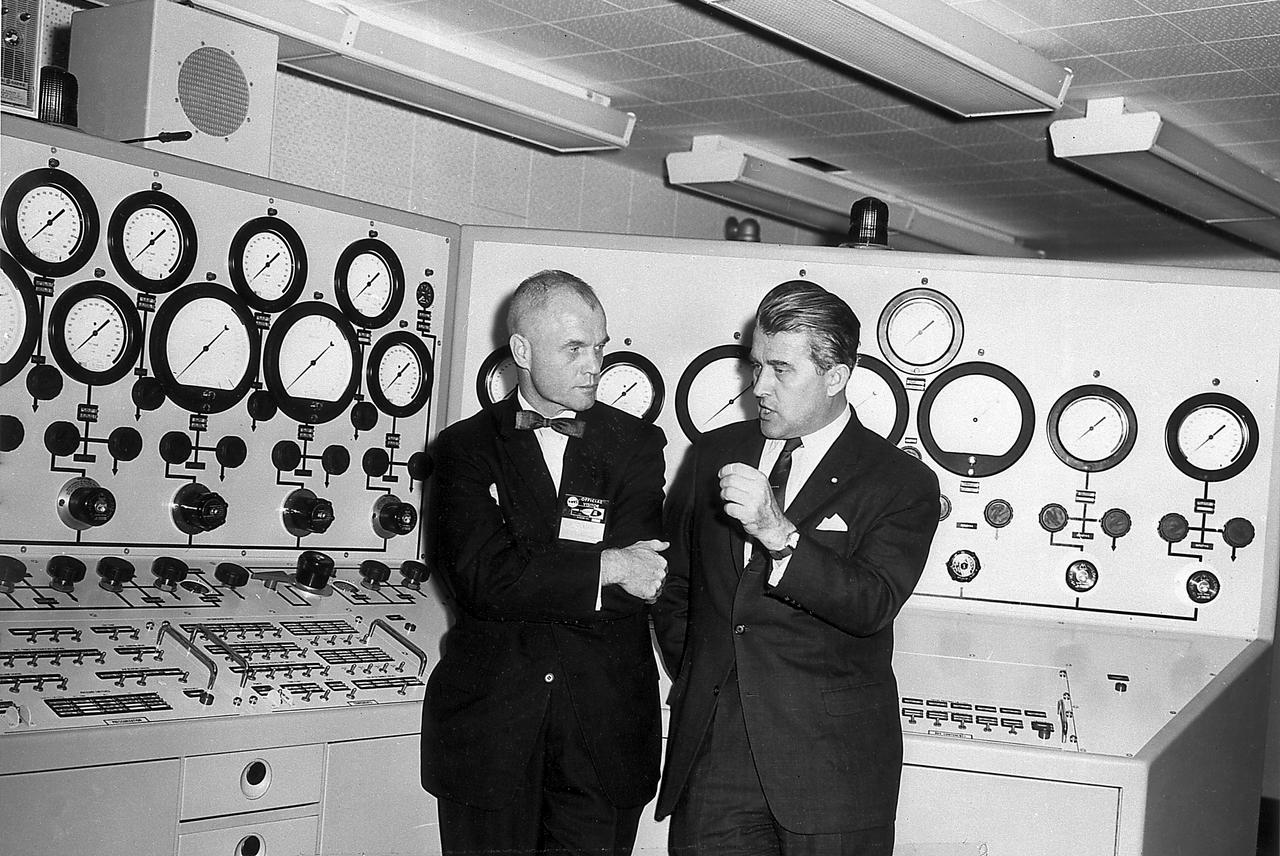

Dr. von Braun briefs Astronaut John Glenn in the control room of the Vehicle Test Section, Quality Assurance Division, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), November 28, 1962.
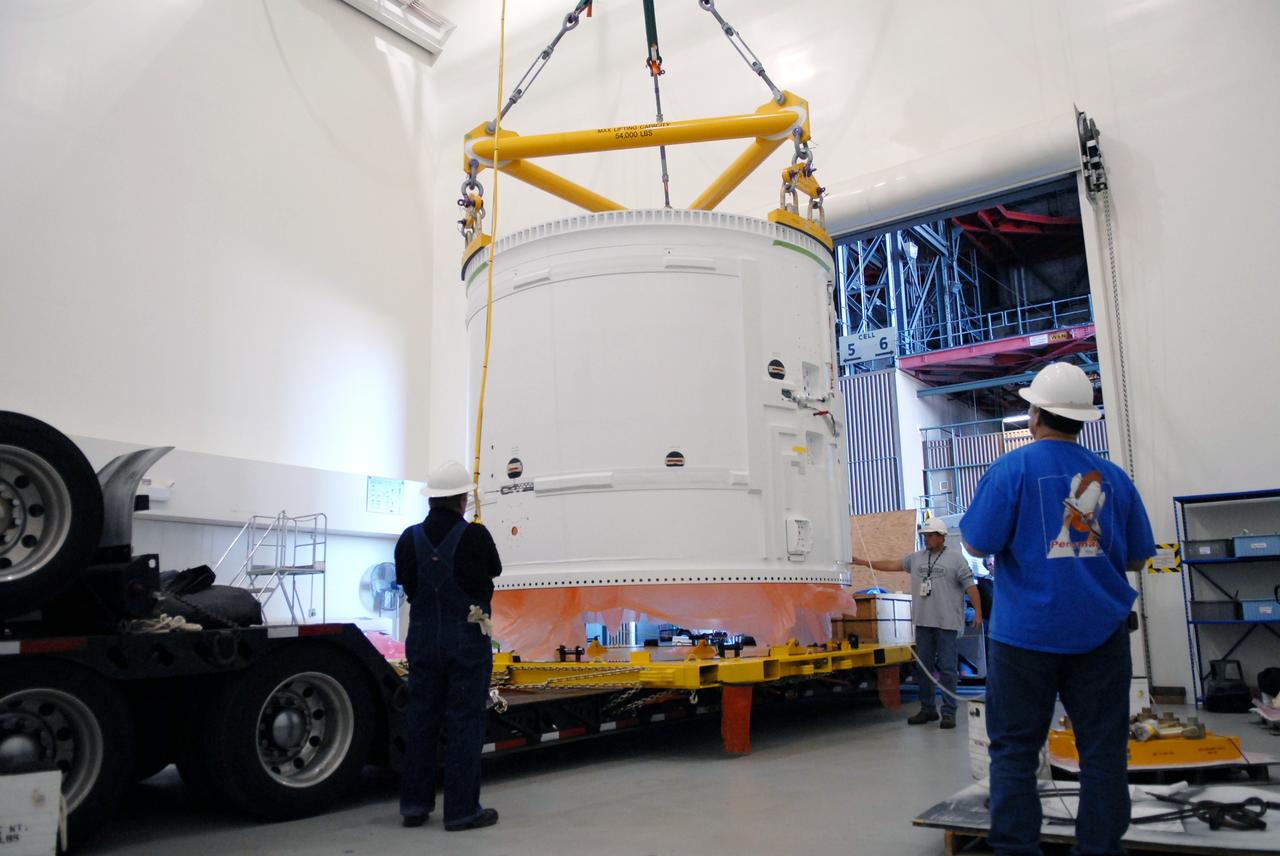

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's extended duration orbiter lab, or EDO, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X fifth segment simulator aft section is lifted by a crane from the transporter. The aft section will be moved to a stand. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
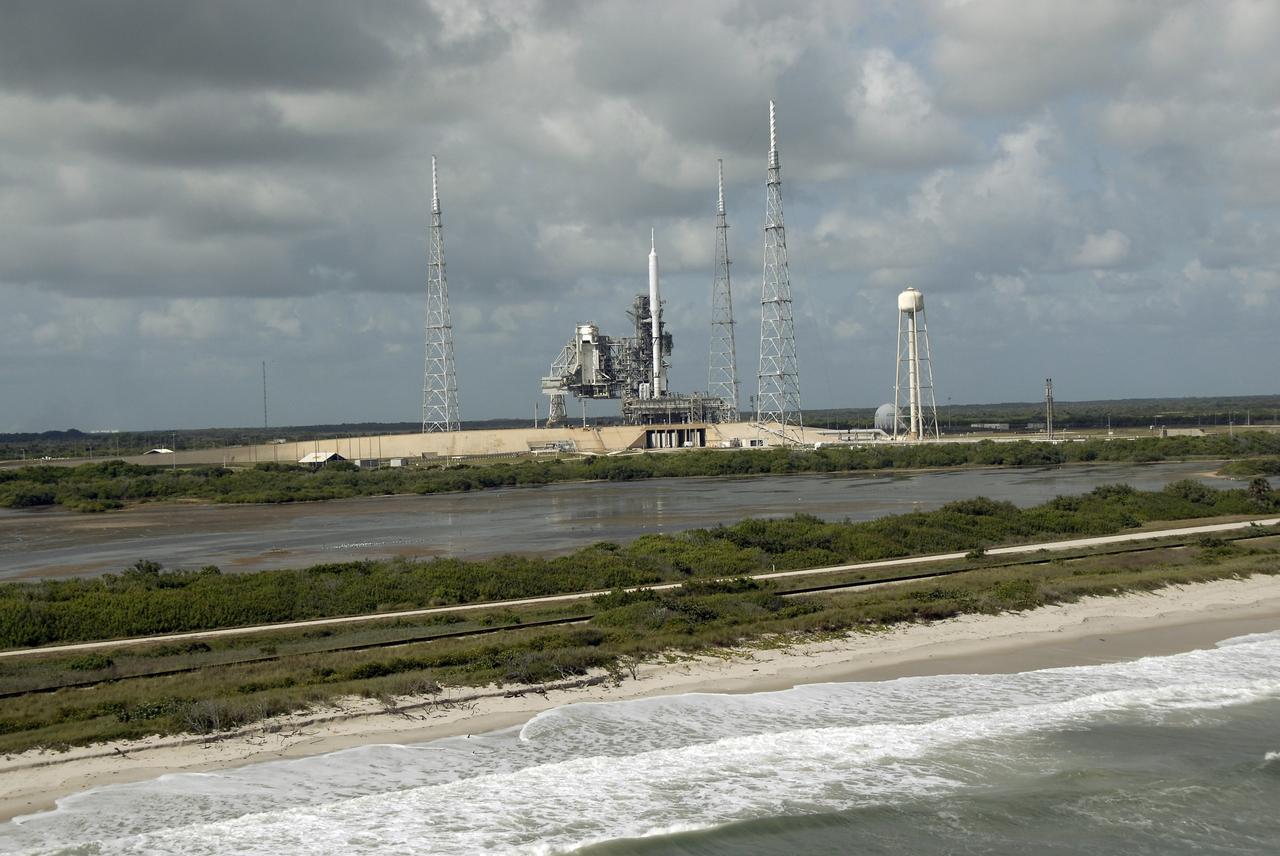

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Waves lap the shore of the Atlantic Ocean near Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On the pad, the Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on its upcoming flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

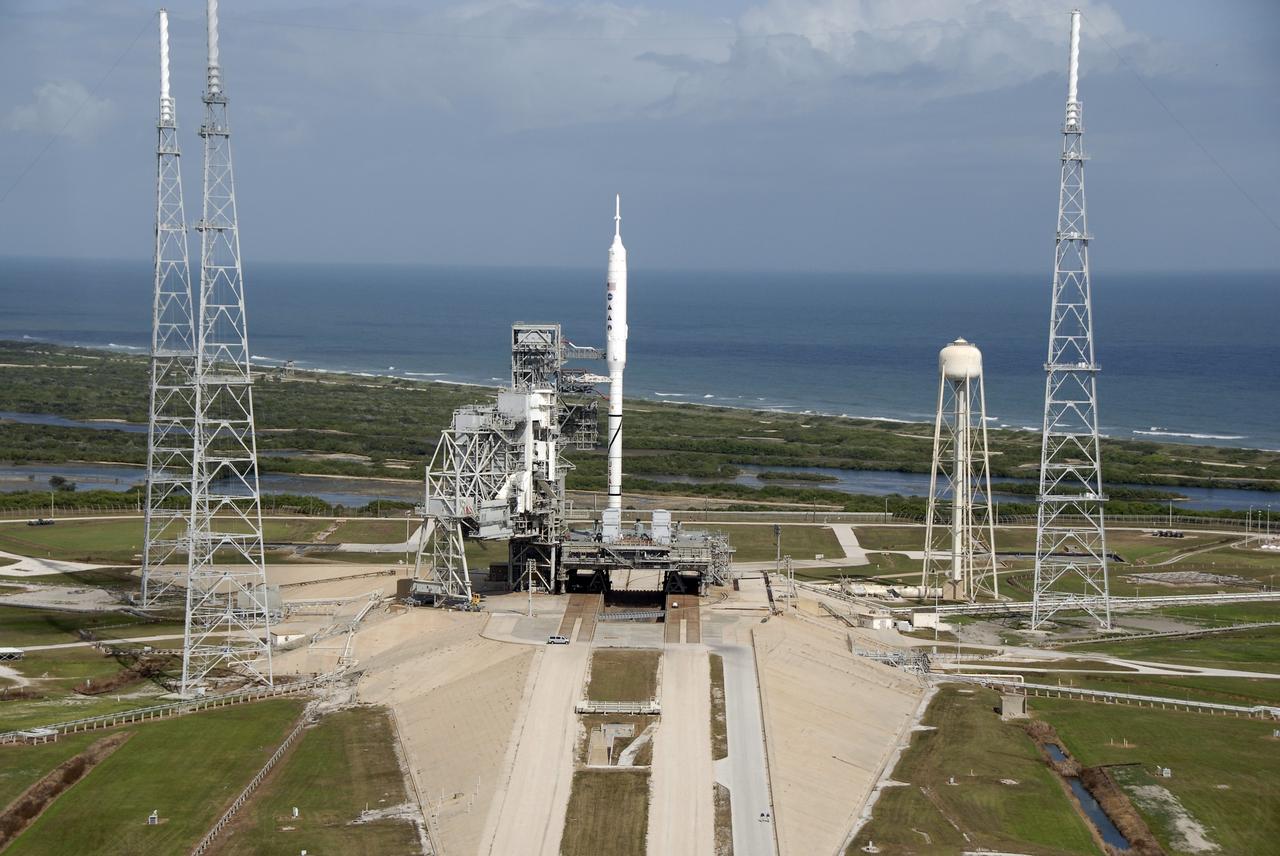
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
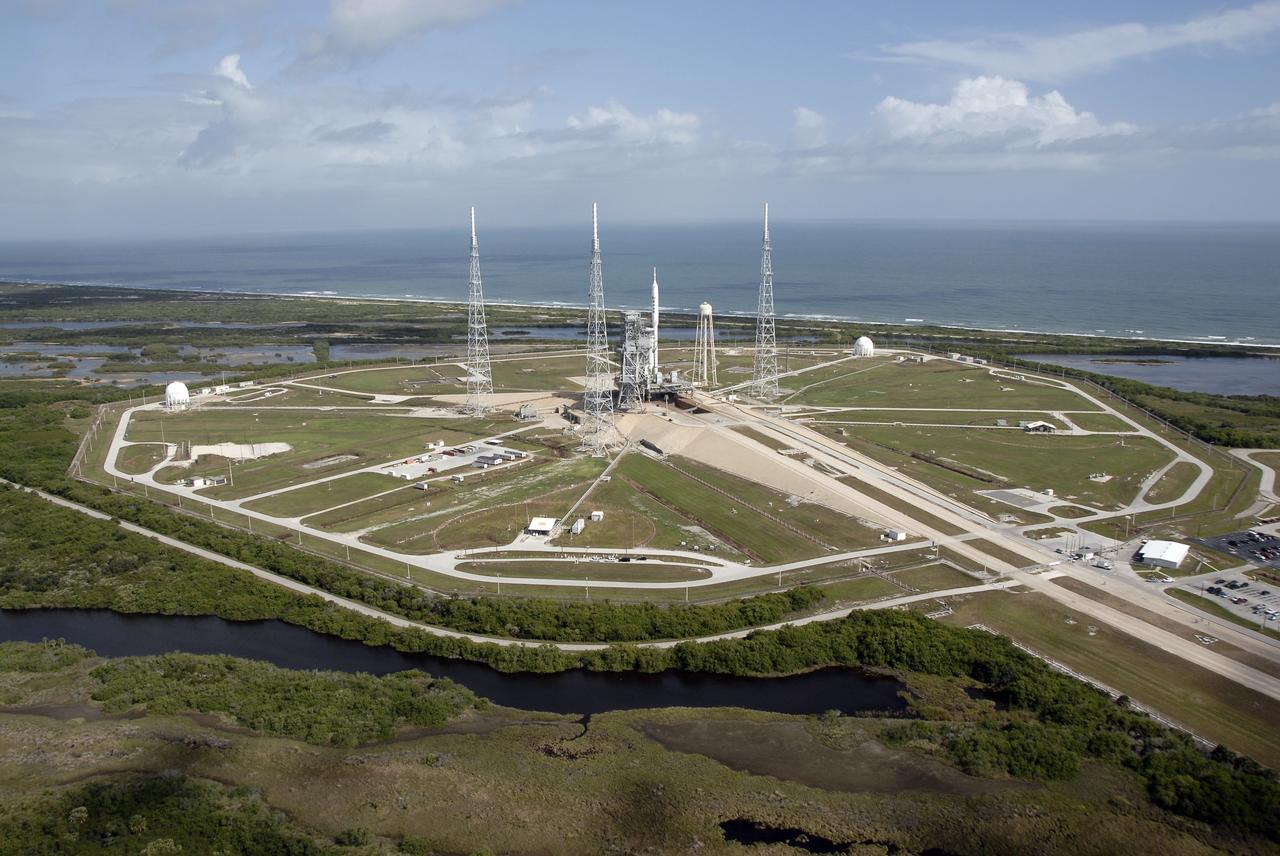

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on the hexagonally shaped Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
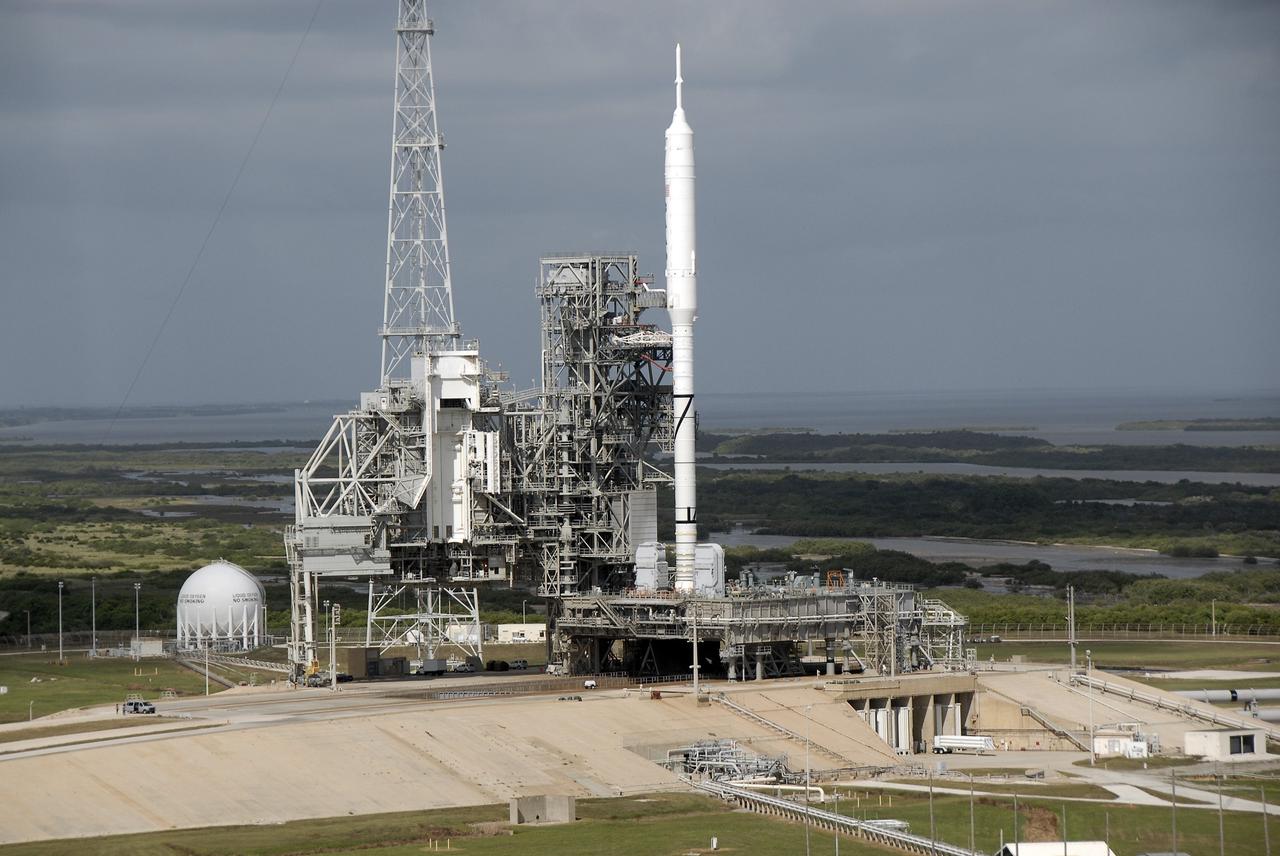

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket, secured to its mobile launcher platform, awaits liftoff on its upcoming flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Waves break along the Atlantic shoreline near Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On the pad, the Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on its upcoming flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
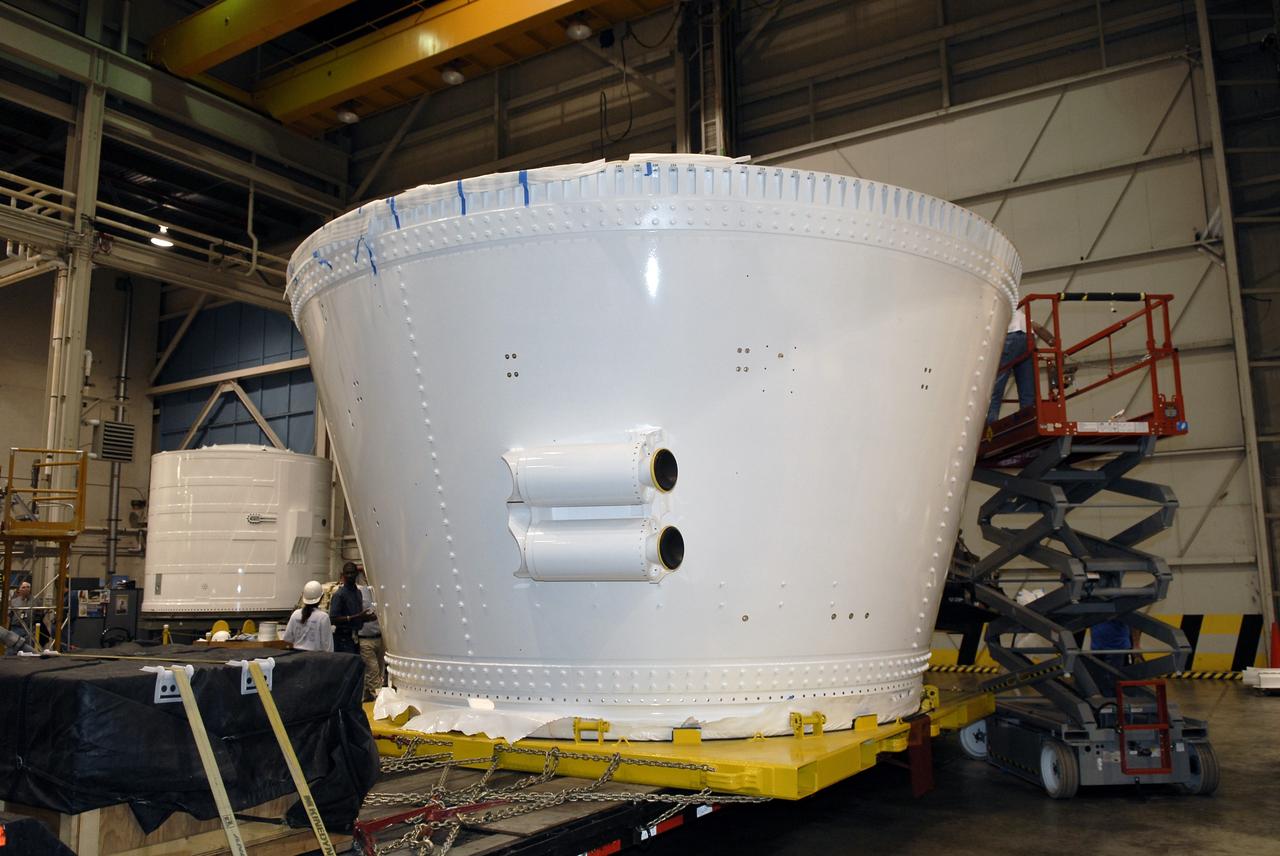

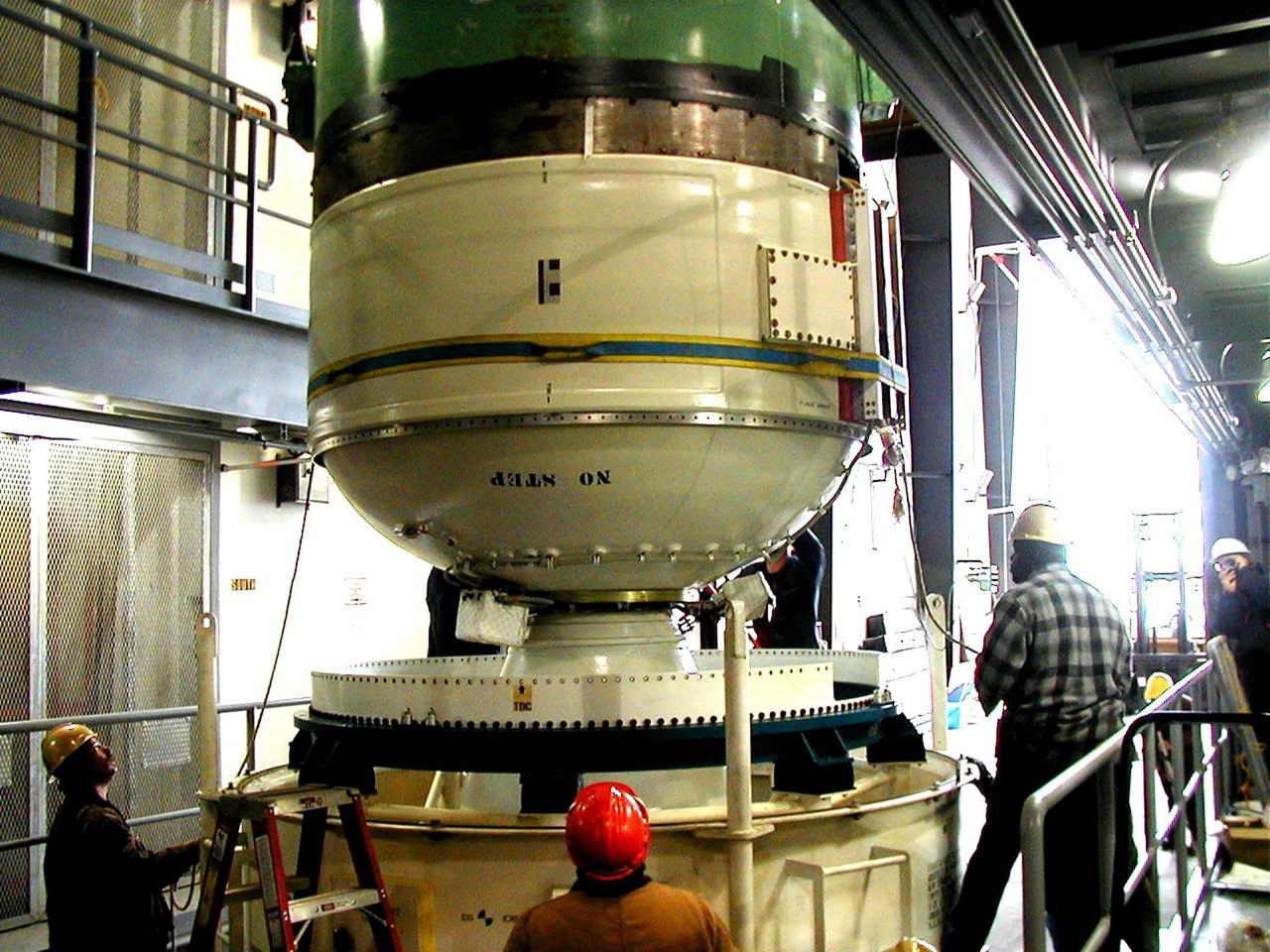
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the last newly manufactured section of the Ares I-X test rocket, the frustum, is revealed after removal of the shipping covers. Resembling a giant funnel, the frustum's function is to transition the primary flight loads from the rocket's upper stage to the first stage. The frustum is located between the forward skirt extension and the upper stage of the Ares I-X. Weighing in at approximately 13,000 pounds, the 10-foot-long section is composed of two aluminum rings attached to a truncated conic section. The large diameter of the cone is 18 feet and the small diameter is 12 feet. The cone is 1.25 inches thick. The frustum will be integrated with the forward skirt and forward skirt extension, which already are in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. That will complete the forward assembly. The assembly then will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking operations, which are scheduled to begin in April. Manufactured by Major Tool and Machine Inc. in Indiana under a subcontract with Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, the Ares I-X is targeted to launch in the summer of 2009. The flight will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I launch vehicle. The flight test also will bring NASA a step closer to its exploration goals of sending humans to the moon and destinations beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
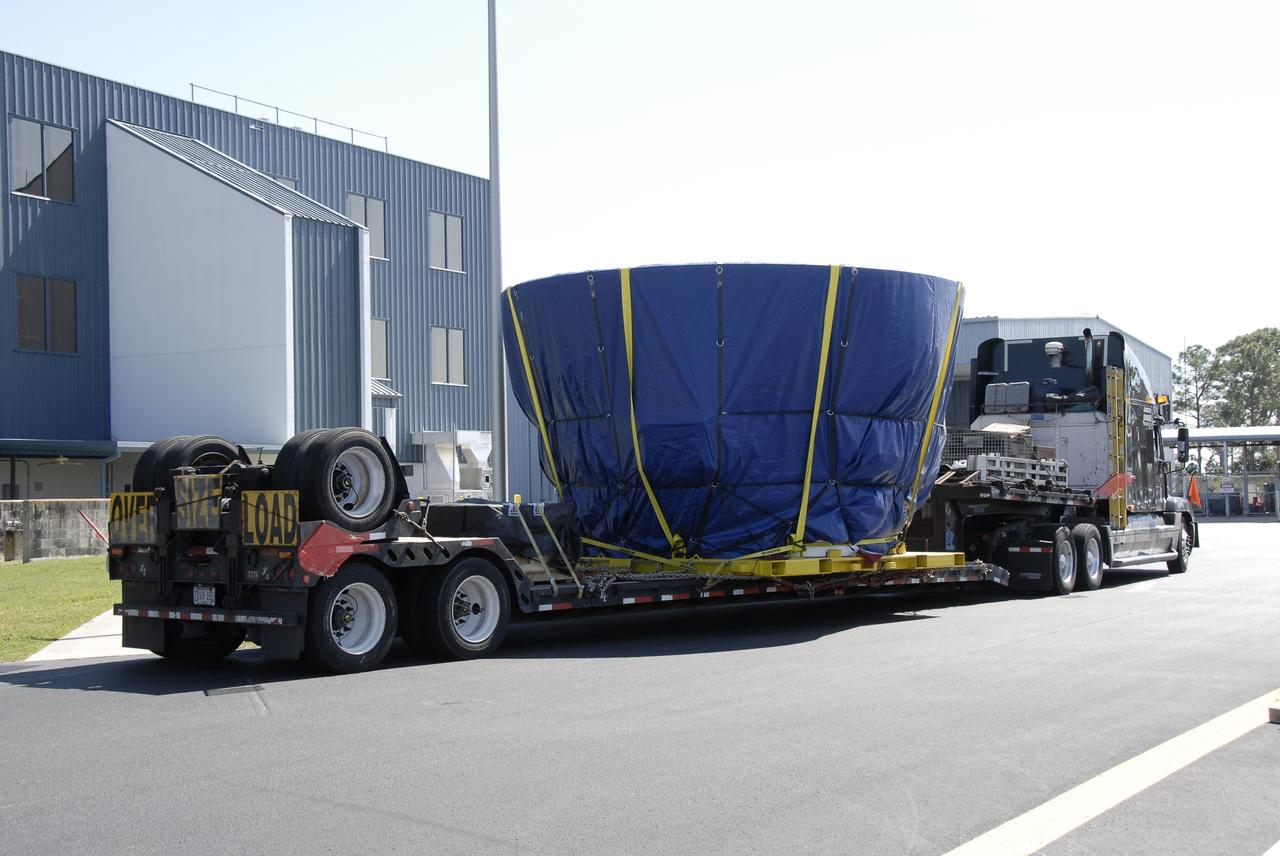

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The last newly manufactured section of the Ares I-X test rocket, the frustum, arrives at the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Resembling a giant funnel, the frustum's function is to transition the primary flight loads from the rocket's upper stage to the first stage. The frustum is located between the forward skirt extension and the upper stage of the Ares I-X. Weighing in at approximately 13,000 pounds, the 10-foot-long section is composed of two aluminum rings attached to a truncated conic section. The large diameter of the cone is 18 feet and the small diameter is 12 feet. The cone is 1.25 inches thick. The frustum will be integrated with the forward skirt and forward skirt extension, which already are in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. That will complete the forward assembly. The assembly then will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking operations, which are scheduled to begin in April. Manufactured by Major Tool and Machine Inc. in Indiana under a subcontract with Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, the Ares I-X is targeted to launch in the summer of 2009. The flight will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I launch vehicle. The flight test also will bring NASA a step closer to its exploration goals of sending humans to the moon and destinations beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
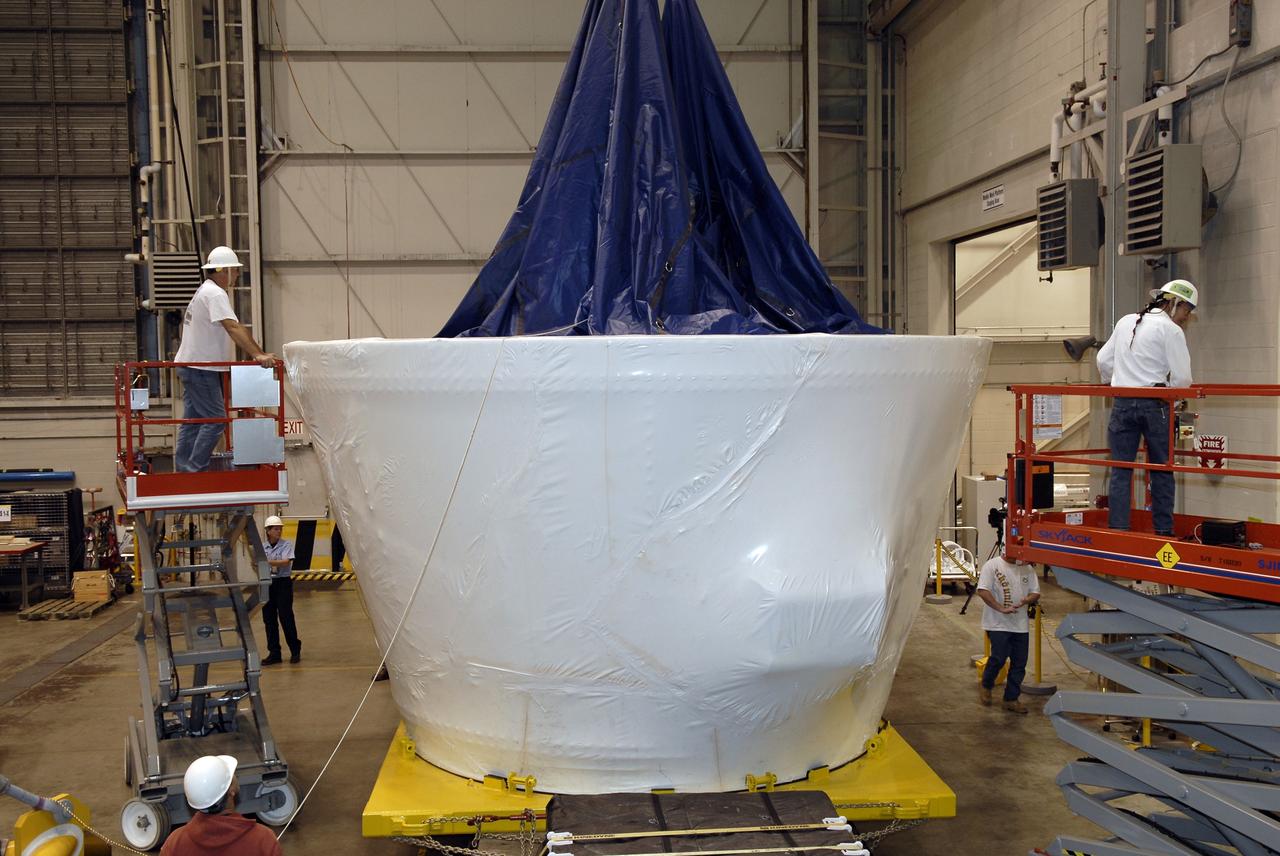

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers remove the cover from the frustum, the last newly manufactured section of the Ares I-X test rocket. Resembling a giant funnel, the frustum's function is to transition the primary flight loads from the rocket's upper stage to the first stage. The frustum is located between the forward skirt extension and the upper stage of the Ares I-X. Weighing in at approximately 13,000 pounds, the 10-foot-long section is composed of two aluminum rings attached to a truncated conic section. The large diameter of the cone is 18 feet and the small diameter is 12 feet. The cone is 1.25 inches thick. The frustum will be integrated with the forward skirt and forward skirt extension, which already are in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. That will complete the forward assembly. The assembly then will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking operations, which are scheduled to begin in April. Manufactured by Major Tool and Machine Inc. in Indiana under a subcontract with Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, the Ares I-X is targeted to launch in the summer of 2009. The flight will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I launch vehicle. The flight test also will bring NASA a step closer to its exploration goals of sending humans to the moon and destinations beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
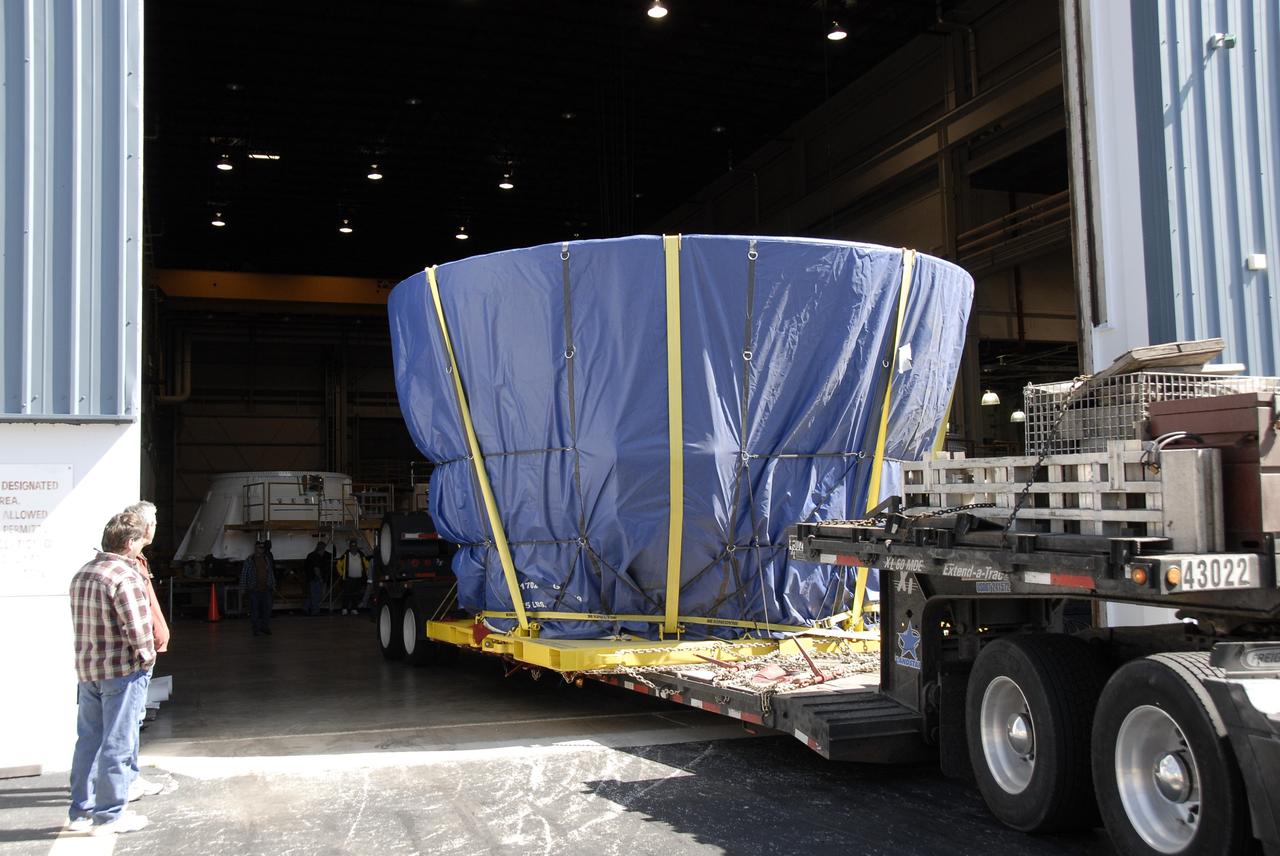

