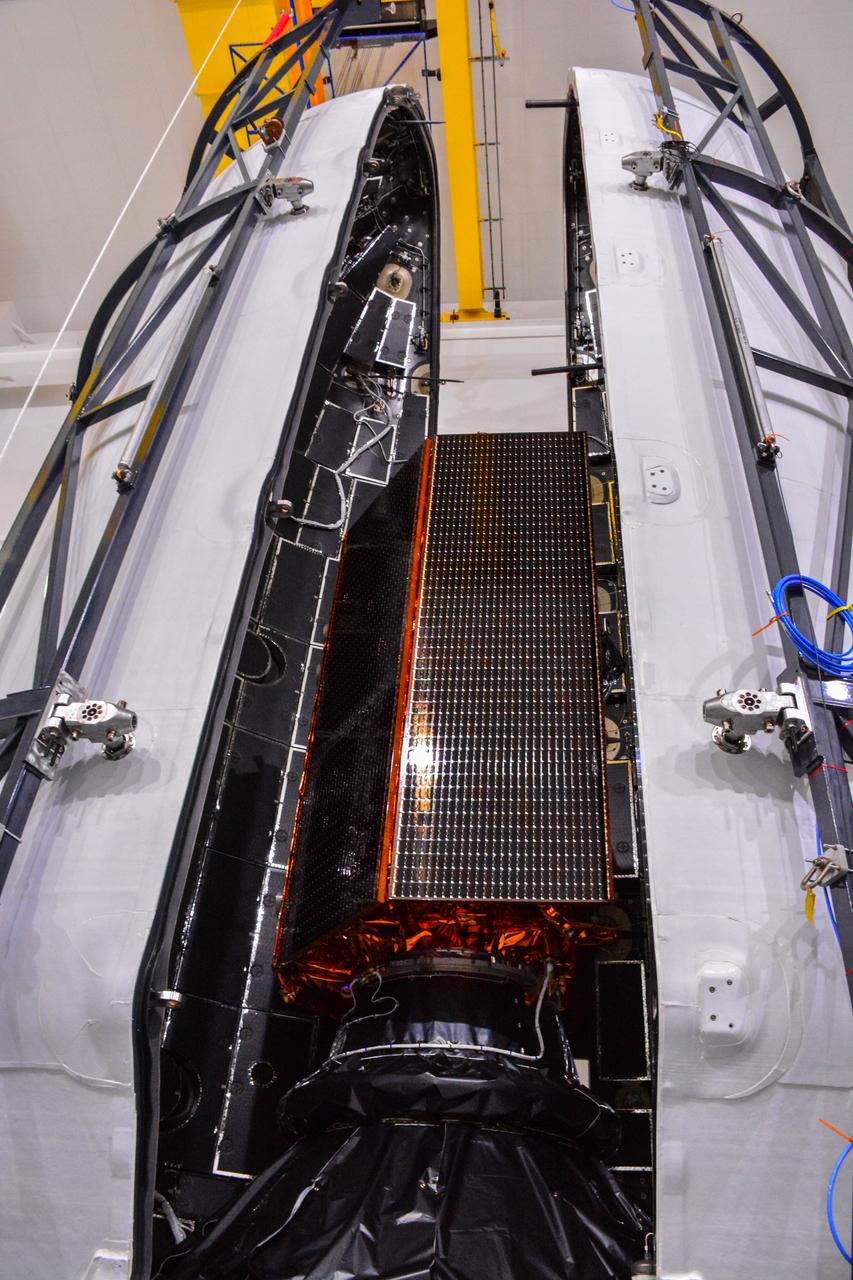
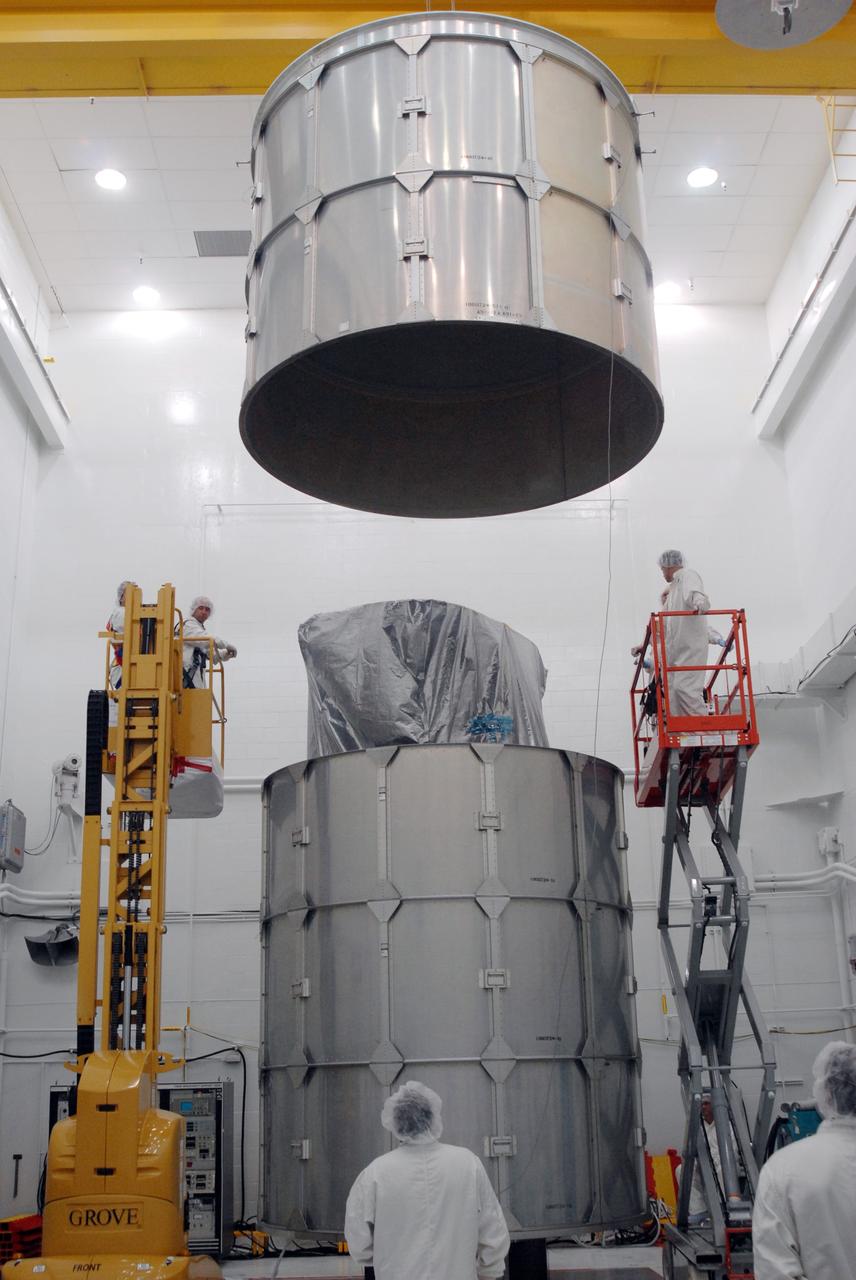
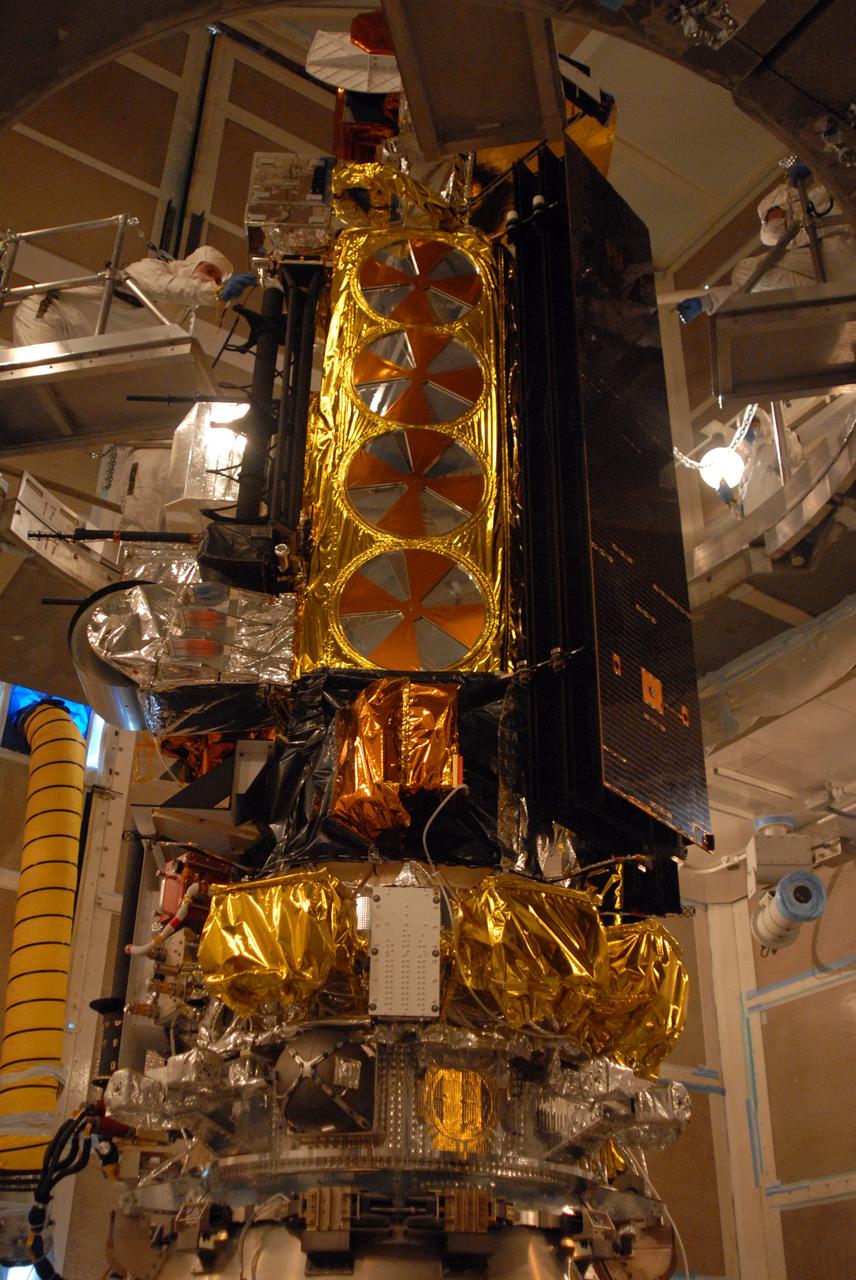
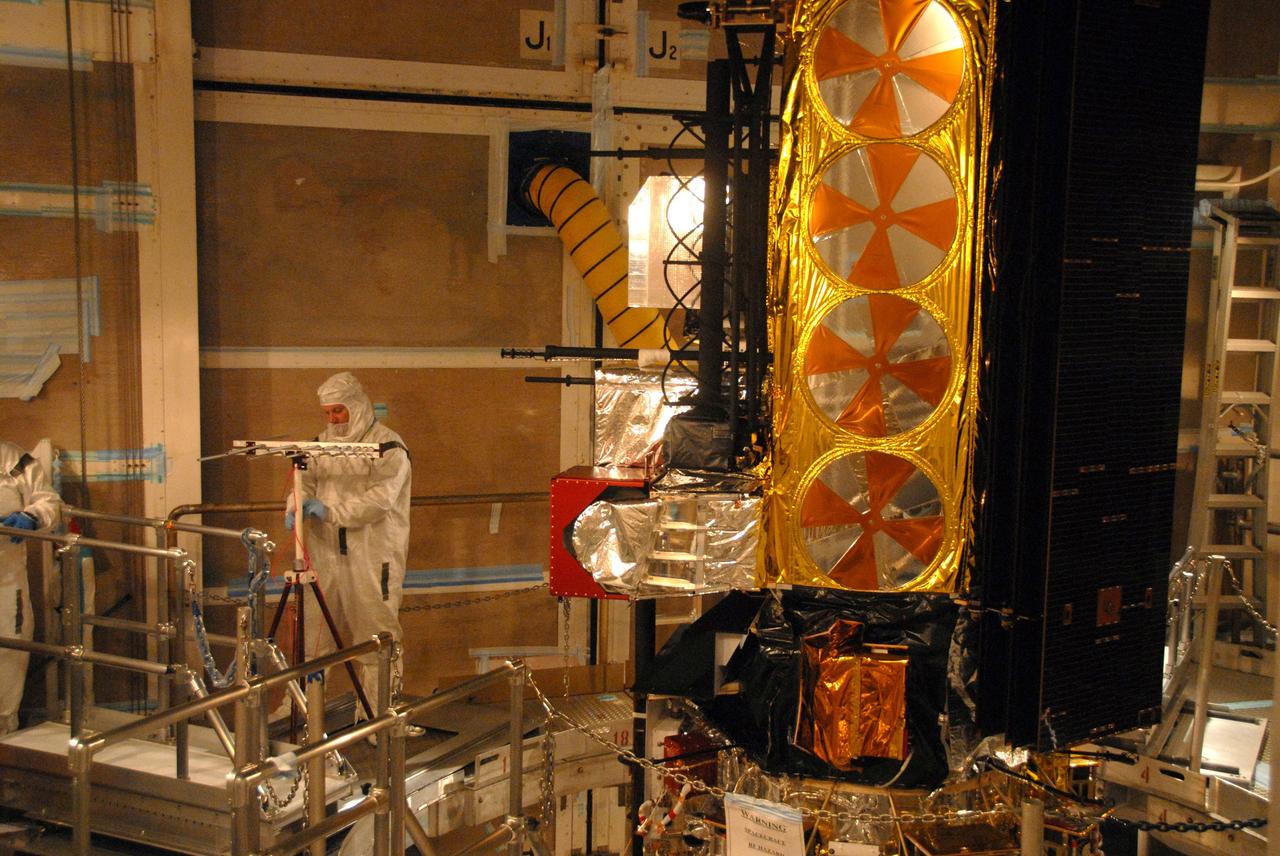
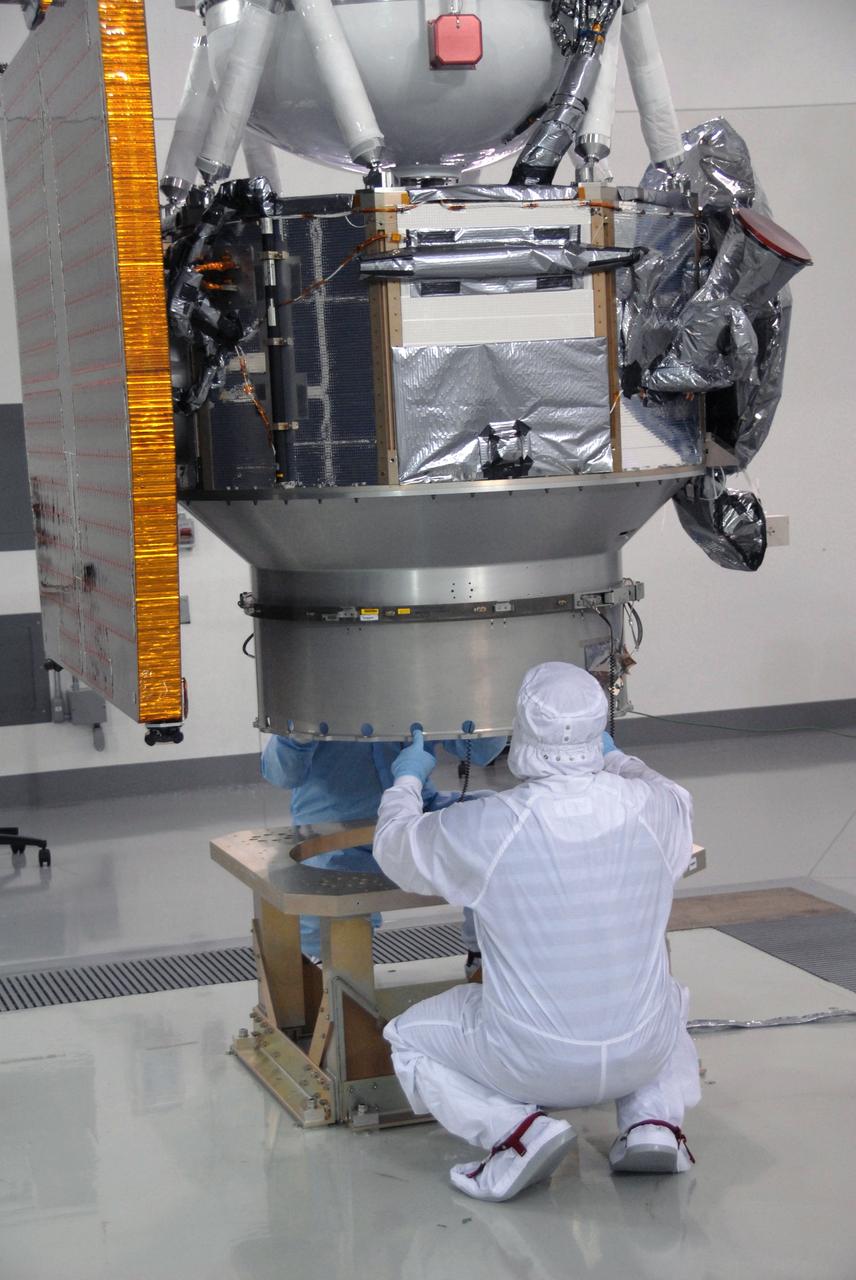
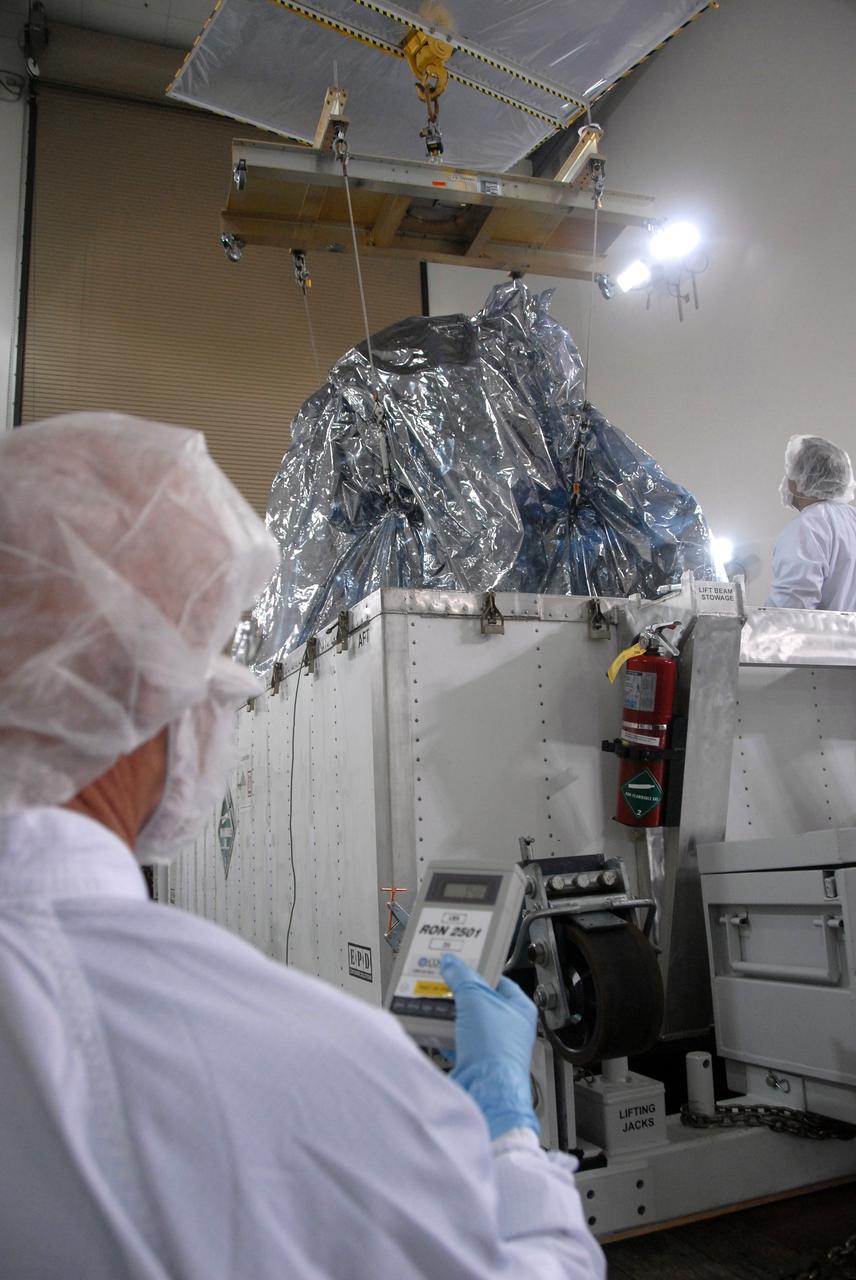
The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite is encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing on Nov. 3, 2020, inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite is being encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing on Nov. 3, 2020, inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite is encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing on Nov. 3, 2020, inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite is being encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing on Nov. 3, 2020, inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
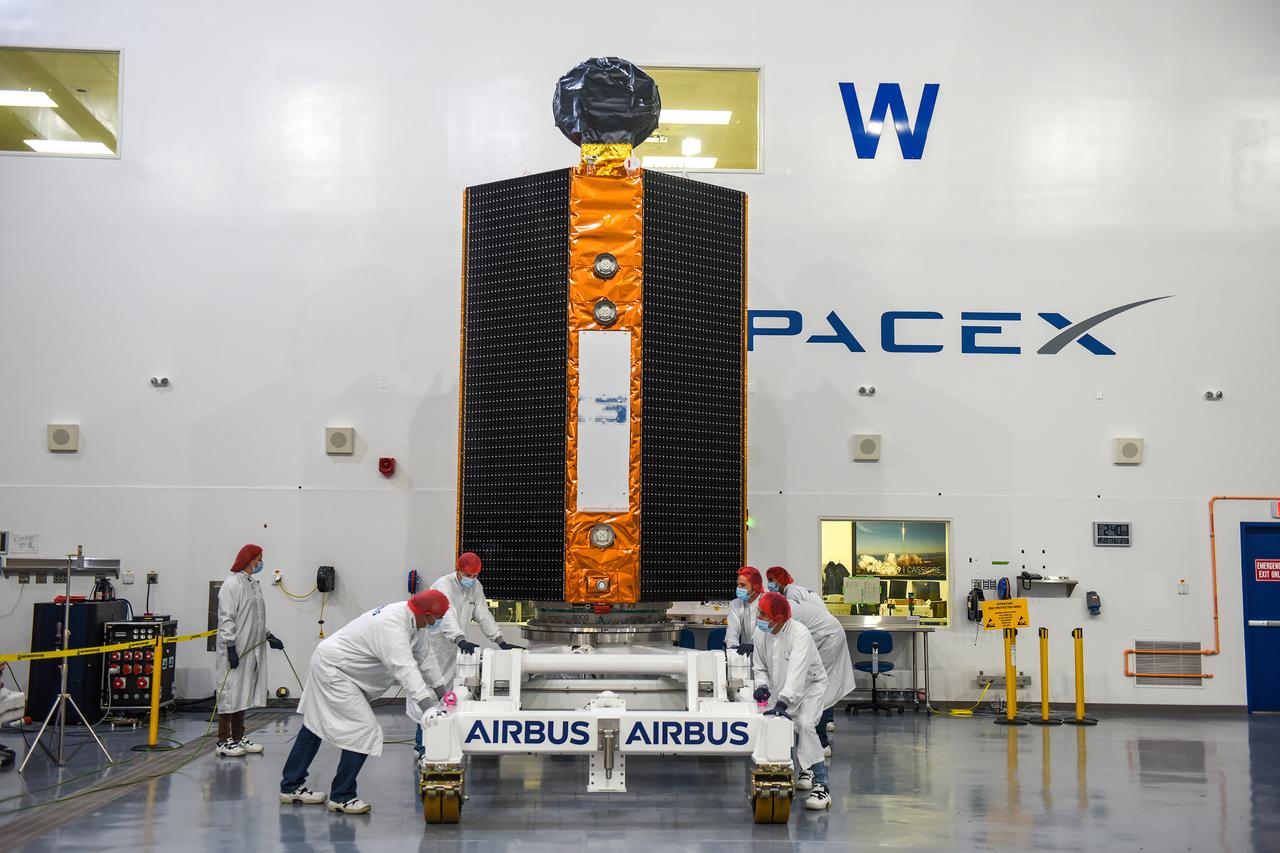

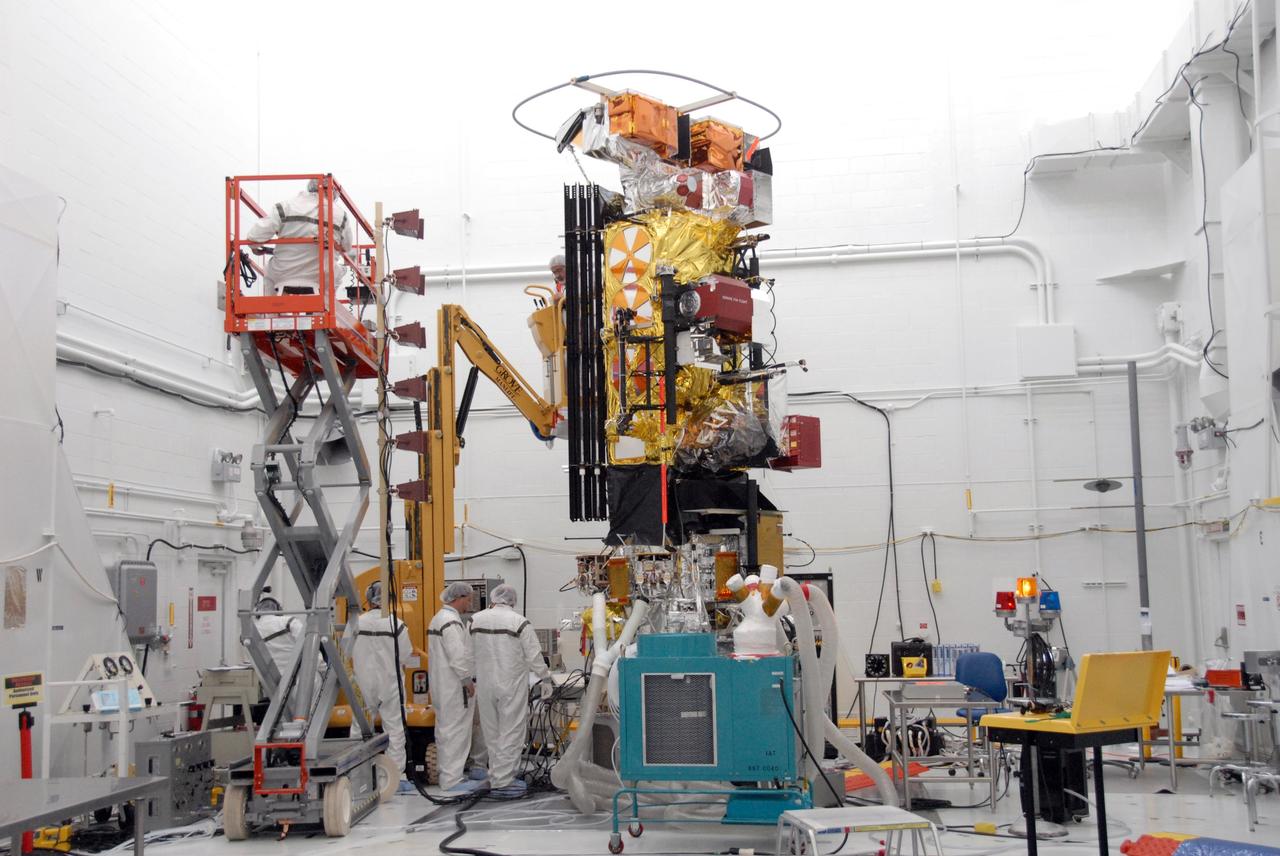
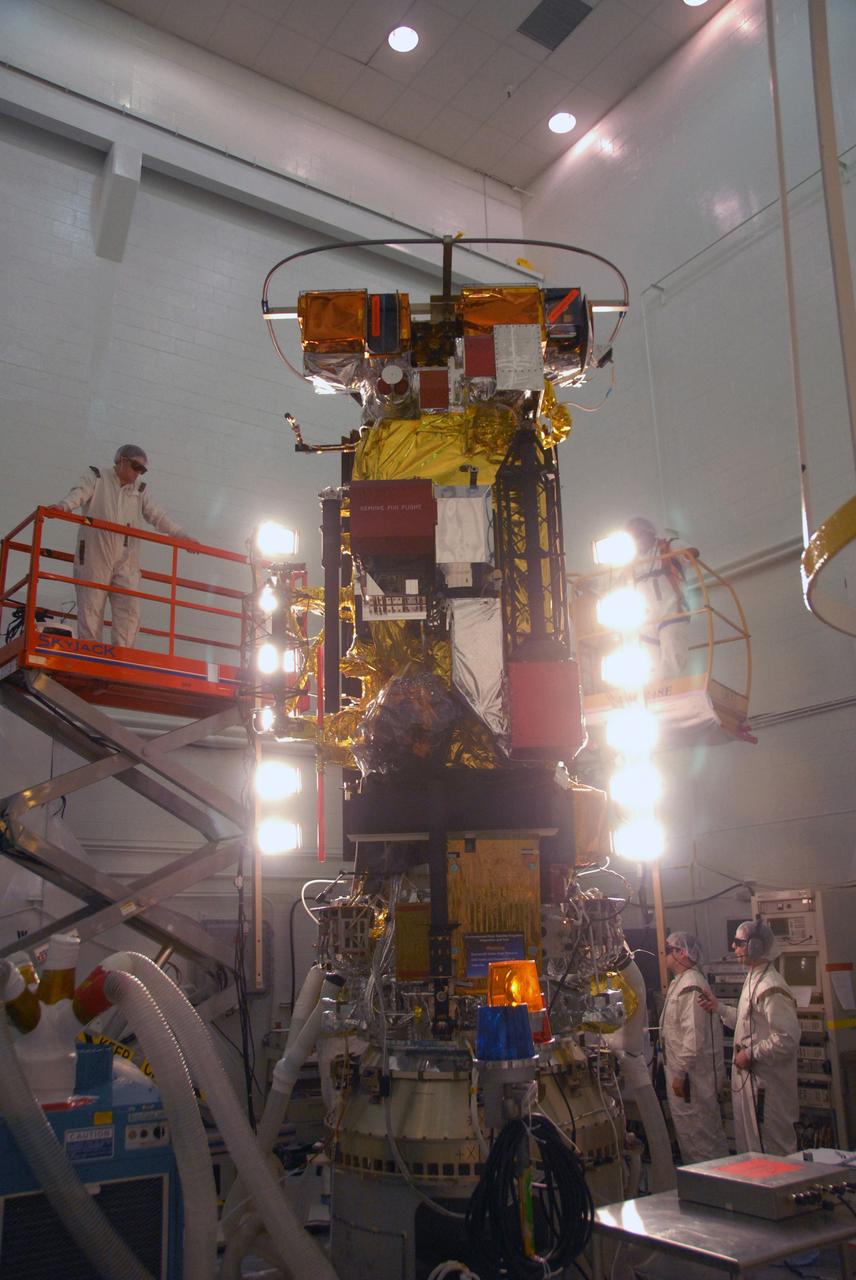
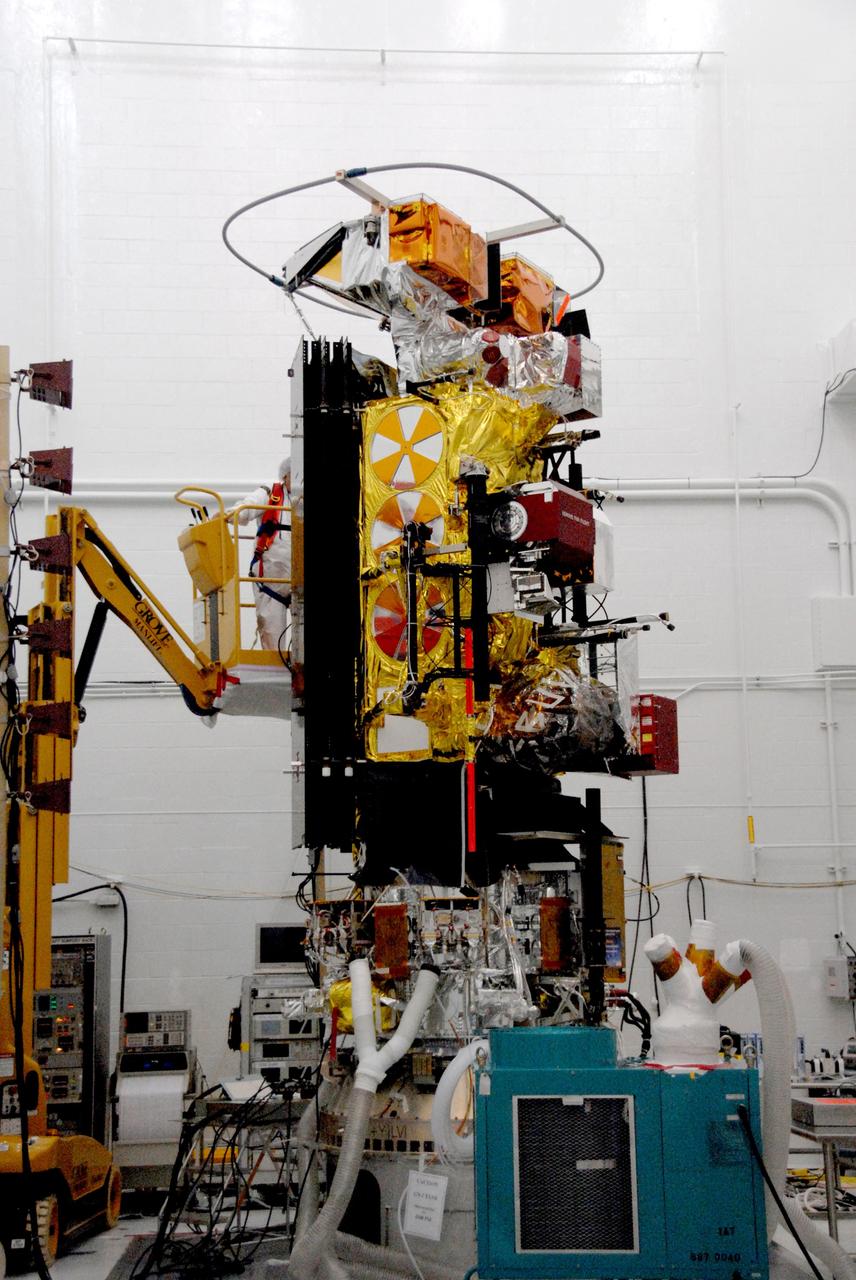
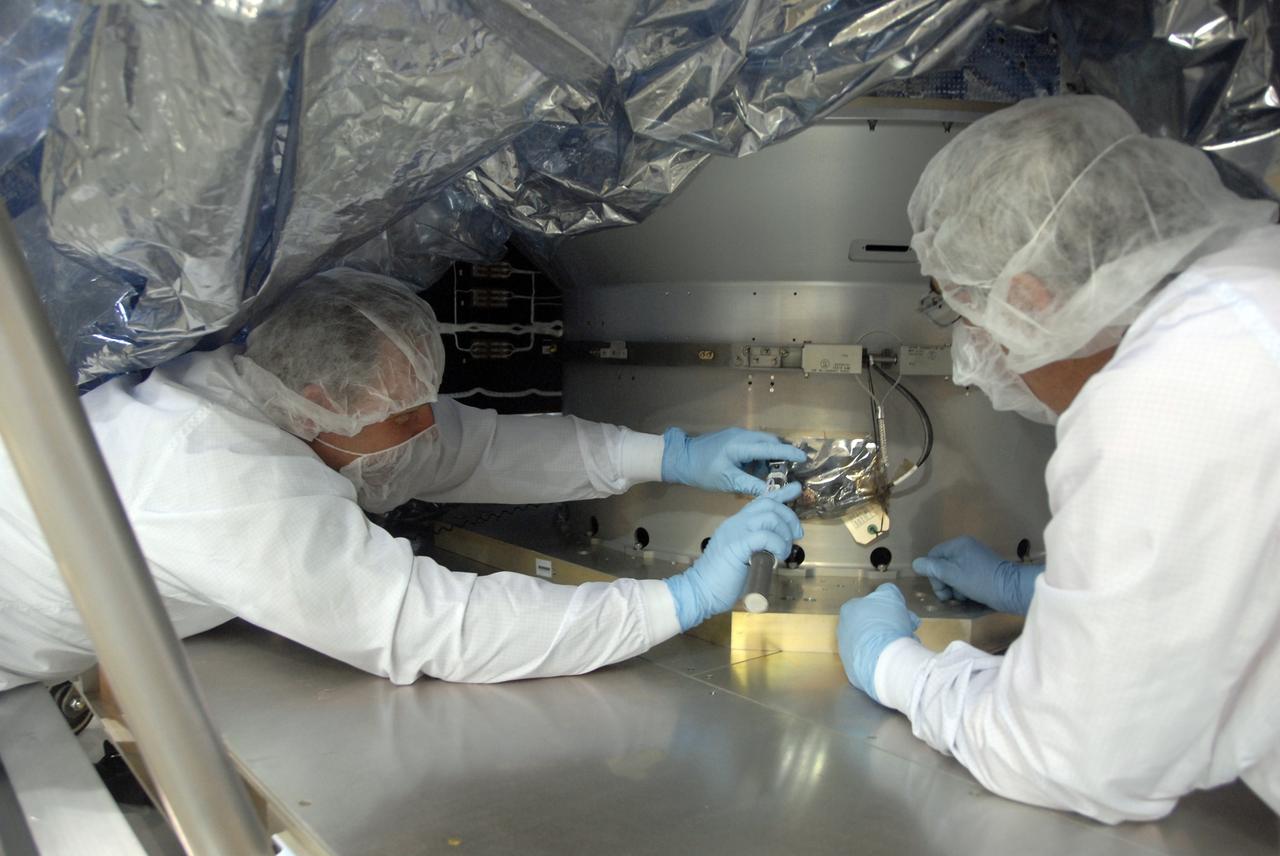
Airbus Defence and Space technicians position the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft for fueling inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California on Oct. 22, 2020. The mission is an international collaboration and will be the first of two satellites launched to continue observing changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is scheduled to launch from VAFB atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
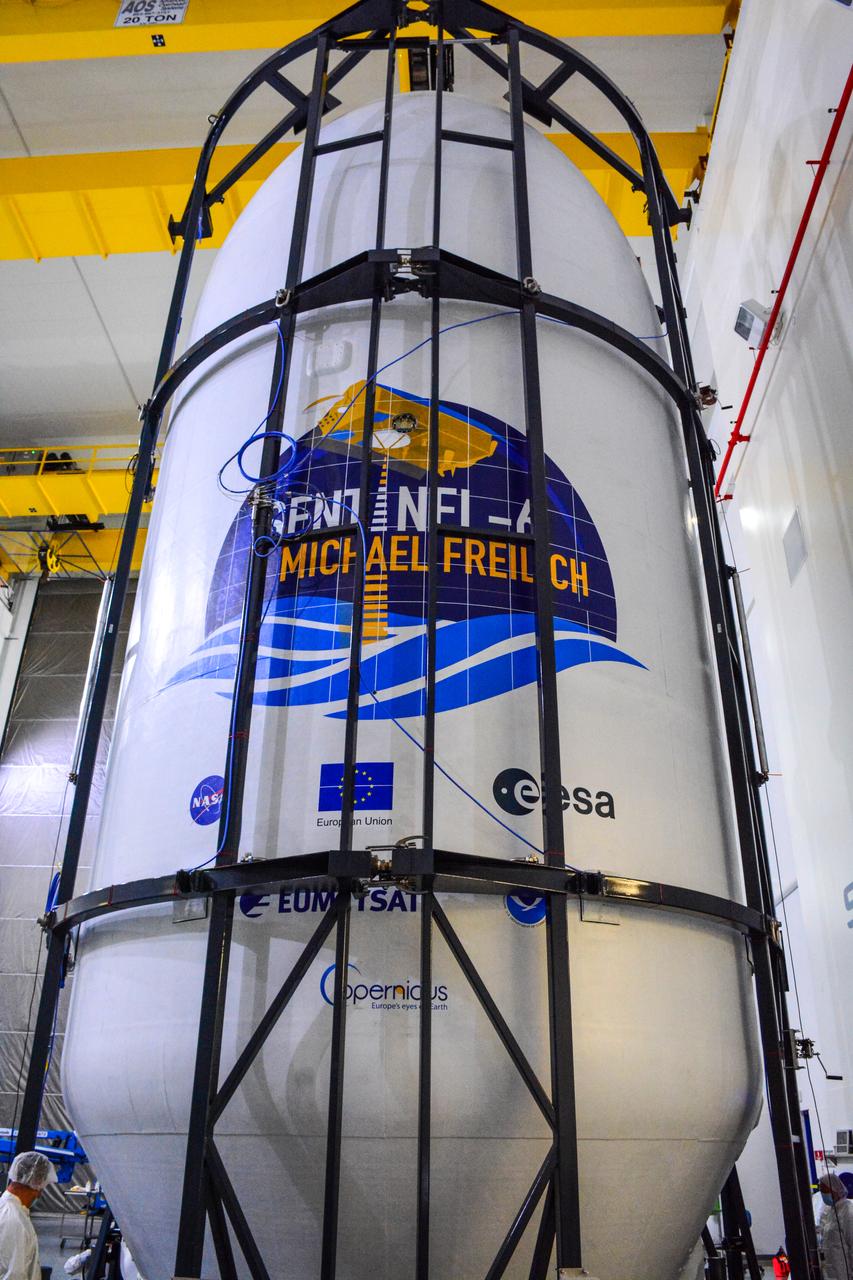

