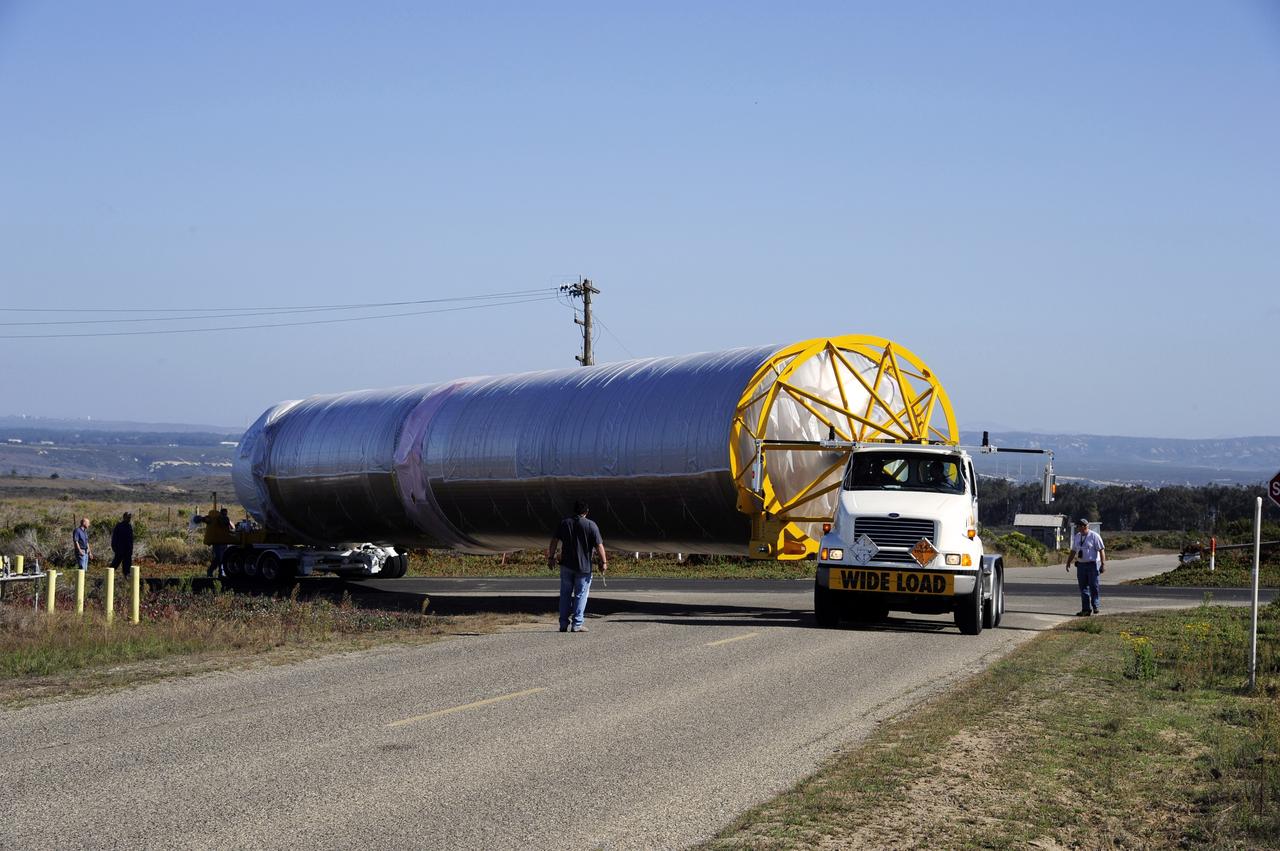

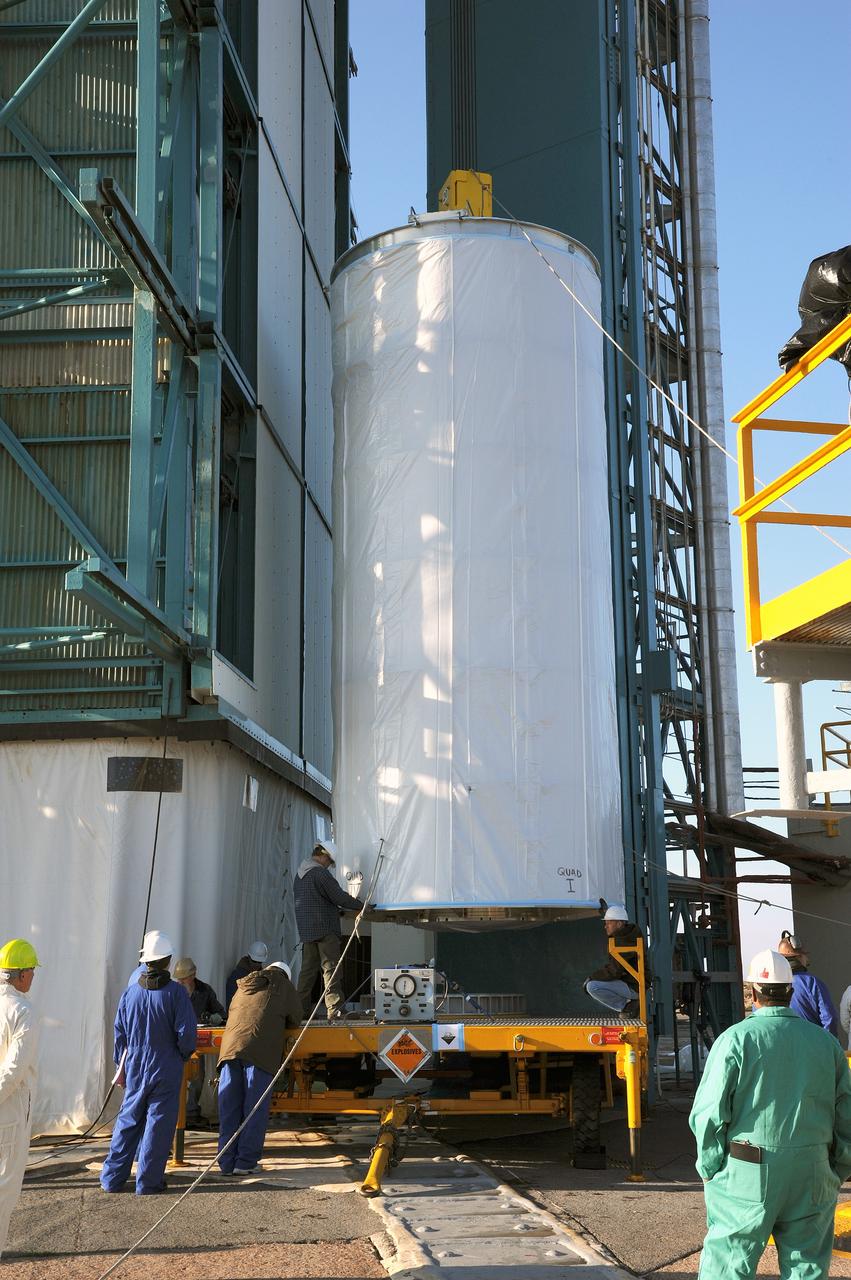
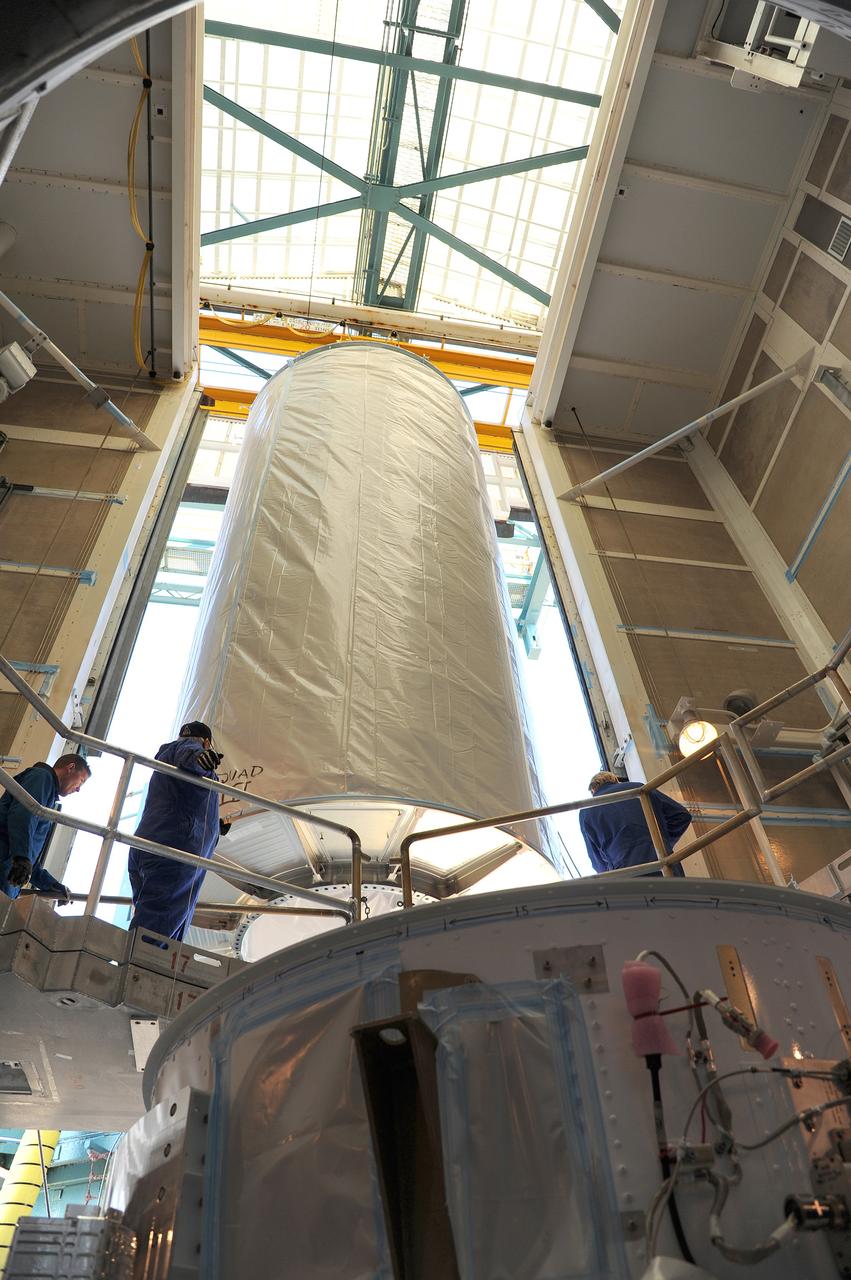
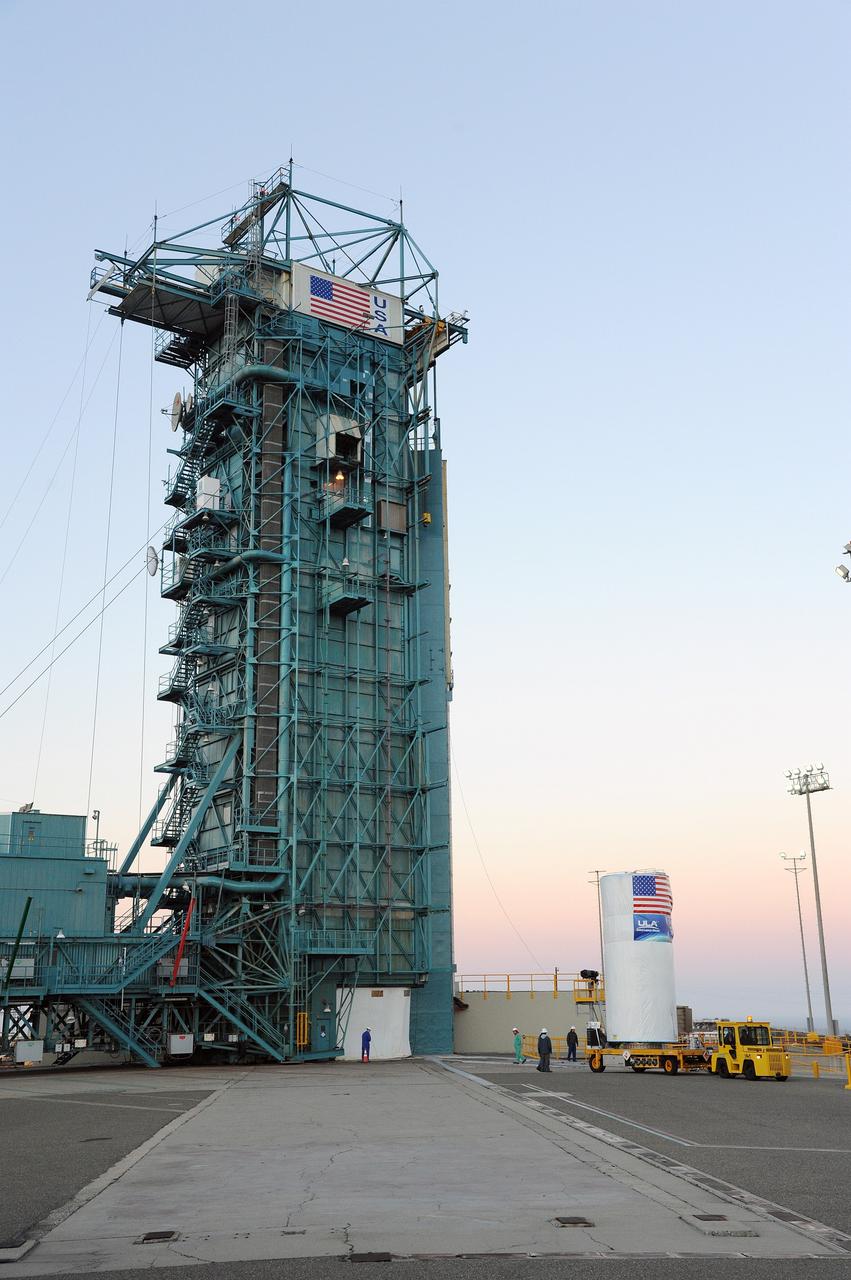
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
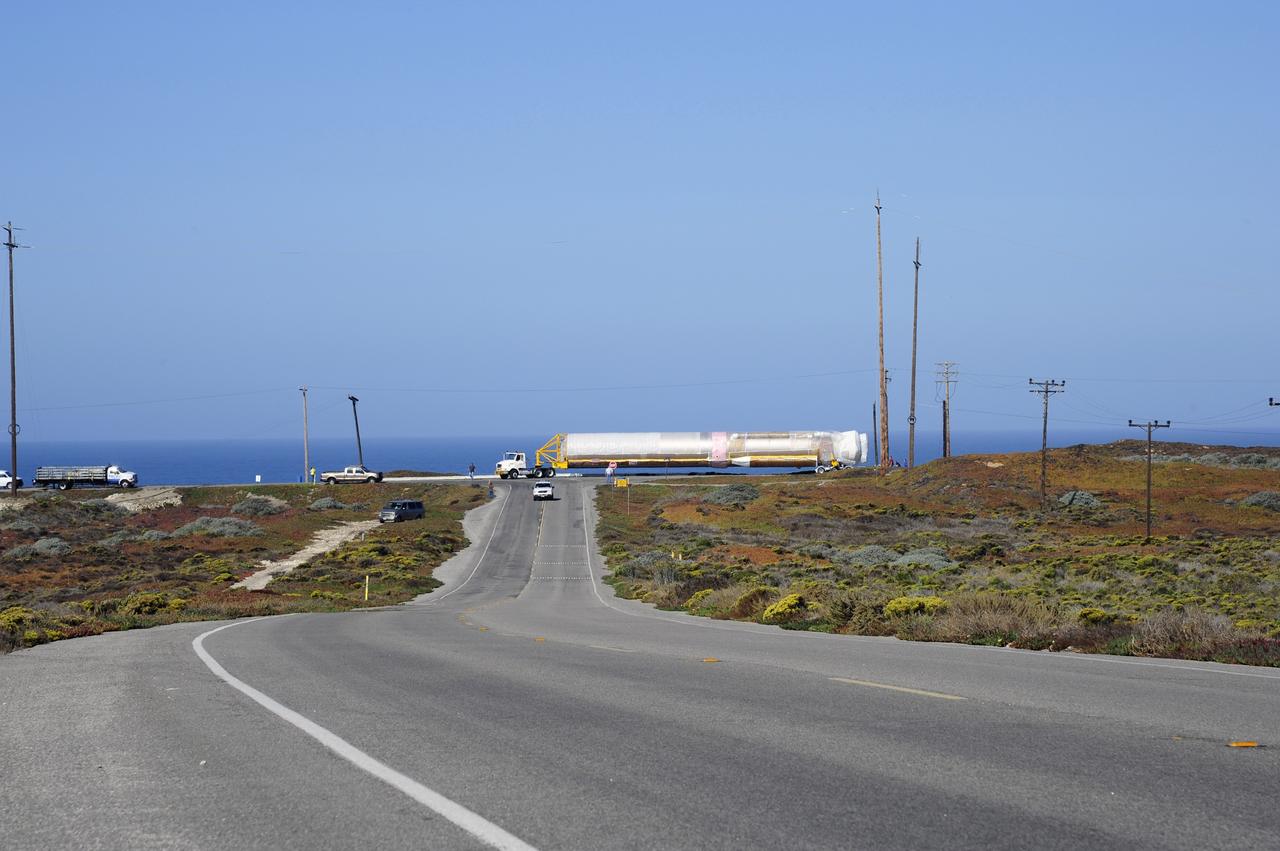

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
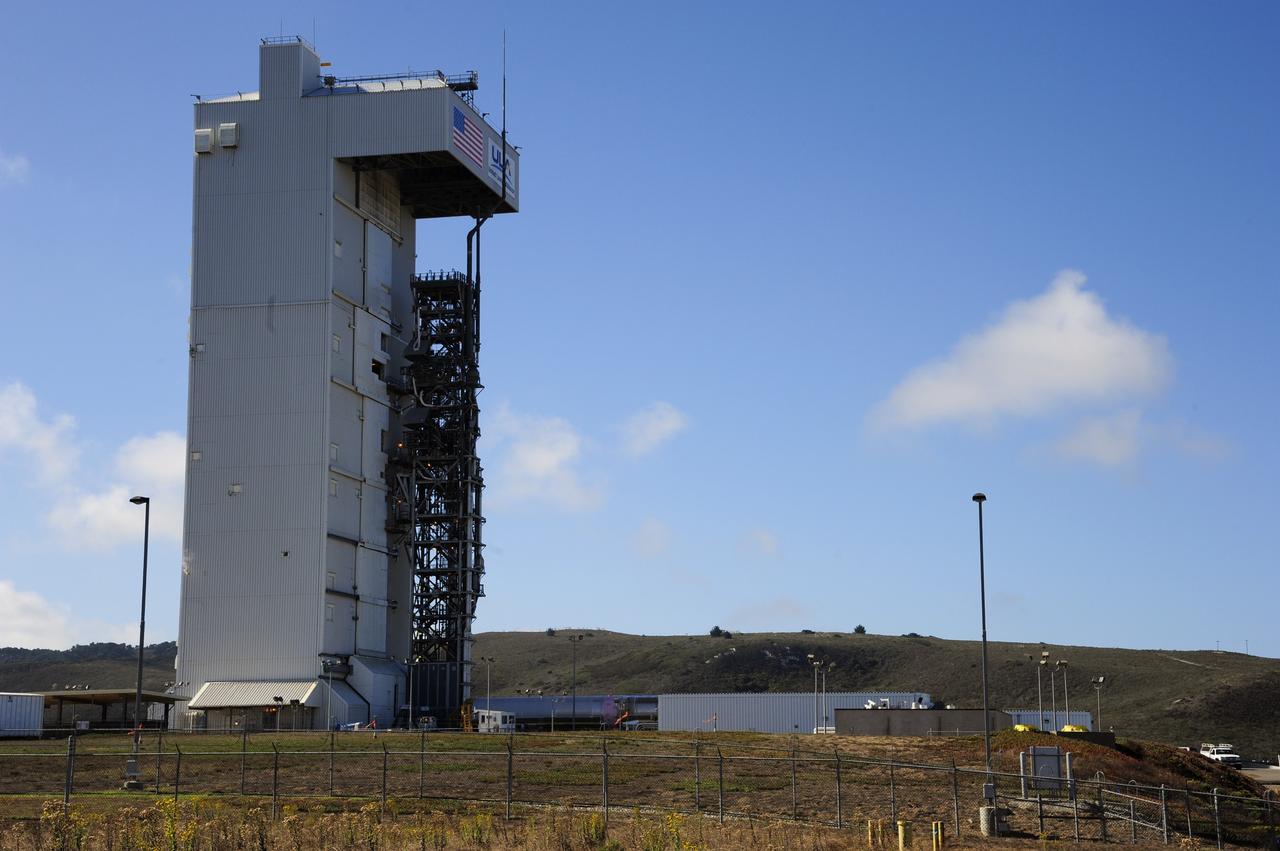

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
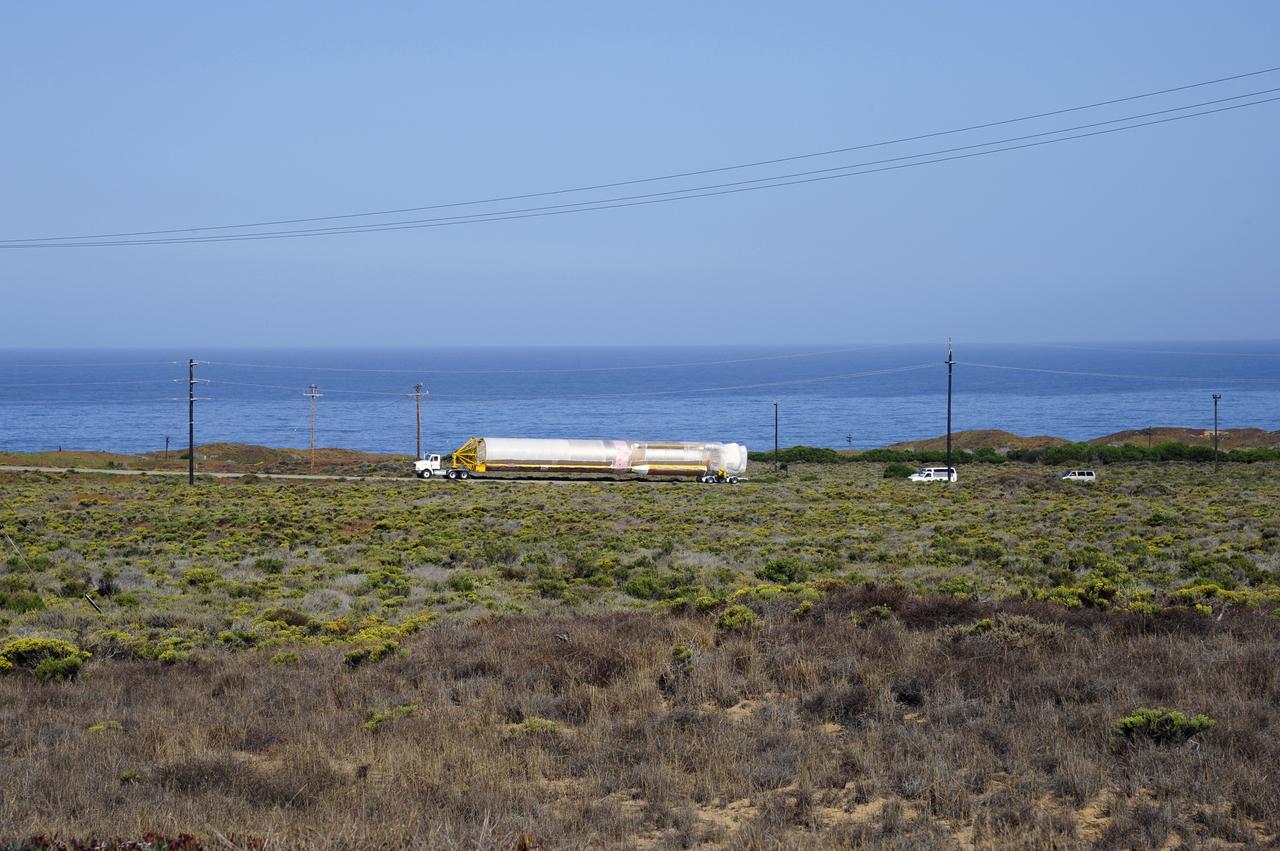

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
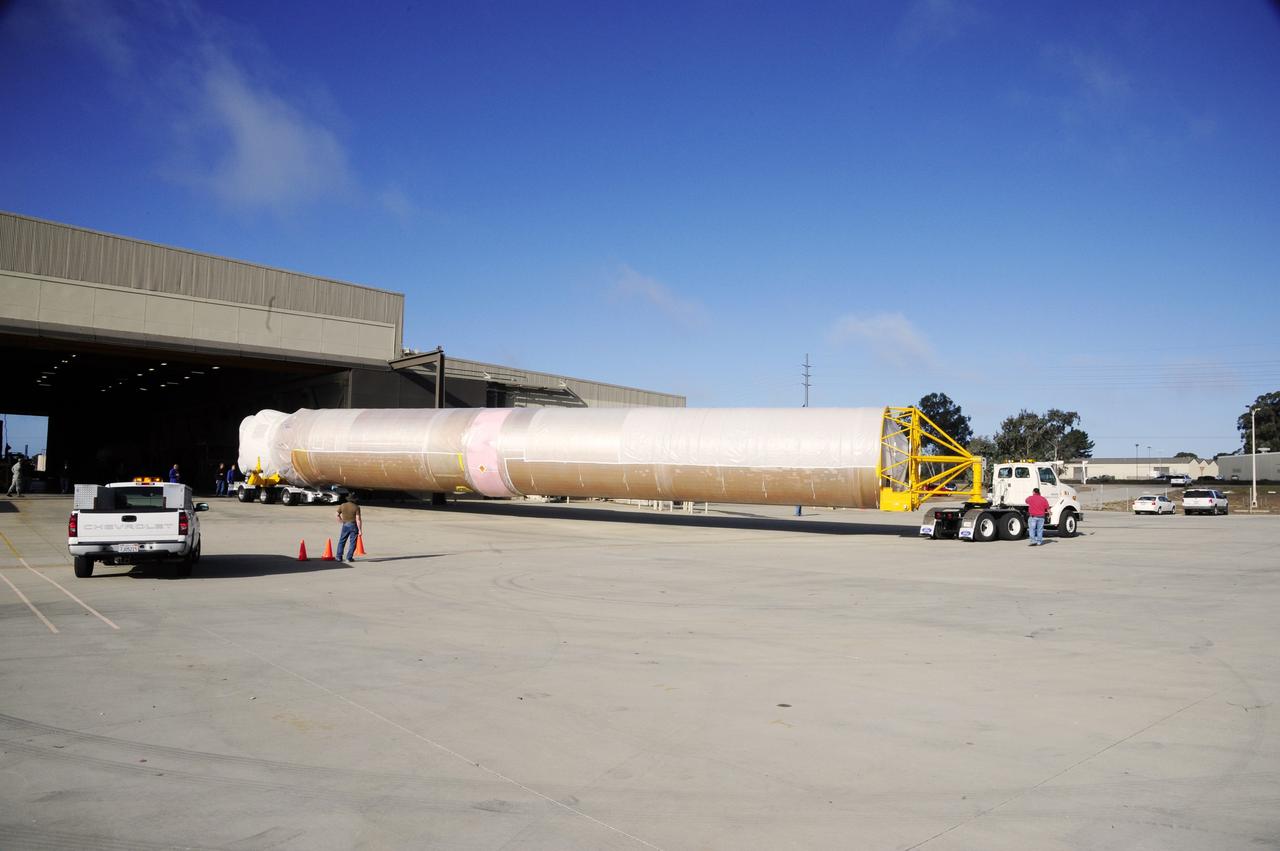

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
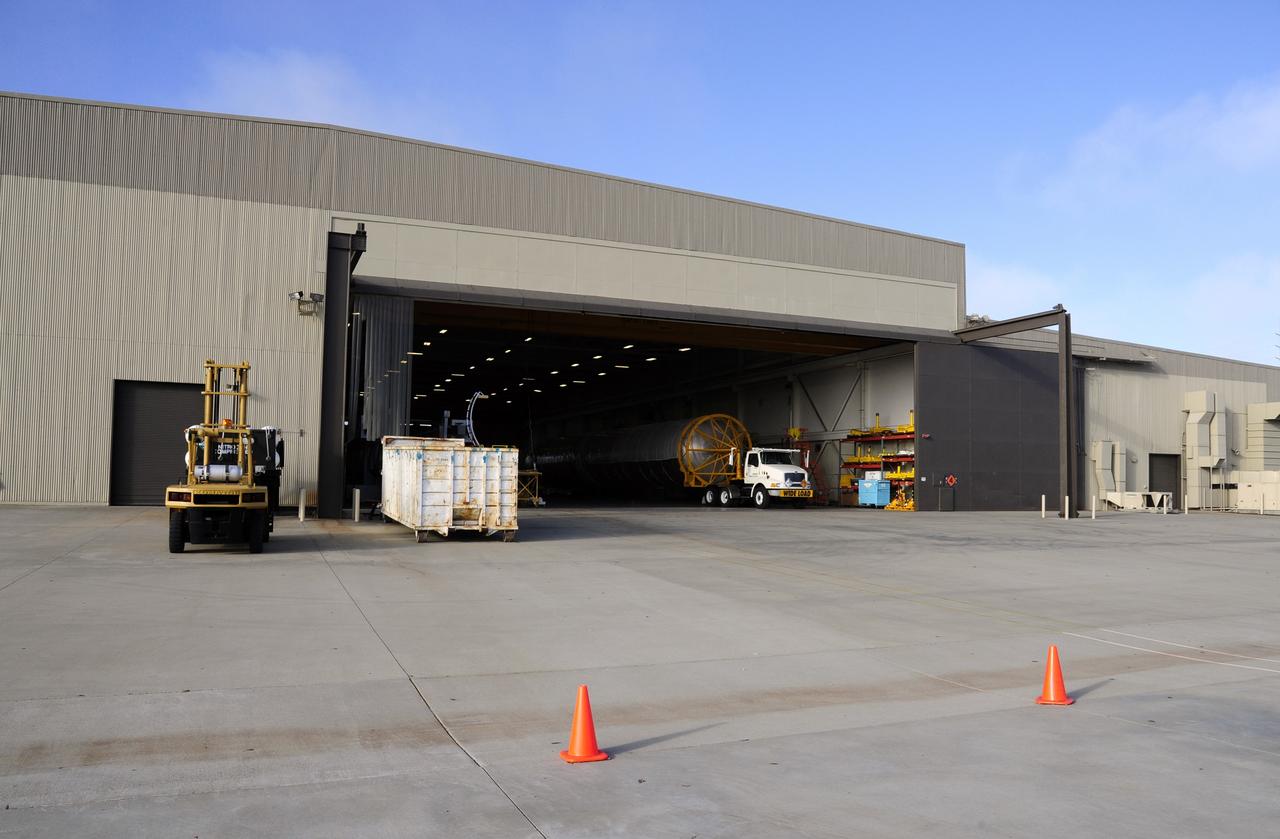

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
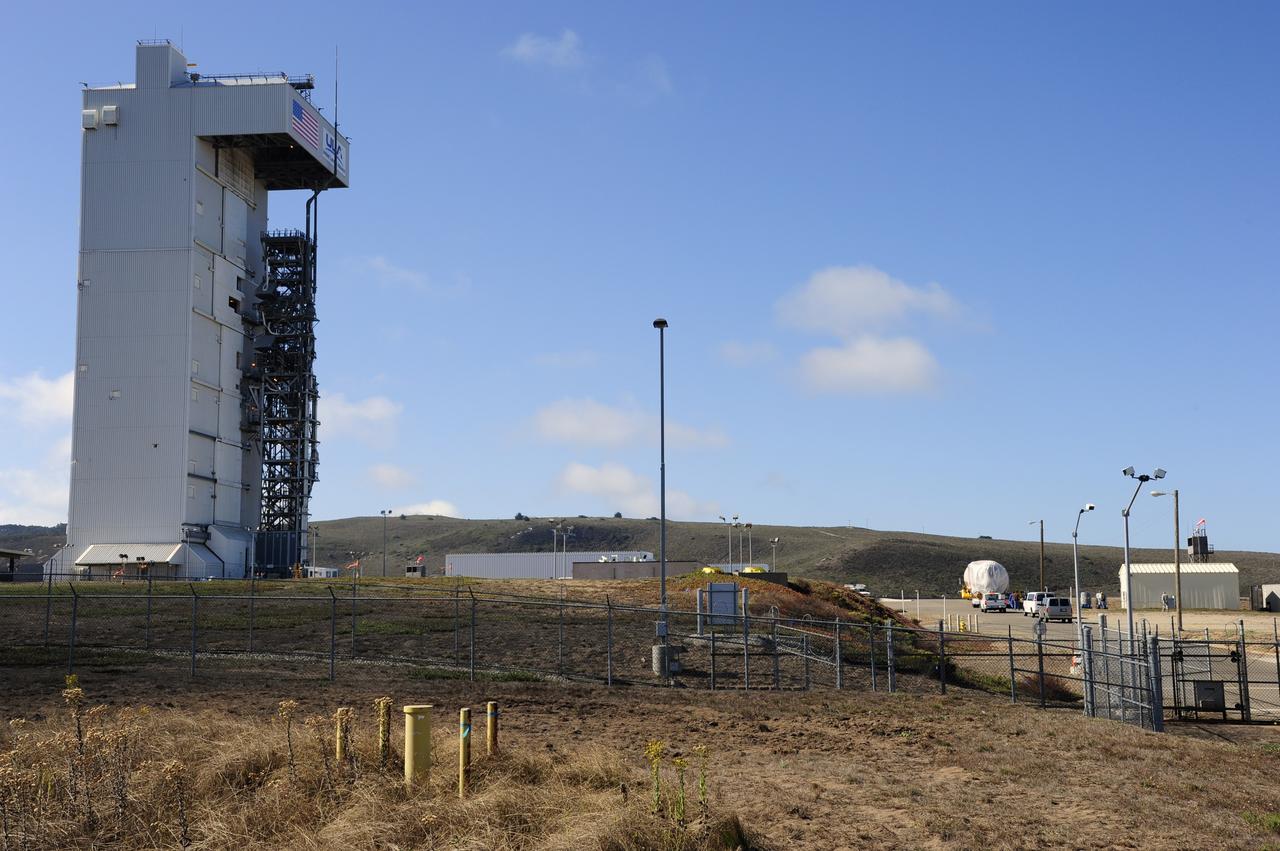

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
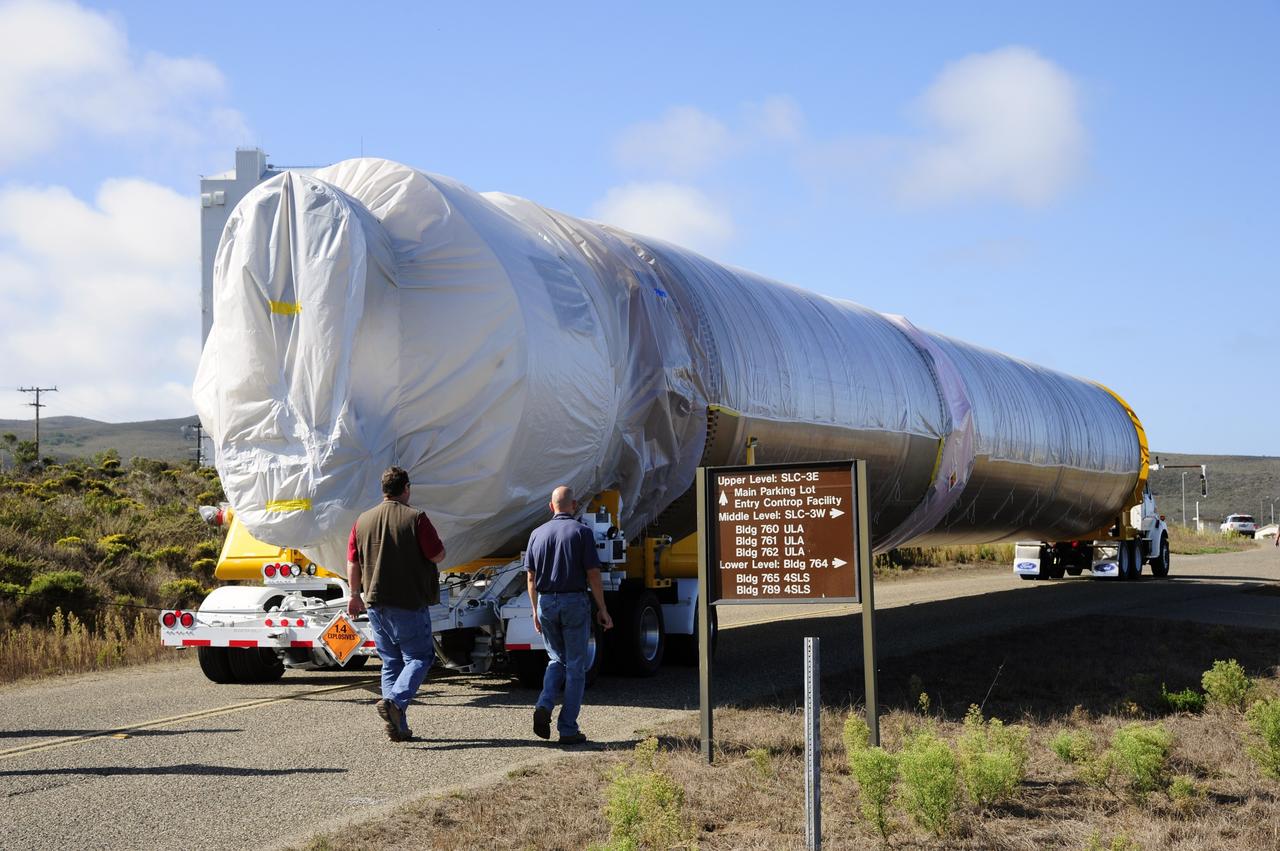

