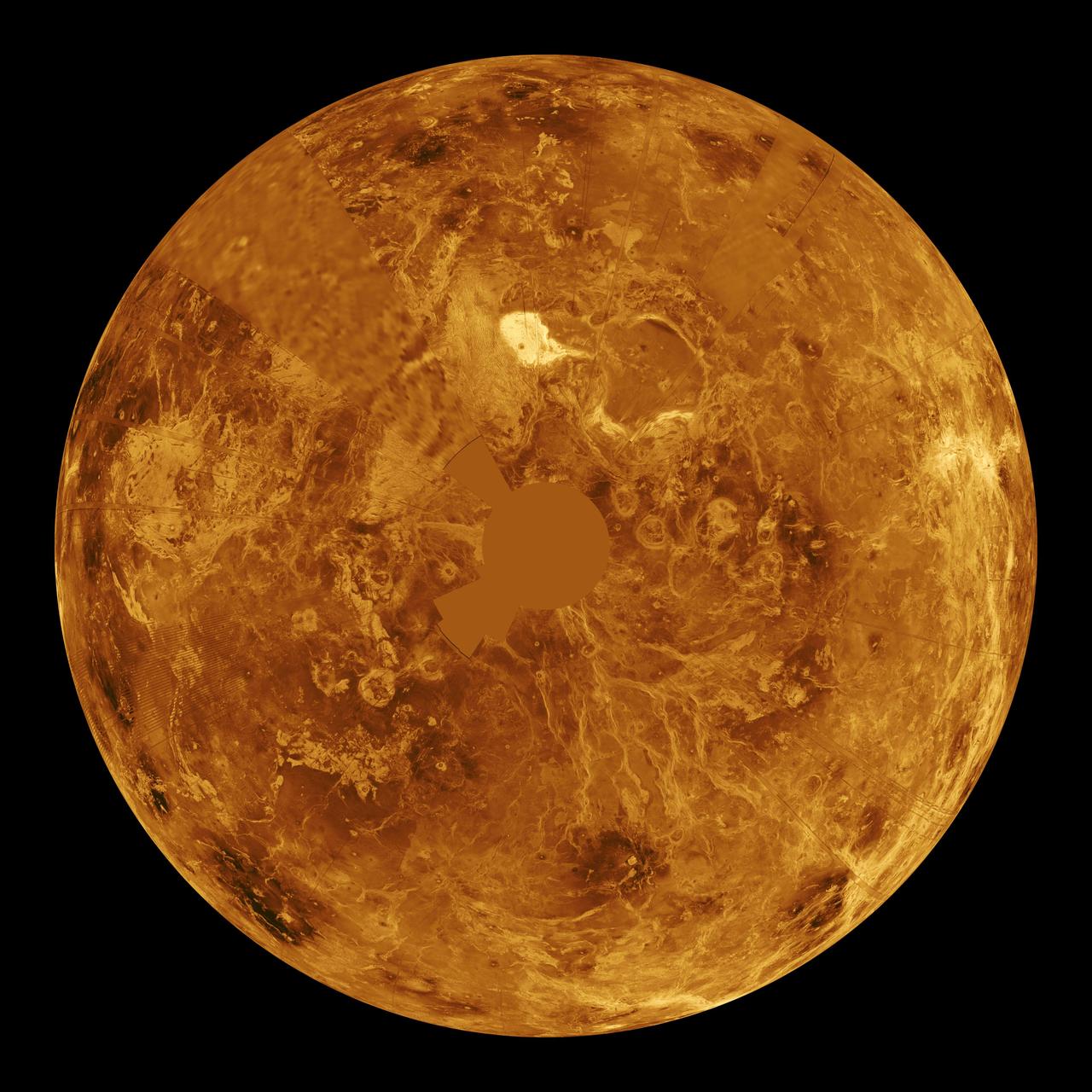

The northern hemisphere is displayed in this global view of the surface of Venus. NASA Magellan synthetic aperture radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magellan mapping were mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create this image. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00252
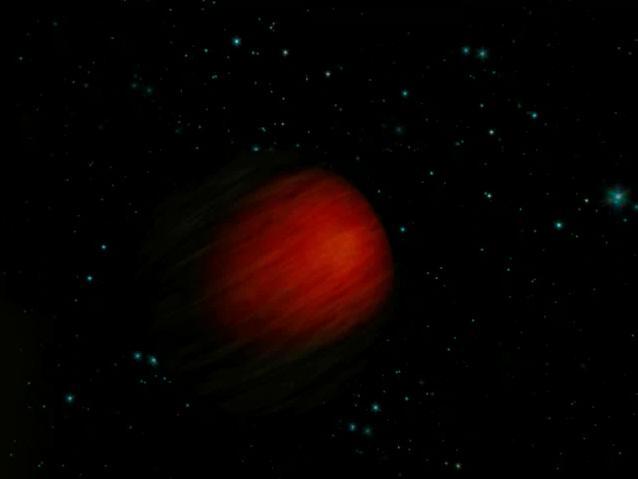

This artist concept illustrates the hottest planet yet observed in the universe. The scorching ball of gas, a hot Jupiter called HD 149026b, is about 3 times hotter than the rocky surface of Venus, the hottest planet in our solar system.
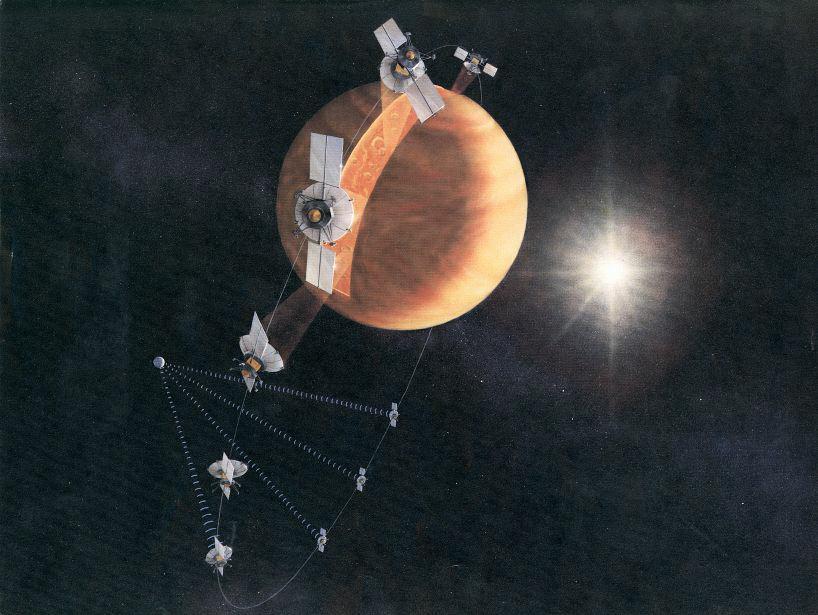
An artist's concept of the Magellan spacecraft making a radar map of Venus. Magellan mapped 98 percent of Venus' surface at a resolution of 100 to 150 meters (about the length of a football or soccer field), using synthetic aperture radar, a technique that simulates the use of a much larger radar antenna. It found that 85 percent of the surface is covered with volcanic flows and showed evidence of tectonic movement, turbulent surface winds, lava channels and pancake-shaped domes. Magellan also produced high-resolution gravity data for 95 percent of the planet and tested a new maneuvering technique called aerobraking, using atmospheric drag to adjust its orbit. The spacecraft was commanded to plunge into Venus' atmosphere in 1994 as part of a final experiment to gather atmospheric data. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18175
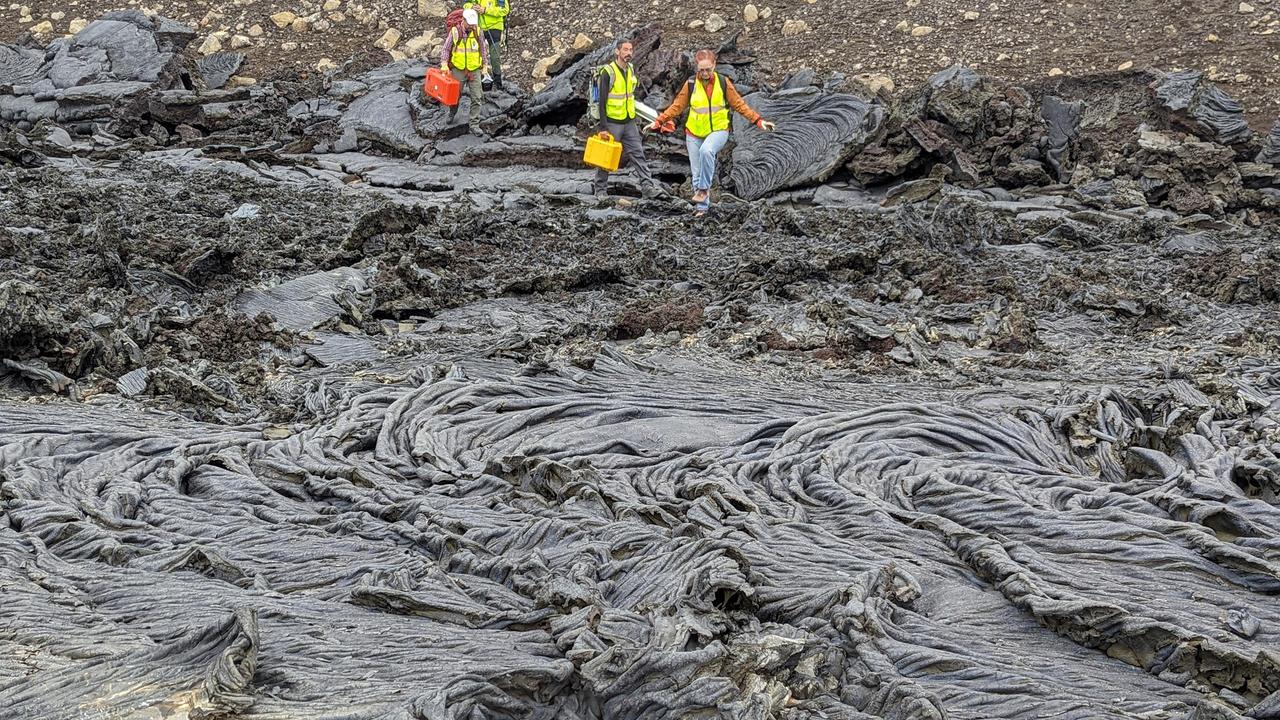

To lay the groundwork for NASA's VERITAS mission (Venus Emissivity, Radio science, InSAR, Topography, And Spectroscopy), members of the mission's international science team traveled in August 2023 to Iceland, using the island as a stand-in, or analog, for Venus. Using several techniques, the team studied a variety of rocky terrain, including this lava field featuring new rock from a recent flow, to better understand what the VERITAS mission will "see" when it studies Venus' surface. The VERITAS orbiter will peer through the planet's thick atmosphere with a suite of powerful science instruments to create global maps of the planet's surface – including topography, radar images, rock type, and gravity measurements – as well as detect surface changes. VERITAS is designed to understand what processes are currently active, search for evidence of past and current interior water, and understand the geologic evolution of the planet, illuminating how rocky planets throughout the galaxy evolve. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25838
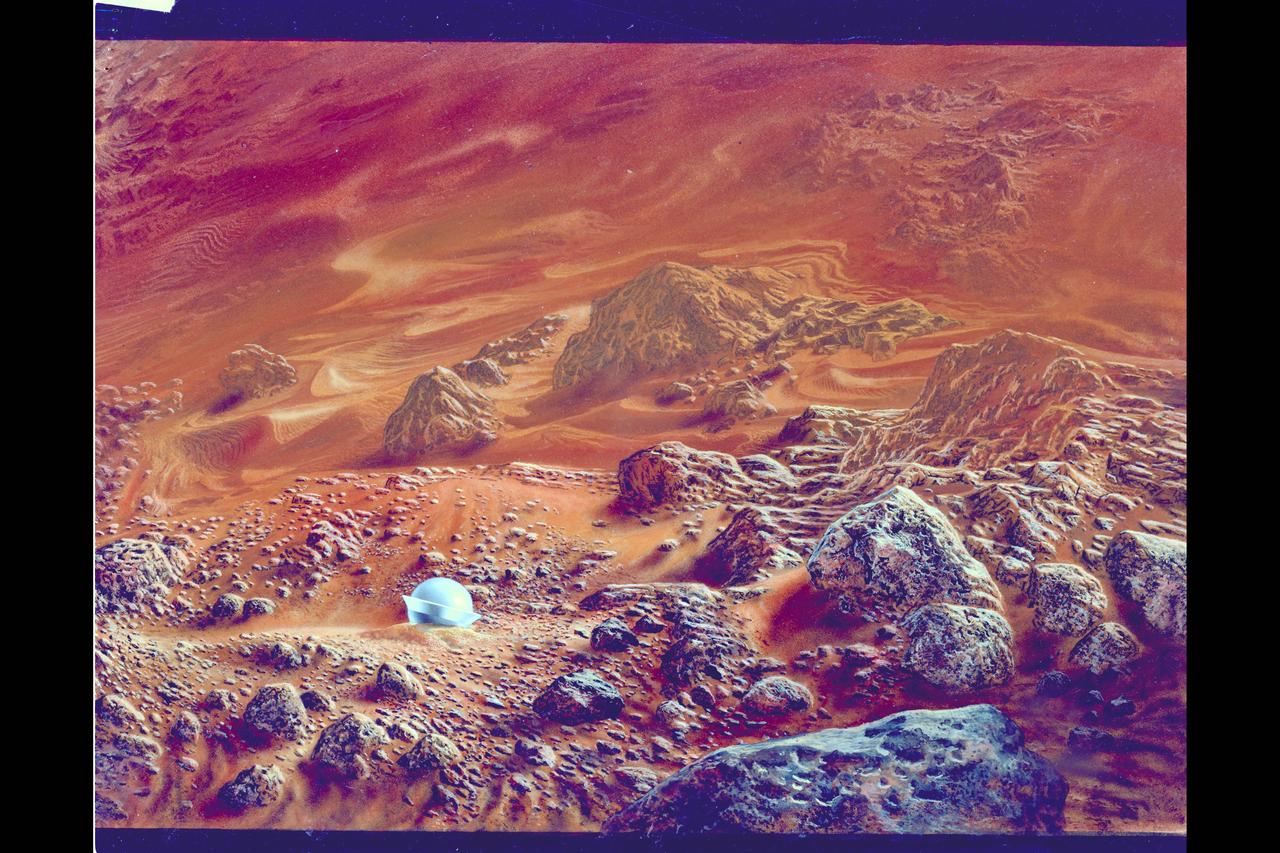

Art By Don Davis Artist's concept of one of the probes on the hot surface of Venus. Although the probes were not designed to withstand impact, there was a chance that one might survive and transmit some data from the surface. A small probe did survive and transmitted data for 67 minutes.
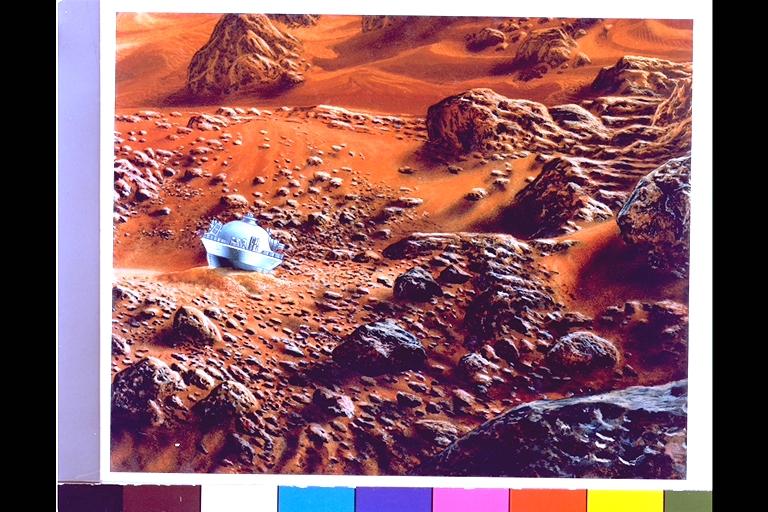

Art By Don Davis Artist's concept of one of the probes on the hot surface of Venus. Although the probes were not designed to withstand impact, there was a chance that one might survive and transmit some data from the surface. A small probe did survive and transmitted data for 67 minutes.
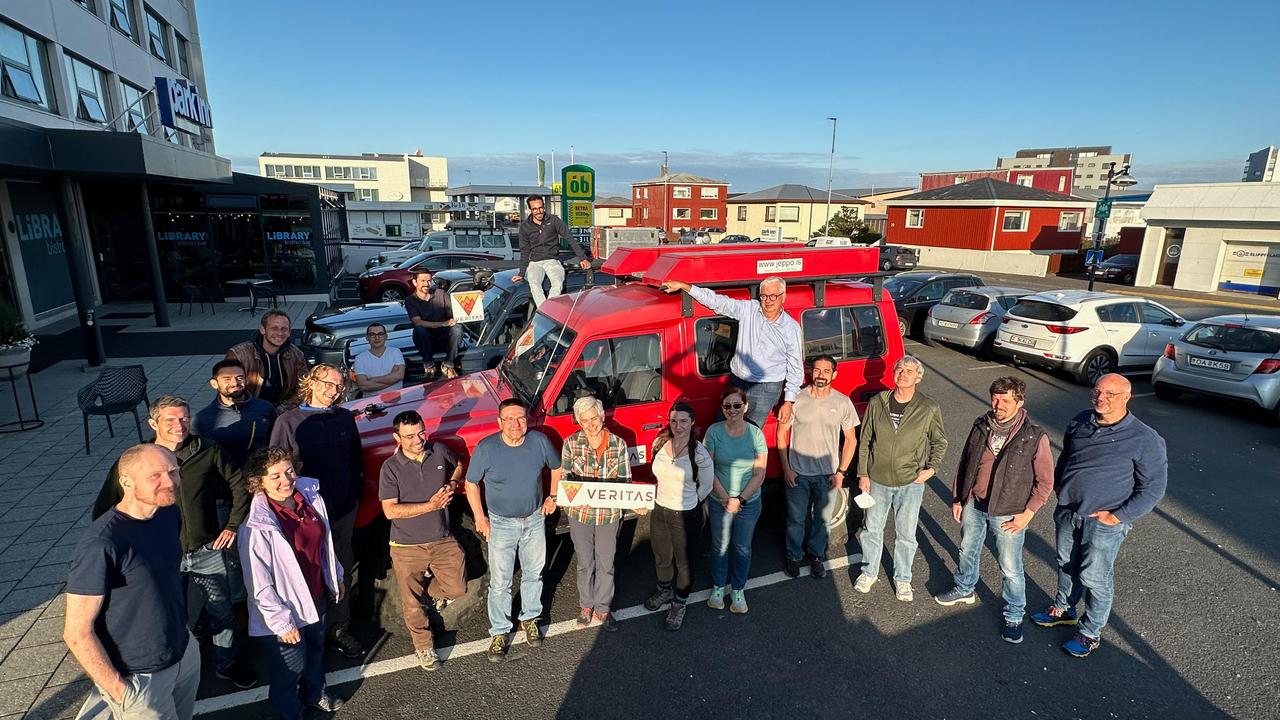

Members of the VERITAS science team pause for a photograph on July 31, 2023, after arriving in Iceland to begin a two-week campaign to study the volcanic island's geology to help the team prepare for NASA's VERITAS (short for Venus Emissivity, Radio science, InSAR, Topography, And Spectroscopy) mission to Venus. From July 30 to Aug. 14, 2023, the international science team, including local participation from the University of Iceland, worked to lay the groundwork for the science that will ultimately be done from Venus orbit. At center, holding the VERITAS mission identifier is the mission's principal investigator and the science team lead, Sue Smrekar, of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Flanking her are science team members from multiple U.S., Italian, and German institutions, including members of the German Aerospace Center (DLR) Flugzeug Synthetic Aperture Radar (F-SAR) airplane team. The DLR F-SAR team was tasked with collecting synthetic-aperture radar data of the regions studied by the field team. A key objective of the campaign is to refine change detection algorithms that will be used to look for global surface change (such as volcanic activity) between NASA's Magellan radar mission from the 1990s and VERITAS, as well as between VERITAS and the ESA (European Space Agency) EnVision mission to Venus, both of which are targeting the early 2030s for launch. NASA's VERITAS is an orbiter designed to peer through Venus' thick atmosphere with a suite of powerful instruments to create global maps of the planet's surface, including topography, radar images, rock type, and gravity, as well as detect surface changes. VERITAS is designed to understand what processes are currently active, search for evidence of past and current interior water, and understand the geologic evolution of the planet, illuminating how rocky planets throughout the galaxy evolve. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25835
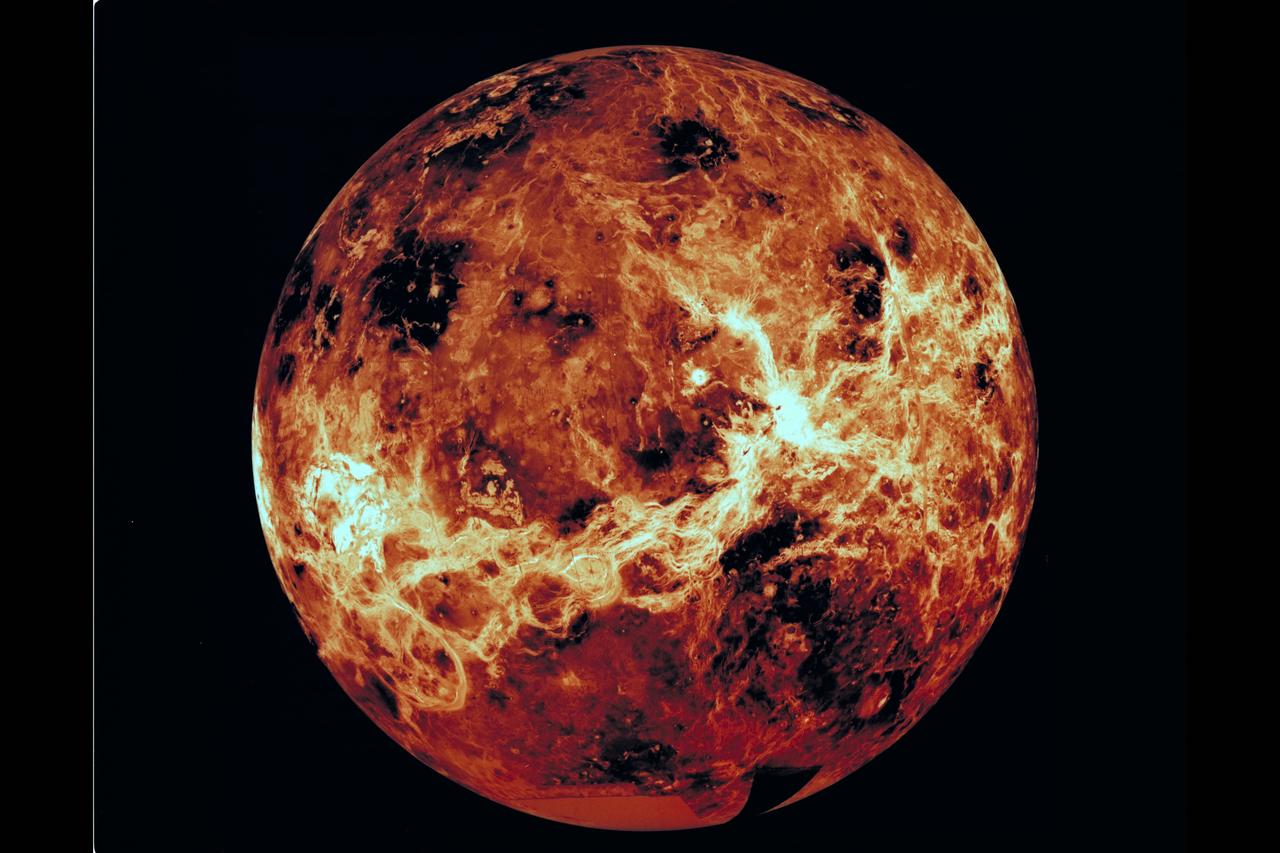
This global view of the surface of Venus is centered at 270 degrees east longitude. Magellan synthetic aperture radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magellan mapping are mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create this image. Data gaps are filled with Pioneer-Venus orbiter data, or a constant mid-range value. Simulated color is used to inhance small-scale structure. The simulated hues are based on color images recorded by the Soviet Venera 13 and 14 spacecraft.
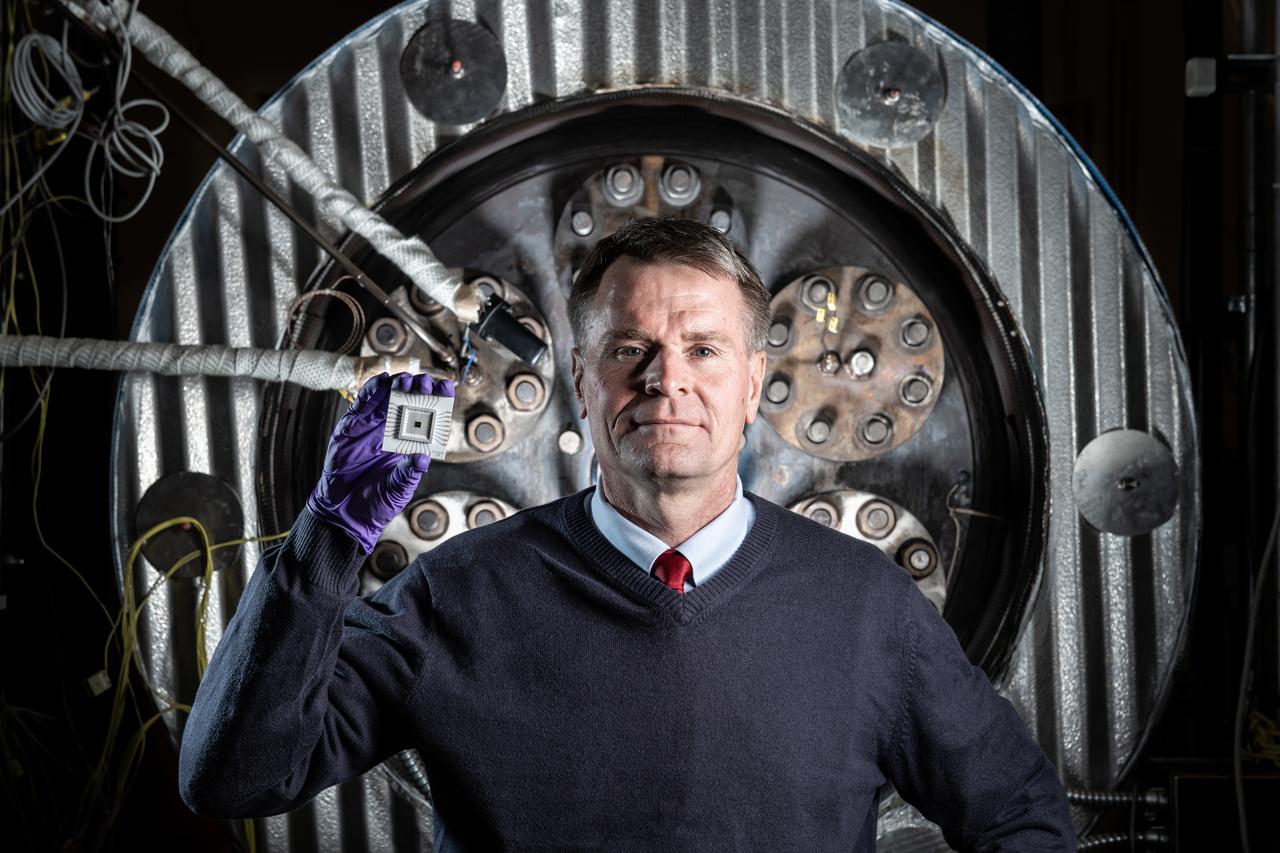