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The last newly manufactured section of the Ares I-X test rocket, the frustum, is offloaded in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Resembling a giant funnel, the frustum's function is to transition the primary flight loads from the rocket's upper stage to the first stage. The frustum is located between the forward skirt extension and the upper stage of the Ares I-X. Weighing in at approximately 13,000 pounds, the 10-foot-long section is composed of two aluminum rings attached to a truncated conic section. The large diameter of the cone is 18 feet and the small diameter is 12 feet. The cone is 1.25 inches thick. The frustum will be integrated with the forward skirt and forward skirt extension, which already are in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. That will complete the forward assembly. The assembly then will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking operations, which are scheduled to begin in April. Manufactured by Major Tool and Machine Inc. in Indiana under a subcontract with Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, the Ares I-X is targeted to launch in the summer of 2009. The flight will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I launch vehicle. The flight test also will bring NASA a step closer to its exploration goals of sending humans to the moon and destinations beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers remove the cover from the frustum, the last newly manufactured section of the Ares I-X test rocket. Resembling a giant funnel, the frustum's function is to transition the primary flight loads from the rocket's upper stage to the first stage. The frustum is located between the forward skirt extension and the upper stage of the Ares I-X. Weighing in at approximately 13,000 pounds, the 10-foot-long section is composed of two aluminum rings attached to a truncated conic section. The large diameter of the cone is 18 feet and the small diameter is 12 feet. The cone is 1.25 inches thick. The frustum will be integrated with the forward skirt and forward skirt extension, which already are in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility. That will complete the forward assembly. The assembly then will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking operations, which are scheduled to begin in April. Manufactured by Major Tool and Machine Inc. in Indiana under a subcontract with Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, the Ares I-X is targeted to launch in the summer of 2009. The flight will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I launch vehicle. The flight test also will bring NASA a step closer to its exploration goals of sending humans to the moon and destinations beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
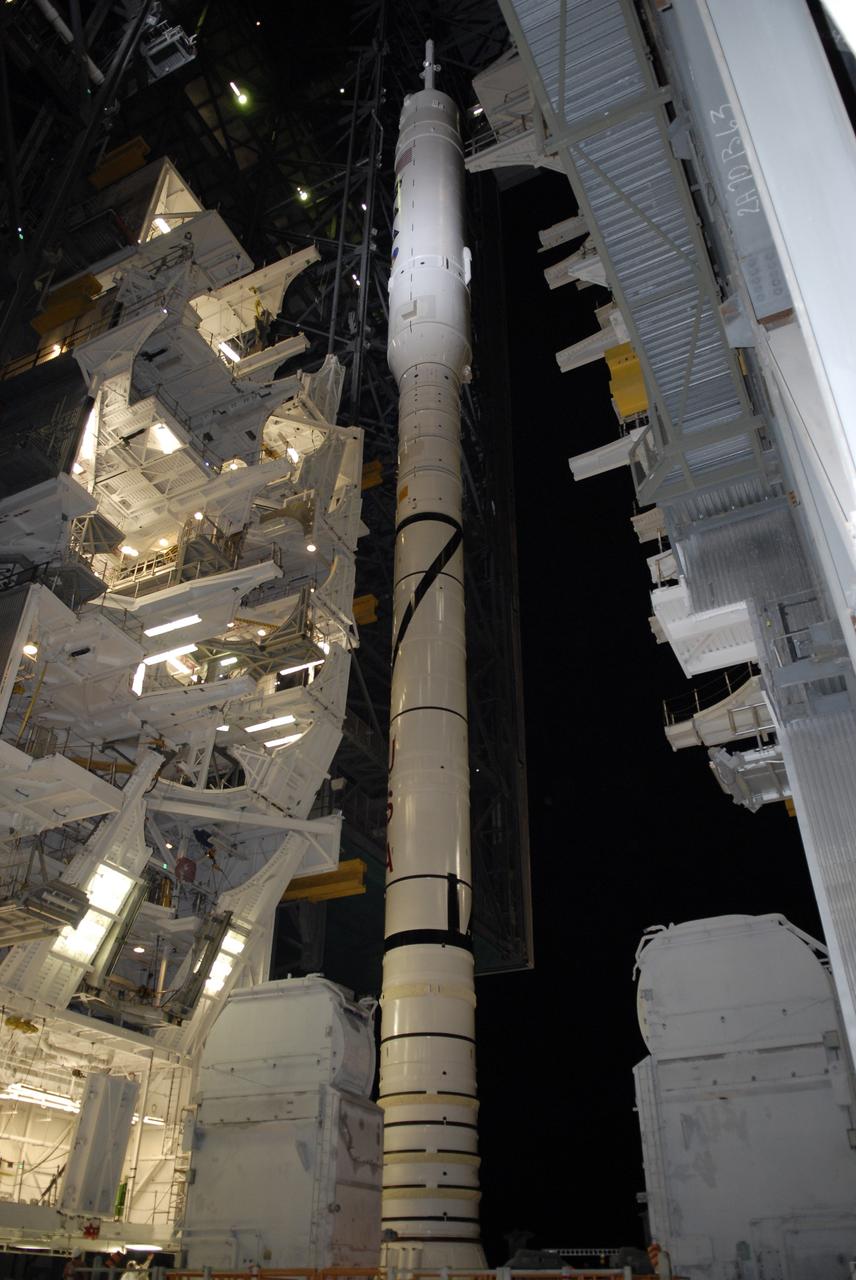

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With the work platforms retracted, the Ares I-X stands tall inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were retracted in preparation for the rocket's rollout to Launch Pad 39B. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
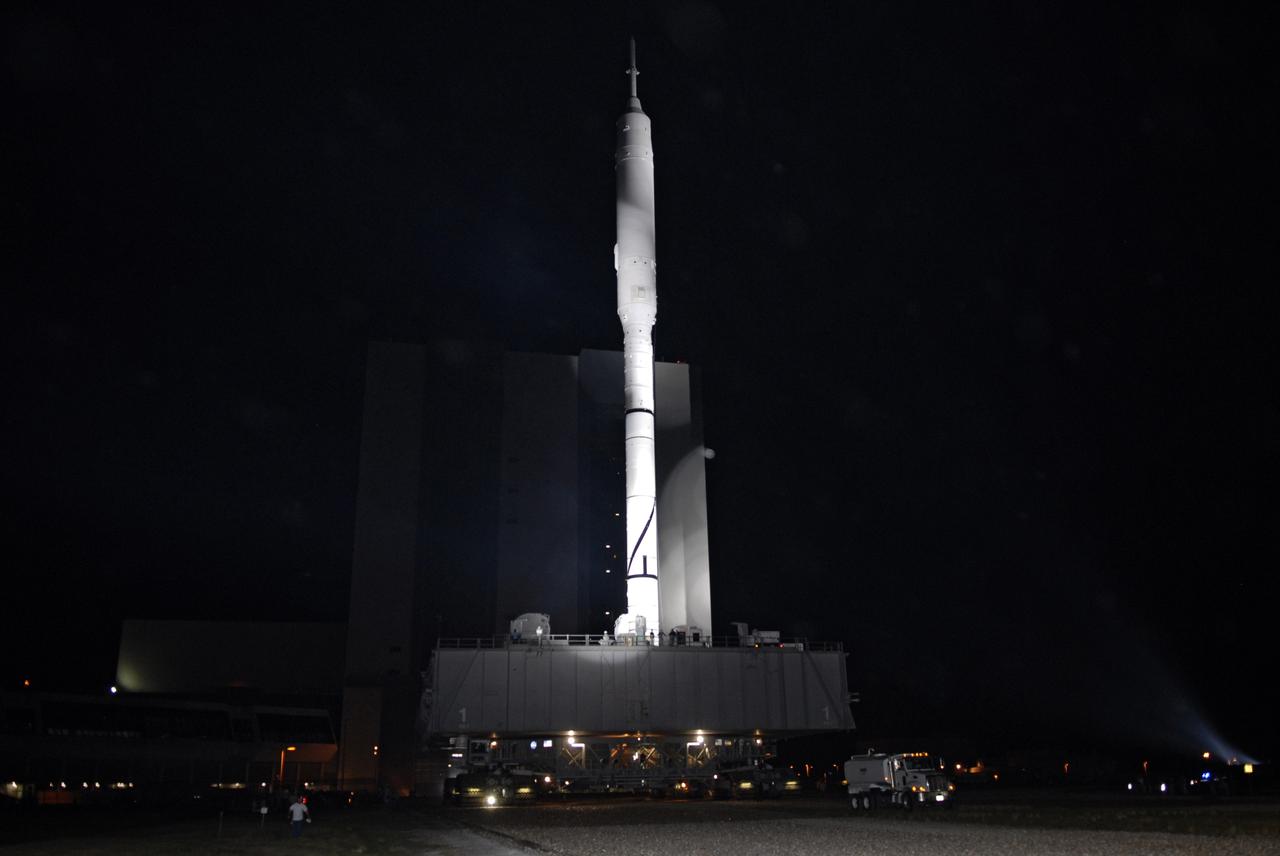

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Ares I-X rocket heads toward Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, riding atop a crawler-transporter. The 4.2-mile trip to the pad from the massive Vehicle Assembly Building began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
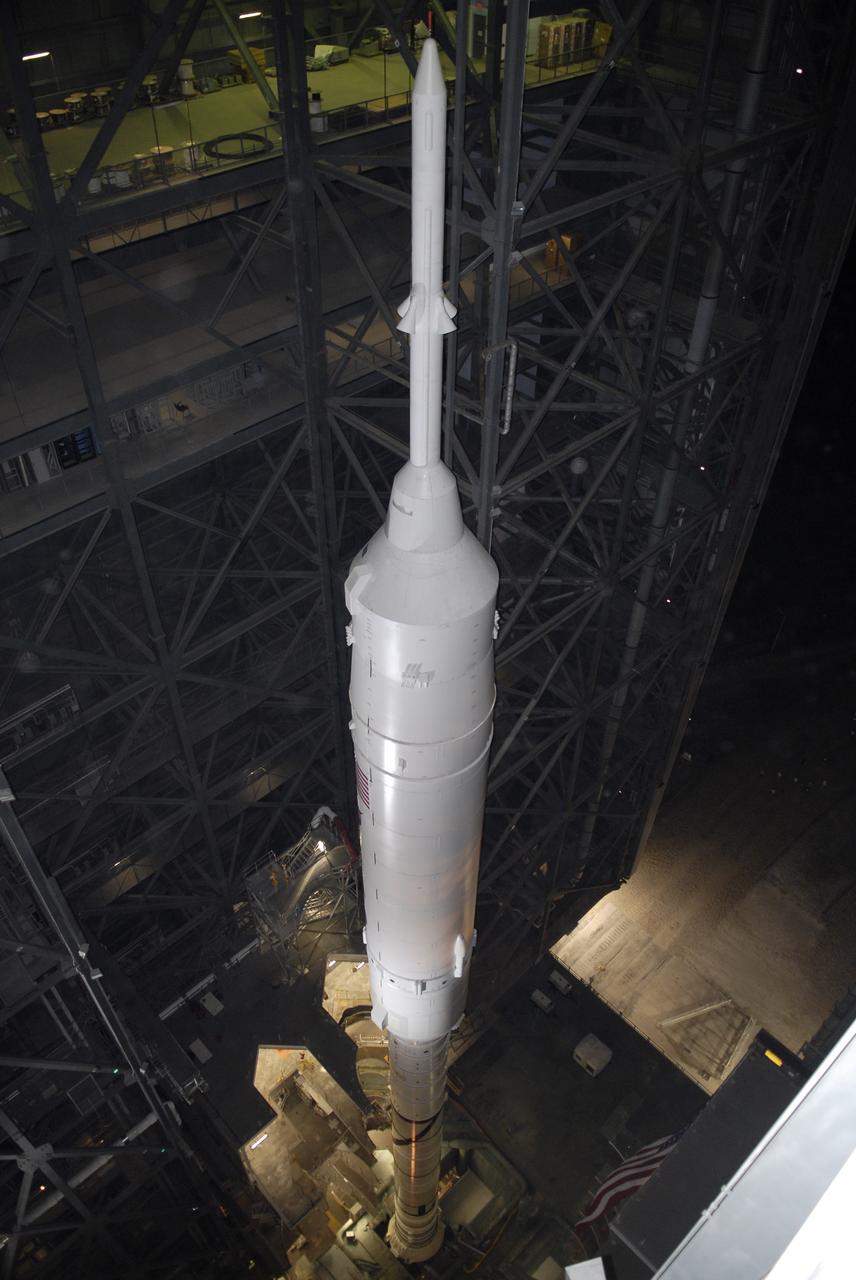

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket stands on its mobile launcher platform. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
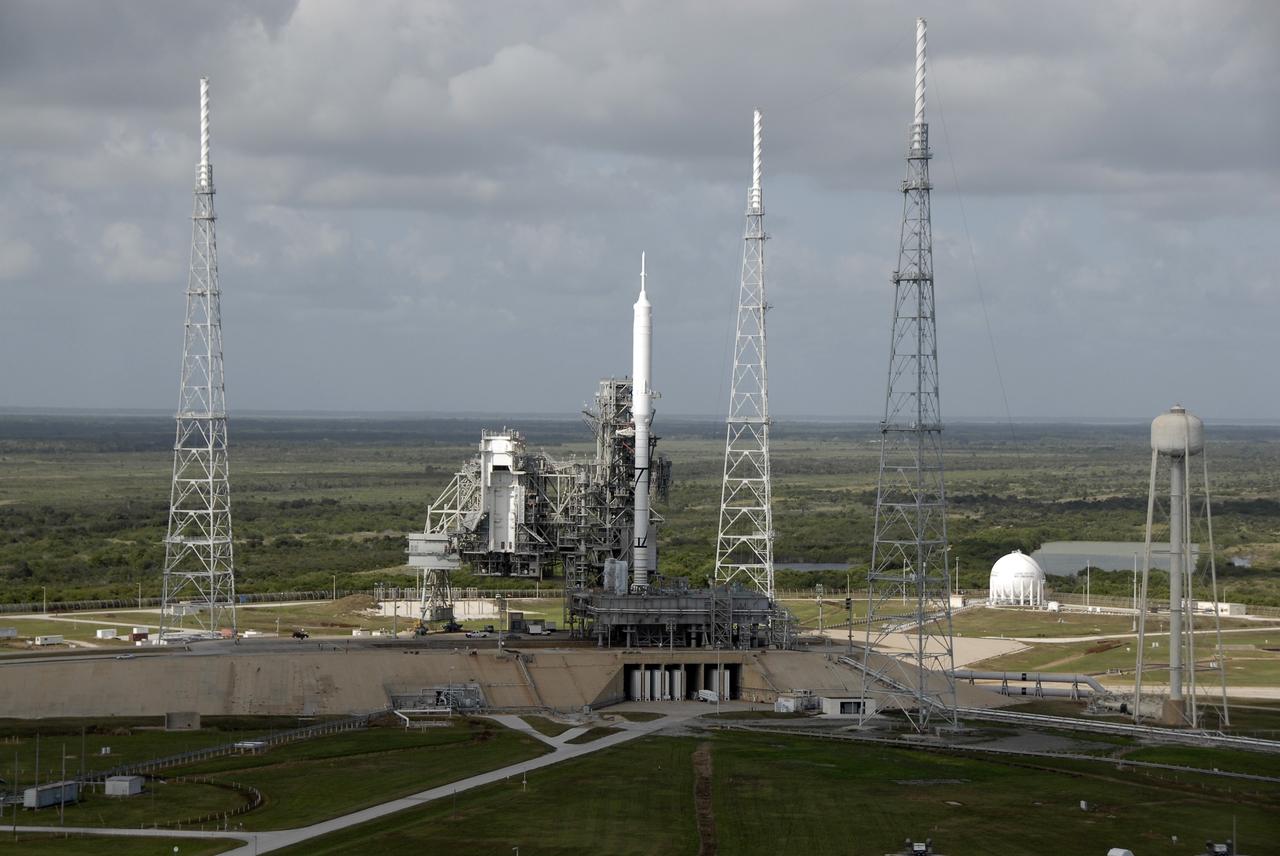

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket is the first vehicle processed on Launch Pad 39B other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
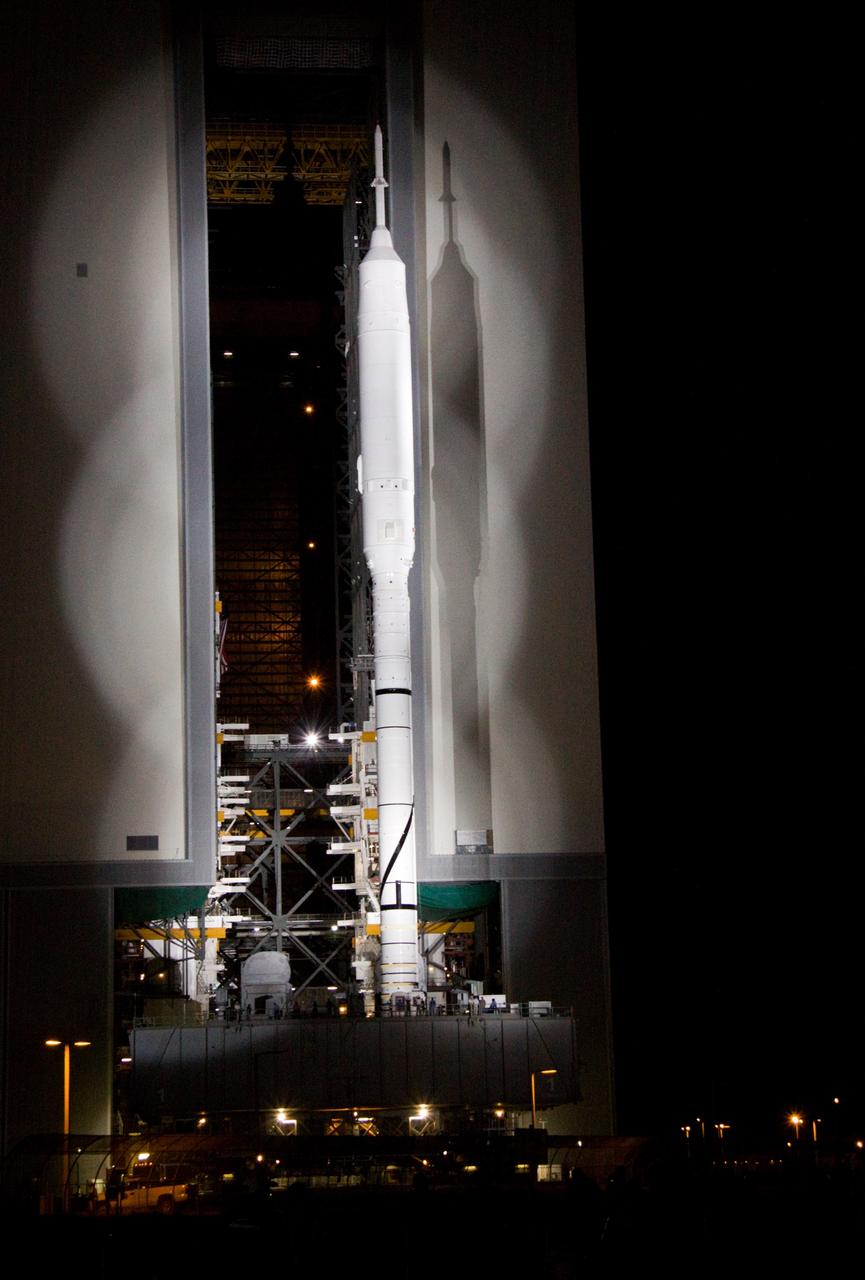

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket clears the door of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on its way to Launch Pad 39B. The move to the launch pad, known as "rollout," began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
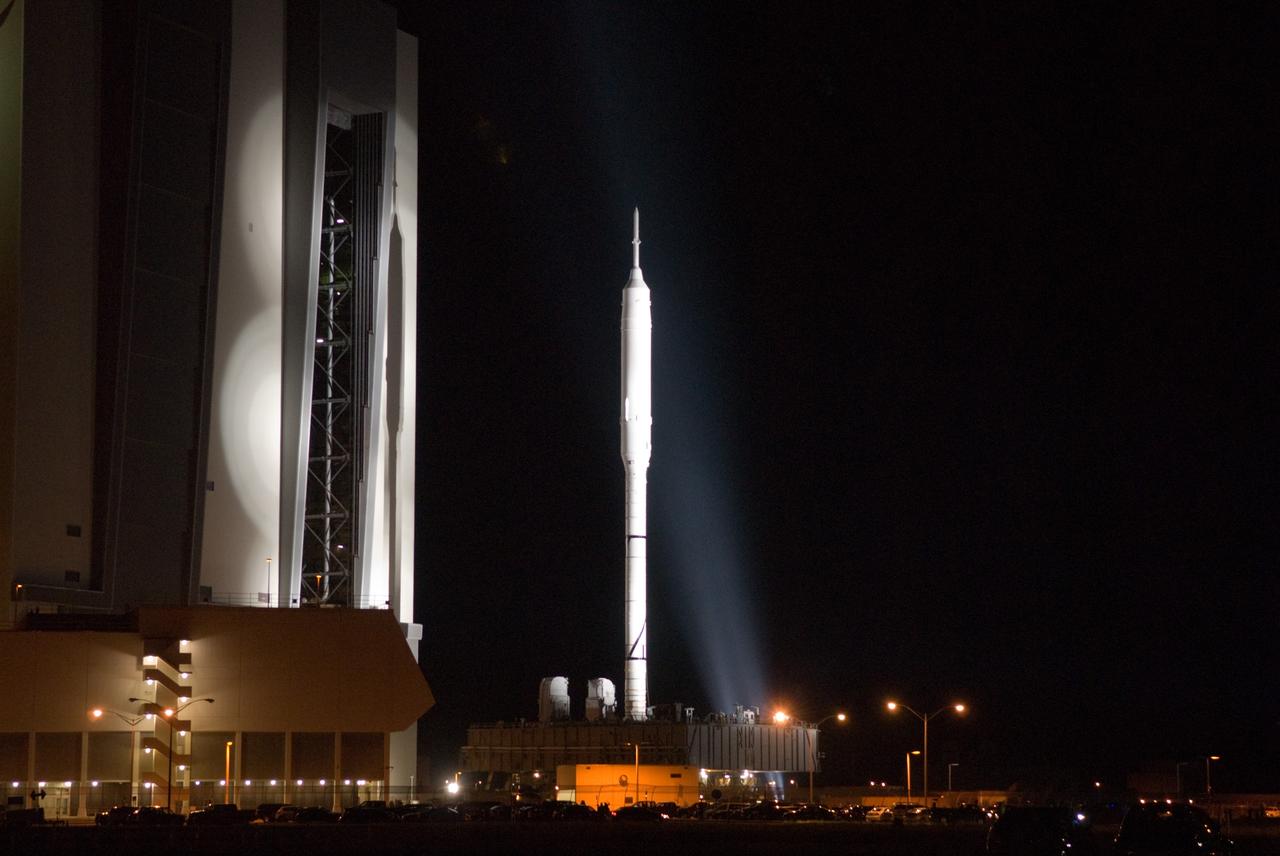

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Standing tall, the Ares I-X rocket rides atop the crawler-transporter as it moves beyond the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Its slow trek to Launch Pad 39B, known as "rollout," began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
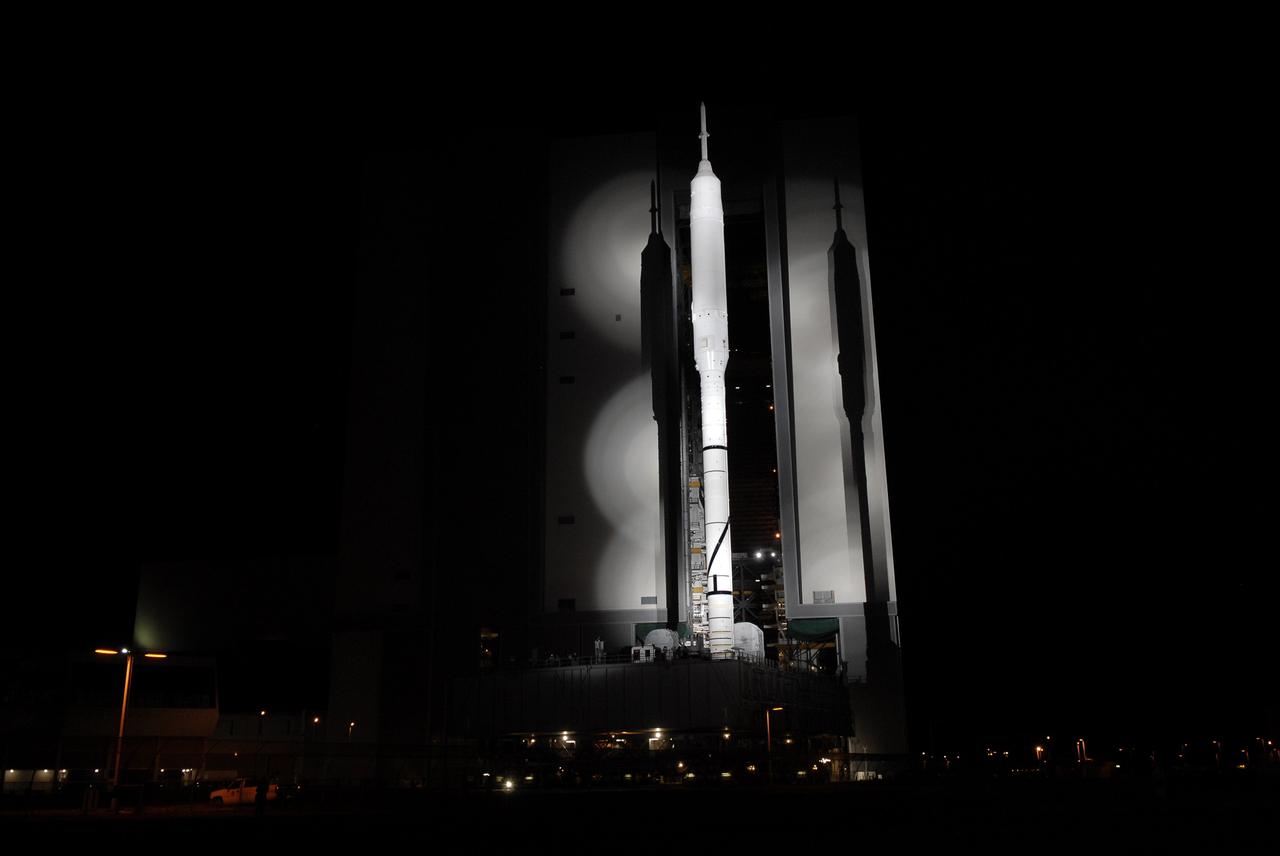

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket rides aboard a crawler-transporter as it exits the massive Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket is bolted to its mobile launcher platform for the move to the launch pad. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
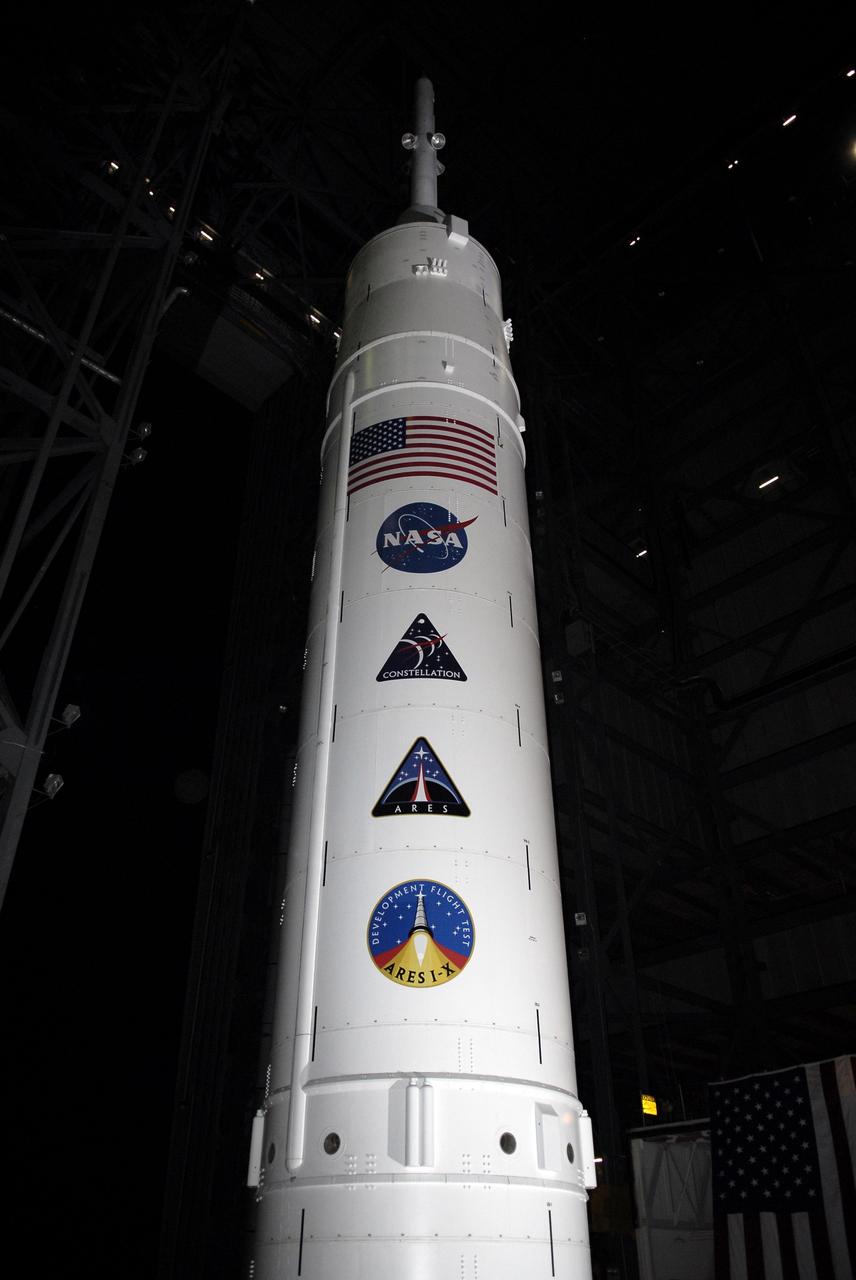

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Poised inside Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket's upper stage is adorned with the American flag, NASA logo, and the logos of the Constellation Program, Ares, and Ares I-X. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
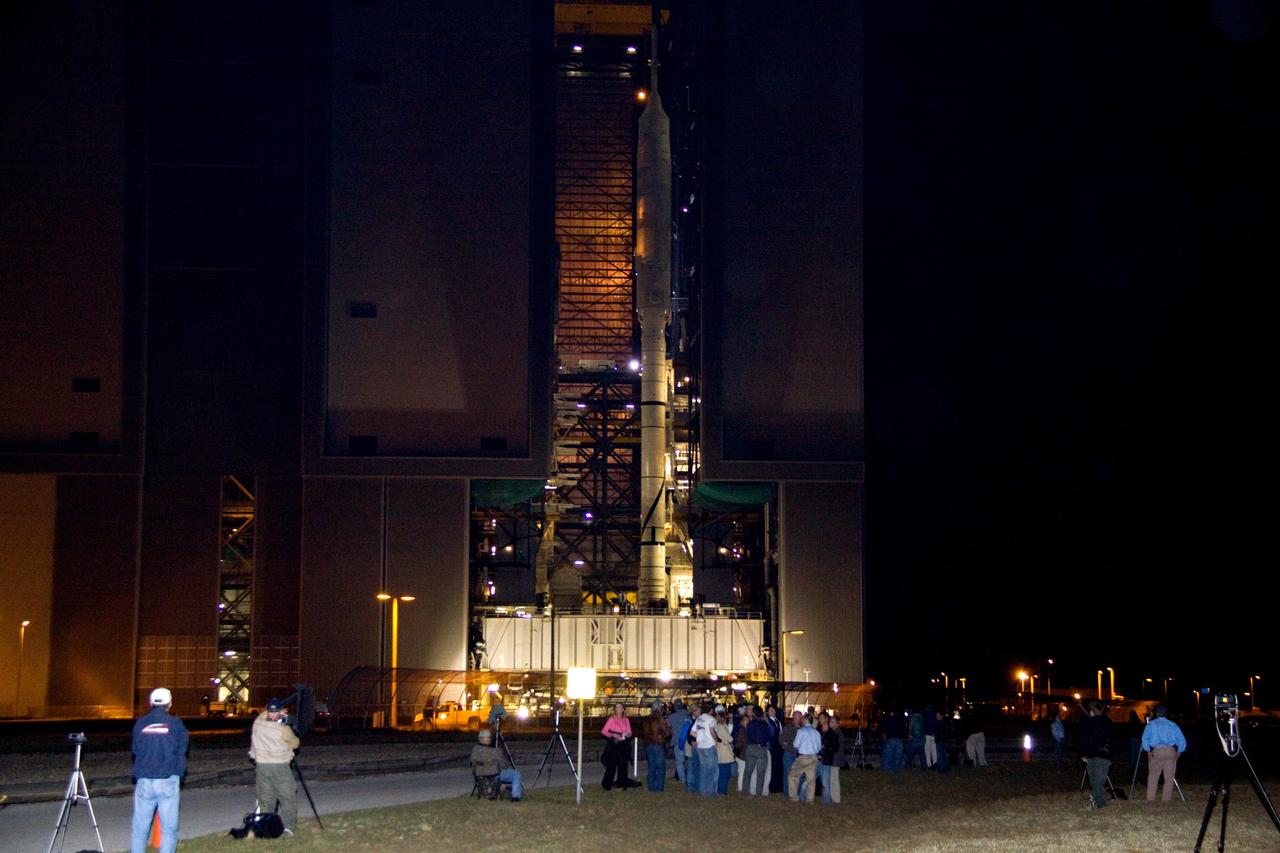

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outside the massive Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the news media (foreground) wait in the dark for the rollout of the Ares I-X to begin. The rocket will travel the 4.2 miles to Launch Pad 39B atop the crawler-transporter. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
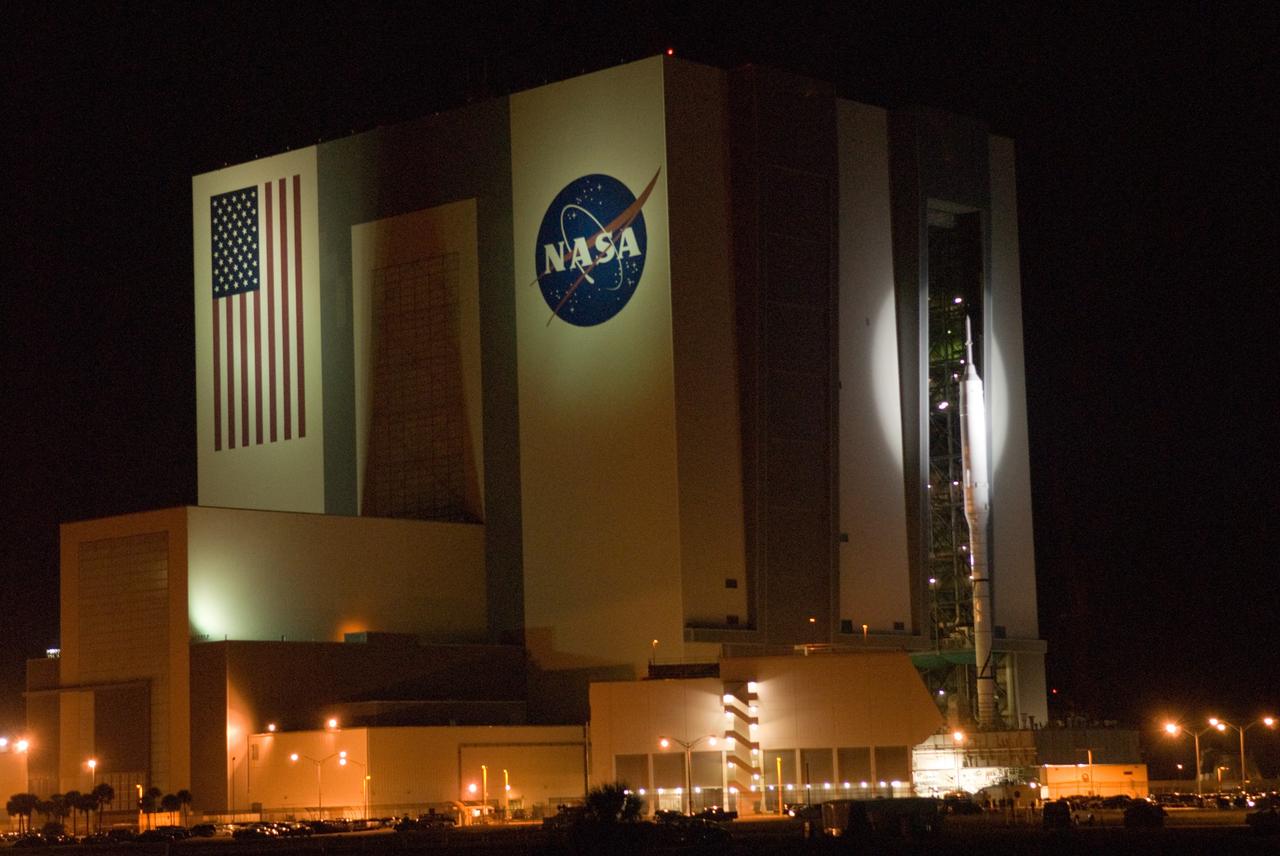

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Spotlighted against the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket begins its slow trek to Launch Pad 39B. The move, known as "rollout," began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
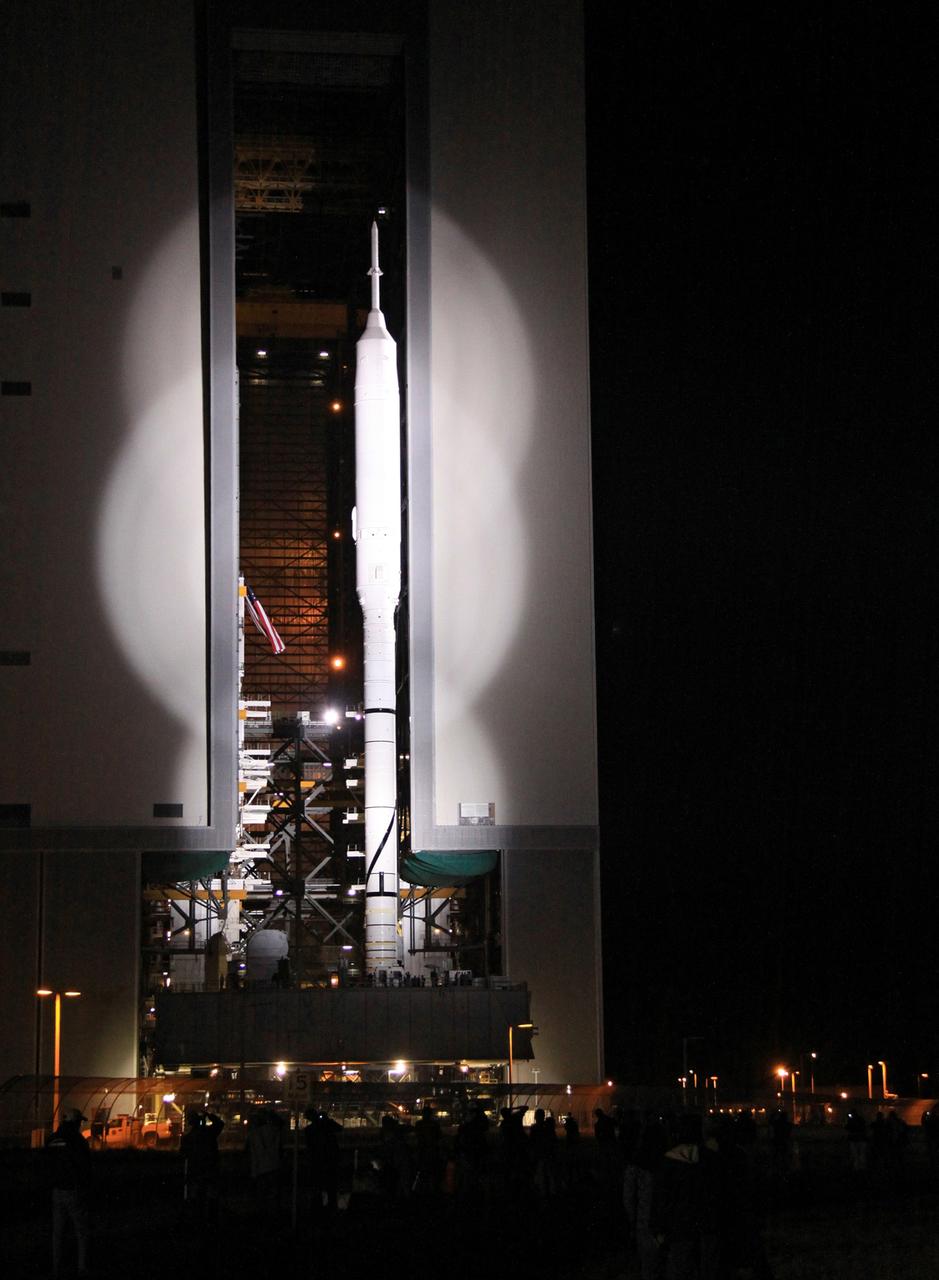