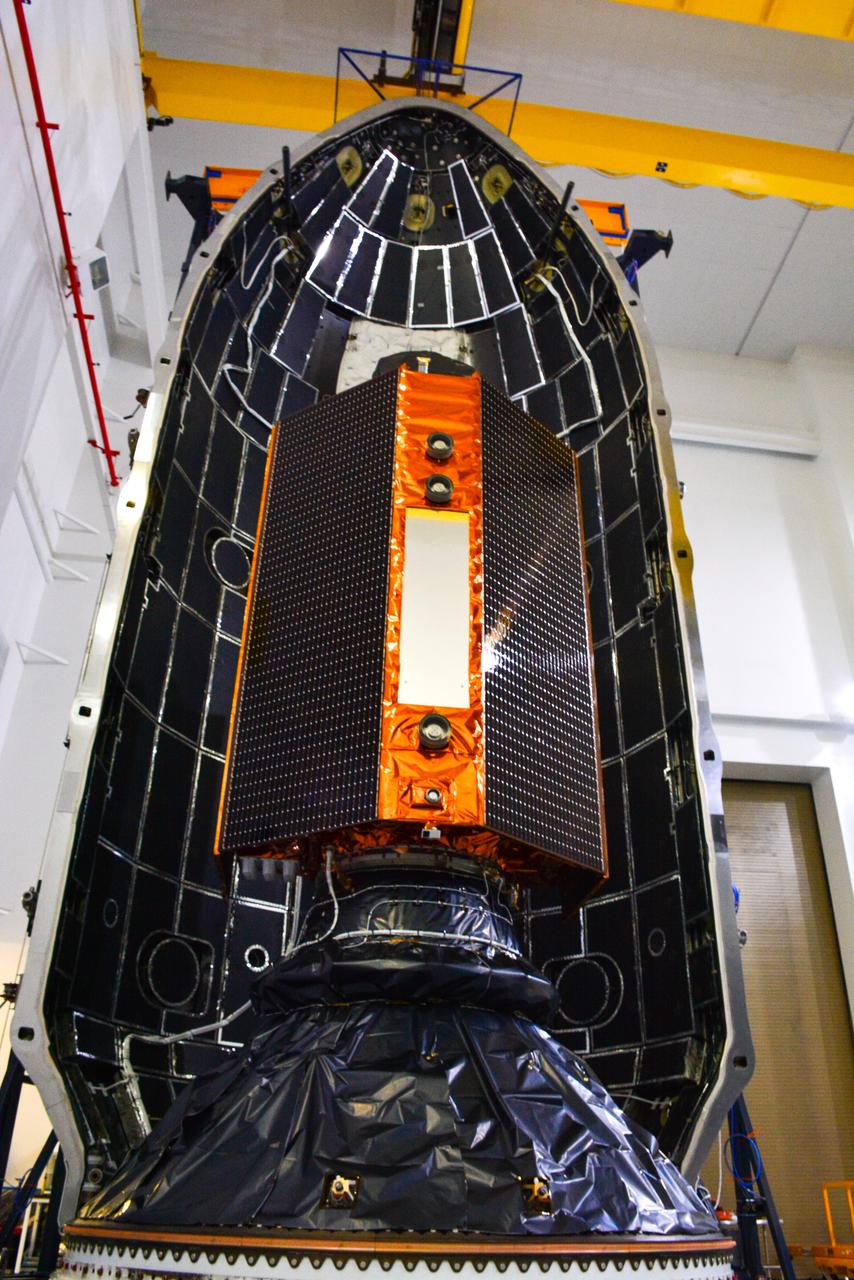
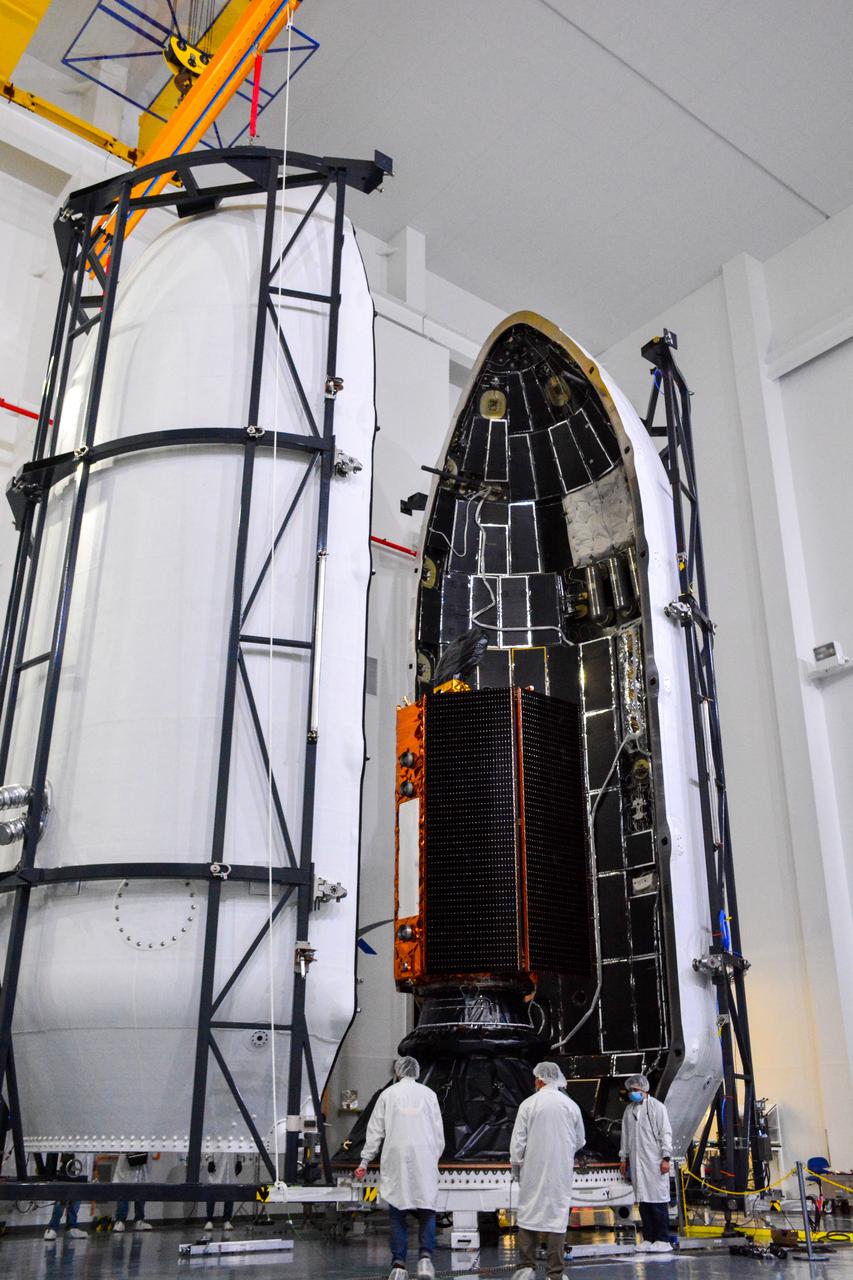
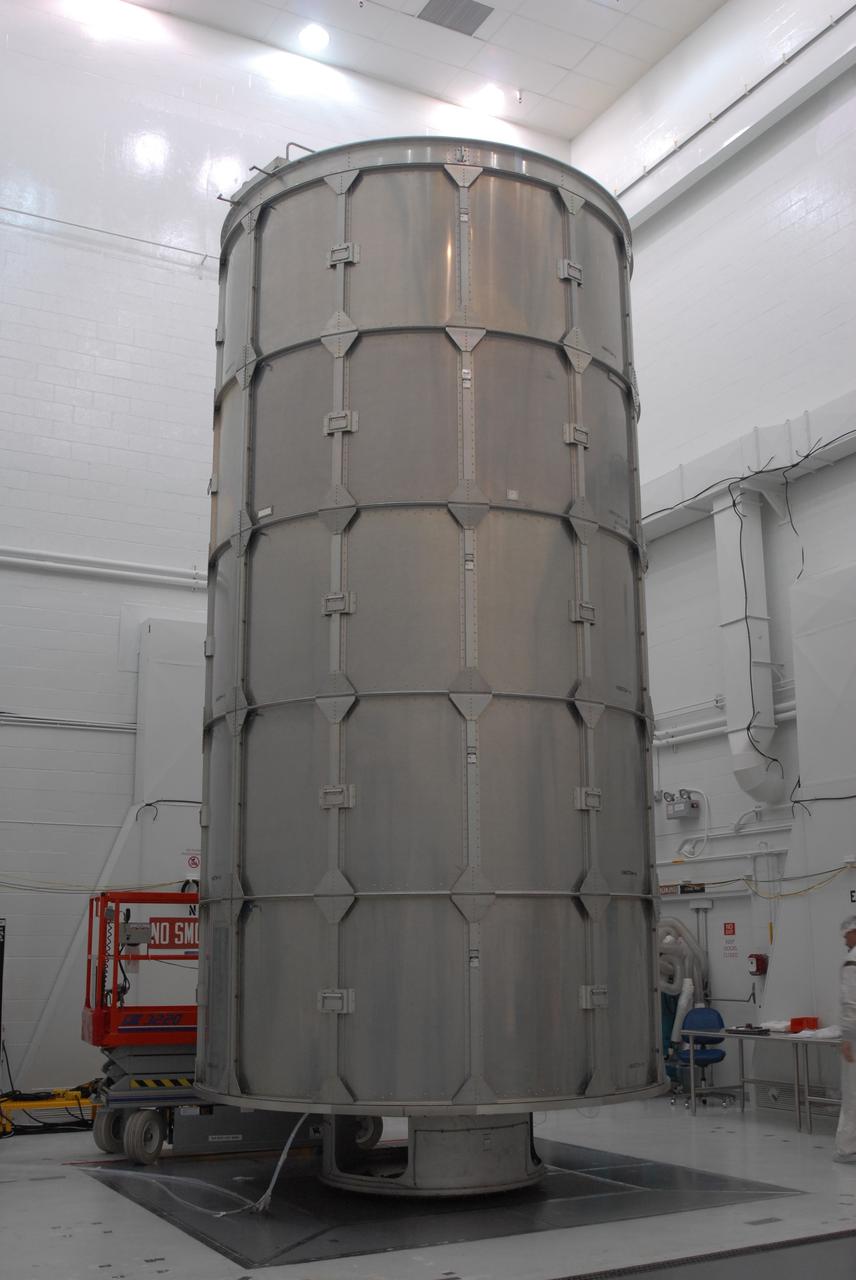
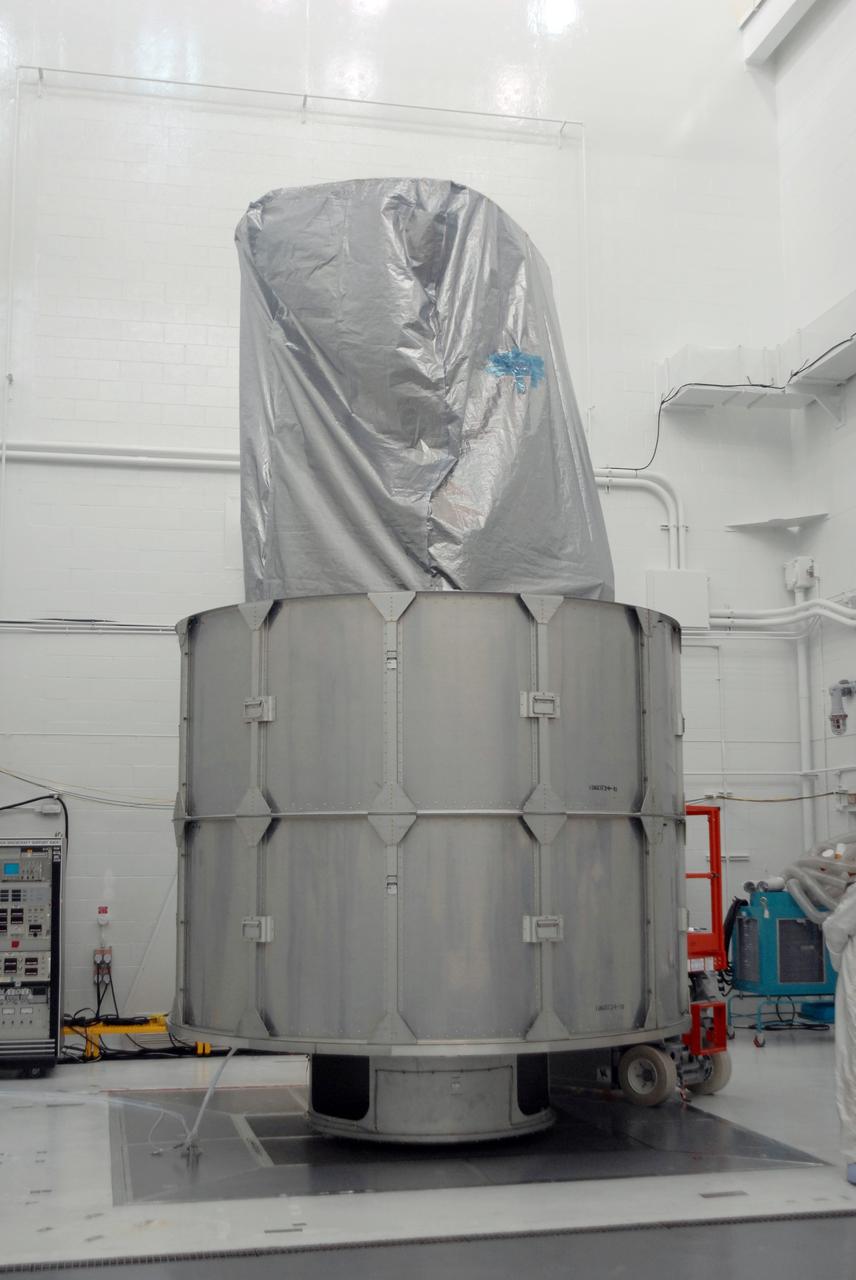
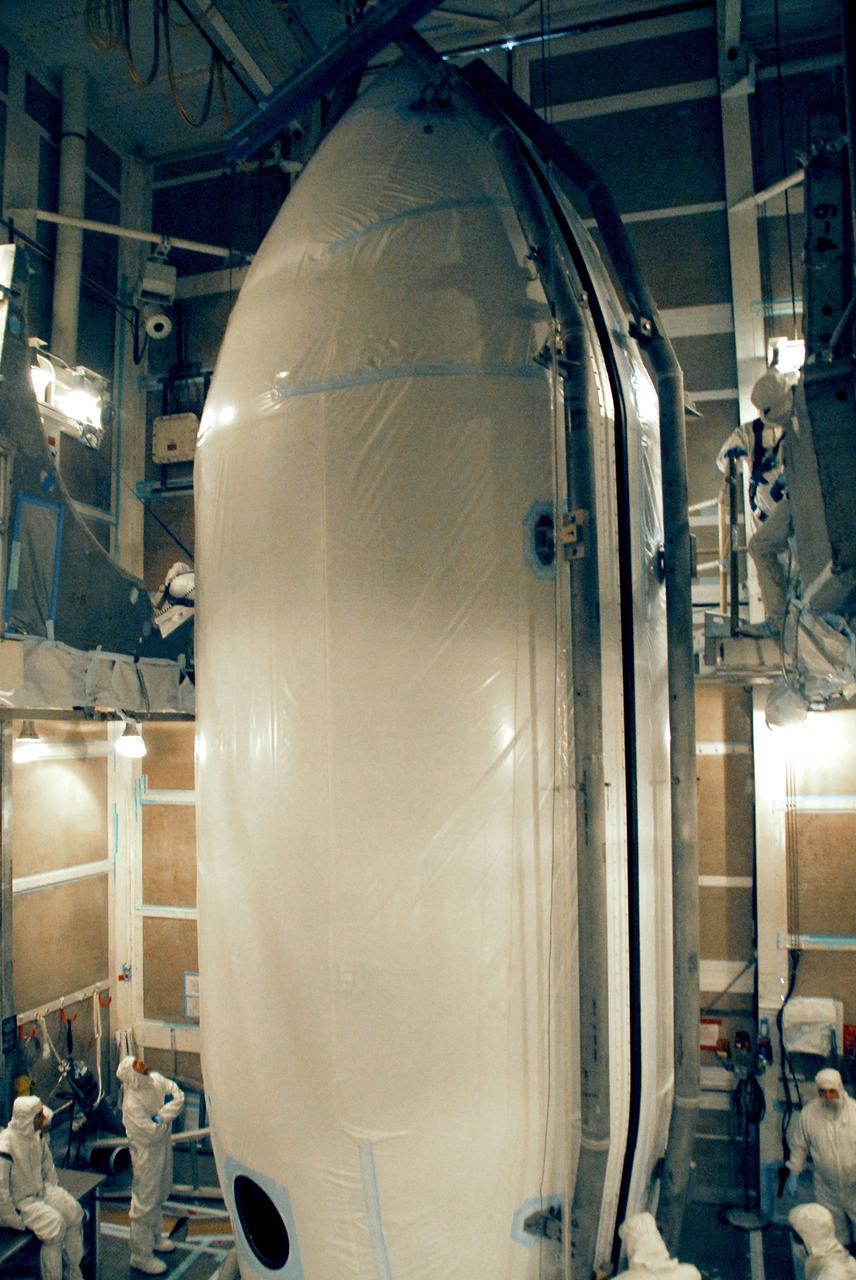
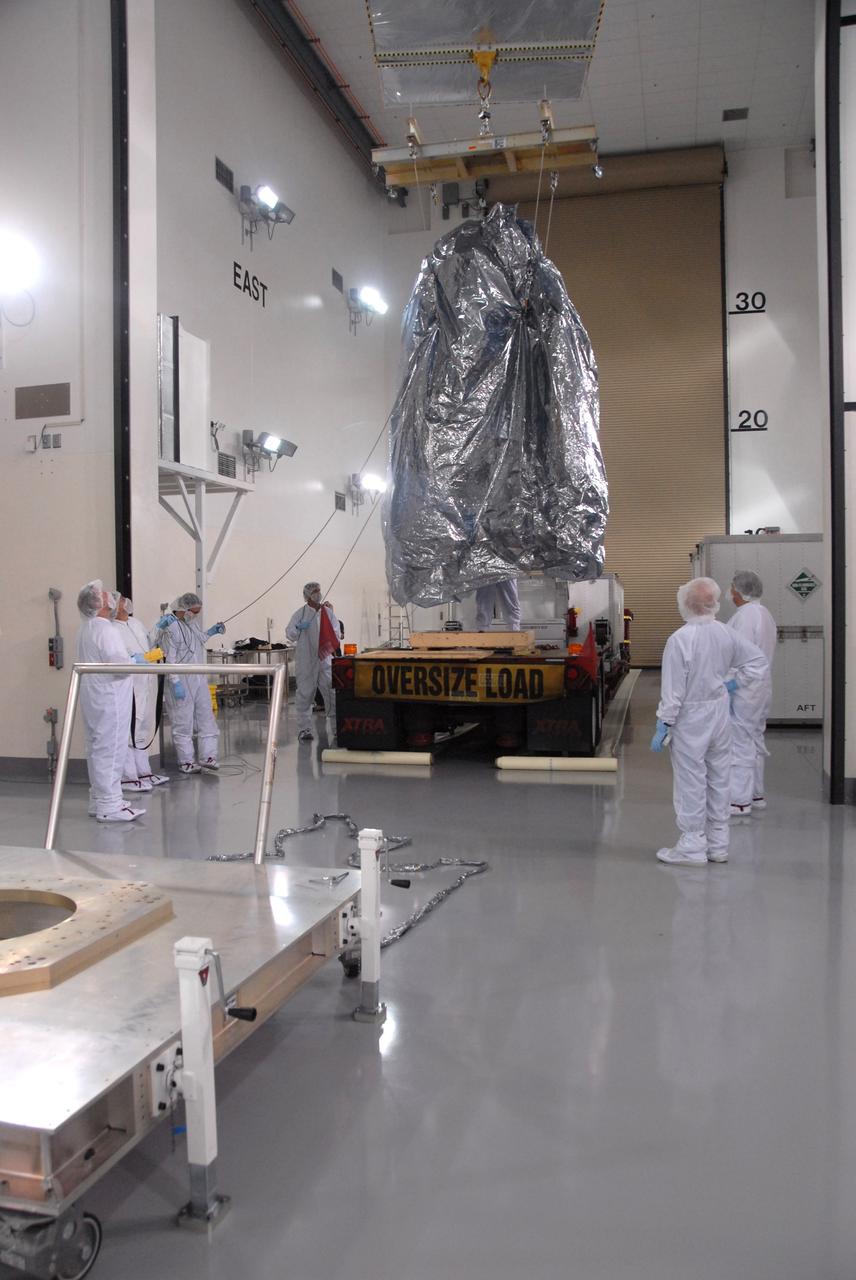
The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich ocean-monitoring satellite, secured inside the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket’s payload fairing, is shown inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California following encapsulation on Nov. 3, 2020. Sentinel-6 is scheduled to launch on Nov. 21, 2020, at 12:17 p.m. EST (9:17 a.m. PST), from Space Launch Complex 4E at VAFB. The Launch Services Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
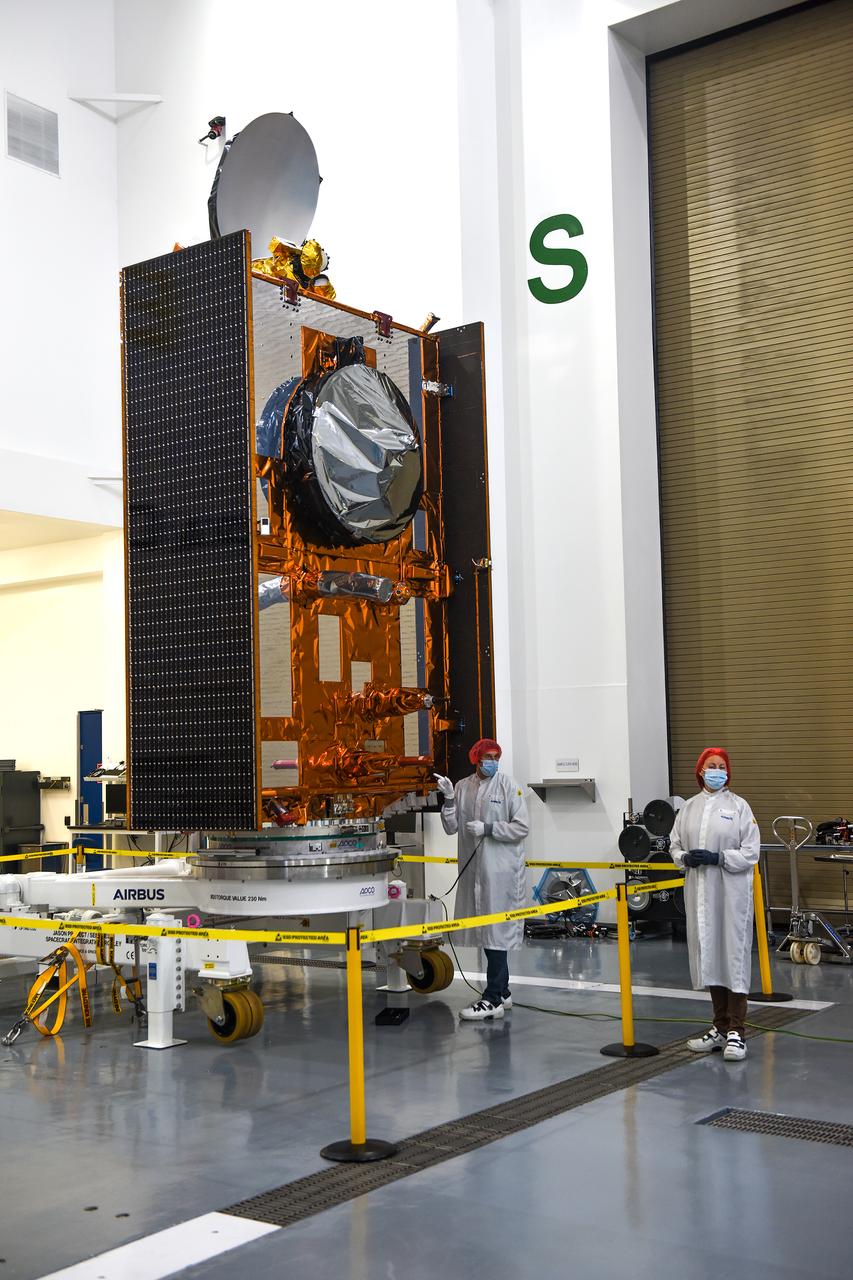

Airbus Defence and Space technicians position the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft for fueling inside SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California on Oct. 22, 2020. The mission is an international collaboration and will be the first of two satellites launched to continue observing changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is scheduled to launch from VAFB atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
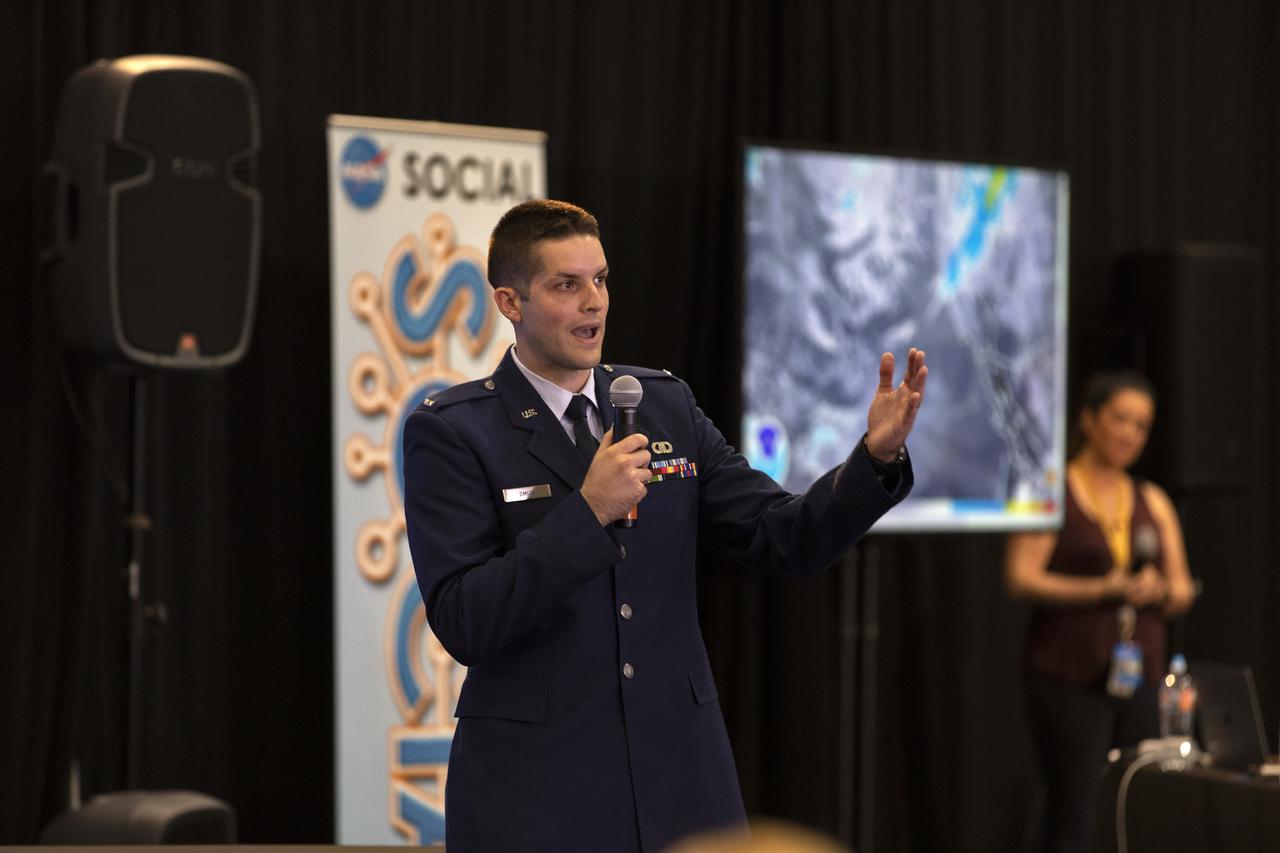

1st Lt. Daniel Smith, launch weather officer, 30th Space Wing, Vandenberg Air Force Base, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
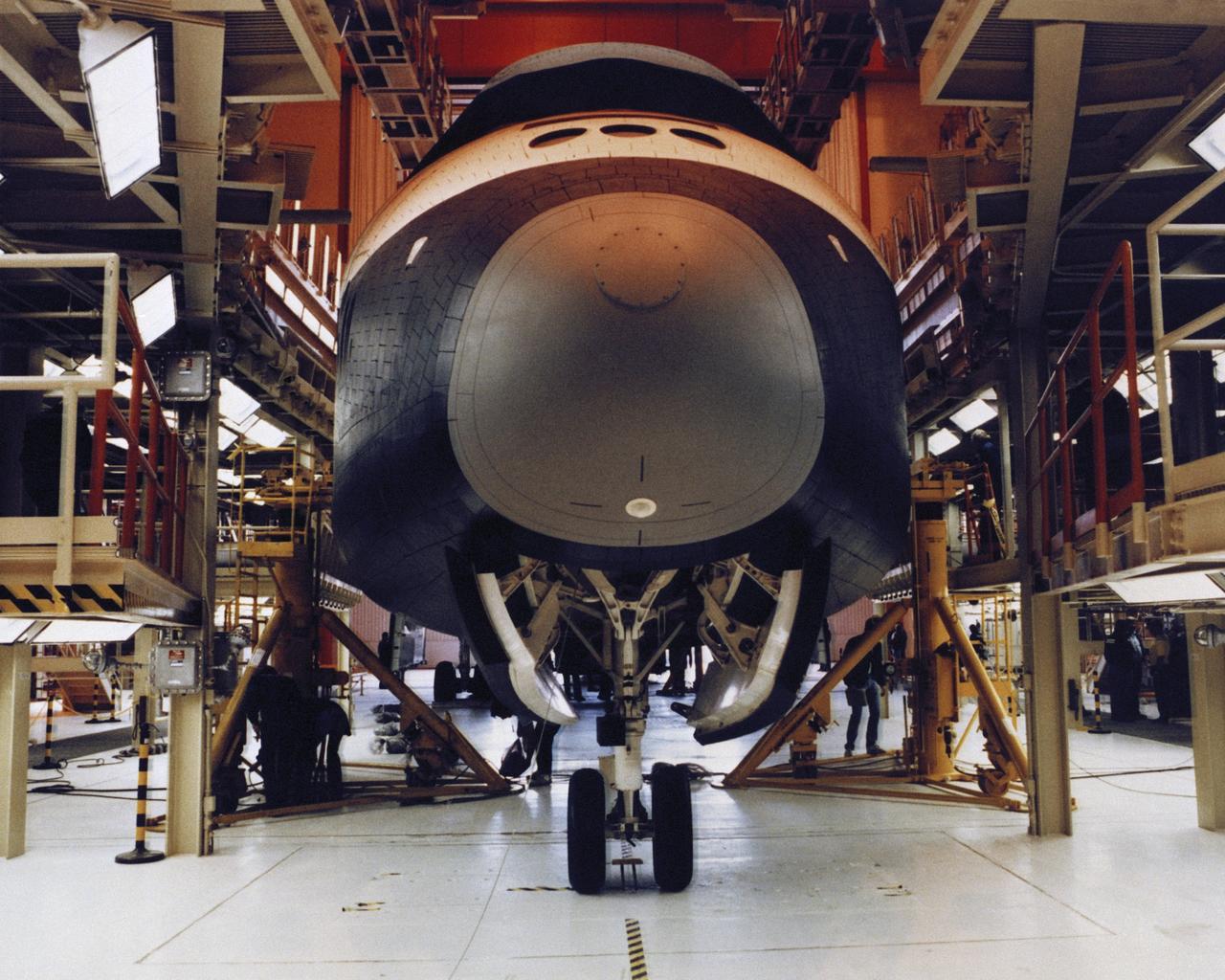

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise in California at VAFB. Photo credit: NASA
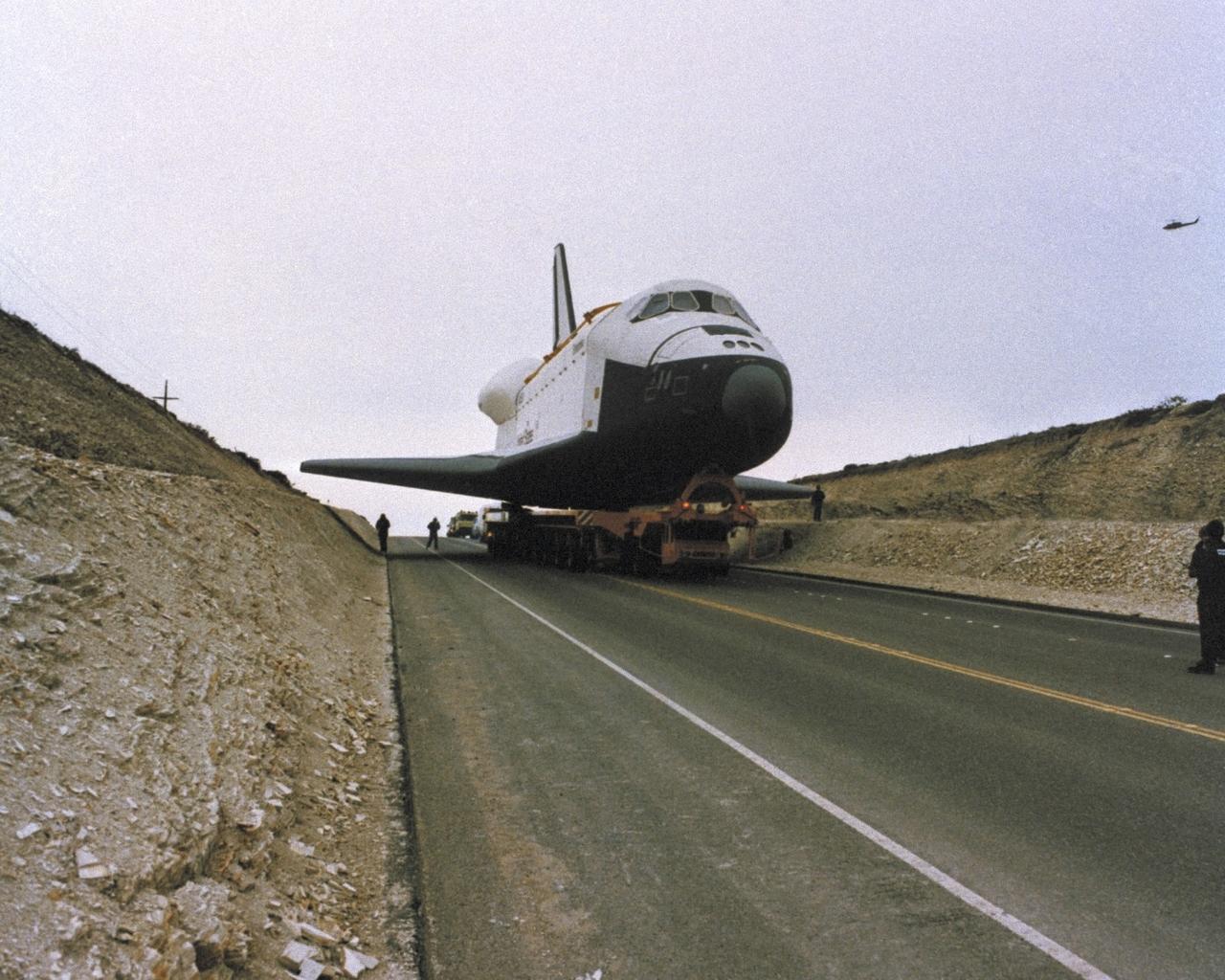

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Enterprise in California at VAFB. Photo Credit: NASA
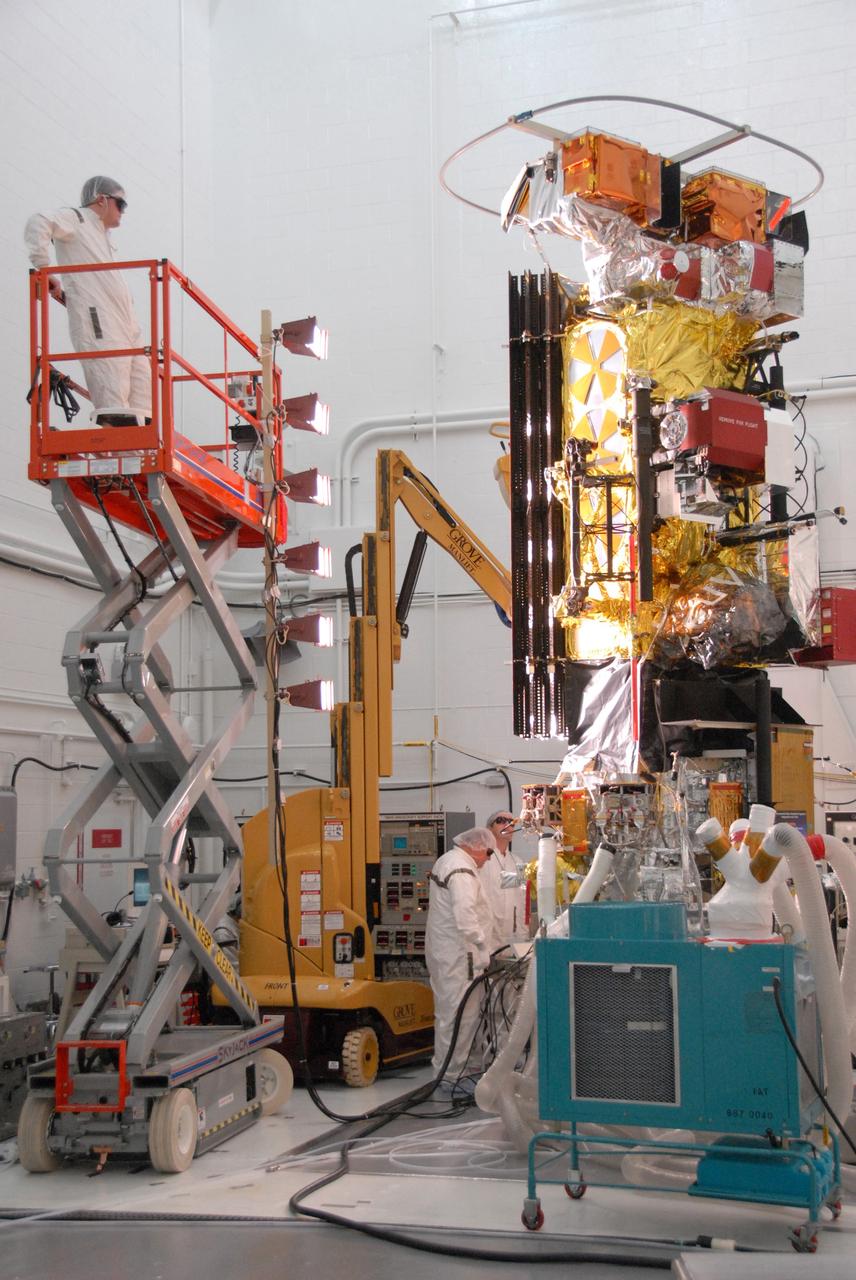