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
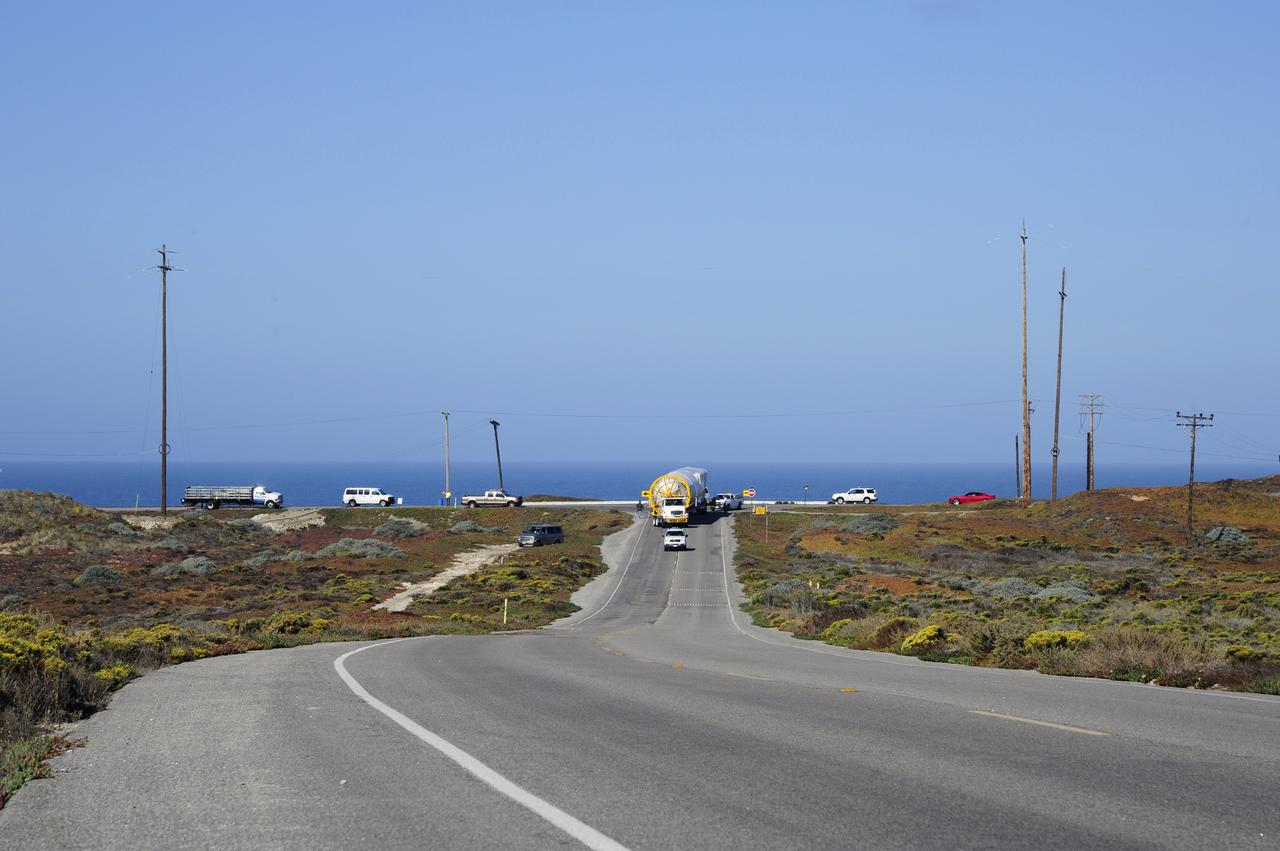

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
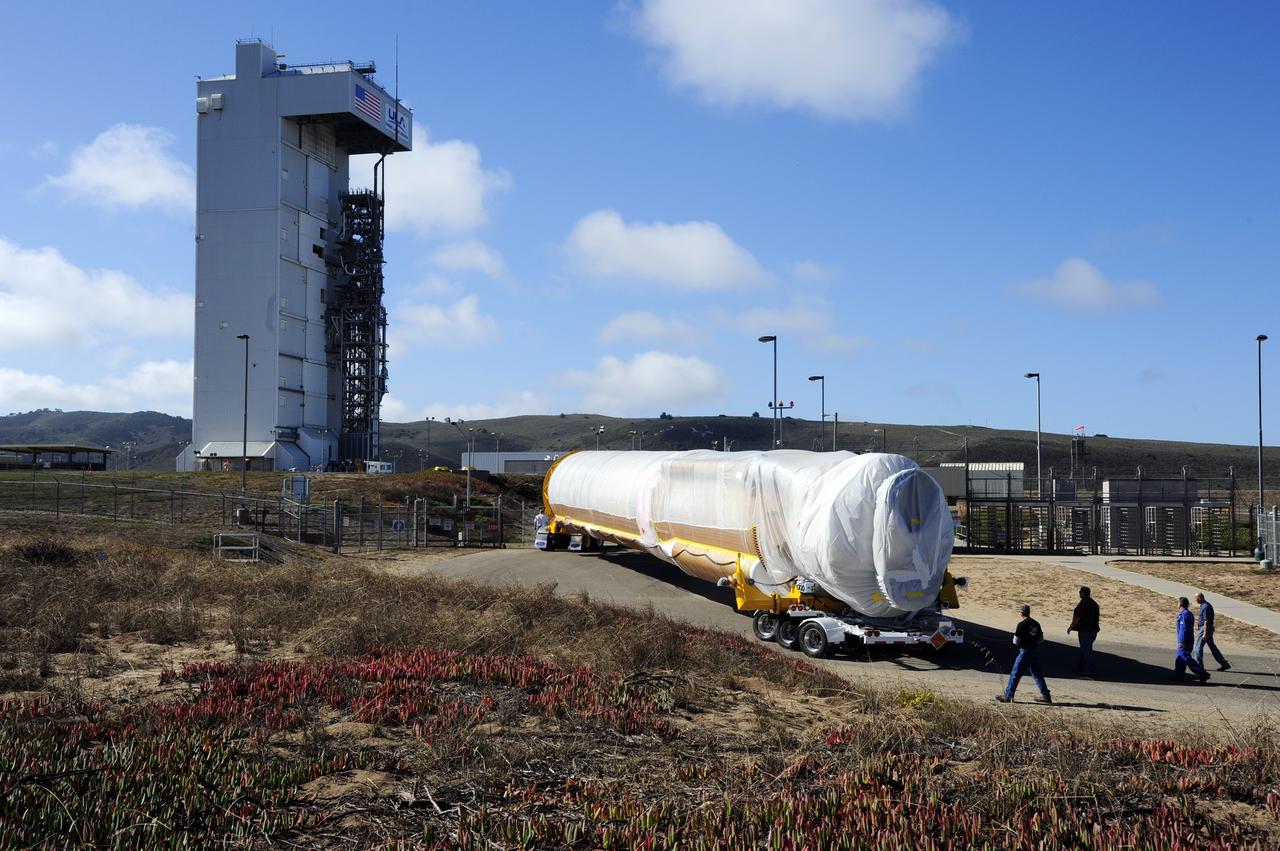

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck moves the first stage booster of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V to Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. in preparation for the launch of the Landsat Data Continuity Mission. The Landsat Data Continuity Mission, or LDCM, is the future of Landsat satellites. It will continue to obtain valuable data and imagery to be used in agriculture, education, business, science, and government. The Landsat Program provides repetitive acquisition of high resolution multispectral data of the Earth's surface on a global basis. The data from the Landsat spacecraft constitute the longest record of the Earth's continental surfaces as seen from space. It is a record unmatched in quality, detail, coverage, and value. Launch is planned for Feb. 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Roy Allison
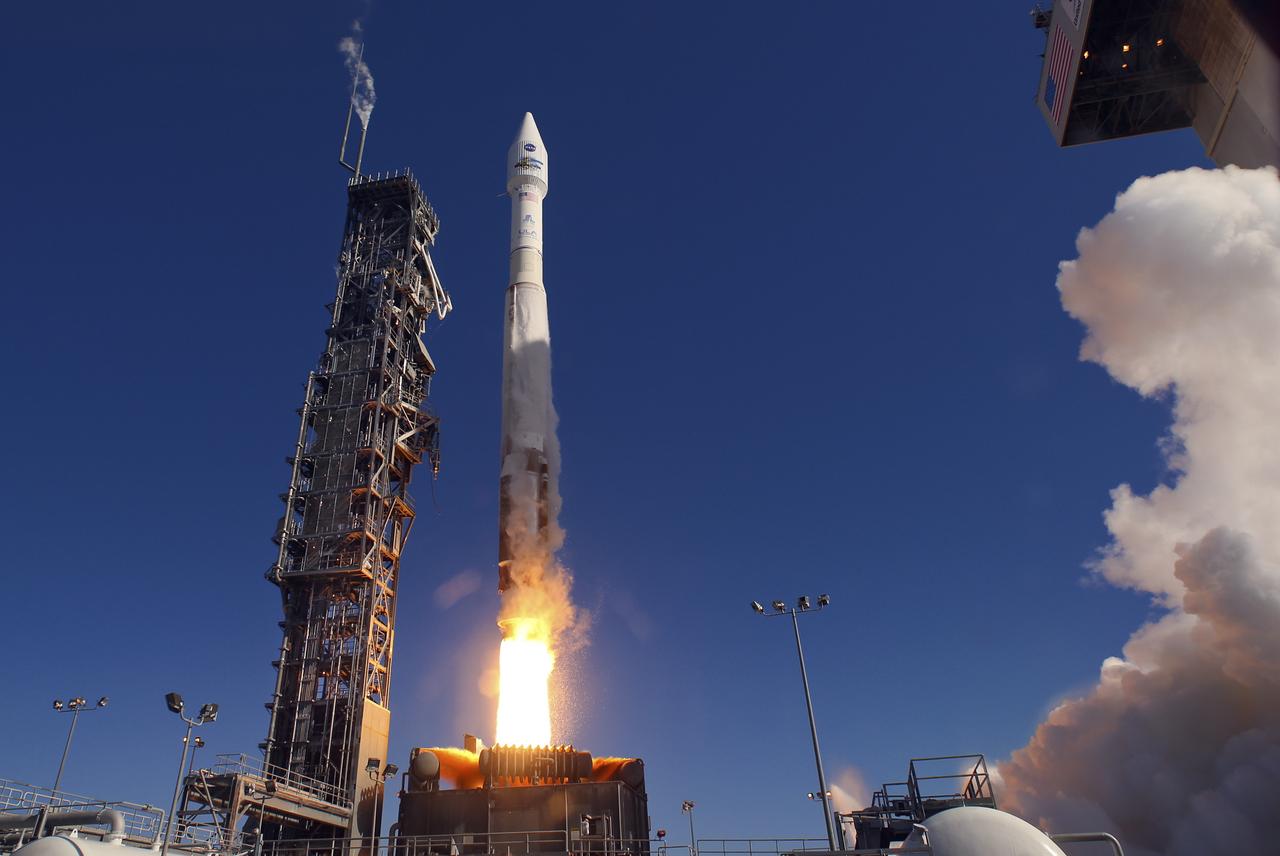

Launch of Atlas V LDCM, from Vandenberg AFB, California
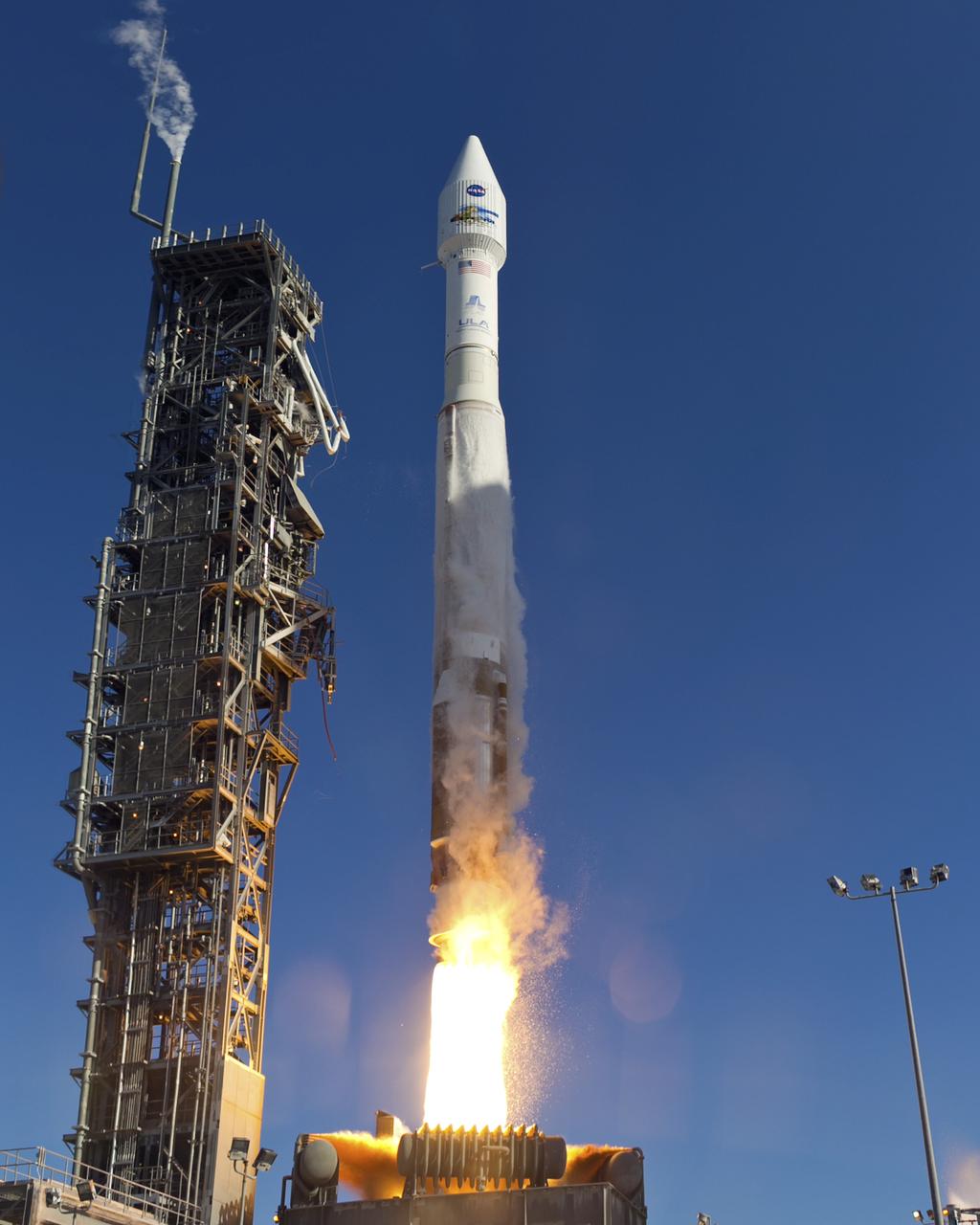

Launch of Atlas V LDCM, from Vandenberg AFB, California
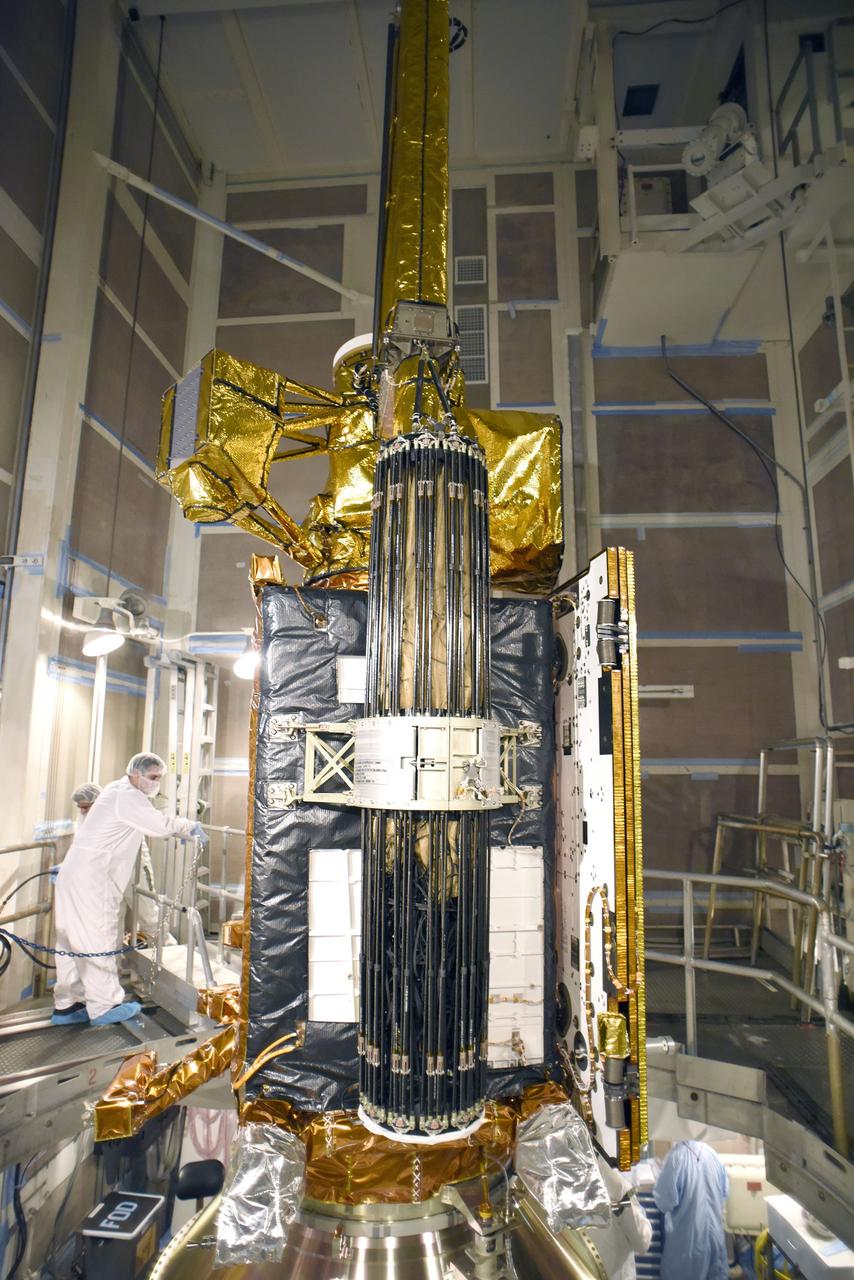

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
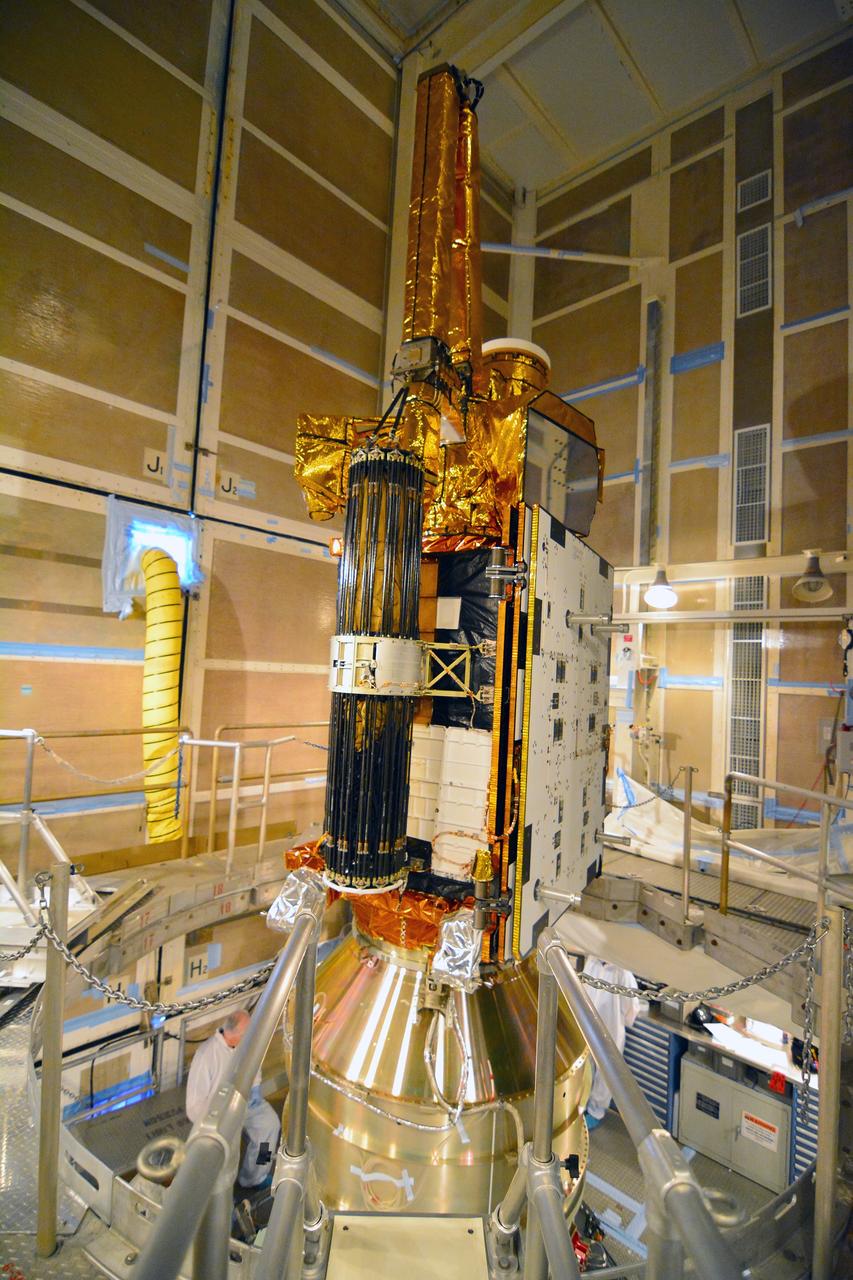
VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
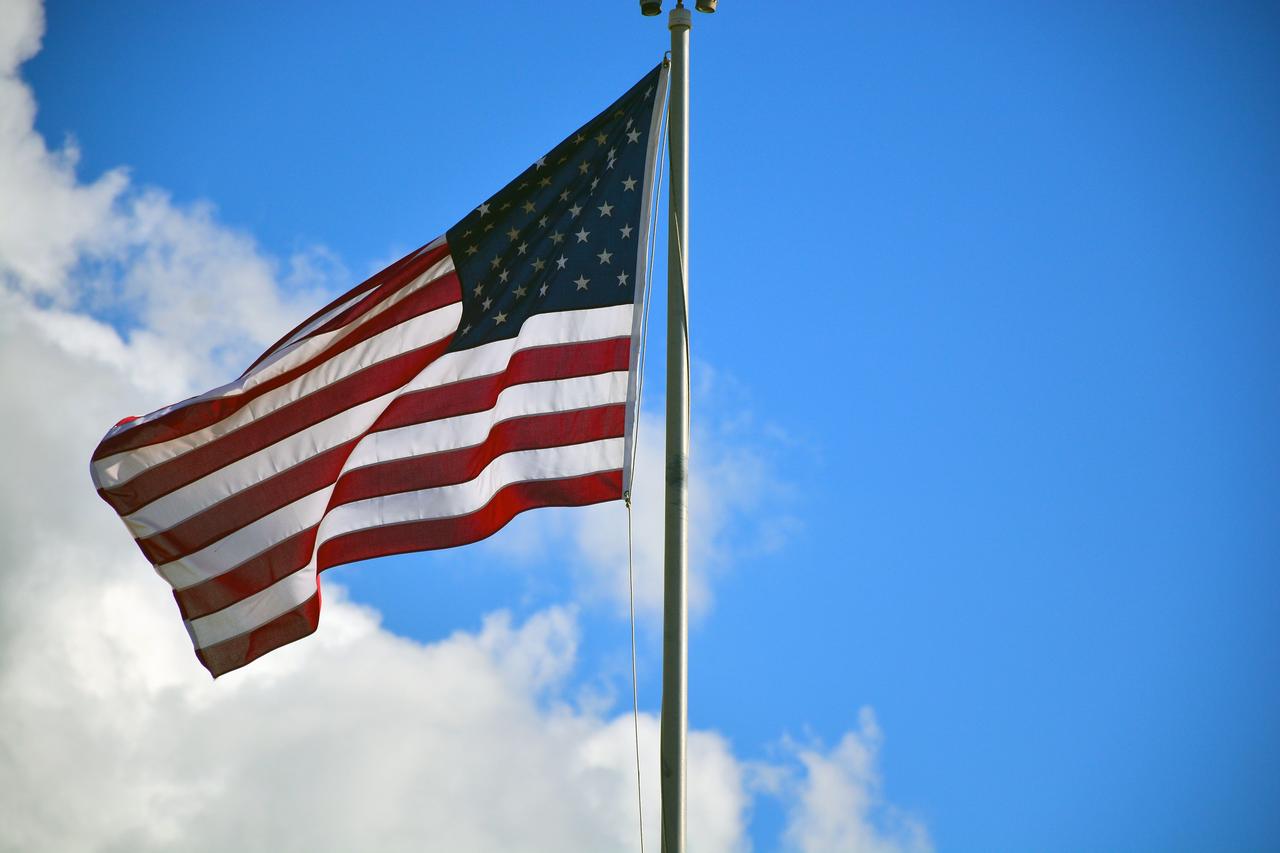

VANDENBERG AFB, California – An American flag flies at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
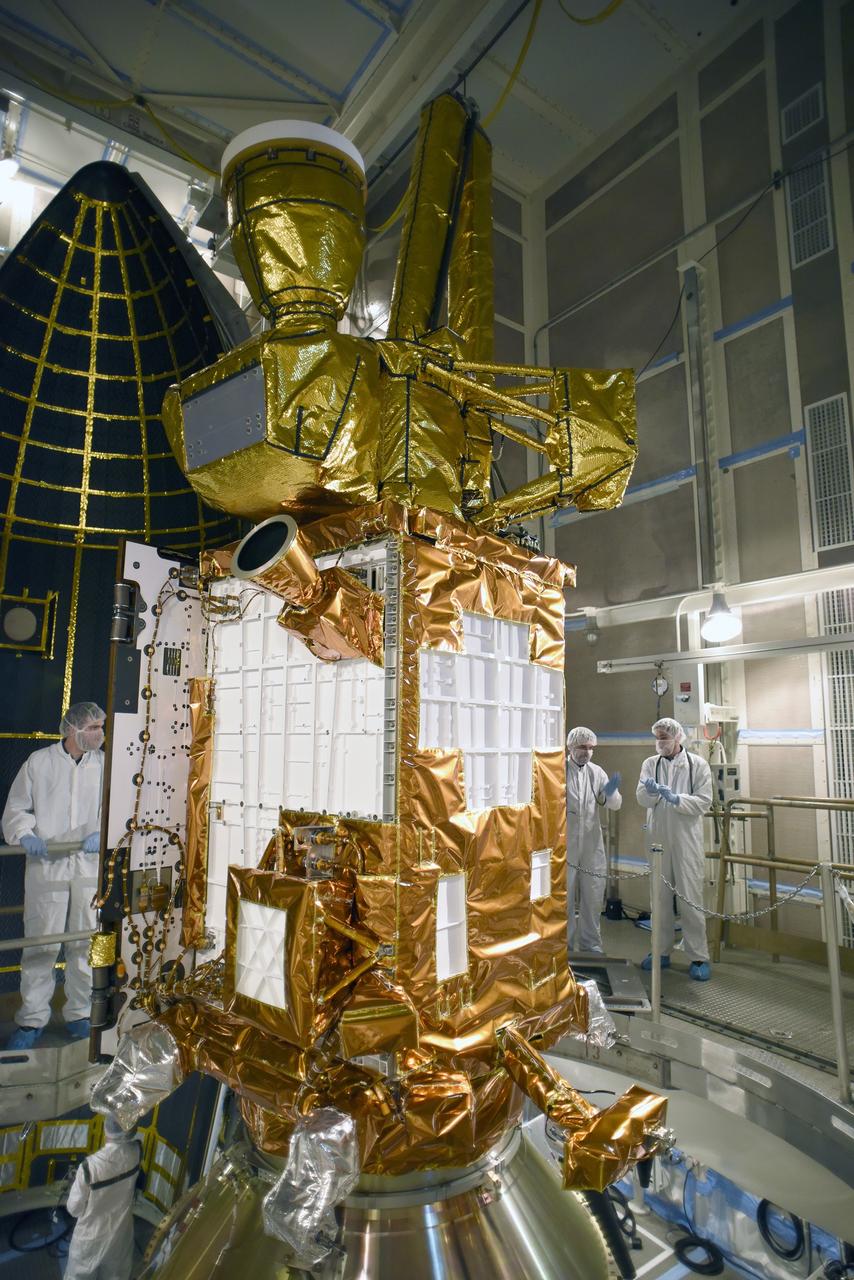

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Detail of mission and NASA logos at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
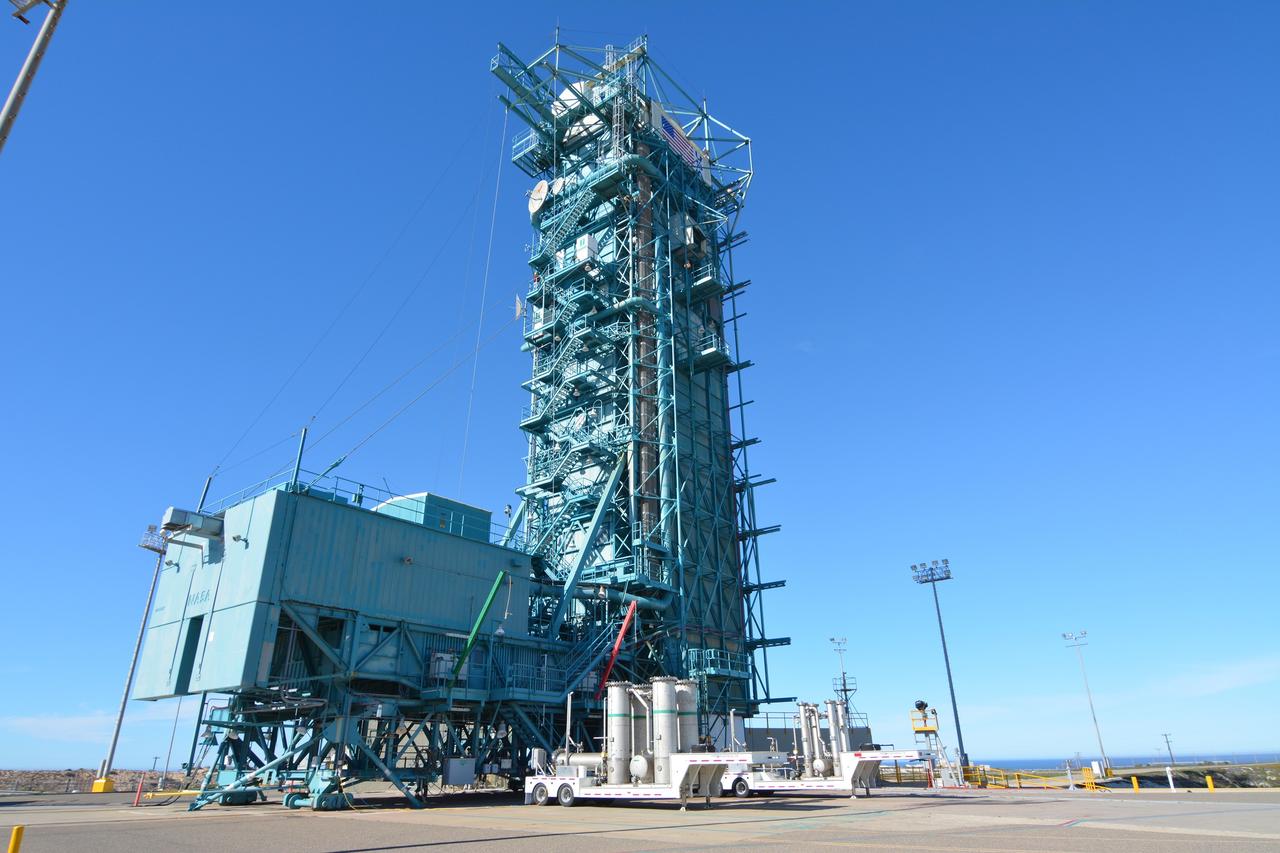

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California, is the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California, is the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
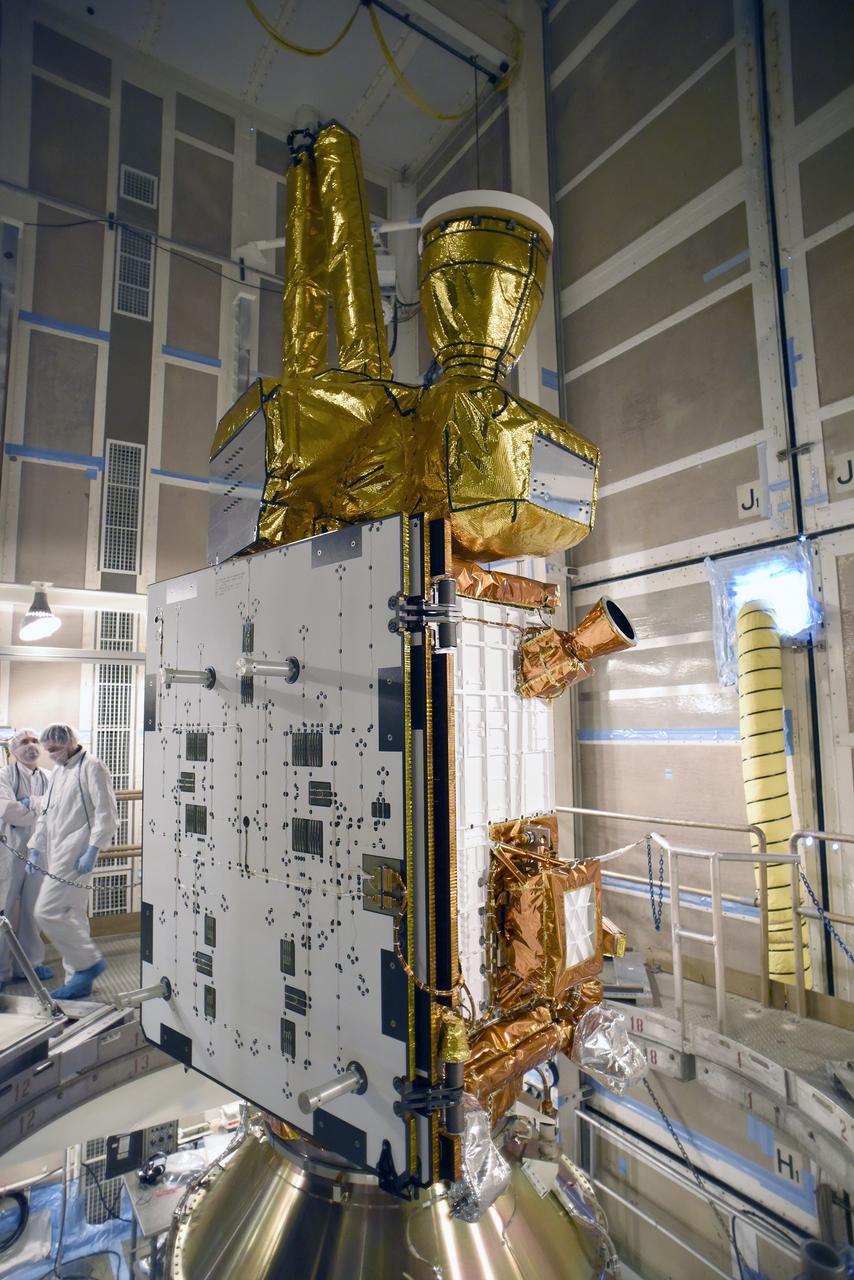