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Spotlighted in brilliant white, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket emerges from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The move to the launch pad, known as "rollout," began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
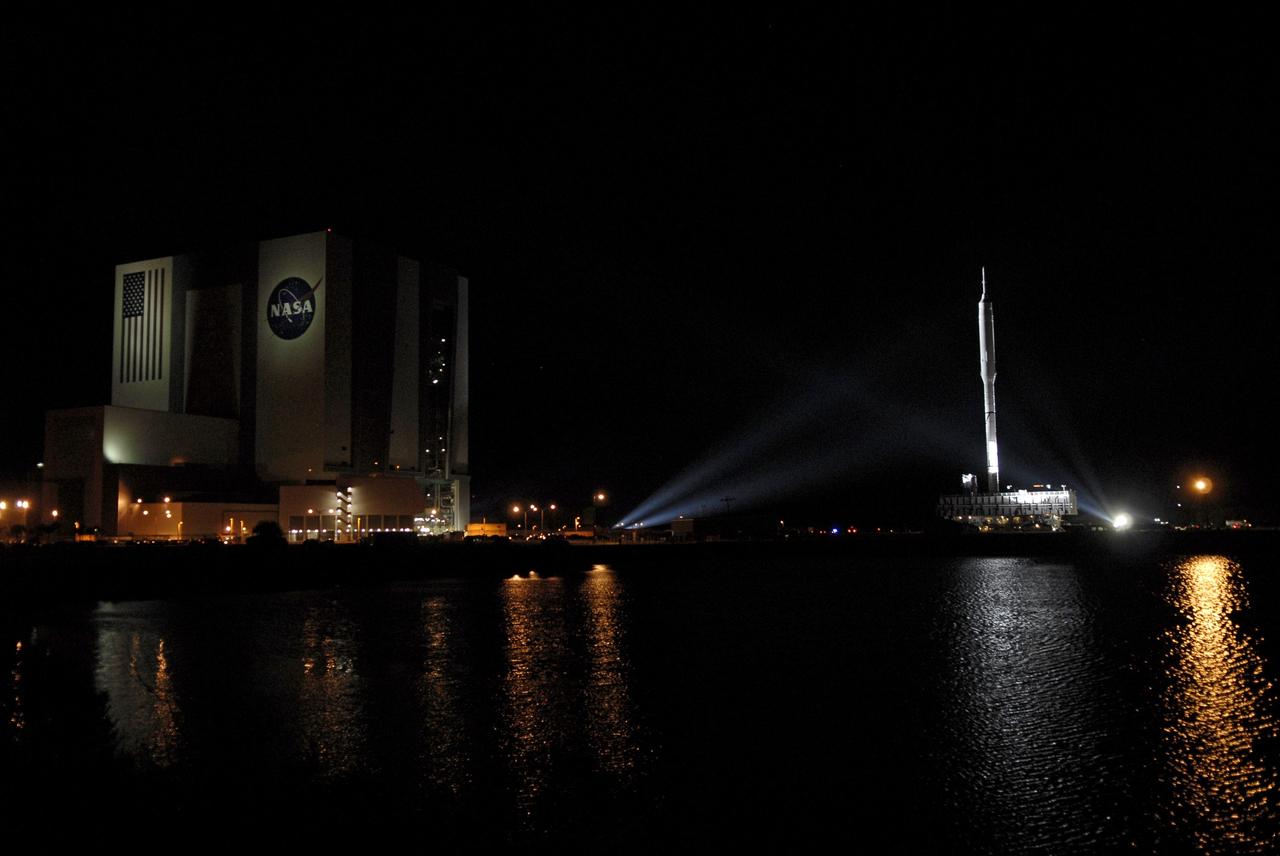

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket moves away from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket's slow, 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B began at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
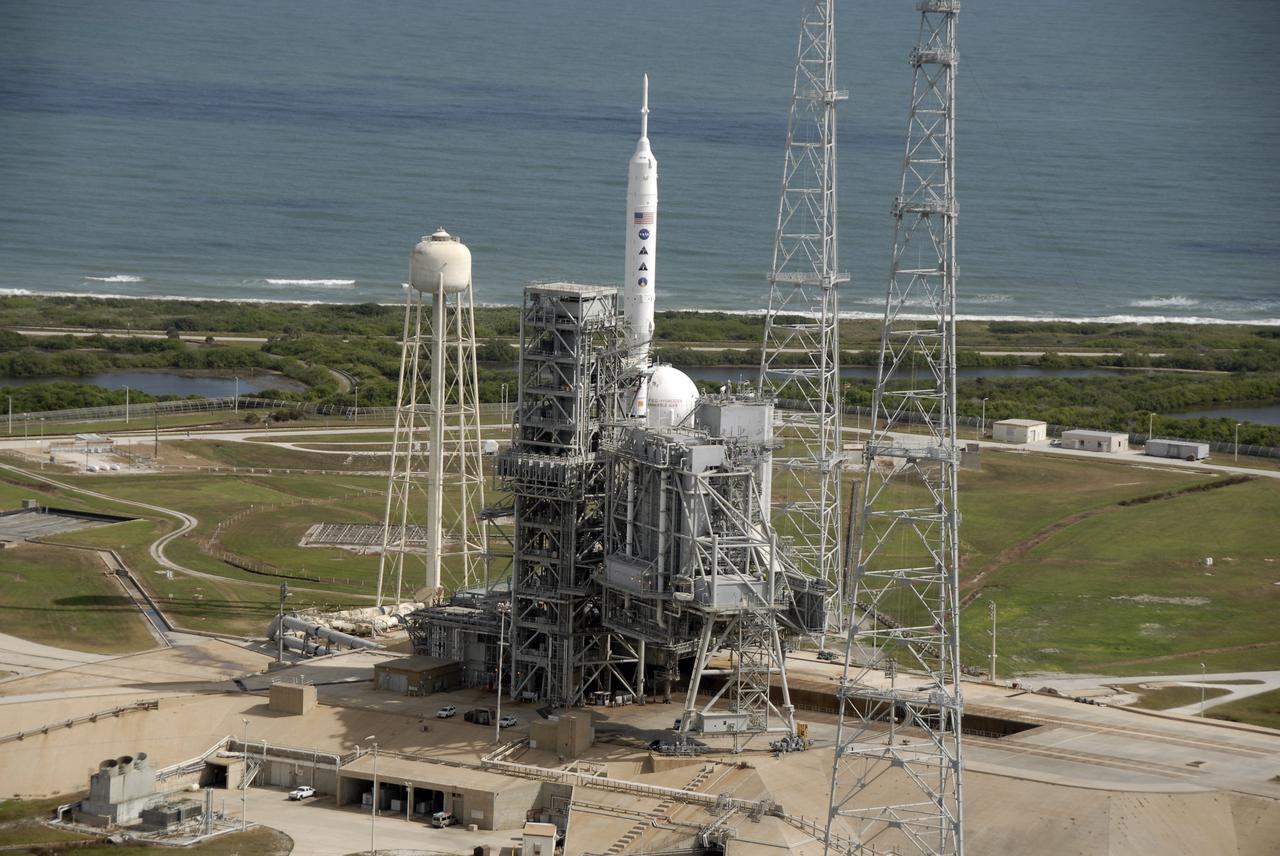

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
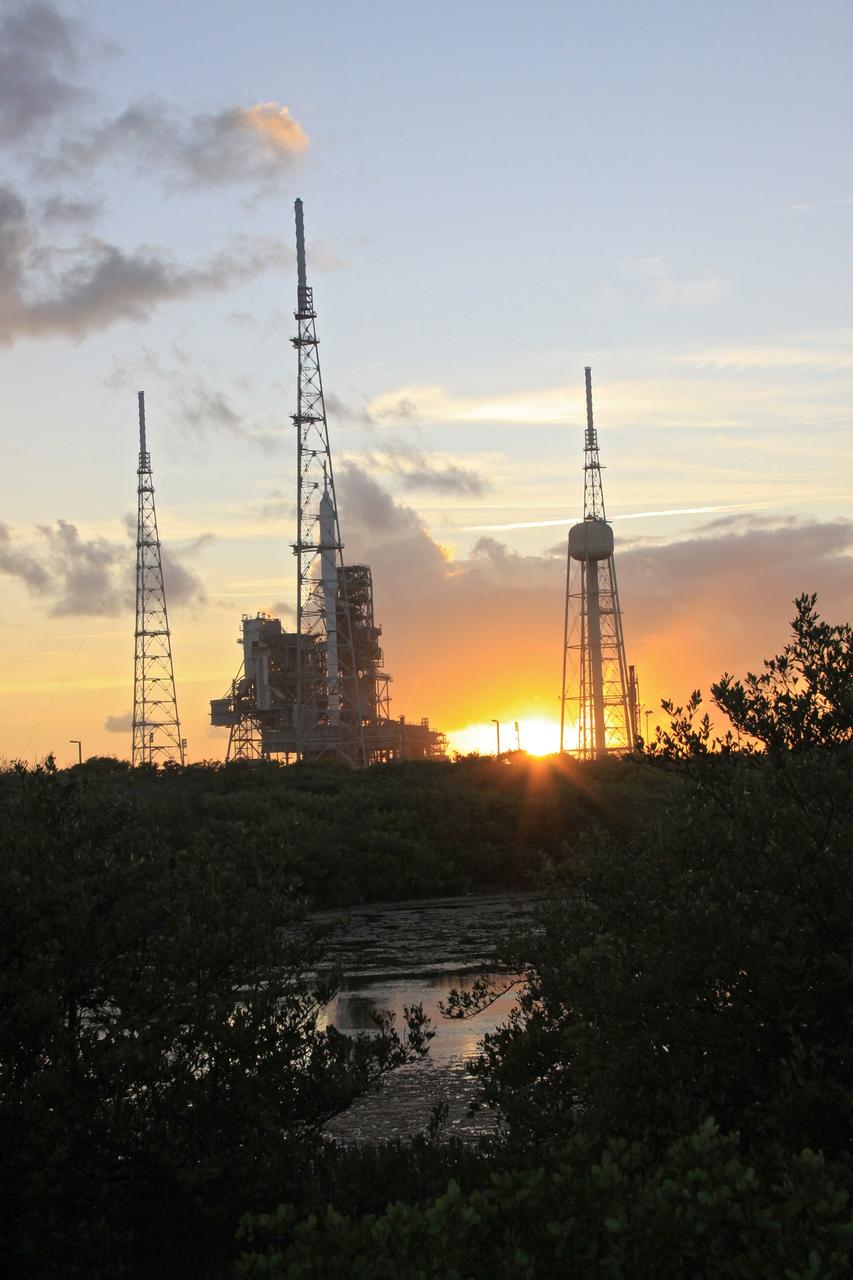

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun falls behind Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the rotating service structure, or RSS, has been retracted from the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket to allow a full test of the rocket to be conducted. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
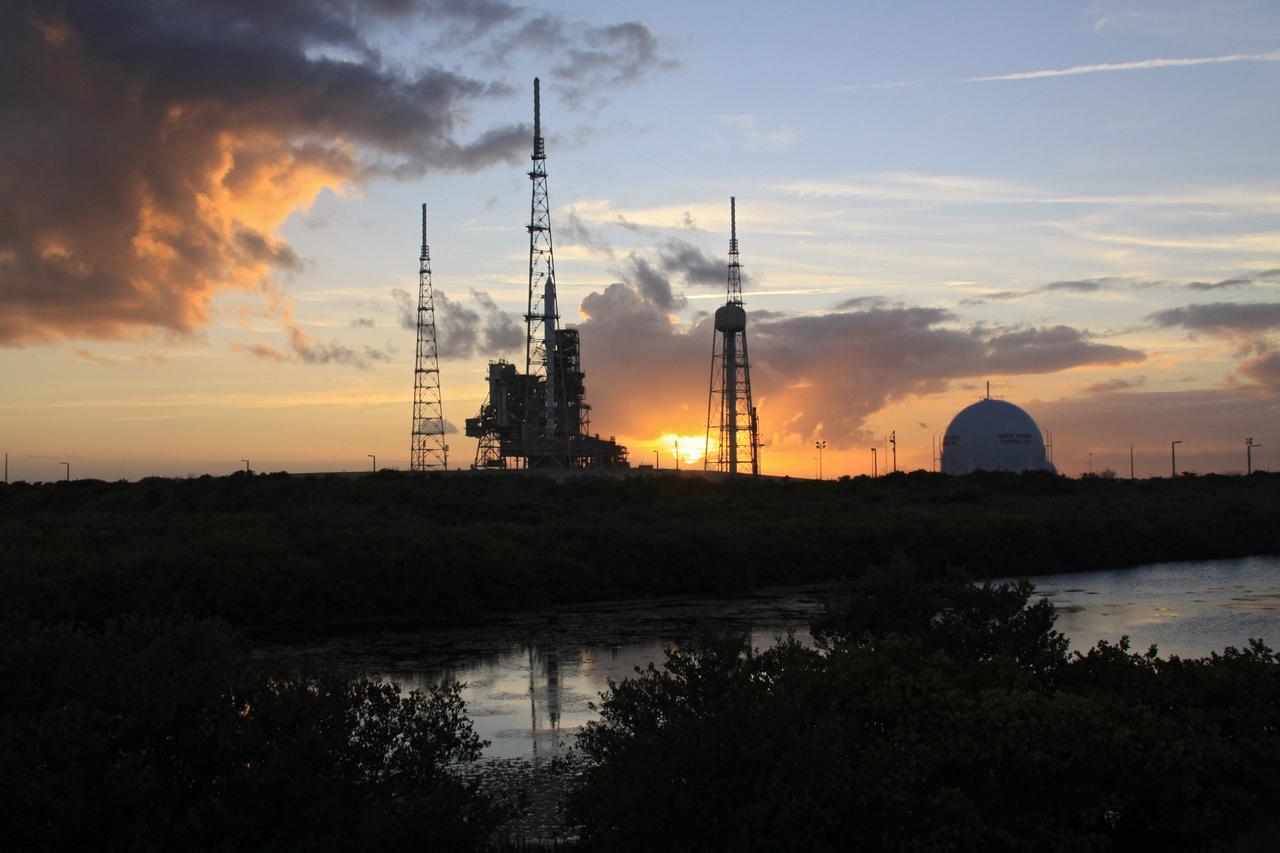

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At sunset at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the rotating service structure, or RSS, has been retracted from the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket to allow a full test of the rocket to be conducted. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
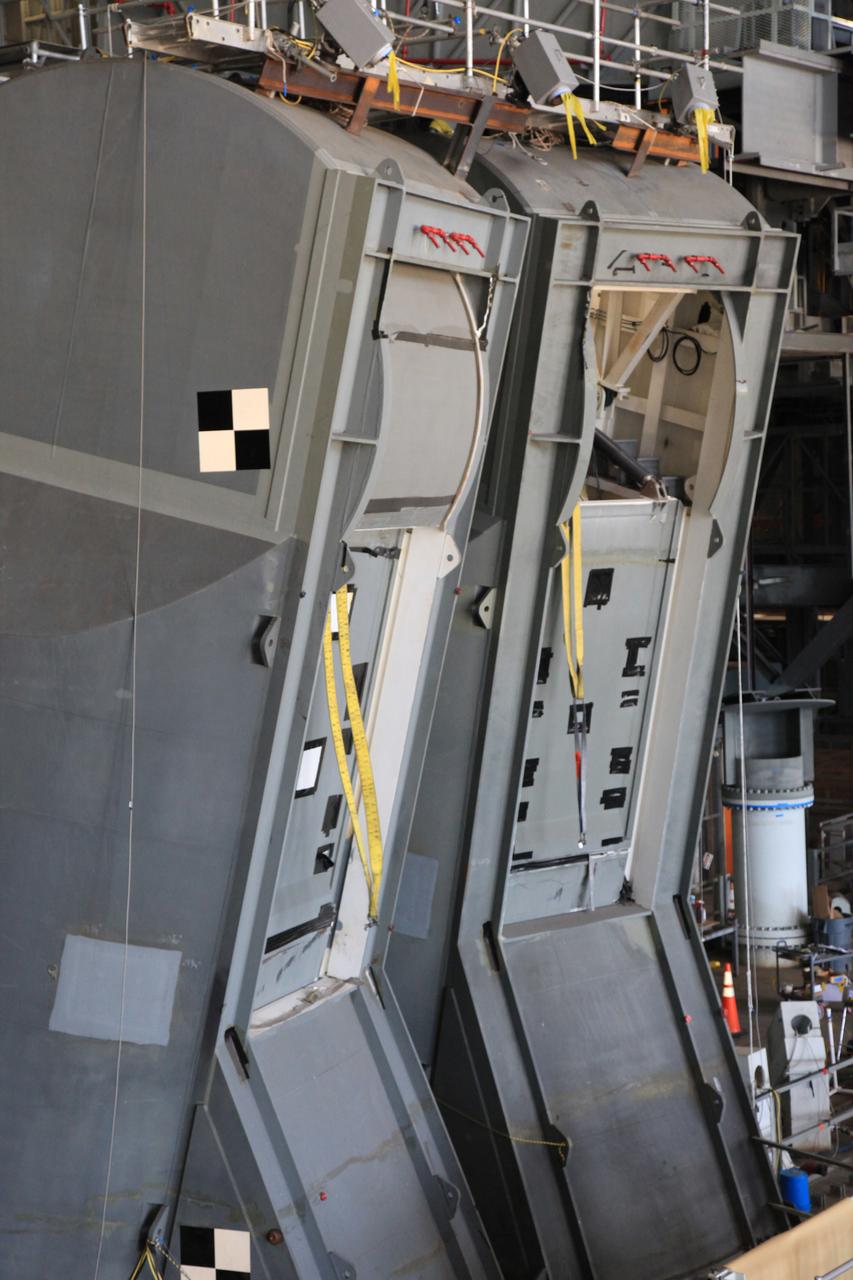

Preparations are underway to conduct a drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
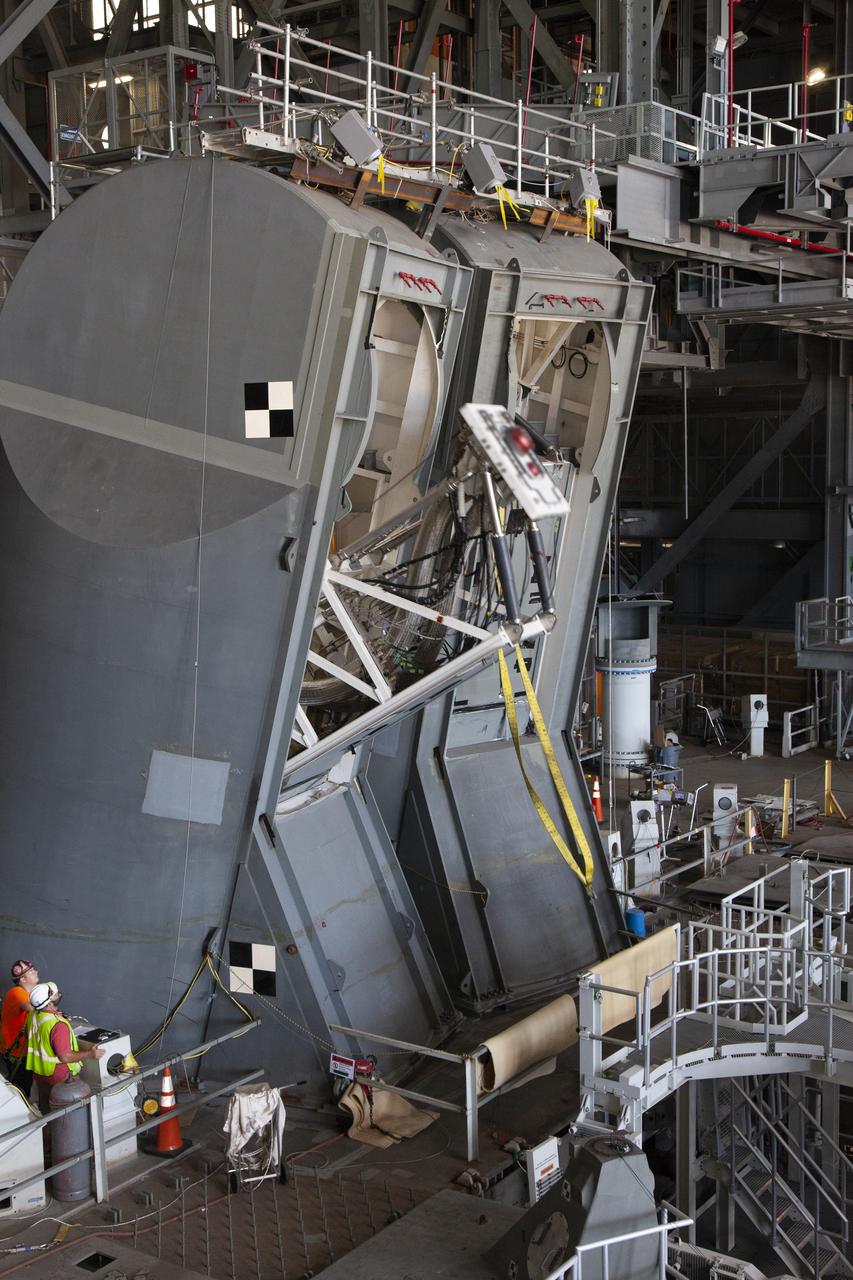

A drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is underway on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
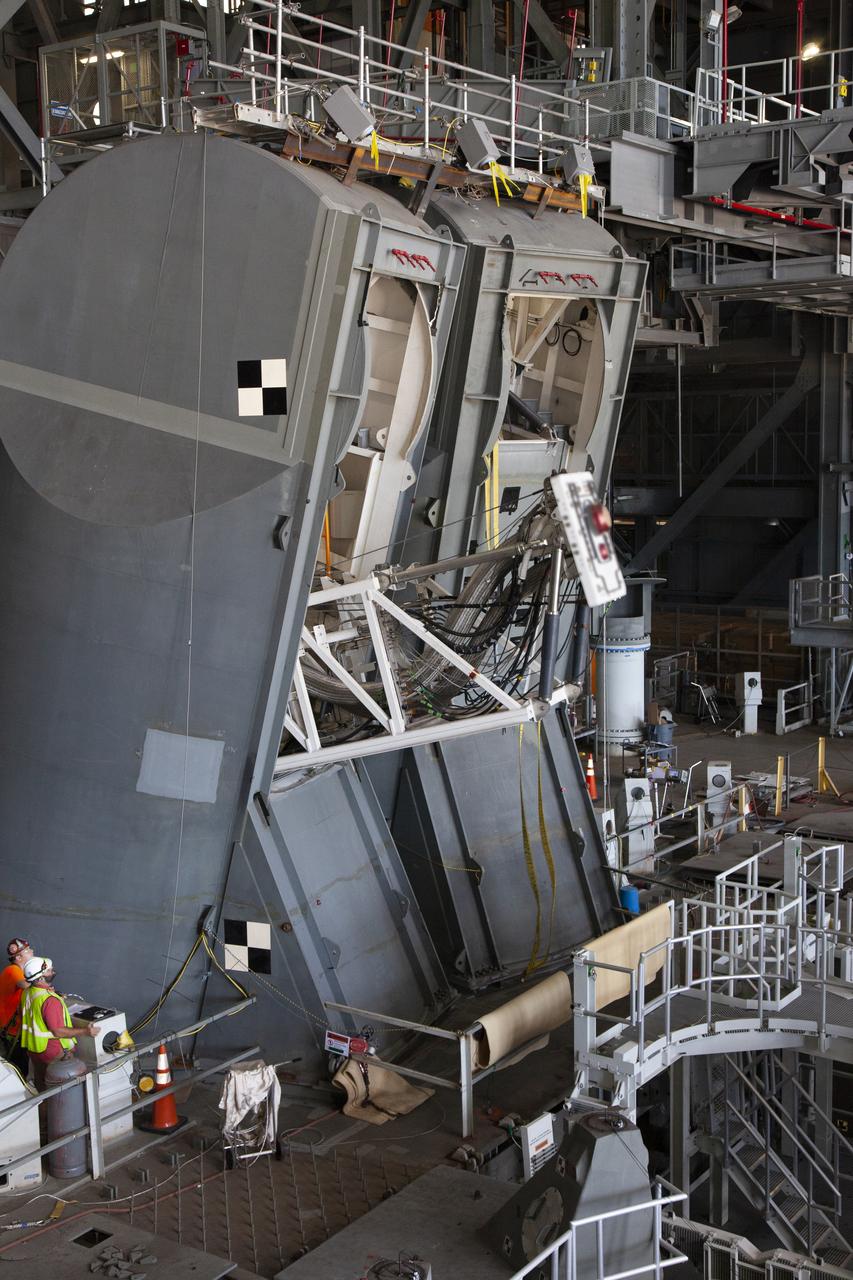

A drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is underway on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
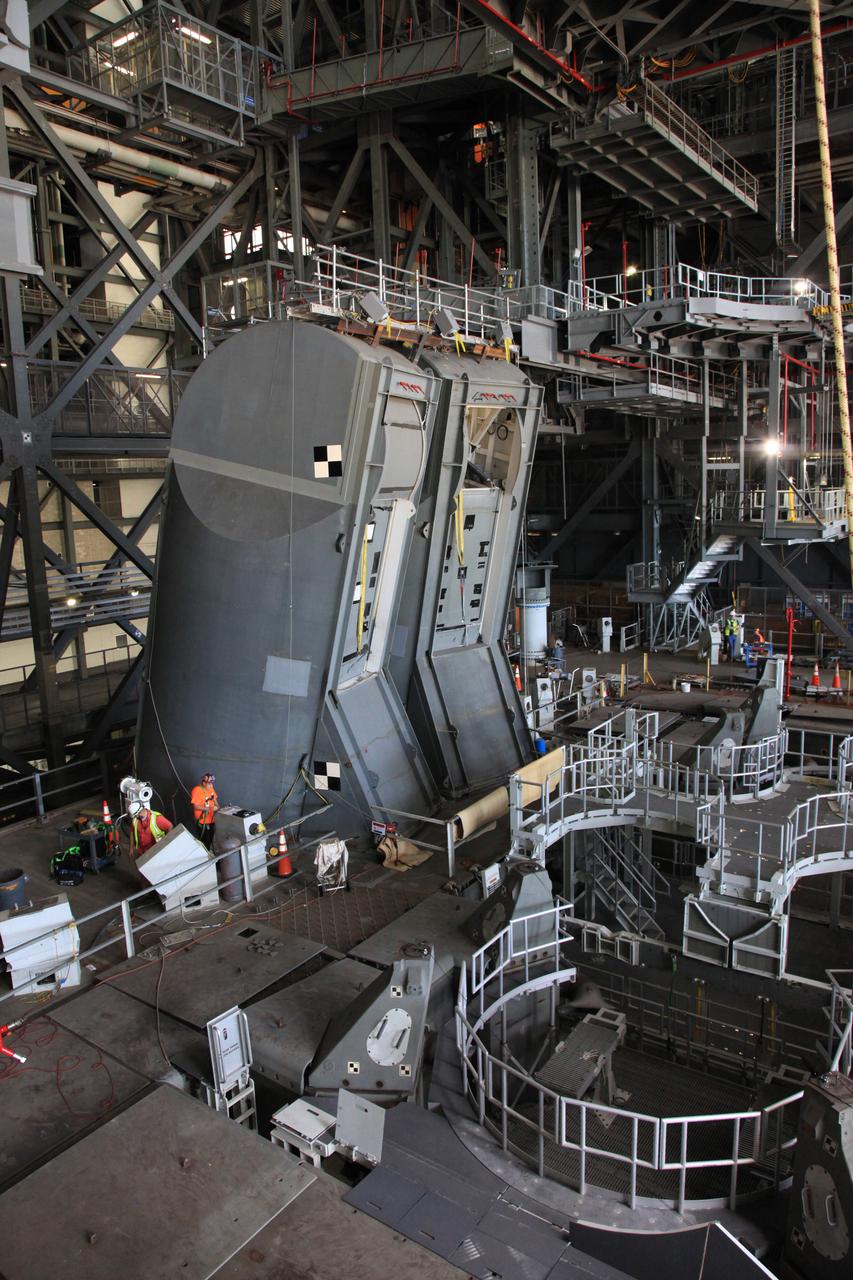
Preparations are underway to conduct a drop test of the Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 19, 2019. The 35-foot-tall TSMUs will connect to the SLS core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The drop test is being performed to ensure that the umbilicals will disconnect before launch of the SLS carrying Orion on its first uncrewed mission, Artemis 1, from Launch Complex 39B. Exploration Ground Systems and Engineering are completing the tests.
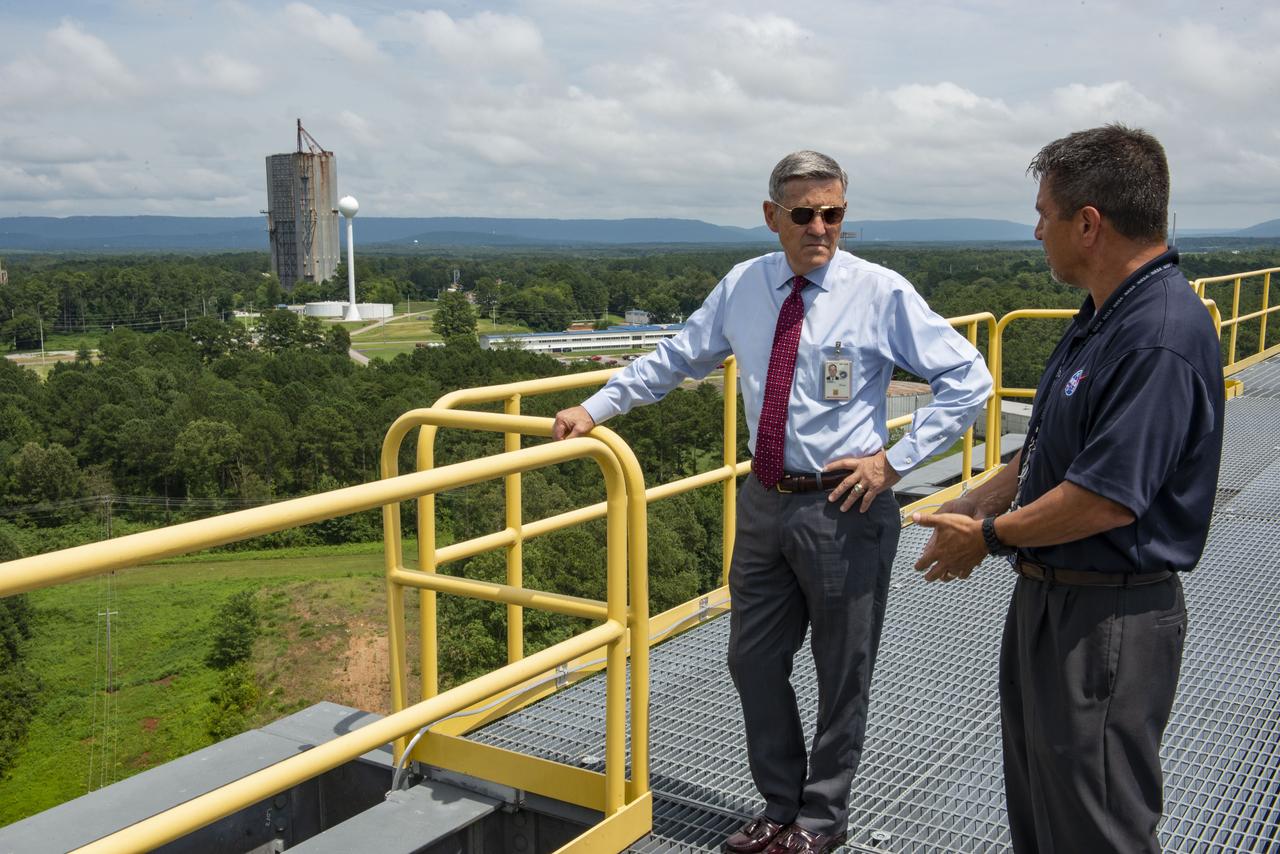

NASA's Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana visited Marshall Space Flight Center July 16. With the Dynamic Test Stand in the background, Cabana, left, talks with Tim Flores, integration manager for stages in the Space Launch System Program Office, on top of Test Stand 4693, NASA’s largest SLS structural test stand. In addition to viewing SLS hardware, Cabana spoke to the Marshall Association and National Space Club Huntsville during his visit.
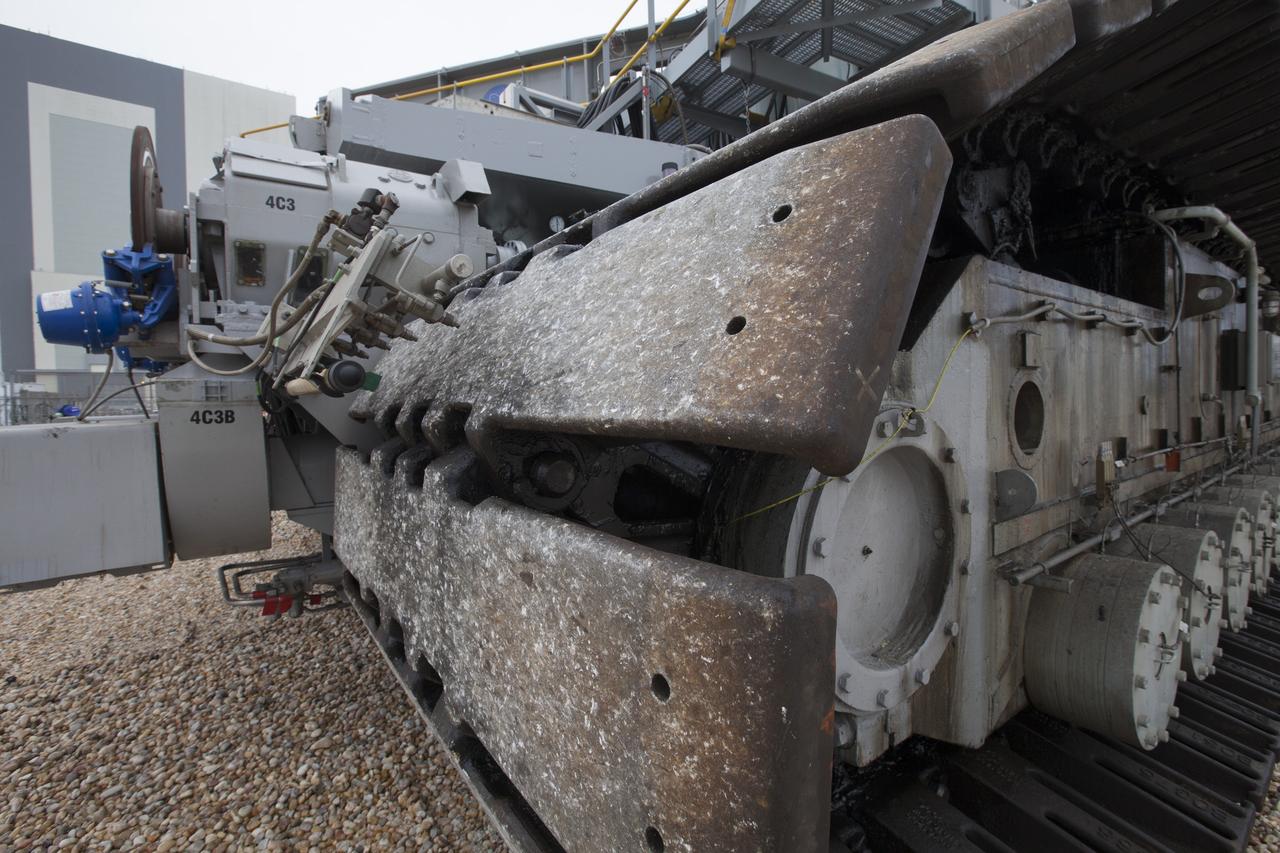

A close-up view of one of the cleats on one section of the tracks that help propel NASA’s upgraded crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the giant vehicle moves along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 was driven to Launch Pad 39B to test recently completed upgrades and modifications to ensure the vehicle will be ready to support NASA’s journey to Mars. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy oversaw upgrades to the crawler in the VAB. The crawler will carry the mobile launcher with Orion atop the Space Launch System rocket to Pad 39B for Exploration Mission 1.
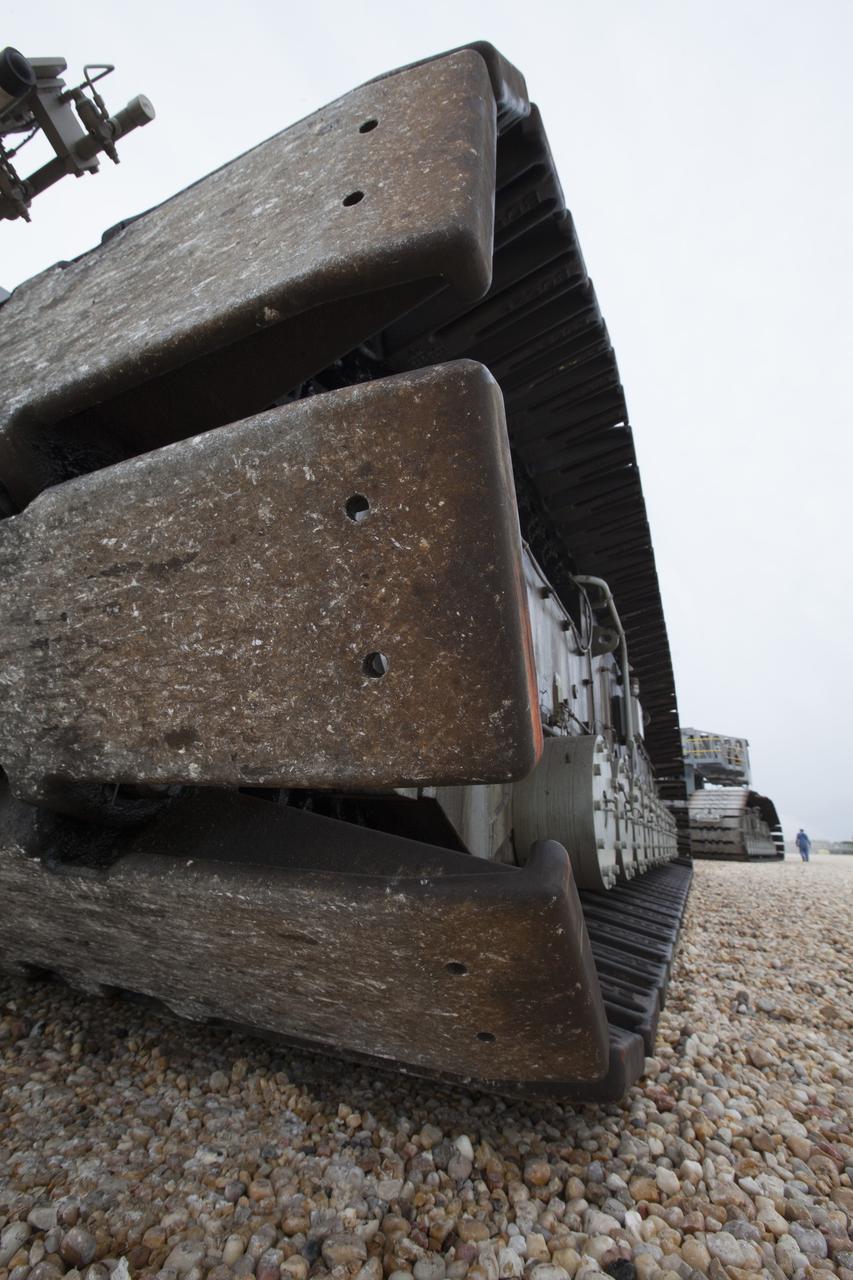