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the NASA payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers conduct solar array illumination on the NOAA-N Prime satellite. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB
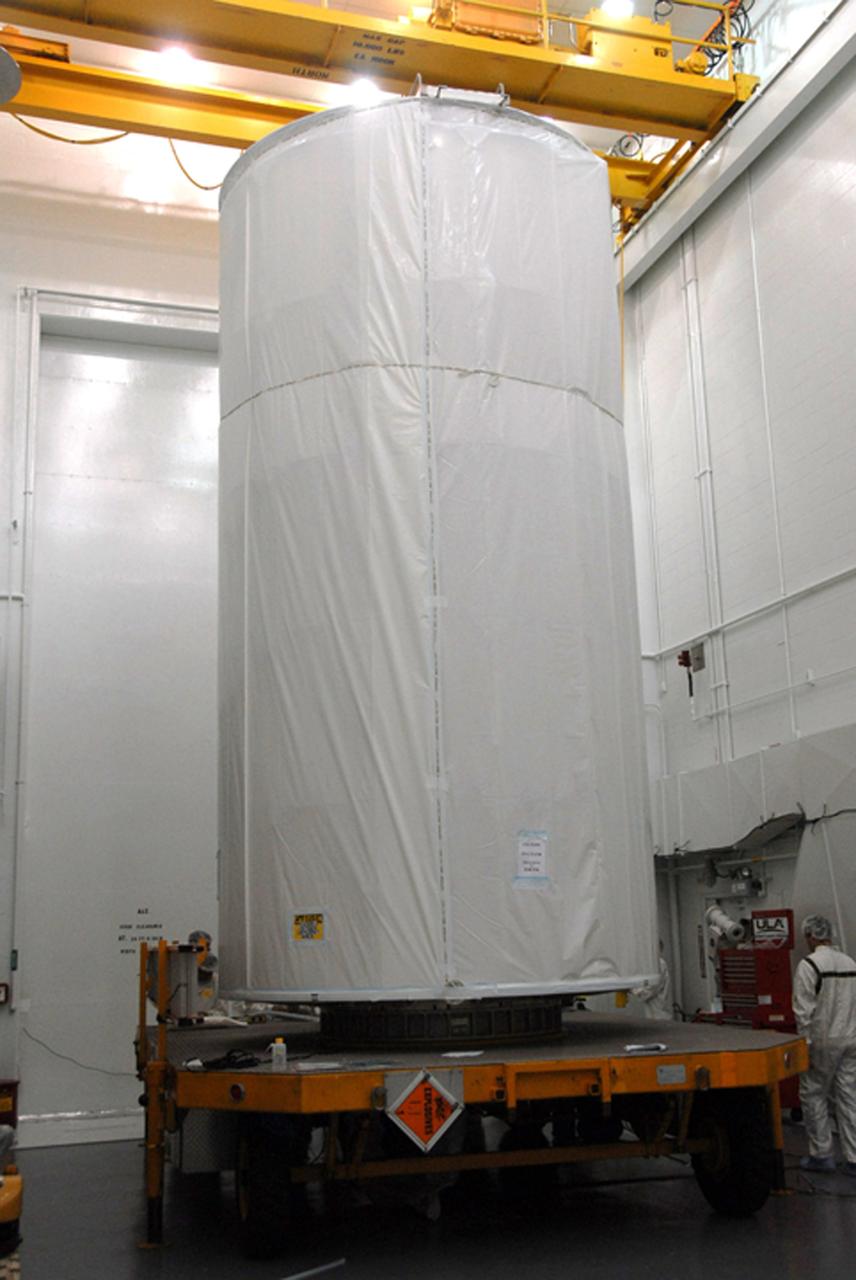

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the covered NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is lowered onto a transporter. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB
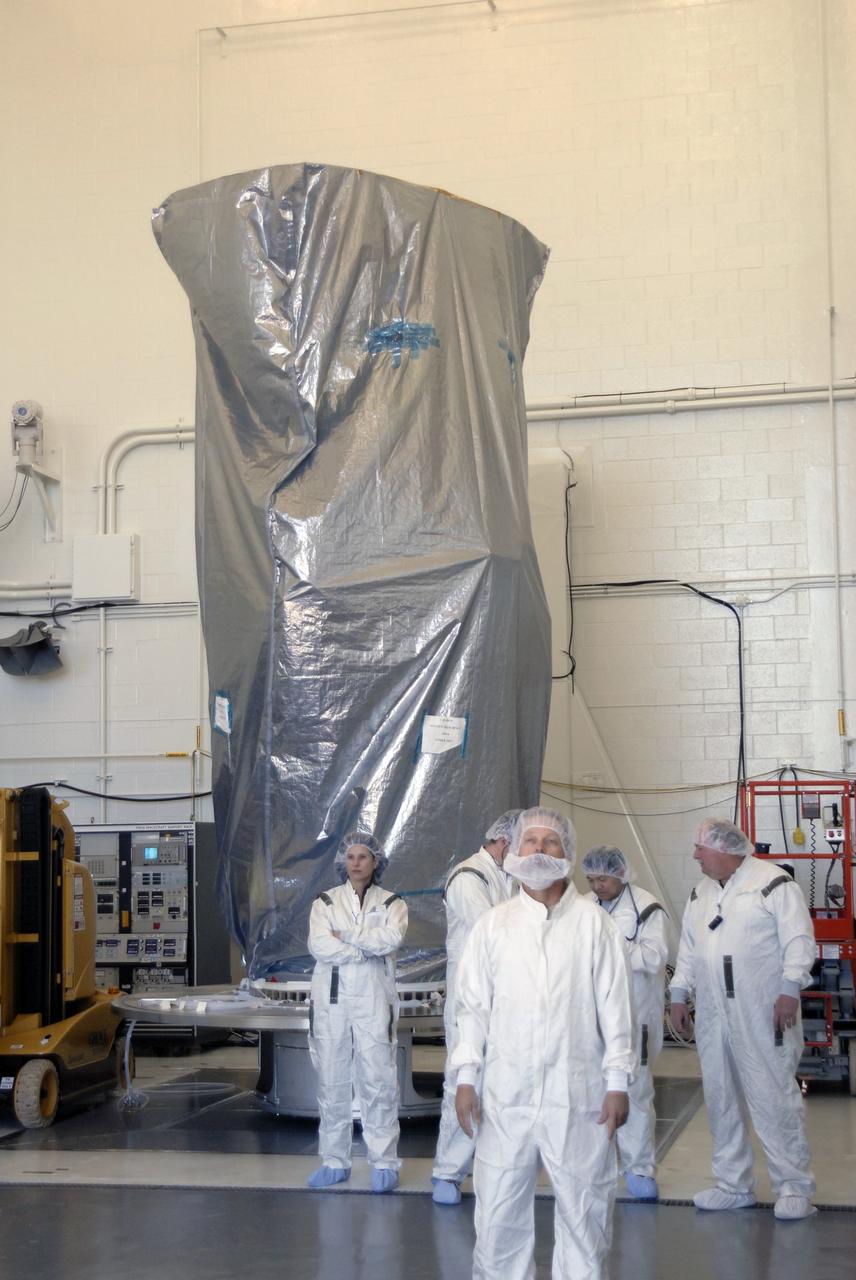

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is waiting for a transportation canister to be placed around it. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB
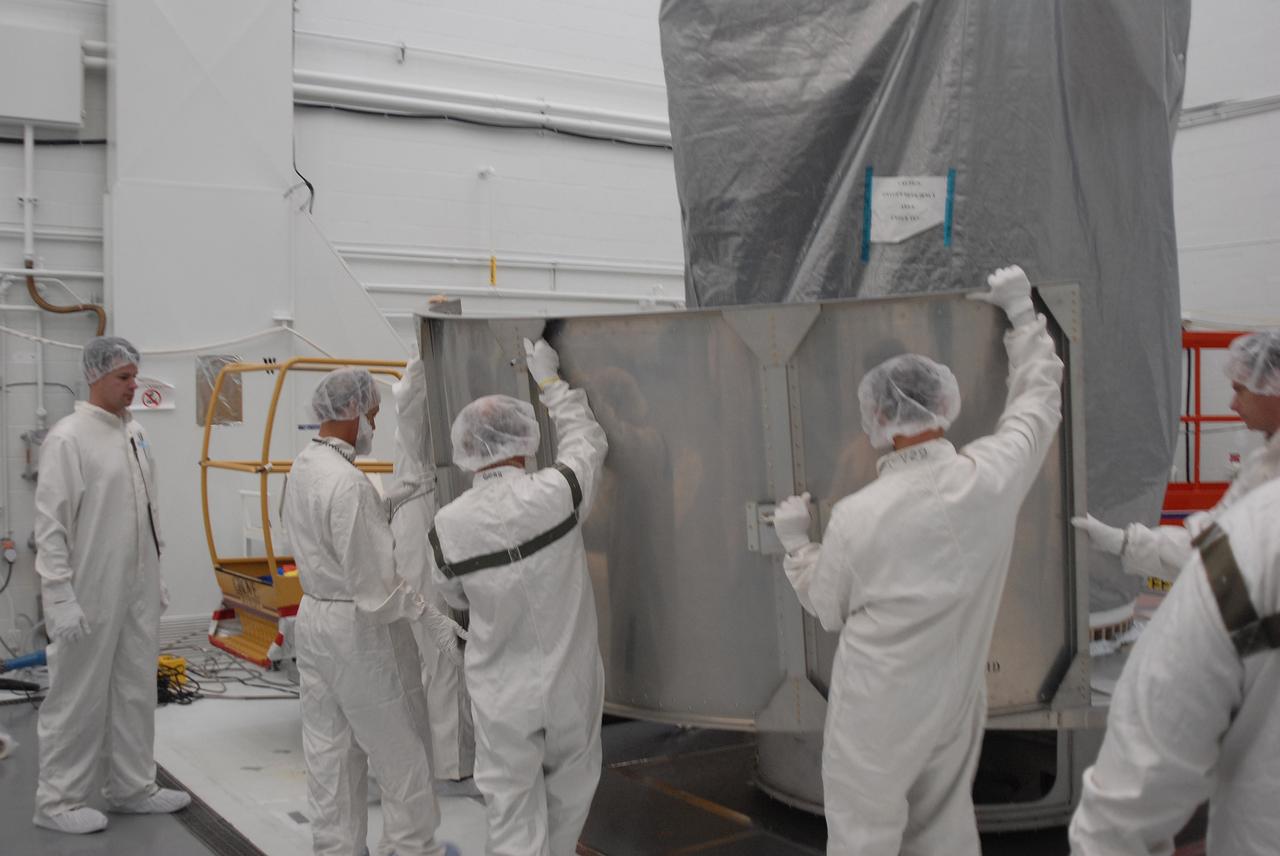

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers place the first of the lower segments of a transportation canister around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

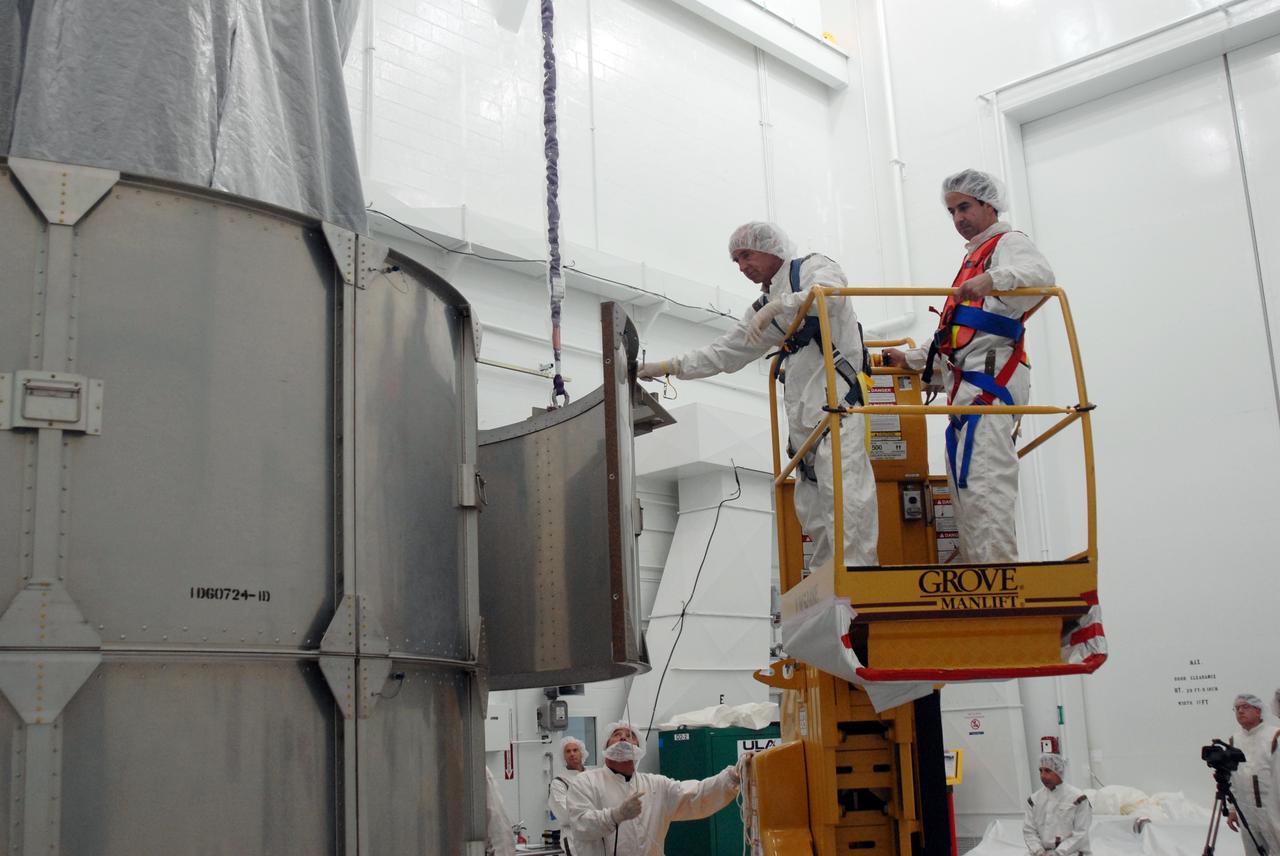
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the covered NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is lifted off its stand. It will be moved to a transporter. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

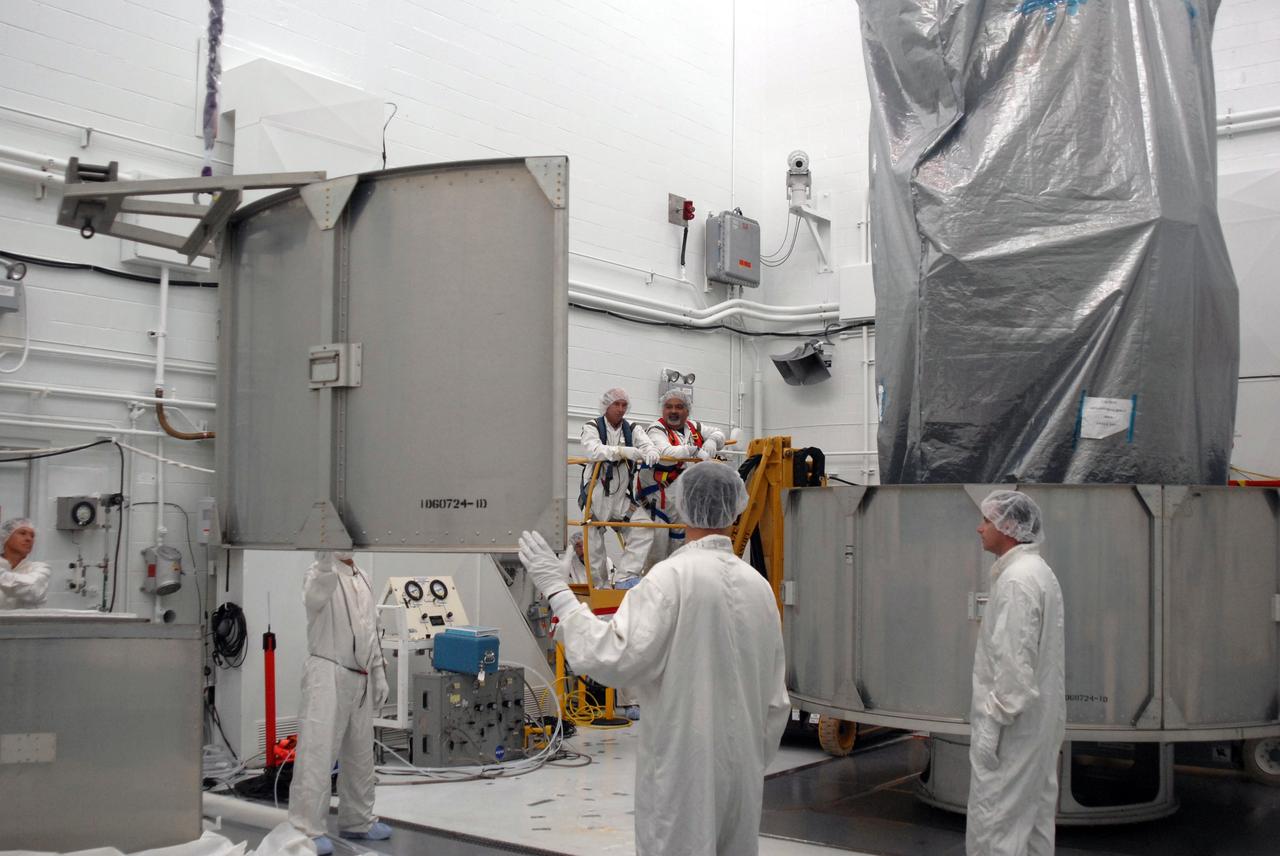
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers guide an upper segment of the transportation canister toward the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers help guide a second-row segment of a transportation canister toward the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft for installation. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the NASA payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers complete the solar array illumination on the NOAA-N Prime satellite. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the NASA payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers conduct solar array illumination on the NOAA-N Prime satellite. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

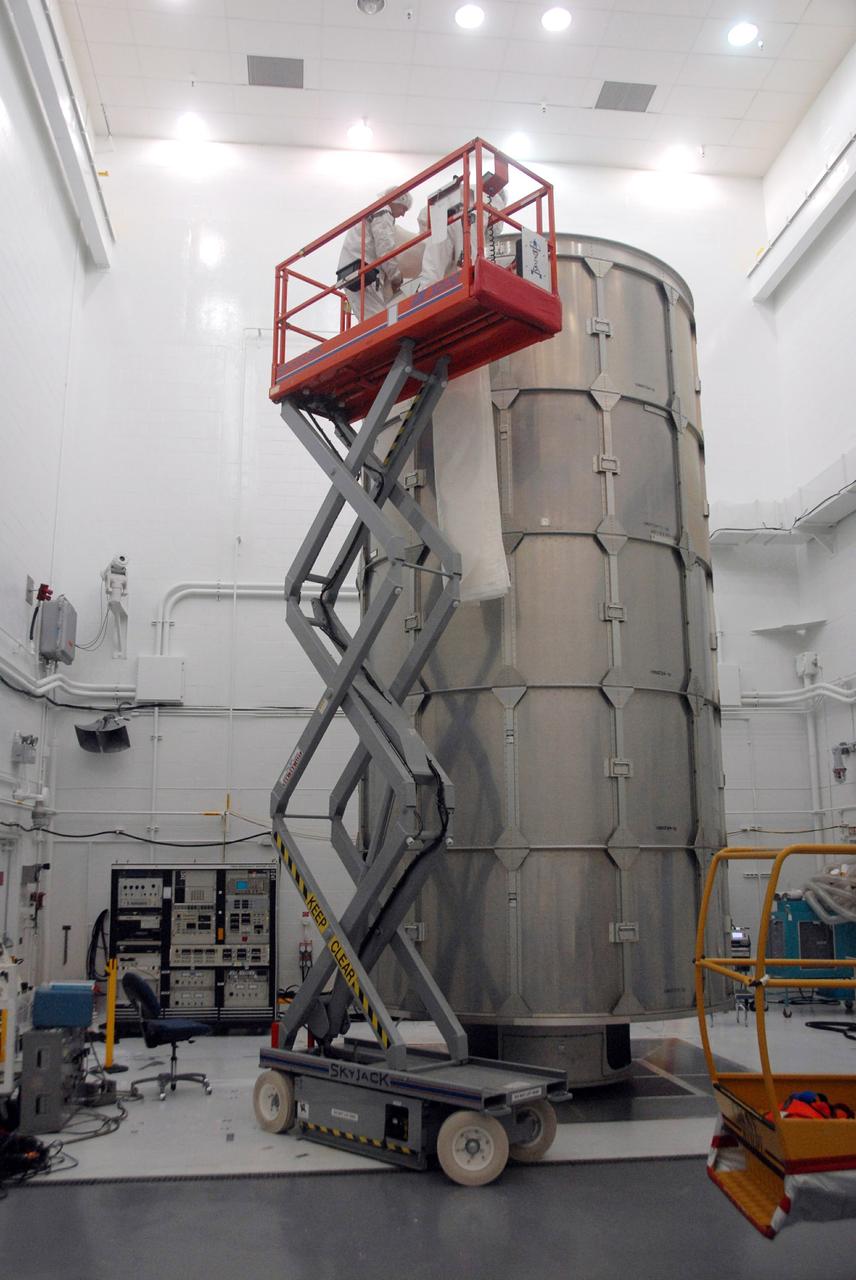
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a transportation canister is being placed around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

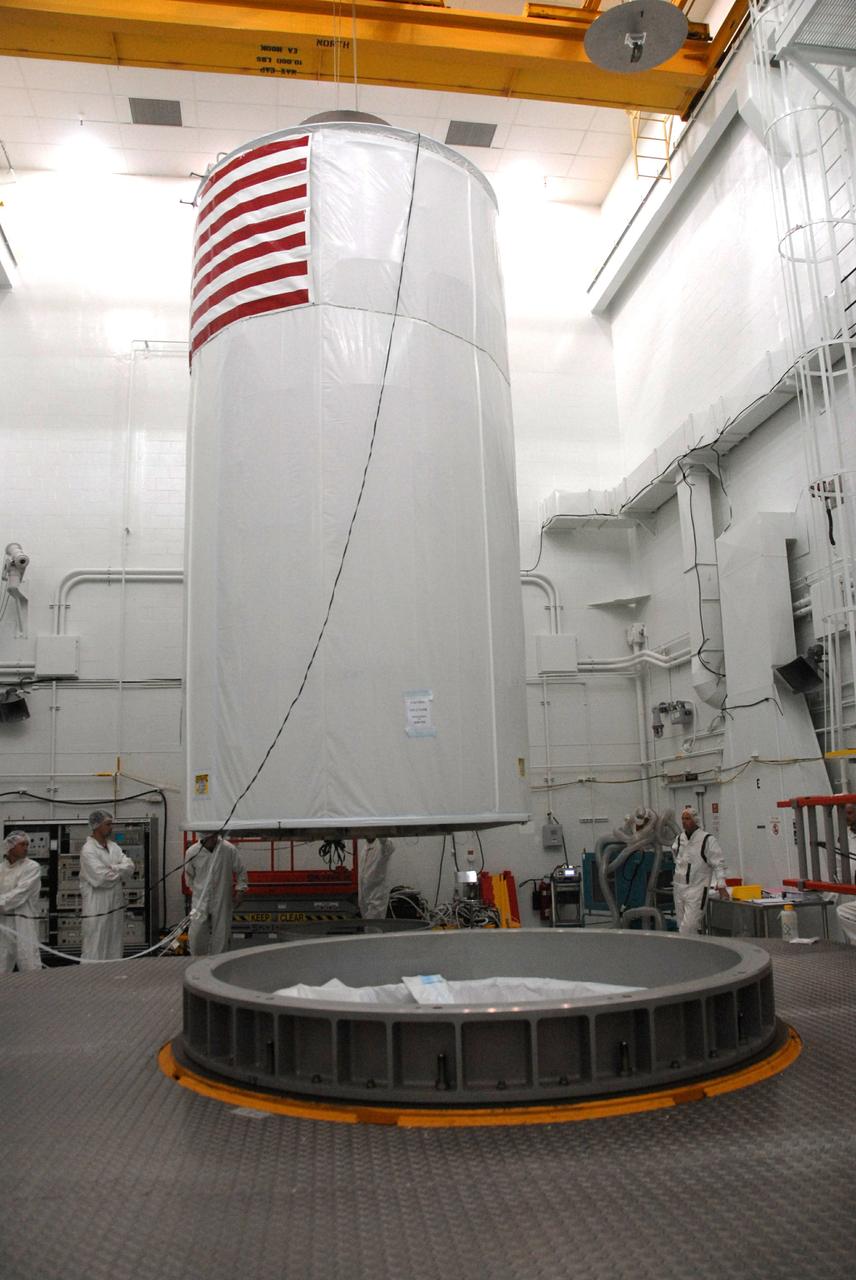
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is encased inside a transportation canister. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB
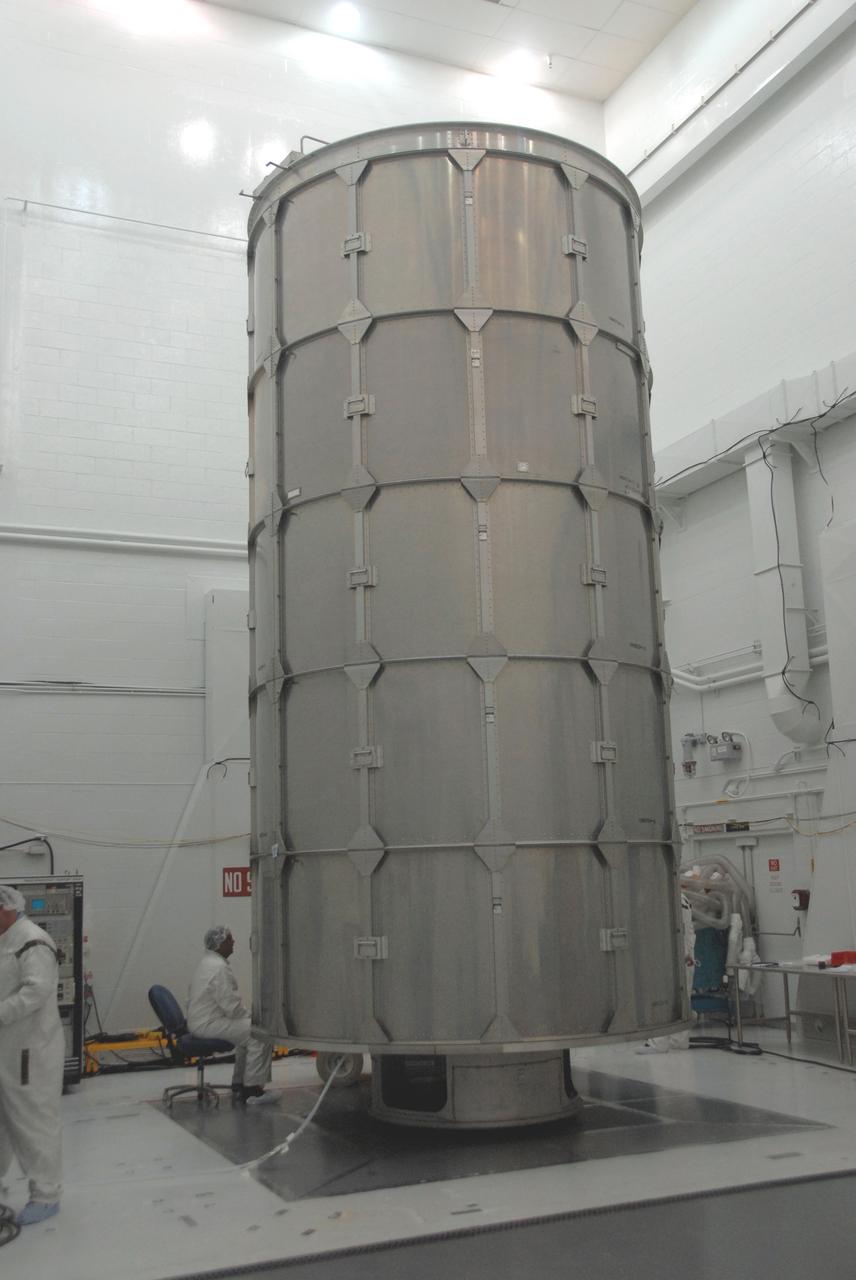

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A transportation canister surrounds the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The spacecraft will be moved to a transporter. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB
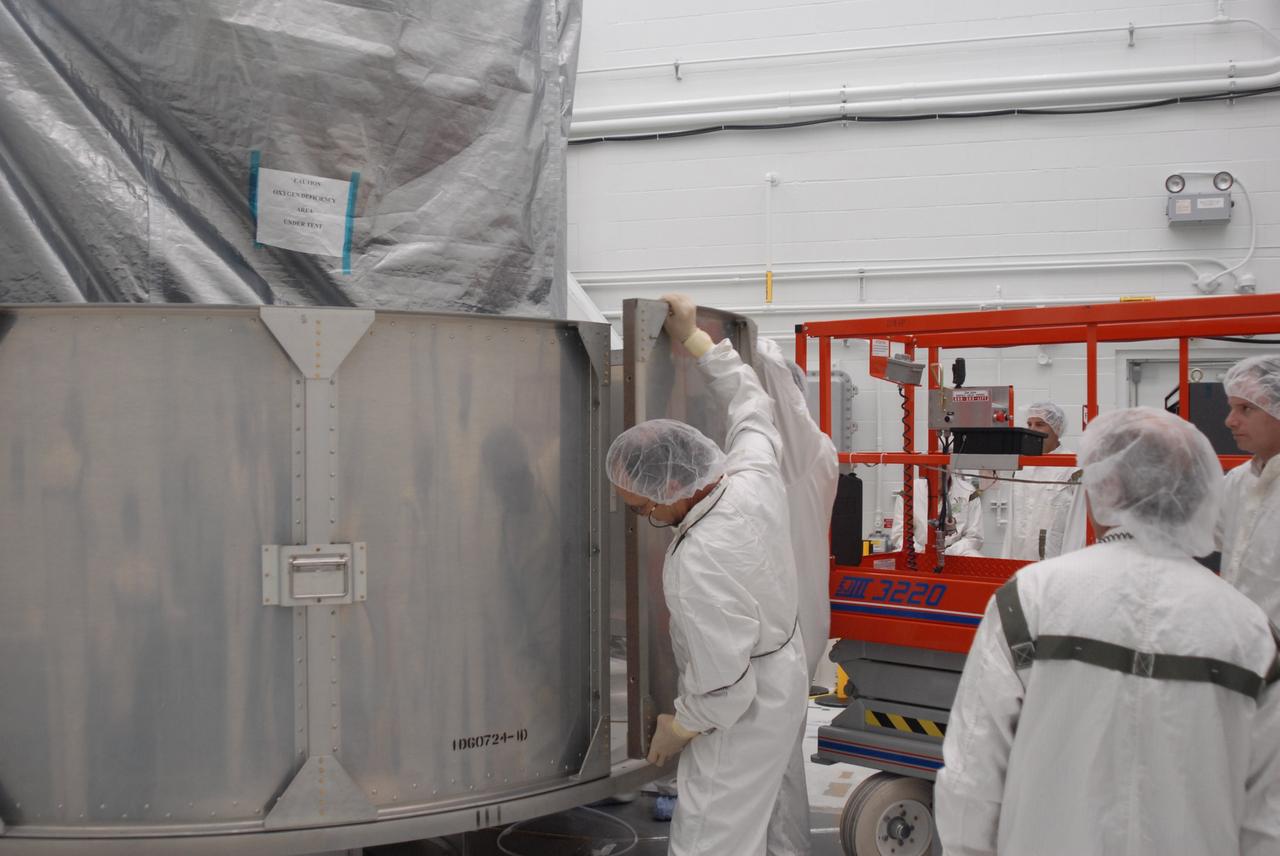

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers place another lower segment of a transportation canister around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a second-row segment of a transportation canister is put in place for installation around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

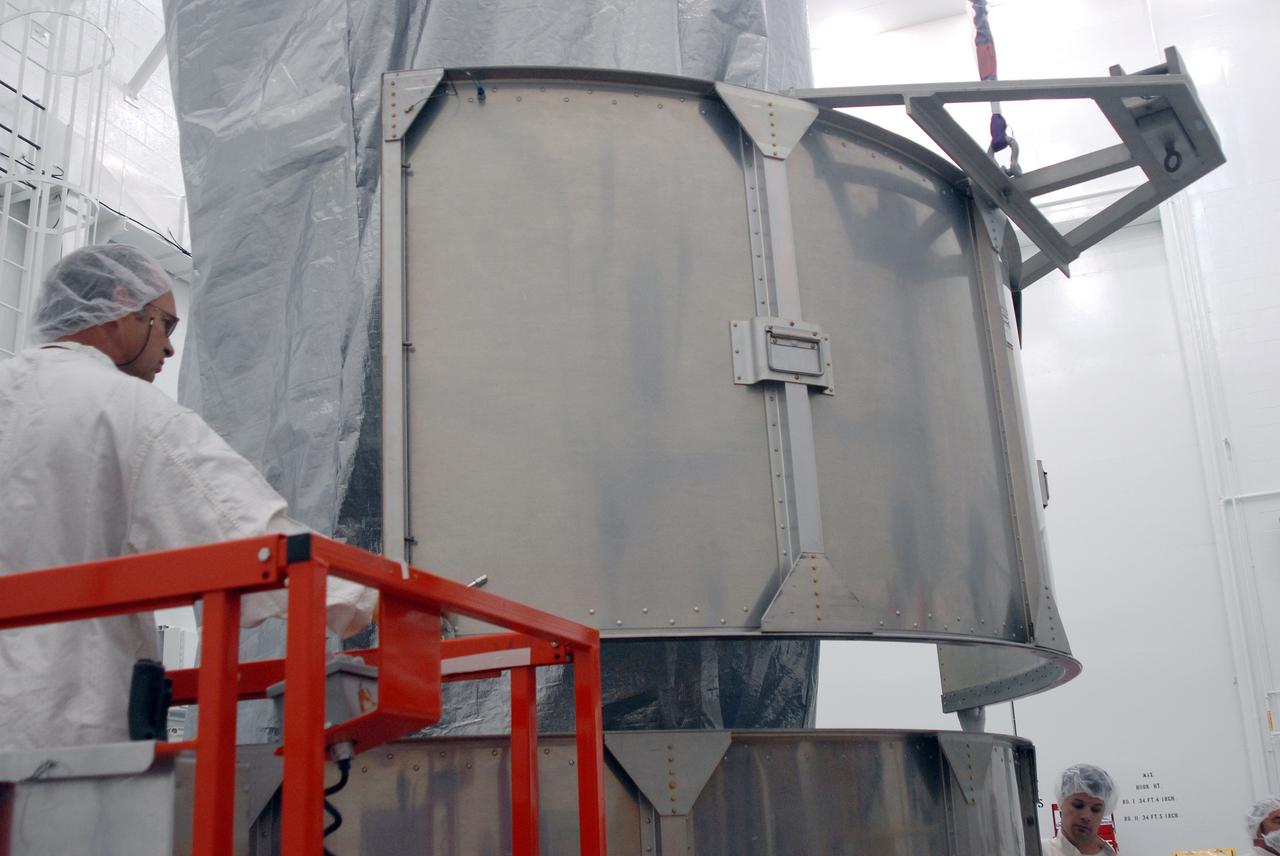
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin attaching a protective cover over the transportation cover of the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. The spacecraft will be moved to a transporter. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the NASA payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime satellite undergoes solar array illumination. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In Bldg. 1610 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, two rows of the transportation canister are installed around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is closed out for encapsulation and installation on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard the Delta II from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft is set up for an RF and other tests. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Liberotti, VAFB

Helen Fricker, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California, ICESat-2 science definition team member, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
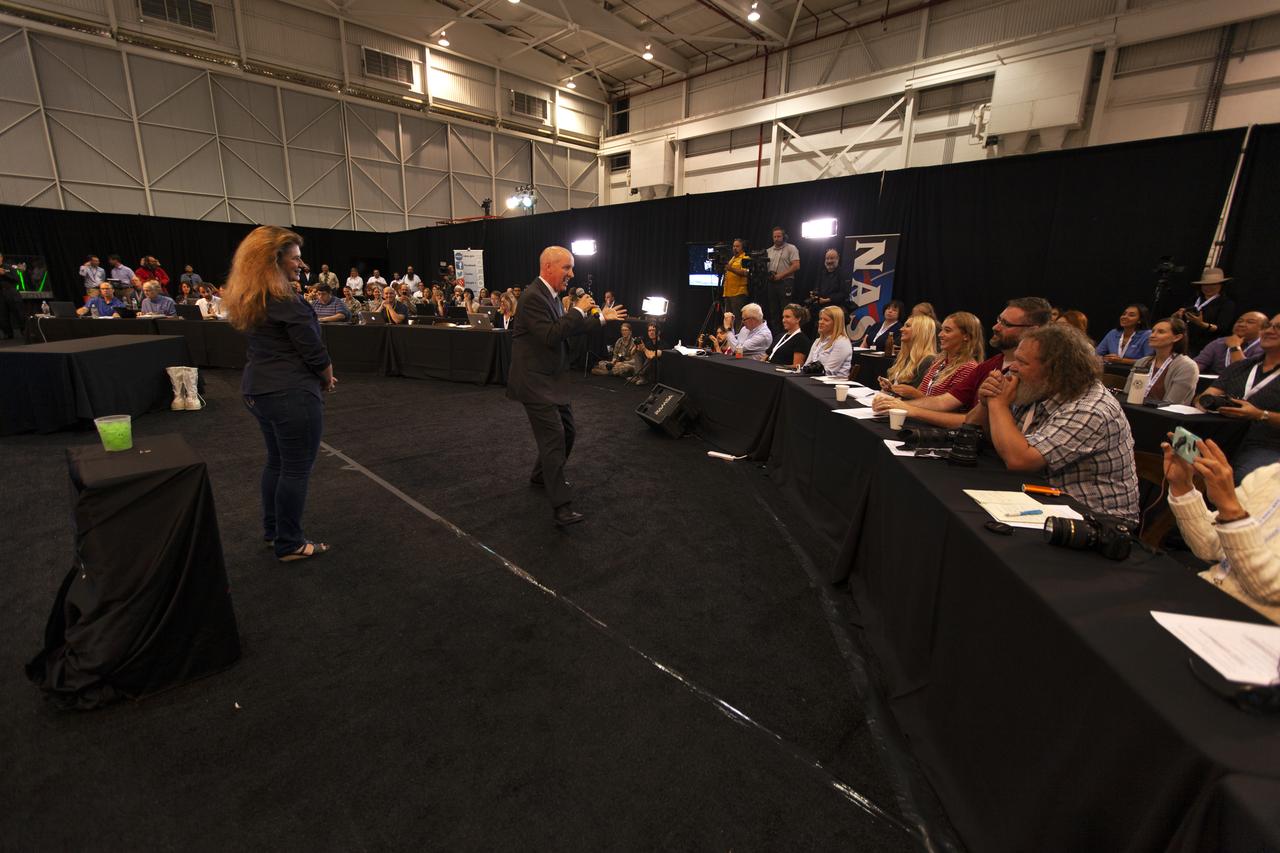

