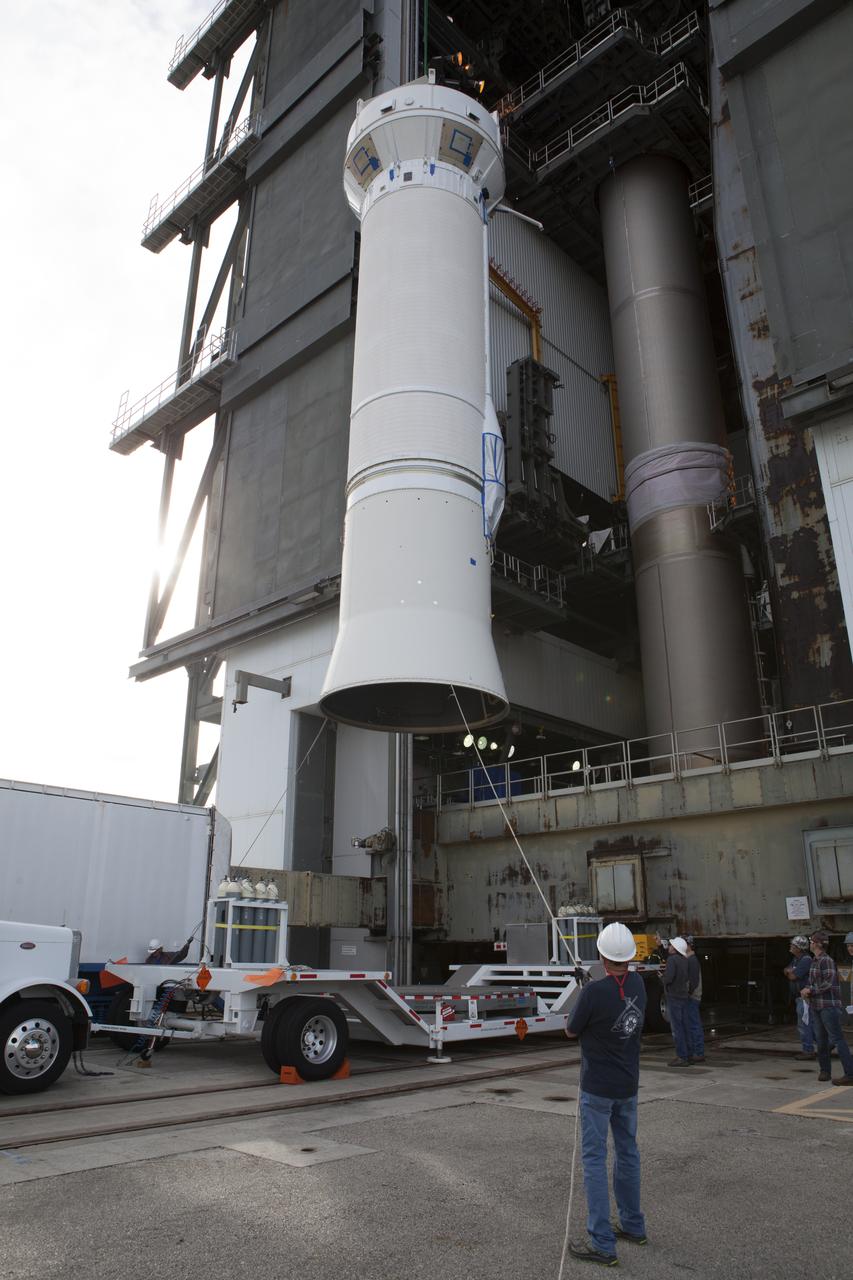

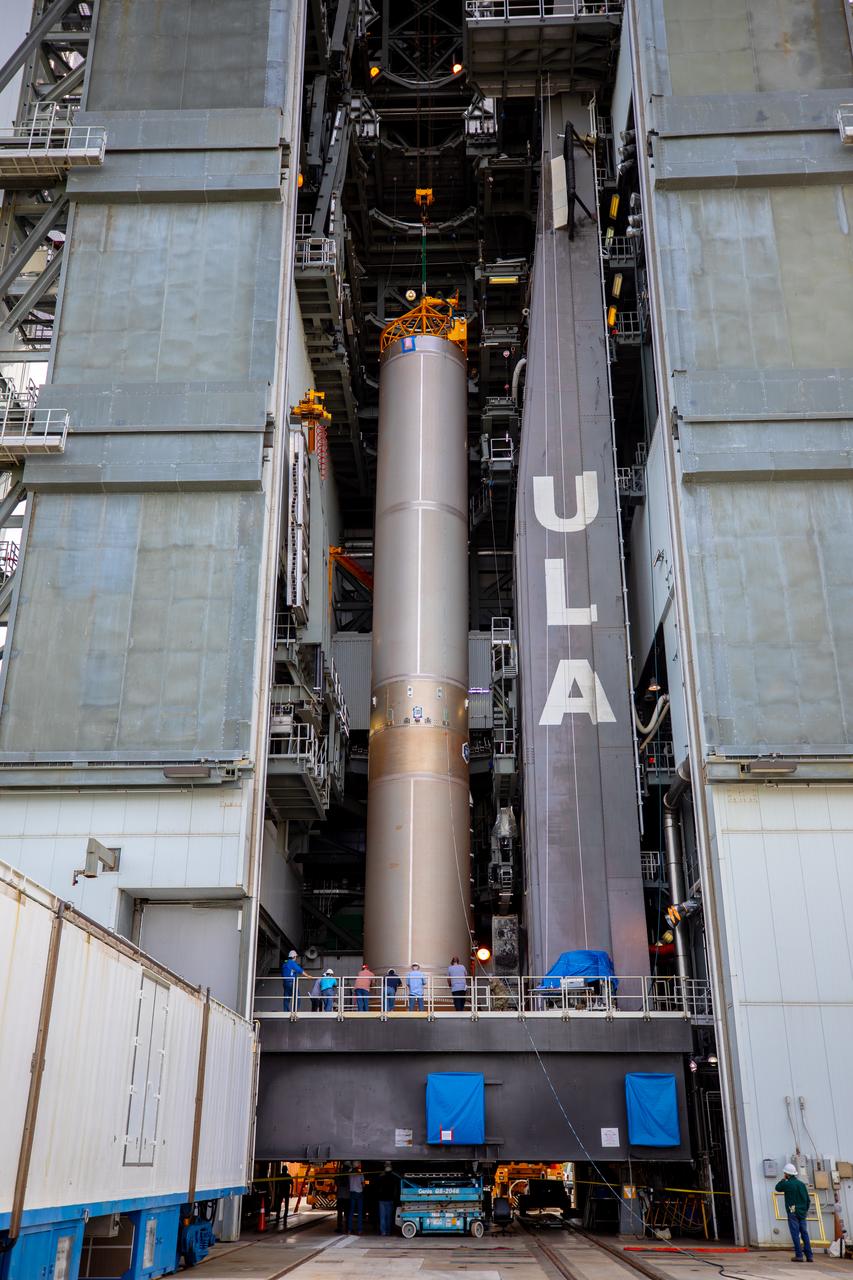
The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is lifted up by crane at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be moved into the VIF, lifted up and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
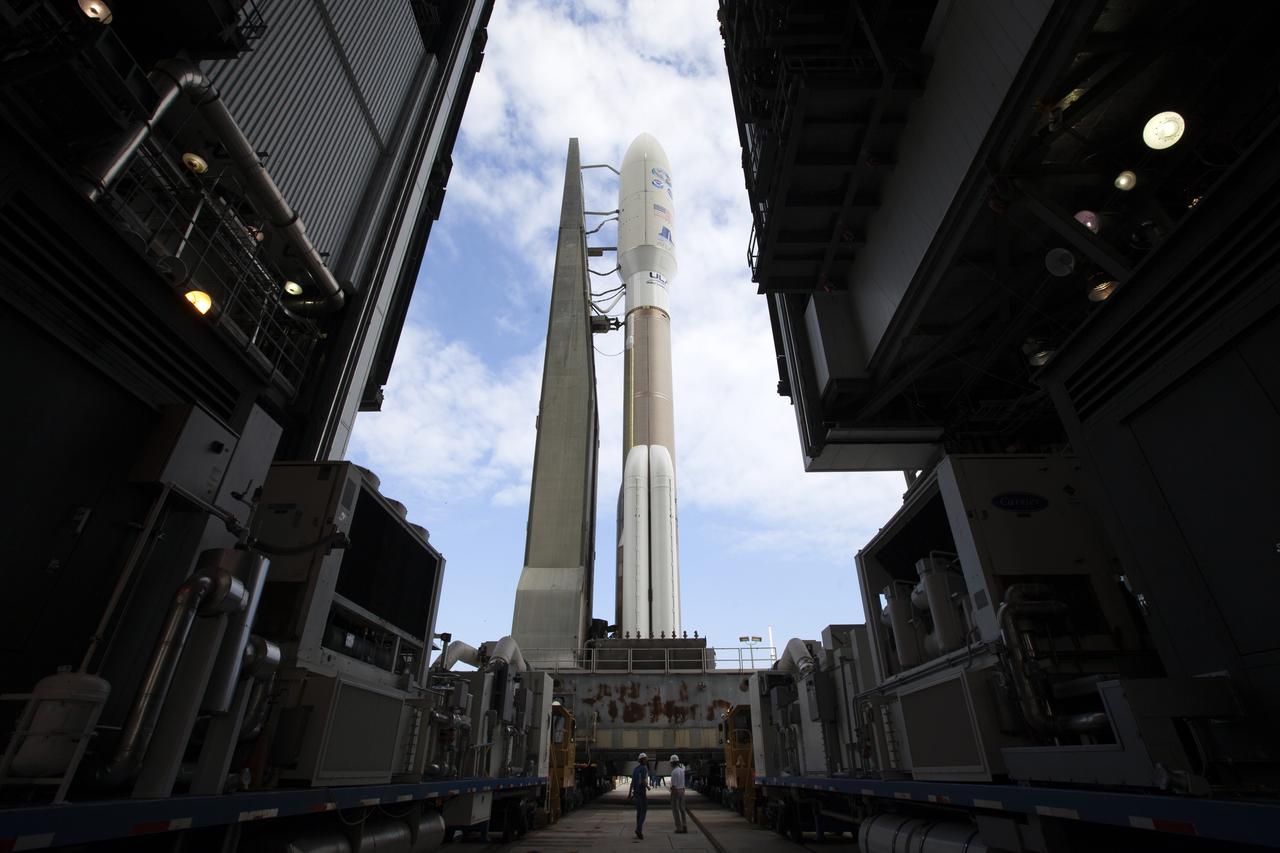

With blue sky in the background, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket begins its rollout from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
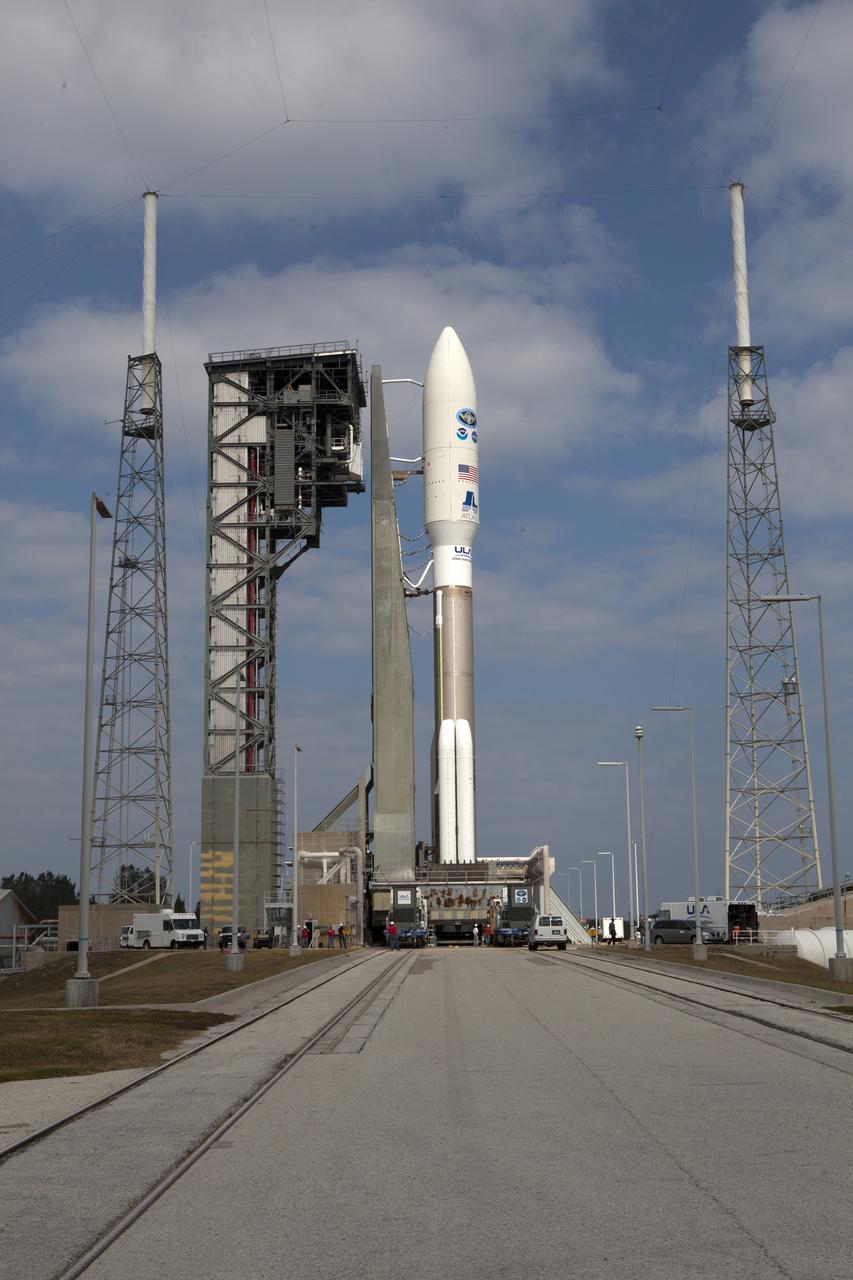

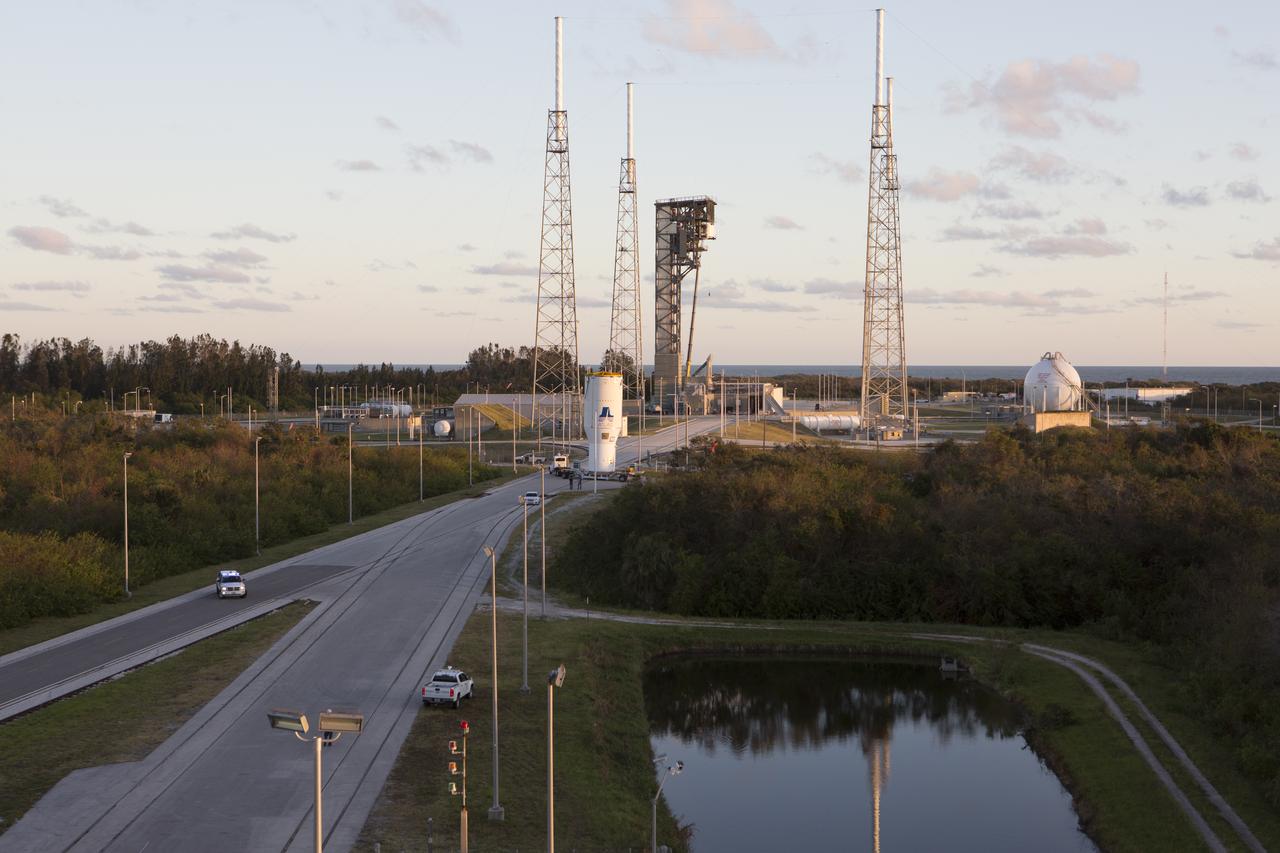
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket rolls out from the Vehicle Integration Facility on its way to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
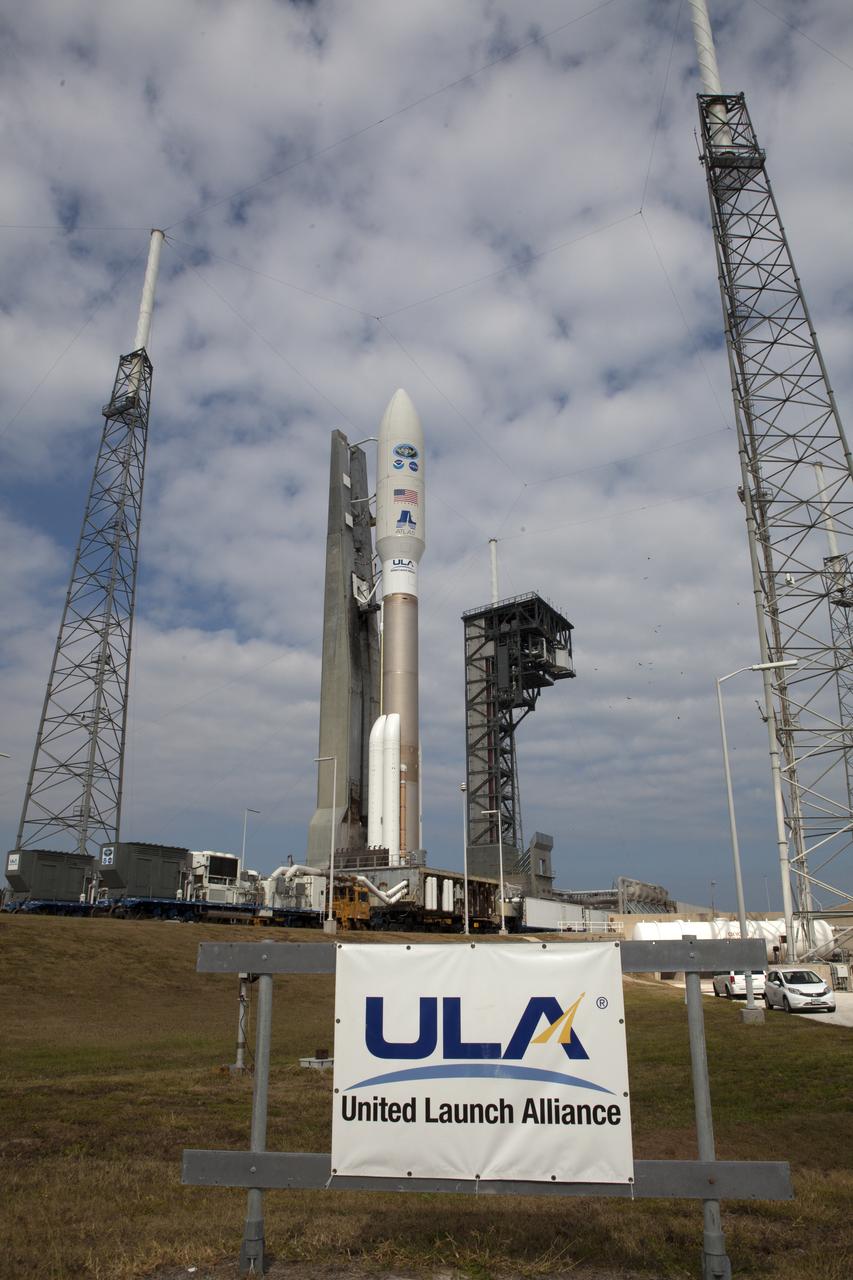

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
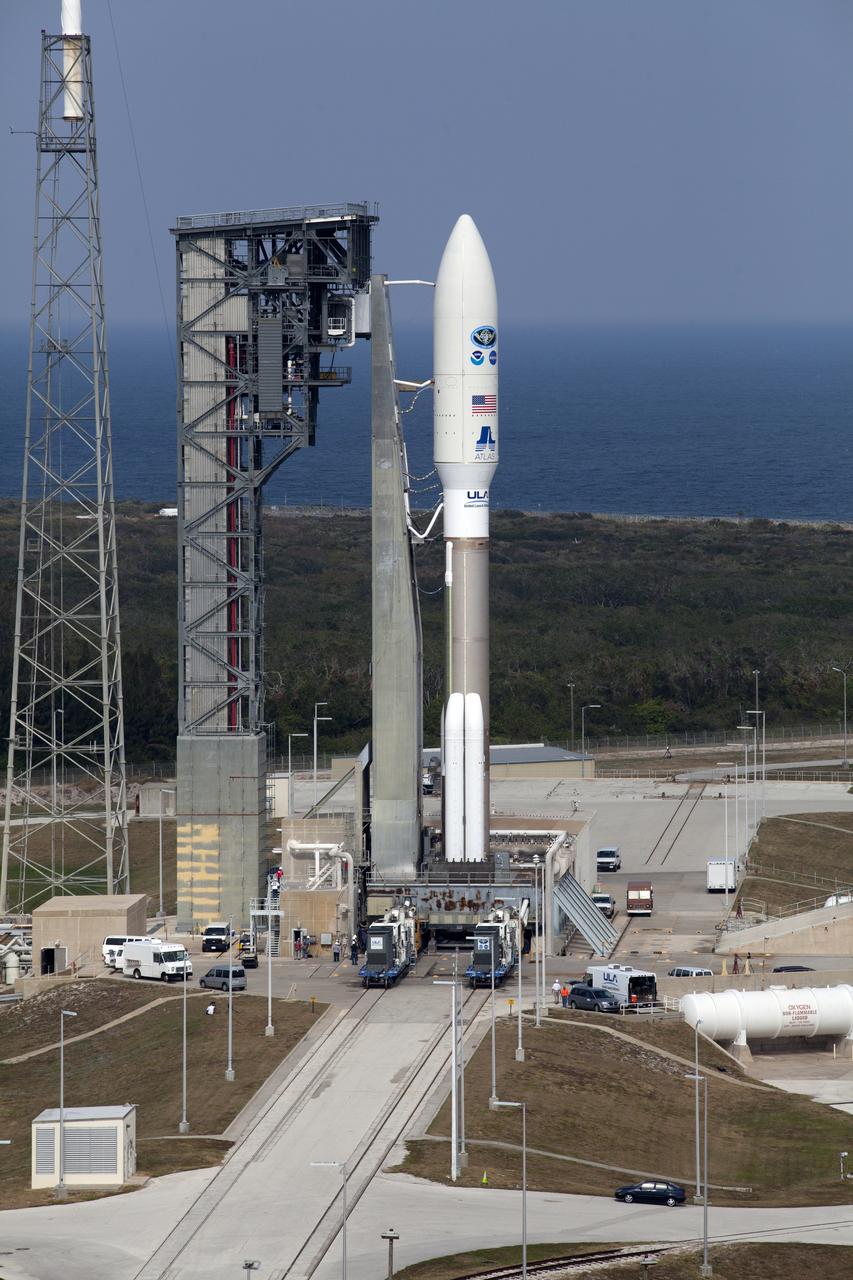

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
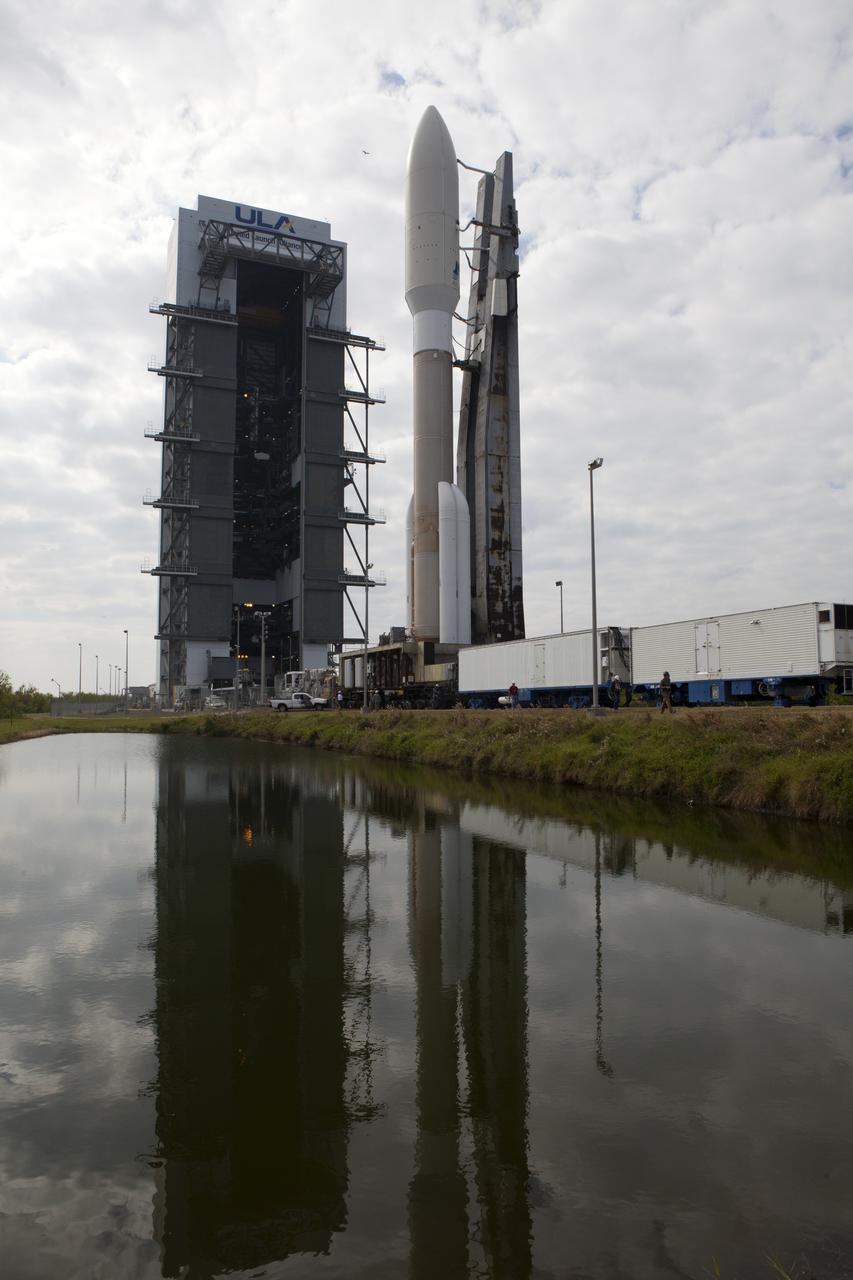

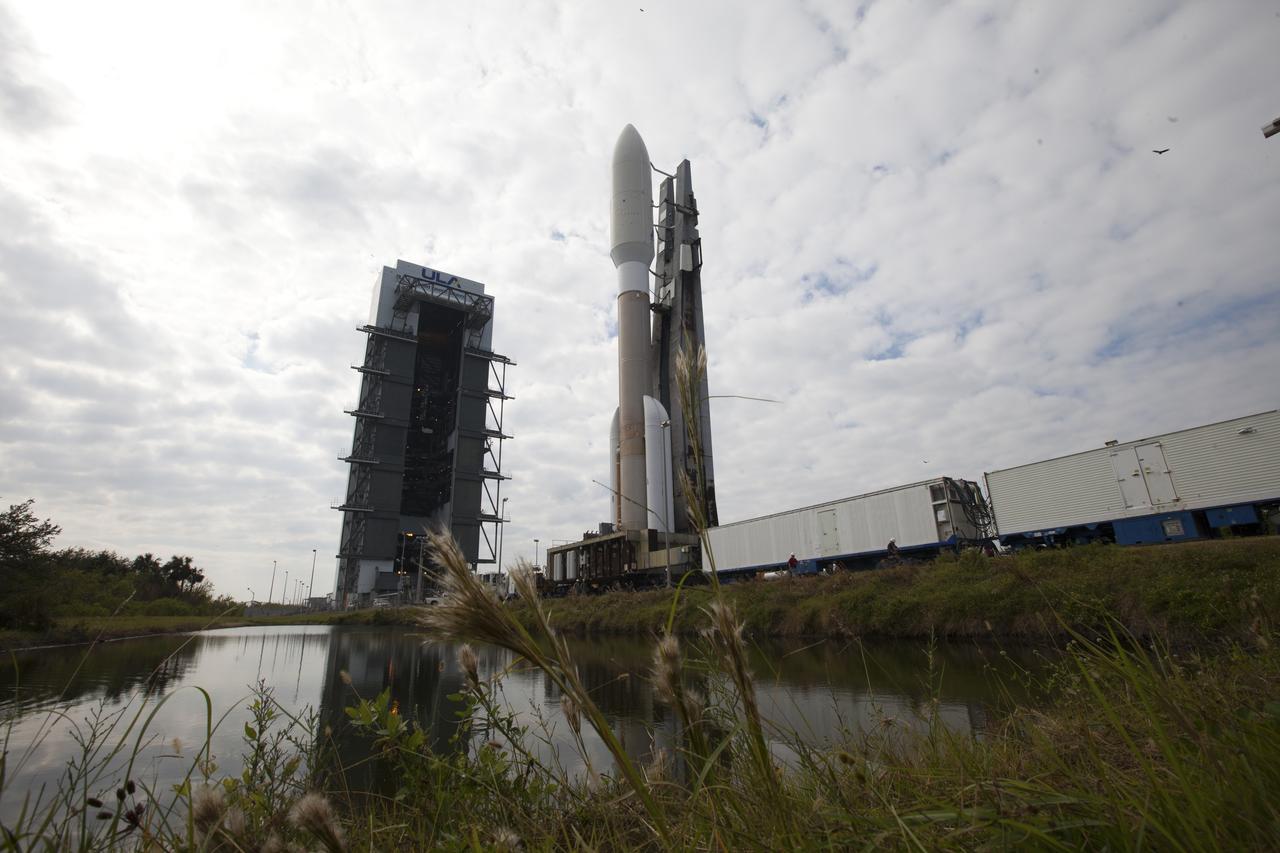
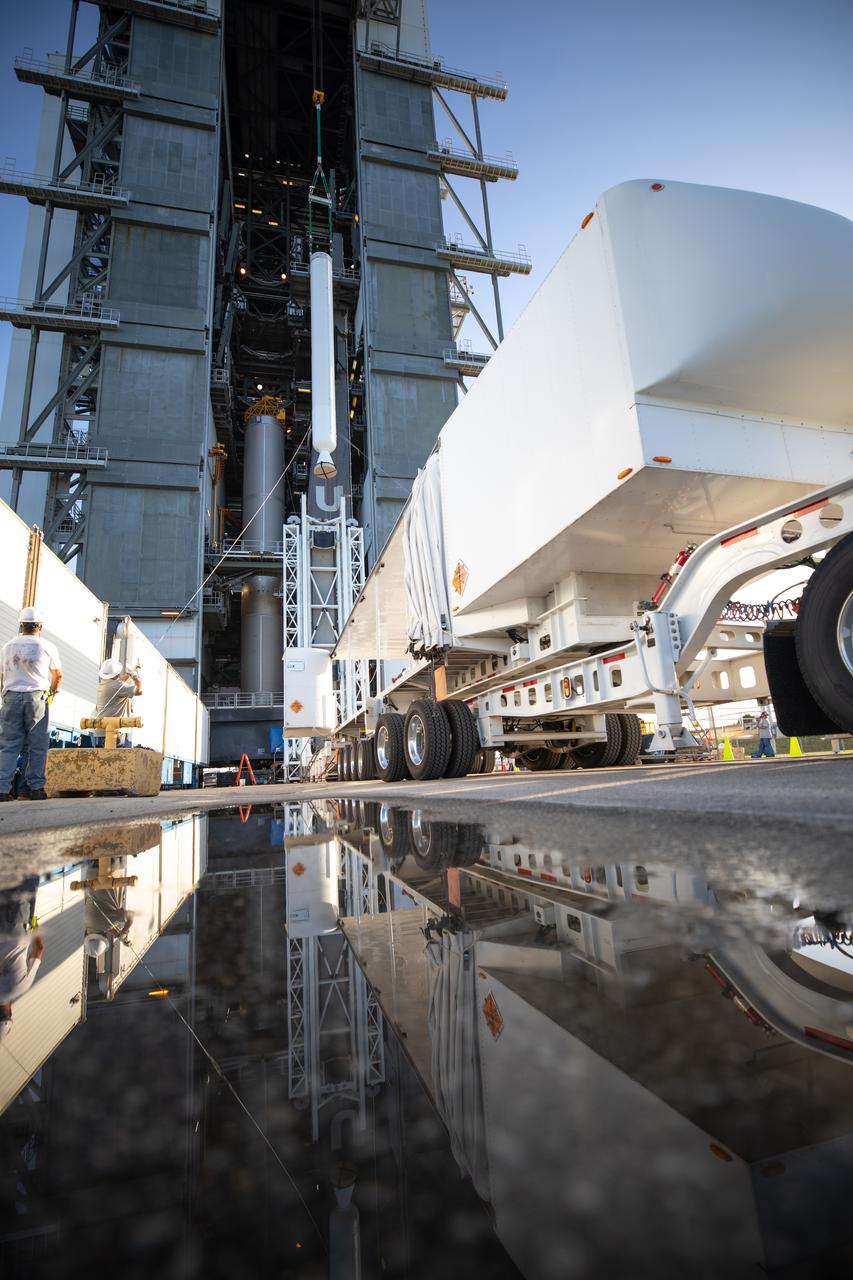
Reflected in the water, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
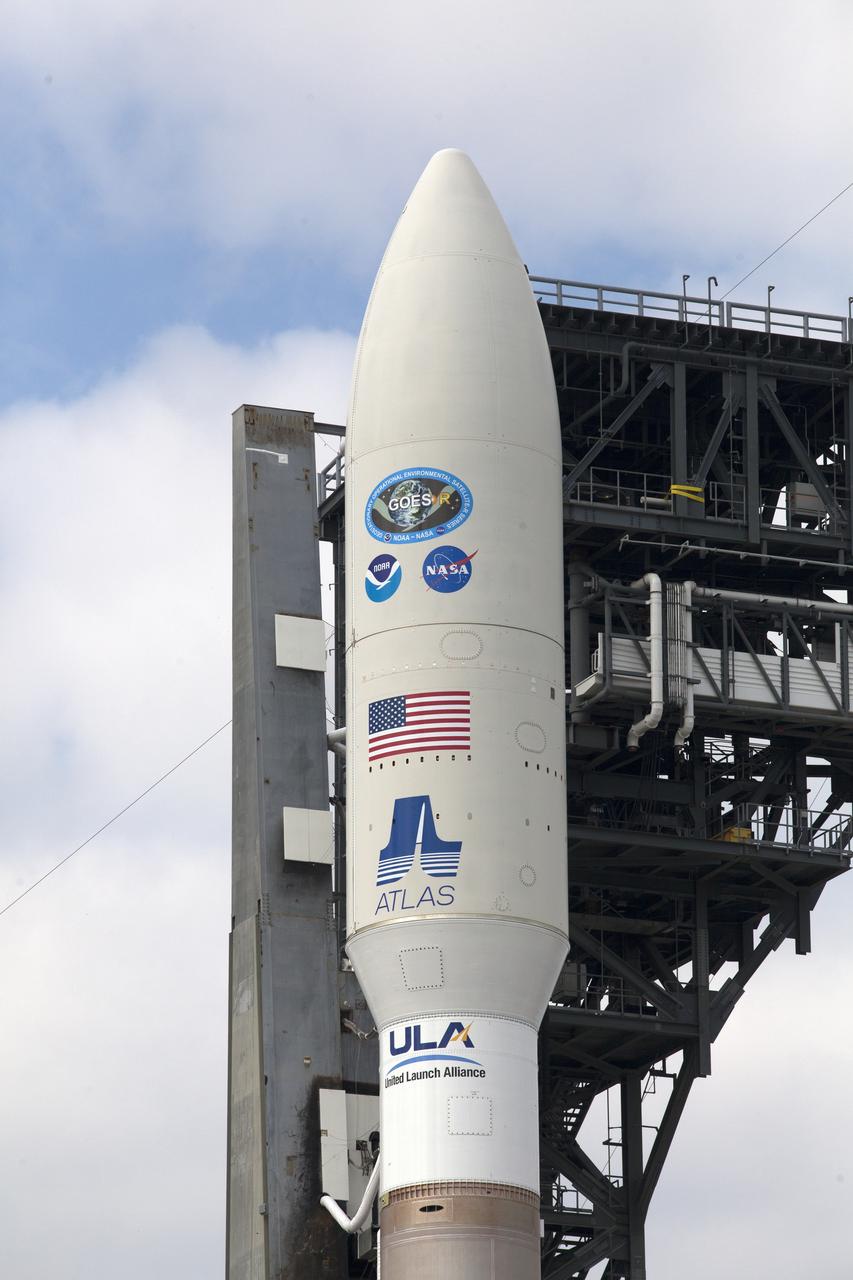