A close-up view of a section of cleats on one of the tracks that help propel NASA’s upgraded crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) as the giant vehicle moves along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 was driven to Launch Pad 39B to test recently completed upgrades and modifications to ensure the vehicle will be ready to support NASA’s journey to Mars. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy oversaw upgrades to the crawler in the VAB. The crawler will carry the mobile launcher with Orion atop the Space Launch System rocket to Pad 39B for Exploration Mission 1.
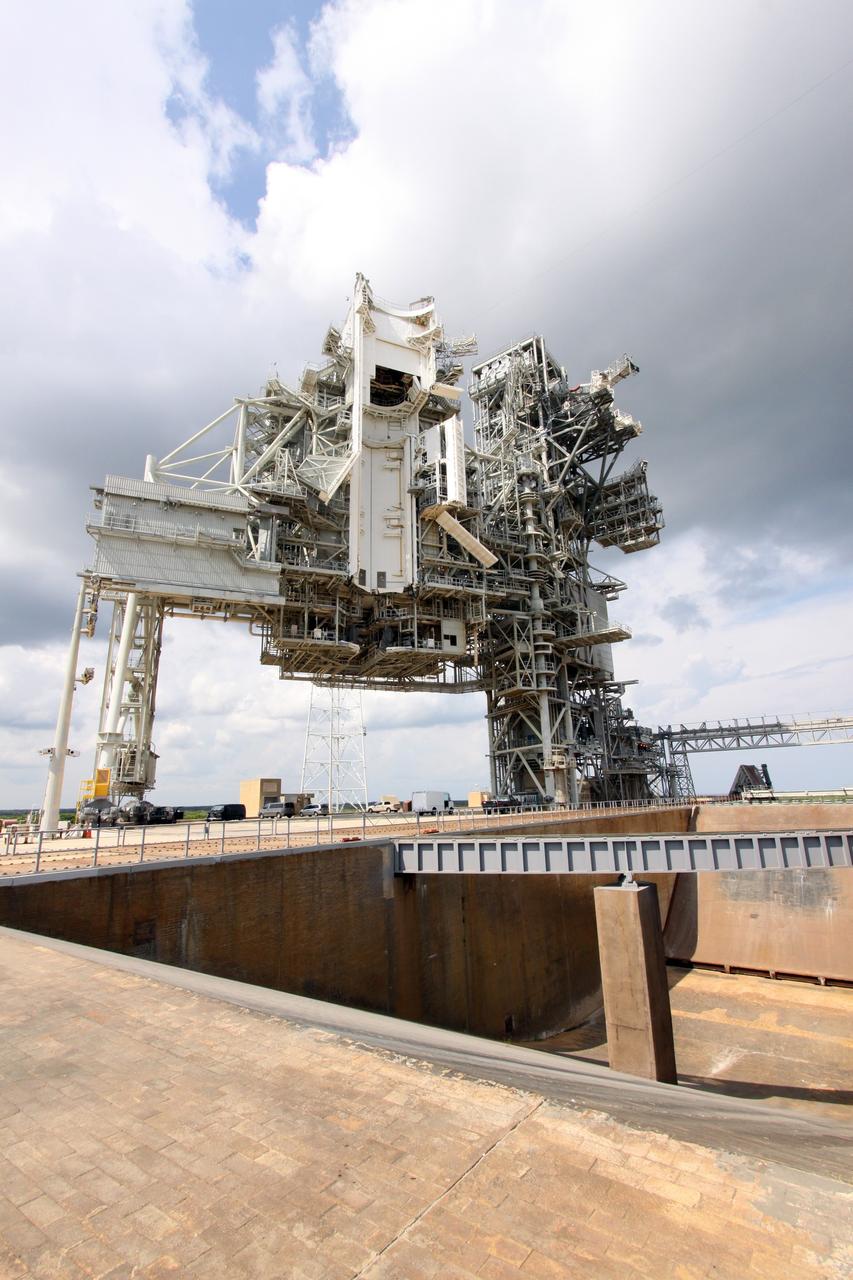

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, modifications to Launch Pad 39B are complete, and the pad is ready to support the Ares I-X rocket. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system designed to carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
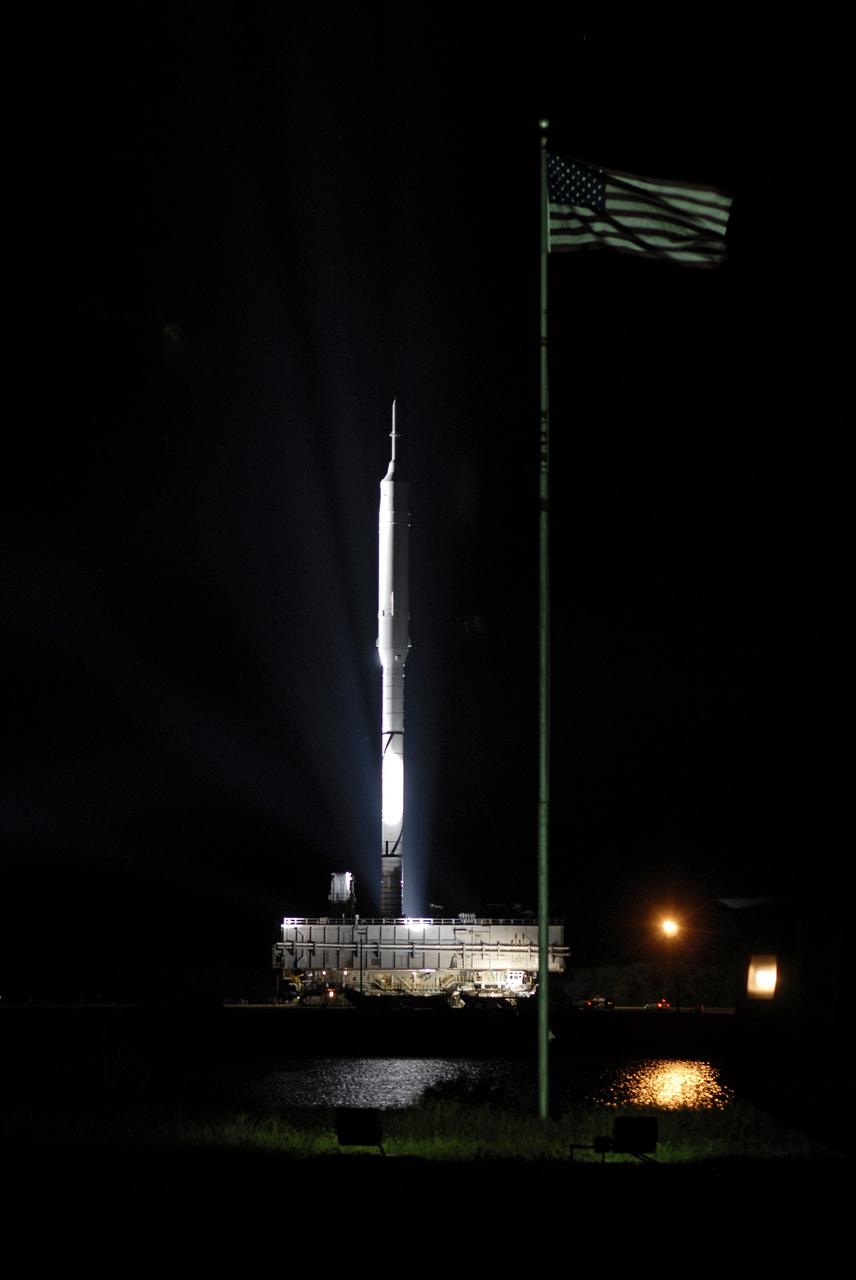

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The American flag waves as the Ares I-X rocket passes by on its slow trek to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket, riding atop a crawler-transporter, began the 4.2-mile journey at 1:39 a.m. EDT. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
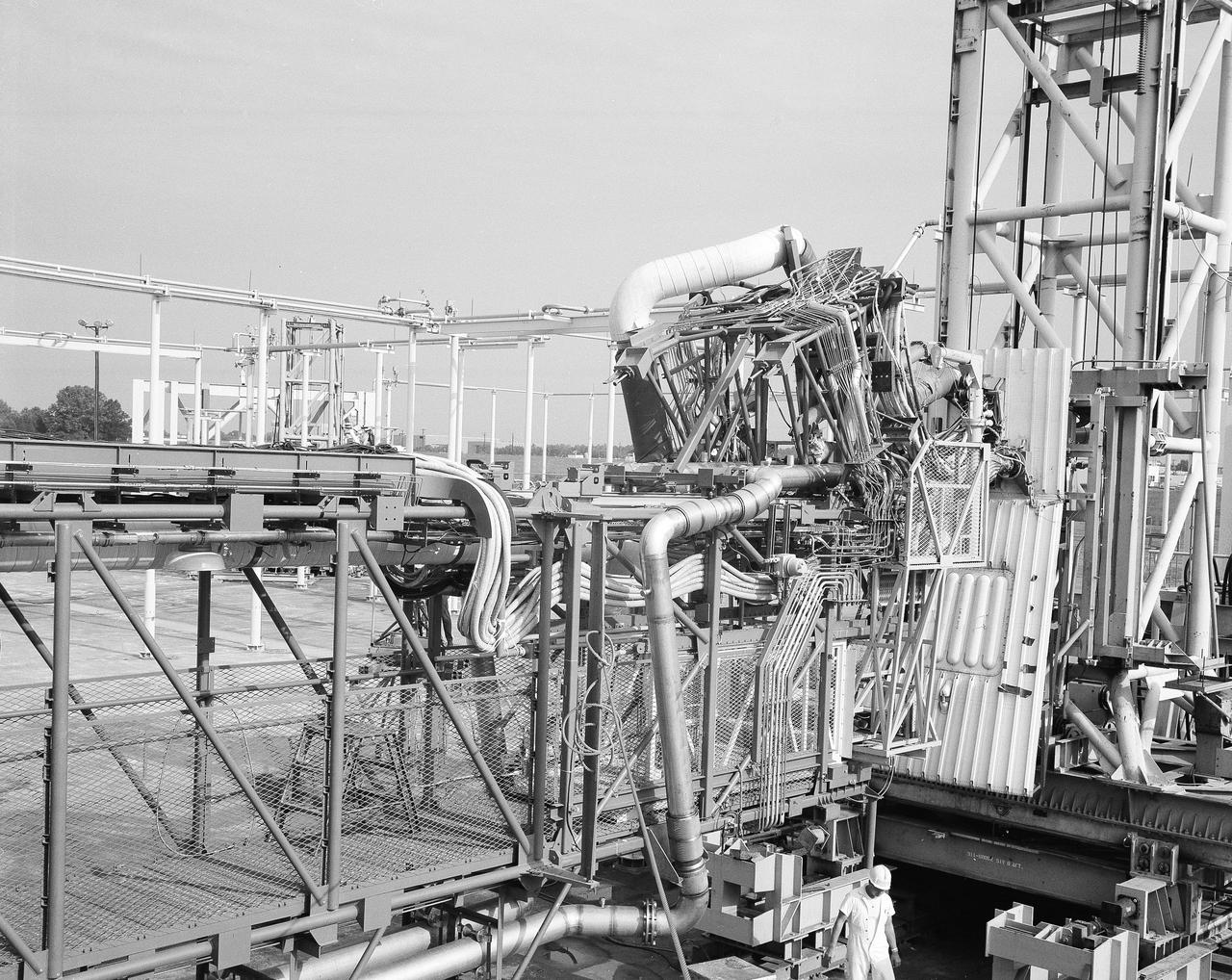

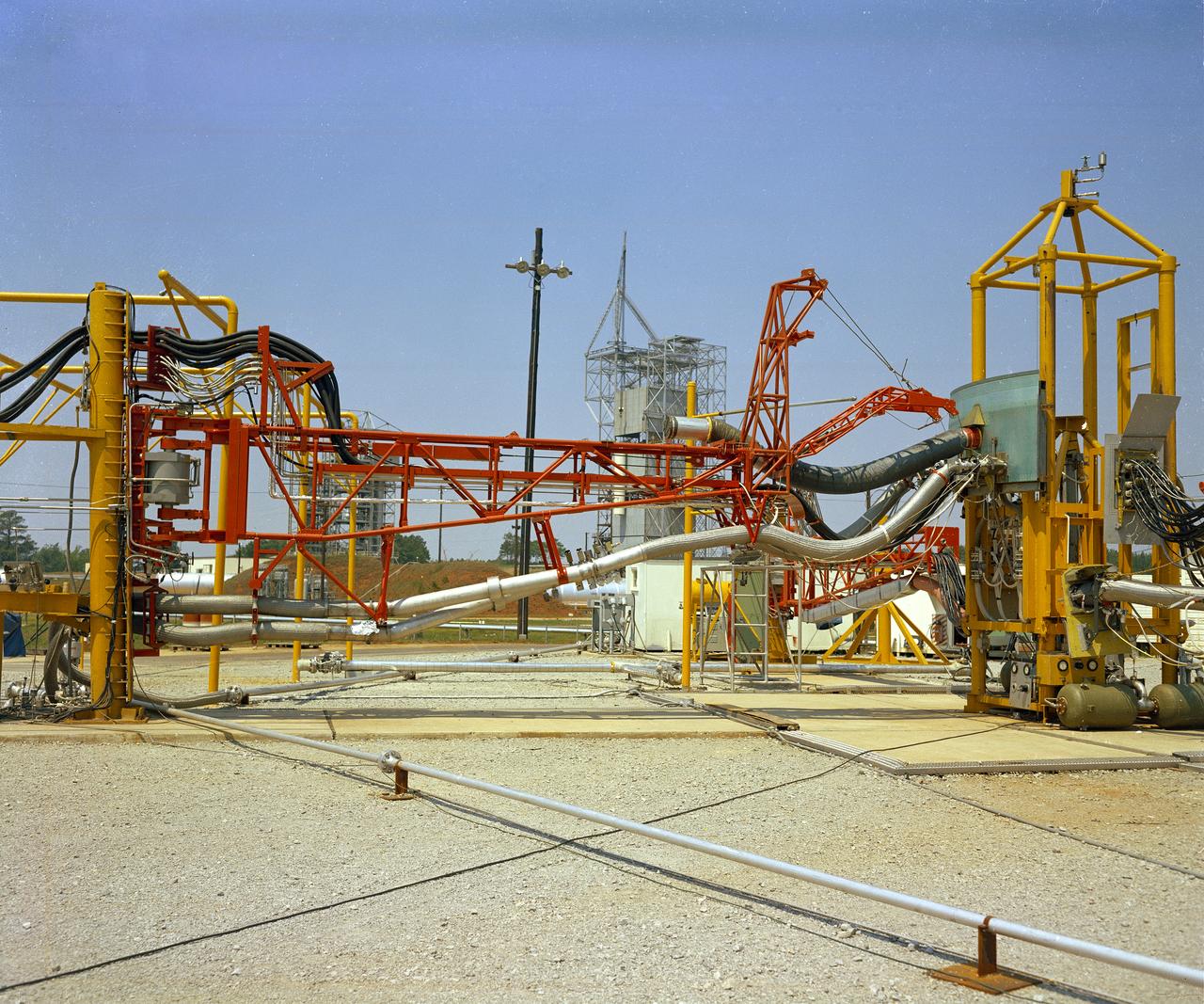
The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
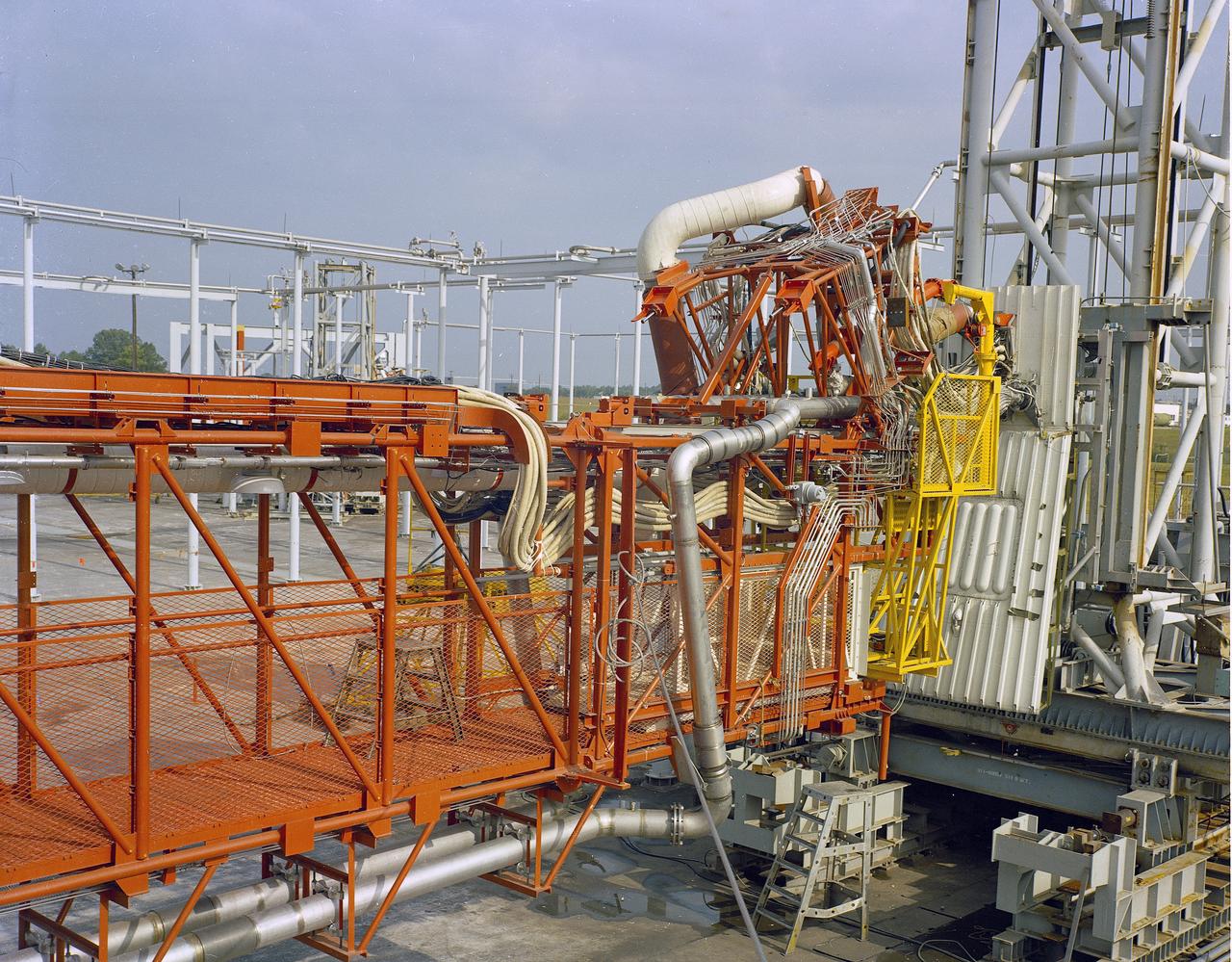

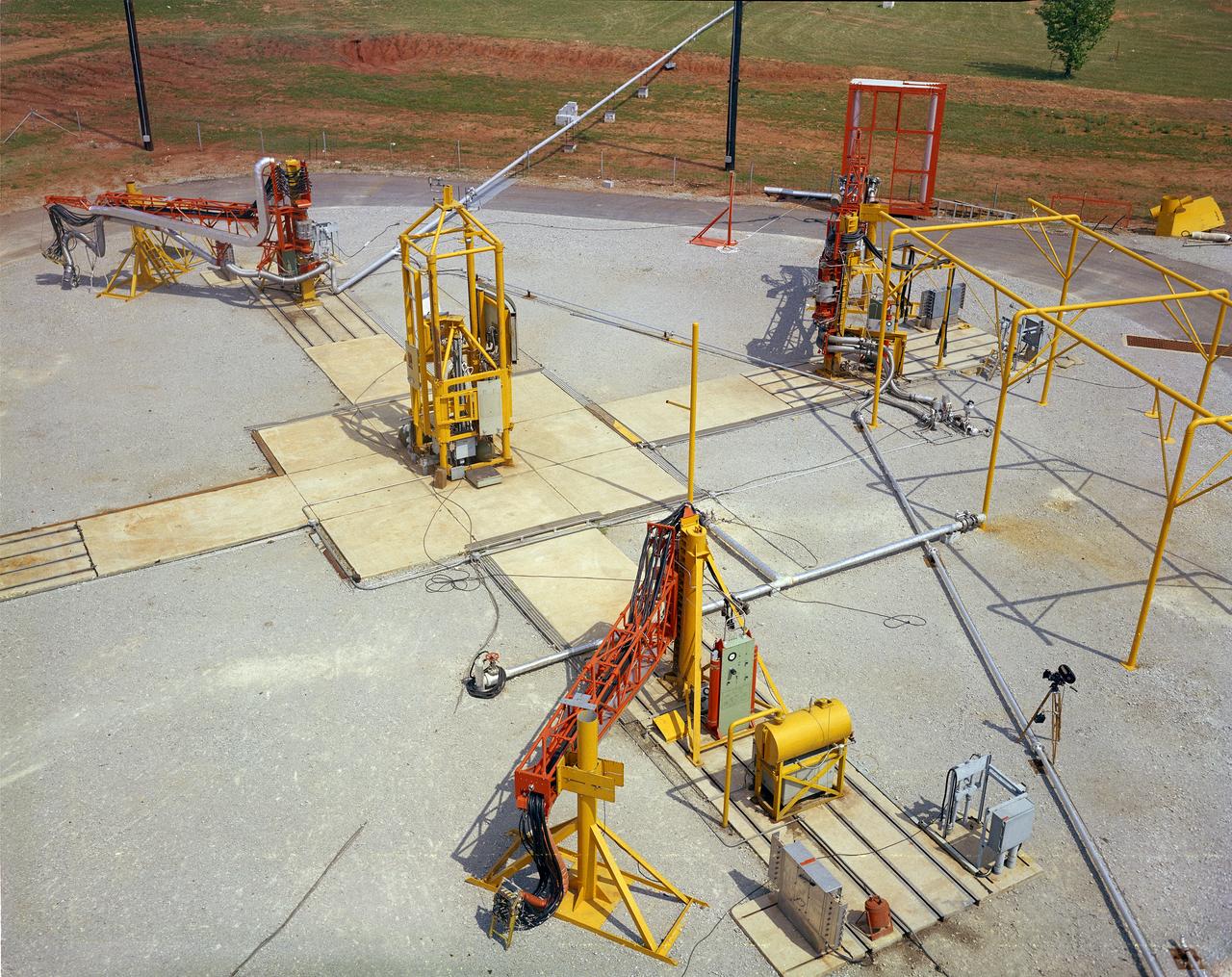
The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
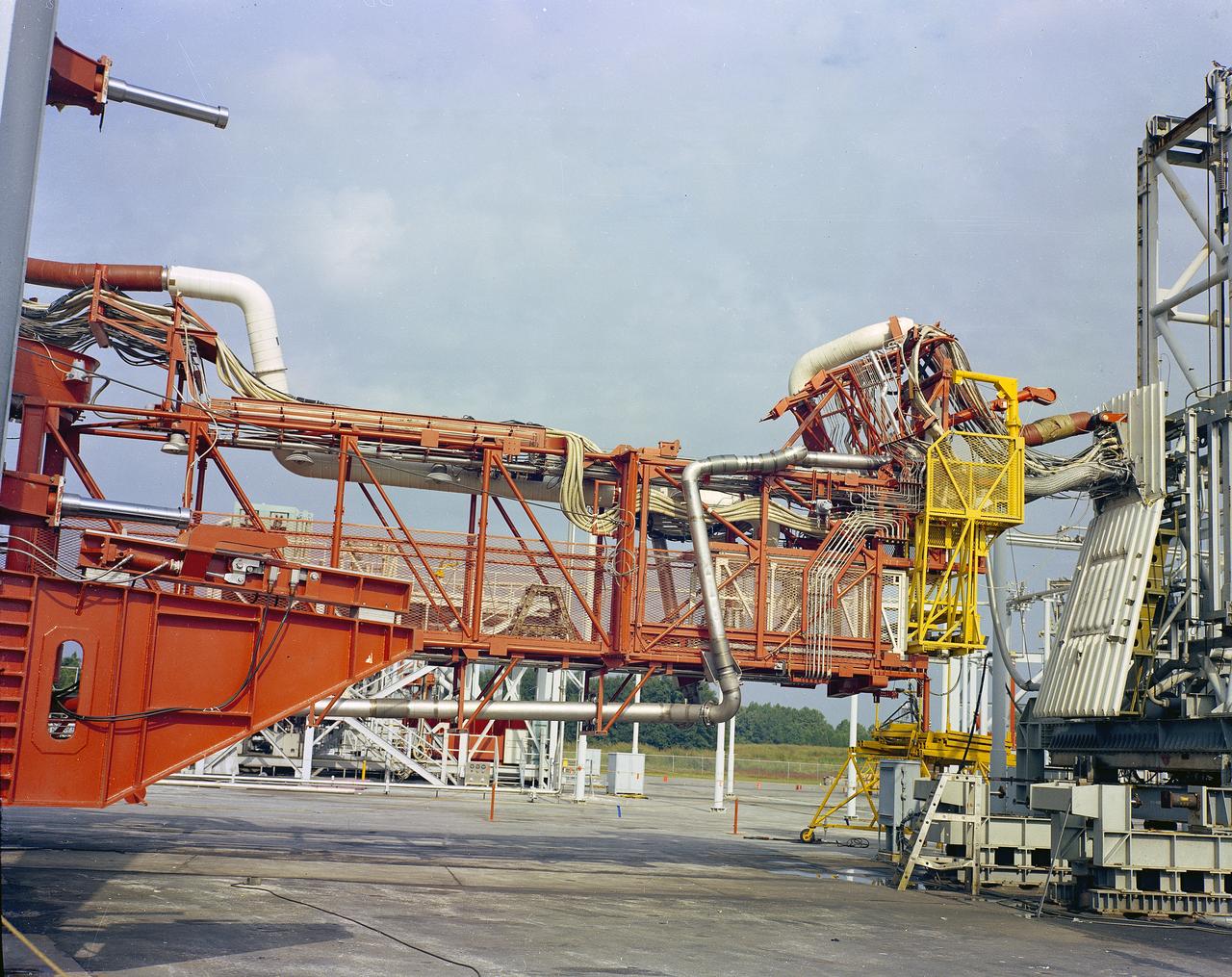

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
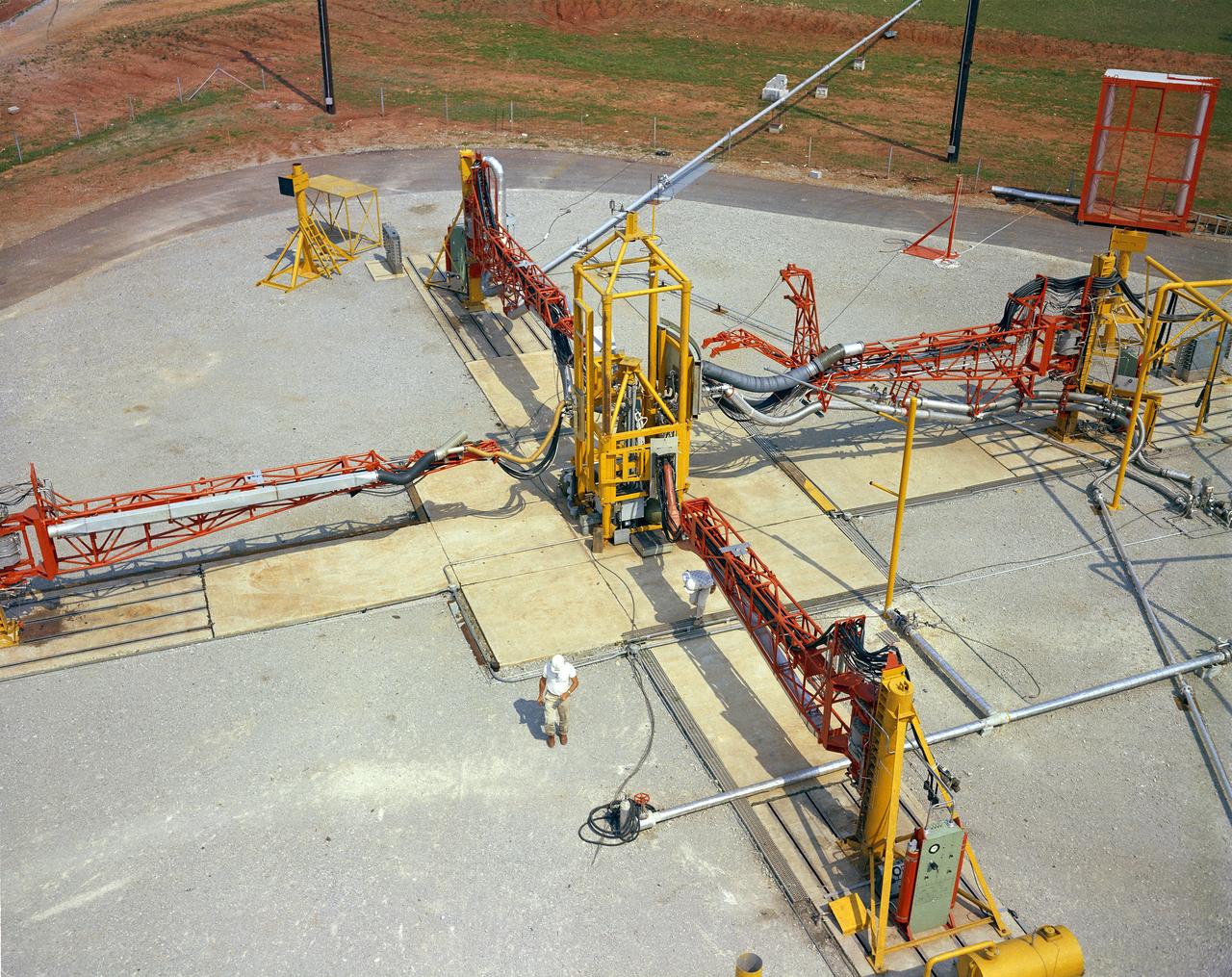

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
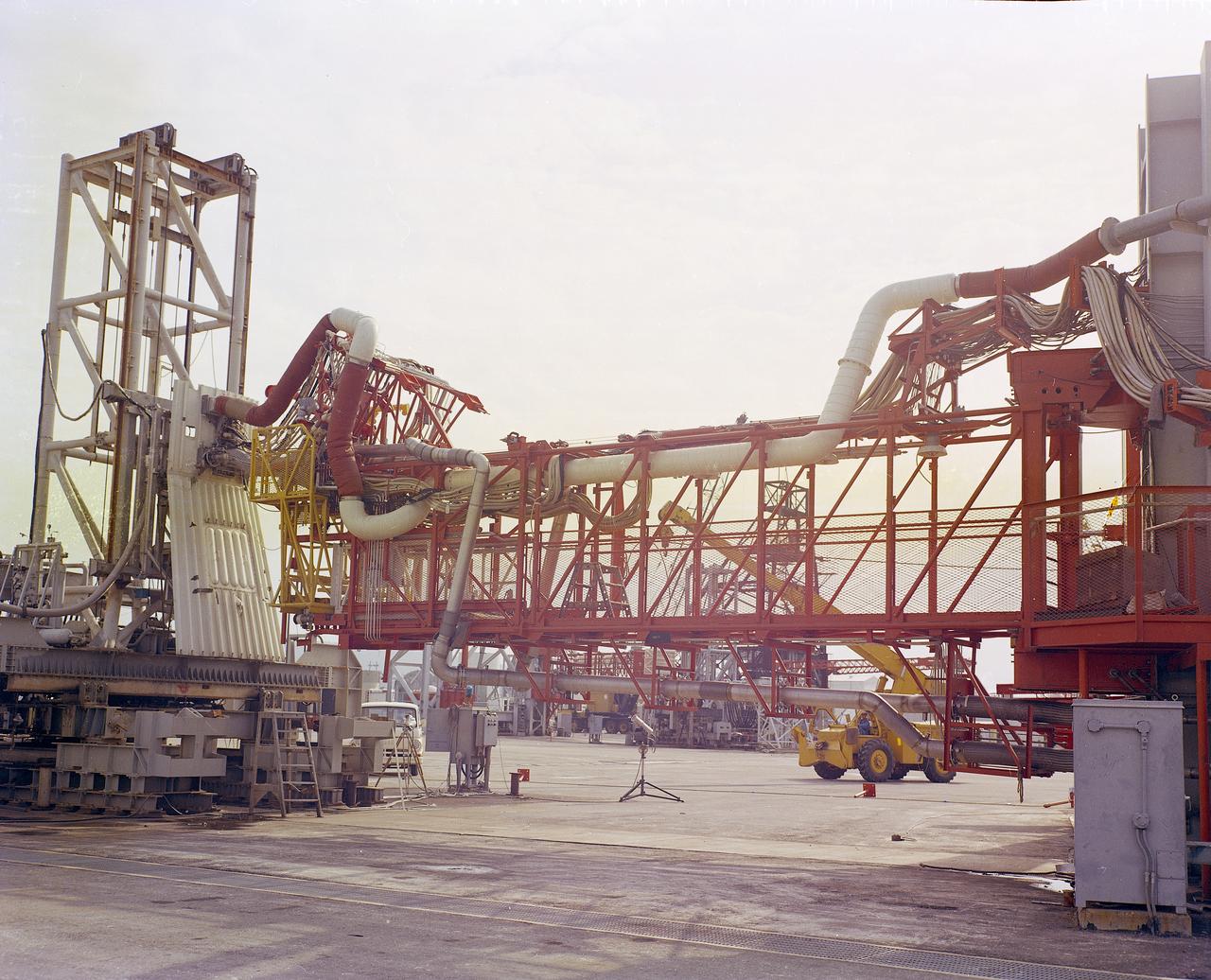

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
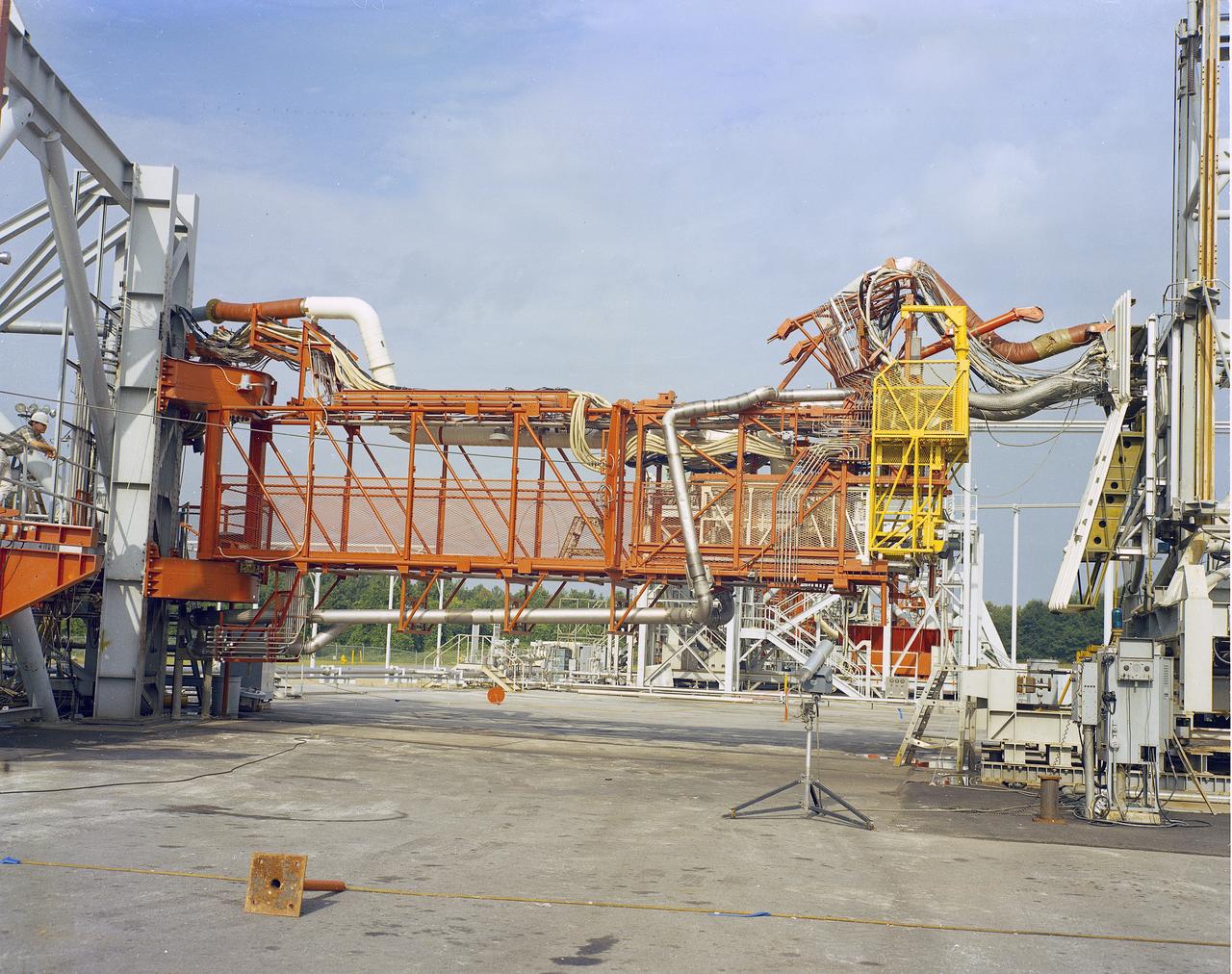

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
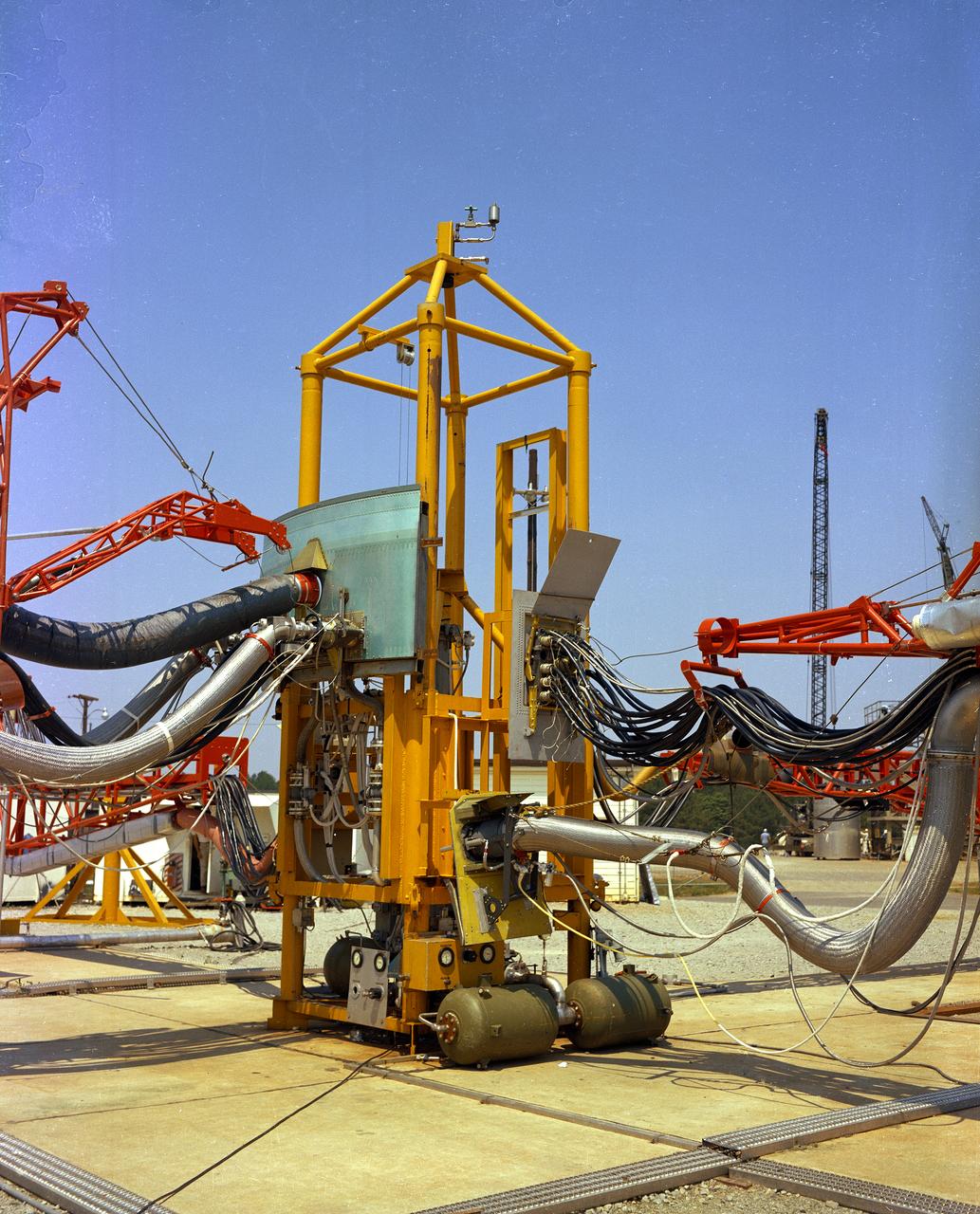