Phil Neudeck- Can Take the Heat When it comes to the heat of extreme environments like Venus, electronics can get fried within a few minutes of arrival. But NASA Researcher Phil Neudeck and his team have developed extremely durable silicon carbide semiconductor integrated circuits to survive those harsh conditions. After successfully testing the electronics in our high-pressure, high-temperature extreme environments chamber, there is now a path forward for Venus landers to survive and operate scientific experiments on the planet’s surface for longer durations.

This global view of Venus, centered at 270 degrees east longitude, is a compilation of data from several sources. Magellan synthetic aperature radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magellan mapping are mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create the image. Data gaps are filled with Pioneer-Venus orbiter data, or a constant mid-range value. Simulated color is used to enhance small-scale structure. The simulated hues are based on color images recorded by the Soviet Venera 13 and 14 spacecraft. The image was produced at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Multimission Image Processing Laboratory and is a single frame from a video released at the JPL news conference, 10-29-91. View provided by JPL with alternate number P-39225 MGN81.
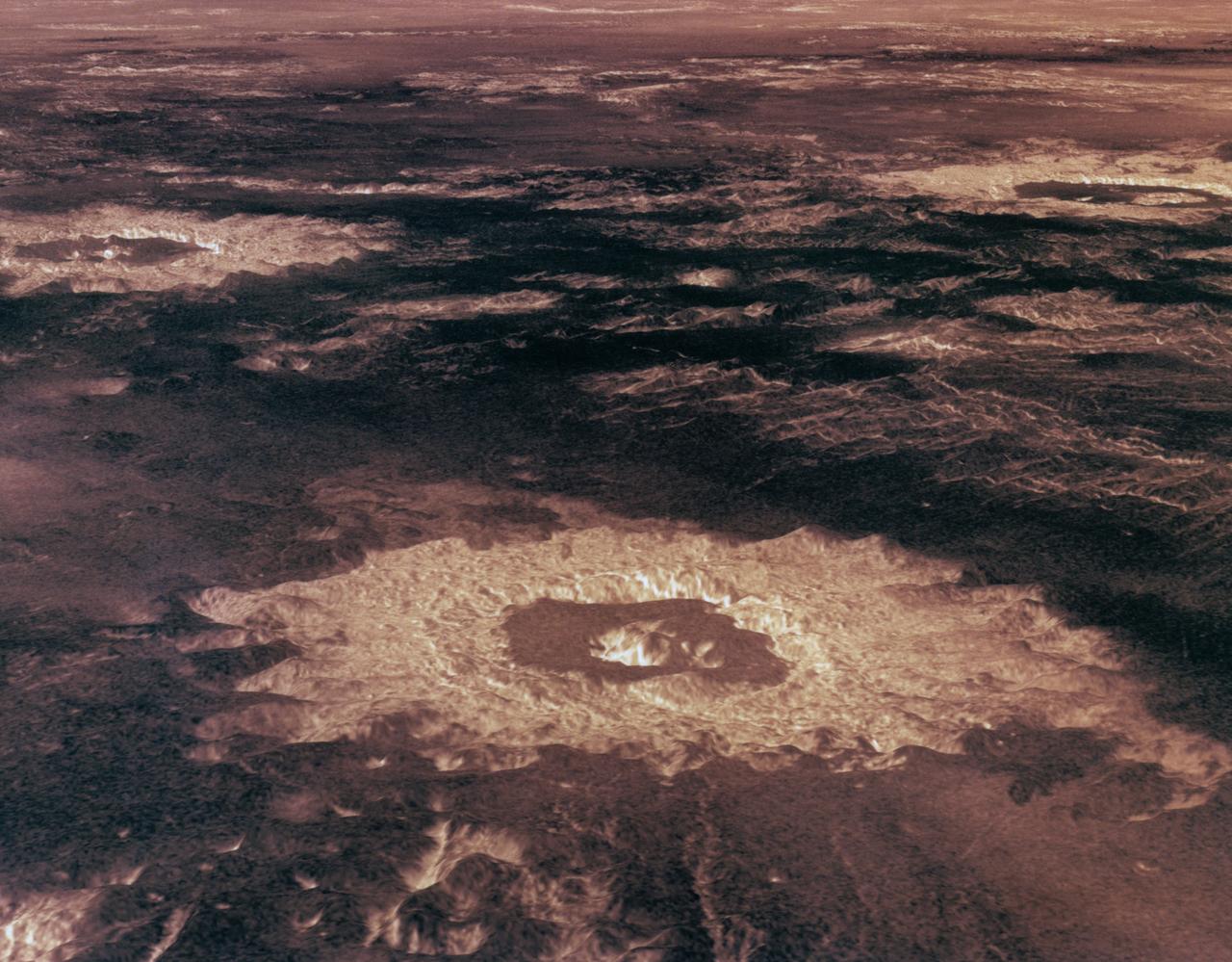

Three impact craters in three-dimensional perspective located approximately 27 degrees south latitude, 339 degrees east longitude in the northwestern portion of Lavinia Planitia. The viewpoint is located southwest of Howe Crater which appears centered in the lower portion of the image. Howe has a diameter of 37.3 kilometers (23.1 miles) located at 28.6 degrees south latitude, 337.1 degrees east longitude. Danilova, a crater with a diameter of 47.6 kilometers (29.5 miles) and located at 26.35 degrees south latitude and 337.5 east longitude, appears above and to the left of Howe in the image. Aglaonice, a crater with a diameter of 62.7 kilometers (38.9 miles) and located at 26.5 degrees south latitude and 340 degrees east longitude is on the right of Danilova. Magellan synthetic aperture radar data is combined with radar altimetry to develop a 3D map of the surface. Rays cast in a computer intersect the surface to create a 3D view. Simulated color and a digital elevation map developed by the United States (U.S.) Geological Survey is used to enhance small-scale structure. The simulated hues are based on color images recorded by the Soviet Venera 13 and 14 spacecraft. The image was processed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Multimission Image Processing Laboratory and is a single frame from a video released at the JPL news conference 05-29-91. View provided by JPL with alternate number P-39146.
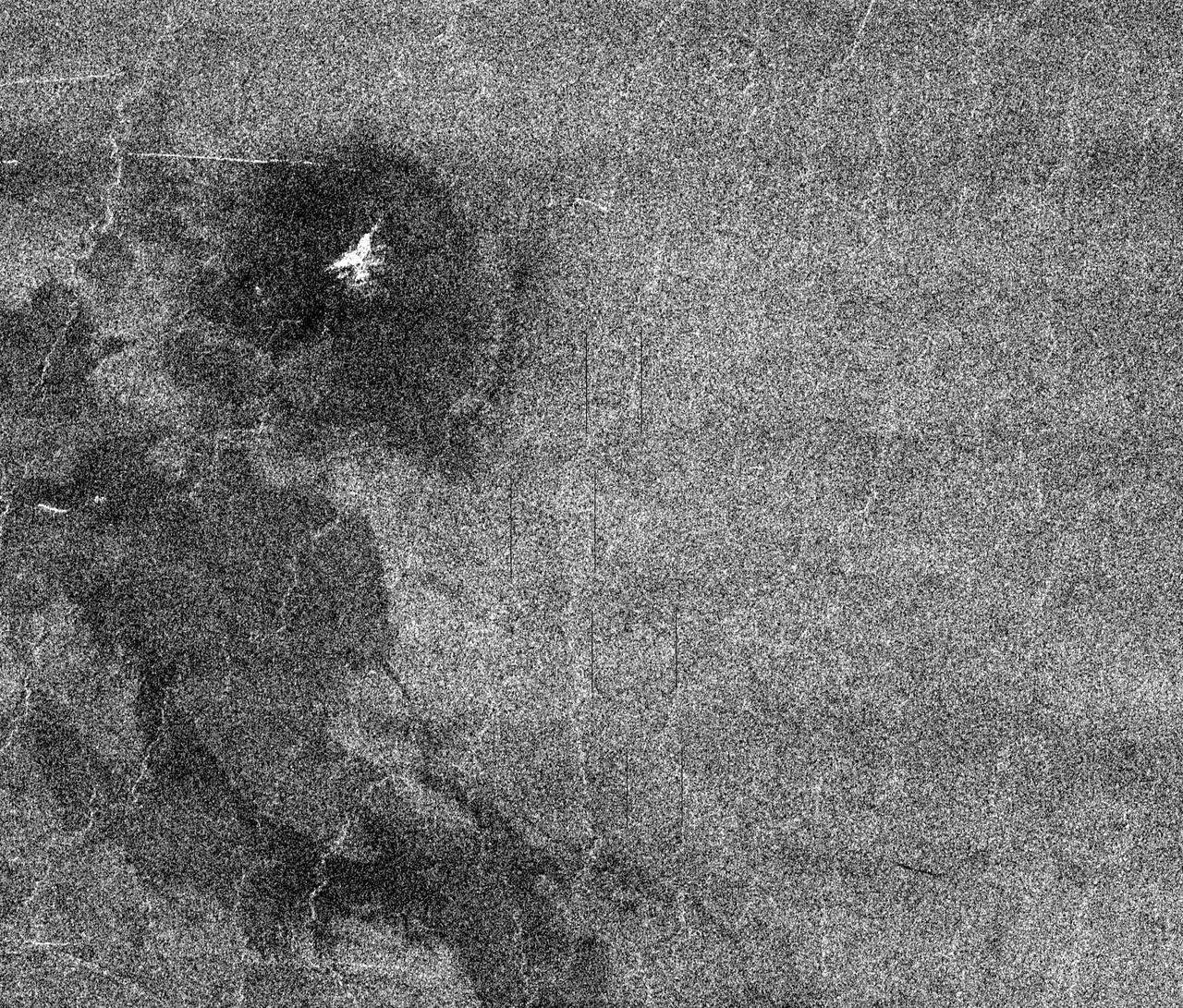
This full resolution mosaiced image covers an area of approximately 100 kilometers by 120 kilometers (62 by 74 miles) and is located in the Lakshmi region of Venus at 47 degrees north latitude and 334 east longitude. Due to the dense Venusian atmosphere, primary impact craters of less than a 3 kilometer (2 mile) diameter are nonexistent. The dark circular region and associated central bright feature in this image are thought to be the remnants of a meteoroid smaller than the size necessary to create an impact crater entering the atmosphere at a low velocity (approximately 350 meters/second.) The central bright feature appears to be a cluster of small secondary impacts, ejecta and debris from the original meteor that broke up in the atmosphere. Even though most of the meteorite did not hit the surface, the atmospheric shock wave could be great enough to modify the surrounding region. One explanation for this radar dark circular formation, called dark margins, could be that the shock wave was energetic enough to pulverize the surface (smooth surfaces generally appear radar dark.) Another explanation is that the surface could be blanketed by a fine material that was formed by the original meteor's breakup through the atmosphere. More than half of the impact craters on Venus have associated dark margins, and most of these are prominently located left of center of the crater. This is another effect which could be caused by the dense atmosphere of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00477
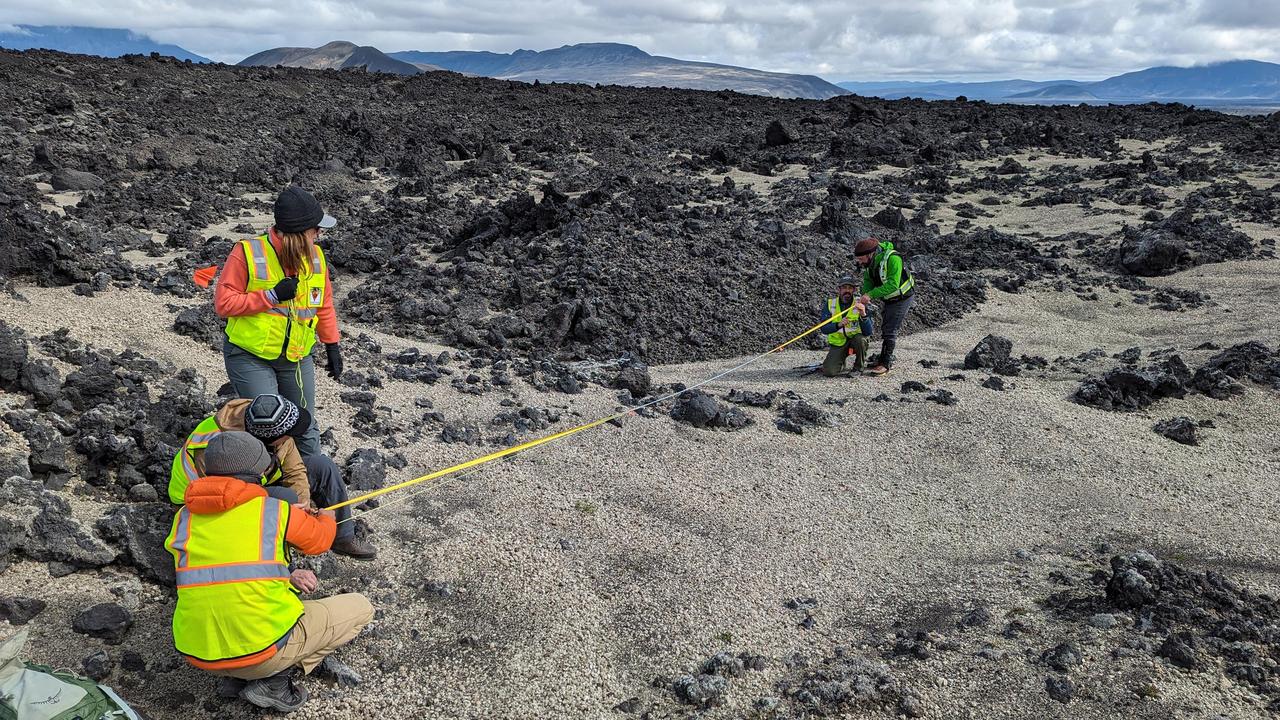