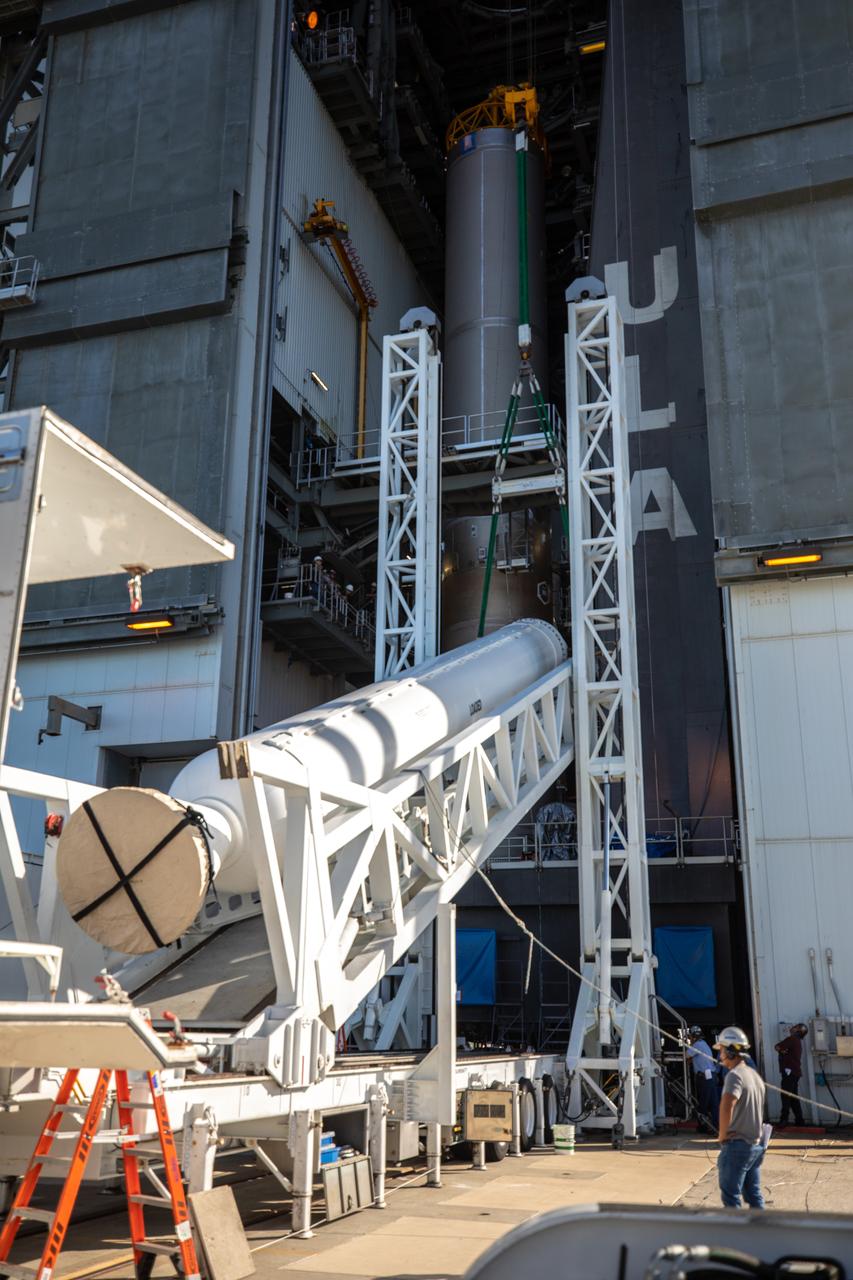
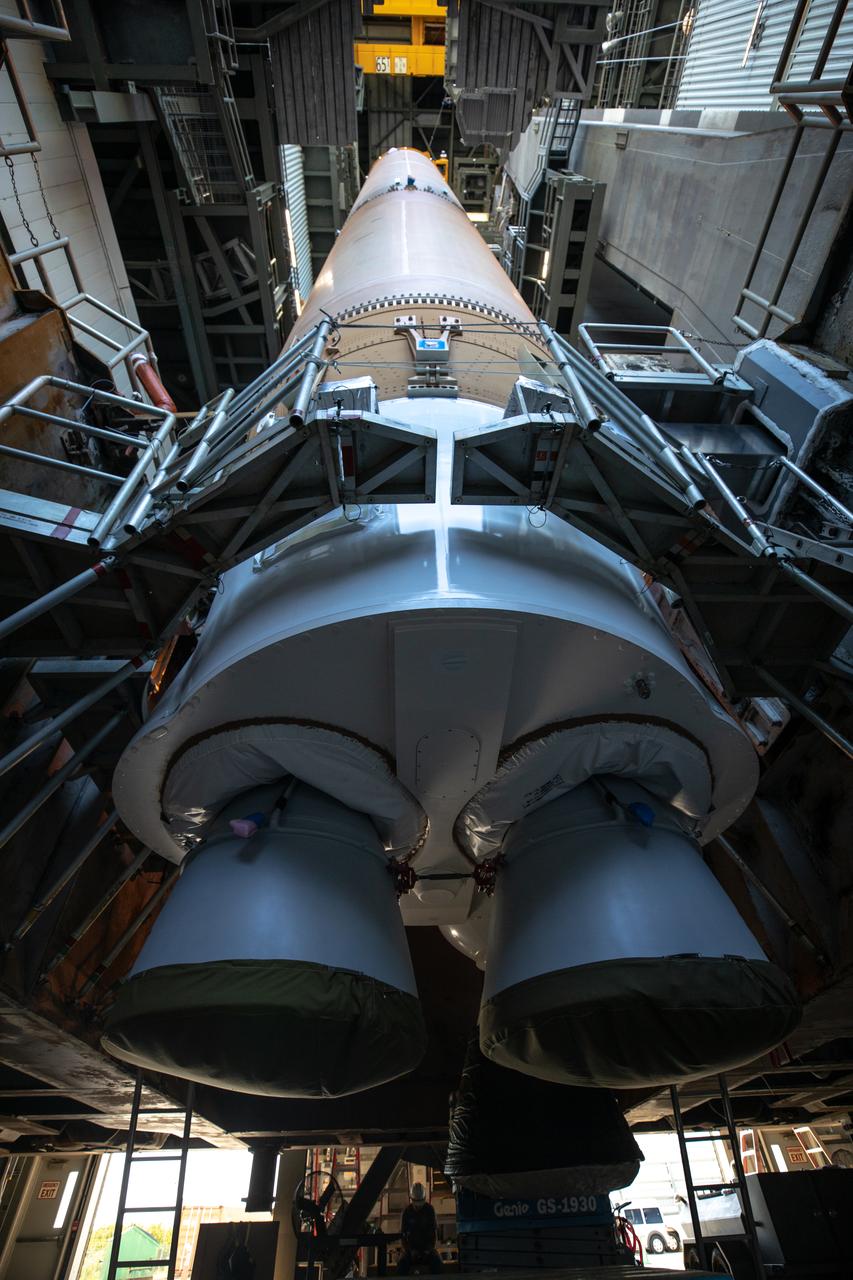
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. In view is the upper stage and payload fairing containing the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R). The launch vehicle will send GOES-R to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
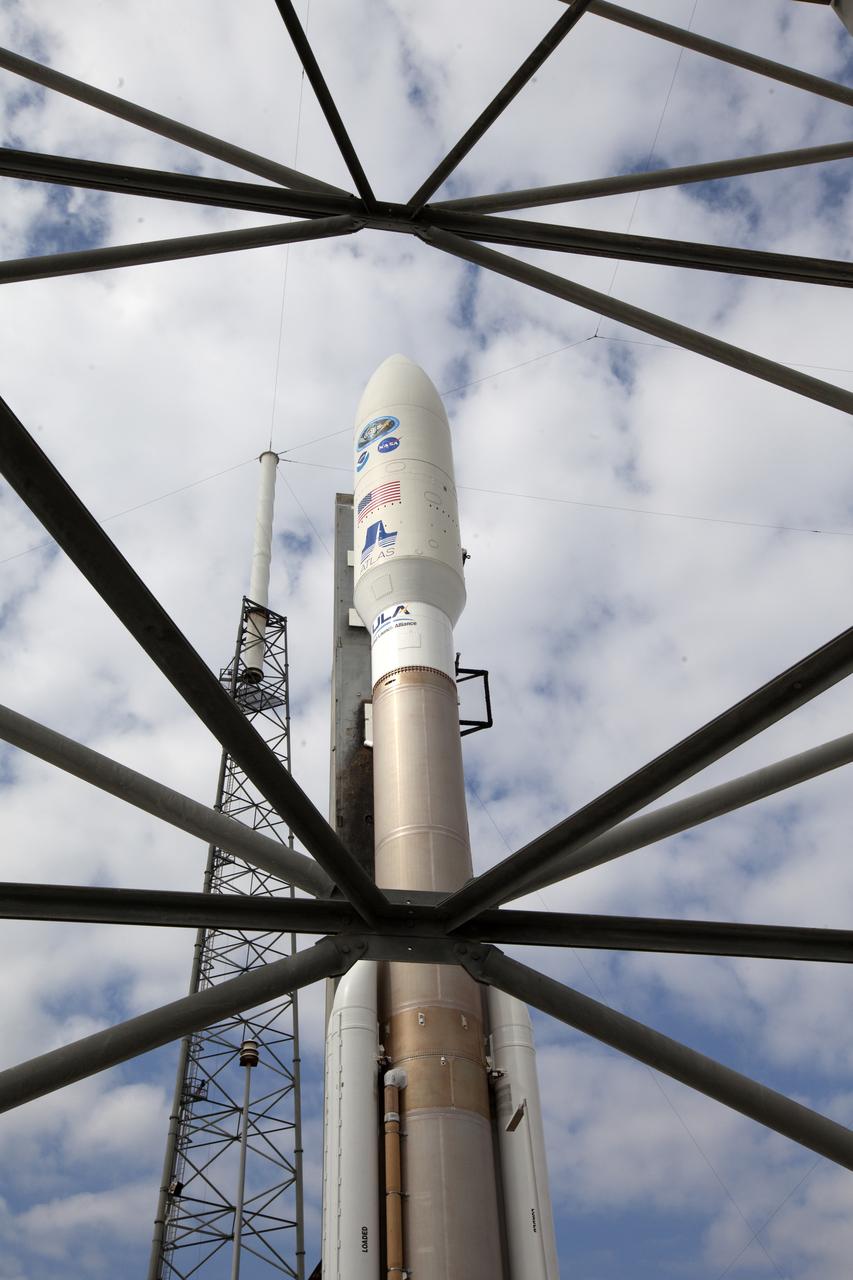

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket rolls out to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
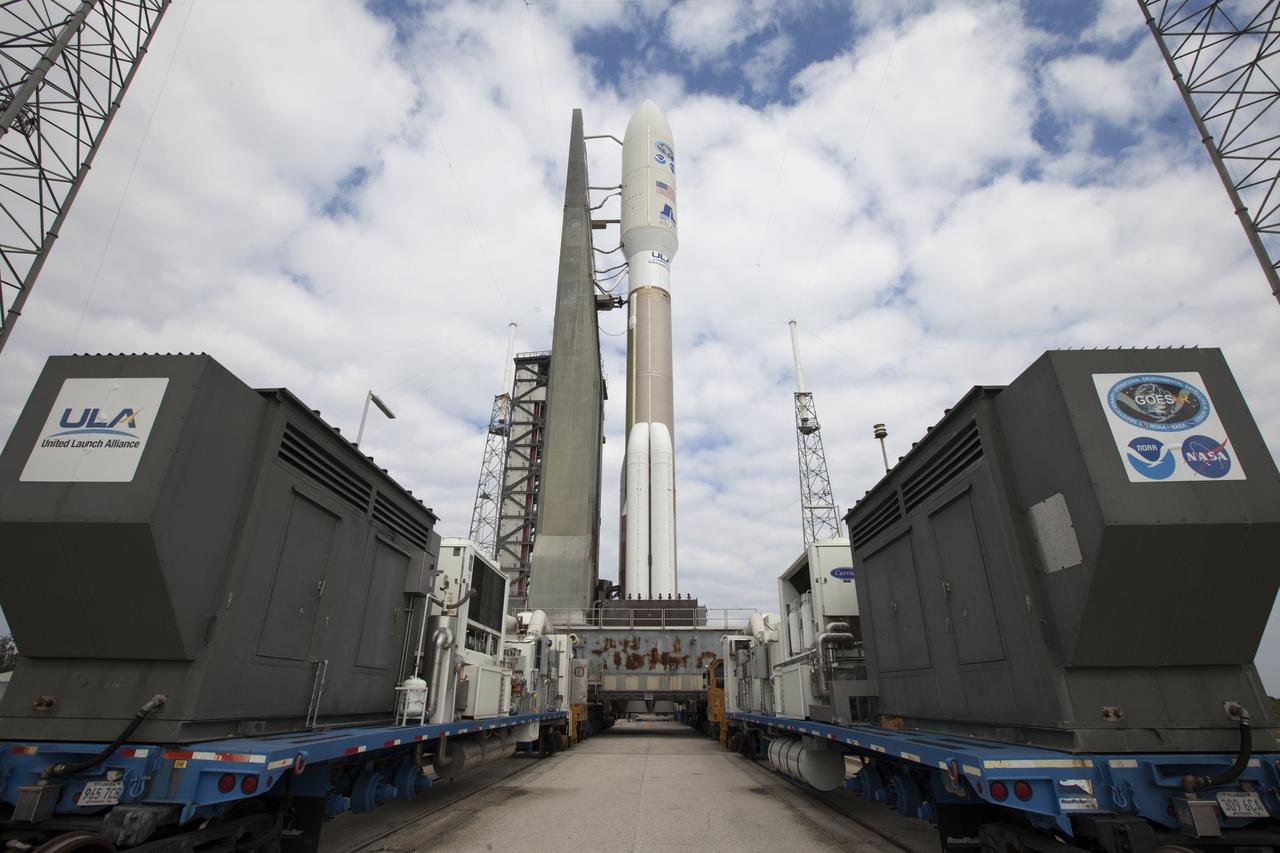

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
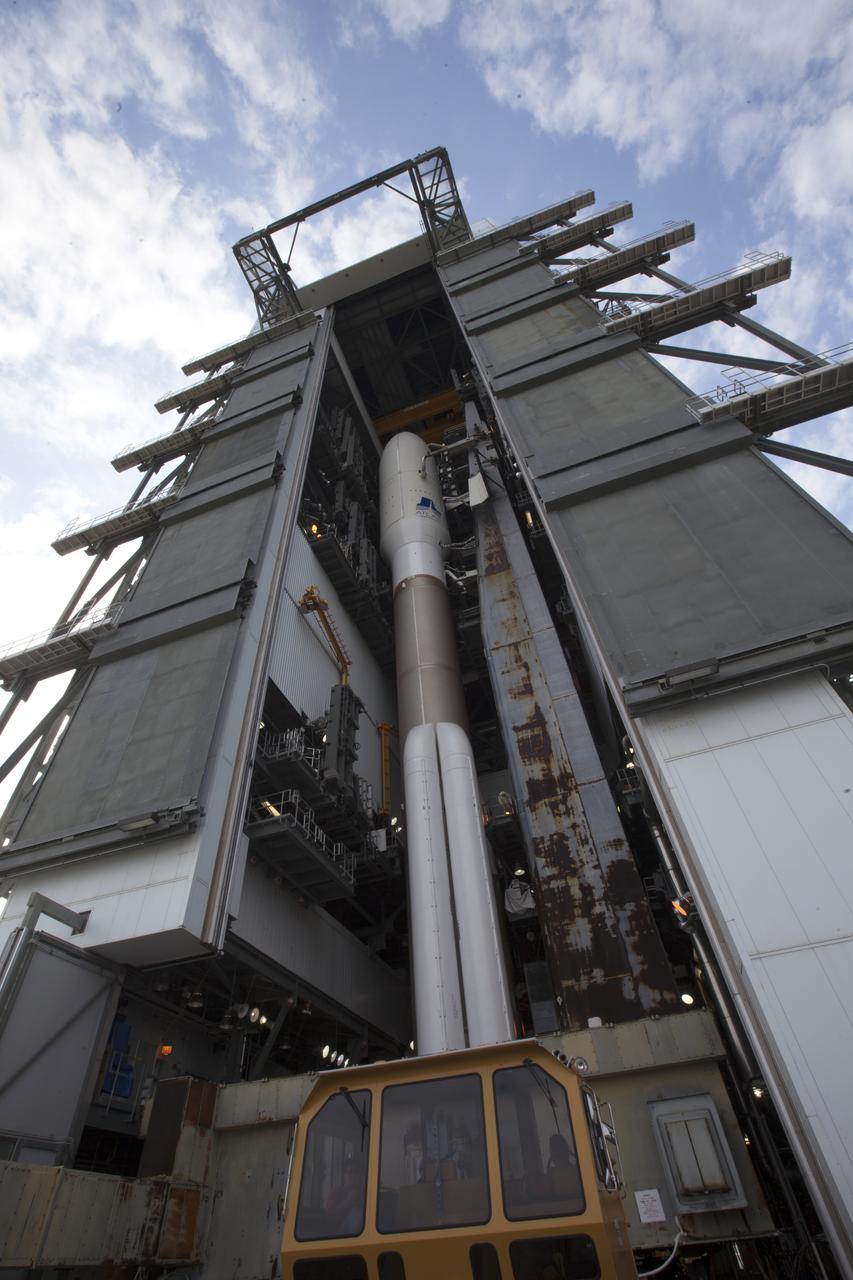

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket begins its rollout from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
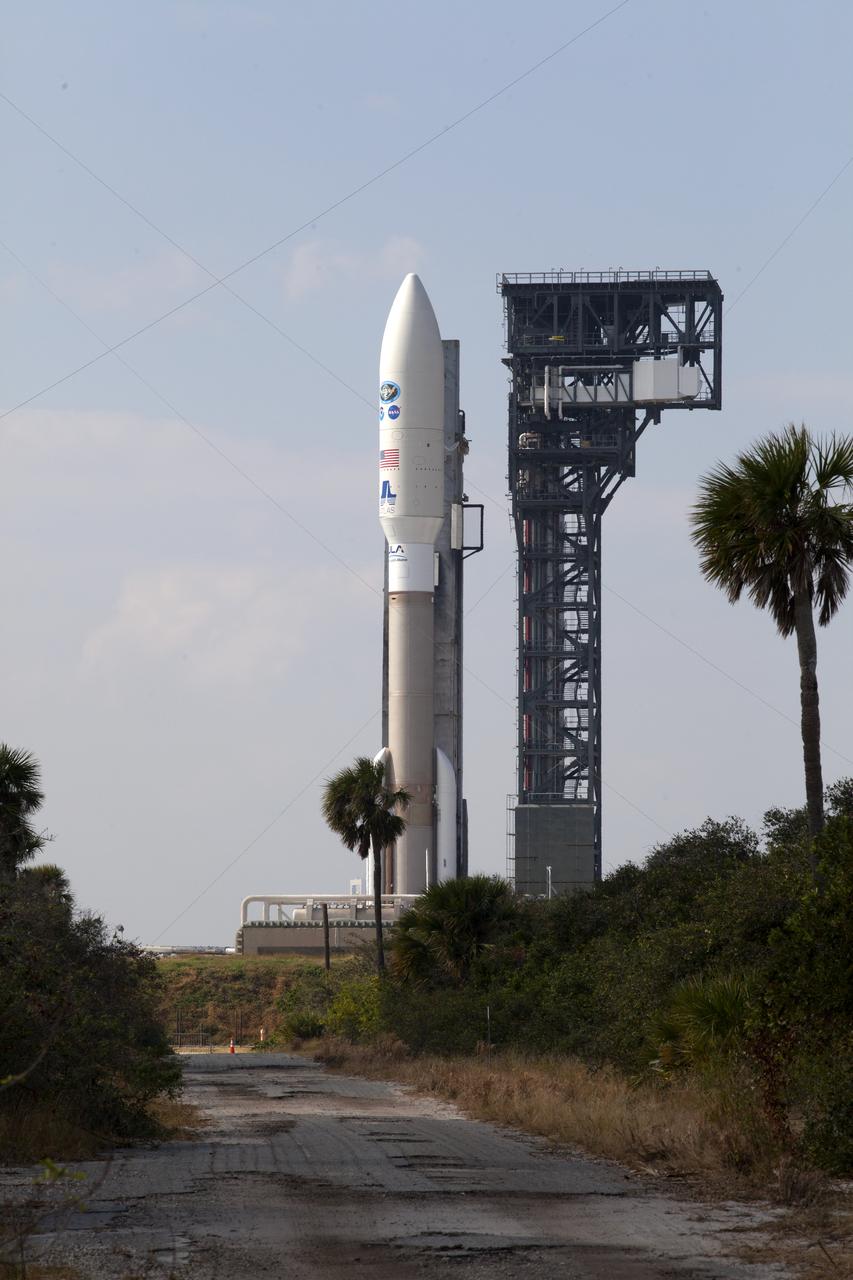

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
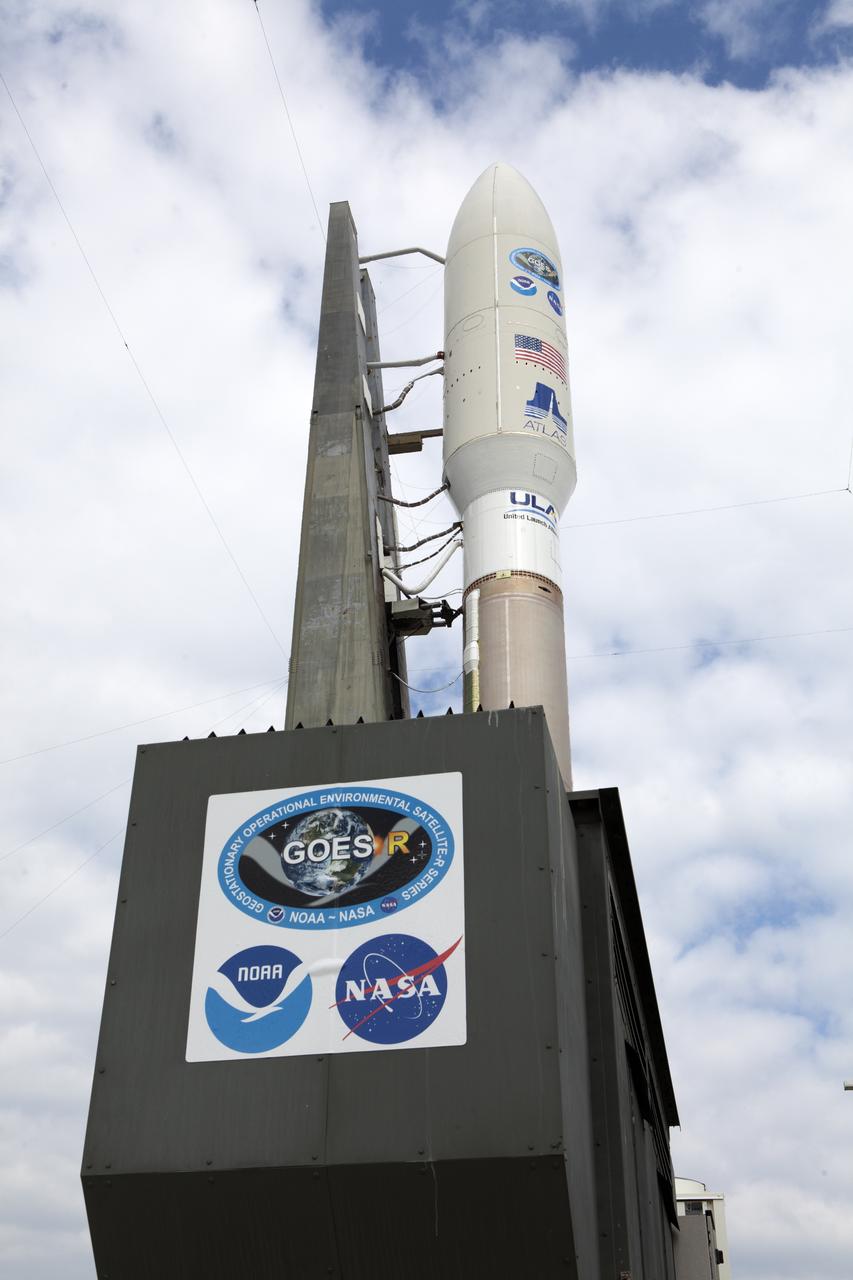

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
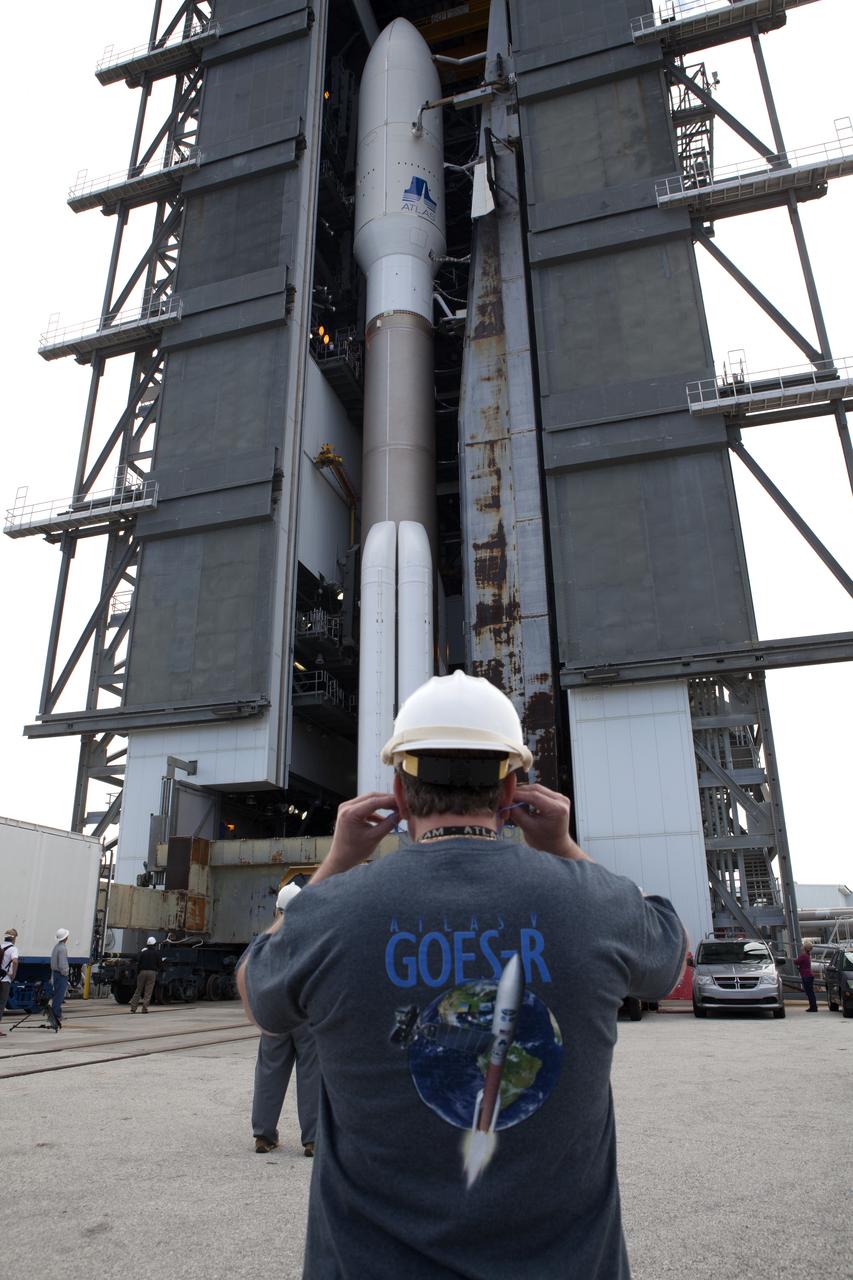

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is ready to roll out from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
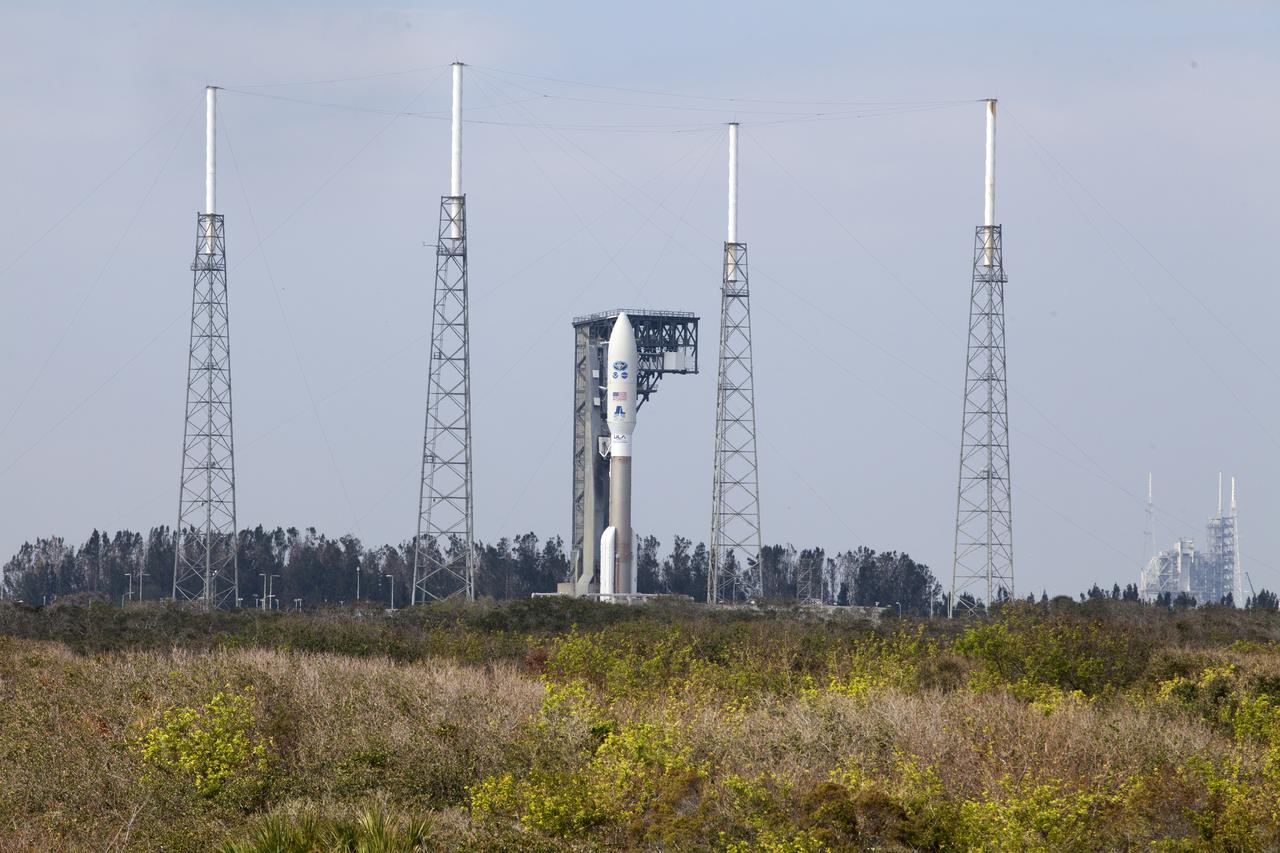

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
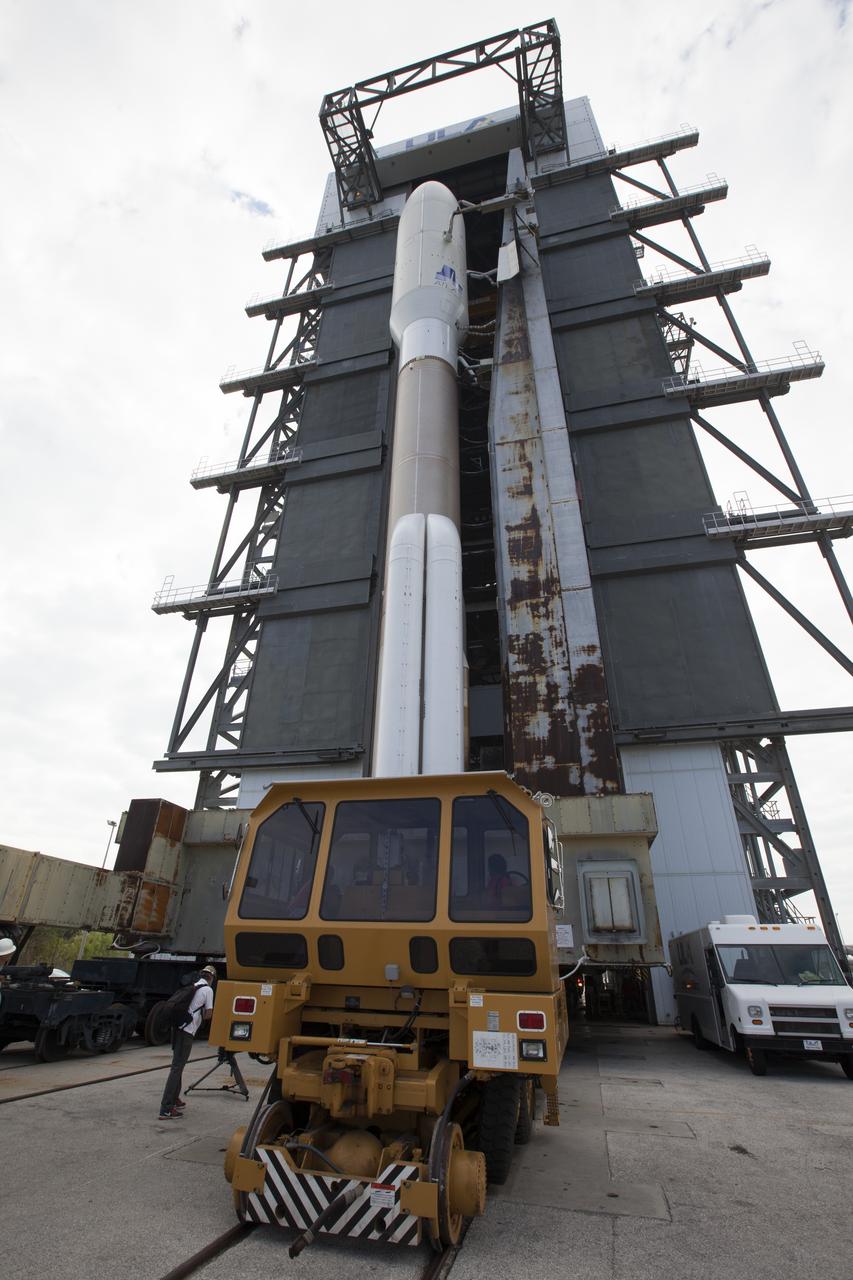

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket begins its rollout from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
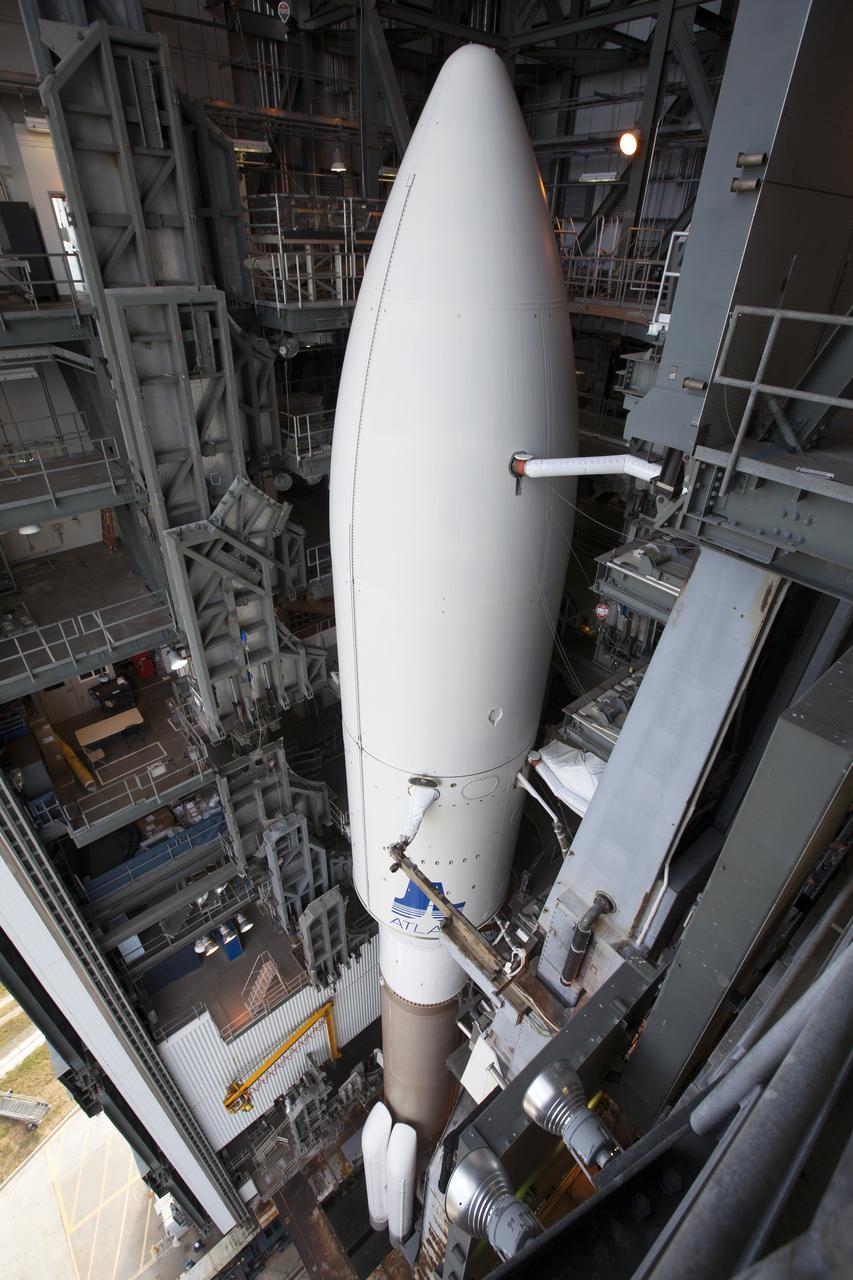

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is ready to roll out from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
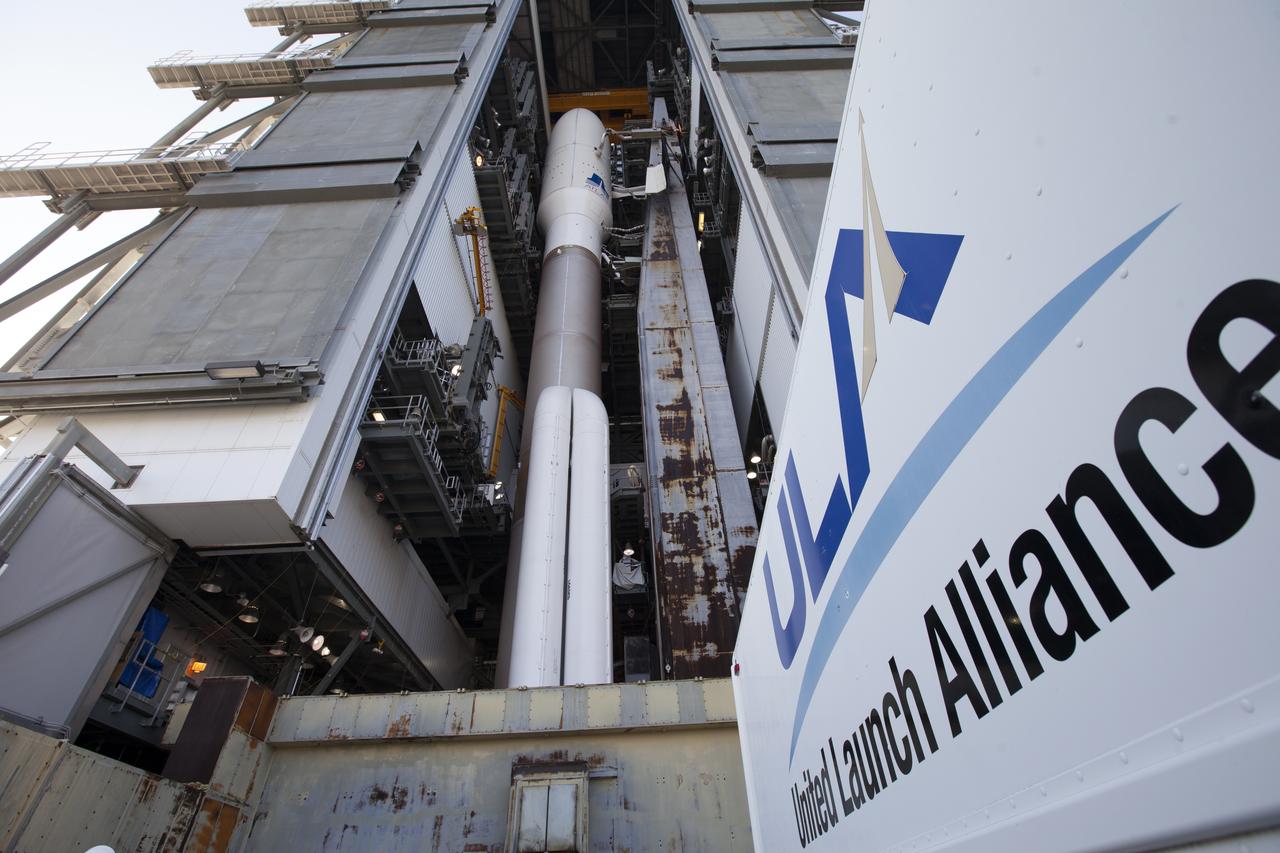