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
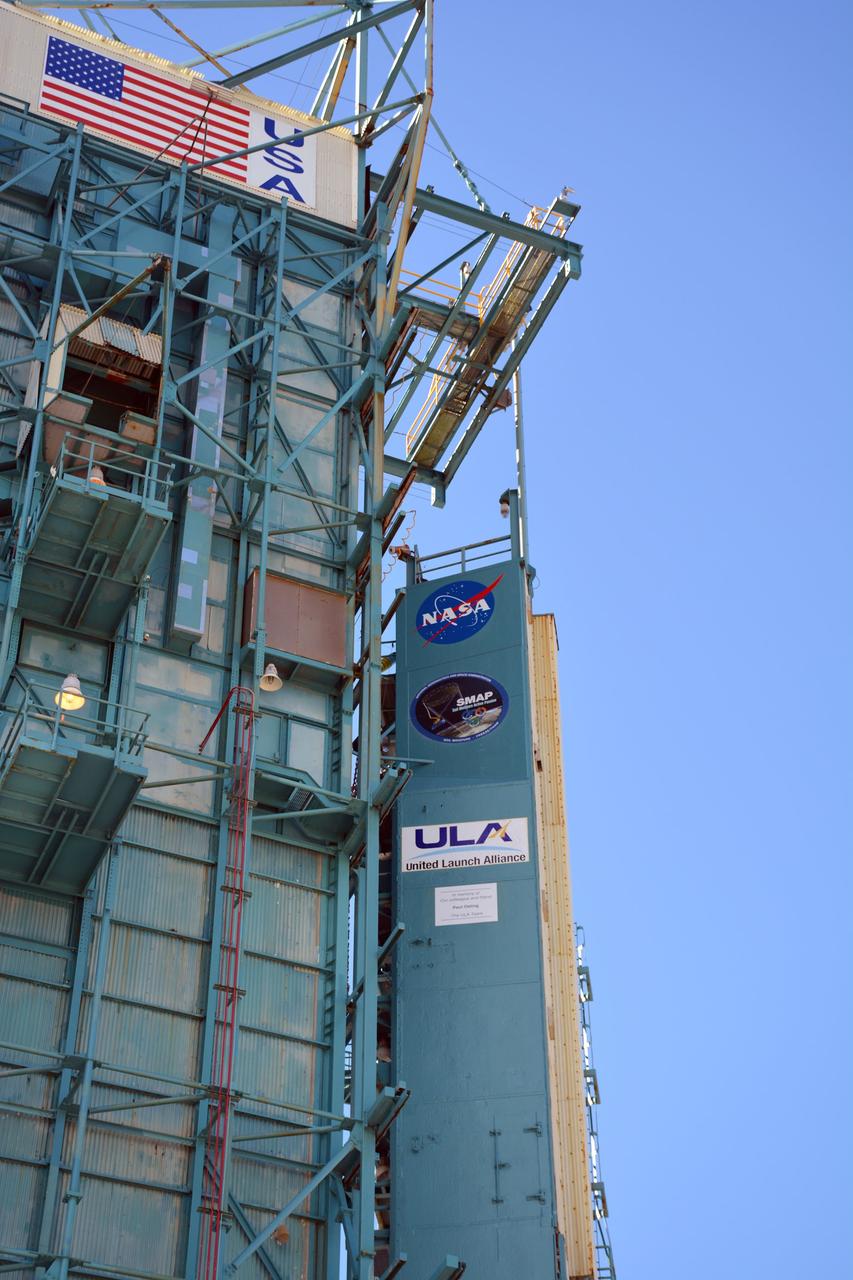

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California, is the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Detail of mission and NASA logos at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
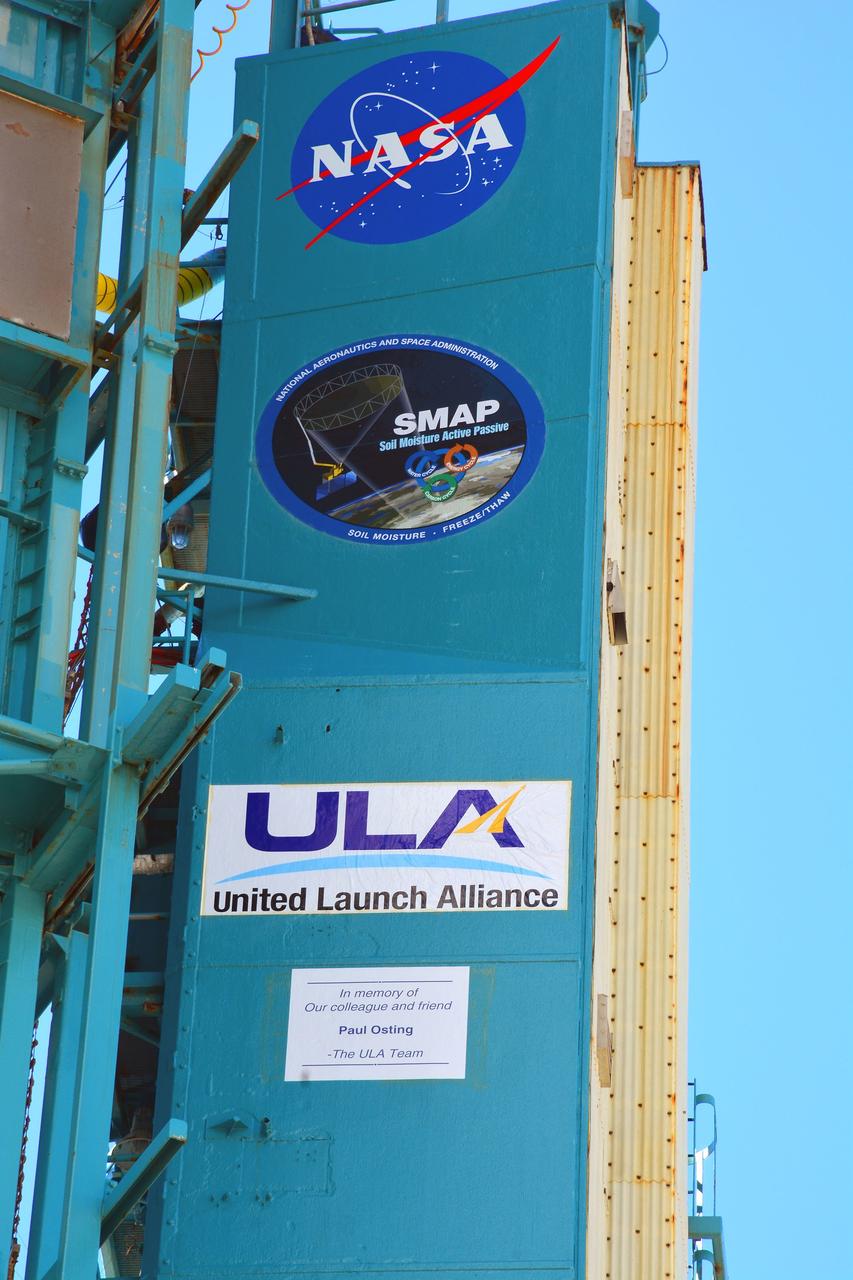

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Detail of mission and NASA logos at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In Orbital Sciences Corp. Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first and second stage of the Taurus XL rocket is being loaded onto an Assembly Integration Trailer in preparation for moving to Pad 576-E on north Vandenberg later this month. The Orbital Sciences Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E, will take NASA's Glory satellite into low Earth. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In Orbital Sciences Corp. Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians monitor the loading of the Taurus XL rocket components onto an Assembly Integration Trailer in preparation for moving to Pad 576-E on north Vandenberg later this month. The Orbital Sciences Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E, will take NASA's Glory satellite into low Earth orbit. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In Orbital Sciences Corp. Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians monitor the loading of the Taurus XL rocket components onto an Assembly Integration Trailer in preparation for moving to Pad 576-E on north Vandenberg later this month. The Orbital Sciences Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E, will take NASA's Glory satellite into low Earth orbit. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
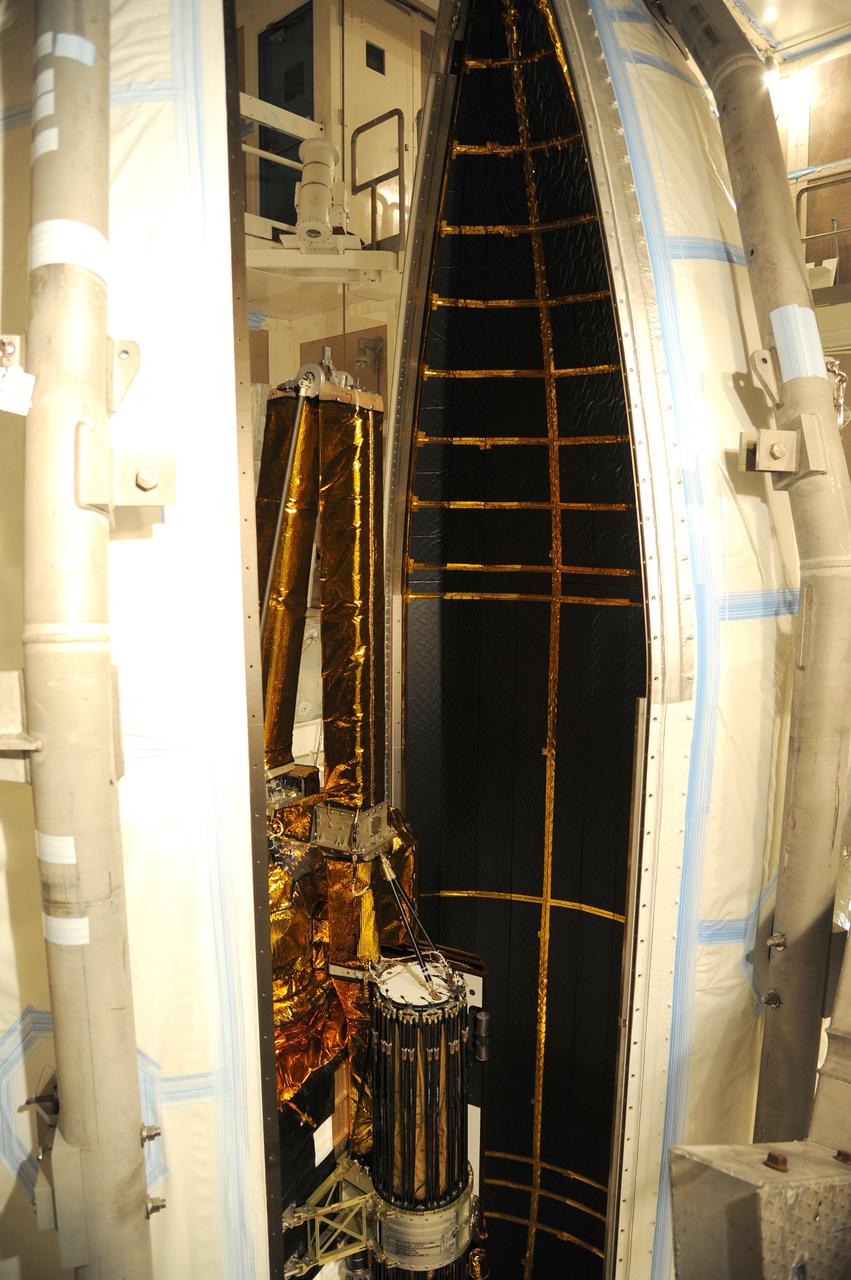

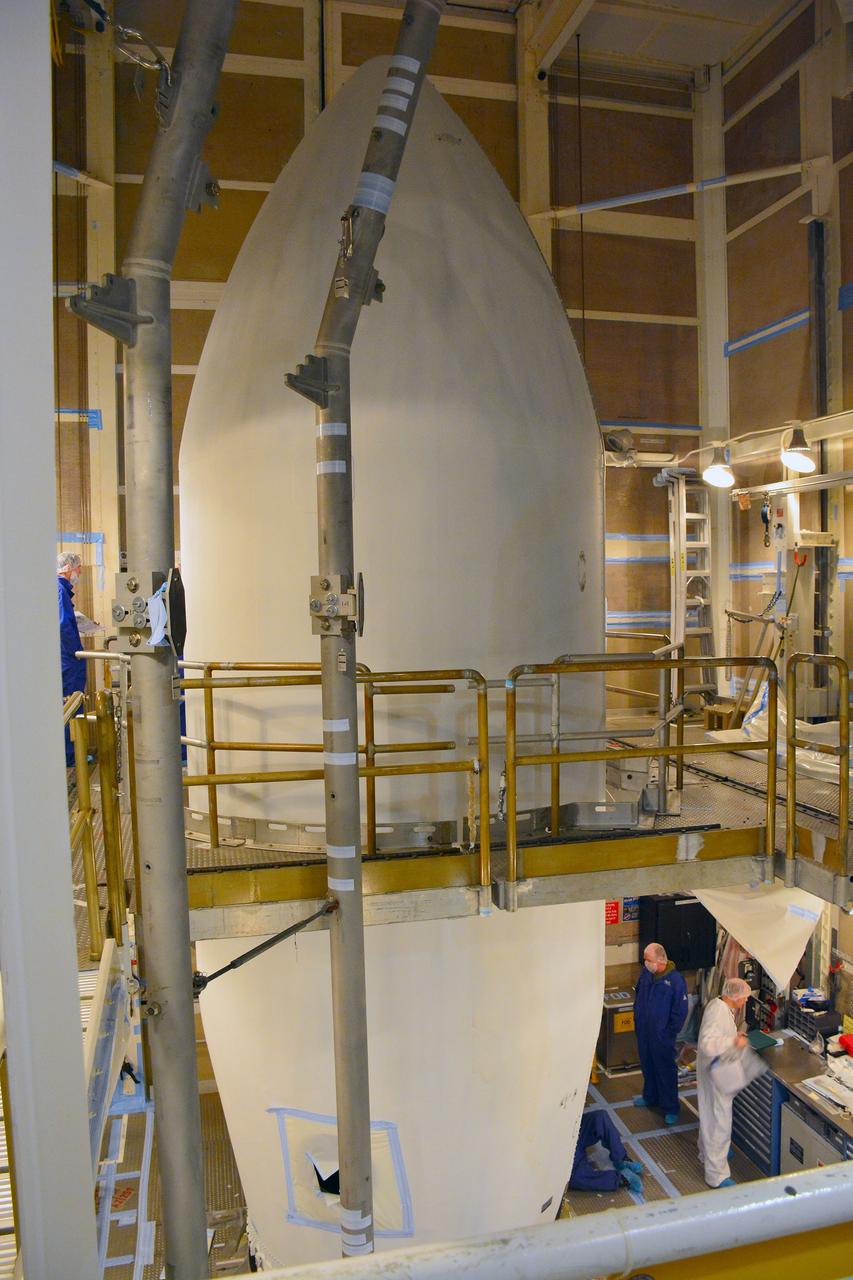
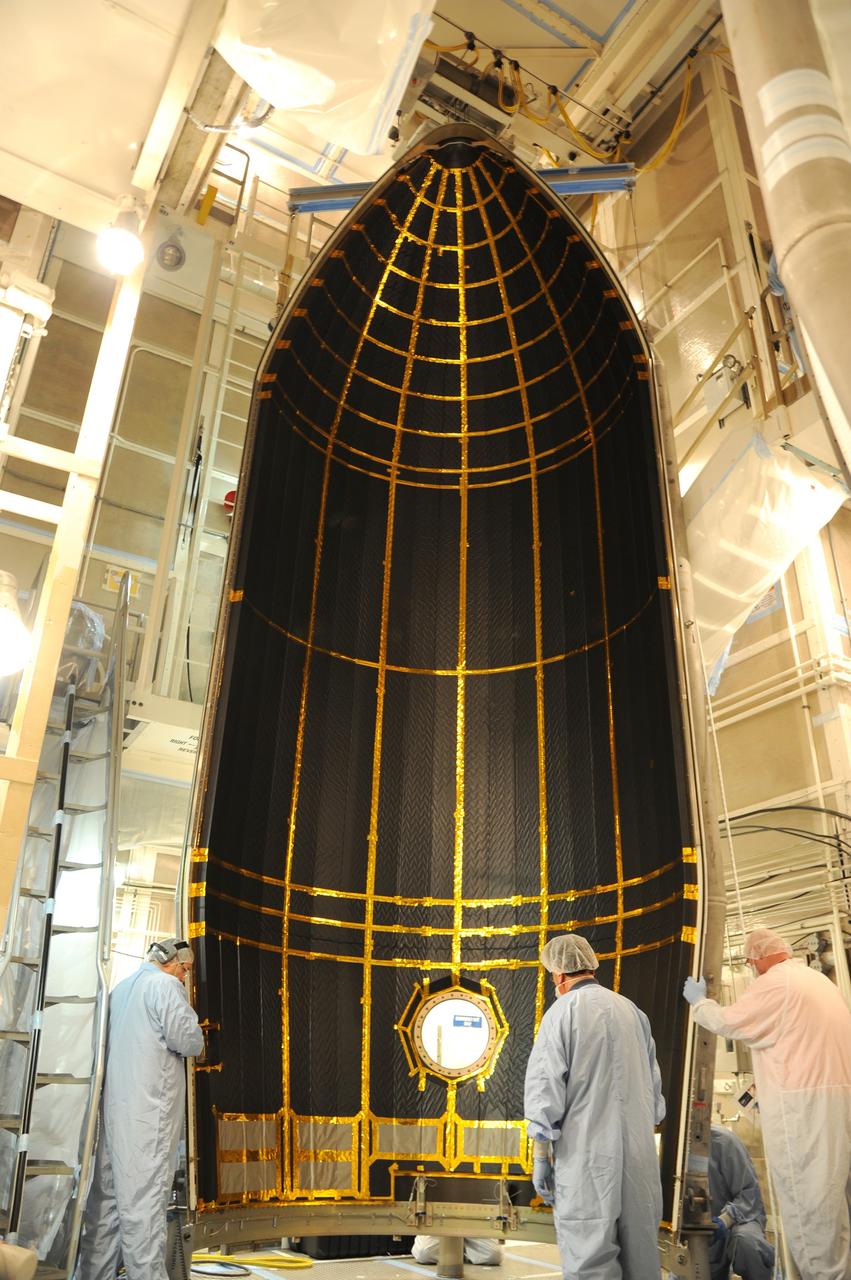
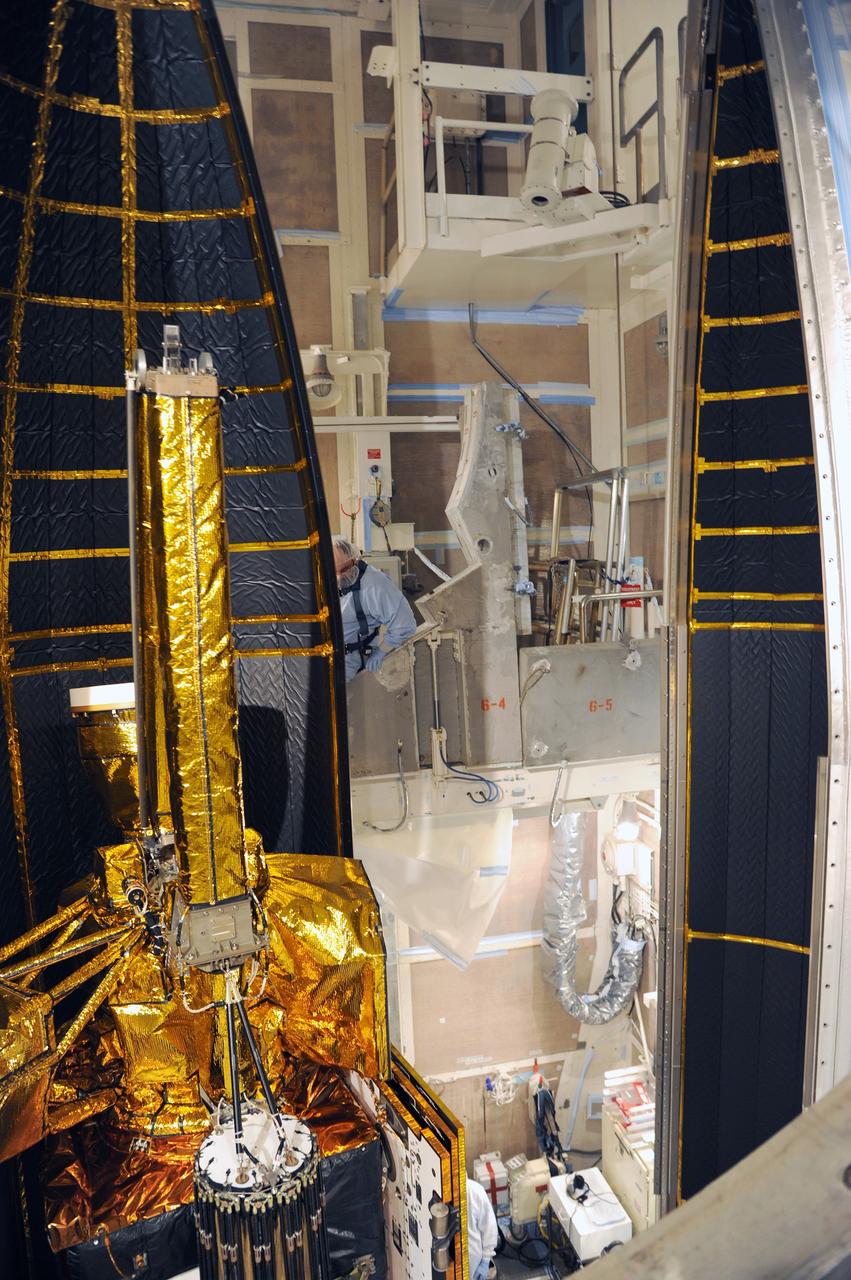
VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
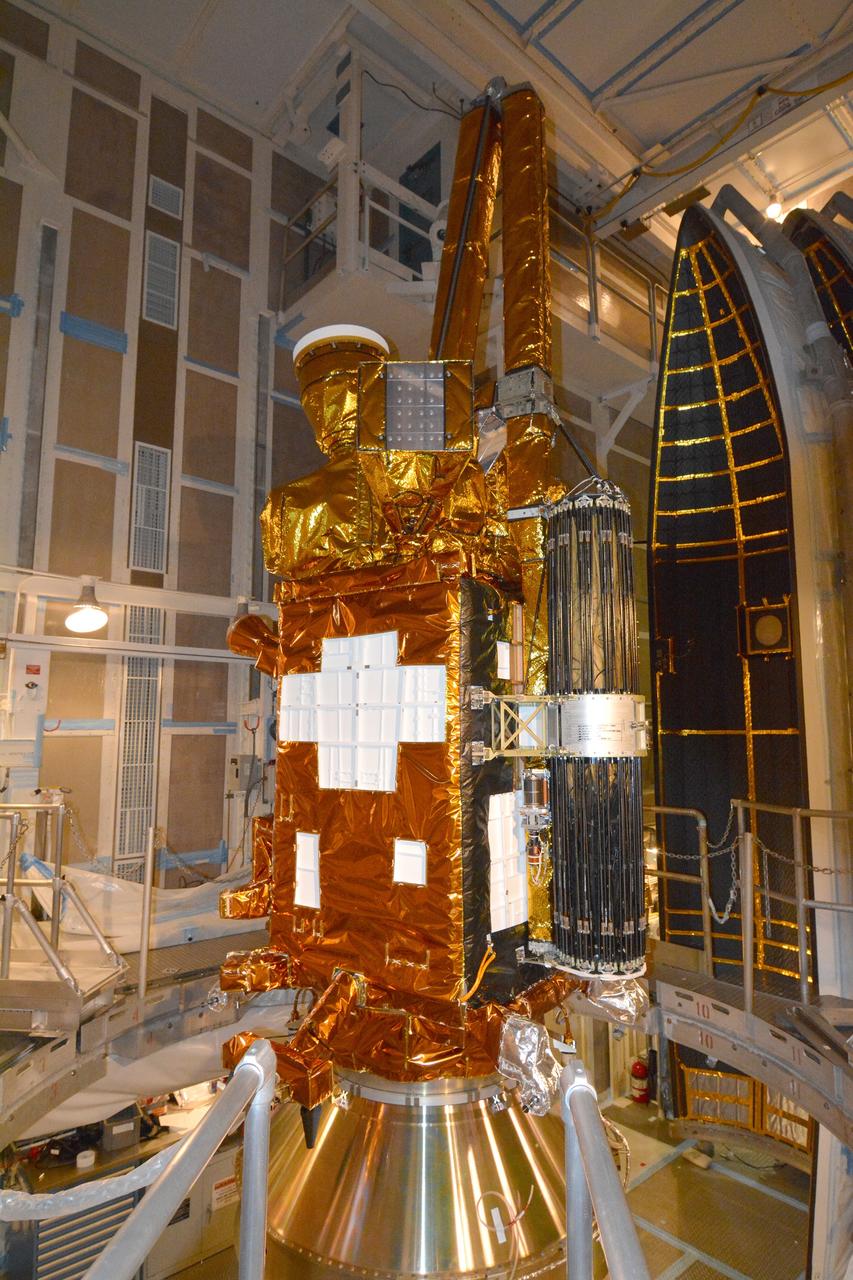

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California, as the payload fairing is prepared for attachment to the rocket to protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
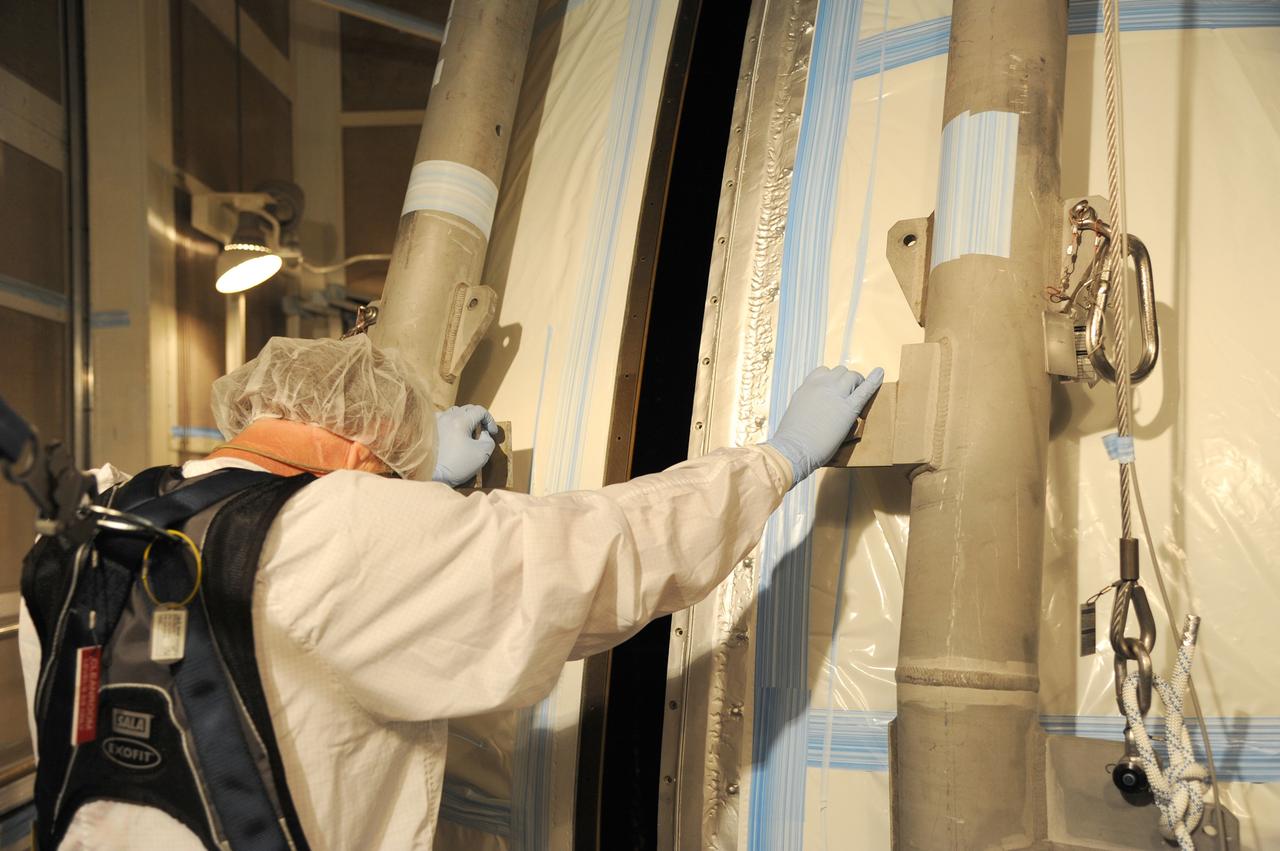

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing in place over NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's SMAP spacecraft inside the service structure at Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg AFB, California - the launch site for NASA's SMAP spacecraft. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
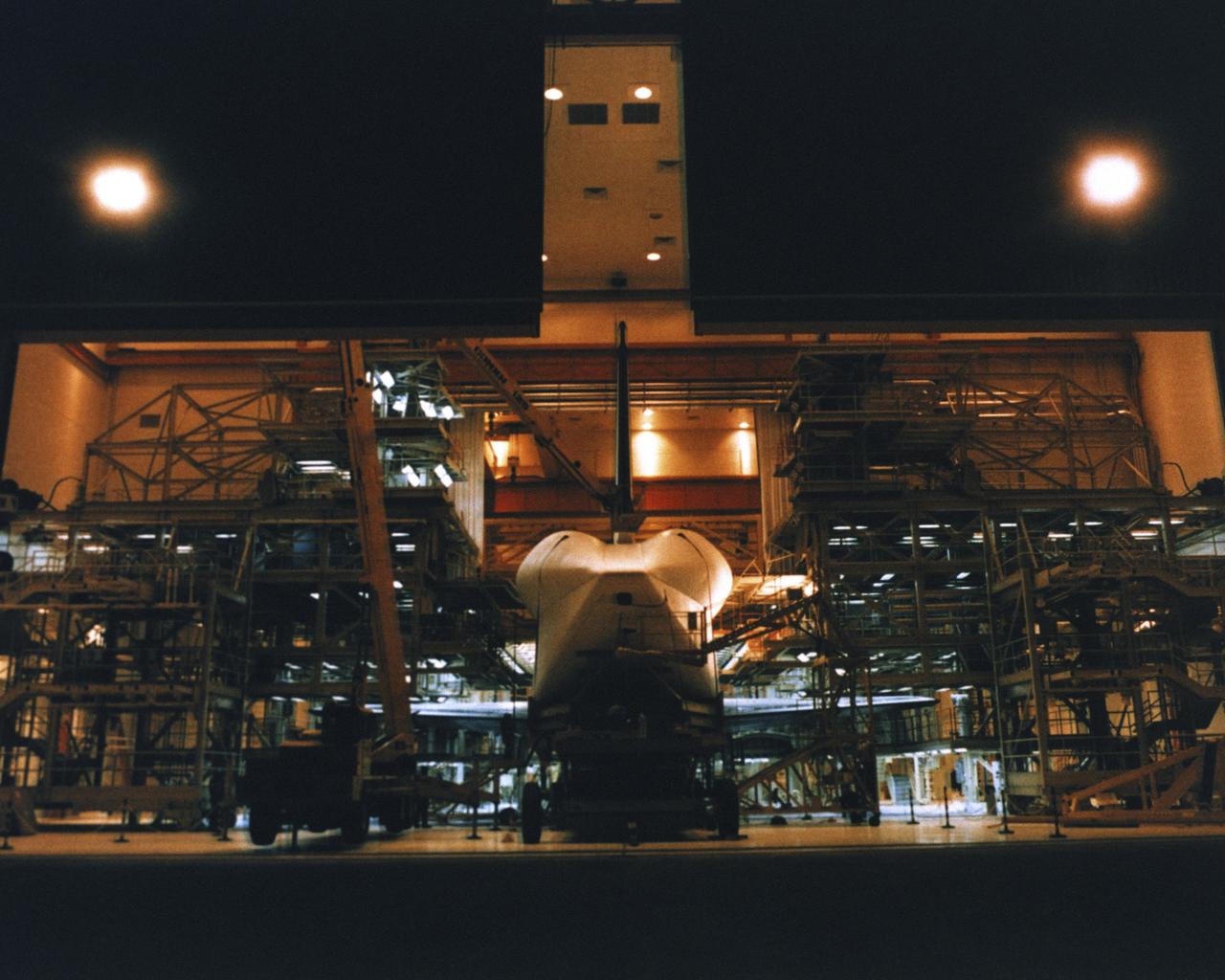

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise inside the Orbiter Maintenance and Checkout Facility at Vandenberg AFB, California. Photo Credit: NASA

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise inside the Orbiter Maintenance and Checkout Facility at Vandenberg AFB, California. Photo Credit: NASA

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying the Landsat Data Continuity Mission spacecraft from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
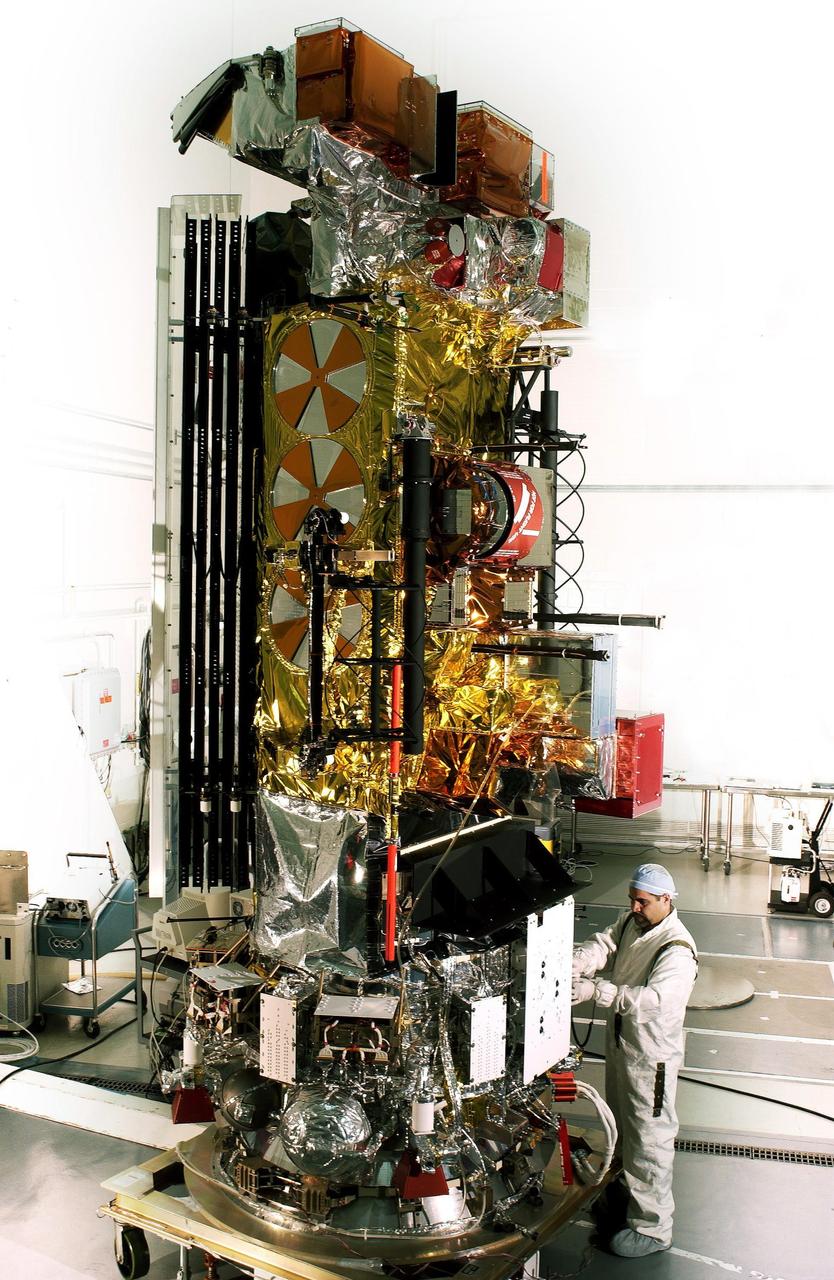