During their August 2023 Iceland field campaign, international science team members of NASA's VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio science, InSAR, Topography, And Spectroscopy) mission prepare for lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) imaging of rocks at a study area. Lidar measurements of rocky terrain can provide information about the material, such as surface roughness. While the science team led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory gathered lidar data on the ground, their partners from the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, or DLR) carried out overflights to gather radar observations of the same study areas. By doing this, the team was able to ground-truth the radar data that will be used to help inform the science that VERITAS will do at Venus. VERITAS will peer through the planet's thick atmosphere with a suite of powerful science instruments to create global maps of Venus' surface – including topography, radar images, rock type, and gravity measurements – as well as detect surface changes. VERITAS is designed to understand what processes are currently active, search for evidence of past and current interior water, and understand the geologic evolution of the planet, illuminating how rocky planets throughout the galaxy evolve. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25839
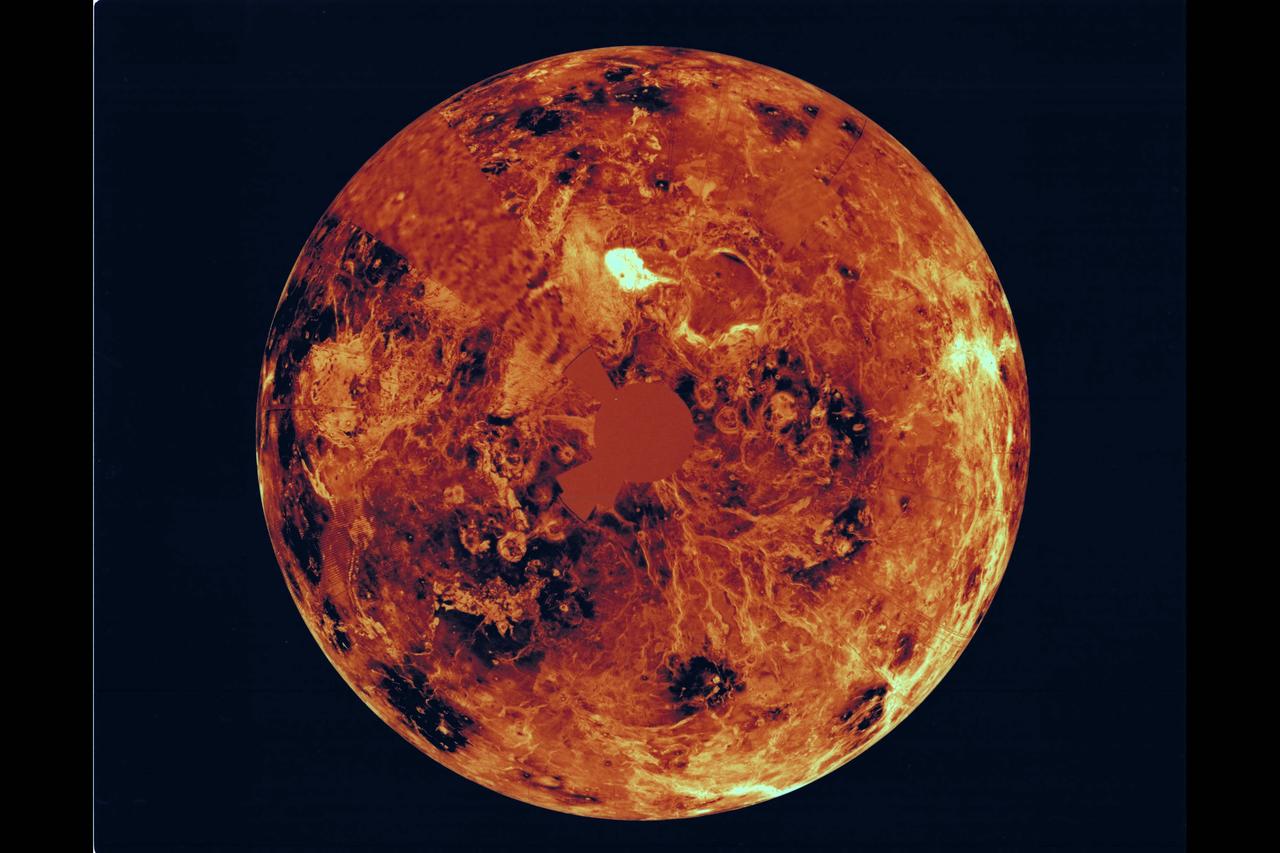
The northern hemisphere is displayed in this global view of the surface of Venus. The north pole is at the center of the image; with 0 degrees, 90 degrees , 180 degrees, 270 degrees east longitudes at 6, 3, 12 and 9 0'clock positions, repectively, of an imagery clock face. Magellan synthetic aperture radar mosaics from the first cycle of Magelolan mapping are mapped onto a computer-simulated globe to create this image. Data gaps are filled with Pioneere-Venus Orbiter data, or a constant mid-range value. Simulated color is used to enhance small-scale structure. The simulated hues are based on color images recorded by the Soviet Venera 13 & 14 spacecraft.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - MESSENGER, a NASA Discovery mission. The MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) mission is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury. MESSENGER will be launched in the summer of 2004 and will enter Mercury orbit in March of 2011, after one Earth flyby, two flybys of Venus, and three of Mercury along the way. The flyby and orbital phases of the mission will provide global mapping and detailed characterization of the planet's surface, interior, atmosphere and magnetosphere.
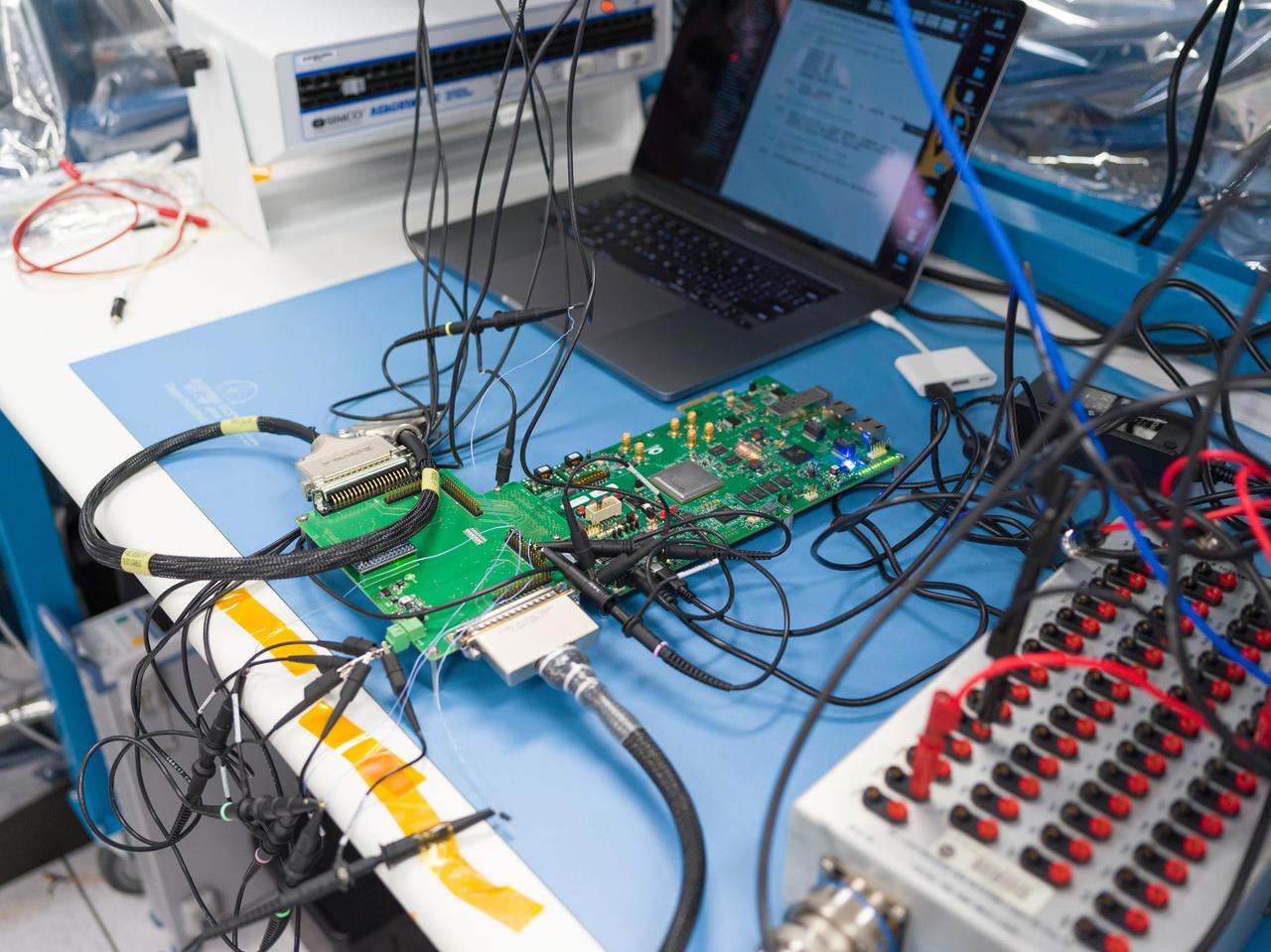
Seen here in March 2023, prototype hardware for the Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR) underwent interface testing at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. VISAR is being developed at JPL for NASA's Venus Emissivity Radio Science, InSAR, Topography & Spectroscopy (VERITAS) mission that will launch within a decade to explore Earth's twin. These early interface tests are the first in a series to be run by JPL and Thales Alenia Space Italy (TASI), an international partner of the VERITAS mission that is contributing hardware to the instrument. Figure A shows TASI engineers Luca Di Marco Napini and Gabriel Mihu working in a JPL cleanroom on the VISAR prototype hardware. When VERITAS arrives in orbit, it will use VISAR to create detailed 3D global maps of Venus. The spacecraft will also carry a near-infrared spectrometer to figure out what the surface is made of. Together, the instruments will offer clues about the planet's past and present geologic processes, help reveal how the paths of Venus and Earth diverged, and how Venus lost its potential as a habitable world. VERITAS is managed by JPL. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25832
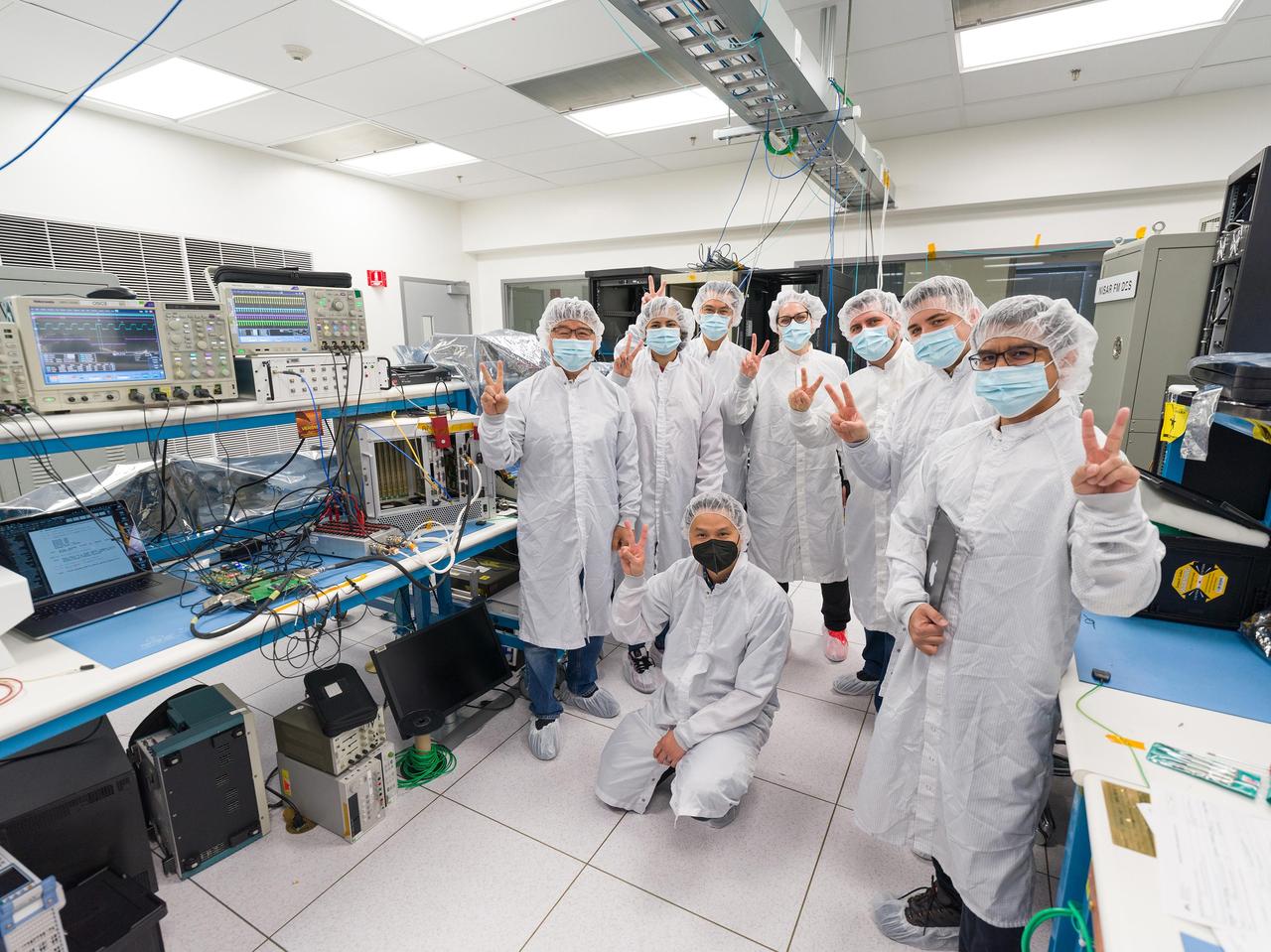

Seen here are members of the international team that participated in recent tests on prototype hardware for the Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. VISAR is being developed at JPL for NASA's Venus Emissivity Radio Science, InSAR, Topography & Spectroscopy (VERITAS) mission that will launch within a decade to explore Earth's twin. In March 2023, the hardware underwent early interface tests in a JPL clean room, representing the first in a series to be run by JPL and Thales Alenia Space Italy (TASI), an international partner of the VERITAS mission that is contributing hardware to the instrument. Dressed in gowns to minimize the risk of contamination with sensitive electronics, the JPL VISAR digital team and TASI engineers pose for a photograph next to the laboratory benches where the tests took place. Figure A shows the same personnel without gowns for a team photo. From left to right: Marvin Cruz (JPL), Chester Lim (JPL), Tim Noh (JPL), Hana Haideri (JPL), Luca Di Marco Napini (TASI), Ernie Chuang (JPL), Dragana Perkovic-Martin (JPL), and Gabriel Mihu (TASI). JPL's Michael Burke, Anusha Yarlagadda, Duane Clark, and TASI's Antonio Delfino also participated in the tests but are not pictured. When VERITAS arrives in orbit, it will use VISAR to create detailed 3D global maps of Venus. The spacecraft will also carry a near-infrared spectrometer to figure out what the surface is made of. Together, the instruments will offer clues about the planet's past and present geologic processes, help reveal how the paths of Venus and Earth diverged, and how Venus lost its potential as a habitable world. VERITAS is managed by JPL. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25833
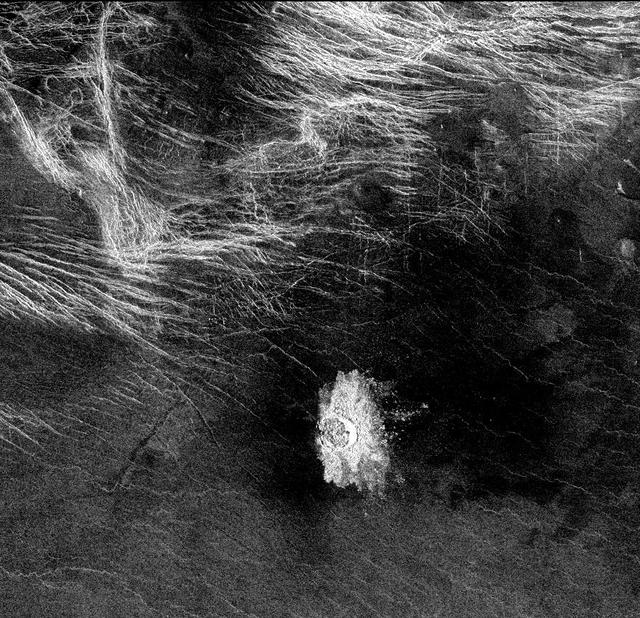
This image from NASA Magellan spacecraft is of Crater Stephania, located at 51.3 degrees latitude, 333.3 degrees longitude in northern Sedna Planitia on Venus. With a diameter of 11 kilometers (6.8 miles) it is one of the smaller craters on Venus. Because many small meteoroids disintegrate during their passage through the dense atmosphere, there is an absence of craters smaller than 3 kilometers (1.9 miles) in diameter, and even craters smaller than 25 kilometers (15.5 miles) are relatively scarce. The apron of ejected material suggests that the impacting body made contact with the surface from an oblique angle. Upon closer observation it is possible to delineate secondary craters, impact scars from blocks ejected from the primary crater. A feature associated with this and many other Venusian craters is a radar-dark halo. Since dark radar return signifies a smooth surface, it has been hypothesized that an intense shock wave removed or pulverized previously rough surface material or that a blanket of fine material was deposited during or after the impact. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00475
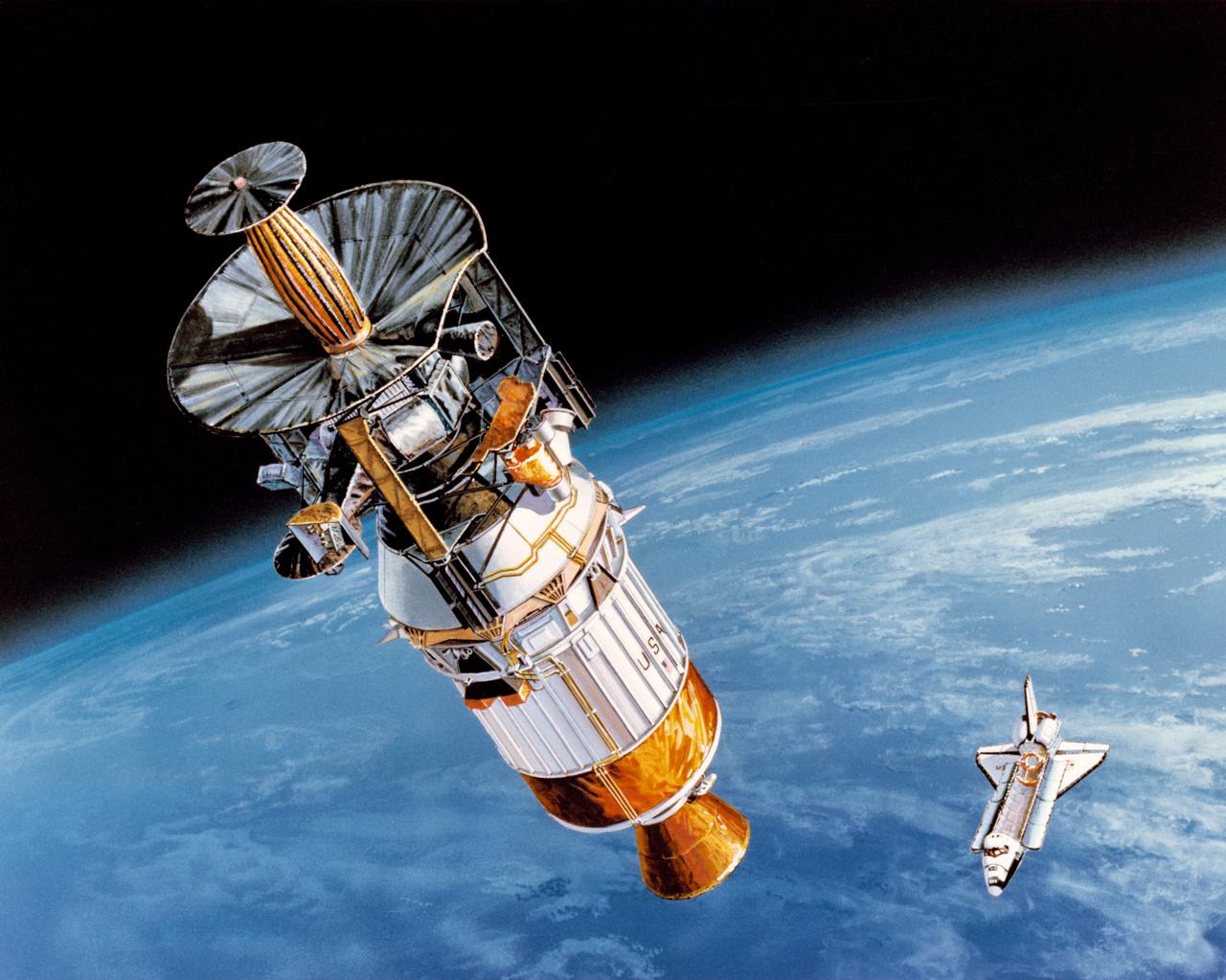

S89-42940 (April 1989) --- In this artist's rendition, the Galileo spacecraft is being boosted into its inter-planetary trajectory by the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) rocket. The Space Shuttle Atlantis, which is scheduled to take Galileo and the IUS from Earth's surface into space, is depicted against the curve of Earth. Galileo will be placed on a trajectory to Venus, from which it will return to Earth at higher velocity and then gain still more energy in two gravity-assist passes, until it has enough velocity to reach Jupiter. Passing Venus, it will take scientific data using instruments designed for observing Jupiter; later, it will make measurements at Earth and the moon, crossing above the moon's north pole in the second pass. Between the two Earth passes, it will edge into the asteroid belt, beyond Mars' orbit; there, the first close-up observation of an asteroid is planned. Crossing the belt later, another asteroid flyby is possible.
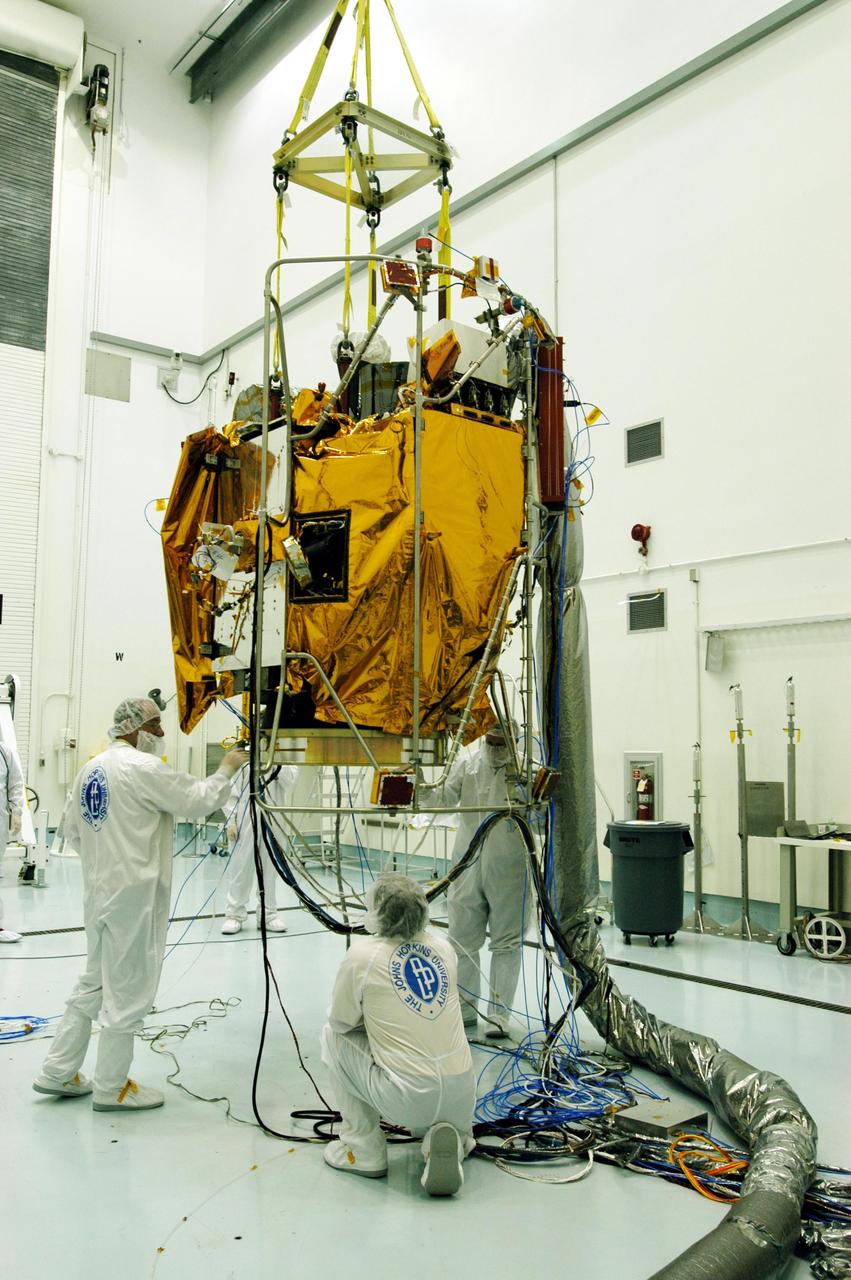

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft is carried across the floor by an overhead crane. MESSENGER is being moved to a turnover fixture that will rotate it for prelaunch testing. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC get ready to attach an overhead crane to the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft before lifting. They are moving it to a turnover fixture that will rotate it for prelaunch testing. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
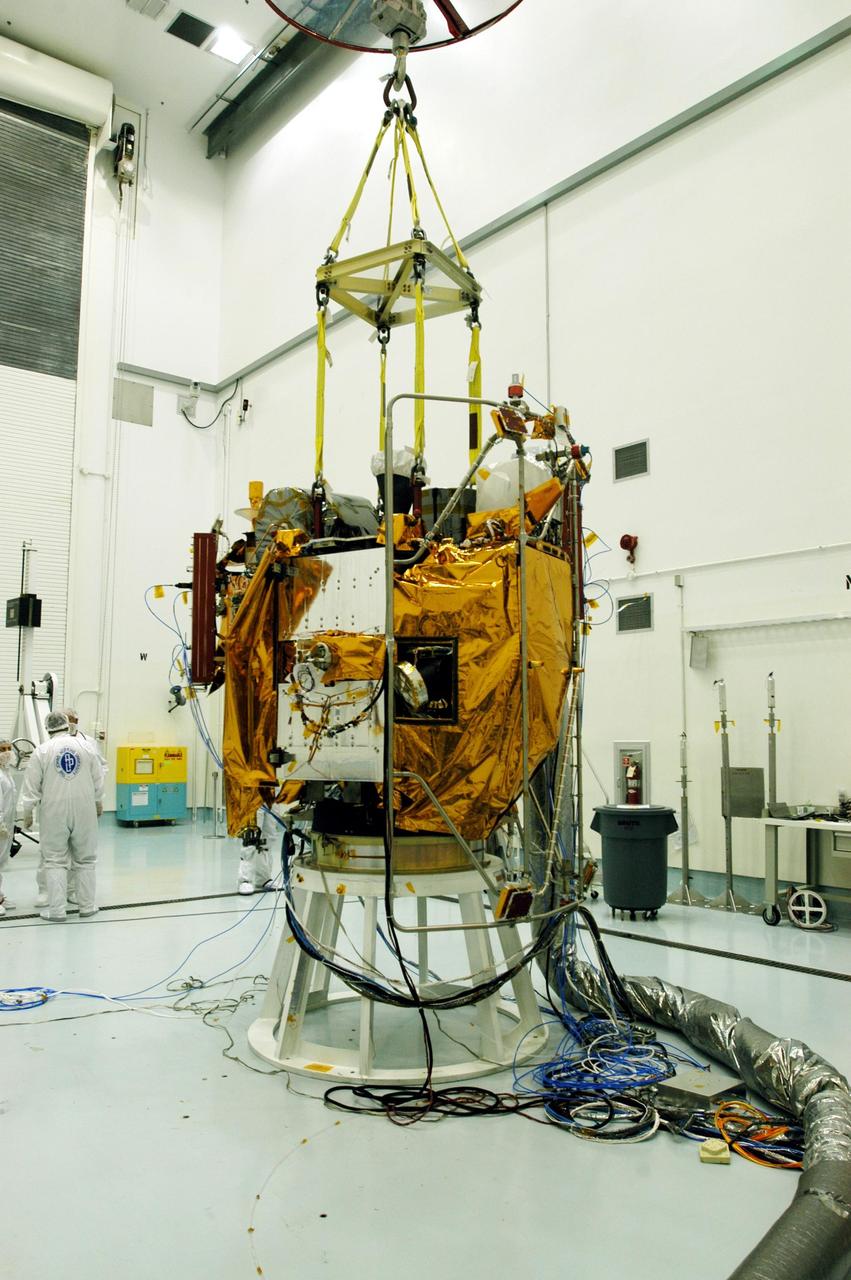

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft is ready for lifting. It is being moved to a turnover fixture that will rotate it for prelaunch testing. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.