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is ready to roll out from the Vehicle Integration Facility to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
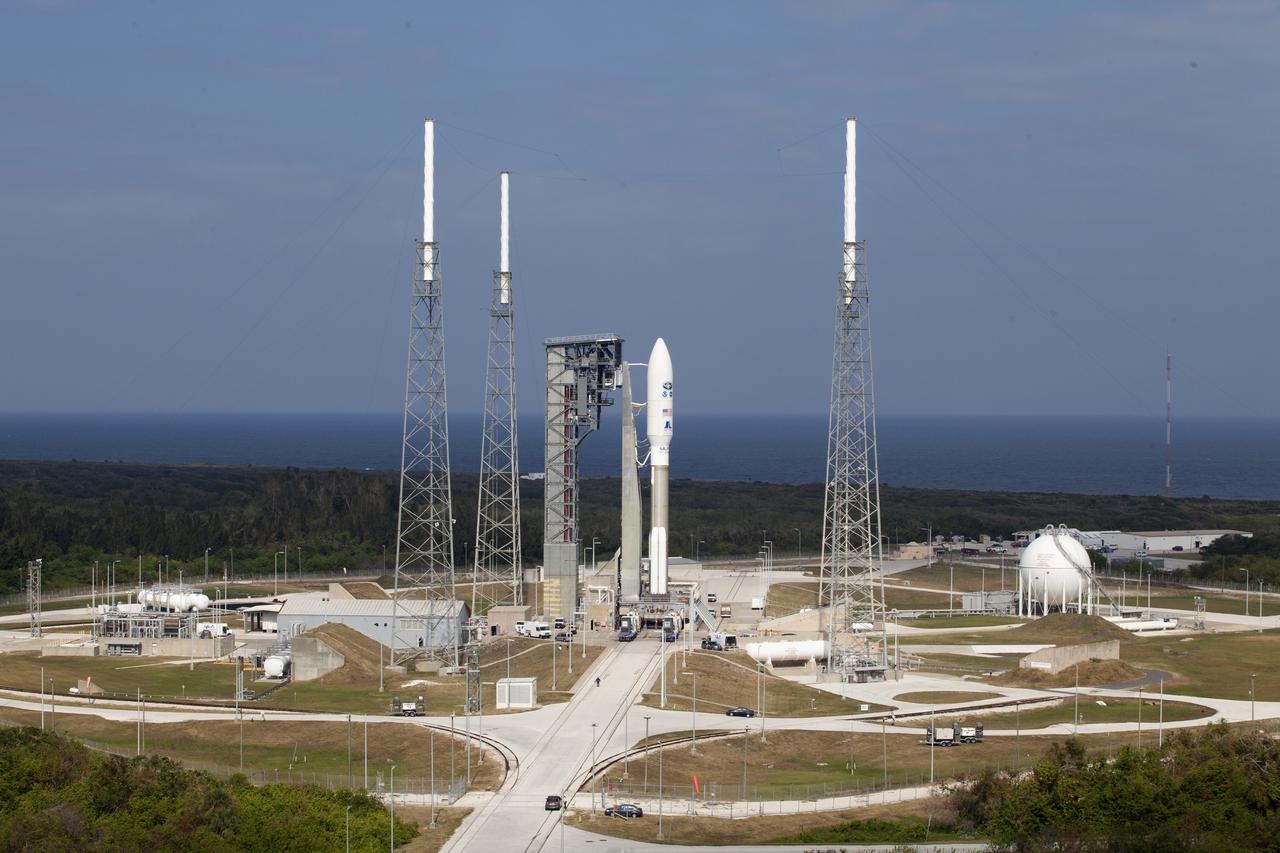

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
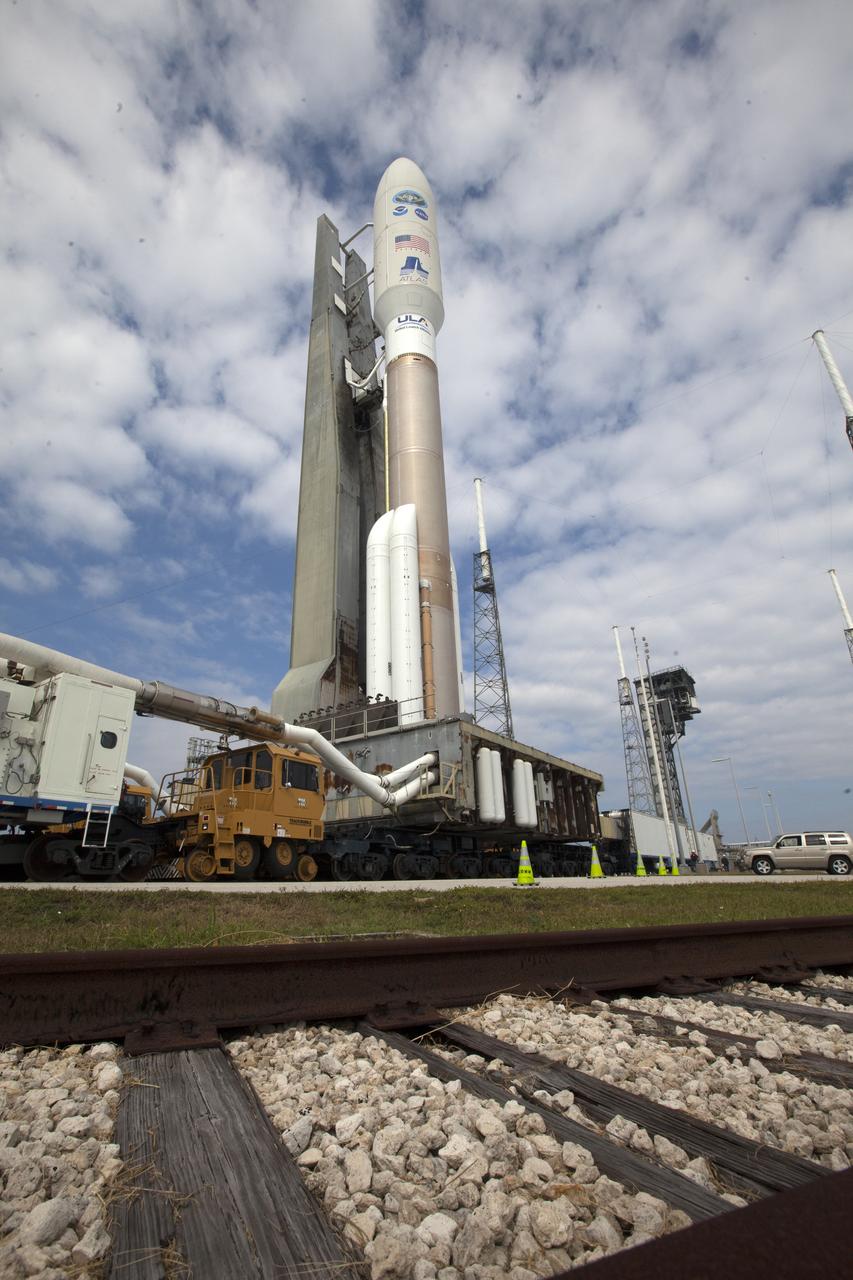

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket rolls out to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
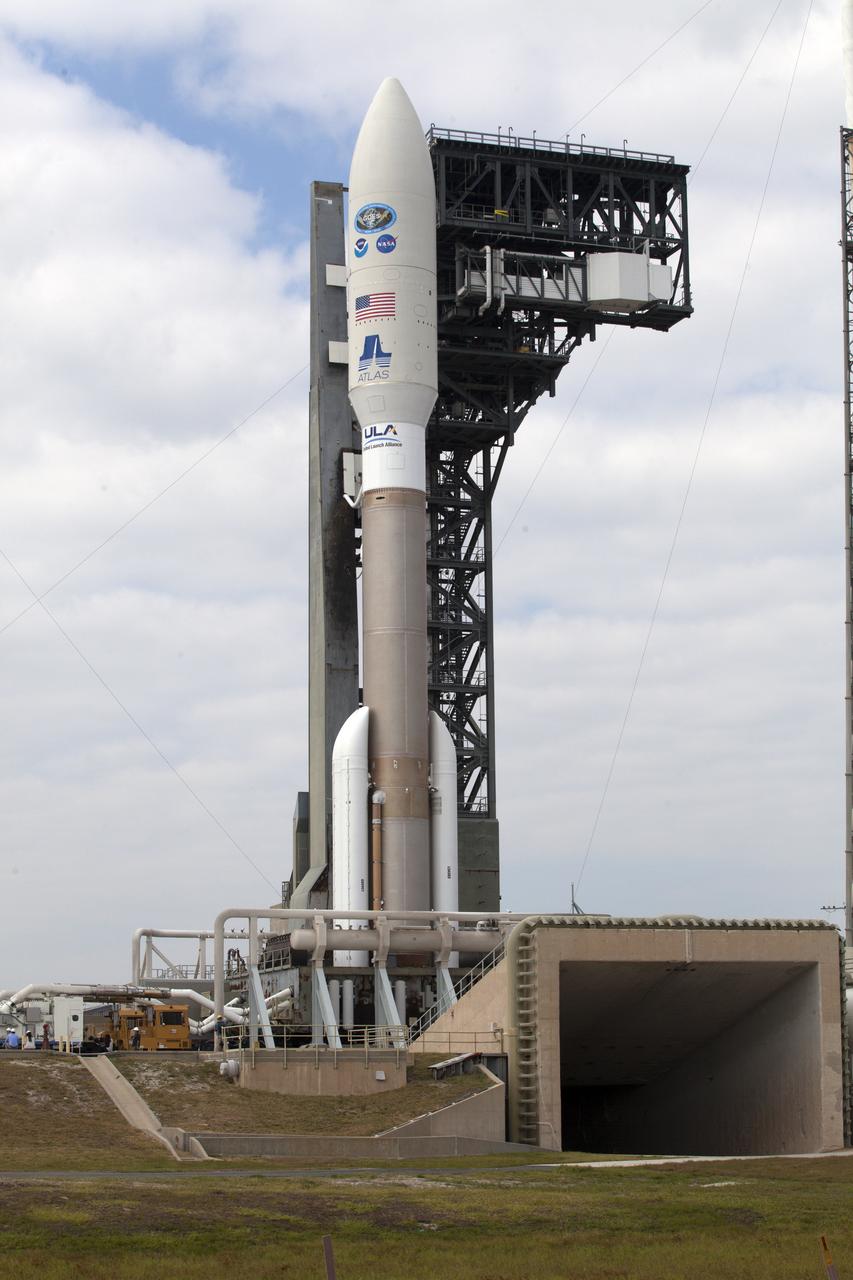

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The launch vehicle will send the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) to a geostationary position over the U.S. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES satellites.
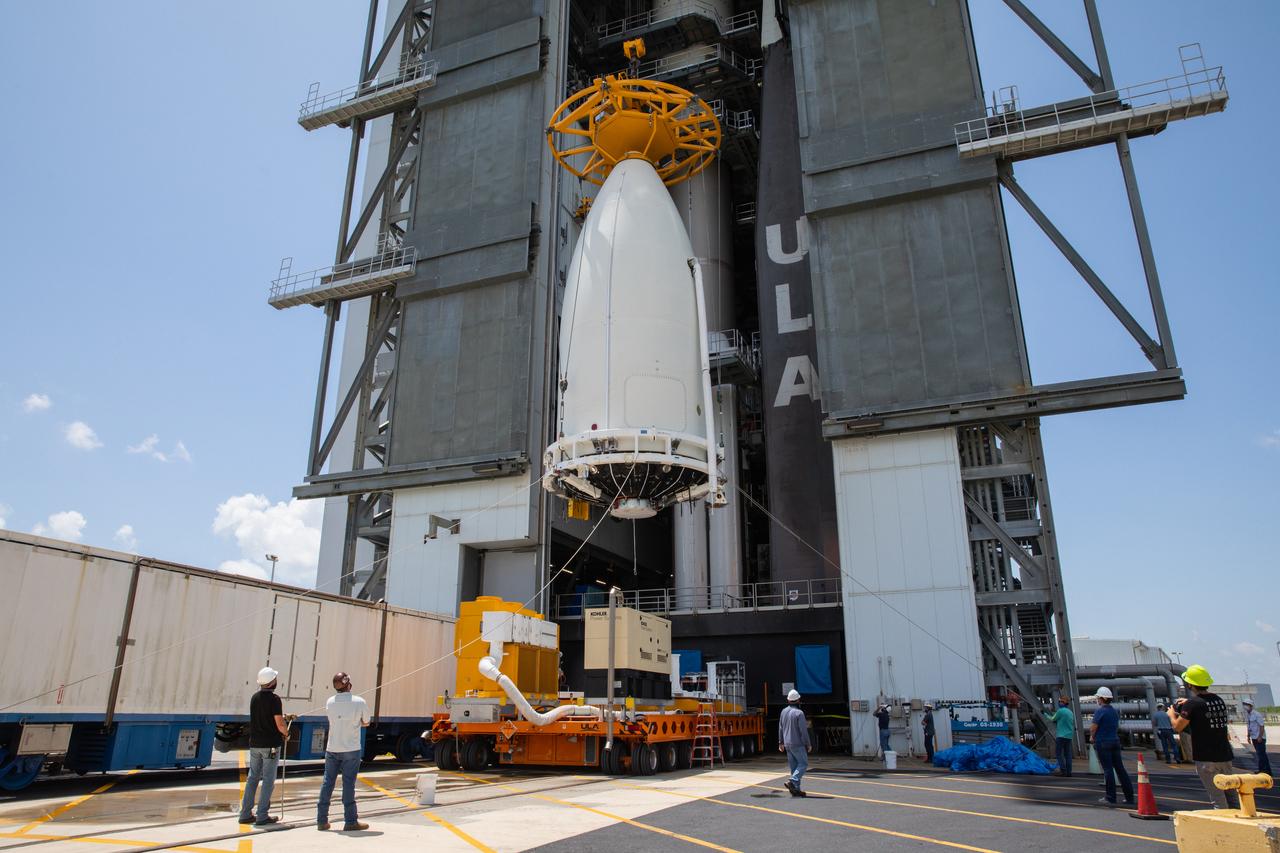

A crane is attached to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
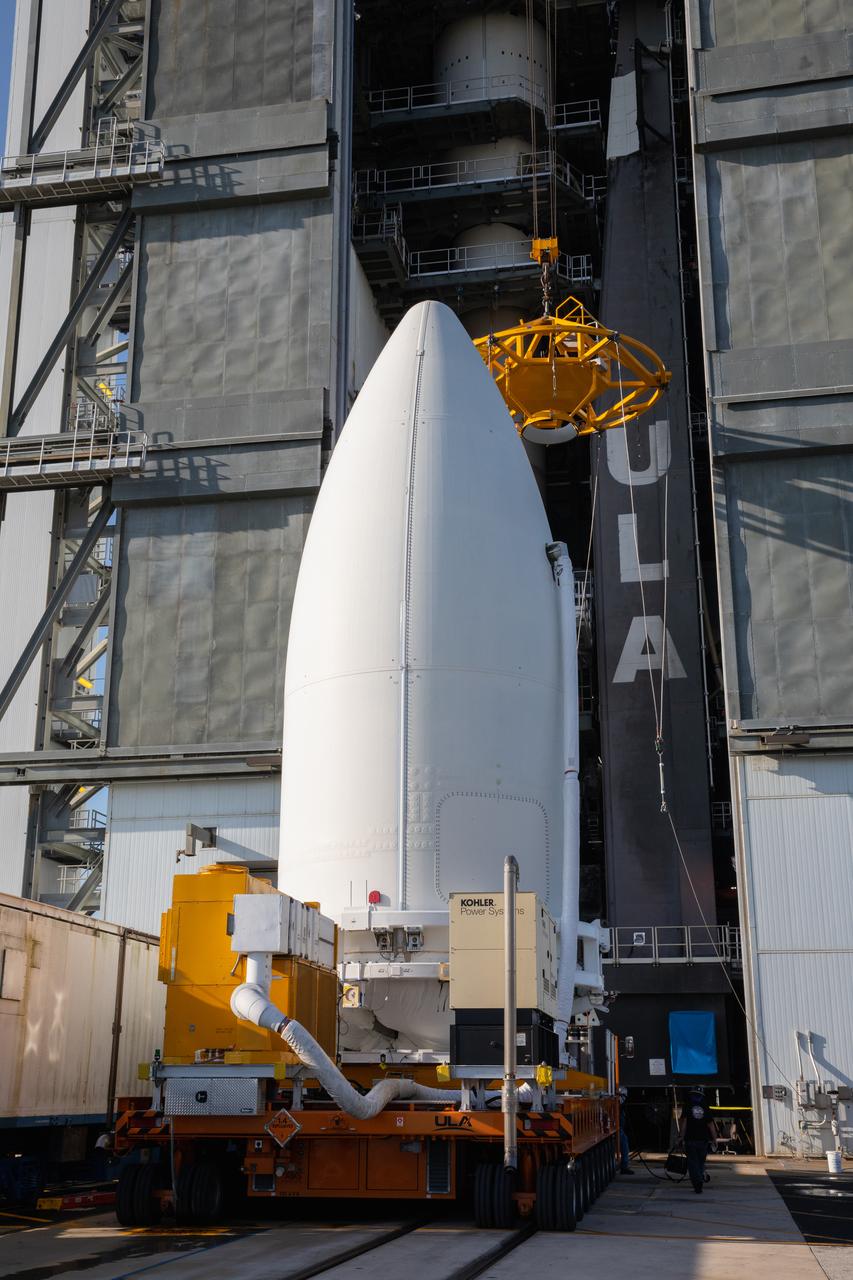

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
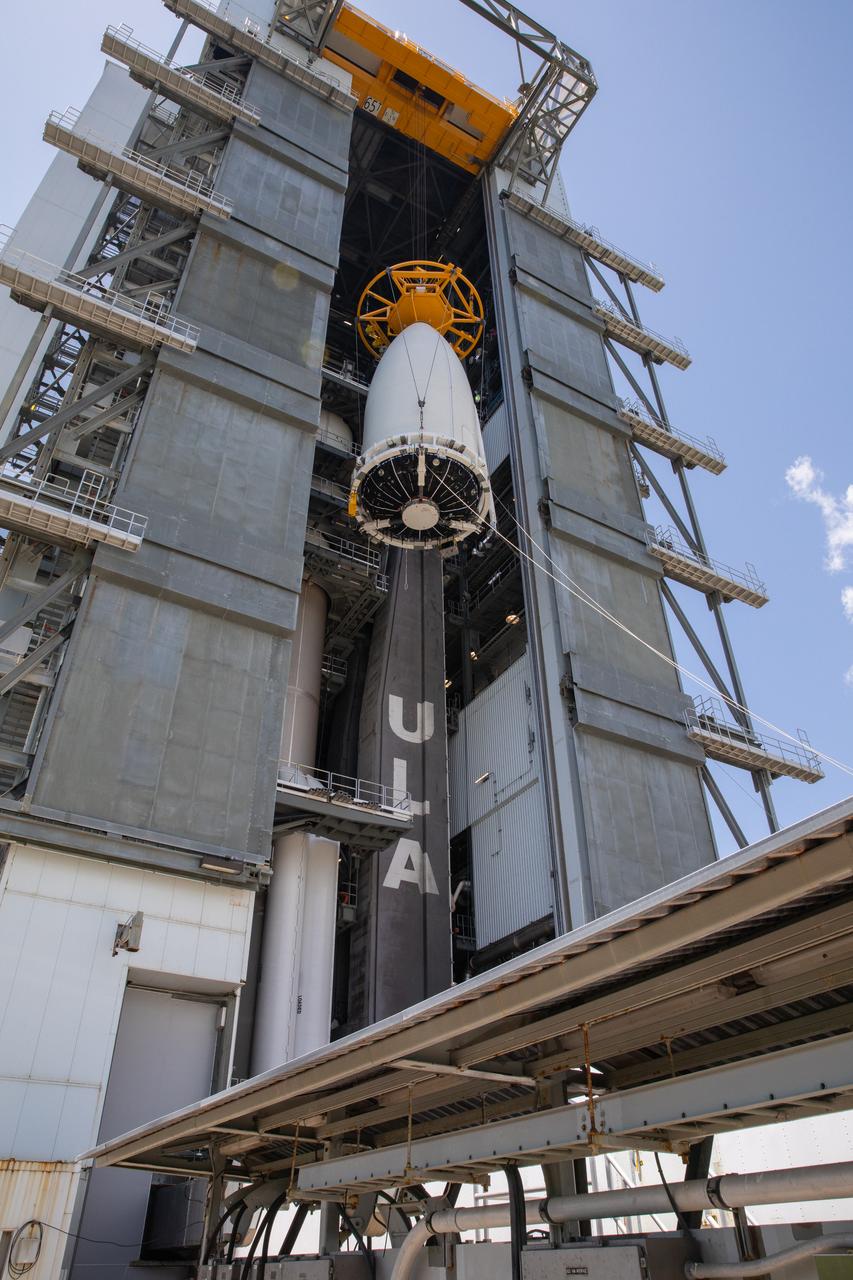

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is lifted high up inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
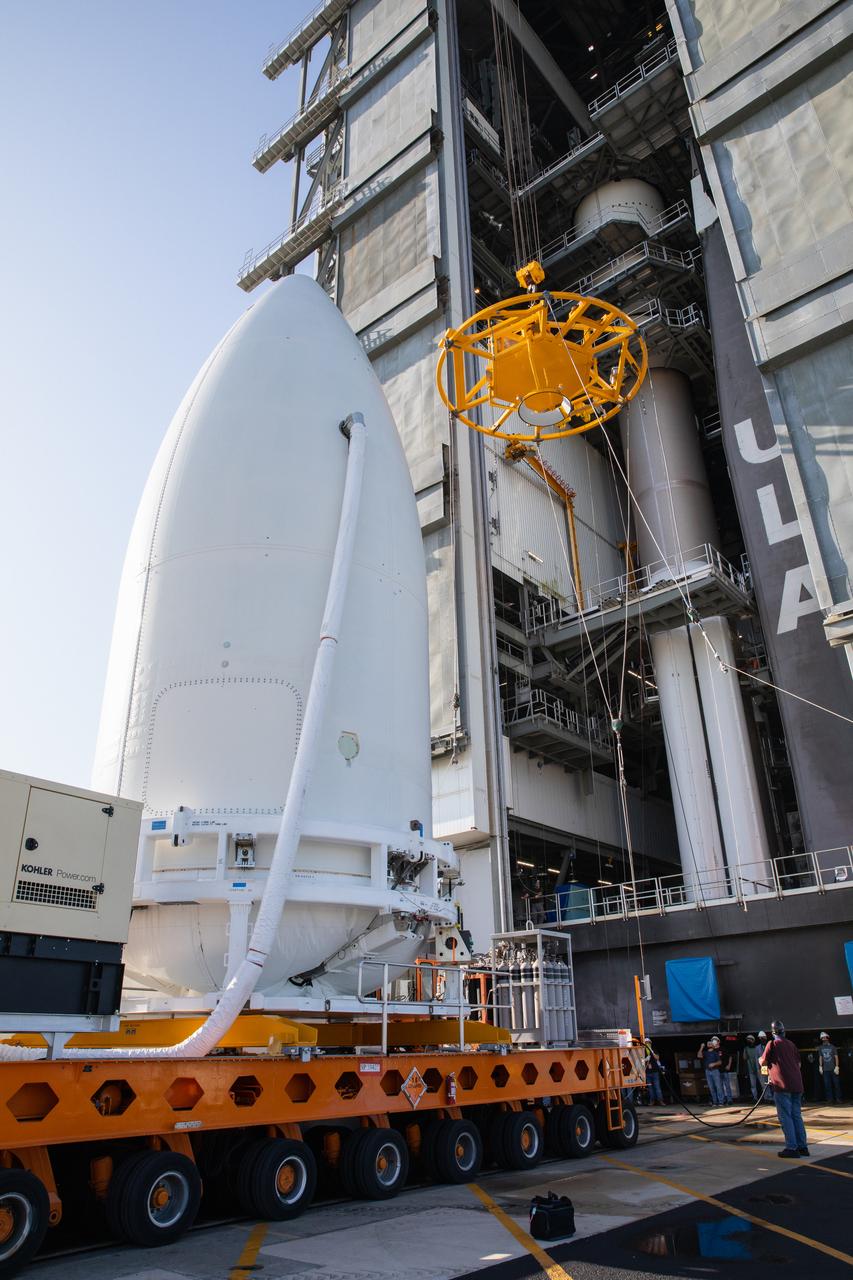

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A crane lifts the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
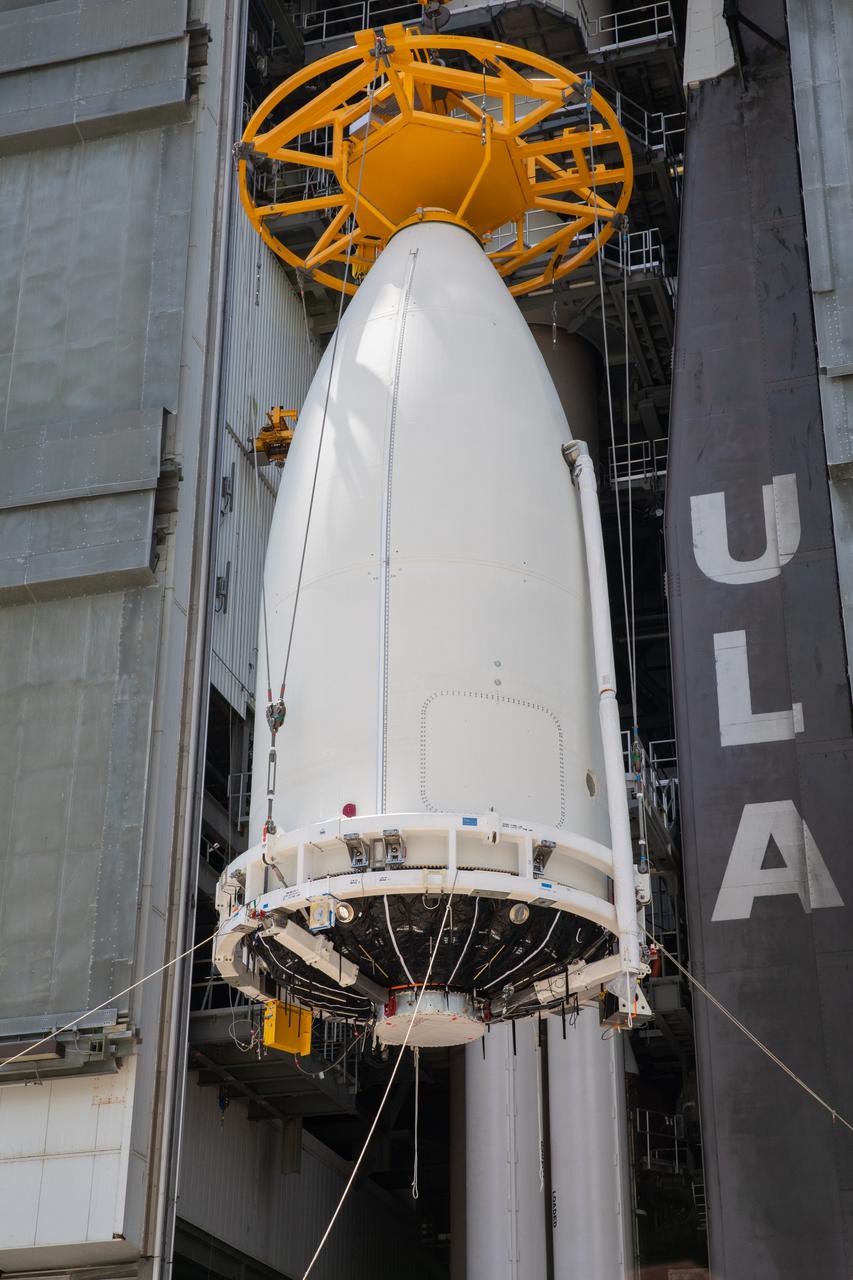

A crane lifts the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
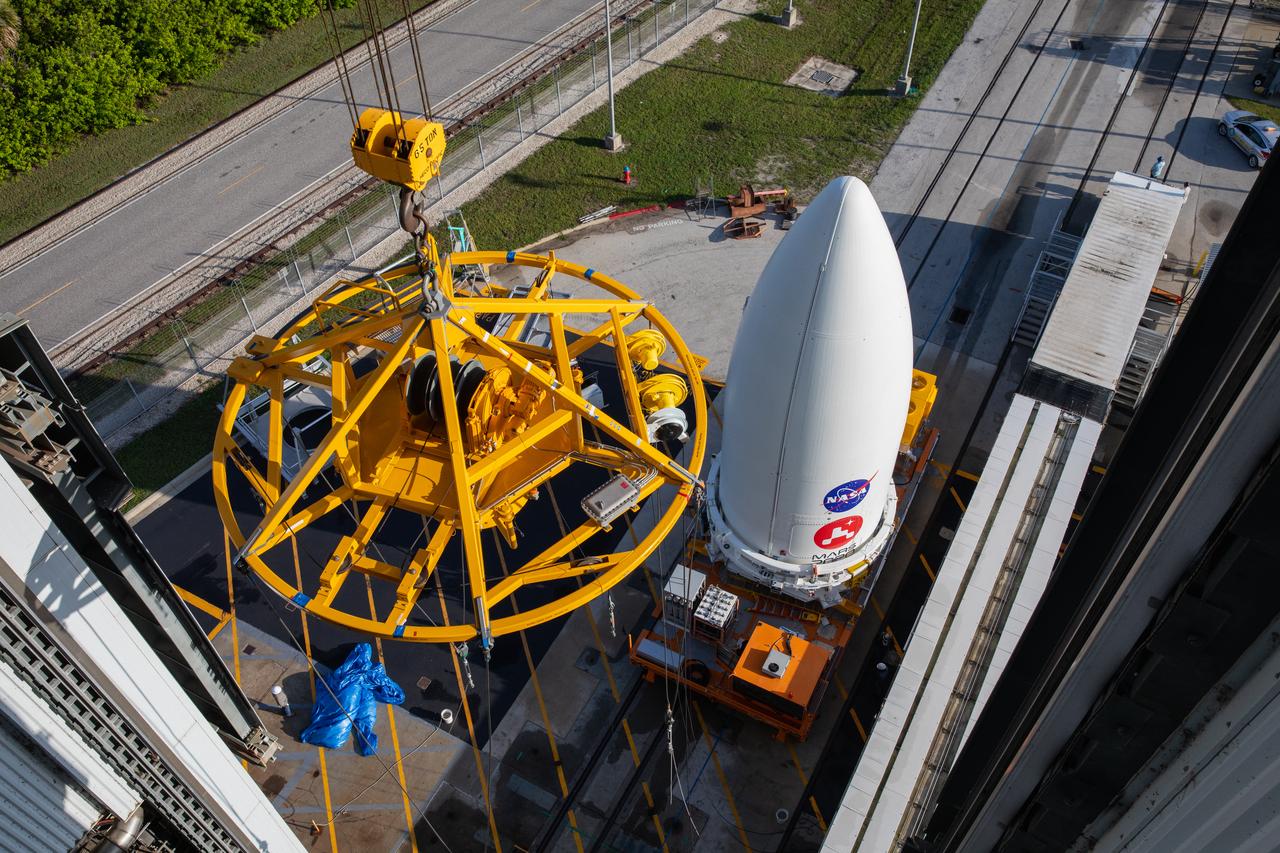

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
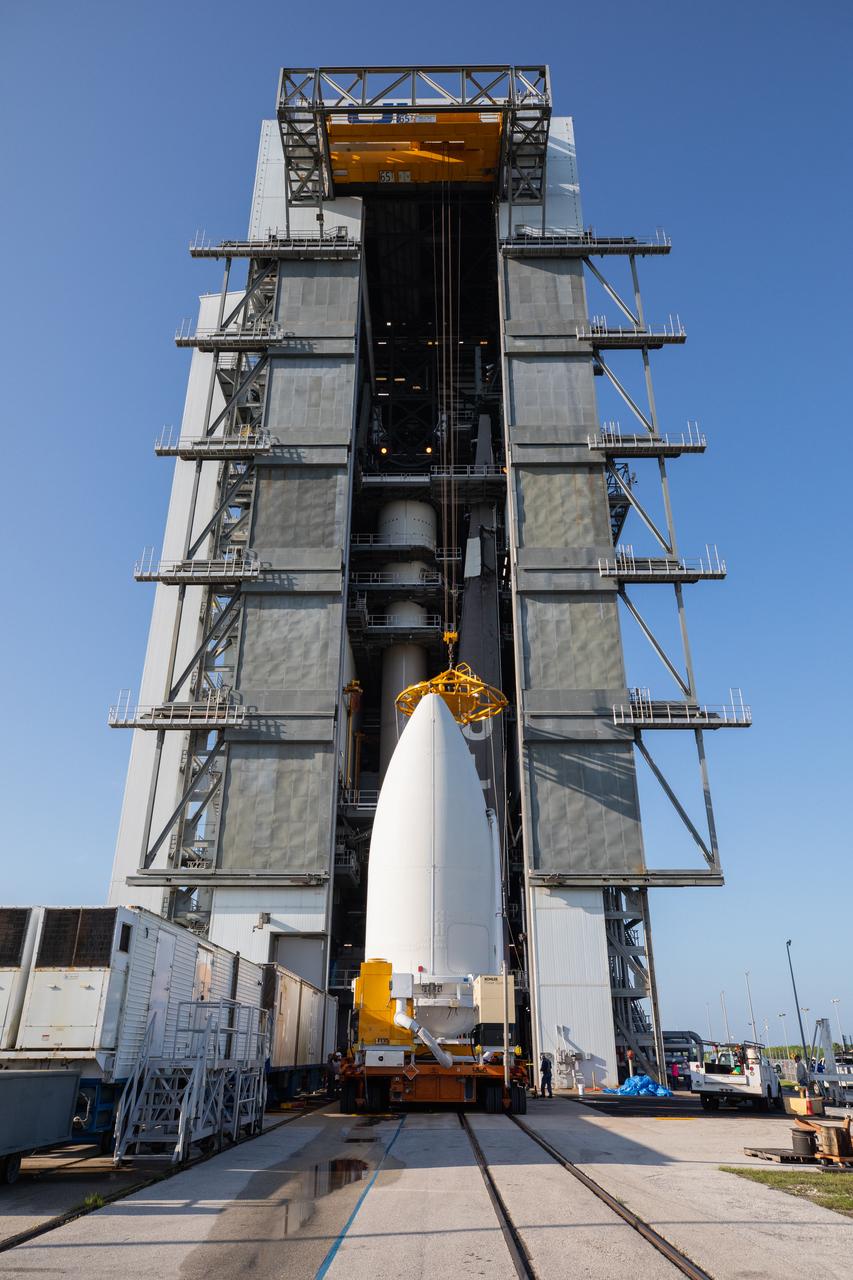

Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside up into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. Inside the VIF, the payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
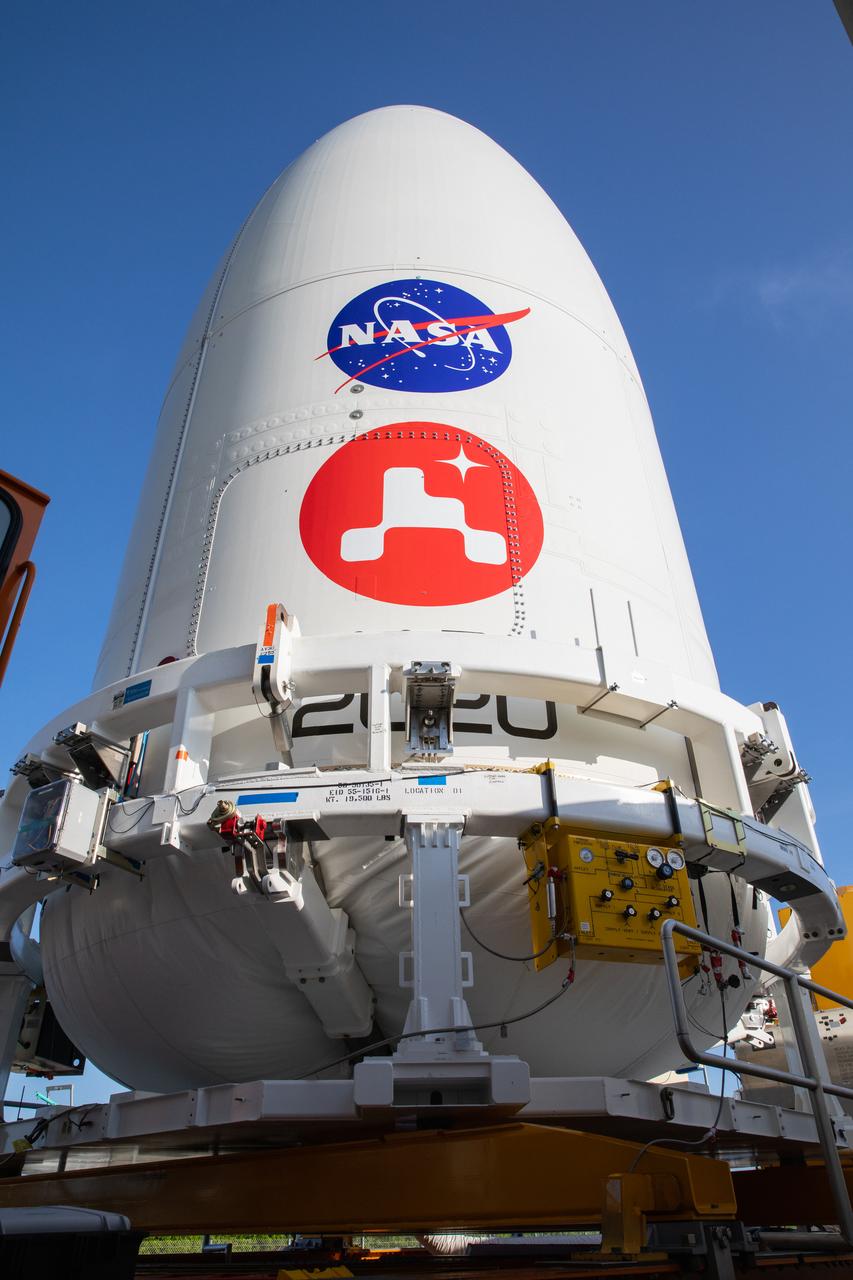

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be lifted up by crane and moved into the VIF where it will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
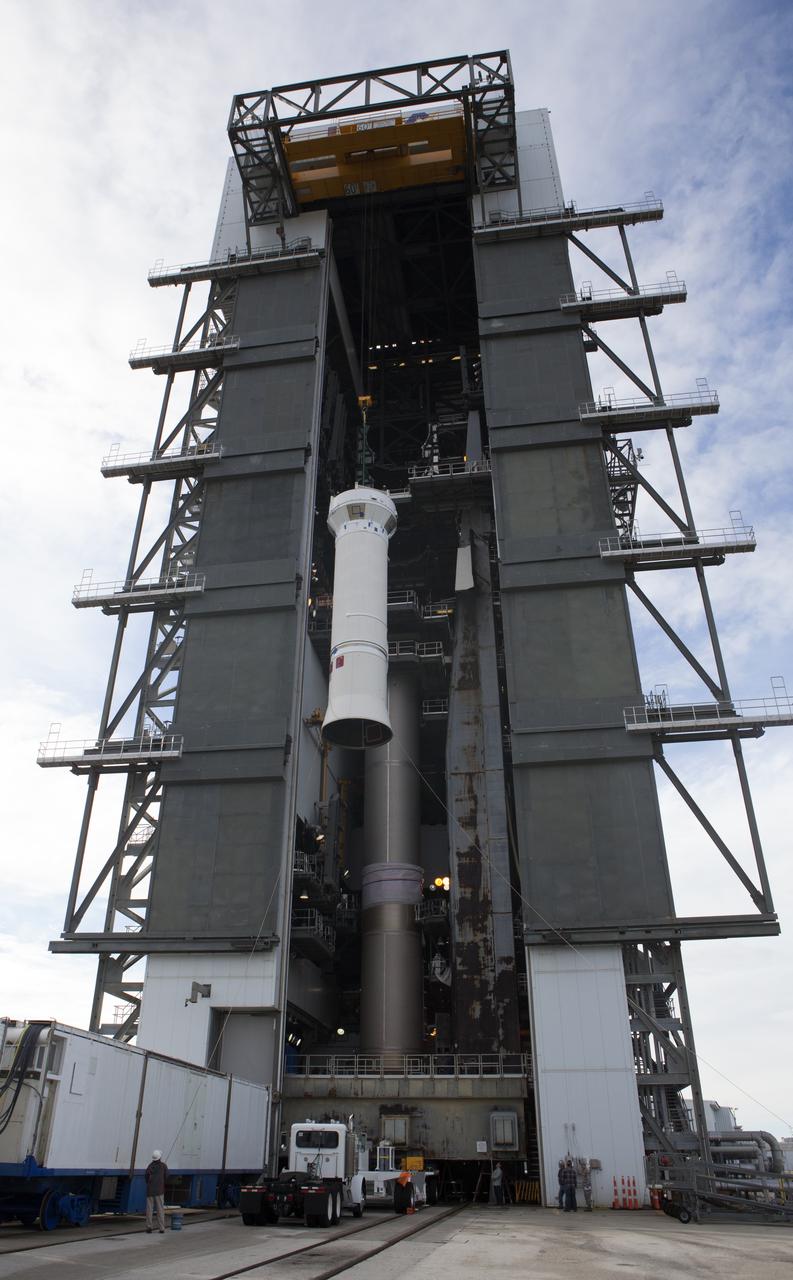