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. --Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's NOAA-M satellite during launch preparation at Vandenberg AFB, Calif. NOAA-M is a polar-orbiting Earth environmental observation satellite that will provide global data to NOAA's short- and long-range weather forecasting systems. Launch of the NOAA-M aboard a Titan II rocket is scheduled for June 24, 2002, from VAFB
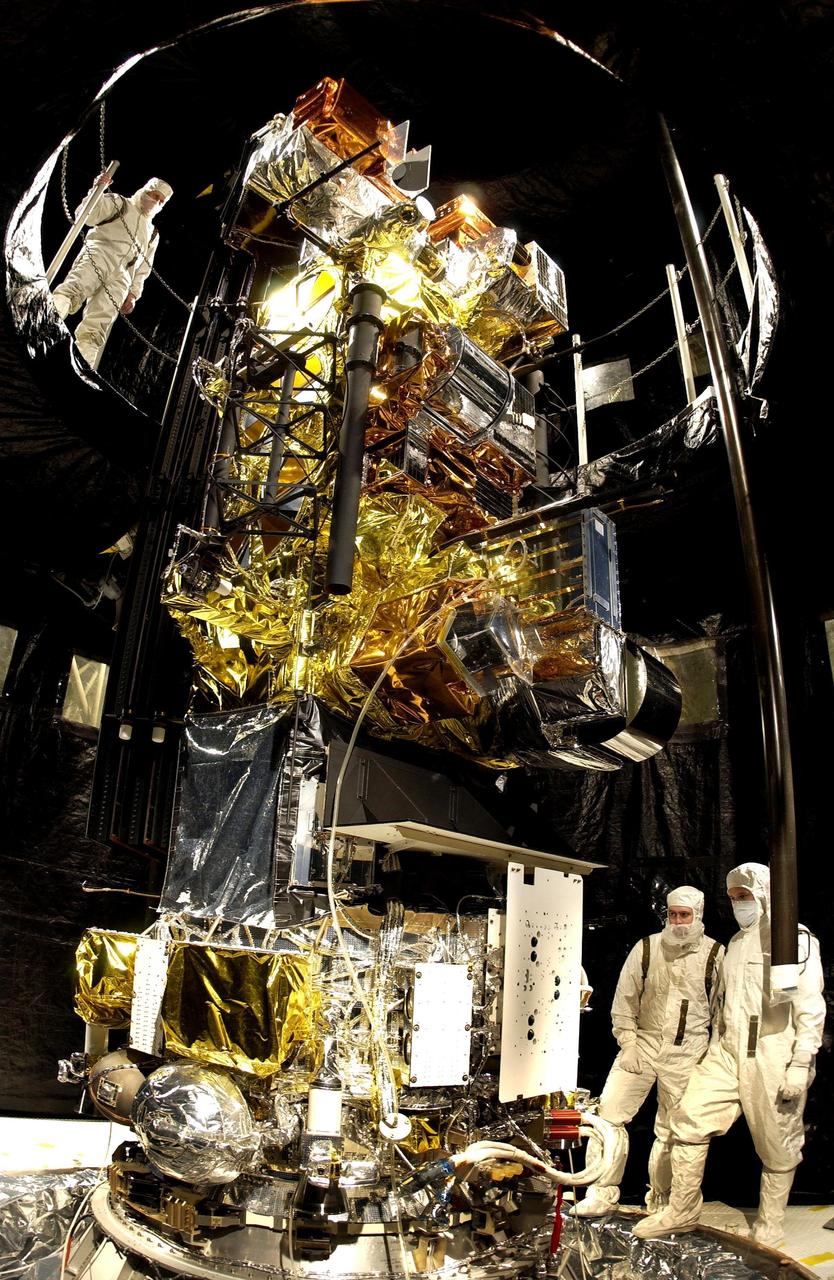

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- The Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's NOAA-M satellite is prepared for launch at Vandenberg AFB, Calif. NOAA-M is a polar-orbiting Earth environmental observation satellite that will provide global data to NOAA's short- and long-range weather forecasting systems. Launch of the NOAA-M aboard a Titan II rocket is scheduled for June 24, 2002, from VAFB

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- Workers at Vandenberg AFB, Calif., prepare the Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's NOAA-M satellite forlaunch. NOAA-M is a polar-orbiting Earth environmental observation satellite that will provide global data to NOAA's short- and long-range weather forecasting systems. Launch of the NOAA-M aboard a Titan II rocket is scheduled for June 24, 2002, from VAFB

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. --Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's NOAA-M satellite during launch preparation at Vandenberg AFB, Calif. NOAA-M is a polar-orbiting Earth environmental observation satellite that will provide global data to NOAA's short- and long-range weather forecasting systems. Launch of the NOAA-M aboard a Titan II rocket is scheduled for June 24, 2002, from VAFB
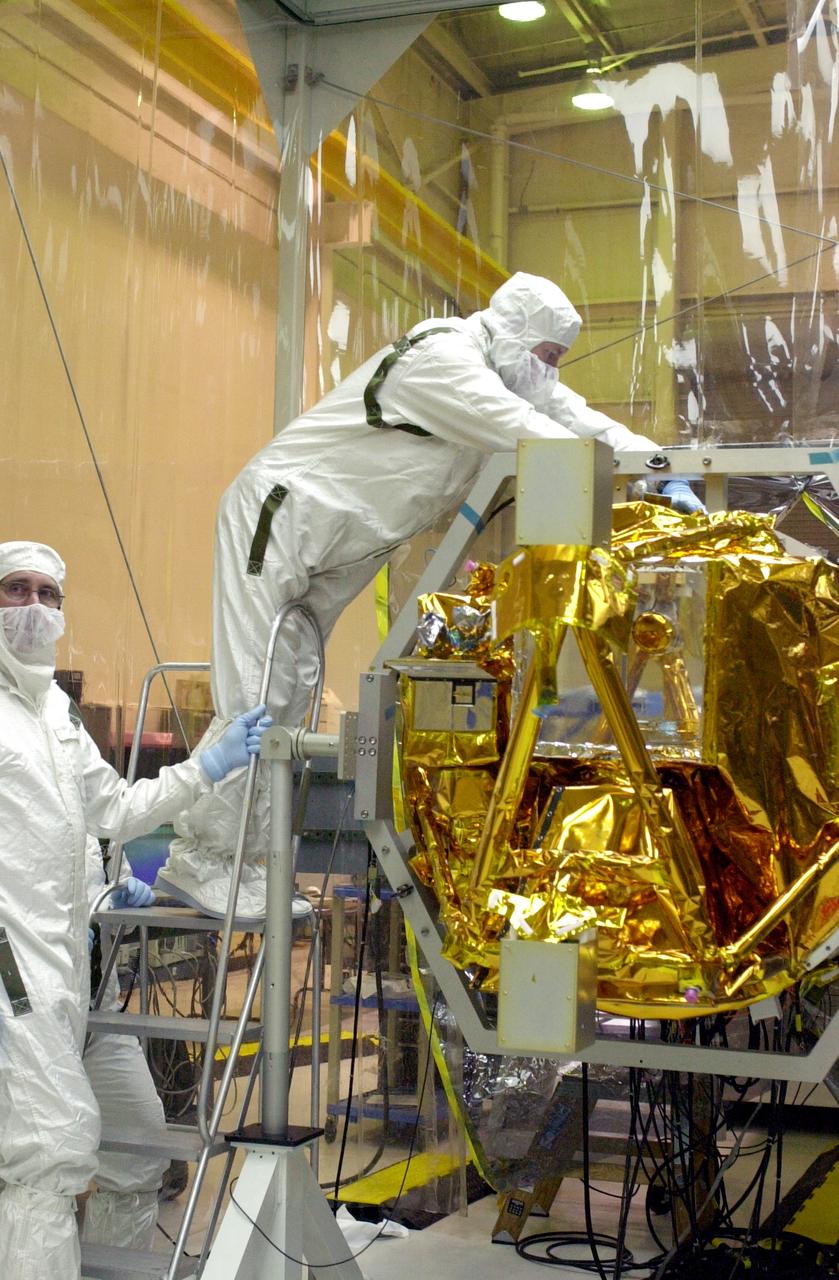

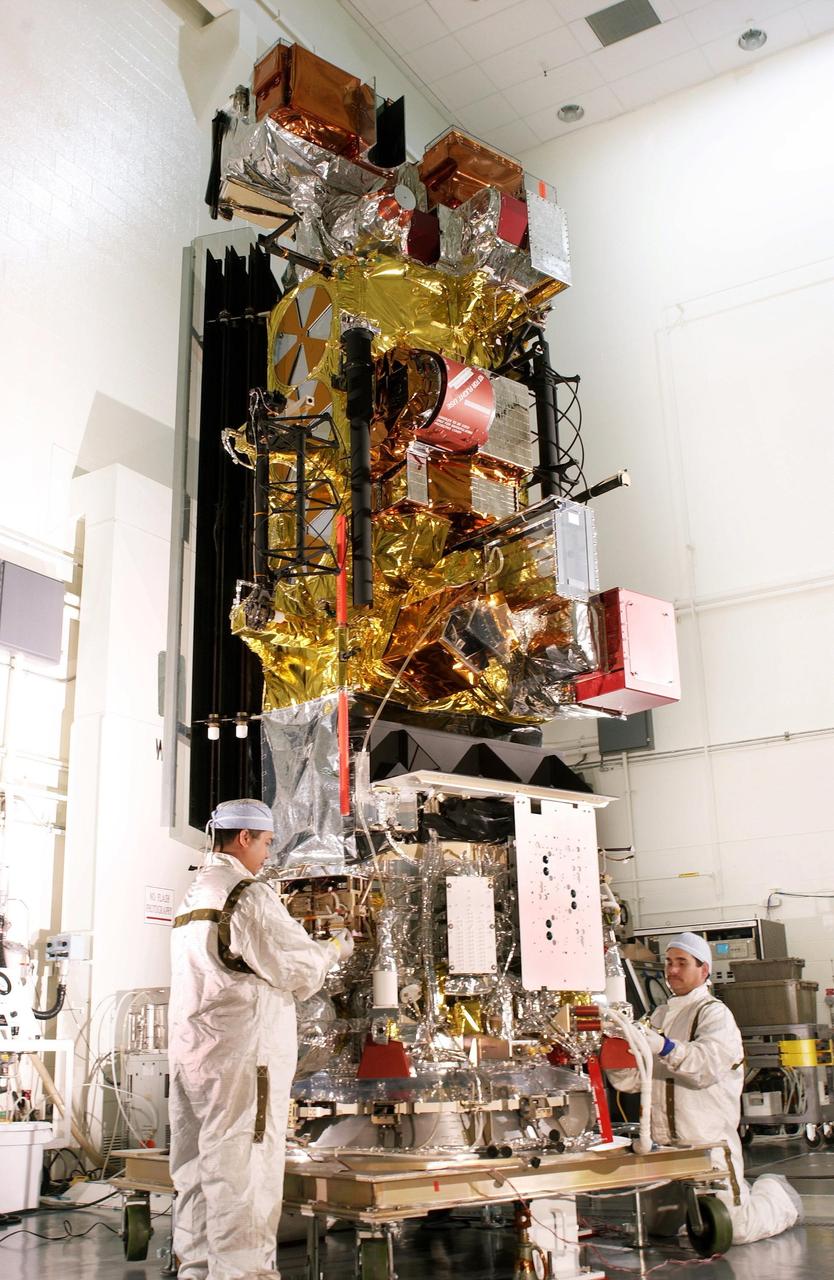
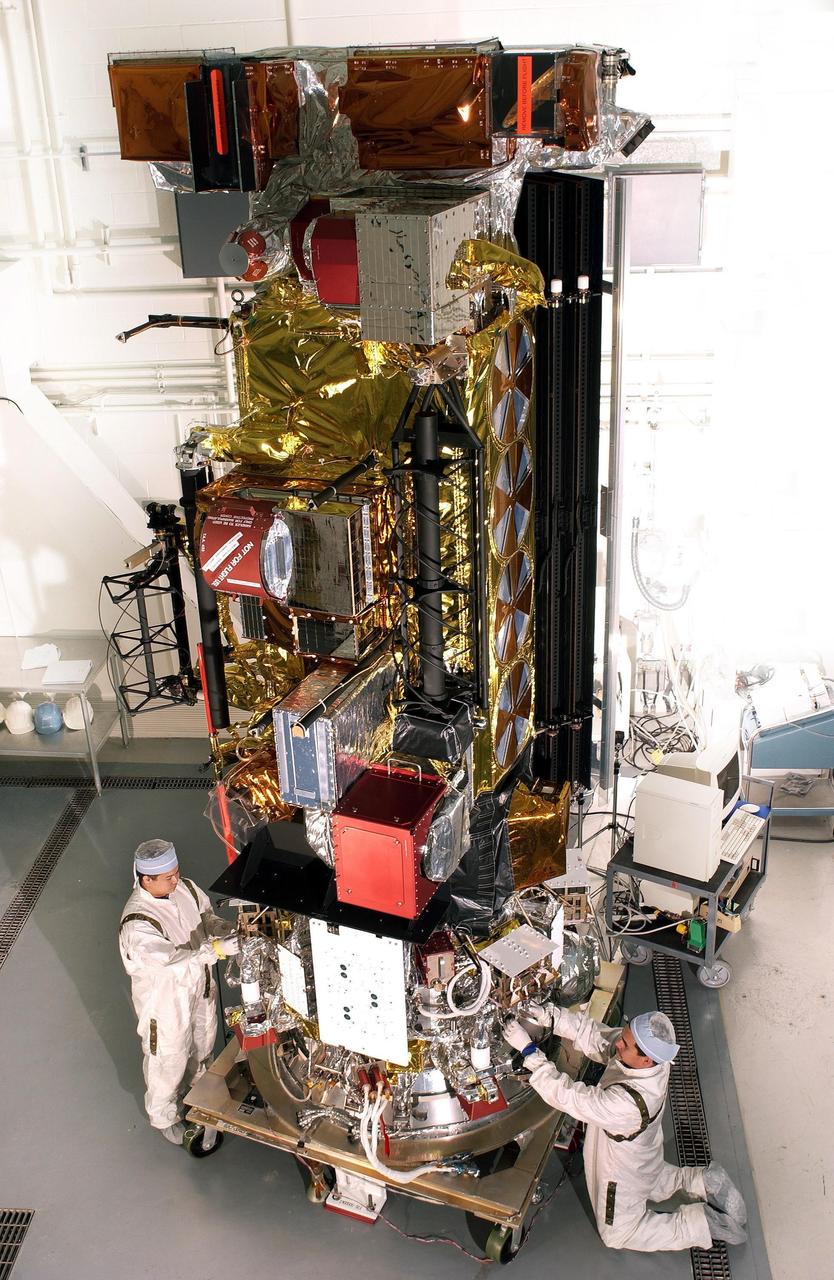
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - At Vandenberg AFB, Calif., a solar array is installed on the SciSat-1 spacecraft. The SciSat-1 weighs approximately 330 pounds and after launch will be placed in a 400-mile-high polar orbit to investigate processes that control the distribution of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The data from the satellite will provide Canadian and international scientists with improved measurements relating to global ozone processes and help policymakers assess existing environmental policy and develop protective measures for improving the health of our atmosphere, preventing further ozone depletion. The mission is designed to last two years.
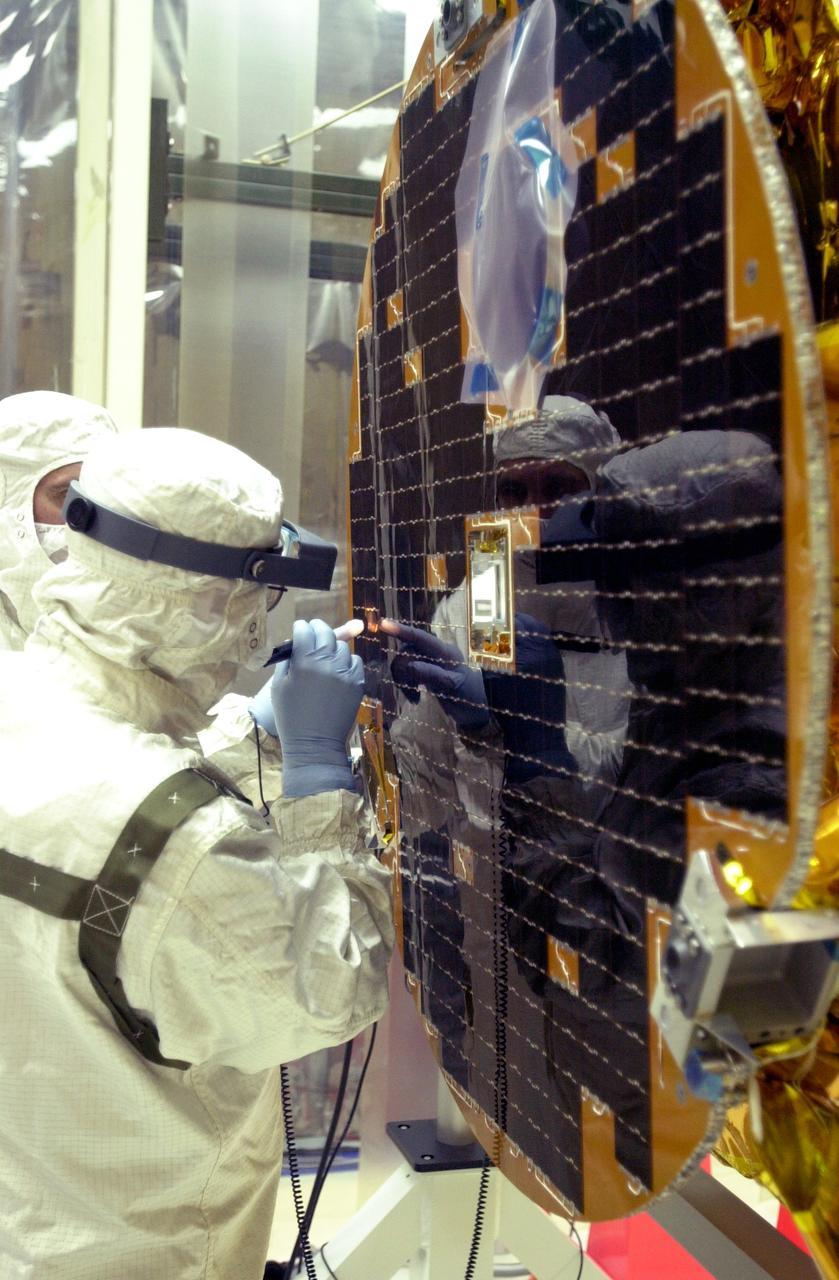

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - At Vandenberg AFB, Calif., a solar array is tested before installing on the SciSat-1 spacecraft. The SciSat-1 weighs approximately 330 pounds and after launch will be placed in a 400-mile-high polar orbit to investigate processes that control the distribution of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The data from the satellite will provide Canadian and international scientists with improved measurements relating to global ozone processes and help policymakers assess existing environmental policy and develop protective measures for improving the health of our atmosphere, preventing further ozone depletion. The mission is designed to last two years.
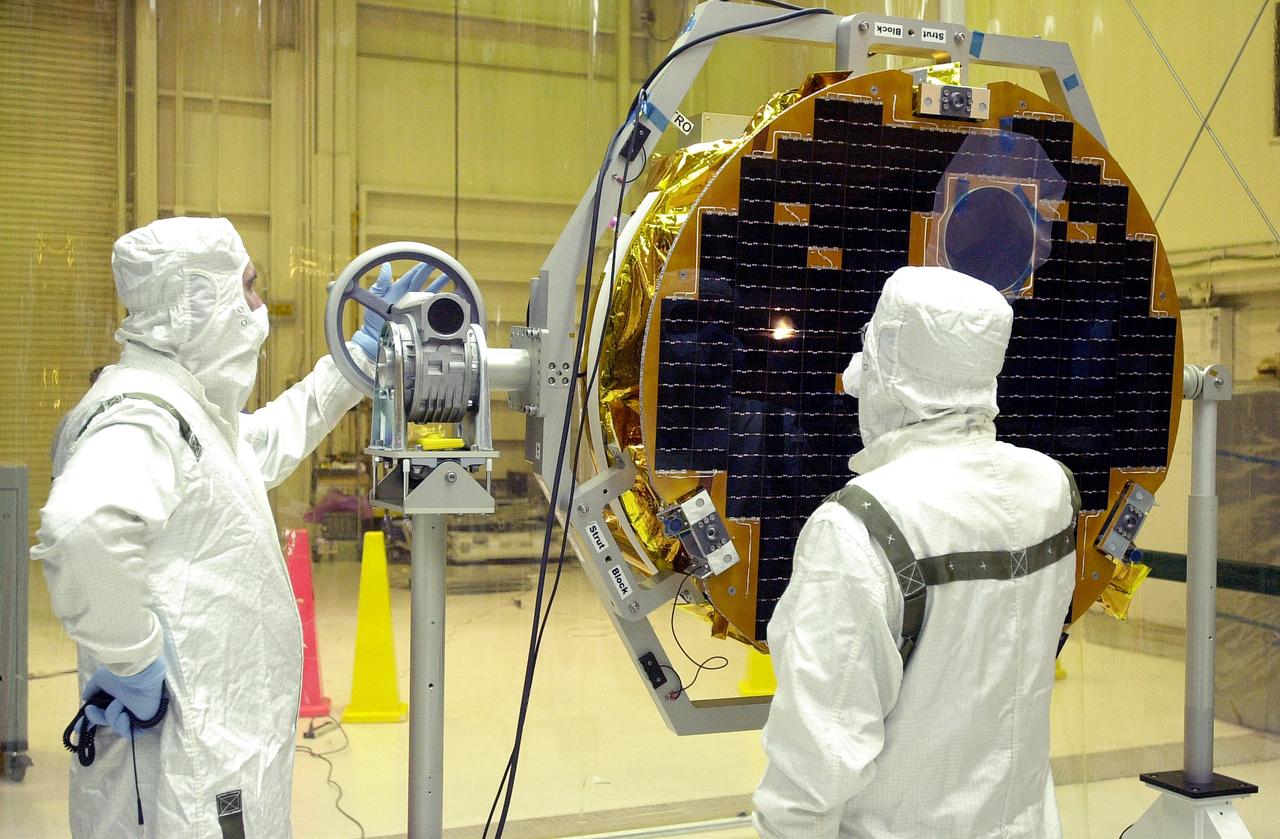

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - At Vandenberg AFB, Calif., a solar array is tested before installing on the SciSat-1 spacecraft. The SciSat-1 weighs approximately 330 pounds and after launch will be placed in a 400-mile-high polar orbit to investigate processes that control the distribution of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The data from the satellite will provide Canadian and international scientists with improved measurements relating to global ozone processes and help policymakers assess existing environmental policy and develop protective measures for improving the health of our atmosphere, preventing further ozone depletion. The mission is designed to last two years.
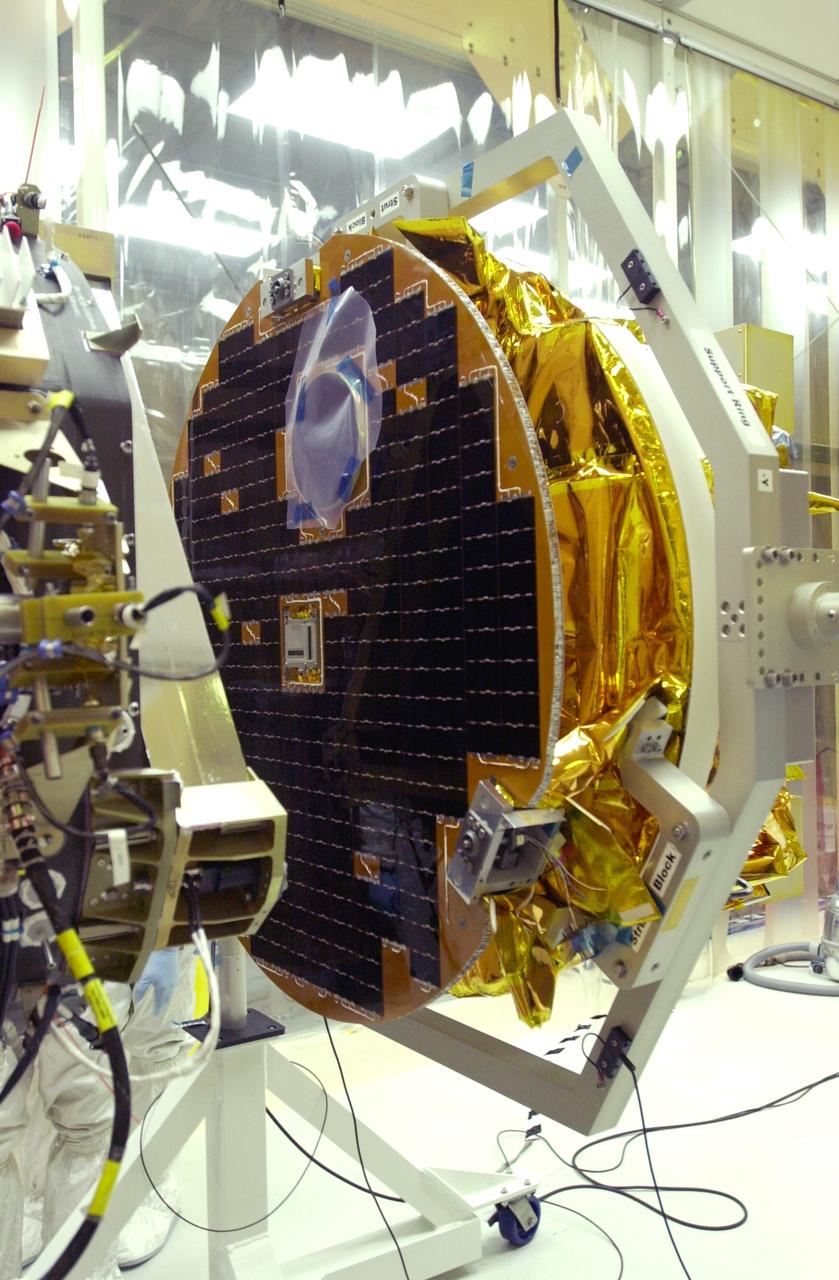

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - At Vandenberg AFB, Calif., a solar array is tested before installing on the SciSat-1 spacecraft. The SciSat-1 weighs approximately 330 pounds and after launch will be placed in a 400-mile-high polar orbit to investigate processes that control the distribution of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The data from the satellite will provide Canadian and international scientists with improved measurements relating to global ozone processes and help policymakers assess existing environmental policy and develop protective measures for improving the health of our atmosphere, preventing further ozone depletion. The mission is designed to last two years.
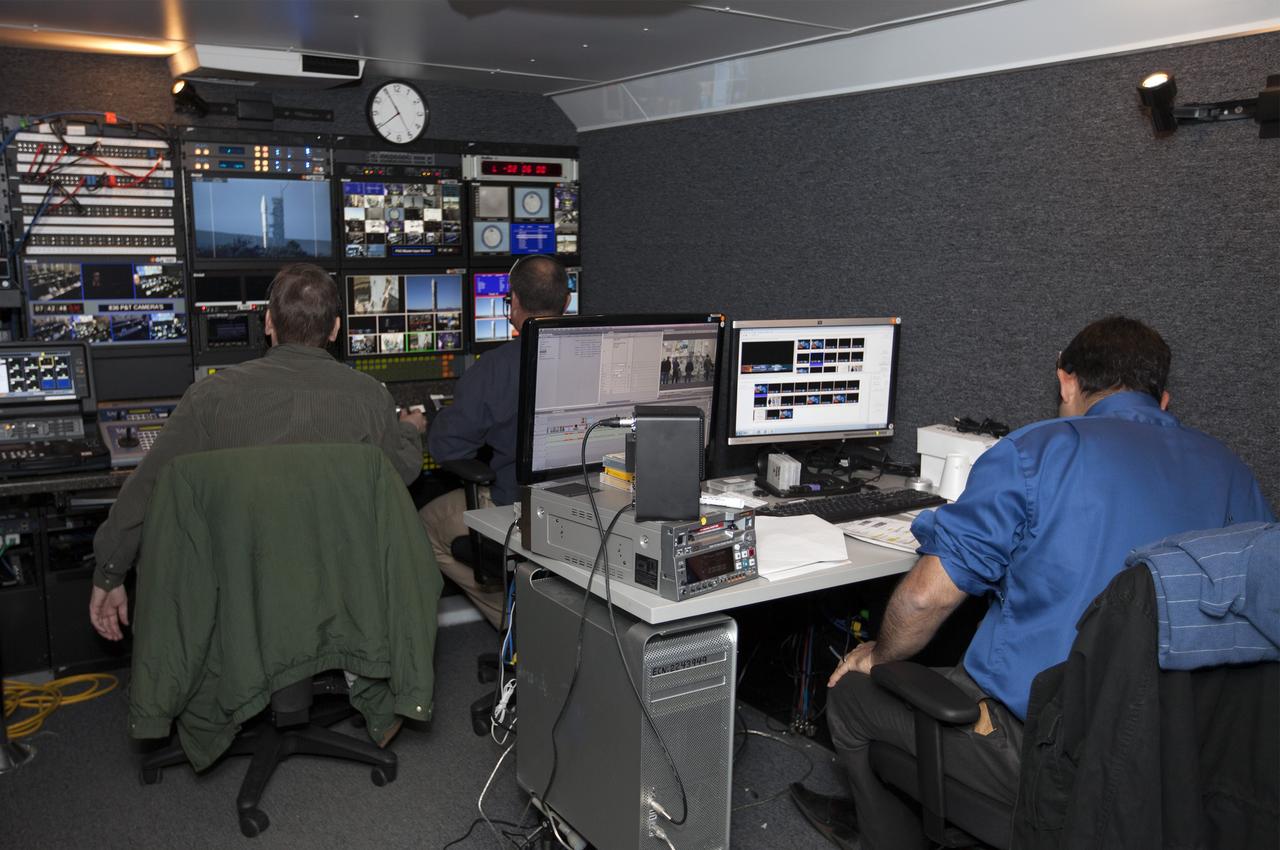

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – NASA TV technicians work on the broadcast for the launch of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying the Landsat Data Continuity Mission spacecraft from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
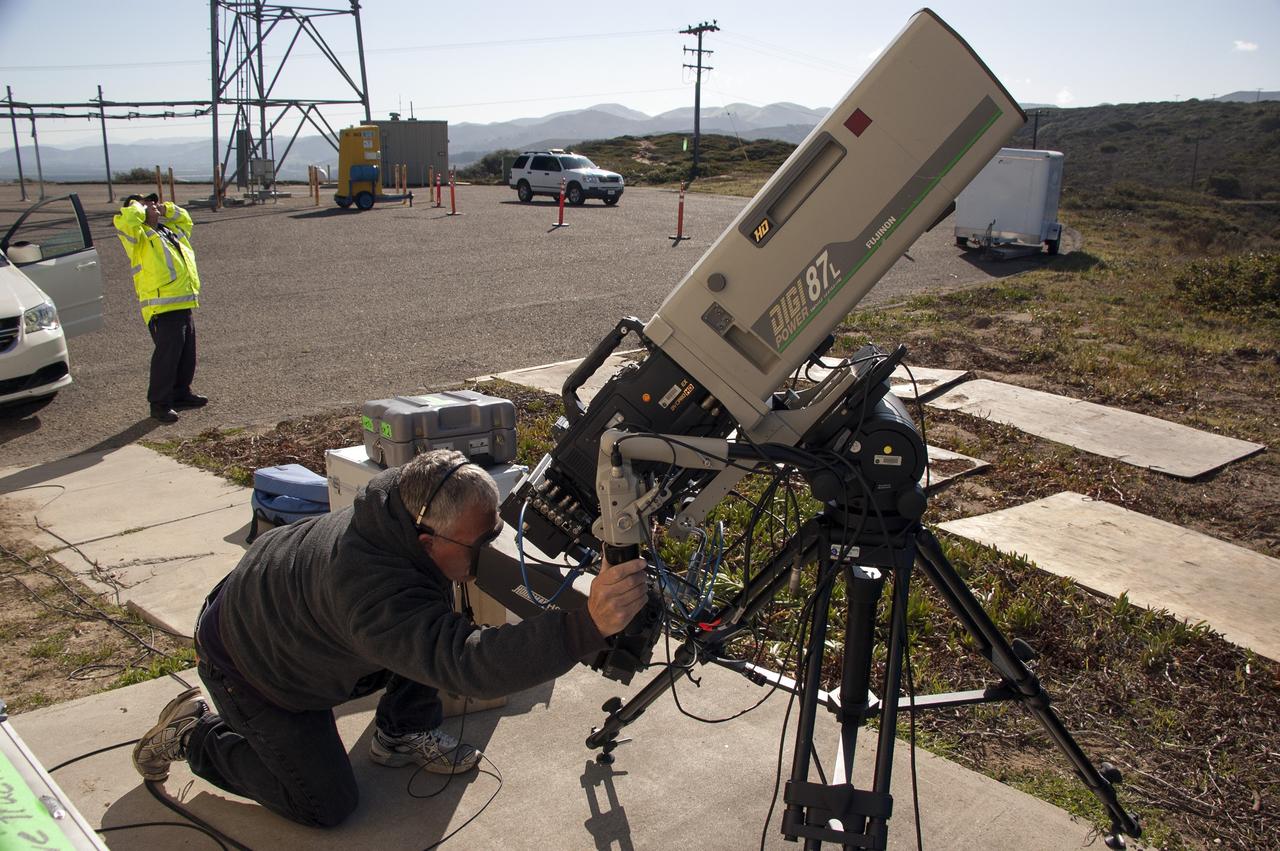

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A NASA TV technician records the launch of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying the Landsat Data Continuity Mission spacecraft from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers begin lifting NASA's SMAP spacecraft to the top of a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft is hoisted to the top of a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft is hoisted to the top of a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft arrives at Space Launch Complex-2 from the Astrotech processing facility for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
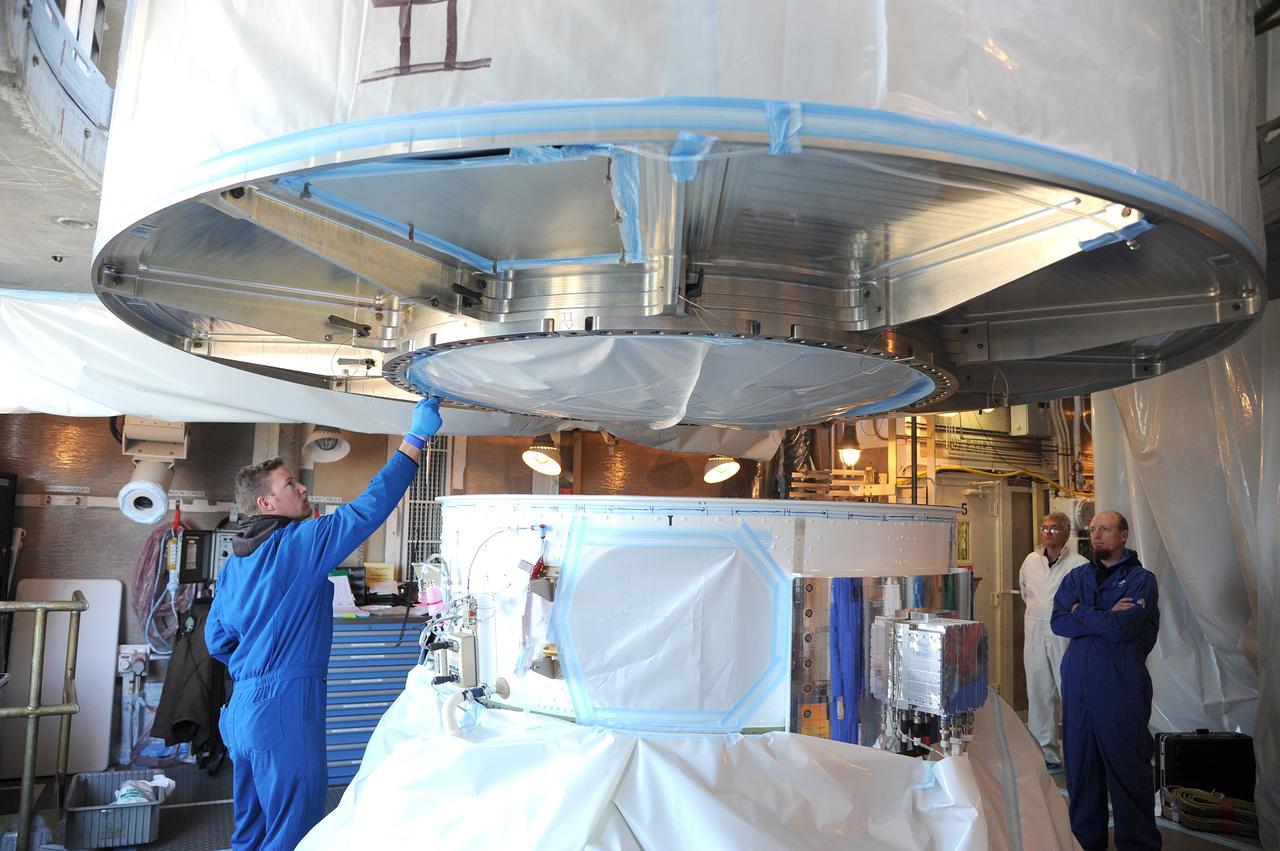

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft is positioned atop a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
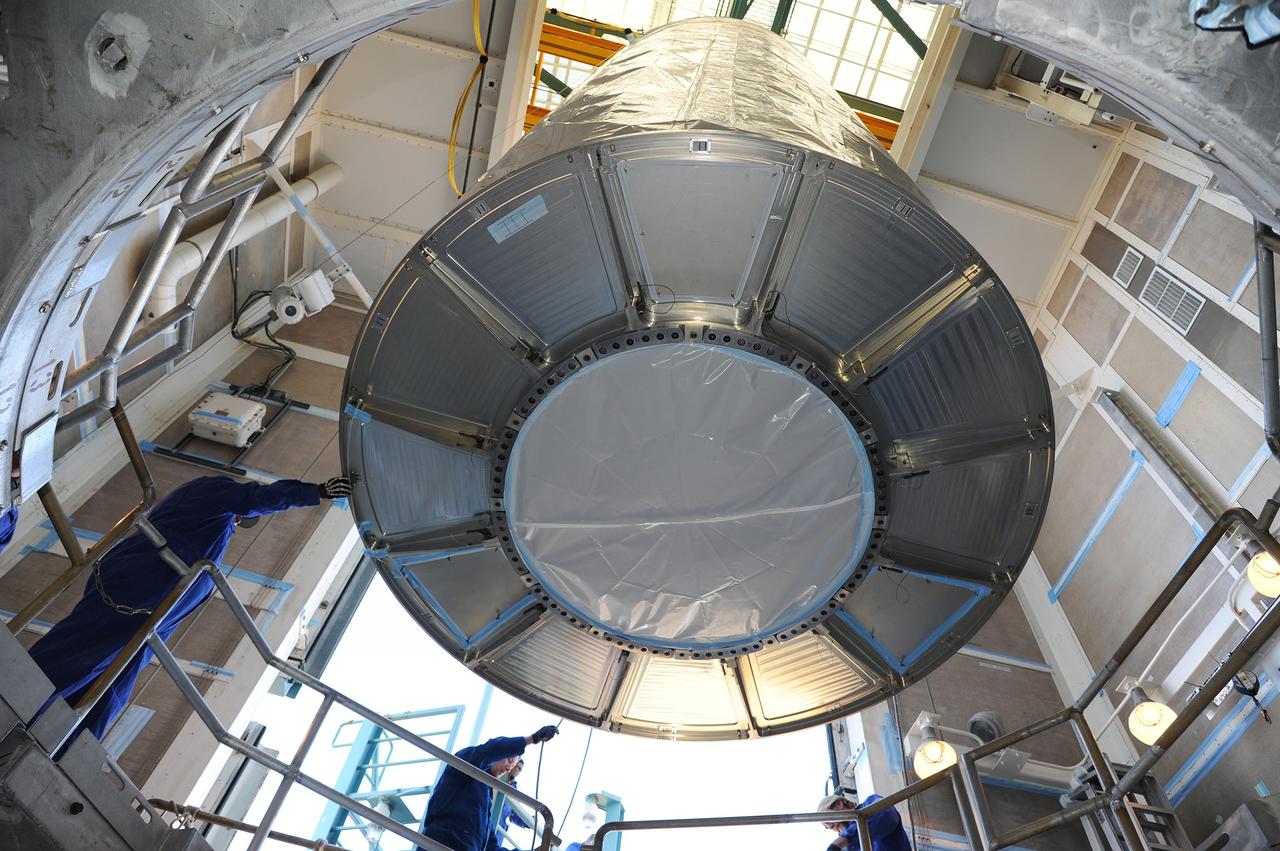

VANDENBERG AFB, California – NASA's SMAP spacecraft is positioned atop a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- A Boeing Delta II rocket soars above the clouds here today at Vandenberg AFB, Calif. The NASA payloads aboard the rocket are the ICESat, an Ice Cloud and land Elevation Satellite, and CHIPSat, a Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer. ICESat, a 661-pound satellite, is a benchmark satellite for the Earth Observing System that will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will observe the ice sheets that blanket the Earth’s poles to determine if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate affect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Geoscience Laser Altimeter System is the sole instrument on the satellite. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide information about the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This launch marks the first Delta from Vandenberg this year. (USAF photo by: SSgt. Lee A Osberry Jr.)