As it sped away from Venus, NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft captured this seemingly peaceful view of a planet the size of Earth, wrapped in a dense, global cloud layer. But, contrary to its serene appearance, the clouded globe of Venus is a world of intense heat, crushing atmospheric pressure and clouds of corrosive acid. This newly processed image revisits the original data with modern image processing software. A contrast-enhanced version of this view, also provided here, makes features in the planet's thick cloud cover visible in greater detail. The clouds seen here are located about 40 miles (60 kilometers) above the planet's surface, at altitudes where Earth-like atmospheric pressures and temperatures exist. They are comprised of sulfuric acid particles, as opposed to water droplets or ice crystals, as on Earth. These cloud particles are mostly white in appearance; however, patches of red-tinted clouds also can be seen. This is due to the presence of a mysterious material that absorbs light at blue and ultraviolet wavelengths. Many chemicals have been suggested for this mystery component, from sulfur compounds to even biological materials, but a consensus has yet to be reached among researchers. The clouds of Venus whip around the planet at nearly over 200 miles per hour (100 meters per second), circling the globe in about four and a half days. That these hurricane-force winds cover nearly the entire planet is another unexplained mystery, especially given that the solid planet itself rotates at a very slow 4 mph (less than 2 meters per second) — much slower than Earth's rotation rate of about 1,000 mph (450 meters per second). The winds and clouds also blow to the west, not to the east as on the Earth. This is because the planet itself rotates to the west, backward compared to Earth and most of the other planets. As the clouds travel westward, they also typically progress toward the poles; this can be seen in the Mariner 10 view as a curved spiral pattern at mid latitudes. Near the equator, instead of long streaks, areas of more clumpy, discrete clouds can be seen, indicating enhanced upwelling and cloud formation in the equatorial region, spurred on by the enhanced power of sunlight there. This view is a false color composite created by combining images taken using orange and ultraviolet spectral filters on the spacecraft's imaging camera. These were used for the red and blue channels of the color image, respectively, with the green channel synthesized by combining the other two images. Flying past Venus en route to the first-ever flyby of Mercury, Mariner 10 became the first spacecraft to use a gravity assist to change its flight path in order to reach another planet. The images used to create this view were acquired by Mariner 10 on Feb. 7 and 8, 1974, a couple of days after the spacecraft's closest approach to Venus on Feb. 5. Despite their many differences, comparisons between Earth and Venus are valuable for helping to understand their distinct climate histories. Nearly 50 years after this view was obtained, many fundamental questions about Venus remain unanswered. Did Venus have oceans long ago? How has its atmosphere evolved over time, and when did its runaway greenhouse effect begin? How does Venus lose its heat? How volcanically and tectonically active has Venus been over the last billion years? This image was processed from archived Mariner 10 data by JPL engineer Kevin M. Gill. The Mariner 10 mission was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23791
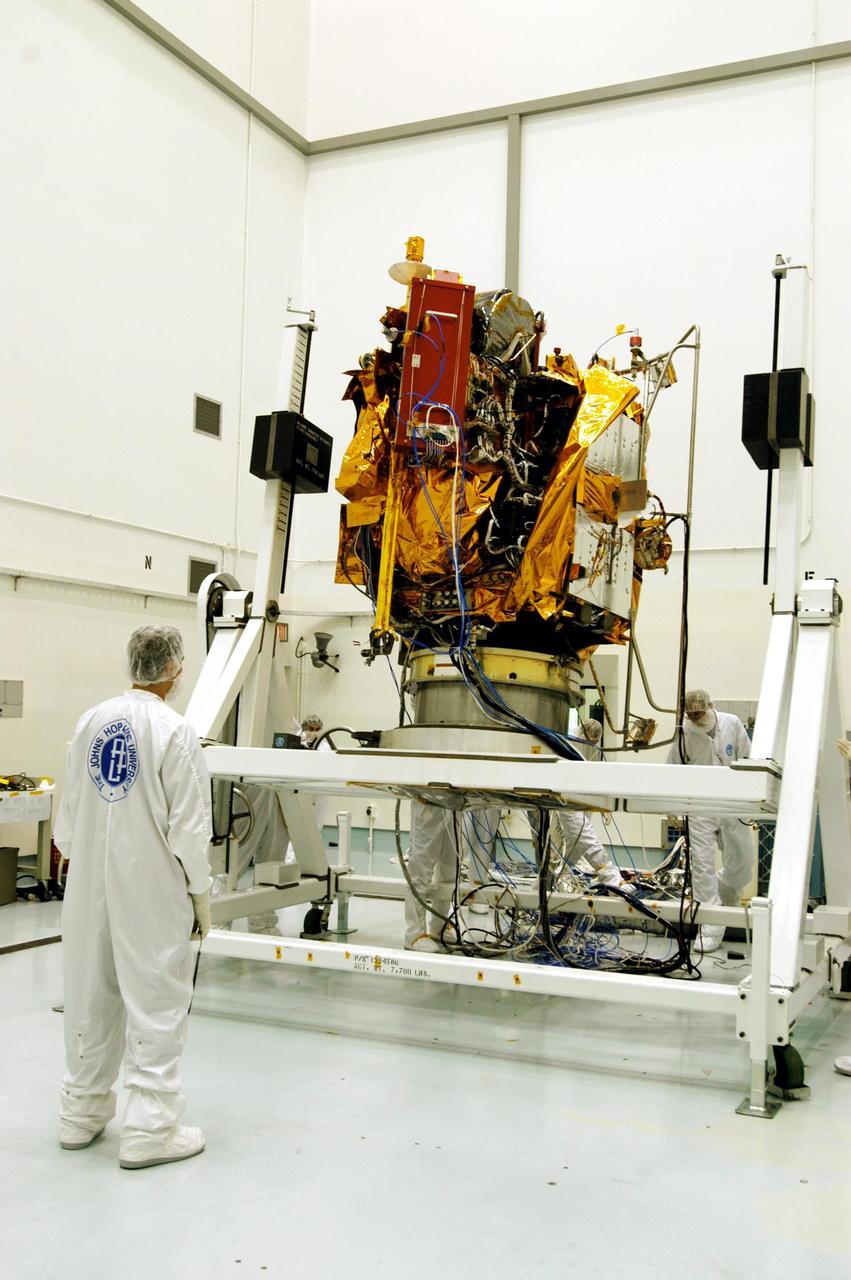

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers begin to rotate the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
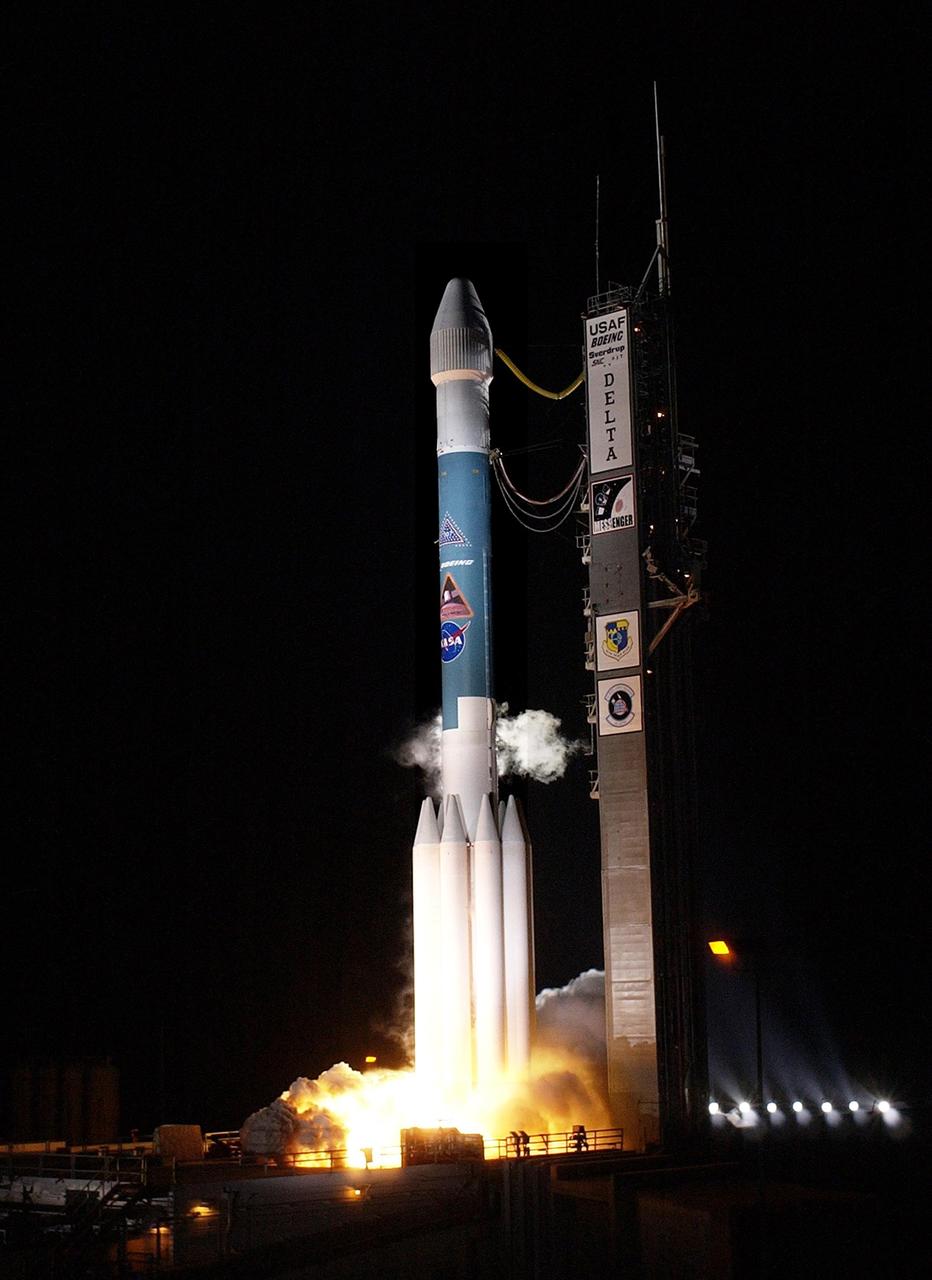

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER spacecraft atop a Boeing Delta II rocket lifts off on time at 2:15:56 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year, 4.9-billion-mile journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times, as well as circling the sun 15 times, to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
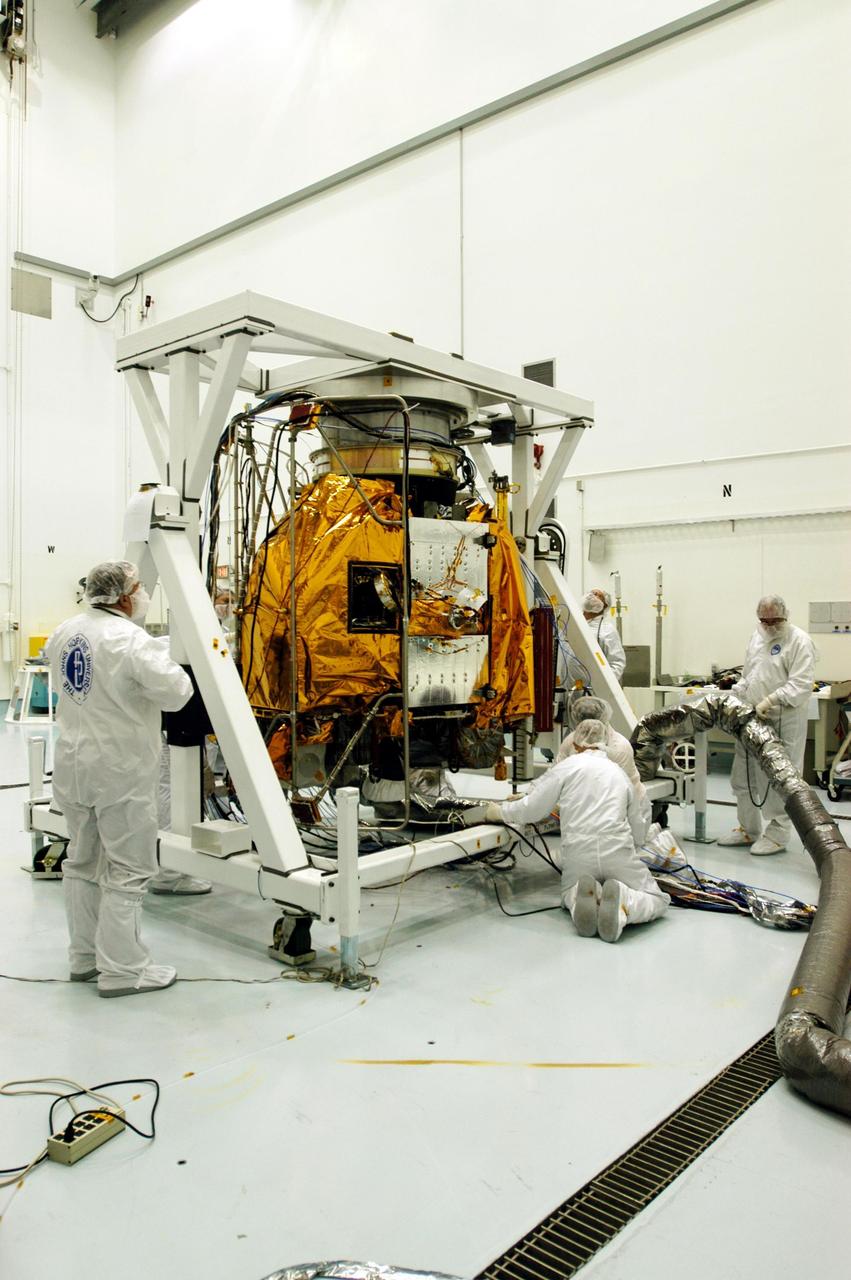

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers complete rotation of the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The tip of the Boeing Delta II rocket with its MESSENGER spacecraft on top breaks through the billows of smoke below as it lifts off on time at 2:15:56 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
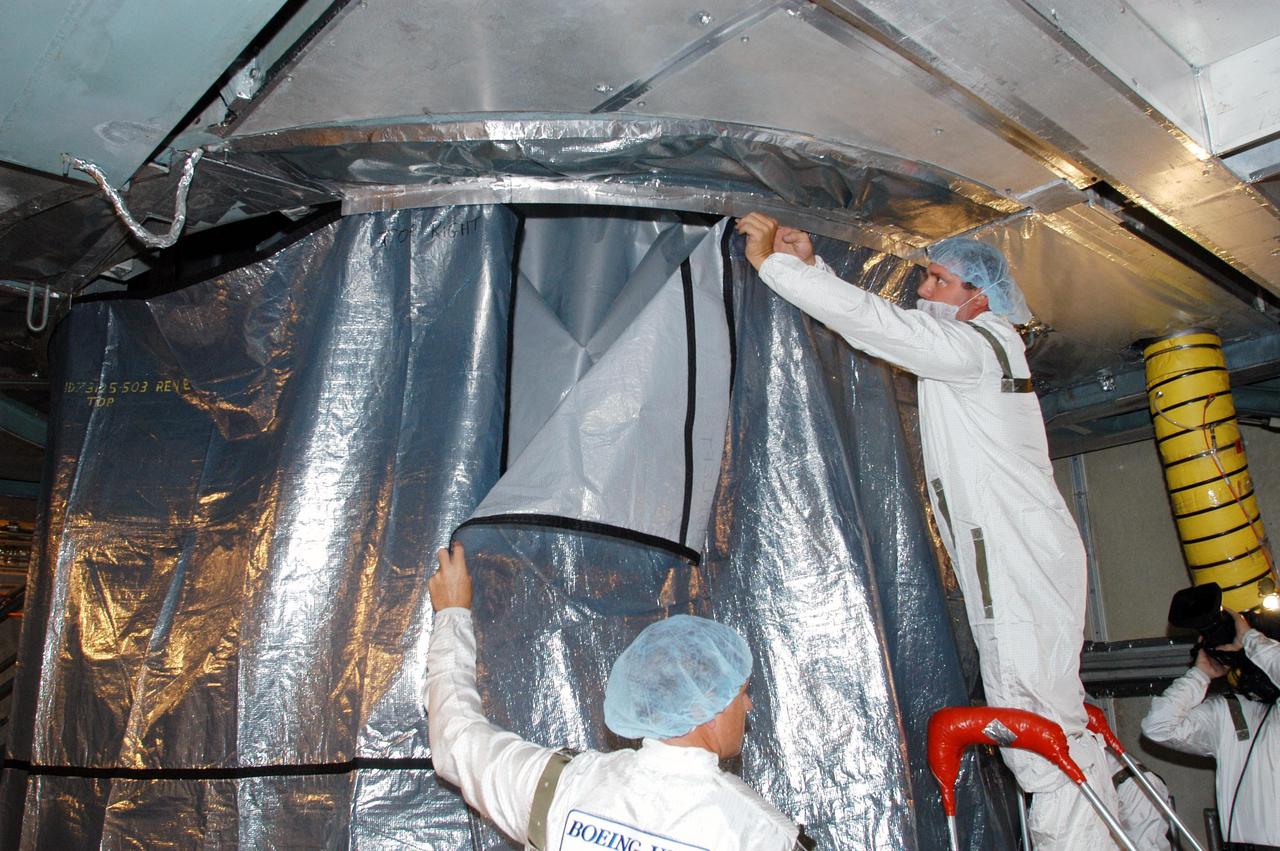

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers suspend an environmental curtain around the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft, which is still wrapped from its journey to the pad. Scheduled to launch Aug. 2, MESSENGER will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Processing is being done at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla.
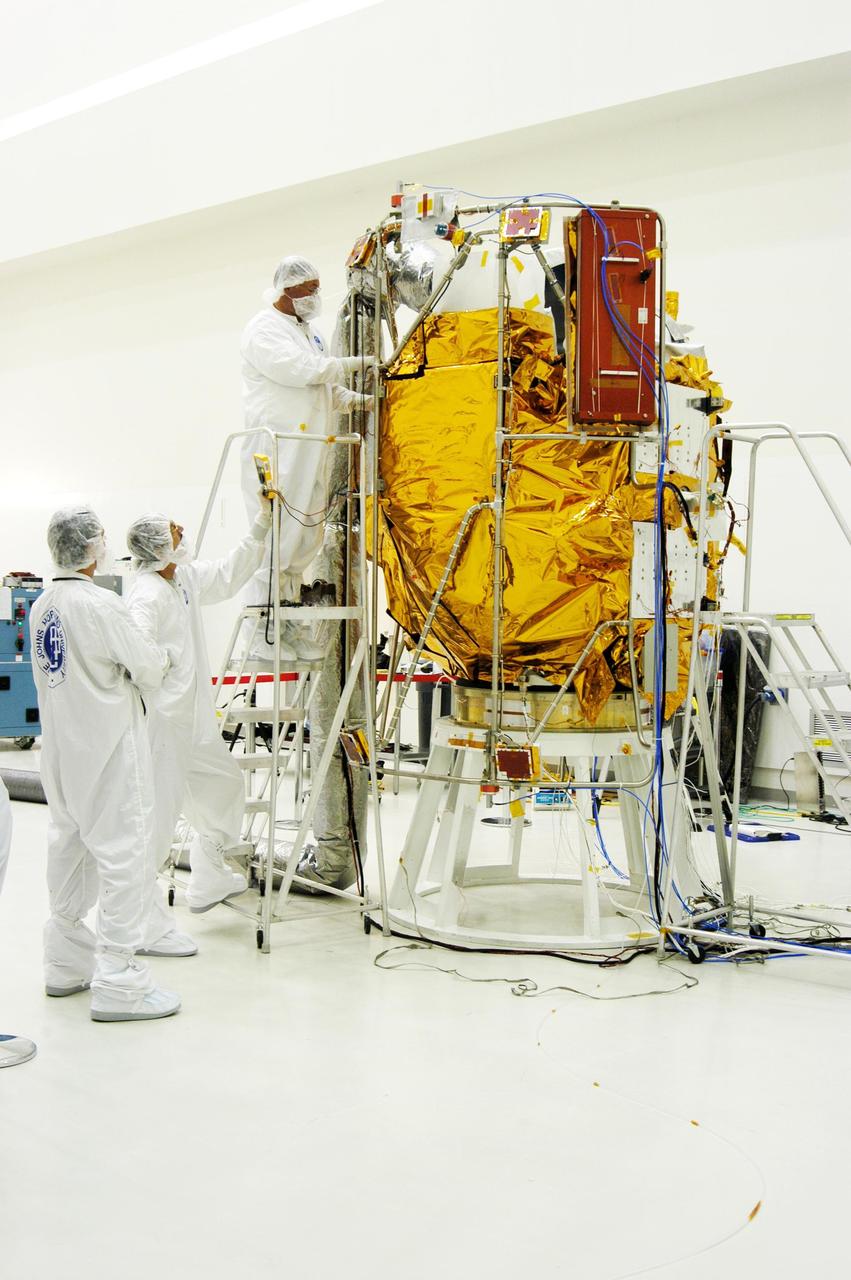

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., workers place insulating blankets around the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. Two solar arrays will be installed June 24-25, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
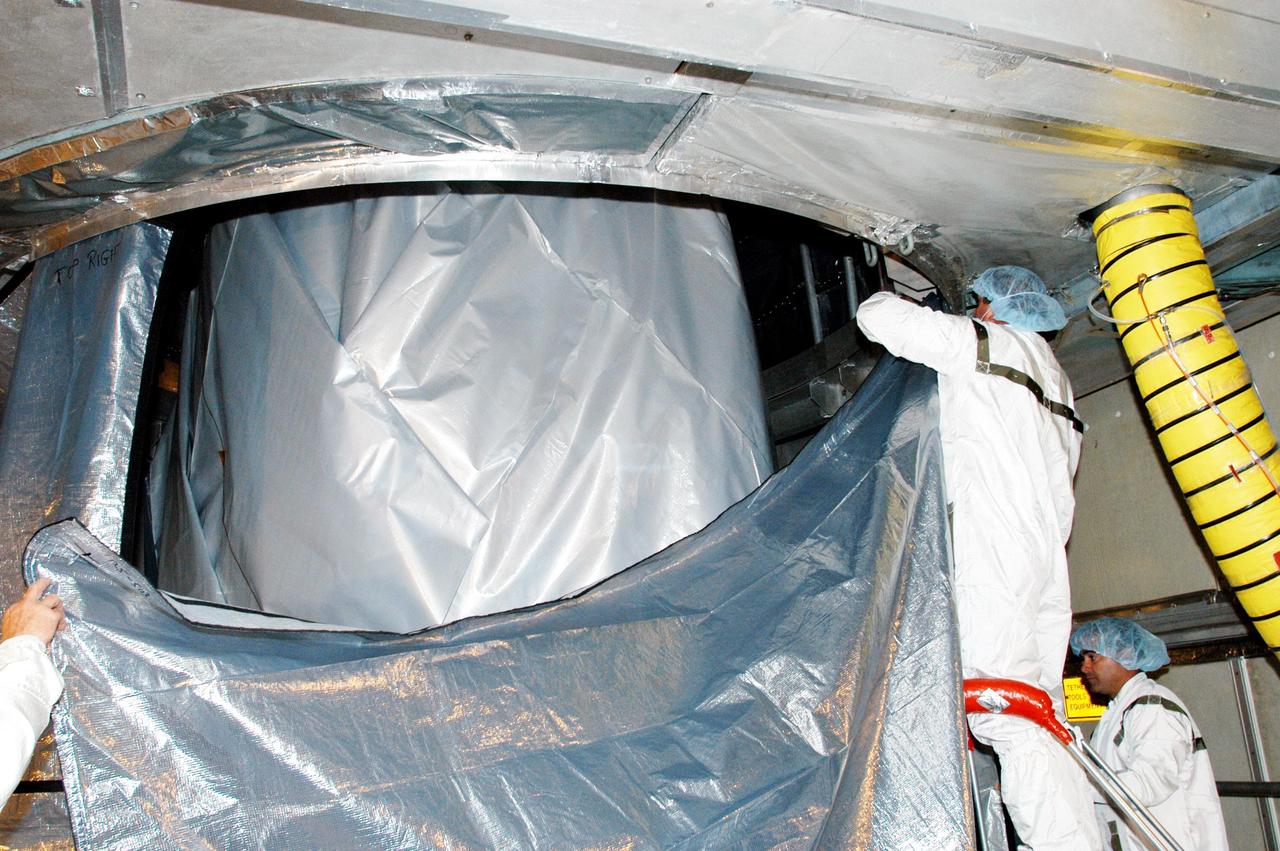