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is lifted up by crane at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted inside the VIF and lowered for mating to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
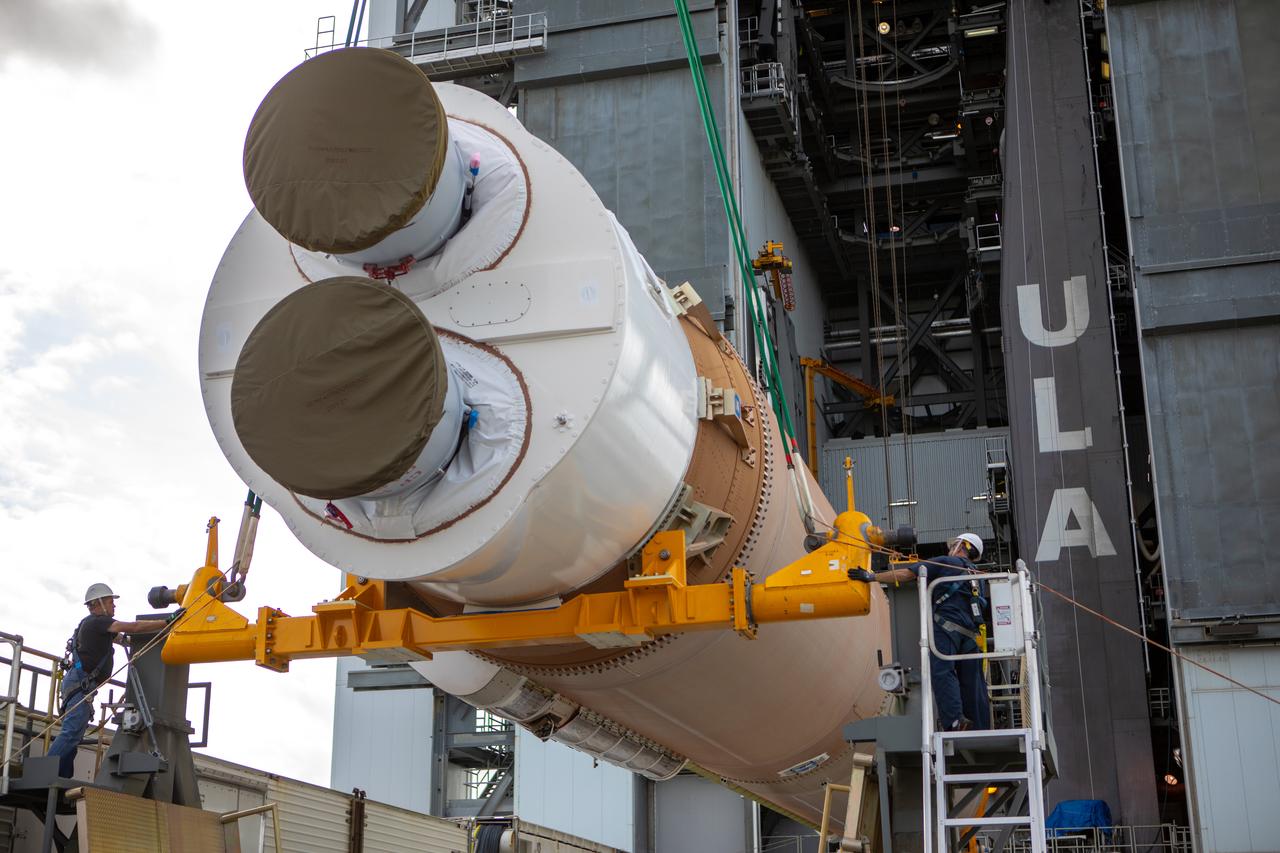

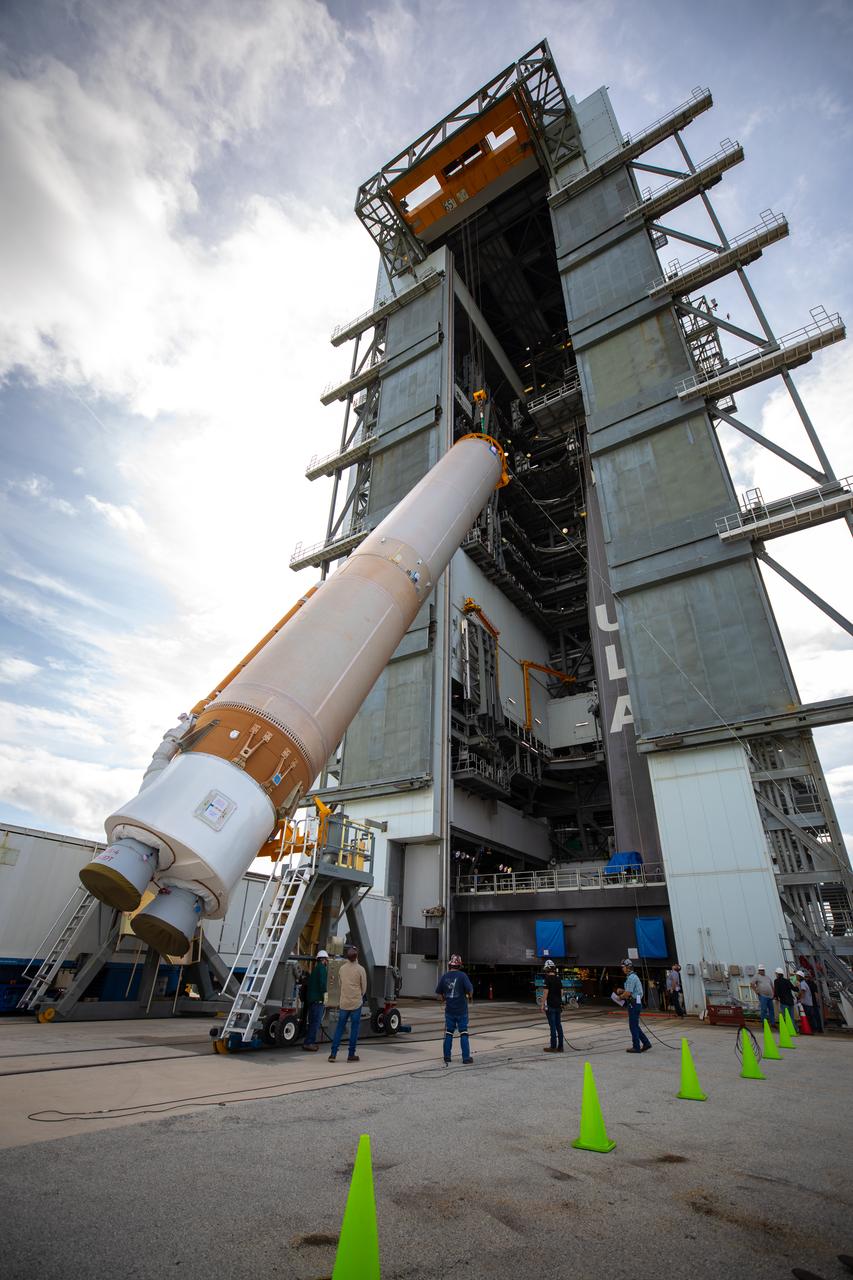
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
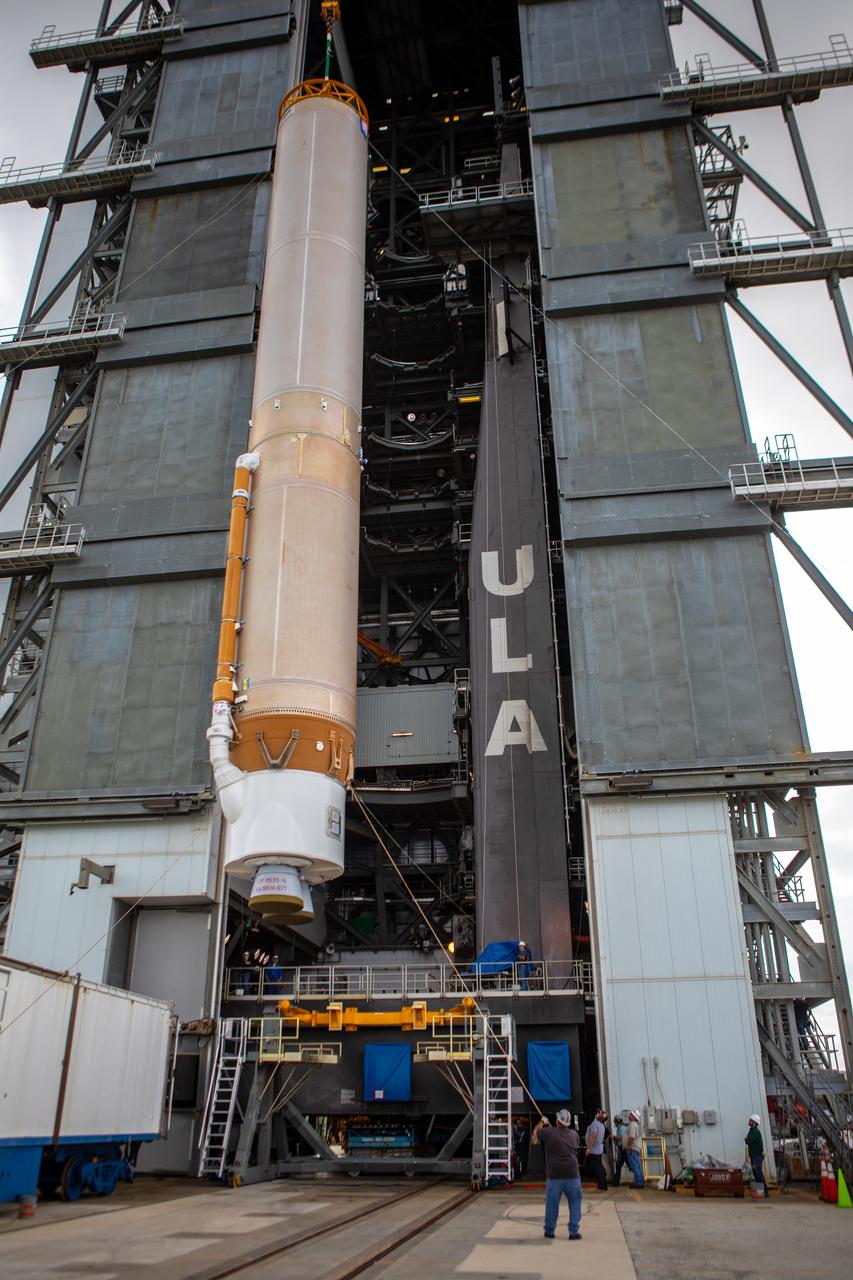

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
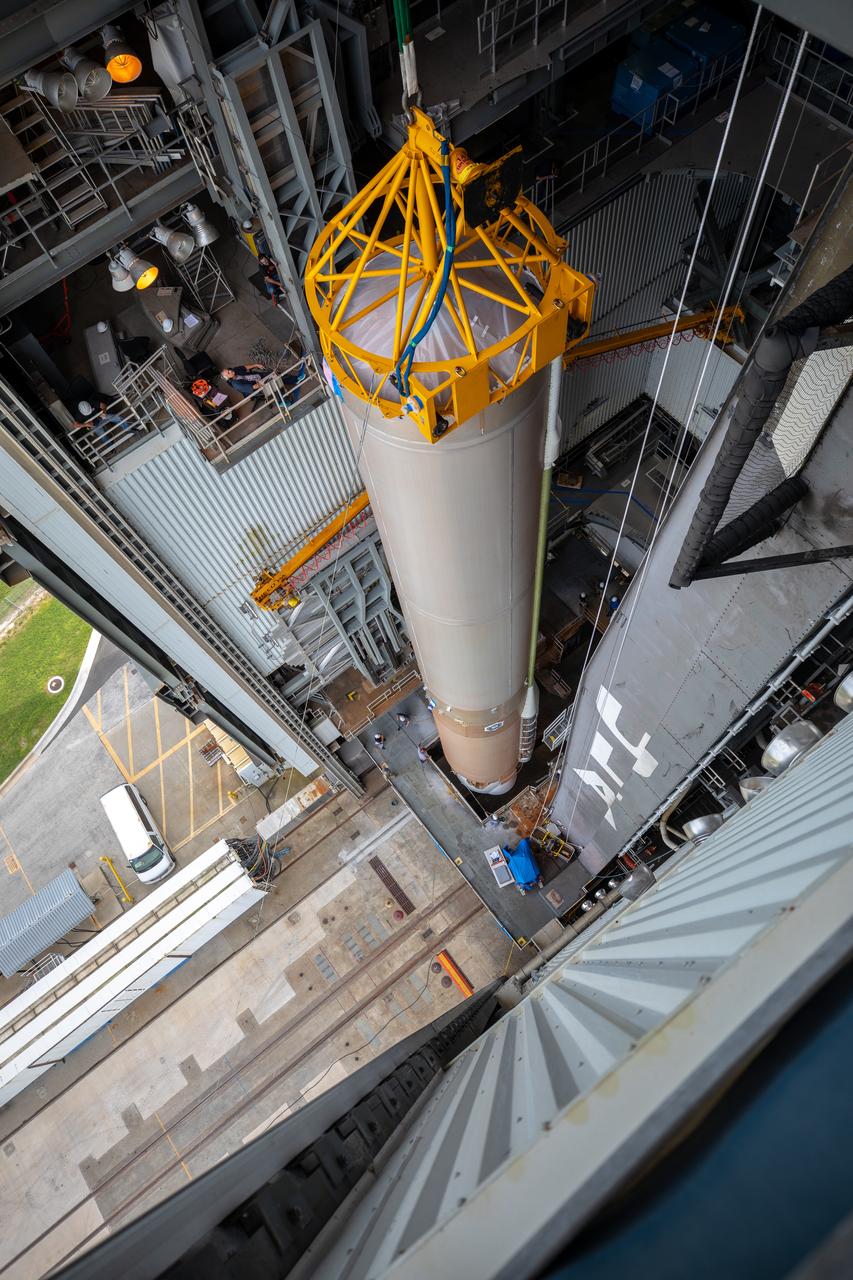

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
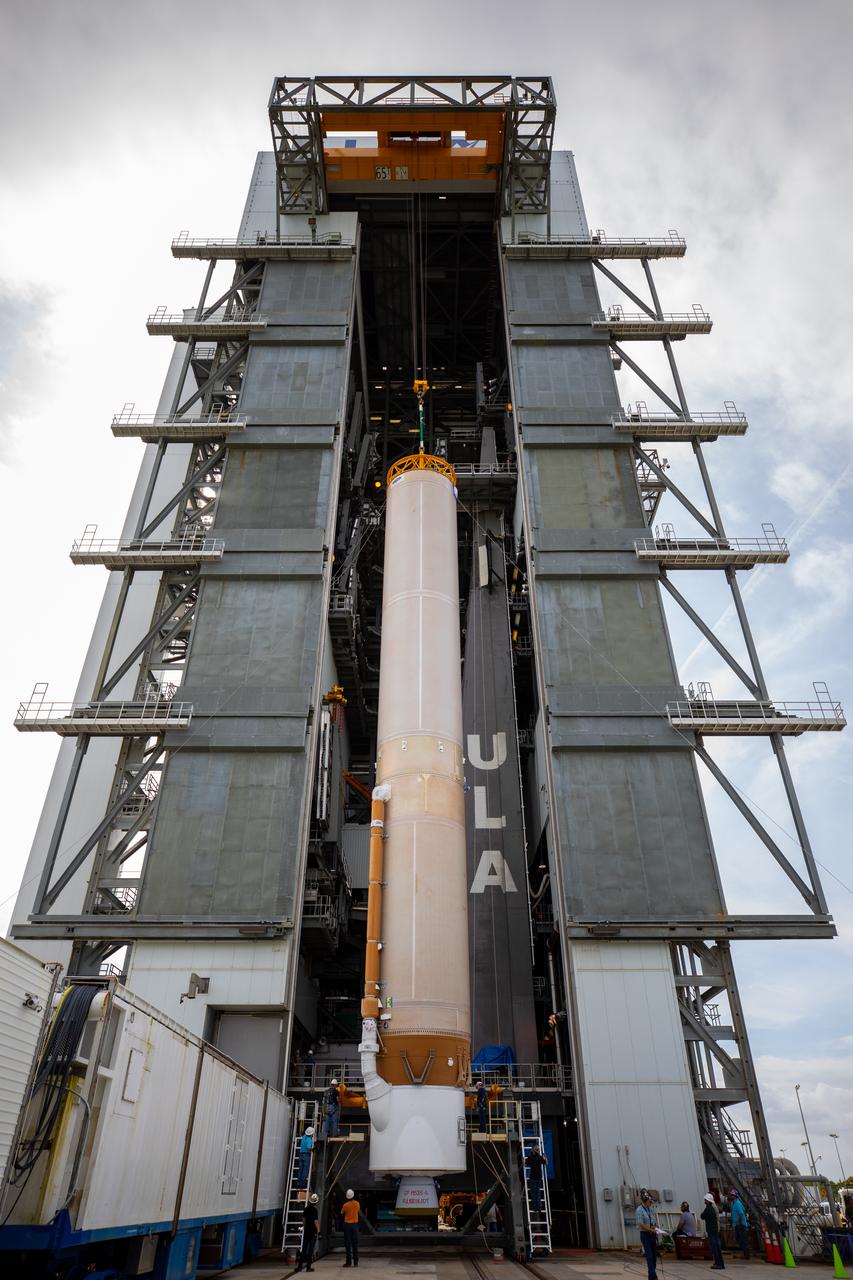

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
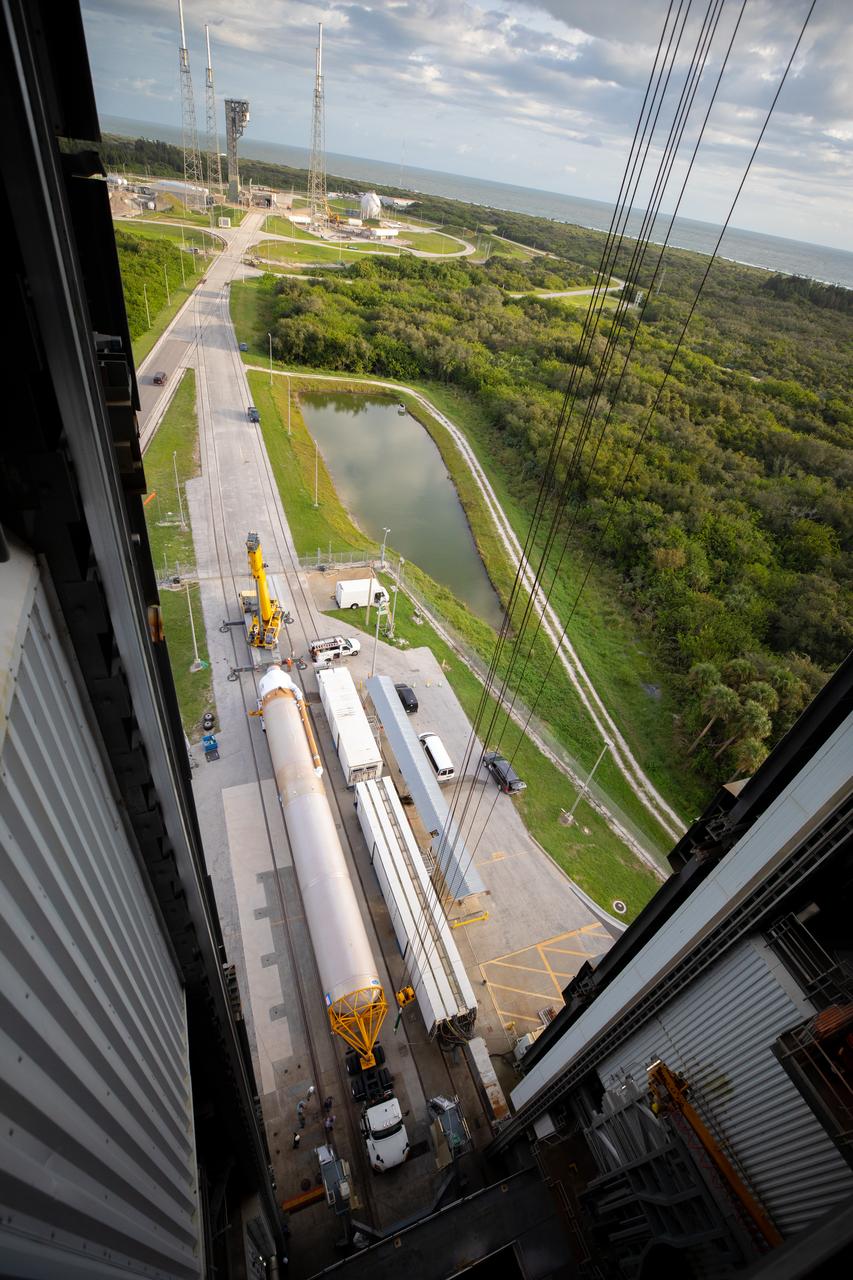

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position on Nov. 4, 2019, in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
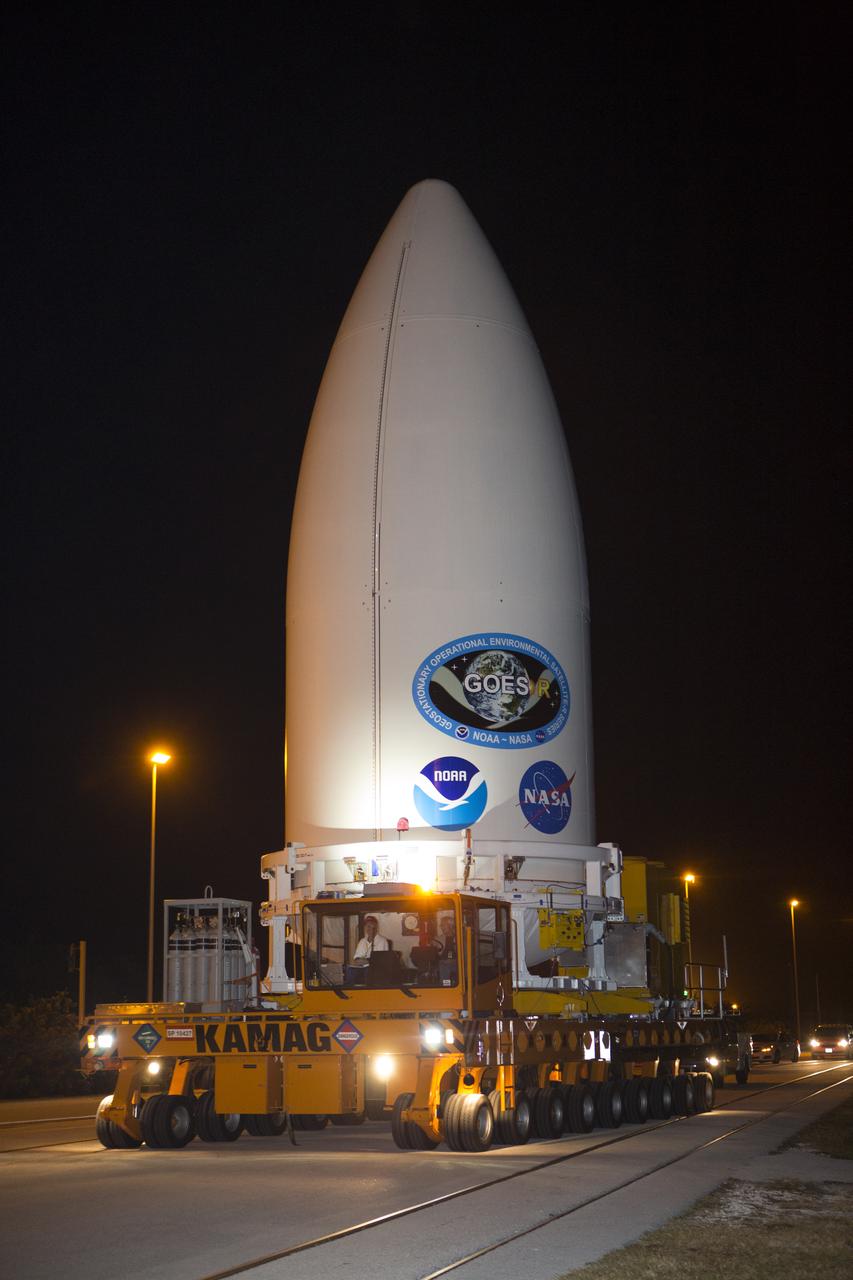

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is being transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
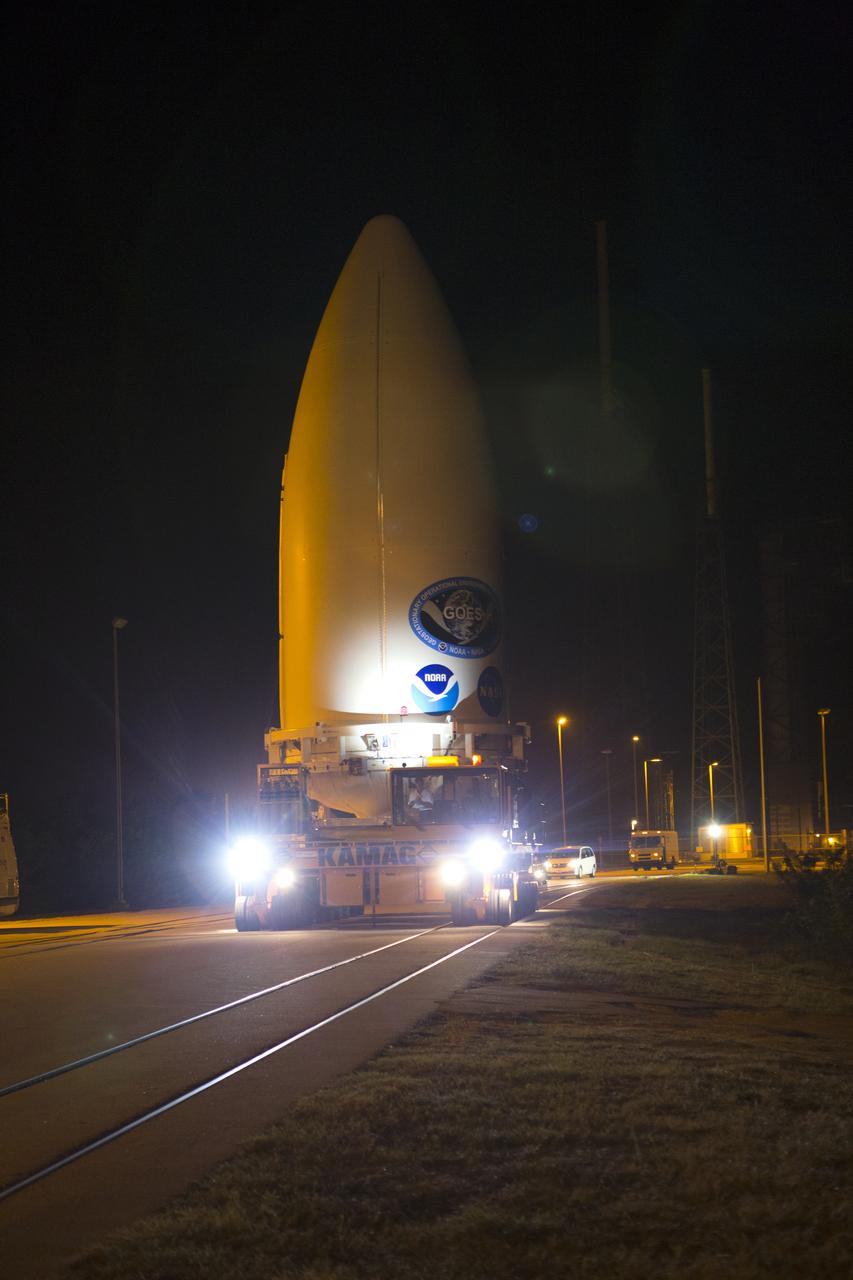

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is being transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
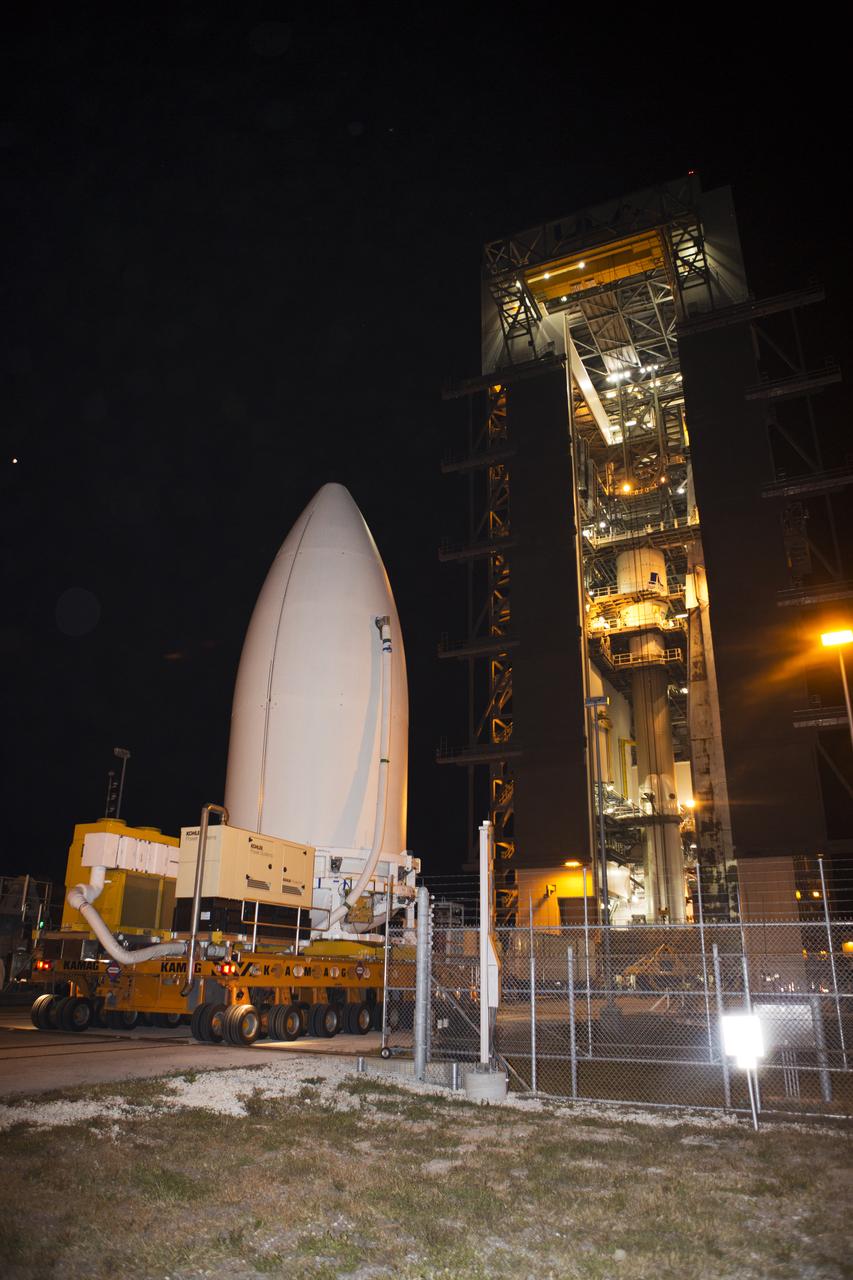

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-R will be stacked atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch atop the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-R will be stacked atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch atop the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
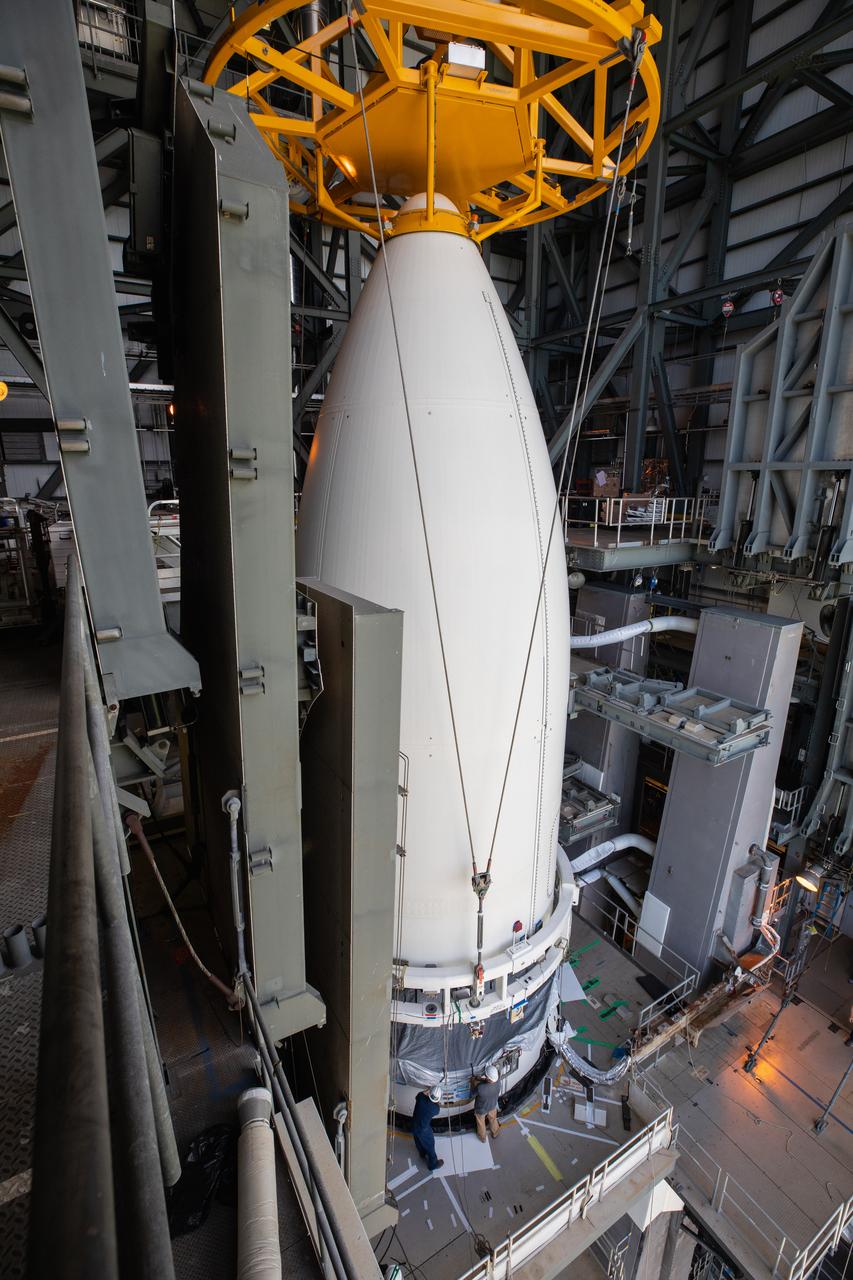

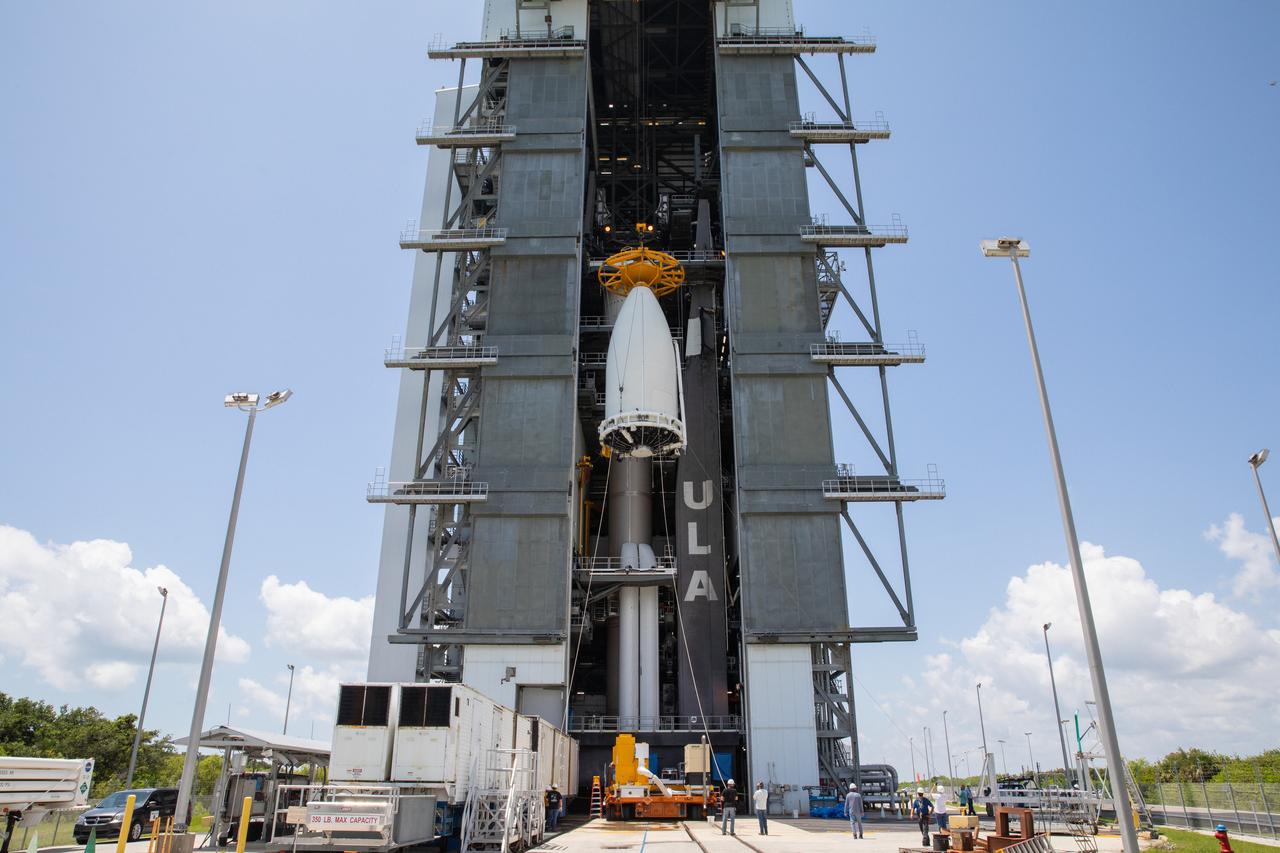
Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside is secured on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket on July 7, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
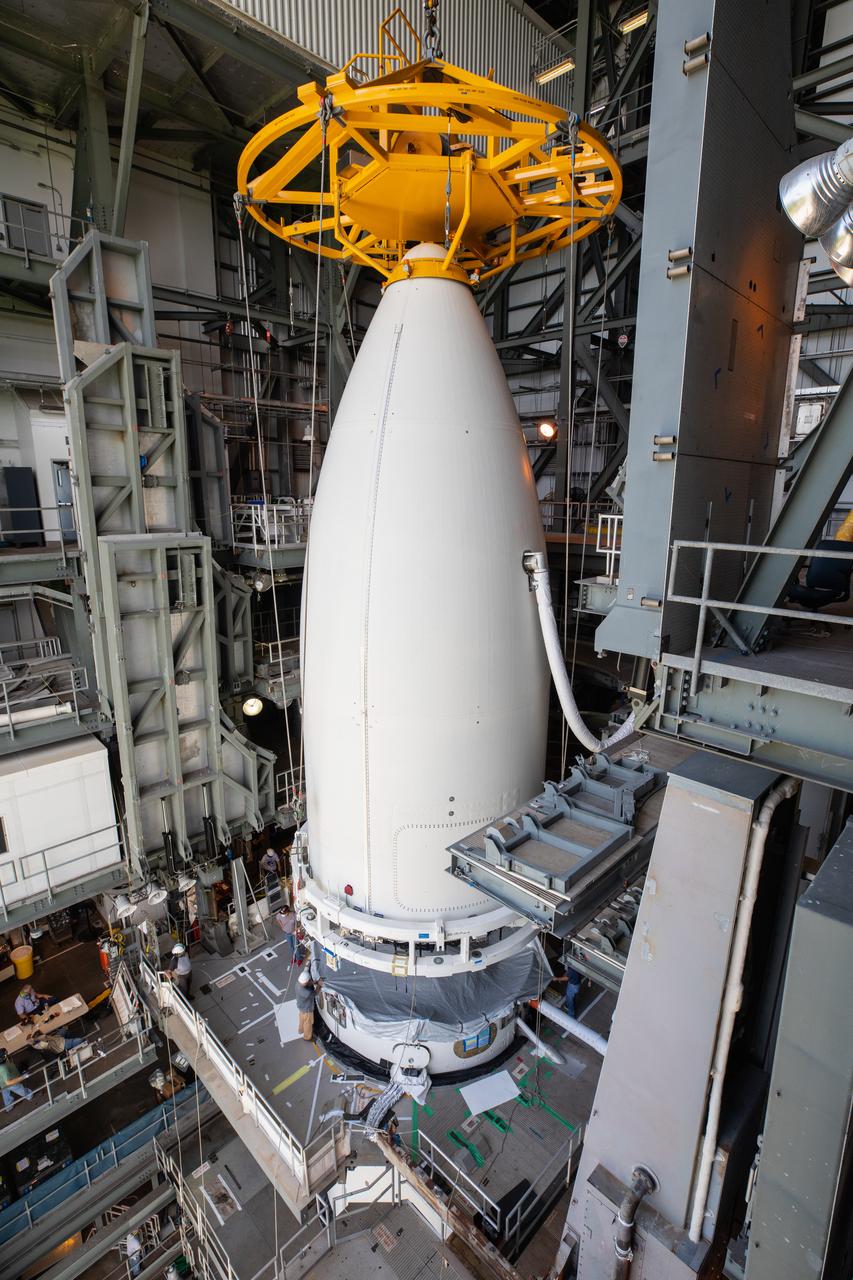