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. -- A Boeing Delta II rocket soars above the clouds here today at Vandenberg AFB, Calif. The NASA payload aboard the rocket are the ICESat, an Ice Cloud and land Elevation Satellite, and CHIPSat, a Cosmic Hot Interstellar Plasma Spectrometer. ICESat, a 661-pound satellite, is a benchmark satellite for the Earth Observing System that will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will observe the ice sheets that blanket the Earth’s poles to determine if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and climate affect polar ice masses and global sea level. The Geoscience Laser Altimeter System is the sole instrument on the satellite. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide information about the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This launch marks the first Delta from Vandenberg this year. (USAF photo by: SSgt Lee A Osberry Jr.)
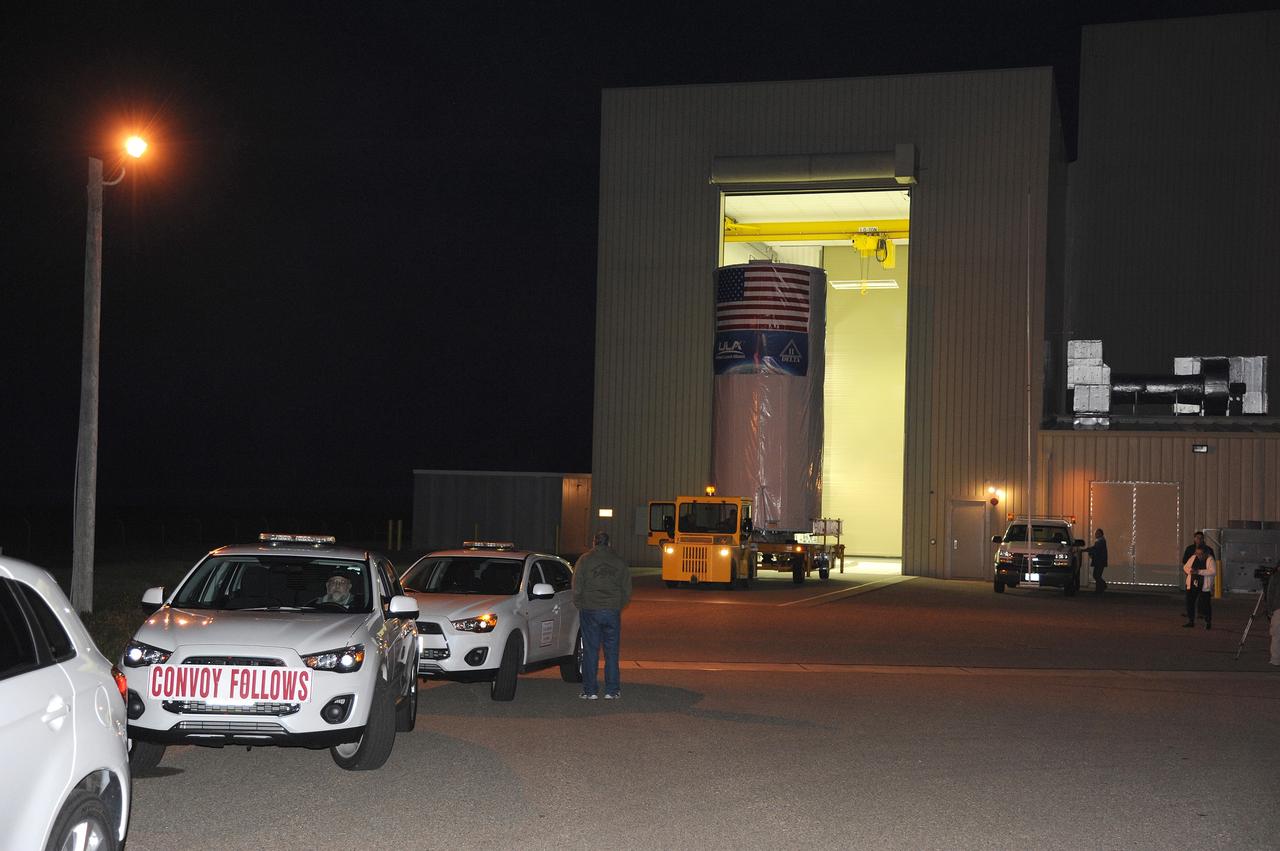

VANDENBERG AFB, California – A convoy assembles to take NASA's SMAP spacecraft from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
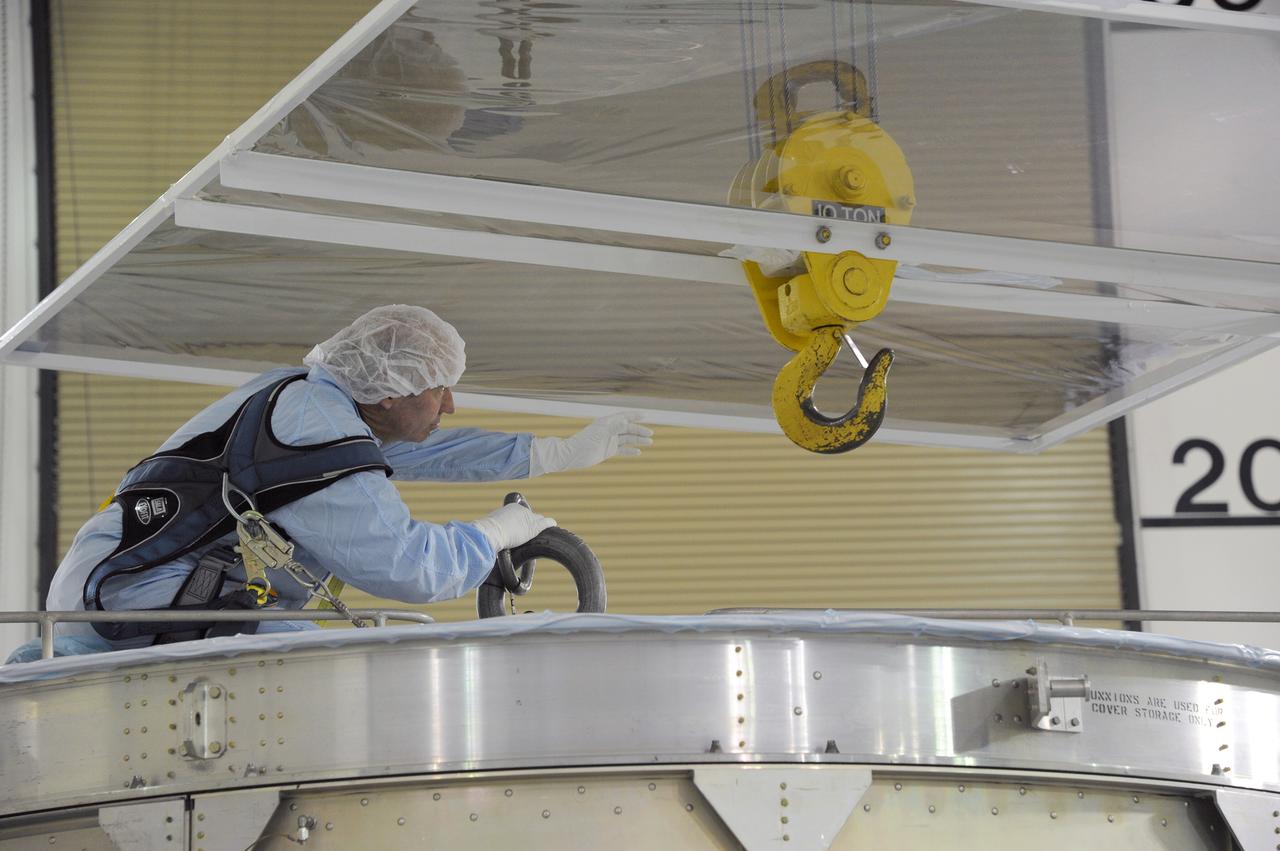

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
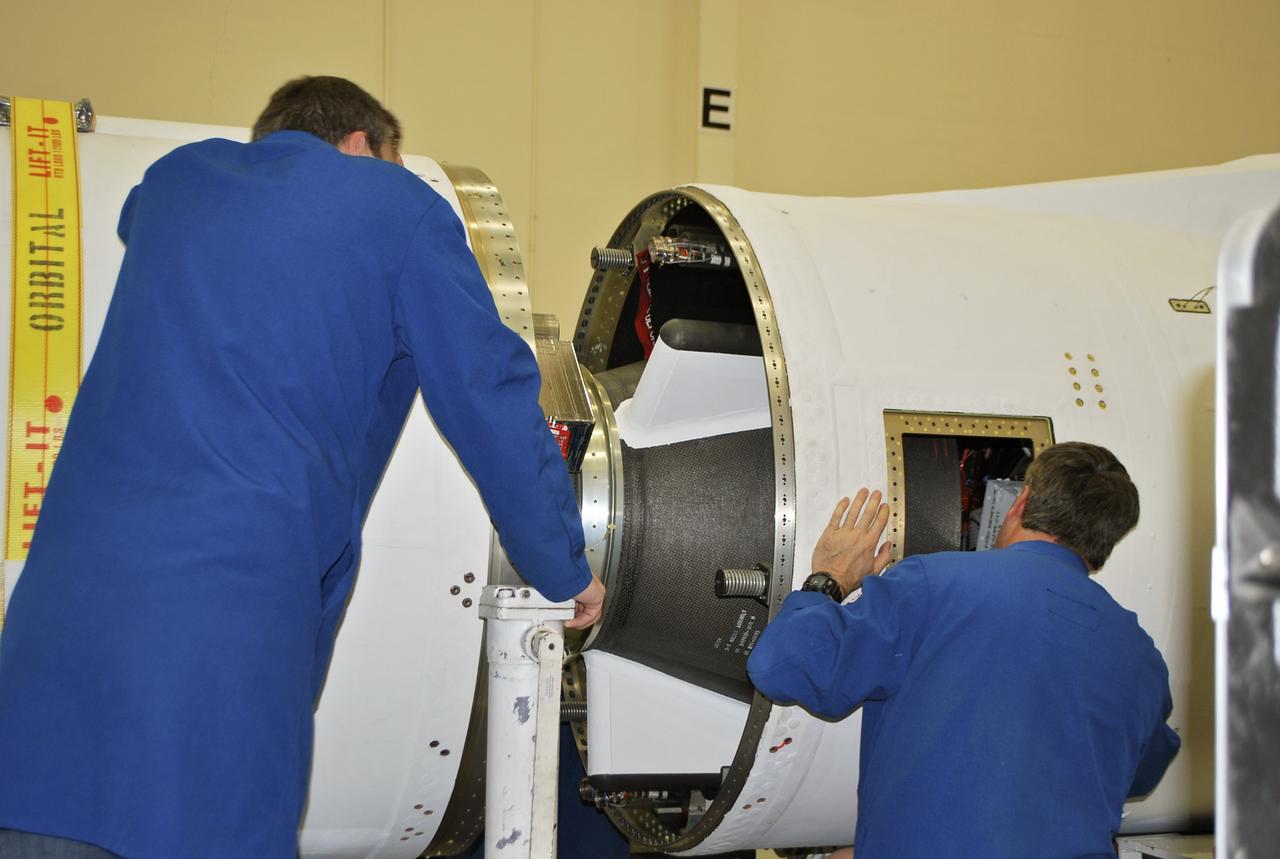

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians monitor the movement of the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
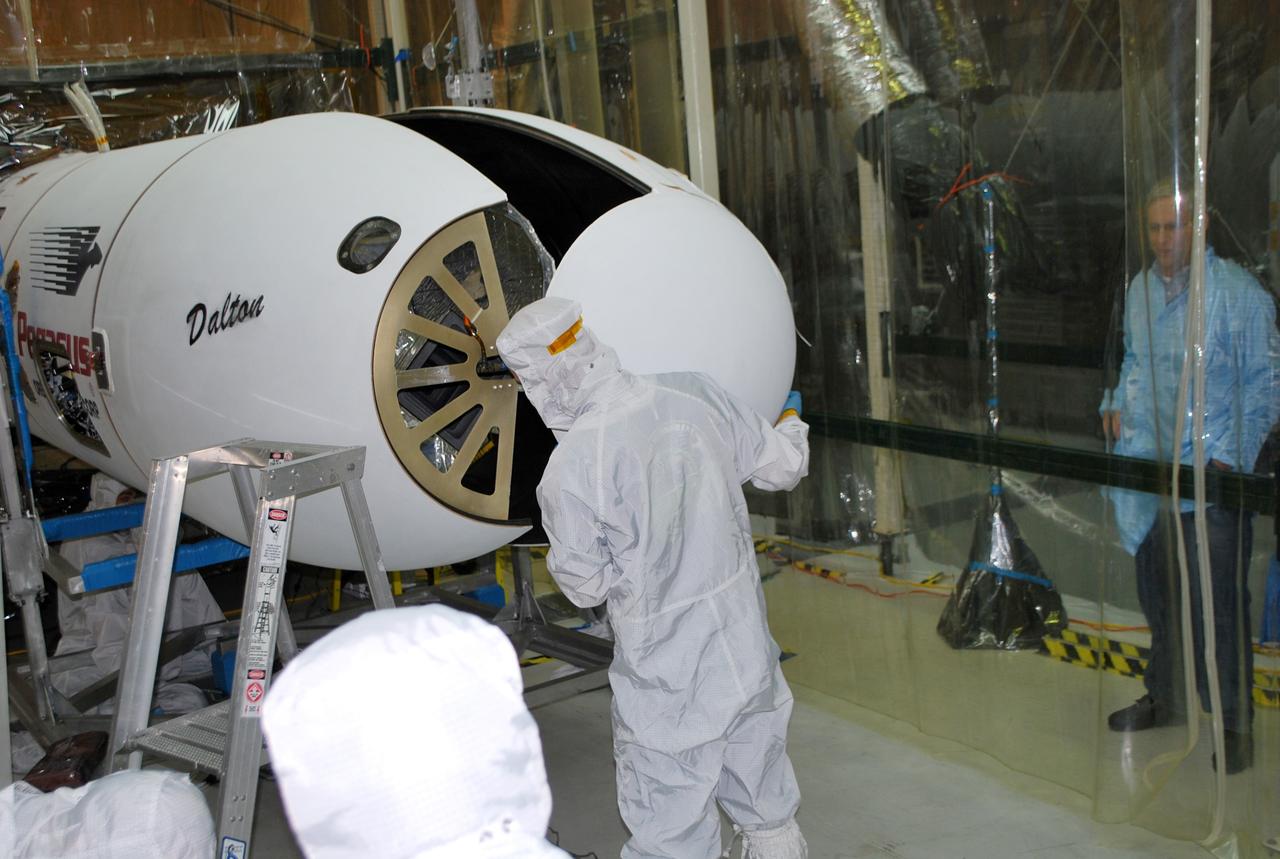

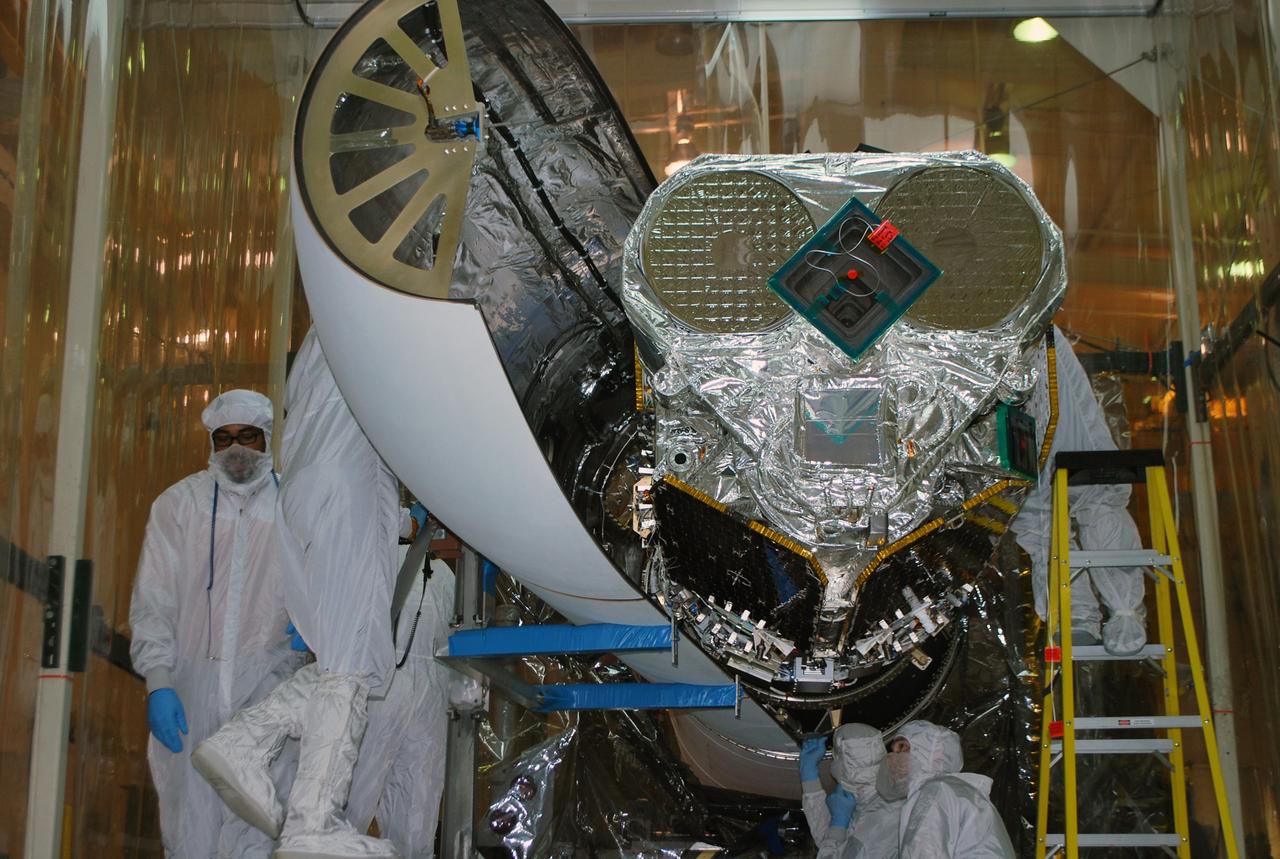
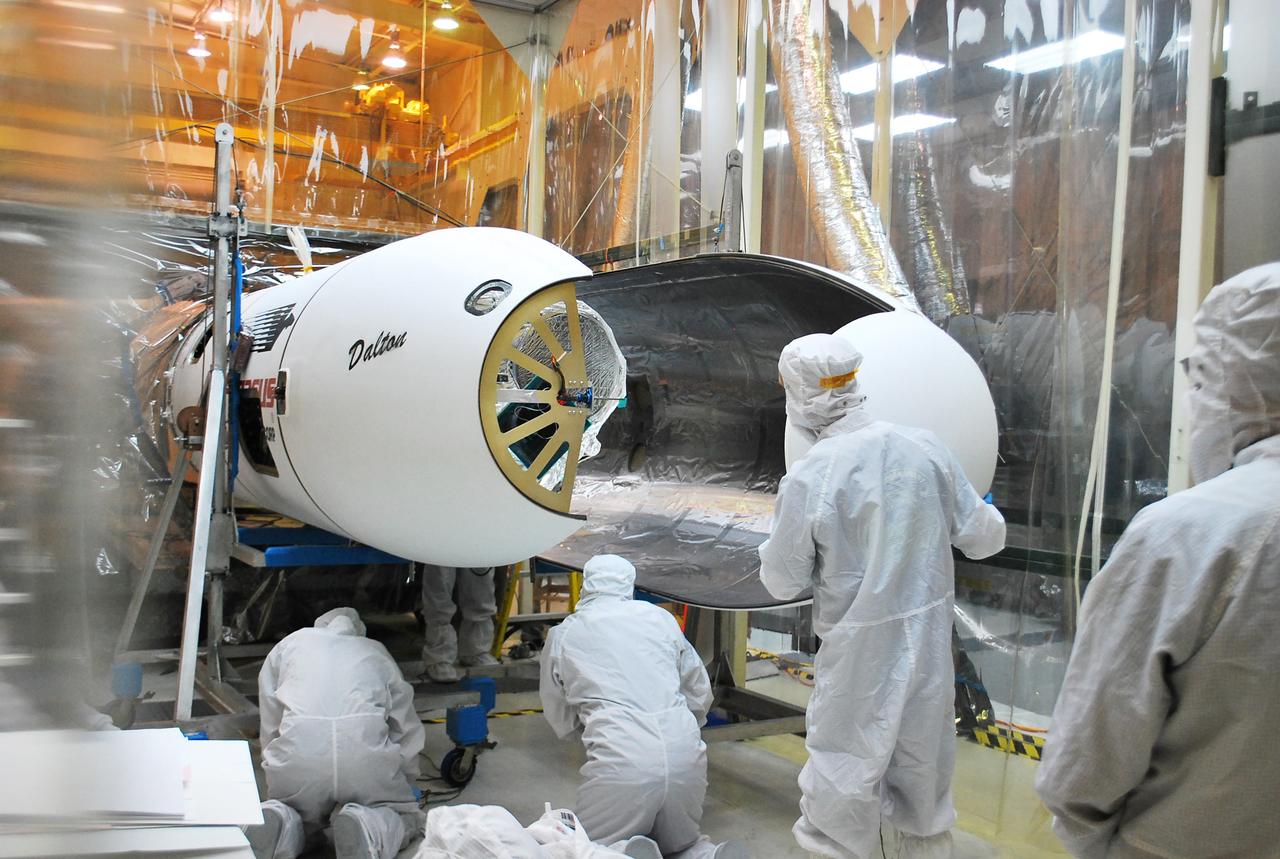
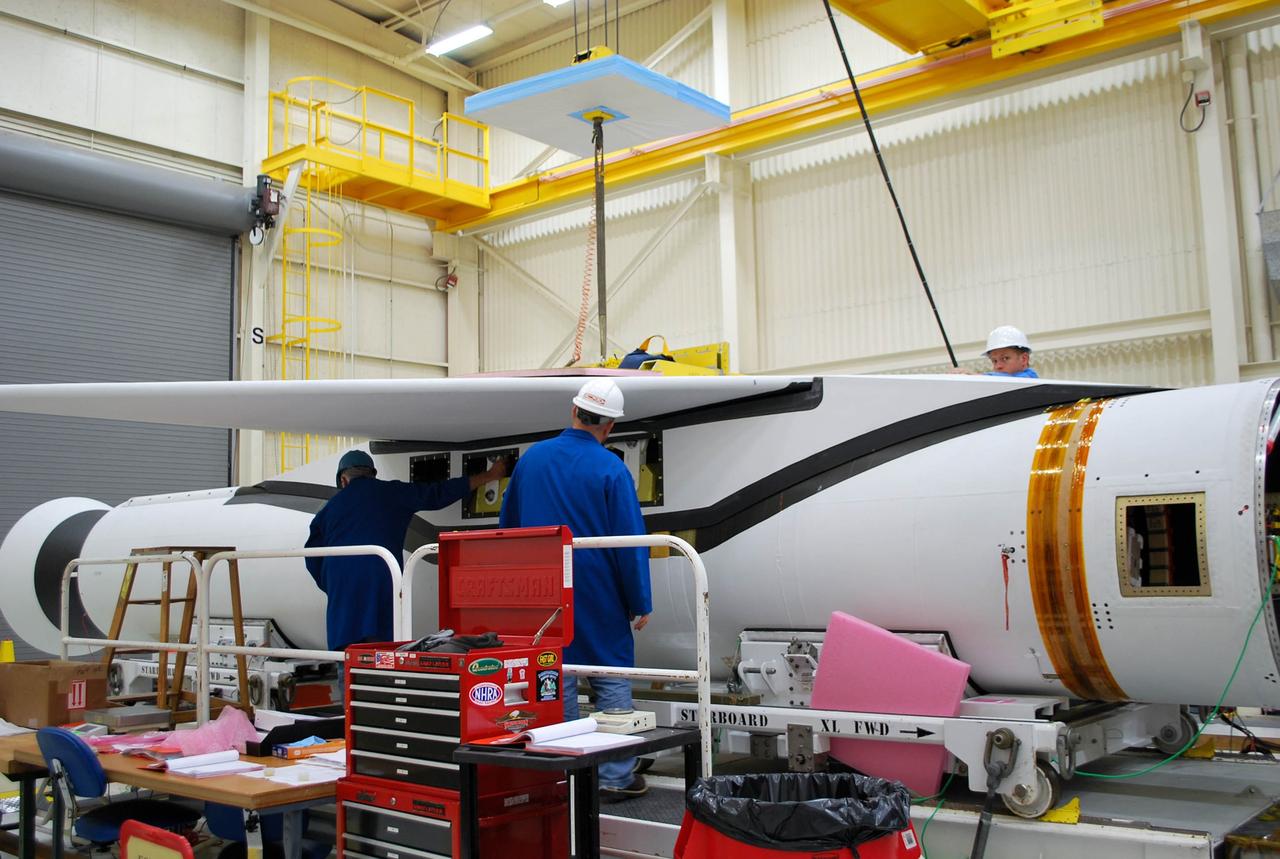
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install the second half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
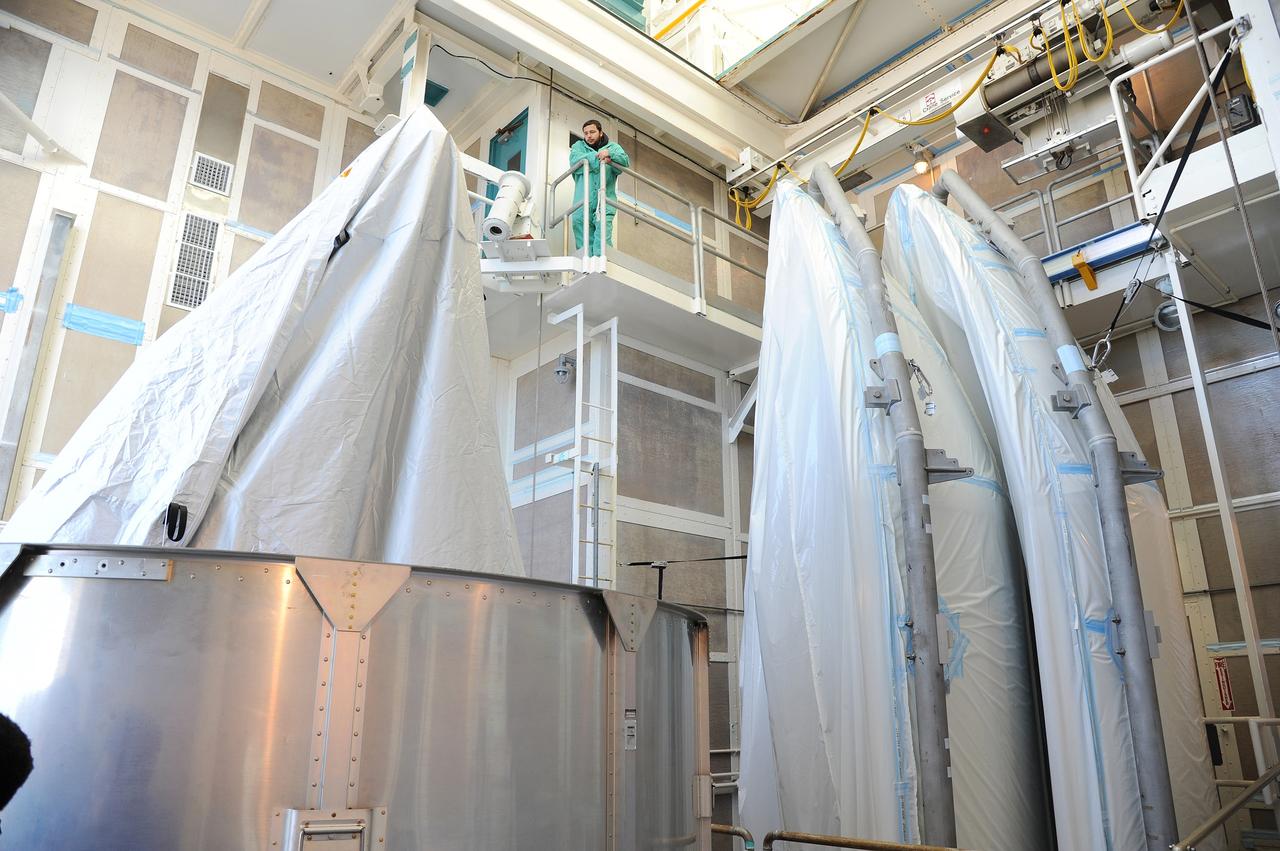

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The transportation canister is removed from around NASA's SMAP spacecraft after positioning the satellite atop a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF
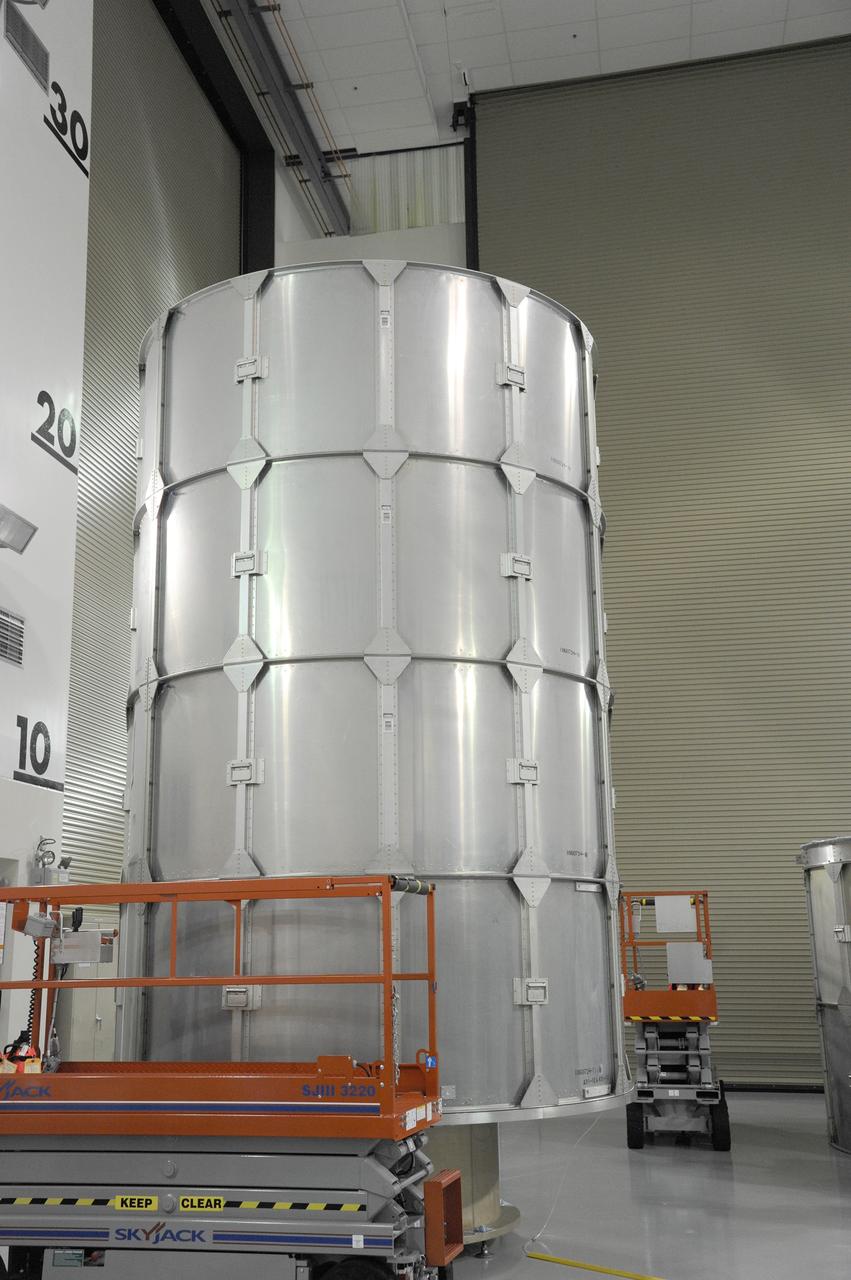