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers place an environmental curtain around the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft, which is still wrapped from its journey to the pad. Scheduled to launch Aug. 2, MESSENGER will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Processing is being done at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla.
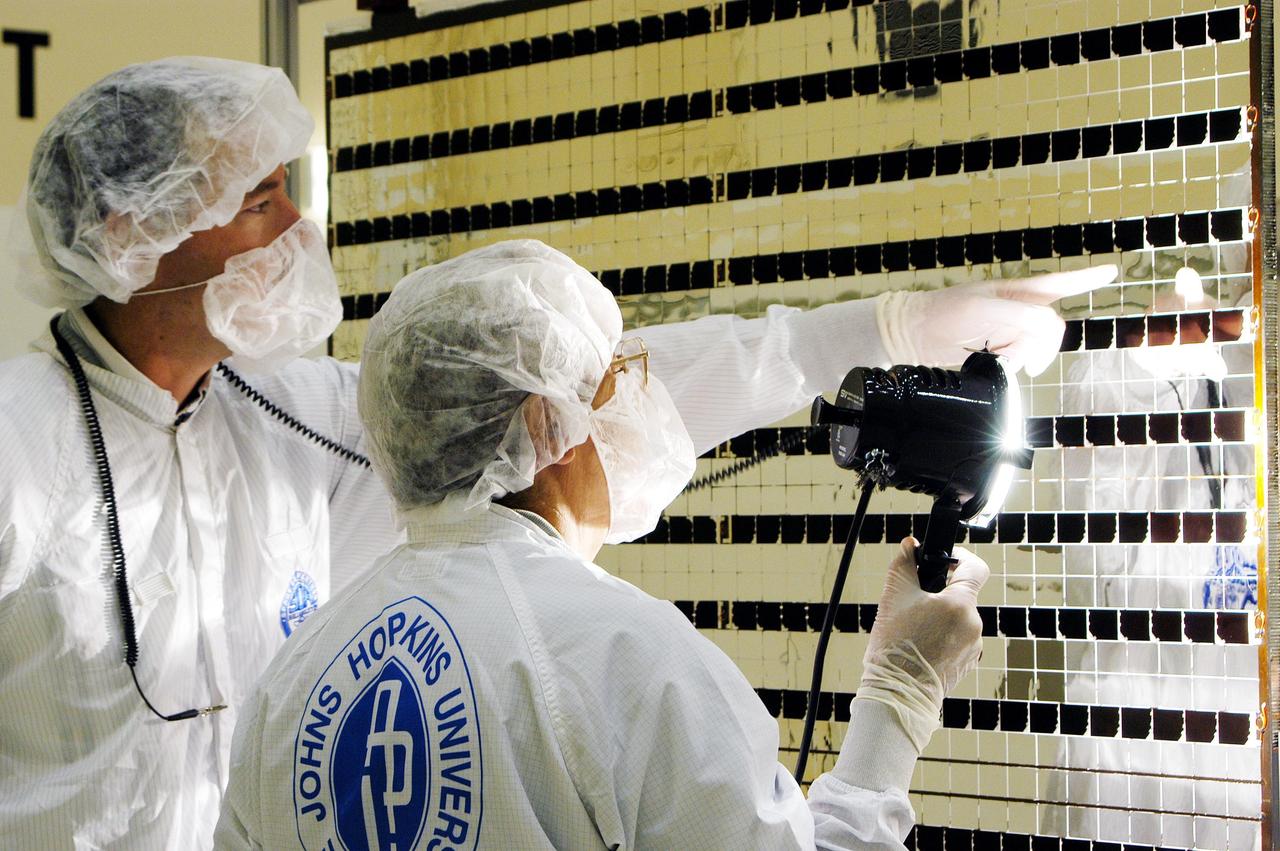

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft’s two solar arrays are undergoing cleaning inspections and voltage checks in preparation for installation on June 24 -25. One array will be installed each day, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., a worker adjusts an insulating blanket around the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. Two solar arrays will be installed June 24-25, followed by a deployment test. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
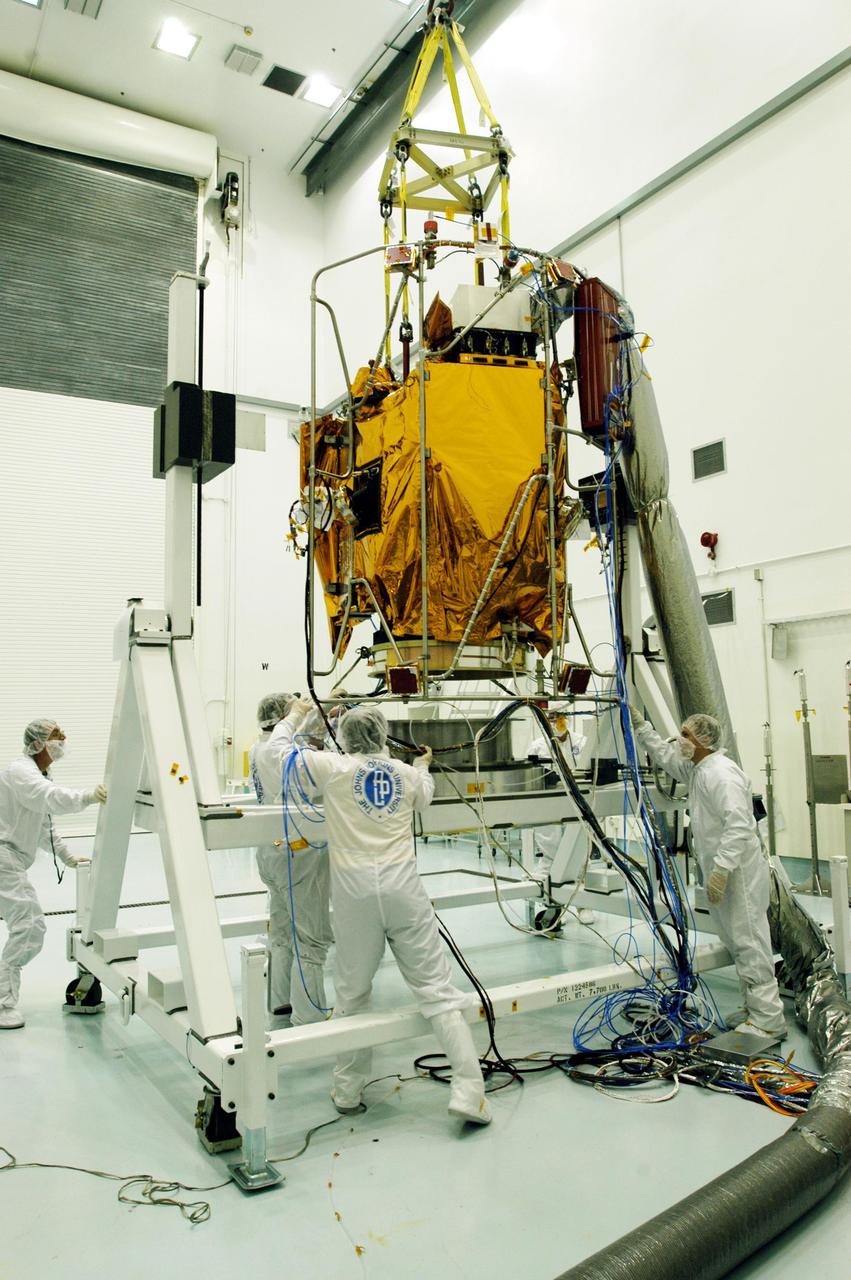

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers help while an overhead crane lowers the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft onto a turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
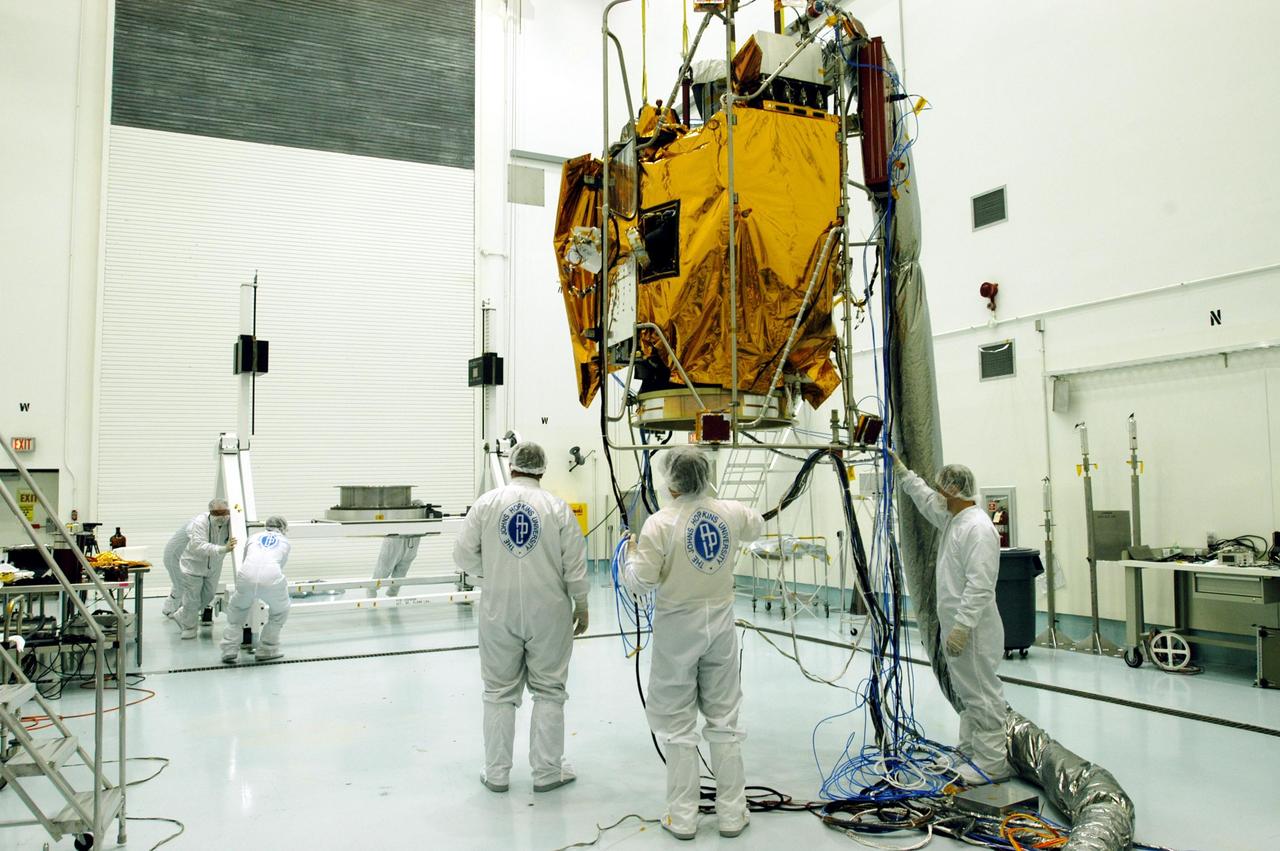

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers at left move a turnover fixture toward the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. The turnover fixture will rotate the spacecraft for prelaunch testing. MESSENGER is undergoing prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
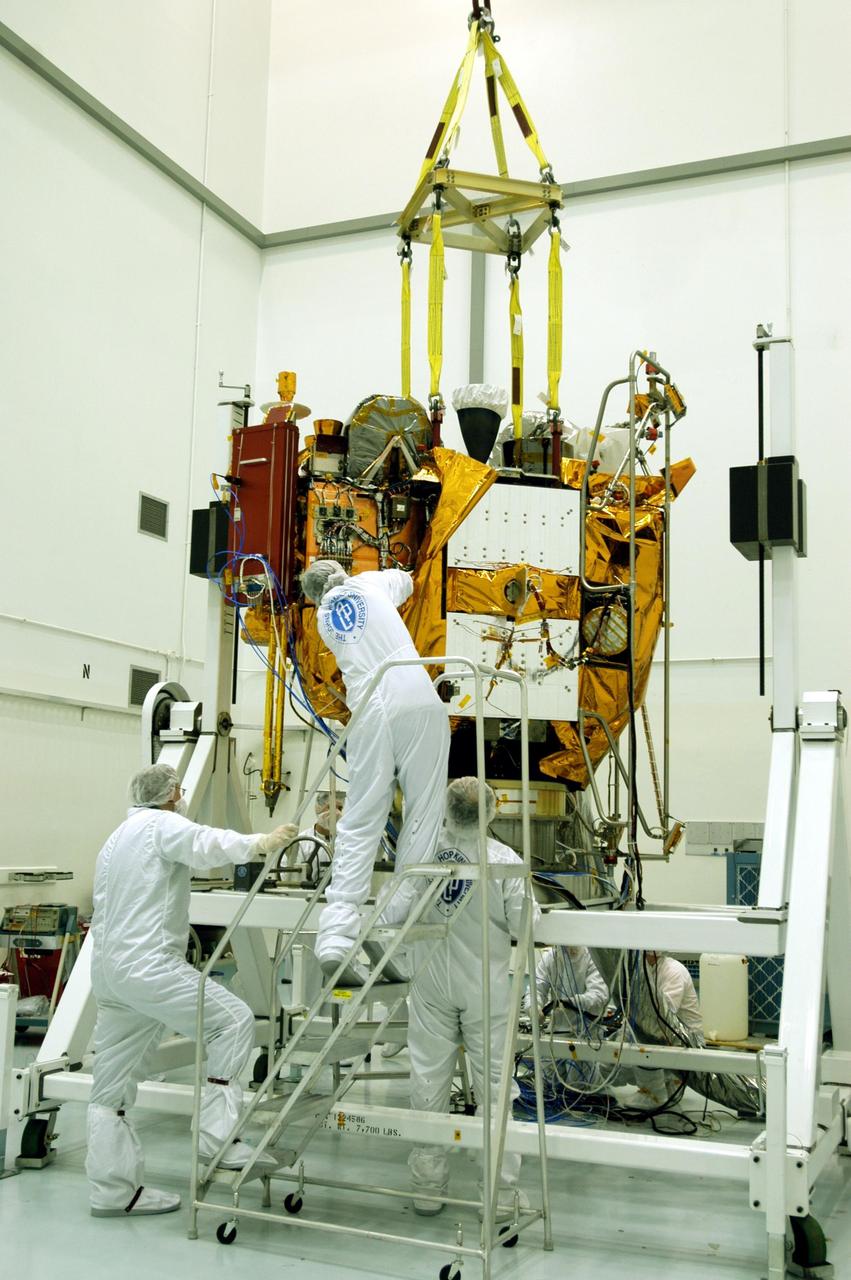

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers remove protective covers from the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft now resting on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft’s two solar arrays are undergoing cleaning inspections and voltage checks in preparation for installation on June 24 -25. One array will be installed each day, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004, from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., a worker adjusts an insulating blanket around the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. Two solar arrays will be installed June 24-25, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
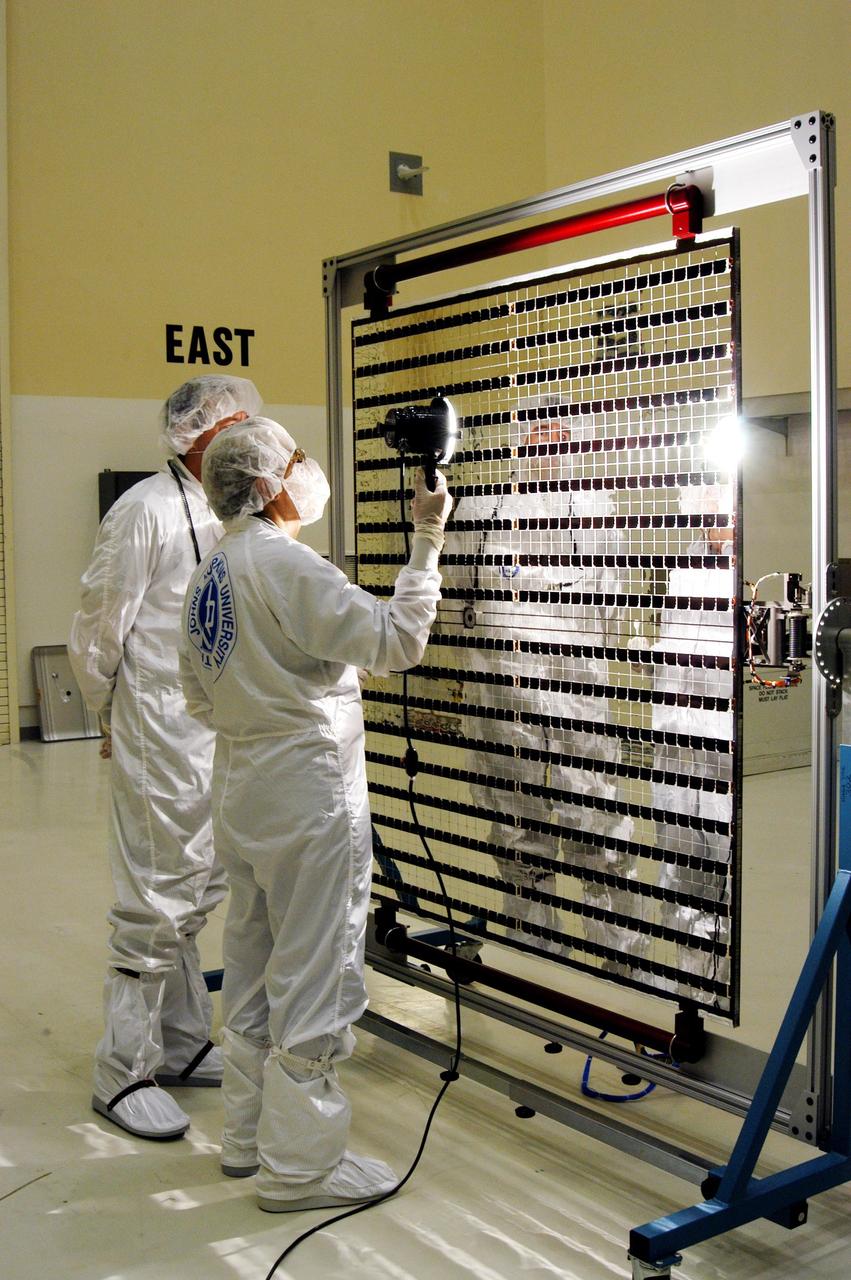

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft’s two solar arrays are undergoing cleaning inspections and voltage checks in preparation for installation on June 24 -25. One array will be installed each day, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
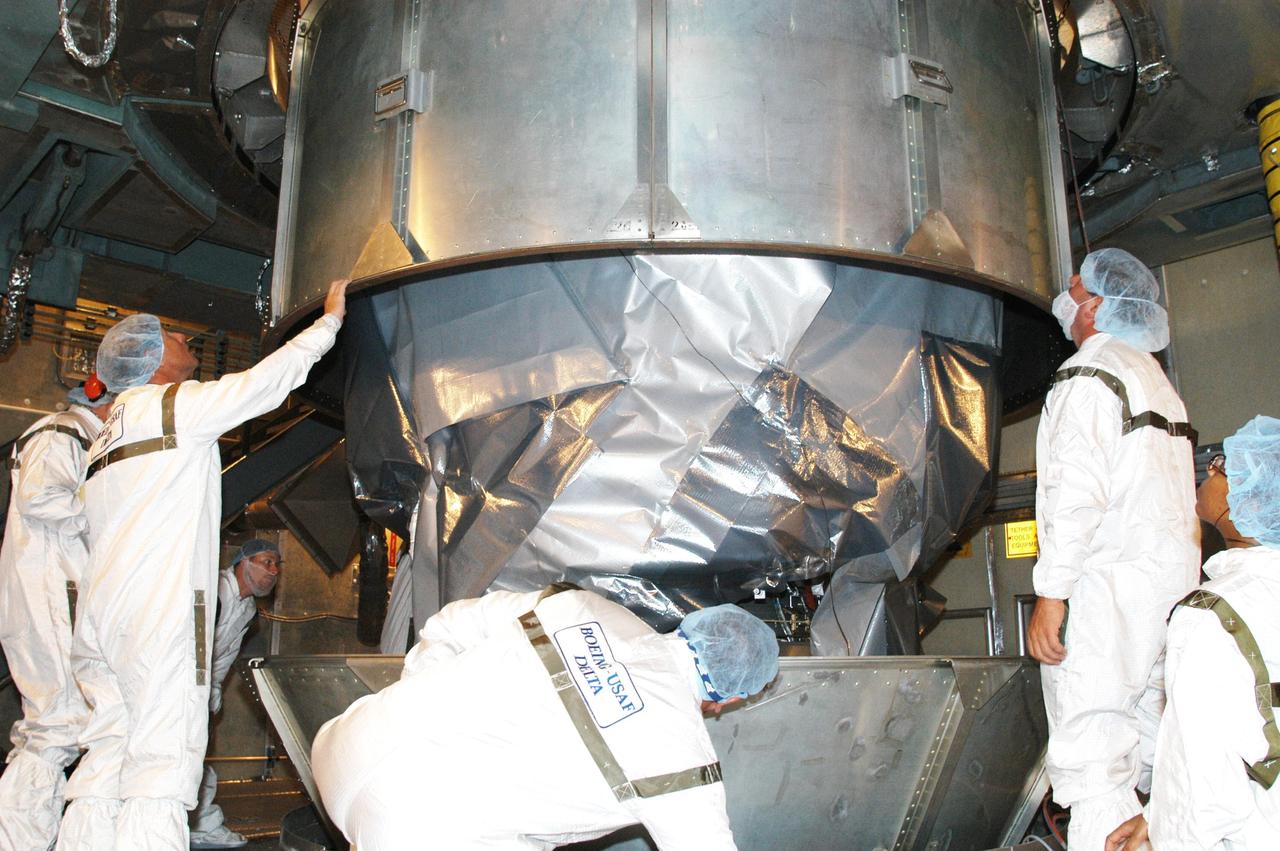

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers oversee removal of the canister from around the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft. Scheduled to launch Aug. 2, MESSENGER will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Processing is being done at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla.
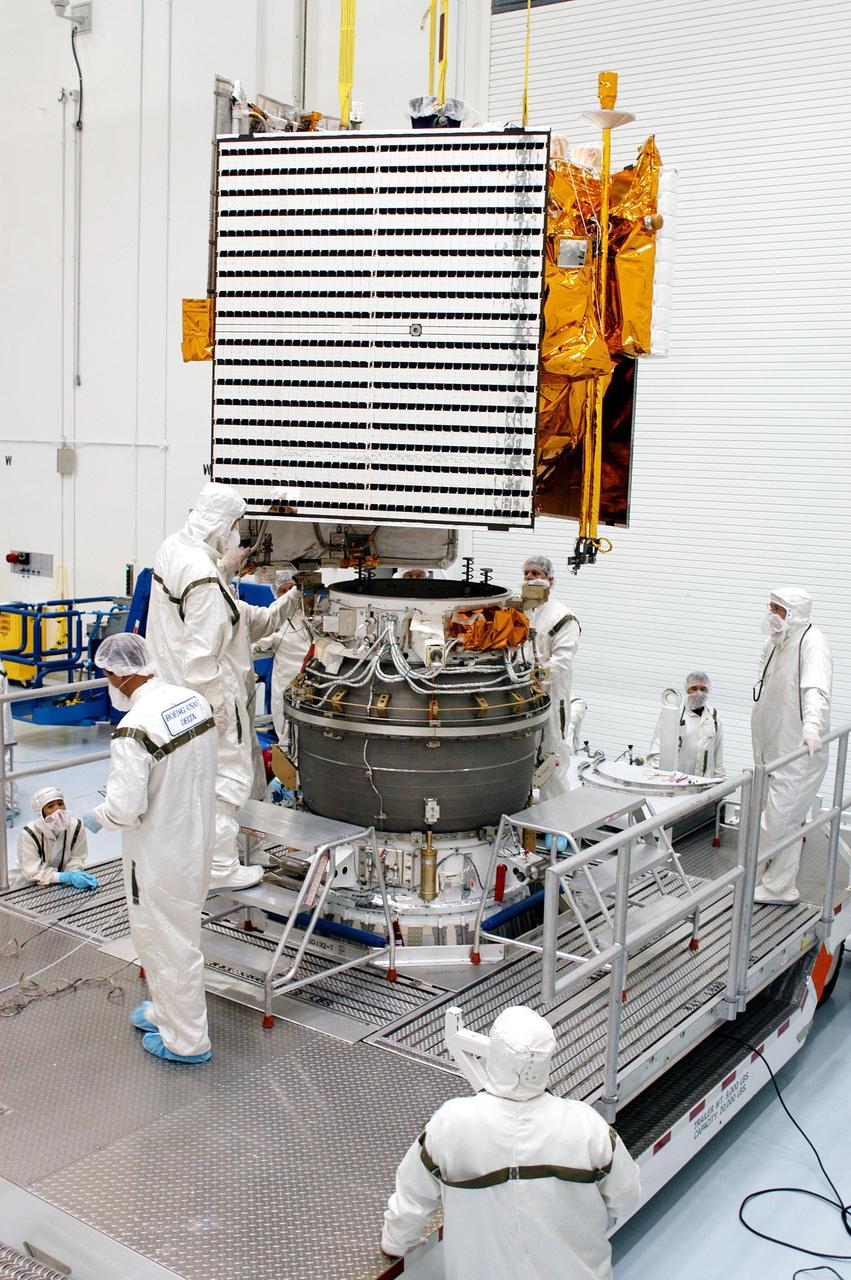