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside is secured on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket on July 7, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
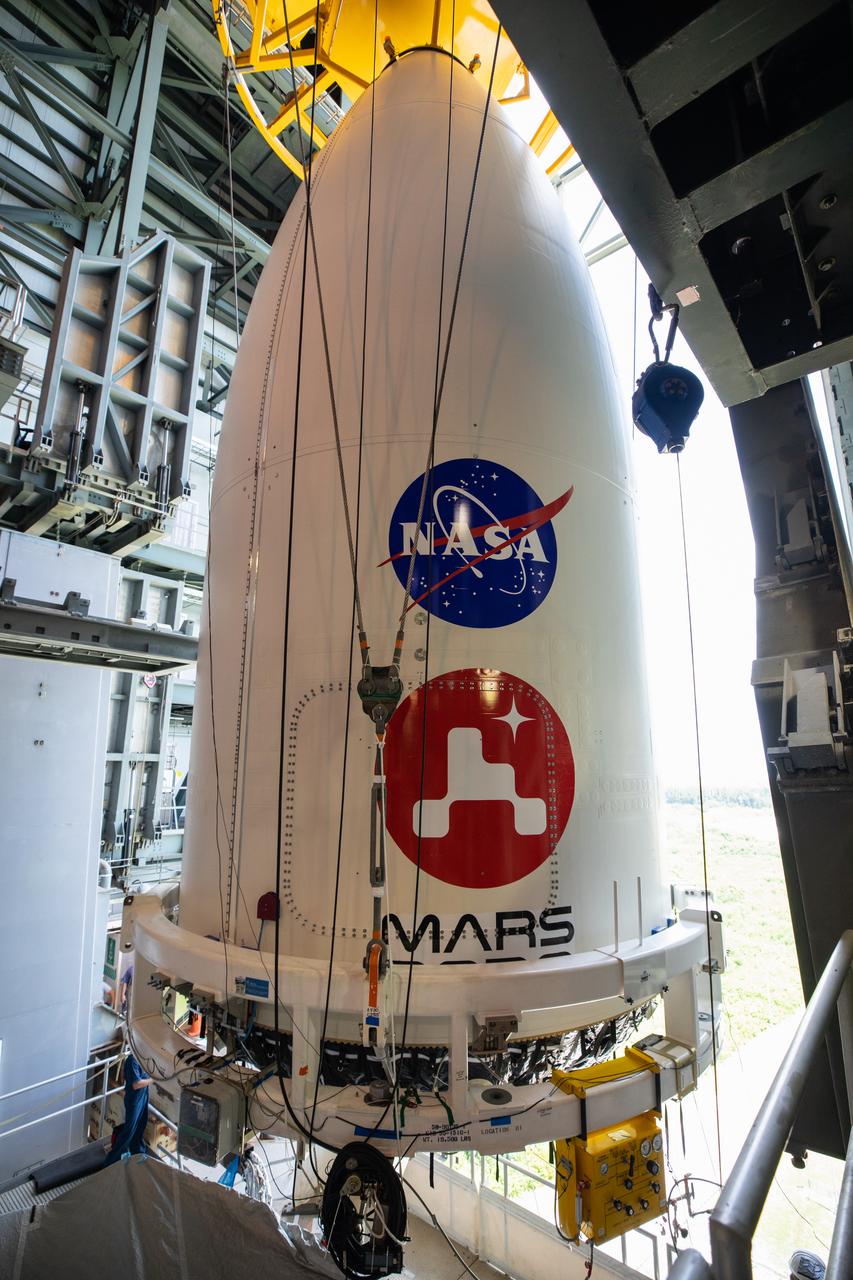

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is positioned on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A close-up view of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover inside in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing is being secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
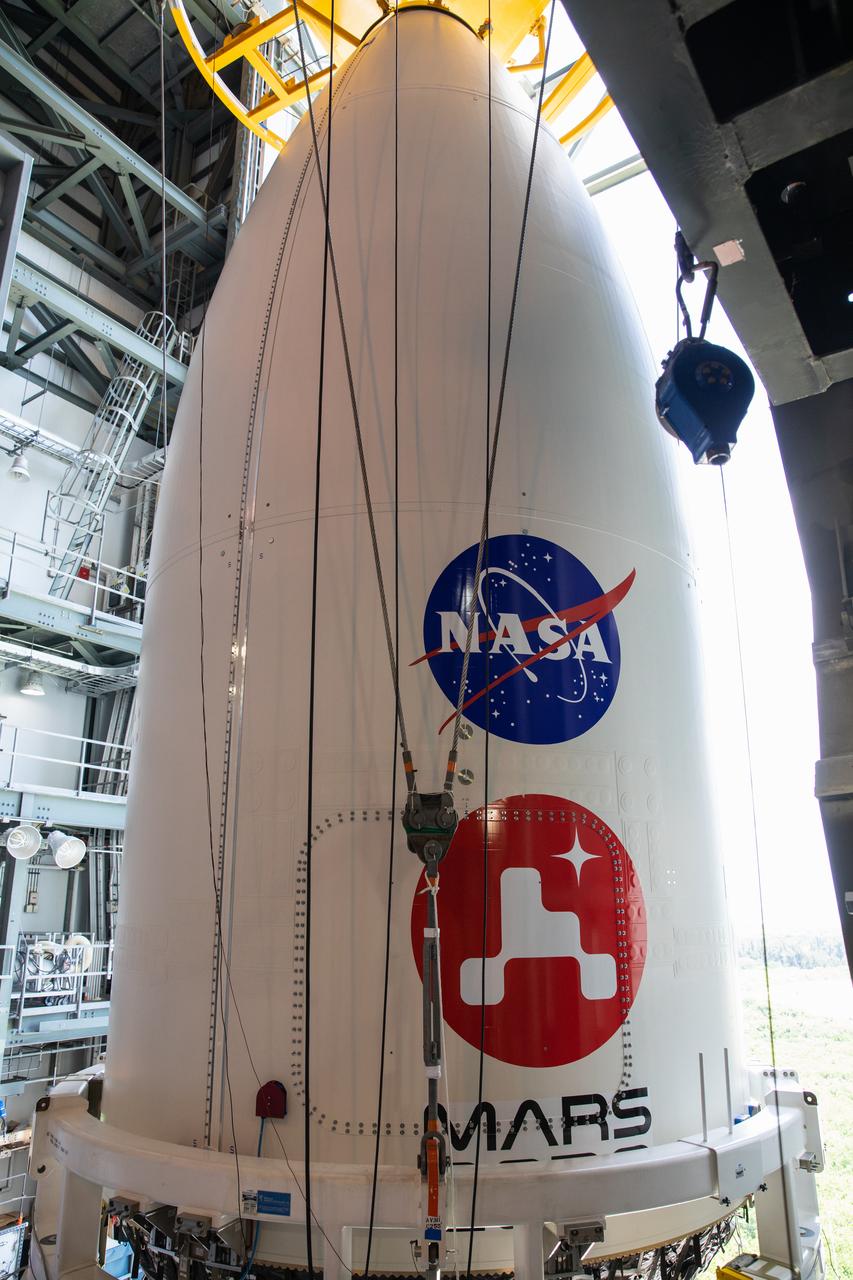
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing with NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover secured inside is positioned on top of the ULA Atlas V rocket inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. The payload fairing will be secured on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 30. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
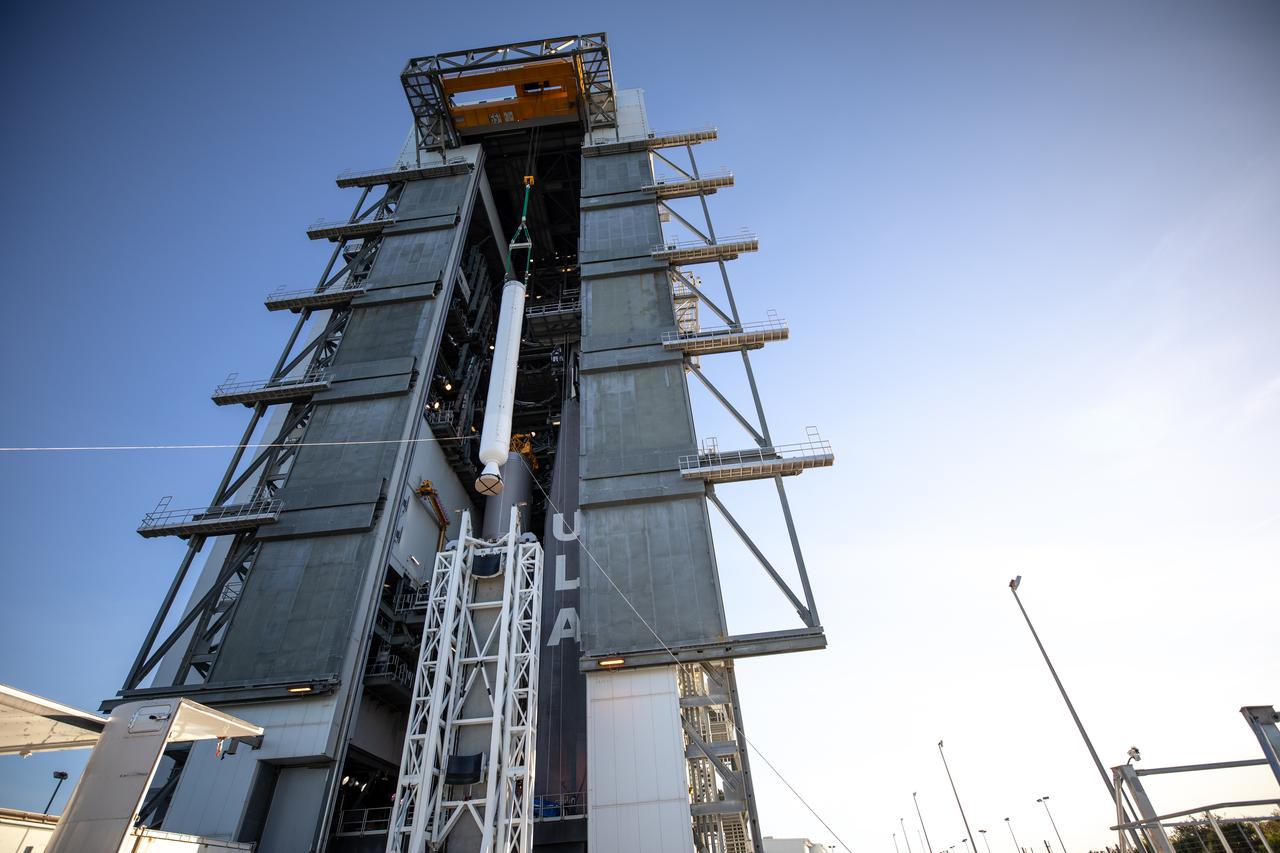

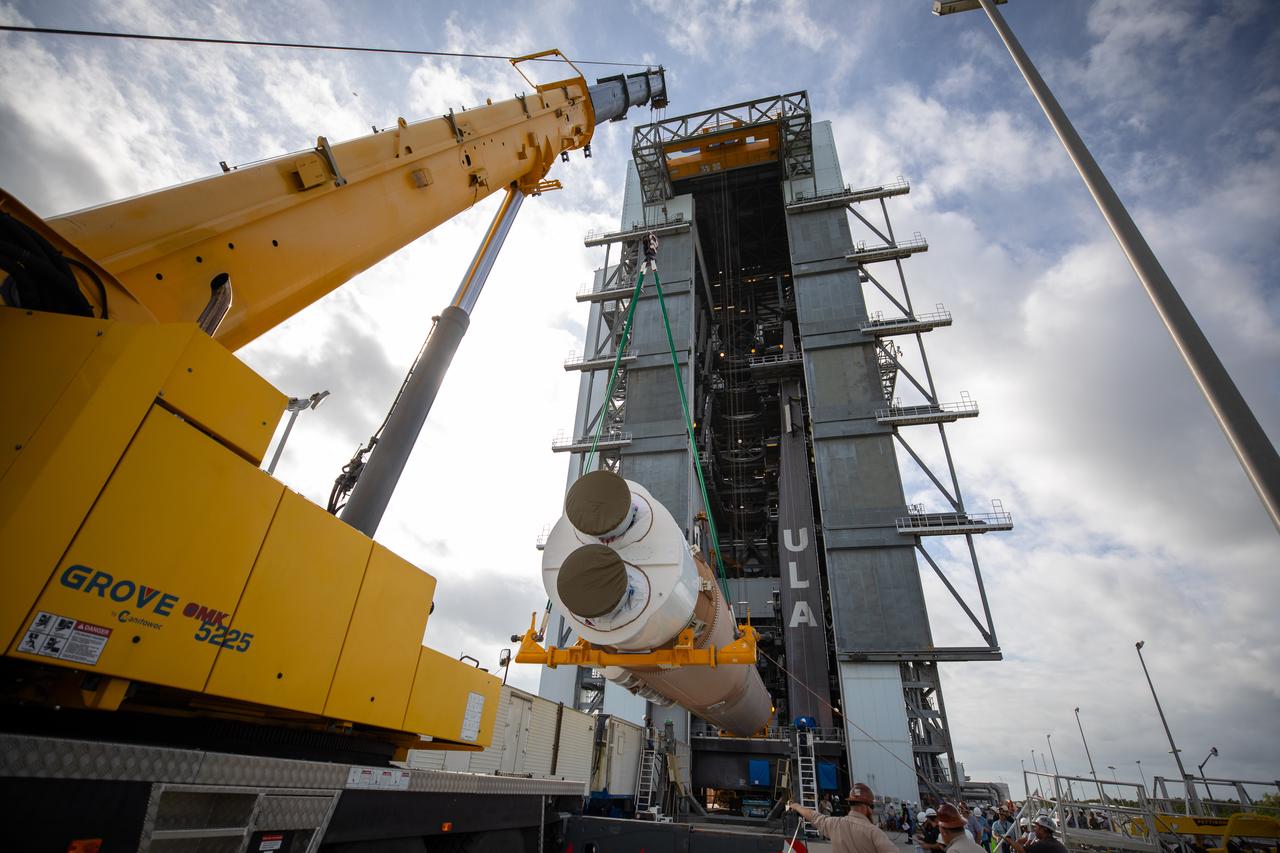
Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
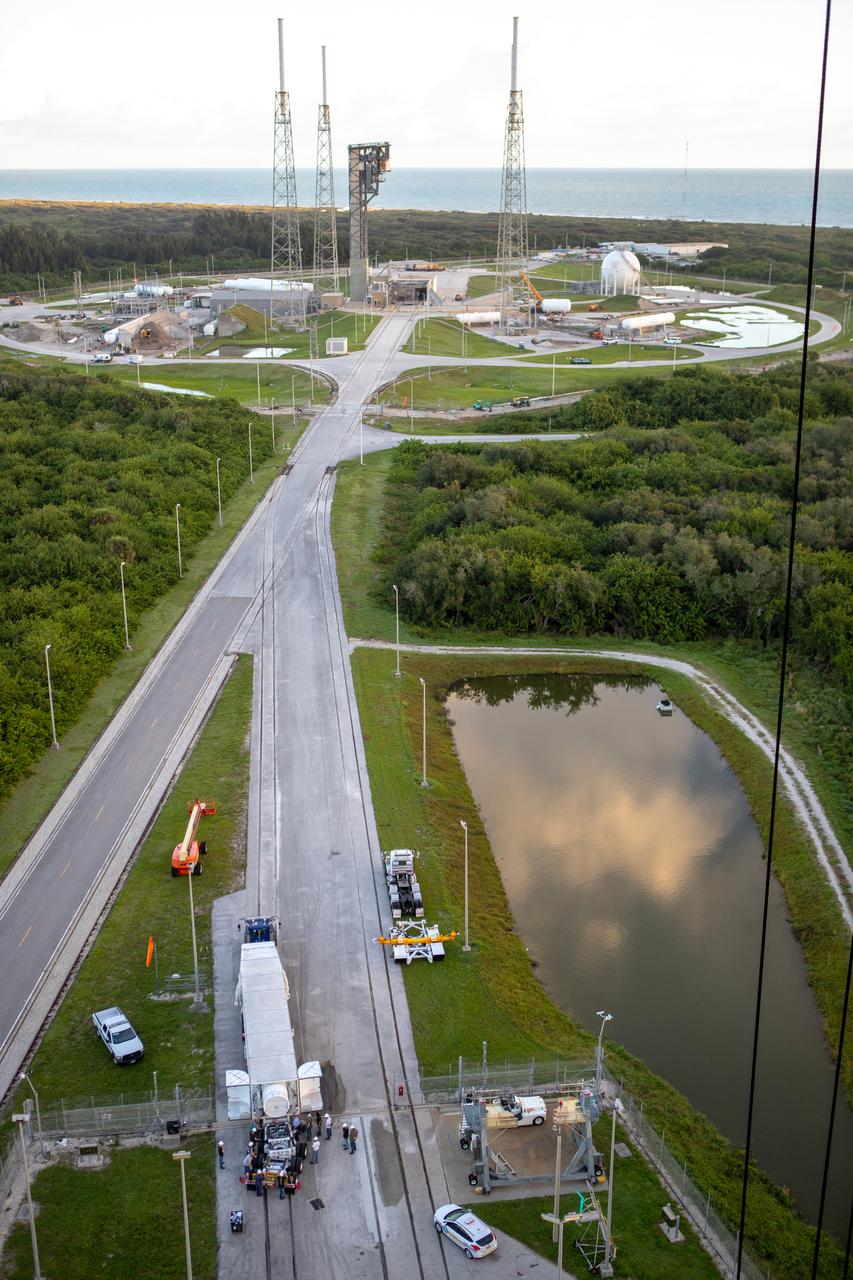

Two solid rocket boosters are delivered to the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019. The boosters were then mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

Two solid rocket boosters are mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.

A test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission arrives at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator will be used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
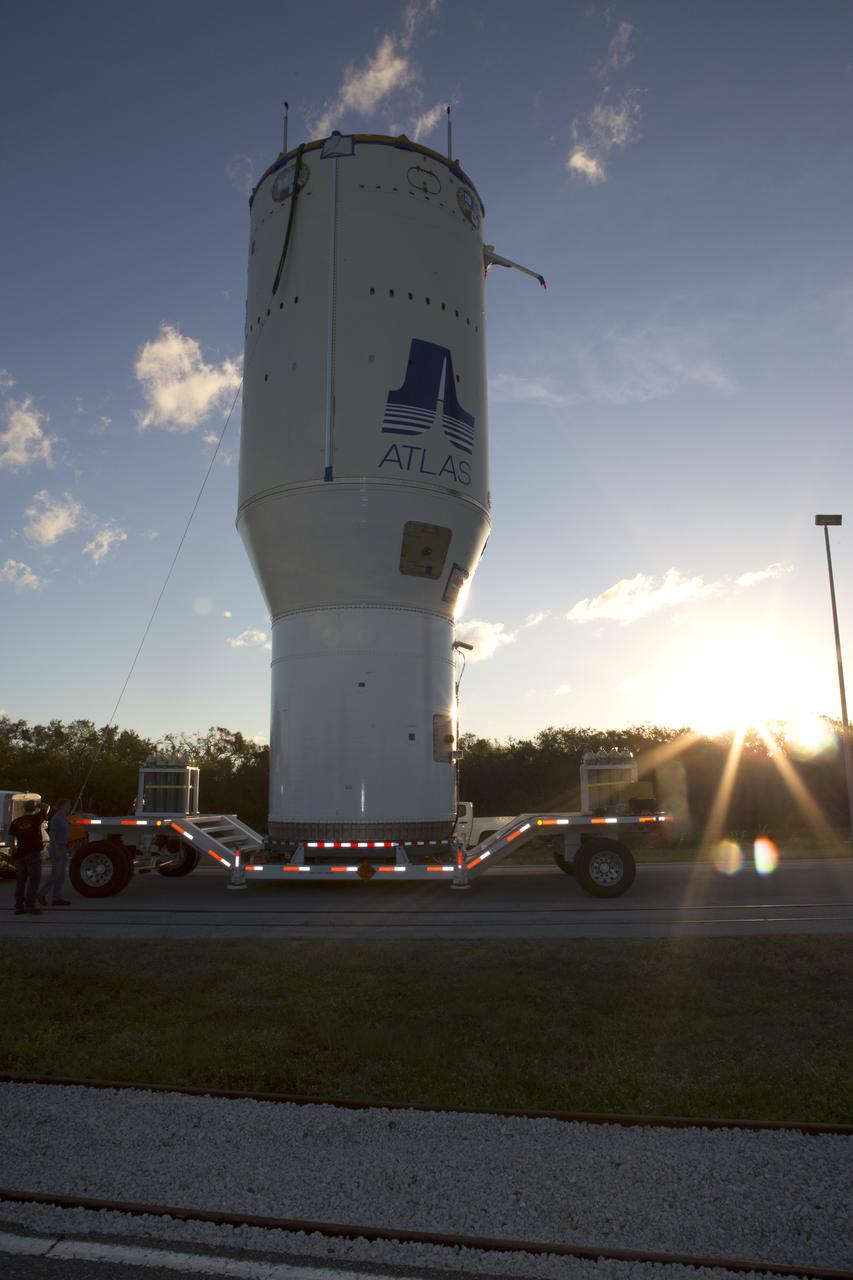

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is on a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
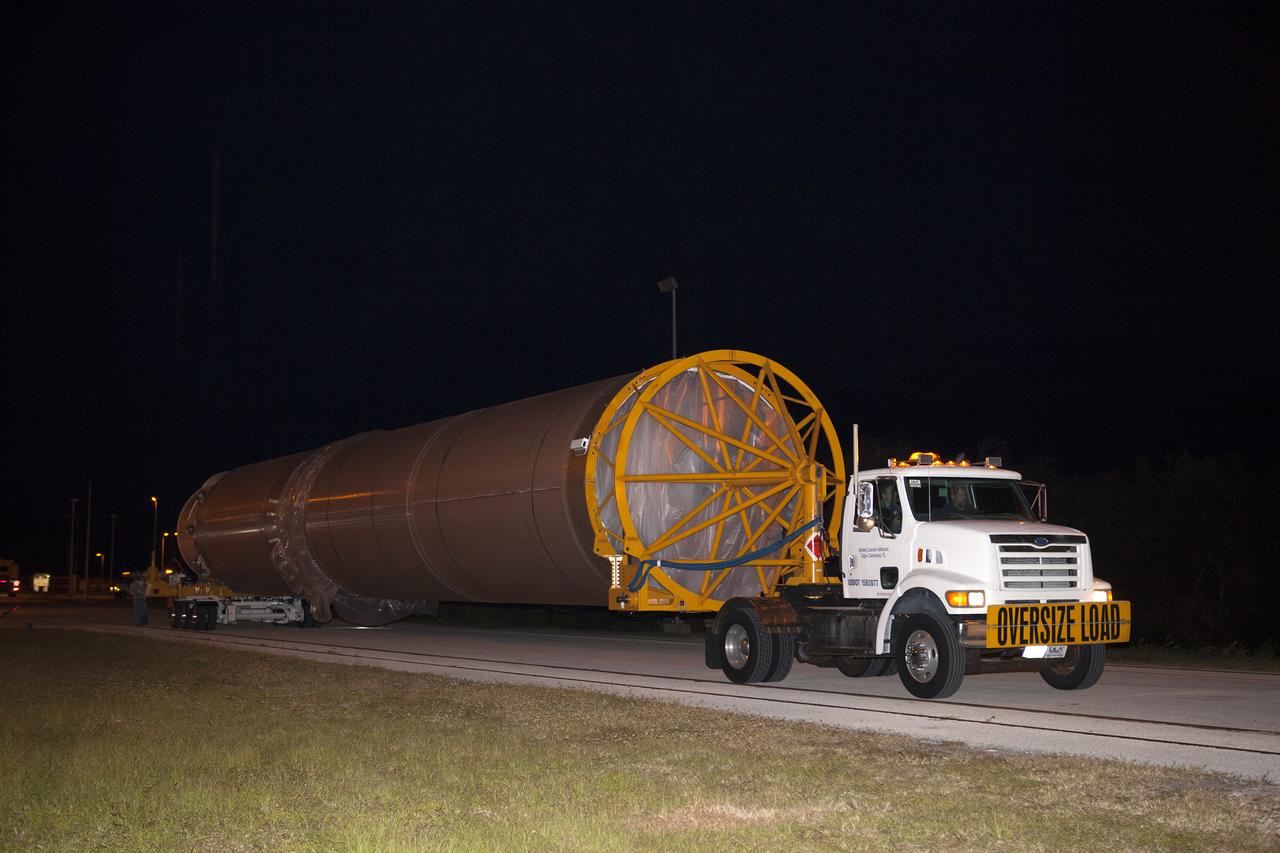

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is on its way from the Atlas Space Operations Center to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
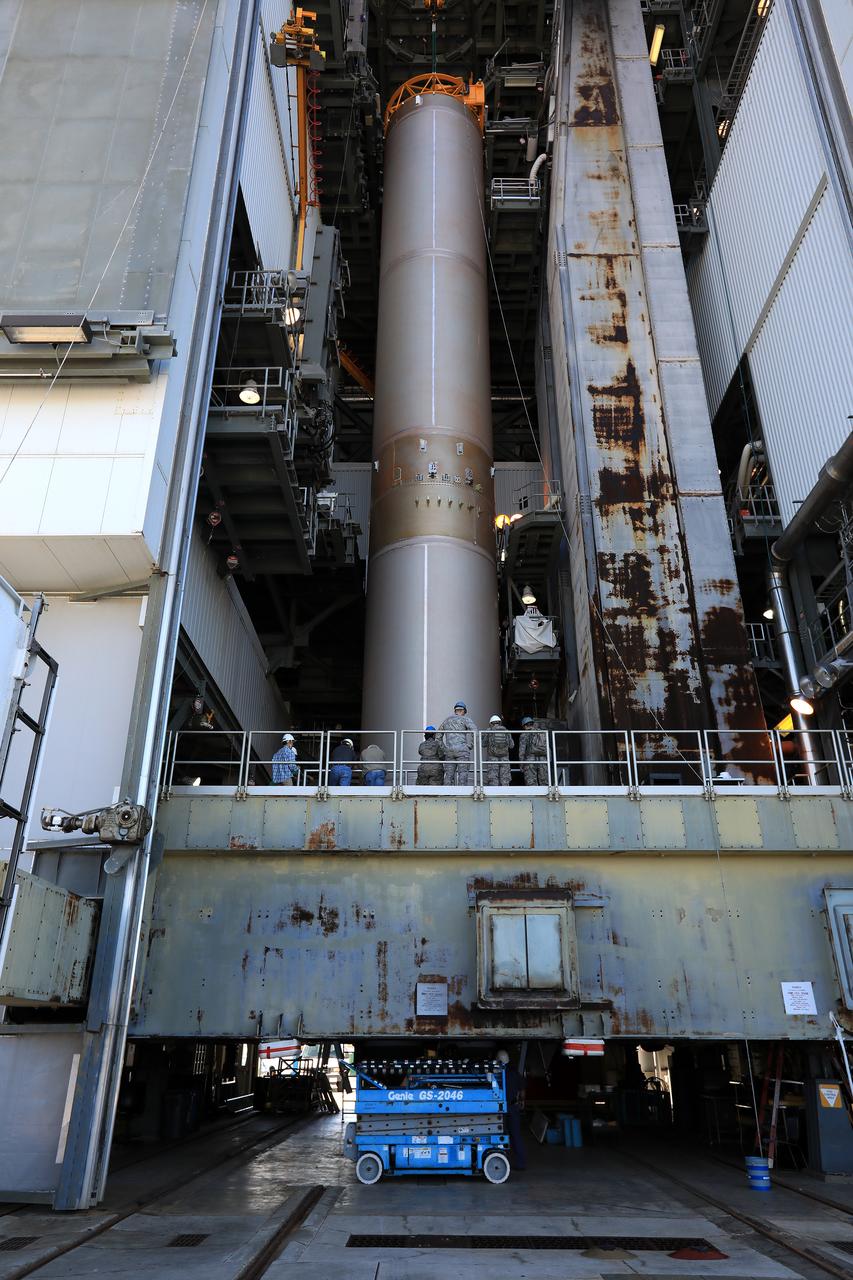

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is in the vertical position in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
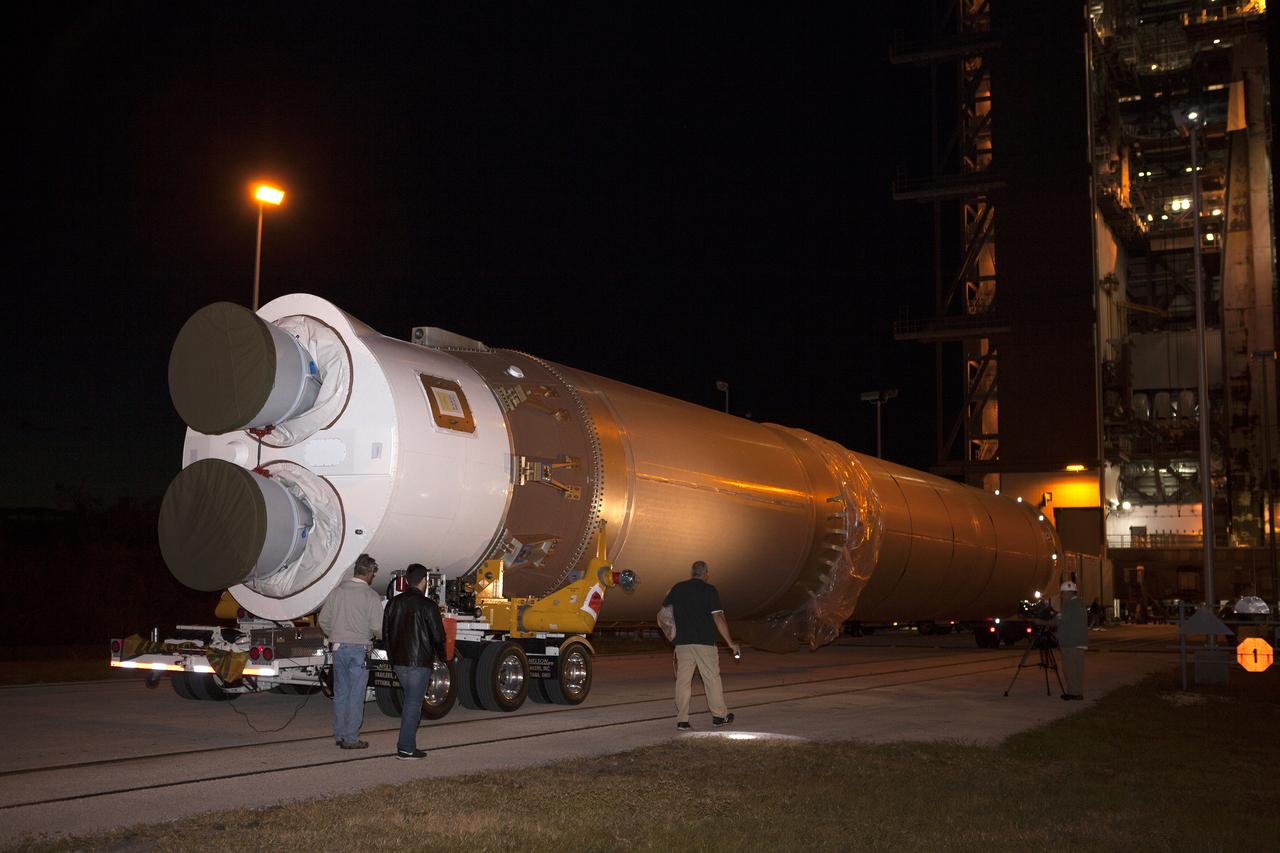

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
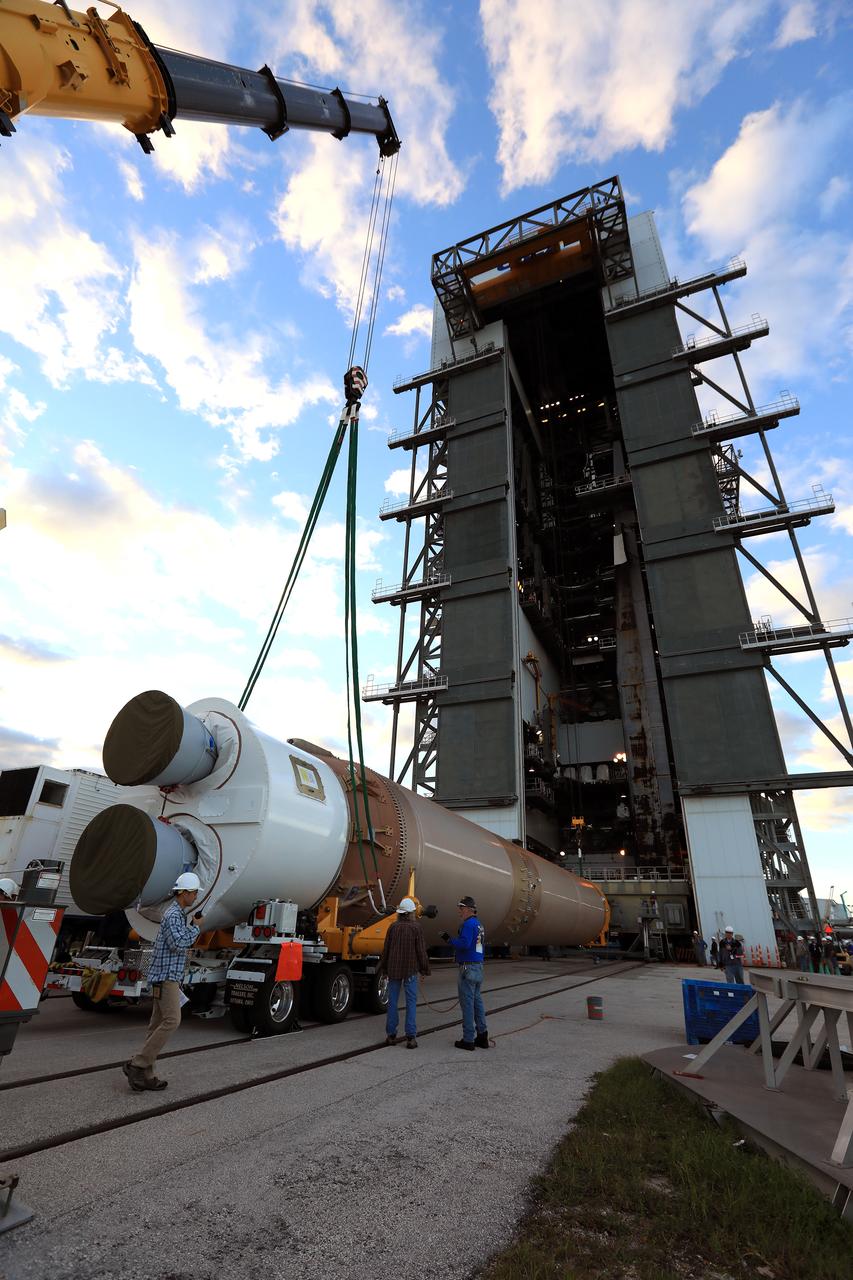

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage has arrived at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. A crane has been attached to the first stage to begin the lift to the vertical position. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is on its way to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
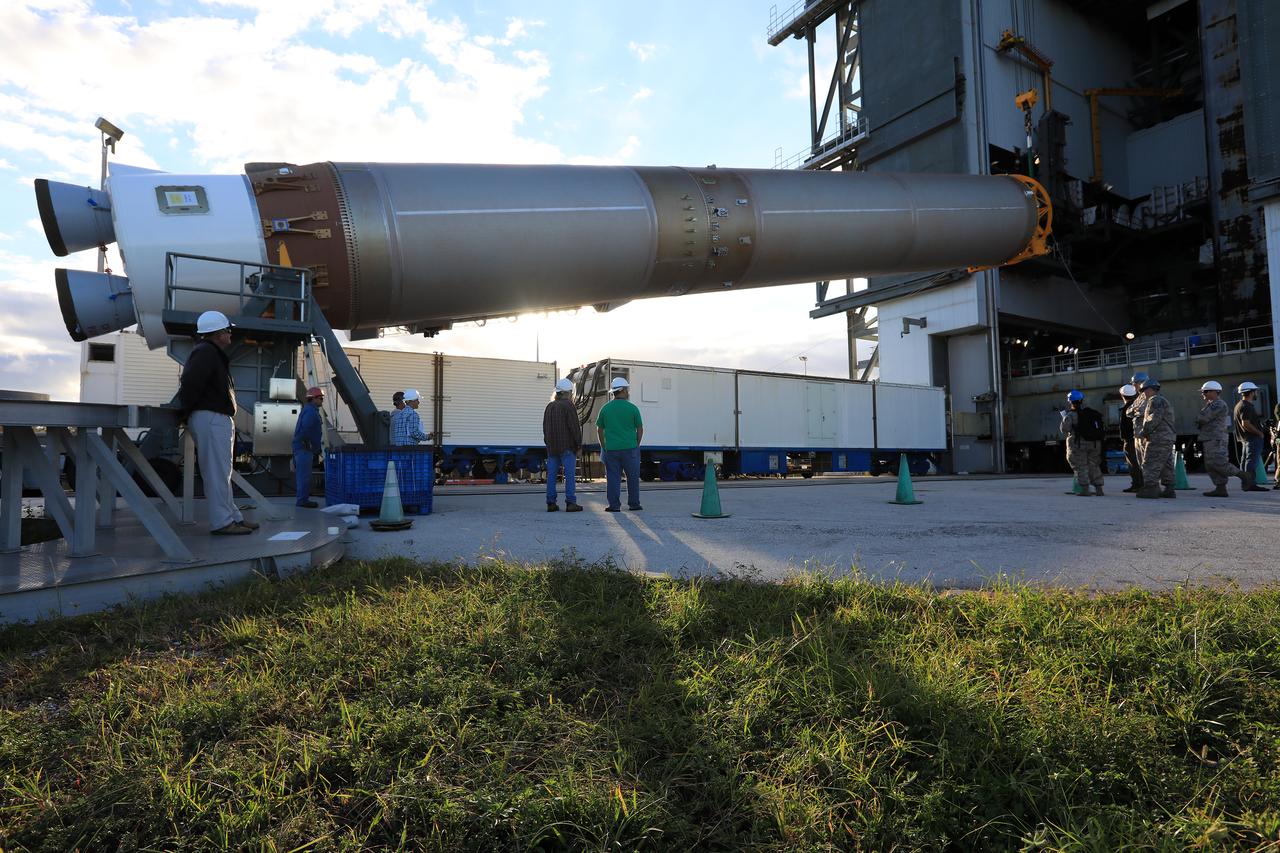