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
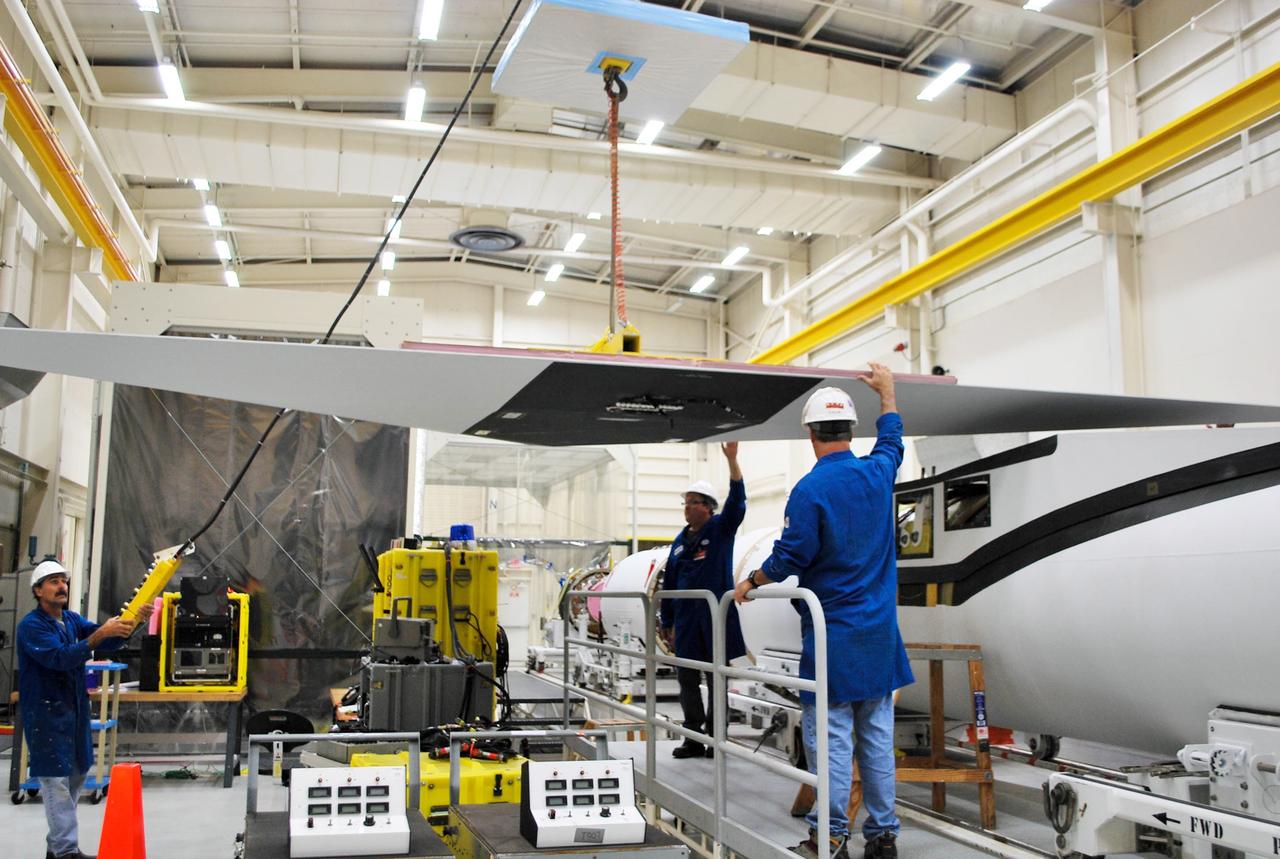

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the wing of the Pegasus to the fuselage. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the portion of the Pegasus that joins the wing to the fuselage, a piece called a fillet. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
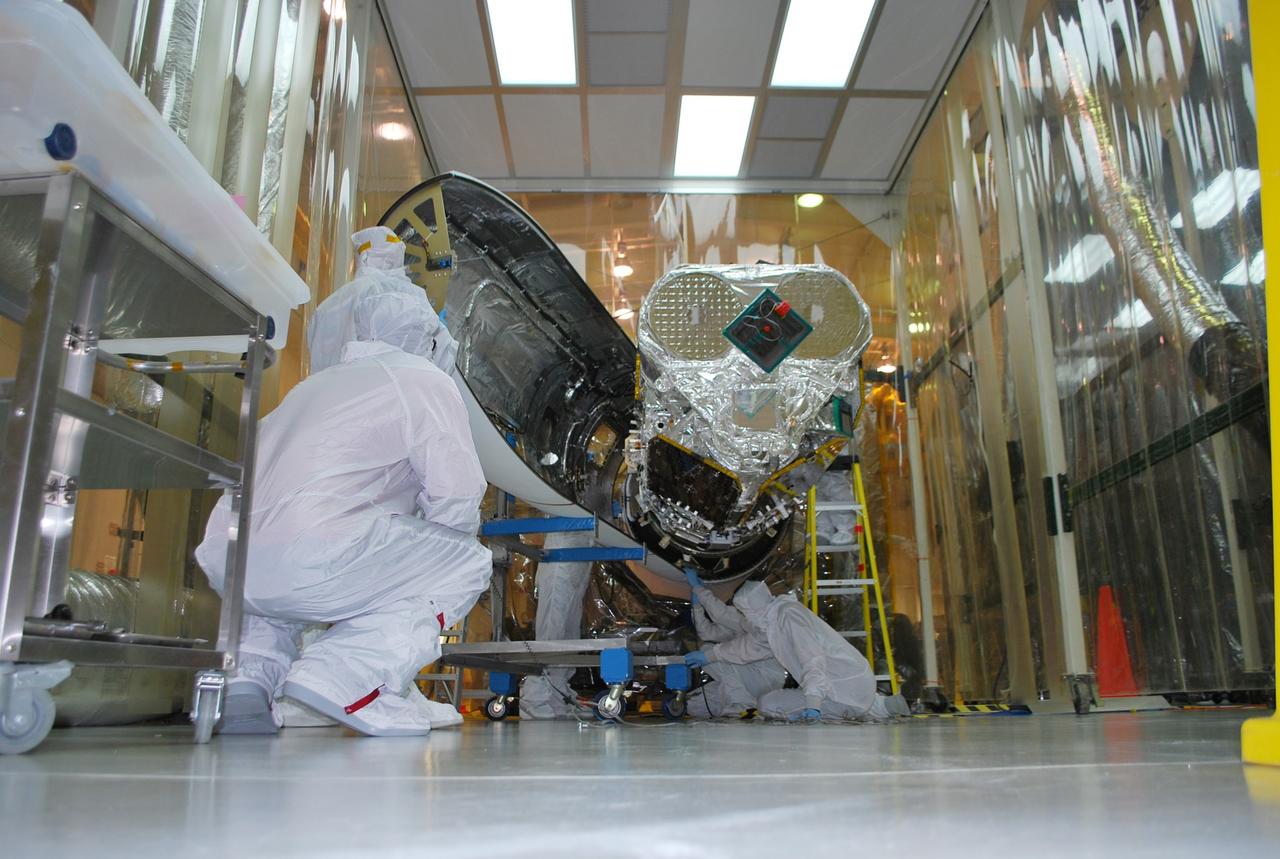

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install one half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
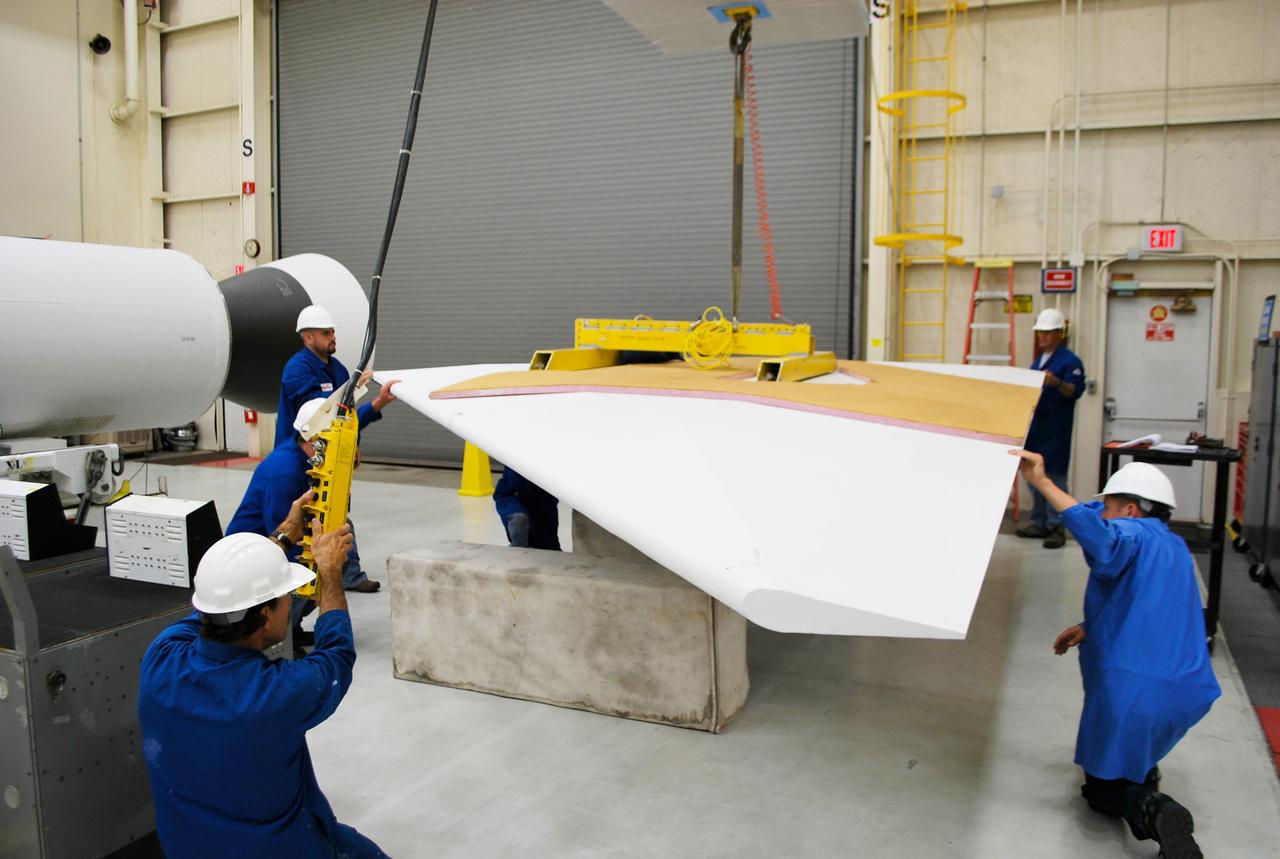

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the wing of the Pegasus to the fuselage. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the portion of the Pegasus that joins the wing to the fuselage, a piece called a fillet. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
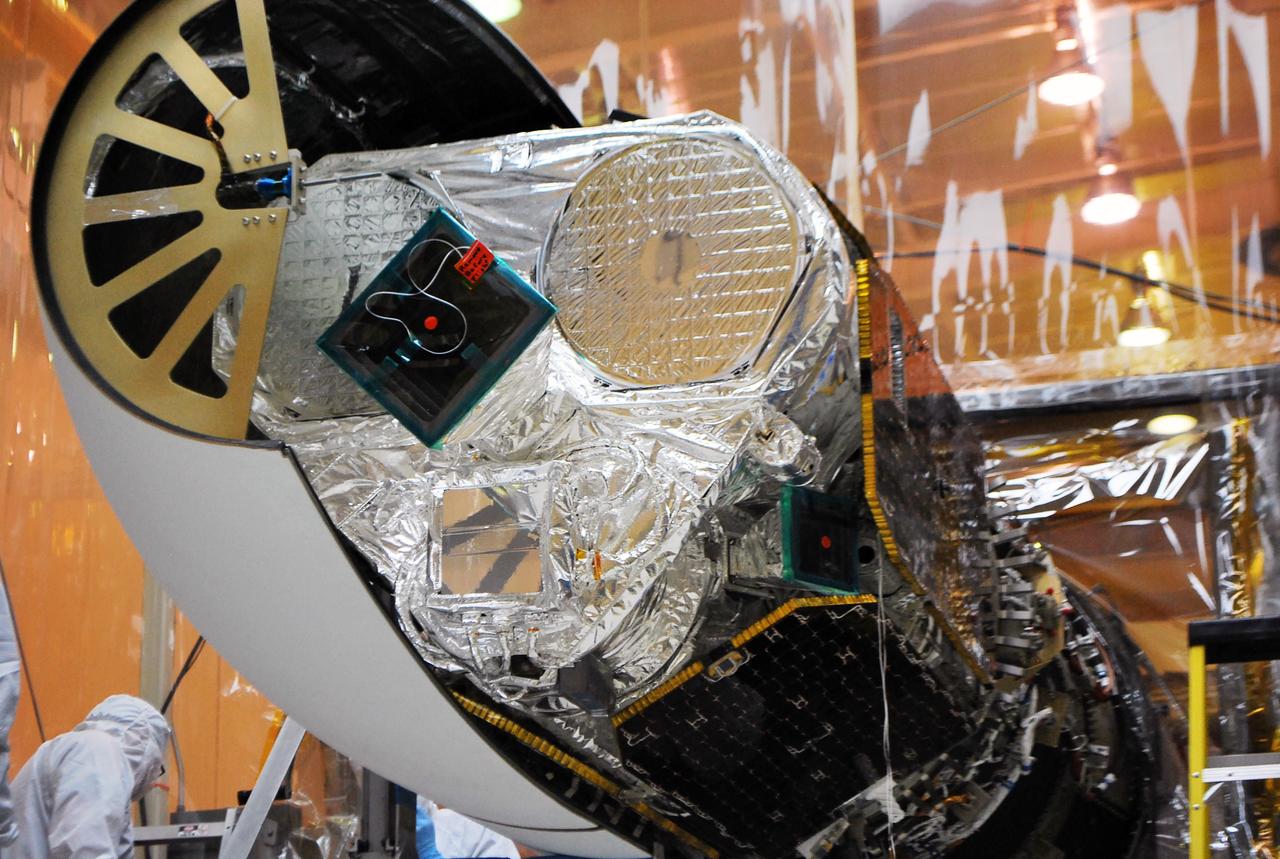
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install one half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
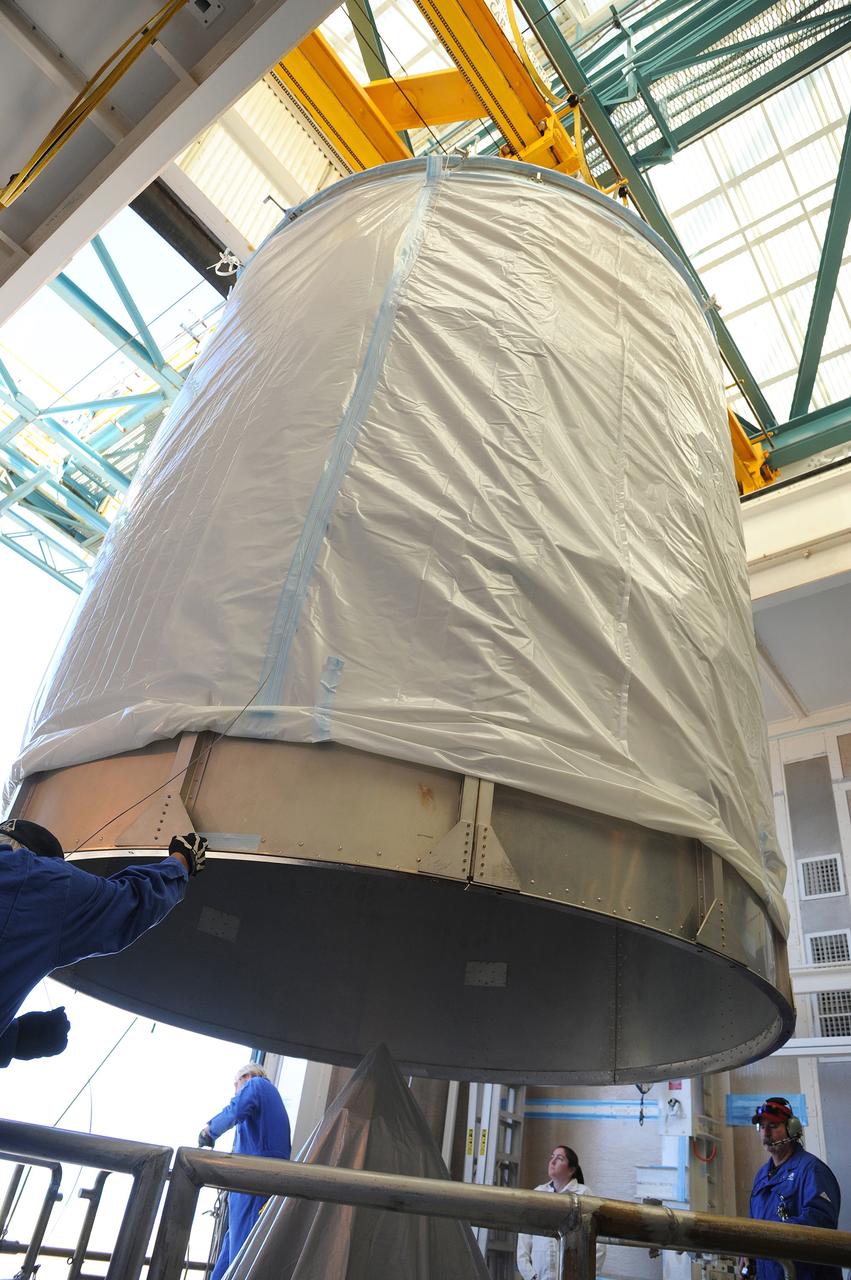

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The transportation canister is removed from around NASA's SMAP spacecraft after positioning the satellite atop a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

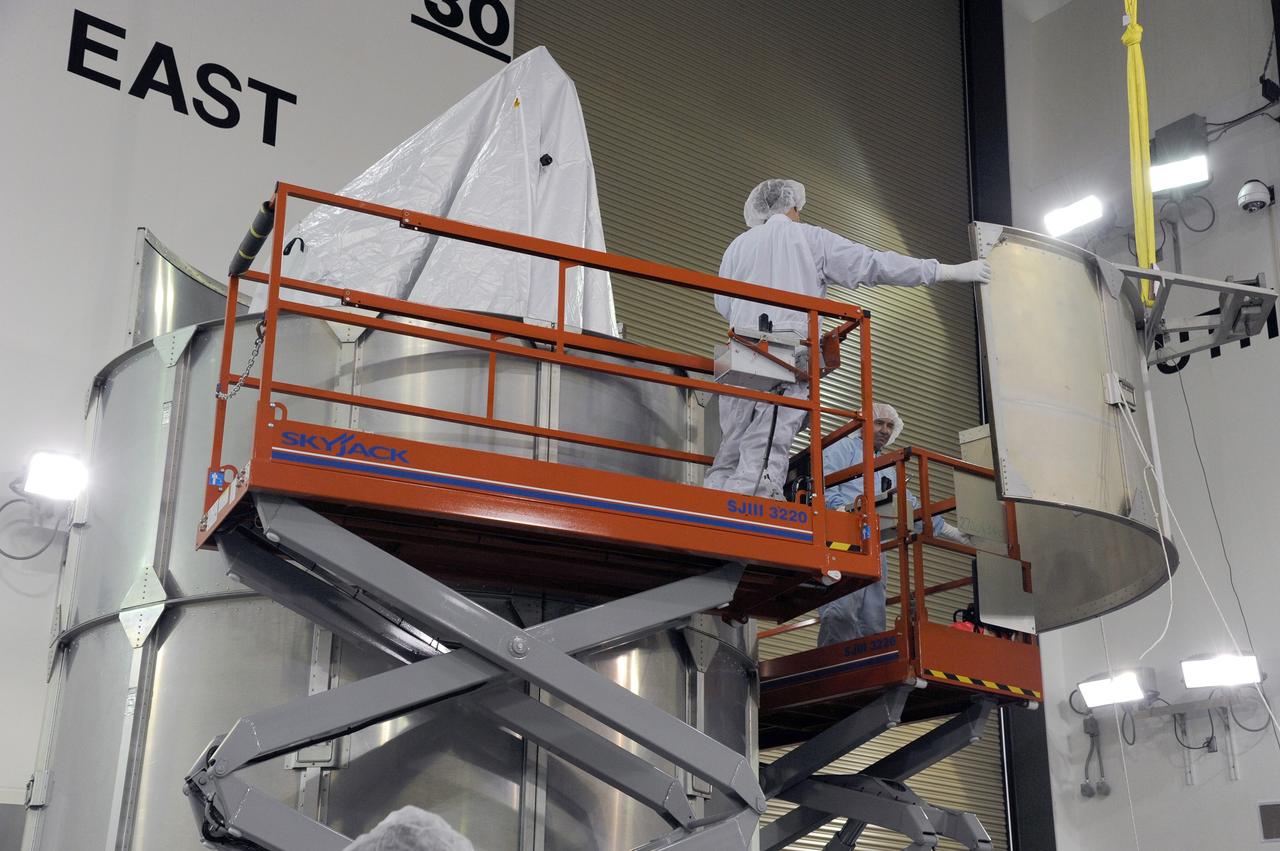
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install one half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install the second half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
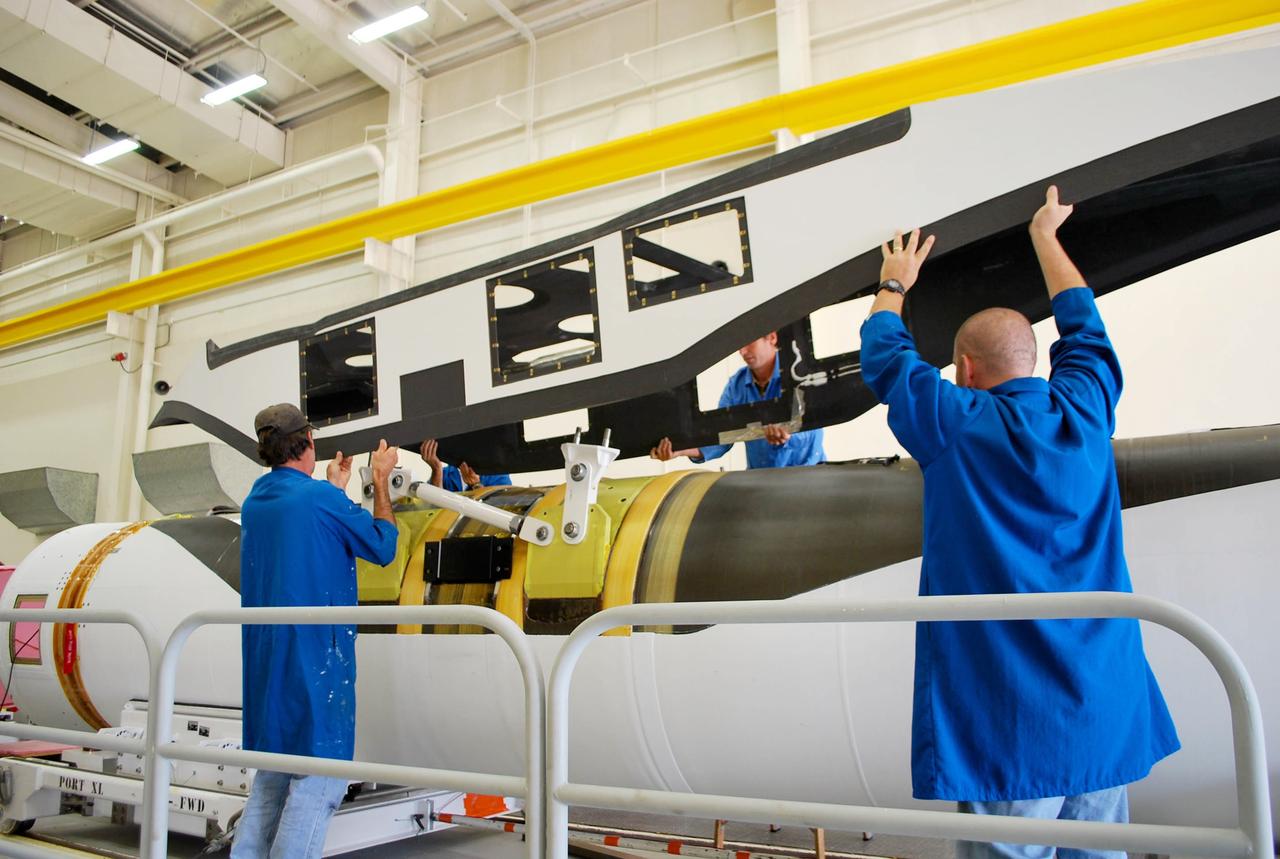

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the portion of the Pegasus that joins the wing to the fuselage, a piece called a fillet. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A technician monitors the movement of the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

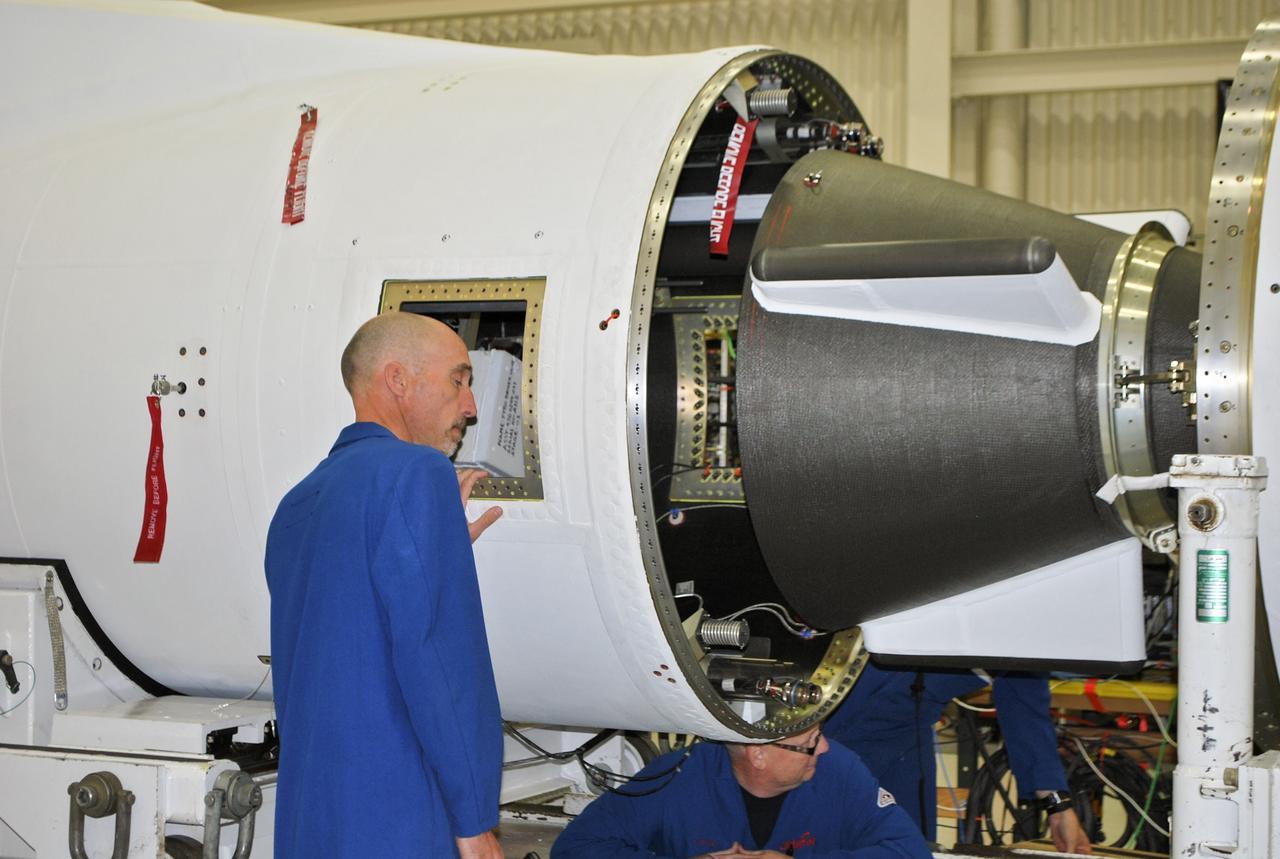
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install one half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. The second half of the fairing stands ready for installation. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
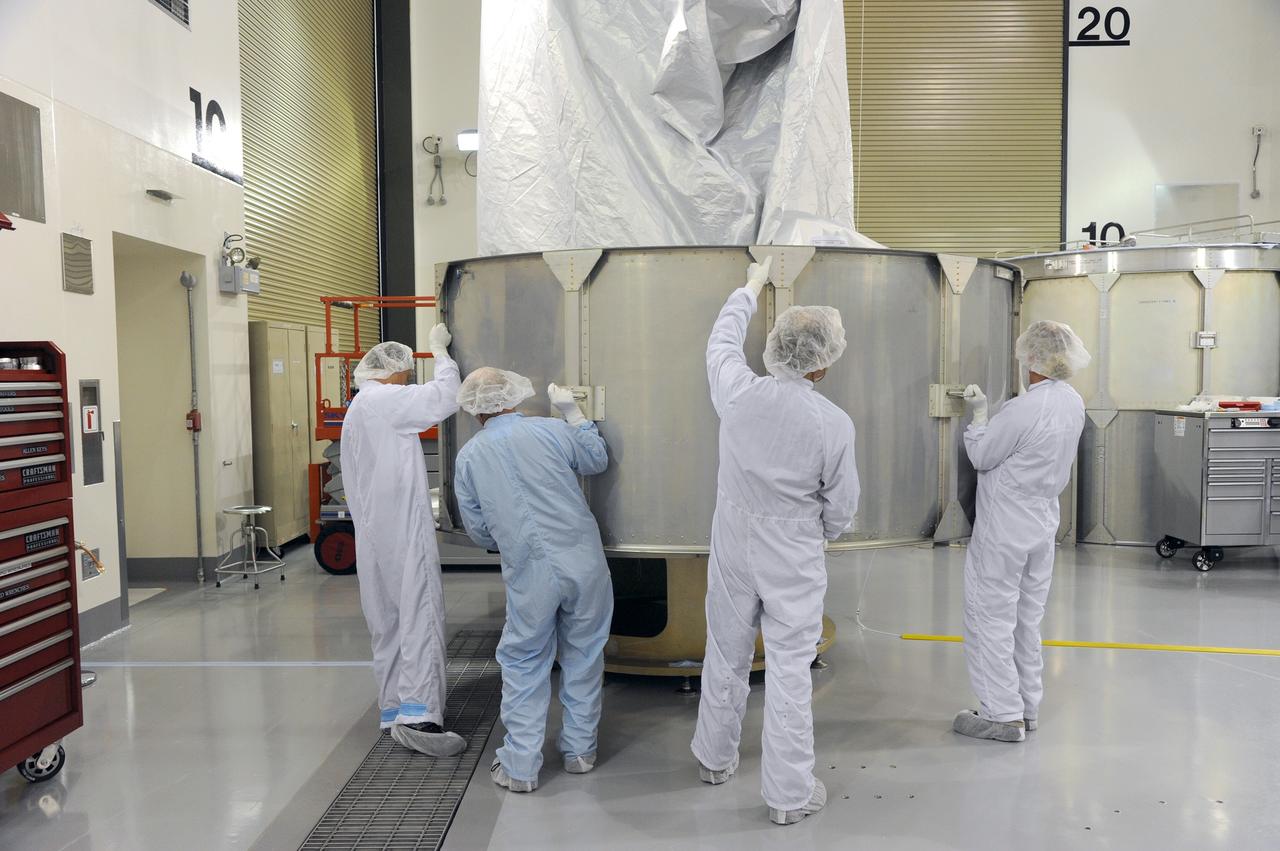

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
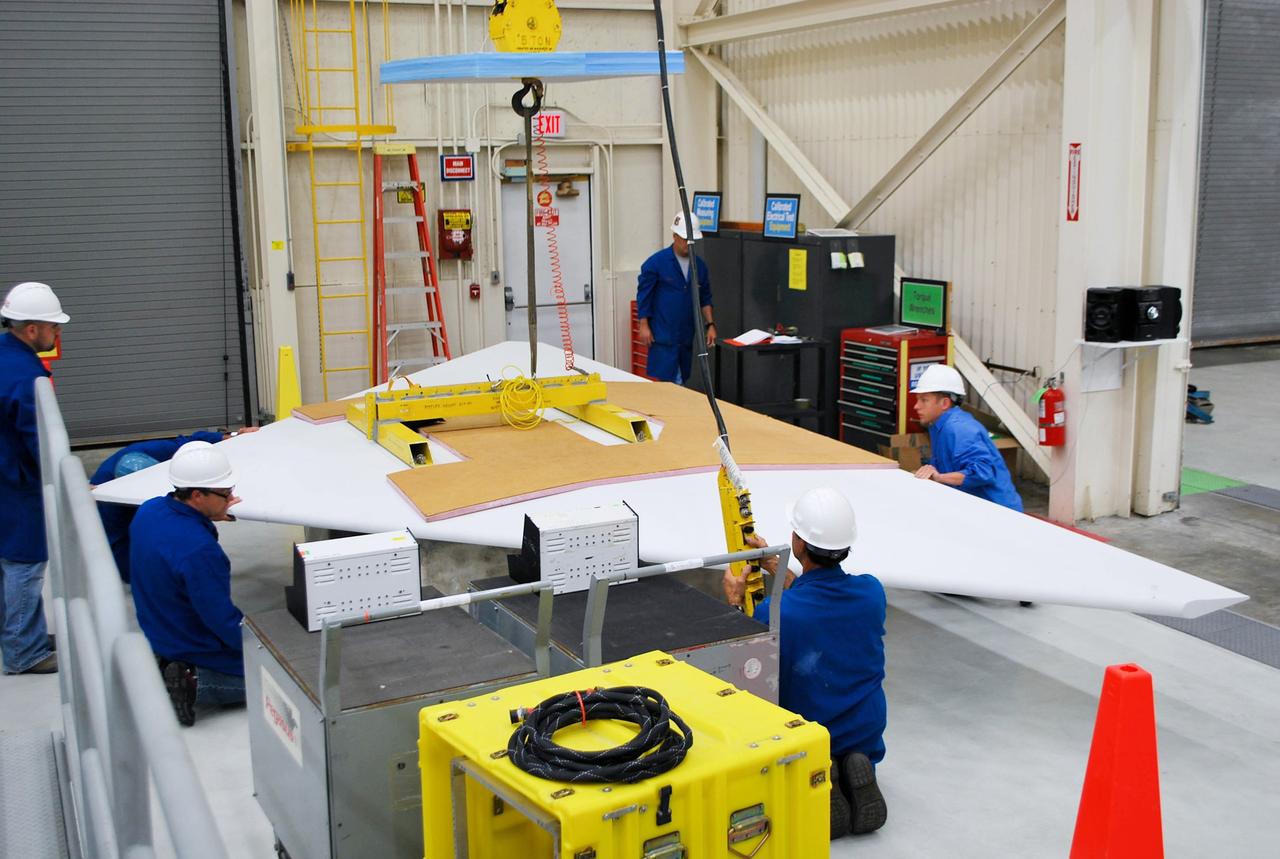