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., oversee the mating of the MESSENGER spacecraft with the Payload Assist Module, the Boeing Delta II third stage, below it. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
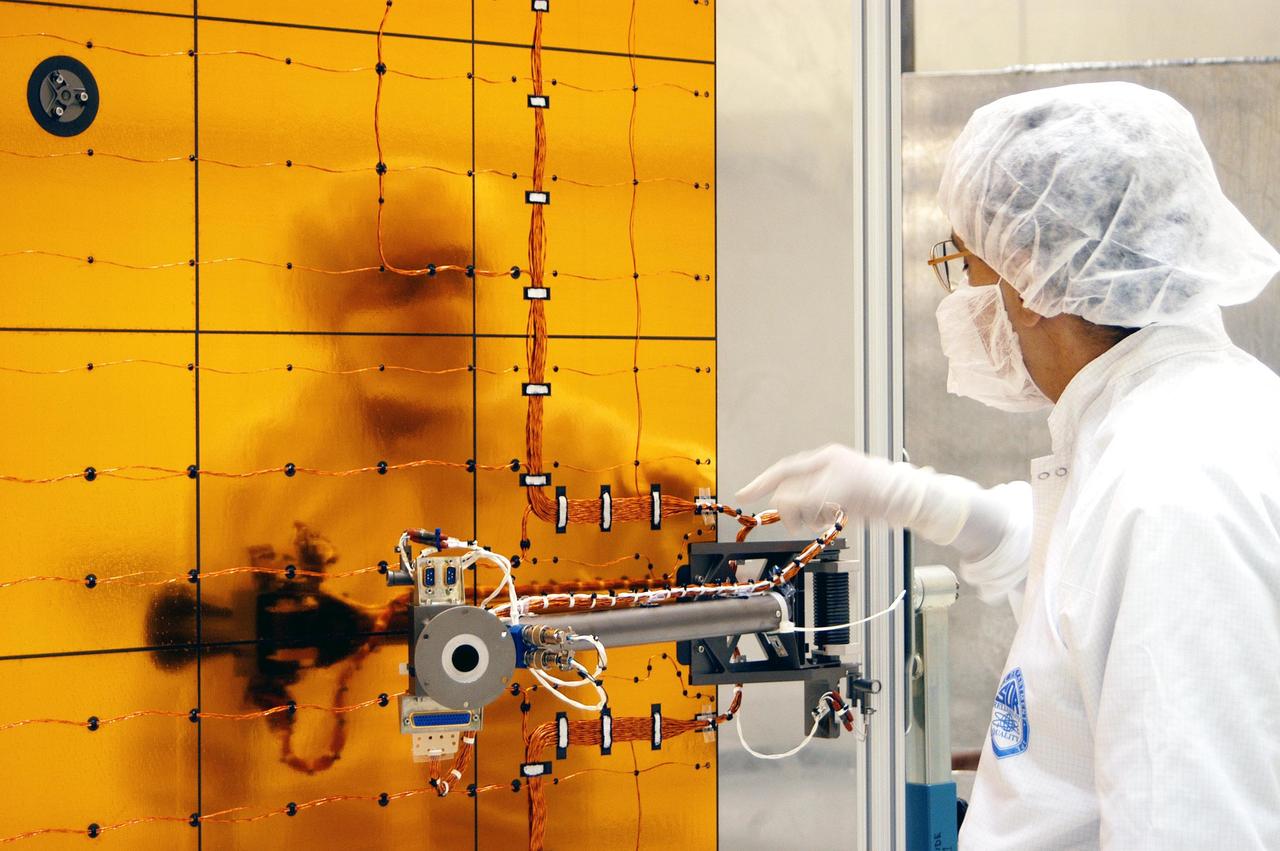
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., a worker checks wiring on the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. Two solar arrays will be installed June 24-25, followed by a deployment testLaunch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
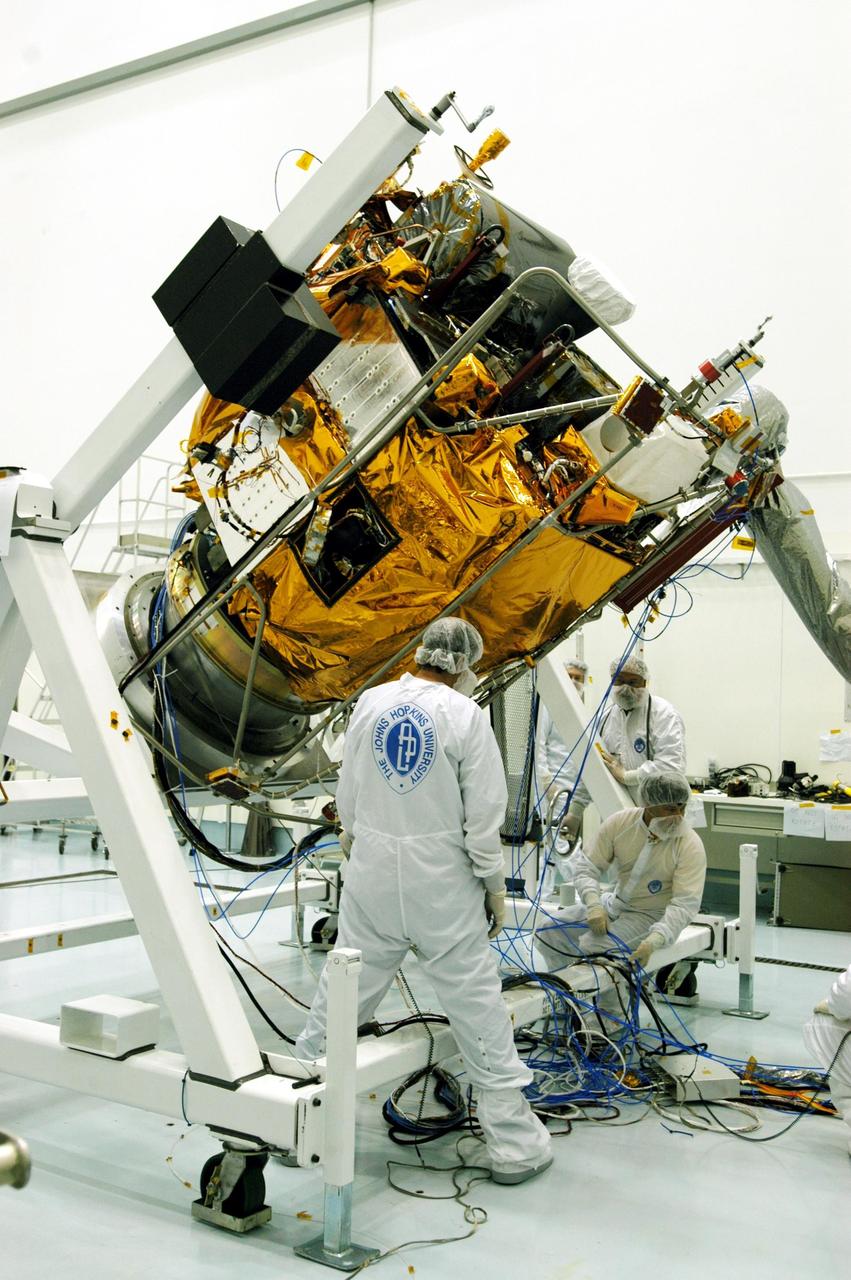

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers begin to rotate the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
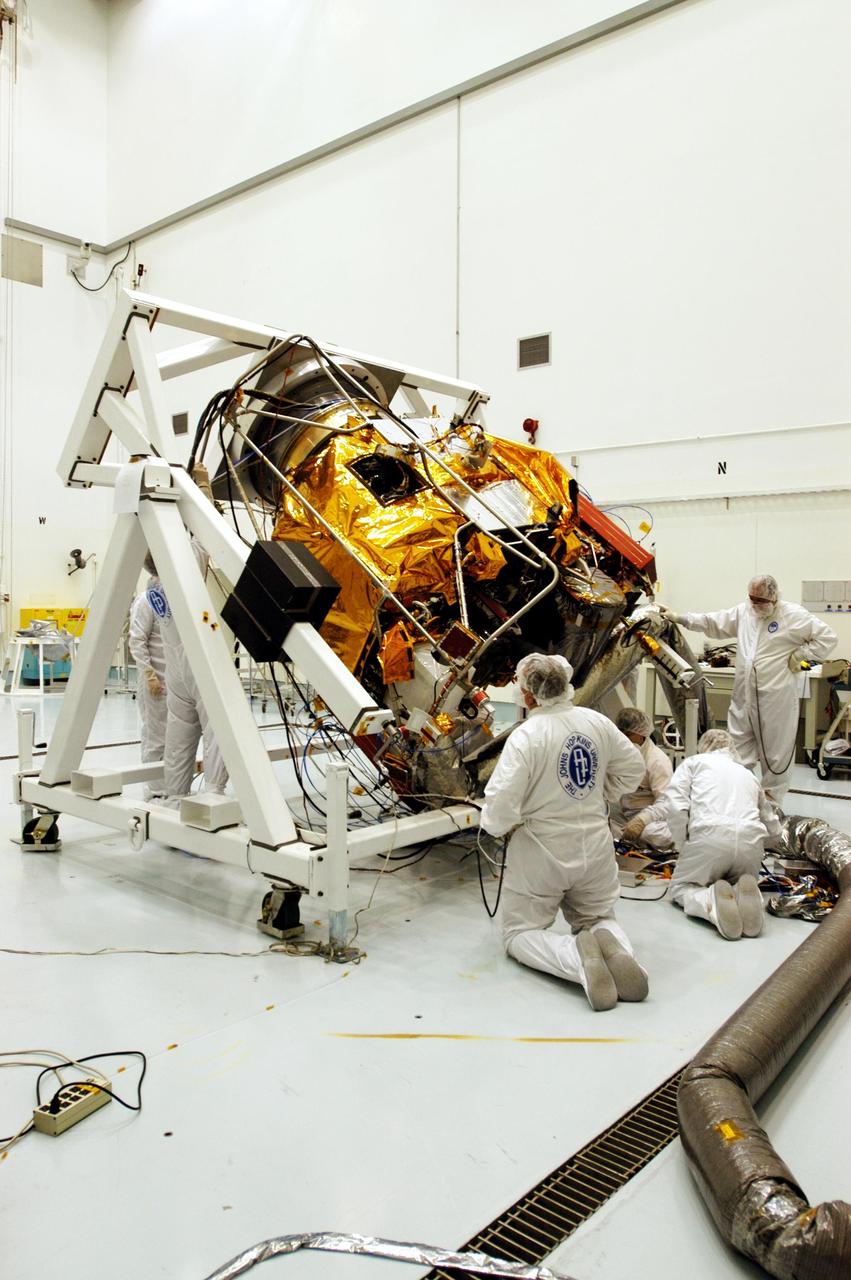

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers again rotate the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
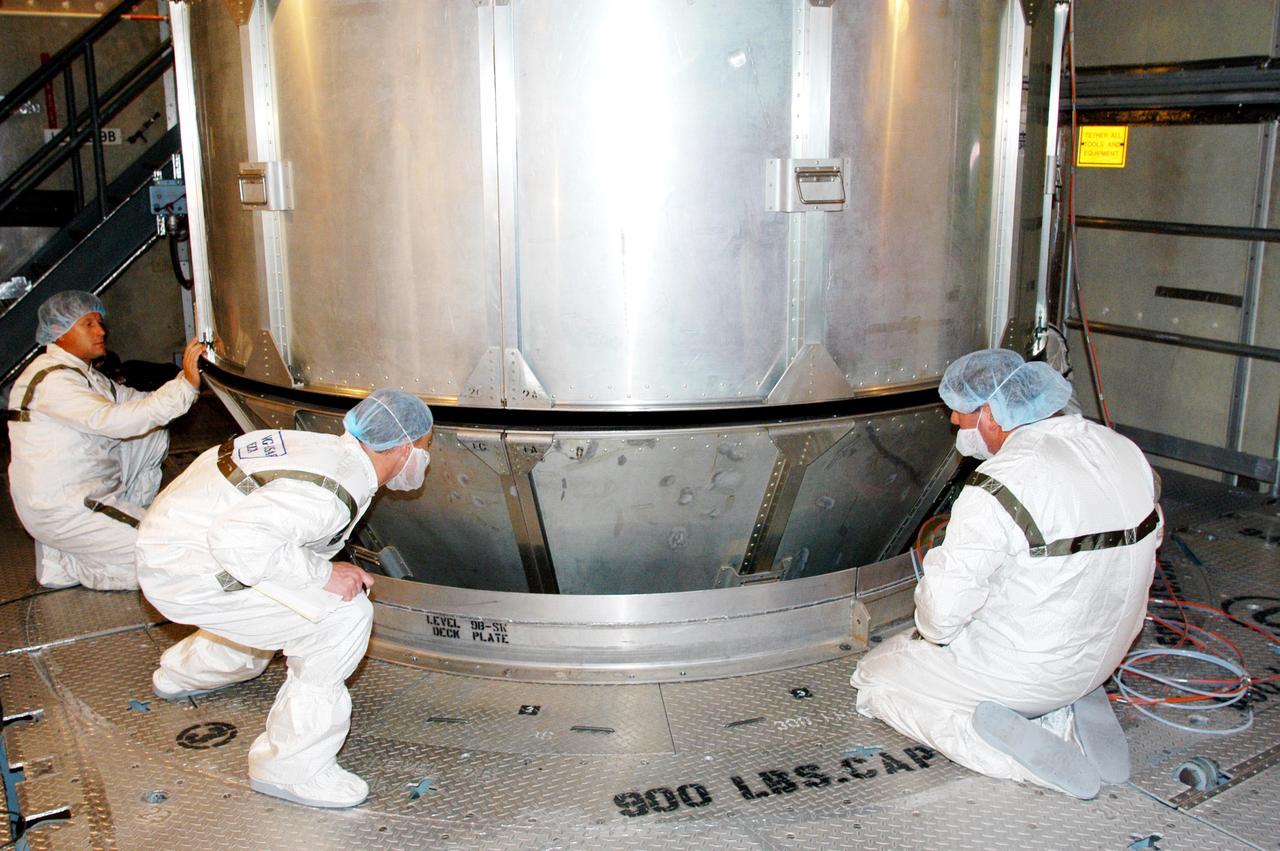

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers watch closely as the upper canister around the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft is detached from the lower panels. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Processing is being done at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla.
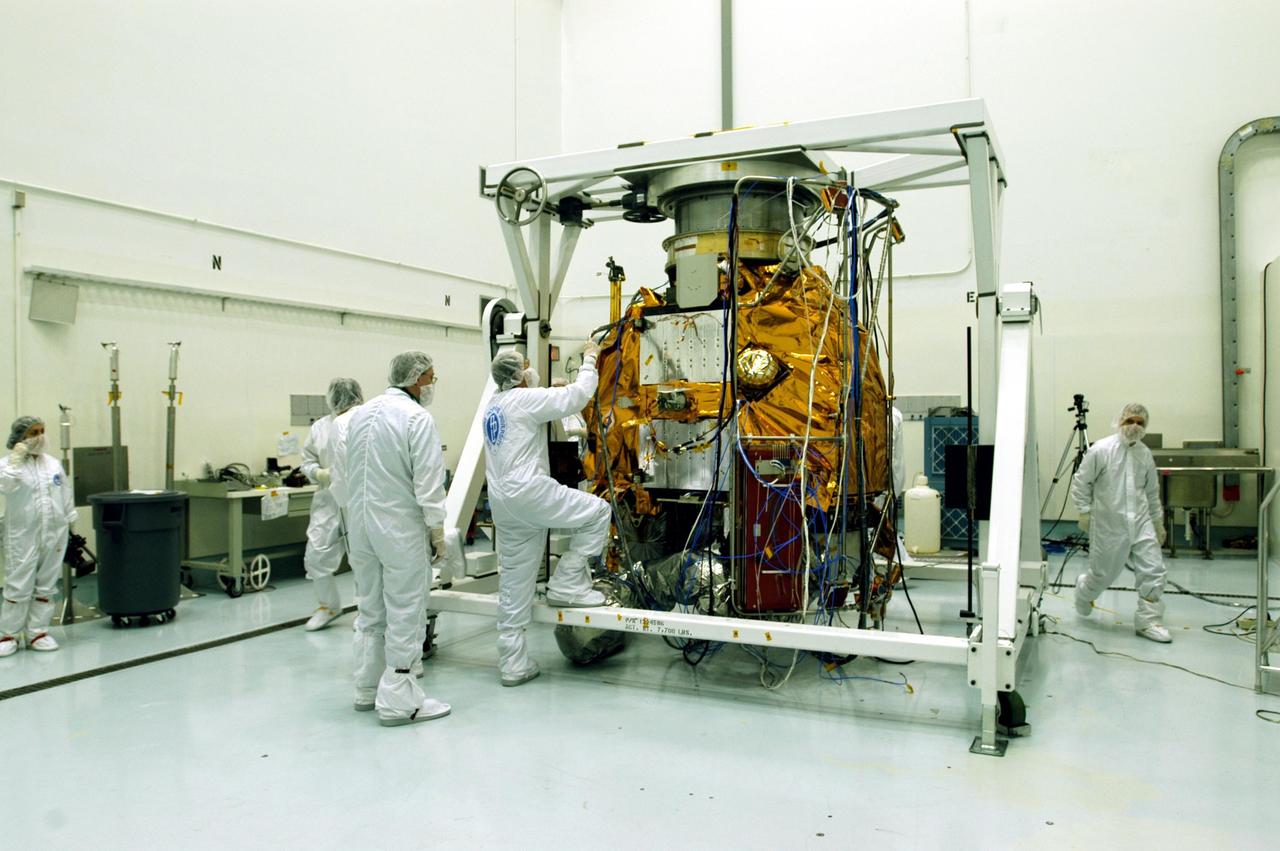

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers check the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft after completing rotation on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
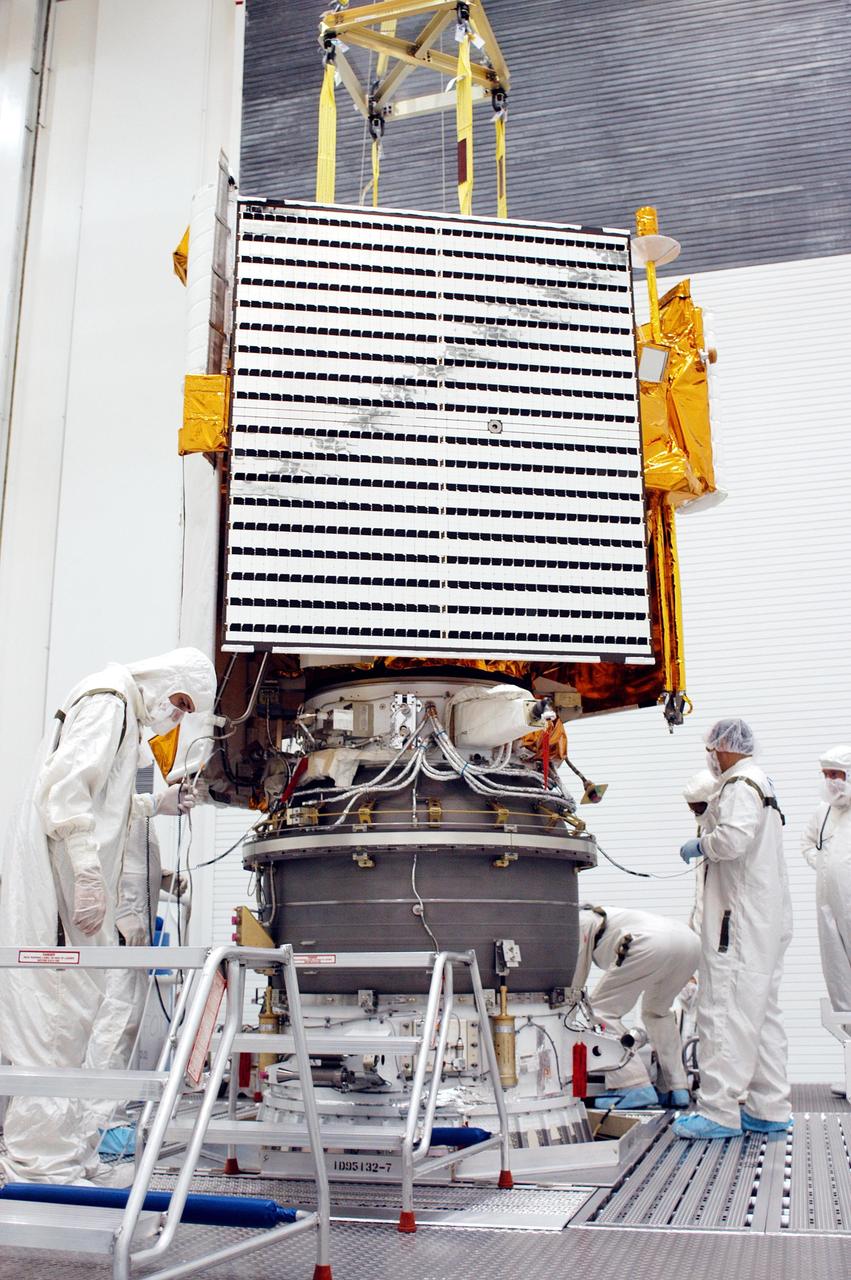
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., complete the mating of the MESSENGER spacecraft with the Payload Assist Module, the Boeing Delta II third stage, below it. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
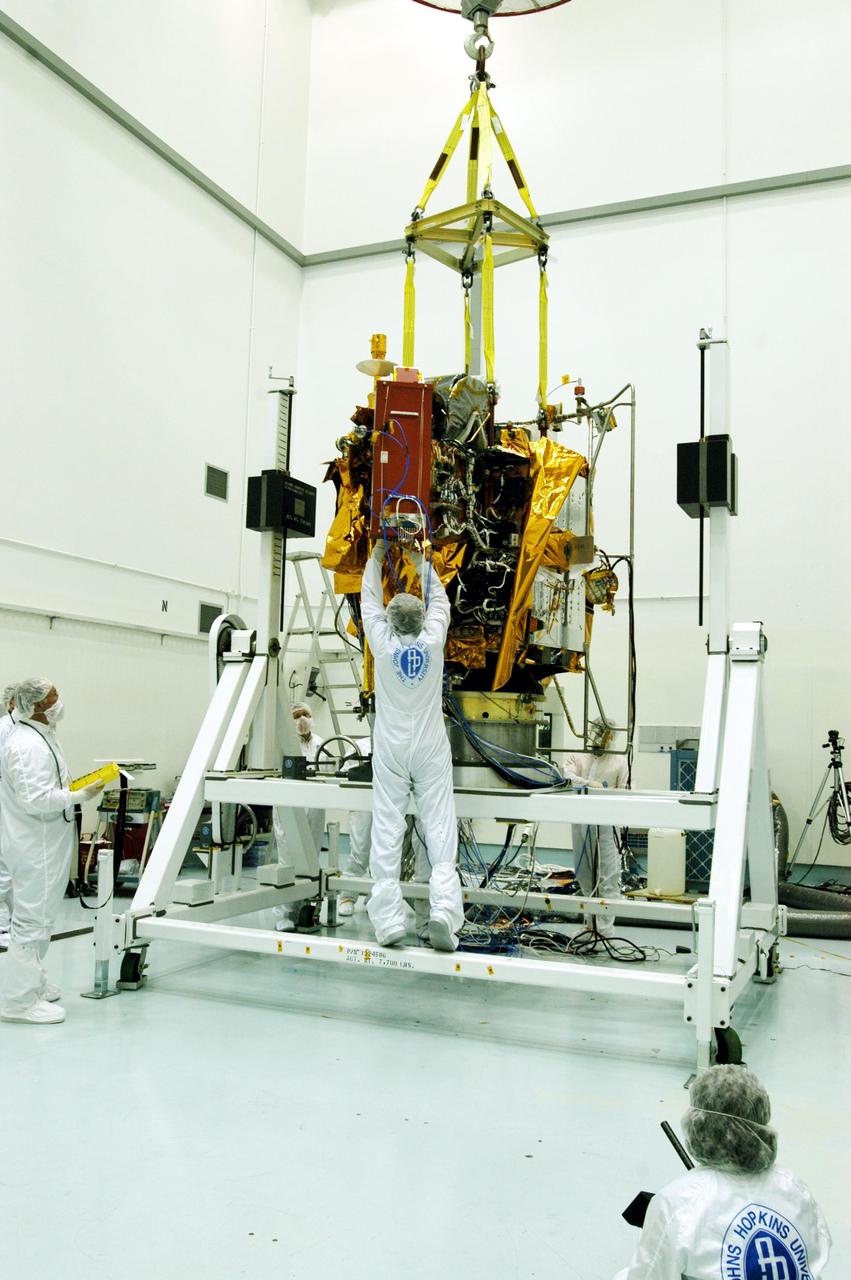