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) played a crucial role in the development of the huge Saturn rockets that delivered humans to the moon in the 1960s. Many unique facilities existed at MSFC for the development and testing of the Saturn rockets. Affectionately nicknamed “The Arm Farm”, the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator was one of those unique facilities. This facility was developed to test the swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off. The Arm Farm provided the capability of testing the detachment and reconnection of various arms under brutally realistic conditions. The 18-acre facility consisted of more than a half dozen arm test positions and one position for testing access arms used by the Apollo astronauts. Each test position had two elements: a vehicle simulator for duplicating motions during countdown and launch; and a section duplicating the launch tower. The vehicle simulator duplicated the portion of the vehicle skin that contained the umbilical connections and personnel access hatches. Driven by a hydraulic servo system, the vehicle simulator produced relative motion between the vehicle and tower. On the Arm Farm, extreme environmental conditions (such as a launch scrub during an approaching Florida thunderstorm) could be simulated. The dramatic scenes that the Marshall engineers and technicians created at the Arm Farm permitted the gathering of crucial technical and engineering data to ensure a successful real time launch from the Kennedy Space Center.
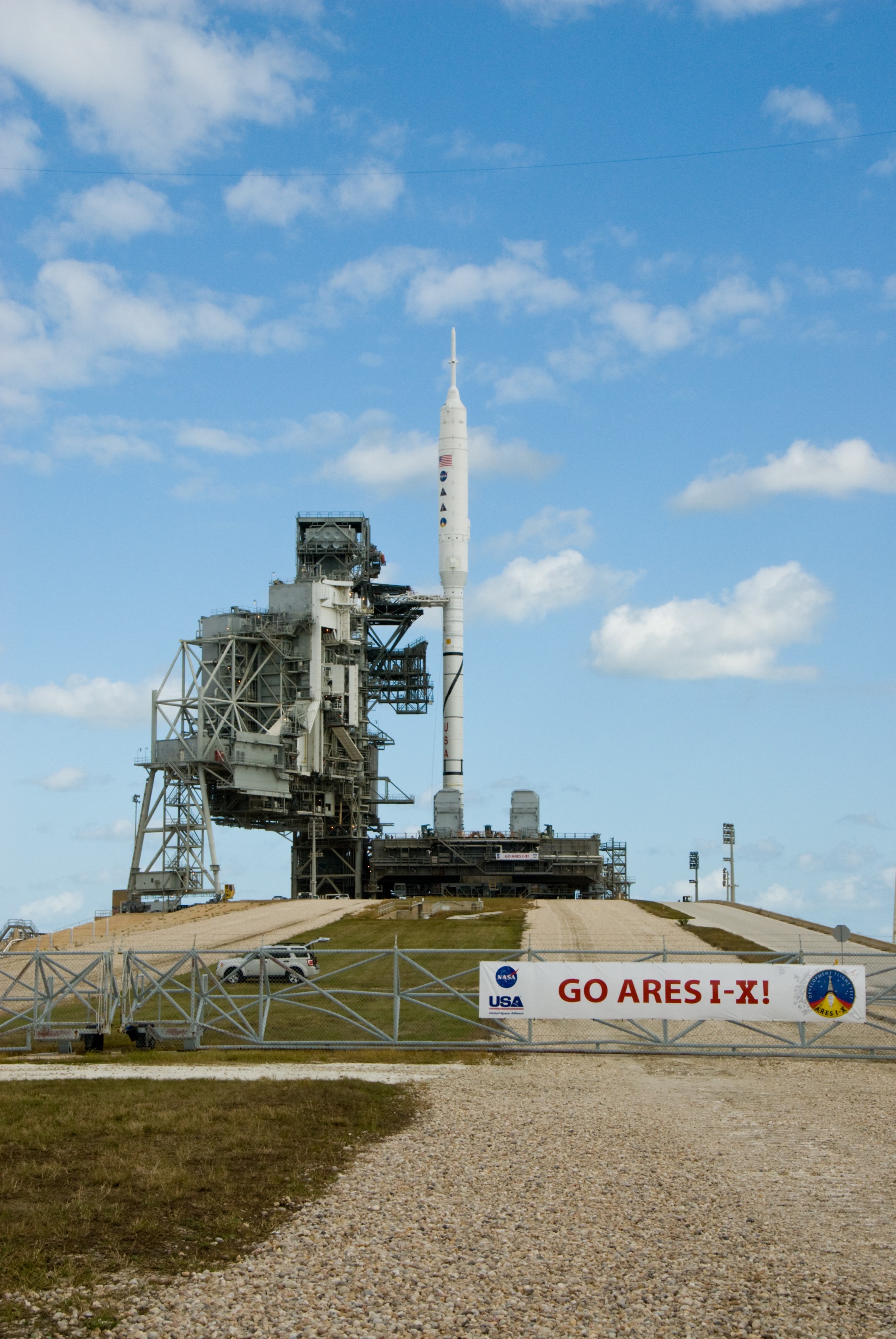

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Go Ares I-X! A banner on the perimeter fence of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida reflects the excitement building in Kennedy's work force in anticipation of the flight test of the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. A Flight Test Readiness Review, a meeting to assess preparations for the flight test, is scheduled for Oct. 23. The flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
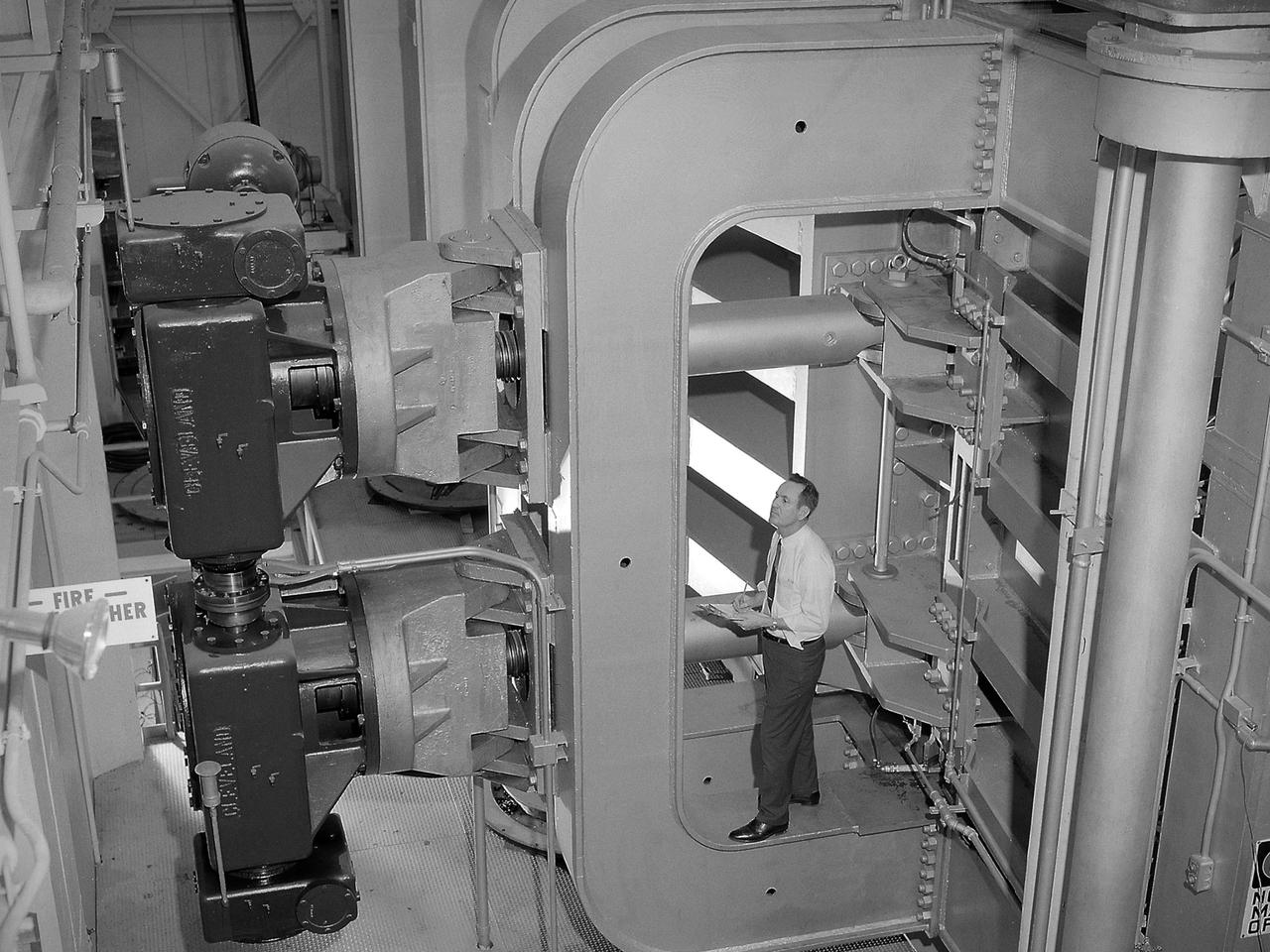

Screwjacks located on the exterior of the second throat section in the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The 10- by 10 tunnel was the most powerful propulsion wind tunnel in the country when it began operating in 1956. The facility can generate wind speeds from Mach 3 to 3.5. A flexible wall nozzle located just upstream from the test section can be adjusted using screw jacks to produce the desired air flow. The 61-foot long second throat, seen here from the outside, was located just beyond the test section. It slows the supersonic air flow down to prevent shock waves. The second throat’s side walls can be adjusted up to three inches on each side using these electrically-driven screwjacks. The air and the 1.25-inch thick walls are cooled by water injection. During the 1960s the 10- by 10-foot tunnel supported the development of virtually all US launch vehicle systems. It was used for Atlas-Centaur, Saturn rockets, and Atlas-Agena testing.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Waves break off the Atlantic Ocean near Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On the pad, the Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on its upcoming flight test. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers prepare to close the arms of the vehicle stabilization system around the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, newly arrived on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
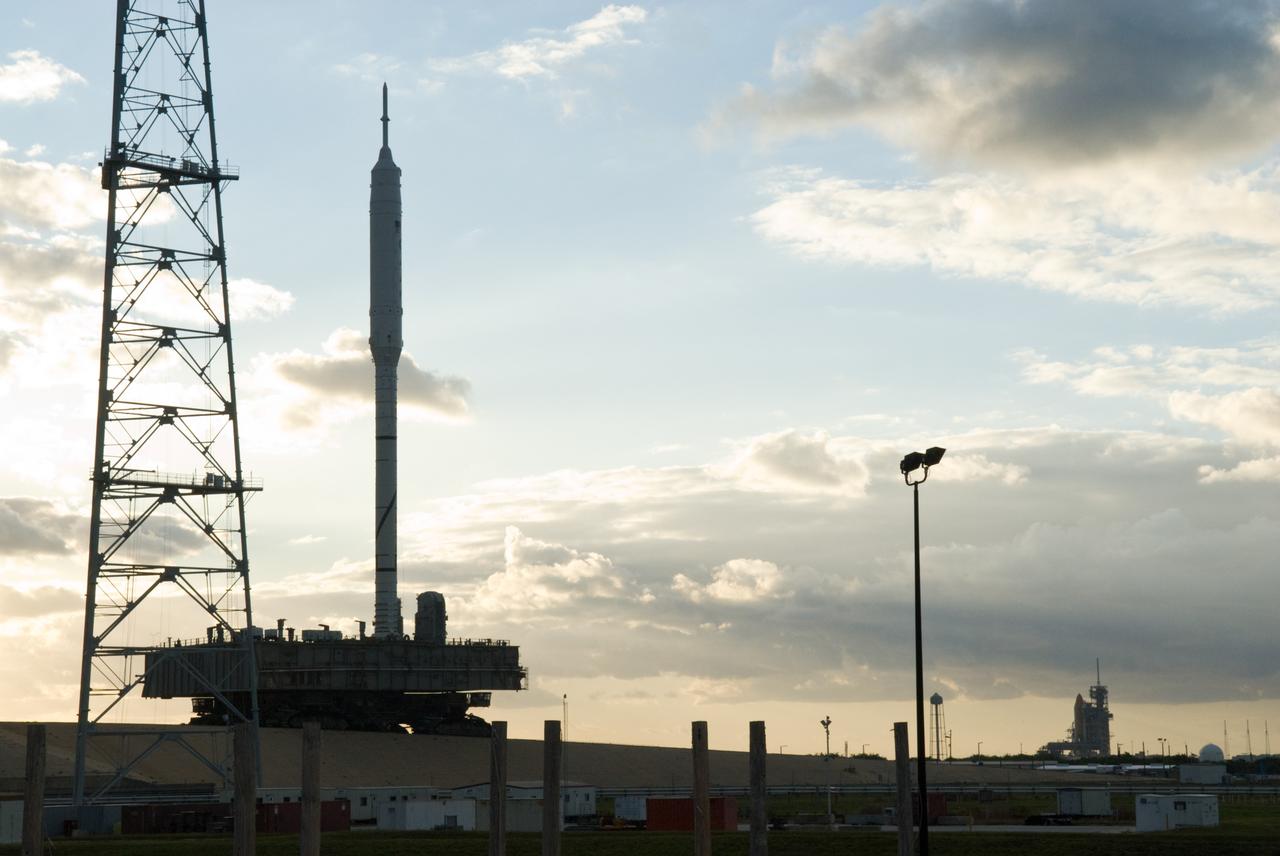

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – It's a full house at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida with launch vehicles on both of the center's pads. The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket is newly arrived on Launch Pad 39B, at left, with space shuttle Atlantis filling Launch Pad 39A in the distance. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
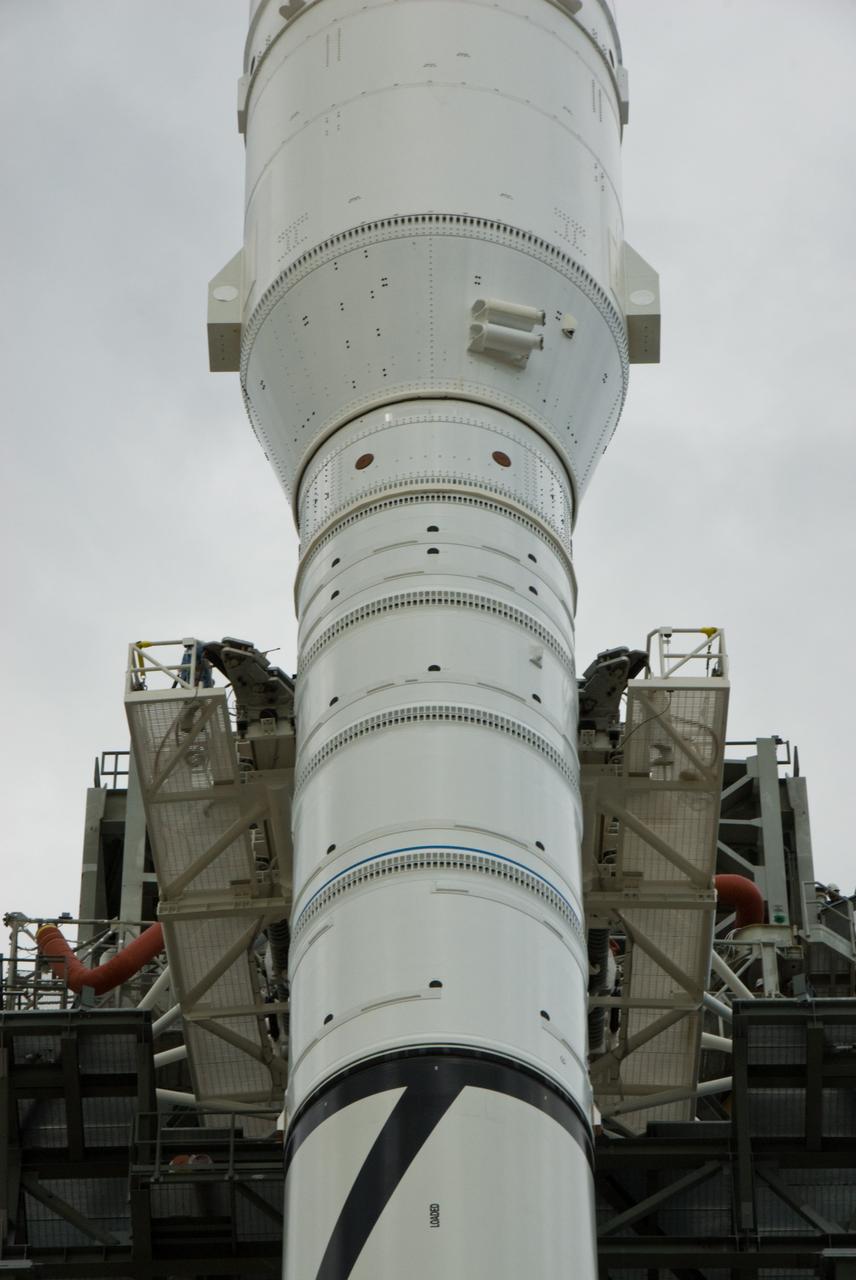

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The arms of the vehicle stabilization system are closed around the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, newly arrived on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
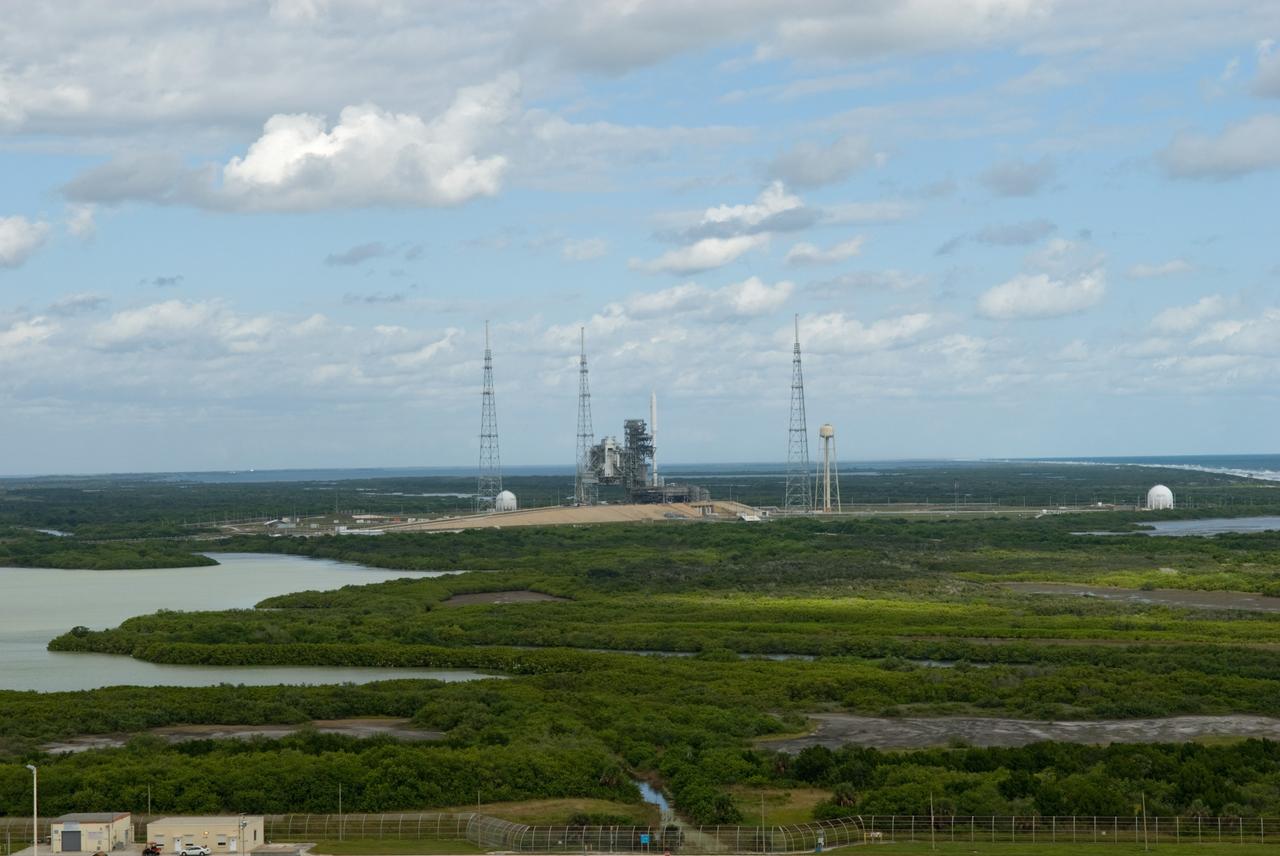

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - This view from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida shows the Ares I-X rocket on Pad 39B, ready for final processing for its upcoming flight test. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
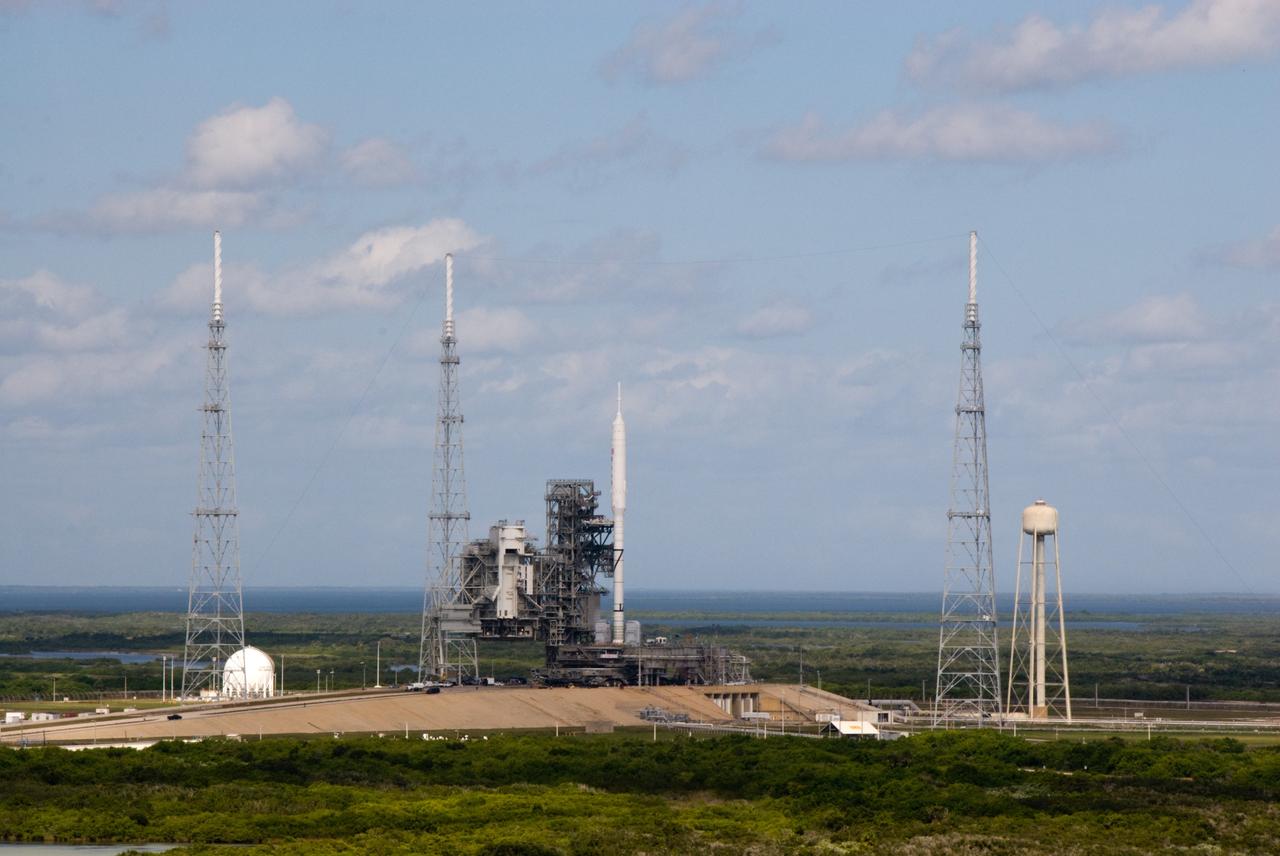

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Ares I-X rocket on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is ready for final processing for its upcoming flight test. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
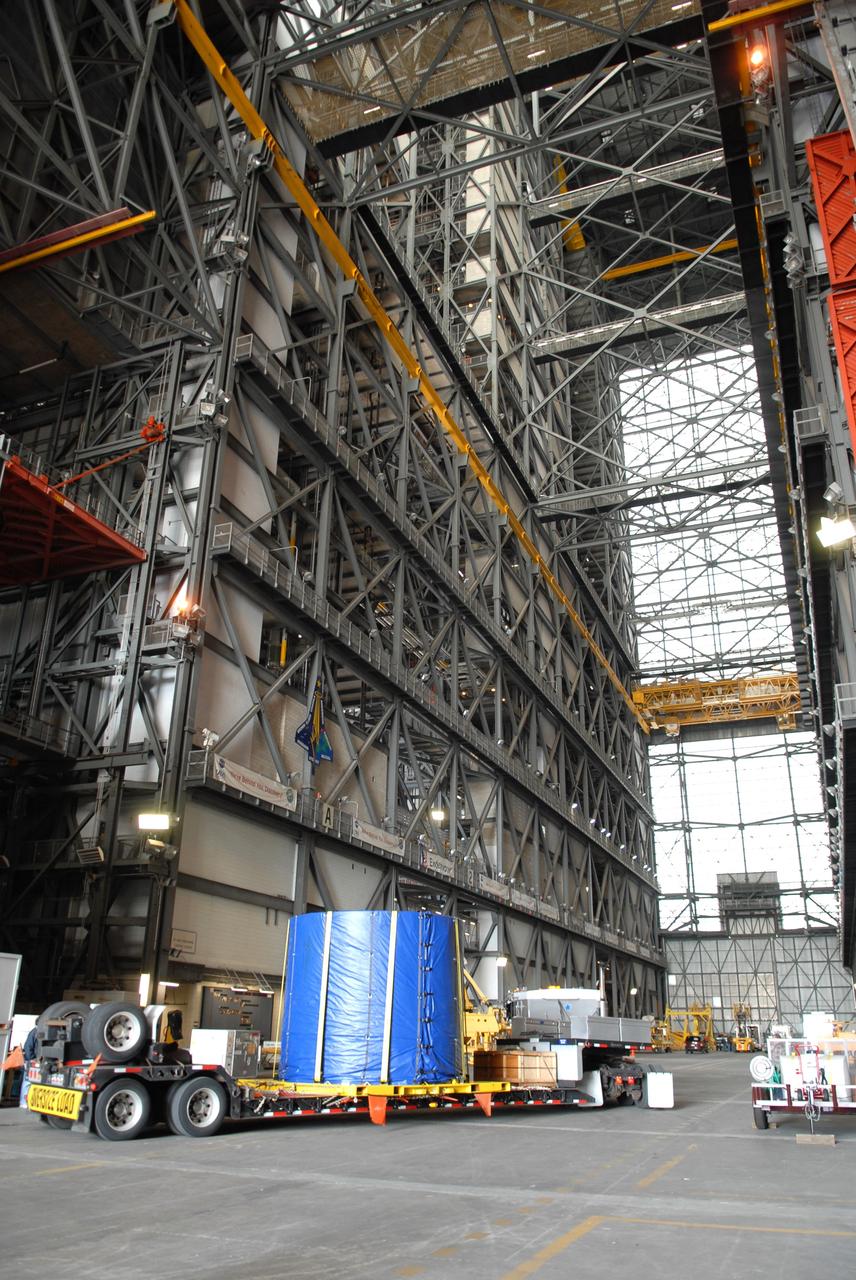

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X fifth segment simulator aft section arrives in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
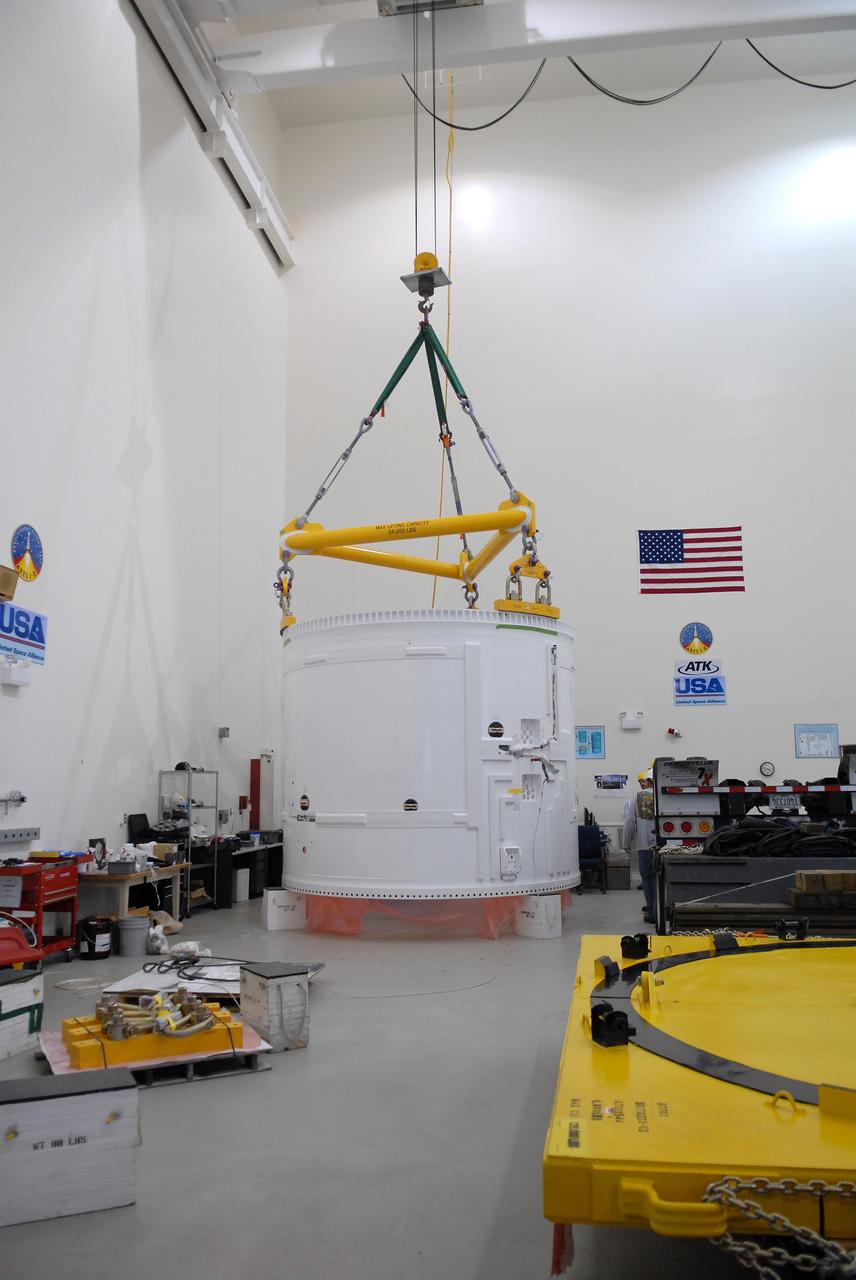

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X fifth segment simulator aft section is lowered onto a stand in the Vehicle Assembly Building's extended duration orbiter lab, or EDO, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
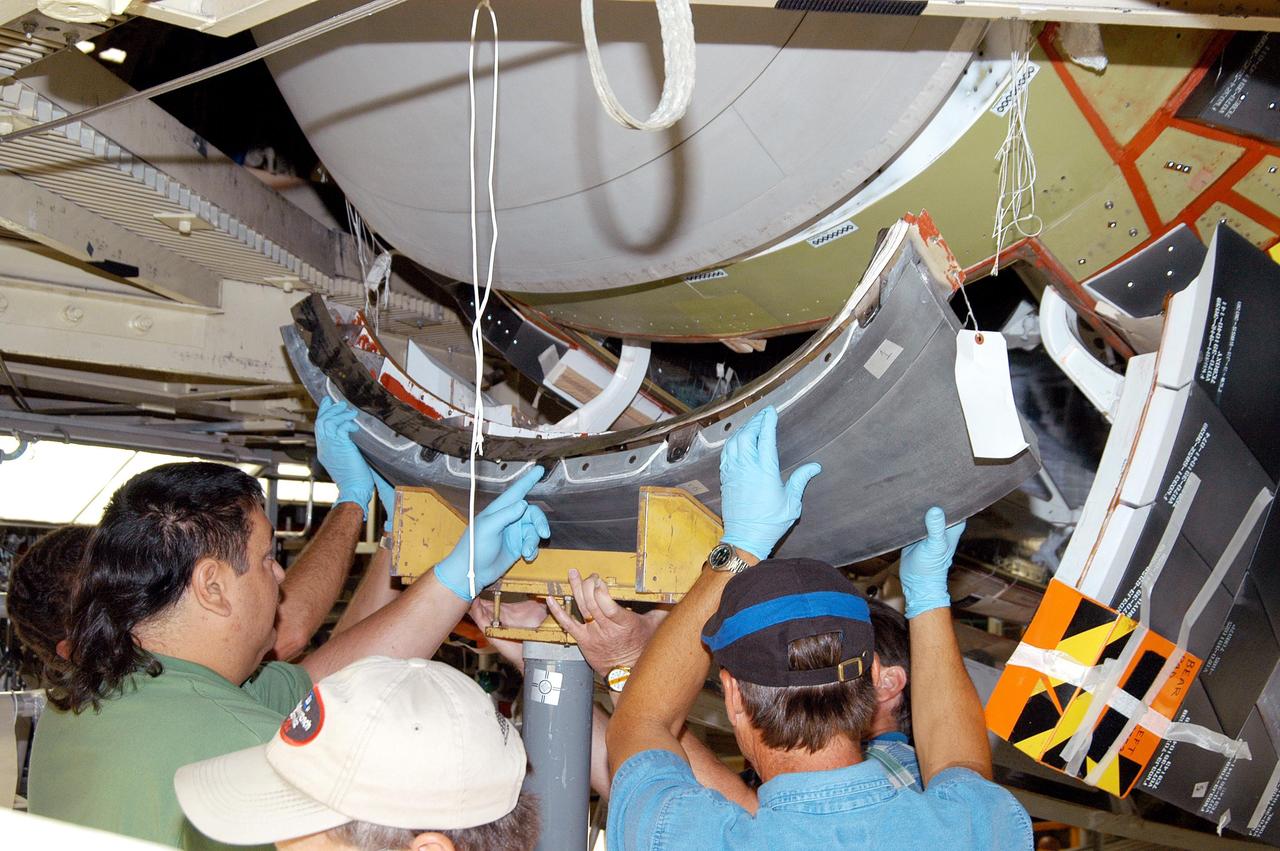

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility check the placement of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel on Discovery. . The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
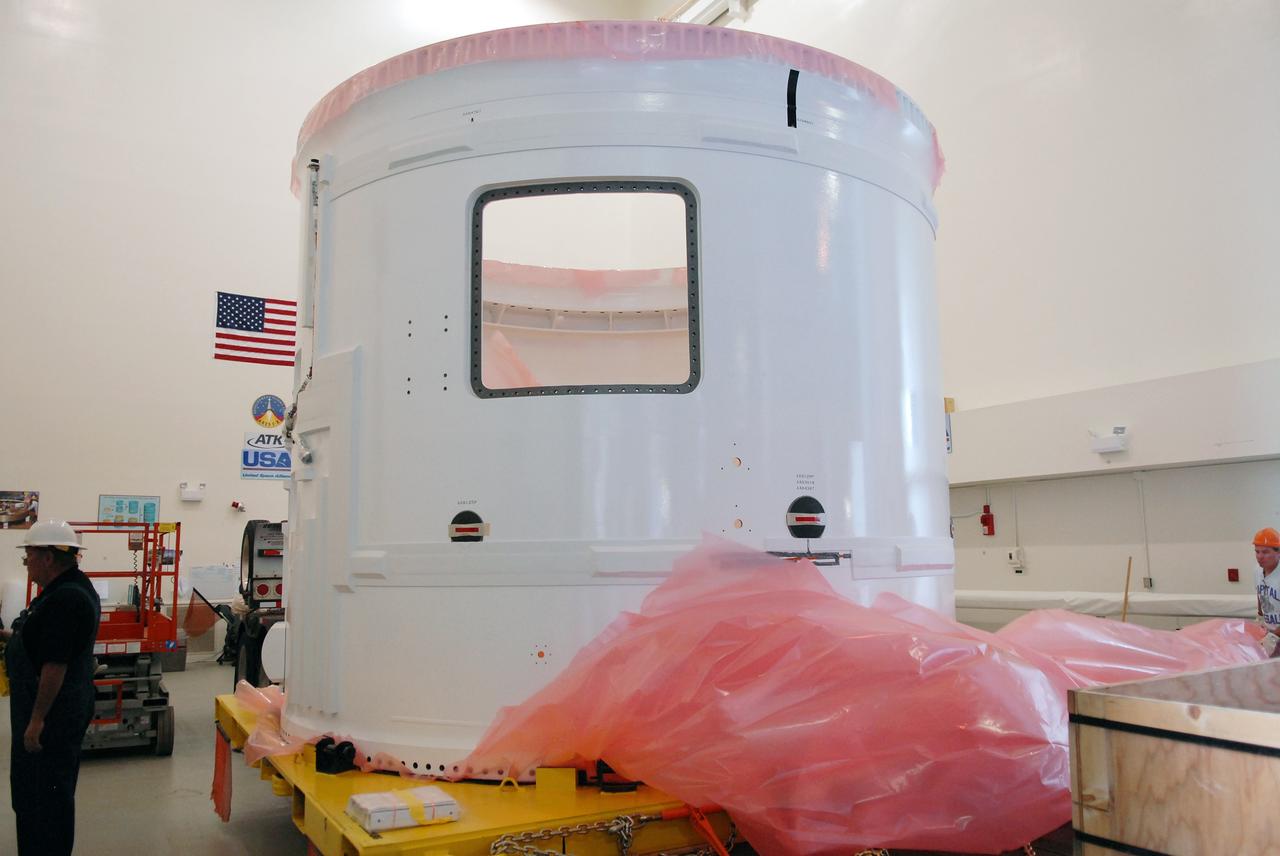