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the wing of the Pegasus to the fuselage. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
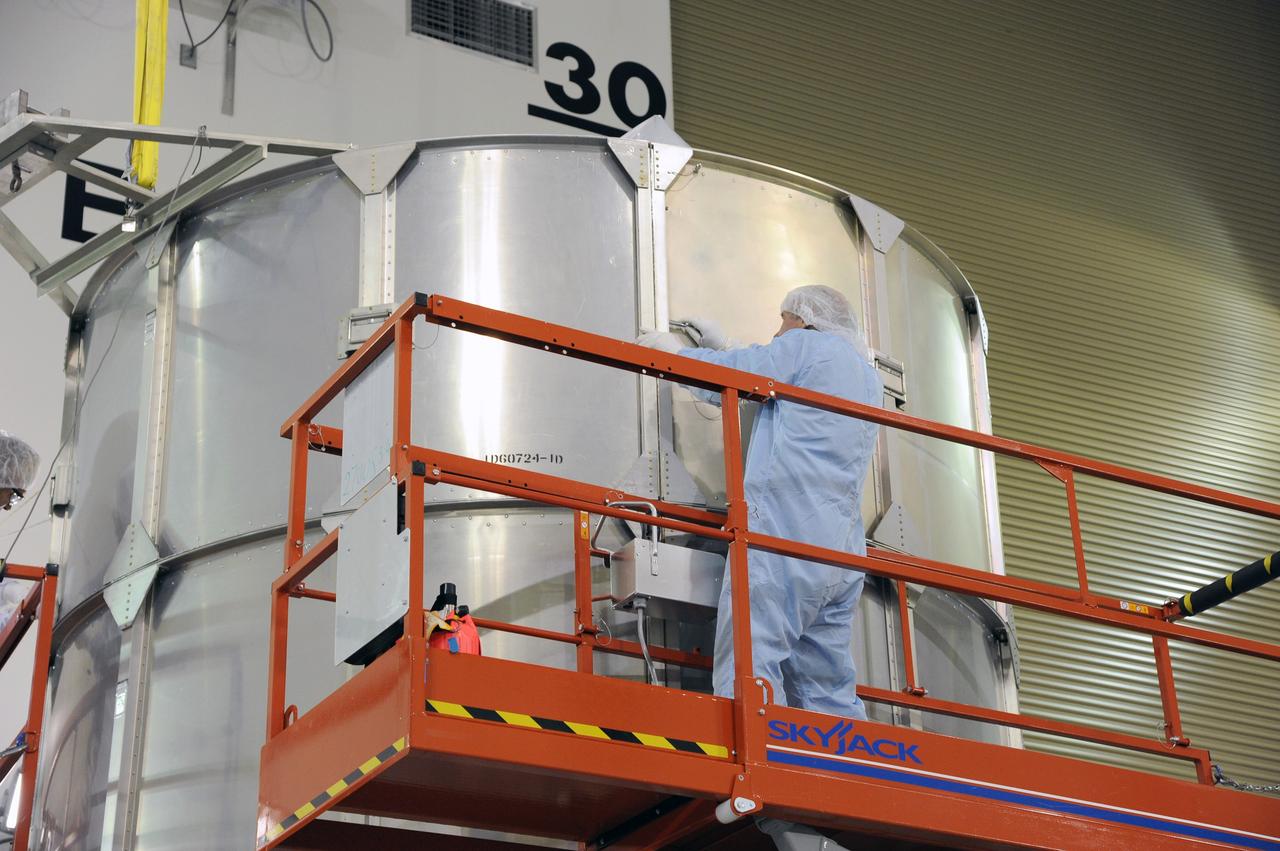

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila

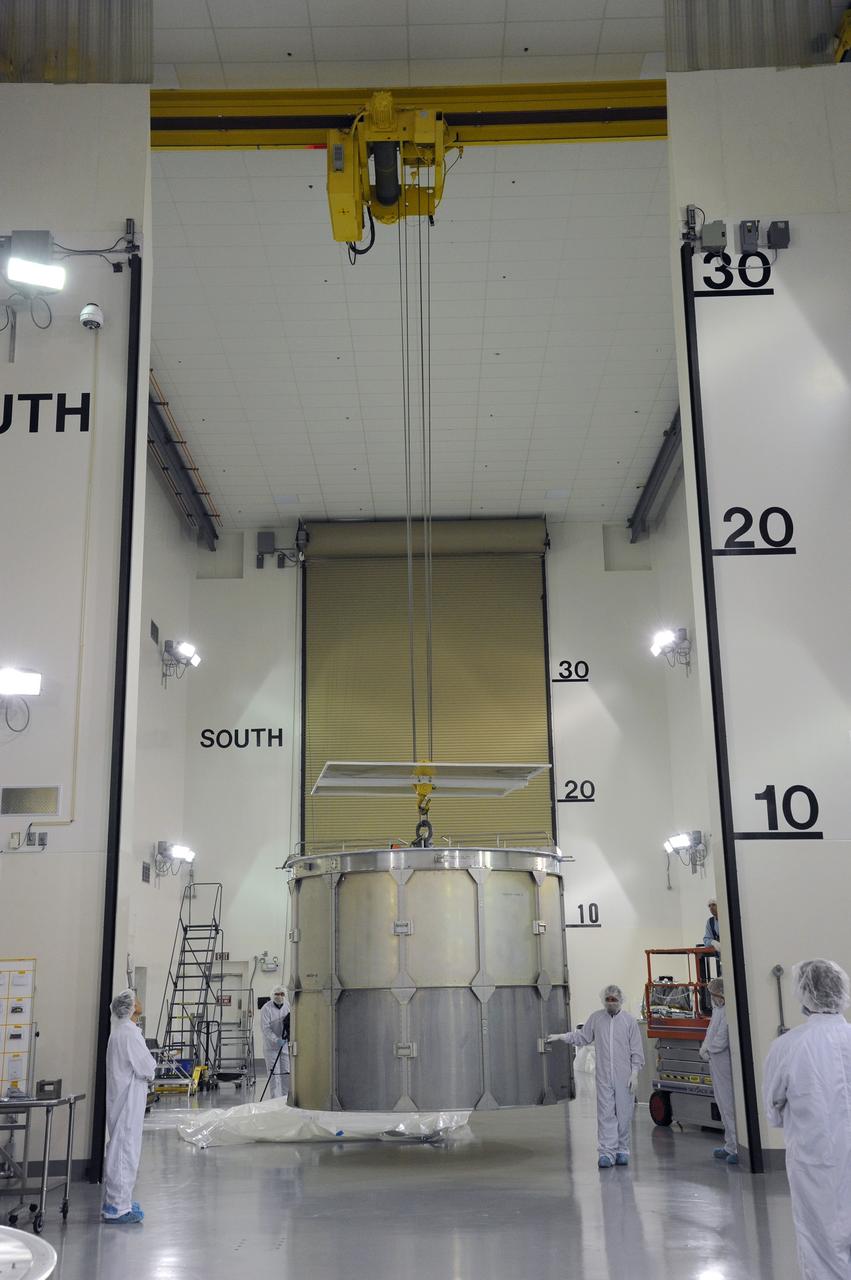
VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
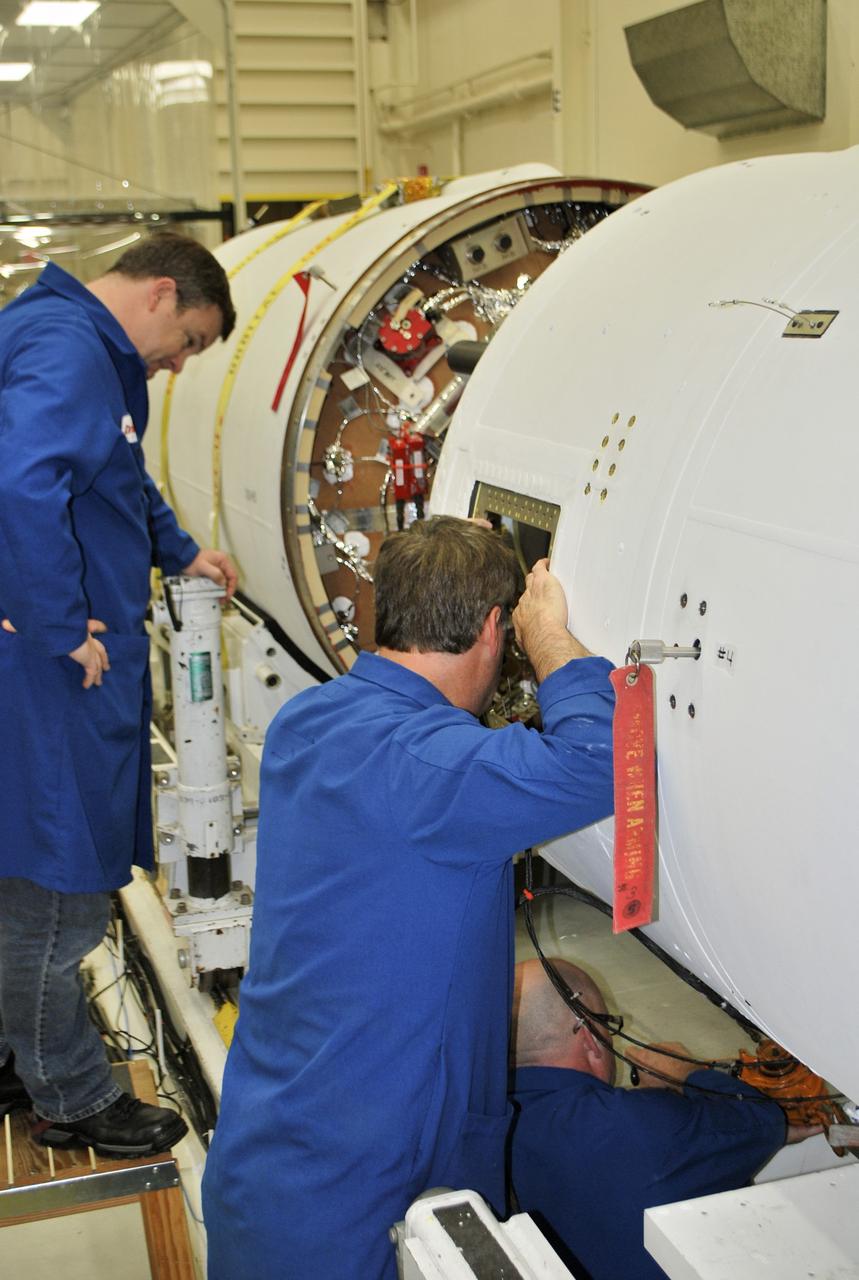

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians monitor the movement of the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians monitor the movement of the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
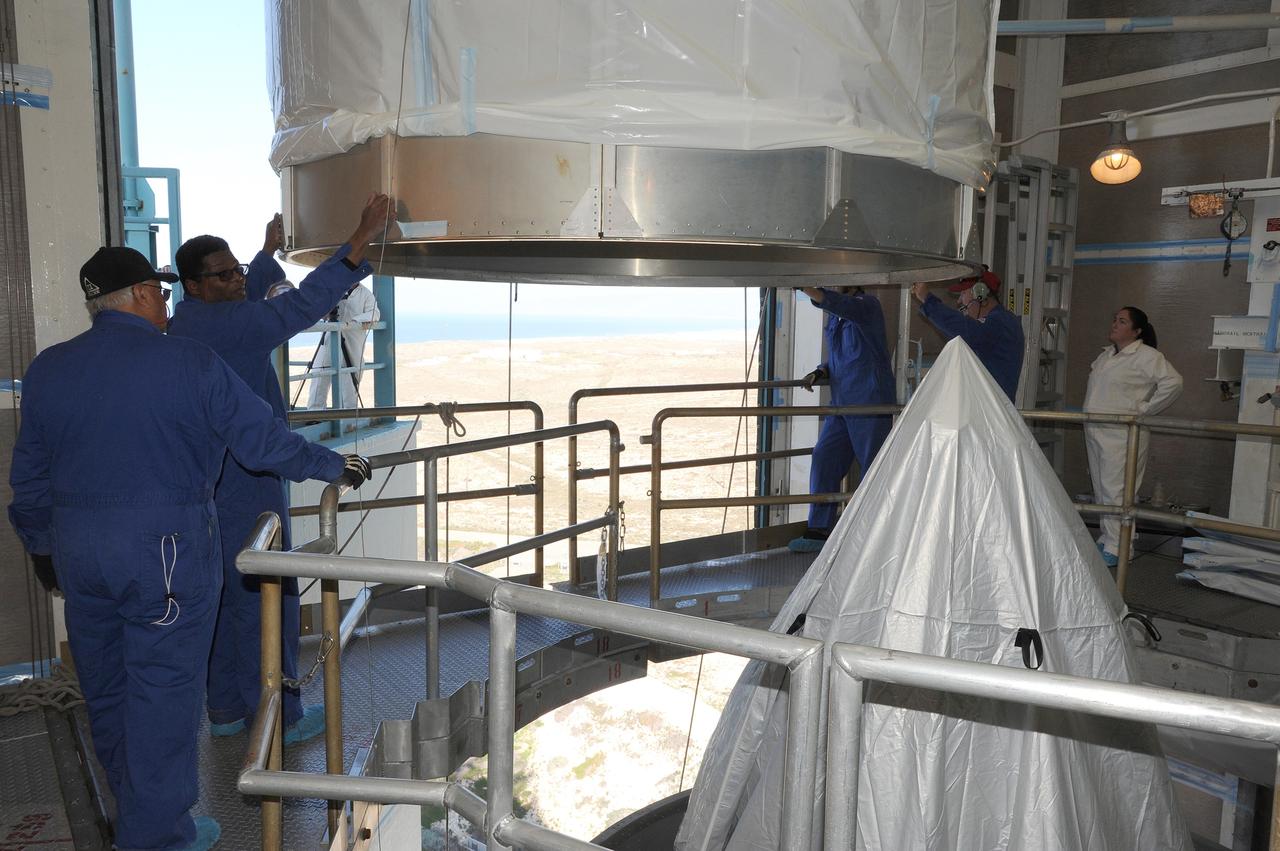

VANDENBERG AFB, California – The transportation canister is removed from around NASA's SMAP spacecraft after positioning the satellite atop a Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex-2 for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
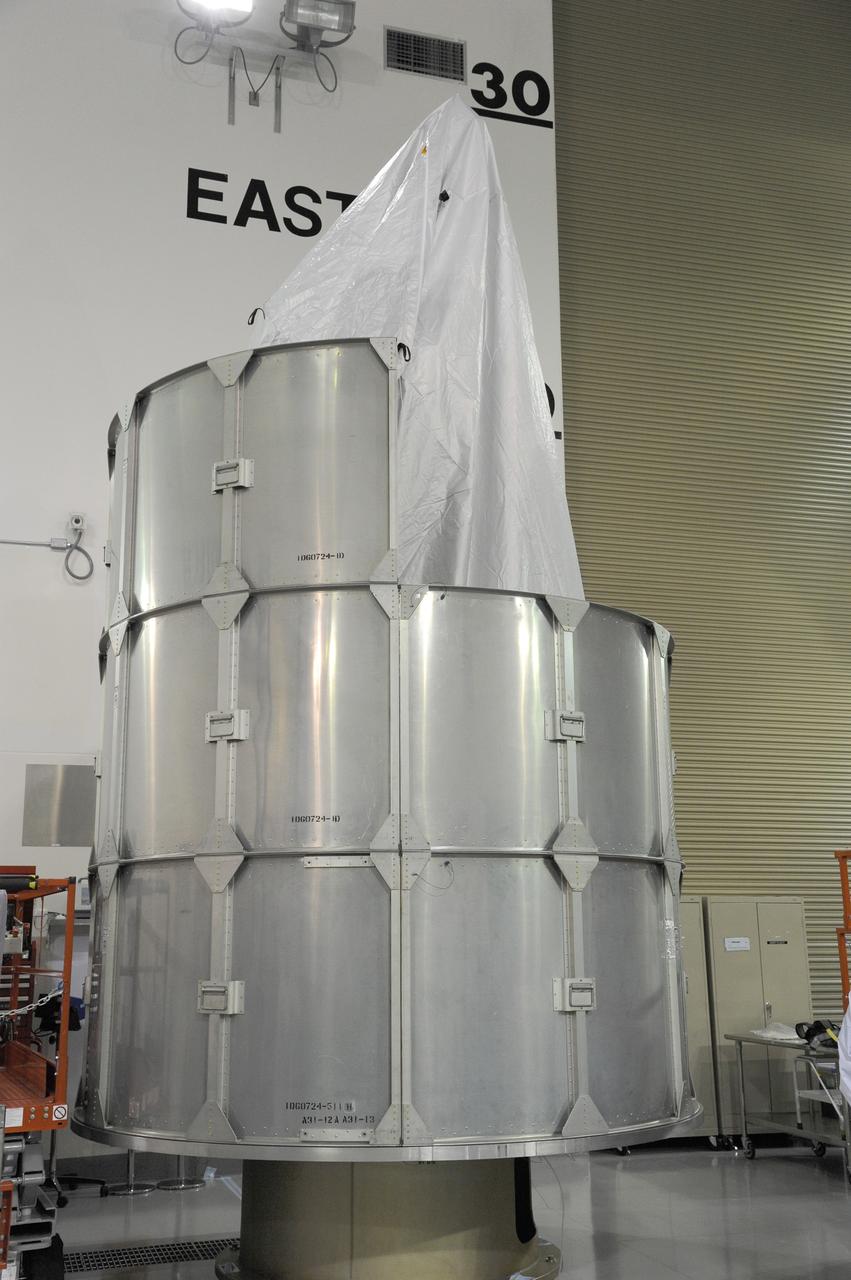

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila

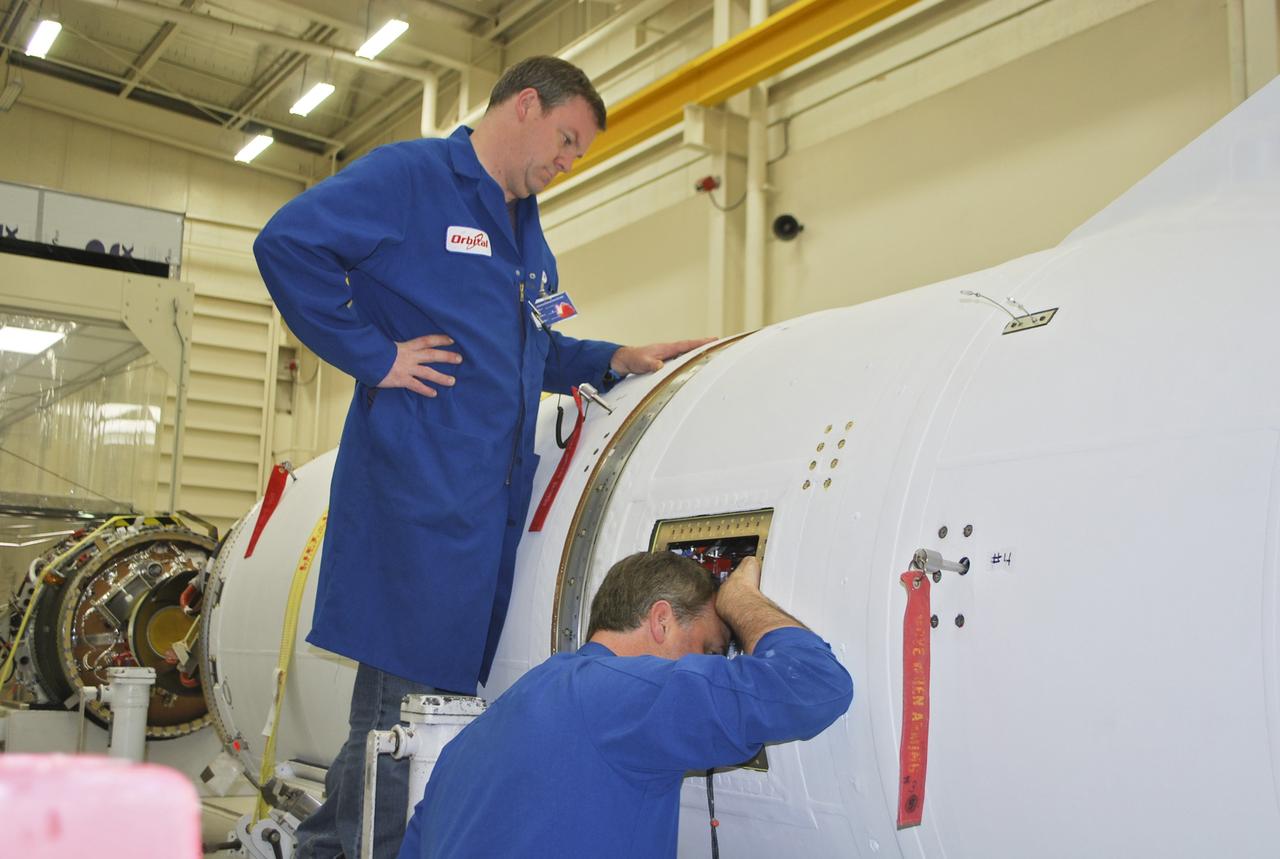
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the wing of the Pegasus to the fuselage. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
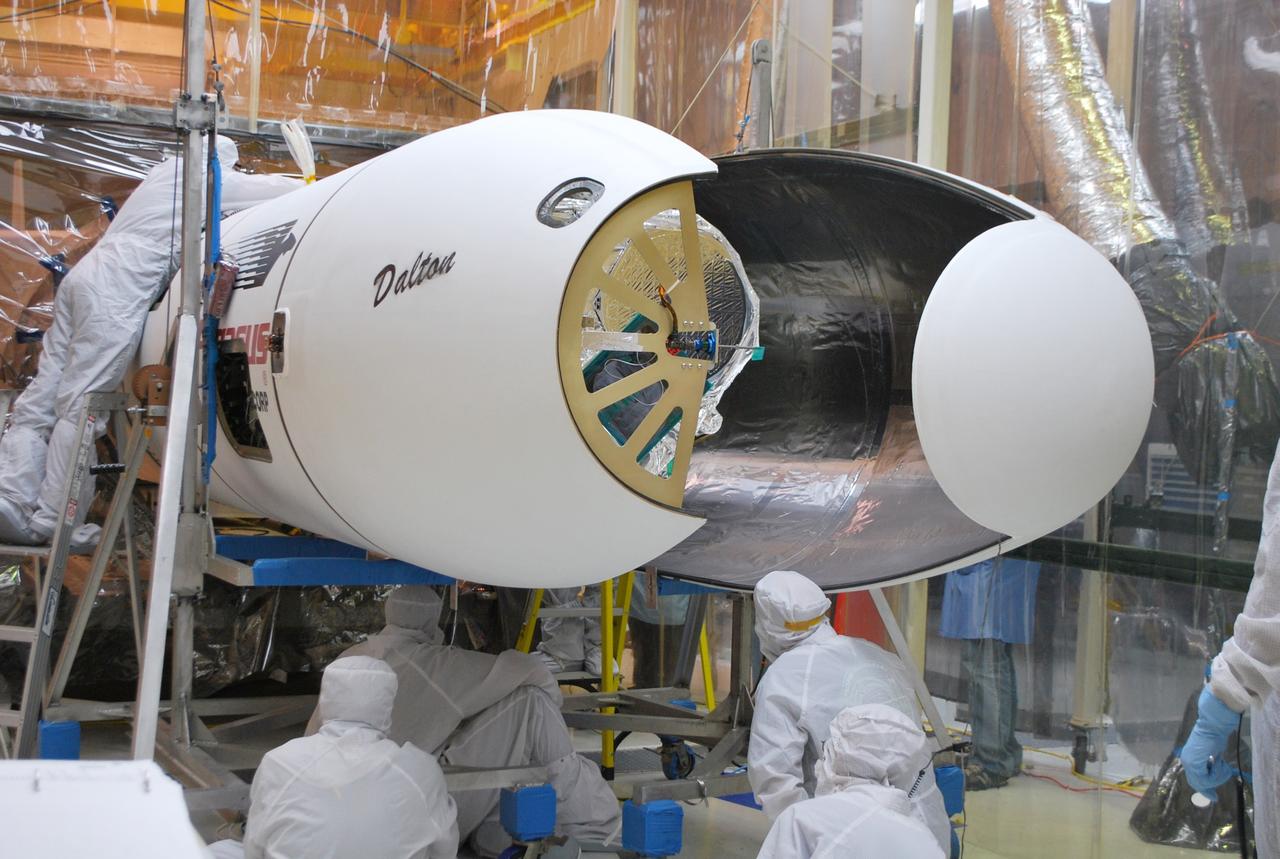

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install the second half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
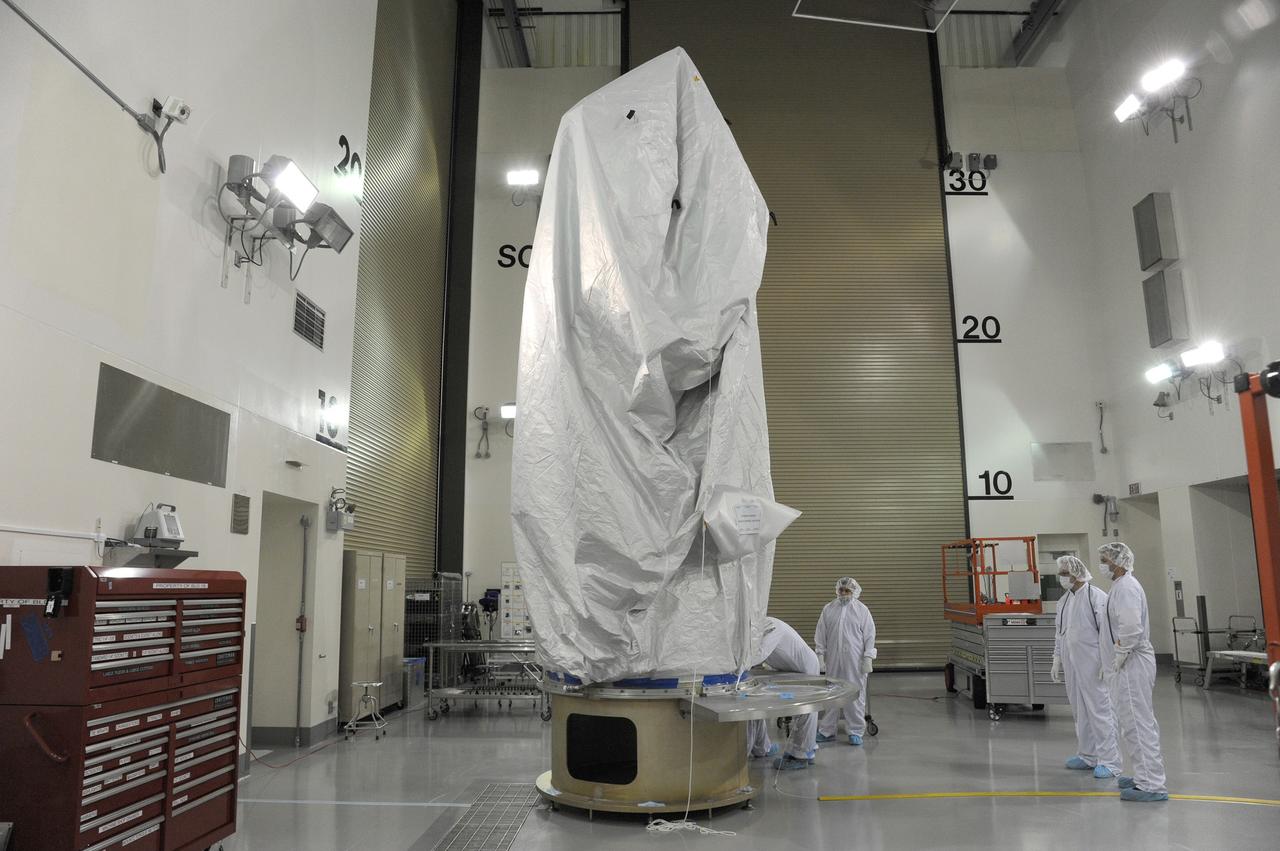

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
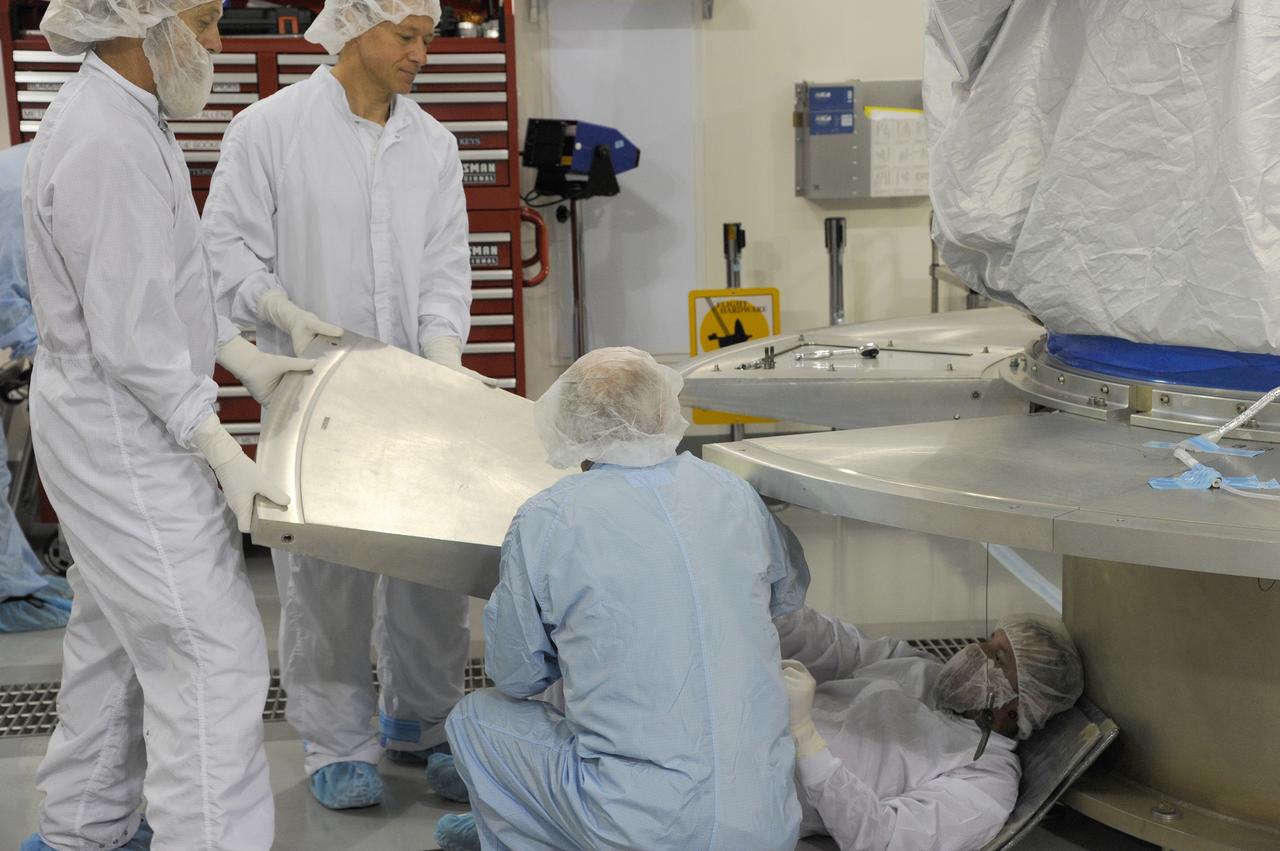

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
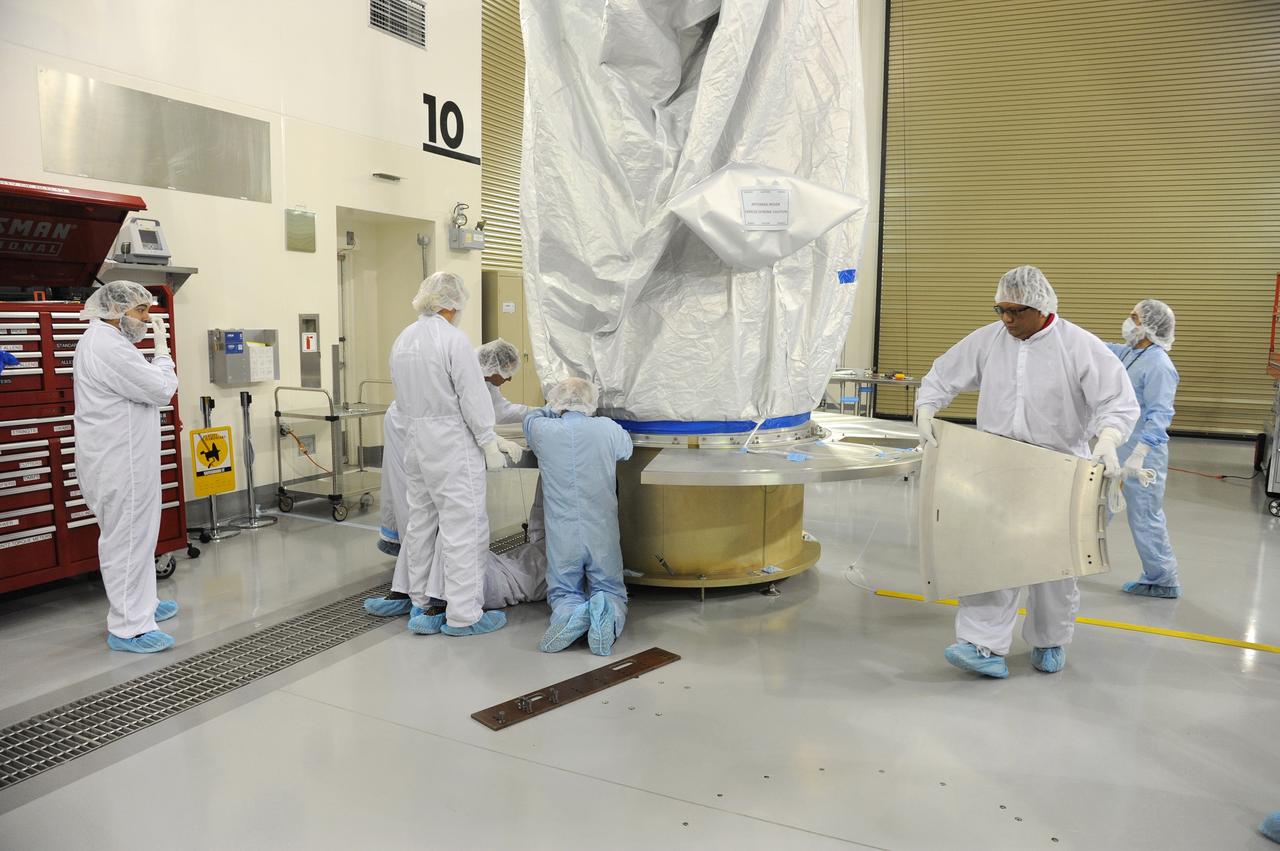

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
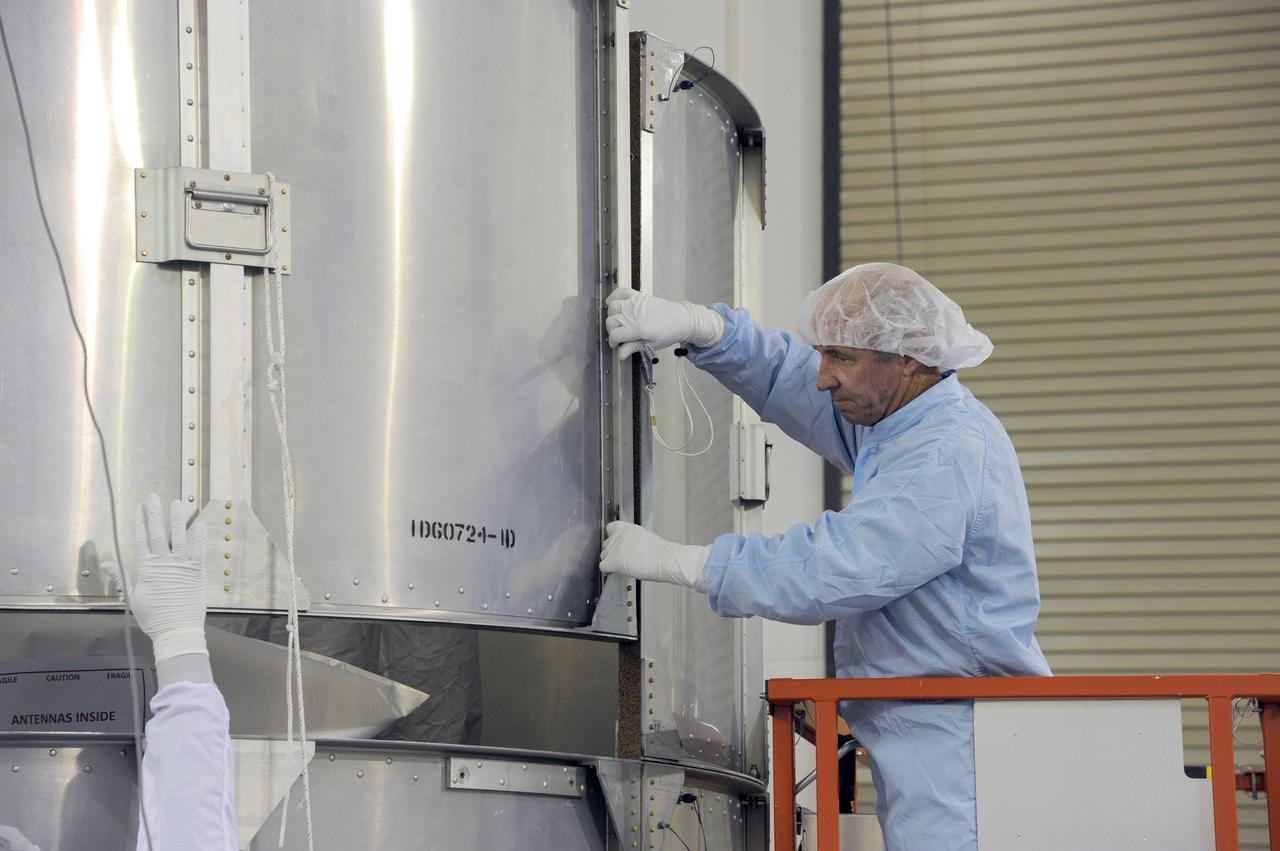