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers make adjustments to the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft now resting on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
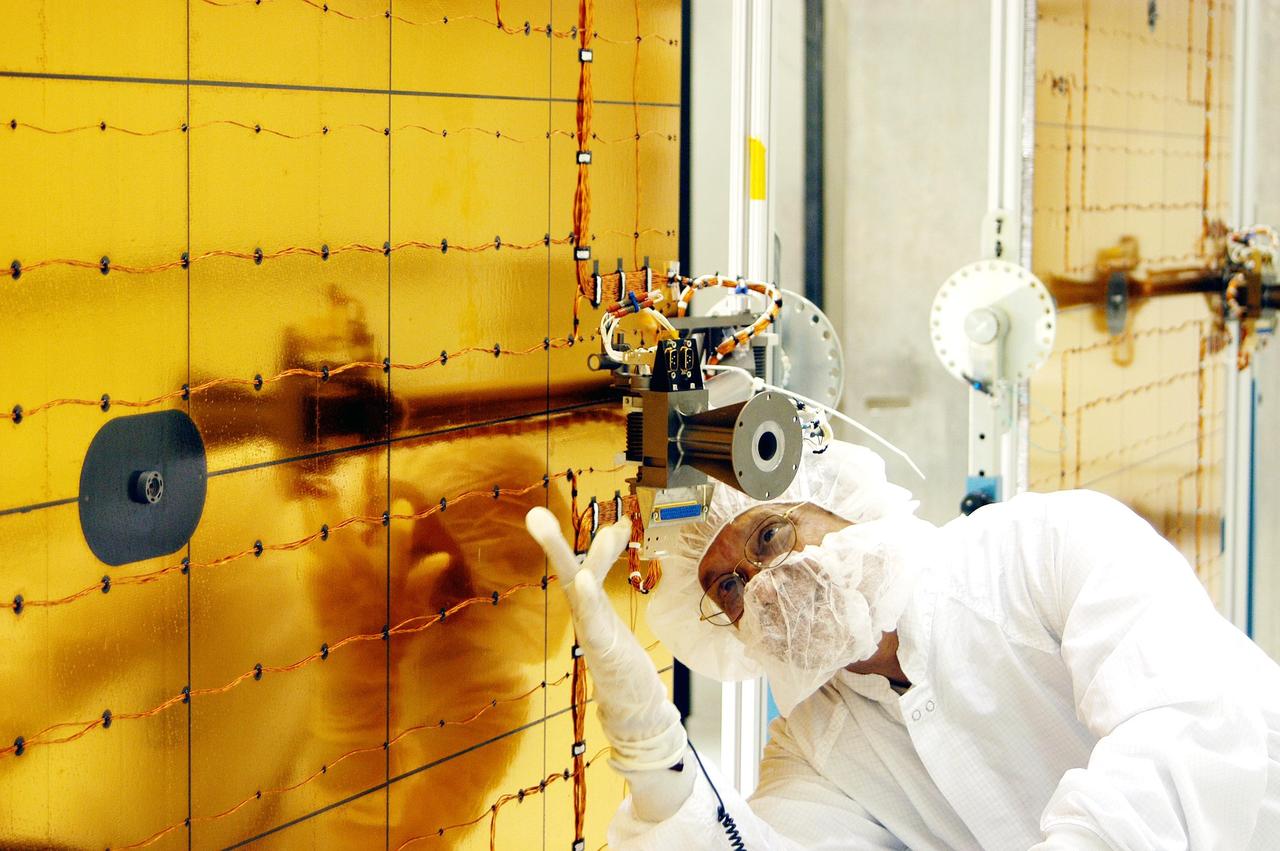

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., a worker checks wiring on the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft. Two solar arrays will be installed June 24-25, followed by a deployment test. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers adjust wires on the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft during rotation on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft’s two solar arrays are undergoing cleaning inspections and voltage checks in preparation for installation on June 24 -25. One array will be installed each day, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
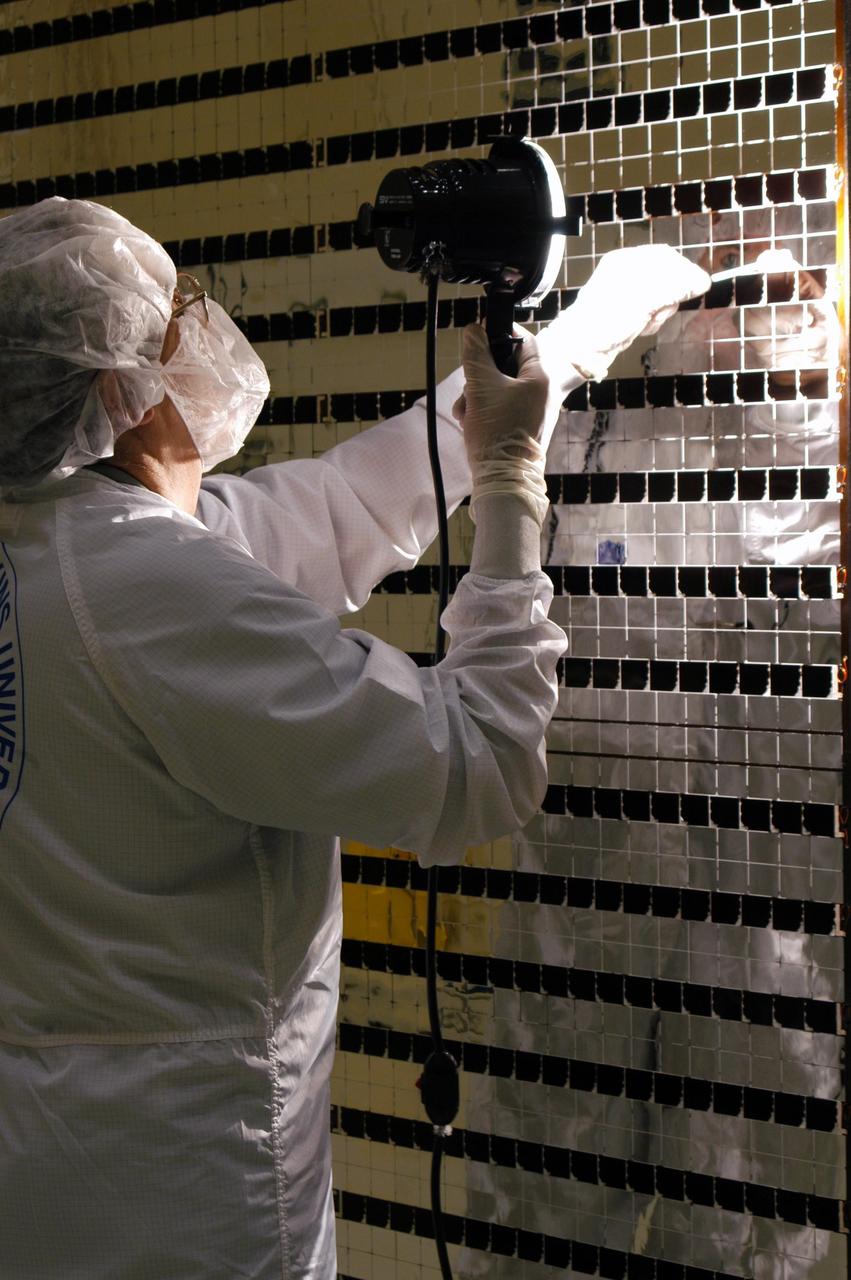

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft’s two solar arrays are undergoing cleaning inspections and voltage checks in preparation for installation on June 24 -25. One array will be installed each day, followed by a deployment test. The spacecraft will fly past Earth once, Venus twice and Mercury three times before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in March 2011. Launch is scheduled for July 30, 2004 from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
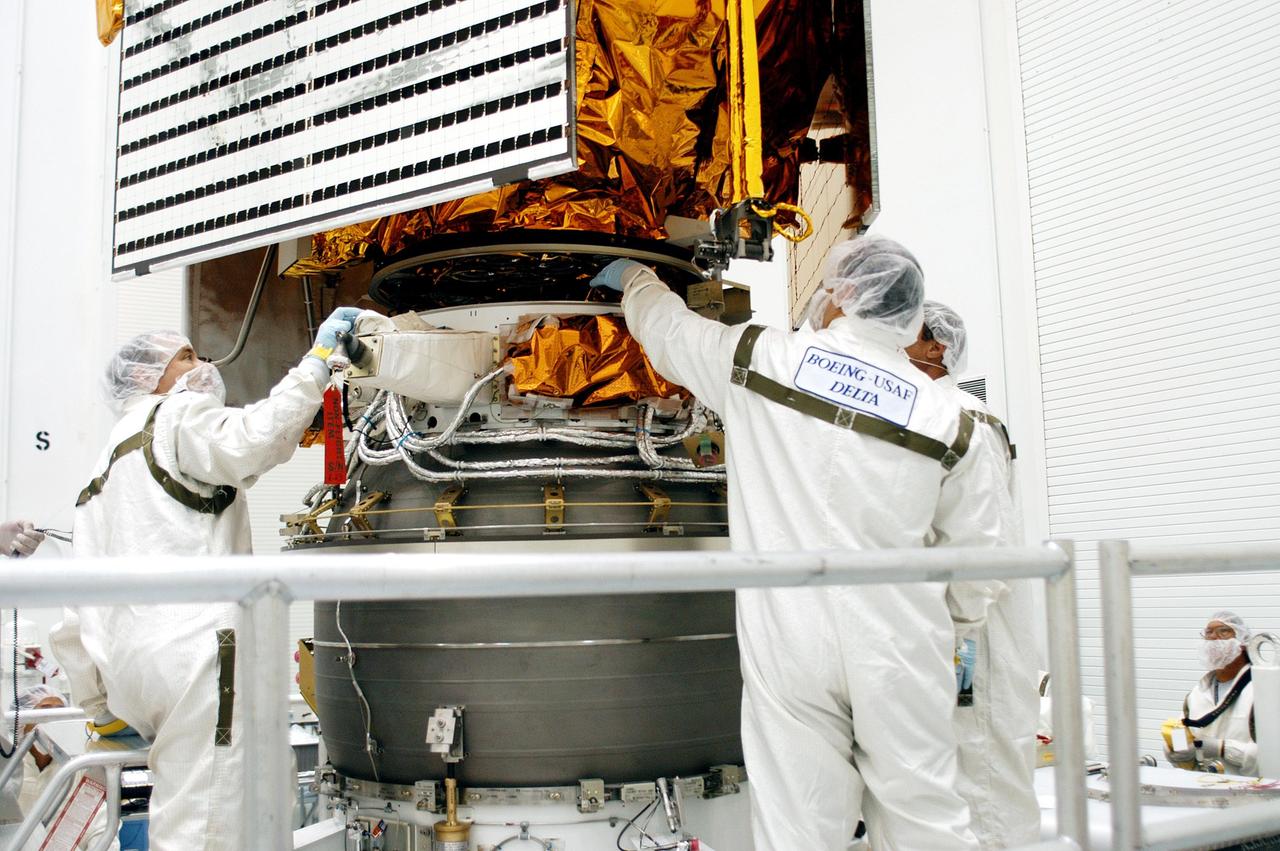

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., watch closely as the MESSENGER spacecraft is lowered toward the Payload Assist Module, the Boeing Delta II third stage, below for mating. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. It is expected to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
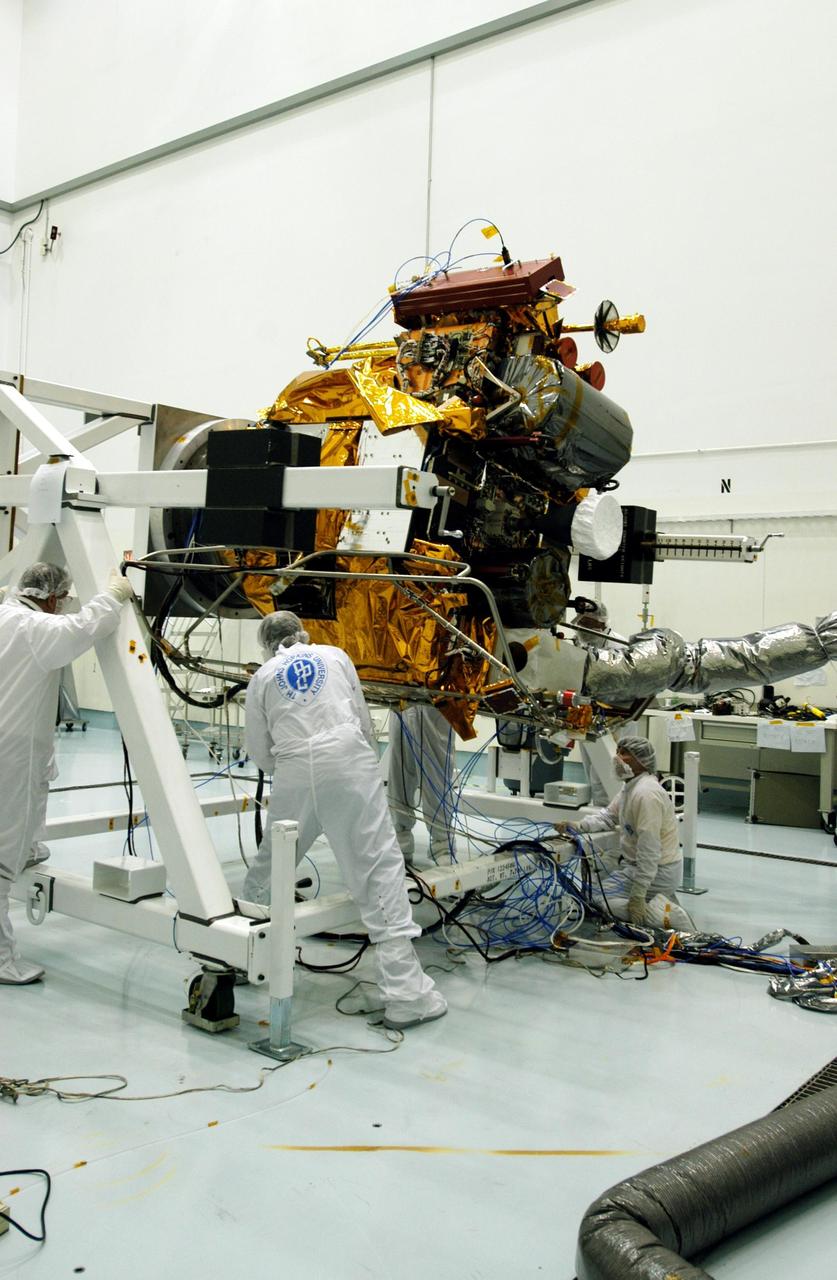

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- - Astrotech Space Operations facilities near KSC, workers check the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft as it rotates on the turnover fixture. Workers will perform the propulsion system phasing test - firing gas through the thrusters in order to verify that the right thrusters fire when expected - as part of prelaunch testing at the site. Launch is scheduled for May 11 from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will fly past Venus three times and Mercury twice before starting a year-long orbital study of Mercury in July 2009.
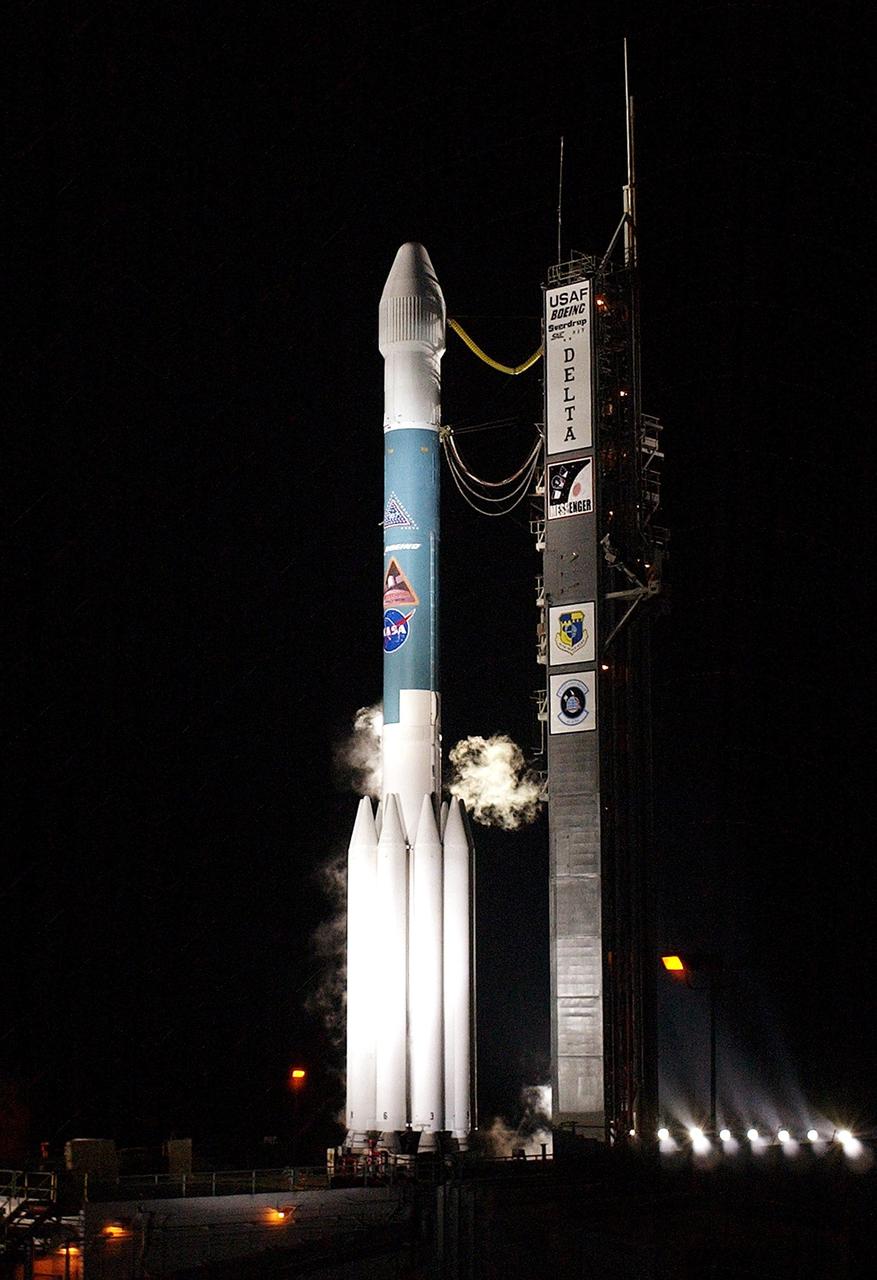