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
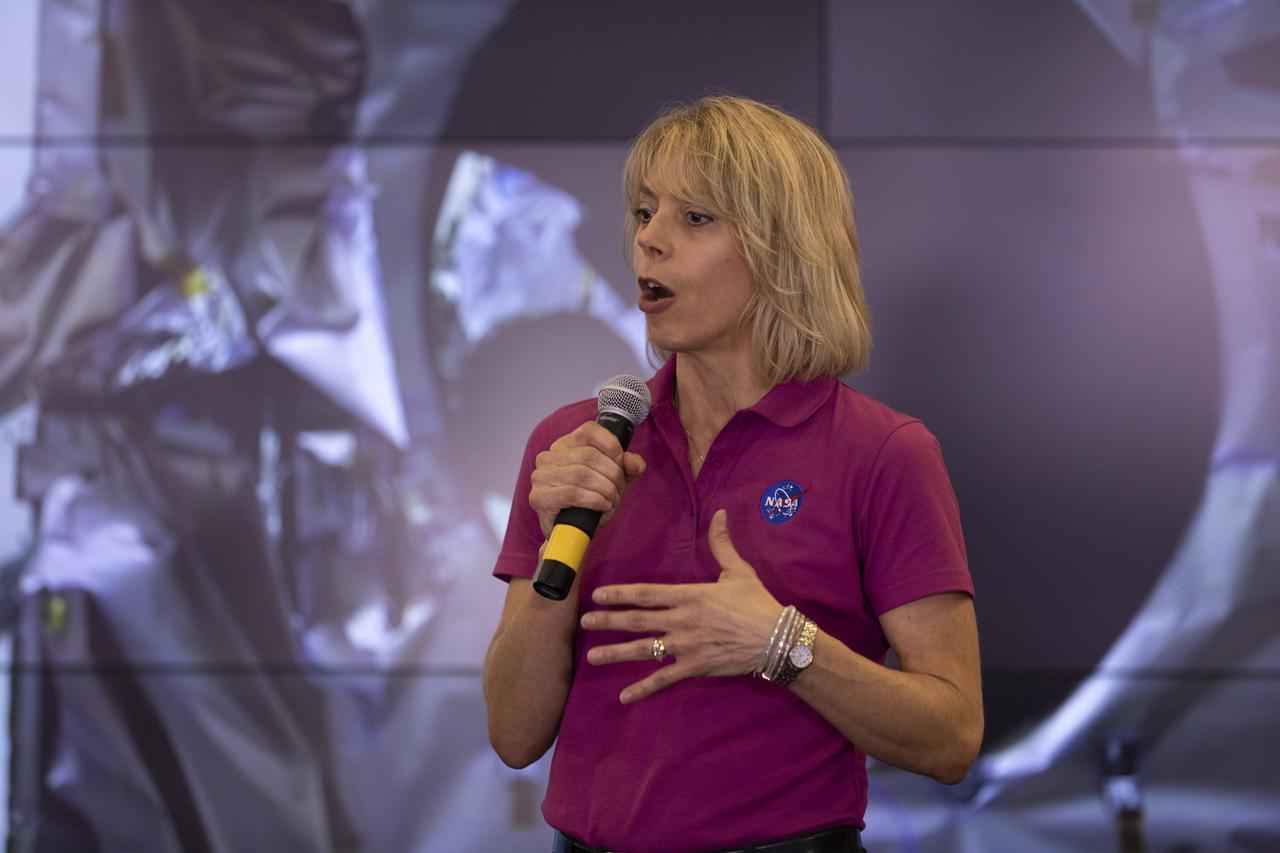

Cathy Richardson, Deputy Program Manager, Earth Science Projects Division, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
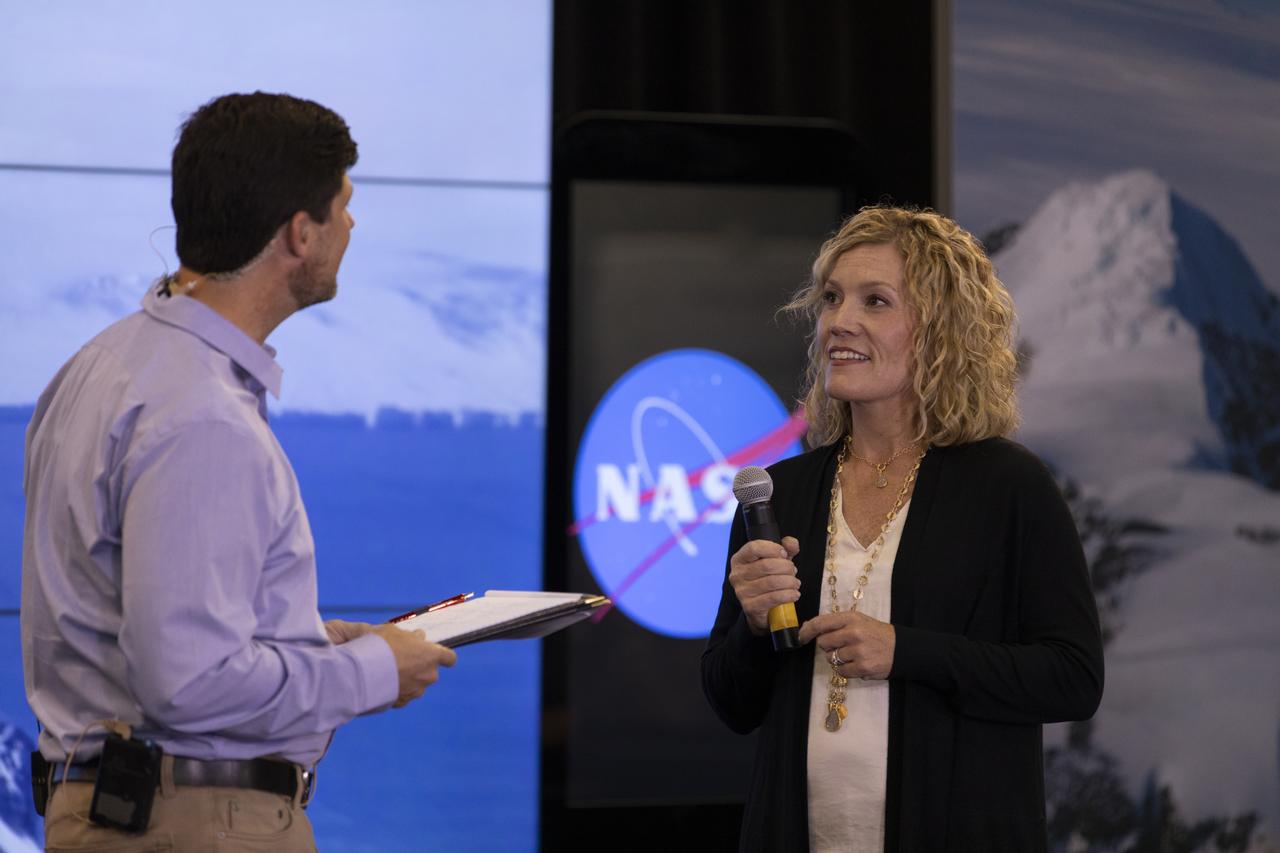

Lori Magruder, University of Texas at Austin, ICESat-2 science definition team lead, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
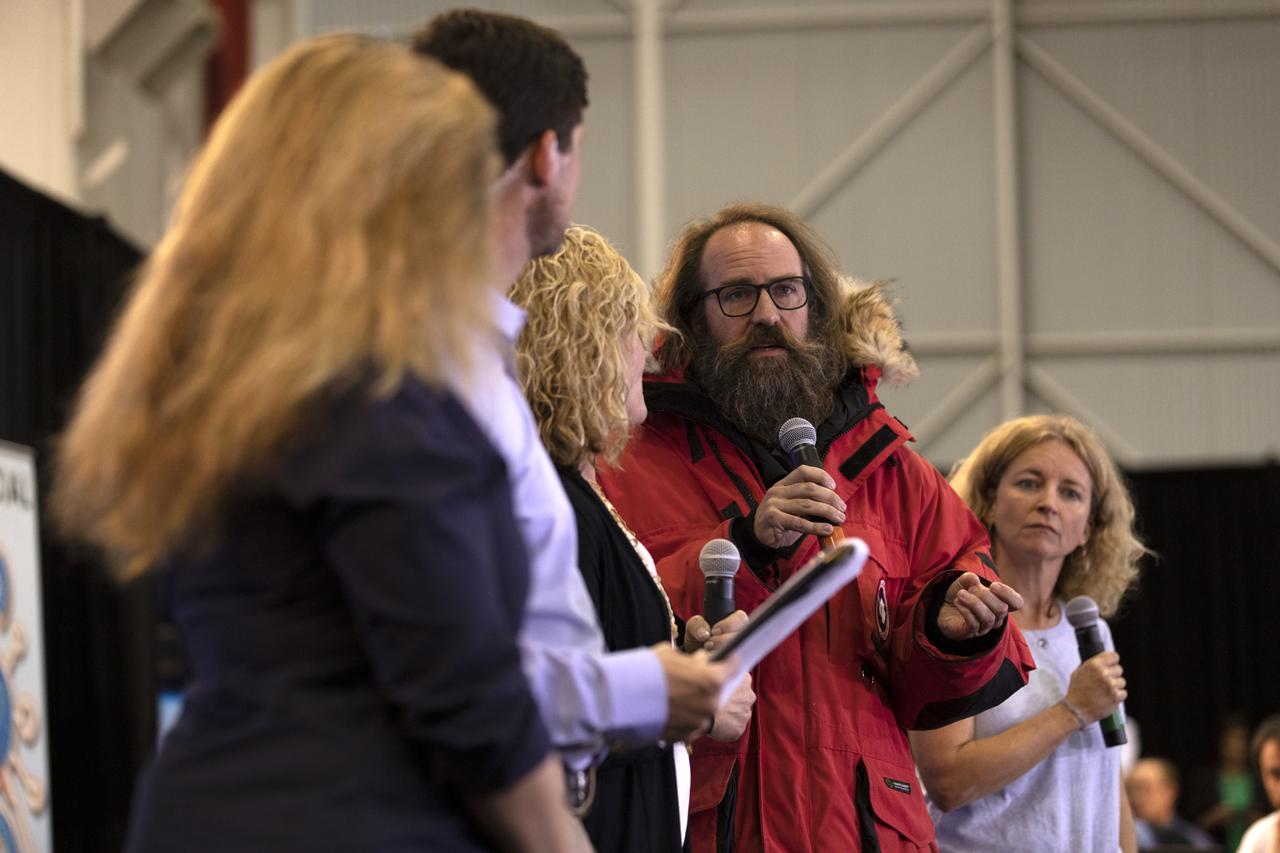

Tom Neumann, ICESat-2 deputy project scientist, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

Michelle Thaller, NASA Communications (left), and Tom Wagner, ICESat-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters (right) speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
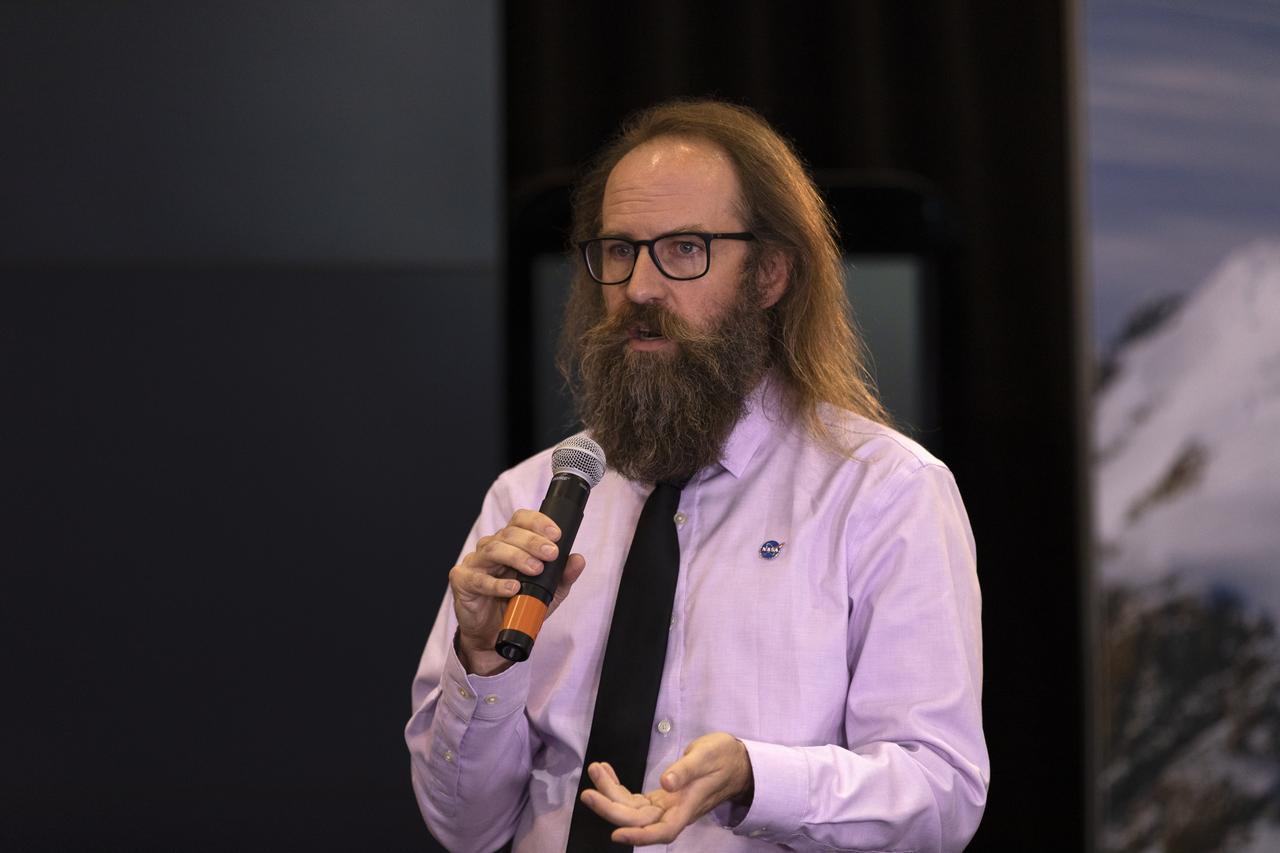

Tom Neumann, ICESat-2 deputy project scientist, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
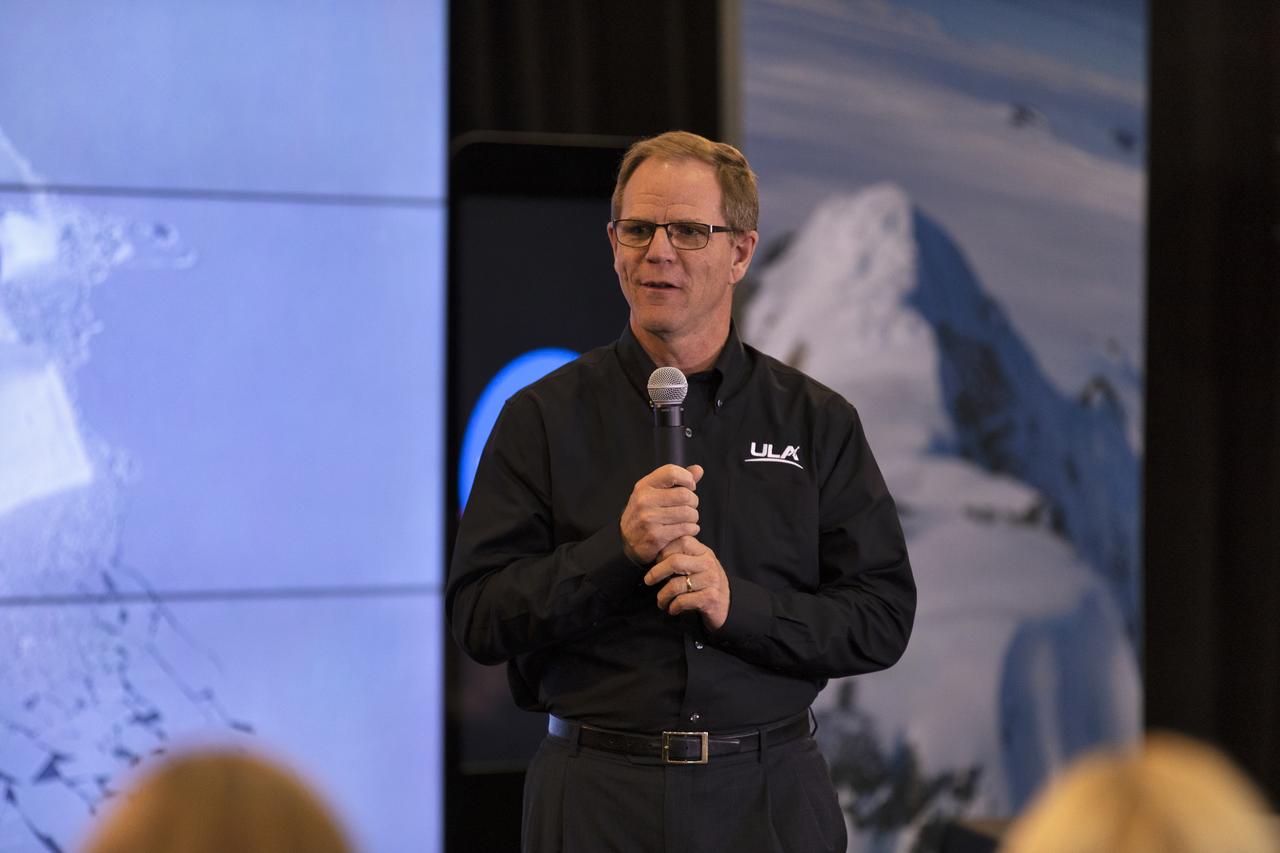

Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Programs, United Launch Alliance, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
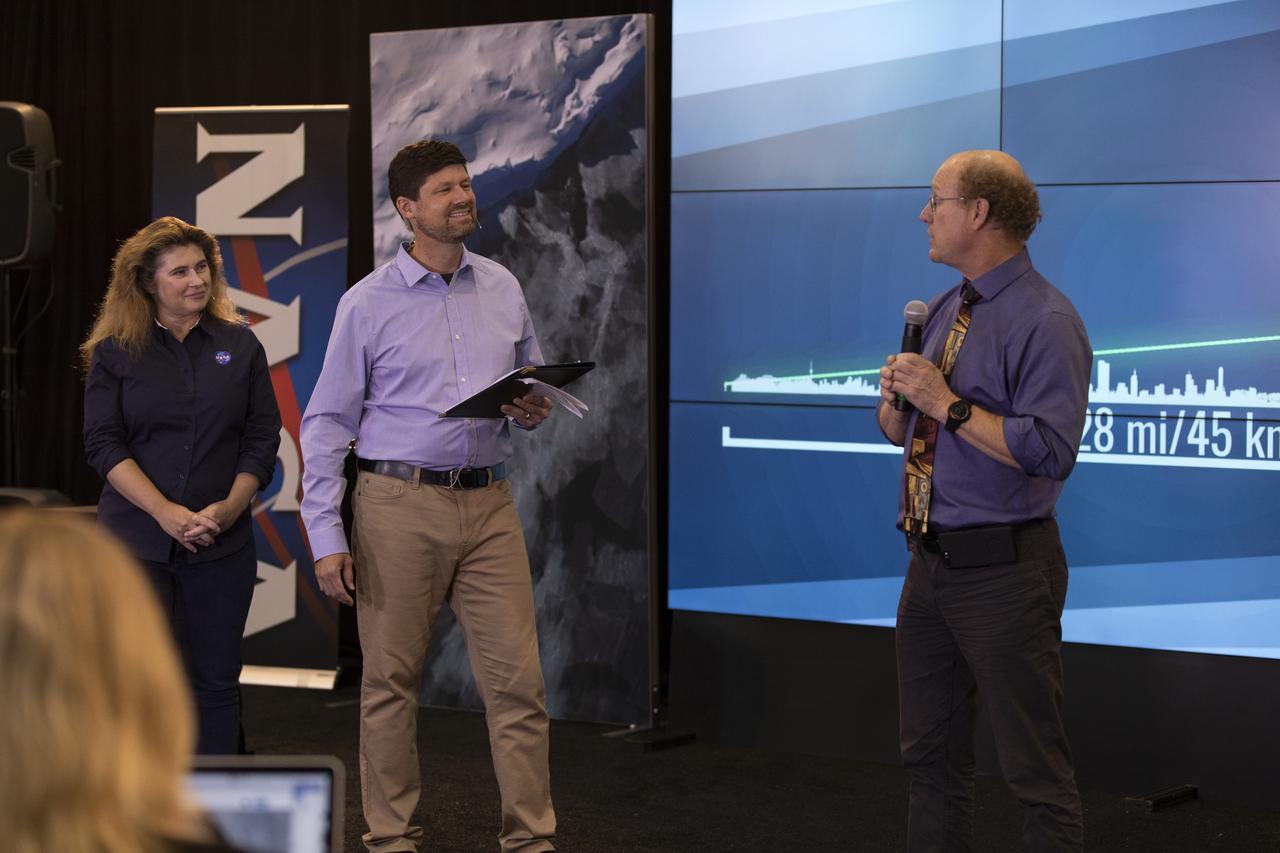

Doug McLennan, ICESat-2 project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

Bill Barnhart, ICESat-2 program manager, Northrop Grumman, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker checks the integration of the Taurus XL Stages 1 and 2. The Taurus is the launch vehicle for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO, a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed after blankets and edge tape were applied. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
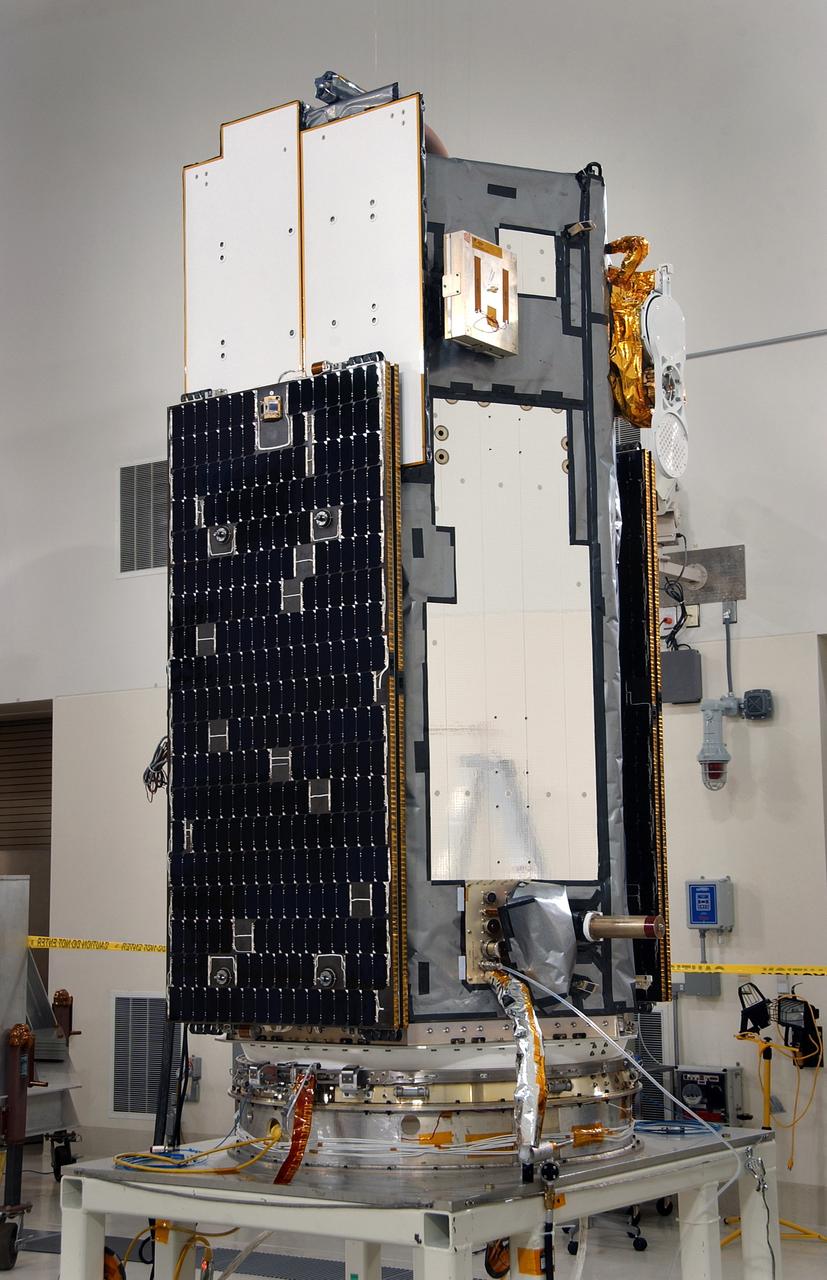
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
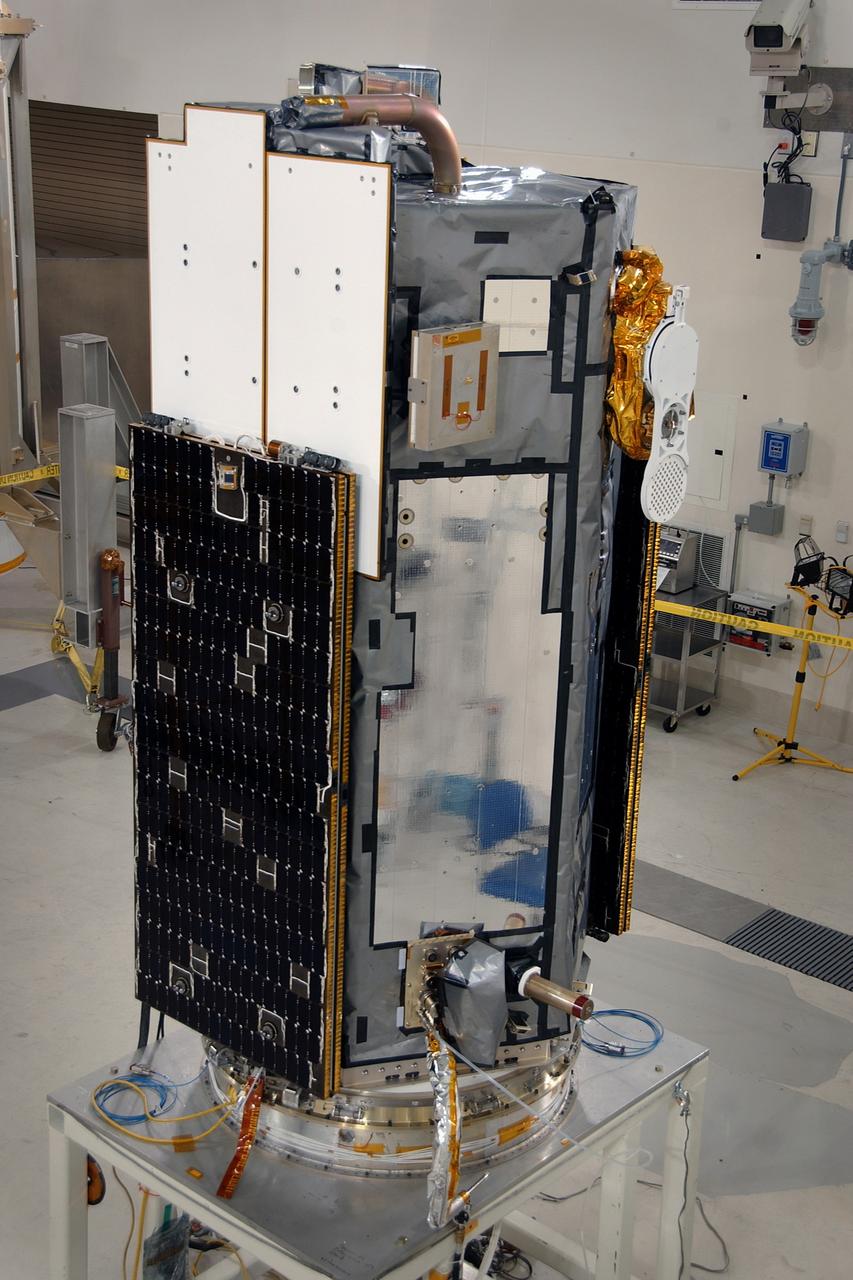

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed after blankets and edge tape were applied. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
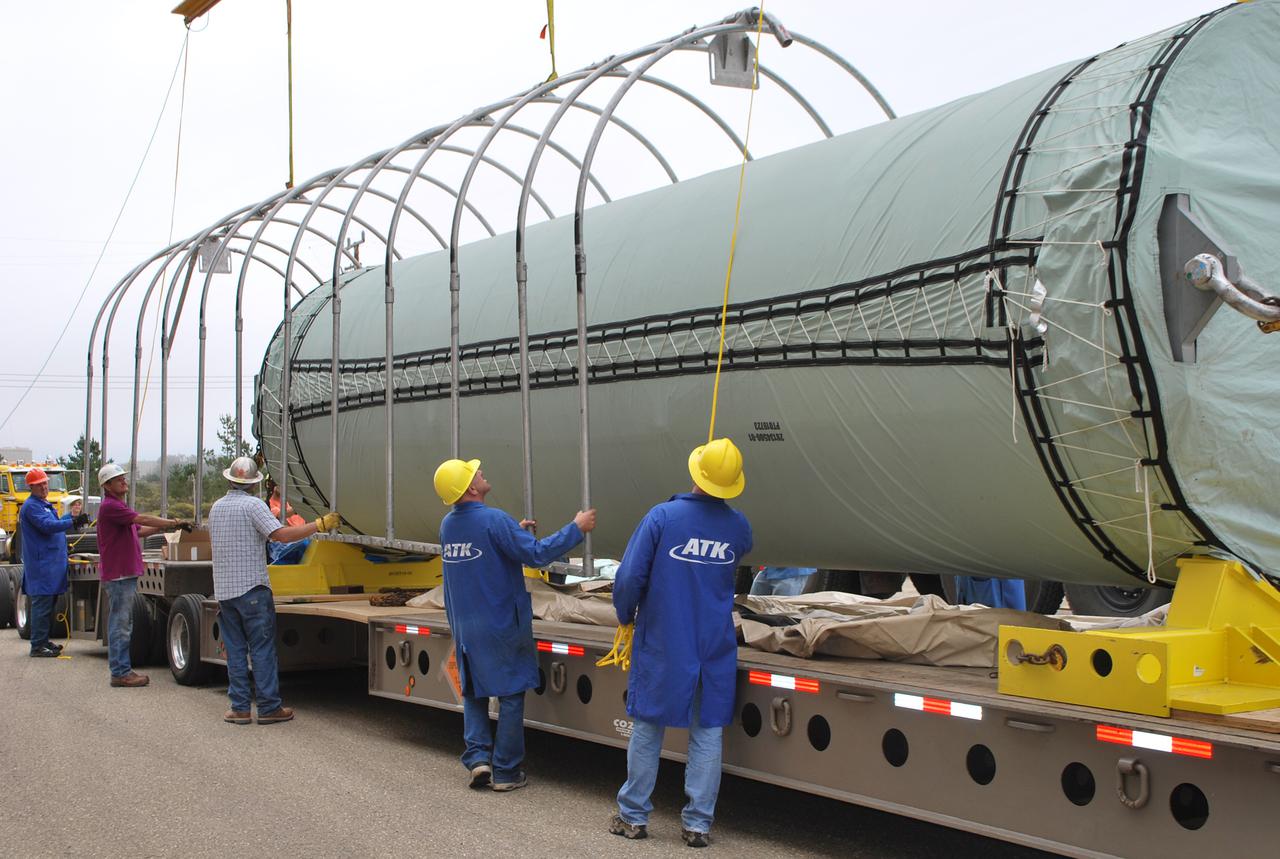

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Stage 0 motor for the Taurus XL launch vehicle is revealed. The motor will help carry NASA's Glory satellite into low Earth orbit. Glory is scheduled to launch in November from Vandenberg's Launch Pad SLC 576-E. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
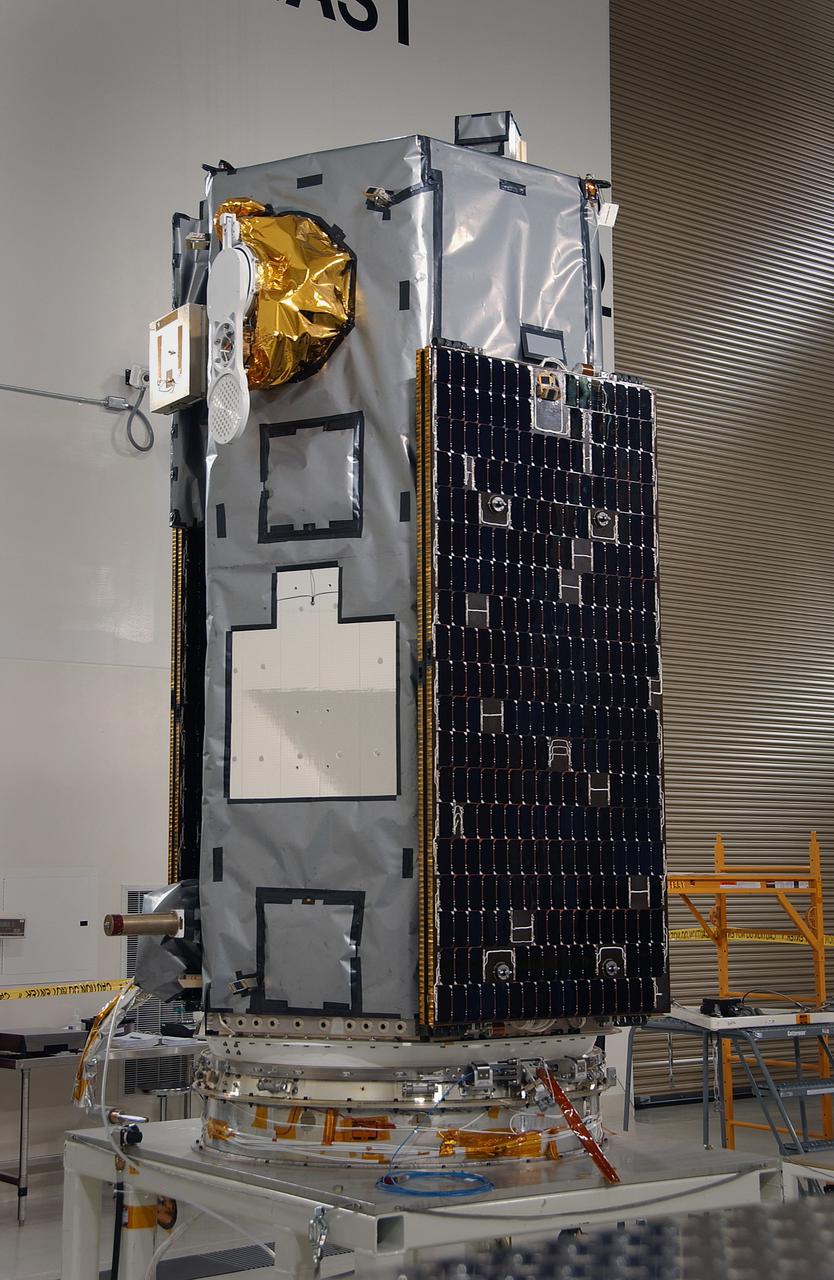

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed after blankets and edge tape were applied. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
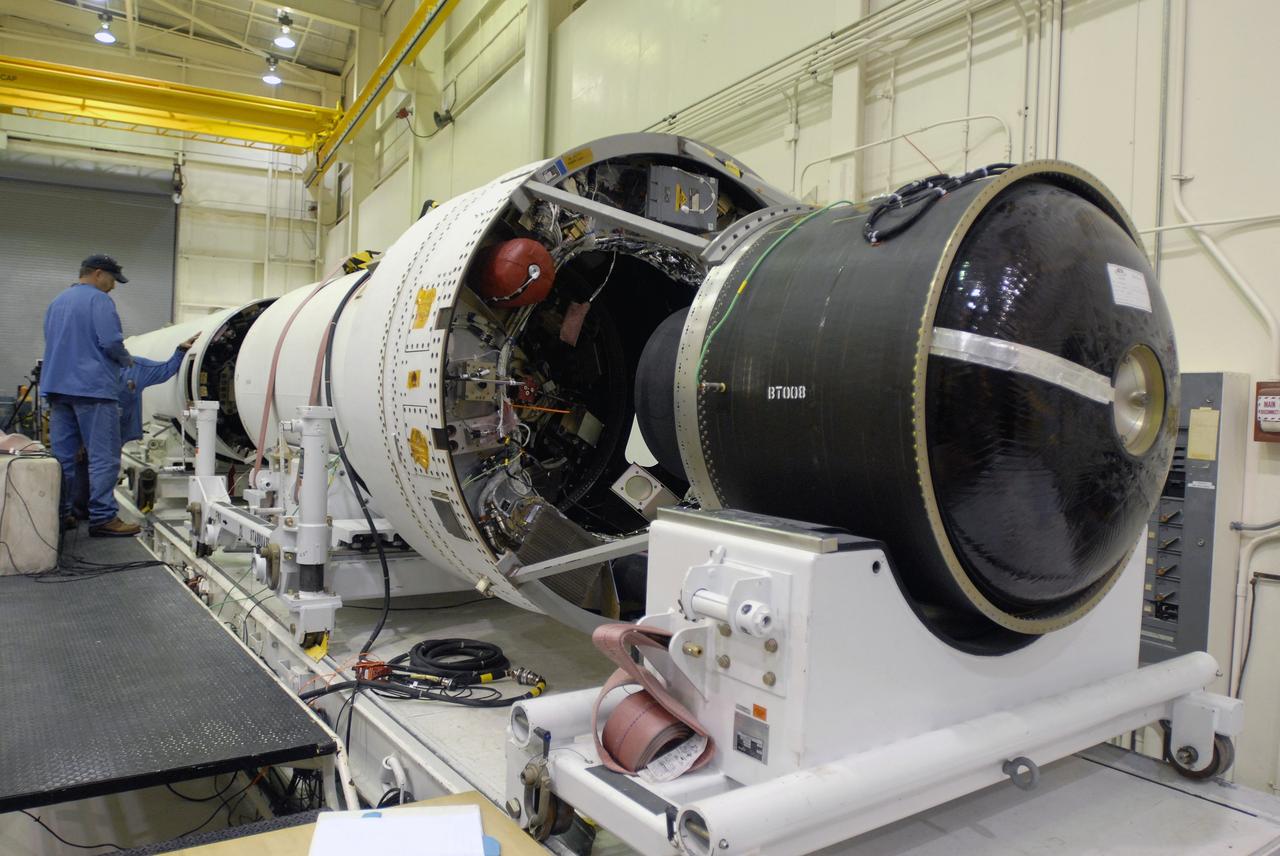

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --In Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Stages 1 and 2 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle are being integrated for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO. OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
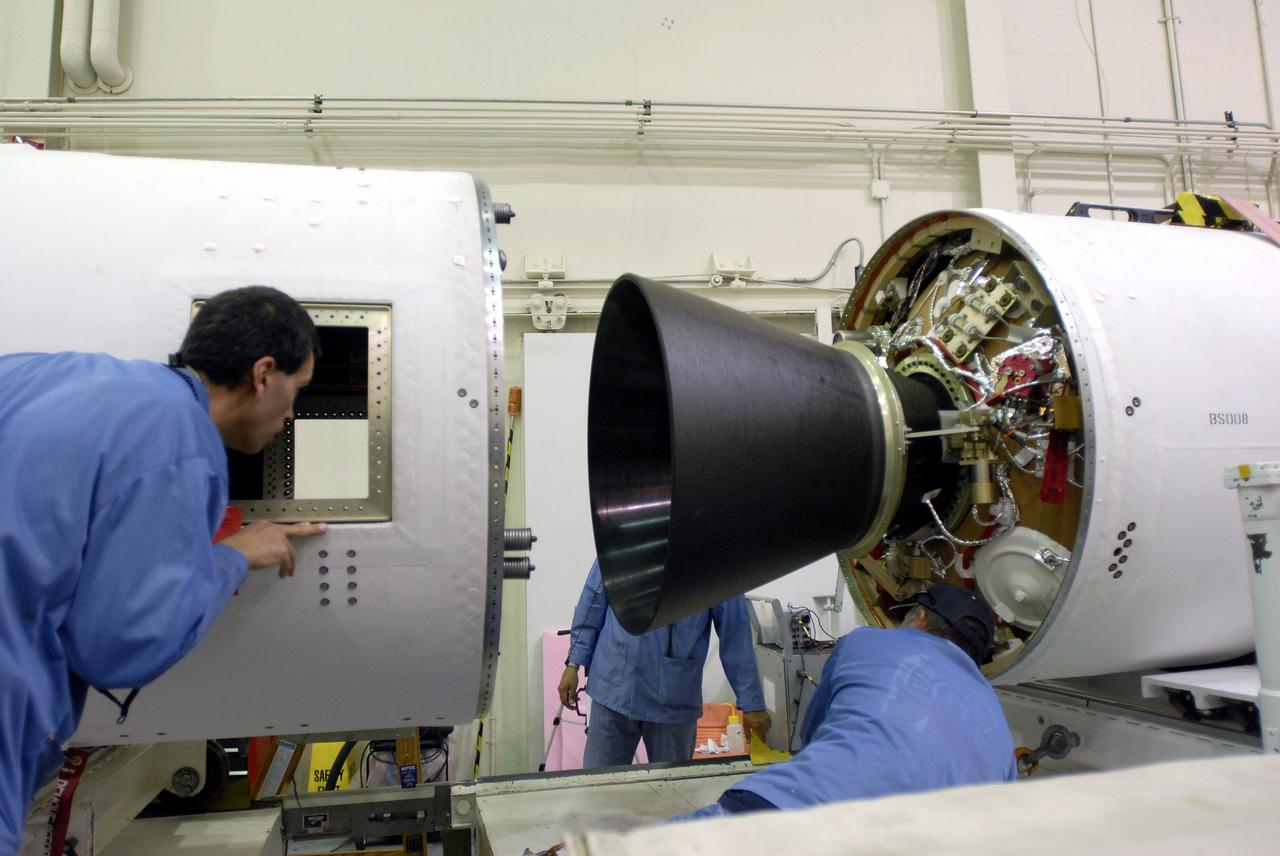