United Launch Alliance team members monitor the progress as the operation begins to lift the Atlas V first stage to the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
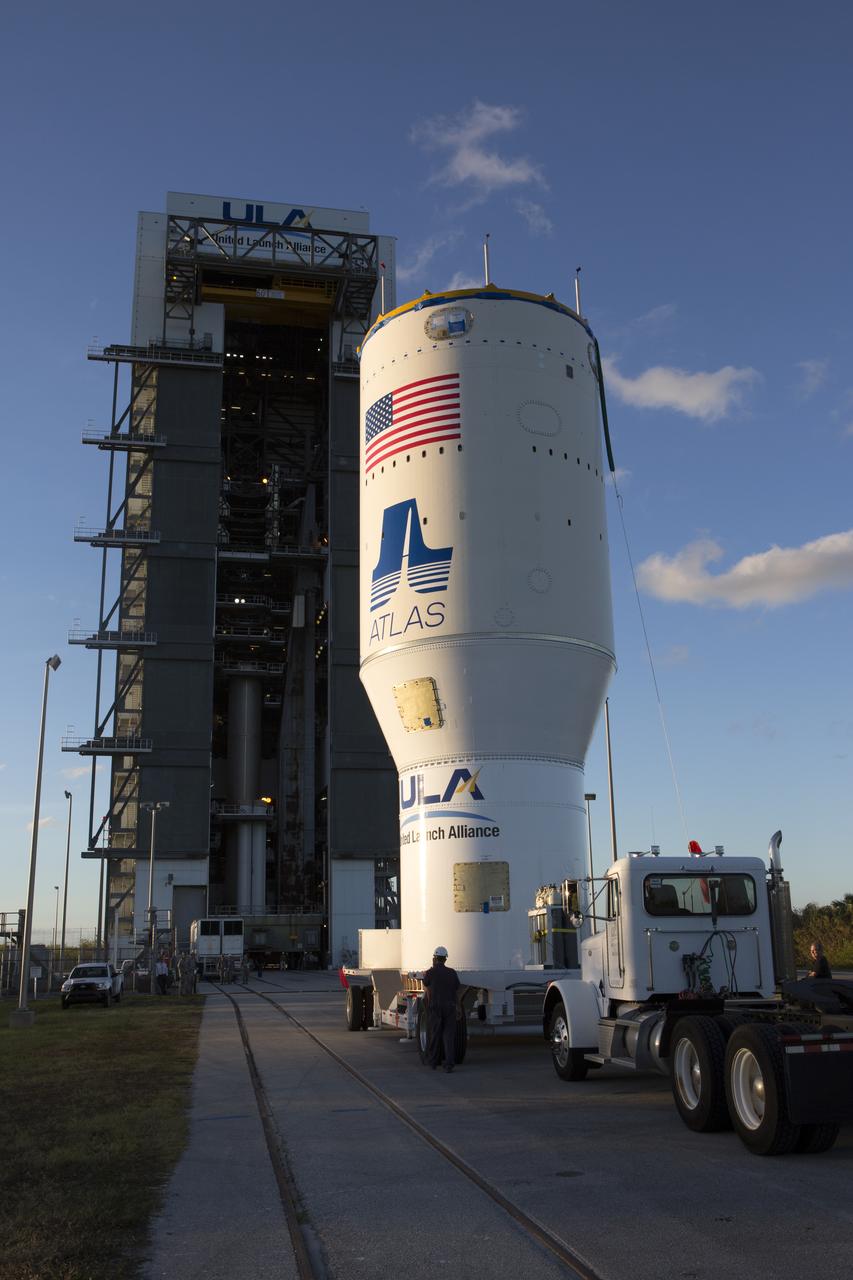

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
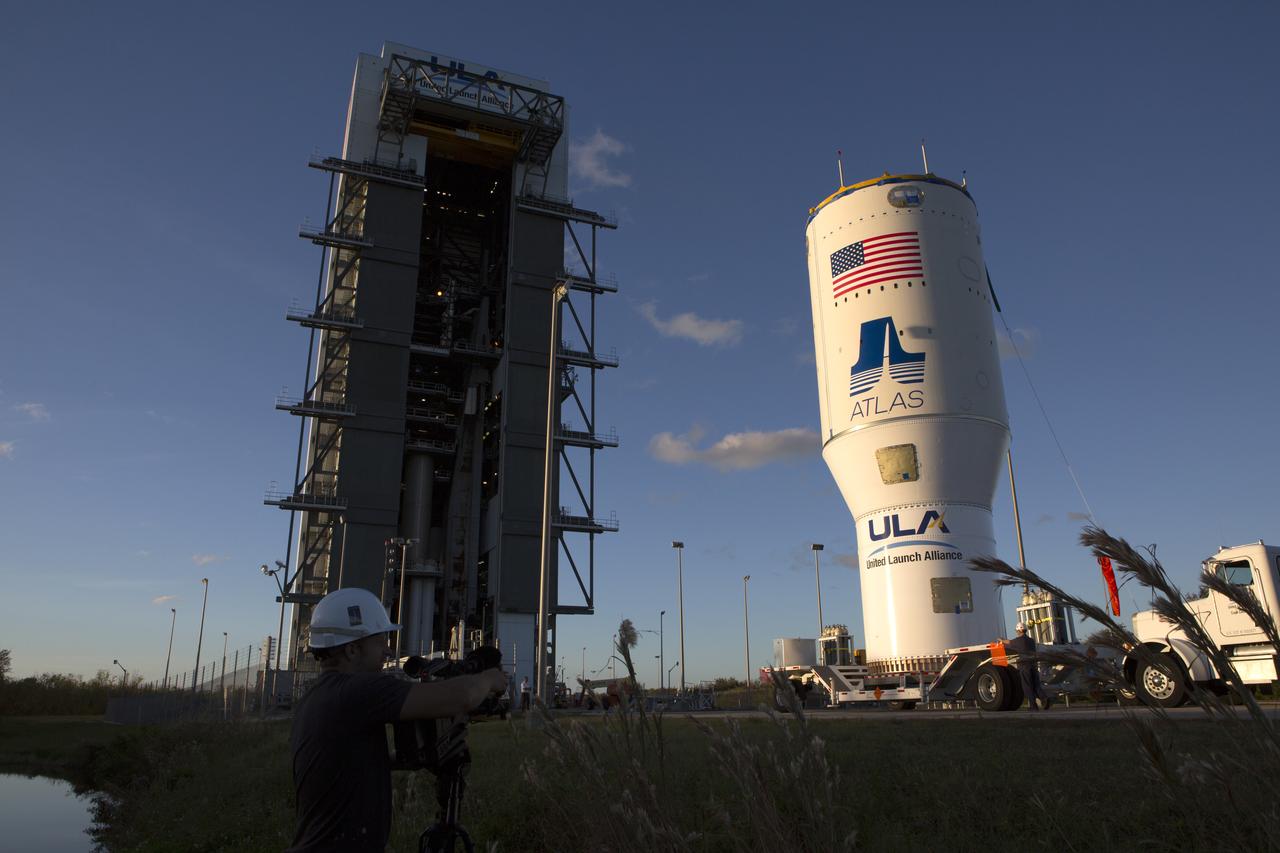

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
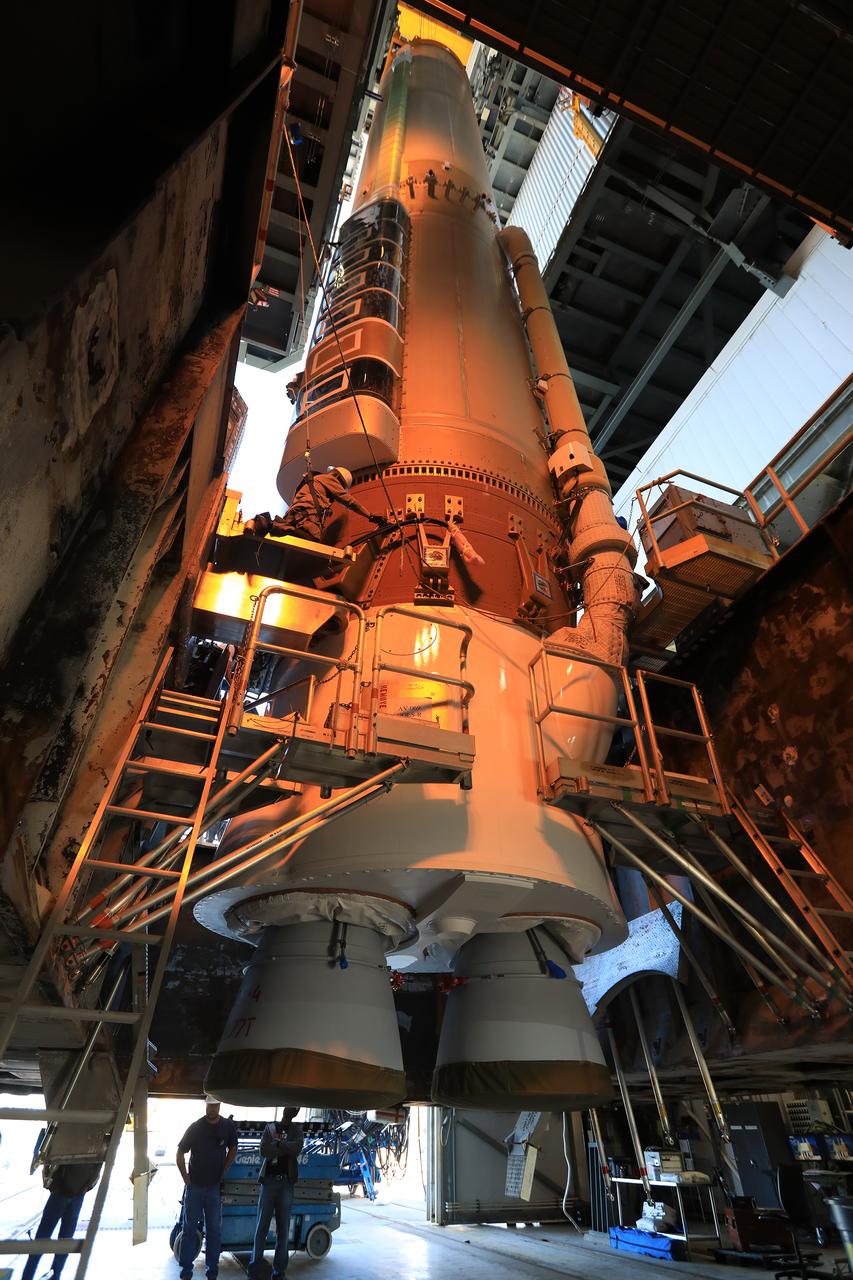

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage has been lifted to the vertical position inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
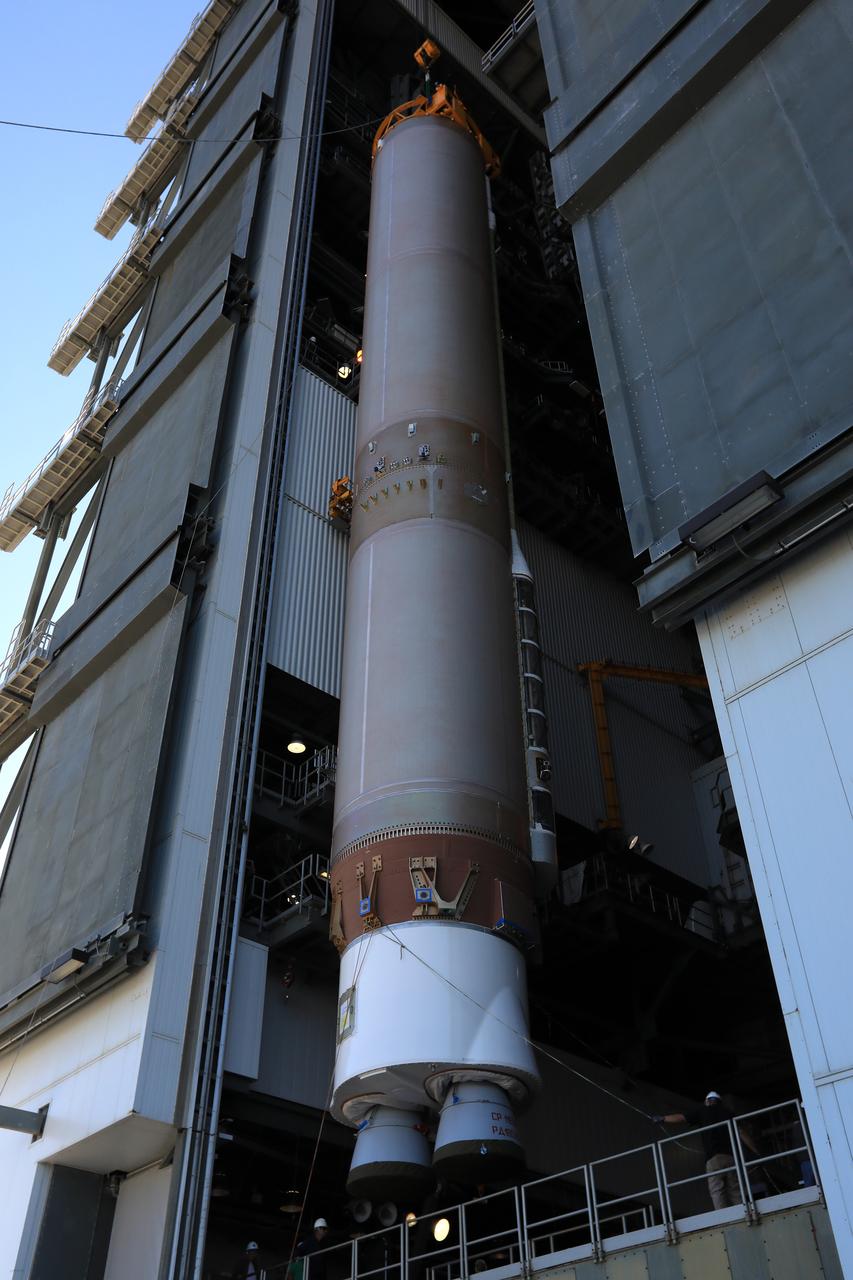

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage has been lifted to the vertical position in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
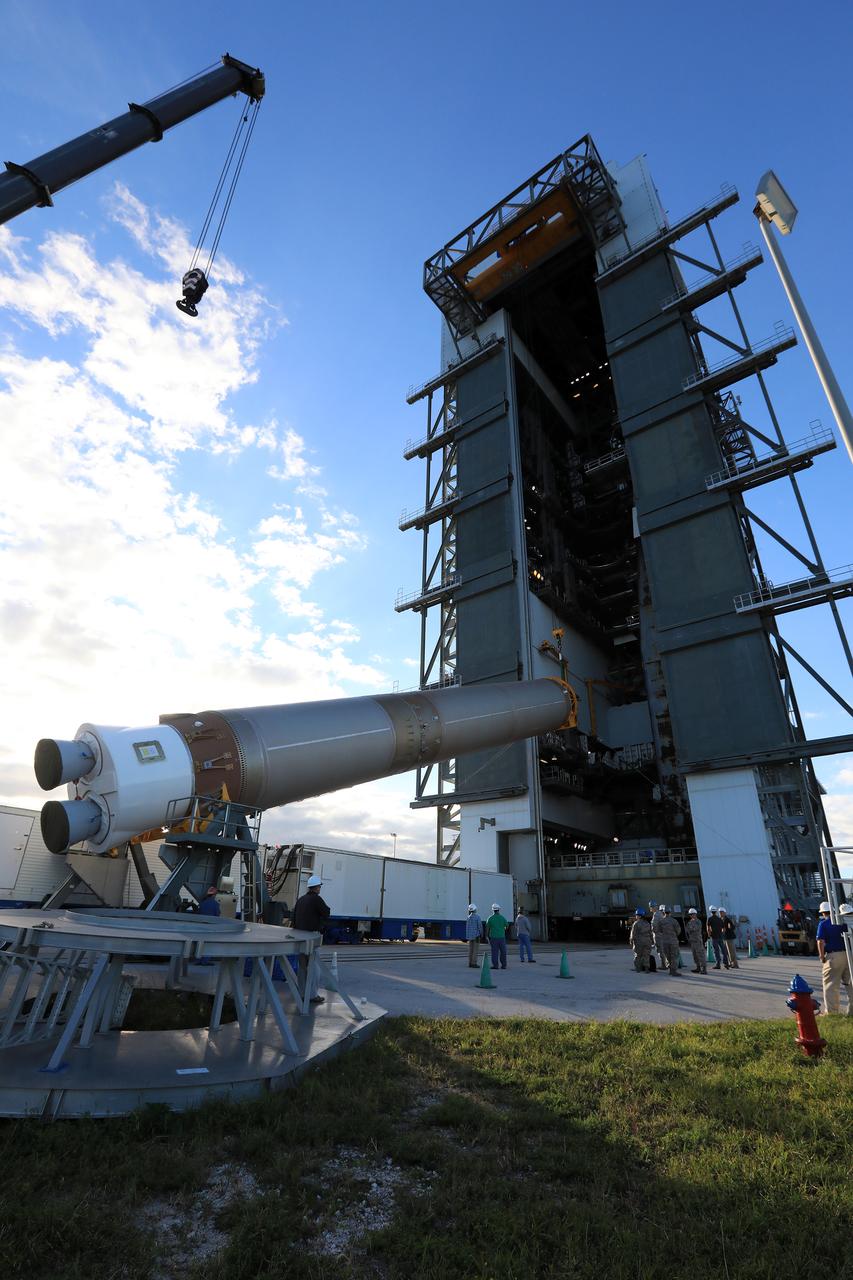

United Launch Alliance team members monitor the progress as the operation begins to lift the Atlas V first stage to the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
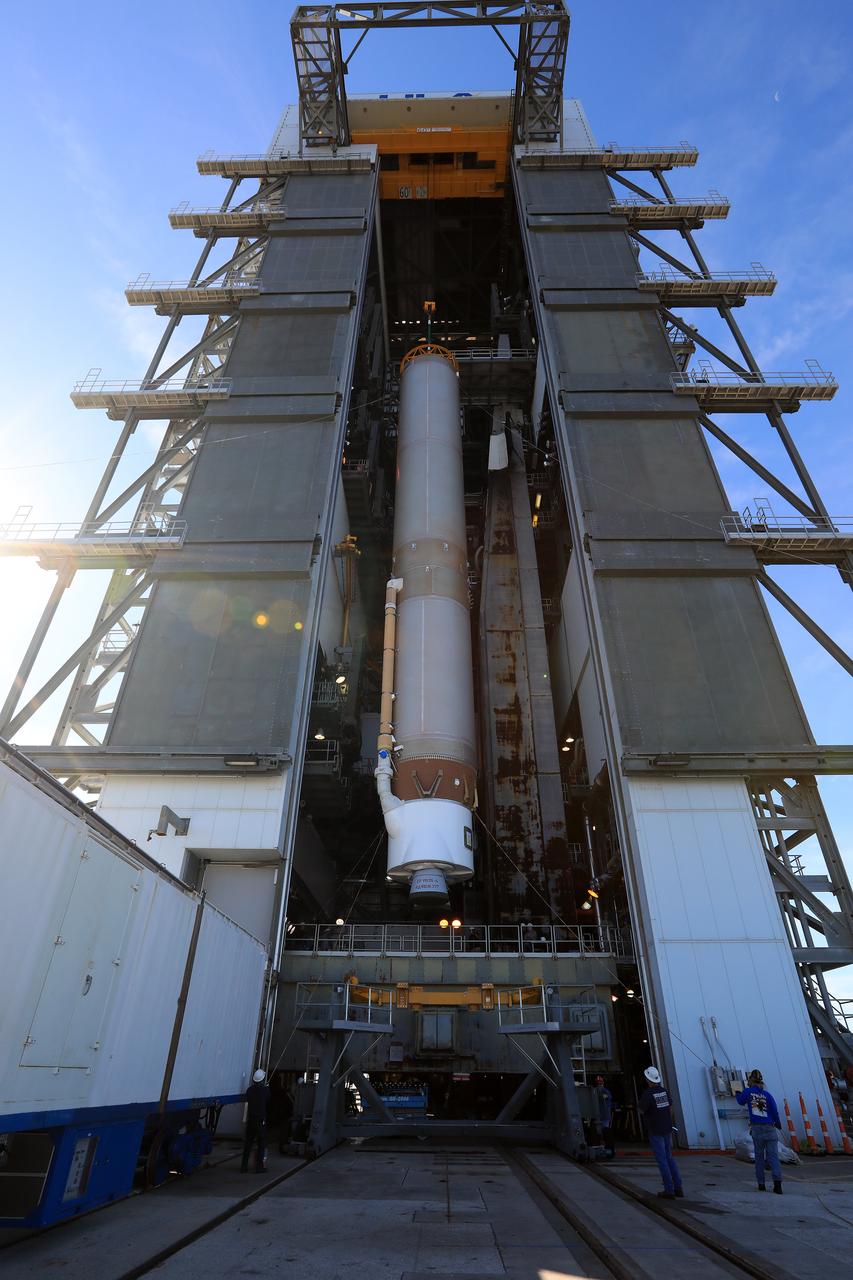

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage has been lifted to the vertical position in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
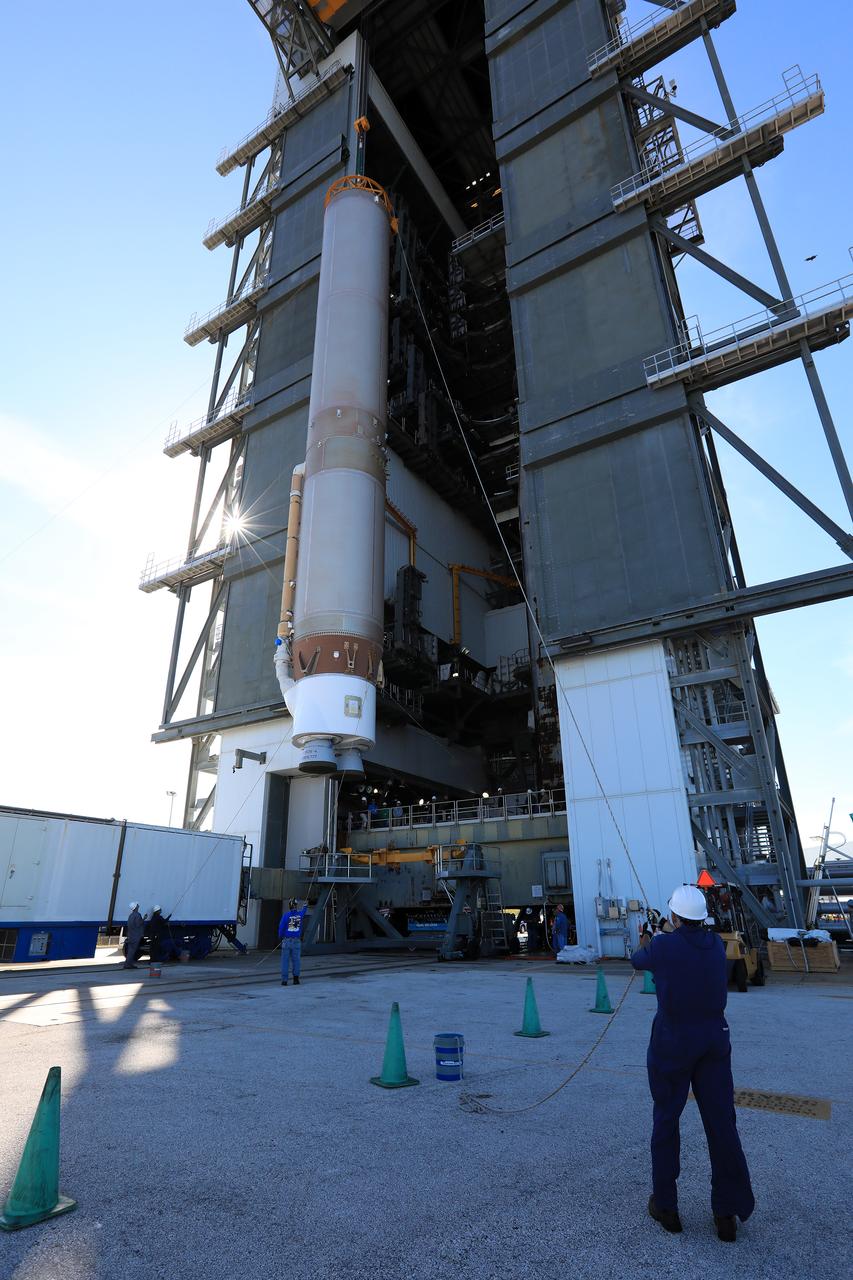

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted to the vertical position in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
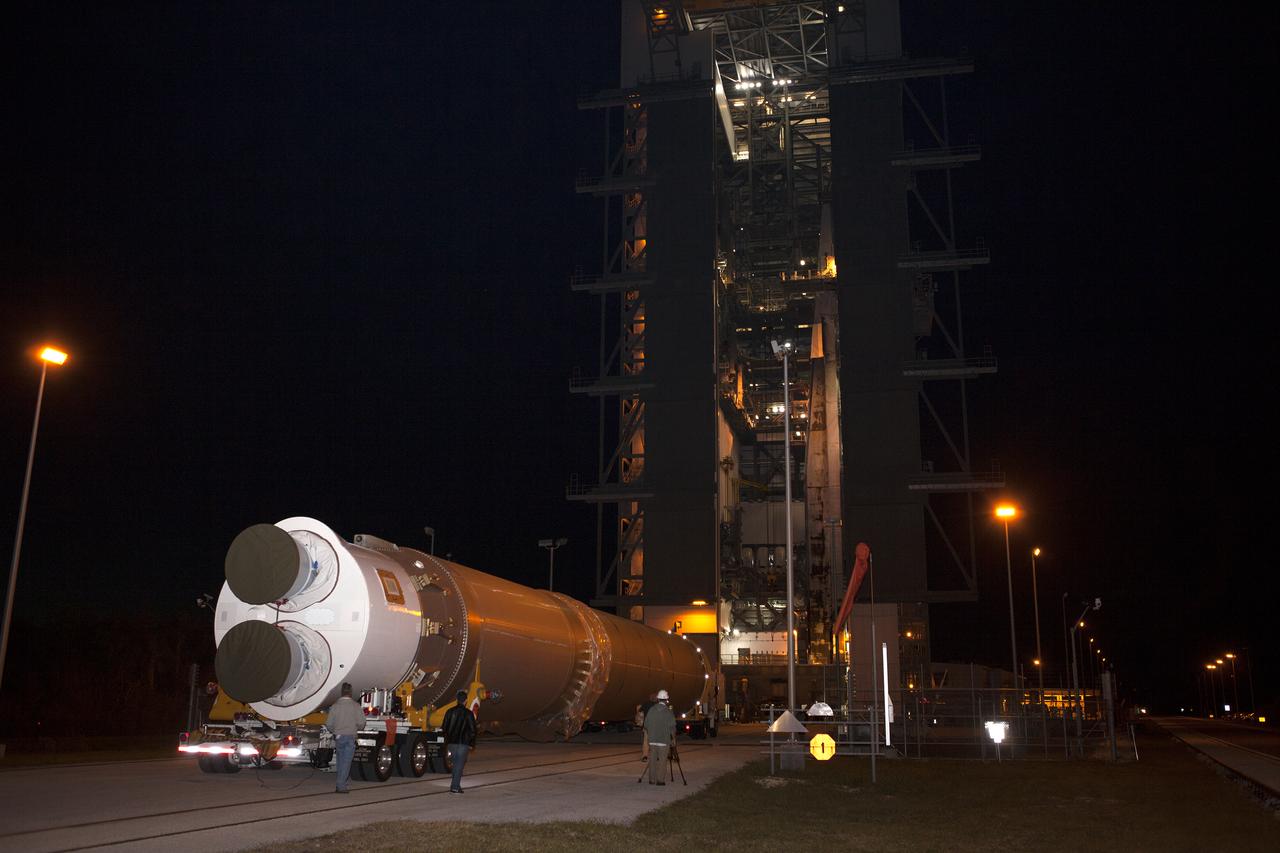

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
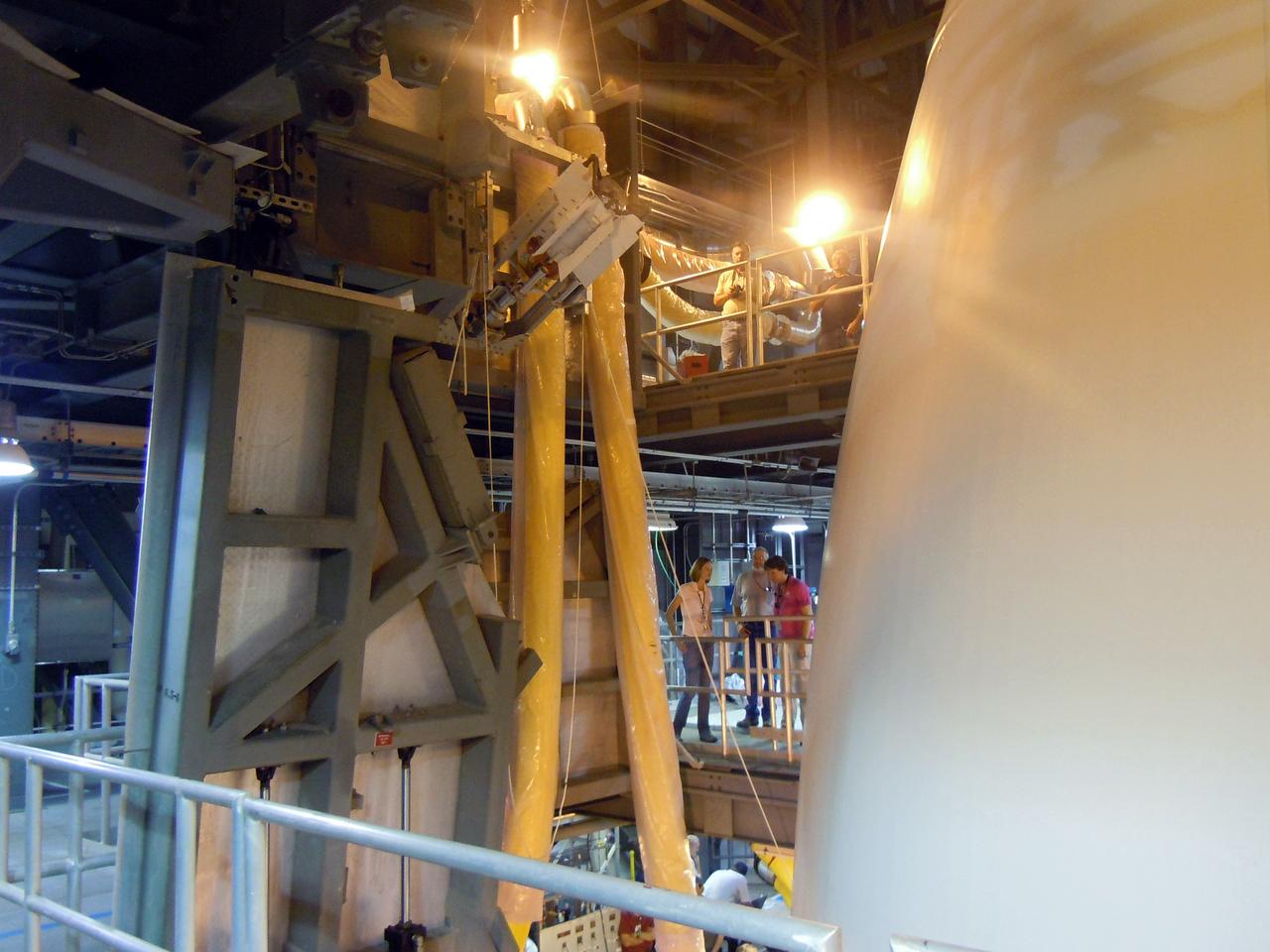

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF

MMRTG Loaded into Spacecraft at VIF
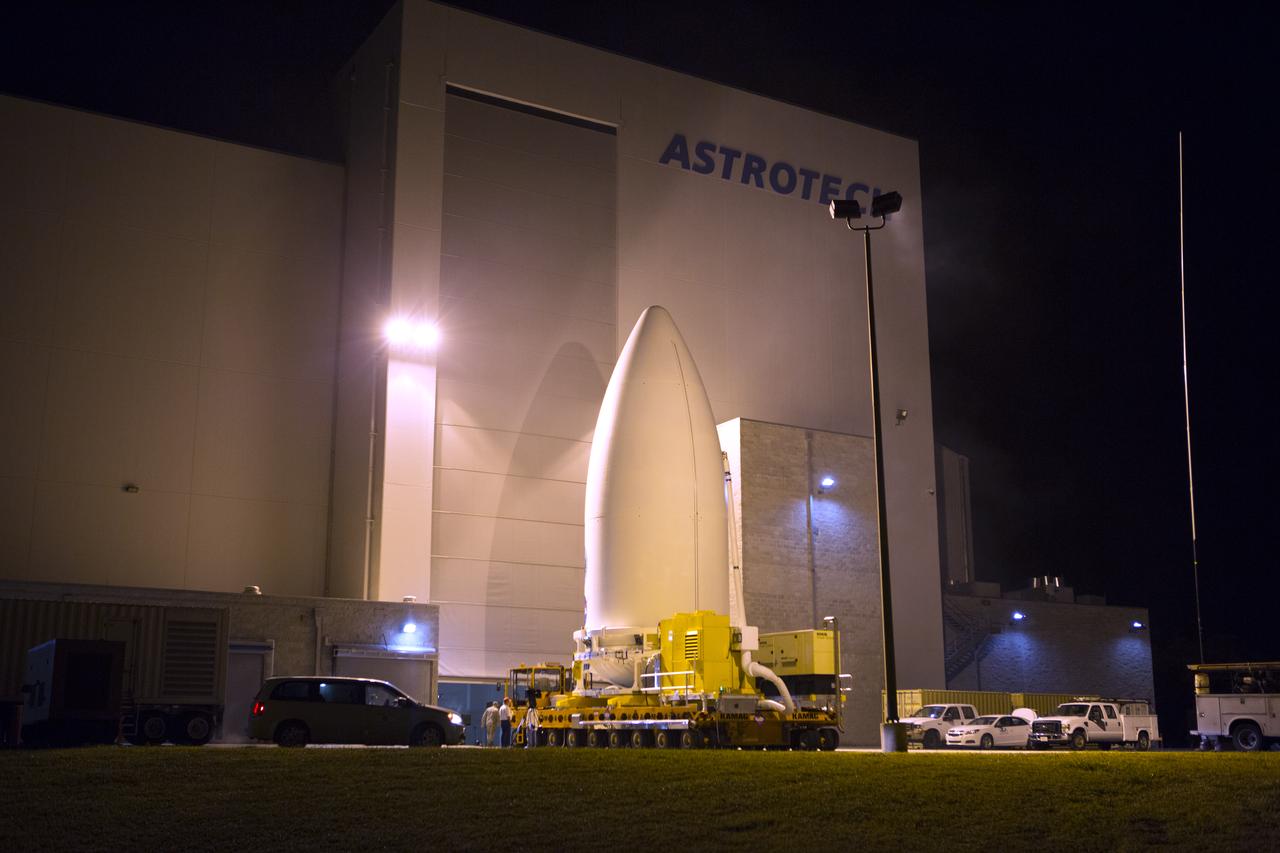

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) departs from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
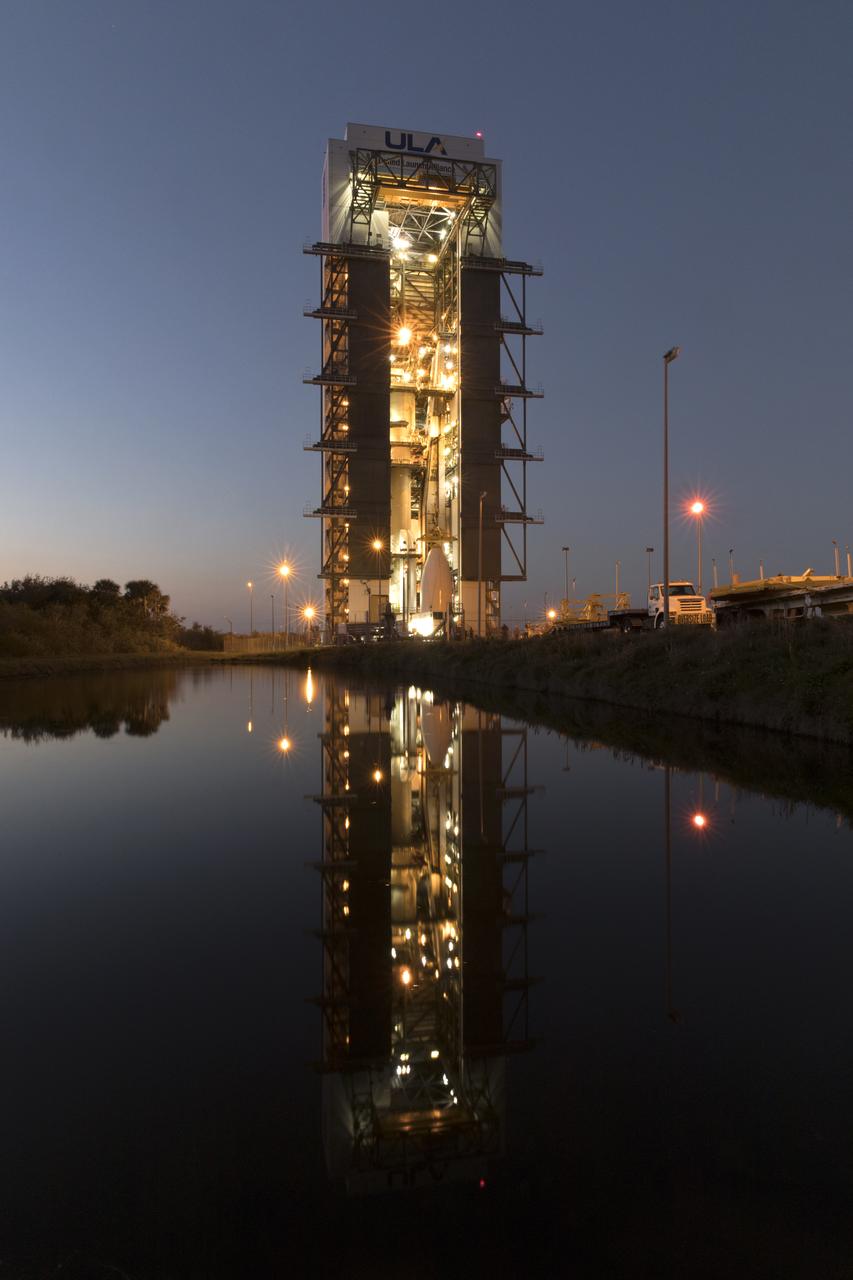

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) is reflected in the water at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, as a crane begins to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). The fairing will be lifted and mated to the ULA Atlas V rocket. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the ULA Atlas V on March 1.
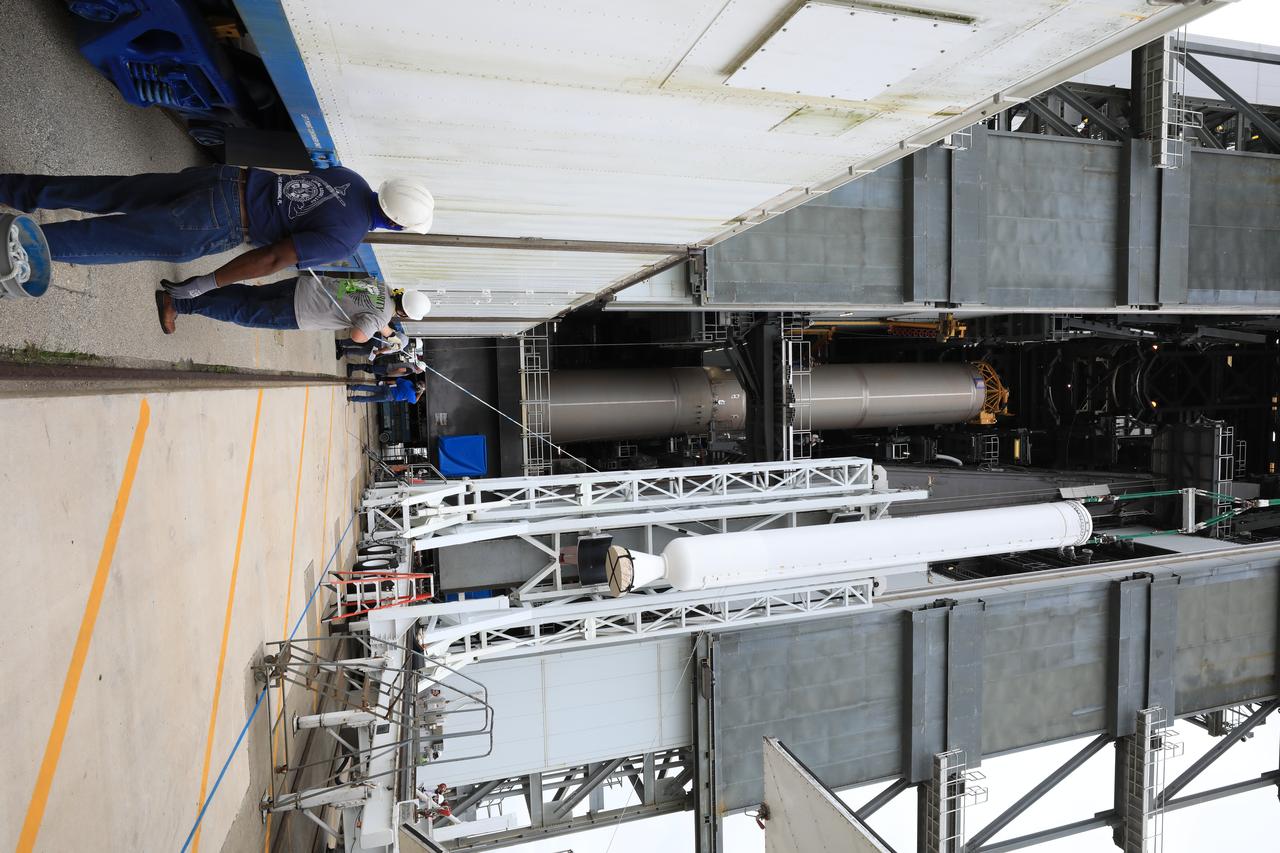