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's extended duration orbiter lab, or EDO, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X fifth segment simulator aft section is rid of its protective cover before being moved to a stand. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
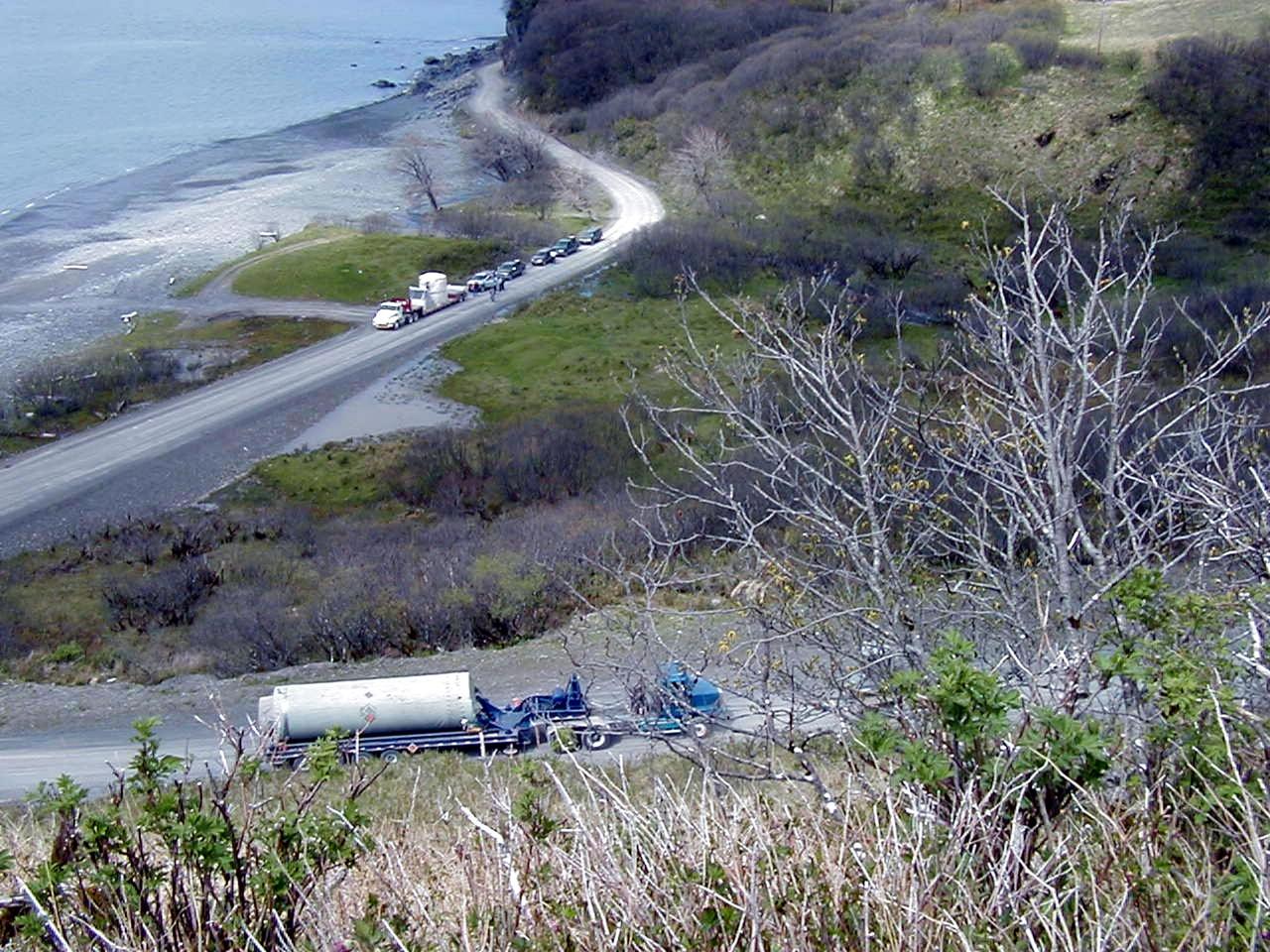

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- The Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, waits for the first stage, Castor 120, to be towed up the steepest part of the road, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
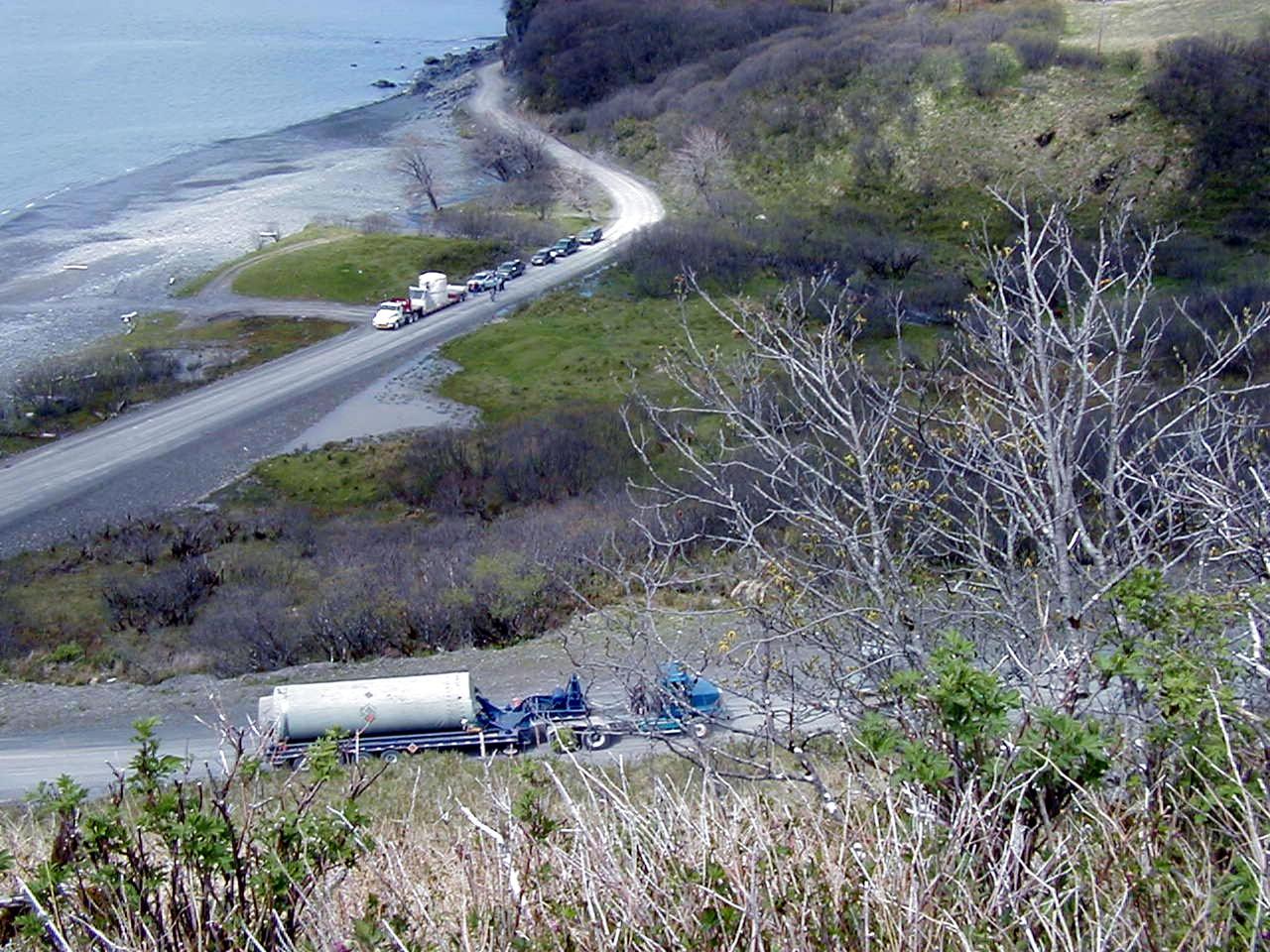

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- The Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, waits for the first stage, Castor 120, to be towed up the steepest part of the road, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel to install on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
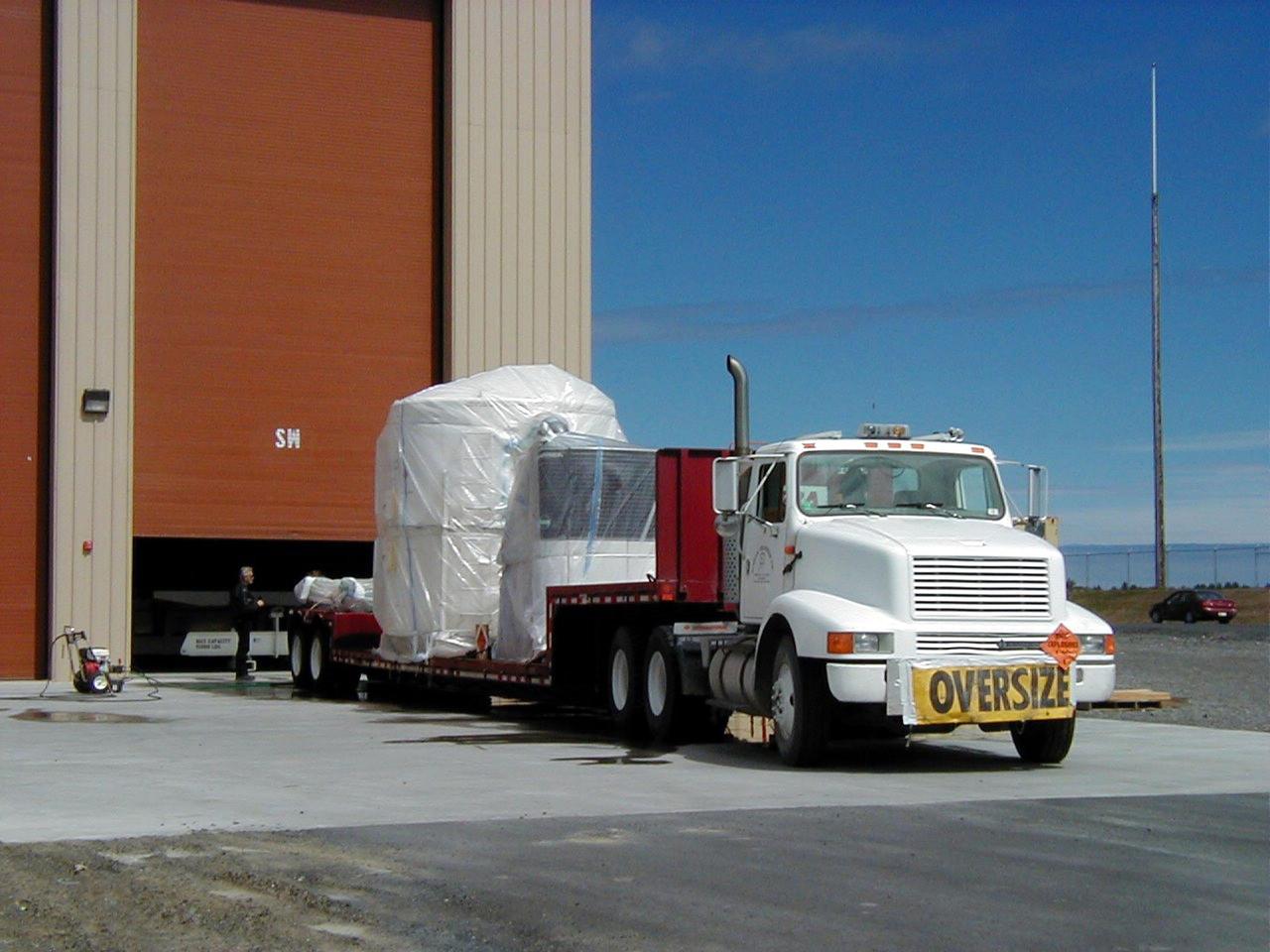

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Trucks transporting Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, arrive at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
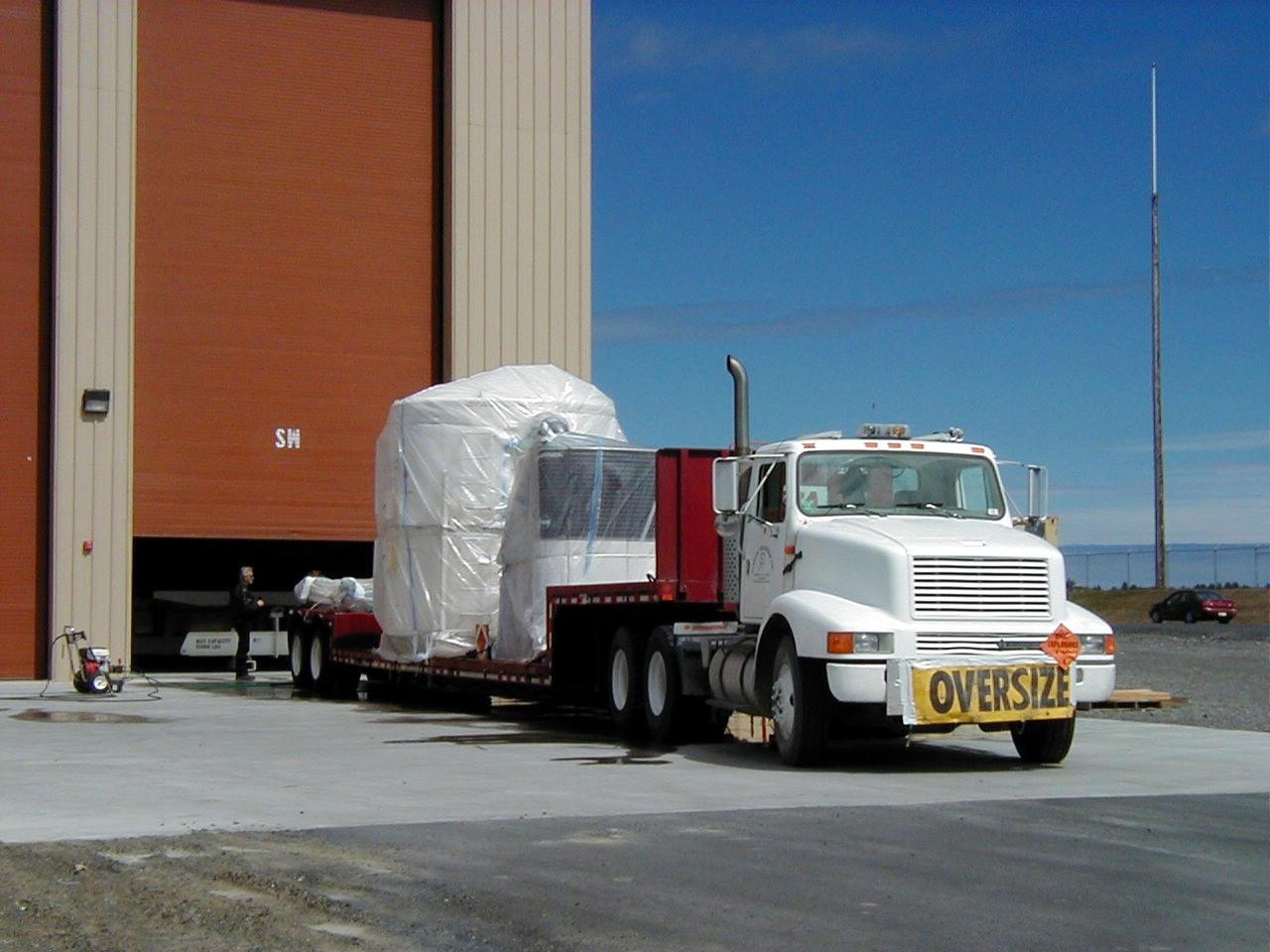

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Trucks transporting Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, arrive at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
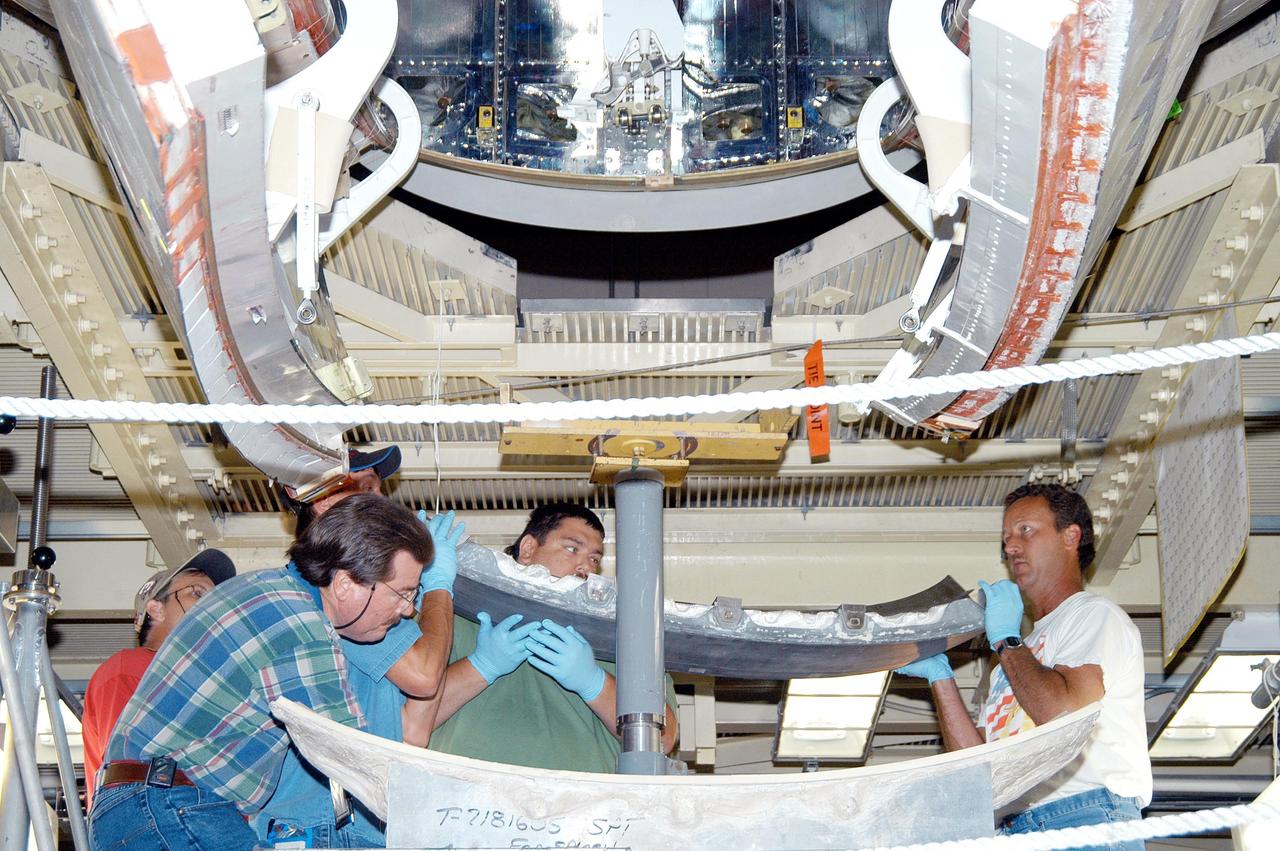

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility lift the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel to install on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
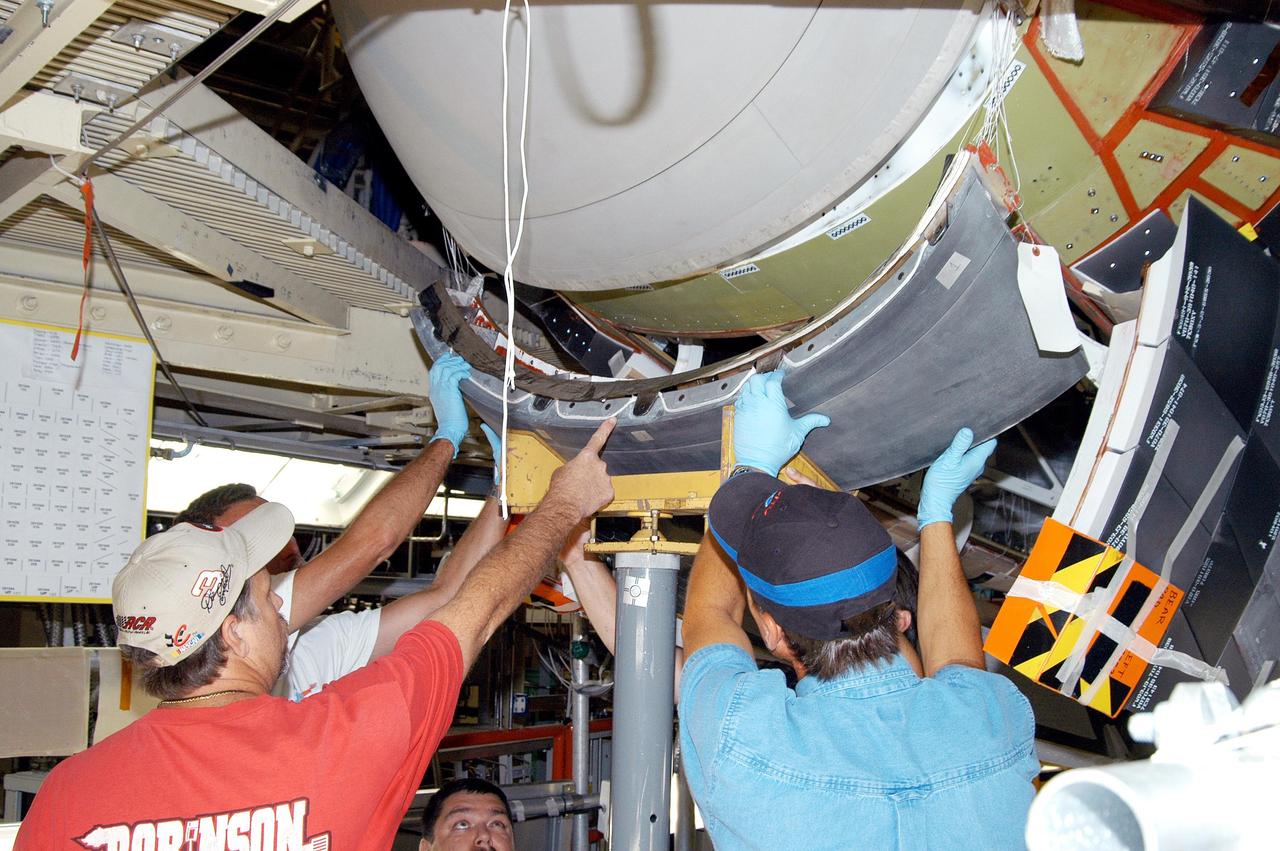

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility check the placement of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon chin panel on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X fifth segment simulator aft section heads for the open door of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
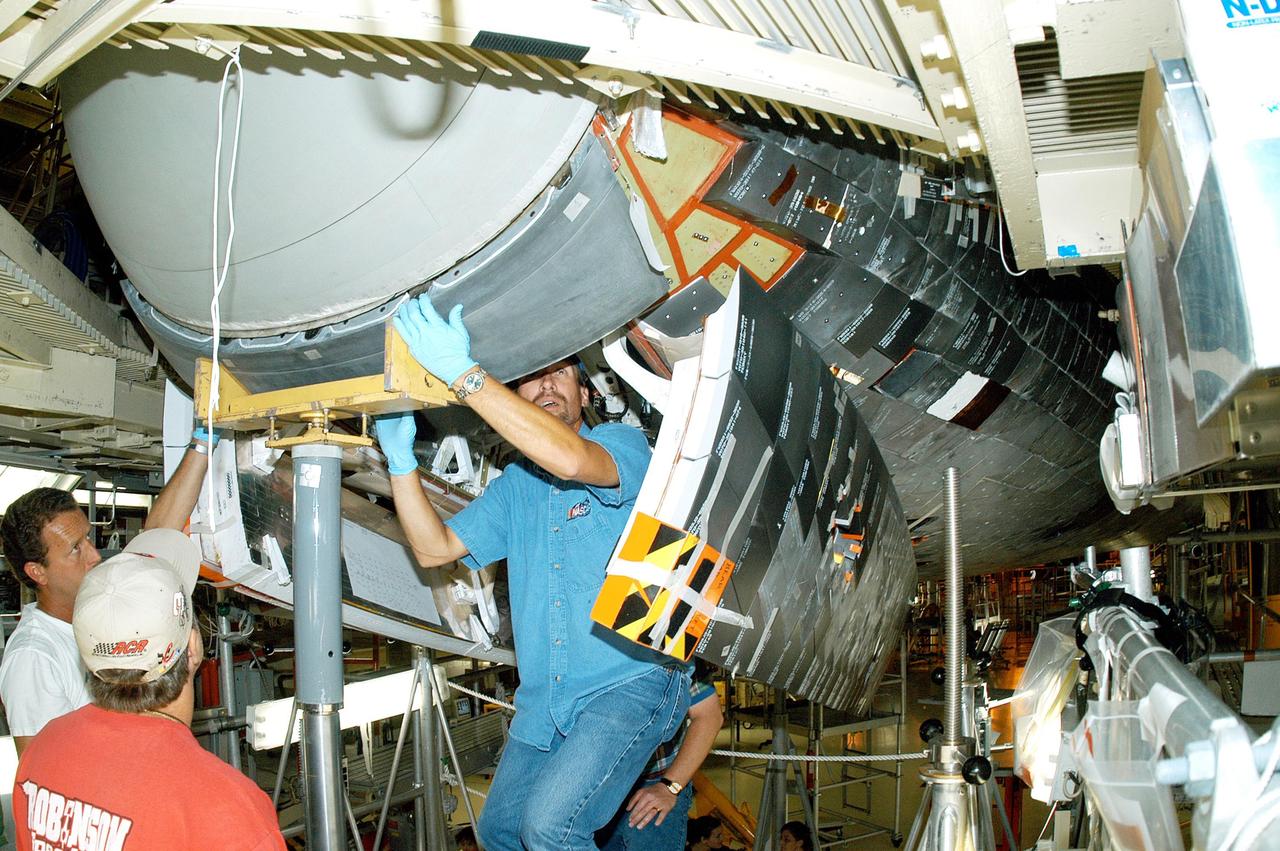

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility complete the installation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panel on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Technicians install Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as processing for the launch of Kodiak Star proceeds. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Technicians install Orbis 21D Equipment Section Boost Motor, the second stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as processing for the launch of Kodiak Star proceeds. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
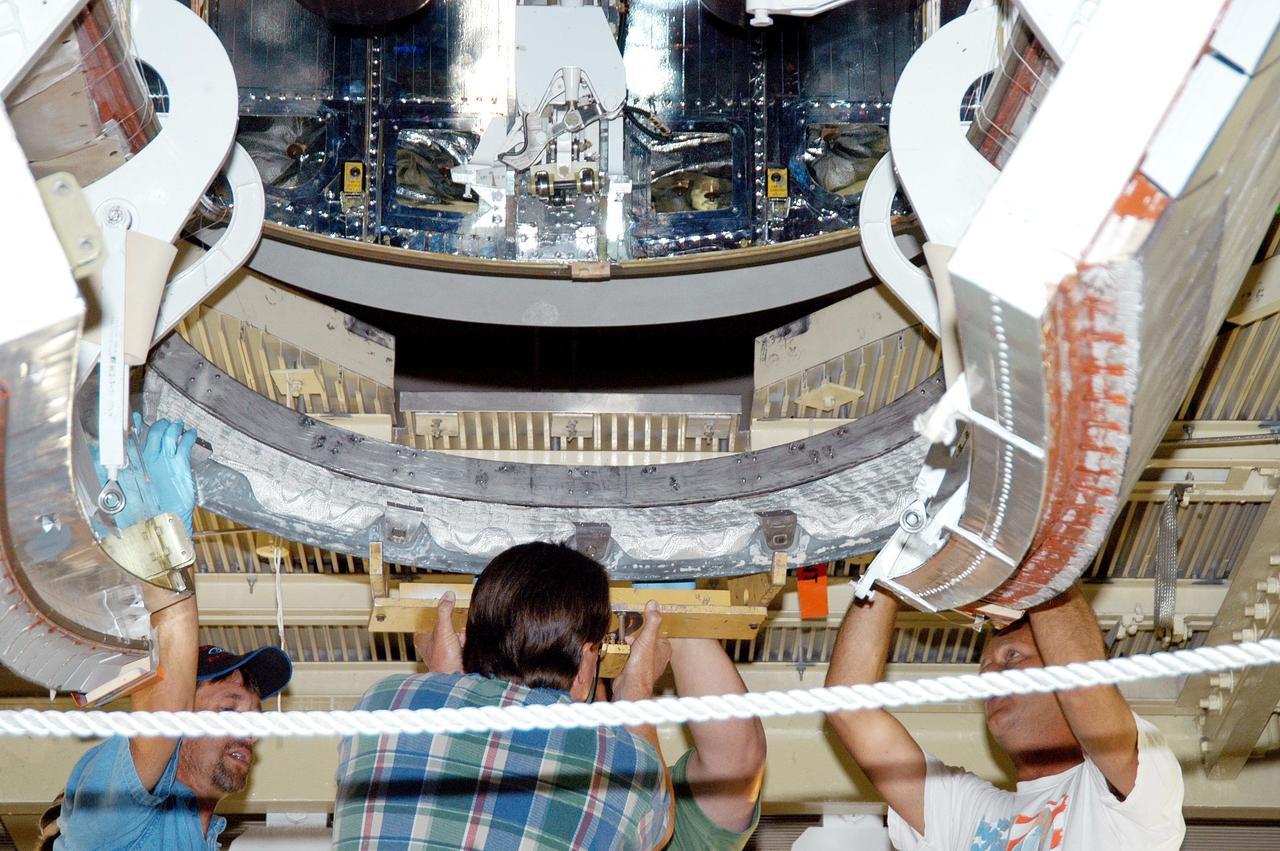

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility lift the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) chin panel into place on Discovery. The chin panel is the smile-shaped section of RCC directly below the nose cap that provides a thermal barrier during re-entry. The nose cap, with chin panel, was removed from the vehicle in the summer of 2003 and returned to the vendor, where it underwent numerous forms of Non-Destructive Evaluation. These tests included X-ray, ultrasound and eddy current to ensure its structural integrity prior to reinstallation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
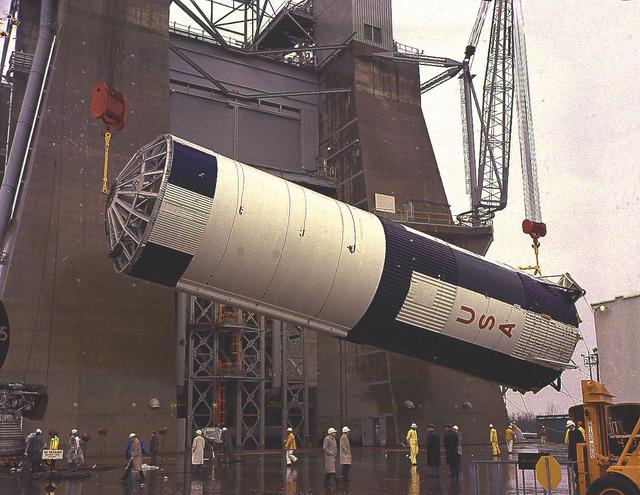

The S-IC-T stage was hoisted into the S-IC Static Test Stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage was a static test vehicle, not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months to prove the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, housed the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that held a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks were cornected by a 26-foot intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
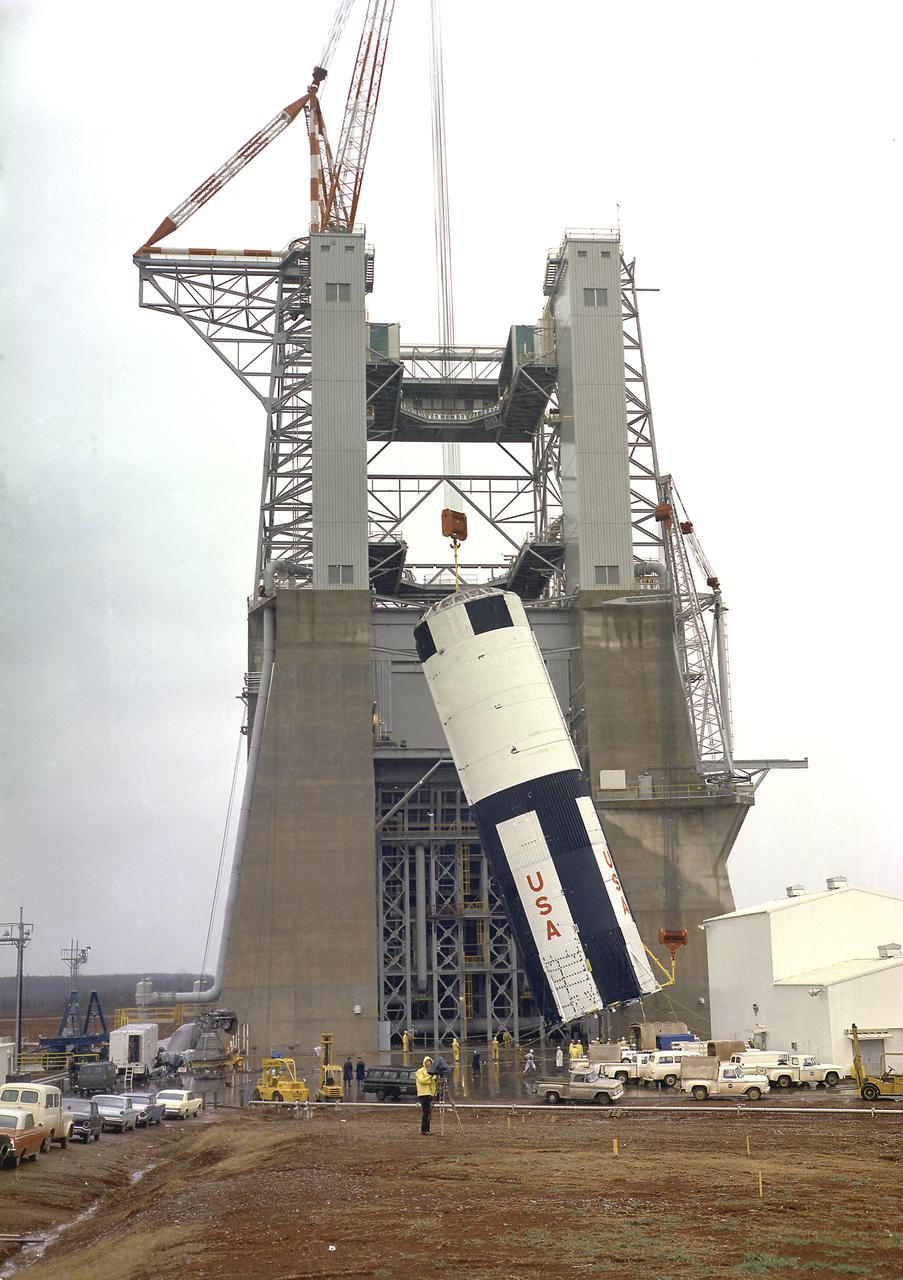

The S-IC-T stage was hoisted into the S-IC static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage was a static test vehicle not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months to prove the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, housed the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that held a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks are cornected by a 26-foot-long intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
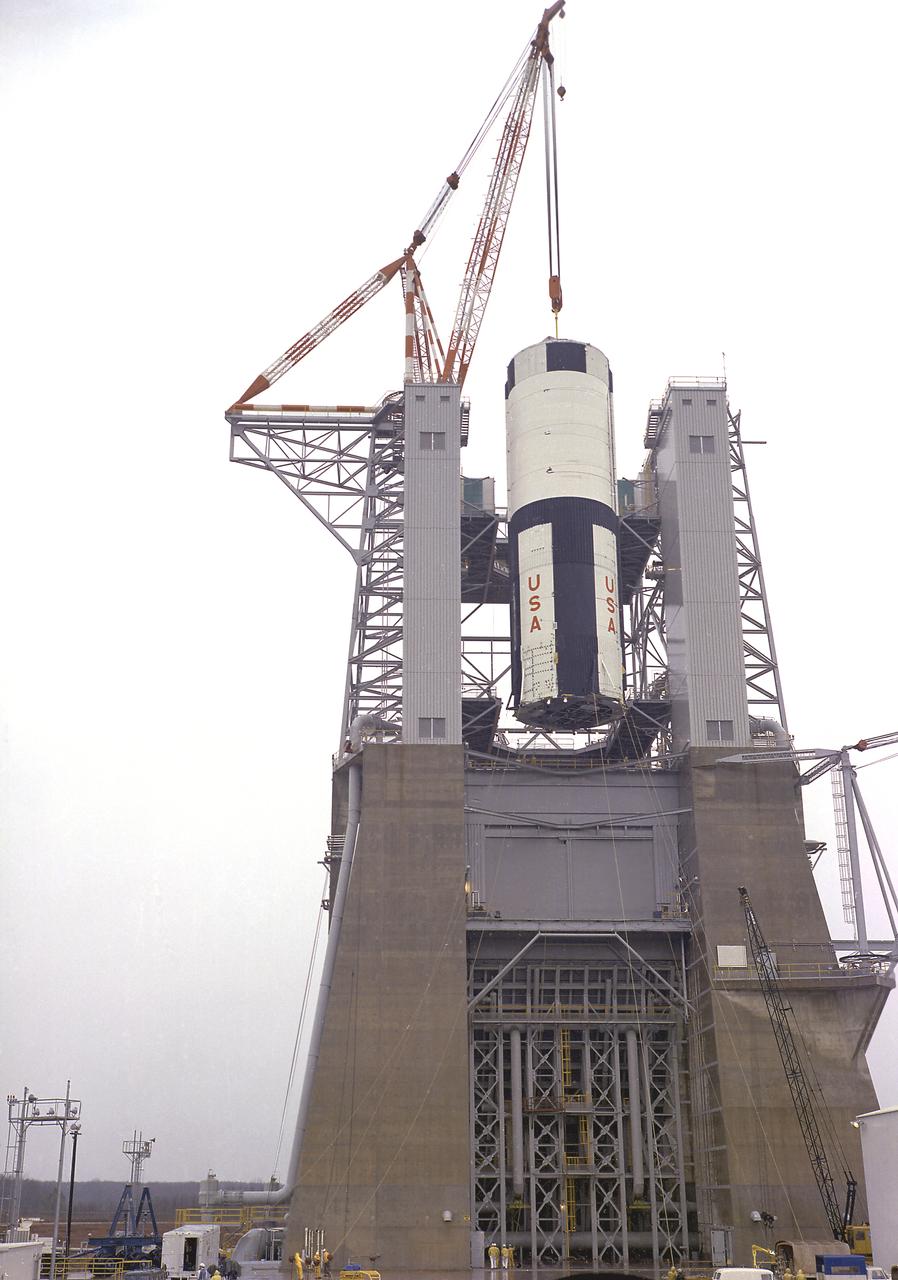

The S-IC-T stage is hoisted into the S-IC static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S-IC-T stage is a static test vehicle not intended for flight. It was ground tested repeatedly over a period of many months proving the vehicle's propulsion system. The 280,000-pound stage, 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter, houses the fuel and liquid oxygen tanks that hold a total of 4,400,000 pounds of liquid oxygen and kerosene. The two tanks are cornected by a 26-foot-long intertank section. Other parts of the booster included the forward skirt and the thrust structure, on which the engines were to be mounted. Five F-1 engines, each weighing 10 tons, gave the booster a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, roughly equivalent to 160 million horsepower.
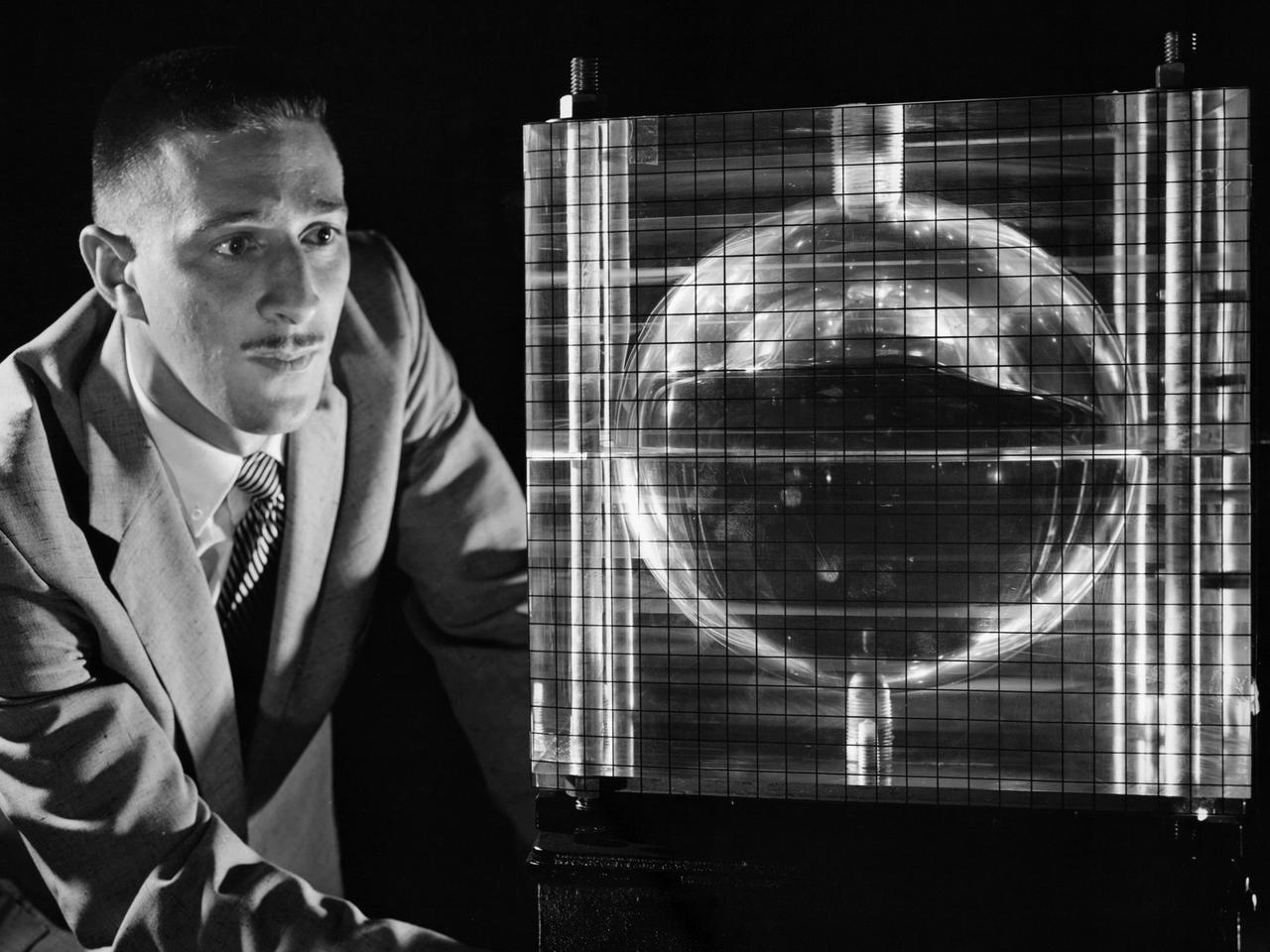