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --In Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Stages 1 and 2 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle are being integrated for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO. OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
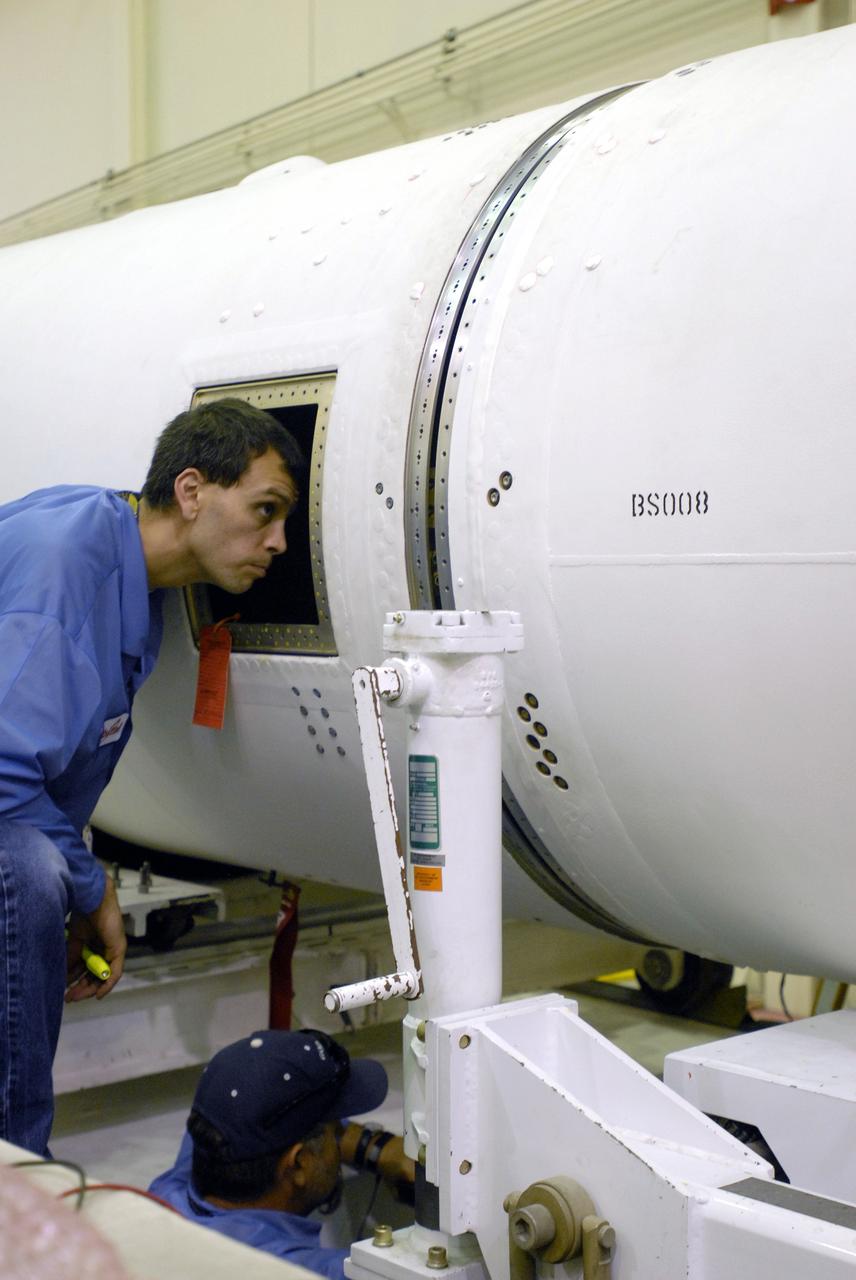

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker checks the integration of the Taurus XL Stages 1 and 2. The Taurus is the launch vehicle for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO, a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
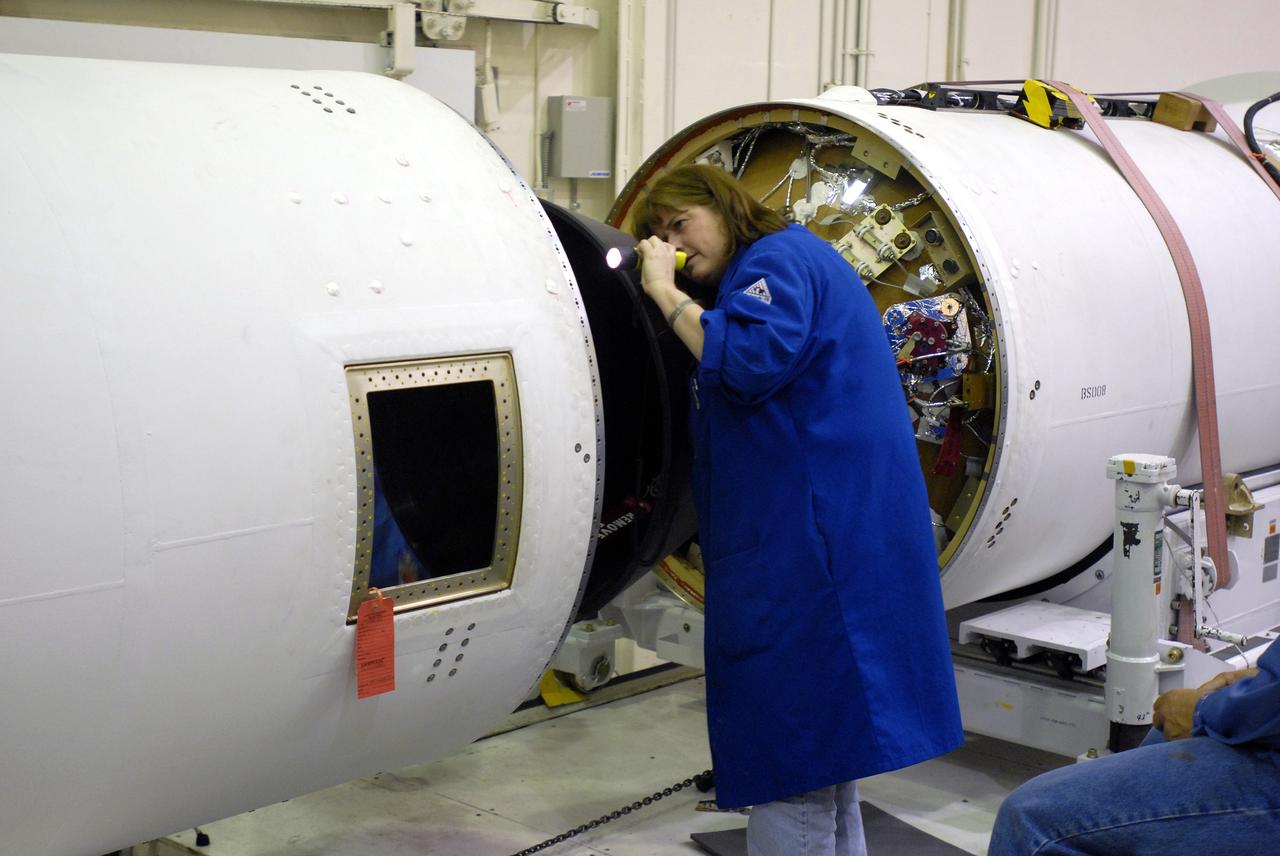

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --In Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Stages 1 and 2 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle are being integrated for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO. OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
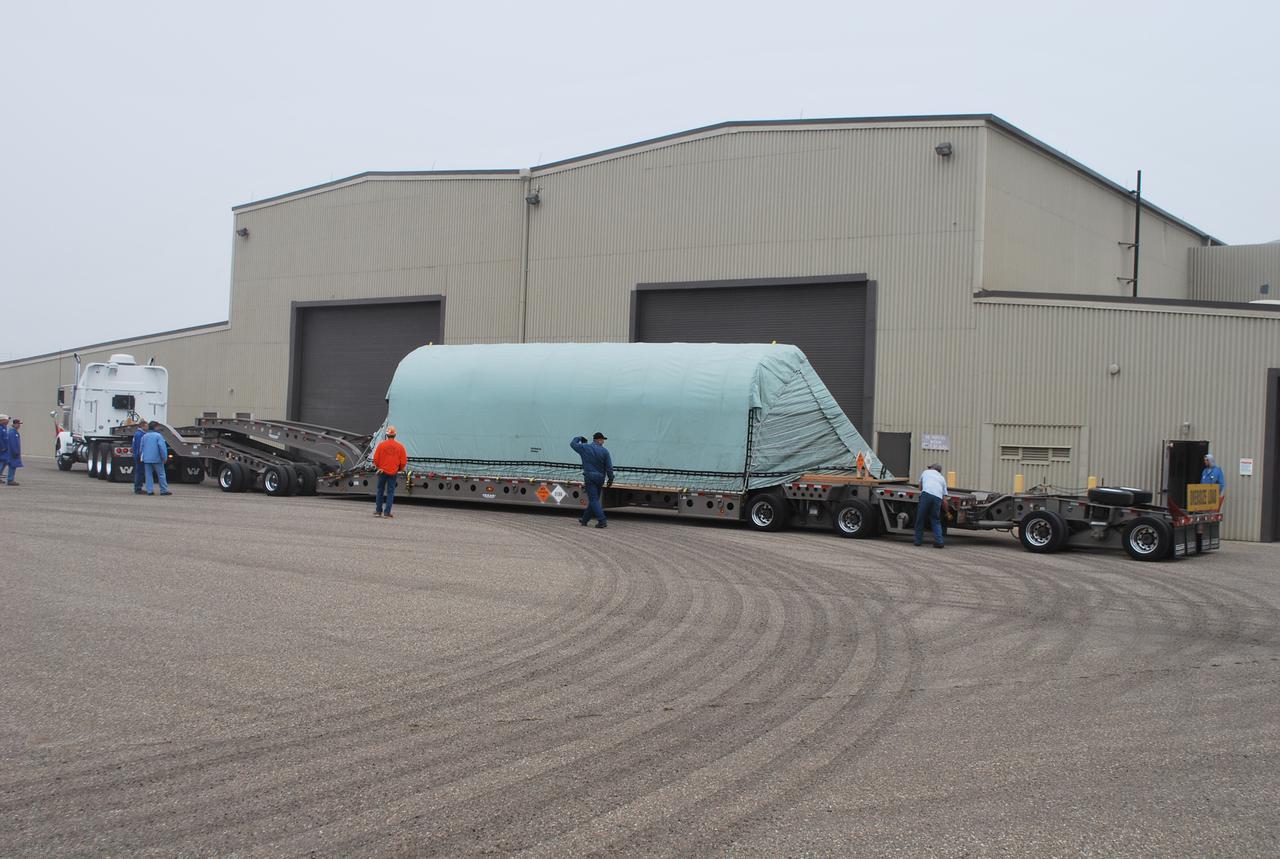

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Stage 0 motor for the Taurus XL launch vehicle arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The motor will help carry NASA's Glory satellite into low Earth orbit. Glory is scheduled to launch in November from Vandenberg's Launch Pad SLC 576-E. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
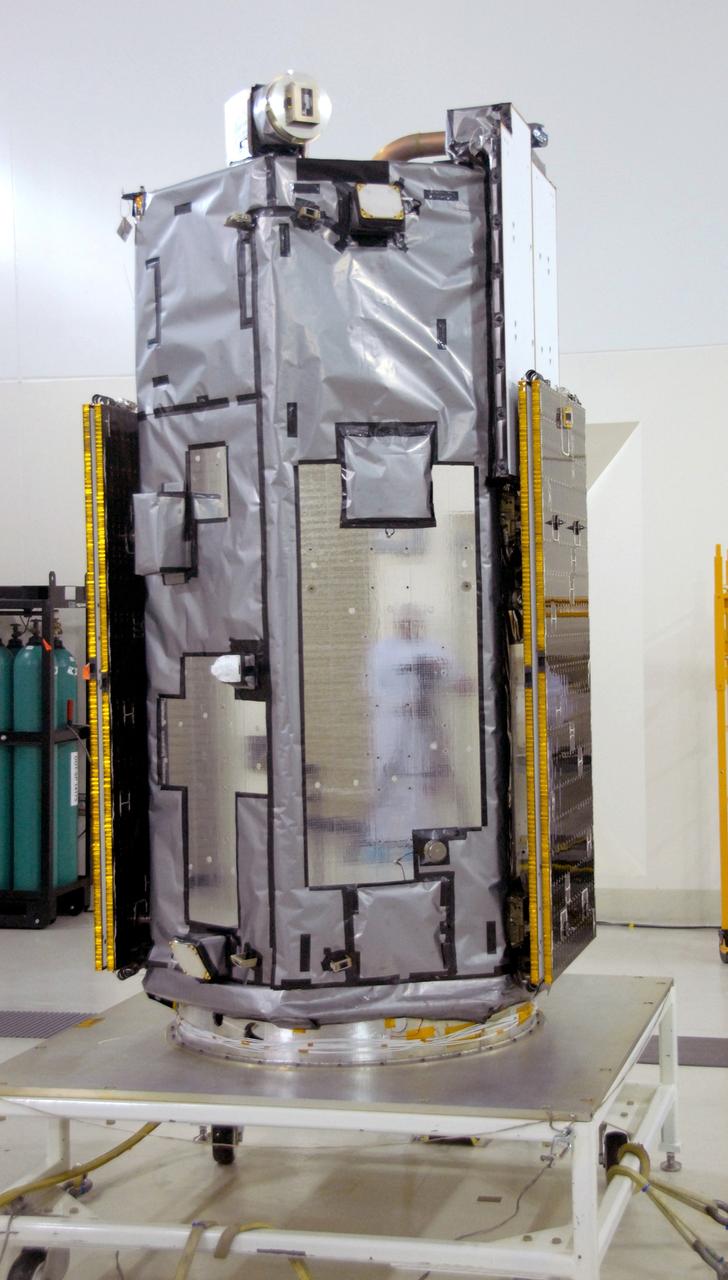

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility, building 1032, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed after blankets and edge tape were applied. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Jan. 15 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB
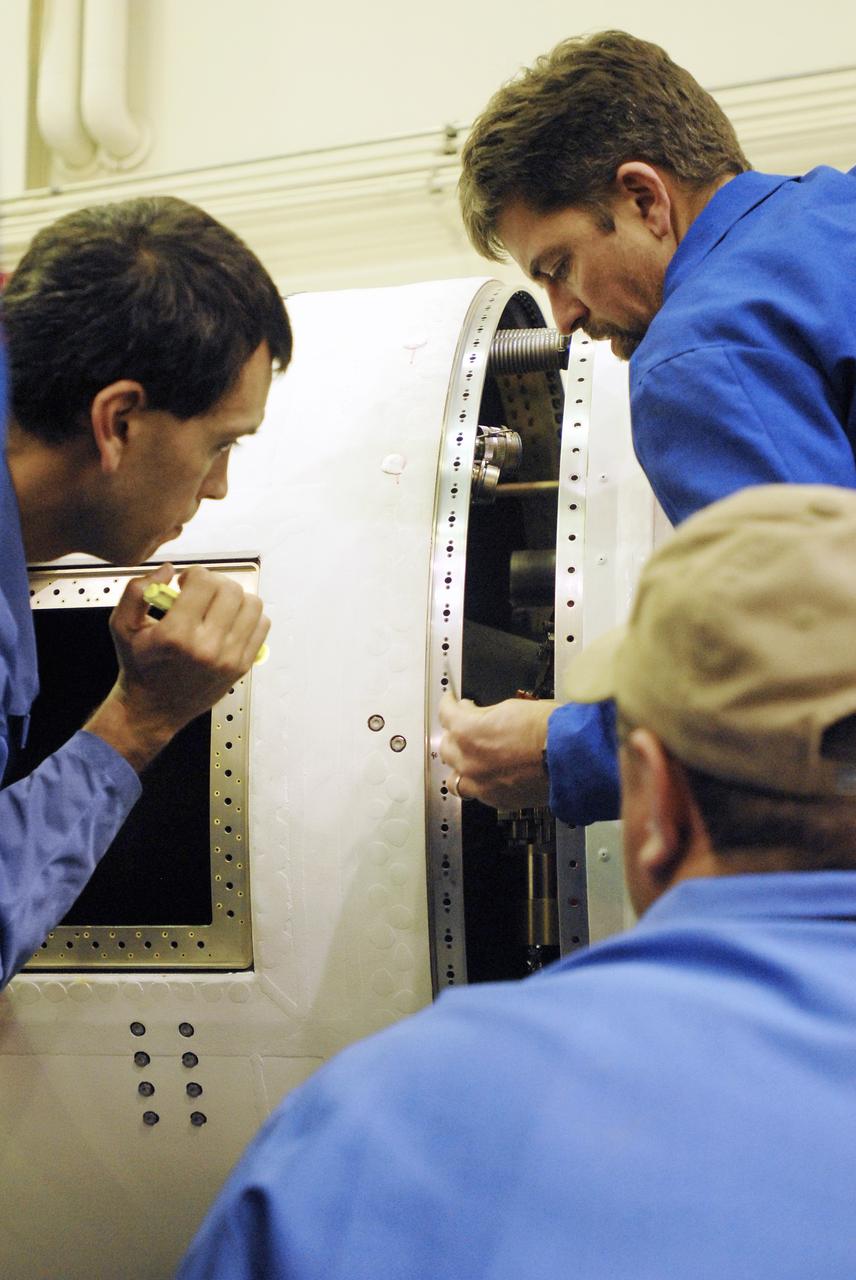

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. --In Space Launch Complex 576-E, Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Stages 1 and 2 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle are being integrated for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, called OCO. OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
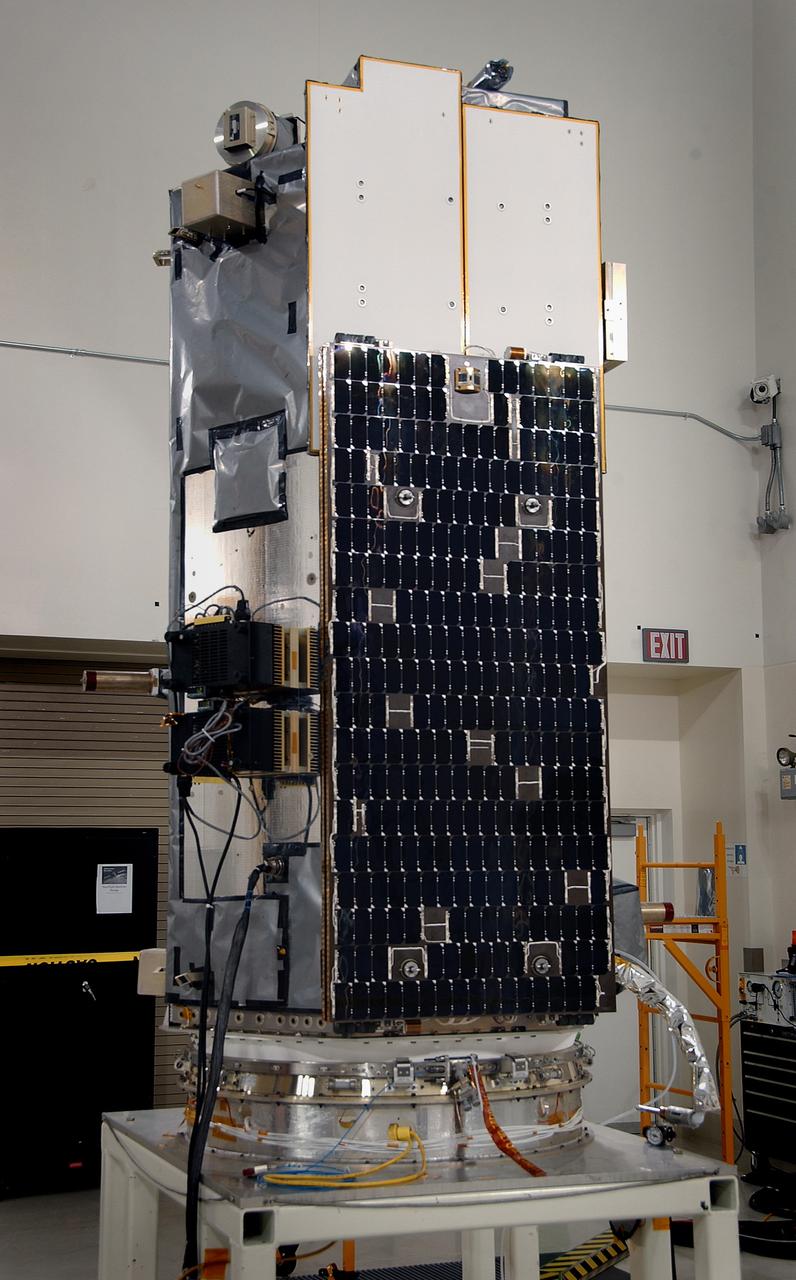

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Feb. 23 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
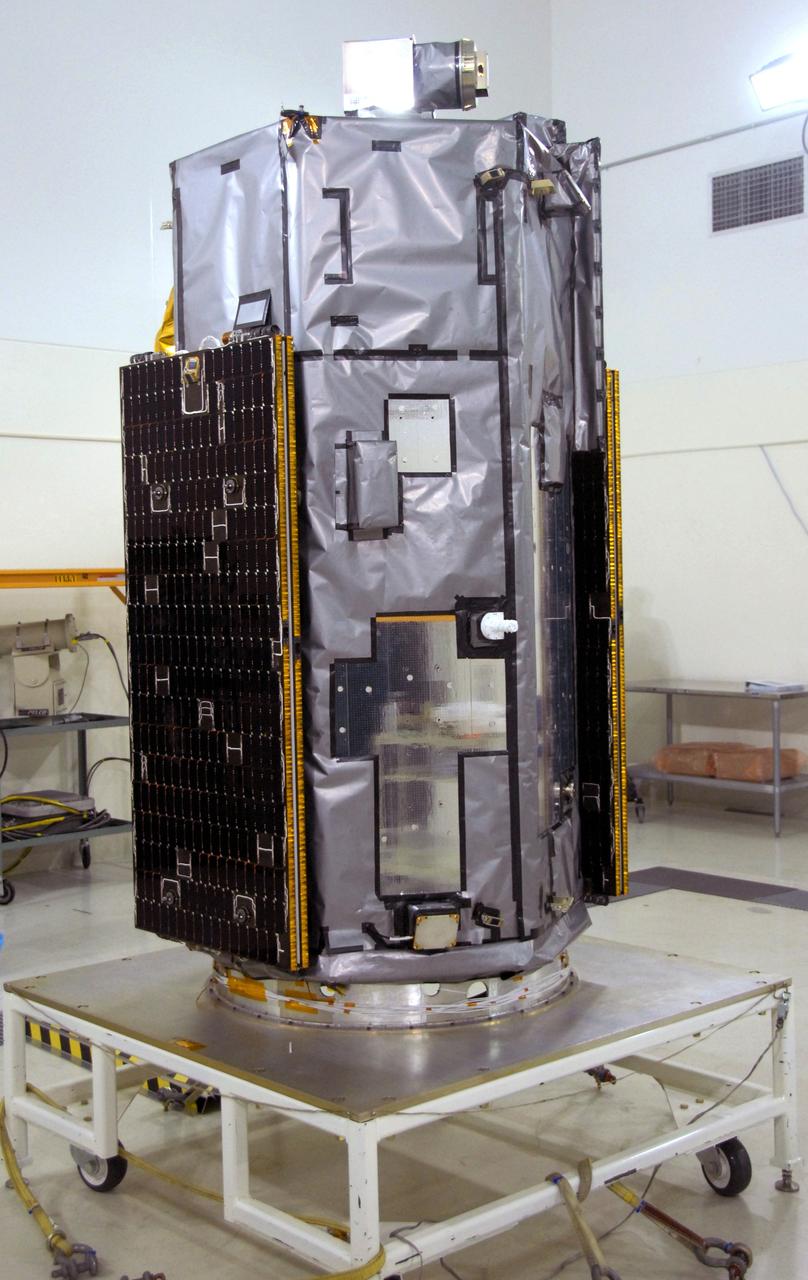

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility, building 1032, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, is displayed after blankets and edge tape were applied. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The observatory is targeted to launch Jan. 15 from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB
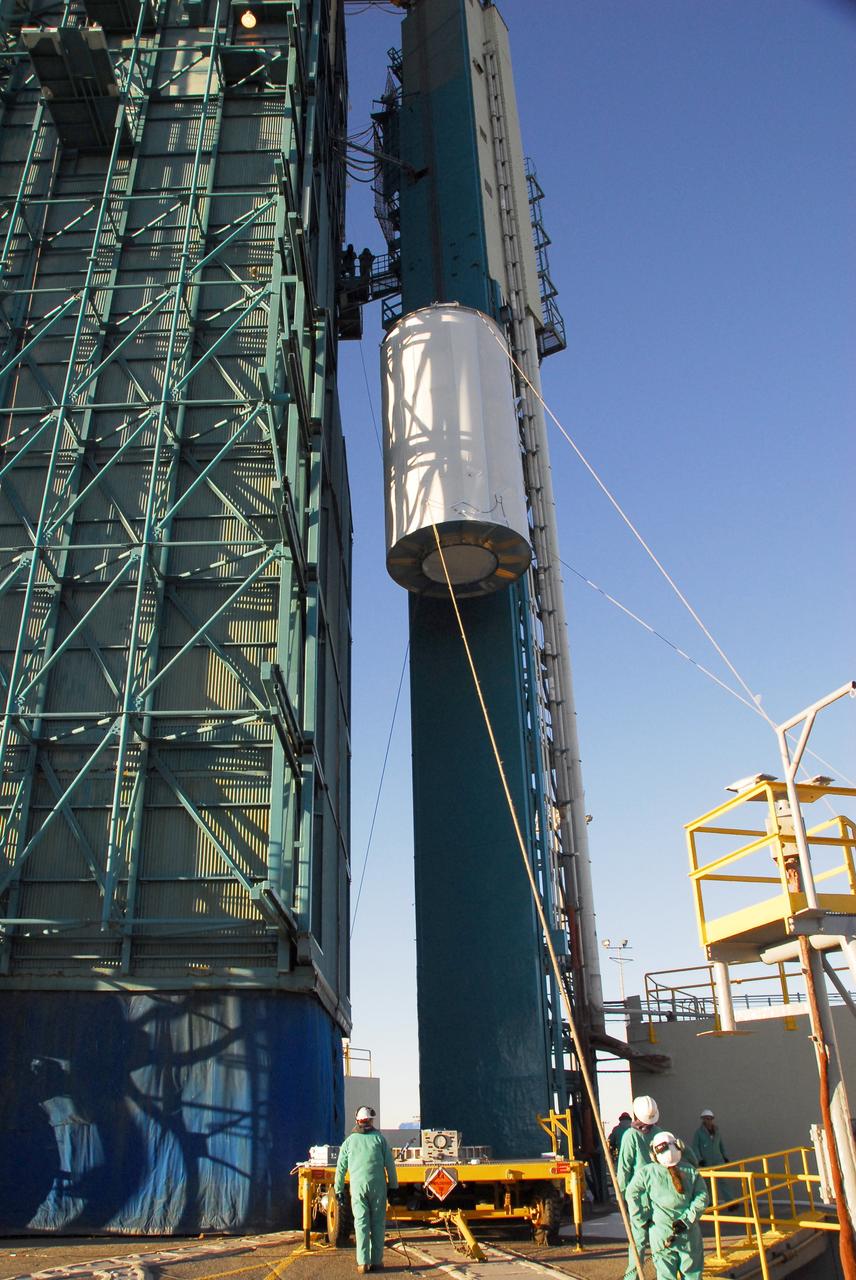

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The NOAA-N Prime satellite, enclosed in a canister for travel, is lifted alongside the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. In the tower, the satellite will be encapsulated and installed on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
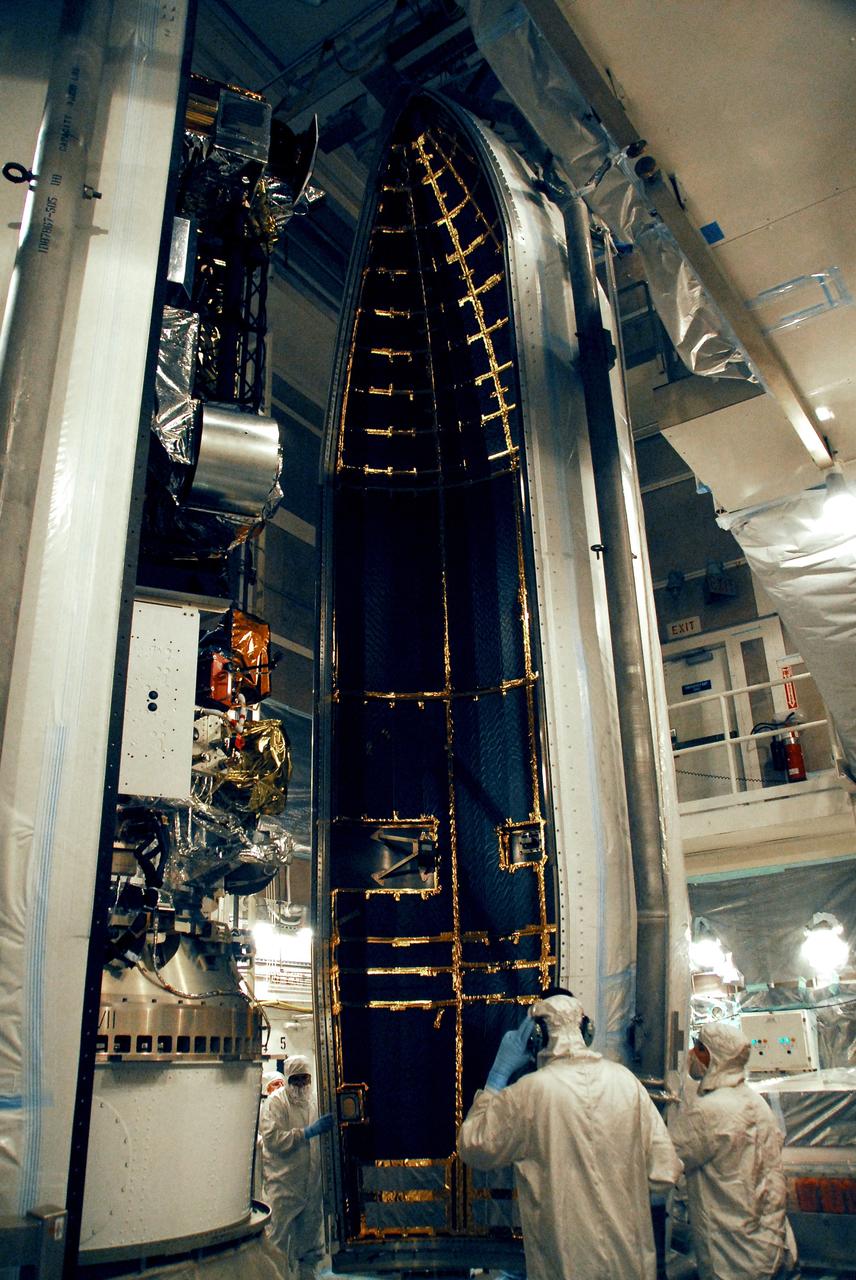
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The second half of the fairing is moved into place around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard the Delta II from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
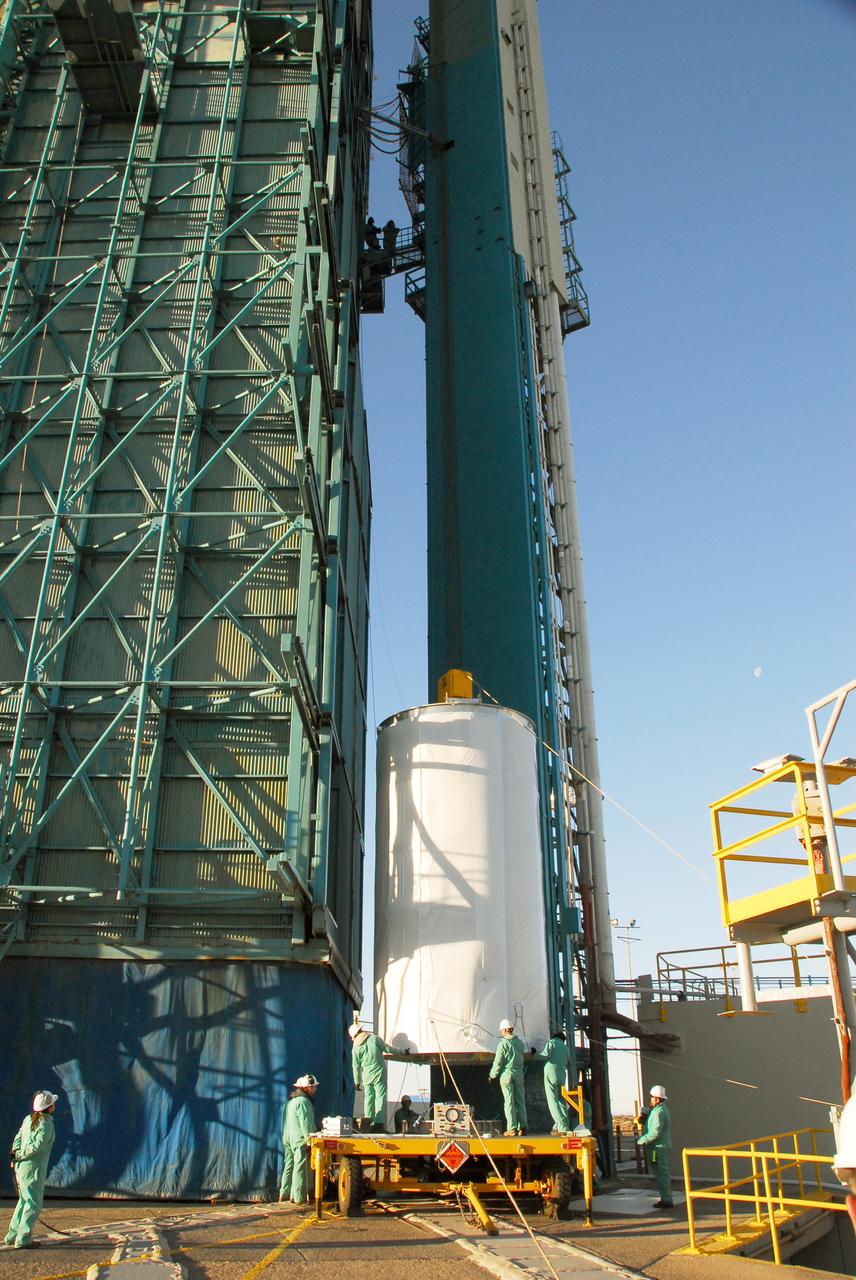

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The NOAA-N Prime satellite, enclosed in a canister for travel, is lifted alongside the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. In the tower, the satellite will be encapsulated and installed on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
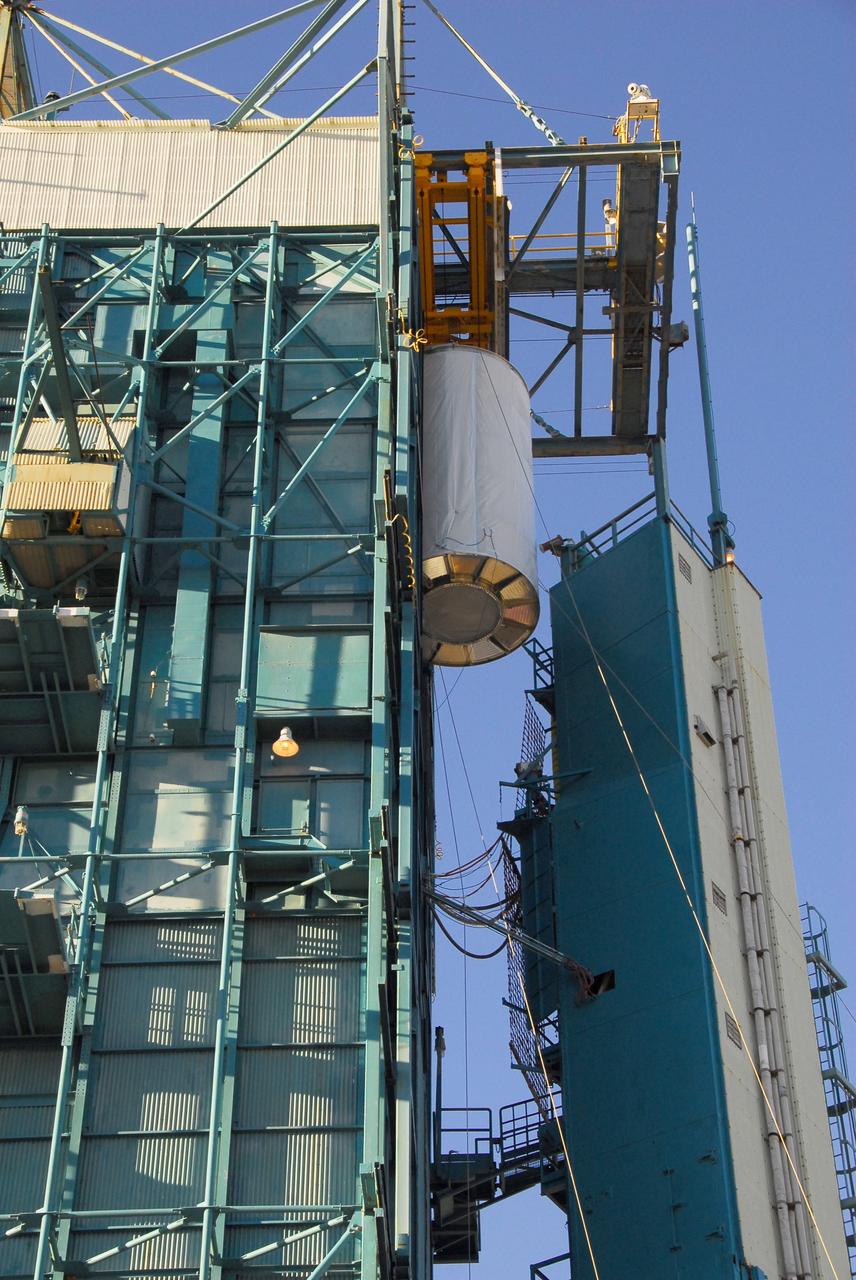