VANDENBERG AFB, California – Technicians and engineers place a transportation canister around NASA's SMAP spacecraft so it can be taken from the Astrotech processing facility to Space Launch Complex-2 for placement atop a Delta II rocket for launch. For more, go to www.nasa.gov/smap Photo credit: USAF/John Davila
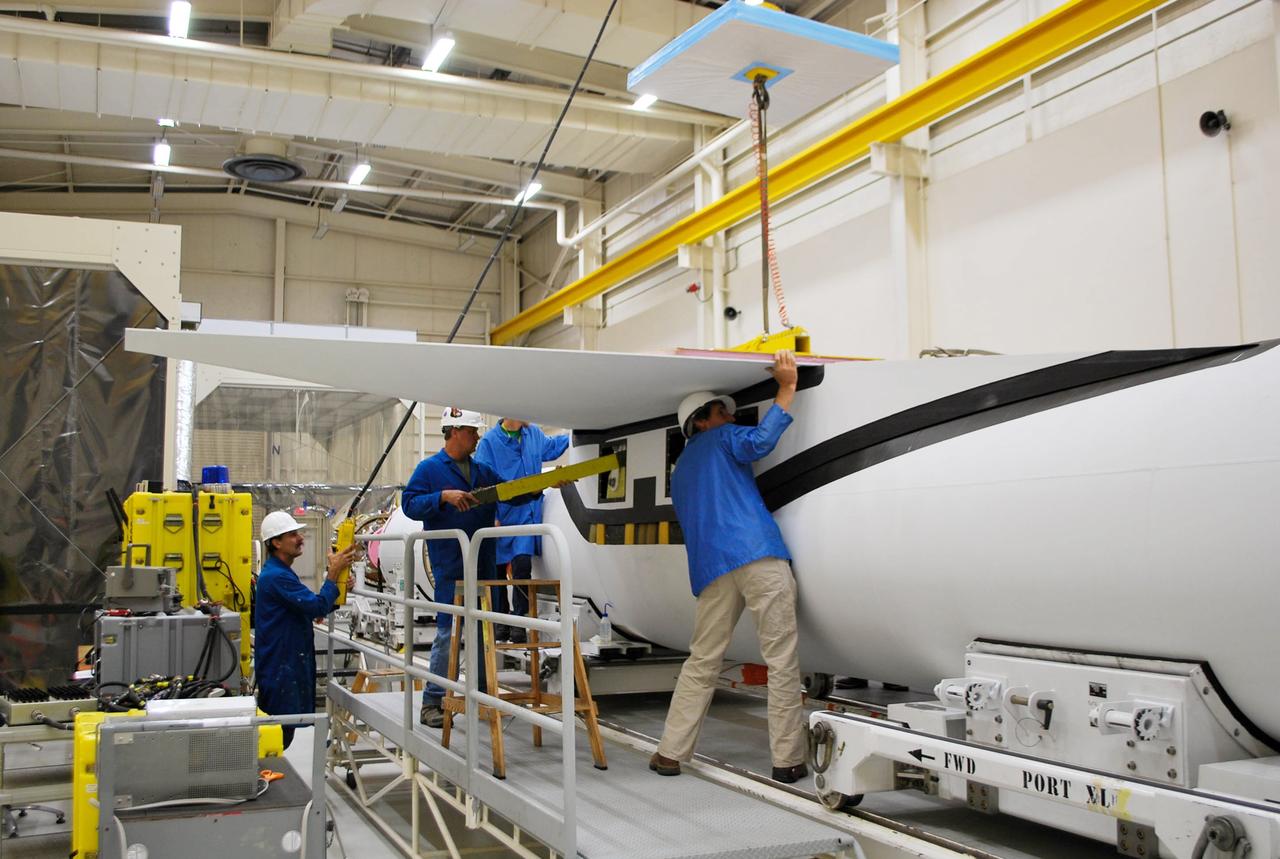

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the wing of the Pegasus to the fuselage. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
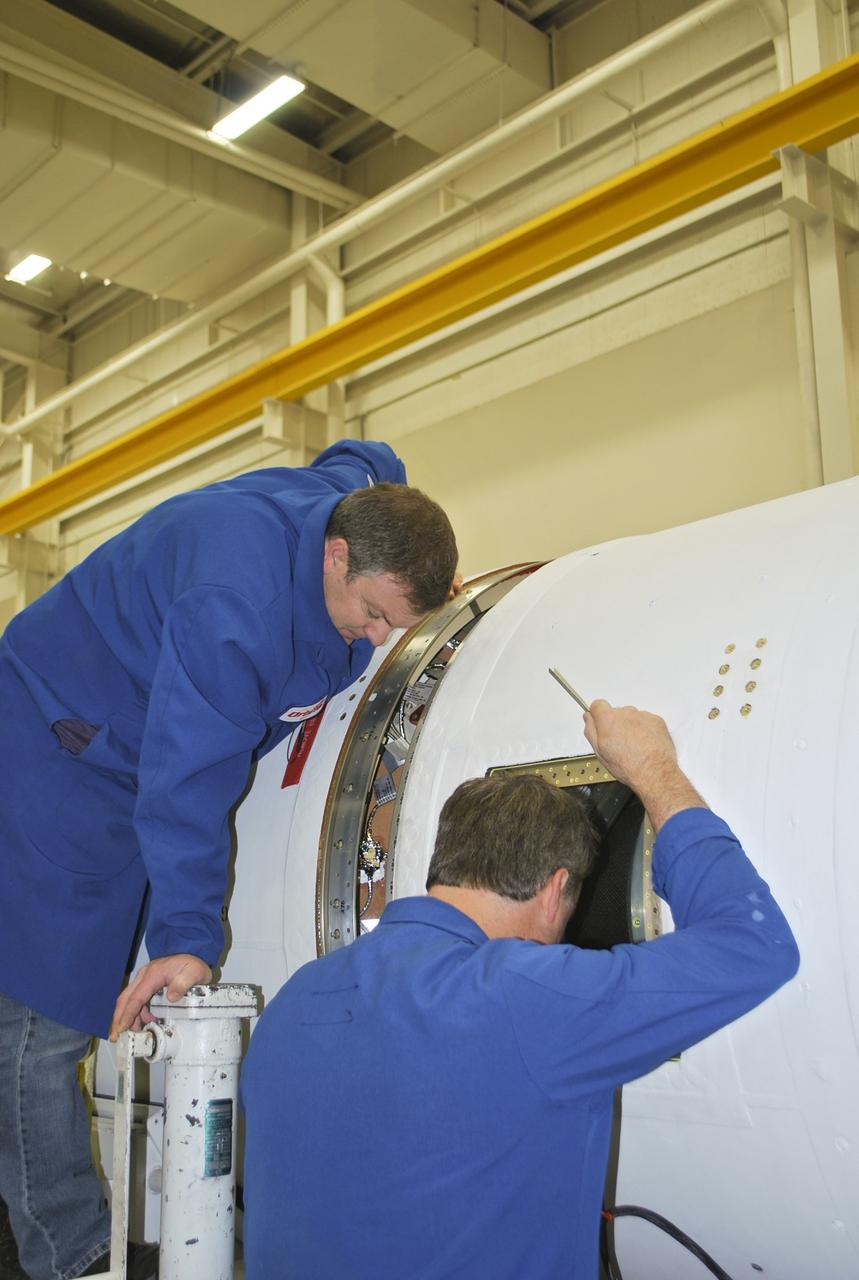

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians monitor the movement of the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
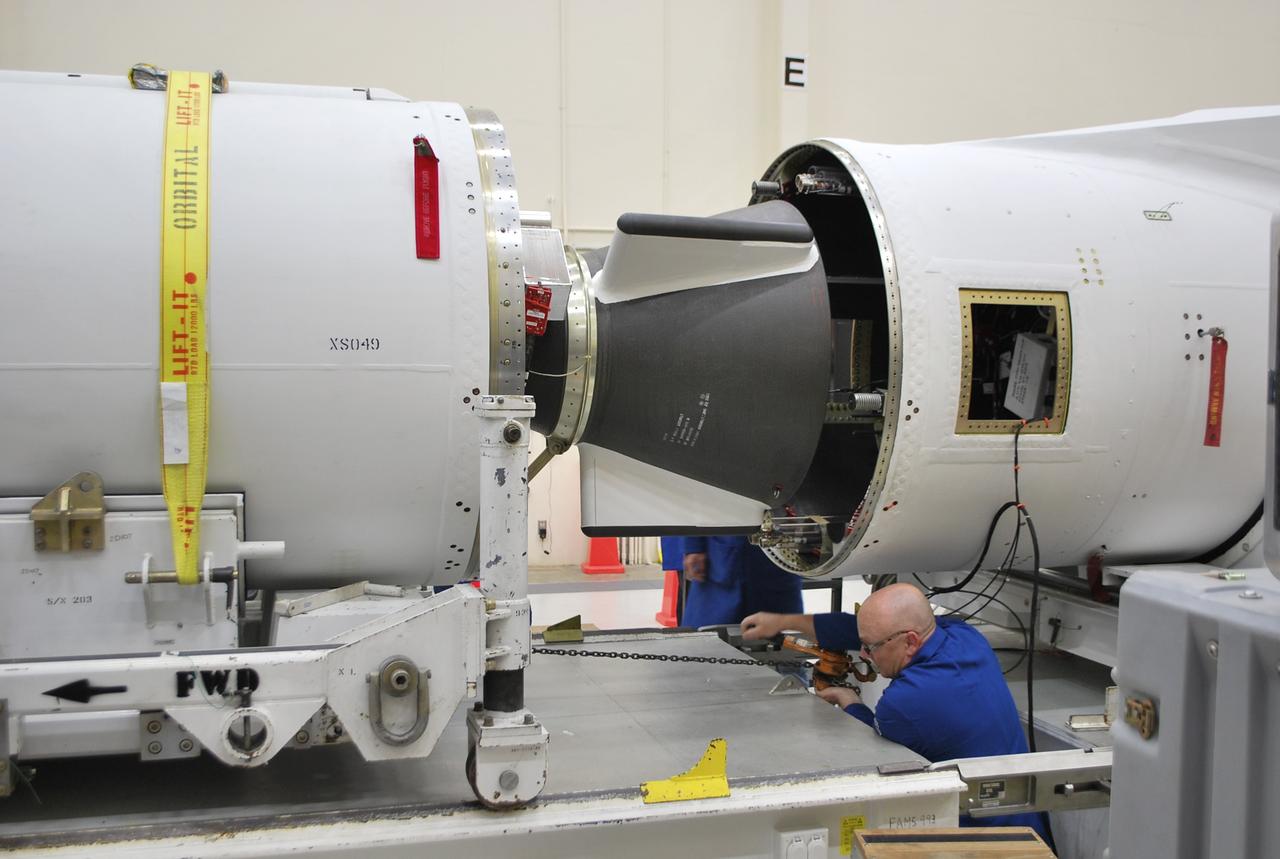

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A technician moves the second stage of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket into the first stage before a separation test is conducted. The Pegasus is being processed to launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission, known as IRIS. Photo credit: Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
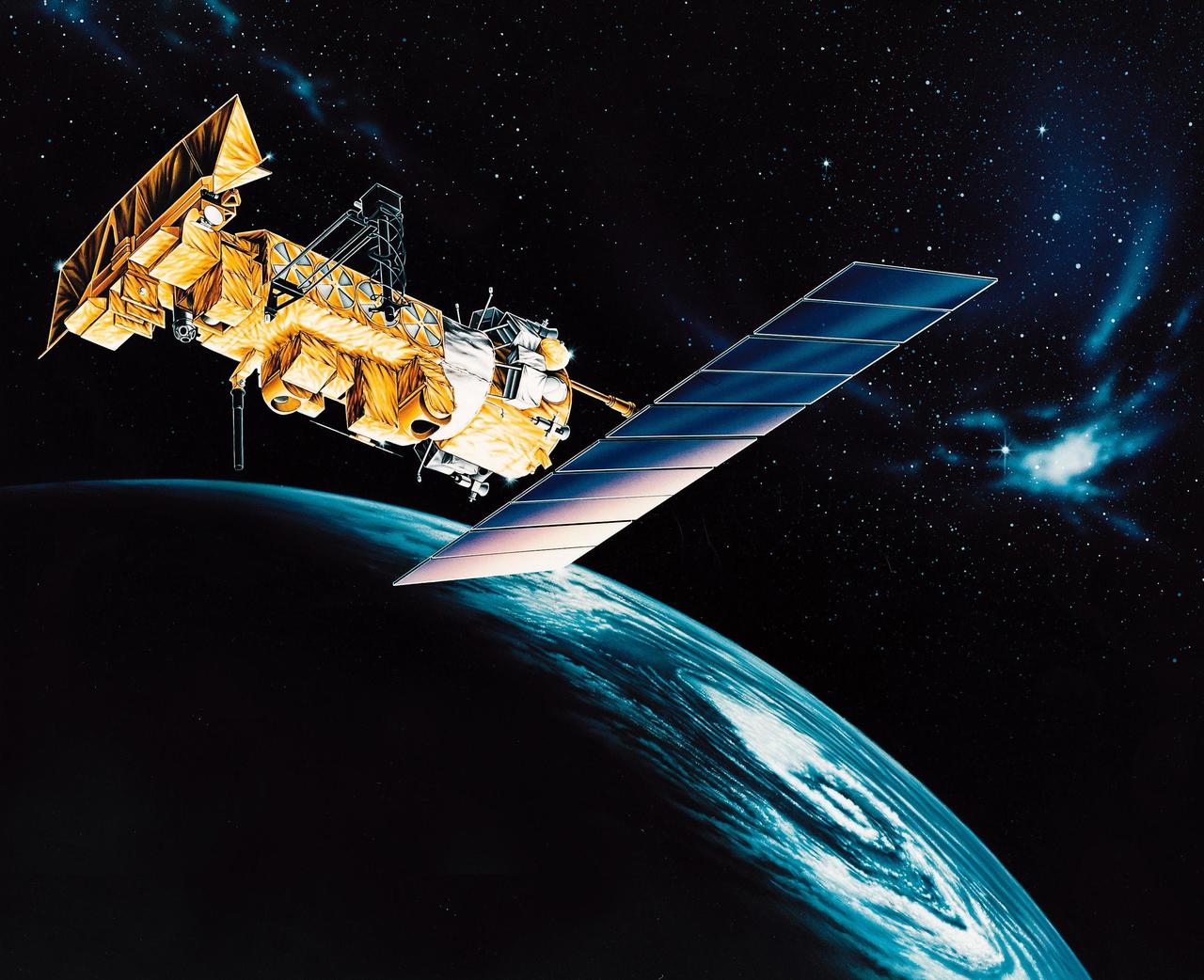

VANDENBERG AFB, CALIF. -- An artist's rendering of the NOAA-M spacecraft, a polar-orbiting Earth environmental observation satellite that will provide global data to NOAA's short- and long-range weather forecasting systems. Launch of the NOAA-M aboard a Titan II rocket is scheduled for June 24, 2002, from VAFB
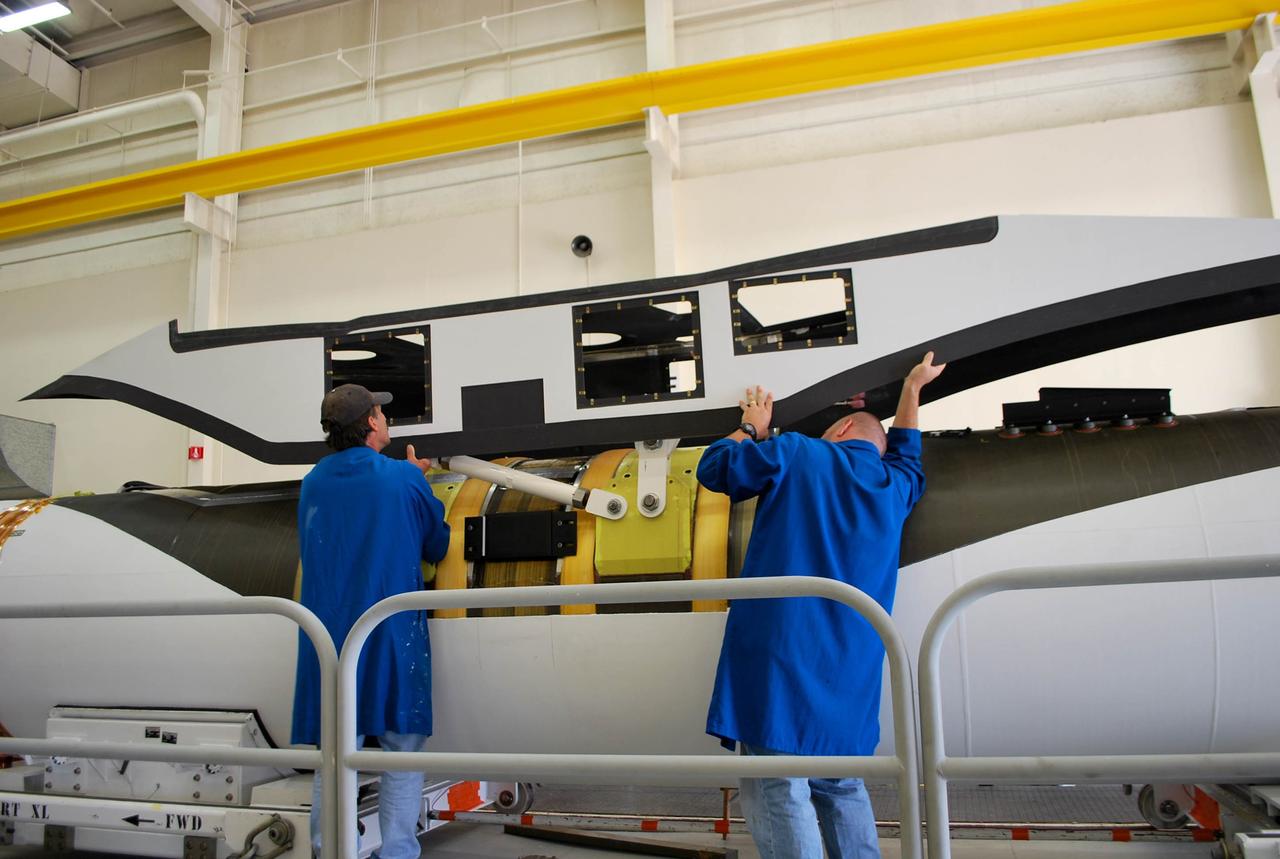

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians perform a fit check on an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket as the launcher is processed for the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph mission known as IRIS. The technicians are attaching the portion of the Pegasus that joins the wing to the fuselage, a piece called a fillet. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
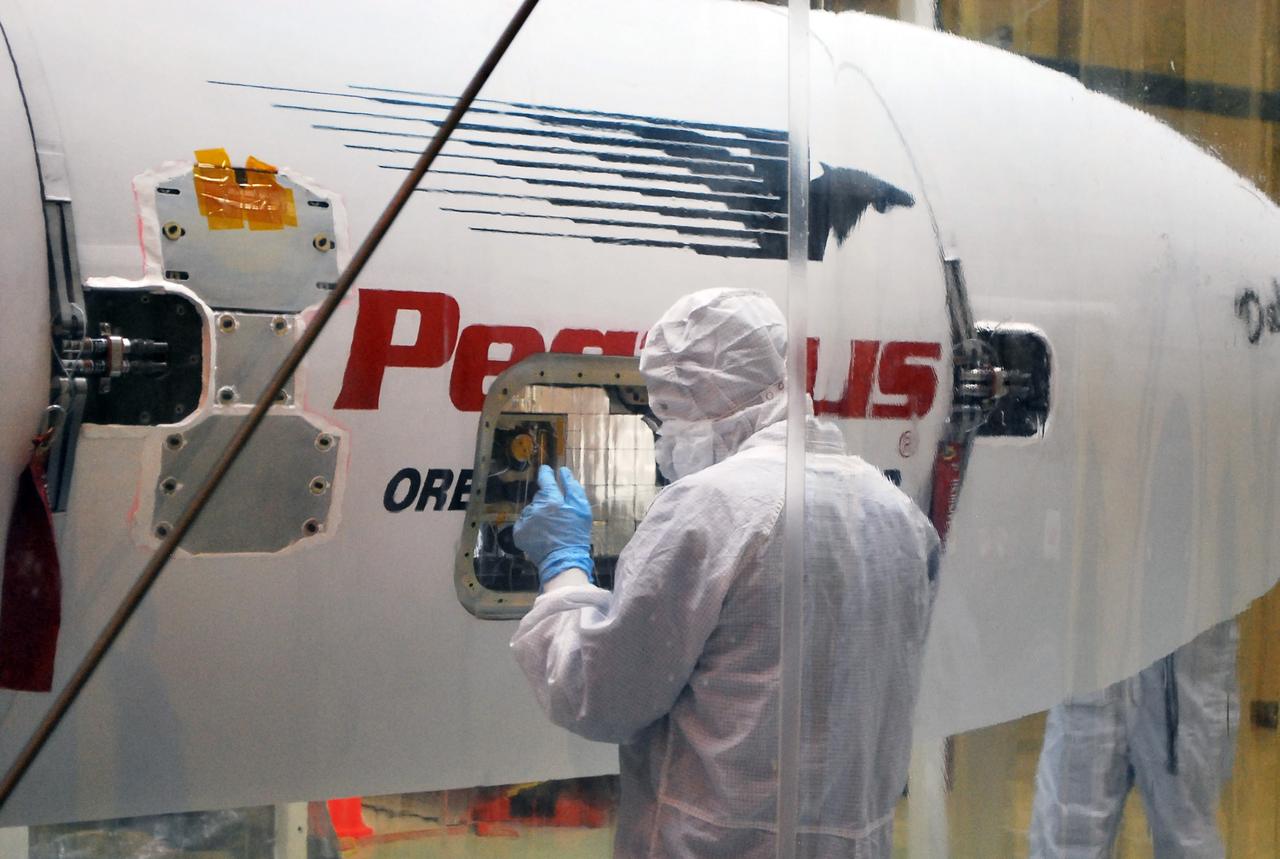

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A technicians checks the installation of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as processing continues for the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
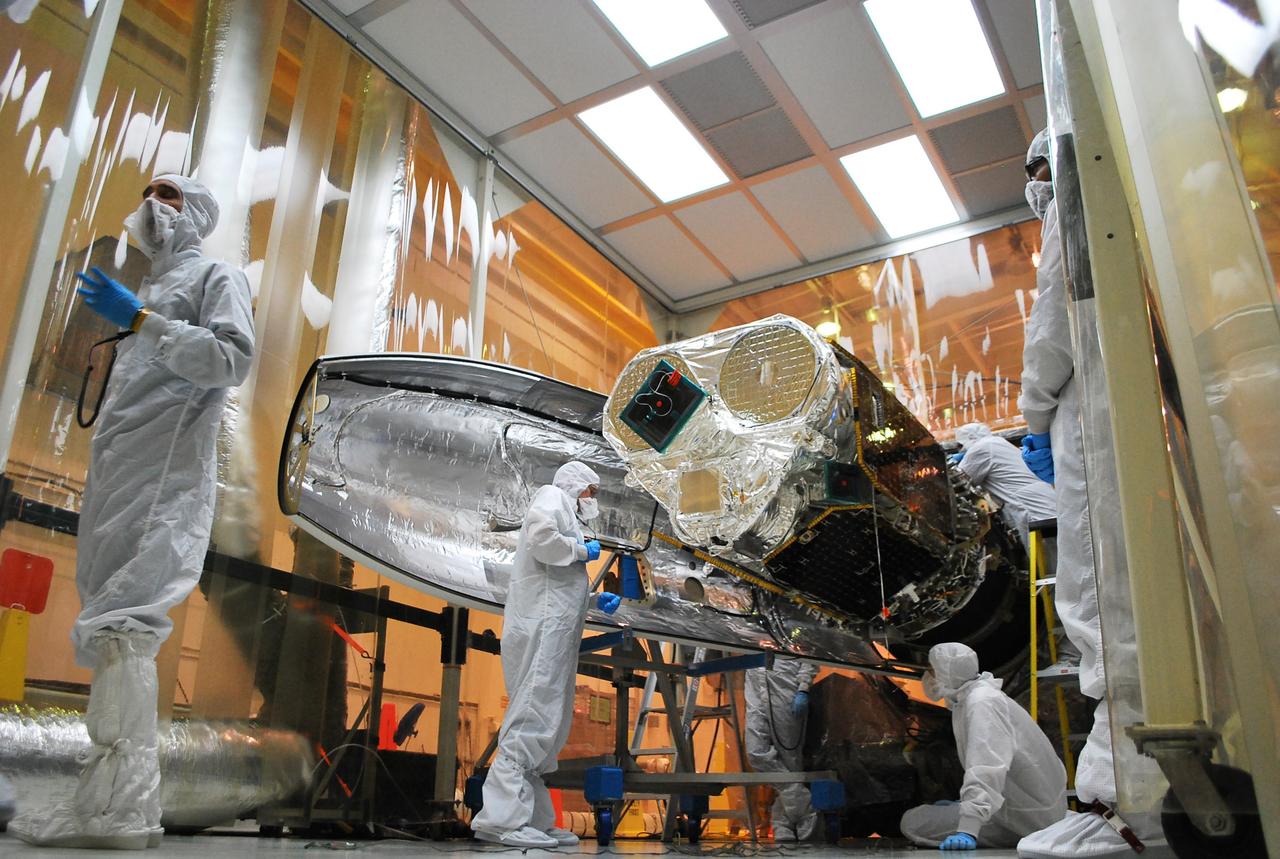

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install one half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
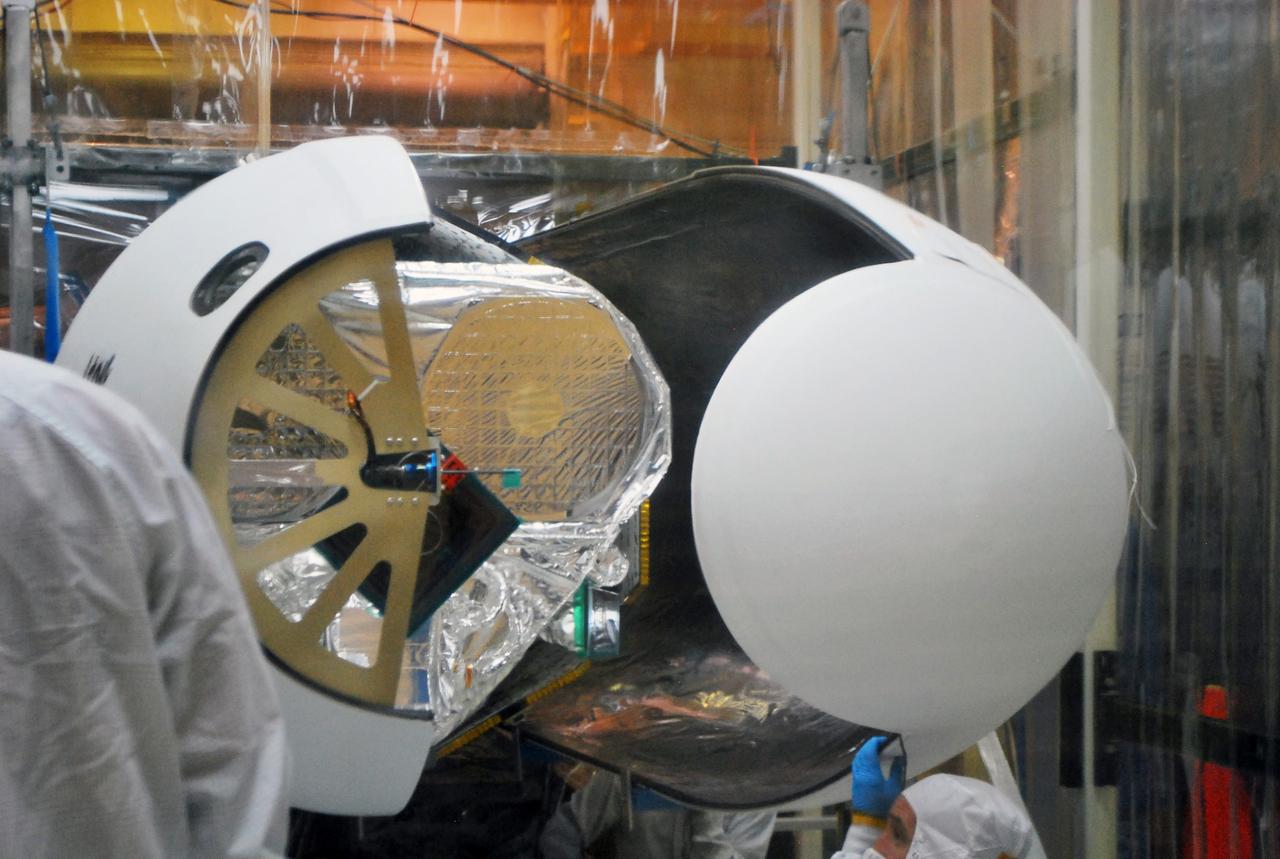

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians install the second half of the payload fairing over the NuSTAR spacecraft as they continue to process the spacecraft and its Pegasus rocket for launch. NuSTAR stands for Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
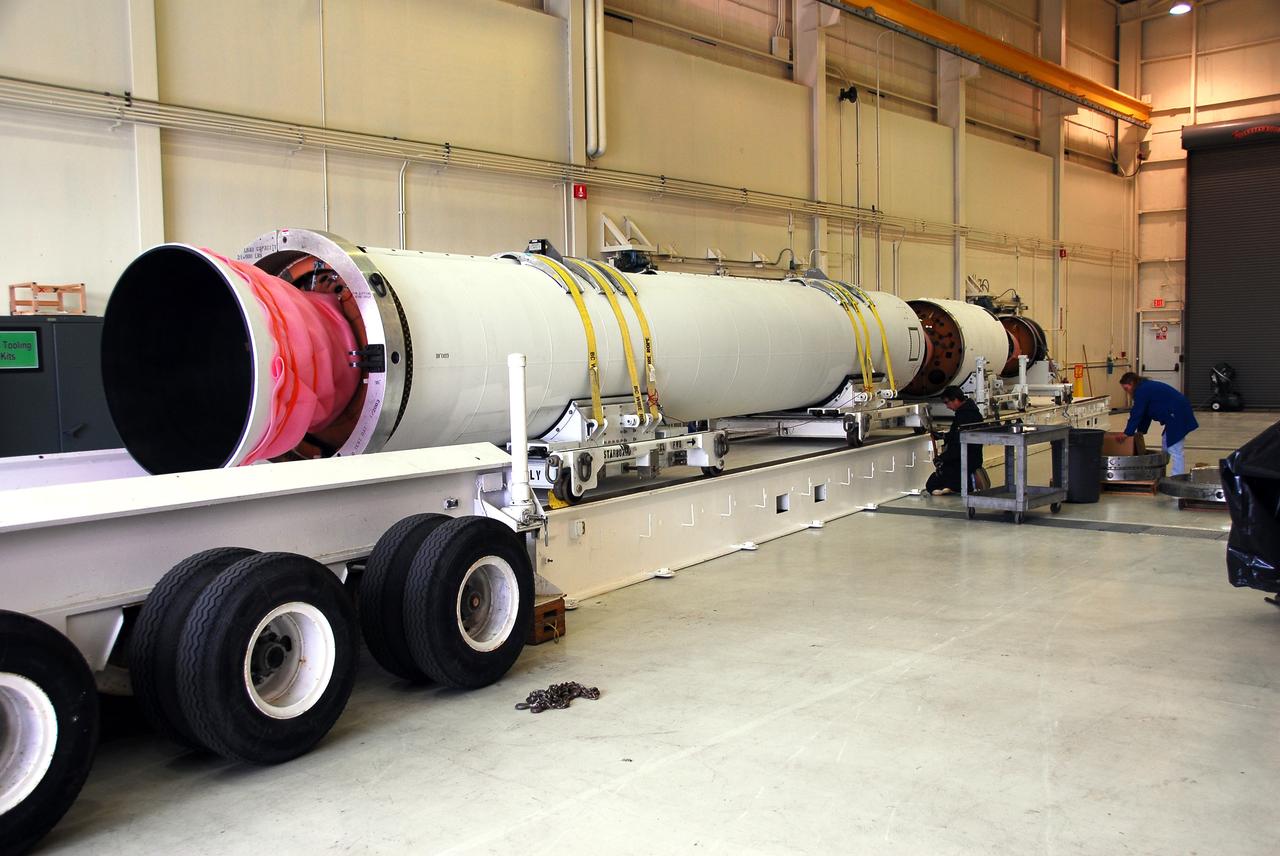

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg AFB, the first stage of the Taurus rocket is being moved onto the stationary rails in Building 1555's west bay. The Taurus will launch the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, in 2009. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
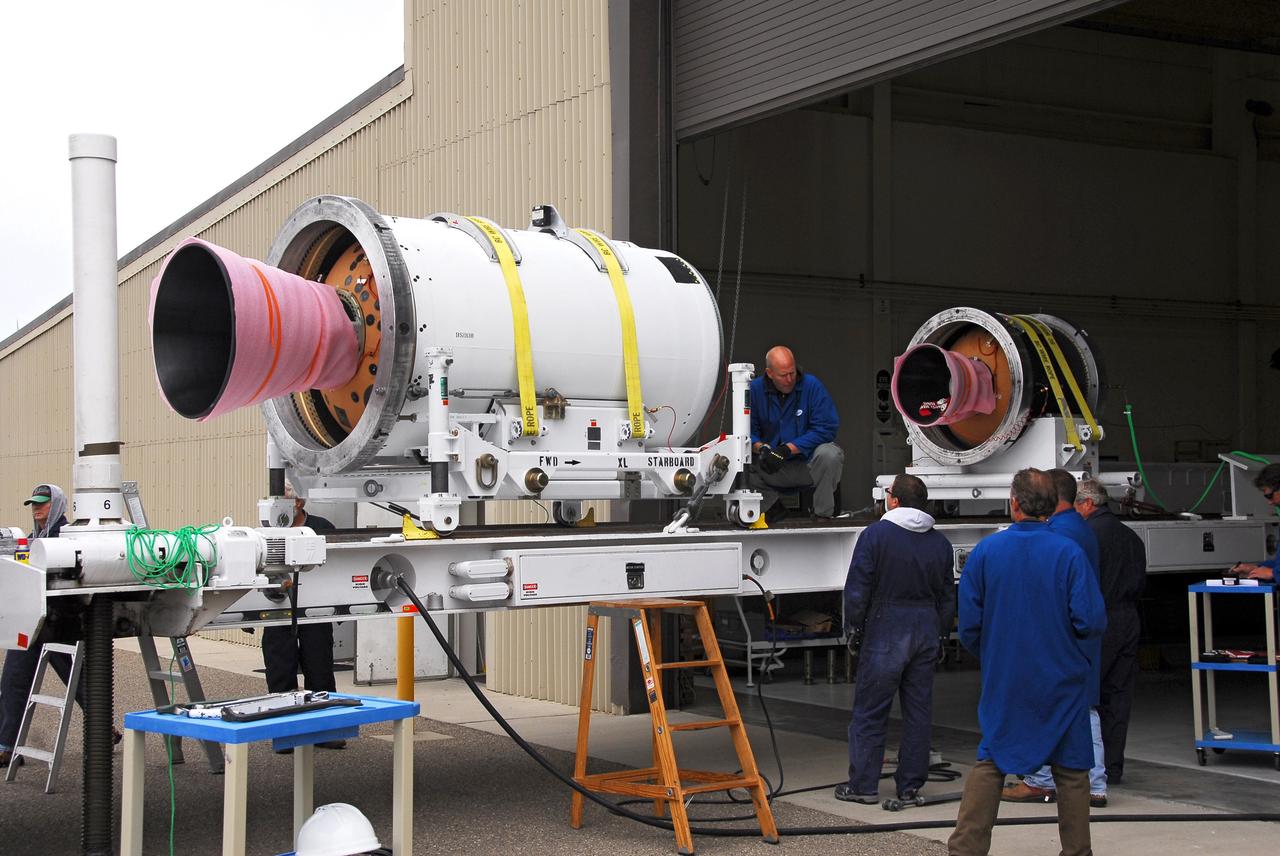

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg AFB, the second stage of the Taurus rocket moves behind the third stage in front of the Building 1555's west bay. The Taurus will launch the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, in 2009. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin