
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter covers a steep west-facing slope in southwestern Ganges Chasma, north of the larger canyons of Valles Marineris. The spot was targeted both for the bedrock exposures and to look for active slope processes. We see two distinct flow deposits: lobate flows that are relatively bright, sometimes with dark fringes, and very thin brownish lines that resemble recurring slope lineae (or 'RSL'). Both flows emanate from rocky alcoves. The RSL are superimposed on the lobate deposits (perhaps rocky debris flows), so they are younger and more active. The possible role of water in forming the debris flows and RSL are the subjects of continuing debate among scientists. We will acquire more images here to see if the candidate RSL are active. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21651
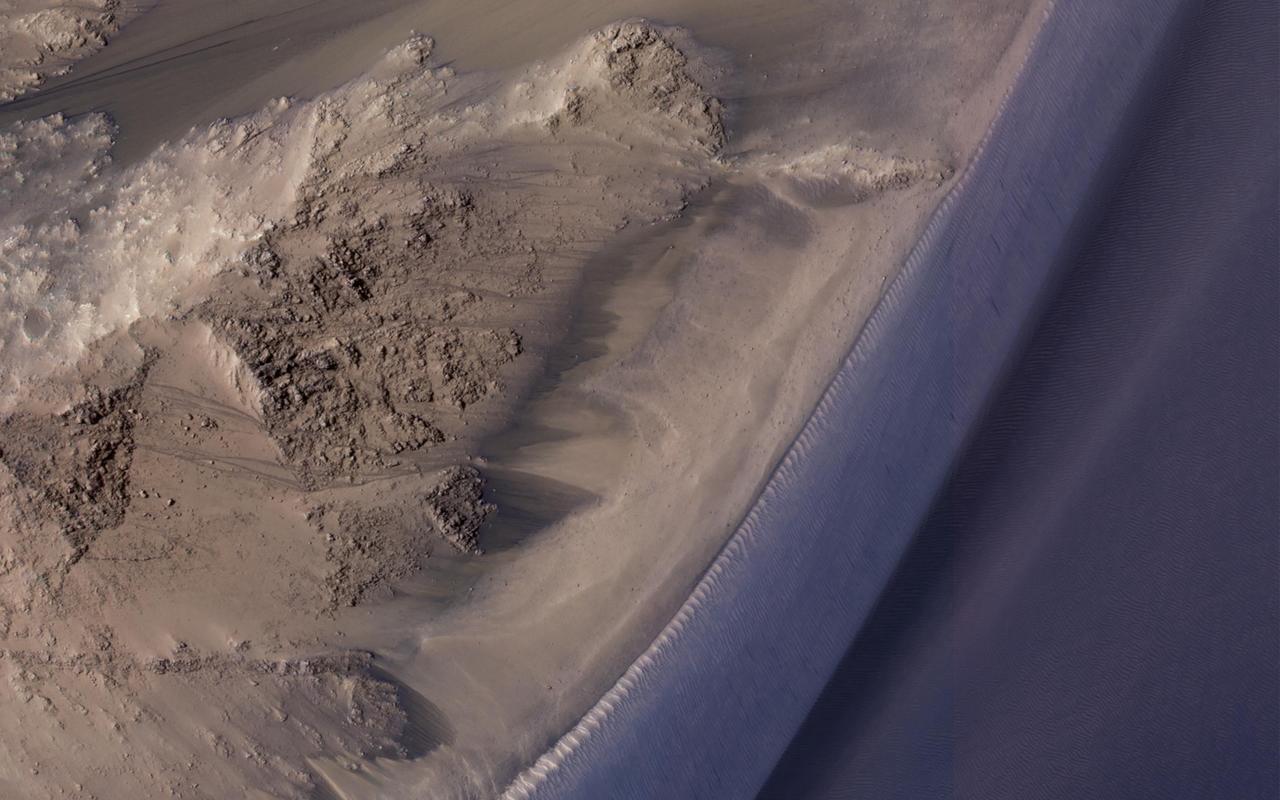

Recurring slope lineae (RSL) are seasonal flows on warm slopes, and are especially common in central and eastern Valles Marineris, as seen in this observation by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This image covers a large area full of interesting features. Here, the RSL are active on east-facing slopes, extending from bouldery terrain and terminating on fans. Perhaps the fans themselves built up over time from the seasonal flows. Part of the fans with abundant RSL are dark, while the downhill portion of the fans are bright. The role of water in RSL activity is a matter of active debate. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21608
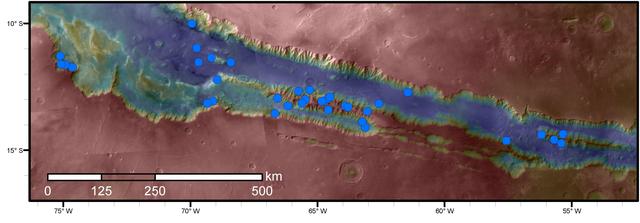
Blue dots on this map indicate sites of recurring slope lineae (RSL) in part of the Valles Marineris canyon network on Mars. RSL are seasonal dark streaks regarded as the strongest evidence for the possibility of liquid water on the surface of modern Mars. The area mapped here has the highest density of known RSL on the Red Planet. The RSL were identified by repeated observations of the sites using the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Map colors represent elevation, where red is high and blue is low. Valles Marineris is the largest canyon system in the solar system. The region shown here includes Melas Chasma and Coprates Chasma, in the central and eastern portions of Valles Marineris. The mapped area extends about 1,500 miles (2,400 kilometers) east to west and about 280 miles (450 kilometers) north to south, at latitudes from 9 to 17 degrees south of Mars' equator. The base map uses data from the Mars Orbiter Camera and Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter of NASA's Mars Global Surveyor mission. RSL extend downslope during a warm season, fade in the colder part of the year, and repeat the process in a subsequent Martian year. A study of 41 RSL sites in this canyon area, published July 7, 2016, provides support for the notion that significant amounts of near-surface water can be found on modern Mars, though the work also indicates that puzzles remain unsolved in understanding how these seasonal features form. Each site includes anywhere from a few to more than 1,000 individual "lineae." http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20756

Although large gullies (ravines) are concentrated at higher latitudes, there are gullies on steep slopes in equatorial regions, as seen in this image captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The colors of the gully deposits match the colors of the eroded source materials. Krupac is a relatively young impact crater, but exposes ancient bedrock. Krupac Crater also hosts some of the most impressive recurring slope lineae (RSL) on equatorial Mars outside of Valles Marineris. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21605
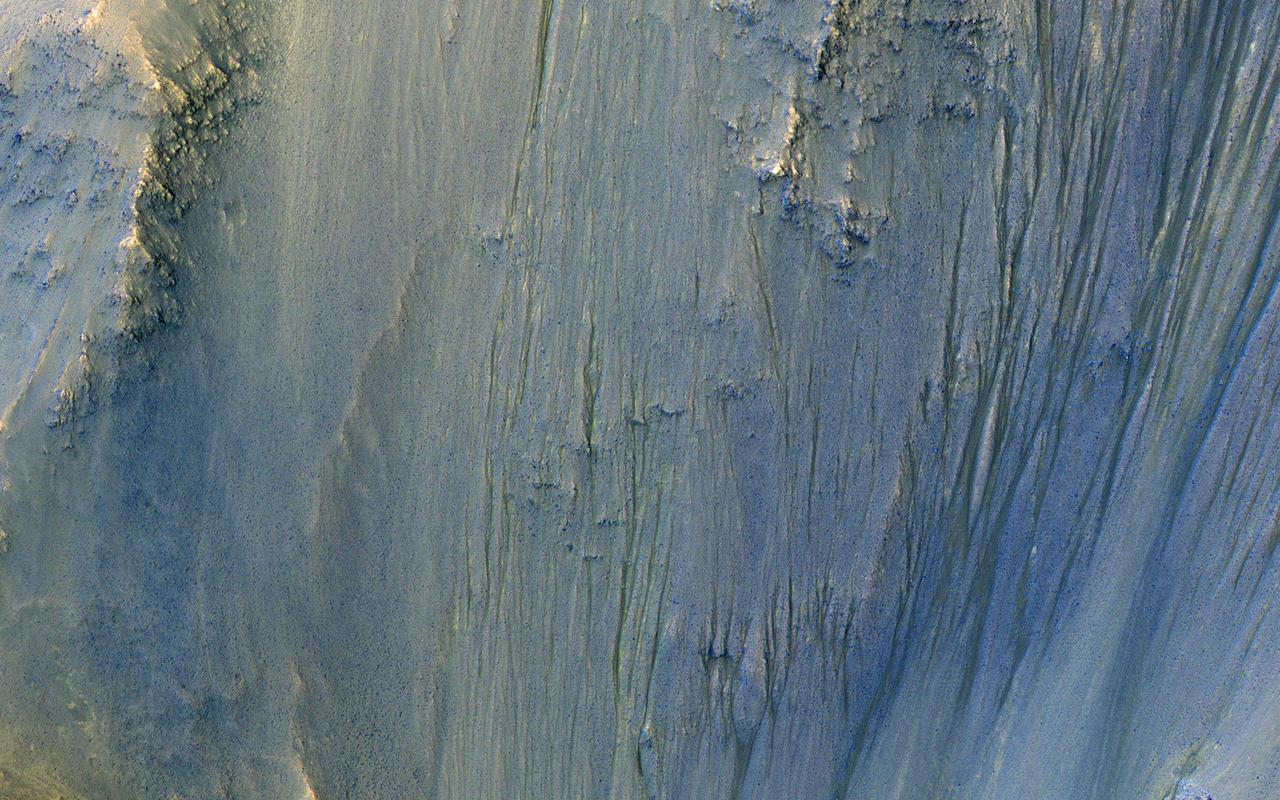