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The NOAA-N Prime satellite is lifted to the top of the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. In the tower, the satellite will be encapsulated and installed on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The two halves of the fairing are closed around the NOAA-N Prime spacecraft in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard the Delta II from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
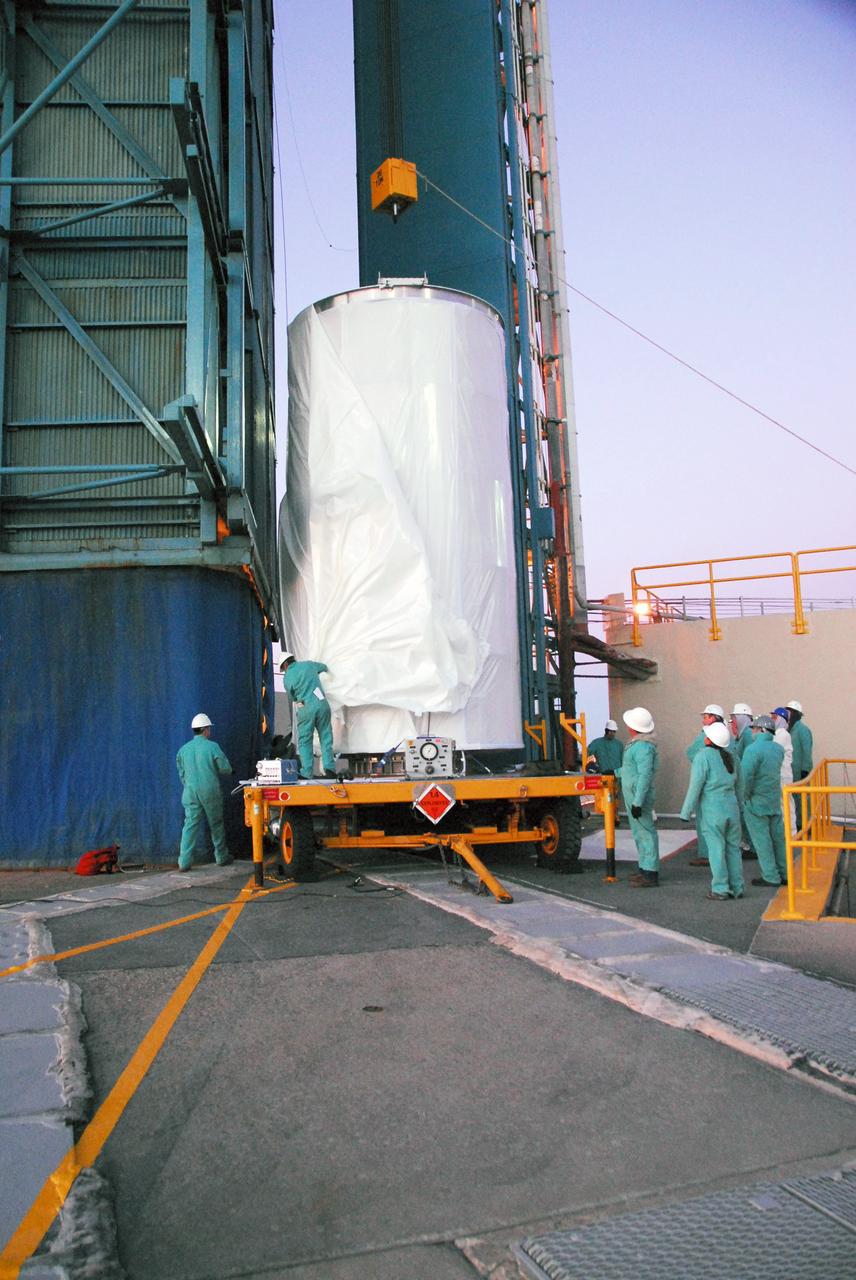

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The NOAA-N Prime satellite, enclosed in a canister for travel, is prepared for its lift into the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. In the tower, the satellite will be encapsulated and installed on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
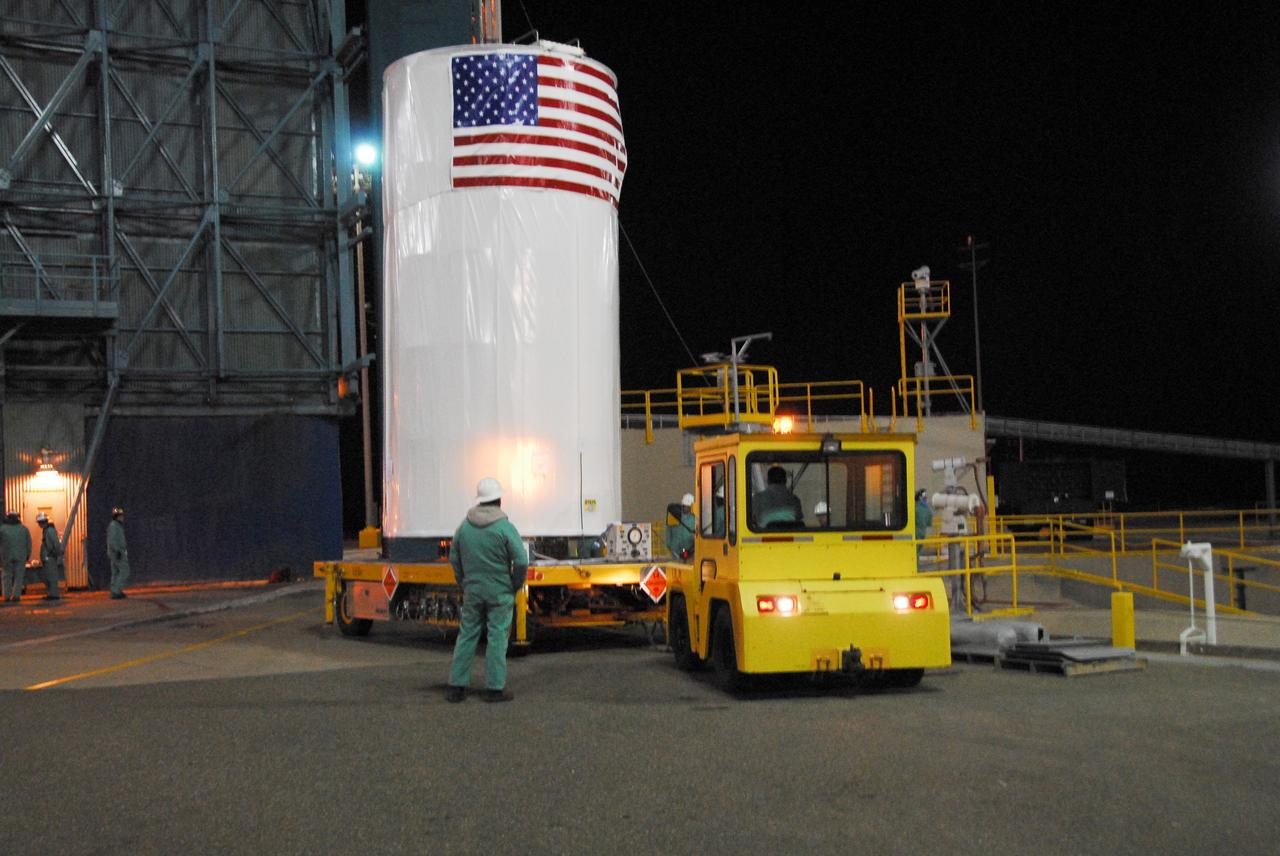

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The NOAA-N Prime satellite, enclosed in a canister for travel, arrives on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The container will be lifted into the mobile service tower for encapsulation and installation on the launch vehicle, a Delta II rocket. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The satellite is scheduled to launch Feb. 4 aboard a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
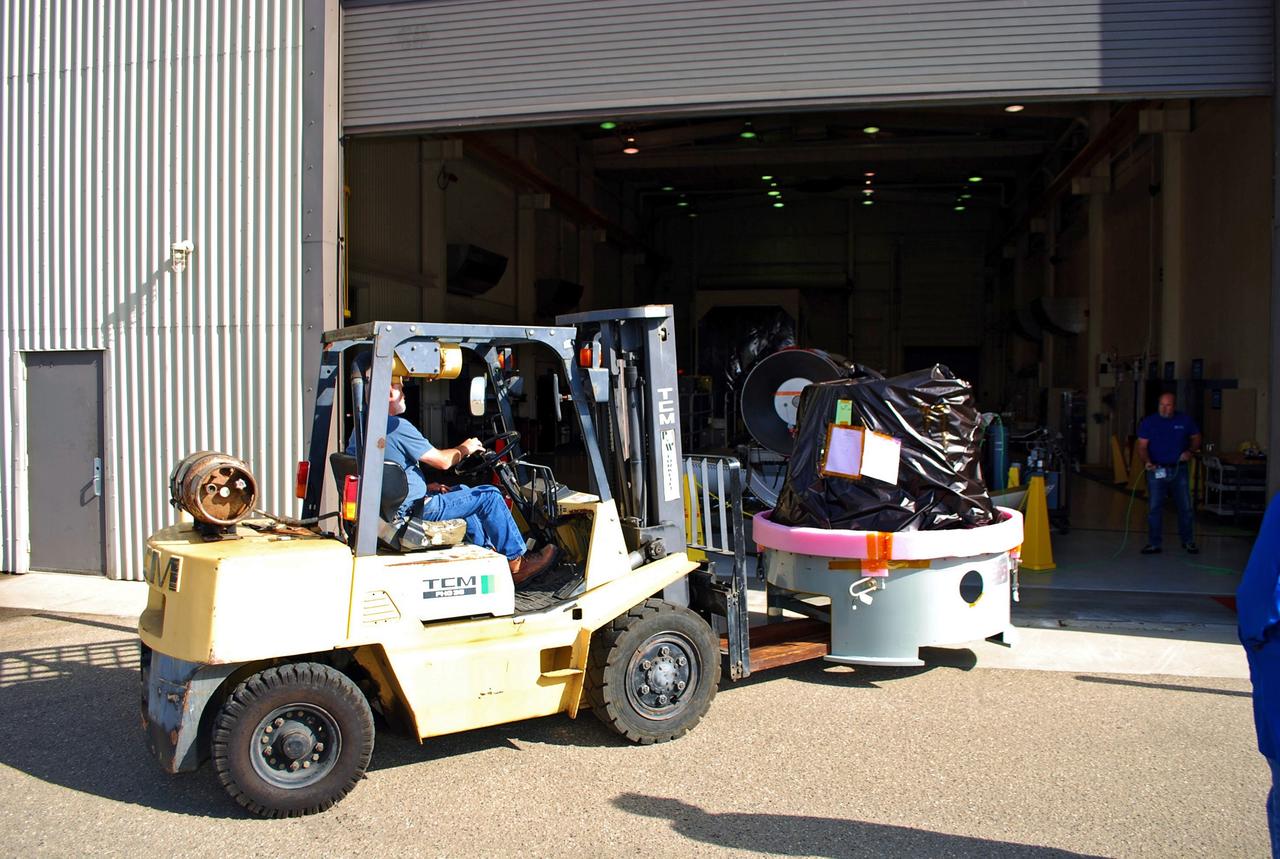

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker user a Hyster lift moves the payload cone for NASA's Glory mission into VAFB's payload processing facility. The payload cone is an adapter that interfaces the Taurus XL rocket with the spacecraft. A four-stage Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 2:09 a.m. PST Nov. 22. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
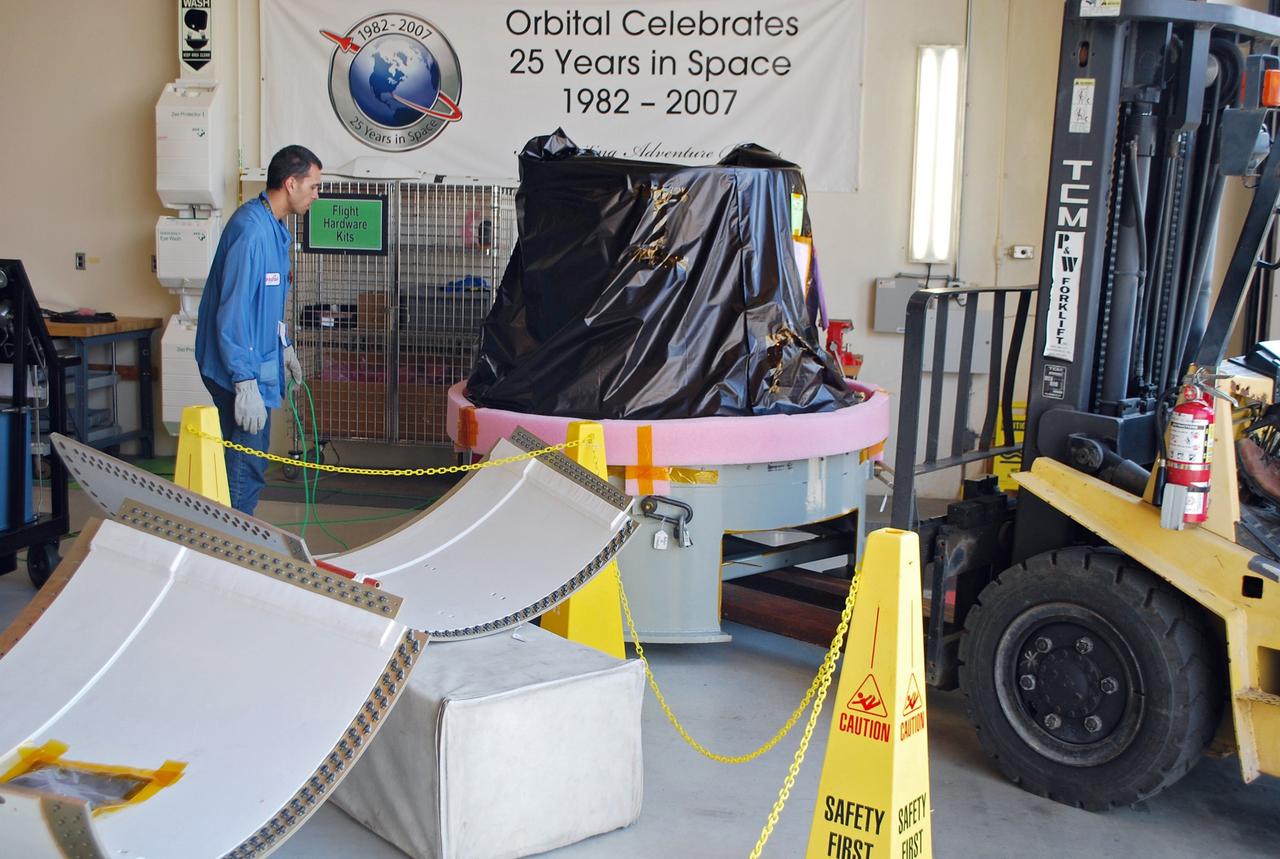

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload cone is lowered onto the floor of VAFB's payload processing facility for NASA's Glory mission. The payload cone is an adapter that interfaces the Taurus XL rocket with the spacecraft. A four-stage Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 2:09 a.m. PST Nov. 22. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
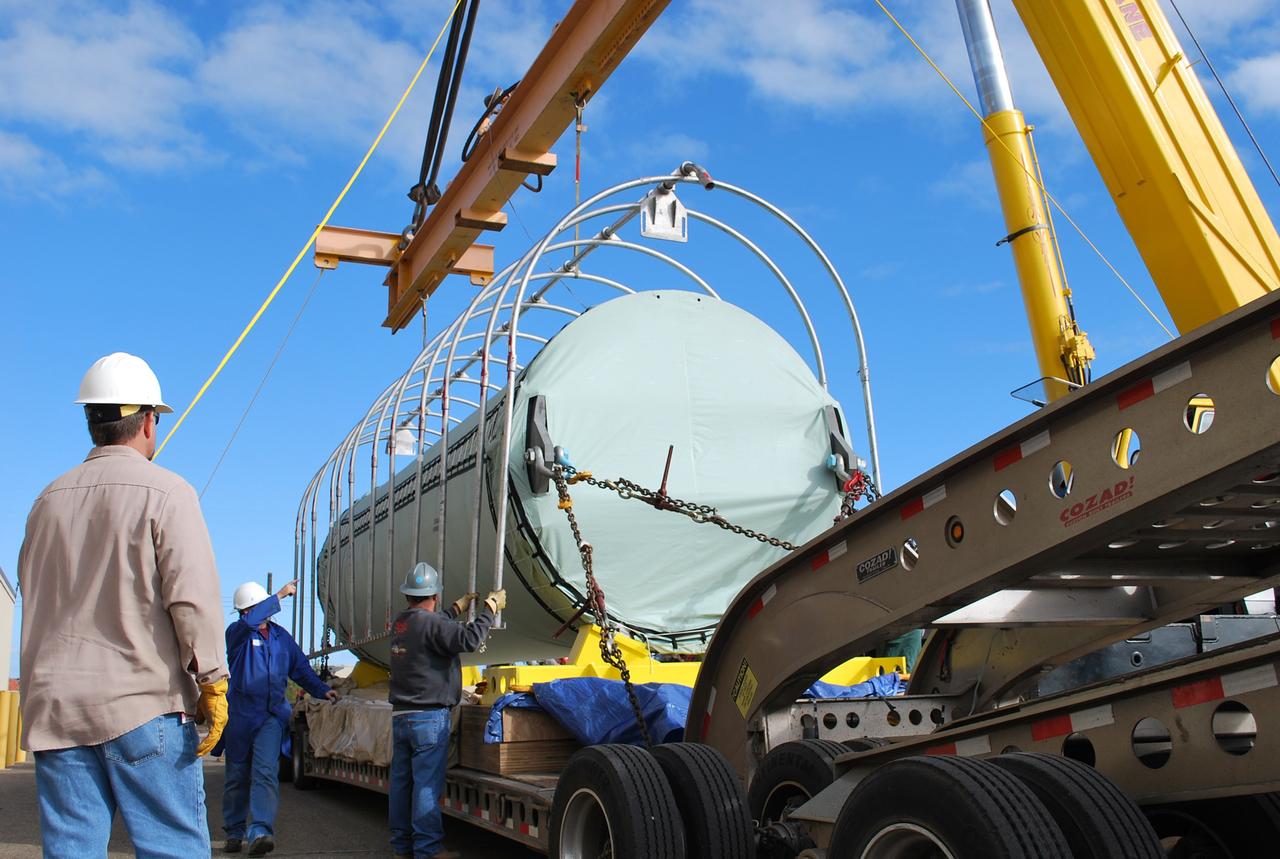

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – After arrival of the Stage 0 motor for the Taurus XL launch vehicle at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts off the protective cage. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
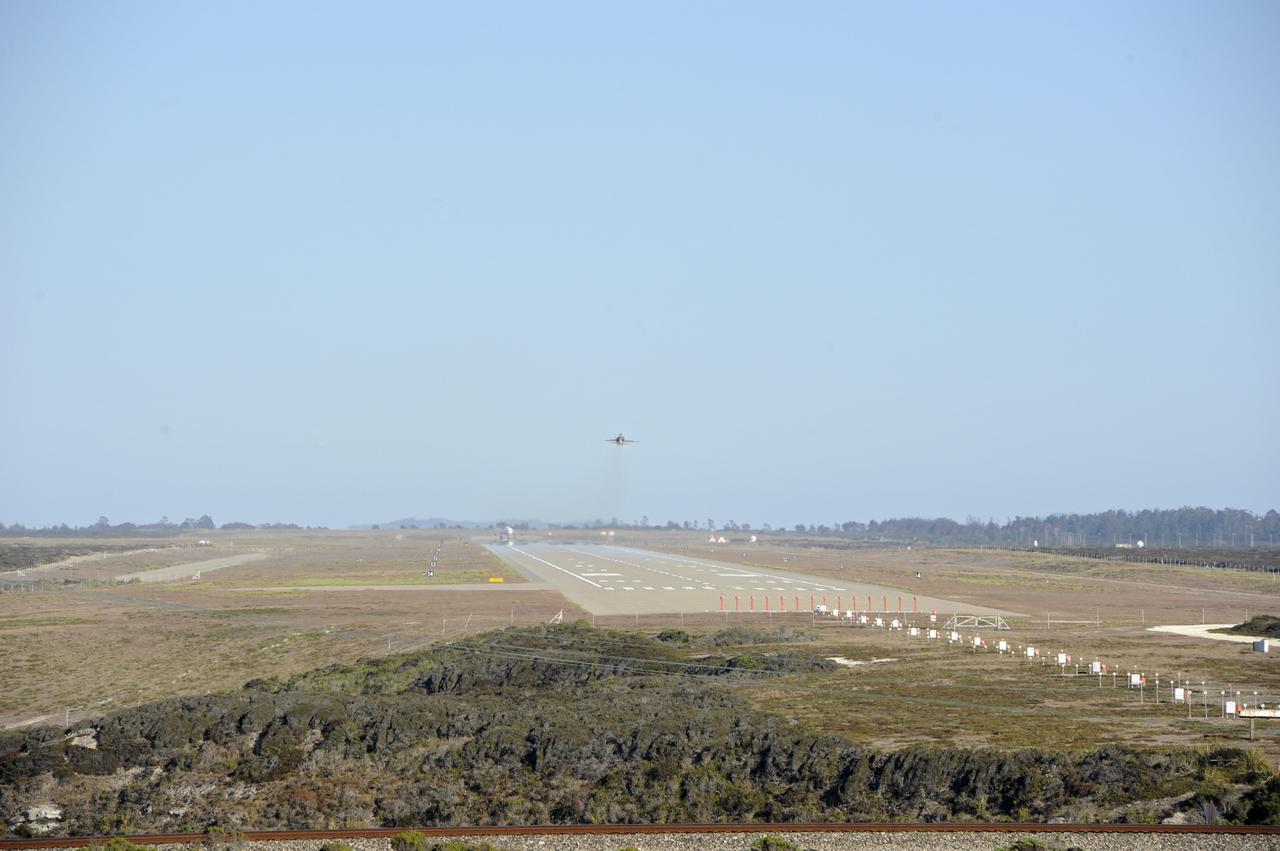

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A NASA F-18 takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., on a mission to record the launch of NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from an L-1011 carrier aircraft. Photo credit: VAFB/Chris Wiant

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts the Taurus XL Stage 0 motor to move it to a flatbed truck. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
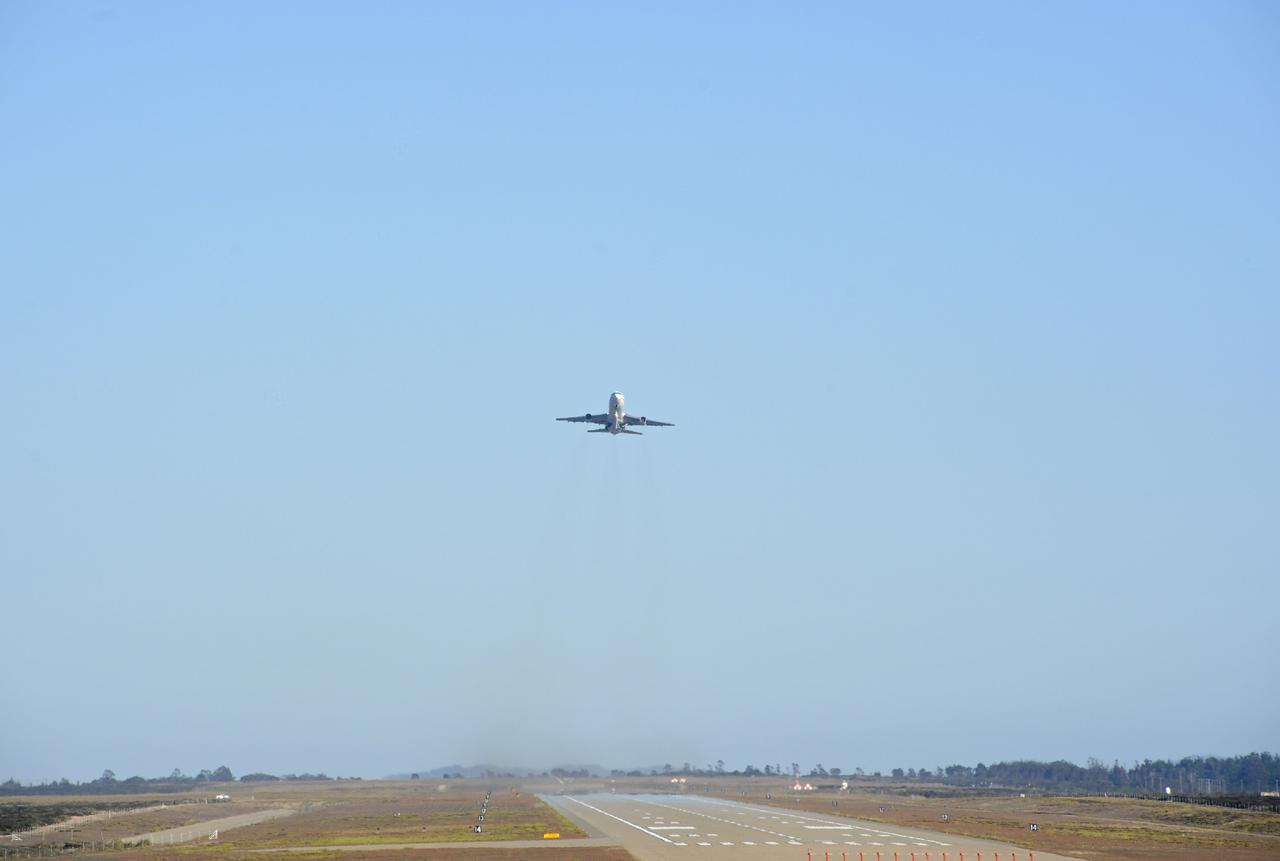

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the L-1011.Photo credit: VAFB/Chris Wiant

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, workers check NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft as it is lowered onto a work stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Moore, VAFB
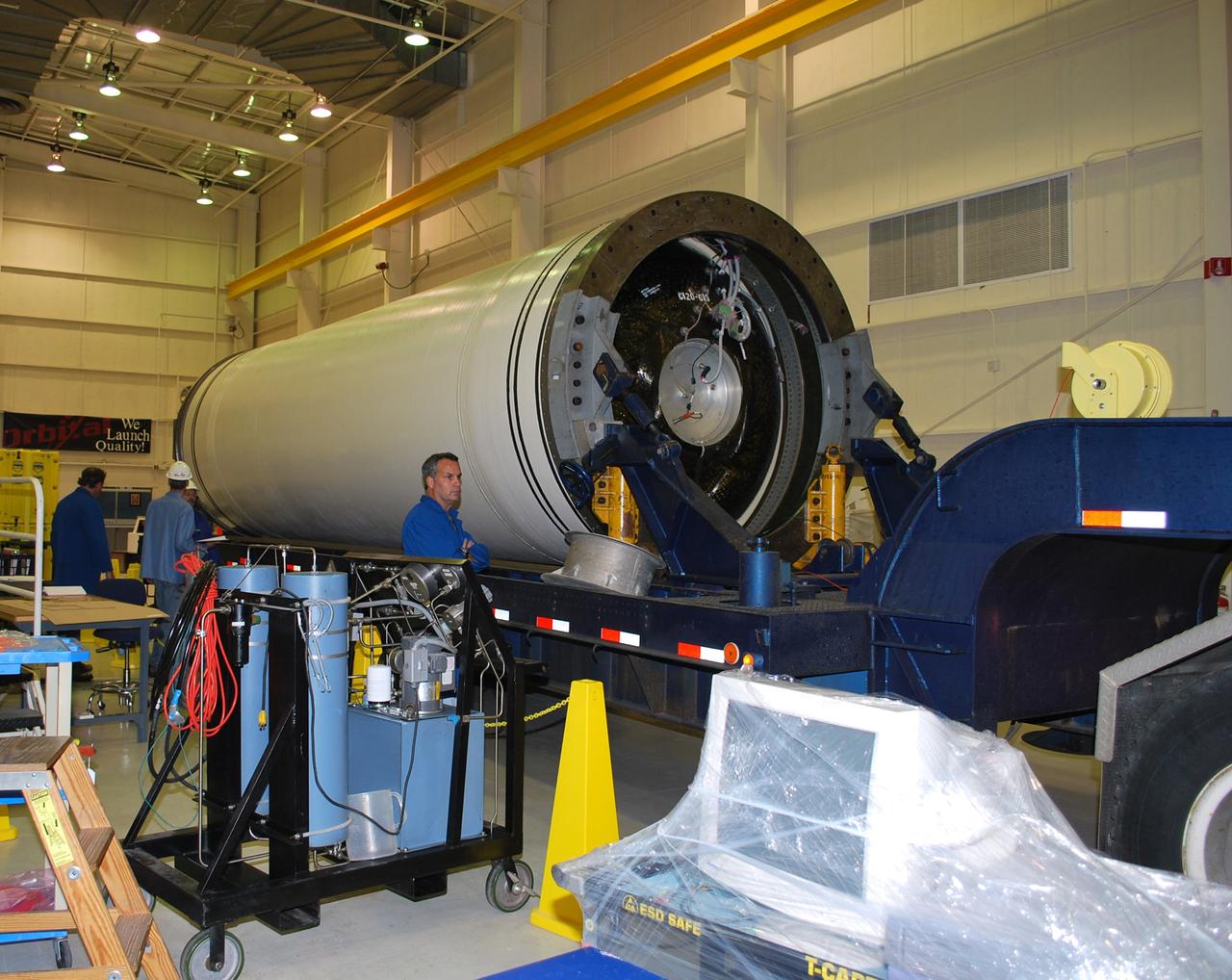

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Taurus XL Stage 0 motor has been moved into Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
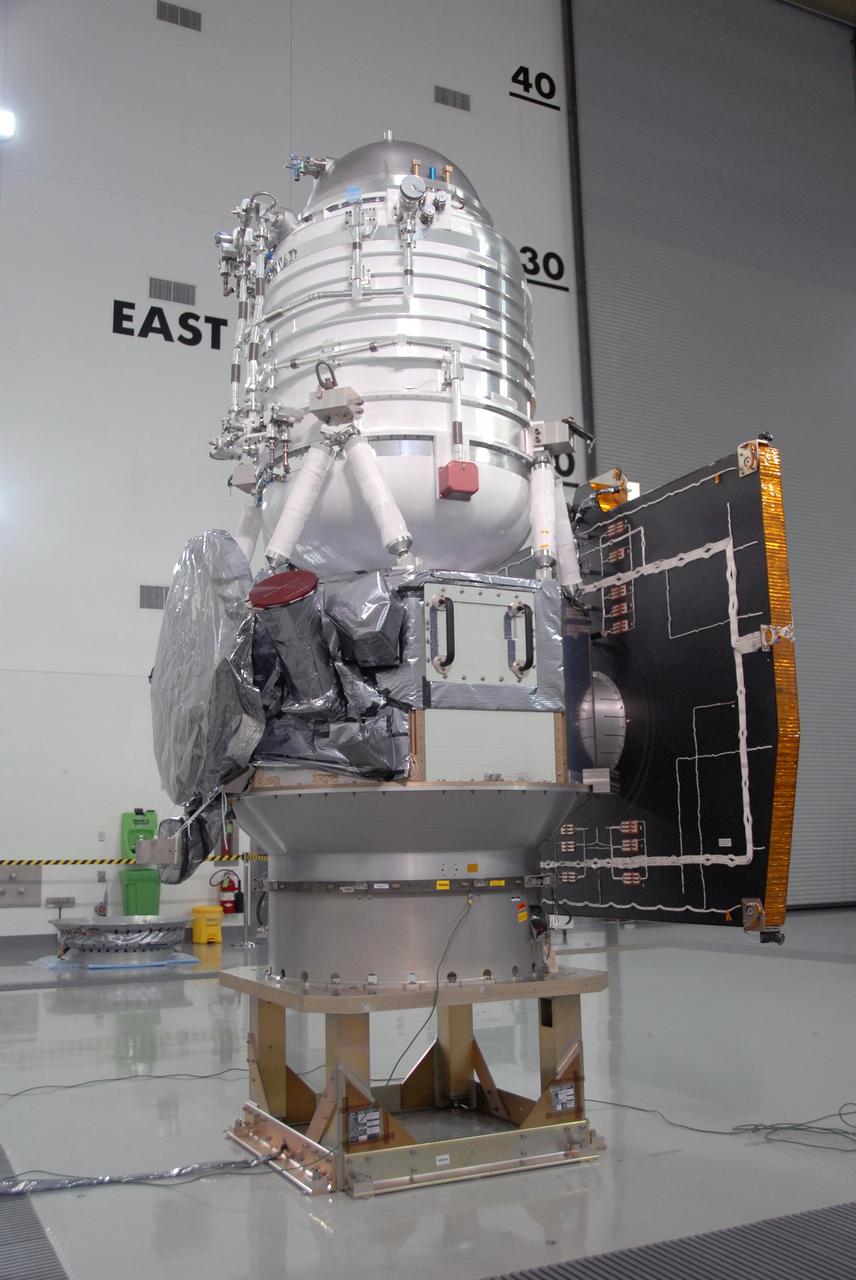

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is situated on a work stand. At right is the fixed panel solar array. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Moore, VAFB
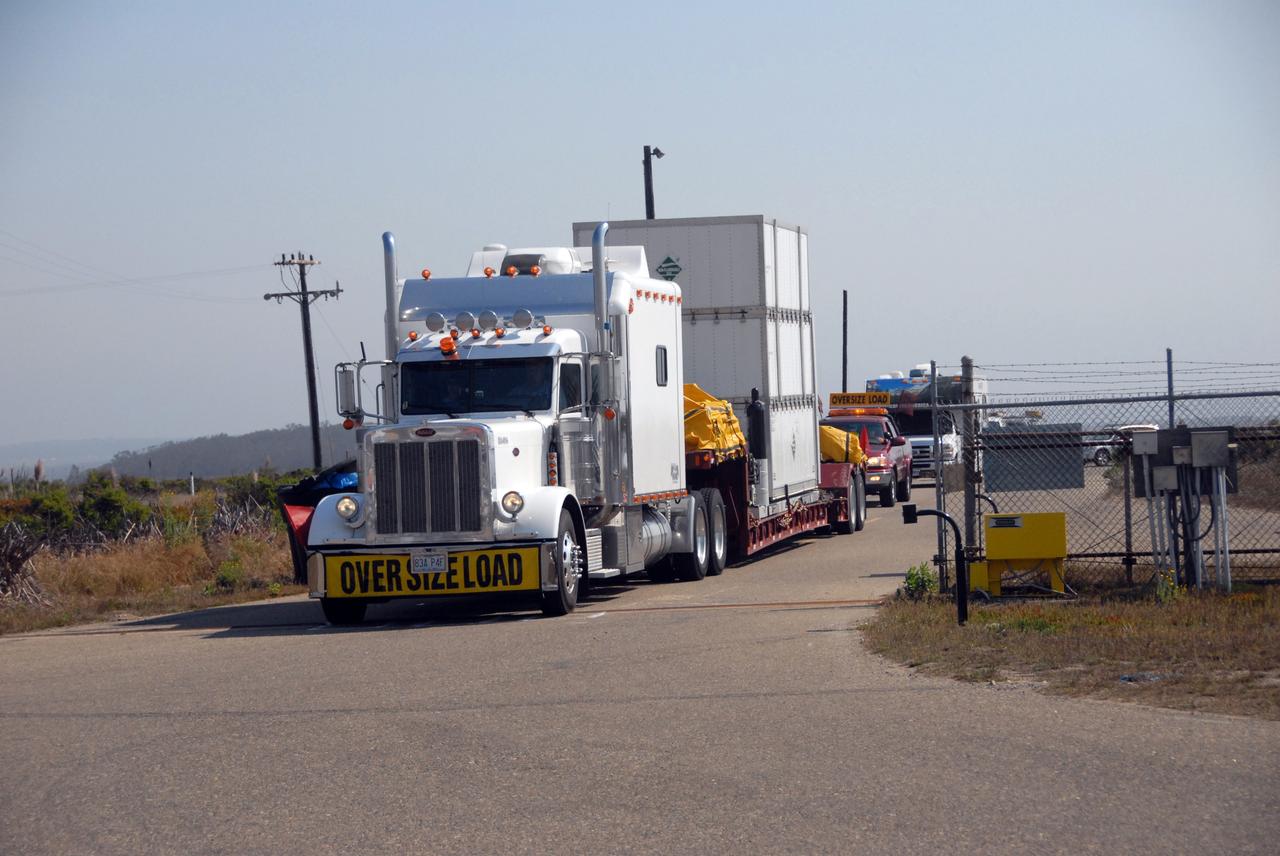

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The truck carrying NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. It will be taken to the Astrotech payload processing facility. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
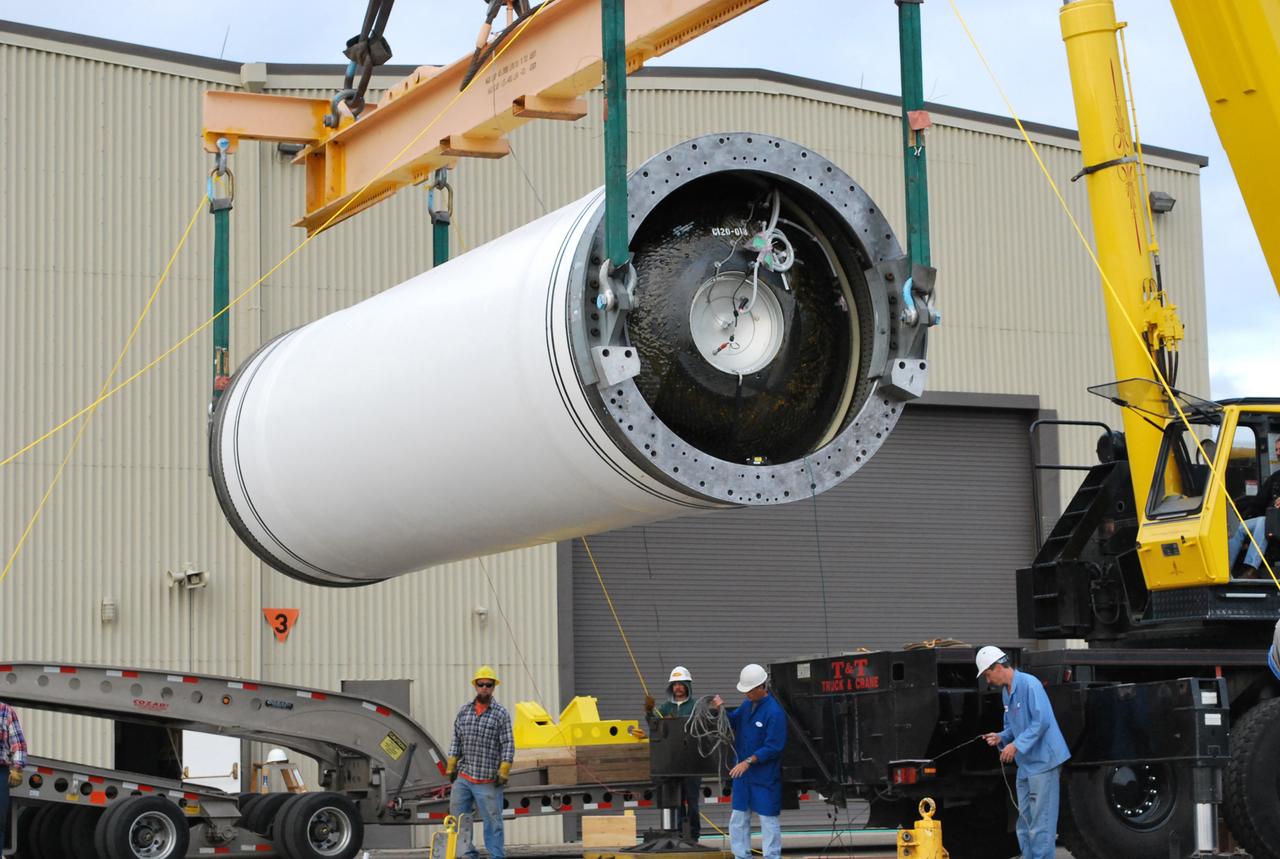

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts the Taurus XL Stage 0 motor to move it to a flatbed truck. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
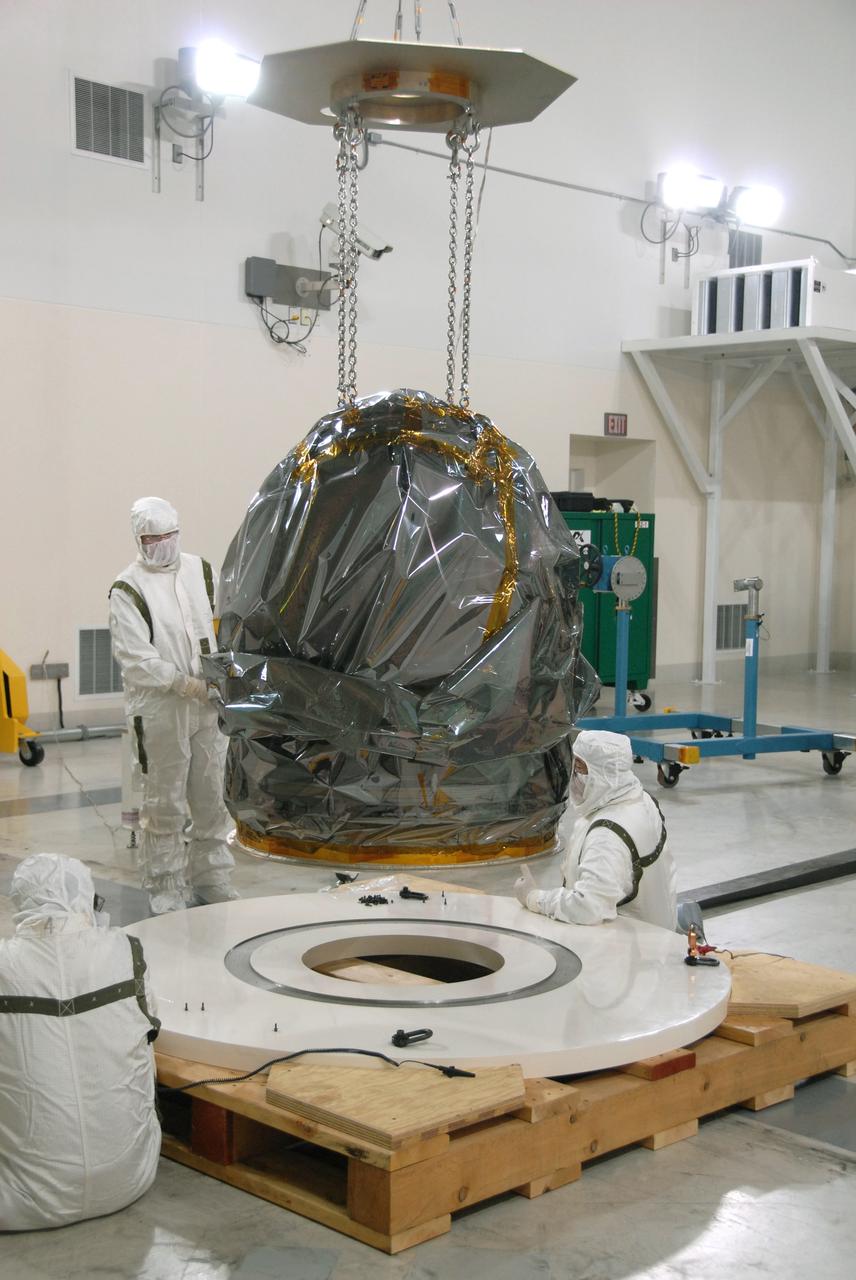

Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, is covered with protective material for a move to the stand in the foreground. The overhead crane will be attached to make the move. Designed to detect the edge of the Solar System, the IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX is targeted for launch from the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, on Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley, VAFB
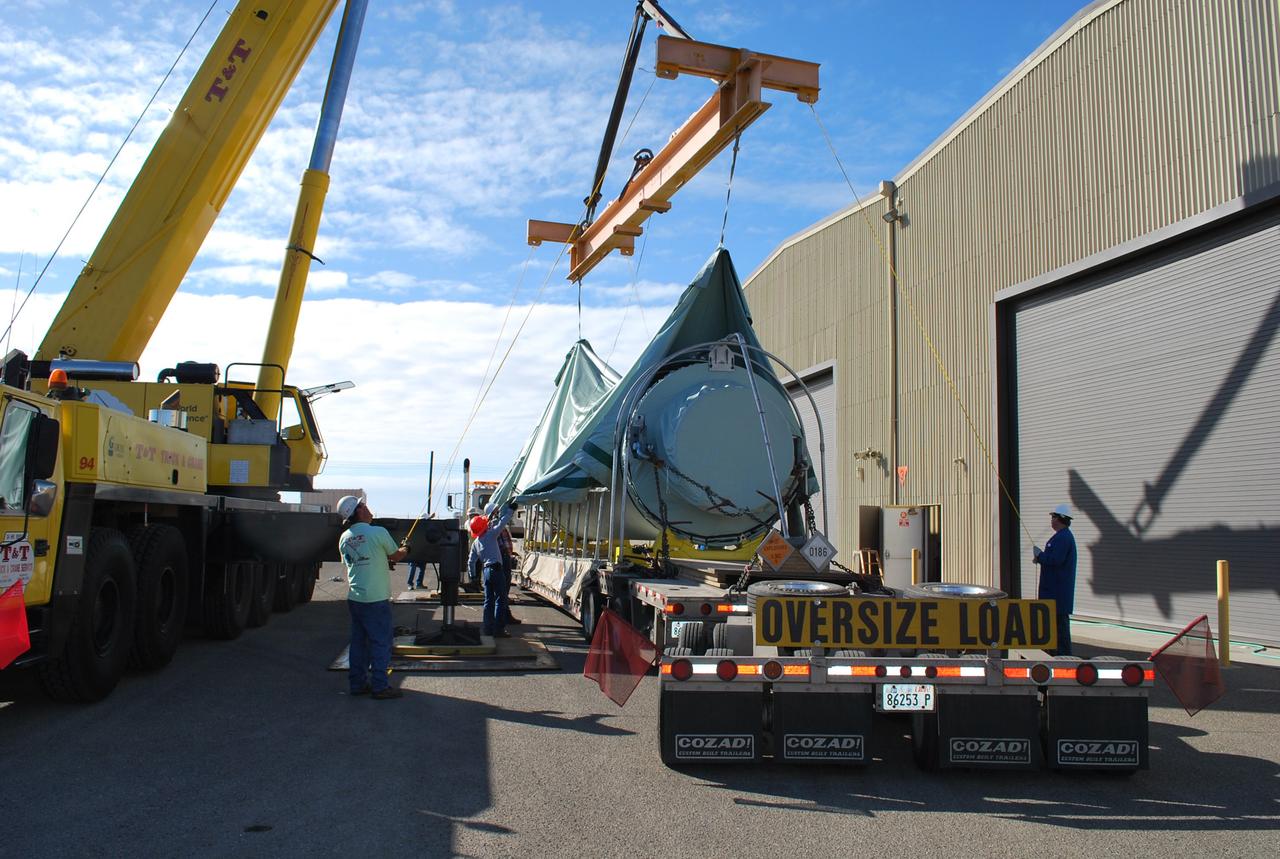

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – After arrival of the Stage 0 motor for the Taurus XL launch vehicle at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts off the protective shipping cover. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
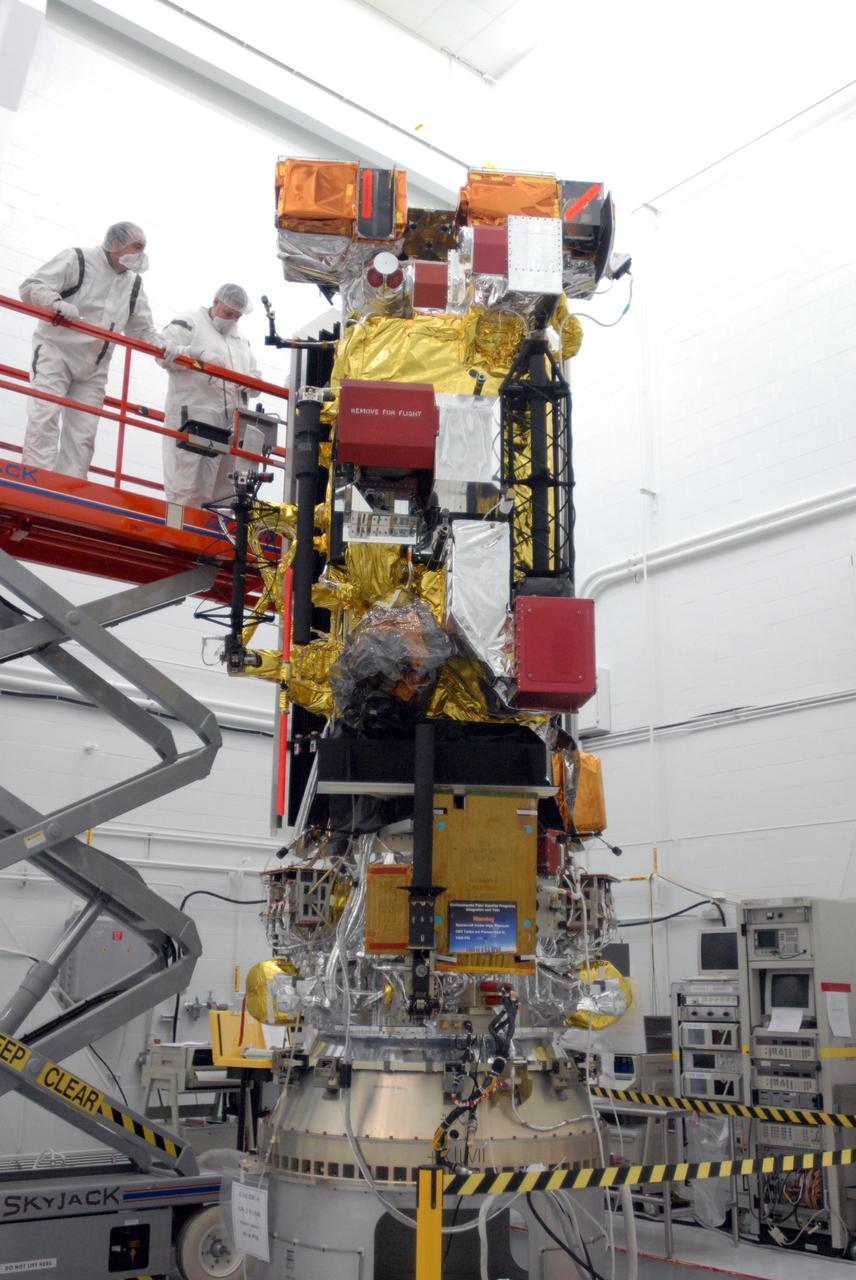

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Another view of the NOAA-N Prime satellite in the payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It is built by Lockheed Martin and similar to NOAA-N launched on May 20, 2005. Launch of NOAA-N Prime is scheduled for Feb. 4. Photo credit: NASA/Joe Davila, VAFB
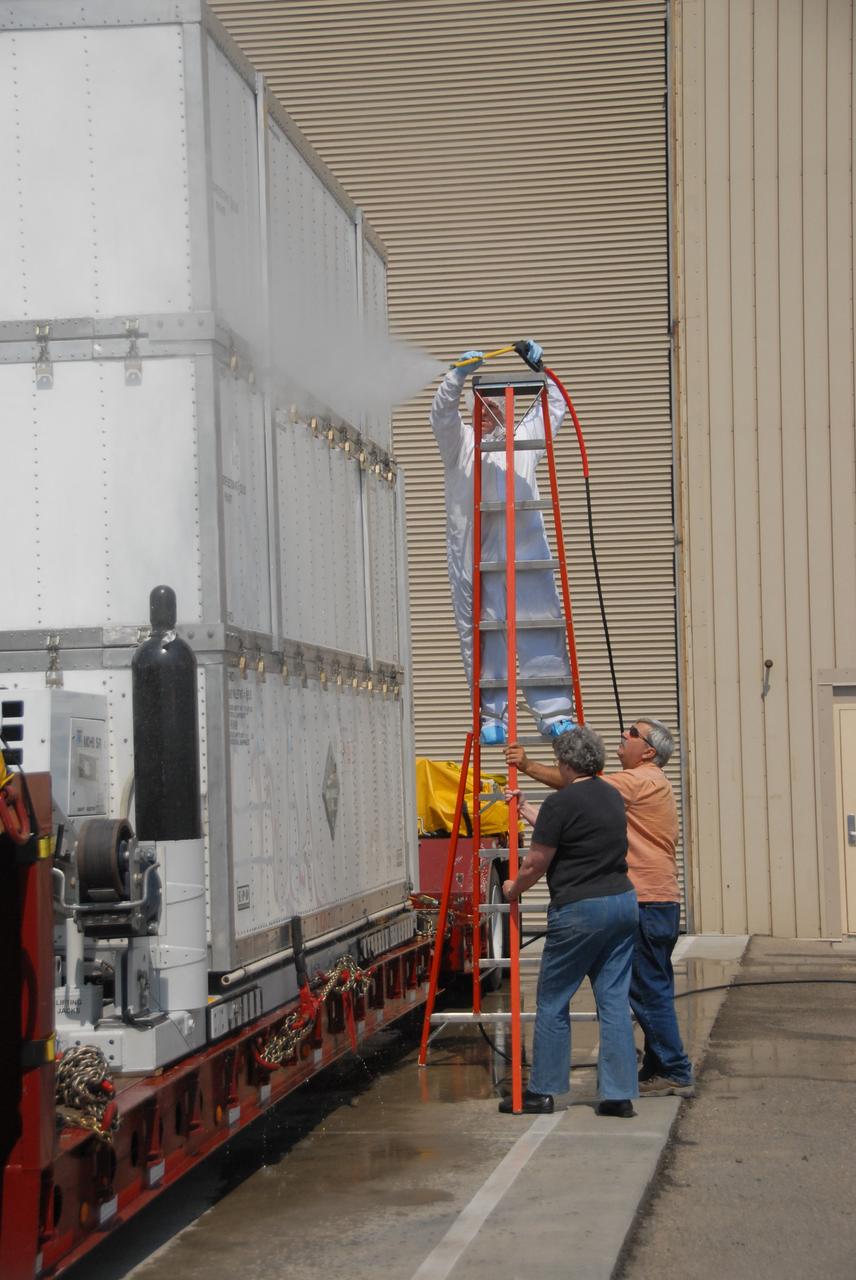

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Outside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers clean the shipping container of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft before moving it inside. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
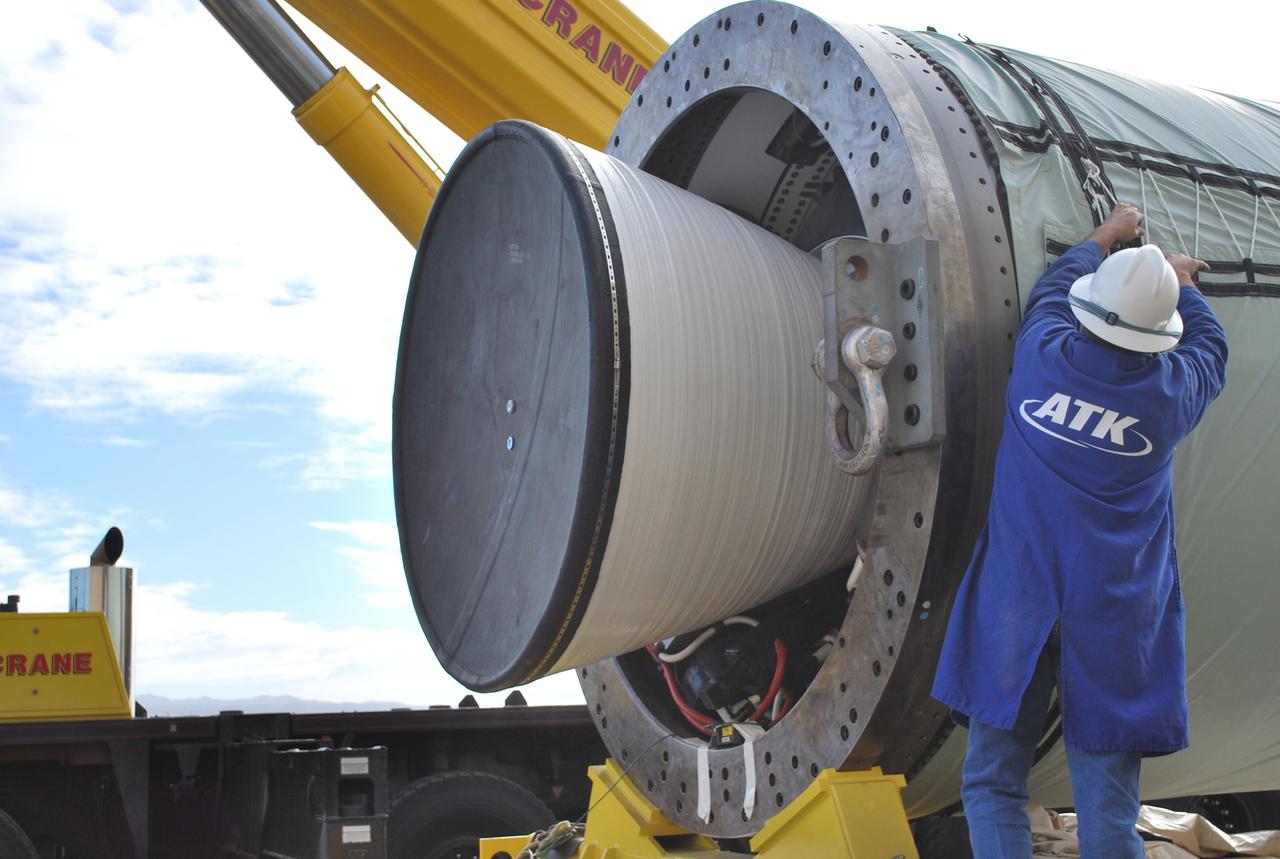

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker secures a crane on the Taurus XL Stage 0 motor. The motor will be lifted onto a flatbed truck and transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
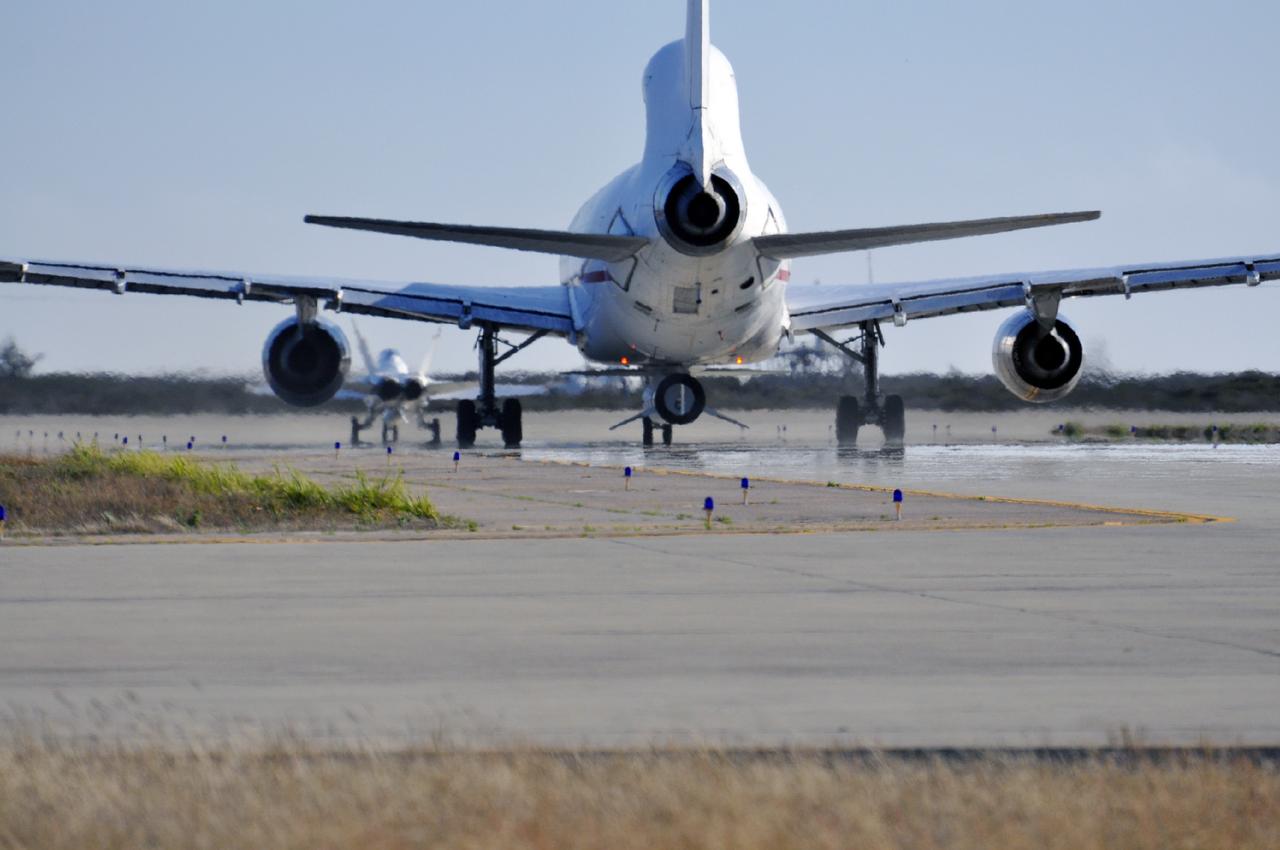

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A NASA F-18 and an Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft taxi to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., before taking off on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the L-1011. Photo credit: VAFB/ Randy Beaudoin

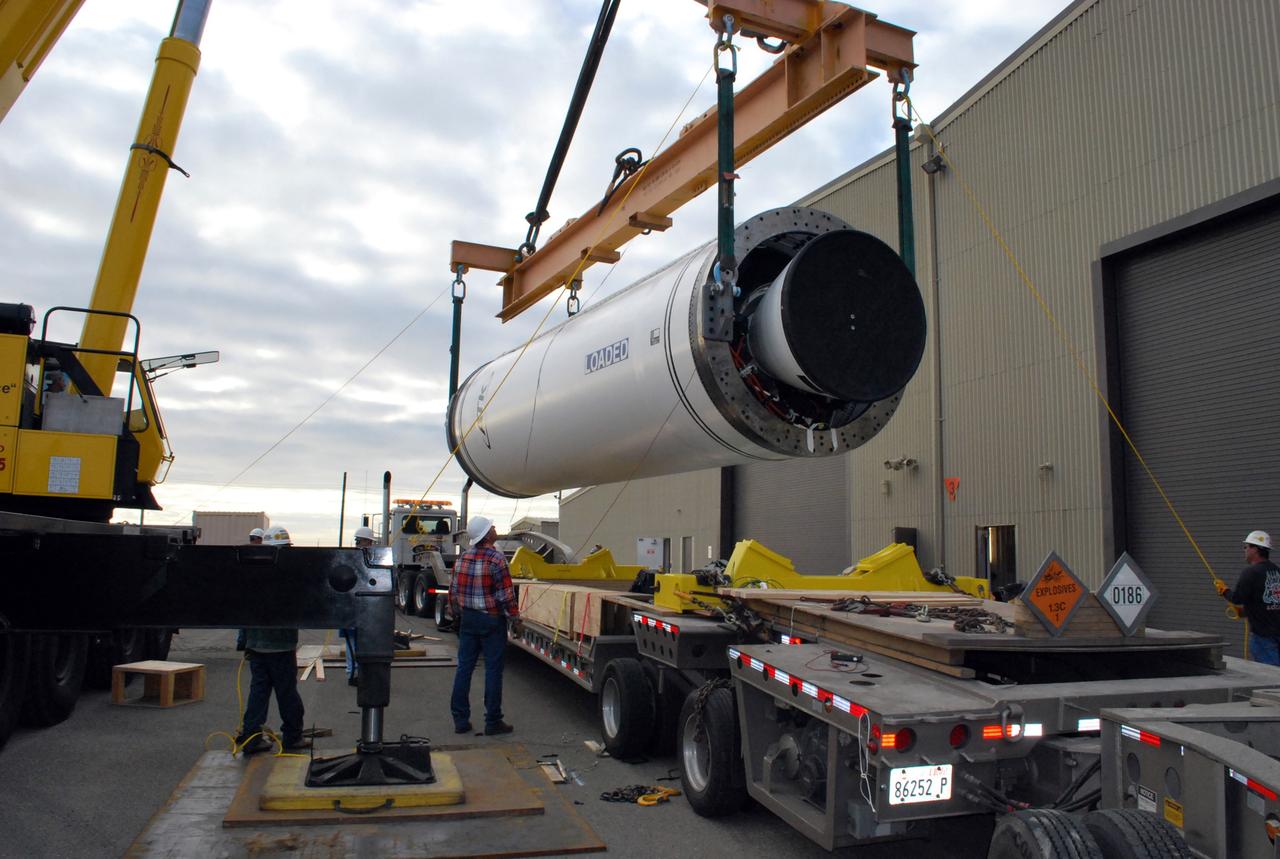
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Stage 0 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle for the Orbiting Carbon Observatory arrives at complex 576E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. It will be mated with stages 1, 2 and 3 for the launch of OCO. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. It is scheduled to launch Feb. 23. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

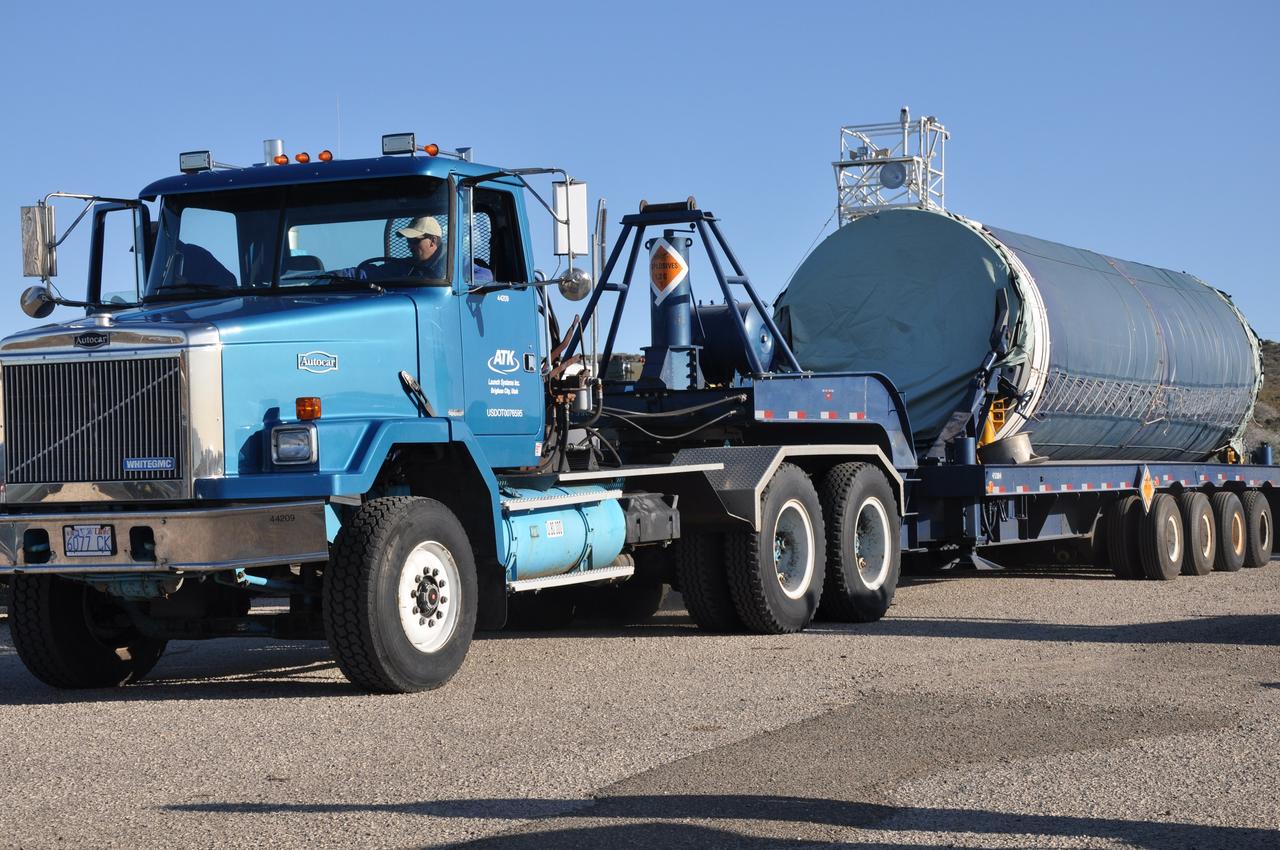
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts the Taurus XL Stage 0 motor to move it to a flatbed truck. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
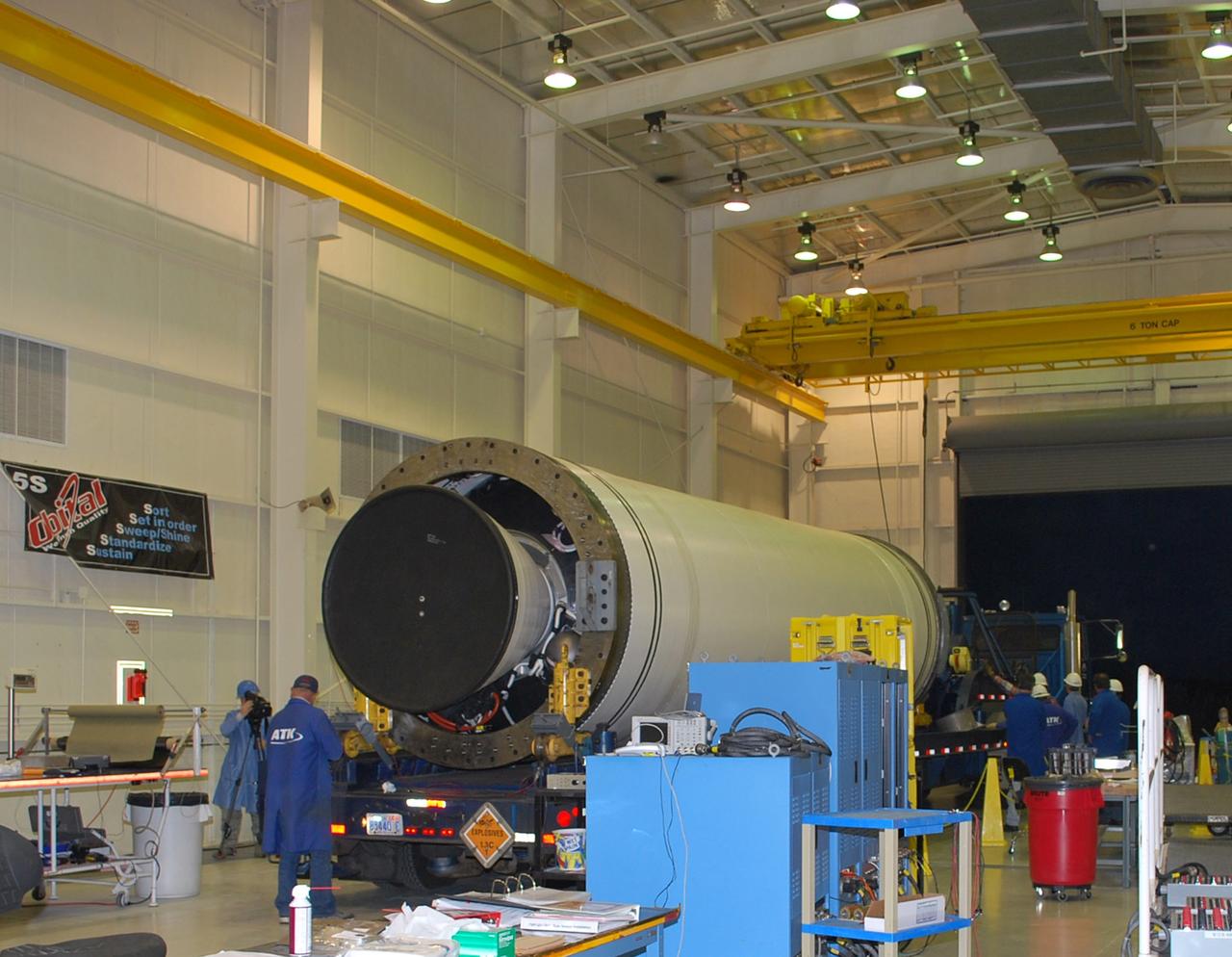

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Taurus XL Stage 0 motor has been moved into Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
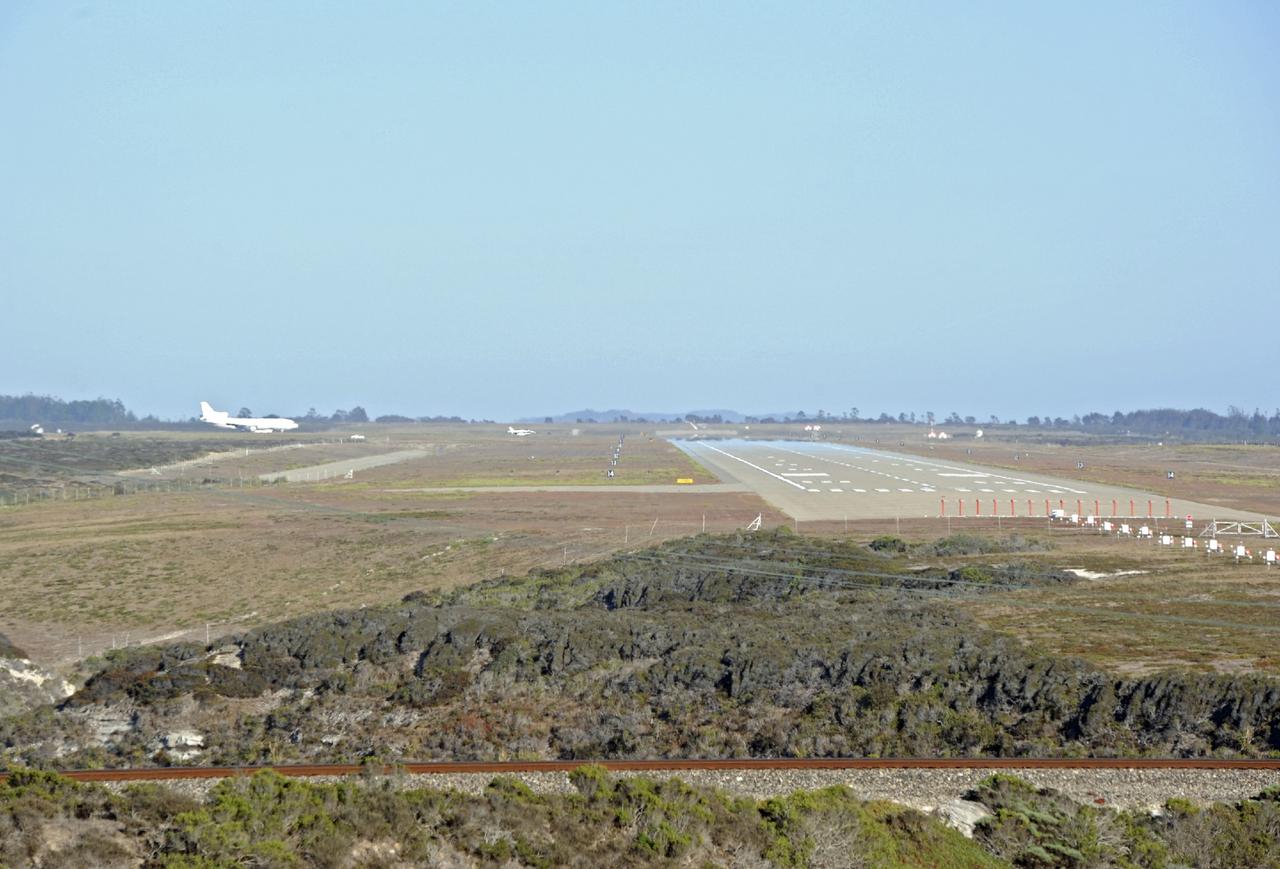

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A NASA F-18 and an Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft taxi to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., before taking off on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the L-1011. Photo credit: VAFB/ Chris Wiant
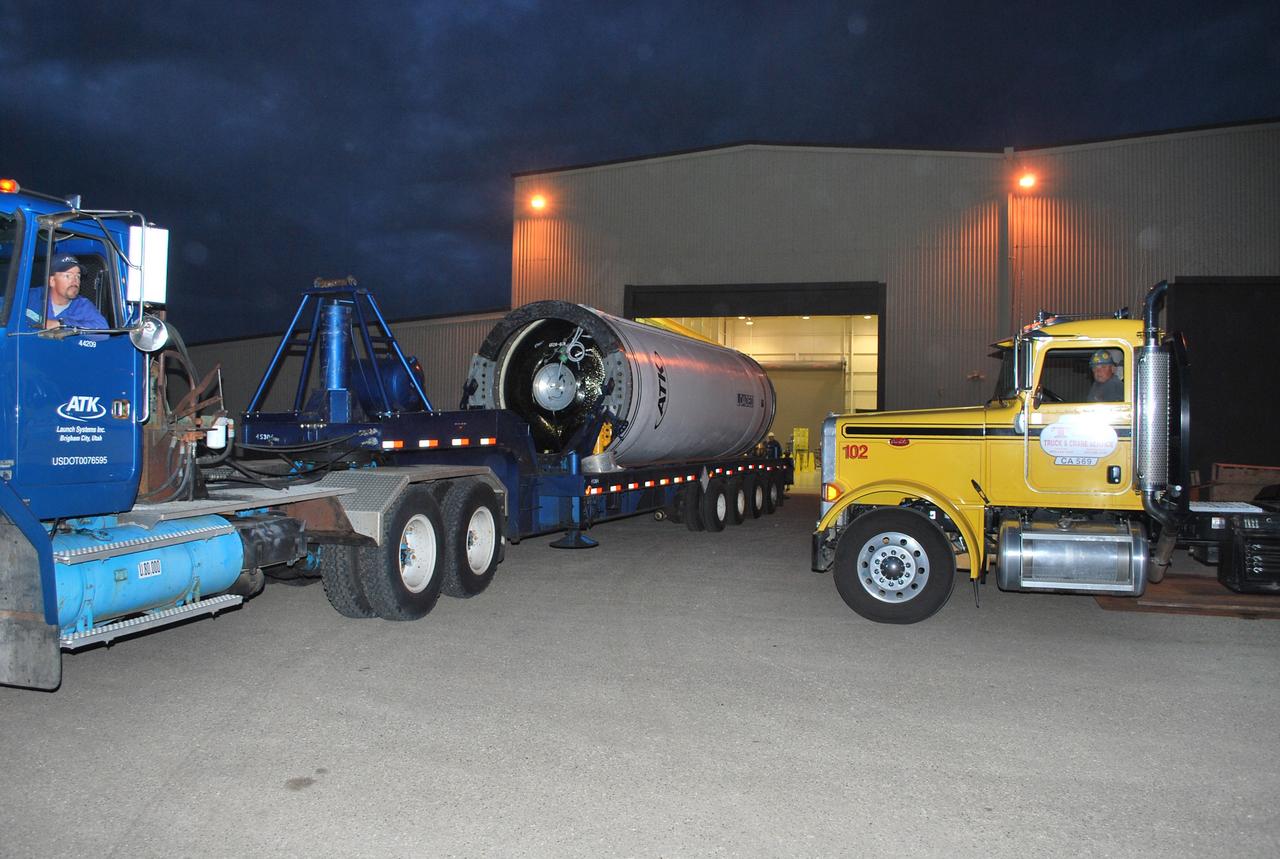

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Taurus XL Stage 0 motor is moved into Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the NASA payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the NOAA-N Prime satellite is bagged before moving it. NOAA-N Prime is the latest polar-orbiting operational environmental weather satellite developed by NASA for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. It is built by Lockheed Martin and similar to NOAA-N launched on May 20, 2005. Launch of NOAA-N Prime is scheduled for Feb. 4. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB
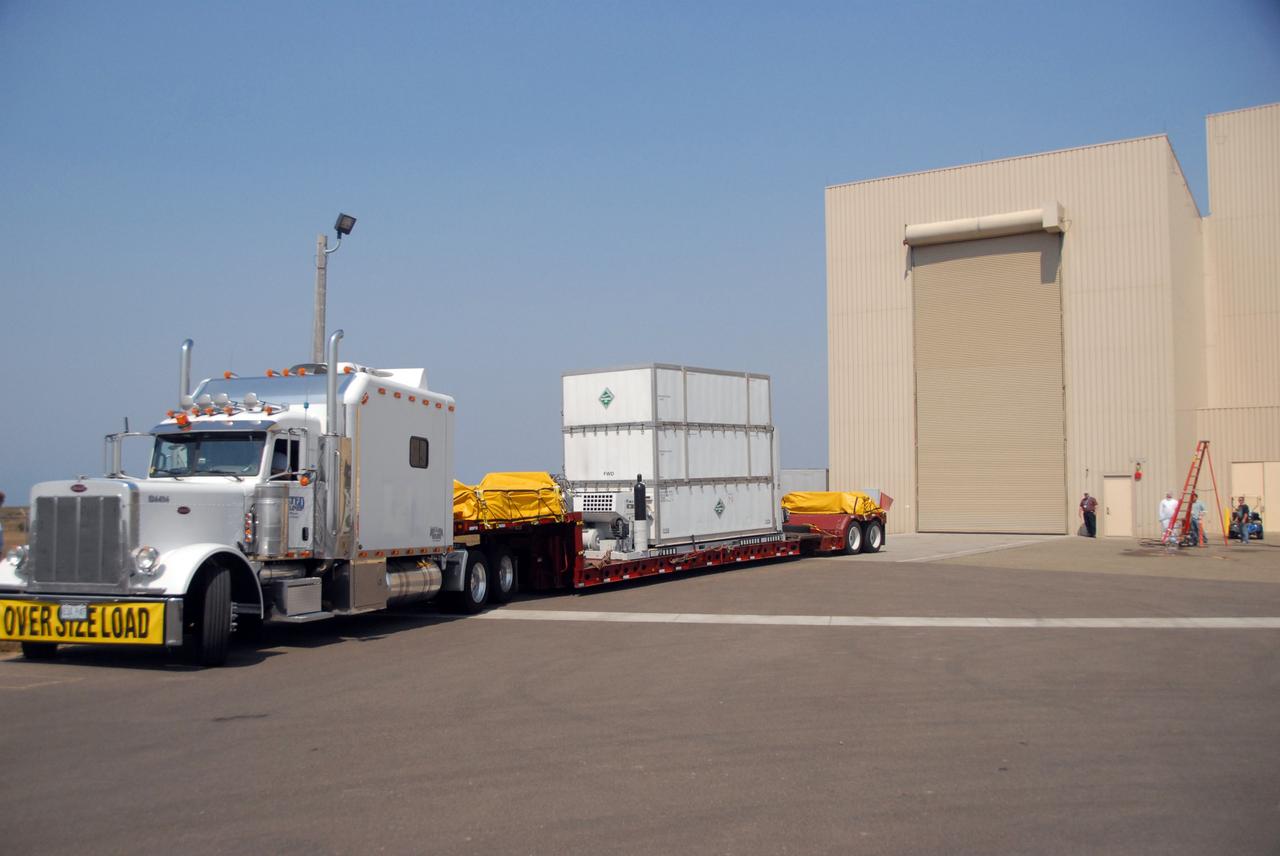