Andy Stofan views a small-scale tank built to study the sloshing characteristics of liquid hydrogen at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Stofan was tasked with the study of propellant motion, or sloshing, in space vehicle propellant tanks. At the time, there was little knowledge of the behavior of fluids in microgravity or the effects of the launch on the propellant’s motion. Sloshing in the tank could alter a spacecraft’s trajectory or move the propellant away from the turbopump. Stofan became an expert and authored numerous technical reports on the subject. Stofan was assigned to the original Centaur Project Office in 1962 as a member of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan was instrumental in solving a dynamic instability problem on the Centaur vehicle and served as the systems engineer for the development of the Centaur propellant utilization system. The solution was also applied to the upper-stages of Saturn. In 1966, Stofan was named Head of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan continued rising through the managerial ranks at Lewis. In 1967 he became Project Manager of a test program that successfully demonstrated the use of a pressurization system for the Centaur vehicle; in 1969 the Assistant Project Manager on the Improved Centaur project; in 1970 Manager of the Titan/Centaur Project Office; in 1974 Director of the Launch Vehicles Division. In 1978, Stofan was appointed Deputy Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Space Science. In 1982, he was named Director of Lewis Research Center.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A digital sign at the fork in the crawlerway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida reminds employees that the flight test of the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, poised for liftoff on Launch Pad 39B in the background, is approaching. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has resided on the pad. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
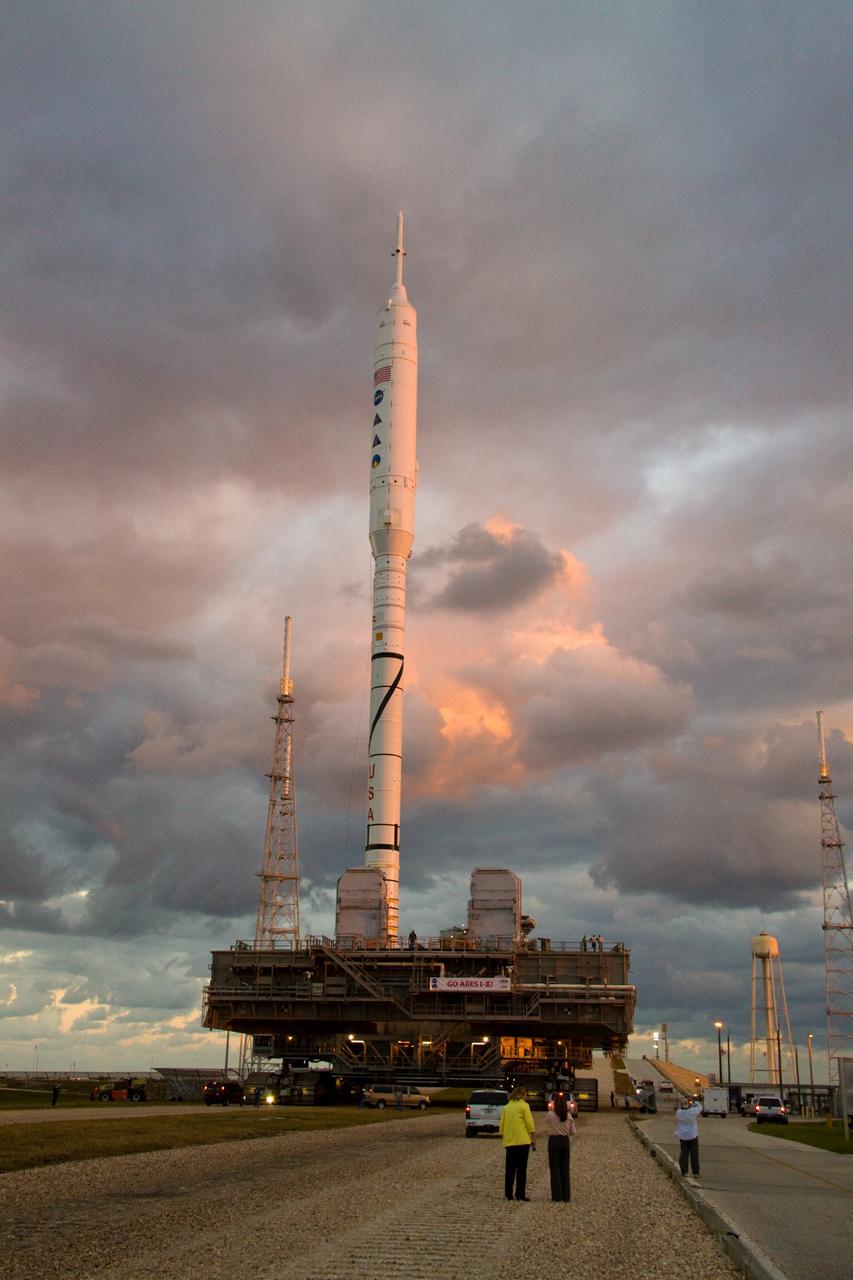

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, approaches the pad's perimeter fence. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
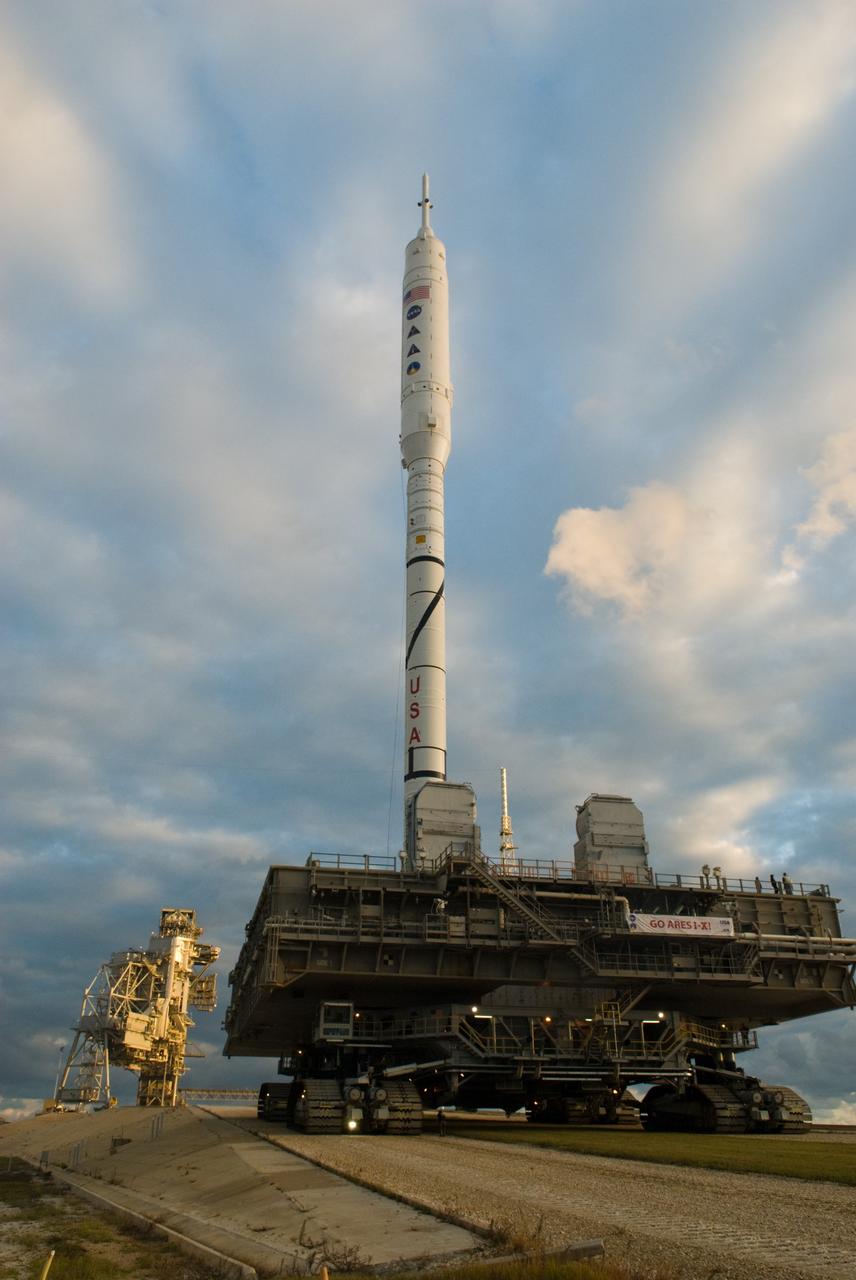

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket slowly approaches the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a 4.2-mile trip that began seven hours earlier. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
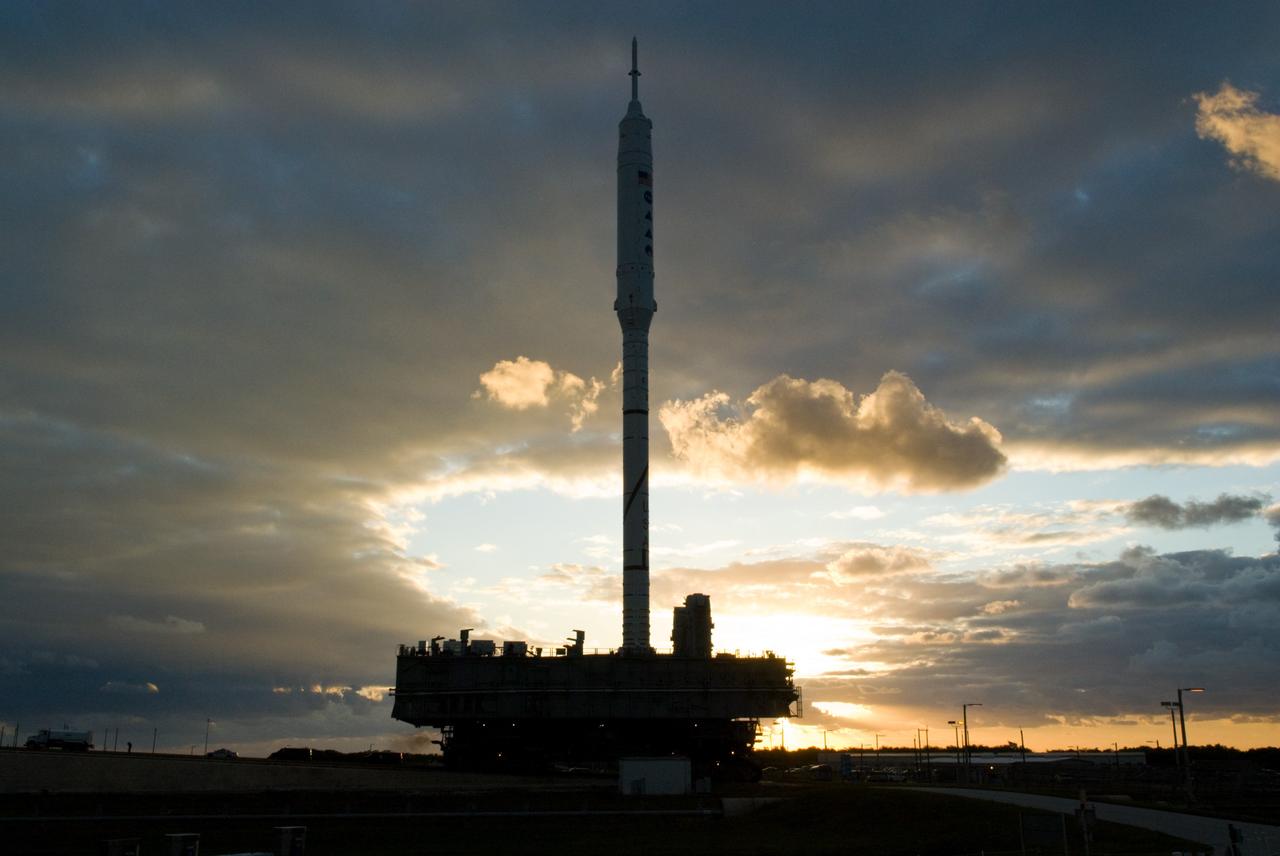

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket is silhouetted again the early morning sky as it lumbers along the 4.2-mile route to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
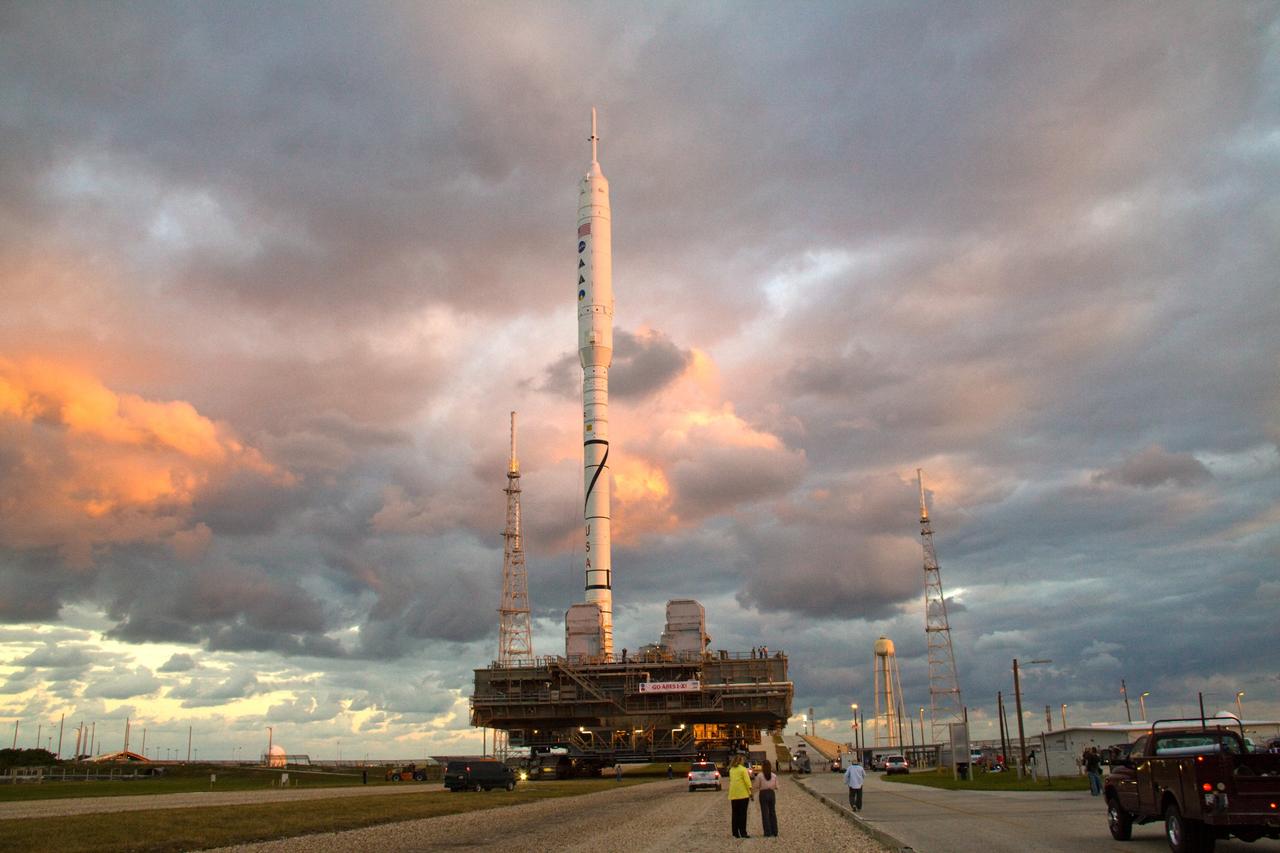

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, prepares to climb the five percent grade of the crawlerway to the top of the pad. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
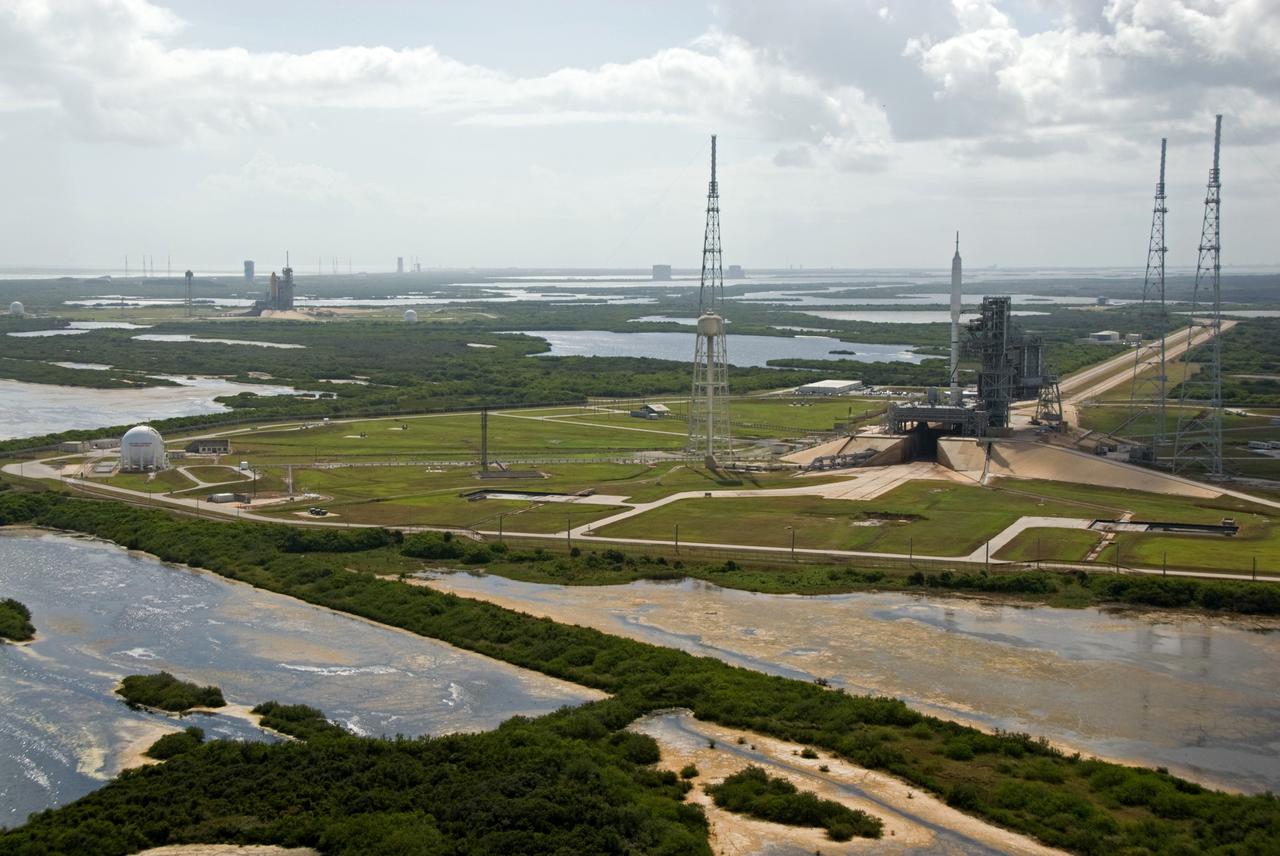

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the distance are space shuttle Atlantis on Kennedy's Launch Pad 39A, and the pads and processing facilities on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
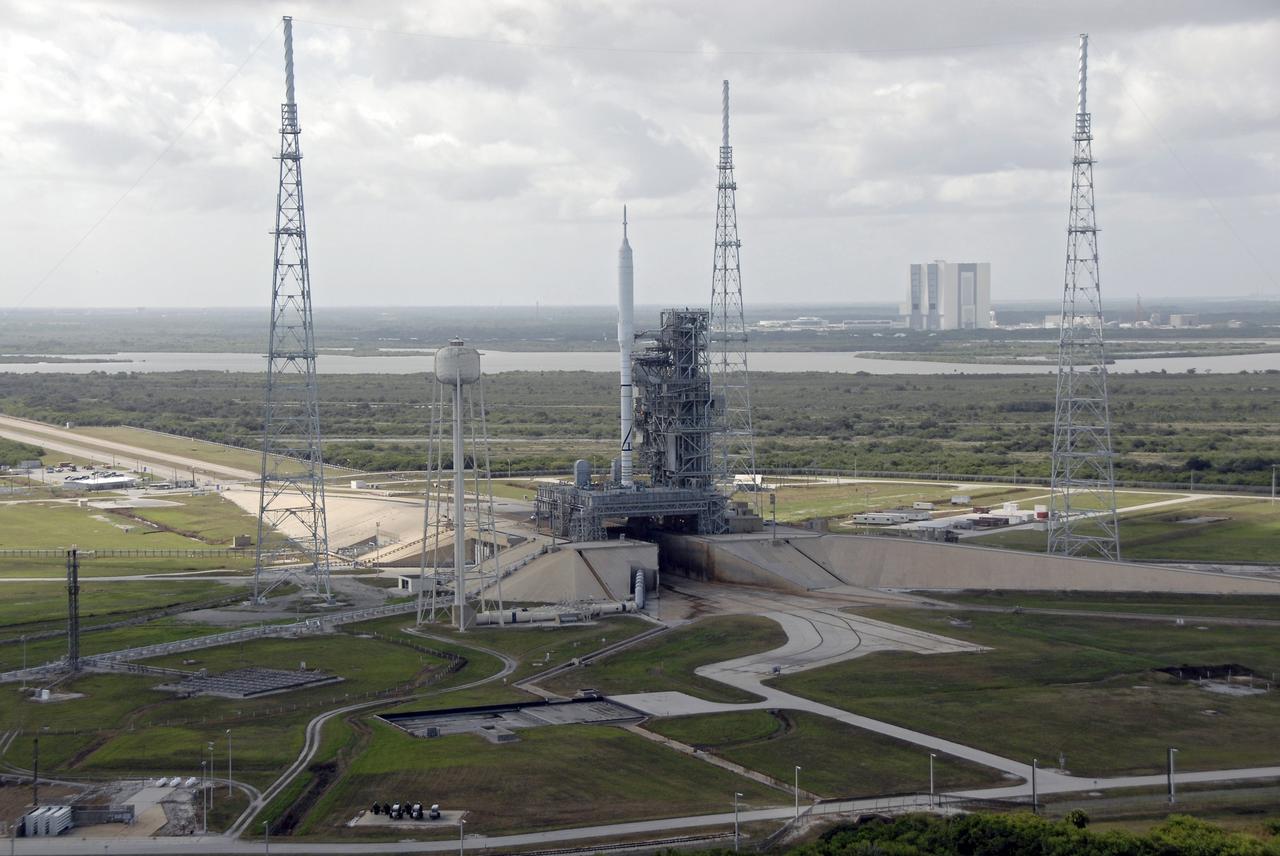

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket undergoes final processing on Launch Pad 39B for its upcoming flight test. The 525-foot Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, where the rocket was assembled is in the background. The rocket's 4.2-mile move from the VAB to the pad, known as rollout, took place Oct. 20. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
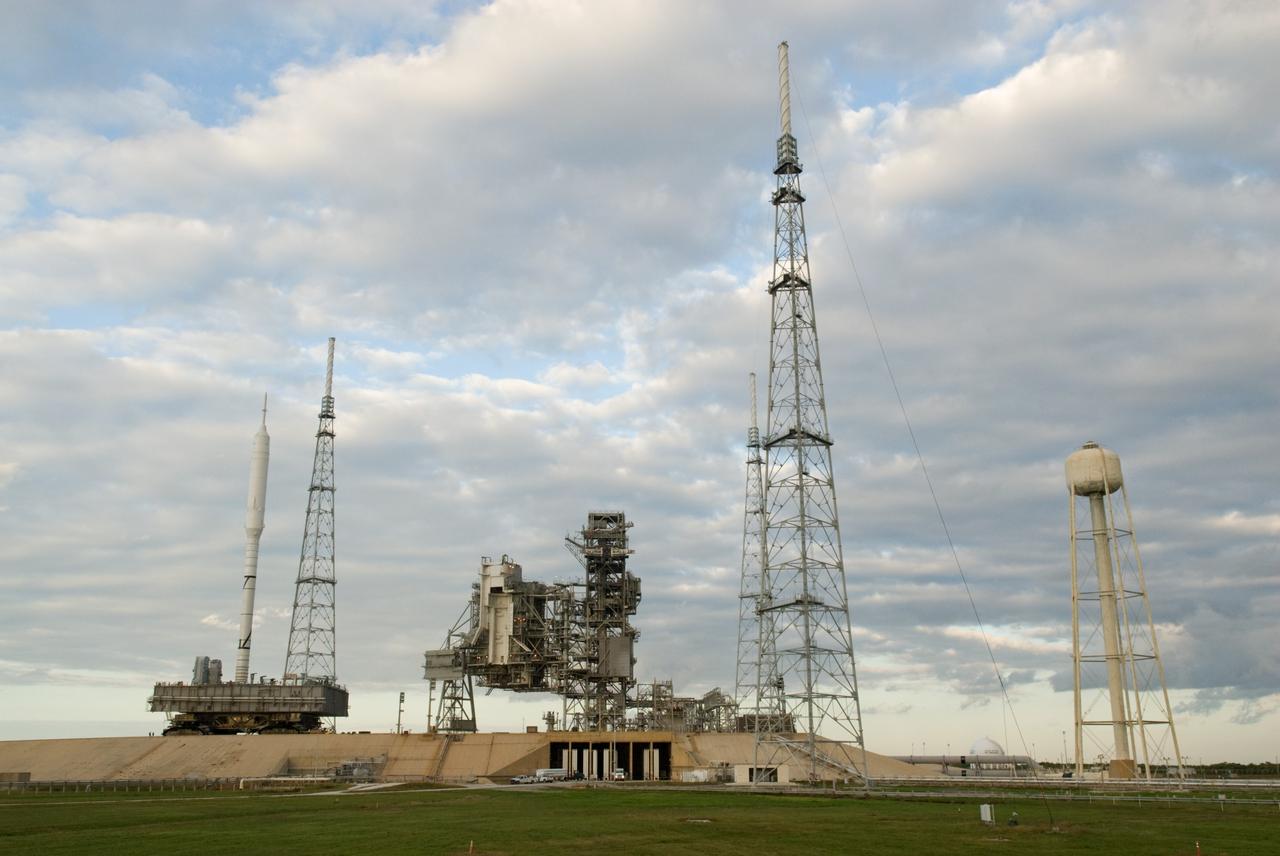

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, nears its place beside the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
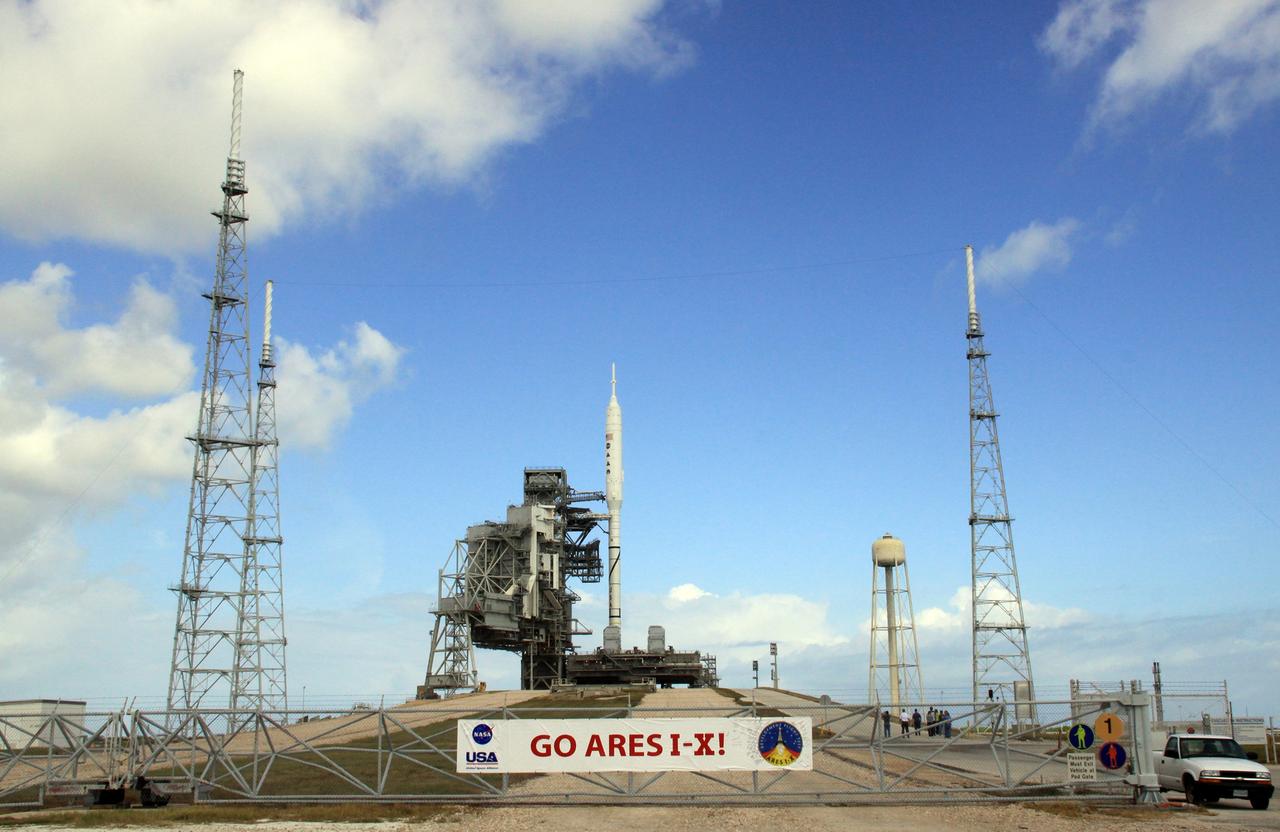

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Go Ares I-X! A banner on the perimeter fence of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida reflects the excitement building in Kennedy's work force in anticipation of the flight test of the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has resided on the pad. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
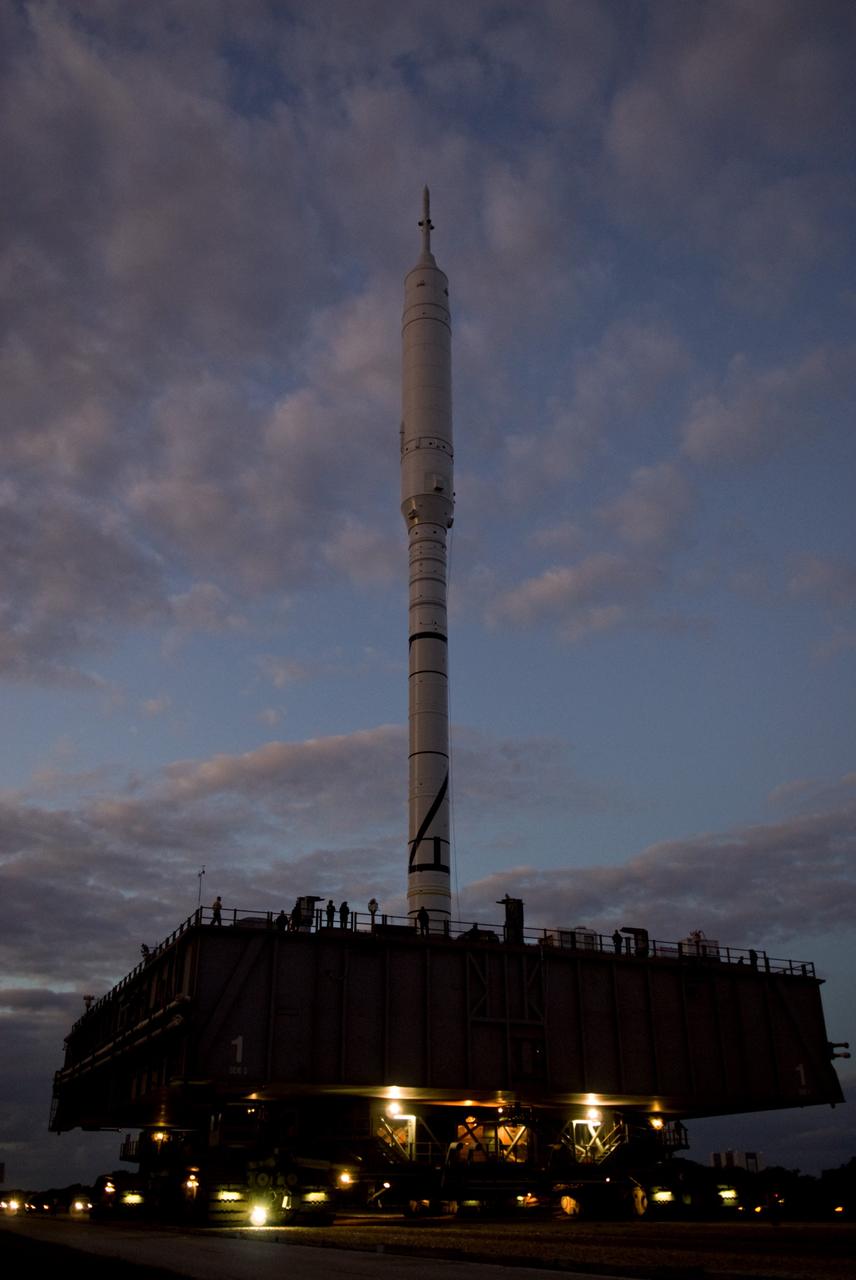

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers hitch a ride on the mobile launcher platform with the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, on its way to Launch Pad 39B. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
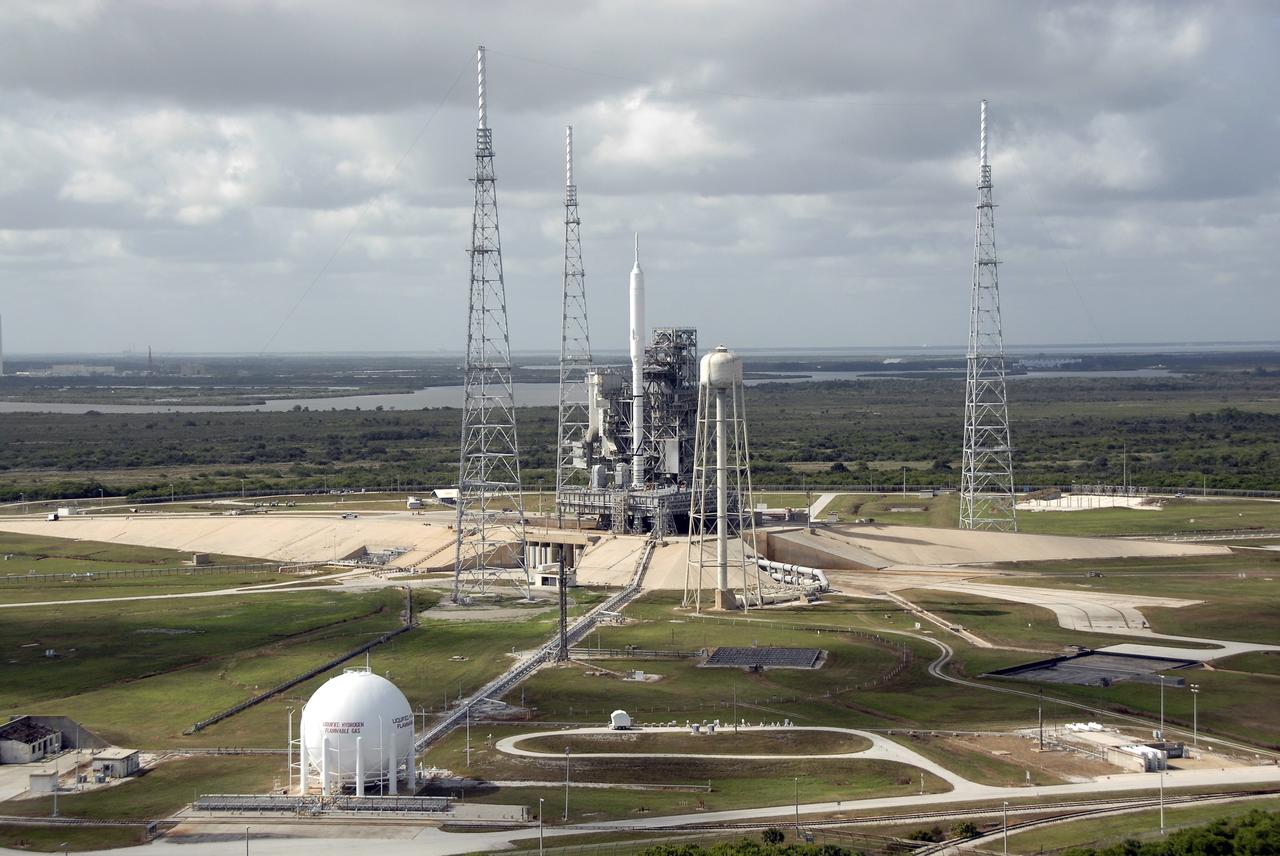

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the distance are the pads and processing facilities on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
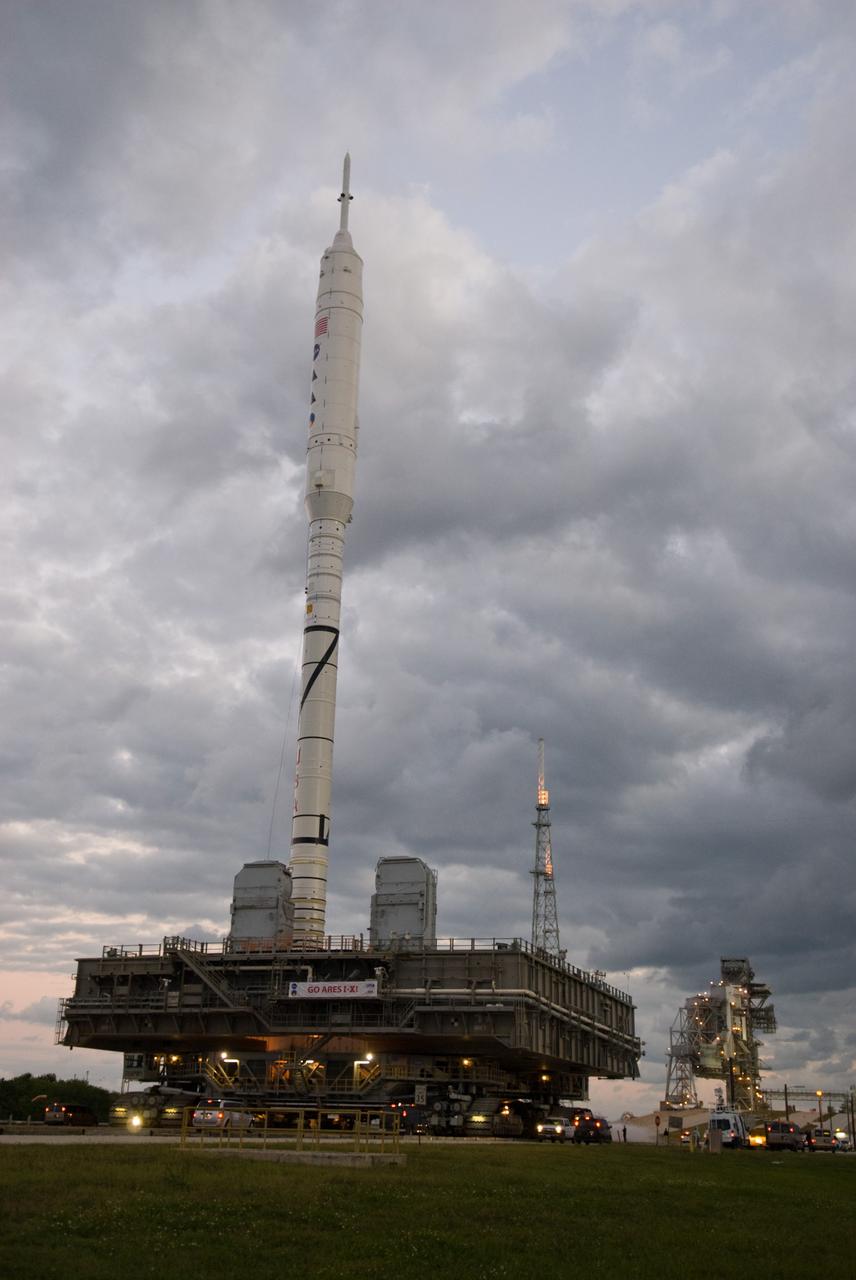