This image was acquired in Ius Chasma, a major section of the western portion of the giant Valles Marineris trough. We see a portion of a steep slope with gullies extending downhill (towards bottom of image). Many of the gully floors are dark, and in some places that dark material extends onto the fan-shaped deposits of the gullies. These dark features are candidates for recurring slope lineae (RSL), which are seasonal features that grow incrementally. The relation between RSL and gullies is not clear: does the RSL activity carve the gullies, or do they simply follow the gully topography created by other processes? Another closeup from this observation shows part of the floor of Ius Chasma, with layered bedrock draped by dunes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23099
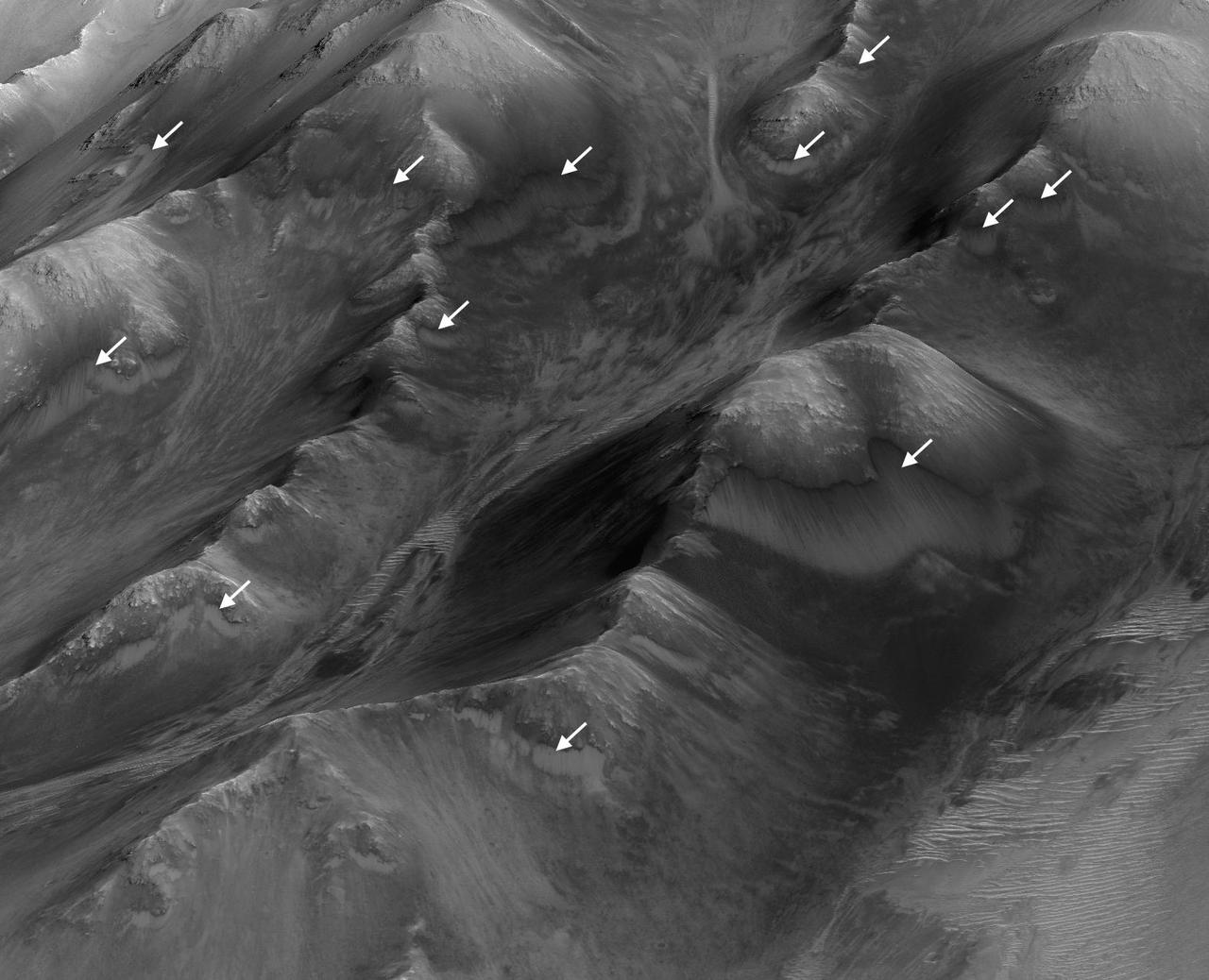
The white arrows indicate locations in this scene where numerous seasonal dark streaks have been identified in the Coprates Montes area of Mars' Valles Marineris by repeated observations from orbit. The streaks, called recurring slope lineae or RSL, extend downslope during a warm season, fade in the colder part of the year, and repeat the process the next Martian year. They are regarded as the strongest evidence for the possibility of liquid water on the surface of modern Mars. This oblique perspective for this view uses a three-dimensional terrain model derived from a stereo pair of observations by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The scene covers an area approximately 1.6 miles (2.5 kilometers) wide. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20757
![This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows what are called "recurring slope lineae"s in Tivat Crater. The narrow, dark flows descend downhill (towards the upper left). Analysis shows that the flows all end at approximately the same slope, which is similar to the angle of repose for sand. RSL are mostly found on steep rocky slopes in dark regions of Mars, such as the southern mid-latitudes, Valles Marineris near the equator, and in Acidalia Planitia on the northern plains. The appearance and growth of these features resemble seeping liquid water, but how they form remains unclear, and this research demonstrated that the RSL flows seen by HiRISE are likely moving granular material like sand and dust. These findings indicate that present-day Mars may not have a significant volume of liquid water. The water-restricted conditions that exist on Mars would make it difficult for Earth-like life to exist near the surface of the planet. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.6 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 77 centimeters (30.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22114](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22114/PIA22114~medium.jpg)
This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows what are called "recurring slope lineae"s in Tivat Crater. The narrow, dark flows descend downhill (towards the upper left). Analysis shows that the flows all end at approximately the same slope, which is similar to the angle of repose for sand. RSL are mostly found on steep rocky slopes in dark regions of Mars, such as the southern mid-latitudes, Valles Marineris near the equator, and in Acidalia Planitia on the northern plains. The appearance and growth of these features resemble seeping liquid water, but how they form remains unclear, and this research demonstrated that the RSL flows seen by HiRISE are likely moving granular material like sand and dust. These findings indicate that present-day Mars may not have a significant volume of liquid water. The water-restricted conditions that exist on Mars would make it difficult for Earth-like life to exist near the surface of the planet. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.6 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 77 centimeters (30.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22114