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The truck carrying NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft arrives at the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
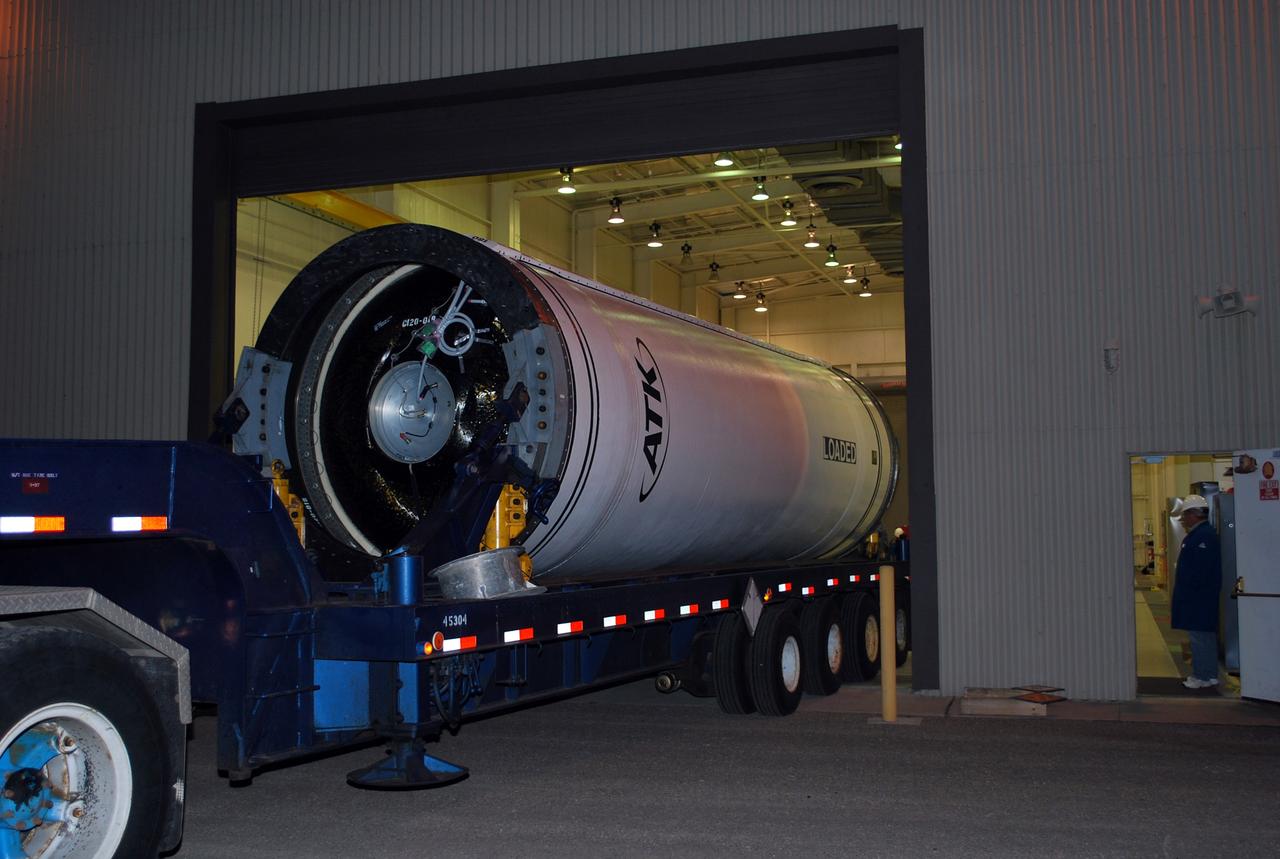

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Taurus XL Stage 0 motor is moved into Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
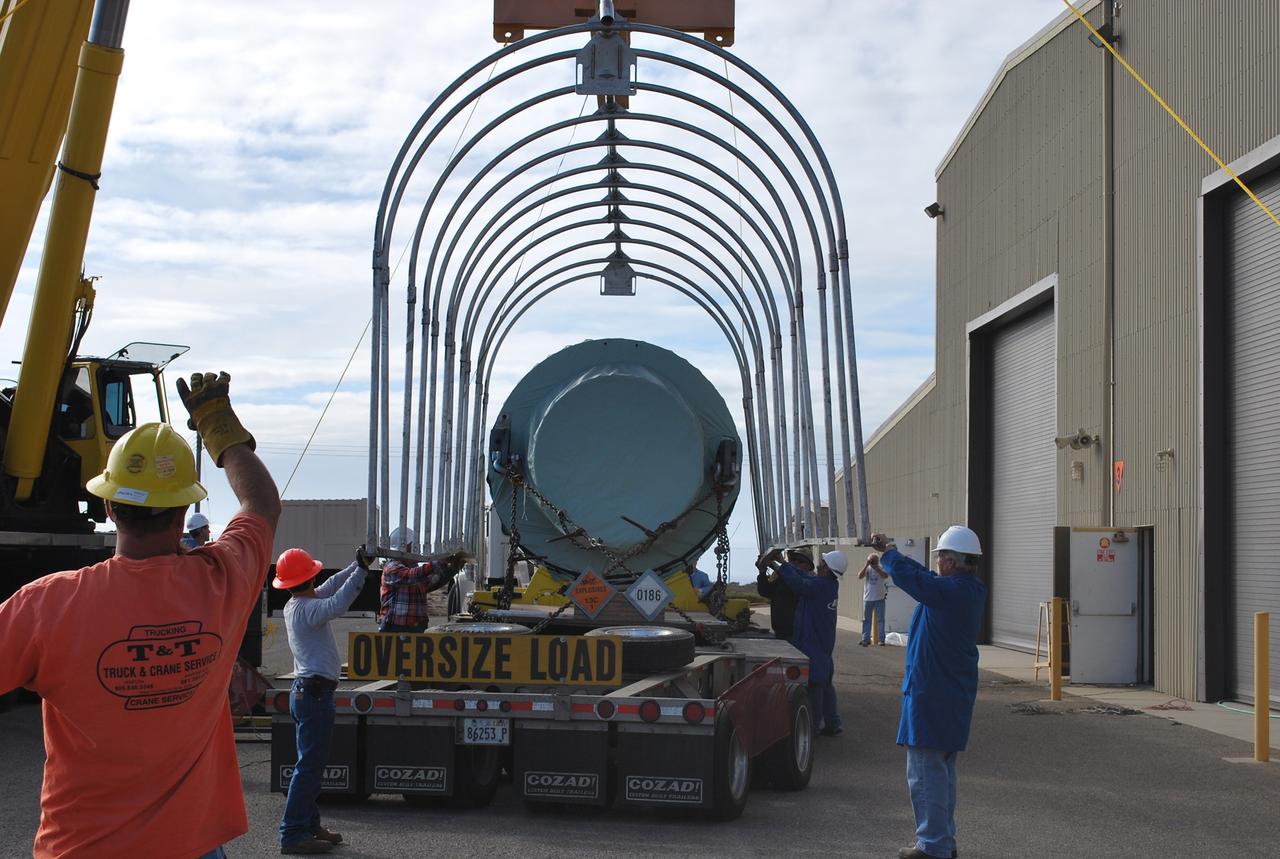

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – After arrival of the Stage 0 motor for the Taurus XL launch vehicle at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts off the protective cage. The motor will be transported to Orbital Sciences' Hangar 1555. The Taurus XL will launch NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, spacecraft targeted for Jan. 15. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
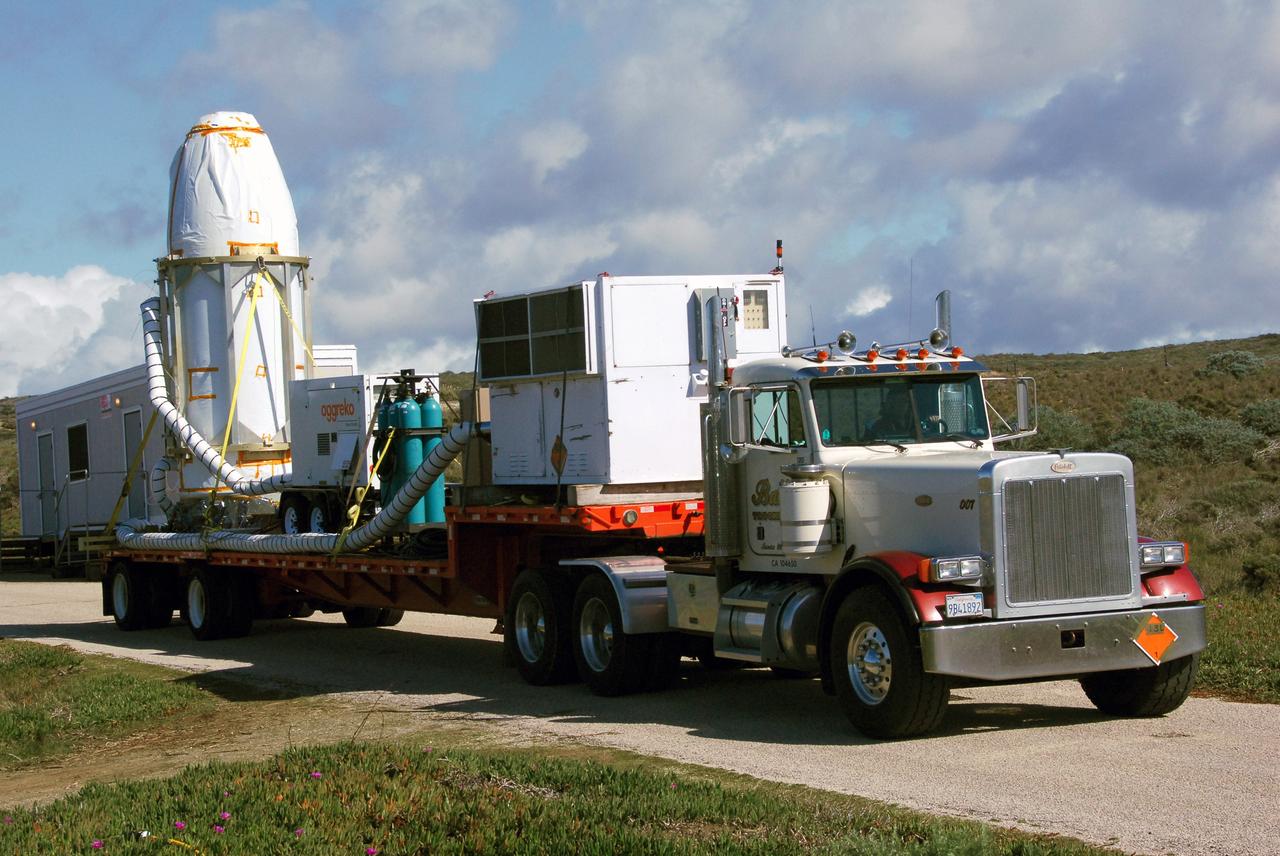

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the transporter holding NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, heads for Launch Complex 576-E. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
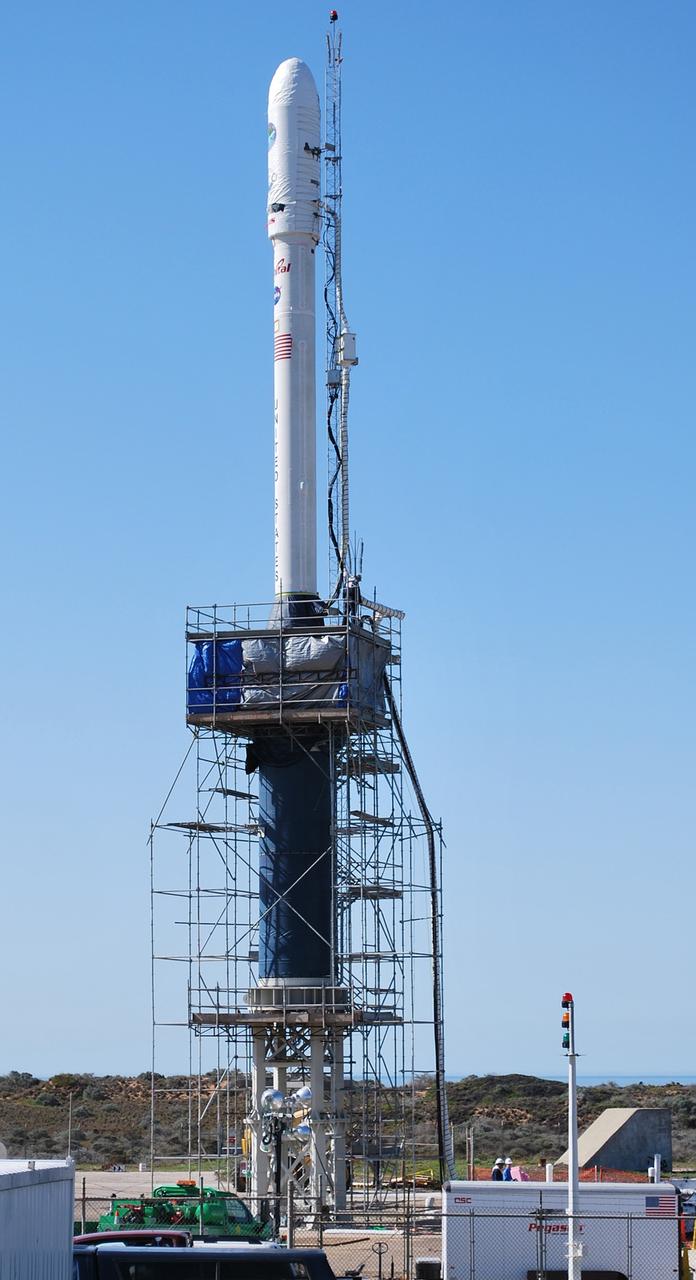

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, has been erected atop Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket for a Feb. 24 launch. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
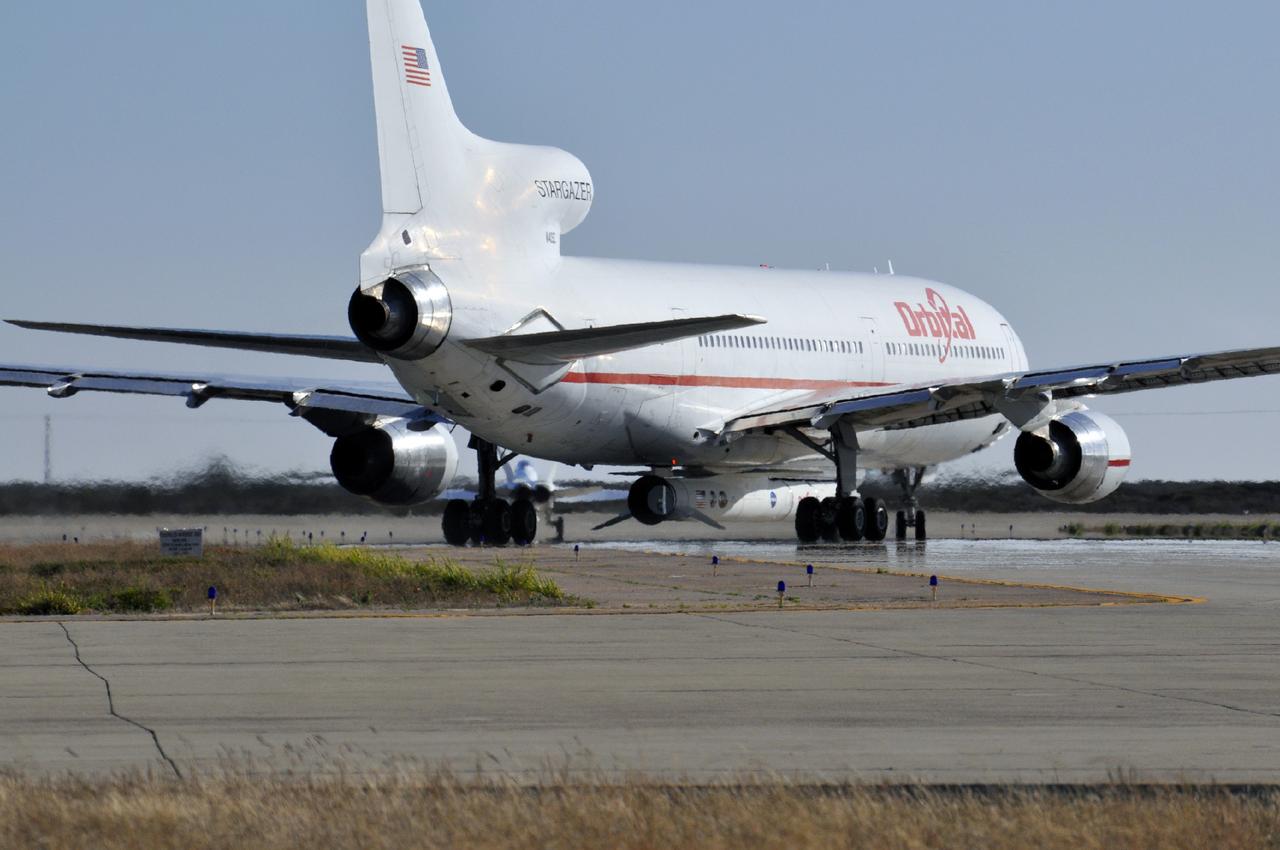

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft taxis to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., before taking off on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the L-1011. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is lifted out of the bottom of the shipping container. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is moved toward a stand seen at front left. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow, VAFB
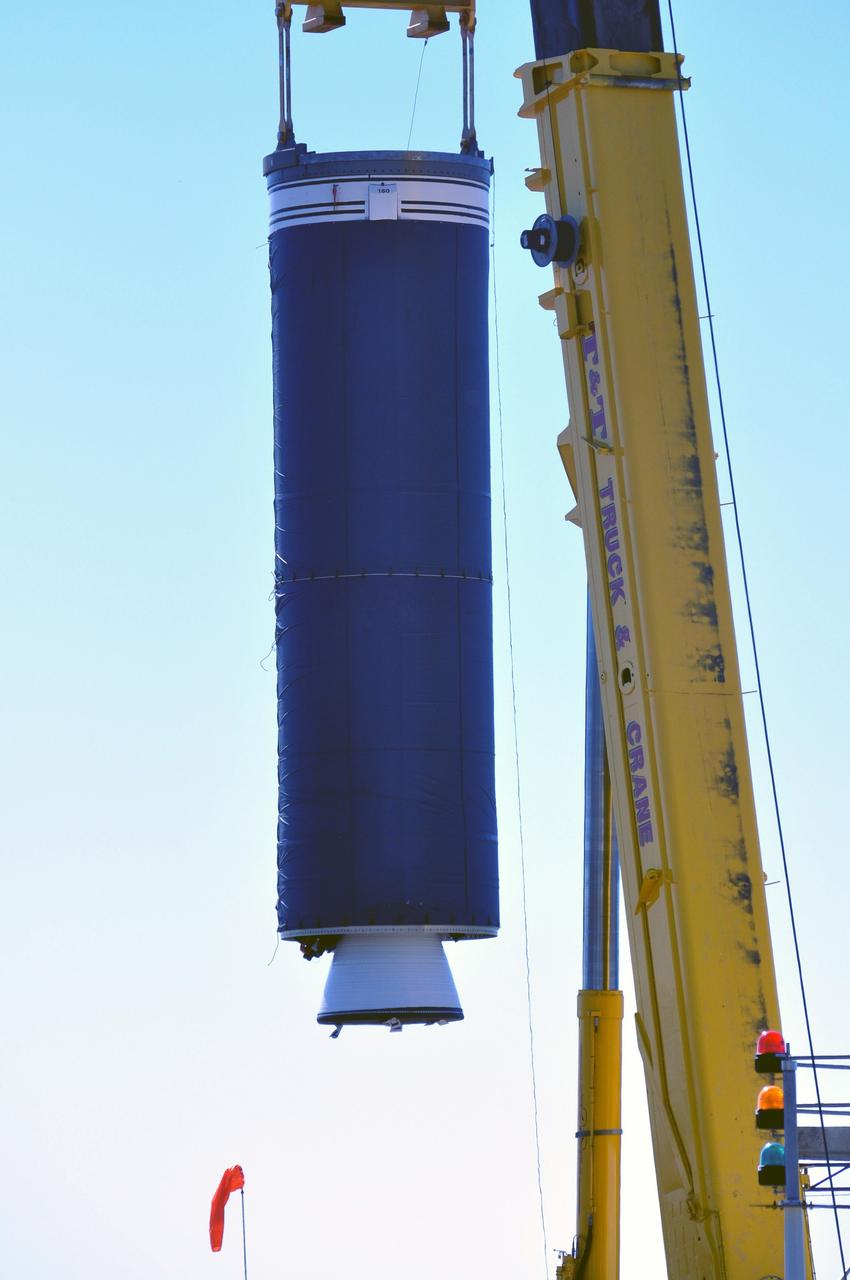

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At complex 576E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts Stage 0 of the Taurus XL launch vehicle for the Orbiting Carbon Observatory from its transporter. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. It is scheduled to launch Feb. 23. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers check the attachment of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft to the stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow, VAFB
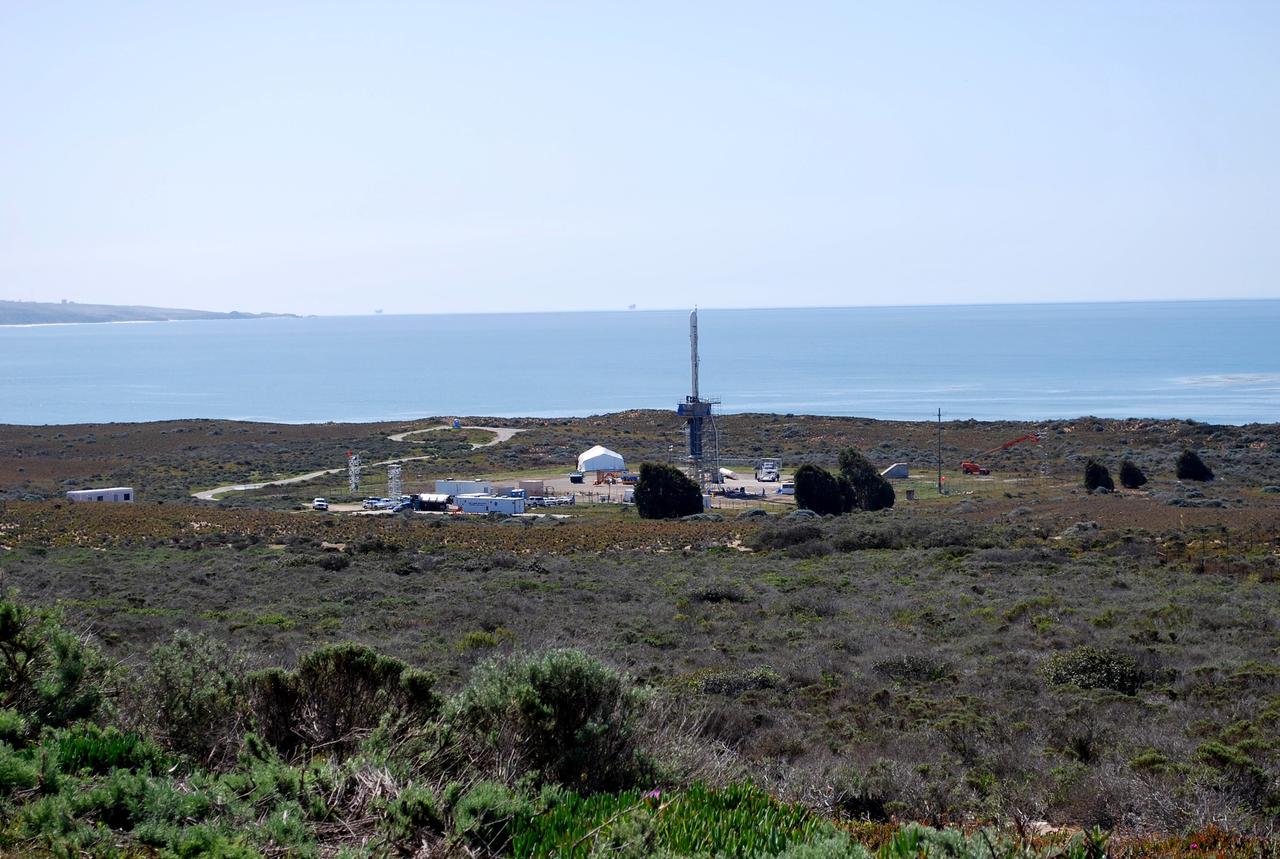

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, has been erected atop Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket for a Feb. 24 launch. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
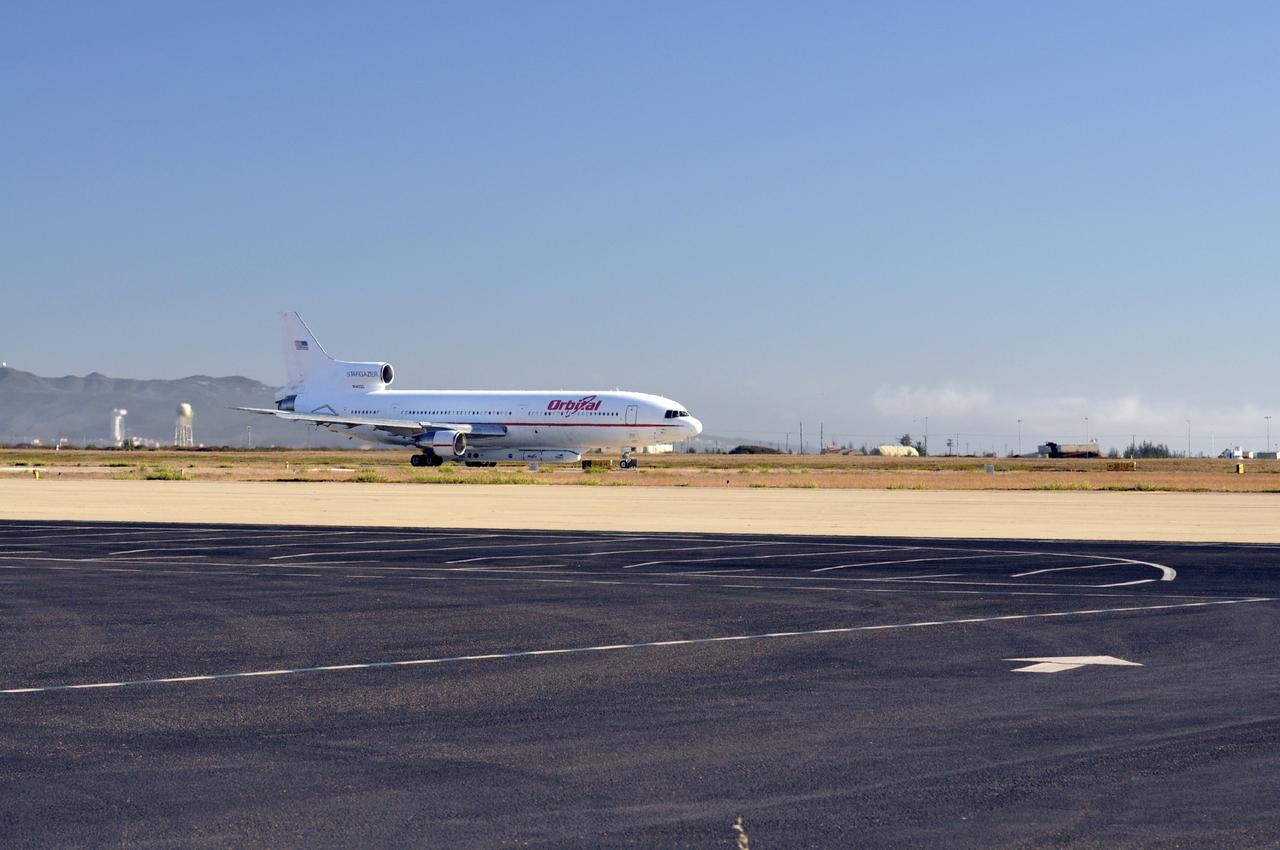

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft taxis to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., before taking off on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the L-1011. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
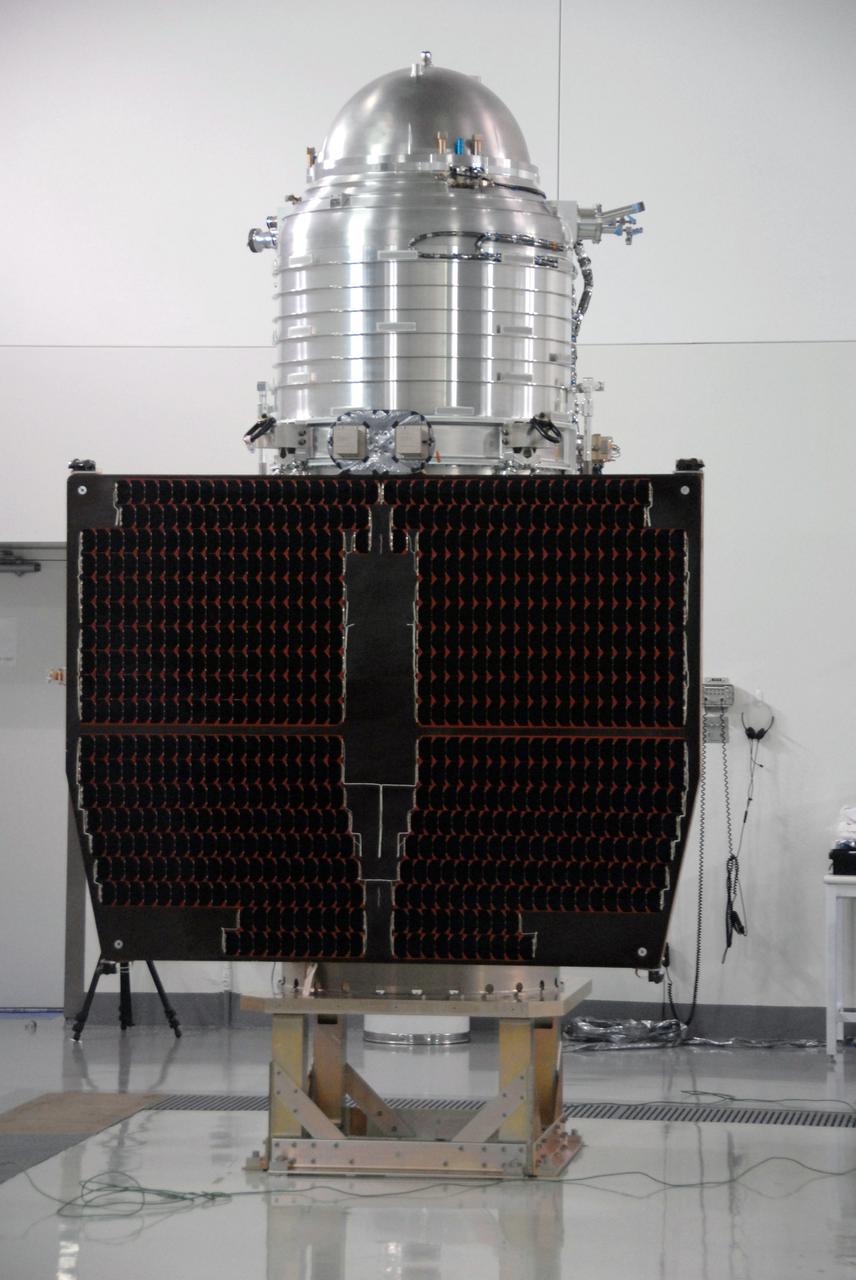
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is situated on a work stand. In front is the fixed panel solar array. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Moore, VAFB
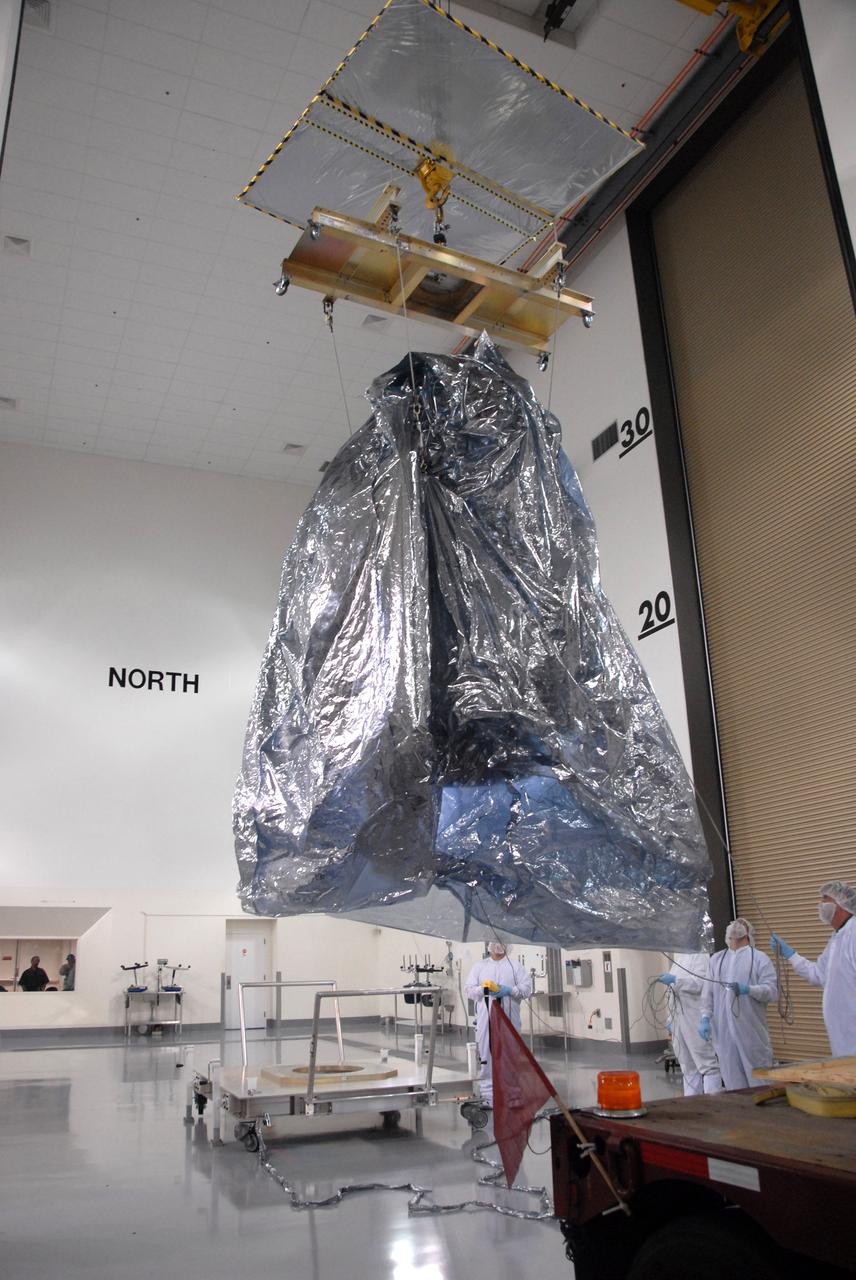

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the Astrotech payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is moved toward a stand seen at bottom center. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow, VAFB
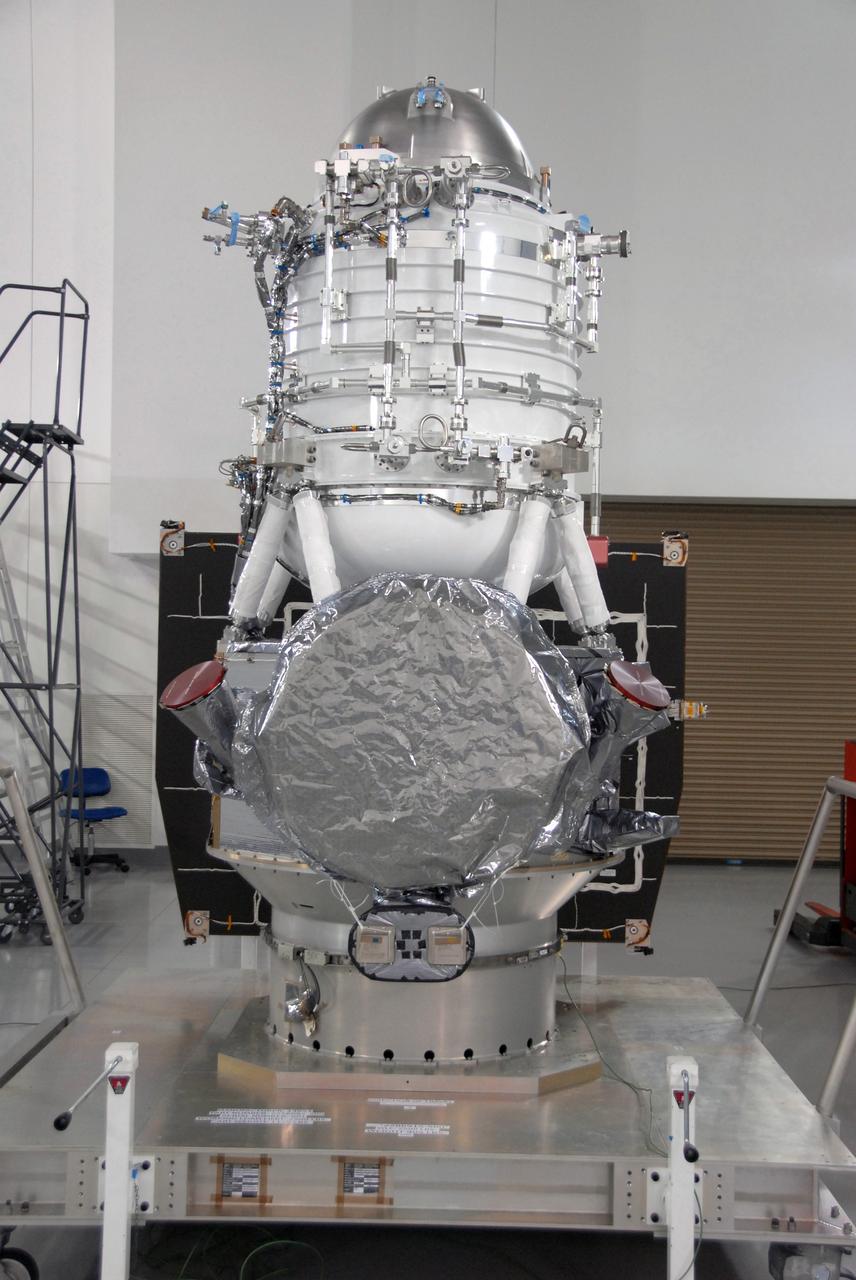

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is seen. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Moore, VAFB