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Against the clear, black sky, spotlights flood the MESSENGER spacecraft aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket as it sits ready for liftoff, scheduled for 2:15:56 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
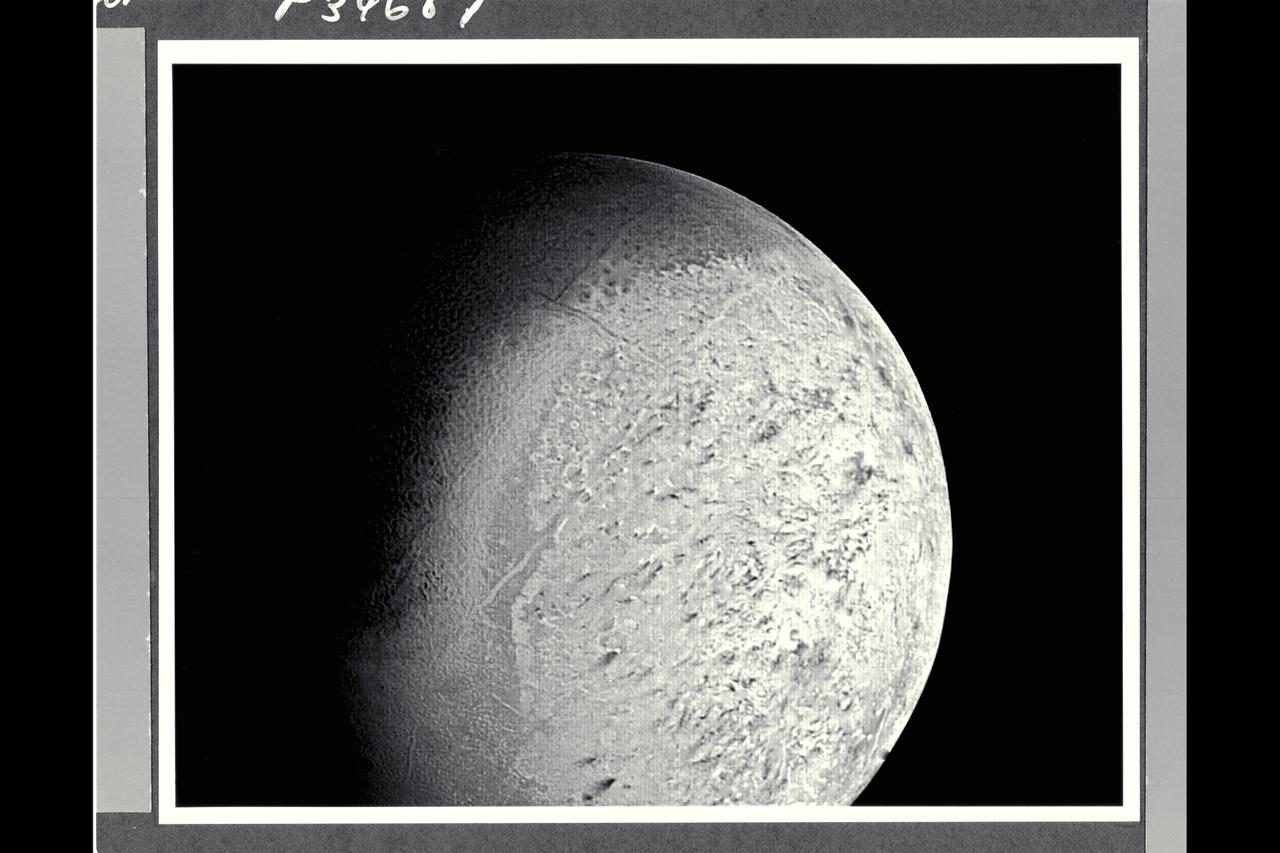
P-34687 Range : 530,000 km. ( 330,000 miles ) Smallest Resolvable Feature : 10 km or 6 miles This Voyager 2 image of Neptune's satellite Triton shows the first photo of Triton to reveal surface topography. The south pole, continuously illuminated by sunlight at this season, ia at bottom left. the boundary between bright southern hemisphere and the darker and the darker, northern hemisphere is clearly visible. Both the darker regions to the north and the very bright sub-equatorial band show a complex pattern of irregular topography that somewhat resembles 'fretted terrain' on parts of Venus and Mars. The pattern of dark and light regions over most of the southern hemisphere will require higher resolution images for interpretation. Also evident are long, straight lines that appear to be surface expressions of internal, tectonic processes. No large impact ctaters are visible, suggesting that the crust of Triton has been renewed relatively recently, that is, within the last bllion years or less.
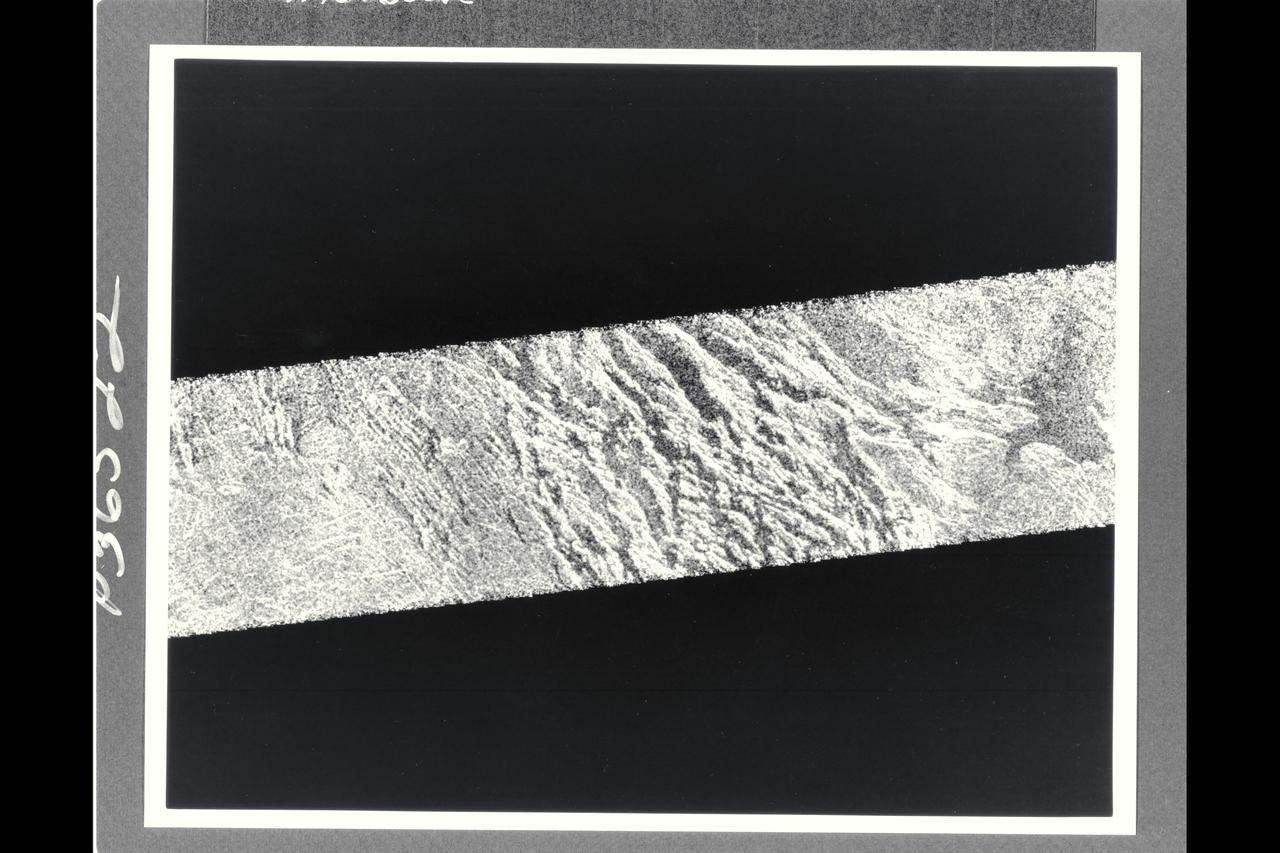

This portion of a Magellan radar image strip shows a small region on Venus 20 km (12.4 mi.) wide and 75 km (50 mi.) long on the east flank of a major volcanic upland called Beta Regio. The image is centerd at 23 degrees north latitude and 286.7 degrees east longitude. The ridge and valley networkin the middle part of the image is formed by intersection faults which have broken the Venusian crust into a clomplex, deformed type of surface called tessera, the Latin word for tile. The parallel mountains and valleys resemble the Basin and Range Province in the western United States. The irregular dark patch near the top of the image is a smooth surface, probably formed by lava flows in a region about 10 km (6 mi.) across. Similar dark surfaces within the valleys indicate lava flows that are younger than the tessera giving an indication of the geologic time relationships of the events that formed the present surface. The image has a resolution of 120 meters (400 feet).
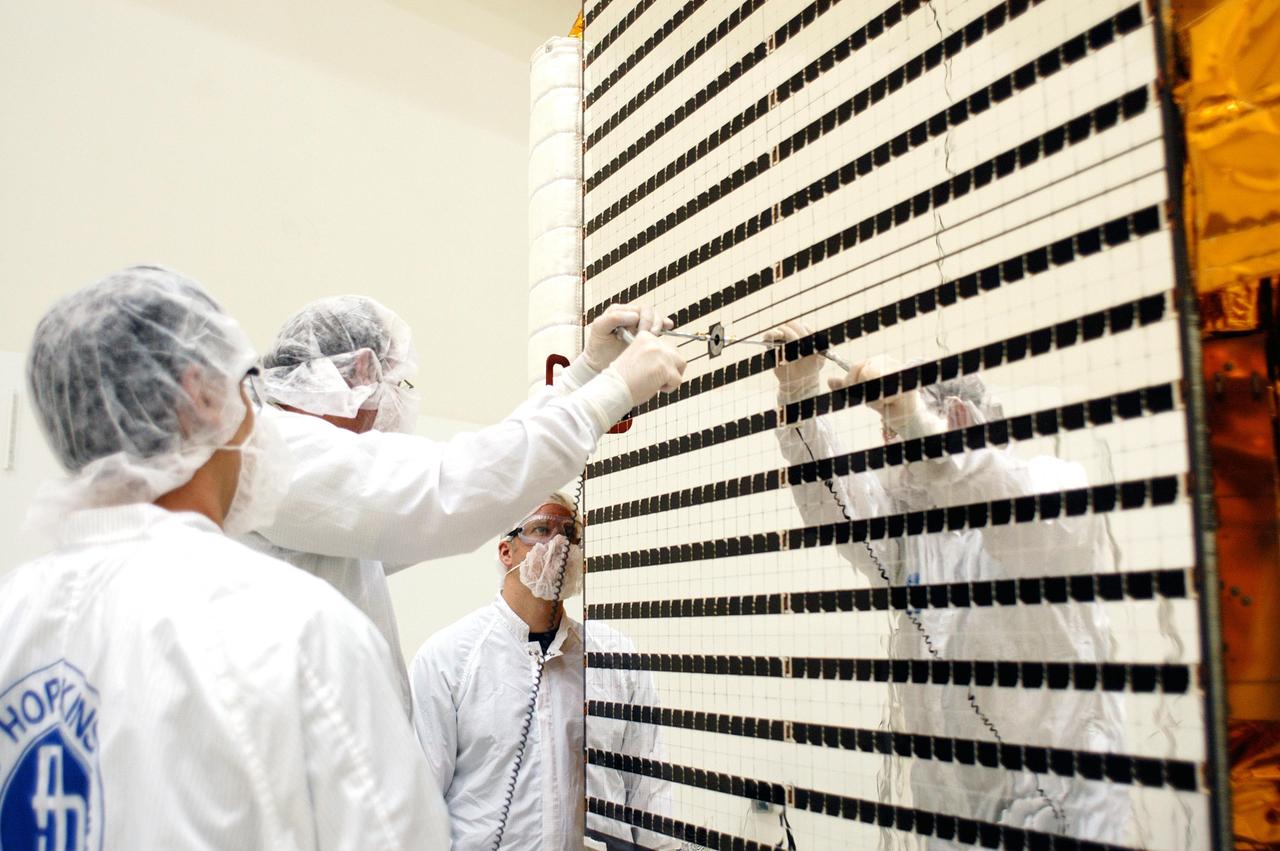

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians with The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) prepare one of two solar array panels on the MESSENGER spacecraft for deployment. The panels will provide MESSENGER’s power on its journey to Mercury. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by APL in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA Mission Integration Manager Cheryle Mako and NASA Launch Site Integration Manager John Hueckel talk before the deployment of the solar array panels on the MESSENGER spacecraft behind them. The solar arrays will provide MESSENGER’s power on its journey to Mercury. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by APL in Laurel, Md.
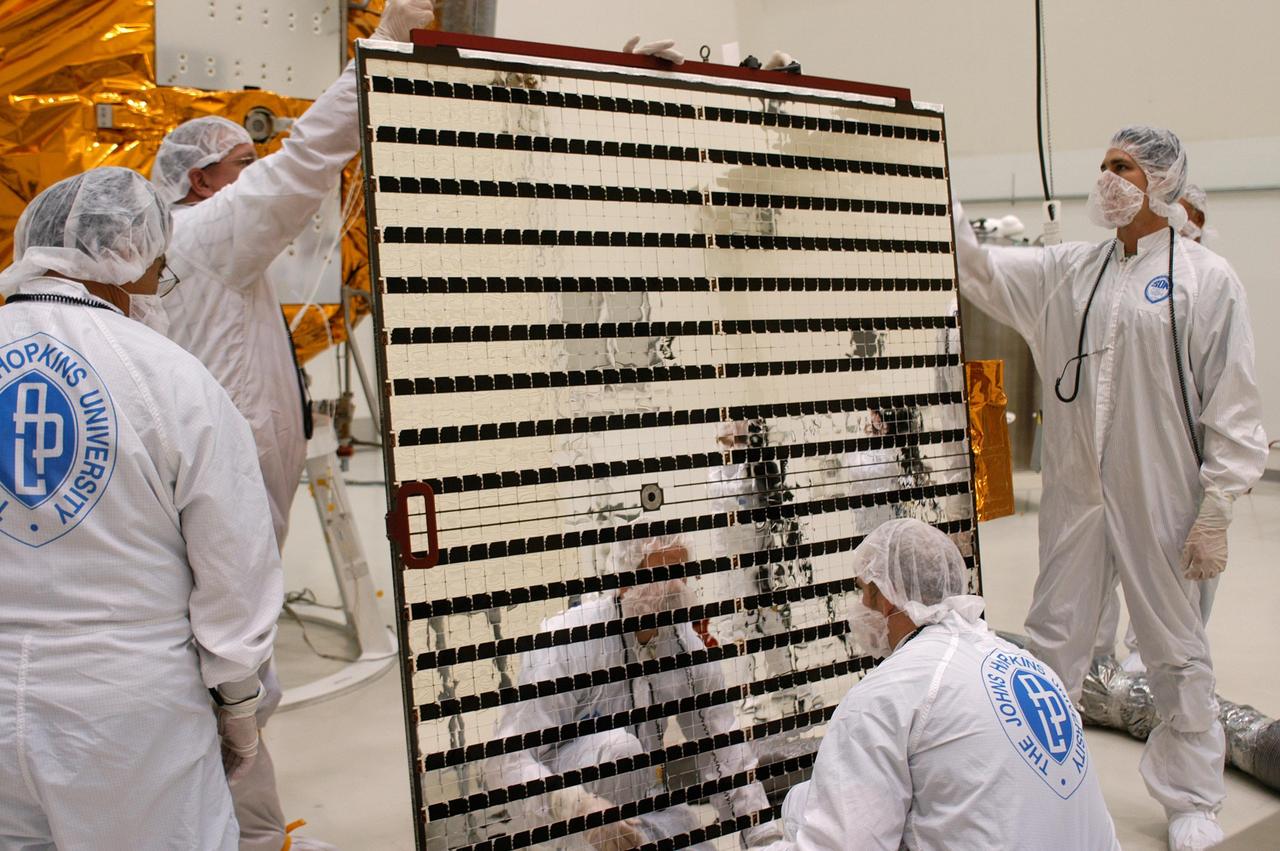

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians check the second solar panel that will be installed on NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft. The two large solar panels, supplemented with a nickel-hydrogen battery, will provide MESSENGER’s power. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure guide wires on the second solar panel to be installed on NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft. The two large solar panels, supplemented with a nickel-hydrogen battery, will provide MESSENGER’s power. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
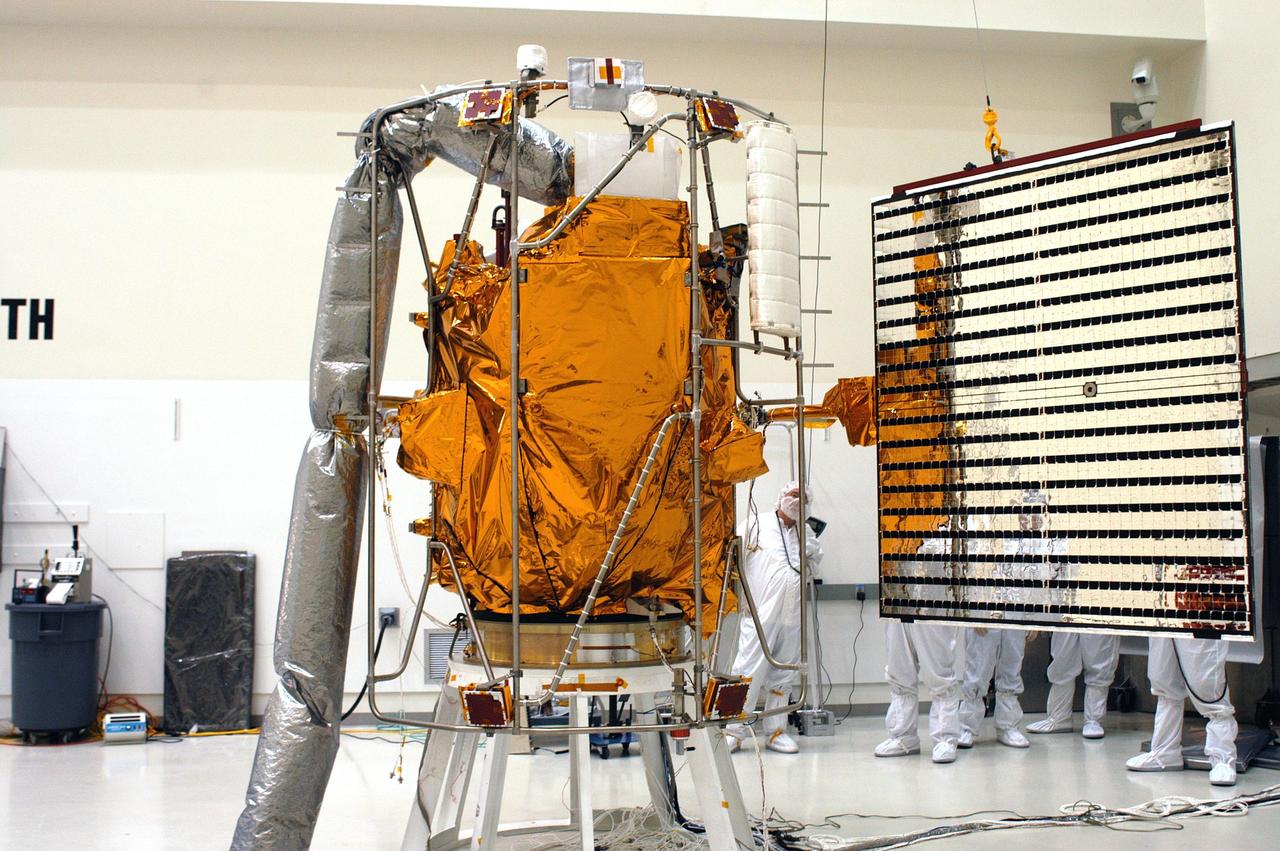

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., help guide a solar panel toward NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft for installation. It is one of two large solar panels, supplemented with a nickel-hydrogen battery, that will provide MESSENGER’s power. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
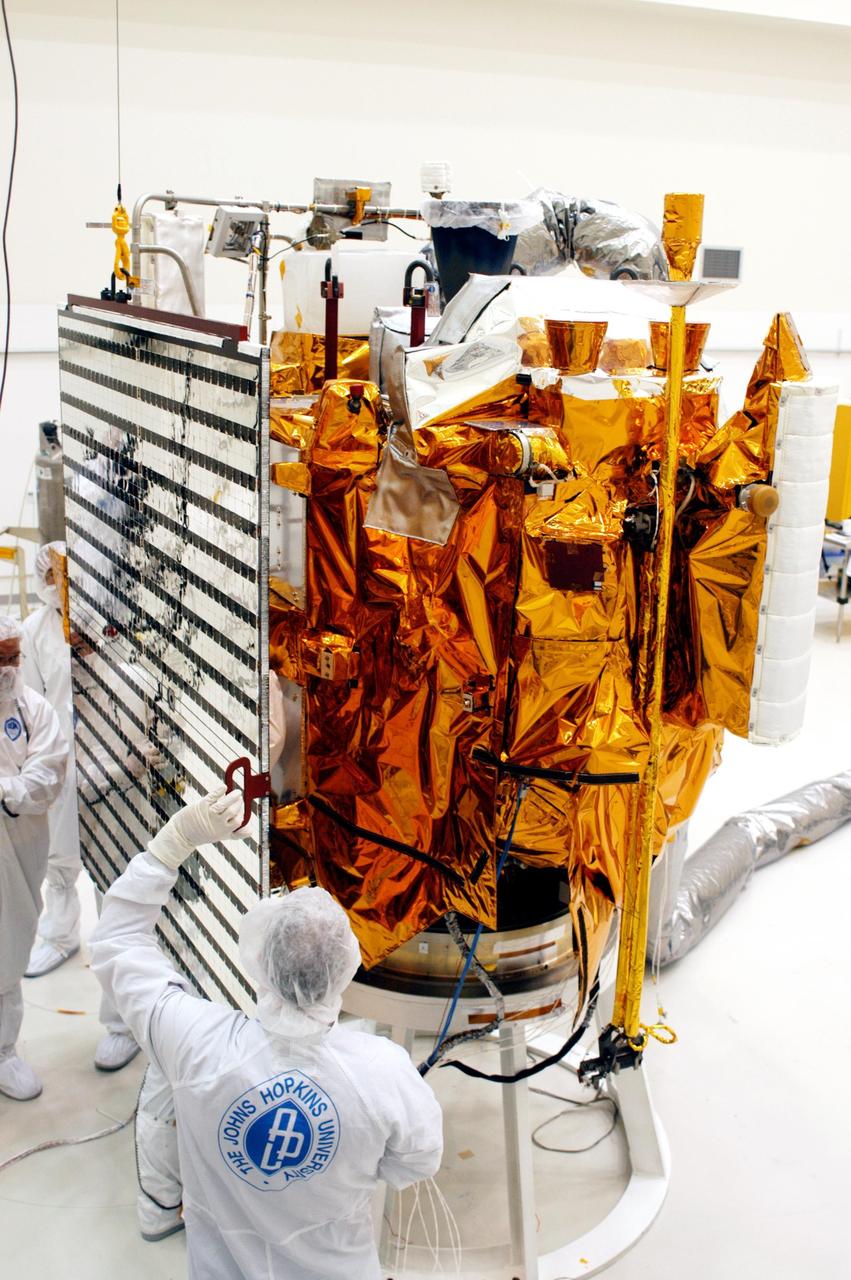

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., maneuver a solar panel into place for installation on NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft. It is one of two large solar panels, supplemented with a nickel-hydrogen battery, that will provide MESSENGER’s power. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
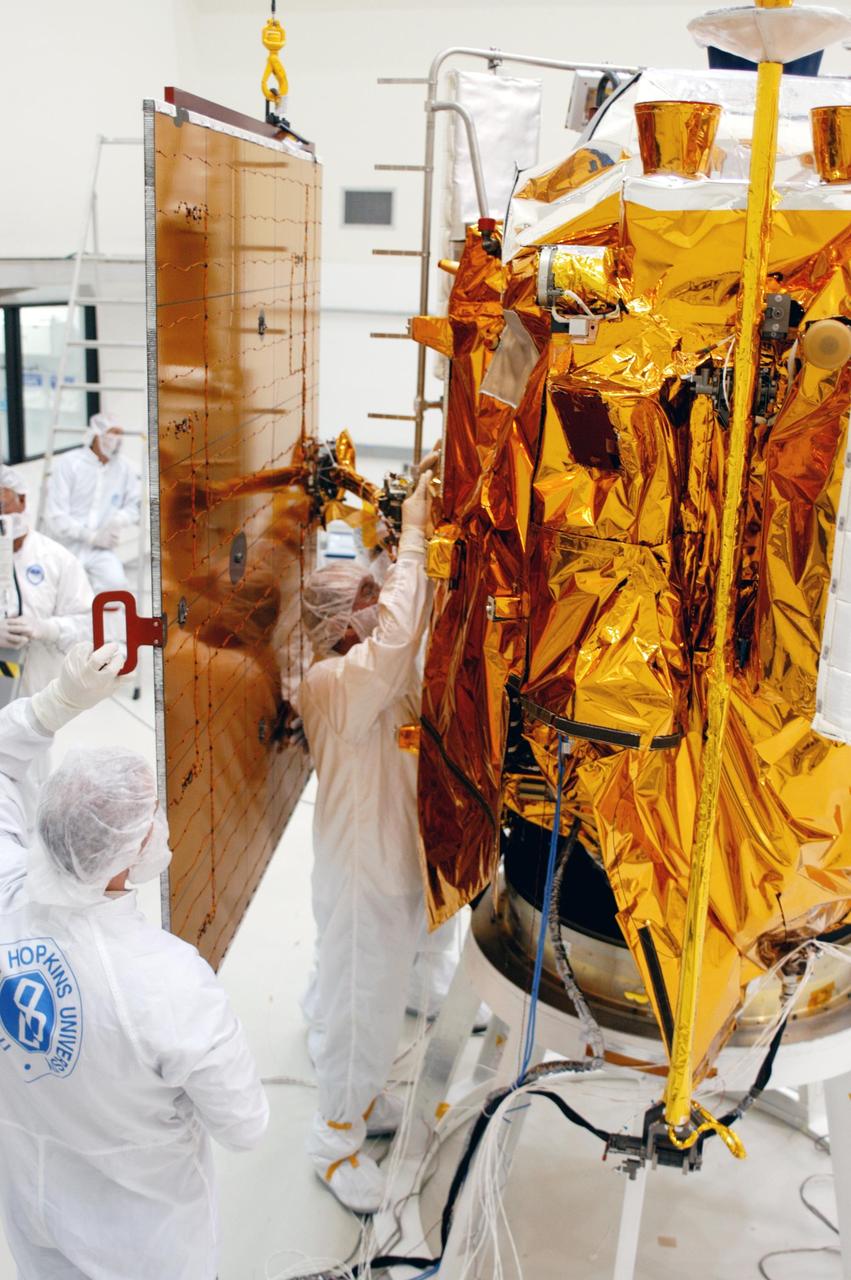

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., steady a solar panel suspended from above as others prepare to install it on NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft. It is one of two large solar panels, supplemented with a nickel-hydrogen battery, that will provide MESSENGER’s power. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch Aug. 2 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. It will return to Earth for a gravity boost in July 2005, then fly past Venus twice, in October 2006 and June 2007. The spacecraft uses the tug of Venus’ gravity to resize and rotate its trajectory closer to Mercury’s orbit. Three Mercury flybys, each followed about two months later by a course-correction maneuver, put MESSENGER in position to enter Mercury orbit in March 2011. During the flybys, MESSENGER will map nearly the entire planet in color, image most of the areas unseen by Mariner 10, and measure the composition of the surface, atmosphere and magnetosphere. It will be the first new data from Mercury in more than 30 years - and invaluable for planning MESSENGER’s year-long orbital mission. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.