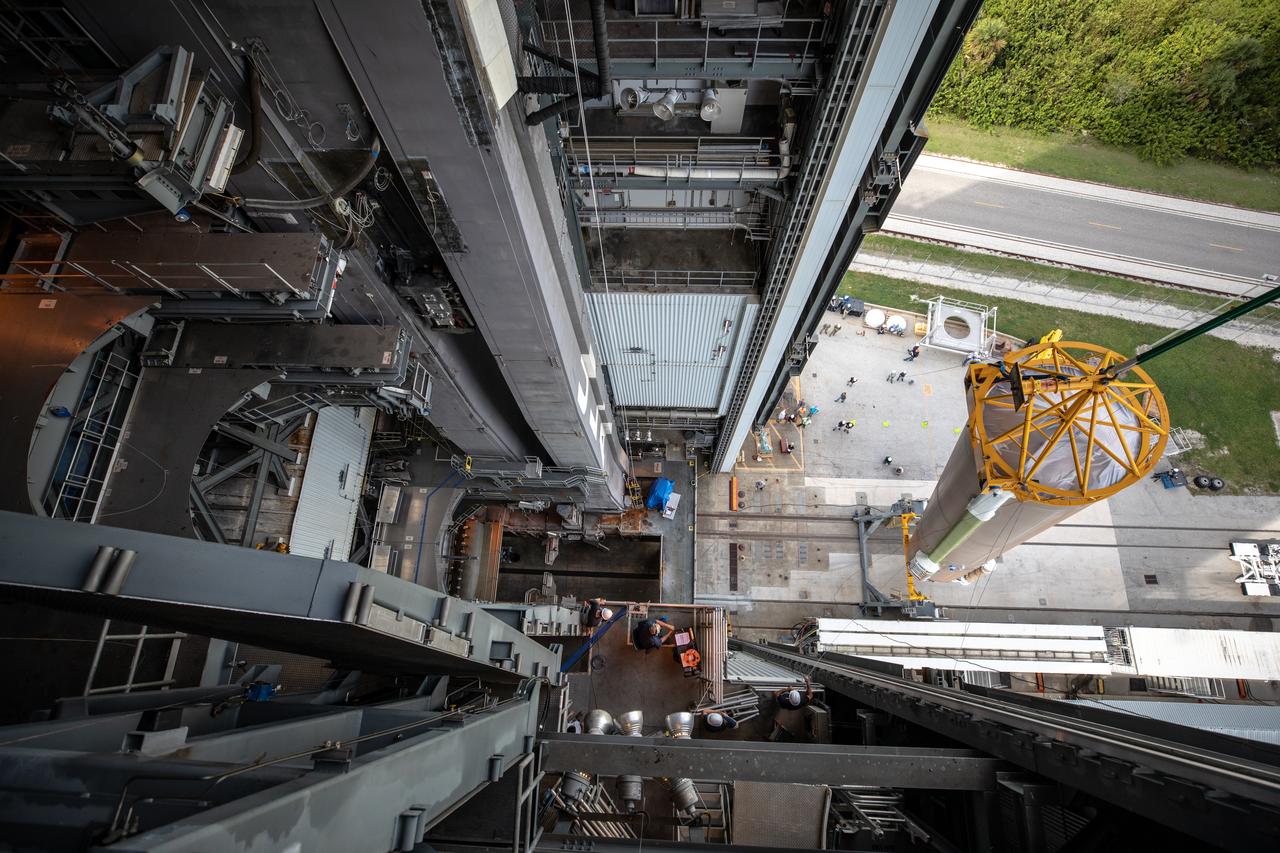
A crane is used to lift the second of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 3, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
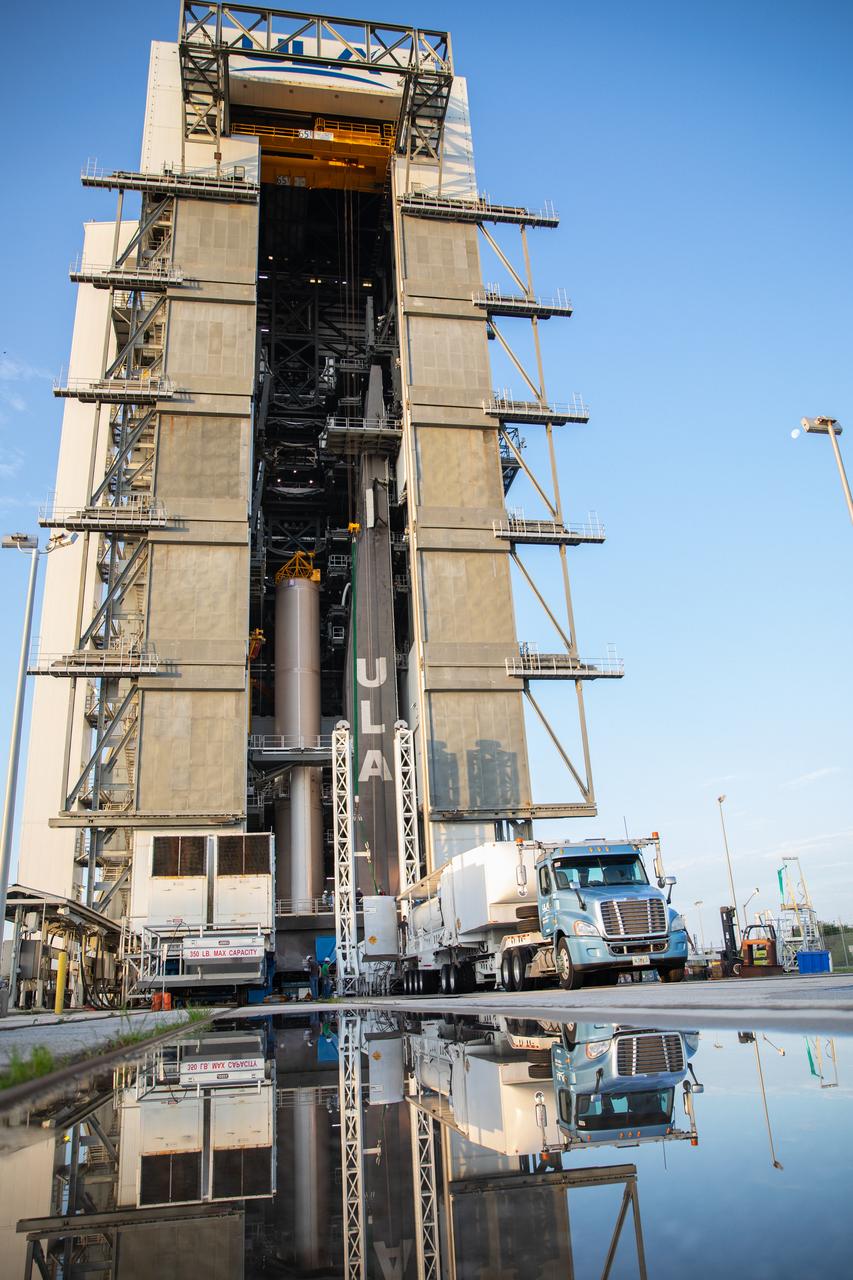

The fourth and final solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 9, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in July 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
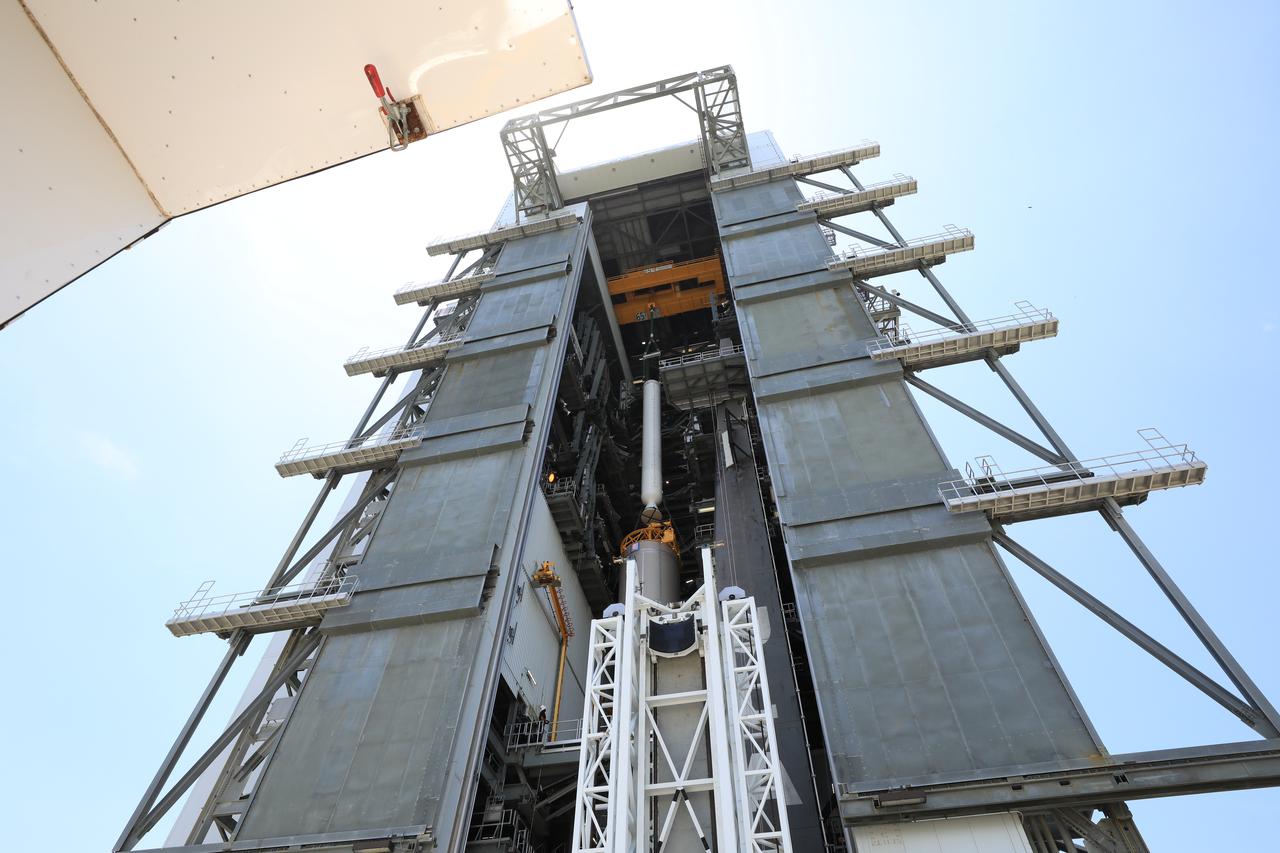

A crane is used to lift the third of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 8, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
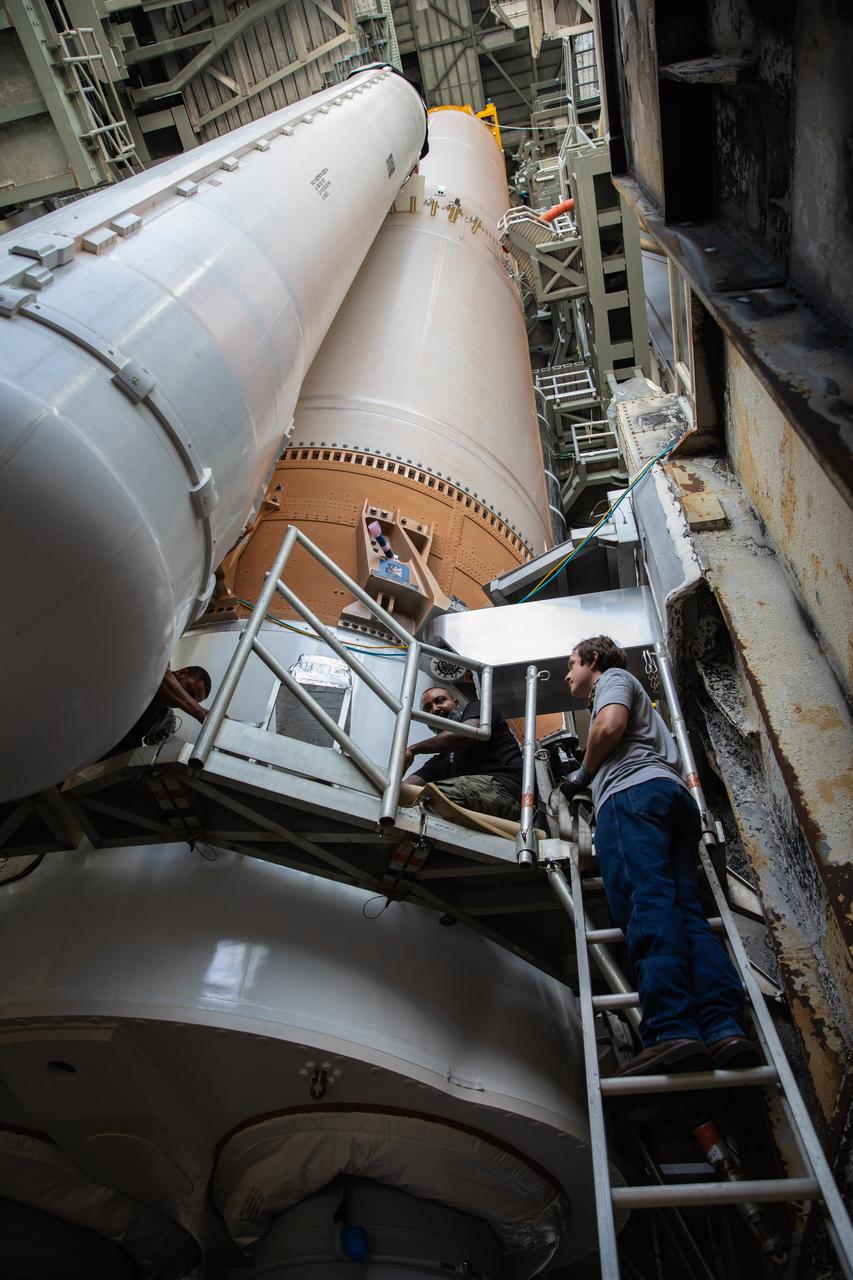

A United Launch Alliance worker is inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 9, 2020. A lifting device is used to raise the fourth and final solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the (VIF) where it will be mated to the booster. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in July 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
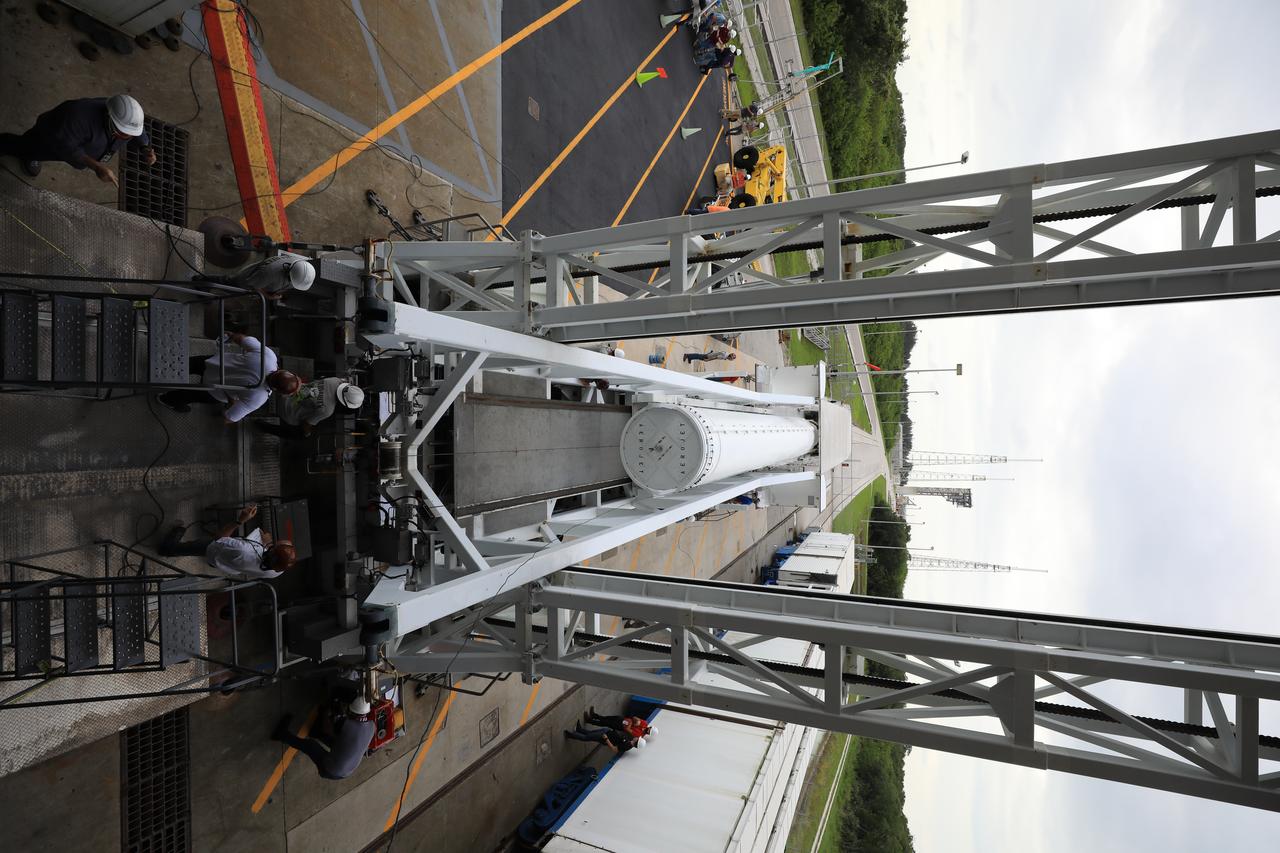

The second of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 3, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
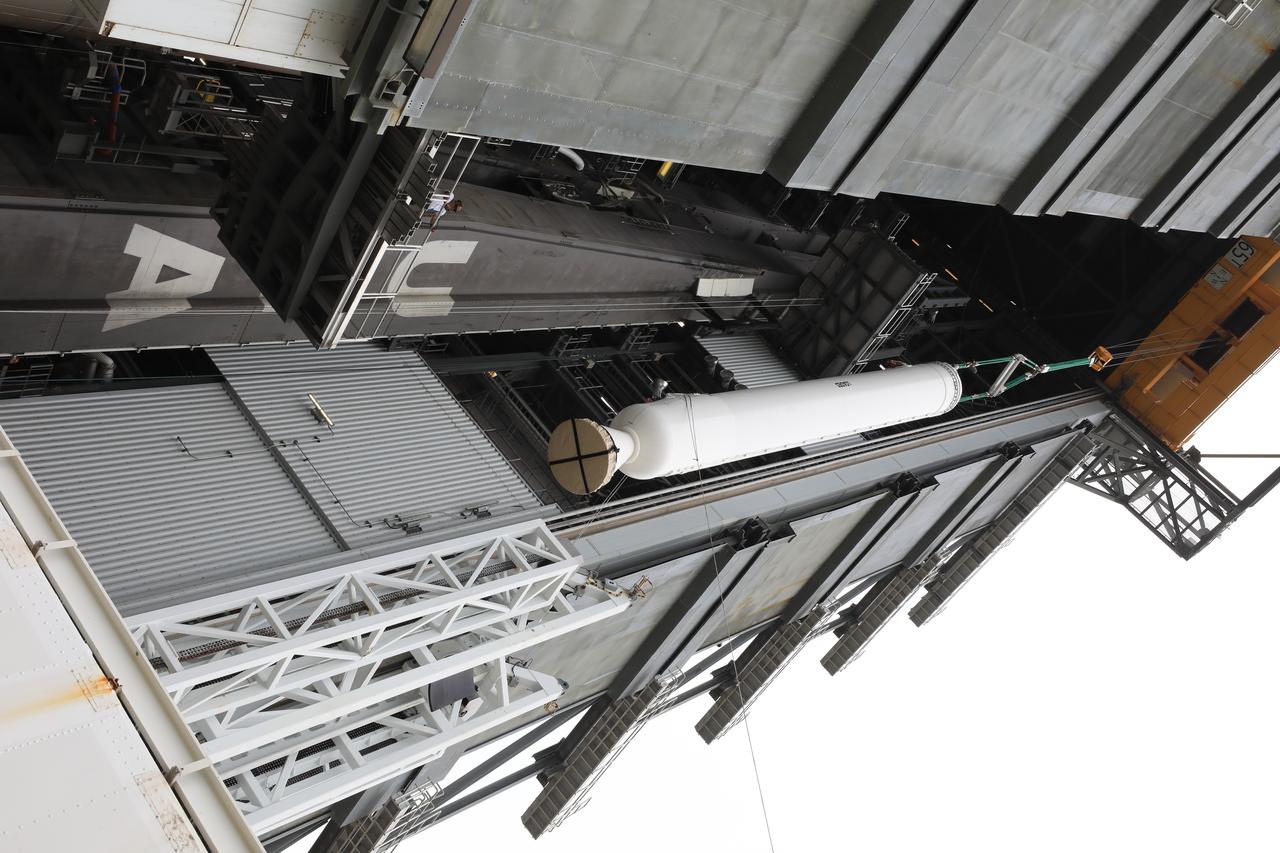

A crane is used to lift the second of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 3, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

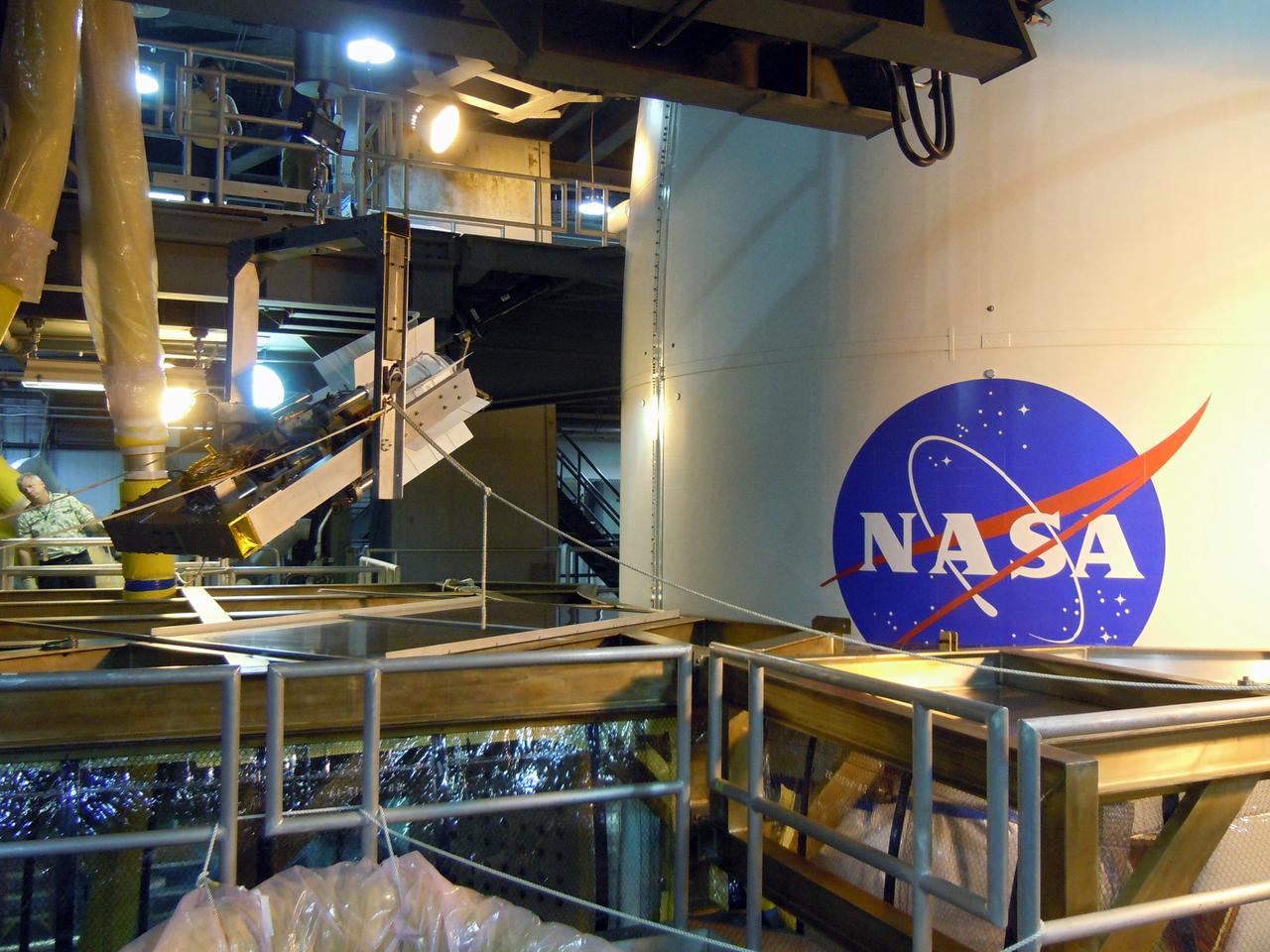
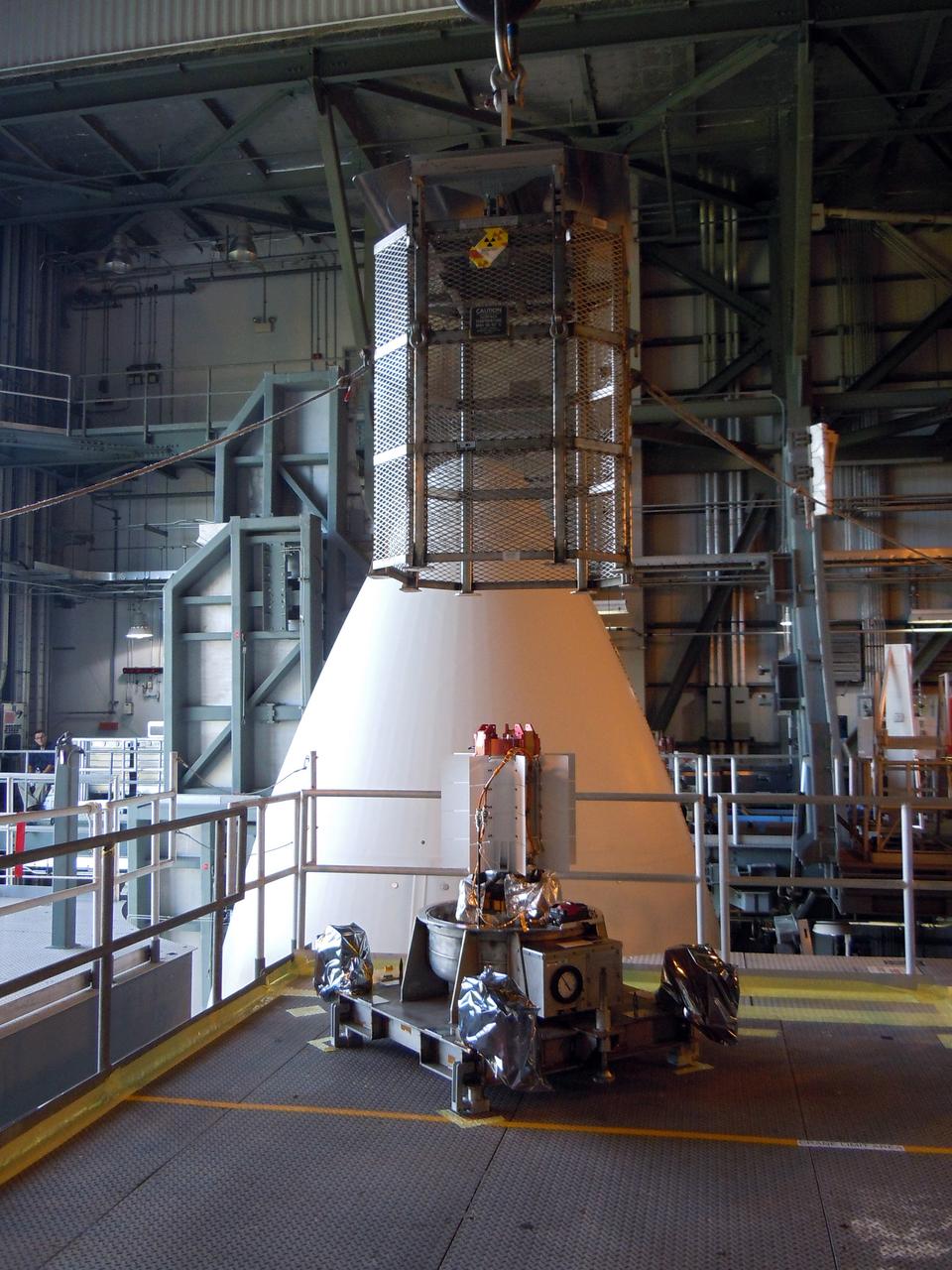
A caution sign marks the presence of a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator will be used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
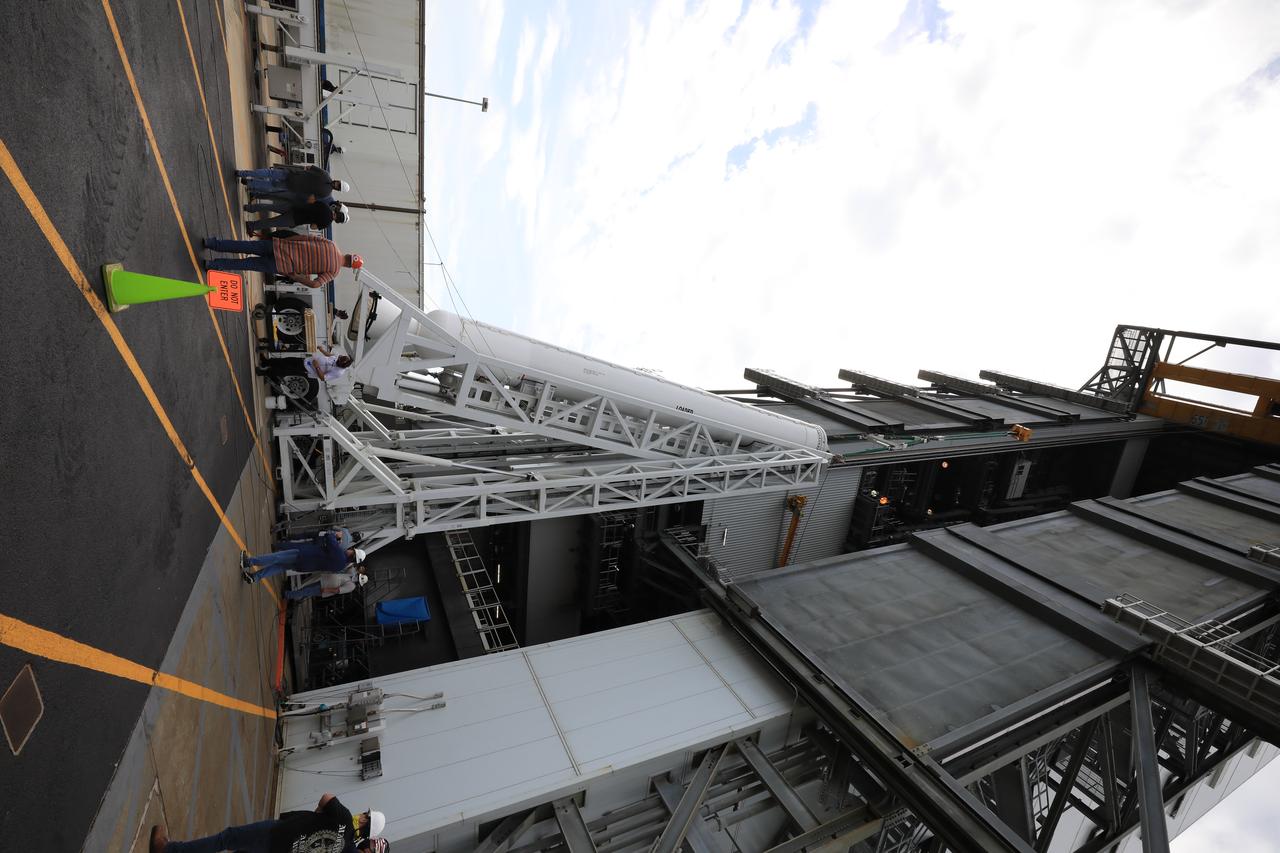

A lifting device is used to raise the third of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 8, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
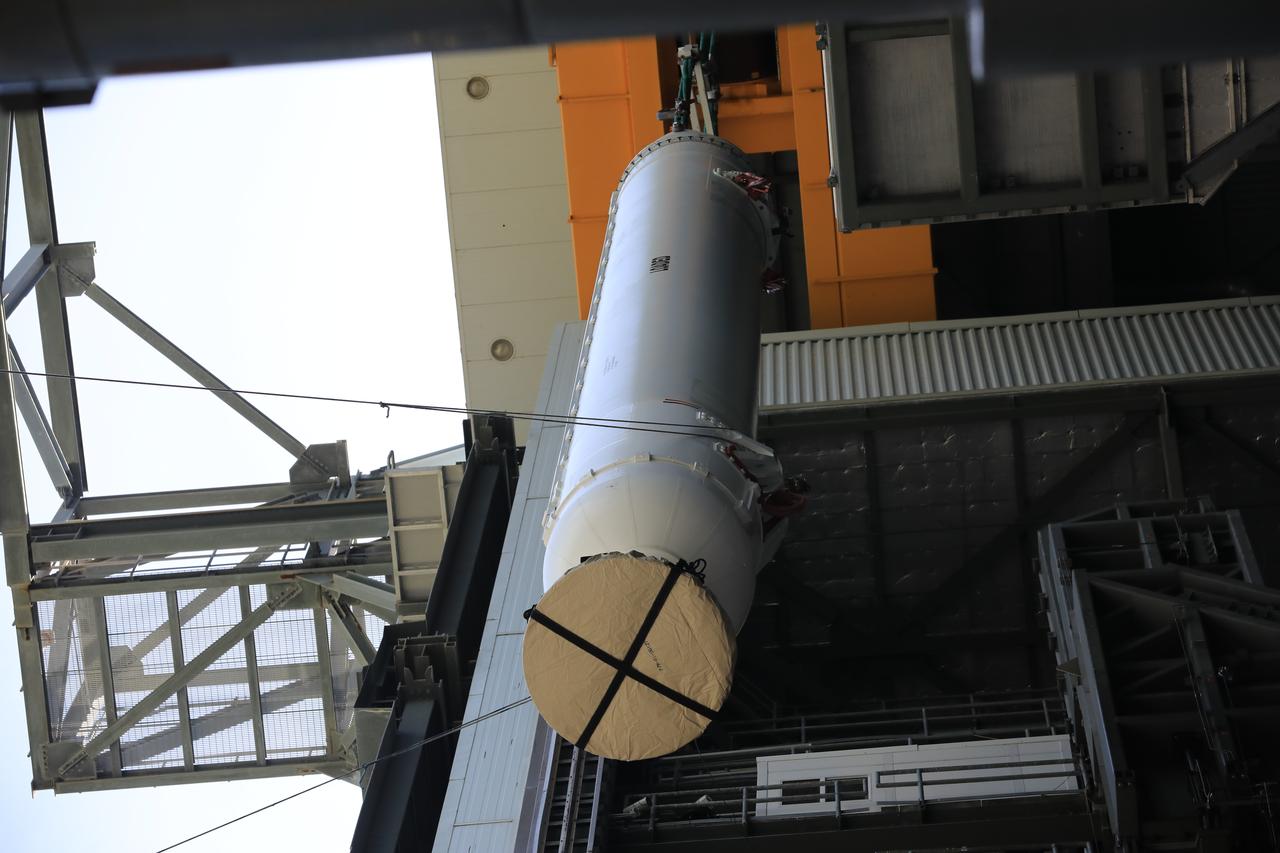

A view from inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, as the third of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is lifted up by crane on June 8, 2020. The SRB will be mated to the Atlas V booster inside the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
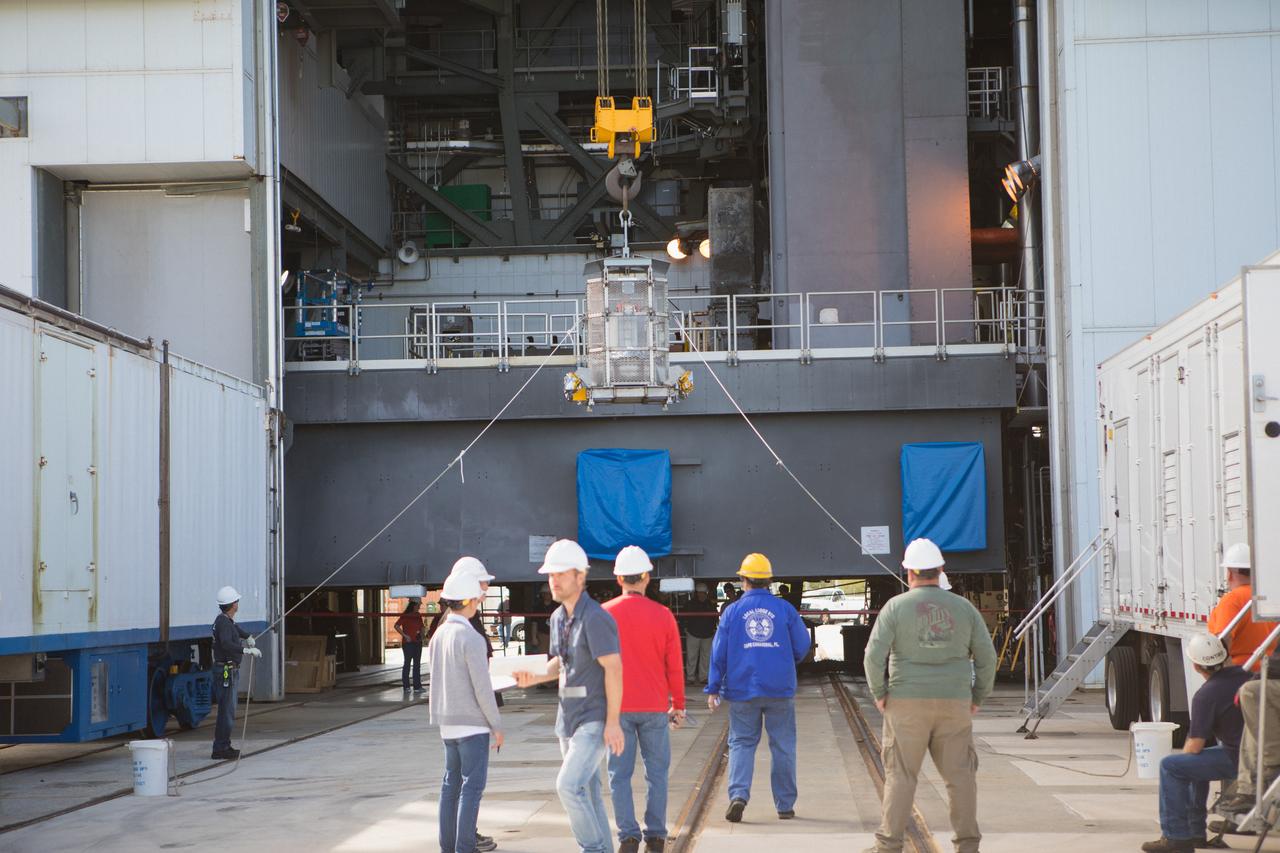

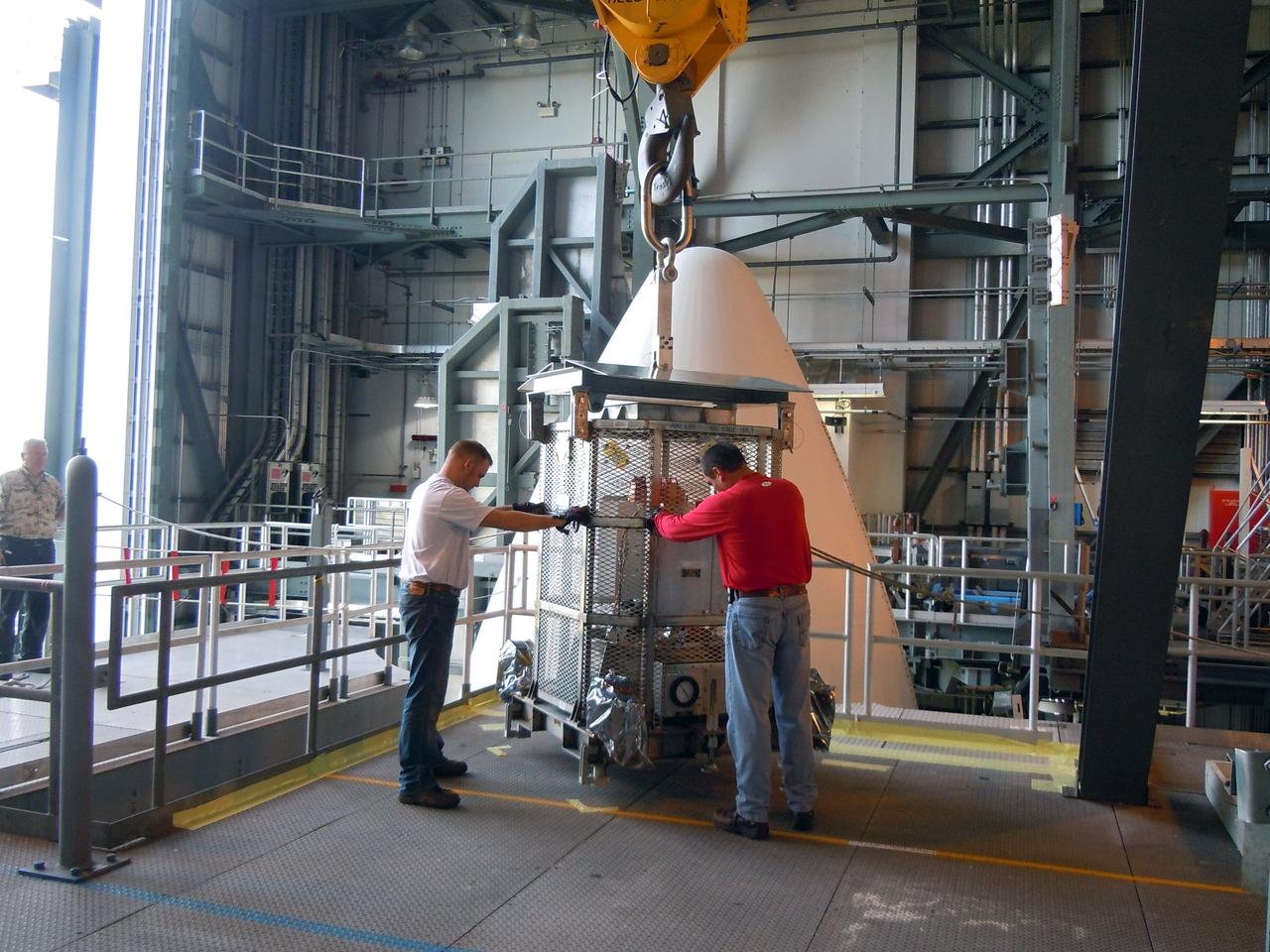
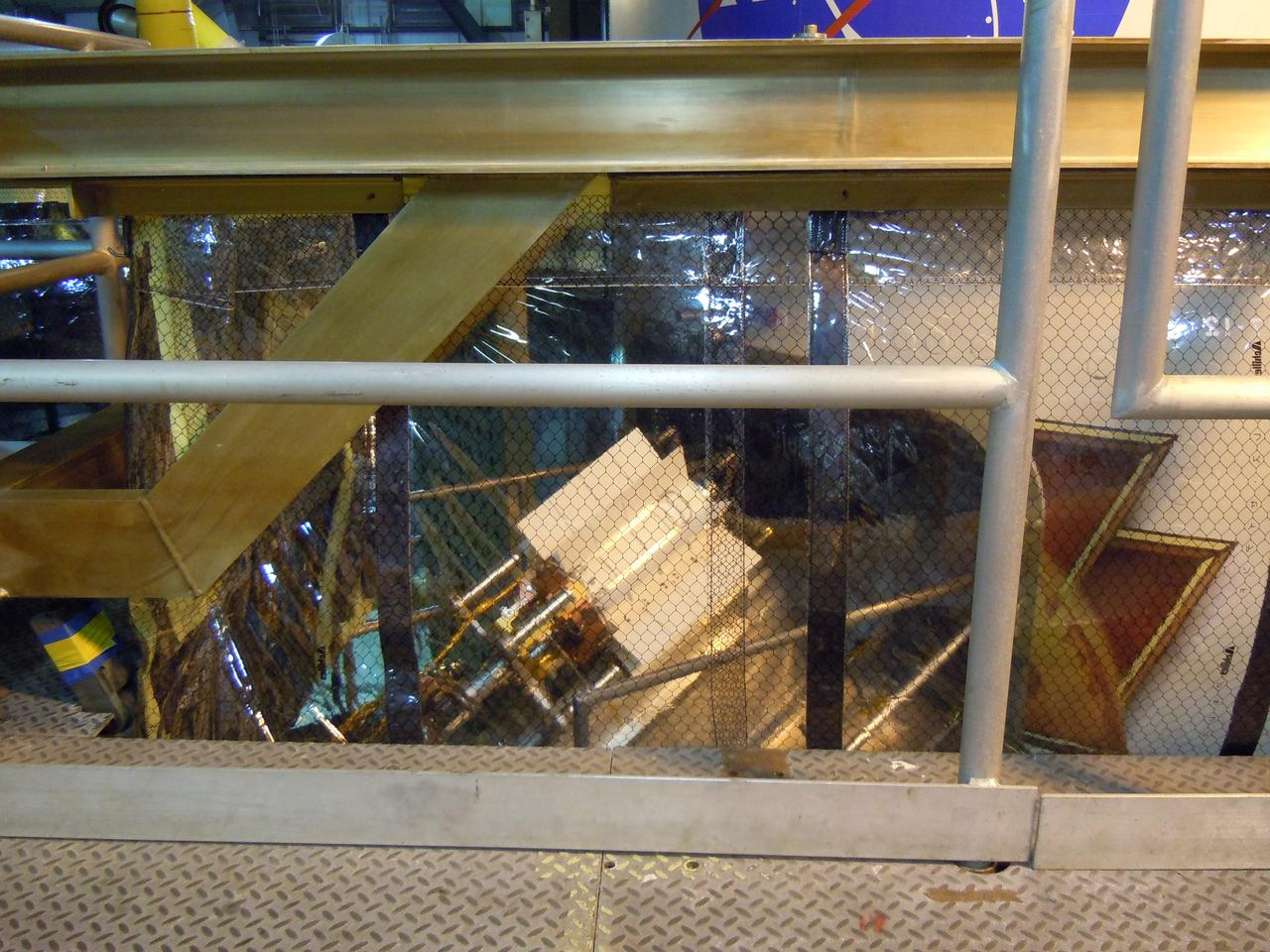
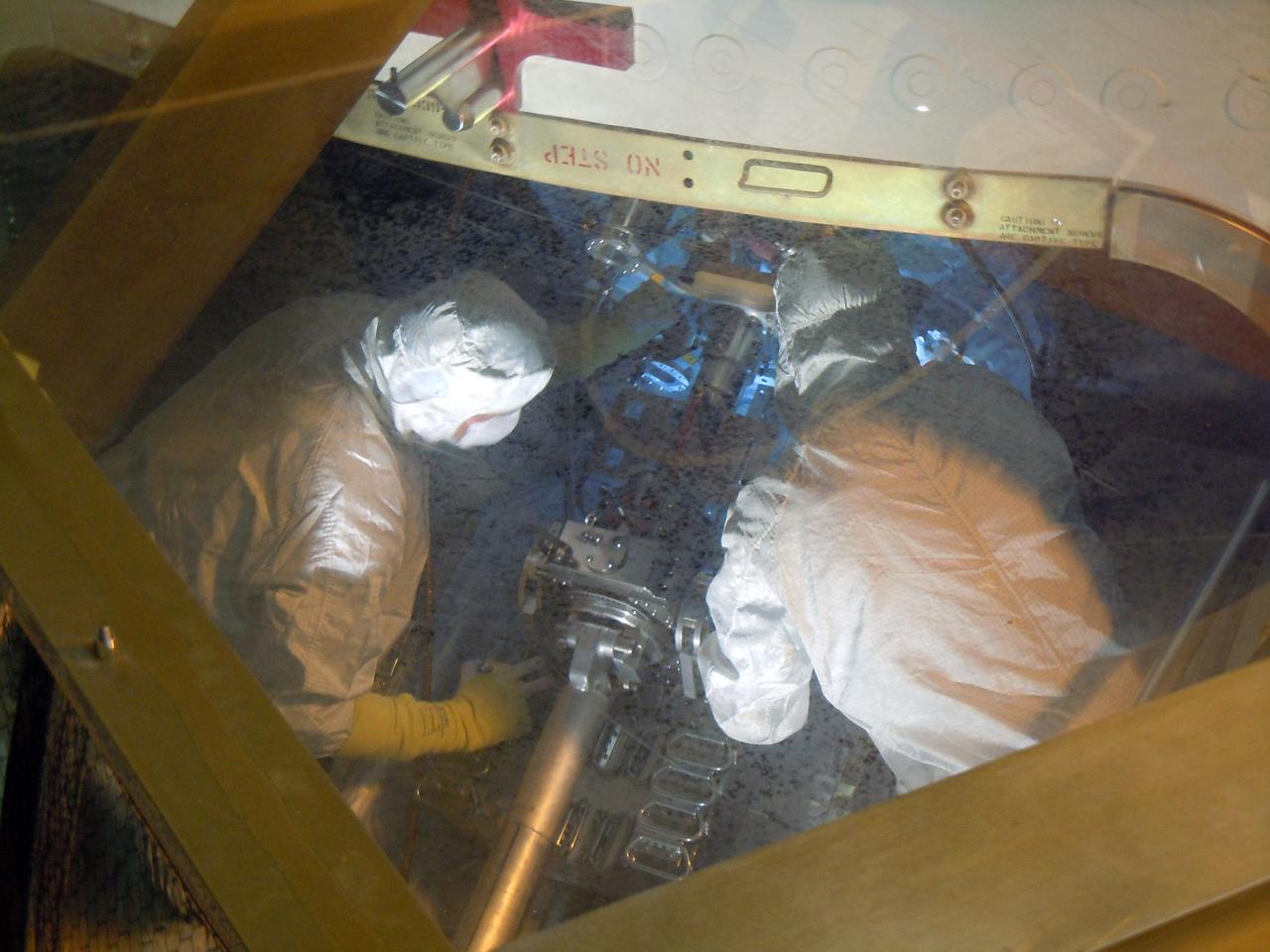
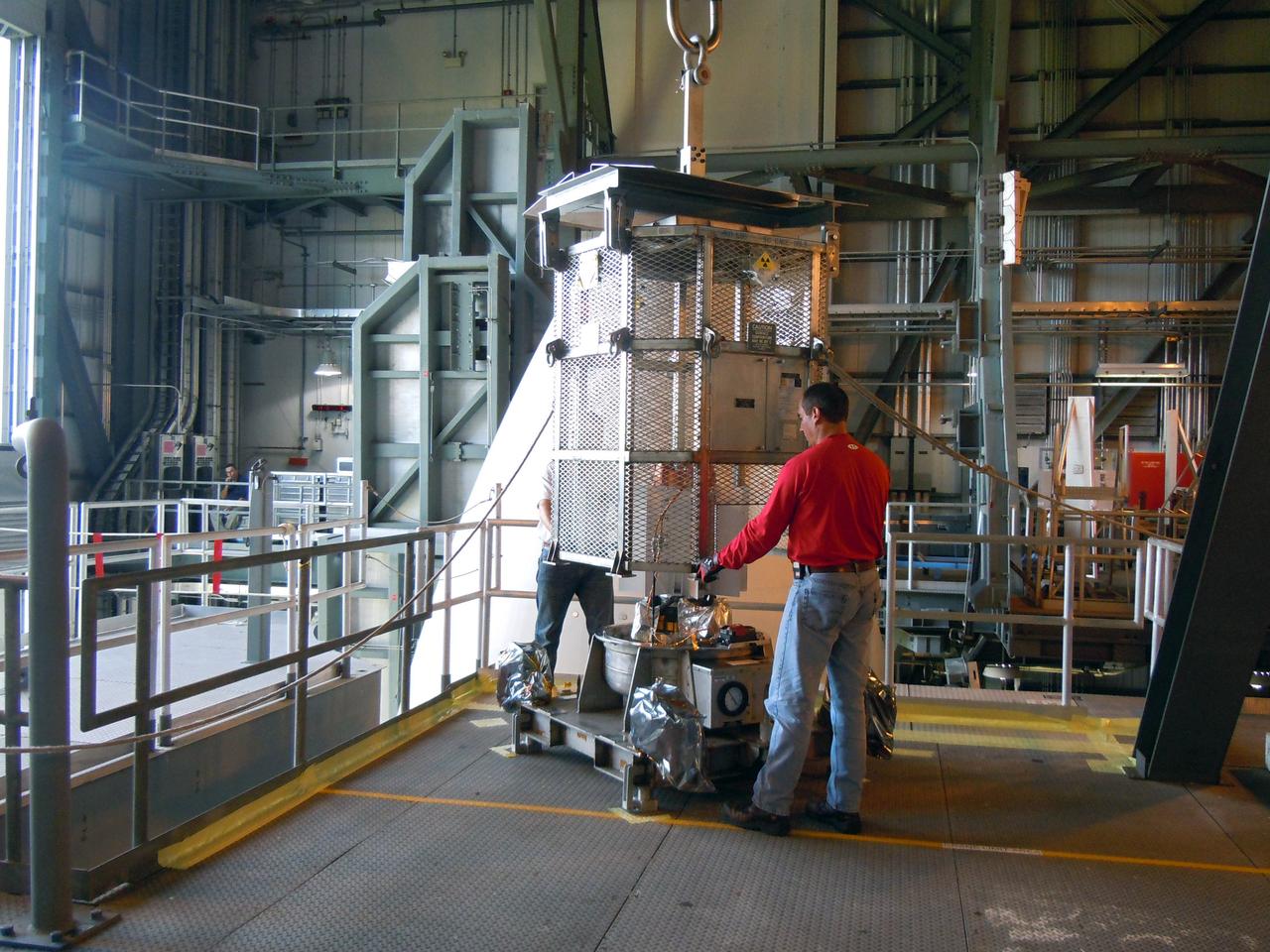
Technicians assist as a crane lifts up a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.

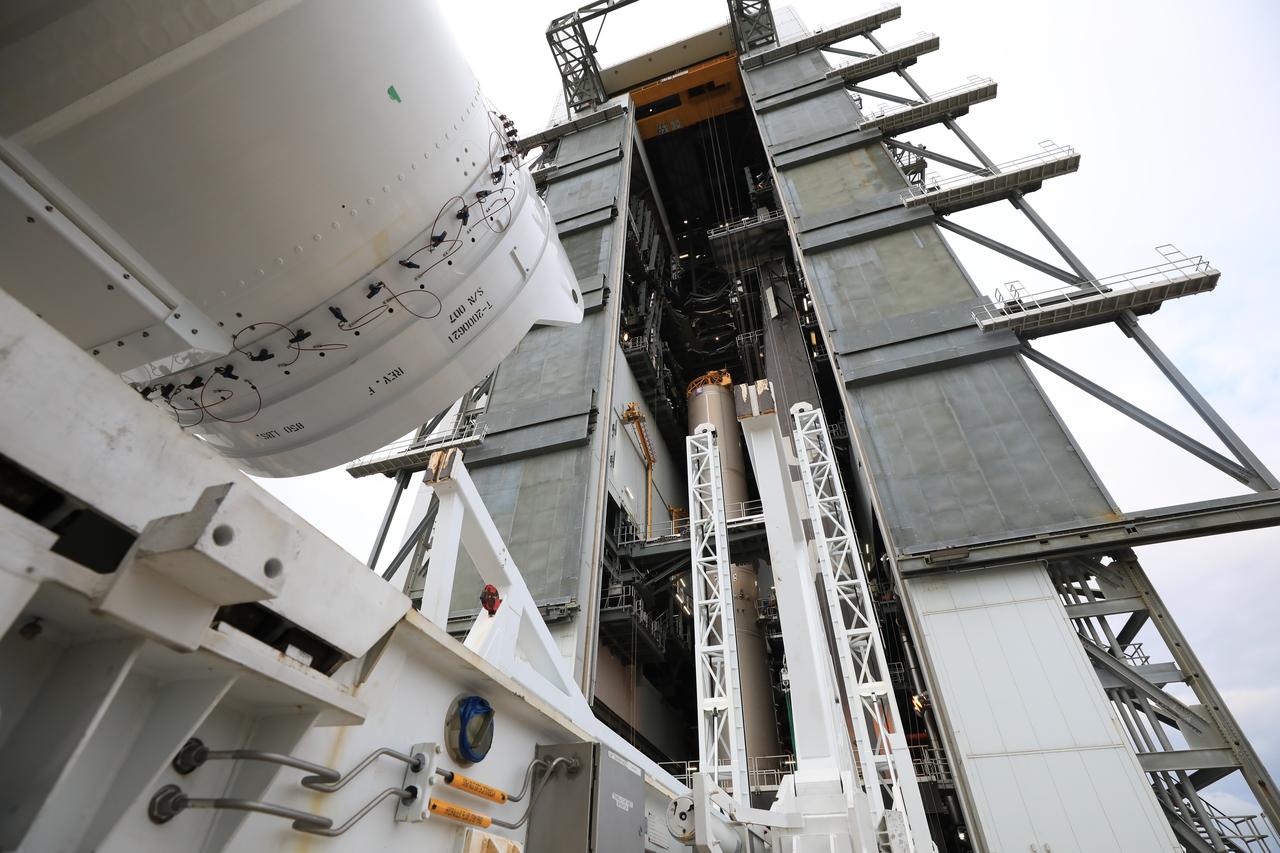
Preparations are underway to lift the fourth and final solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 9, 2020. The SRB will be lifted and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in July 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A lifting device is used to raise the second of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 3, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
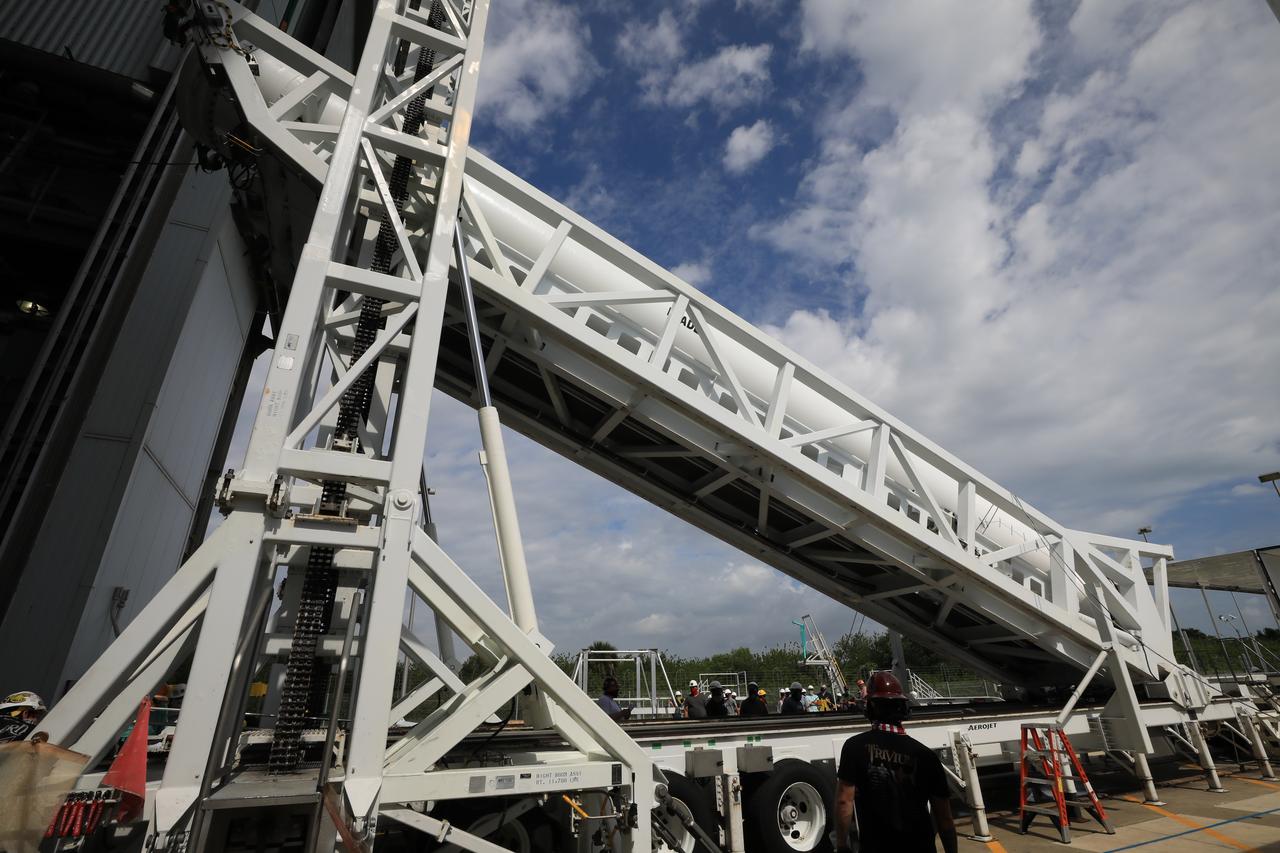

A lifting device raises the third of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 8, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

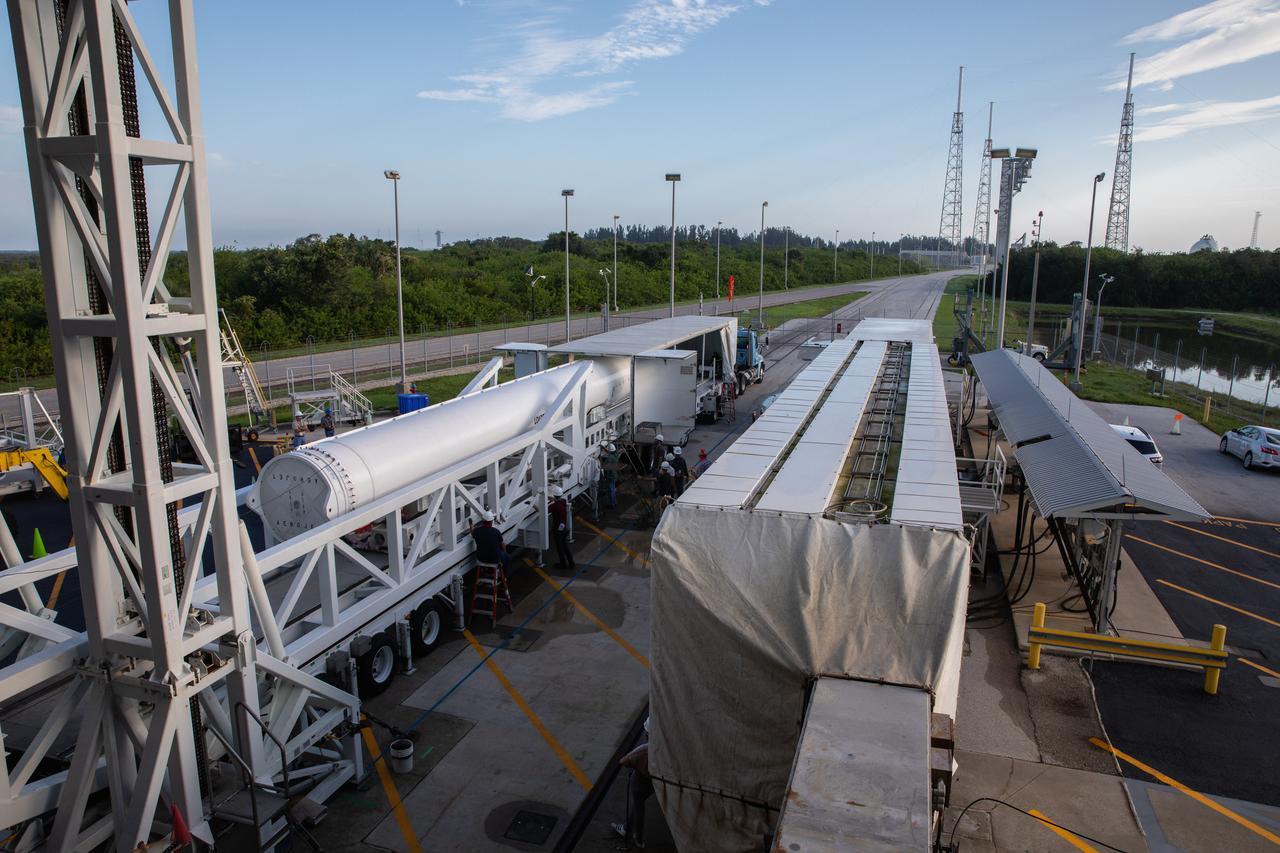
The second of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 3, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
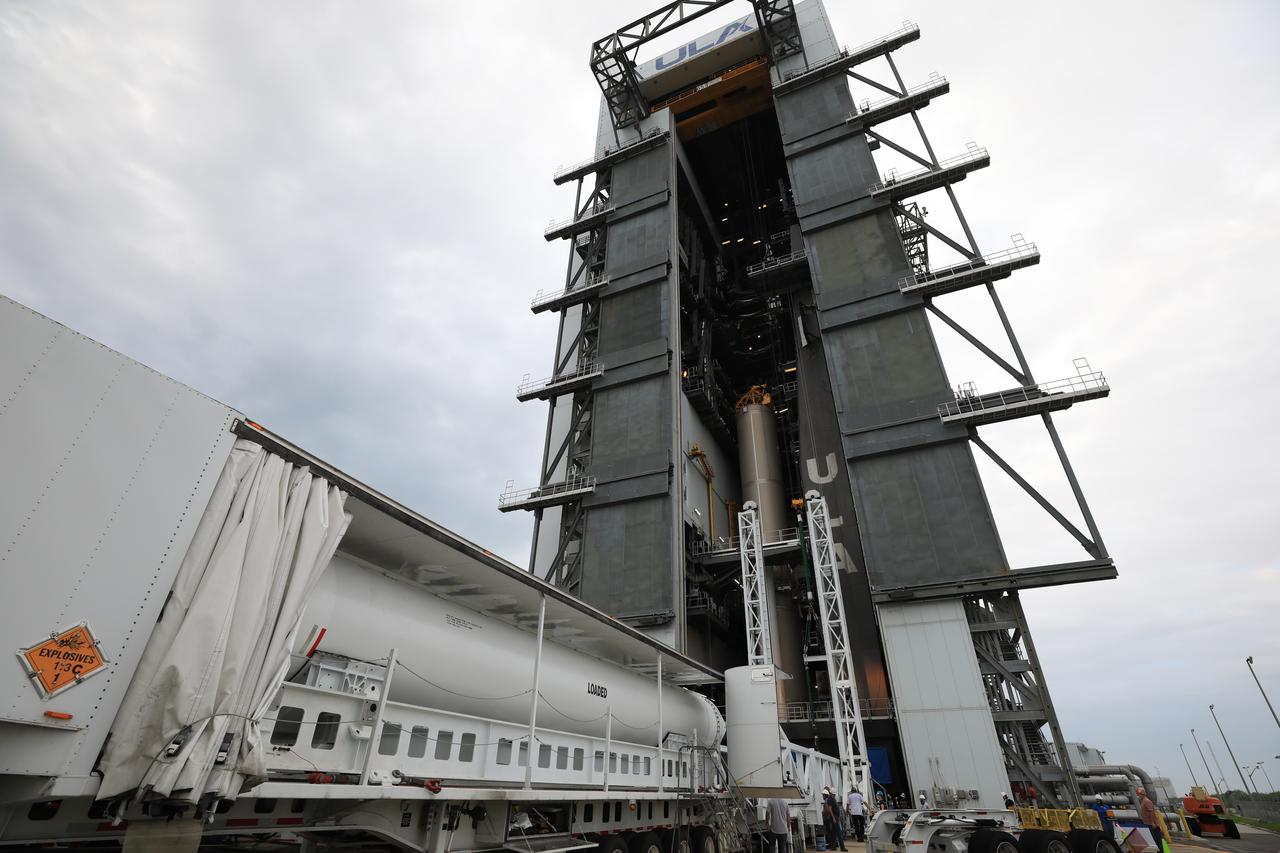

The third of four solid rocket boosters (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 8, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 20, 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
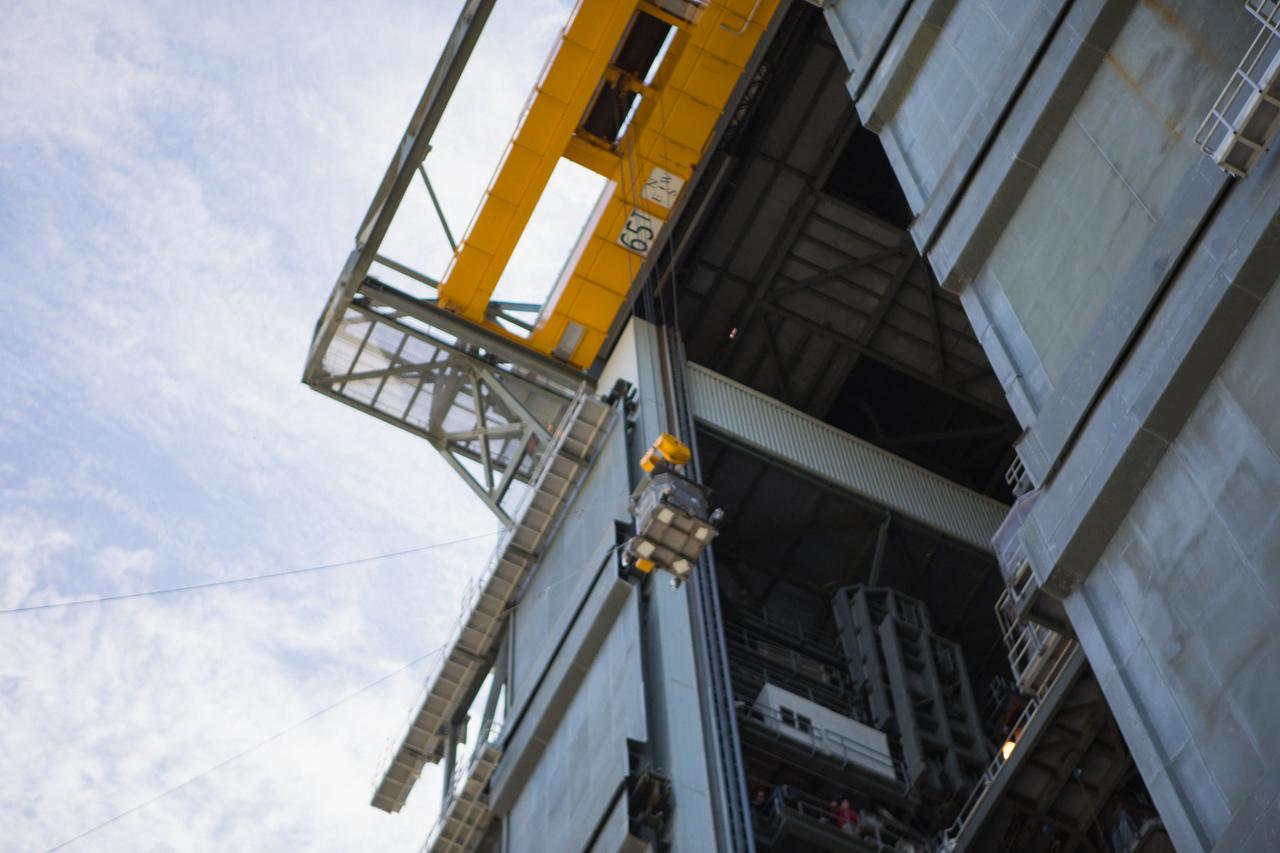

A crane is used to hoist a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully lifting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
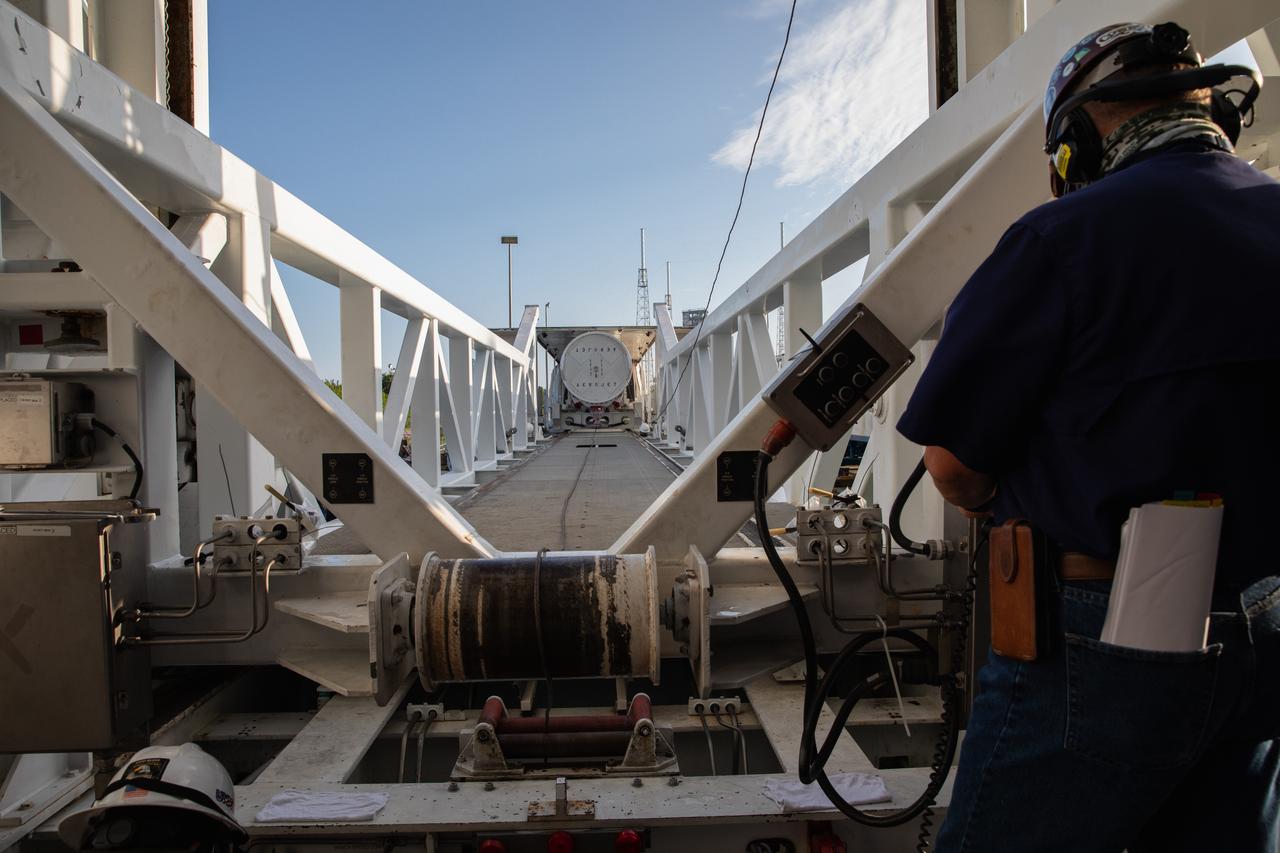

Preparations are underway to lift the fourth and final solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 9, 2020. The SRB will be lifted and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in July 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
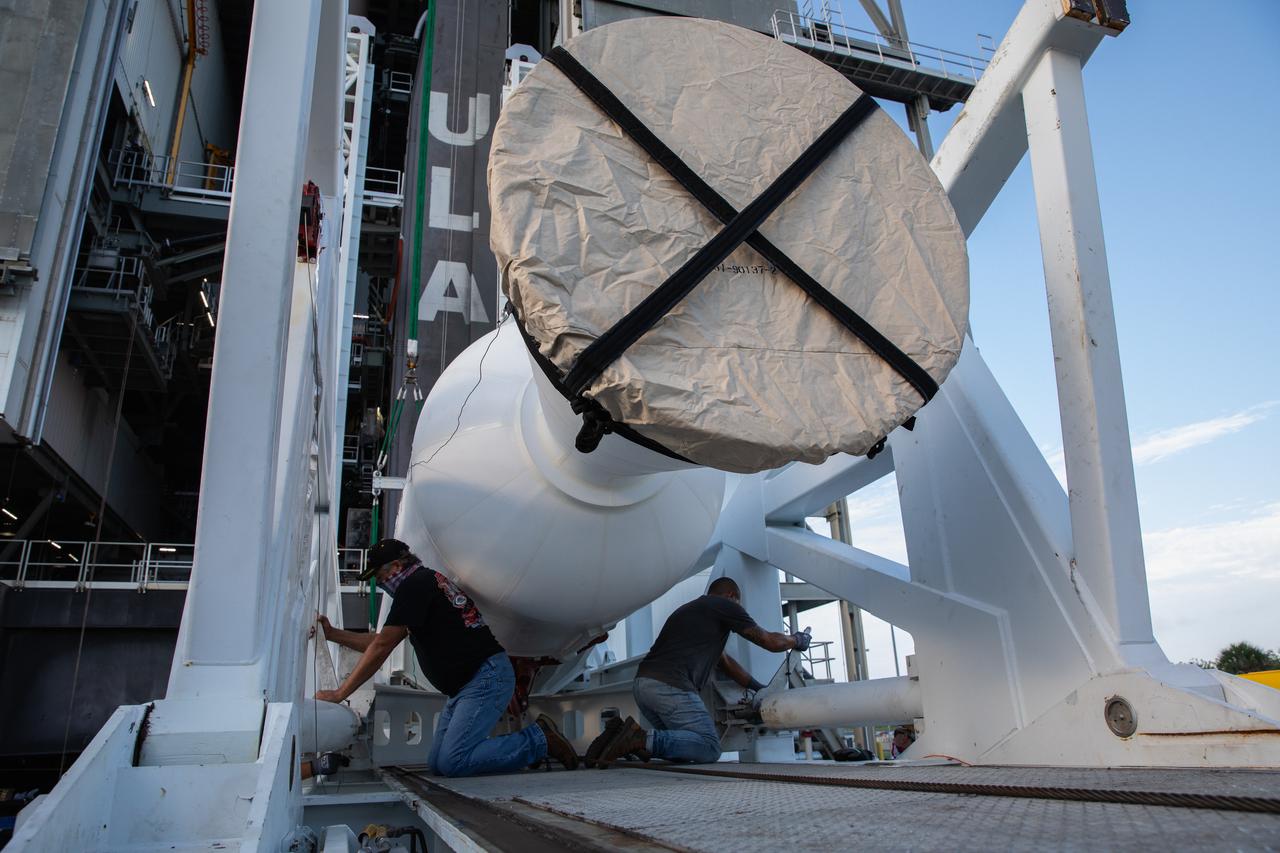

A lifting device raises the fourth and final solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket into the vertical position at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on June 9, 2020. The SRB will be lifted up and mated to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in July 2020, atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.