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, nears its destination beside the pad's fixed service structure. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A digital sign at the fork in the crawlerway announces the details of the upcoming flight test of NASA's 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, poised for liftoff on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, in the background. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has resided on the pad. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Pad modifications to support the Ares I-X include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
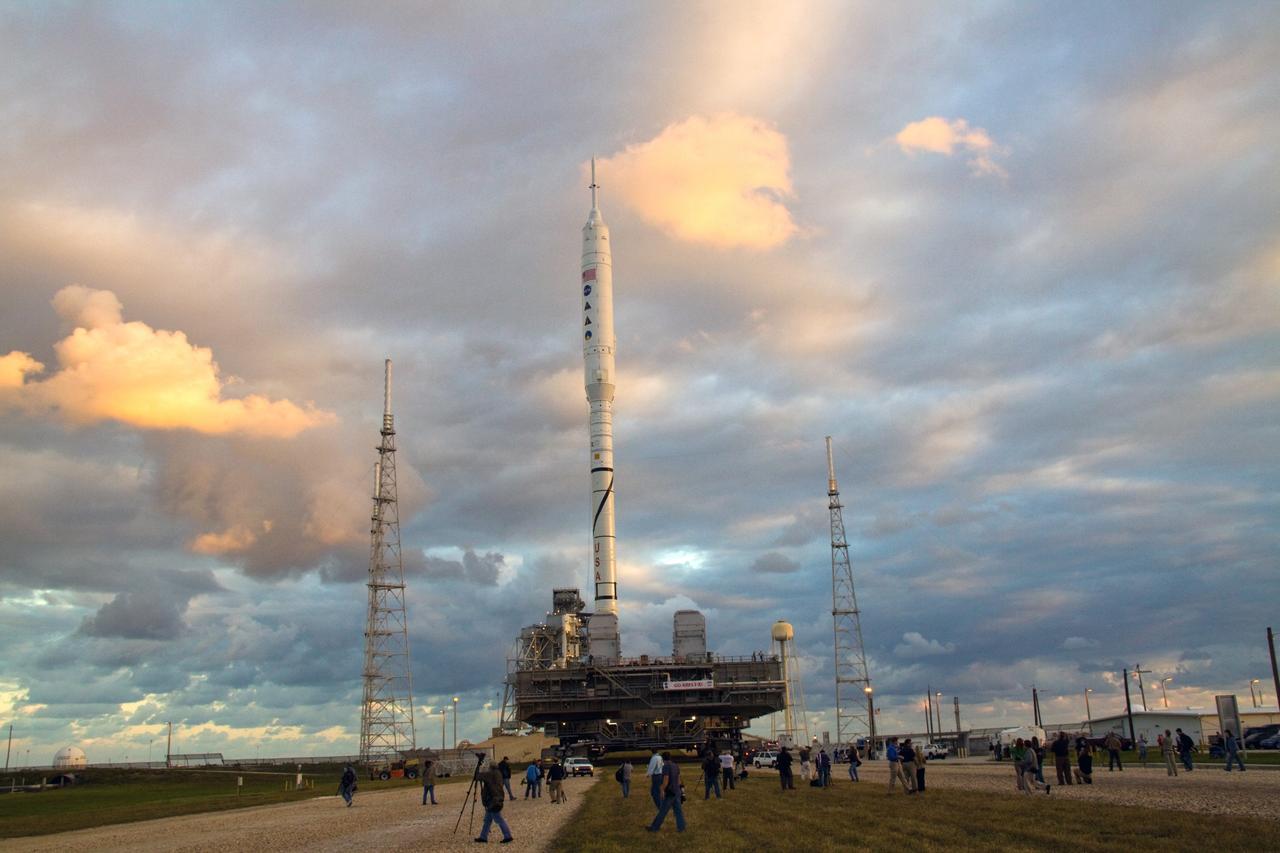

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Sunrise over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida reveals the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, nearing its destination on Launch Pad 39B. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
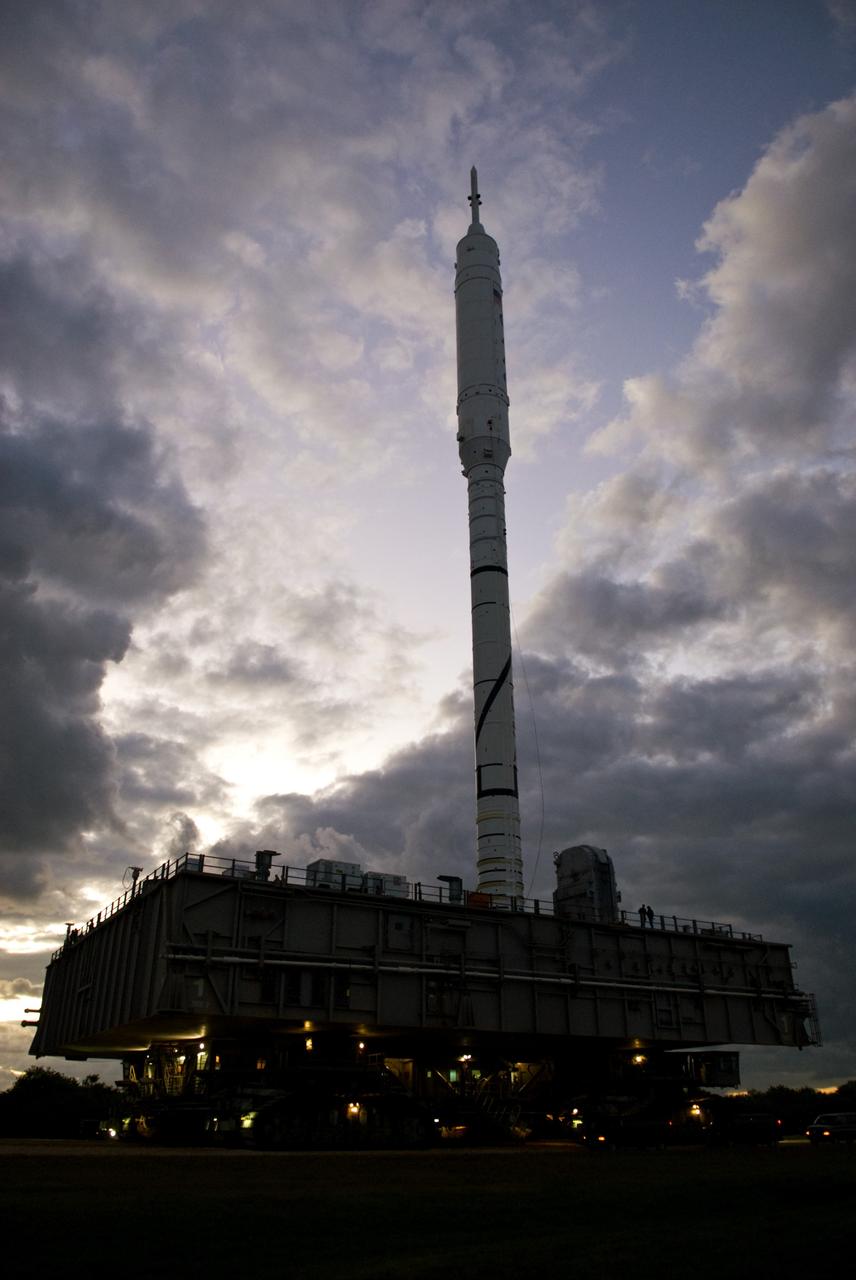

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, moved by the power of a crawler-transporter, is revealed on its 4.2-mile trip to Launch Pad 39B by the sun rising over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
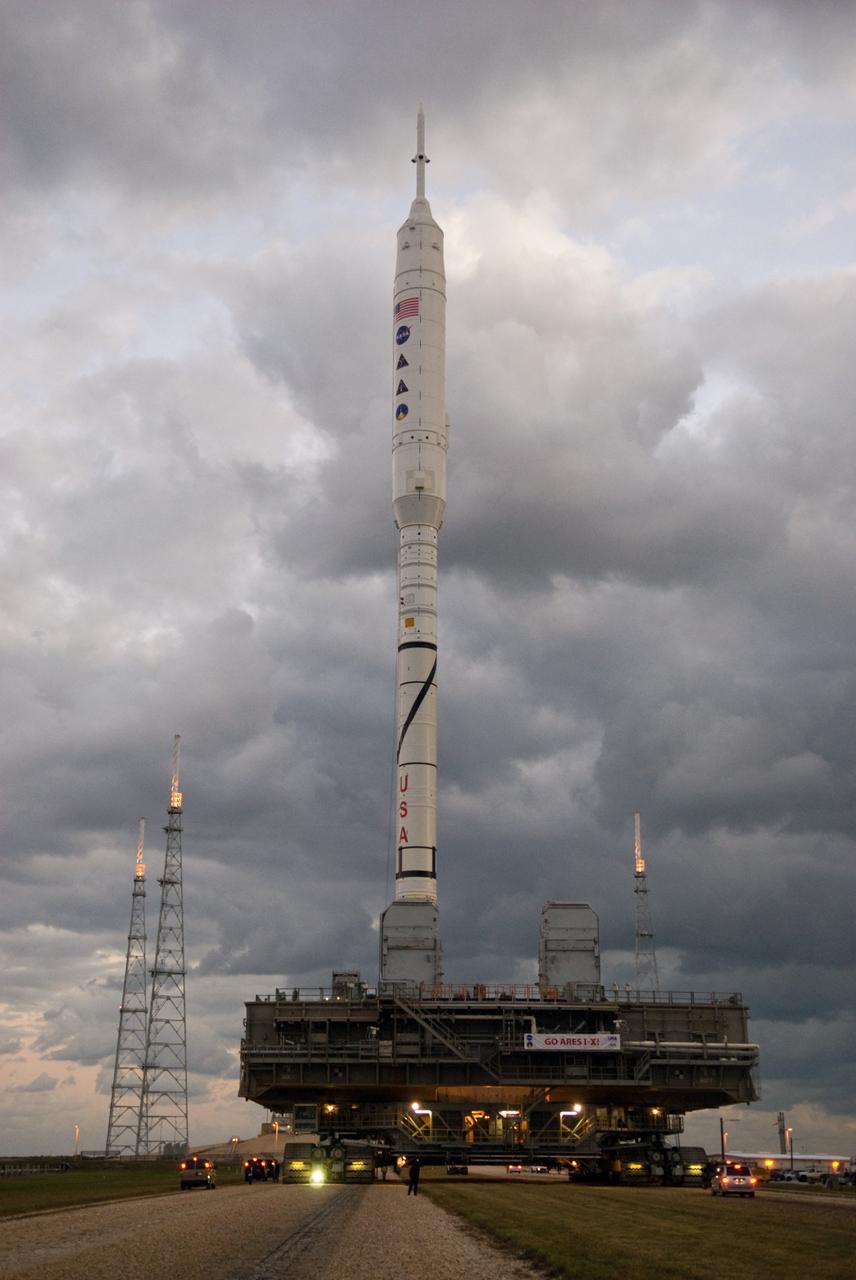

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, approaches the pad's perimeter fence. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
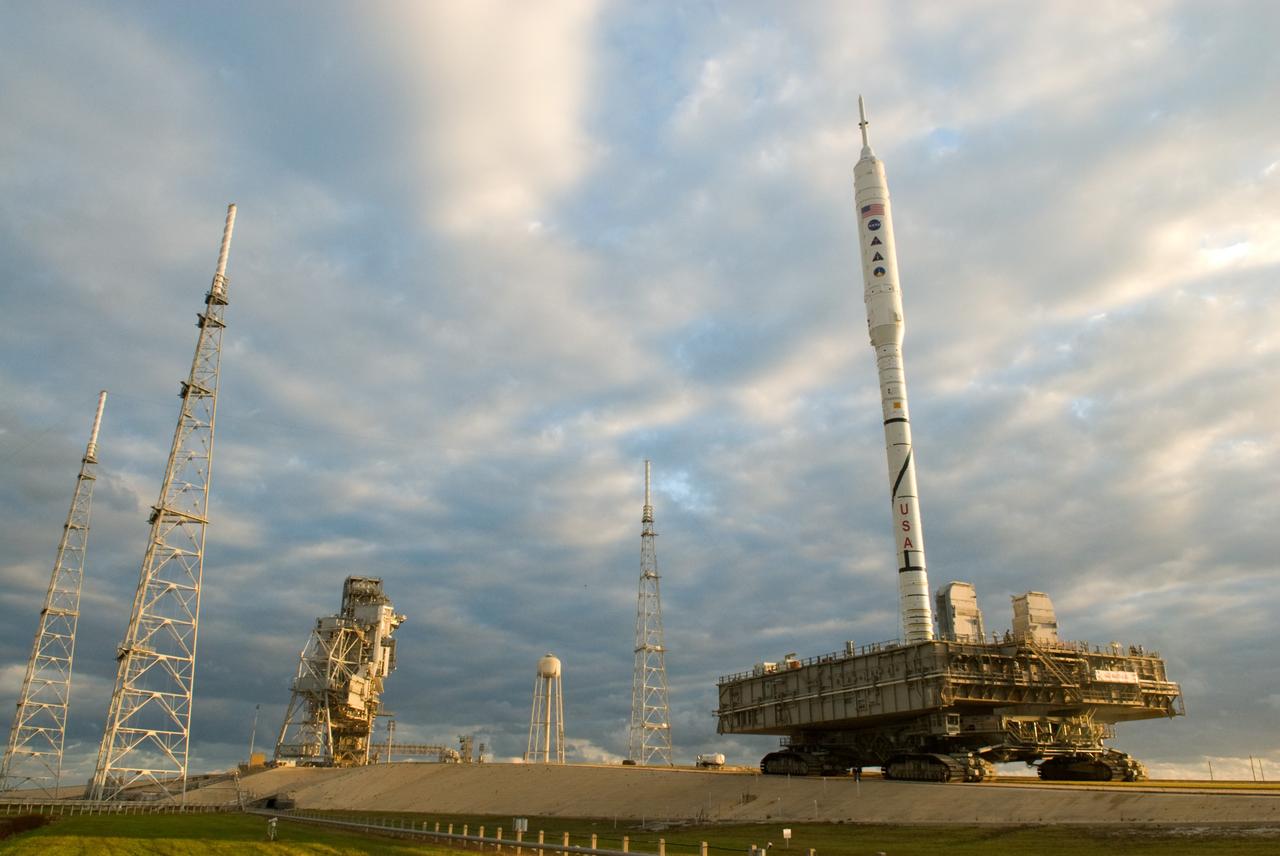

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Daybreak finds the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket slowly making its way up the five percent grade of the crawlerway on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a 4.2-mile trip that began seven hours earlier. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
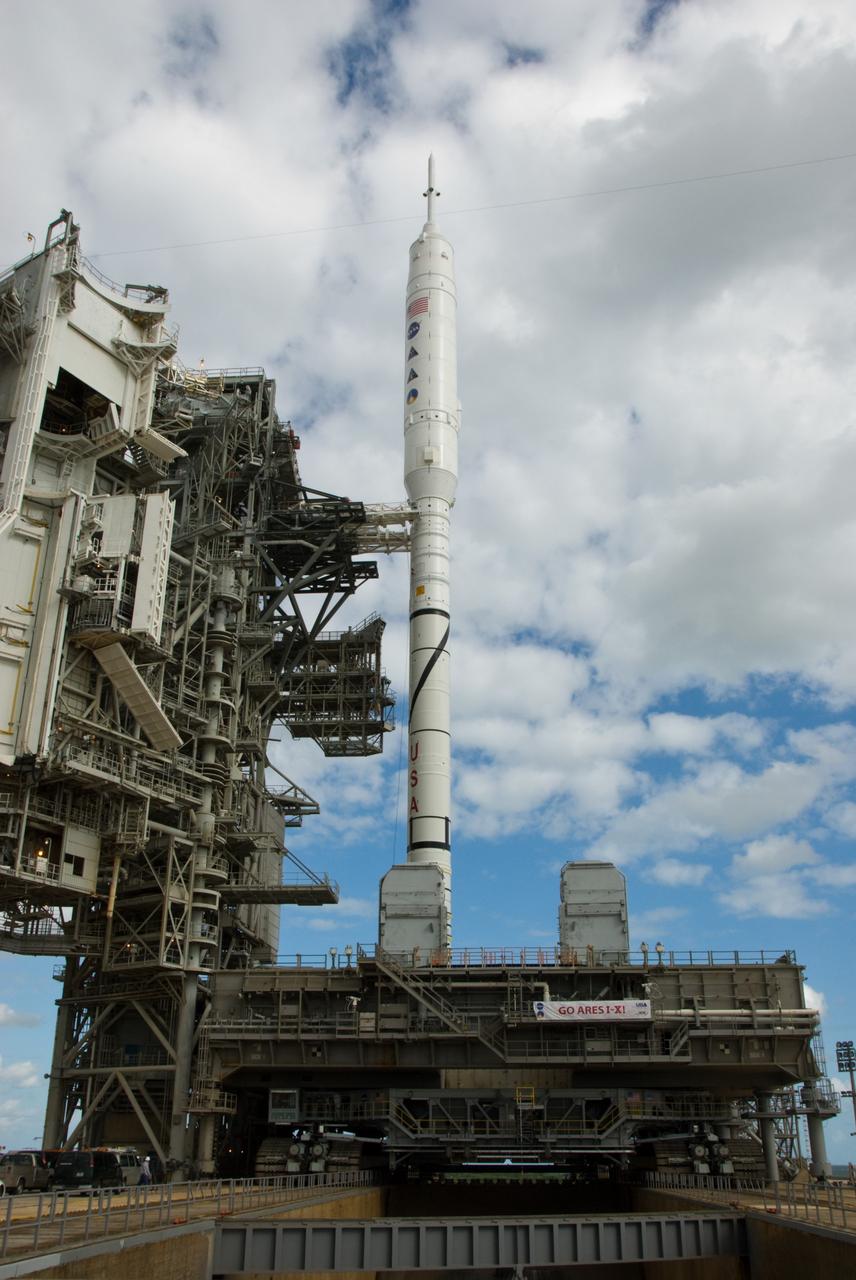

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, newly arrived on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, rests securely on its mobile launcher platform following its seven-hour early-morning trek. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Early morning finds a crawler-transporter moving the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket slowly and steadily along the 4.2-mile route to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
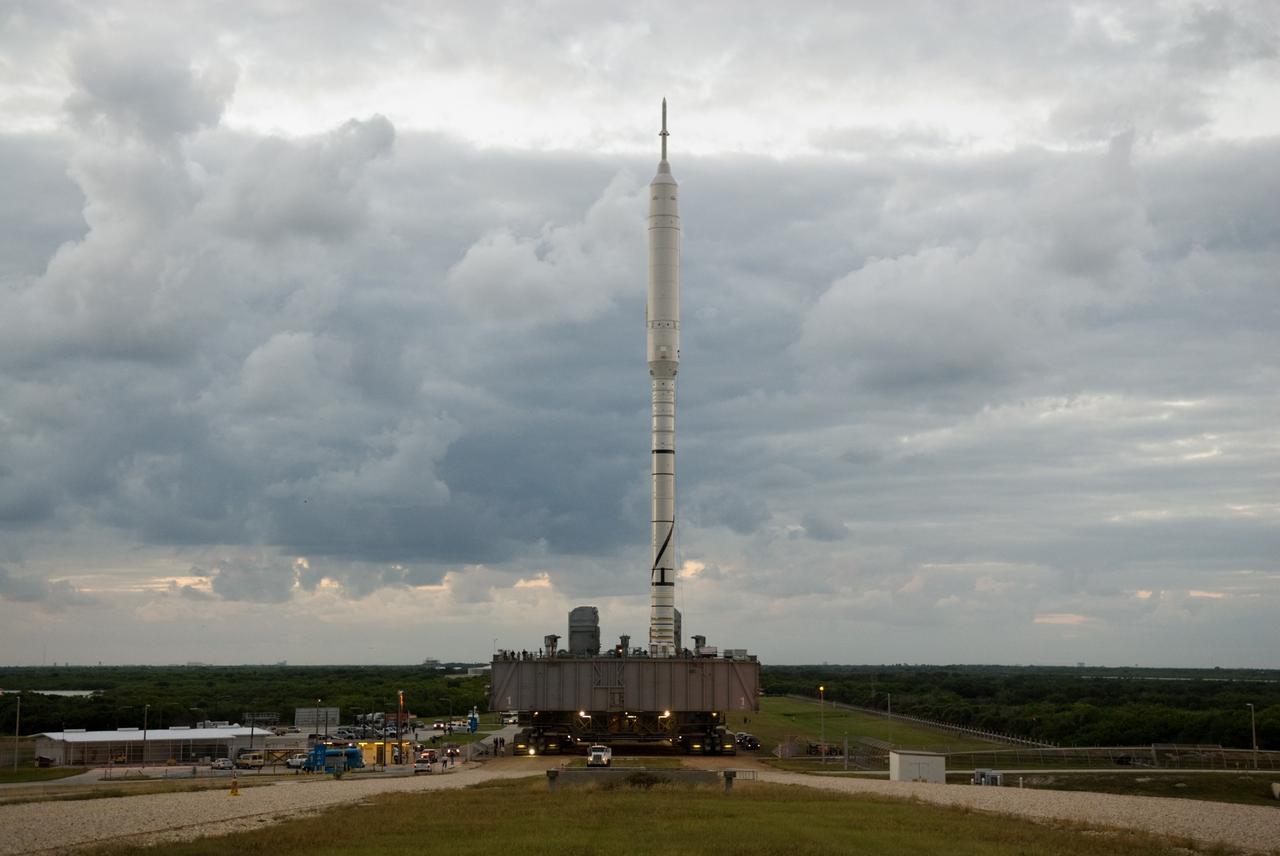

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, makes steady progress toward the top of Launch Pad 39B. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
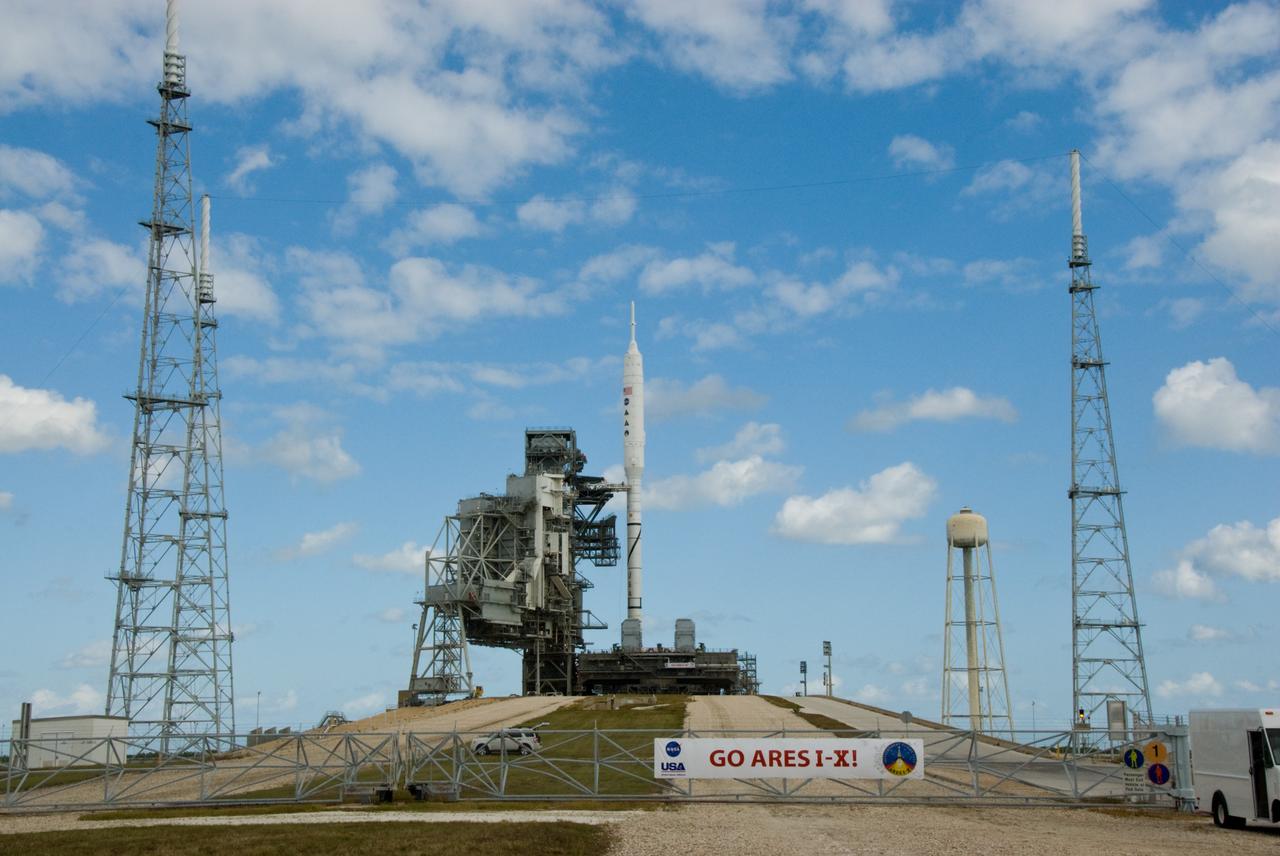

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The perimeter fence on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is closed following the arrival of the towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket following its seven-hour early-morning trek. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
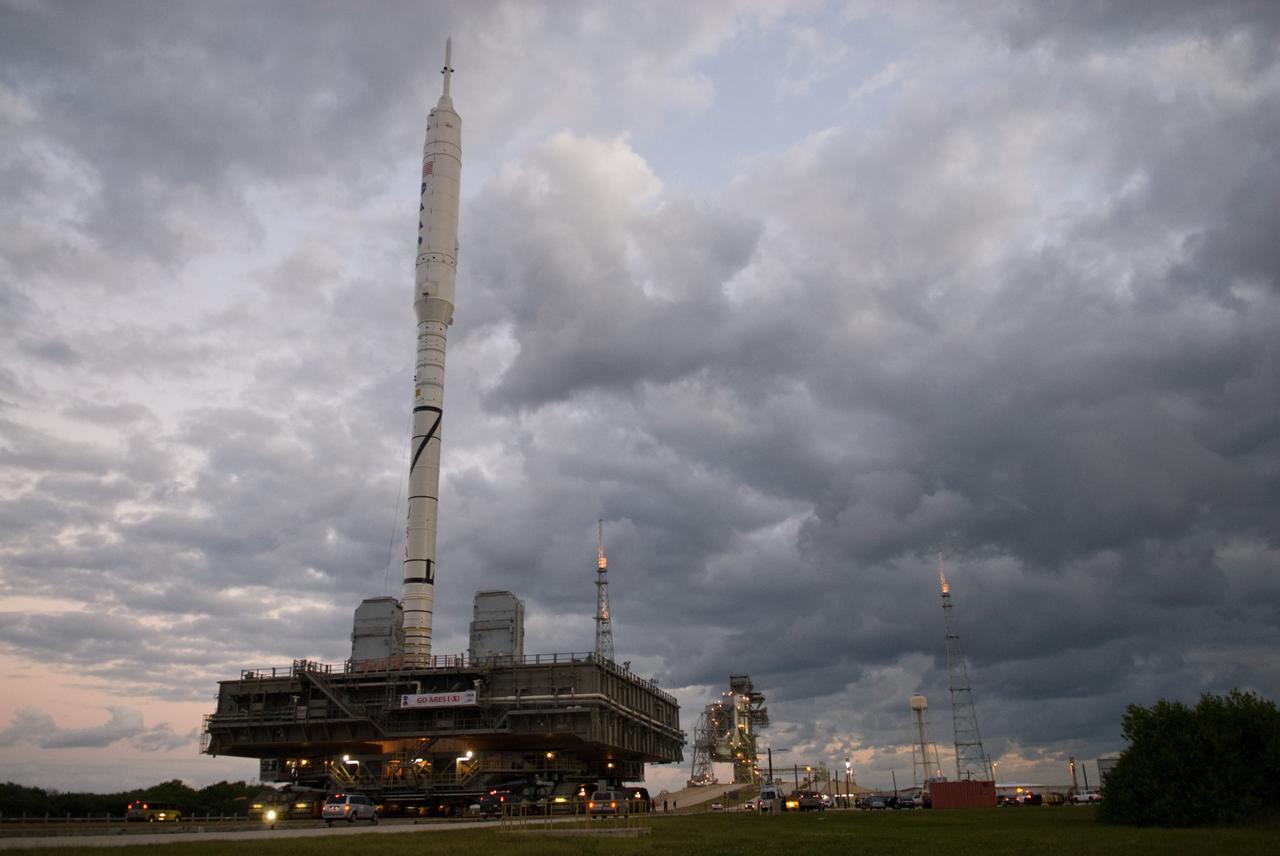

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, secured to a mobile launcher platform, prepares to climb the five percent grade of the crawlerway to the top of the pad. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39B on its upcoming flight test. In the distance are space shuttle Atlantis on Kennedy's Launch Pad 39A, and the pads and processing facilities on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Modifications to the pad to support the Ares I-X included the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, and the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
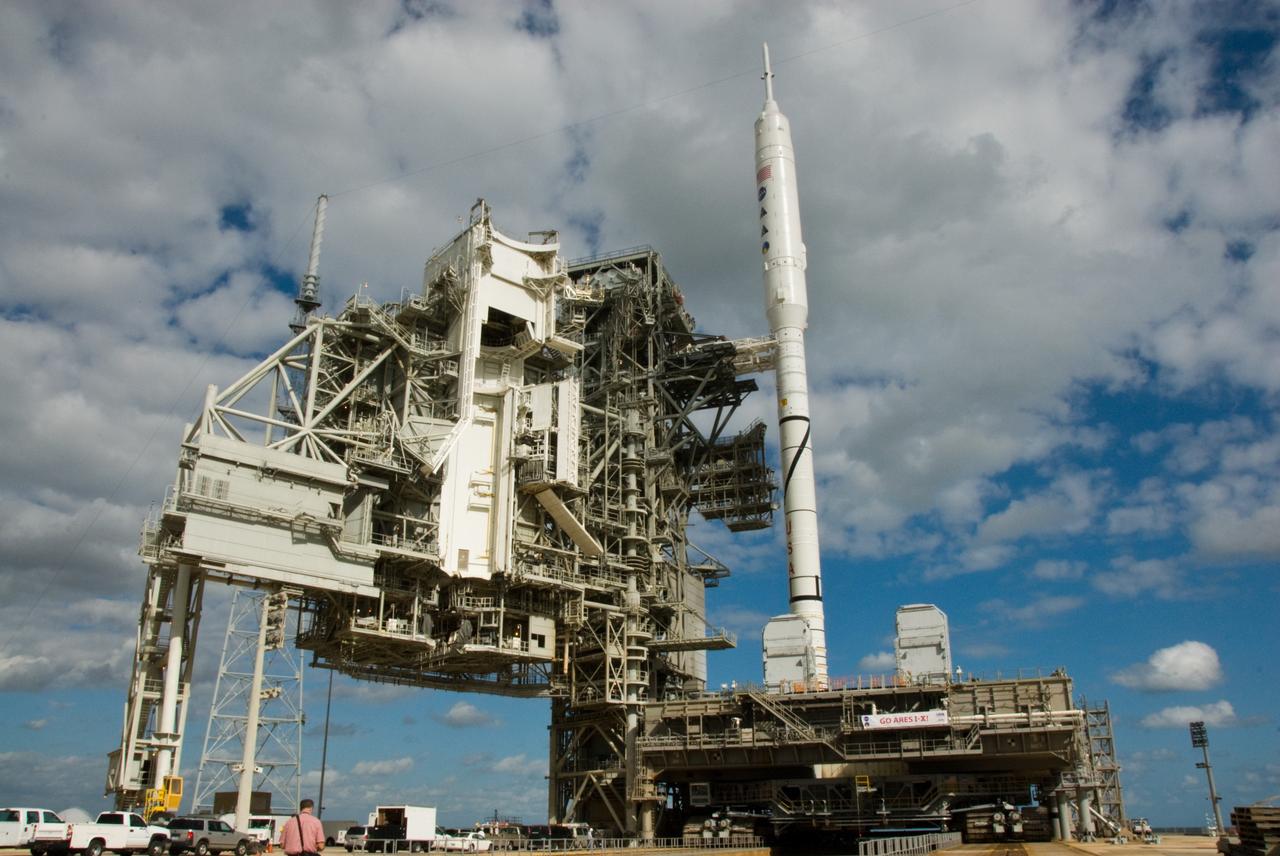

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The towering 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket, newly arrived on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, confidently greats the day following its seven-hour early-morning trek. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
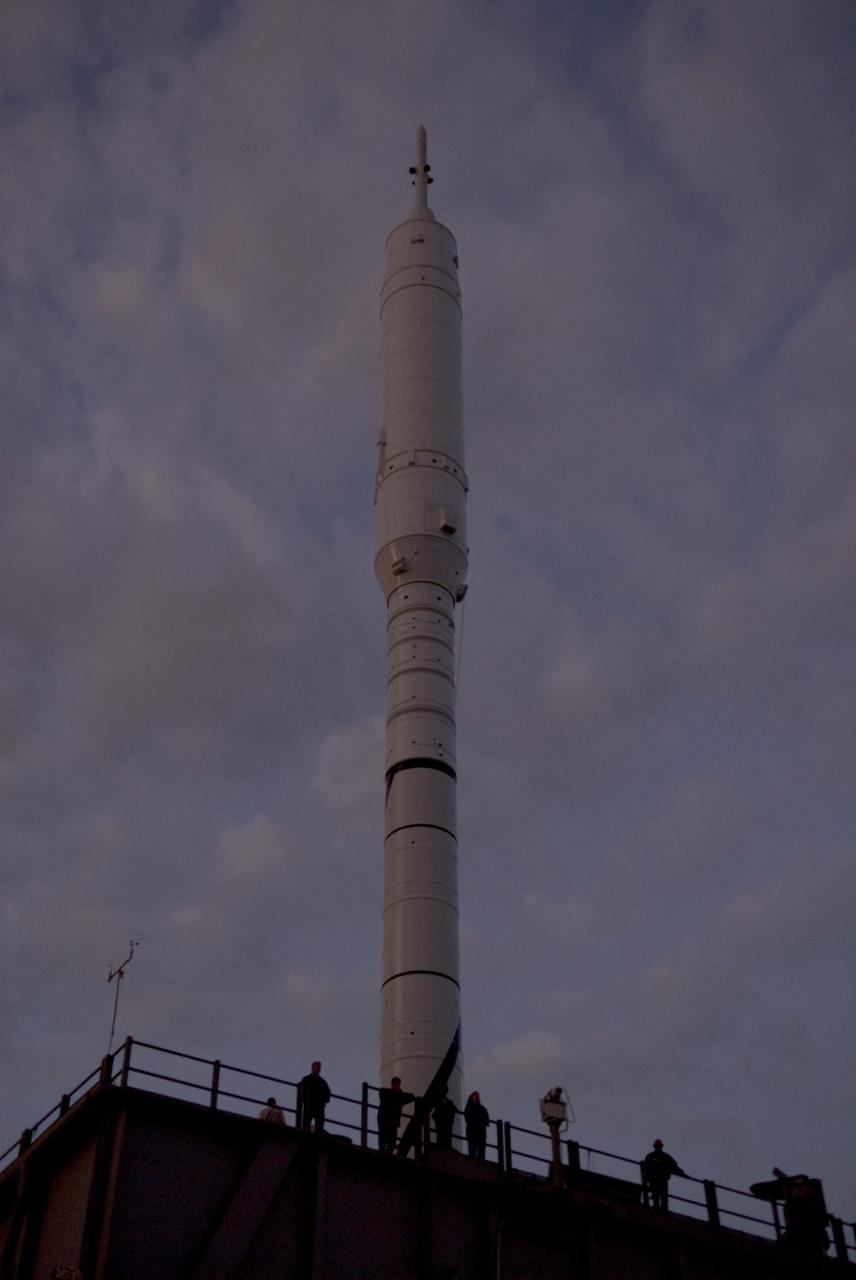

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – As the sun rises over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers ride on the mobile launcher platform to Launch Pad 39B with the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket. The test rocket left the Vehicle Assembly Building at 1:39 a.m. EDT on its 4.2-mile trek to the pad and was "hard down" on the pad’s pedestals at 9:17 a.m. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
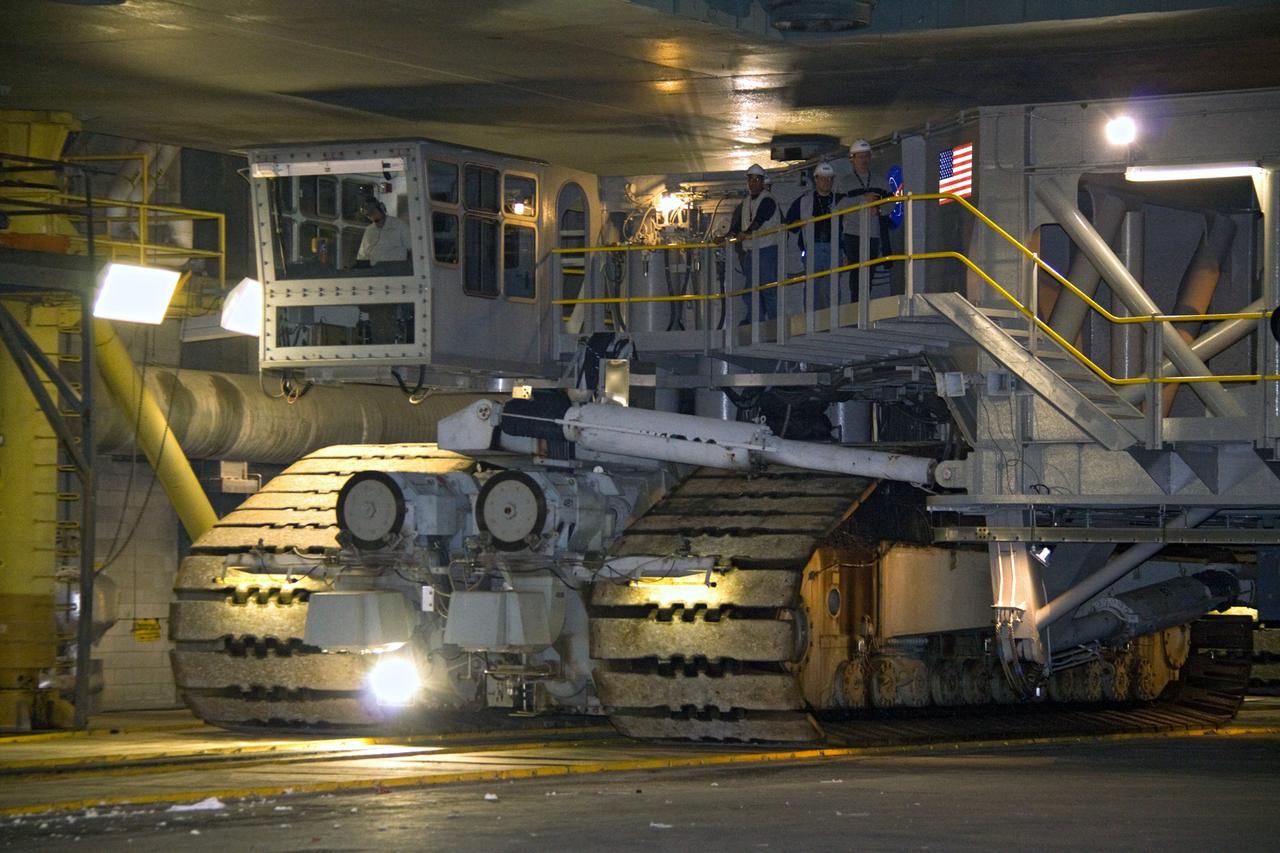

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the driver of the crawler-transporter (upper left) slowly maneuvers the huge vehicle under the mobile launcher platform holding the 327-foot-tall Ares I-X rocket. The crawler-transporter will carry the rocket on the 4.2-mile journey to Launch Pad 39B. The transfer of the pad from the Space Shuttle Program to the Constellation Program took place May 31. Modifications made to the pad include the removal of shuttle unique subsystems, such as the orbiter access arm and a section of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, along with the installation of three 600-foot lightning towers, access platforms, environmental control systems and a vehicle stabilization system. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller